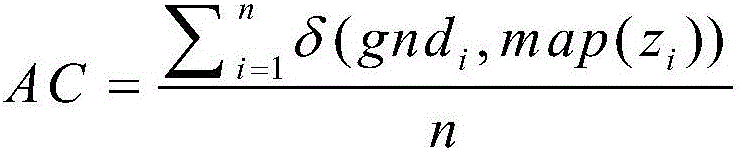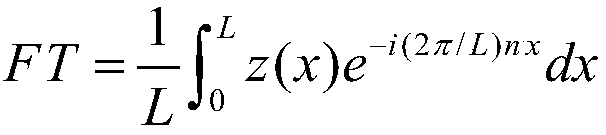Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154 results about "Random projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and statistics, random projection is a technique used to reduce the dimensionality of a set of points which lie in Euclidean space. Random projection methods are known for their power, simplicity, and low error rates when compared to other methods. According to experimental results, random projection preserves distances well, but empirical results are sparse. They have been applied to many natural language tasks under the name random indexing.
Detecting duplicate and near-duplicate files
ActiveUS20080044016A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsToken frequencyRandom projection
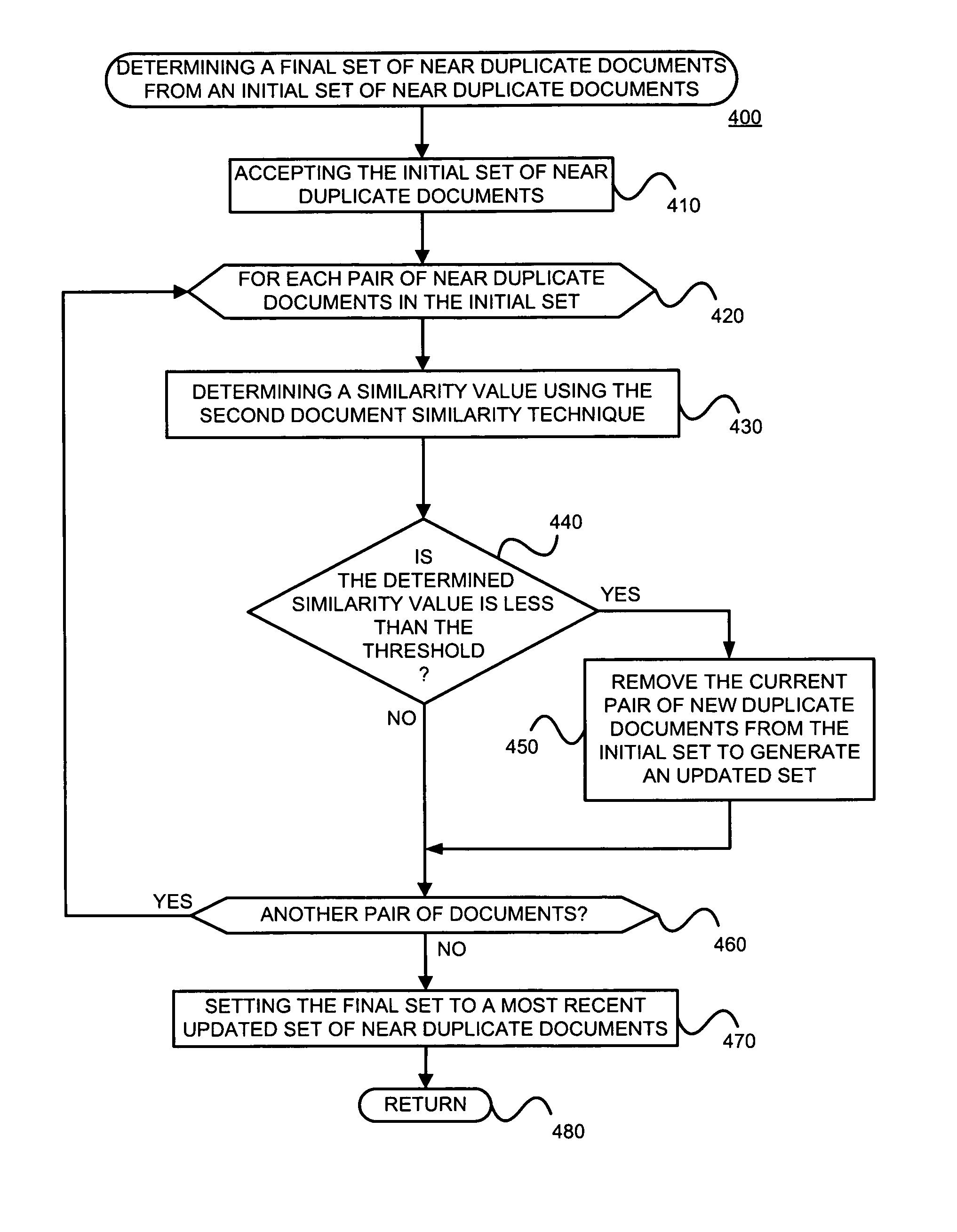
Near-duplicate documents may be identified by processing an accepted set of documents to determine a first set of near-duplicate documents using a first technique, and processing the first set to determine a second set of near-duplicate documents using a second technique. The first technique might be token order dependent, and the second technique might be order independent. The first technique might be token frequency independent, and the second technique might be frequency dependent. The first technique might determine whether two documents are near-duplicates using representations based on a subset of the words or tokens of the documents, and the second technique might determine whether two documents are near-duplicates using representations based on all of the words or tokens of the documents. The first technique might use set intersection to determine whether or not documents are near-duplicates, and the second technique might use random projections to determine whether or not documents are near-duplicates.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and method
ActiveCN102510282AResolve SensitivitySolve the small size of the arrayPulse techniqueDigital micro mirror deviceData acquisition
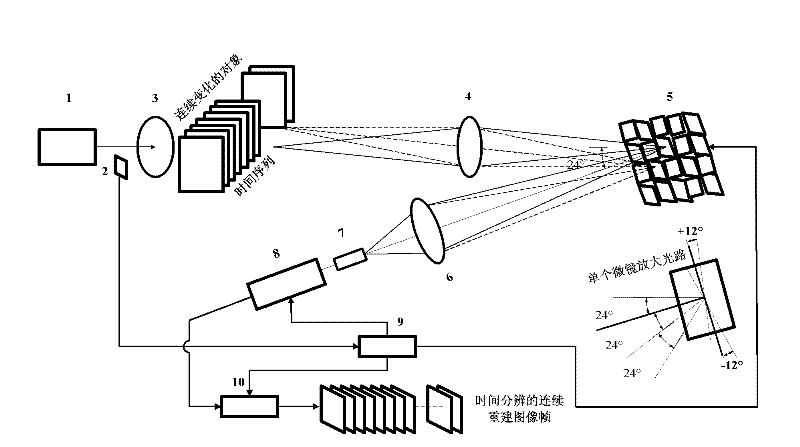
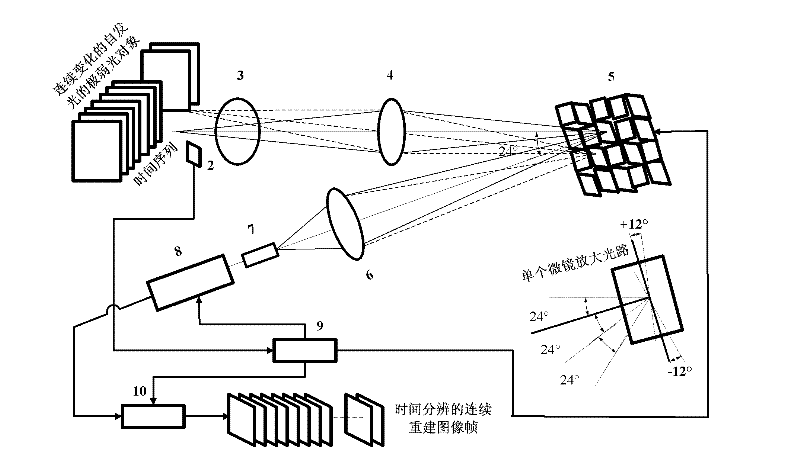
The invention provides a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging method and belongs to the technical field of extremely-weak light detection. A trigger 2 is triggered to start sampling, centralized sampling is performed at t time intervals, and measurement and counting are performed if light comes at the intervals, so that time resolving of an extremely-weak light object is realized, and a time sequence image is generated. Imaging is performed on the basis of a compressive sensing (CS) theory, a digital micro-mirror device (DMD5) performs linear random projection on a compressible two-dimensional image, the compressible two-dimensional image is optically modulated and then synchronously detected by using a single-photon counter, and a high-resolution extremely-weak light image can be reconstructed by a small amount of sampling operation. The measurement process is linear and non-adaptive, the reconstruction process is non-linear, and the invention has the advantages of high generality, robustness, expandability, superposition and computation asymmetry, and can be widely applied to the fields of life science, medical imaging, data acquisition, communication, astronomy, military affairs, hyper-spectral imaging and quantum measurement.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
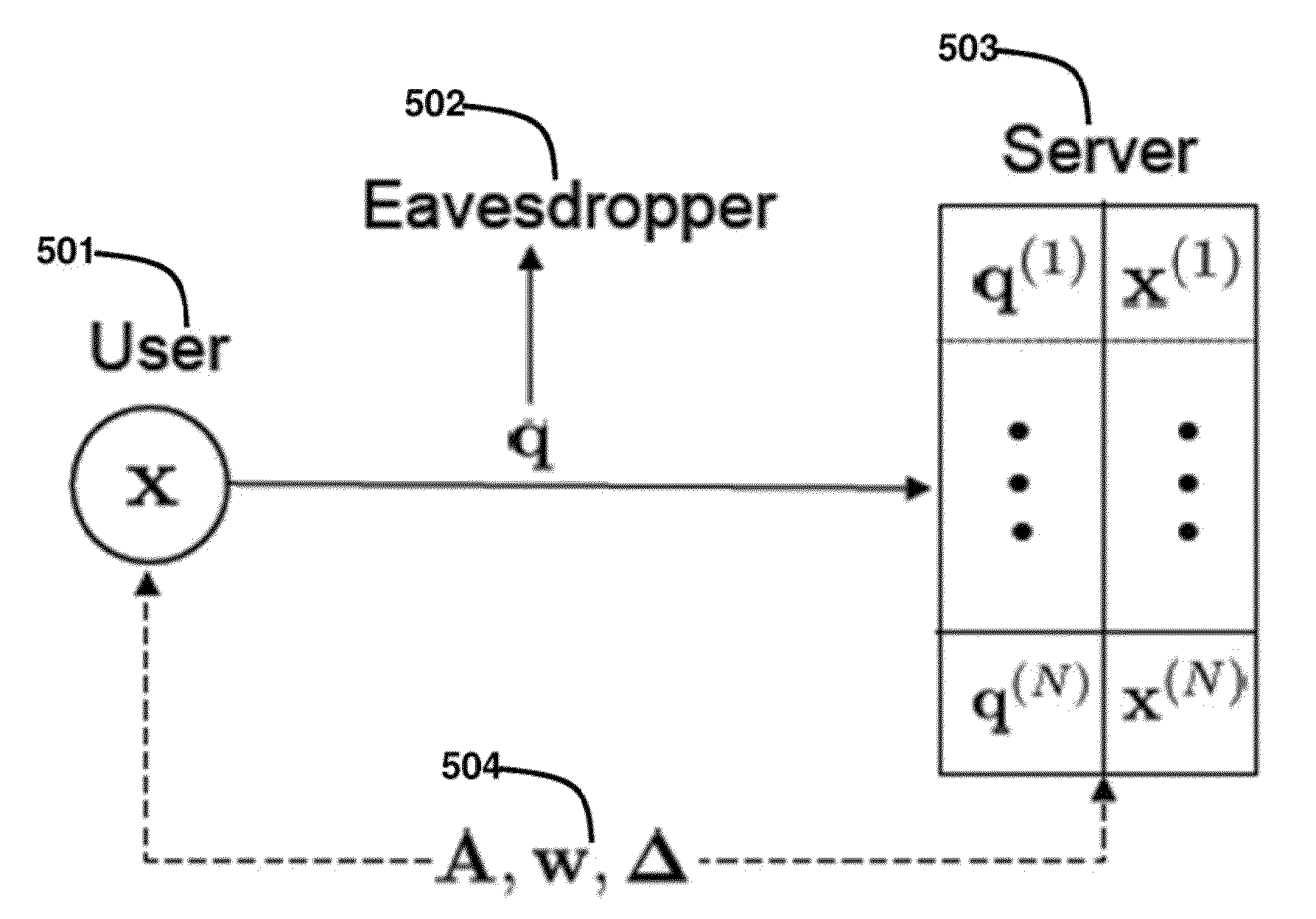
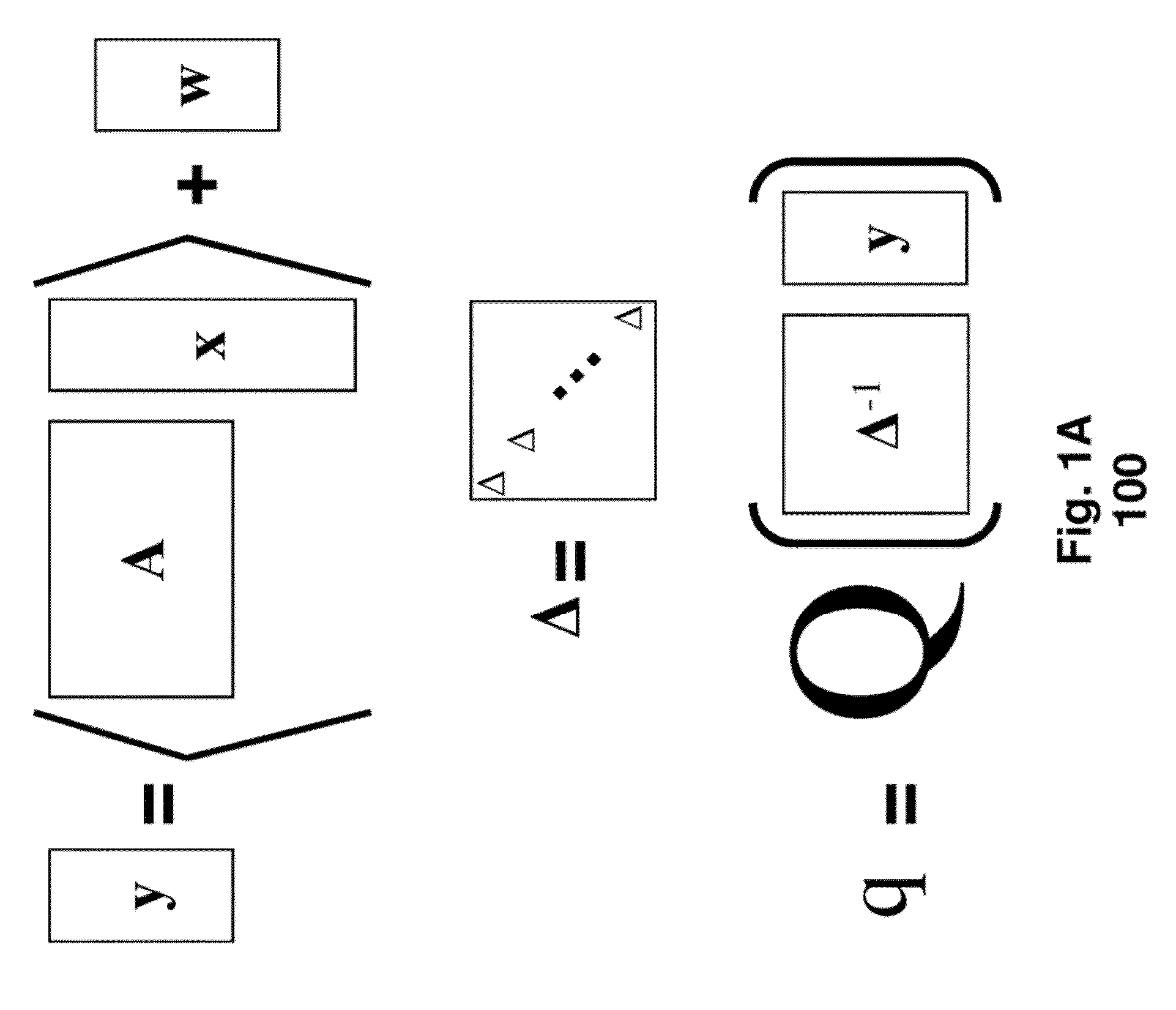
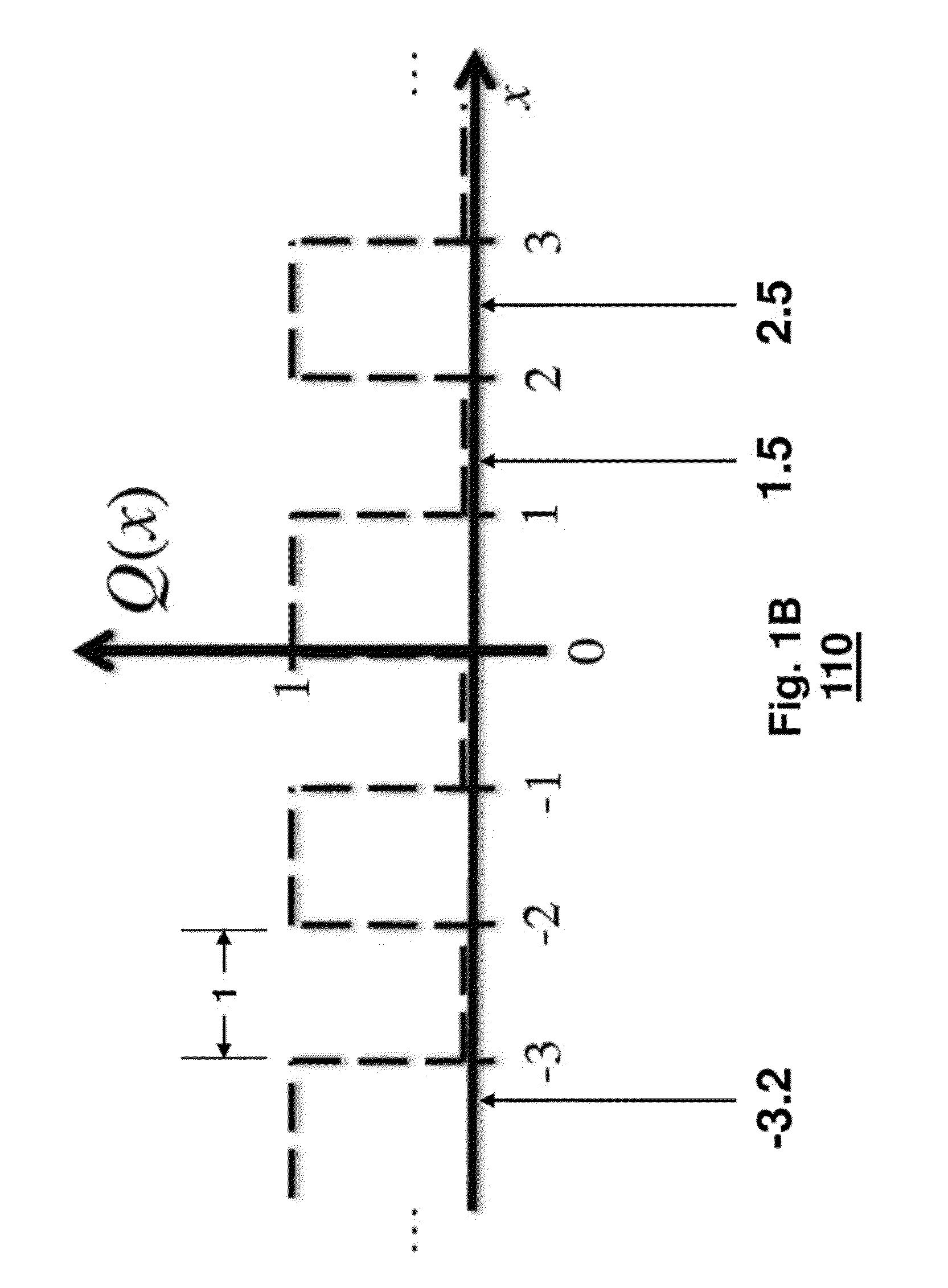
Method for Privacy Preserving Hashing of Signals with Binary Embeddings
ActiveUS20130114811A1Reduce complexityEfficiently determinedSecret communicationInternet privacyPrivacy preserving
A hash of signal is determining by dithering and scaling random projections of the signal. Then, the dithered and scaled random projections are quantized using a non-monotonic scalar quantizer to form the hash, and a privacy of the signal is preserved as long as parameters of the scaling, dithering and projections are only known by the determining and quantizing steps.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
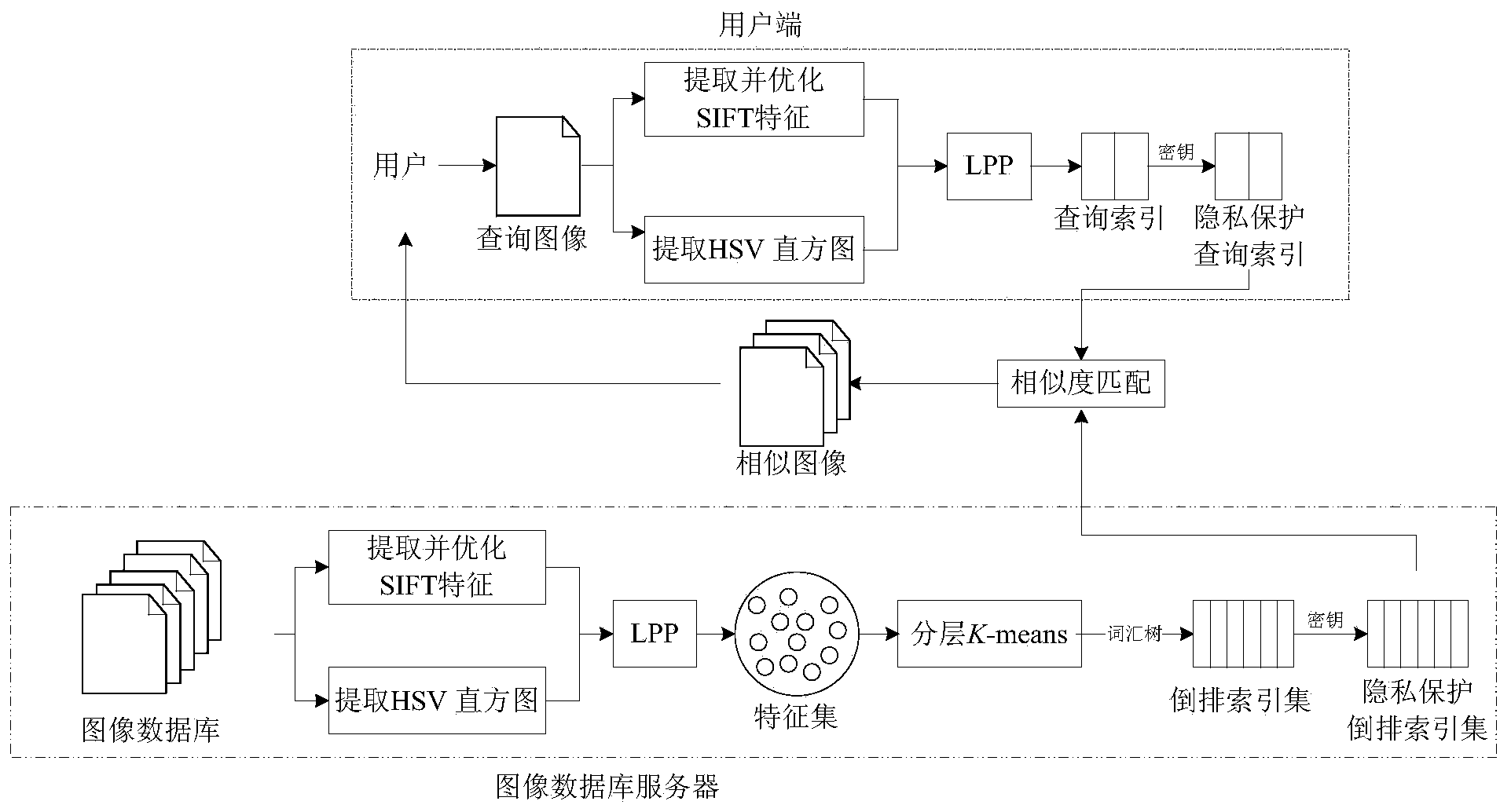
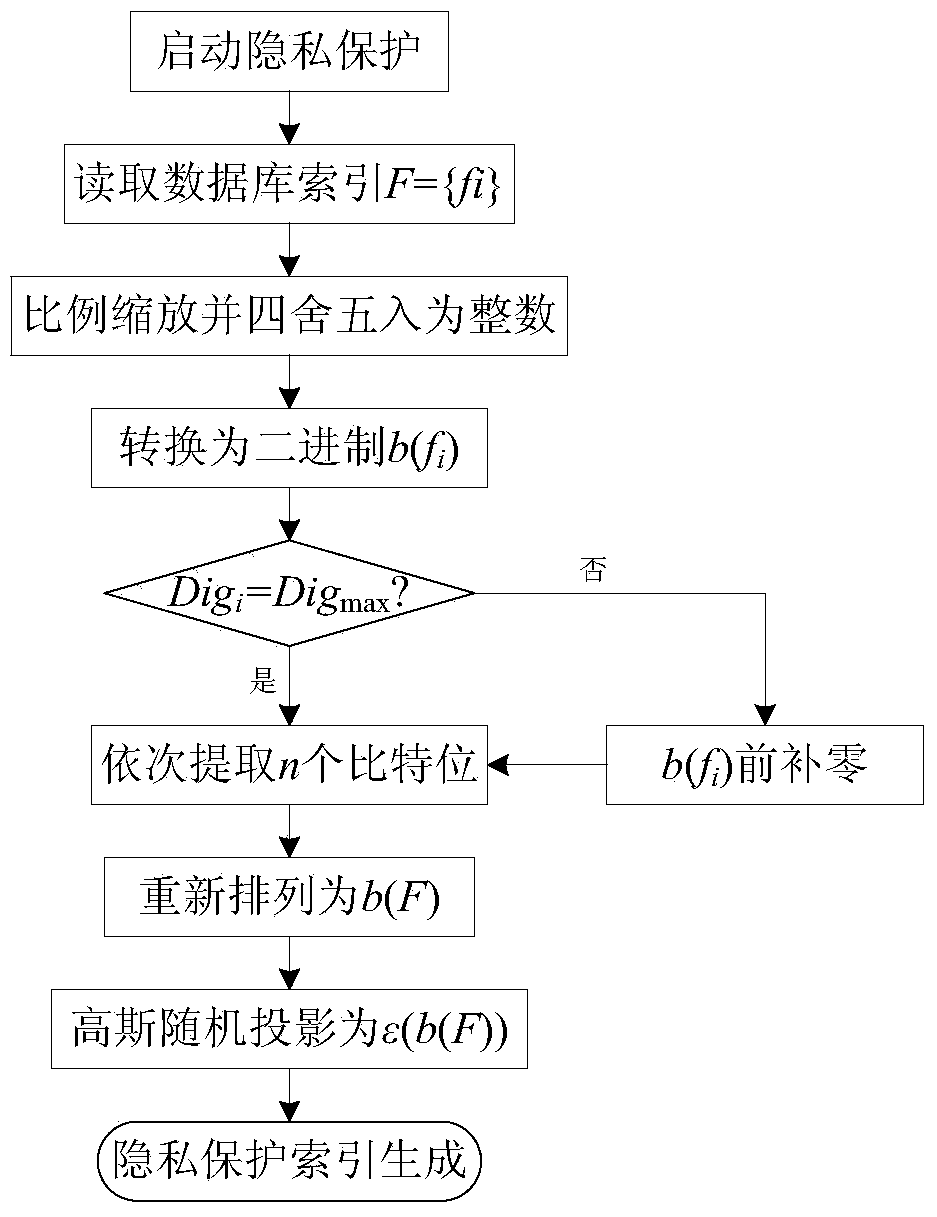
Privacy-protection index generation method for mass image retrieval
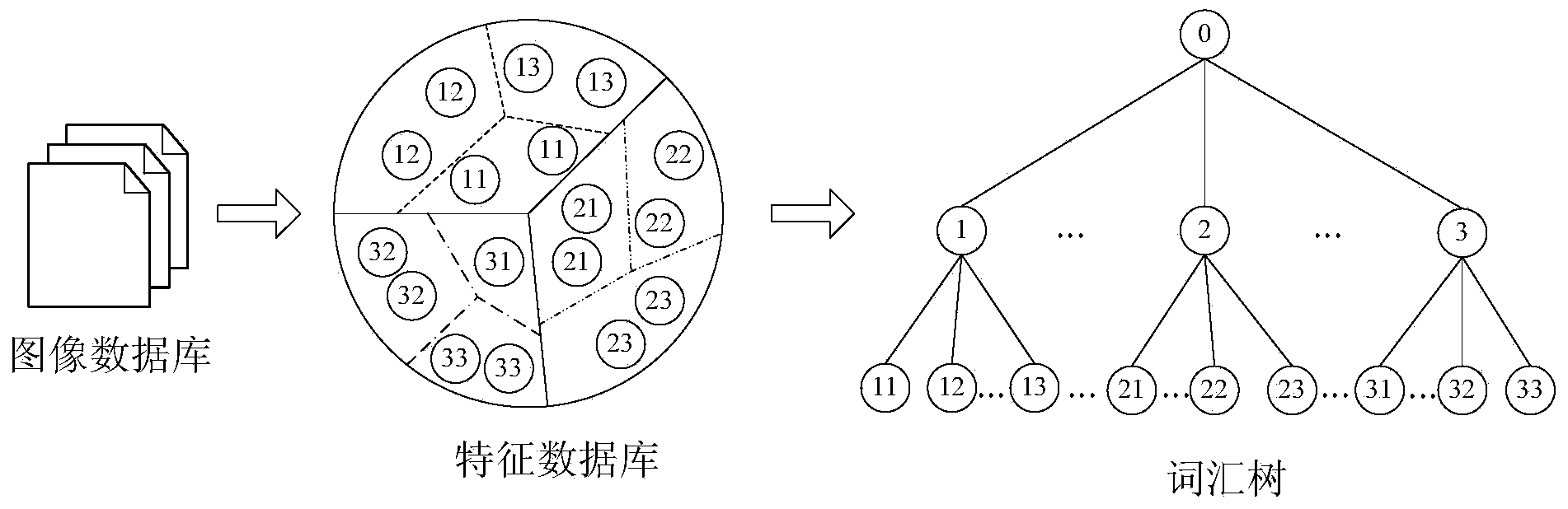
ActiveCN104008174AImprove performanceReduce the numberCharacter and pattern recognitionProgram/content distribution protectionFeature DimensionScale-invariant feature transform
The invention discloses a privacy-protection index generation method for mass image retrieval, relates to the privacy protection problem in mass image retrieval and involves with taking privacy protection into image retrieval. The method is used for establishing an image index with privacy protection, and therefore, the safety of the privacy information of a user can be protected while the retrieval performance is guaranteed. The method comprises the steps of firstly, extracting and optimizing SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) and HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value) color histogram, performing feature dimension reduction by use of a use of a manifold dimension reduction method of locality preserving projections, and constructing a vocabulary tree by using the dimension-reduced feature data. The vocabulary tree is used for constructing an inverted index structure; the method is capable of reducing the number of features, increasing the speed of plaintext domain image retrieval and also optimizing the performance of image retrieval. The method is characterized in that privacy protection is added on the basis of a plaintext domain retrieval framework and the inverted index is double encrypted by use of binary random codes and random projections, and therefore, the image index with privacy protection is realized.
Owner:数安信(北京)科技有限公司
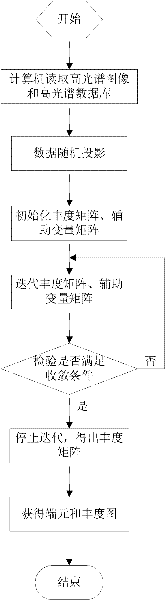
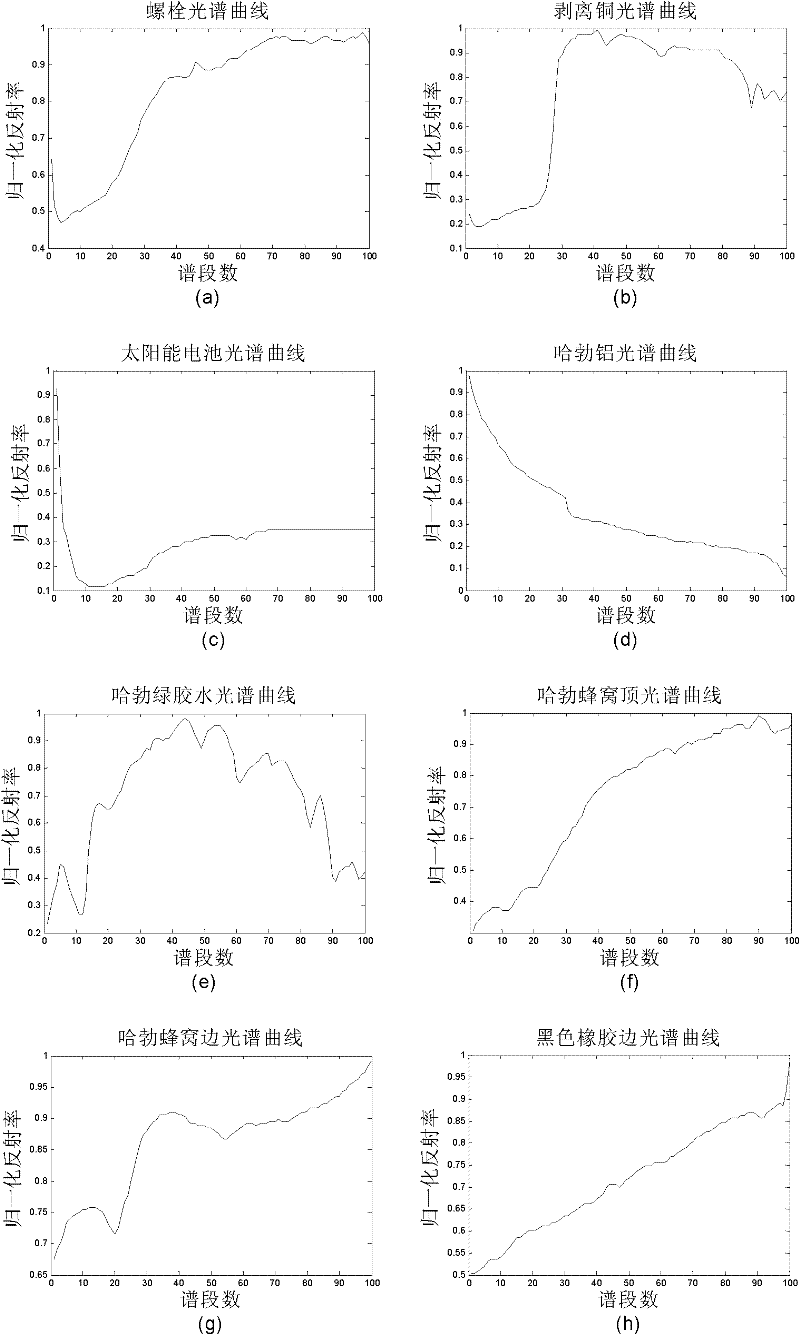
Hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on random projection
ActiveCN102314685AAchieve acquisitionReduce data dimensionalityImage analysisSpectral databaseMATLAB
A hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on random projection includes the following four main steps: (1) data are read by a computer under the environment of MATLAB R2008b; (2) the hyperspectral image data and the hyperspectral library data are randomly projected by the computer; (3) a target function for sparse unmixing is constructed, and the split Bregman algorithm is used for optimizing the target function and working out an extremum until reaching convergence and stopping conditions; (4) an appropriate threshold value is set to process a abundance fraction matrix, so that a final abundance fraction graph and end members can be obtained. The hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on random projection utilizes a hyperspectral database to choose the end members, and overcomes the defect that the end members worked out by the conventional algorithm cannot strictly correspond to the spectra of pure materials in the standard hyperspectral database; and moreover, the hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on random projection uses the random projection technology to carry out dimensionality reduction on raw data, thus achieving the effects of saving memories and reducing the calculation load. The hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on random projection realizes rapid quantitative analysis on hyperspectral images, and has practical value and a broad application prospect in the field of hyperspectral remote sensing image analysis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
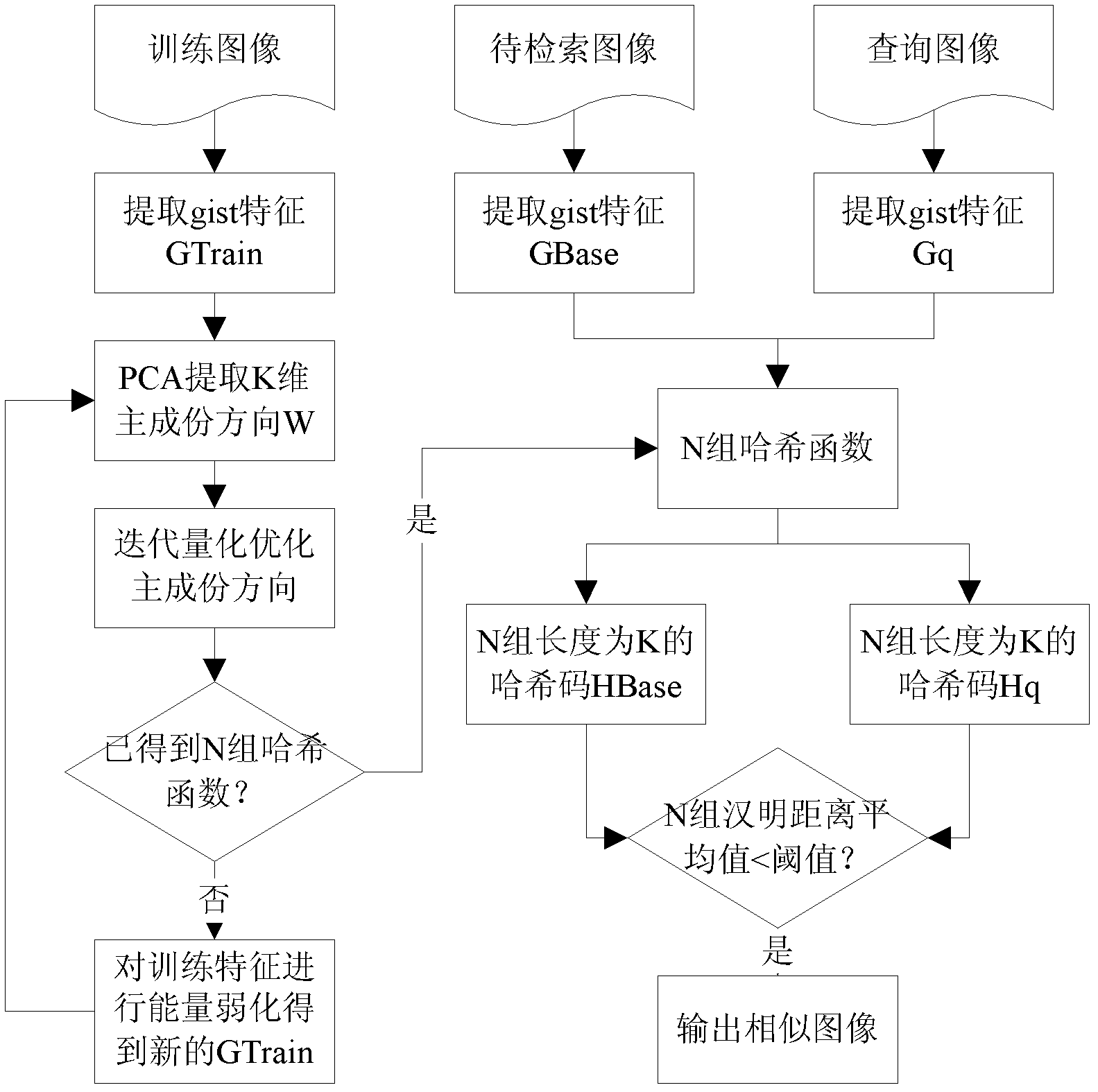
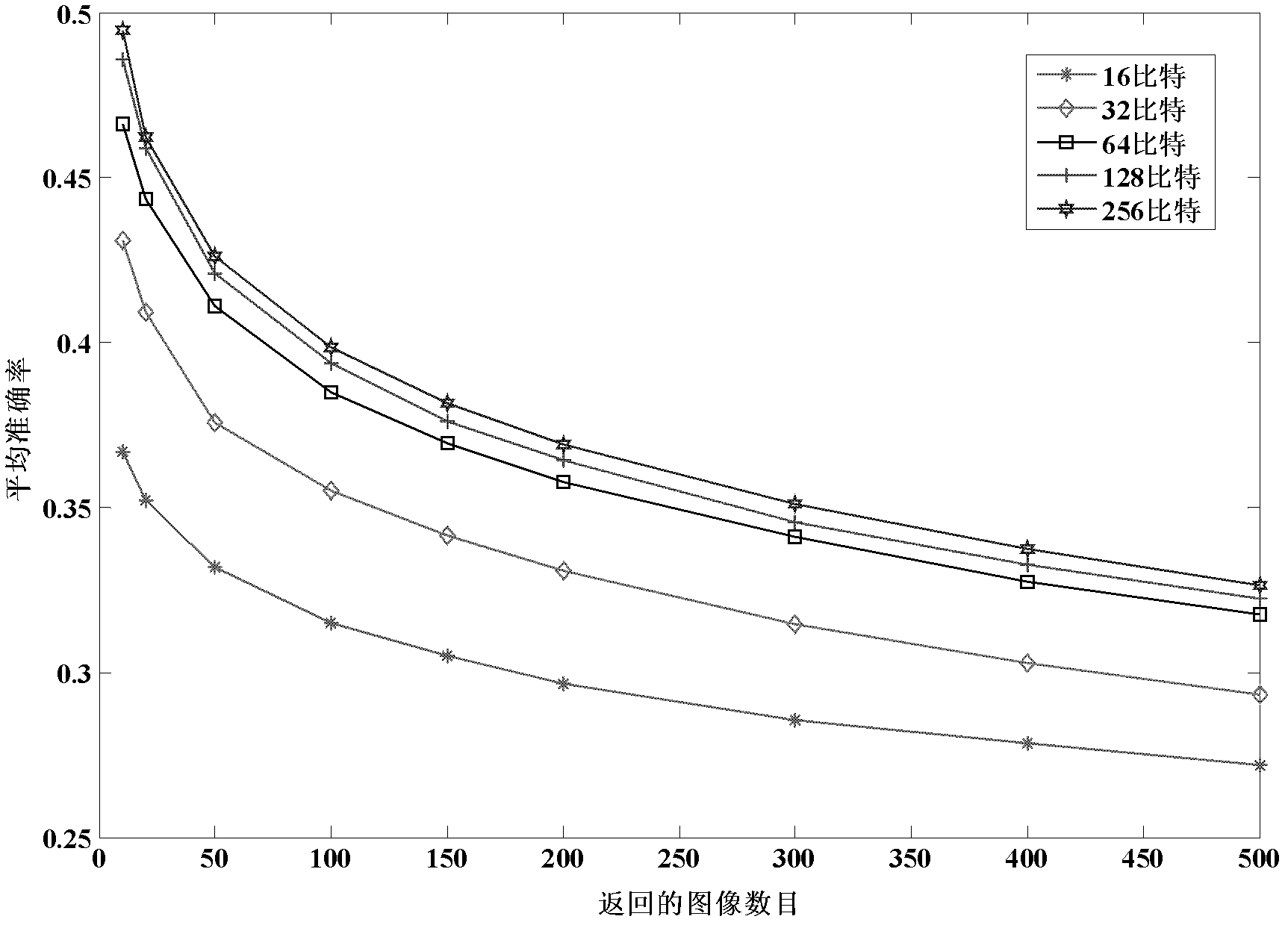
Image retrieval method based on minimum projection errors of multiple hash tables
InactiveCN102508910AImprove accuracyEnergy efficient computingSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalHamming distance
An image retrieval method based on minimum projection errors of multiple hash tables belongs to the technical field of image retrieval, and is characterized in that the gist features of an image to be retrieved, a training image and a query image are respectively extracted; the principal component direction of training features is calculated and optimized through the iterative quantization method, and features to be retrieved and query features are projected on the optimized principal component direction to acquire the corresponding hash codes; the training features go through energy reduction to get new training features, and the process is repeated until the Num groups of hash codes are acquired; and the Hamming distance between the Num group of hash codes of the query image and the Num group of hash codes of the image to be retrieved is calculated, so that the similarity between the image to be retrieved and the query image can be measured according to the distance. The invention has the effects and benefits that the image retrieval method overcomes the shortcoming that the Hamming spherical radius of a single harsh table is large in case of a high recalling rate, as well as the problem that random projection hashing needs too many hash tables in case of a high recalling rate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Automatic fast segmenting method of tumor pathological image
ActiveCN104933711AReduce workloadImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal tissue growthFilter algorithm
The invention discloses an automatic fast segmenting method of a tumor pathological image. The method comprises the following steps: firstly filtering a tumor original pathological image through the adoption of a Gaussian pyramid algorithm to respectively obtain pathological images with equal resolution, double resolution, fourfold resolution, eightfold resolution and 16-fold resolution; determining an initial region of interest containing the tumor on the equal resolution image through a RGB color model and morphological close operation; iteratively optimizing the initial regions of interest from the equal resolution to the fourfold resolution through the adoption of bhattacharyya distance; judging that the contribution of the RGB color model to the tumor region of interest has been reduced to zero when the bhattacharyya distance achieves a set threshold value; performing the self-adaptive high resolution selection of the deep precise segmentation through the adoption of a convergence exponent filtering algorithm, thereby further segmenting under the most suitable high resolution; and finally segmenting out a normal tissue and a tumor tissue in the tumor region of interest through the adoption of a bag of words model based on random projection. The method disclosed by the invention has the features of being accurate, fast and automatic.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
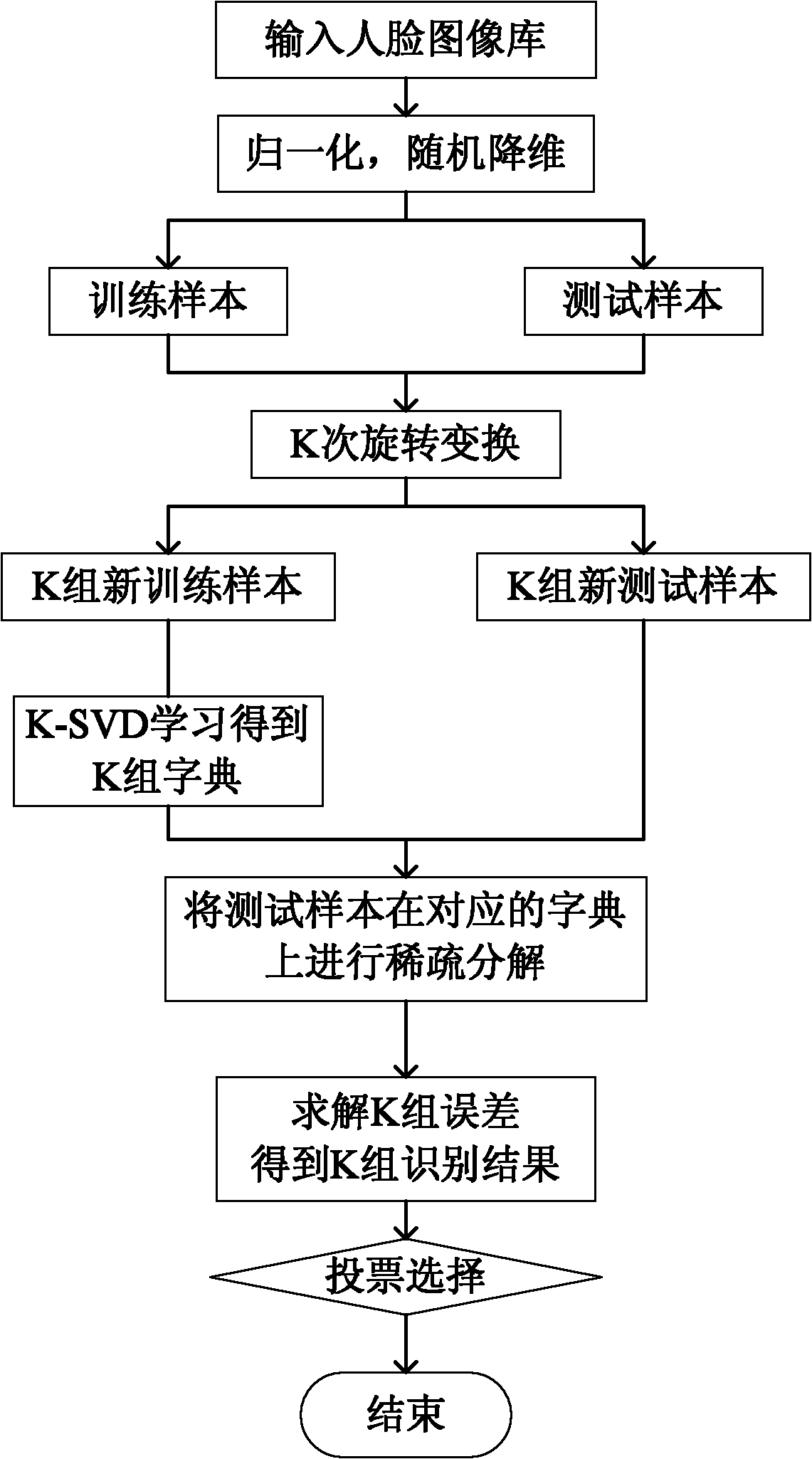
Integration method for face recognition by using sparse representation
InactiveCN102073880AEasy to distinguishImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningOriginal data
The invention discloses an integration method for face recognition by using sparse representation, which mainly solves the problem of low recognition stability in the conventional K-SVD dictionary learning method. The integration method is realized by the following steps of: generating a rotation matrix by a rotation forest algorithm; randomly projecting the same face sample data to different coordinate systems through the rotation matrix, wherein the projected face sample data is easier to distinguish than the original data; recognizing the projected face sample data by a sparse representation classification method; and voting to select the recognition result of a projected face sample to acquire the recognition result of the original face sample. Compared with the conventional sparse representation-based classification method, the integration method has the characteristics of improving the recognition correctness and the recognition stability, and can be used for a safety verification system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Content based similarity detection
Content Based Similarity Detection. A computer implemented method includes computing a hash of each word in a collection of books to produce a numerical integer token using a reduced representation and computing an Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) vector comprising the number of books the token appears in, for every token in the collection of books. The method also includes creating a token occurrence count vector for each book in the collection and normalizing the token occurrence count vector using the IDF vector to create a Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) vector. Further, the method includes reducing each TF-IDF vector by using random projections to obtain a final signature representing each book in the collection, reducing each TF-IDF vector by using random projections to obtain a final signature representing each book in the collection and using a trained machine learning algorithm, determining whether each of the list of candidate books is similar to the target book.
Owner:RAKUTEN KOBO
Detecting duplicate and near-duplicate files
ActiveUS8015162B2Analogue secracy/subscription systemsNatural language data processingToken frequencyTheoretical computer science
Near-duplicate documents may be identified by processing an accepted set of documents to determine a first set of near-duplicate documents using a first technique, and processing the first set to determine a second set of near-duplicate documents using a second technique. The first technique might be token order dependent, and the second technique might be order independent. The first technique might be token frequency independent, and the second technique might be frequency dependent. The first technique might determine whether two documents are near-duplicates using representations based on a subset of the words or tokens of the documents, and the second technique might determine whether two documents are near-duplicates using representations based on all of the words or tokens of the documents. The first technique might use set intersection to determine whether or not documents are near-duplicates, and the second technique might use random projections to determine whether or not documents are near-duplicates.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Image perceptual hashing method based on two-sided random projection
InactiveCN103412960AOvercome the disadvantage of instabilityThe optimal projection vector has high stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsTerminal equipmentImage retrieval
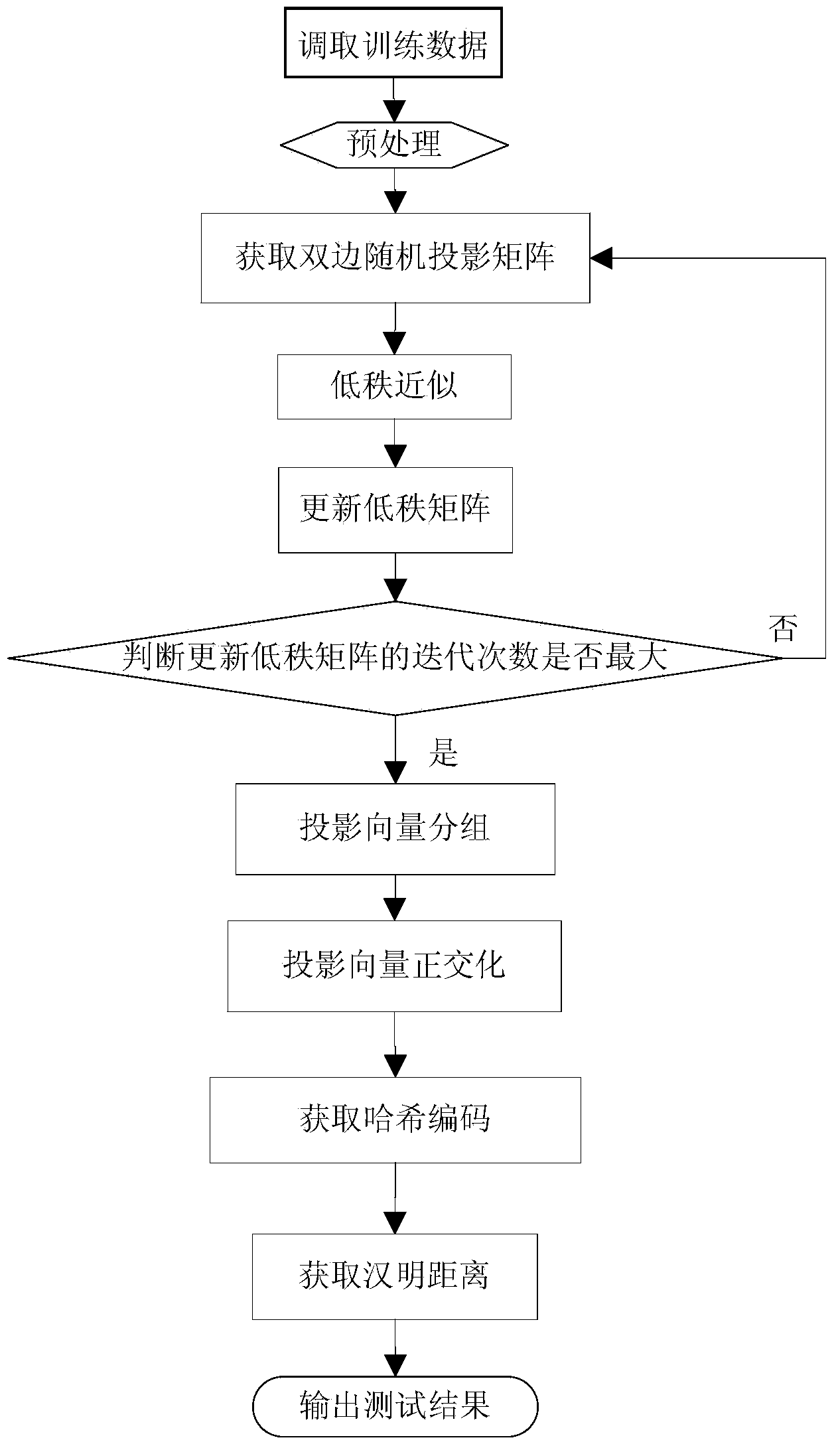
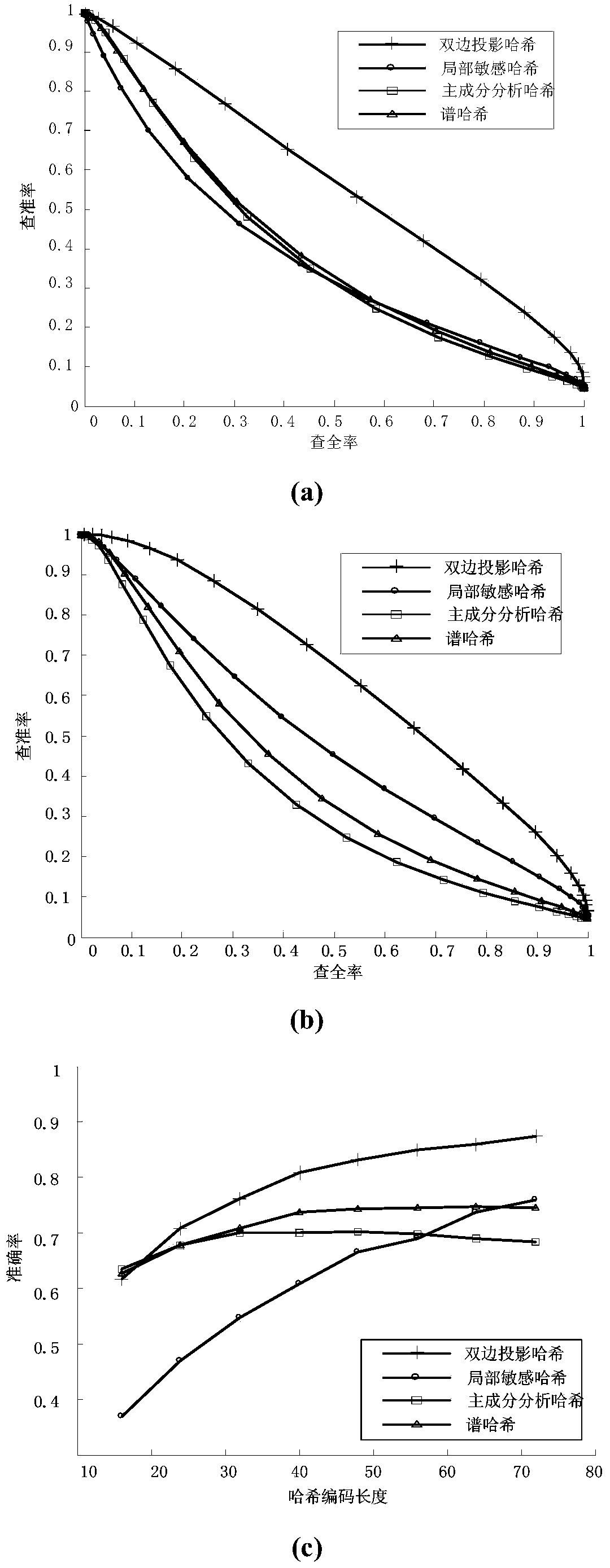
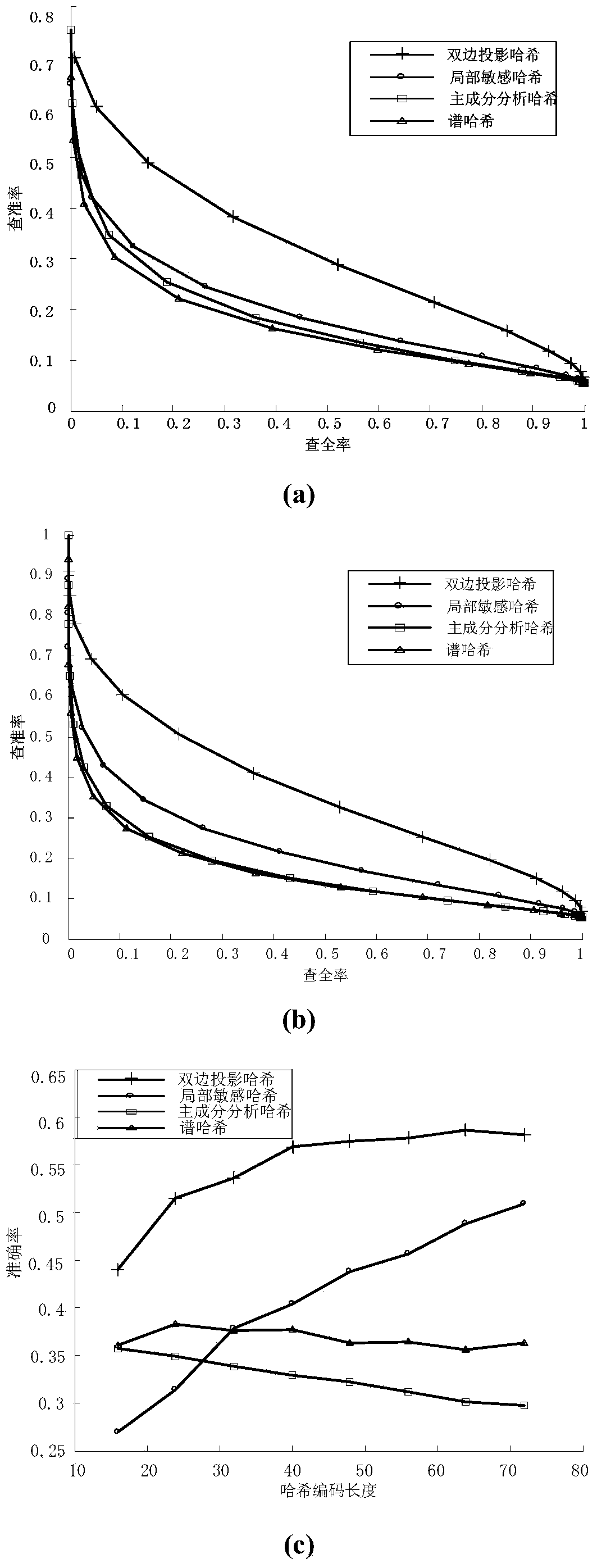
The invention discloses an image perceptual hashing method based on two-sided random projection, which mainly solves the problem of quick searching of massive image data. The method comprises the following steps of (1) preprocessing original image data; (2) obtaining a two-sided random projection matrix; (3) carrying out low-rank approximating; (4) updating a low-rank matrix; (5) judging if the number of iteration times of the updated low-rank matrix is maximum or not; (6) grouping projection vectors; (7) orthogonalizing the projection vectors; (8) obtaining hashing codes; (9) obtaining a hamming distance; and (10) outputting test results. The hashing method has the advantages that the better projection vector can be obtained, the effective hashing codes can be obtained, the memory consumption is reduced, the searching time is saved, the comprehensive performance of precision ratio and recall ratio of image searching can be improved, and the hashing method is applied to the image searching services of electronic businesses and mobile terminal equipment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Automatic electrocardiosignal classification method based on single channel
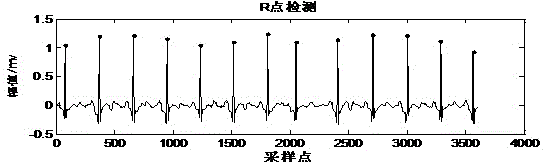
ActiveCN109077715ARelieve pressureOvercoming ECG specificity issuesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature vectorEcg signal
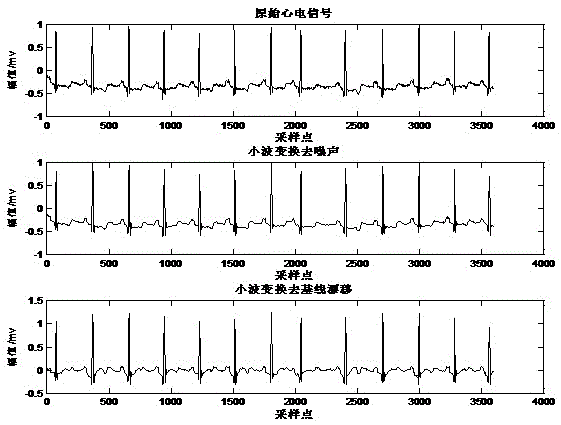
The invention provides an automatic electrocardiosignal classification method based on single channel. The method comprises the steps that a limb channel electrocardiosignal is received through Web socket; a wavelet median threshold method is adopted to perform electrocardiosignal denoising; a Pan-Tompkins method is used for conducting R wave detection, the electrocardiosignal is segmented based on R wave to resolve RR period characteristics, corresponding characteristics vectors are obtained by sequentially conducting empirical mode decomposition, Gaussian random projection matrix, polynomialfitting and interval extremum on obtained electrocardiogram segments; normalization is conducted on obtained characteristic features to allow the characteristic features to be conformed to standardized normal distribution, the standardized characteristic vectors are input to a trained XGboost model, and a corresponding detecting value is output. By means of the method, the problem of personal electrocardiosignal specificity is solved, the method is run at a server end, the pressure on a client is relieved, and the method has higher reference value on N and V type arrhythmias detection results.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nonnegative matrix factorization method based on low-rank recovery
ActiveCN105930308AGuaranteed to be free from interferenceLow-dimensional data represent goodCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsInformation processingOriginal data
The invention belongs to the technical field of information processing and particularly relates to a nonnegative matrix factorization method based on low-rank recovery. The method comprises following steps: 1. each image sample in a raw database is converted into a vector to form an m*n original data matrix X, wherein m is the dimension of the image sample, n is the number of image samples; 2. low-rank sparse factorization is performed on the original data matrix X; 2.1 the rank of the low-rank matrix is set as r, and the sparseness of the sparse matrix is set as k; 2.2 a low-rank matrix L with the rank of r and a sparse matrix S with the rank of k of the original data matrix X is solved by means of the bilateral random projection algorithm; 3. nonnegative matrix factorization is performed on the low-rank matrix L obtained in step 2. to obtain a basis matrix W and an encoding matrix H. According to the nonnegative matrix factorization method based on low-rank recovery, data low-rank components and sparse components are obtained through low-rank sparse factorization and nonnegative matrix factorization is performed on the low-rank components removed of sparse noise parts to make the nonnegative matrix factorization results free from noise interference.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wireless sensor network early warning method and system based on clustering compressed sensing
InactiveCN105636094AImprove real-time performanceImprove fault toleranceNetwork topologiesFault toleranceGeolocation
The invention discloses a wireless sensor network early warning method and system based on clustering compressed sensing. The method comprises the following steps: S1) calculating optimal cluster number and optimum cluster head space distribution by a gateway according to geographic position and an energy consumption model of each sensor node in a wireless sensor network; S2) obtaining monitoring data in a cluster, and converting the monitoring data into binary reading and a binary bit string sequence according to a threshold value; S3) carrying out dense random projection and sparse random projection thereon to obtain a compressed sensing sequence, and carrying out reconstruction on the compressed sensing sequence to obtain a reconstructed sequence; S4) carrying out judgment according to estimated value of the reconstructed sequence, and summarizing the number of effective neighbor nodes executing a majority vote method; and S5) if the number of the effective neighbor nodes is larger than a preset threshold value, determining that the node has an abnormal event. Real-time performance and fault tolerance of the monitoring method can be improved; influence of the fault nodes on abnormal event detection reliability is reduced; and network energy consumption in the data collection process can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
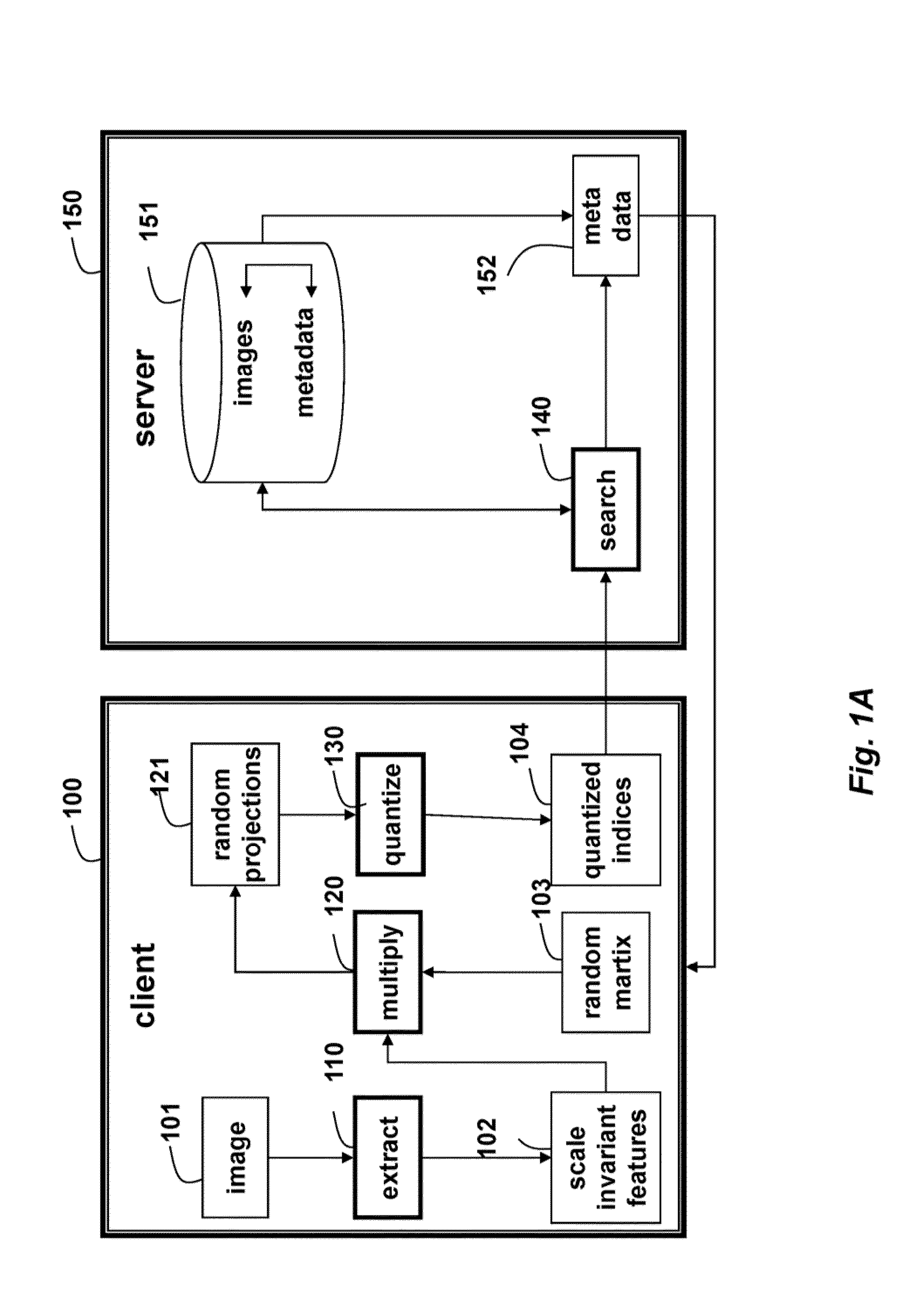
Method for Representing Images Using Quantized Embeddings of Scale-Invariant Image Features
ActiveUS20130336588A1Efficient retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging FeatureEuclidean vector
Scale-invariant features are extracted from an image. The features are projected to a lower dimensional random projection matrix by multiplying the features by a matrix of random entries. The matrix of random projections is quantized to produce a matrix of quantization indices, which form a query vector for searching a database of images to retrieve metadata related to the image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
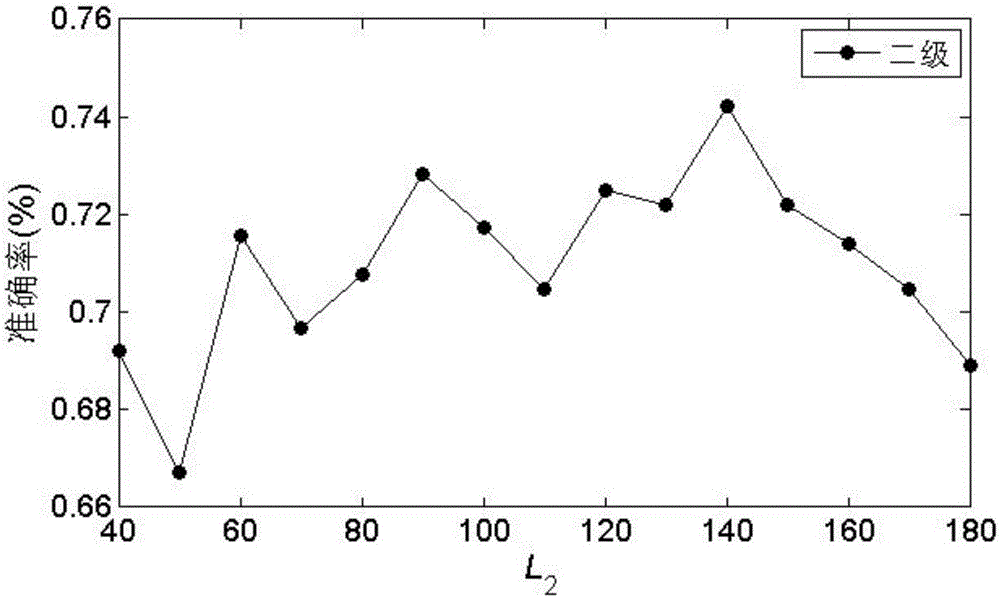
Progressive type mild cognitive impairment identification method based on neuroimaging
InactiveCN106096636AImprove classification performanceImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFeature DimensionVoxel
The invention discloses a progressive type mild cognitive impairment identification method based on neuroimaging, and belongs to the technical field of computer image processing. The MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) graph and the PET (Positron Emission Tomography) graph of a test sample are downloaded from an ADNI (Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative) database and are subjected to preprocessing and sample screening to obtain N groups of sample images; the AAL (Anatomical Automatic Labeling) template of the human is selected to independently manufacture 90 cerebral region templates for the sample images, and the grey matter voxel value of a corresponding cerebral region is obtained to obtain N*180-dimensional data; and finally, a second level integration classifier is constructed, feature dimension reduction is carried out on the obtained data, a reduced dimension is subjected to optimization, and the data is applied to the second level integration classifier to carry out classification identification on progressive type MCI (Mild Cognitive Impairment) patients and non-progressive type MCI patients. The data is subjected to the dimension reduction processing by a random projection method, then, the data is applied to the second level integration classifier, classification accuracy is 74.22%, sensitivity is 66.25%, specificity is 82.19%, operation speed is improved, and the classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
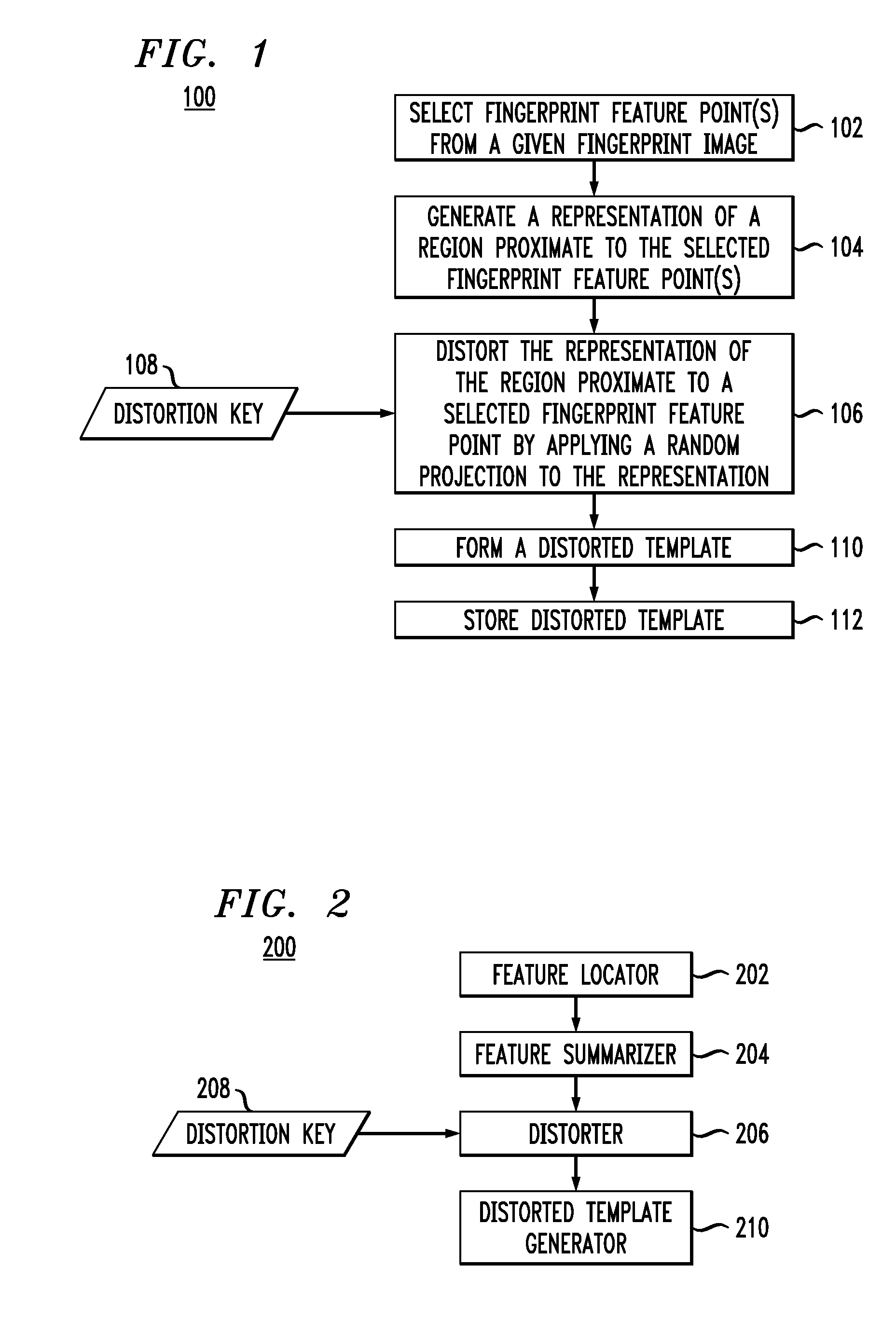
Methods and Apparatus for Generation of Cancelable Fingerprint Template
InactiveUS20090175513A1Programme controlElectric signal transmission systemsRandom projectionDistortion
Techniques for generating a distorted fingerprint representation for a given fingerprint image are provided. First, at least one fingerprint feature point from a given fingerprint image is selected. At least one representation of a region proximate to the selected fingerprint feature point is then generated. Next, the representation of the region proximate to the selected fingerprint feature point is distorted. The distortion comprises applying a random projection to the representation to generate a randomly projected representation of the region proximate to the selected fingerprint feature point. A distorted template is then formed, wherein the distorted template comprises the randomly projected representation of the region proximate to the selected fingerprint feature point.
Owner:IBM CORP
Body sensor network system based on compressed sensing
InactiveCN104933846ADownsampleReduce transmission power consumptionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsData displayIntegrator
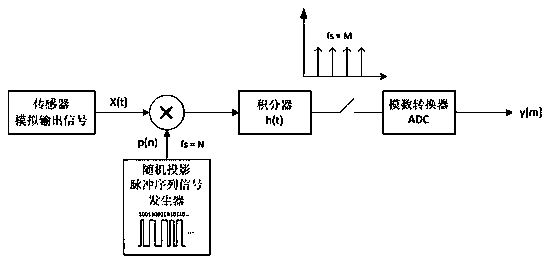
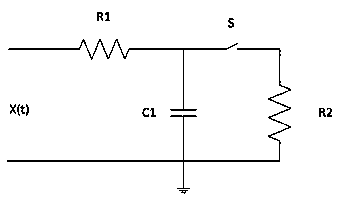
The invention discloses a body sensor network system based on compressed sensing. The body sensor network system comprises sensor nodes, a wireless receiving module, a PC communication module, a signal reconstruction module, a data display module and a data analysis module, wherein each sensor node comprises a sensor module, a compressive sampling module and a wireless transmission module; the compressive sampling modules comprise random projection pulse-train generators, integrators, electronic switches and analog-digital conversion modules; the compressive sampling modules are suitable for signals of different frequencies, and meet collection requirements of signals of different frequencies by adjusting the parameters of the random projection pulse-train generators and the integrators; the compressive sampling modules achieve different compression ratios and different compression degrees of original signals by adjusting the parameters of the electronic switches. Based on a compressed sensing technology, the invention provides the novel body sensor network system and method which can achieve the purpose of compressing and sampling synchronously, and sampling and transmitting power consumption of the nodes in a body sensor network can be reduced effectively.
Owner:苏州康迈德医疗科技有限公司
Real-time electrocardiogramclassification method based on random projection
InactiveCN105550659AImprove efficiencyEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionEcg signalData acquisition
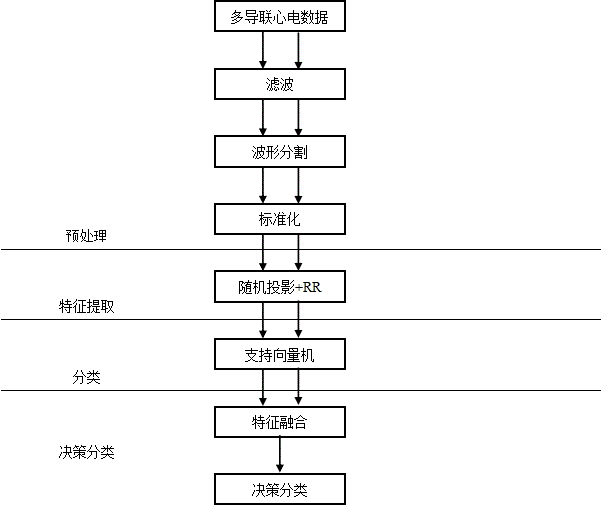
The invention requests to protect a real-time electrocardiogram classification method based on random projection, and aims to solve the problems of data acquisition and computation and power consumption transmission with which a remote electrocardiogram monitoring system faces and the problem that electrocardiogram cannot be classified in real time. Five types of heartbeat are classified into normal pulsation, atrial premature beat, ventricular premature beat, left bundle branch block and right bundle branch block. The method comprises the following steps: (1) data preprocessing; (2) characteristic extraction: on the basis of a compressed sensing principle, compressing data, calculating an RR interval and an RR weight, and splicing characteristic vectors to form second characteristics; (3) classification: dividing secondary characteristic data into training data and test data, wherein the training data and the test data are independently used for modeling ant testing; and (4) decision classification: carrying out multiple-lead classification result data fusion. The step of data preprocessing comprises the following specific steps: 1) filtering an electrocardiosignal, and removing interference; 2) carrying out waveform detection and segmentation; 3) carrying out data standardization. The electrocardiogram data classification method provided by the invention is accurate in a classification result, and improves data processing capability.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Ultra-broadband analogue signal parallel sampling system based on accidental projection
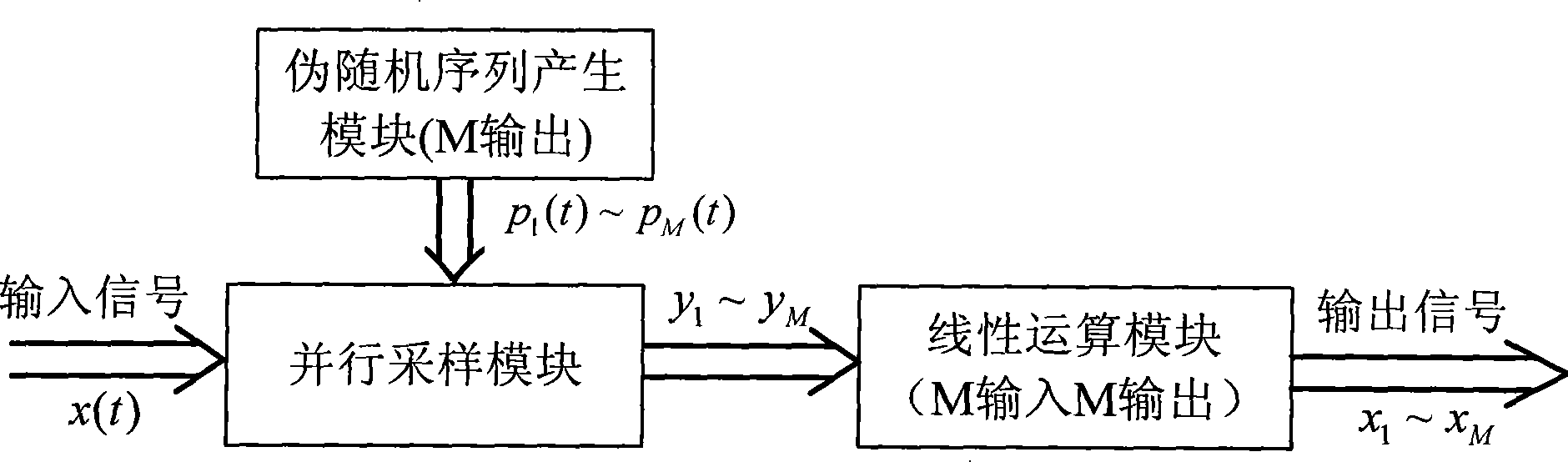
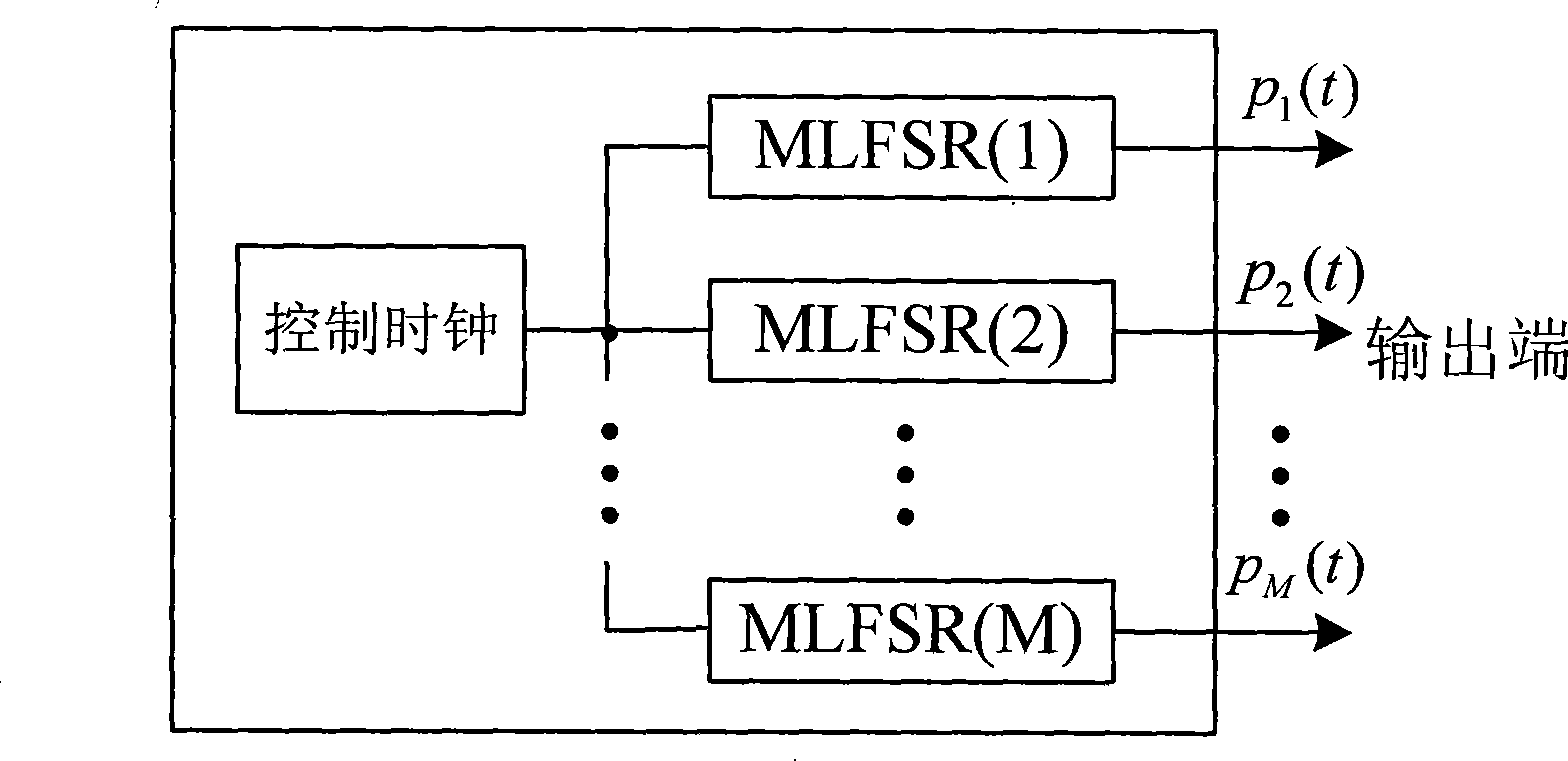
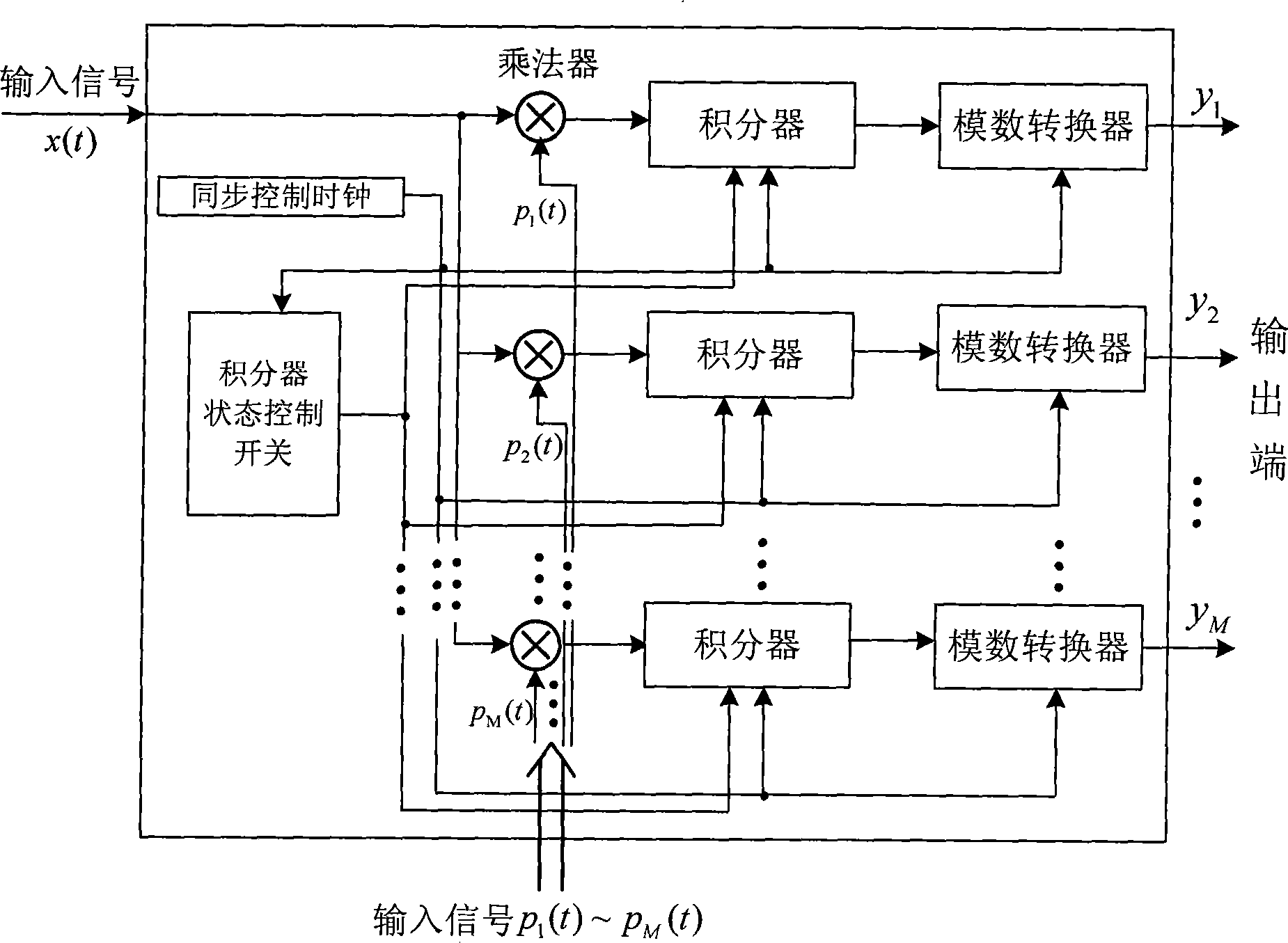
InactiveCN101247137AEasy to implementAchieving Process StabilityAnalogue-digital convertersTransmissionAnalog signalBroadband
The present invention discloses a parallel sampling system basing on the super-wideband which is projected randomly, and the invention mainly settles the problem of complex realization and no suitability for processing the common super-wide band in the homogeneous system. The system is mainly composed of a function generating module, a parallel sampling module and a linear operating module. In the system the function generating module adopts a pseudorandom sequence generating module for generating a group of pseudorandom sequence for inputting to the parallel sampling module. The parallel sampling module realizes the projection operation of the upper-wide band analog signal on the self-contained pseudorandom space and obtains the digital projection coefficient signal for inputting to the linear operating module. The linear operating module adopts the M-input and M-output linear structure and conveys the output projection coefficient signal of the parallel sampling module to the parallel digital sampling signal and then outputs. The invention has the advantages of low complexity in the circuit operation, being easily realized and broad applying sphere. The invention can be used for executing digitization sampling processing to the super-wideband signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
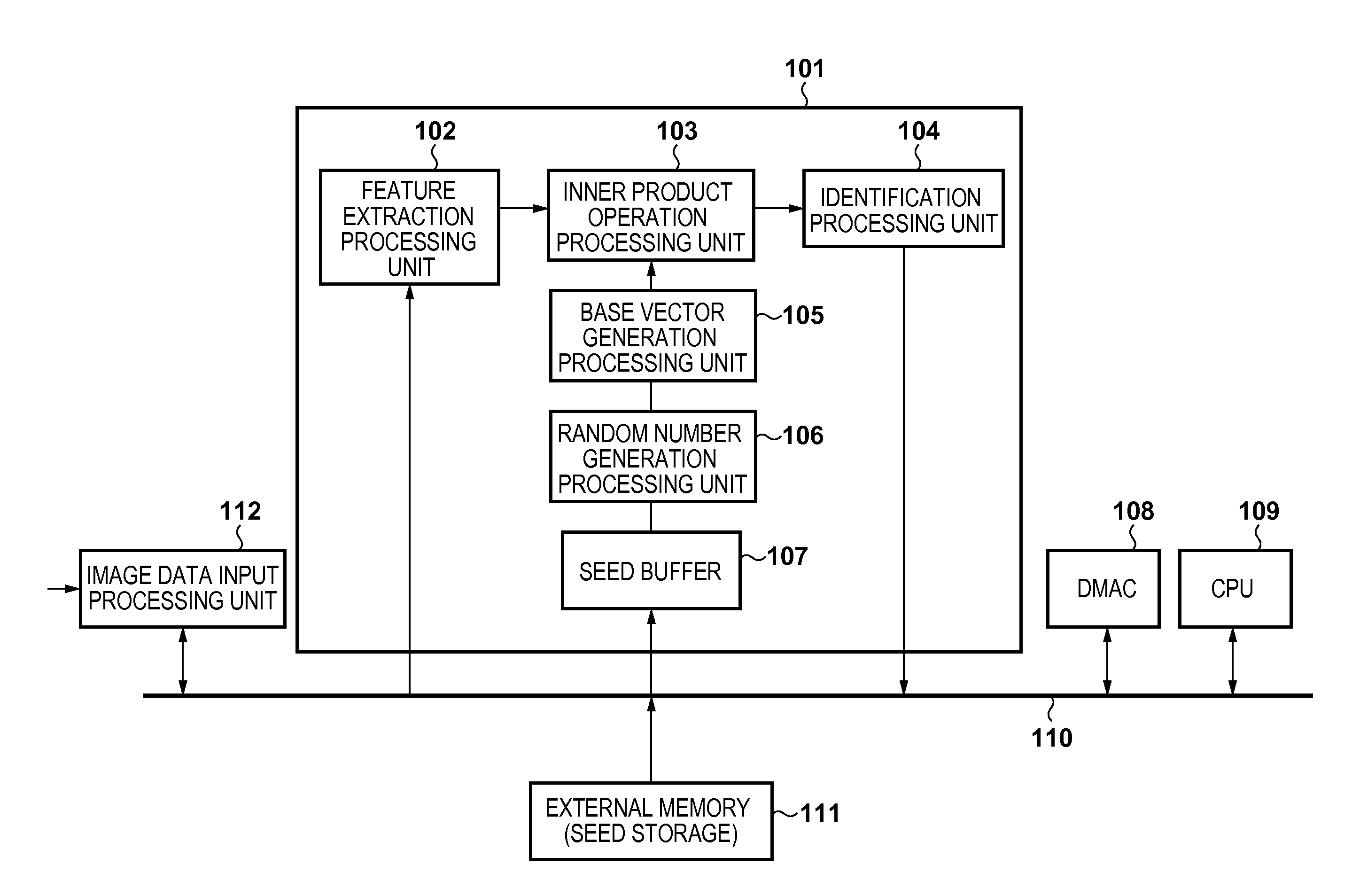
A plurality of random number sequences are generated using a plurality of random number seeds stored in a memory, and a plurality of base vectors are generated based on the plurality of random number sequences. A transformation source vector is transformed into a lower-dimensional vector by performing random projection for the transformation source vector using the plurality of generated base vectors.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for automatically adjusting smoothness of projection surface
InactiveCN105791786AGuaranteed no distortionPicture reproducers using projection devicesProjection imageProjection system
The invention provides a system and a method for automatically adjusting smoothness of a projection surface. The system is characterized in that the system comprises a storage unit for storing a standard corrected image; and a control unit which reads the standard corrected image from the storage unit and projects the standard corrected image on a random projection surface through a projection unit; the method comprises the steps of acquiring the corrected projection image of the standard corrected image on the projection surface through an image sensing unit; correcting the corrected projection image so that the corrected projection image is similar with the standard corrected image, thereby obtaining a correction parameter; correcting the to-be-projected image according to the correction parameter; and projecting the corrected image on the projection surface through the projection unit. The other technical solution of the invention provides a projection surface evenness automatic adjustment method based on the system. The system and the method provided by the invention can realize no distortion of the image which is projected out of the projection system without the projection surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATECH INFORMATION TECH
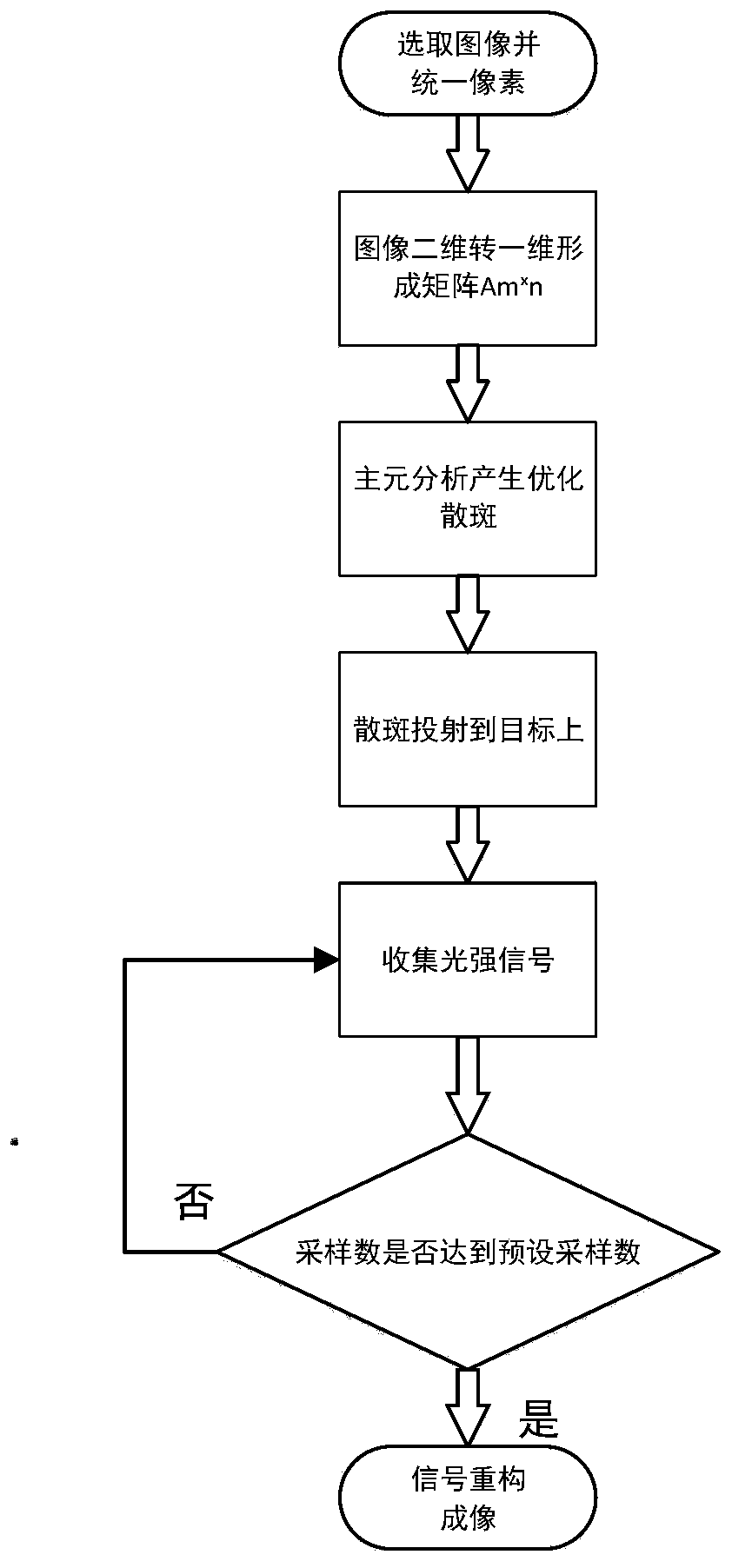
Speckle optimal-compressed sensing ghost imaging method and system
ActiveCN110646810AImprove image qualityAchieve a high level of refactoringElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging qualityLight spot
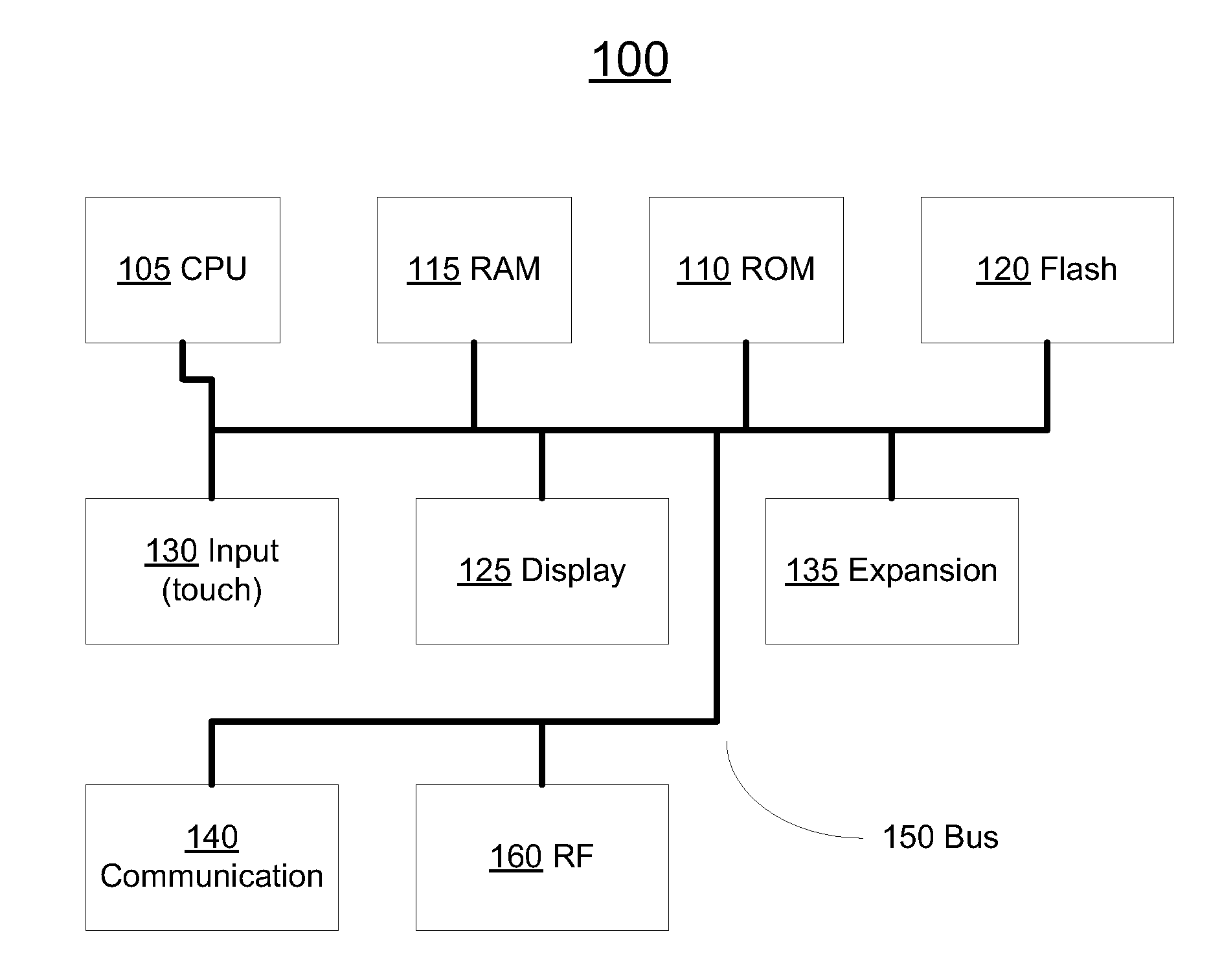
The invention discloses a speckle optimal-compressed sensing ghost imaging method and system, and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging. An implementation method of the invention comprisesthe following steps of generating an optimized speckle matrix through a principal component analysis method; generating light spots according to the generated speckle matrix, projecting the generatedlight spots onto a target image, receiving a light intensity signal reflected by the target image, and transmitting the signal to a compression processing module; projecting the obtained light intensity signals to a sparse base in a compression processing module to obtain sparse signals, wherein the sparse signals are subjected to an over-complete measurement matrix to obtain a series of non-adaptive linear random projection value matrixes; solving an optimal solution of the series of non-adaptive linear random projection value matrixes to realize the high reconstruction of the original lightintensity signal, and realizing the speckle optimal-compressed sensing ghost imaging, thereby improving imaging quality of the three-dimensional ghost imaging. The invention further discloses a computational ghost imaging system based on compressed sensing. The ghost imaging method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being fast in imaging speed, less in times of receiving the light intensity signal, and flexible in form.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
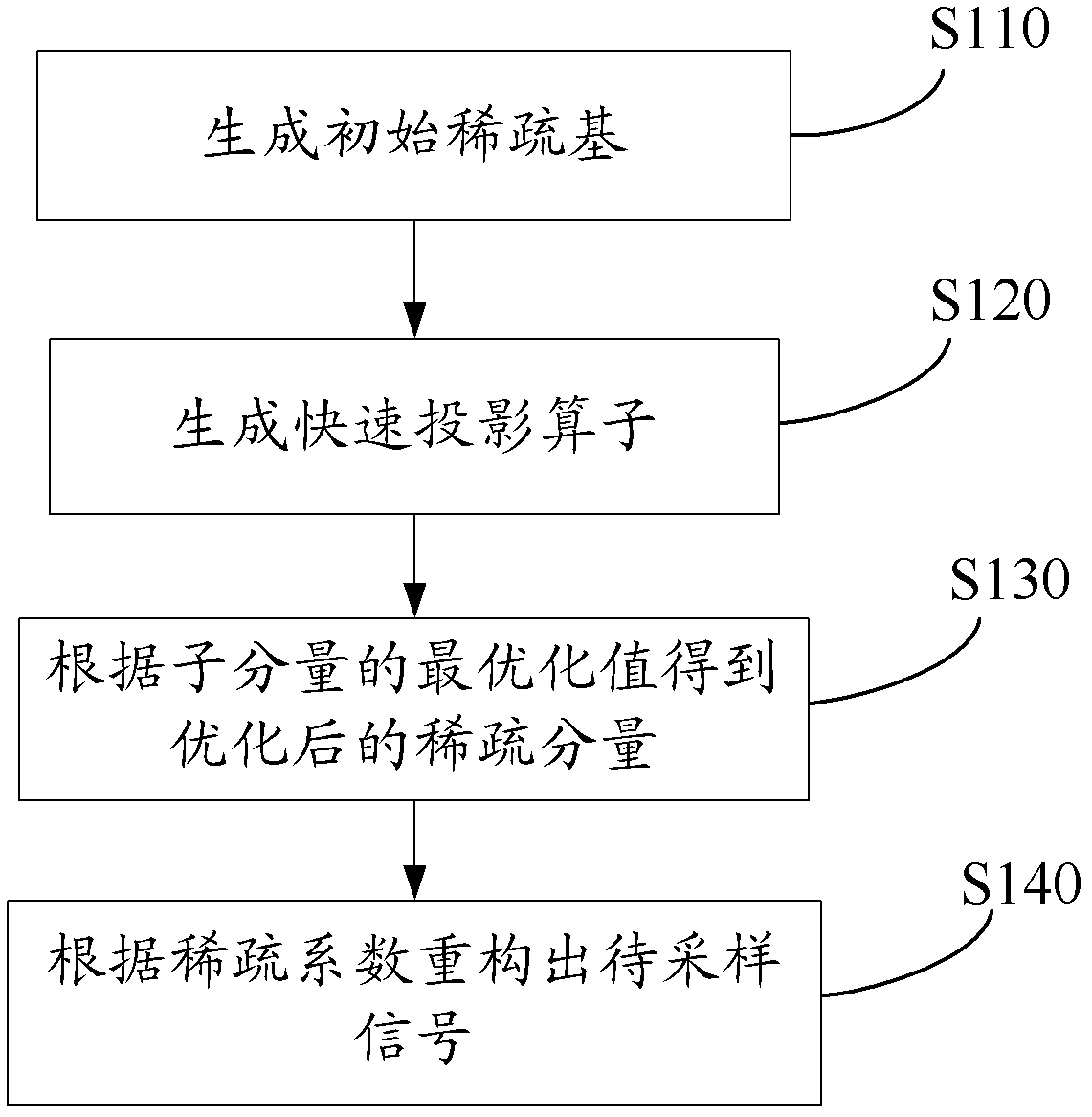
Compressive sampling method and device
ActiveCN102523450AQuality improvementReduce computational complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputation complexityRandom projection
The invention provides a compressive sampling method, which includes: acquiring signals of a target object, selecting a sparse base capable of indicating the signals of the target object sparsely; generating quick projection operators according to the initial sparse base, a preset random permutation matrix and a random matrix, solving the optimum value of subcomponents according to the quick projection operators, and obtaining optimized sparse components; determining the sparse coefficient of the optimized sparse components in the initial sparse base, and reconfiguring to-be-sampled signals according to the sparse coefficient. Data in different data quantity can be acquired on blocks different in sparse degree by the quick compressive sampling method, and the random projection operators have lower computing complexity so that higher reconfiguring quality can be obtained. Besides, the invention discloses a compressive sampling device.
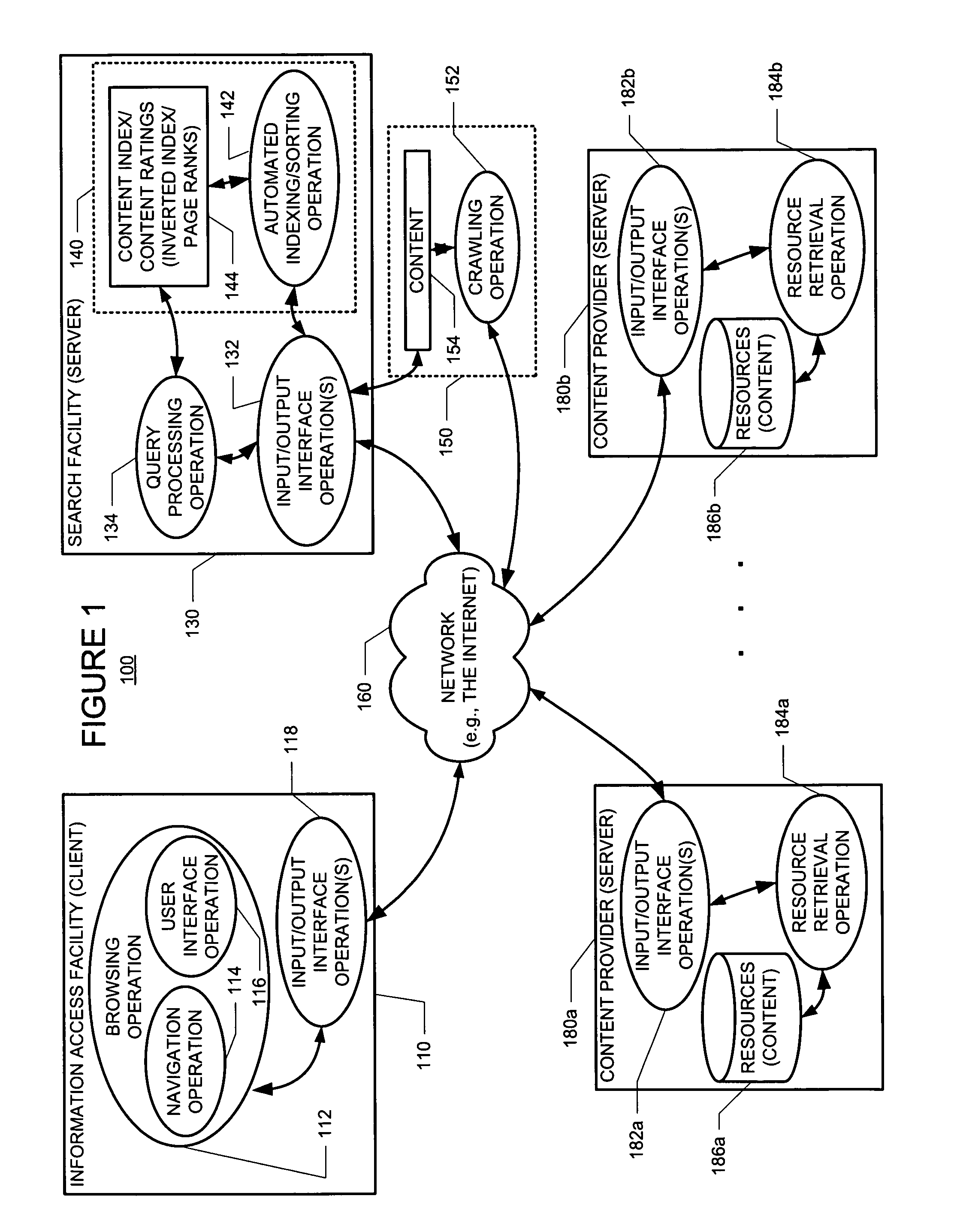
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
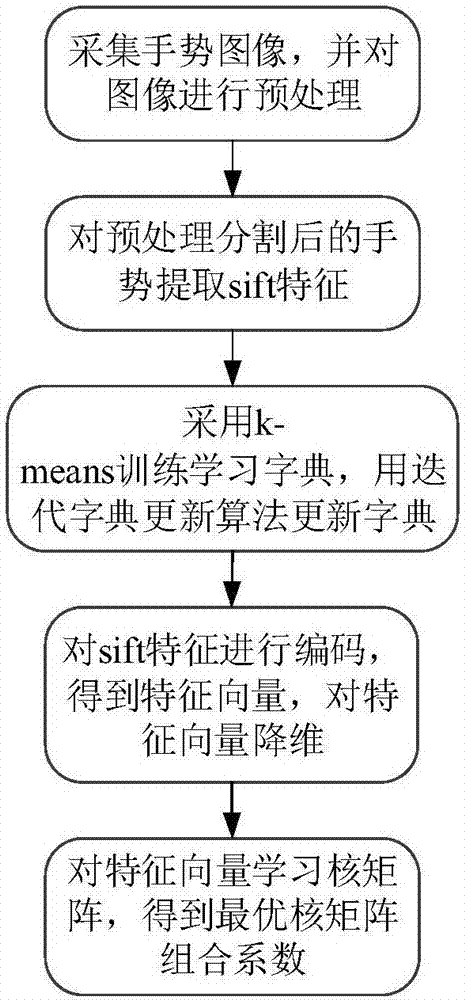
Random projection multi-kernel learning-based hand gesture identification method
ActiveCN106909895AReduce the impact of gesture segmentationImprove recognition efficiencyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorLearning based
The invention discloses a random projection multi-kernel learning-based hand gesture identification method comprising the following steps: hand gesture images are collected and preprocessed, preprocessing operation comprises hand gesture positioning operation and hand gesture segmenting operation, sift characteristics are extracted from preprocessed and segmented hand gestures, a K-means algorithm is adopted for training a learning dictionary, an iteration dictionary is used for updating the algorithm and the dictionary, the gesture images are subjected to space pyramid dividing operation, the trained dictionary is used for encoding the sift characteristics of the hand gesture images in each space pyramid layer, and therefore characteristic vectors can be obtained and subjected to cascading operation; random projection is adopted for subjecting the characteristic vectors to dimensional reducing operation; as for a characteristic vector learning kernel matrix after dimensional reducing of each pyramid layer, a multi-kernel model learning algorithm is adopted for classified learning, and an optimal kernel matrix combination coefficient is obtained. Via the method disclosed in the invention, problems of background interference, high complexity, long time consumption, low identification rate and the like in a conventional hand gesture identification method can be solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
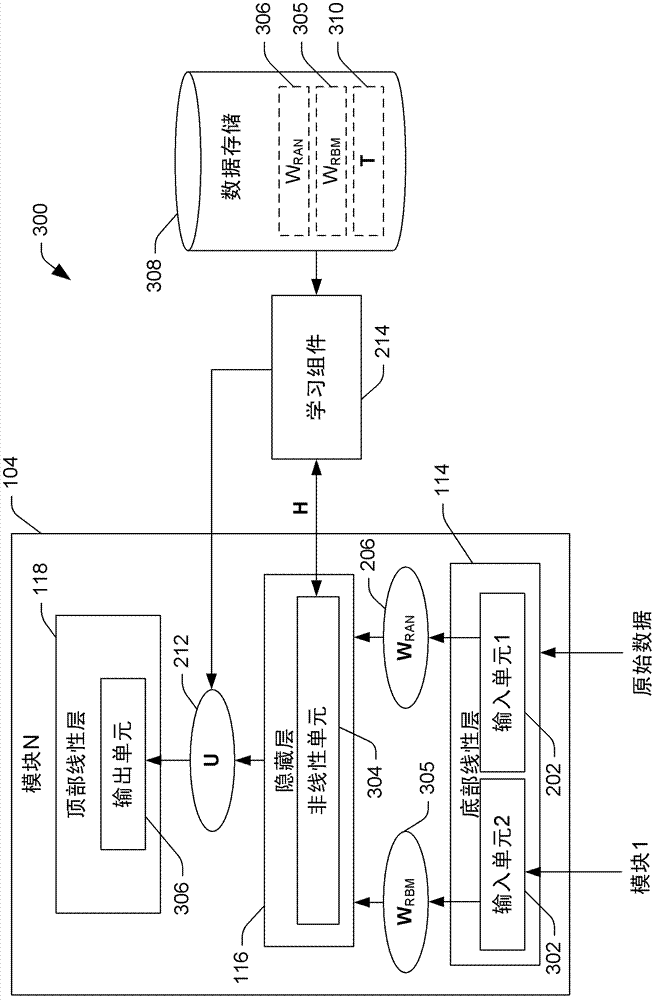
Deep convex network with joint use of nonlinear random projection, restricted boltzmann machine and batch-based parallelizable optimization
ActiveCN102737278ACharacter and pattern recognitionSpeech recognitionStructured modelRestricted Boltzmann machine
A method is disclosed herein that includes an act of causing a processor to access a deep-structured, layered or hierarchical model, called deep convex network, retained in a computer-readable medium, wherein the deep-structured model comprises a plurality of layers with weights assigned thereto. This layered model can produce the output serving as the scores to combine with transition probabilities between states in a hidden Markov model and language model scores to form a full speech recognizer. The method makes joint use of nonlinear random projections and RBM weights, and it stacks a lower module's output with the raw data to establish its immediately higher module. Batch-based, convex optimization is performed to learn a portion of the deep convex network's weights, rendering it appropriate for parallel computation to accomplish the training. The method can further include the act of jointly substantially optimizing the weights, the transition probabilities, and the language model scores of the deep-structured model using the optimization criterion based on a sequence rather than a set of unrelated frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
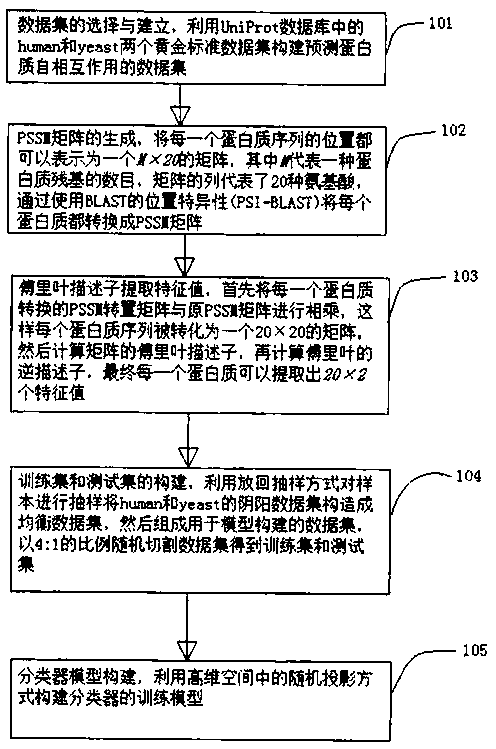
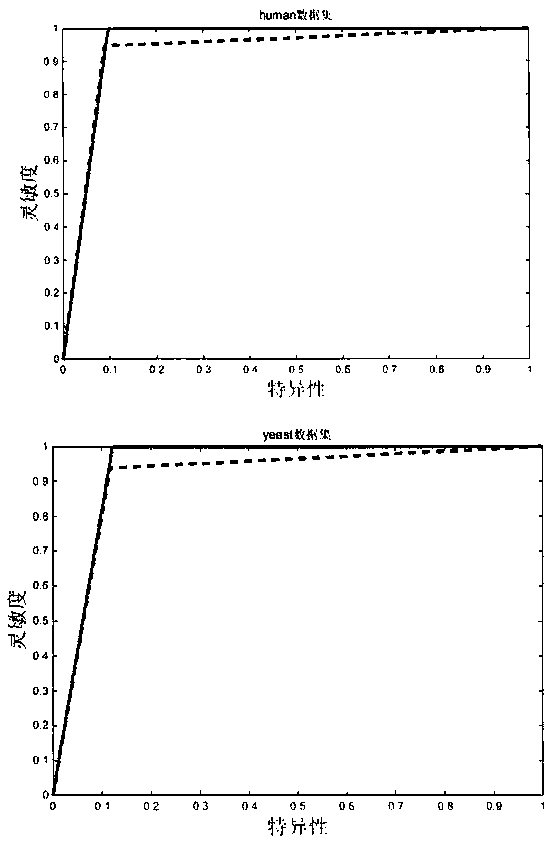
Method for predicting self-interaction effect of protein
ActiveCN107609352ASelf-interacting effectiveThe prediction of self-interactions worksSpecial data processing applicationsData setFourier descriptor
The invention discloses a method for predicting self-interaction effect of protein. The method comprises the steps of selection and establishment of a data set, generation of a PSSM matrix, extractionof a feature value by a Fourier descriptor, construction of a training set and a testing set and construction of a classifier model. According to the method, the feature value of a sample set is extracted by the Fourier descriptor, the number of times of multiplication required for discrete Fourier transform of a computing data set of a computer is greatly reduced, and the computing quantity is reduced. A model can be constructed by a random projection method, the prediction precision is greatly improved, and a good prediction effect can be achieved. The method is low in computing cost and small in power consumption; the self-interaction effect of the protein can be predicted effectively; and the prediction effect can reach 93% or above.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tracking method based on sparse subspace
PendingCN105469431AReduce complexityImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisRandom projectionLow complexity
The invention discloses a tracking method based on a sparse subspace, comprising the steps of firstly learning a plurality of initial frame images by using a random projection matrix and a robust principal component analysis (RPCA) method, and obtaining a low-rank matrix of the images; and extracting the sparse subspace where a tracked target is located from the low-rank matrix. The sparse subspace obtained according to the method has the characteristics of low complexity and high robustness. Compared with the traditional particle filter method based on the target color, target texture or target template, the algorithm based on the target features mentioned in the text has the characteristics of being less in the number of required particles, high in timeliness and strong in stability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
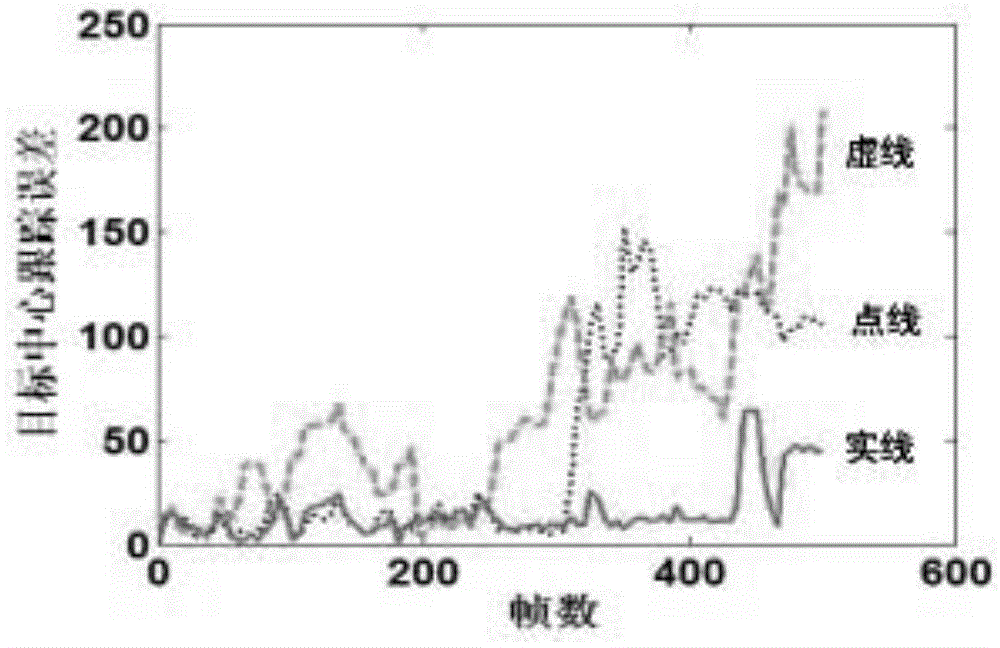
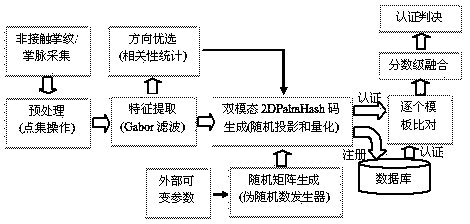
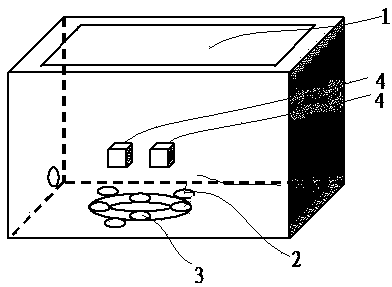
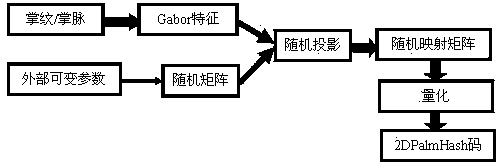
Non-contact revocable palm print bimodal authentication method
InactiveCN104268533AWith replacementCapable of republishingCharacter and pattern recognitionPalm printRandom projection
The invention discloses a non-contact revocable palm print bimodal authentication method. A non-contact device is used for collection a palm print. Point set operation is adopted for preprocessing. A Gabor filter is adopted for extracting texture features. Random projection and quantization are conducted on the texture features and a random matrix with the participation of external variable parameters. A revocable template of a 2DPalmHash code is generated, and the generation direction of the revocable template is optimized according to a low correlation policy. During registration, the template of the bimodal 2DPalmHash code is stored in a database; during authentication, the template is extracted from the database and contrasted with authentication templates one by one, fractional order integration is conducted, and revocable palm print authentication is realized. According to the non-contact revocable palm print bimodal authentication method, the accuracy of the template is improved as the point set operation is adopted; the revocable template is given updating capacity; the feature template is optimized according to a proper strategy, and authentication precision is improved without increasing time and space complexity.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
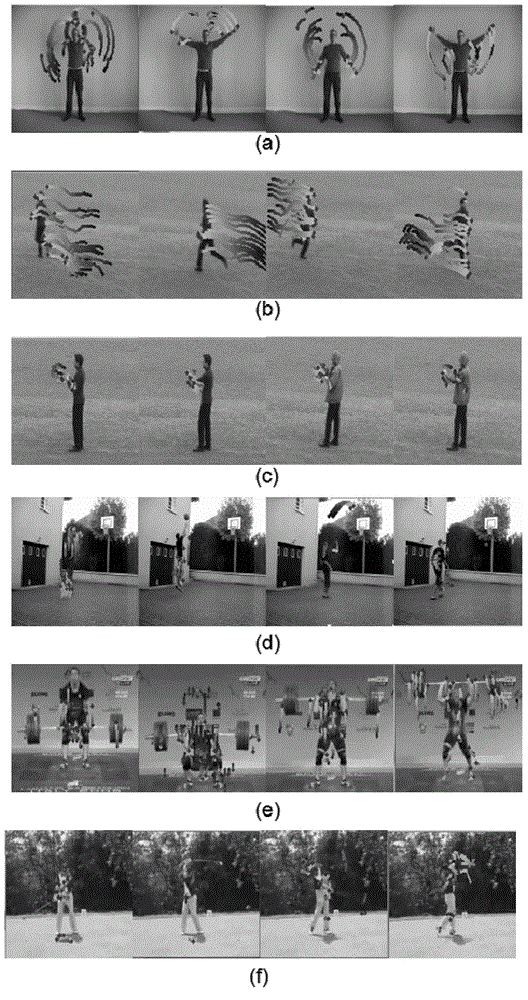
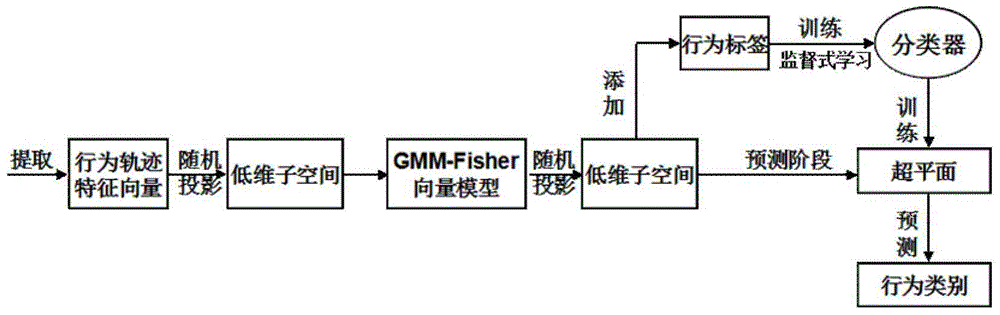
Figure behavior identification method based on random projection and Fisher vectors
ActiveCN104881651ANo misinterpretationRich feature expressionCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a figure behavior identification method based on random projection and Fisher vectors. The method employs a random projection theorem method to replace a principal component analysis method for characteristic dimension reduction, for the purpose of solving the problems of large time consumption, indeterminate reservation of principle components and the like. A random projection theorem indicates that through a compression measurement matrix, original signals with a sparse property can be projected to a certain low-dimension subspace, and the point distance between a vector after mapping and an original high-dimension characteristic vector maintains basically unchanged, i.e., data distortion is not generated in a whole compression process. Besides, different from hard division of a BoW model, the method provided by the invention employs a GMM-Fisher vector hybrid model for soft division of locus characteristic vectors, is integrated with the characteristics of a Fisher nucleus generation mode and a discrimination mode, can calculate the occurrence frequency of each characteristic descriptor, can also describe the probability distribution conditions of these characteristic descriptors in the perspective of statistics, enriches characteristic expression of behavior motion and also improves the behavior identification efficiency.
Owner:NANJING NANJI INTELLIGENT AGRI MASCH TECH RES INST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
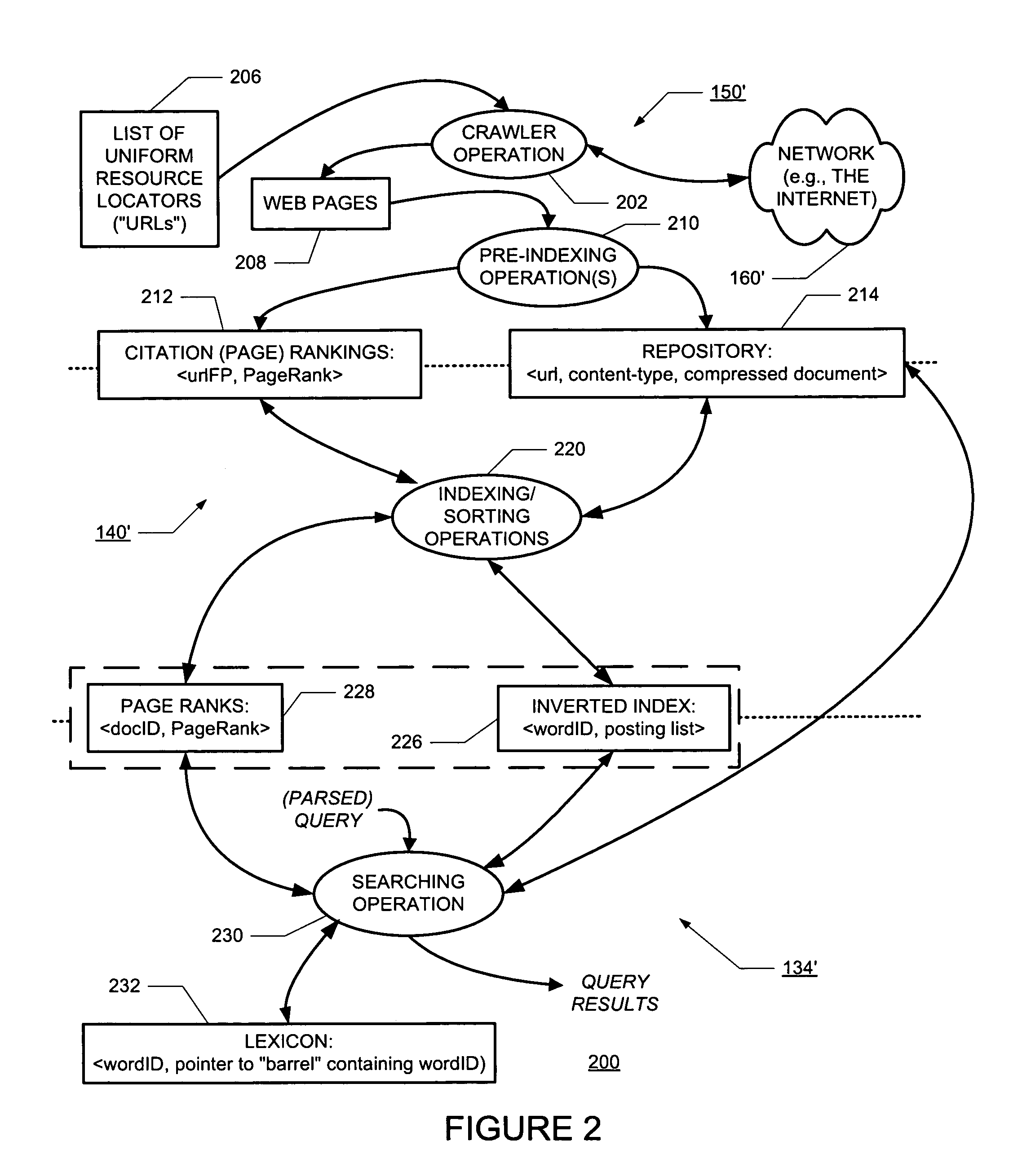
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com