Tracking method based on sparse subspace
A subspace and sparse technology, applied in the field of tracking based on sparse subspace, can solve the problems of inability to adapt to target changes, large amount of calculation, and lack of robust features of programs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
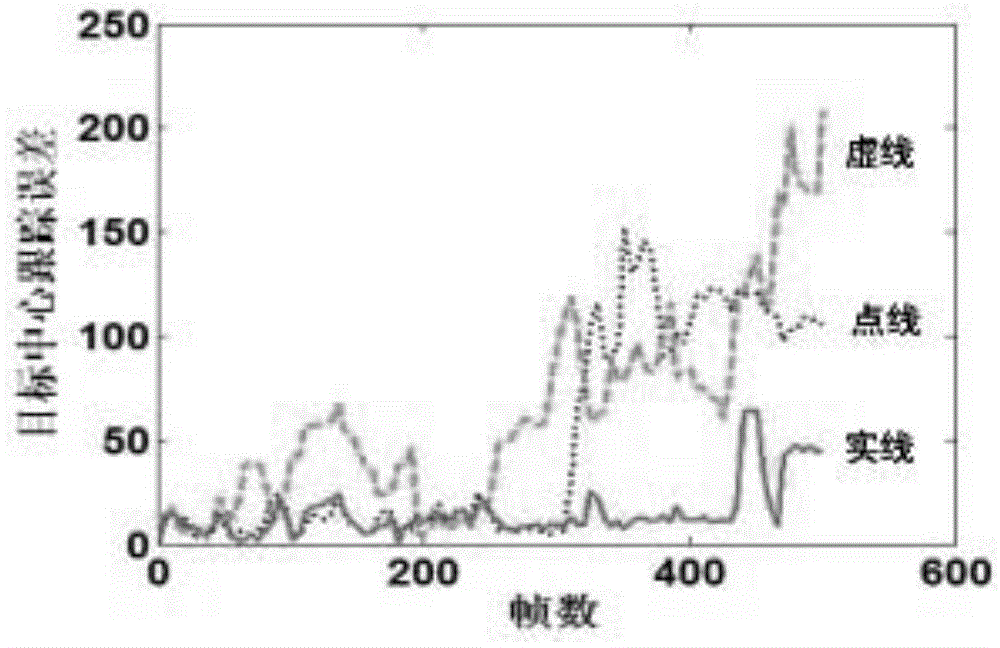
[0085] The 1st group test video originates from GirlTracking in a certain website on the Internet, we have chosen #310, #352, #384, #472 total 4 frame images to test the present invention (the 1st row), IVT algorithm (the 2nd row), The robustness of the three algorithms of L1T algorithm (row 3) when the appearance of the target changes: in frame #310, the target begins to change, at this time the tracking window of the IVT algorithm begins to drift, and the tracking window of the L1T algorithm has completely The tracking window of the present invention can still lock the target firmly. In the next few frames, the tracking windows of IVT and L1T have drifted randomly in areas other than the target, and the target cannot be recaptured.
Embodiment 2
[0087] The second group of test videos comes from Singer1Tracking in a certain website, mainly to investigate the immunity of the tracking algorithm to scale changes and illumination changes. We selected frames #50, #117, #217, and #314 to compare the present invention (No. 1 row), IVT algorithm (second row), Frag-basedTracker algorithm (third row). From image 3It can be seen that due to the change of optical flow in frame #117, the Frag-basedTracker tracking window has drifted seriously; after the light recovery in #217, although the tracking window has returned to some extent, due to the change of scale and appearance, the tracking effect Already far from ideal. In comparison, the sensitivity of the present invention and the IVT algorithm to illumination and scale changes is much lower.
Embodiment 3
[0089] The third group of test videos comes from DeerTracking in a certain website. This video mainly investigates the stability of the tracking algorithm for the target in the case of fast movement. We selected frames #6, #20, #31, and #55 to compare the present invention (the first row), the IVT algorithm (the second row), and the L1T algorithm (the third row). It can be clearly seen that due to the rapid and large jump of the target, the L1T tracking window has already drifted seriously at frame #6, and failed to return to the target. Although the IVT tracking window can cover the tracked target stably before #24 frame, but at #26 frame, the tracking window begins to deviate from the target with the rapid movement of the target, and the deviation reaches the maximum at #46 frame. It can be seen from several representative image frames that the tracking window of the present invention can firmly lock the tracked target, so in comparison, the robustness of the present inventi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com