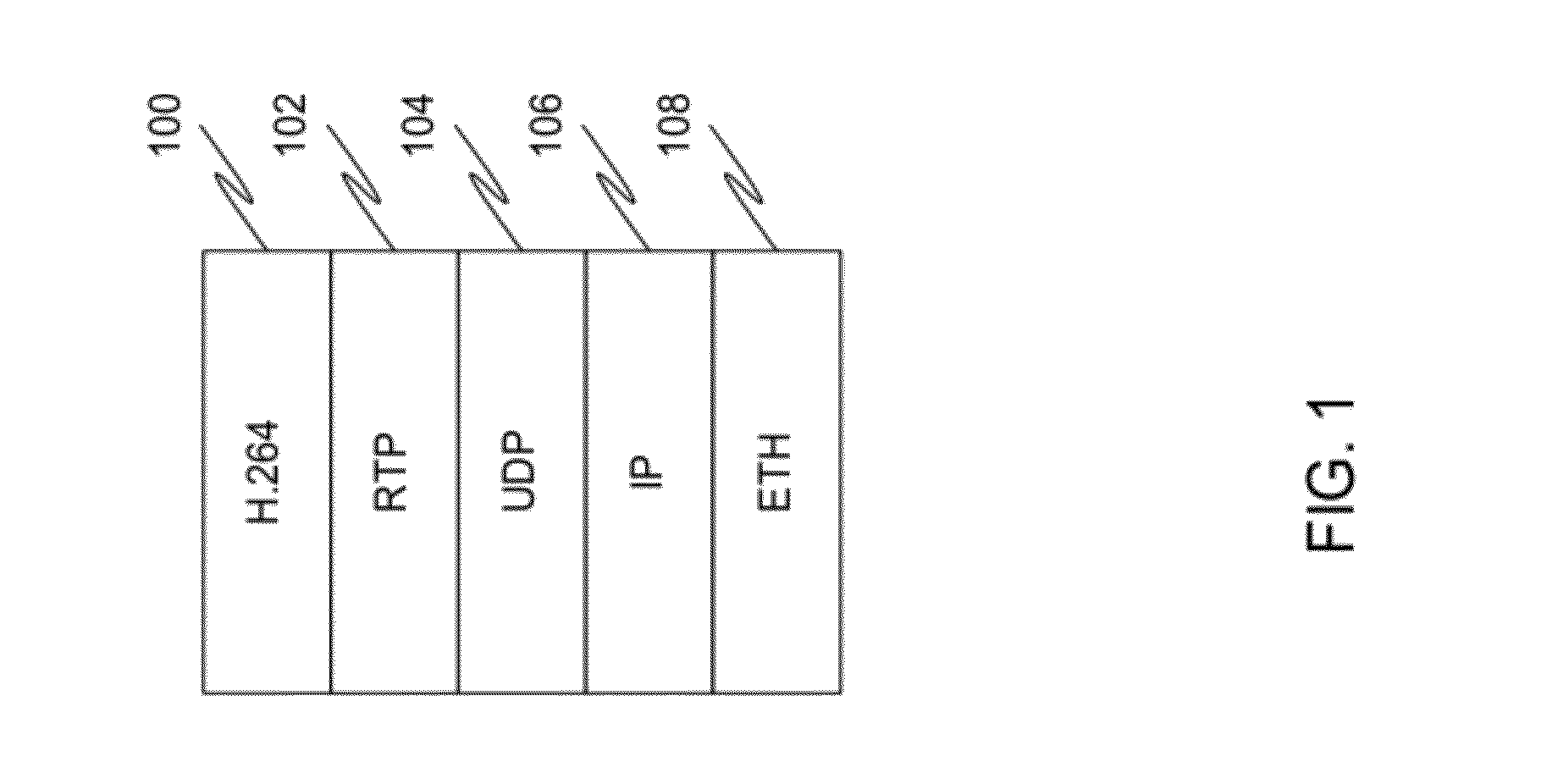
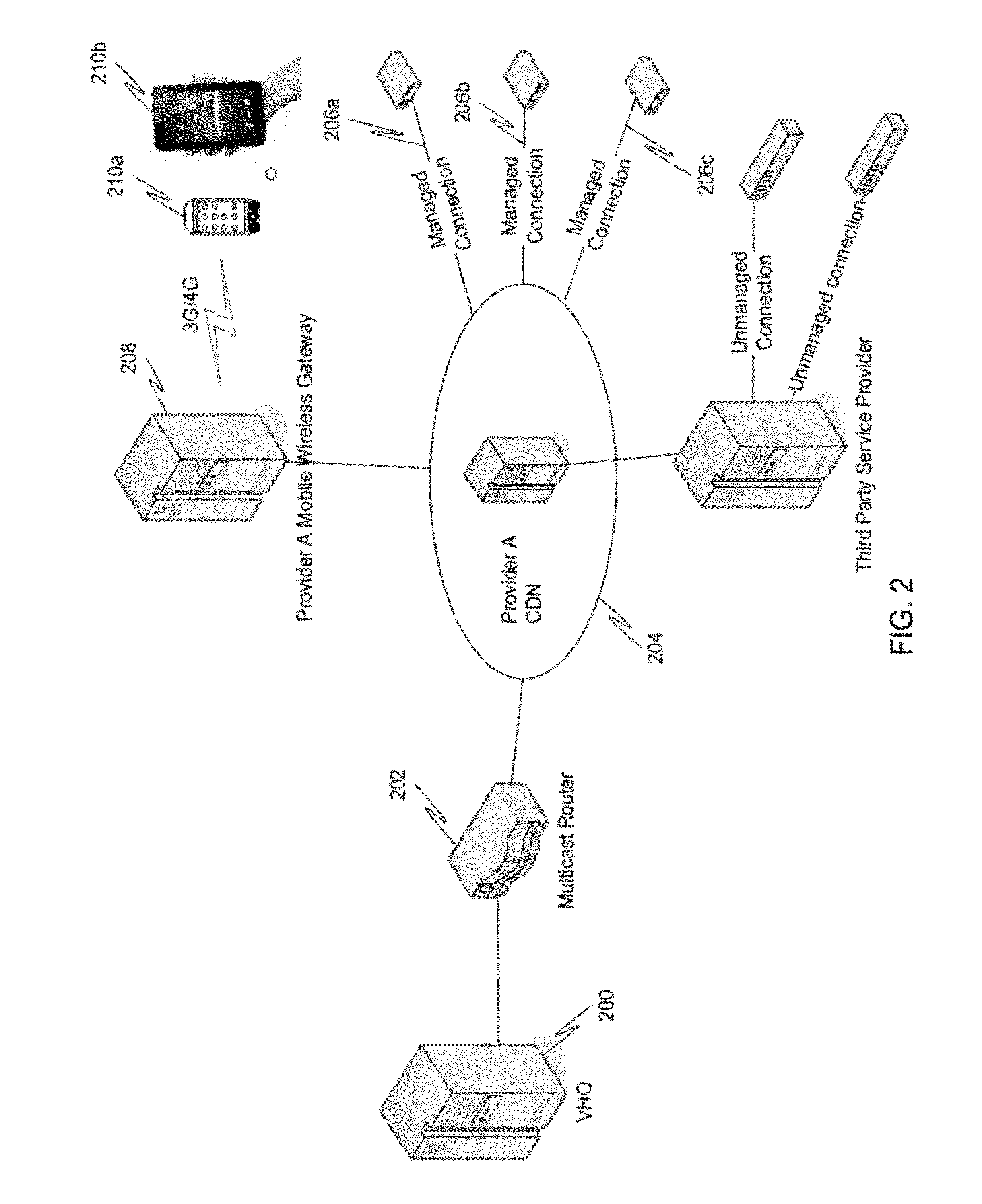
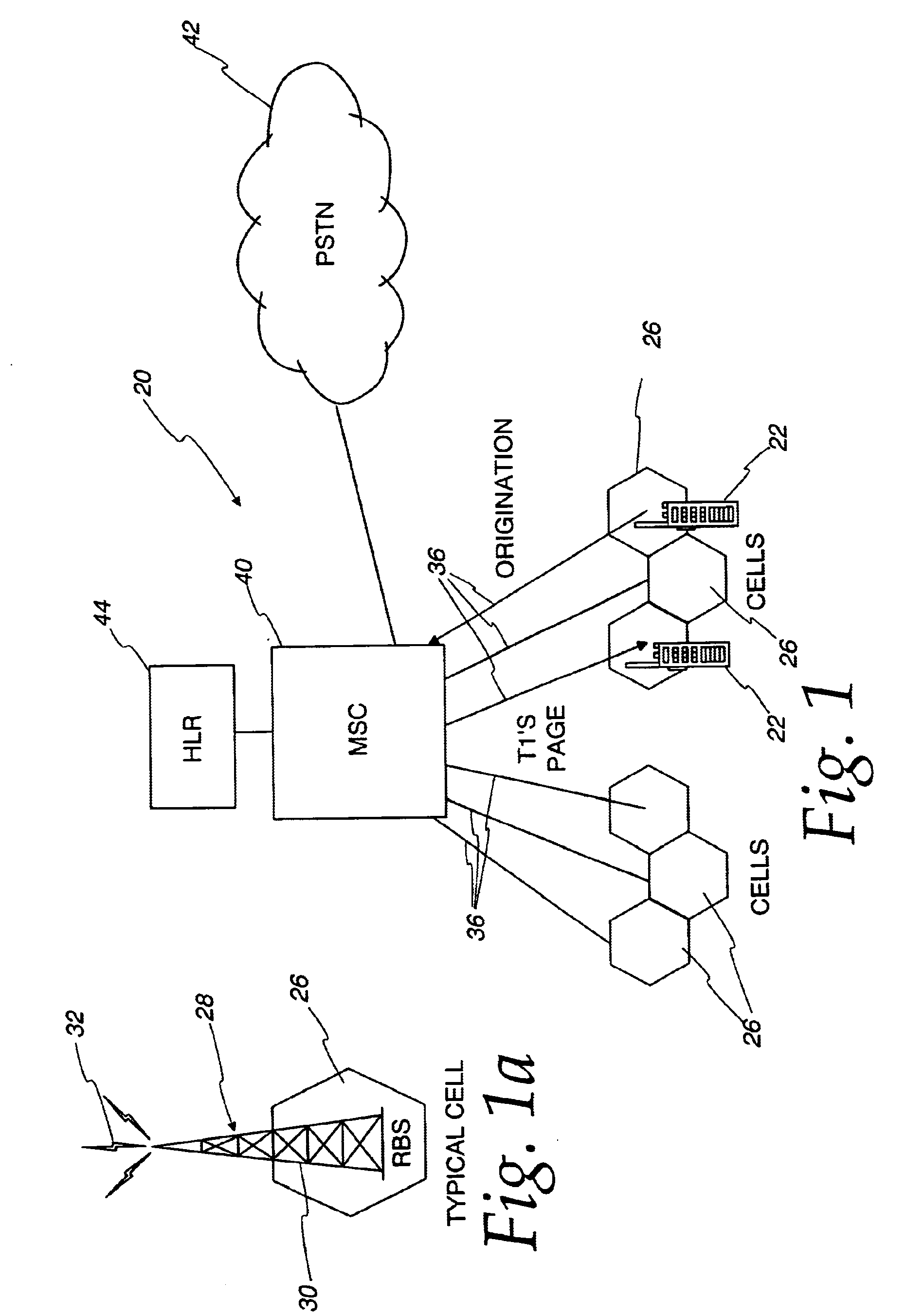
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Broadband connection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
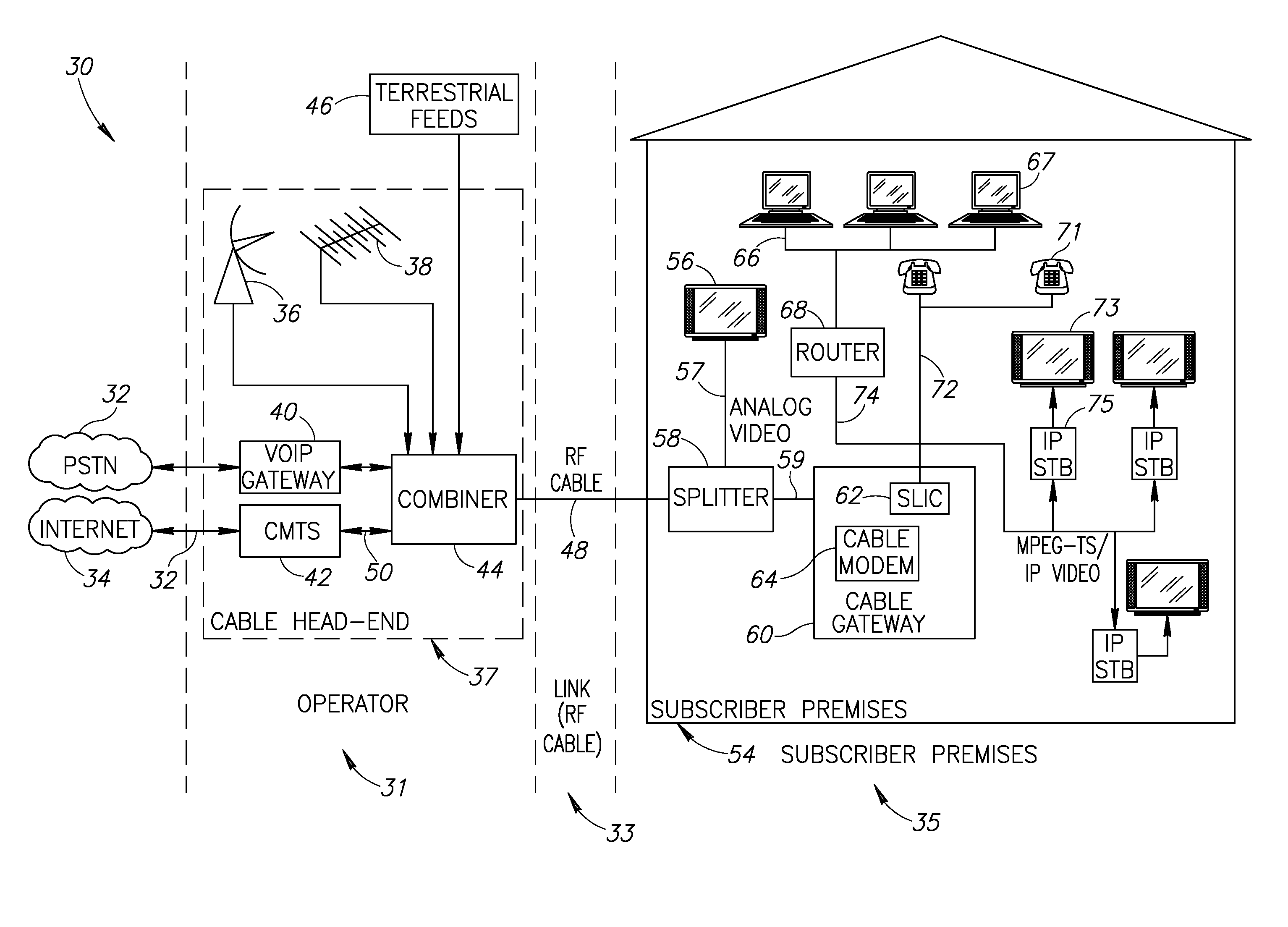
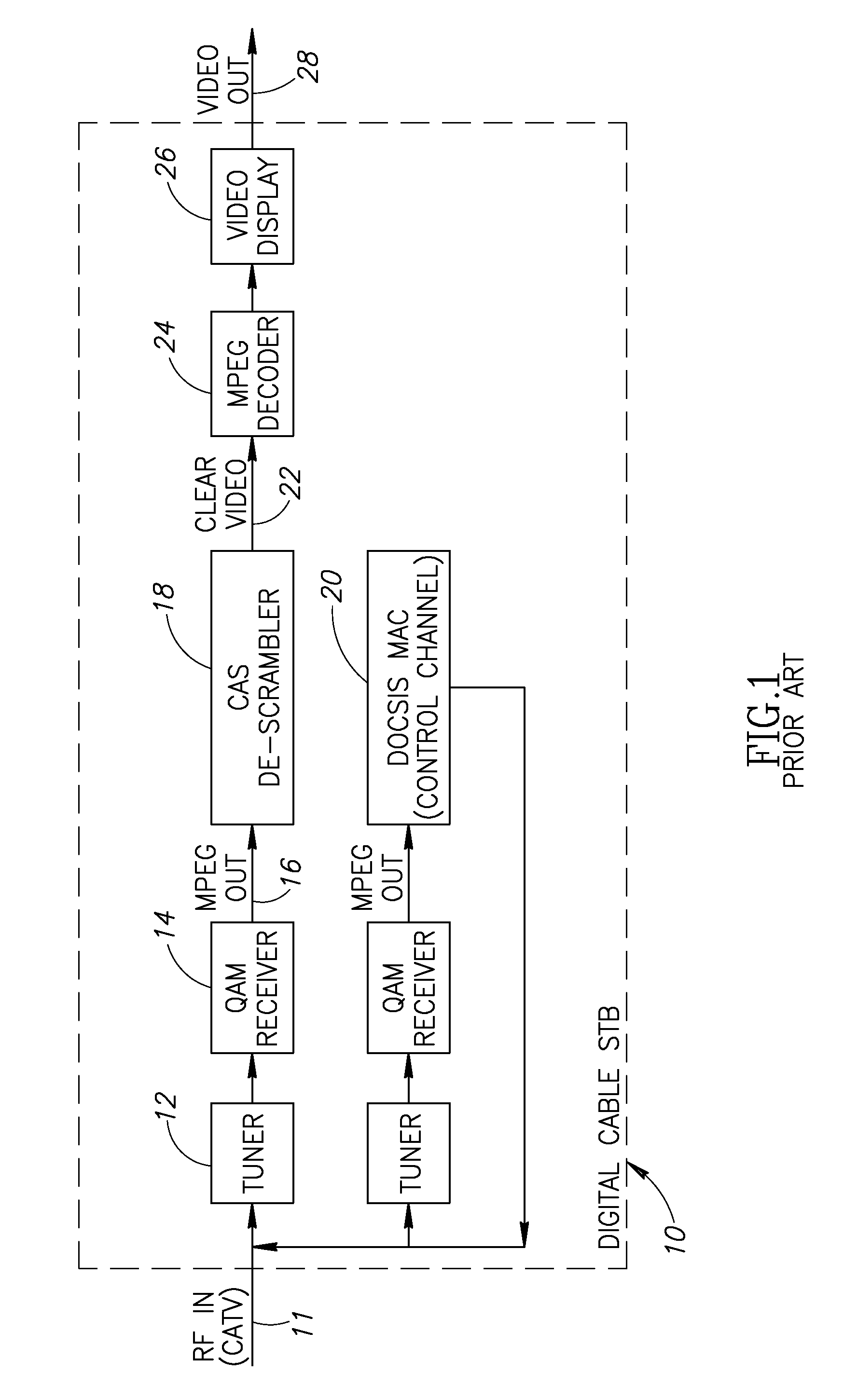
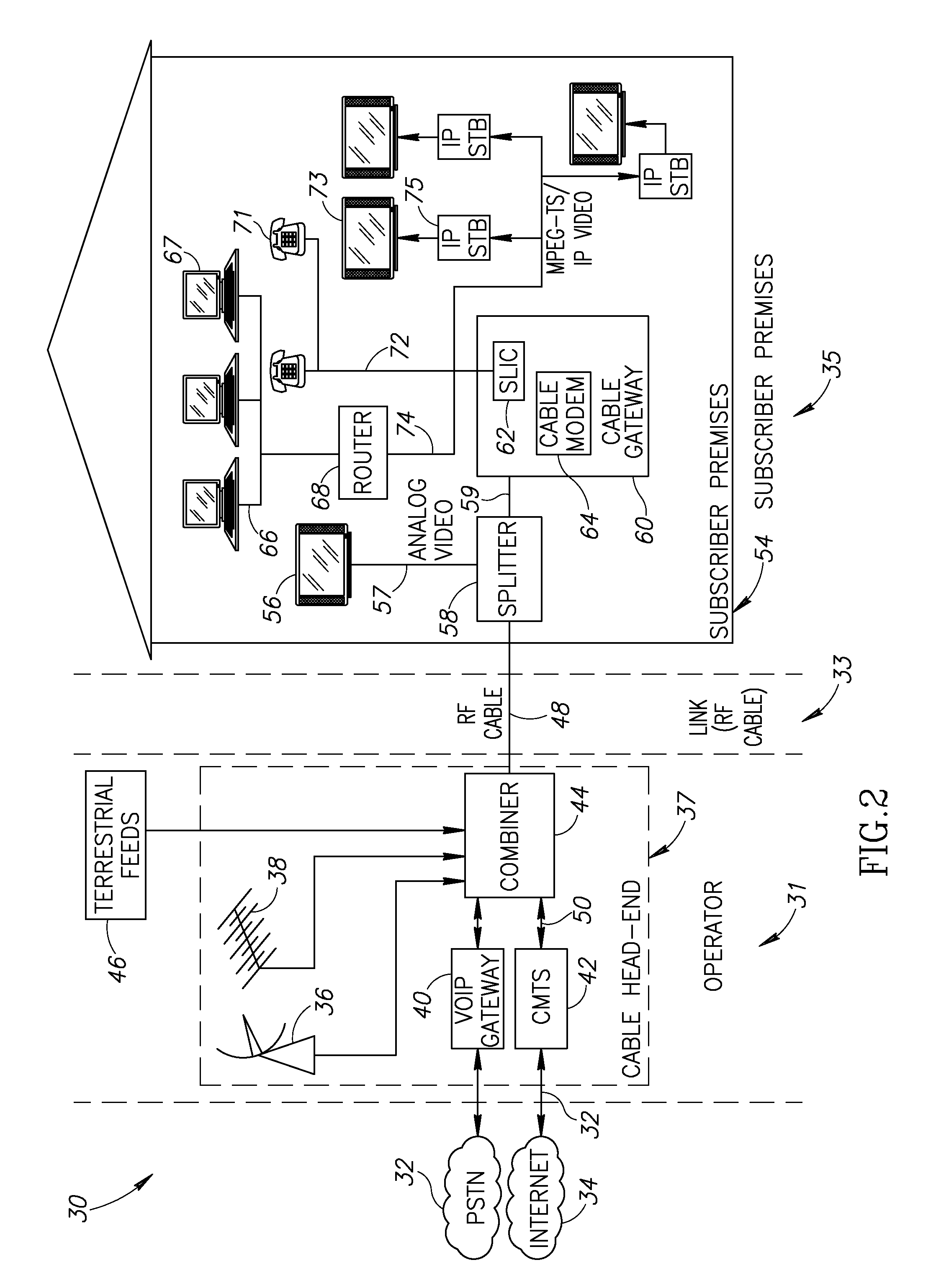
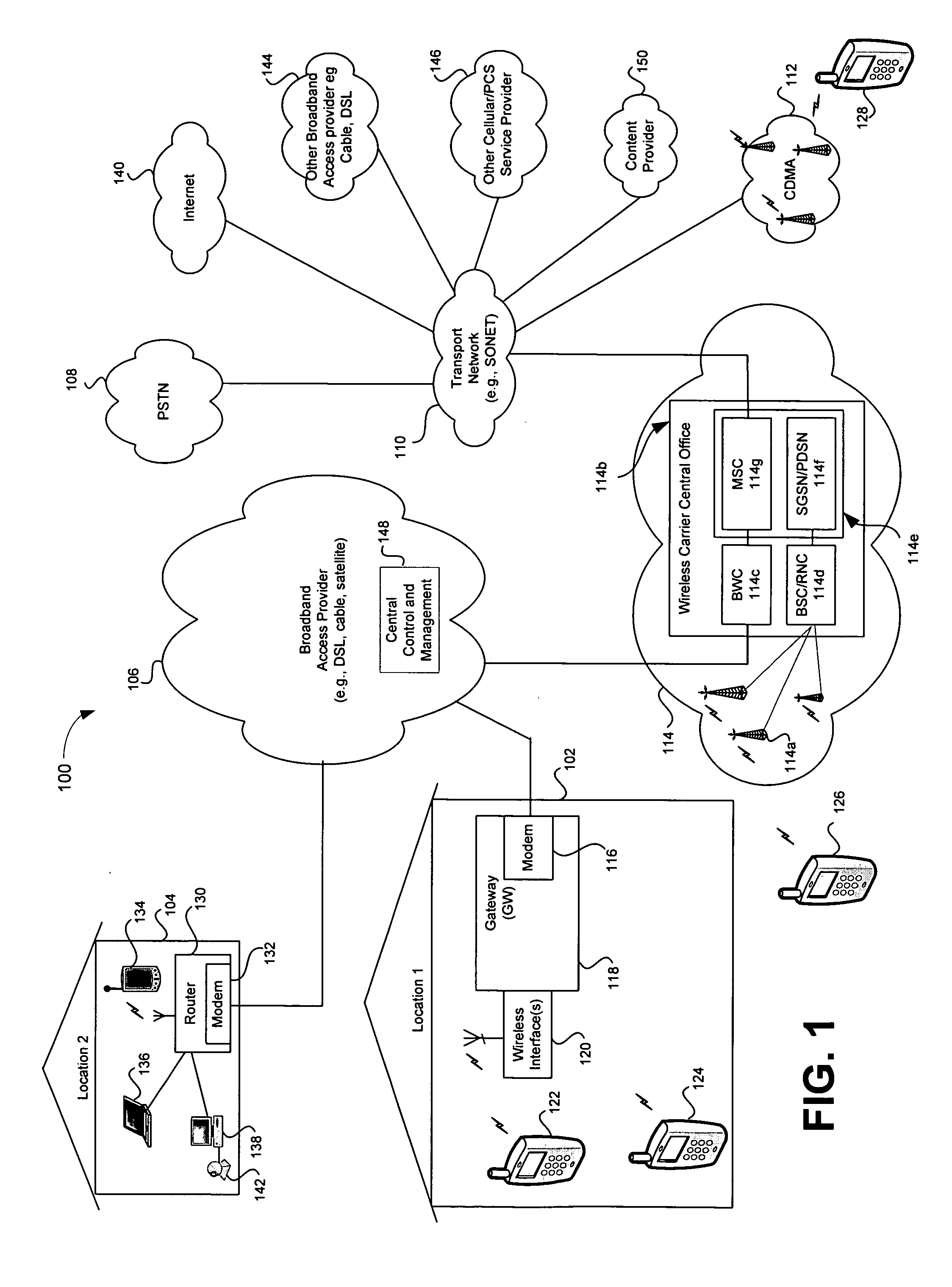
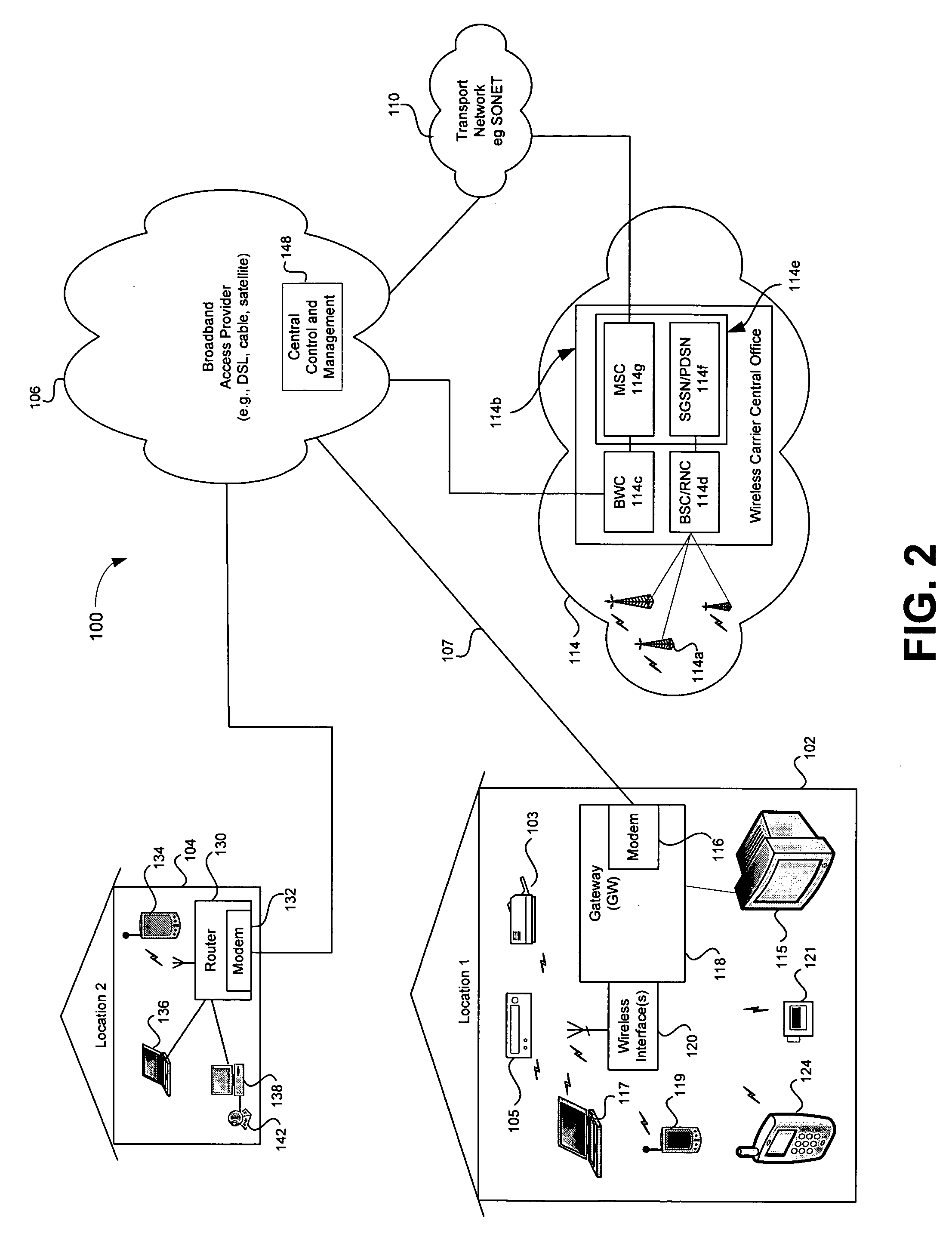
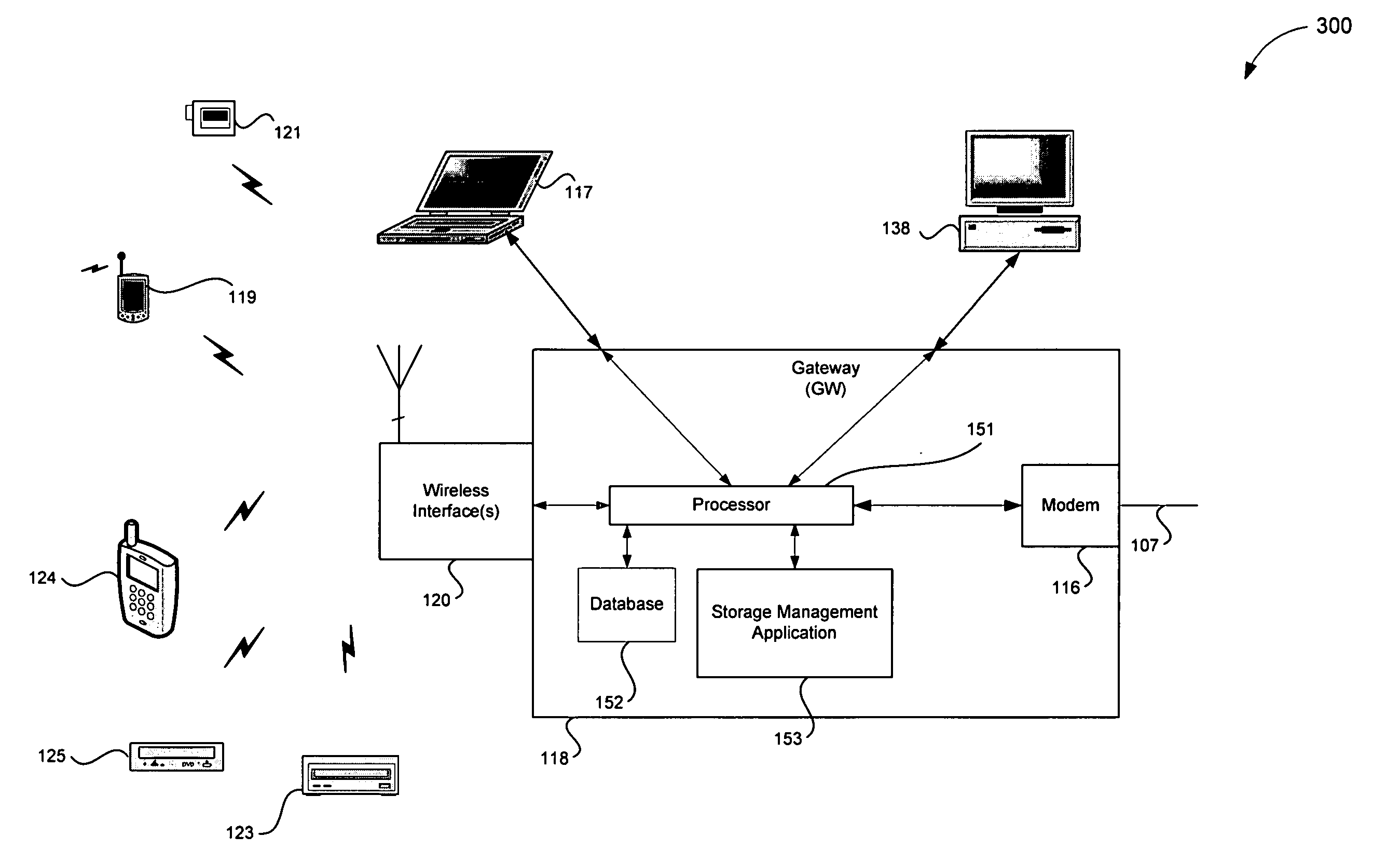
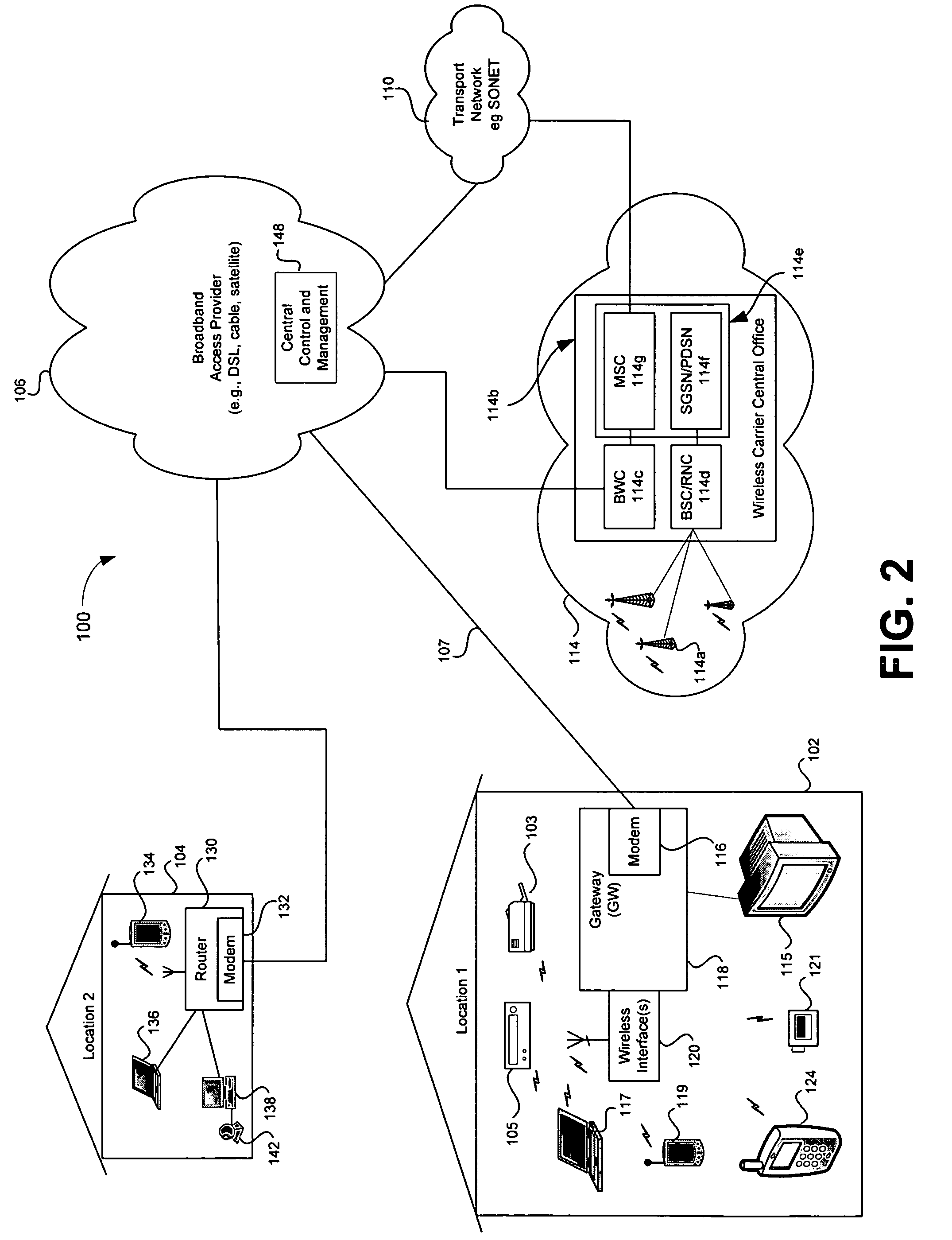
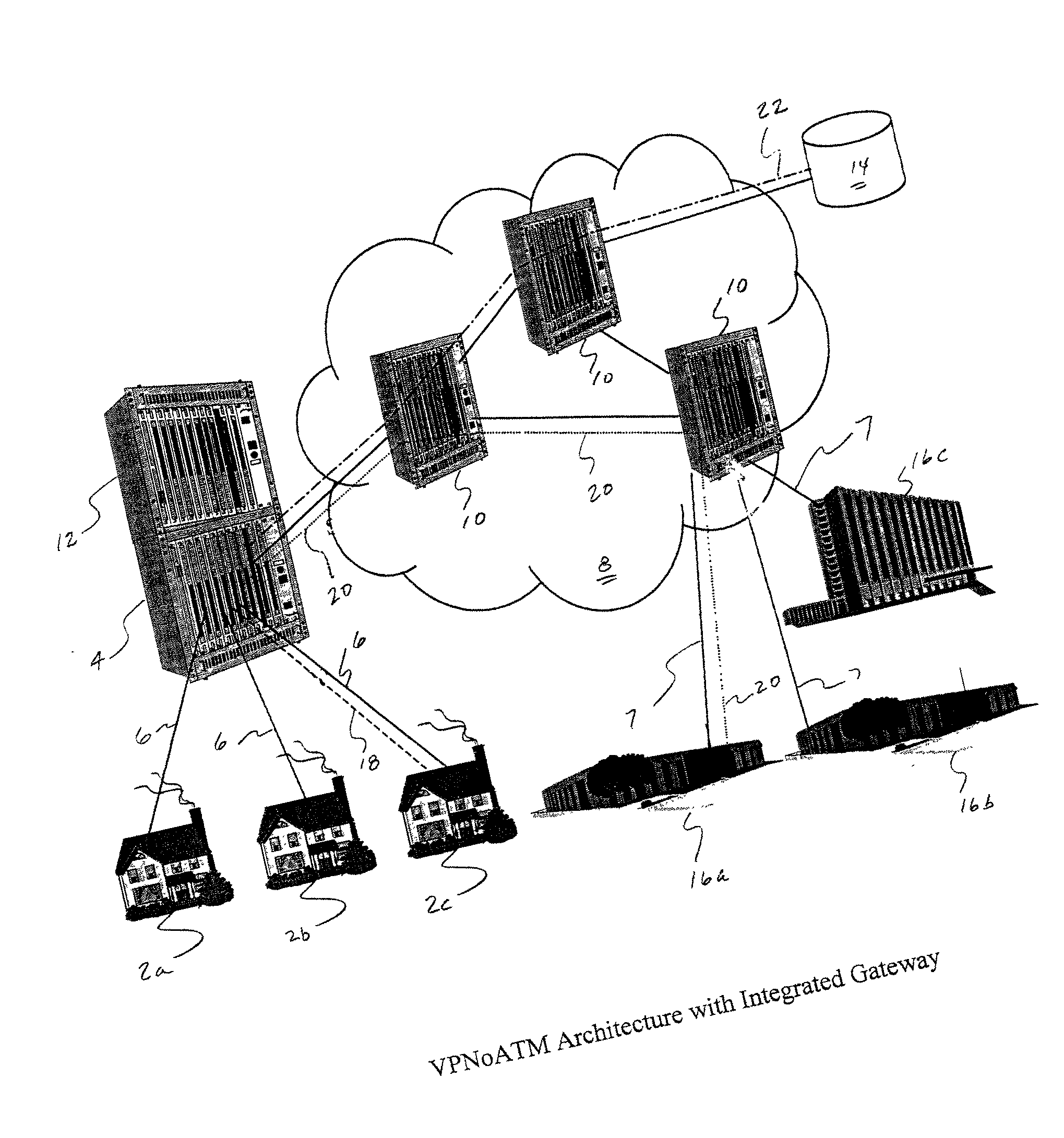
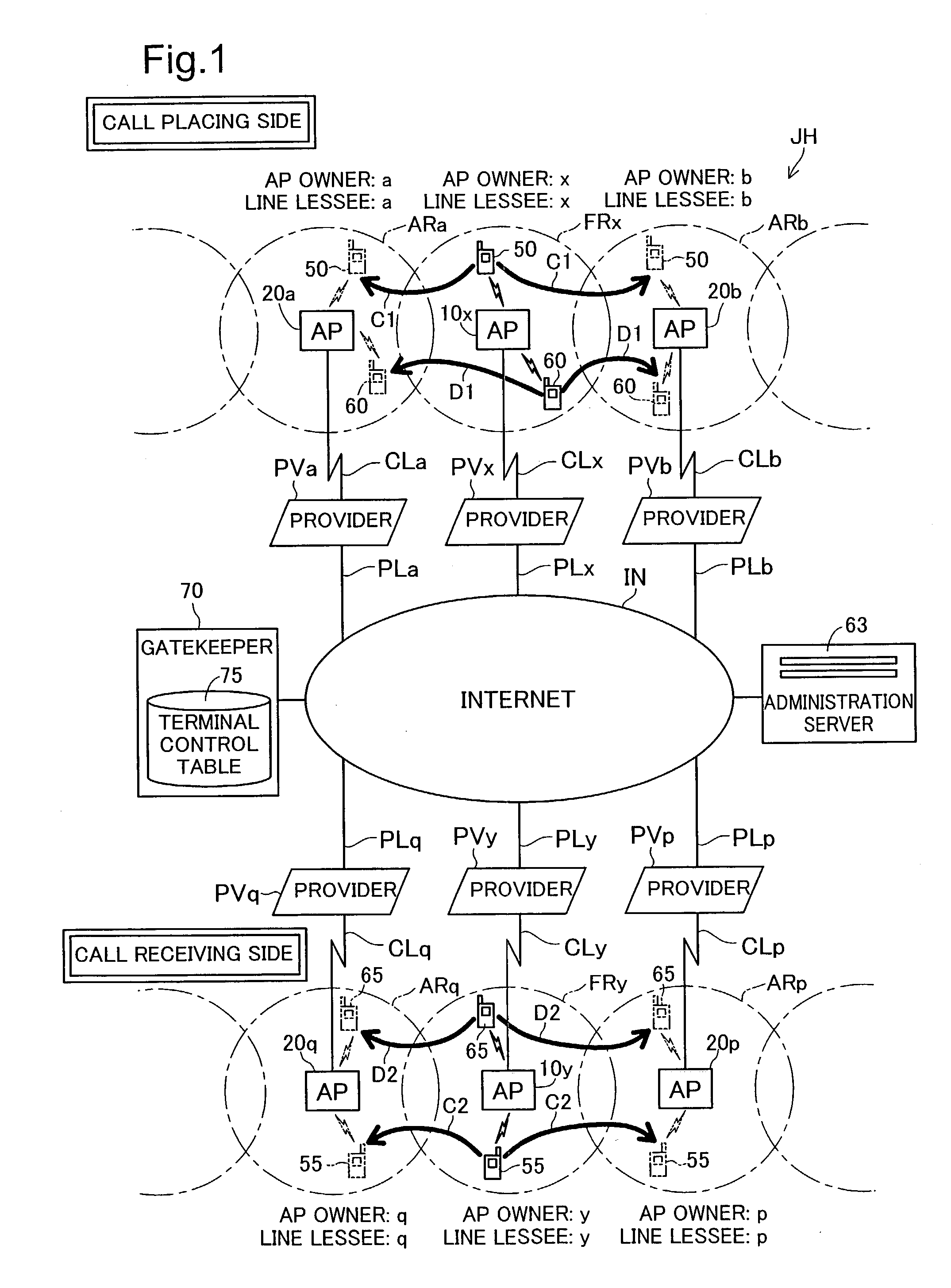
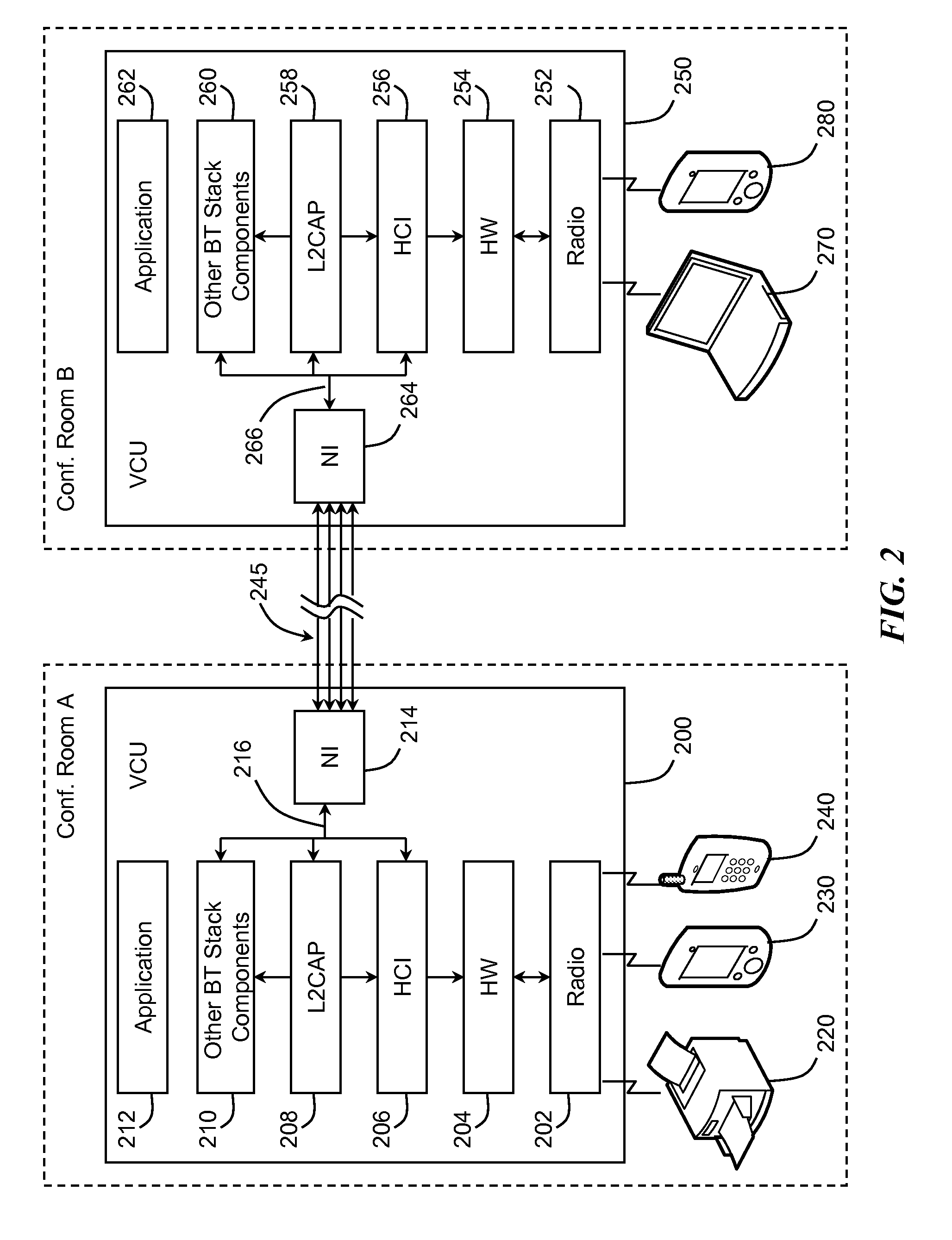
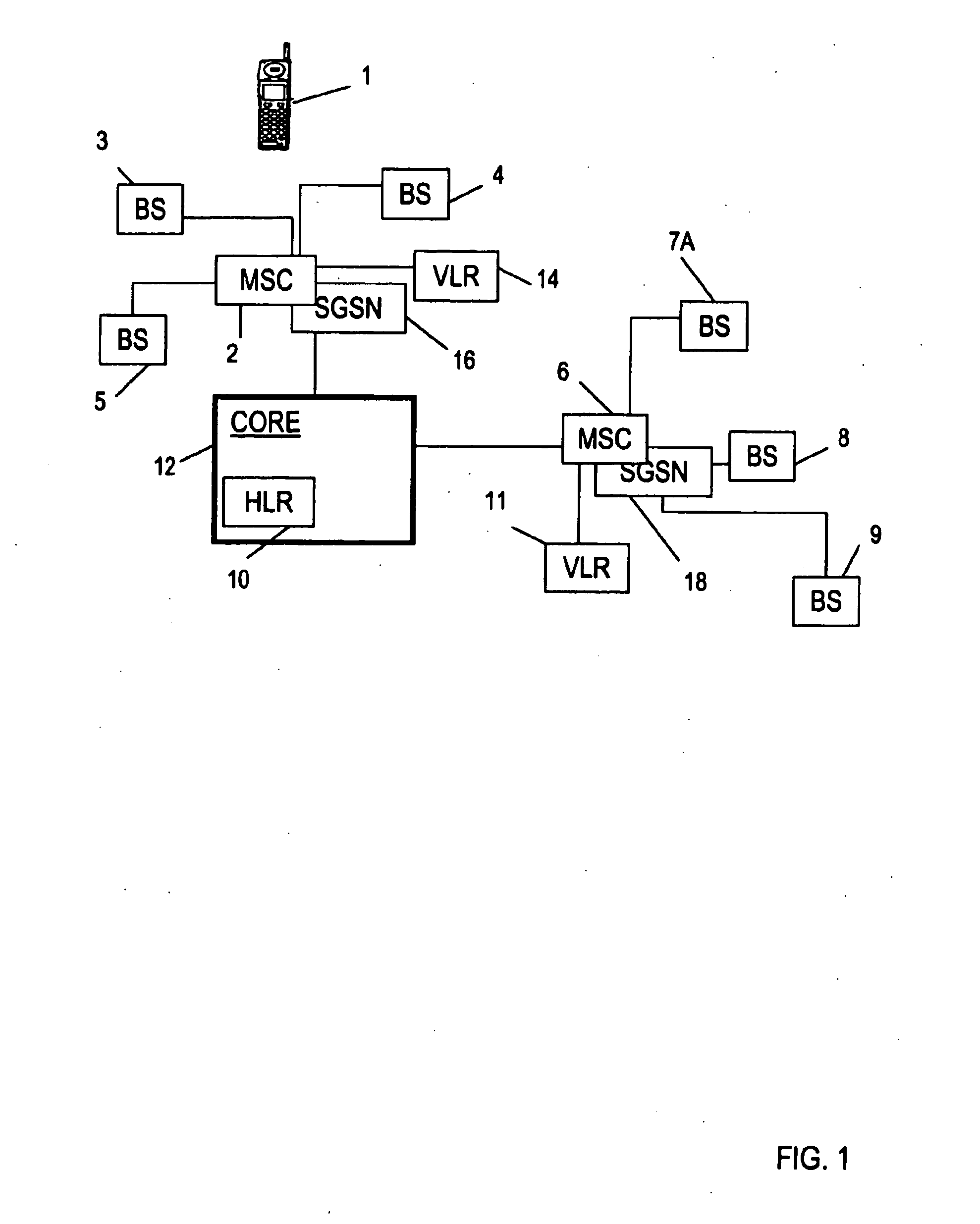
Hybrid mpeg/ip digital cable gateway device and architecture associated therewith
A novel cable gateway system and architecture incorporating a hybrid digital video transceiver. The digital cable system architecture combines reception of legacy video such as MPEG-TS based DVB-C streams with that of original IP video over DOCSIS channels. The system comprises a hybrid DVB / IP cable gateway STB capable of receiving both legacy DVB-C video and original IP video streams. The cable gateway device performs the front-end functionality (including QAM receiver, tuner and broadband connection) while the back-end functionality of video decoding and display is performed by one or more standard IP-STBs connected to the cable gateway device over a network (e.g., home LAN). Legacy MPEG-TS based DVB-C video is captured and encapsulated into packets for distribution over the network to the IP-STBs. The cable gateway distributes the original IP video received over the CATV source and the encapsulated legacy video as video over IP packets over the network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
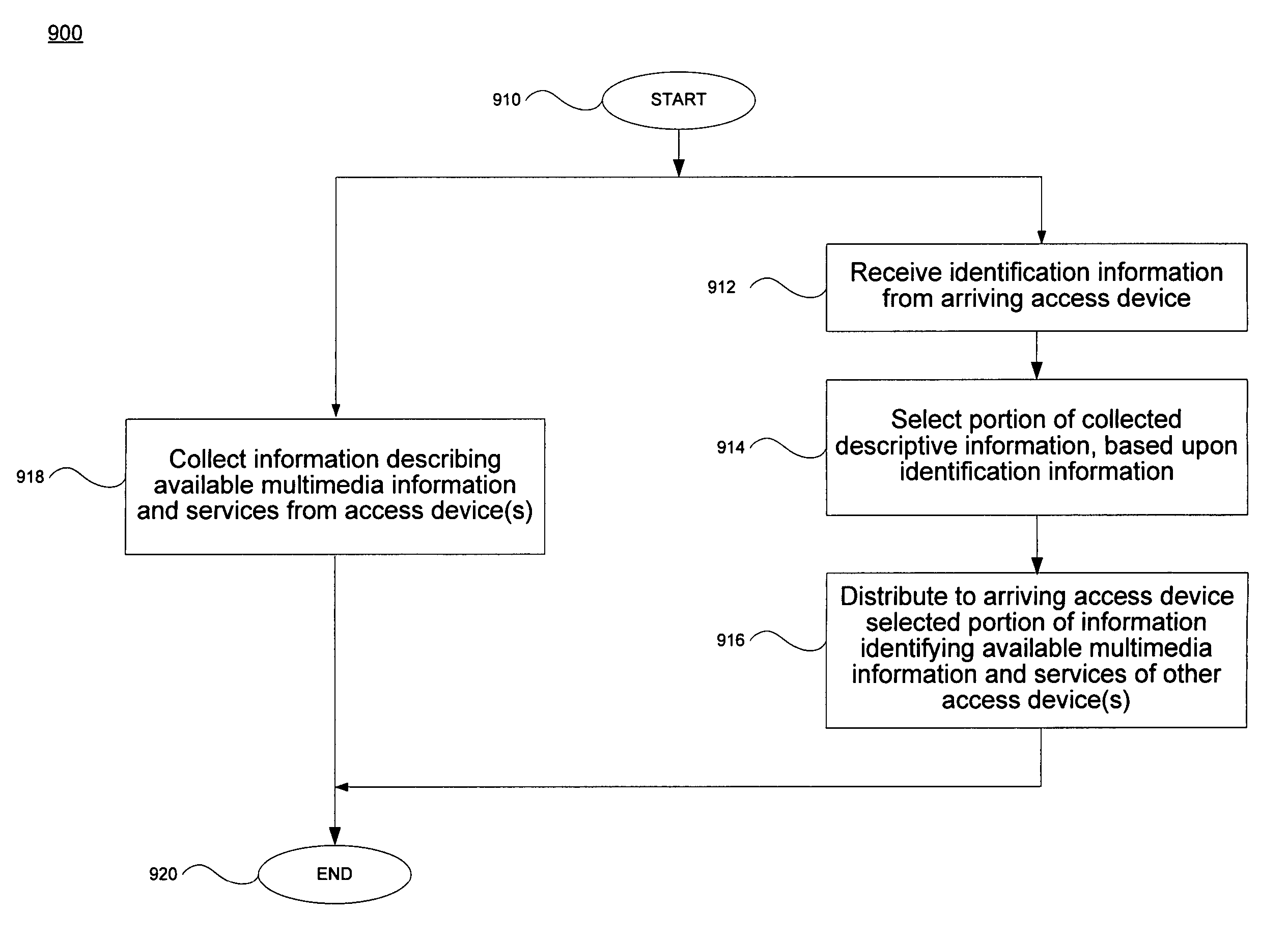
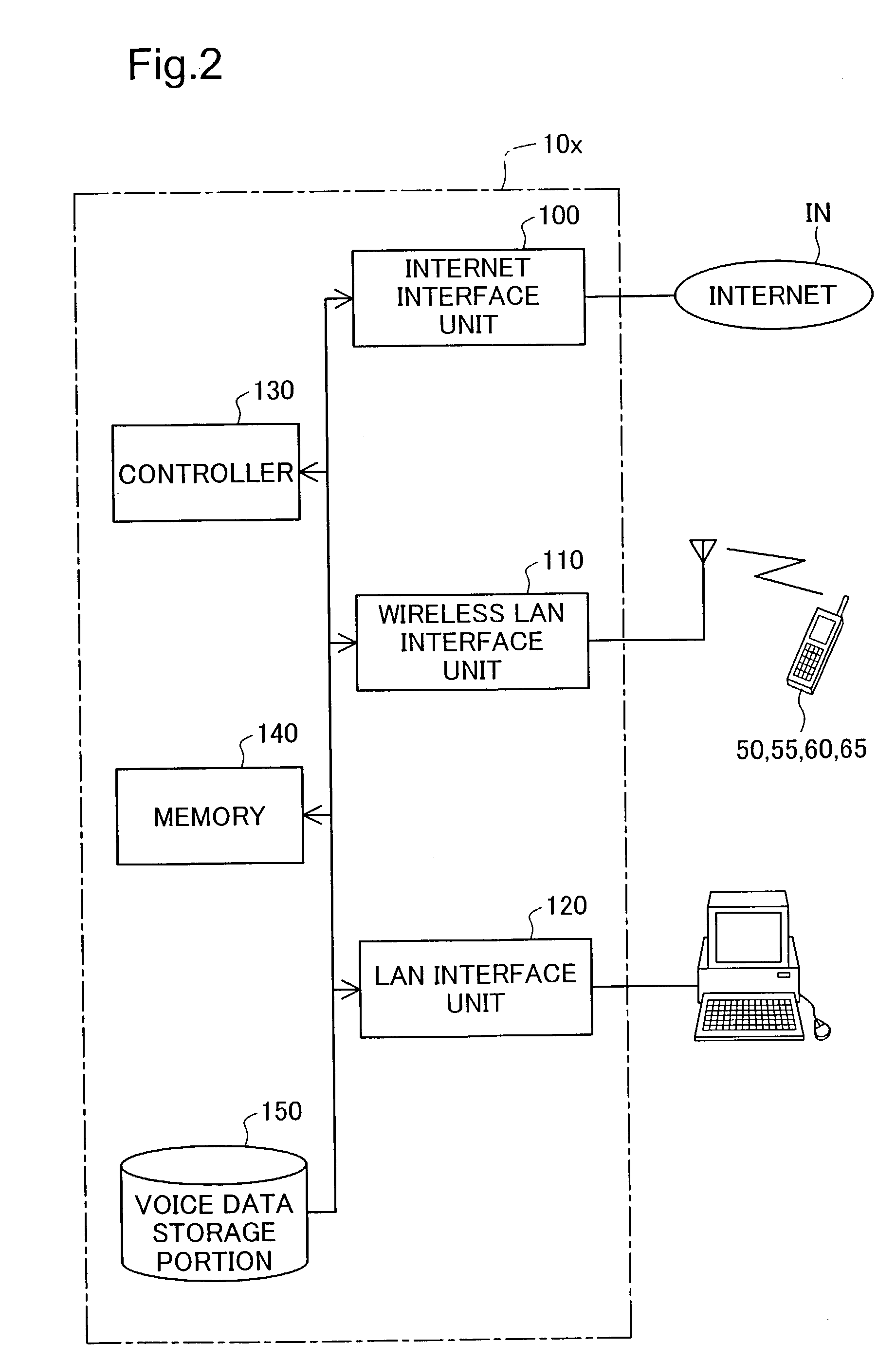
Registering access device multimedia content via a broadband access gateway
A system and method of registering or exchanging information about the availability of multimedia information and services is disclosed. Access devices in a wireless local area network (WLAN) and / or personal area network (PAN) may register, with a wireless broadband access gateway, selected information about multimedia information and services that they have and may share. Information about the available multimedia information and services may be shared by the wireless broadband access gateway with other access devices within the coverage area of the WLAN or PAN. Access devices may then access the multimedia information and services of other access devices via the wireless broadband access gateway, based upon information identifying and authenticating the recipient. A broadband connection permits the gateway to pass multimedia information and service activity to and from the access devices within the coverage area of the WLAN or PAN.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
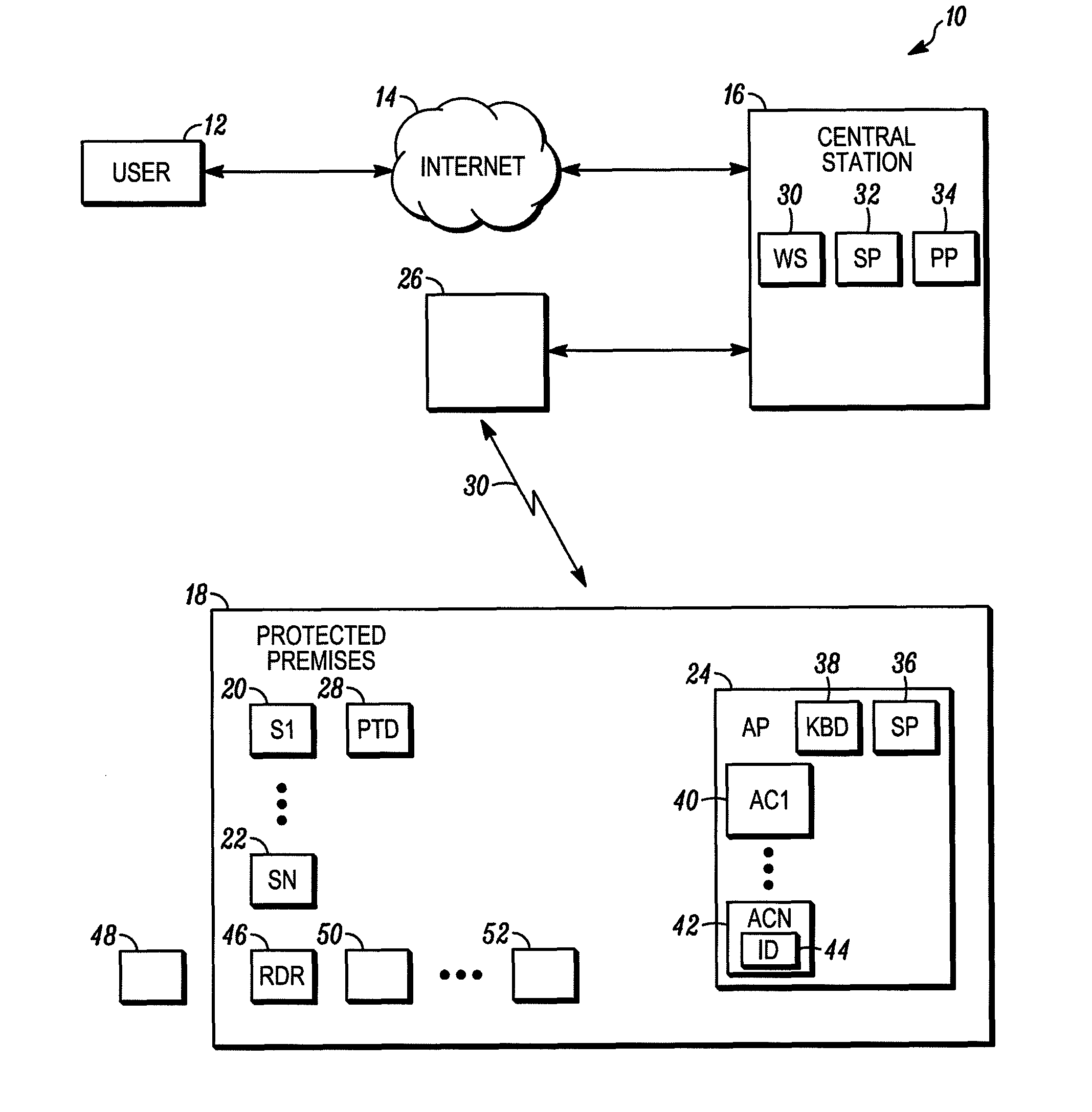
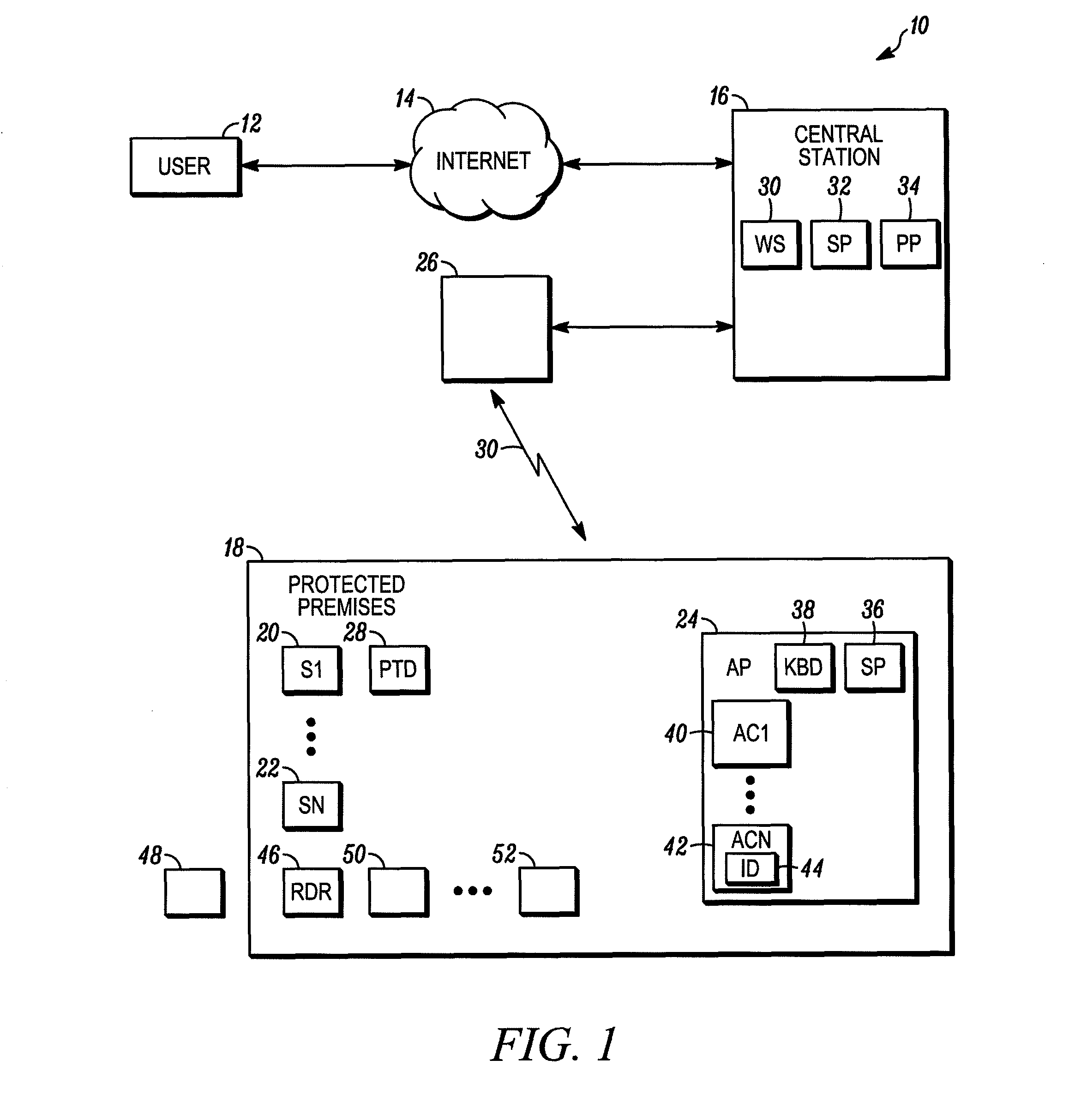
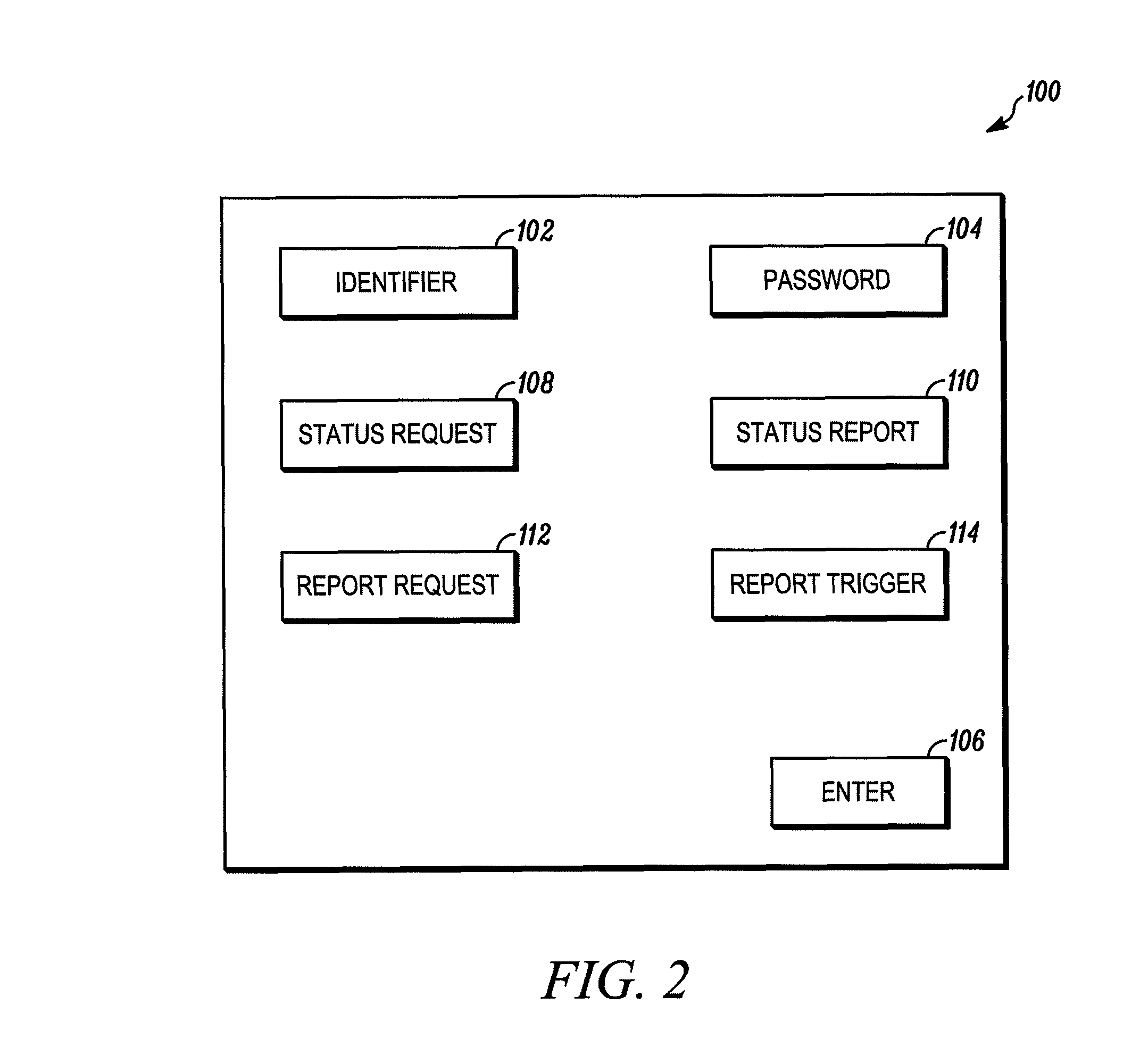
Method and apparatus for interrogation of a security system
ActiveUS8269623B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionWide bandSecurity system
A method and apparatus are provided for obtaining the status of a security system. The method includes the steps of providing a security system for a protected premises, coupling the security system to a central monitoring station through a short-range radio and a broadband connection that receives polling messages from the protected premises where the broadband connection forwards the polling message to the central station, the central station receiving a status request from an authorized user of the protected premises, in response to the polling message, the central station transmitting the status request to the security system through the broadband connection and short range radio system and the security system transmitting a status report through the short range radio and the broadband connection to the central monitoring station in response to the request.
Owner:ADEMCO INC
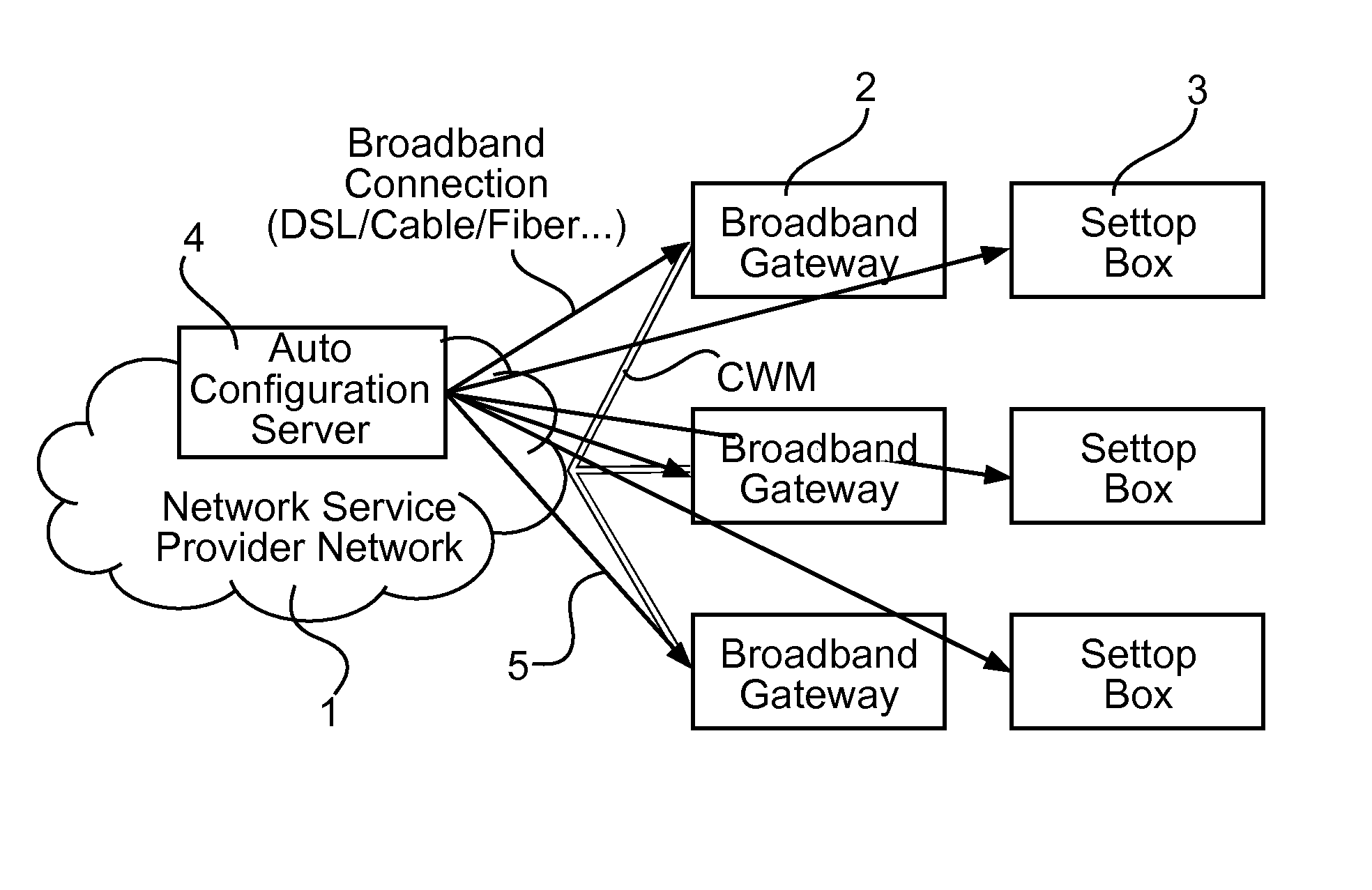
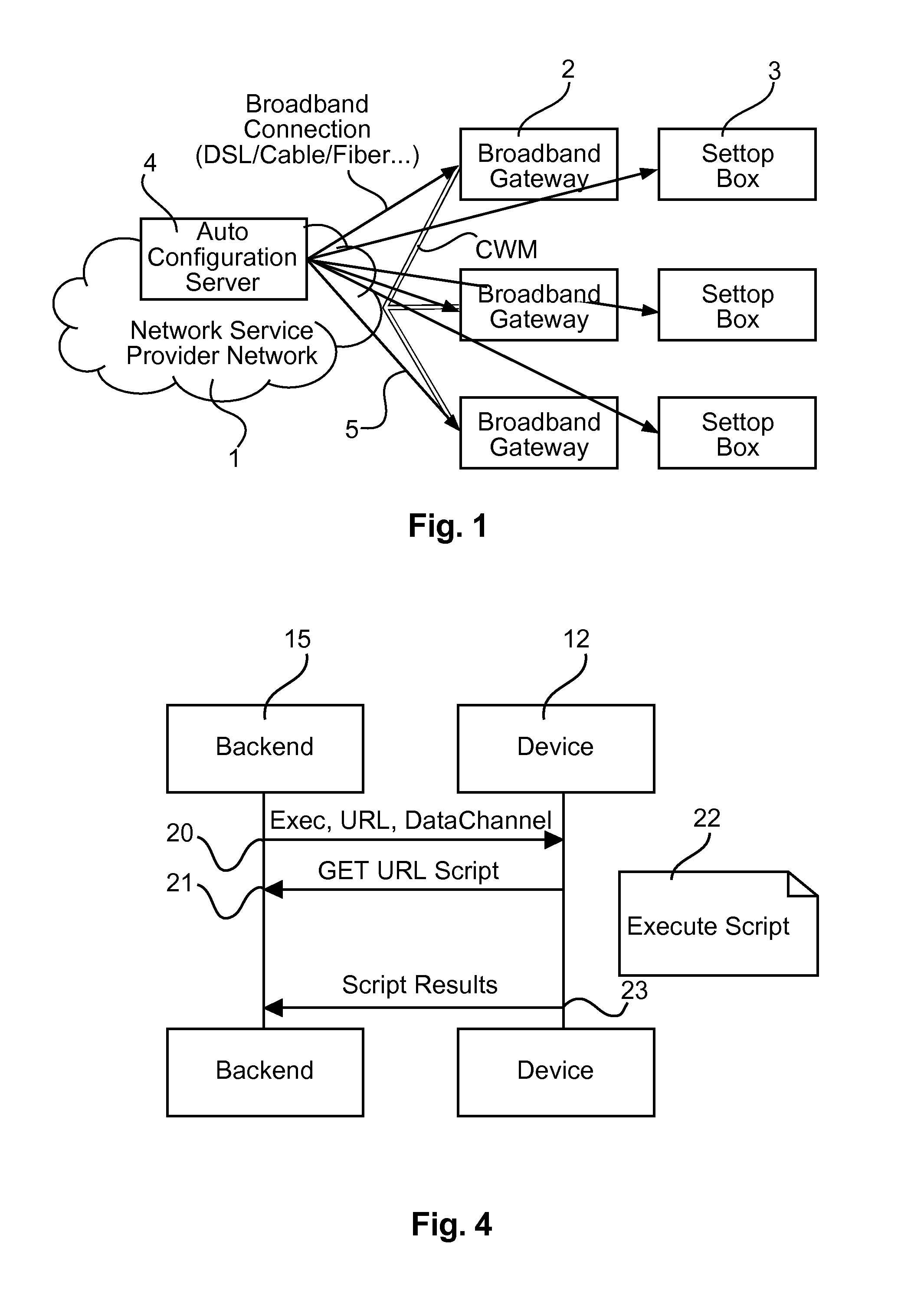
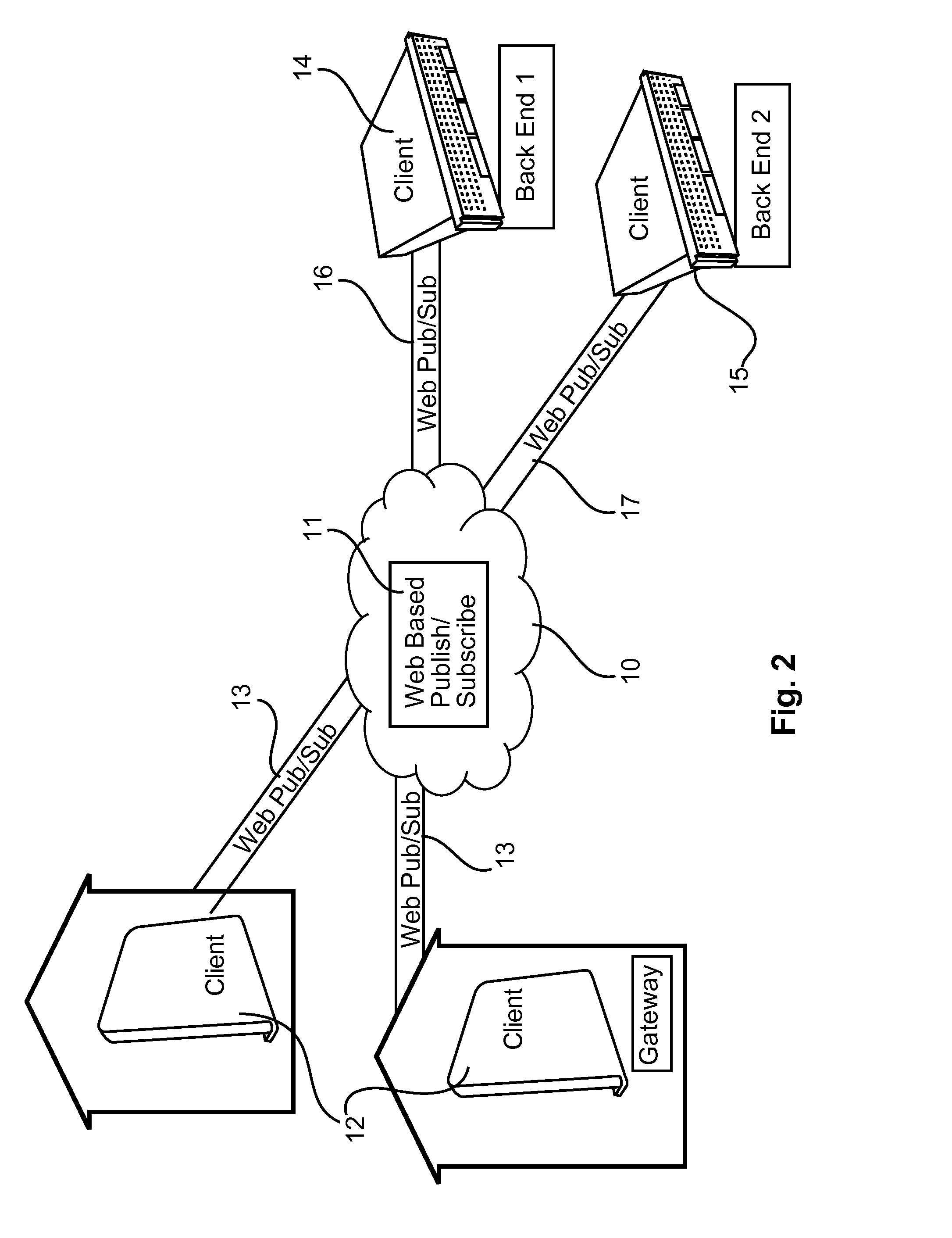
System comprising a publish/subscribe broker for a remote management of end-user devices, and respective end-user device
The present invention provides a method for sending a message to a network device with a specific MAC address, in an IP network implementing a internet group management protocol IGMP, comprising: sending, by a network terminal, to the network device, a multicast group management status message including a destination address set as the specific MAC address A system comprises a multitude of end-user devices coupled via a broadband connection with a service provider network, a publish / subscribe broker adapted to communicate with the multitude of end-user devices and at least a first back-end entity coupled with the service provider network. The first back-end entity includes a first client software application for connecting to the publish / subscribe broker and publishes control data via a control data channel for a device management of the end-user devices. The end-user devices include a second client software application for connecting to the publish / subscribe broker for subscribing to the control data channel and for receiving the control data, and for publishing device data and action data as instructed by the control data. The backend entity authorization is validated in particular by using a control data signature.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Distributed storage and aggregation of multimedia information via a broadband access gateway
ActiveUS20050232210A1Television system detailsBroadcast transmission systemsBroadcastingDigitization
A system and method for the aggregation of multimedia information storage via a broadband access gateway is disclosed. Information about storage resources accessible to a broadband access gateway may be collected and used in selecting storage capacity used for storing multimedia information such as, for example, streaming video, broadcast video, digitized video, digitized audio, text, and digitized images. The gateway may manage storage and retrieval of the multimedia information based upon user defined criteria and characteristics of the available storage resources. Multimedia information may be parsed for storage across multiple storage resources, and the location and nature of the storage resources used for storage of multimedia information items may be unknown to the user. Storage services accessible via a broadband connection may also be used as storage resources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
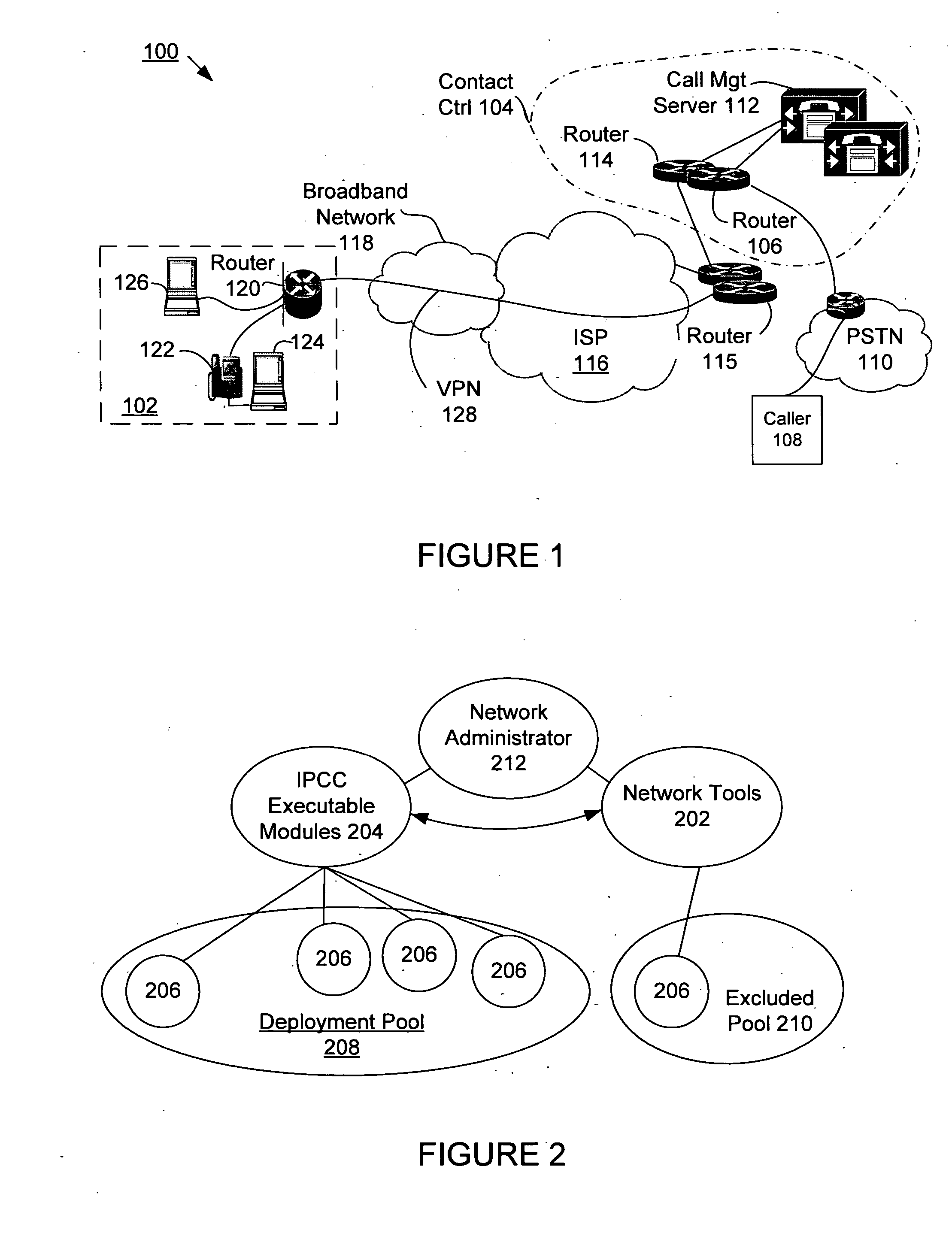
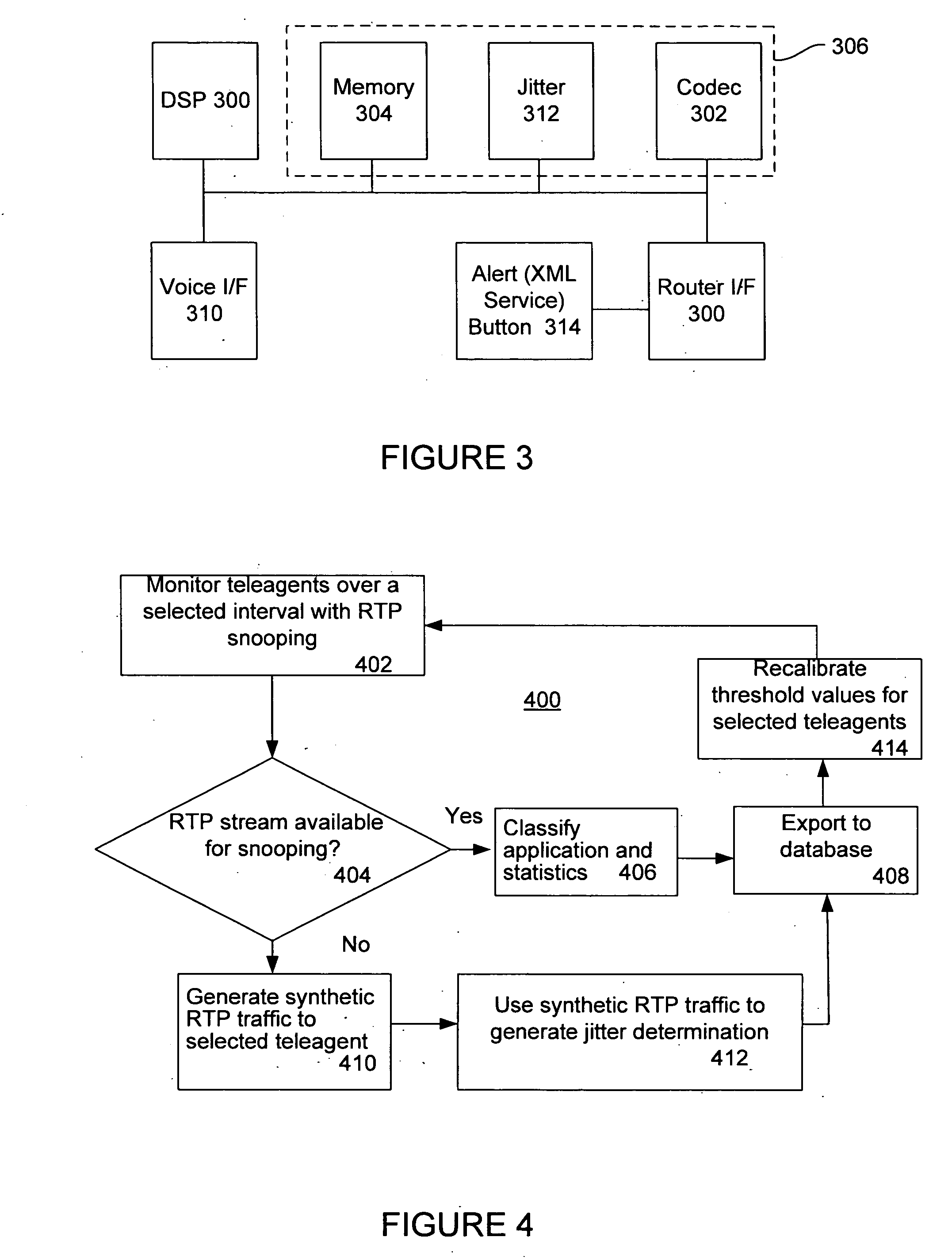
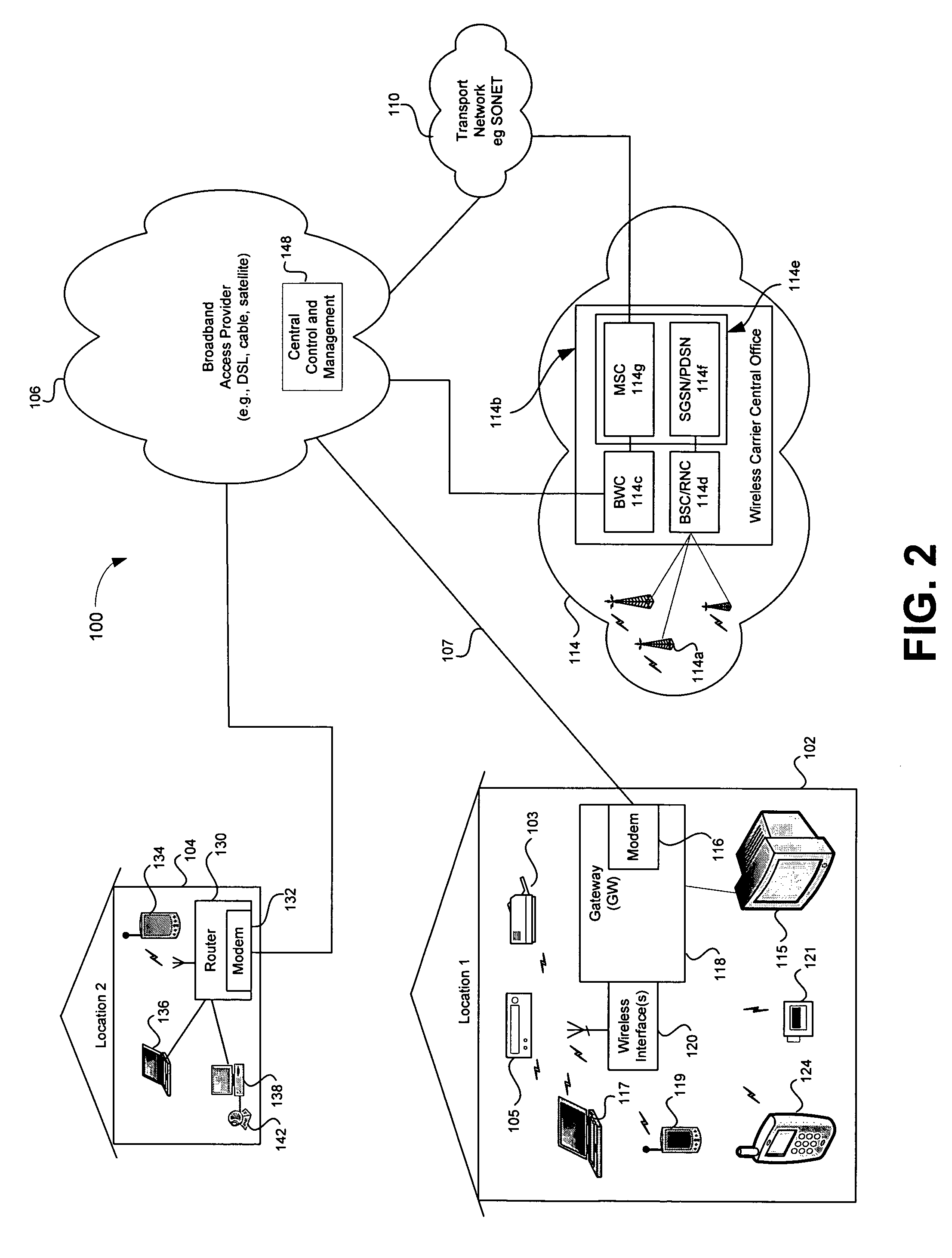
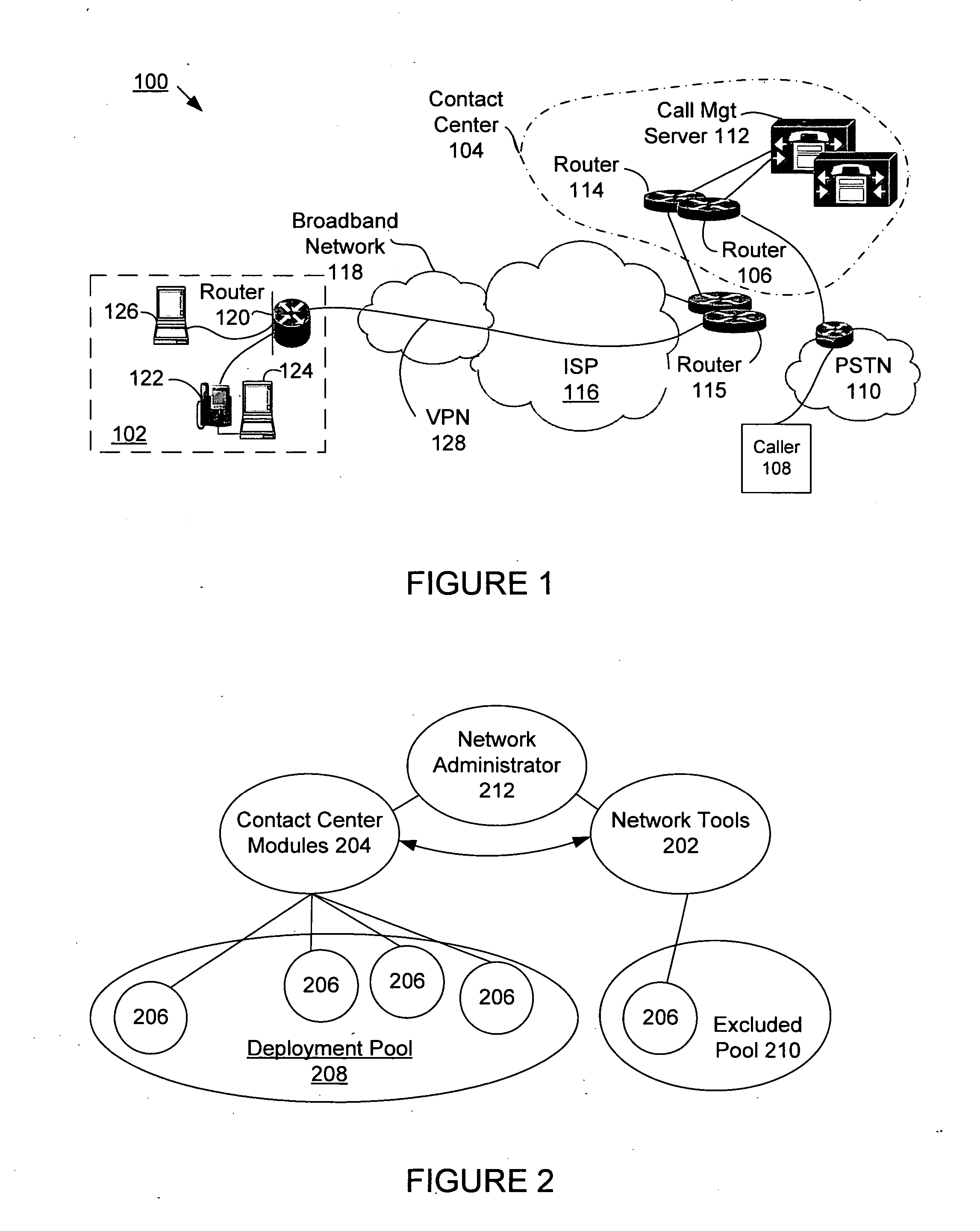
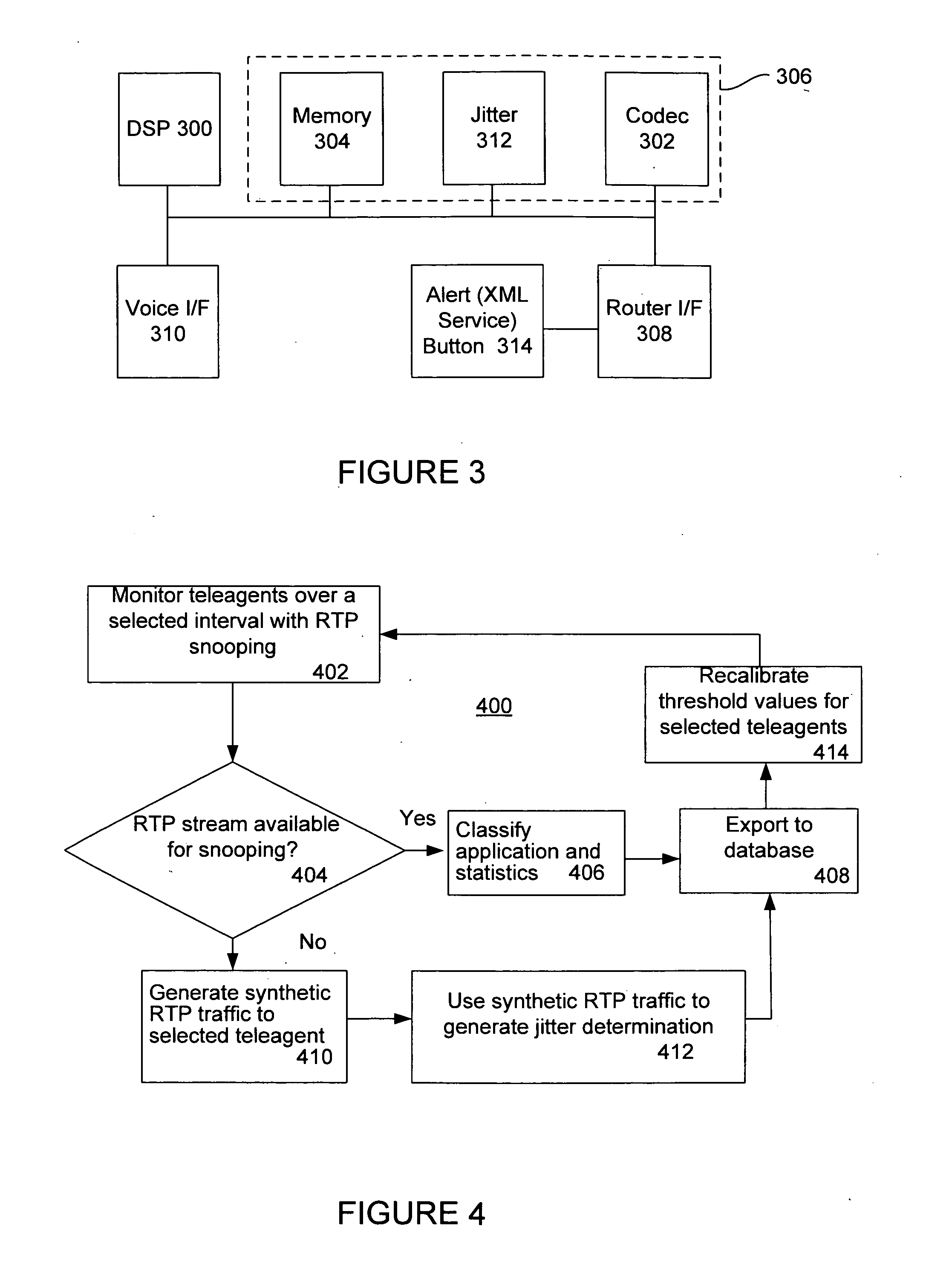
Method for managing the quality of encrypted voice over IP to teleagents
A voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) system and more particularly, an improved VoIP system serving a distributed group of teleagents. Network parameters that affect voice quality over broadband connections are rapidly detected by generating both detected and subjective alerts when problems with the quality of a IP telephone connection are detected and correcting the detected problems. Network parameters are monitored during an actual VoIP telephone call or by using synthetic traffic. If the voice quality degrades for a particular teleagent, the teleagent is removed from the pool of available agents until voice quality improves. Alternatively, the voice quality of each teleagent may be ranked according to the service provided.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Registering access device multimedia content via a broadband access gateway
ActiveUS7522549B2Television system detailsDigital computer detailsWireless broadband accessPersonal area network
A system and method of registering or exchanging information about the availability of multimedia information and services is disclosed. Access devices in a wireless local area network (WLAN) and / or personal area network (PAN) may register, with a wireless broadband access gateway, selected information about multimedia information and services that they have and may share. Information about the available multimedia information and services may be shared by the wireless broadband access gateway with other access devices within the coverage area of the WLAN or PAN. Access devices may then access the multimedia information and services of other access devices via the wireless broadband access gateway, based upon information identifying and authenticating the recipient. A broadband connection permits the gateway to pass multimedia information and service activity to and from the access devices within the coverage area of the WLAN or PAN.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
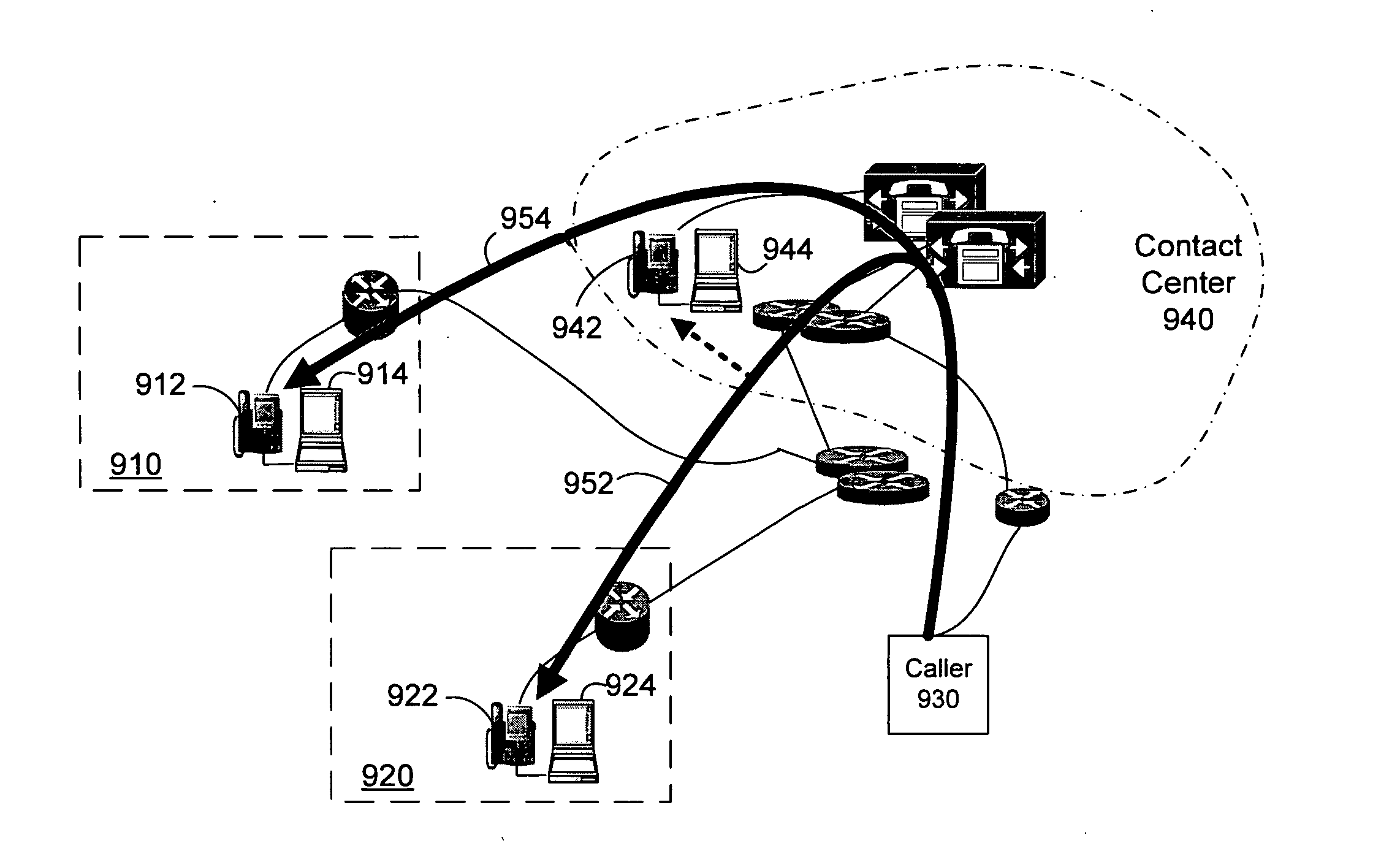
Supervisor intercept for teleagent voice over internet protocol communications
ActiveUS20070019618A1Special service for subscribersNetwork connectionsTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A system for transferring a call from one teleagent to another in response to a loss of voice quality in a voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) communication system. Network parameters that affect voice quality over broadband connections are detected manually or automatically and an alert is generated. In response to the alert, a supervisor can transfer the call in progress to a second agent so that a better communication link can be provided and voice quality restored. Such transfer can be seamless to the caller. In different embodiments, transfer, or intercept, can occur manually or automatically (e.g., without supervisor intervention).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for efficient content distribution using a peer-to-peer networking infrastructure
ActiveUS20050216559A1Effective distributionImprove the corresponding efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent distributionTime sensitive
Disclosed is a method for efficiently distributing content by leveraging the use of a peer-to-peer network infrastructure. In a network of peers, a handful peers can receive content from centralized servers. These peers can then flood this content out to more clients who in turn can send the content along to others. Ultimately, a request for content can be fulfilled by locating the closest peer and obtaining the content from that peer. In one embodiment the method can be used to distribute content by creating content distribution groups of one or more client computing devices and redirecting requests for content from the server to the content distribution group. A further contemplated embodiment efficiently streams time sensitive data through the use of a spanning tree architecture of peer-to-peer clients. In yet another embodiment the present invention provides for more efficient use of bandwidth for shared residential broadband connections.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
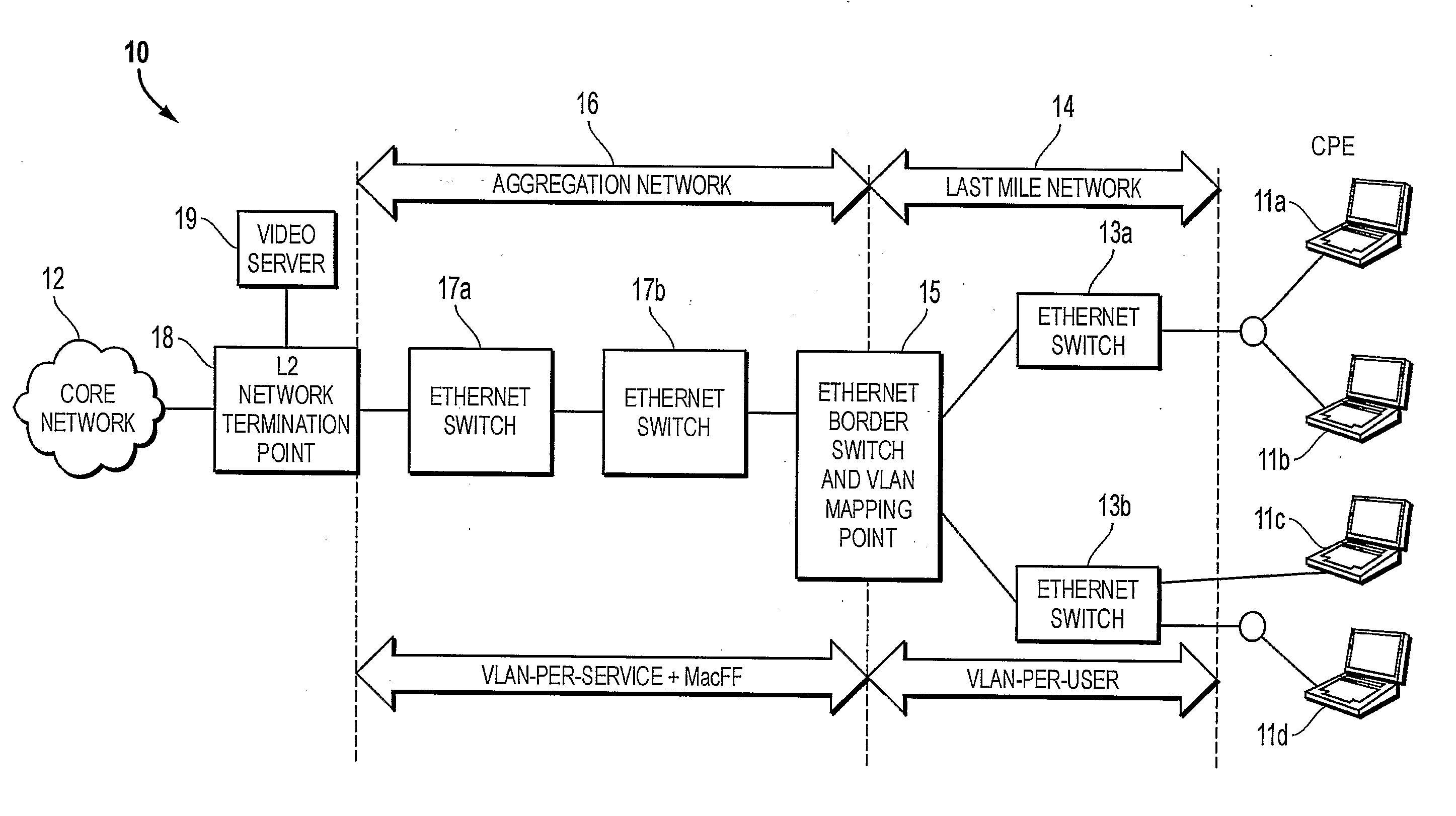
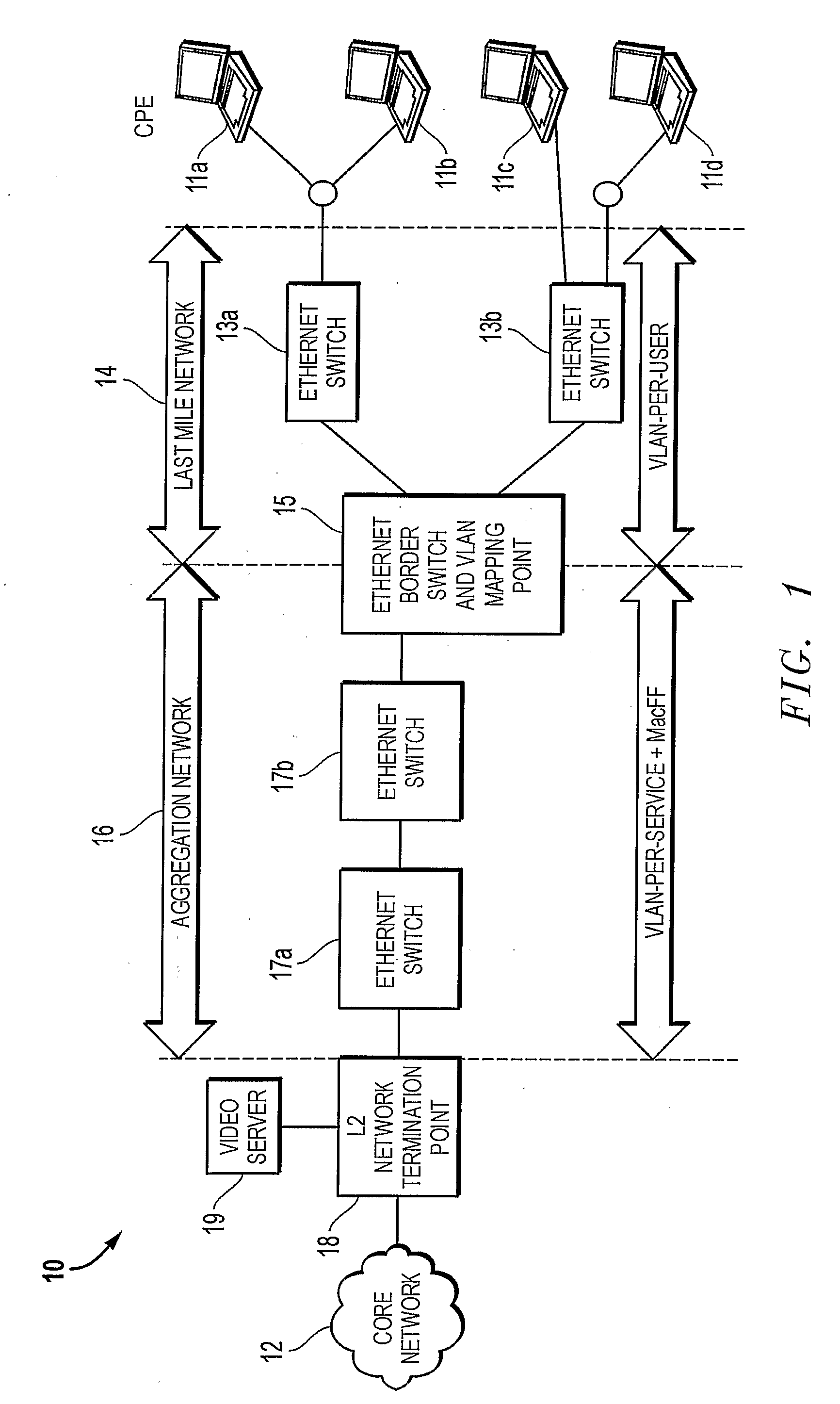
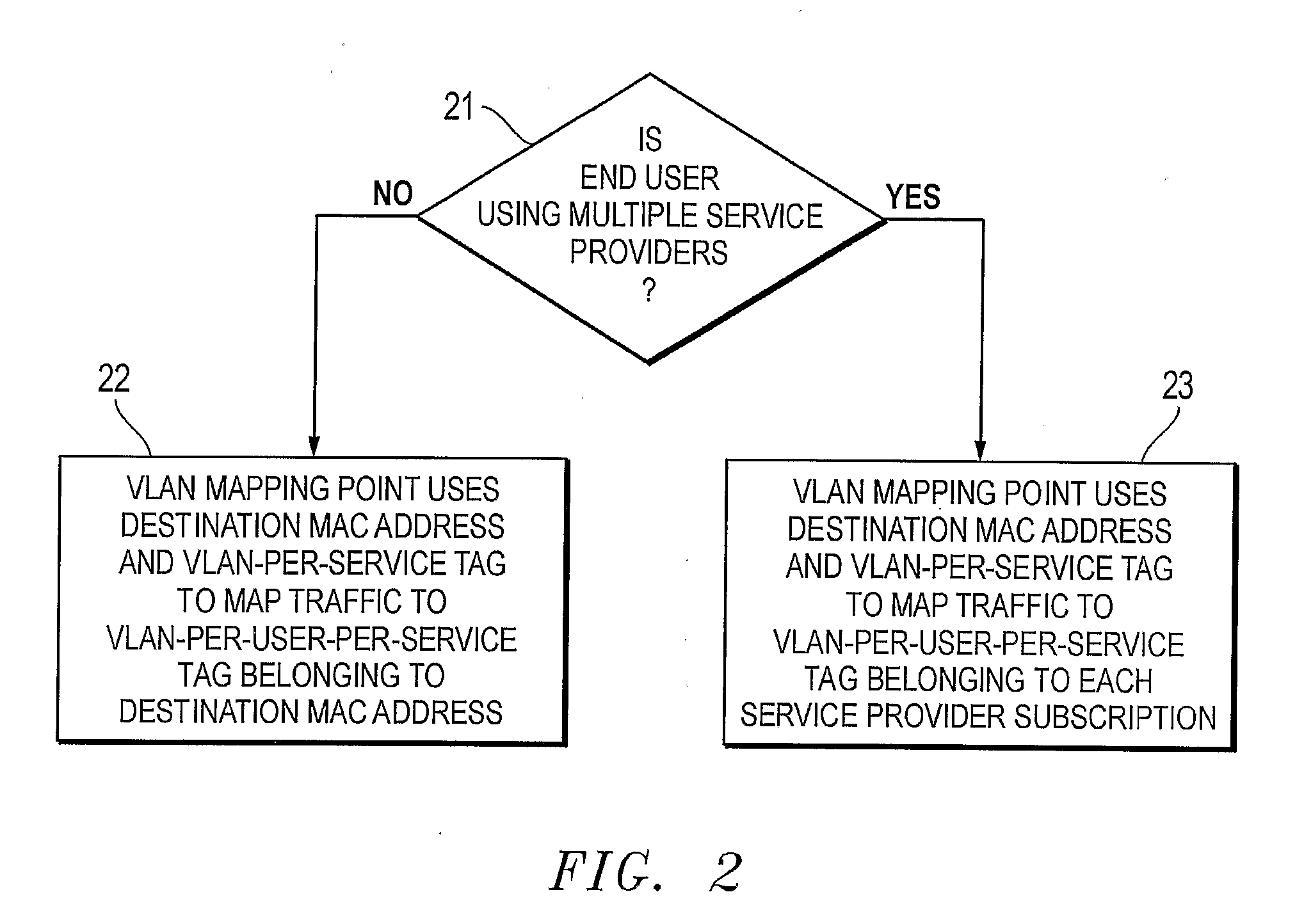
Vlan Mapping For Multi-Service Provisioning
A Virtual Local Area Network, VLAN, Mapping Point enables an end user to simultaneously access multiple services through a single broadband connection. The VLAN Mapping Point is implemented at a border between first and second independently tagged VLAN regions, and includes a mapping function that receives traffic packets from each of the VLAN regions, maps VLAN tags in the packets to associated VLAN tags for the other VLAN region, and forwards the packets using the associated VLAN tags. The first VLAN region may be a last-mile network that connects to end users. and the second VLAN region may be an aggregation network that connects to a core network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Distributed storage and aggregation of multimedia information via a broadband access gateway
A system and method for the aggregation of multimedia information storage via a broadband access gateway is disclosed. Information about storage resources accessible to a broadband access gateway may be collected and used in selecting storage capacity used for storing multimedia information such as, for example, streaming video, broadcast video, digitized video, digitized audio, text, and digitized images. The gateway may manage storage and retrieval of the multimedia information based upon user defined criteria and characteristics of the available storage resources. Multimedia information may be parsed for storage across multiple storage resources, and the location and nature of the storage resources used for storage of multimedia information items may be unknown to the user. Storage services accessible via a broadband connection may also be used as storage resources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
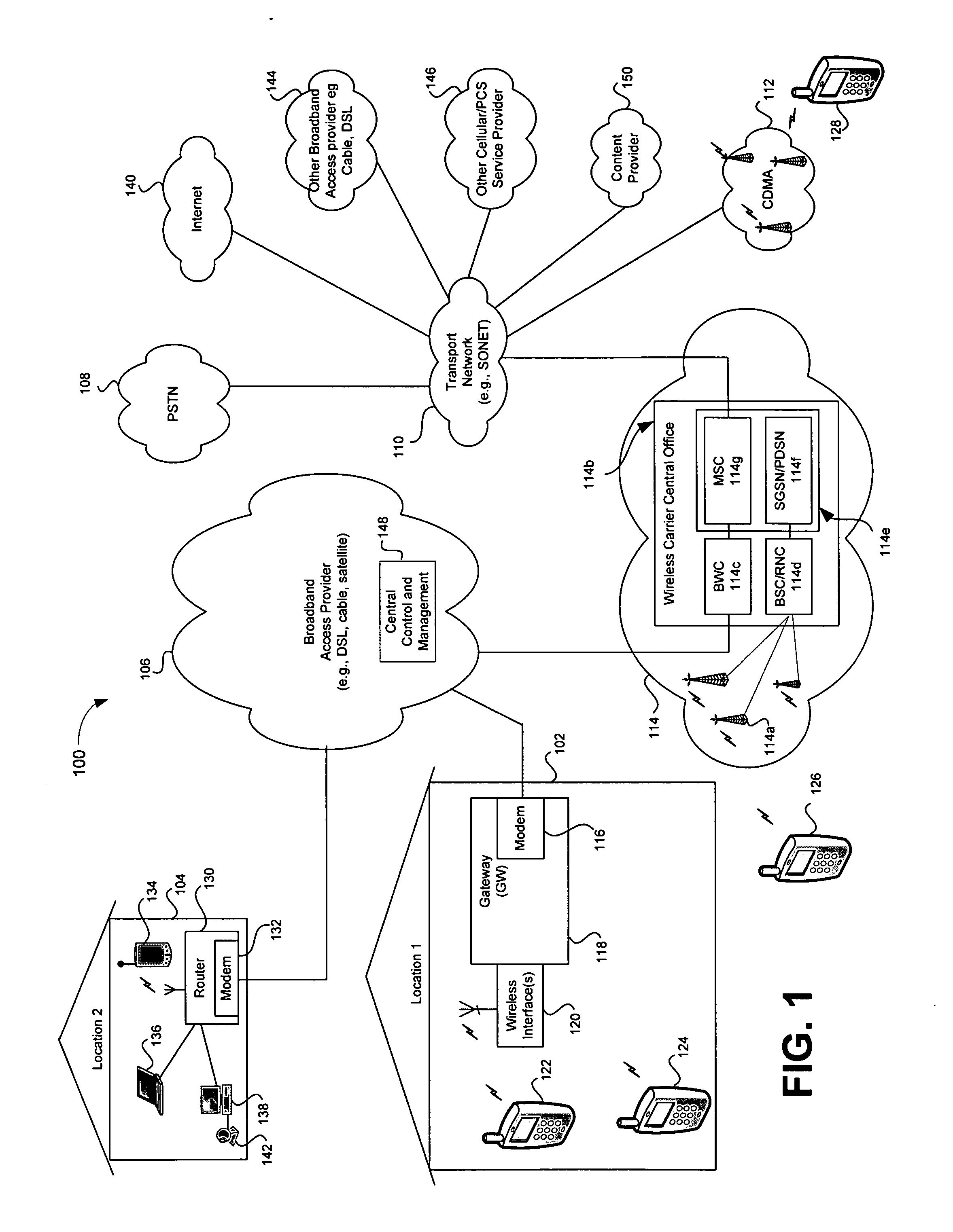
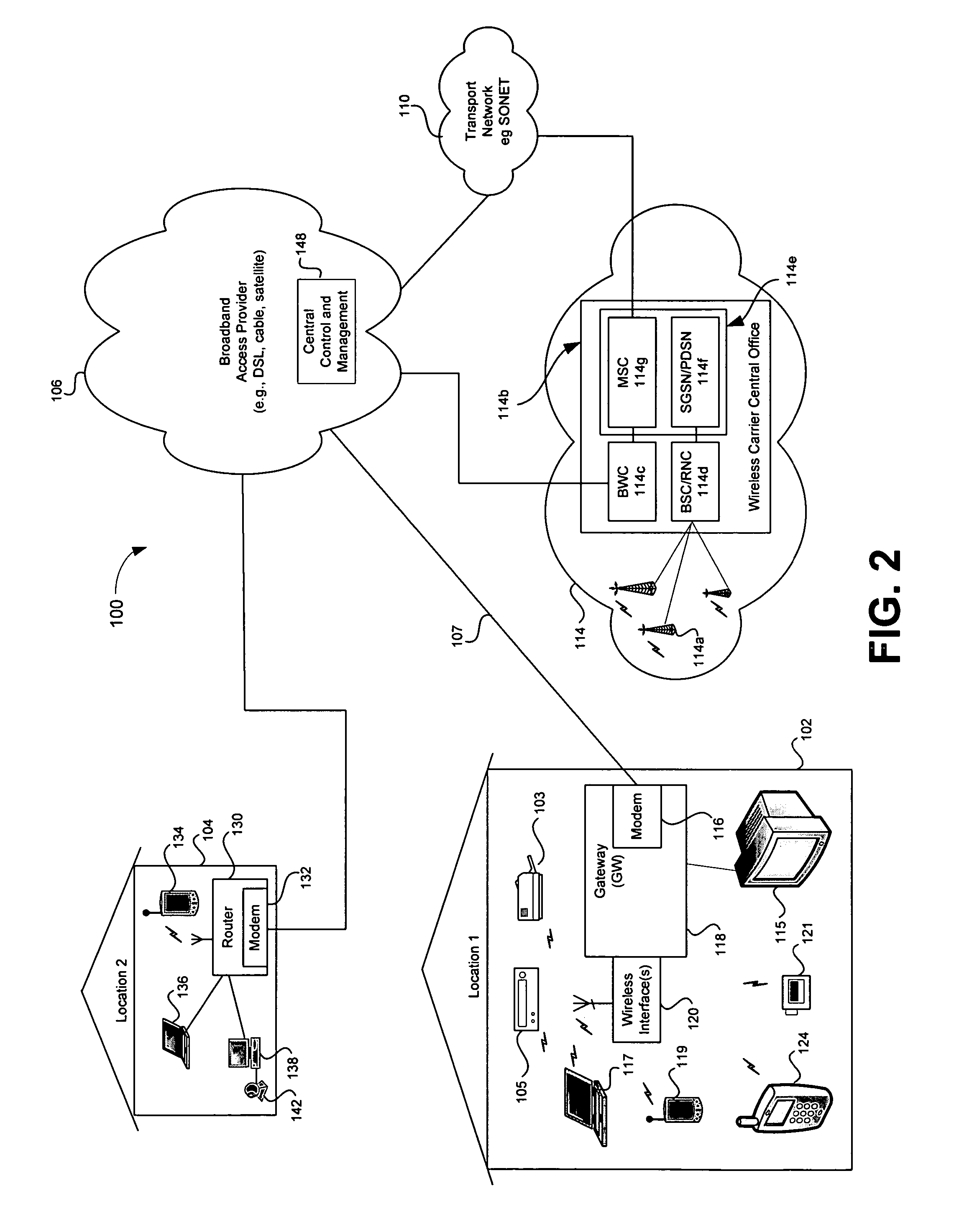
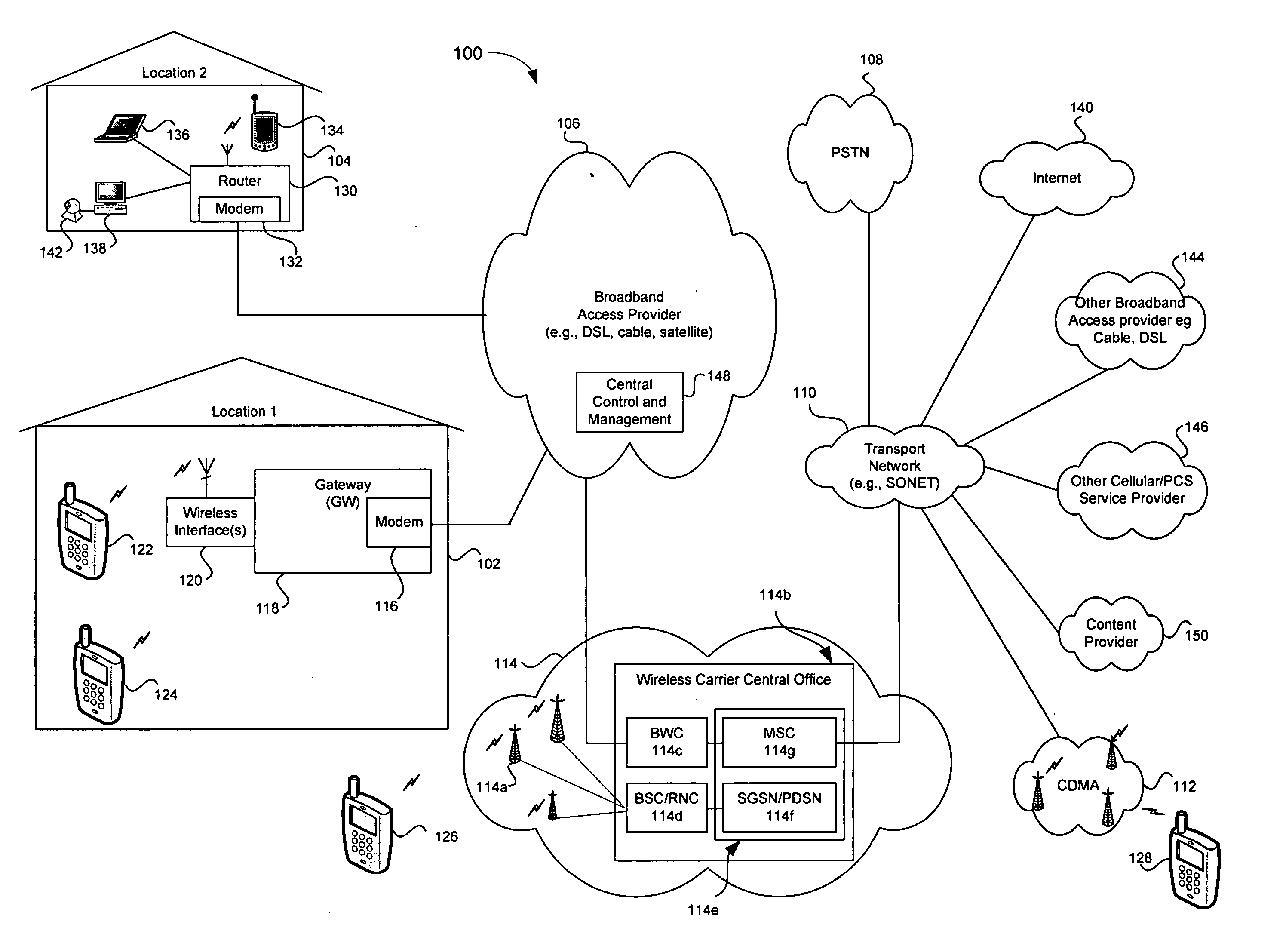
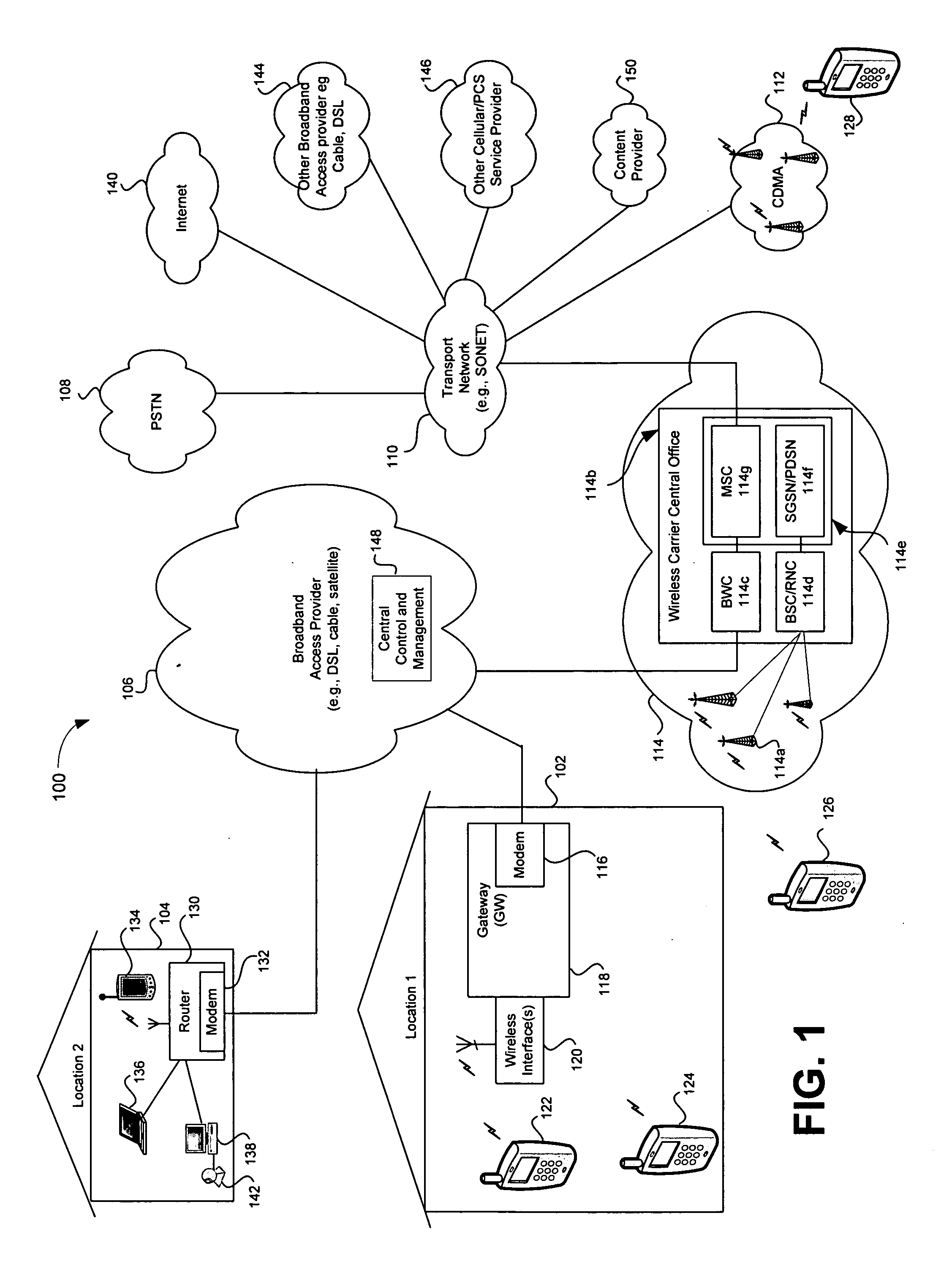
Telecommunications networks and devices
InactiveUS20110263274A1Reduce usageNeed can be usedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesBroadband connectionBase station
A GSM, UMTS or LTE mobile telecommunications network includes a radio access network comprising base stations, and further includes one or more additional access points. An access point may be connected to the network core by an IP transport broadband connection. The access point is configured to appear to the mobile terminal as a base station. Arrangements are disclosed which allow the network to restrict access to the network via these access points whilst also minimizing signaling requirements. The access points may be excluded from traditional Tracking Areas, but associated therewith by a network controller in a mapping in order to notify authorized mobile terminals of the Access Point's existence.
Owner:VODAFONE GRP PLC
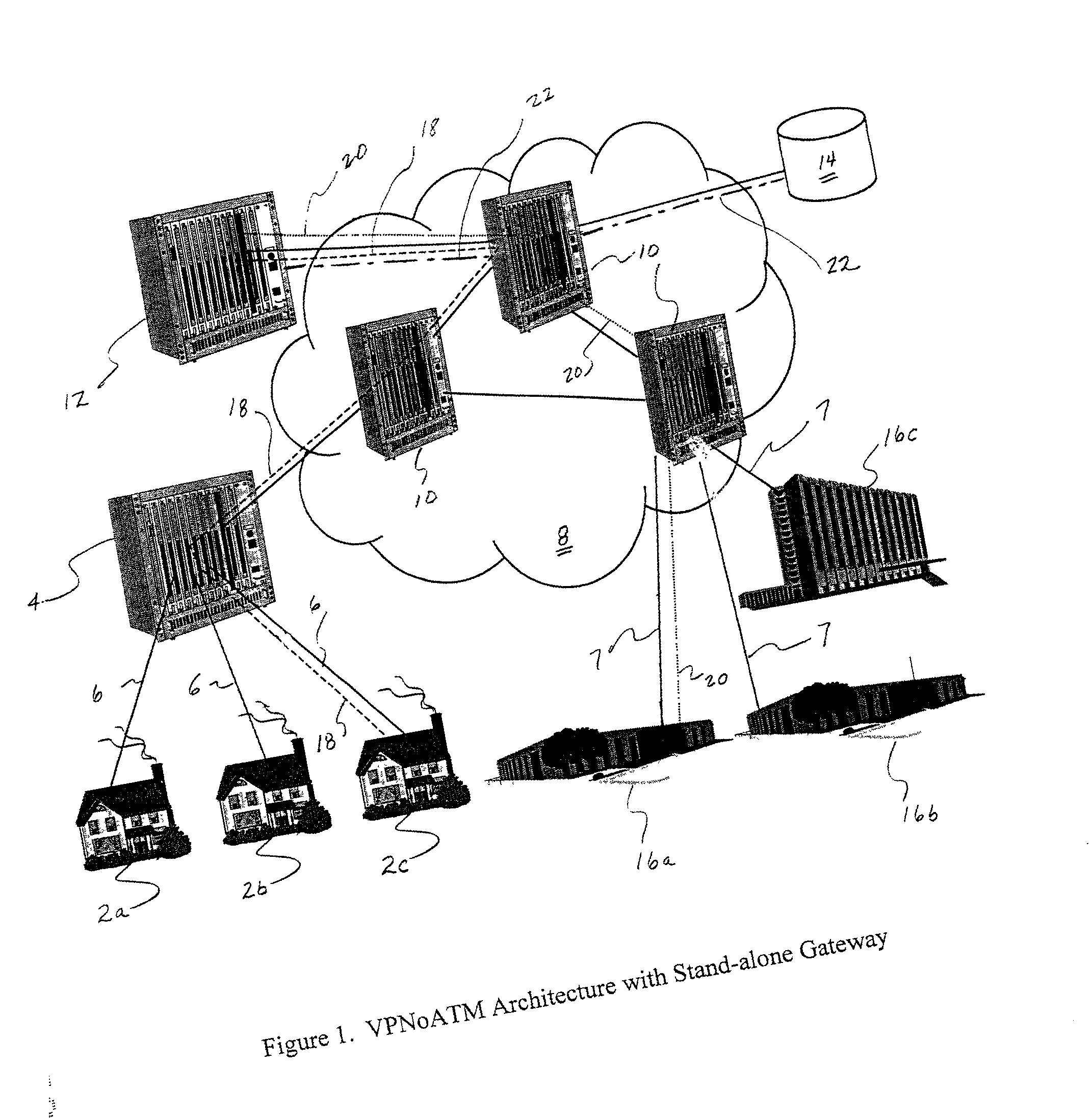
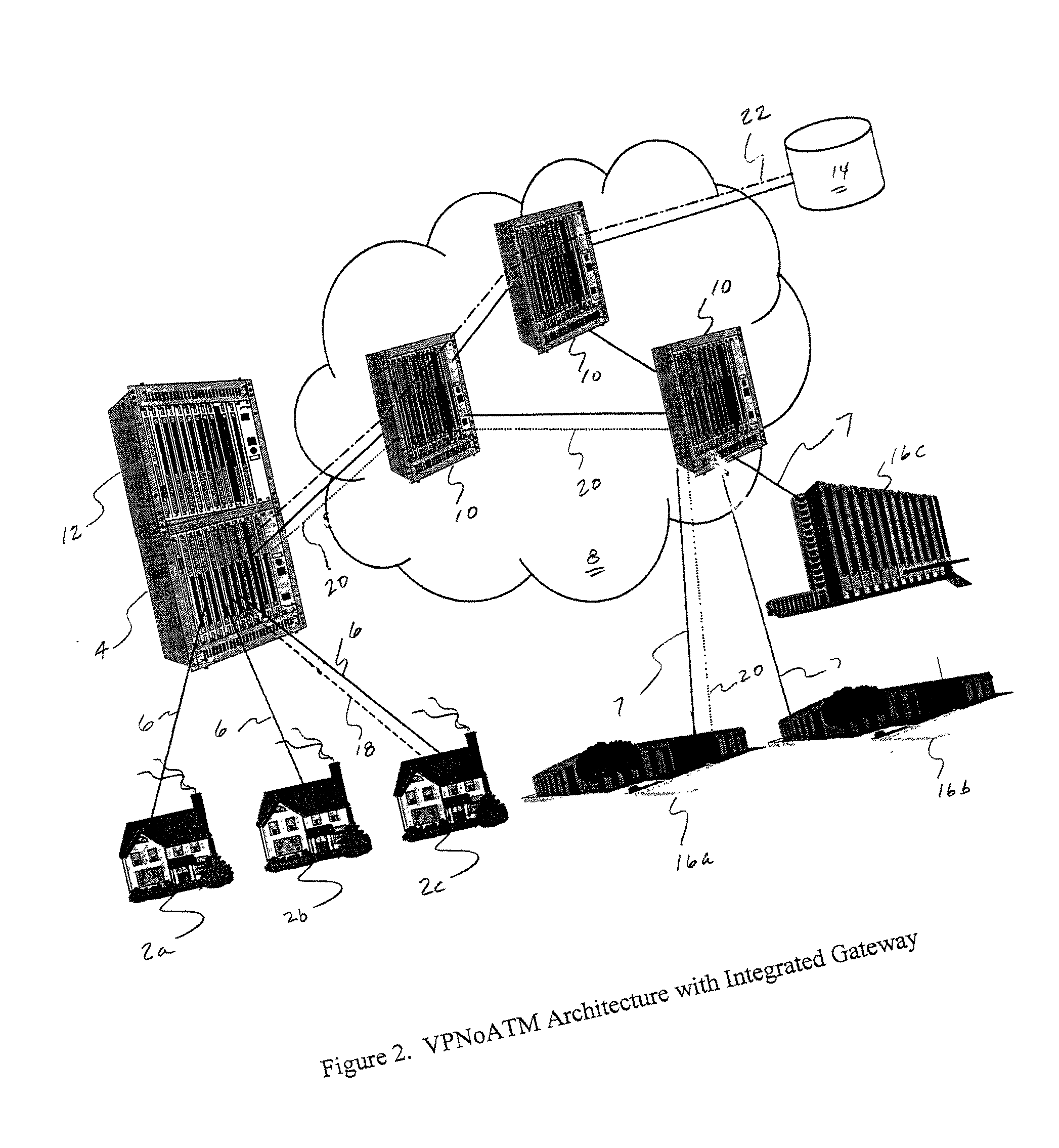
Virtual private network over asynchronous transfer mode
InactiveUS20030016676A1Data switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionPrivate networkNetwork address
A communications network and method enable broadband service subscribers to dynamically select broadband service destinations they wish to access from subscriber customer premises equipment. The communications network is an ATM network including a plurality of ATM switches. The network also includes at least one directory server connected to the ATM network, at least one fiber terminating device connected to the at least one directory server, and at least one broadband destination connected to the ATM network. Furthermore, the subscribers' customer premise equipment is connected to the at least one fiber terminating device. The method includes receiving a session request, which identifies a destination, in the at least one service gateway, wherein the session request is transmitted over a broadband connection using an Internet protocol. Next, using the at least one service gateway, an ATM network address of the destination from the at least one directory server is retrieved. Then an SVC is launched over the ATM network from the at least one service gateway to connect the subscriber to the ATM network address. Finally, the subsequent packets are forwarded to the destination over the ATM SVC connection.
Owner:SBC TECH RESOURCES
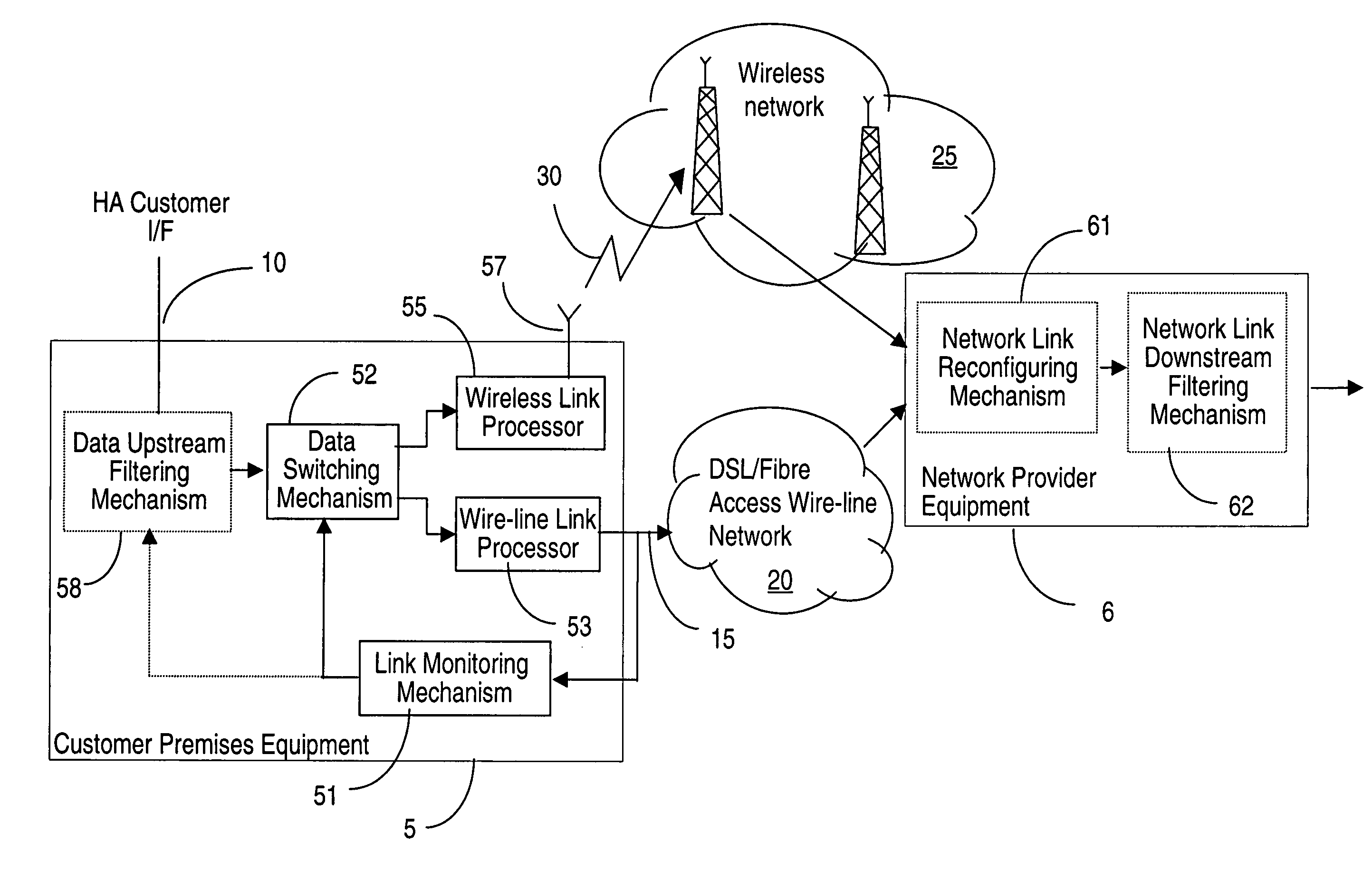
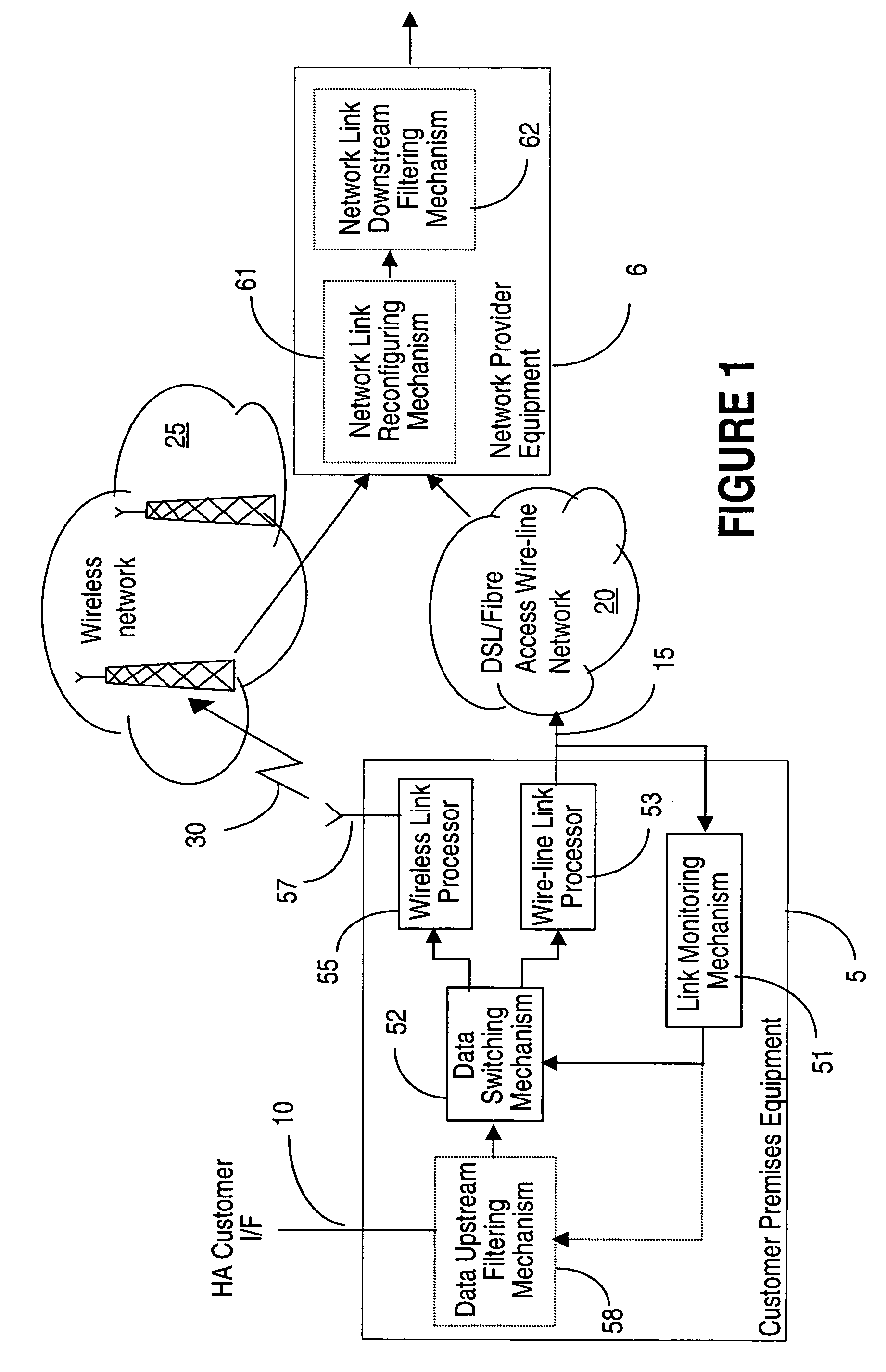
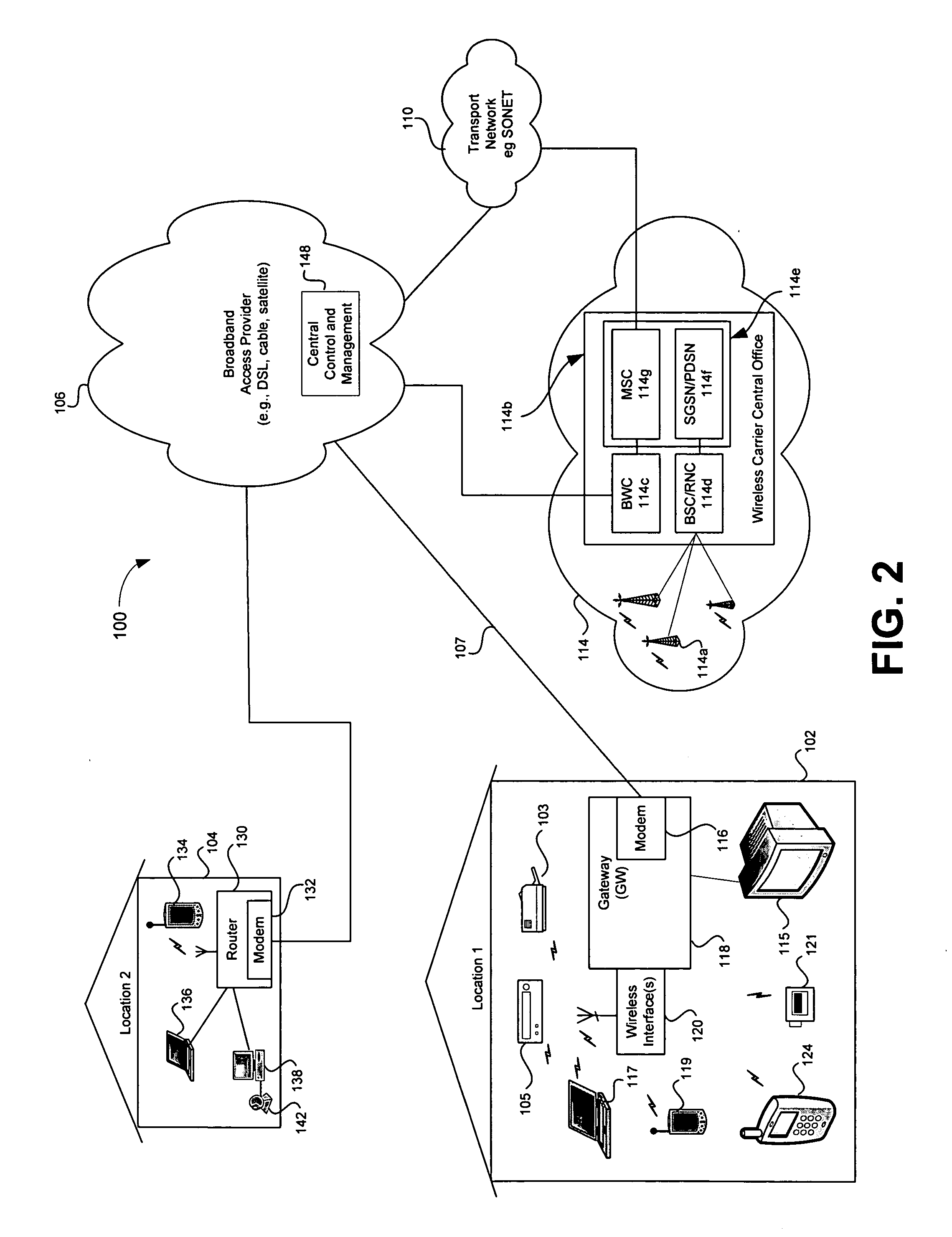
High availability broadband connections through switching from wireline to diverse wireless network
InactiveUS20050174935A1Improve usabilityReduce bandwidth costsInterconnection arrangementsError preventionHigh availabilityProtection system
A broadband access connection carried over a wireline link is backed-up by a wireless connection to create a high availability communication channel. This protection system comprises a wireline link processor for connecting a user site to a provider network over a broadband access connection and a wireless link processor for connecting the user site and the provider network over a backup connection. A link monitoring mechanism supervises operation of the wireline link and generates a fault signal upon detection of a specified under-performance, failure, or overloading condition of the broadband wireline access connection. A data switching mechanism switches the user traffic received over the user interface between the wireline and the wireless link according to the fault signal. A method for protecting the wireline link is also provided.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
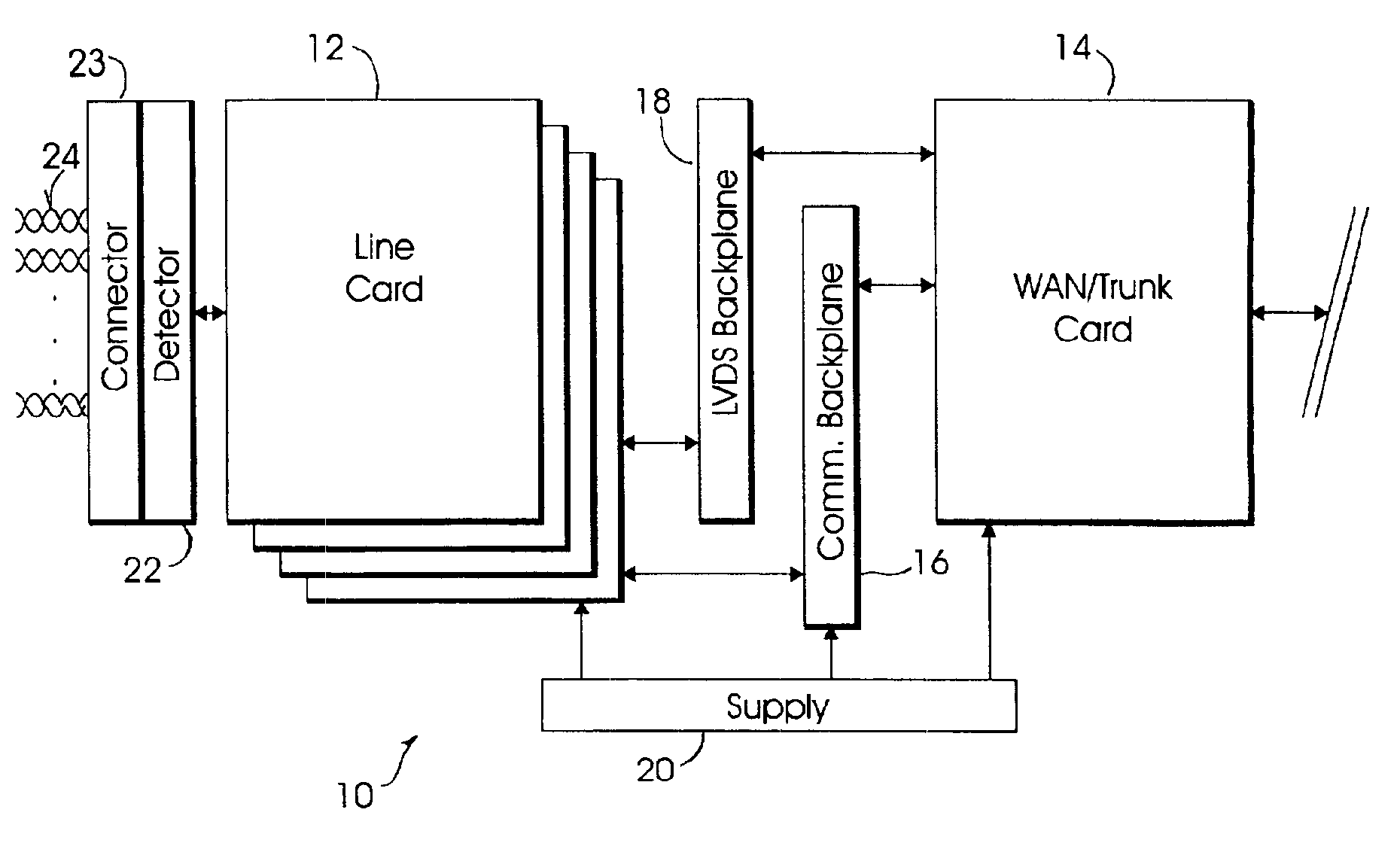
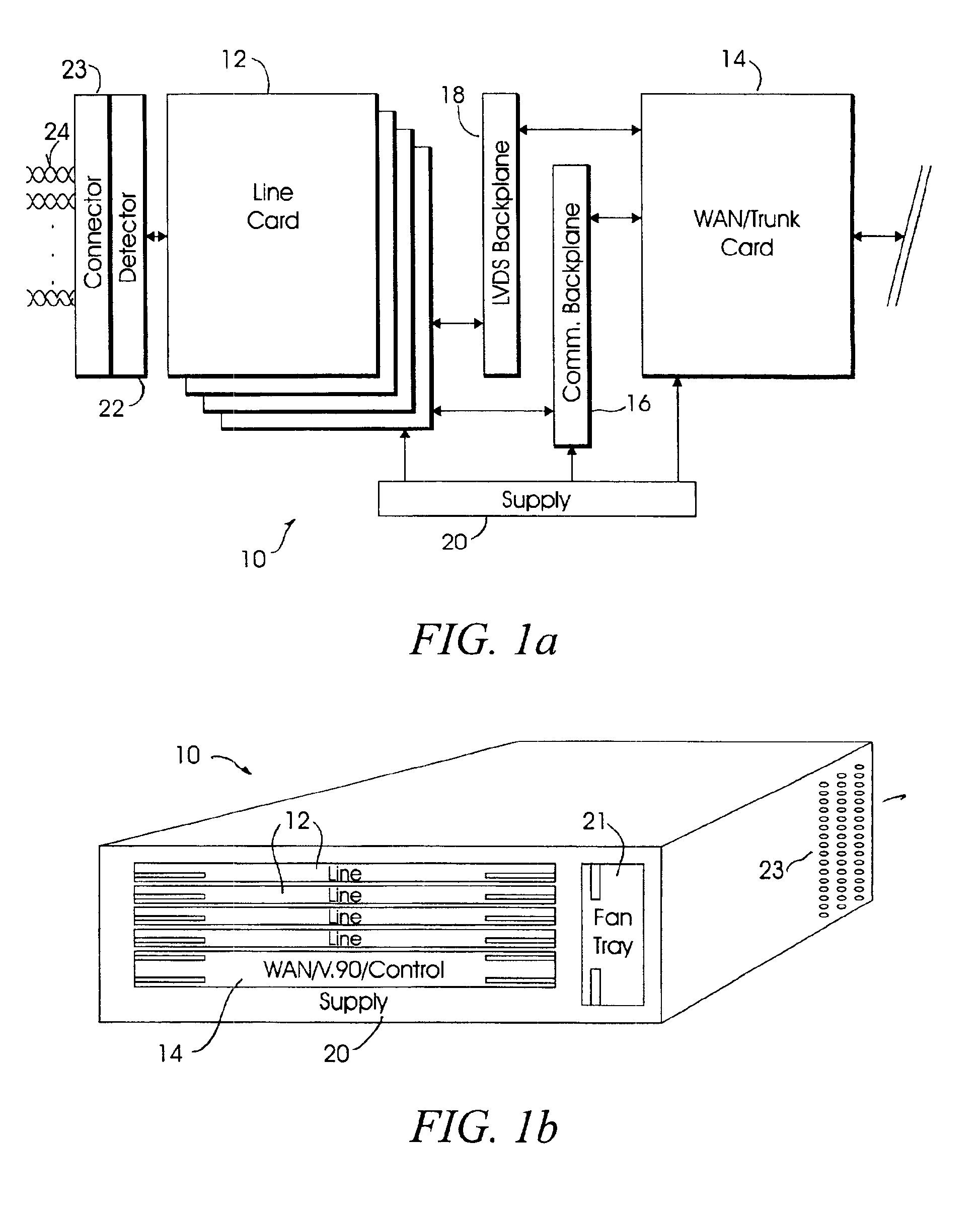
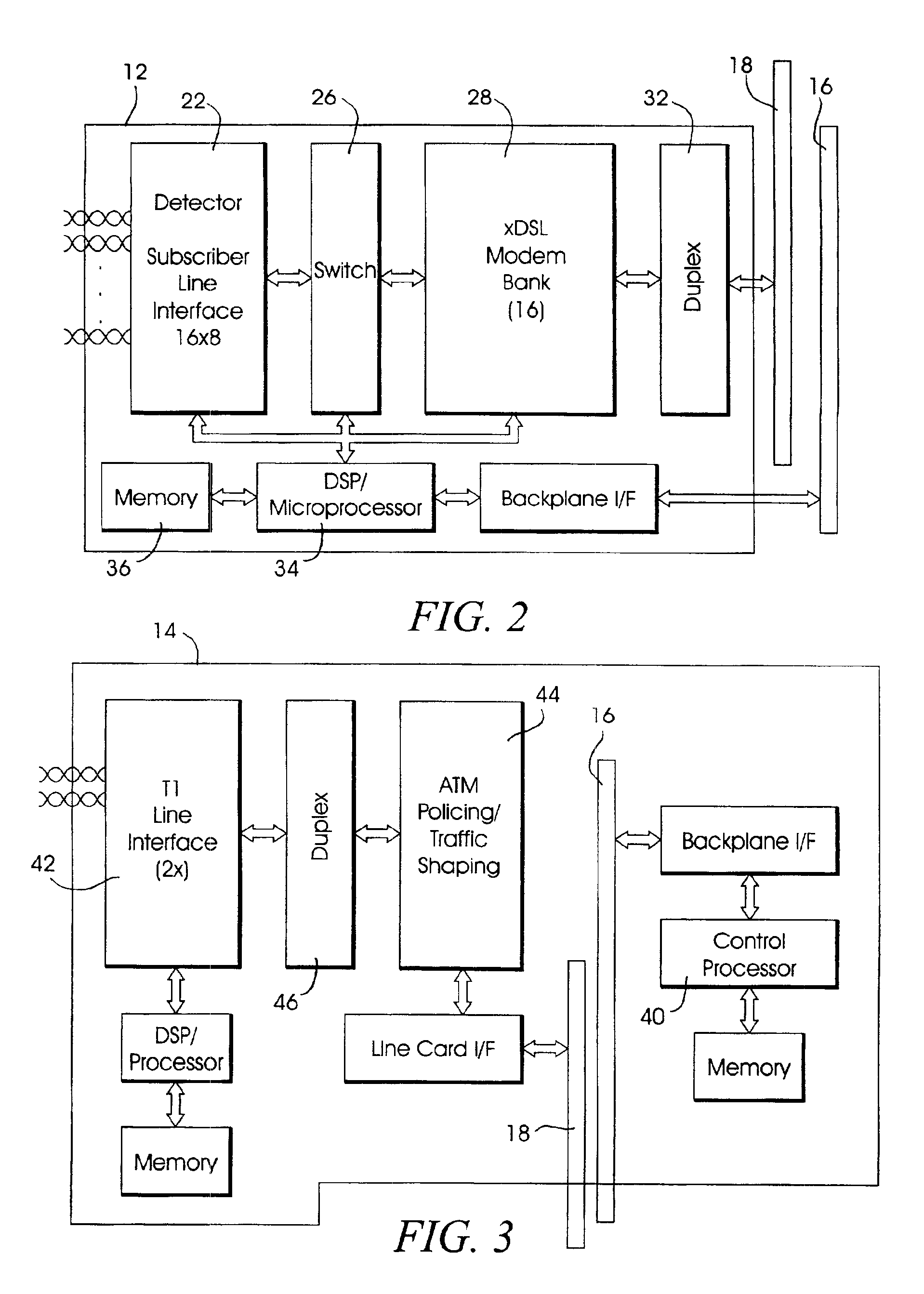
System and method for broadband roaming connectivity using DSL
InactiveUS6963579B2Facilitate multiple simultaneous communication sessionTelephonic communicationNetwork connectionsModem deviceHigh density
A broadband communication appliance allows multiple, simultaneous access by a multiplicity of users to a high-speed broadband wide area network connection. Multiple data lines, facilitated within a user premises are aggregated, by high-density connectors, into a system that includes multiple DSL modems, coupled to a wide area network through a high-speed network interface device. Data service requests are detected and particular ones of the DSL modems are assigned to service a particular data line. Bi-directional communication, using the modem bank, is concentrated through the high-speed network interface device, such that multiple users are able to obtain broadband connectivity, using DSL data rates. Users are authenticated as DSL subscribers, by maintaining their subscription profile information on an authentication server. The system retrieves a subscriber's profile information from their local authentication server, and maintains it locally, such that a user is able to effect DSL communication in accordance with DSL service, as obtained from their own service provider. A user is able to therefore “roam” while maintaining DSL connectivity.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
System and method for a private wireless network interface
InactiveUS20070060133A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationResidenceService provision
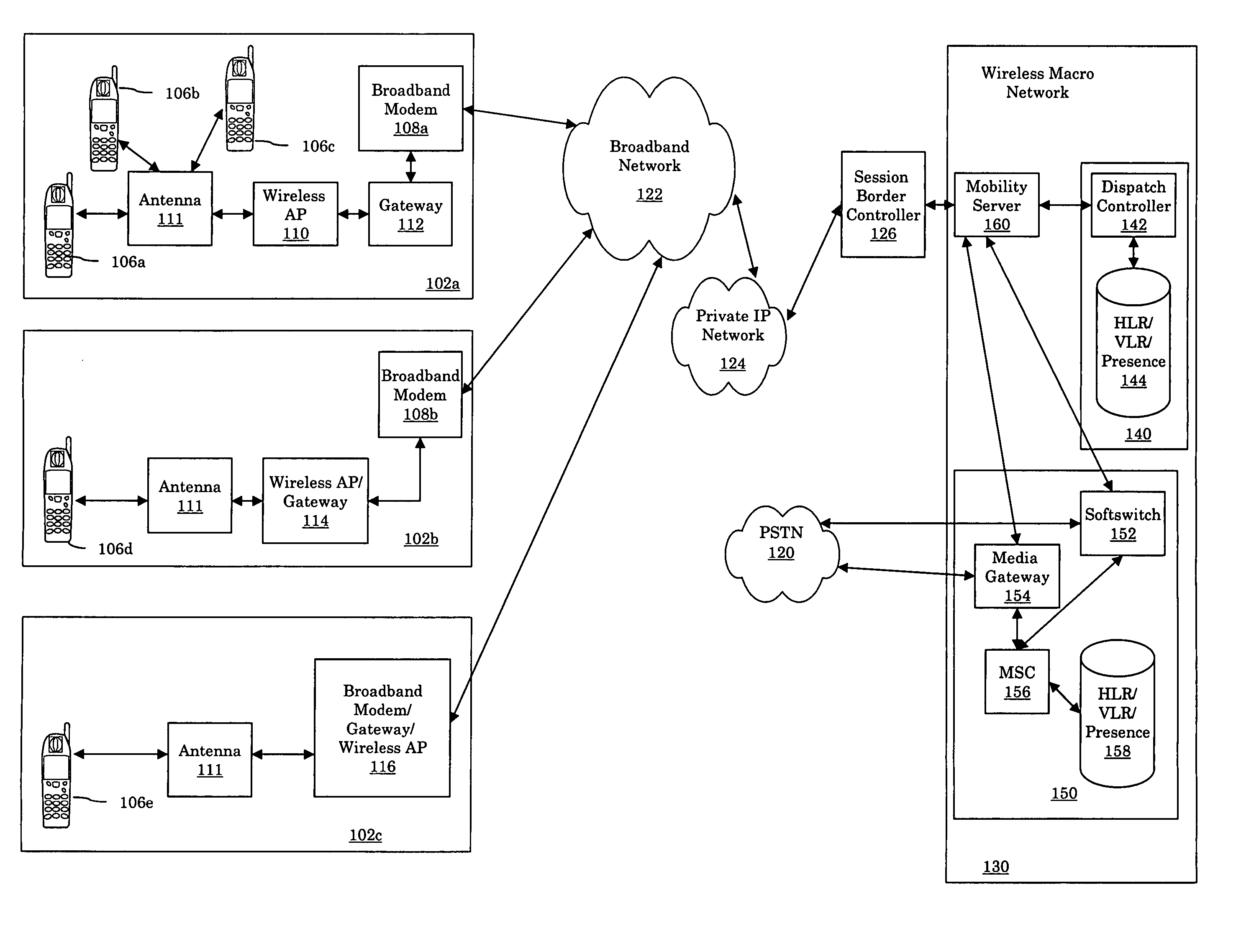
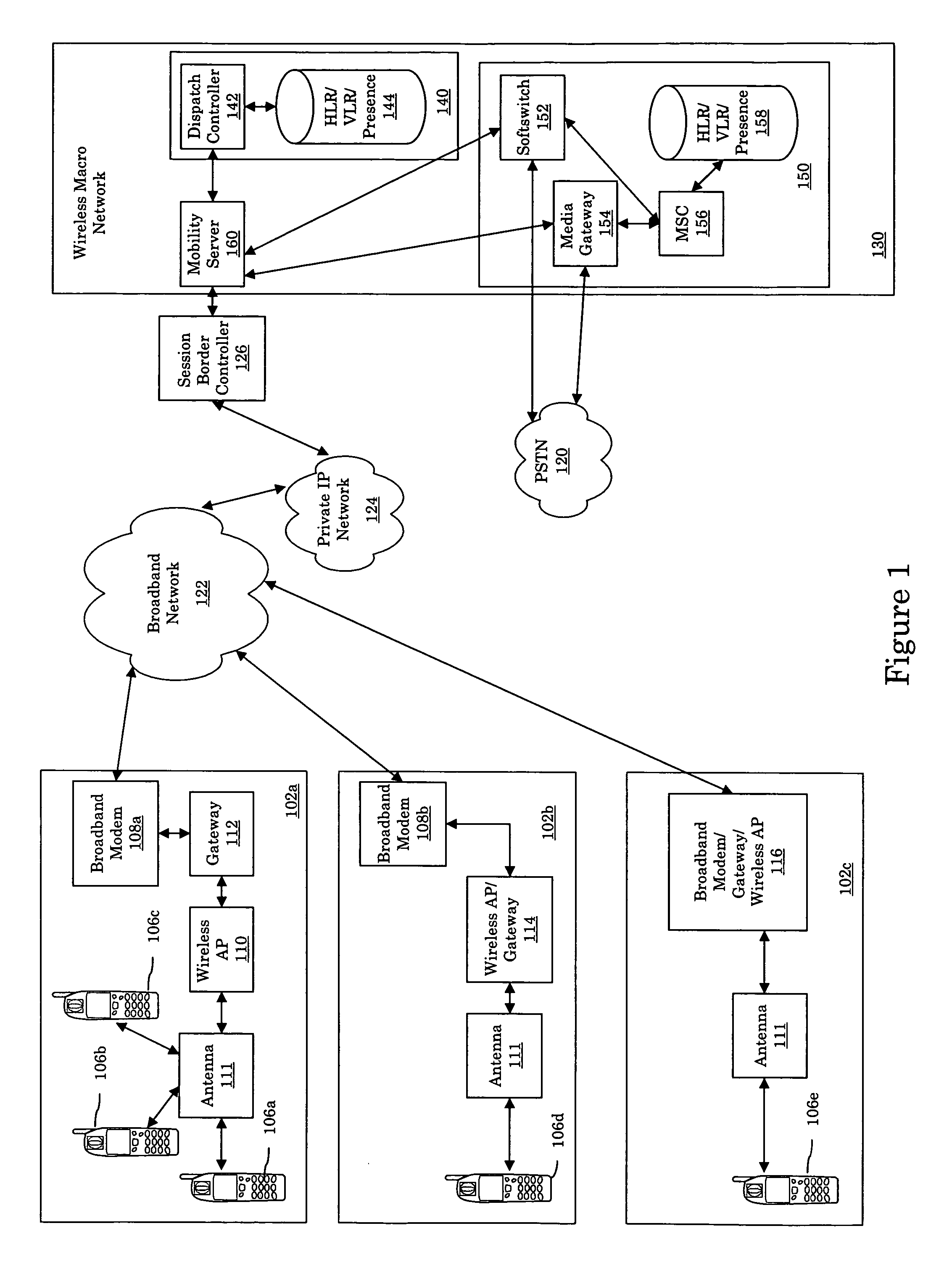
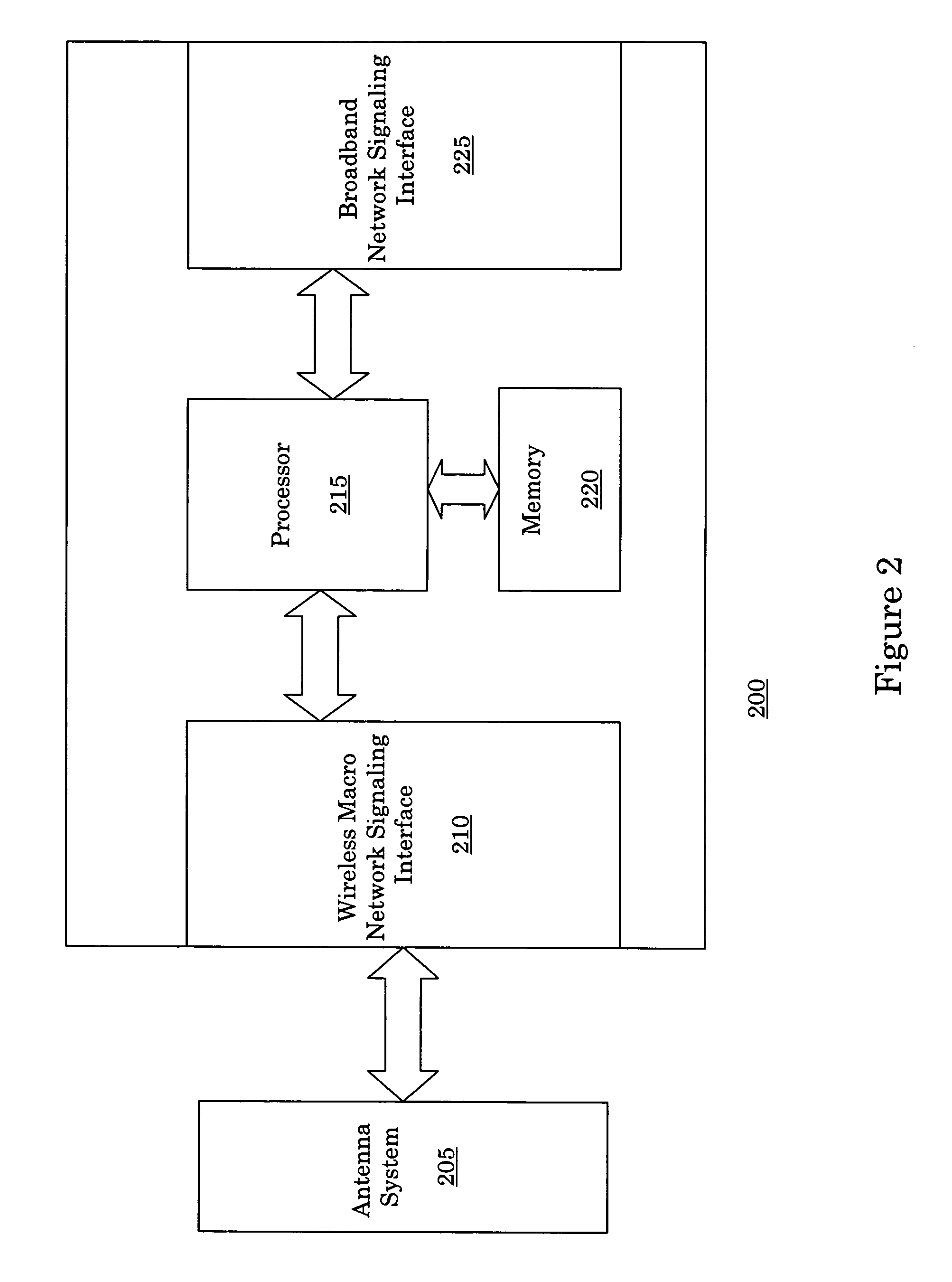
A private wireless network interface provides wireless signaling and protocols of a wireless macro network to allow a consumer to operate over a private wireless network. The private wireless network interface receives wireless signals compatible with a wireless macro network and transmits the signals over a broadband connection to a wireless service provider's wireless macro network. The private wireless network interface allows the use of mobile stations which are compatible with a wireless macro network to operate in a residence and have the signals backhauled over the residence's broadband connection. The private wireless network interface can provide wireless macro network coverage in any location with some type of coupling to the Internet.
Owner:NEXTEL COMMUNICATIONS
Method for providing voice communication services and system for the same
InactiveUS20040076144A1Imposing significant equipment costIncrease the areaMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesThird partyVoice communication
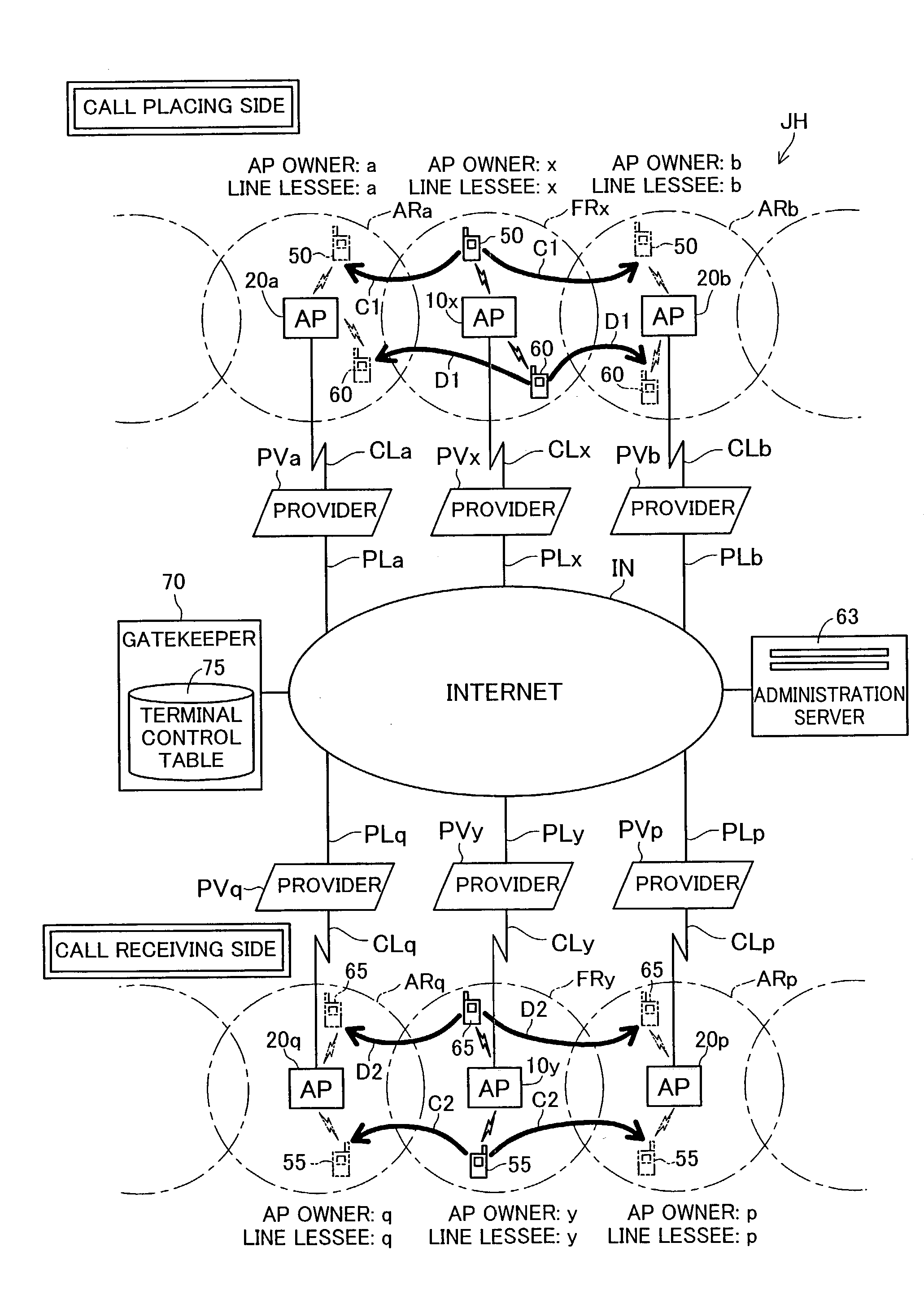
To expand the call area for wireless IP phones without imposing significant economic costs on IP telephony service providers. In a voice communication service system JH, a service provider provides voice communication service to a subscriber who has paid a predetermined service charge, using an authorized access point and spare bandwidth available on an authorized broadband connection. Where spare bandwidth on an authorized broadband connection is used by a third party, the authorized access point owner and line lessee of the authorized broadband connection receive a rebate, based on usage of the spare bandwidth, from the service provider.
Owner:MELCO INC
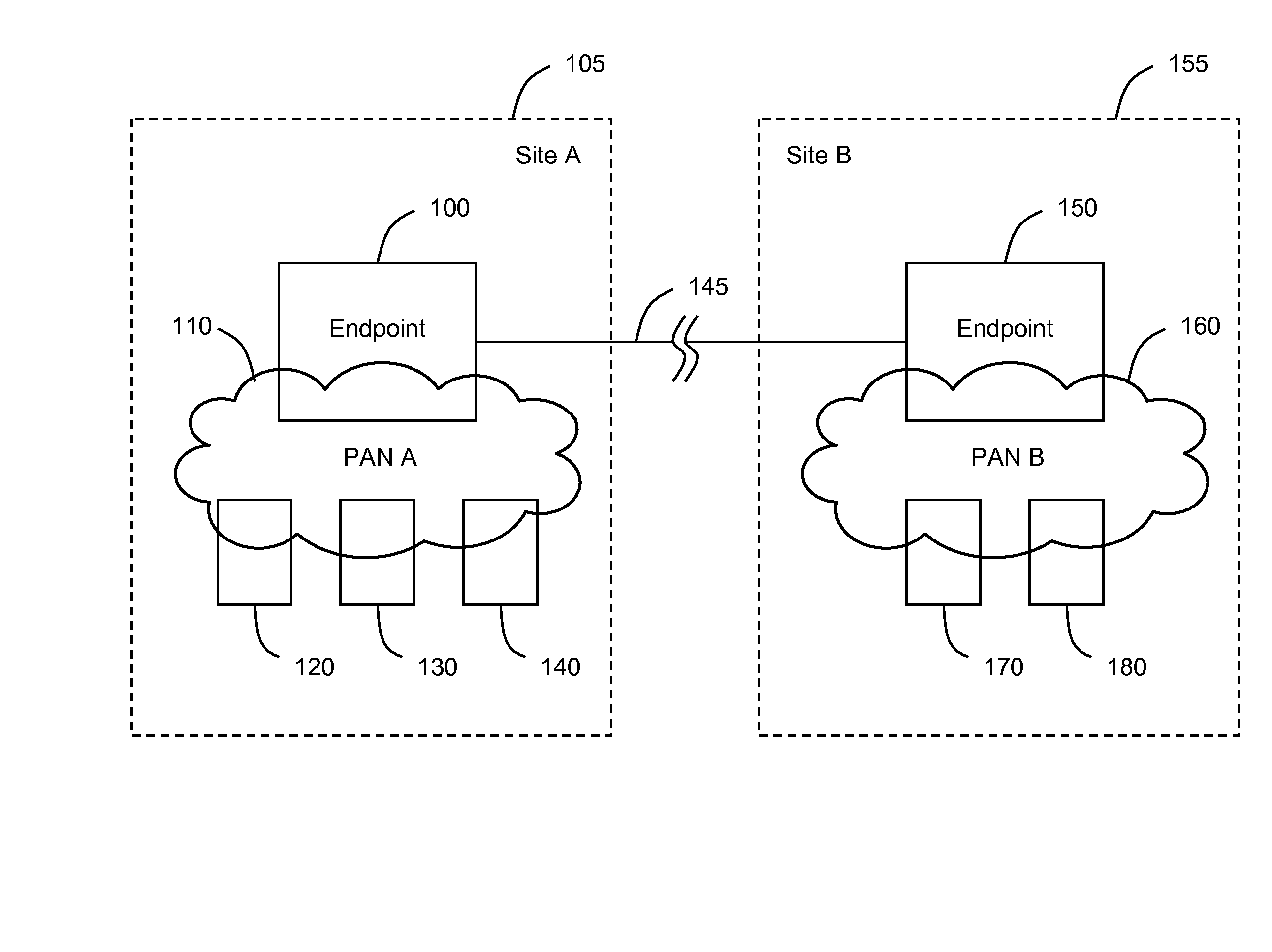
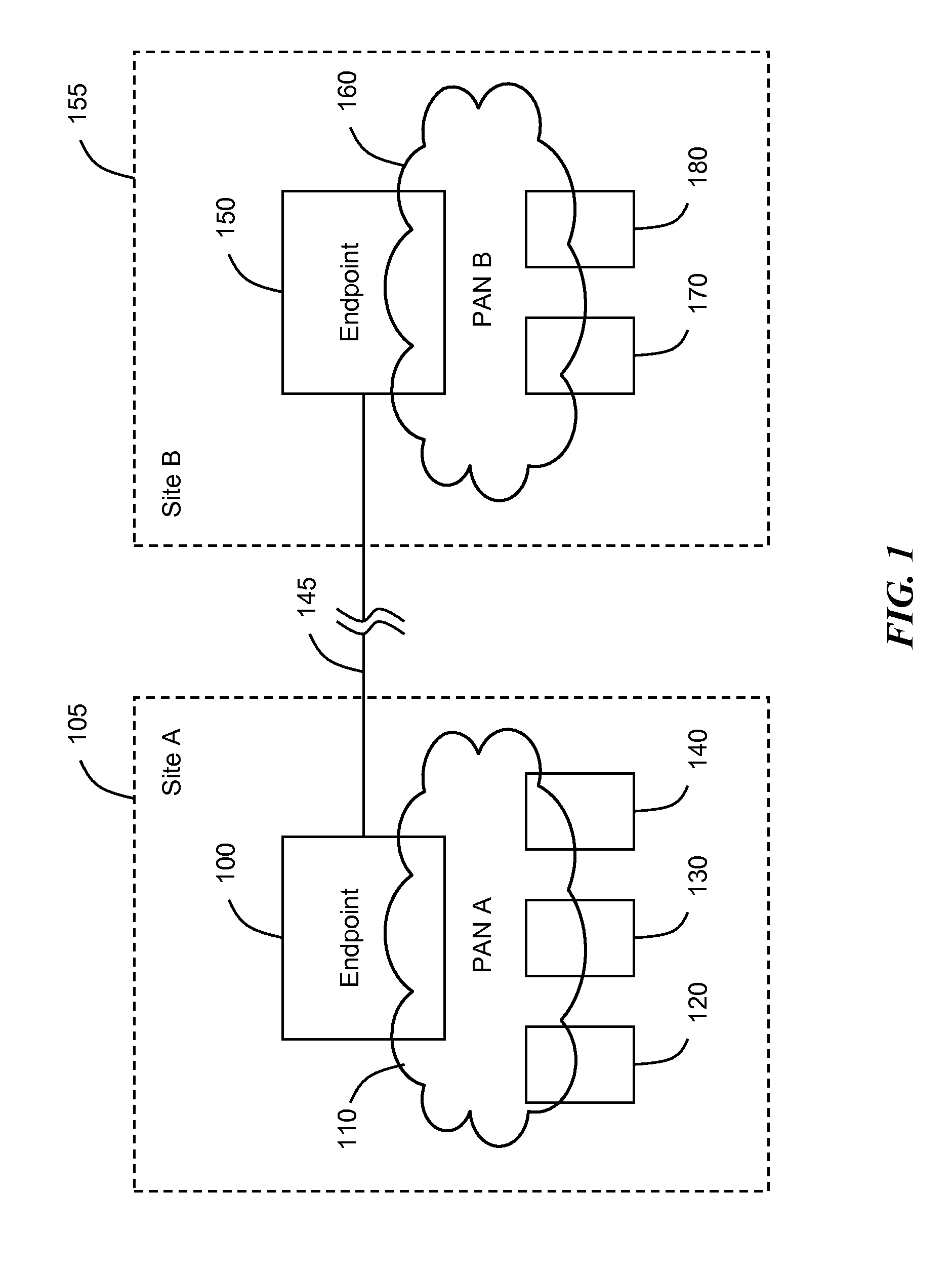
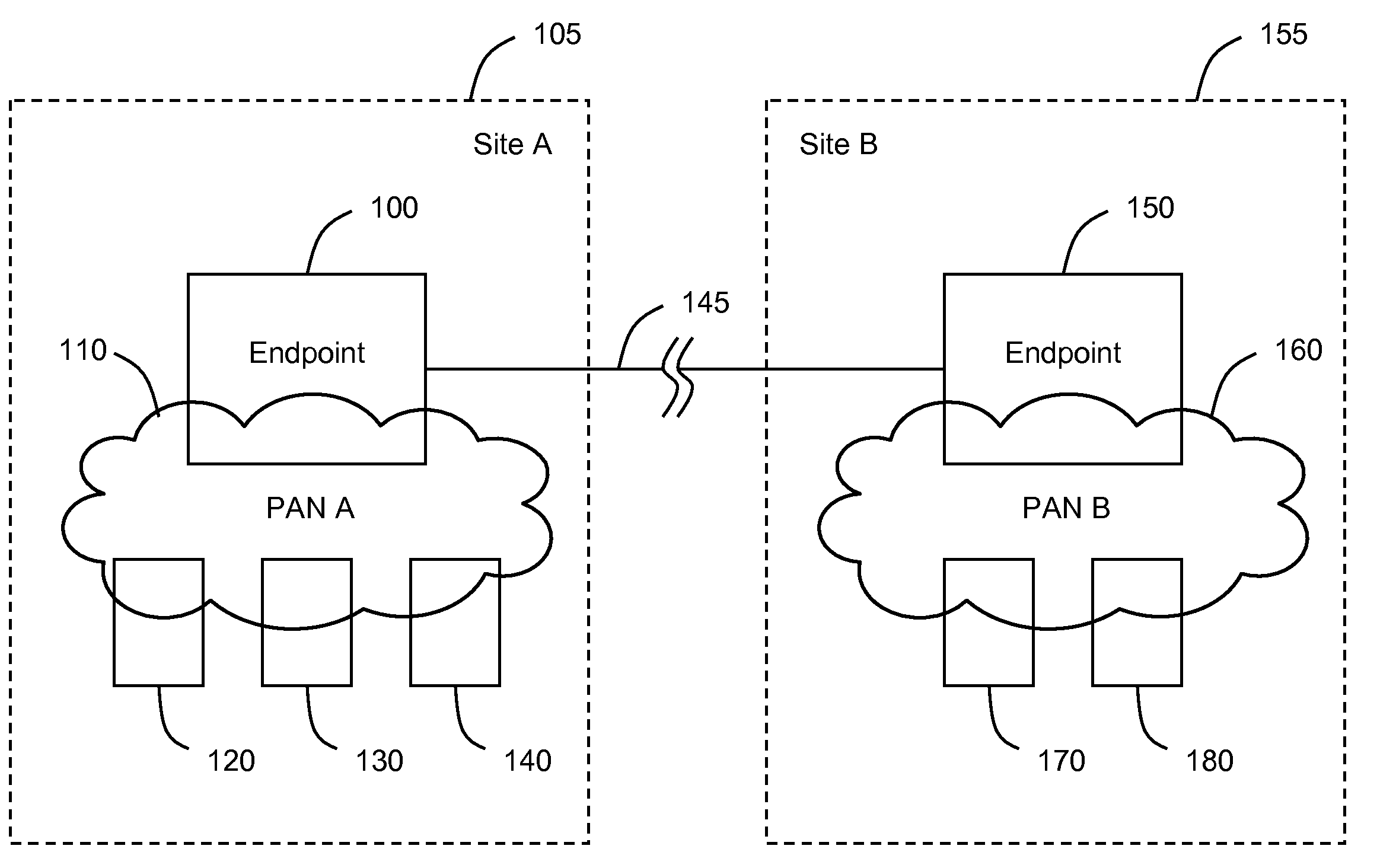
System, method, and apparatus for extending wireless personal area networks using conferencing connection
ActiveUS20070264988A1Provide goodEliminate clutterSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsBluetooth piconetsControl channel
A system, method, and apparatus are disclosed whereby a wireless Personal Area Network such as a Bluetooth piconet may be extended to a remote location beyond the normal range by means of a conferencing connection. The conferencing connection may comprise, for example, one or more ISDN lines or an IP connection between two or more conference endpoints. The broadband connection may include a video channel, an audio channel, a control channel, and a Bluetooth channel.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Enhanced caller ID information based on access device information via a broadband access gateway
InactiveUS20050233735A1Enhanced caller identification informationSpecial service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer scienceWorld Wide Web
A system and method for providing enhanced caller identification (caller ID) information to a user is described. A broadband access gateway communicatively coupled to a plurality of access devices may collect information about multimedia content available on the access devices and / or information exchanged with access devices. The gateway may search the collect information upon receiving information identifying a called or calling party, to find information that may be associated with the called or calling party. Selected items of the information associated with the called or calling party may then be delivered to the access device of the called or calling party. Information accessible to the gateway via a broadband connection may also be made available to the user of the access device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System, method, and apparatus for extending wireless personal area networks using conferencing connection
ActiveUS7675537B2Eliminate clutterProvide goodSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsBluetooth piconetsControl channel
A system, method, and apparatus are disclosed whereby a wireless Personal Area Network such as a Bluetooth piconet may be extended to a remote location beyond the normal range by means of a conferencing connection. The conferencing connection may comprise, for example, one or more ISDN lines or an IP connection between two or more conference endpoints. The broadband connection may include a video channel, an audio channel, a control channel, and a Bluetooth channel.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Managing alternative networks for high quality of service communications
ActiveUS20160330108A1Broadband local area networksHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceService use
Methods and systems are provided. Exemplary methods may include: providing a first data packet to a first interface, the first data packet including a first address and being received from a computing device, the computing device being at a premises and coupled to a third interface, the first interface coupled to a first broadband connection received at the premises, the first broadband connection being coupled to a service using a first data network; determining at least one second data packet to be received at the first interface from the service is lost or delayed; supplying a second address to the computing device for communications with the service, in response to the determining; receiving from the computing device a third data packet including the second address; modifying the third data packet including replacing the second address with the first address; and giving the modified third data packet to a second interface.
Owner:OOMA
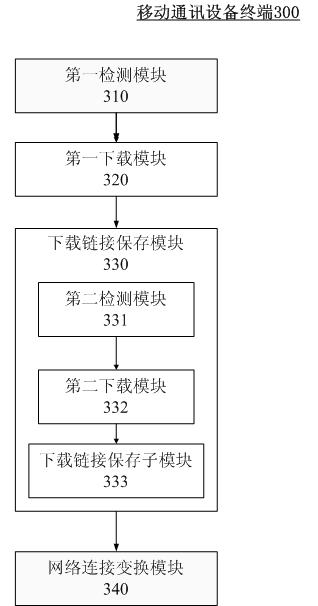
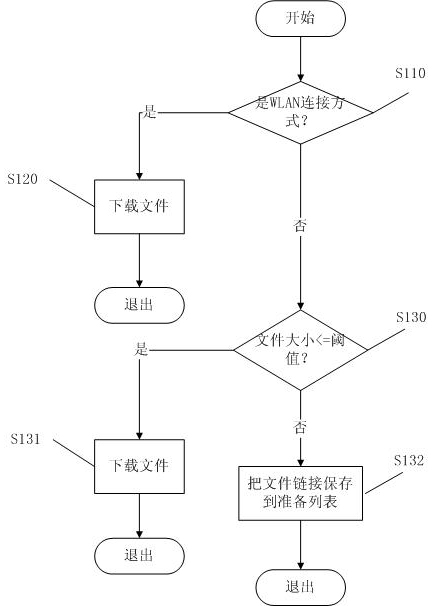
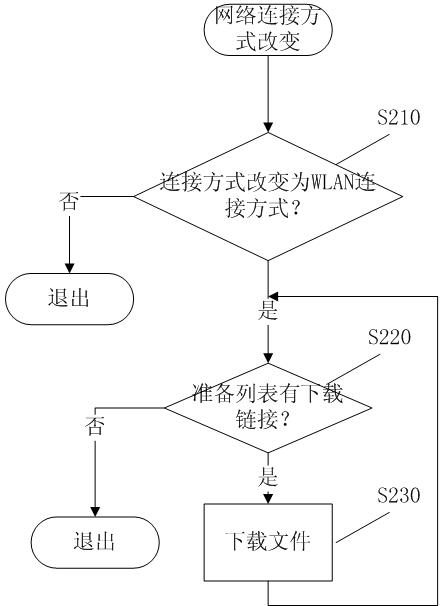
Downloading method and device for mobile communication equipment terminal
ActiveCN101951404AAvoid occupyingDownload does not affectTransmissionTraffic capacityNetwork connection
The invention relates to the technical field of downloading of mobile communication equipment terminals, in particular to a downloading method and a downloading device for a mobile communication equipment terminal. The method comprises that: the mobile communication equipment terminal receives a file downloading request which comprises a file downloading link and detects whether the network connection mode meets the first rule; if the network connection mode meets the first rule, the mobile communication equipment terminal downloads the file according to the file downloading link acquired from the file downloading request; and if the network connection mode does not meet the first rule, the mobile communication equipment terminal saves the file downloading link acquired from the file downloading request in a preparation list, wherein when acquiring network connection mode change information, the mobile communication equipment terminal detects whether the network connection mode meets the first rule, and downloads the file according to the file downloading link saved in the preparation list if the network connection mode meets the first rule. During mobile network connection, when high flow downloading is carried out, a downloading process is hung so as to avoid greatly occupying the mobile network bandwidth for a long time; however, a large file is downloaded under the condition of broadband connection. Therefore, the flow is saved and the downloading efficiency is improved on the premise of not influencing user downloading.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
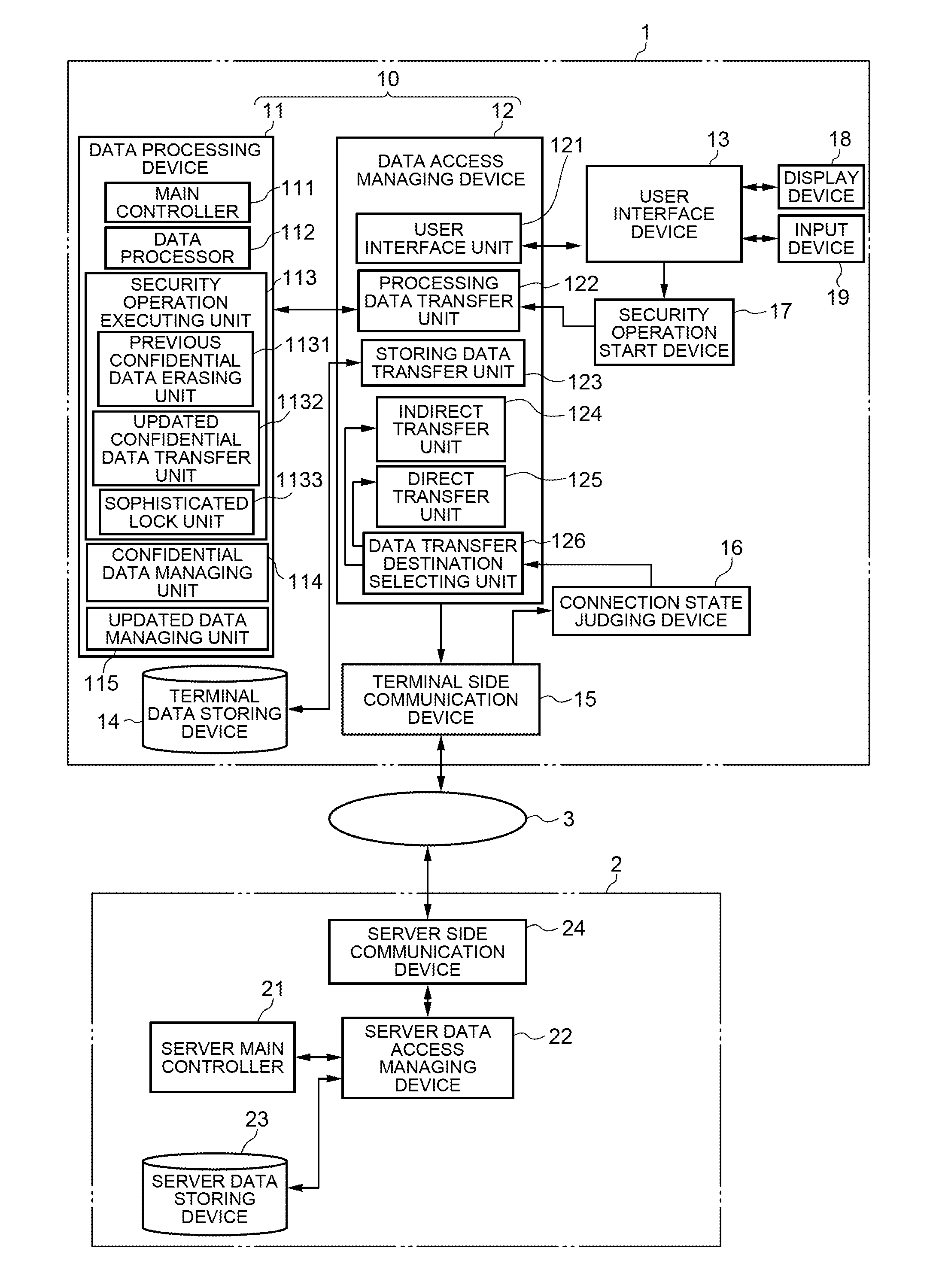
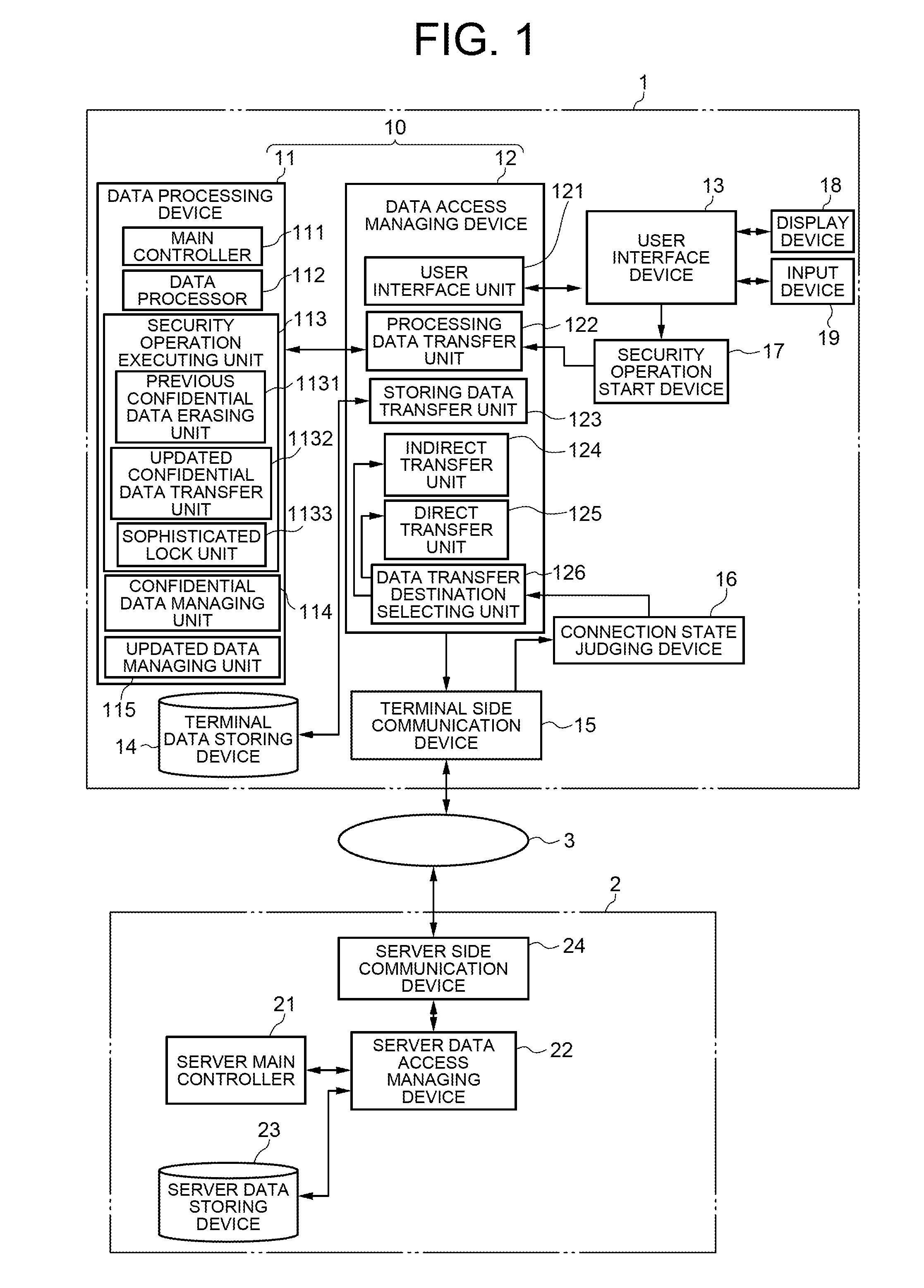
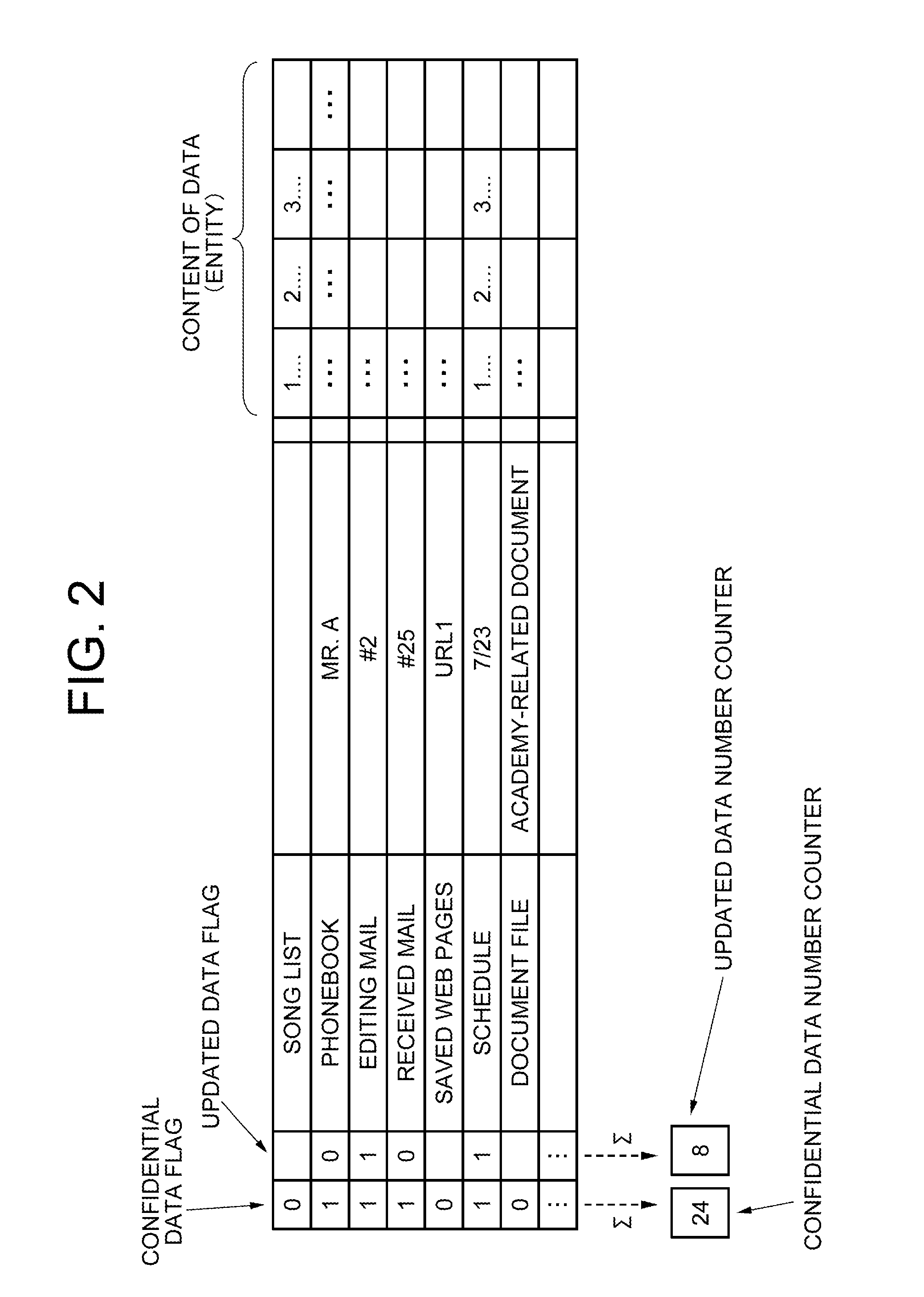
Confidential information management by mobile terminal
ActiveUS8254883B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemComputer terminal
To provide a communication system including a mobile terminal which can prevent leak of information even if the mobile terminal is lost and reproduce previously accumulated confidential data without losing newly created and updated confidential data. A mobile terminal includes connection state judging device which detects a line connection state with a server. When the line connection state is a broadband connection, the data is read directly from and written directly into a data storing device of the server. When the line connection state is a narrowband connection, the data is temporarily read out and written into a data storing device of the terminal. When the operation of the mobile terminal is completed or a security operation starting instruction is issued by a user, the updated confidential data is written into the data storing device of the server and then the confidential data is erased from the mobile terminal.
Owner:NEC CORP
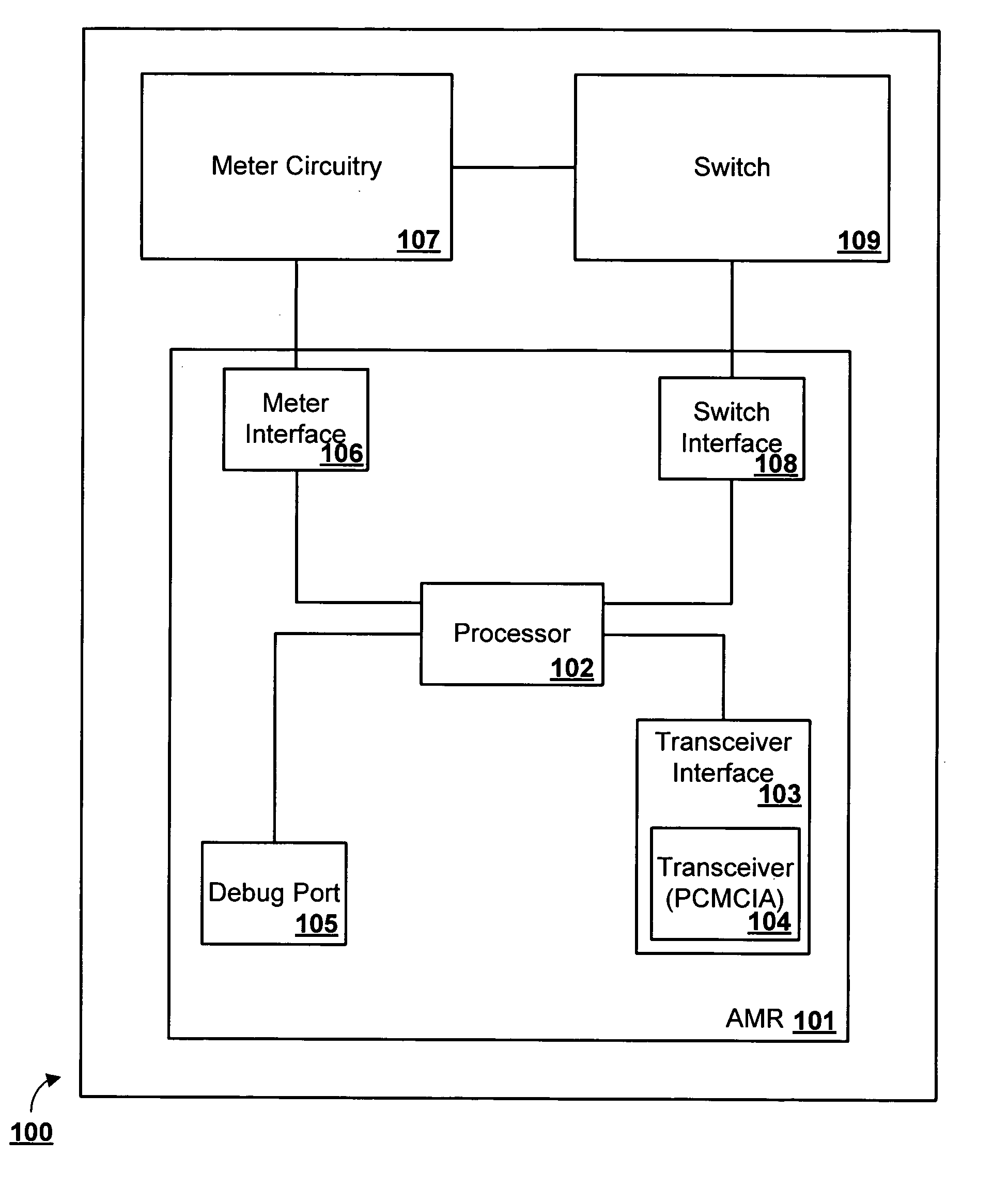
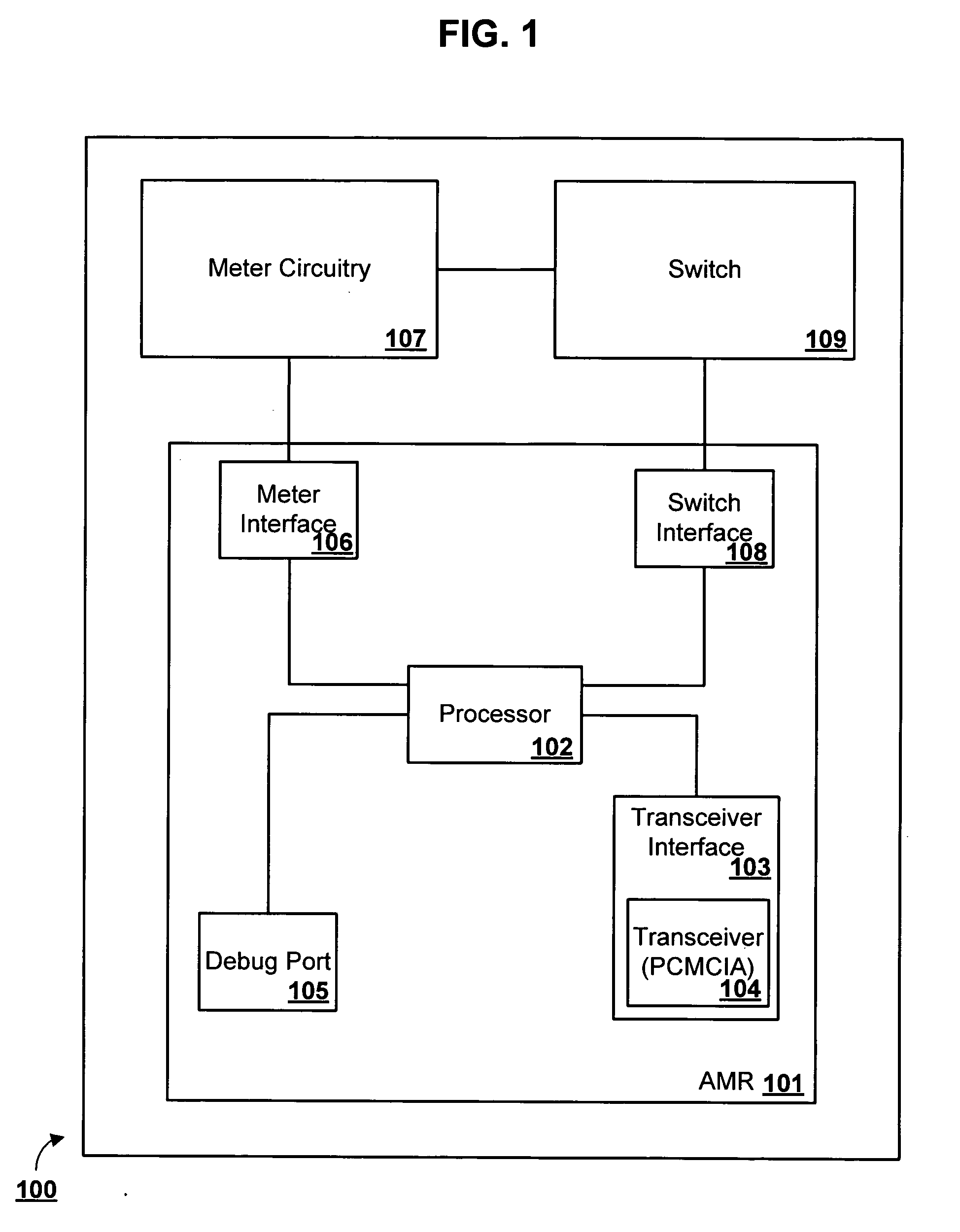
Methods and systems for meter reading and high speed data transfer
ActiveUS20060044158A1Without costElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusService personnelService provision
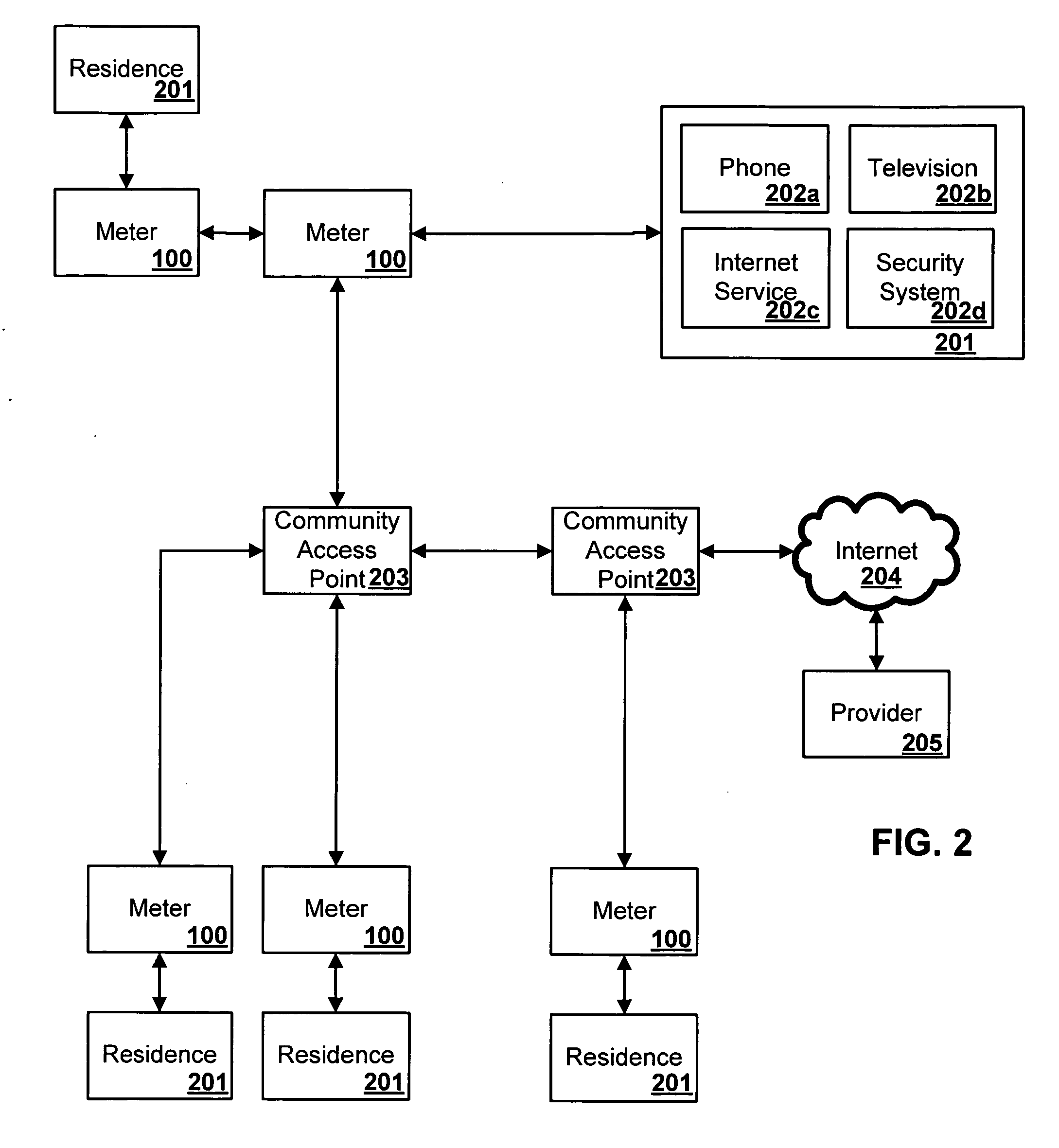
A secure automatic meter reading (“AMR”) method and apparatus which utilizes a microprocessor and a bidirectional broadband connection to access the Internet and can form a wireless distribution network is provided. In addition to AMR, this connection and the network can provide high speed data transmission for other devices and services. As a result of the methods and apparatuses of the present inventions, legacy utility infrastructure and communications equipment can be integrated into a data transmission and collection network and remotely monitored without the costs associated with deploying service personnel or more costly equipment and services.
Owner:BOH TECH
Adaptive audio/video streams proxy
ActiveUS20120192230A1Television system detailsColor television detailsVideo transmissionSelf adaptive
A method is provided comprising: receiving a constant bit rate video stream representing a single video from a video source via a managed broadband connection; converting the constant bit rate video stream into a single non-adaptive bit rate video stream by modifying a video transport stack of the video to be compatible with a home device media player video transport stack; modifying a video control stack of the video to be compatible with a device in a home network; adding a home networking transport stack to the video stream, wherein the home networking transport stack is such that it would appear to the device in the home network as if the video stream came from a server local to the home network; and delivering the video stream to a device in the home network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
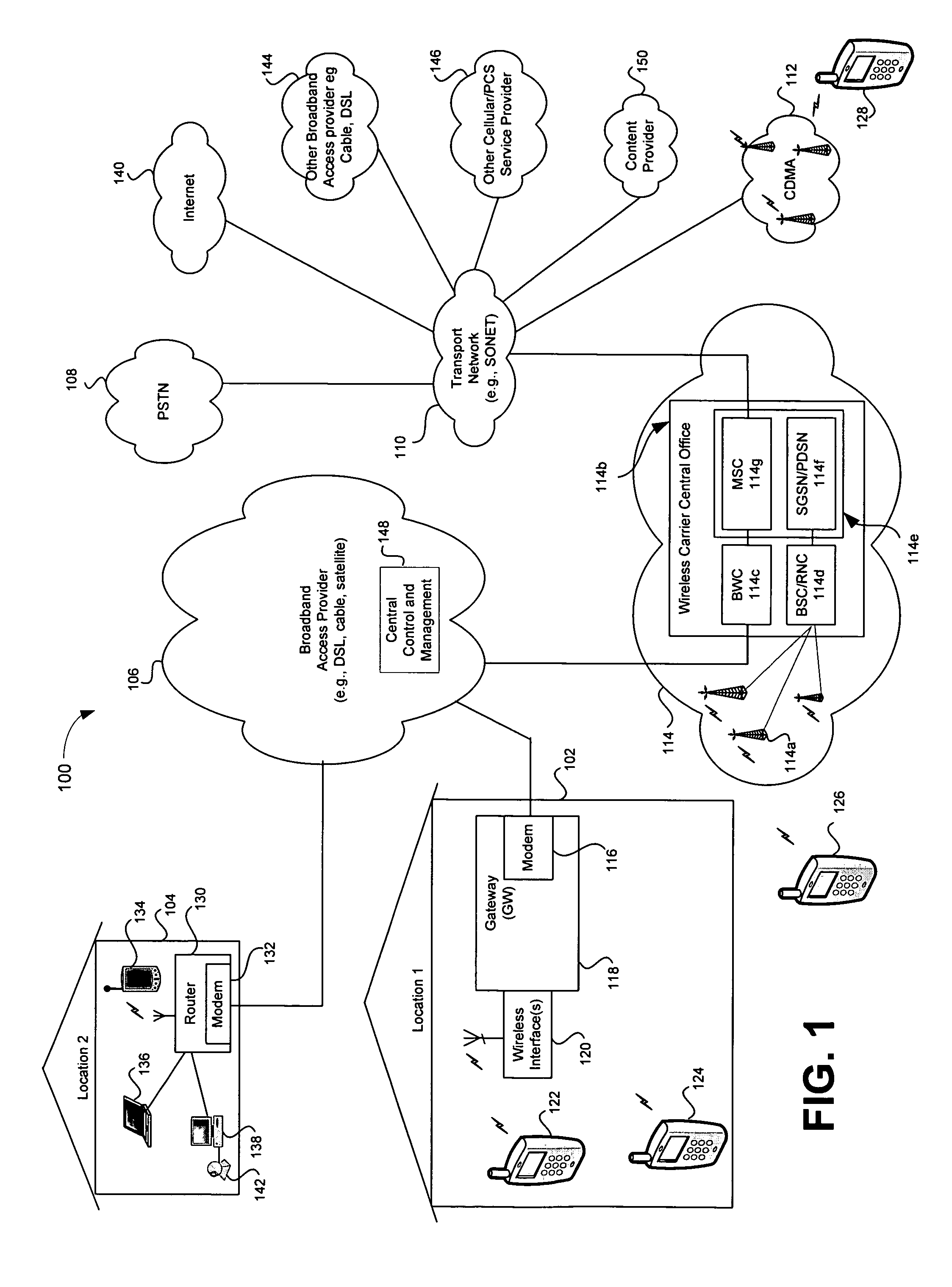
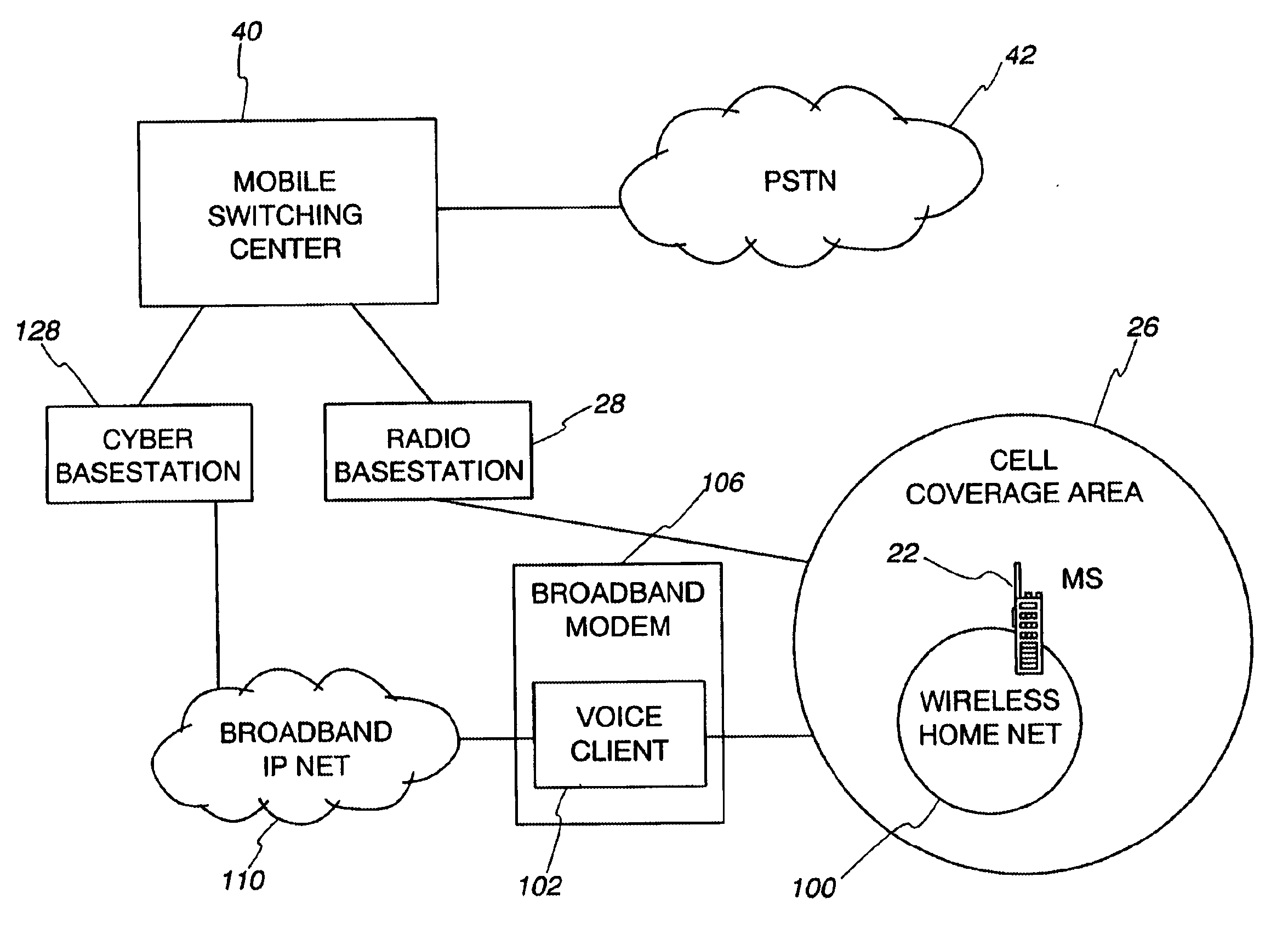
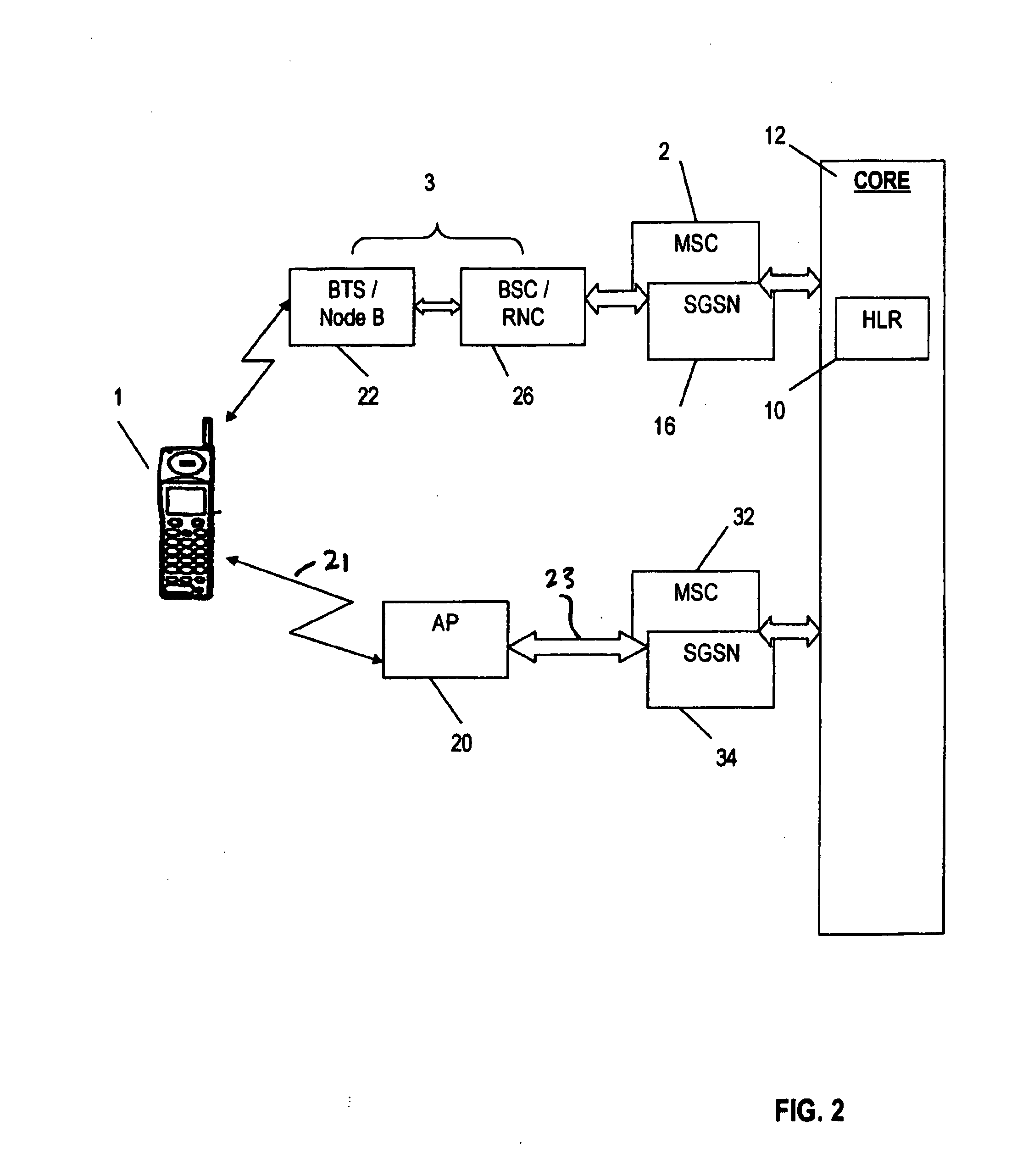
Cellular system with cybercells
A local site communication system, including a broadband connection between the local site and an internet, a wireless local site network in the local site and communicating data between the broadband connection and the mobile terminal when the mobile terminal is located at the local site, and a cyber base station connected to the internet and communicating data between the broadband connection and a mobile switching center whereby the mobile terminal when located at the local site connects to a mobile switching center via the wireless local site network, the broadband connection, the internet and the cyber base station. A voice client converts data between wireless signals on the wireless local site network and internet protocol signals on the broadband connection, and the cyber base station mimics a radio base station to the mobile switching center. The communication system is included in a cellular system including a plurality of low power wireless local site networks located in cells and served by the cyber base station. The wireless local site networks include a low power transceiver for communicating with mobile terminals. Methods of handing off a mobile terminal between cells and cybercells, and of placing and receiving calls in cybercells are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
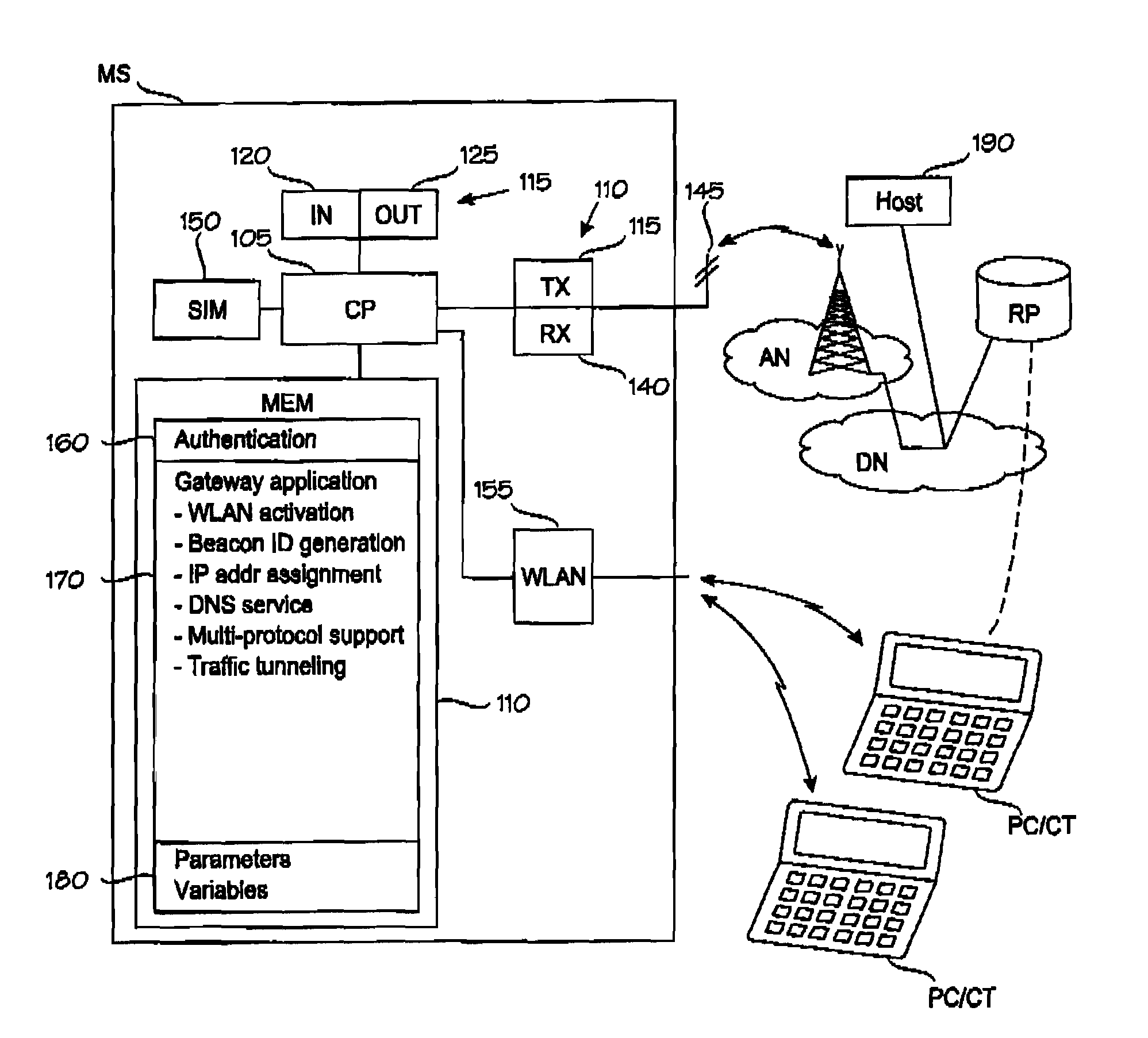
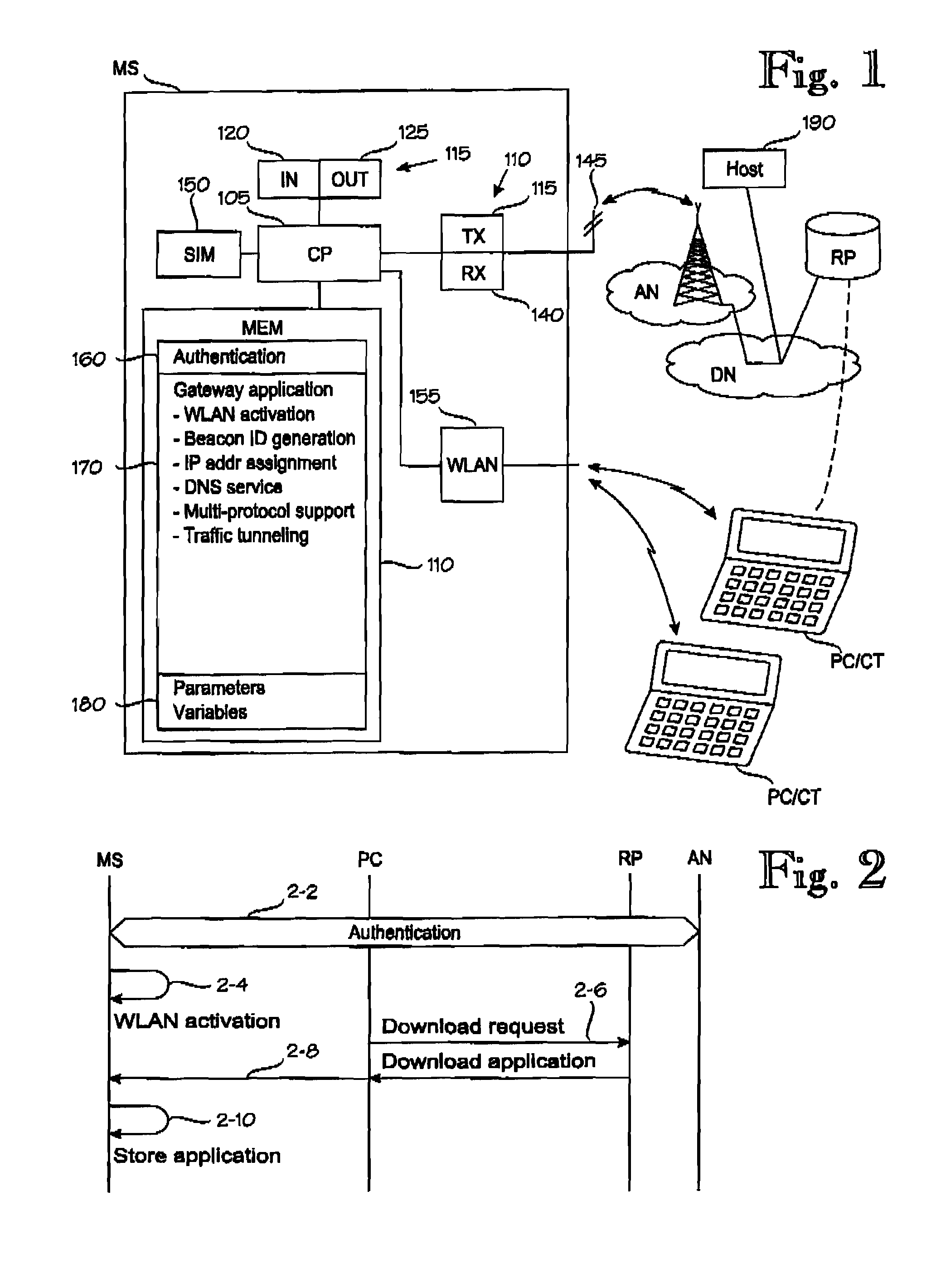
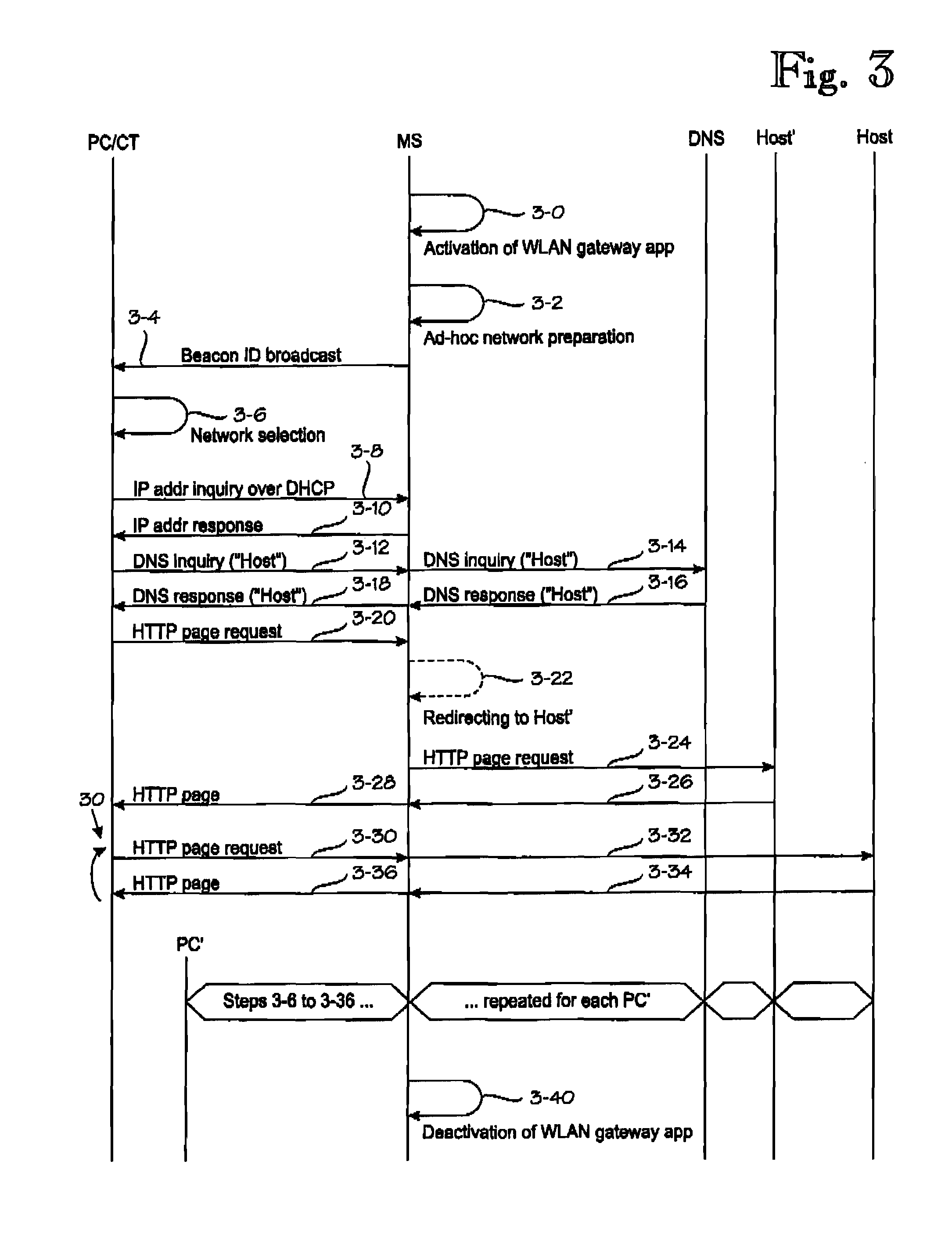
Mobile WLAN Gateway
ActiveUS20090180449A1Reduce decreaseNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesDomain nameTTEthernet
A technique for operating a mobile station as wireless local-area network [“WLAN”] gateway. The mobile station is provided with a gateway application to control the following operations: activating (3-0) the WLAN means as a WLAN base station capable of communicating with at least one WLAN terminal over a WLAN network; creating a network identifier (3-2, 3-4) for the WLAN base station; assigning (3-8, 3-10) an Internet protocol address for the at least one WLAN terminal; resolving domain name service [“DNS”] queries (3-12 . . . 3-18) in cooperation with an external DNS service system; assigning at least one port number for each protocol supported by the gateway application; and tunneling Internet traffic (3-30 . . . 3-36) between the at least one WLAN terminal and an Internet host over the broadband connection.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Establishing and Managing Alternative Networks for High Quality of Service Communications
ActiveUS20170034062A1Broadband local area networksHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceBroadband connection
Methods and systems are provided. Exemplary methods may include: providing a first data packet to a first interface, the first data packet including a first address and being received from a computing device, the computing device being at a premises and coupled to a third interface, the first interface coupled to a first broadband connection received at the premises, the first broadband connection being coupled to a service using a first data network; determining at least one second data packet to be received at the first interface from the service is lost or delayed; supplying a second address to the computing device for communications with the service, in response to the determining; receiving from the computing device a third data packet including the second address; modifying the third data packet including replacing the second address with the first address; and giving the modified third data packet to a second interface.
Owner:OOMA
Controlling the use of access points in a telecommunication system
ActiveUS20100240369A1Reduce quality problemsQuality improvementRadio transmission for post communicationWireless commuication servicesTelecommunications networkRadio access network
A mobile telecommunications network includes a radio access network with base stations and one or more additional access points. An access point is connected to a network core by an IP transport broadband connection. The access point is configured to appear to a mobile terminal as a conventional base station—that is, for example, it communicates with the mobile terminal using GSM or UMTS transport protocols and does not require any modification to a standard GSM or UMTS mobile terminal. Arrangements are disclosed which monitor the quality of the broadband connection between the access point and the network core and which cause the mobile terminal to handover to a neighbouring base station in the event that the quality of the broadband connection becomes too poor for the class of communication between the mobile terminals registered with the access point to be performed satisfactorily.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
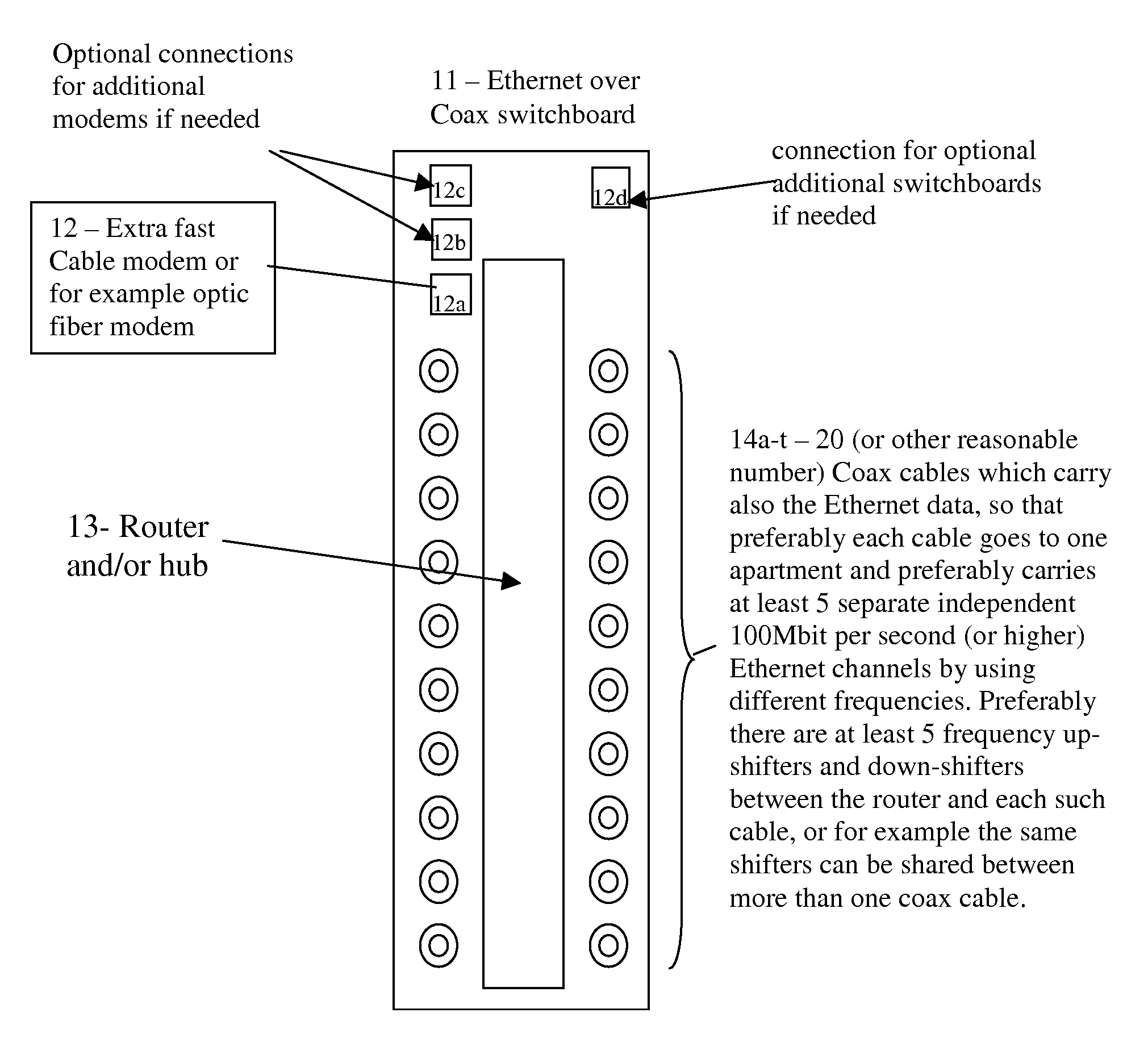
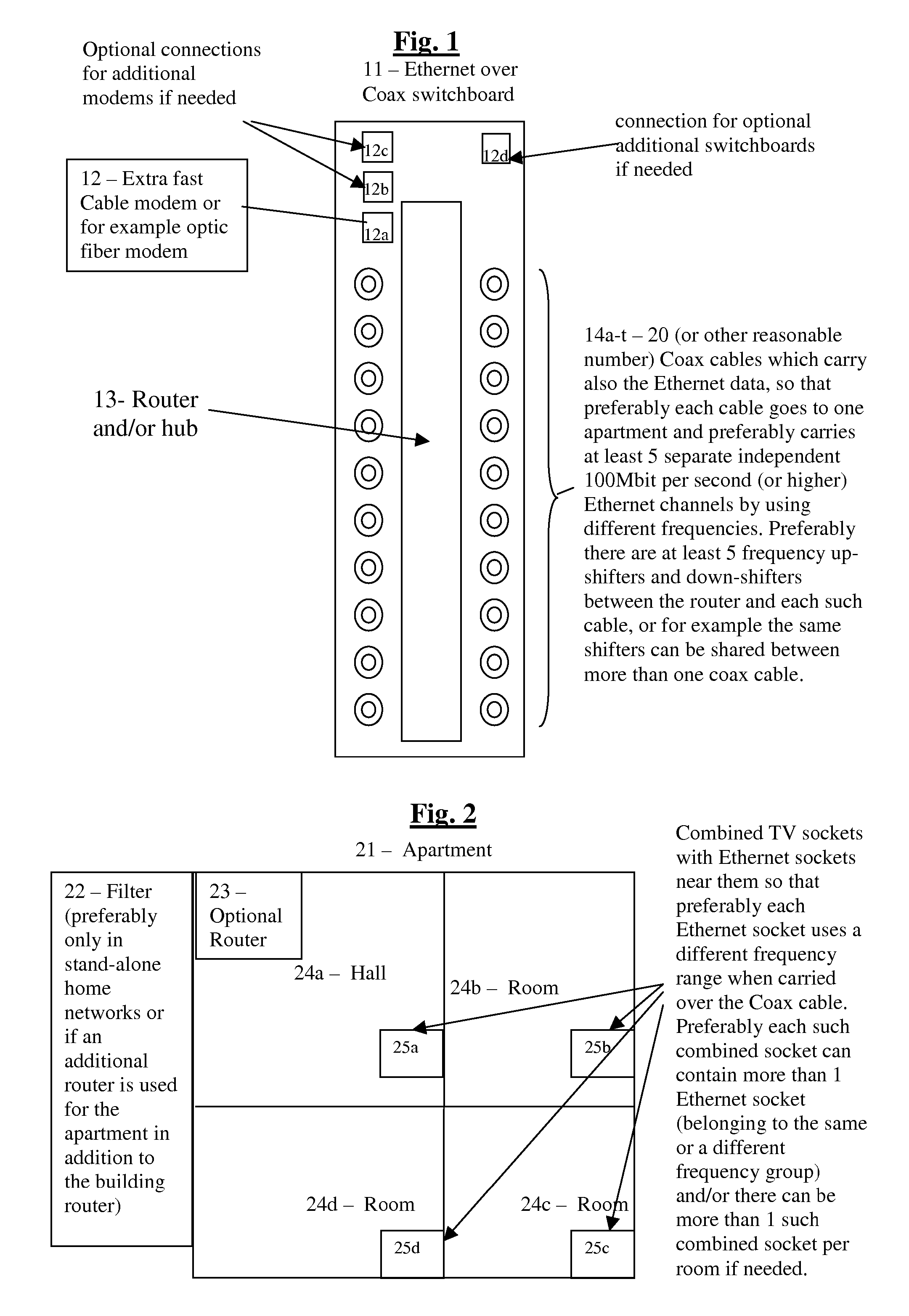
System and method for creating cheap efficient high-speed home networks.
InactiveUS20080025723A1Avoid bandwidthImprove securityTelephonic communicationOptical multiplexModem deviceWeb service
Broadband connections of end users to the Internet are becoming more and more common today, and the most common types of these fast connections are ADSL and Cable modems. These connections are typically still very slow compared to the speeds that are expected in the next few years and typically also highly asymmetric and allow typically 750-2000 Kbit per second (most typically 1500 Kbit) for the downlink and typically for example 96 Kbit or 128 Kbit per second for the uplink (although standard ADSL can in principle support up to 8 Mbit per second download speed and up to 800 Kbit per second upload speed), based on the assumption that most users download much more data than they upload. However, for many users these limitations are highly undesirable, and these are for example home users or small businesses or organizations who want to use the connection also for example for VOIP (voice over IP) communications and / or Video-over IP communications and / or conferences and / or for example running web servers and / or for example various p2p applications, and in fact the low uplink also many times slows down the downlink due to the overhead needed for dealing with relatively small packets, so that any additional uplink by the user can severely limit the real downlink that can be achieved below the downlink bandwidth which the user is paying for. Actually ADSL is beginning to be replaced in some places by VDSL where the distance to the nearest street switchboard is about 1.2 Kilometers or less, which in principle allows up to 52 Mbit per second Download speed and up to 16 Mbit per Second Upload speed. However, these modems are expensive and are only slowly entering the market and only in a few countries. On the other hand there is no need to upgrade typical cable modems for enabling faster speeds, such as for example 20 Mbit downlink and 2 Mbit uplink, as is offered for example in France, when the ISPs start offering such speeds—since the typical common cable modem is already capable of such speeds. The present invention enables an improved Ethernet-over-coax solution which enables using one or a few very high speed modems, each for multiple users or apartments, preferably in combination with very cheap and very fast home networks (offering preferably at least up to 100 Mbit per second for each computer, preferably at full duplex), preferably based on the Cable TV coax cables, so that multiple computers can share the same internet connection for example in the same apartment and / or communicate between themselves. This preferably includes using a different frequency for the Ethernet-over coax channel for each computer in the apartment. Also shown are for example improved home networks using the second set of normally unused 2 phone wires and for example some improvement in HPNA networks, such as for example using HPNA also to connect between the street switchboard and the home or office instead of having to use also for example an ADSL or VDSL modem.
Owner:MAYER YARON +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com