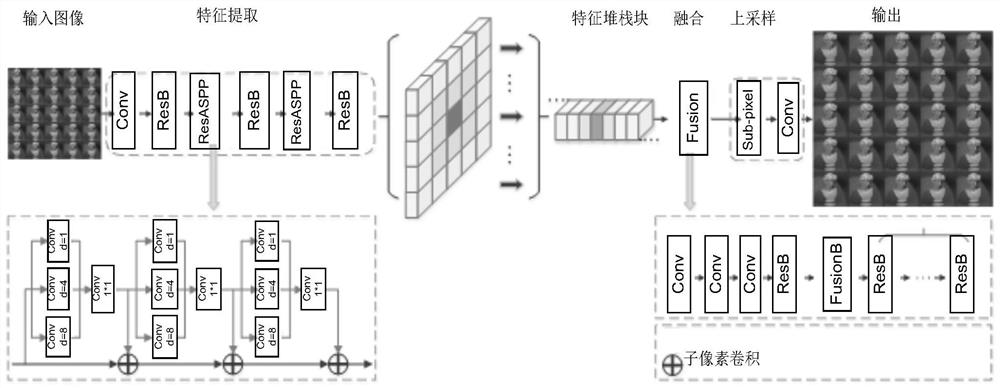
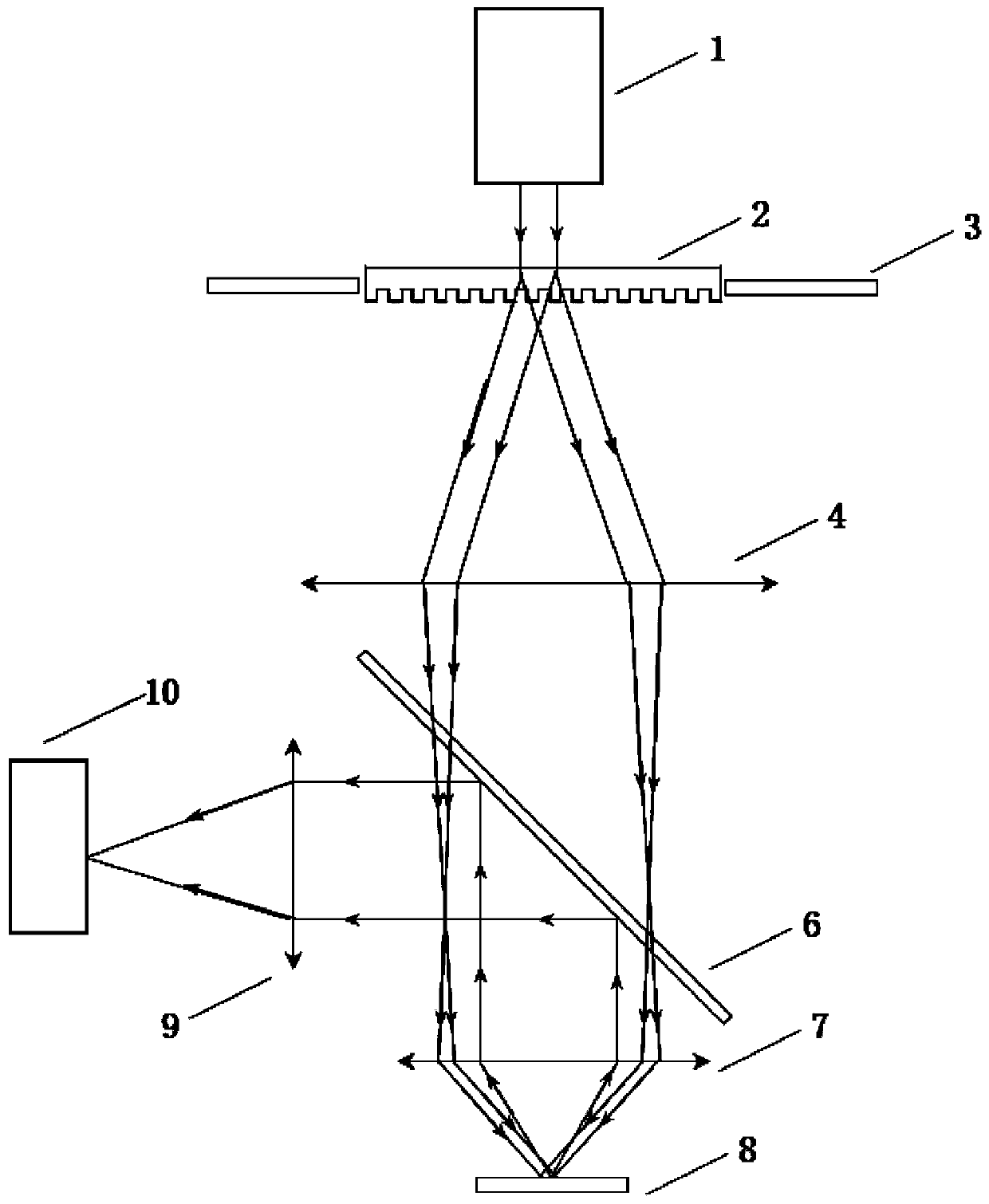
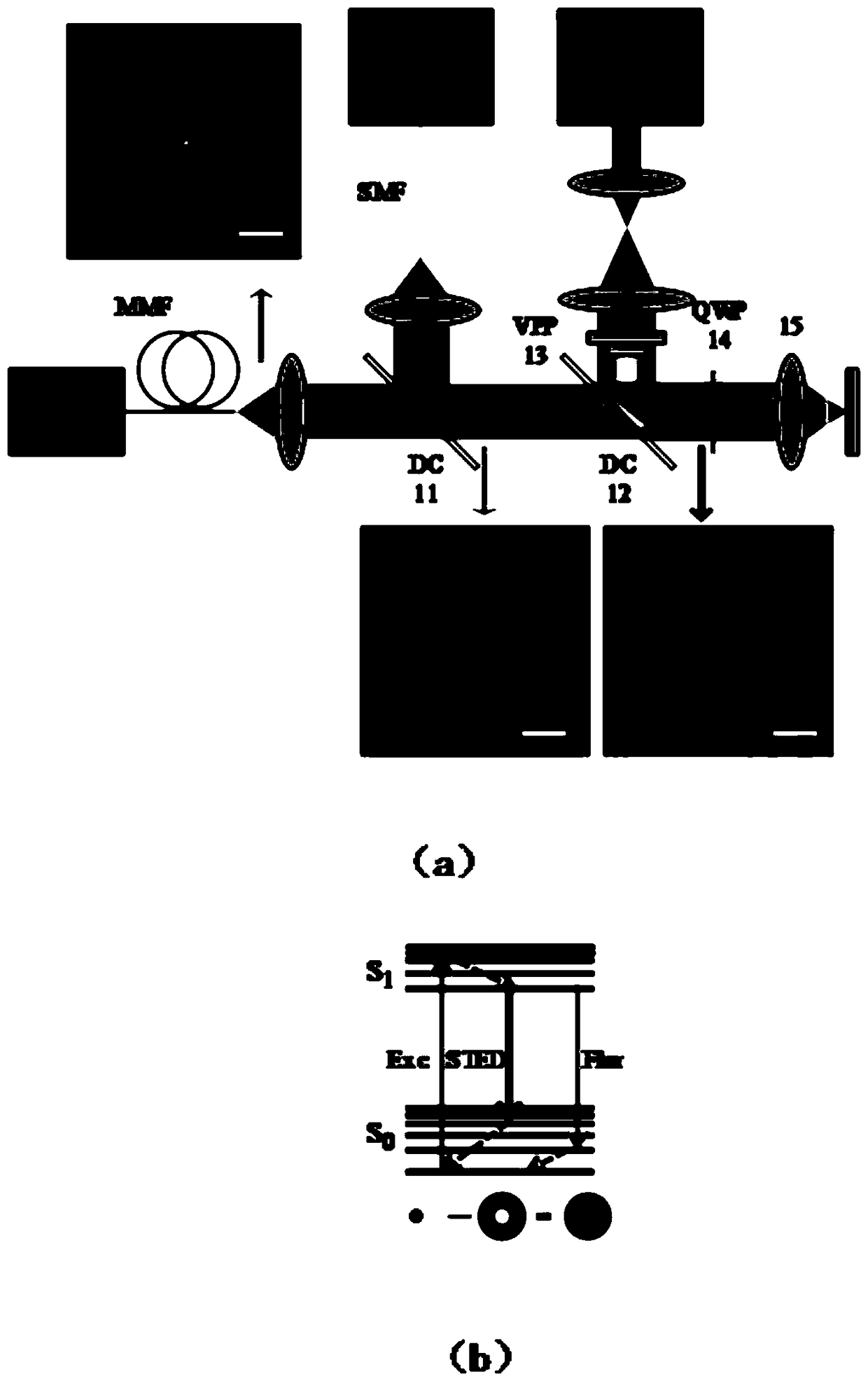
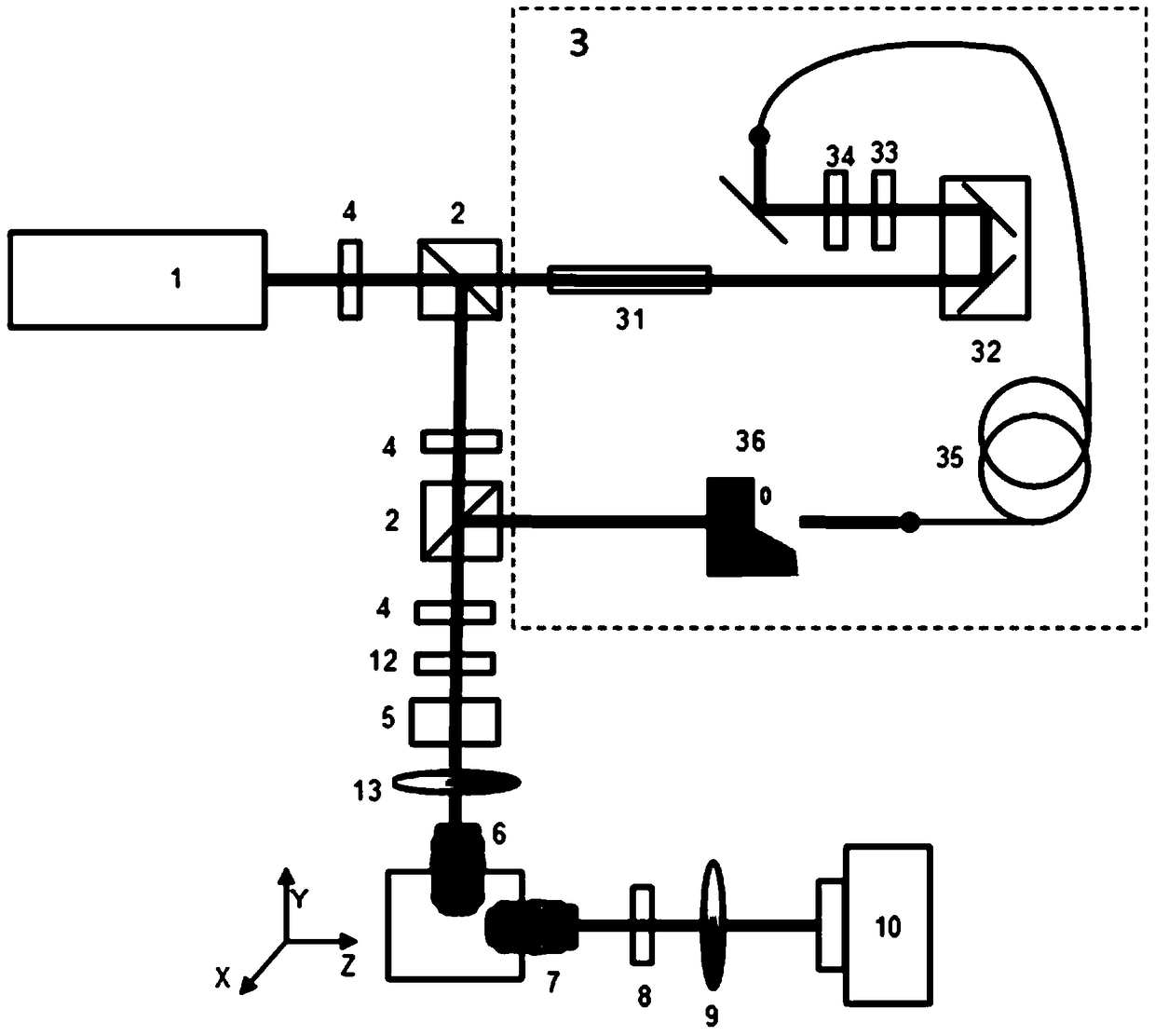
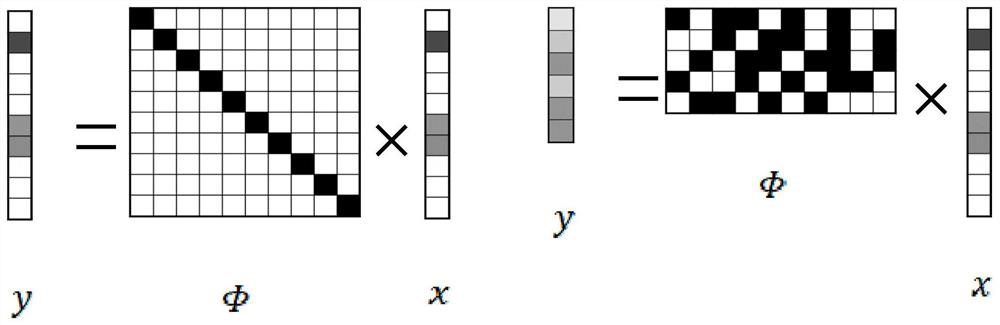Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Achieve super resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
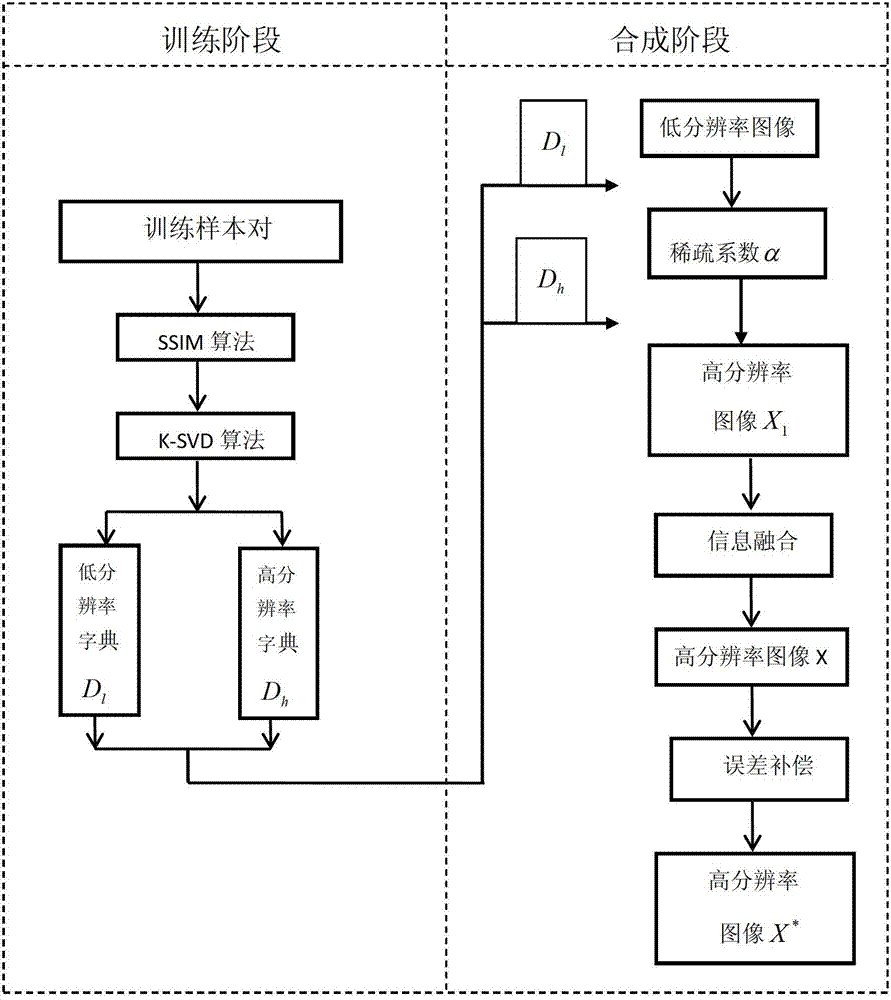
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity
ActiveCN103077511ASparse coefficients are accurateReasonably high resolution dictionaryImage enhancementK singular value decompositionReconstruction method
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity, mainly solving the problem that a reconstructed image based on the prior art has a fuzzy surface and a serious marginal sawtooth phenomenon. The image super-resolution reconstruction method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) acquiring a training sample pair; (2) learning a pair of high / low-resolution dictionaries by using structural similarity (SSIM) and K-SVD (K-Singular Value Decomposition) methods; (3) working out a sparse expression coefficient of an input low-resolution image block; (4) reestablishing a high-resolution image block Xi by using the high-resolution dictionaries and the sparse coefficient; (5) fusing the high-resolution image block Xi to obtain a high-resolution image X'I subjected to information fusion; (6) obtaining a high-resolution image X according to the high-resolution image X'I; and (7) carrying out high-frequency information enhancement on the high-resolution image X through error compensation to obtain a high-resolution image subjected to high-frequency information enhancement. A simulation experiment shows that the image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages of clear image surface and sharpened margin and can be used for image identification and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method
InactiveCN103310427AImprove image qualityHigh resolutionImage enhancementImaging qualityHorizontal and vertical
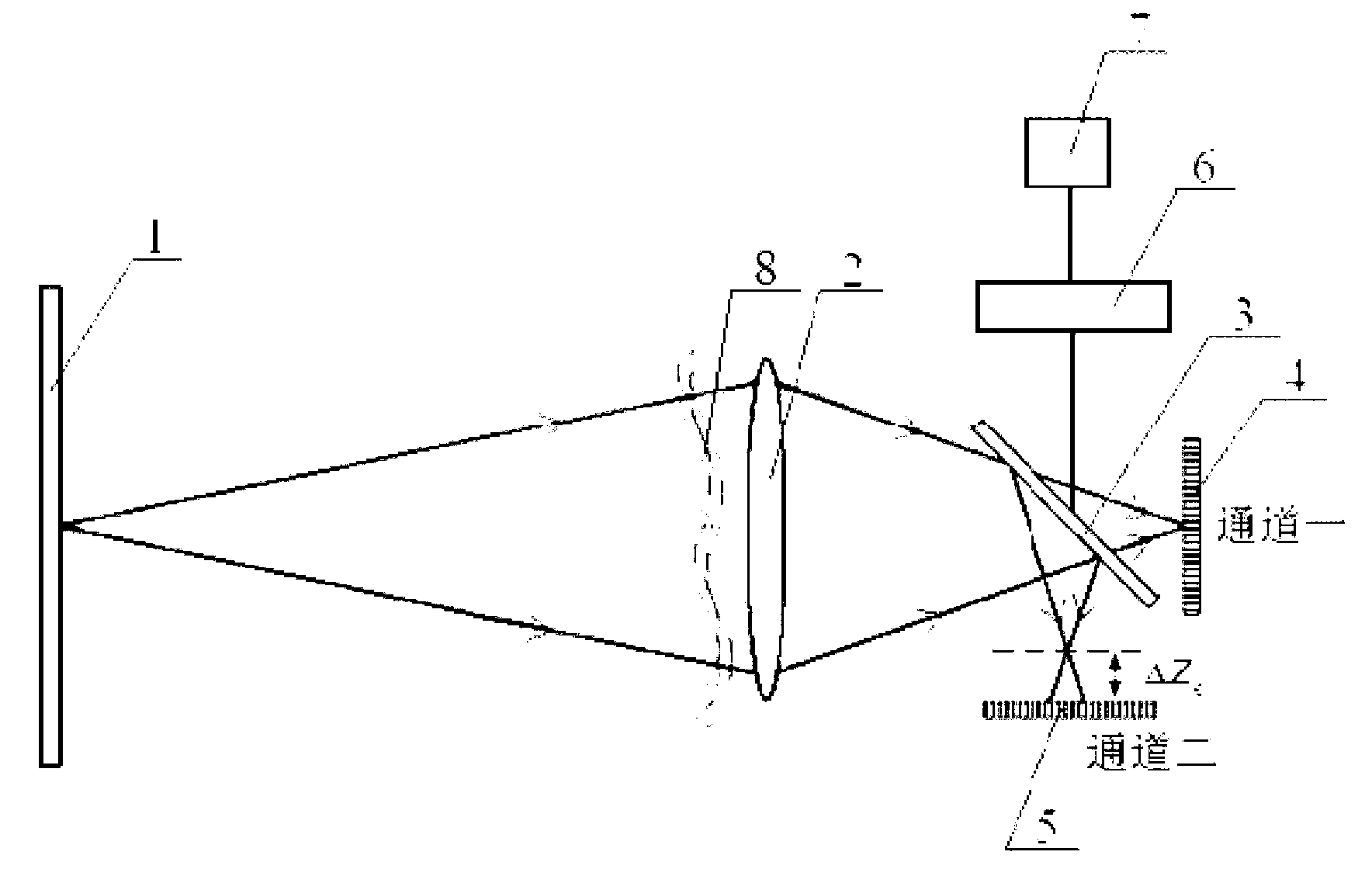
The invention provides an image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method and relates to the technical field of digital image processing in a space remote sensing imaging system. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method solves the problems that optimization elements which can be utilized are less, the improvement space of the image quality is limited, and accordingly the image quality cannot be effectively improved in the existing Wiener filtering image restoration method. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method comprises utilizing a light beam splitter to collect in-focus images and out-of-focus images in two channels respectively and collect N staggered in-focus images which enable 1 / N pixels to be staggered in the horizontal and vertical direction relative to the in-focus images; performing PD (Phase Diversity) processing on the in-focus images and the out-of-focus images; utilizing a conjugate gradient algorithm to obtain an aberration coefficient; obtaining restored target images after the PD processing and calculating an objective function; performing Wiener filtering processing on the staggered in-focus images and the restored target images; and performing sub-pixel integration on the two restored images to obtain a restored image with ultrahigh resolution. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method achieves super-resolution and high definition of images and improves the resolution by 1.4 times.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
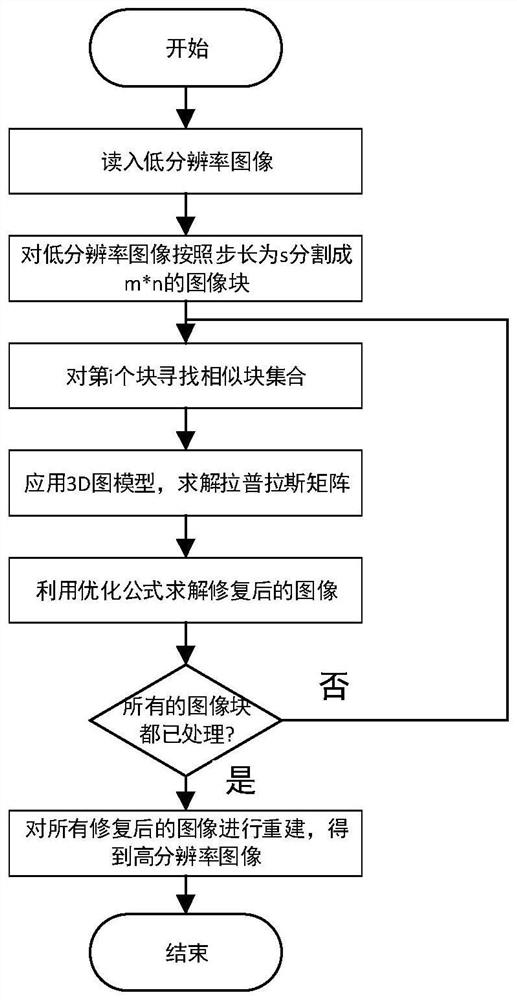
Graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method
ActiveCN107680043AAchieve super resolutionSuper Resolution FitGeometric image transformationImage resolutionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method. The graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method includes the following steps: 1) according toa preset sampling rate, performing interpolation on an input single image by means of a bicubic interpolation method, obtaining a low resolution image, segmenting the obtained low resolution image into m*n image blocks, calculating the Euclidean distance of the pixel value of each image block, and according to the Euclidean distance, determining a set of similar blocks, wherein each image block in the segmented low resolution image has one set of similar blocks; 2) constructing a graph model for the set of similar blocks; 3) performing Laplace transformation on the obtained two dimensional matrix to obtain a Laplace matrix, and then carrying out restoration of the image blocks through solution by means of an optimization formula; and 4) averaging and reconstructing the restored image block set, and finally obtaining a super-resolution image. The graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method can overcome the defect that a machine learning method needs mass image data totrain a model, thus being more suitable for image super resolution.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Light field multi-view image super-resolution reconstruction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN112750076AAchieve super resolutionImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionLight-field camera
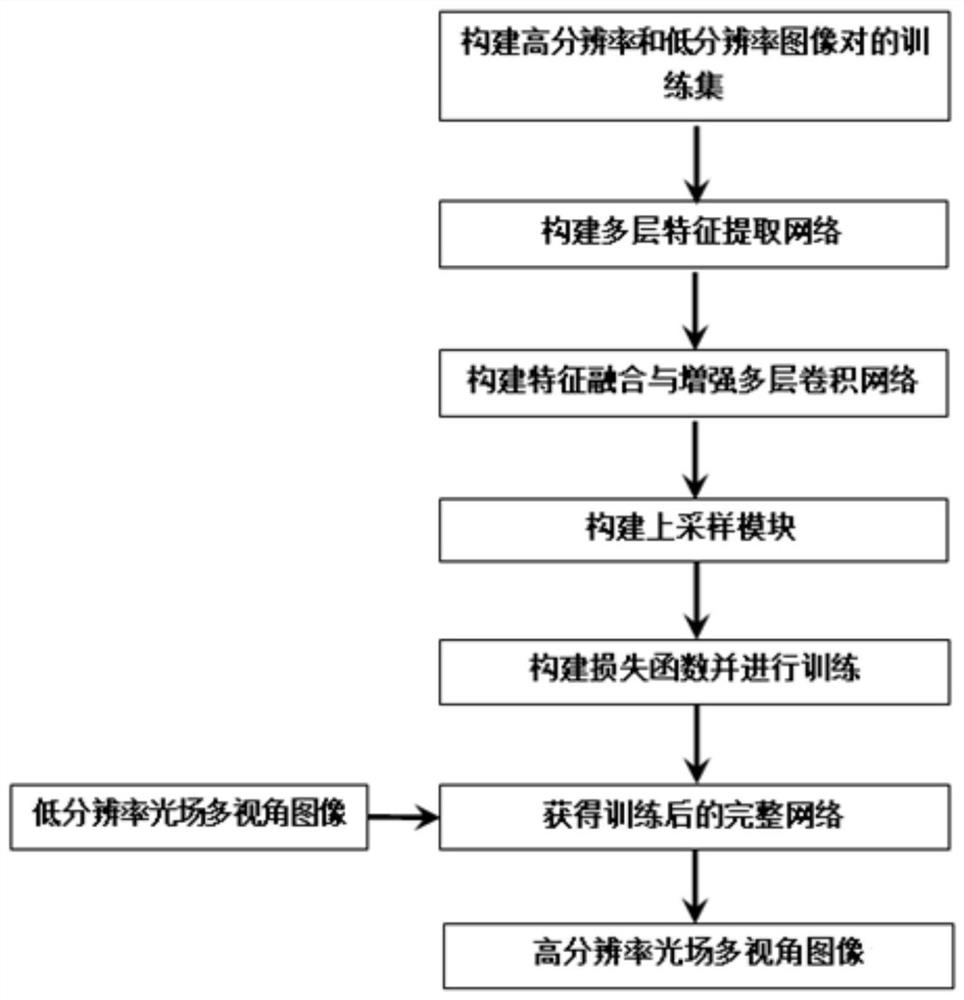
The invention discloses a light field multi-view image super-resolution reconstruction method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a training set of high-resolution and low-resolution image pairs by adopting multi-view images which are obtained from a light field camera or a light field camera array and are distributed in an N * N array shape; constructing a multi-layer feature extraction network from the N * N light field multi-view image array to the N * N light field multi-view feature image; stacking the feature images and constructing a feature fusion and enhanced multi-layer convolutional network to obtain 4D light field structure features capable of being used for reconstructing a light field multi-view image; constructing an up-sampling module to obtain a nonlinear mapping relation from 4D light field structure features to a high-resolution N * N light field multi-view image; constructing a loss function based on the multi-scale feature fusion network, training the loss function, and finely adjusting network parameters; and inputting a low-resolution N * N light field multi-view image into the trained network to obtain a high-resolution N * N light field multi-view image.
Owner:VOMMA (SHANGHAI) TECH CO LTD
MIMO radar waveform separation method based on compressive sensing
ActiveCN107037409ASuppression distance to high sidelobeEasy to separateWave based measurement systemsRadar waveformsImage resolution
The present invention discloses a MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) radar waveform separation method based on compressive sensing. The method comprises: (1) emitting orthogonal waveforms; (2) receiving a target echo; (3) constructing a sensing matrix; and (4) performing sparse reconstruction of a target one-dimensional distance image. Based on the sparsity of a radar target on a distance direction, the MIMO radar waveform separation method based on the compressed sensing constructs the sensing matrix related to a transmitted waveform set and employs the joint sparse recovery algorithm to realize the orthogonal separation of different waveform components in the MIMO radar echo. The method provided by the invention replaces a traditional matched filtering process, effectively inhibits the high sidelobe of the distance direction caused by non-orthogonal waveforms, breaks through the restriction of signal bandwidth for the distance resolution, and improves the distance resolution.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system
The invention discloses a multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system. The multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system comprises a center optical imaging system and four secondary optical imaging systems having complete identical optical structures, wherein the center optical imaging system is a rotary symmetric system, the optical axis and the system center axis are superposed, the four secondary optical imaging systems are arranged at the back of the center optical imaging system, from the perspective of image cross sections, four optical axes of the secondary optical imaging systems are distributed on tip tops of a rectangle which takes the optical axis of the center optical imaging system as the center, and parallel lights emitted from different perspectives by a target are respectively imaged through the center optical imaging system and the four secondary optical imaging systems on different coordinate points on an image plane of one same detector. Independent multiple target images can be acquired by applying the multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system to acquire target object information, the center image resolution is higher than the secondary image resolution, images respectively have certain pixels superposed in the field of view, and the multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system can provide excellent support for subsequent data processing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Improved dimension-reduction space-time adaptive processing-based ship-borne high-frequency ground wave radar sea clutter suppression method
InactiveCN105372635AGood sea clutter suppressionAchieve super resolutionWave based measurement systemsSpace-time adaptive processingMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to an improved dimension-reduction space-time adaptive processing-based ship-borne high-frequency ground wave radar sea clutter suppression method and belongs to the clutter suppression field. The objective of the invention is to solve the problems of large calculation amount and poor clutter suppression effect of an adaptive processing algorithm in the prior art. The improved dimension-reduction space-time adaptive processing-based ship-borne high-frequency ground wave radar sea clutter suppression method includes the following specific steps that: step one, distance transformation and Doppler transformation are performed on high-frequency ground wave radar echo baseband signals, so that distance unit and Doppler unit data can be formed; step two, azimuth processing is performed on the data of any one distance unit and any one Doppler unit through utilizing the MUSIC algorithm; and step three, dimension-reduction space-time adaptive processing is performed on the data which have been processed by the MUSIC algorithm, so that sea clutter can be suppressed. The improved dimension-reduction space-time adaptive processing-based ship-borne high-frequency ground wave radar sea clutter suppression method of the invention is applied to the clutter suppression field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Super-resolution method for reconstructing potential image based on dynamic vision sensor
ActiveCN113837938APixel values are stable and continuousHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVision sensor
The invention discloses a super-resolution method for reconstructing a potential image based on a dynamic visual sensor, relates to the technical field of event camera application, and solves the problems that edge details of a grayscale image are not sharp enough, the grayscale of the same pixel value is not stable enough, the dynamic range is liable to lose and the like in a reconstruction junction in the prior art. The method is realized through a neural network structure, and comprises two steps of potential grey-scale map reconstruction and multi-image fusion; a high-quality high-resolution grey-scale map is reconstructed through a neural network architecture, and event signals and grey-scale map signals are considered at the same time, a series of potential grey-scale maps are reconstructed on the basis of the grey-scale map, and the pixel value of the fused high-resolution grey-scale map is stable and continuous. A plurality of potential grayscale frames are reconstructed, and the super-resolution of the APS grayscale image is realized by adopting a multi-image super-resolution method, so that the quality of super-resolution reconstruction is greatly superior to the reconstruction effect of the previous related methods. According to the method, the quality of the image super-resolution is improved by using a deep learning method.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Method for distinguishing radar detection target based on information theory
ActiveCN108845311ASolve complex integralsReasonable resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing a radar detection target based on the information theory. The method comprises steps that S1, signals are received by a radar system receiving end;S2, the received signals are down-converted to a base band, and discretization is performed through sampling at a sampling rate B to obtain a discrete sequence; S3, the received signals of N receivingantennas in a radar system are processed in the S2 to form a sampling signal matrix Z, and the multidimensional probability density function p (Z|X, Y) of Z is calculated under the condition of the given target position X and the target amplitude Y; and S4, the number of p(Z|X, Y) peaks is calculated, namely, the number of distinguished radar detection targets. The method is advantaged in that signal bandwidth restriction can be broken through, and a problem of relatively poor resolution of a radar system in the prior art is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity
ActiveCN103077511BSparse coefficients are accurateReasonably high resolution dictionaryImage enhancementK singular value decompositionReconstruction method
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure similarity, mainly solving the problem that a reconstructed image based on the prior art has a fuzzy surface and a serious marginal sawtooth phenomenon. The image super-resolution reconstruction method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) acquiring a training sample pair; (2) learning a pair of high / low-resolution dictionaries by using structural similarity (SSIM) and K-SVD (K-Singular Value Decomposition) methods; (3) working out a sparse expression coefficient of an input low-resolution image block; (4) reestablishing a high-resolution image block Xi by using the high-resolution dictionaries and the sparse coefficient; (5) fusing the high-resolution image block Xi to obtain a high-resolution image X'I subjected to information fusion; (6) obtaining a high-resolution image X according to the high-resolution image X'I; and (7) carrying out high-frequency information enhancement on the high-resolution image X through error compensation to obtain a high-resolution image subjected to high-frequency information enhancement. A simulation experiment shows that the image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages of clear image surface and sharpened margin and can be used for image identification and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
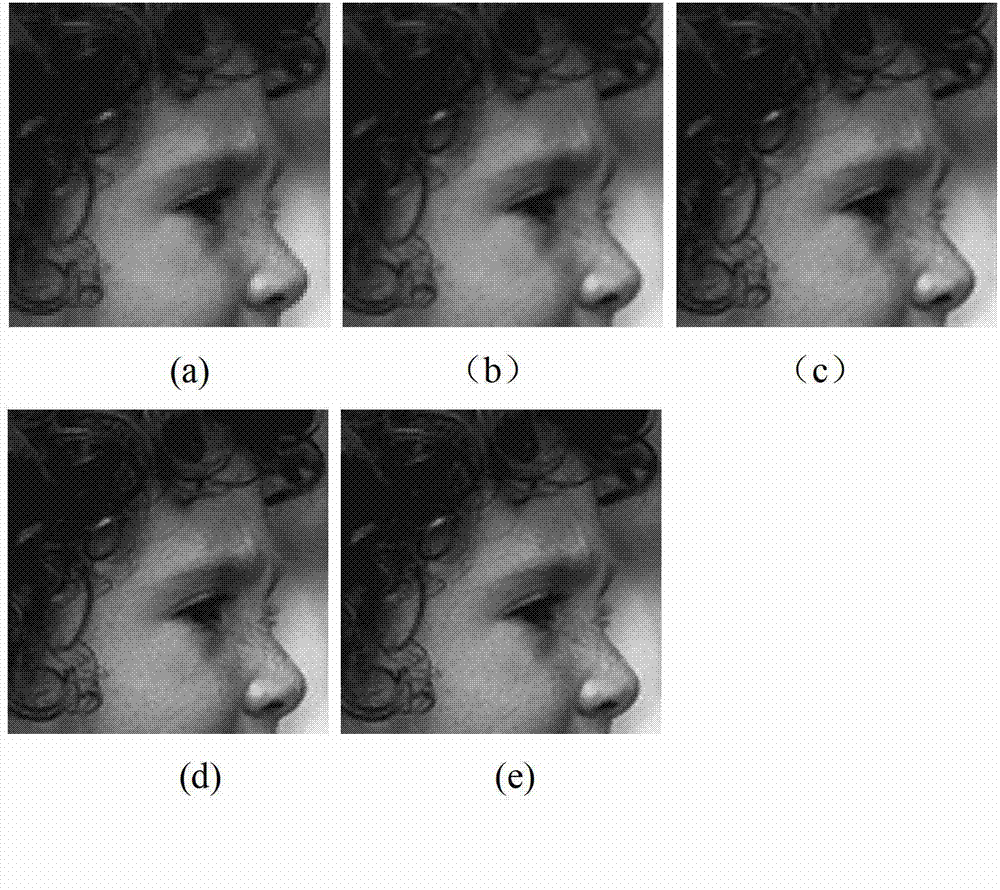
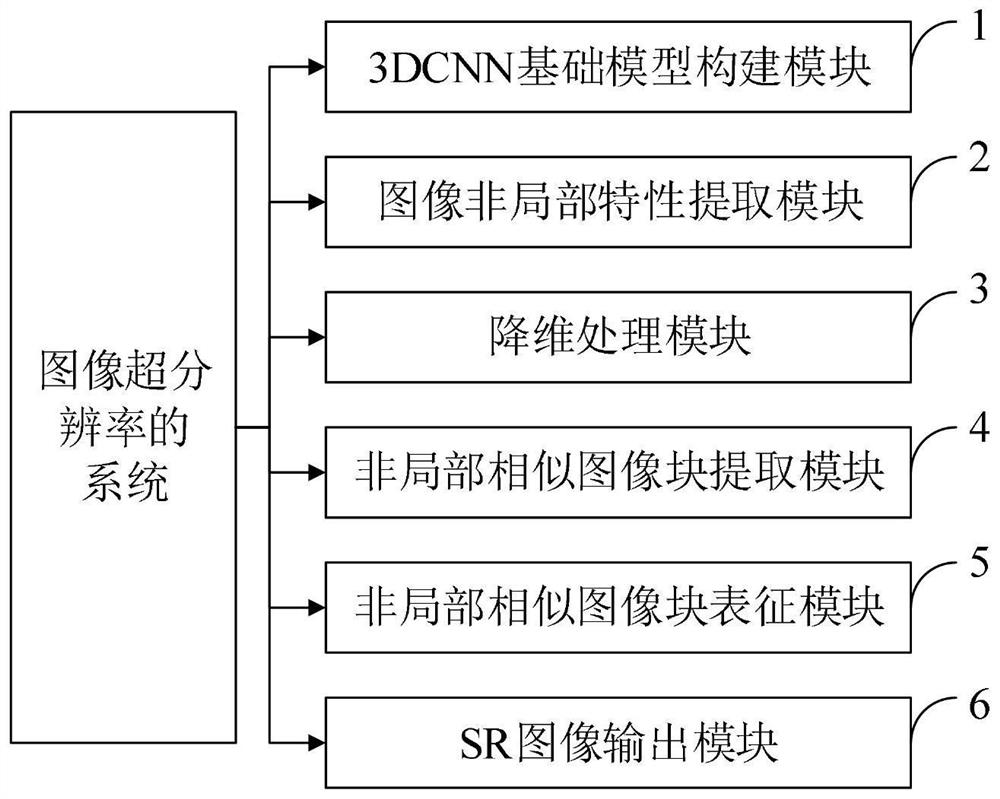
Image super-resolution method and system
PendingCN113191947AAchieve super resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionConvolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of image super-resolution, and discloses an image super-resolution method and system, and the method comprises the steps of processing an image SR through employing a 3D convolutional neural network 3DCNN in combination with the non-local self-similarity of an image, and proposing a 3DCNN-based non-local super-resolution method; modeling non-local similarity by directly utilizing 3DCNN, and extracting non-local similarity information of a natural image; constructing a 3DCNN basic model based on an eight-layer full convolutional network; designing a 3D convolutional neural network in 3DCNN, and proposing an RNN-based improved model, so that a basic model becomes a special example of the improved model. By using the non-local operation provided by the invention, the non-local similar information in the image can be effectively captured, and the SR reconstruction performance is improved; compared with an existing CNN model, the invention shows obvious reconstruction advantages, and is prominent in image scenes with rich structural information.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Stibium bismuth phase-change alloy mask read-only ultra-resolution CD-disc
InactiveCN101409086ASimple structureLow read powerRecord information storageOptical record carriersOptoelectronicsAlloy
A antimony and bismuth intersection alloy mask read-only super-resolution CD structurally comprises a dielectric layer, a mask layer and a disk base and is characterized in that the dielectric layer consists of silicon nitride; the mask layer consists of antimony and bismuth alloy, that is, SbxBi(1-x) film, wherein, the variation range of x is from 0.7-0.9. The super-resolution CD is characterized by simple structure, low read-out power, high sensibility, good read-out cyclicity, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiscale Multiaperture Optical Imaging System
The invention discloses a multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system. The multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system comprises a center optical imaging system and four secondary optical imaging systems having complete identical optical structures, wherein the center optical imaging system is a rotary symmetric system, the optical axis and the system center axis are superposed, the four secondary optical imaging systems are arranged at the back of the center optical imaging system, from the perspective of image cross sections, four optical axes of the secondary optical imaging systems are distributed on tip tops of a rectangle which takes the optical axis of the center optical imaging system as the center, and parallel lights emitted from different perspectives by a target are respectively imaged through the center optical imaging system and the four secondary optical imaging systems on different coordinate points on an image plane of one same detector. Independent multiple target images can be acquired by applying the multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system to acquire target object information, the center image resolution is higher than the secondary image resolution, images respectively have certain pixels superposed in the field of view, and the multi-scale multi-aperture optical imaging system can provide excellent support for subsequent data processing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Membrane for retaining a microsphere
PendingCN108351501ASave spaceAchieve super resolutionMicroscopesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesNanometreChemistry
The present invention relates to a novel optical nano-imaging scheme by using a transparent particle as an optical lens in order to achieve super-resolution nano-imaging. In particular, the present invention relates to a membrane for retaining a microsphere. The present invention relates to the membrane, and its application in super-resolution nano-imaging. In an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a membrane having a first surface and a second surface, the first and second surfaces oppose each other, the membrane comprising: (a) an opening penetrating through the membrane and is sized to retain a microsphere, wherein the opening is tapered, the size of the opening on the first surface is larger than the size of the opening on the second surface.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
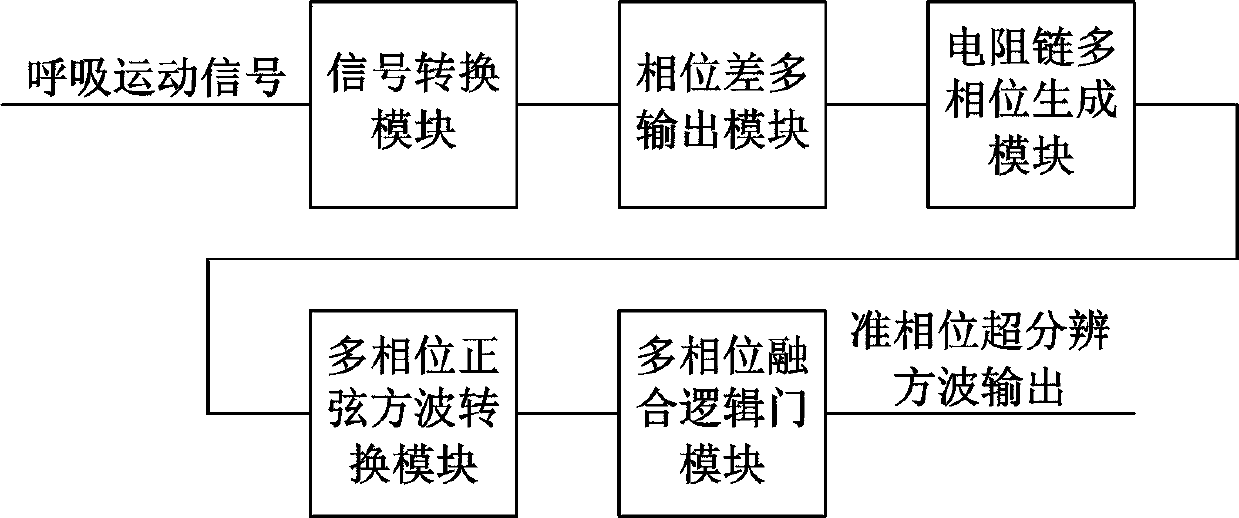
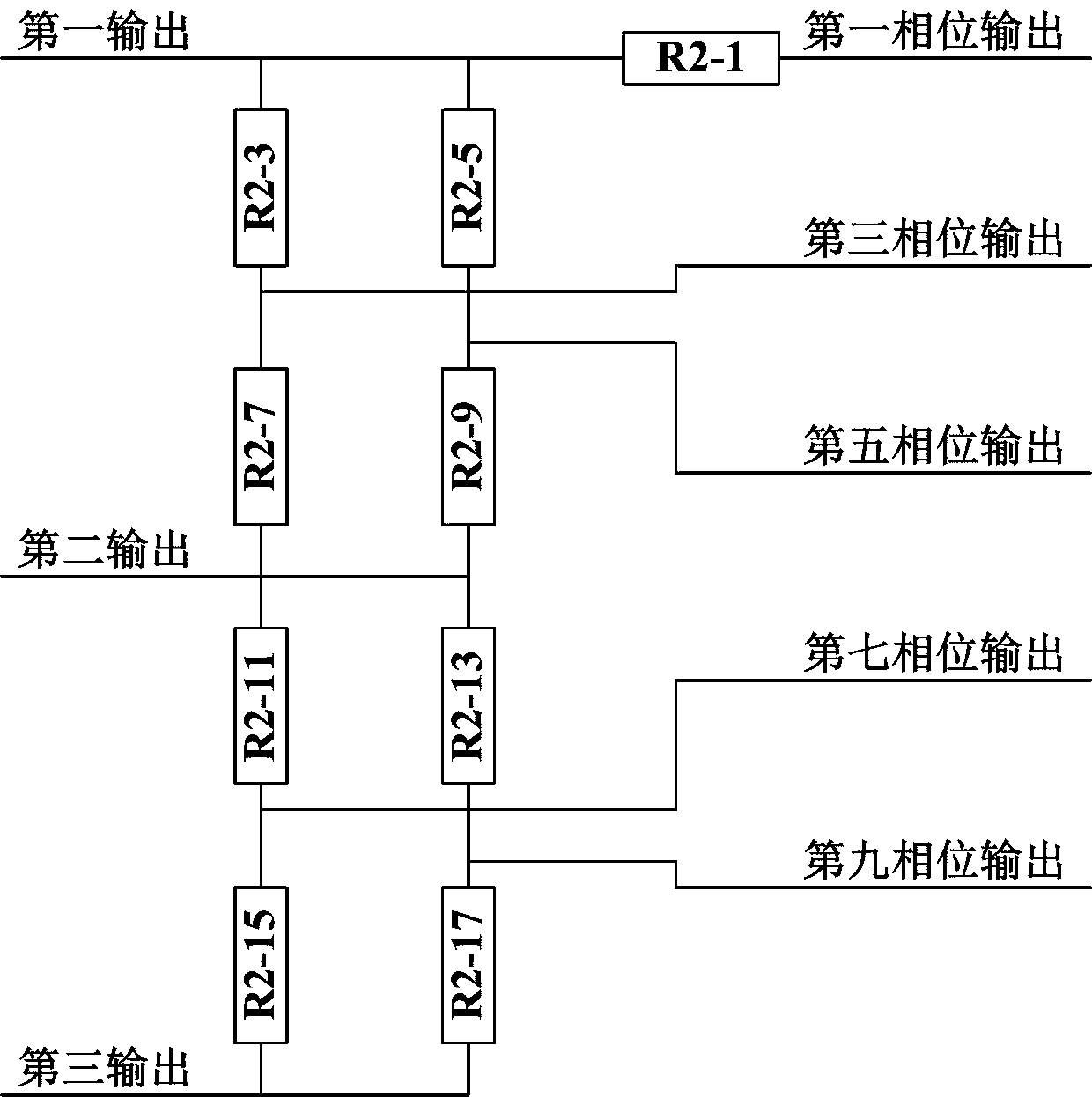
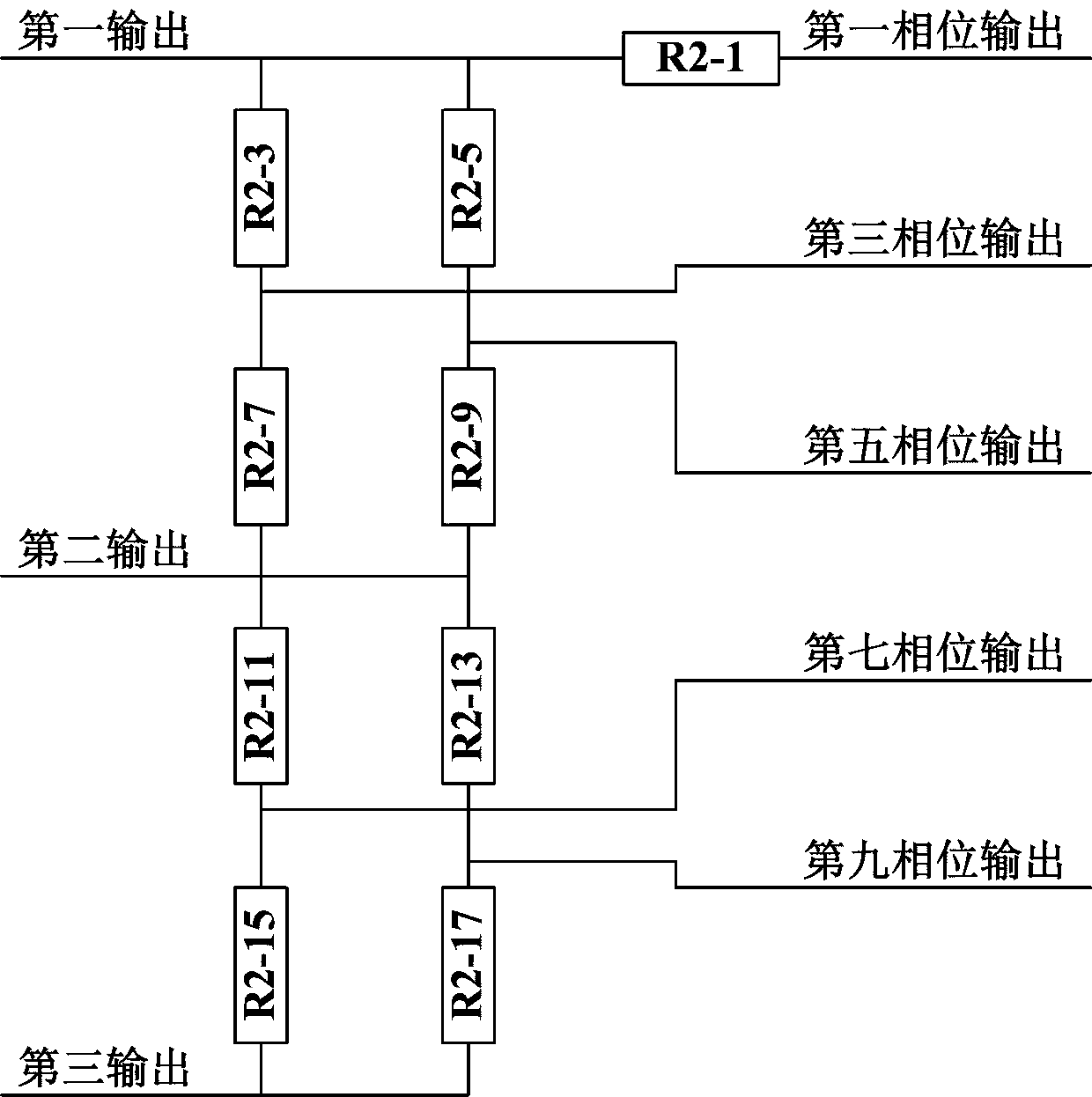
A phase-staggered super-resolution method for respiration motion signals on the thoracoabdominal surface
InactiveCN111135481BAchieve super resolutionShort analysis timeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySignal onEngineering
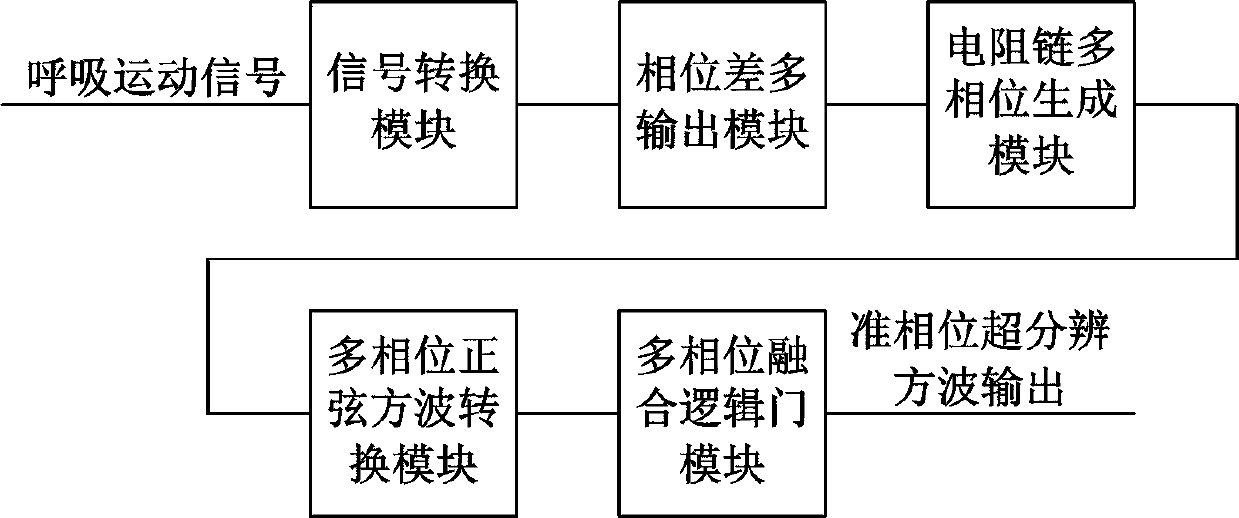
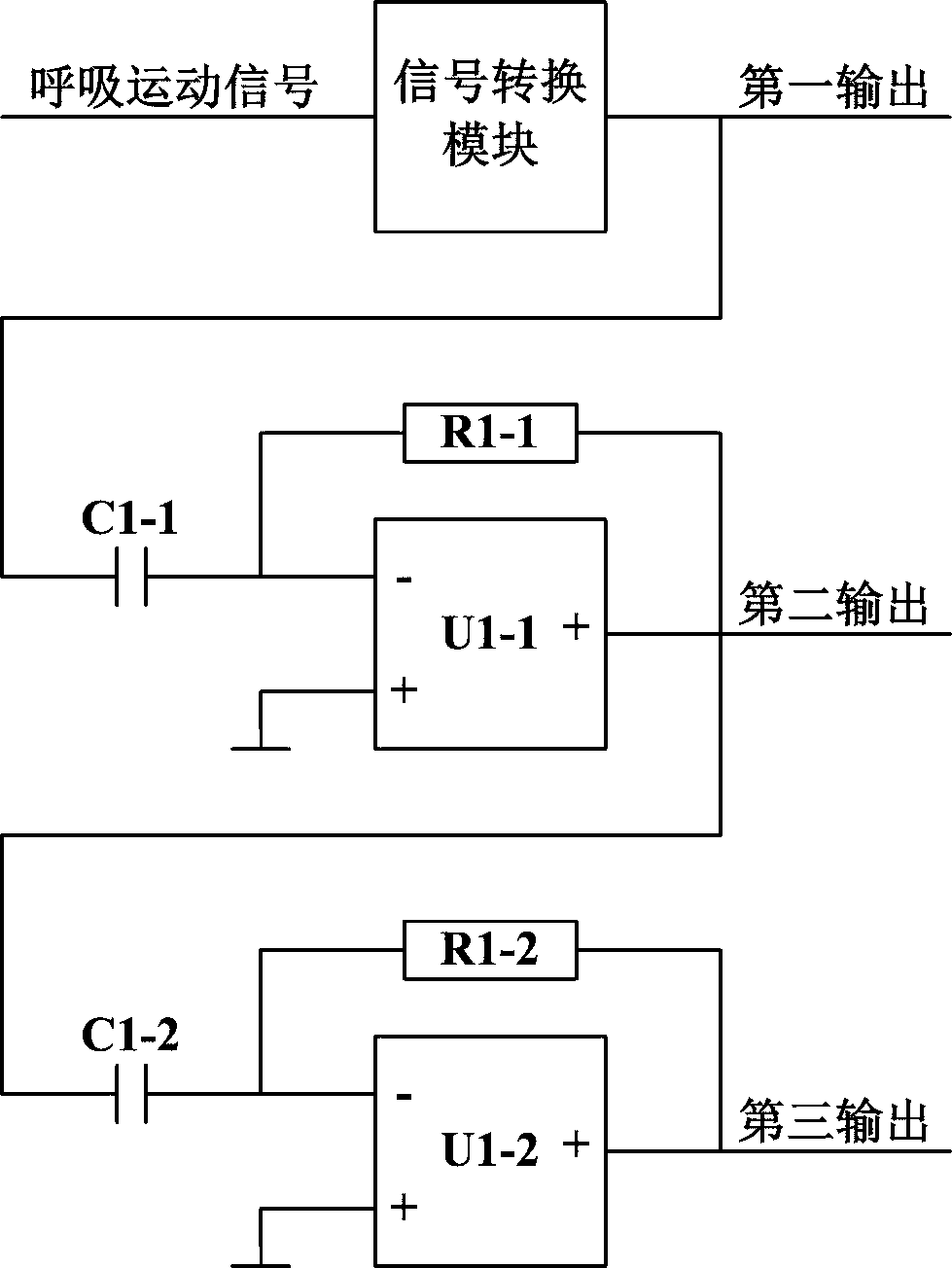
The invention relates to a phase-staggered super-resolution method for respiratory motion signals on the surface of the chest and abdomen, which belongs to the technical field of precision instruments and thoracoabdominal radiotherapy; the method first converts the respiratory motion signal into a periodic signal through a signal conversion module, and then through a phase difference multi-output module , forming three outputs with equal phase difference with a phase difference of π / 2, and then forming five outputs with equal phase difference with a phase difference of π / 5 through the resistance chain multiphase generating module, and then forming a square wave through a multiphase sine square wave conversion module, And through the multi-phase fusion logic gate module to form the out-of-phase super-resolution square wave output, that is, to realize the transformation of one cycle of respiratory motion signal into a multi-cycle out-of-phase square wave signal, and the phase error phase super-resolution square wave output signal quarter cycle of .
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A structured light illumination super-resolution microscopy imaging method
ActiveCN106770147BReduce in quantityAchieve super resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceDigital imagingFrequency spectrum
Owner:PEKING UNIV
An Ultrasonic Ranging Method in Long-distance Scenarios
ActiveCN112346062BRealize high-precision distance measurementGuaranteed stabilityAcoustic wave reradiationFar distanceMultipath channels
The invention discloses an ultrasonic ranging method in a long-distance scene. The method includes: generating a measurement signal according to a measurement criterion of compressed sensing, and transmitting it through an ultrasonic transducer at a transmitting end; sampling and summing the received signal at a receiving end. After filtering, the effective signal interception is performed on the filtered sampling signal; the sparse channel signal is recovered from the intercepted effective signal by using the compressed sensing recovery algorithm; the first path signal and the first channel signal are obtained by peak screening from the sparse channel signal. The arrival time of the first path; multiply the arrival time of the first path by the propagation velocity to get the distance from the transmitting end to the receiving end. The method of the invention can measure accurate multi-path channels, realize high-precision distance measurement, and simultaneously ensure measurement stability; can acquire signals at a lower sampling frequency, realize super-resolution of distance measurement, and reduce distance measurement cost.
Owner:北京奥特雷柏科技有限公司
Single-wavelength realization of multiphoton pulsed sted-spim microscopy system
The invention relates to a multiphoton subpulse STED-SPIM (Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy) microscopic system realized by single wavelength, characterized in that the femtosecond pulse laser emitted by a femtosecond single wavelength laser is transmitted to a first splitter through a first polarization regulator to be divided into two beams of light, and a first beam of light is successively transmitted to a second polarization regulator, a second splitter, a third polarization regulator and a quarter-wave plate along a Y-axial direction to form an excitation light beam; a second beam of light is transmitted to an STED photoquenching system, and the light outputted by the STED photoquenching system is successively emitted into the second splitter, the third polarization regulator and the quarter-wave plate to be modulated into donut-shaped focus spots to form a quenching light beam; a scanner is used for scanning the excitation light beam and the quenching light beam to generate an excitation plate light source and an STED quenching plate light source; an excitation plate light source and an STED quenching plate irradiate an object to be imaged through an excitation objective lens to allow the flourescent dye of the object to be imaged to excite fluorescence, and excited fluorescence is imaged through an imaging objective lens, and is emitted to a photosensitive element or an analysis element successively through an optical filter and a convergent lens.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
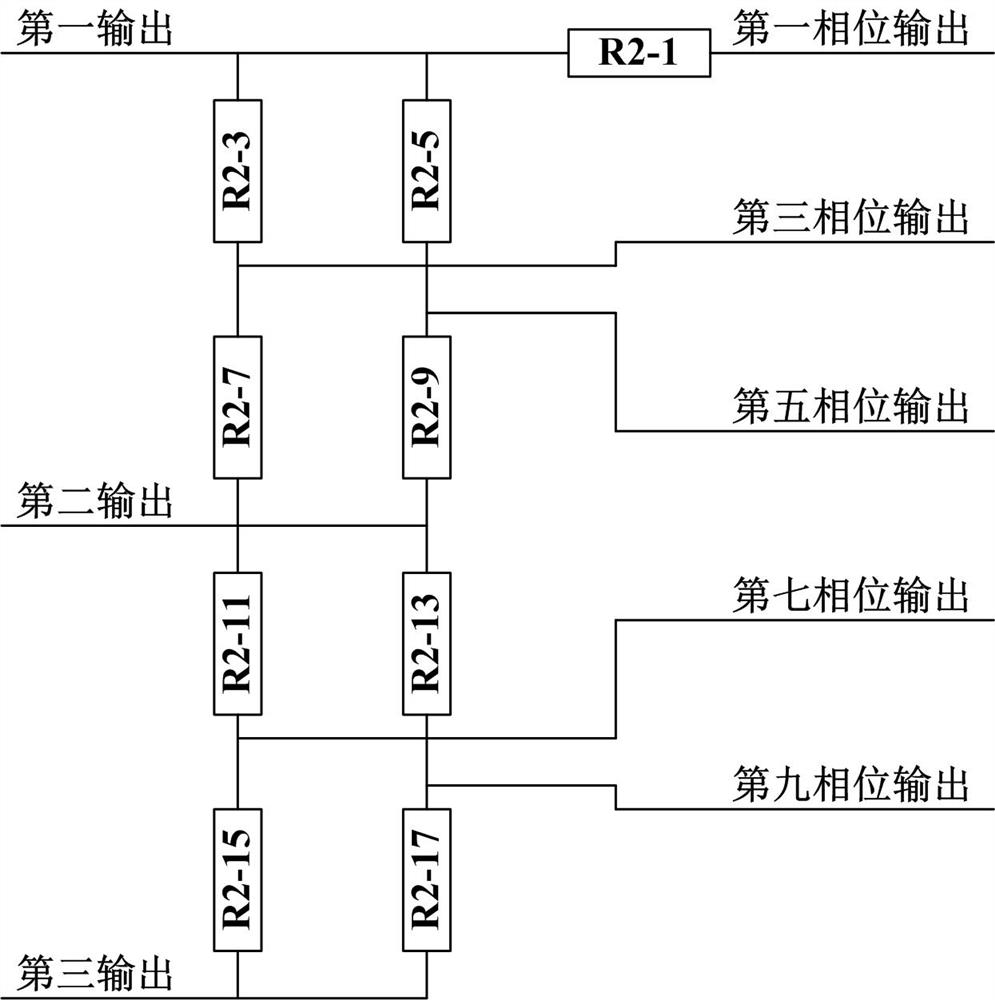
Quasi-phase super-resolution circuit of thoracoabdominal surface respiratory movement signals
PendingCN111135478AAchieve super resolutionShort analysis timeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySquare waveformRespiratory frequency
The invention relates to a quasi-phase super-resolution circuit of thoracoabdominal surface respiratory movement signals, and belongs to the technical fields of precision instruments and thoracoabdominal radiotherapy. The circuit comprises a signal conversion module, a phase difference multiple output module, a resistor chain multiphase generation module, a multiphase sinusoidal square wave conversion module and a multiphase fusion logic gate module; the modules are indispensable as a whole, and convert the respiratory movement signals of one cycle into quasi-phase square wave signals of multiple cycles jointly, and the null cycle of the signals is output by a super-resolution square wave with phase difference of a quasi phase; that is to say, super resolution of the thoracoabdominal surface respiratory movement signals is achieved, and further technical advantages which can be brought by the result are that in a process of multiple respiratory cycles, by judging frequency change of square wave signals, change of the respiratory frequency can be judged, and more importantly, due to the fact that the cycle of the super-resolution square wave is much smaller than the respiratory movement cycle, change of the respiratory frequency can be judged in a time range smaller than one respiratory cycle.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Microwave Radar Super-resolution Method Based on Spatial Frequency Dispersion
ActiveCN110568410BAchieve super resolutionRealize regulationWave based measurement systemsAntennasMechanical engineeringMicrowave radar
The invention discloses a microwave radar super-resolution method of spatial frequency dispersion, comprising: designing a phase-space variable dispersion antenna with adjustable amplitude and phase distribution on the aperture surface as the transmitting antenna; optimizing the amplitude and phase distribution on the antenna aperture surface; A point at the center of the variable phase is used as the center of rotation of the antenna. During detection, the dispersive antenna rotates and scans around the center of rotation, and the signal in the form of a pulse is used as the transmission signal, which is equivalent to forming a variable phase with the distance between the center of rotation and each variable phase center as the radius. Multi-section arc virtual antenna array in the center; the phase space-varying signal corresponding to the rotation center as the reference point is used as the reference signal, and the spatial matching filter is used to realize the focusing of the multi-section arc virtual antenna array. When the effective aperture of the multi-section arc virtual antenna array is larger than the actual Angle super-resolution of microwave radar can be achieved when the dispersive antenna aperture is small.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Auto-locating confocal scan microscope with optical fibre
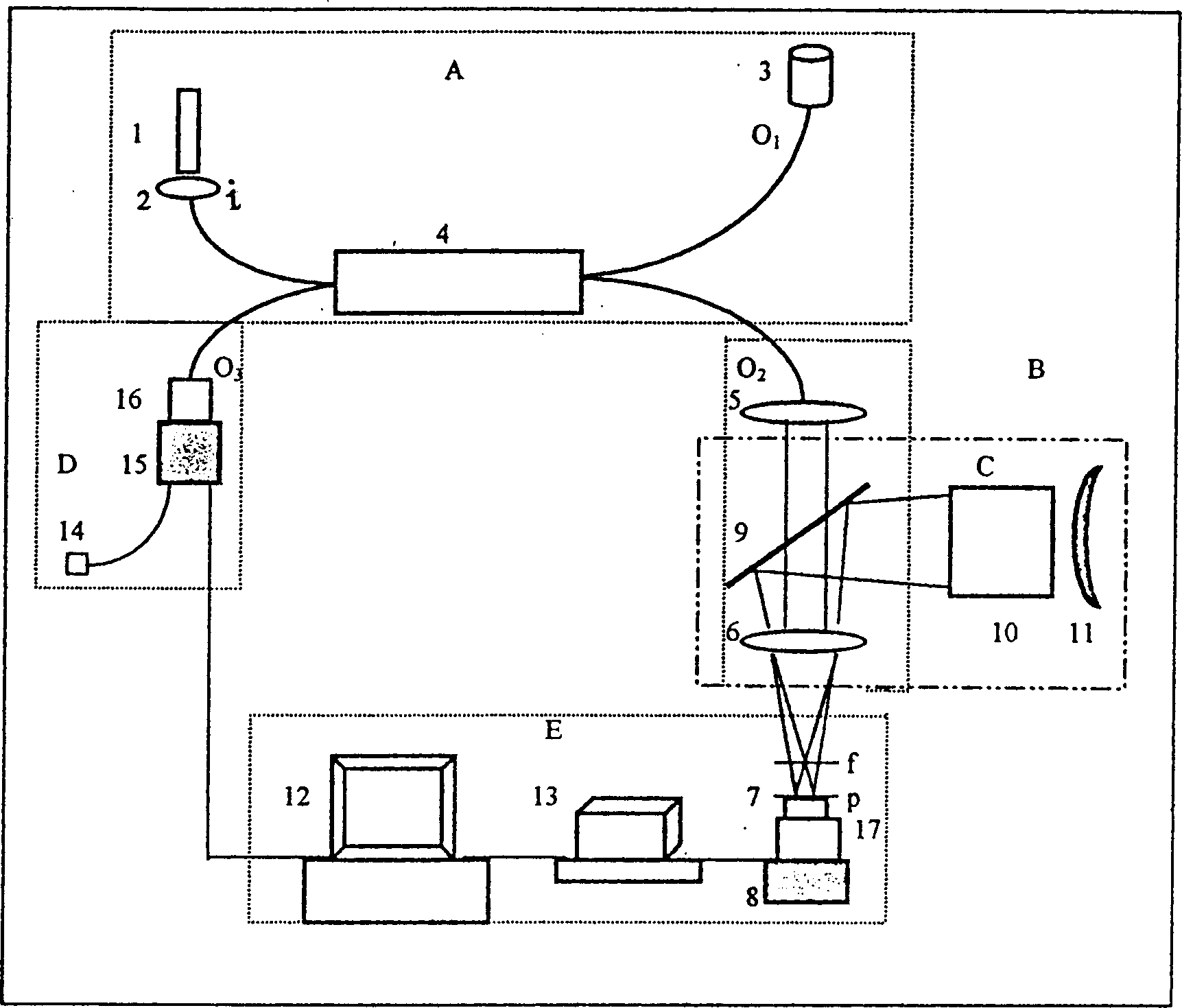
An auto-locating confocal scan microscope using optical fibre is composed of light beam input unit A, optical fibre scan unit B, measurement locating unit C alternative with B, probing-sampling unit D and control data acquisition and processing unit E. Said A, B, D and E constitute an optical fibre confocal scan microscope. Said A, B and C constitute a quasi-confocal small-view-field microscope. That is, it has both the microscan-tomographic imaging function and one-pass imaging function. It is suitable for examining 3D structure with nm depth and submicron width.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quasi-phase super-resolution method for chest-and-belly surface breathing movement signals
InactiveCN111135482AAchieve super resolutionShort analysis timeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySquare waveformMedicine
The invention relates to a super-resolution method for chest-and-belly surface breathing movement signals and belongs to the technical fields of precise instruments and chest-and-belly radiotherapy. According to the method, firstly, breathing movement signals are converted into periodic signals through a signal conversion module, then, equal-phase-difference III output with the phase difference ofPI / 2 is formed through a phase difference multi-output module, then, equal-phase-difference V output with the phase difference of PI / 5 is formed through a resistance chain multi-phase generation module, then, square waves are formed through a multi-phase sine square wave conversion module, and quasi-phase super-resolution square wave output is formed through a multi-phase merged logic gate module, so that the breathing movement signals of one period can be changed into quasi-phase square wave signals of multiple periods, and phasic difference is a zeroth period of the quasi-phase super-resolution square wave output signals.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Image super-division method based on progressive residual generative adversarial network
PendingCN114140323AAchieve super resolutionImprove the effect of super resolutionGeometric image transformationNeural architecturesPattern recognitionAlgorithm
The invention discloses an image super-division method based on a progressive residual generative adversarial network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing down-sampling processing on a given real target image to obtain a series of low-resolution picture sets; building a residual generative adversarial network, and starting layer-by-layer training from the lowest sub-network layer until a vivid reconstructed picture with the same resolution as the original real picture is generated; and finally, further performing up-sampling on the image according to a required super-resolution value, overlapping noise and inputting the noise into a higher layer of sub-network for iterative training, and finally obtaining a required super-resolution image. On the basis of the generative adversarial network model in deep learning, a weighted cascade residual structure is fused, feature information of the input picture can be efficiently and fully utilized, data features of the input picture can be fitted, and super-resolution of the picture is achieved. Compared with the prior art, the method is low in cost and easy to implement, and the super-resolution effect of the image can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Single image super-resolution output method based on graph model
ActiveCN107680043BAchieve super resolutionSuper Resolution FitGeometric image transformationAlgorithmImage resolution
The invention discloses a graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method. The graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method includes the following steps: 1) according toa preset sampling rate, performing interpolation on an input single image by means of a bicubic interpolation method, obtaining a low resolution image, segmenting the obtained low resolution image into m*n image blocks, calculating the Euclidean distance of the pixel value of each image block, and according to the Euclidean distance, determining a set of similar blocks, wherein each image block in the segmented low resolution image has one set of similar blocks; 2) constructing a graph model for the set of similar blocks; 3) performing Laplace transformation on the obtained two dimensional matrix to obtain a Laplace matrix, and then carrying out restoration of the image blocks through solution by means of an optimization formula; and 4) averaging and reconstructing the restored image block set, and finally obtaining a super-resolution image. The graph-model-based single image super-resolution output method can overcome the defect that a machine learning method needs mass image data totrain a model, thus being more suitable for image super resolution.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Terahertz super-resolution imaging system and method based on confocal waveguide
InactiveCN109683341AAchieving Subwavelength FocusingAchieve super resolutionMicroscopesFocal positionWaveguide
The invention discloses a terahertz super-resolution imaging system and method based on a confocal waveguide. The system comprises a terahertz or millimeter wave source, a pinhole, the confocal waveguide, an imaging target, a two-dimensional scanning mechanism, a second waveguide body and a detector. The terahertz or millimeter wave source is used for giving out a terahertz or millimeter wave; thepinhole is formed in an incident light path of the source and used for obtaining terahertz or millimeter transmission light; the confocal waveguide is composed of two confocal waveguide bodies, wherein the first waveguide body is arranged on an incident light path after the terahertz or millimeter wave transmits the pinhole and used for transmitting and focusing the terahertz or millimeter wave;the imaging target is arranged on the focal position of the first waveguide body; the two-dimensional scanning mechanism is used for controlling the imaging target to conduct scanning imaging; the second waveguide body is arranged on a transmission or reflection light path of the imaging target and used for transmitting and focusing a transmission wave; the detector is arranged on the focal position of the second waveguide body and used for detecting the intensity of the terahertz or millimeter wave, and finally imaging is achieved. According to the system, the confocal waveguide is used for replacing a traditional confocal lens to achieve focal imaging, the transmission loss of the terahertz or millimeter wave is reduced, the diffraction limit can be broken through, and super-resolution imaging is achieved.
Owner:龚诚
Radar distance super-resolution calculation method based on sparse Bayesian learning algorithm
ActiveCN113406575AAchieve super resolutionMathematical modelsGeometric image transformationAlgorithmCalculation methods
The invention discloses a radar distance super-resolution calculation method based on a sparse Bayesian learning algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of S1, carrying out the pulse compression of an echo signal of a radar, and determining a group target radar signal segment, S2, performing frequency dechirp processing on the group target radar signal segment to obtain a single-frequency signal, S3, performing super-resolution processing on the single-frequency signal by using a sparse Bayesian learning algorithm to obtain a frequency point position of a group target radar signal, and S4, determining a radar distance according to the frequency point position of the group target radar signal. Compared with a traditional pulse compression processing algorithm, the resolution effect of the radar distance super-resolution algorithm based on the sparse Bayesian learning algorithm can be improved by more than one time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Waveform Separation Method for MIMO Radar Based on Compressive Sensing
ActiveCN107037409BSuppression distance to high sidelobeEasy to separateWave based measurement systemsRadar waveformsImage resolution
The invention discloses a MIMO radar waveform separation method based on compressed sensing, which includes: (1) transmitting orthogonal waveforms; (2) receiving target echoes; (3) constructing a sensing matrix; (4) sparsely reconstructing one-dimensional targets distance like. Based on the sparsity of the radar target in the distance upward, the invention realizes the orthogonal separation of different waveform components in the MIMO radar echo by constructing a perception matrix related to the transmitted waveform set and using a joint sparse restoration algorithm. This method replaces the traditional matched filtering process, effectively suppresses the high range sidelobe caused by non-orthogonal waveforms, and breaks through the limitation of the signal bandwidth on the range resolution, improving the range resolution.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Meter-wave radar low-elevation height measurement method based on robust principal component analysis noise reduction
PendingCN114814830AHigh angular stabilityExcellent signal matrixCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionNoiseSignal modeling
The invention relates to a meter-wave radar low-elevation height measurement method based on robust principal component analysis noise reduction, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the modeling of an array receiving signal of a meter-wave radar into a two-dimensional receiving signal matrix, and obtaining an array receiving signal model; establishing a convex optimization model of a low-rank signal matrix and a sparse noise matrix by adopting a noise reduction method based on robust principal component analysis; solving the convex optimization model by using an improved non-precise augmented Lagrangian multiplier method to obtain an optimal low-rank signal matrix without noise pollution; establishing a covariance matrix by using the optimal low-rank signal matrix, and constructing the maximum likelihood estimation of the direct wave elevation direction of arrival in combination with the covariance matrix and the synthetic steering vector to obtain a target elevation estimation value; and calculating the target height by using the target elevation angle estimated value. According to the method, the problems that in the prior art, under the conditions of non-uniform noise, low signal-to-noise ratio and few snapshots, the angle measurement performance is reduced, and the angle resolution is insufficient are solved, and the method has high angle measurement stability and good angle resolution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
New usage of photo-discolor diarylethene compound
InactiveCN100428349CAchieve super resolutionImprove compatibilityRecord information storageTenebresent compositionsHigh densityOptical storage
This invention discloses a new usage of photochromic diarylethenes compound, in which, the inventer verifies from experiments that the near field super resolution optical storage CD with photochromic diarylethenes compound as the mask layer has the advantages of high density and small size in recording information.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com