Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
412 results about "Adjacent-channel interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
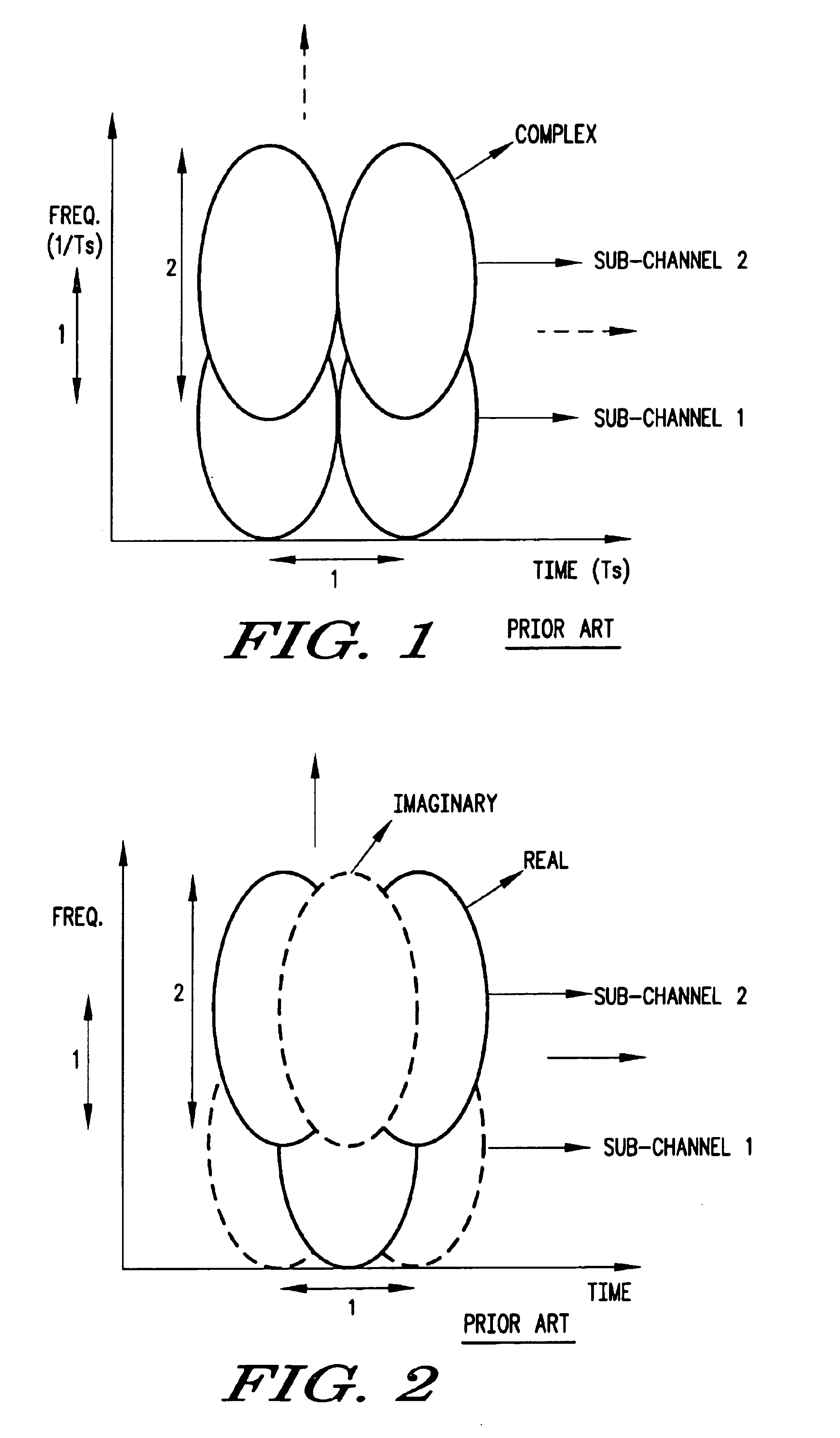
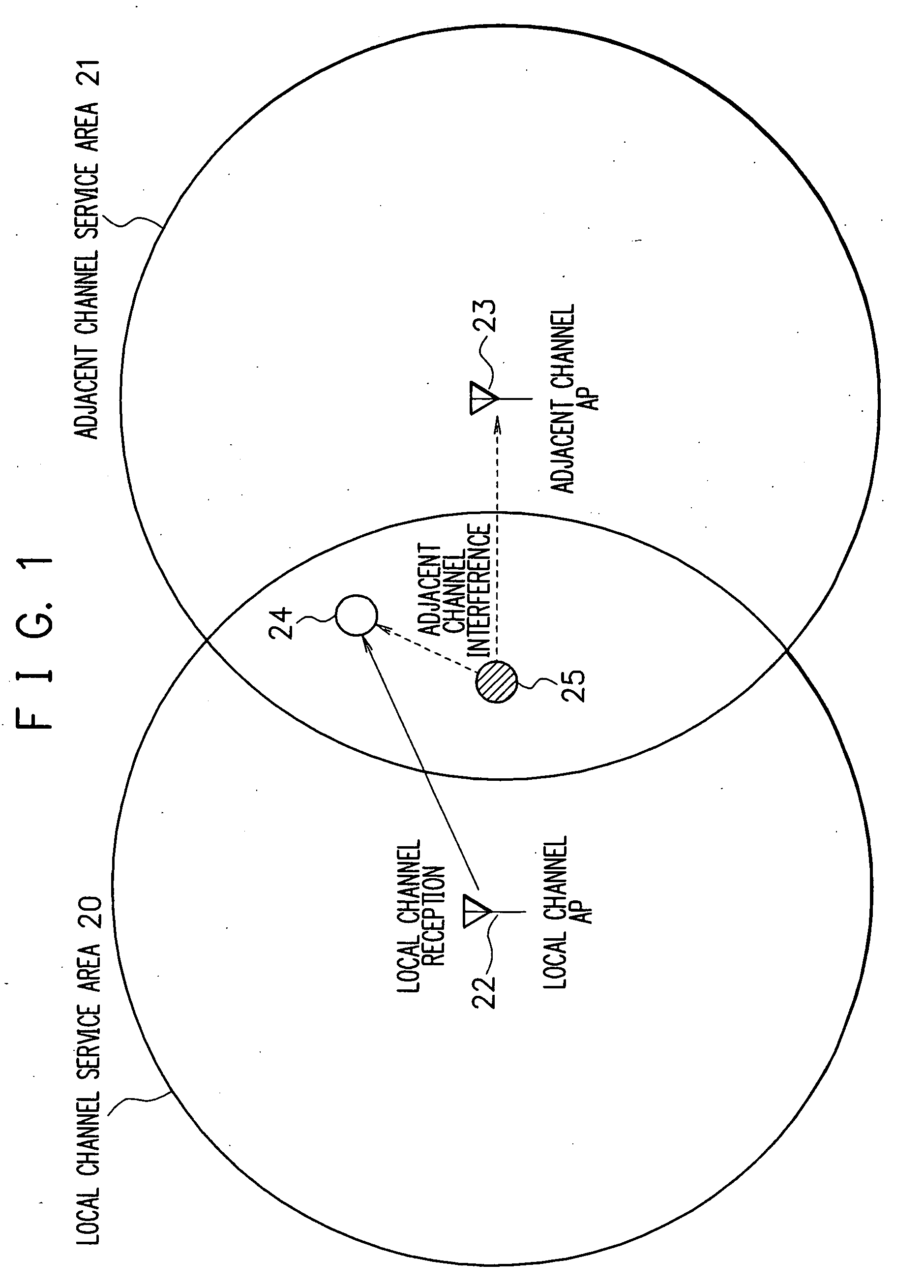
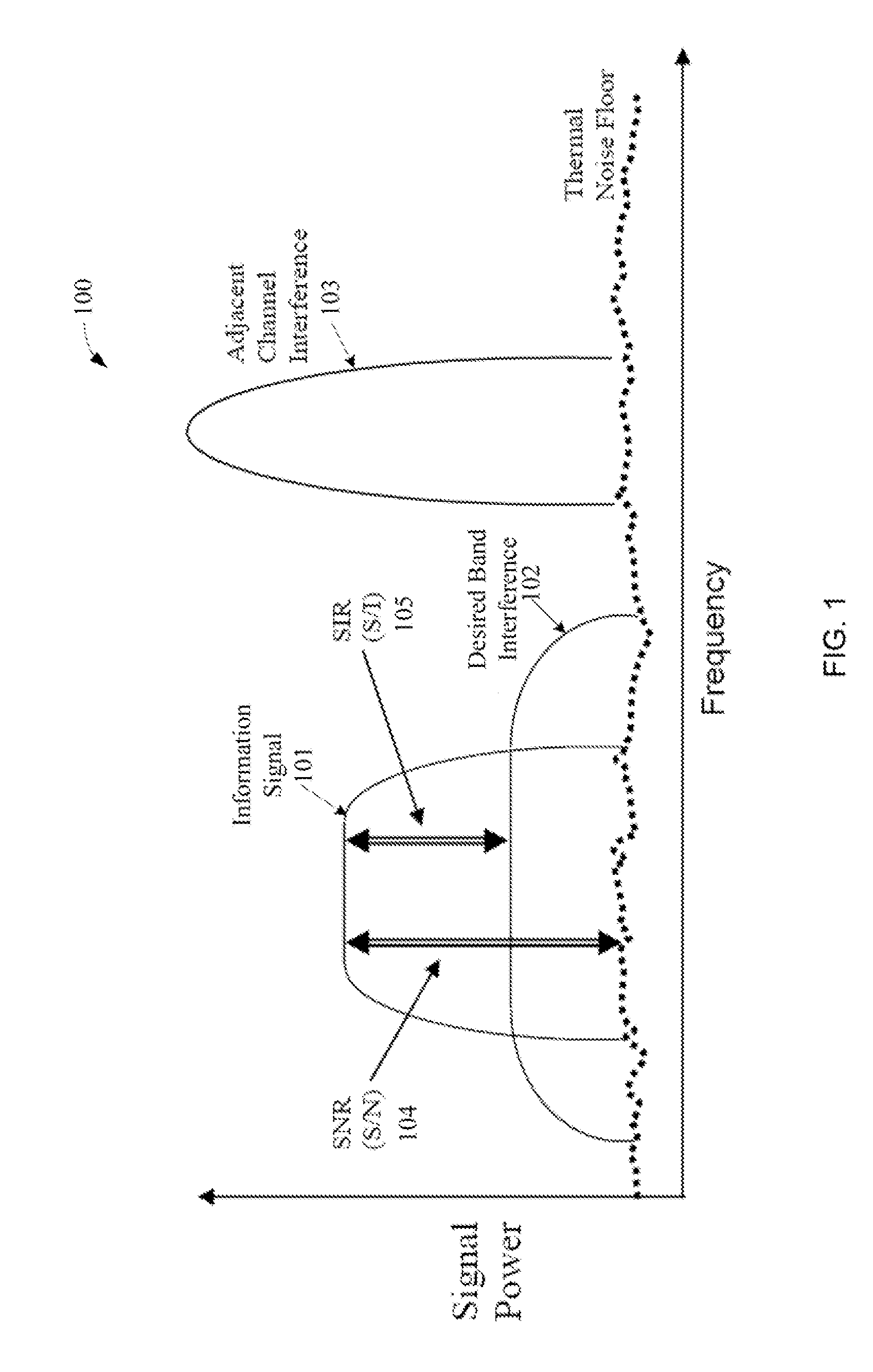
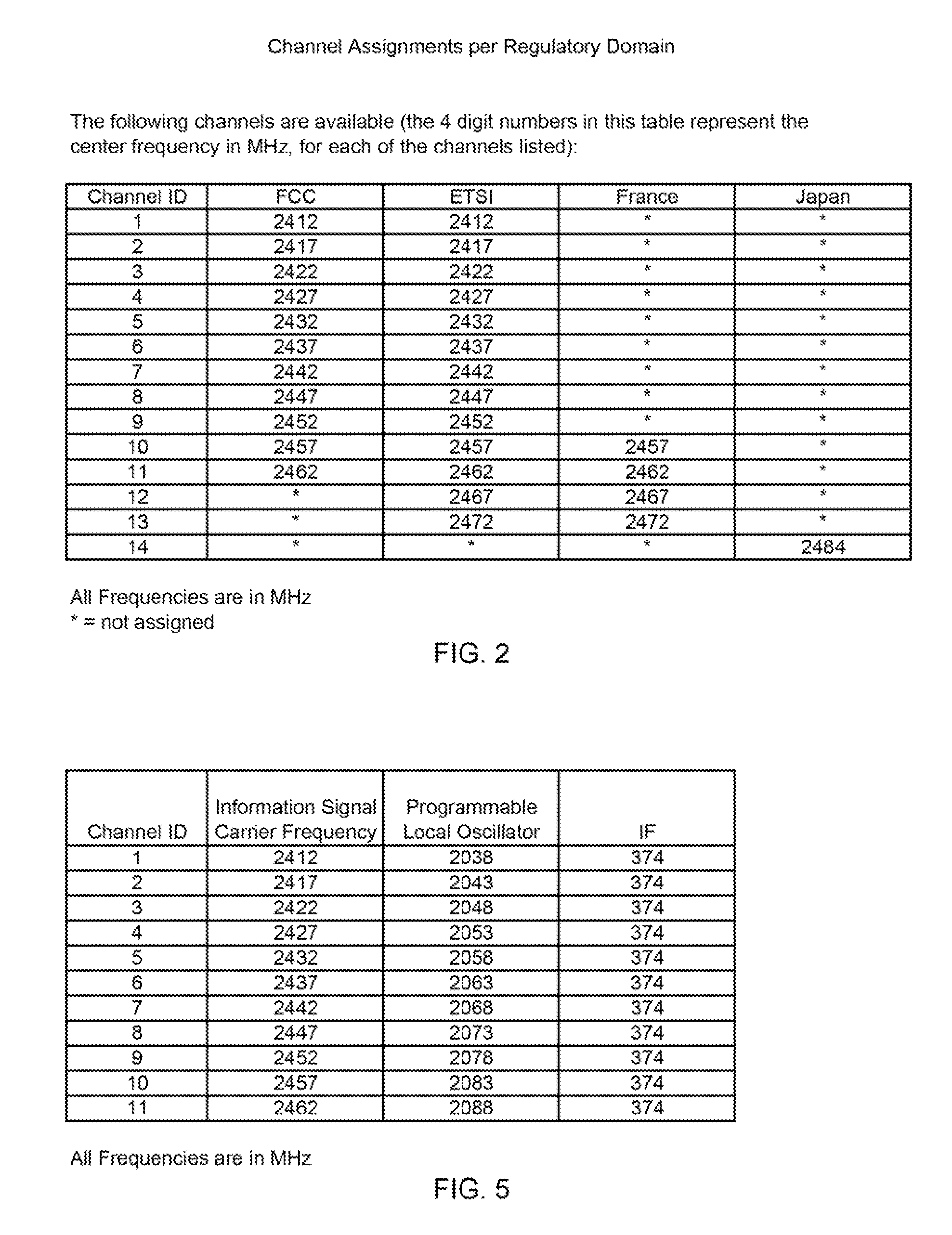
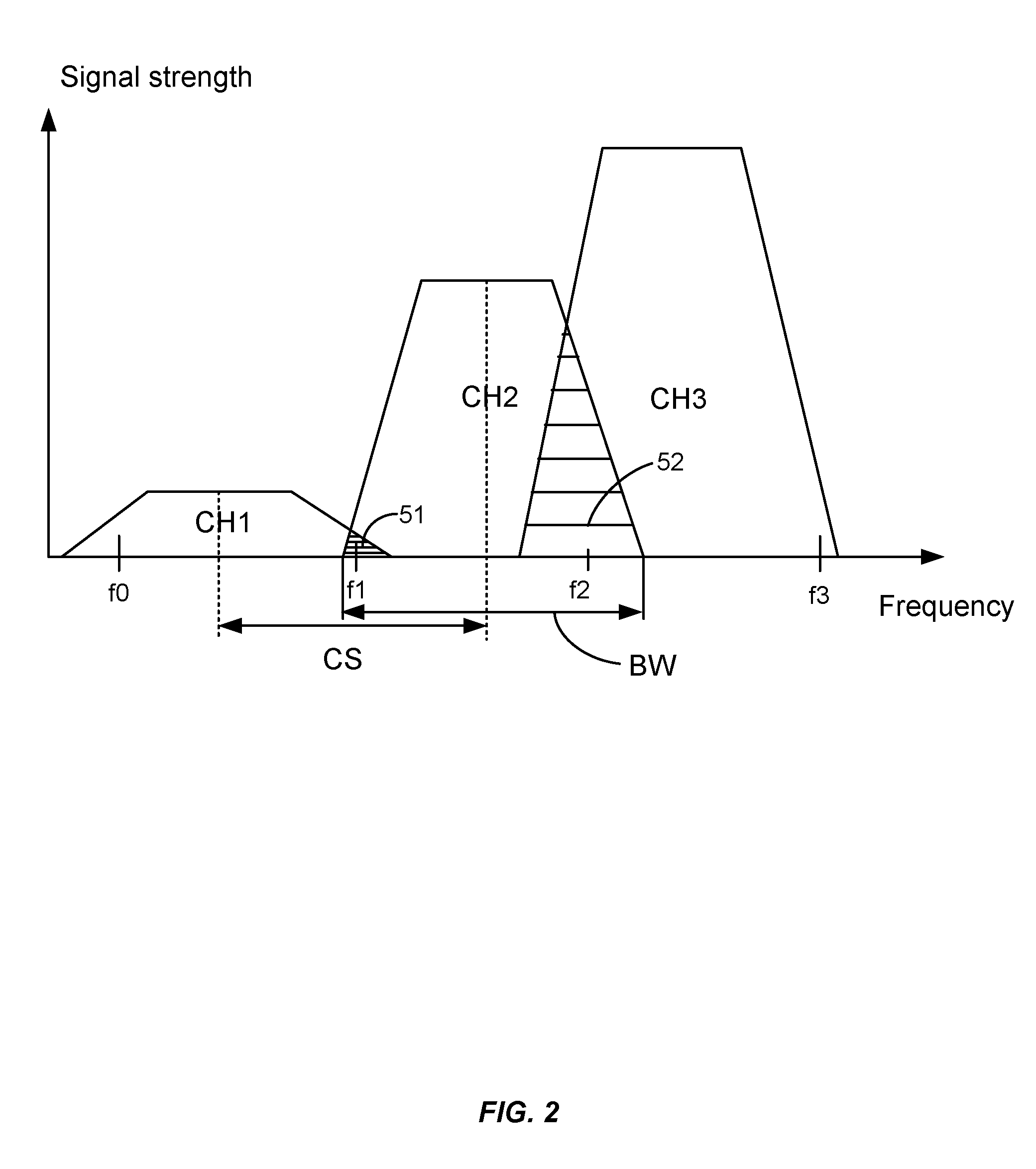
Adjacent-channel interference (ACI) is interference caused by extraneous power from a signal in an adjacent channel. ACI may be caused by inadequate filtering (such as incomplete filtering of unwanted modulation products in FM systems), improper tuning or poor frequency control (in the reference channel, the interfering channel or both).
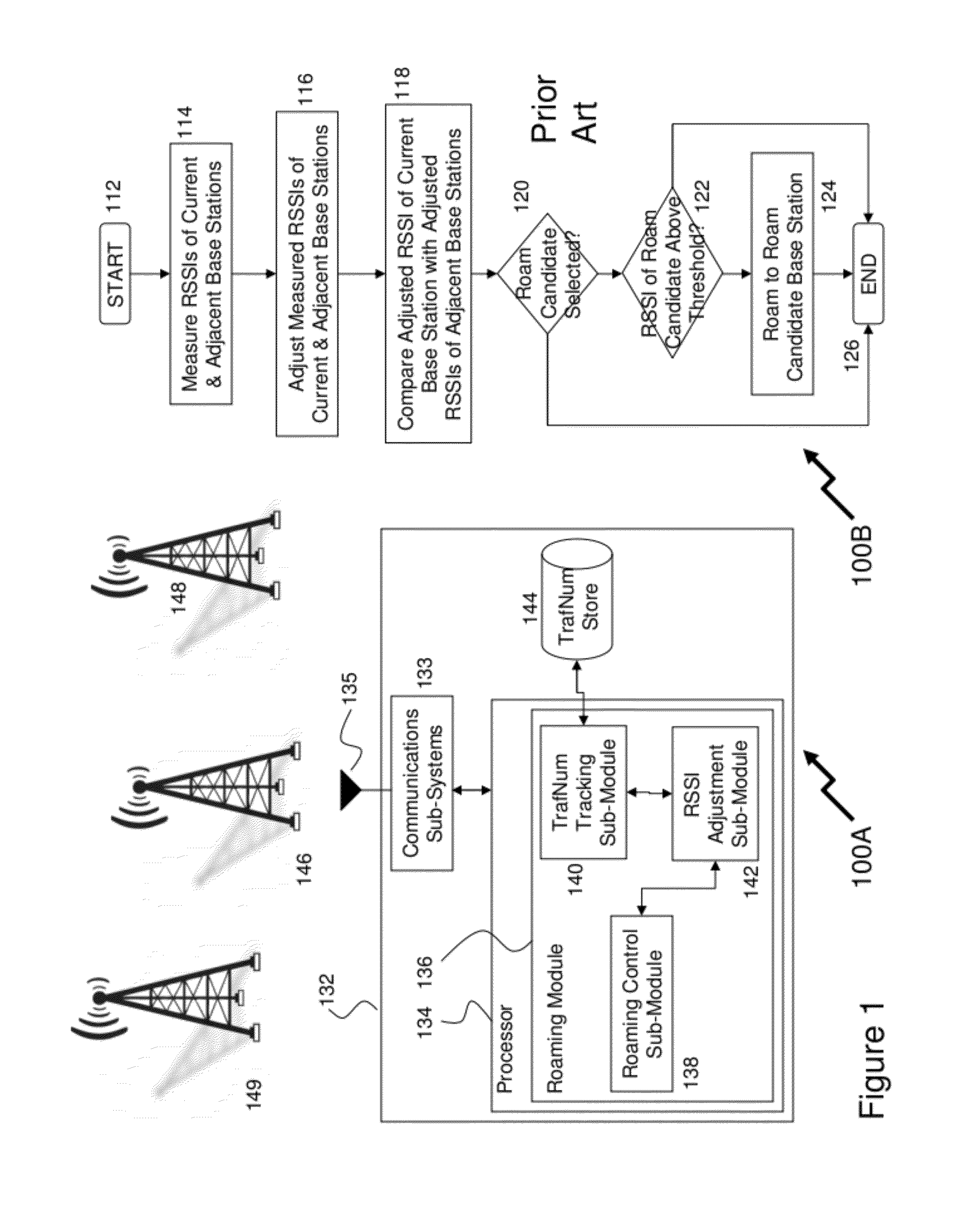
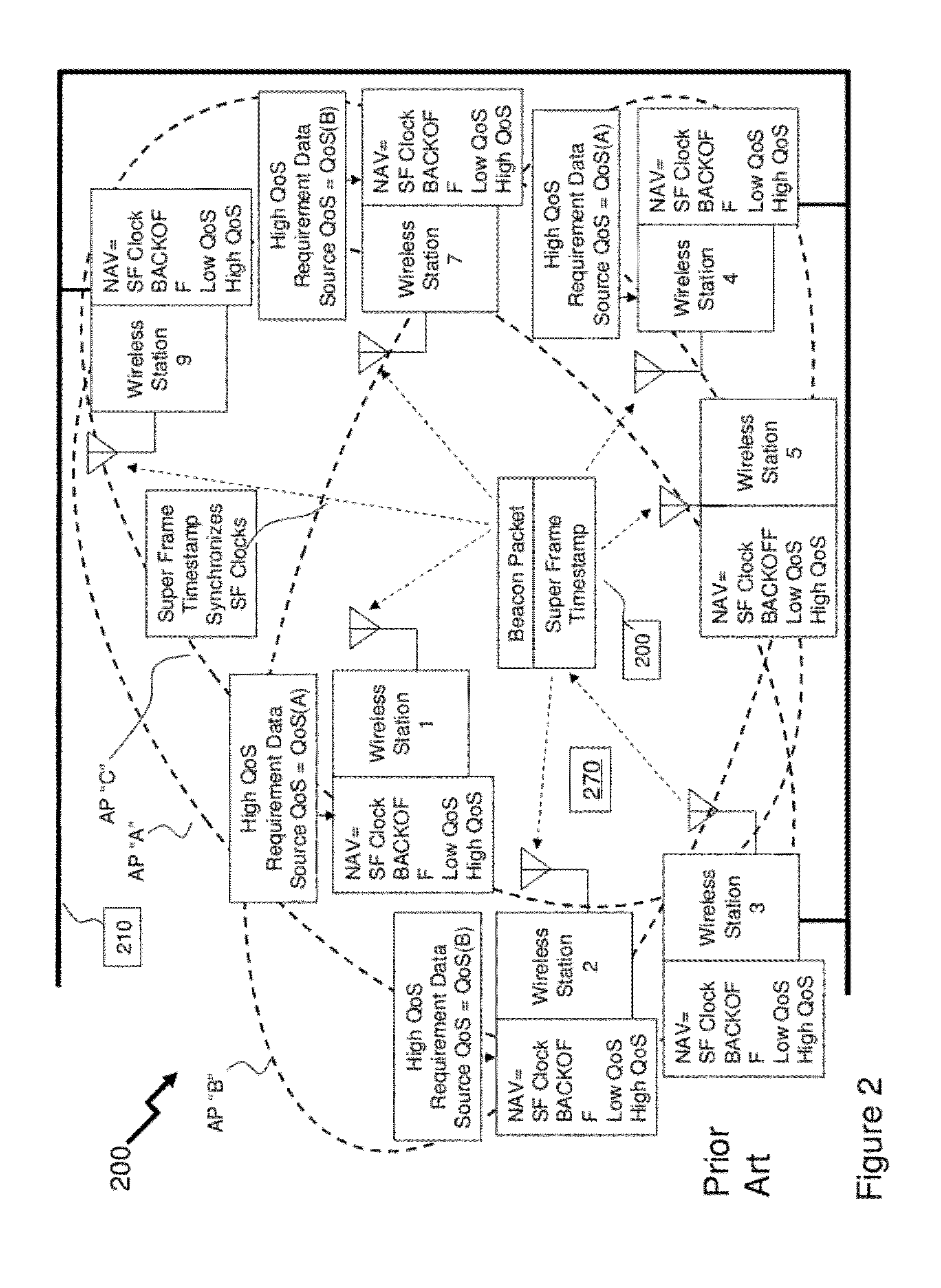
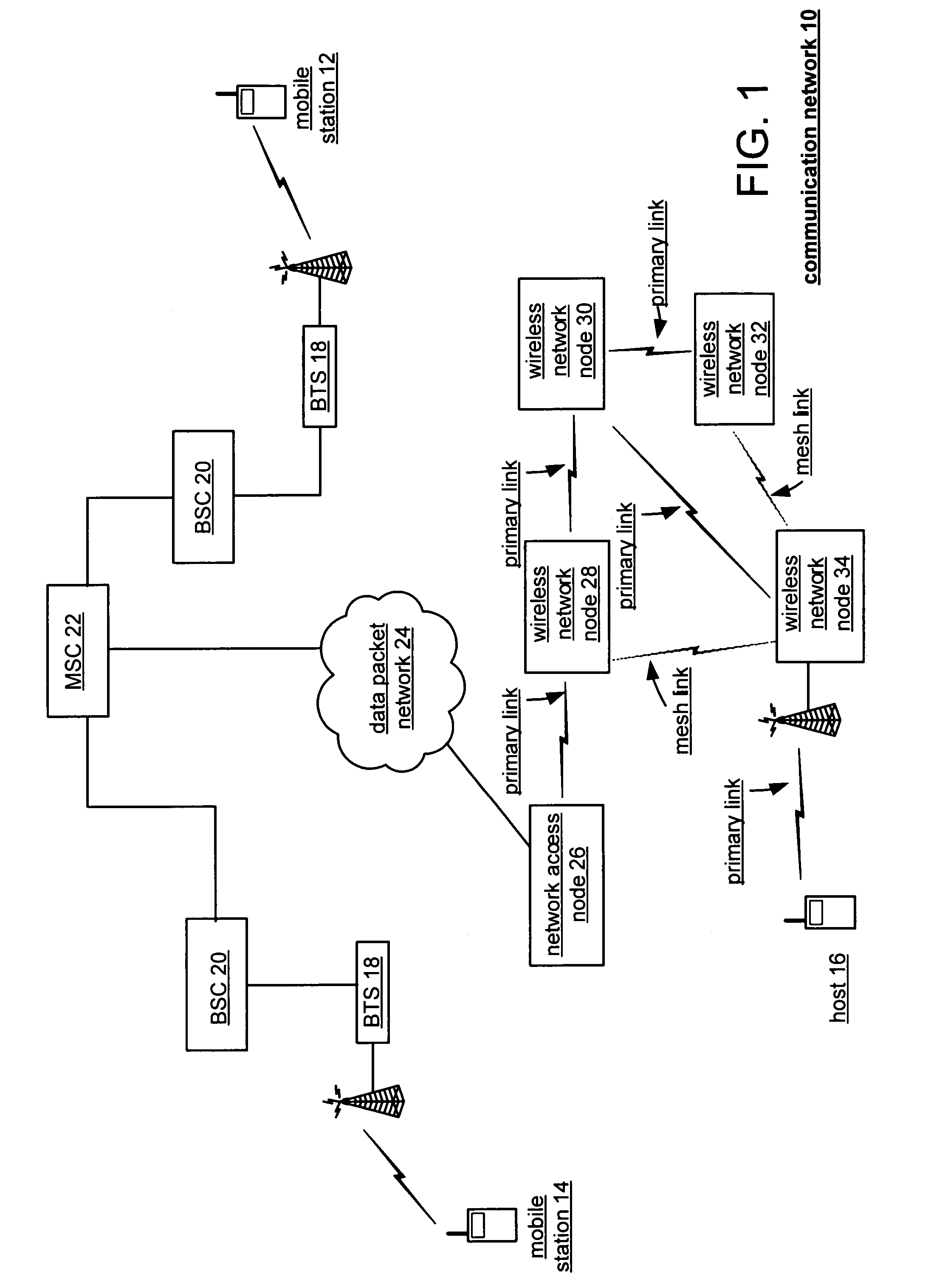
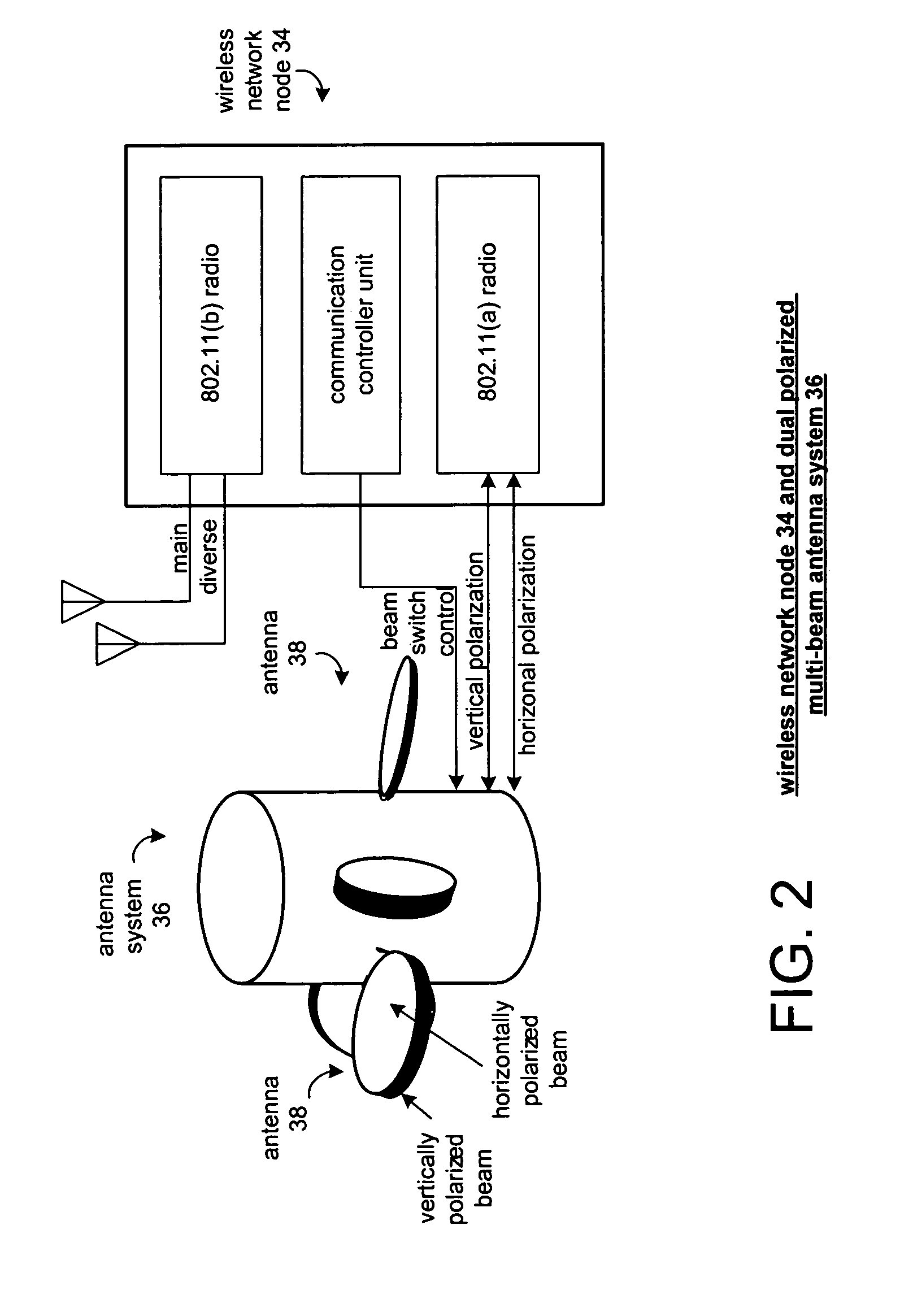
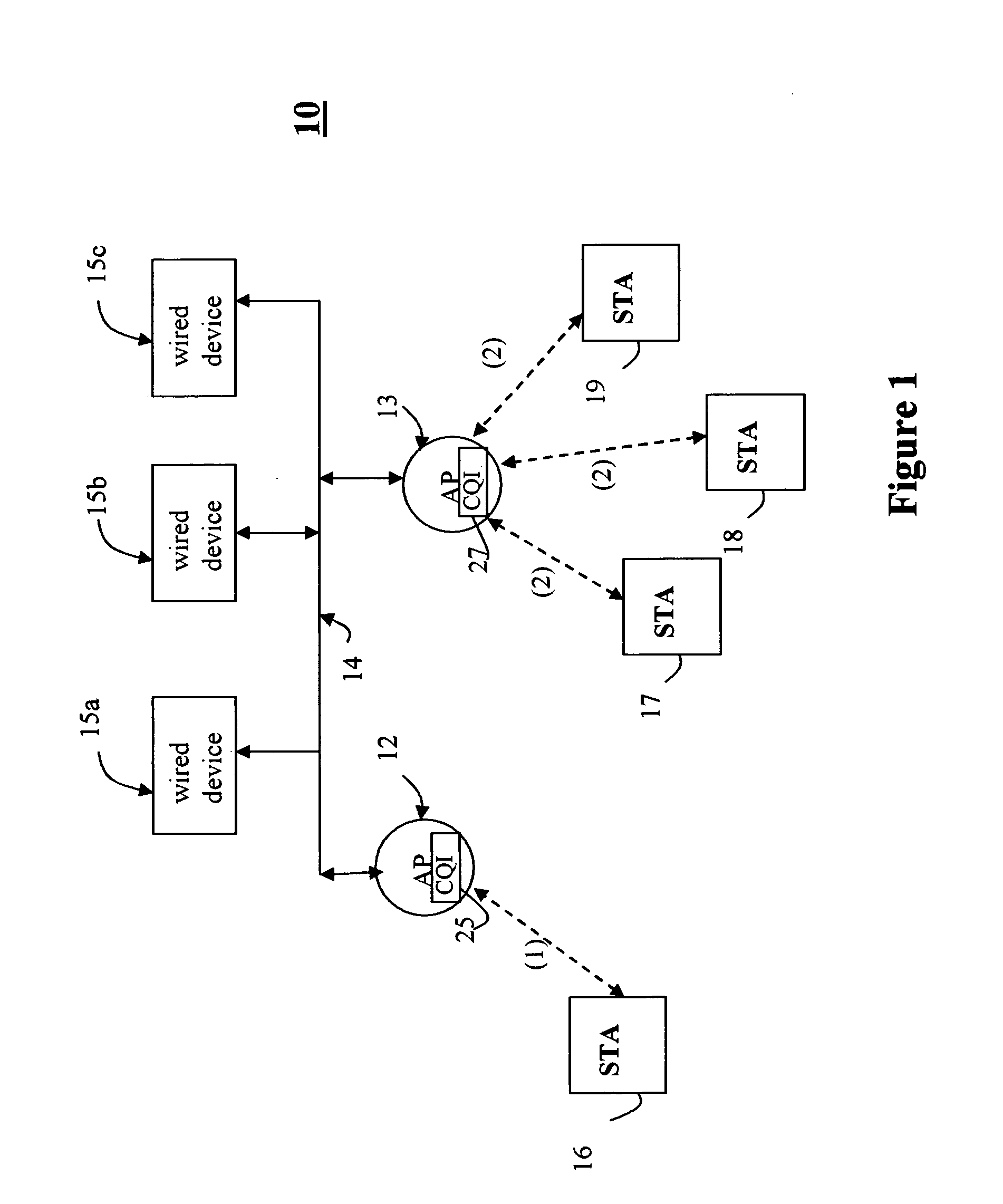
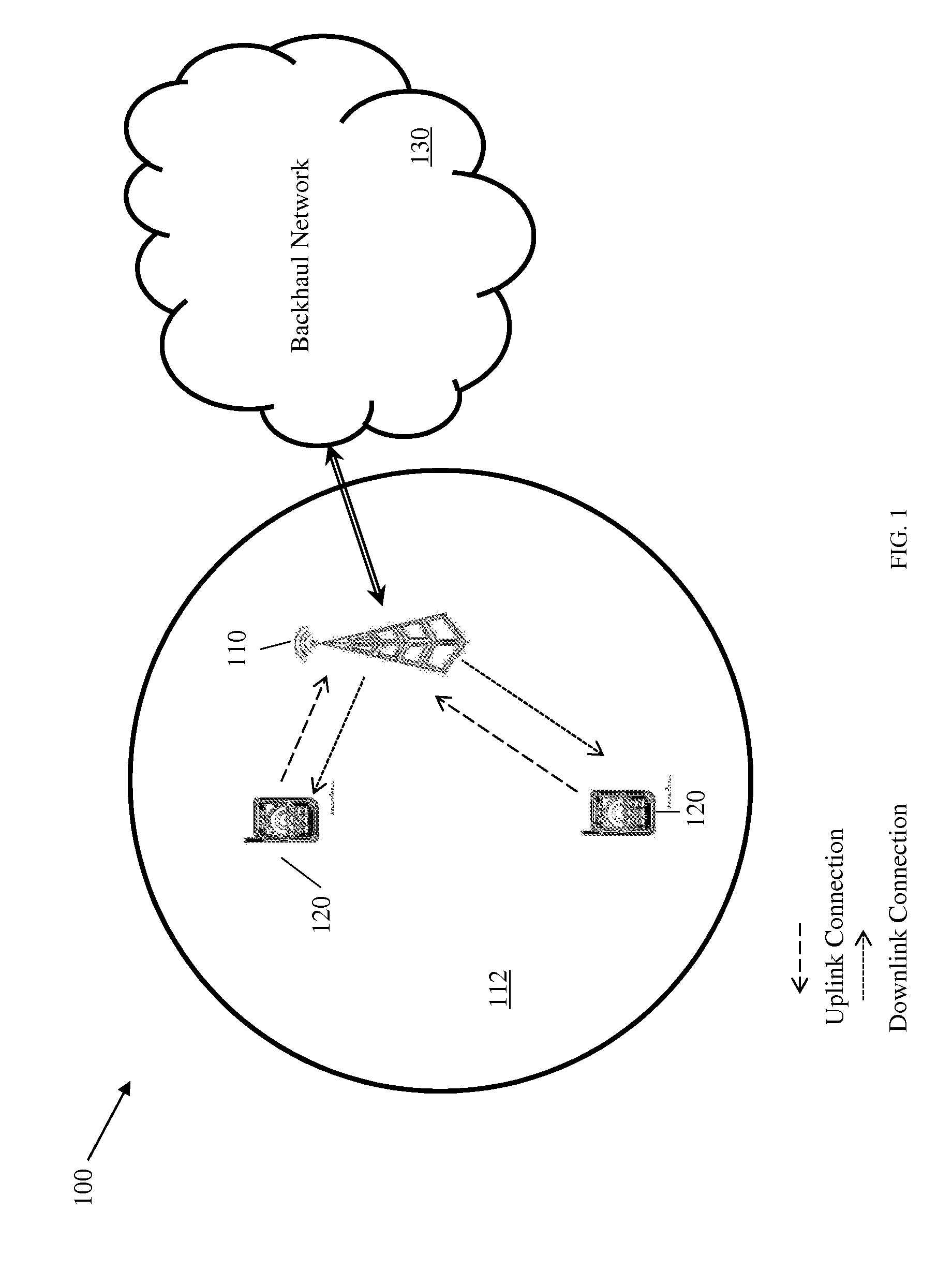
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
InactiveUS20120224484A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementInterference ratio
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
InactiveUS20120224481A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementInterference ratio
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
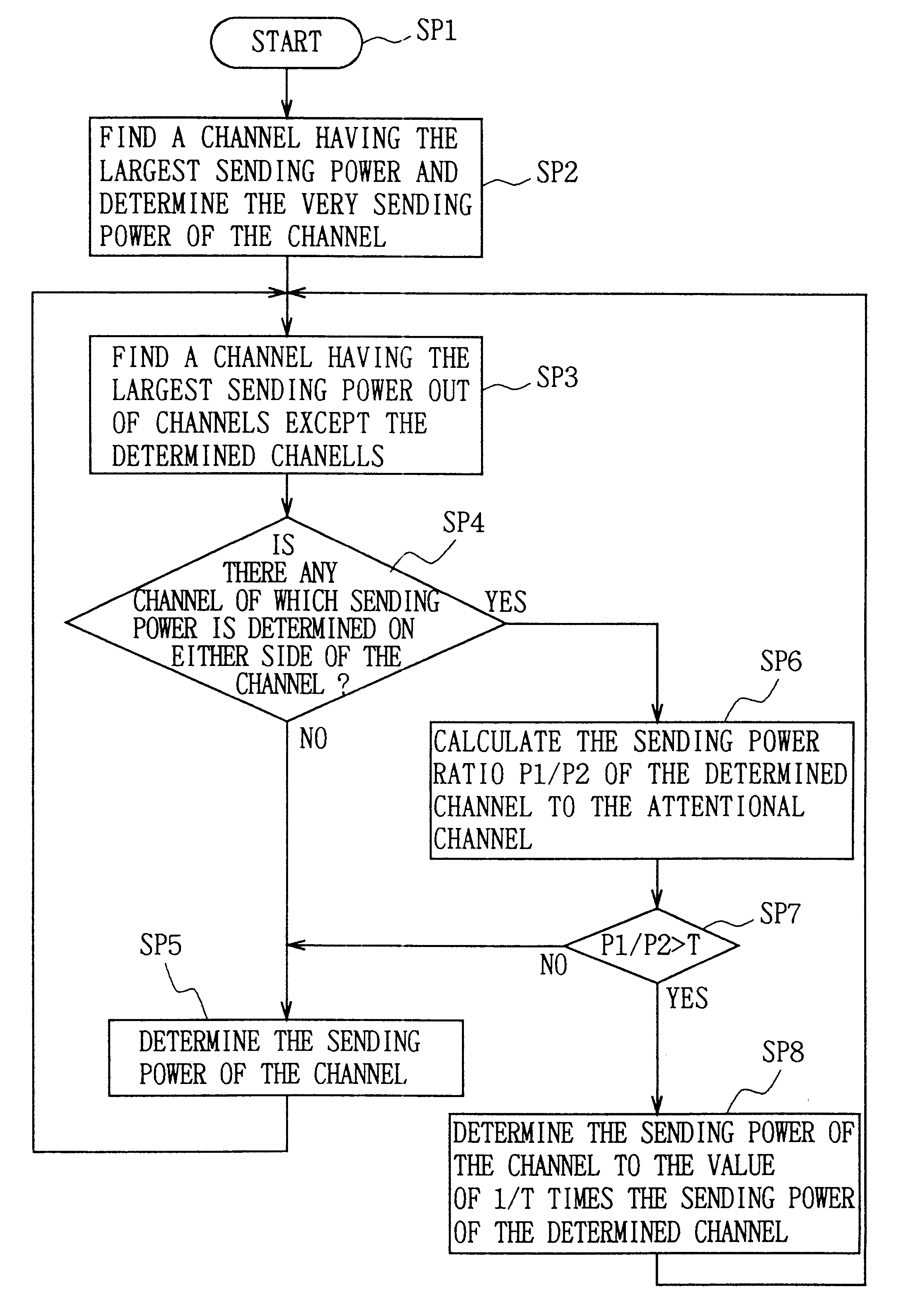
Transmitting method and apparatus, and sending power controlling method
In a transmitting method, it is possible to avoid influences of adjacent-channel interference to perform communication satisfactorily. In the case of performing transmission with a previously set sending power, the transmission is performed with the set sending power with respect to a channel having the largest sending power. With respect to a channel having the next largest sending power, if its adjacent channel is the determined channel, the transmission is performed such that the sending power is corrected on the basis of the sending power of the determined channel. Thereby, it is possible to prevent the signal-to-interference wave power ratio C / I of the channel from deteriorating due to the leakage signal (interference wave) from the adjacent channel. Thus, it is possible to avoid the influences of adjacent-channel interference to thereby perform communication satisfactorily.
Owner:SONY CORP
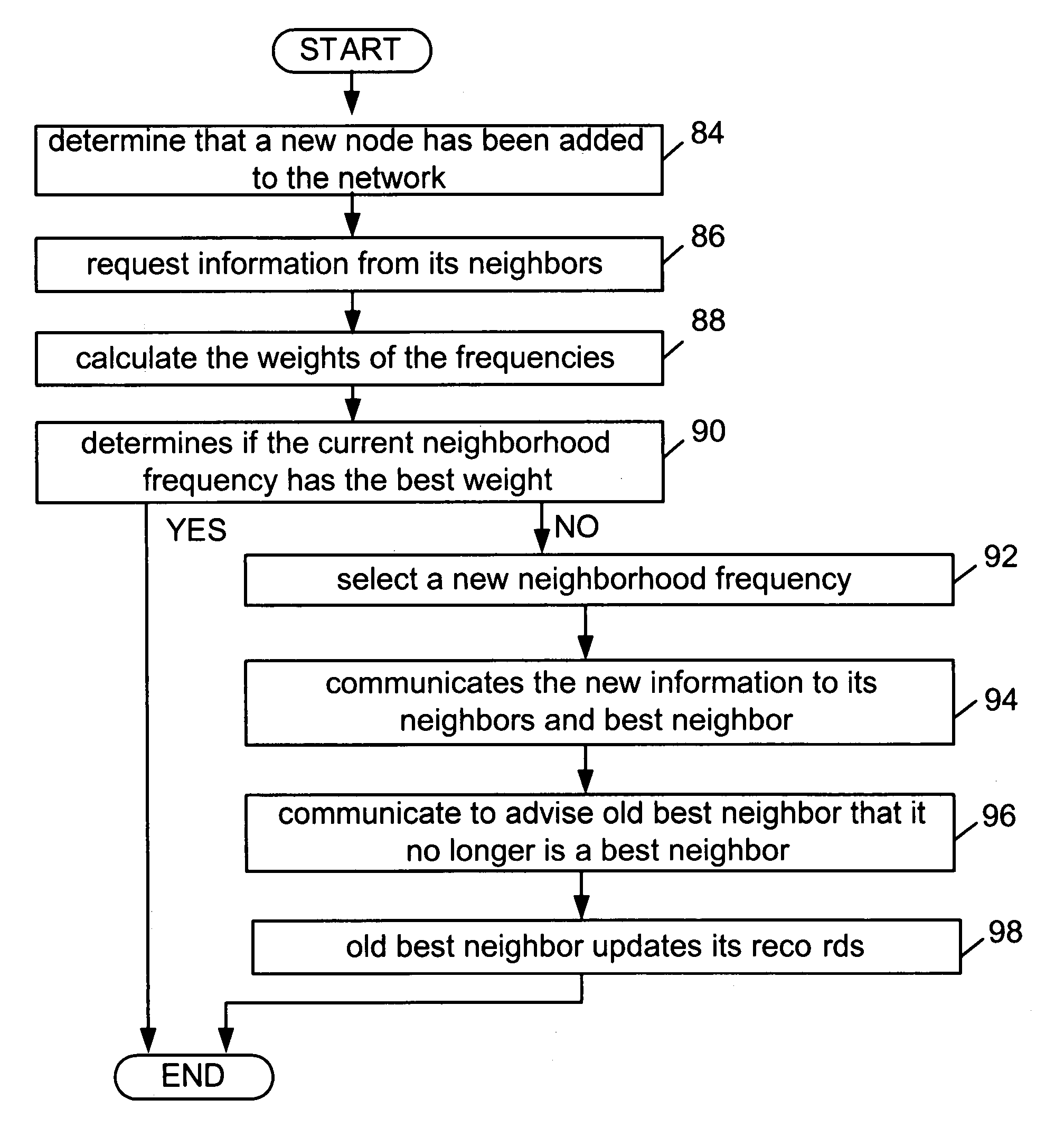
Self-selection of radio frequency channels to reduce co-channel and adjacent channel interference in a wireless distributed network
ActiveUS7174170B2Low costShorten the timeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAdjacent-channel interferenceRadio frequency
A wireless network node and a network provide for automatic self-deployment of the radio frequency channels without the need for preplanning. Each wireless network node adapts to the inclusion of a new node and to changing local conditions without requiring manual configuration at deployment or re-deployment. When a node is added to the network, it scans and finds its neighbors, and enters a frequency self-selection phase of its initialization process. The method for frequency self-selection involves transmitting and receiving a sequence of messages to / from neighbors and performing related processing within the controller unit of the node. Three sets of parameters are used in the frequency self-selection algorithm. The three parameter sets include a routing cost function, the frequencies in use by neighbors (and those that may be blocked), and the antenna beams used for the respective frequencies.
Owner:APPLE INC
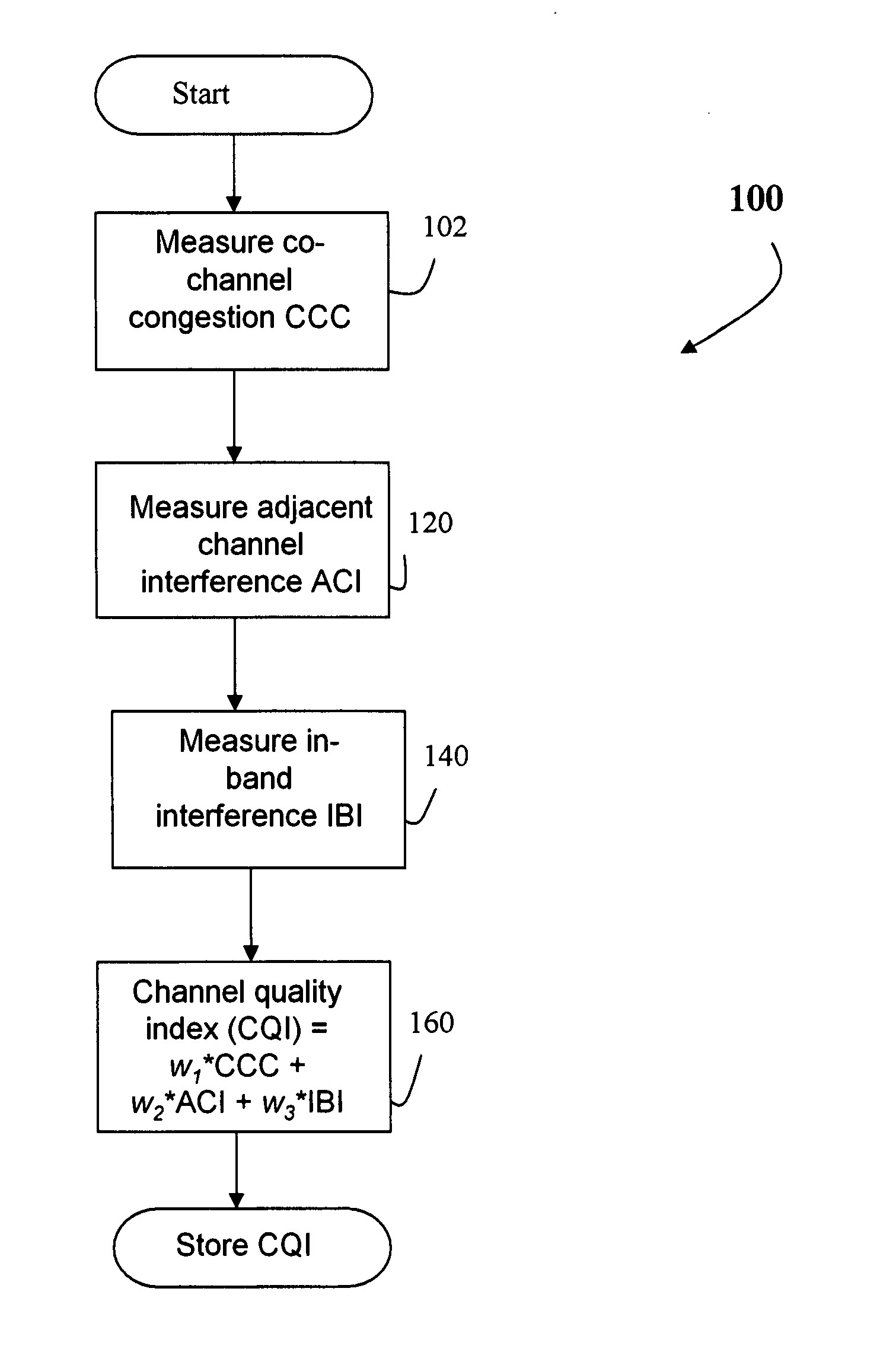
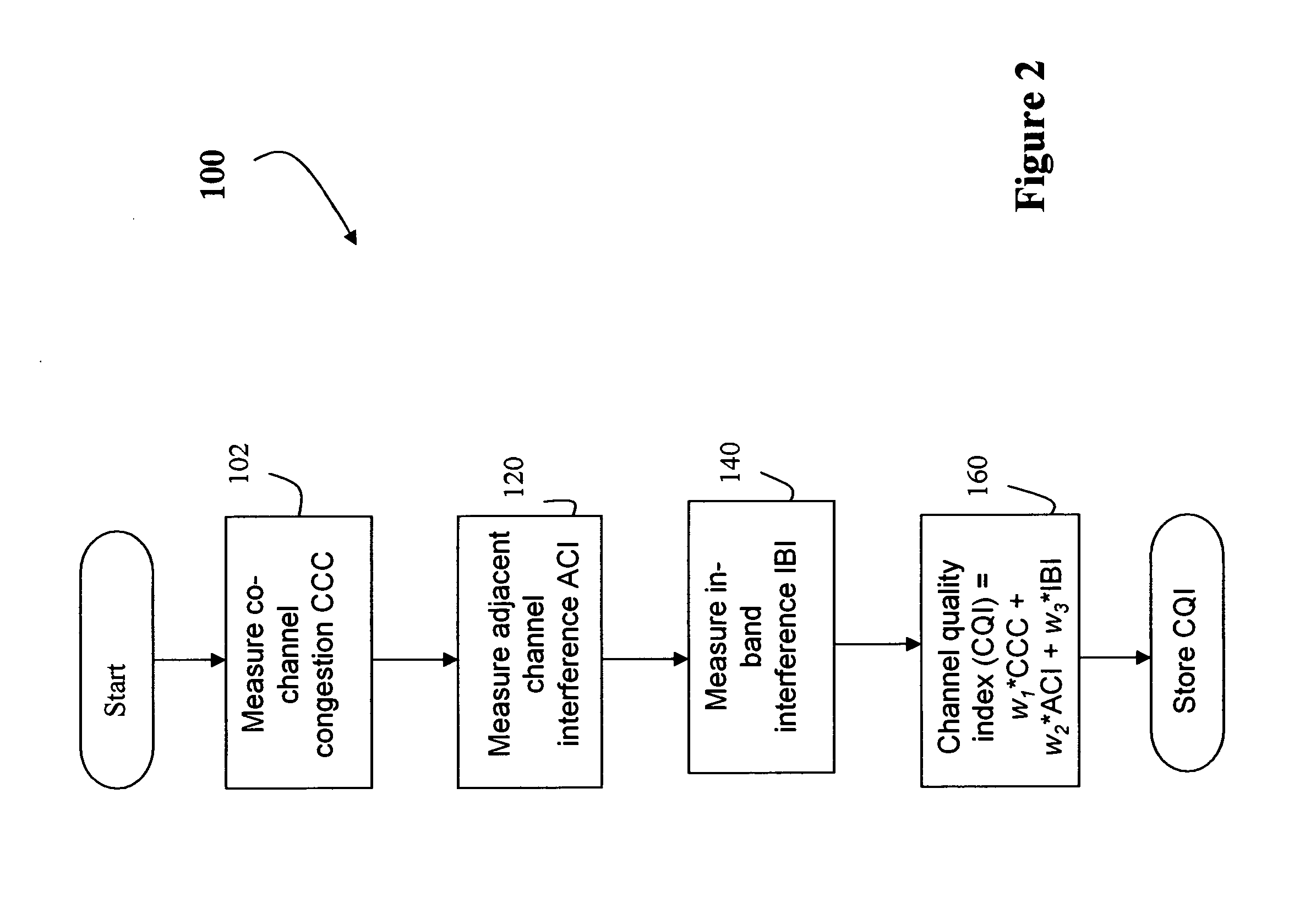
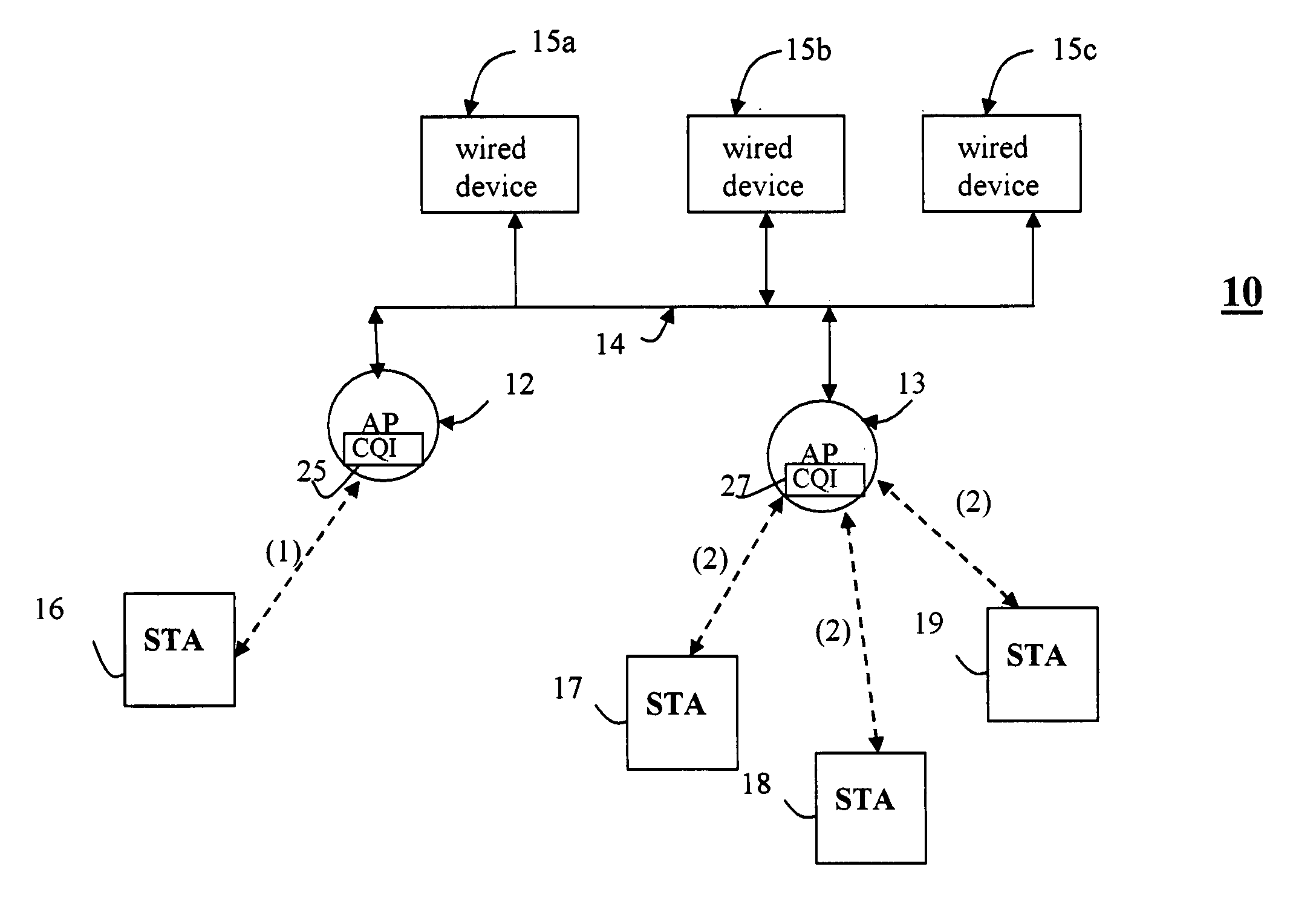
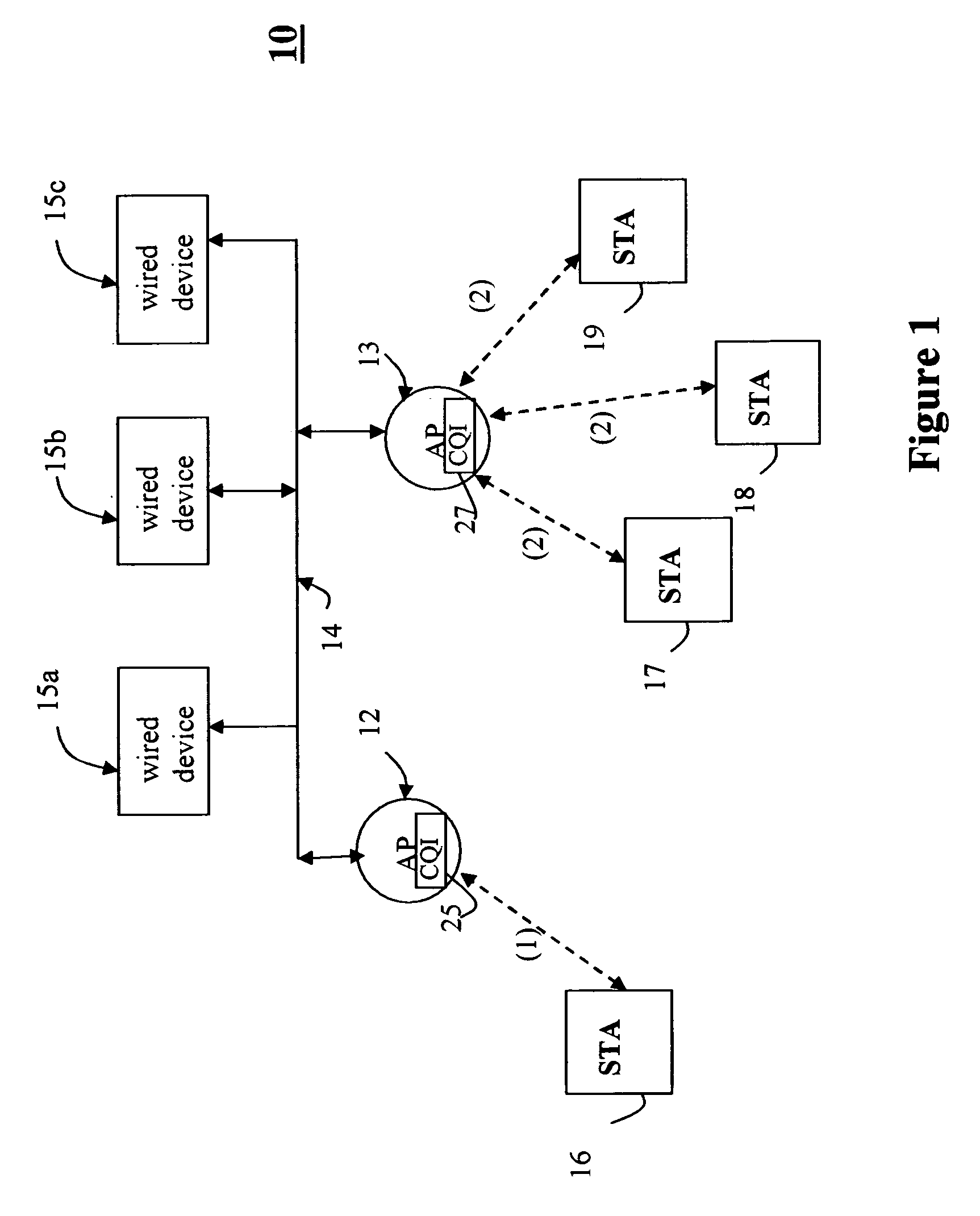
System and method for determining channel quality in a wireless network
ActiveUS20060292988A1Quick identificationTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionAdjacent-channel interferenceTelecommunications
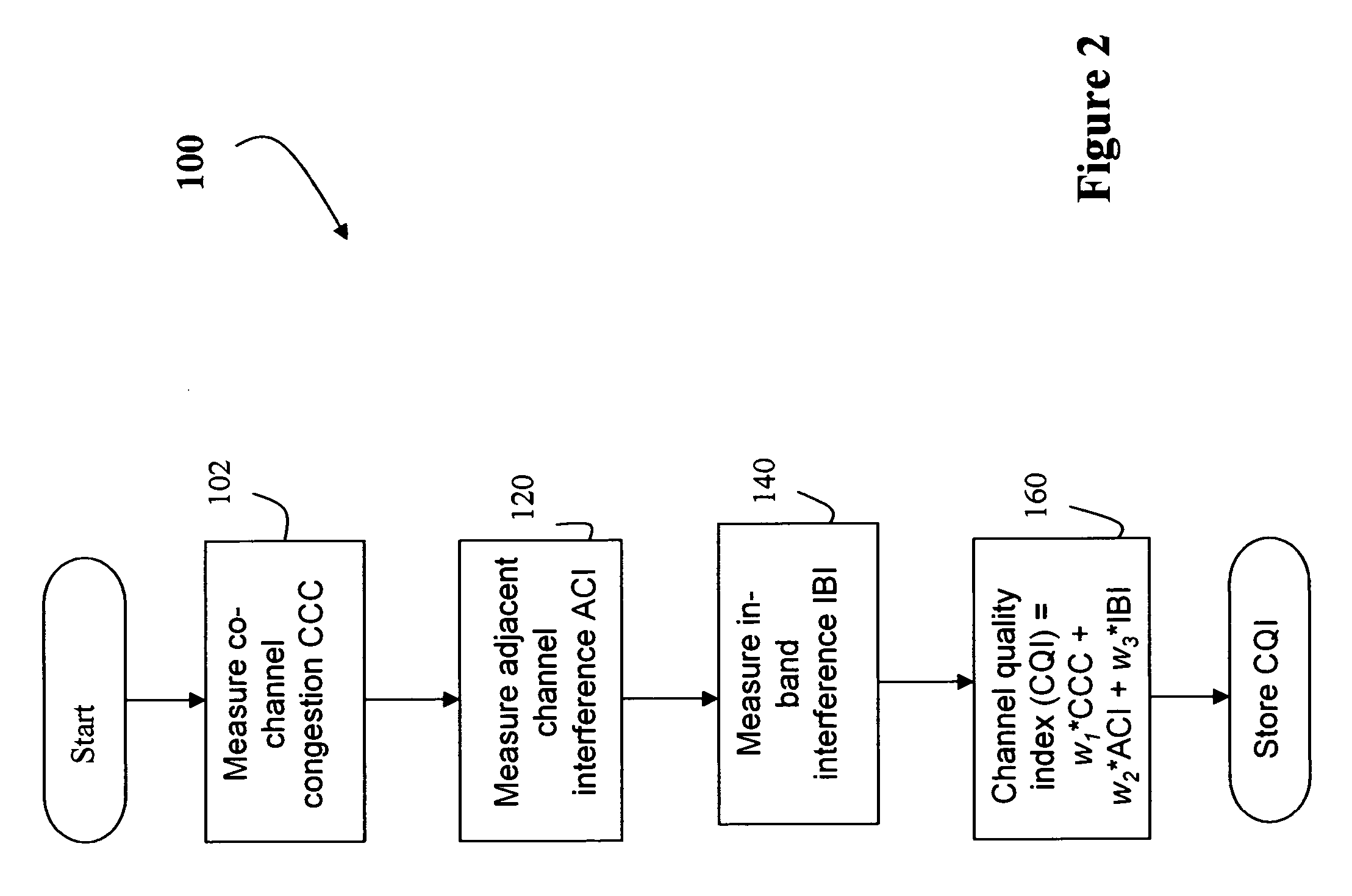
A system and method for Access Point (AP) channel selection based upon a Channel Quality Index (CQI) is described. The Channel Quality Index (CQI) is a value which quantifies a transmission quality of a channel. The transmission quality is evaluated based on a combination of different types of measured interference in the channel. In one embodiment the different types of measured interference include co-channel congestion, adjacent channel interference and in-band interference. The CQI is a value derived from the measurements, and for example may be a sum of all of the measurements. Each AP of the present invention determines the CQI of potential transmission channels, and selects a channel for use which has the ‘best’ CQI; for example if the CQI is a sum of all measured interferences, the ‘best’ AP is the one with the lowest CQI
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
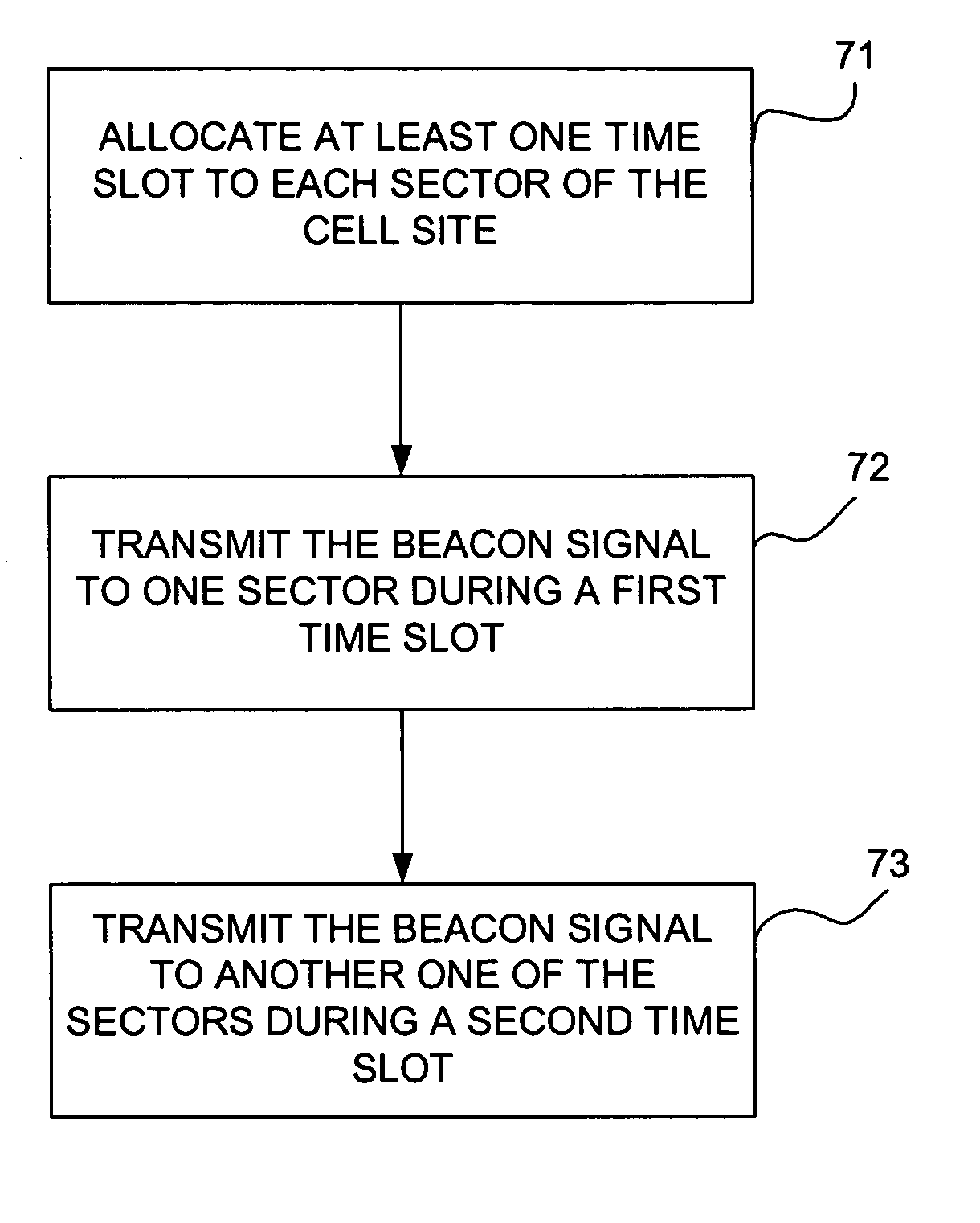
Method and apparatus for allocating a beacon signal in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20060089141A1Improve spectral efficiencyReduce power consumptionAssess restrictionPosition fixationAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
A method and apparatus for transmitting beacon signals in a wireless communications network. For a given cell site, a single frequency may be used for the beacon signal by assigning different beacon signal time slots to different sectors of the cell site. During one time slot, the beacon signal is transmitted to one of the sectors, and during another one of the time slots, the beacon signal is transmitted to a different one of the sectors. Because a single frequency can be used for all of the sectors of a cell site, more frequencies are available for other purposes, such as for user traffic, for example. The invention improves spectral efficiency, reduces adjacent channel interference and co-channel interference and allows power consumption to be controlled.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
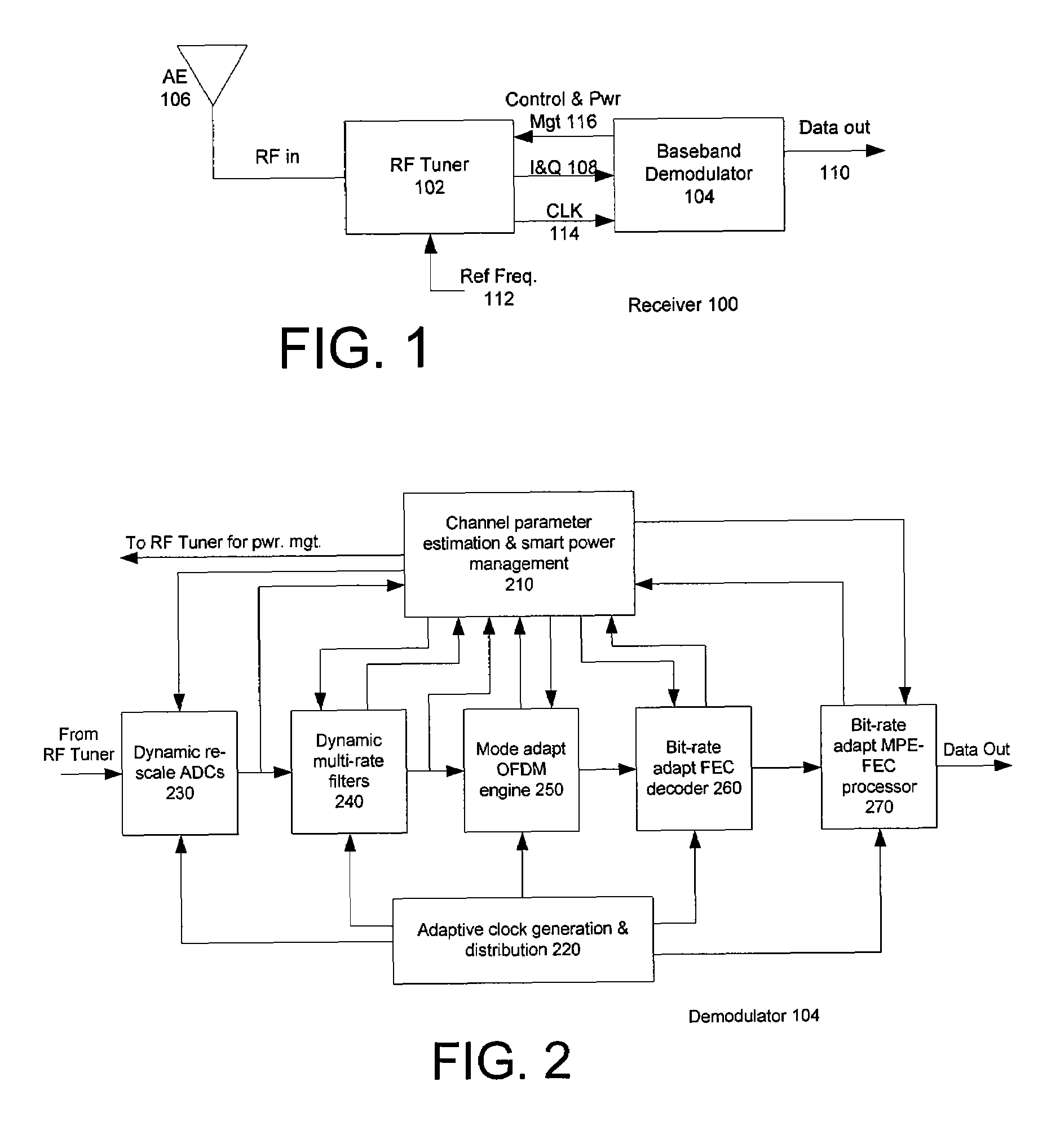
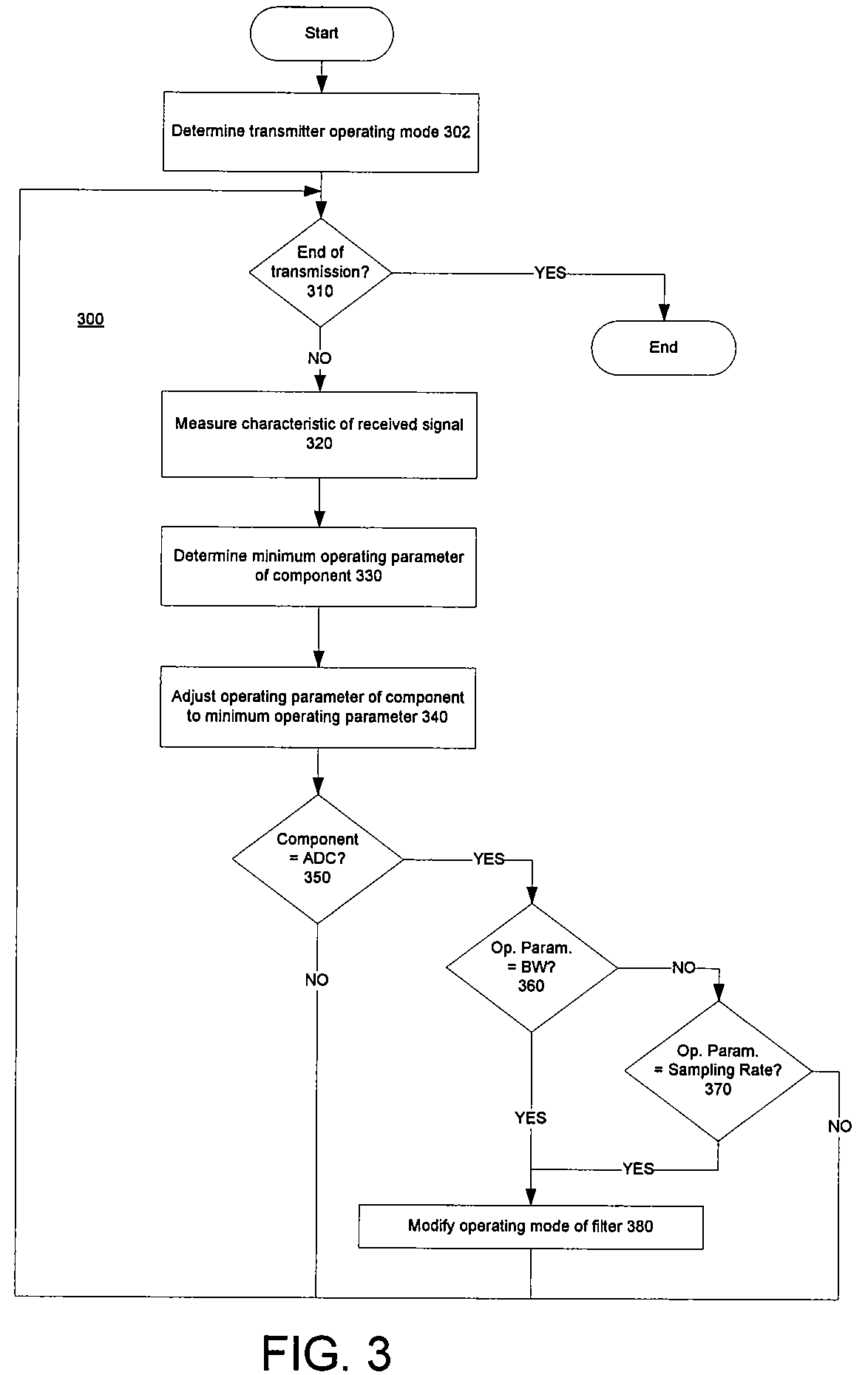
Power Management in Digital Receivers
ActiveUS20070064839A1Unnecessary power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceControl power
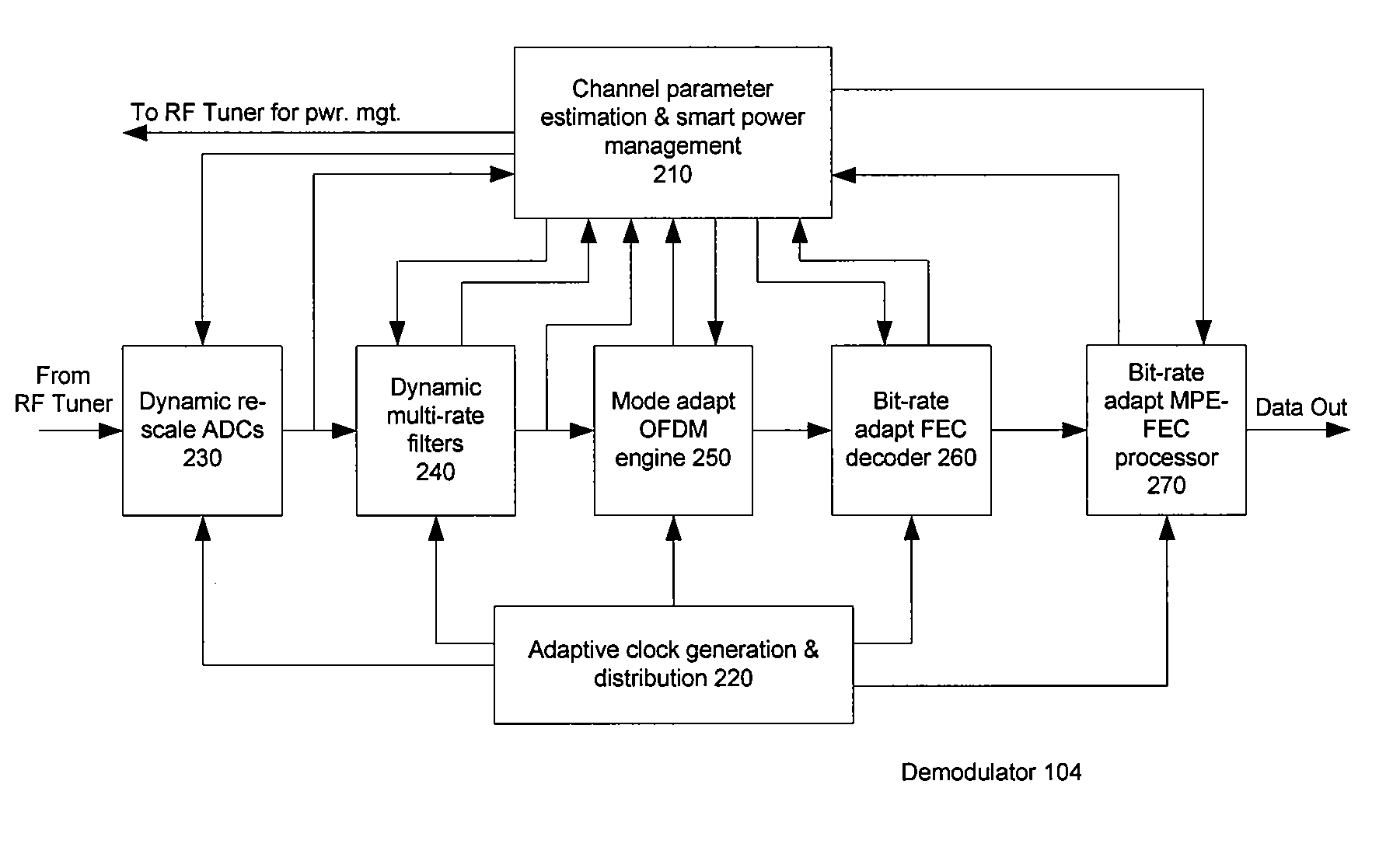
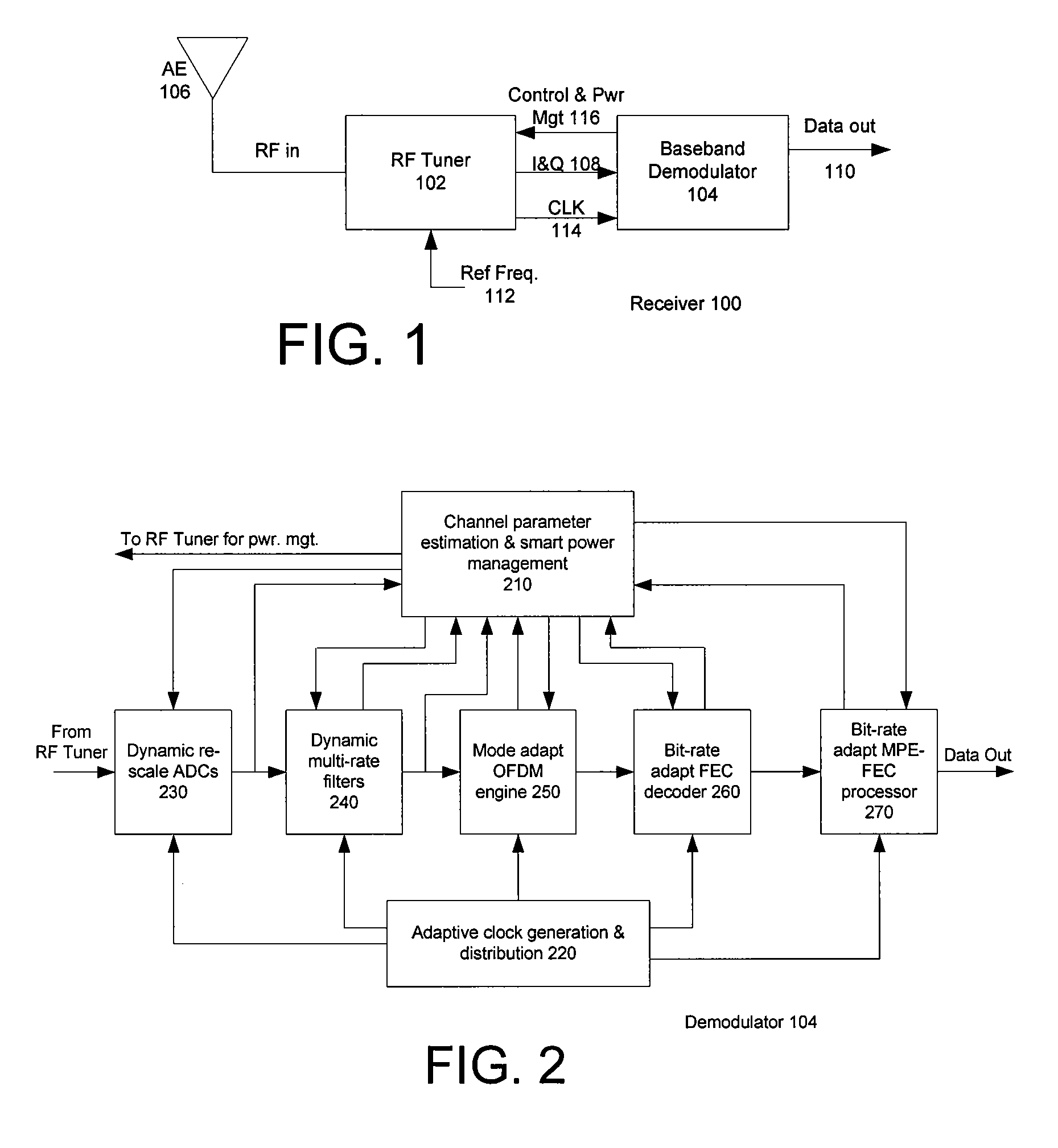
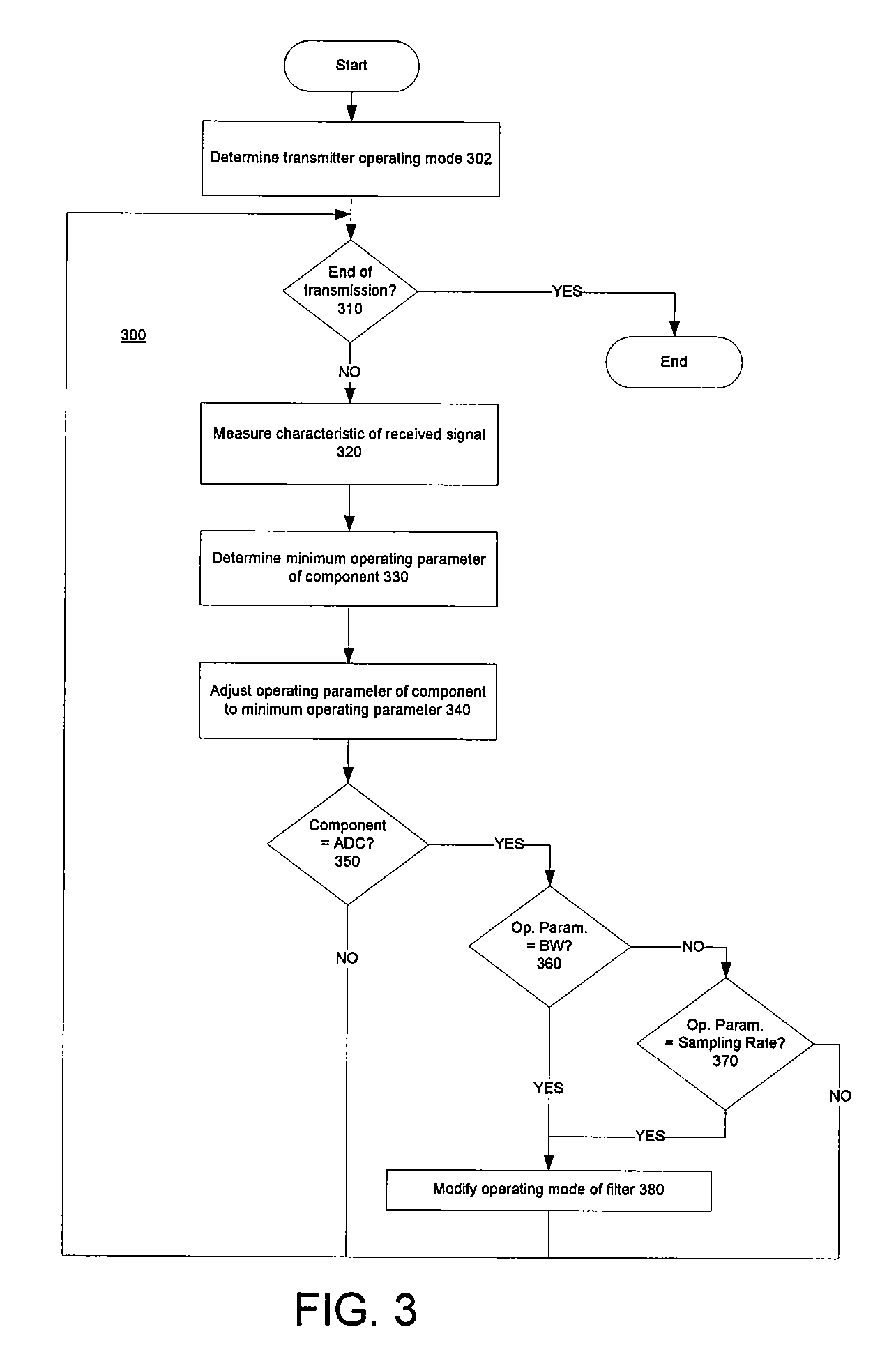
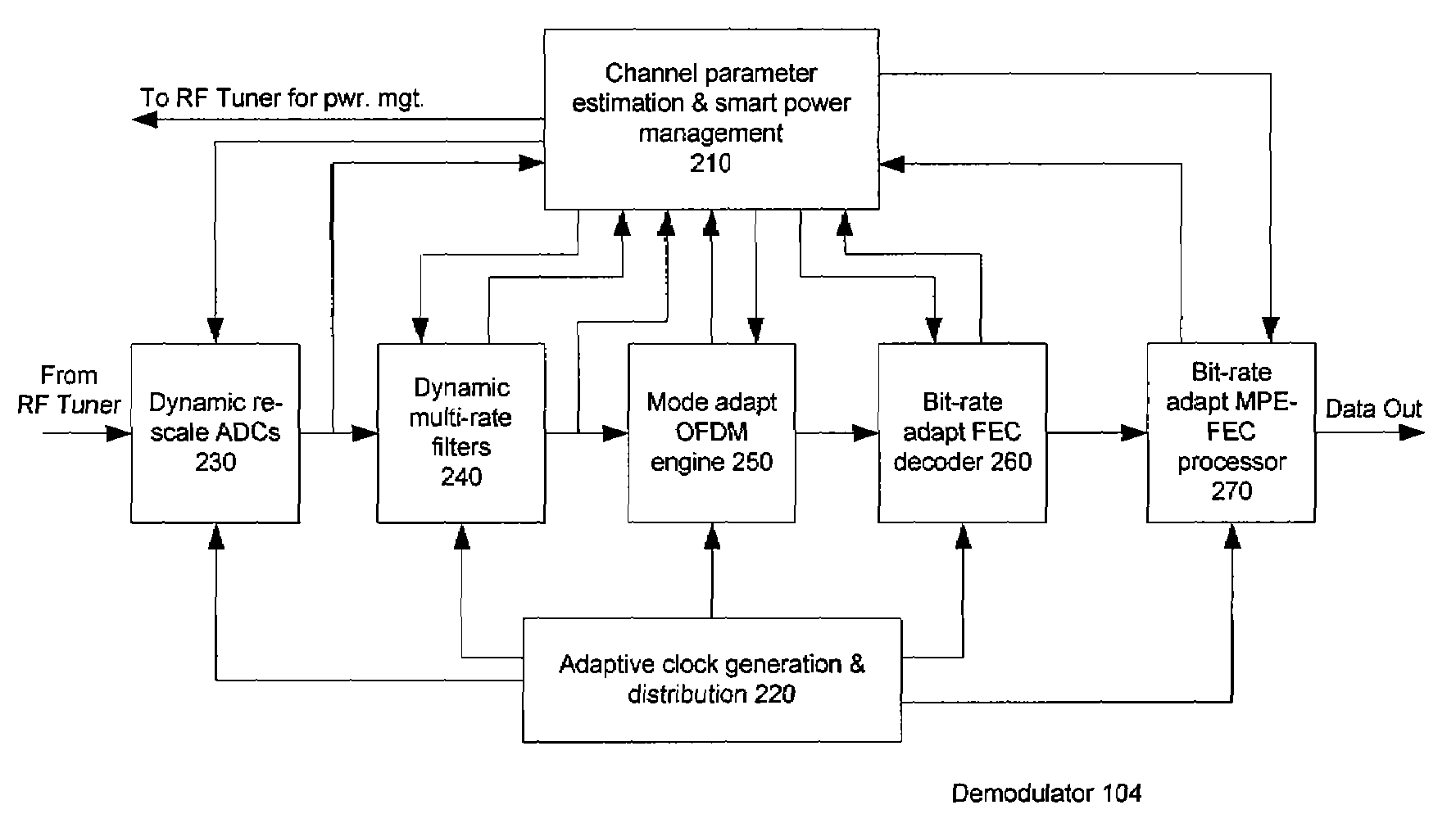
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention provide a method for dynamically controlling power consumption in a digital demodulator circuit by varying clock rates and bit widths of demodulator components including an analog to digital converter, decimation filter, OFDM operating engine, FEC decoder, and MPE-FEC processor, according to parameters and conditions of the received signal including modulation mode, signal to noise ratio, effective bit transmission rate, bit error rate, packet error rate, adjacent channel interference, and co-channel interference.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
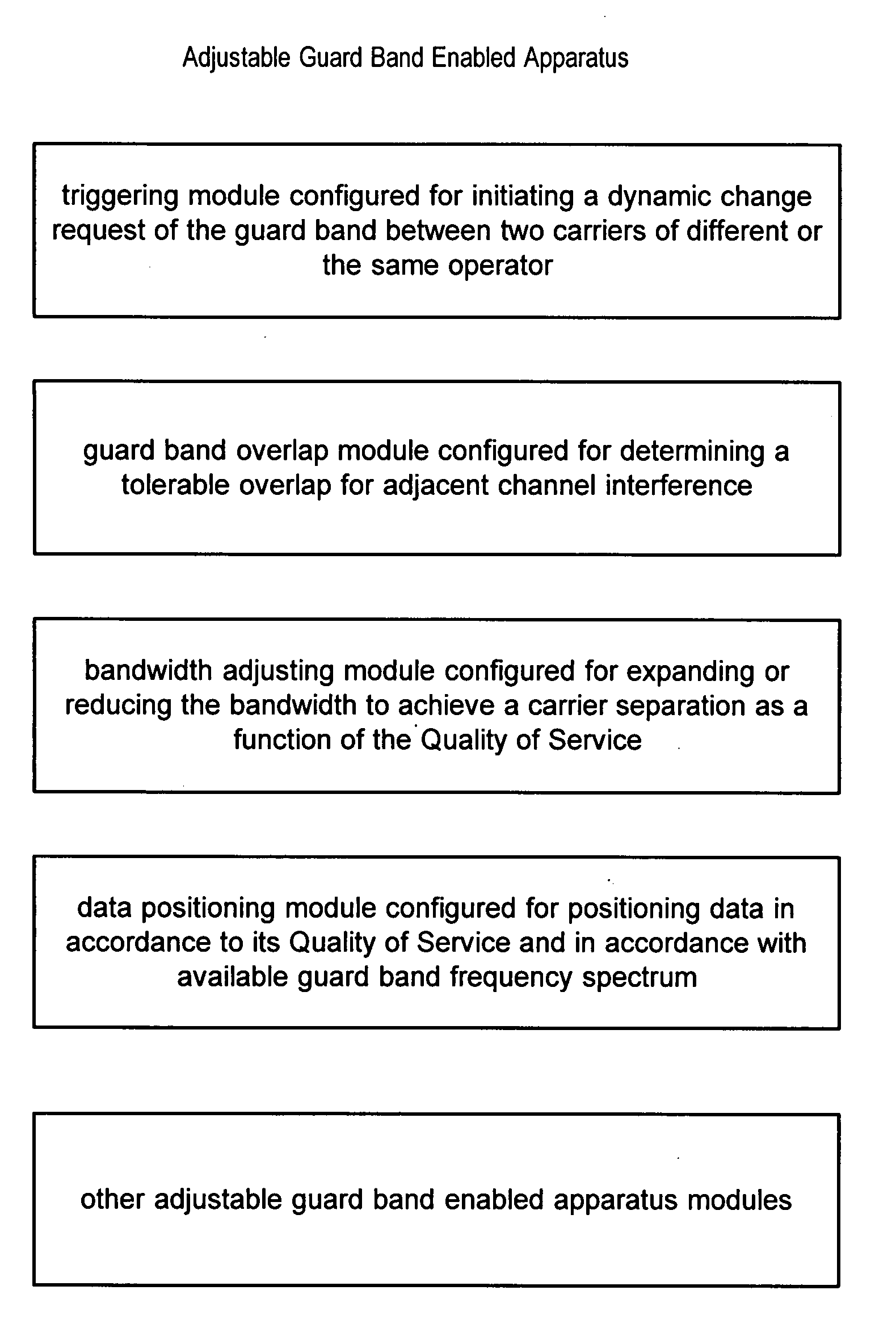
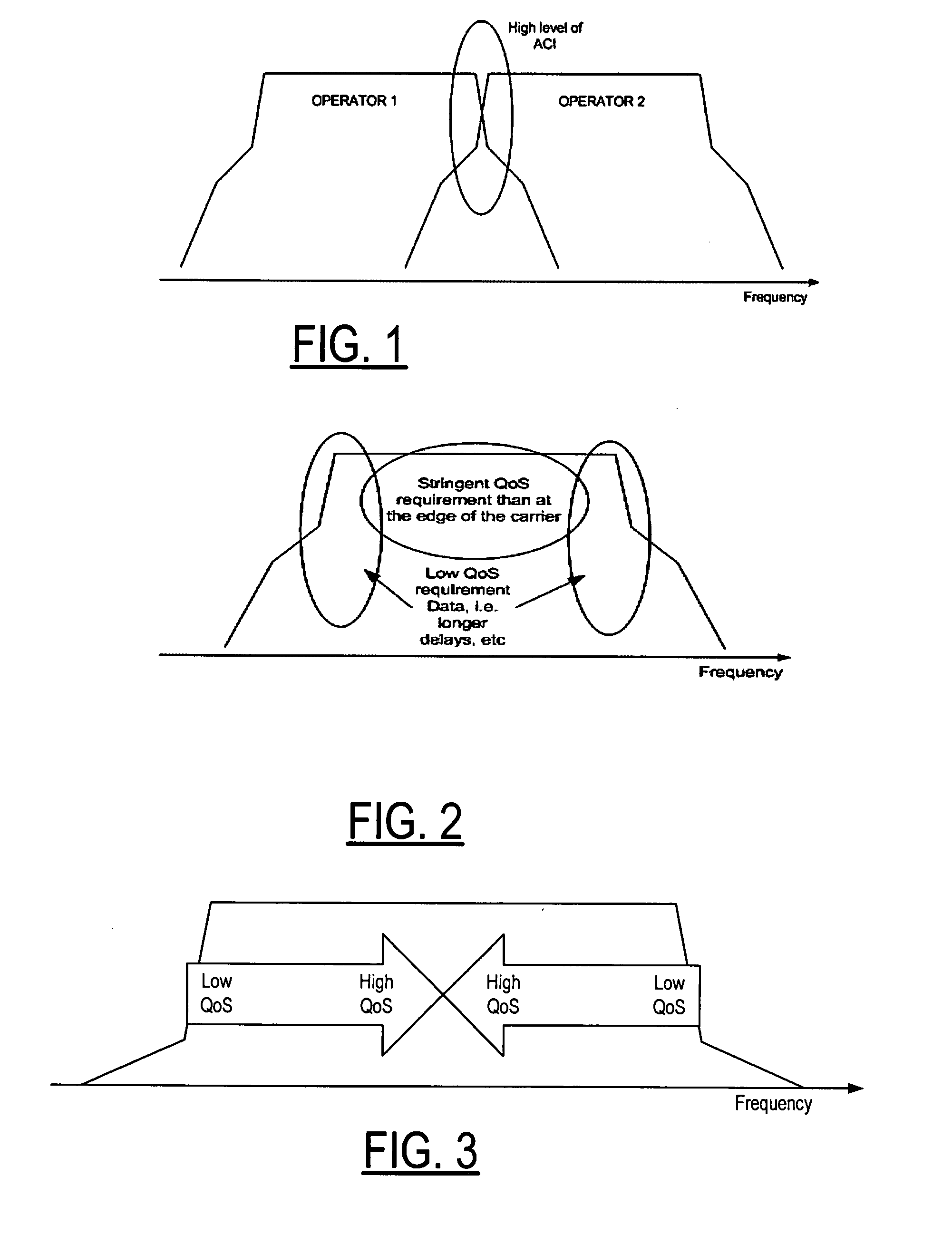
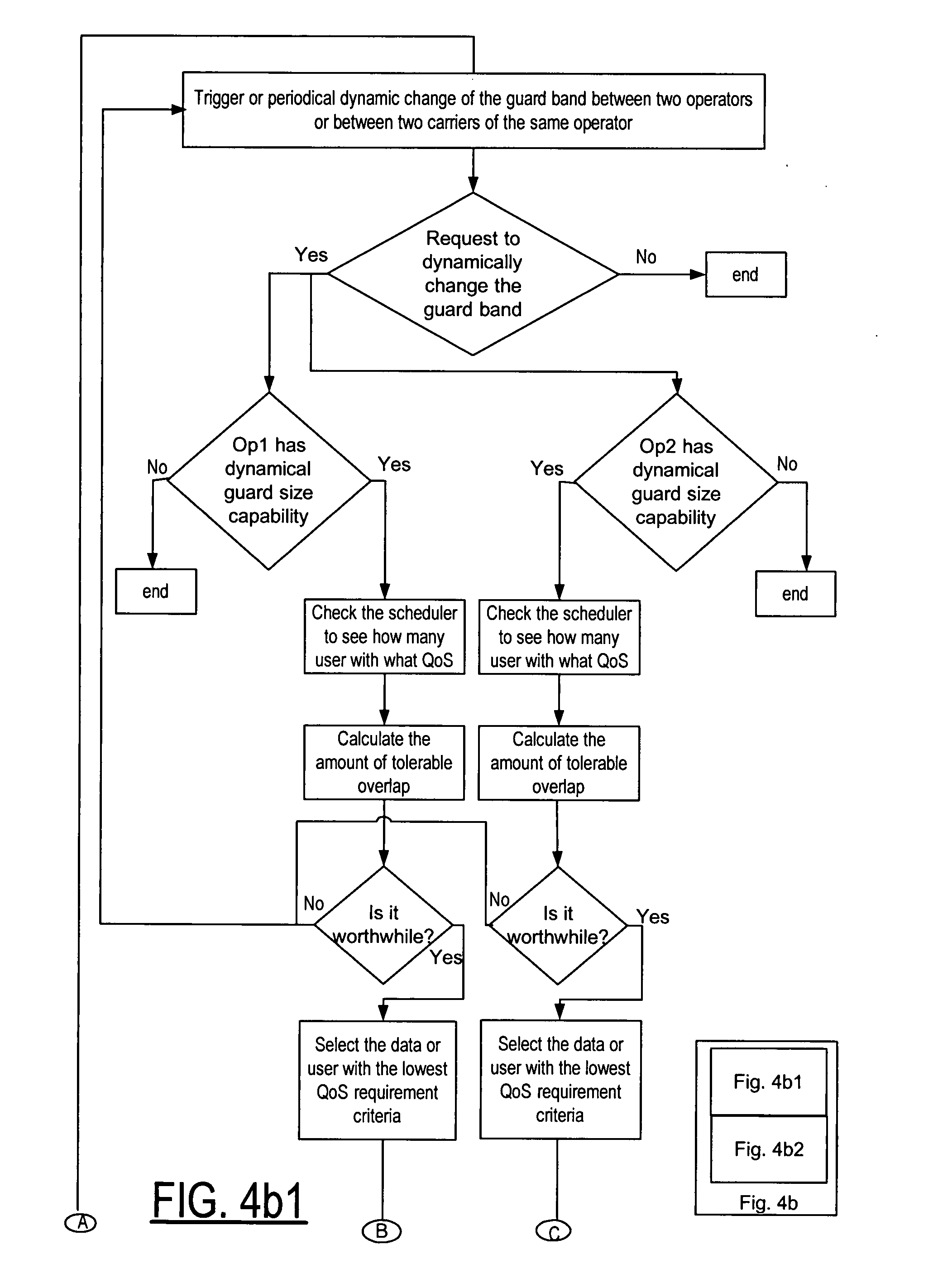
Method and apparatus for adjusting guard band size between two carriers by quality of service data positioning in the spectrum band
InactiveUS20080070586A1Reduce adjustmentMinimize impactTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCarrier signalAdjacent-channel interference
The guard band between two carriers of the same or different operators is reduced or dynamically adjusted by initiating a dynamic change request of the guard band between the two carriers to allow for flexible spectrum use by adjusting the tolerable guard band overlap. The data is distributed or positioned in the carrier spectrum band as a function of the Quality of Service so that the lowest Quality of Service constrained data are positioned at the edges of the carrier spectrum band and the highest Quality of Service constrained data are positioned in the middle of the carrier spectrum band to minimize any impact from the increased adjacent channel interference due to the guard band overlap and narrower guard band.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
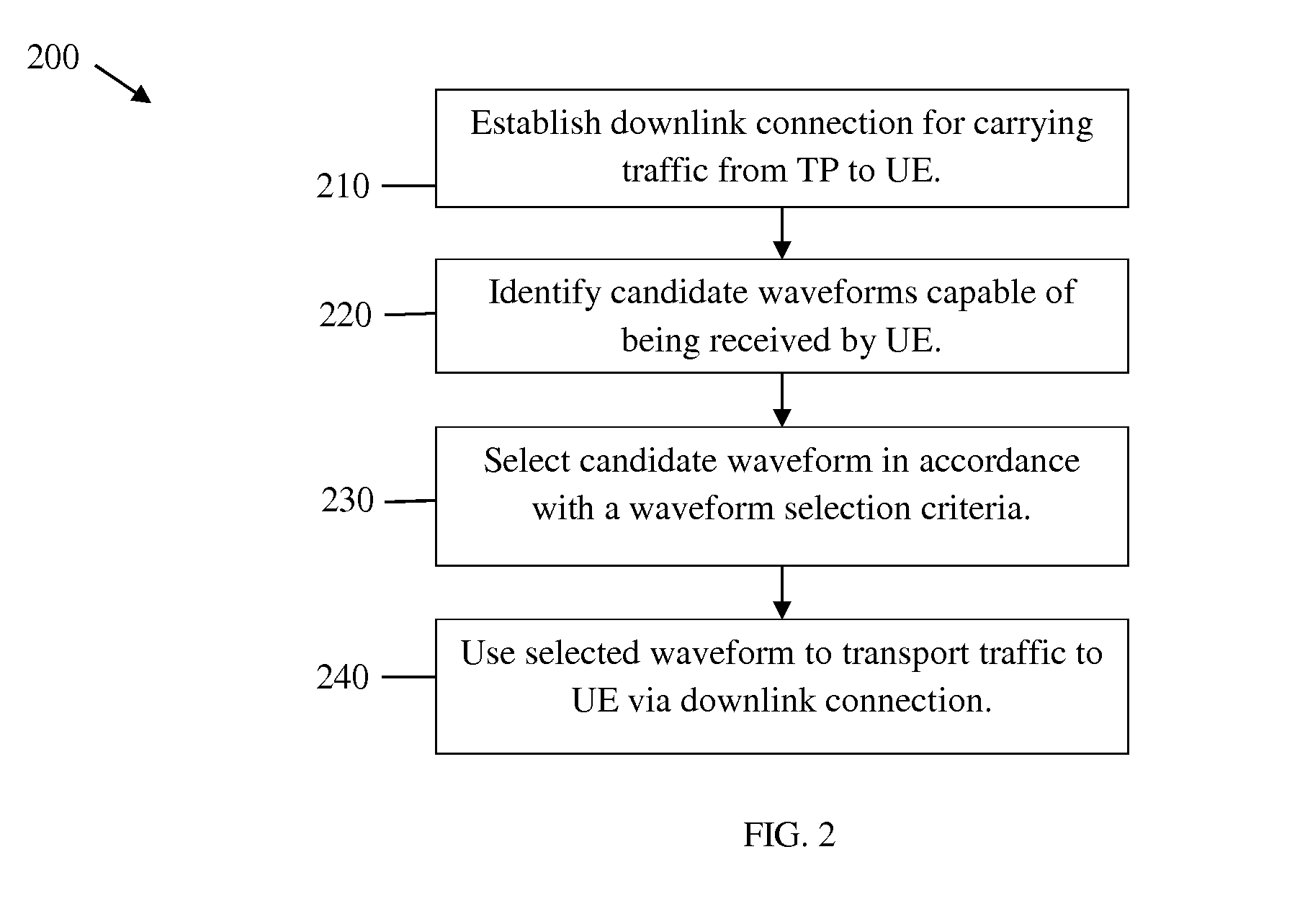
Systems and Methods for Waveform Selection and Adaptation
ActiveUS20140146754A1Wireless commuication servicesLink quality based transmission modificationAdjacent-channel interferenceTraffic characteristic
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for providing waveform adaptation are provided. In an example, a method is provided for identifying a plurality of candidate waveforms, and selecting one of the candidate waveforms for data transmission. The candidate waveforms may be identified in accordance with one or more criteria, such as a transmission capability of the transmitting device, a reception capability of the receiving device, a desired Peak-to-Average-Power-Ratio (PAPR) characteristic, adjacent channel interference (ACI) rejection requirements, spectrum localization requirements, and other criteria. The waveform selected for data transmission may be selected in accordance with one or more waveform selection criteria, such as traffic characteristic, application types, etc.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System for reducing adjacent-channel interference by pre-linearization and pre-distortion
InactiveUS6621340B1Reduce interferenceReduce channel interferenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAdjacent-channel interferenceAudio power amplifier
A circuit for reducing adjacent-channel interference by pre-linearizing and pre-distorting an input signal to be transmitted via a power amplifier having a non-linear transmission characteristic is disclosed. A portion of the input signal exceeding a dynamic range of the power amplifier is determined and expanded along the time axis to produce an expanded version thereof. The expanded version and the input signal are combined, such that the expanded version is subtracted from the input signal, to produce a pre-linearized signal. The circuit further has a pre-distorting unit for pre-distorting the pre-linearized signal using complex pre-distortion coefficients, such that the distortion introduced by the non-linear transmission characteristic of the power amplifier is substantially compensated for according to magnitude and phase.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
Method and system for reducing channel interference in a frame-synchronized wireless communication system
InactiveUS7177598B2Reduce channel interferenceReduce co-channel interferenceFrequency-division multiplexTransmission monitoringAdjacent-channel interferenceCommunications system
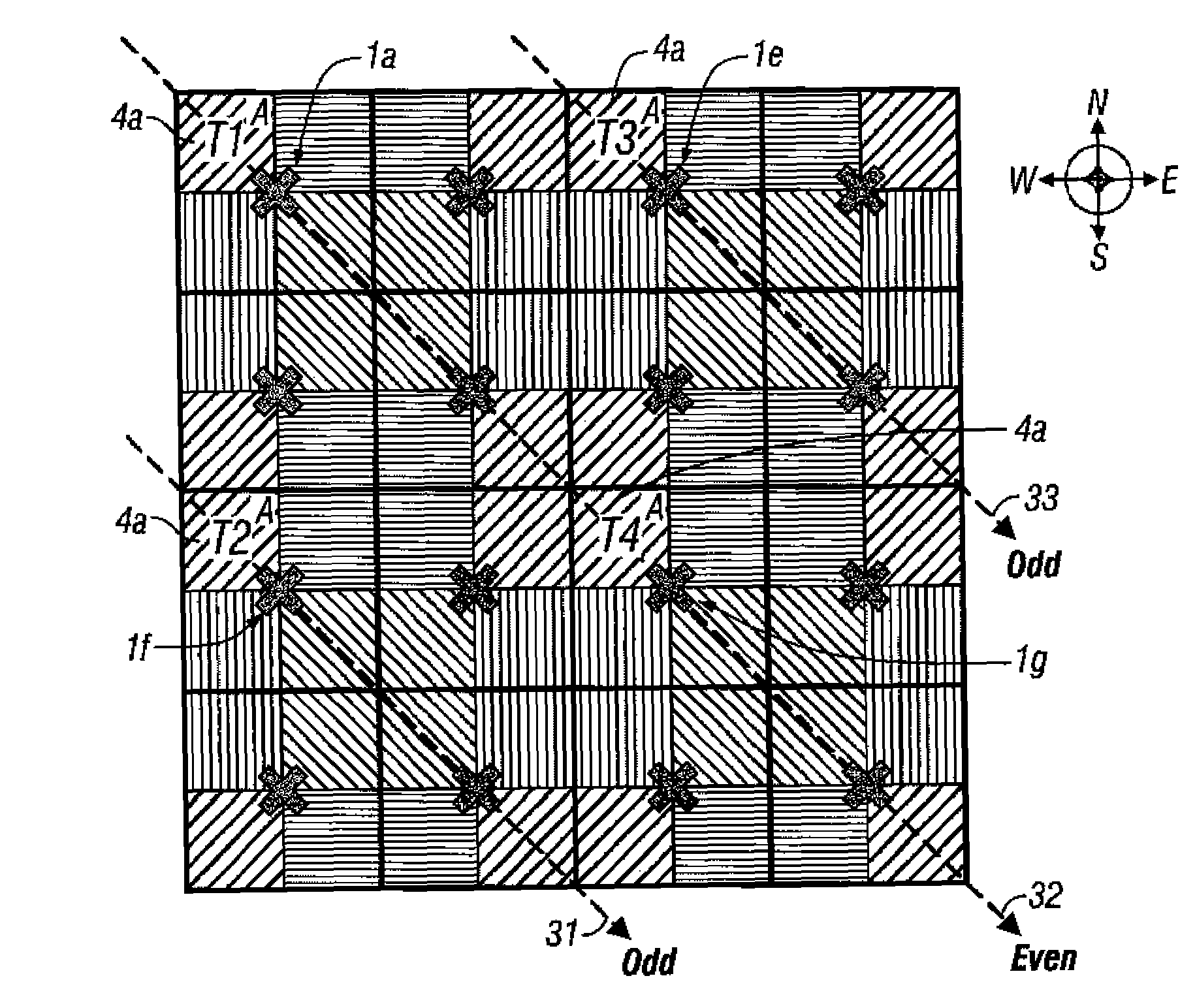
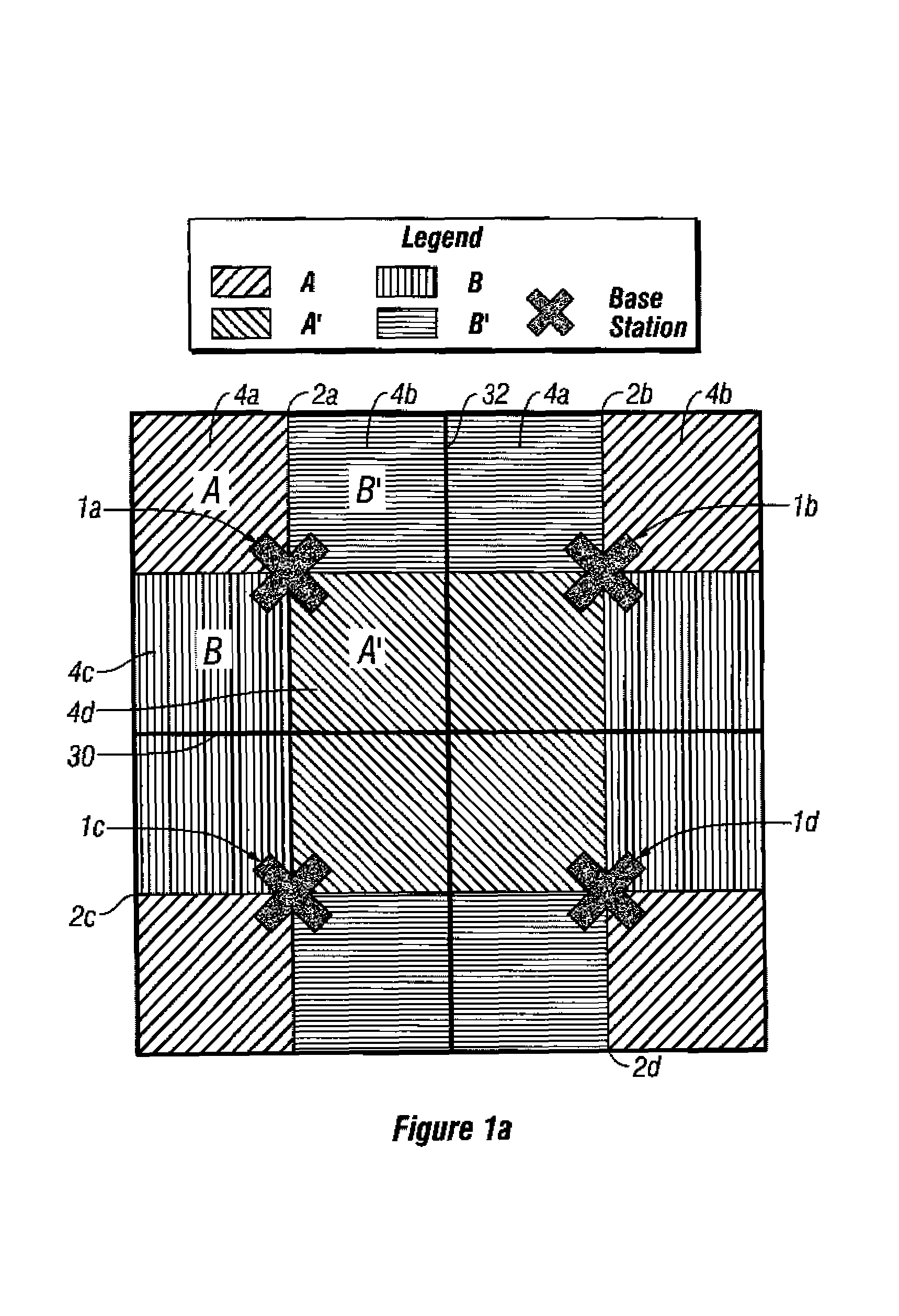
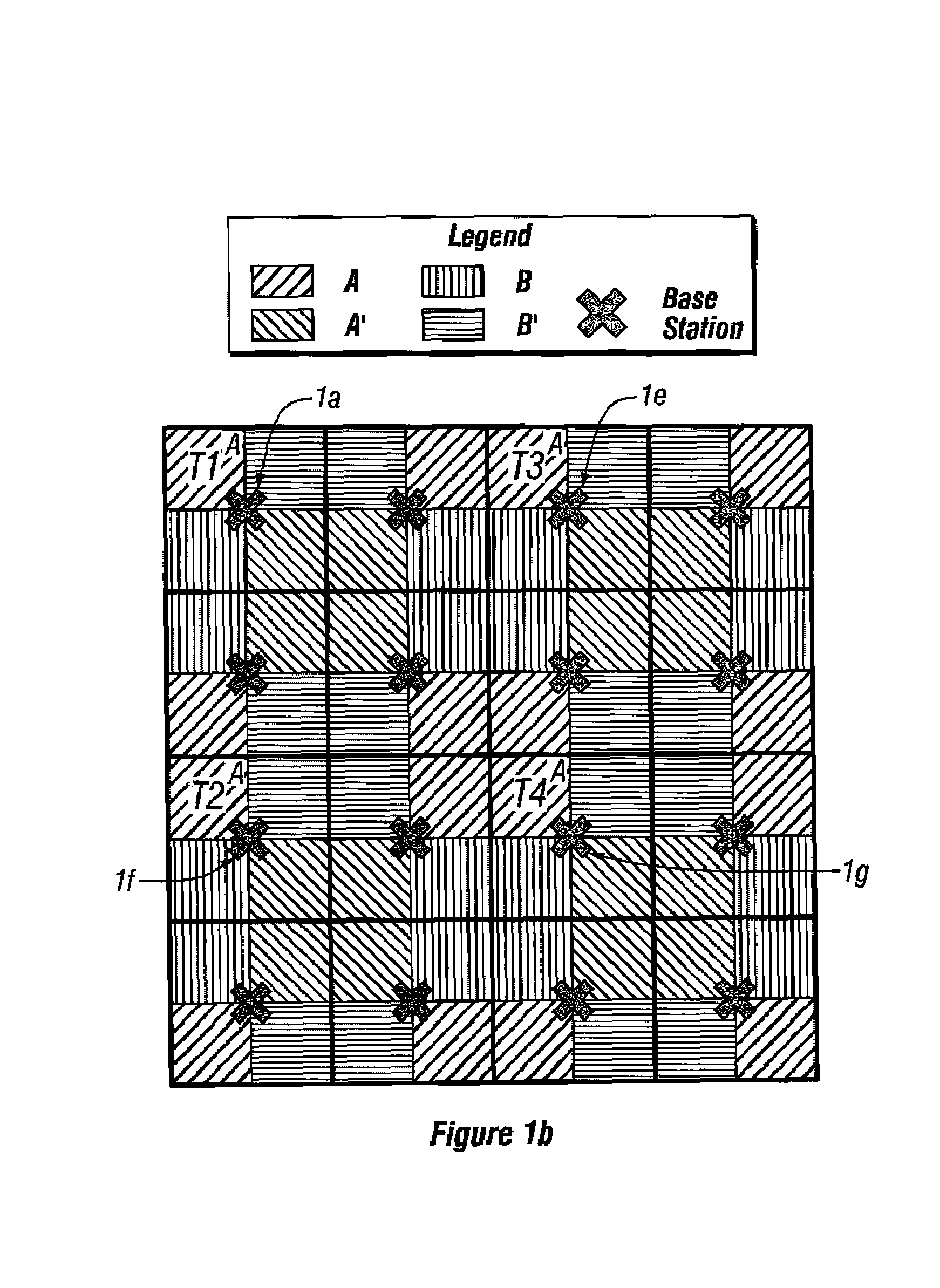
Base stations having potentially interfering terminal stations that are geographically located on the same or similar diagonal or Line of Sight (relative to the base station) operate on a first set of time frames (e.g., “even” time frames). Similarly, base stations having potentially interfering terminal stations that are not geographically located on the same or similar diagonals operate on a second set of time frames (e.g., “odd” time frames). By alternating in their use of the even and odd frames, the potential for co-channel interference between terminal stations is minimized. Systems and methods are disclosed which reduce co-channel and adjacent channel interference between terminal stations of different cells as well as adjacent channel interference between terminal stations of adjacent cells. The methods and systems so described can be used during the deployment or expansion of a communication system in a region.
Owner:WI LAN INC
System and method for reducing adjacent channel interference (ACI) in a multicarrier modulation system
InactiveUS6934246B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyReasonable power sensitivity lossError preventionTime-division multiplexAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
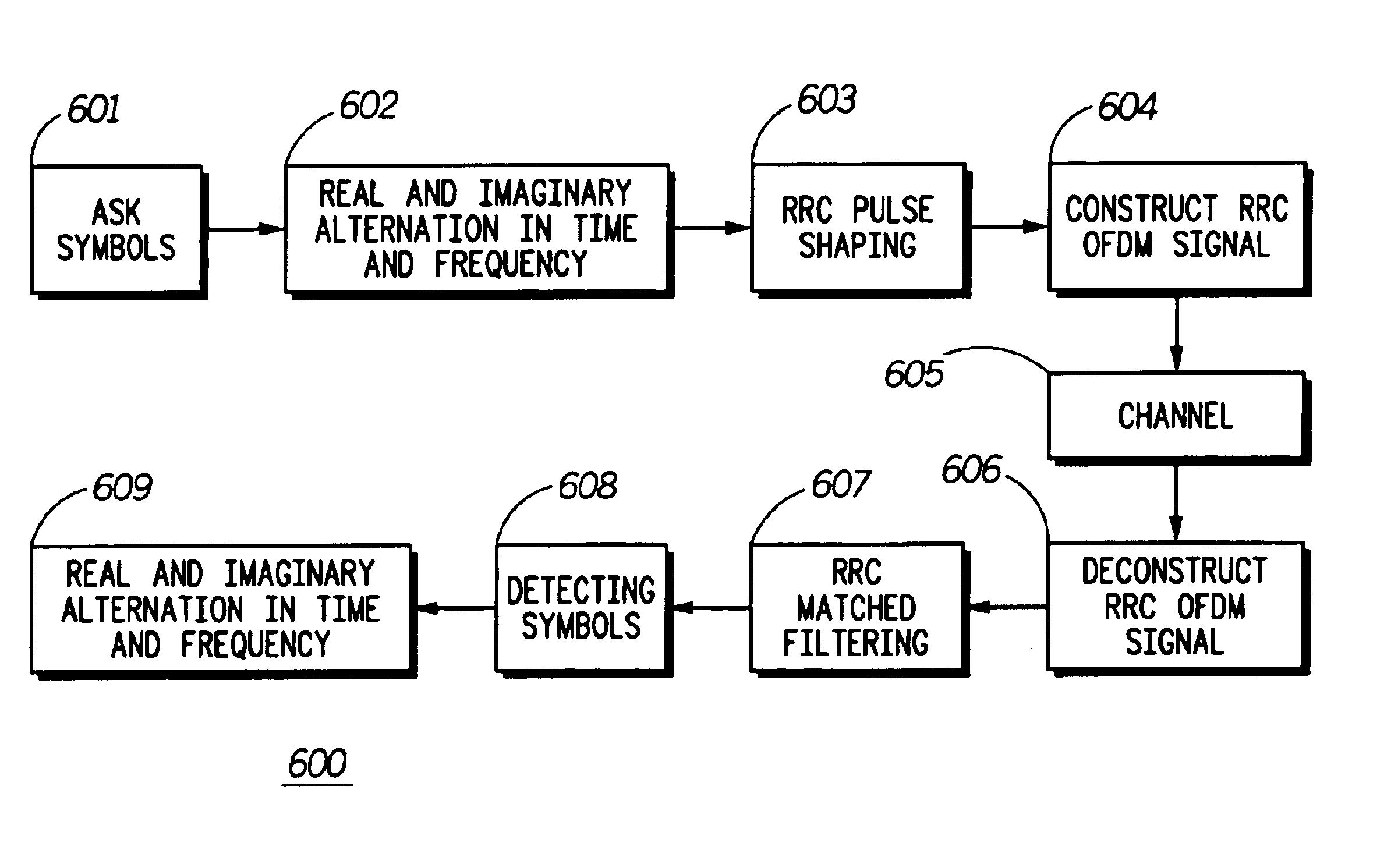
An improved multicarrier modulation system and method, which has the advantages of both isotropic orthogonal transfer algorithm orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (IOTA OFDM) and scalable advanced modulation (SAM), is introduced. The invention is root raised cosine (RRC) OFDM using the most spectrally efficient RRC filter without sacrificing the compact subchannel spacing of OFDM. The invention further provides an adjacent channel interference (ACI) suppression scheme and a modified RRC for better suppressing ACI of RRC OFDM. The ACI suppression scheme can also be applied to SAM with the modified RRC and to IOTA OFDM with a modified IOTA. The invention greatly improves a major problem of conventional OFDM namely ACI due to the use of a wide subchannel filter. Thus, the invention allows OFDM to meet even the strictest ACI requirements, which was not possible by using a conventional raised cosine windowing method.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
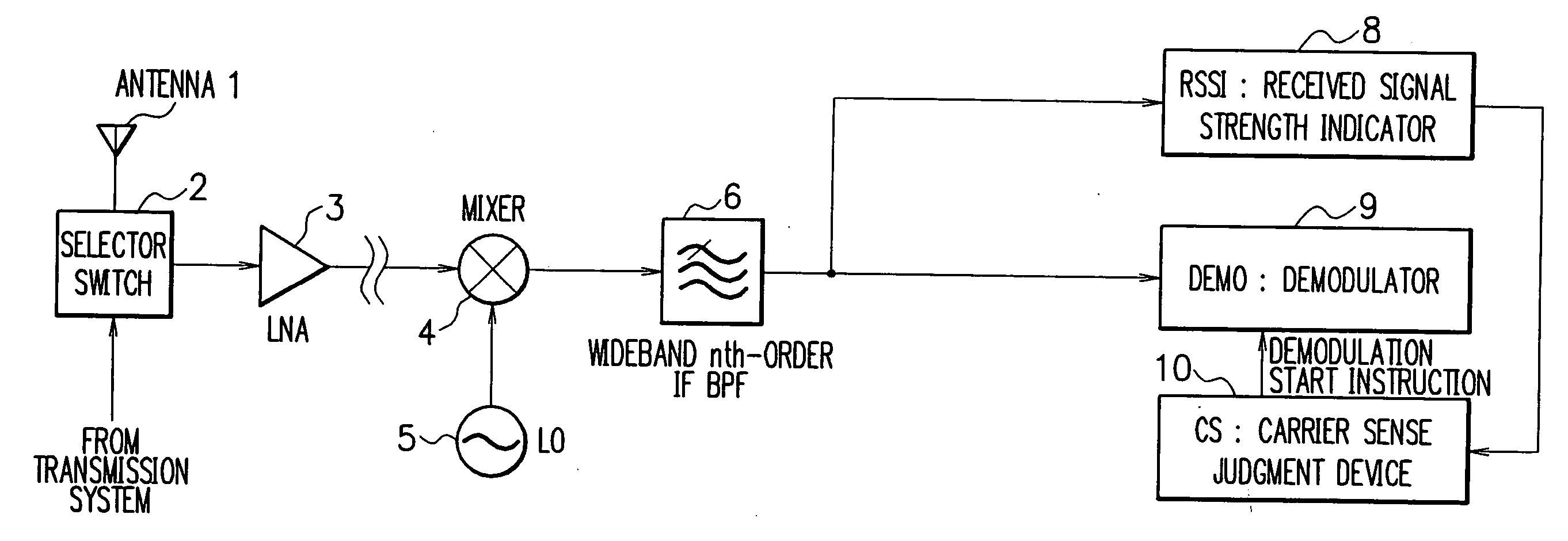
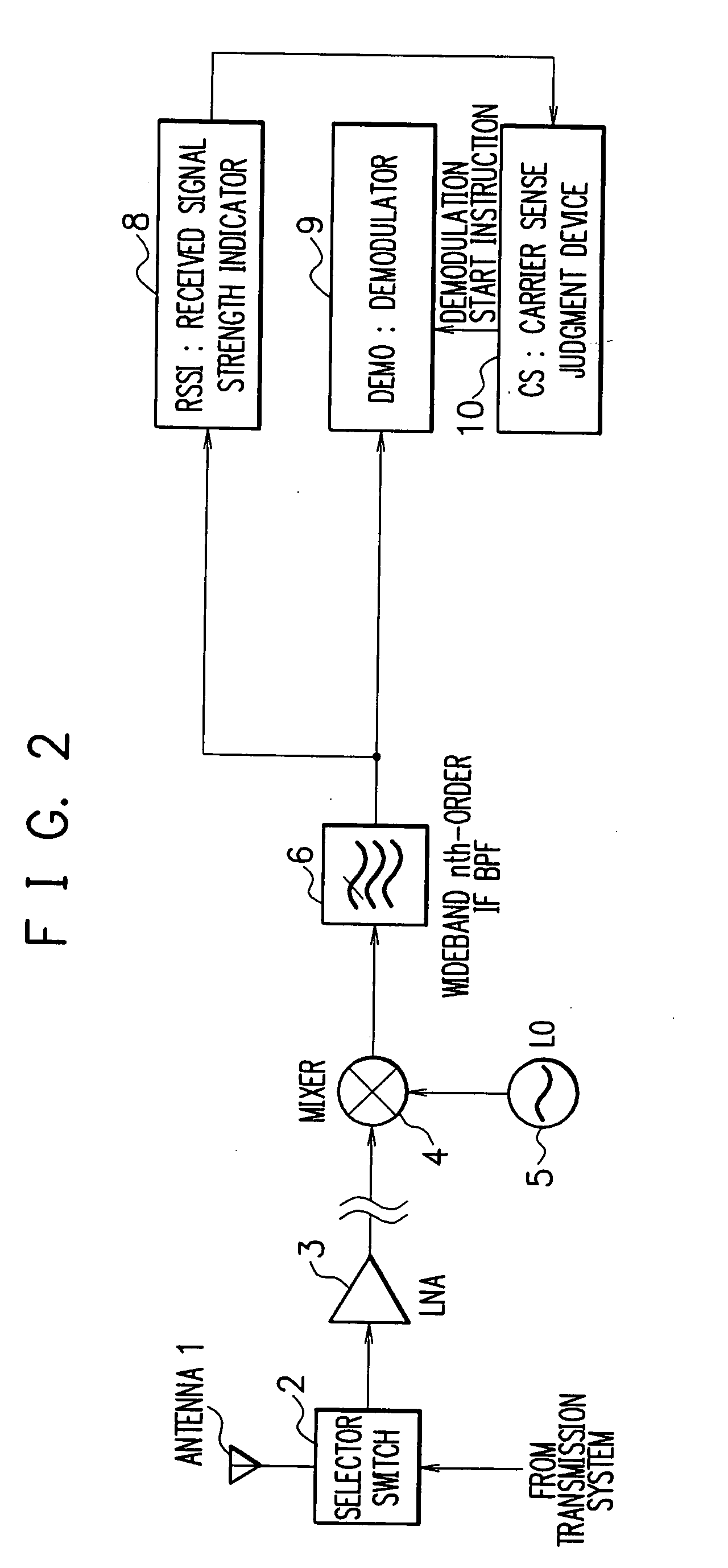
Receiver of carrier sense multiplexing connection method and interference suppressing method thereof
A broad band packet radio communication system is characterized by the carrier sense multiplexing connection method operated on a harsh frequency arrangement where an occupied band width of a modulation transmission / reception wave and a modulation side lobe are wide and the frequency channel interval is narrow. It is possible to improve the reception adjacent channel interference characteristic among a plurality of terminals belonging to the respective cells existing in the vicinity of adjacent frequency cell boundary area. The RSSI system is subjected to a narrow-band channel filtering (a narrow-band filter (BPF or LPF) having a band narrower than one-channel occupied band width) while the reception / demodulation system is subjected to a wide-band channel filtering (a wide-band filter (BPF or LPF) having a pass band equal to or wider than the one-channel occupied band width).
Owner:NEC CORP
ETC lane anti-jamming method based on multi-beam antenna
ActiveCN103268639AIncrease traffic speedAvoid interferenceTicket-issuing apparatusAdjacent-channel interferenceAnti jamming
The invention discloses an ETC lane anti-jamming method based on a multi-beam antenna. The ETC lane anti-jamming method comprises the steps that signal and position detection is carried out through the multi-beam antenna on vehicle-mounted electronic tags in an antenna communication area of a lane where the multi-beam antenna exists; when the multi-beam antenna detects that the vehicle-mounted electronic tags exist in the communication area, an orientation downlink beam is emitted to each vehicle-mounted electronic tag, each downlink beam forms an independent and relatively small communication subdomain, and concurrent communication of the downlink beams with the vehicle-mounted electronic tags is achieved through a space division multiplexing mode. According to the ETC lane anti-jamming method based on the multi-beam antenna, beam forming technology is utilized, effective communication areas for ETC trading can be regulated, an OBU accurate position of an ETC lane is detected in real time, the orientation downlink beam is regulated and emitted according to positions of the electronic tags, the concurrent communication of the downlink beams with the vehicle-mounted electronic tags is achieved through the space division multiplexing mode, and therefore the lane passage speed is improved, and meanwhile vehicles on the ETC lane are prevented from car following jamming and adjacent channel interference.
Owner:北京速通科技有限公司
Method and system for transmitting/receiving data in a communication system
InactiveUS20070287465A1Improve system performancePower managementSpectral gaps assessmentAdjacent-channel interferenceCommunications system
A method and system for transmitting and receiving data to prevent Adjacent Channel Interference (ACI) in a Cognitive Radio (CR) communication system are provided, in which a second system using a second frequency band measures a first channel interference that a first frequency band used by a first system causes to the second frequency band, determines a frequency spreading parameter according to the first channel interference, measures a second channel interference that the second frequency band causes to the first frequency band, receives link information from the first system according to the second channel interference, determines a power allocation map according to the link information and transmits and receives data according to the frequency spreading parameter and the power allocation map.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Power management in digital receivers that adjusts at least one a of clock rate and a bit width based on received signal
ActiveUS7555661B2Modulated-carrier systemsVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringCo-channel interference
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention provide a method for dynamically controlling power consumption in a digital demodulator circuit by varying clock rates and bit widths of demodulator components including an analog to digital converter, decimation filter, OFDM operating engine, FEC decoder, and MPE-FEC processor, according to parameters and conditions of the received signal including modulation mode, signal to noise ratio, effective bit transmission rate, bit error rate, packet error rate, adjacent channel interference, and co-channel interference.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
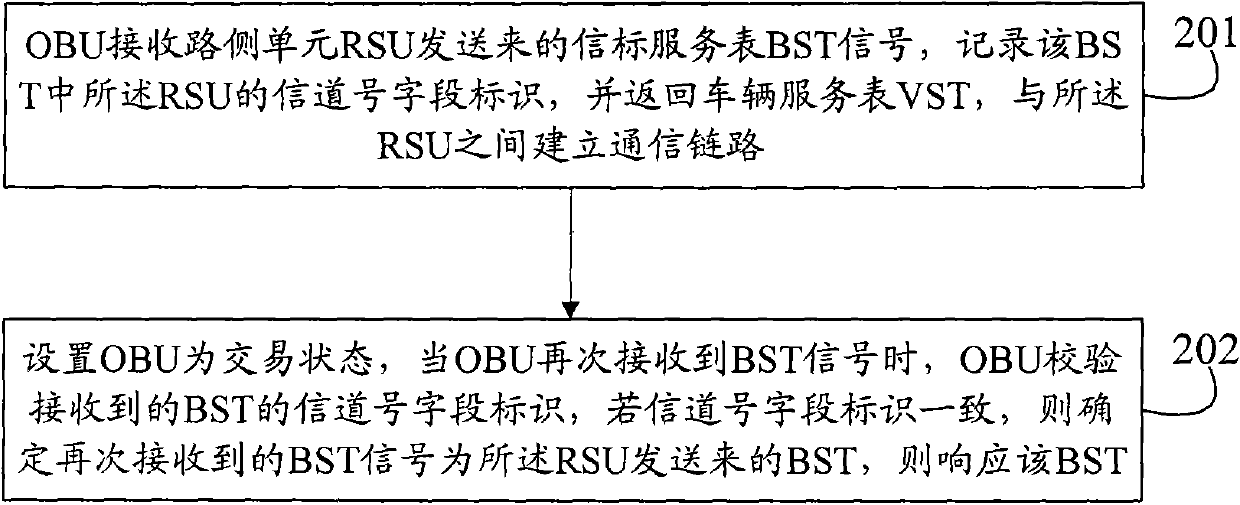
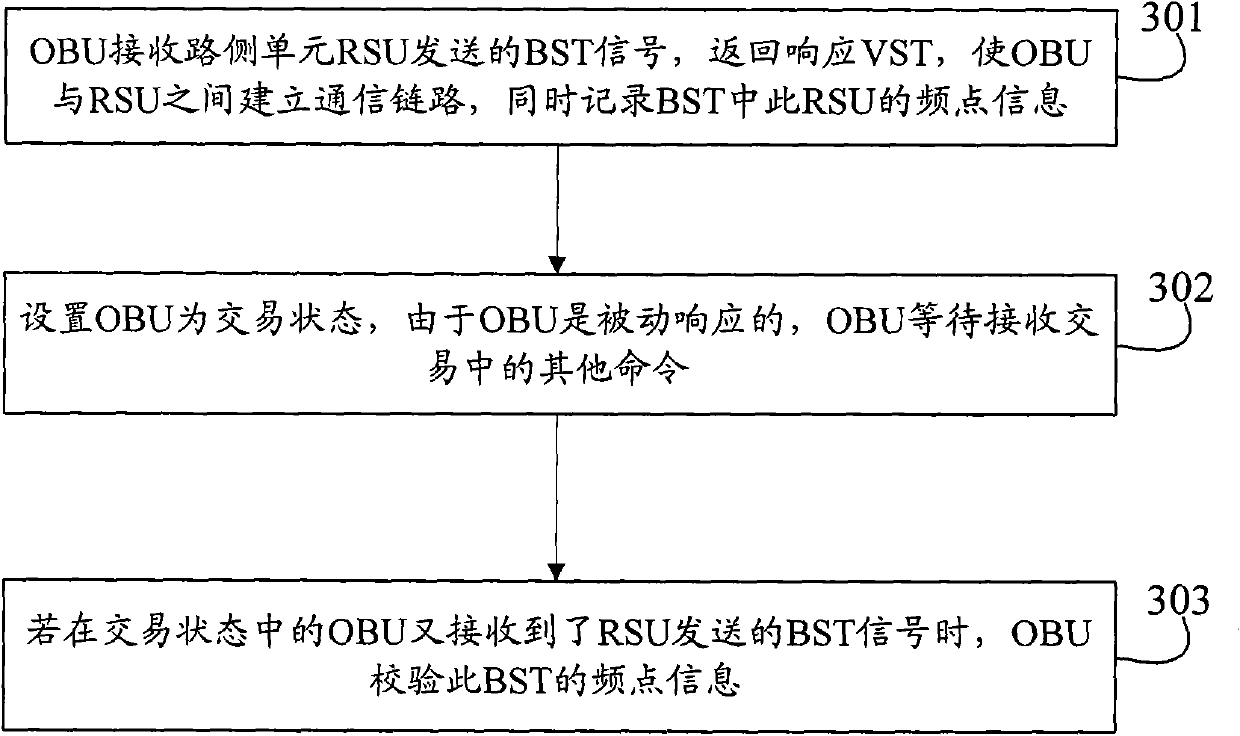
Implementation method and system for avoiding adjacent channel interference in electronic toll of collection (ETC)
InactiveCN102088705AReduce distractionsTicket-issuing apparatusConnection managementAdjacent-channel interferenceTelecommunications link
The invention discloses an implementation method and device for avoiding adjacent channel interference in electronic toll of collection (ETC). The method comprises the following steps that: an on-board unit (OBU) receives a beacon service table (BST) signal transmitted by a road-side unit (RSU), records a channel number field identifier of the RSU in the BST and establishes a communication link with the RSU, wherein RSUs of adjacent lanes are provided with different channel number field identifiers; and when the OBU receives the BST signal once again in an area covered by an RSU antenna, the OBU verifies a channel number field identifier in the BST, determines that the BST signal which is received once again is transmitted by the RSU if the channel number field identifier is consistent with the recorded channel number field identifier, and completes charging operation with the RSU in response to the BST signal which is received once again. After the method and the device are adopted, two communicating parties are arranged at the same fixed frequency point during a transaction between the RSU and the OBU, so that the probability of adjacent channel interference is effectively lowered.
Owner:ZTE CORP
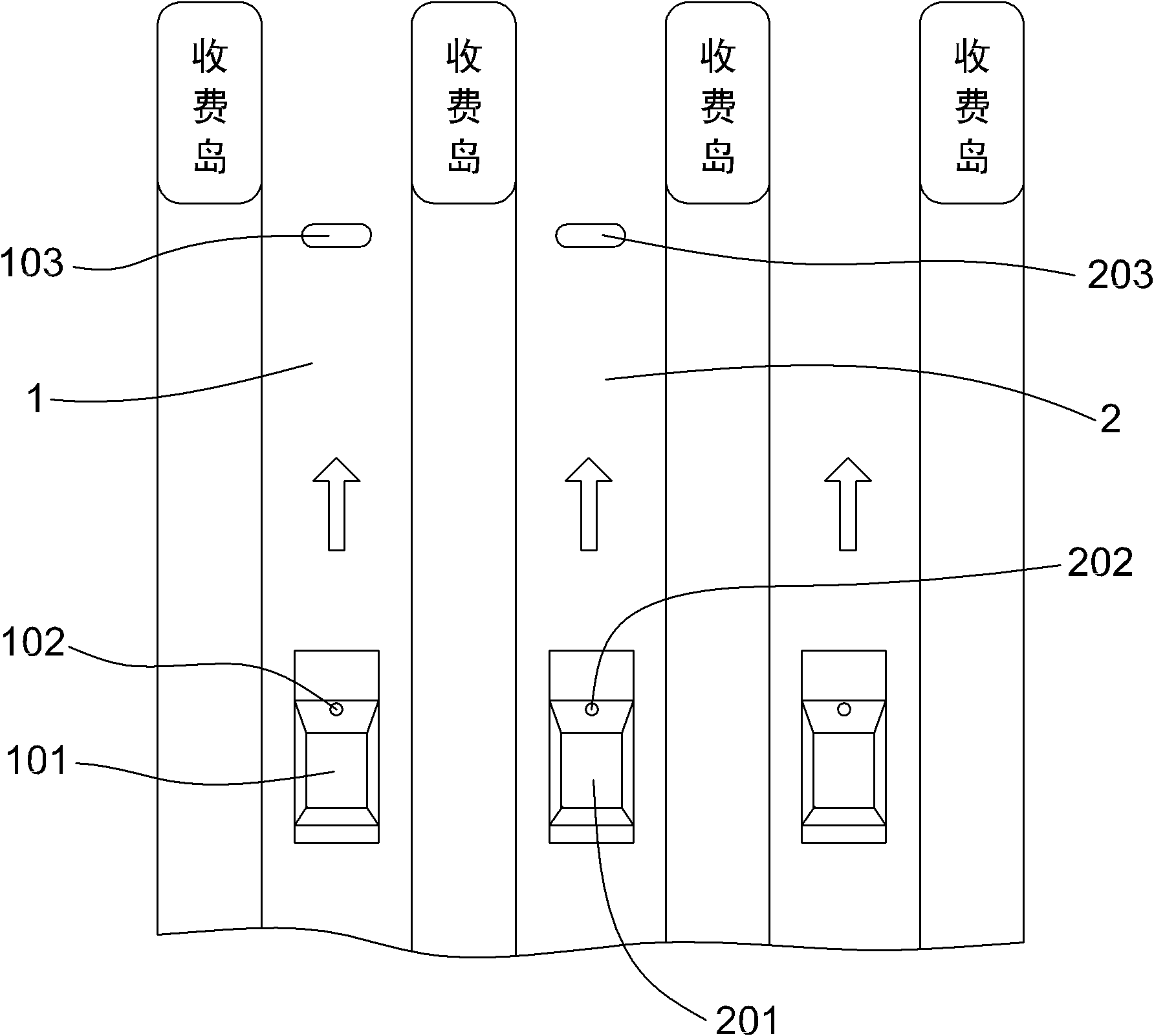
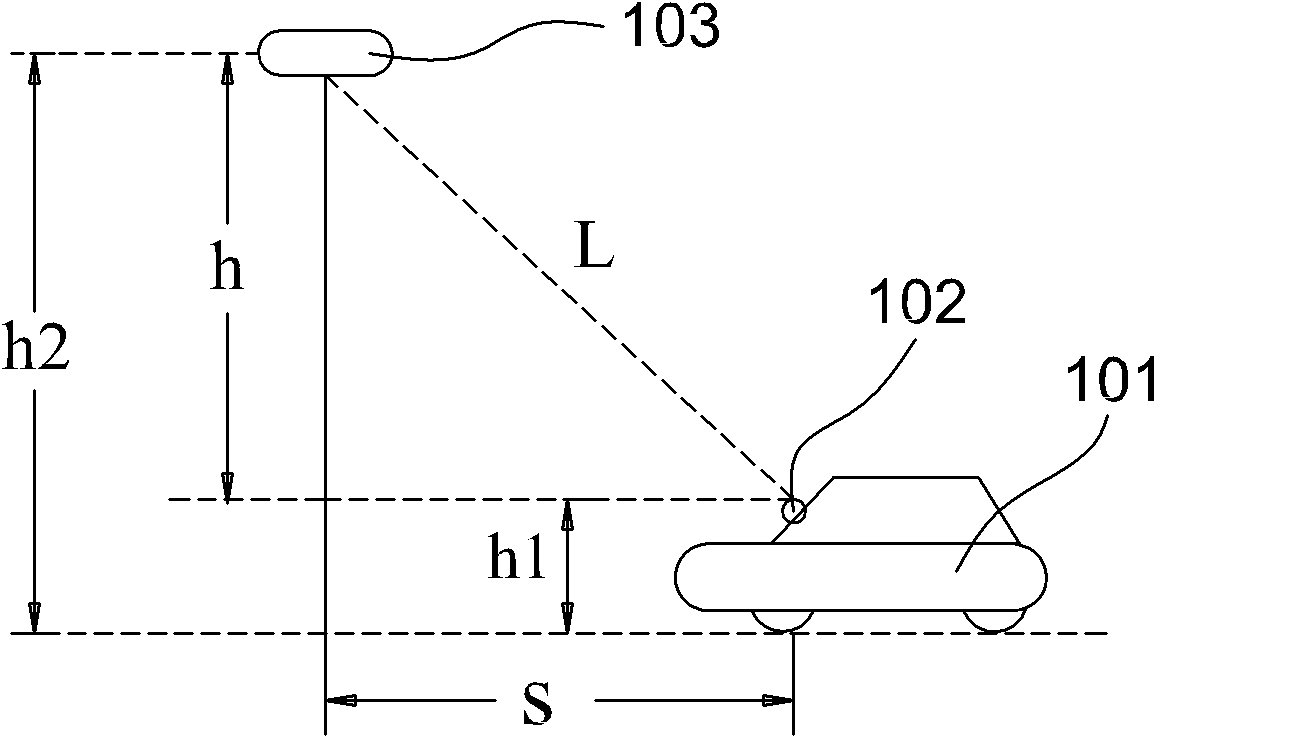
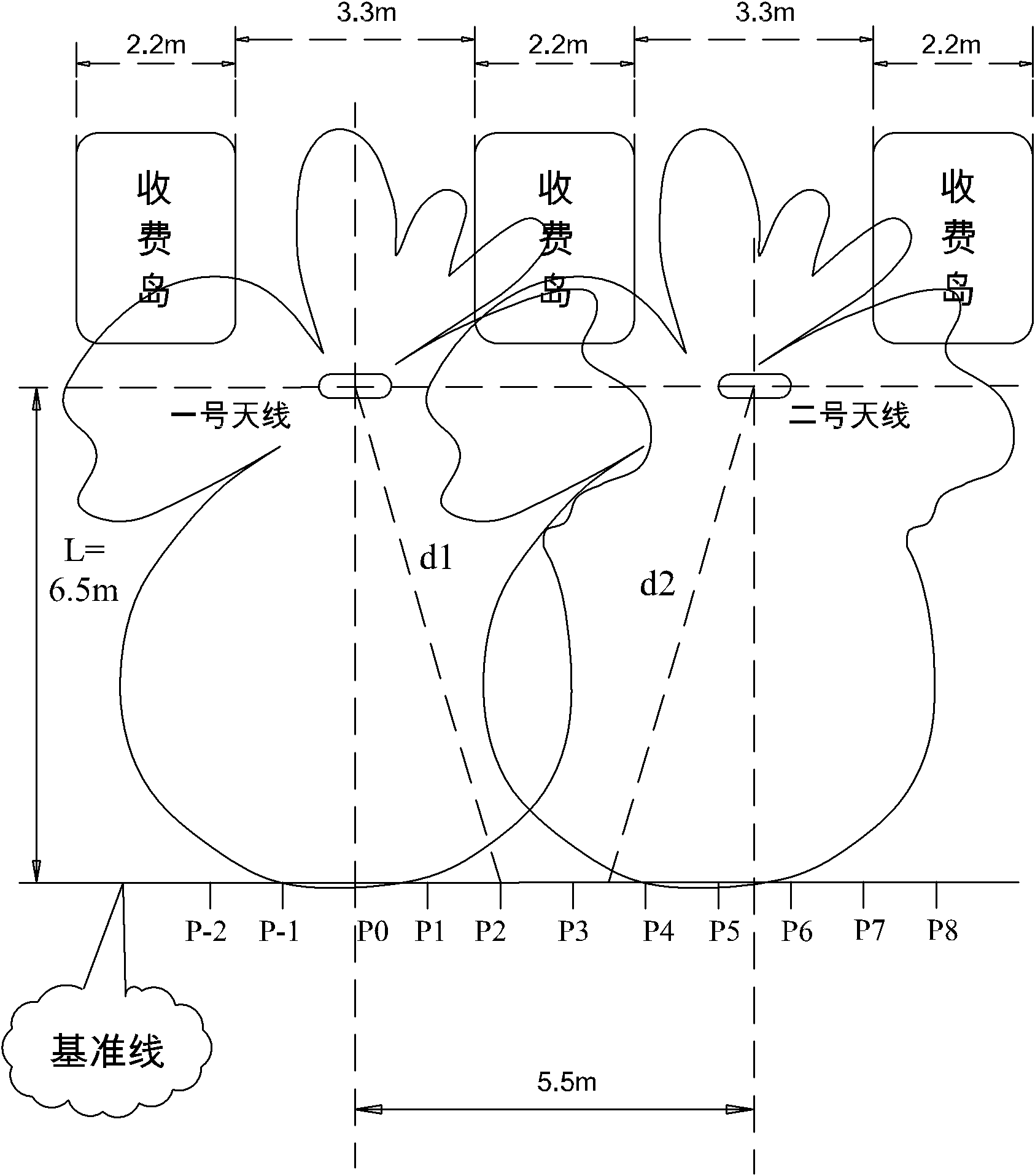
Method for solving problem of adjacent channel interference through multi-antenna co-location
ActiveCN102045122AAvoid communicationEliminate adjacent channel interferenceSpatial transmit diversityTicket-issuing apparatusAdjacent-channel interferenceInterference problem
The invention discloses a method for solving a problem of adjacent channel interference through multi-antenna co-location, and the method is applied to parallelly-arranged ETC (electronic toll collection) antenna systems. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dividing scaling points; 2, calculating the distances between the scaling points and No.1 and No.2 antennas; 3, determining the basic link transmission losses of the No.1 antenna and the No.2 antenna relative to the scaling points; 4, theoretically calculating an uplink signal strength value of each scaling point received by a No.1 antenna receiver; 5, theoretically calculating an uplink signal strength value of each scaling point received by a No.2 antenna receiver; 6, adjusting the uplink signal strength value of each scaling point received by the No.1 antenna receiver through actual measurement so as to obtain a reference value; 7, adjusting the uplink signal strength value of each scaling point received by the No.2 antenna receiver so as to obtain a reference value; and 8, through carrying out matched fitting with the reference values, determining the position of a vehicle. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the problem of adjacent channel interference can be solved, and the reliability of the ETC antenna system can be improved.
Owner:北京速通科技有限公司
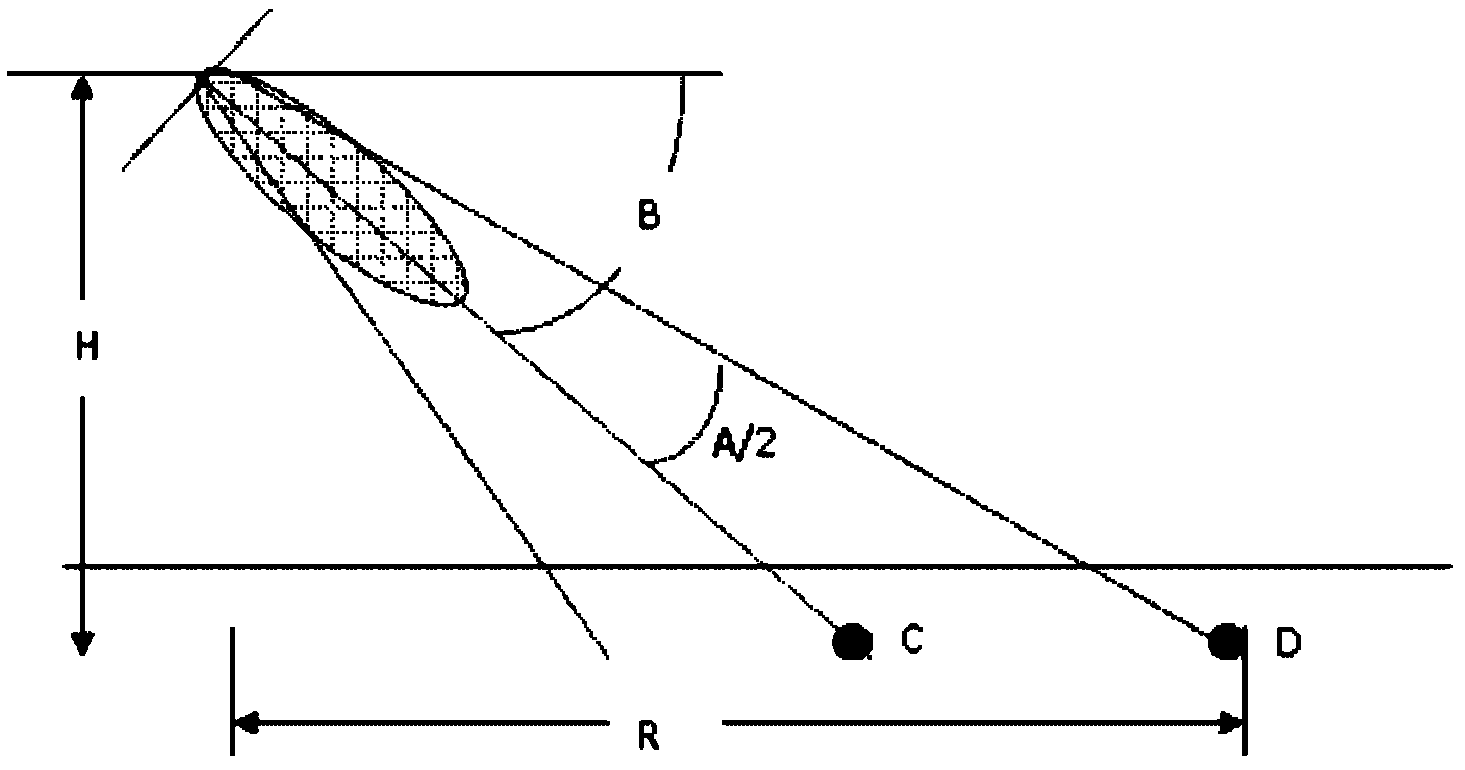
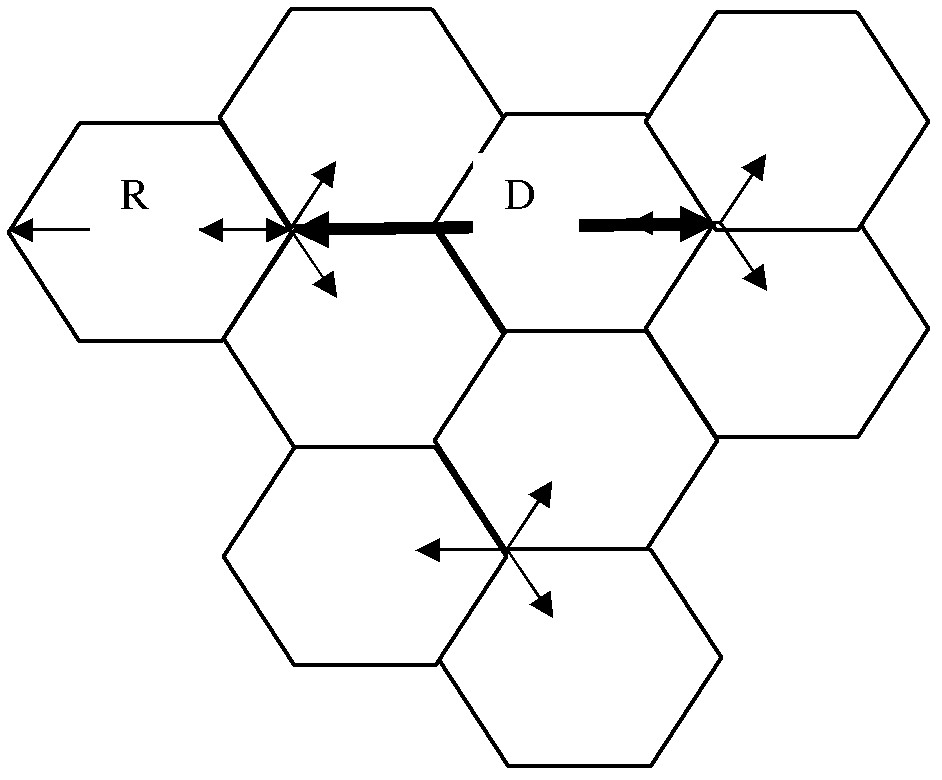
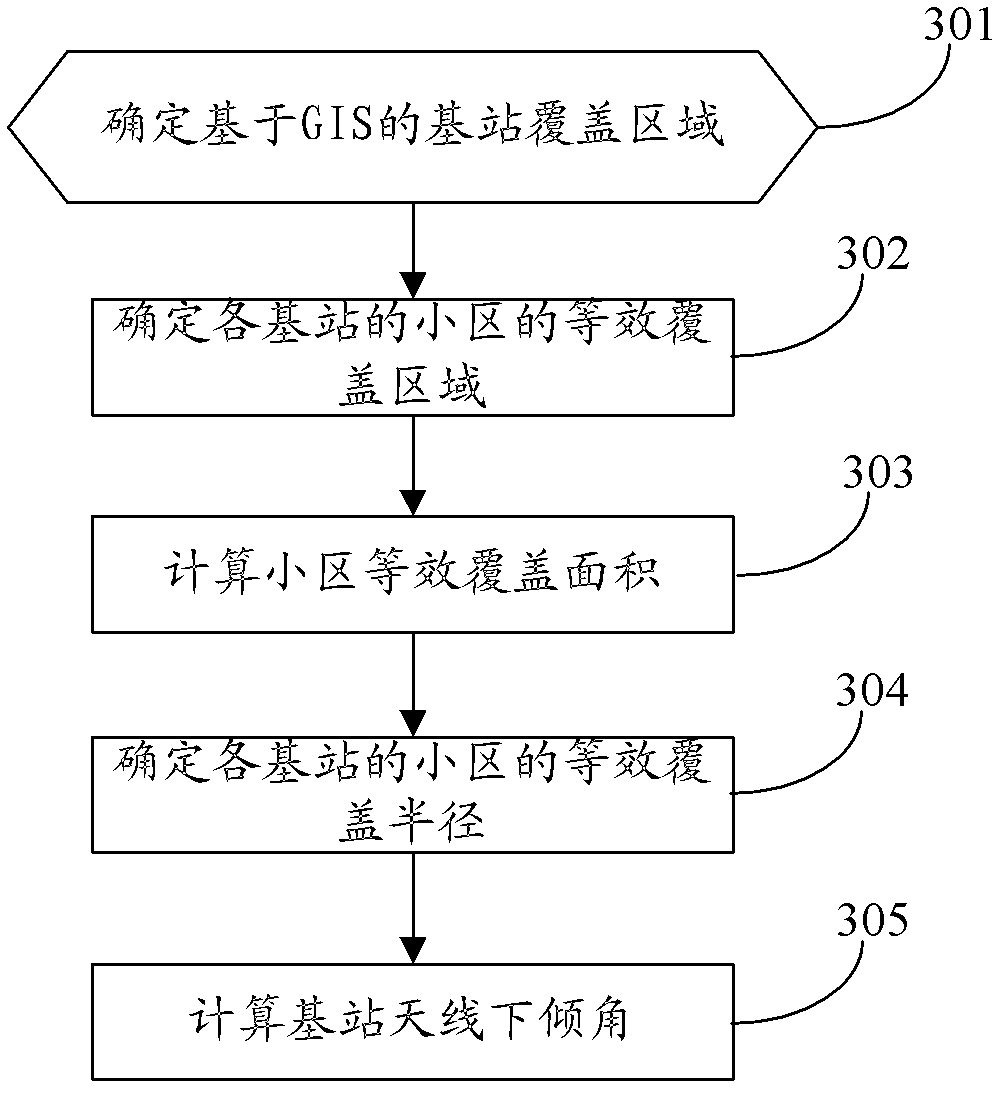
Antenna downward inclination angle determination method and device based on geographic information system (GIS)
ActiveCN103188693AAvoid overlapping coverageAvoid throughput drop issuesNetwork planningAdjacent-channel interferenceTime-Division Long-Term Evolution
The invention discloses an antenna downward inclination angle determination method and device based on a geographic information system (GIS). The method comprises the following steps: determining an equivalent coverage radius of a cell of each base station according to base station location information in the GIS and the Thiessen polygon principle and determining a maximum coverage radius of the cell of each base station according to an application scene which the cell of each base station is located in; when the equivalent coverage radius is ascertained to be smaller than or equal to the maximum coverage radius, determining the antenna downward inclination angle of the base station which the cell belongs to based on the equivalent coverage radius; and when the equivalent coverage radius is ascertained to be larger than the maximum coverage radius, determining the antenna downward inclination angle of the base station which the cell belongs to based on the maximum coverage radius. According to the technical scheme of the antenna downward inclination angle determination method and device based on the GIS, the problems, that handling capacity in a border cell is reduced and a resource usage ratio is low, caused by unreasonable arrangement of the antenna downward inclination angle of the base station in same-frequency networking in a time division-long term evolution (TD-LTE) system can be avoided, same and adjacent channel interference among cells can be reduced effectively and network service quality and user experience effects are improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP JIANGSU
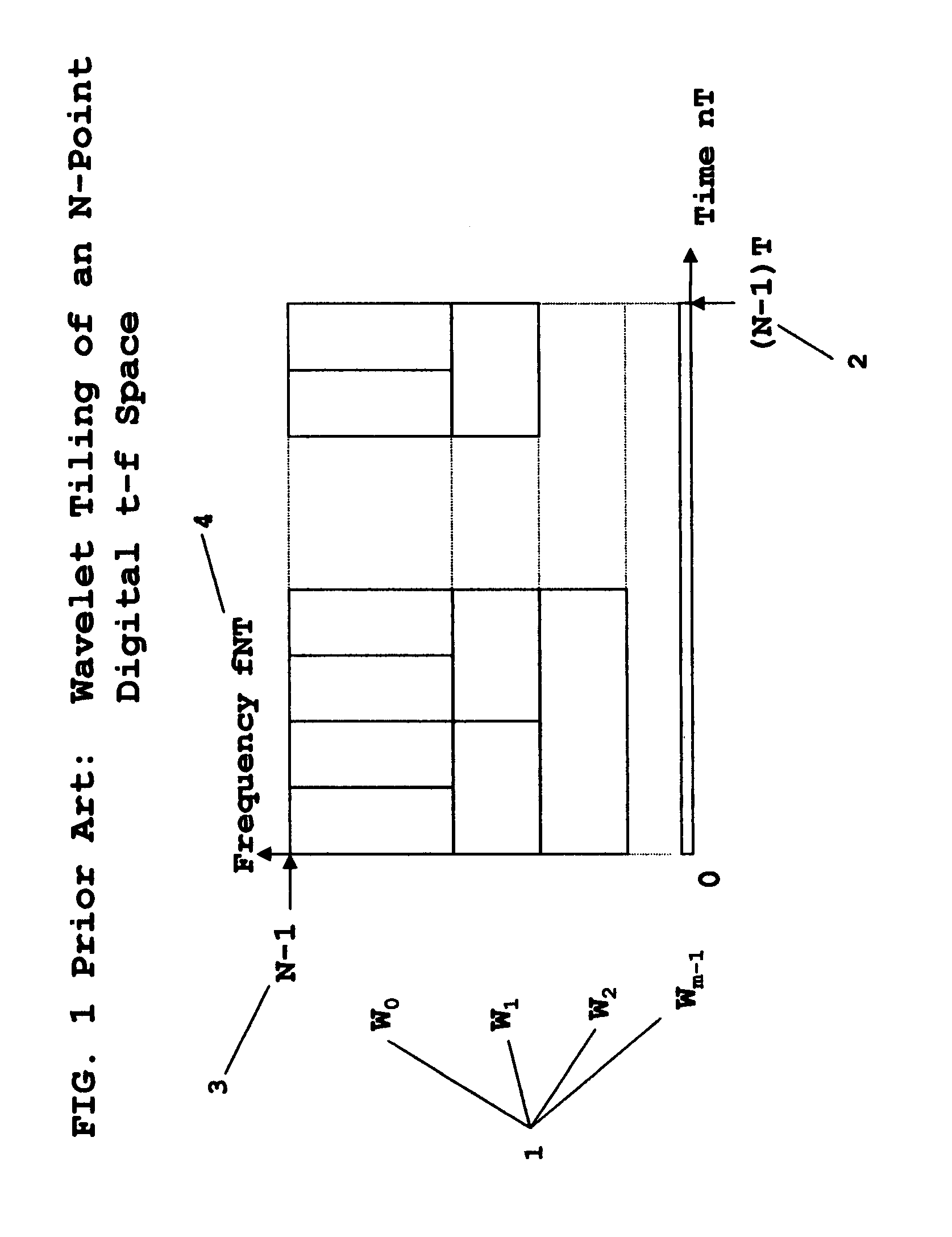
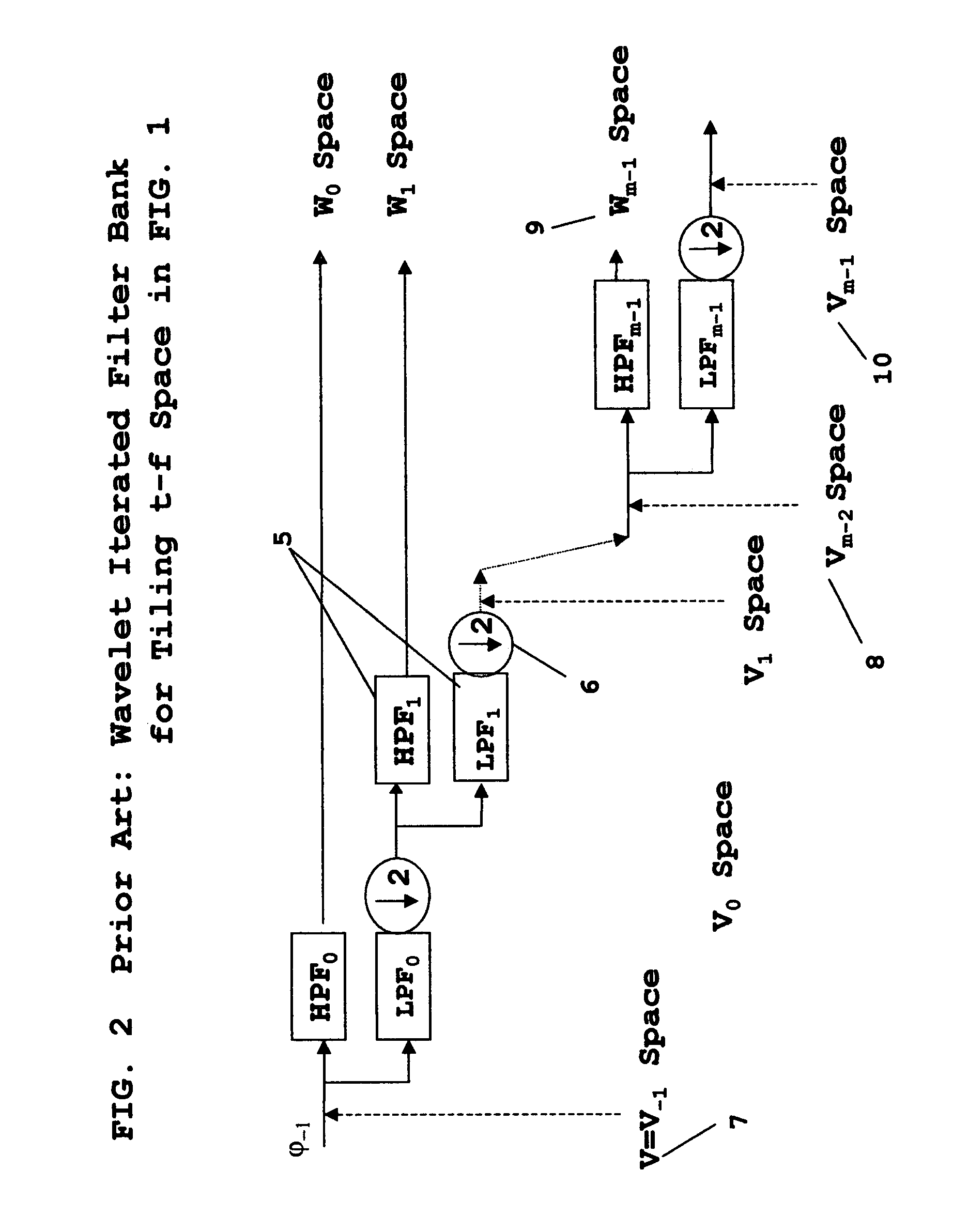
Wavelet multi-resolution waveforms
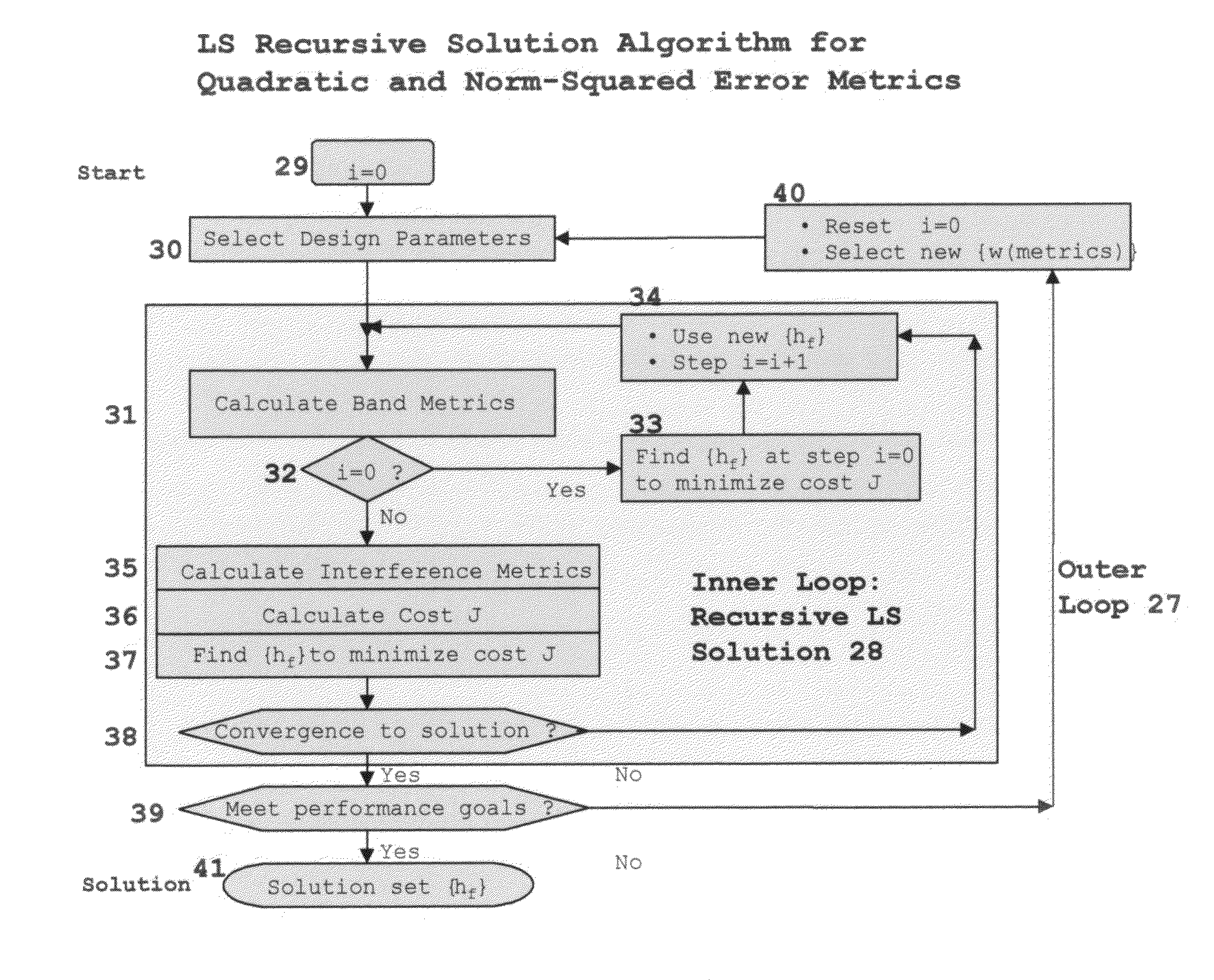
InactiveUS7376688B1Improve performanceModulated carrier system with waveletsComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseSynthetic aperture radar
A method for designing Wavelets for communications and radar which combines requirements for Wavelets and finite impulse response FIR filters including no excess bandwidth, linear performance metrics for passband, stopband, quadrature mirror filter QMF properties, intersymbol interference, and adjacent channel interference, polystatic filter design requirements, and non-linear metrics for bandwidth efficient modulation BEM and synthetic aperture radar SAR. Demonstrated linear design methodology finds the best design coordinates to minimize the weighted sum of the contributing least-squares LS error metrics for the respective performance requirements. Design coordinates are mapped into the optimum FIR symbol time response. Harmonic design coordinates provide multi-resolution properties and enable a single design to generate Wavelets for arbitrary parameters which include dilation, down-sampling, up-sampling, time translation, frequency translation, sample rate, symbol rate, symbol length, and set of design harmonics. Non-linear applications introduce additional constraints. Performance examples are linear communications, BEM, and SAR.
Owner:VON DER EMBSE URBAIN A
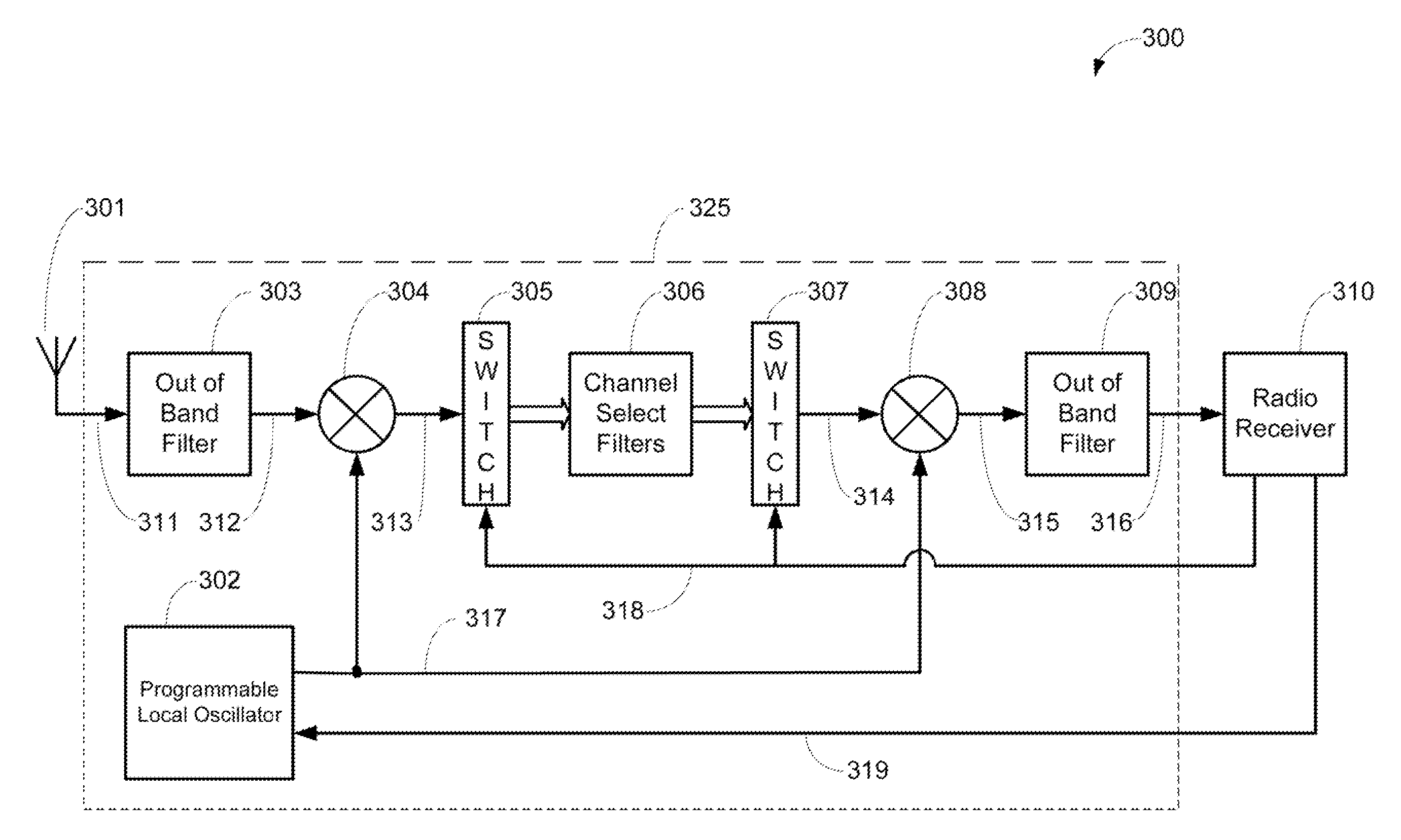
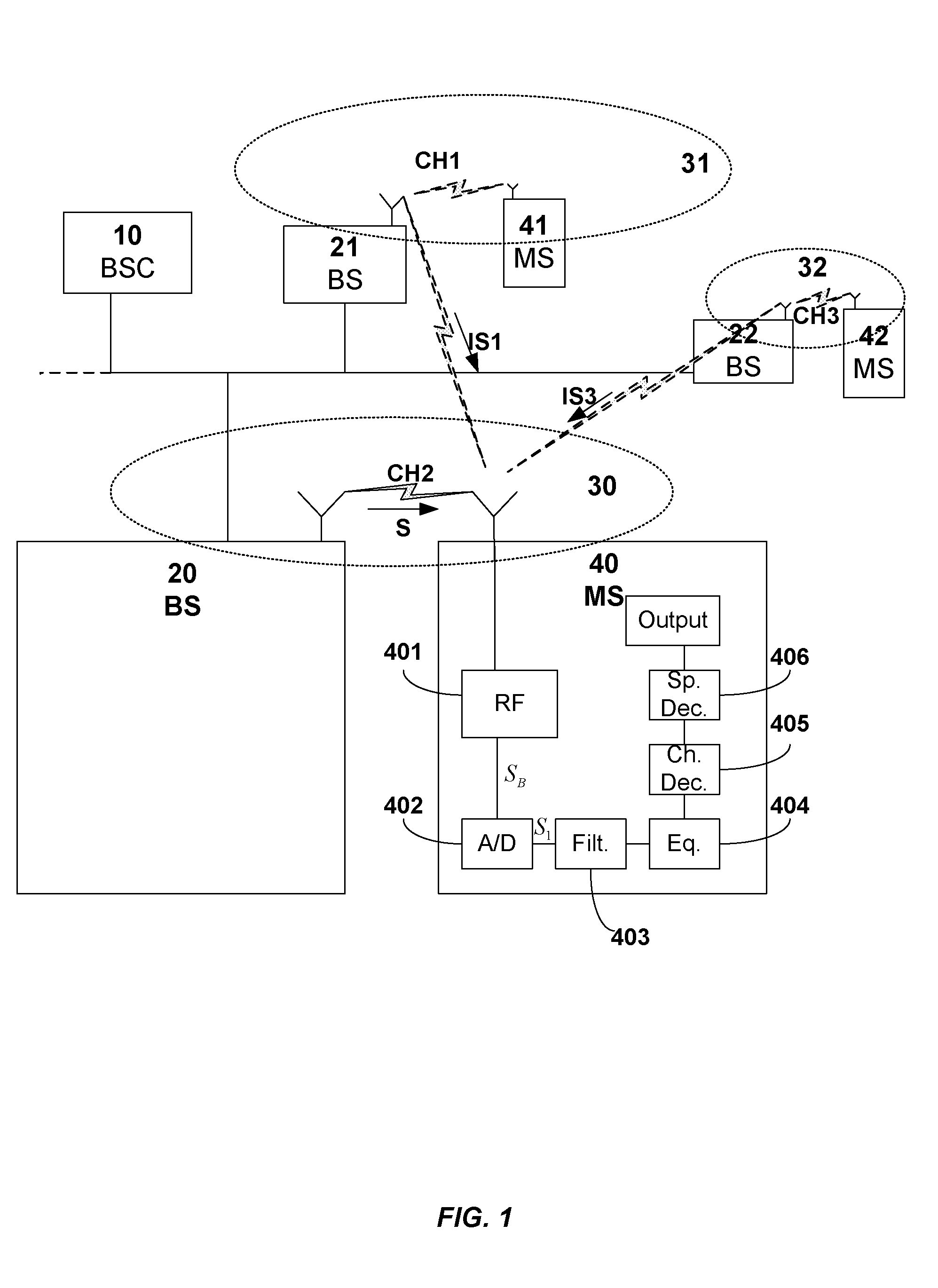
Adjacent channel optimized receiver
ActiveUS20110117870A1Improve performanceHigh selectivityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumRadio receiver
The present invention offers significant improvements in the performance of a radio receiver operating in an environment with high desired band interference. The present invention comprises a high selectivity RF circuit that is located between the antenna and the radio receiver, and utilizes superheterodyne technology to filter adjacent channel interference in the desired band frequency spectrum. This type of interference is problematic for IEEE 802.11 radio receivers that are implemented with the popular direct conversion radio receiver architectures. The present invention may be utilized in many types of radio receivers.The high selectivity RF circuit comprises channel select filters, a down-converter, an up-converter and a programmable local oscillator. The radio receiver provides control signals to the high selectivity RF circuit that permits the selection of an appropriate channel select filter and permits the generation of a local oscillator that subsequently generates the proper intermediate frequency in a mixer.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
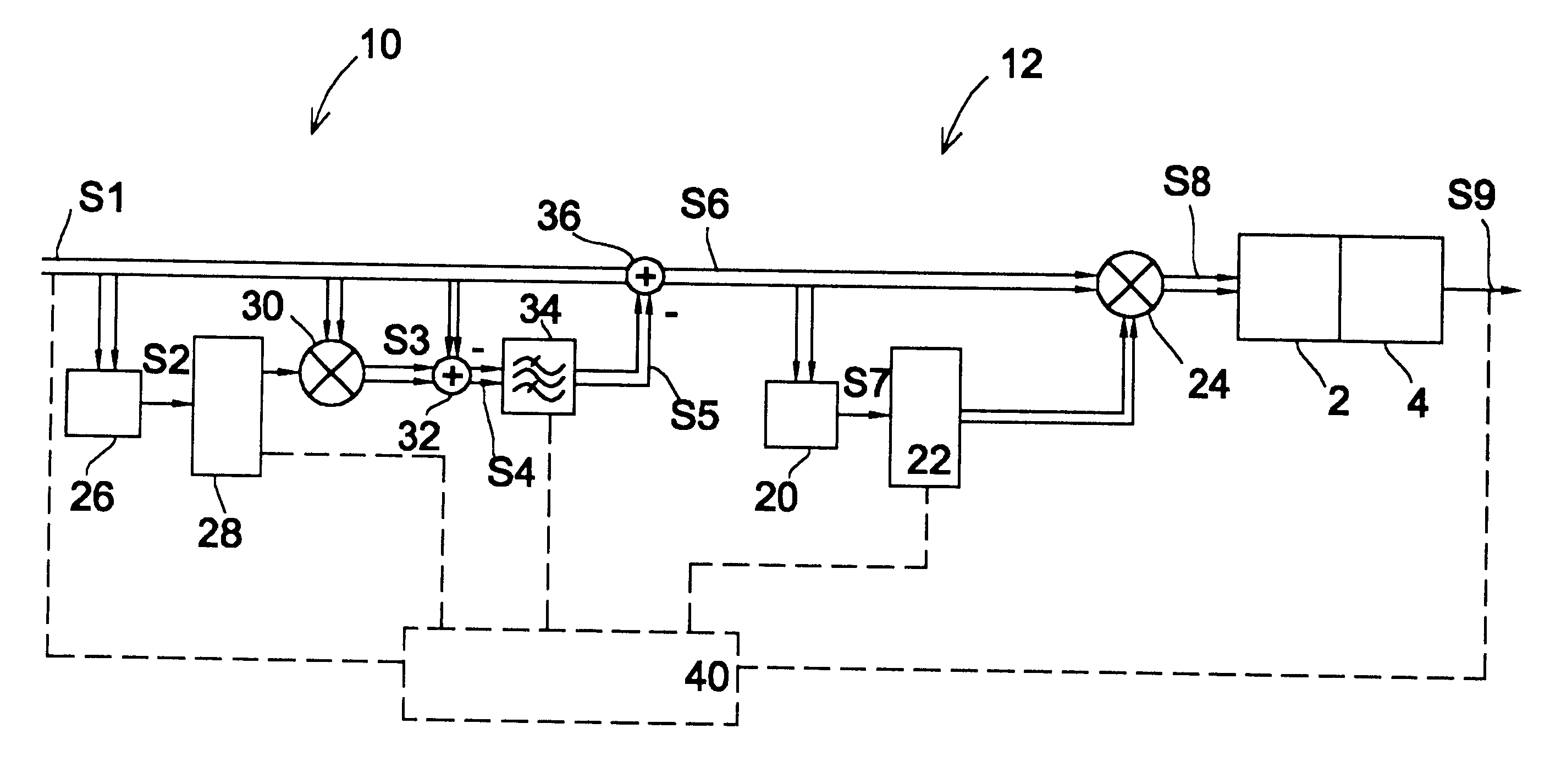
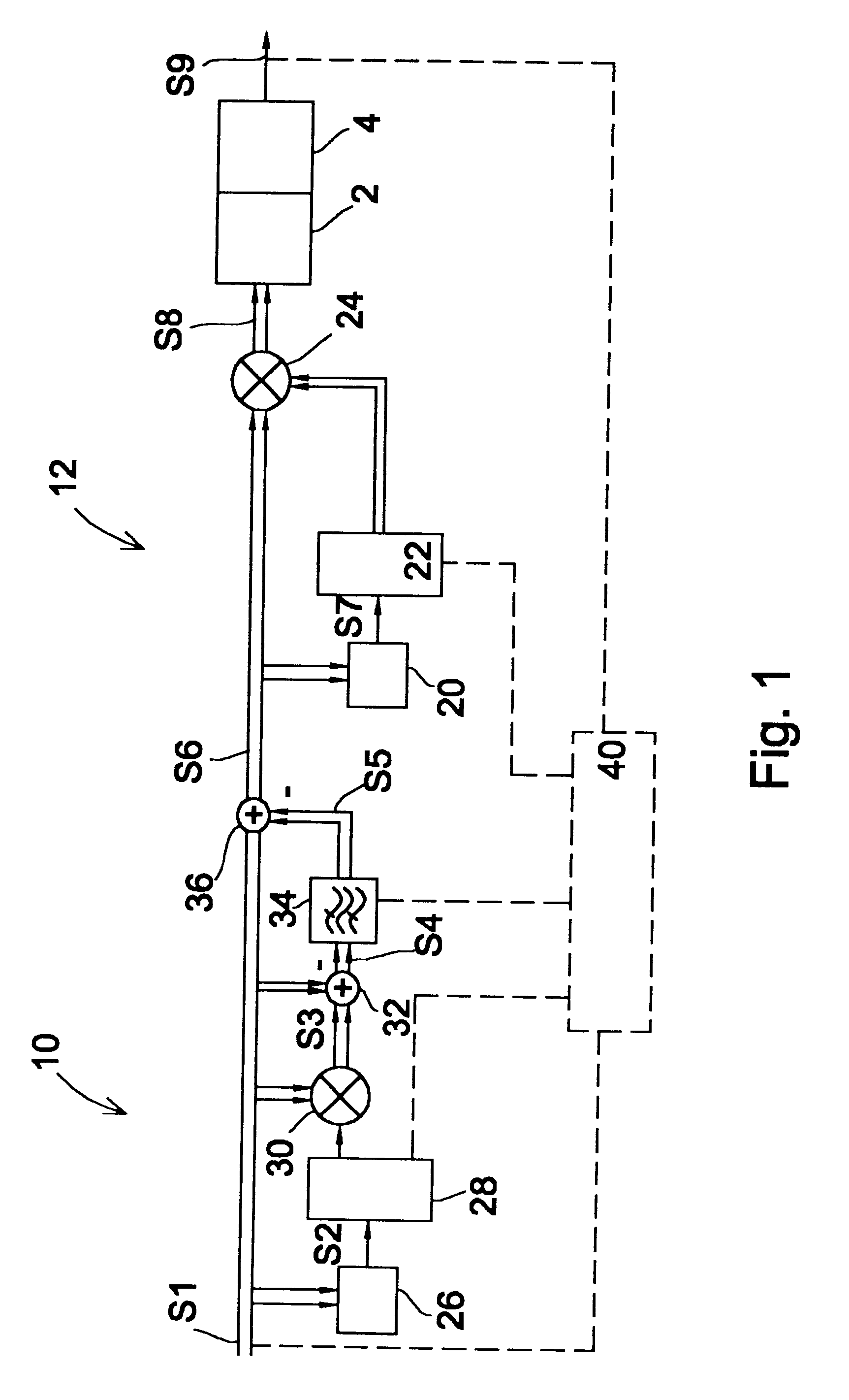
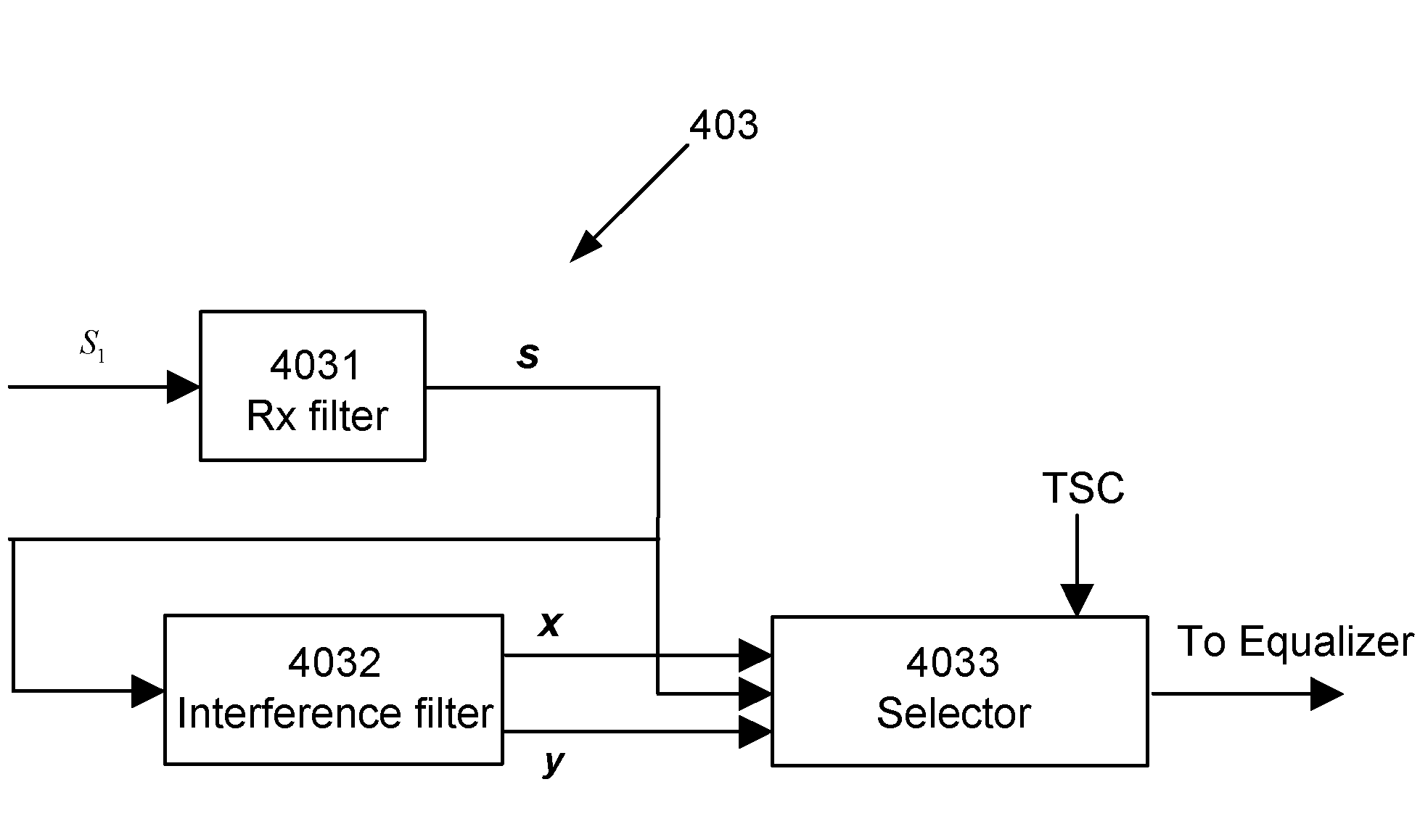
Filter and Method for Suppressing Effects of Adjacent-Channel Interference
ActiveUS20090135973A1Reduced processing power requirementsReduced Power RequirementsDigital technique networkModulated-carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceLow frequency band
A filter device and method for suppressing effects of Adjacent-Channel Interference of a received signal in a Frequency-Division-Multiple-Access system by filtering a baseband signal of the received signal. The filter device comprises an interference filter, which is a complex digital Single-Input-Multiple-Output, SIMO, filter that is adapted to simultaneously generate a first signal filtered at an upper-frequency-band and a second signal filtered at a lower-frequency-band, wherein the first signal is separate from the second signal. The filter device also comprises a selector adapted to select one of the signals as the output from the filter device.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
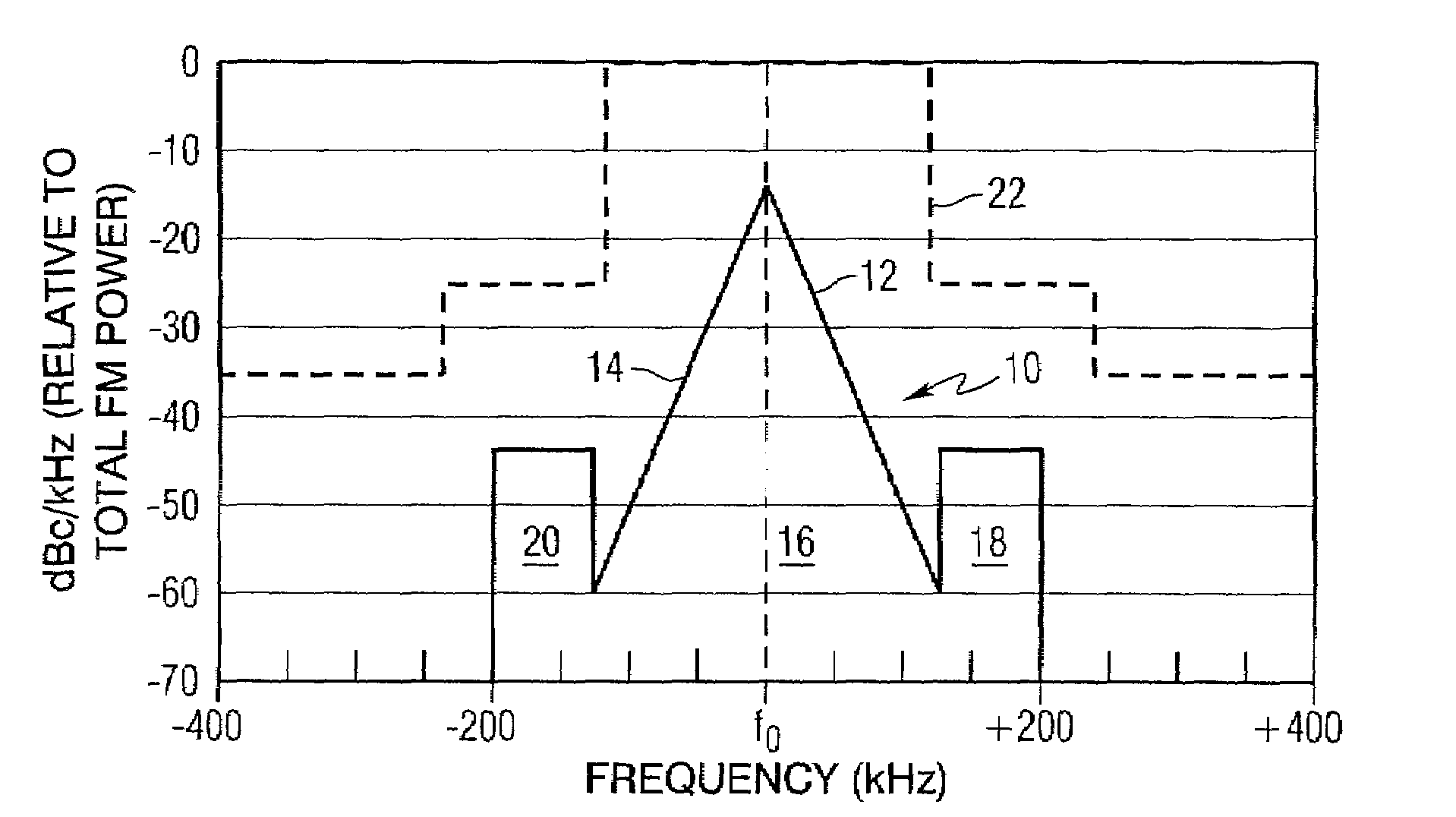
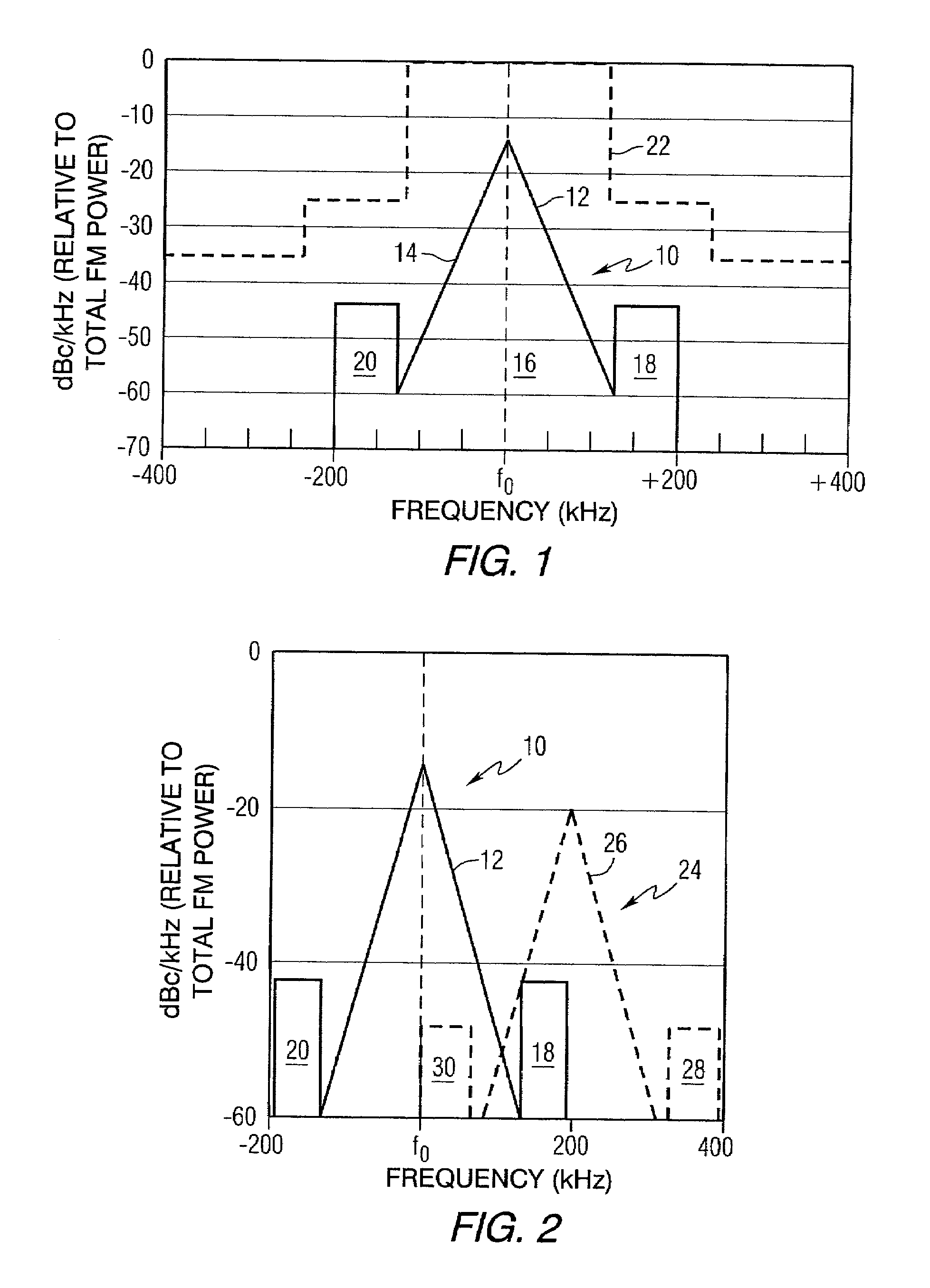
Adjacent channel interference mitigation for FM digital audio broadcasting receivers
ActiveUS7221917B2Electric pulse generatorPlural information simultaneous broadcastBandpass filteringAdjacent-channel interference
A method of receiving an FM digital audio broadcasting signal including a first plurality of subcarriers in an upper sideband of a radio channel and a second plurality of subcarriers in a lower sideband of the radio channel comprises the steps of mixing the digital audio broadcasting signal with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency signal, passing the intermediate frequency signal through a bandpass filter to produce a filtered signal, determining if one of the upper and lower sidebands of the digital audio broadcasting signal is corrupted, and adjusting the local frequency oscillator signal to change the frequency of the intermediate frequency signal such that the bandpass filter removes the subcarriers in the upper or lower sideband that has been corrupted. A receiver that processes a digital audio broadcasting signal in accordance with the method is also provided.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Co-channel congestion method and apparatus
ActiveUS20060291401A1Good choiceError preventionTransmission systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceTelecommunications
A system and method for Access Point (AP) channel selection based upon a Channel Quality Index (CQI) is described. The Channel Quality Index (CQI) is a value which quantifies a transmission quality of a channel. The transmission quality is evaluated based on a combination of different types of measured interference in the channel. In one embodiment the different types of measured interference include co-channel congestion, adjacent channel interference and in-band interference. The CQI is a value derived from the measurements, and for example may be a sum of all of the measurements. Each AP of the present invention determines the CQI of potential transmission channels, and selects a channel for use which has the ‘best’ CQI; for example if the CQI is a sum of all measured interferences, the ‘best’ AP is the one with the lowest CQI
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
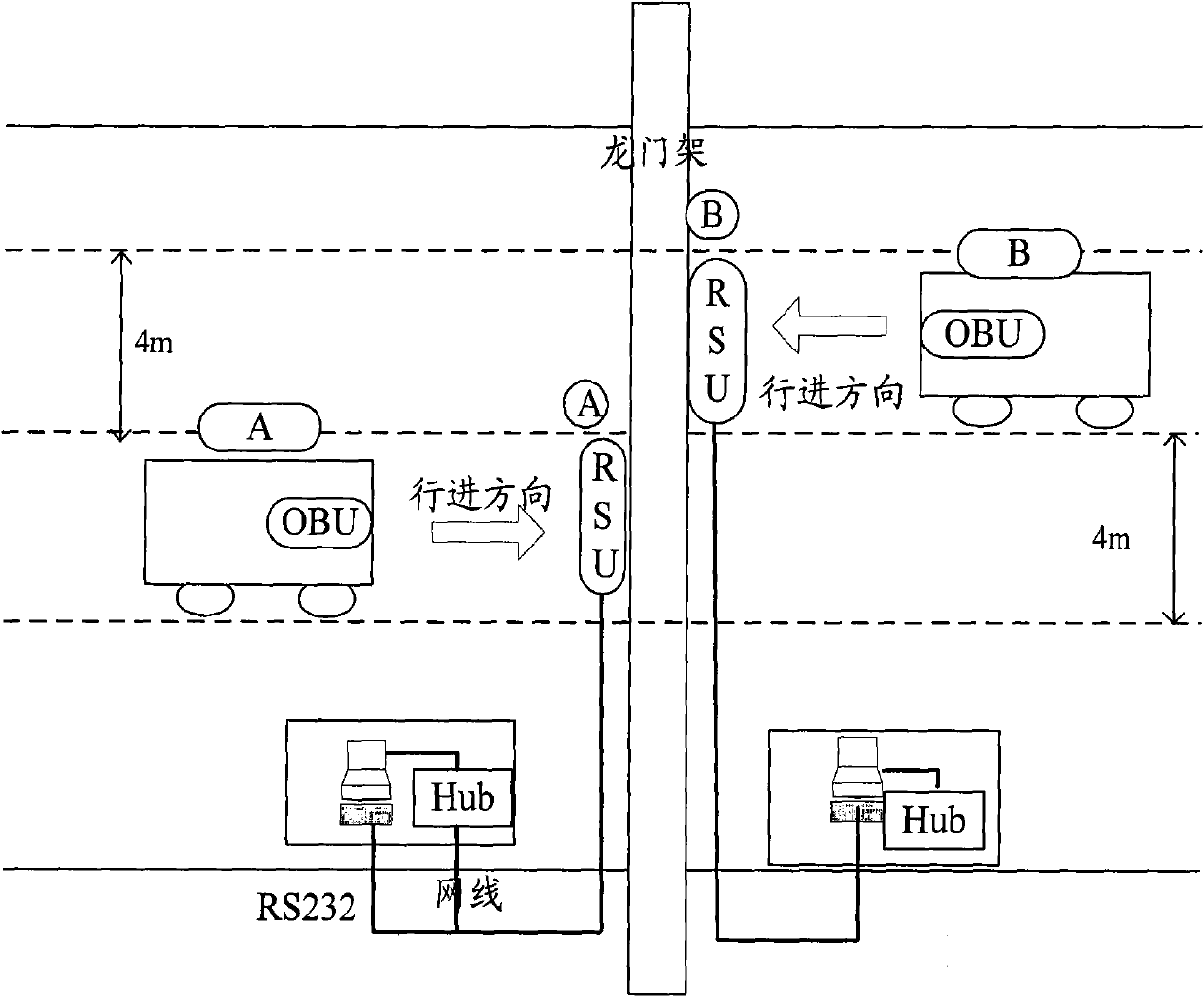
Adaptive wireless communication receiver
ActiveUS20120288043A1Consumes less powerInexpensive circuitEnergy efficient ICTAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsStart timeBluetooth
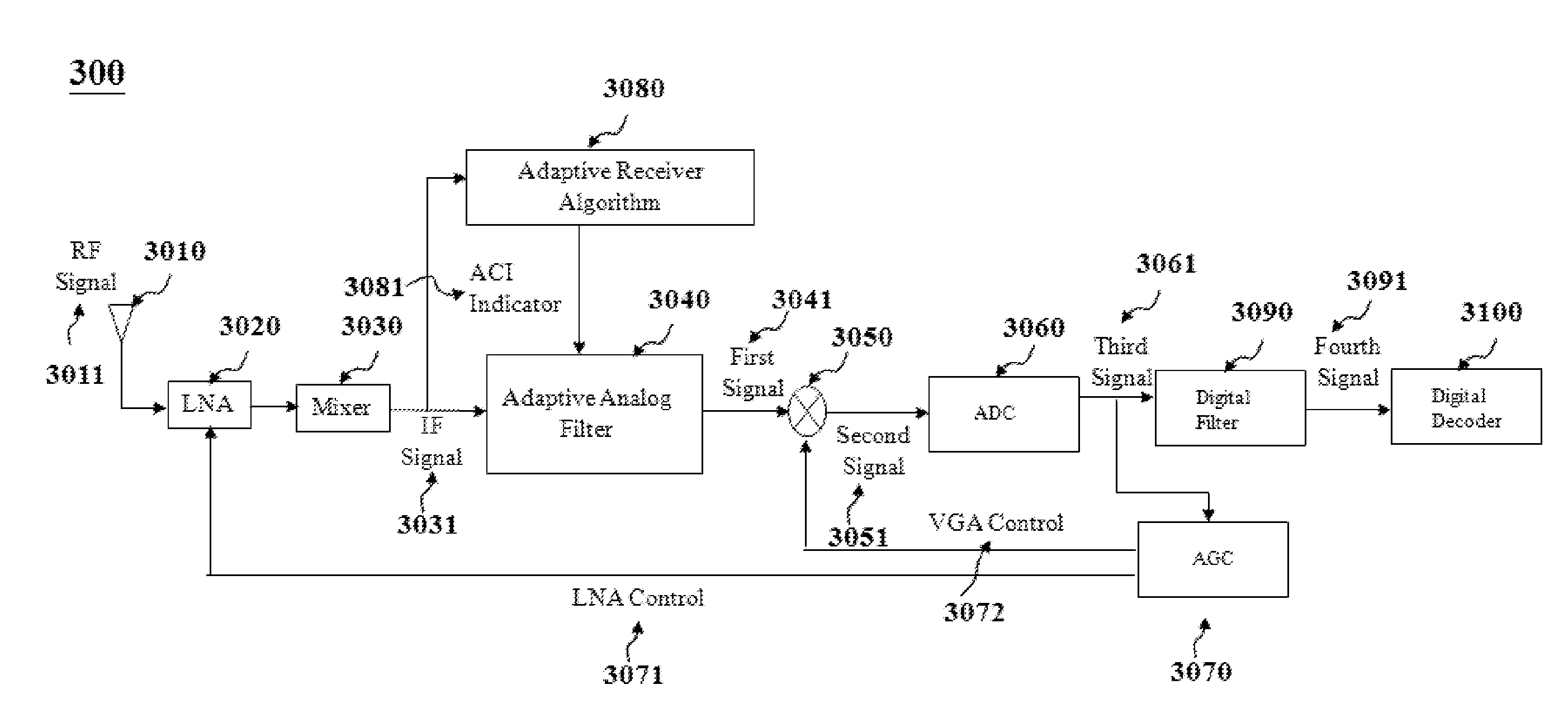
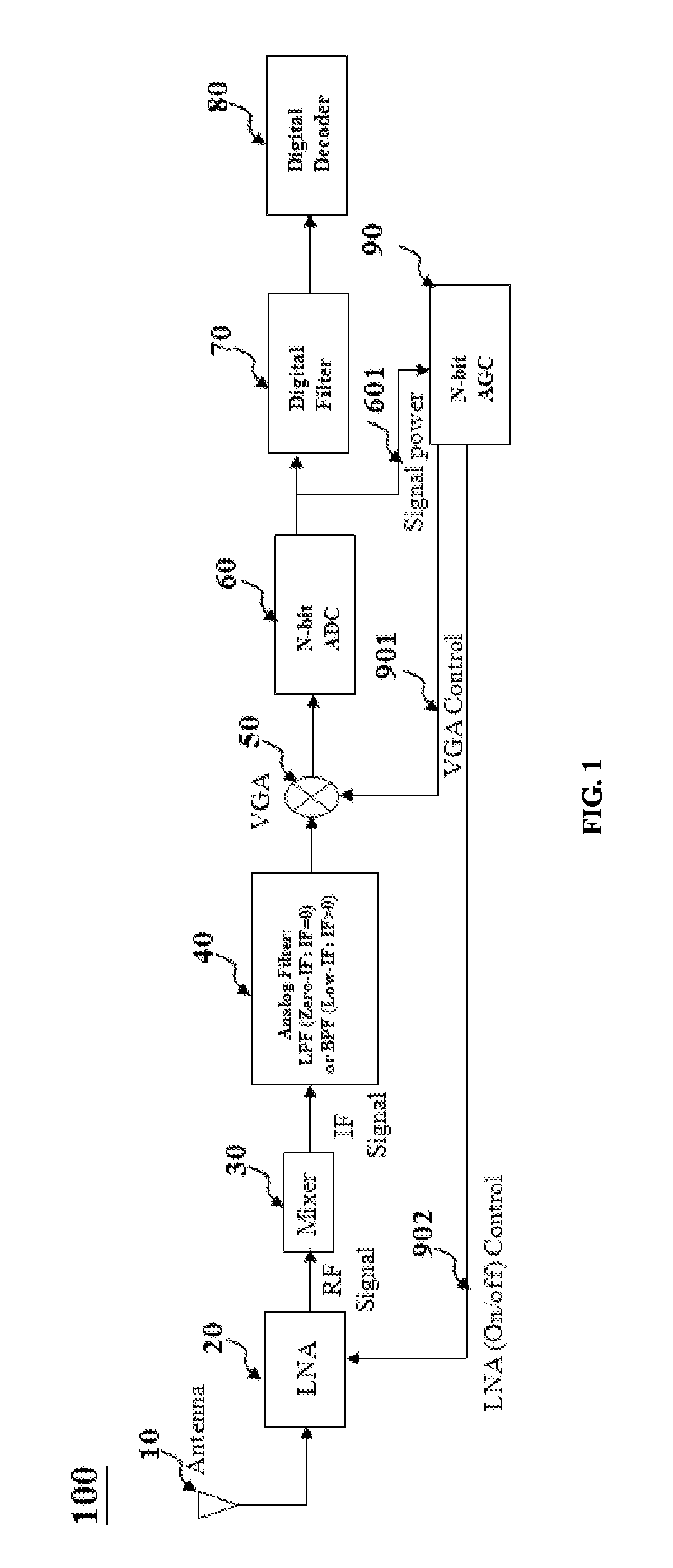
The present invention relates to an adaptive, cost-performance efficient, power-saving apparatus for wireless communication systems, such as but not limited to Bluetooth (BT) receivers, and in particular to a packet-based receiver's decoding algorithm which can detect the presence or absence of the adjacent channel interference (ACI) before the scheduled starting time for receiving a Bluetooth packet, and accordingly set the receiver configurations including the filter's pass-band bandwidth (BW), filter's order, the sampling rate, the number of analog-to-digital-converter (ADC) output bits, and the automatic-gain-control (AGC) algorithm unit to determine the low noise amplifier (LNA) and variable gain amplifier (VGA) settings.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
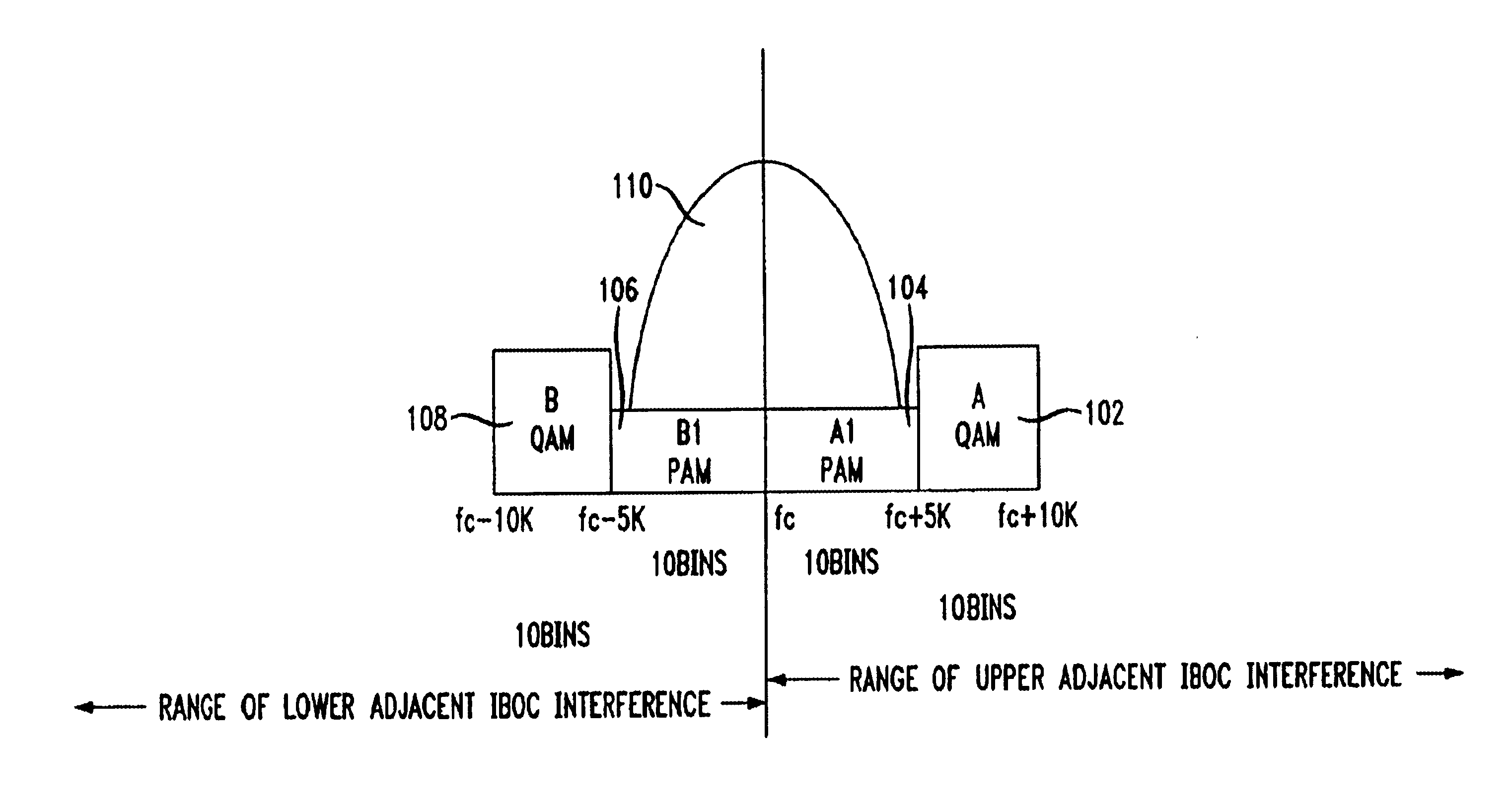
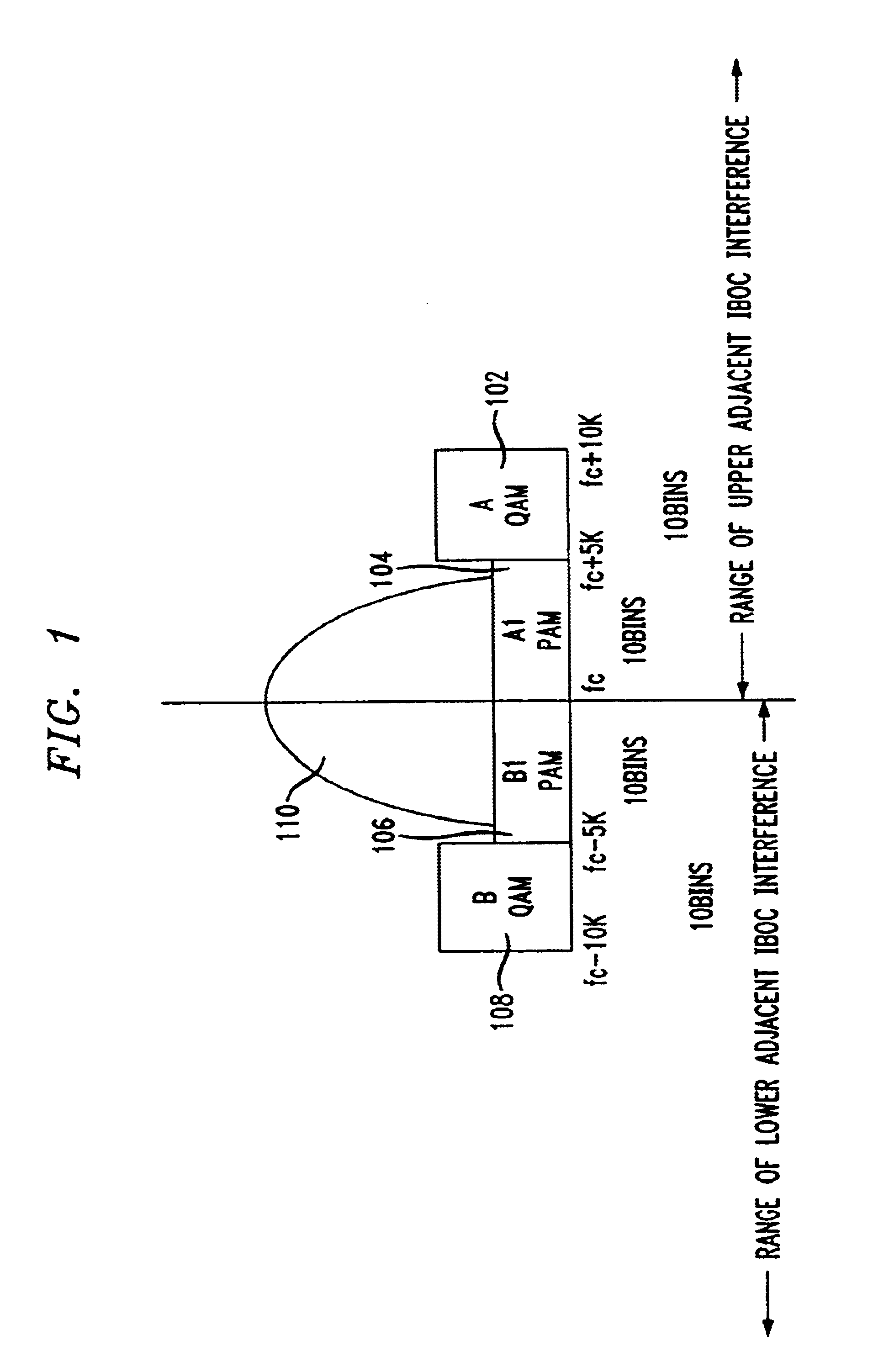
Asymmetric pulse amplitude modulation transmission of multi-stream data embedded in a hybrid IBOC channel
InactiveUS6650717B1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierDigital dataFrequency spectrum
In accordance with the principles of the present invention, in addition to conventional use of frequency division multiplexed upper and lower side bands, the spectral area occupied by the analog host will be utilized by applying a one-dimensional modulation, e.g., pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) as opposed to the conventional use of a two-dimensional modulation, e.g., quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). Furthermore, the analog and digital information within the analog host bandwidth may be combined in quadrature to keep the signals orthogonal. Thus, should one side band under the analog carrier be deteriorated or obliterated by adjacent channel interference, the other side band under the analog carrier can still provide useful data and hence better digital audio codec performance. By transmitting one or two digital data streams asymmetrically with respect to the center frequency, particular digital side bands can be rendered useless as environmental conditions warrant (e.g., as they become detrimentally affected by adjacent channel interference), reducing bandwidth capacity but not affecting the quality of the received digital data transmitted in any of the remaining digital side band regions.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
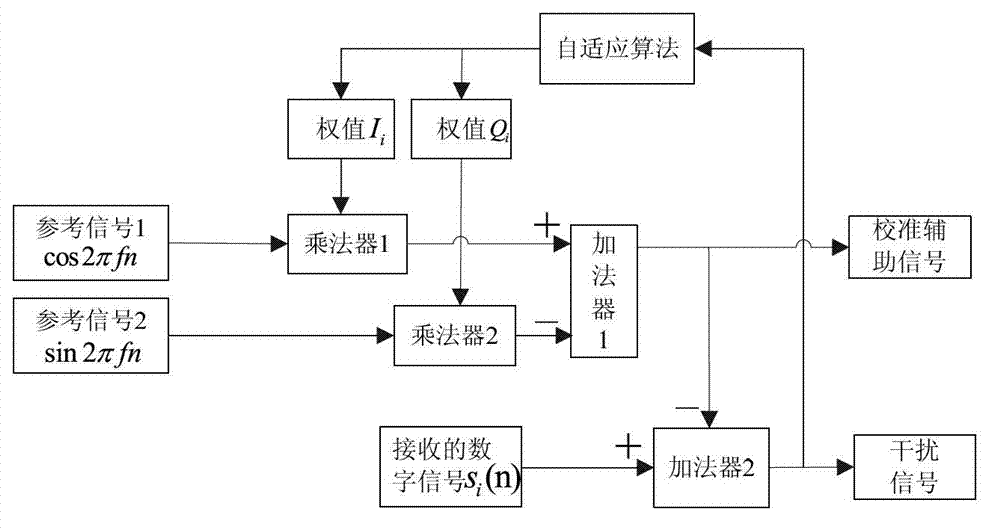
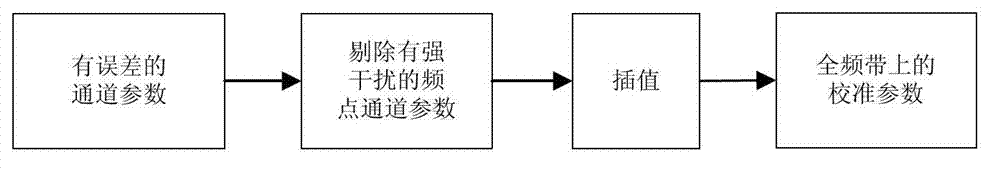
Method and device for antenna array calibration under complex electromagnetic environment
InactiveCN103117781AAutomatic suppression of influenceAccurate acquisitionTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityAdjacent-channel interferenceSmall amplitude
The invention discloses a method and a device for antenna array calibration under complex electromagnetic environment. The device transmits calibration signals from a center point of an antenna array, and extracts array antennas and receives front-end amplitude inconsistency and phase inconsistency by means of wiener solution according to the principle of adaptive filter. The influence of small-amplitude same frequency interference or adjacent channel interference upon the result of frequency array calibration can be inhibited automatically in the complex electromagnetic environment with intense interference. When high-amplitude same frequency interference or adjacent channel interference has great influence on channel parameters, the extracted channel parameters can be processed to eliminate or greatly weaken the influence of the interference; received array signals are then subjected to broadband compensation or multiple narrowband compensation, and accordingly errors caused by channel inconsistency are eliminated. The method and device are applicable to real-time channel parameter extraction and automatic compensation for circular antenna arrays and receiving channels operating in any frequency range under the complex electromagnetic environment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
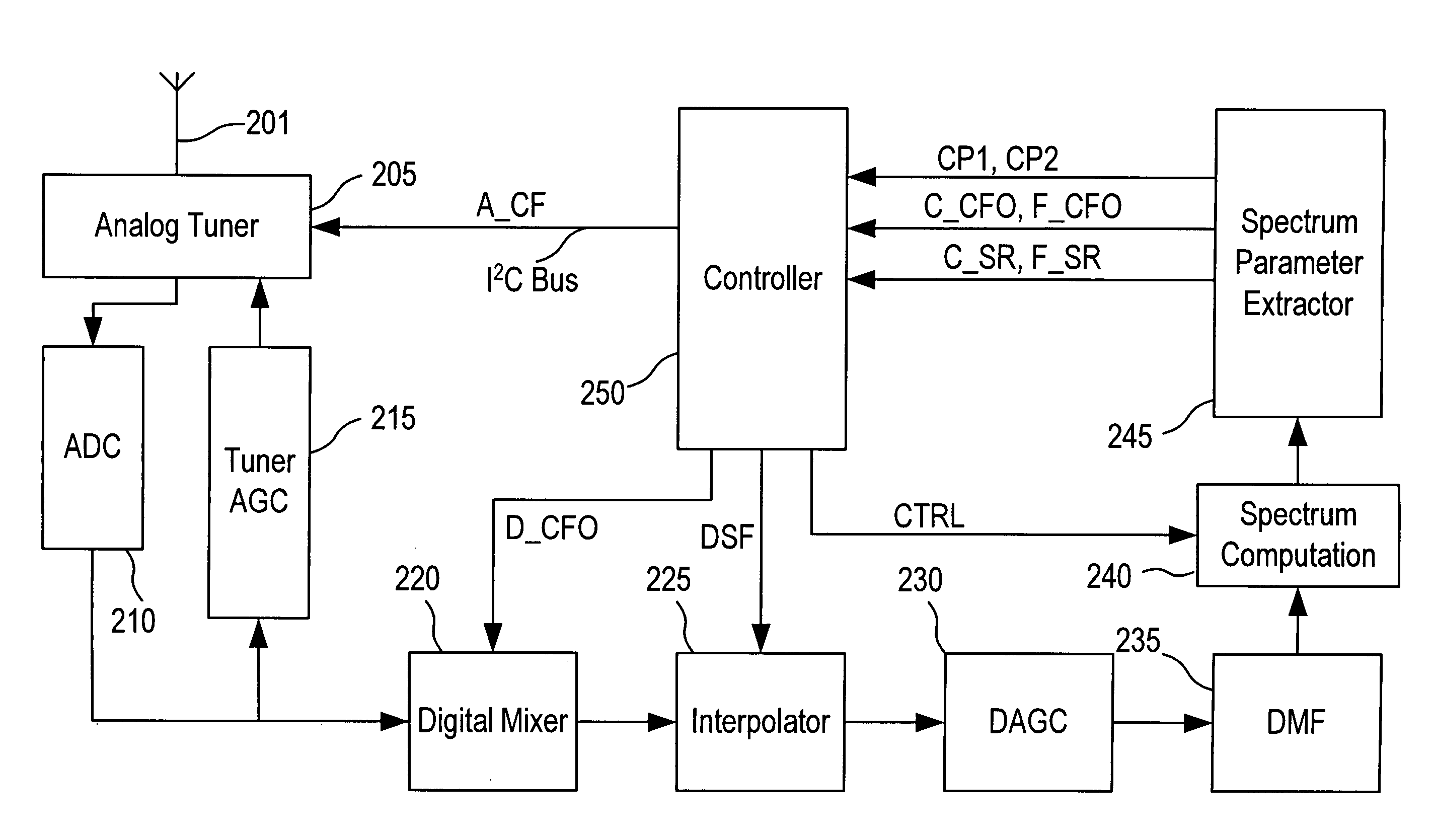
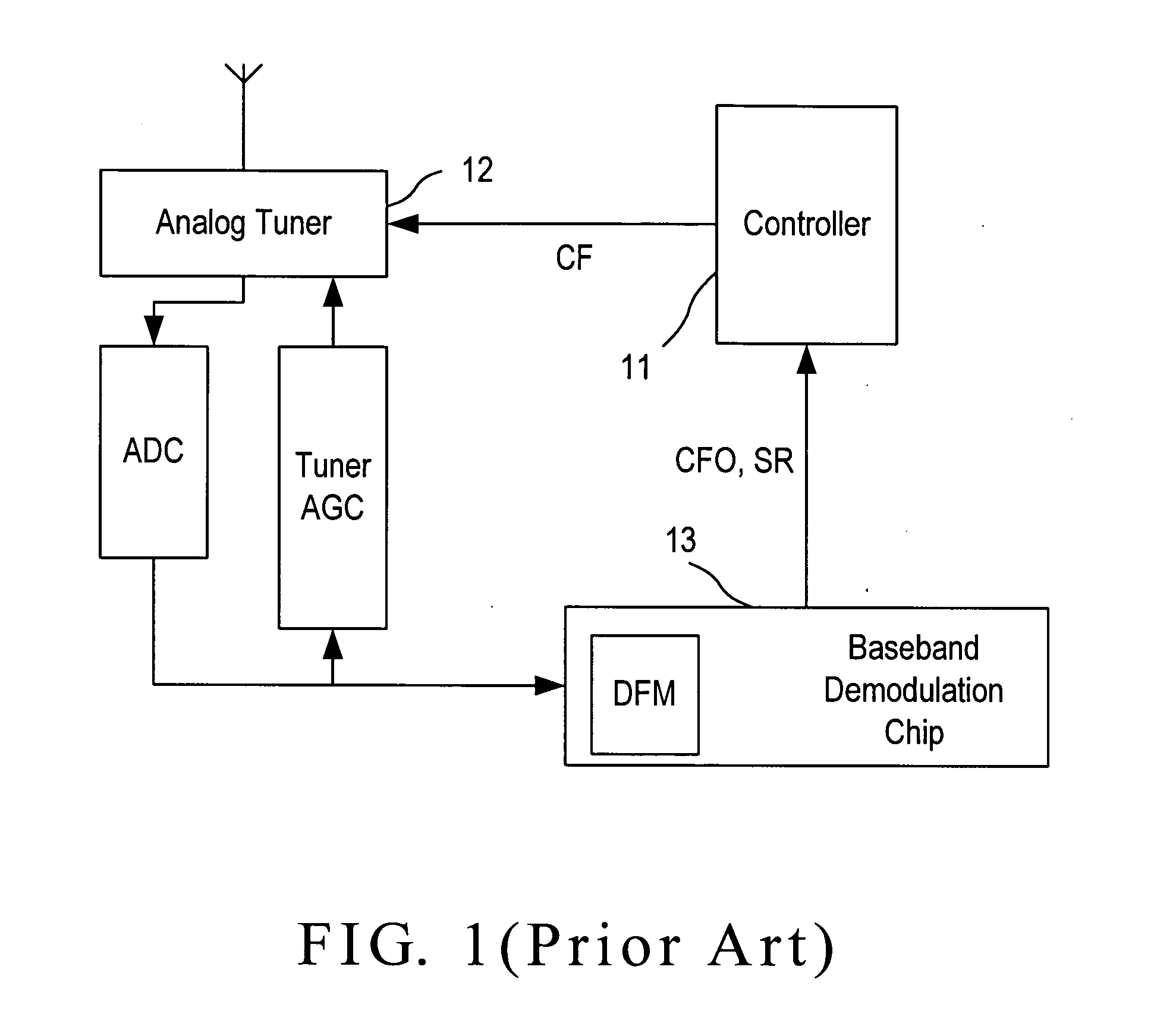
Blind scan system and method in a DVB-S system
InactiveUS20110135042A1Carrier regulationTime-division multiplexAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
A blind scan system in a DVB-S system includes a spectrum parameter extractor to fetch and calculate a coarse carrier frequency offset and coarse symbol rate of a signal; a digital mixer to depend on the coarse frequency offset to shift the center of a spectrum of the signal to a position where a DC part of a working spectrum of a digital matched filter locates, so as to produce an offset signal; and an interpolator to perform a down-sampling on the offset signal according to the coarse symbol rate in order to improve the in-band signal-to-noise ratio of the digital matched filter and mitigate impacts due to adjacent channel interferences. Thus, the fine carrier frequency offset and fine symbol rate estimation can be performed accurately.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
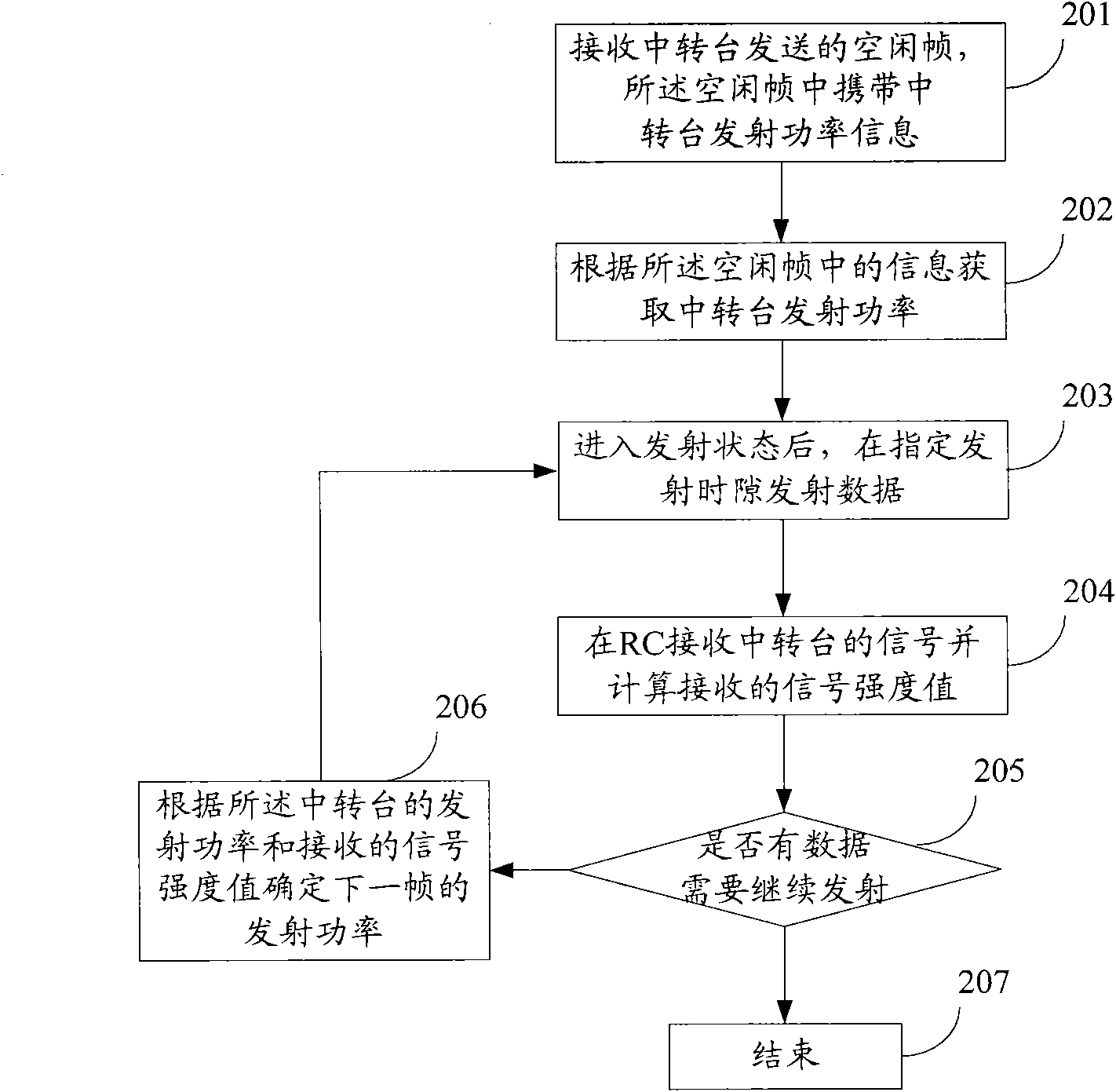
Terminal of digital mobile wireless transferring system, method for adjusting transmission power thereof and system thereof
ActiveCN101902807AReduce consumptionReduce distractionsPower managementEnergy efficient ICTAdjacent-channel interferenceTransmitted power
The invention relate to the technical field of mobile communication, disclosing a terminal of a digital mobile wireless transferring system, a method for adjusting the transmission power thereof and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving an idle frame transmitted by a transferring table, wherein the idle frame carries the information of transferring table transmitting power; obtaining the transferring table transmitting power according to the information in the idle frame; transmitting data at appointed transmitting time slot after entering into a transmitting status; receiving a single of the transferring table and computing a received signal strength value in a reversal signal path; ensuring the transmitting power of the next frame according to the transmitting power of the transferring table and the received signal strength value when needing to continuously transmit the data; and transmitting the next frame data at the appointed transmitting time slot according to the ensured transmitting power of the next frame. The invention can lead the terminal to adaptively adjust the transmitting function thereof, reduces the power consumption, and reduces the adjacent channel interference and radiation.
Owner:HYTERA COMM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com