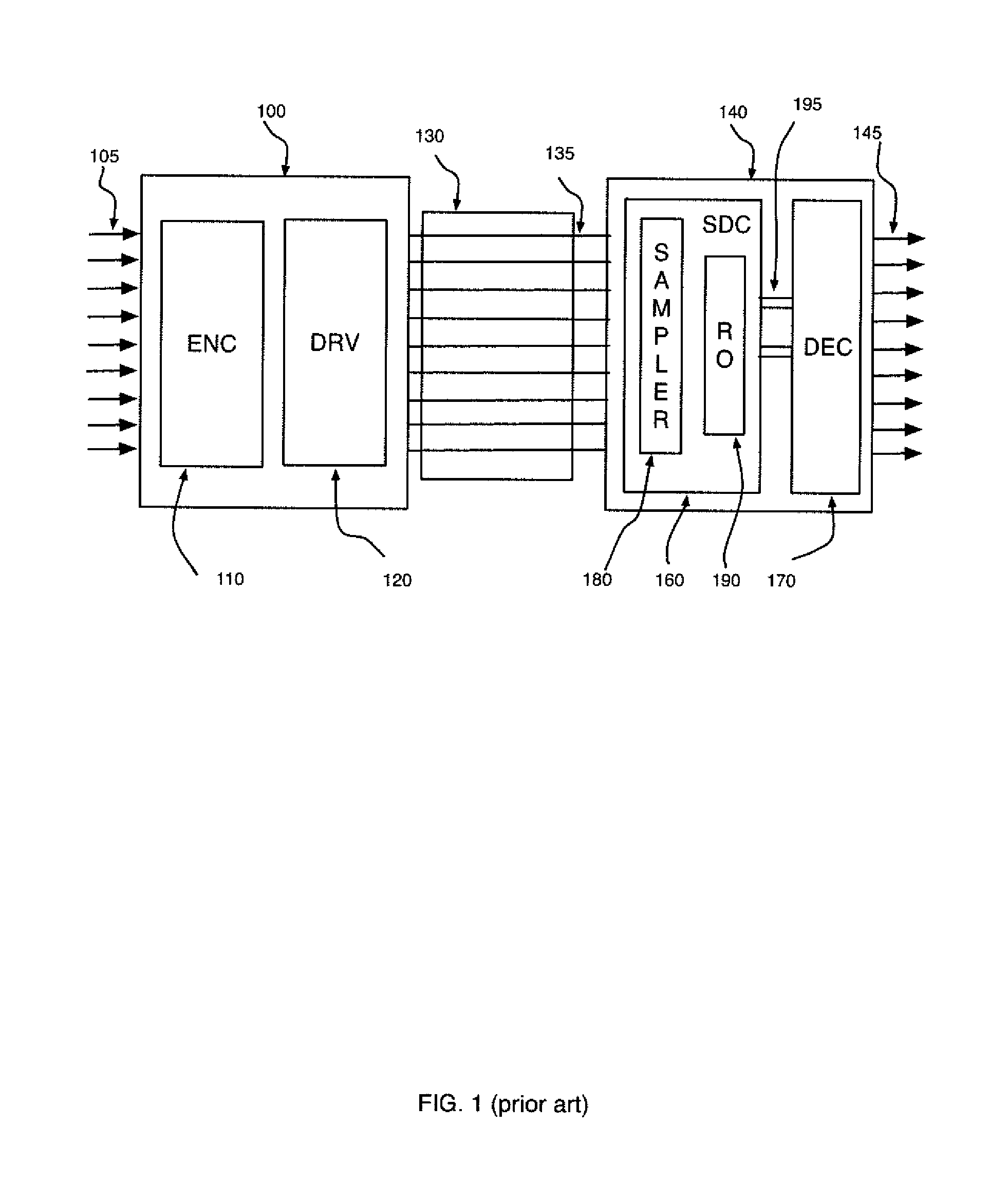
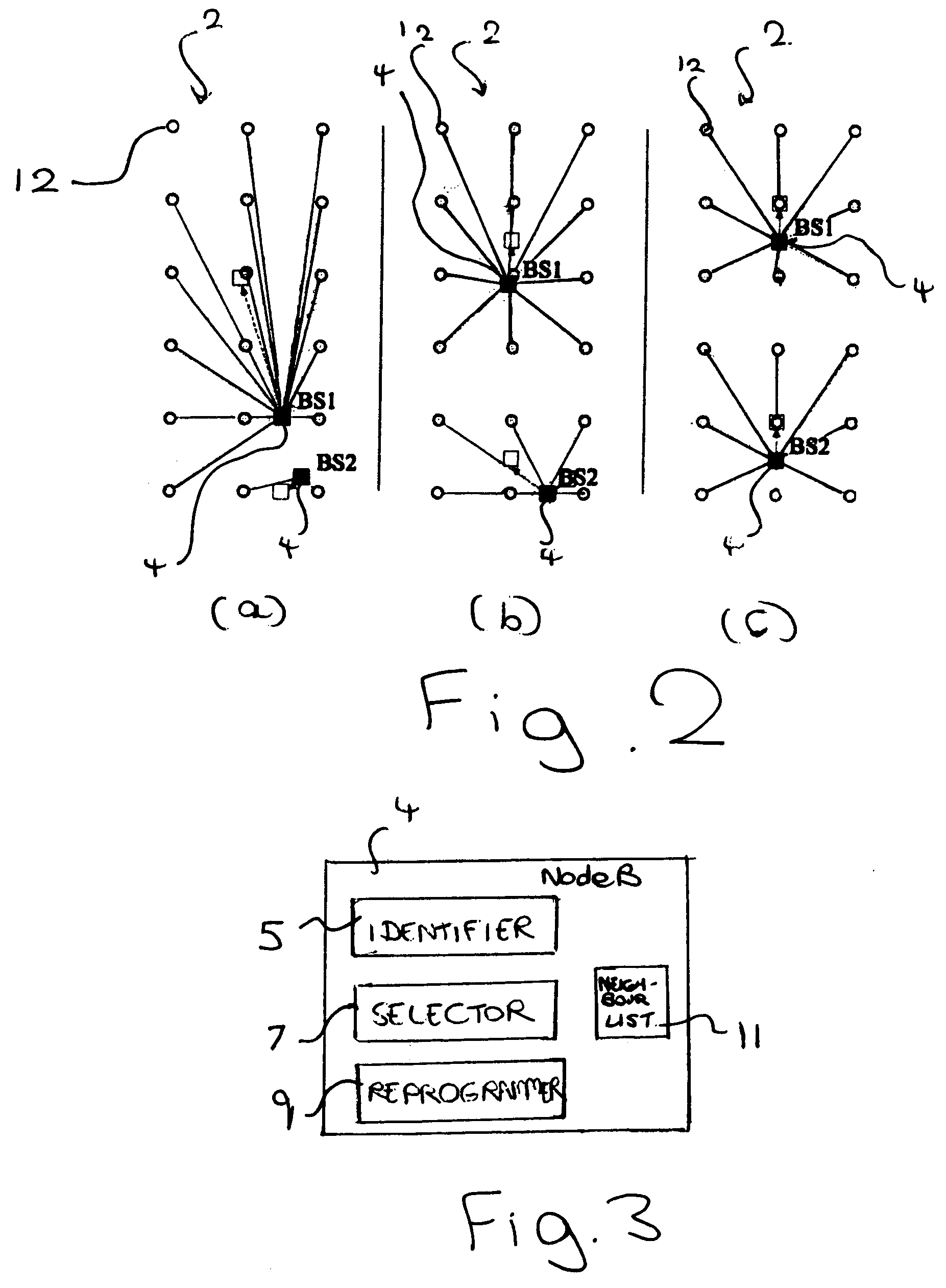
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
687results about "Link quality based transmission modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
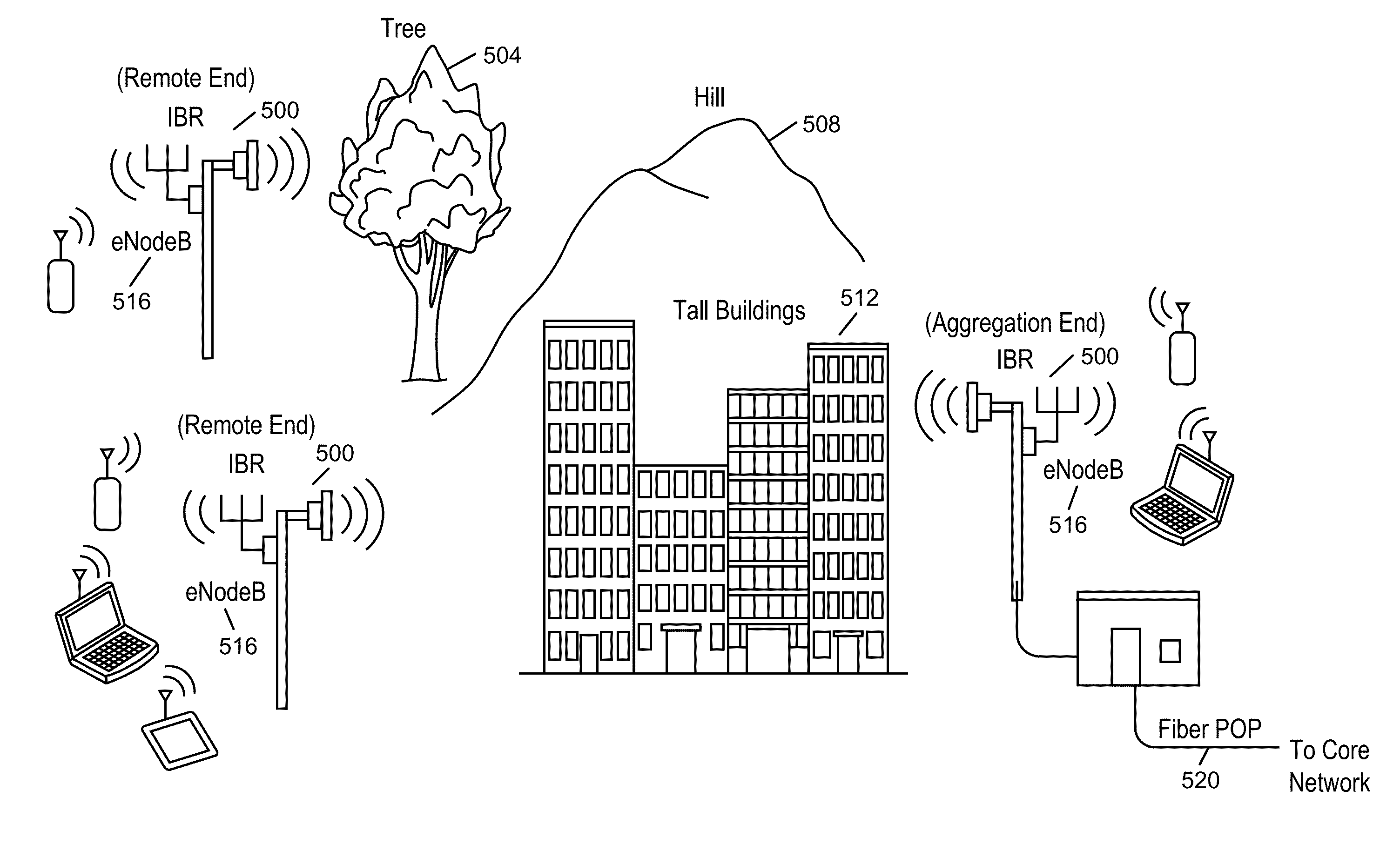
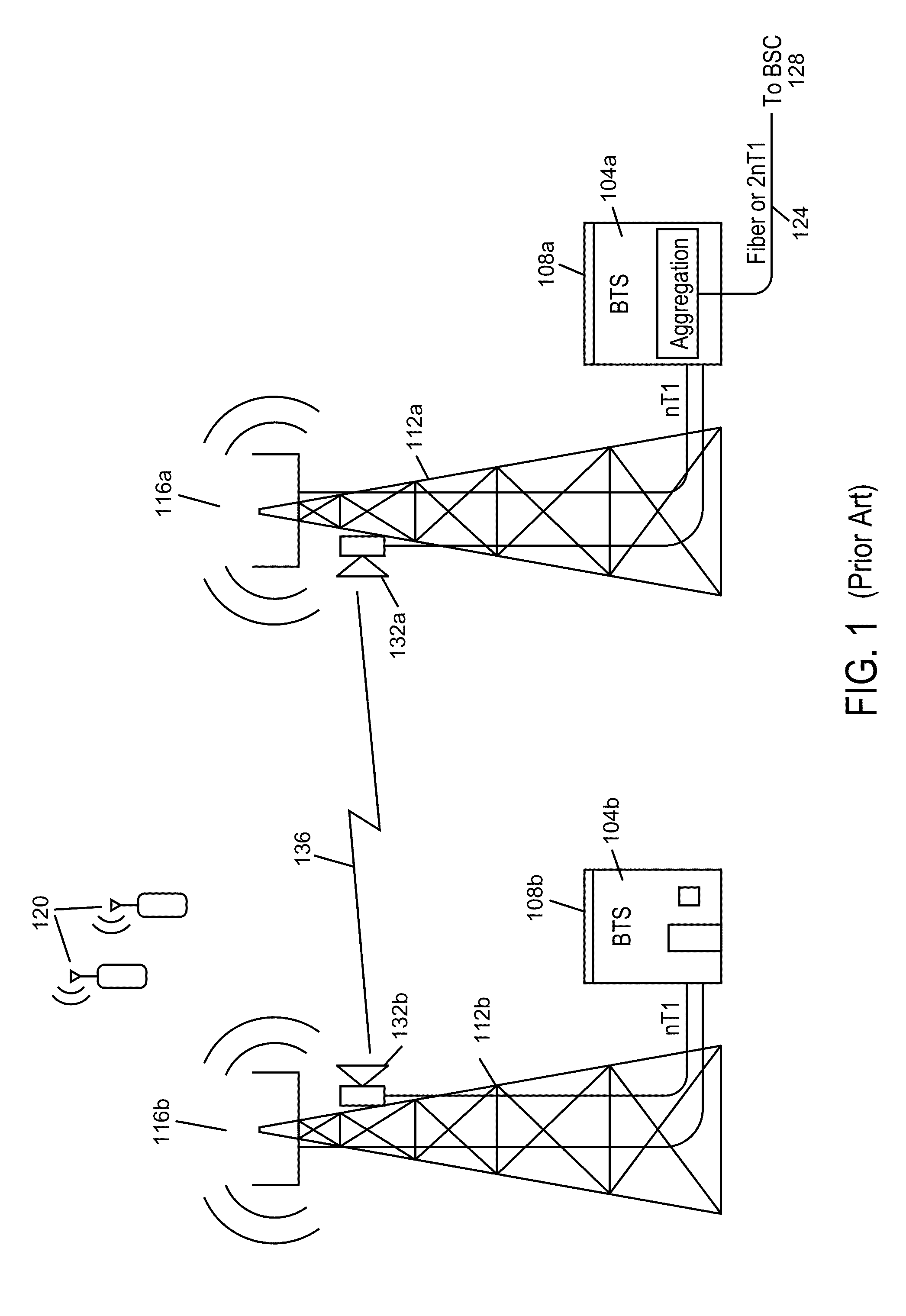
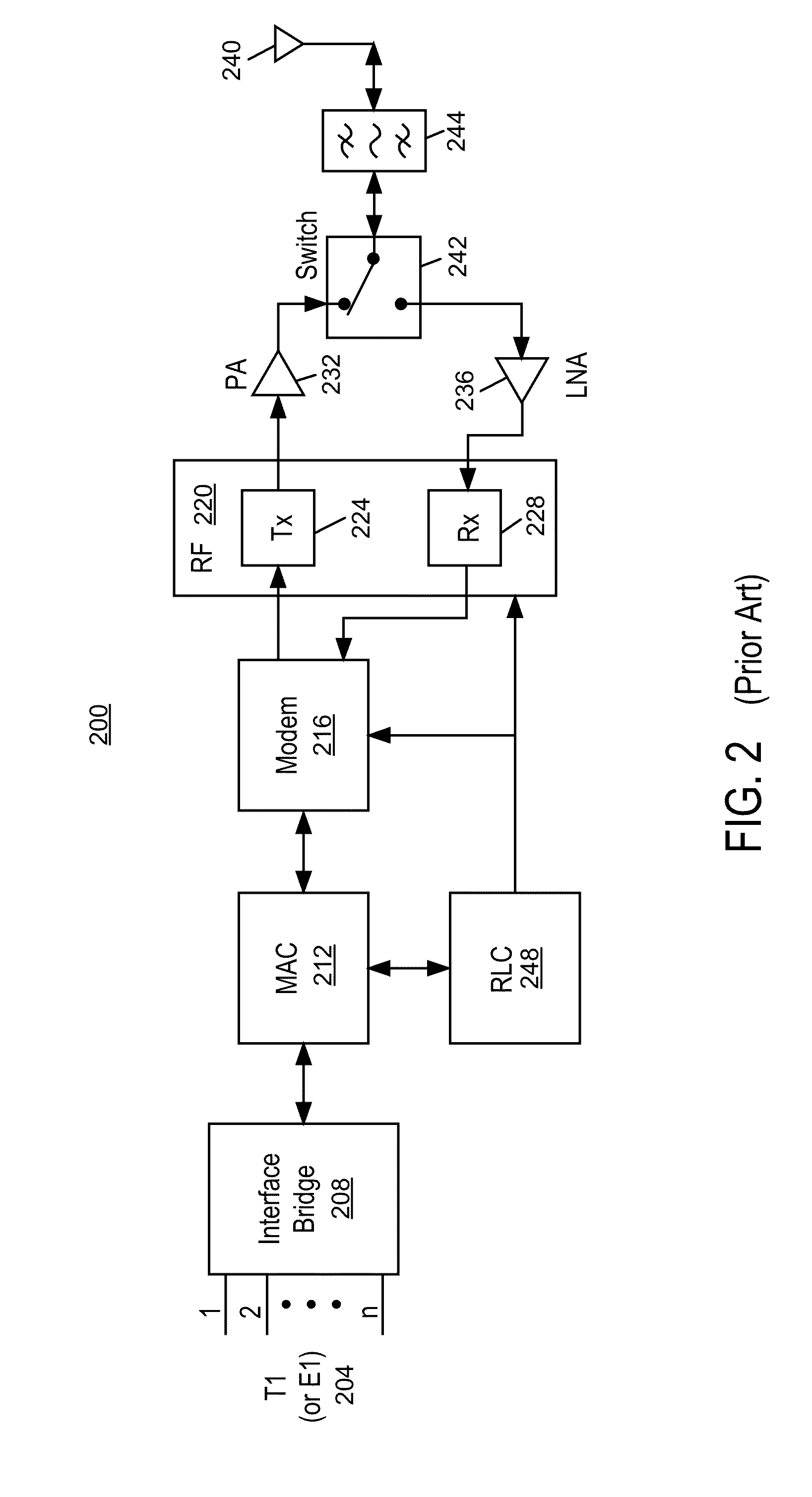
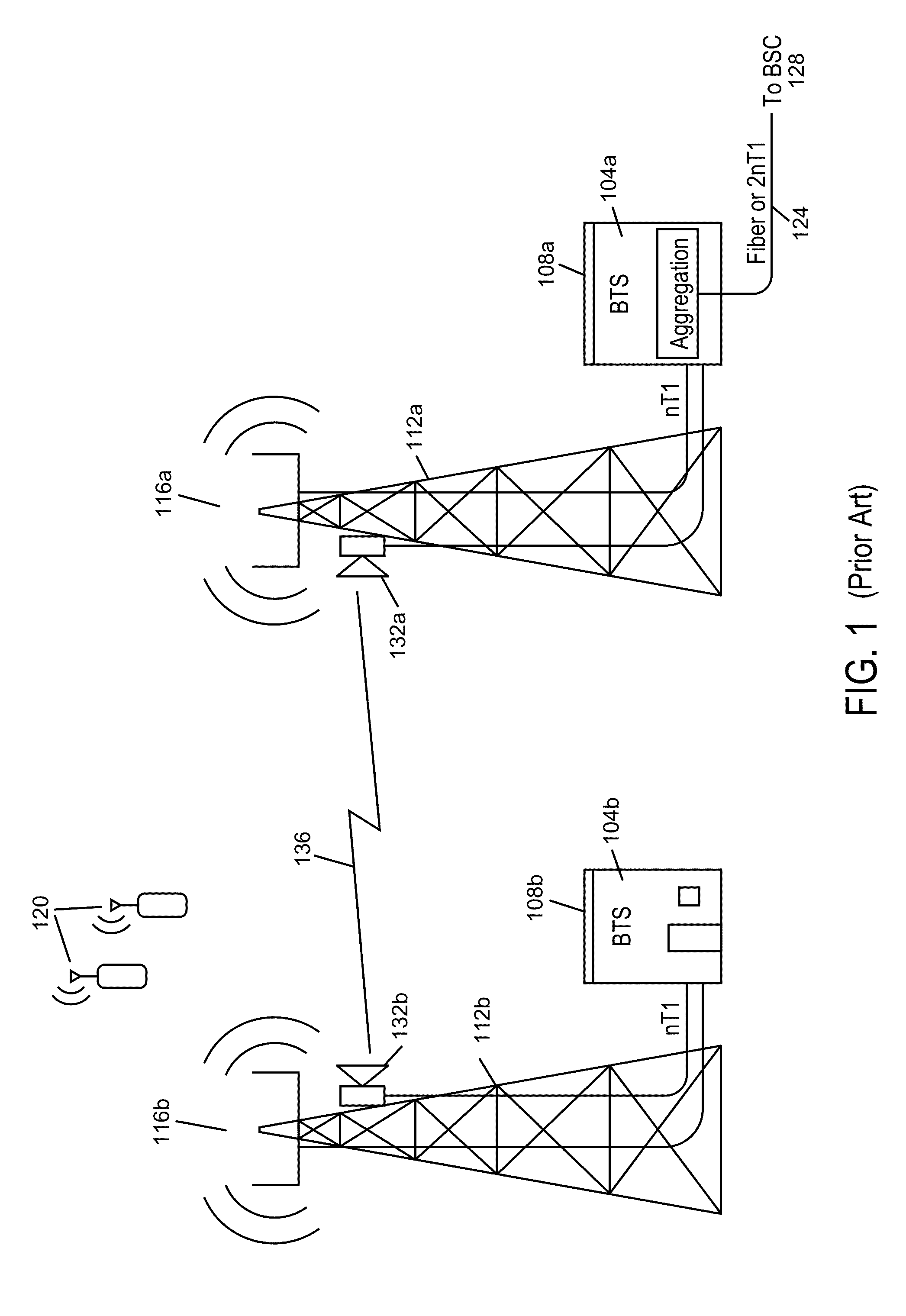
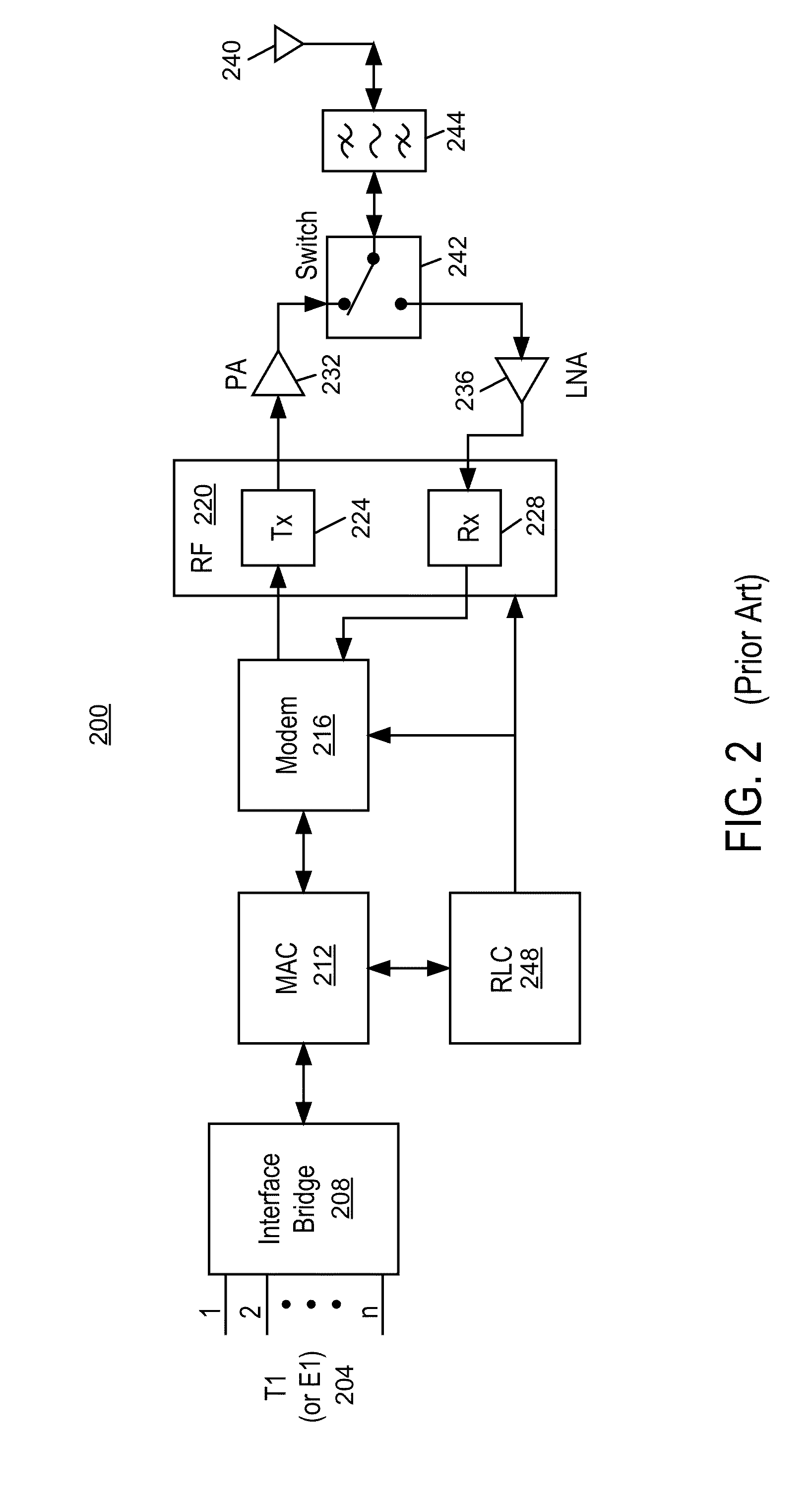
Intelligent backhaul radio and antenna system
ActiveUS8467363B2High path loss exponentWide angular-spreadError prevention/detection by using return channelPolarisation/directional diversitySide informationMimo transmission
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Intelligent backhaul radio and antenna system
ActiveUS20130044028A1Without any loss in diversityMinimum angular widthError prevention/detection by using return channelPolarisation/directional diversitySide informationMimo transmission
A intelligent backhaul radio have an advanced antenna system for use in PTP or PMP topologies. The antenna system provides a significant diversity benefit. Antenna configurations are disclosed that provide for increased transmitter to receiver isolation, adaptive polarization and MIMO transmission equalization. Adaptive optimization of transmission parameters based upon side information provided in the form of metric feedback from a far end receiver utilizing the antenna system is also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
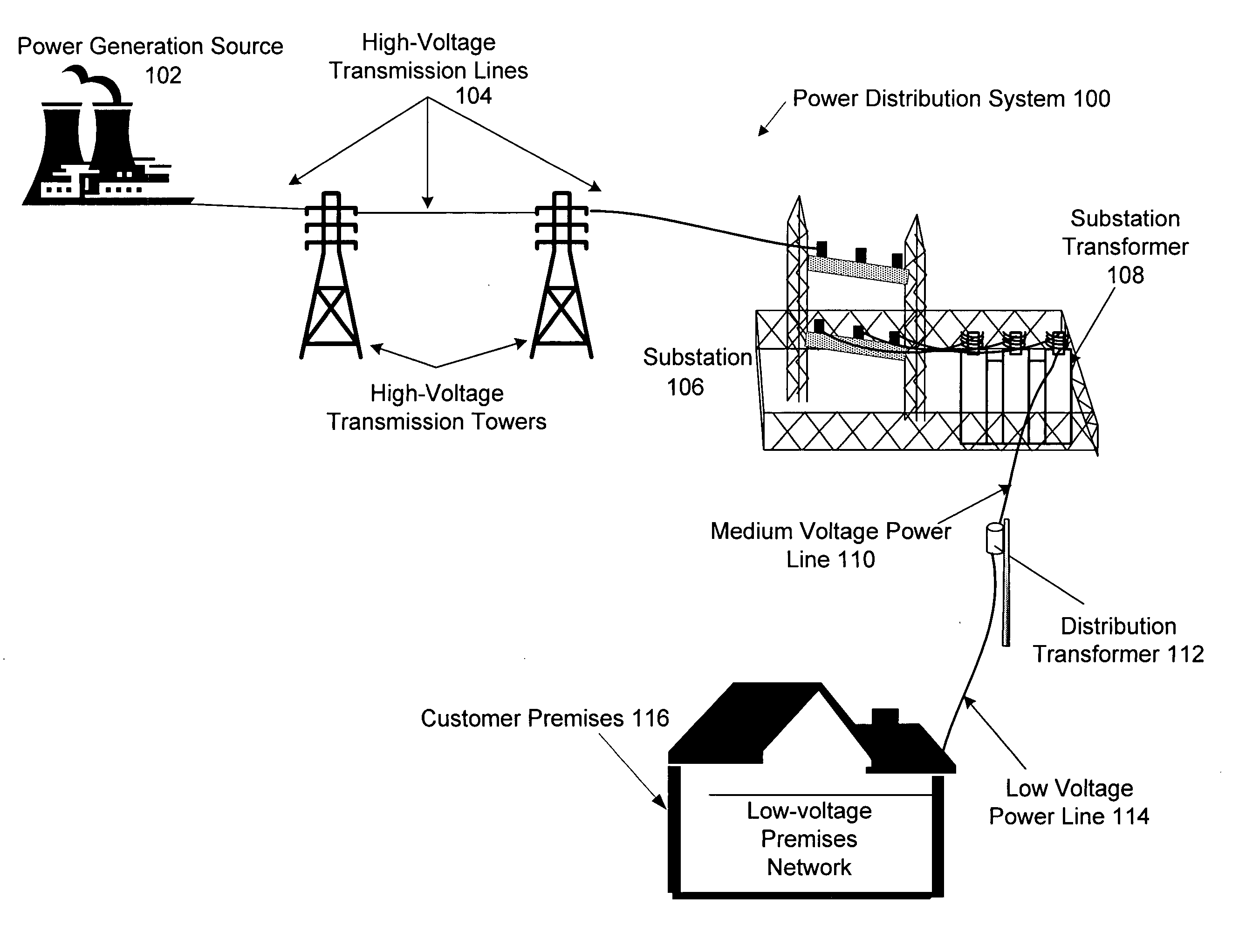
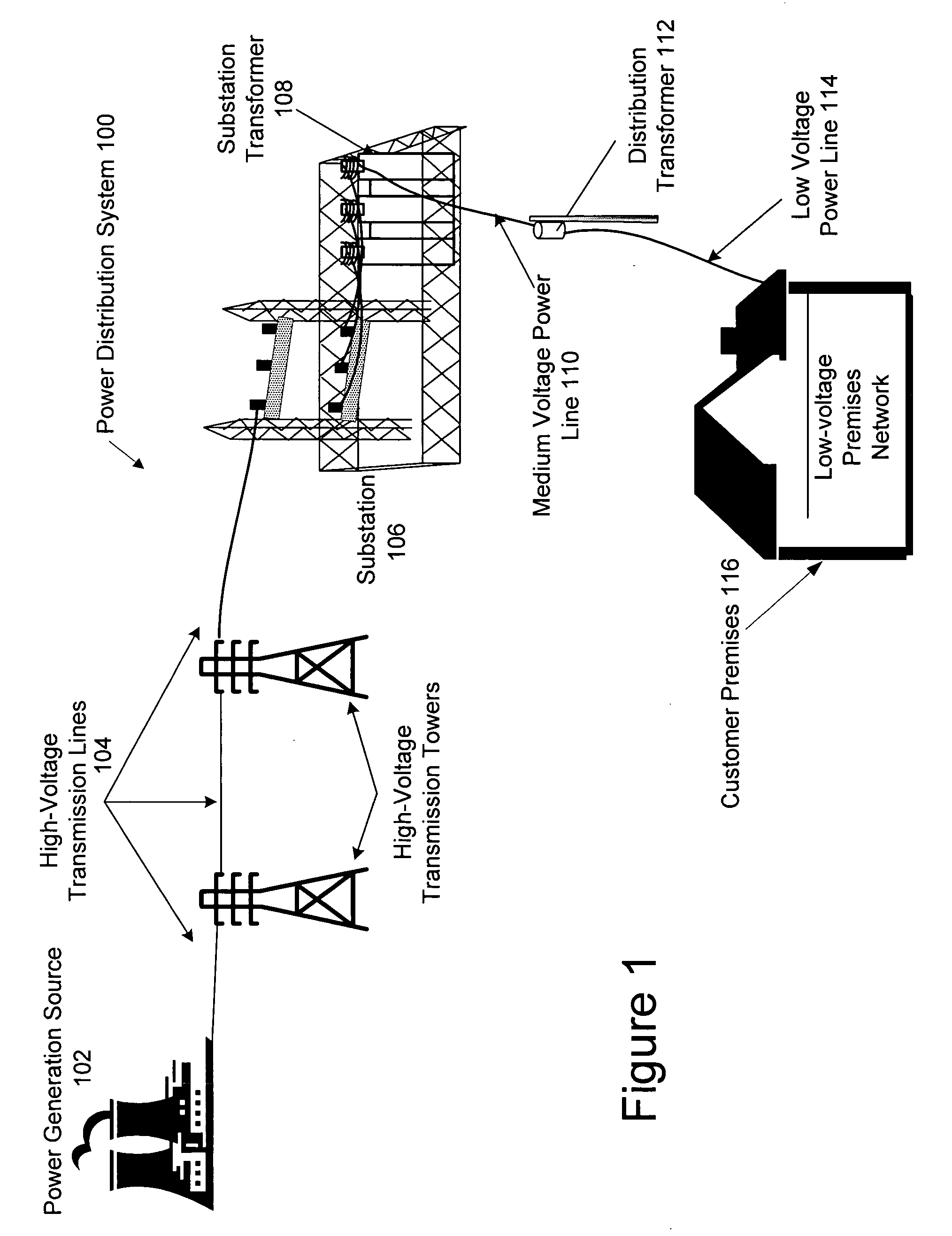
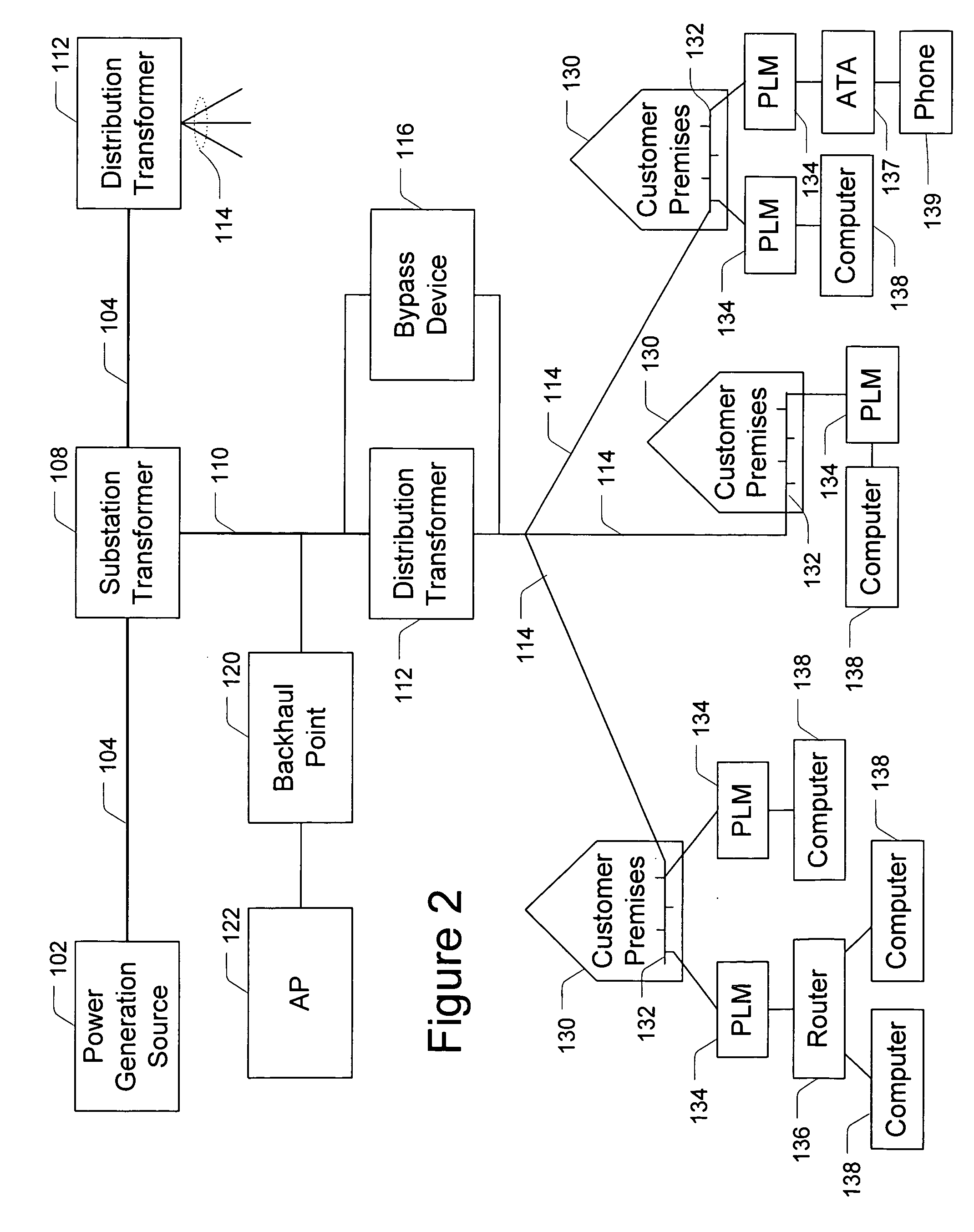
Hybrid power line wireless communication system
InactiveUS20070054622A1Increase system capacityLower latencyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunication interfaceTelecommunications link
In a hybrid communication system a wireless communication link is maintained between a power line communication medium and a non-power line communication medium. Wireless communication is established within an unlicensed frequency band and monitored for quality. If the quality falls below a threshold, a wireless communication link is established within a licensed frequency band. The wireless link may be maintained between a power line communication system (PLCS) backhaul point and an internet protocol (IP) network access point, and / or between a PLCS endpoint communication interface and a premises communication device.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
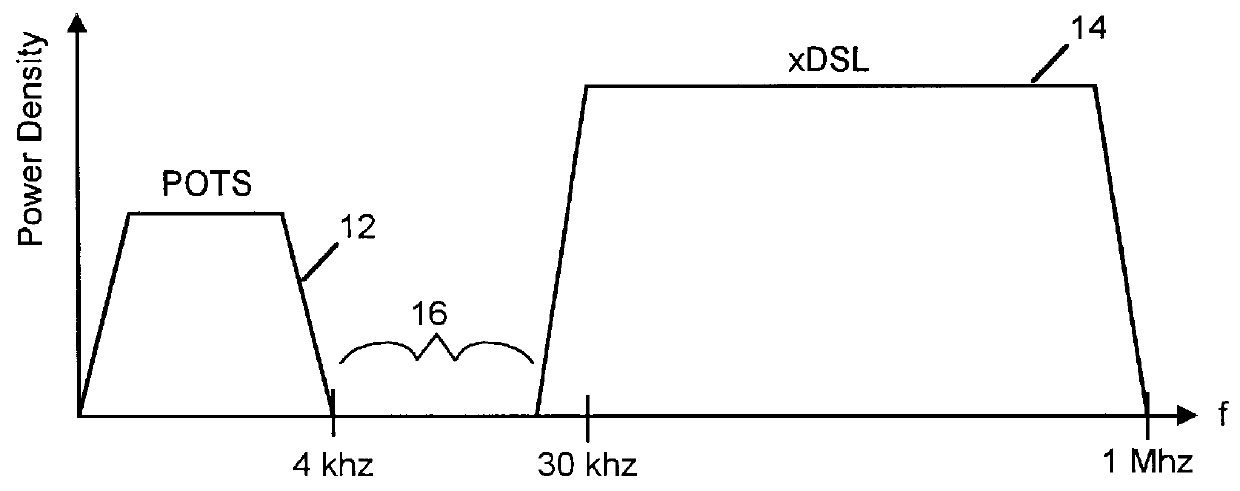
Apparatus and method for communicating voice and data between a customer premises and a central office
InactiveUS6061392AEfficient implementationLow costFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationTelecommunications linkModem device
A method and apparatus are provided for communicating data across a communication link, in a manner that senses and dynamically adapts to the simultaneous transmission of voice information across the local loop. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a method is provided for dynamically communicating data over a local loop using a modem comprising the steps of transmitting data in a full-band transmission state, sensing a band-limiting condition, and adjusting the transmission of data from the full-band transmission state to a bandlimited transmission state, in response to the sensing step. In accordance with the method, data may be transmitted by the modem across the local loop at the same time that voice information is communicated via telephone across the same local loop. A significant aspect of the present invention is the dynamic allocation of the data transmission bandwidth, whereby the invention senses a condition indicative of whether voice information is being communicated. If so, then the system shifts and / or narrows the data transmission bandwidth to allow for voice communications without interference from or with the data transmission. However, when no voice information is being communicated, the invention dynamically allocates the data transmission bandwidth to utilize at least a portion, if not all, of the frequency band otherwise used for communicating voice information.
Owner:PARADYNE CORP
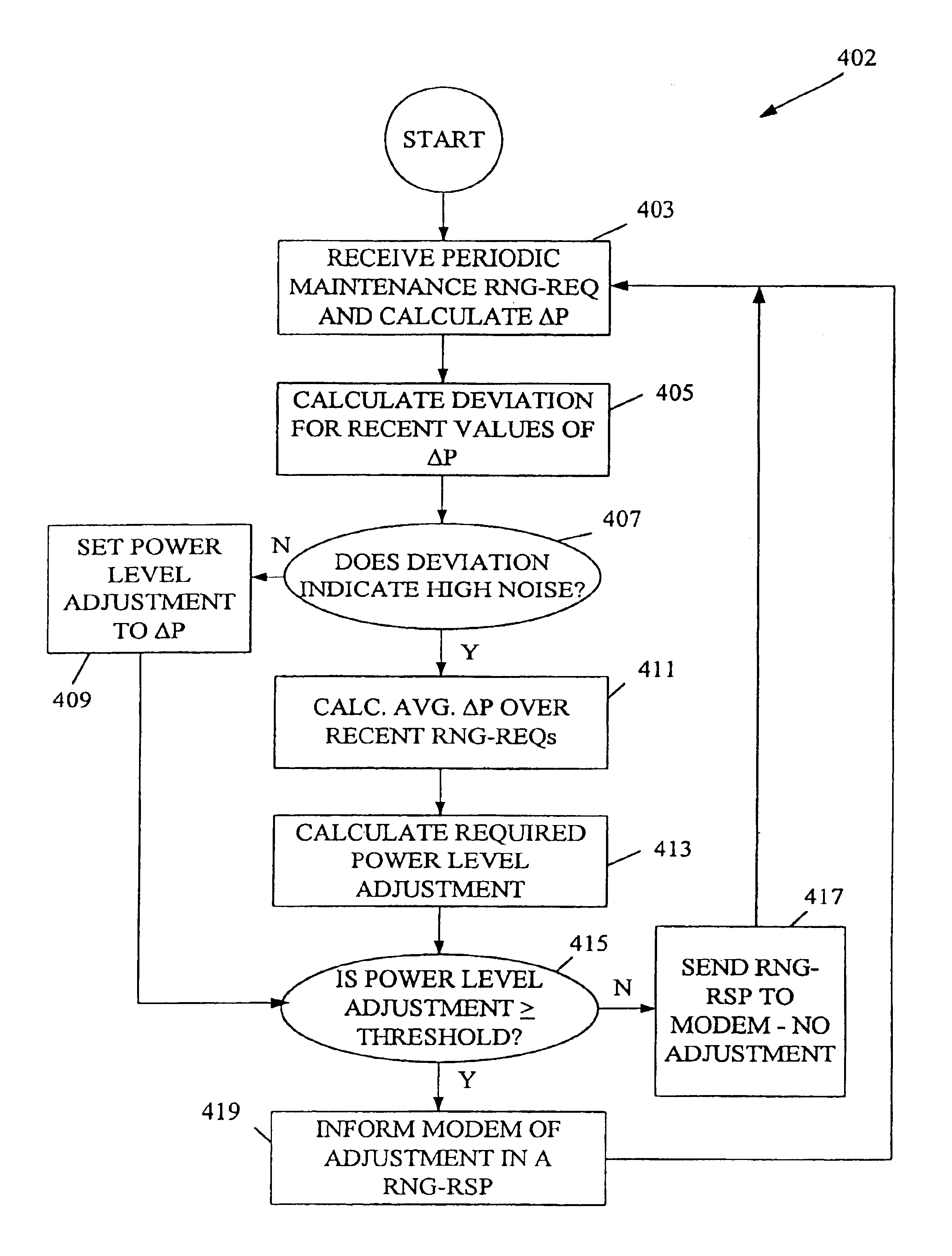
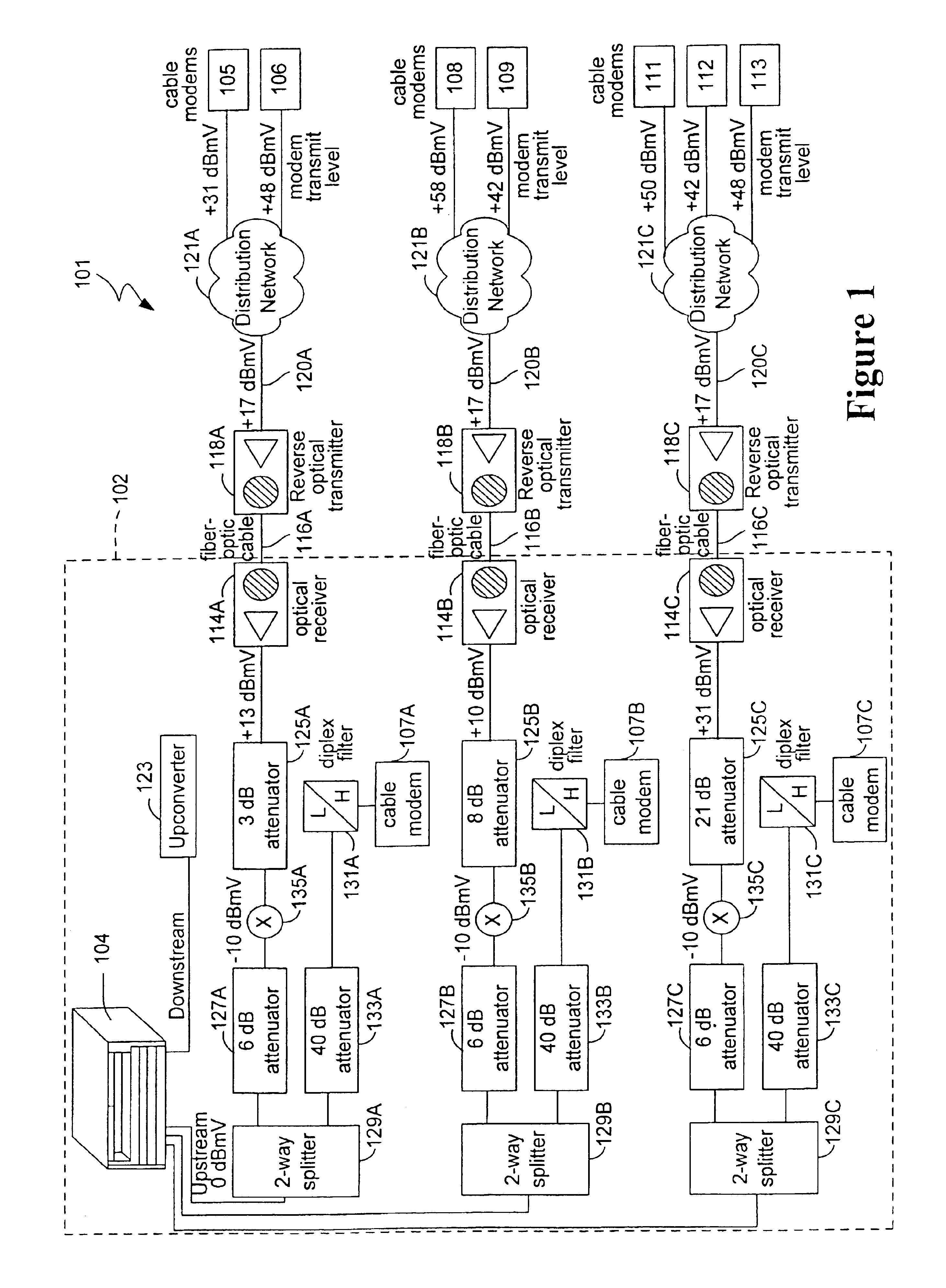
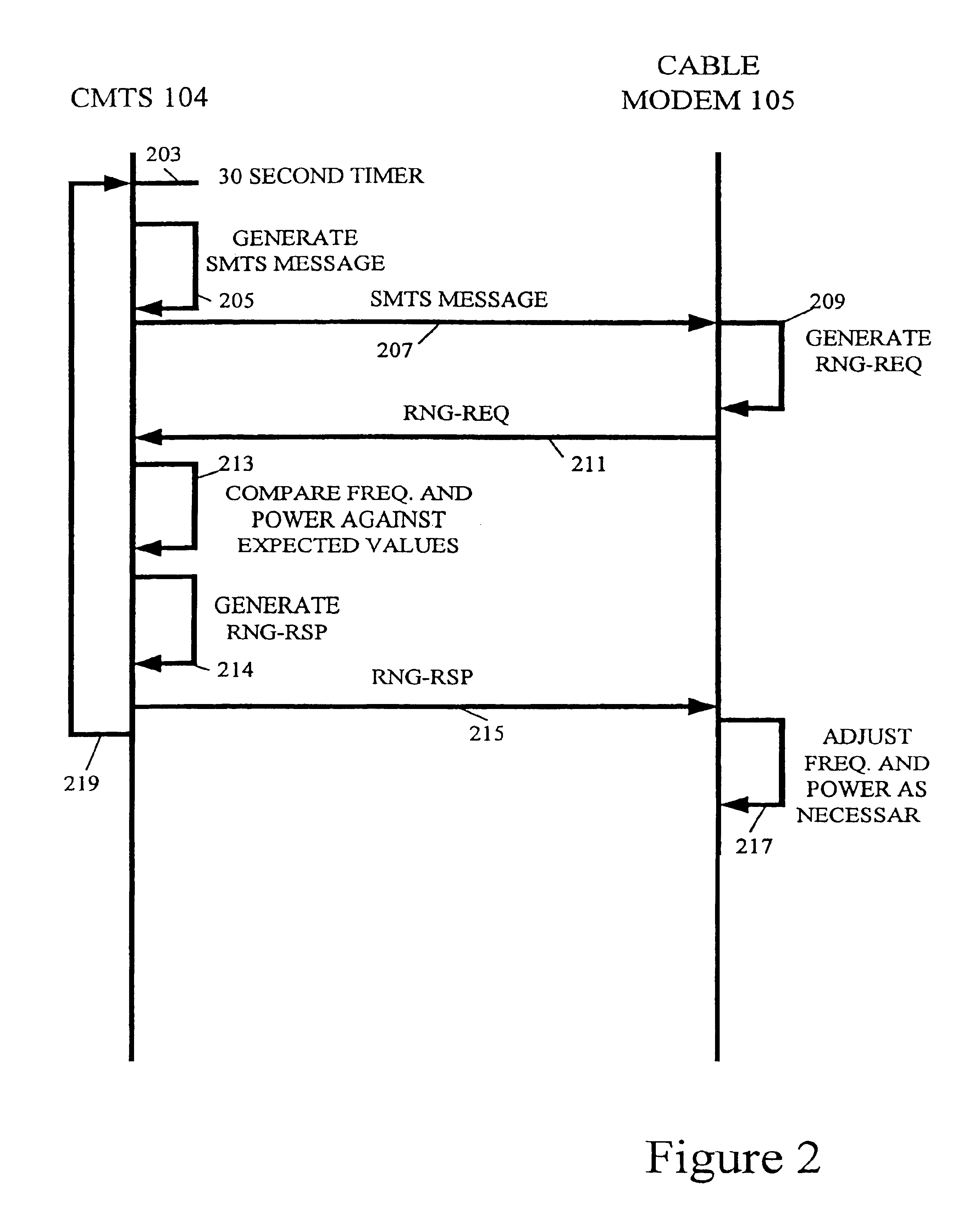
Intelligent power level adjustment for cable modems in presence of noise
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multiradio management through quality level control
InactiveUS20080207253A1Balance performanceStable storageSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringQuality levelSignal quality
A system for managing the operation of a plurality of radio modules integrated within the same wireless communication device. In at least one embodiment of the present invention, a control strategy may be employed to regulate the quality level of a signal delivered by a codec in order to balance the performance realized in the reproduction certain signals with overall communication stability in the wireless communication device. The regulation of signal quality level may be affected by reducing the bit rate of a codec, changing the codec to select another codec with a lower bit rate, or by performing bitrate scaling with the codec signal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
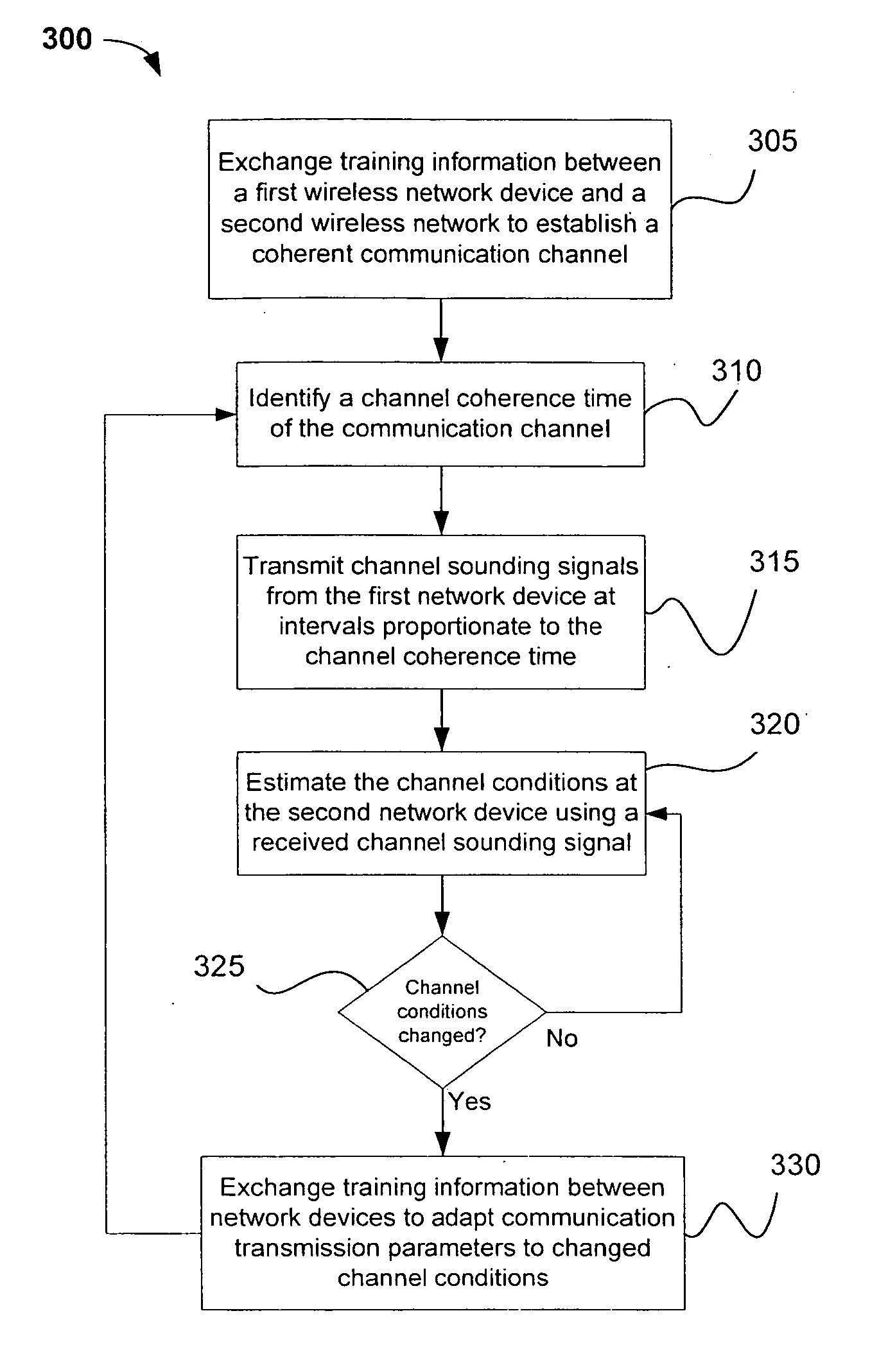
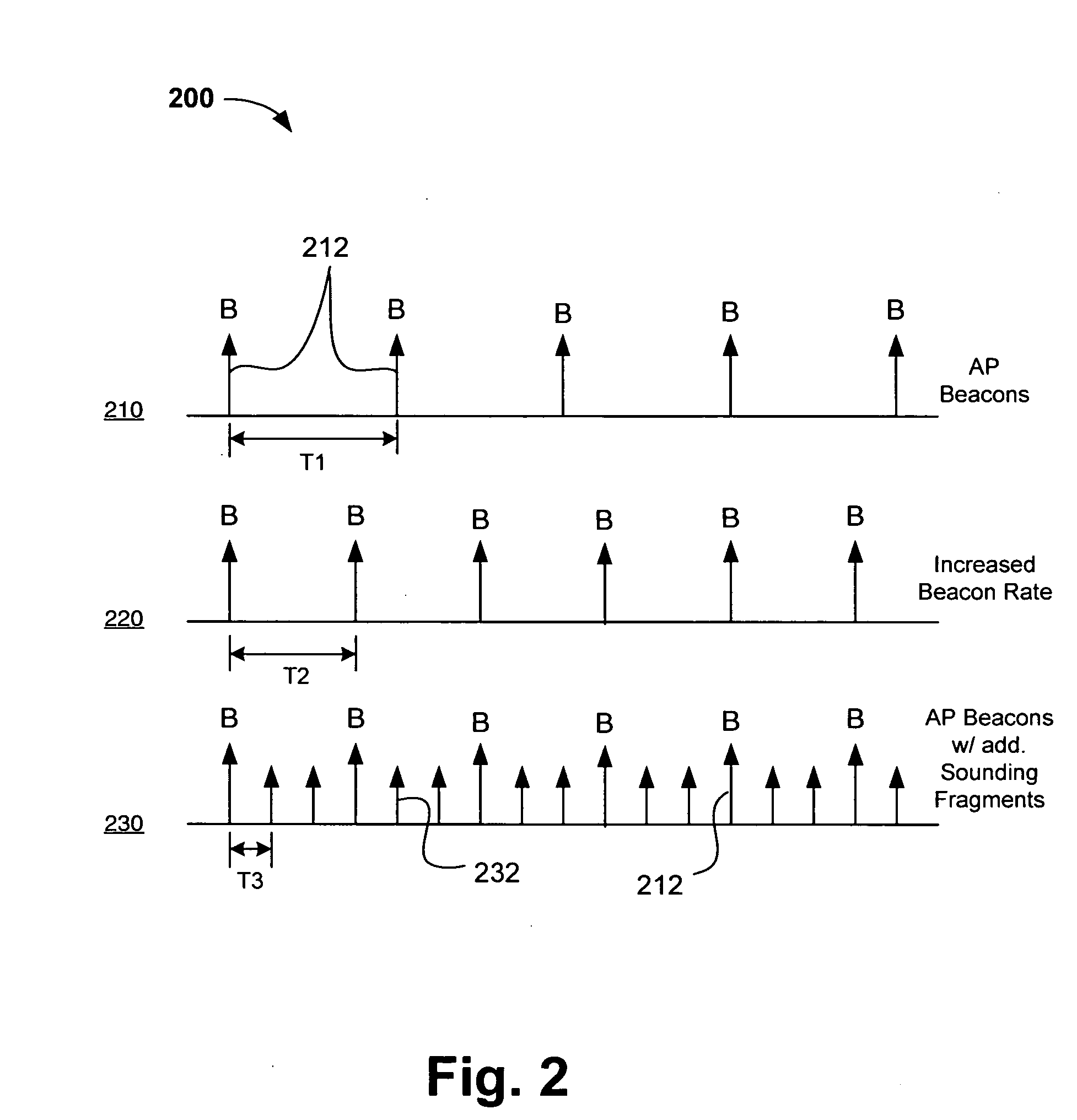
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
InactiveUS20050170781A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsCoherence timeLink adaptation
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and unit for controlling the flow of a TCP connection on a flow controlled network
InactiveUS6925060B2Easy to implementAvoid congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsMultiplexingComputer science
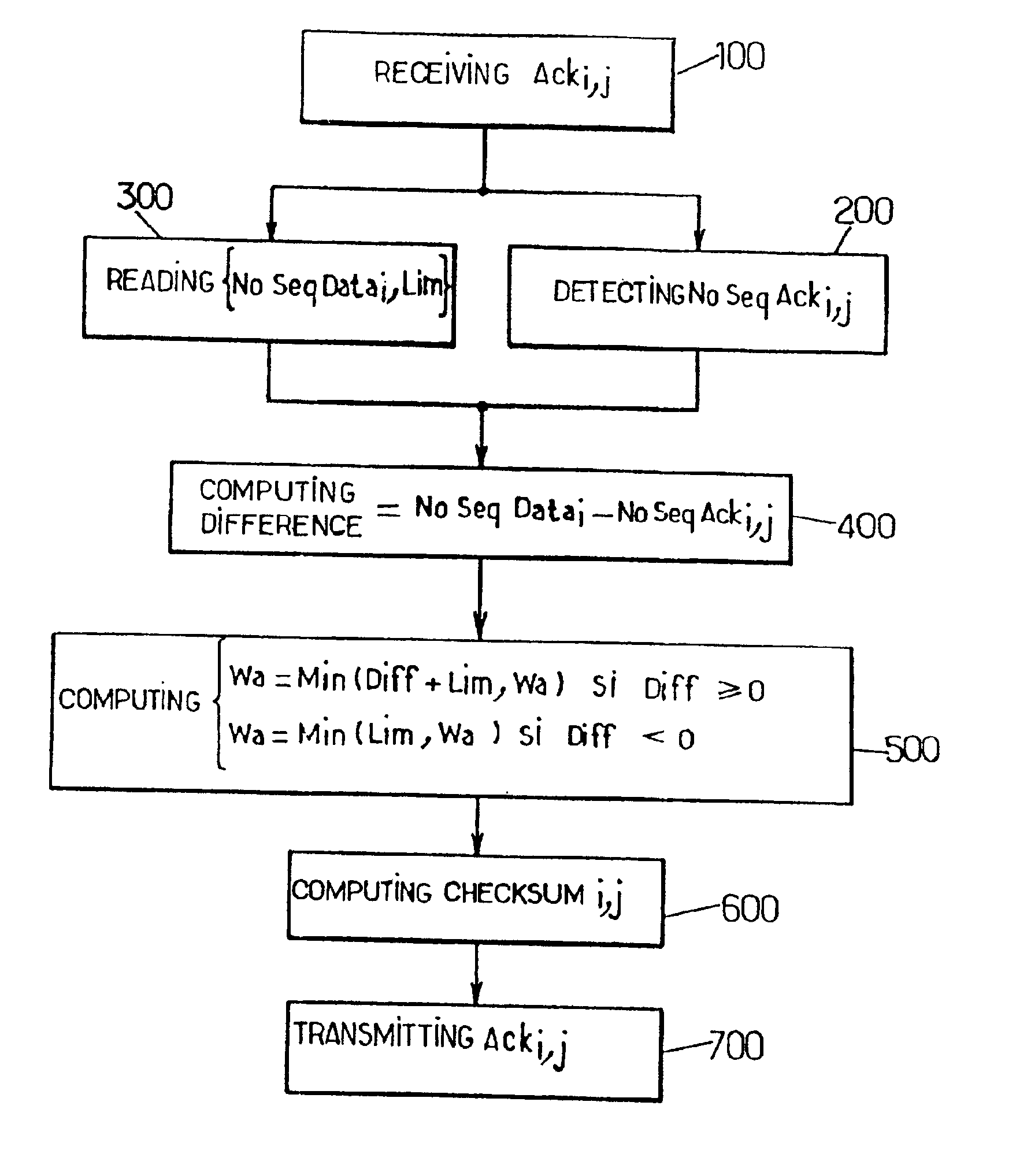
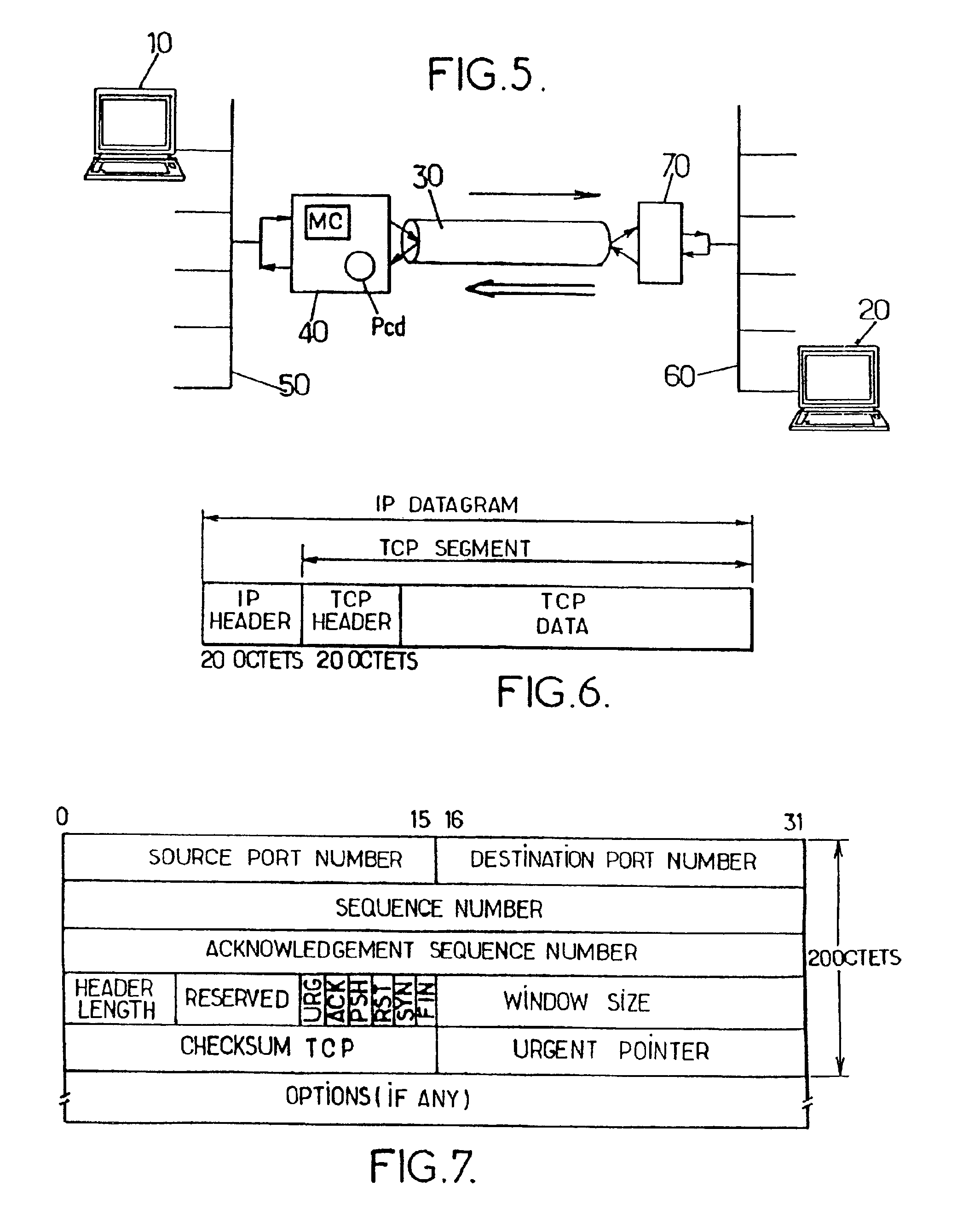
The invention proposes a method and a unit for controlling the flow of at least one TCP connection between a sender and a receiver. The method is of the type which consists in controlling, at the level of a given multiplexing node through which TCP segments relevant to the connection pass, a window size parameter contained in acknowledgement segments sent back by the receiver. The method comprises the steps of:a) receiving an acknowledgement from the receiver on the up link (receiver to sender) of the connection at the level of said given multiplexing node;b) controlling a window size parameter contained in, said acknowledgement segment on the basis of the difference between, firstly, a first context value associated with the TCP connection, defined as being the sequence number of the last segment that was transmitted from said given multiplexing node on the down link (sender to receiver) of the connection, to which the length of said segment is added, and, secondly, the sequence number indicated in said acknowledgement segment;c) transmitting the acknowledgement segment to the sender the up link of the connection from said multiplexing node with the window size parameter thus controlled.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
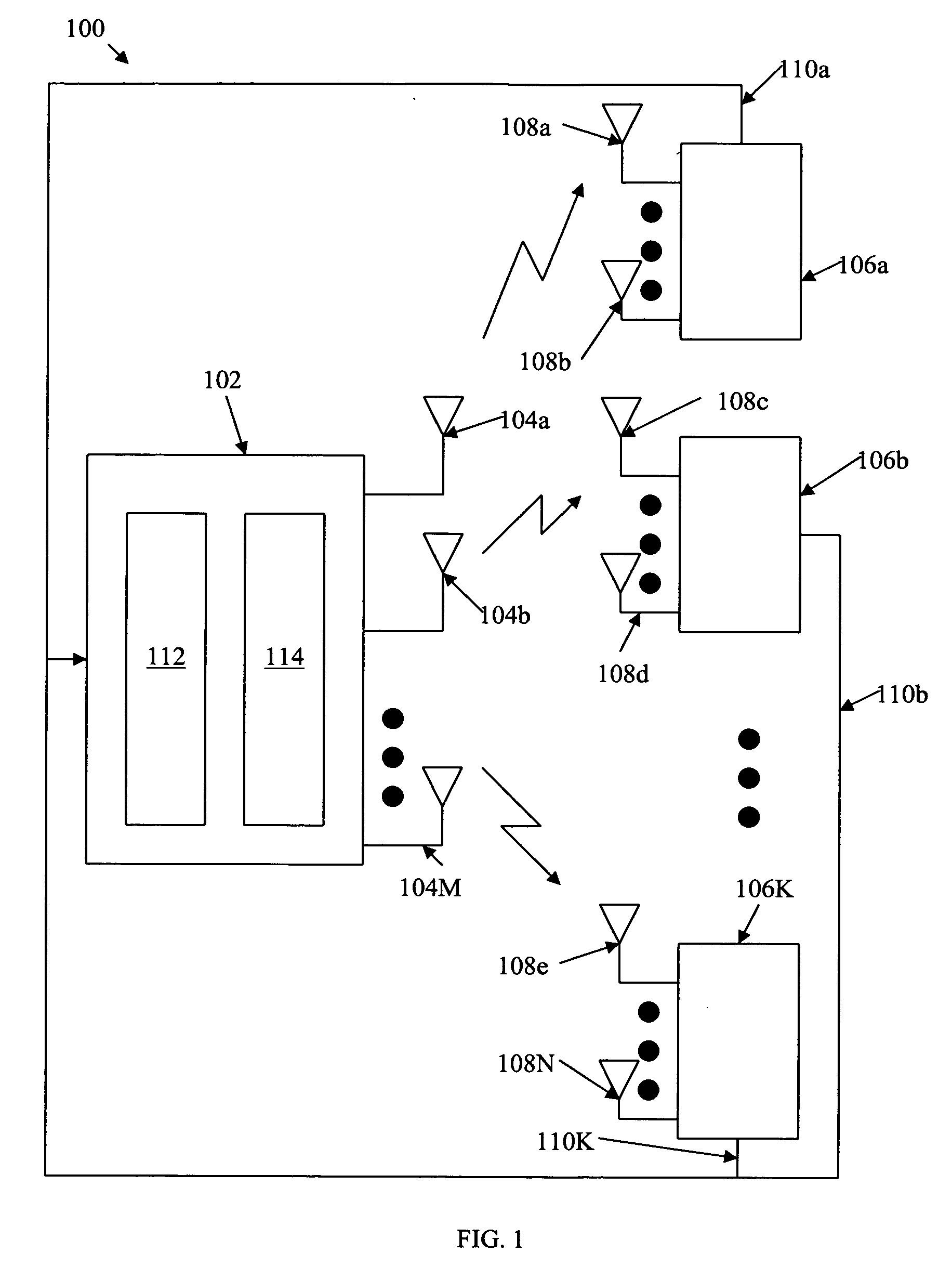
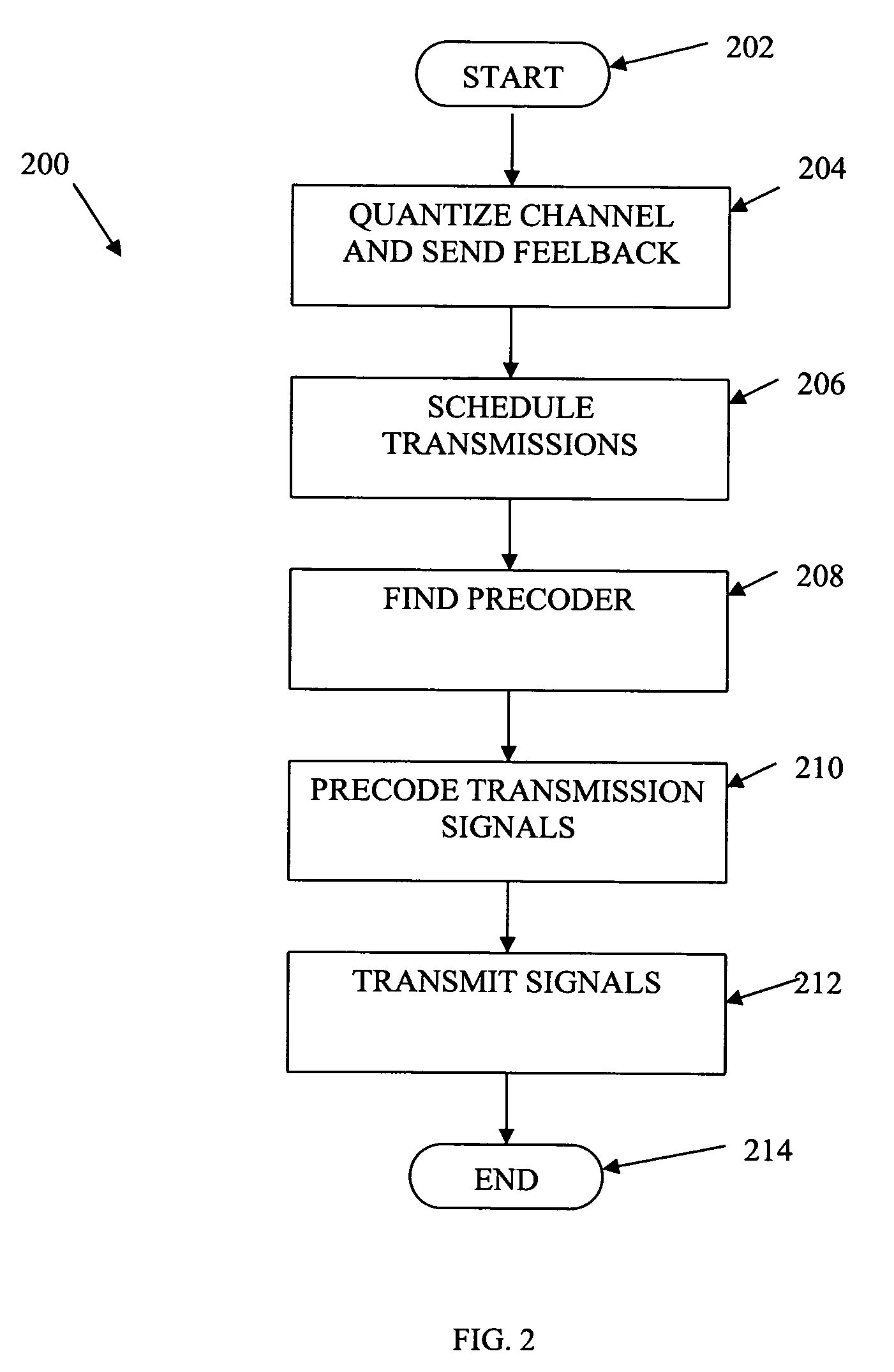
Design of multi-user downlink linear MIMO precoding systems
ActiveUS20080159425A1Maximize throughputSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityEngineeringMimo systems
Multi-user (MU-) MIMO systems with quantized feedback are designed to maximize the sum-rate via scheduling and linear precoding. To maximize throughput over the network, quantized CSIT is sent through a low-rate feedback link feedback from a plurality of users back to a base station. The base station then determines a subset of the plurality of users to transmit one or more signals to based on the received feedback and determines a preceding matrix based on the received feedback from the plurality of users wherein the precoding matrix maximizes a sum-rate throughput for the subset of the plurality of users. Additionally, based on the received feedback, the base station designs a quantization codebook. This codebook may be designed off-line and / or online. The codebook and / or precoding matrix are used to transmit signals to the users.
Owner:NEC CORP
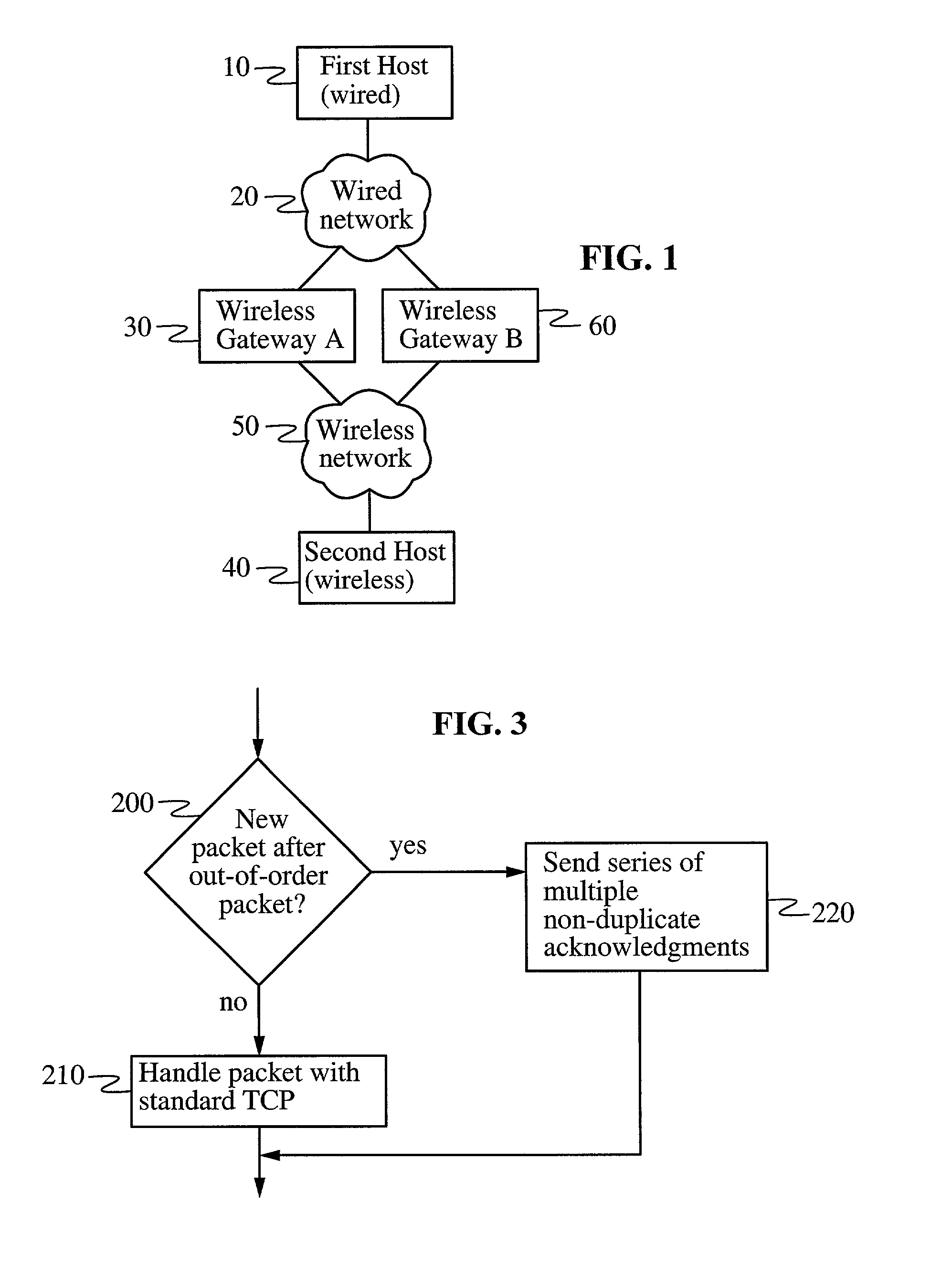
Data throughput over lossy communication links
InactiveUS7061856B2Promote recoveryError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData connectionTelecommunications link
In a heterogeneous data network including both wired and wireless / lossy links, a transport protocol method implemented at the wireless host is fully compatible with existing wired networks and wireless gateways, and requires no modification to transport protocols at existing wired hosts. The wireless host calculates a temperament parameter [100] characterizing the error-proneness of the data connection and uses this parameter to determine whether error-induced losses or congestion-losses dominate the data connection [110]. If congestion-losses dominate the data connection, then the host uses a standard technique for acknowledging data packets [130]. If, on the other hand, error-induced losses dominate the connection, the host uses a modified technique for acknowledging data packets [120]. According to this modified technique, the wireless host sends a plurality of non-duplicate acknowledgements of a single packet whenever a packet is received after an out-of-order packet is received. By acknowledging distinct fragments of the packet, rather than identical (i.e., duplicate) acknowledgments of the packet, the acknowledgments have the effect of accelerating recovery of maximal window size at the wired host and increasing data throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Dual mode satellite/cellular terminal
InactiveUS6084865APower managementTransmission control/equalisingTime division multiple accessDual mode
A method and apparatus of communicating information using Time Division Multiple Access and adaptive transmission and reception are disclosed. Signal bursts are transmitted from TDMA transmitters to a TDMA receiver wherein the transmitter codes the information and transmits coded information to the receiver using at least one of two timeslots of a plurality of timeslots in a repetitive TDMA frame period. Both of the two timeslots are received whether or not the transmitter has transmitted using one or two timeslots and the received signals are classified as intended and non-intended. Successively received signals classified as intended are then assembled into a block for decoding to reproduce the information.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
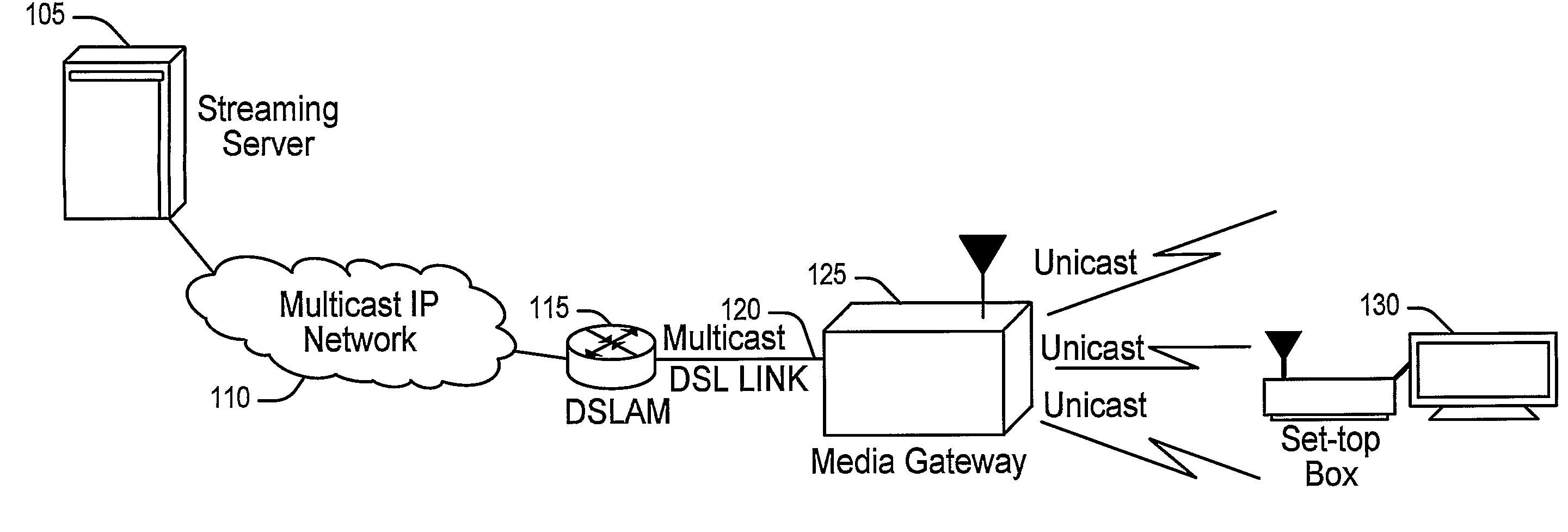
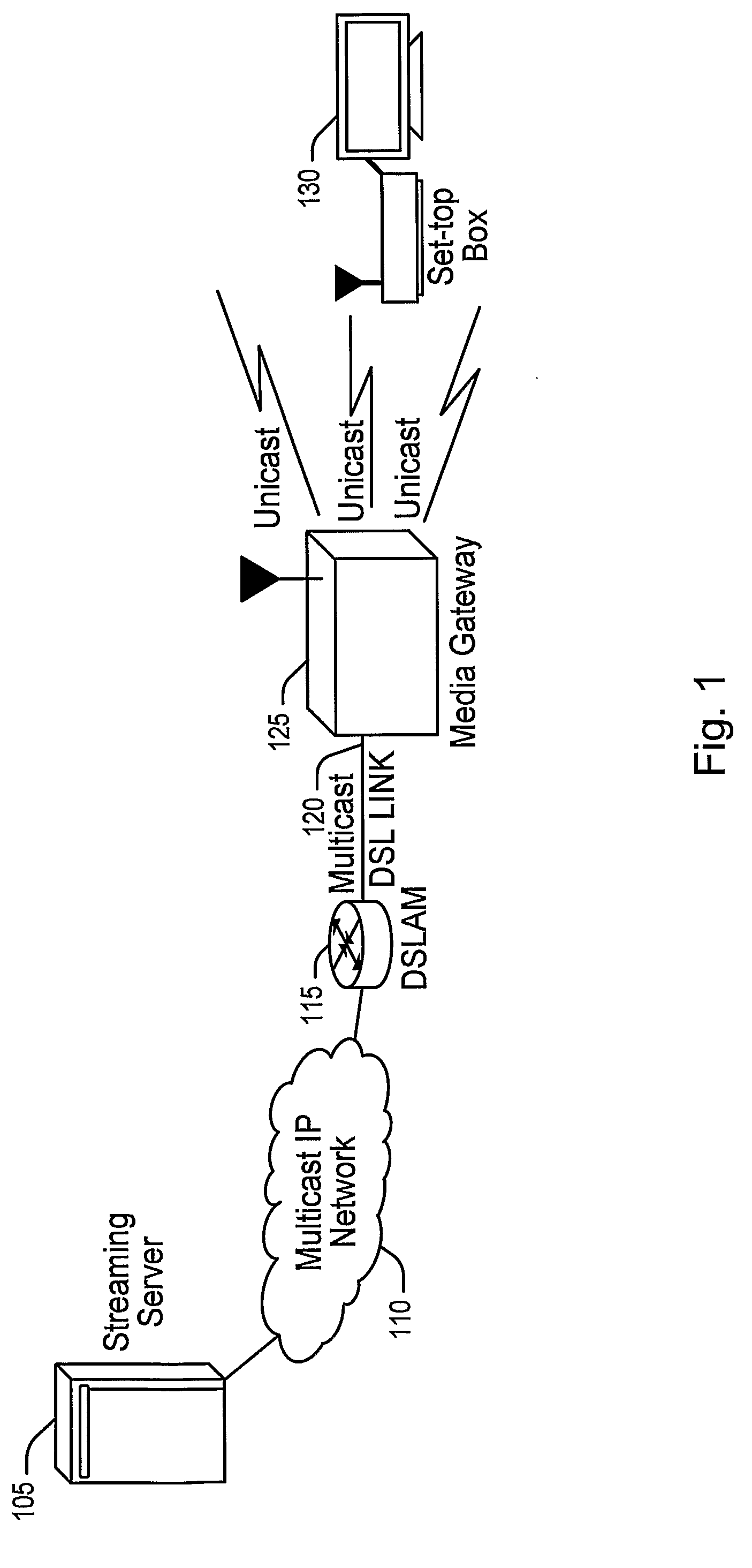
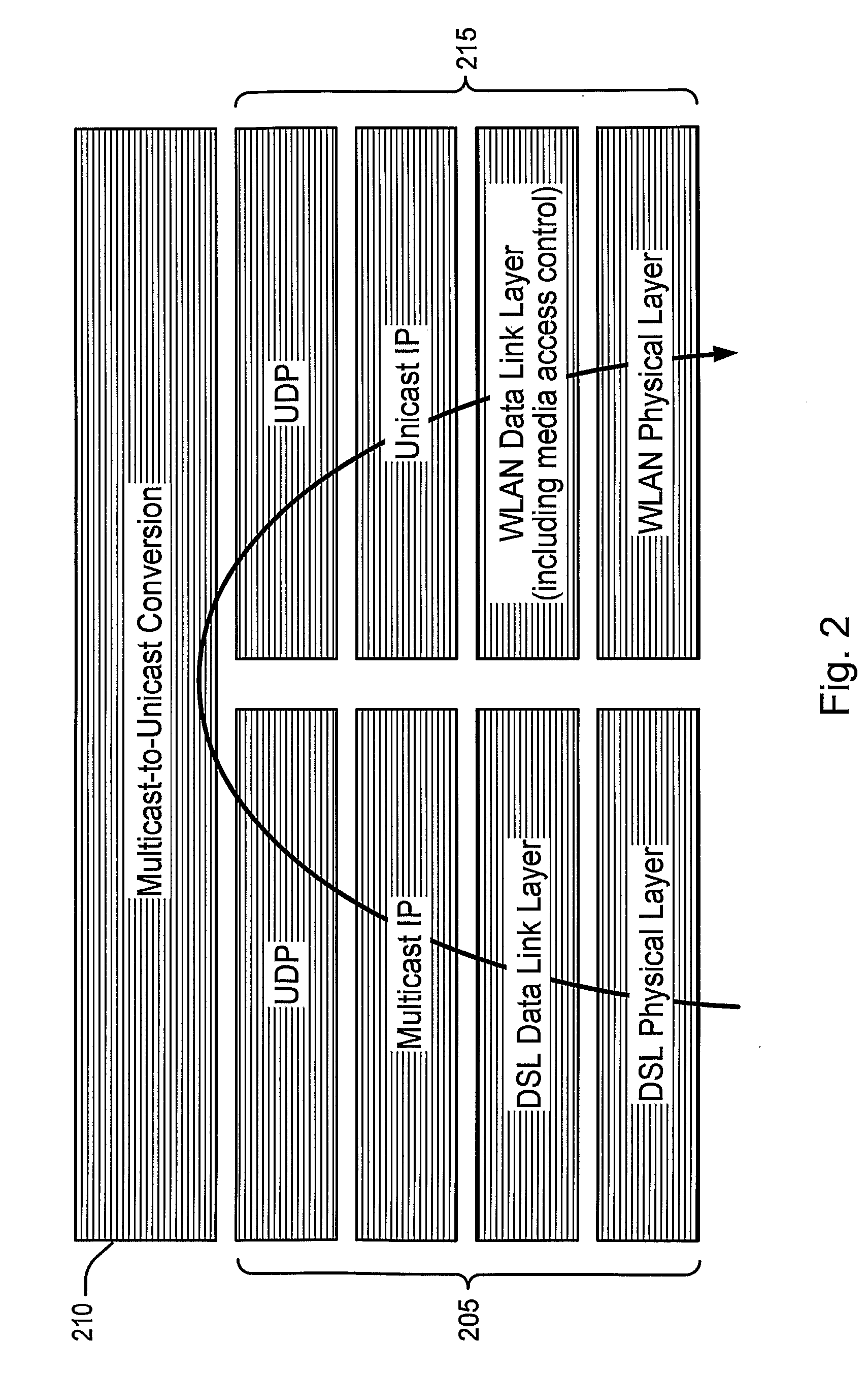
Method and Apparatus for Reliably Delivering Multicast Data
ActiveUS20090147718A1Reliable deliveryReliable transmissionSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast transmission systemsNetwork packetMulticast address
A method and apparatus are described including mapping a multicast connection to a unicast uniform resource identifier, establishing a state for a multicast-to-unicast conversion, allocating ports, receiving multicast addressed data packets and converting the multicast addressed data packets to unicast addressed data the packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
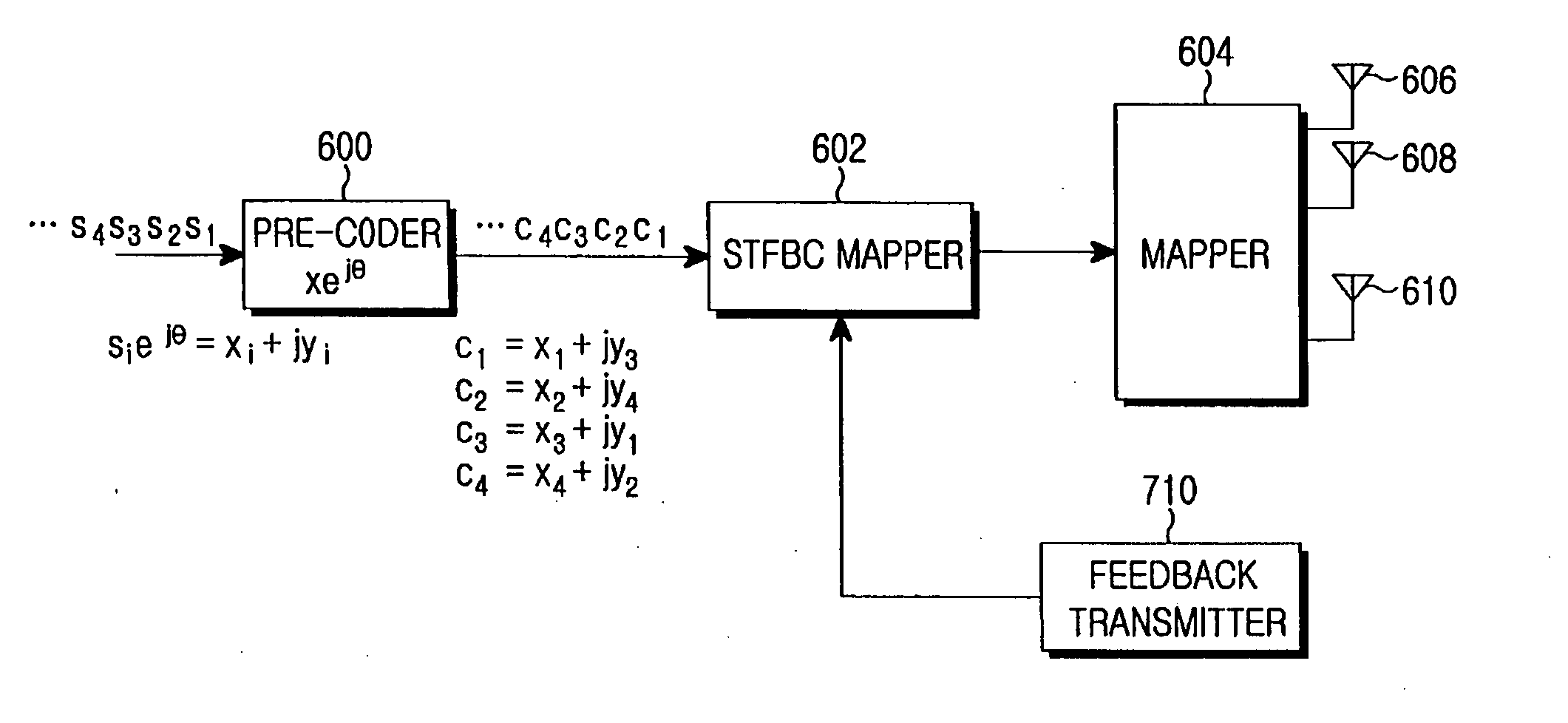
Apparatus and method for space-time-frequency block coding for increasing performance
ActiveUS20060039500A1Improve performancePolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationTransmission matrixComputer science
A space-time-frequency block coding apparatus and method in a transmitter with three transmit (Tx) antennas are provided. An input symbol sequence is transmitted through three Tx antennas according to a permutation method using a selected transmission matrix in order to improve the performance of an STFBC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
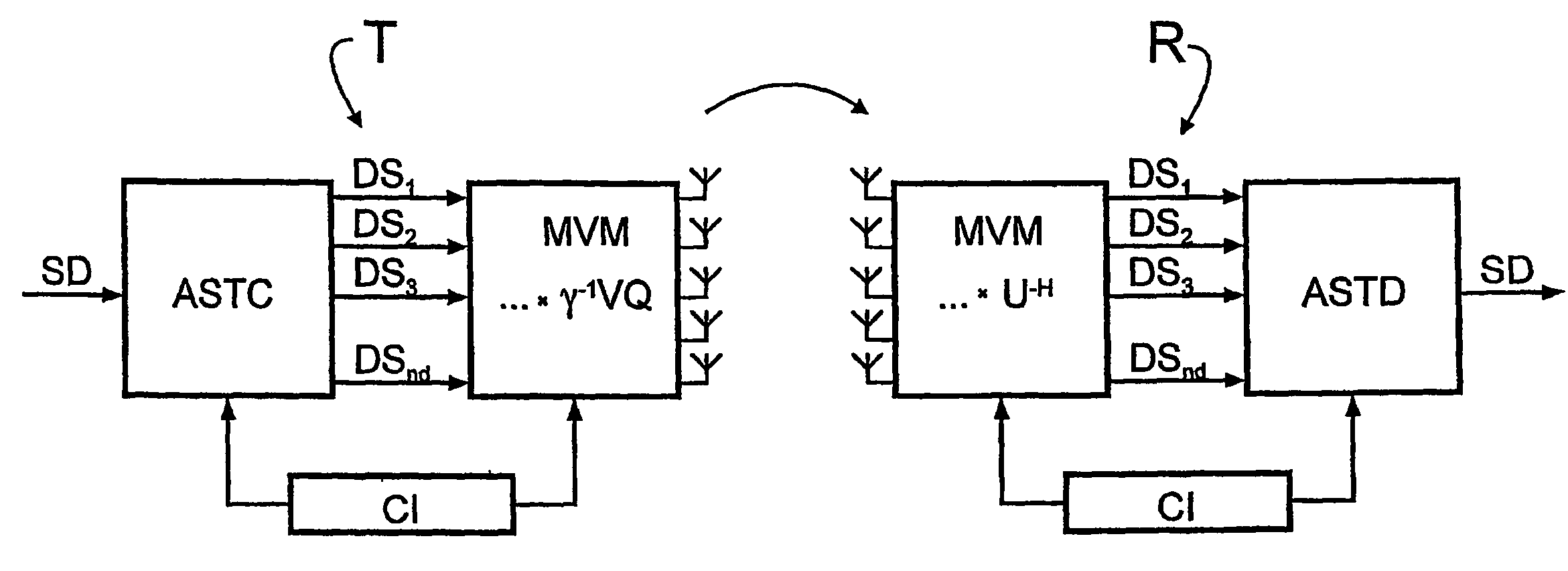
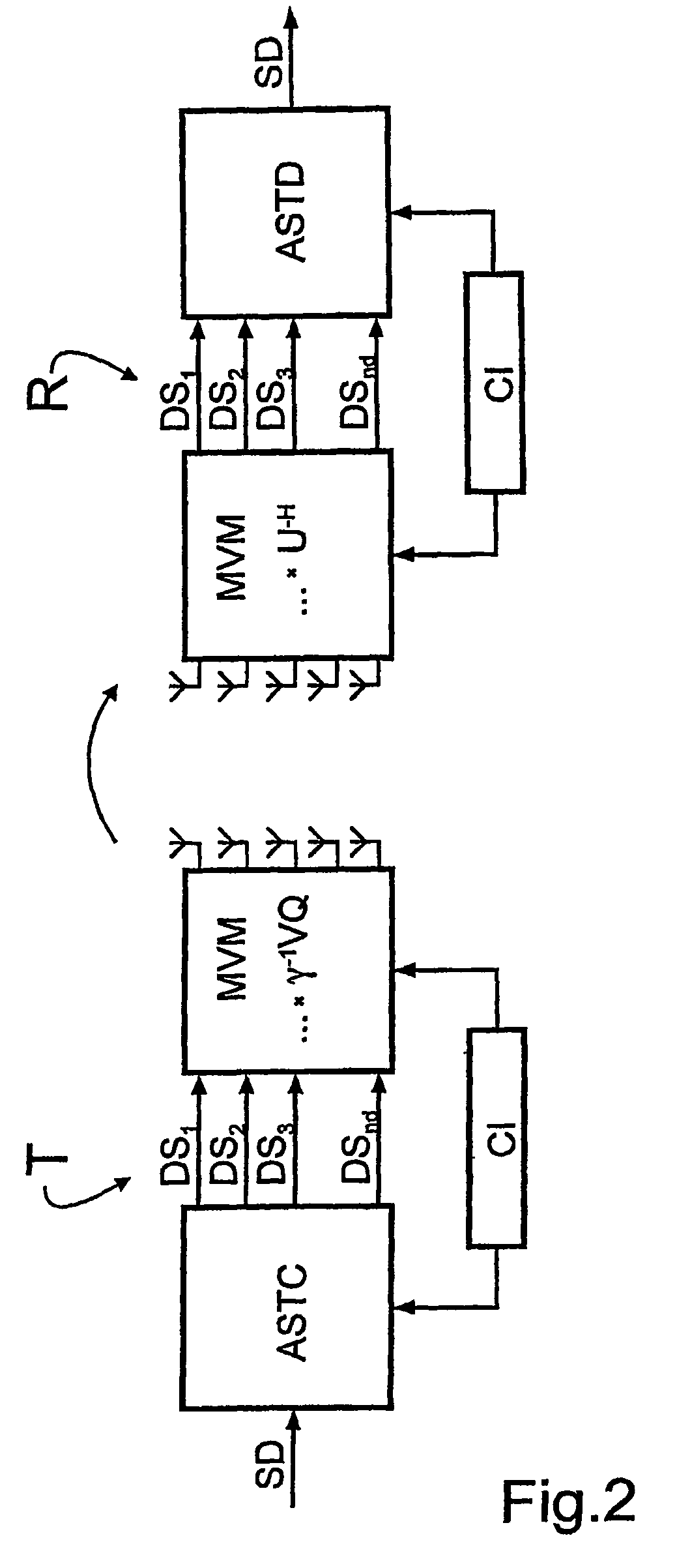
Mimo signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
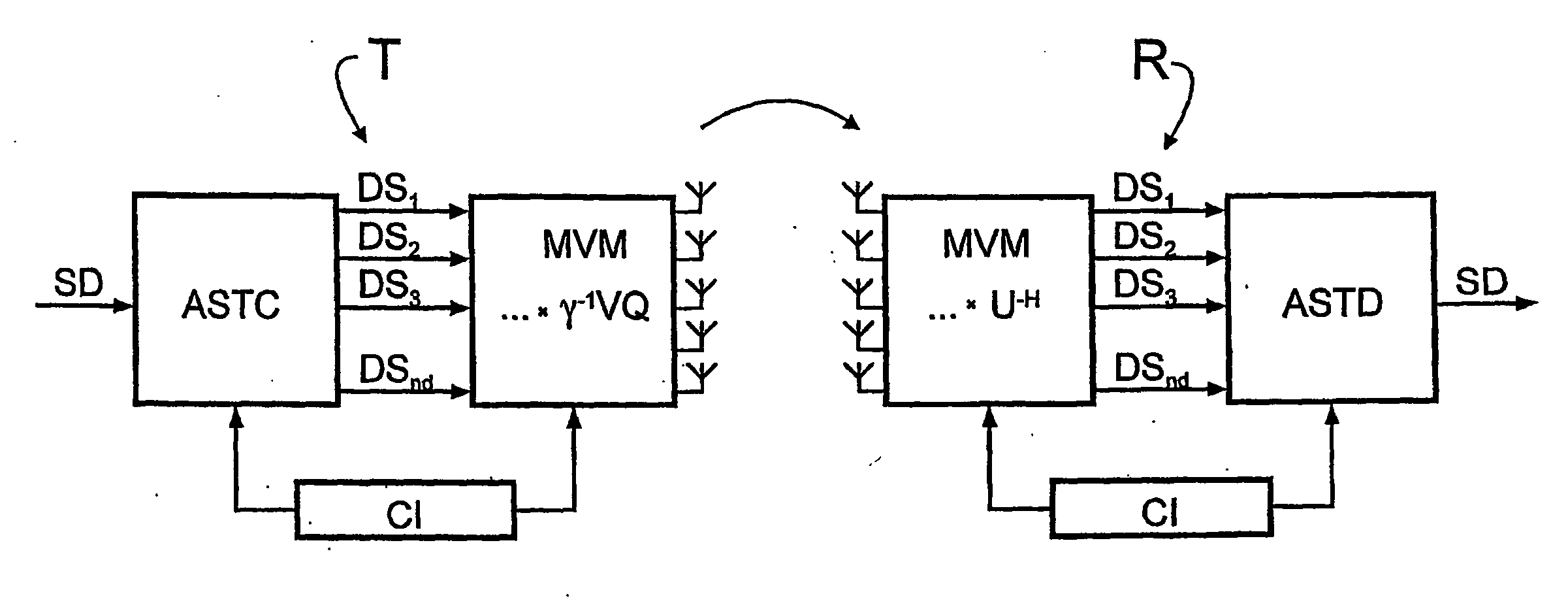
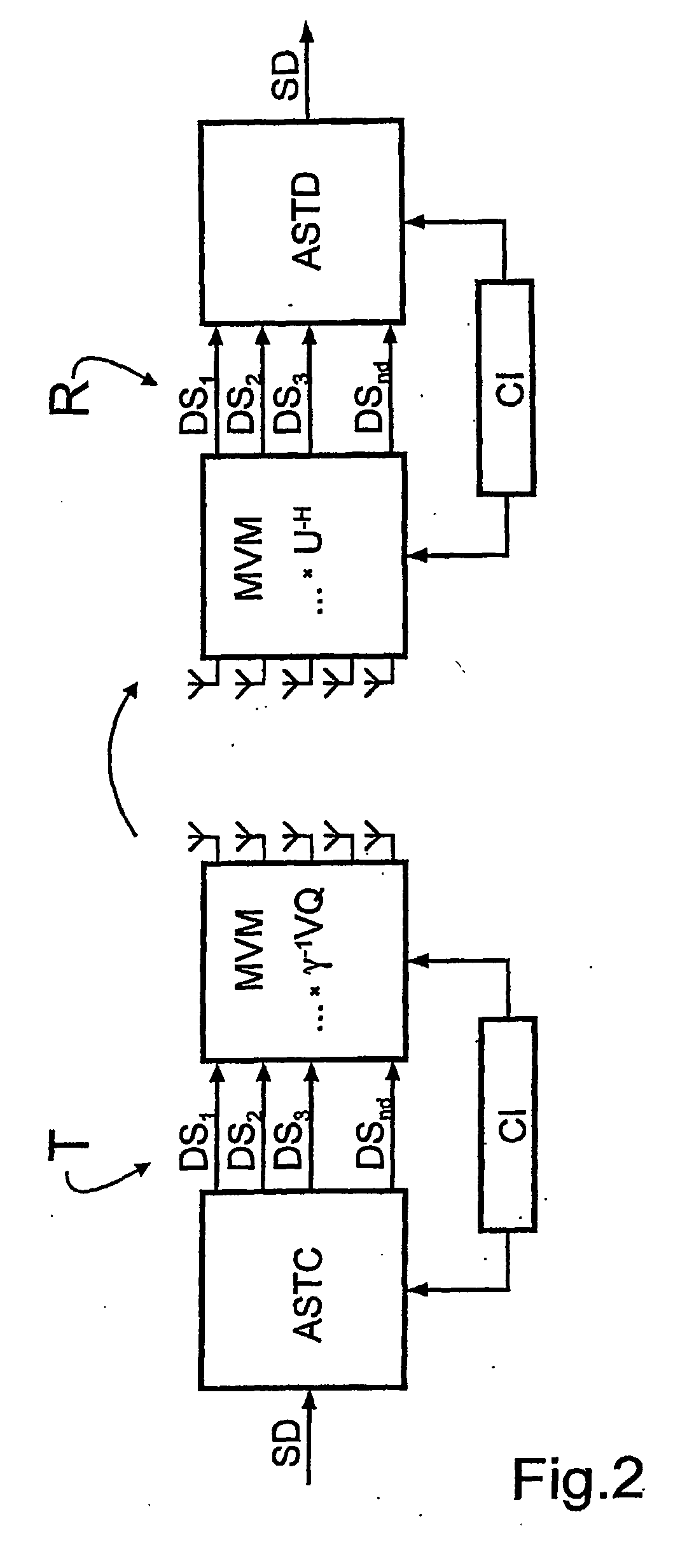
InactiveUS20060193294A1Reduce complexityReliable data transmissionPower managementTransmission control/equalisingData streamTransmitted power
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Vector network analyzer applique for adaptive communications in wireless networks
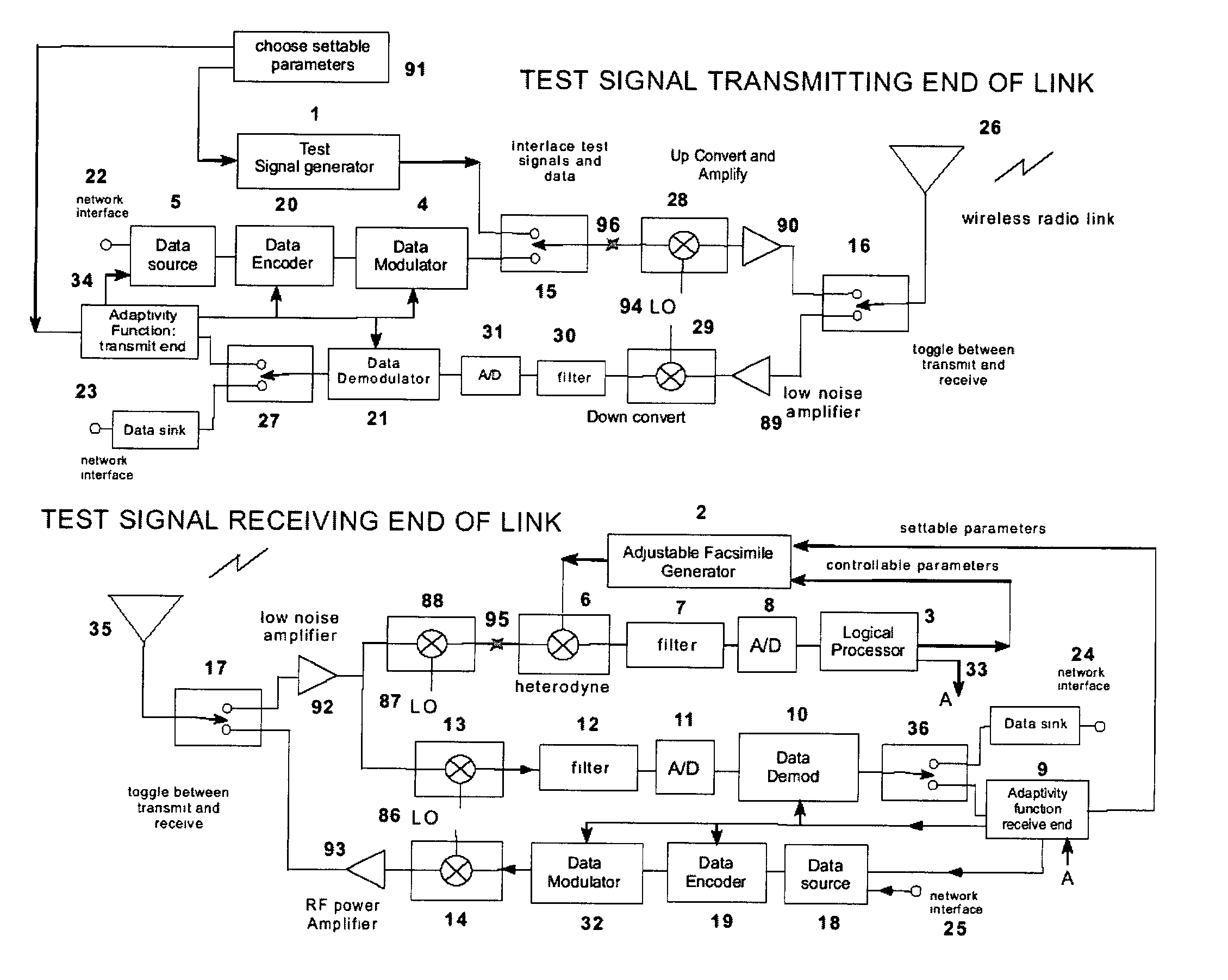
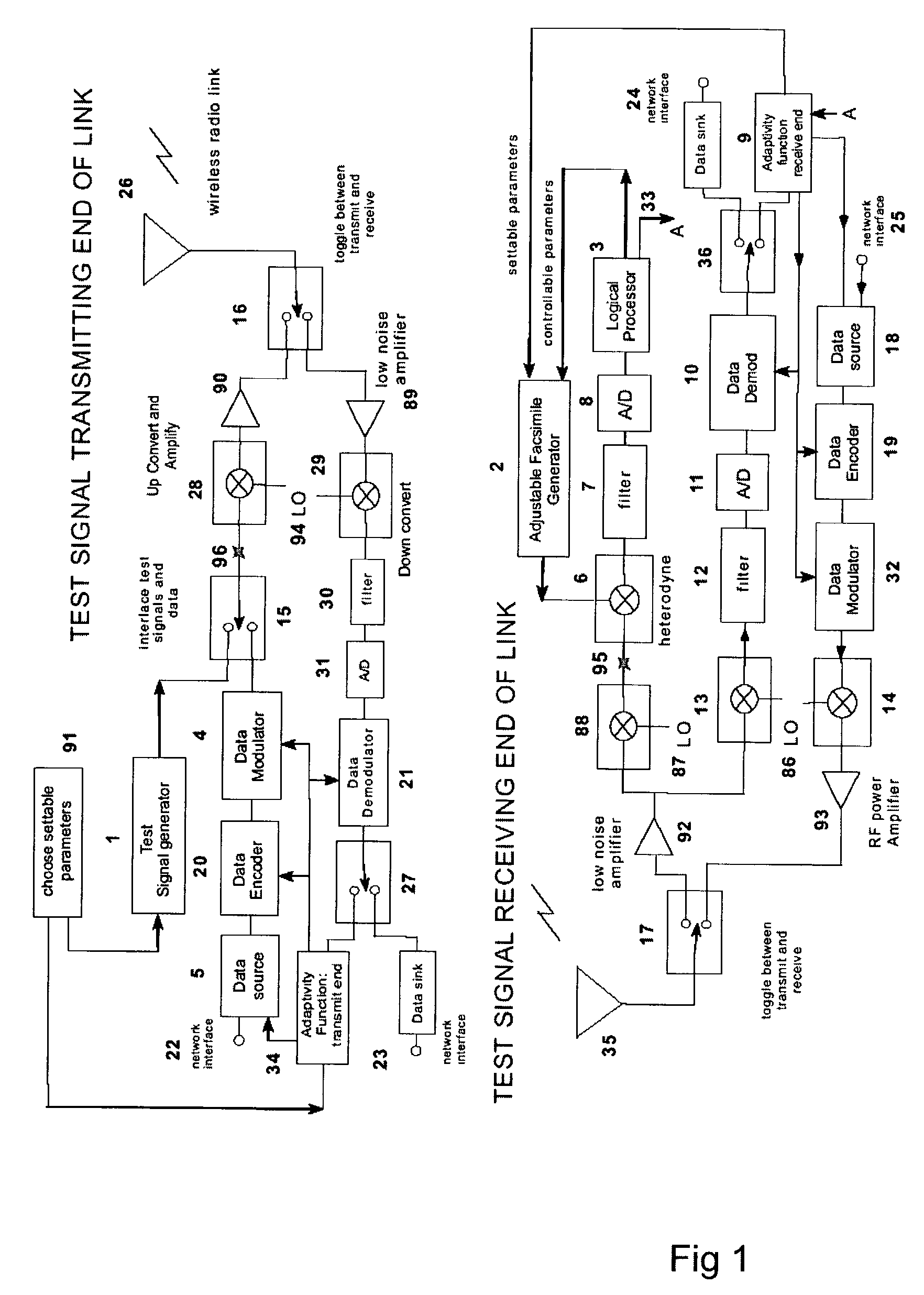
A test signal generator at a transmitter station and a facsimile generator at a receiver station go through an acquisition and tracking process which aligns the two signals so that a logical processor can compute the frequency transfer function of the entire propagation path for use in an adaptive, concurrently sent communication signal. The frequency transfer function is conveyed back to the transmit end via a control channel permitting an adaptivity function at the transmit end to influence subsequent selection of communication parameters, among which are typically transmitted data rate, selection of modulation, selection of forward error correcting coding, and selection of frequency band for transmission. The same measurement is conveyed to an adaptivity function at the receive end for use in the communications receiver to select demodulator variables such as gain control, and equalization of amplitude and phase, versus frequency. The adaptivity function also permits interspersing of reverse-direction communications over the same frequency bands in a time-share mode between forward-direction and reverse-direction communication with the measurement signals having to be transmitted in only one direction. An alternate embodiment invention of this type is described which is additionally useful for mobile communications channels. Another variation embodiment is described for pure propagation measurements only, absent conveyance of end-user information.
Owner:SARABAND WIRELESS
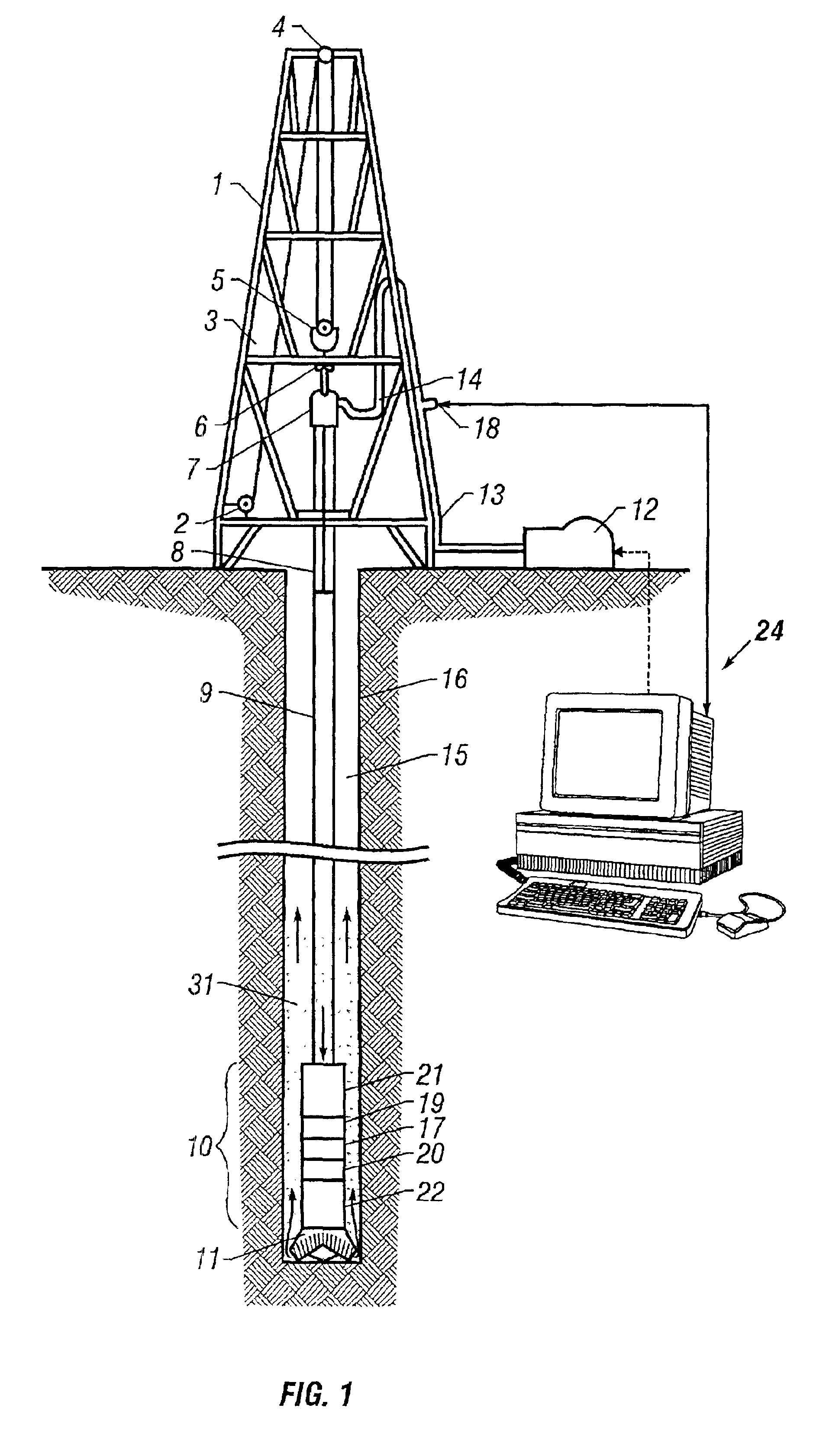
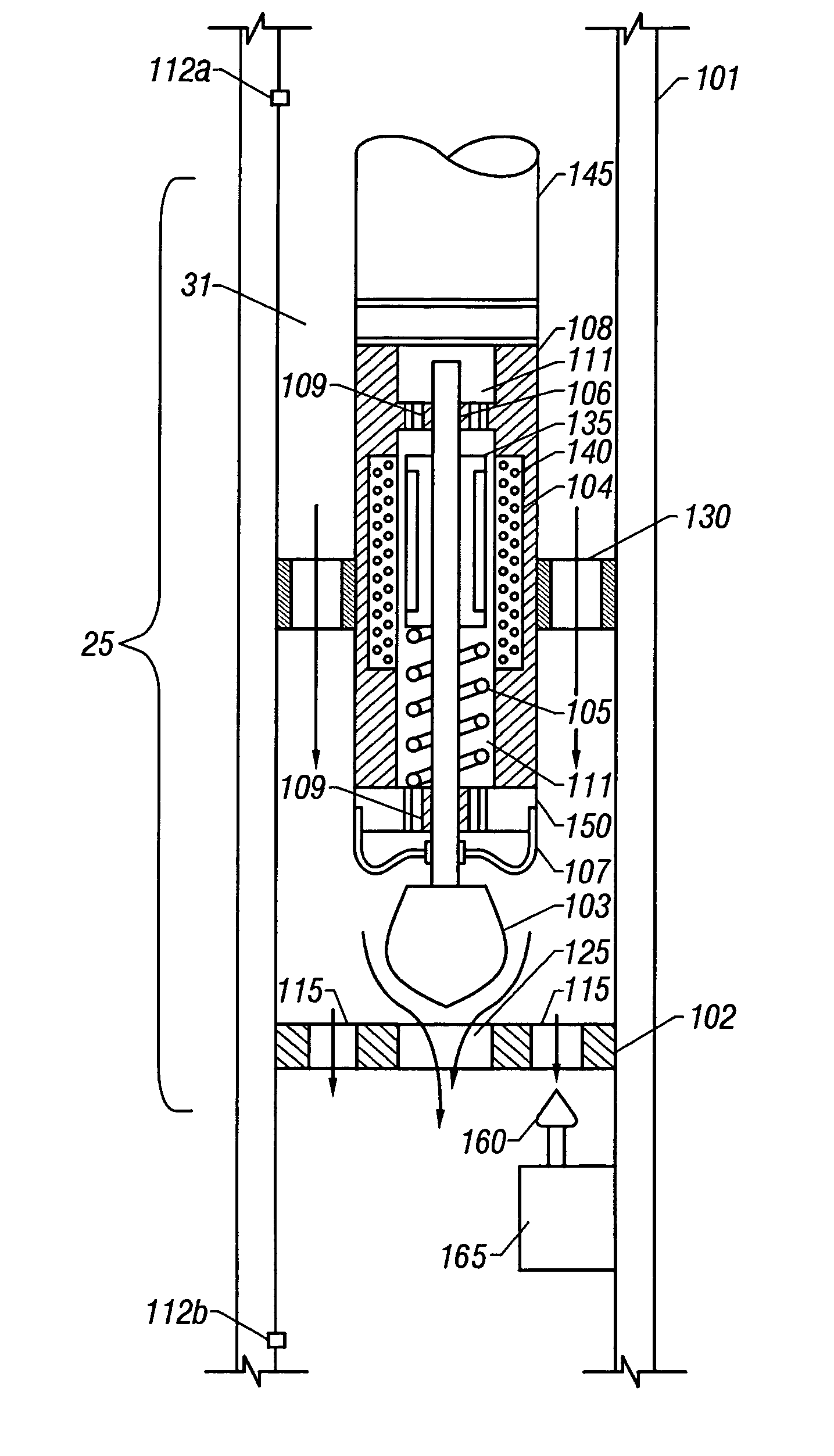
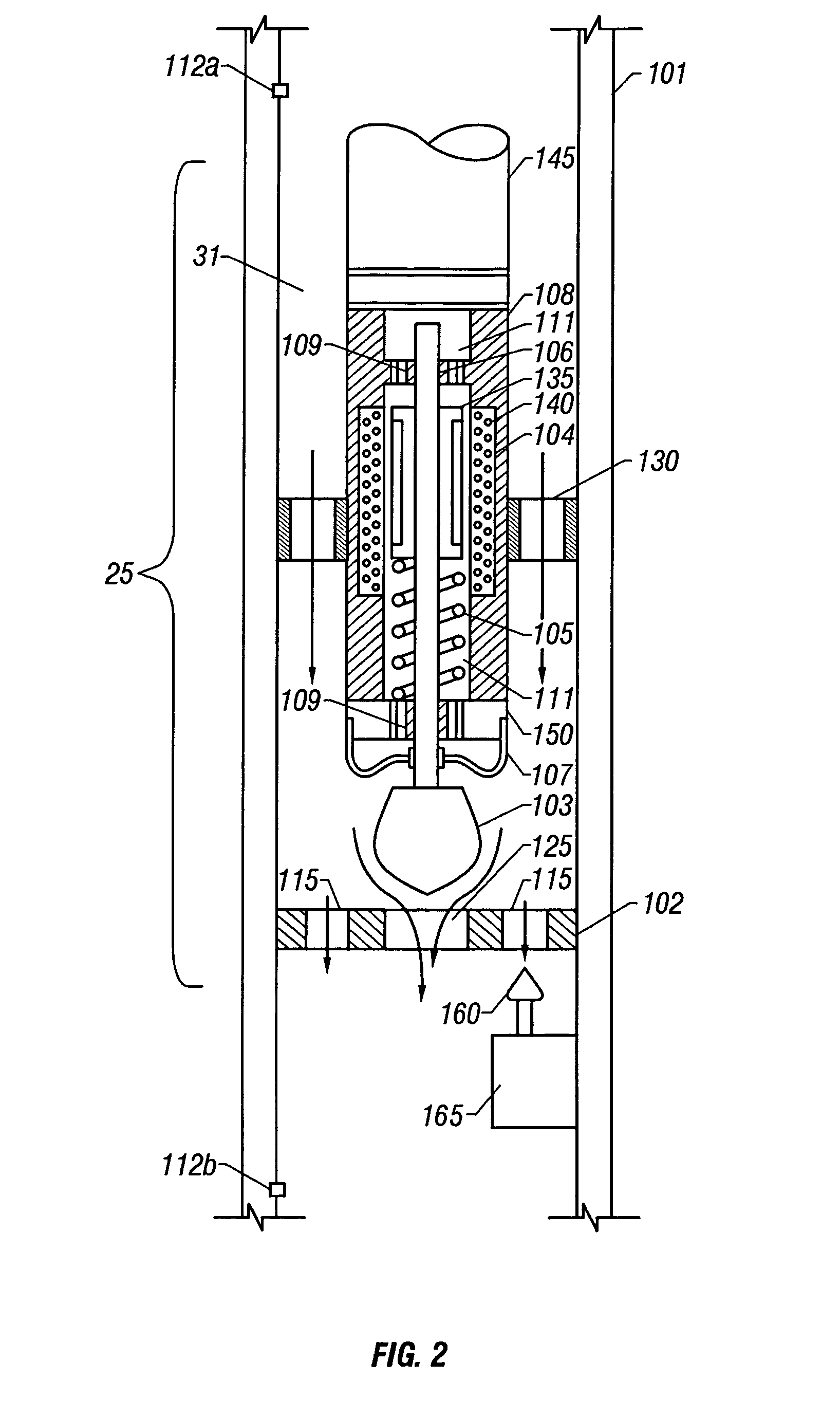
Hydraulically balanced reciprocating pulser valve for mud pulse telemetry
ActiveUS6898150B2Improve data transfer rateSurveyMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsDifferential pressureReciprocating motion
A reciprocating pulser system for generating pressure fluctuations in a flowing drilling fluid comprising a reciprocating poppet and a stationary valve assembly with axial flow passages. The poppet reciprocates in close proximity to the valve assembly, at least partially blocking the flow through the valve assembly and generating oscillating pressure pulses. The poppet passes through two zero speed positions during each cycle, enabling rapid changes in signal phase, frequency, and / or amplitude thereby facilitating enhanced data encoding. The poppet is driven by a linear electric motor disposed in a lubricant filled housing. In one embodiment, the housing to shaft seal is a flexible bellows. In one embodiment, a force balance spring is used to essentially offset the hydraulic flow forces on the poppet. In one embodiment, a bypass poppet is used to adjust the differential pressure across the valve assembly.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
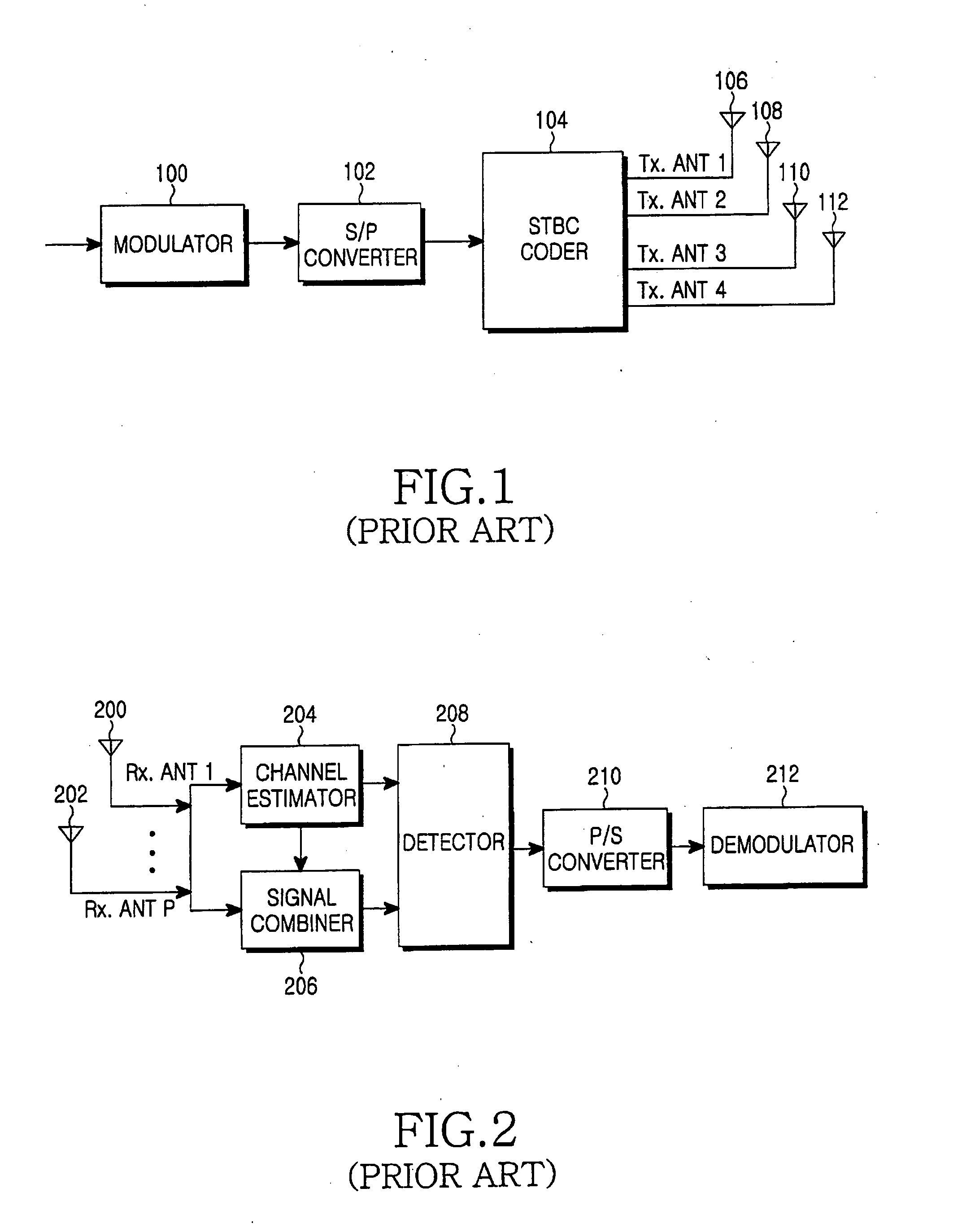
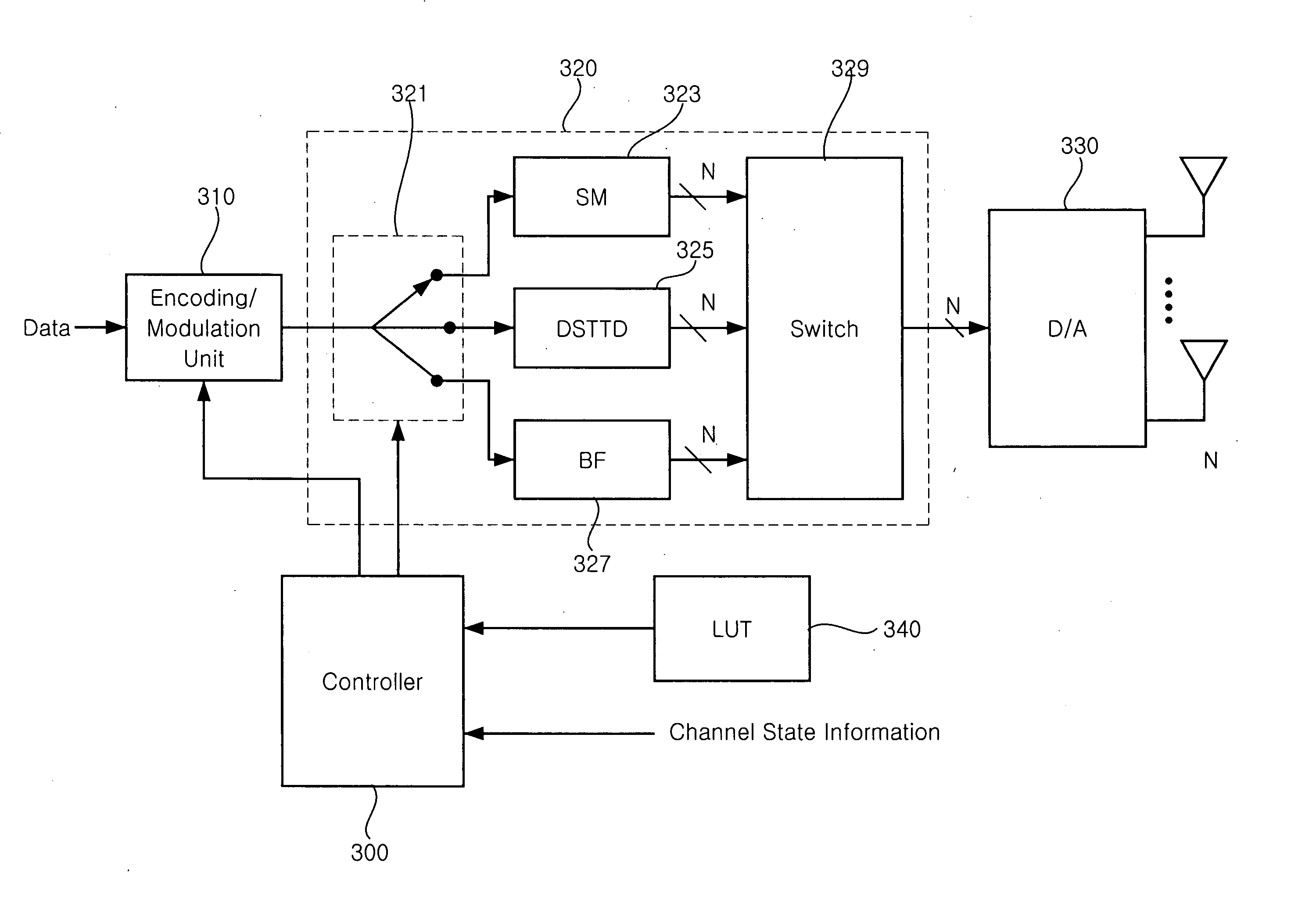
MIMO communication system using an adaptive transmission mode switching technique
ActiveUS20060083195A1Improve spectral efficiencyMultiplex communicationRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumMimo transmission
A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless communication system. A transmitter that includes a plurality of transmit antennas selects one of a spatial multiplexing scheme and a spatial diversity scheme, processes a signal in the selected transmission scheme, and transmits the signal through the plurality of transmit antennas. A receiver that includes a plurality of receive antennas processes a signal in a reception scheme mapped to a transmission scheme of the transmitter. The transmission schemes include a transmission scheme for maximizing diversity gain and a transmission scheme for maximizing spectral efficiency. The MIMO communication system using an adaptive transmission mode switching technique performs switching between MIMO transmission modes using spatial selectivity of a channel, thereby obtaining maximum gain in a signal to noise ratio (SNR) and spectral efficiency according to channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Adaptive TCP delayed acknowledgment
InactiveUS20020159396A1Improve throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsTransmission throughputTCP delayed acknowledgment
This invention relates to reception and transmission of data over a network. More specifically, this invention relates to Transmission Control Protocol's delayed acknowledgment and improving transmission throughput by adaptively adjusting the use of delayed acknowledgment.
Owner:IBM CORP
Automatic Retransmission Request Control System and Retransmission Method in Memo-Ofdm System
ActiveUS20070255993A1Improvement of data throughput performanceReduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesData streamAutomatic repeat request
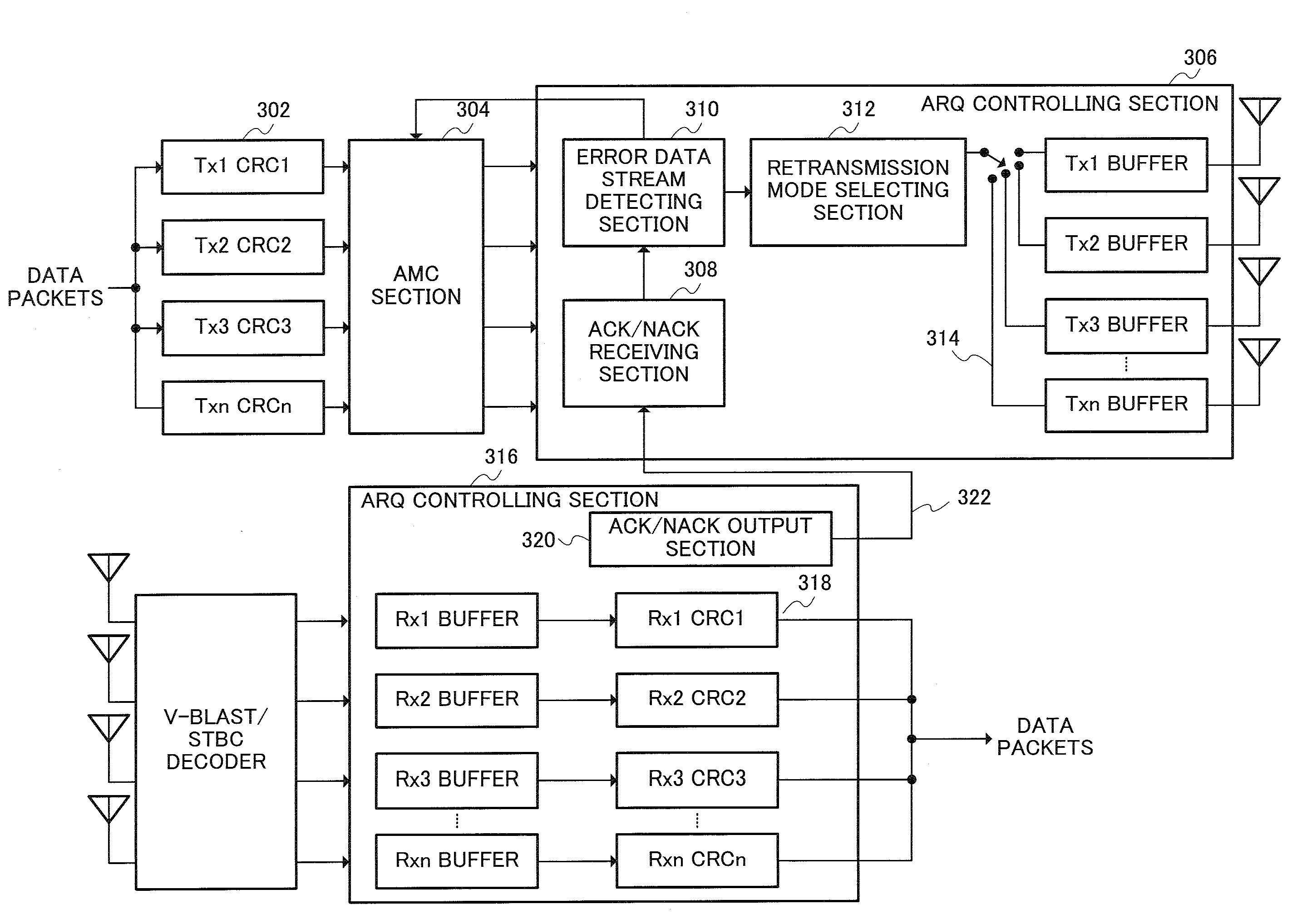
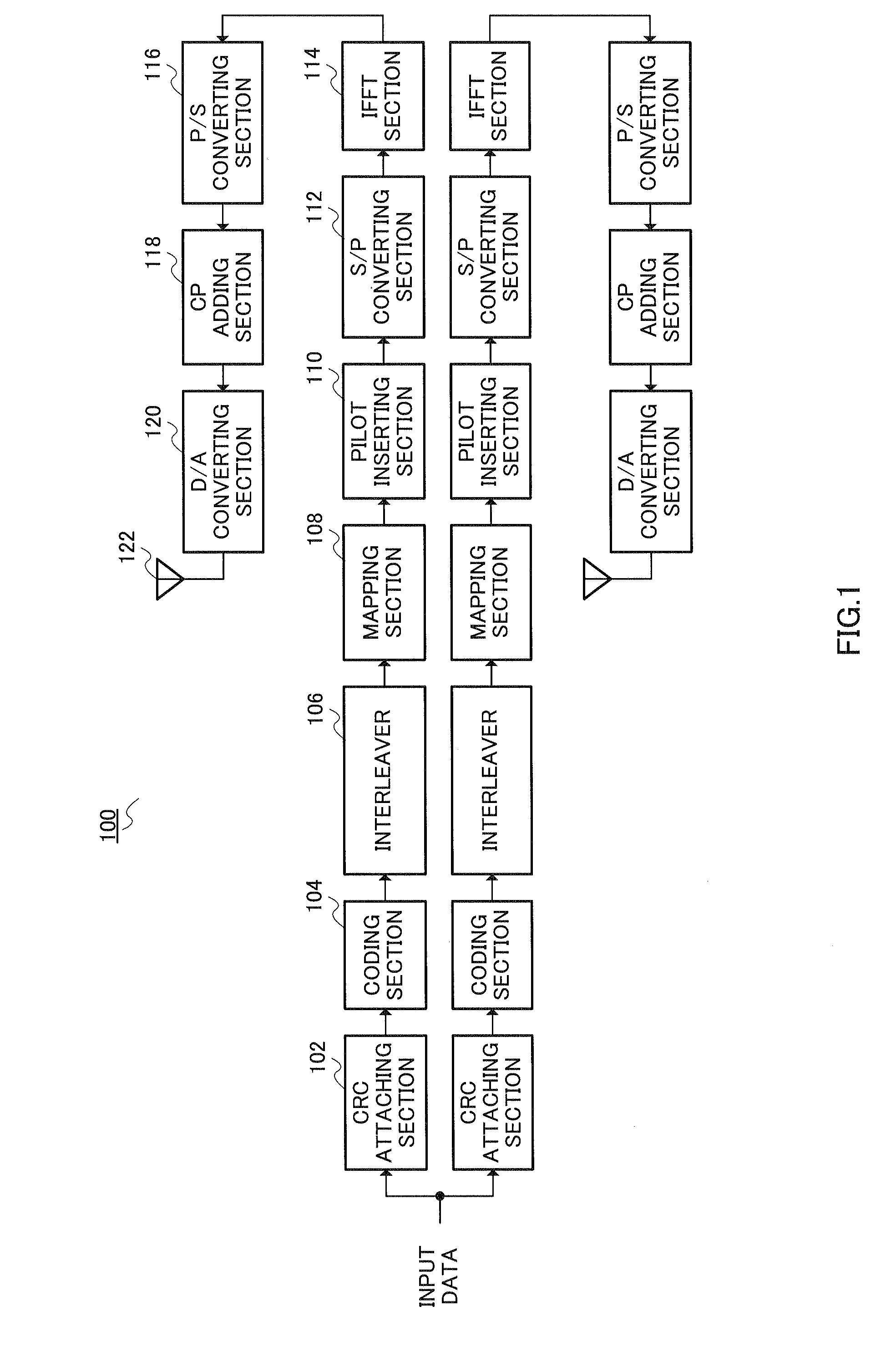
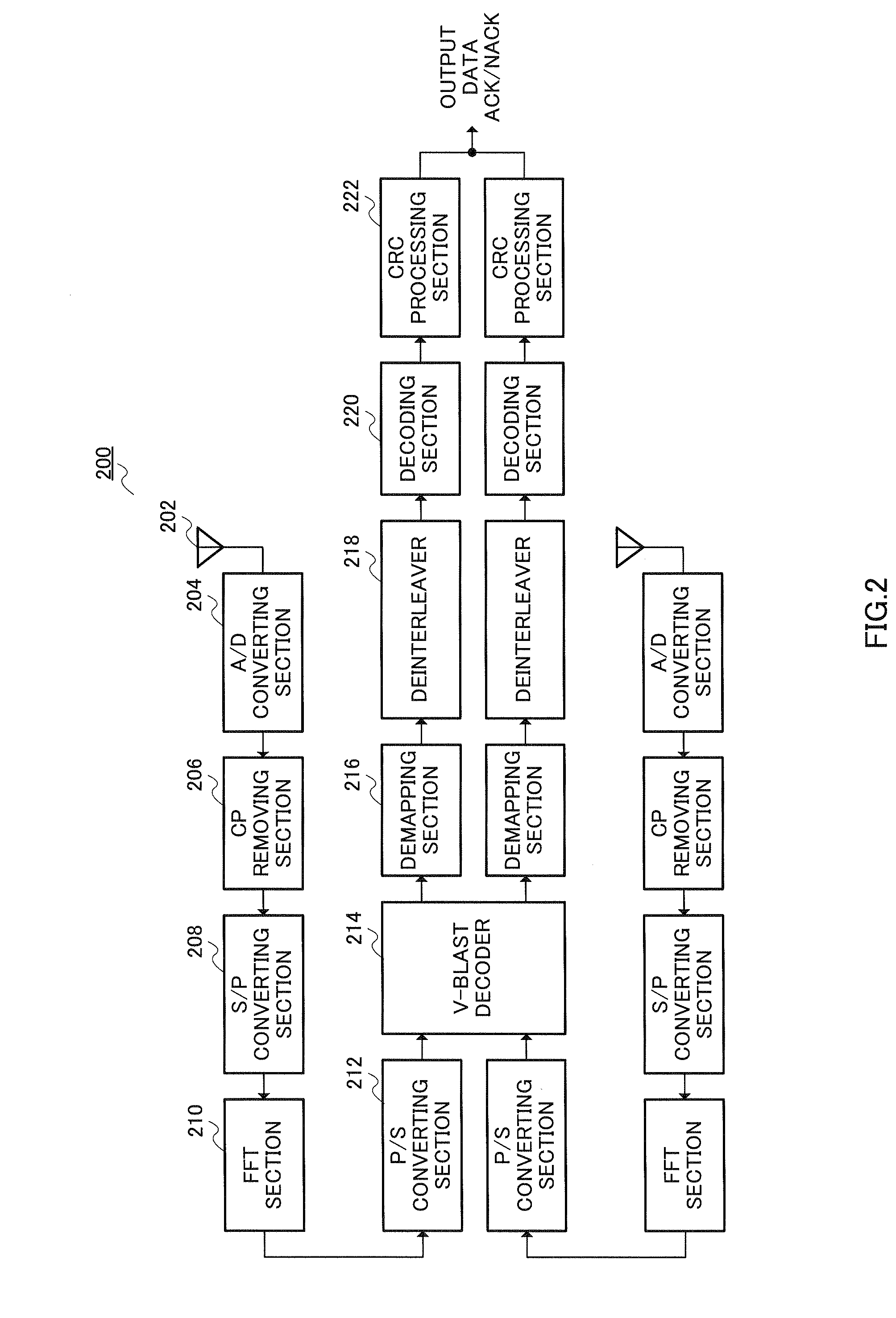
An automatic retransmission request control system in OFDM-MIMO communication system. In this system, an ACK / NACK output part (320) of a receiver transmits, to a transmitter, a feedback information of positive or negative response based on the result of a cyclic redundancy check. An error data stream decision part (310) of the transmitter determines, based on the feedback information, a data stream that need be retransmitted, and a retransmission mode selection part (312) selects a retransmission mode from among (a) a mode in which to transmit the data, which are to be retransmitted, via the same antenna as in the previous transmission, while transmitting, at the same time, new data by use of an antenna via which no data retransmission is requested; (b) a mode in which to transmit the data, which are to be retransmitted, via an antenna via which no retransmission is requested, while transmitting new data via another antenna at the same time; (c) a mode in which to use STBC to retransmit the data via an antenna via which no retransmission is requested; and (d) a mode in which to use STBC to retransmit the data via all the available antennas.
Owner:INVT SPE LLC
Control loop management and differential delay correction for vector signaling code communications links
ActiveUS9059816B1Exact reproductionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLink quality based transmission modificationCommunications systemTelecommunications link
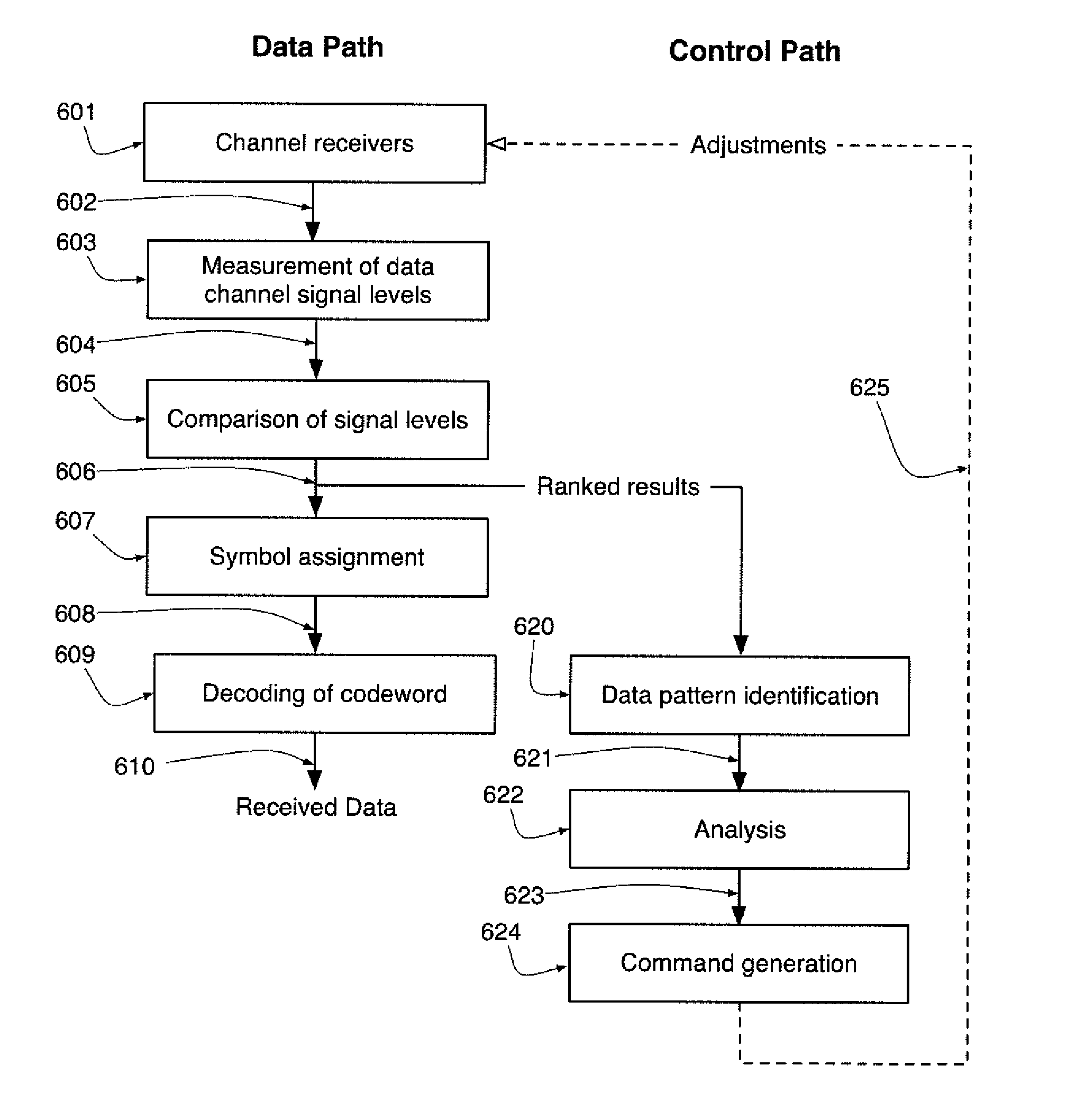
Vector signaling code communications systems rely on group transmission of code symbols using multiple signaling channels that may have differing propagation characteristics, resulting in differing received signal levels, waveforms, and symbol arrival times, and thus that should be actively monitored and adjusted to minimize differential signal characteristics. Information obtained during symbol decode may be analyzed to identify channel operational characteristics during normal operation and perform non-disruptive channel adjustments, including per-channel adjustment of sample-and-hold timing to realign code symbol groups. Initialization or start-up adjustment may also be performed using intentionally-transmitted training patterns.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Changing the scrambling code of a base station for wireless telecommunications
A method is provided of a base station for wireless telecommunications changing scrambling code to be applied to pilot signals for transmission. The method comprises automatically:identifying a need to change scrambling code,selecting a new scrambling code for use,reprogramming the base station to use the scrambling code, andusing the new scrambling code for subsequent pilot signal transmissions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Effective protocol for high-rate, long-latency, asymmetric, and bit-error prone data links
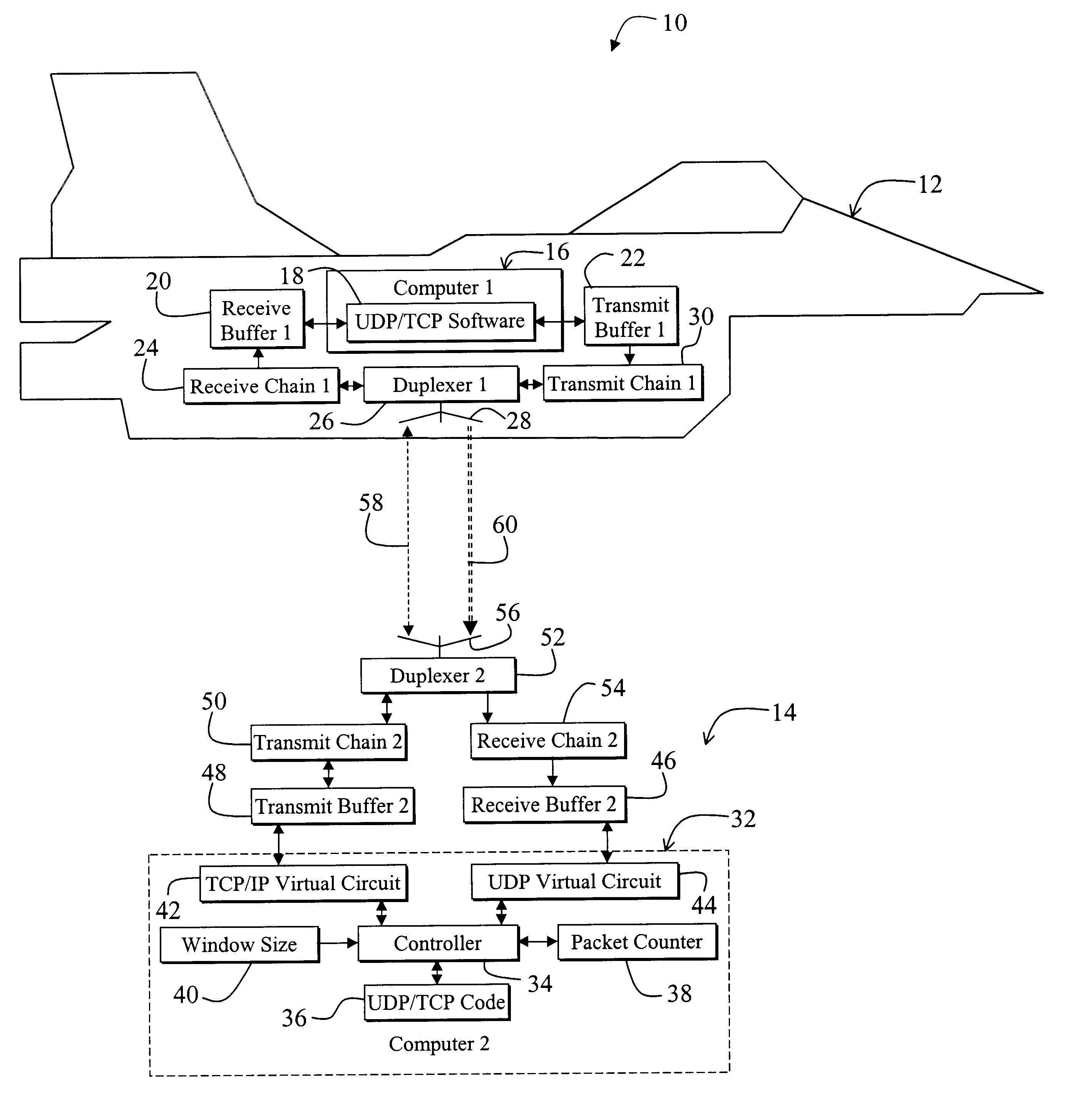
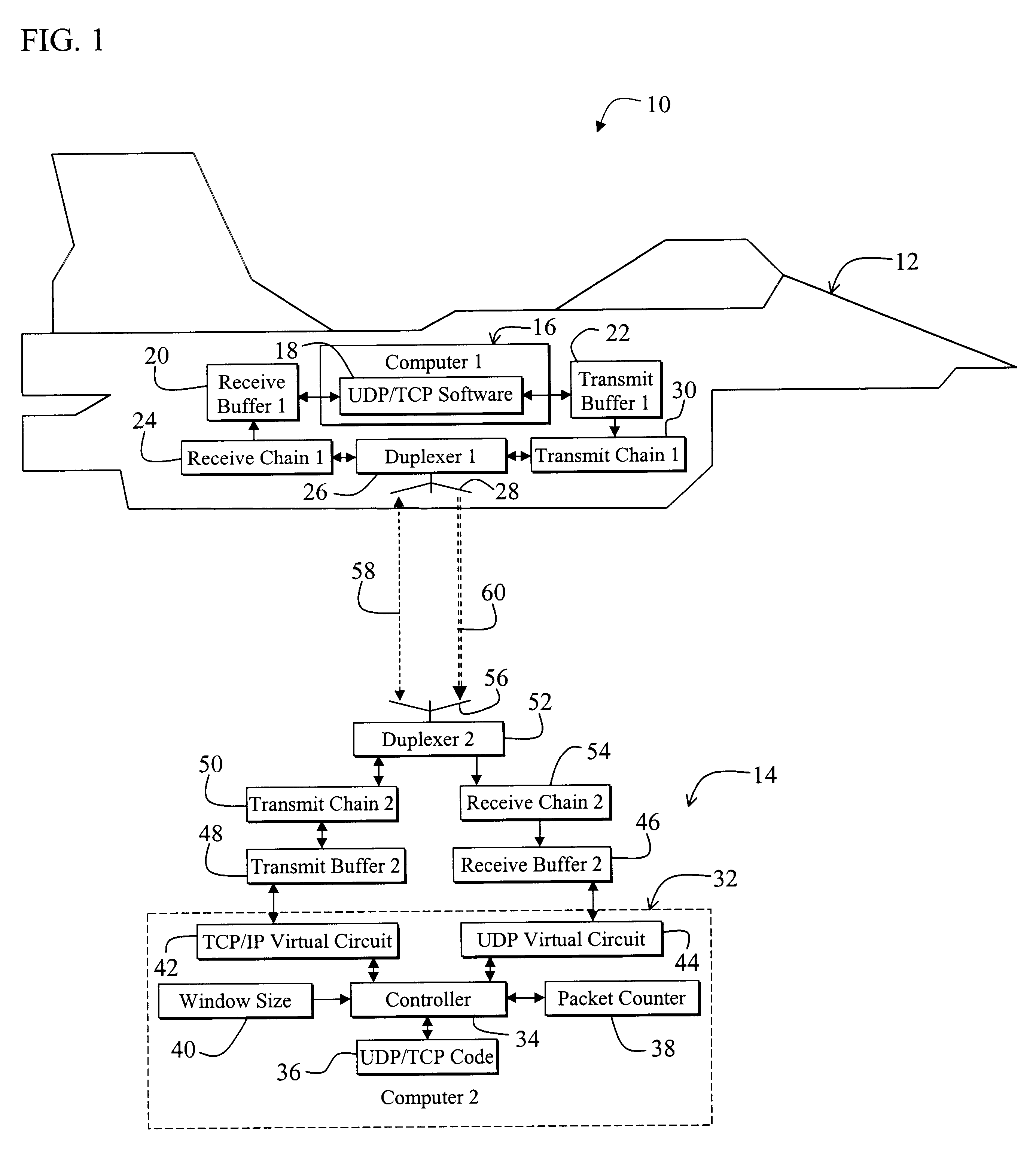
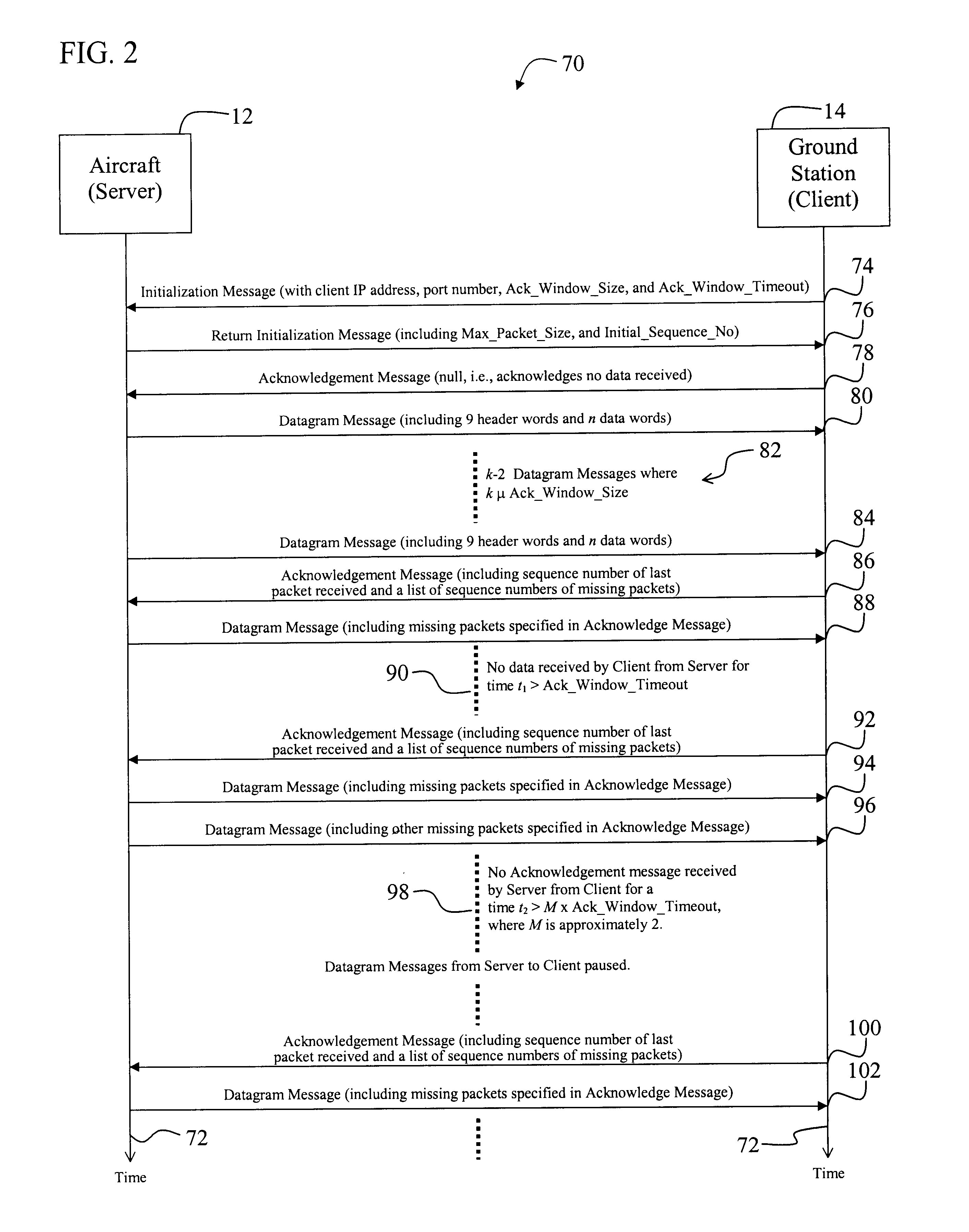
InactiveUS6831912B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsLong latencyTelecommunications link
A system for efficiently and reliably communicating over a high-speed asymmetric communications link. The system includes a first mechanism for connecting a first device to a second device via a channel. A second mechanism delivers data packets over the channel from the first device to the second device. Each packet is associated with a window of packets. A third mechanism selectively employs the second mechanism to re-send data packets not received by the second device after each window of packets. The window of packets is sized in accordance with the bandwidth of the communications link between the first device and the second device, and the round trip delay time. In a specific embodiment, the first mechanism (includes Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) functionality on the first device and the second device for establishing a first TCP / IP link from the second device to the first device. The first mechanism also includes Universal Datagram Protocol (UDP) functionality on the first device and the second device for transferring UDP packets from the first device to the second device. The third mechanism sends acknowledgement messages from the second device to the first device specifying the packets not received by the second device. The system further includes a fourth mechanism for selectively disabling the second mechanism when first device does not receive an acknowledgement message after a predetermined time interval. The predetermined time interval is a function of a window timeout variable. The predetermined function is (M)x(window timeout), where M is approximately 2. The window timeout is greater than N multiplied by a number of packets included in the window of packets divided by the data rate of the communications link between the first device and the second device, here N is an integer greater than 1. N is between 3 and 10.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
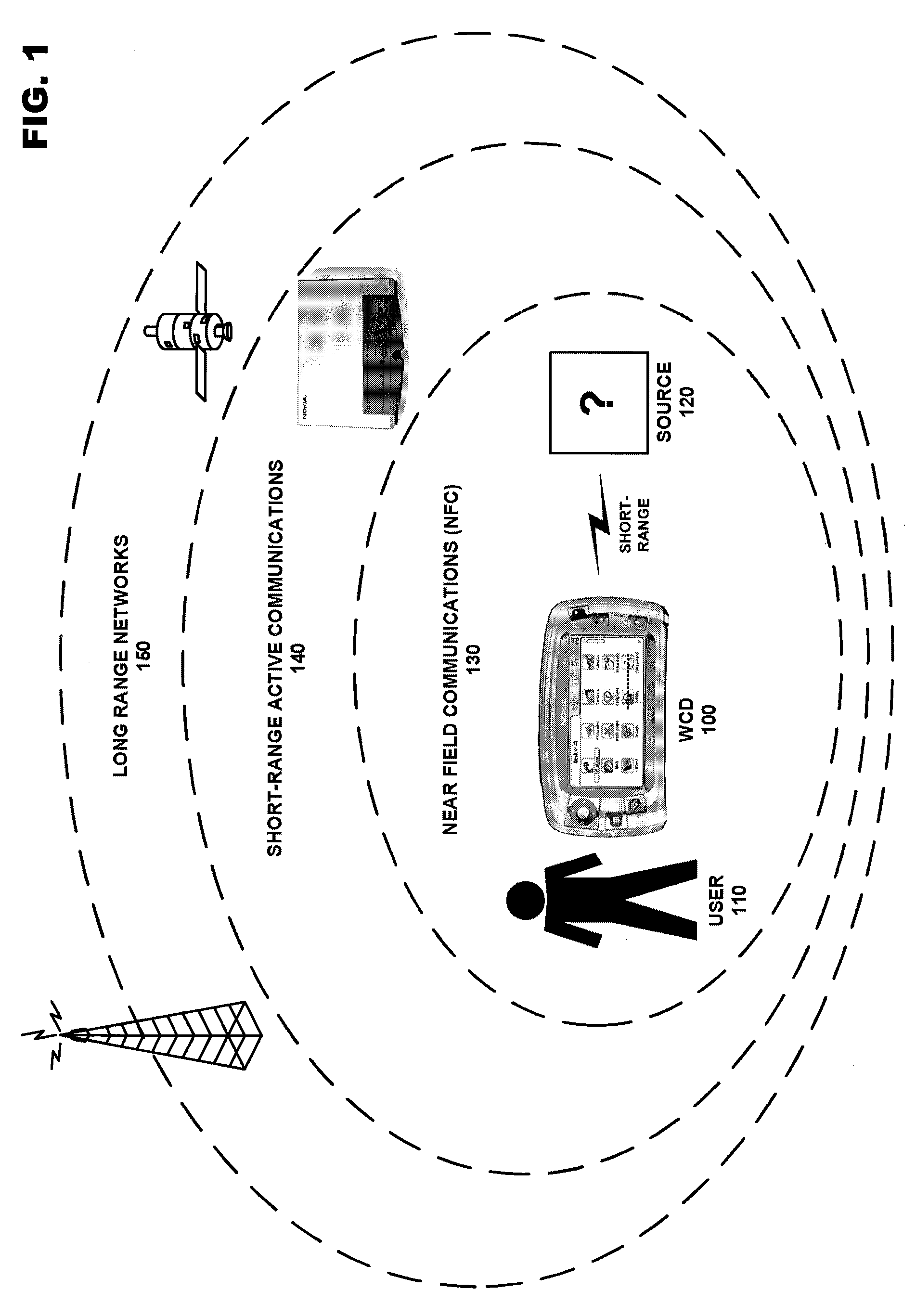
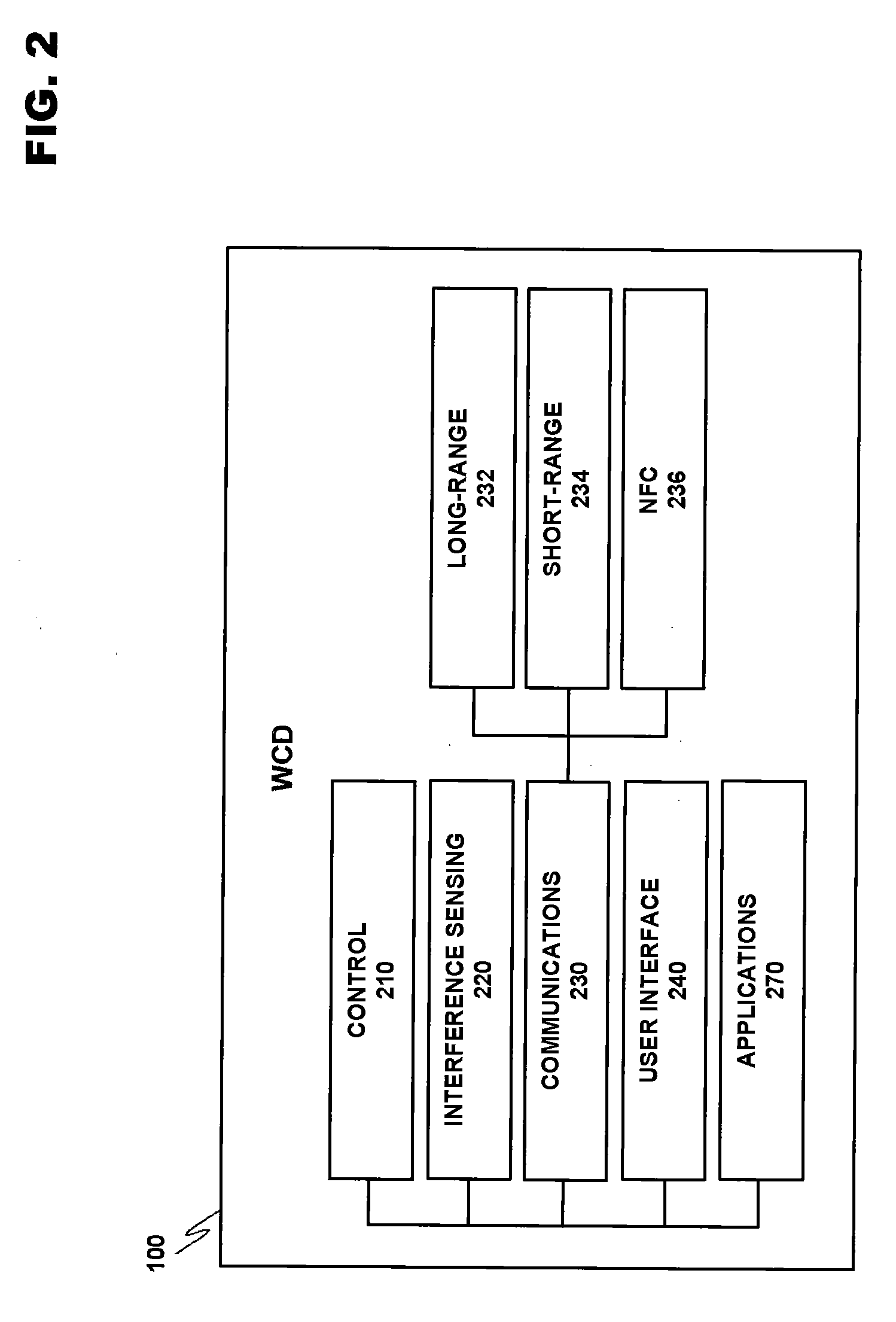
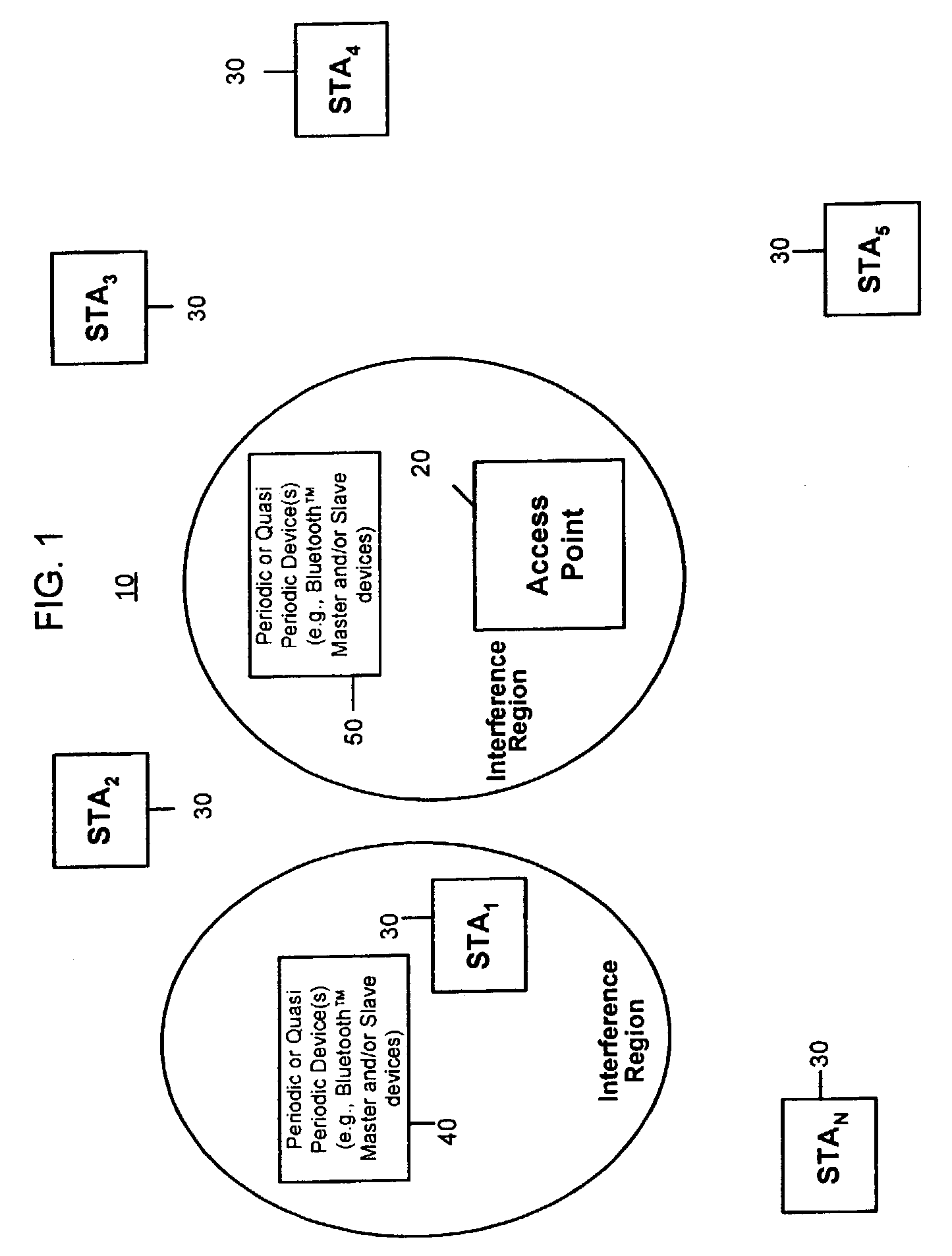
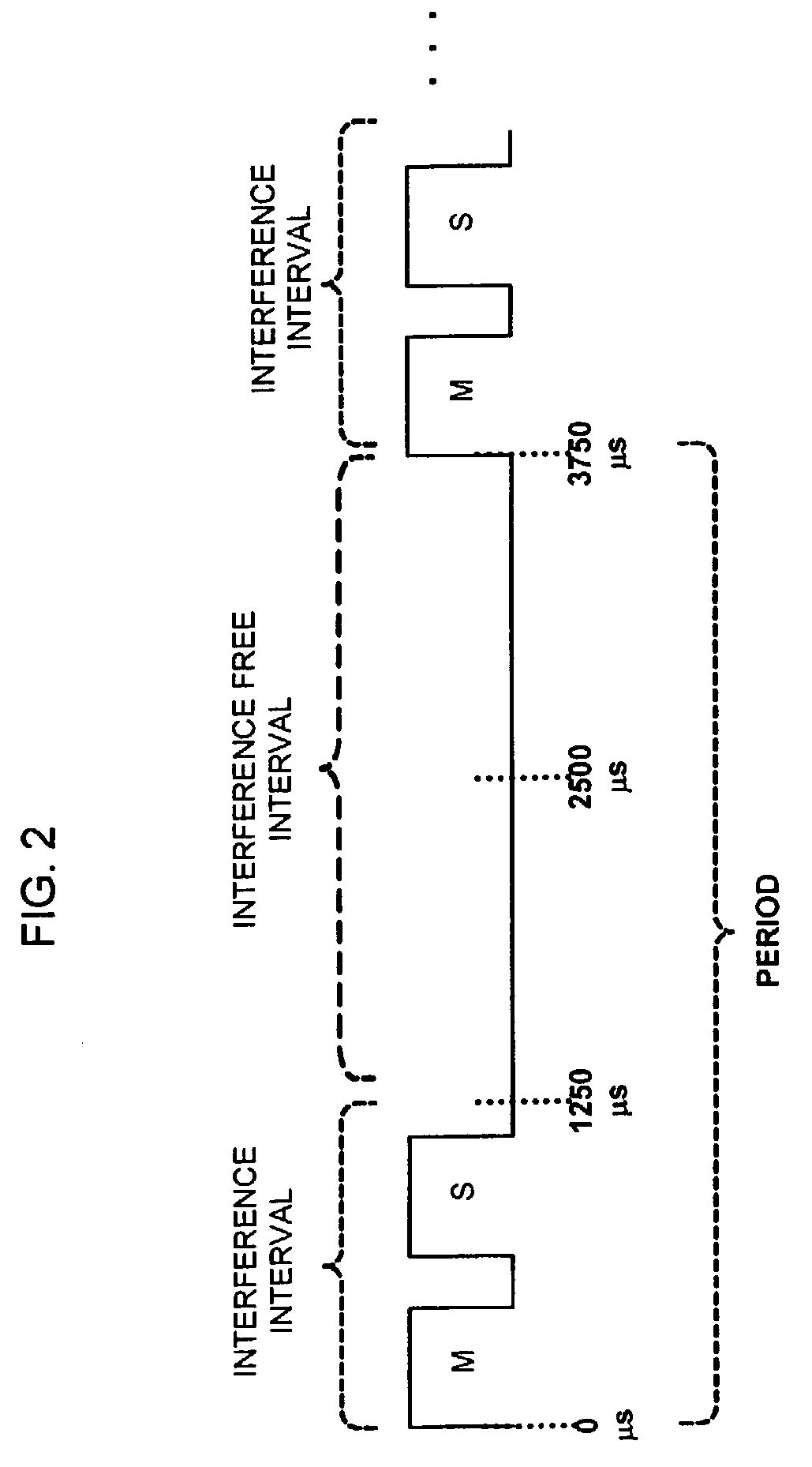
Systems and methods for interference mitigation with respect to periodic interferers in short-range wireless applications
InactiveUS7079812B2Improve service qualityAvoid interferenceData switching by path configurationTransmission monitoringQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
Several techniques are provided for use by wireless devices to avoid interference with signals that are of a periodic or quasi-periodic nature that may operate in the same frequency band and proximity. In some cases, the periodic signals are detected and their timing is determined so as to predict when a next interfering event will occur. Devices that are affected by the periodic signal (such as an affected device with information to be transmitted or devices that have information to be transmitted to the affected device) are controlled to prevent transmissions during the interfering intervals. In addition, a process is provided to dynamically fragment a transmit frame of information to transmit part of the information before the interfering interval and the remainder of the information after the interfering interval, rather than waiting to transmit the entire frame until after the interfering interval. Moreover, techniques are provided to correct for clock drift between the periodic signal and a device affected by the periodic signal, as well as for clock drift between a device affected by the periodic signal and other devices that communicate with that device. These techniques prevent interference with periodic signals and in so doing, improve the quality of service of the communication link for both the interfering devices and the other devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for reduced peak-to-average-power ratio in a wireless network
InactiveUS20070081604A1Modulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityTelecommunicationsFrequency spectrum
A wireless transmission device capable of communicating with a receiver according to a DFT-spread OFDM protocol. The wireless transmission device comprises a configurable spectral shaping filter block capable of performing spectral shaping of an outgoing signal. The wireless transmission device configures the configurable spectral shaping filter block to perform spectral shaping according to a peak-to-average power (PAPR) value associated with the outgoing signal. The multi-carrier protocol comprises one of orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
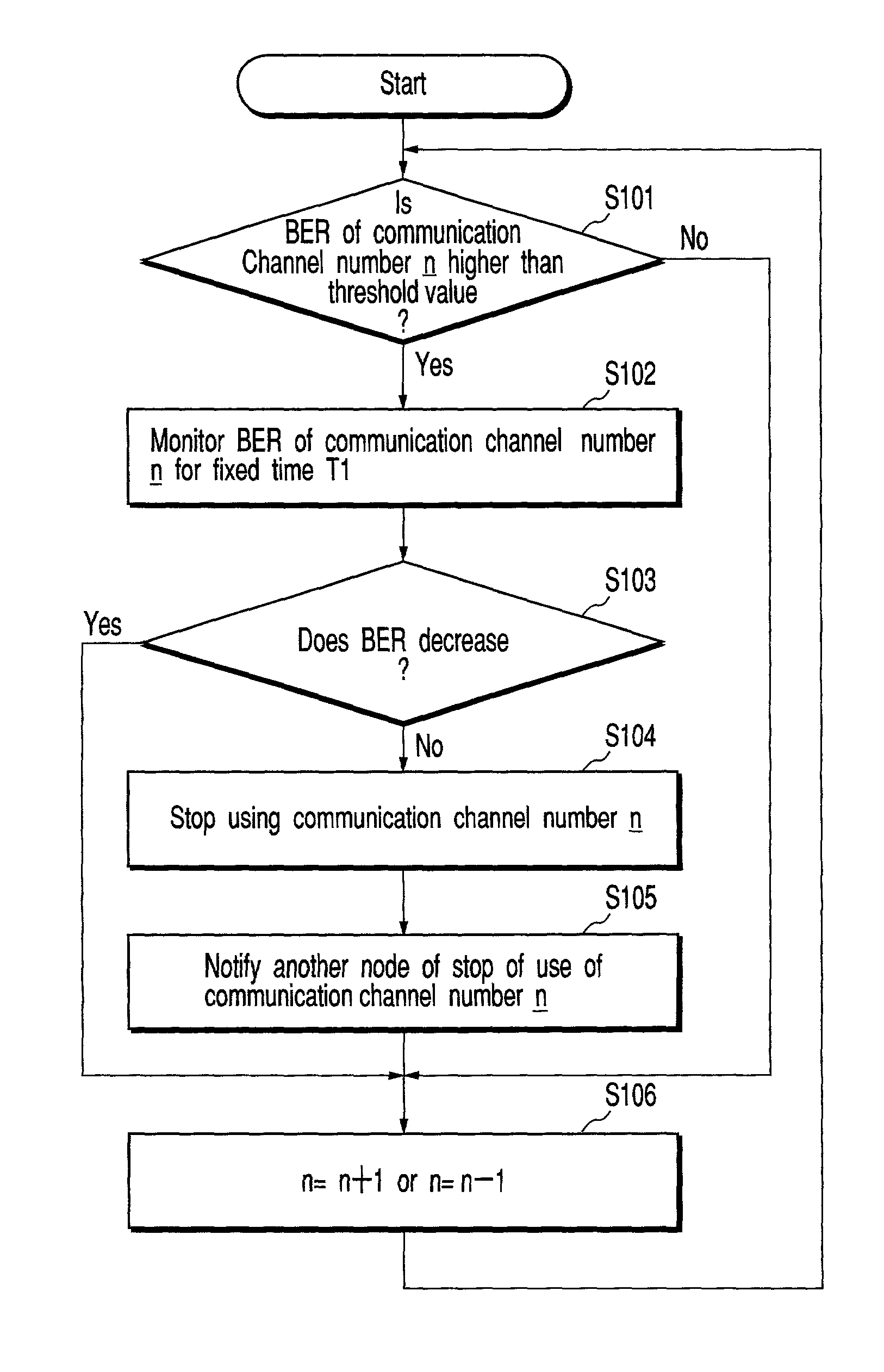
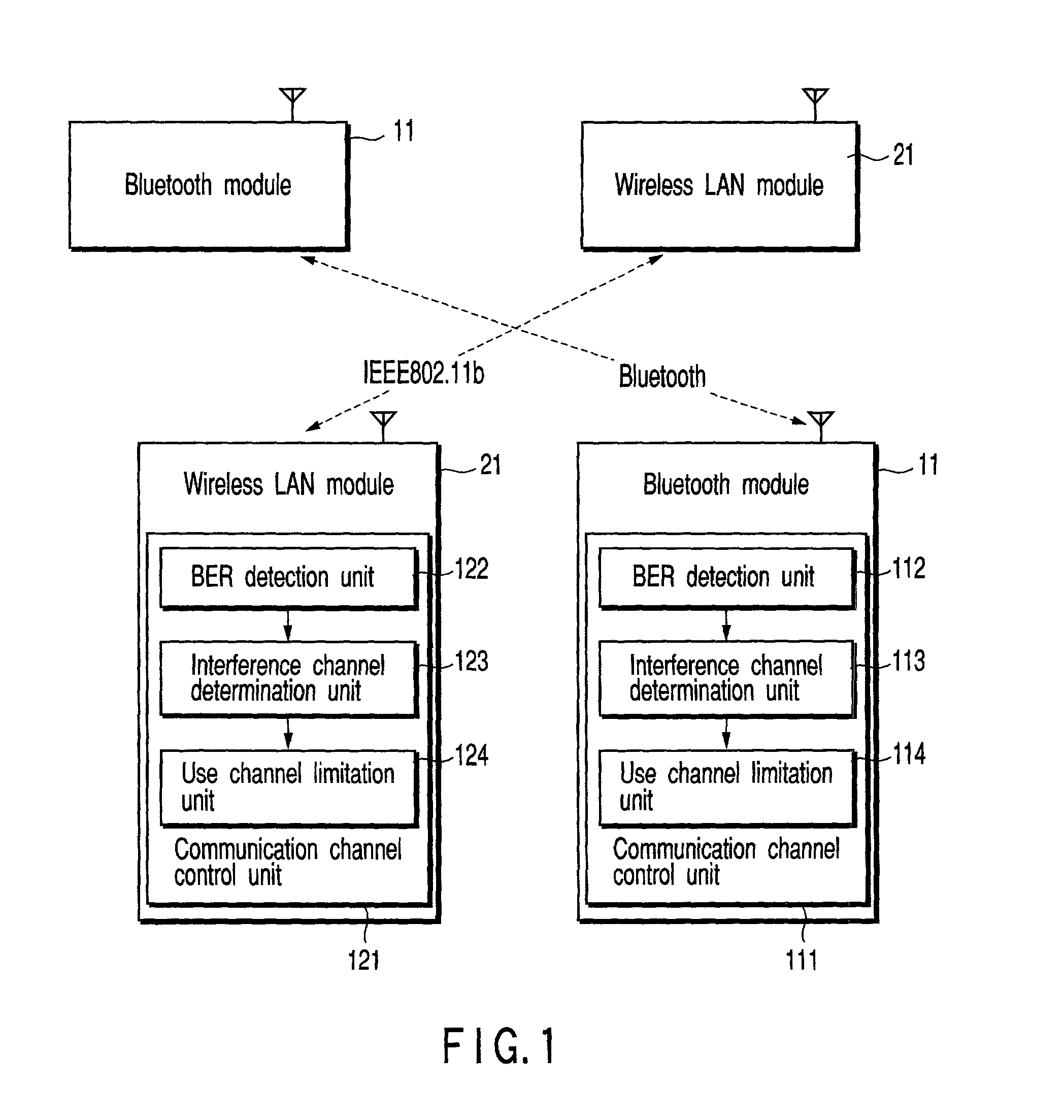
Method and apparatus for performing wireless communication using a plurality of frequency channels
InactiveUS7006451B2Avoid interferenceFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationCommunications systemCommunication device
A wireless communication apparatus performs wireless communication using a plurality of frequency channels. In order to prevent a radio signal from interfering with another wireless communication system, the apparatus includes a unit which detects an error rate of each of the plurality of frequency channels, a unit which determines whether the detected error rate is higher than a specific threshold value, and a unit which suspends use of a frequency channel whose error rate is determined to be higher than the threshold value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
MIMO signal processing method involving a rank-adaptive matching of the transmission rate
InactiveUS7450548B2Reduce complexityNo loss of transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingMulti inputData stream
A bidirectional signal processing method uses parallel transmission of digital transmitted data streams in a multiple input-multiple output system. Related art methods generate high bit error rates mostly in singular transmission channels. For this reason, the rank-adaptive signal processing method provides that the number nd of active subchannels are varied according to the actual channel behavior in order to effect a robust data transmission even in singular radio channels based on a transmit-side and receive-side channel knowledge and a modification of the data vector by a linear matrix vector multiplication while introducing a factor gamma for limiting the maximum transmit power. The maximum transmit power is then only distributed to the currently activated subchannels so that no transmit power remains unused. Another optimization of the number of subchannels nd occurs when selecting the modulation and encoding methods. During the optimal rank-adaptation according to the water-filling principle, another power is allocated to each subchannel. Another modulation and encoding method is accordingly selected for each data stream. During the suboptimal rank-adaptation according to the channel inversion principle, all subchannels have the same power whereby enabling the data streams to be modulated and encoded in a common source.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
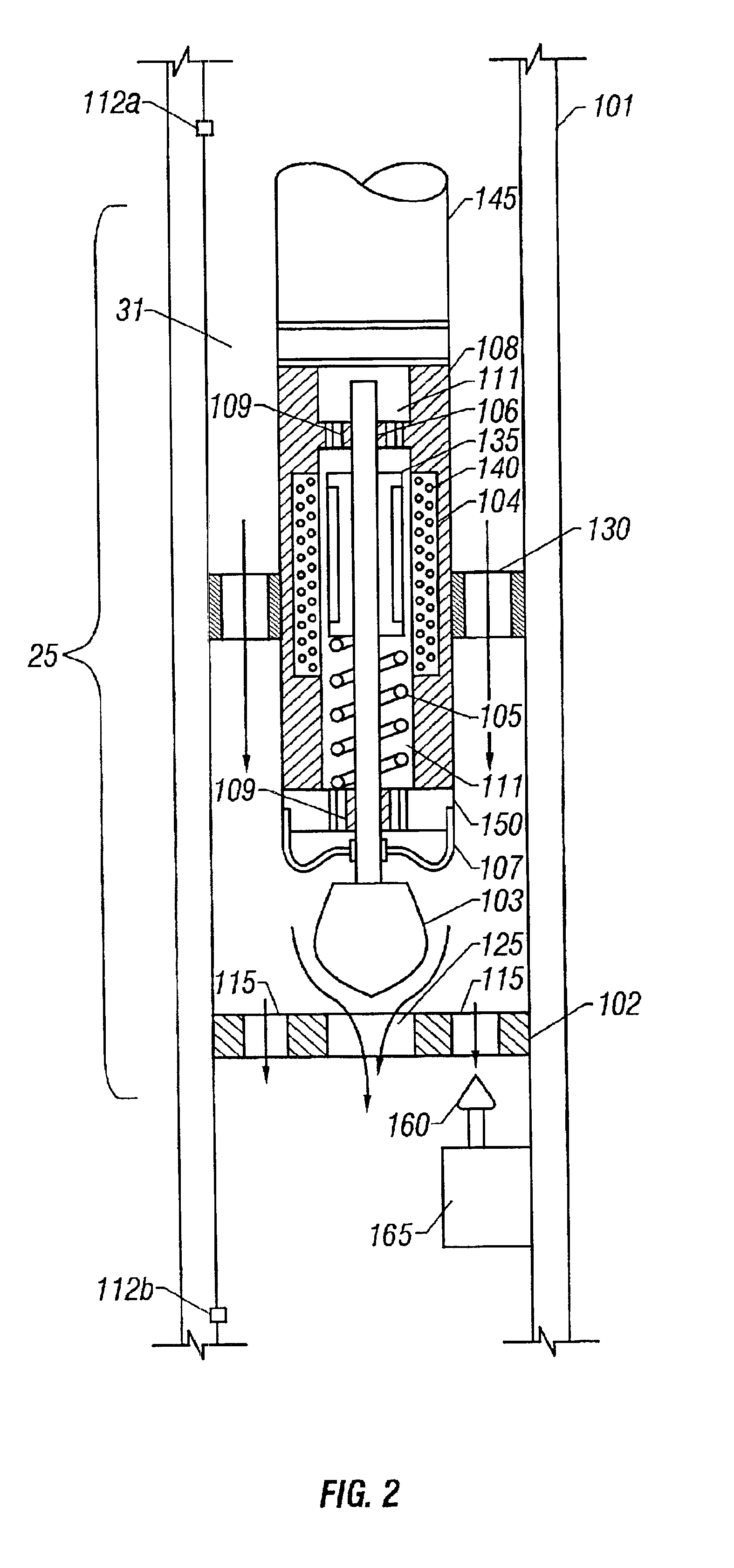
Reciprocating pulser for mud pulse telemetry
A method of transmitting pressure pulses from a downhole location through a flowing fluid in a wellbore comprises using a linear actuator to controllably move a reciprocating member axially back and forth between a first position and a second position to at least partially obstruct flow of the flowing fluid to generate the pressure pulses. A reciprocating pulser for generating pressure pulses in a fluid flowing in a wellbore, comprises a fluid passage that allows flow of the fluid through the pulser, and a reciprocating member. A linear actuator is coupled to the reciprocating member, such that the linear actuator moves the reciprocating member in a first axial direction and then in a reverse direction to at least partially obstruct flow of the fluid through the pulser to generate pressure pulses in the flowing fluid.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
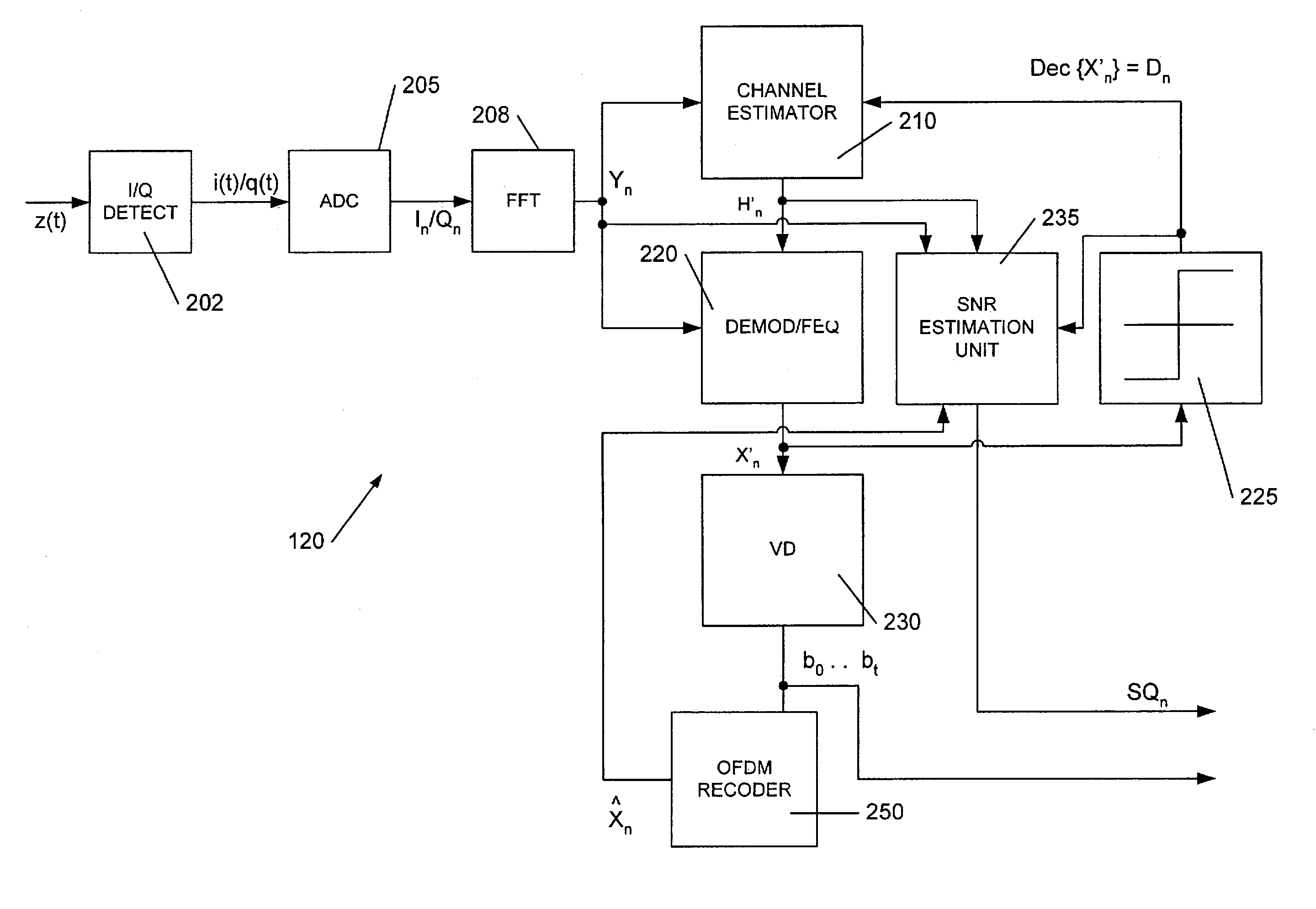
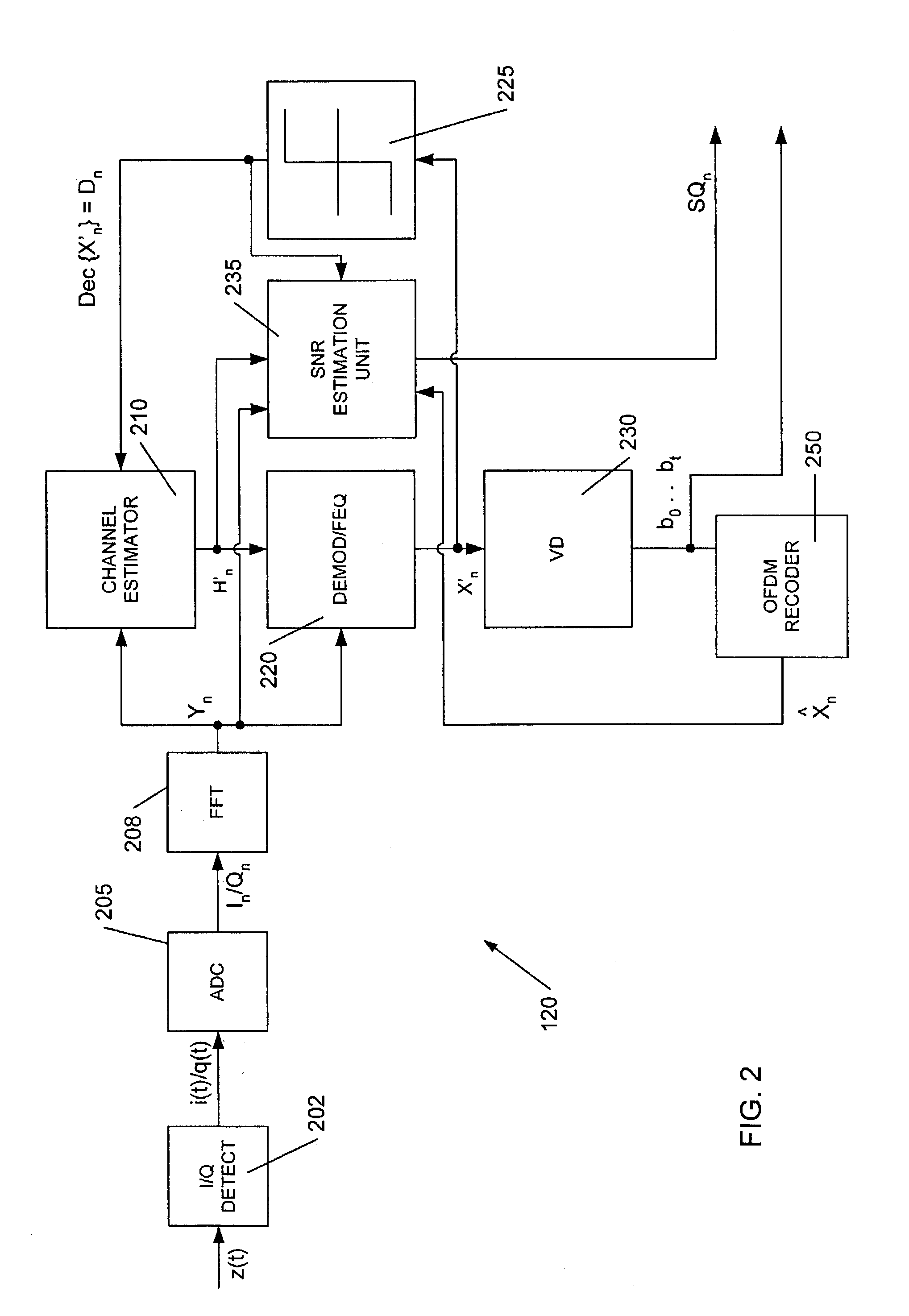
Apparatus and method for measuring signal quality of a wireless communications link
ActiveUS7016651B1Way accurateAccurate geometric SNR estimateResonant long antennasError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
Techniques for measuring signal quality in a communications link supporting OFDM symbol transfer across plural sub-carriers are disclosed. These techniques employ a link interface receiving OFDM symbol(s) from the link, and a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimation unit generating an estimate of a geometric SNR (SNRgeo) for the received symbols based on an average of the logrithmic difference between soft decision and hard decisions for the received symbol. SNRgeo here defines a scalar measure of the link signal quality, which results in a computationally efficient yet accurate link signal quality assessment, and thereby permit selective link characteristic alteration. Only sub-carrier subsets need be used to derive a relatively an accurate SNRgeo estimate. Sharing calculation resources between SNR estimation and soft decision units further reduce implementation complexity. Hard decision generation may use a relatively quick slicer or more accurate viterbi decoder / OFDM re-coder combination, as design goals dictate.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
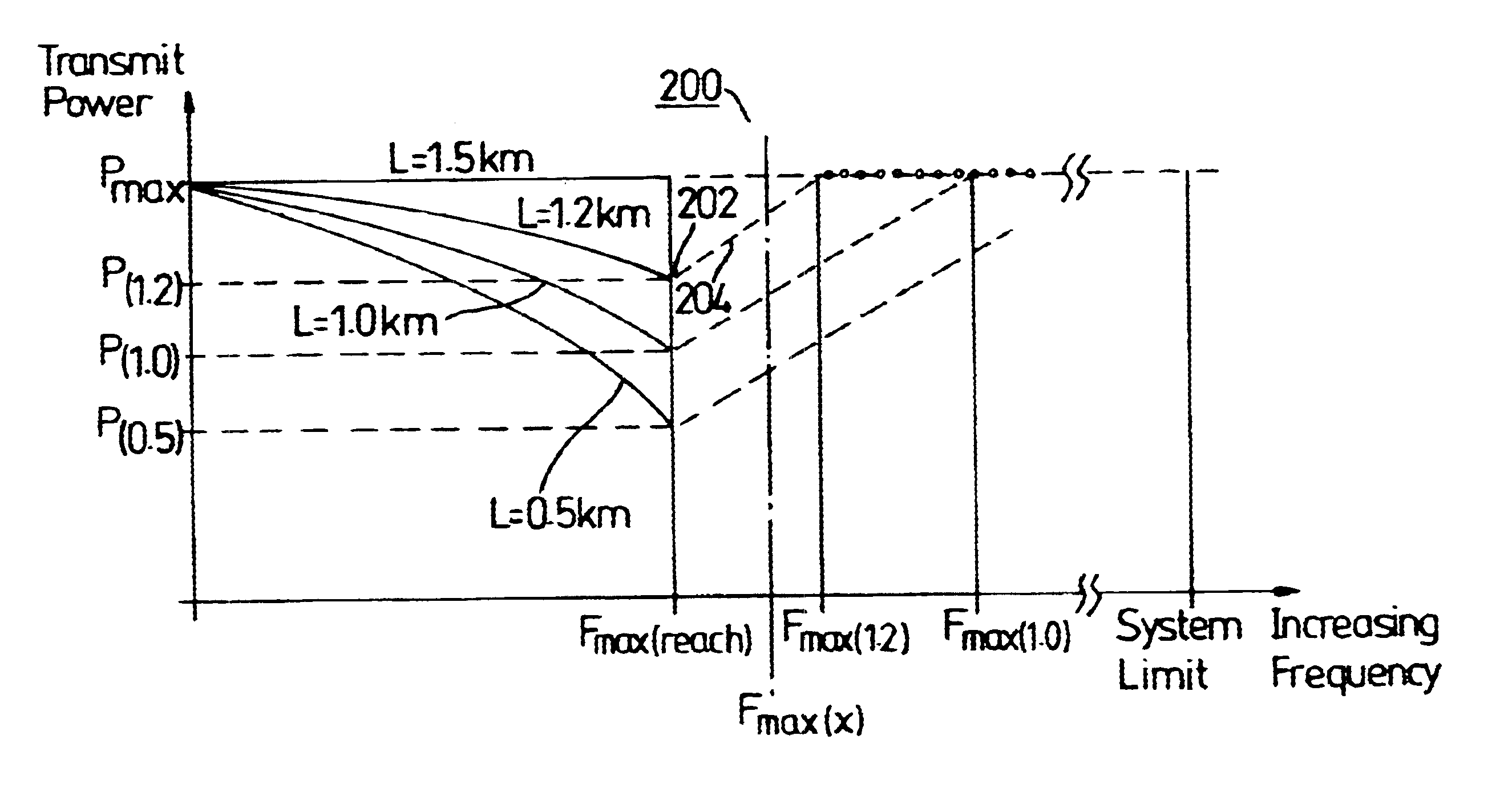
Wireline communication system and method of frequency allocation therein
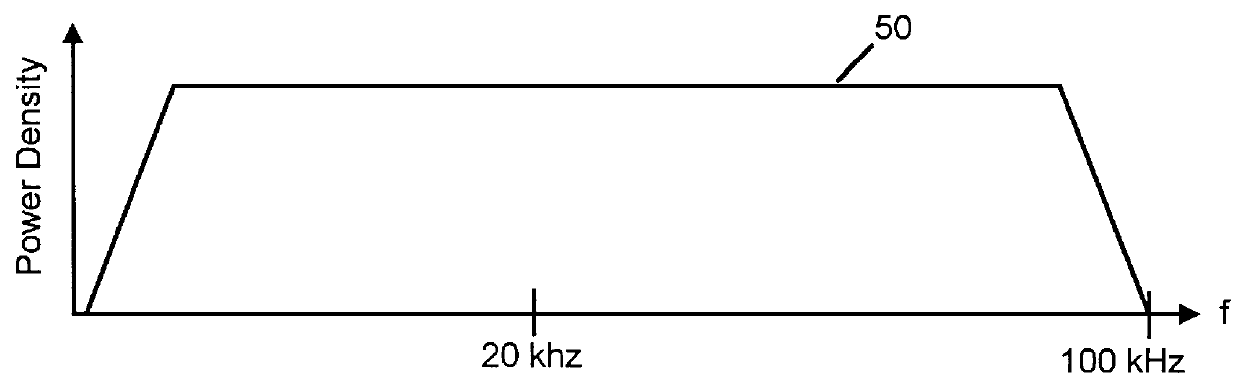
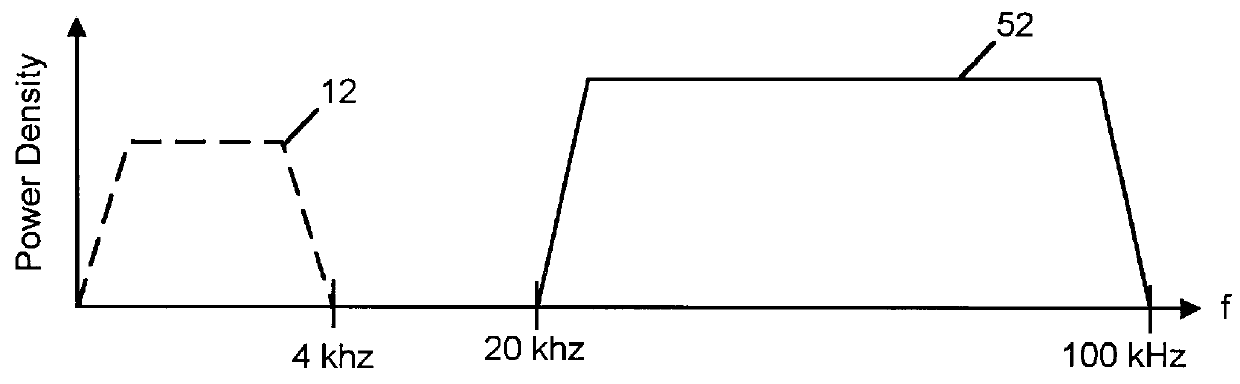
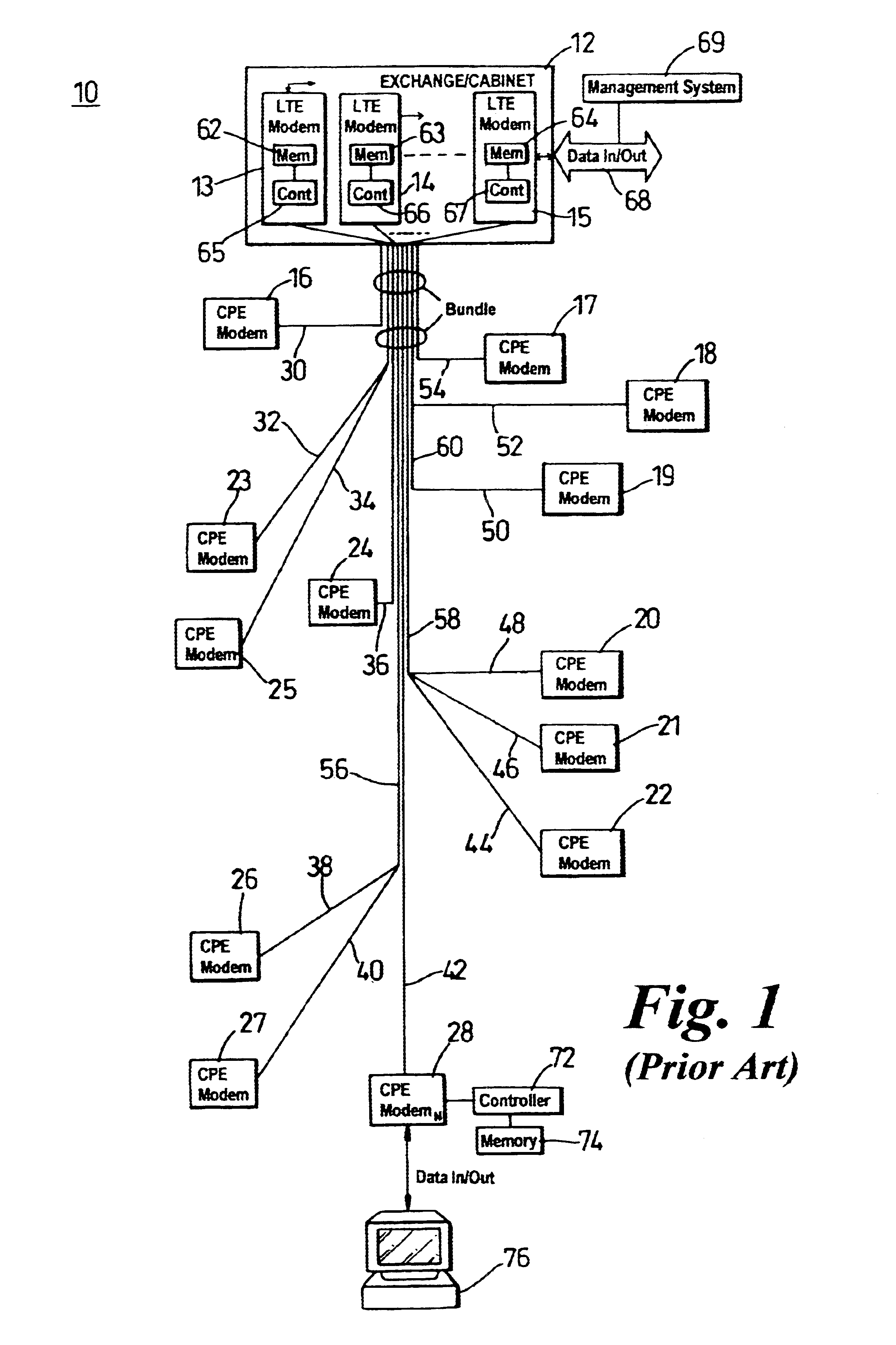
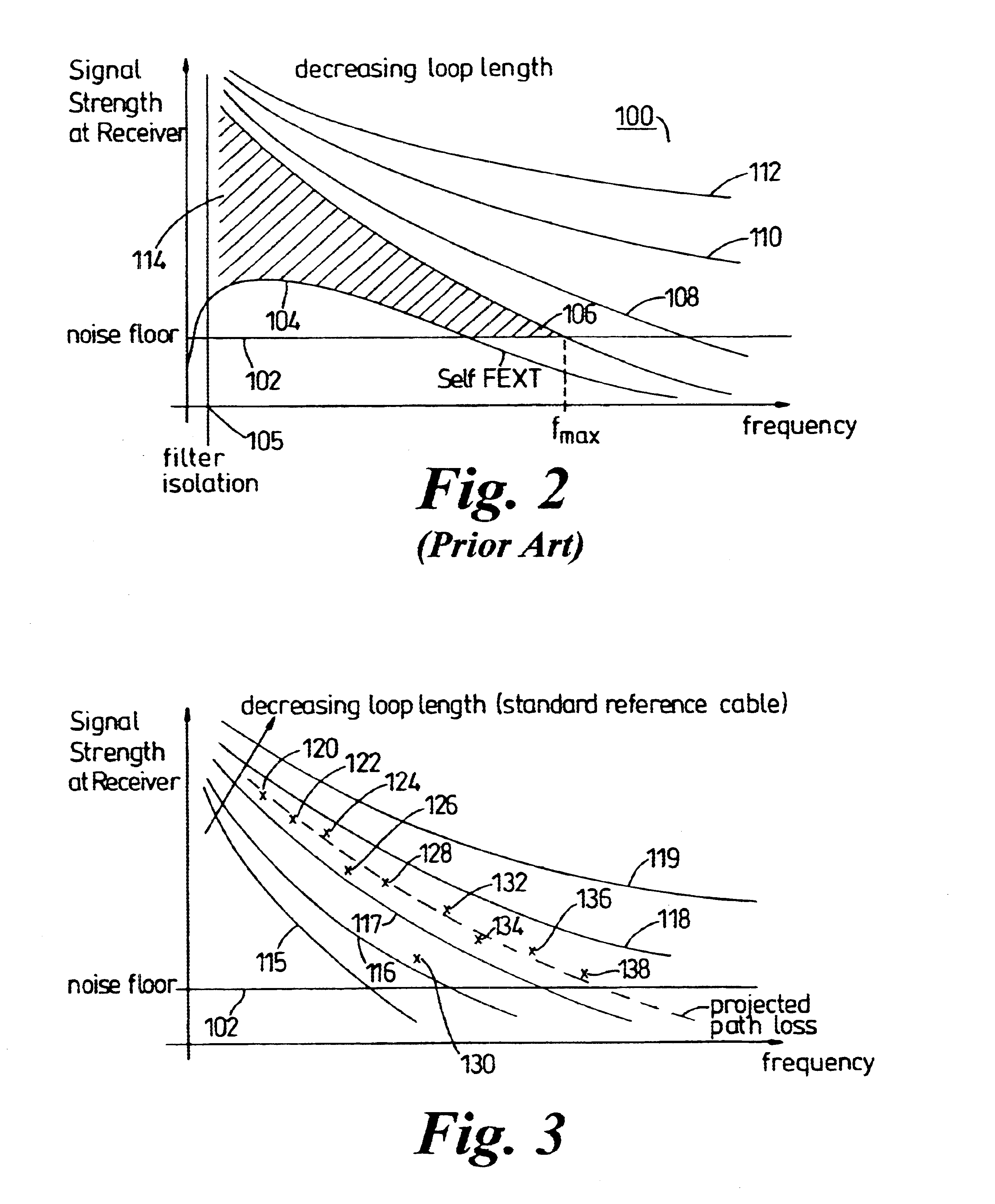
InactiveUS6650697B1Reduce impactImprove performanceTelephonic communicationLink quality based transmission modificationModem deviceFrequency spectrum
To alleviate the requirement to back-off all up-link performance, such as by limiting power spectral density, to overcome far-end cross-talk problems otherwise associated with relatively short loop-length wireline links, the present invention partitions the frequency spectrum based on an estimate of the loop length of a subscriber unit (CPE) modem from an exchange (LTE) modem. Up to a threshold frequency (fmax) at which received transmissions from a subscriber having a longest loop length (115) become indistinguishable by the LTE modem from a noise floor (102), up-link performance on all loop lengths is limited to correspond to that of the longest loop. At frequencies above the threshold frequency (fmax), subsets of subscribers (152-154) having relatively short loop lengths (116-119) use high frequency carriers that have signal to noise ratios sufficient to support information transmission in these elevated frequency bands.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
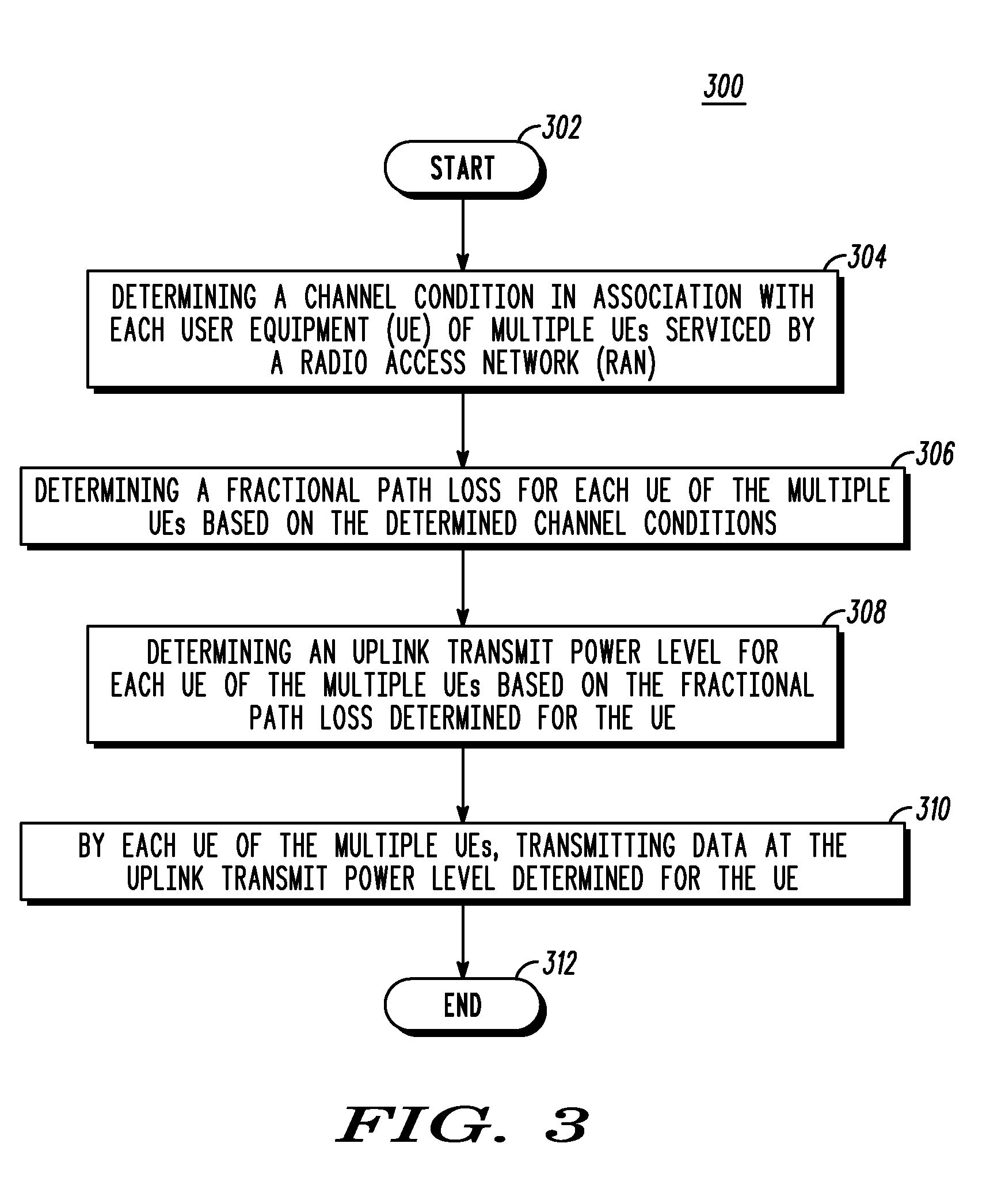
Method and apparatus for uplink resource allocation in a frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS20070178930A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumCommunications system
To address the need for a resource allocation scheme that results in a better tradeoff between the cell-edge performance and the overall spectral efficiency, a communication system is provided that allocates uplink transmit power to user equipment (UEs) based on a fractional power control scheme. In another embodiment, since the cell-edge users are also likely to be power limited, the communication system may implement a minimized uplink transmission bandwidth resource allocation scheme that may work with the fractional power control scheme to achieve a level of performance desired for uplink transmissions in 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project) and 3GPP2 Evolution communication systems.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com