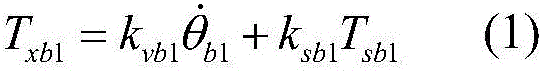Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
331results about How to "Avoid sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
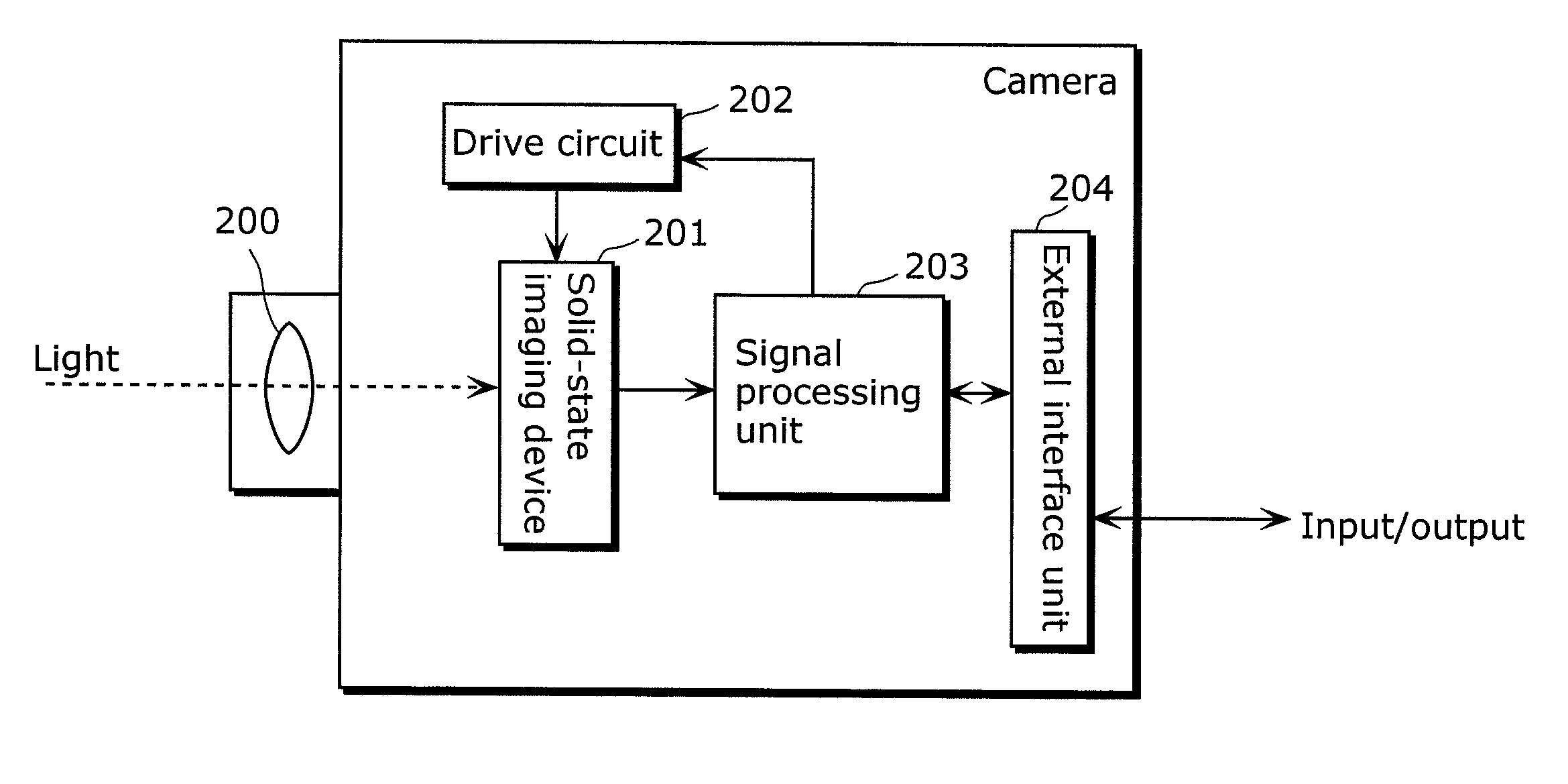
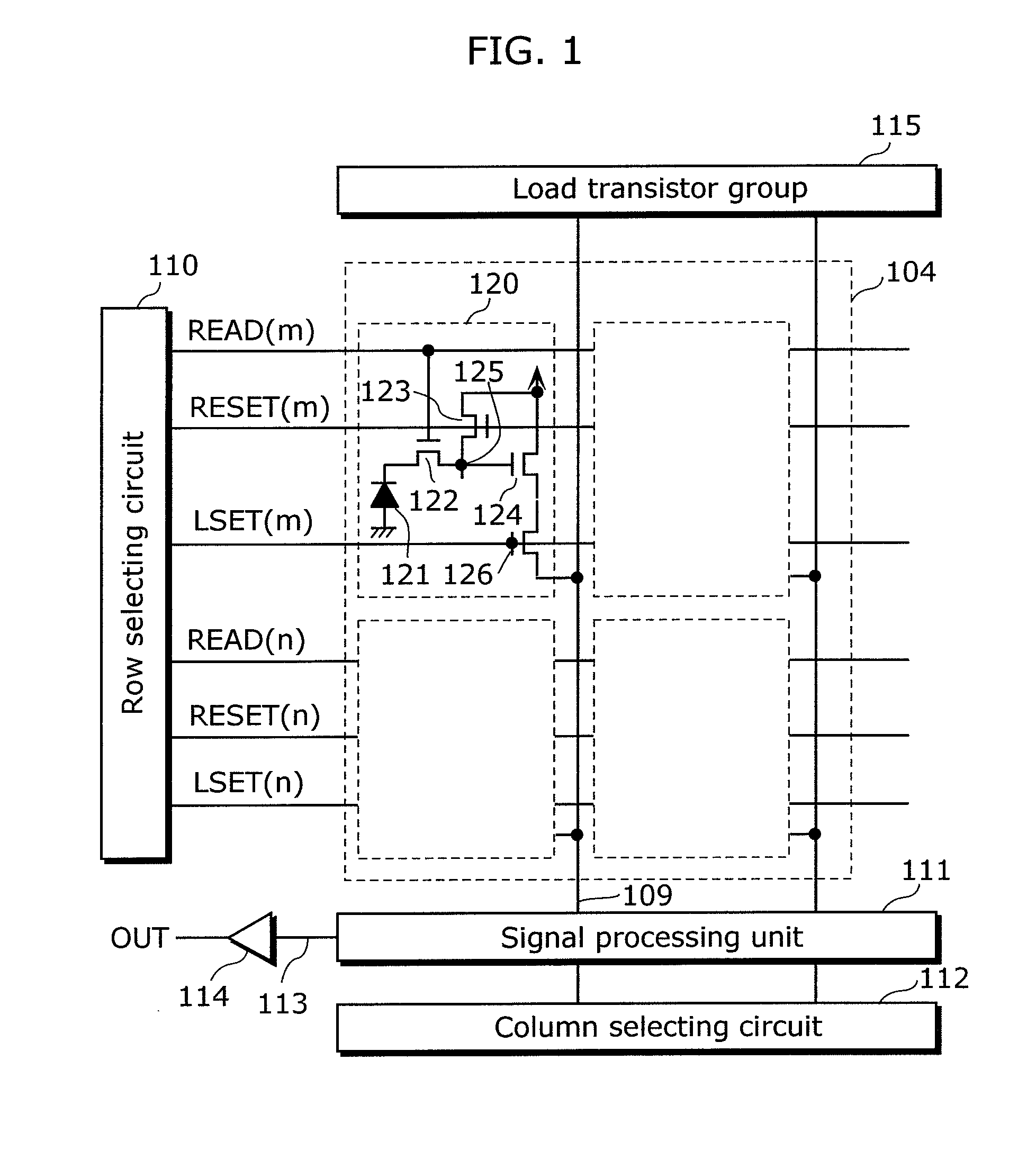
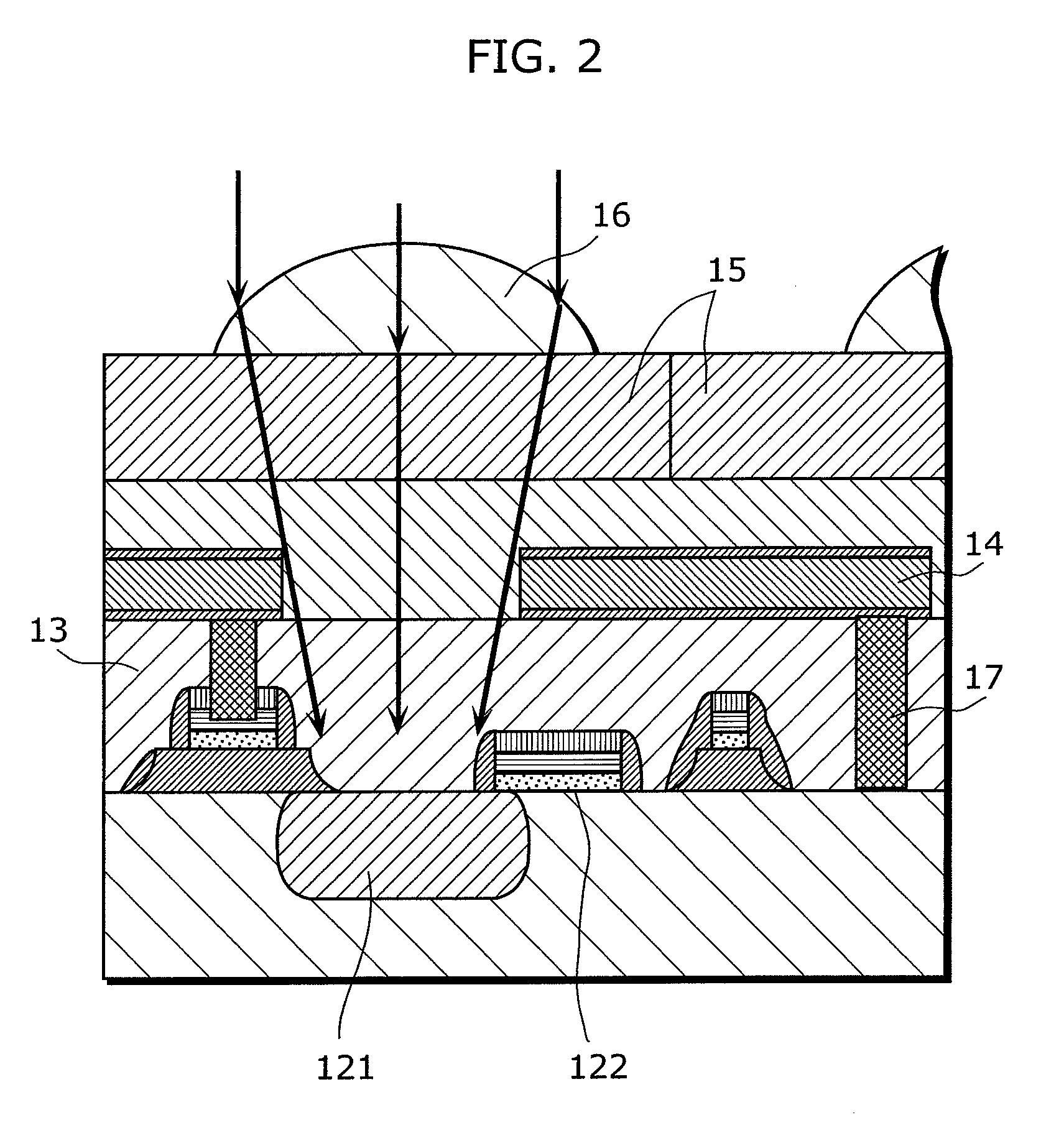
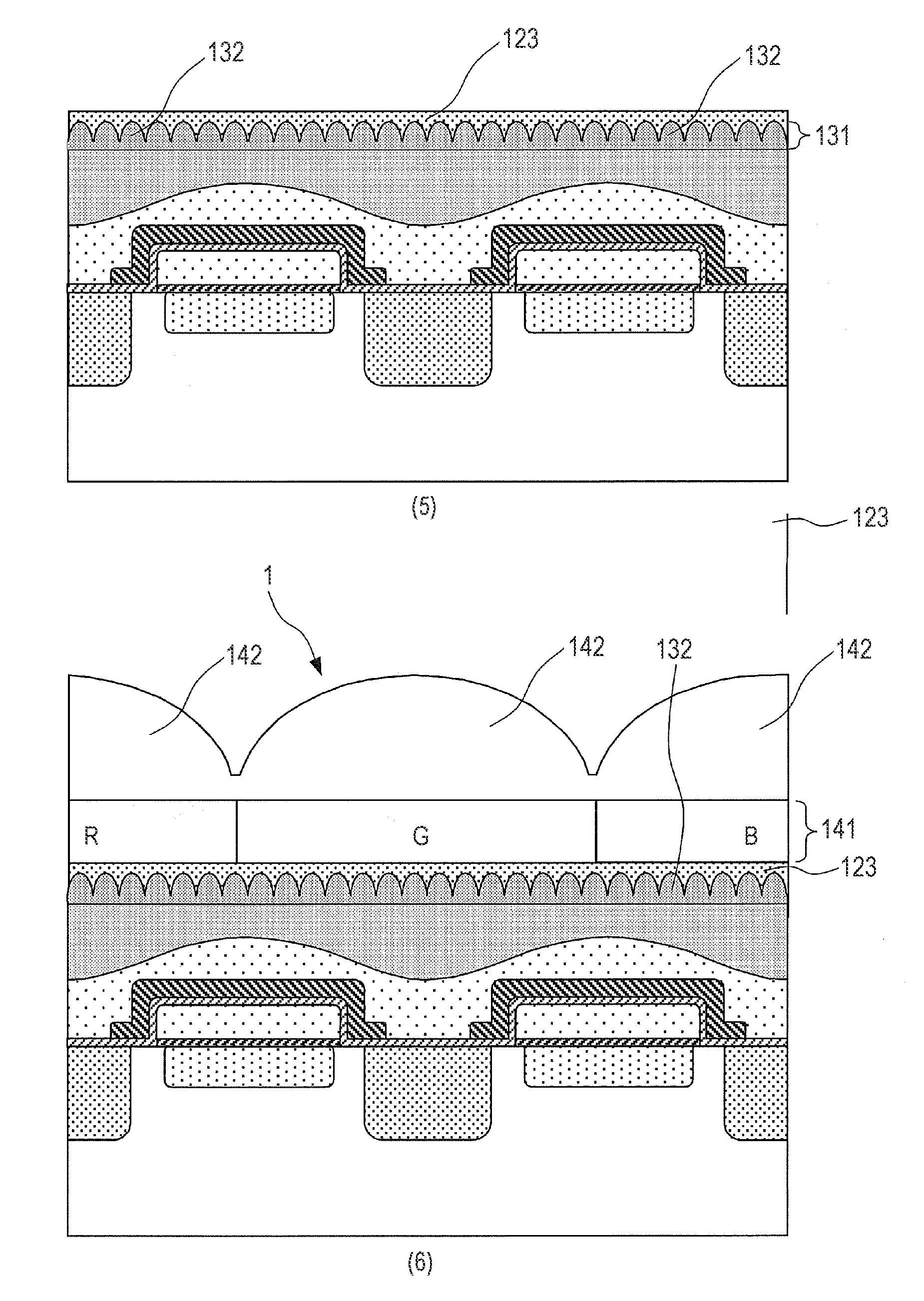
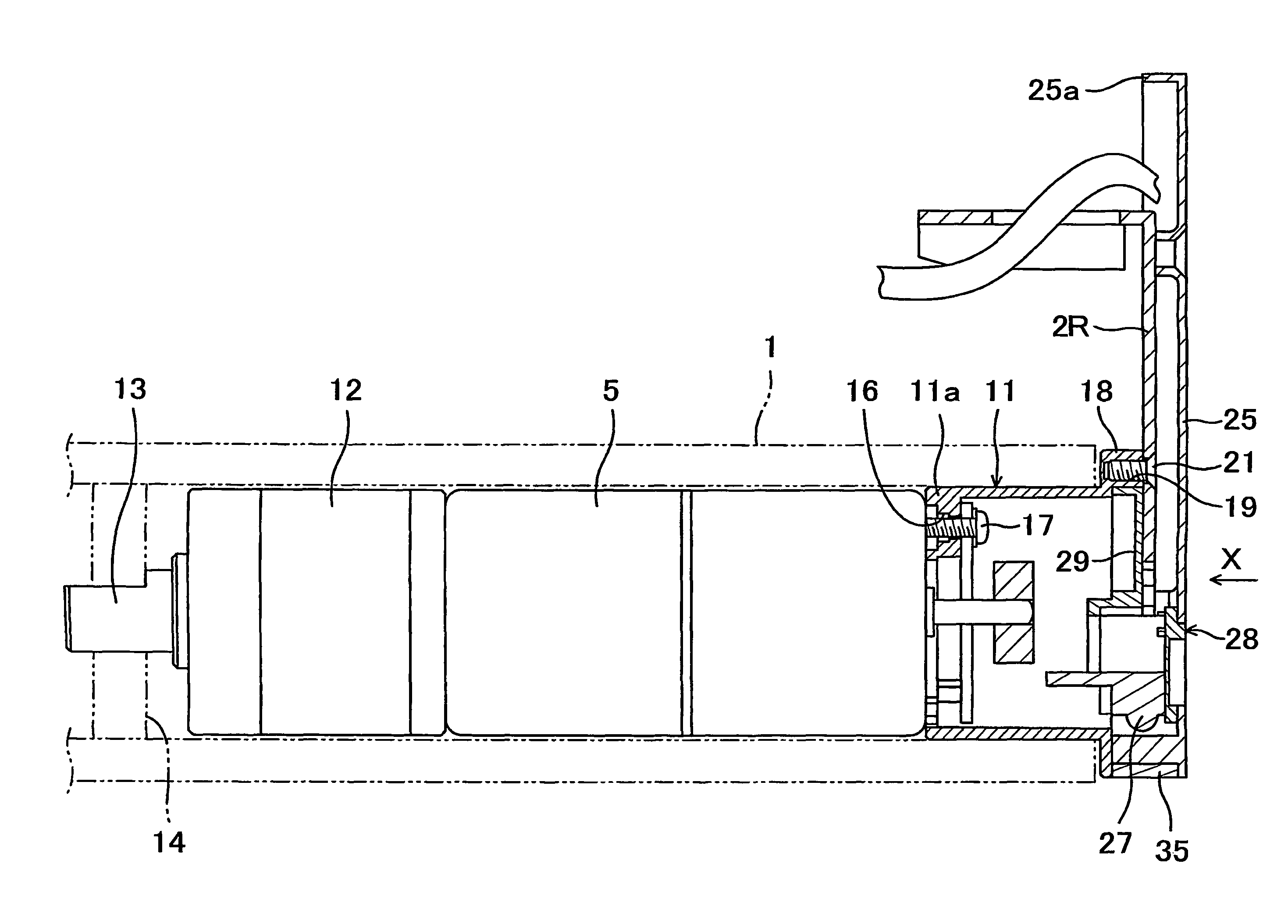
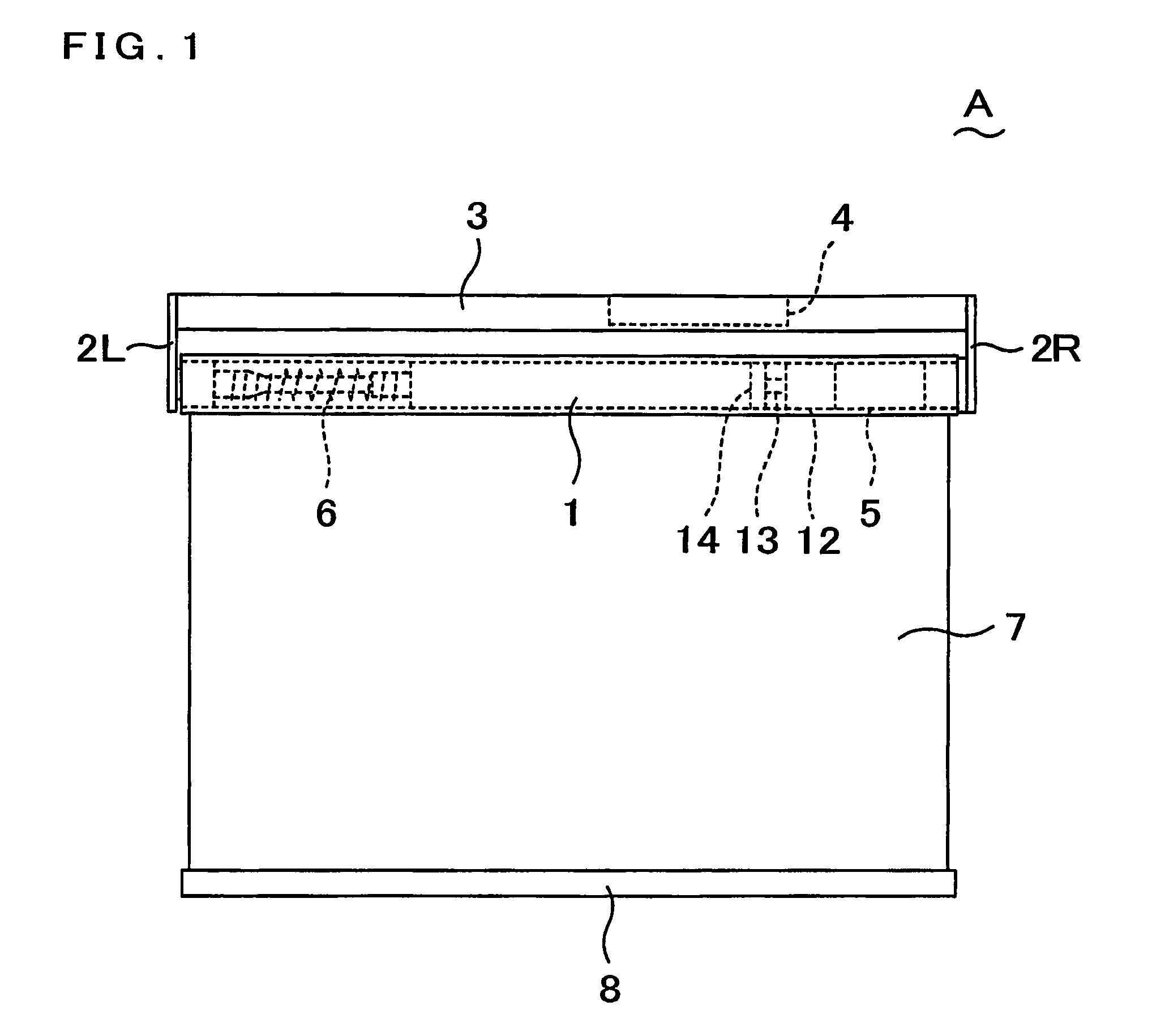
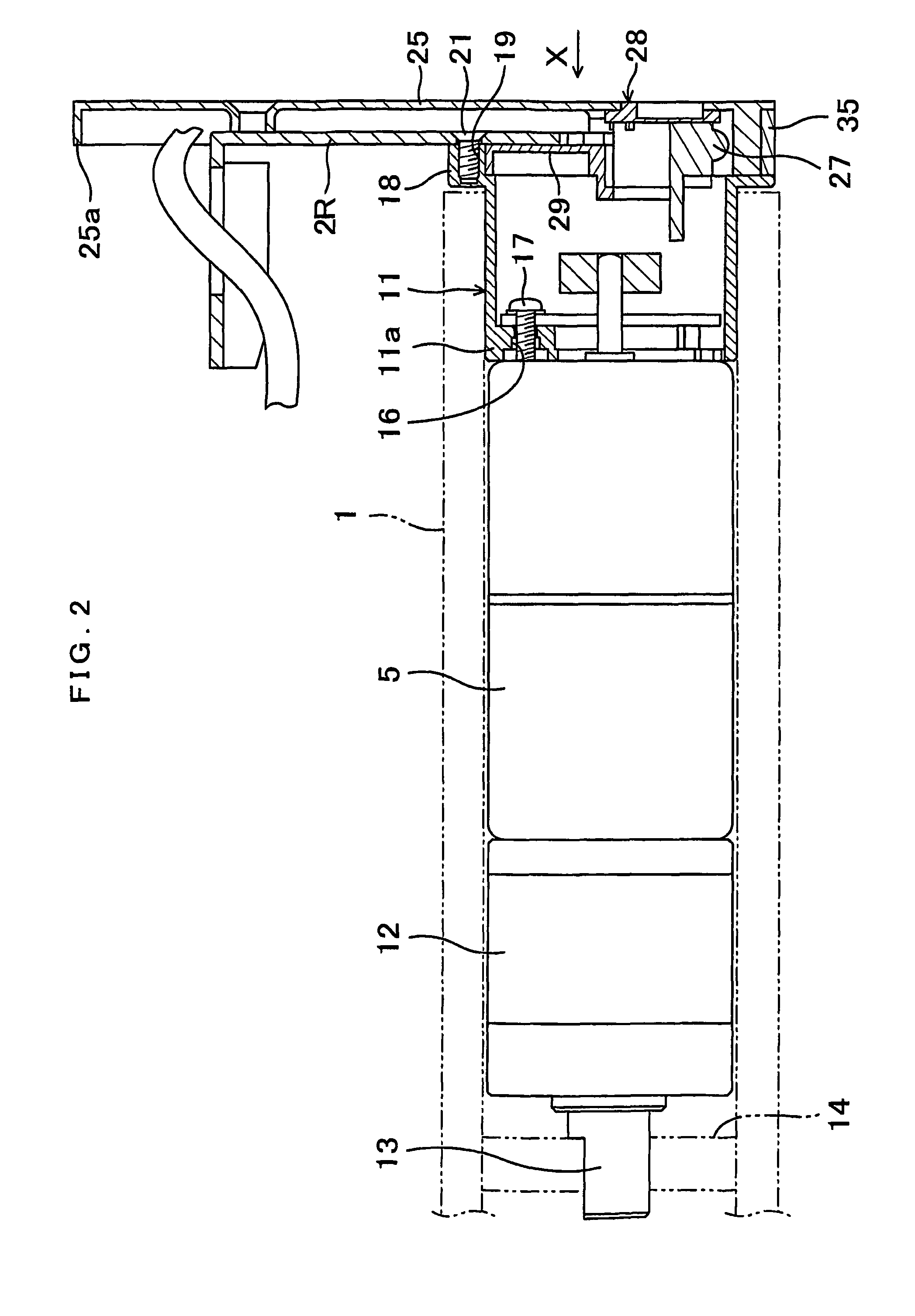
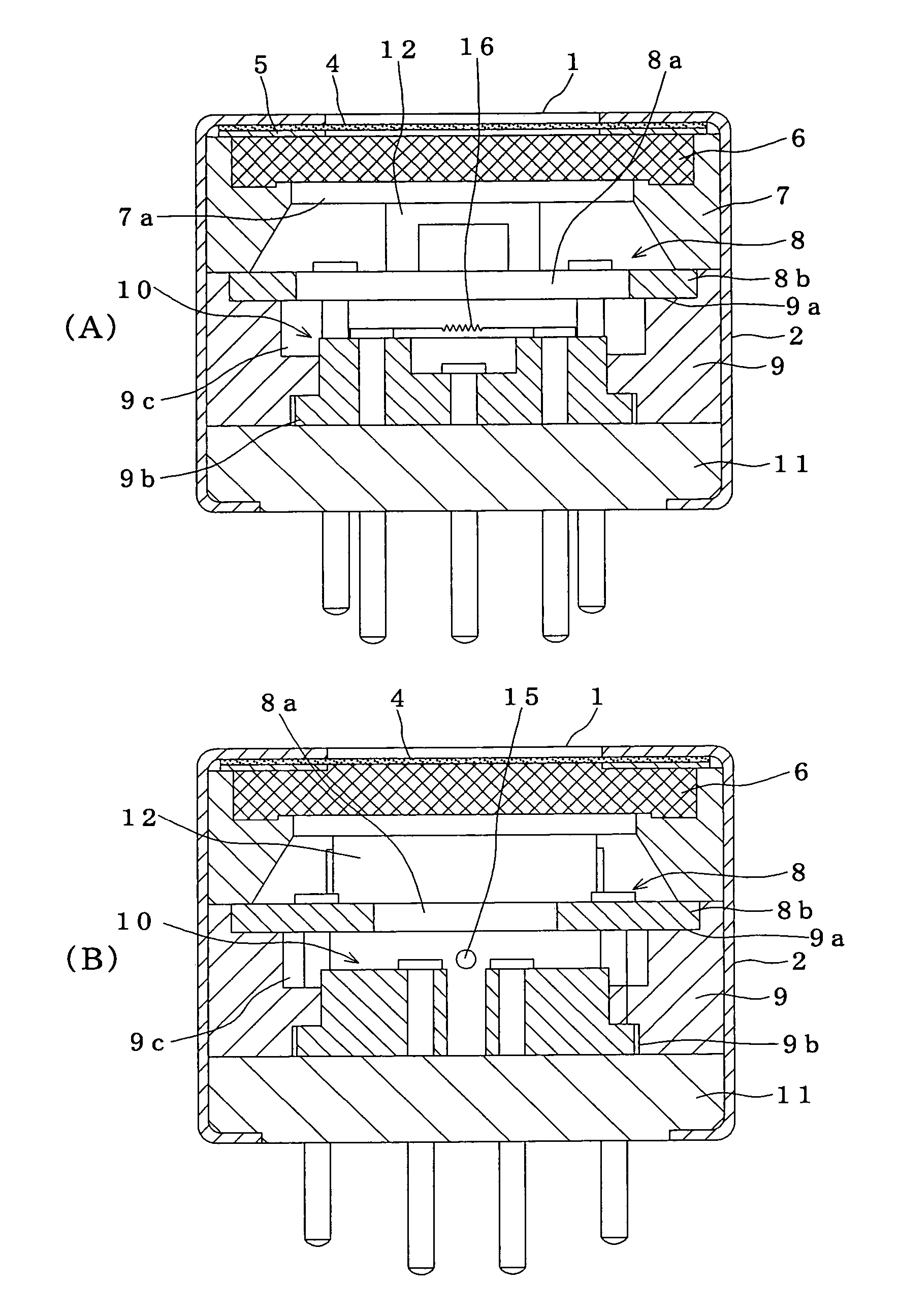
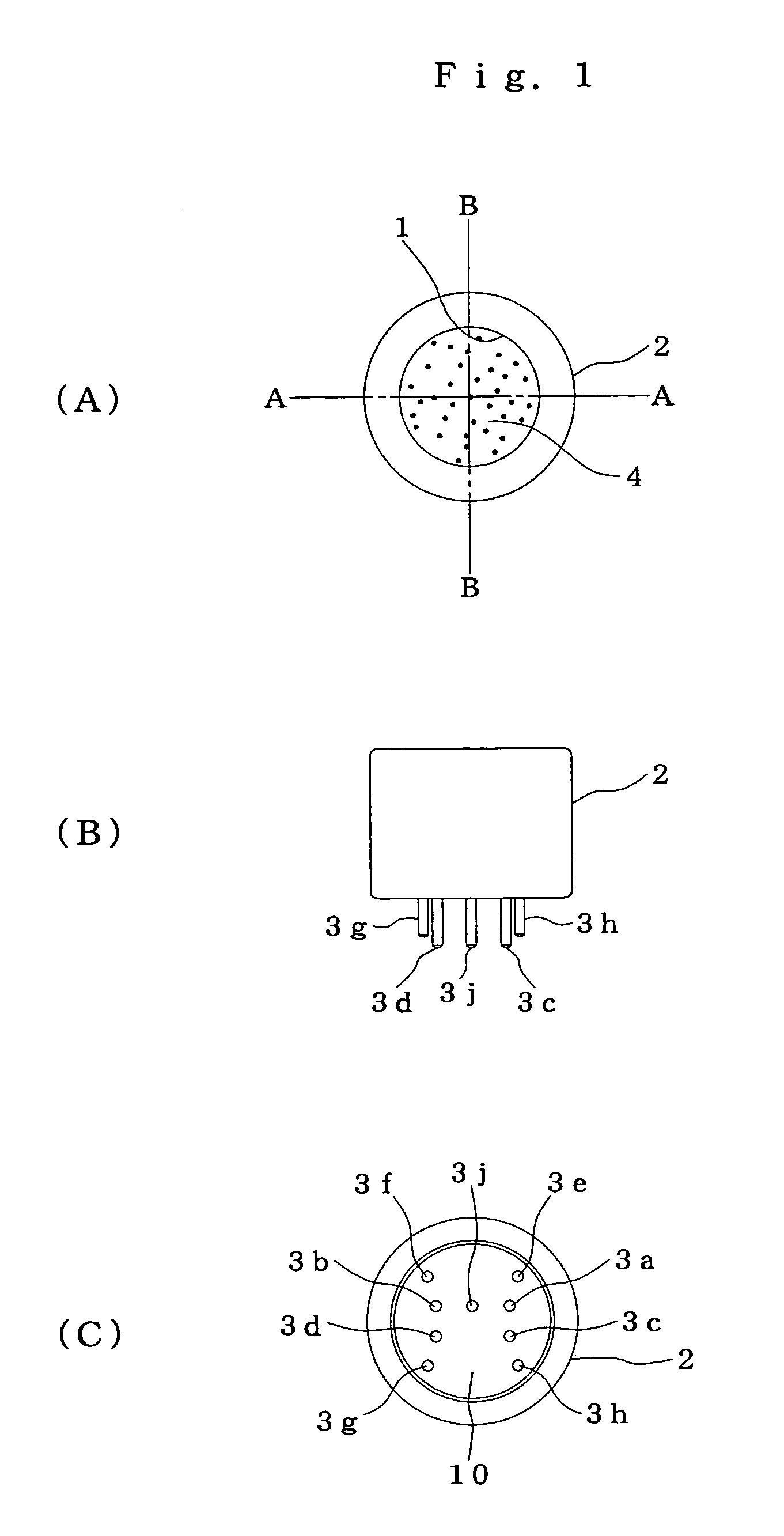
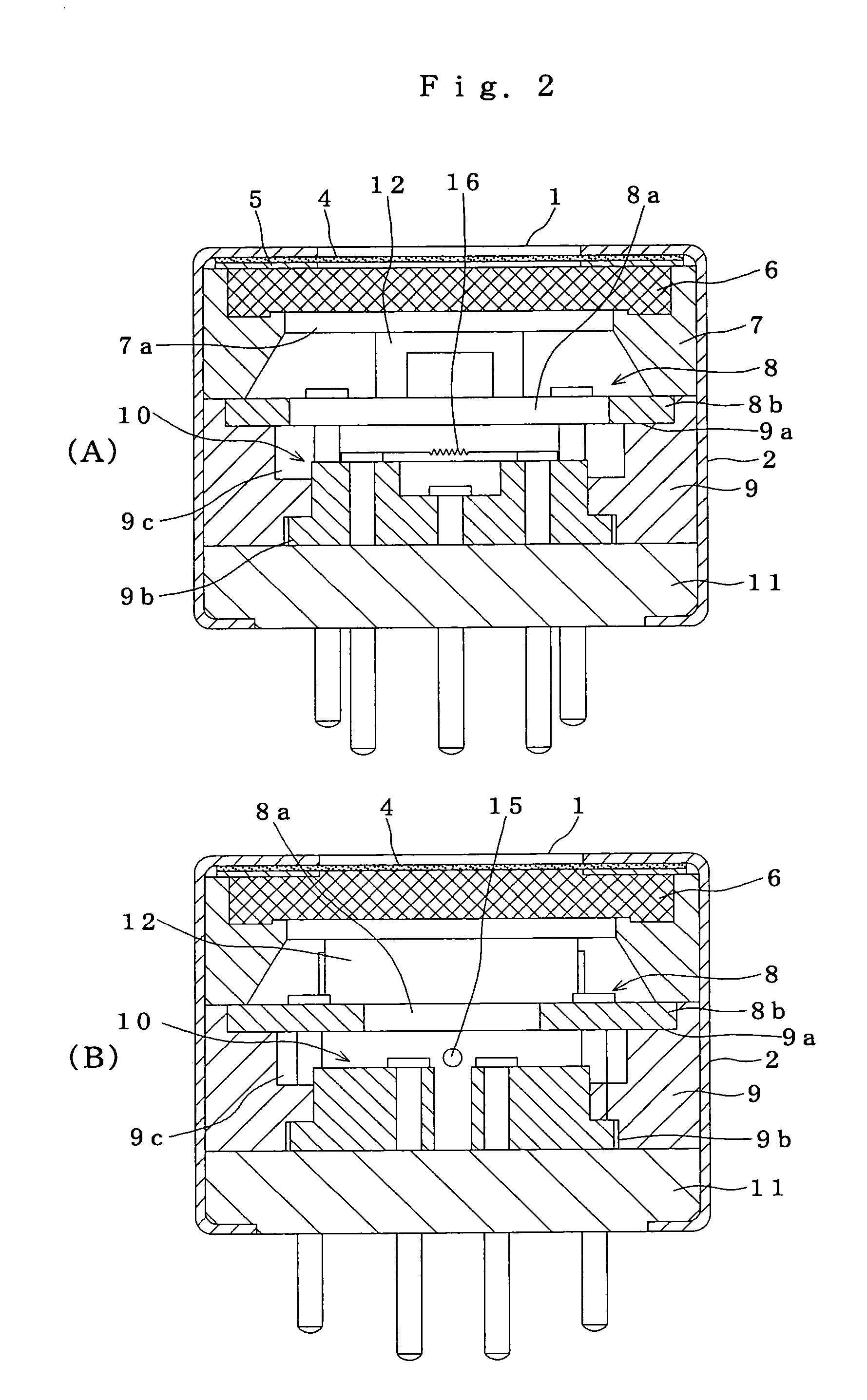
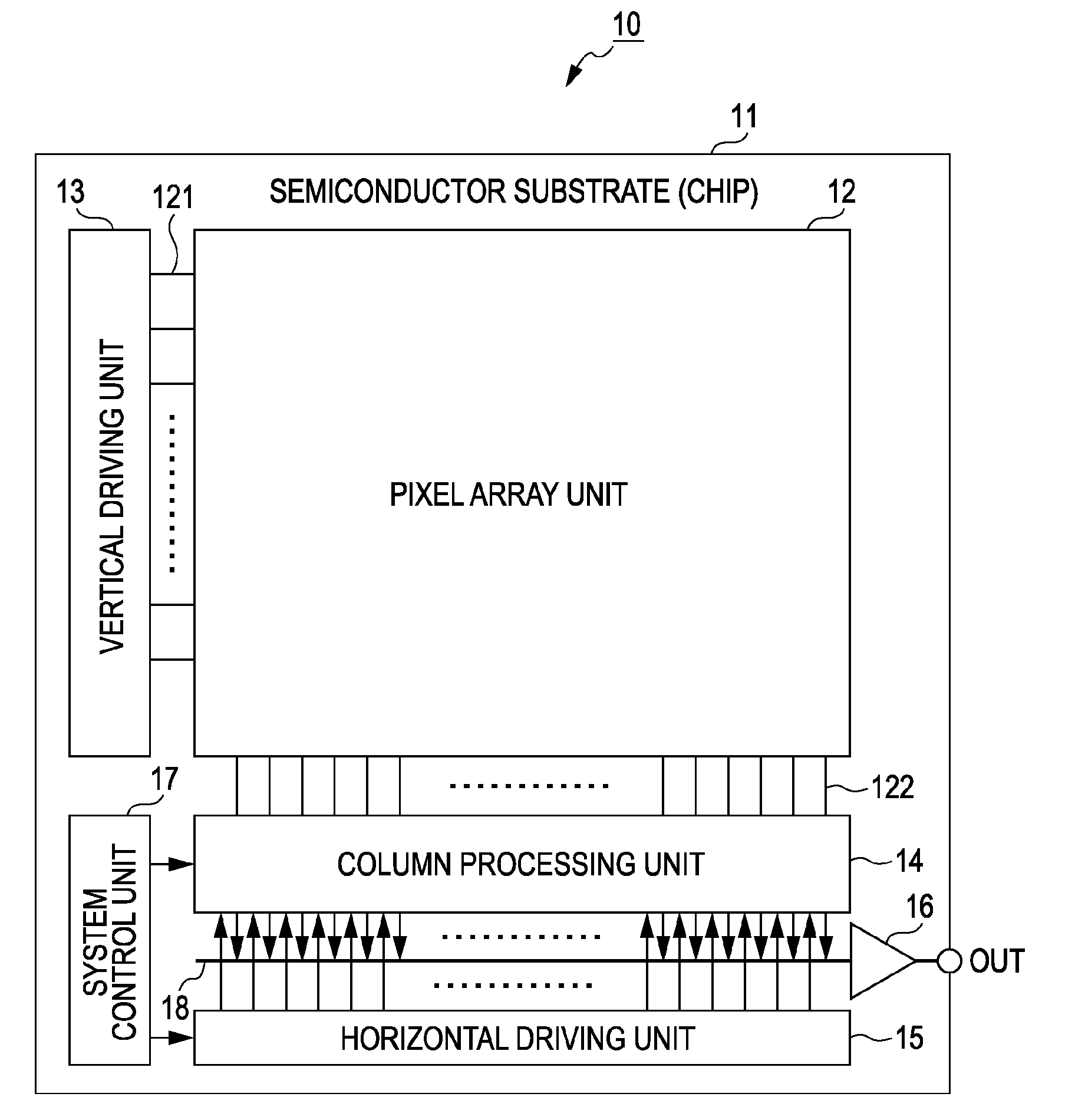
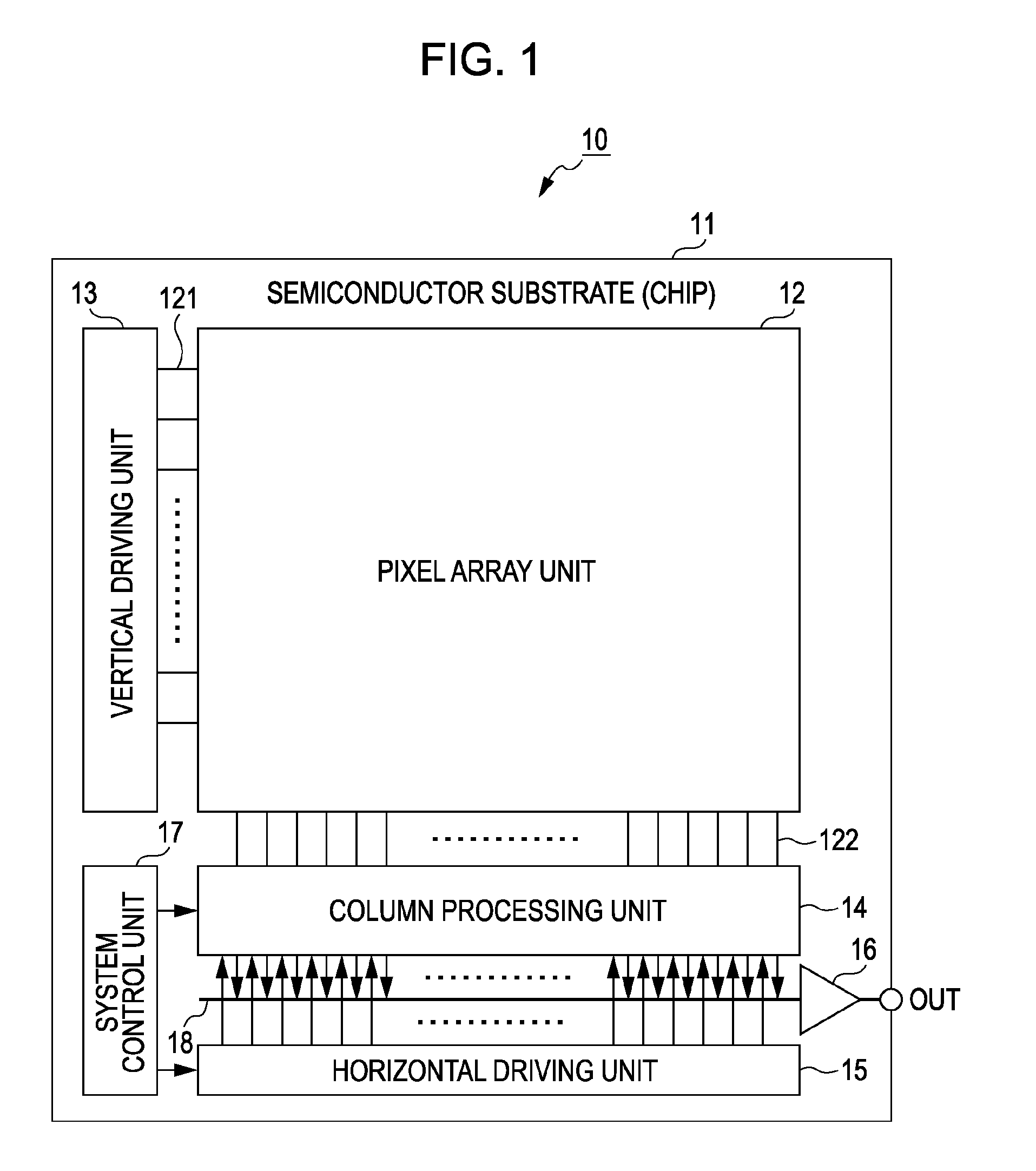
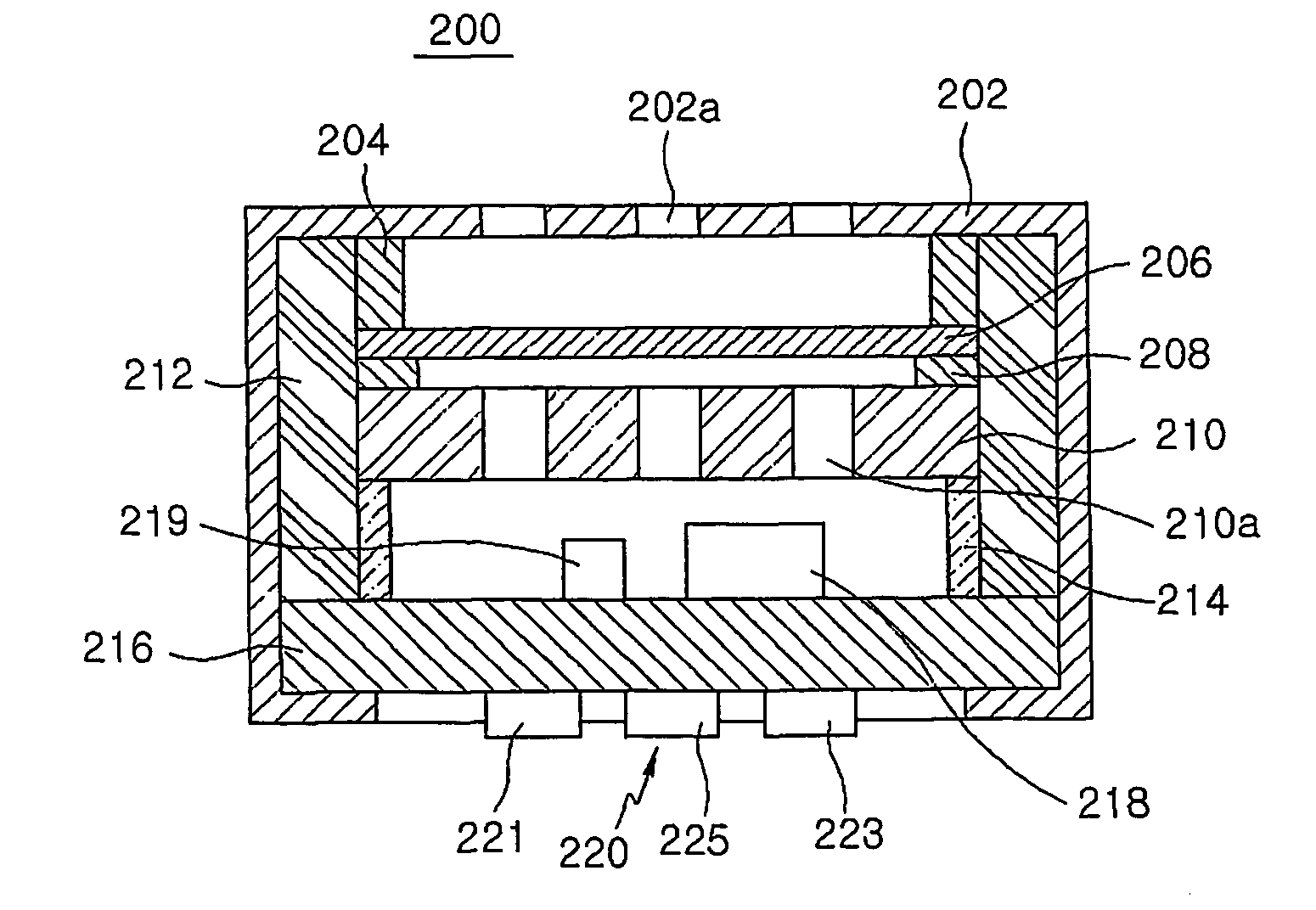
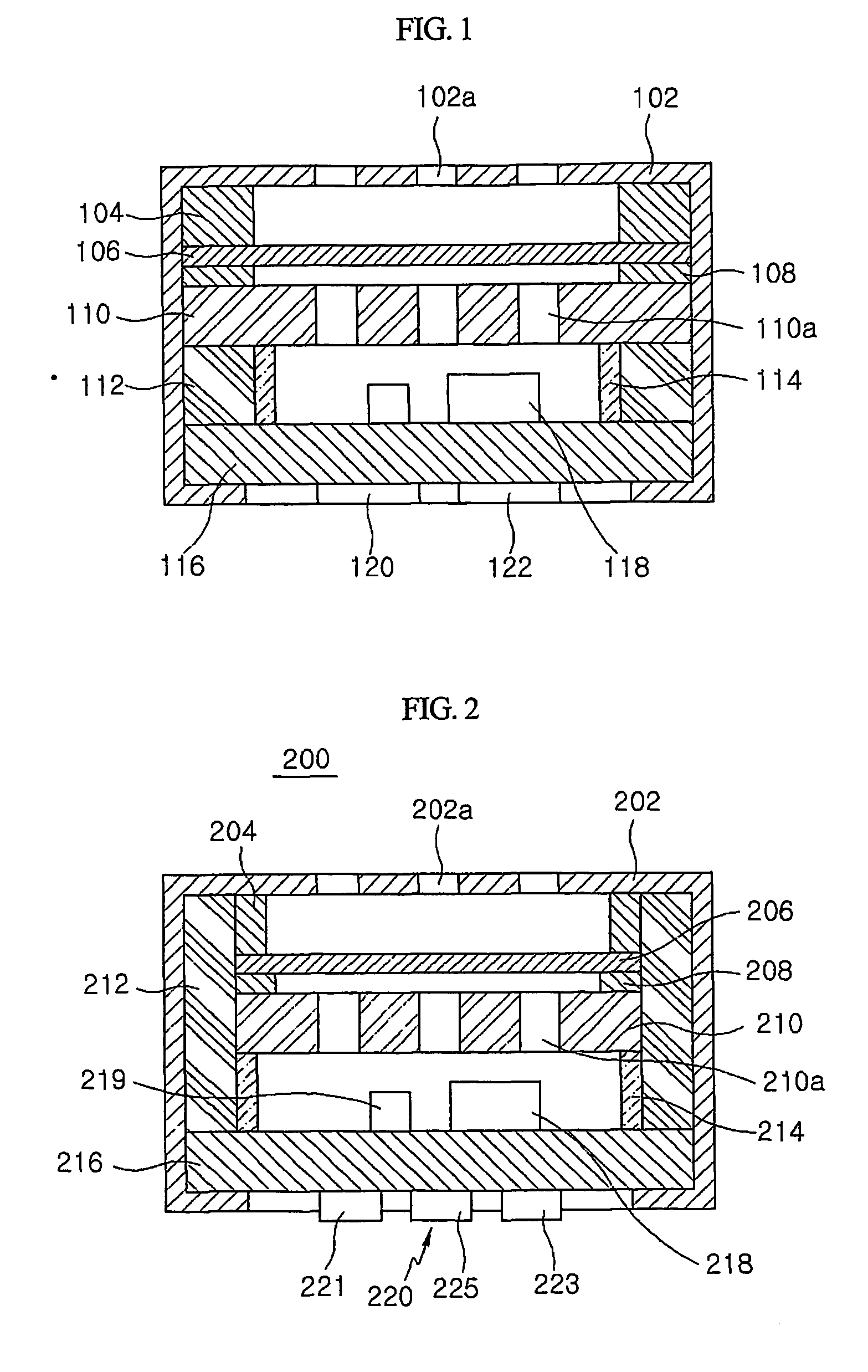
Solid-state imaging device and camera using the same
InactiveUS20080170143A1Improve picture qualityHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLength waveScale down
The object of the present invention is to provide a solid-state imaging device equipped with a color filter which is highly durable, inexpensive to manufacture, and adaptable to the scaling down of pixels, and a camera using the solid-state imaging device. The solid-state imaging device includes a photodiode, and a metal optical filter formed above the photodiode, which allows light of a desired wavelength to be transmitted. The metal optical filter is made of a metal thin film in which plural cylinder-shaped apertures are periodically arrayed. The size of each of the apertures is smaller than the desired wavelength, and an inter-aperture distance between a predetermined aperture and an aperture adjacent to the predetermined aperture is shorter than the desired wavelength.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
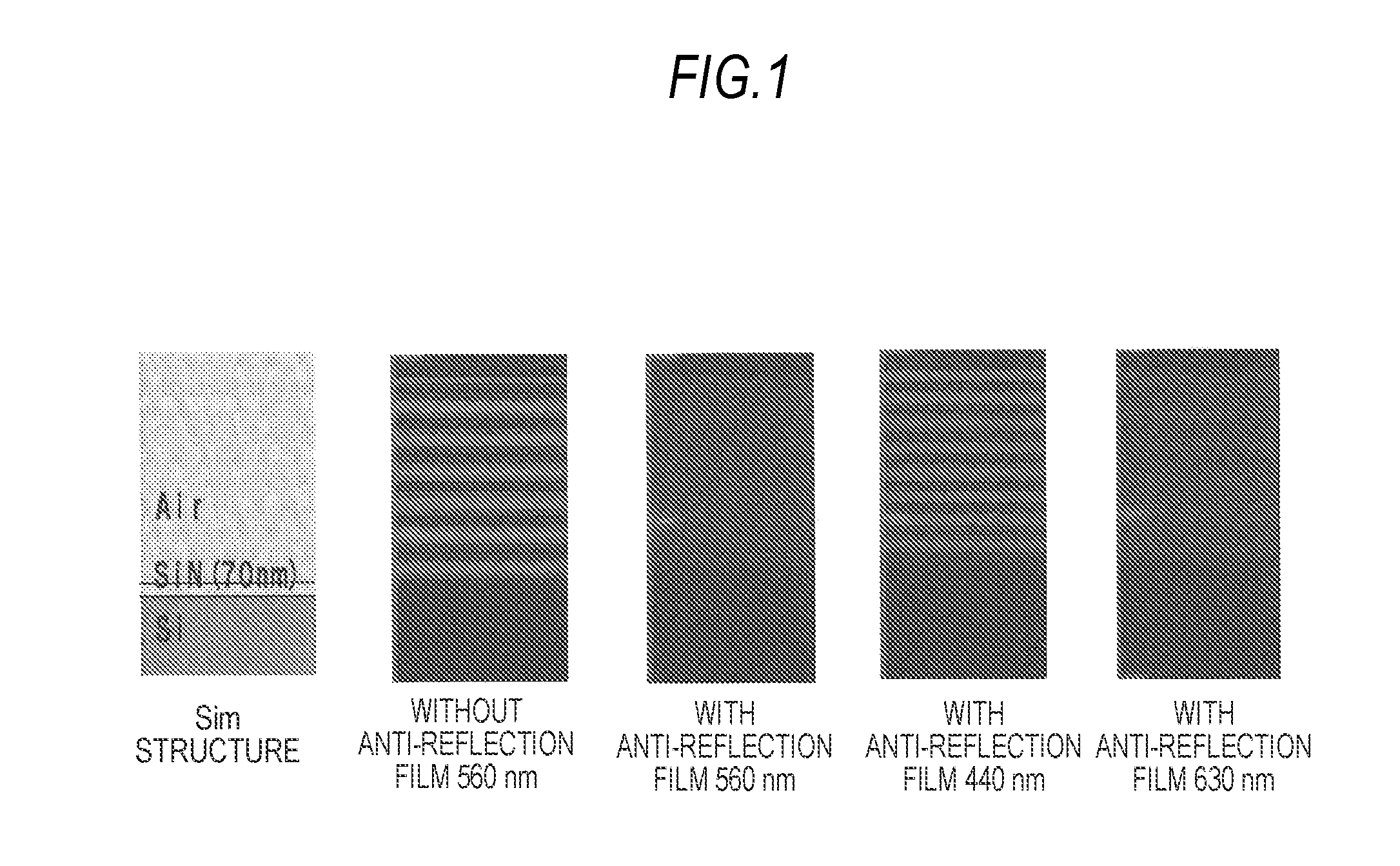
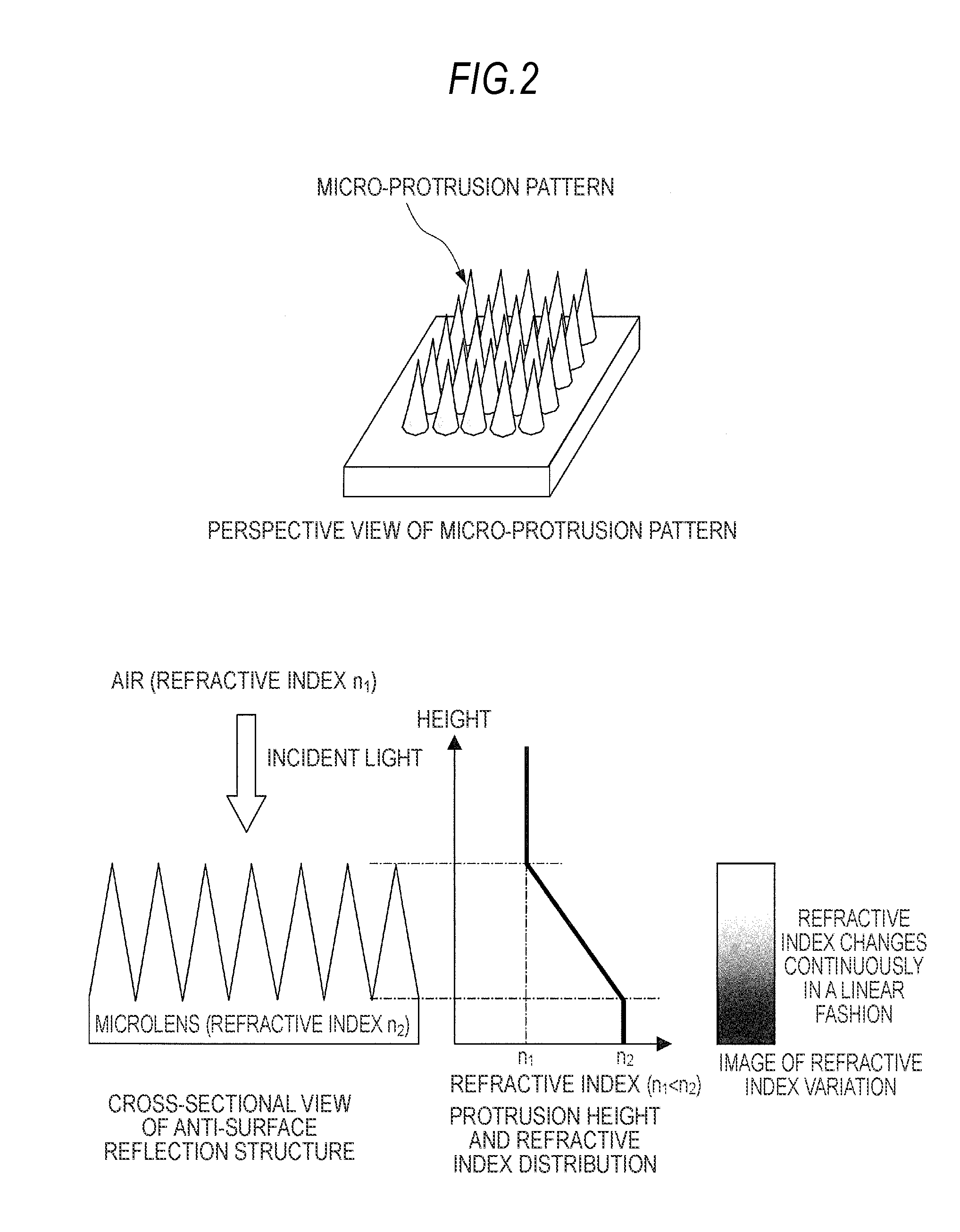
Solid-state imaging device, fabrication method thereof, imaging apparatus, and fabrication method of Anti-reflection structure
InactiveUS20100244169A1Avoid sensitivityHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin membraneSurface shape
A fabrication method of an anti-reflection structure includes the steps of: forming a resin film having micro-particles dispersed therein on a surface of a substrate; forming a protrusion dummy pattern on the resin film by etching the resin film using the micro-particles in the resin film as a mask while gradually etching the micro-particles; and forming a protrusion pattern on the surface of the substrate by etching back the surface of the substrate together with the resin film having the protrusion dummy pattern formed thereon, and transferring a surface shape of the protrusion dummy pattern formed on a surface of the resin film to the surface of the substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
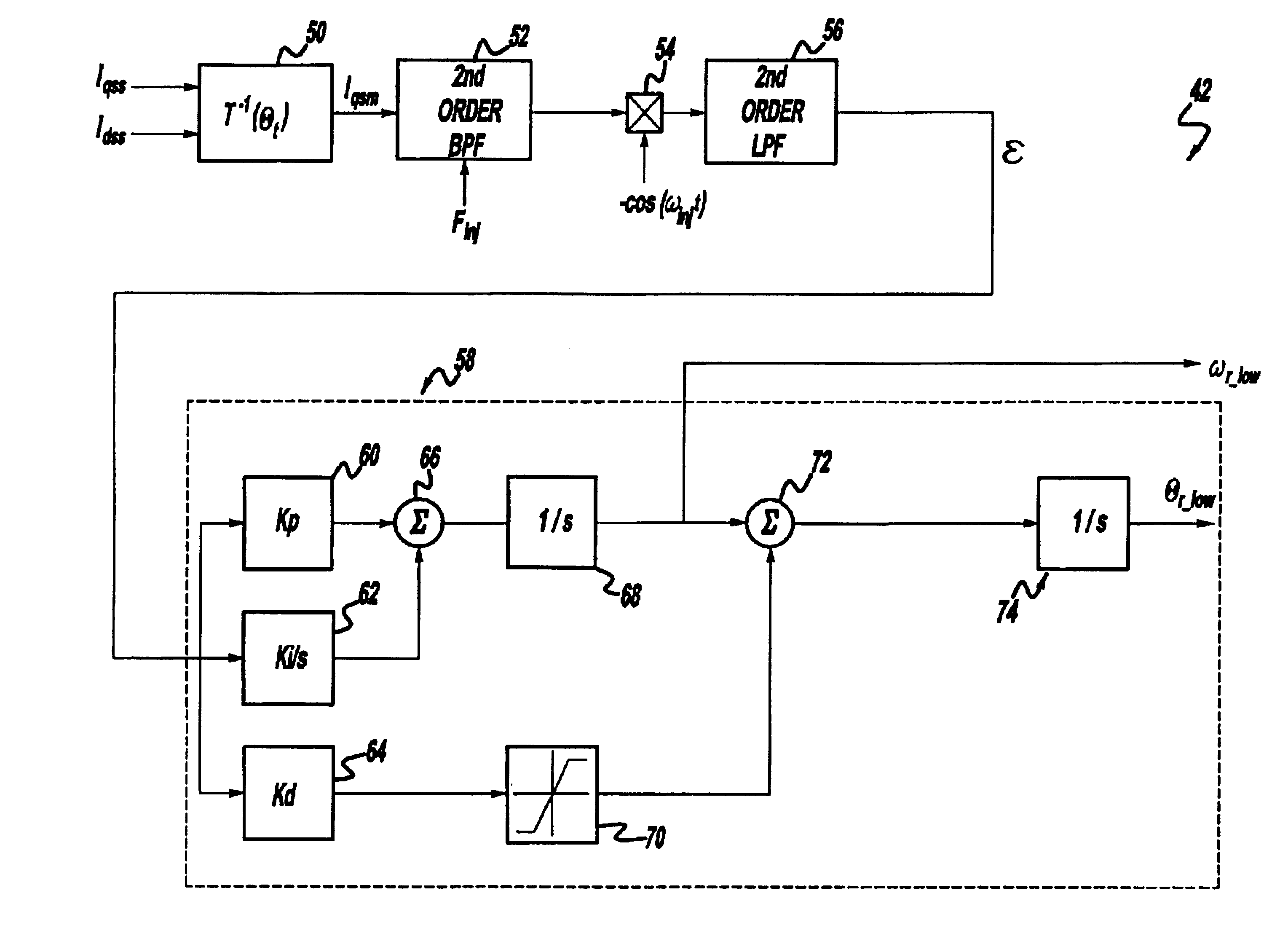
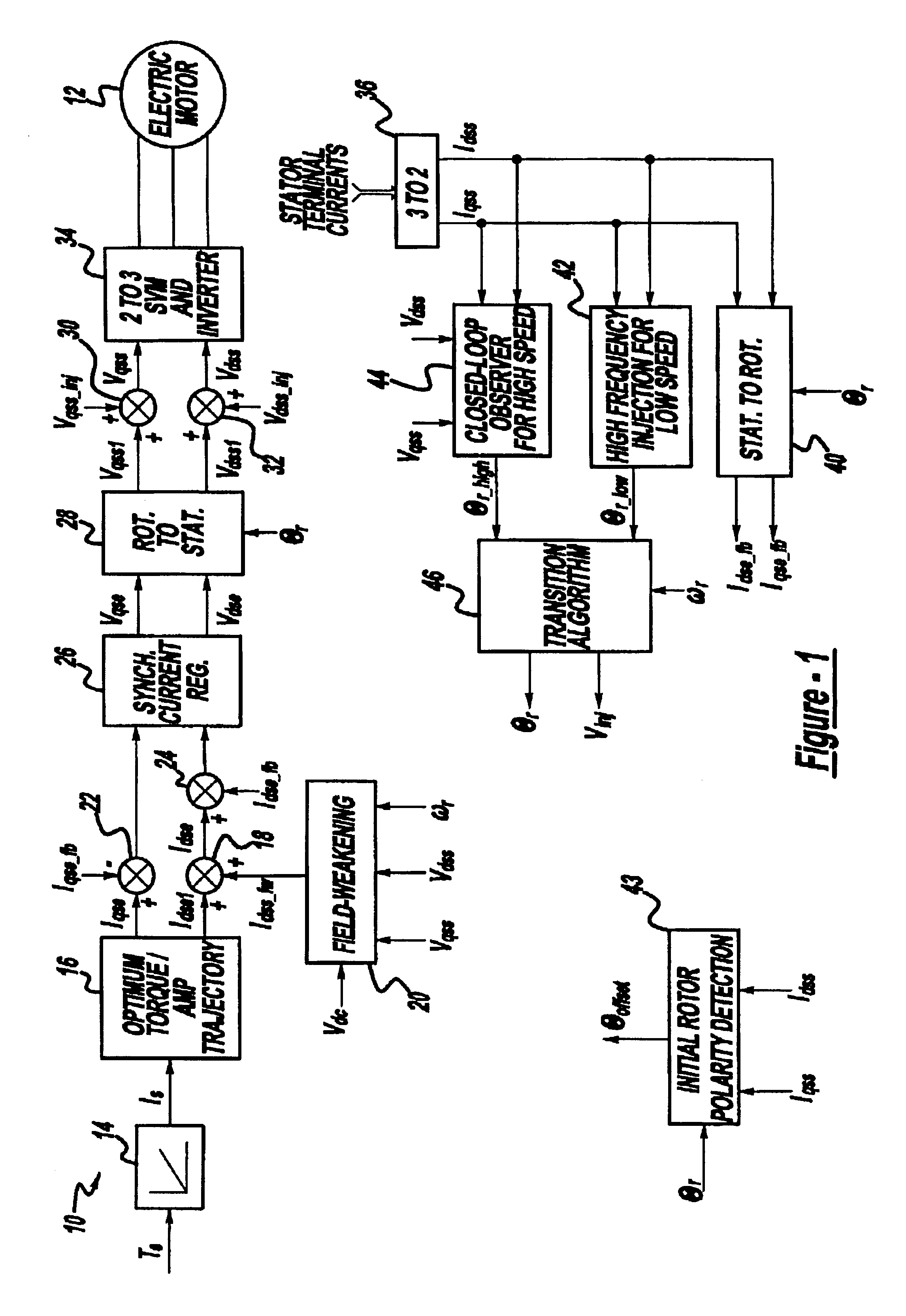
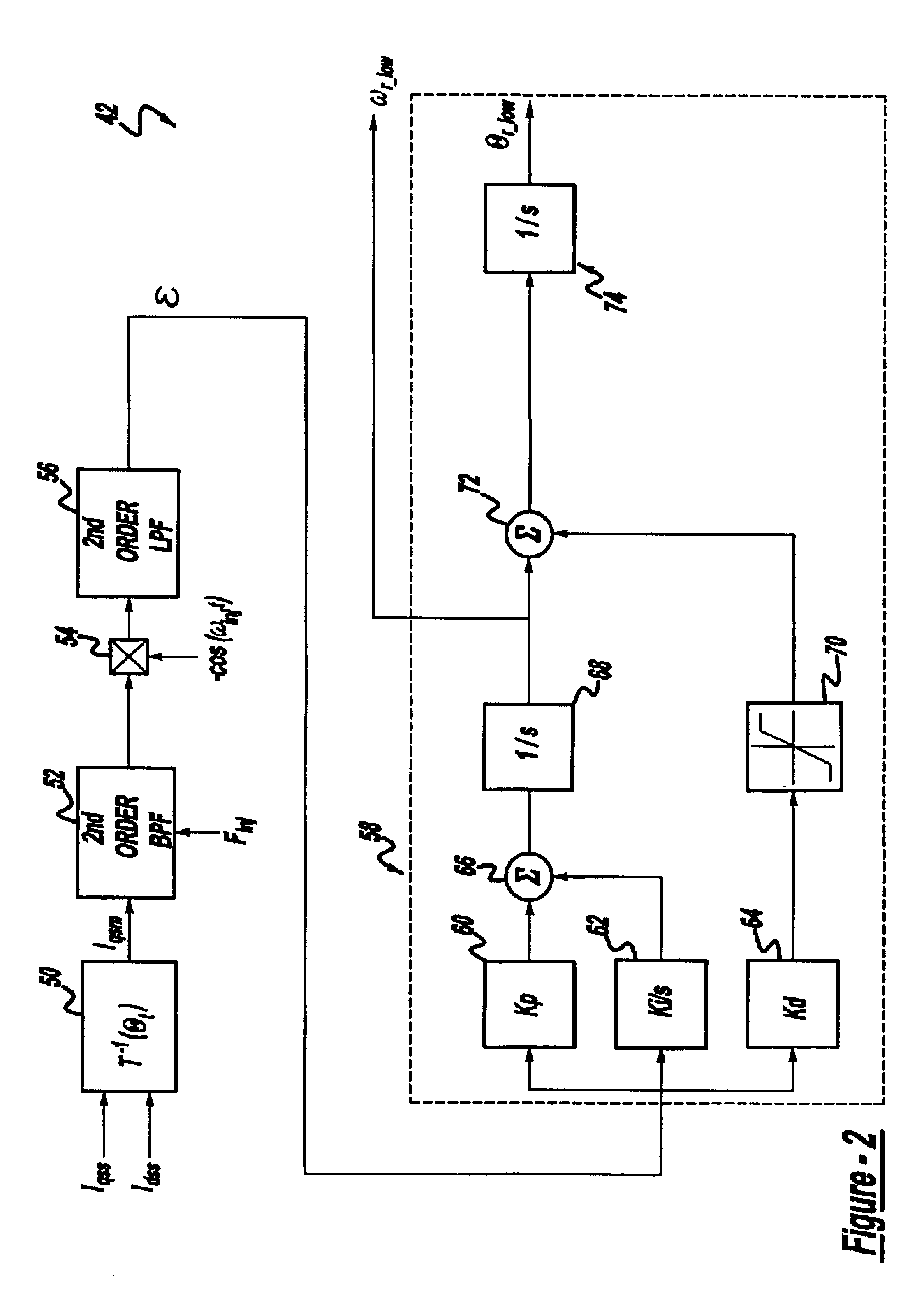
Position sensorless control algorithm for AC machine
InactiveUS6894454B2Less sensitiveFaster dynamic performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor speedControl system
A control system for an electric motor including an inverter for providing power to the electric motor, a controller for controlling the inverter, a first motor speed control block in the controller injecting a high frequency signal into the electric motor to determine the speed and position of the electric motor, a second motor speed control block in the controller detecting the back electromotive force to determine the speed and position of the electric motor, and a transition control block in said controller to vary operation between the first motor speed control block and the second motor speed control block.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
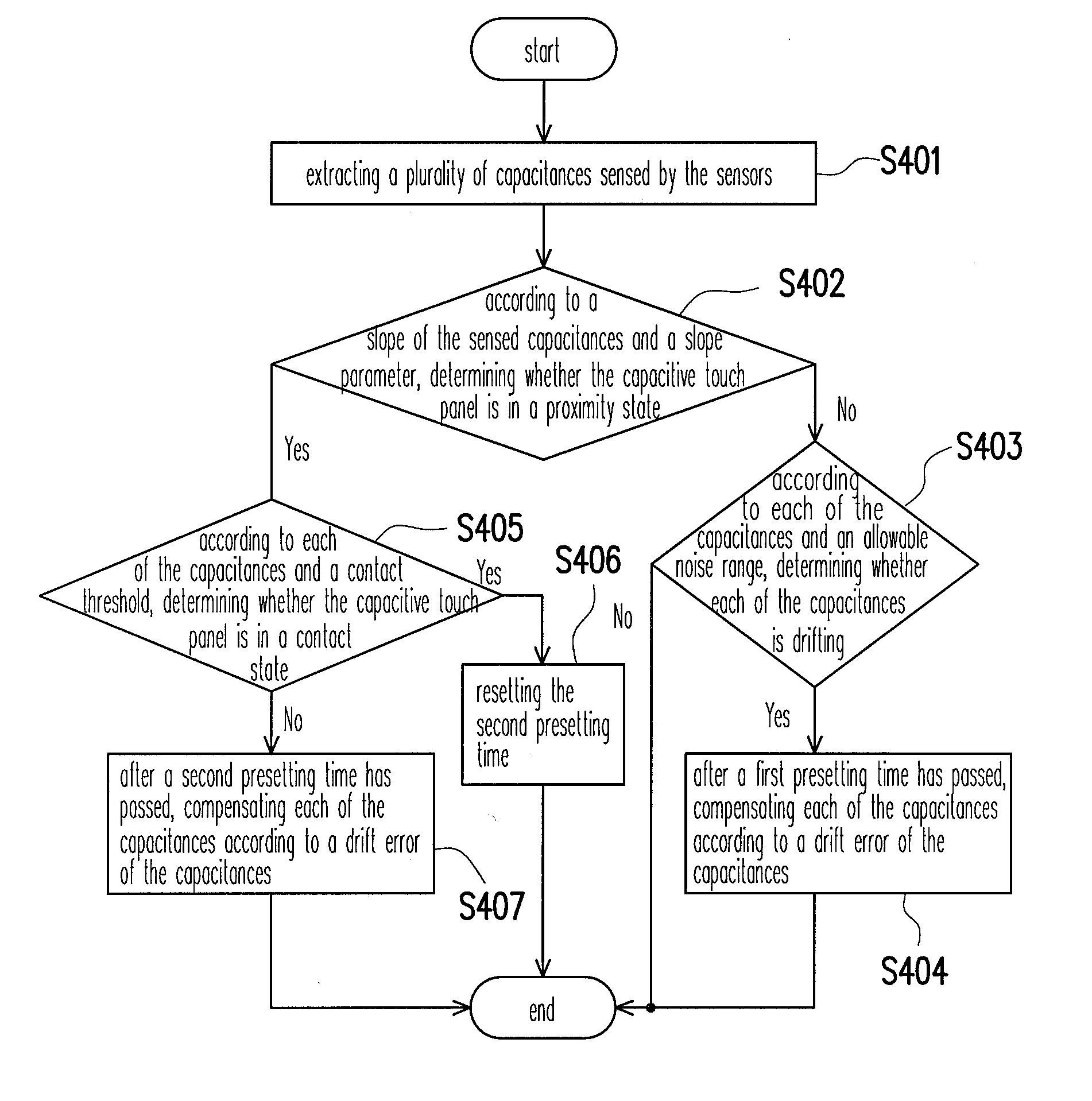
Drift compensation apparatus of capacitive touch panel and drift compensation method thereof
InactiveUS20100214253A1High sensitivityEasy to implementInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouchpad
A method and an apparatus adapted to a capacitive touch panel for drift compensation are provided, wherein the touch panel includes a plurality of sensors. In the method for drift compensation, a plurality of capacitances respectively sensed by each of the sensors are extracted. Whether the touch panel is in a proximity state is determined upon a slope of the sensed capacitances and a slope parameter. Whether each of the capacitances is drifted is determined upon the capacitance and an allowable noise range. When the touch panel is not in the proximity state and each of the capacitances is drifted, each of the capacitances is compensated according to a drift error of each of the capacitances after a first presetting time has passed.
Owner:ITE TECH INC
Graphene/ stannic oxide nanometer compounding resistance type film gas sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102636522AFine 3D NanostructuresLarge specific surface areaMaterial resistanceResponse sensitivityNano structuring
The invention discloses a graphene / stannic oxide nanometer compounding resistance type film gas sensor, which takes ceramics as a basal body. The surface of the ceramic basal body is photo-etched and evaporated with multiple pairs of interdigital gold electrodes, and is coated with gas-sensitive films of graphene and stannic oxide nanometer composite, and the manufactured resistance type film gas sensor has the advantages of simple manufacturing process and low cost. The gas-sensitive film is composed of a grapheme namosheet layer in a three-dimensional nano-structure and stannic oxide crystal particle composite with an orientated growth characteristic, the introduction of the graphene can favorably reduce the resistance of sensor elements, and the formation of the three-dimensional nano-structure can obviously enhance the specific surface area of the composite, thus the absorption and the diffusion of the gas can be promoted so as to greatly enhance the room temperature gas sensitive response sensitivity of elements. The graphene / stannic oxide nanometer compounding resistance type film gas sensor has the characteristics of high response sensitivity to low concentration ammonia, fast response, favorable recovering performanc, capability of carrying out the detection at the room temperature, and the like, which can be widely applied in the agricultural and industrial production process, and the room temperature detection and control of the concentration of ammonia in the atmospheric environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
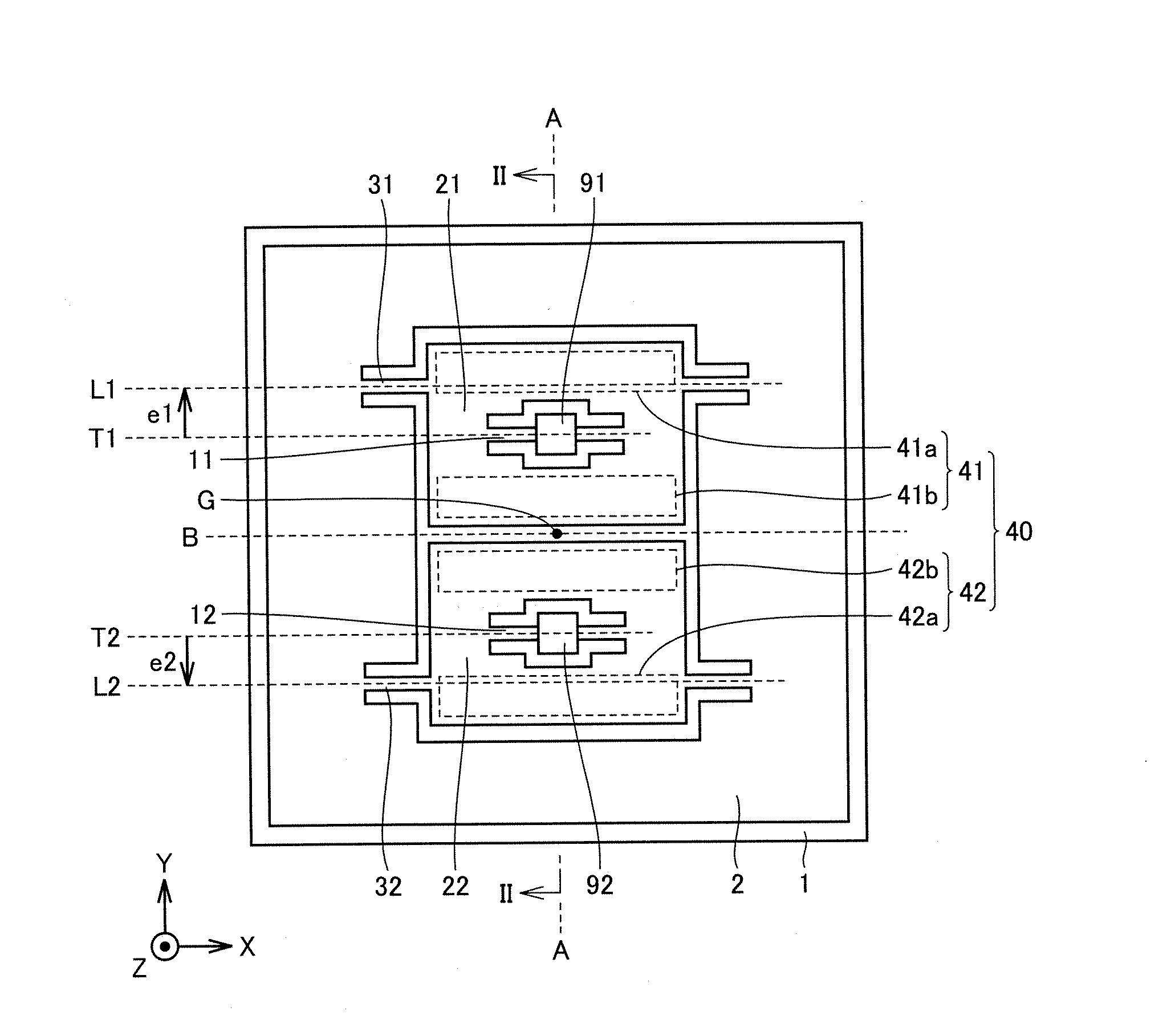
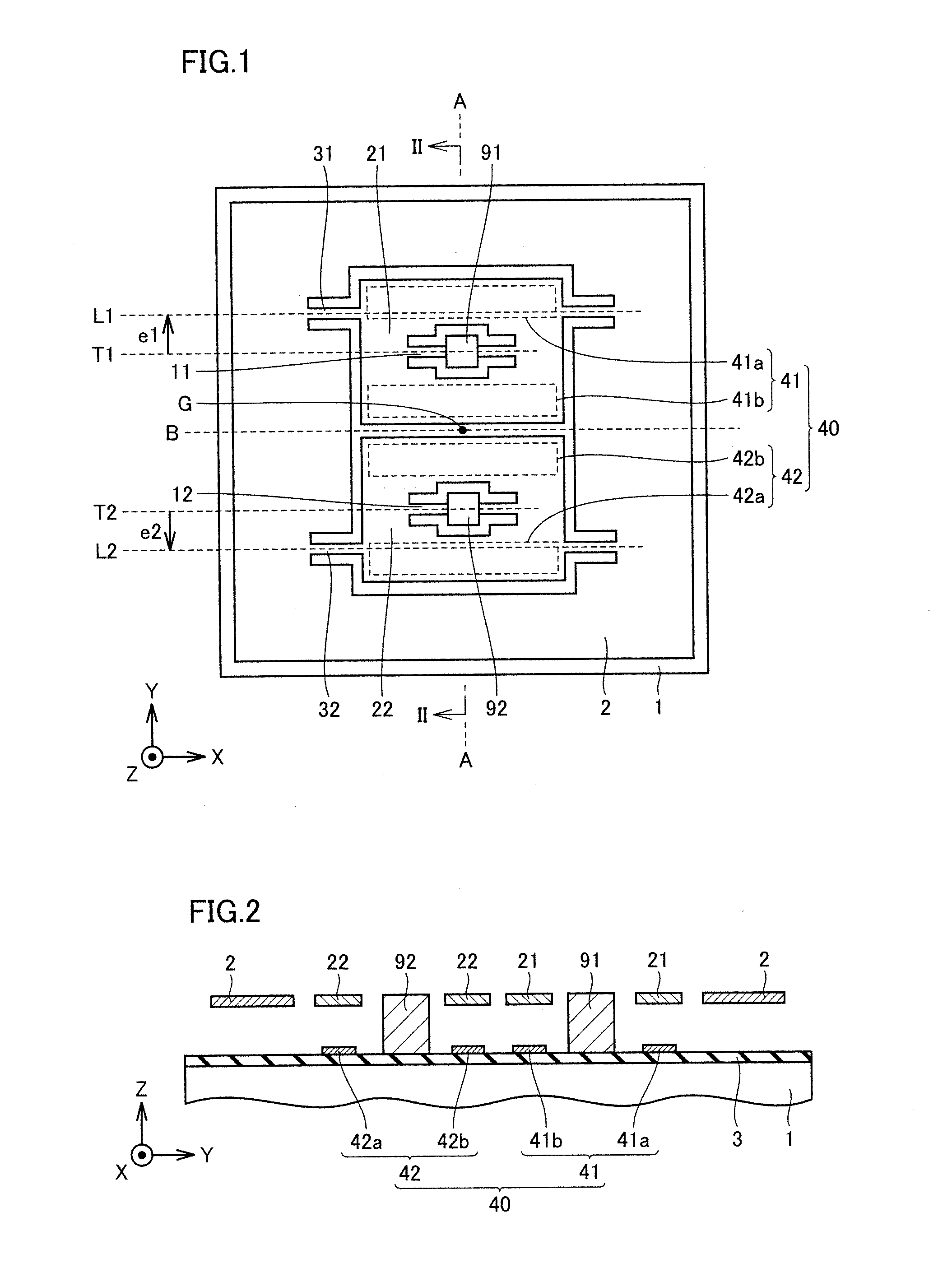
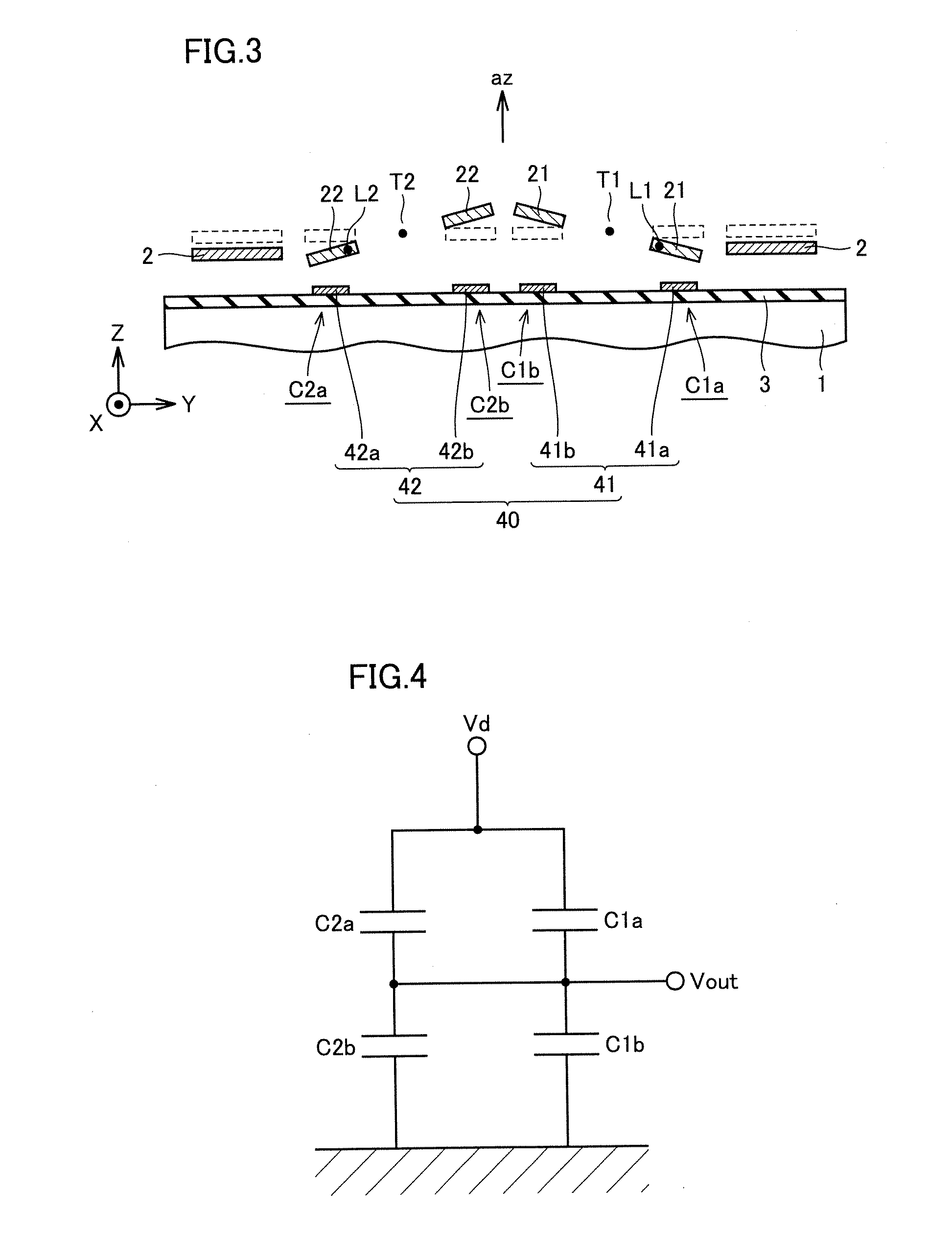
Acceleration sensor
ActiveUS20080110260A1Suppress sensitivityIncreased sensitivityAcceleration measurementInertiaPosition shift
First and second detection frames are supported by a substrate to be rotatable about first and second torsion axes. A first link beam is connected to the first detection frame on an axis located at a position moved from a position of the first torsion axis in a first direction crossing the first torsion axis and directed to one end side of the first detection frame. A second link beam is connected to the second detection frame on an axis located at a position shifted from a position of the second torsion axis in a second direction opposite to the first direction. An inertia mass body is displaceable in a thickness direction of the substrate by being linked with the first and second detection frames by the first and second link beams, respectively. This constitution makes it possible to obtain a highly precise acceleration sensor hardly influenced by disturbances.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
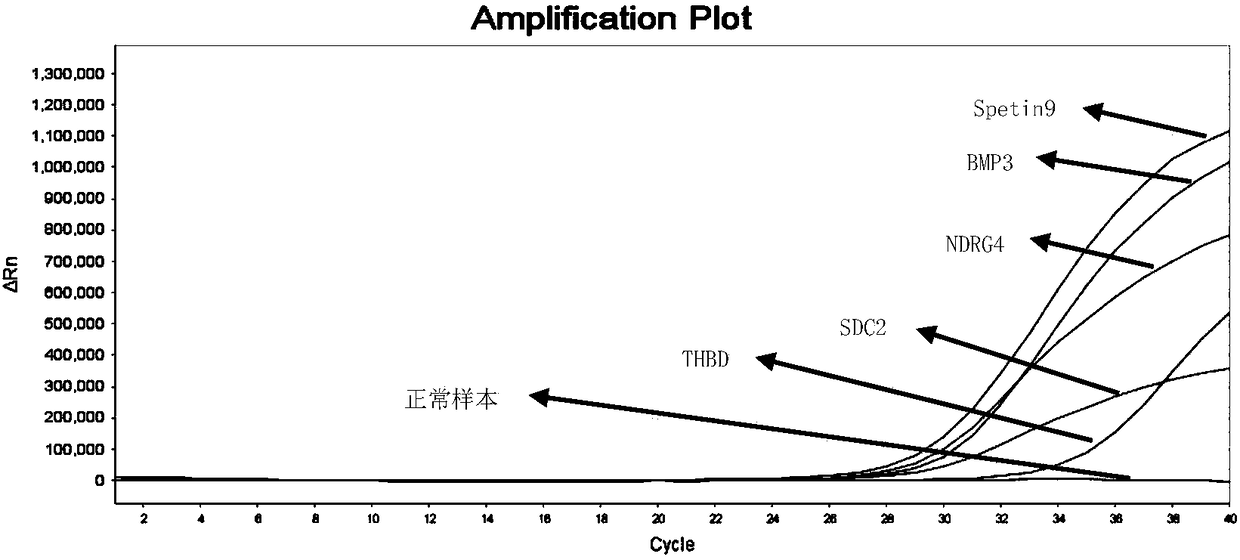
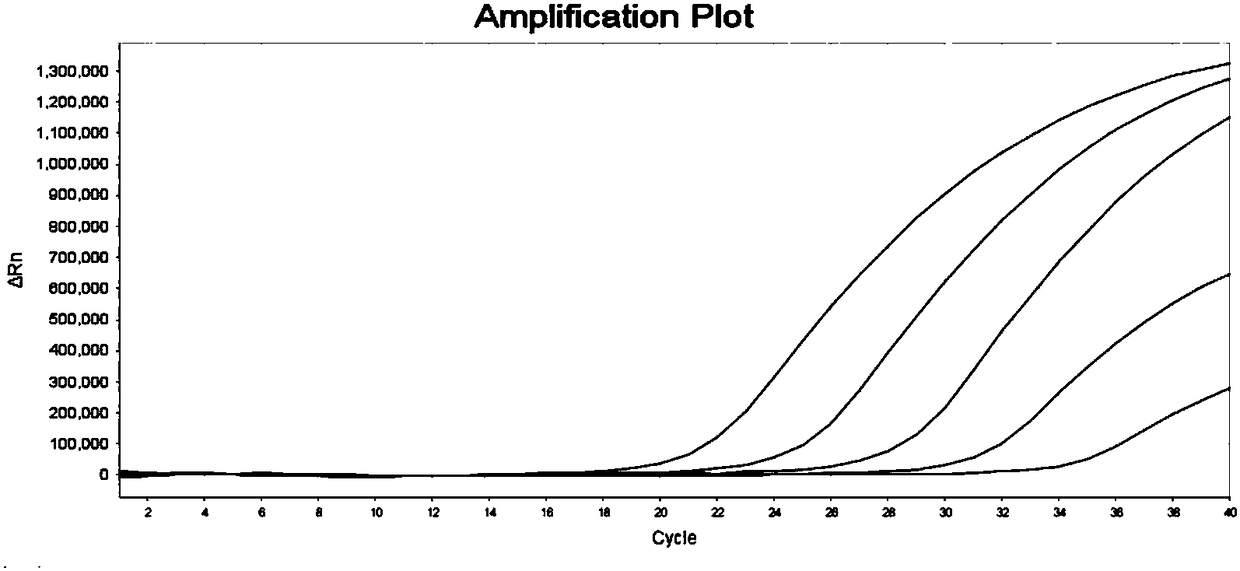
Primer pair, probe and kit used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer and applications thereof
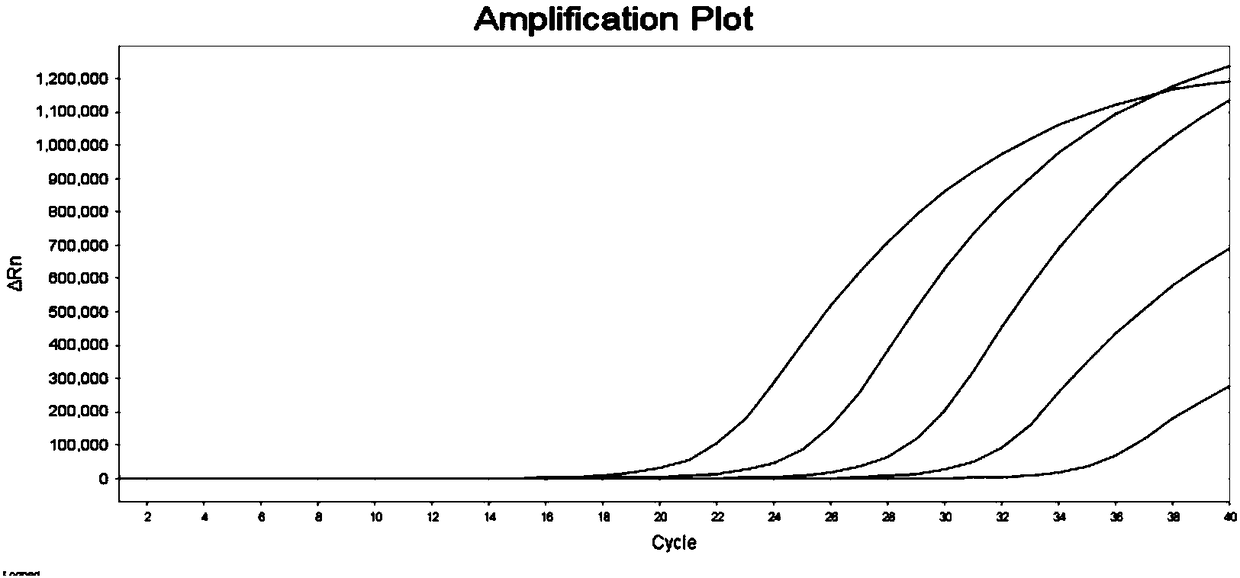
ActiveCN108103195AEasy to sampleSampling non-invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationFluorescence
The invention relates to a primer pair and a probe used for noninvasive polygene methylation combination detection for early stage colorectal cancer, and includes the primer pair and the probe used for detecting methylation of genes Spetin9, NDRG4, BMP3, THBD and SDC2 and the primer pair and the probe for internal reference ACTB; the sequences of the primer pair and the probe are represented as the SEQ ID No.1 to the SEQ ID No.18. The invention also provides a kit containing the primer pair and the probe and applications thereof. The application method includes free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, sulfite conversion, PCR amplification reaction, fluorescent signal detection and result determination. The kit and the method are suitable for methylation detection of the five genes Spetin9, THBD, SDC2, NDRG4 and BMP3 in human peripheral blood; compared with a conventional colorectal cancer diagnosis method, the application method fully utilizes the free DNA extraction from a plasma specimen, the DNA methylation and QPCR associated technologies, thus developing the kit having high sensitivity and specificity. The primer pair, probe and kit are used for performing early stage noninvasive screening to human colorectal cancer.
Owner:上海酷乐生物科技有限公司
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130082701A1Avoid sensitivityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceIn plane
The present invention has an object to provide a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus or the like that avoids a region with zero sensitivity of an optical magnetometer and allows imaging by strong magnetic resonance when a common magnetic field is used as a bias field of an optical magnetometer and as a magnetostatic field to be applied to a sample. When a direction of a magnetostatic field application unit applying a magnetostatic field to a sample is a z direction, alkali metal cells of a plurality of scalar magnetometers are arranged so as not to overlap a region to be imaged in a z direction, and so as not to intersect the region to be imaged in an in-plane direction perpendicular to the z direction.
Owner:CANON KK
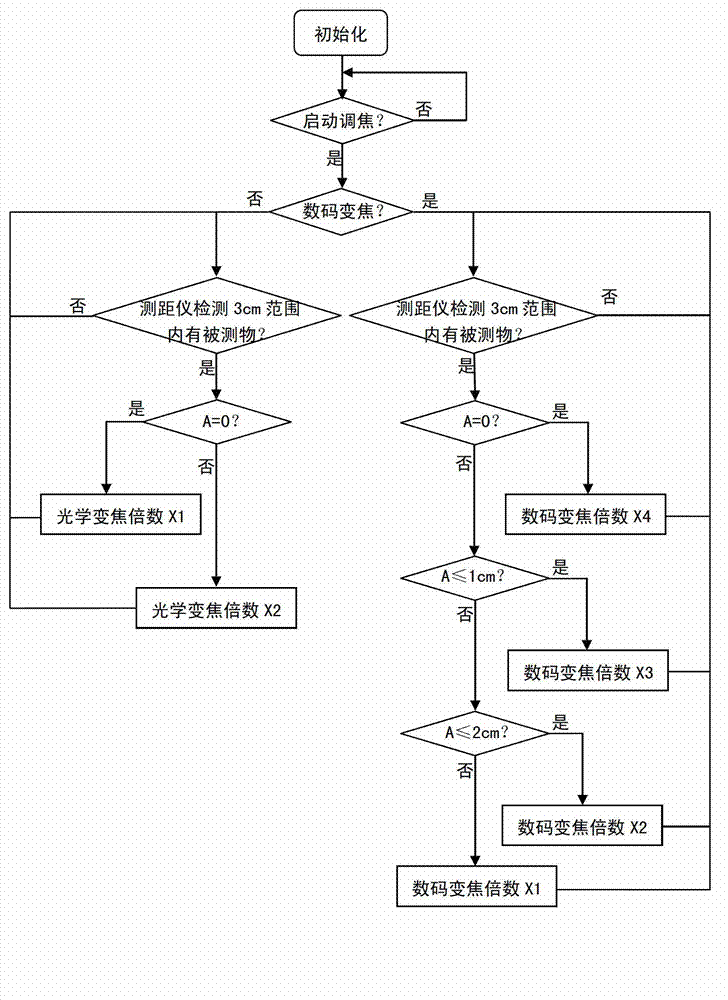
Camera focusing device and method
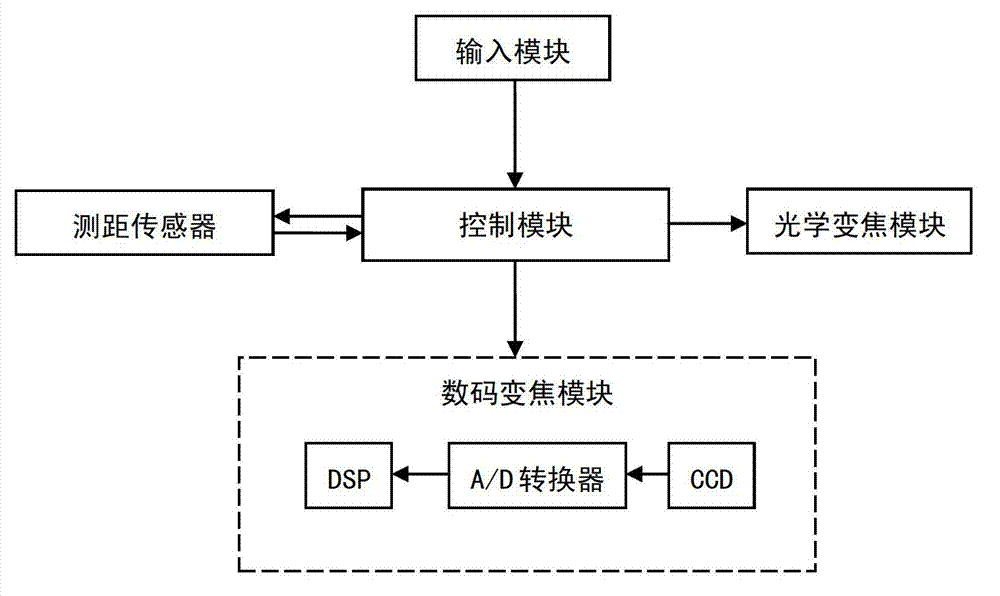
InactiveCN103048765AFlexible and fast focusingFlexible and fast focus adjustmentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalComputer module
The invention discloses a camera focusing device, which comprises a ranging sensor, a control module and a focusing module. The invention further discloses a camera focusing method. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the ranging sensor measures a distance from a tested object to the ranging sensor, and transmits the measured distance information to the control module; (2) the control module receives the distance information transmitted by using the ranging sensor, judges according to the distance information, and transmits a control signal to the focusing module; and (3) the focusing module focuses according to the control signal transmitted by using the control module. According to the camera focusing device and the camera focusing method, the focusing times are not required to be controlled through a focusing key, and the zooming magnitude is determined according to the distance of the tested object for adjusting a focal length, sensed by the range sensor, so that the defects of slow response, poor sensitivity and low accuracy of the focusing key used in the prior art are overcome, and camera focusing can be realized flexibly and rapidly.
Owner:TIANJIN SAMSUNG OPTO ELECTRONICS +1
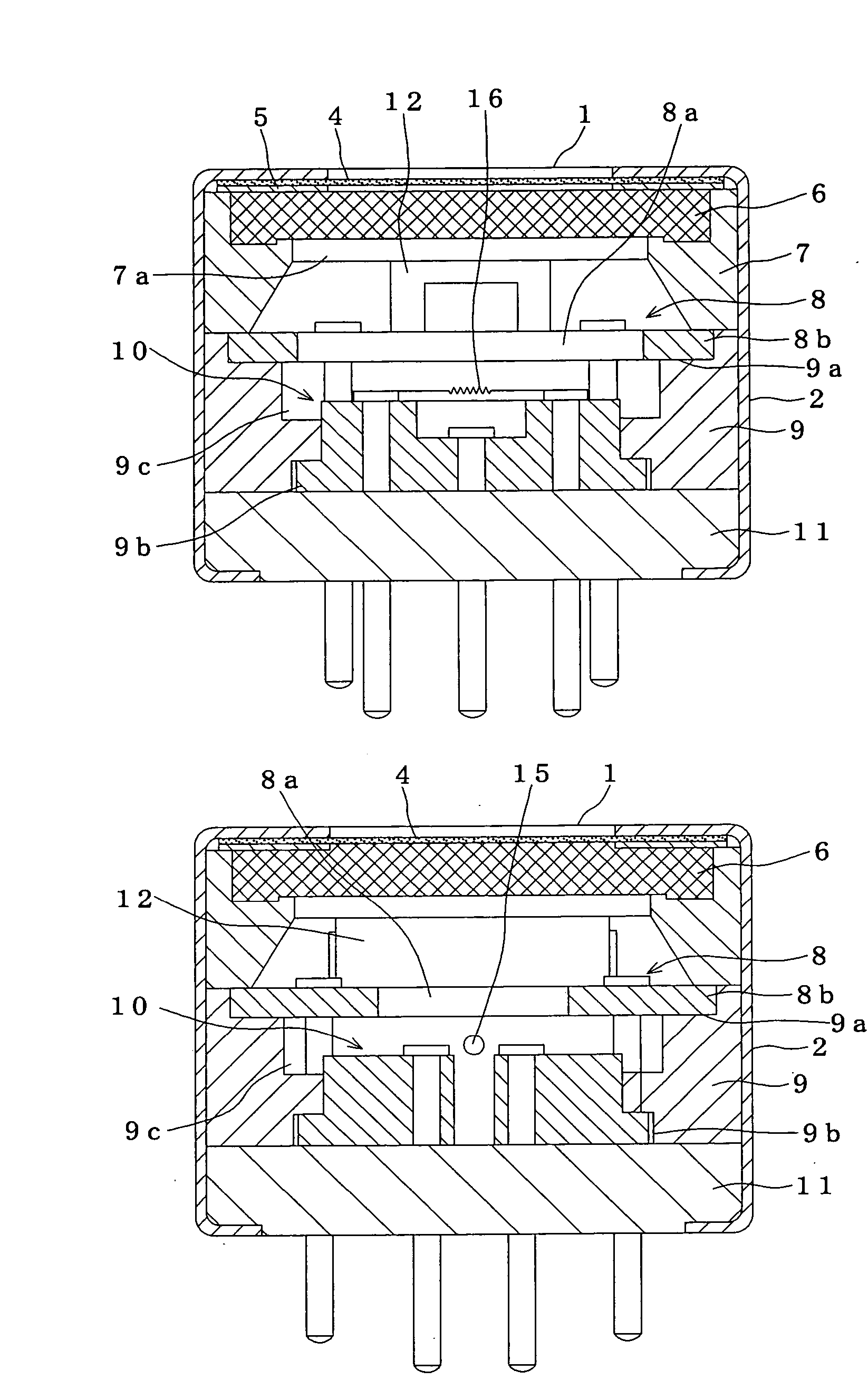
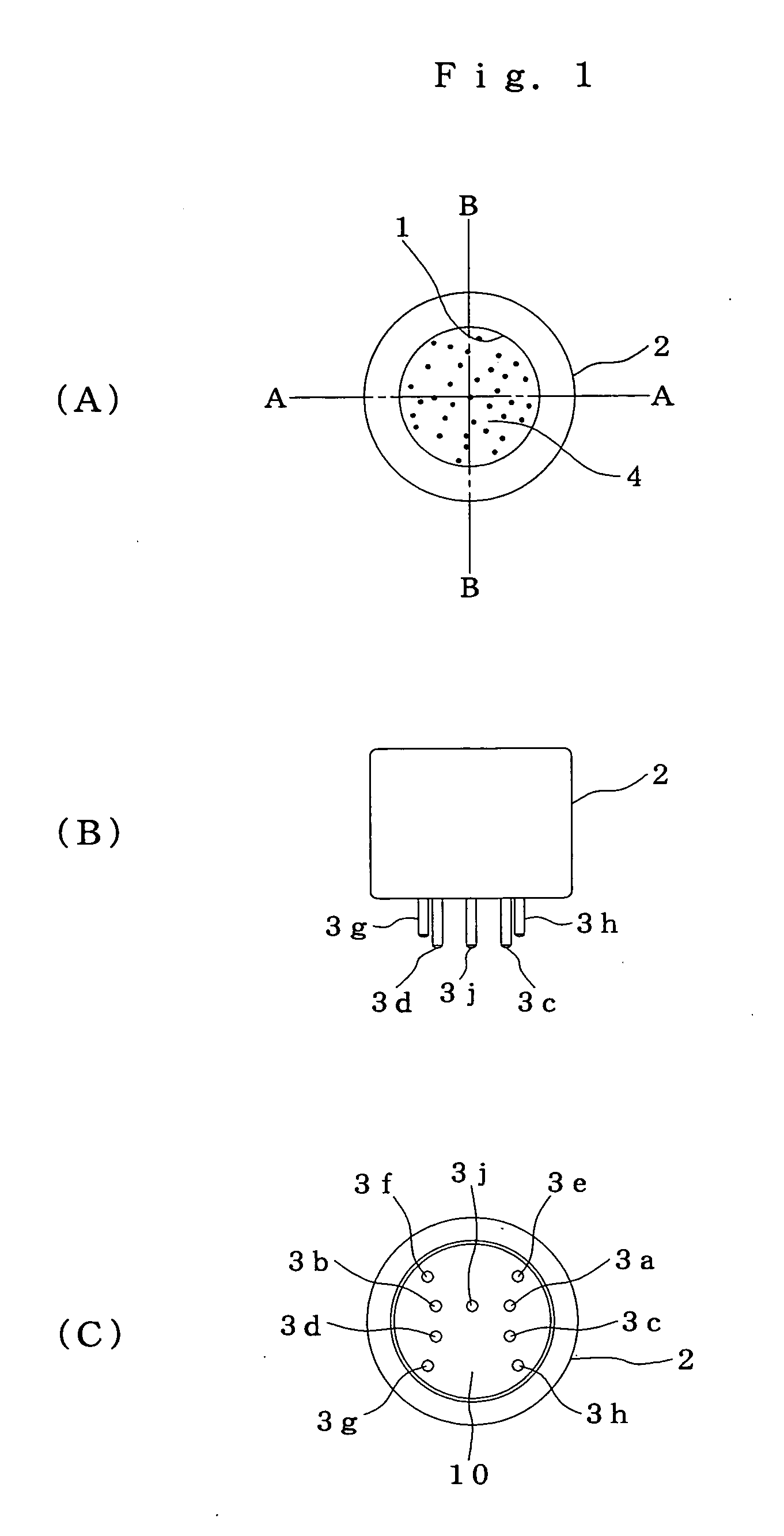
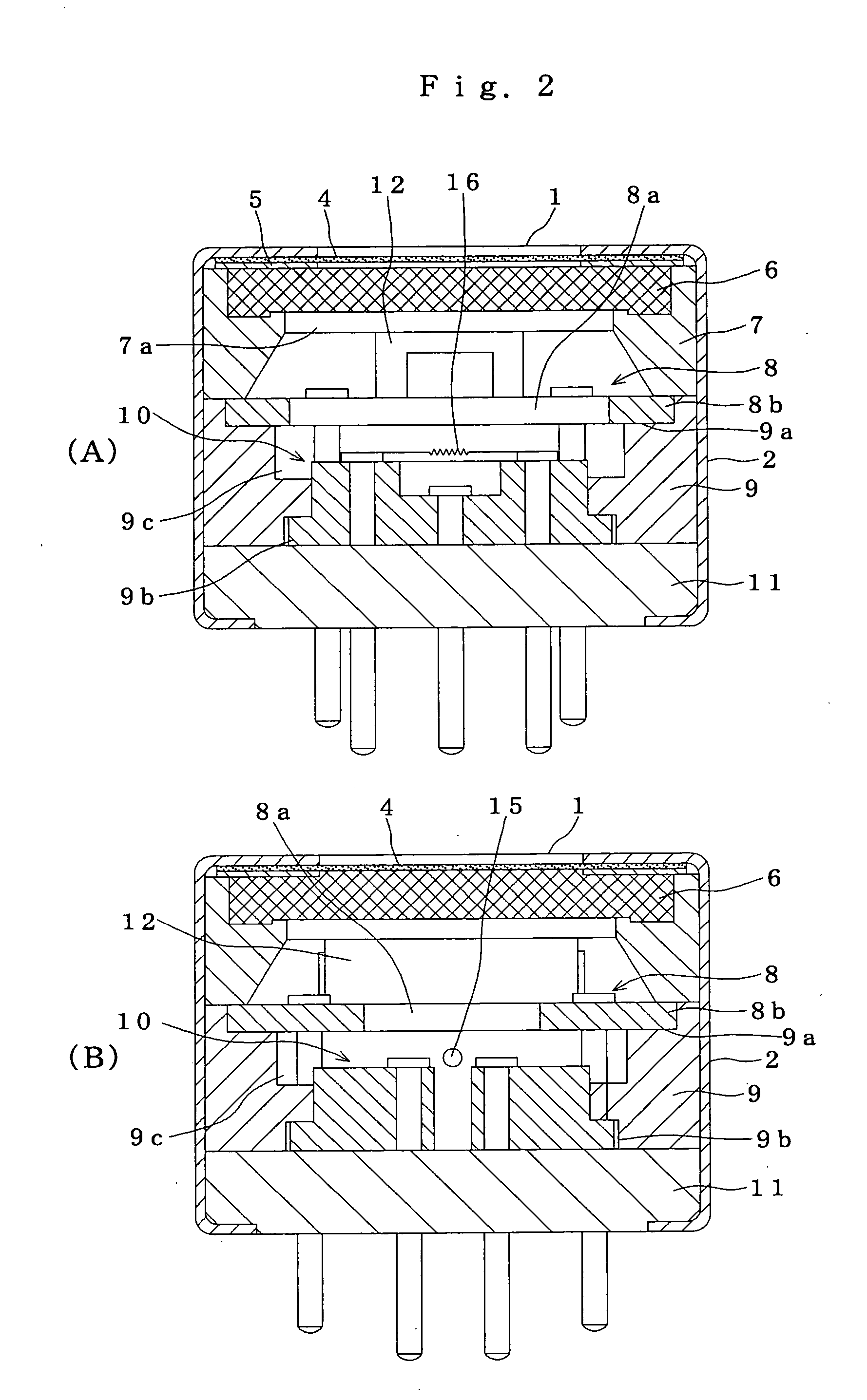
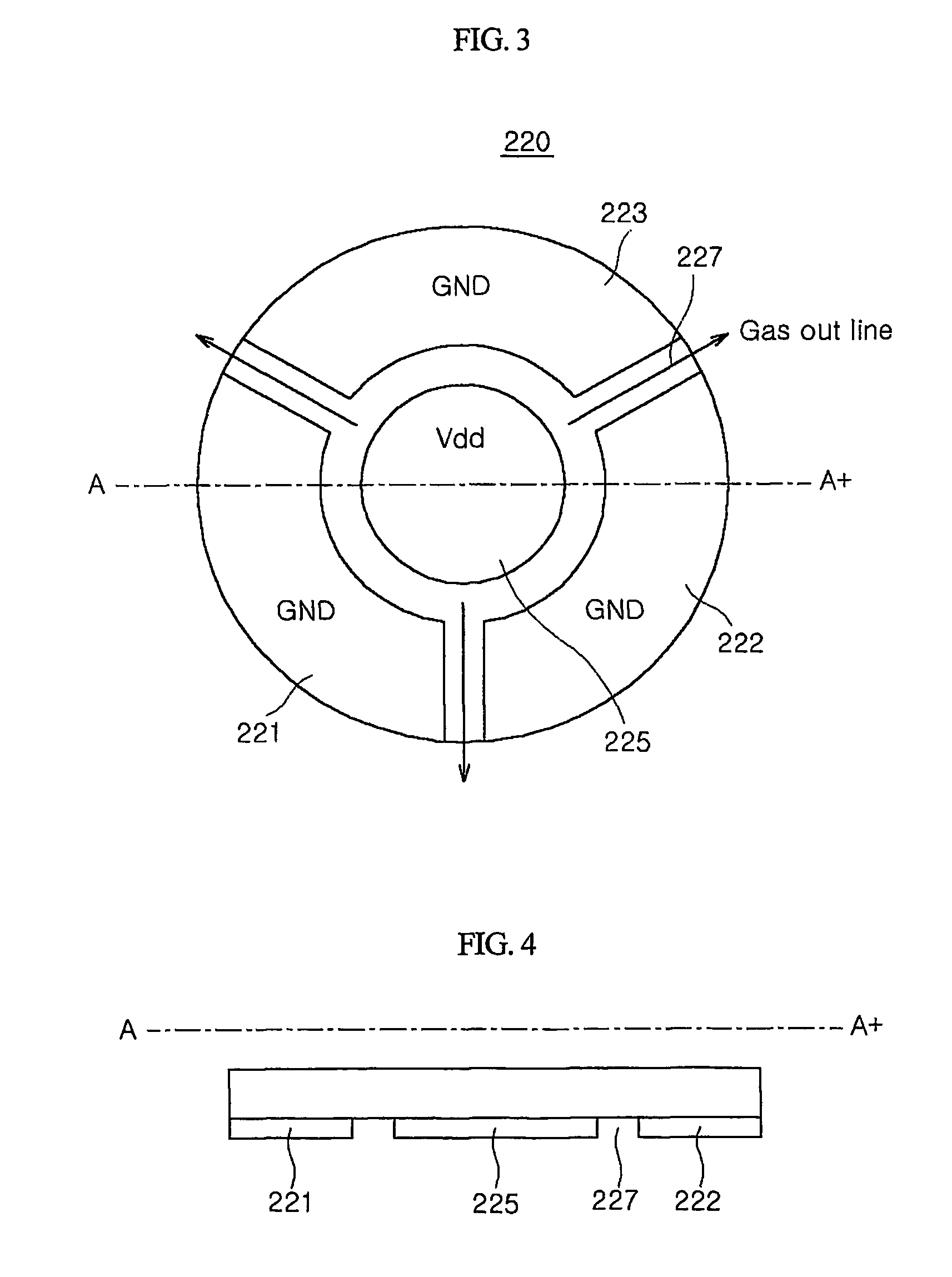
Gas sensor
ActiveUS20050042141A1Avoid desensitizationReduce sensitivitySolid electrolytesChemical analysis using combustionEngineeringHydrogen sensor
A hydrogen sensor 25 has a fitting base plate 29 in which a gas-sensing chamber 34 is formed, a specimen gas intake 35 formed on said fitting base plate 29, opening toward an exit passage 24 and introducing hydrogen gas into the gas-sensing chamber 34, a gas-sensing element 39 held in the gas-sensing chamber 34 and adapted to sense hydrogen gas, and a water-repelling filter 44 covering the specimen gas intake 35.
Owner:RIKEN KEIKI KK
Remote-controlled light receiving structure of electric roll screen for blind
InactiveUS8258993B2Improve convenienceSimple structureScreensElectric signal transmission systemsRemote controlEngineering
Owner:SHINSEI SEIKI
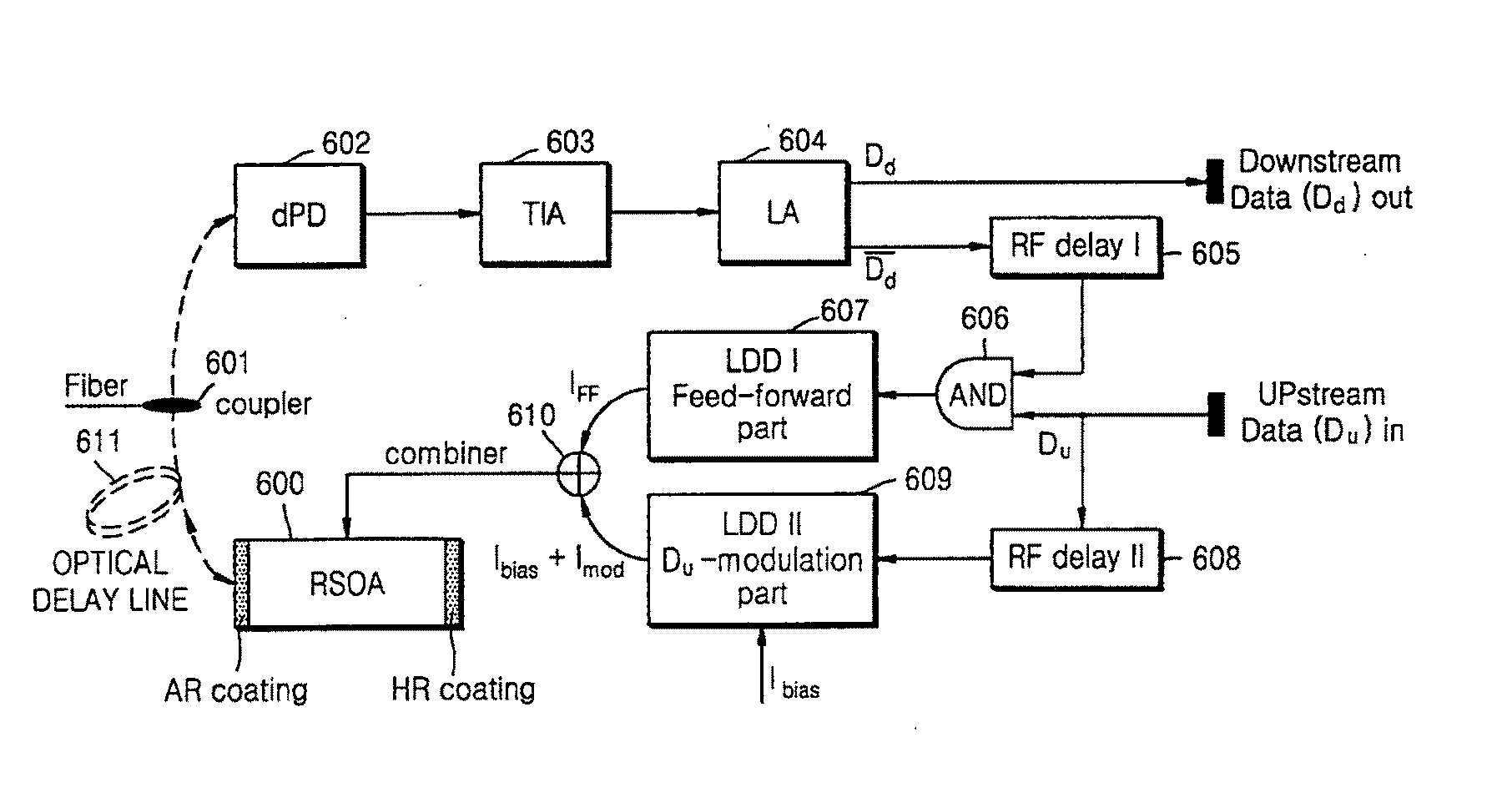
Apparatus and method for olt and onu for wavelength agnostic wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical networks
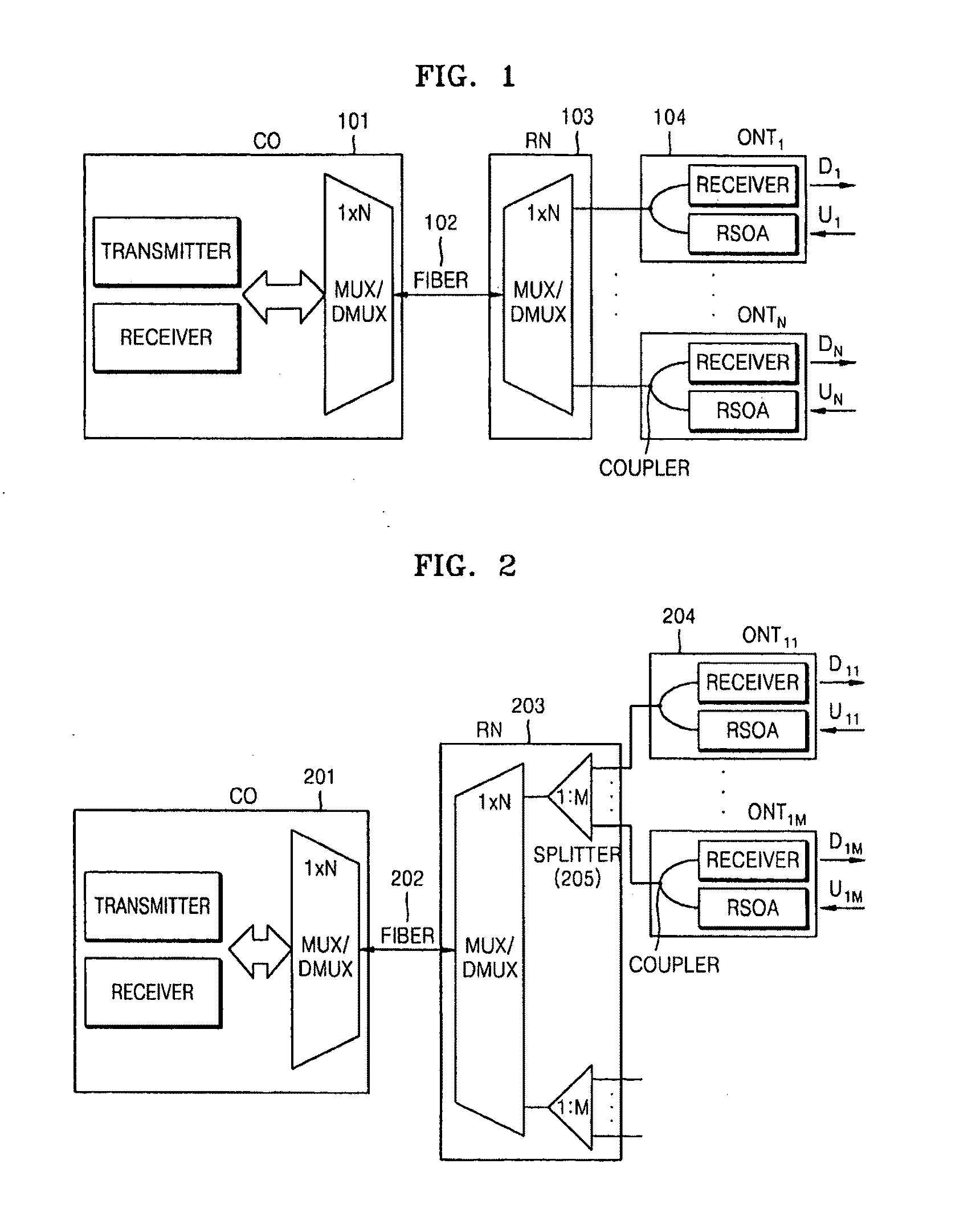
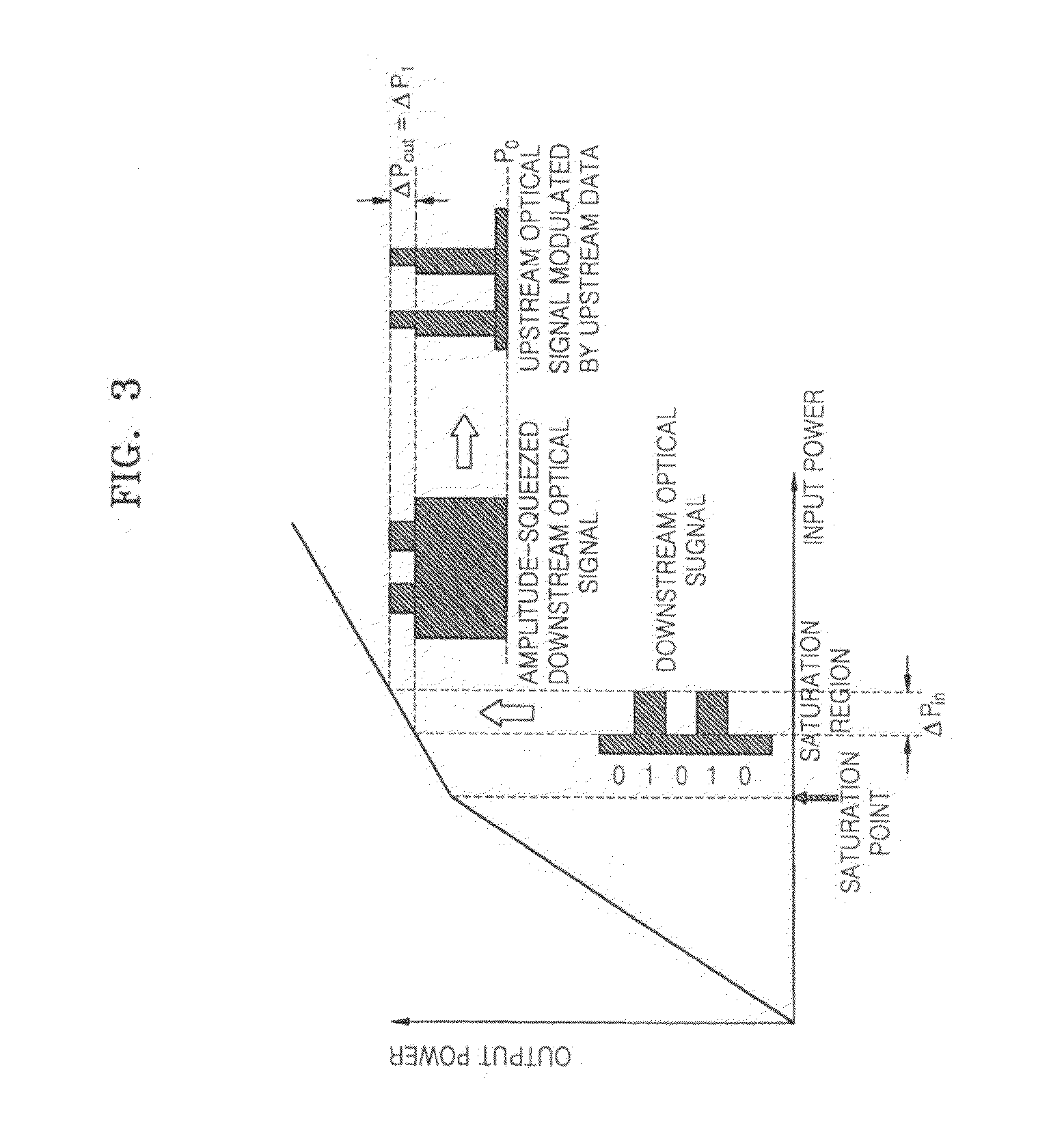
ActiveUS20110026923A1Lowering in extinction ratioPossible to transmitLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer terminalLength wave
In a Wavelength-Division-Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) utilizing a conventional downstream optical signal reusing method, there is an inventory problem that different optical transmitter types need to be provided for the operation, management, replacement, etc. of a system. A WDM-PON system according to the present invention, includes: a seed light (SL) unit generating a seed light whose wavelength intervals and center wavelengths are adjusted using at least one seed light source; an optical line terminal (OLT) receiving the wavelength-multiplexed seed light from the seed light unit, transmitting a downstream optical signal to a subscriber of the WDM-PON, and receiving a upstream optical signal from the subscriber; and an optical network unit (ONU) receiving the downstream optical signal from the OLT, flattening and modulating the downstream optical signal with upstream data so that the downstream optical signal is reused for carrying upstream data. It is possible to improve the quality and reliability of downstream transmission by sufficiently increasing an extinction ratio, and improve the quality and reliability of upstream transmission by sufficiently flattening an input downstream optical signal in a semiconductor optical amplifier.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Image pickup apparatus
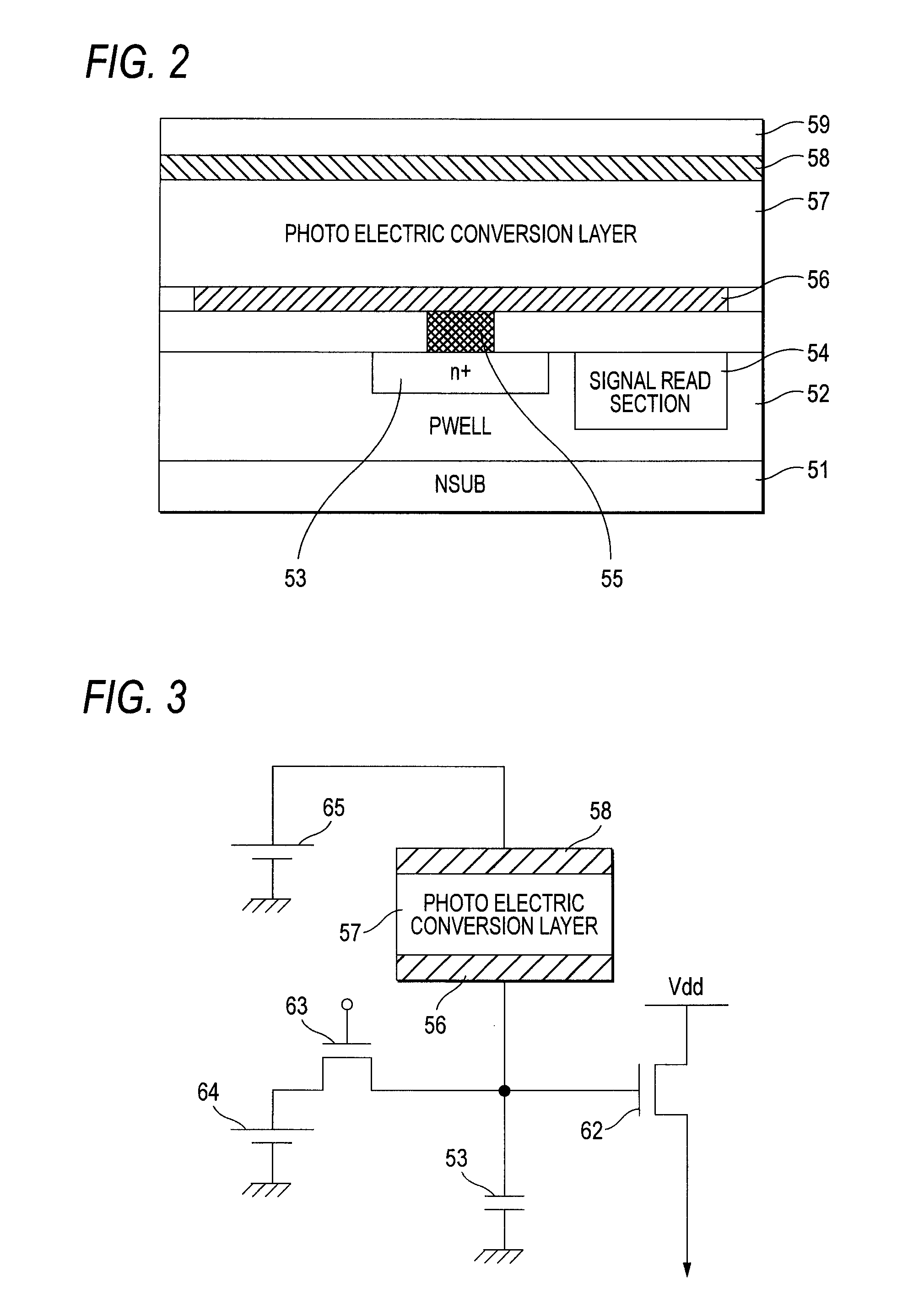
ActiveUS20080211954A1Preventing degradationAvoid sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsExposure End TimeEngineering
A lower electrode, a photoelectric conversion layer, and an upper electrode are stacked in order above a semiconductor substrate, and a charge storage section that stores charge generated in the photoelectric conversion layer is connected to the lower electrode. The charge stored in the charge storage section is swept away by a charge sweeping away section for a given time from the endpoint of exposure. The given time is a time taken until the residual image charge existing in the photoelectric conversion layer at the exposure end point time is sufficiently discharged to the outside of the photoelectric conversion layer in a state in which the same bias as that at the exposure start time point is applied to the photoelectric conversion layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Gas sensor
ActiveUS7479255B2Reduce sensitivityProlong lifeSolid electrolytesChemical analysis using combustionEngineeringHydrogen sensor
A hydrogen sensor 25 has a fitting base plate 29 in which a gas-sensing chamber 34 is formed, a specimen gas intake 35 formed on said fitting base plate 29, opening toward an exit passage 24 and introducing hydrogen gas into the gas-sensing chamber 34, a gas-sensing element 39 held in the gas-sensing chamber 34 and adapted to sense hydrogen gas, and a water-repelling filter 44 covering the specimen gas intake 35.
Owner:RIKEN KEIKI KK
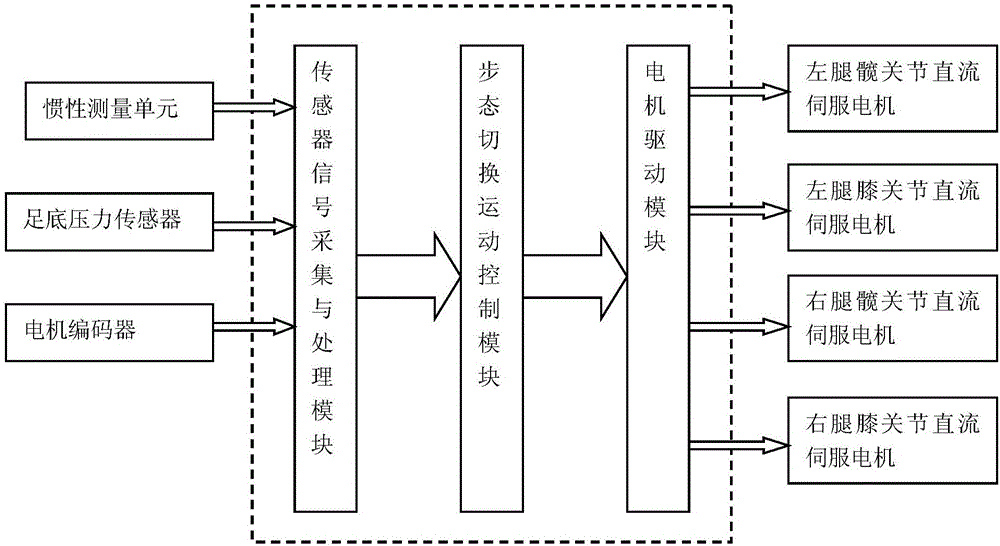
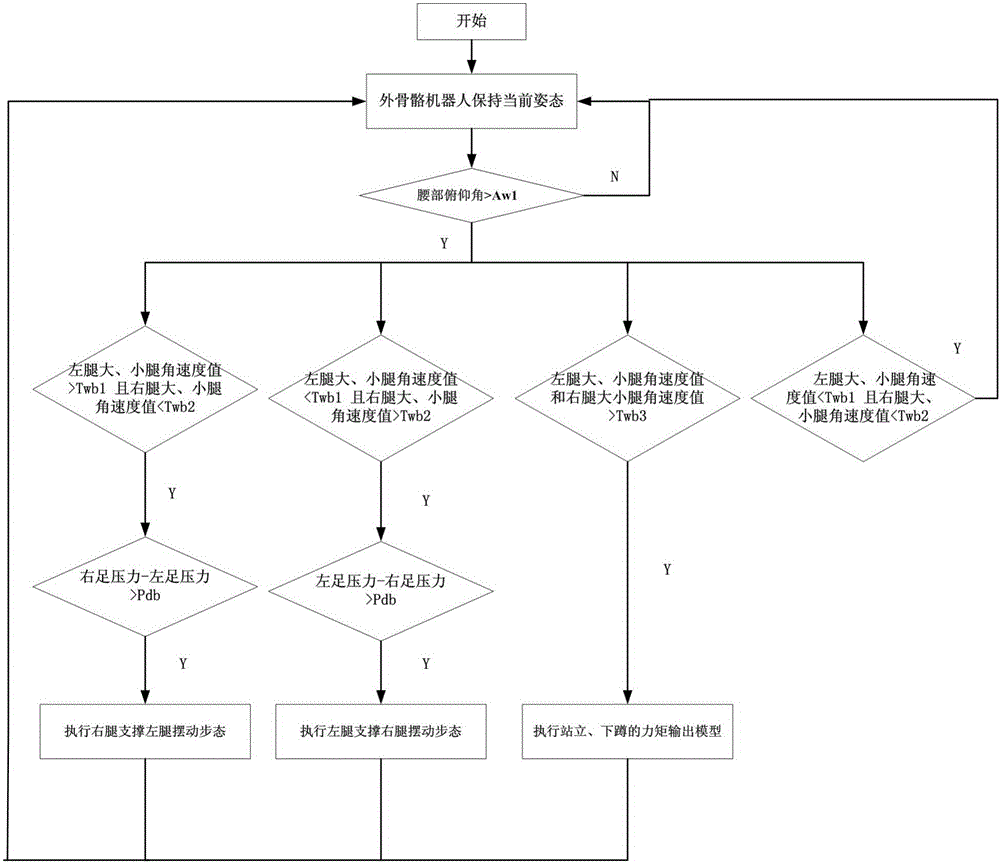
Multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for power-assisted exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN106325273AProtect personal safetyImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPosition/course control in two dimensionsExoskeleton robotMotor power
The invention discloses a multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for a power-assisted exoskeleton robot. The multi-phase gait switching control system is characterized in that the multi-phase gait switching control system includes a sensor module, a signal acquisition and processing module, a gait switching motion control module and a motor driving module; and sensors comprise inertial measurement units, plantar pressure sensors and motor encoders. With the multi-phase gait switching control system and control method for the power-assisted exoskeleton robot of the invention adopted, the output of lower hip joint and knee-joint motor power-assisted torque under various of phase gaits and smooth switching between the phase gaits can be planned under a condition that the exoskeleton robot bears a heavy object, and the coordination and flexibility of the movement of the limbs of the weight-bearing exoskeleton equipment can be realized.
Owner:江苏中科伟思智能机器人科技有限公司
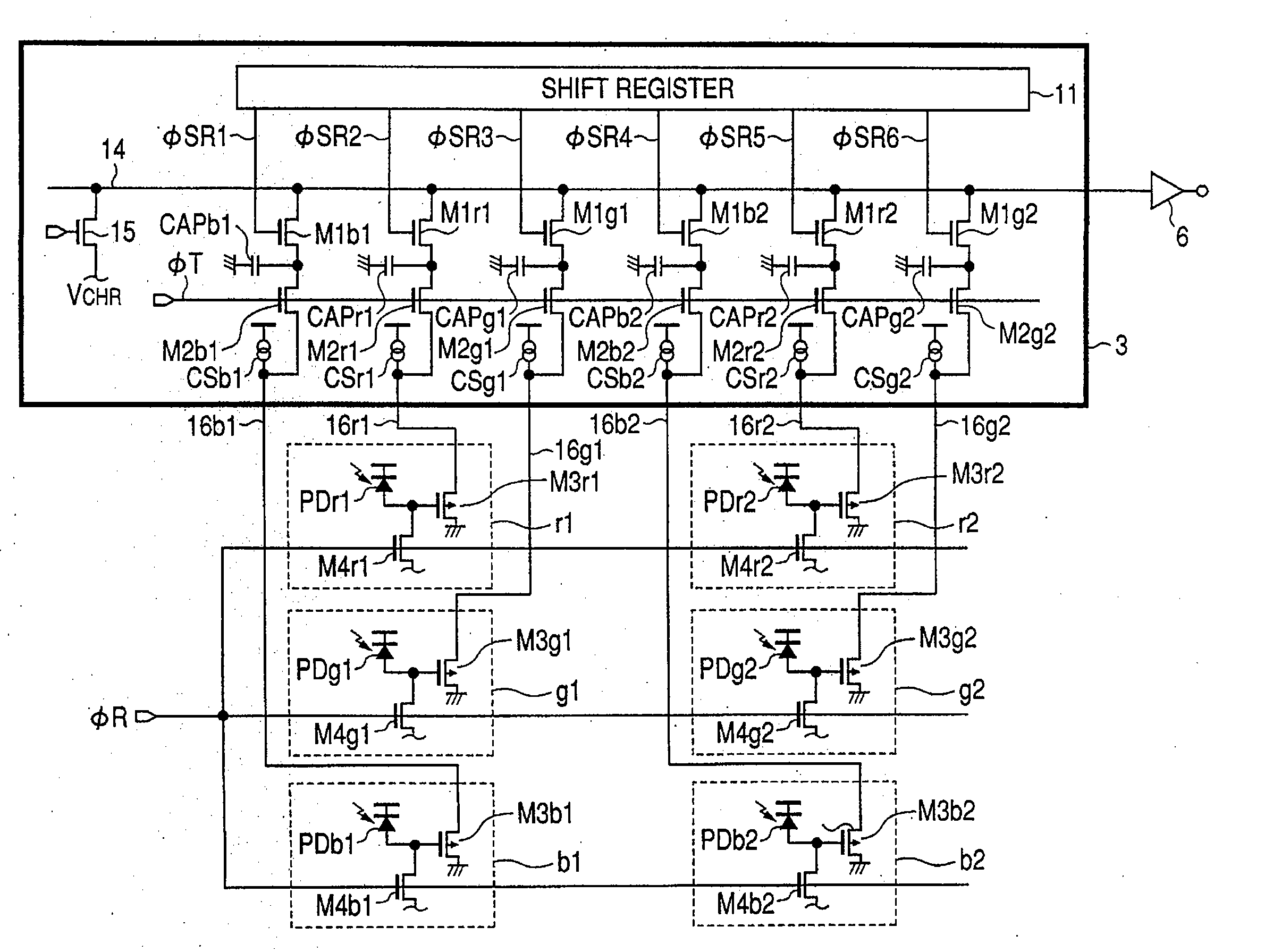
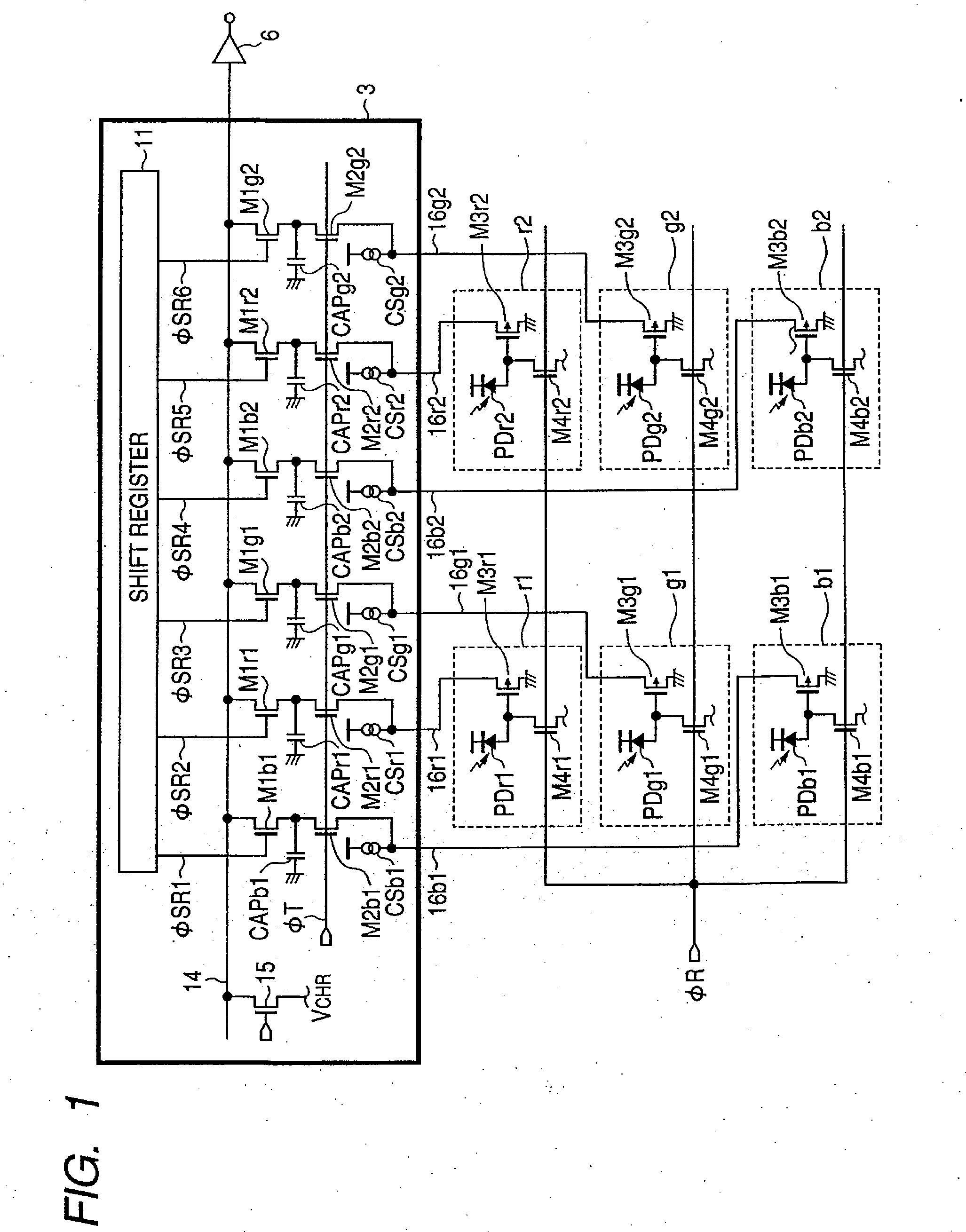
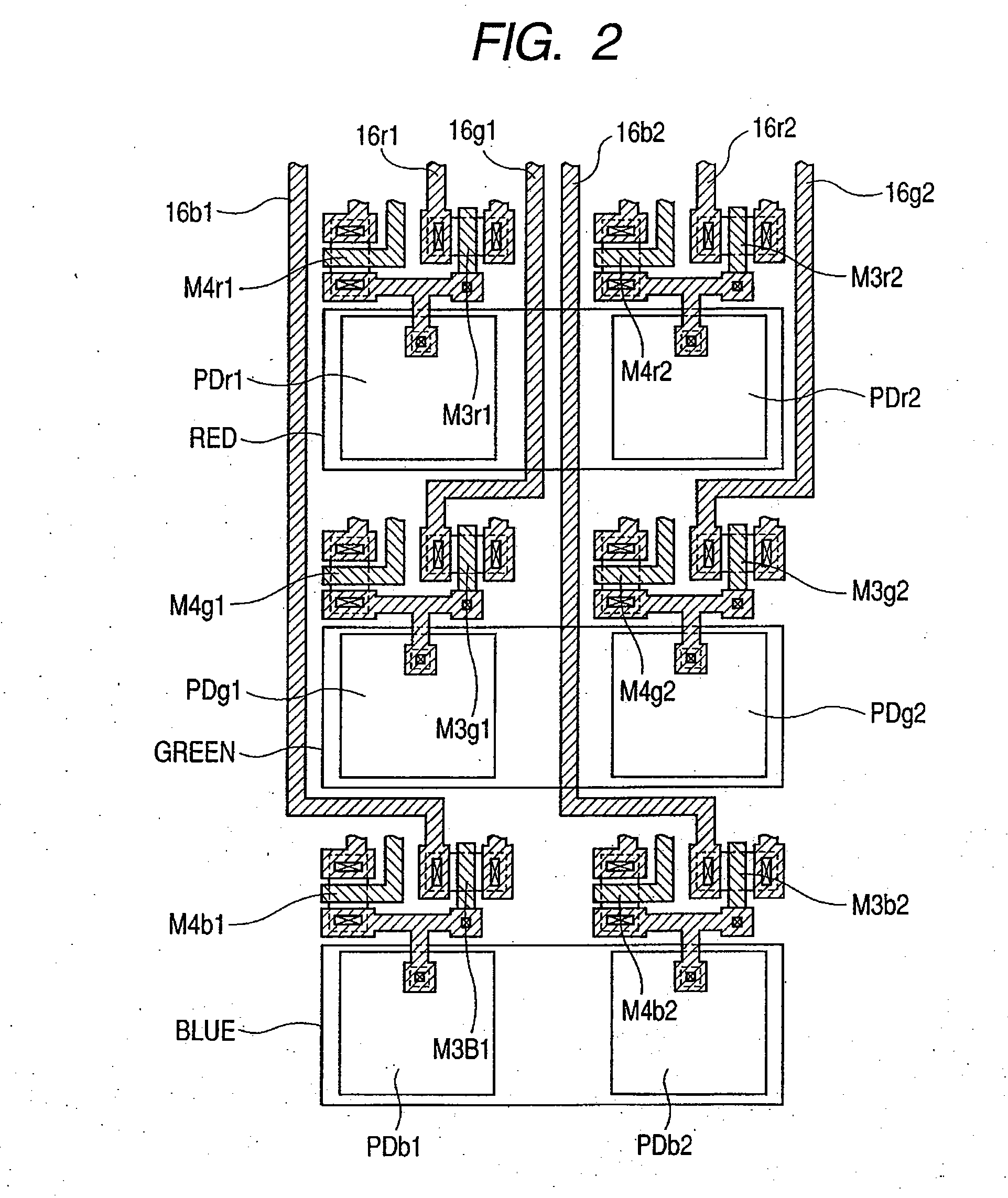
Photoelectric conversion device, multichip image sensor, contact image sensor, and image scanner
InactiveUS20060169871A1Reduce sensitivitySensitivity differenceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsContact image sensorPhotoelectric conversion
The invention provides a photoelectric conversion device, in which a decrease in sensitivity and a crosstalk between wirings are suppressed. Plural pixel columns are arranged in one direction, plural pixels are arranged in a different direction to the one direction in a column manner in the pixel column, and the pixel includes a photodiode PD, a reset transistor M4 for resetting the photodiode PD, and a source follower input transistor M3 for receiving a signal from the photodiode PD. An independent readout wiring 16 is individually provided for each pixel. The reset transistor M4 and the source follower input transistor M3 included in one pixel column or another pixel column are arranged between the photodiode column in one pixel column and the photodiode column in another pixel column arranged adjacent to the one pixel column.
Owner:CANON KK
Screen unlocking method
InactiveCN102779015AAchieving Convenience and VersatilityEasy to operateInput/output processes for data processingEmbedded systemElectronic equipment
The invention relates to a screen unlocking method. The screen unlocking method comprises the following steps: an electronic device receives an unlocking operation of a user; the electronic device judges whether the unlocking operation is matched with an existing unlocking scheme or not and unlocks when the unlocking operation is matched with the existing unlocking scheme, wherein the existing unlocking scheme comprises the unlocking operation in an unlocking region, the unlocking region is a touch screen any region or an appointed unlocking region, and the unlocking operation is one or combination of single click, double click, and long-press; therefore, the convenience and the variety of the unlocking manner are realized; after being unlocked, the touch screen can automatically enter an appointed application program interface according to the configuration of the user so that the operation is simplified; simultaneously, the position of the unlocking region on the touch screen is random so that the problem of reduced abrasion, sensitivity and precision of the touch screen caused by long-term operation on a constant region can be effectively avoided.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Antenna coil to be mounted on a circuit board and antenna device
InactiveUS20080007473A1Easily mountEasy to installLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsMagnetic coreEngineering
In an antenna coil including a first magnetic core, a second magnetic core, and a flexible board, coil conductors are provided on a surface of the flexible board. By winding the flexible board around the first magnetic core and the second magnetic core, a first coil portion is disposed around the first magnetic core and a second coil portion is disposed around the second magnetic core. The winding direction of the second coil portion is opposite to that of the first coil portion. The first coil portion and the second coil portion are connected to define one coil as a whole.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
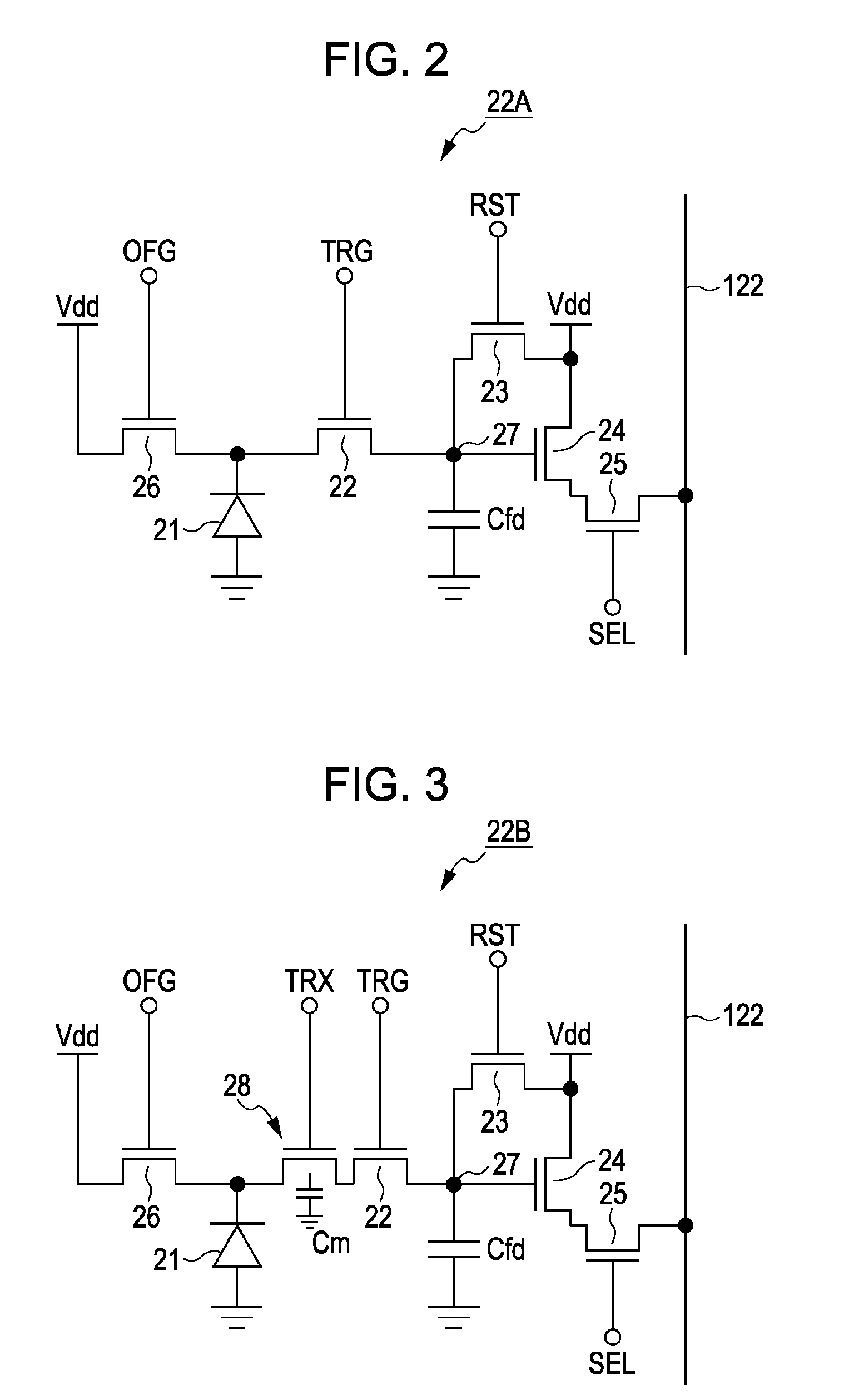
Solid-state image capturing apparatus, driving method thereof and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20100188543A1Improve layout efficiencyHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCharge dischargeEngineering
A solid-state image capturing apparatus includes: a pixel array unit including two-dimensionally arranged pixels each including a photoelectric conversion unit, a transfer transistor that transfers charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion unit, and a charge discharging transistor that selectively discharges the charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion unit; and a driving unit that performs driving for reading signals from each pixel of the pixel array unit, and drives the charge discharging transistor by using a signal for the driving.
Owner:SONY CORP
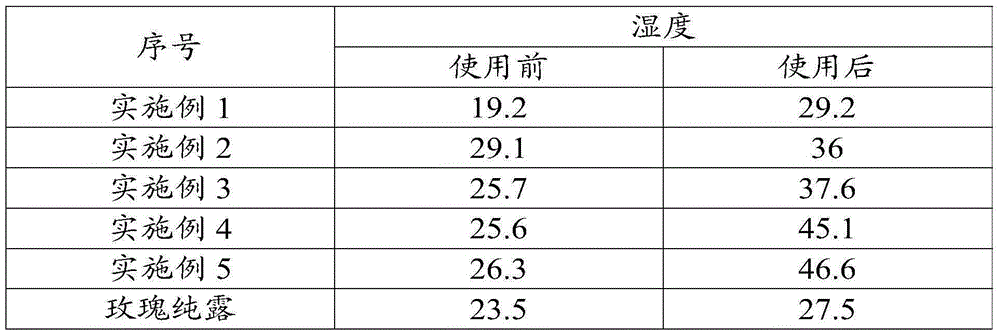
Skin caring product made from roses and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105411919AAvoid sensitivityPrevent peelingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMedicineTremella
The invention provides a skin caring product made from roses and a preparation method thereof. The skin caring product is prepared from, by weight, 20-130 parts of rose hydrosol, 2-3 parts of glycerol, 2-4 parts of butanediol, 1-4 parts of tremella extracts, 0.5-2 parts of low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, 0.5-2 parts of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid and 4-20 parts of deionized water. The skin caring product made from roses comprises the rose hydrosol with the feature beautifying function and has the functions of moistening skin and keeping the skin moist and refreshing. Besides, the skin caring product made from roses has the functions of conditioning skin, relieving patches and preventing skin sensitivity and decrustation and also has many effective components for supplementing water and preserving moisture, and functions of making the water supplementing and moisture preserving effect last long and prolonging the effect of the rose hydrosol are also achieved. The preparation method of the skin caring product made from roses has the advantages of being convenient to use, simple and easy to master, rose essence water and rose essence cream can be respectively obtained through different operating methods, and products are diversified.
Owner:WUHAN GUANGYINSHU ECOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Positive photosensitive composition
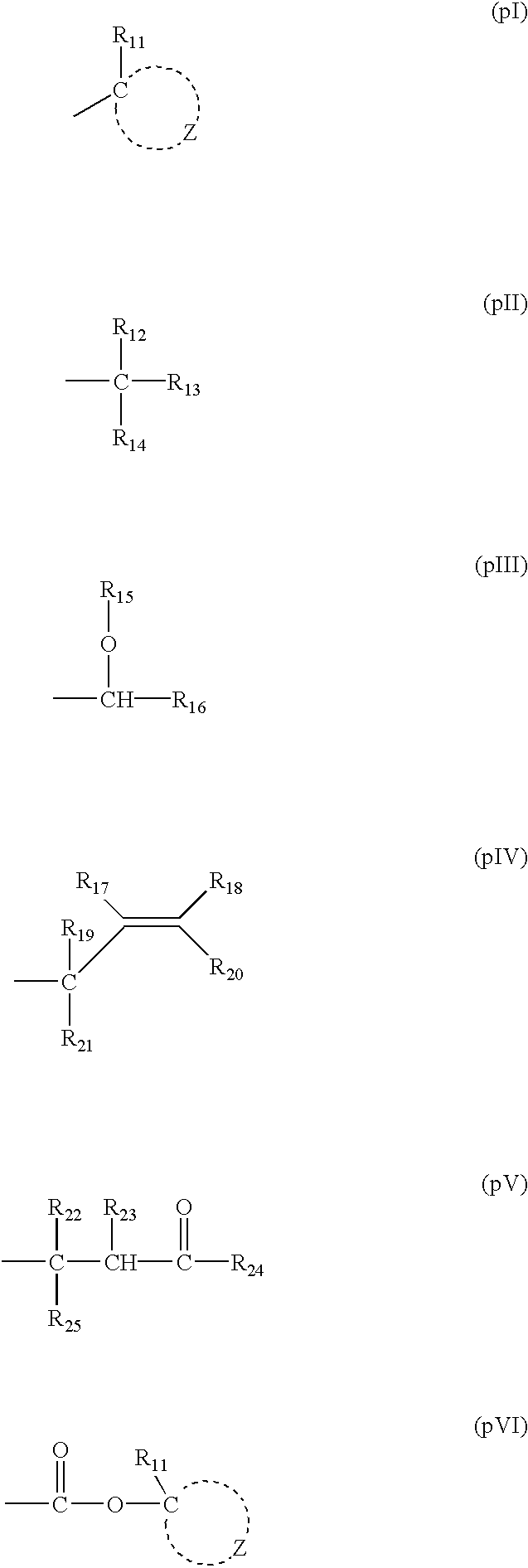
InactiveUS6858370B2Increase exposureAvoid sensitivityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsActinic RaysAlicyclic Hydrocarbons
A positive photosensitive composition comprises: (A) an acid generator capable of generating an acid upon irradiation with one of an actinic ray and a radiation; and (B) a resin having a monocyclic or polycyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and capable of decomposing by the action of an acid to increase the solubility in an alkali developer, wherein the acid generator (A) comprises at least two compounds of a sulfonium salt compound not having an aromatic ring, a triarylsulfonium salt compound, and a compound having a phenacylsulfonium salt structure.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
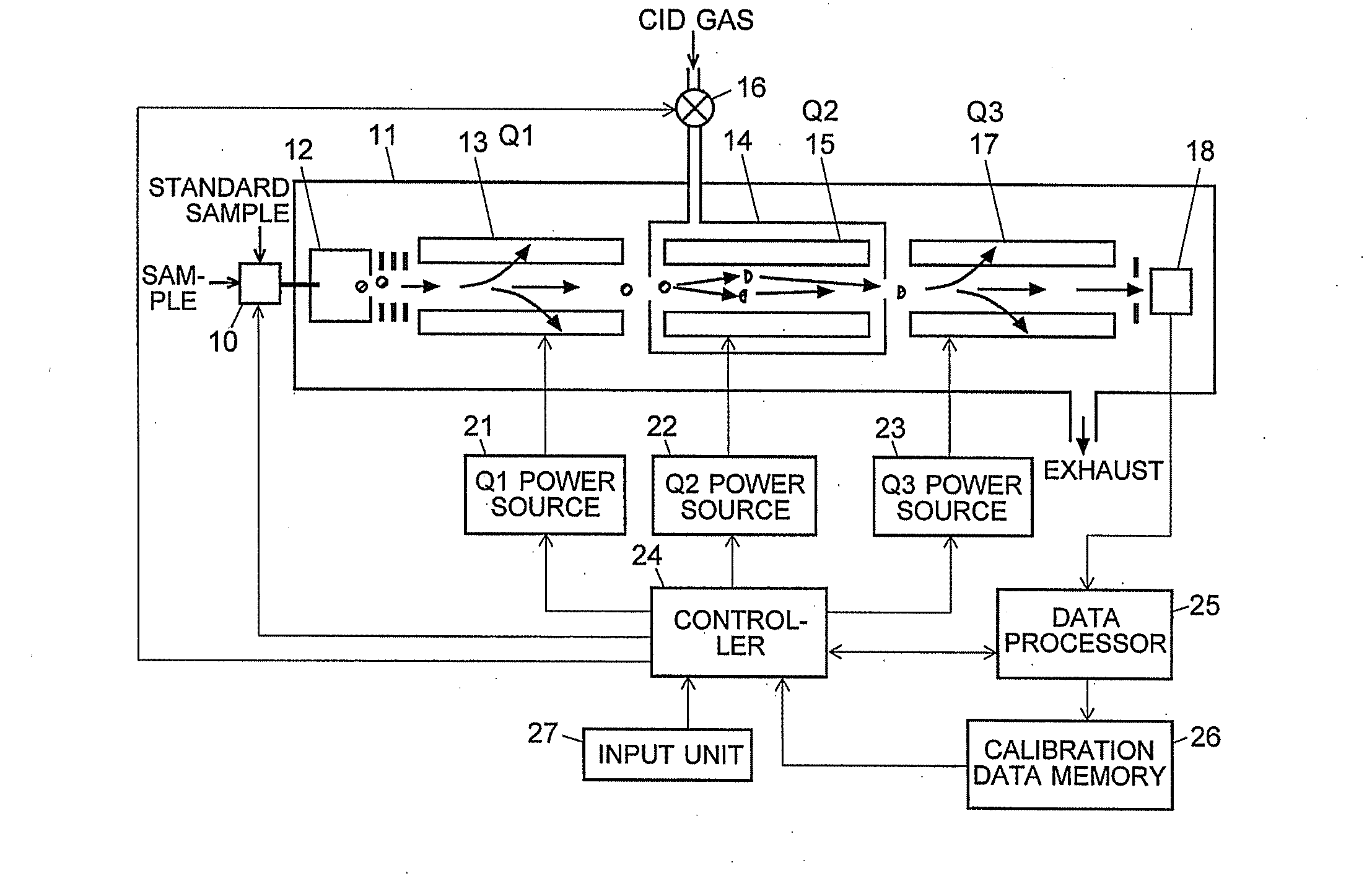
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20110284740A1High detection sensitivityIncrease in mass accuracySamples introduction/extractionParticle spectrometer methodsData memoryQuadrupole
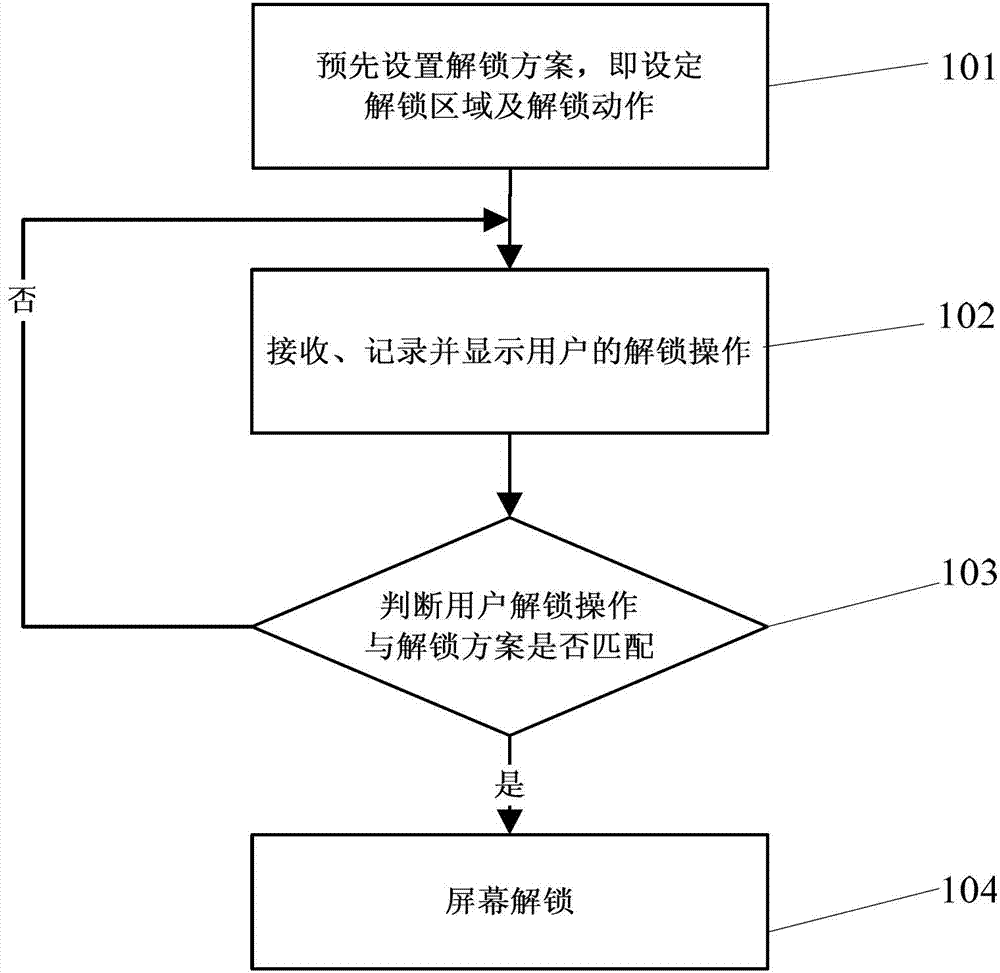
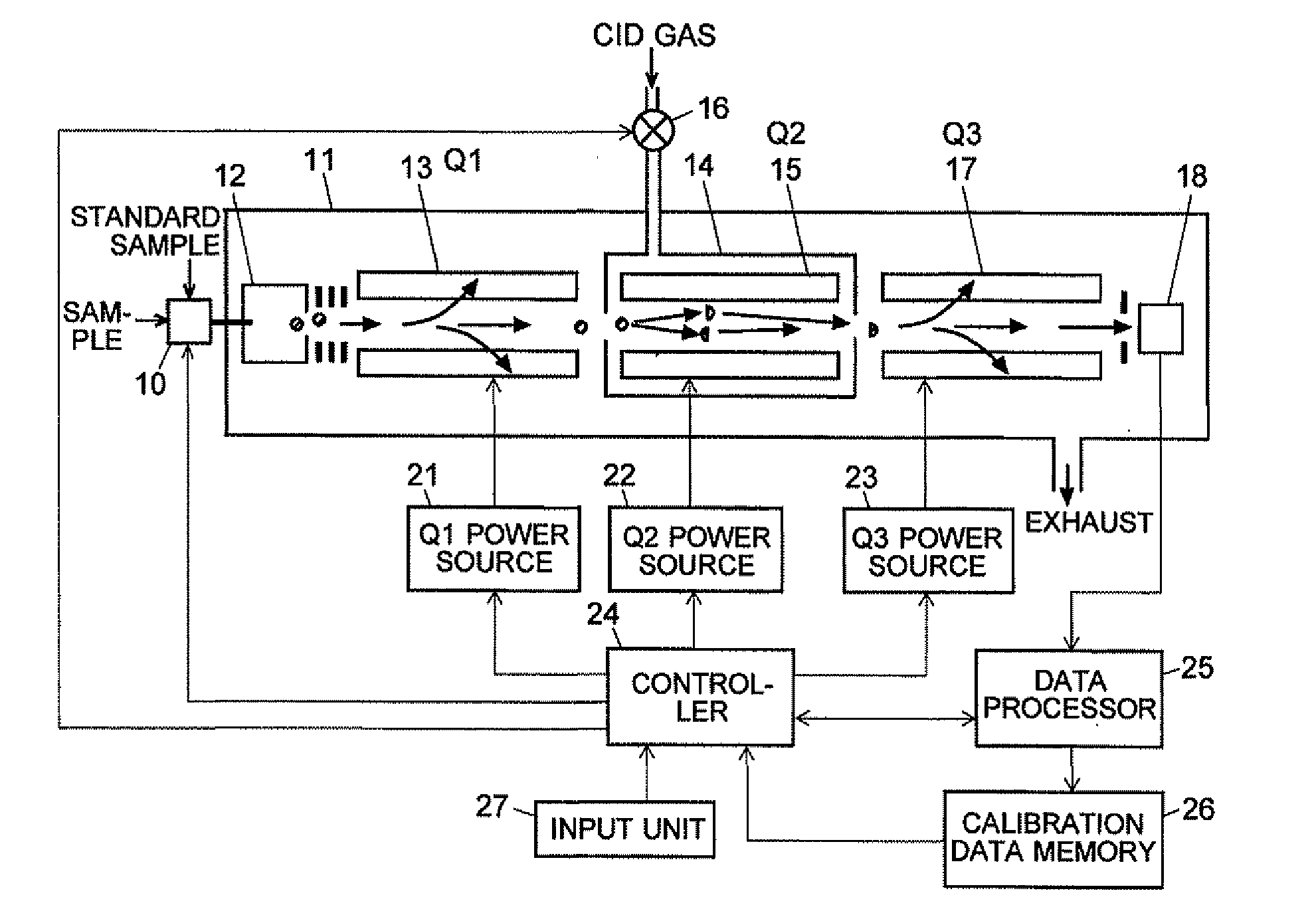
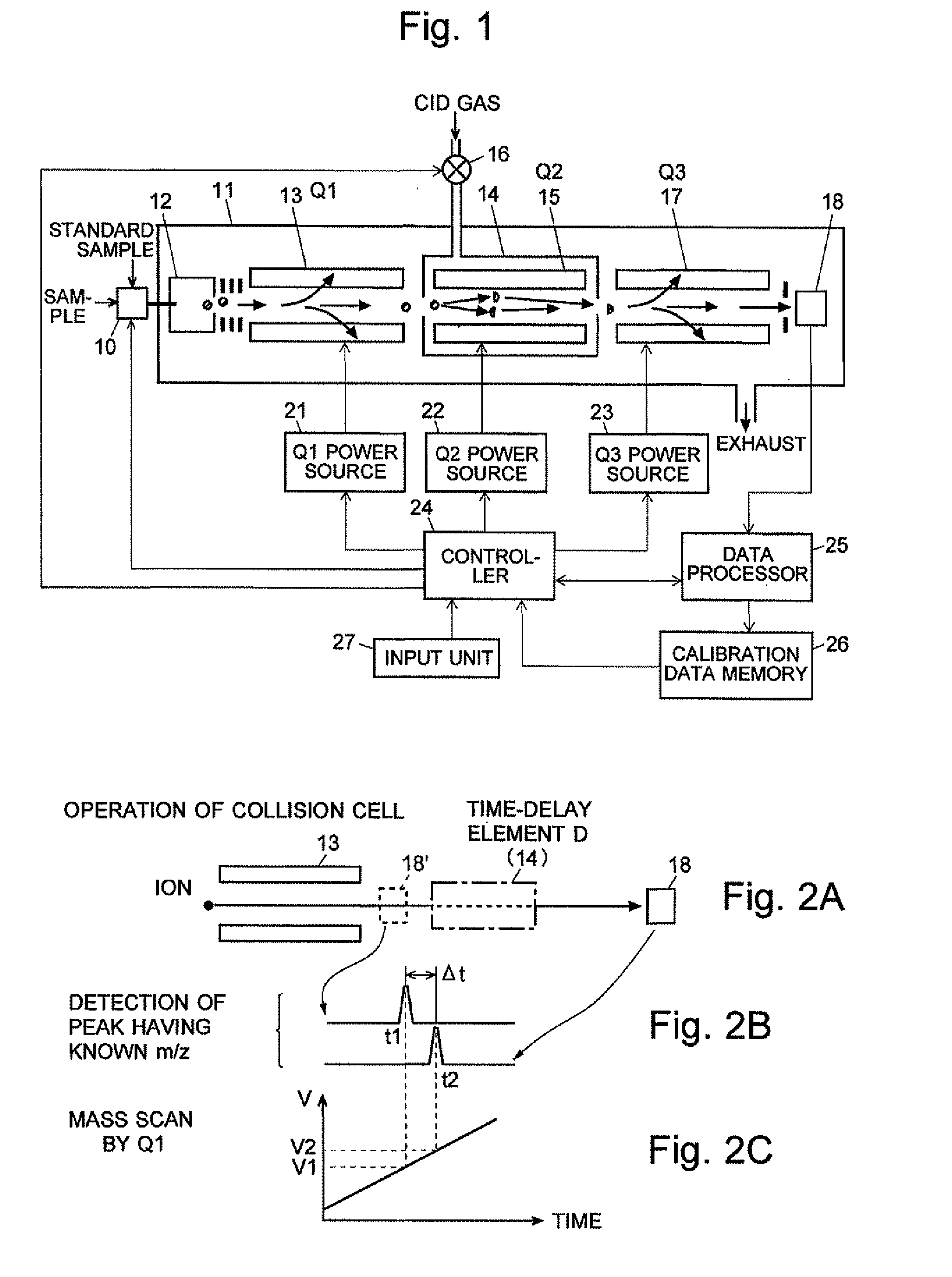
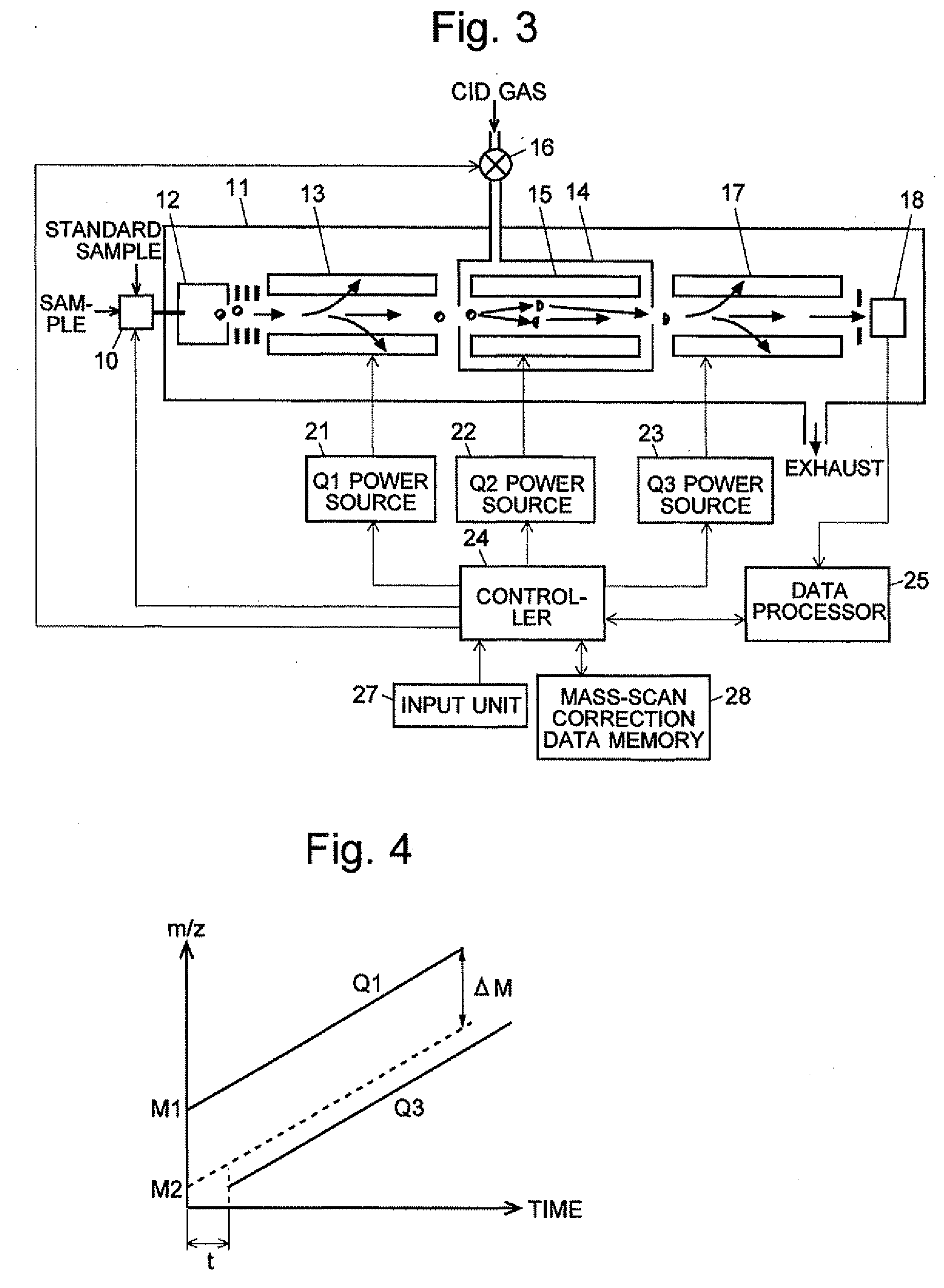
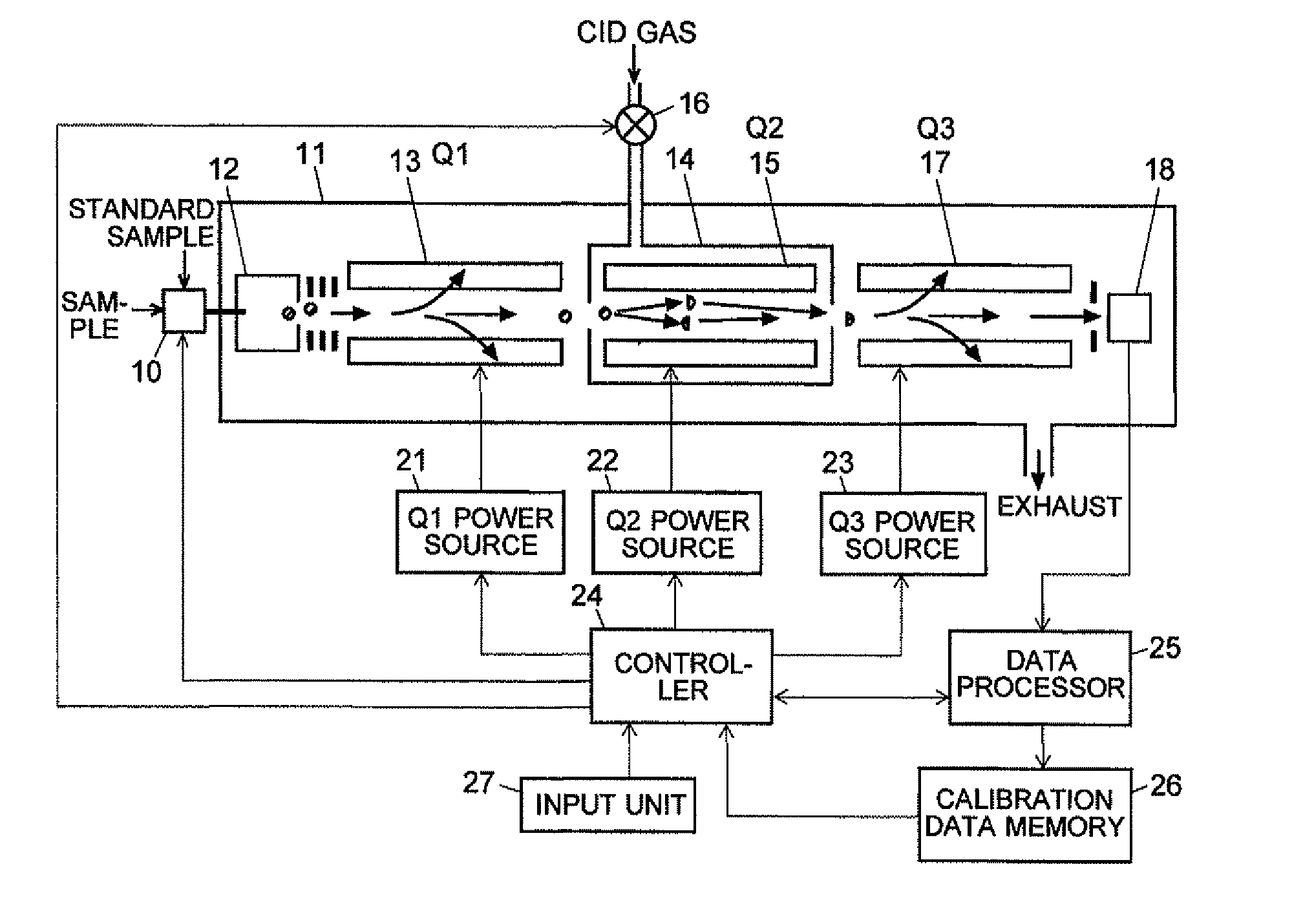
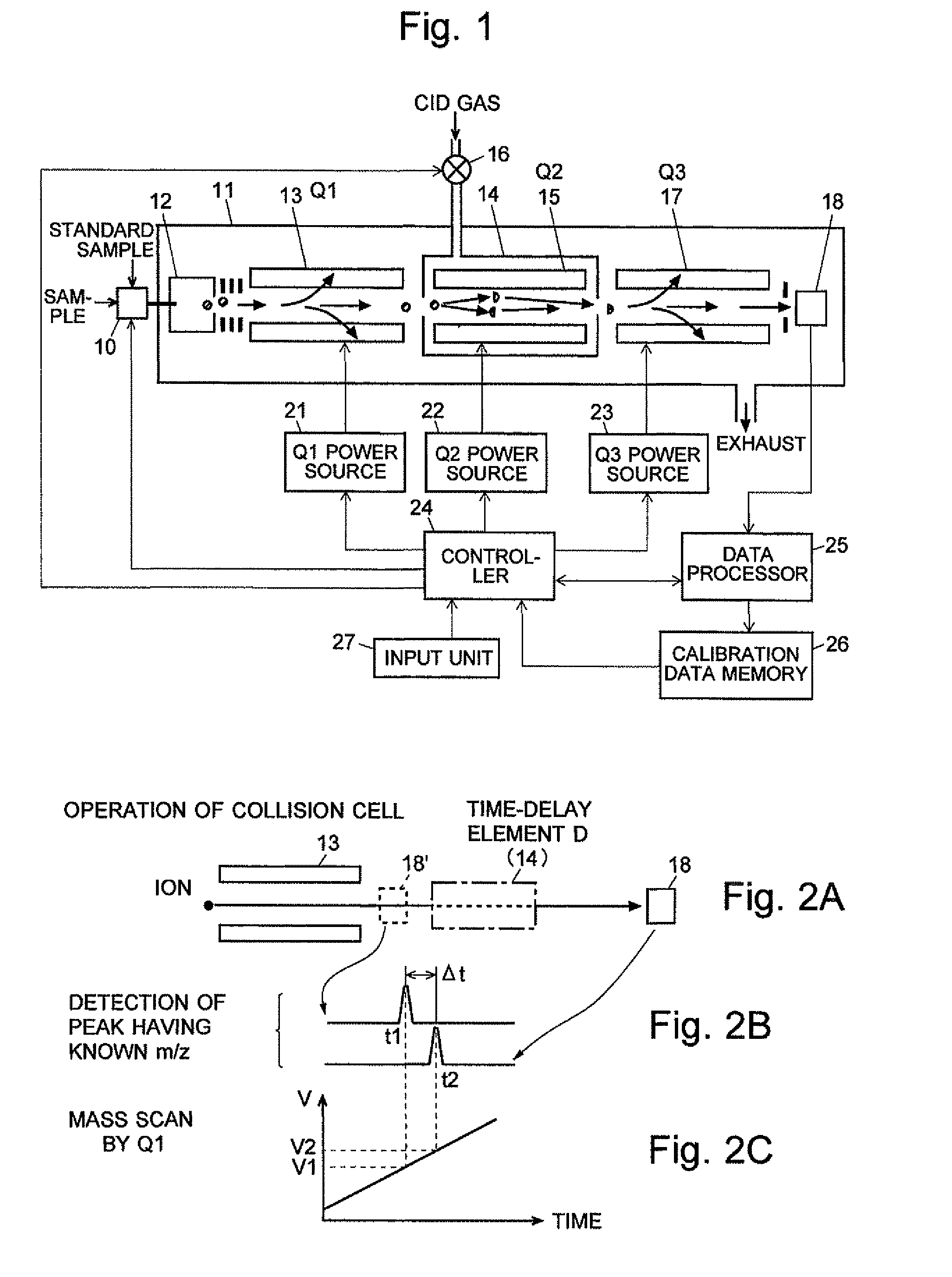
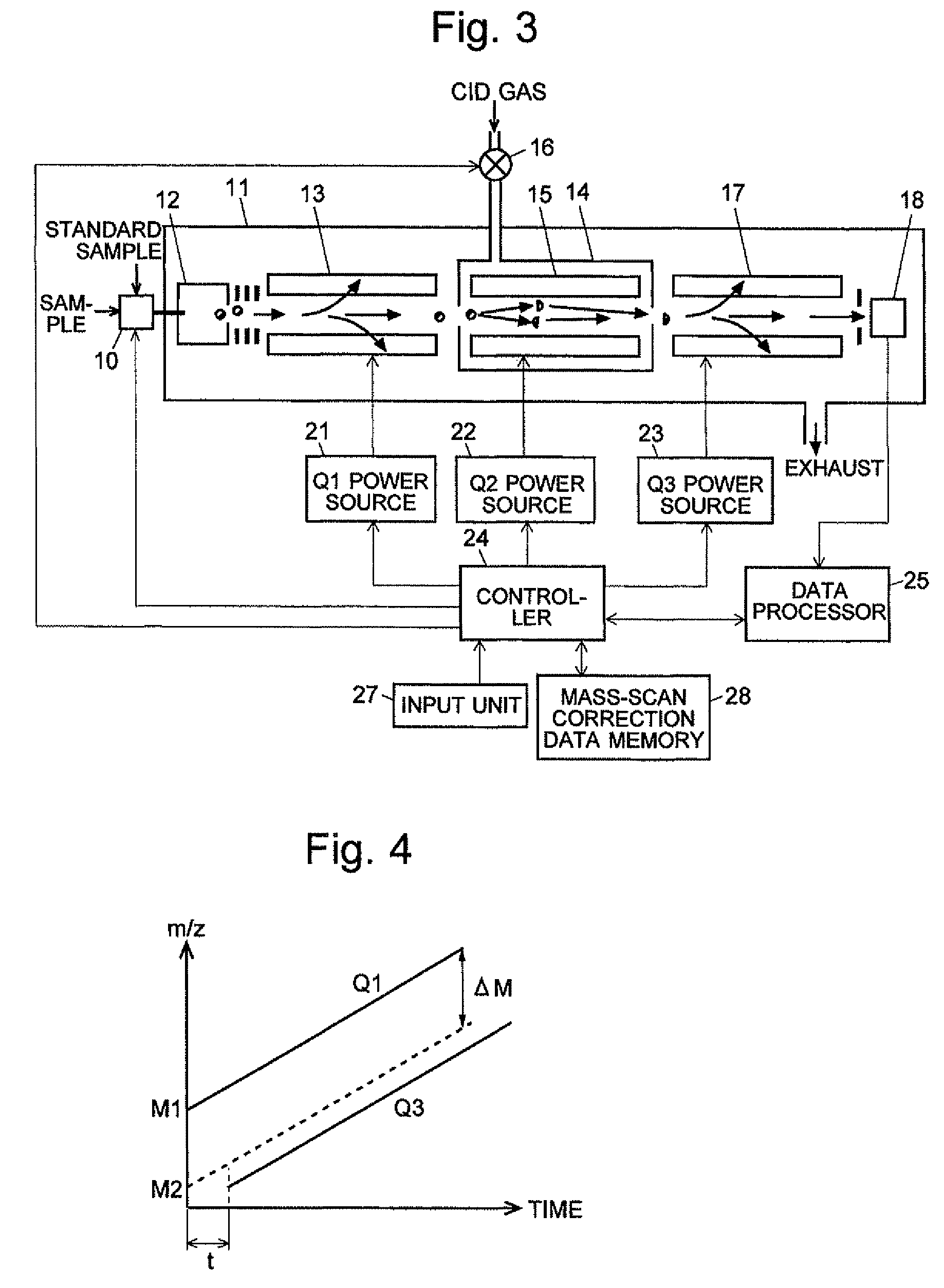
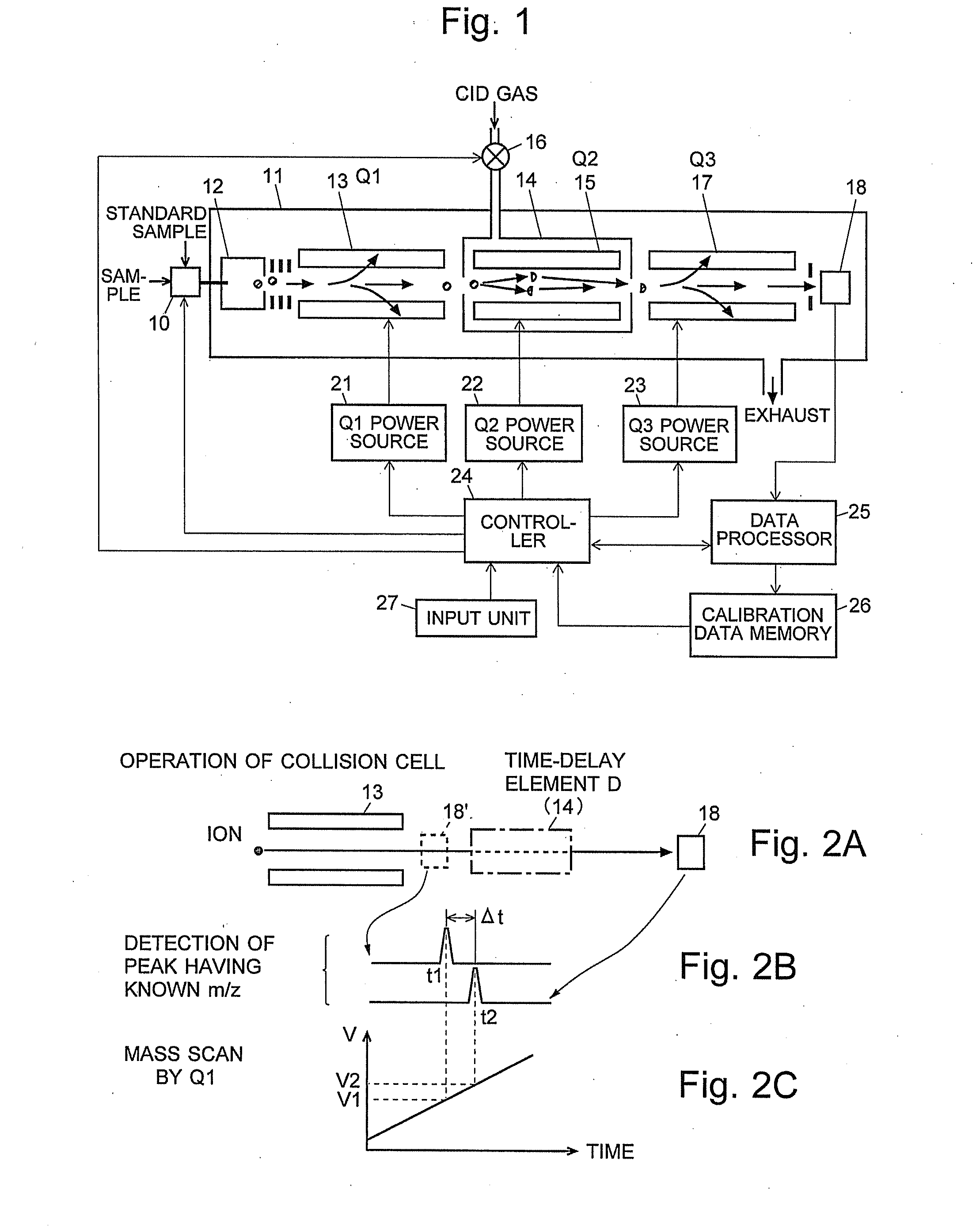
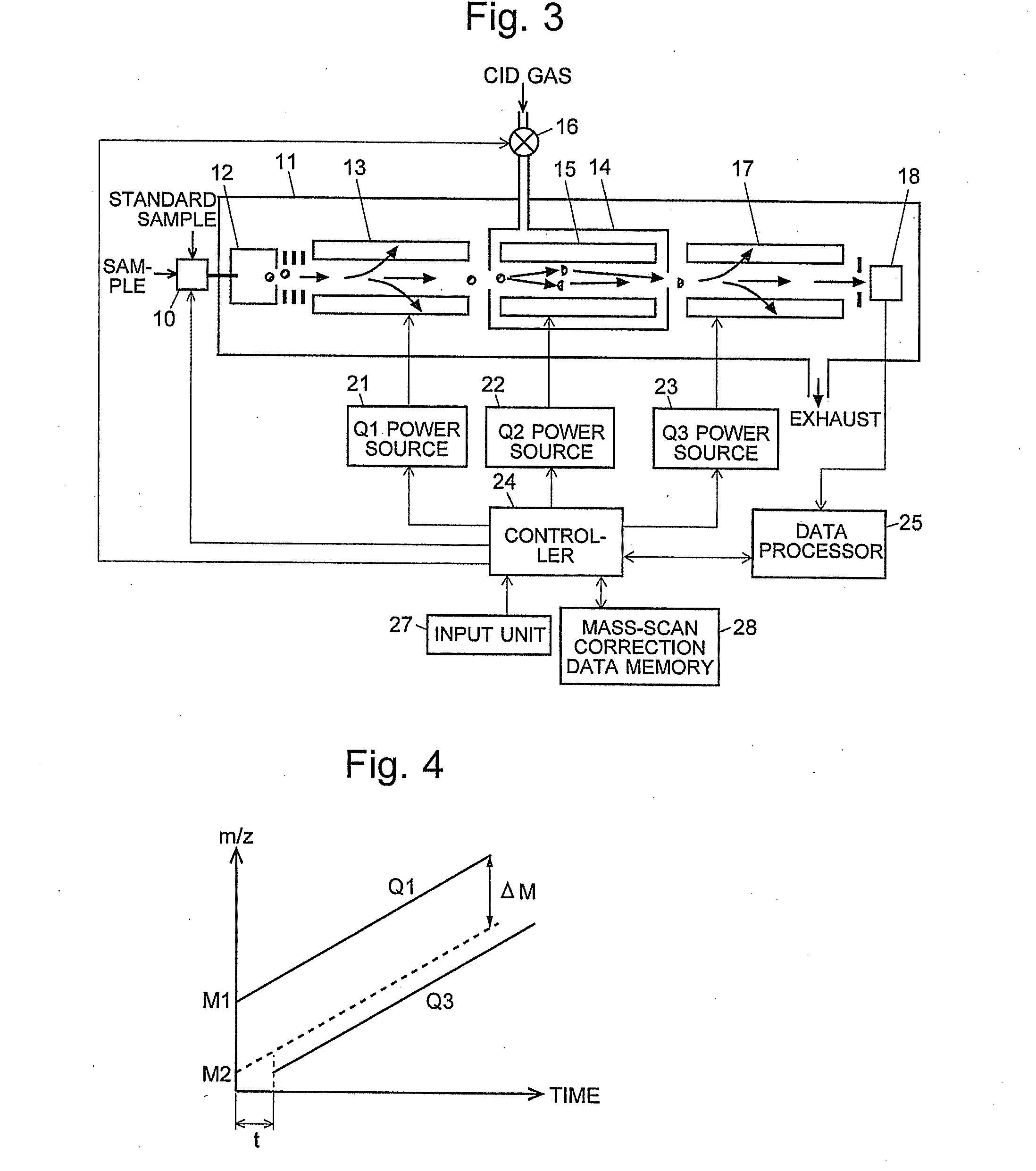
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Touch screen panel
ActiveUS20100182255A1Reduce resistanceAvoid sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingCouplingTouchscreen
The touch screen panel of the present invention includes first sensing patterns formed on a transparent substrate, a first insulating film formed on the first sensing patterns, second sensing patterns formed on the first insulating film, a plurality of metal patterns disposed on edge regions of the first and second sensing patterns, and a plurality of auxiliary metal patterns formed in the same layer as the metal patterns. Each of the first and second sensing patterns has sensing cells and coupling lines. Each of the coupling lines connects two of the sensing cells. Each of the metal patterns is coupled to the first sensing pattern or to the second sensing pattern, and each of the auxiliary metal patterns being formed on one of the first coupling lines or on one of the second coupling lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
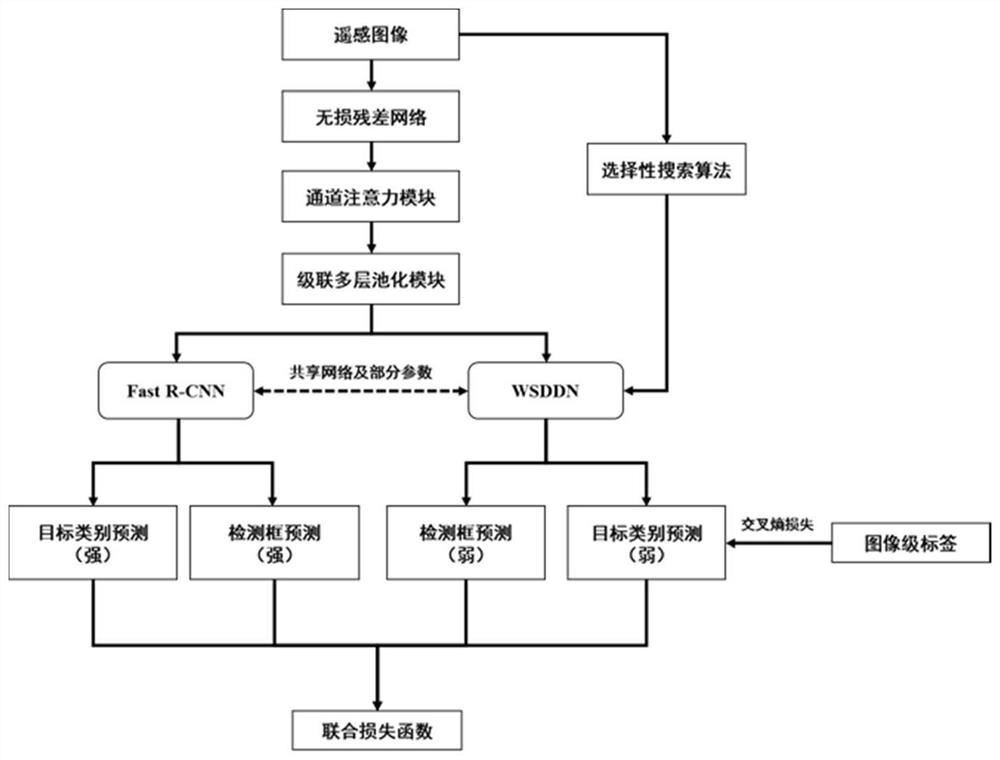
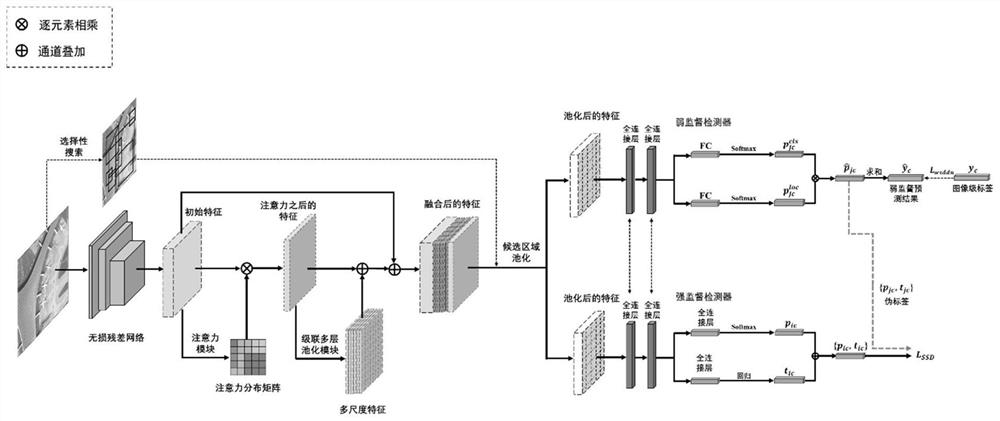
Weak supervision remote sensing target detection method based on hybrid hole convolution
PendingCN112183414AImprove robustnessAvoid lossScene recognitionNeural architecturesFeature extractionEngineering
The invention provides a weak supervision remote sensing target detection method based on hybrid hole convolution. According to the method, various customized designs such as hybrid hole convolution,attention mechanism and multi-layer pooling are adopted, multi-scale feature extraction and fusion are enhanced, and the robustness of objects of different sizes is improved. Besides, asynchronous iteration alternate training between a strong supervision detector and a weak supervision detector is utilized, training and detection can be carried out only through an image-level real label, and the purpose of cooperatively improving the detection performance is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Video error concealment mechanism for block based video decompression
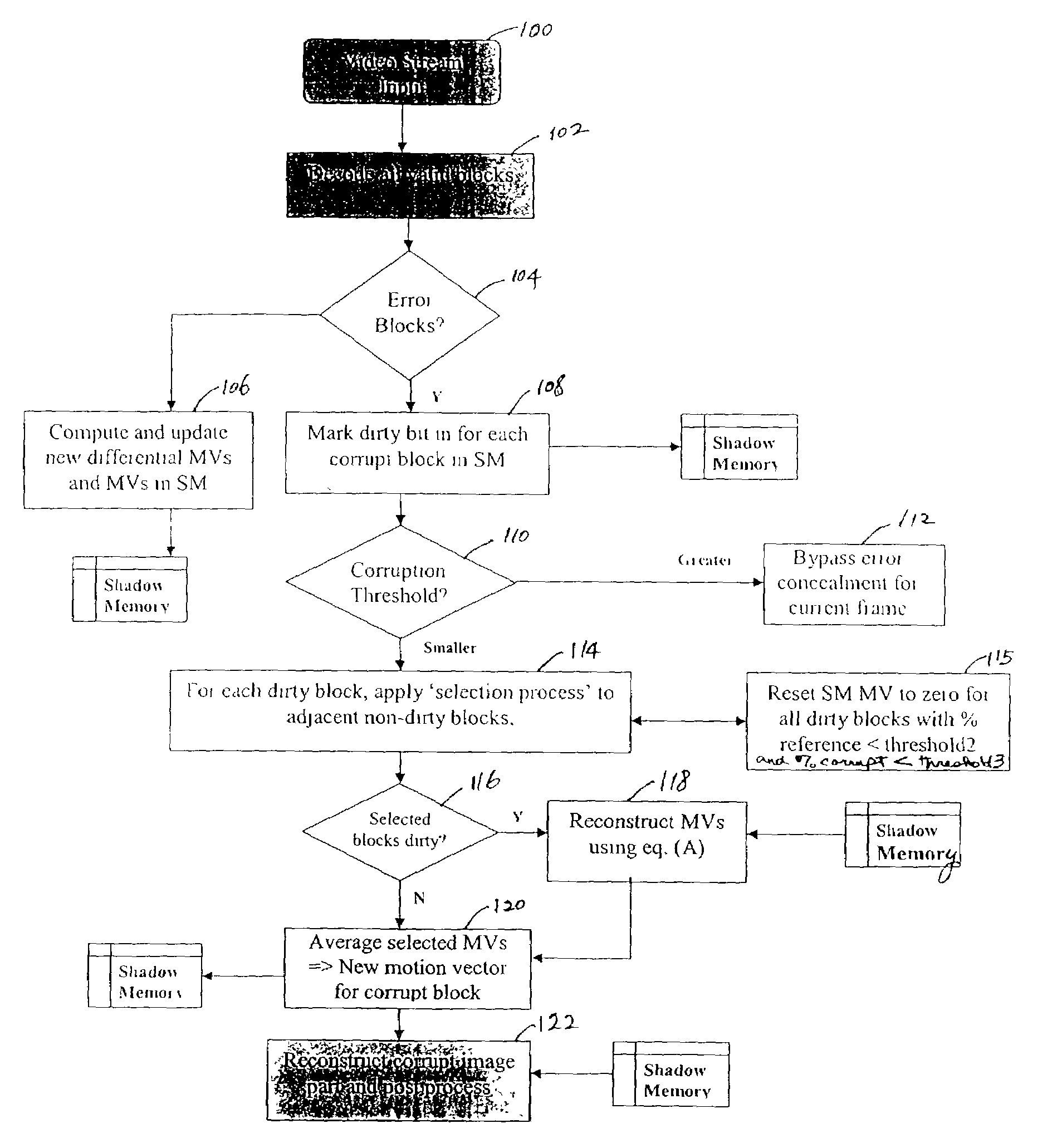
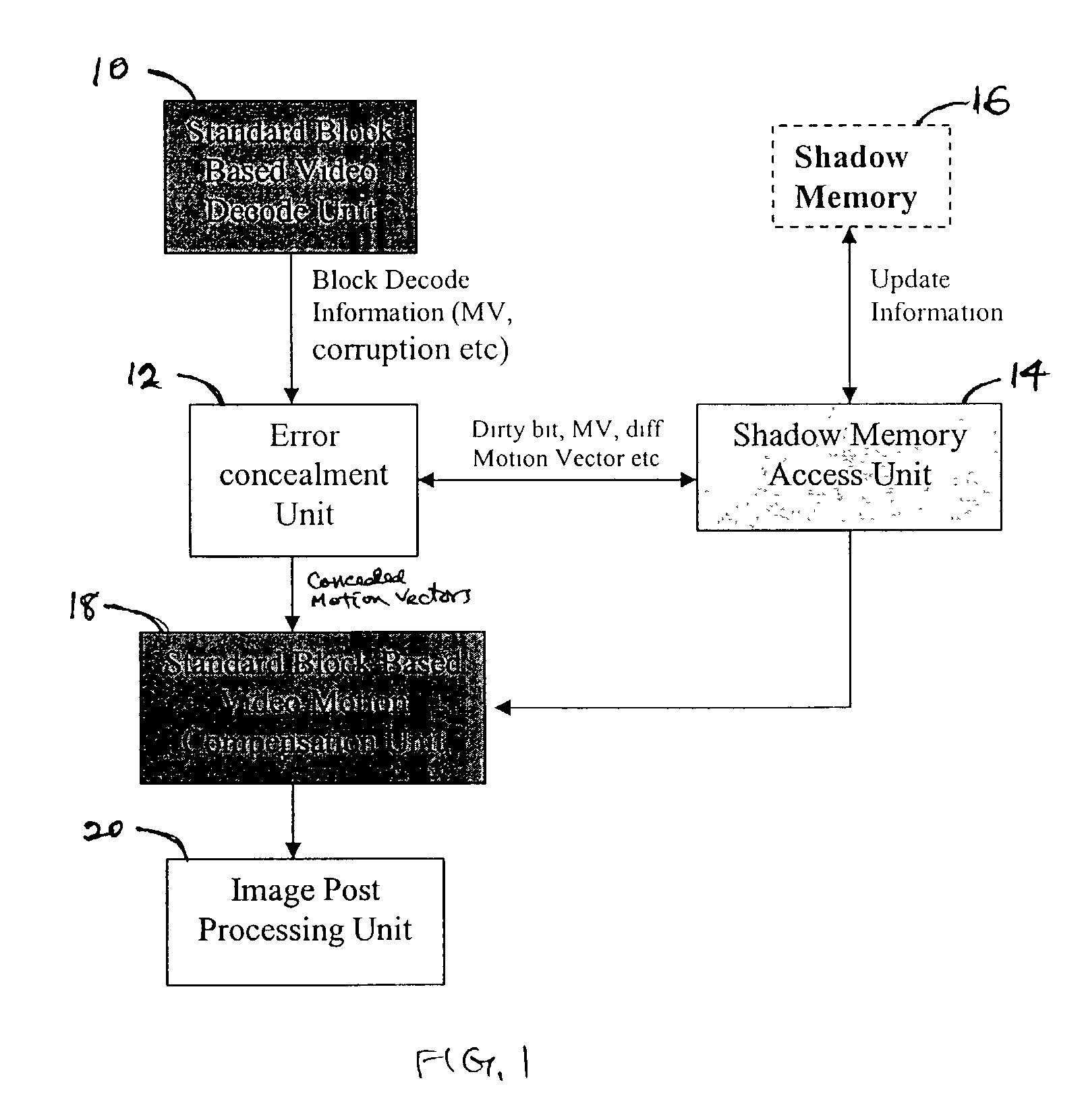
InactiveUS7020207B1Prevent and minimize degradationReduce artifact effectColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMotion vector
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and apparatus for decoding digital video or motion picture signals with error concealment to prevent or minimize degradation of the picture quality. When corruption occurs, the method determines whether error concealment is needed according to a preset criterion. If so, motion vectors for the corrupt region are calculated using the motion vectors and rates of change of motion of current blocks in the current frame and / or old blocks in a previous frame according to a best matching block selection process. The method also determines if the “time” relative motion of content is small by defining a percentage use parameter. In some cases, once the error concealment is complete, the “weight” or visual sensitivity of the restored block is decreased in order to reduce boundary artifact effects. This is accomplished by a quantization mask employing the human visual system (HVS) concept.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
MS/MS mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8269166B2Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a standard sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a mass scan at a first-stage quadrupole (13) over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation (CID) gas is introduced into a collision cell (14) and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole (17) is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various kinds of product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole (13) arrive at and are detected by a detector (18) without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor (25) can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole (13) and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell (14) reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory (26), to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like. By using this relationship, a mass shift due to the time delay in the collision cell (14) can be cancelled, so that the product ions can be detected with high sensitivity over the entire mass range. Furthermore, a mass spectrum having an accurate mass axis can be created.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Surface mountable electret condenser microphone
InactiveUS20060280320A1Reduce sensitivityNotElectrets selectrostatic transducerElectrostatic transducer microphonesCapacitanceSurface mounting
Disclosed is an electret condenser microphone capable of surface mounting which has a structure highly resistant to high temperature. The electret condenser microphone comprises a case, a polar ring, a diaphragm, a spacer, a back-plate, a first base, a second base and a printed circuit board (PCB), wherein the first base surrounds the diaphragm, the spacer and the back-plate, so that the first base prevents characteristics of an electret formed on any one of the diaphragm and the back-plate from being deteriorated in a reflow process for surface mounting. Further, in order to prevent sensitivity of the electret condenser microphone from being lowered due to decrease of an electrical potential value of the electret in the reflow process. High gain IC devices are used. The electret condenser microphone capable of surface mounting can be obtained by, first, using main components made from a high-temperature resistant insulating material, for example, a polymer-, a plastic- or a fluoro resin-based material, second, constructing the first base to surround acoustic based components, third, using a cream solder for high temperature to bond components to the PCB, fourth, using the high gain IC devices, fifth, providing the connecting terminal with gas discharge grooves and protruding the connecting terminal to be higher than a curled surface of the electret condenser microphone.
Owner:BSE CO LTD
MS/MS Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20130214146A1Reduce impactHigh detection sensitivityIsotope separationTube calibration apparatusTime delaysData memory
A mass analysis of a sample having a known mass-to-charge ratio is carried out by performing a scan at a first-stage quadrupole over a predetermined mass range, under the condition that a collision induced dissociation gas is introduced into a collision cell and a voltage applied to a third-stage quadrupole is set so that no substantial mass separation occurs in this quadrupole. Various product ions originating from a precursor ion selected by the first-stage quadrupole arrive at and are detected by a detector without being mass separated. Accordingly, based on the detection data, a data processor can obtain a relationship between the voltage applied to the first-stage quadrupole and the mass-to-charge ratio of the selected ions, with a time delay in the collision cell reflected in that relationship. This relationship is stored in a calibration data memory, to be utilized in a neutral loss scan measurement or the like.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
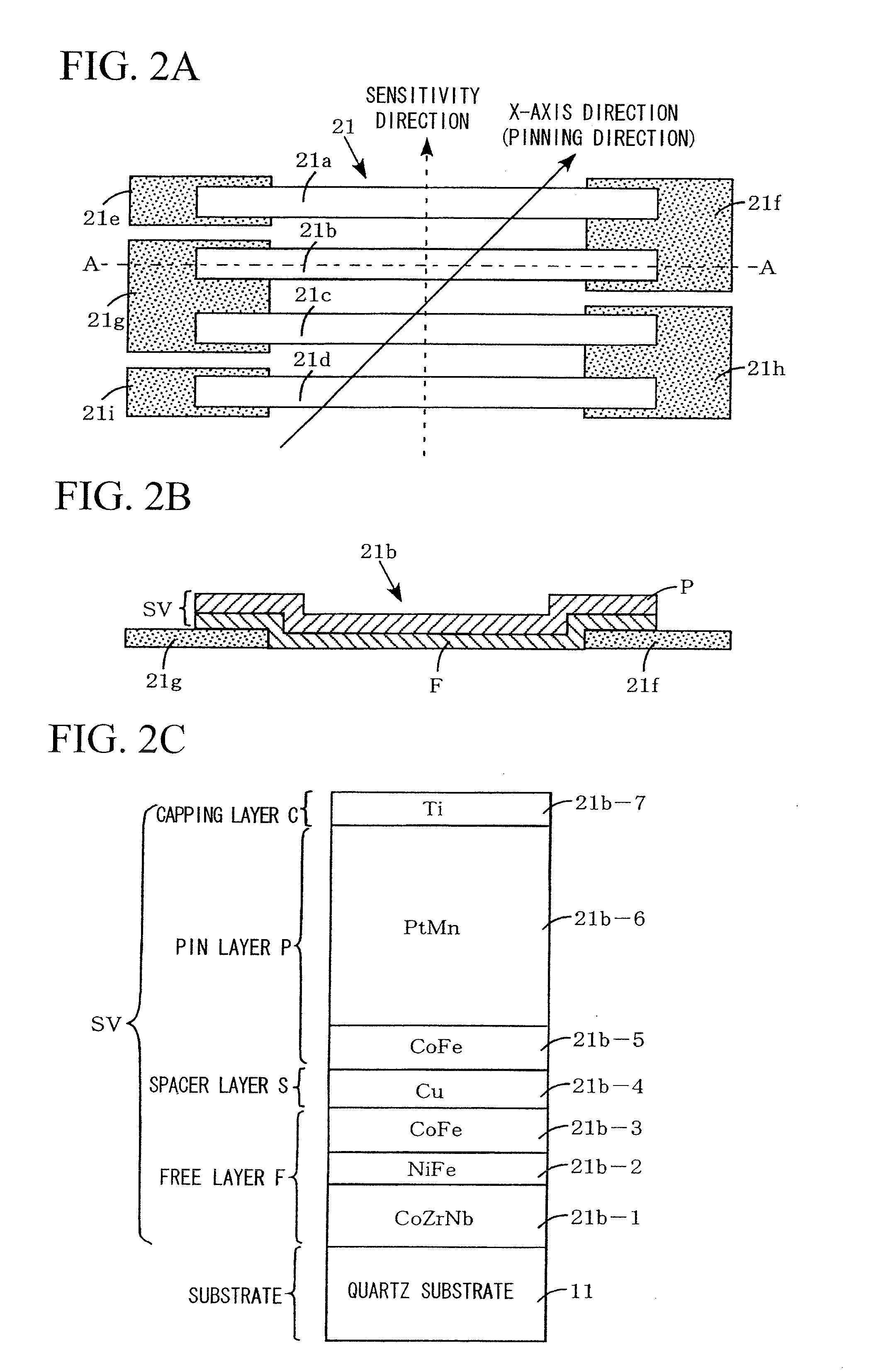
Three-axis magnetic sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120268113A1Avoid sensitivityEasy and inexpensiveNanomagnetismWave amplification devicesMagnetizationMagnet
In a three-axis magnetic sensor, a plurality of magnetoresistive effect element bars are connected in series by means of bias magnets formed on a flat surface parallel to the flat surface of the substrate to constitute magnetoresistive effect elements. The sensitivity direction of magnetization is a direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of each of the magnetoresistive effect element bars. Magnetoresistive effect elements forming X-axis and Y-axis sensors have magnetization directions that are orthogonal to each other. Magnetoresistive effect elements of the Z-axis sensor are formed on a tilted surface substrate in such a way that the magnetization direction is inside the tilted surface. The sensitivity direction of the Z-axis sensor is perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the magnetoresistive effect element bar.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
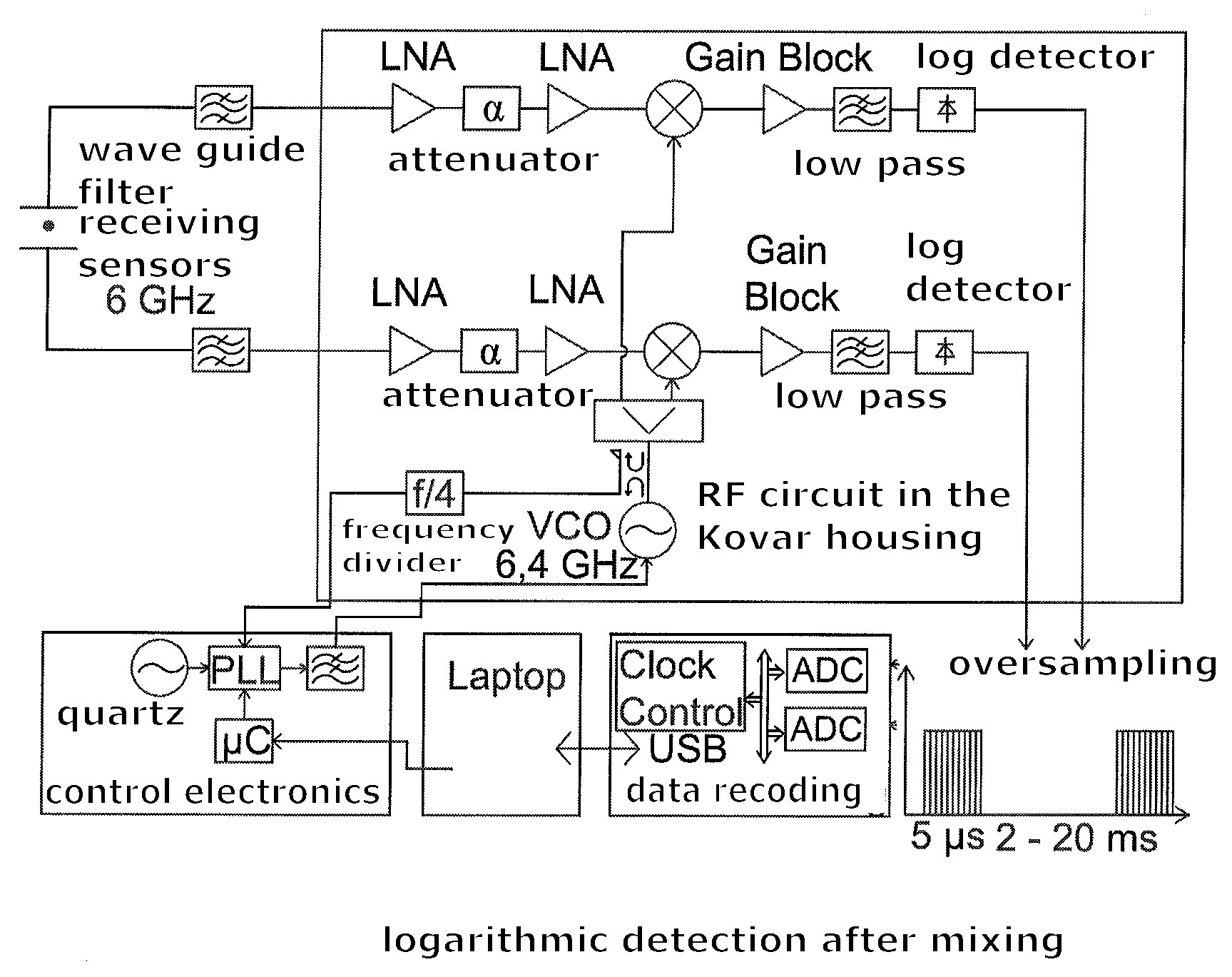
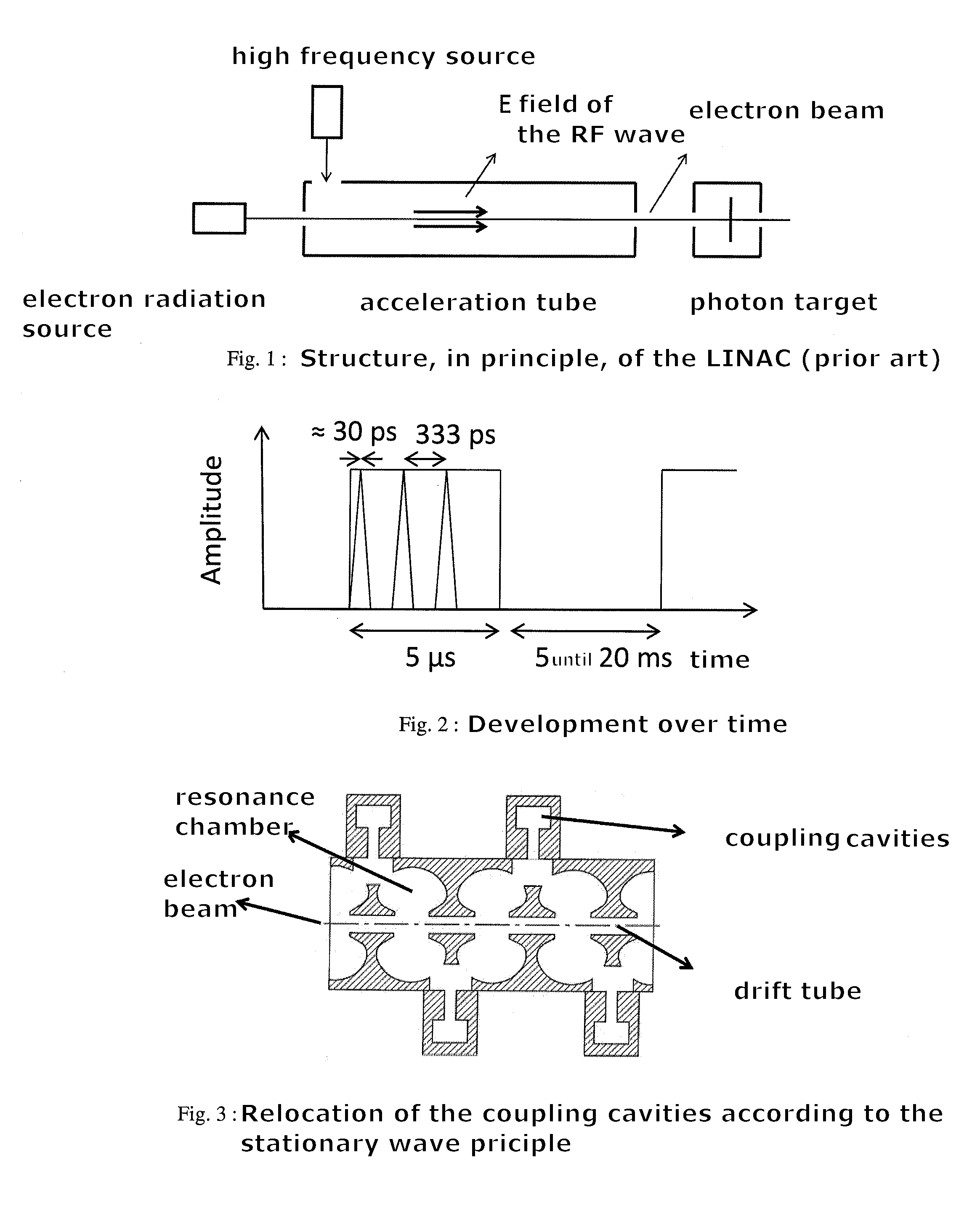
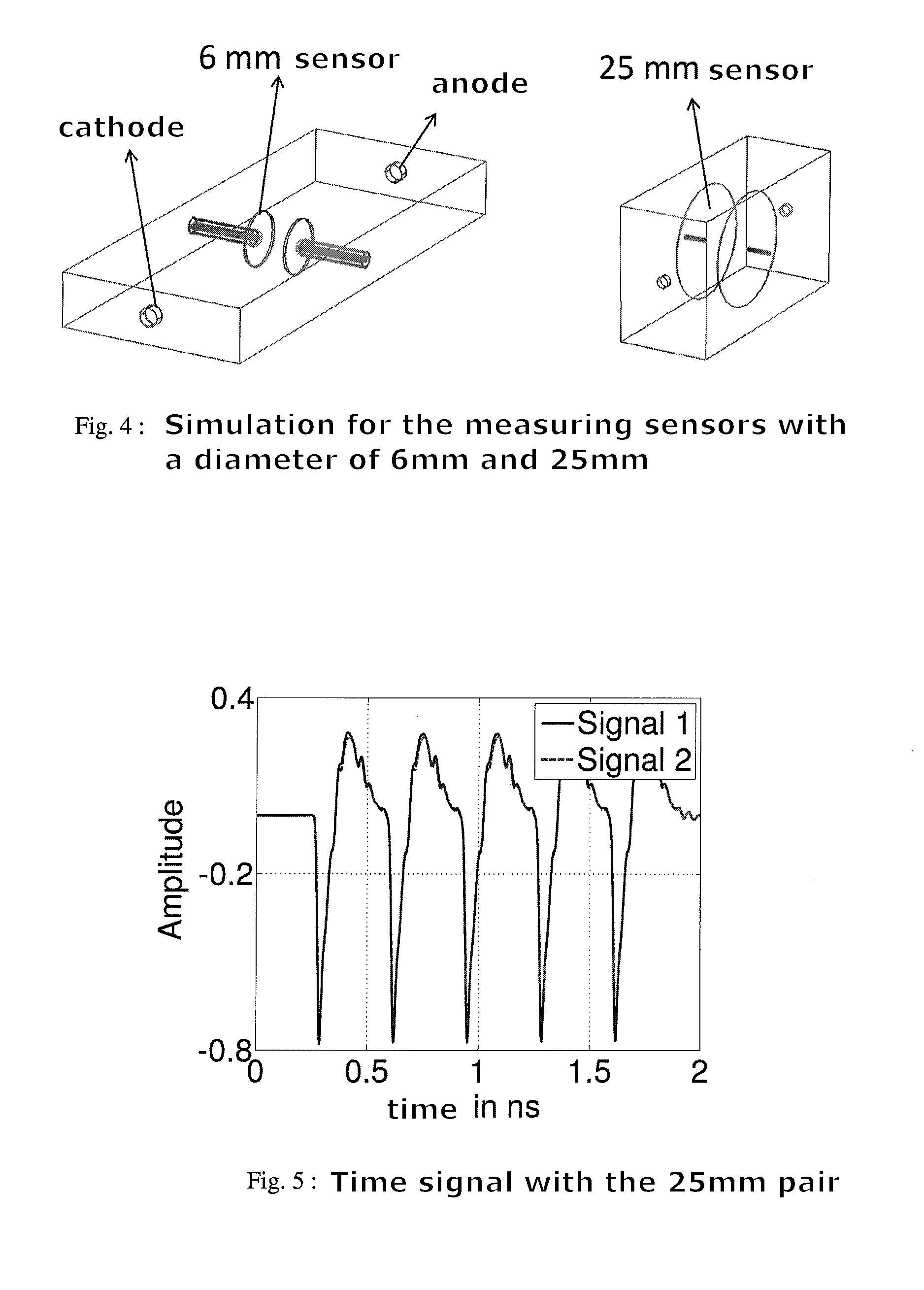
Beam position monitor for electron linear accelerator
ActiveUS20120262333A1Low hardware complexityHigh frequency selectivityAcceleratorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency mixerDrift tube
Owner:CRUISE MUNICH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com