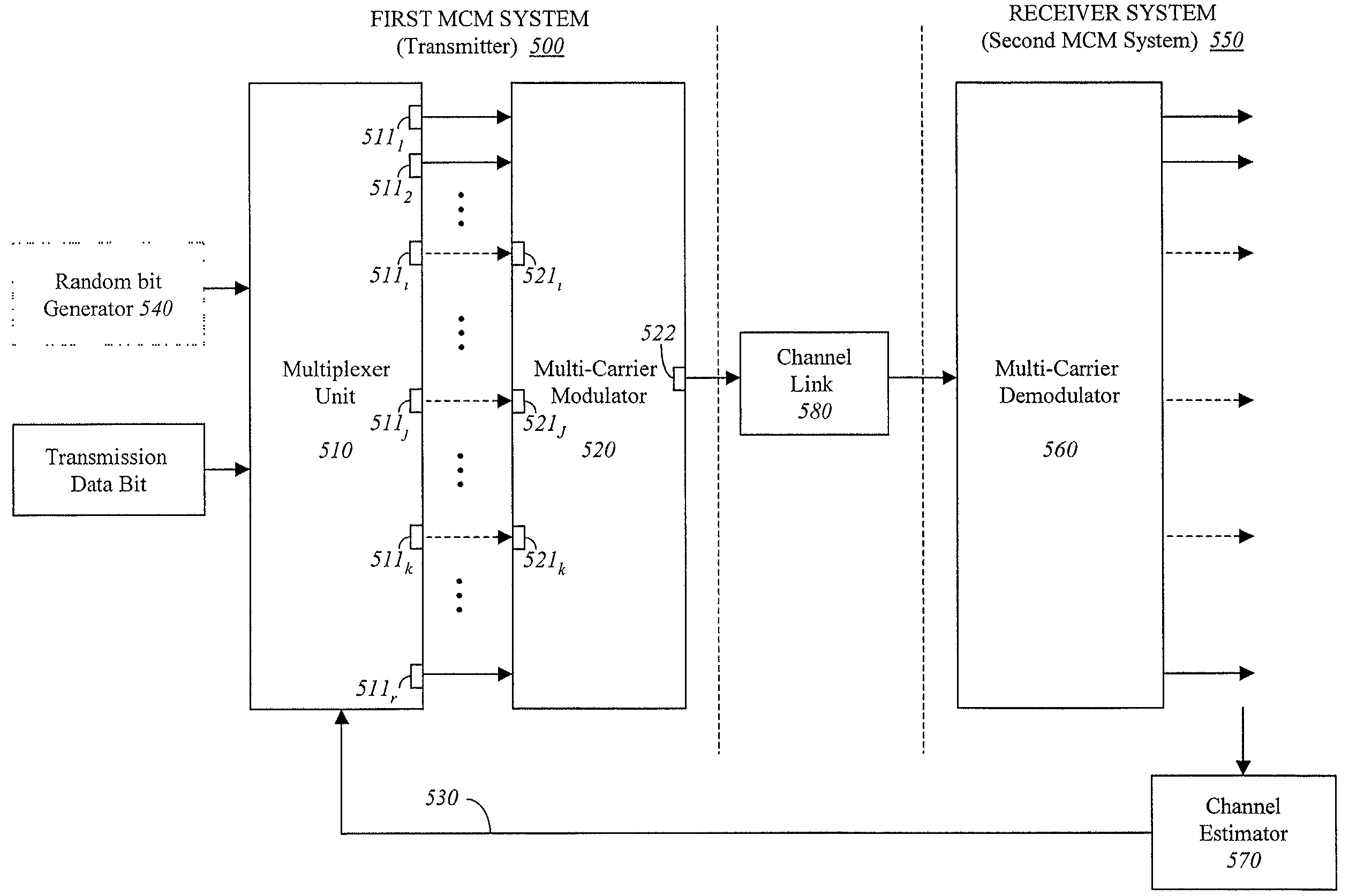
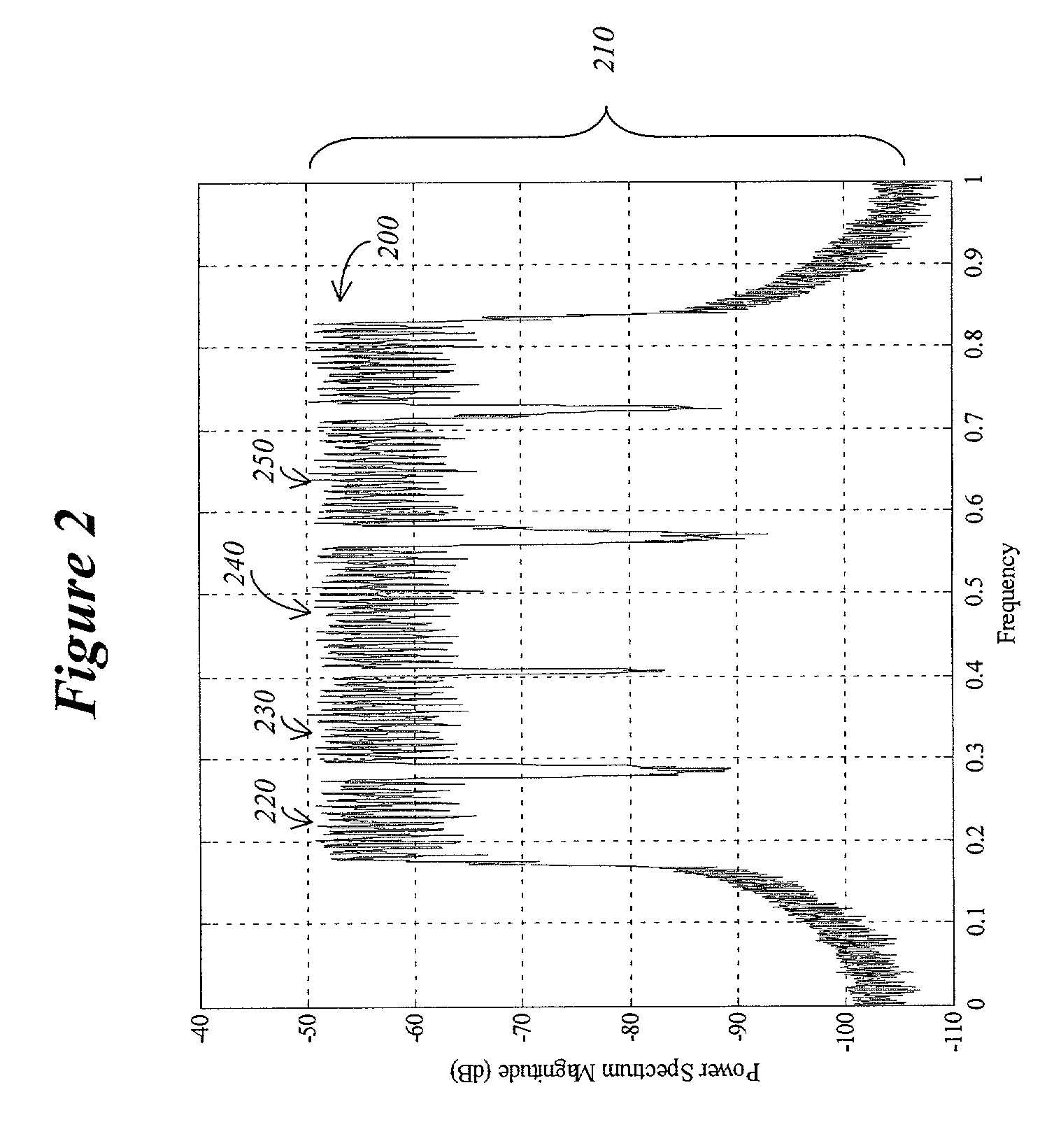
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
451 results about "Multi carrier modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
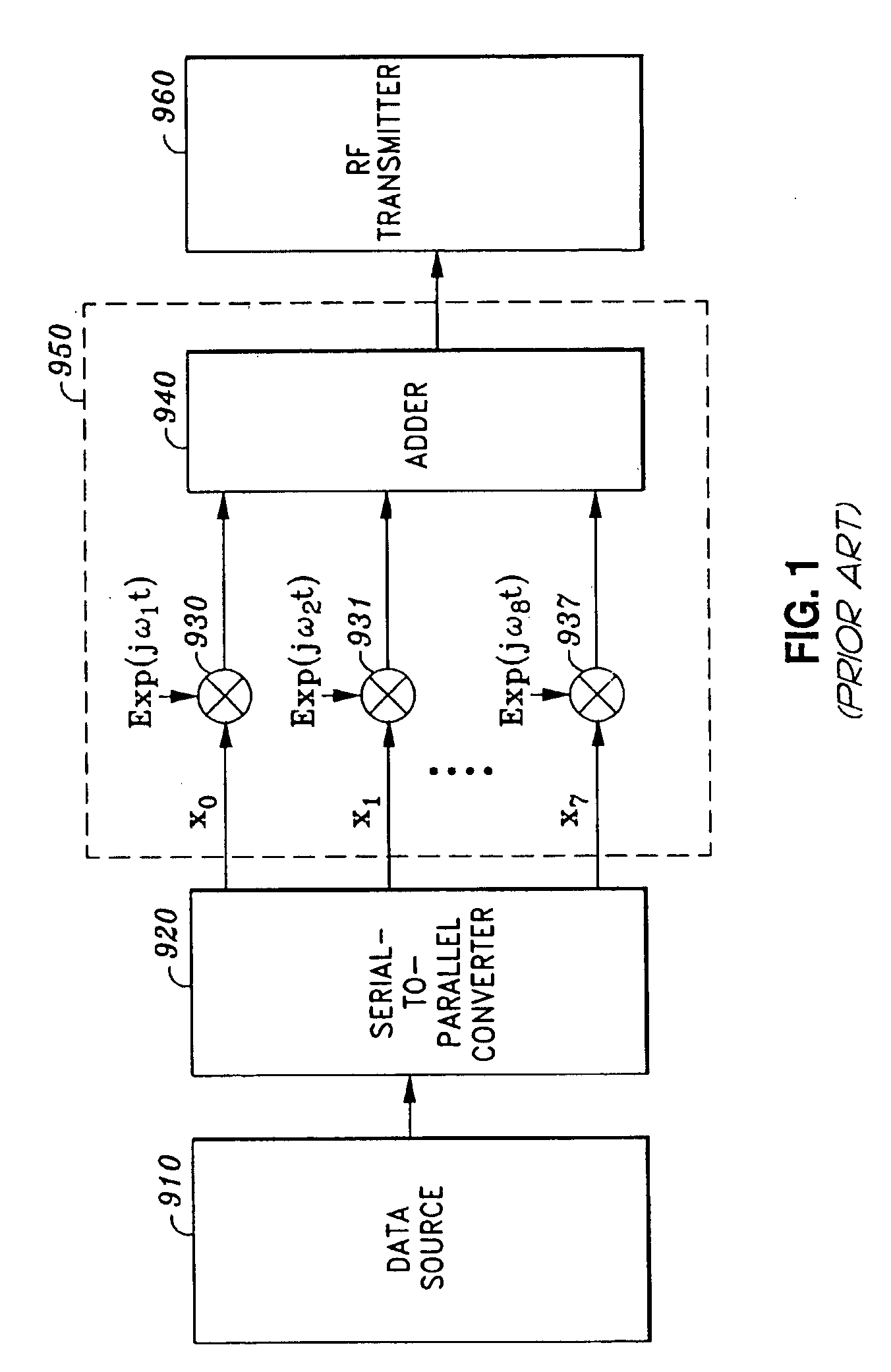
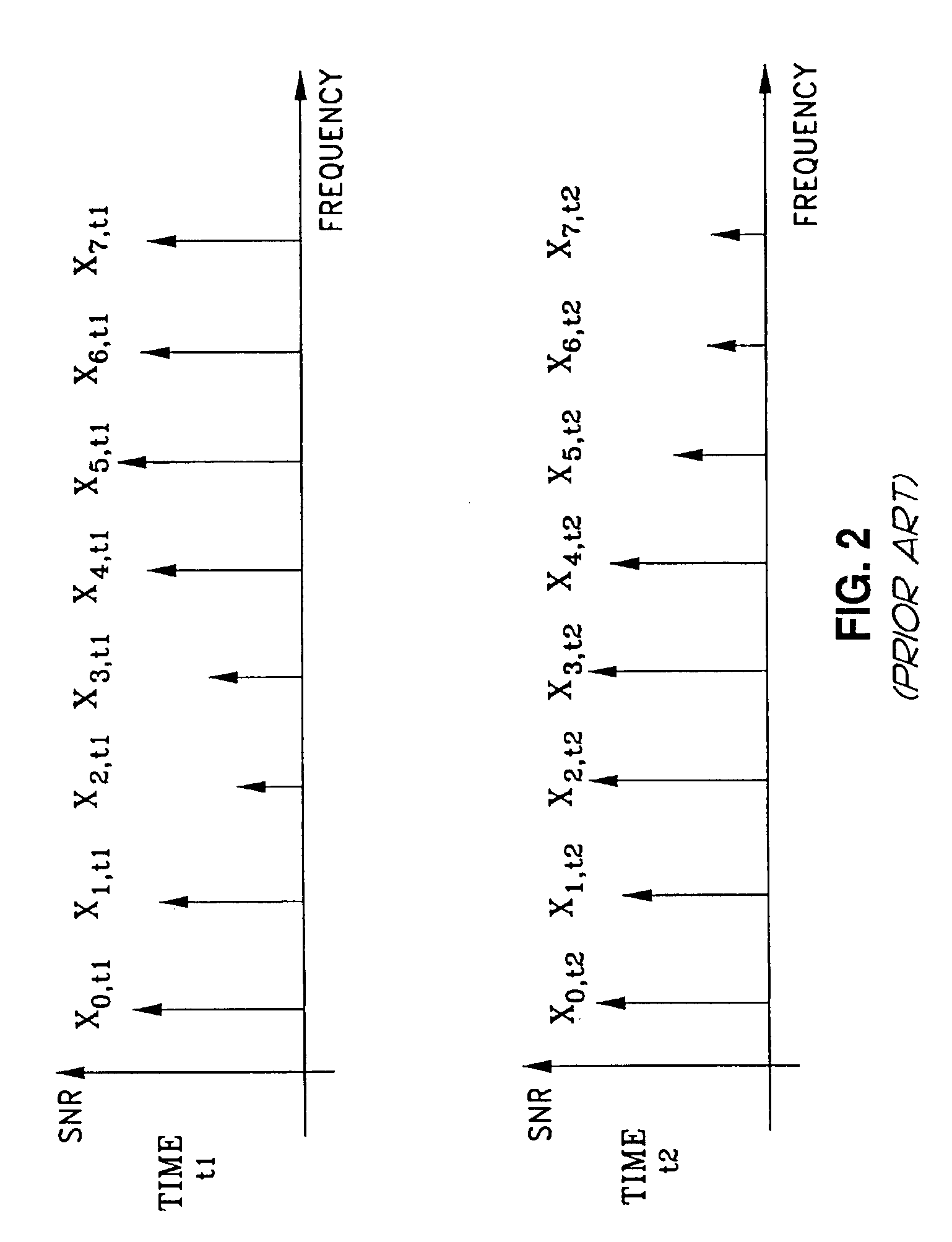
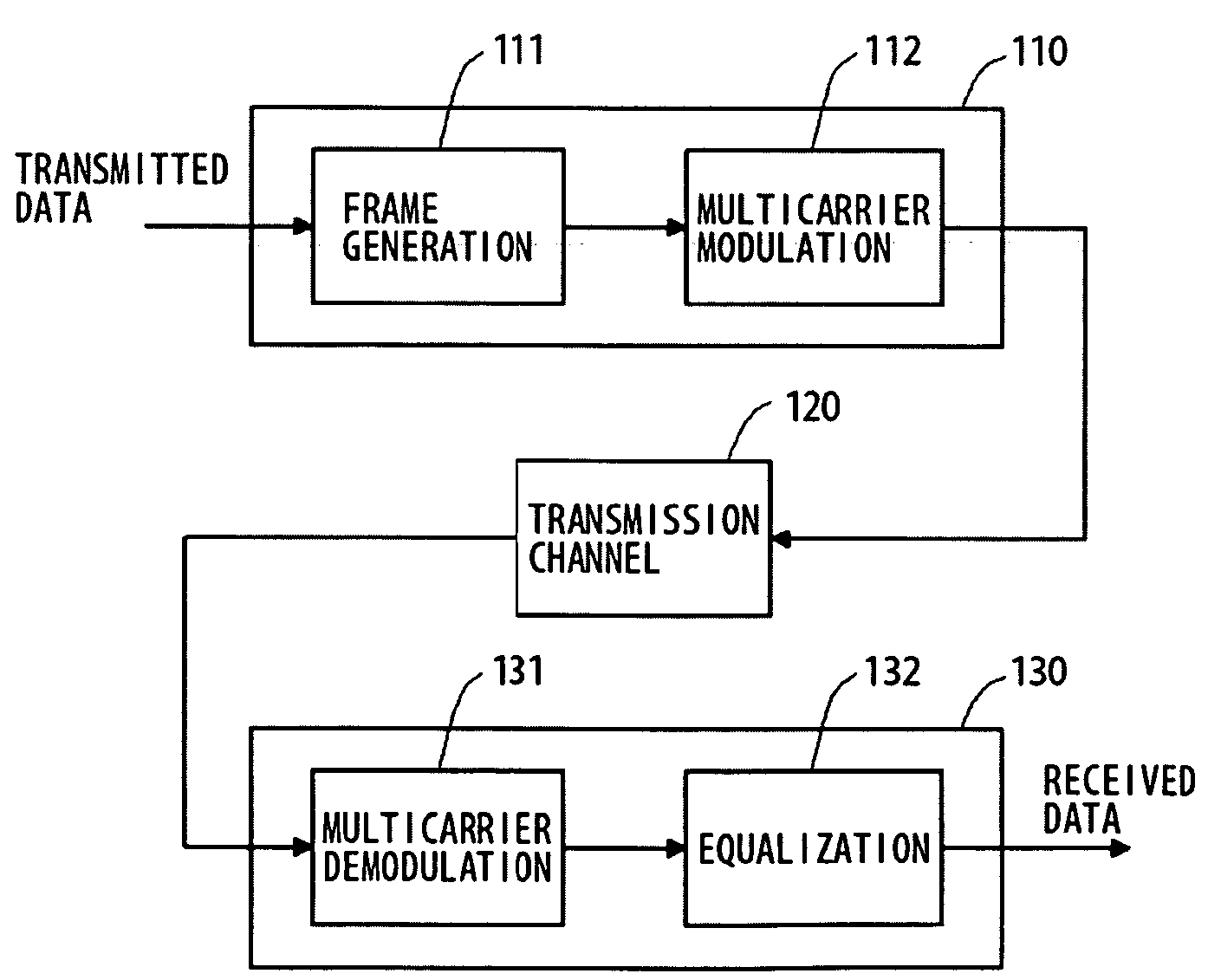
Multi-carrier modulation or MCM is an approach to data transmission that involves segregating the data into several more or less equal components. The individual components are then routed across different carrier signals. At the point of termination, the individual components are reassembled and delivered.
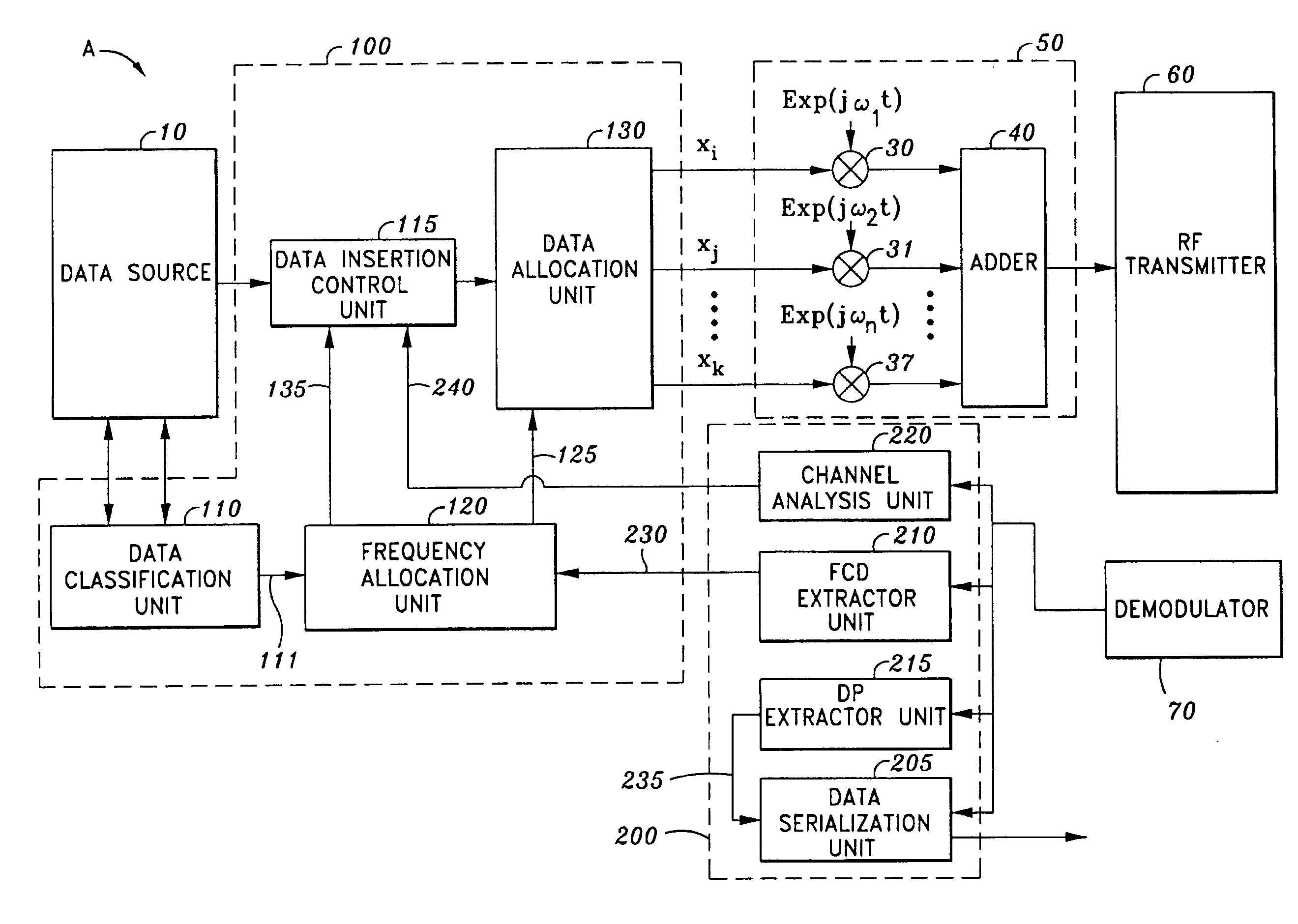
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
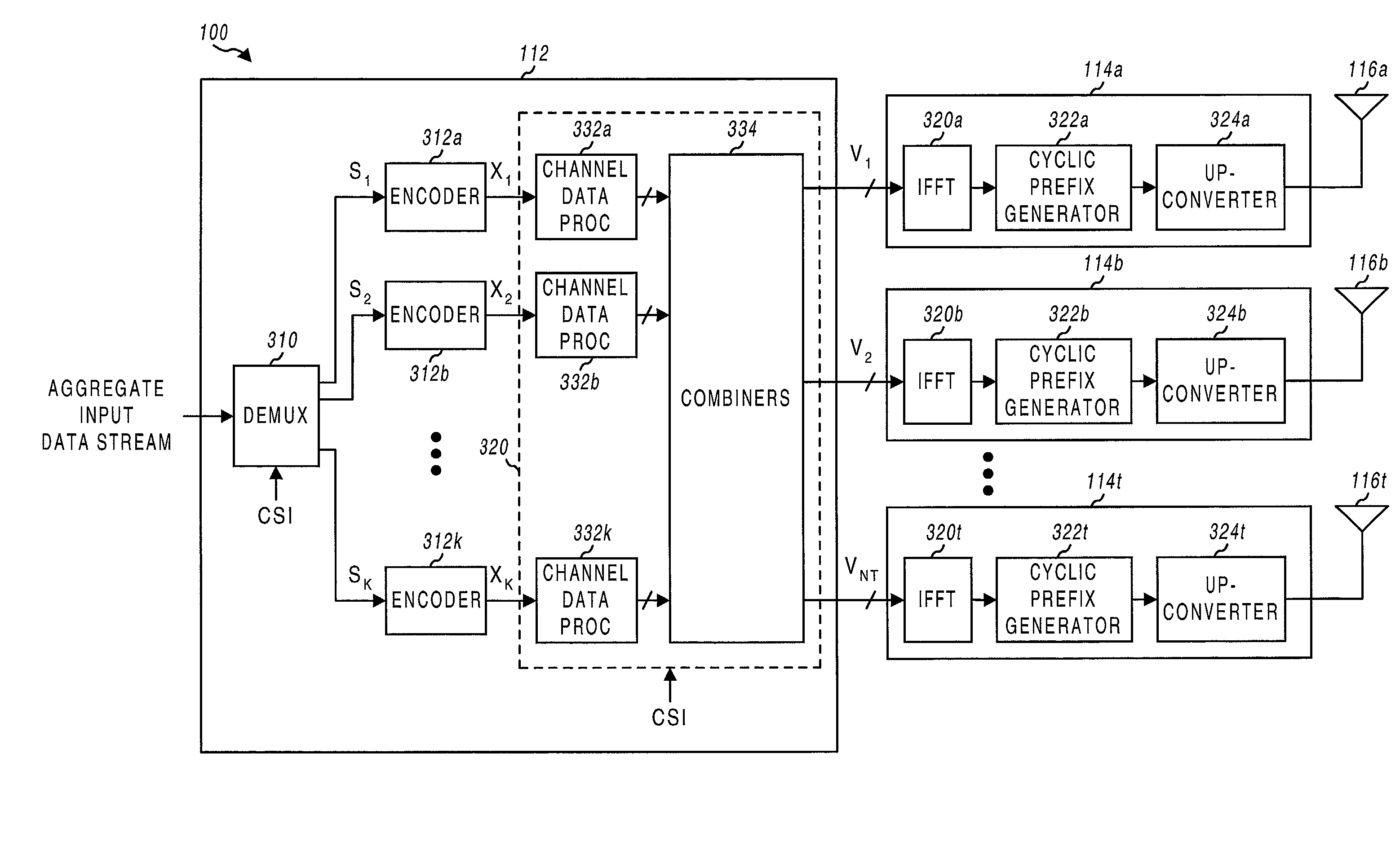
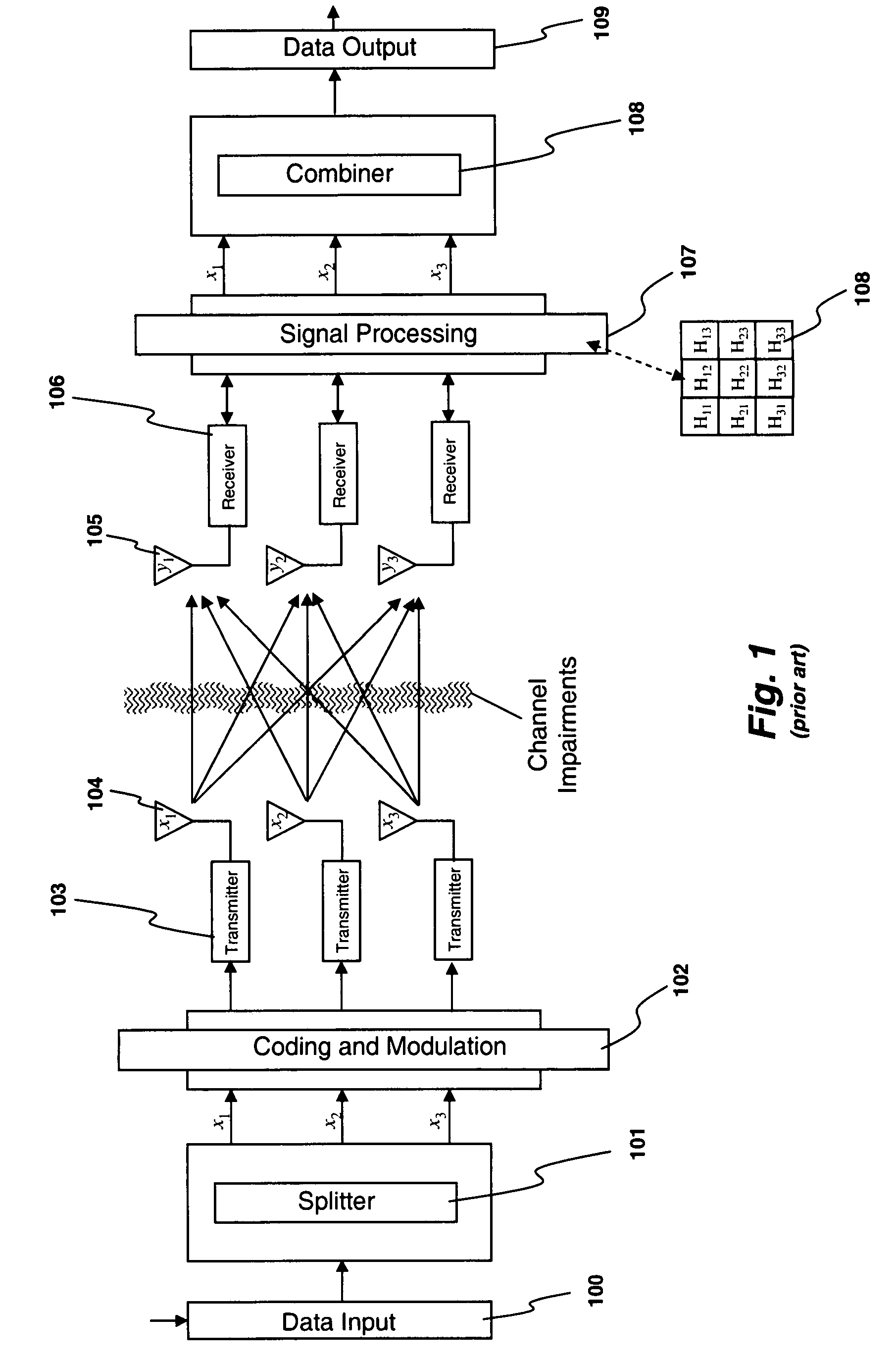
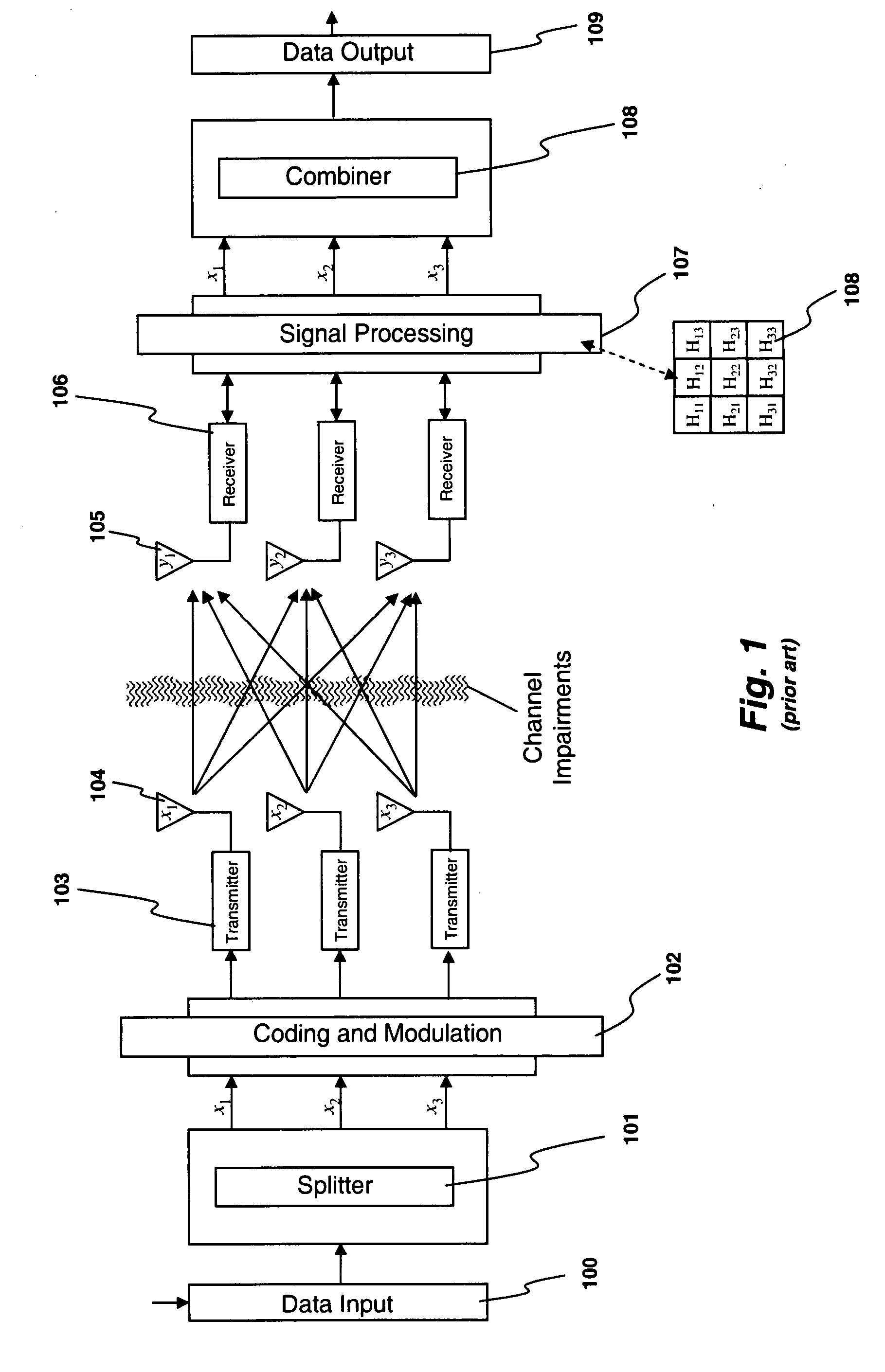
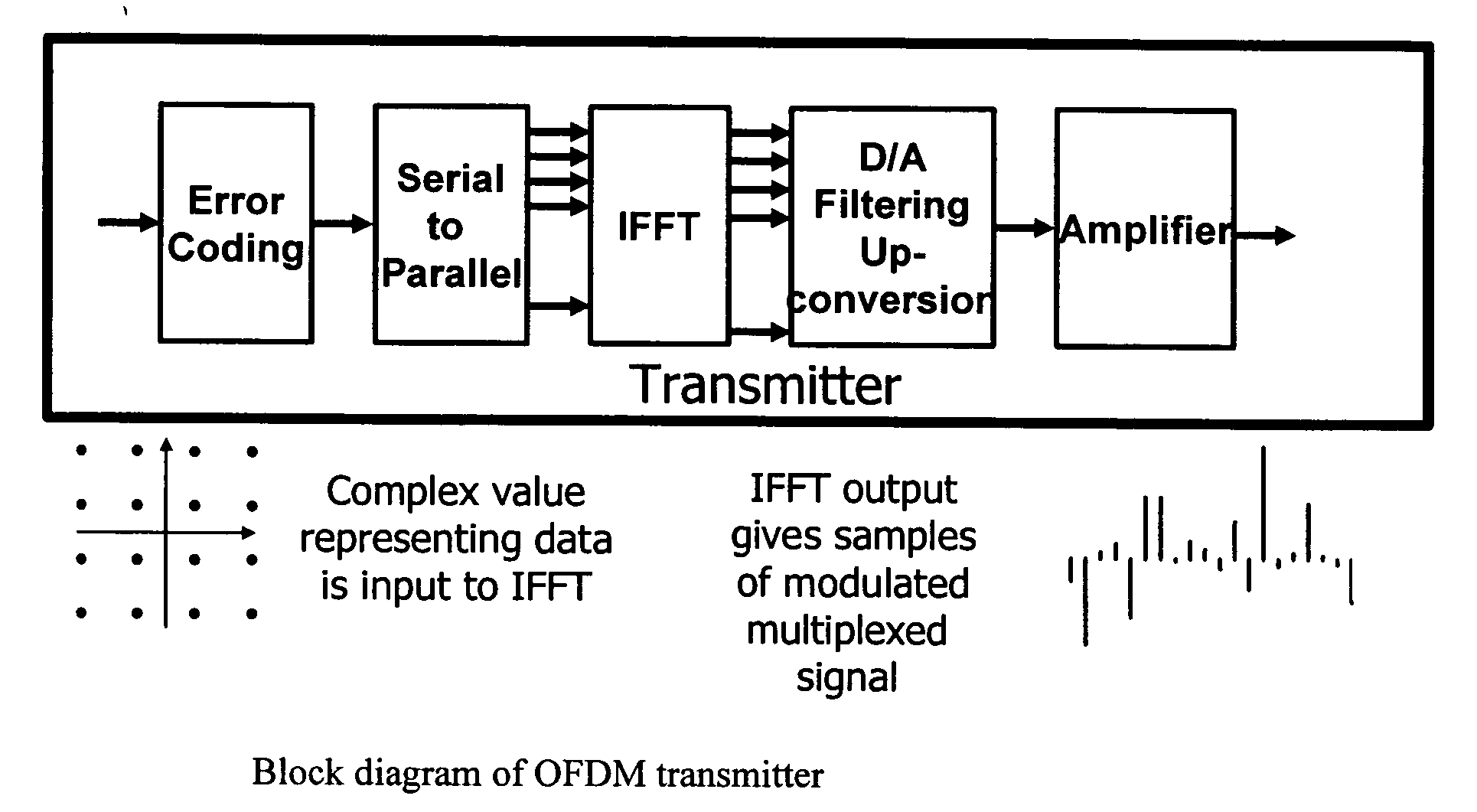
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
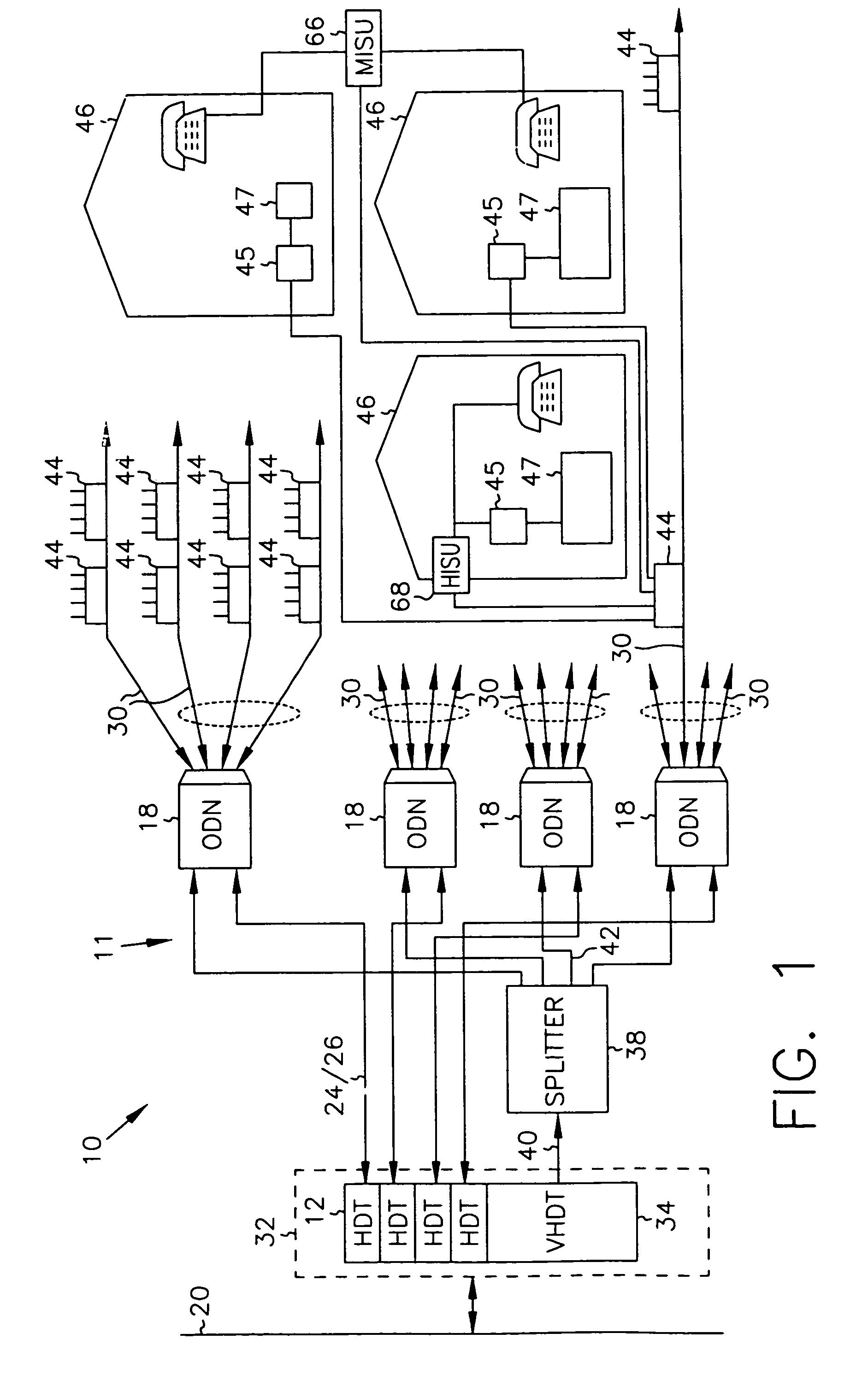
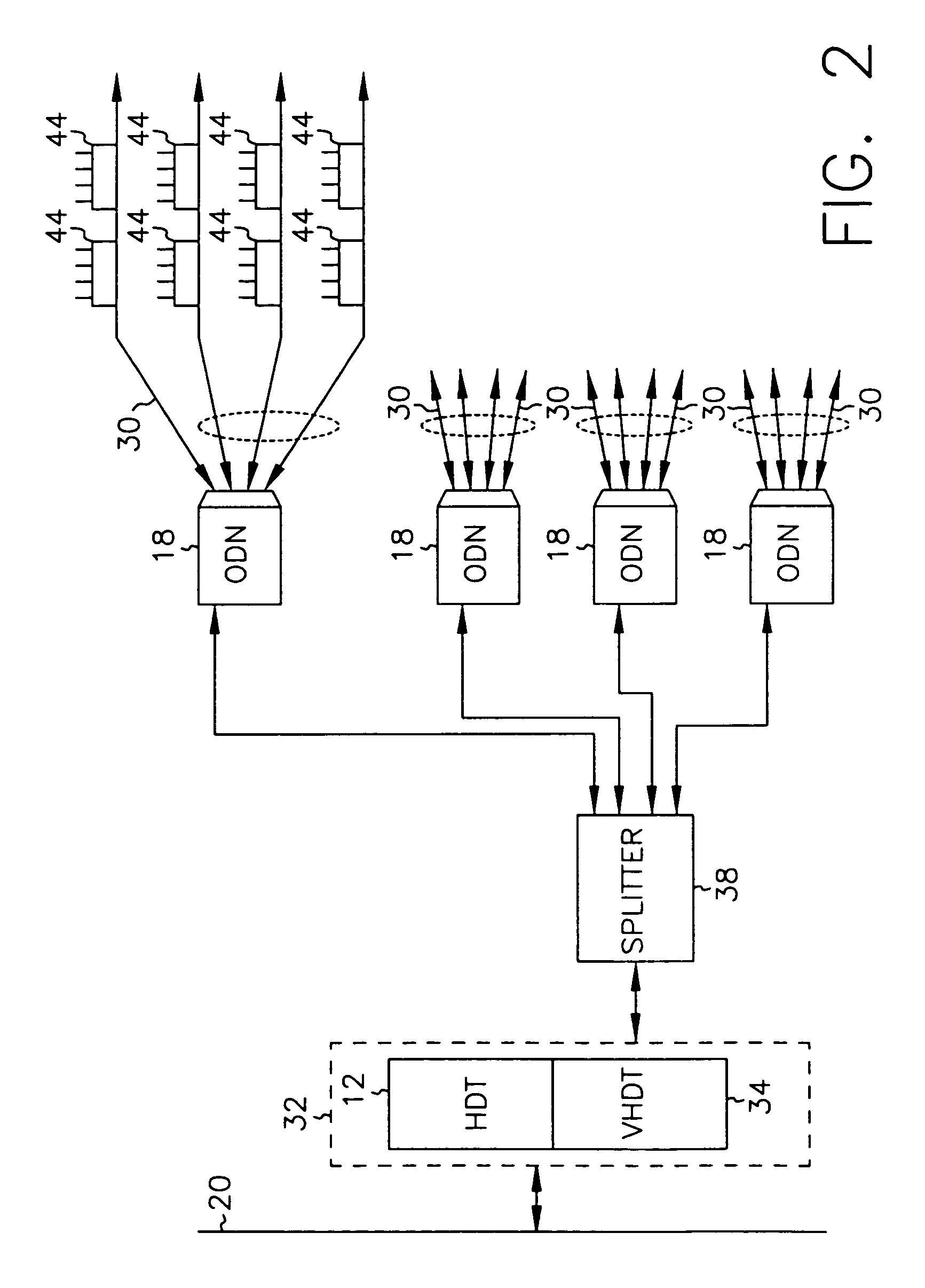
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
Multi-user multicarrier allocation in a communication system
InactiveUS20050111406A1Improve spectral efficiencyImprove throughputCriteria allocationFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemCarrier signal
In a multicarrier modulation communication system, subcarriers are allocated to a plurality of users using a plurality of sets of sequential subcarriers. The plurality of sets of sequential subcarriers may be allocated for transmitting information to the plurality of users or for transmitting information from the plurality of users. A multicarrier modulation communication system and the multicarrier modulation communications device is also discussed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
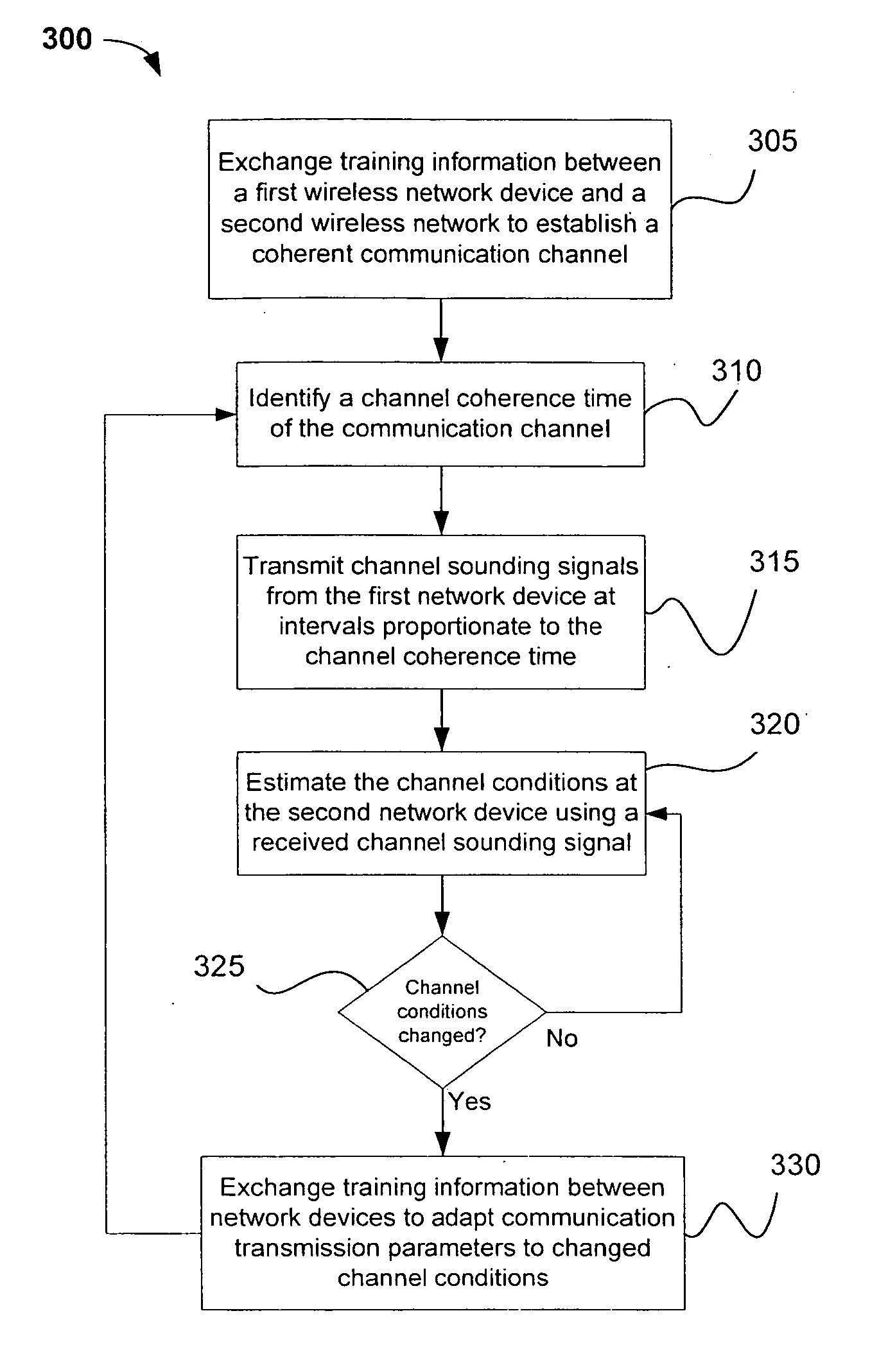
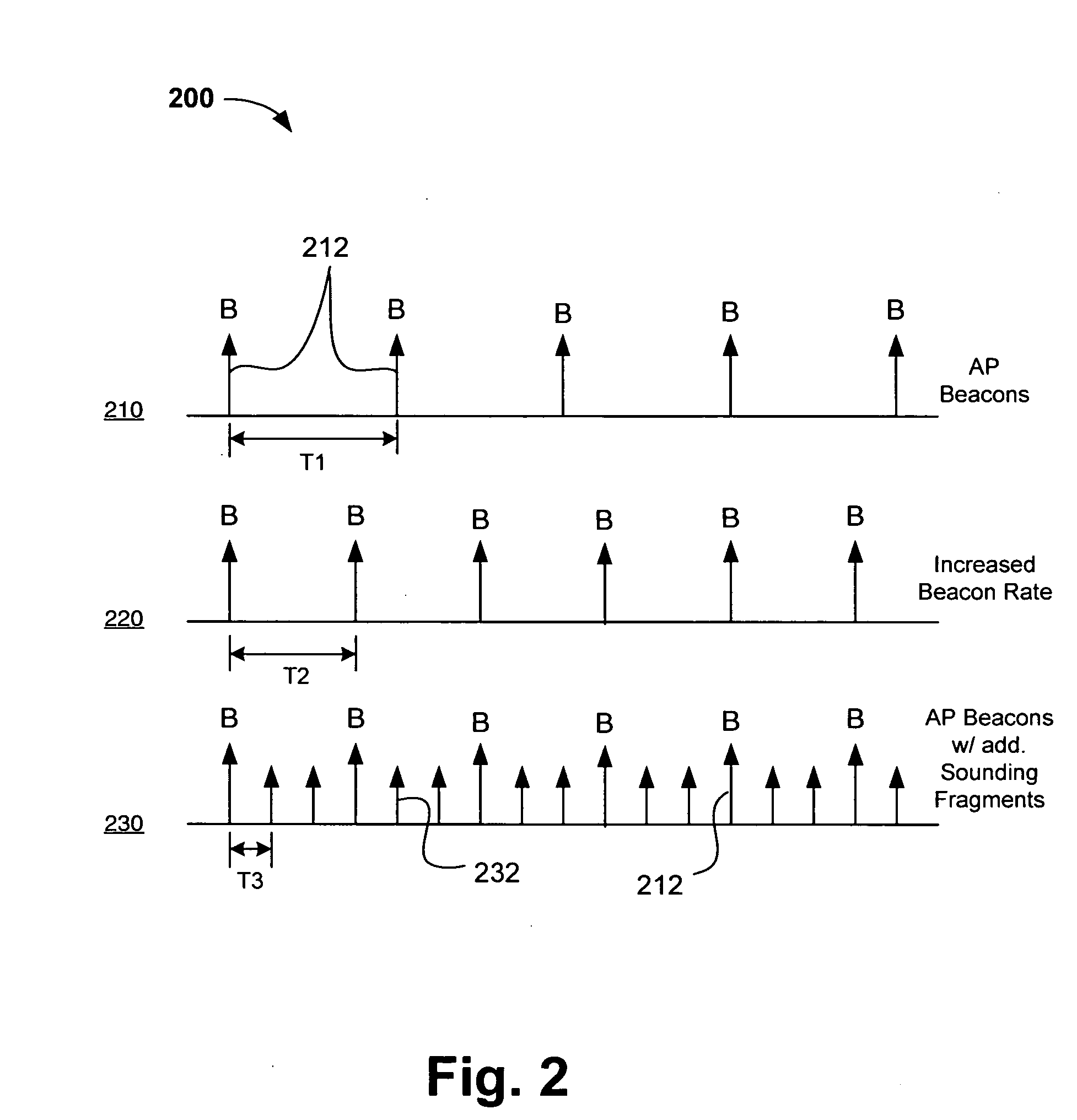
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
InactiveUS20050170781A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsCoherence timeLink adaptation
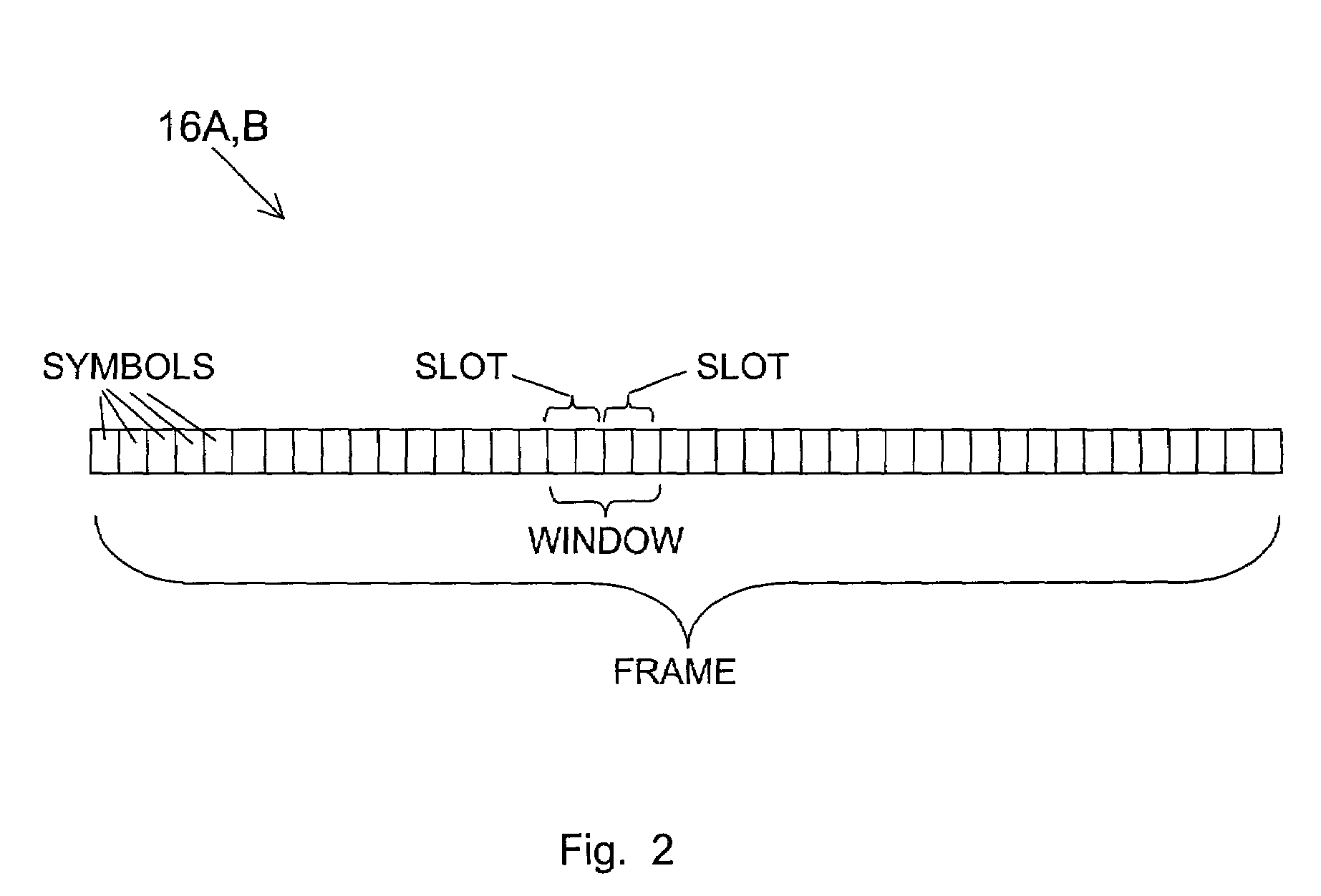
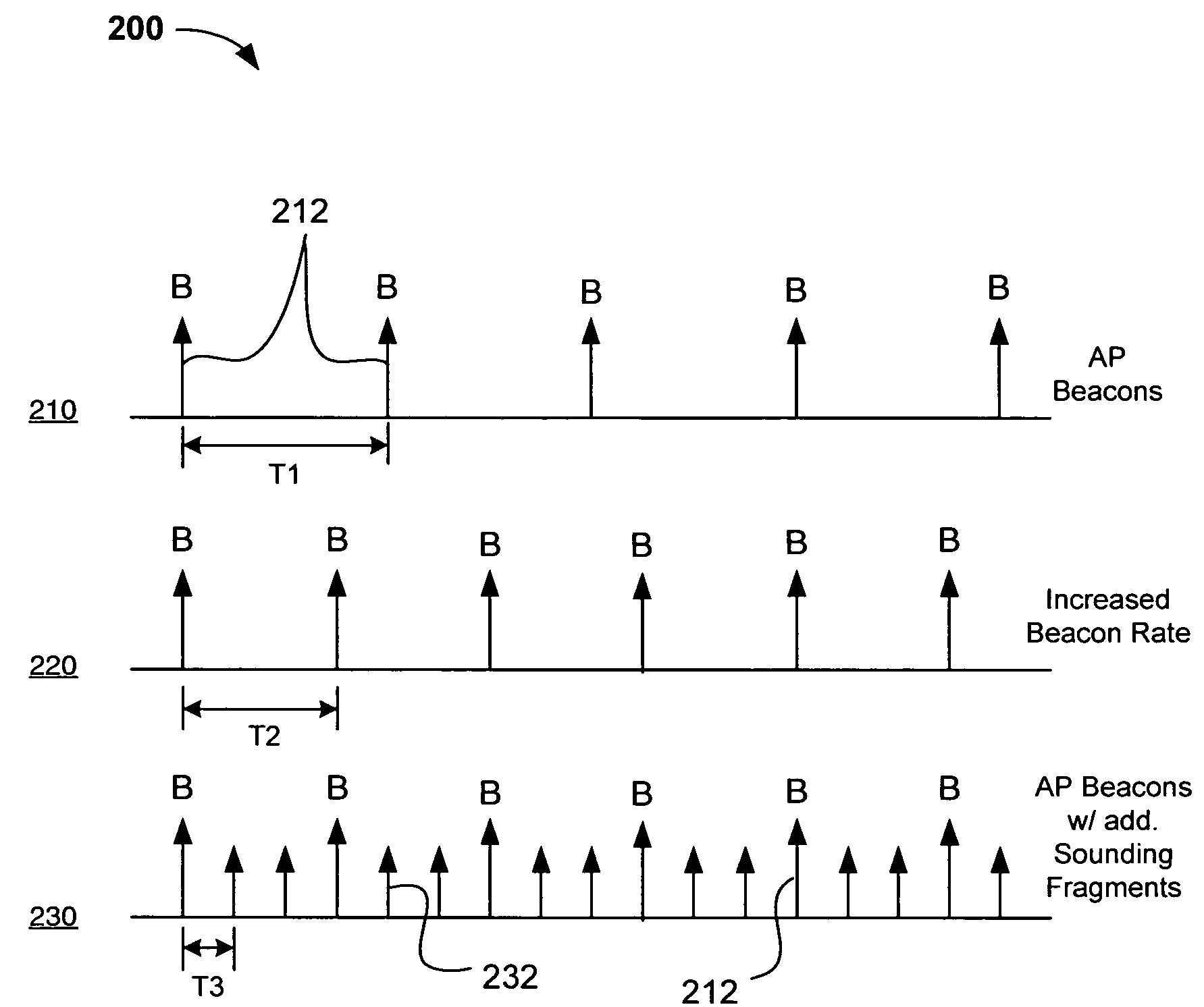
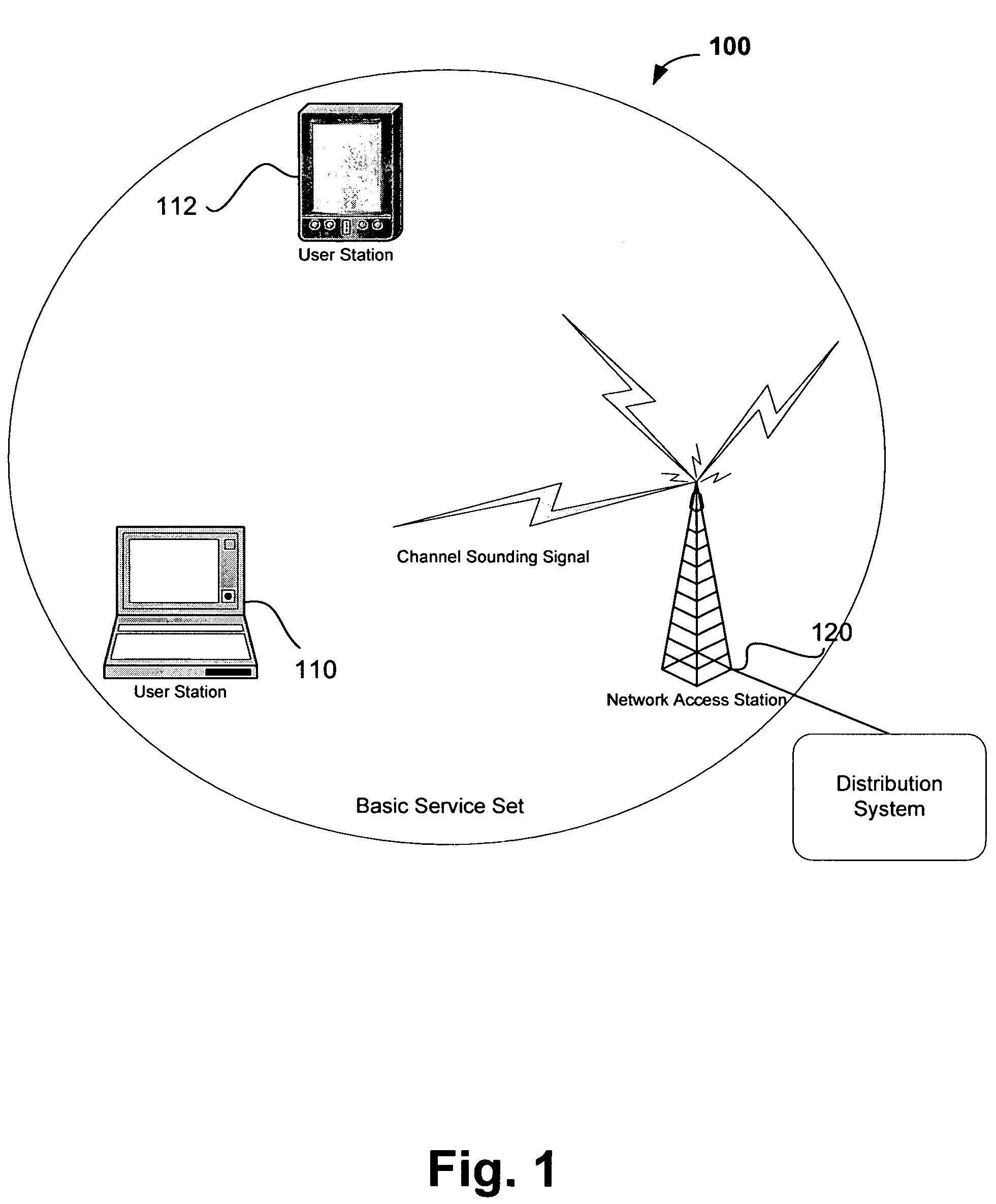
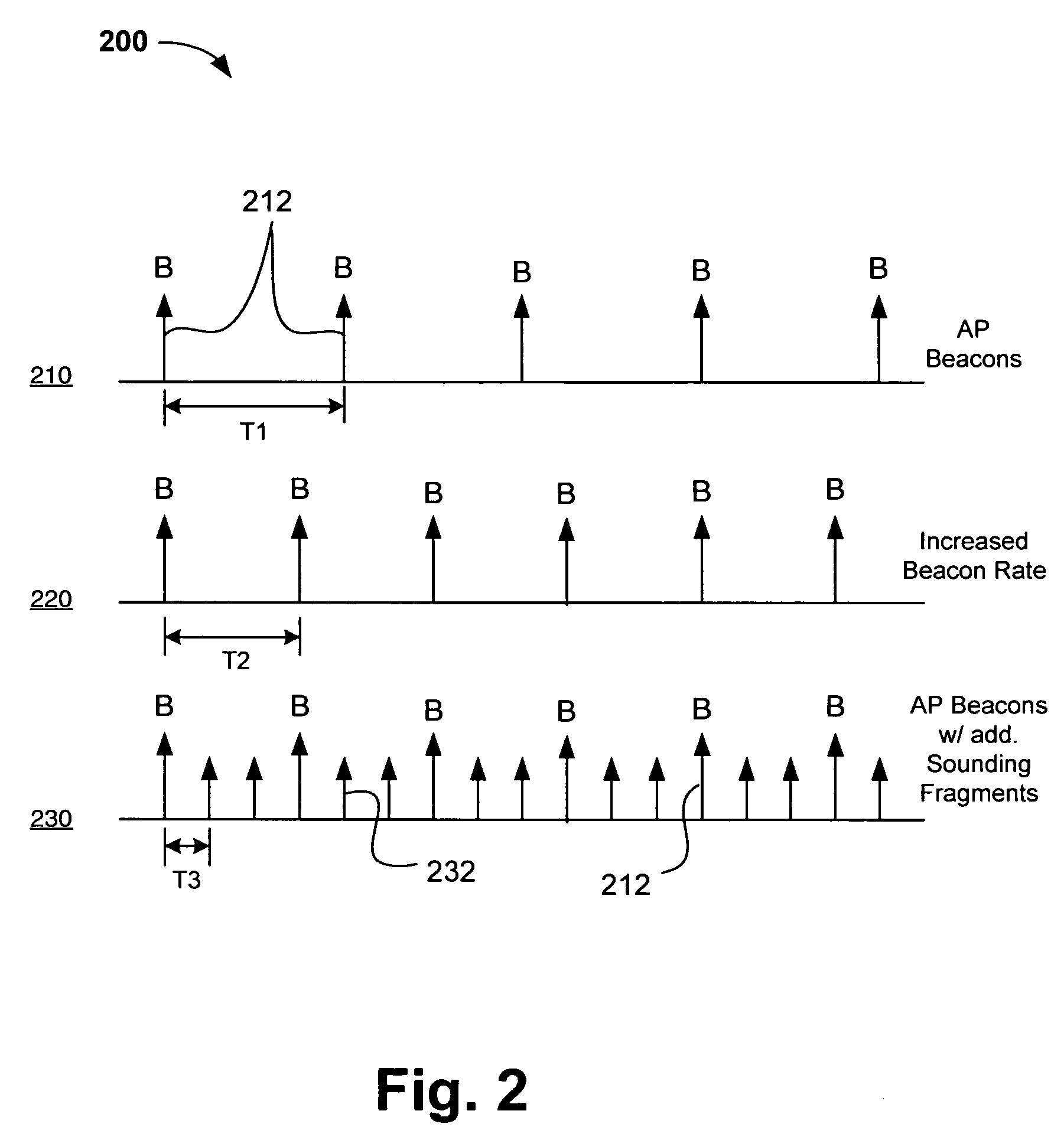
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
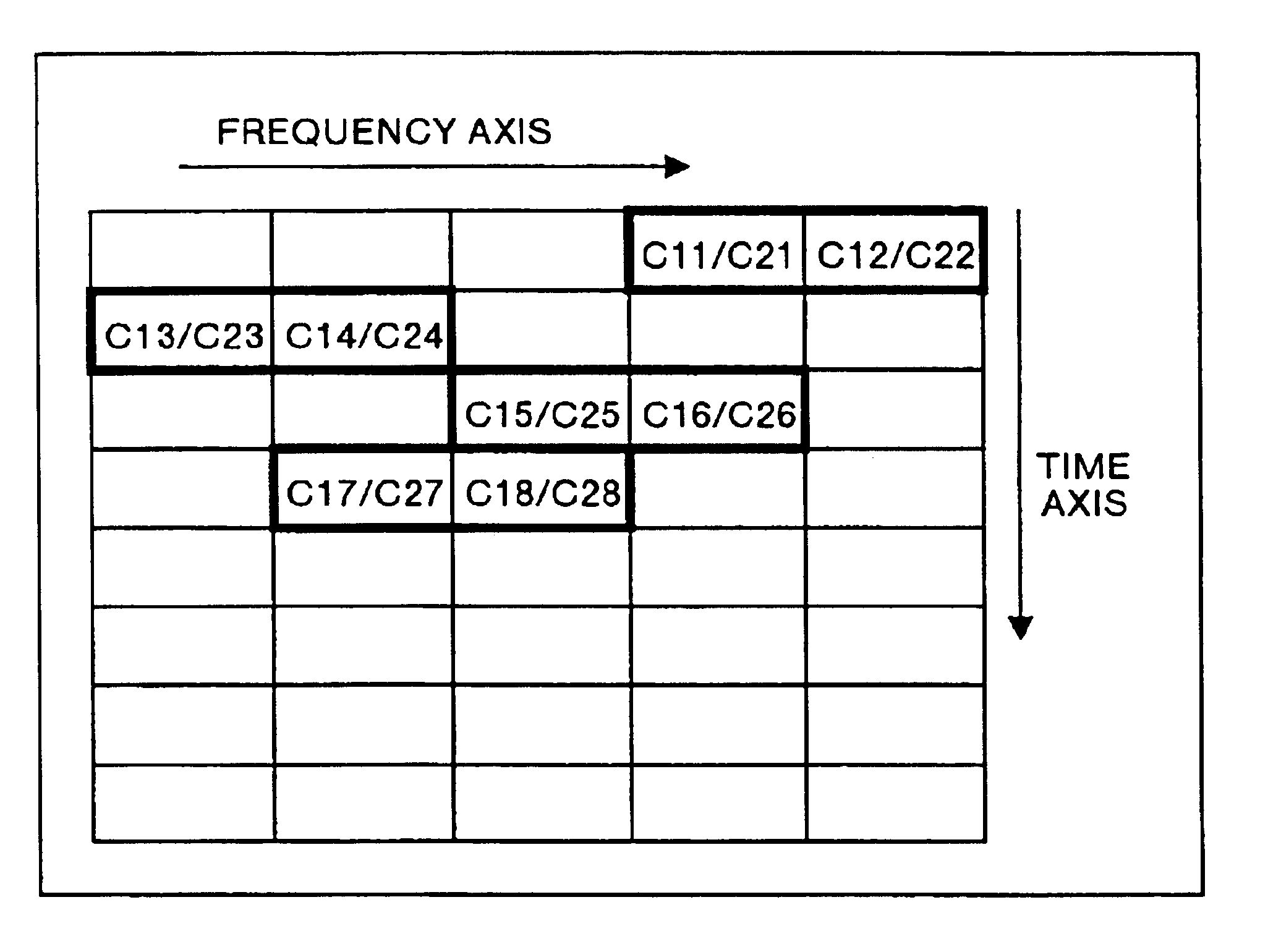
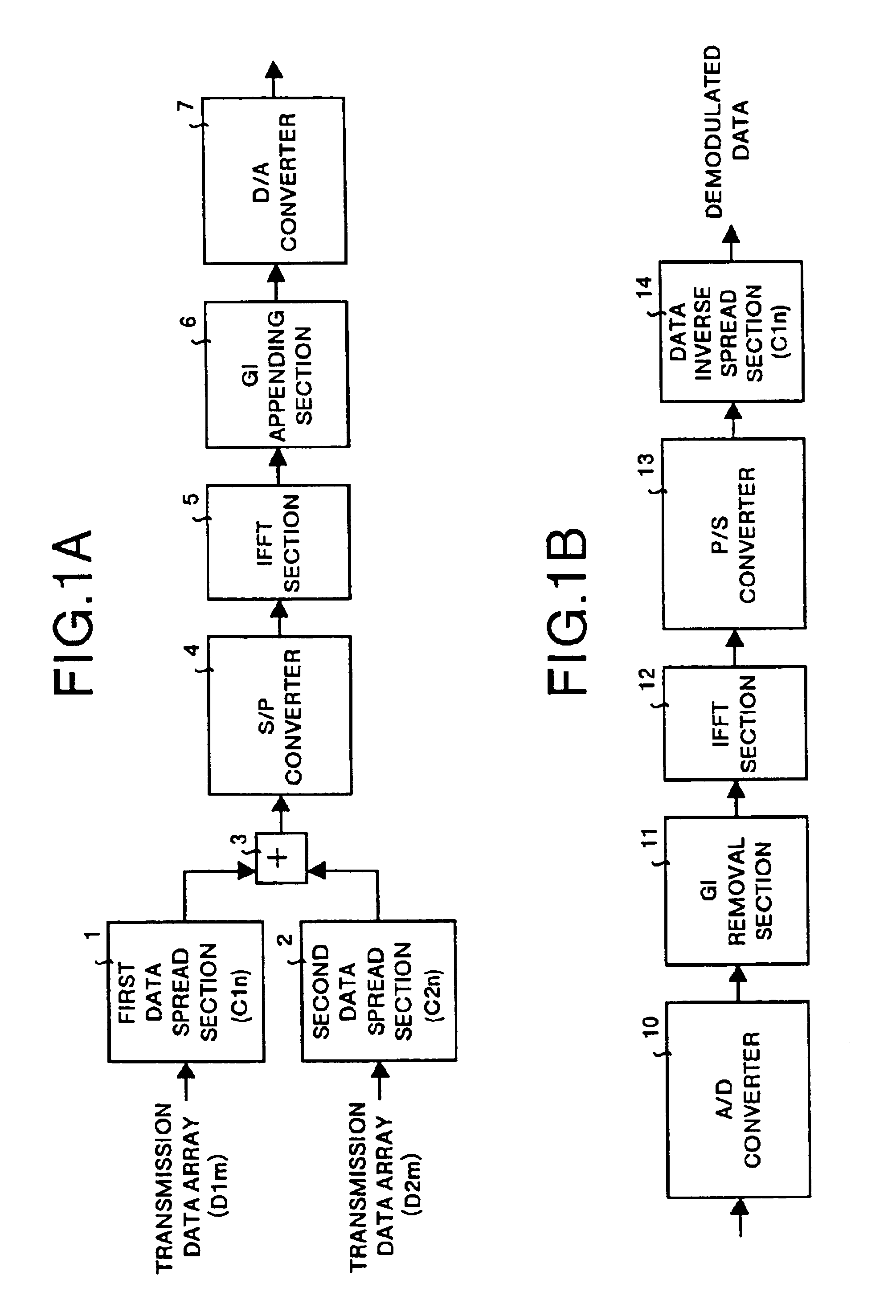
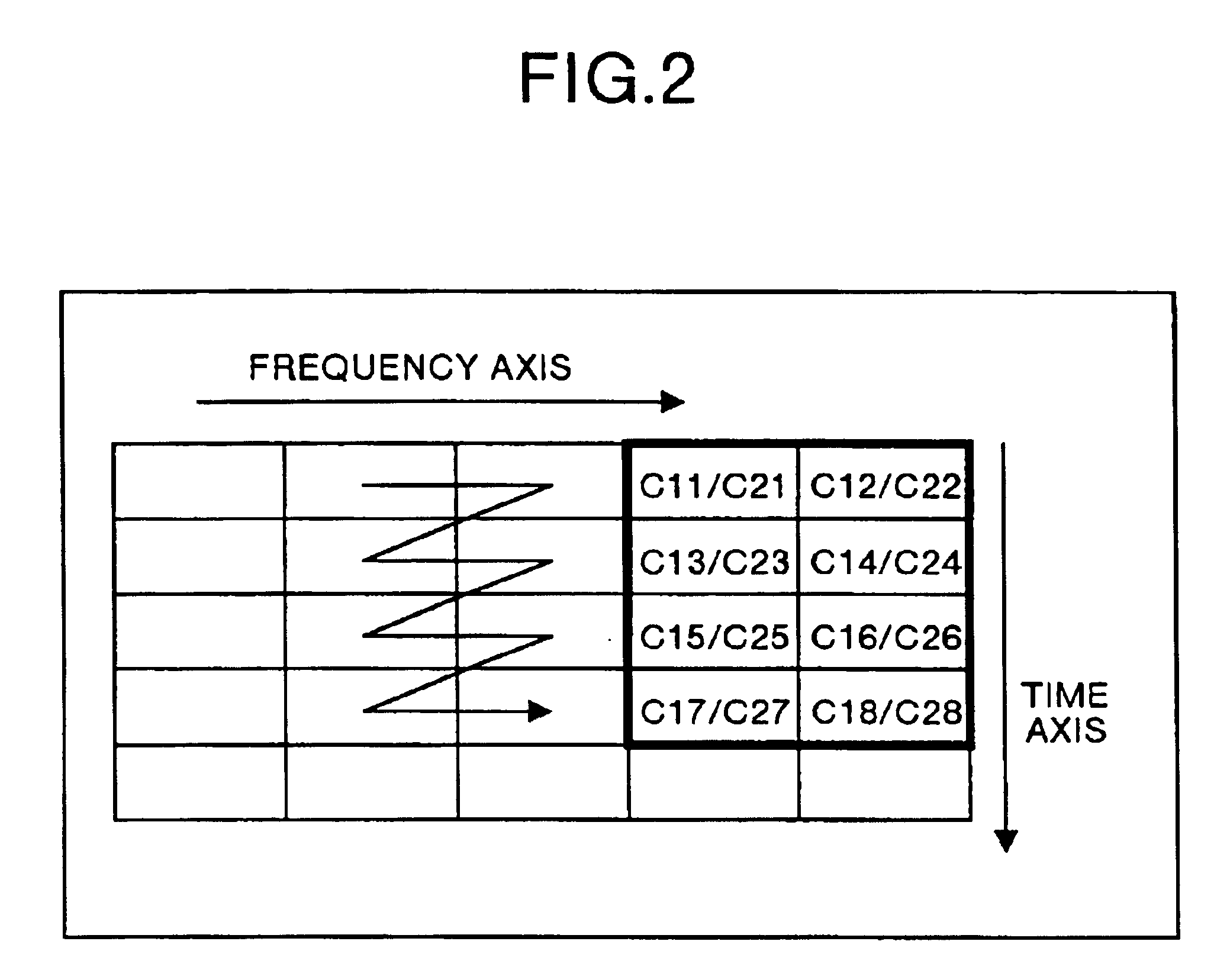
Multicarrier transfer system and multicarrier modulation method
InactiveUS6870826B1Increase the number ofNetwork traffic/resource managementModulated-carrier systemsSoftware engineeringCarrier signal
The multicarrier transfer system employing the OFDM / CDMA modulation system comprises a transmitter having an S / P converter which two-dimensionally arranges spread signals for a transmission data array on a frequency and time axes system and then rearrange the spread signals for one transmission data array arranged two-dimensionally. The transmitter transmits the signals generated in the S / P converter. A receiver receives the signals transmitted by the transmitter and demodulates the signal to reconstruct the transmission data array.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Method and apparatus for mobile platform reception and synchronization in direct digital satellite broadcast system
InactiveUS6956814B1Overcome disadvantagesImprove continuityPolarisation/directional diversityActive radio relay systemsEngineeringDiversity scheme
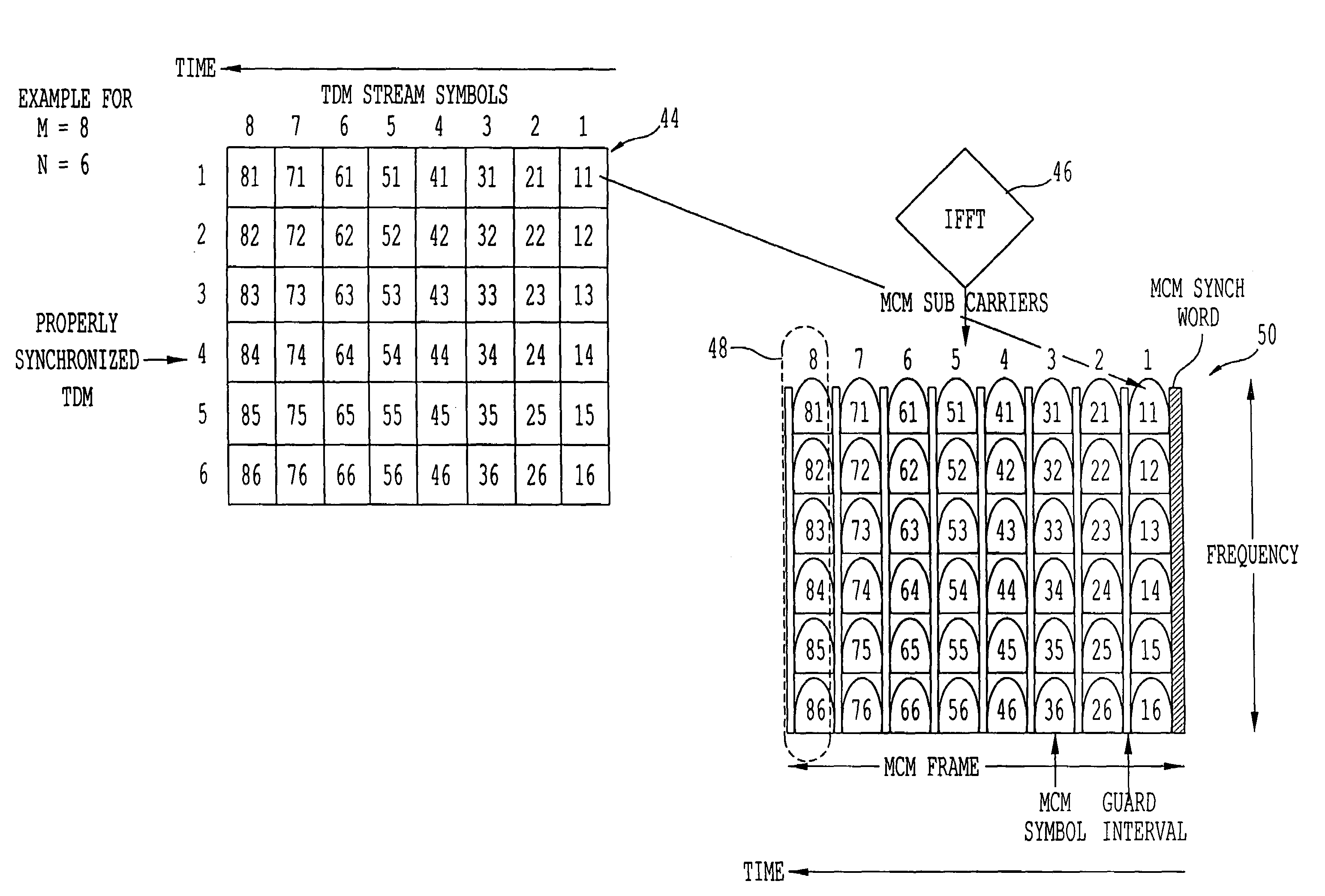
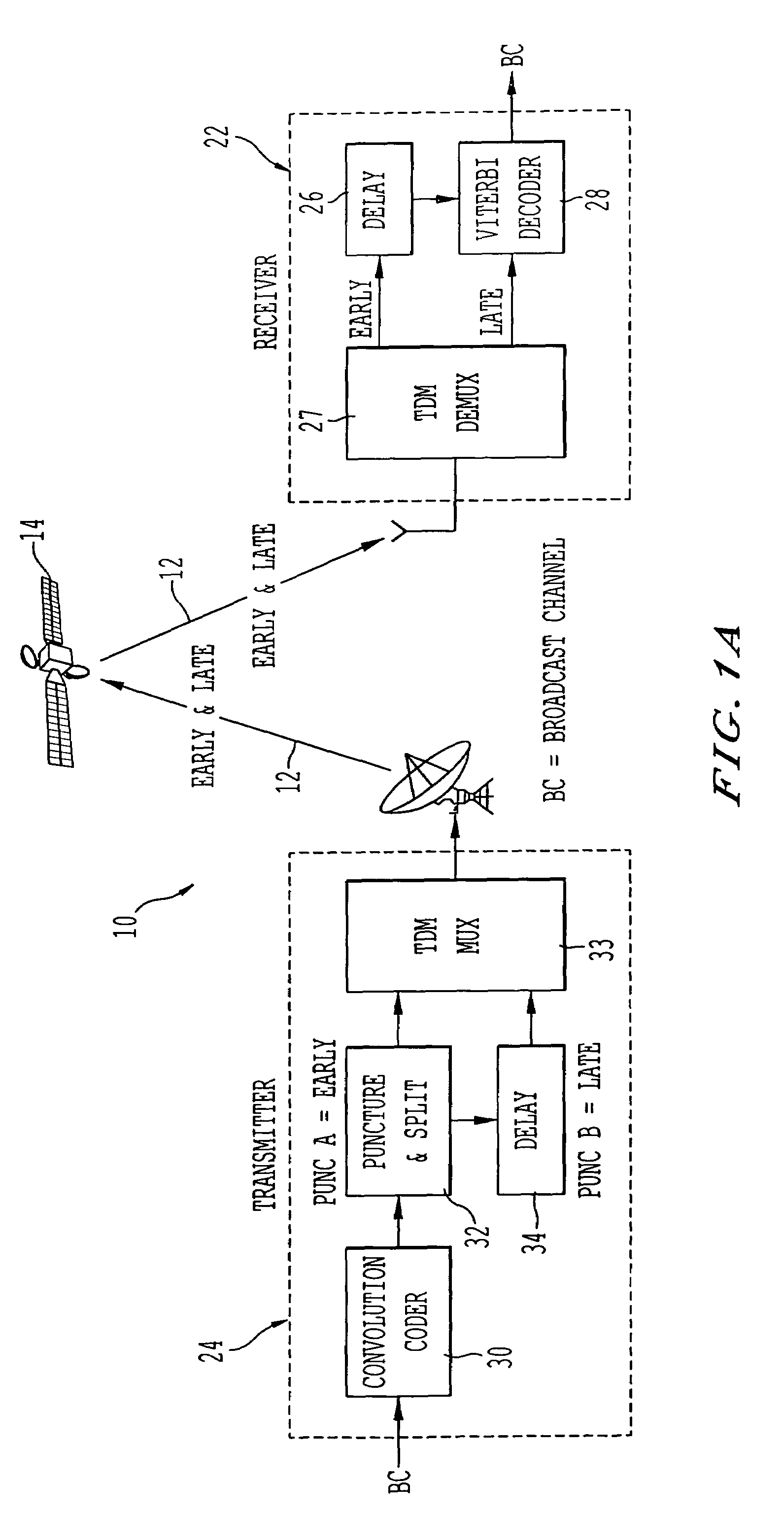
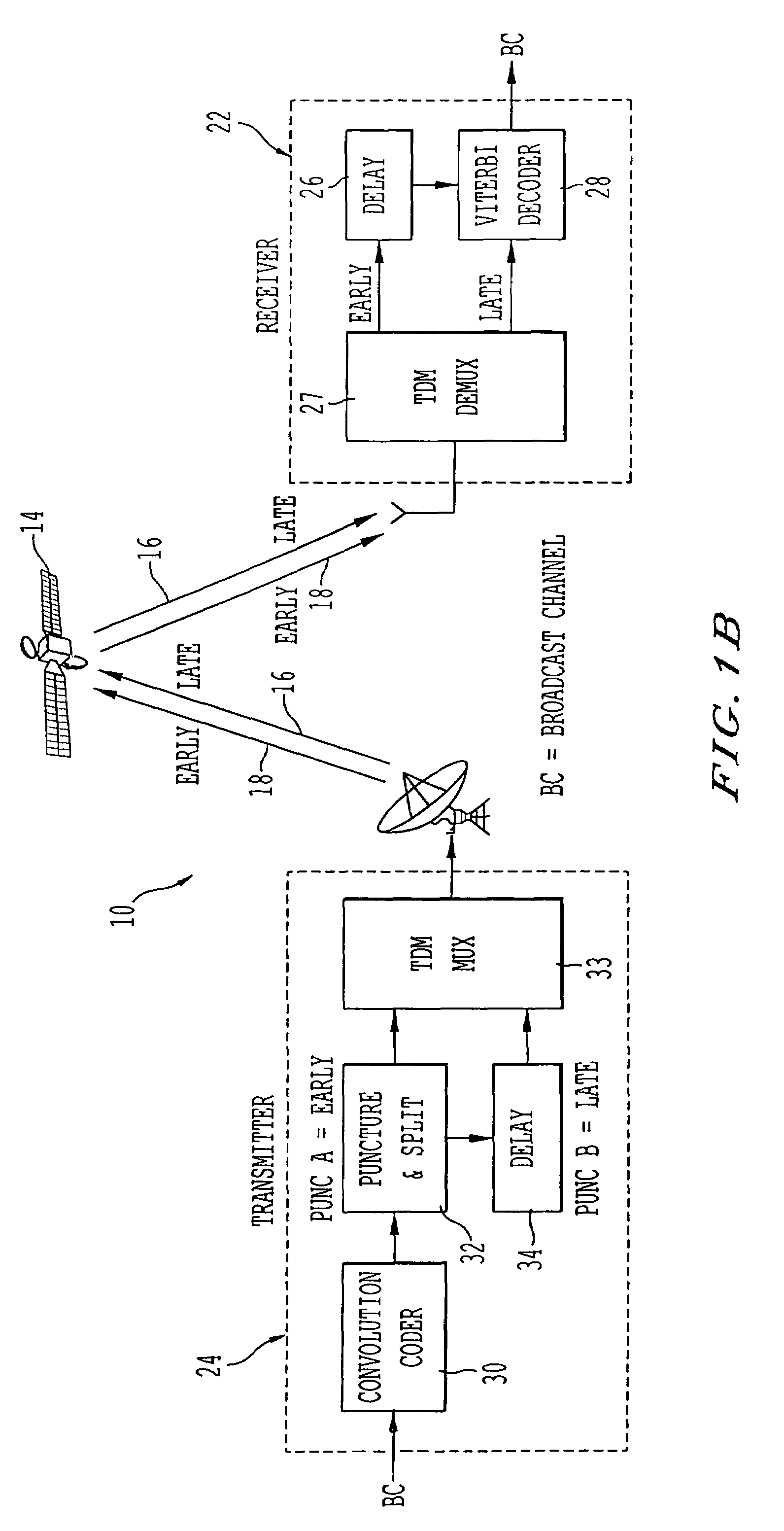
A satellite system employing time diversity and a single frequency network of terrestrial re-radiation stations is provided wherein each terrestrial re-radiation station inserts a delay into a terrestrial signal. The delay allows the time of arrival of the early time diversity signal at the center of terrestrial coverage to coincide with the arrival of the corresponding late time diversity signal, thereby improving hand-off between terrestrial and satellite signals at a receiver. The delay also adjusts for distance differences between each terrestrial re-radiation station and the satellite and between each station and the center of the terrestrial coverage region. This adjustment optimizes the TDM-MCM reception by synchronizing at the center of the SFN the phase of the MCM signals re-radiated from the re-radiating stations of the SFN. The delay also compensates for the processing delay encountered when converting a satellite LOS TDM stream into a multicarrier modulated stream for transporting the satellite LOS TDM stream to user receivers and for the diversity delay between the early and late signals.
Owner:WORLDSPACE INC
System and method for distributed input-distributed output wireless communications
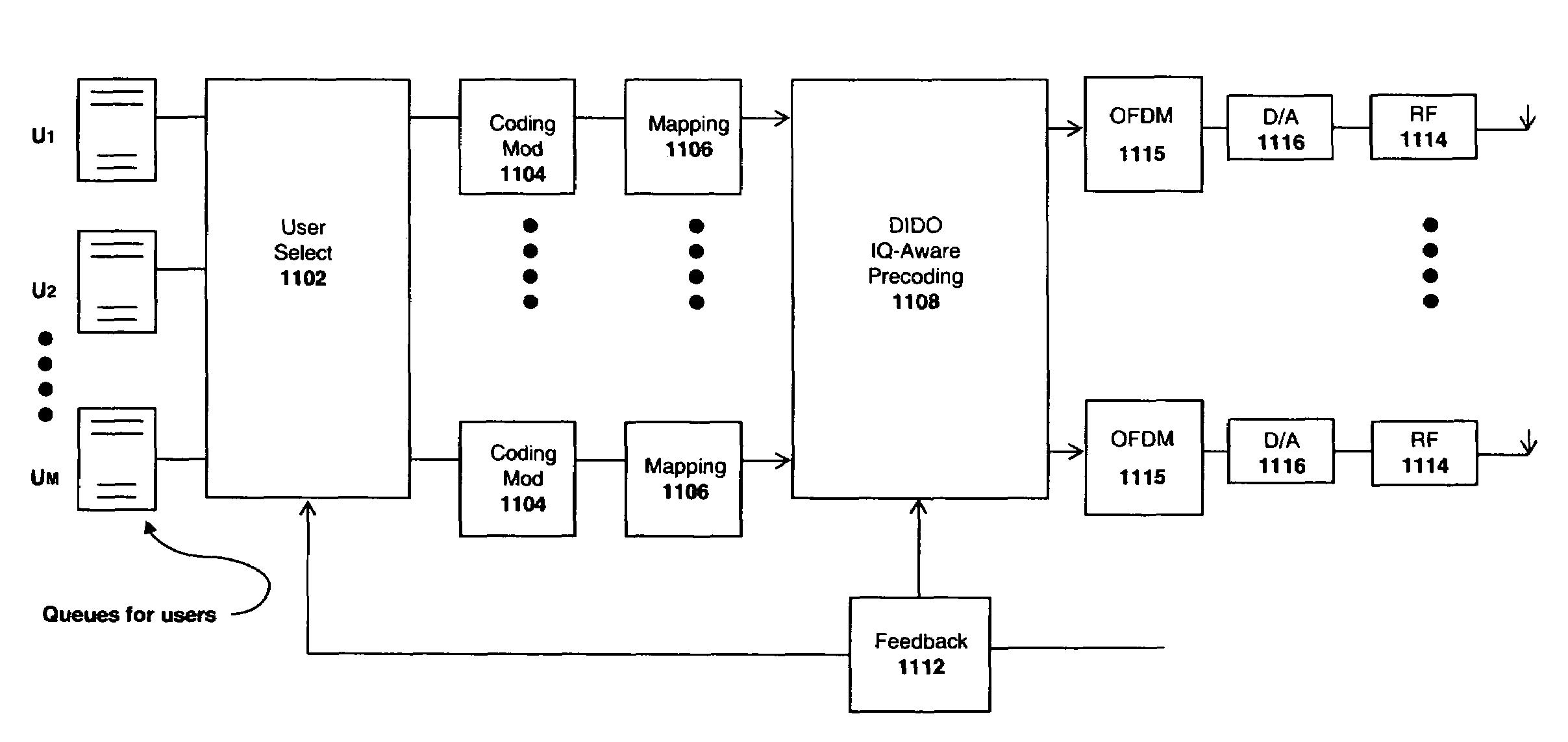
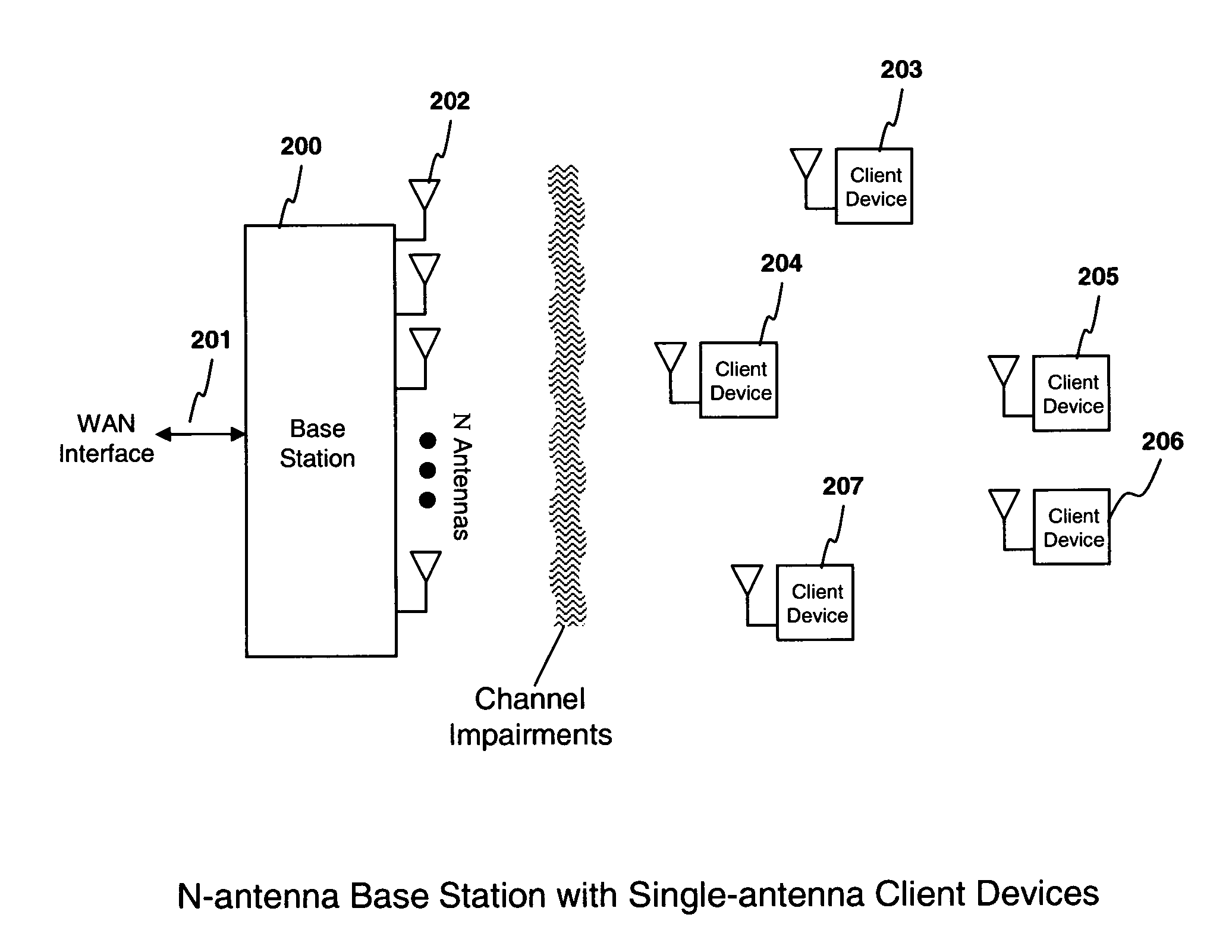
A system for compensating for in-phase and quadrature (I / Q) imbalances for multiple antenna systems (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (defined with the acronym MU-MAS), such as distributed-input distributed-output (DIDO) communication systems, comprising multicarrier modulation, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). For example, one embodiment of the system comprises one or more coding modulation units to encode and modulate information bits for each of a plurality of wireless client devices to produce encoded and modulated information bits; one or more mapping units to map the encoded and modulated information bits to complex symbols; and a MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding unit to exploit channel state information obtained through feedback from the wireless client devices to compute MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding weights, the MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware preceding unit precoding the complex symbols obtained from the mapping units using the weights to pre-cancel interference due to I / Q gain and phase imbalances and / or inter-user interference.
Owner:REARDEN
System and method for distributed input-distributed output wireless communications
A system for compensating for in-phase and quadrature (I / Q) imbalances for multiple antenna systems (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (defined with the acronym MU-MAS), such as distributed-input distributed-output (DIDO) communication systems, comprising multicarrier modulation, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). For example, one embodiment of the system comprises one or more coding modulation units to encode and modulate information bits for each of a plurality of wireless client devices to produce encoded and modulated information bits; one or more mapping units to map the encoded and modulated information bits to complex symbols; and a MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding unit to exploit channel state information obtained through feedback from the wireless client devices to compute MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware precoding weights, the MU-MAS or DIDO IQ-aware preceding unit precoding the complex symbols obtained from the mapping units using the weights to pre-cancel interference due to I / Q gain and phase imbalances and / or inter-user interference.
Owner:REARDEN
Multicarrier modulation systems
ActiveUS20050243938A1Reduce probabilityMinimize degradationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides a new approach which is better suited to FFT design as applied to multicarrier modulation systems such as OFDM. The signals are scaled so that overflow, rather than being completely avoided, occurs with low probability throughout the IFFT and FFT structures. The size of the error that results from an overflow depends on how overflow is handled in the DSP. To minimize the degradation, overflow should result in saturation of the value at the maximum positive or negative value option. This is equivalent to clipping the signal. Using the new technique, signals within the FFT structure are scaled to balance the effect of clipping and round-off. Clipping may result in comparatively large errors in a few signal values but because of the spreading effect of the FFT and because OFDM systems typically include error coding / correction, system performance depends on the total error or, in other words the total noise power, across all of the FFT outputs rather than on any individual value.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Broadband network for coaxial cable using multi-carrier modulation
ActiveUS7295518B1Speed up the descentOvercome problemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A broadband local area data network uses coaxial cable wiring for interconnection of terminal devices. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with bit loading is used to overcome channel impairments and provide a path for terminal devices to transmit to and receive from other terminal devices. Probe messages are sent between devices to characterize the communication channel and determine optimum bit loading. The data network shares the cable spectrum with other services and uses frequency bands not used by other services. Adaptive power control can be used to maintain signal to noise ratio in a communication between terminal devices. Frequency coordination can be used to avoid interference between the LAN communications and other services transmitted on the cable.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
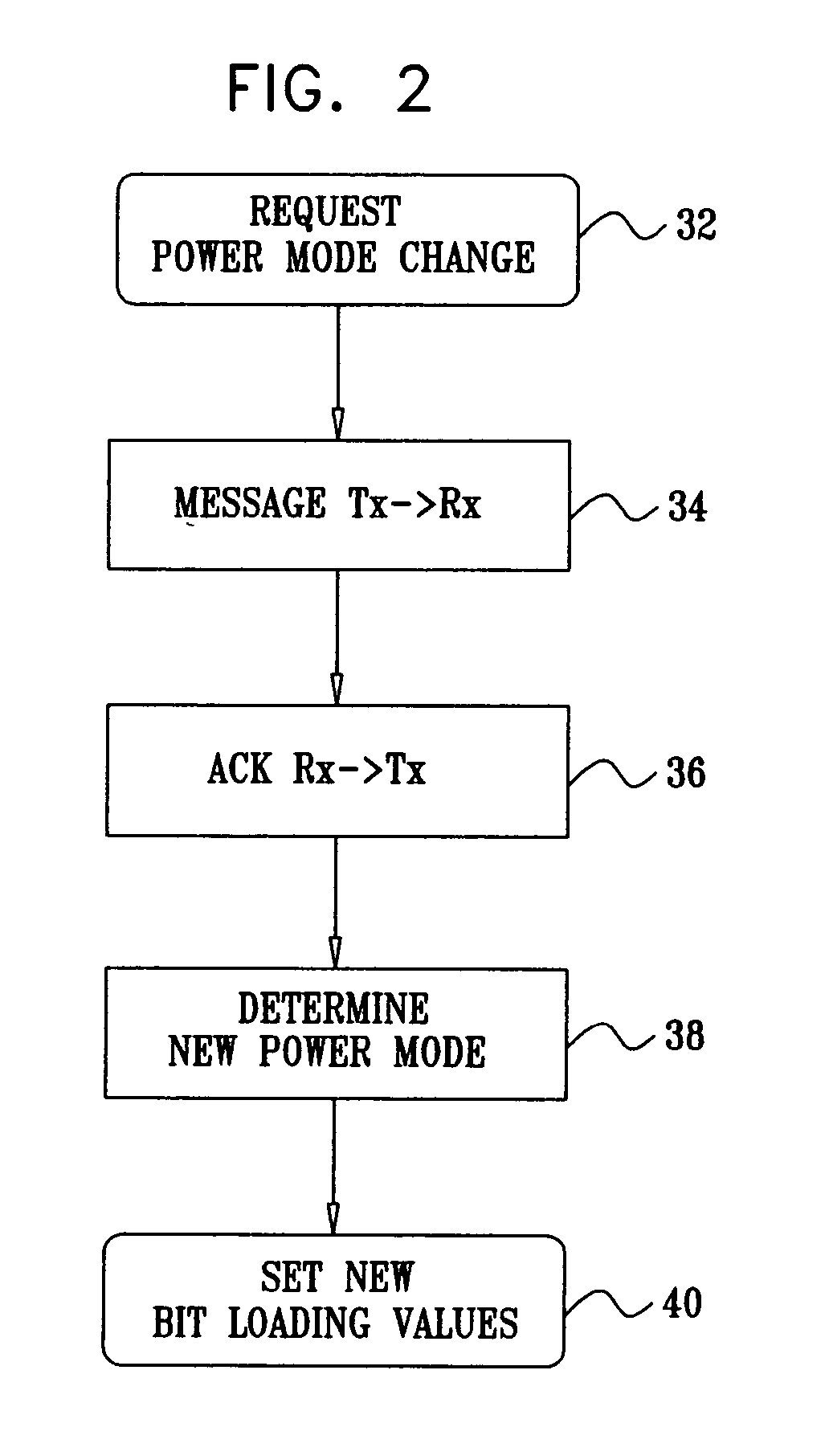
Power save mode transition using loading translation function
Methods and systems provide an efficient power save mode for multi carrier modems, such as DMT based ADSL and VDSL modems. Fast transitions from power save mode to full operational mode occur, without the overhead of transmitting large quantities of configuration information between the transmitter and receiver. Signal constellation size changes occurring while operating in power save mode to continue to apply once full operational mode is resumed. Multiple power save modes are enabled, each having a different level of power dissipation and crosstalk, both far end crosstalk and near end crosstalk. Power dissipation and crosstalk can thus be graduated on a line, according to a user-requested bit rate.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
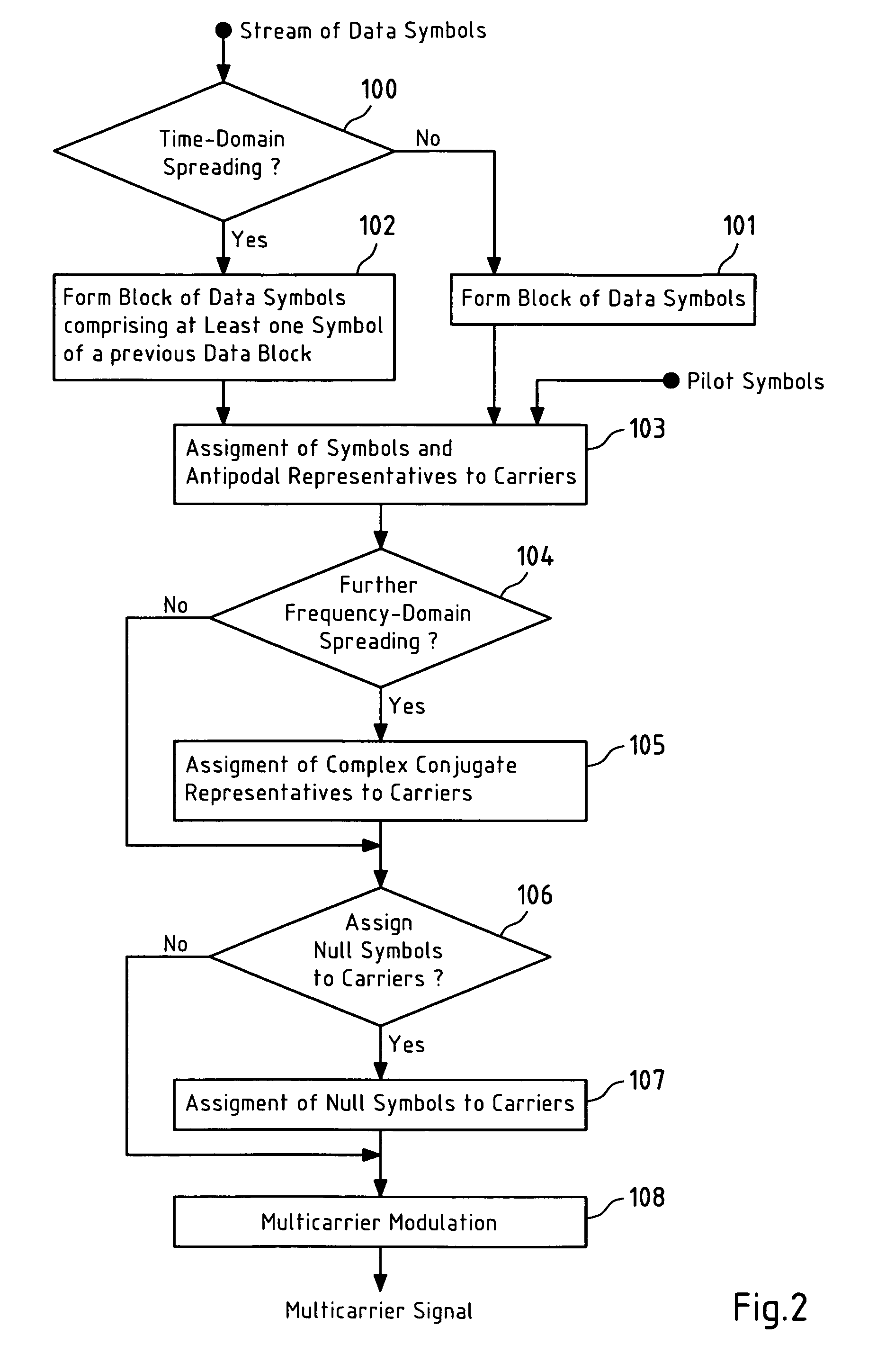
Multicarrier modulation with enhanced frequency coding
ActiveUS7808883B2Reduce distractionsReduce the required powerError preventionTransmission path divisionCarrier signalMulti carrier
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, a transmitter and a receiver for a multicarrier modulation, wherein symbols are assigned to carriers of a set of N carriers, the method comprising assigning at least one of the symbols to a first carrier of the set of N carriers, and assigning an antipodal representative of the at least one of the symbols to a second carrier of the set of N carriers.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a pilot signal in a communication system using a multi-carrier modulation scheme
InactiveUS20050084035A1Minimize limitationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemCarrier signal
In an MCM communication system in which one frame includes at least one pilot symbol of a predetermined length and at least one data symbol of the predetermined length, to transmit the pilot symbol for time synchronization and frequency synchronization, a first pilot sequence of a length shorter than the predetermined length is generated, and a second pilot sequence of a length shorter than the predetermined length is generated. Here, the second pilot sequence is different from the first pilot sequence. The first and second pilot sequences are repeated a predetermined number of times. The pilot symbol is generated by combining the repeated first and second pilot sequences, and then transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for the dynamic allocation of frequencies for multicarrier modulation systems
InactiveUS7039120B1Multiple EffectsEfficiently transmitting informationTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCarrier signalEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
Reduction of spectral leakage in OFDM system
ActiveCN104823402AMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransmission path multiple useFrequency spectrumResource block
A resource block (RB)-based multicarrier modulation (MCM) transmitter and receiver structure for spectral agile systems are disclosed. The transmitter and the receiver are capable of sharing opportunistically available and non-contiguous channels with other users. The RB-MCM partitions the available spectrum, contiguous or non-contiguous, into multiple RBs (same or different sizes), applies a baseband MCM or single carrier modulation, or coded single carrier or multicarrier schemes in each RB with a type of spectral leakage reduction technique, and applies RB modulation for each RB to modulate the signal from baseband to the frequency band of that RB. At the receiver, the received signal may be filtered and RB demodulation may be applied to put each RB signal in baseband and a baseband multicarrier or single carrier or coded single carrier or coded multicarrier demodulation may be applied to each RB signal. Different RBs may use different modulation schemes.
Owner:IDAC HLDG INC
Receiver
ActiveUS20030210749A1Improve integrityFacilitate communicationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCarrier signalFourier transform on finite groups
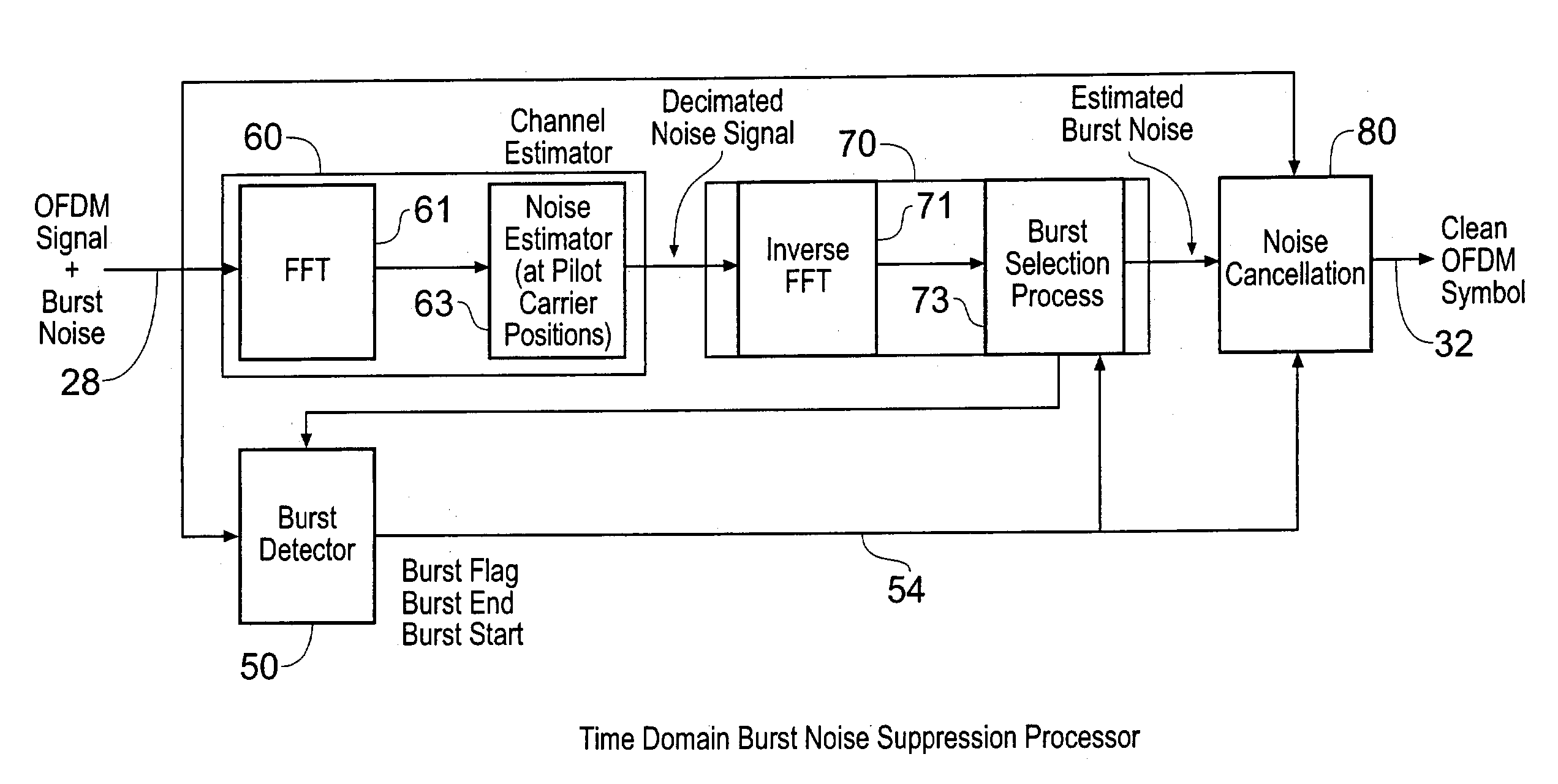
A receiver for receiving a multi-carrier modulated symbol is arranged to suppress a burst noise signal which may have been induced in the symbol. The symbol includes a plurality of pilot carriers as well as a plurality of data bearing carriers. The receiver comprises a burst noise detection processor operable to detect the temporal position of the burst noise signal which may have corrupted the symbol within a period occupied by the symbol, and a channel estimation processor operable to generate a decimated noise signal corresponding to the burst noise, from the recovered pilot carriers. An inverse Fourier transform of the decimated noise signal provides a plurality of estimated versions of the burst noise signal. A noise signal processor is operable to generate an estimate of the burst noise signal by identifying one of the plurality of estimated burst noise versions at the detected temporal location of the burst noise signal. The noise signal processor may be operable to set the signal samples other than the identified estimate of the burst noise signal to zero and to perform a Fourier transform, to provide a frequency domain version of the burst noise signal, thereby interpolating the decimated noise signal. The frequency domain noise signal estimate may be cancelled from the symbol by a noise cancellation processor in the frequency domain, before data is recovered from the symbol. The receiver finds application for Digital Video Broadcasting in which COFDM is employed.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC +1
Mixed waveform configuration for wireless communications
ActiveUS20030012302A1Minimize complexityMaintain powerFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationChannel impulse responseCarrier signal
A mixed waveform configuration for wireless communications including a first portion that is modulated according to a single-carrier modulation scheme and a second portion that is modulated according to a multi-carrier modulation scheme. The waveform is specified so that a channel impulse response (CIR) estimate obtainable from the first portion is reusable for acquisition of the second portion. The first portion includes a preamble and header and the second portion typically incorporates the payload.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
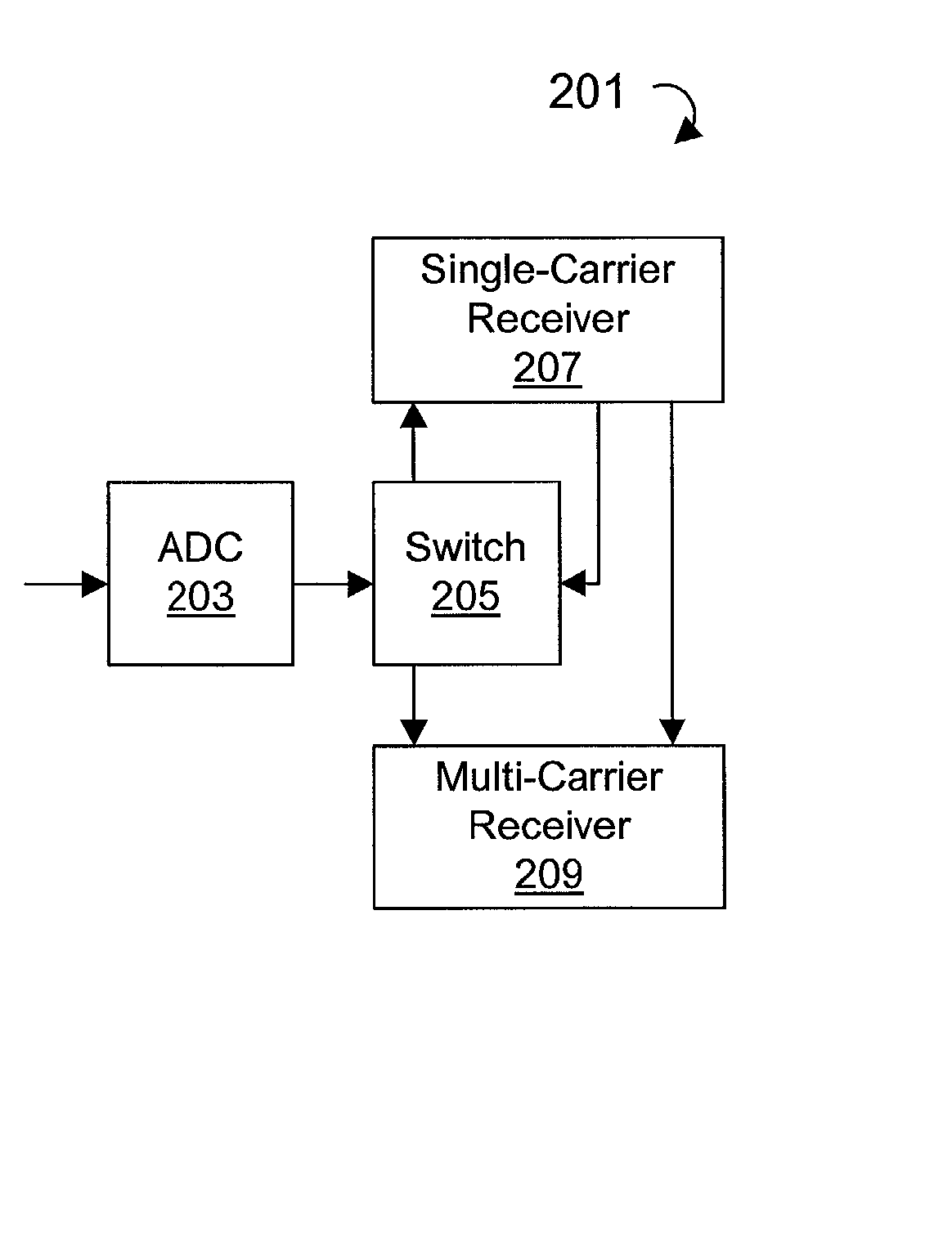
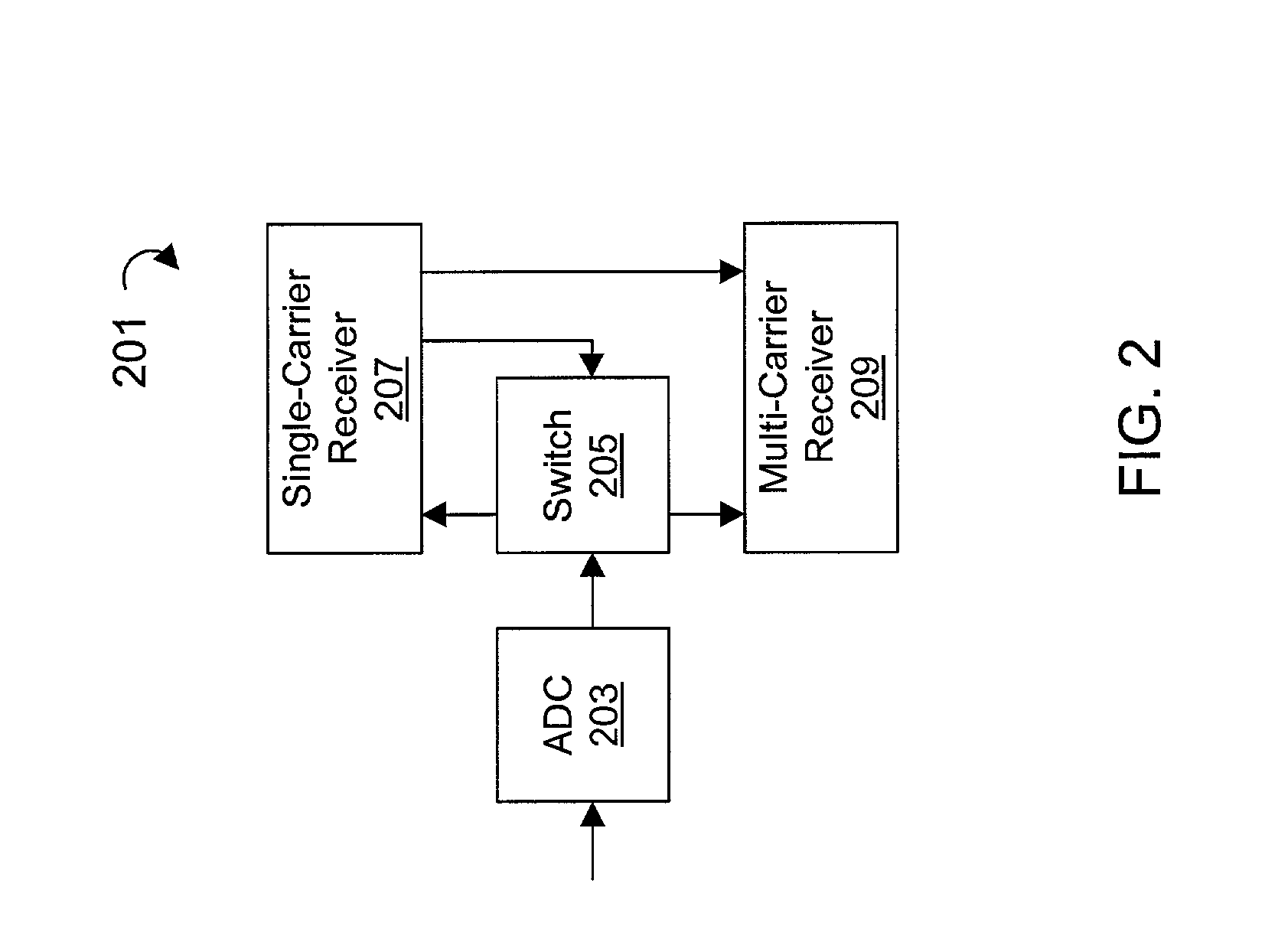
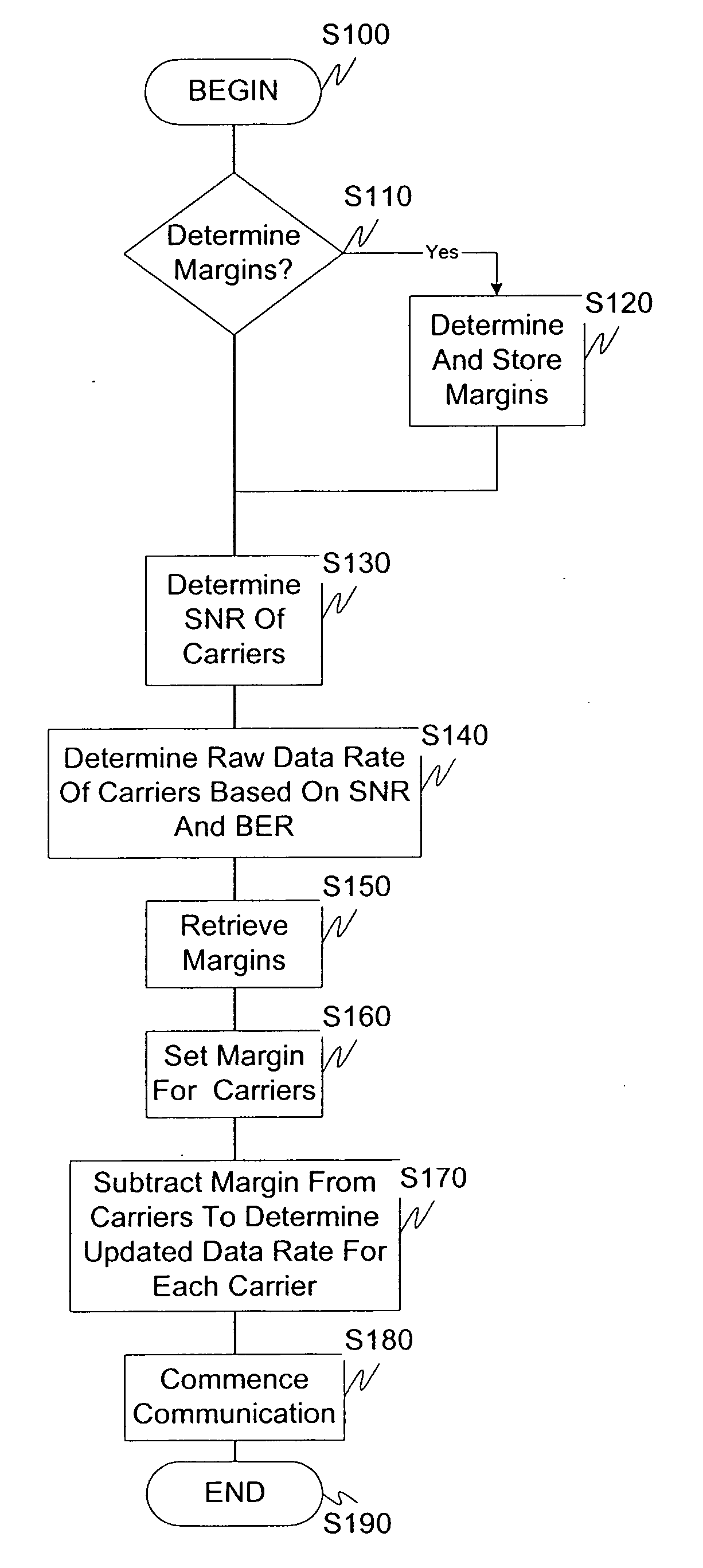
Systems and methods for a multicarrier modulation system with a variable margin
InactiveUS20060018395A1Effect on its overall performanceHigh levelError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceData rate
Owner:AWARE INC
Multicarrier modulation with data dependent frequency-domain redundancy
ActiveUS7075999B2Eliminate distractionsIncreasing data rate lossSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsData streamModem device
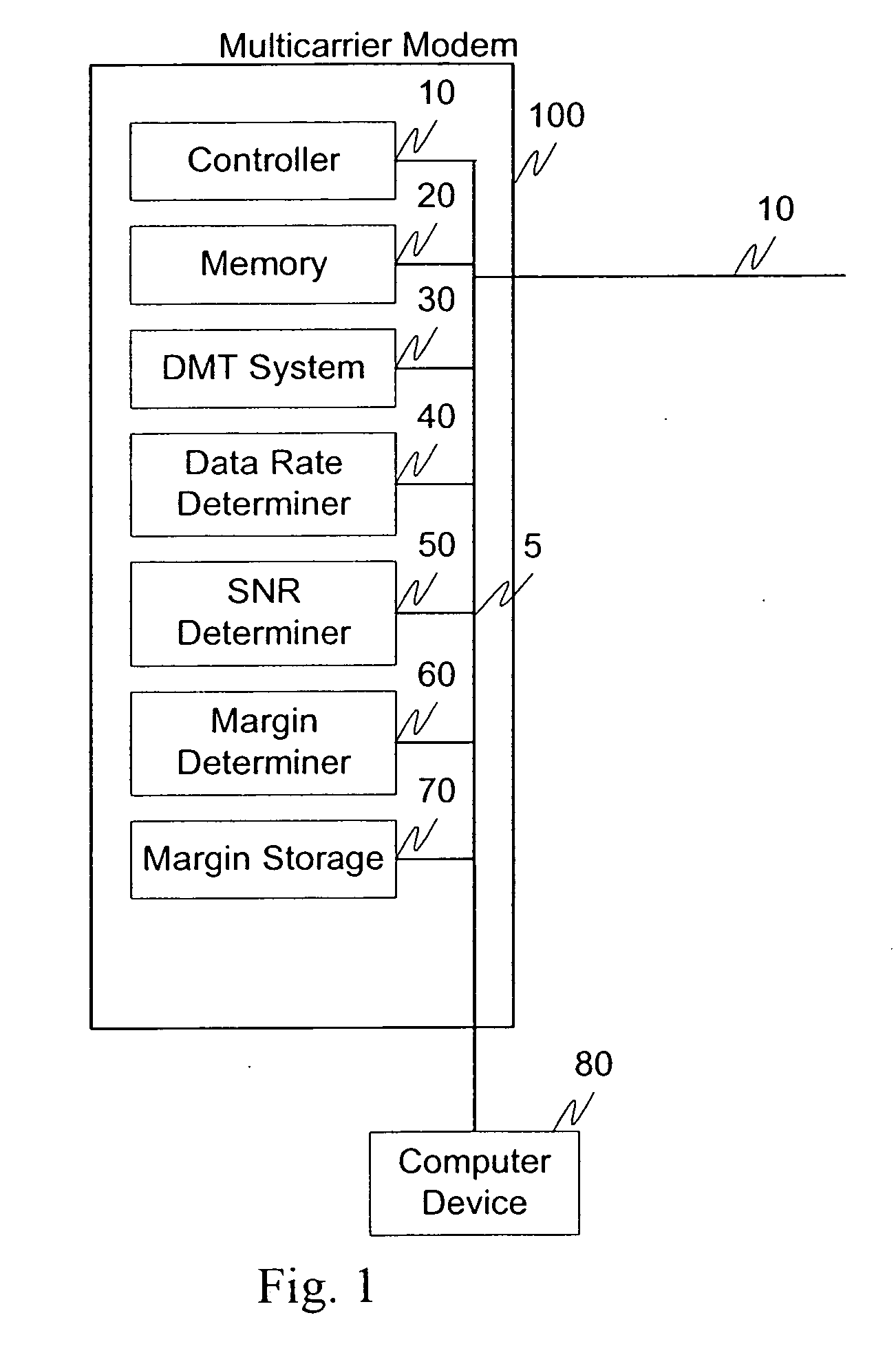
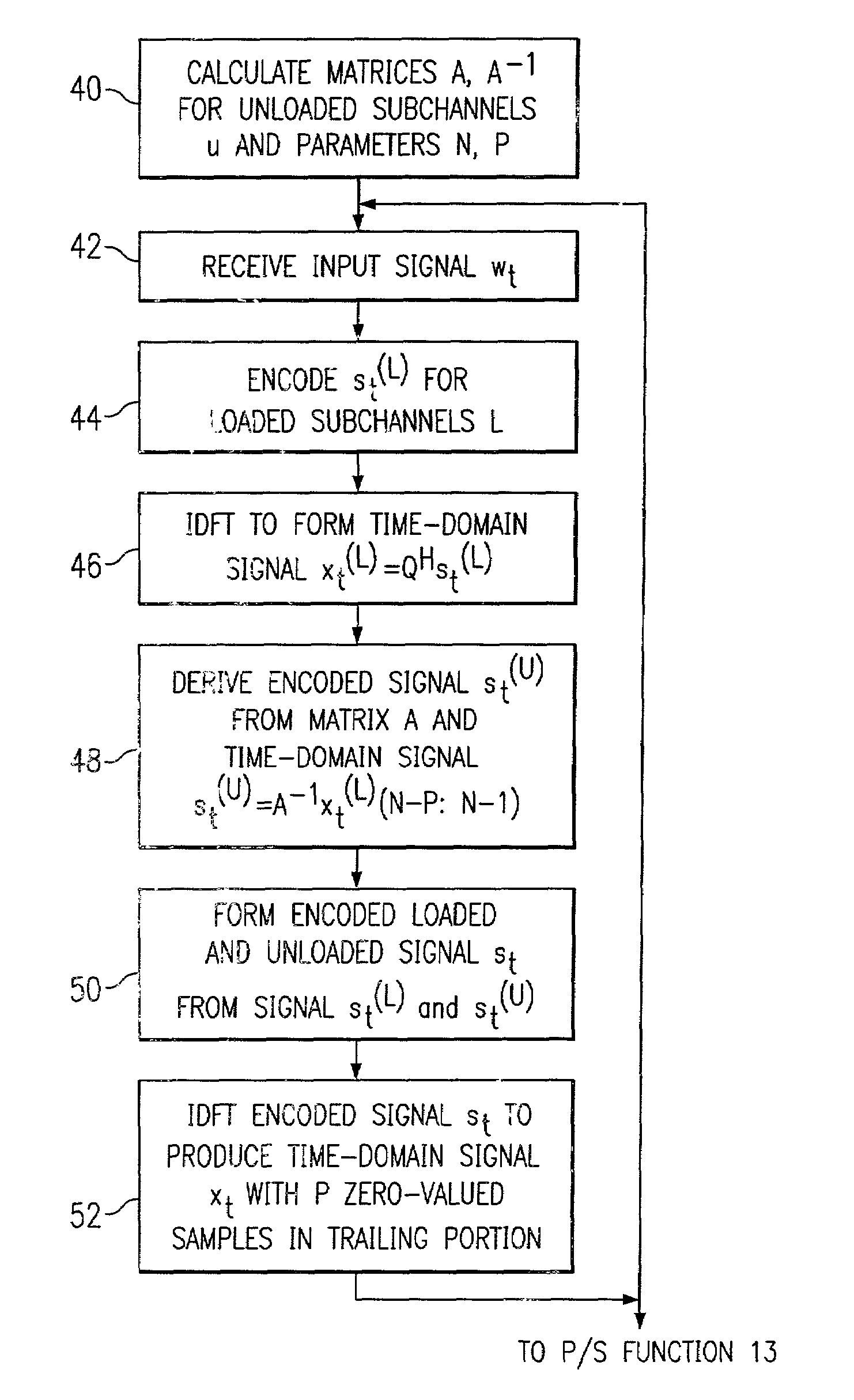
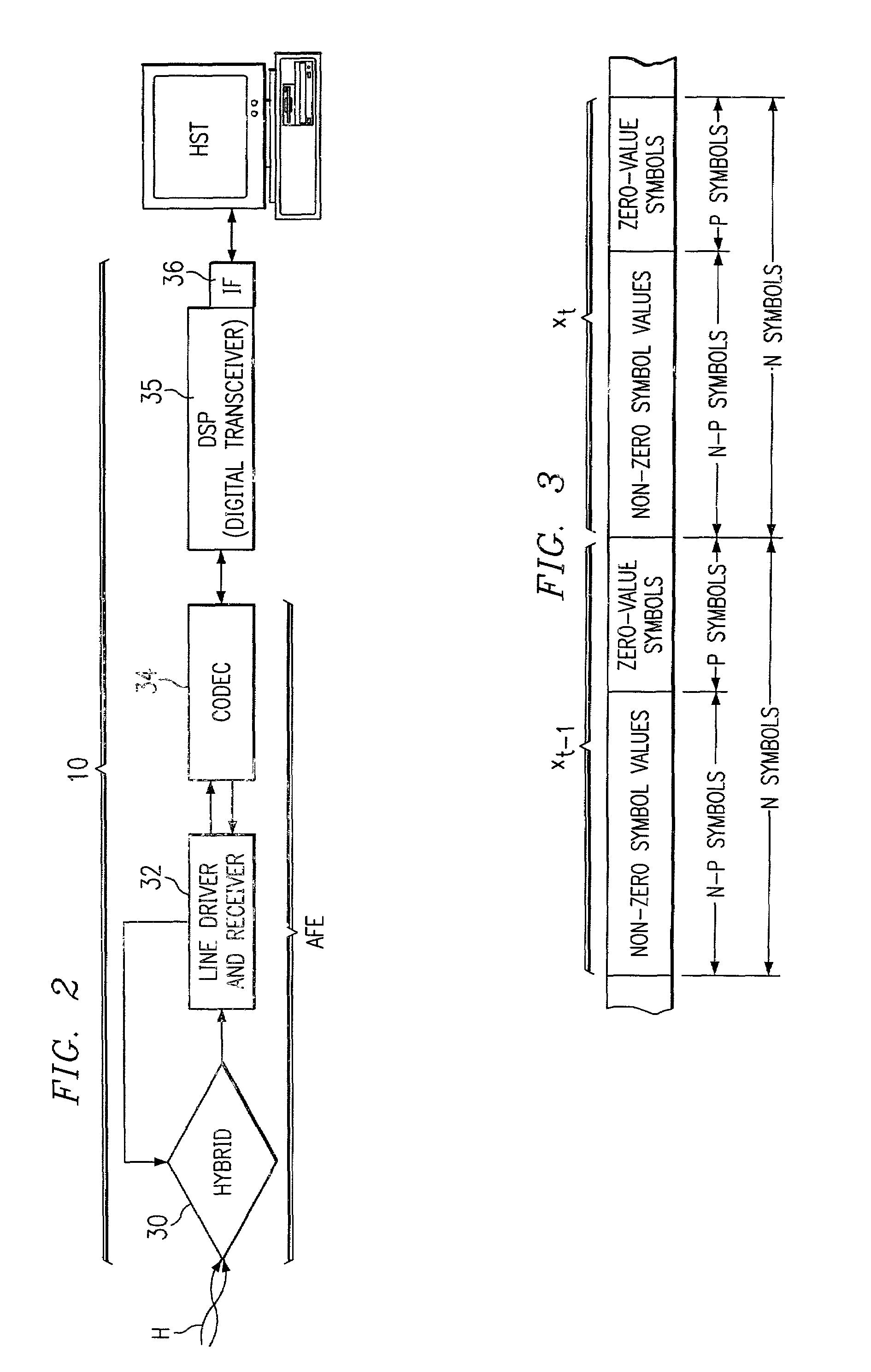
A modem (10) for transmitting a discrete multitone modulated (DMT) signal over a communications channel (H) is disclosed. In the encoding of an input bitstream, unloaded subchannels in the DMT spectrum are assigned signal values so that a trailing portion of each block or frame of the resulting datastream are forced to a known value, for example zero. The known-valued trailing portion of each block provides the effect of a cyclic prefix, without necessitating the prepending of an actual cyclic prefix and incurring the corresponding data rate loss; alternatively, the effect of a cyclic prefix can be augmented by the forcing of the trailing portion of the blocks to known values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multicarrier modulation scheme as well as transmission apparatus and reception apparatus using the scheme
ActiveUS20090268837A1Reduce transmit powerSpatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionGeneration processCarrier signal
An object is to generate a pilot signal for estimating transmission characteristic of a transmission channel which is suitable for the OFDM / OQAM multicarrier modulation. A phase reference pilot symbol of which a modulation amplitude is suppressed to zero, and an amplitude reference pilot signal obtained through modulation performed by using an amplitude known to a reception end are transmitted from a transmission end, and the transmission characteristic of the transmission channel is estimated and compensated by using the phase reference pilot signal and the amplitude reference pilot signal at the reception end. Thus, it is possible to simplify frame generation process performed at the transmission end, and reduce transmission power for the phase reference pilot signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
System and method for modulation of non-data bearing carriers in a multi-carrier modulation system
For one aspect of the invention, a method is described for mitigating power spectral density irregularities in a multi-carrier modulation environment. The method involves identifying at least one carrier of a plurality of carriers that is in a non-data bearing state. Thereafter, that carrier is modulated with random data.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Method for reducing peak-to-average power ratio of filter bank multi-carrier system
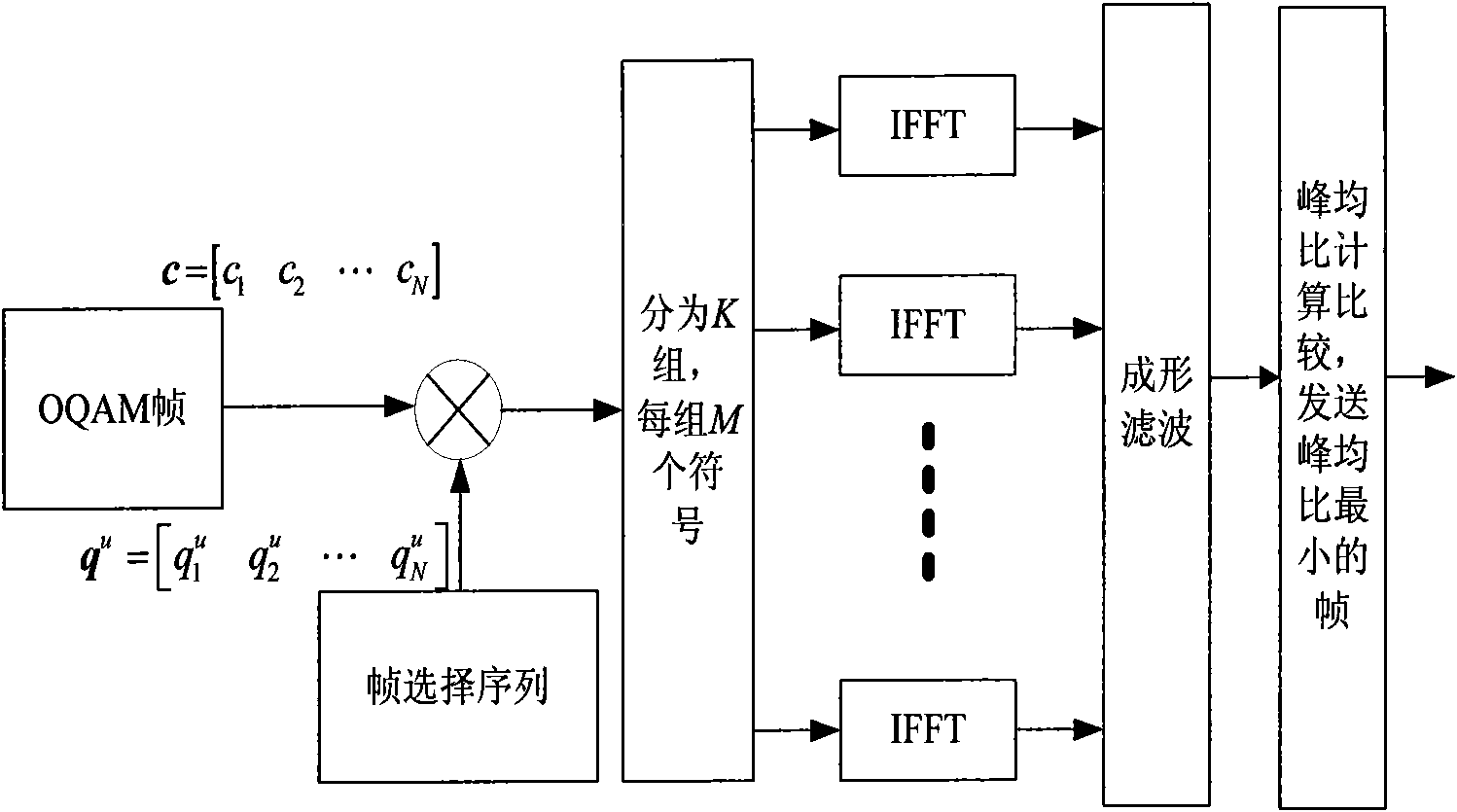
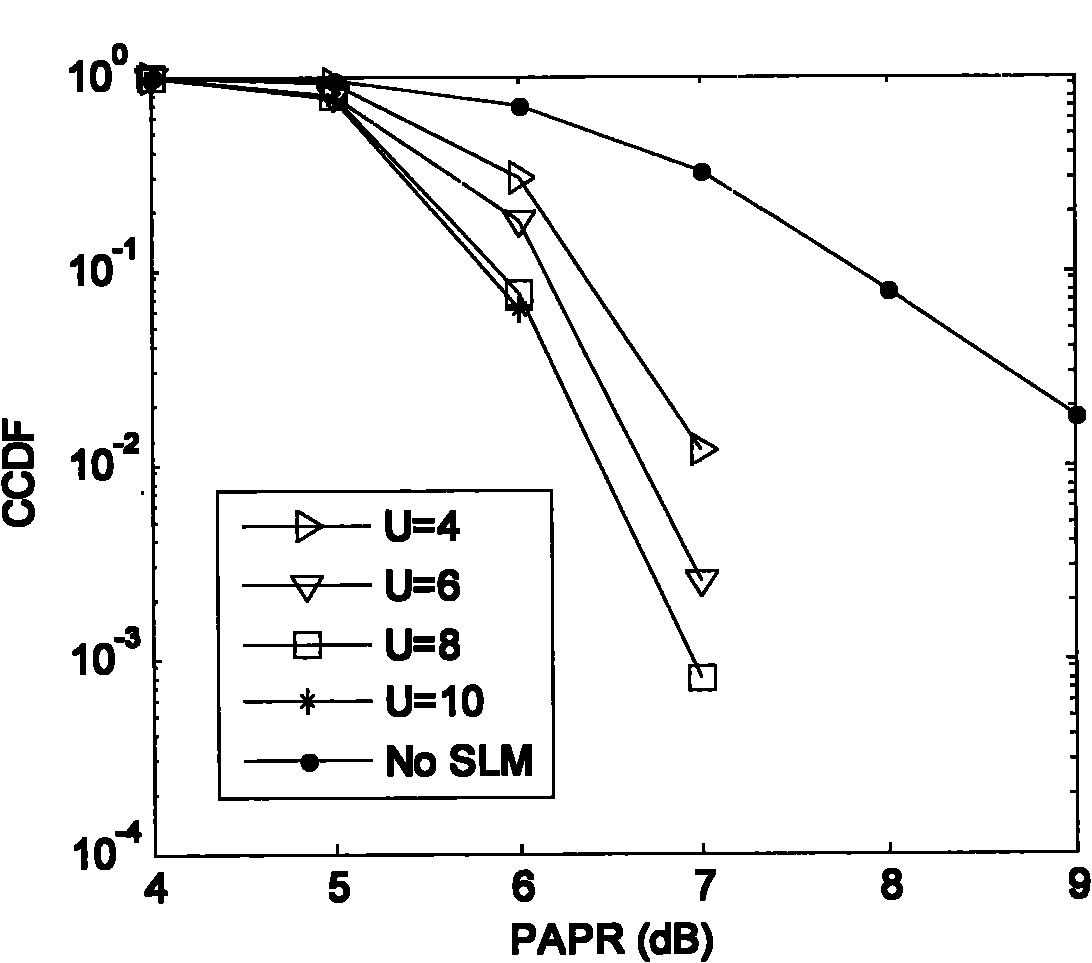
InactiveCN101867547AGuaranteed low peak-to-average ratio requirementsImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainCommunications system
The invention provides a method for reducing peak-to-average power ratio of a filter bank multi-carrier system, and relates to the field of multi-carrier modulation method. The method comprises the following steps: the analysis of main factors affecting the peak-average power ratio of the FBMC system through the establishment of the FBMC system model and the definition of the peak-average power ratio of the FBMC system, the construction of an FSLM method and the check analysis of Monte Carlo simulation experiments, and is characterized in that: a frame selection mapping method is called as the FSLM method, is a signal non-distortion technique, selects sequences for FBMC signal frames and design frames, constructs FBMC carrier frame signals which have the same information and are independent from one another according to the frame selection sequences, and then selects a frame of symbols allowing the time domain signals to have minimum PAPR, and the method can reduce the PAPR of the FBMC system without distortion, and effectively reduce the PAPR of the FBMC system. The invention can ensure that the requirements of the low peak-to-average power ratio of the system, and further optimize the performance of the system. In practice, the invention can provide certain reference value for the application of Beyond3G, 4G, 802.16 and other communications systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
System and method for reducing adjacent channel interference (ACI) in a multicarrier modulation system
InactiveUS6934246B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyReasonable power sensitivity lossError preventionTime-division multiplexAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
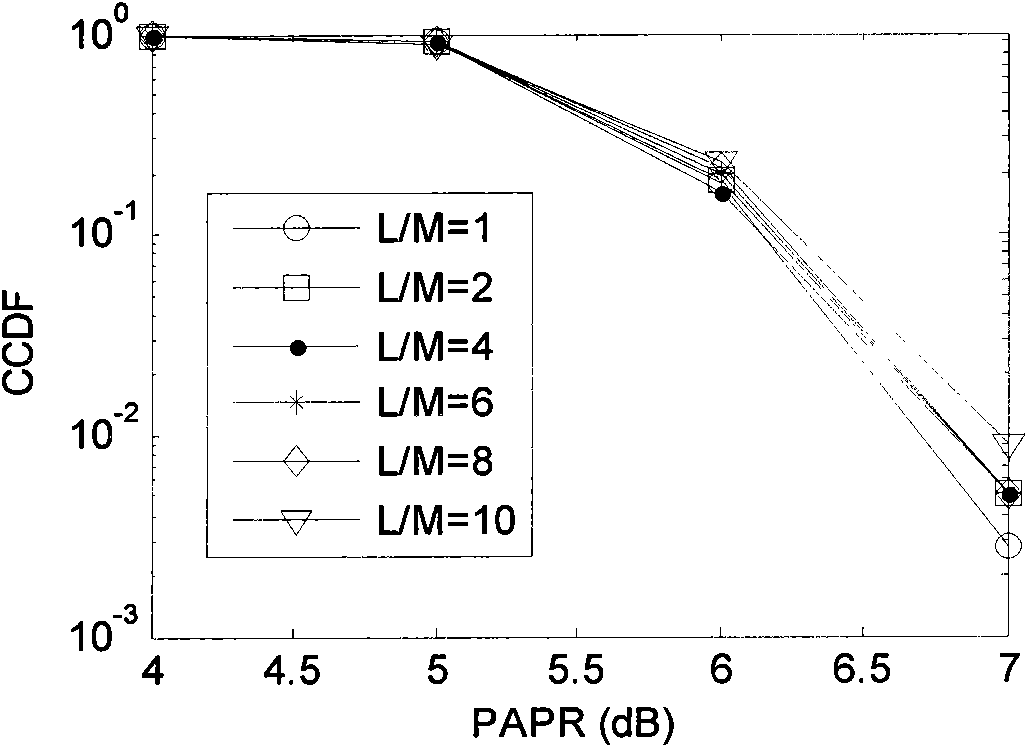
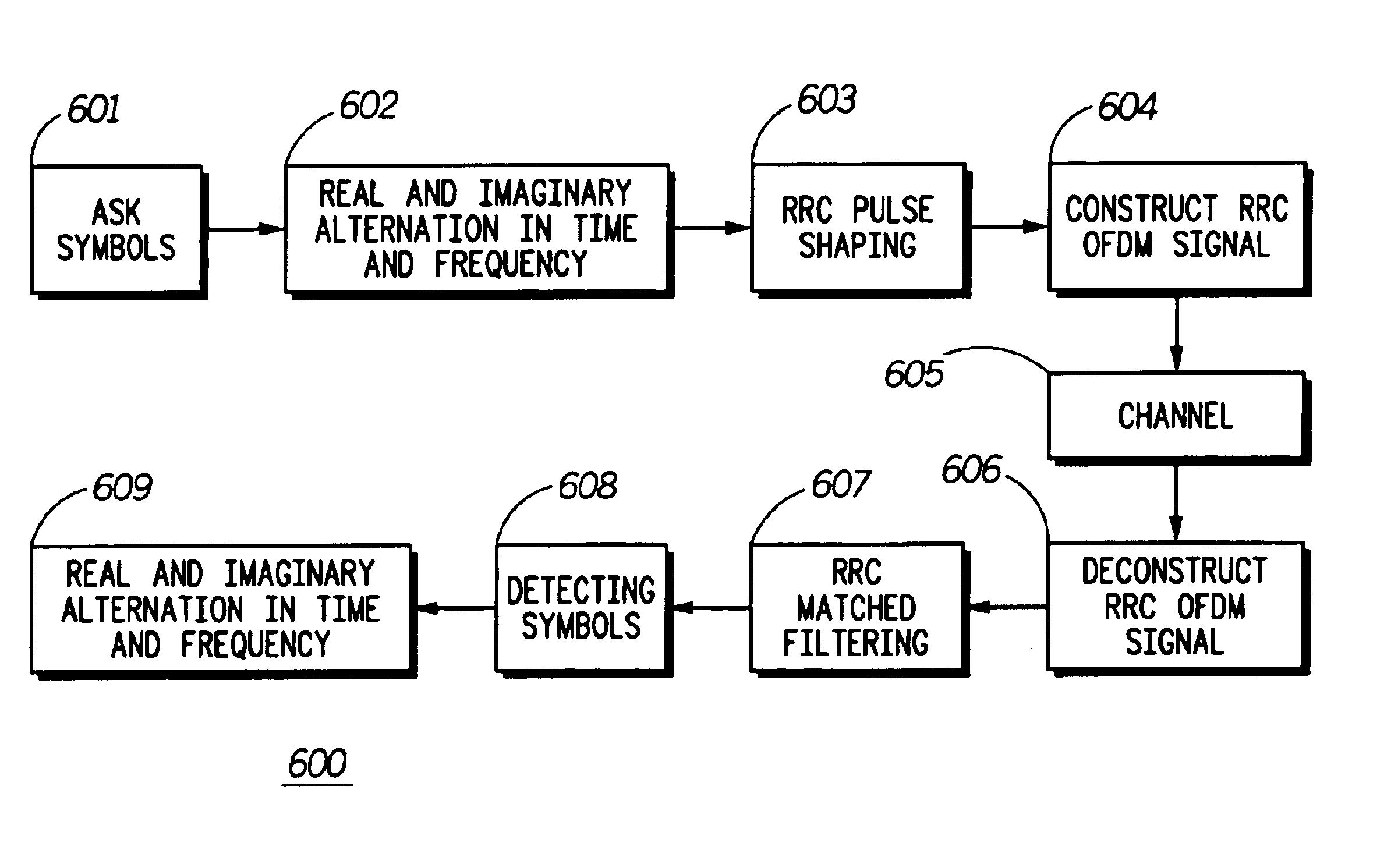
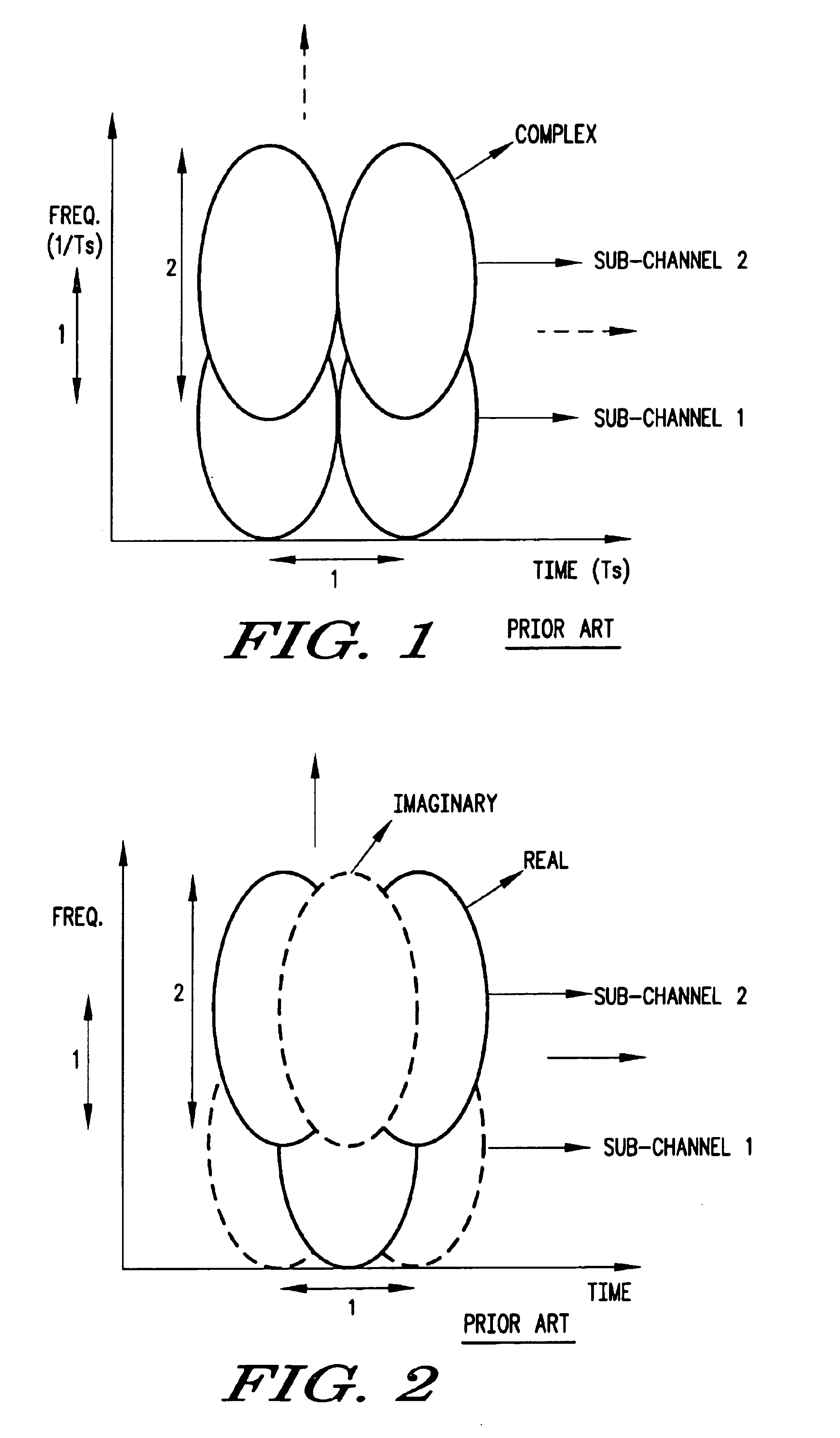
An improved multicarrier modulation system and method, which has the advantages of both isotropic orthogonal transfer algorithm orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (IOTA OFDM) and scalable advanced modulation (SAM), is introduced. The invention is root raised cosine (RRC) OFDM using the most spectrally efficient RRC filter without sacrificing the compact subchannel spacing of OFDM. The invention further provides an adjacent channel interference (ACI) suppression scheme and a modified RRC for better suppressing ACI of RRC OFDM. The ACI suppression scheme can also be applied to SAM with the modified RRC and to IOTA OFDM with a modified IOTA. The invention greatly improves a major problem of conventional OFDM namely ACI due to the use of a wide subchannel filter. Thus, the invention allows OFDM to meet even the strictest ACI requirements, which was not possible by using a conventional raised cosine windowing method.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
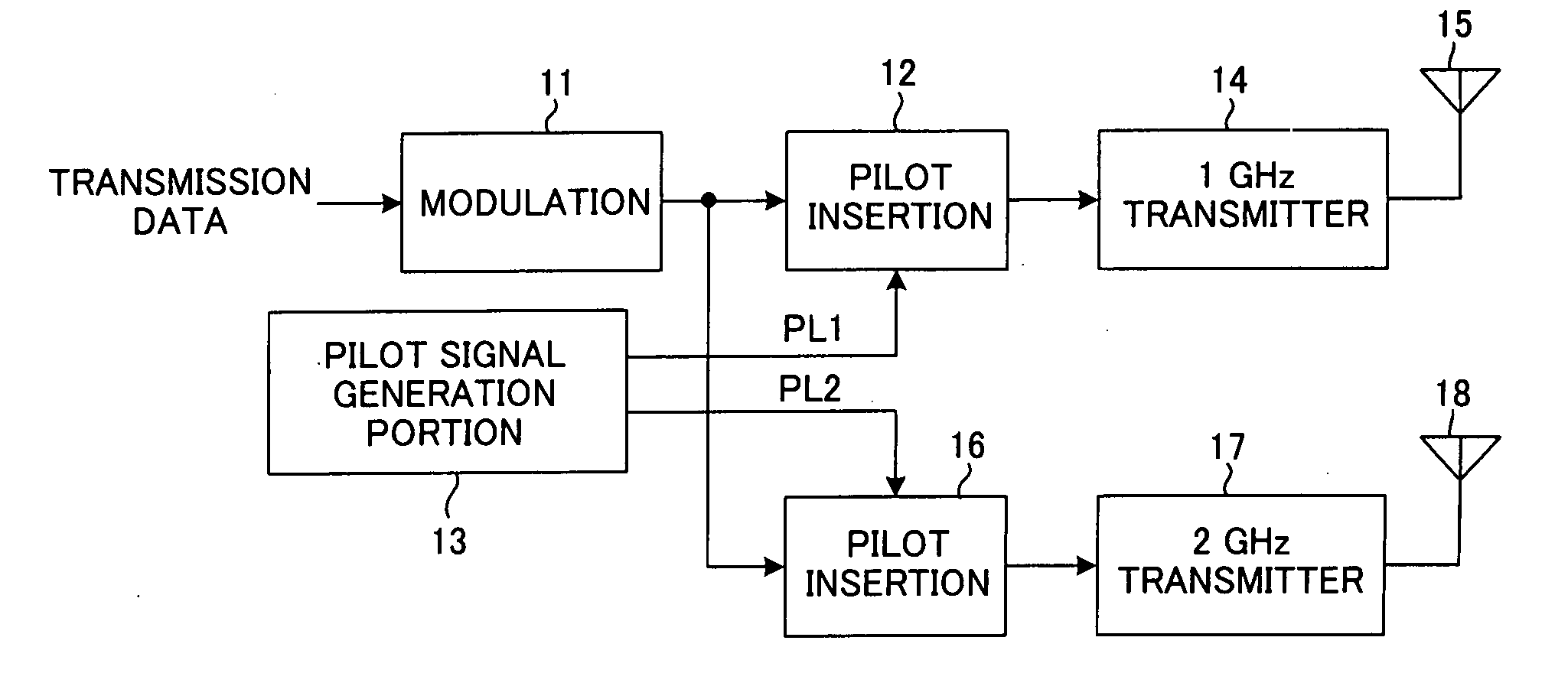
Radio communication system
InactiveUS20070254693A1Improve reception performanceHigh precisionSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemGuard interval
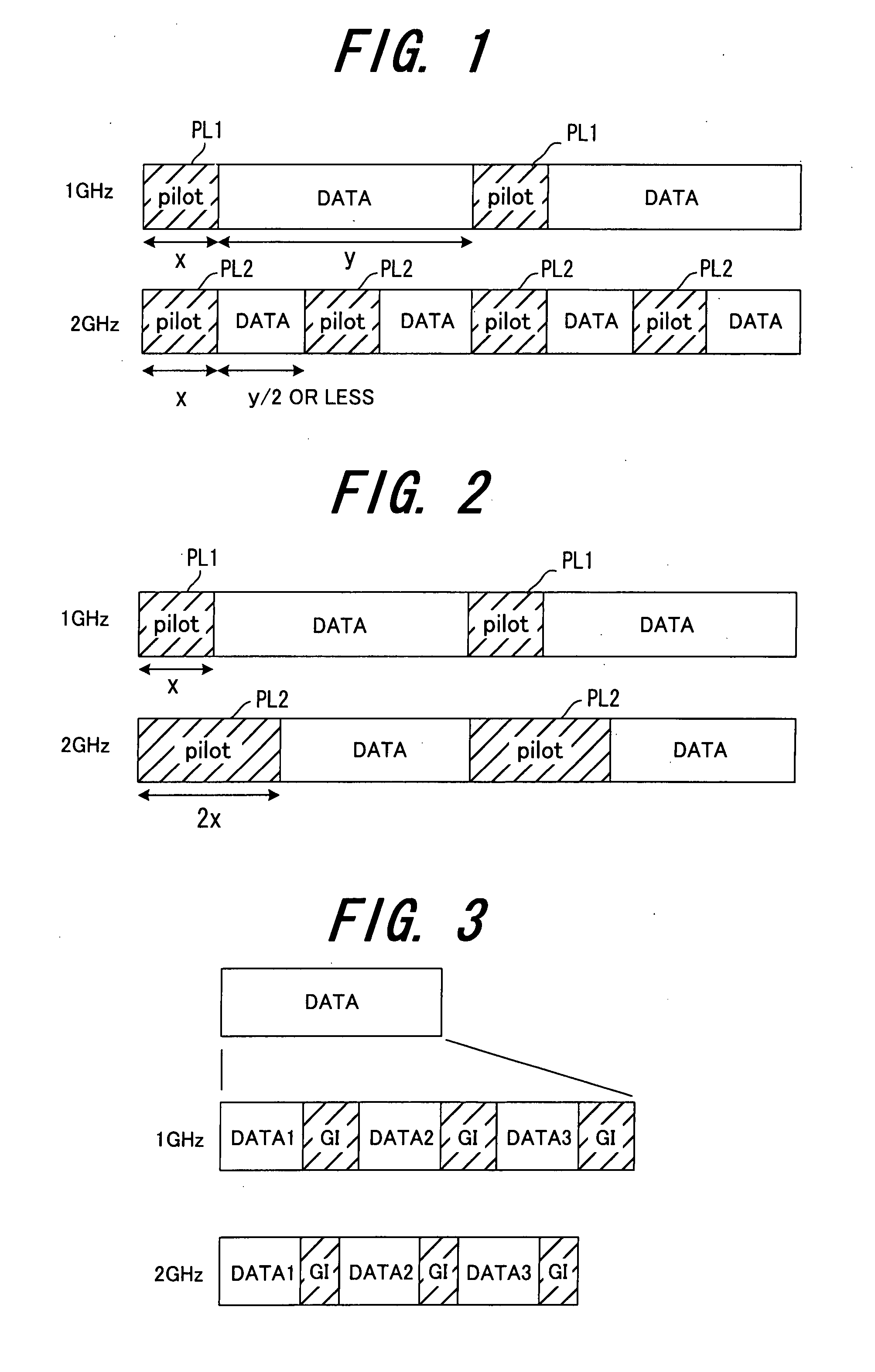
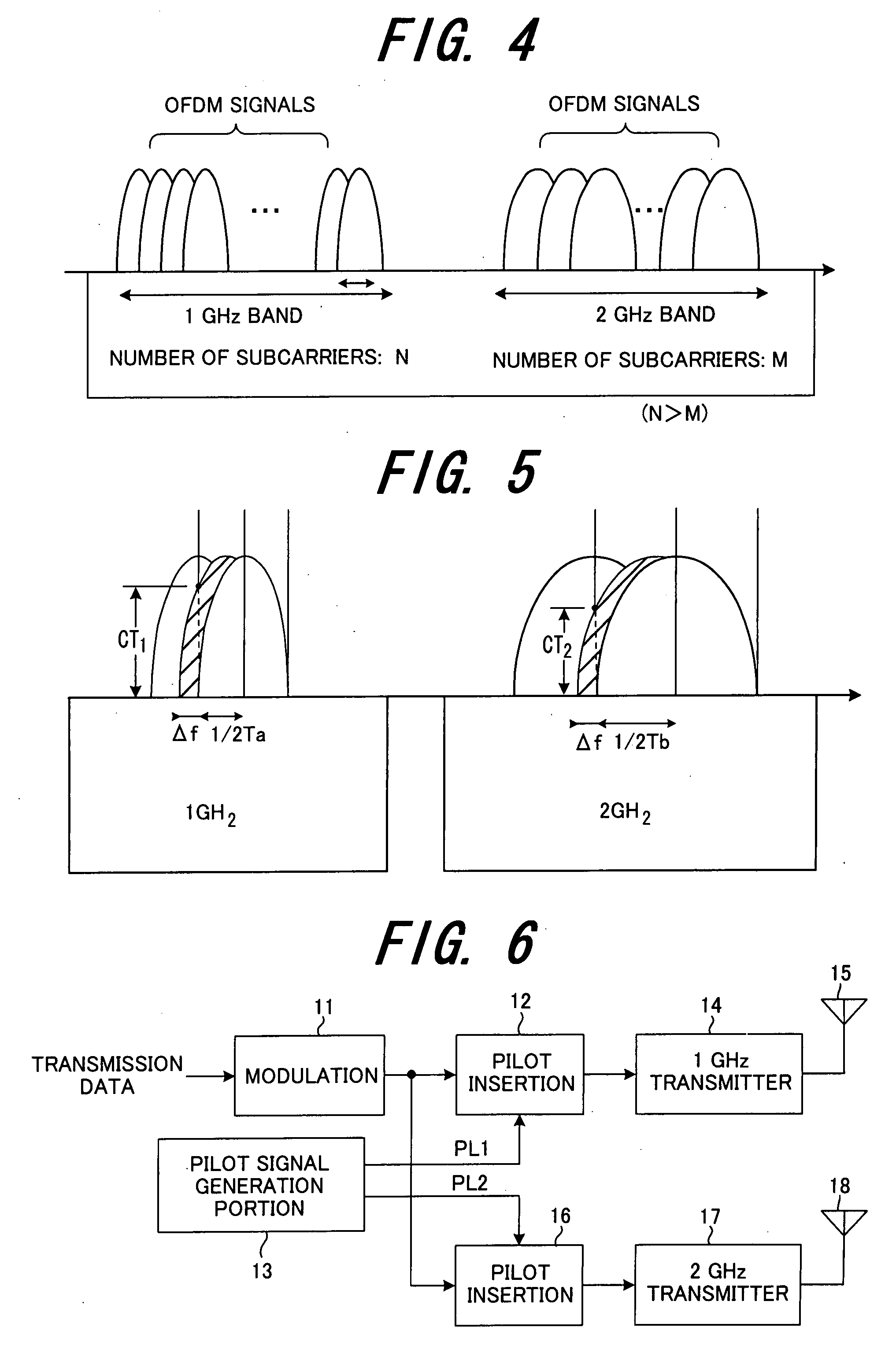
In a radio communication system in which multiple bands or a plurality of different radio frequencies are used, a different radio transmission method is used in each band or at each radio frequency. For example, by transmitting data using radio formats which are different in each band or at each radio frequency, the radio transmission method is made different in each band or at each radio frequency. In order to vary the radio format, (1) the pilot length is varied at each radio frequency; or (2) the pilot interval is varied at each radio frequency; or (3) the guard interval length is varied in each band or at each radio frequency; or (4) when multicarrier modulation is used for radio communication in each band, the subcarrier interval for multicarrier transmission is varied in each band.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
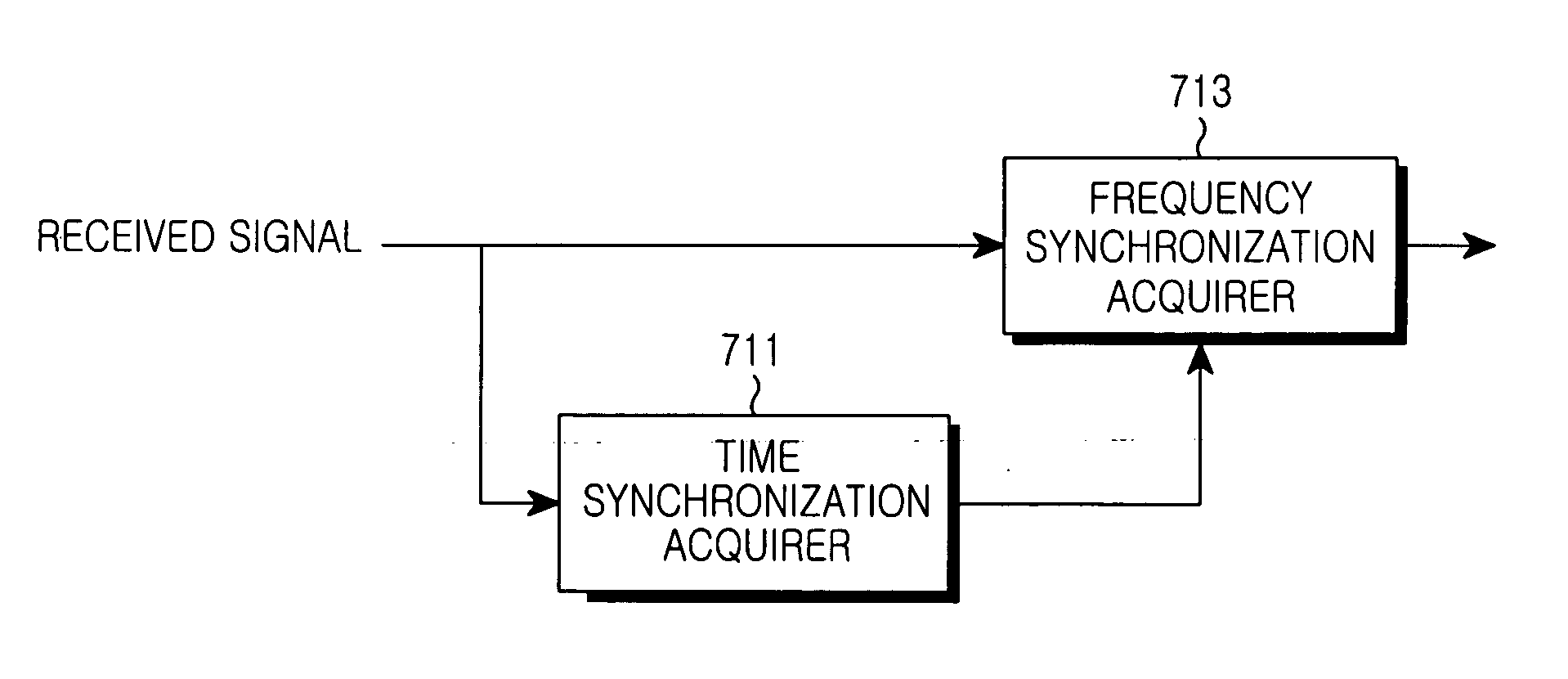
Method and device in a communication system
InactiveUS6252908B1Simple and inexpensive to implementSymbol rateMulti-frequency code systemsSynchronising arrangementCommunications systemSymbol rate
The present invention concerns a method and a device for the synchronization of a transmitter (1) and at least one receiver (3) in multi-carrier modulated communication systems in which FFT technology is used for the modulation and demodulation of data transmitted between the transmitter (1) and the receiver (3). According to the invention the transmitter (1) transmits synchronization symbols (15, 16) as training symbols (15, 16) at the beginning of a transmission, until a result is obtained that may indicate where a synchronization symbol starts. The result is used for the adjustment of the symbol rate in the receiver (3). Data symbols may then be transmitted after the synchronization symbols (15, 16).
Owner:WI FI ONE
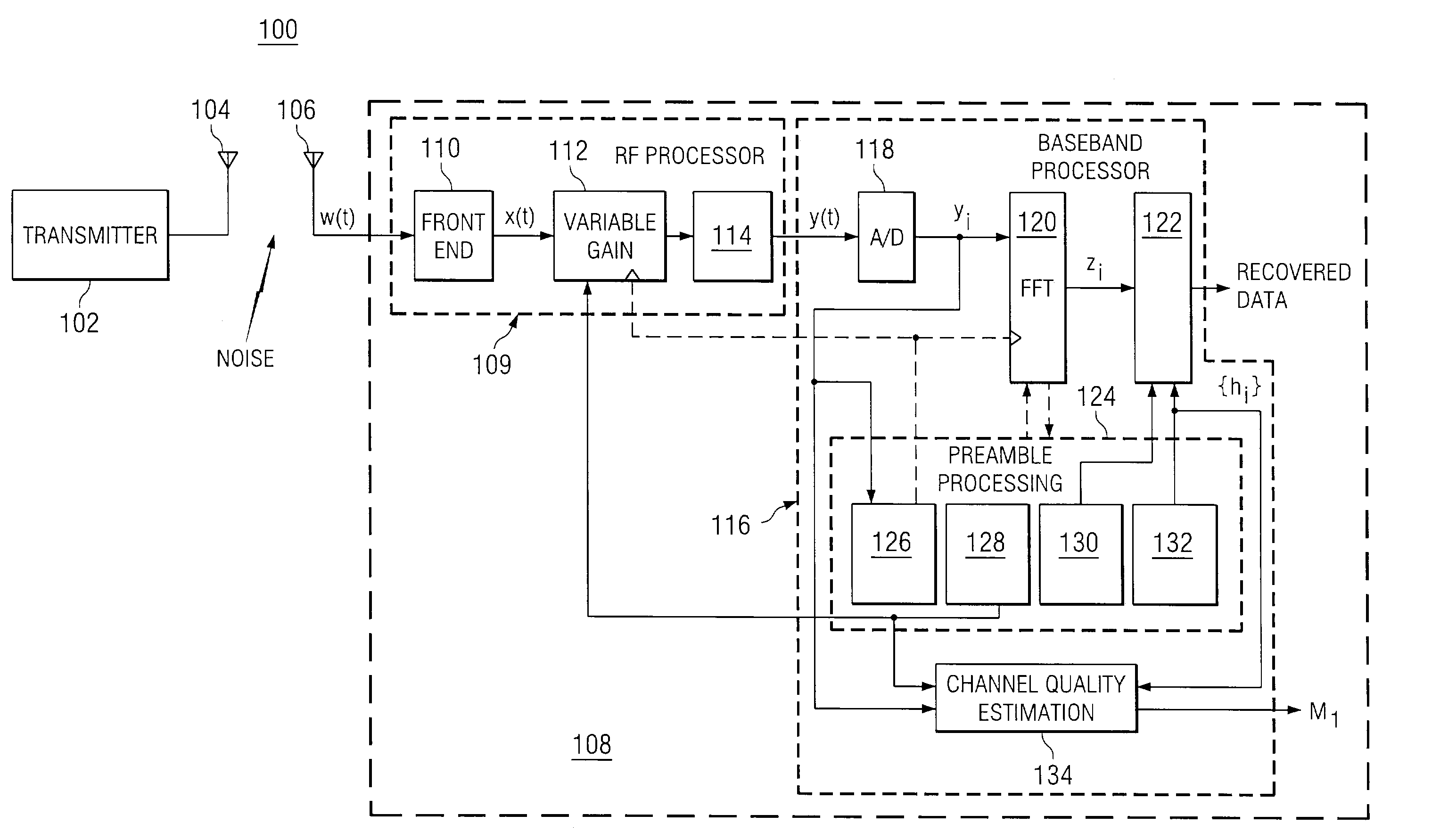
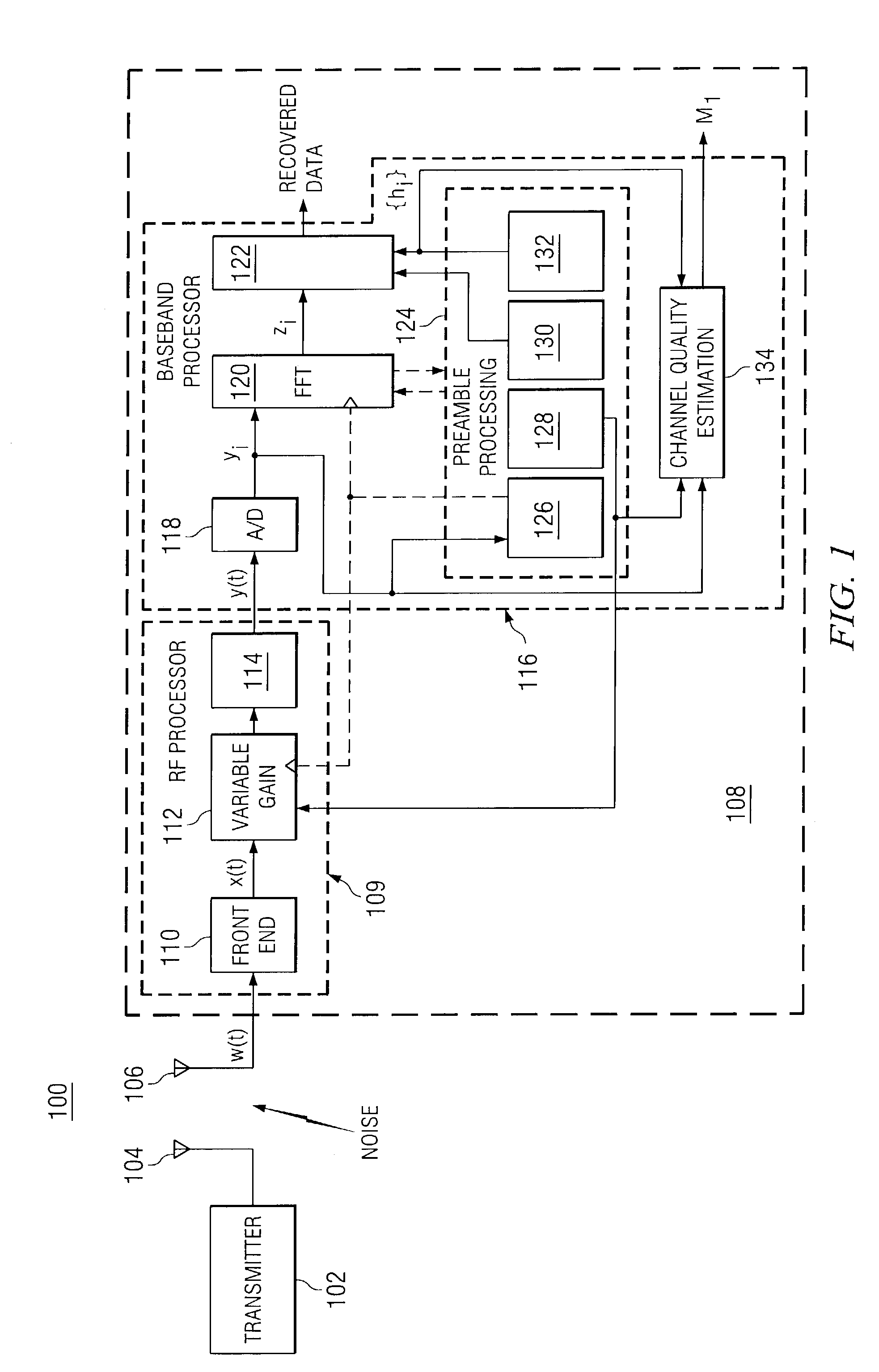
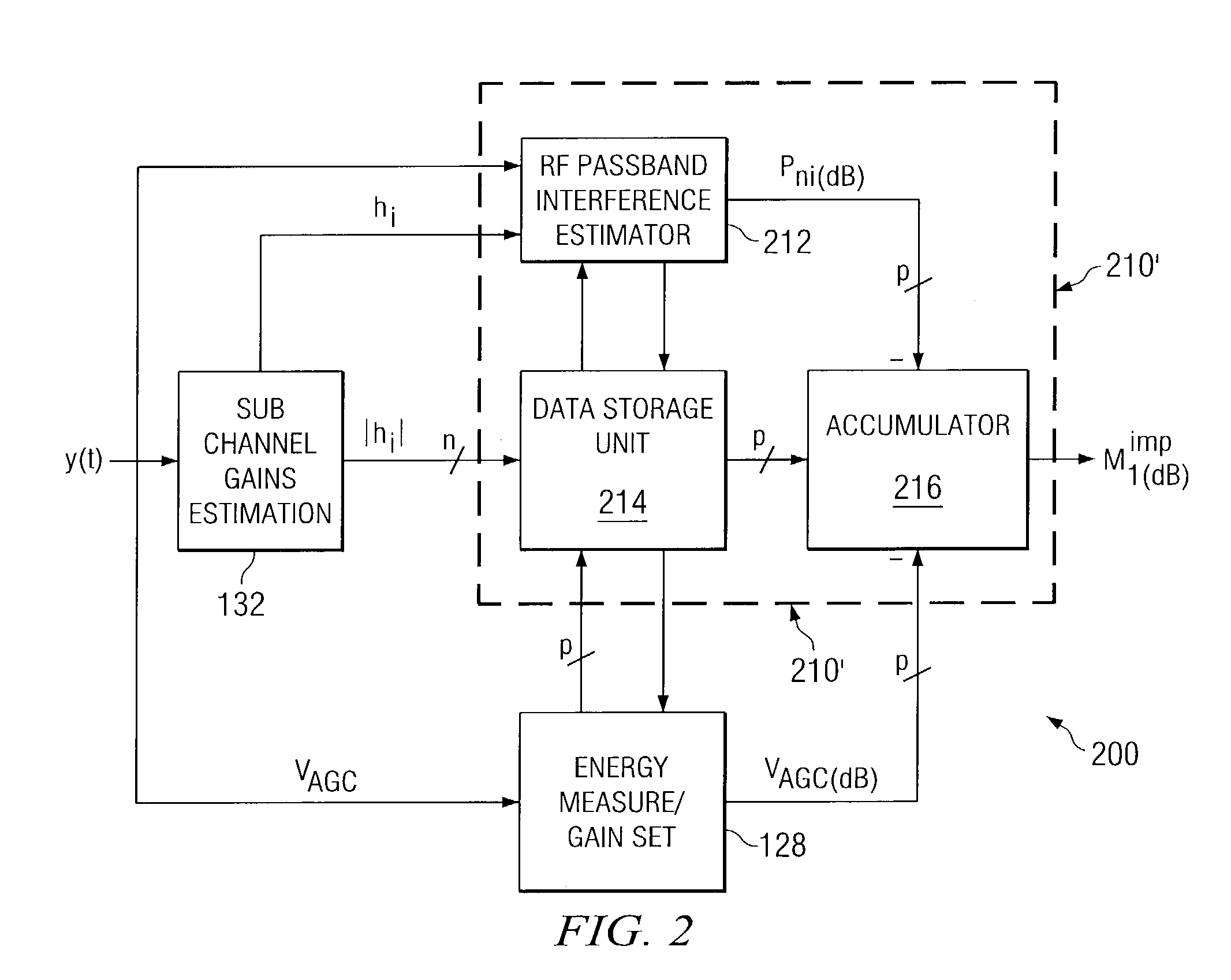
Method and apparatus for channel quality metric generation within a packet-based multicarrier modulation communication system
ActiveUS7295517B2Quality assuranceSimple calculationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl setCommunications system
A communication system includes a receiver having a variable gain module and a baseband processor. The baseband processor measures the power of the signal received and derives a variable gain control setting that is inversely proportional to the power of that signal and sends the variable gain control setting to the variable gain module. The baseband processor generates a channel quality metric that is equivalent to the normalized geometric mean of the squared magnitudes of the gain estimation, divided by the total noise-plus-interference power.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
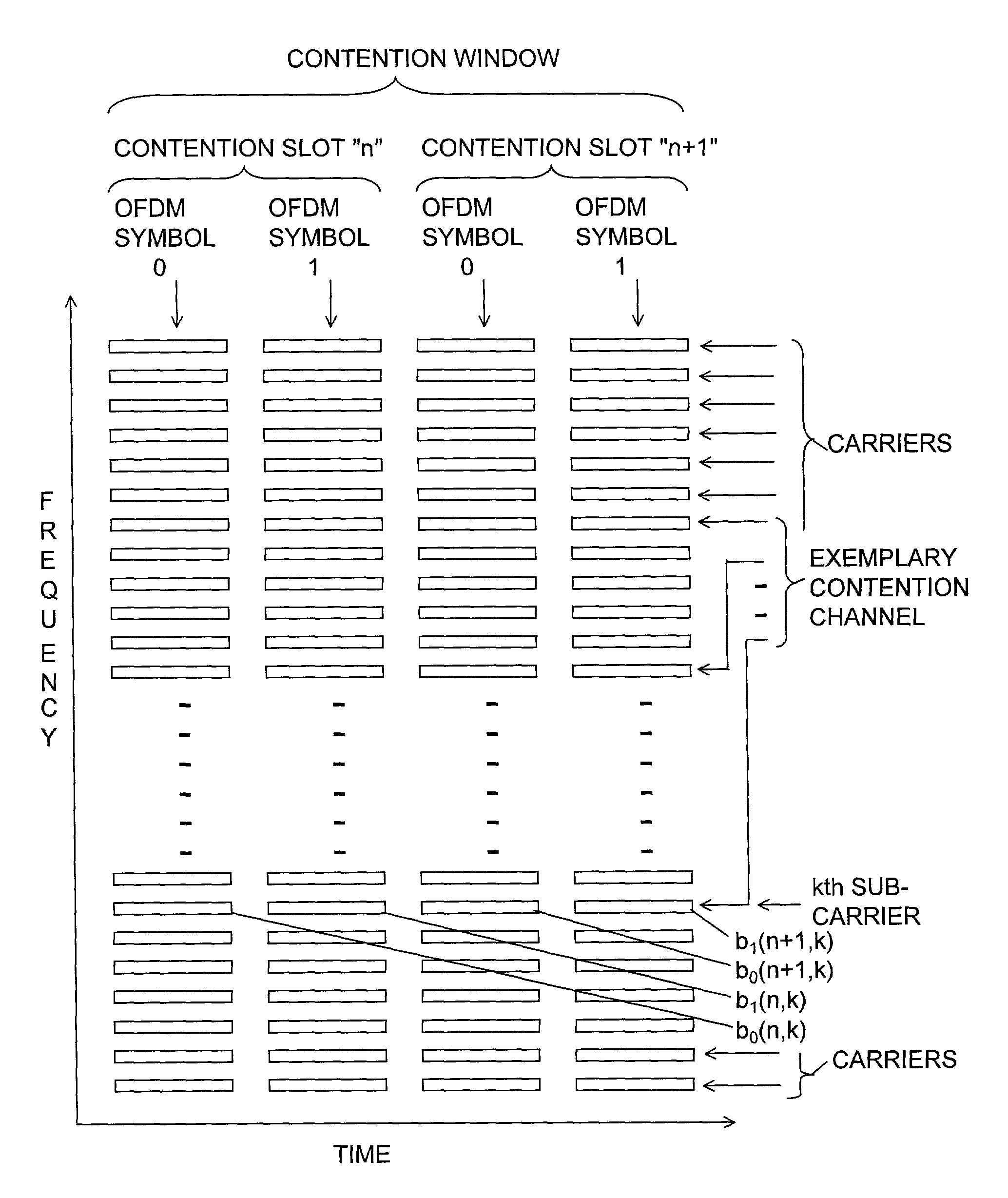
Method and apparatus for multiuser access in a multicarrier modulation network
ActiveUS7184393B1Eliminate needSolve excessive overheadTransmission path divisionAllocation timingTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
A multiple access system for a network using multicarrier modulation. To contend for service a subscriber station selects an upcoming frame in whose contention window it will contend, selects a contention slot within the window, selects a contention channel corresponding to a subset of the carriers used by the network, and imposes a contention code differentially on the carriers in the contention channel.
Owner:RADIA COMM
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
InactiveUS7280804B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsCarrier signalCoherence time
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
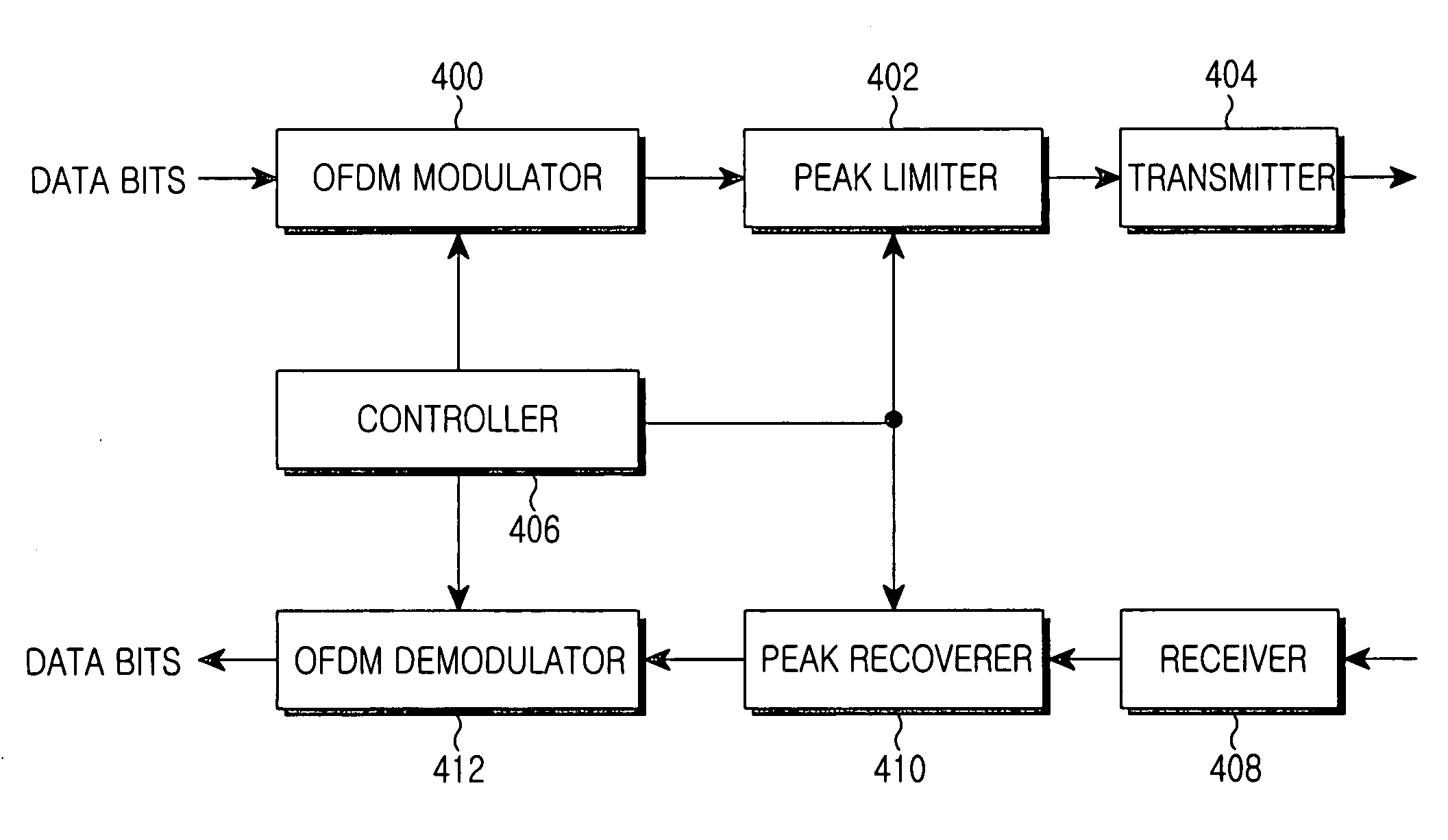
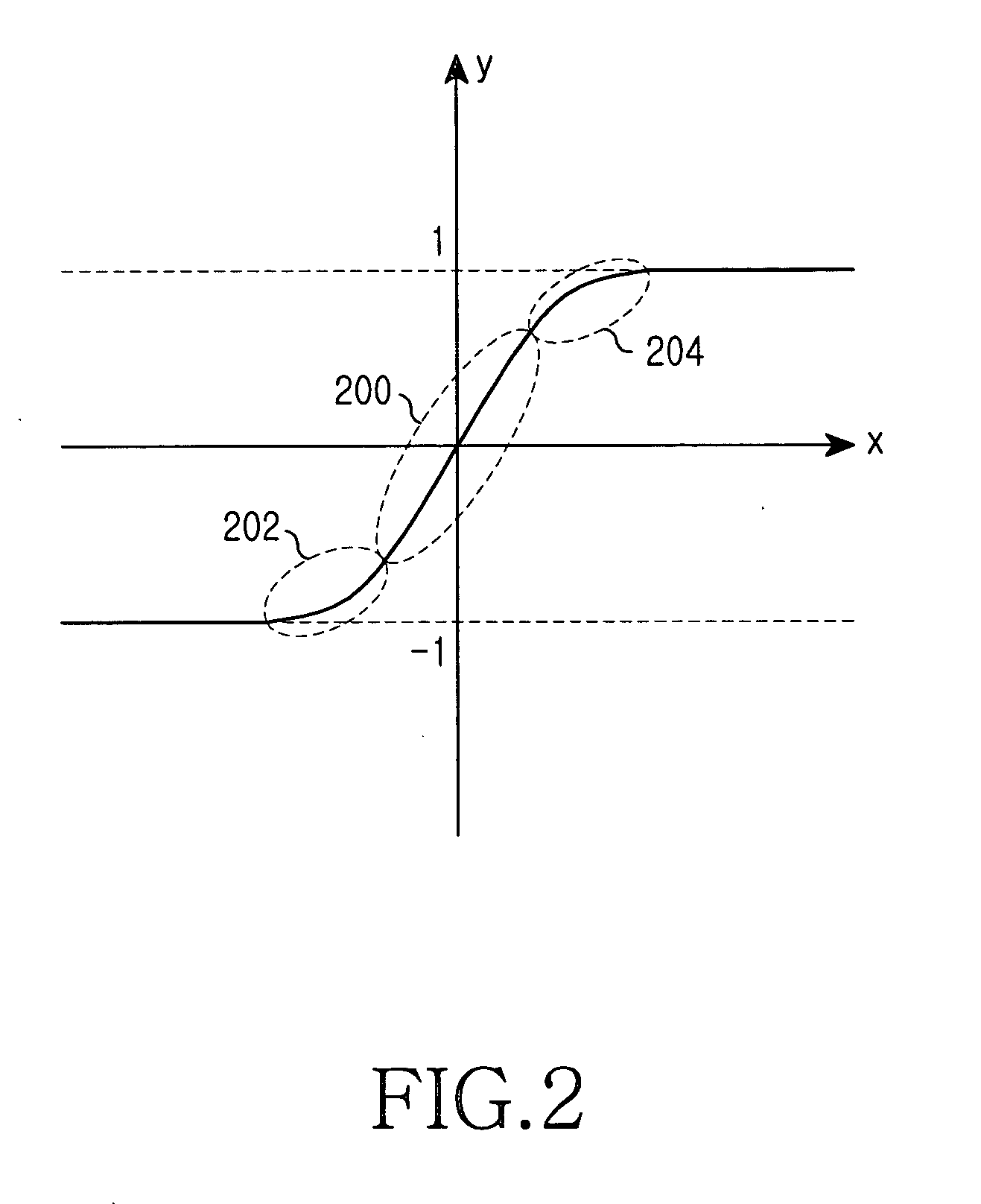
Transmitting and receiving apparatuses for reducing a peak-to-average power ratio and an adaptive peak-to-average power ratio controlling method thereof
InactiveUS20050254587A1Easy to implementSuppress BER performance degradationSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalEngineering
Transmitting and receiving apparatuses for PAPR reduction and an adaptive PAPR control method thereof are provided. Prior to transmission, the transmitting apparatus limits the peak of a multi-carrier modulated signal using a mapping function that increases an output value with an input value and converges the output value to a predetermined value. The receiving apparatus receives the peak-limited signal, recovers the peak of the signal using a demapping function of the mapping function, and recovers data from the peak-recovered signal according to the multi-carrier modulation scheme used. According to the adaptive PAPR control method, a scaling factor can be set variably for the mapping function and the demapping function according to a sub-carrier modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
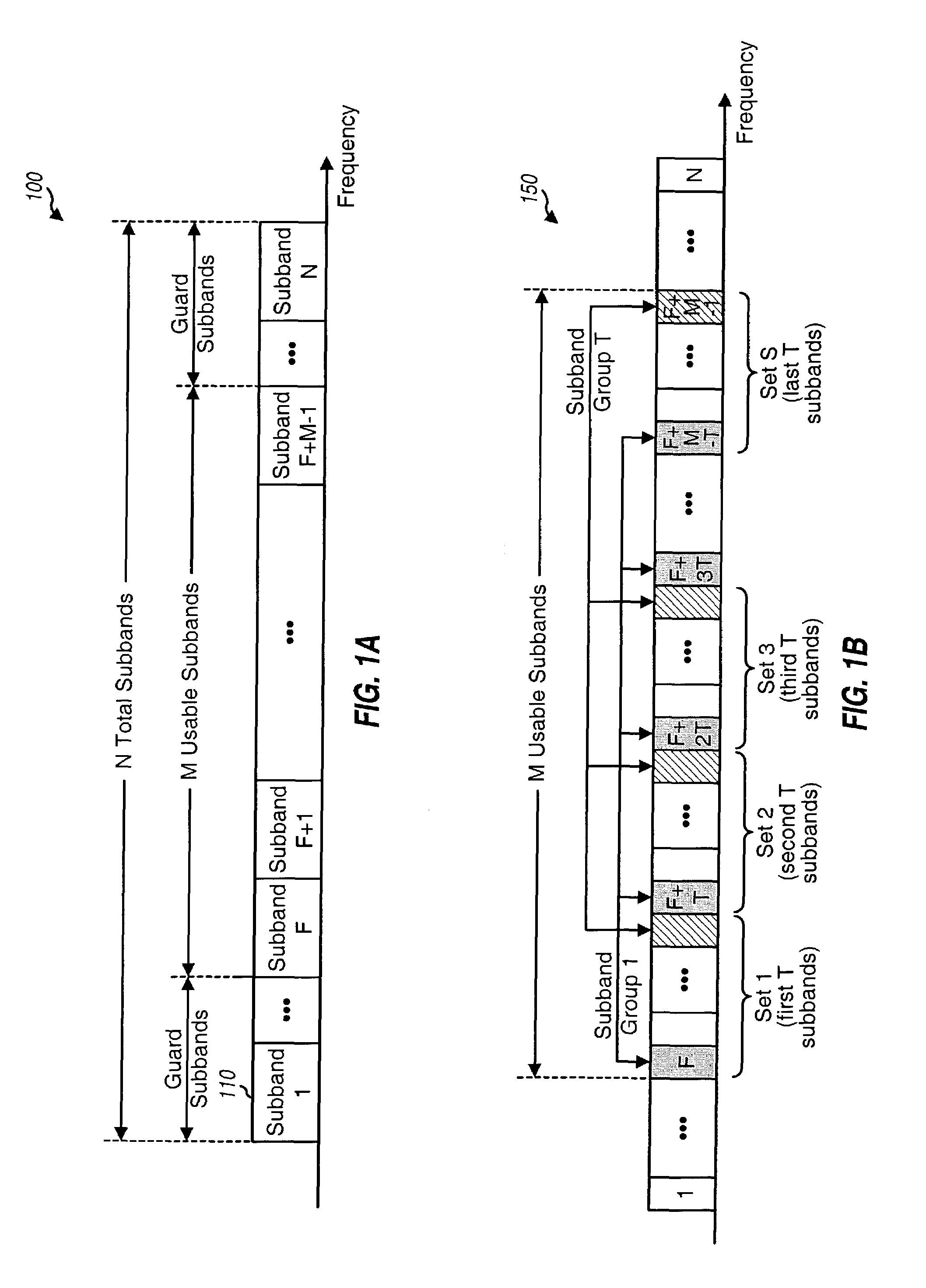
Transmission schemes for multi-antenna communication systems utilizing multi-carrier modulation
ActiveUS7095790B2Avoid interferenceImprove performancePower managementSpatial transmit diversityMultiplexingCommunications system
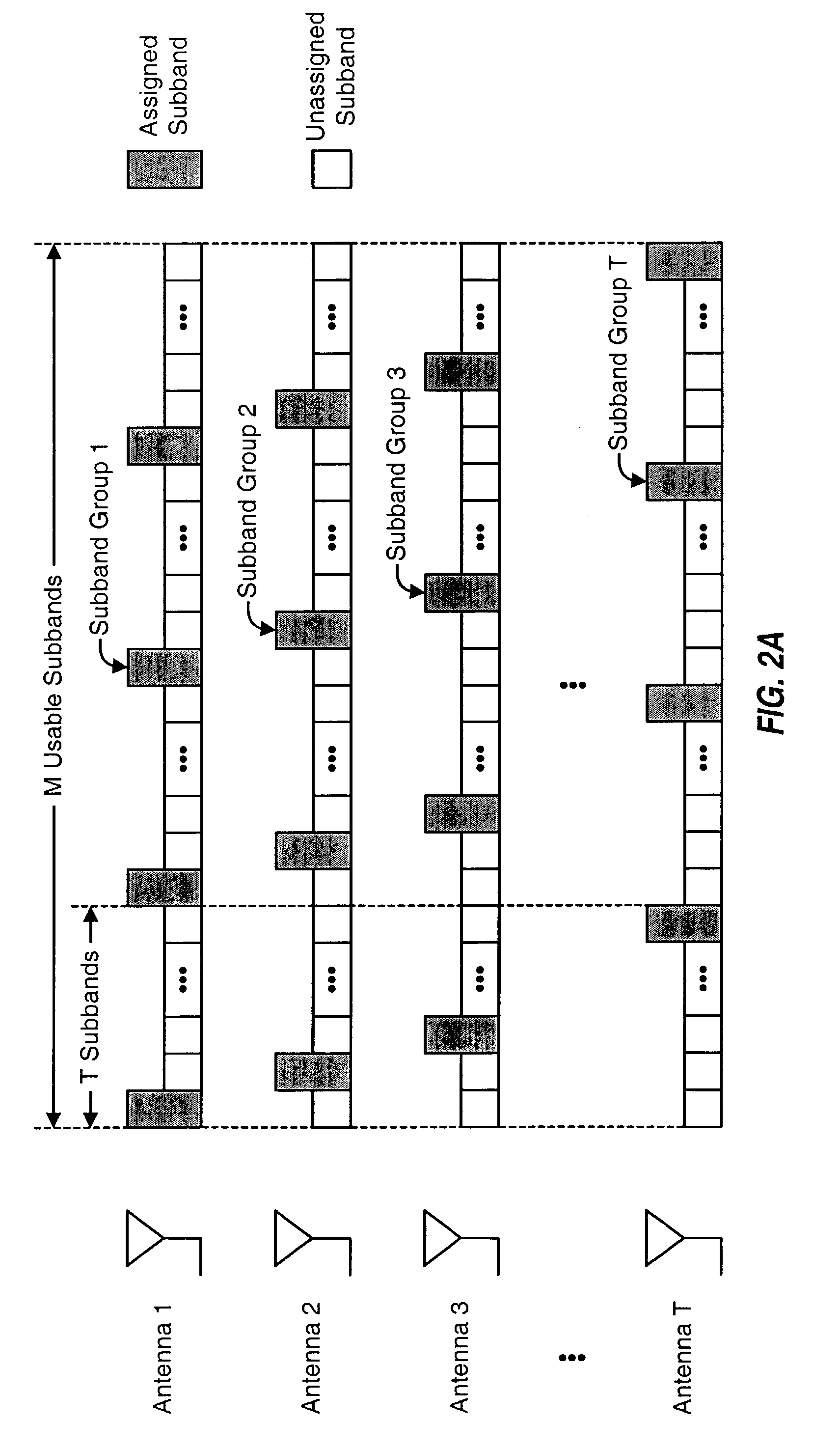
Pilot and data transmission schemes for multi-antenna communication systems utilizing multi-carrier modulation are provided. Subband multiplexing is used to avoid interference resulting from transmitting multiple signals simultaneously from multiple antennas. M usable subbands are initially arranged to form multiple groups of subbands, with each group including a different subset of the usable subbands. Each of T transmit antennas is then assigned one or possibly more subband groups for pilot transmission and typically one subband group for data transmission. Pilot and data may then be transmitted from each antenna on the subbands assigned to that antenna for pilot and data transmission. For each transmit antenna, the transmit power for each assigned subband may be scaled higher such that all of the total transmit power available for the antenna is used for transmission. Pilot and / or data may be transmitted simultaneously from all T antennas on all usable subbands without causing mutual interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com