Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
248 results about "Rogue access point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
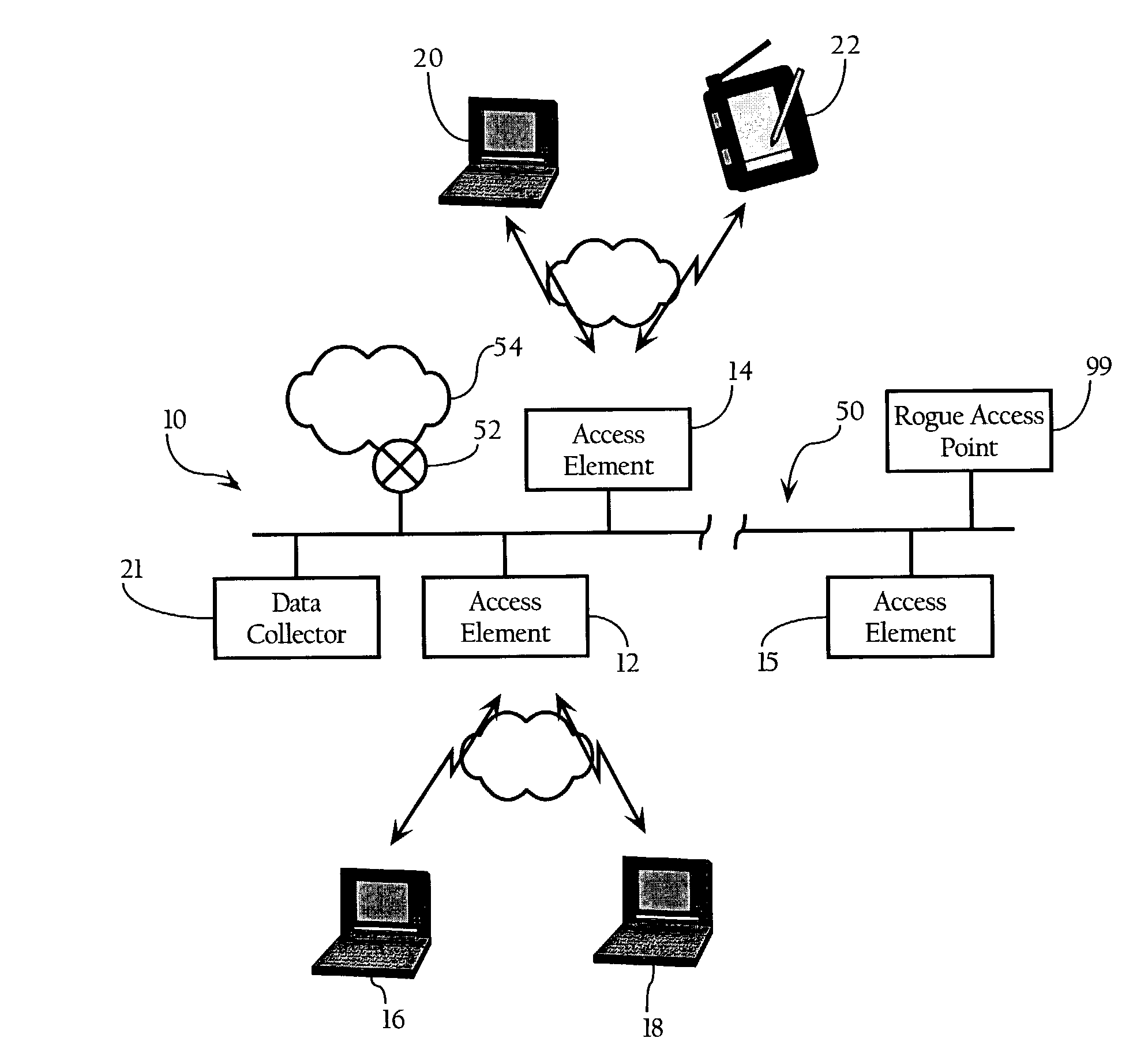
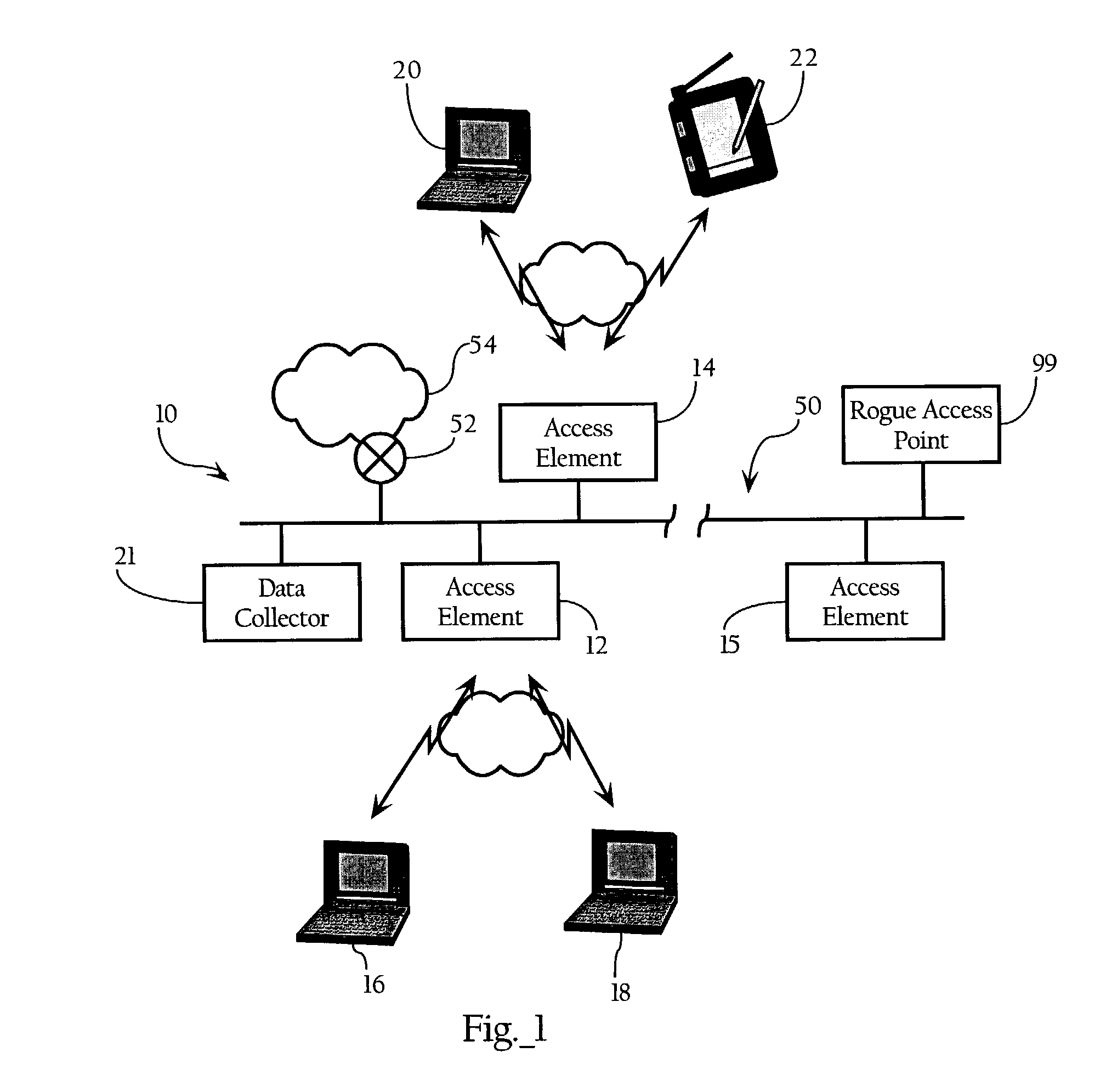
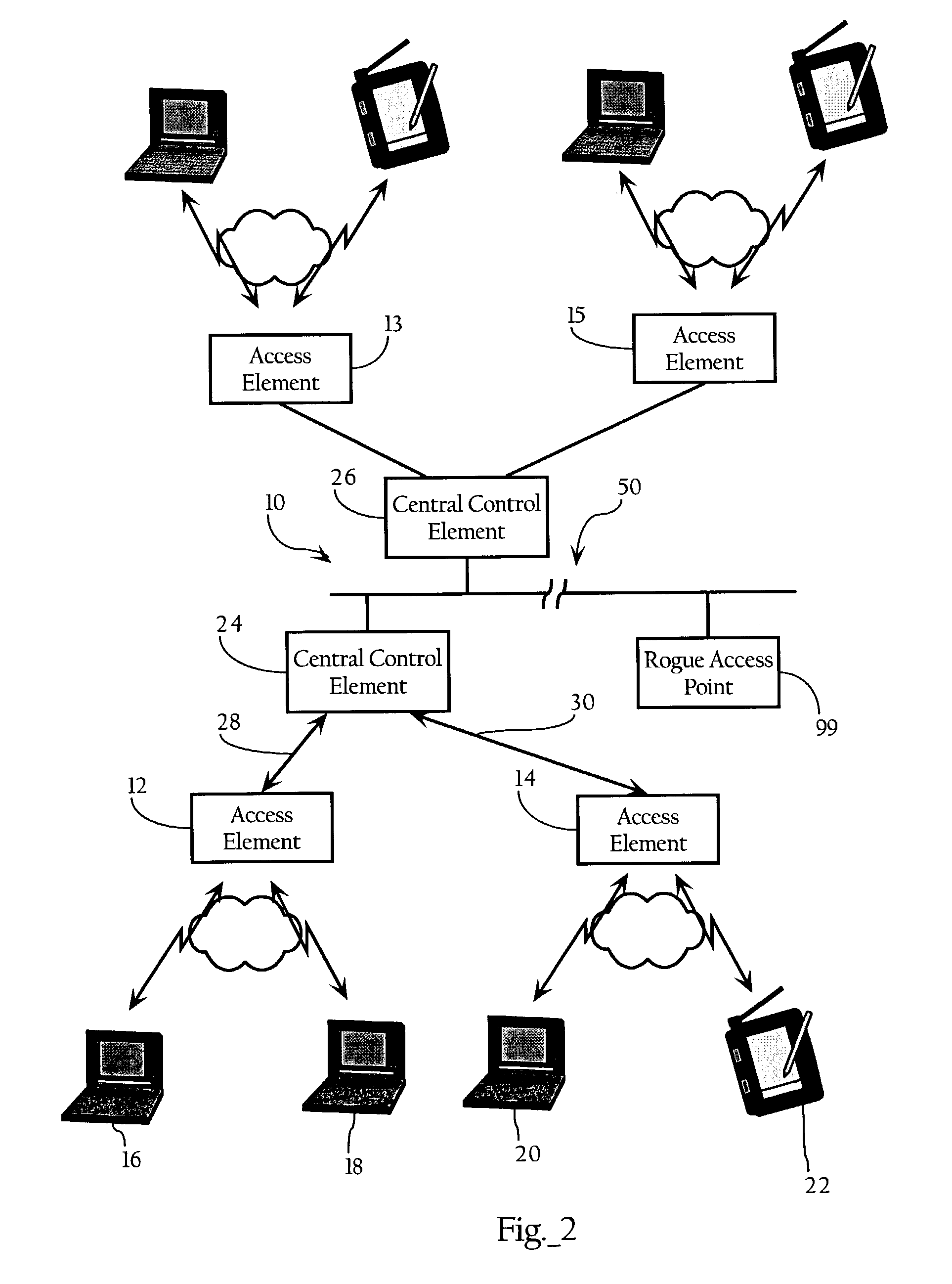
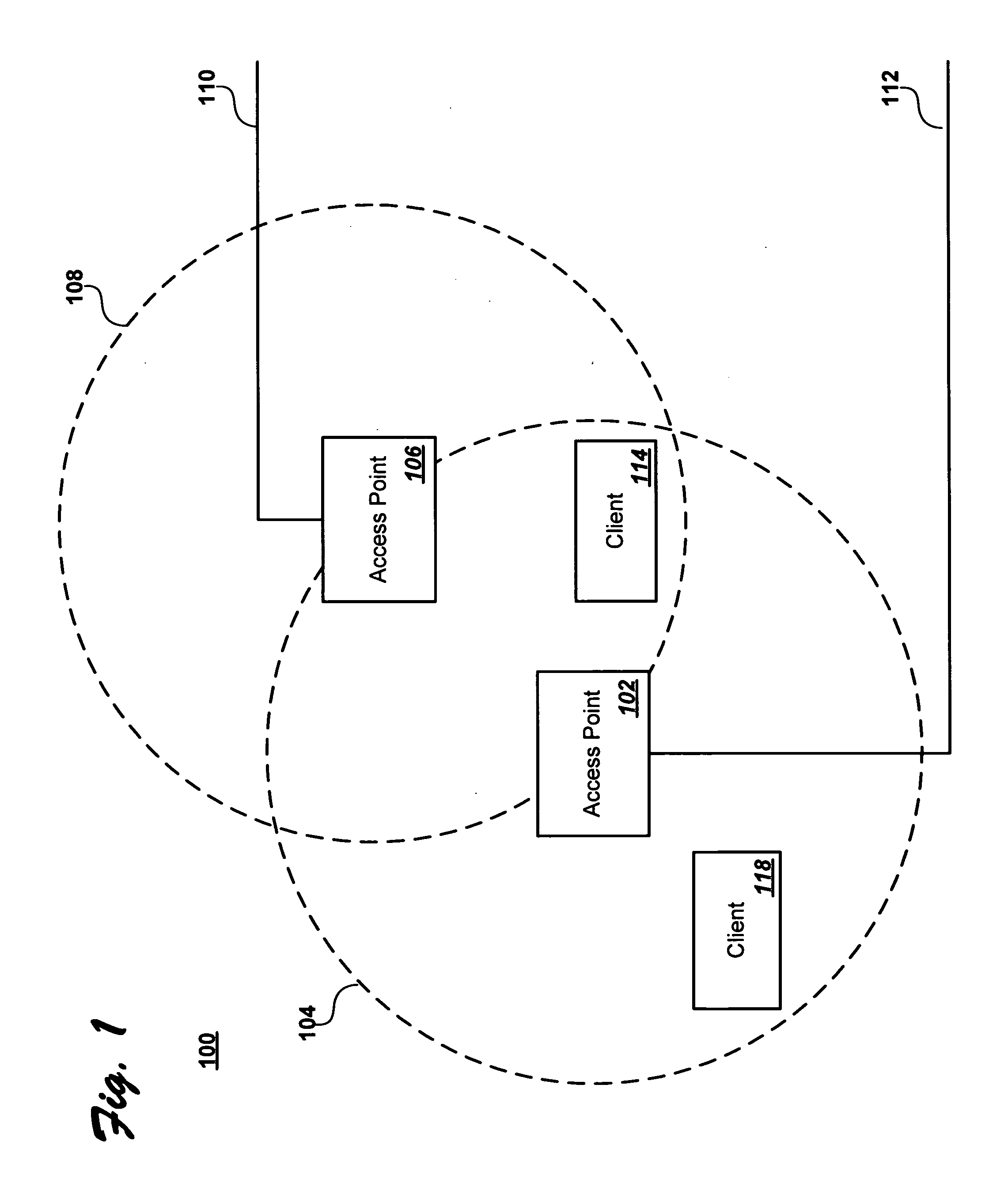
A rogue access point is a wireless access point that has been installed on a secure network without explicit authorization from a local network administrator, whether added by a well-meaning employee or by a malicious attacker.
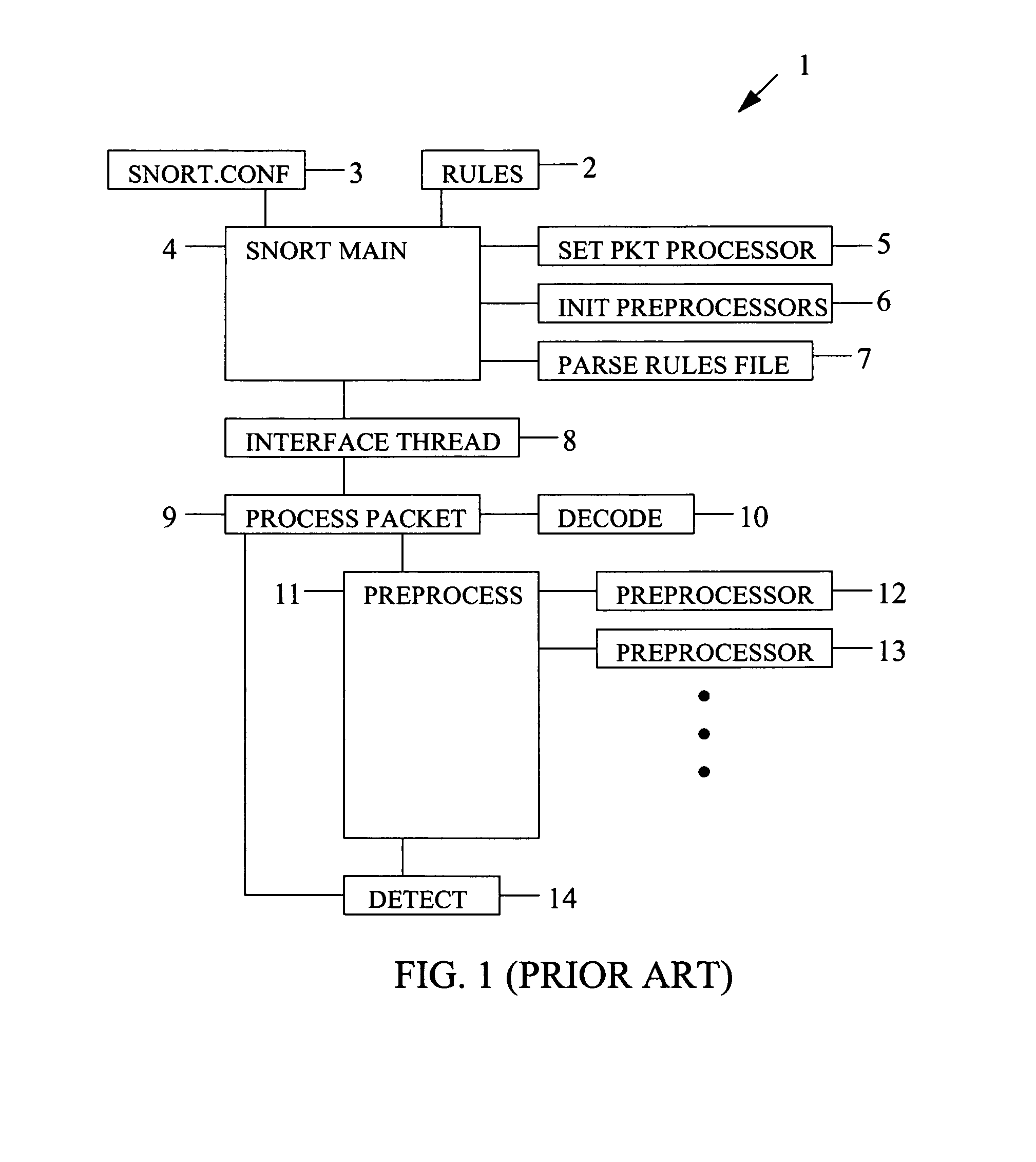
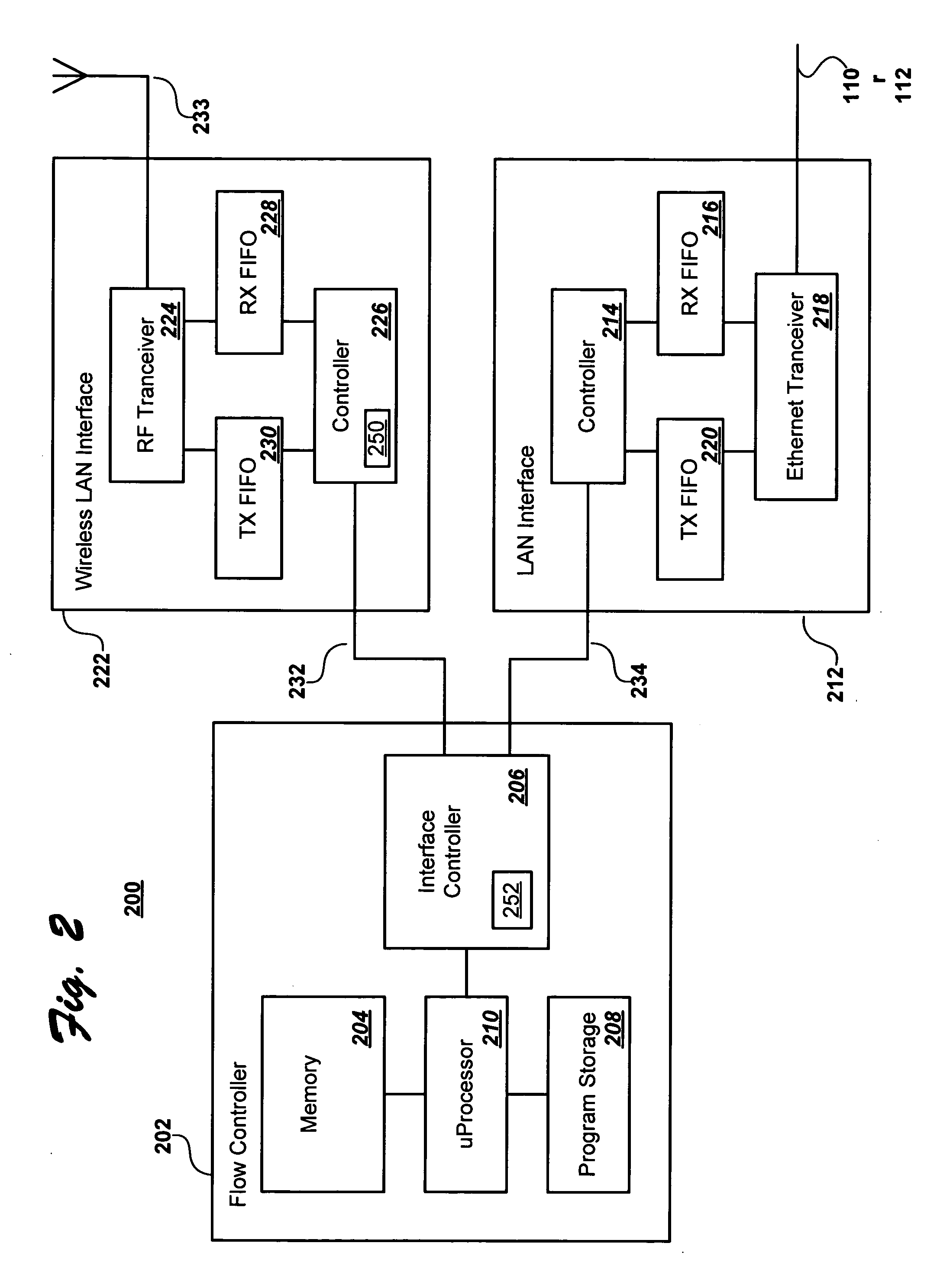
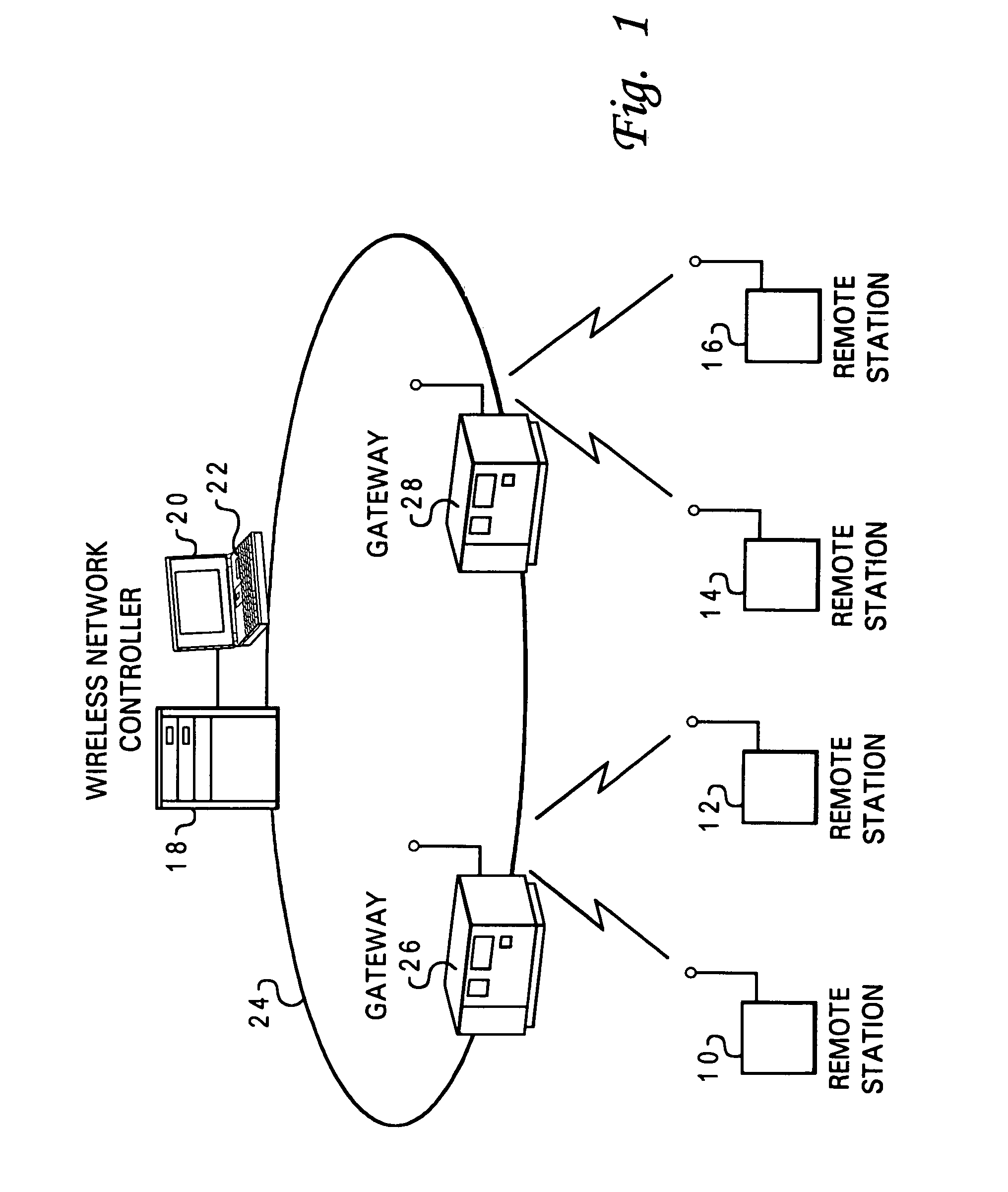
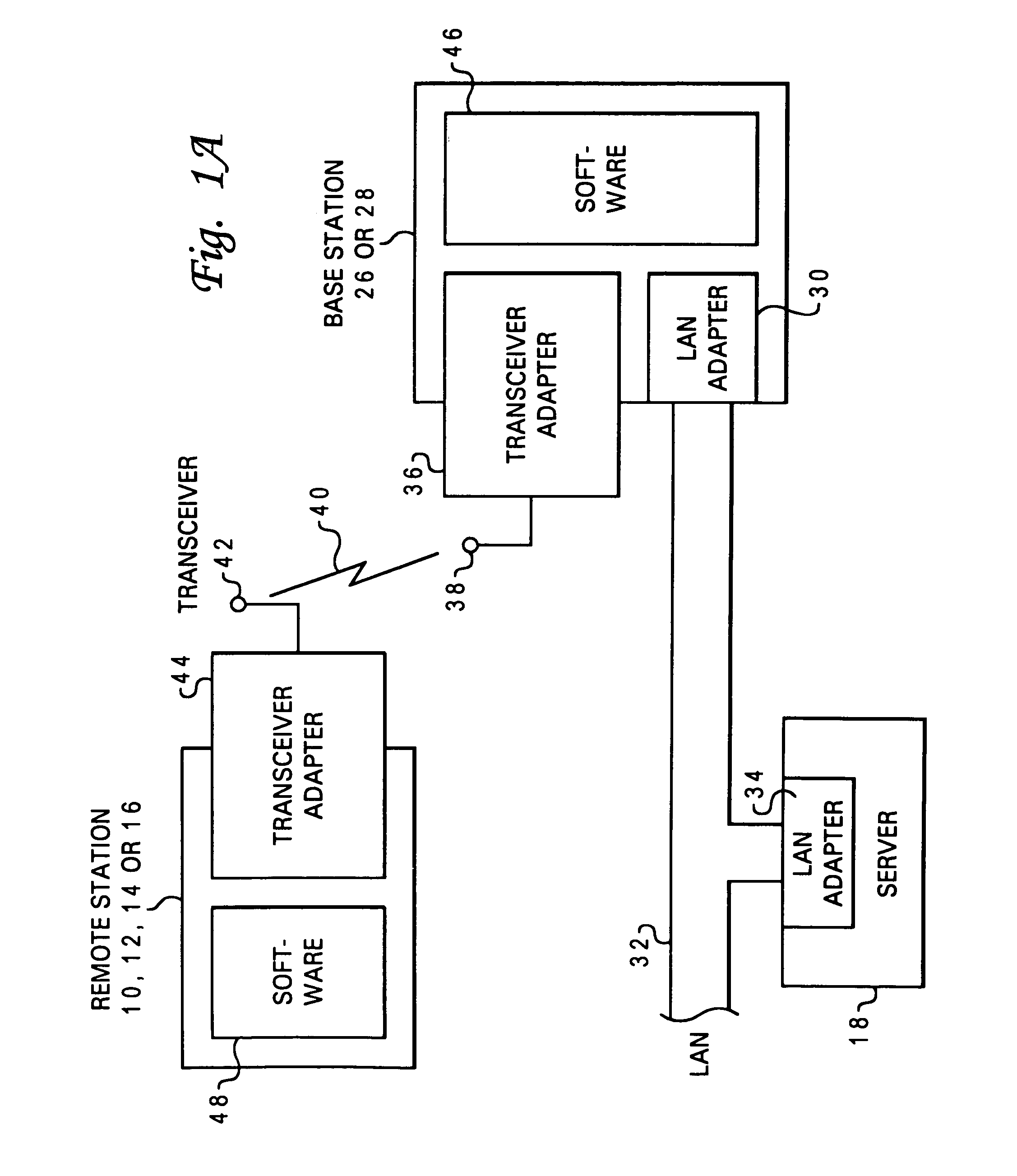
Device for and method of wireless intrusion detection
A device for and method of detecting intrusion into a wireless network that includes a configuration file, a rules files, a main processor, a set packet processor, an initialize preprocessor, a parse rules file, an interface thread unit, a process packet unit, a decoder, a preprocess unit connected to the process packet unit; at least one preprocessor consisting of a rogue access point and transmit channel preprocessor, a NETSTUMBLER preprocessor, a MAC spoofing preprocessor, a DEAUTH flood preprocessor, an AUTH flood preprocessor, a rogue client preprocessor, a bridged network preprocessor, a rogue client valid access point preprocessor, valid client rogue access point preprocessor, an ad-hoc network preprocessor, a wrong channel preprocessor, a cloaking policy violation preprocessor, an encryption policy violation preprocessor, and a null SSID association policy violation preprocessor; and a detector.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY
Wireless network system including integrated rogue access point detection
ActiveUS7346338B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsRogue access pointWireless access point
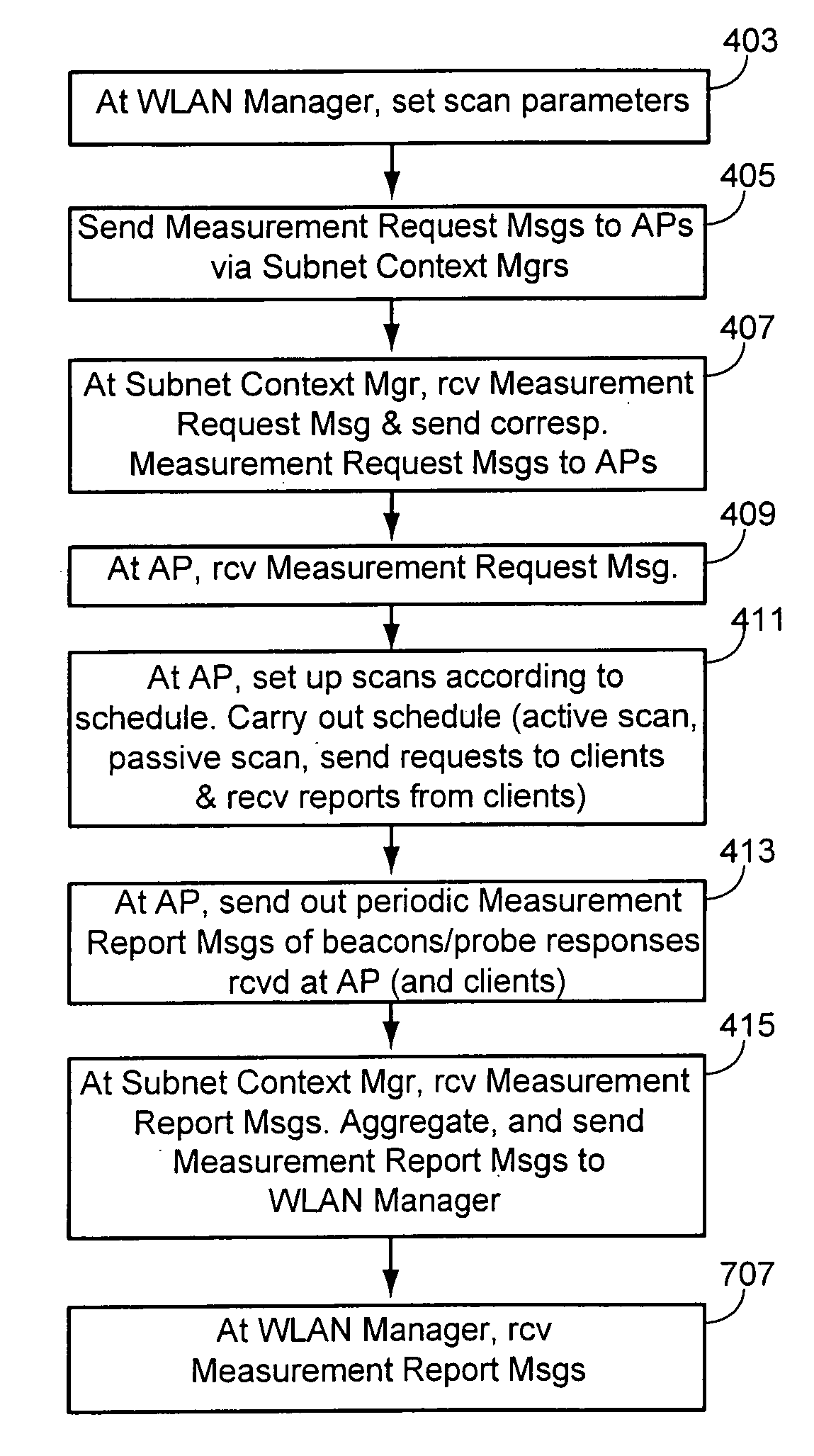
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating automated detection of rogue wireless access points in a wireless network environment. The present invention, in one embodiment, integrates automated detection of rogue access points into wireless network systems. As discussed more fully below, the present invention can be applied to a variety of wireless network system architectures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mobile virtual LAN
InactiveUS6847620B1Not burdened with associated computational overheadNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsCommunications systemVirtual LAN
A communication system in which multiple protocols and proxy services are executed by an access point. In one embodiment of the invention, GVRP and GMRP registrations are combined in a single packet when a wireless device roams to a different VLAN. In addition, outbound GVRP and GMRP multicast messages are handled by an access point (also referred to as a GVRP and GMRP “gateway”) such that the wireless device is not burdened with the associated computational overhead. In a further embodiment, a wireless device may dynamically switch between a VLAN-aware state and a VLAN-unaware state depending on the nature of a detected access point. For example, if a relevant access point supports GVRP, the wireless device may operate as a VLAN terminal. If a wireless device is not attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, the wireless device sends and receives VLAN tagged frames. If a wireless device configured with a VLAN ID is attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, or if the wireless device is attached to a non-VLAN access point, then the wireless device may send and receive raw / untagged frames. In addition to the gateways described below, the ability of a wireless device to detect when it can send untagged frames is considered novel. In another embodiment of the invention, a special ID that is different than the native VLAN ID for a switch port is used for VLAN-unaware devices. This allows such devices that do not issue tagged frames to belong to a single VLAN ID.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for locating rogue access point switch ports in a wireless network related patent applications
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for locating and disabling the switch port of a rogue wireless access point. In one embodiment, a network management device is configured to detect the presence of a rogue access point on a managed wireless network. Once detected, the management device may then instruct a special client, such as a scanning AP, to associate with the rogue access point and send a discovery packet through the rogue access point to network management device. The network management device upon receiving the discovery packet may thereby determine that the rogue access point is connected to a network managed by said network device. The network device may then utilize information contained in the discovery packet to locate the switch port to which the rogue access point is connected, and ultimately disable the switch port to which the rogue access point is connected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
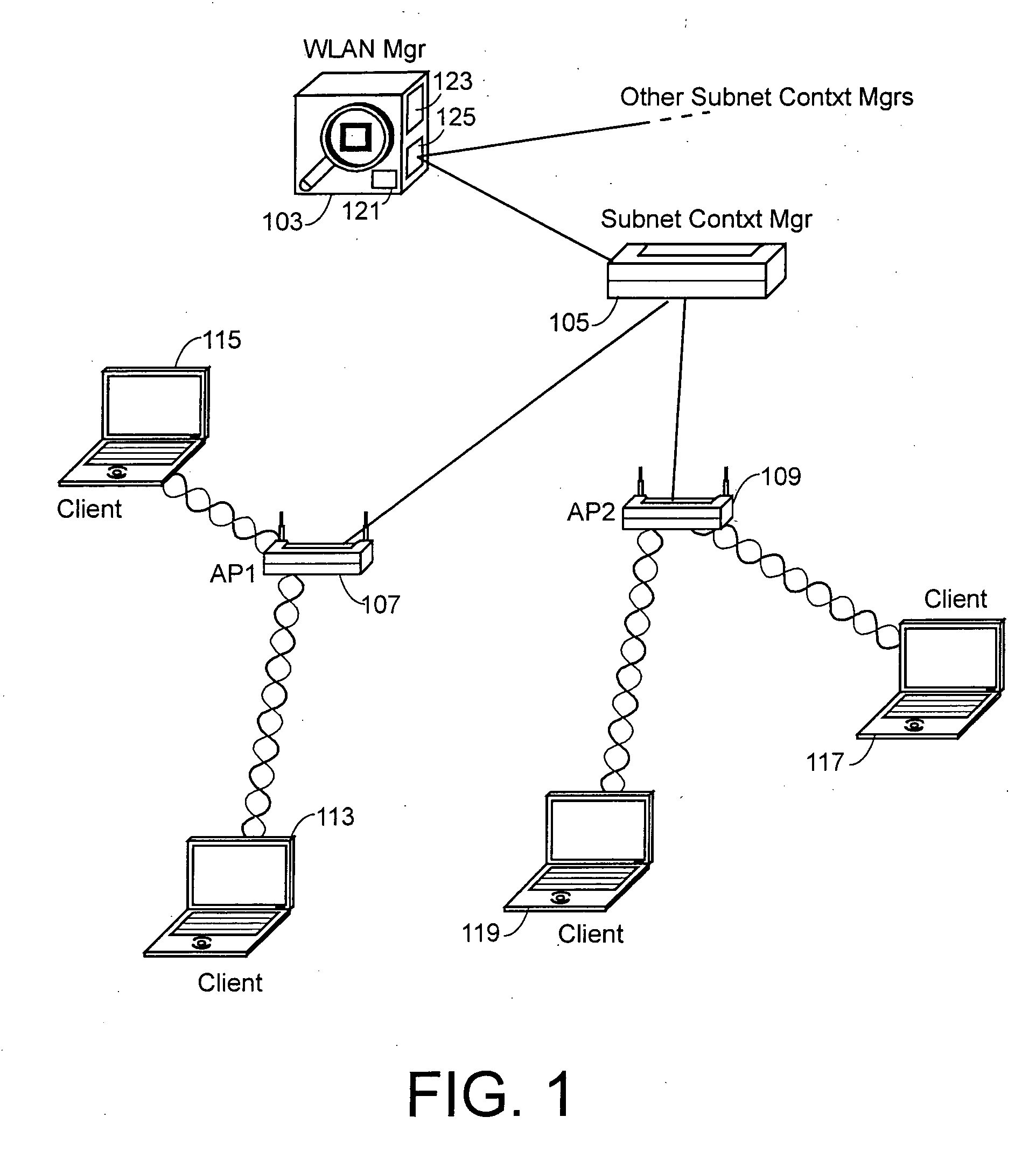
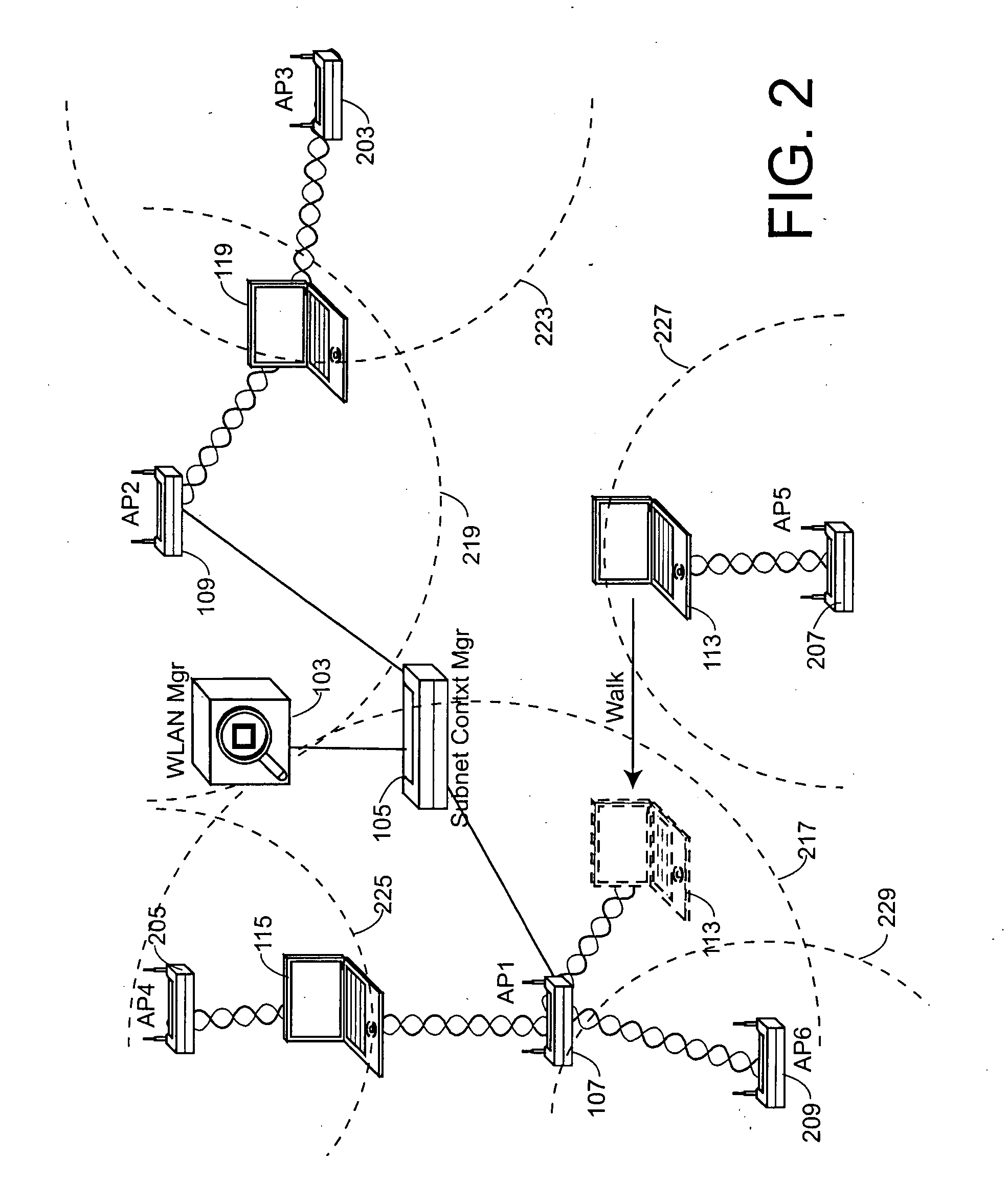
802.11 using a compressed reassociation exchange to facilitate fast handoff
ActiveUS7350077B2Reduce the burden onUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesComputer networkRogue access point
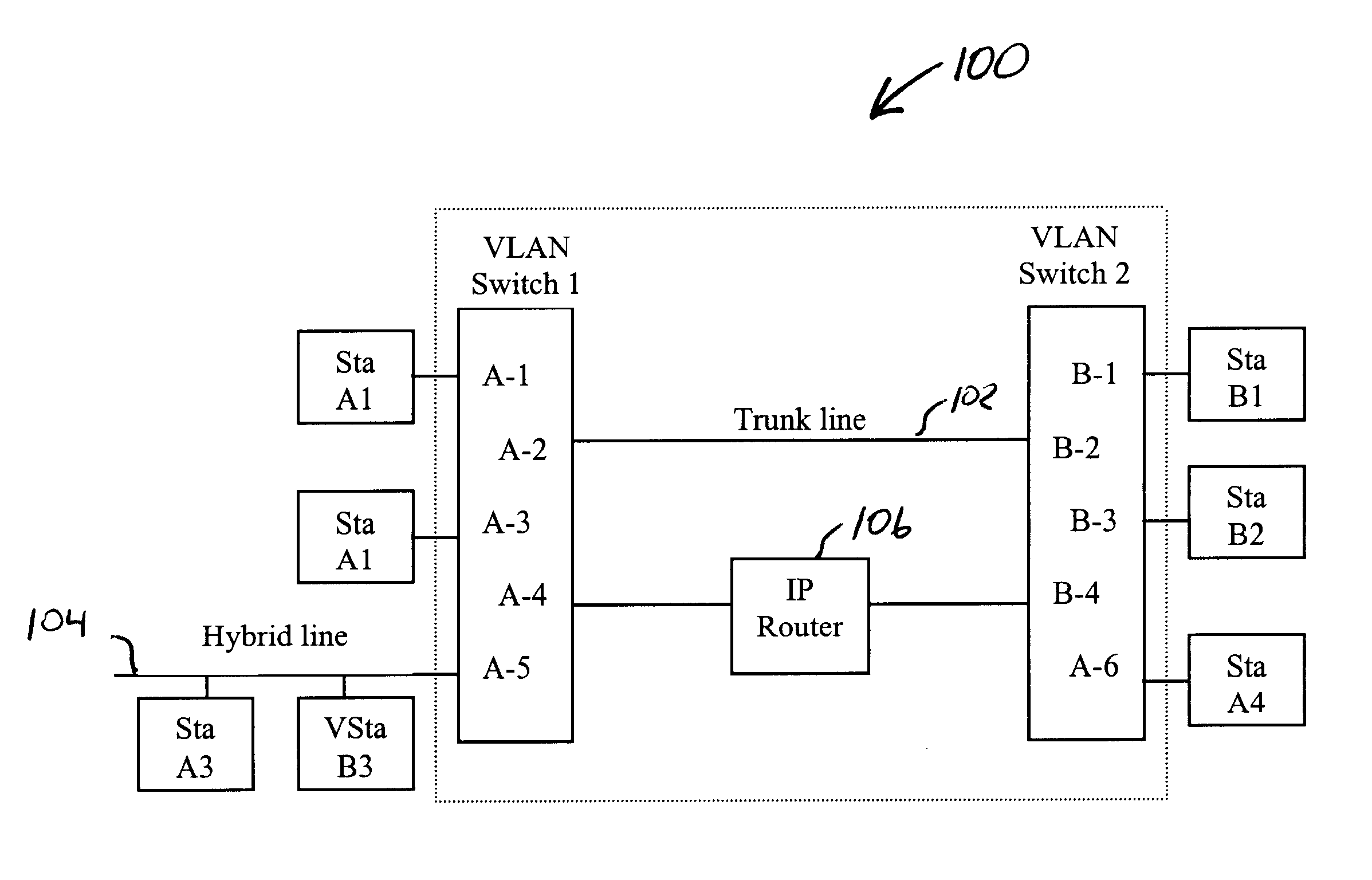
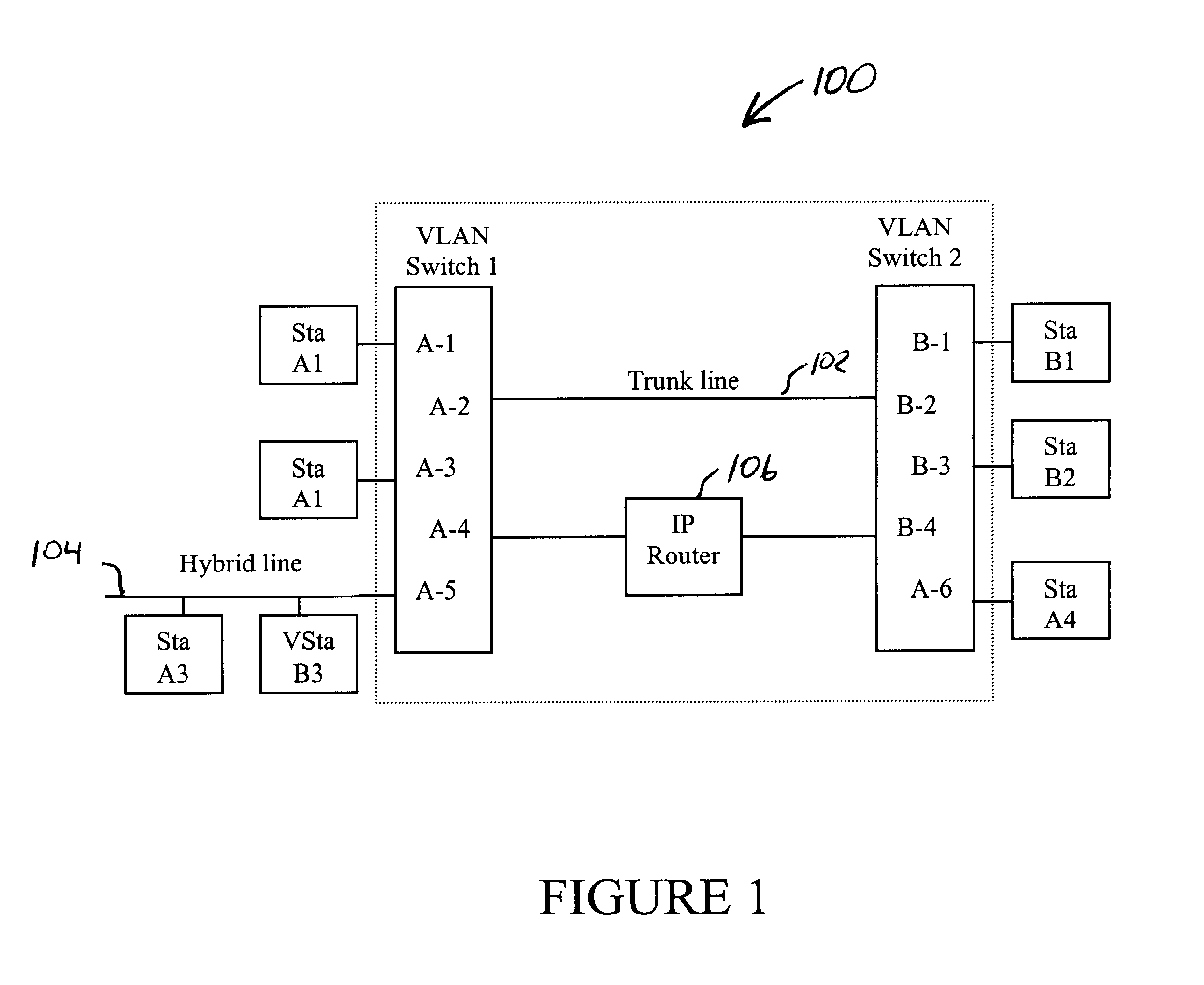
A method and system for handling roaming mobile nodes in a wireless network. The system uses a Subnet Context Manager to store current Network session keys, security policy and duration of the session (e.g. session timeout) for mobile nodes, which is established when the mobile node is initially authenticated. Pairwise transit keys are derived from the network session key. The Subnet Context Manager handles subsequent reassociation requests. When a mobile node roams to a new access point, the access point obtains the network session key from the Subnet Context Manager and validates the mobile node by computing a new pairwise transient key from the network session key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
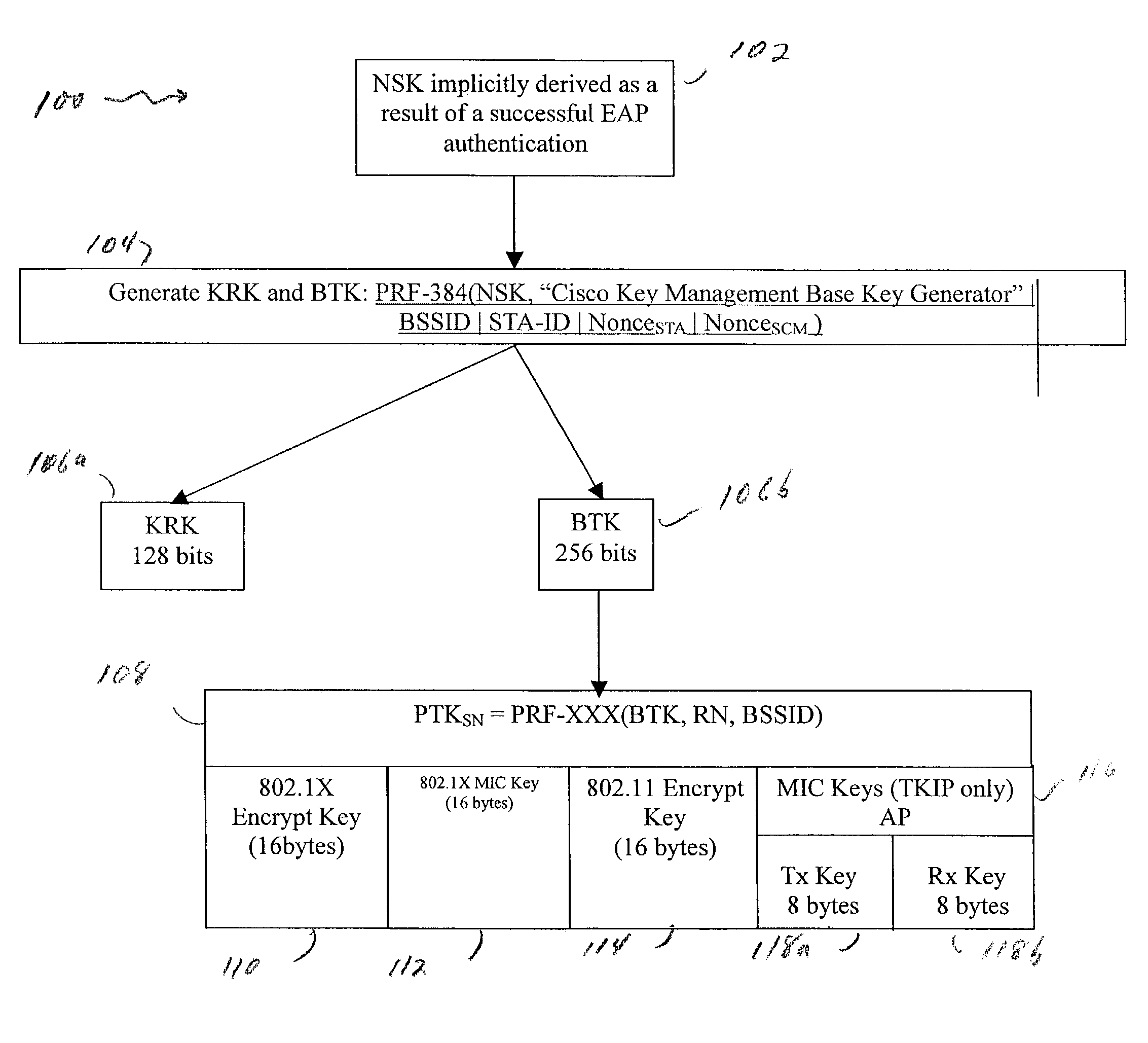
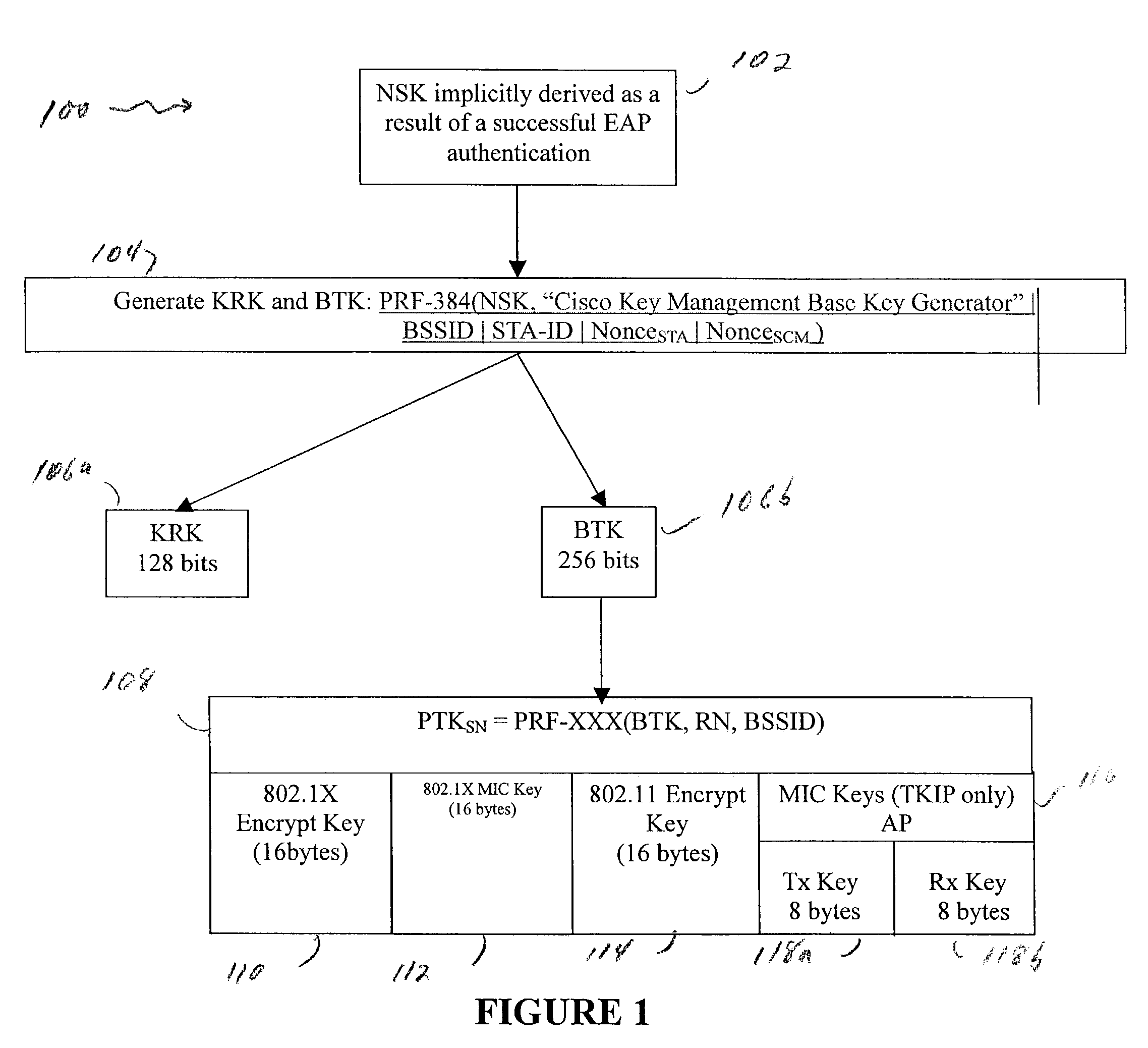
Rogue AP detection
InactiveUS7181530B1Quick launchReduce complexityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionRogue access pointNetwork access point
A method of detecting a rogue access point is disclosed. A message is directed from a supplicant to a network through an access point. A network response message is received by the supplicant from the access point. A step of determining whether the access point is one of a valid network access point and a rogue access point is performed based on whether the received network response message is respectively in conformity or nonconformity with predetermined expectations. If the access point is determined to be a rogue access point, it is reported to the network. If the access point is determined to be a valid network access point, the supplicant is authenticated to the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method of seamlessly roaming between multiple wireless networks using a single wireless network adaptor
InactiveUS20080069065A1Reduce in quantityConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsRogue access point
A method of roaming between access points on the same or different wireless networks using a single wireless network interface adaptor. A device will establish a connection with a second wireless network access point while still connected with a first wireless network access point such that the device can concurrently communicate with both wireless access points. During and after connection with the second wireless network access point real-time IP data transfer is maintained with another network device by switching between the first and second access points for concurrently sending and receiving data packets via both access points using a switching strategy based at least in part on a number of the data packets to be send to each network access point. The method also determines when to roam, scans for candidate wireless network access points to connect to and selects the best access point for roaming based on selection criteria.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
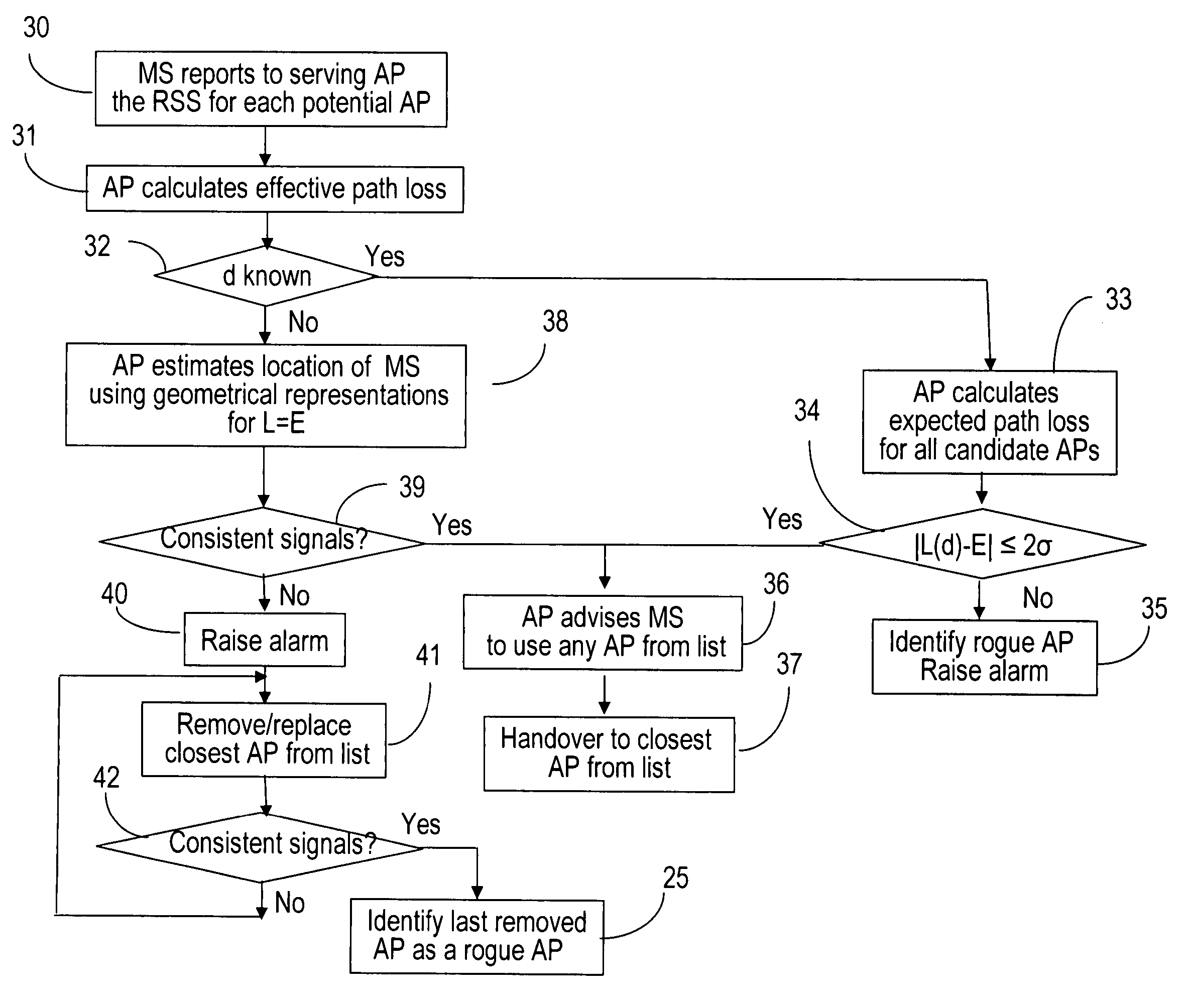
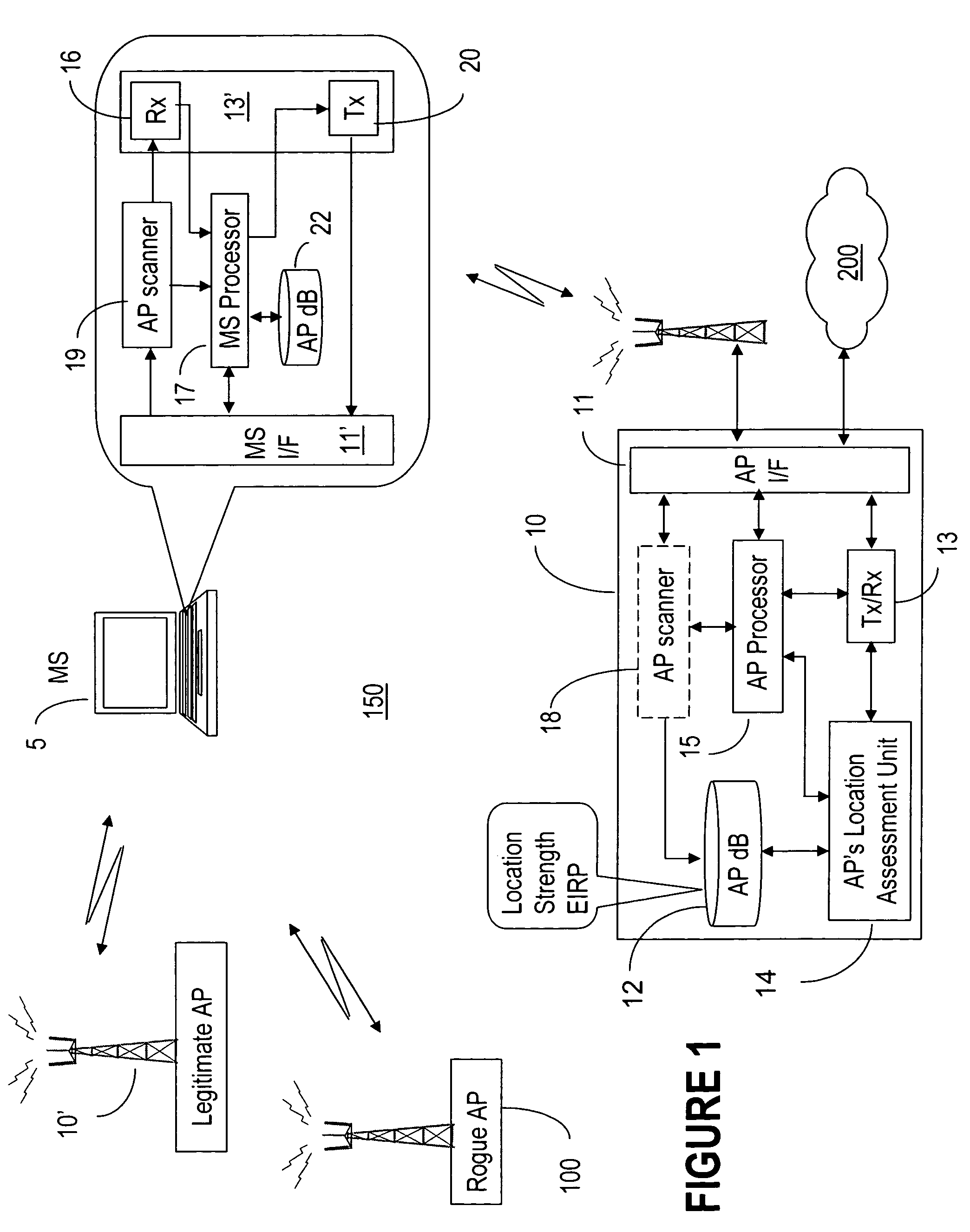
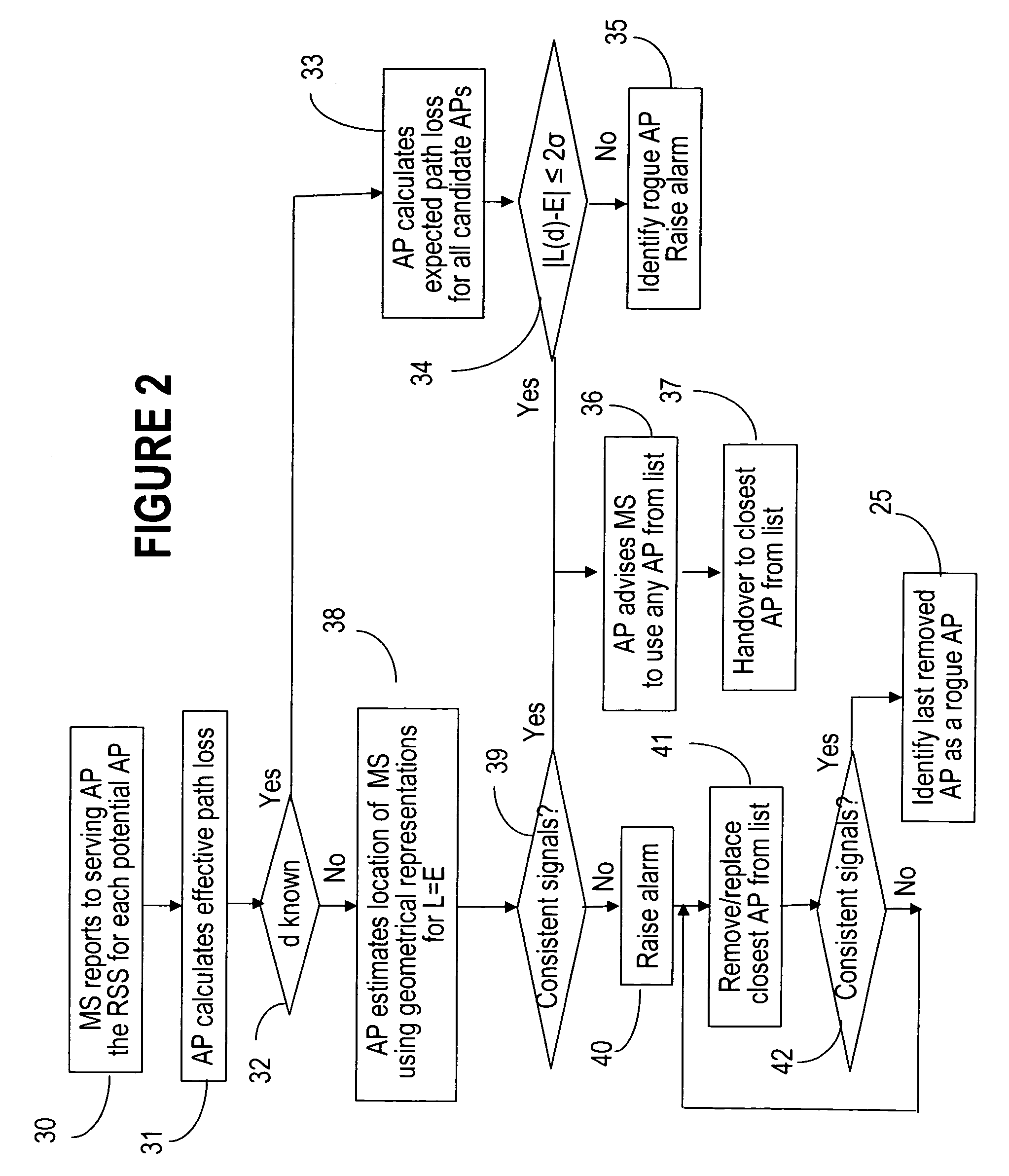
Rogue access point detection in wireless networks
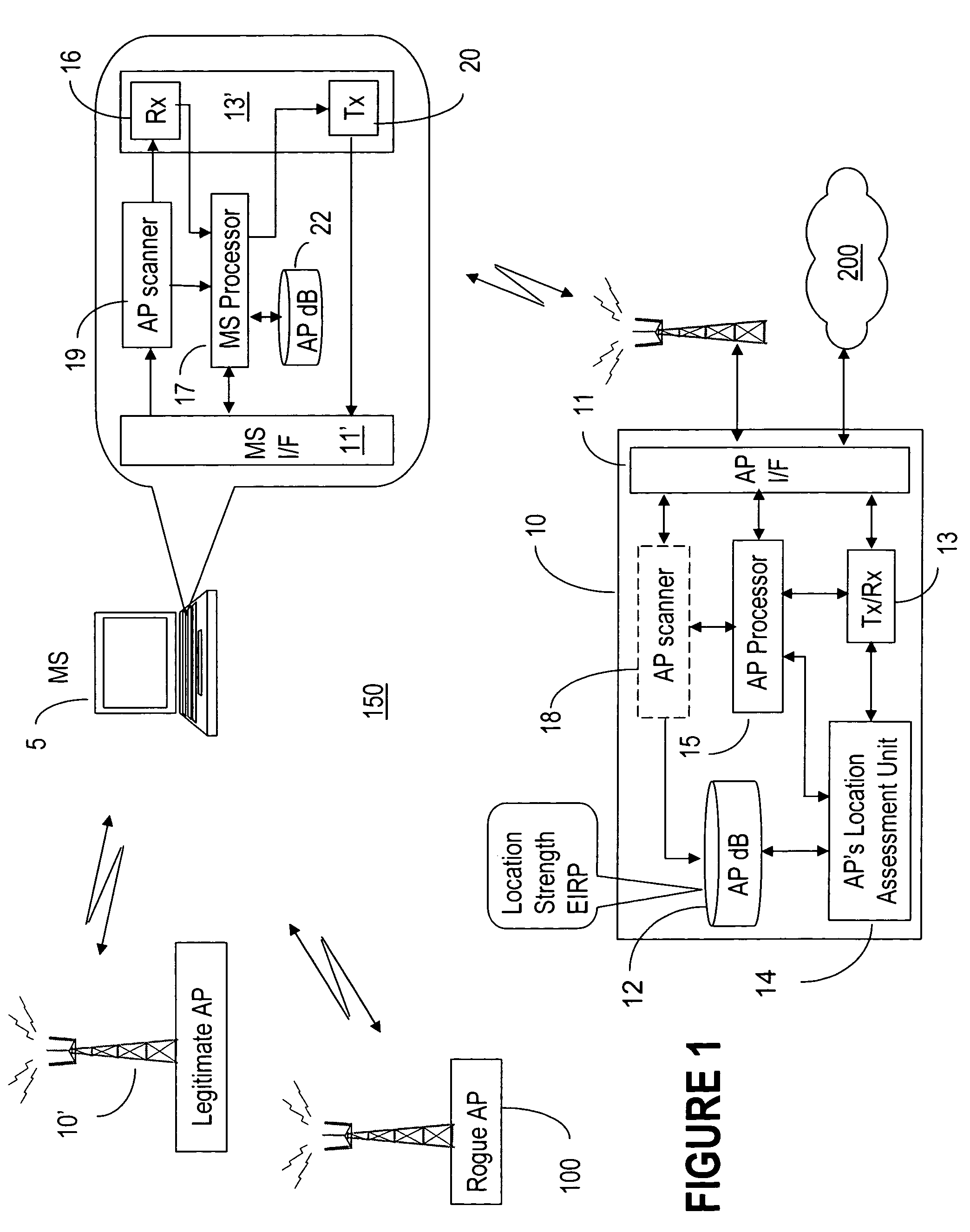
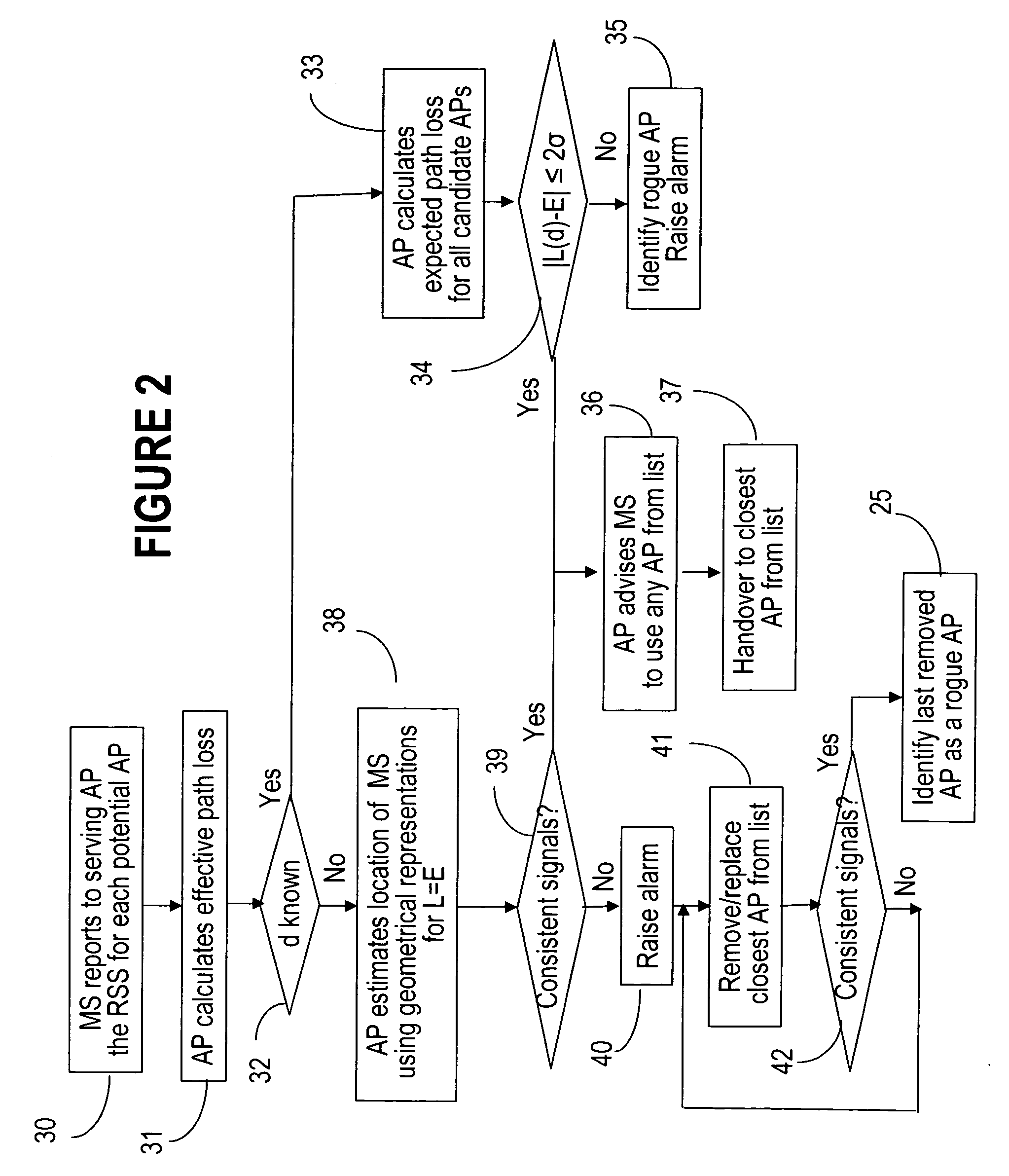
InactiveUS20070079376A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsWireless mesh networkRogue access point
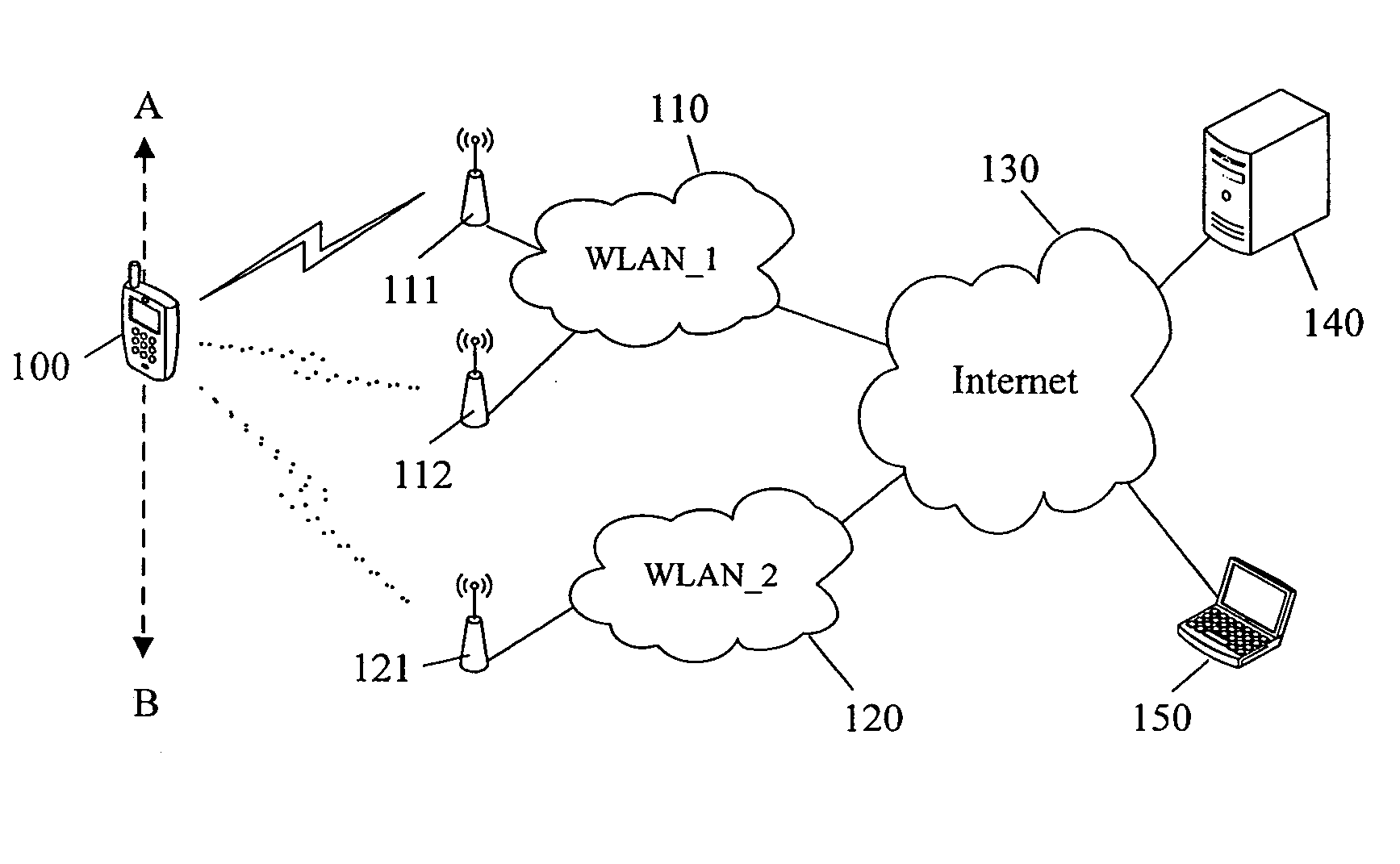
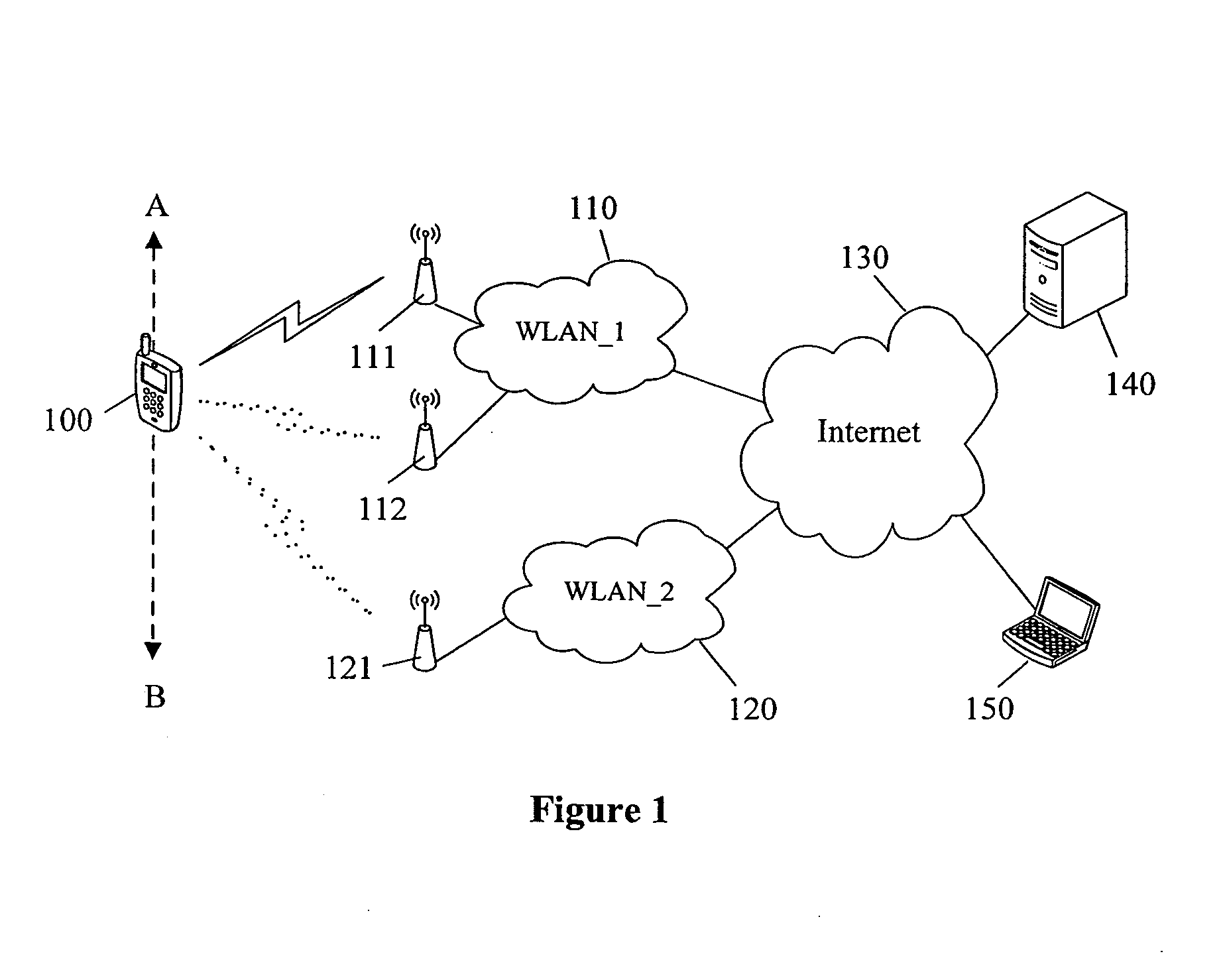
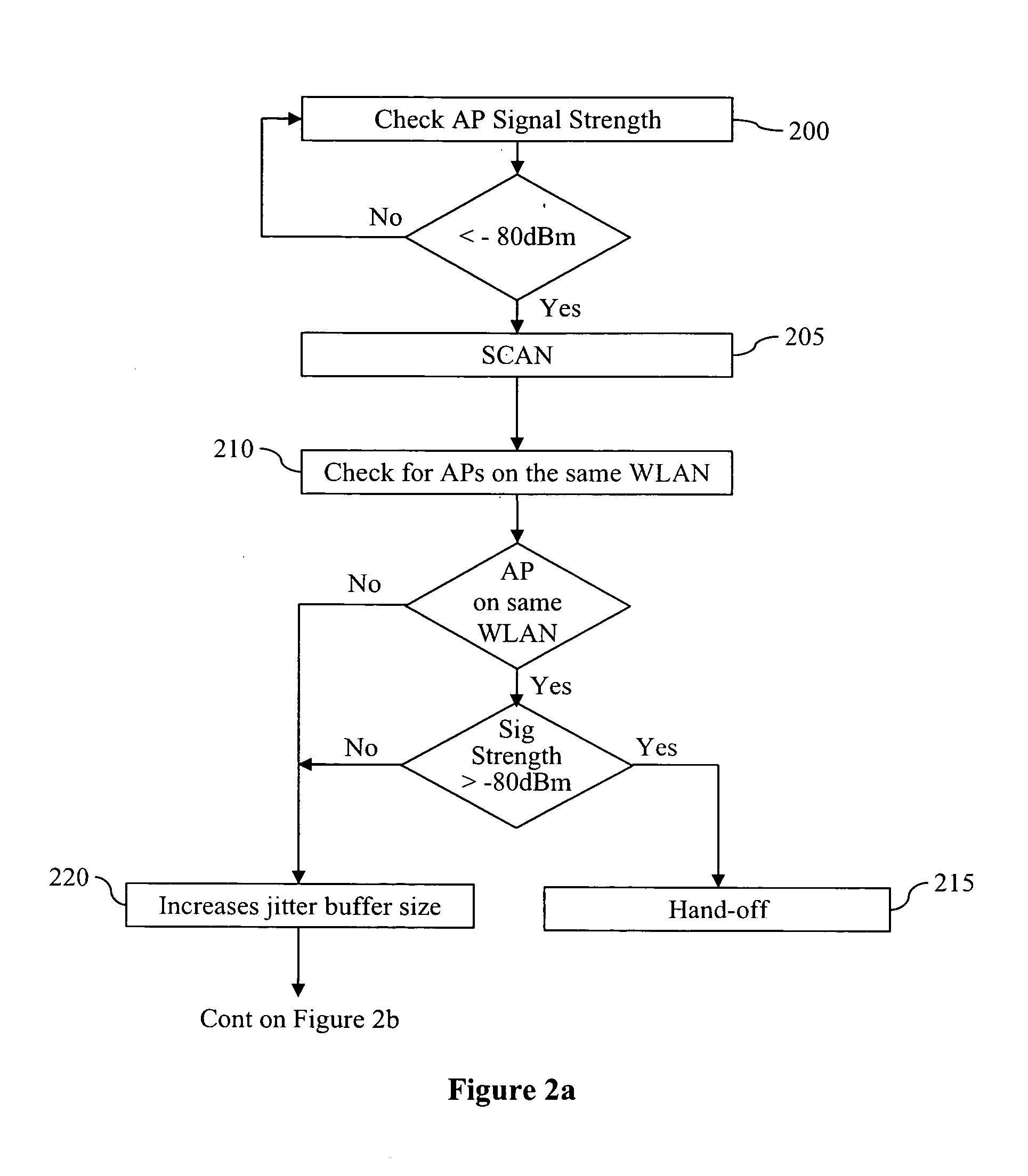
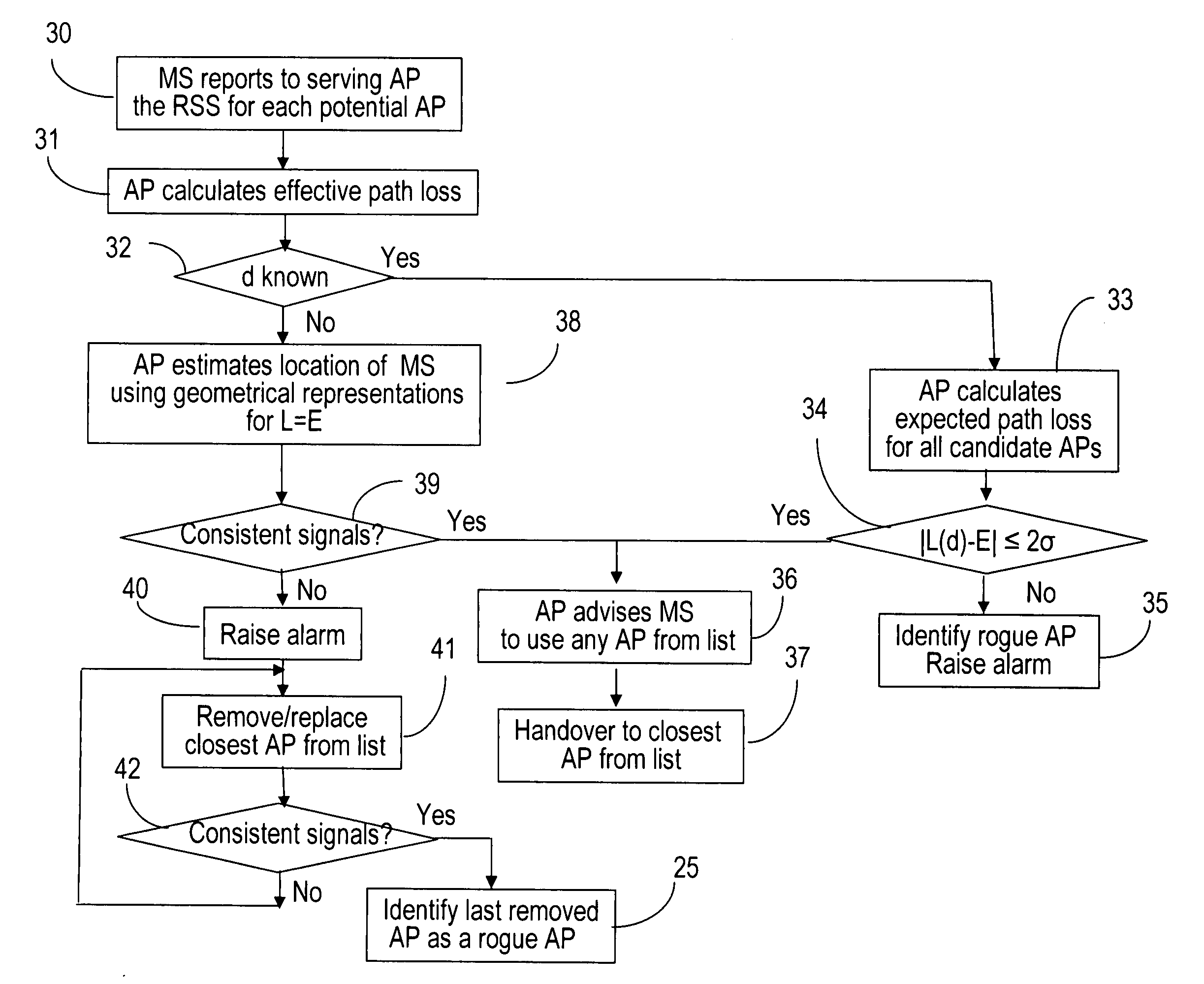
Methods to detect rogue access points (APs) and prevent unauthorized wireless access to services provided by a communication network are provided. A mobile station (MS) reports to a serving AP the received signal strength (RSS) for all APs in the area it travels. The serving AP detect a rogue AP based on inconsistencies perceived in the RSS reports, assessed during the handover phase or whilst the communication is active.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
System and Method For Mapping Wireless Access Points
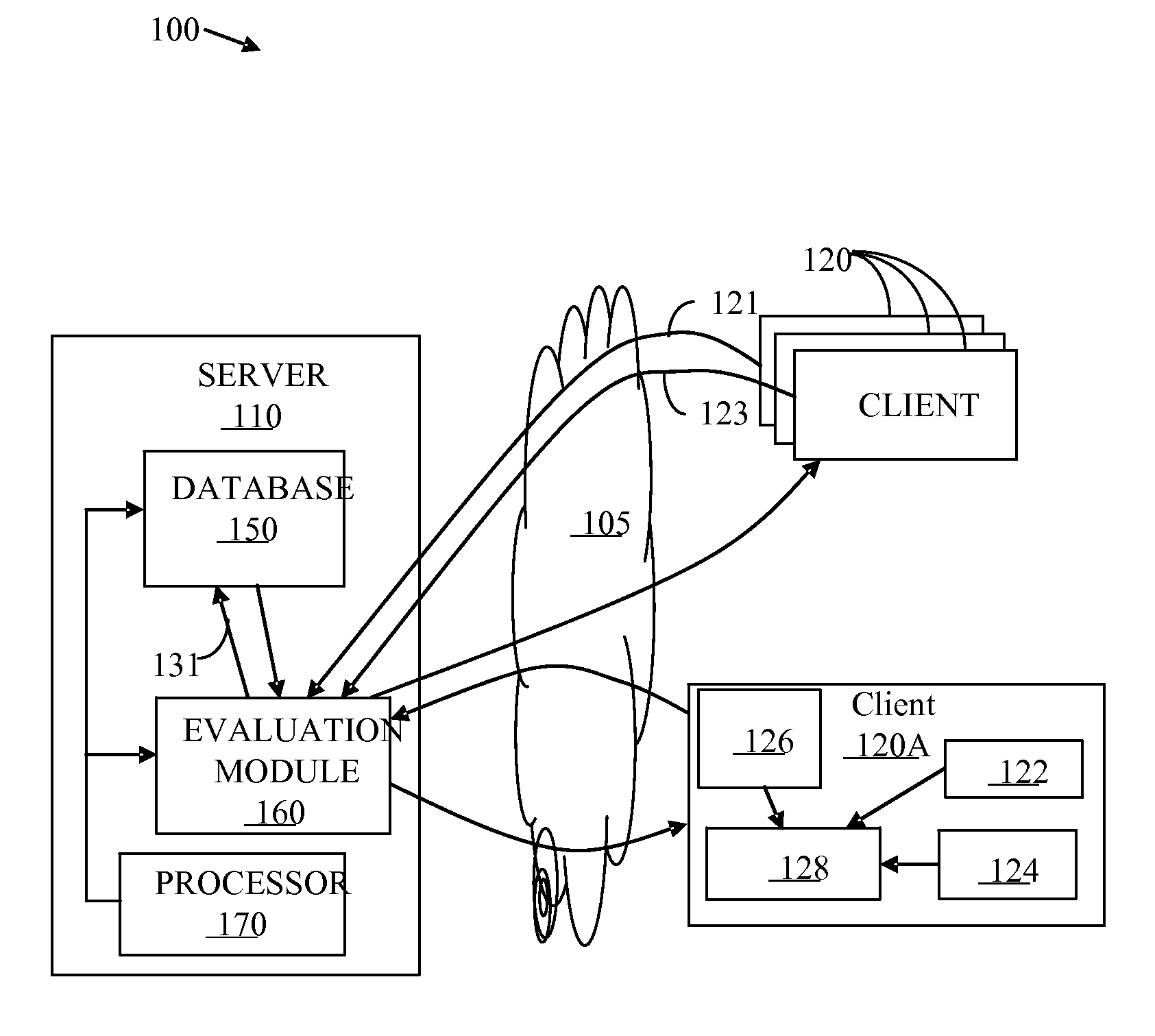
ActiveUS20090042557A1Effective serviceMinimal interventionAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesLocation detectionRadio access point
An improved connectivity to radio access point is enabled by a server that includes a database storing data about various radio access points, and an evaluation module evaluating the quality of connection to each of the access points. Clients receive updates about relevant access points from the server and use the information to connect to the preferred access point. The clients also check connectivity to other access points in the vicinity, and report the findings to the server. The server uses the reports to update its database, and send corresponding updates to the clients. The database can include information about the location of the access points. The information about the location of the access points can be manually input or determined using GPS information. The location of an access points can be determined as a function of available information about other access points detected at the same location. An access point can be presumed to be located in approximately the same location as another access point detected in the same location by the same user terminal. Where more than one access point having a known location is detected in the same location as an unmapped access point (having an unknown location), the location of the unmapped access point can be determined as function of a weighted average of the known locations of the other access points and signal strength of the signal received from each access point.
Owner:WEFI
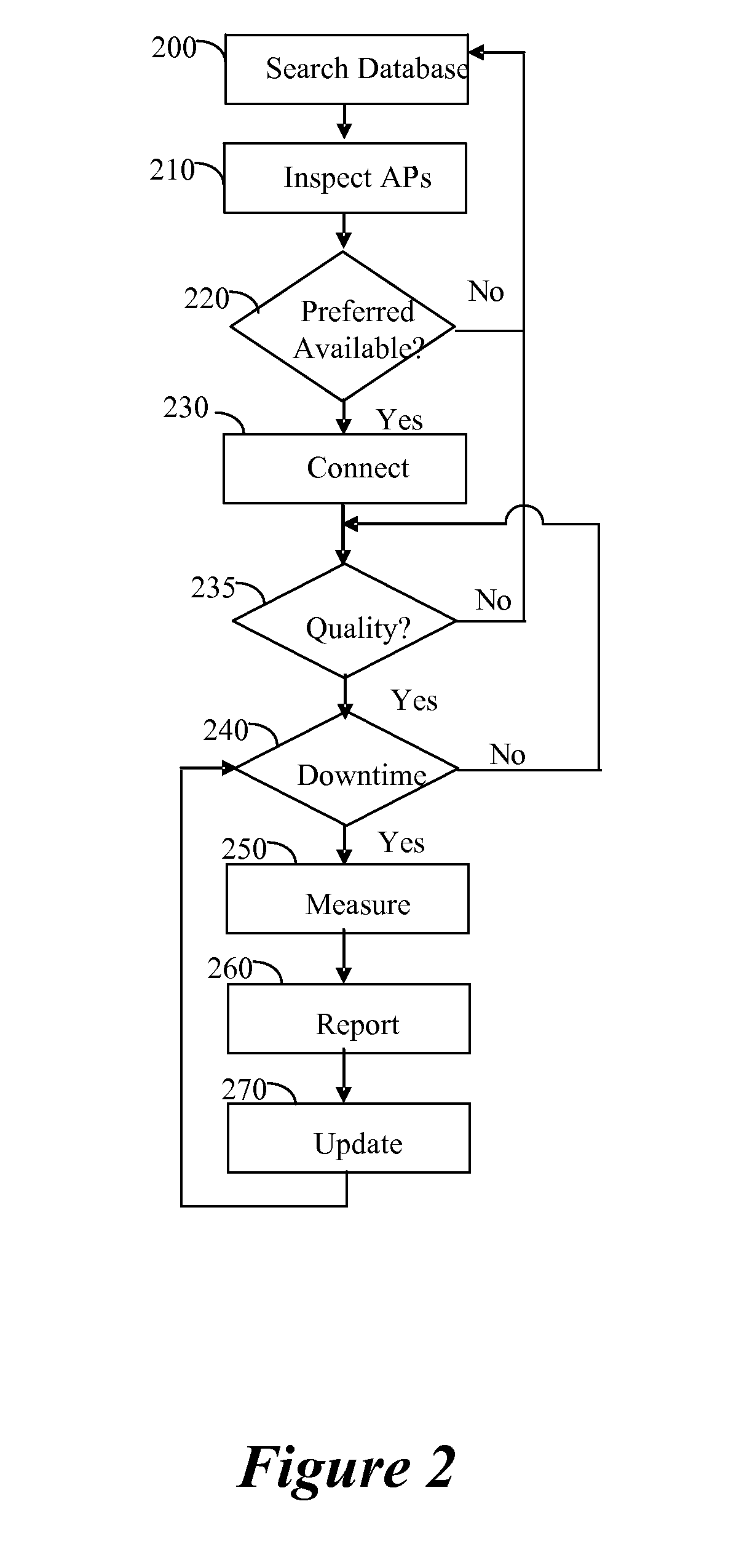
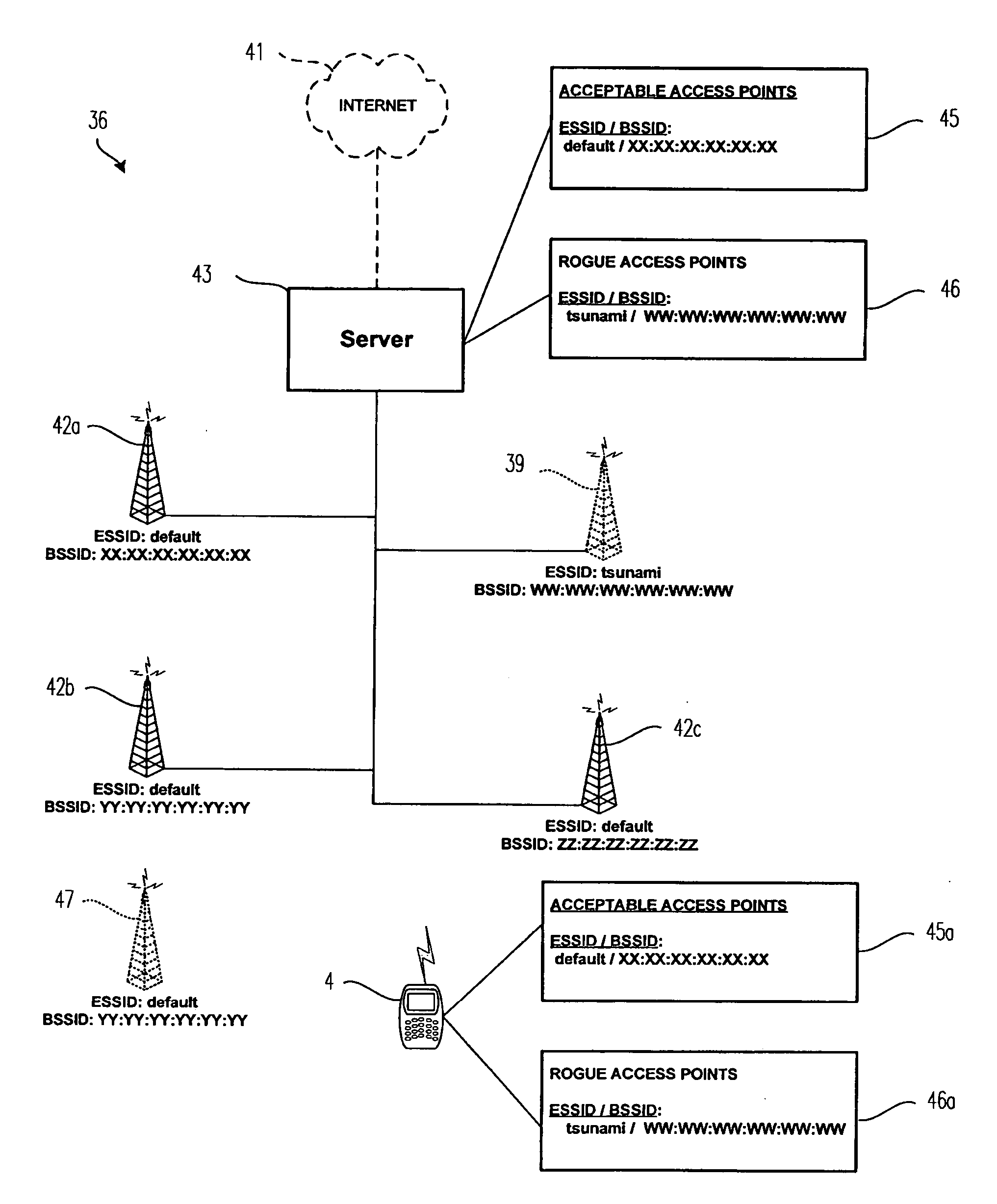
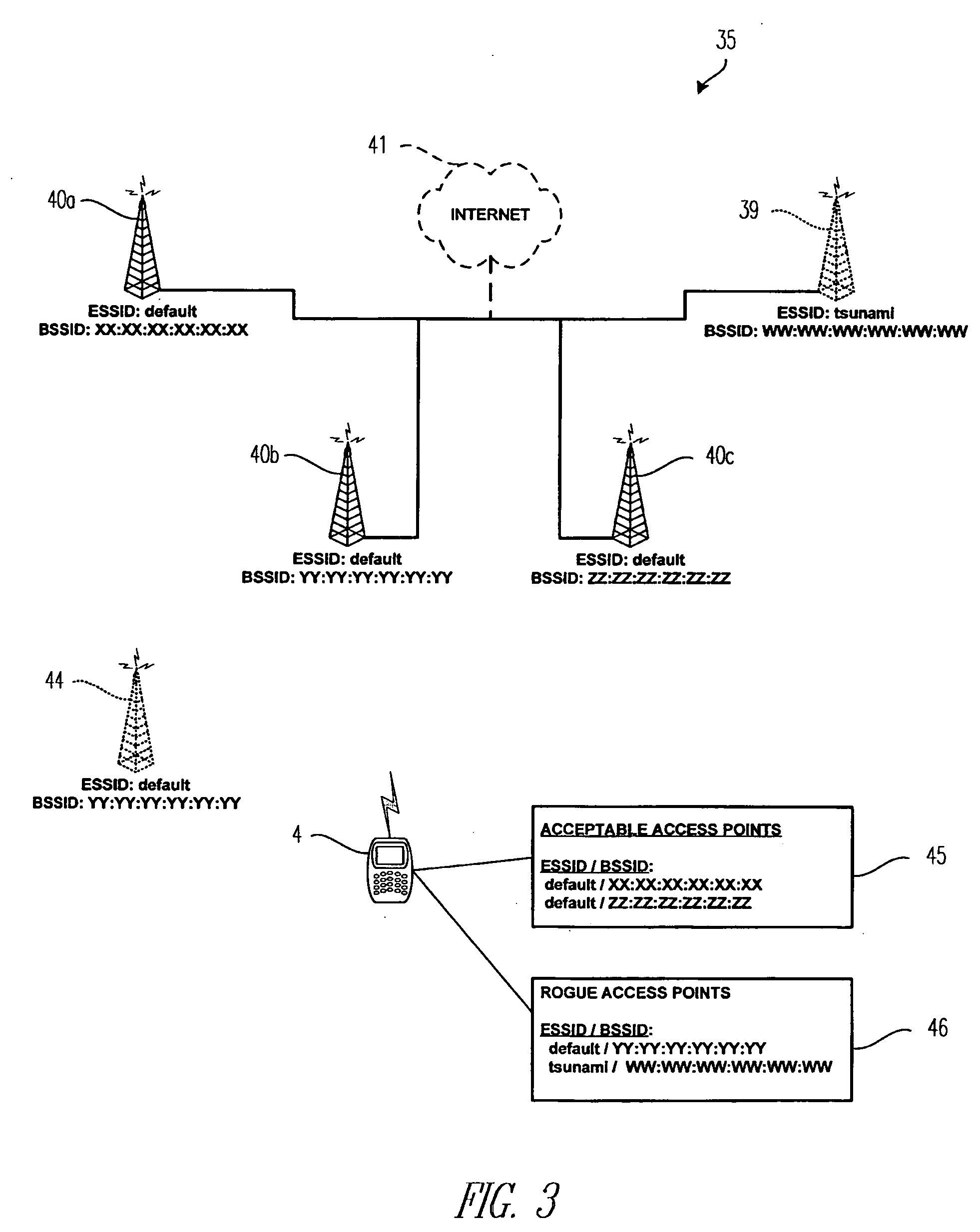
Rogue access point detection and restriction
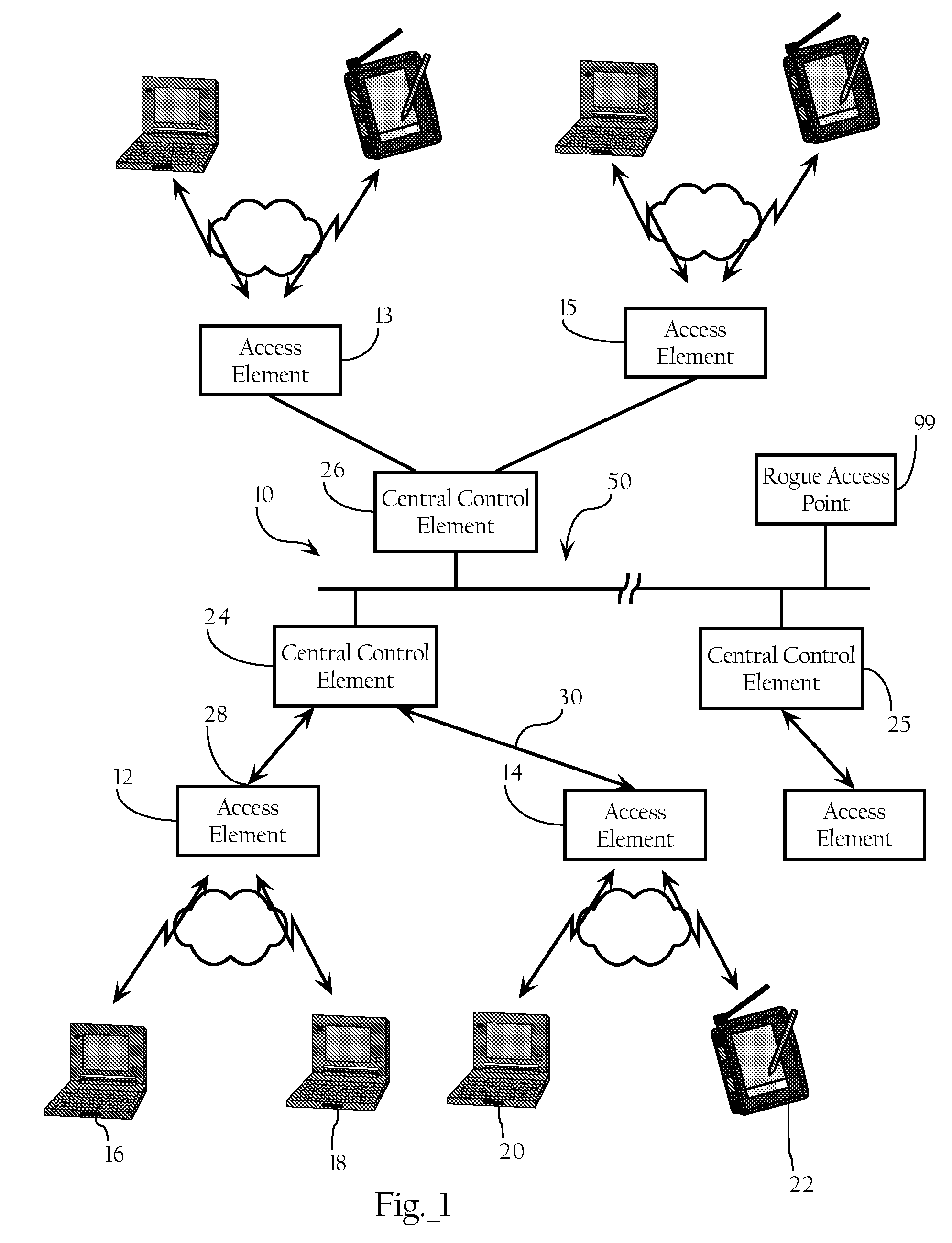
A method for securing a network having a number of access points which comprises detecting a rogue access point and responsive to the detecting, hindering a client from accessing the network via the rogue access point. The network comprises a number of access points and a first device having stored thereon a list of access points determined to be acceptable access points. The network is structured to enable communication between the first device and a second device through at least one of the number of access points. Furthermore, the network is structured to hinder the second device from accessing the first device via an access point other than an acceptable access point.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
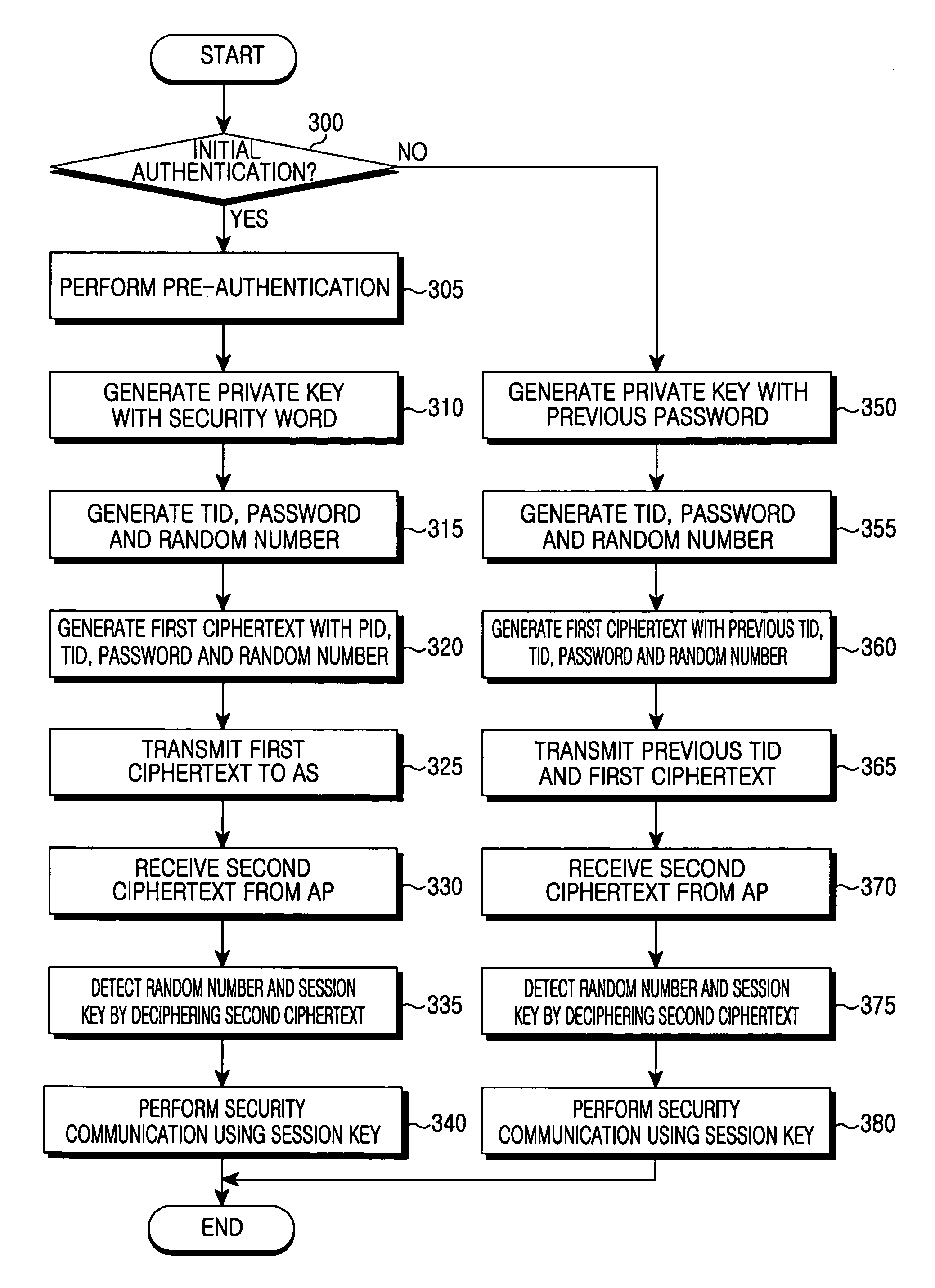
Authentication method for fast handover in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS7158777B2Communication securityIncrease speedUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionData taking preventionSecure communicationFast handover
Disclosed is a method for authenticating a mobile node in a wireless local area network including at least two access points and an authentication server. When the mobile node associates with a first access point and performs initial authentication, the mobile node receives a first session key for secure communication from the authentication server by using a first private key generated with a secret previously shared with the authentication server, and the first access point receives the first session key from the authentication server by using a second private key previously shared with the authentication server. When the mobile node is handed over from the first access point to a second access point and performs re-authentication, the mobile node receives a second session key for secure communication from the authentication server by using a third private key generated with authentication information generated during previous authentication and shared with the authentication server and the second access point receives the second session key from the authentication server by using the second private key previously shared with the authentication server.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Local IP access scheme
Local IP access is provided in a wireless network to facilitate access to one or more local services. In some implementations, different IP interfaces are used for accessing different services (e.g., local services and operator network services). A list that maps packet destinations to IP interfaces may be employed to determine which IP interface is to be used for sending a given packet. In some implementations an access point provides a proxy function (e.g., a proxy ARP function) for an access terminal. In some implementations an access point provides an agent function (e.g., a DHCP function) for an access terminal. NAT operations may be performed at an access point to enable the access terminal to access local services. In some aspects, an access point may determine whether to send a packet from an access terminal via a protocol tunnel based on the destination of the packet.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
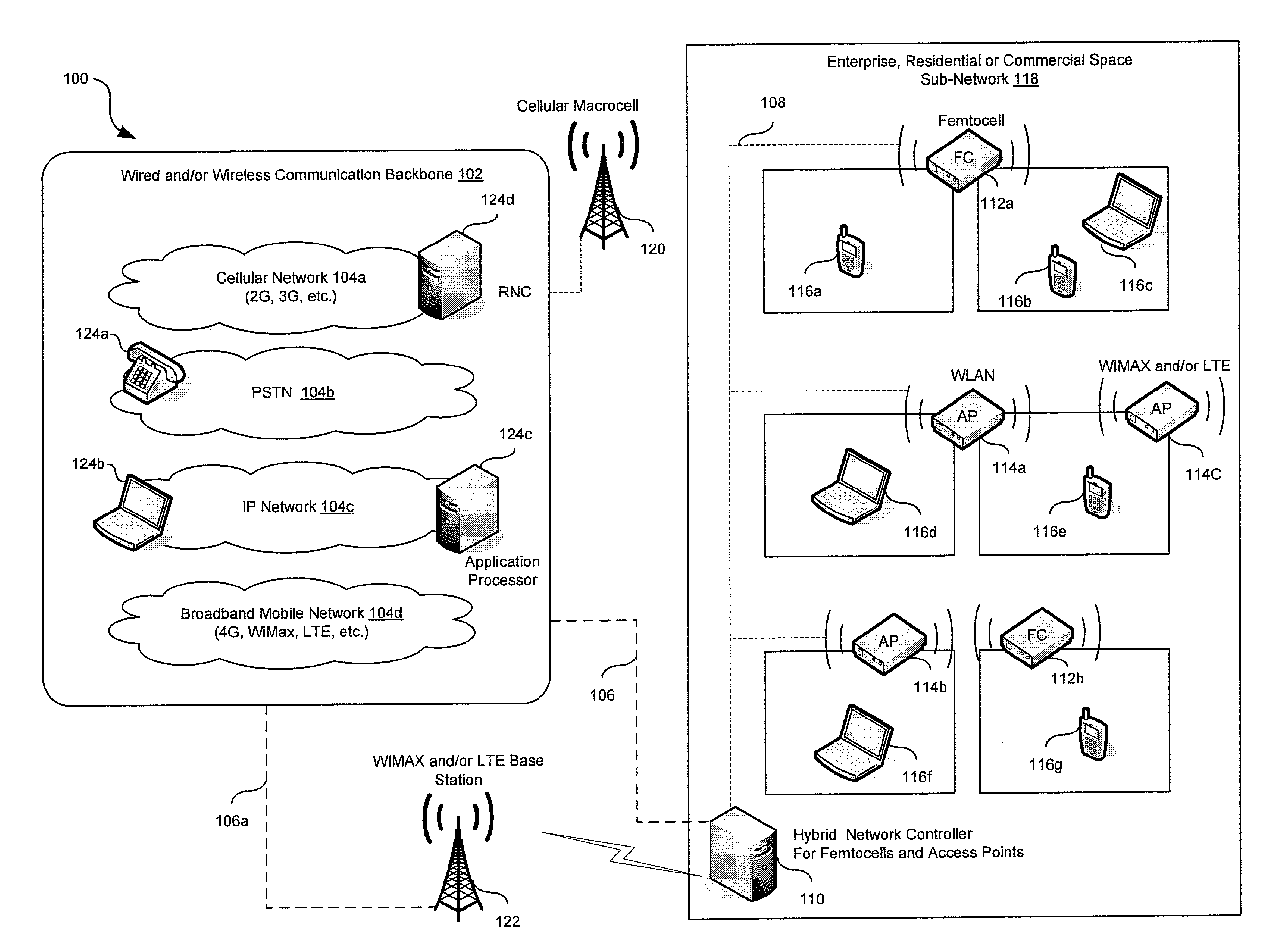
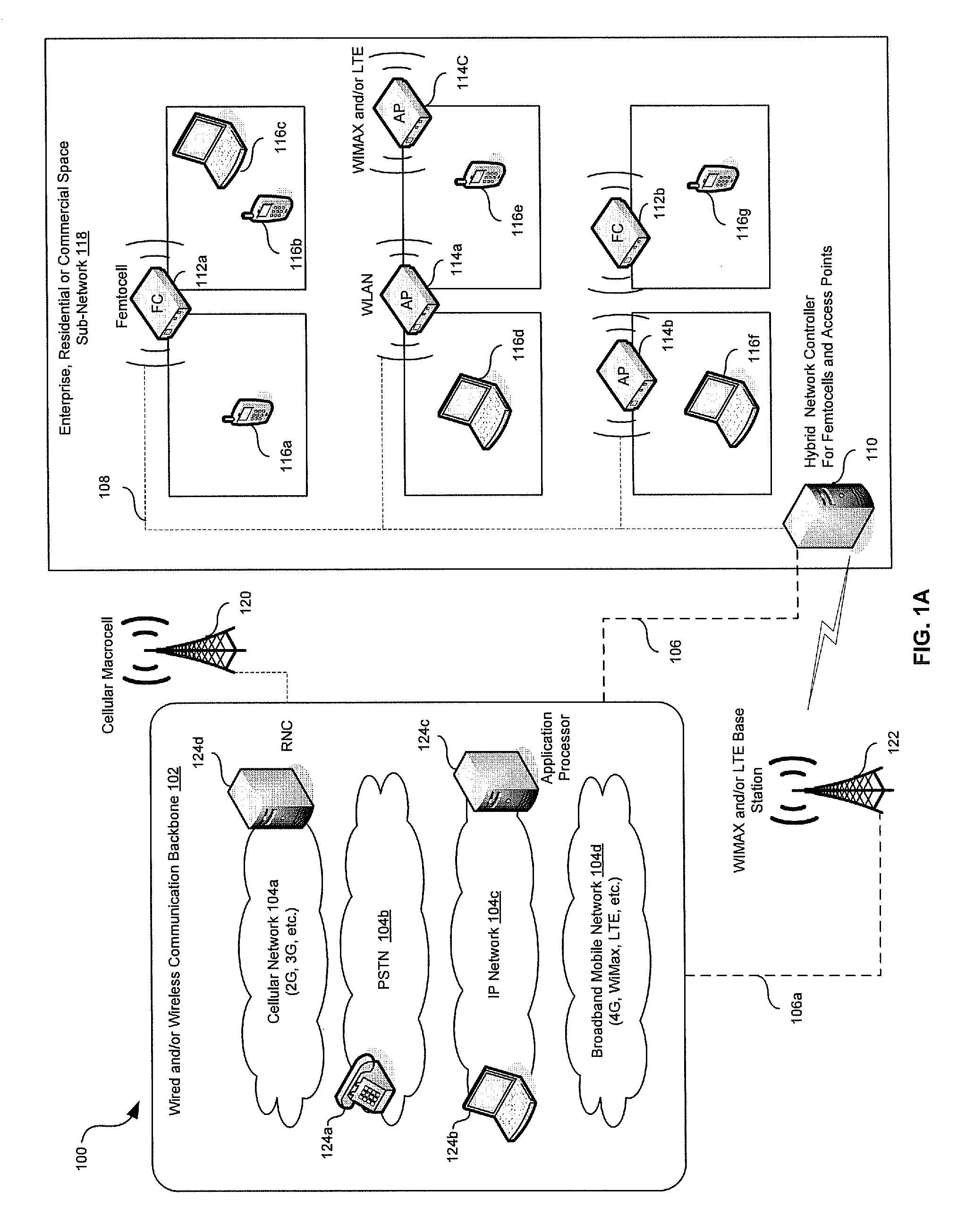
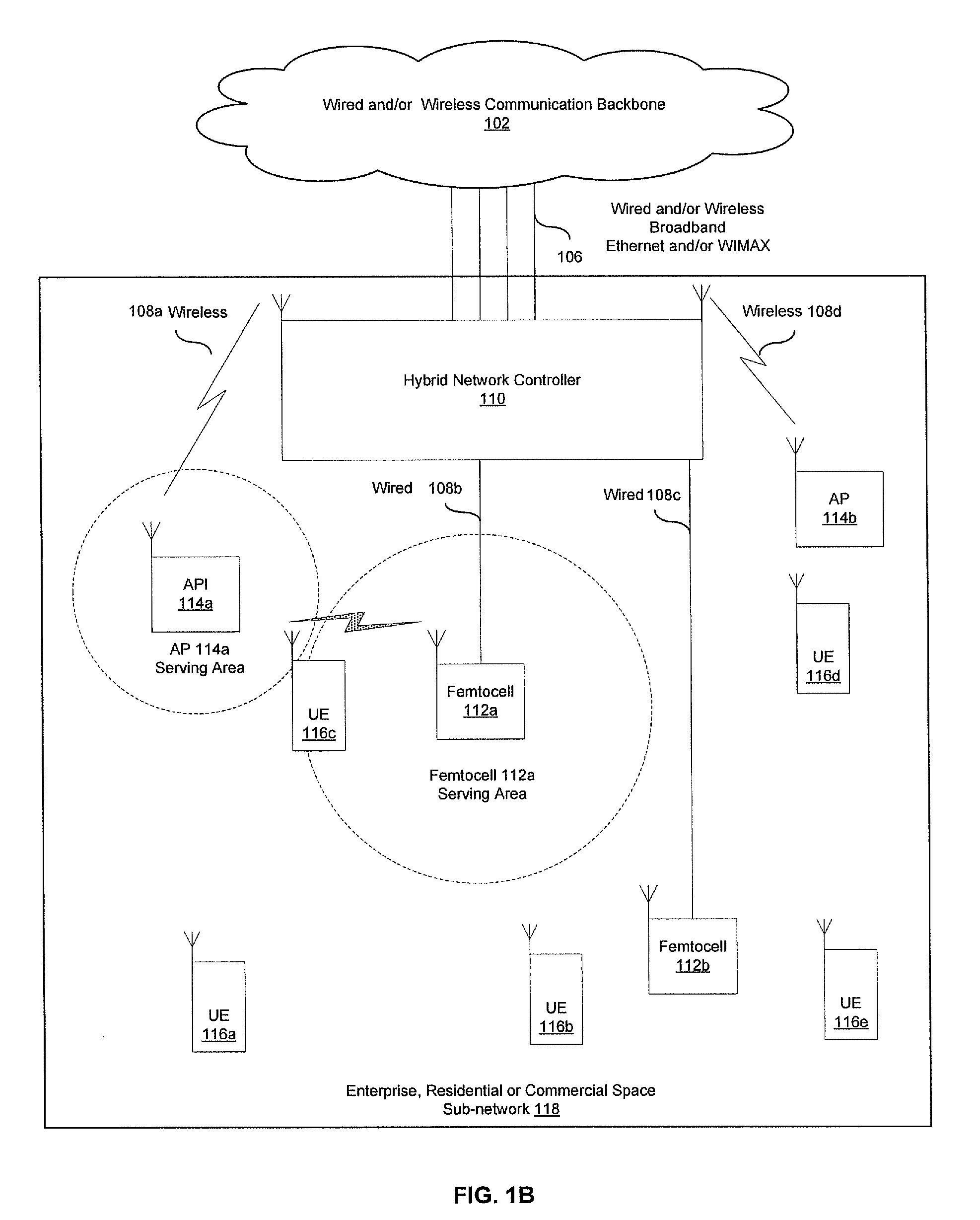
Traffic management in a hybrid femtocell/wlan wireless enterprise network
A hybrid network controller may determine and / or communicate traffic management information for enabling setup and / or handoff of call and / or communication session among femtocells, access points and / or end-point devices. Traffic management information may comprise set-up instructions, handoff instructions, transmit power, neighbor list information, signal quality thresholds, frequency assignments, transmission time, code assignments and / or antenna pattern assignments. The hybrid network controller and / or an end-point device may control handoffs between a communication device external to the communication system and the femtocells, access points and / or end-point devices. Received signal strength, interference levels, SNR, signal path delay, power consumption, traffic loads, bandwidth usage and / or radio resource availability may be monitored and / or analyzed by the hybrid network controller. The hybrid network controller may assign time slots, codes, antenna patterns as well as a serving femtocell and / or AP for a set up and / or a handoff. The information may be communicated via wired, optical and / or wireless interfaces.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
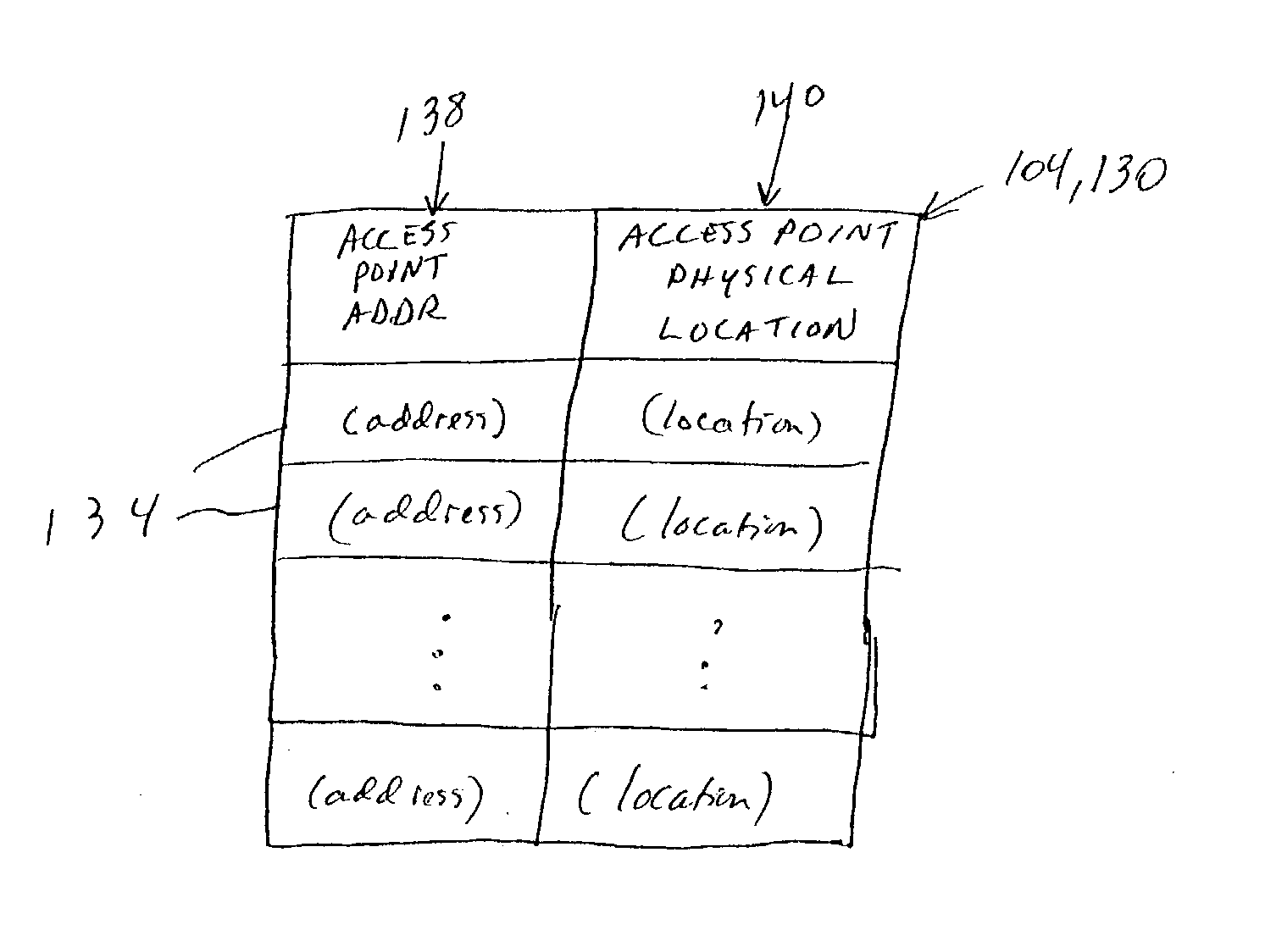
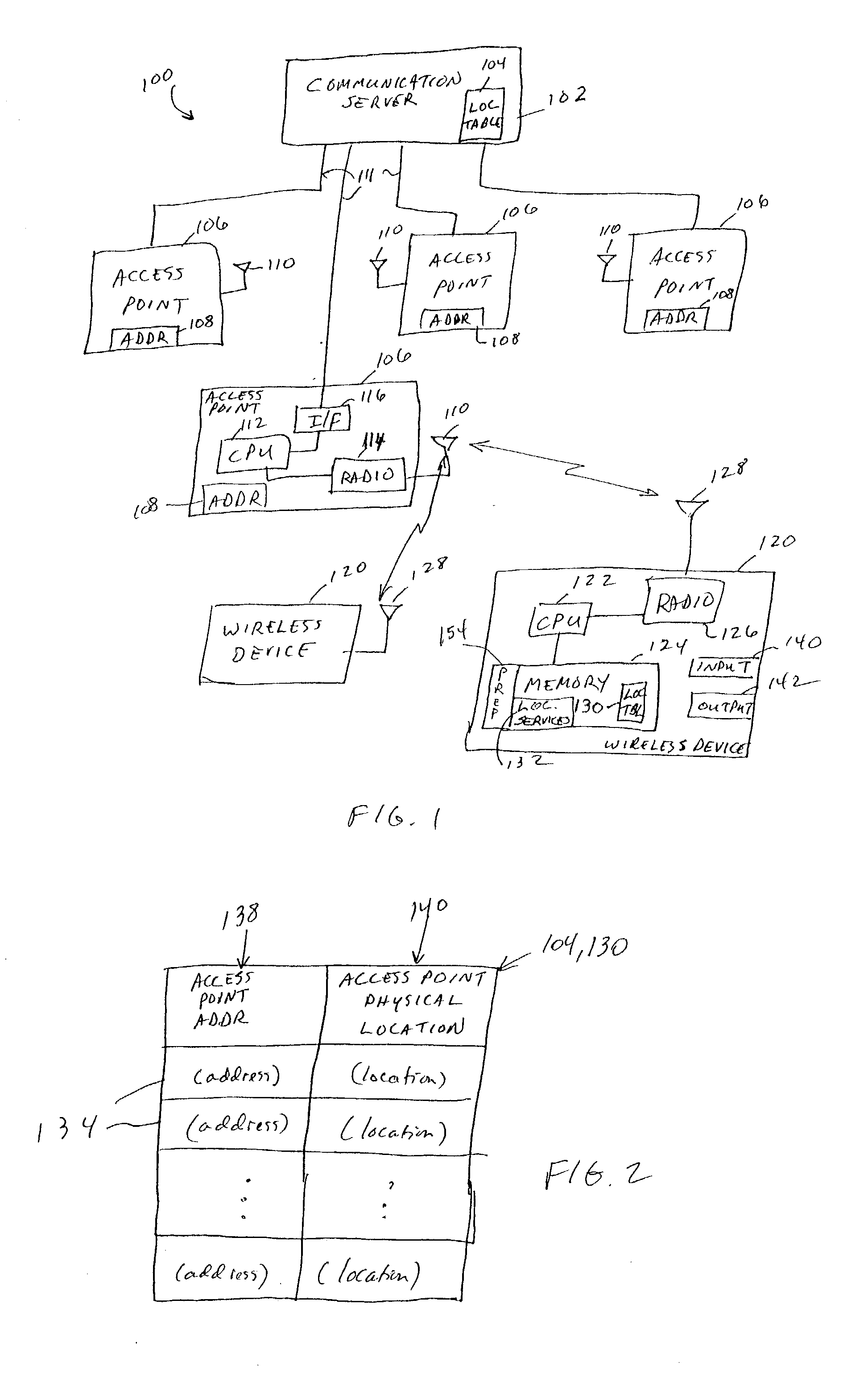
Location determination in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20040002343A1The process is simple and clearImprove privacySubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork addressingRogue access point
A wireless network permits wireless devices to determine their own location and receive location-based services. The network includes a communication server coupled to a plurality of access points and at least one mobile wireless device that wirelessly communicates through the access points. Each wireless device includes a location table through which the wireless device can determine its physical location. The location table includes the physical location of the various access points indexed by their network addresses. When the wireless device communicates with an access point, the access point provides the wireless device its address. The wireless device uses the address of the access point as an index into the location table to determine its own location based on the location of the access point. Once the wireless device has determined its own physical location, it requests location-based services from or through the communication server.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Roaming Network Stations Using A Mac Address Identifier To Select New Access Point
There is disclosed a method of helping mobile stations such as voice over IP devices to roam between wireless access points, by each access point transmitting the MAC address of a spanning tree algorithm root switch of the local network domain. This MAC address is used by mobile stations to detect if two access points are in a common network domain.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
Network infrastructure validation of network management frames
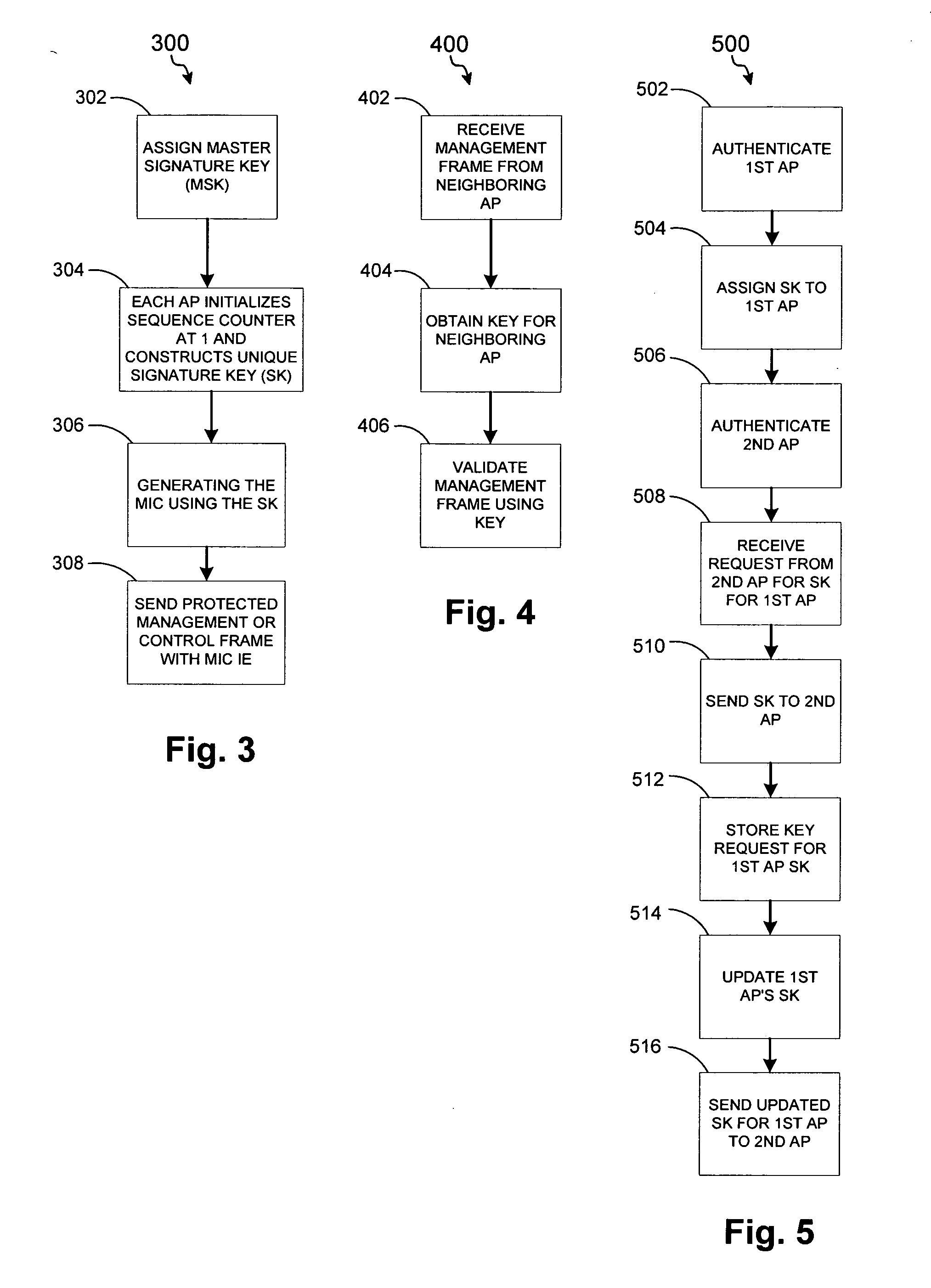
ActiveUS20050141498A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationNetwork managementMessage integrity
A detection-based defense to a wireless network. Elements of the infrastructure, e.g., access points or scanning-only access points, detect intruders by detecting spoofed frames, such as from rogue access points. Access points include a signature, such as a message integrity check, with their management frames in a manner that enables neighboring access points to be able to validate the management frames, and to detect spoofed frames. When a neighboring access point receives a management frame, obtains a key for the access point sending the frame, and validates the management frame using the key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Discovery of Rogue Access Point Location in Wireless Network Environments
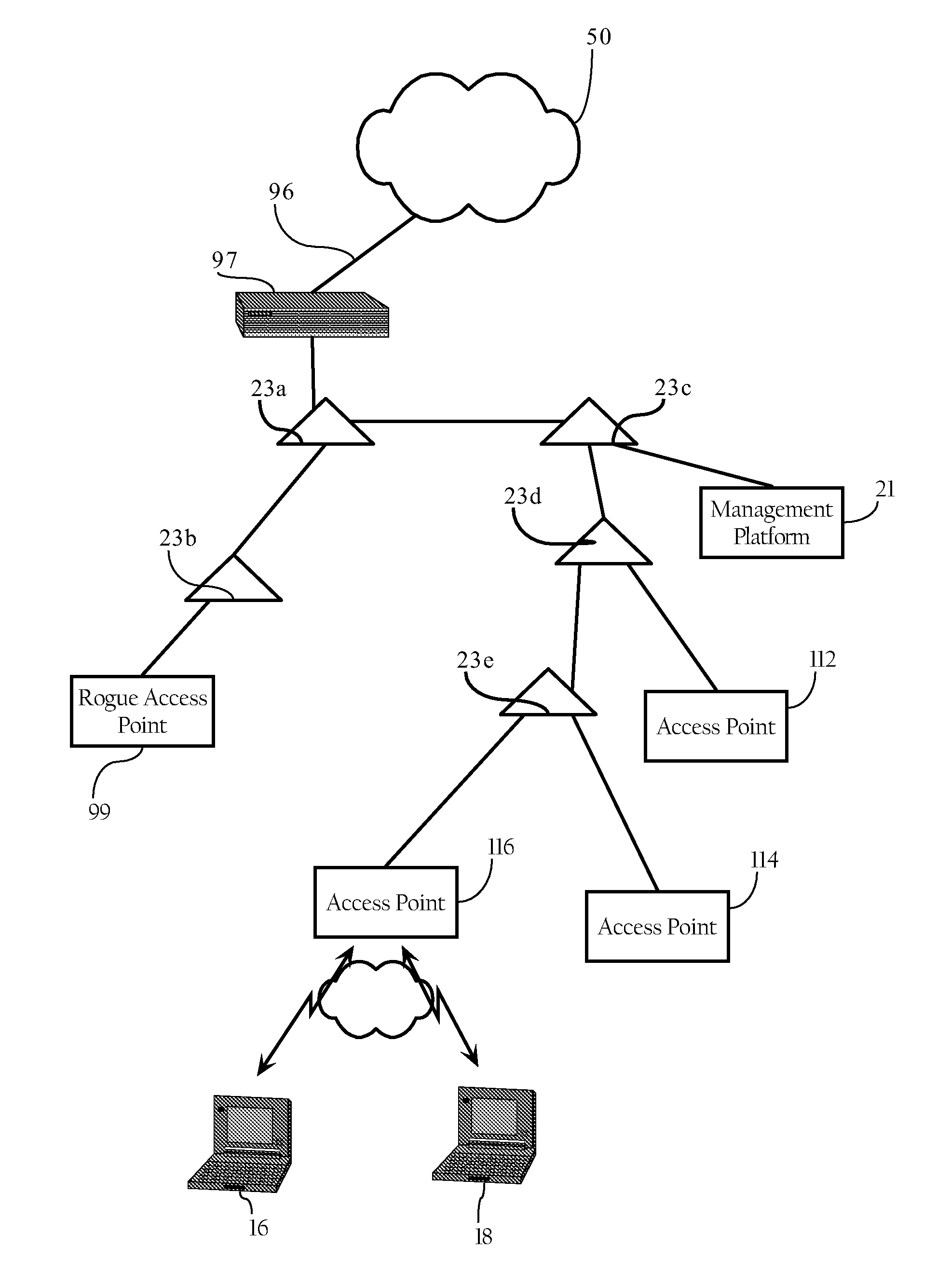
ActiveUS20080101283A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkNetworked system
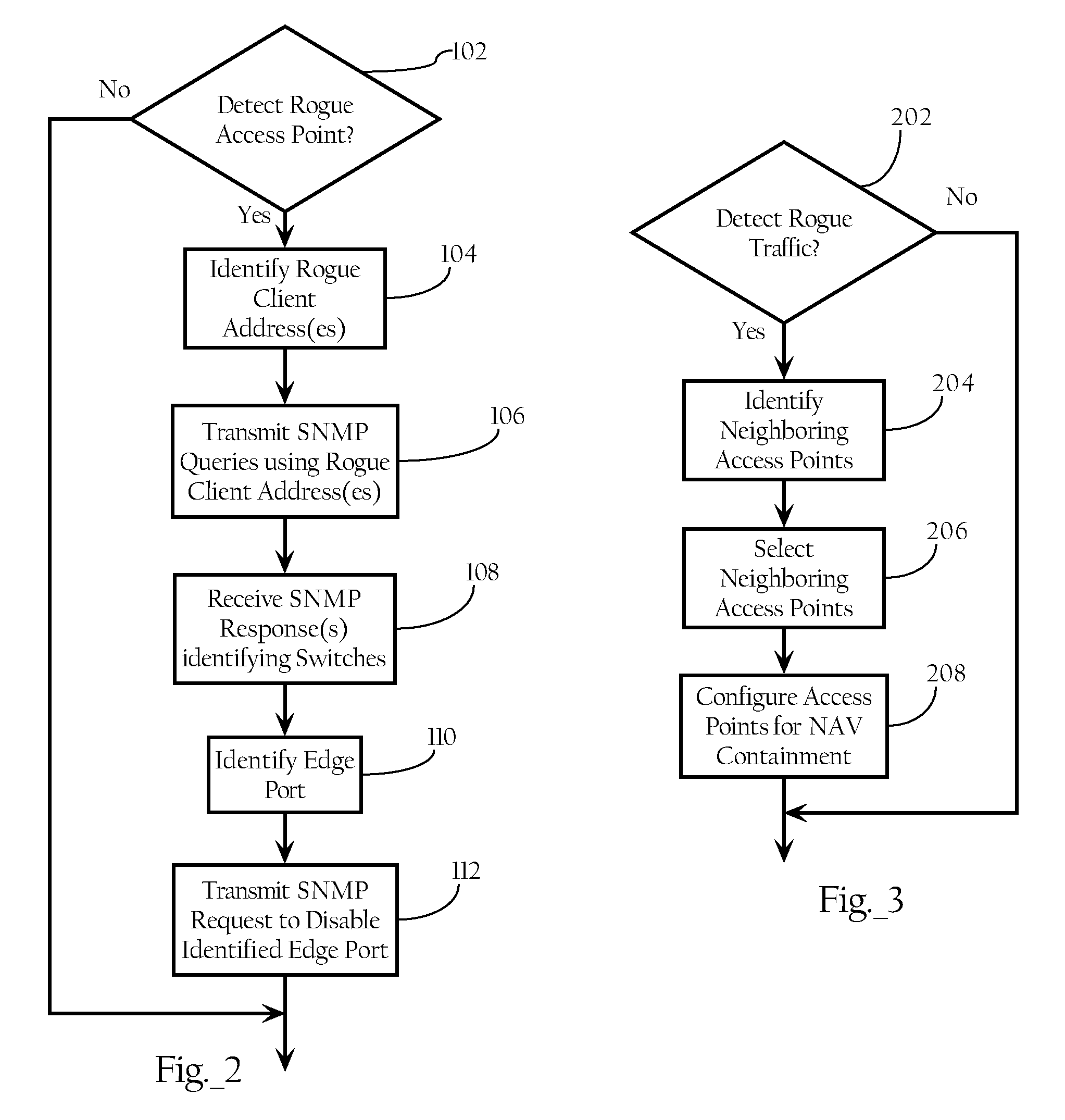
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating location or containment of rogue or unauthorized access points on wireless computer network environments. Embodiments of the present invention support one to a plurality of rogue containment methodologies. A first rogue containment type involves identification of the physical connection of the rogue access point to the wired network infrastructure and, thus, allows for disabling of that physical connection to contain the rogue access point. Other rogue containment methods involve wireless techniques for containing the effect of rogue access points. In some embodiments, the present invention provides methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating network location of rogue access points to determine whether one or more rogue containment methodologies should be applied. As discussed below, the rogue location and containment functionality described herein can be applied to a wide variety of wireless network system architectures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
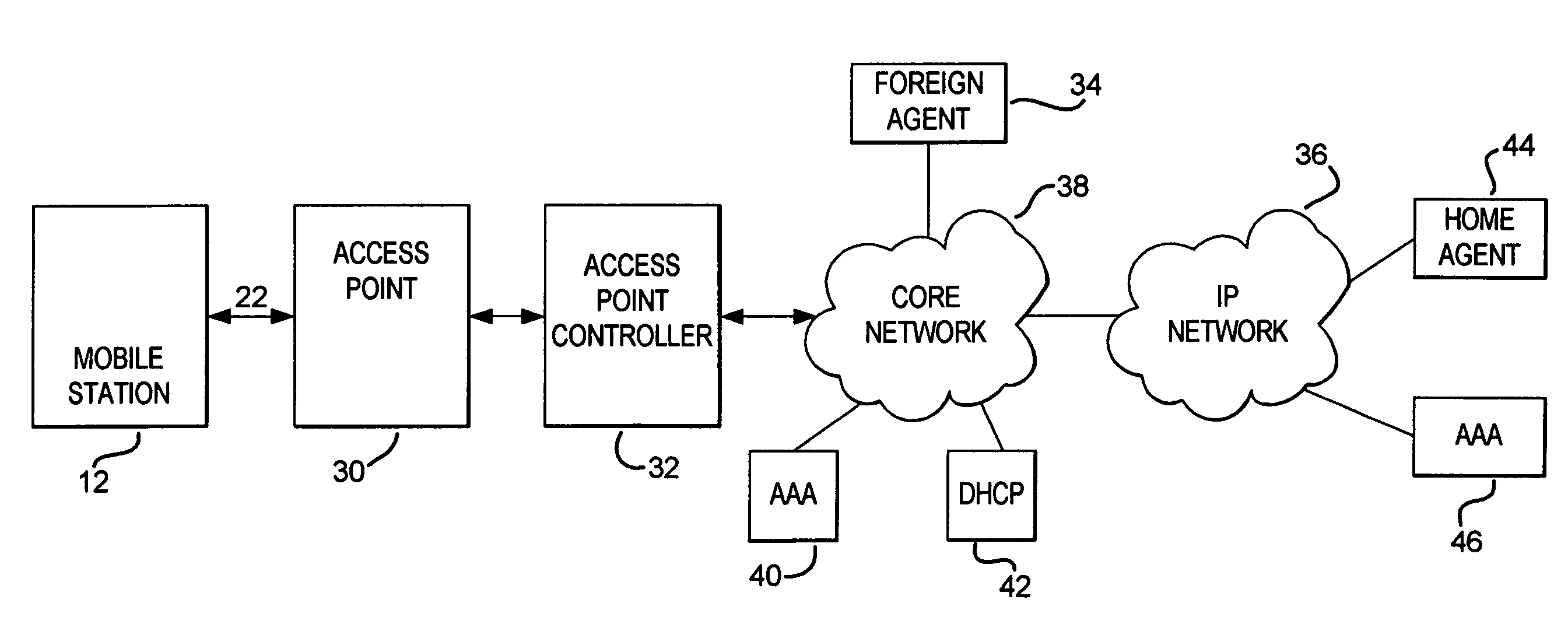
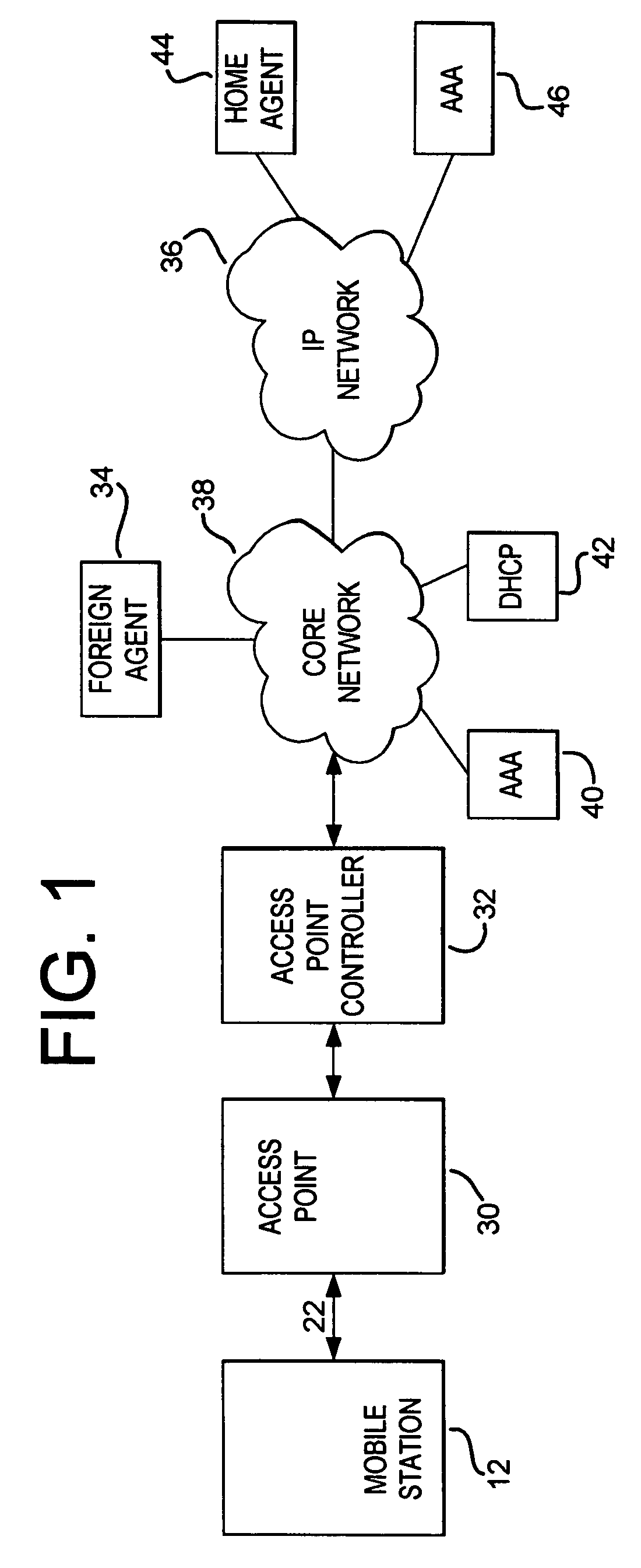
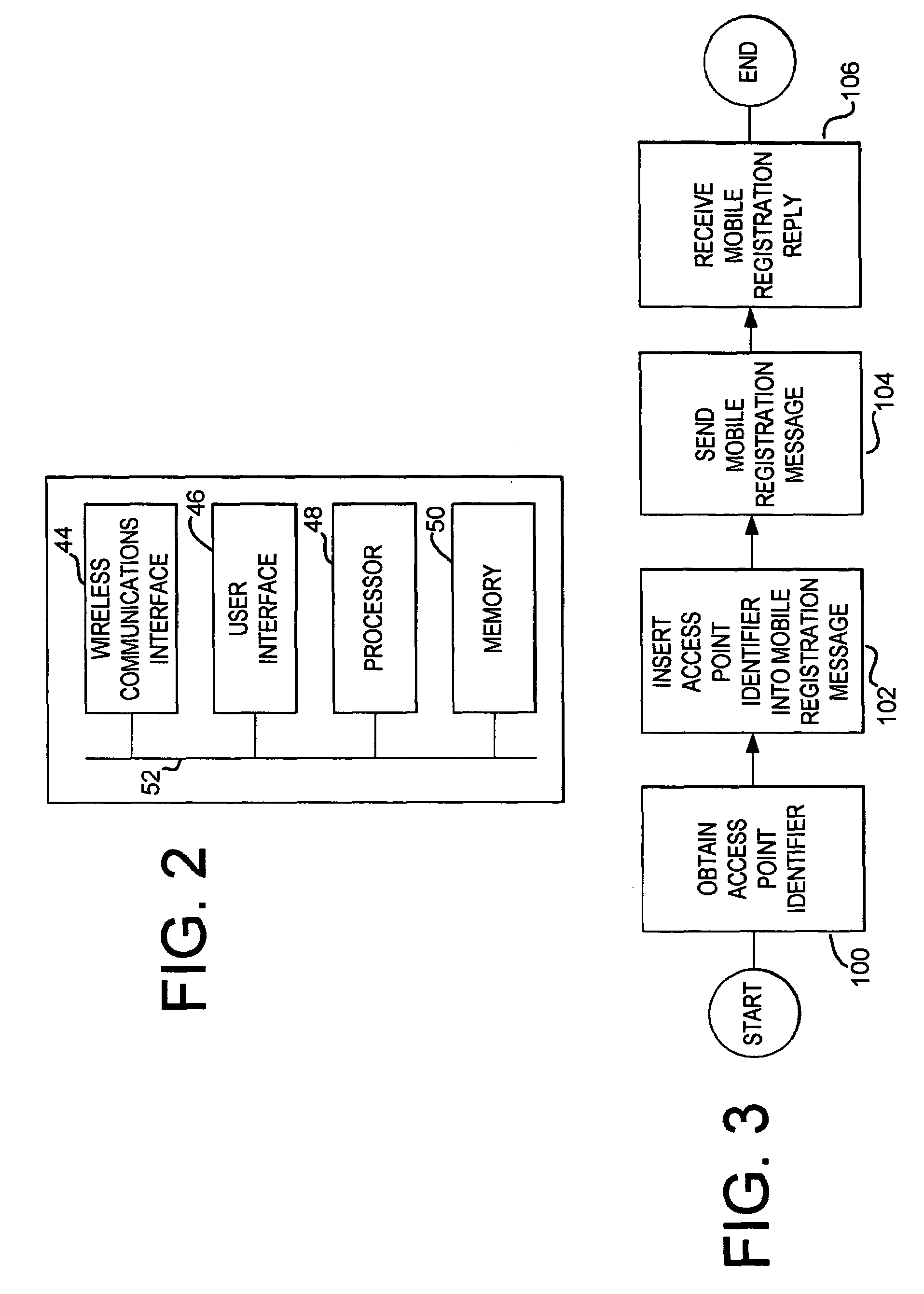
Method and system for identifying an access point into a wireless network
A method and system for a mobile station to identify to a wireless network agent, an access point into a wireless network. The mobile station obtains an indication of an access point into the wireless network and inserts the indication into a mobile registration message. The access point identifier identifies an access point into the wireless network. Then, the mobile station sends the mobile registration message to the wireless network agent via the access point identified by the access point identifier. The wireless network agent receives the mobile registration message and provides the access point identifier to an authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server. The AAA server uses the access point identifier to provide location-based services to the mobile station.
Owner:III HLDG 1
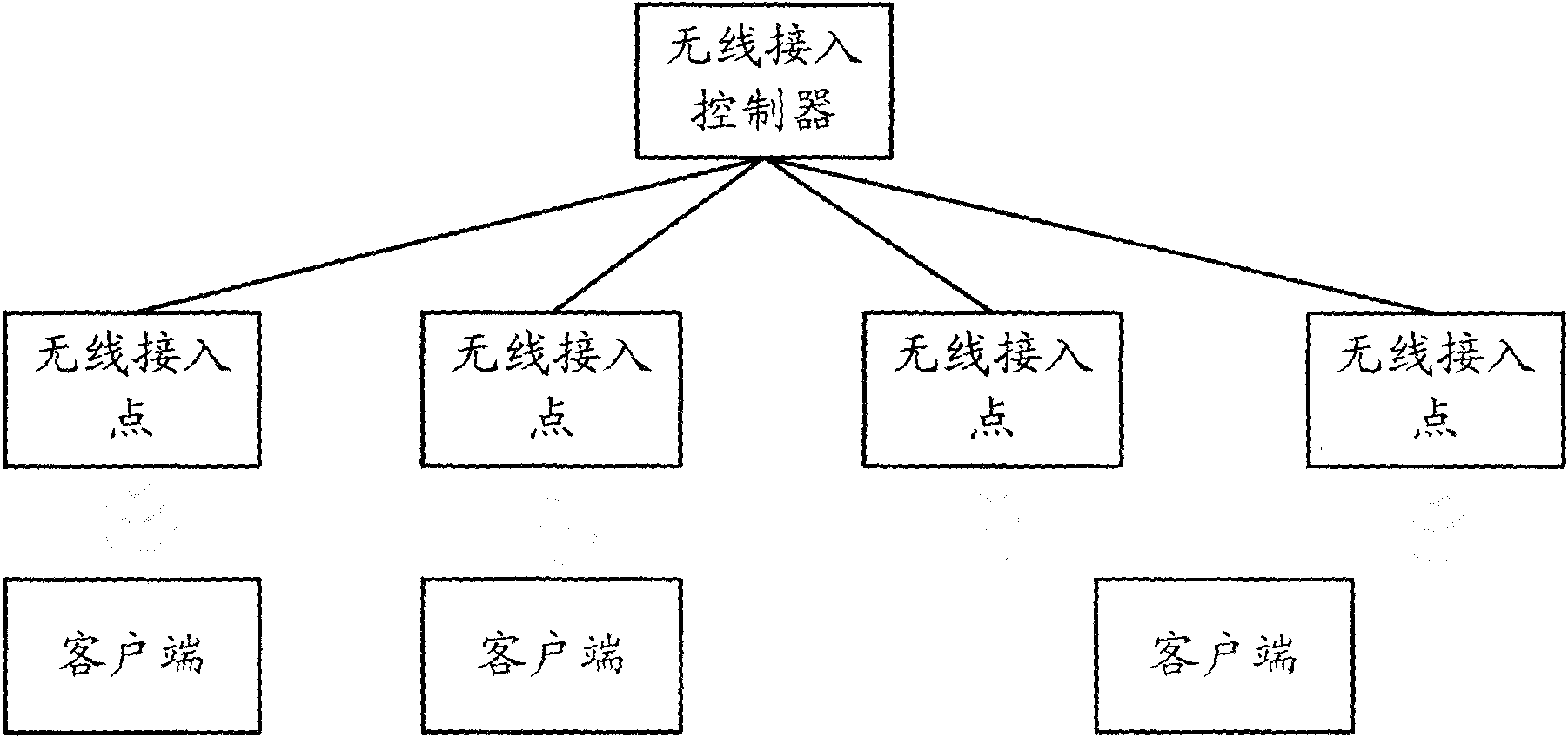
Method and equipment for selecting access points (APs)
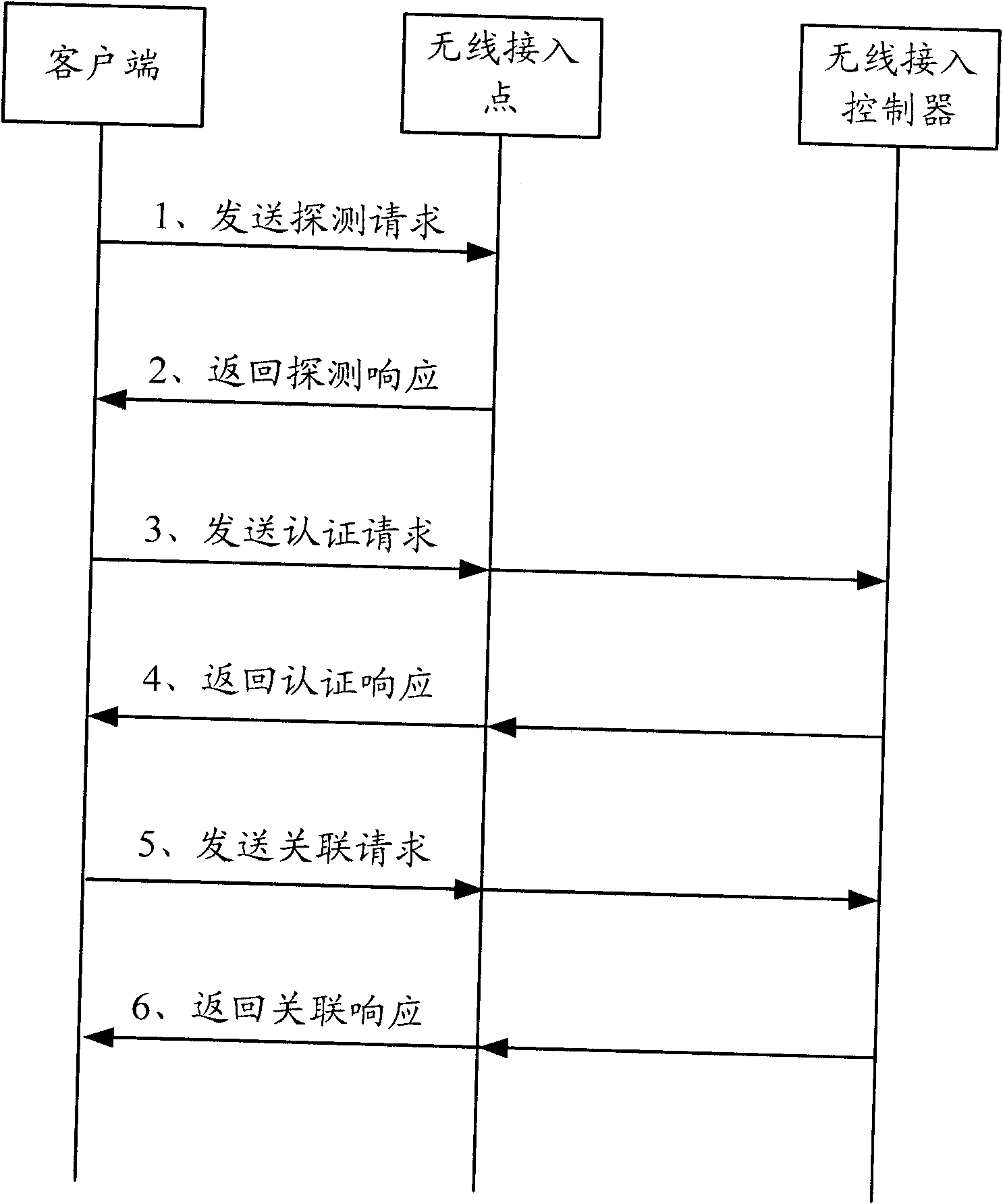
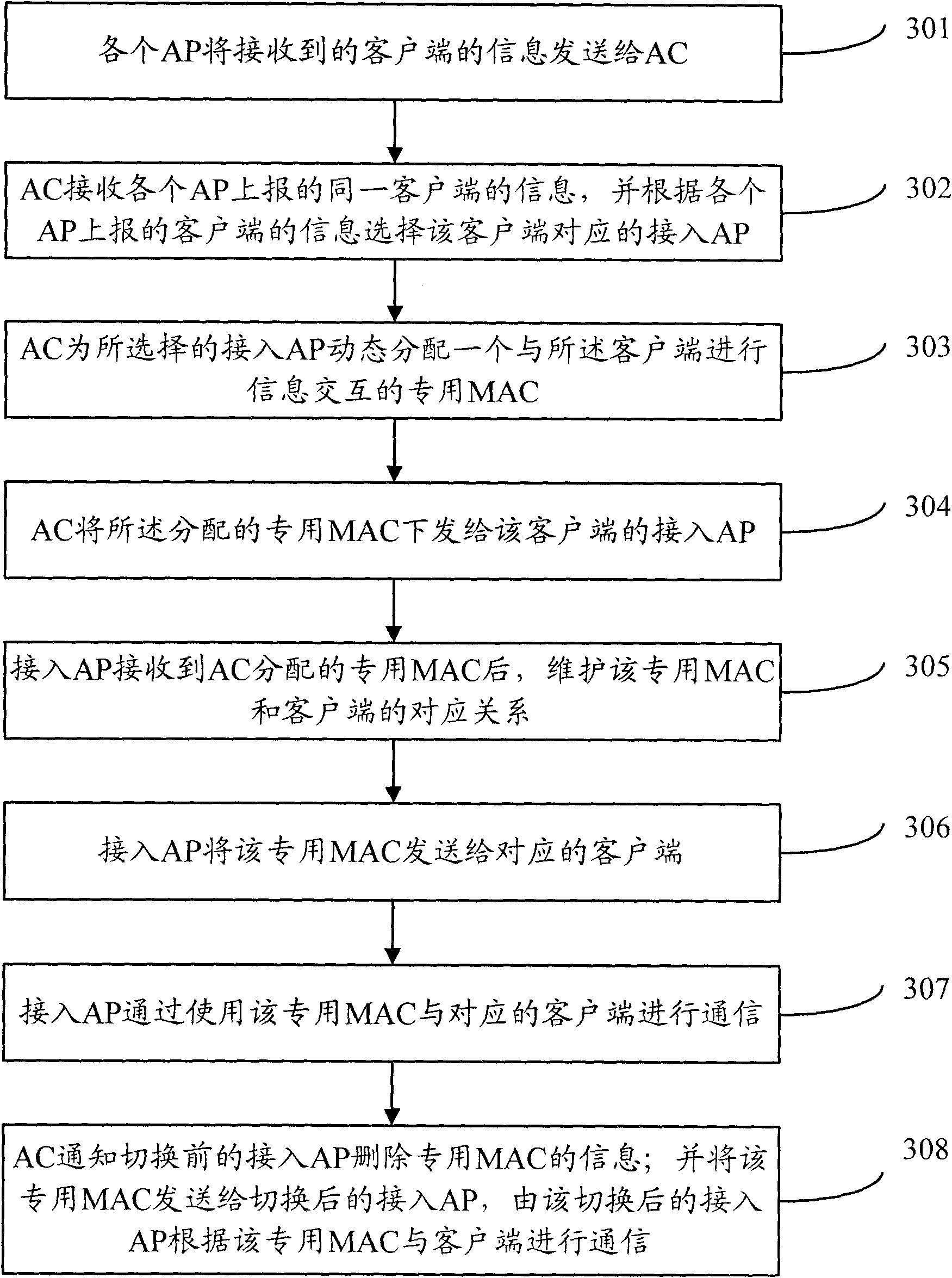
InactiveCN101801051AReduce workloadRoam quicklyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesRogue access pointMedia access control
The invention discloses a method for selecting access points (APs), comprising the following steps: an access controller (AC) is made to receive the information on the same client side, which is reported by all access points (APs), and the AC is made to select the APs of the client side according to the information on the client side, which is reported by all the APs; the AC is made to dynamically allot the special media access control (MAC) which is used to communicate with the client side to the selected APs, send the special MAC to the APs and communicate with the client side by the APs according to the special MAC. In the invention, the selection of the APs by the user can be controlled by the client side, and the work load of the client side can be reduced.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Methods, device and system for access point facilitated fast handoff
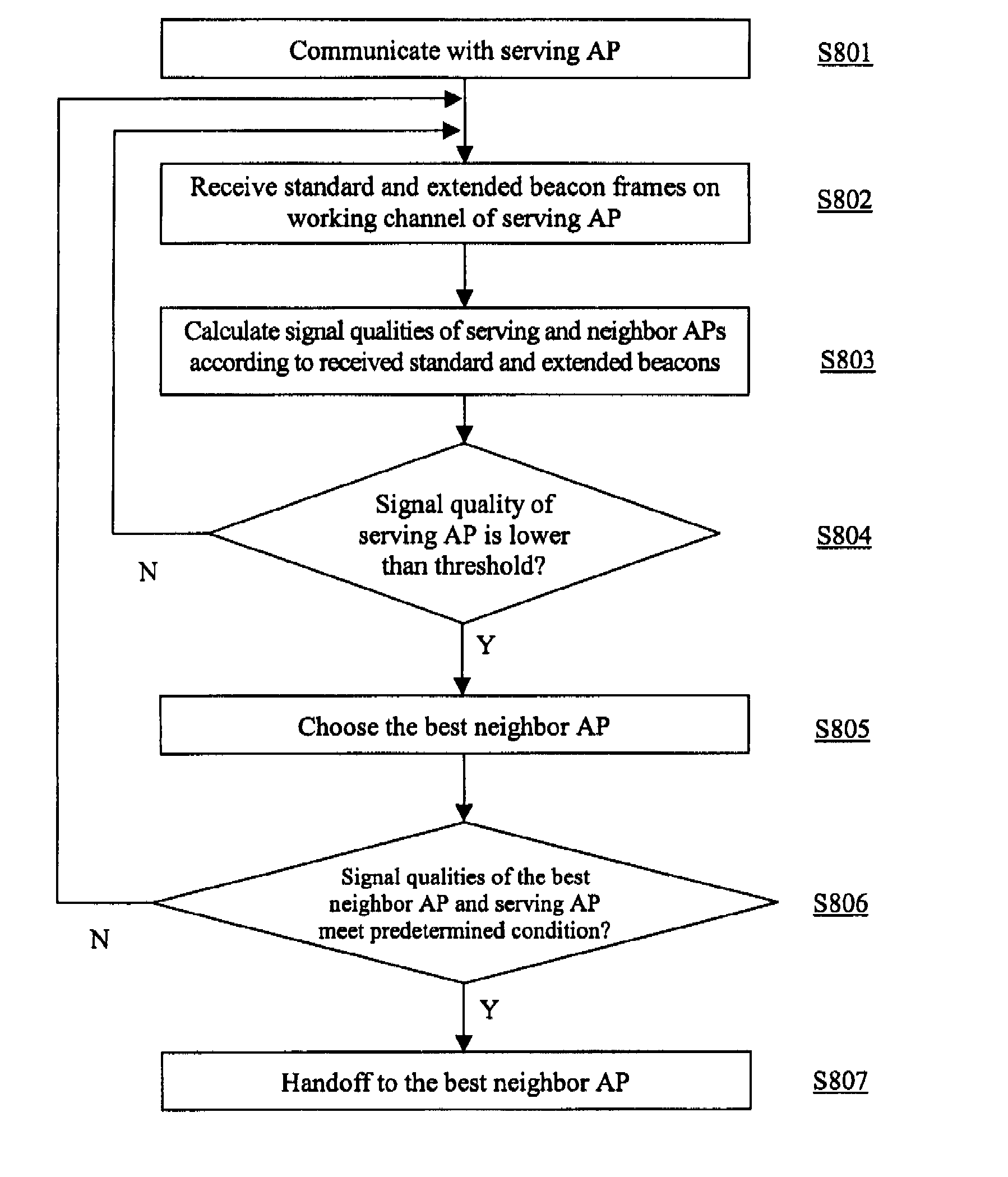
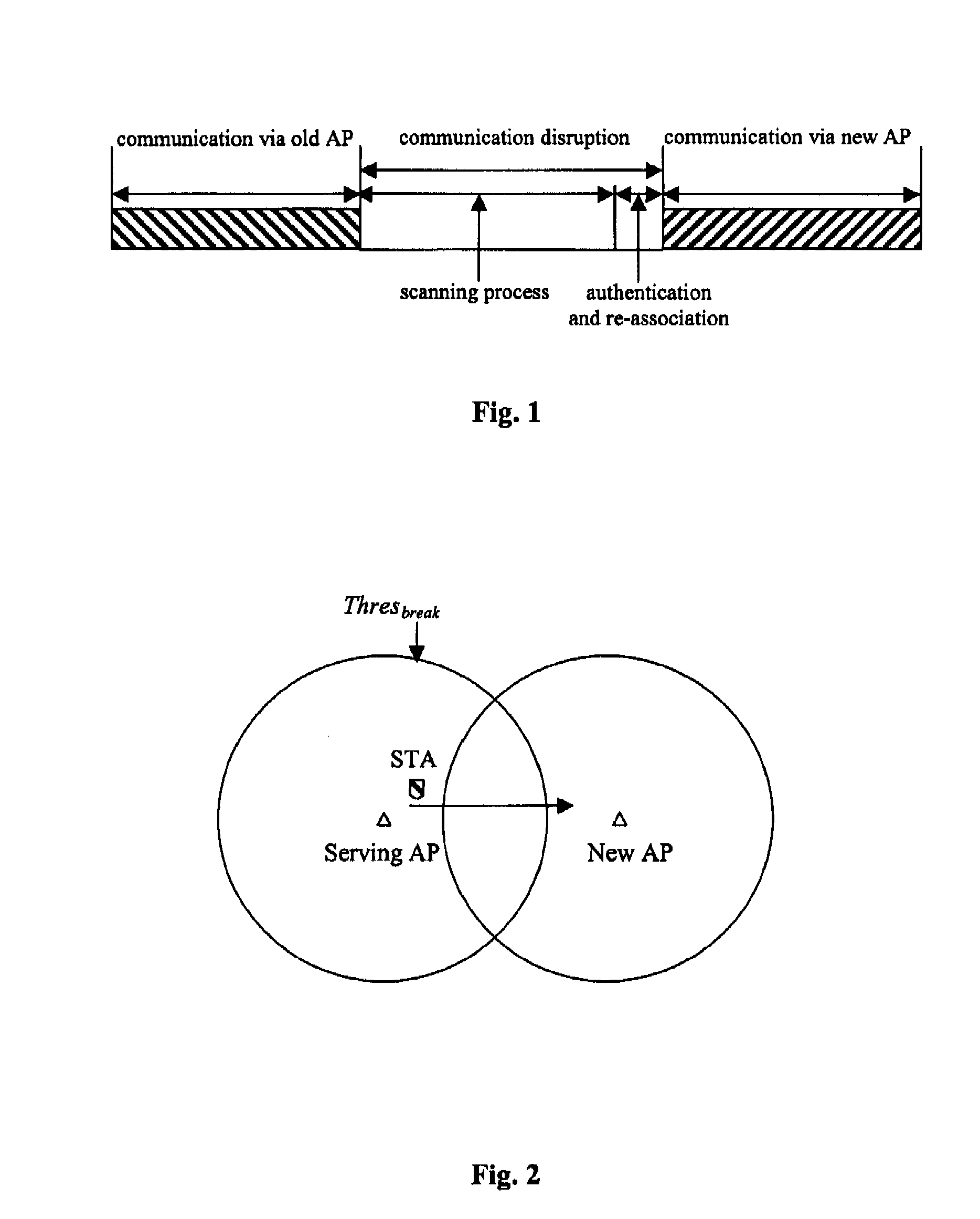
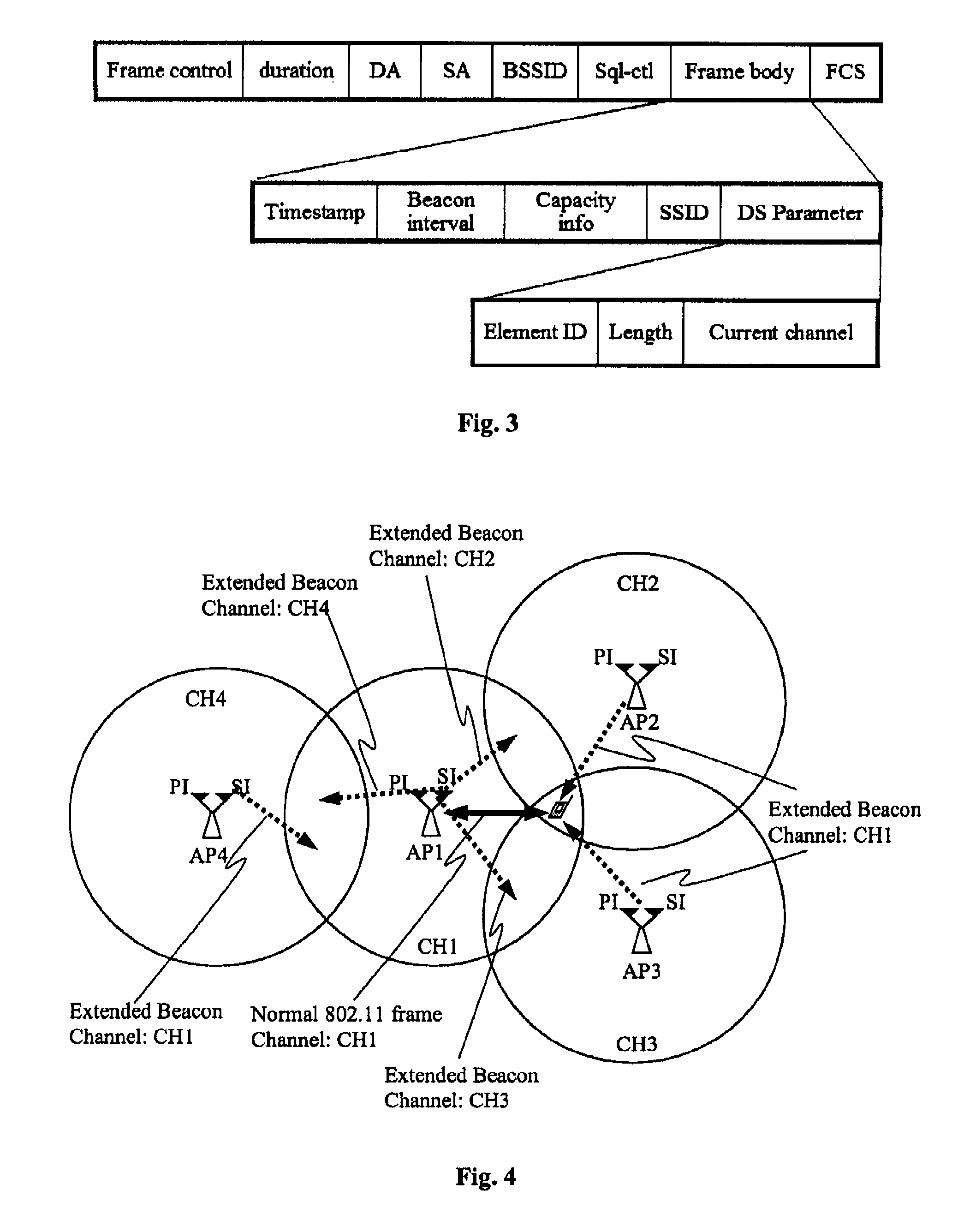
InactiveUS20080062933A1Reduce switching delayEliminate power consumptionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal qualityBeacon frame
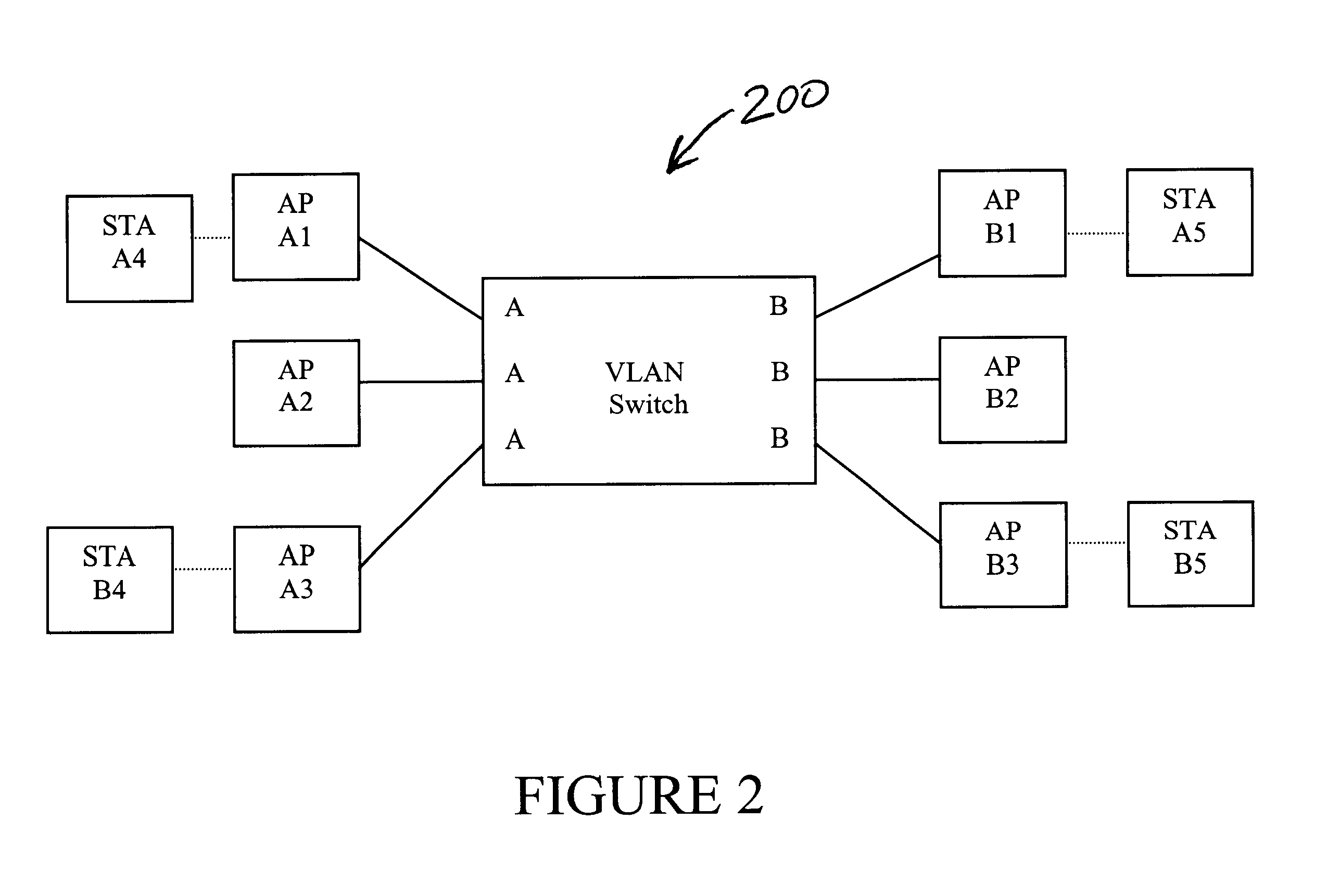
Methods, devices and system for access point facilitated fast handoff are provided. Each access point (AP) in a wireless local area network is provided with a primary interface and a secondary interface wherein the primary interface performs normal communication with user terminals and broadcasts standard beacon frames on its working channel, and the secondary interface broadcasts extended beacon frames on working channels of neighbor APs sequentially. The extended beacon frame includes at least information of BSSID, SSID, working channel and the like of the primary interface of the corresponding AP. The user terminal may receive the standard beacons from the serving AP it is communicating with and the extended beacons from the neighbor APs, and according to the two kinds of beacons, the terminal may calculate the signal quality with the primary interface of the serving AP and the signal qualities with the neighbor APs at the current position. By an algorithm of comparing the signal qualities of the best neighbor AP and the serving AP, the terminal may accurately and quickly determine whether to perform handoff with minimized cost.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Method and system for enabling centralized control of wireless local area networks
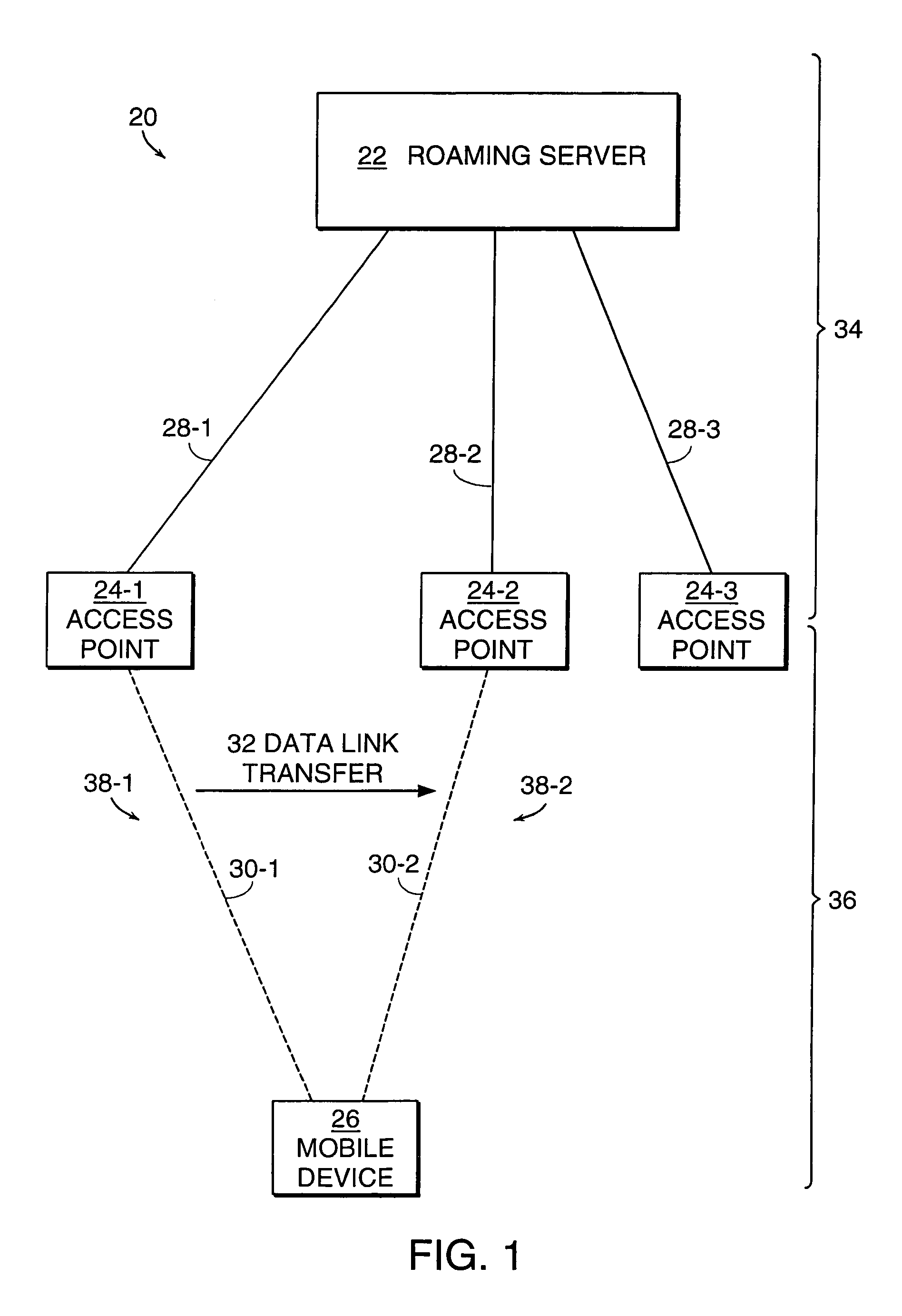
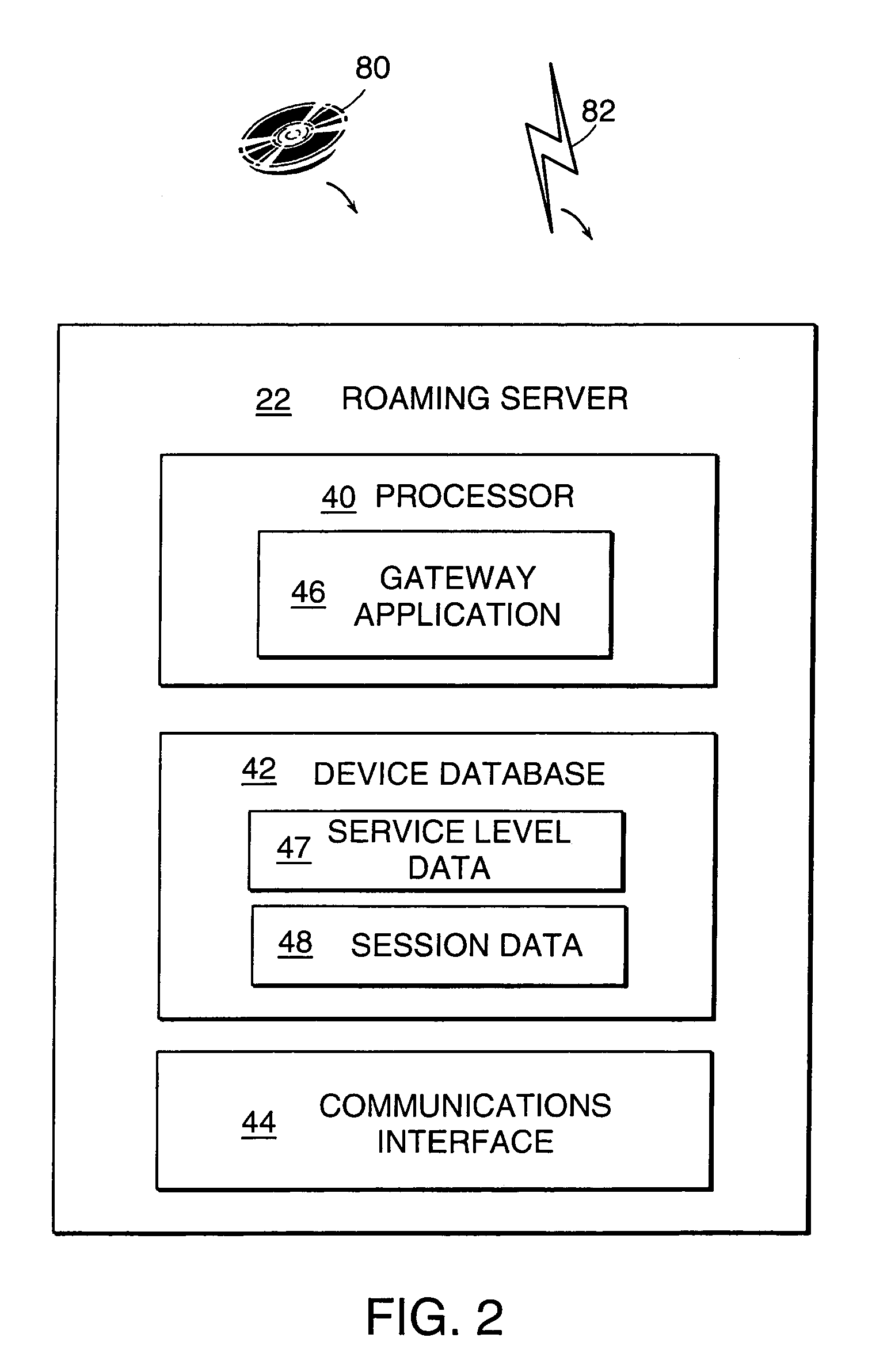
ActiveUS7146636B2Improve link performanceImproving radio link quality of serviceUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsWireless connectivitySeamless handoff
A wireless local area network (WLAN) includes mobile devices that are allowed to transfer wireless connections between WLAN subnets or channels having different access points. The access points connect to a central controller or roaming server that supports seamless hand-offs of mobile devices from one access point to another access point. The roaming server supports the reassignment of session data parameters from one access point to another (e.g., access point address spoofing) so that the mobile device can use the same parameters for communicating to a new access point. The roaming server also supports the seamless handoff of a mobile device from one access point to another by using a master-slave switch technique across two piconets. The roaming server also facilitates the control of access points by establishing a host controller interface and wireless protocol stack in the roaming server and another, complementary wireless protocol stack in the access point. The roaming server then encapsulates host controller commands in a packet based network protocol used for communication between the roaming server and the access points.
Owner:BLUESOCKET
Autonomic client reassociation in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050135310A1Degraded backbone performanceData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRogue access pointClient-side
A wireless network client is described which obtains access to the resources of a backbone network provided by a wireless access point. The client is adapted to receive a reassociation request from an access point which is able to detect a degraded condition on the backbone network and inform clients of the degraded condition. Upon detecting the degraded condition, the access point transmits or broadcasts a reassociation request to one or more clients associated with the access point. Information can also be sent identifying the degraded performance of the backbone network and can include other information useful to clients. Once a client has received the reassociation request and / or the informed identifying the degraded performance, the clients seek access to the backbone network through other access points which are not experiencing degraded performance. The seek preferably omits the access point identified as experiencing degraded backbone performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
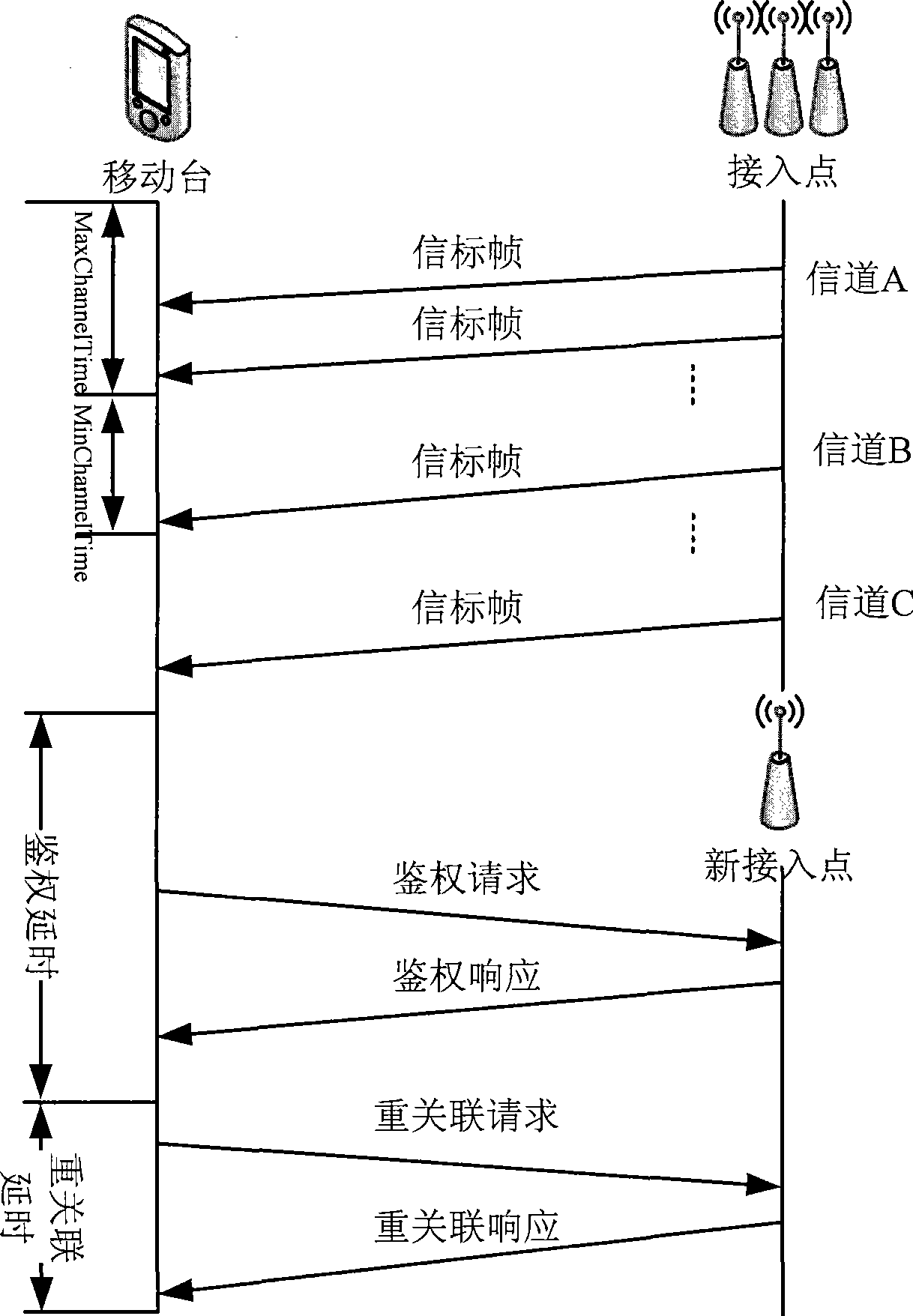
Fast switching method for WLAN
The invention relates to a rapid switching method for a wireless local area network, wherein, in a beacon frame being sent, an access point contains a channel used by an adjacent access point, SSID (service set identifier) and BSSID (basic service set identifier) information; a mobile station receives and stores the information of a target access point in the beacon frame, and when switching condition is satisfied, the information is used as a reference for selecting the target access point in switching. The mobile station preferentially searches the beacon frame or sends a polling request frame on a channel appointed by the information, and selects a next access point needing to be switched according to the RSSI (received signal quality indication) of the beacon frame or a polling response frame. Through the rapid switching algorithm of the invention, the mobile station does not need to scan all channels in the wireless local area network, thus greatly reducing switching delay.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
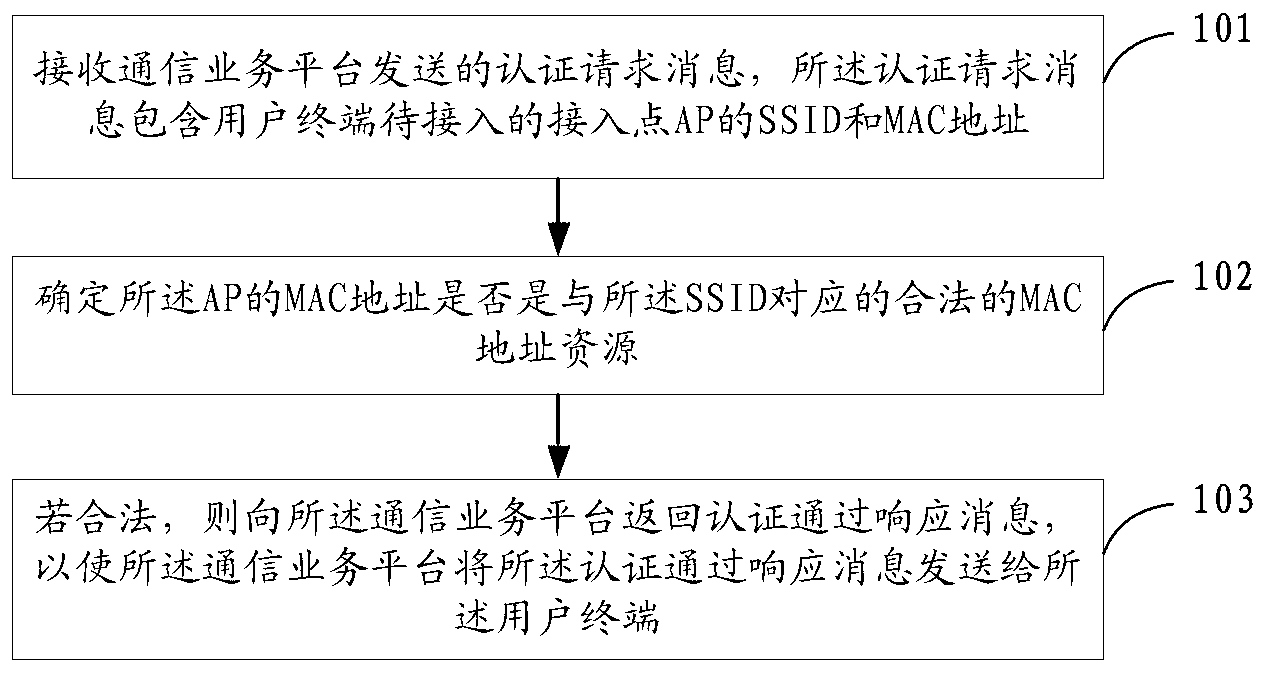
Access point authorizing method, device and system
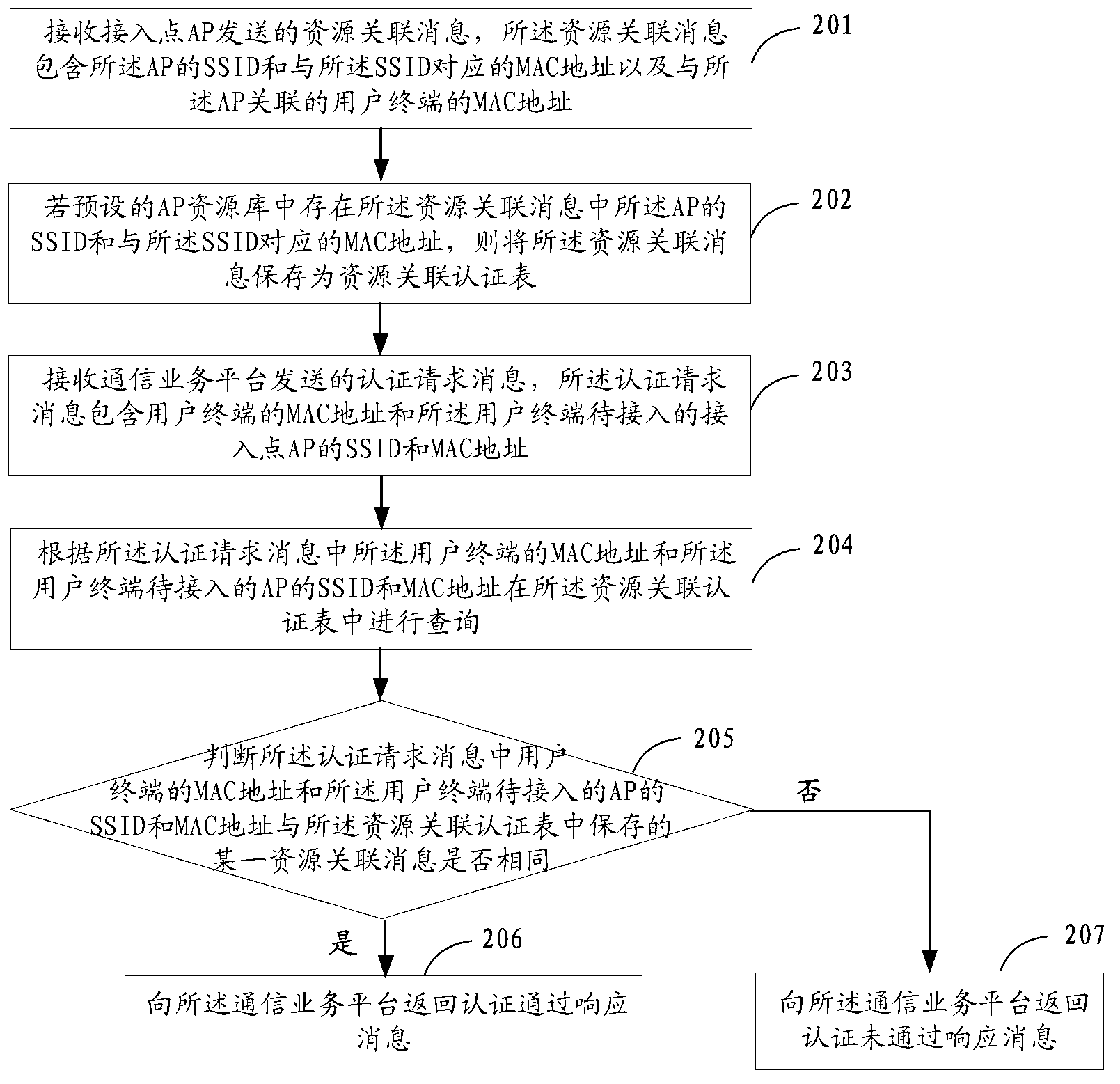
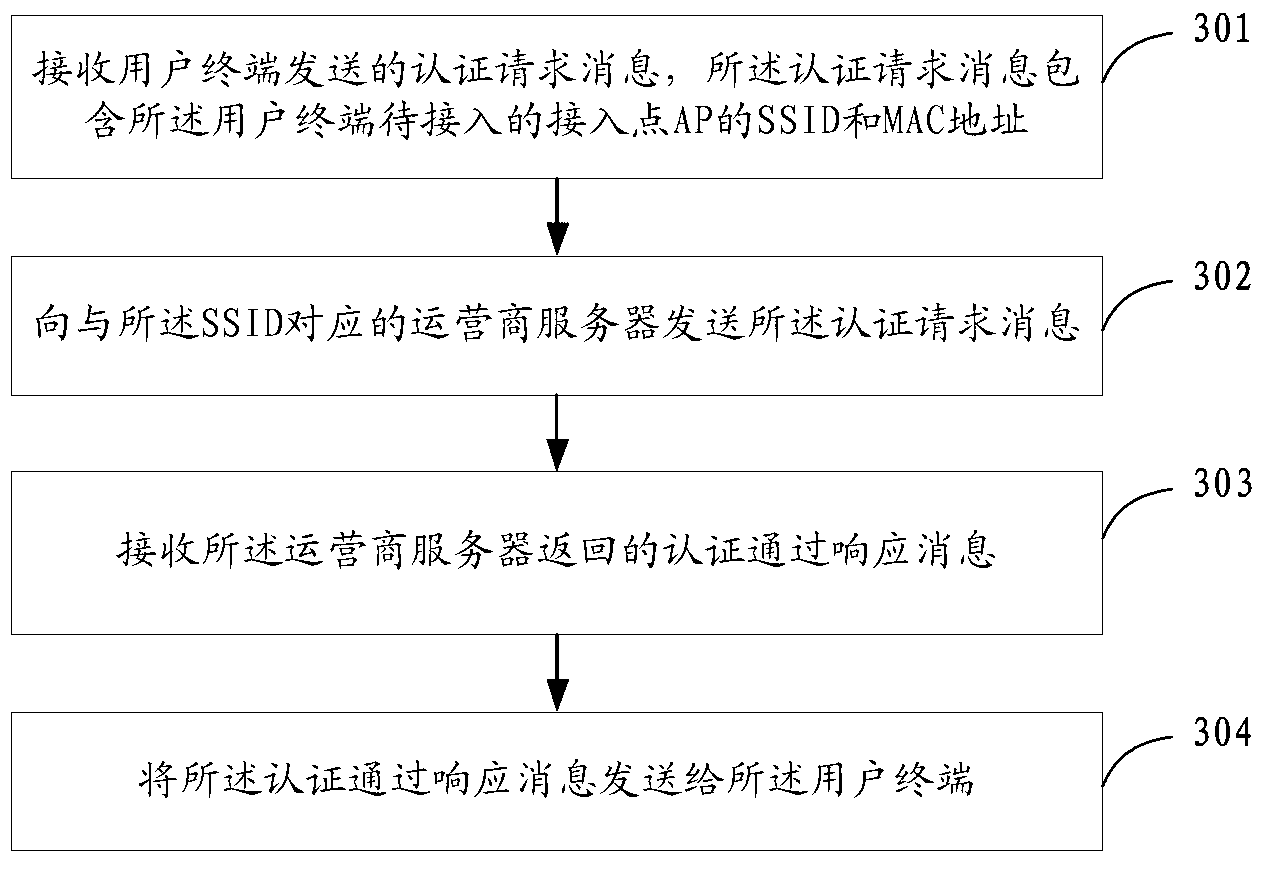
ActiveCN102843682ADetermination of legalitySecurity arrangementRogue access pointMedia access control
The invention provides an access point authorizing method, device and system. The access point authorizing method comprises the following steps of: receiving an authorization request message sent by a communication service platform, wherein the authorization request message comprises an SSID (Service Set Identifier) and an MAC (Media Access Control) address of an access point (AP) to be accessed of a user terminal; determining whether the MAC address of the AP is a legal MAC address resource corresponding to the SSID; if yes, returning an authorization passing response message to the communication service platform to ensure that the communication service platform sends the authorization passing response message to the user terminal. According to the invention, the user terminal authorizes an authorization request of legality of the AP to be accessed, which is initiated by the communication service platform, and an authorization passing result is returned to the user terminal through the communication service platform, therefore the guarantee is provided for accessing the safety AP to the user terminal.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
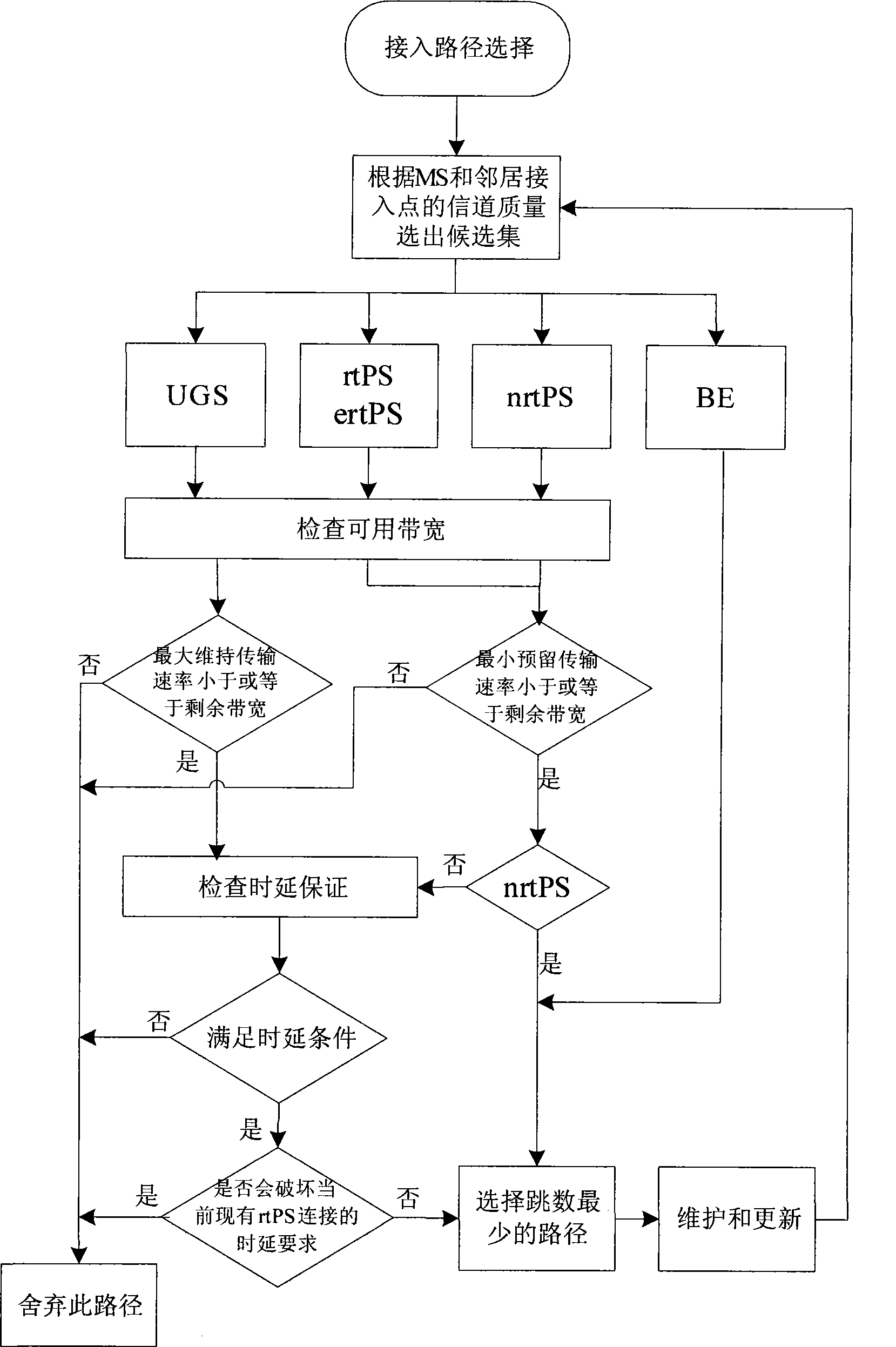
Fast access point switching method based on dynamic access path selection mechanism
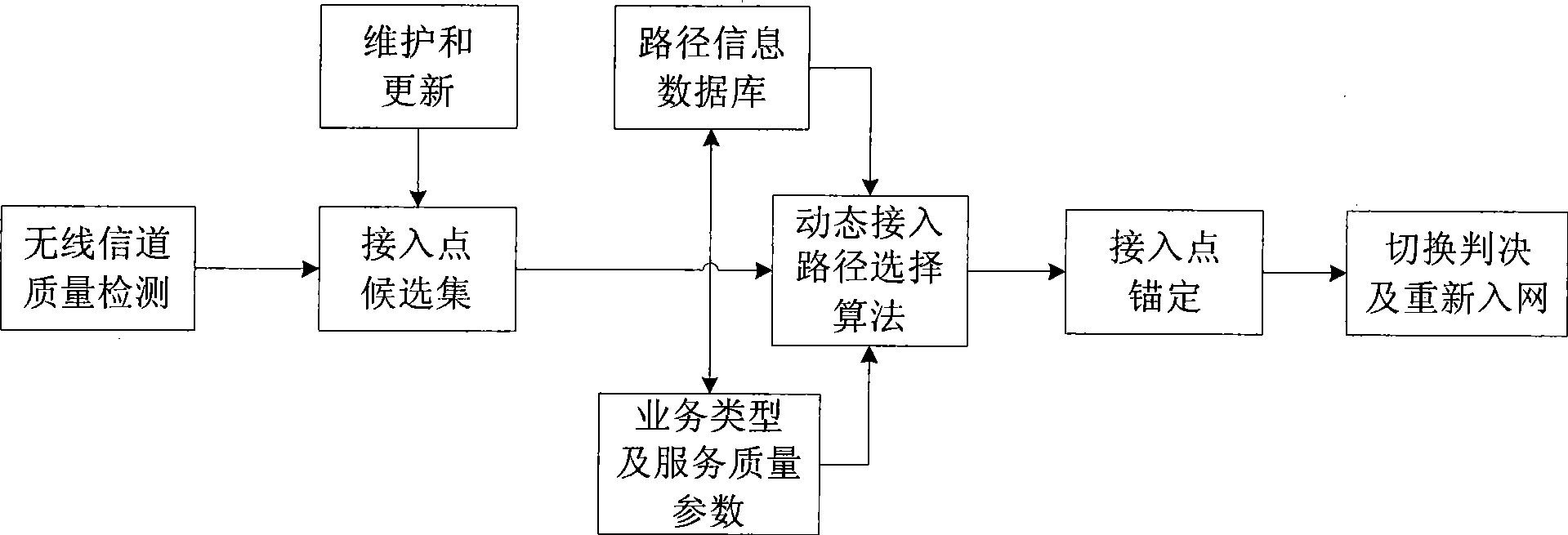
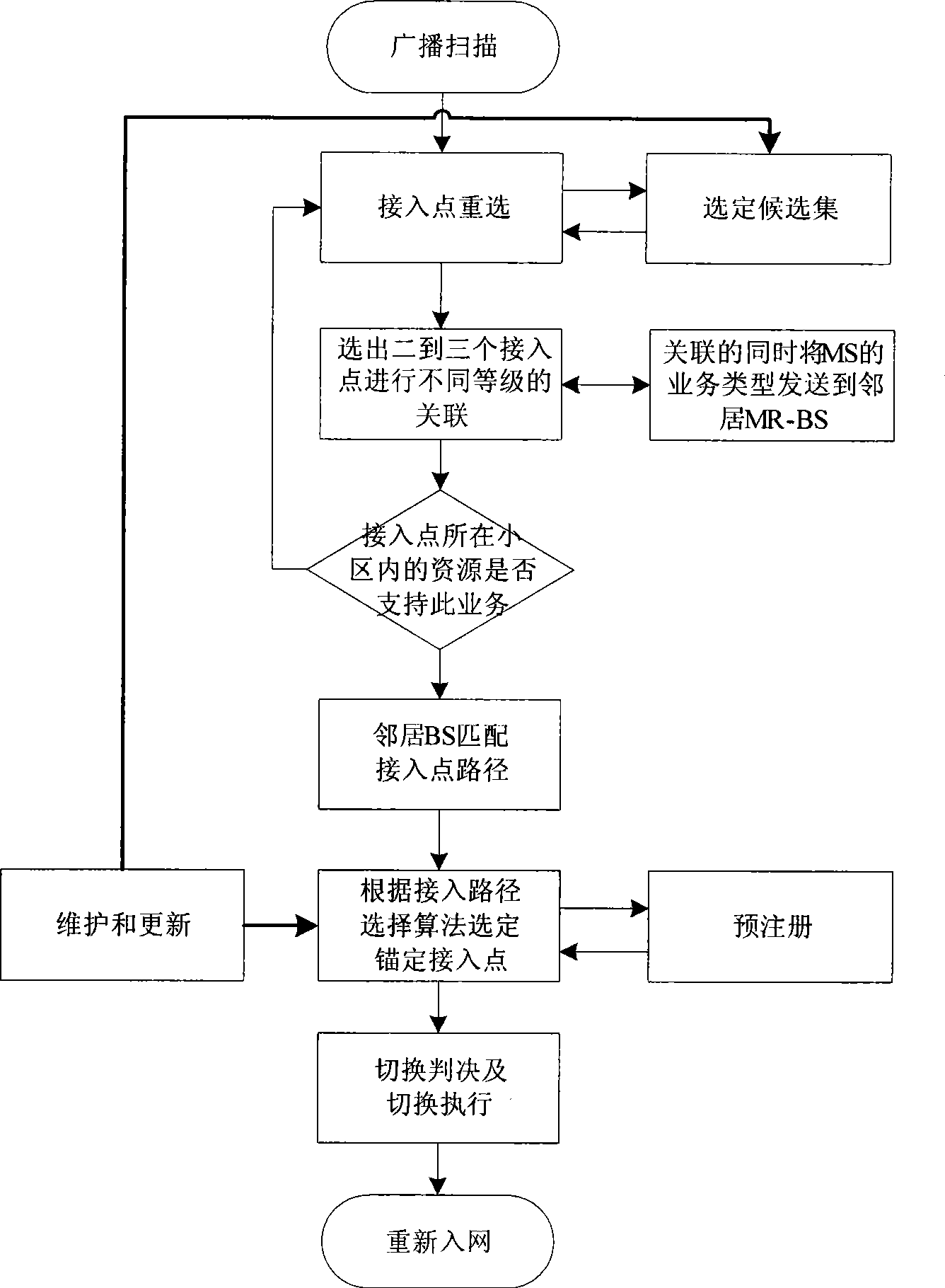
InactiveCN101483893AGuaranteed connection qualityReduce switching delayWireless communicationQuality of serviceUser needs
The invention discloses a rapid access point switching method based on a dynamic access path selection mechanism, wherein, in a multi-hop relay broadband radio access network, each district exists a plurality of access points, including a base station and a delay station, a mobile user dynamically and rapidly switches to the access point of an adjacent district in a moving process according to the quality of a current radio channel with the aid of access path selection algorithm. By means of access point reselection, information such as the bandwidth, delay and hop count of a candidate access point path, and the current connection business type of the mobile user and service quality parameter thereof, the method of the invention selects the access path that satisfies current traffic condition from the candidate access points, and according to a best anchoring access point selected from business information obtained beforehand from a reserved network, the best access path is determined. When the mobile user needs switching, a target access point is switched rapidly, and the rapid access point switching method reduces switching delay, and different treatment on business with different priority improves switching connection rate.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Rogue access point detection in wireless networks
InactiveUS7716740B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsWireless mesh networkRogue access point
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Efficient multicast control processing for a wireless network
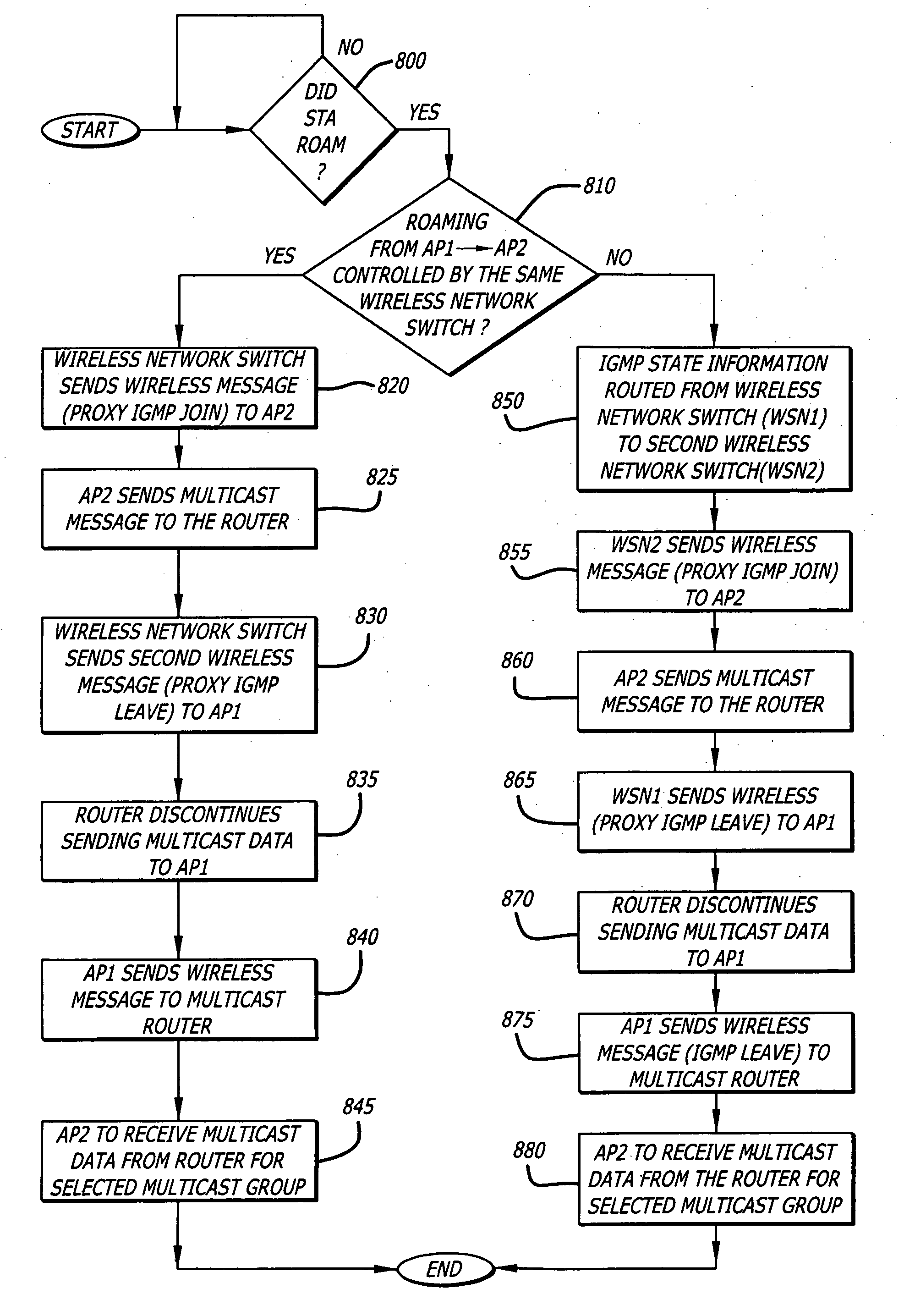
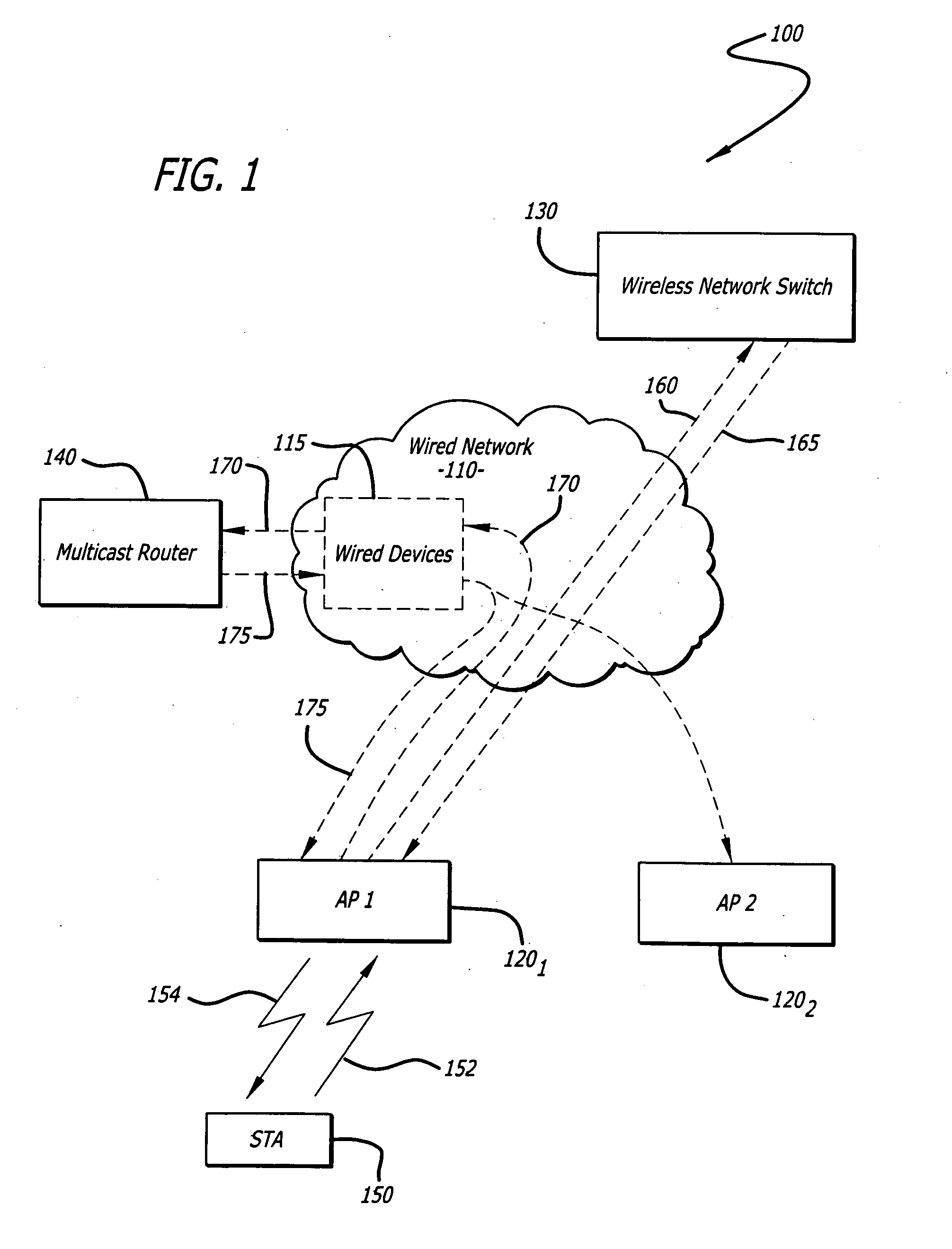
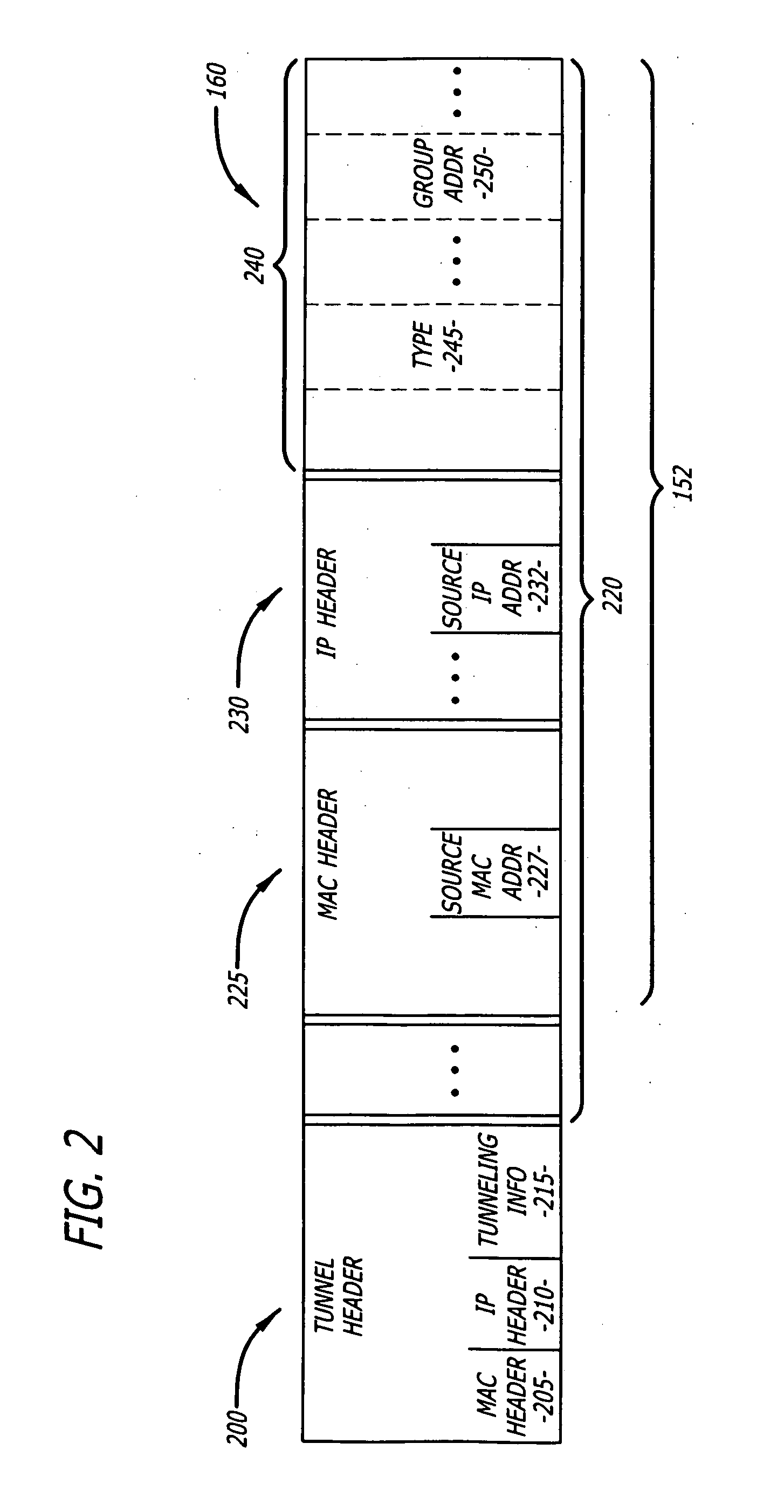
ActiveUS20070286137A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsWireless mesh networkRogue access point
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method comprises an exchange of messages between an access point and a wireless network switch. One message, a PROXY IGMP JOIN message, is transmitted to the access point for propagation to a multicast router. This is performed so that multicast data associated with the multicast group identified by the PROXY IGMP JOIN message is routed to the access point without any unnecessary involvement by the wireless network switch.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Trustworthiness decision making for access authentication
ActiveUS20110225632A1Improve resource utilizationEfficient measurementDigital data processing detailsAssess restrictionAccess networkRadio access network
There are provided measures for trustworthiness decision making for access authentication, for example relating to the trustworthiness of non-3GPP access networks within a 3GPP-compliant packet data system, exemplary comprising receiving an indication about a provisional trustworthiness of an access network, which provides packet data access for a roaming user, with respect to a visited network of said user from a network element of said visited network, determining the applicability of local breakout or home routing for each subscribed access point name of said user, and deciding about a final trustworthiness of said access network based upon the received provisional trustworthiness indication and the determined routing applicability for each subscribed access point name of said user.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Bandwidth management in a wireless network
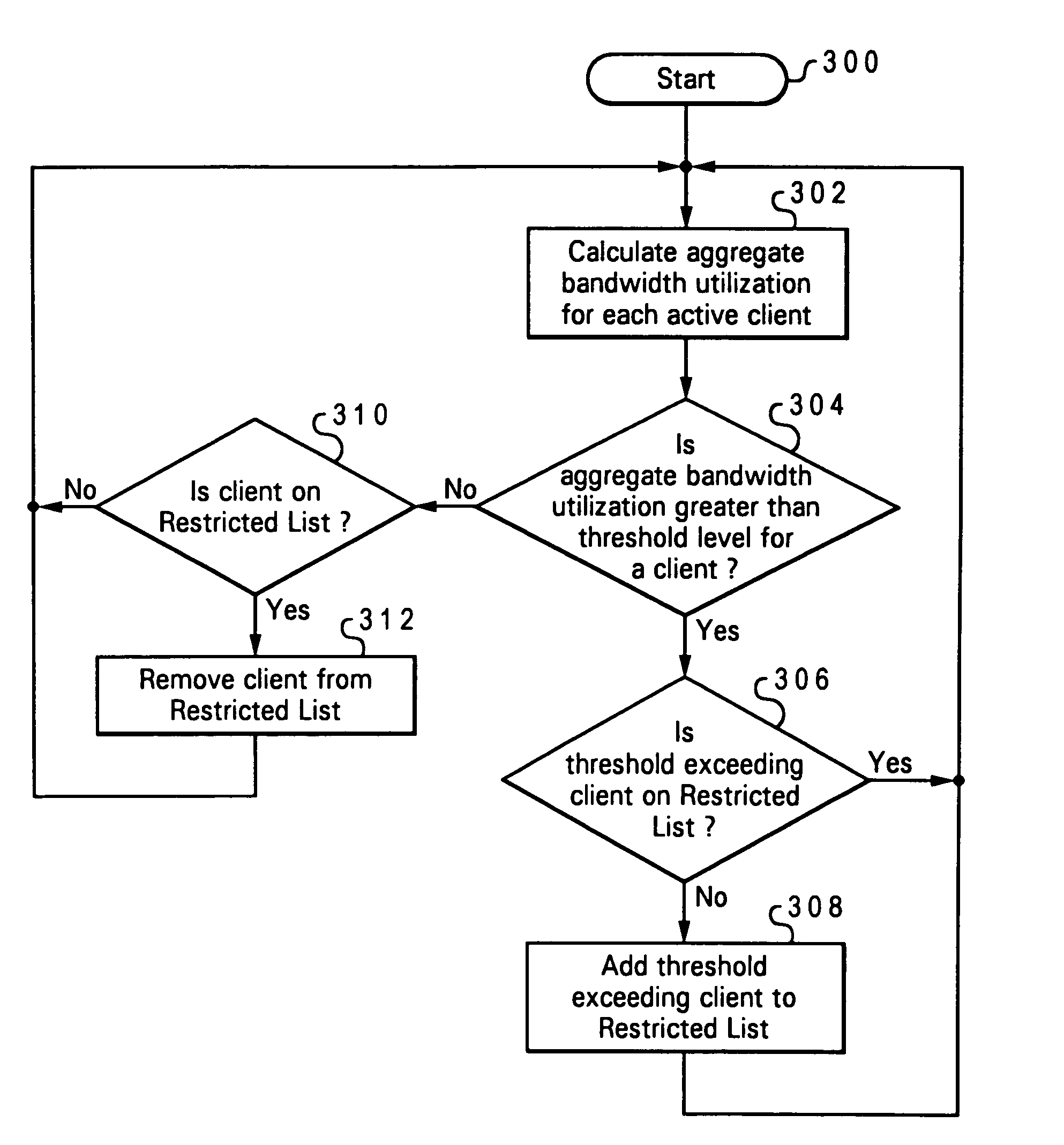
ActiveUS7113497B2Avoid spreadingBroadcast with distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless mesh networkDynamic load balancing
In accordance with the preferred embodiment, an access point provides dynamic load balancing of network bandwidth between access points within the 802.11 wireless LAN. The access point uses the RTS / CTS protocol to reduce the bandwidth available to a single device using an excessive amount of network bandwidth. The access point places a device that has been monopolizing a network channel on a Restricted List, and regulates bandwidth on the network by not returning a CTS to any client on the Restricted List. When the client's network usage drops below a policy driven threshold set by the number of network users, the client is removed from the list and the access point will respond to a RTS from the client with a CTS.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Wireless node search procedure
InactiveCN101622887AReduce power consumptionOptimize search programAssess restrictionLocation information based serviceRogue access pointComputer science
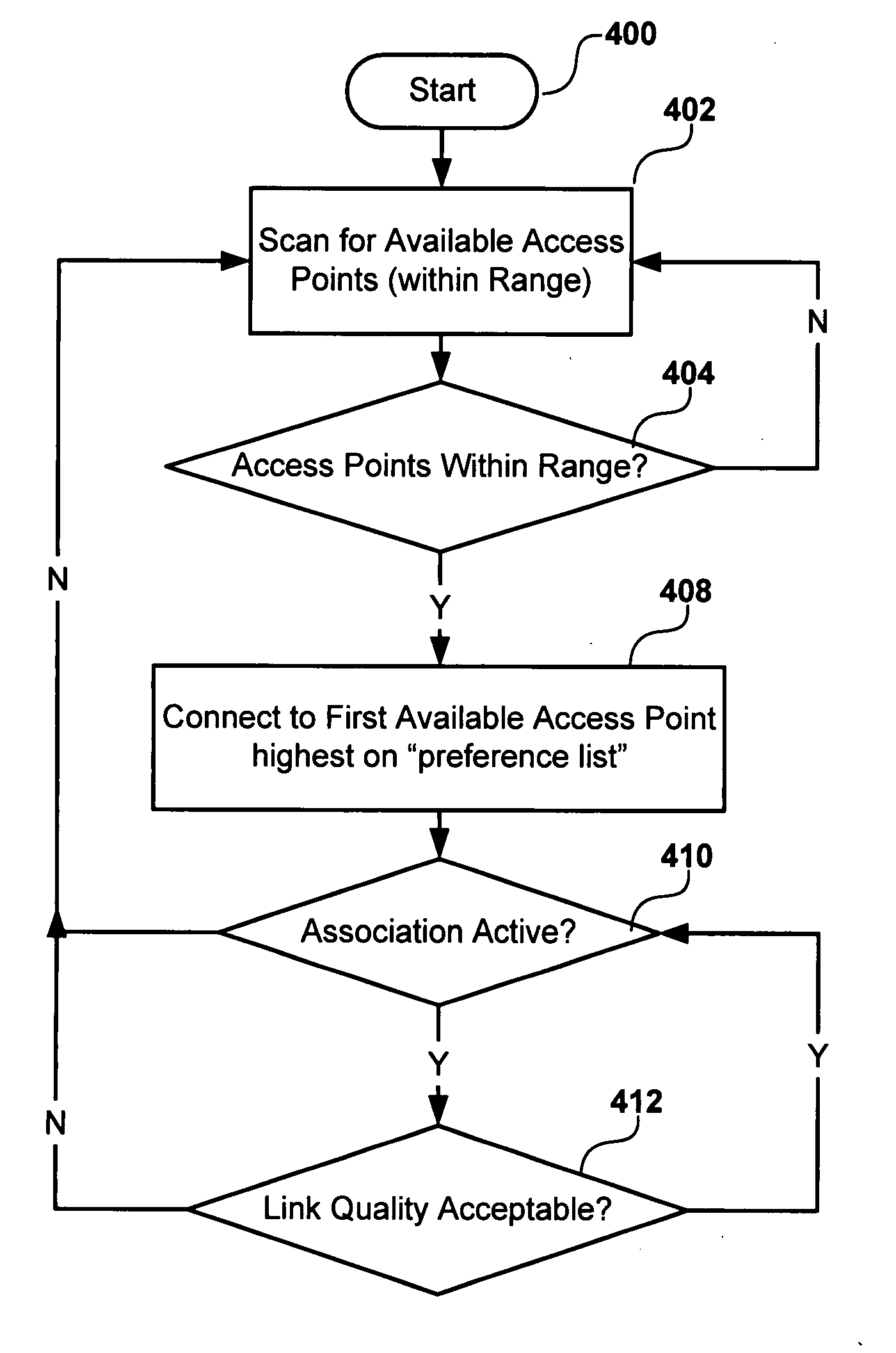
An access terminal scans for nearby access points and maintains a candidate list of access point with which the access terminal may associate in the event the access terminal's communication with its current access point deteriorates for some reason. This search procedure may be performed in a proactive manner whereby the access terminal repeatedly performs scans and updates its list of candidateaccess points when it is powered on. In some aspects, the search procedure used by the access terminal may be based on a state of the wireless device. In addition, different states of the access terminal may be associated with different optimization criteria.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com