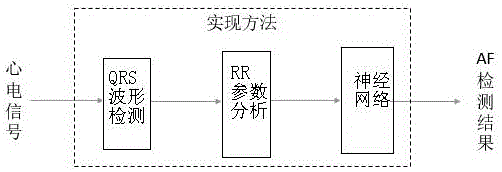
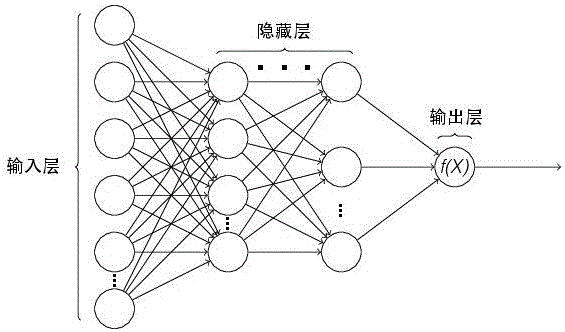
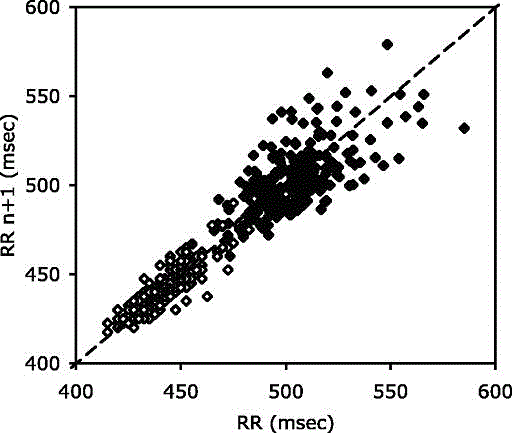
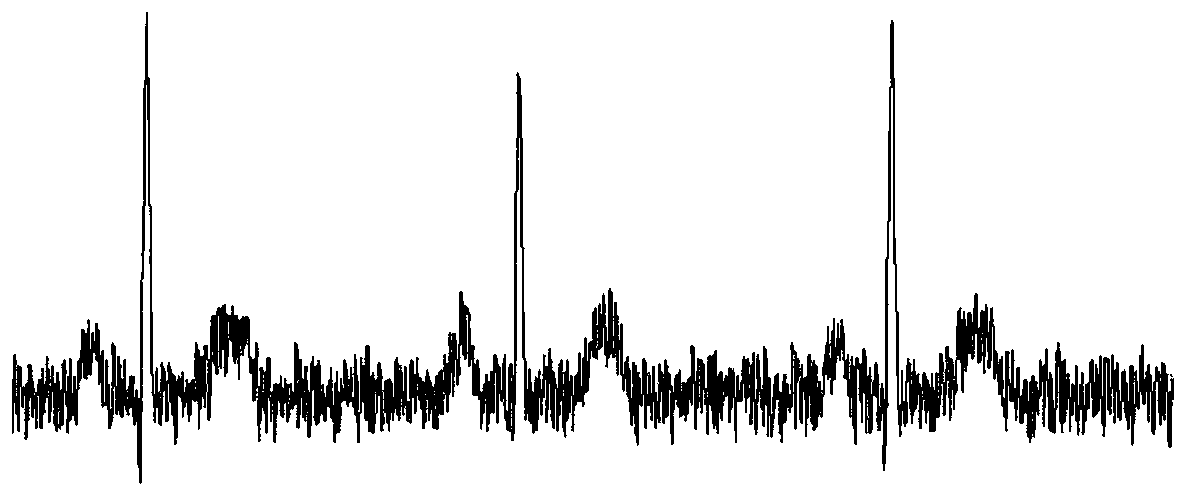
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Sinus rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
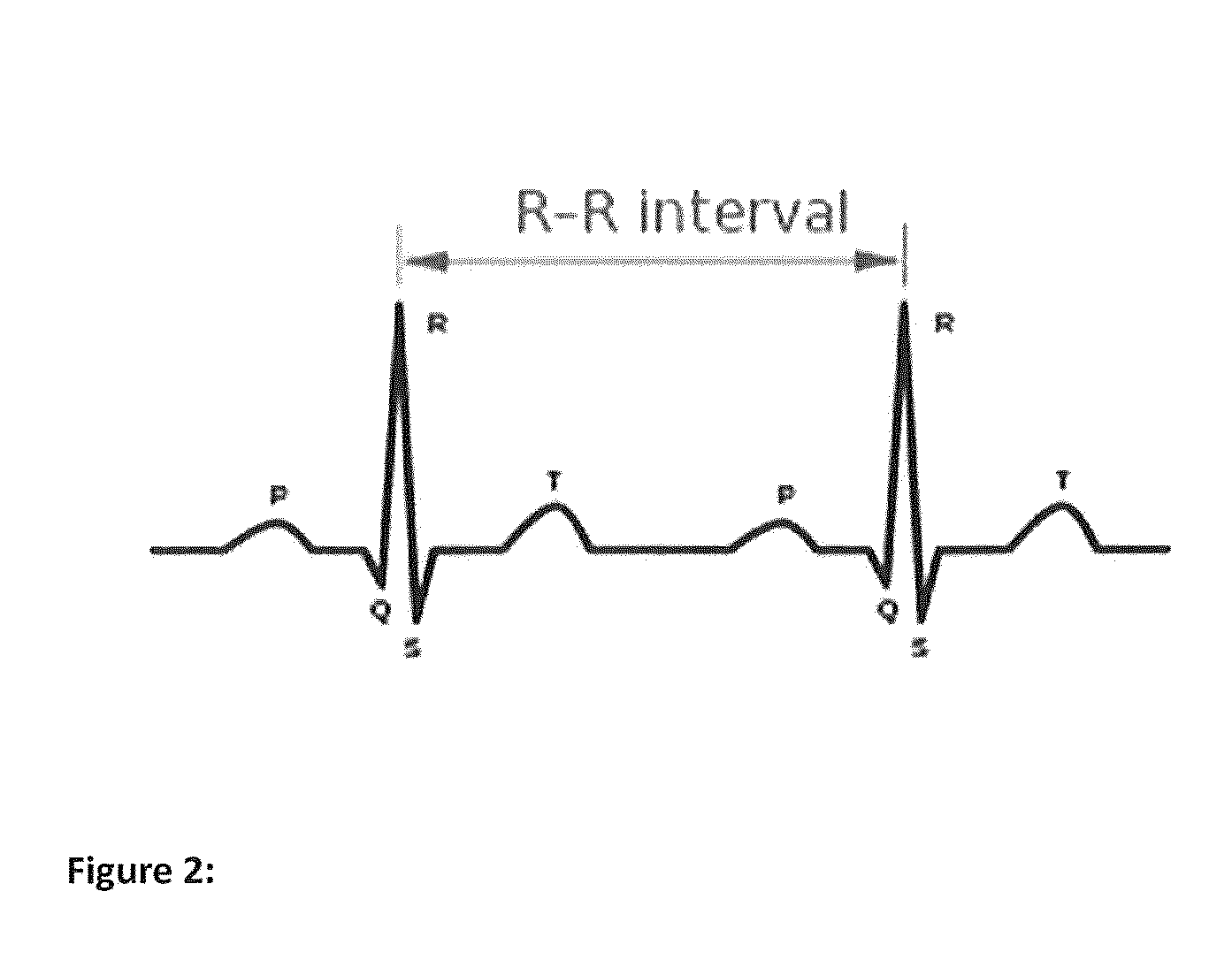
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarization of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is characterised by the presence of correctly oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG). Sinus rhythm is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart.
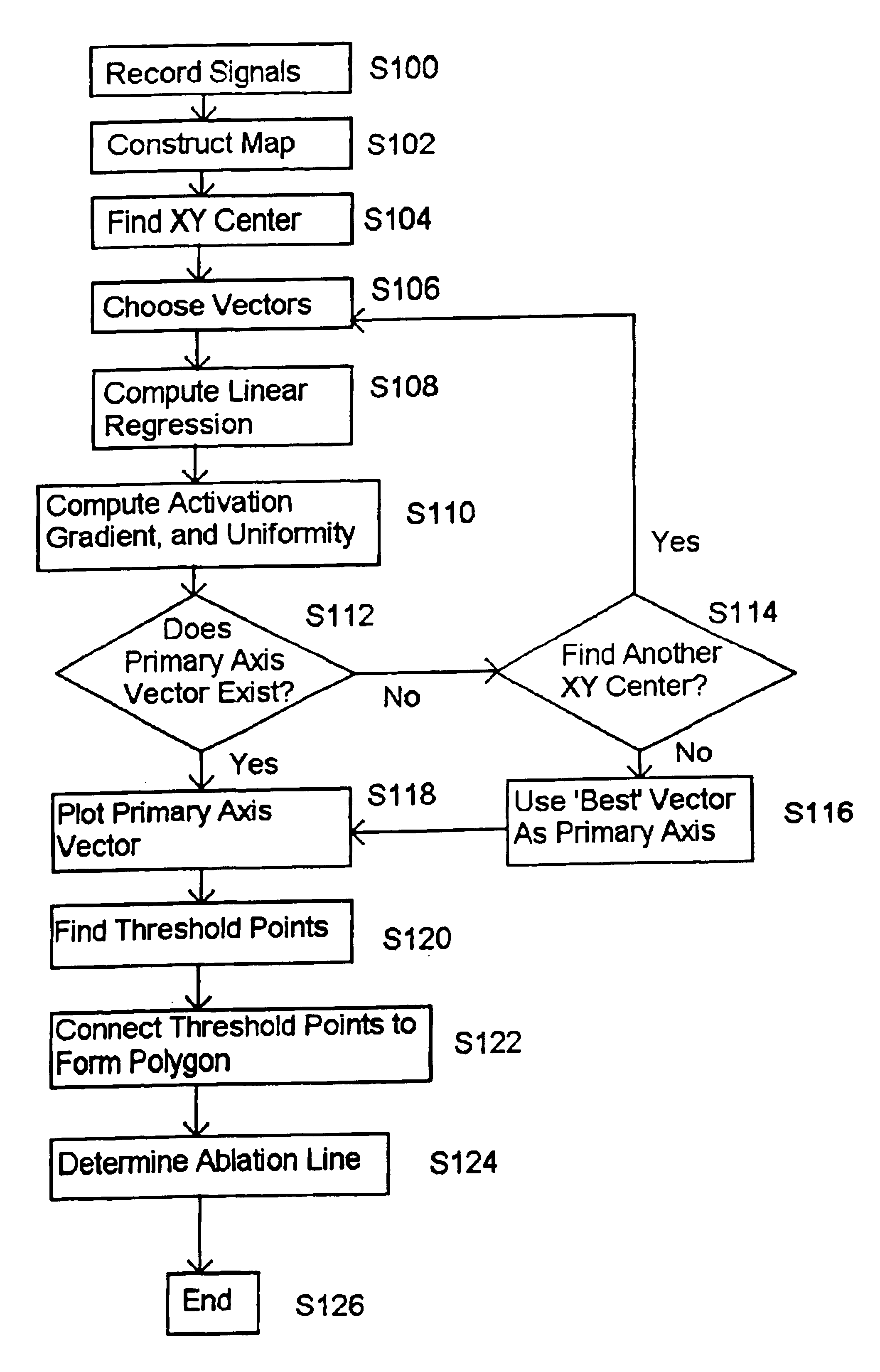
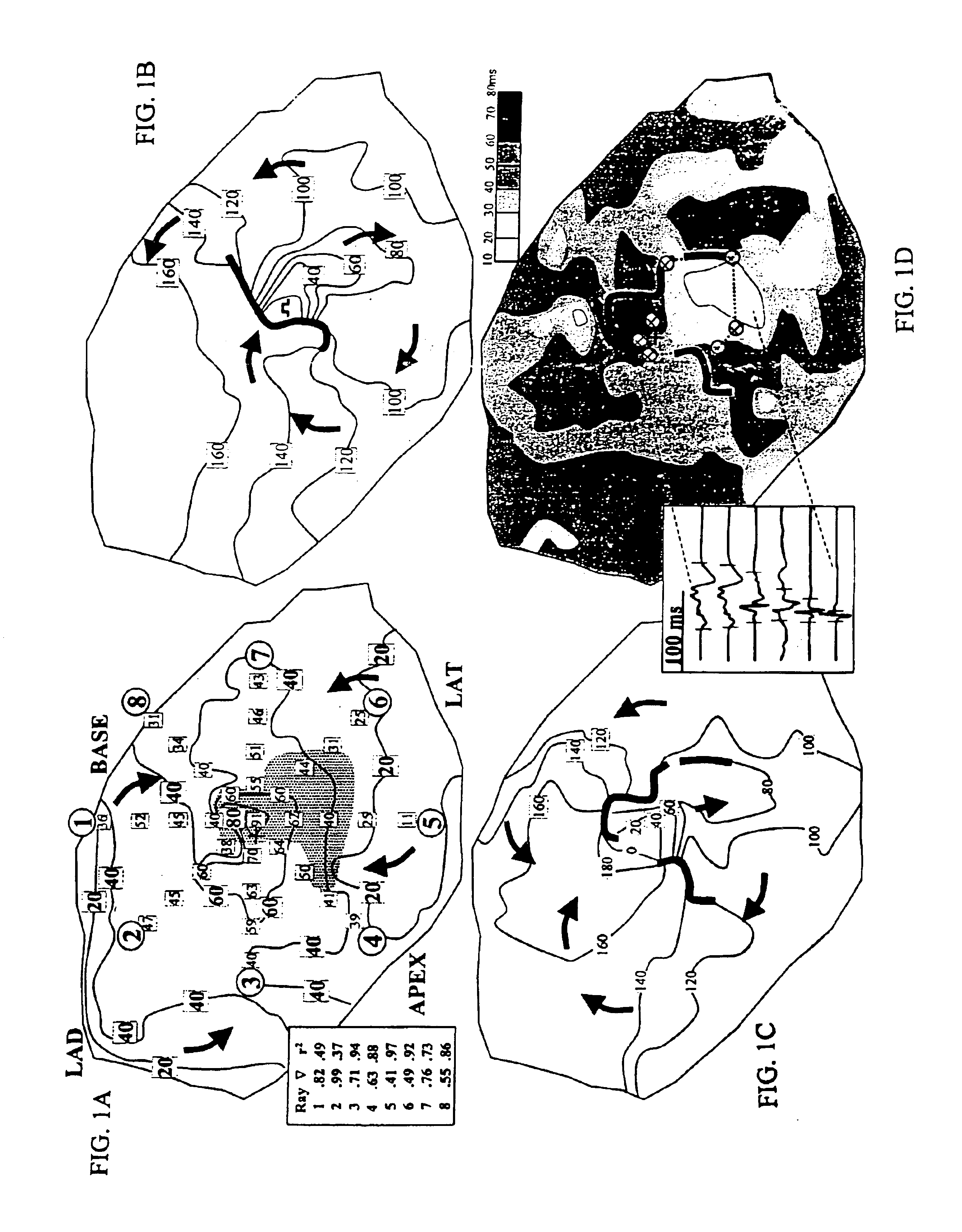
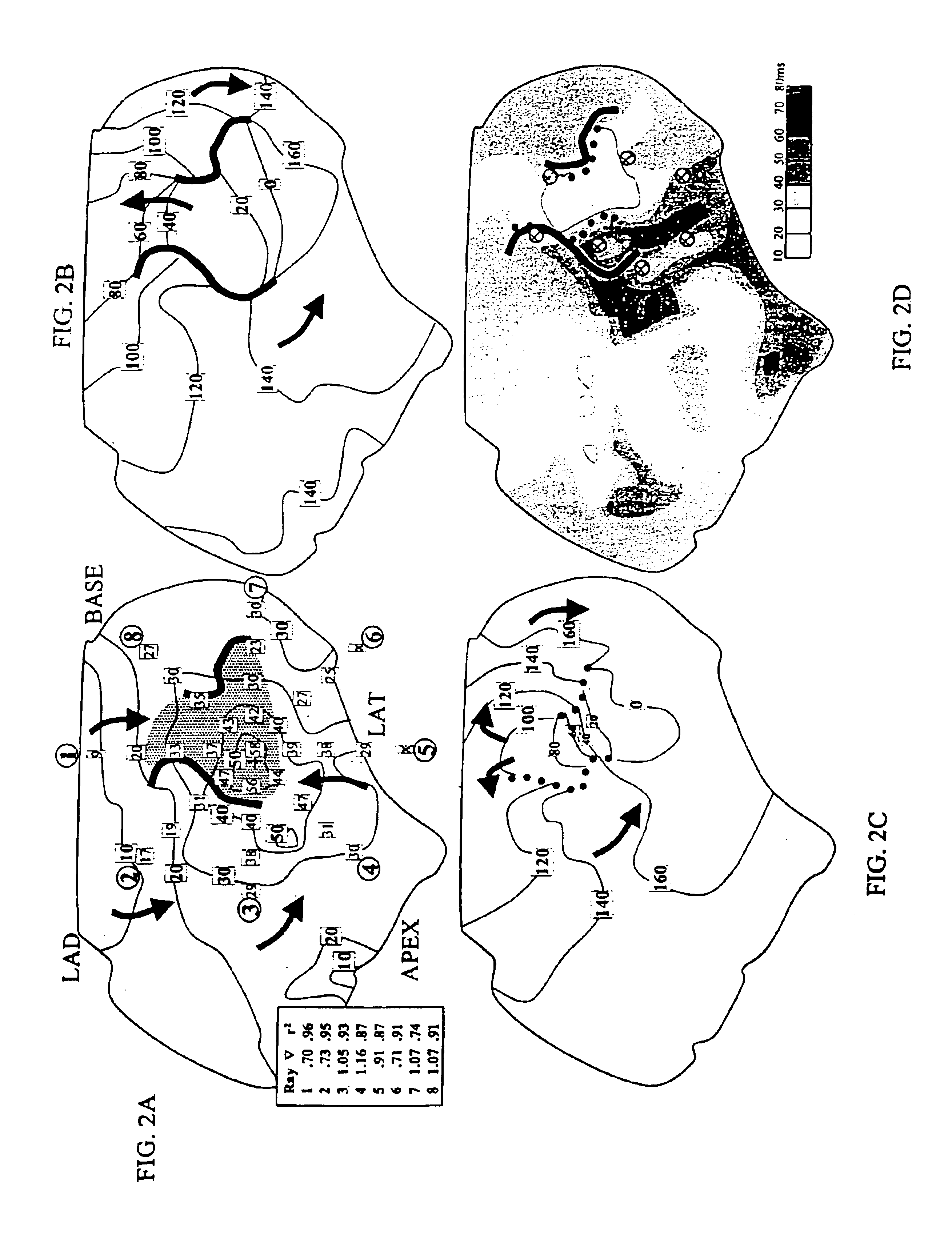
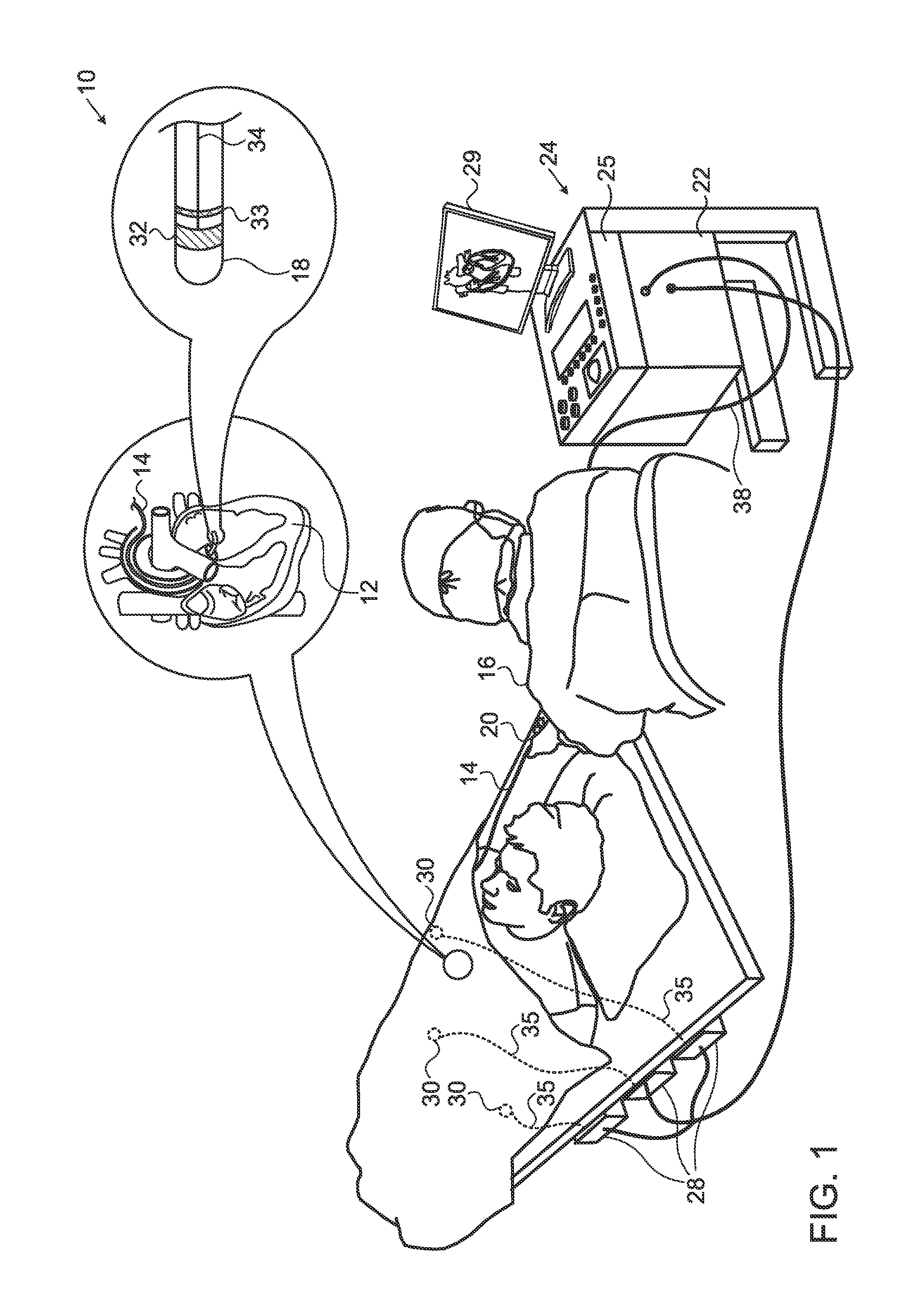
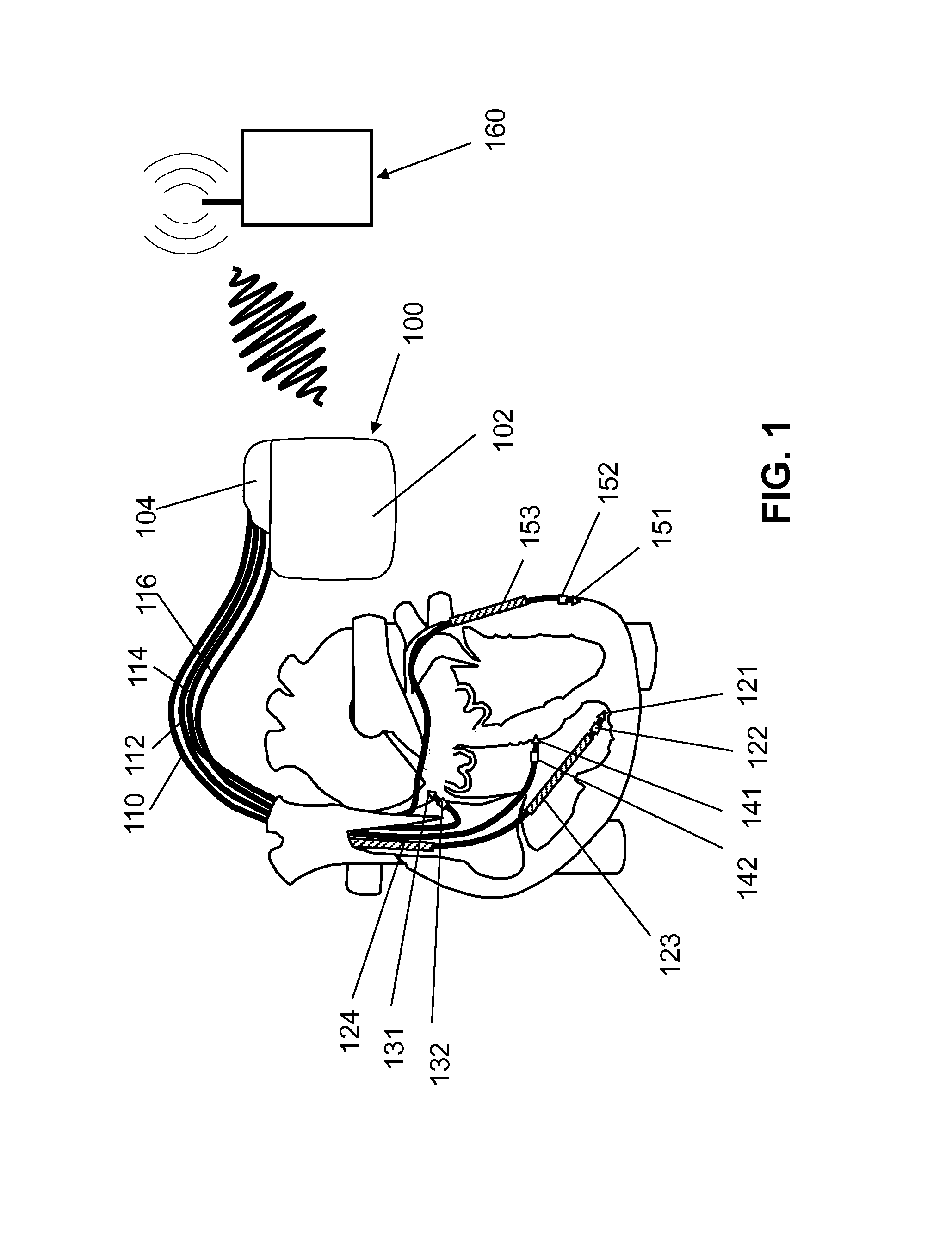
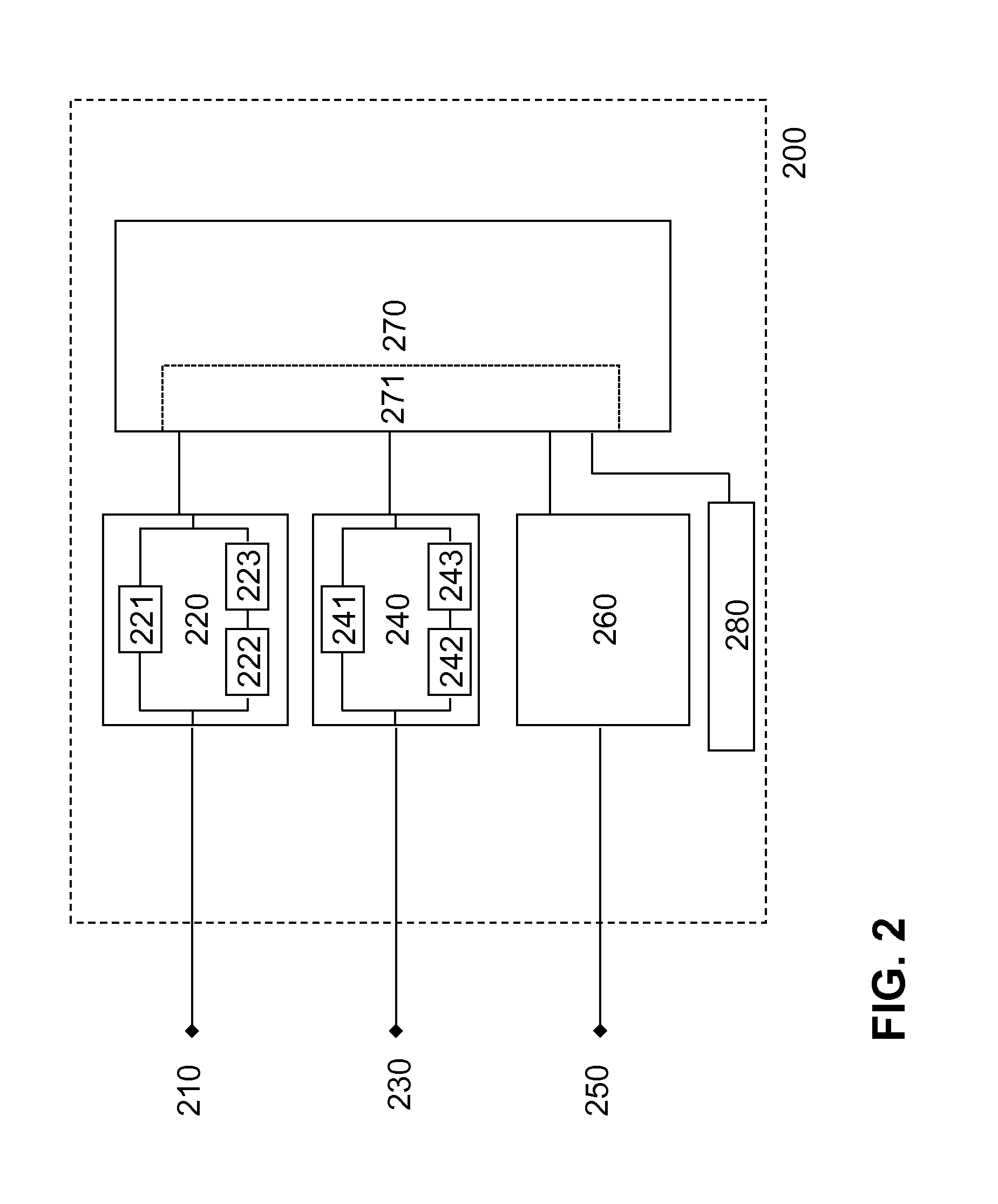
System and method for determining reentrant ventricular tachycardia isthmus location and shape for catheter ablation
A method for identifying and localizing a reentrant circuit isthmus in a heart of a subject during sinus rhythm, including: a) receiving electrogram signals from the heart during sinus rhythm via electrodes; b) storing the electrogram signals; c) creating a map based on the electrogram signals; d) finding a center reference activation location on the map; e) defining measurement vectors originating from the center reference activation location; f) selecting from the measurement vectors a primary axis vector indicating a location of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart; g) finding threshold points of electrogram signals on the map; h) connecting the threshold points to form a polygon indicating a shape of the reentrant circuit isthmus in the heart.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Heart Monitor
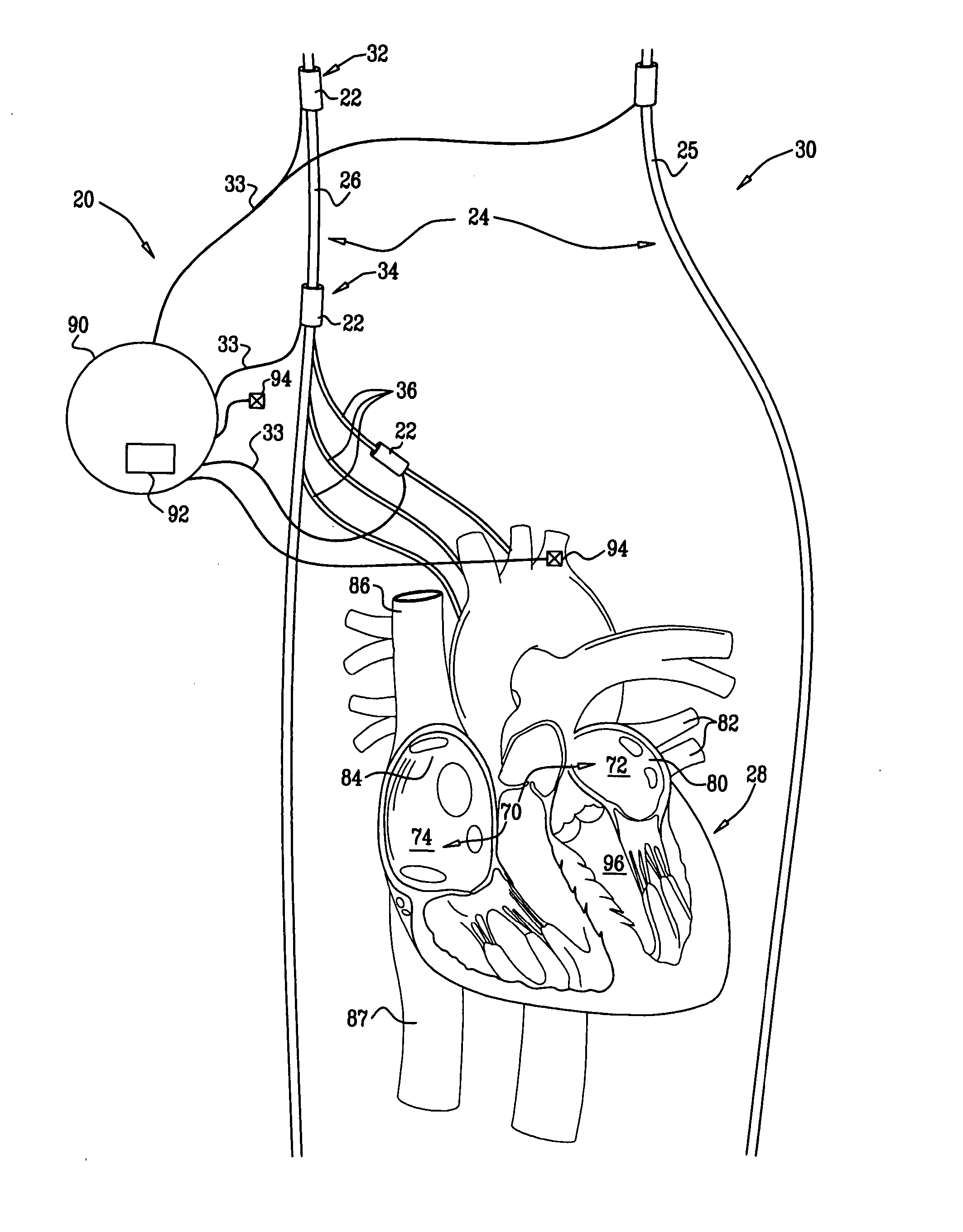
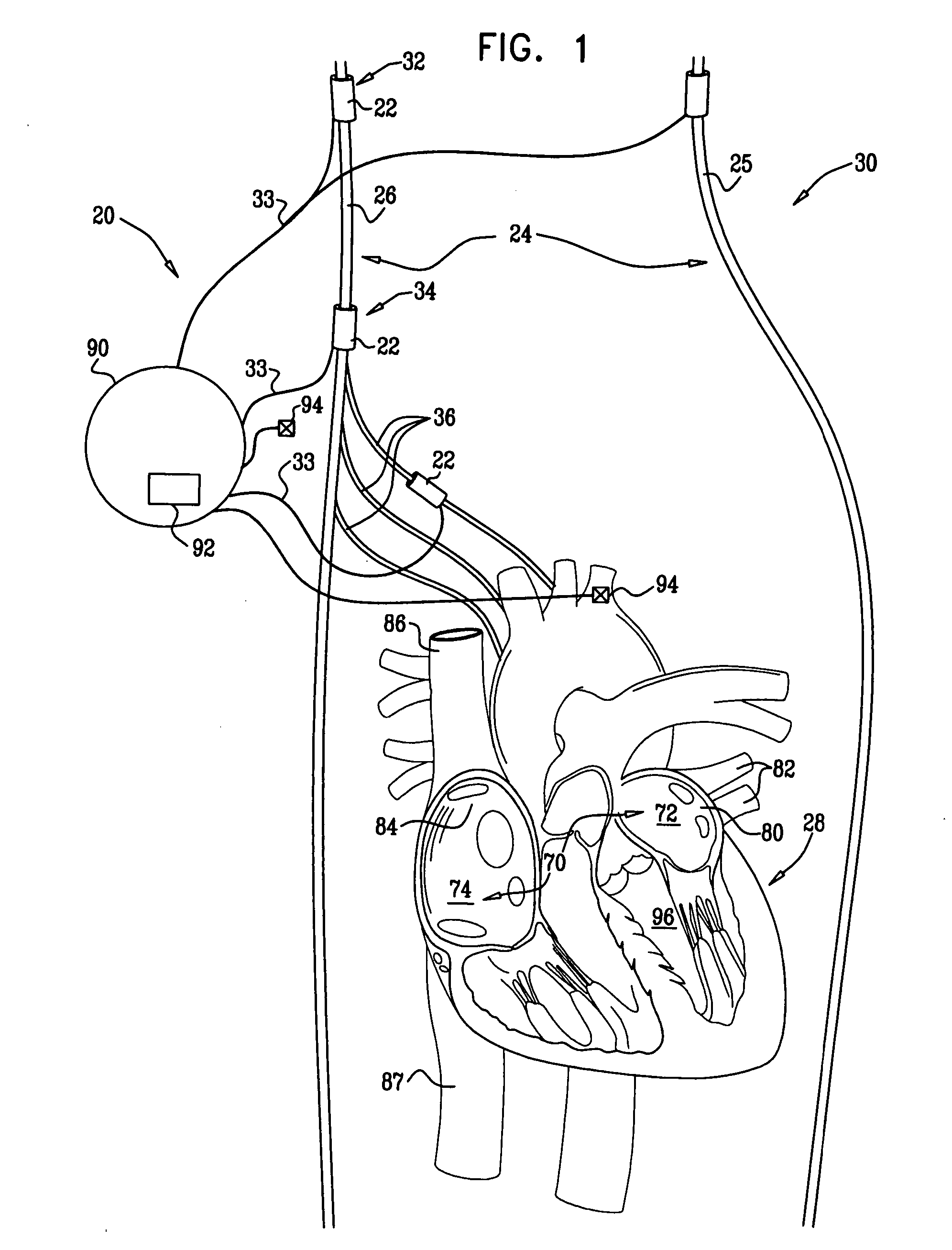
A heart monitor for use as a non-invasive screening tool for identifying potential atrial fibrillation in patients comprises a sensor for producing an output waveform of the patient's actual sinus rhythm, a processing unit arranged to store the normalised waveform of an ideal sinus rhythm and to compare the actual and ideal sinus rhythm waveforms and to produce an output dependant on the difference on a display. The value of the output is indicative of whether the patient is atrial fibrillation or other cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:MELYS DIAGNOSTICS
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
ActiveUS7218966B2Inhibiting therapeutic deliverySurgical needlesHeart defibrillatorsPulse rateNormal Sinus Rhythm
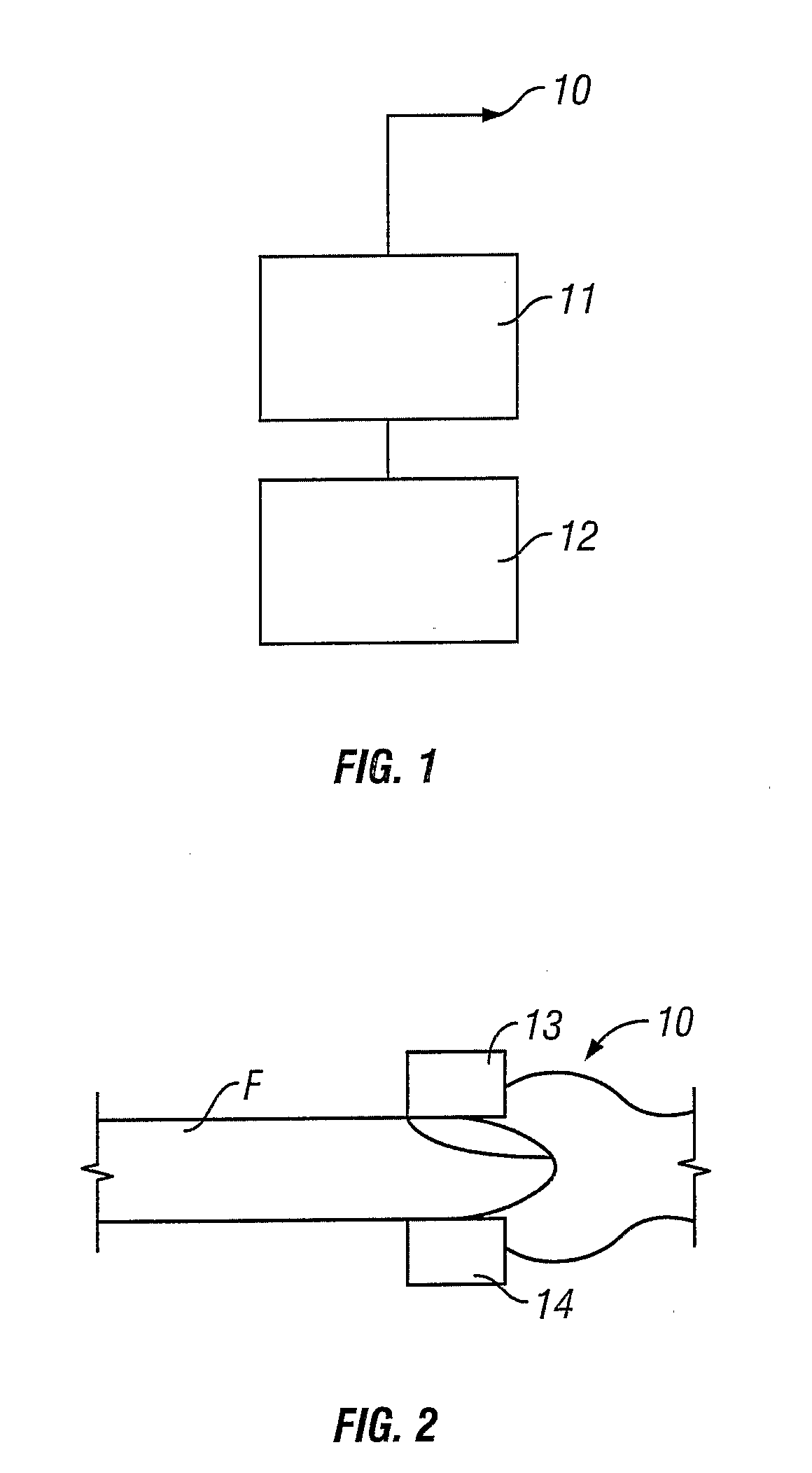
An arrhythmia discrimination device and method involves receiving electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals at subcutaneous locations. Both the electrocardiogram-signals and non-electrophysiologic signals are used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia may be detected using electrocardiogram signals, and verified using the non-electrophysiologic signals. A detection window may be initiated in response to receiving the electrocardiogram signal, and used to determine whether the non-electrophysiologic signal is received at a time falling within the detection window. Heart rates may be computed based on both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals. The rates may be used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and arrhythmia, and used to determining absence of an arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Intravascular parasympatheticstimulation for atrial cardioversion
InactiveUS20080046016A1Avoid stimulationHigh strengthInternal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
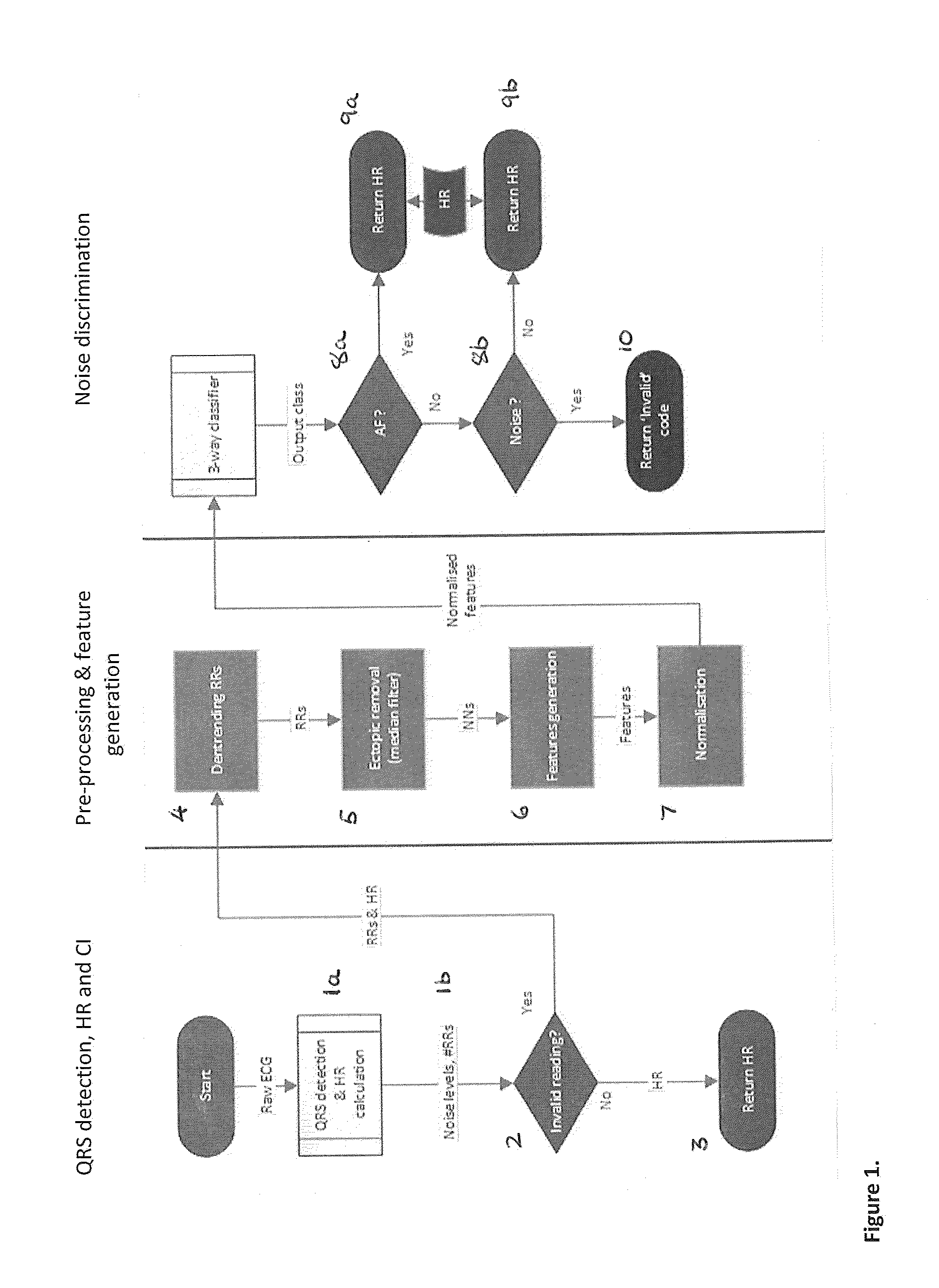
Method for confidence level determination of ambulatory hr algorithm based on a three-way rhythm classifier
ActiveUS20150327781A1Improve monitoring effectLow costElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisEcg signalAmbulatory
A method of determining a confidence level in a heart rate obtained from an ECG signal of a patent comprises determining a heart rate from a segment of an ECG signal, the segment having a pre-determined length, and determining a first confidence level in the determined heart rate. If the first confidence level exceeds a predetermined value, the heart rate is output. Otherwise, the method further comprises determining a set of features from the segment of the ECG signal; and classifying the segment of the ECG signal, based on one or more features selected from the determined set of features and the heart rate, into one of at least three classes: noise, an abnormal sinus rhythm and a normal sinus rhythm.
Owner:SENSIUM HEALTHCARE
Bayesian discriminator for rapidly detecting arrhythmias
InactiveUS20030216654A1Improve algorithm performanceImprove performanceMedical data miningElectrocardiographyDiscriminatorData set
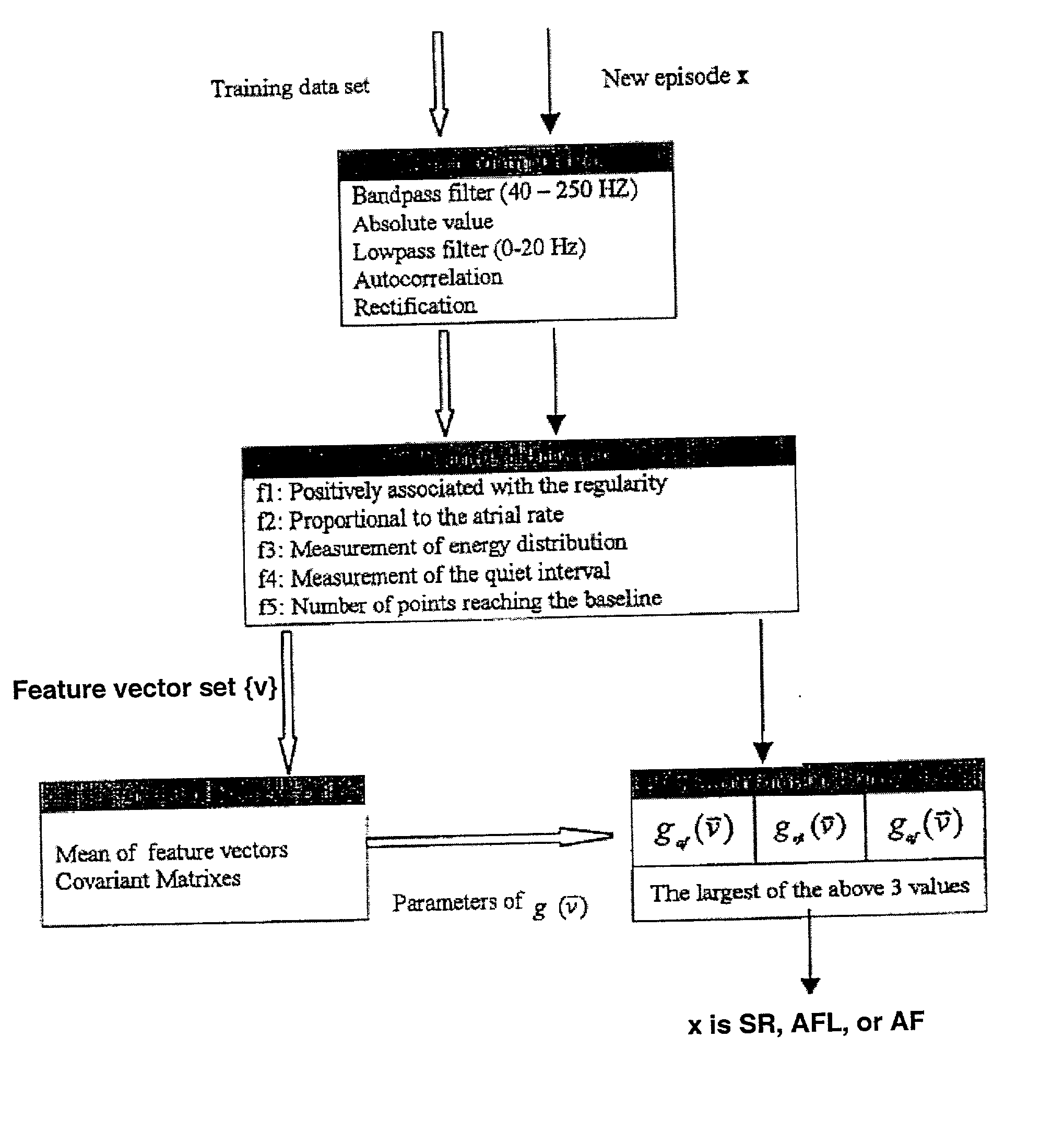
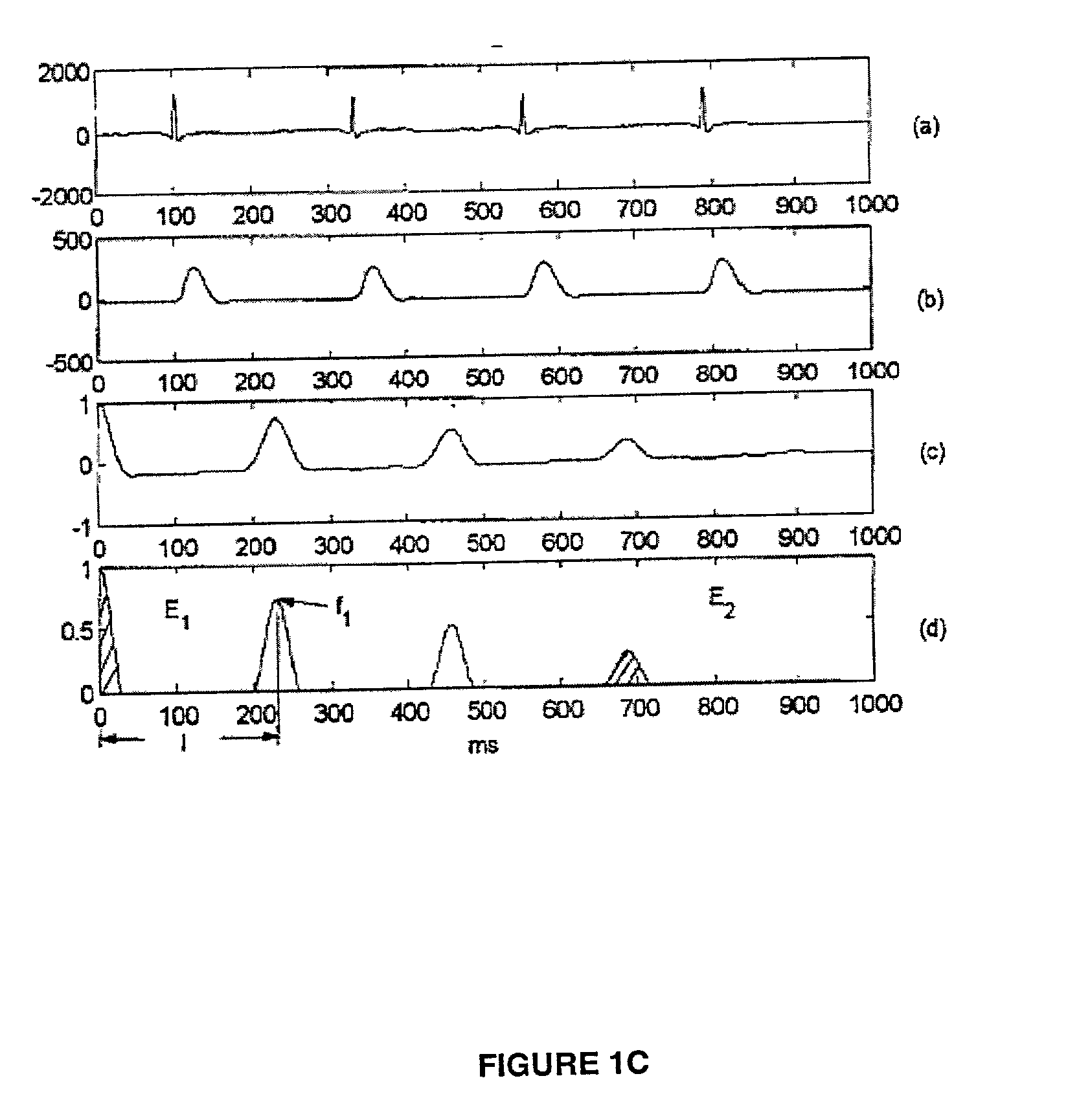
A method for accurate and rapid automated detection of atrial fibrillation (AF), sinus rhythm (SF), and atrial flutter (AFL) is disclosed, which allows distinguishing of these cardiac signals with lowered risk of errors by implanted pacemakers and like devices. The method includes training episodes of intra-cardiac signals (called the closed data set CDS) to evaluate five feature parameters with a discriminator classifying the signal into AF, AFL or sinus rhythm (SR). Comparison with the independent decisions of experienced physicians for each episode reveals specificity, accuracy and sensitivity of greater than 97%. Each episode is a window of intracardiac signal of interval 1-2 seconds with the discriminator providing results in less than 0.25 s. In another aspect, the method is resistant to the presence of noise in the data. In yet another aspect, more feature parameters may be used in alternative implementations including for detecting signals other than AF, AFL & SR.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF
Single chamber implantable medical device for confirming arrhythmia through retrospective cardiac signals
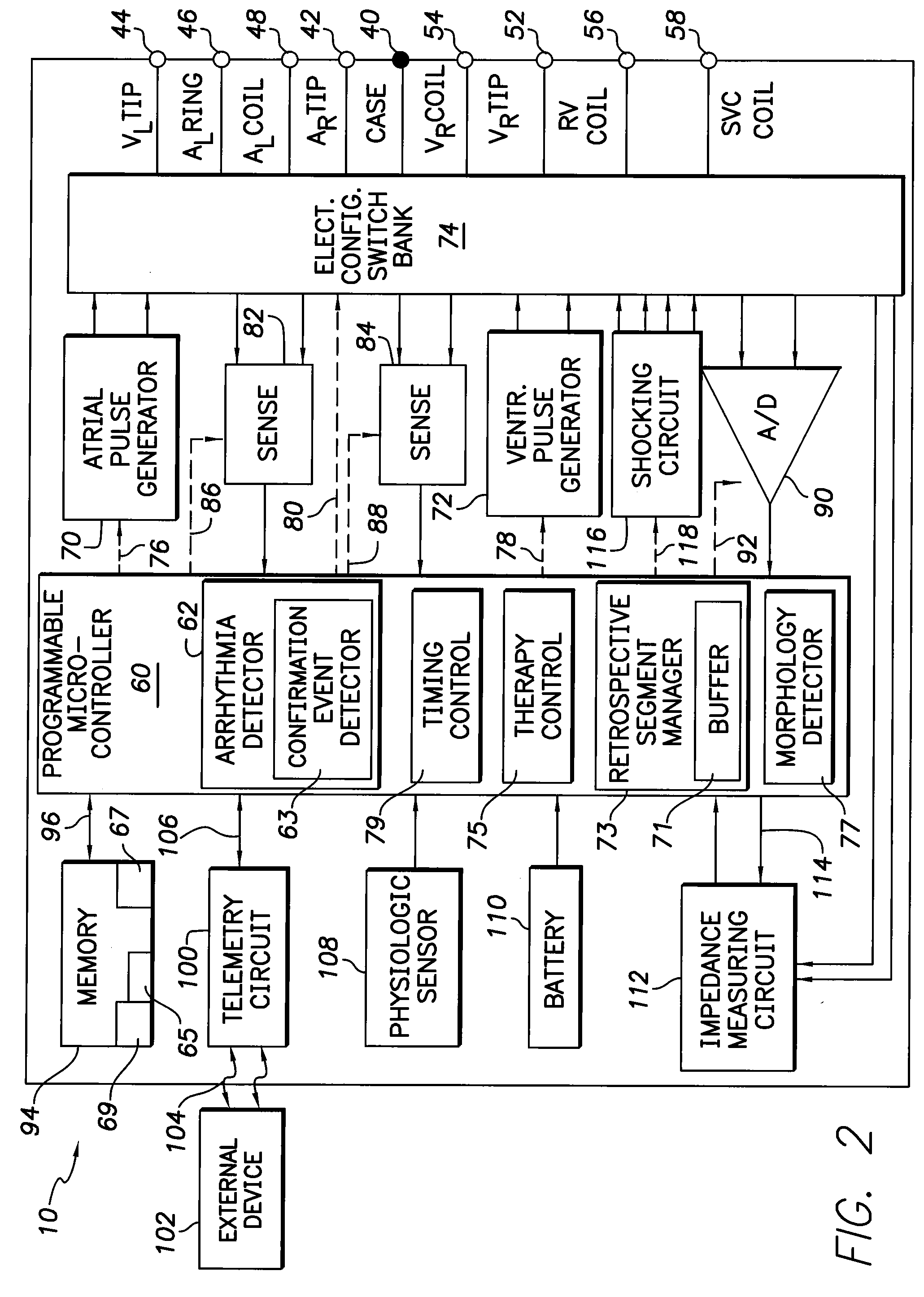
InactiveUS20110125206A1Improve performanceReduce the amplitudeElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsNormal Sinus RhythmSingle chamber
Owner:PACESETTER INC
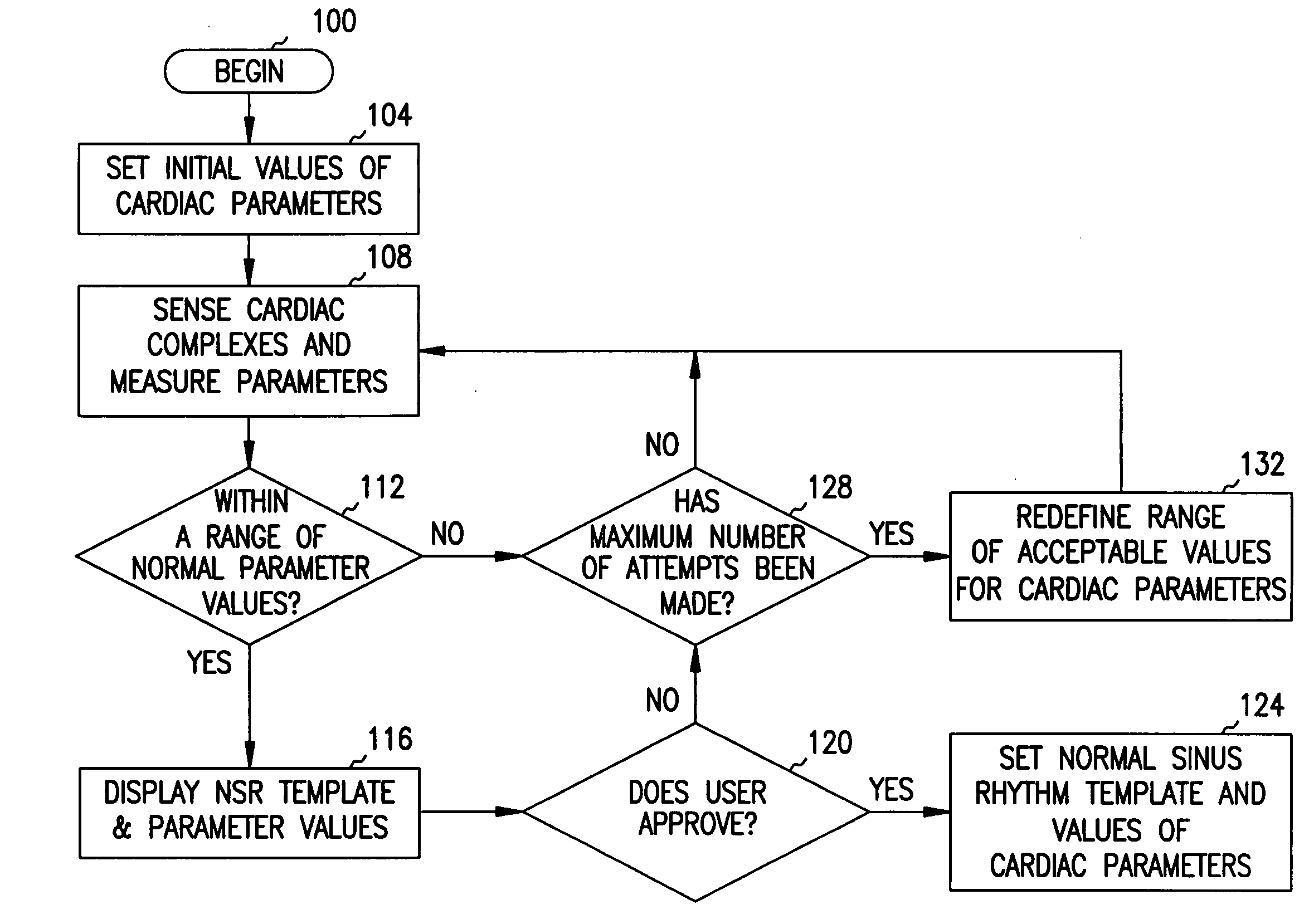
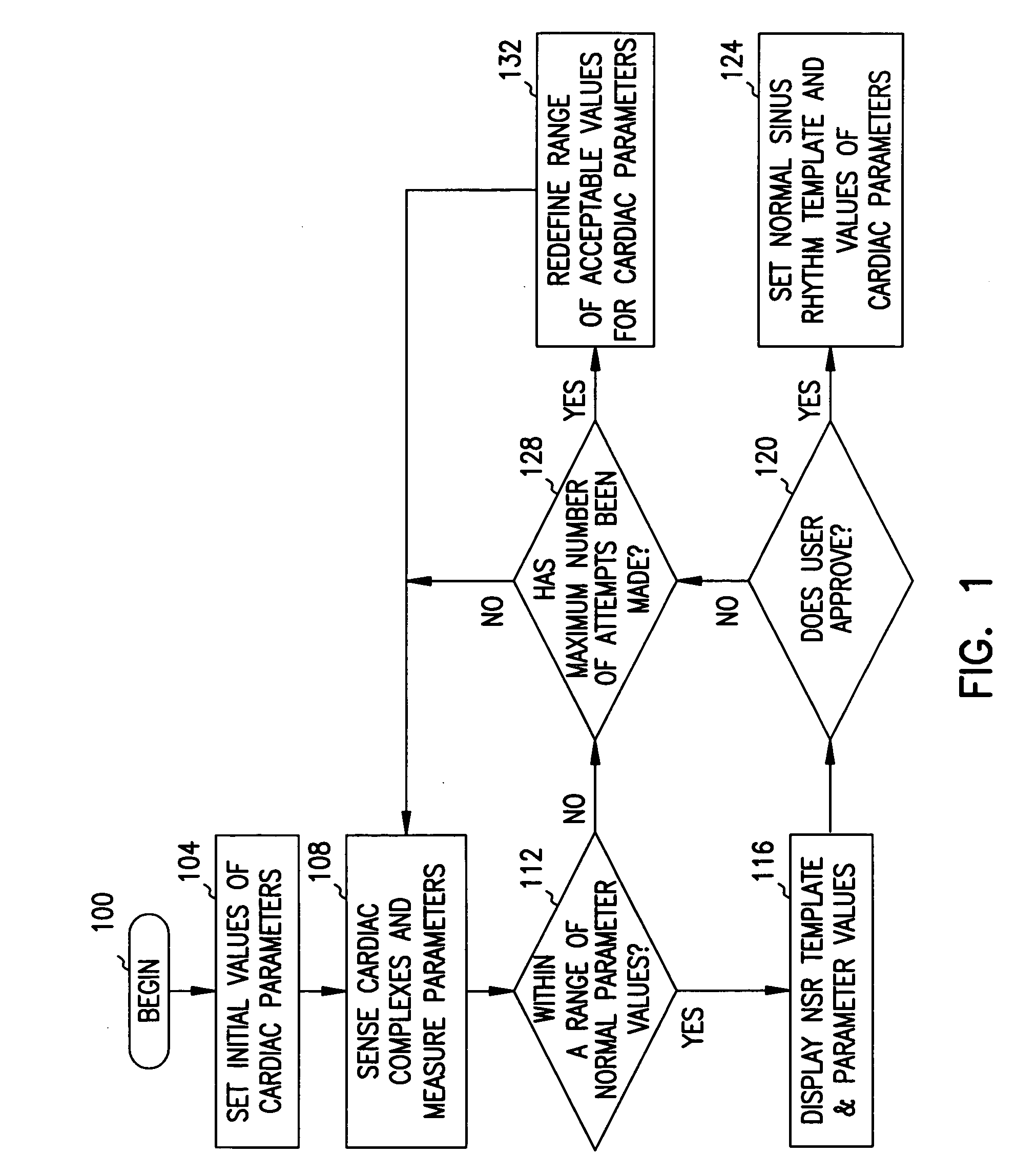
Method and system for verifying the integrity of normal sinus rhythm templates
InactiveUS20060079796A1Classified more accuratelyAccurate classificationElectrocardiographySensorsNormal Sinus RhythmSinus rhythm
A method and system for verifying the integrity of normal sinus rhythm (NSR) templates and updating the NSR template after selected time intervals. At selected time intervals after establishing a NSR template, cardiac complexes are sensed and values for one or more cardiac parameters are measured. The values of the cardiac parameters are compared to predetermined value ranges for NSR cardiac complexes. When the values of the cardiac parameters fall within the predetermined value ranges, values for the differences between the values of the cardiac parameters for the cardiac complexes and the values for the cardiac parameters of the NSR cardiac complexes are calculated. When the values of the differences are greater than one or more threshold values, the NSR template is updated as a function of the sensed cardiac complexes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for classifying tachycardia arrhythmias having 1:1 atrial-to-ventricular rhythms
An implantable cardioverter / defibrillator includes a tachycardia detection system that detects one-to-one (1:1) tachycardia, which is a tachycardia with a one-to-one relationship between atrial and ventricular contractions. When the 1:1 tachycardia is detected, the system discriminates ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) based on analysis of a cardiac time interval. Examples of the cardiac time interval include an atrioventricular interval (AVI) and a ventriculoatrial interval (VAI). A template time interval is created during a known normal sinus rhythm. The system measures a tachycardia time interval after detecting the 1:1 tachycardia, and indicates a VT detection if the tachycardia time interval differs from the template time interval by at least a predetermined percentage of the template time interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for realizing automatic recognition of atrial fibrillation on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment
InactiveCN106073755AImprove the detection rateEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalHuman body
The invention discloses a method for realizing automatic recognition of atrial fibrillation on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment. The method includes: calling an MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, an MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database and a long-time atrial fibrillation database as training samples, and introducing an artificial neural network for learning training; setting a weight value for each layer of the artificial neural network, and inputting the training data samples to repeatedly and iteratively correct the weight value of each layer until training errors are less than a certain specified value, through the means, a weight value matrix capable of judging occurrence of atrial fibrillation can be found; utilizing the weight value matrix, and adding the same into an original artificial neural network to build a new artificial neural network; using collected electrocardiosignals of a target human body, processing the electrocardiosignals of the human body, acquiring a target human body feature vector X, and performing prediction operation according to the target human body feature vector X and the new artificial neural network.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
System, method and computer program product for detection of changes in health status and risk of imminent illness
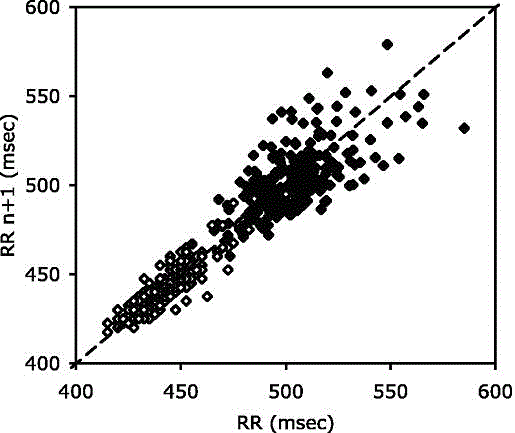
A method for analysis of cardiac rhythm and RR interval time series based on entropy related data and entropy based measures. The information is related to but distinct from entropy, and is derived from histograms of interval match counts in which the y-axis is the frequency of intervals of length in that have the match count given on the x-axis. The phenotype of the histogram informs on the presence of atrial fibrillation or, in the presence of sinus rhythm, the degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
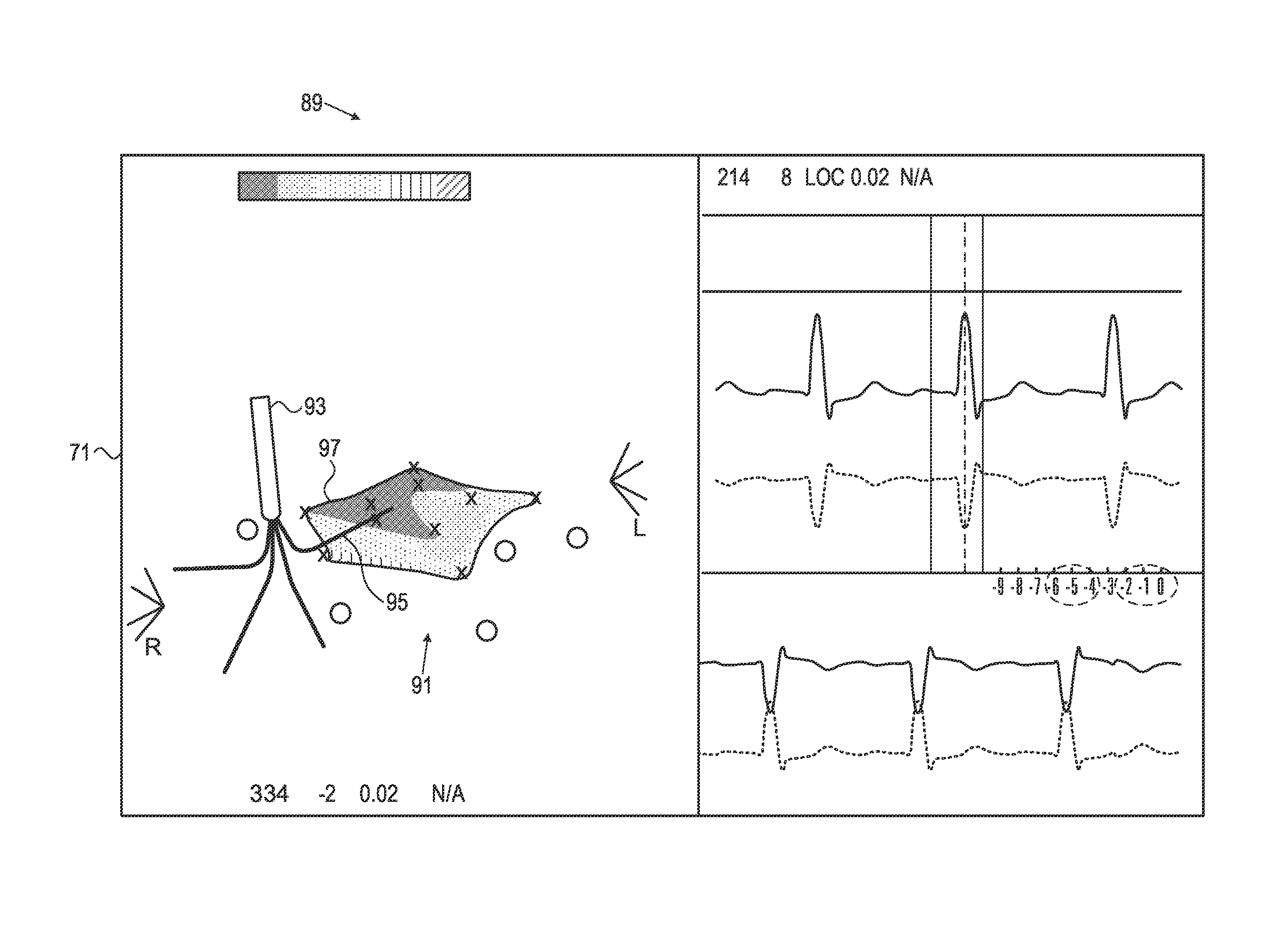
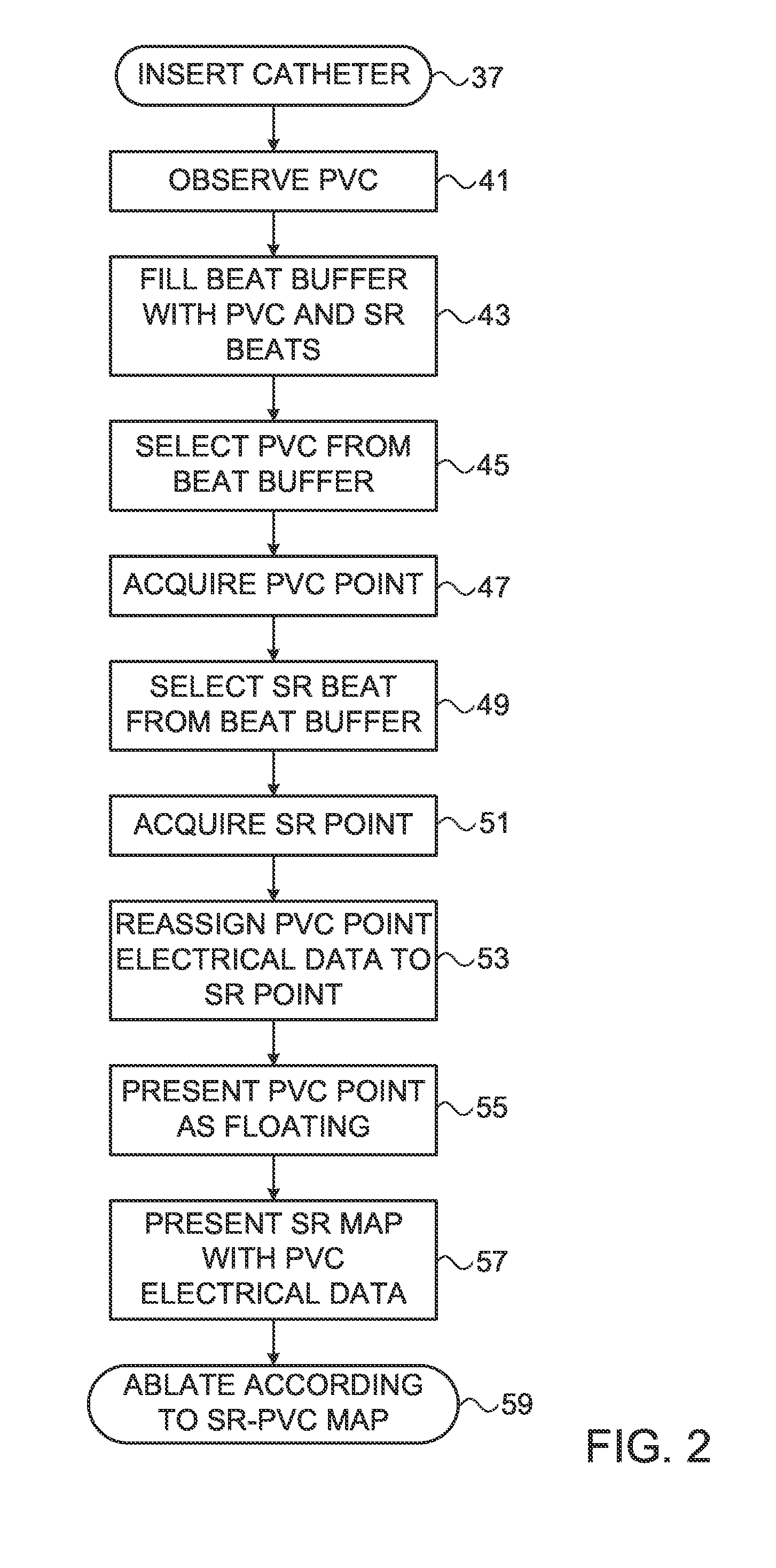
Method for mapping ventricular/atrial premature beats during sinus rhythm
While detecting a cardiac arrhythmia, a mapping electrode of a probe is used to associate a local activation time with a first location in a region of interest in the heart. While detecting an absence of the cardiac arrhythmia, the local activation time is associated with a second location in the heart. Electrical data of the first location is assigned to the second location, and an electroanatomic map of the heart is generated that includes the second location in association with the assigned electrical data of the first location.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Anti-tachycardia pacing methods and devices
Improved methods and devices perform anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a ventricular tachycardia (VT) to normal sinus rhythm. In one embodiment of the invention bi-ventricular (BV) ATP is employed. In this embodiment the right ventricle and left ventricle of a patient's heart are independently paced based on signals sensed in each chamber.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Interventricular delay as a prognostic marker for reverse remodeling outcome from cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS20070239037A1Increase geometryFunction increaseInternal electrodesCatheterLeft ventricular sizeMortality rate
In heart failure (HF) patients diagnosed according to the New York Heart Association (NYHA) rating scale as either Class III or Class IV, with QRS duration ≧120 ms, left ventricular (LV) EF≦35% (when in sinus rhythm), cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) can predict sustained improvement in at least LV structure and function. The knowledge of aetiology of a subject's HF status and of a few simple echocardiographic characteristics provides useful information as to whether such patients and undergo significant and beneficial reverse remodelling of the LV in particular and, in the long term can be expected to experience an improvement in all-cause mortality, for example such patients can be reasonably expected to survive and enjoy a relatively enhanced quality of life (QOL). A patient who qualifies according to the invention can be termed a reverse remodelling responder (RRR) or the like.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Discriminating between tachycardias of ventricular origin and supra entricular origin, methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20100249626A1Risk minimizationReduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedical deviceTachycardia
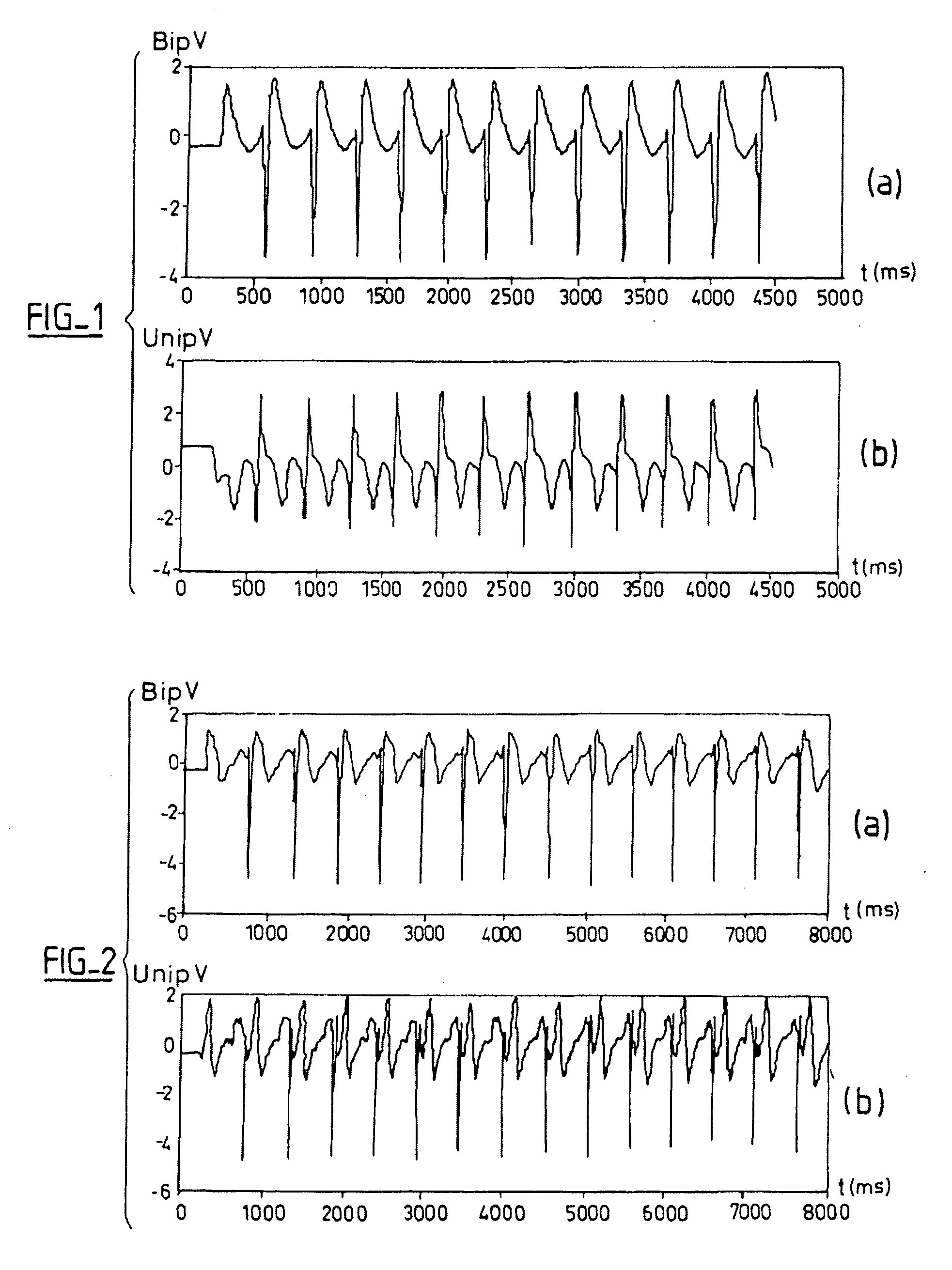
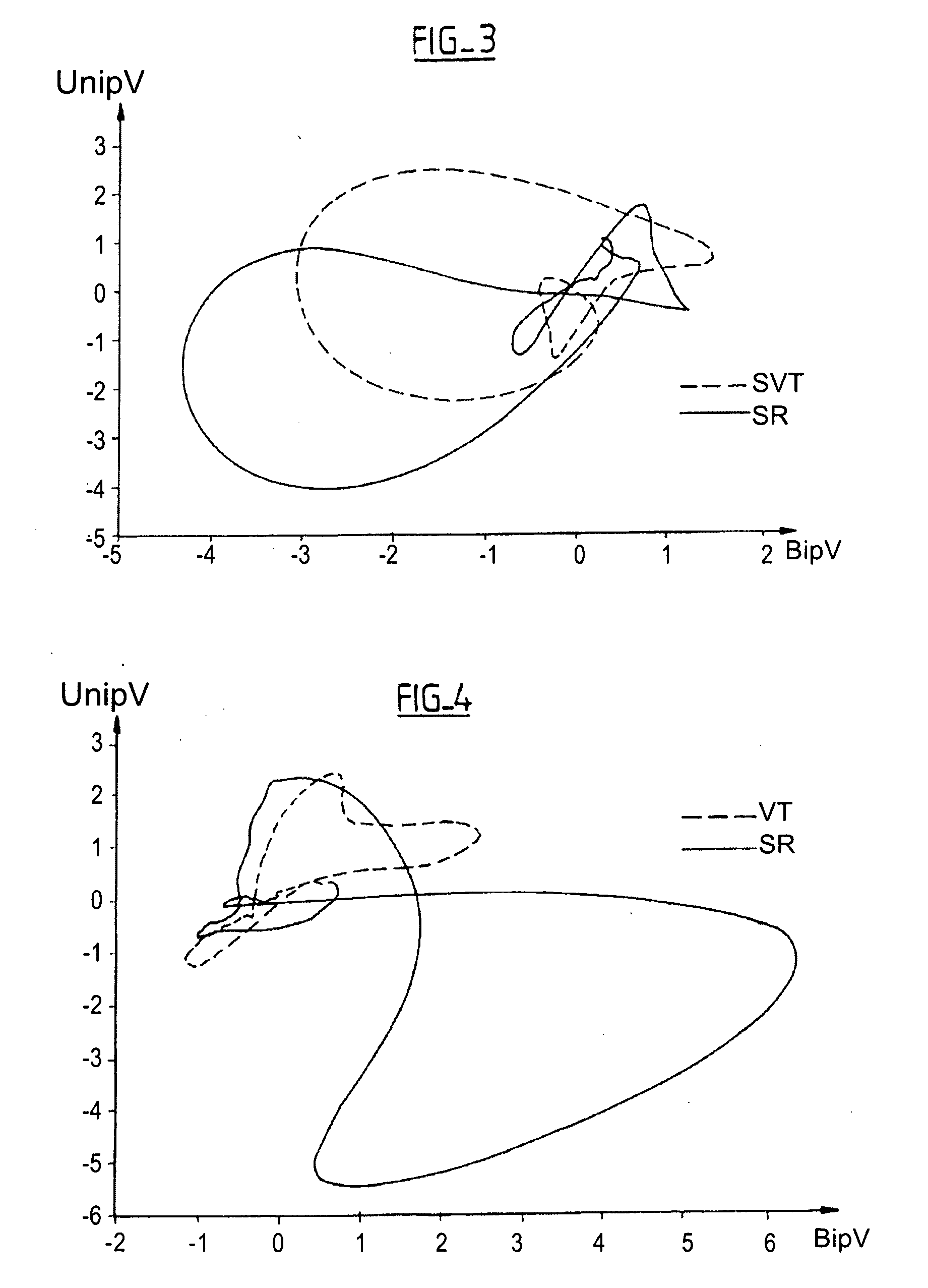
An active medical device able to discriminate between tachycardias of ventricular origin and of supra-ventricular origin. Two distinct temporal components (UnipV, BipV) are obtained corresponding to two EGM signals of ventricular electrograms. The diagnosis operates in at least two-dimensional space to determine, from the variations of one temporal component as a function of the other temporal component, a 2D characteristic representative of a heart beat and, this, for a reference beat collected in Sinus Rhythm (SR) in the absence of tachycardia episodes, and for a heart beat in Tachycardia. The discrimination of the tachycardia type, VT or SVT, is then realized by a classifier operating a comparison of the two current and reference 2D characteristics.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Method for arrhythmias treatment based on spectral mapping during sinus rhythm
ActiveUS7819862B2Facilitate conductionIncrease contractilityInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac muscleSpectral analysis
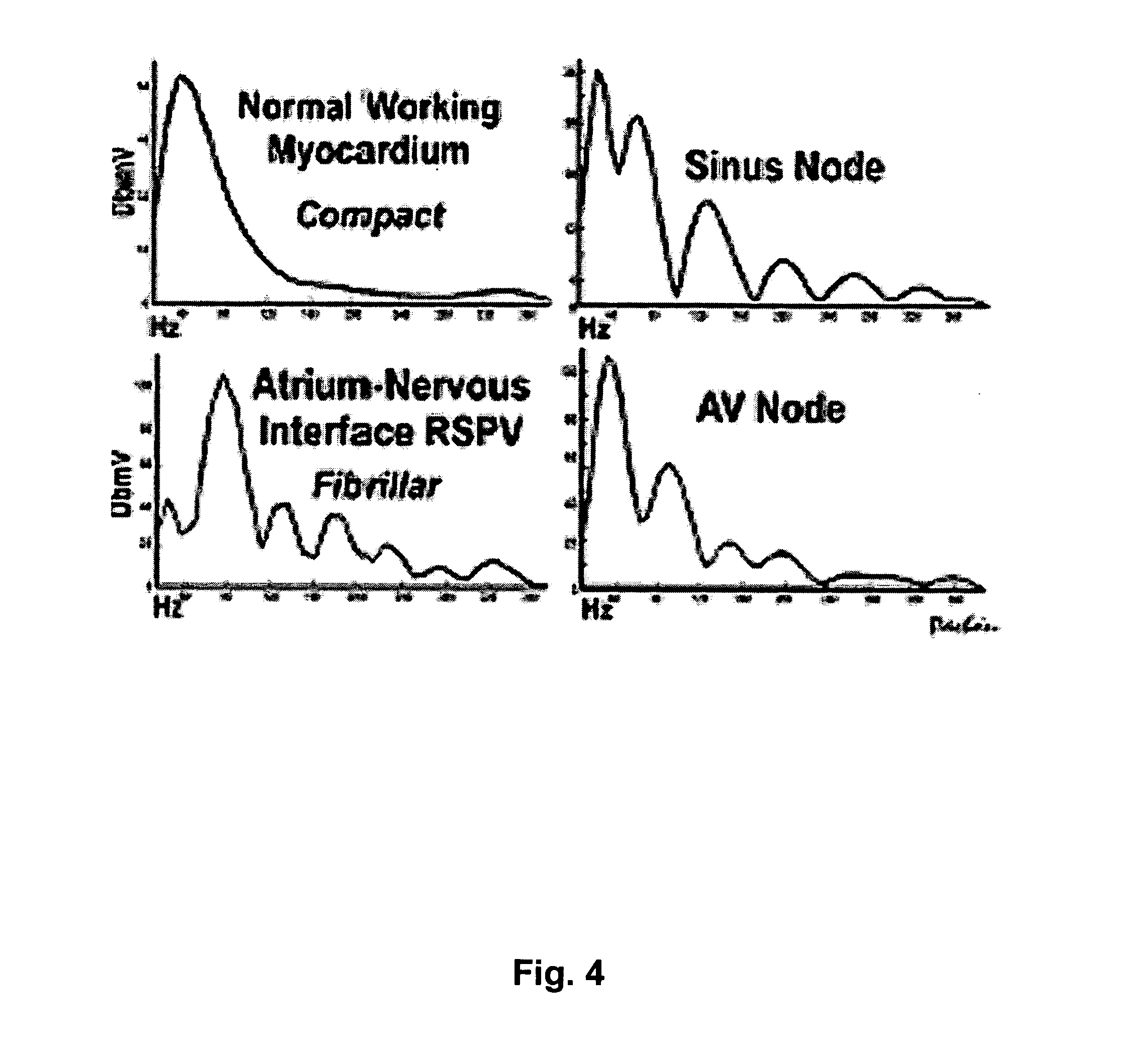
Methods for curative ablation are provided to achieve the inactivation or destruction of fibrillar myocardium of the so-called AF nests. In addition, fibrillar myocardium may be identified and mapped by spectral analysis and phase study of the tissue during sinus rhythm. The procedure may be performed by transseptal puncture using only one catheter for ablation and mapping. The methods may be used to localize the application targets even during an arrhythmia.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for obtaining artificial neural network weighted value matrix for identifying atrial fibrillation
ActiveCN106066933AReal-time automatic detectionSave livesMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsEcg signalNormal Sinus Rhythm
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an artificial neural network weighted value matrix for identifying atrial fibrillation. The method includes the steps of calling an MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, an MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database and a long-time atrial fibrillation database as trainning samples, introducing an artificial neural network for learning training, randomly setting the weighted value of each layer of artificial neural network, and inputting training data samples to conduct repeated iteration to correct the weighted value of each layer until the training error is smaller than a designated value. In this way, the weighted value matrix for determining occurrence of atrial fibrillation can be found, the weighted value matrix is added into an original artificial neural network to establish a new artificial neural network, and human electrocardiosignals are processed with the acquired target human electrocardiosignals as data to obtain a target human body characteristic vector X. The prediction operation is carried out according to the target human body characteristic vector X and the new artificial neural network.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
Method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium for electrocardiogram signal detection and classification
ActiveCN110226921AImprove accuracyAbnormal rhythm is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalClassification methods
The invention relates to a method, a device, electronic equipment and a storage medium for electrocardiogram signal detection and classification. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a signal waveform from an electrocardiogram signal; acquiring a morphological characteristic and a deep characteristic of the signal waveform, wherein the morphological characteristic comprises anyone of a TR wave amplitude difference characteristic, a PR wave quantity ratio characteristic, an ST wave band characteristic and a P wave variation characteristic, and the deep characteristic comprises a depth characteristic and a hierarchy characteristic; inputting the morphological characteristic and the deep characteristic into a classifier; and acquiring a classification result output by theclassifier so as to obtain the signal type of the electrocardiogram signal, wherein the classification result is a result that the classifier performs classification according to the morphological characteristic and the deep characteristic, and the signal type comprises an atrial fibrillation rhythm, a non-atrial fibrillation abnormal rhythm, a normal sinus rhythm and noise. The method can accurately identify various types of abnormal rhythms, avoids the situation that abnormal rhythms of non-atrial fibrillation types such as tachycardia, bradycardia and arrhythmia are classified into atrial fibrillation types in error, and improves the accuracy of classification of electrocardiogram signals.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for obtaining risk predictions of sudden death with weight value matrices of artificial neural network
InactiveCN106021941ATimely measuresLimit detectabilityHealth-index calculationBiological neural network modelsEcg signalNormal Sinus Rhythm
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the weight value matrix of the artificial neural network for sudden death risk prediction. The sudden cardiac death database and the MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database are constructed into training data samples and cross-validation samples, and each layer of the artificial neural network is randomly set first. Input training data samples to iteratively correct the weight values of each layer until the training error is less than a specified value, find the weight value matrix that can predict the risk of sudden death, and then use the weight value matrix to add the weight value matrix to the original artificial neural network to construct a new model. The artificial neural network, and then use the collected target human ECG signal as data, process the human ECG signal to obtain the target human feature vector X, and perform prediction calculations according to the target human feature vector X and the new artificial neural network, and finally Get the predicted value.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
Method for arrhythmias treatment based on spectral mapping during sinus rhythm
ActiveUS20070038251A1Facilitate conductionIncrease contractilityInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsRf ablationCardiac muscle
A new method for curative radiofrequency AF ablation to achieve the inactivation or distruction of fibrillar myocarcium and of the AF nests. In addition, evidence that fibrillar myocardium could be of the real AF substratum was found. Identified and mapped by spectral analysis and phase study of the tissue, which seems to have intermediate features between nervous and myocardium. The procedure by transeptal puncture which requires only one catheter for ablation and mapping. The new method may be localize the application targets even during arrhythmia.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method of using vagal stimulation to assess autonomic tone and risk of sudden cardiac death in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS7869870B1Eliminate riskEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsVentricular contractionPremature ventricular complex
A method and apparatus for using vagal stimulation to detect autonomic tone and assess a patient's risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) are presented. The method involves stimulating the patient's vagus nerve in order to induce a drop in arterial blood pressure, which simulates the patient's cardiovascular response to a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). Sinus rhythm data just before and immediately following the stimulation is recorded and analyzed for a degree of heart rate turbulence (HRT) in order to detect abnormalities in autonomic tone and assess the risk of SCD. In an embodiment, the method is implemented in an implantable cardiac device (ICD), which can deliver arrhythmia prevention therapy based on the risk of SCD. The method can assess the patient's vagal activity on-demand by measuring HRT without relying on naturally occurring PVCs and eliminates the risk of causing arrhythmia associated with artificially inducing PVCs in order to measure HRT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
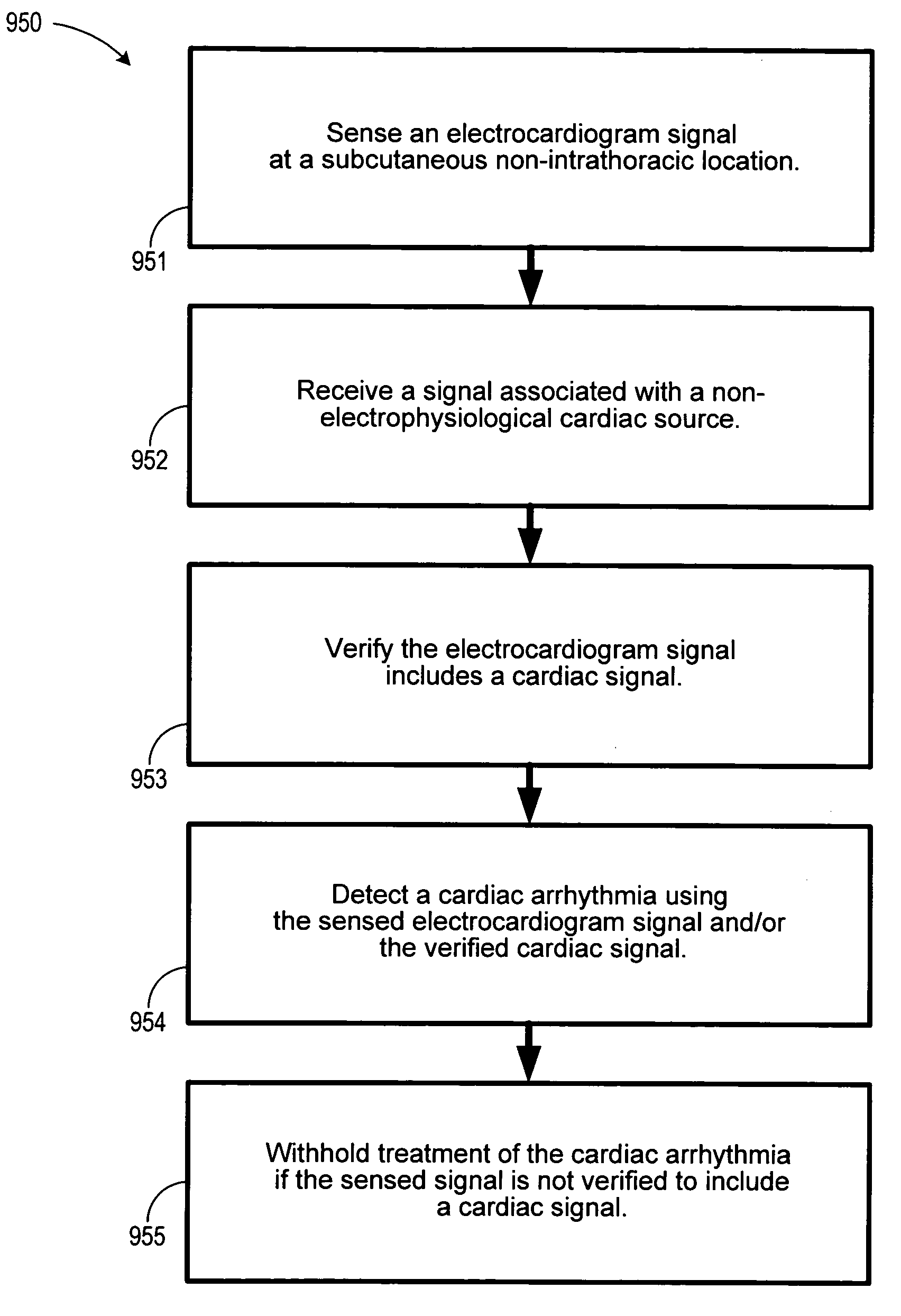
An arrhythmia discrimination device and method involves receiving electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals at subcutaneous locations. Both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals are used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia may be detected using electrocardiogram signals, and verified using the non-electrophysiologic signals. A detection window may be initiated in response to receiving the electrocardiogram signal, and used to determine whether the non-electrophysiologic signal is received at a time falling within the detection window. Heart rates may be computed based on both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals. The rates may be used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia, and used to determine absence of an arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
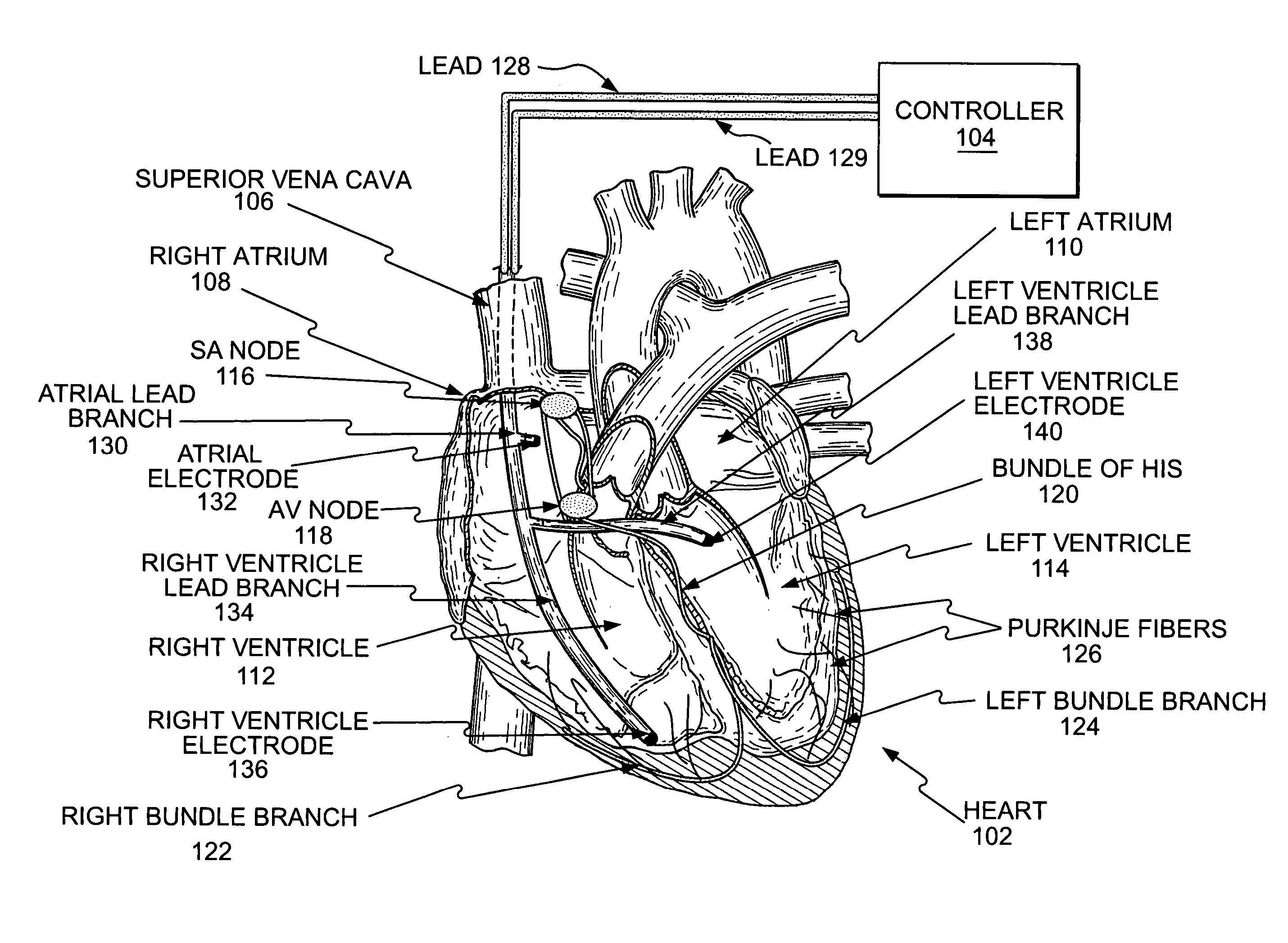
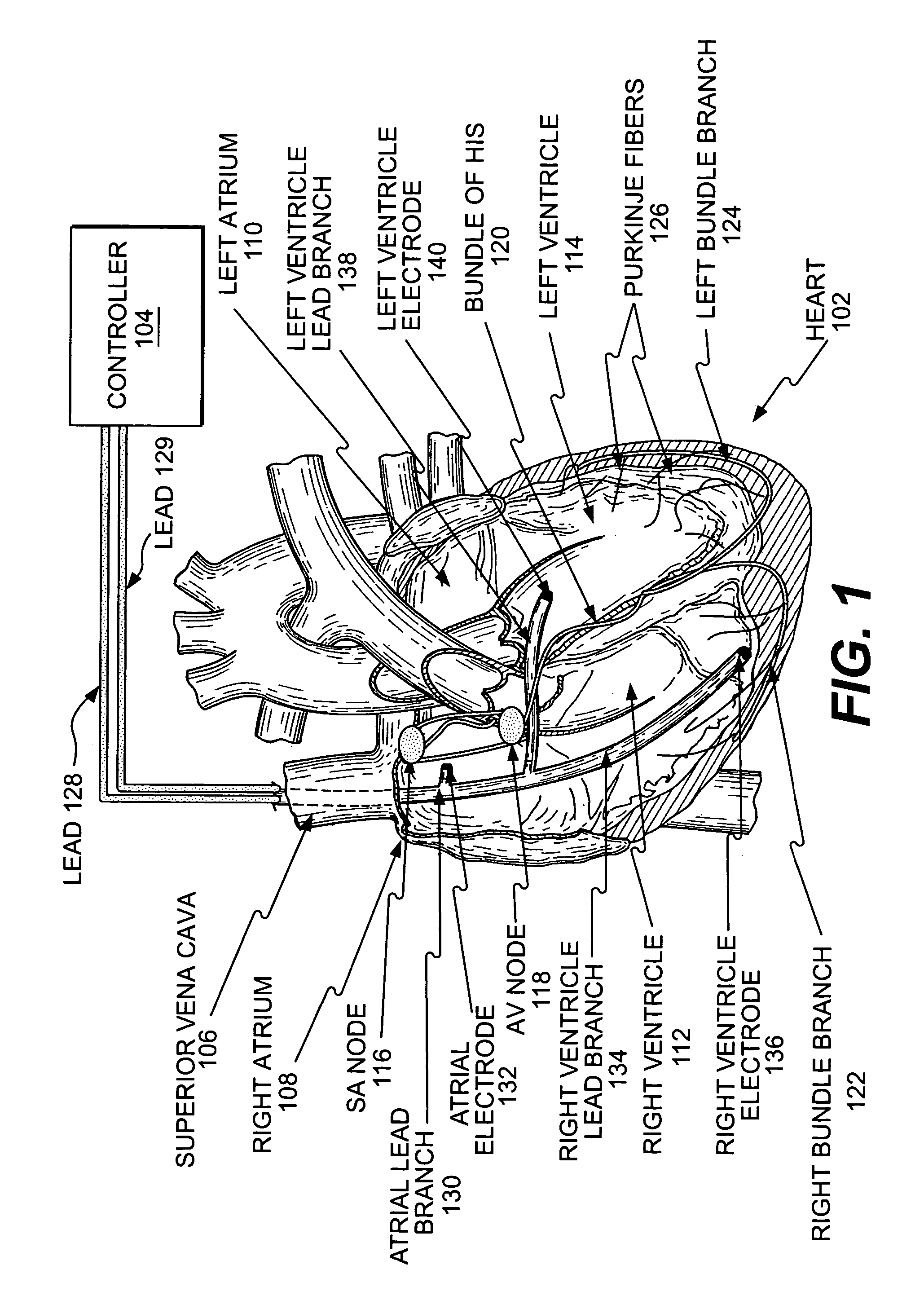
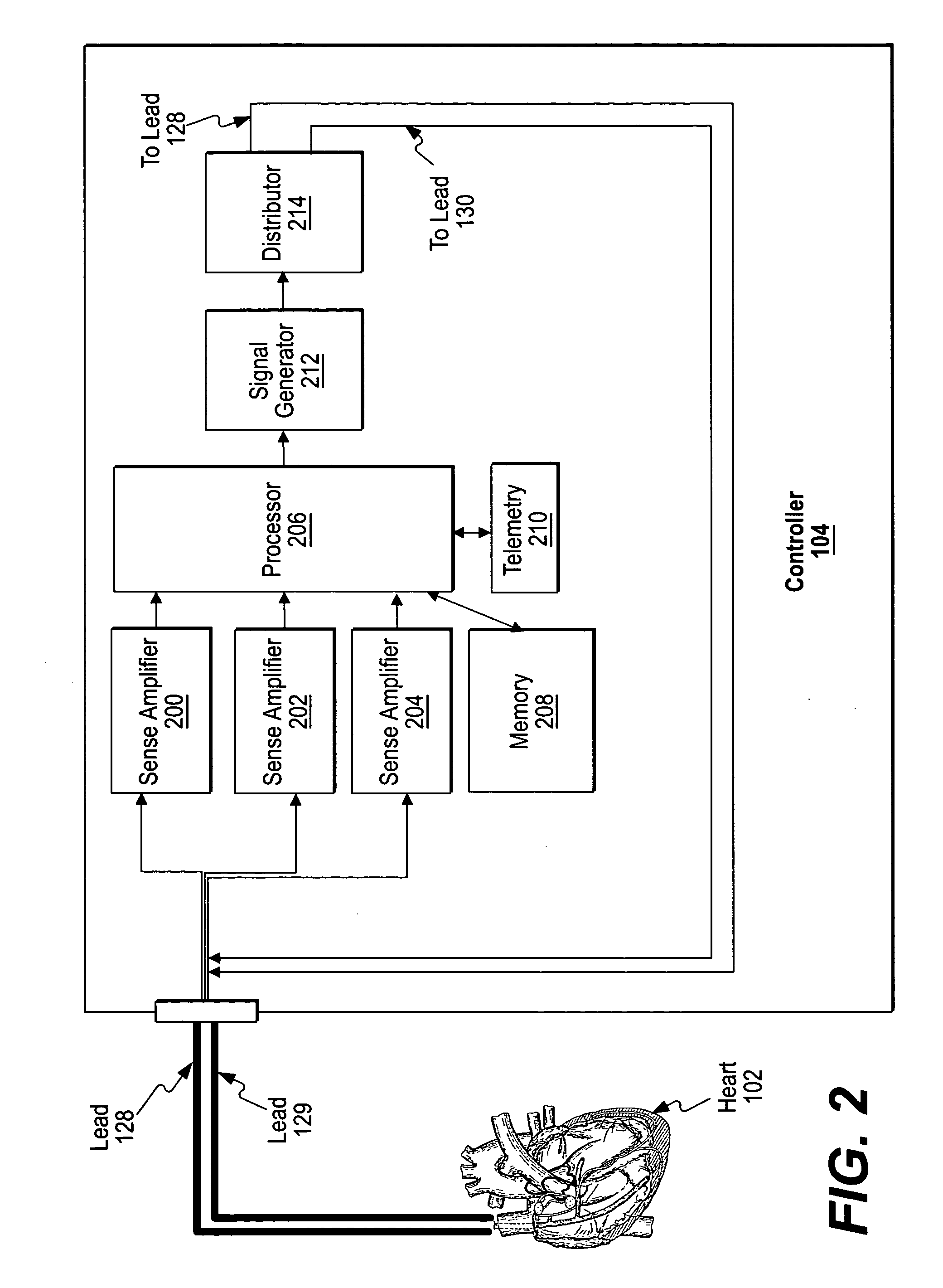
Methods, apparatus, and systems for multiple stimulation from a single stimulator
Methods, apparatus, and systems are provided to stimulate multiple sites in a heart. A controller senses electrical activity associated with sinus rhythm of the heart. A signal generator is configured to generate an electrical signal for stimulating the heart. Based on the electrical signal, a distributor circuit then distributes the stimulating signals, such as pacing pulses, to a heart. The distributor circuit may vary the delay time between stimulating signals, inhibit a stimulating signal, trigger application of a stimulating signal, or vary the characteristics, such as the pulse width and amplitude, of a stimulating signal.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
System And Method For Determining The Origin Of A Sensed Beat
InactiveUS20080281369A1Improve heart functionElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method for monitoring a biological cardiac pacemaker is provided. The method may include stimulating a heart at a region selected for implantation of a biological pacemaker and sensing at least one electrical signal indicative of a cardiac depolarization originating in the region selected for implantation of the biological pacemaker. The method may further include sensing at least one subsequent electrical signal produced by the heart and determining if the subsequent electrical signal originated in the region selected for the biological pacemaker or another region of the heart. In an alternative embodiment, the method may include determining a template time difference between two points on cardiac complexes sensed in two or more different cardiac locations during normal sinus rhythm. The method may further include determining a time difference between two points on a subsequent cardiac complex sensed in two or more different cardiac locations. The time differences may be compared to determine if the subsequently-sensed cardiac complex originates in a left ventricular biological pacemaker site or in another cardiac site.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Anti-tachycardia pacing method and apparatus for multi-chamber pacing
Improved methods and devices perform tachycardia detection and anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a tachycardia (e.g., VT or AT) to normal sinus rhythm. According to one embodiment, an anti-tachycardia pacing method includes sensing, during sinus rhythm, first and second cardiac signals at first and second sites, respectively, in a patient's heart. The first and second sites include left and right ventricles or left and right atria, for example. The method further includes sensing third and fourth cardiac signals at the first and second sites, respectively, during a tachycardia (e.g., ventricular tachycardia or atrial tachycardia). The cardiac signals are processed to provide respective values. One or more anti-tachycardia pacing pulses are delivered at the site closest to the reentrant circuit based on a comparison of a first ratio of the first and third values and a second ratio of the second and fourth values. Unipolar sensing of the cardiac signals may be employed by, for example, shorting together pairs of electrodes implanted at each site.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Level crossing detector for detecting noise, sinus rhythm and ventricular fibrillation in subcutaneous or body surface signals
A SubQ ICD that is entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and associated with subcutaneous leads provides distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. A level crossing detection system and process is implemented to detect noise, sinus rhythm and ventricular fibrillation in subcutaneous or body surface signals to deliver therapies as needed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
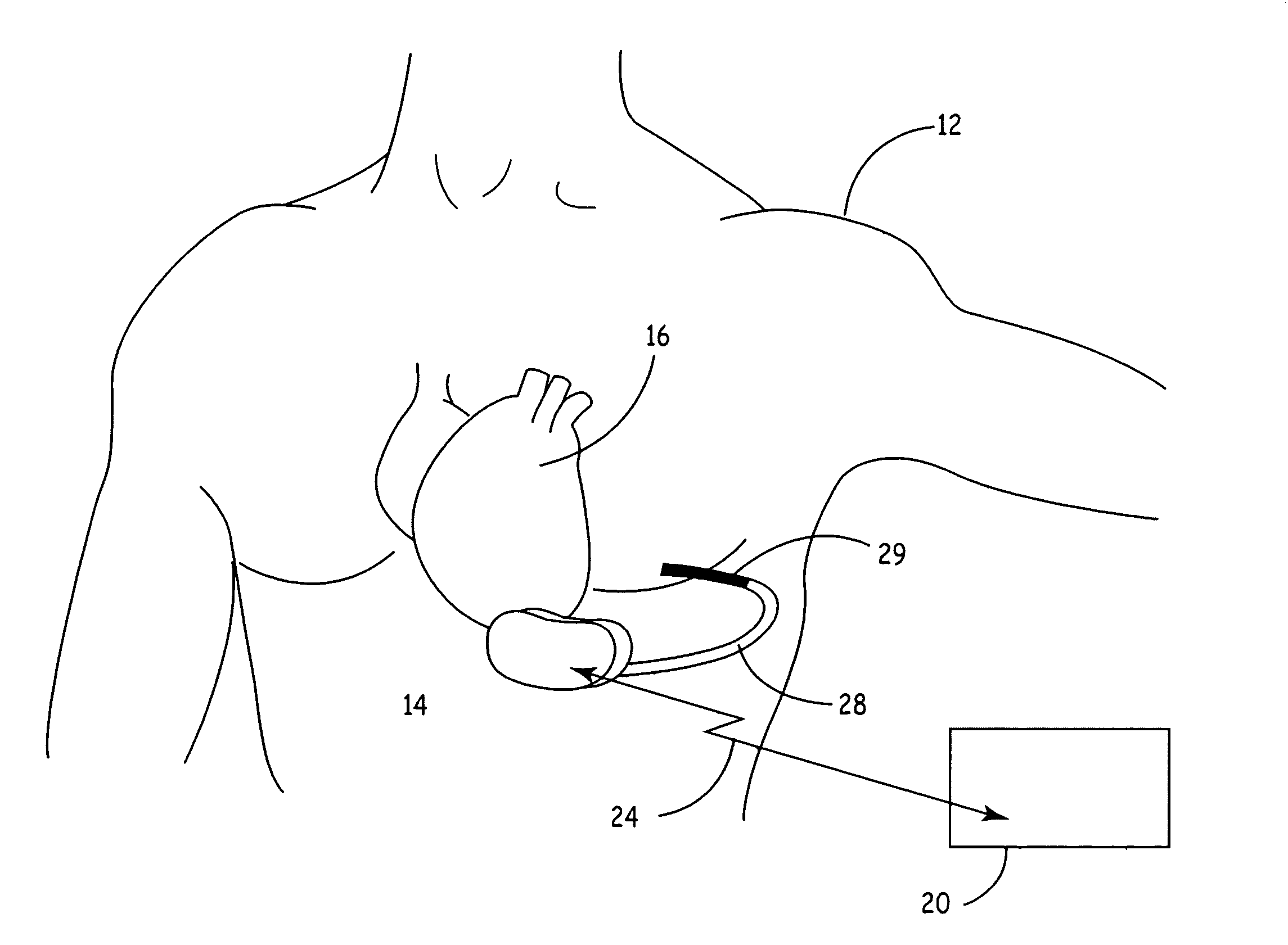
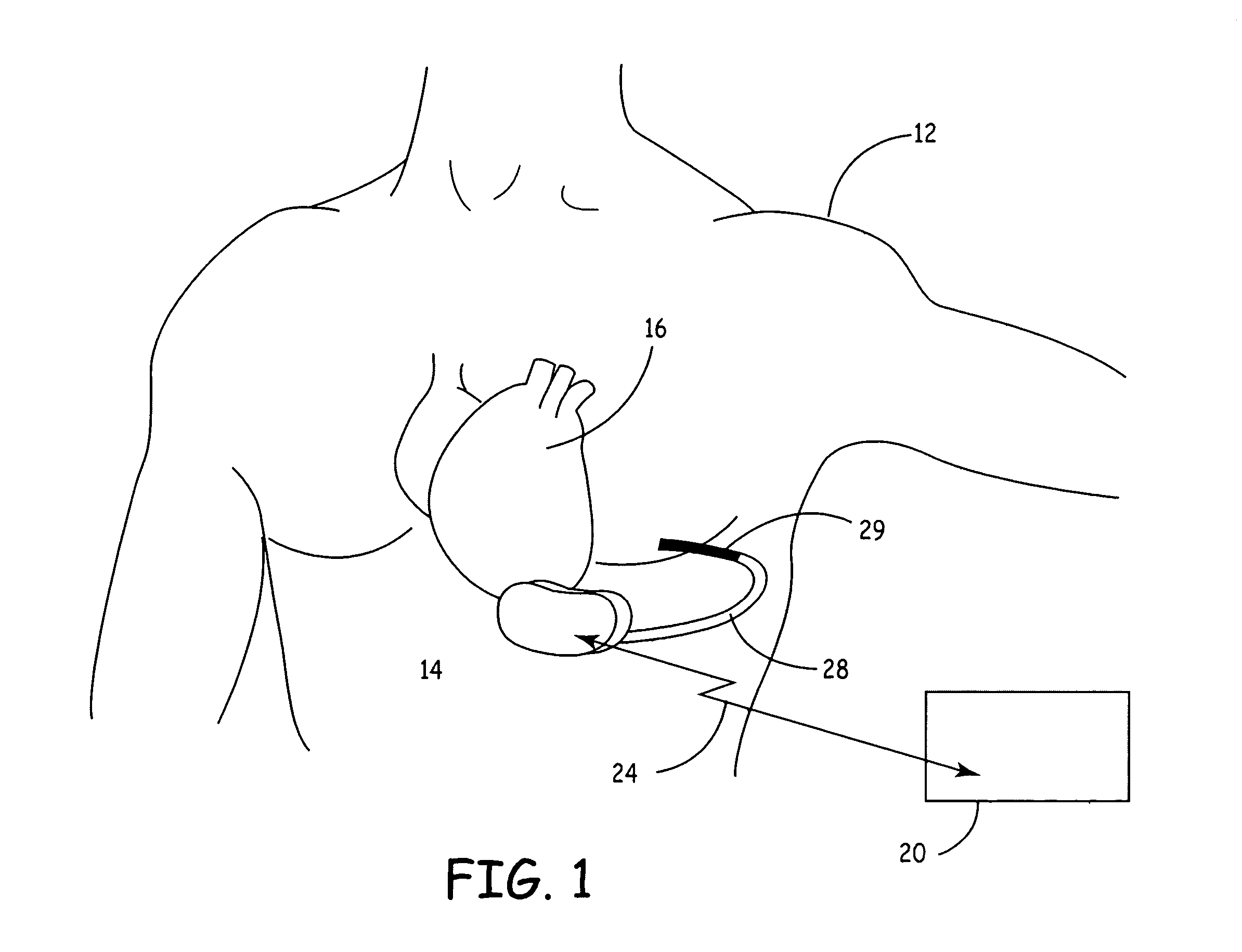
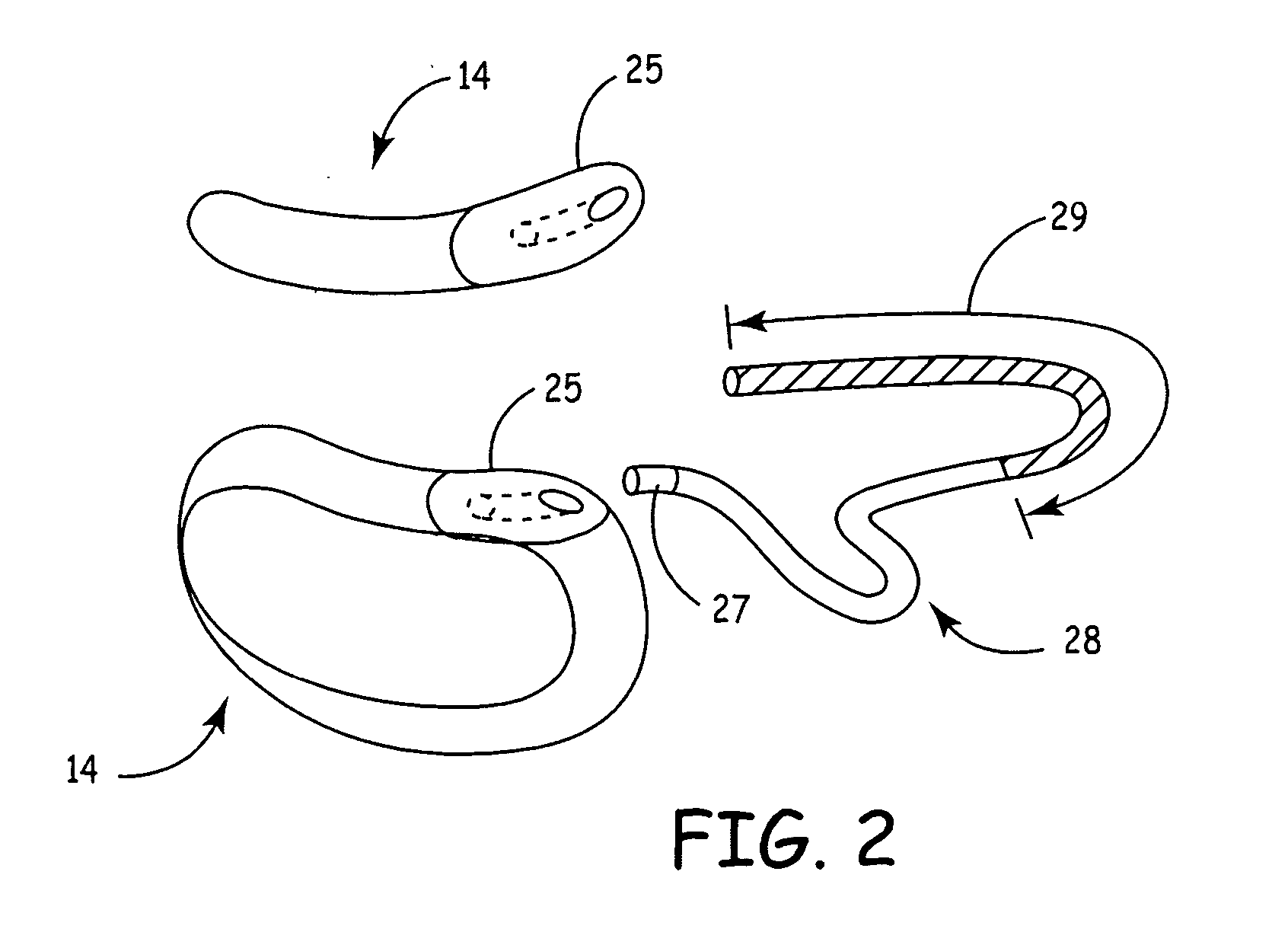
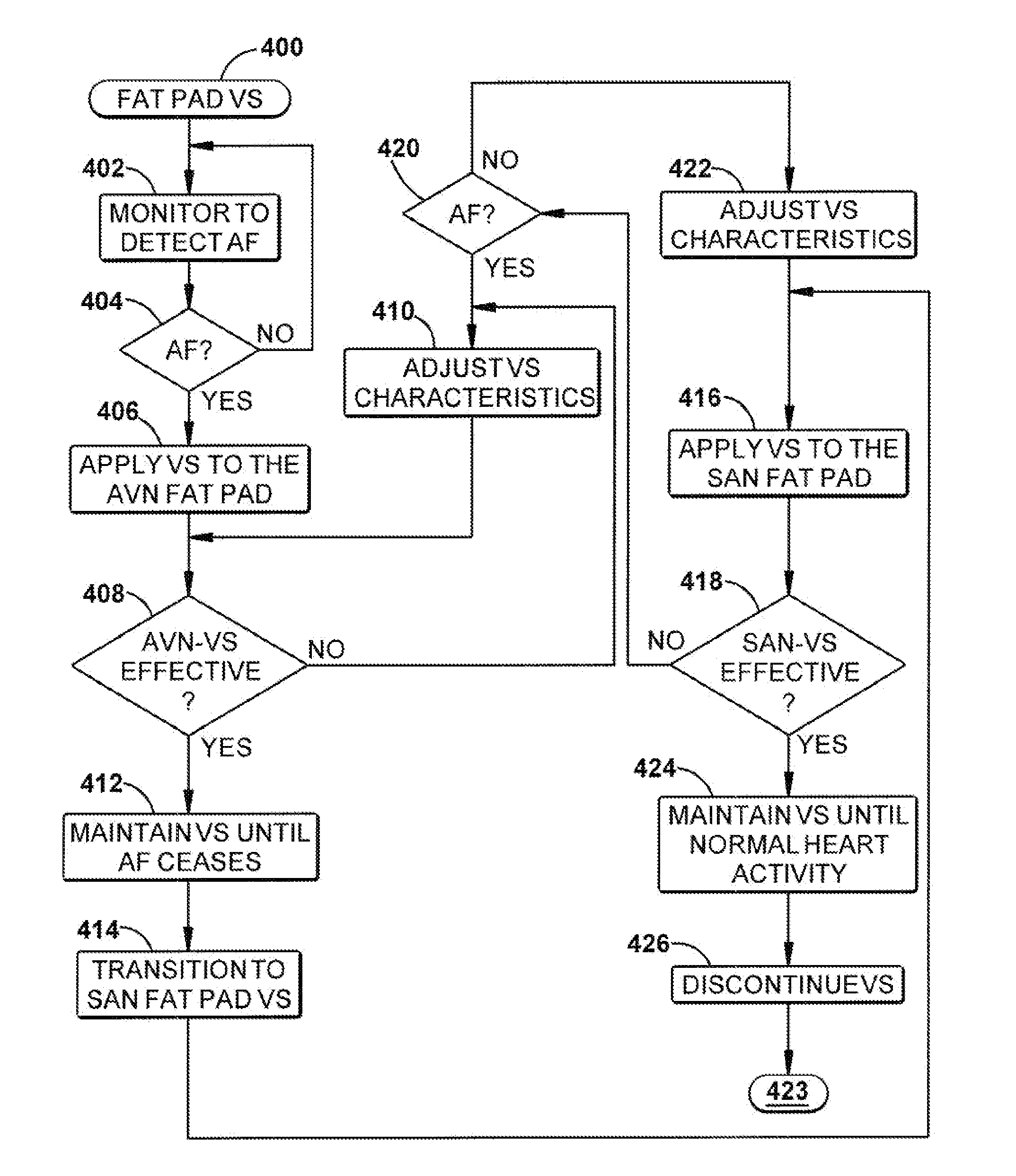
Control of cardiac arrhythmia by vagal stimulation at the atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodal fat pads of the heart
Vagal stimulation applied to the atrioventricular nodal (“AVN”) fat pad and the sinoatrial nodal (“SAN”) fat pad via epicardial leads is useful for controlling cardiac arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation (‘AF”). In the case of AF, for example, vagal stimulation may be applied initially to the AVN fat pad to reduce ventricular rate, and vagal stimulation may be applied to the SAN fat pad after restoration of sinus rhythm to control atrial rate. The technique is applicable to control acute AF and chronic AF. The vagal stimulation may be optimized for exciting ganglia in the fat pads to produce dromotropic and chronotropic effects in the atrioventricular node and the sinoatrial node, respectively. In addition, the SAN fat lead can also be used to pace the atrium in case of sinus bradycardia.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Atrial fibrillation detecting method and system
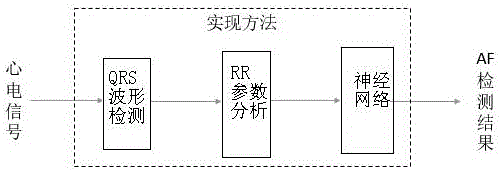
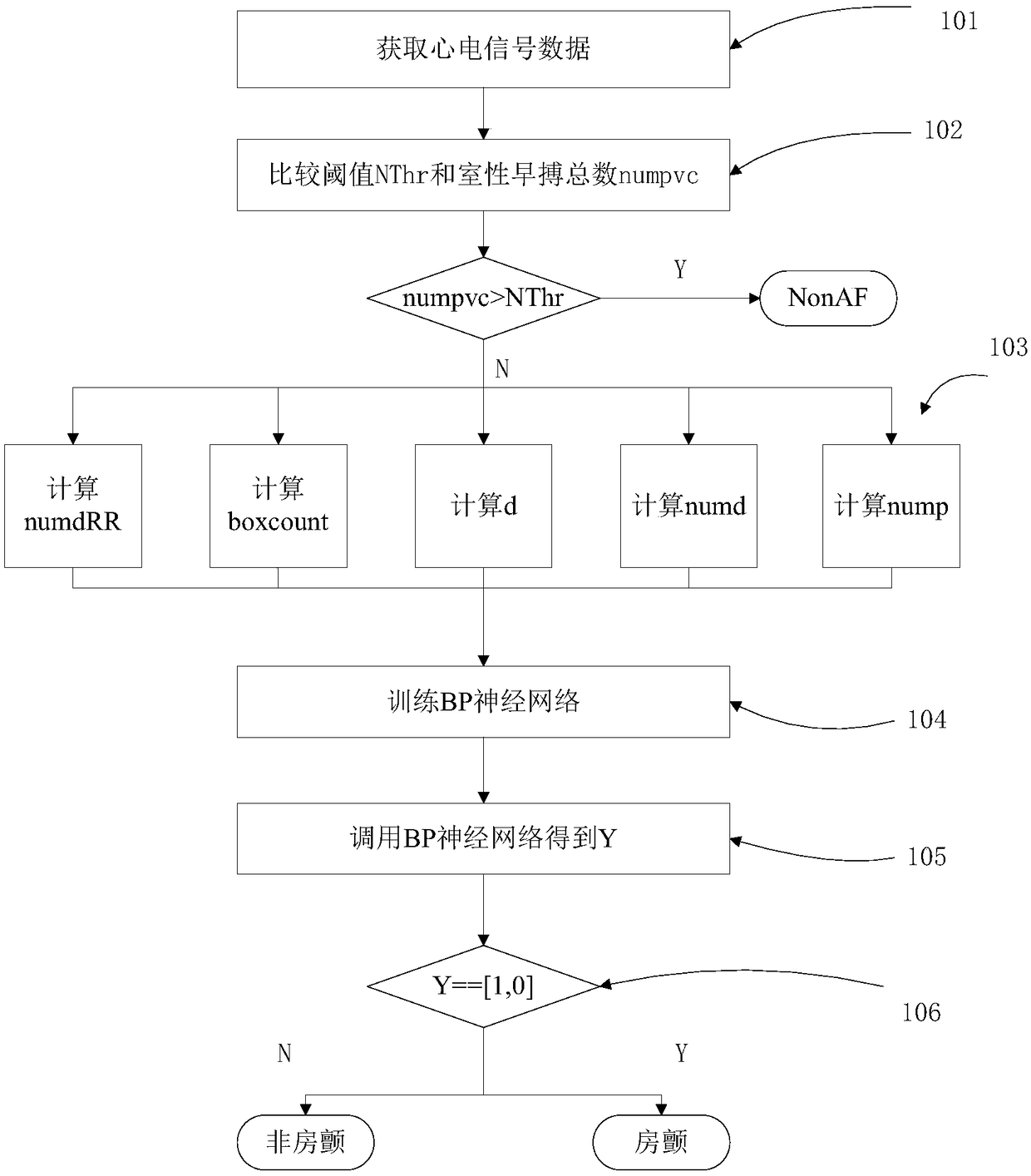
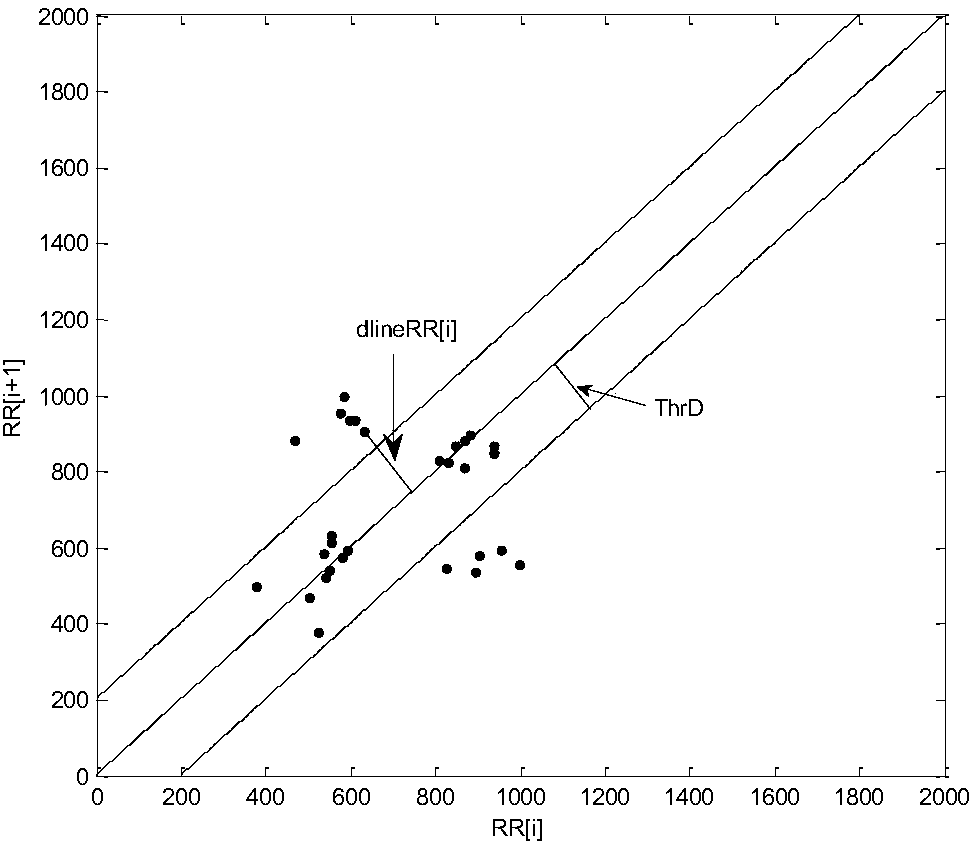
InactiveCN108324264ASolve the problem of false detectionImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRR intervalMedicine
The invention relates to an atrial fibrillation detection method and system. A condition that whether signals have P wave or not is added while the characteristic reflecting RR interval irregularity of the ECG signals is extracted, so that the problem of false detection of sinus arrhythmia signals is solved; a BP neural network method is adopted to replace simple logic conditions to judge atrial fibrillation signals, so that atrial fibrillation detecting accuracy when input RR interval number is small is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU KONSUNG BIOMEDICAL TECH
Cardiac stimulator for delivery of cardiac contractility modulation therapy
ActiveUS20130006319A1Immense clinical benefitGreat therapeutic benefitHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleContractility
A combination cardiac stimulator for CRT stimulation and CCM stimulation, which is connected to a rhythm evaluation unit which can either detect a sinus rhythm that is present, or classify an atrial arrhythmia, and which comprises an additional therapy selection unit, wherein the therapy selection unit selects the delivery of either CRT therapy or CCM therapy on the basis of the classification of the atrial rhythm such that CRT therapy is preferred in the case of sinus rhythm, and CCM therapy is delivered in the case of atrial arrhythmia.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com