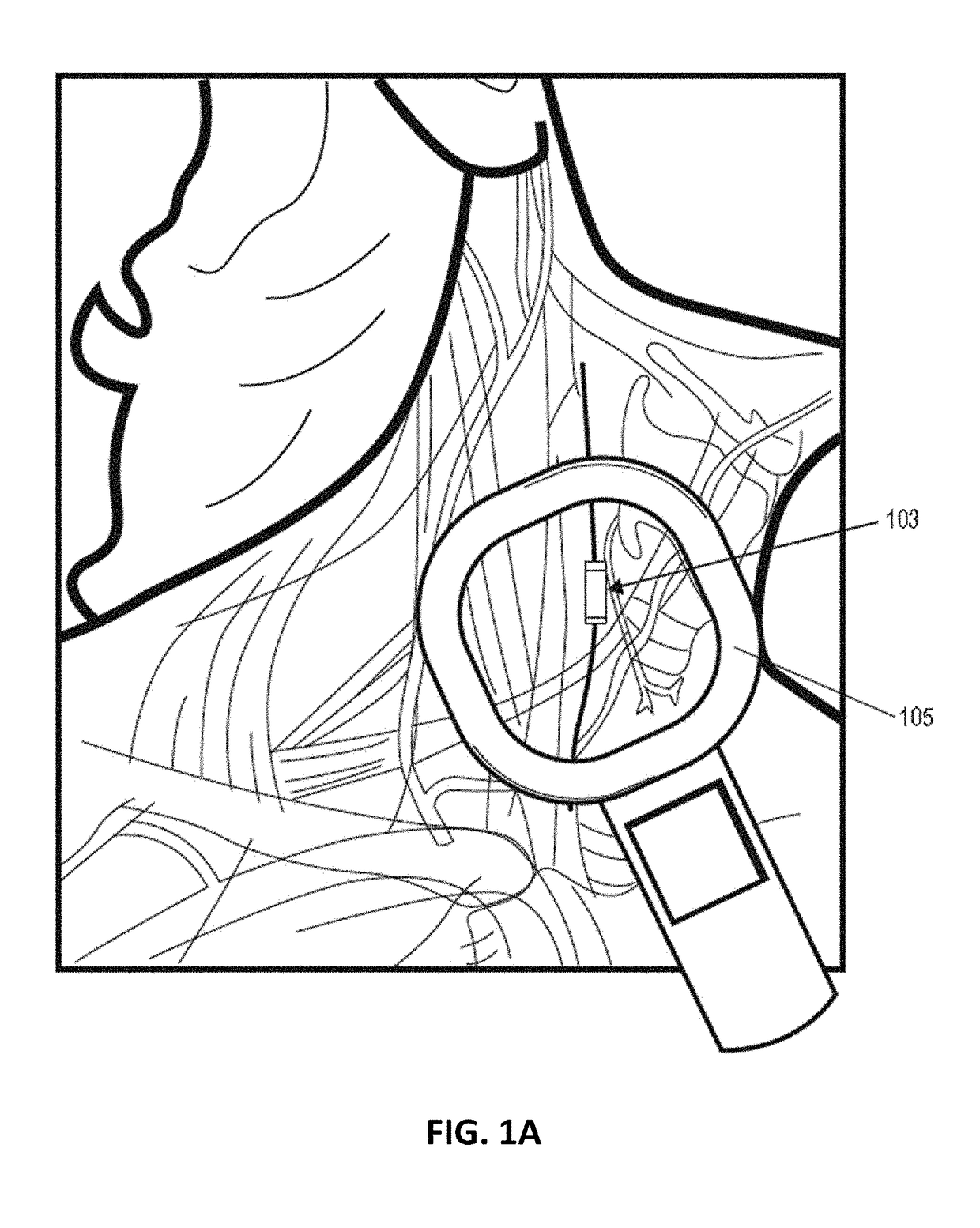
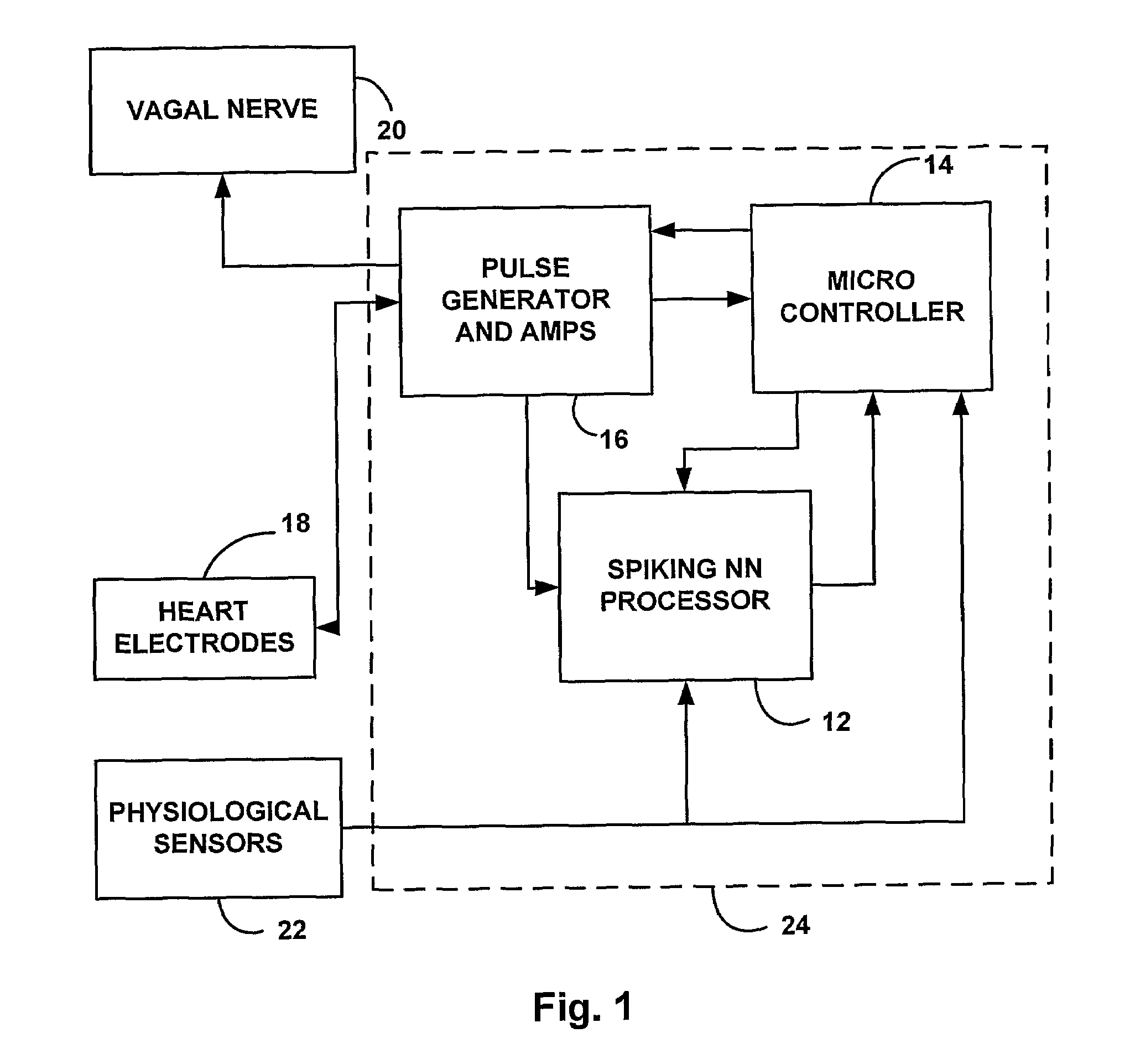
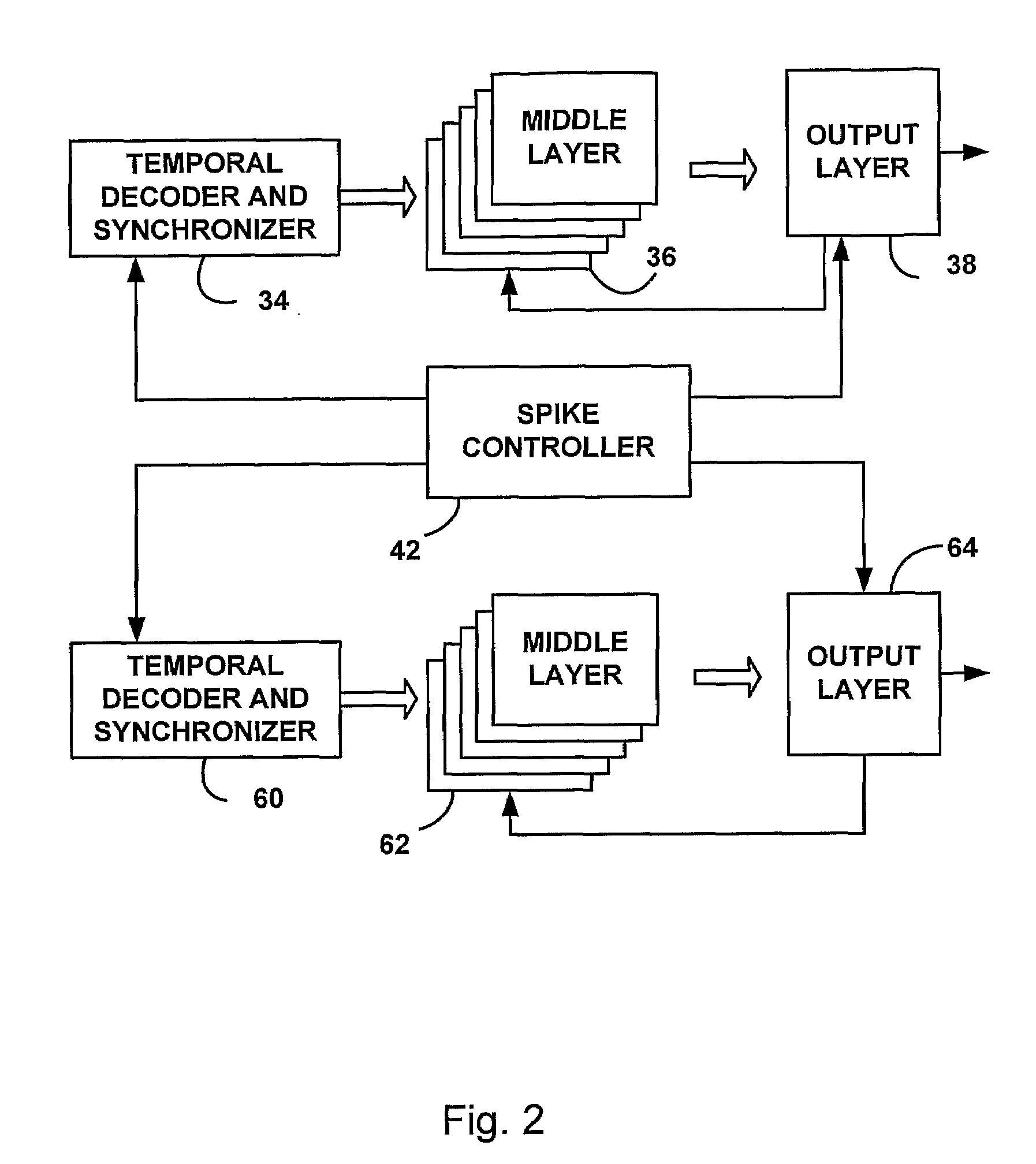
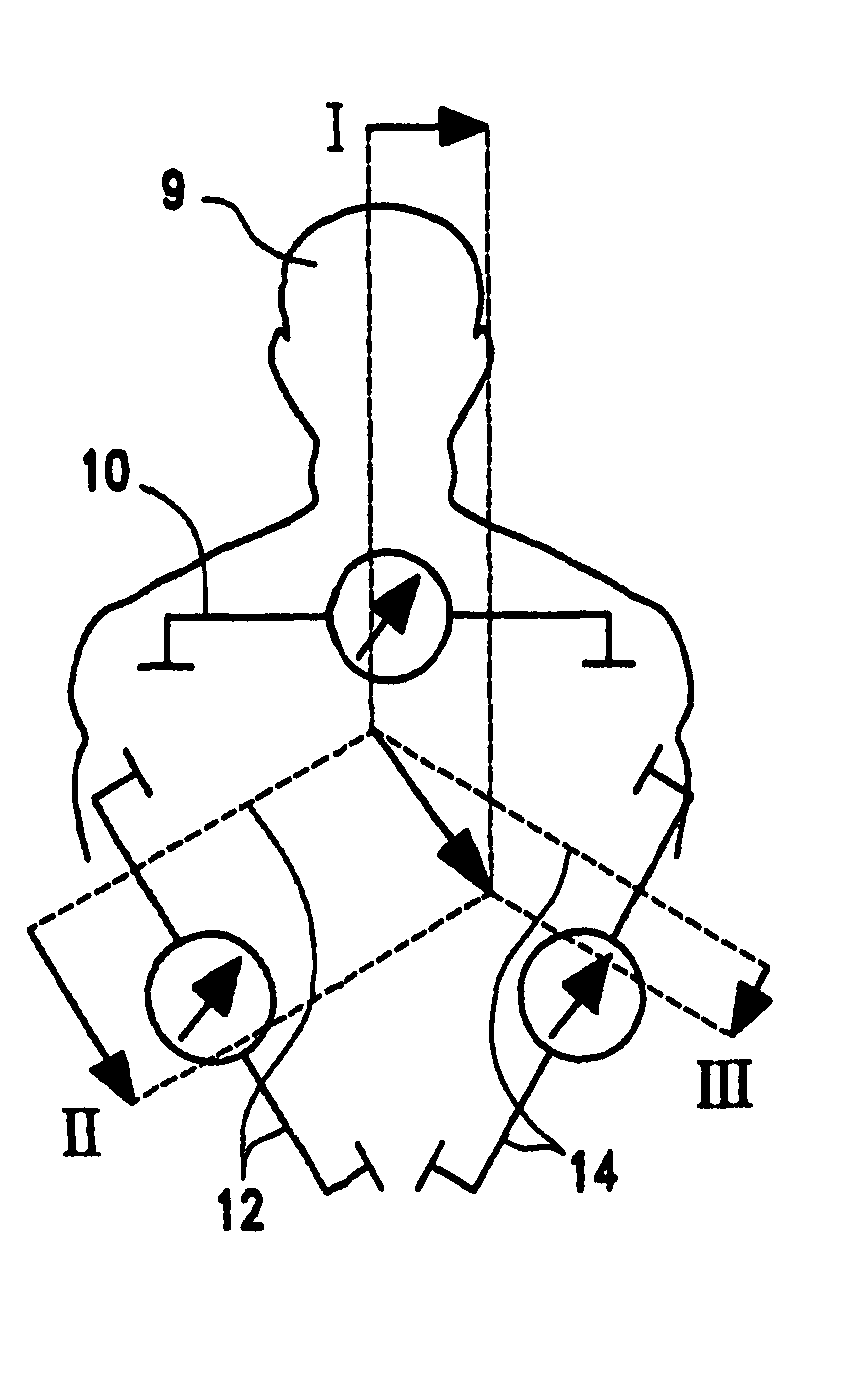
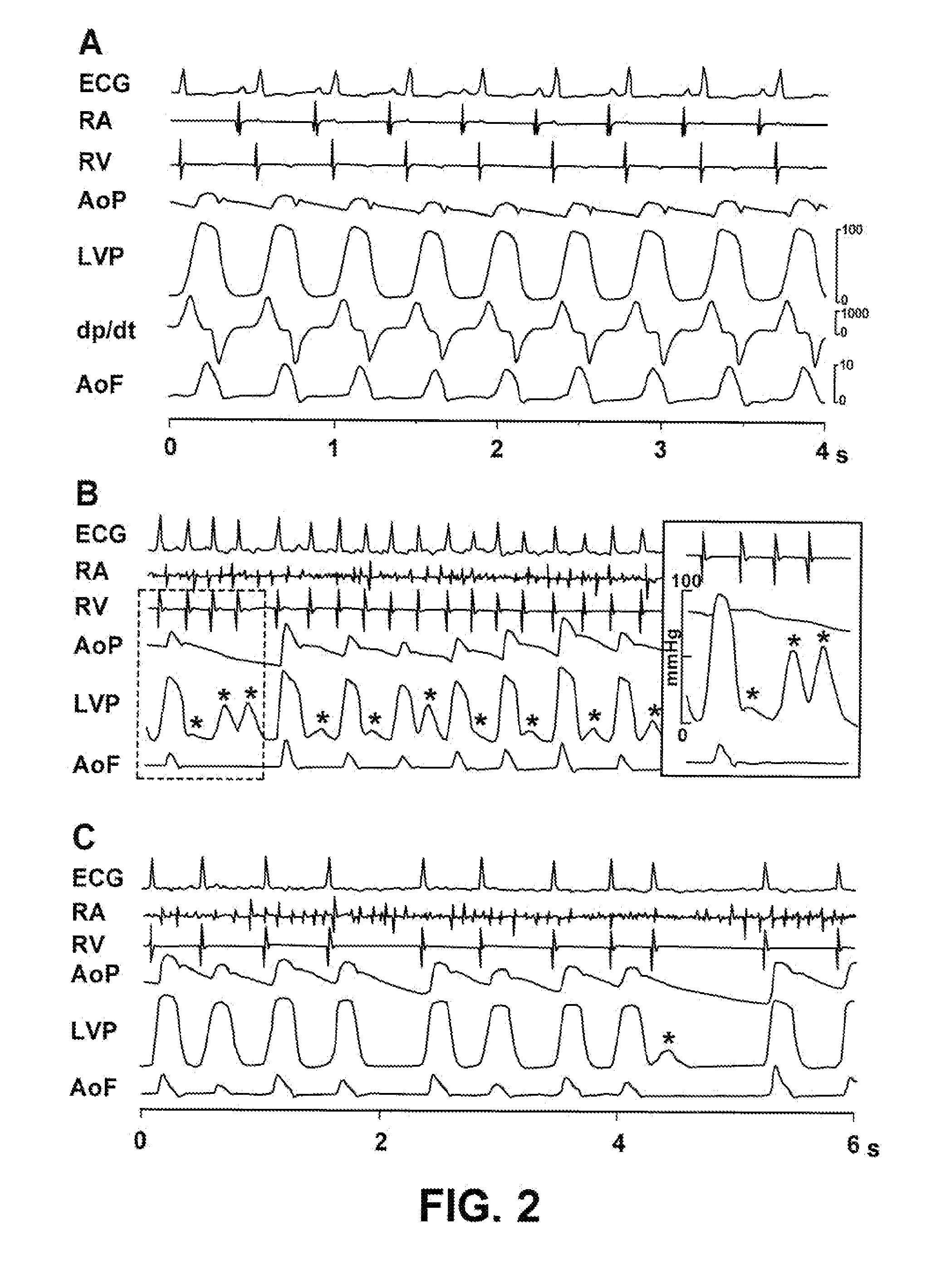
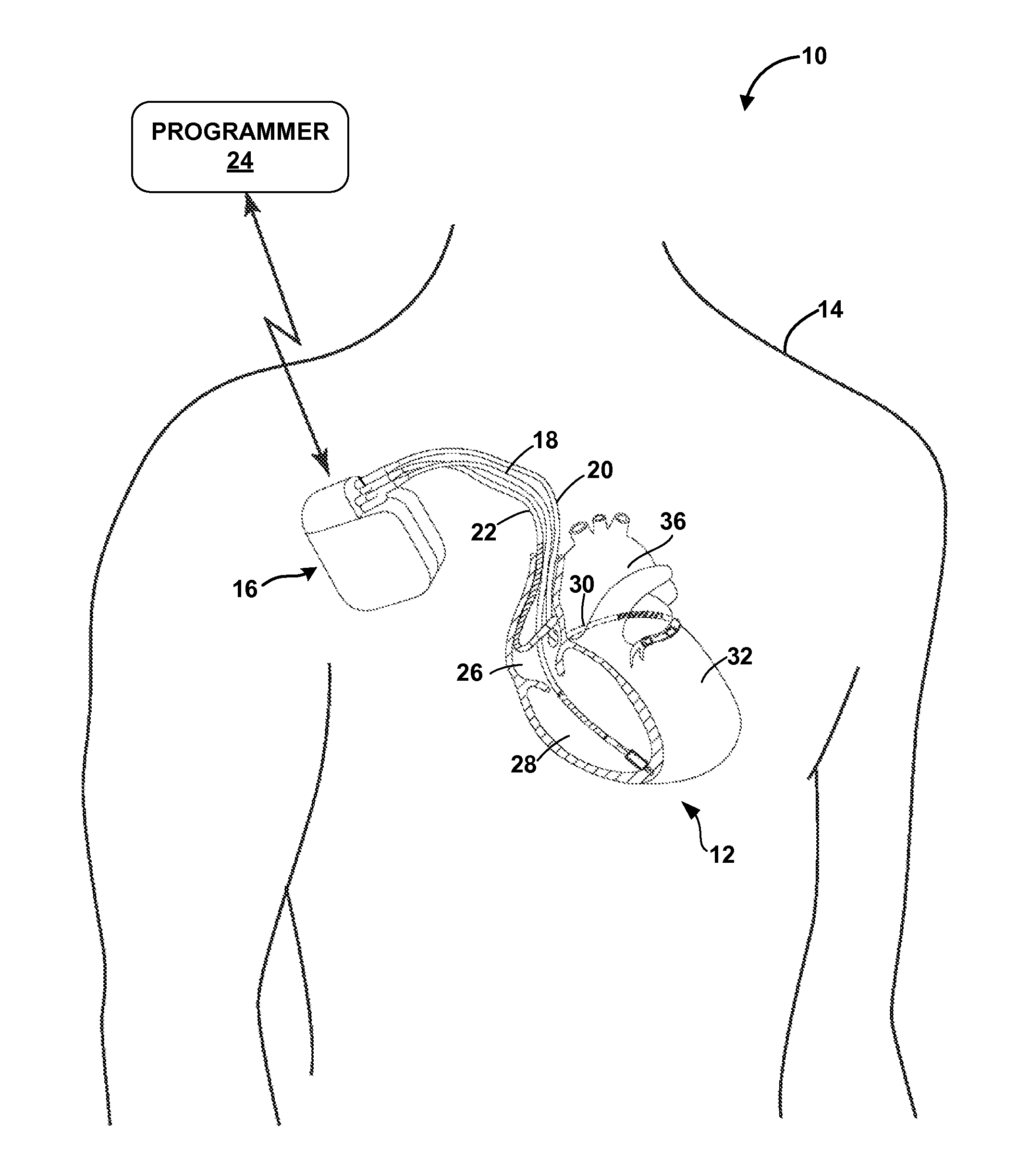
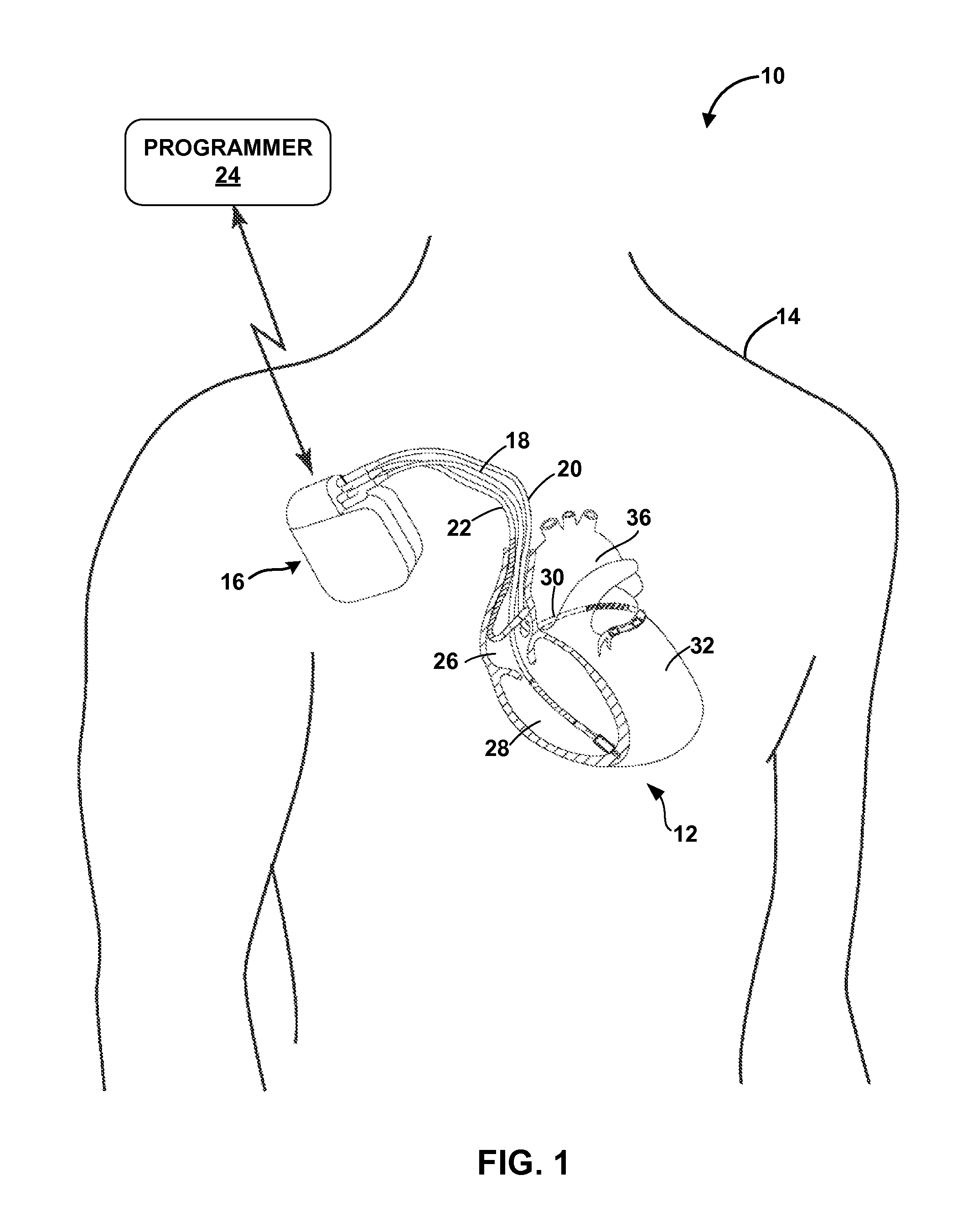
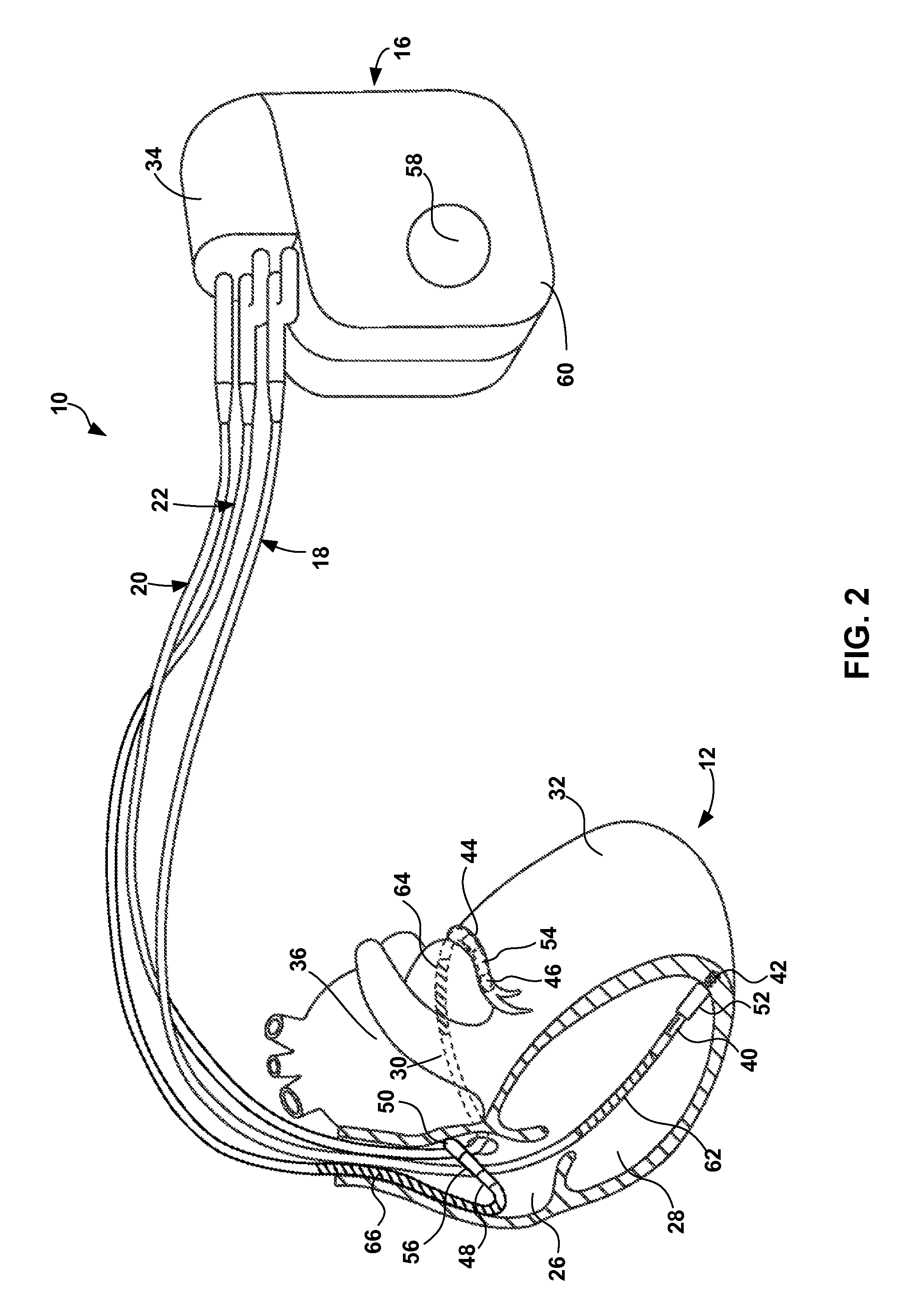
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Vagal stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
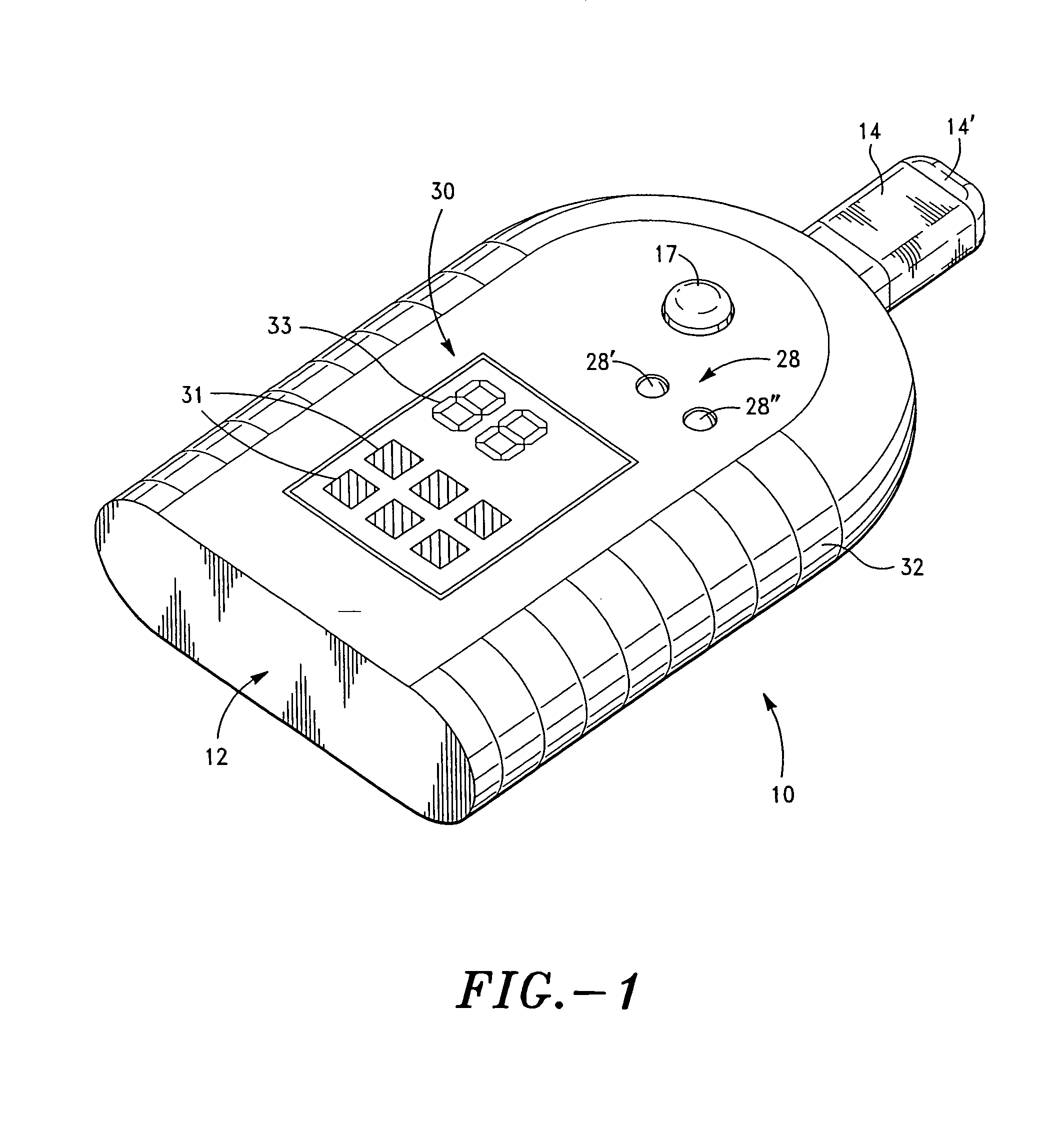
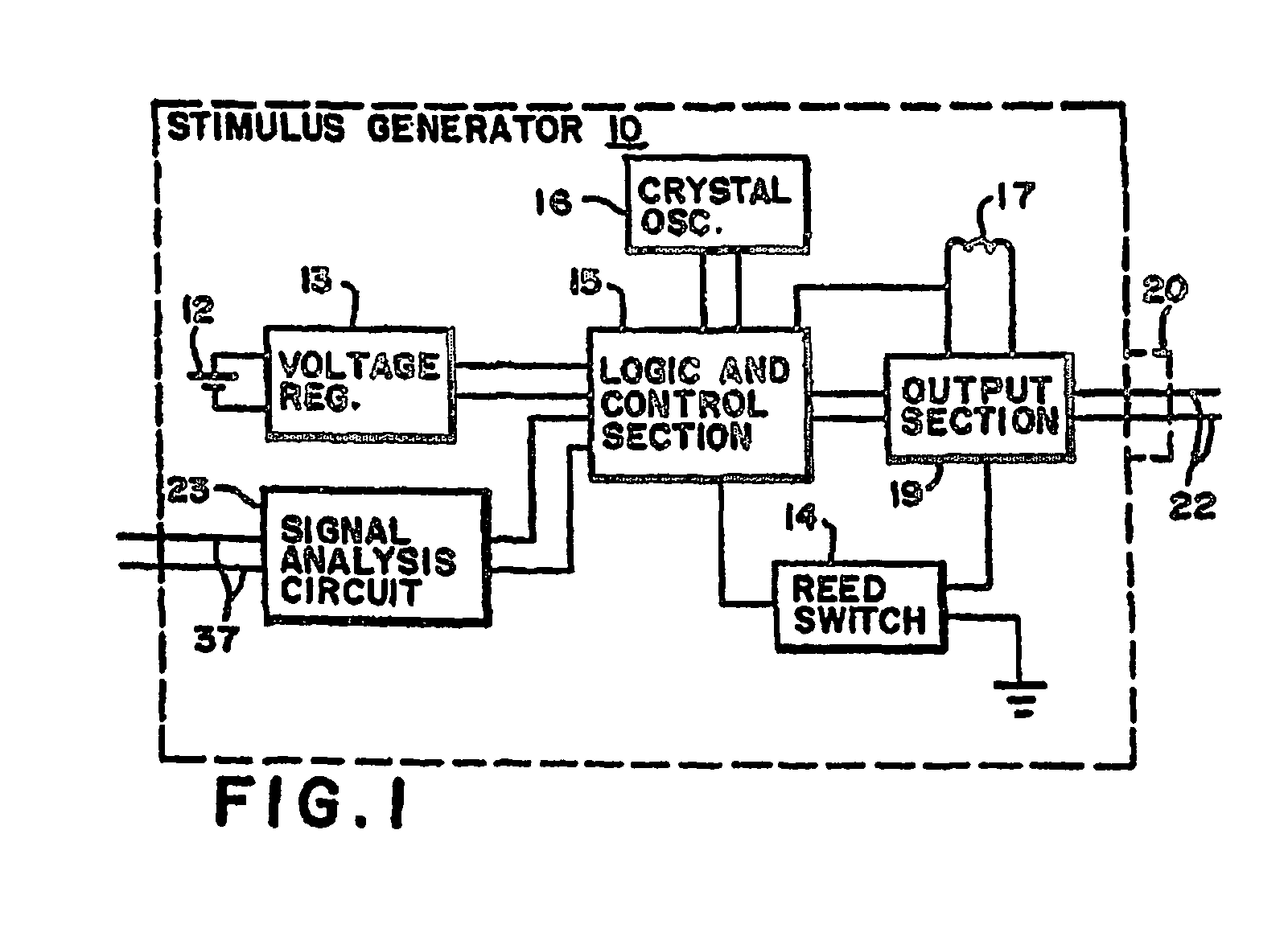
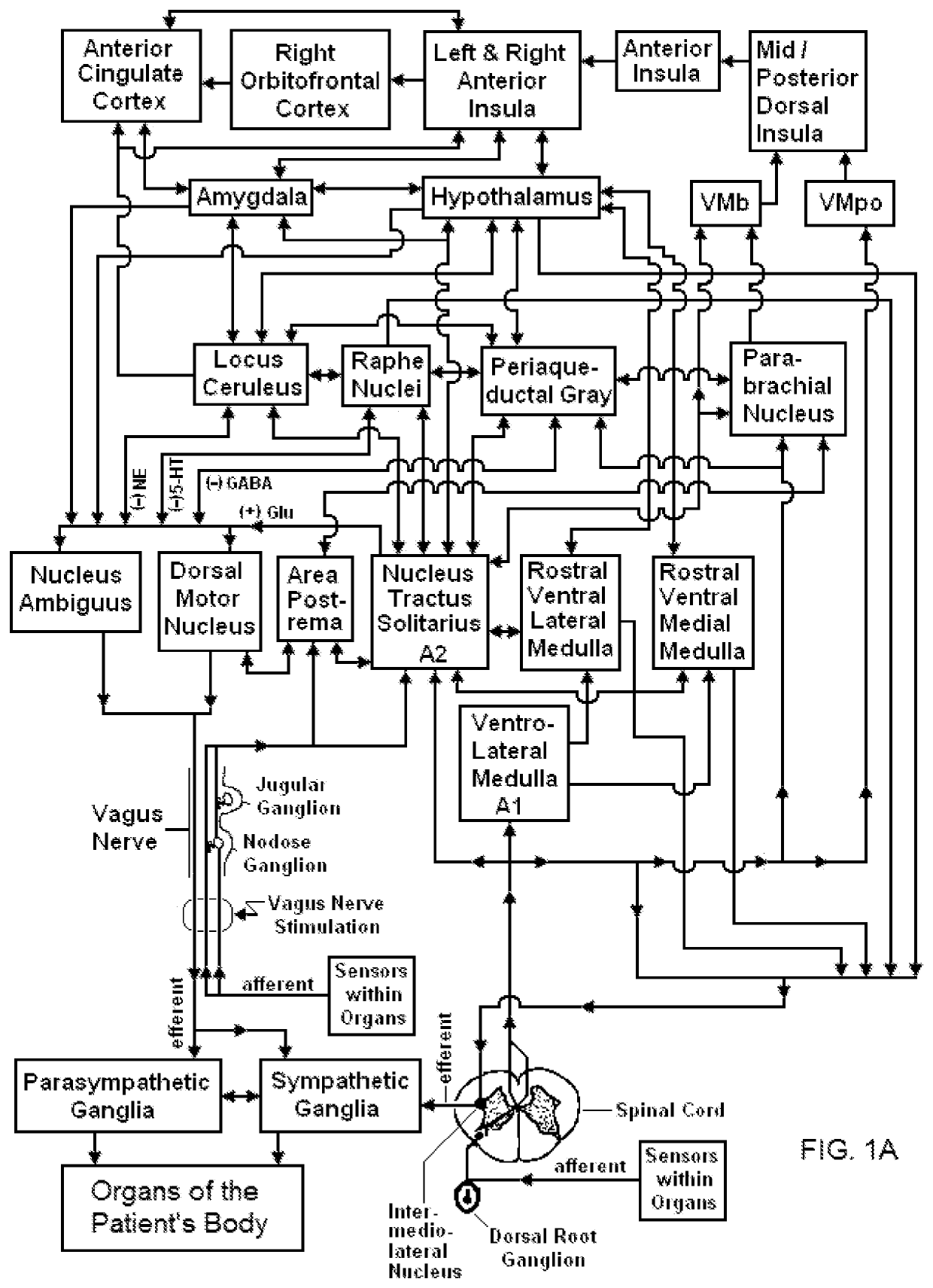
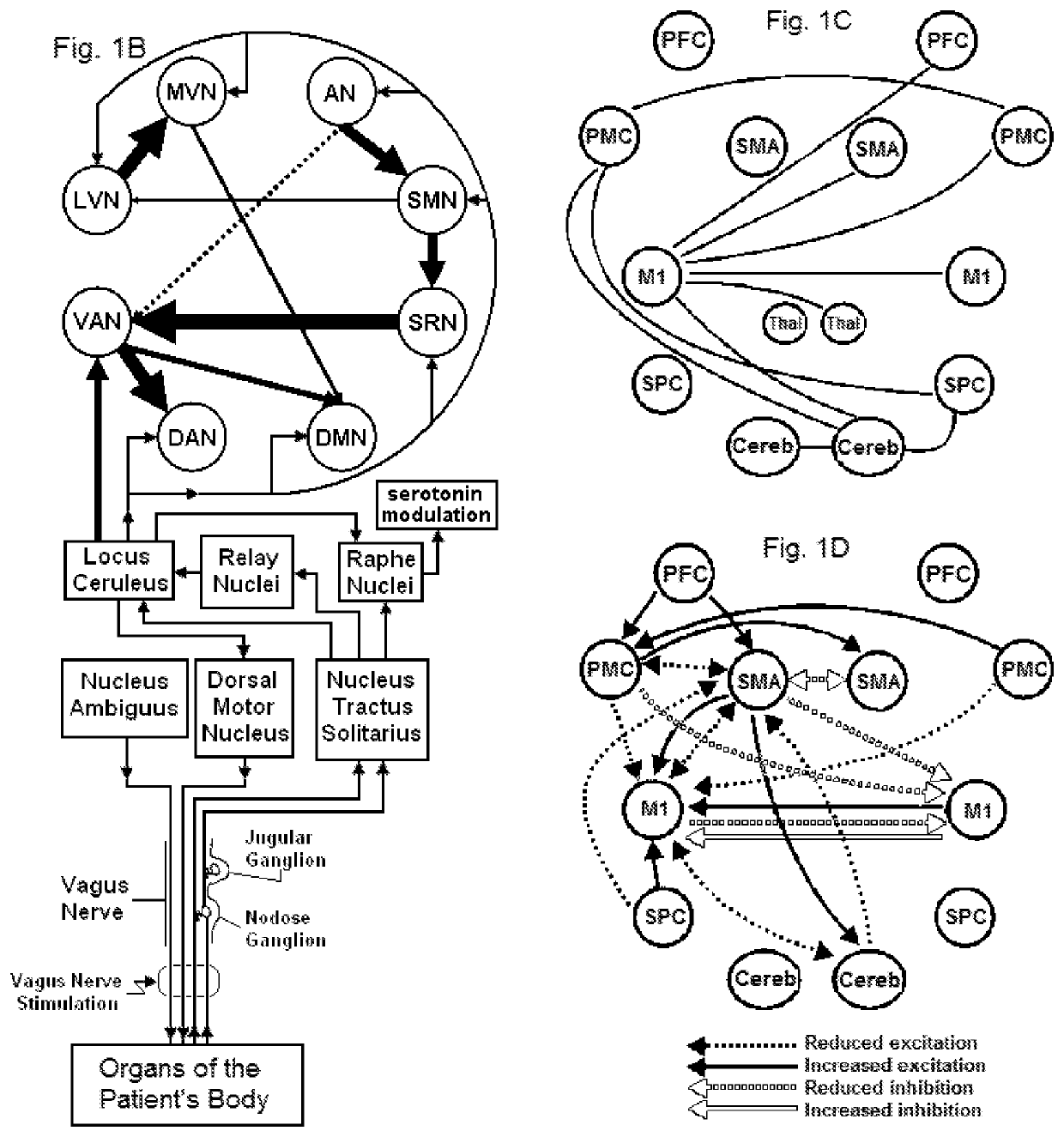
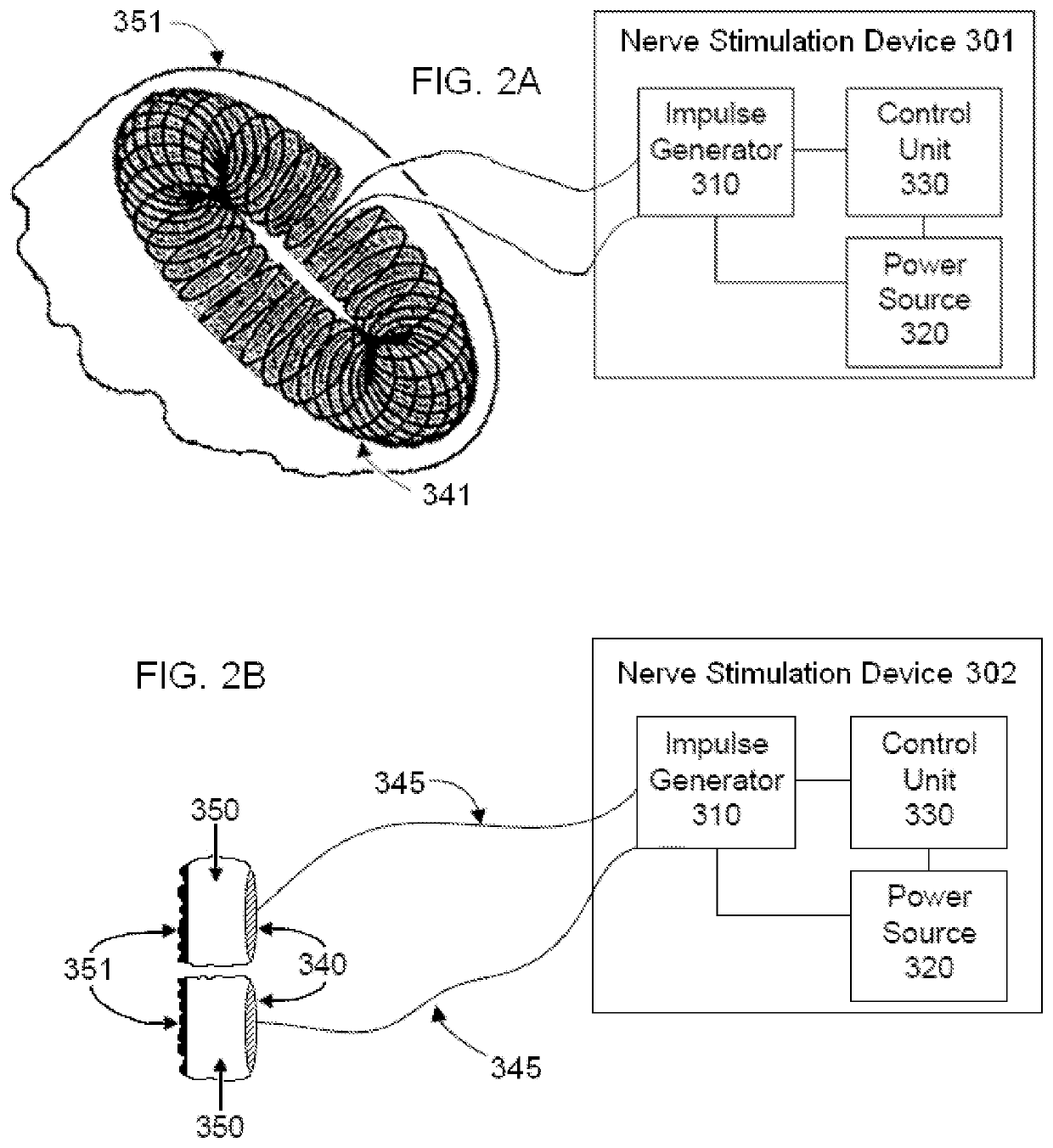
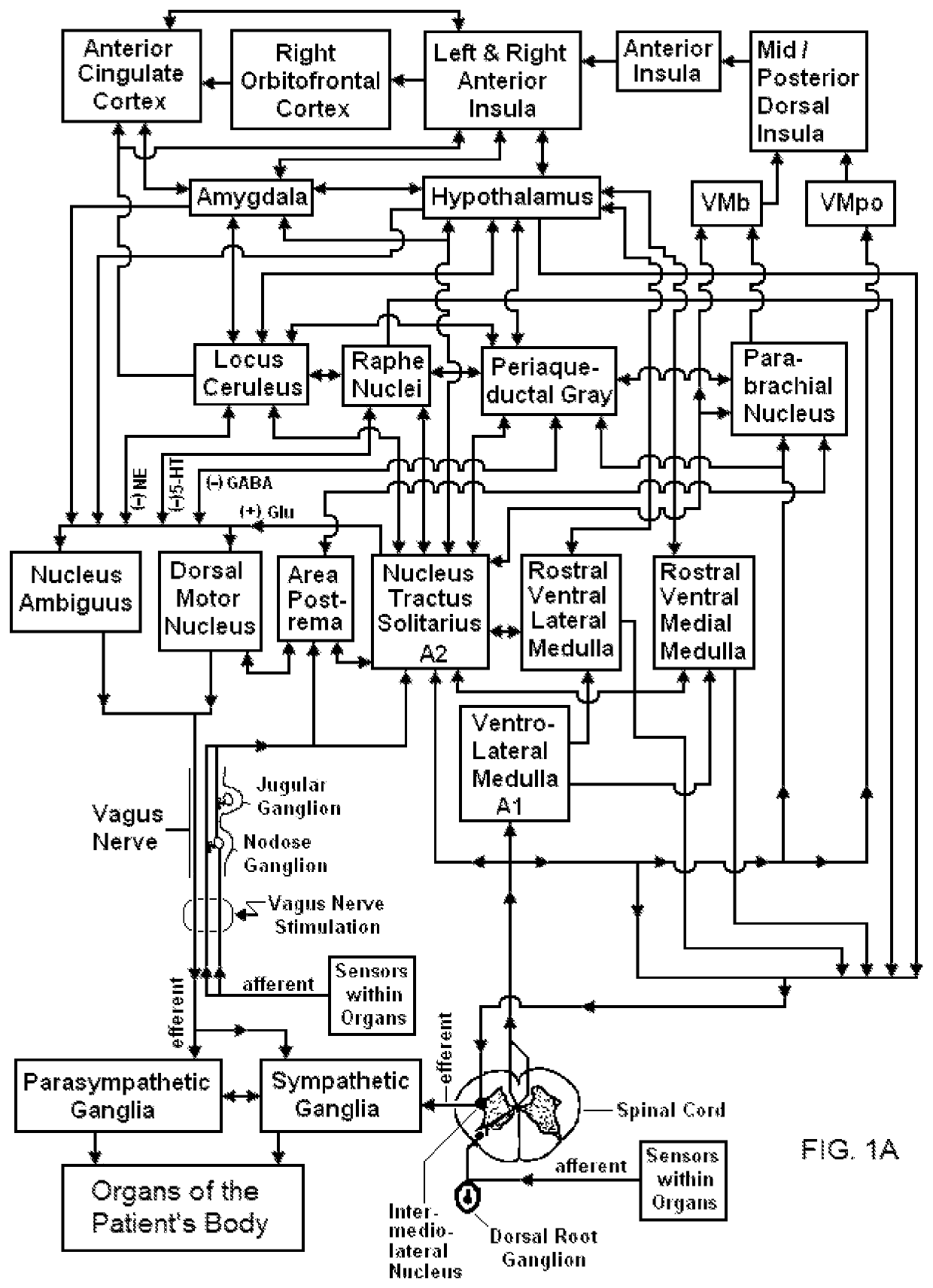
Method and system for vagal blocking and/or vagal stimulation to provide therapy for obesity and other gastrointestinal disorders
InactiveUS20050137644A1Eliminates repeated surgeryOvercomes shortcomingElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseDisease irritable bowel
Method and system to provide therapy for obesity and gastrointestinal disorders such as FGIDs, gastroparesis, gastro-esophageal reflex disease (GERD), pancreatitis and ileus comprises vagal blocking and / or vagal stimulation. Vagal blocking may be in the afferent or efferent direction, and may be with or without stimulation pulses. Blocking may be provided by one of a number of different electrical blocking techniques. Electrical signals may be provided with an external stimulator in conjunction with an implanted stimulus-receiver, or an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for temporary power source. In one embodiment, the external stimulator may comprise an optional telemetry unit. The addition of the telemetry unit to the external stimulator provides the ability to remotely interrogate and change stimulation programs over a wide area network, as well as other networking capabilities,
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
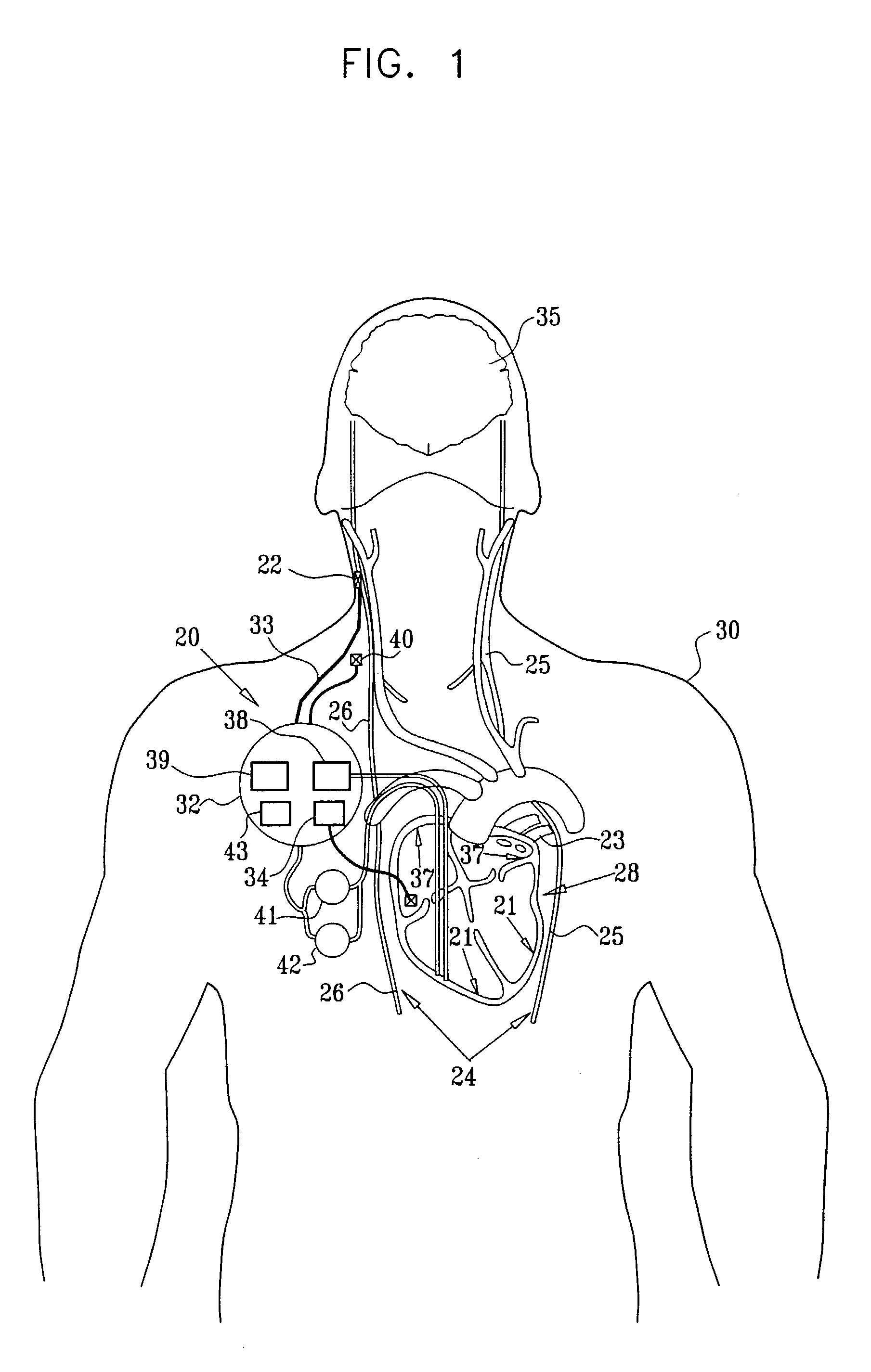
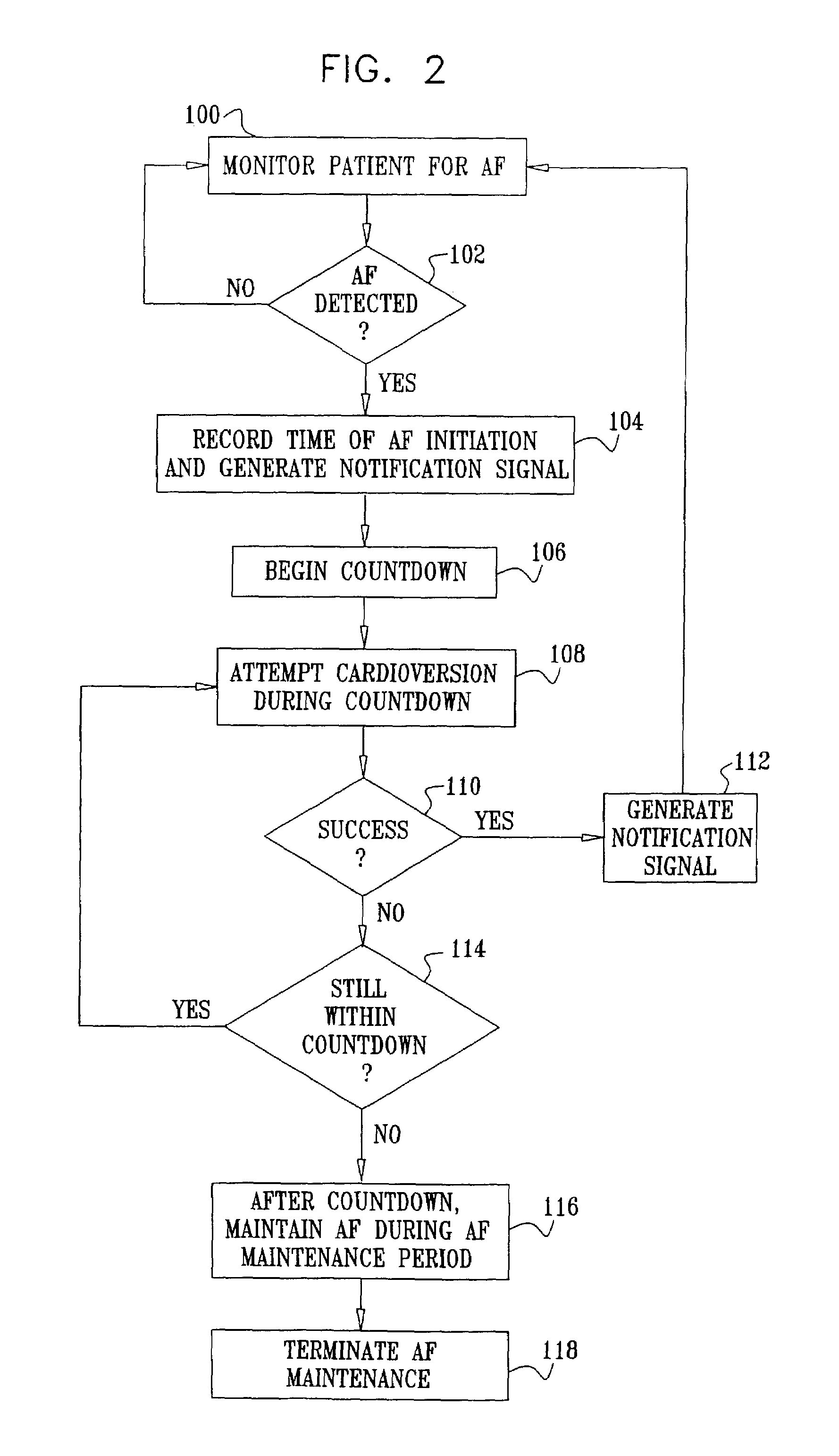
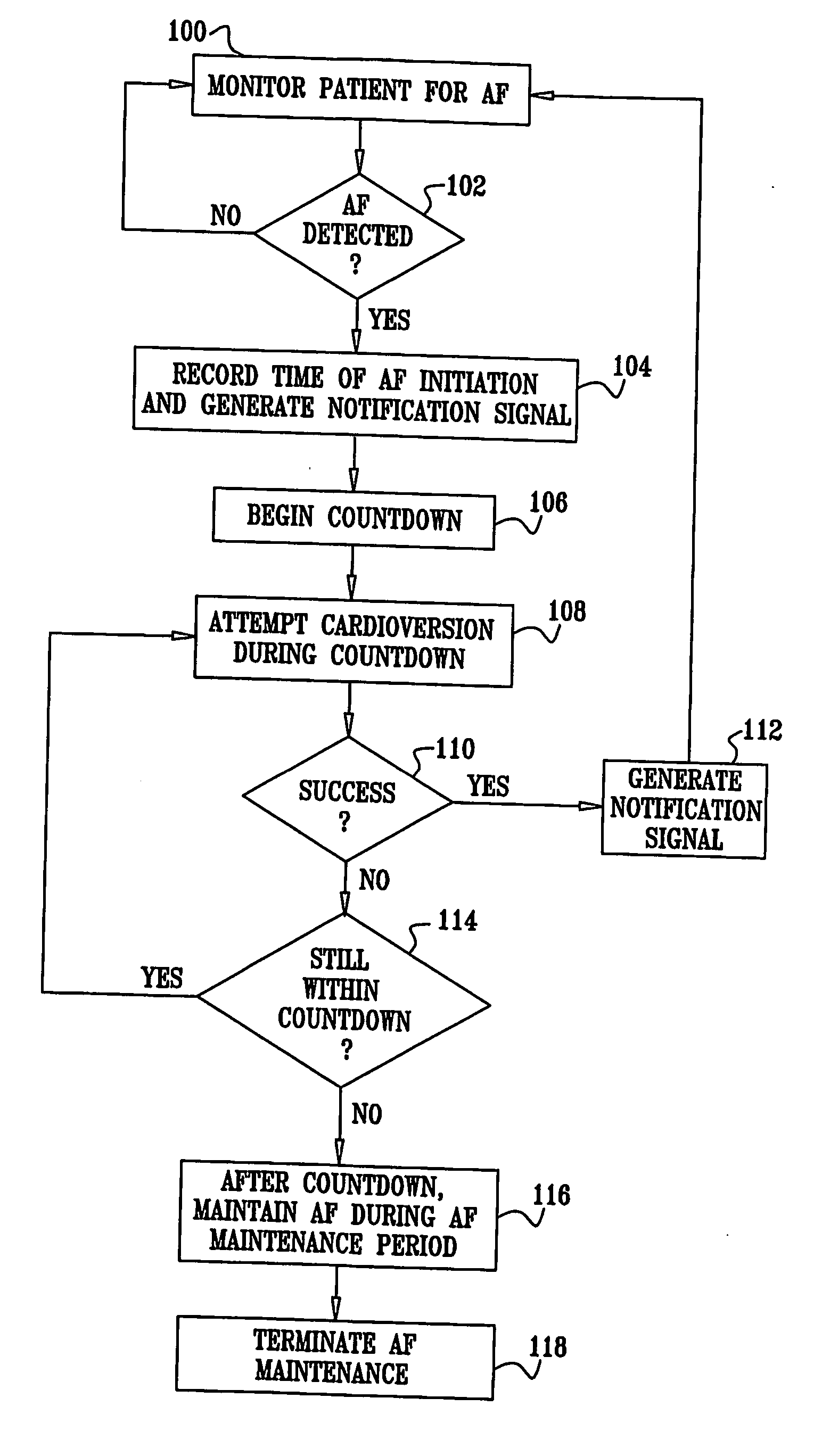
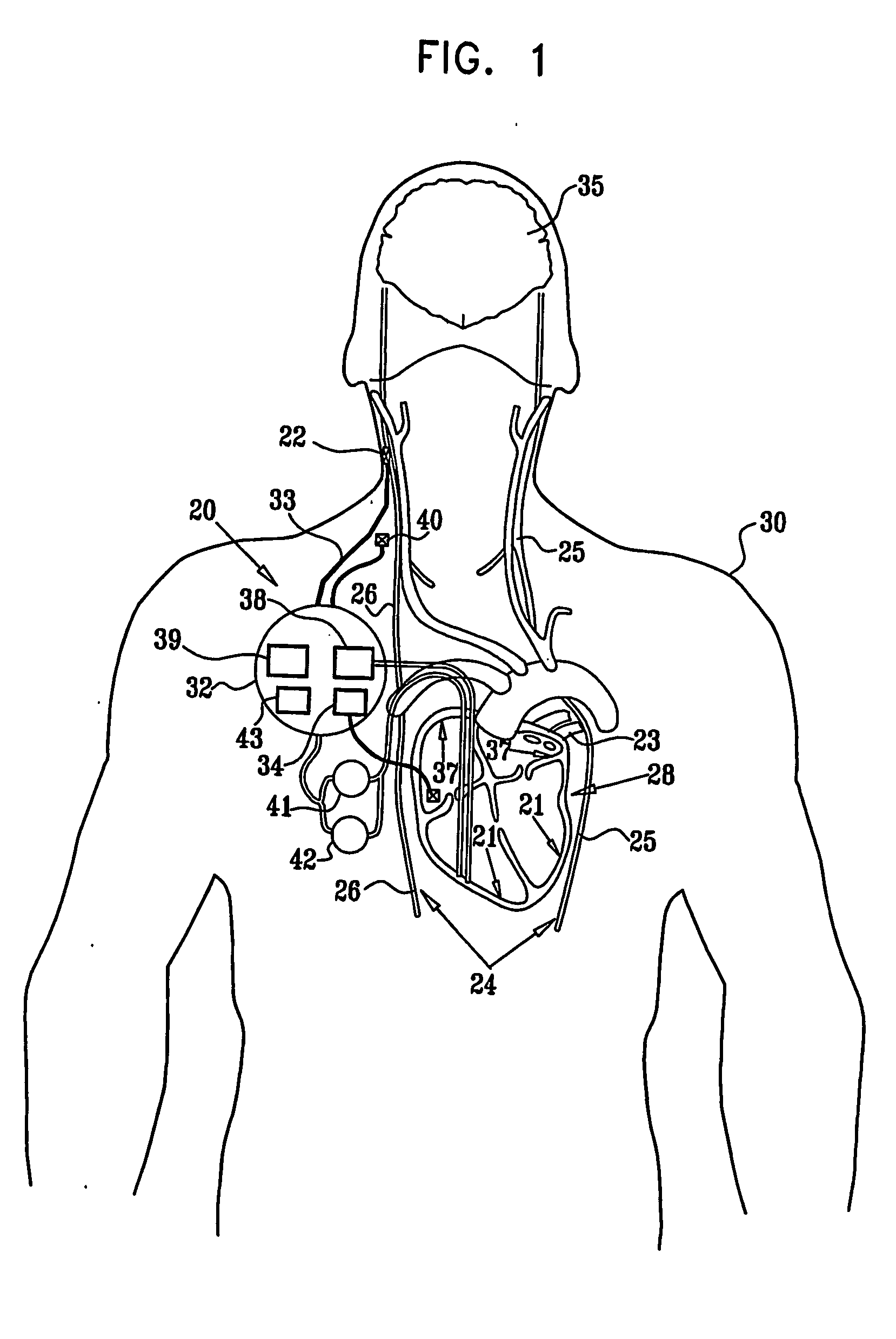
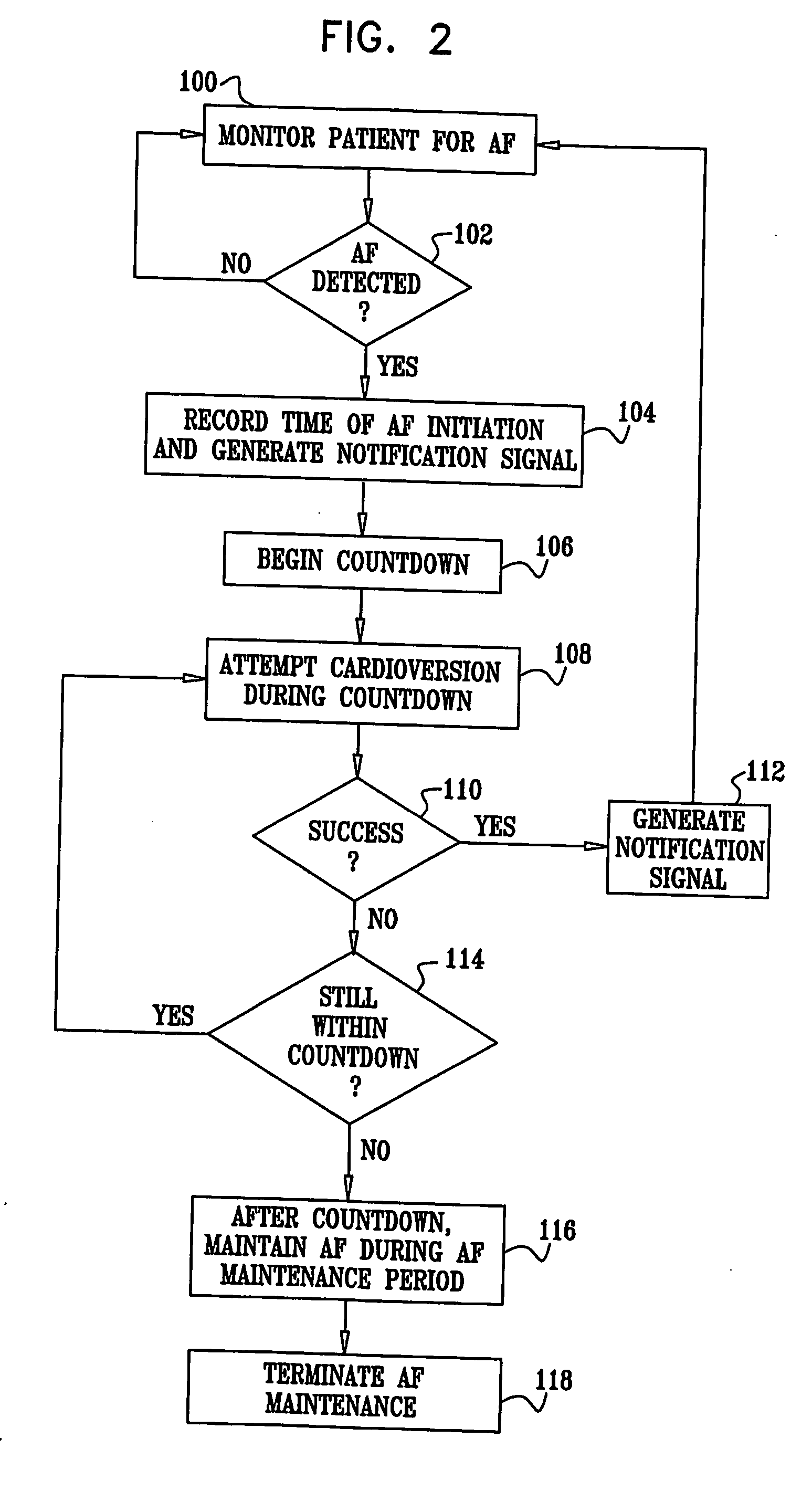
Vagal stimulation for atrial fibrillation therapy
InactiveUS7321793B2Reduce frequencyIncreased riskHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPower flowThrombus
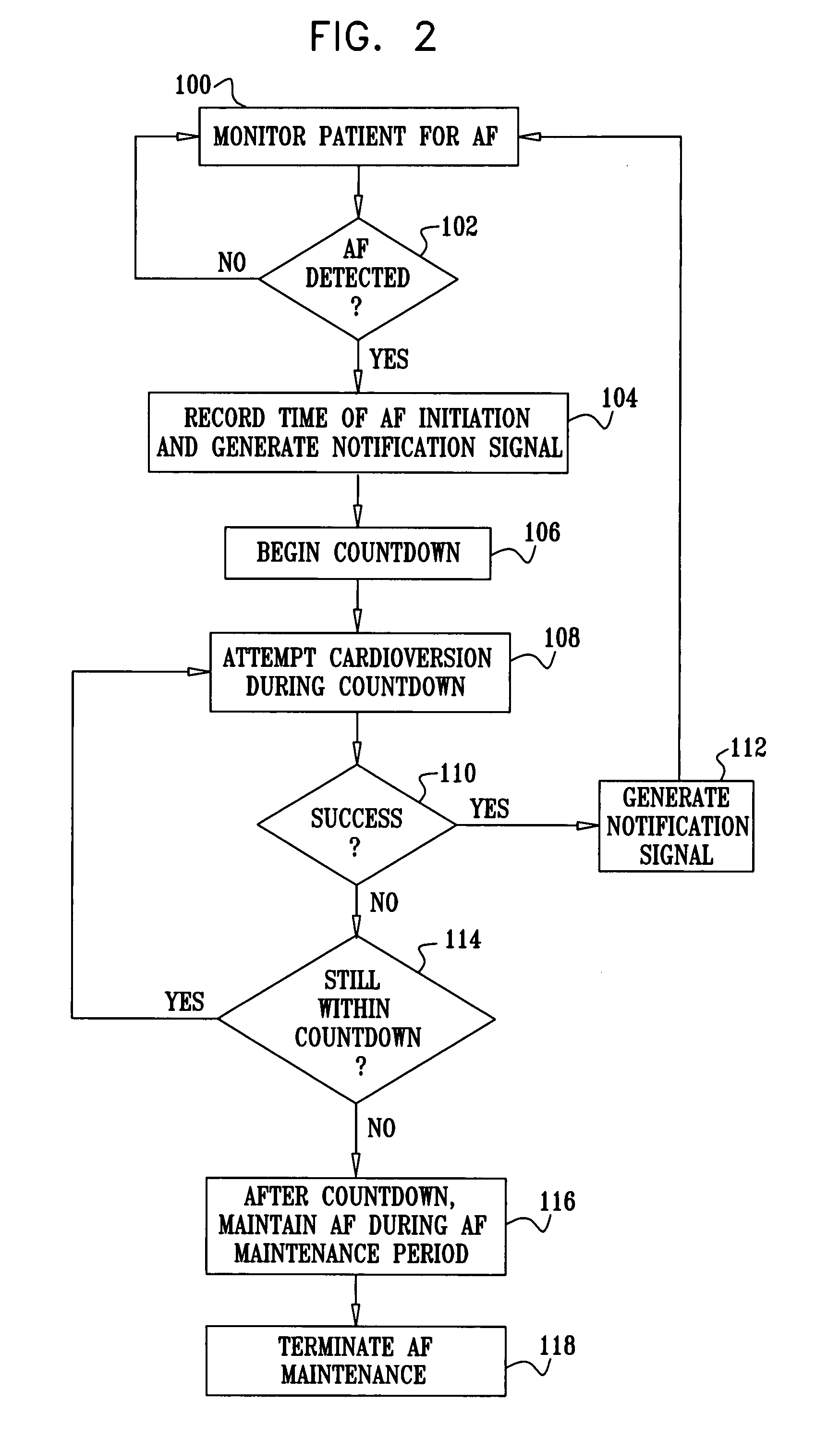
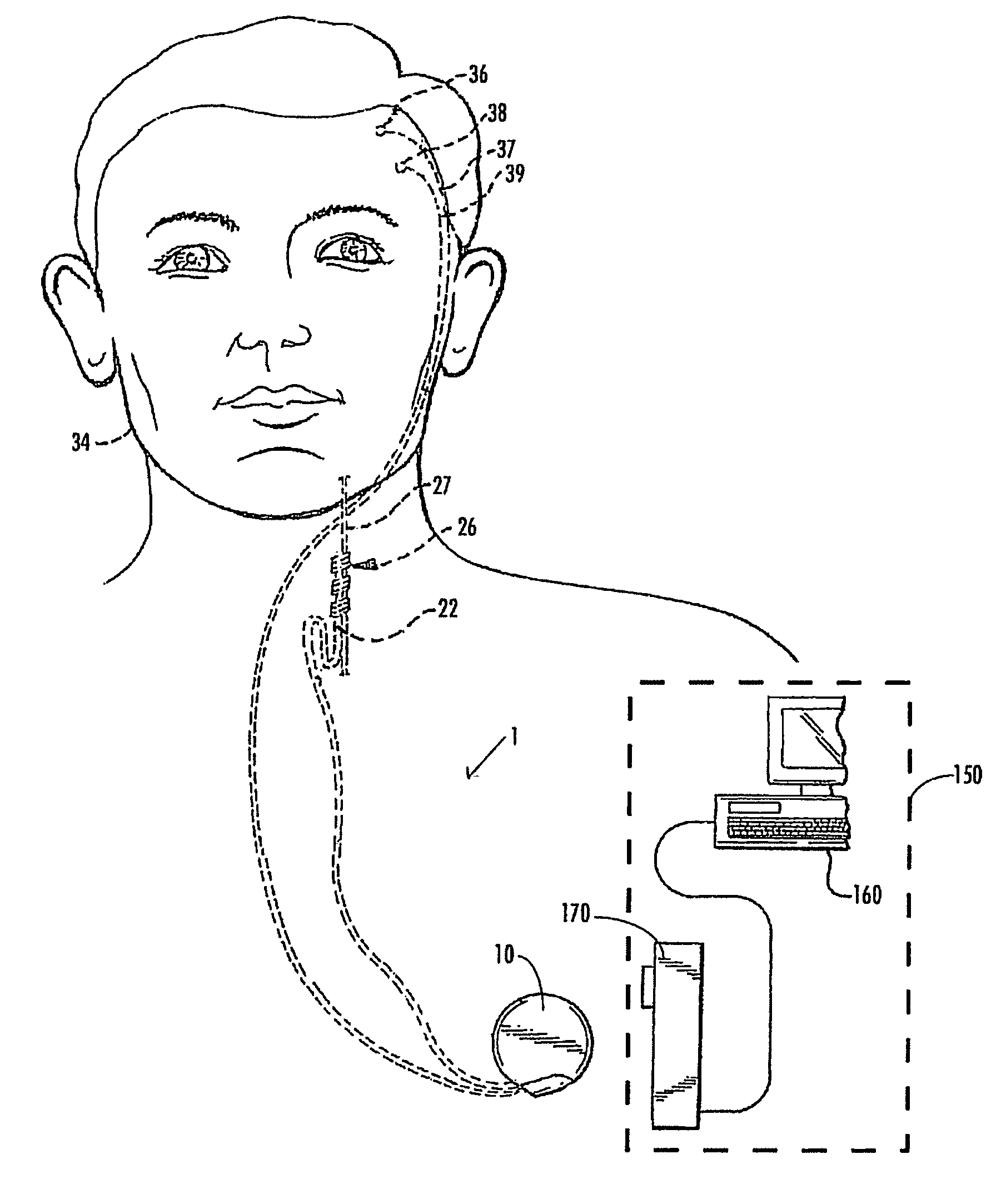
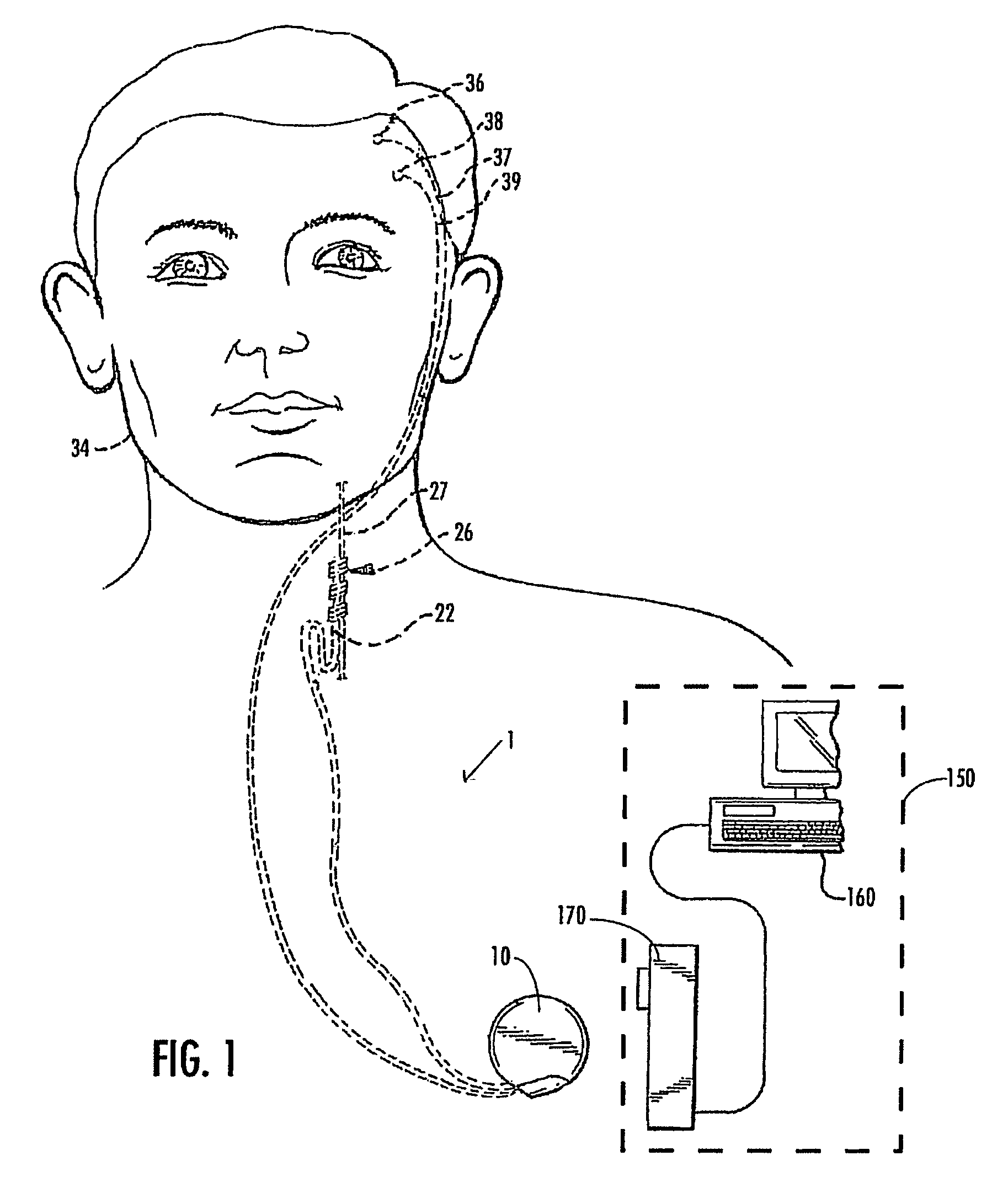
Apparatus for treating a subject suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of the subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the vagus nerve, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
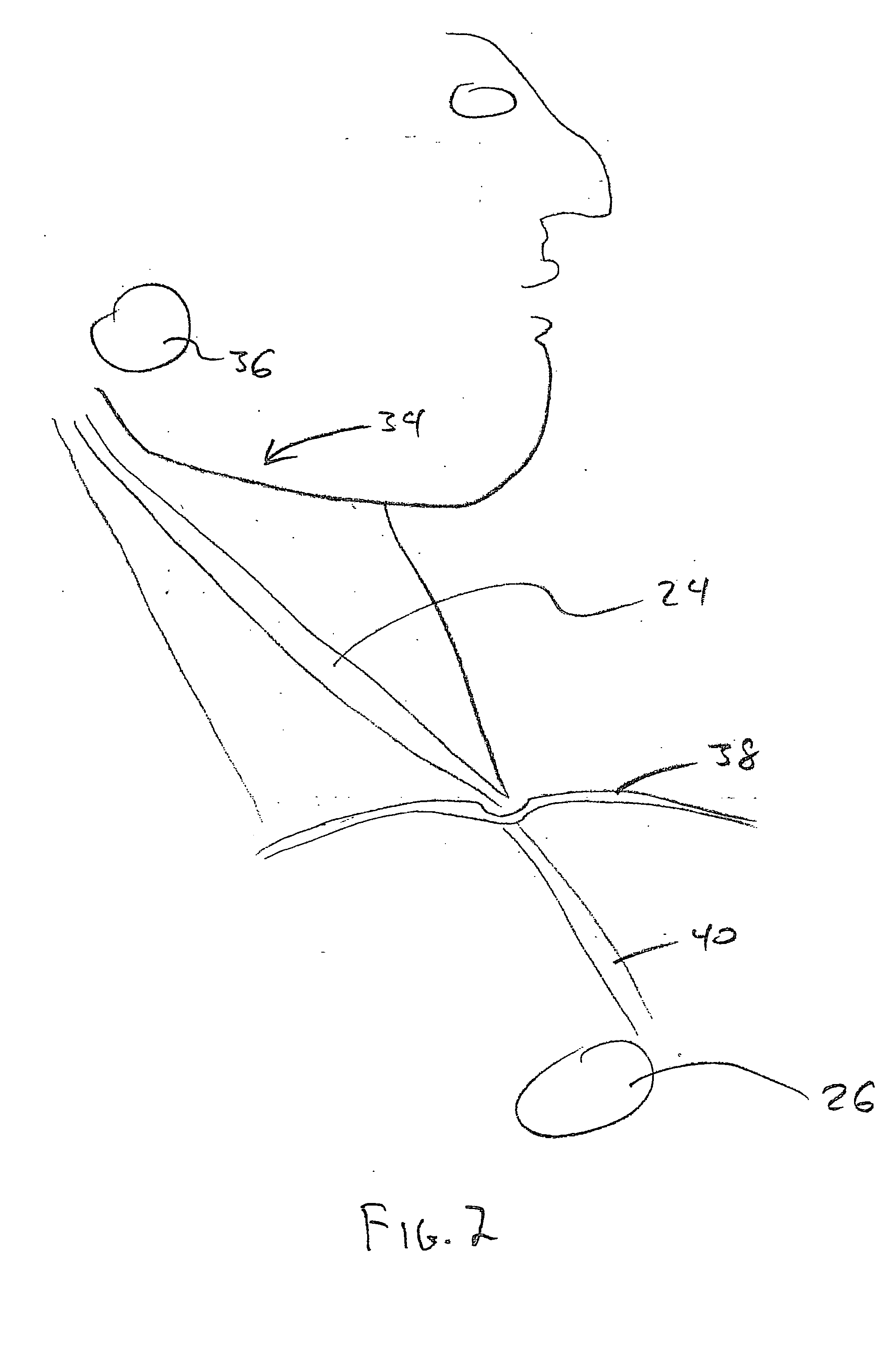
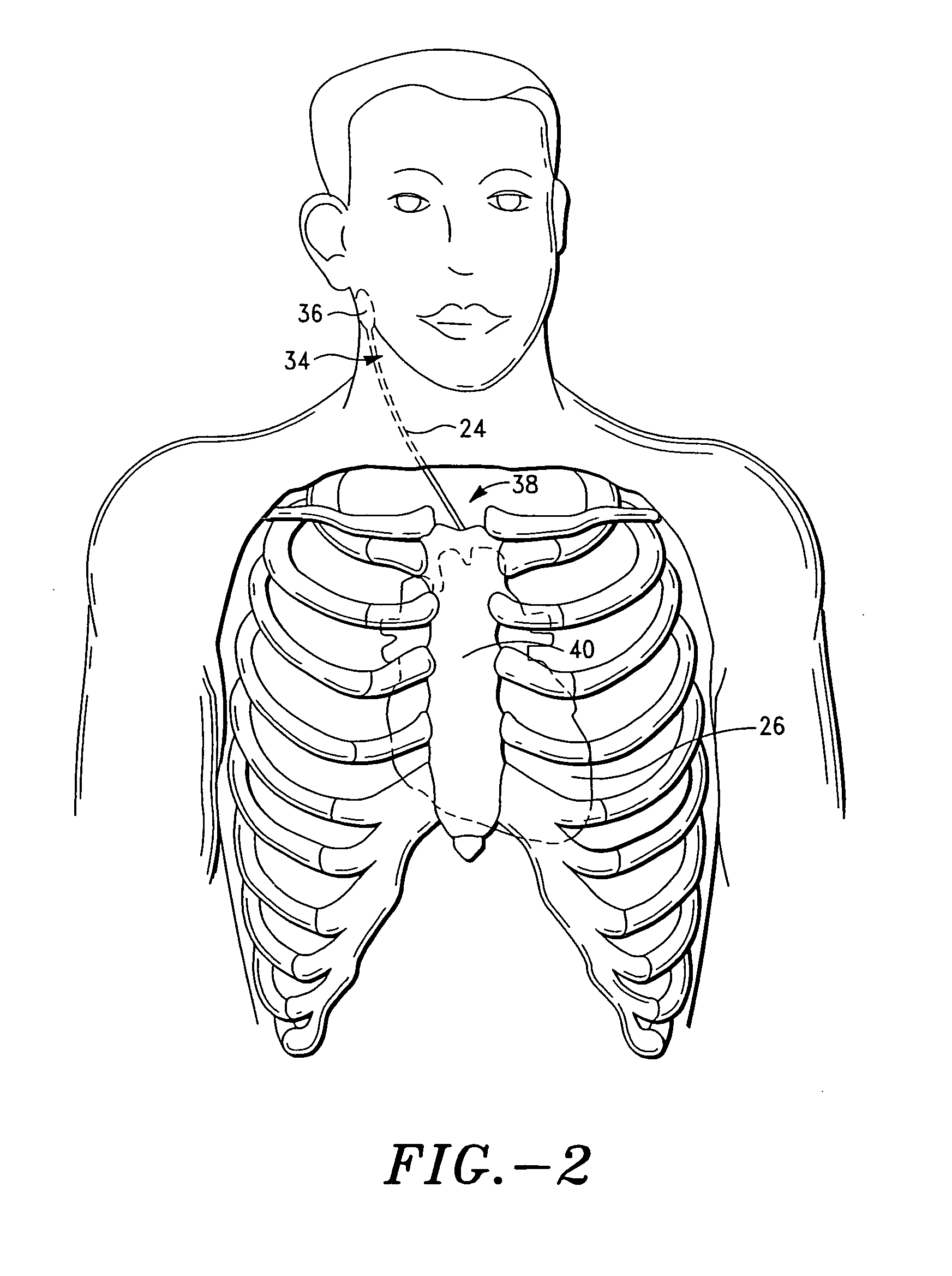
Vagal stimulation for anti-embolic therapy
InactiveUS20060271115A1Increase volumeIncrease stimulationSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsEmbolization TherapyBlood flow
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
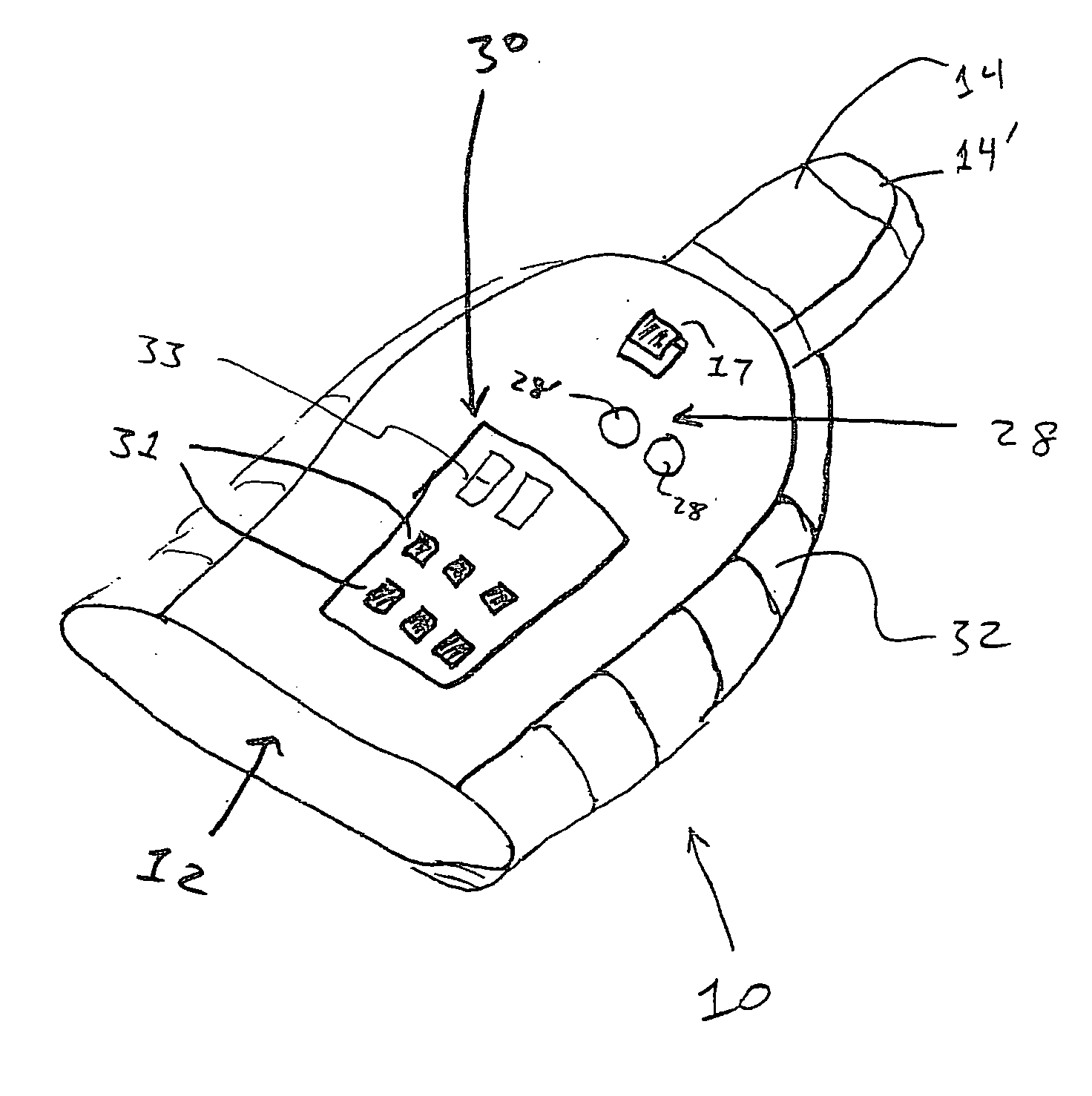
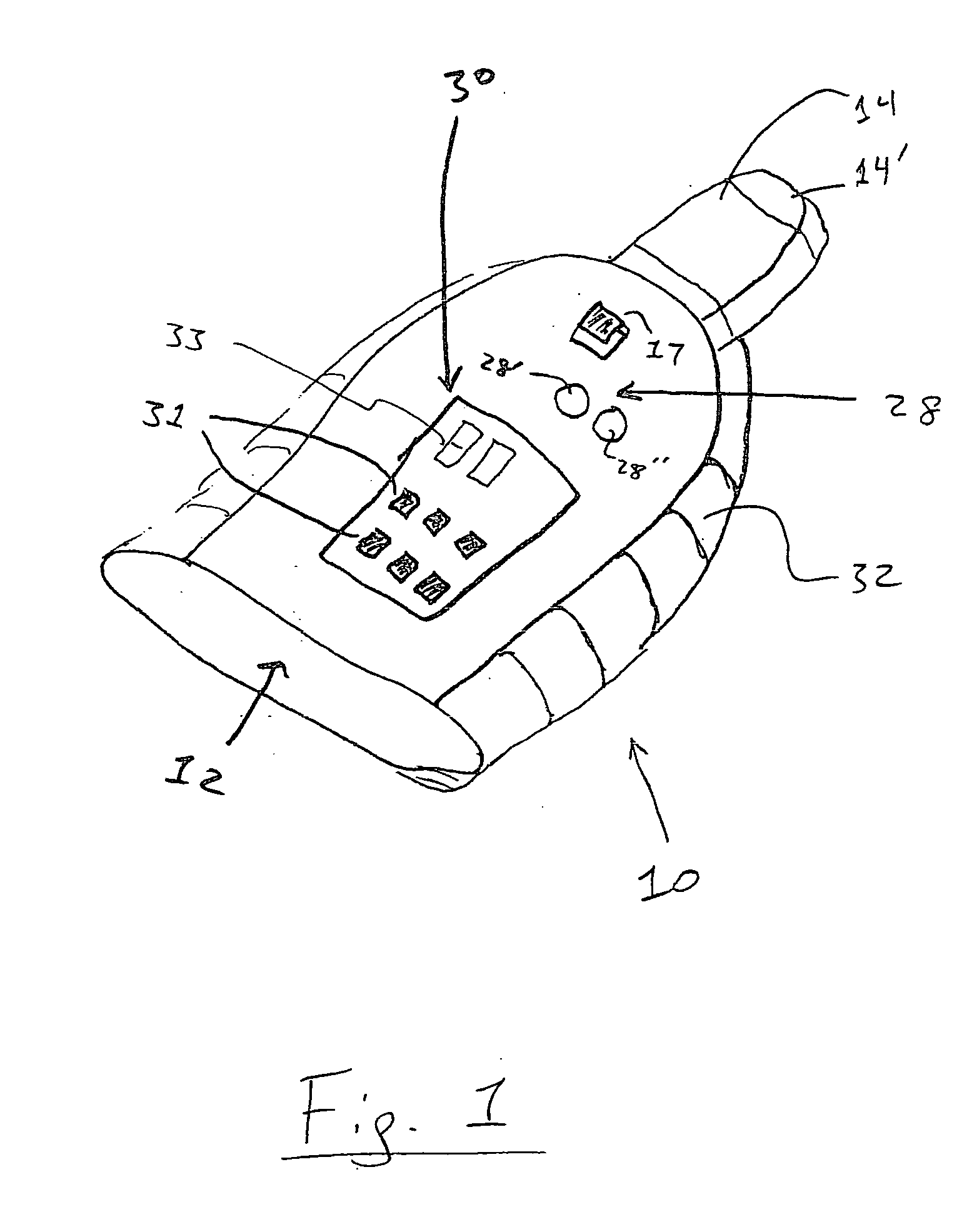
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:NEUROSIGNAL TECH
Implantable digital device for tissue stimulation
InactiveUS20080281368A1Power Loss MinimizationLower impedanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsHigh energyDigital device
An implantable vagal stimulation device with high-energy efficiency and novel data sensing is provided for use in a wide variety of applications where neural stimulation is required, including human heart rate control. The stimulation device uses low-impedance circuitry and digital waveforms to minimize energy losses, thereby requiring a relatively small battery. Front-loaded, passive filtering is employed to reduce electromagnetic noise sensitivity, leaving a clear physiological signal without degradations. This physiological signal is processed by a derivative zero transition detector (DZD), which is immune to variations in input signal dynamic range unlike traditional methods. Information that the DZD receives can be then interpreted and used along with an algorithm to execute appropriate vagal nerve stimulation.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:ORTIZ & LOPEZ PLLC
Vagal stimulation for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20080091241A1Reduce frequencyIncreased riskSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsBlood flowThrombus
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Selective neurostimulation for treating epilepsy
A method and device for treating epilepsy are disclosed which provide for electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of epilepsy. Deep brain stimulation is combined with vagus nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Some embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
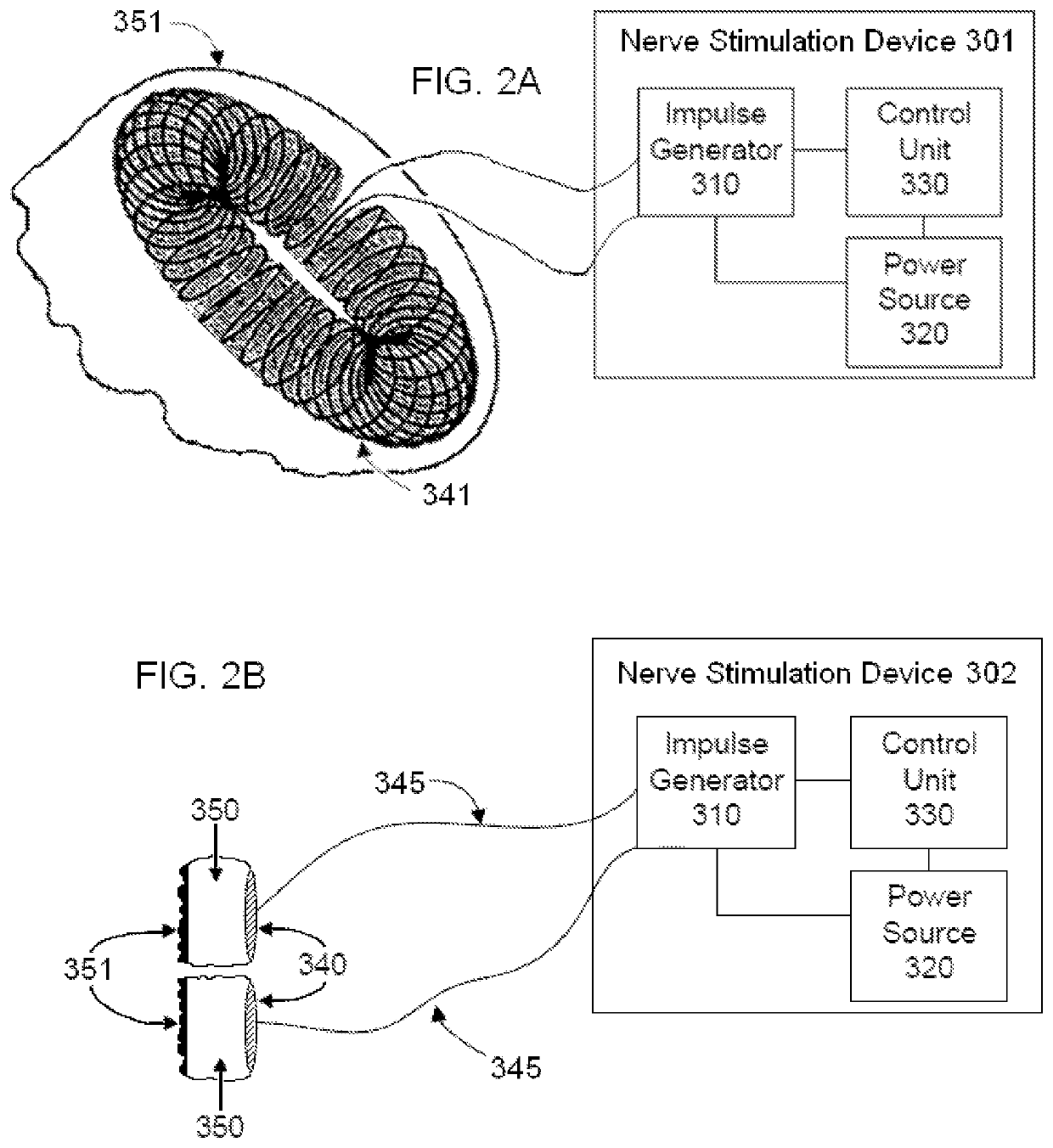
Control of vagal stimulation
ActiveUS20170203103A1Increase amplitudeLower Level RequirementsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsRR intervalT-regulatory cell
Methods and apparatuses for stimulation of the vagus nerve to treat inflammation including adjusting the stimulation based on one or more metric sensitive to patient response. The one or more metrics may include heart rate variability, level of T regulatory cells, particularly memory T regulatory cells, temperature, etc. Stimulation may be provided through an implantable microstimulator.
Owner:SETPOINT MEDICAL CORP
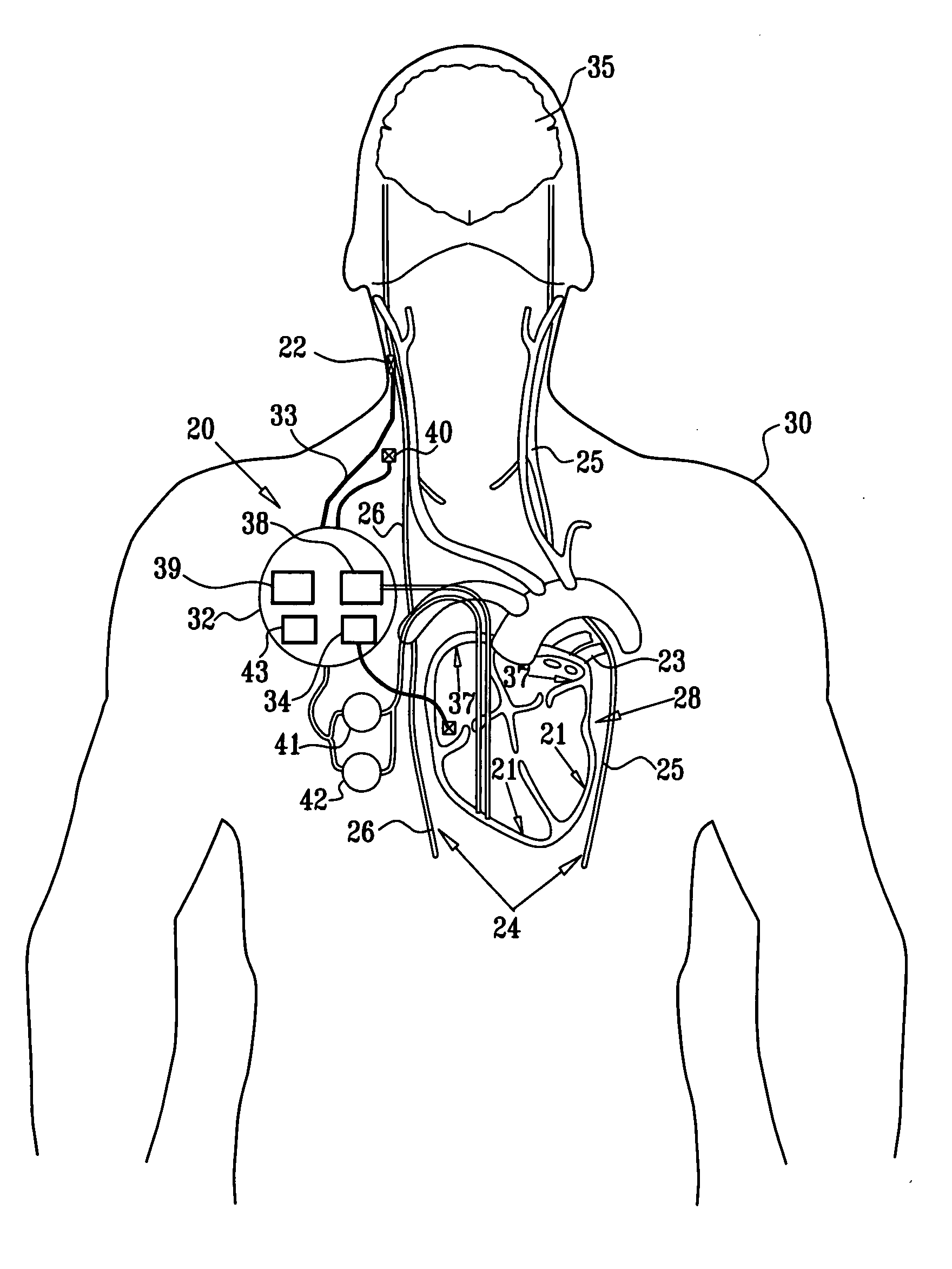
Adaptive cardiac resyncronization therapy and vagal stimulation system
An adaptive feed-back controlled system for regulating a physiological function of a heart in which a hemodynamic sensor continuously monitors the physiological performance of the heart. Three implanted electrodes sense and pace the right atrial, right ventricle and left ventricle. A learning neural network module receives and processes information for the electrodes (18) and sensors (22), and is controlled by a deterministic module for limiting said learning module. A pulse generator (16), is also controlled by the deterministic module, and stimulates both the heart and the vagus (20).
Owner:ROM RAMI
System and method of using vagal stimulation to assess autonomic tone and risk of sudden cardiac death in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS7869870B1Eliminate riskEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsVentricular contractionPremature ventricular complex
A method and apparatus for using vagal stimulation to detect autonomic tone and assess a patient's risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) are presented. The method involves stimulating the patient's vagus nerve in order to induce a drop in arterial blood pressure, which simulates the patient's cardiovascular response to a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). Sinus rhythm data just before and immediately following the stimulation is recorded and analyzed for a degree of heart rate turbulence (HRT) in order to detect abnormalities in autonomic tone and assess the risk of SCD. In an embodiment, the method is implemented in an implantable cardiac device (ICD), which can deliver arrhythmia prevention therapy based on the risk of SCD. The method can assess the patient's vagal activity on-demand by measuring HRT without relying on naturally occurring PVCs and eliminates the risk of causing arrhythmia associated with artificially inducing PVCs in order to measure HRT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
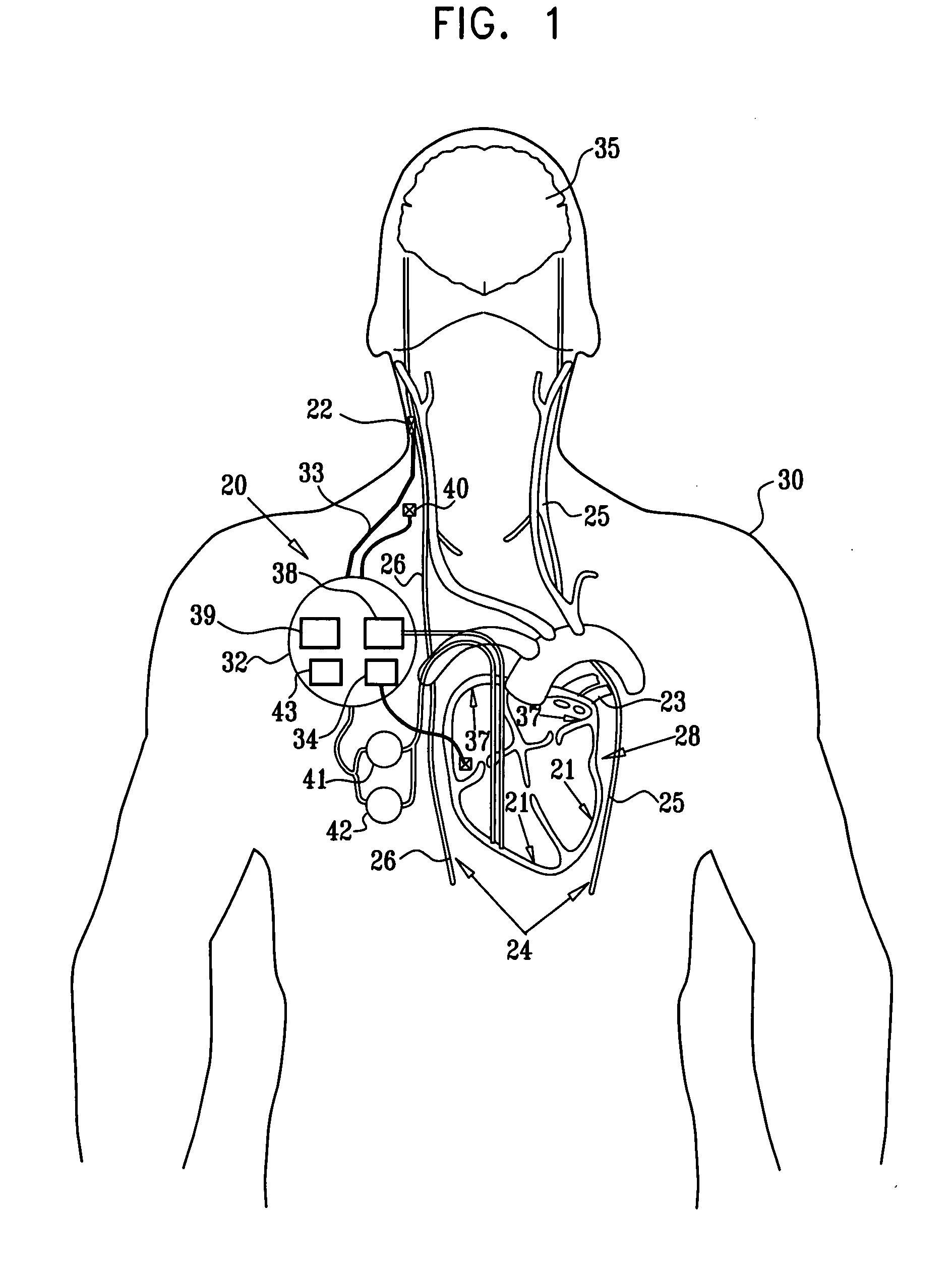
Adaptive Cardiac Resyncronization Therapy and Vagal Stimulation System
An adaptive feed-back controlled system for regulating a physiological function of a heart in which a hemodynamic sensor continuously monitors the physiological performance of the heart. Three implanted electrodes sense and pace the right atrial, right ventricle and left ventricle. A learning neural network module receives and processes information for the electrodes (18) and sensors (22), and is controlled by a deterministic module for limiting said learning module. A pulse generator (16), is also controlled by the deterministic module, and stimulates both the heart and the vagus (20).
Owner:ROM RAMI
Heart rate variability analysis method, apparatus and application
The invention relates to a heart rate variability (HRV) analysis method, apparatus and application. A low-cost, portable and wearable signal acquisition device is employed to obtain electrocardiography (ECG) signals of an epileptic patient within 24 hours before operation, the time domain, the frequency domain and the non-linear index of long-range and short-range ECG are calculated by means of a stylized HRV analysis method, based on the characteristic parameter representing the modulating effect degree of the vagus nerve to the heart rate, i.e., the vagus nerve activity, the curative effect of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) operation to medically intractable epileptic patients is predicted accurately and efficiently, unnecessary appropriation expenditure is avoided, the optimal opportunity for treatment is prevented from being delayed, by means the HRV characteristic parameter of ECG, VNS operation indication patients are selected definitely, and the curative effect of the VNS therapy is improved on the whole.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method of vagal stimulation to treat patients suffering from congestive heart failure
InactiveUS8457743B2Shorten the progressReduce failureElectrotherapyInertial sensorsCardiac cycleClosed loop
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
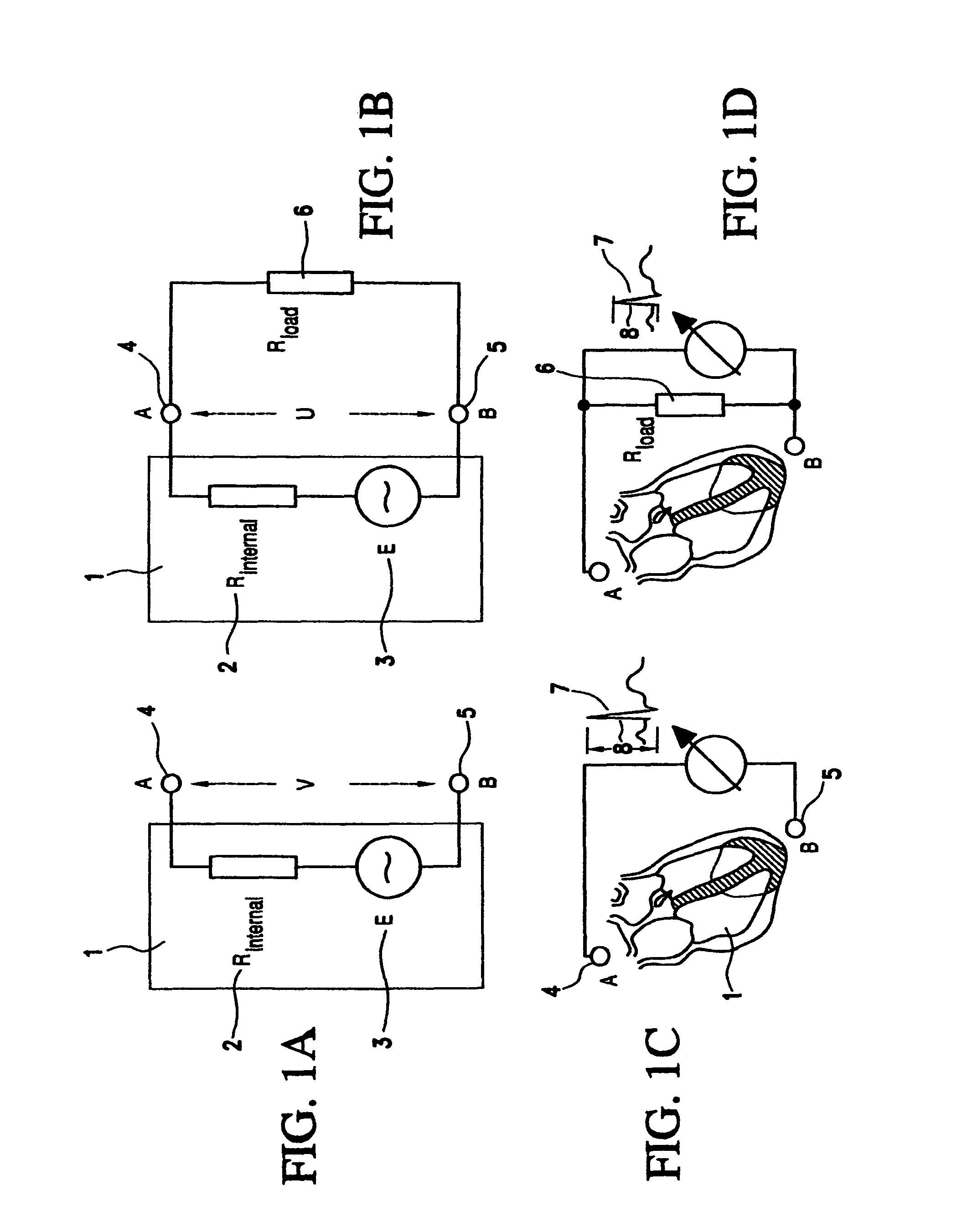
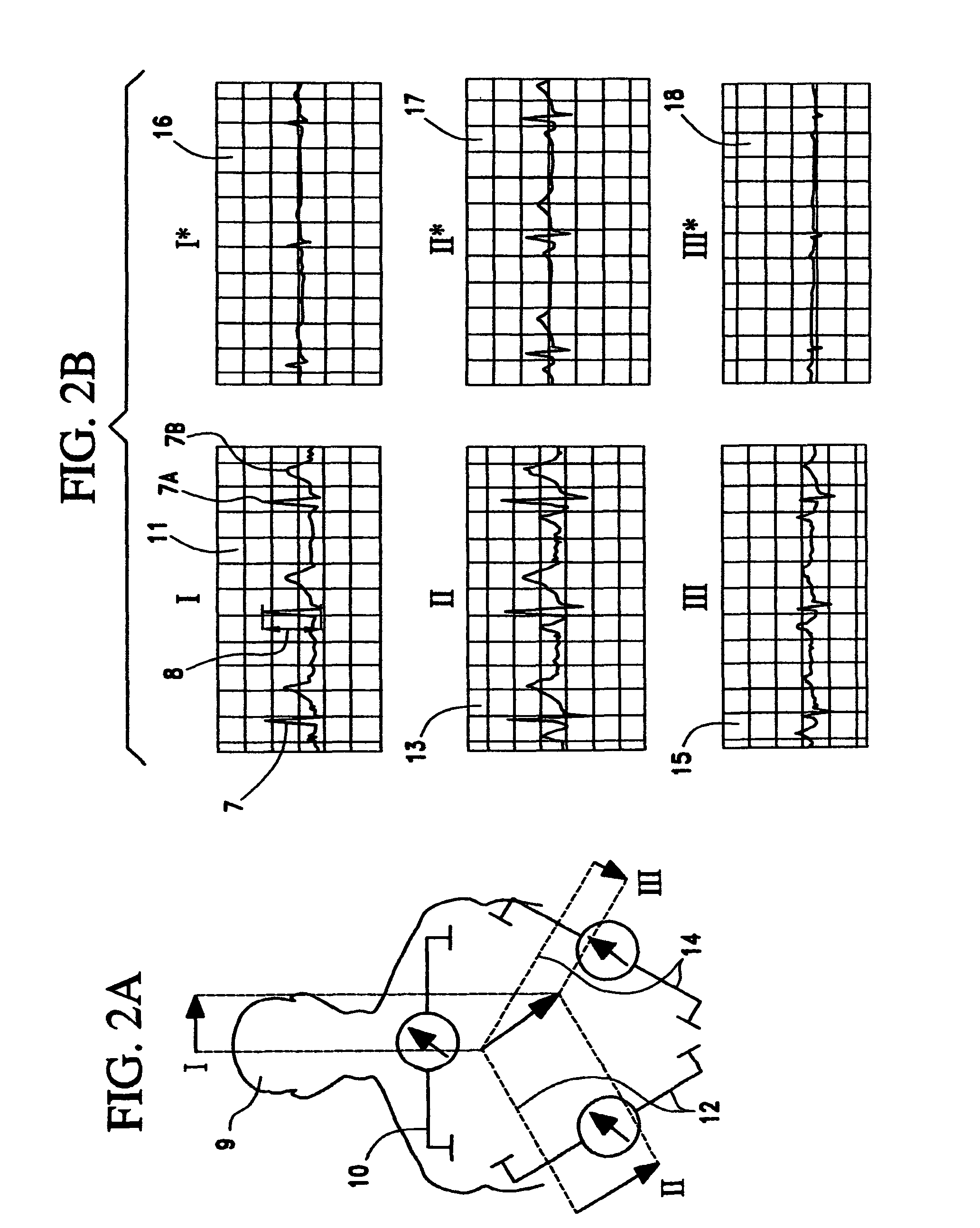
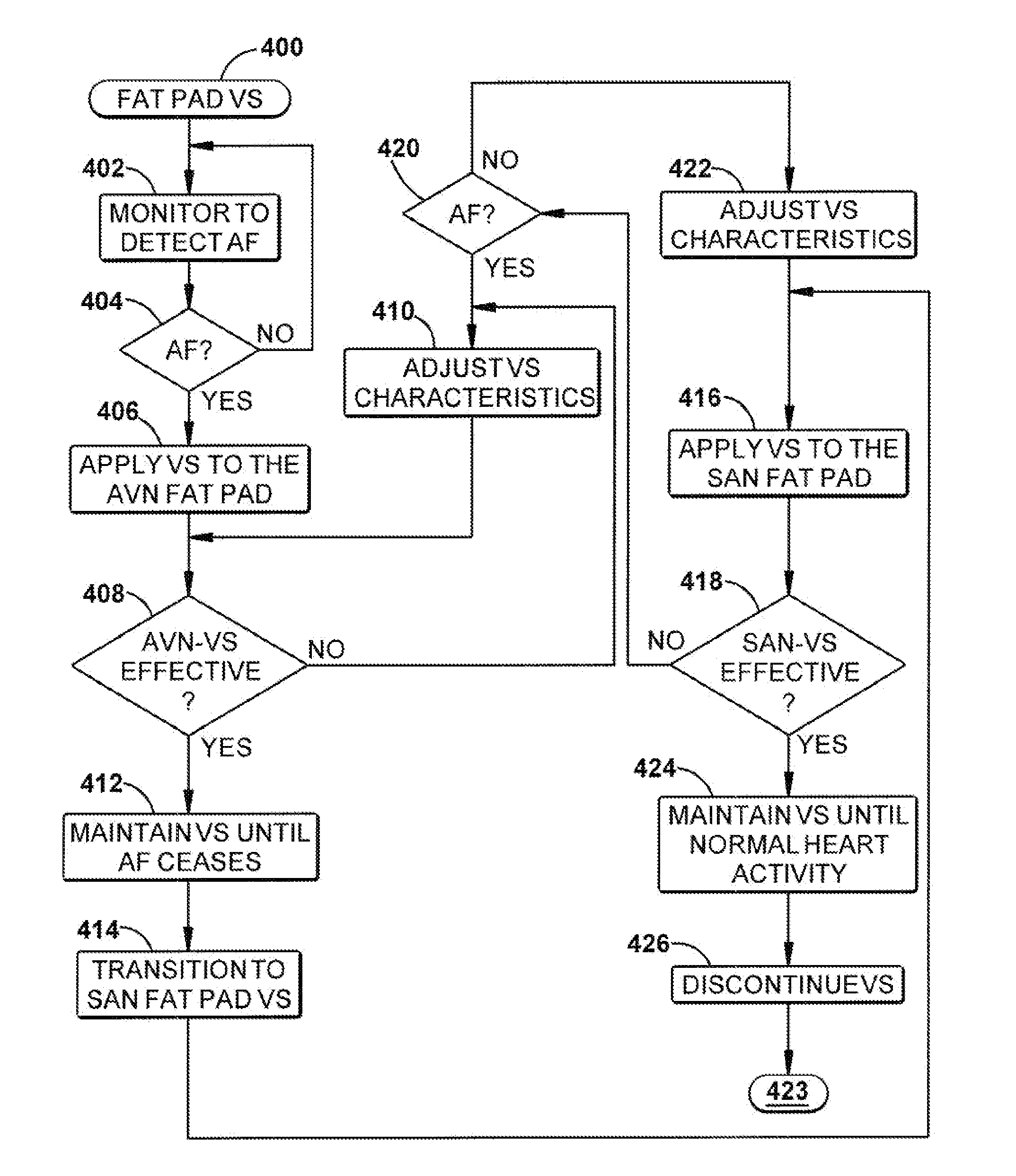
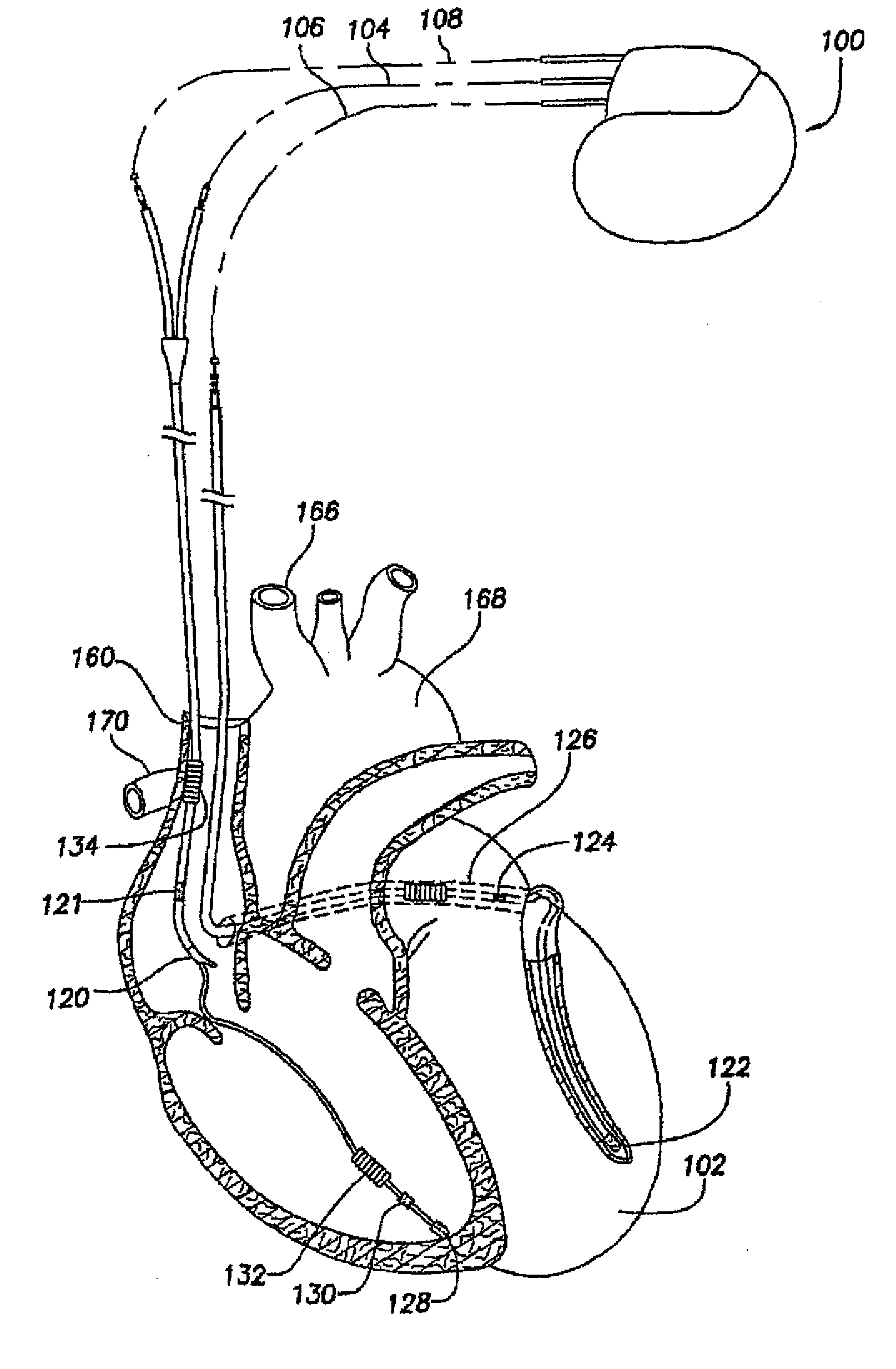
Control of cardiac arrhythmia by vagal stimulation at the atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodal fat pads of the heart
Vagal stimulation applied to the atrioventricular nodal (“AVN”) fat pad and the sinoatrial nodal (“SAN”) fat pad via epicardial leads is useful for controlling cardiac arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation (‘AF”). In the case of AF, for example, vagal stimulation may be applied initially to the AVN fat pad to reduce ventricular rate, and vagal stimulation may be applied to the SAN fat pad after restoration of sinus rhythm to control atrial rate. The technique is applicable to control acute AF and chronic AF. The vagal stimulation may be optimized for exciting ganglia in the fat pads to produce dromotropic and chronotropic effects in the atrioventricular node and the sinoatrial node, respectively. In addition, the SAN fat lead can also be used to pace the atrium in case of sinus bradycardia.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Vagal stimulation during atrial tachyarrhythmia to facilitate cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS20130138173A1Increased and variable ventricular rateMore intrinsic ventricular depolarizationsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrial cavity
The disclosure describes techniques for delivering vagal stimulation to decrease the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation. Decreasing the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia may facilitate increased ventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and may also reduce the likelihood of inappropriately detecting a ventricular tachyarrhythmia during the atrial tachyarrhythmia. Furthermore, the vagal stimulation may augment vagal tone, which may facilitate long term left ventricular reverse remodeling and decrease atrial and ventricular arrhythmic burden in heart failure patients. An example system that delivers CRT comprises a processor that detects an atrial tachyarrhythmia in one or more atria of the heart, and monitors at least one of a ventricular rate or degree of ventricular pacing subsequent to the detected atrial arrhythmia. The processor controls a stimulation generator to deliver vagal stimulation based on the least one of a ventricular rate or degree of ventricular pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cervical vagal stimulation induced weight loss
Apparatus and methods for treating obesity using chronic cervical vagal nerve stimulation (cVNS) of the left vagus trunk are disclosed. Four men and ten women, average age 46 years (SD±10) were treated with output current typically 0.75 mA, pulse frequency 30 Hz and width 250 or 500 μs, and duty cycle of 30 s power per five minutes. Mean intake weight was 91 kg (SD±27, range 46 to 137 kg) with body mass index (BMI) 43 kg / m2 (SD±5, range 18 to 49 kg / mn2). After 6-12 months, obese patients had marked weight loss while normal weights were maintained. Decrease in BMI was consistently proportional to initial BMI. Average weight loss at one year was 7 kg (SD±3, range −6 to +24) with mean drop in BMI of 2 kg / m2 (SD±3, range −2 to +8)k. All patients denied any major dieting or exercise.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
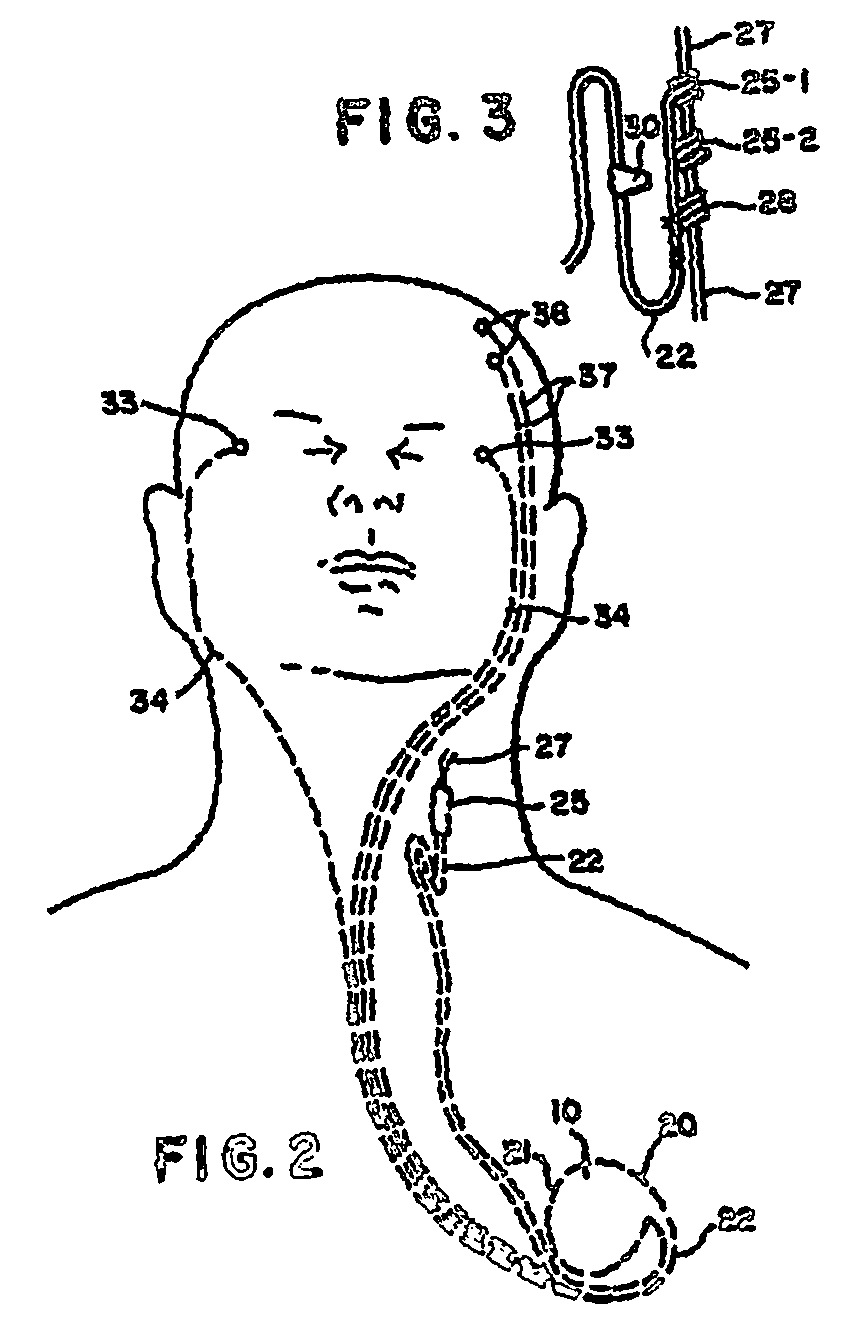
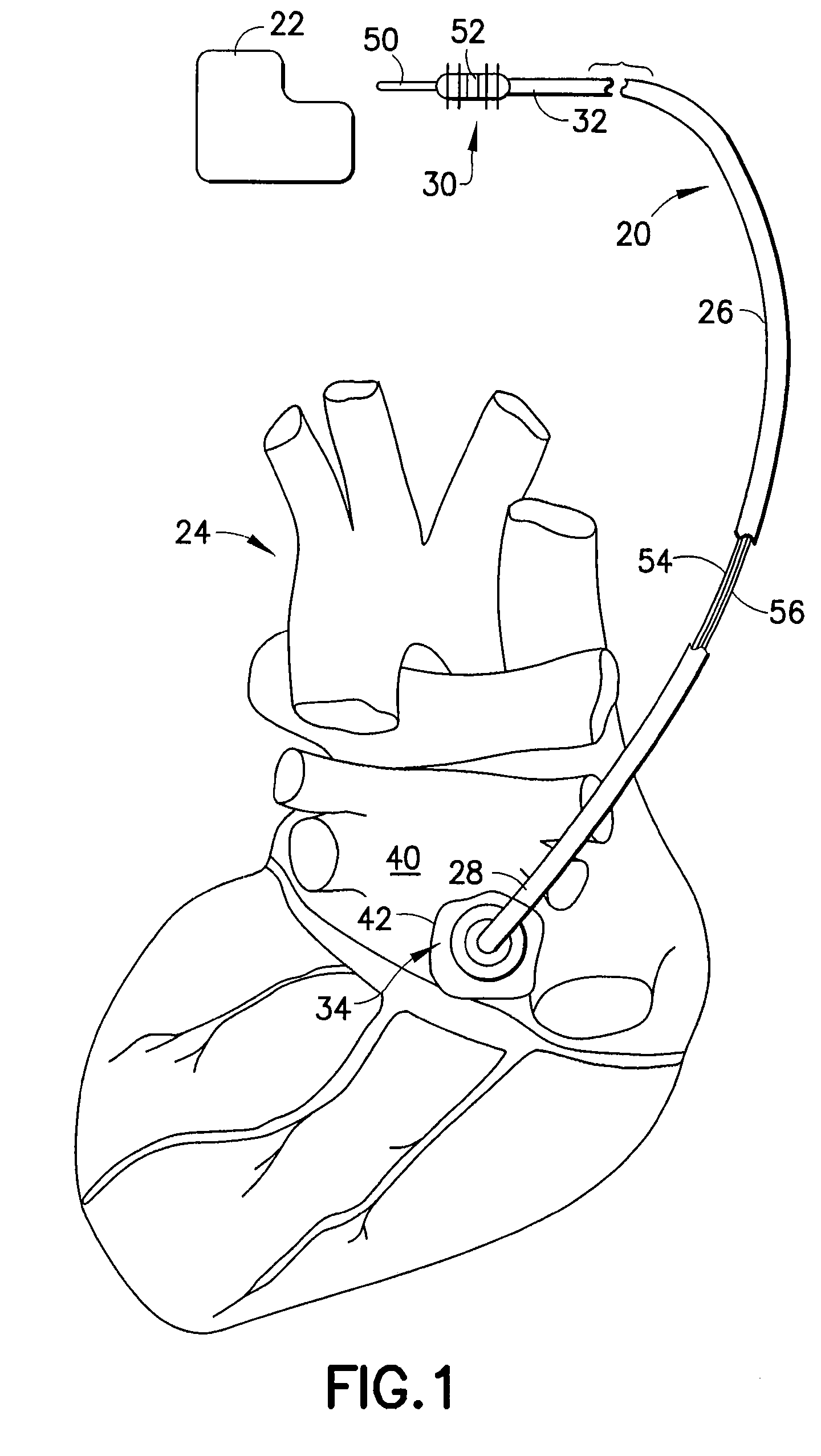
Lead for AV nodal vagal stimulation through an epicardial fat pad
InactiveUS7783366B1Increase surface areaIncrease contactEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesNODALElectrical conductor
A medical electrical lead for conducting electrical signals between an electrical stimulator and a heart site includes a lead body extending from a distal non-conductive disk member to a proximal connector for attachment to the stimulator, first and second spaced electrodes protruding from the disk member for puncturing engagement with the epicardial surface of the heart in the region of an AVN fat pad containing ganglia which extend to the AV node providing an electrical connection between the atrium and the ventricle, a first conductor extending from the first electrode to a first terminal of the connector, and a second conductor extending from the second electrode to a second terminal of the connector such that electrical current from the electrical stimulator is caused to flow through the ganglia between the first and second electrodes to stimulate the AV node to control ventricular rate in the presence of atrial fibrillation.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
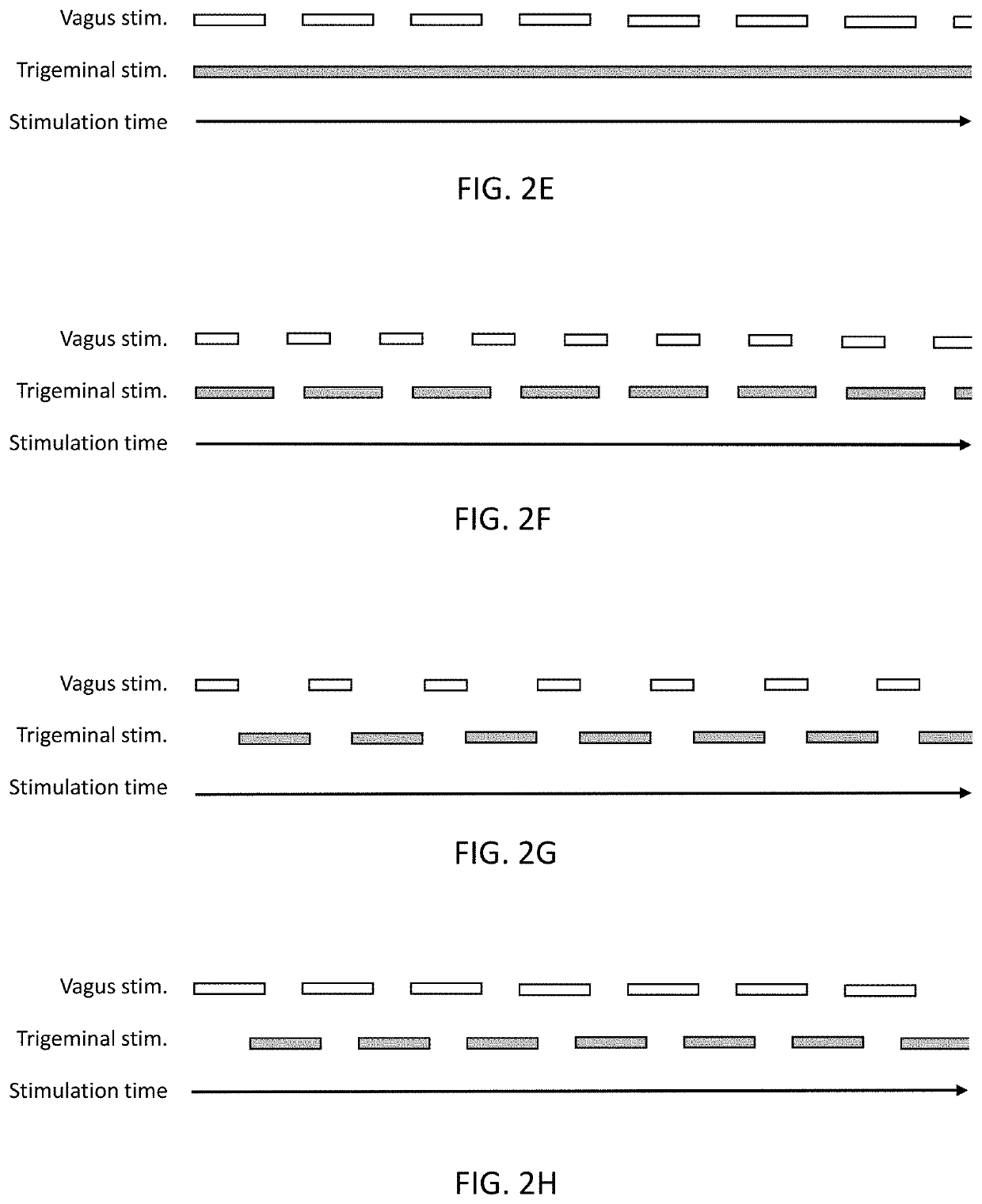
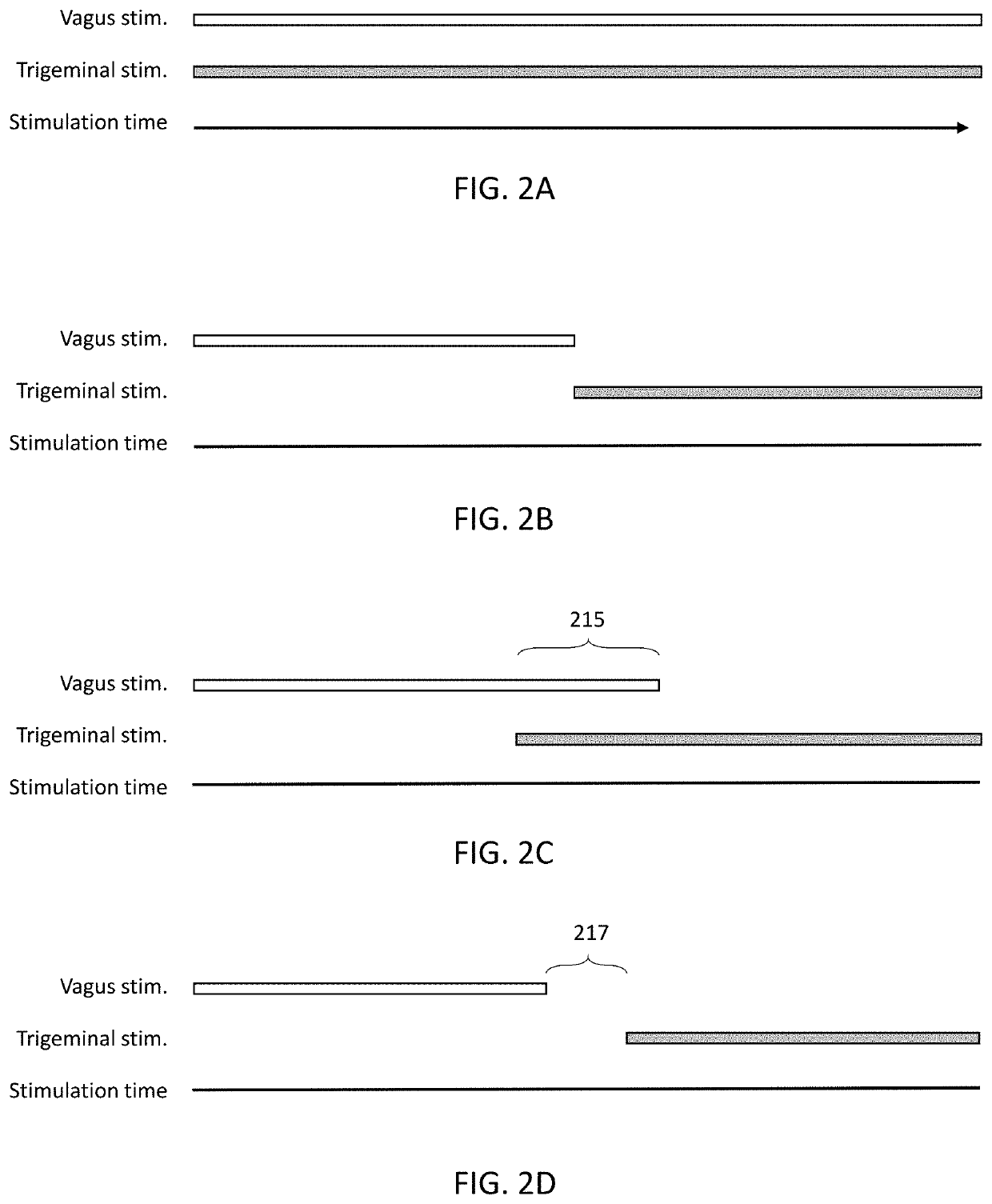
Methods and apparatuses for reducing bleeding via coordinated trigeminal and vagal nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20200094055A1Shorten bleeding timeBleeding timeHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsTrigeminal nerve stimulationBleeding time
Disclosed are apparatuses and methods for reducing or limiting blood loss and reducing bleed time in a subject by combined vagus and trigeminal stimulation. The apparatuses and methods may activate (e.g., electrically) one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve and may concurrently (at overlapping or near-overlapping time) independently activate the vagus nerve. This activation may be invasive or non-invasive.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Vagal nerve stimulation to avert or treat stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS10537728B2Improve the level ofInhibition of excitementSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNerve fiber bundleAdrenergic
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Systems and methods for vagal nerve stimulation
ActiveUS11191953B2Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSerotoninAdrenergic
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve to treat or prevent disorders in a patient. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy to the vagus nerve according to a treatment paradigm that includes single doses administered 2 to 5 times per day. The treatment paradigm may further comprise one or more daily treatment sessions that each include one or more doses for prophylactic or acute treatment of the patient's condition. Vagus nerve stimulation is used to modulate the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain, such as GABA, norepinephrine, and / or serotonin.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
System and method for controlling a heart stimulator
ActiveUS20100010555A1Reduce riskReduce generationHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse rateHeart rate turbulence
In a system and method for controlling an implantable stimulator capable of producing pacing pulses to be delivered to cardiac tissue, as well as vagal stimulation pulses to be delivered to vagus nerve sites, upon detection of a premature cardiac event, such as a premature ventricular or atrial contraction, a simulated heart rate turbulence (HRT) procedure is applied if the intrinsic heart rate turbulence is weakened or absent. The simulated HRT includes a first phase in which the heart rate is increased, from the existing level, for a number of heart beats, a second phase in which the heart rate is decreased for a number of heart beats, and an optional third phase in which the heart rate is returned to said existing level.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Wireless implant for motor function recovery after spinal cord injury
ActiveUS20190038899A1Improve stimulation efficiencyImprove efficacySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProsthesisRetinal Prosthesis
A wireless implant and associated system for motor function recovery after spinal cord injury, and more particularly a multi-channel wireless implant with small package size. The wireless implant can further be used in various medical applications, such as retinal prostheses, gastrointestinal implant, vagus nerve stimulation, and cortical neuromodulation. The system also includes a method and its implementation to acquire the impedance model of the electrode-tissue interface of the implant.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and apparatuses for reducing bleeding via coordinated trigeminal and vagal nerve stimulation
ActiveUS11260229B2Shorten bleeding timeHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsTrigeminal nerve stimulationBleeding time
Disclosed are apparatuses and methods for reducing or limiting blood loss and reducing bleed time in a subject by combined vagus and trigeminal stimulation. The apparatuses and methods may activate (e.g., electrically) one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve and may concurrently (at overlapping or near-overlapping time) independently activate the vagus nerve. This activation may be invasive or non-invasive.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Wireless implant for motor function recovery after spinal cord injury
ActiveUS11129983B2Stimulation efficacyImprove efficiencySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSpinal cord lesionSpinal cord
A wireless implant and associated system for motor function recovery after spinal cord injury, and more particularly a multi-channel wireless implant with small package size. The wireless implant can further be used in various medical applications, such as retinal prostheses, gastrointestinal implant, vagus nerve stimulation, and cortical neuromodulation. The system also includes a method and its implementation to acquire the impedance model of the electrode-tissue interface of the implant.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Control of vagal stimulation
ActiveUS10695569B2Lower Level RequirementsIncrease amplitudeSpinal electrodesElectrocardiographyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRR interval
Methods and apparatuses for stimulation of the vagus nerve to treat inflammation including adjusting the stimulation based on one or more metric sensitive to patient response. The one or more metrics may include heart rate variability, level of T regulatory cells, particularly memory T regulatory cells, temperature, etc. Stimulation may be provided through an implantable microstimulator.
Owner:SETPOINT MEDICAL CORP
Cardiac defibrillation with vagus nerve stimulation
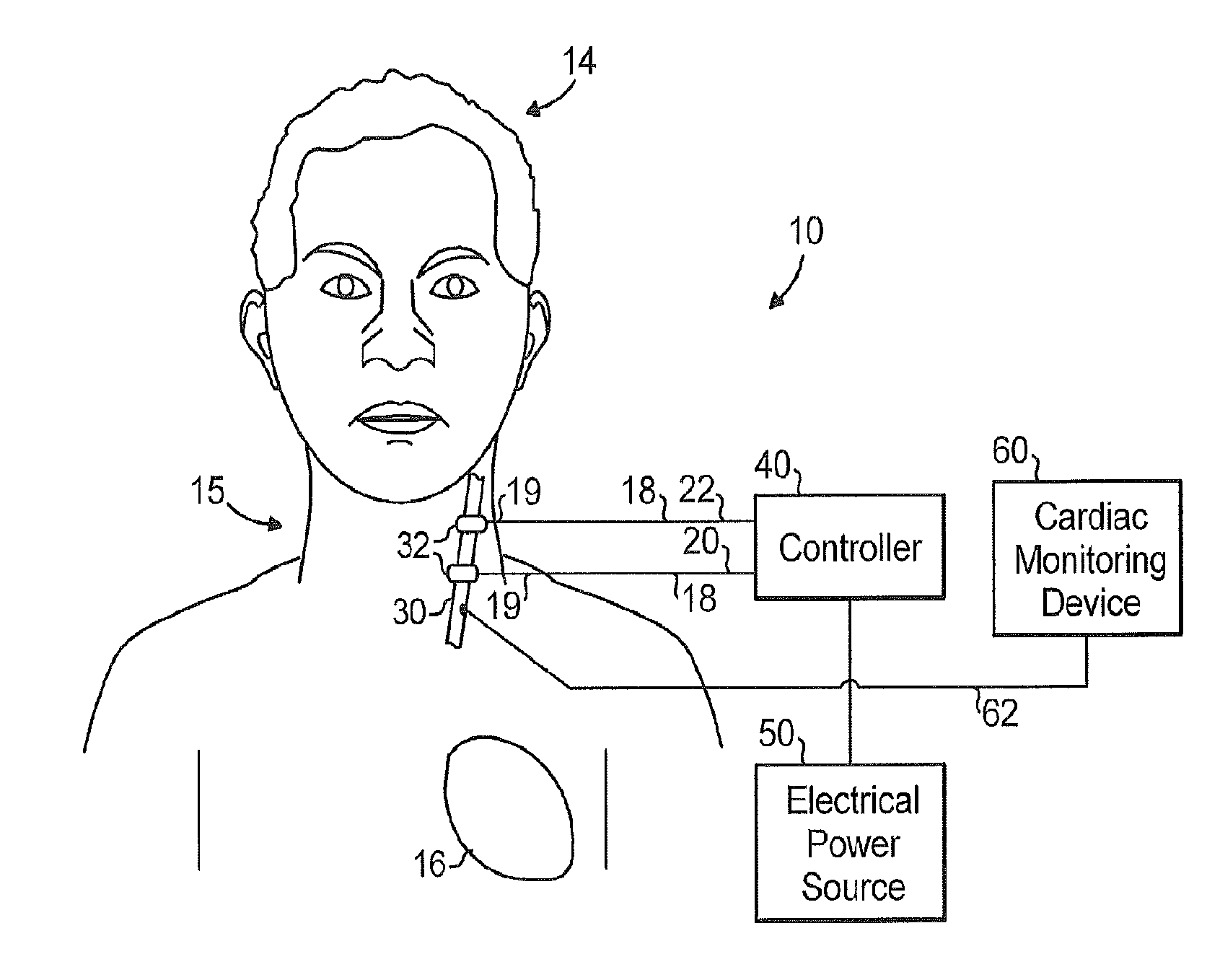
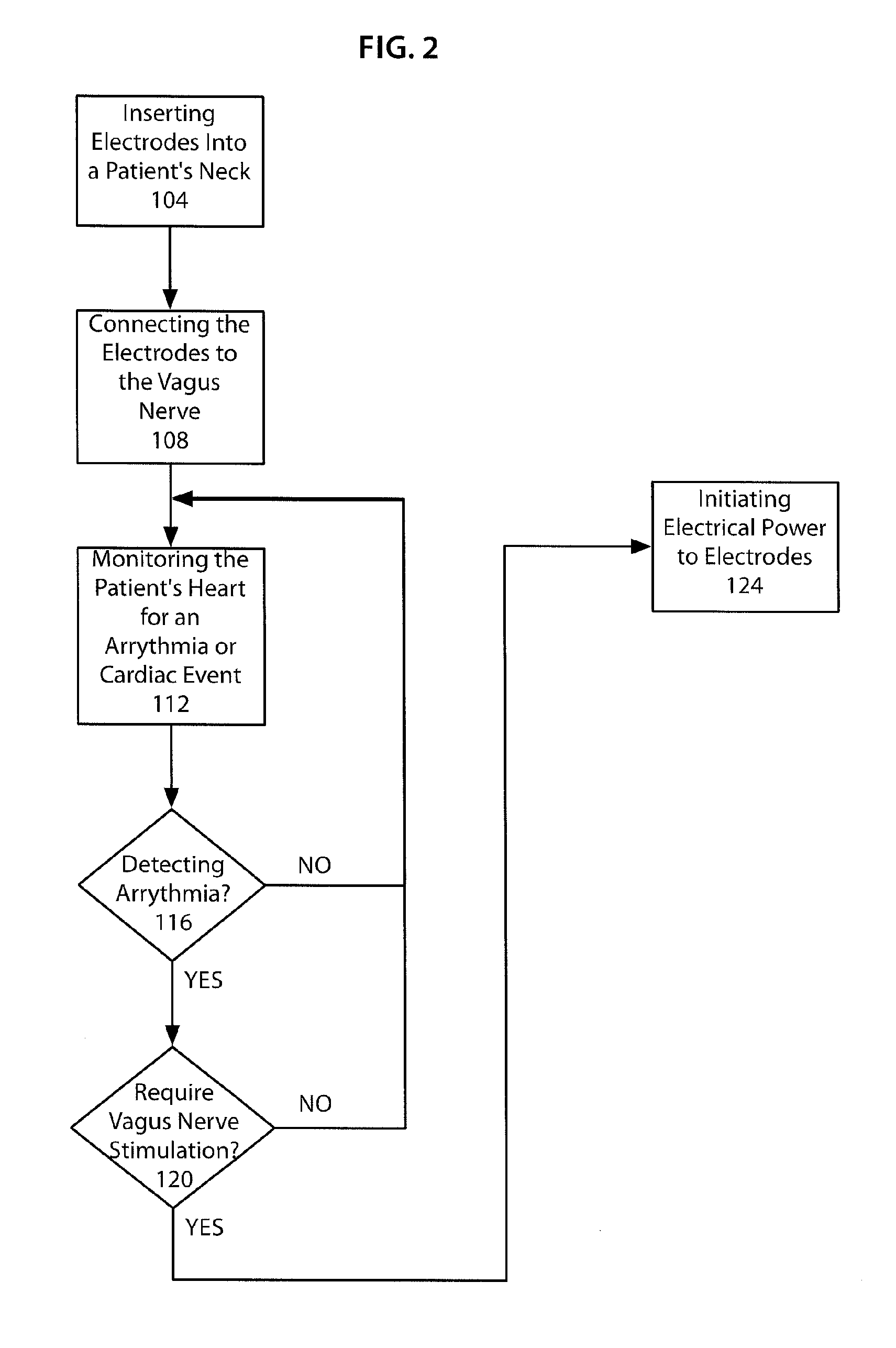
A method and system for treating cardiac arrhythmias which includes inserting one or more electrodes into a patient's neck, and connecting the electrodes to the vagus nerve in the patient's neck. A cardiac monitoring device detects a cardiac arrhythmia. A controller connected to an electrical power source provides electrical power to the electrodes to apply electrical stimulation to the vagus nerve when a cardiac arrhythmia is detected.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Vagus nerve stimulation pre-screening test
Owner:SETPOINT MEDICAL CORP
Pairing vagus nerve stimulation with emg-controlled functional electrical stimulation to enhance neuroplasticity and recovery
A combined closed-loop functional electrical stimulation (FES) and Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy system for treating neurological injuries. Detected EMG signals are used to determine movement (or intended movement) of an extremity. FES is then delivered to help evoke the movement, and VNS is delivered to enhance neuroplasticity and recovery.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
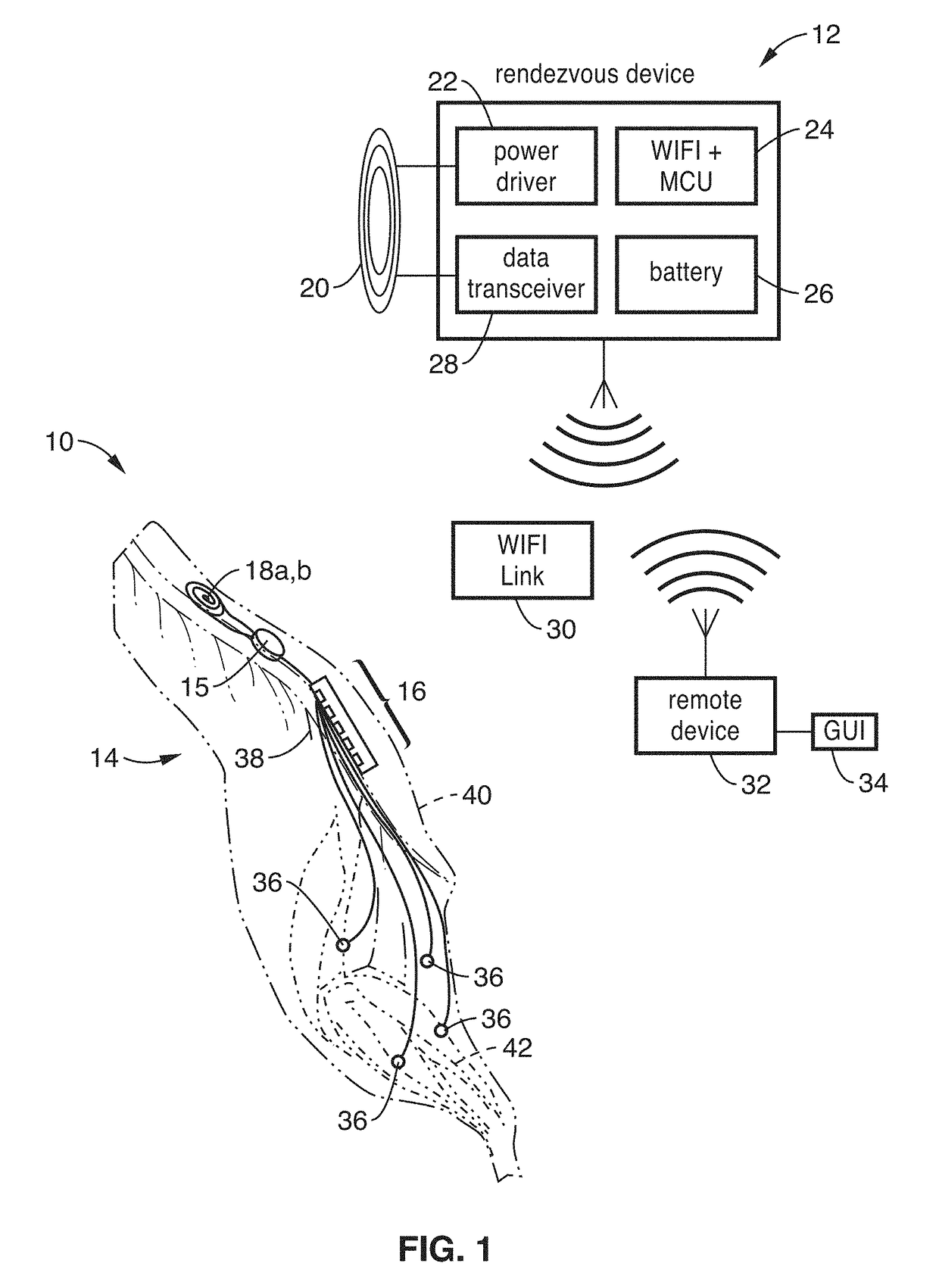
Closed-loop percutaneous auricular concha vagal stimulator based on electroencephalogram signals
PendingCN114042246AFlexible size adjustmentEasy to wearInternal electrodesExternal electrodesControl systemAnatomy
The invention provides a closed-loop percutaneous auricular concha vagal stimulator based on electroencephalogram signals. The closed-loop percutaneous auricular concha vagal stimulator comprises a support body, and further comprises an induction electrode, a stimulation electrode and a feedback control system which are arranged on the support body, wherein the induction electrode and the stimulation electrode are electrically connected with the feedback control system; and the support body comprises a U-shaped bracket and two groups of ear brackets arranged at two ends of the U-shaped bracket, a group of plug connectors which are slidably inserted into inner cavities of the ear brackets are arranged at the end part of each end of the U-shaped bracket, and the U-shaped bracket is telescopically connected with the ear brackets through the plug connectors. According to the closed-loop percutaneous auricular concha vagal stimulator based on the electroencephalogram signals, a U-shaped bracket structure is used, so the closed-loop percutaneous auricular concha vagal stimulator can be conveniently worn on the head of the human body; and meanwhile, the U-shaped bracket and the ear brackets are in telescopic connection, and the size of the support body can be flexibly adjusted according to the head size difference of different individuals, so better compatibility is obtained, and the wearing of the vagal stimulator is more convenient.
Owner:BEIJING SHIJITAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIVERSTY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com