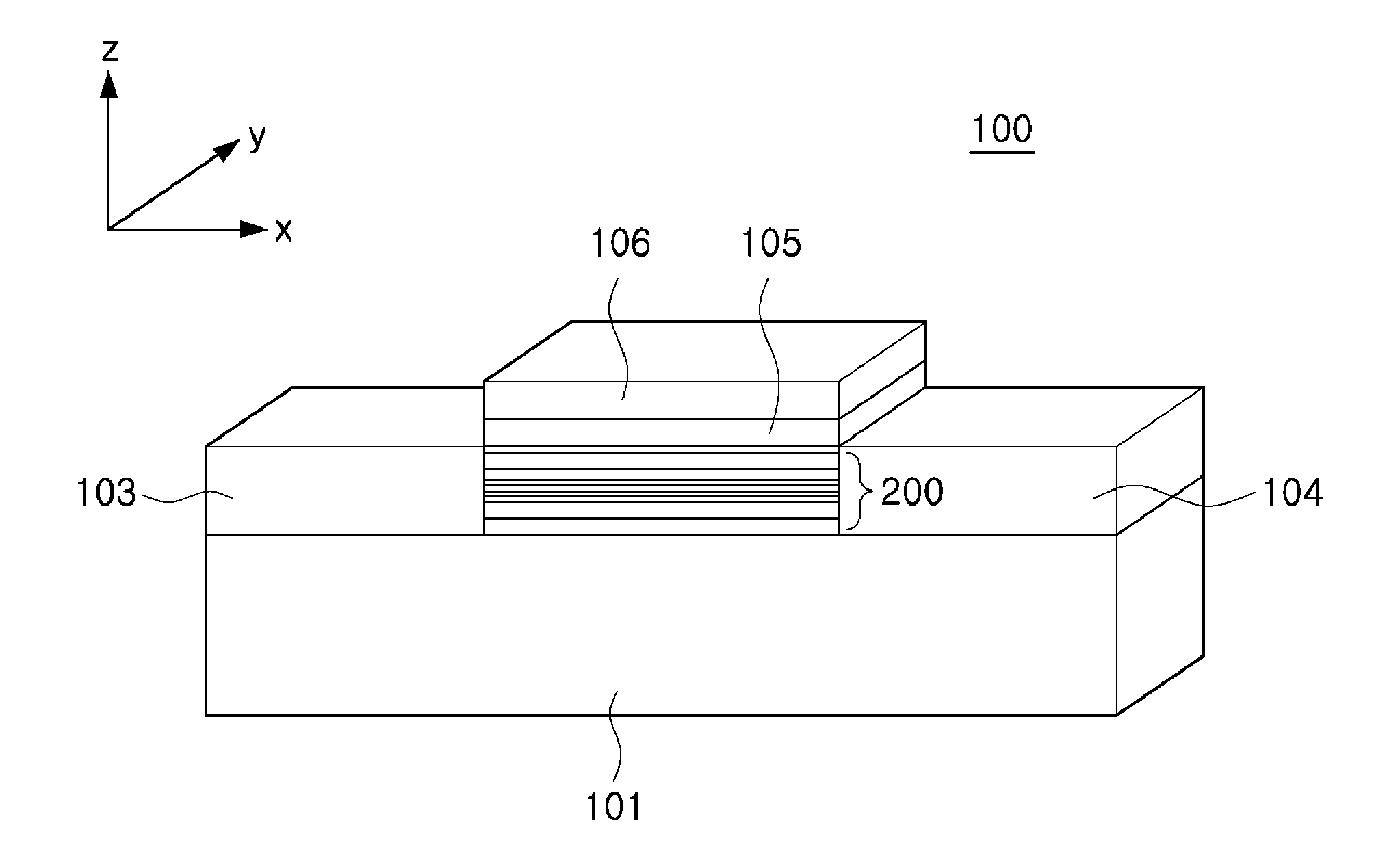
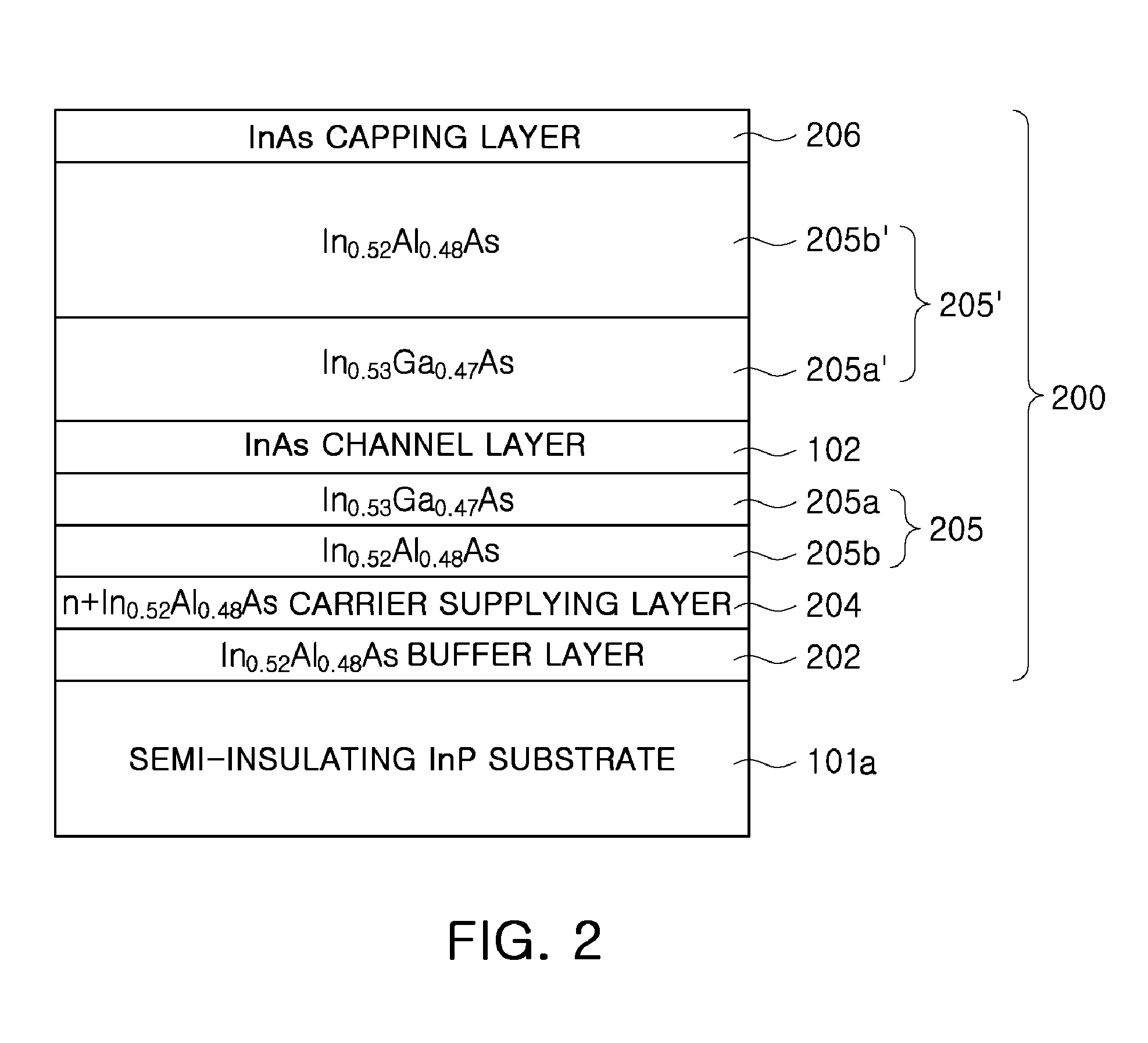
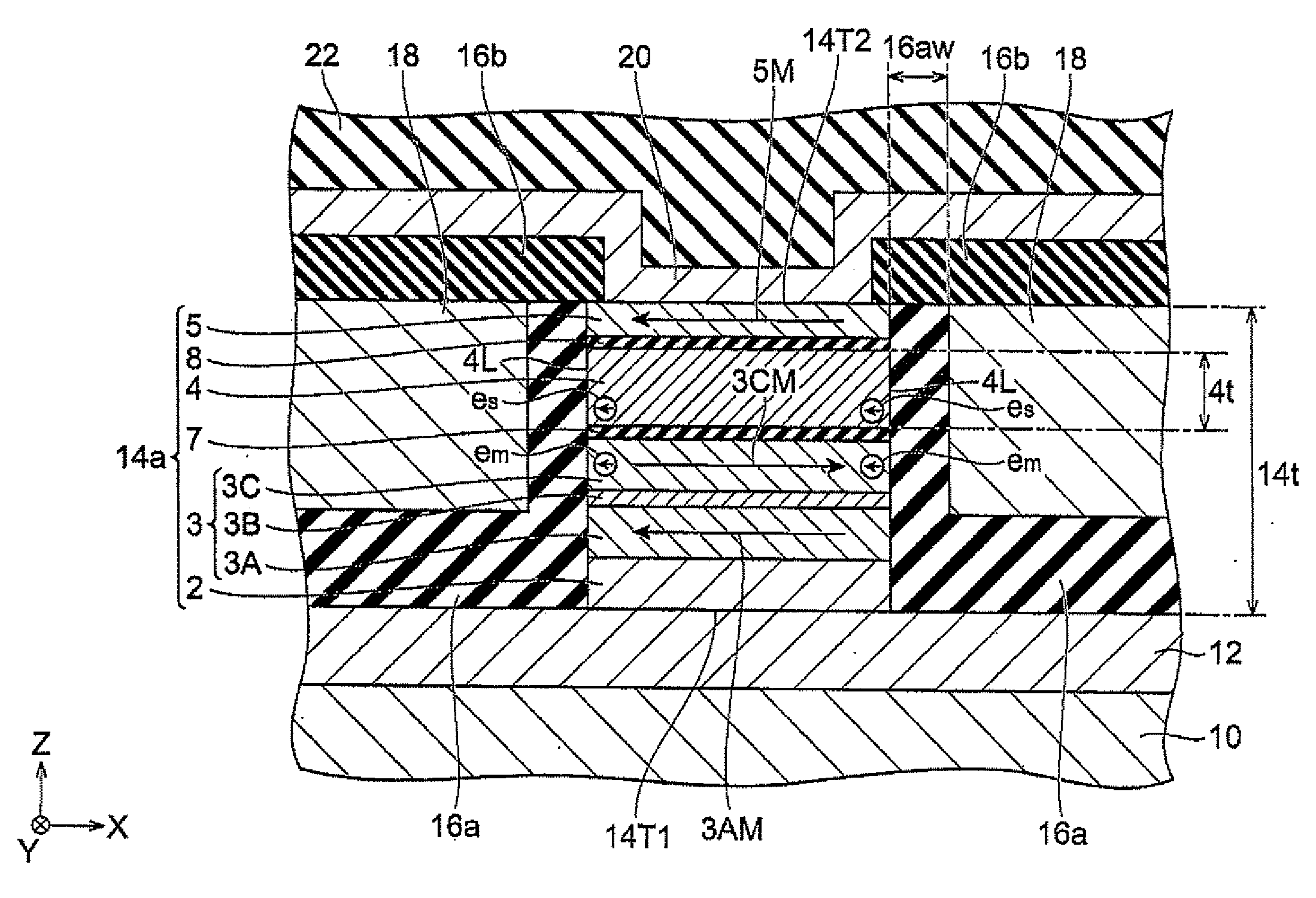
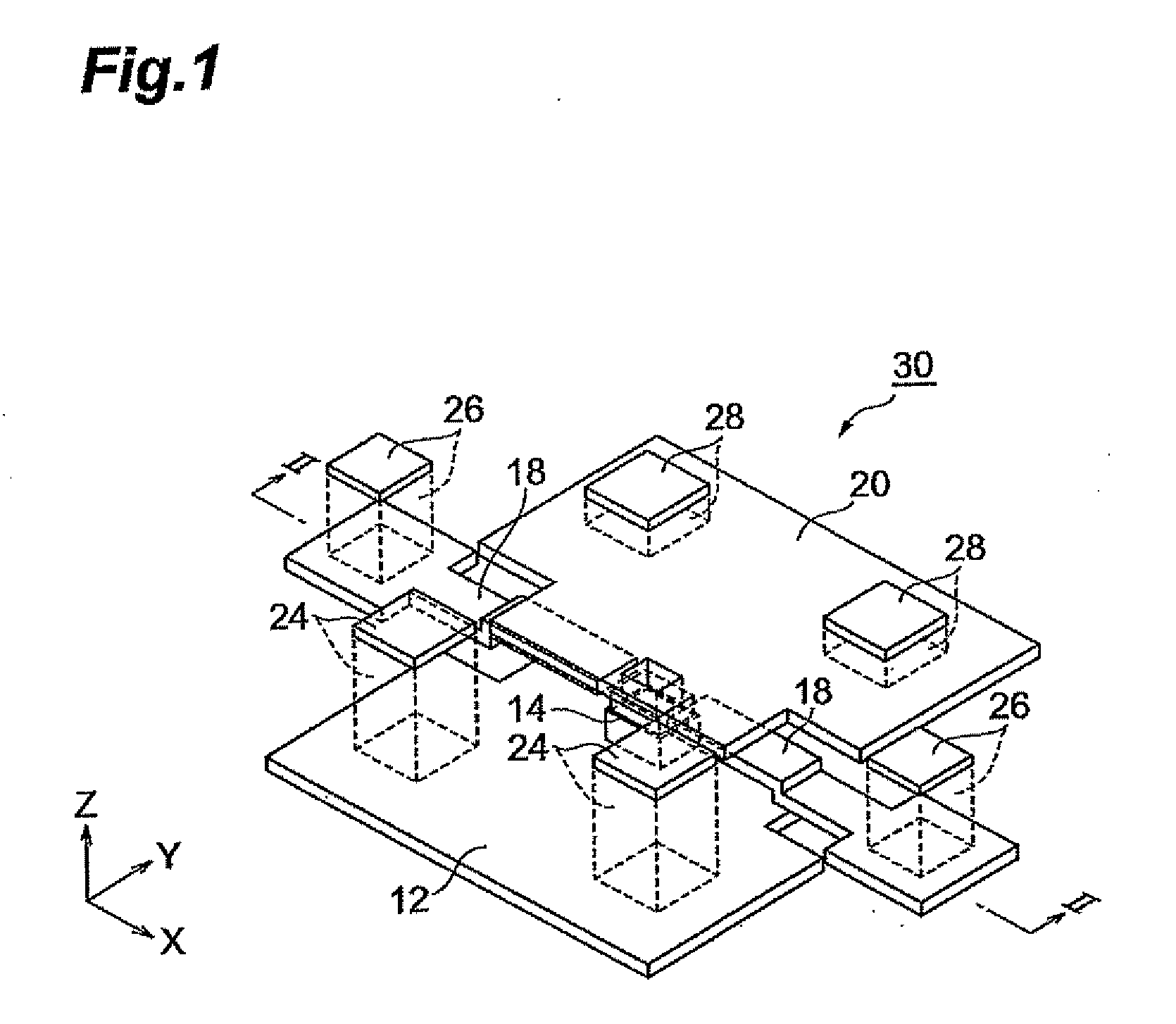
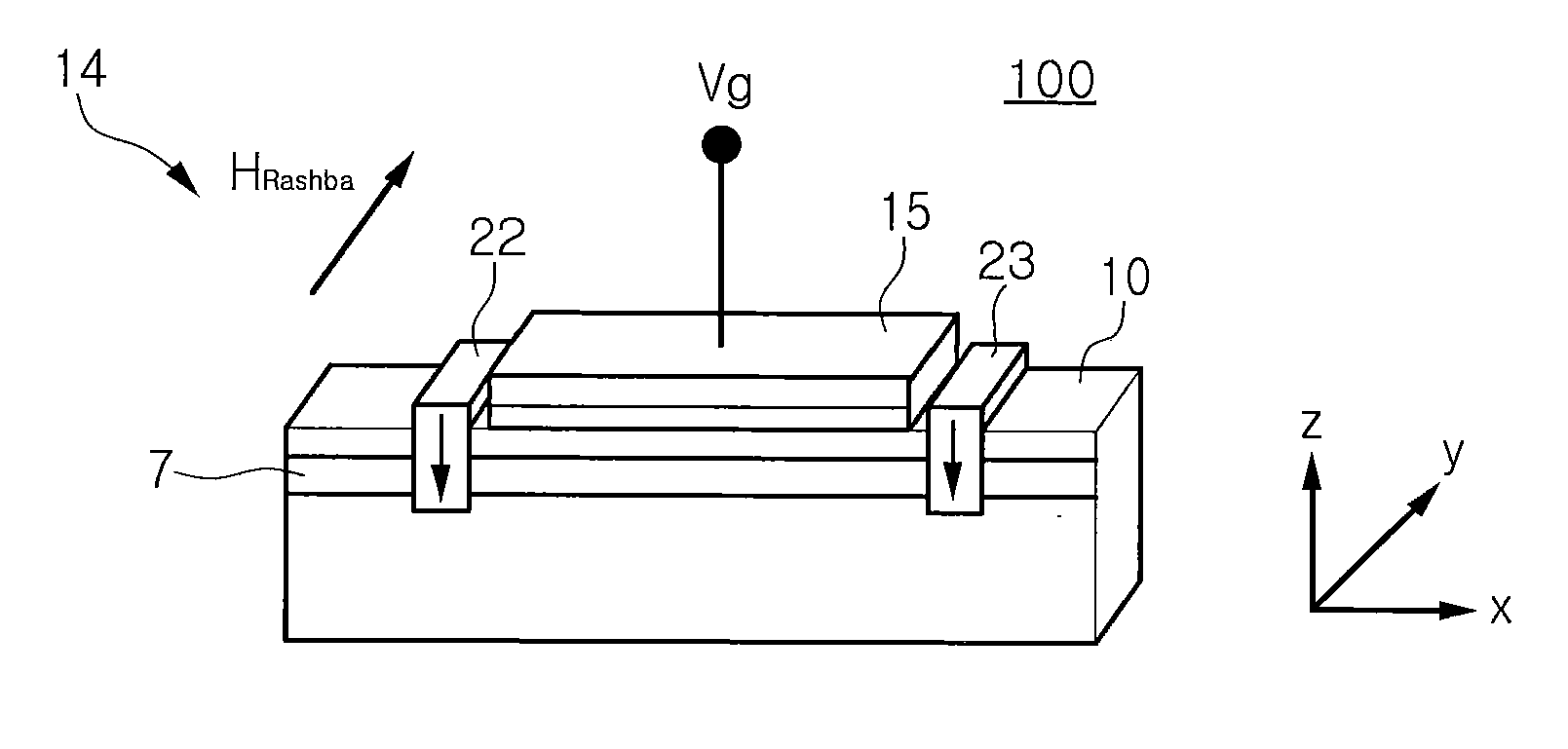
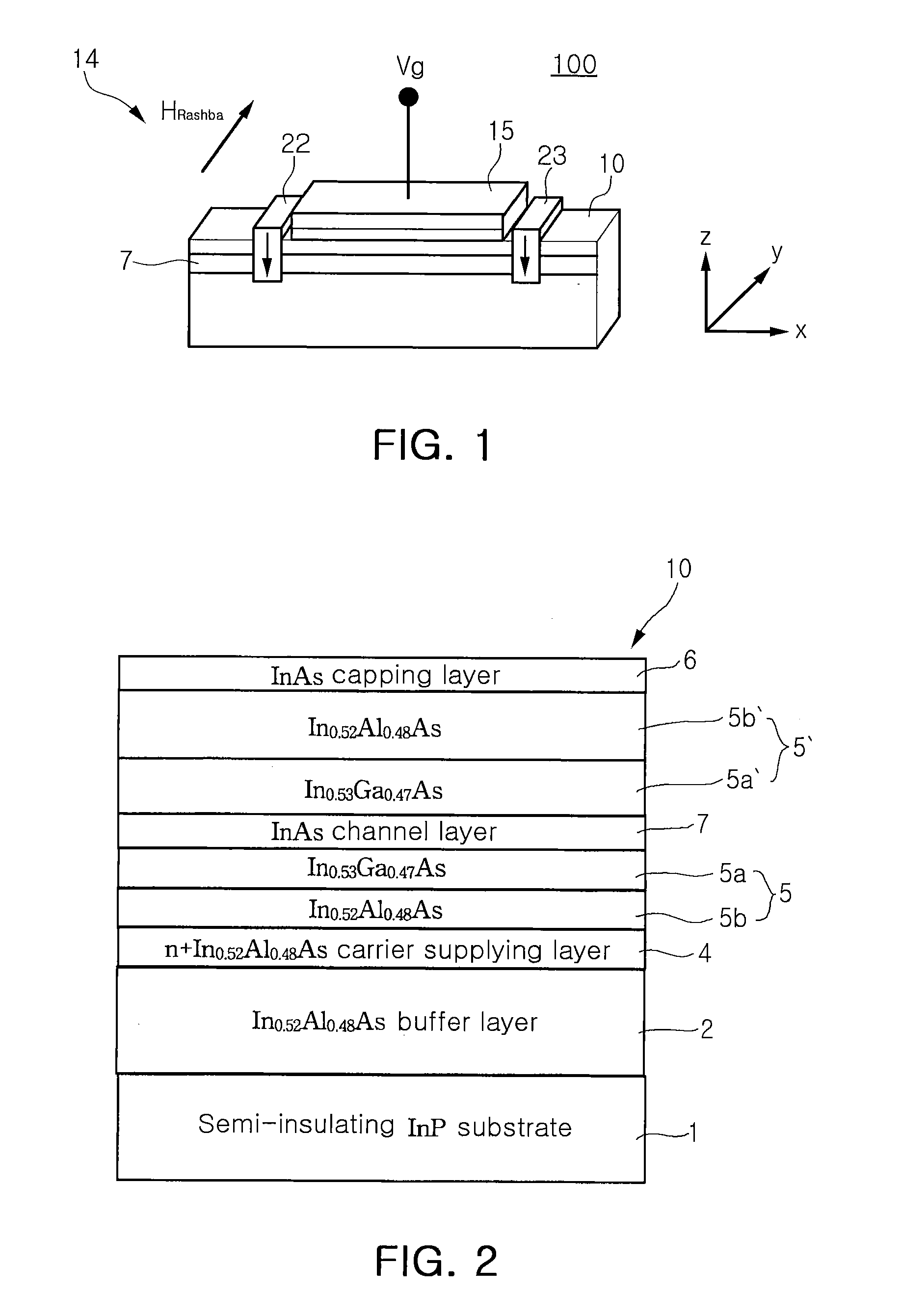
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Spin transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
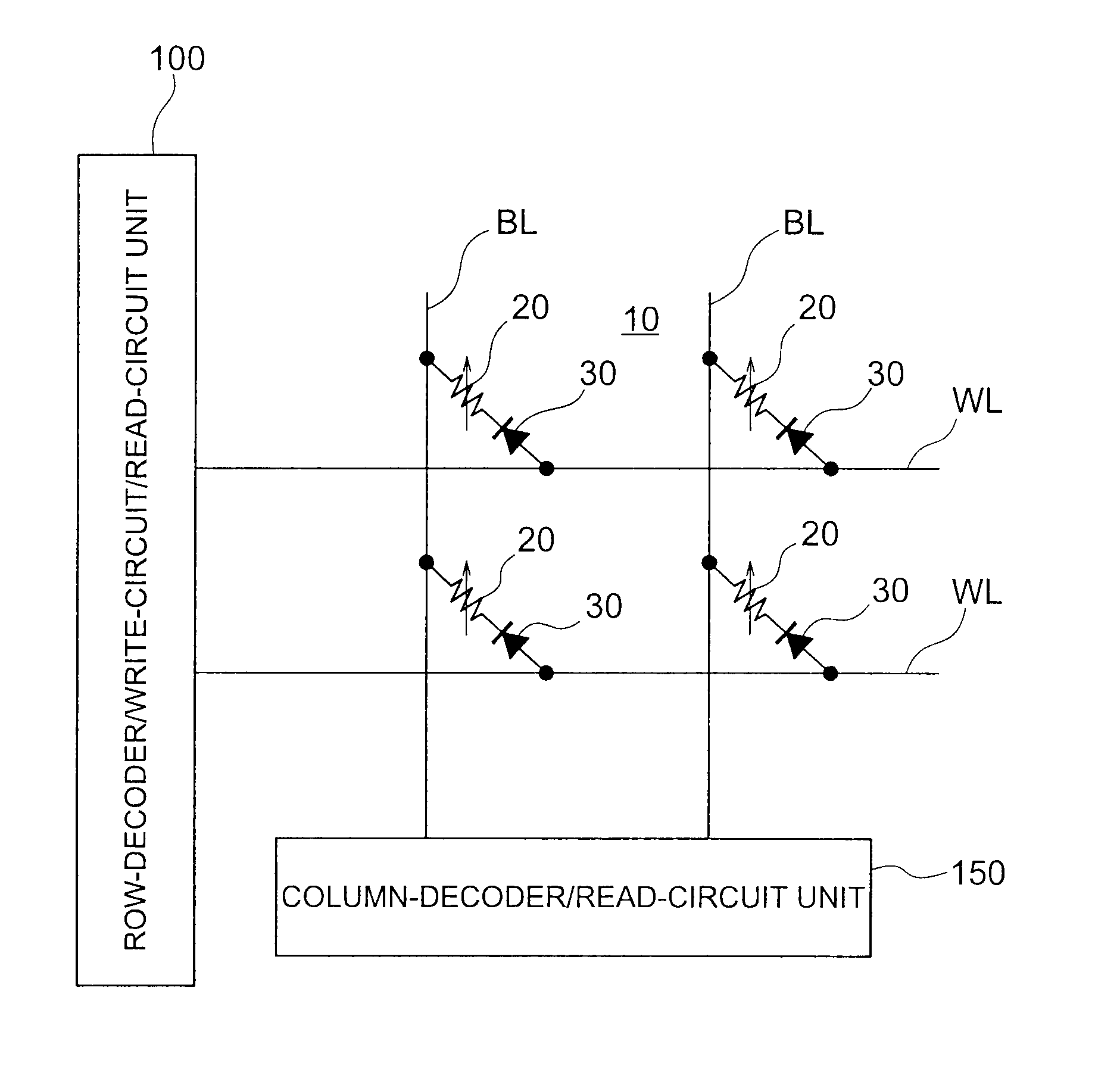
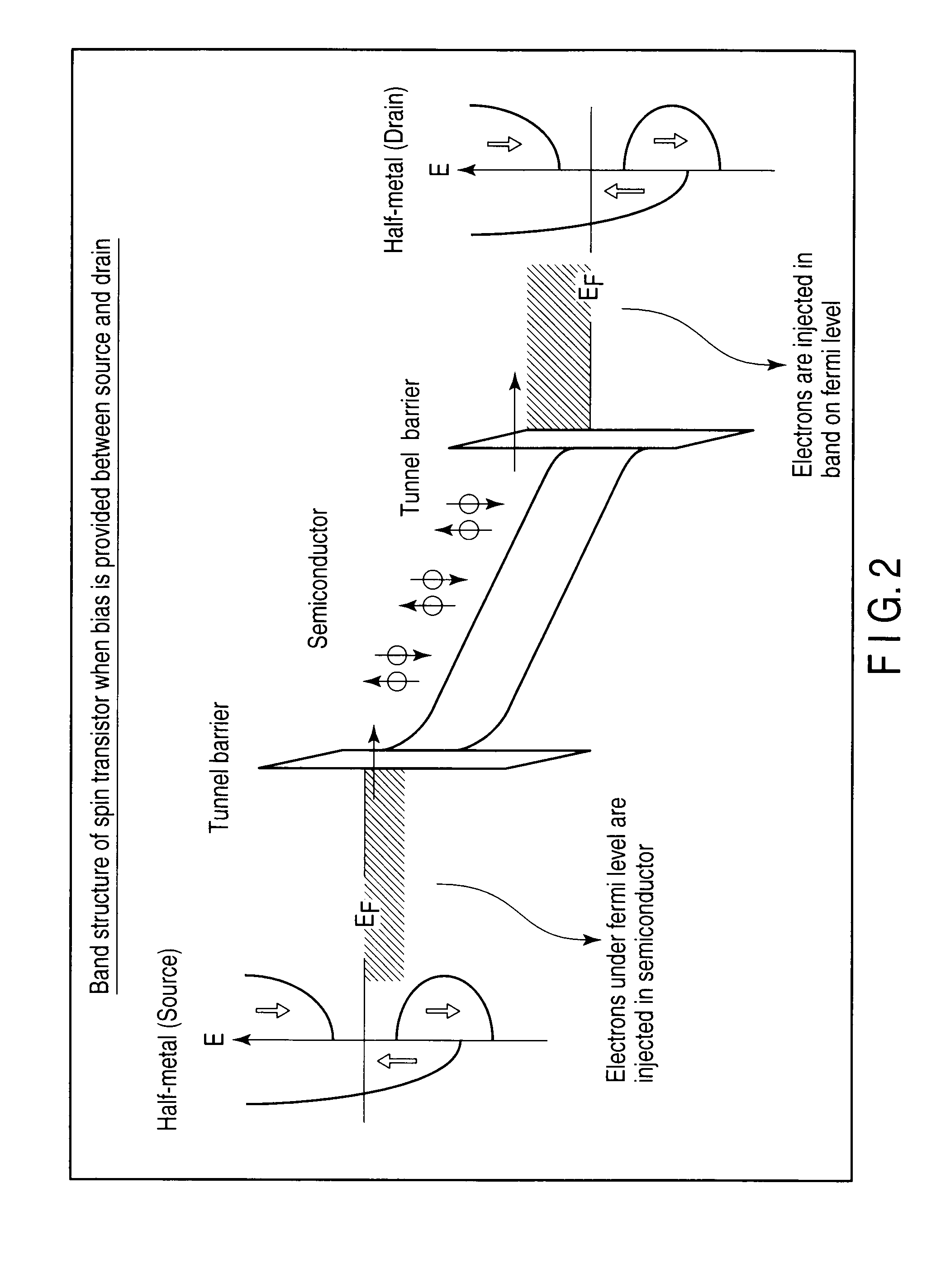
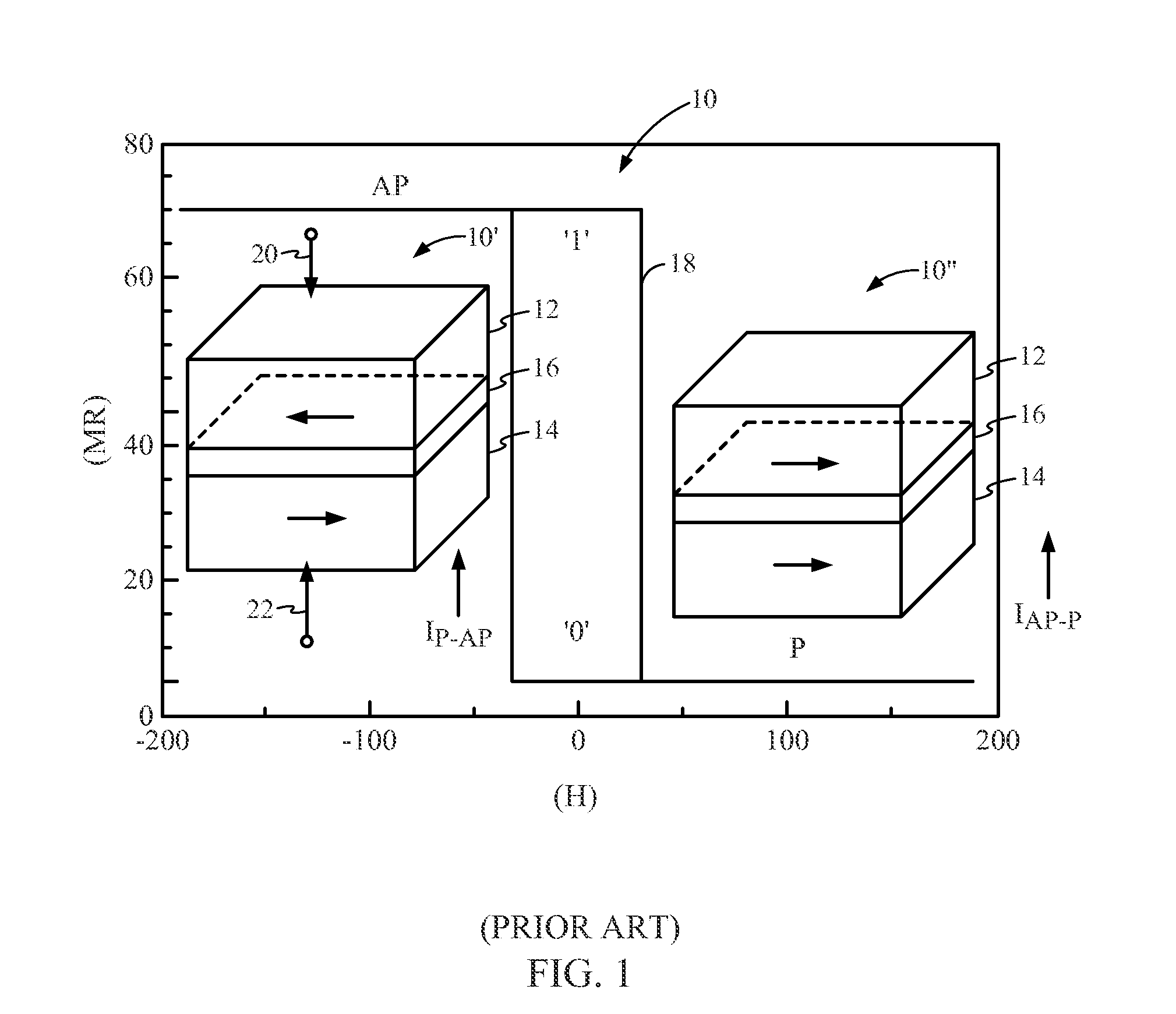
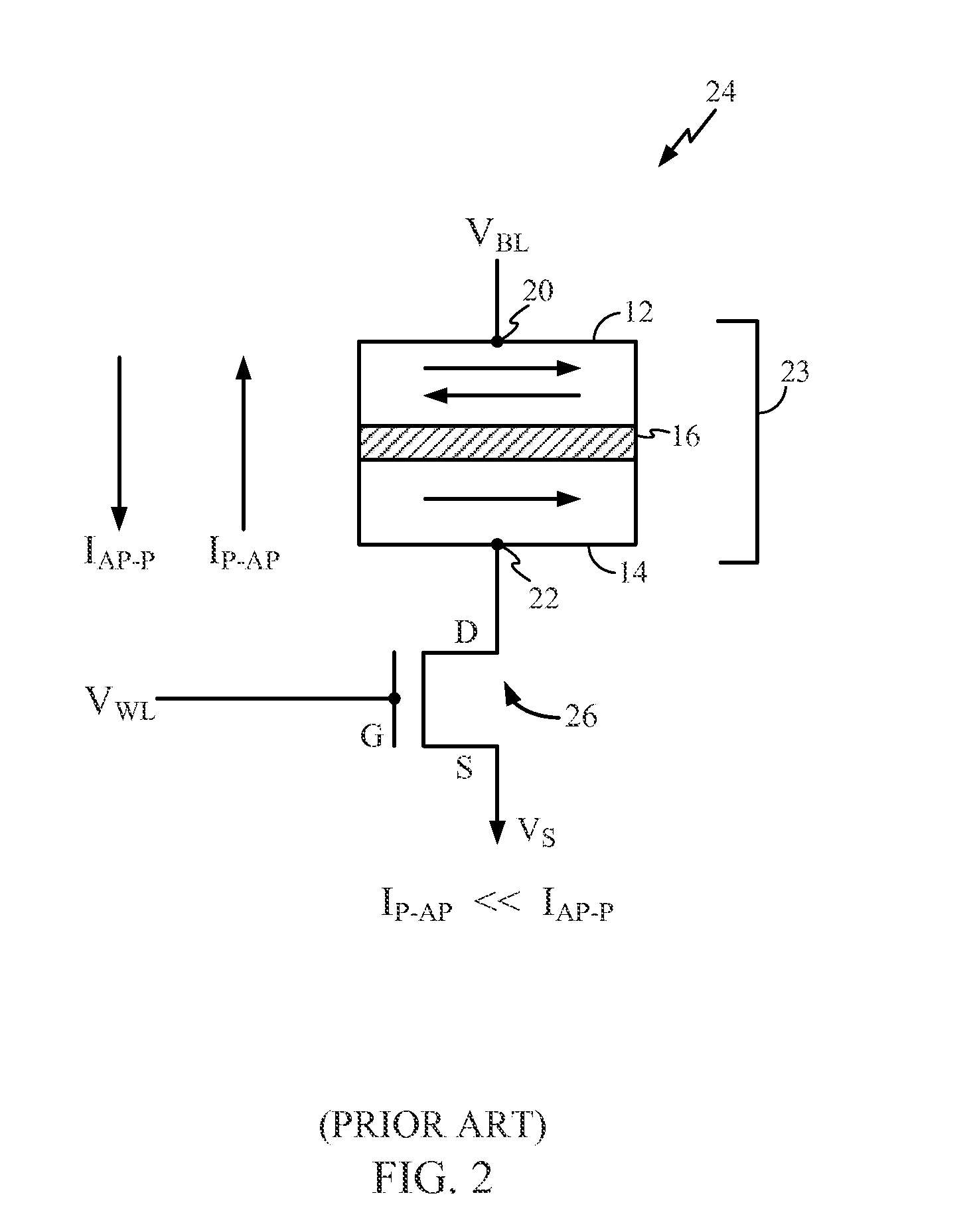
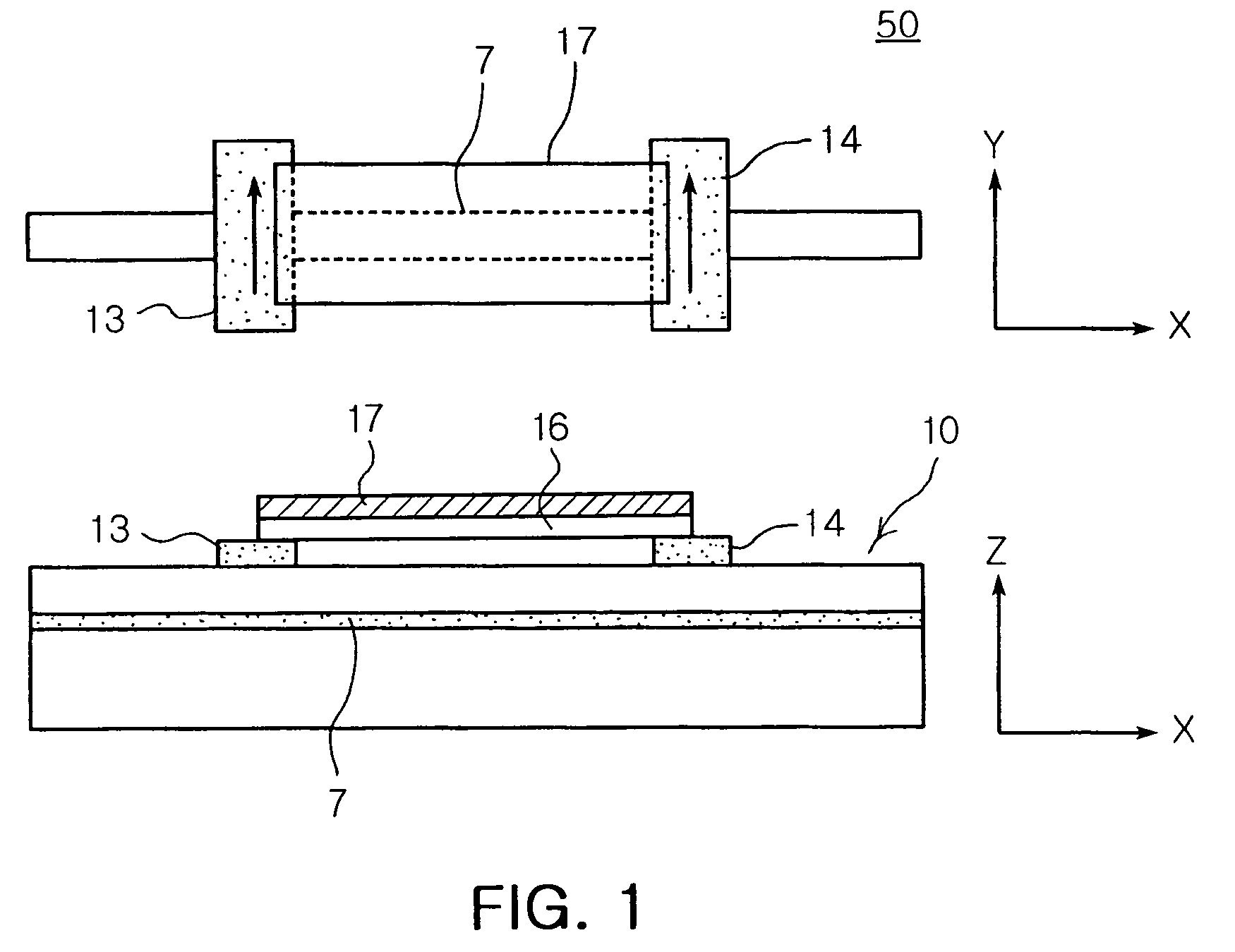
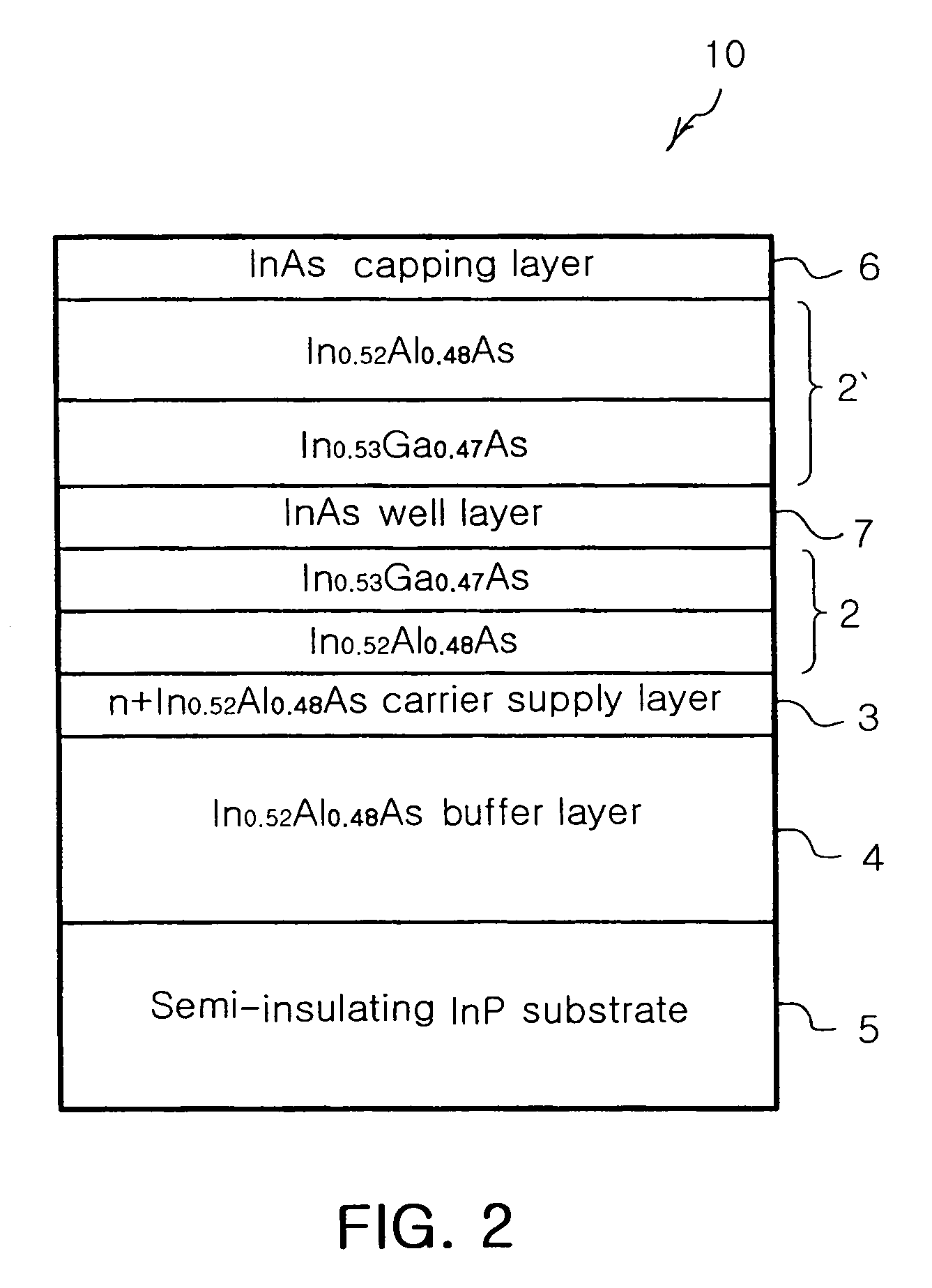
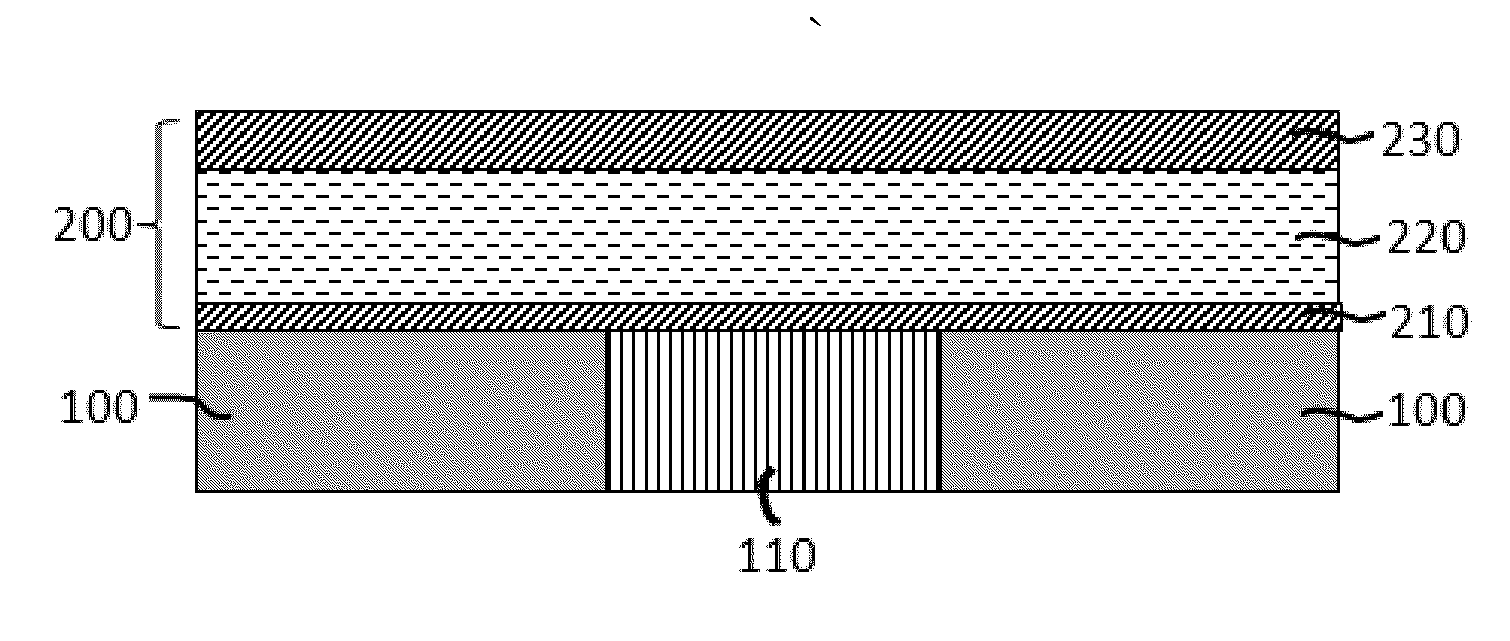
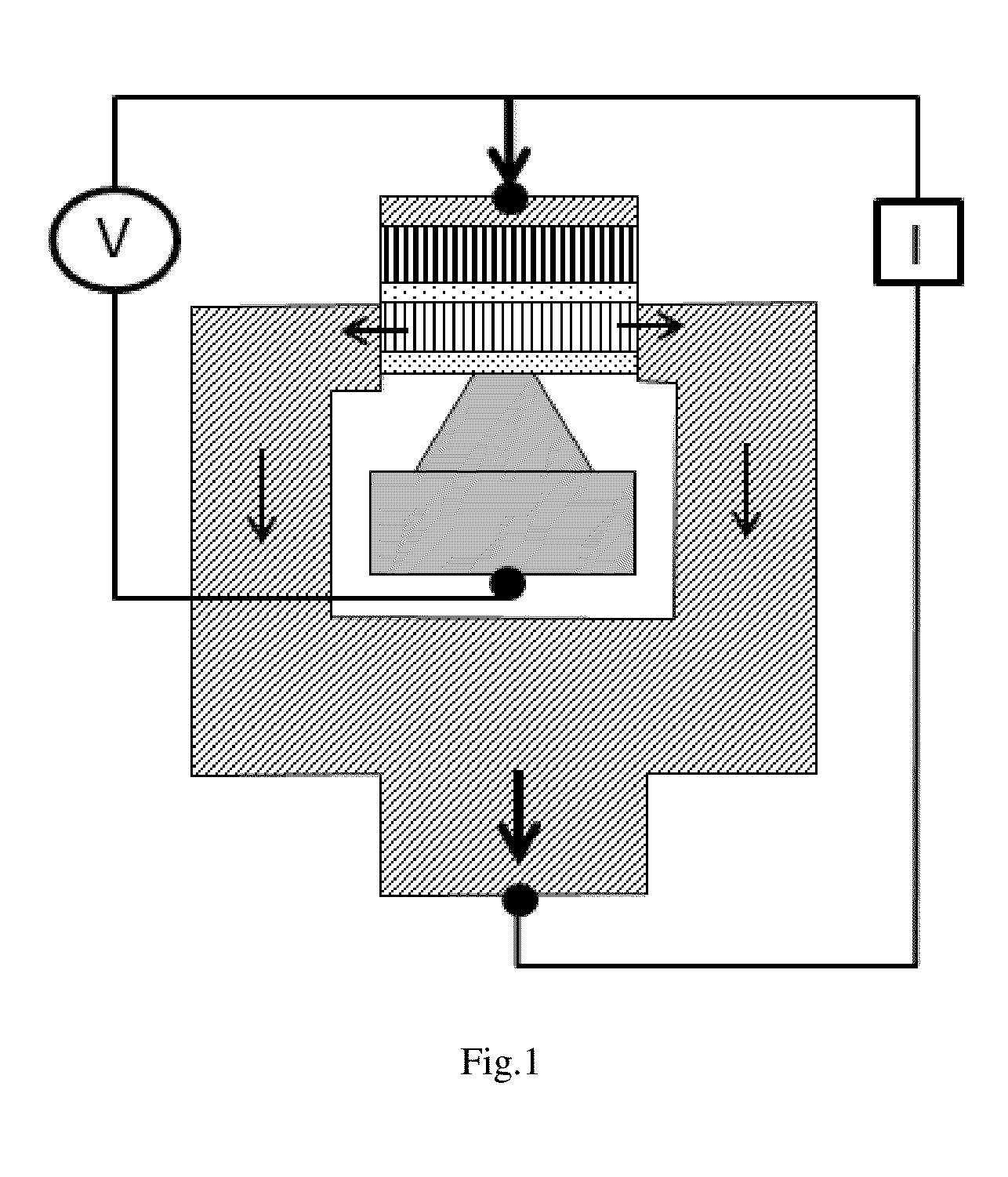
The magnetically sensitive transistor (also known as the spin transistor or spintronic transistor—named for spintronics, the technology which this development spawned), originally proposed in 1990 by Supriyo Datta and Biswajit Das, currently still being developed, is an improved design on the common transistor invented in the 1940s. The spin transistor comes about as a result of research on the ability of electrons (and other fermions) to naturally exhibit one of two (and only two) states of spin: known as "spin up" and "spin down". Thus, spin transistors operate on electron spin as embodying a two-state quantum system. Unlike its namesake predecessor, which operates on an electric current, spin transistors operate on electrons on a more fundamental level; it is essentially the application of electrons set in particular states of spin to store information.
Close shaped magnetic multi-layer film comprising or not comprising a metal core and the manufacture method and the application of the same
InactiveUS7936595B2High densitySmall scaleNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic beadMagnetic logic
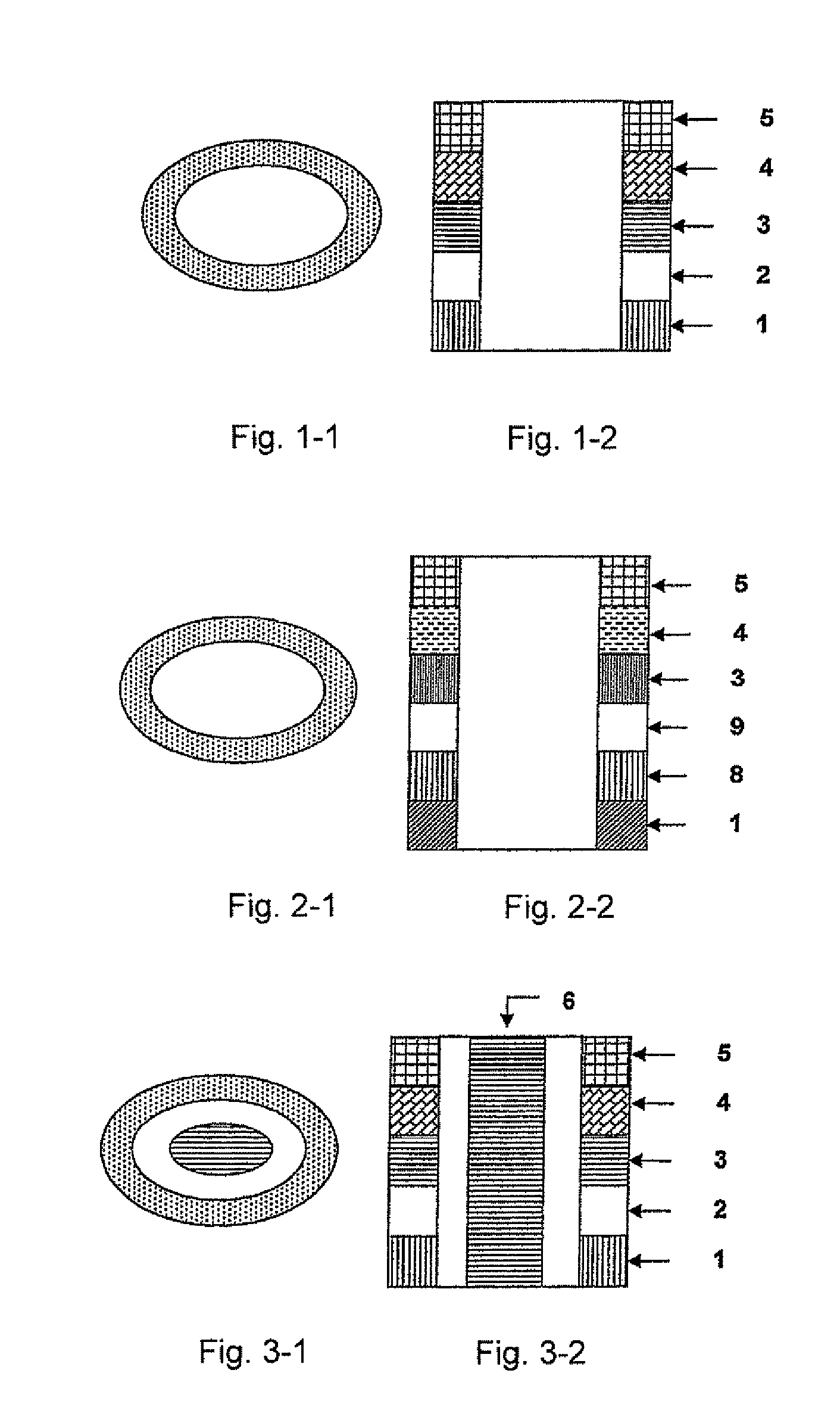
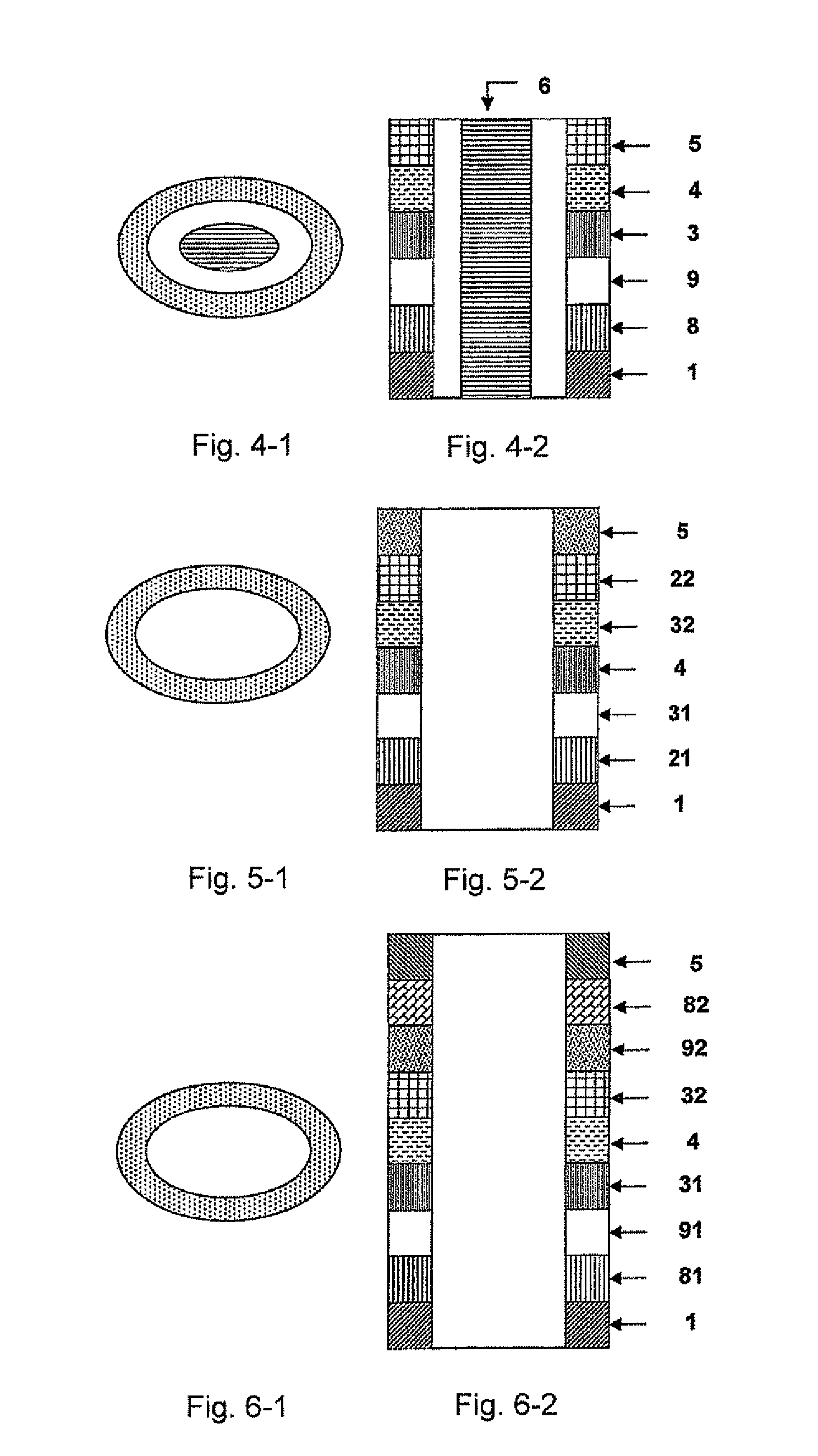
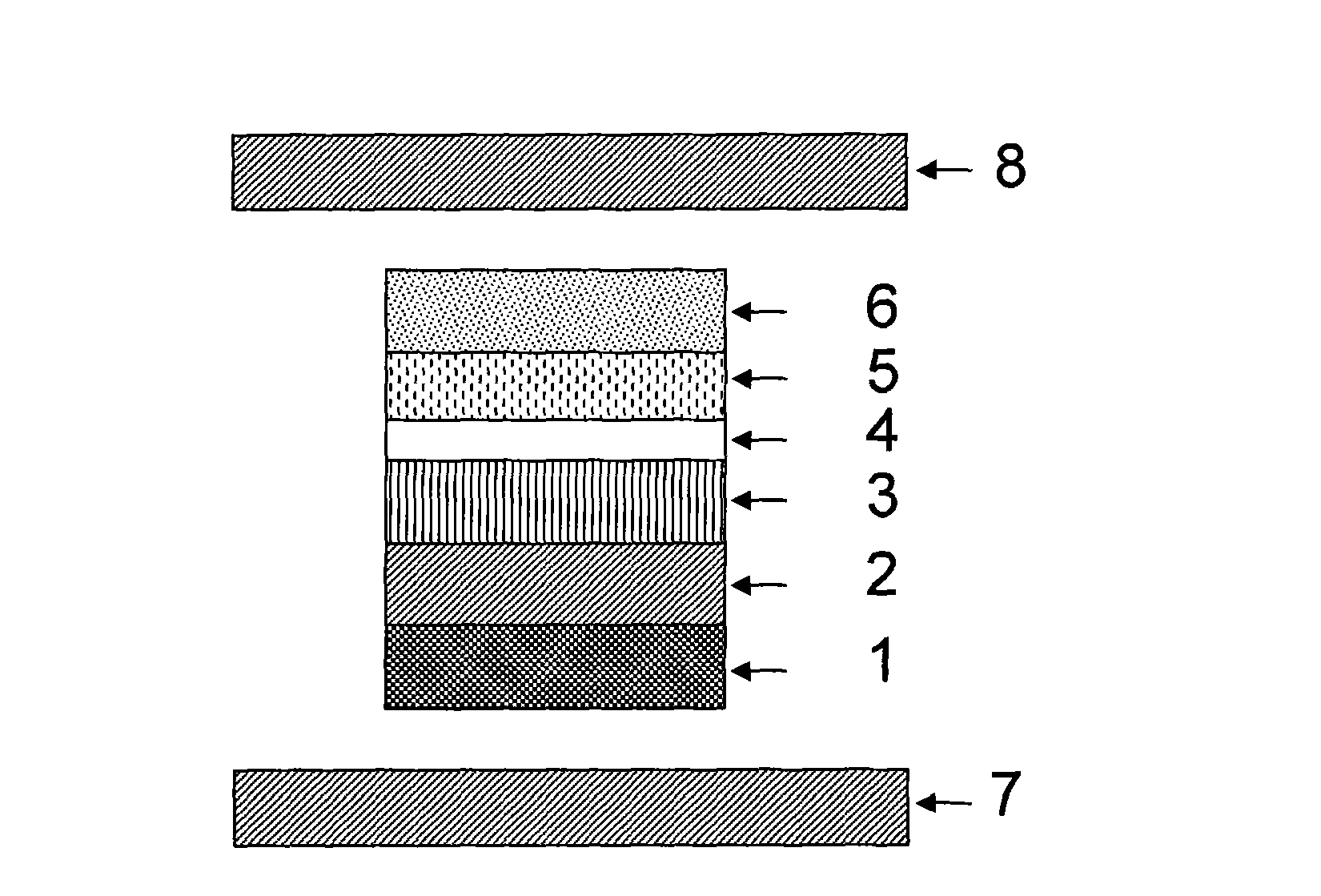
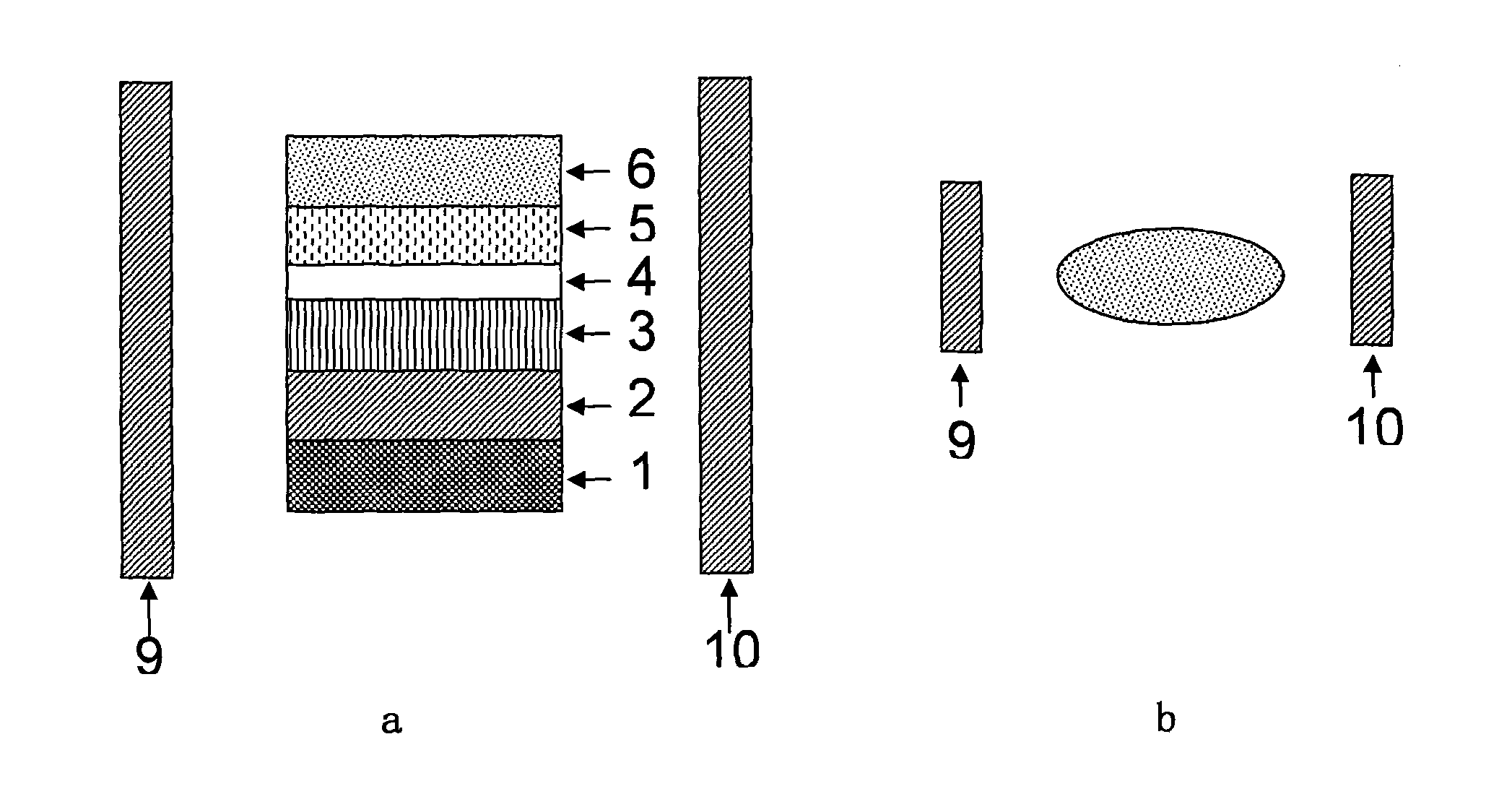
Each layer in the magnetic multilayer film is a closed ring or oval ring and the magnetic moment or flux of the ferromagnetic film in the magnetic unit is in close state either clockwise or counterclockwise. A metal core is put in the geometry center position in the close-shaped magnetic multilayer film. The cross section of the metal core is a corresponding circular or oval. A MRAM is made of the closed magnetic multilayer film with or without a metal core. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film is formed by micro process method. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film can be used broadly in a great variety of device that uses a magnetic multilayer film as the core, such as MRAM, magnetic bead in computer, magnetic sensitive sensor, magnetic logic device and spin transistor.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Close shaped magnetic multi-layer film comprising or not comprising a metal core and the manufacture method and the application of the same
InactiveUS20090168506A1High densitySmall scaleNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic beadMagnetic logic
Each layer in the magnetic multilayer film is a closed ring or oval ring and the magnetic moment or flux of the ferromagnetic film in the magnetic unit is in close state either clockwise or counterclockwise. A metal core is put in the geometry center position in the close-shaped magnetic multilayer film. The cross section of the metal core is a corresponding circular or oval. A MRAM is made of the closed magnetic multilayer film with or without a metal core. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film is formed by micro process method. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film can be used broadly in a great variety of device that uses a magnetic multilayer film as the core, such as MRAM, magnetic bead in computer, magnetic sensitive sensor, magnetic logic device and spin transistor.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
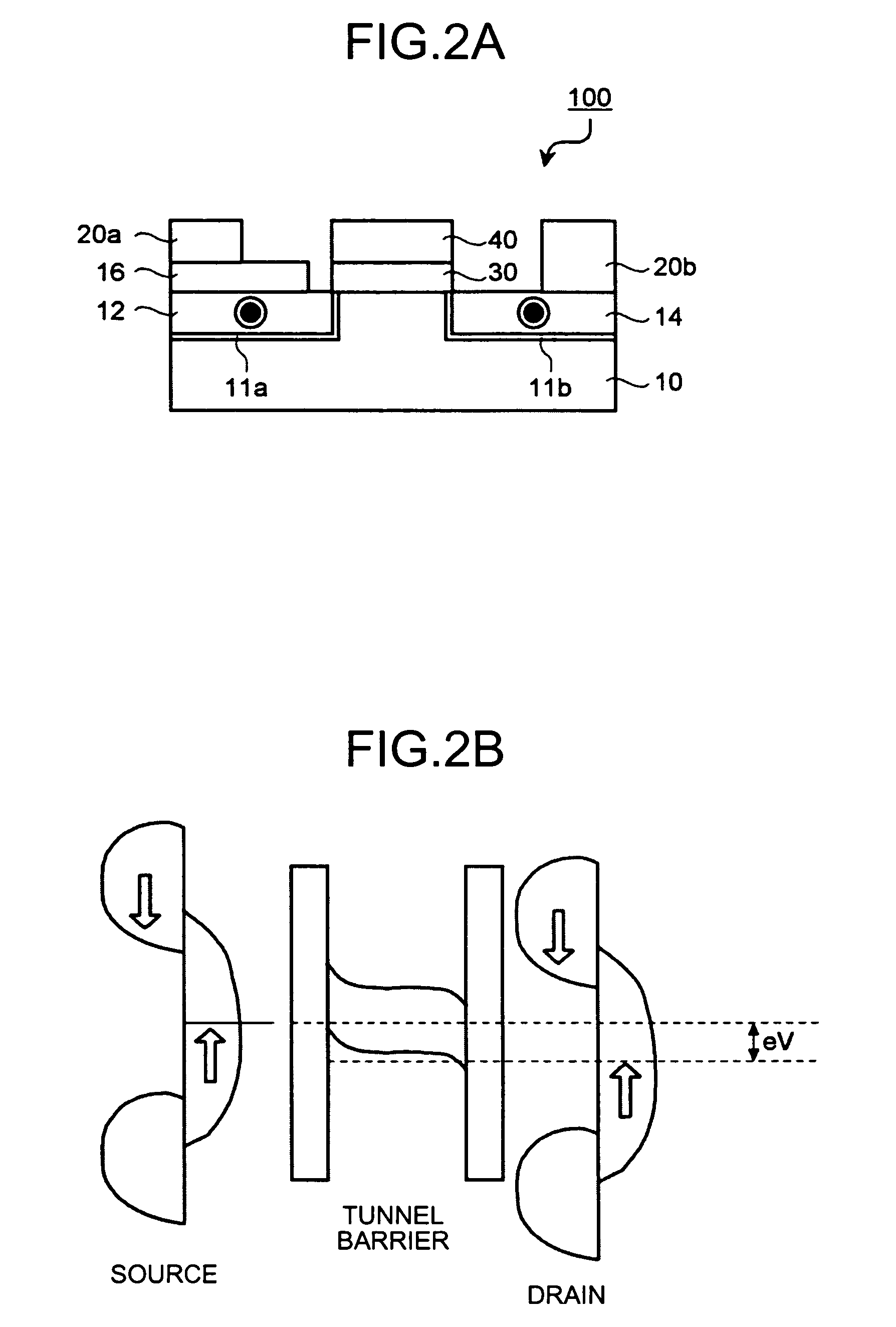
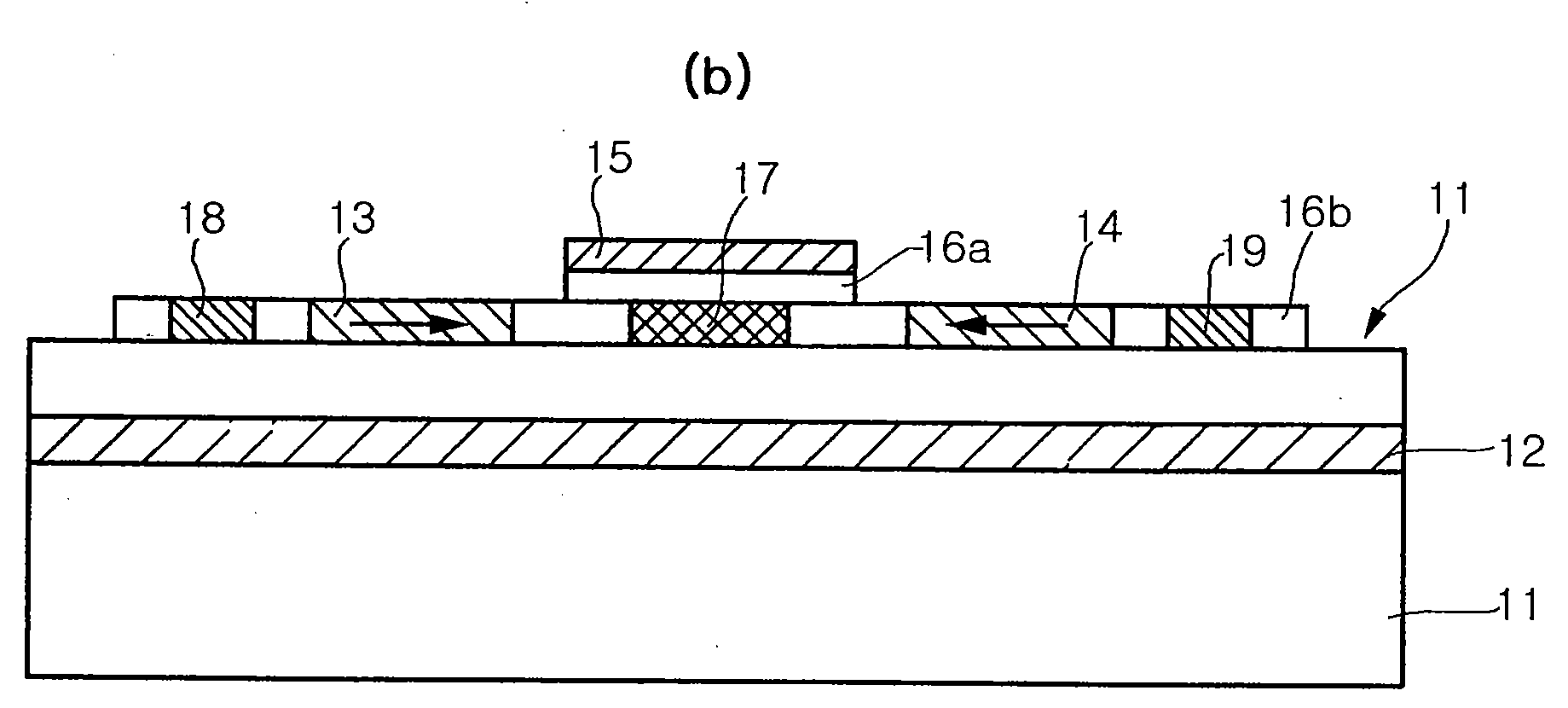
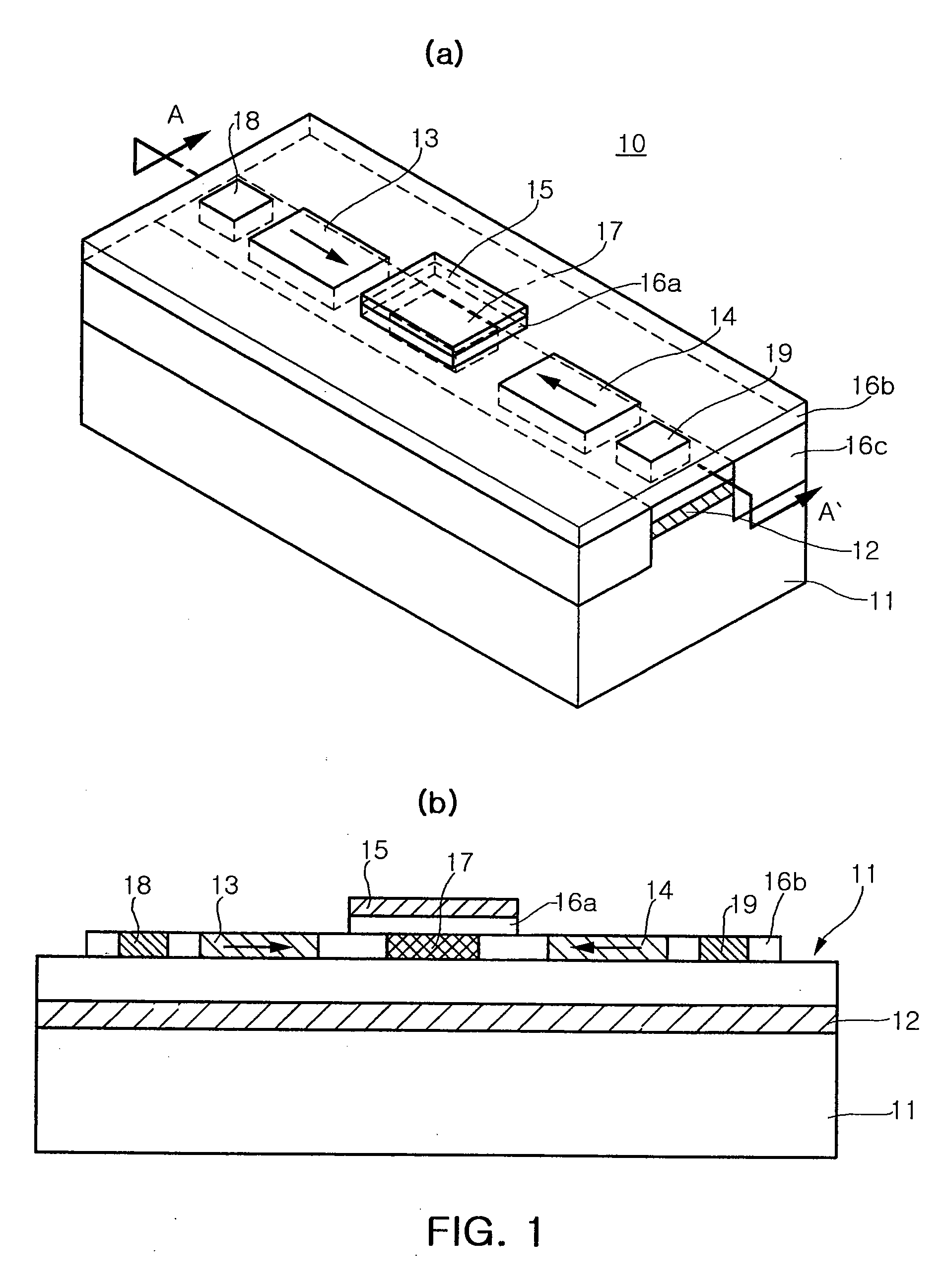
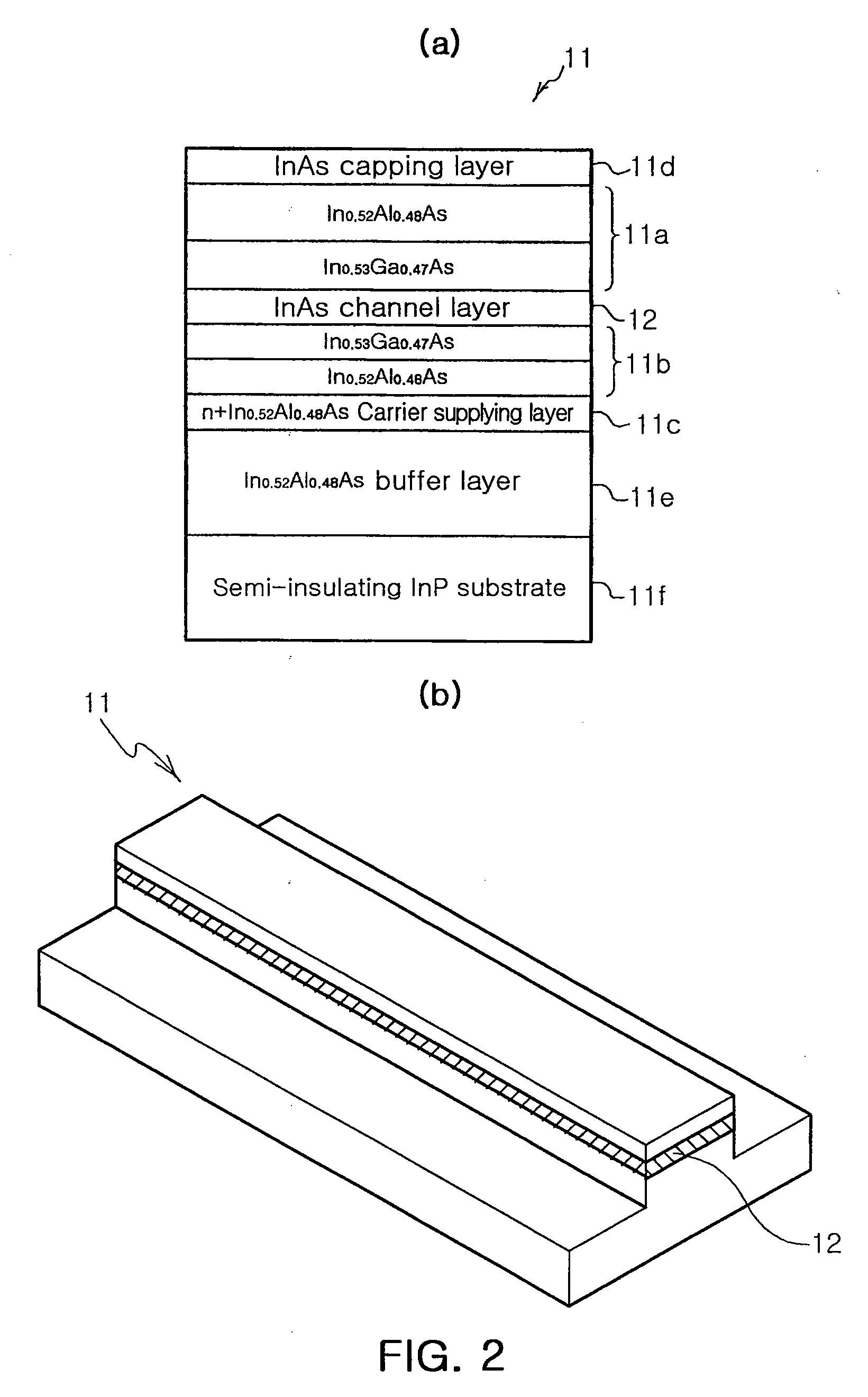
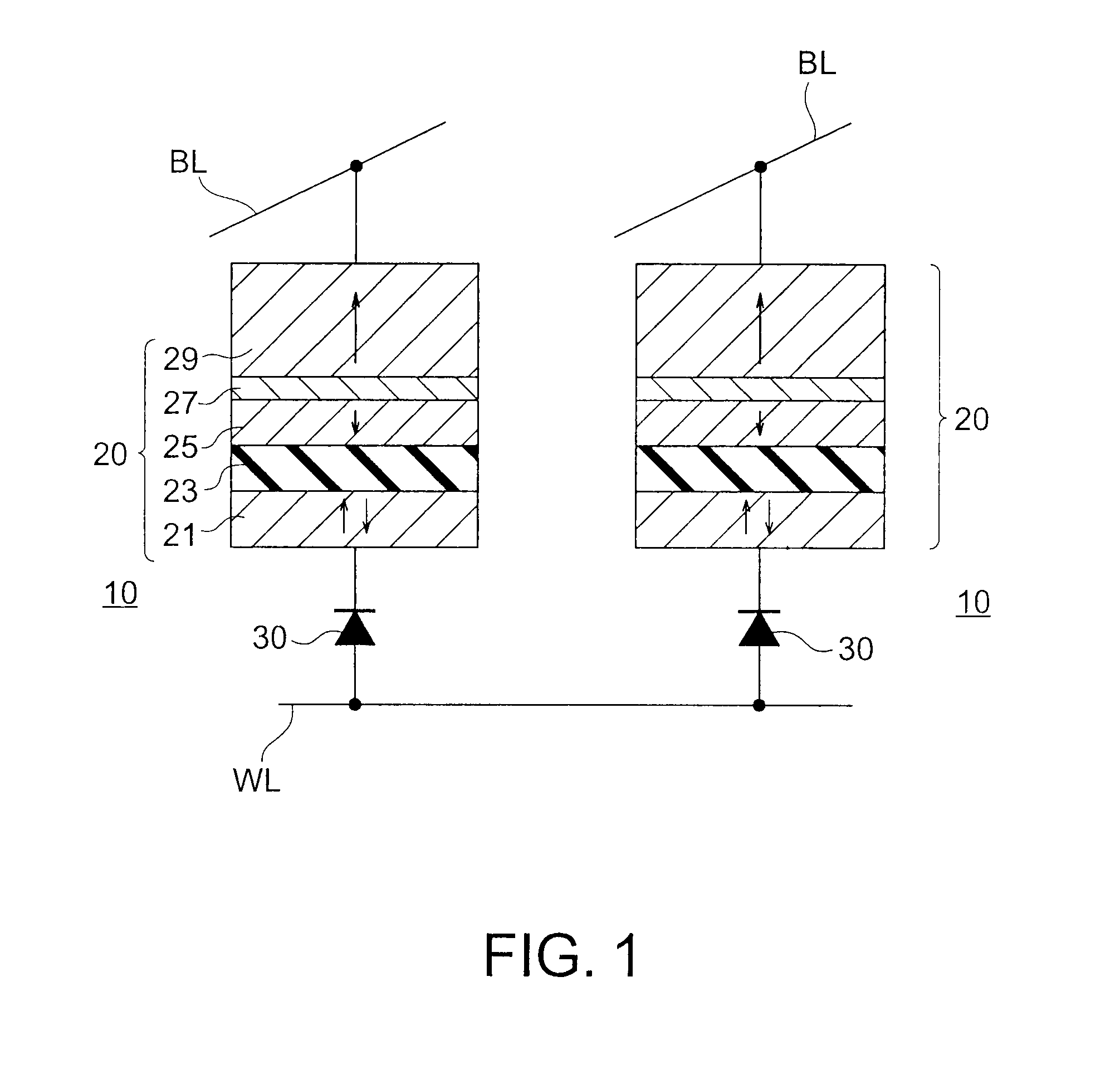
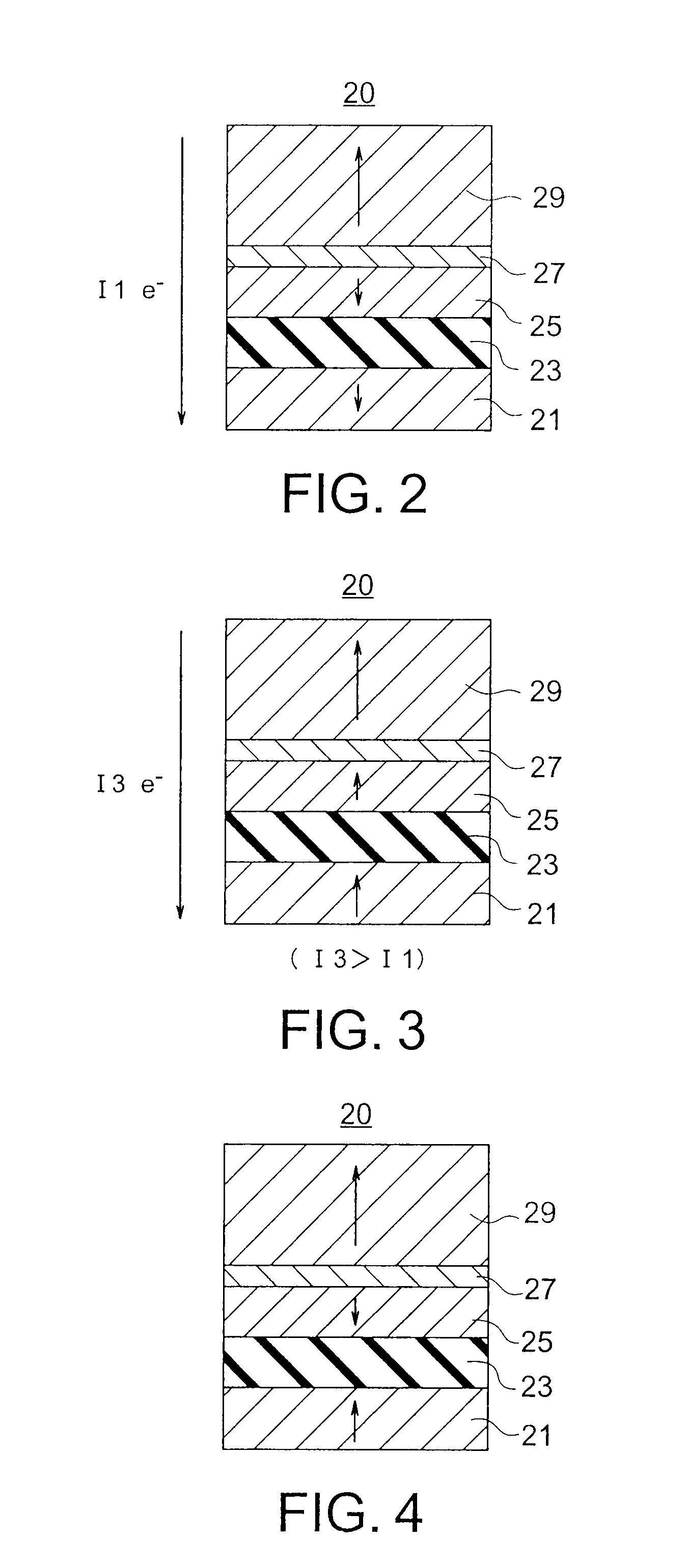
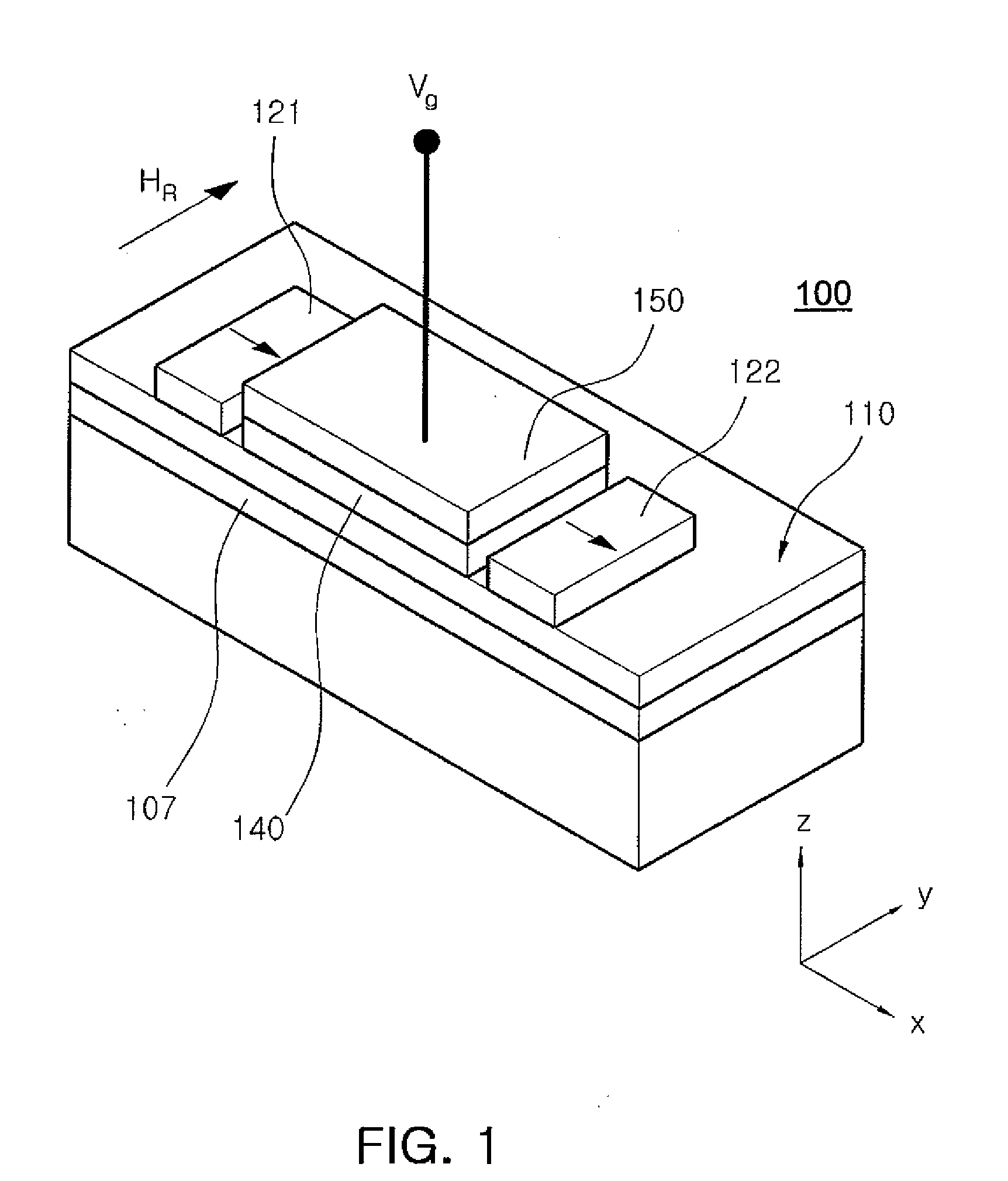
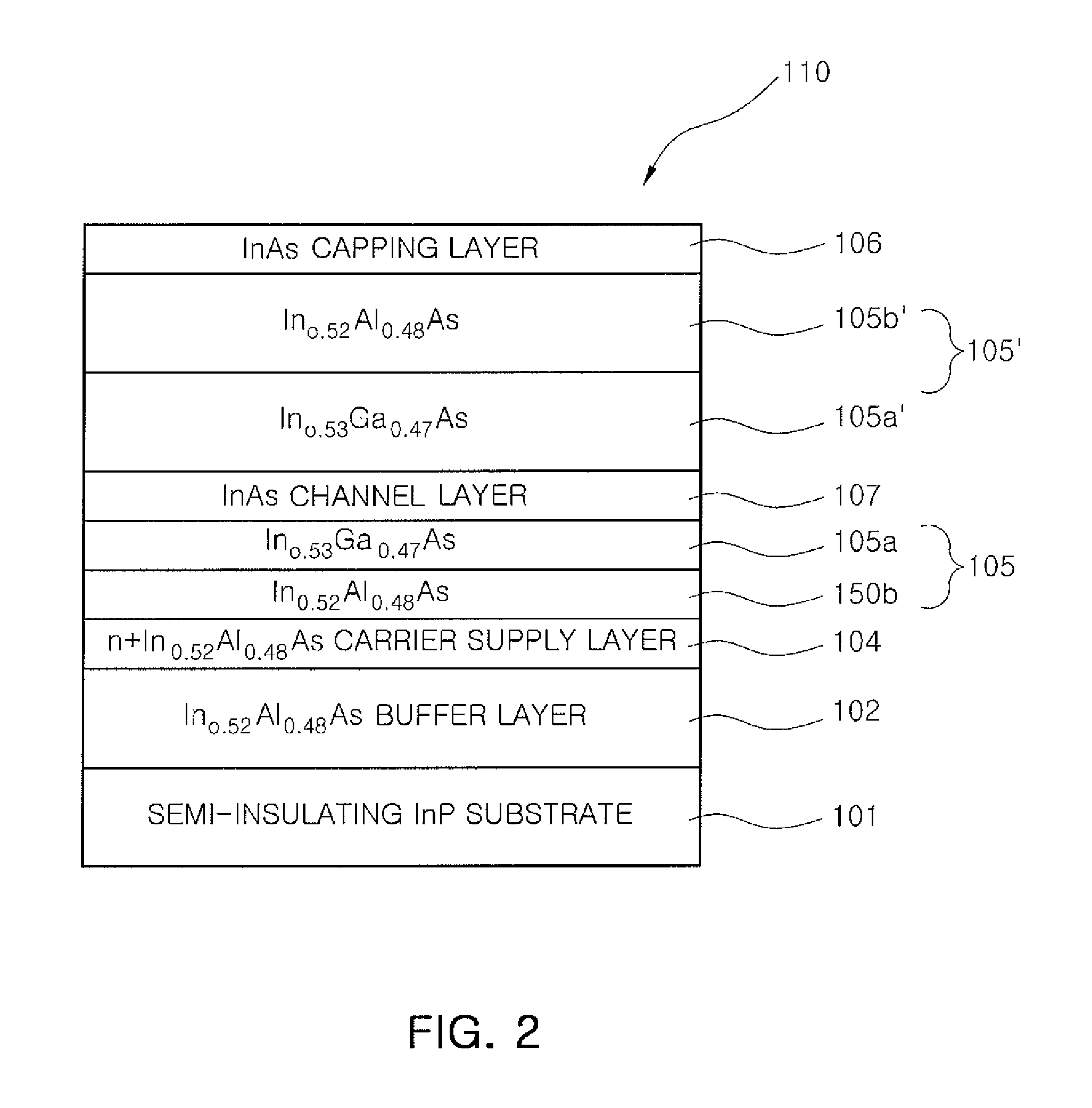
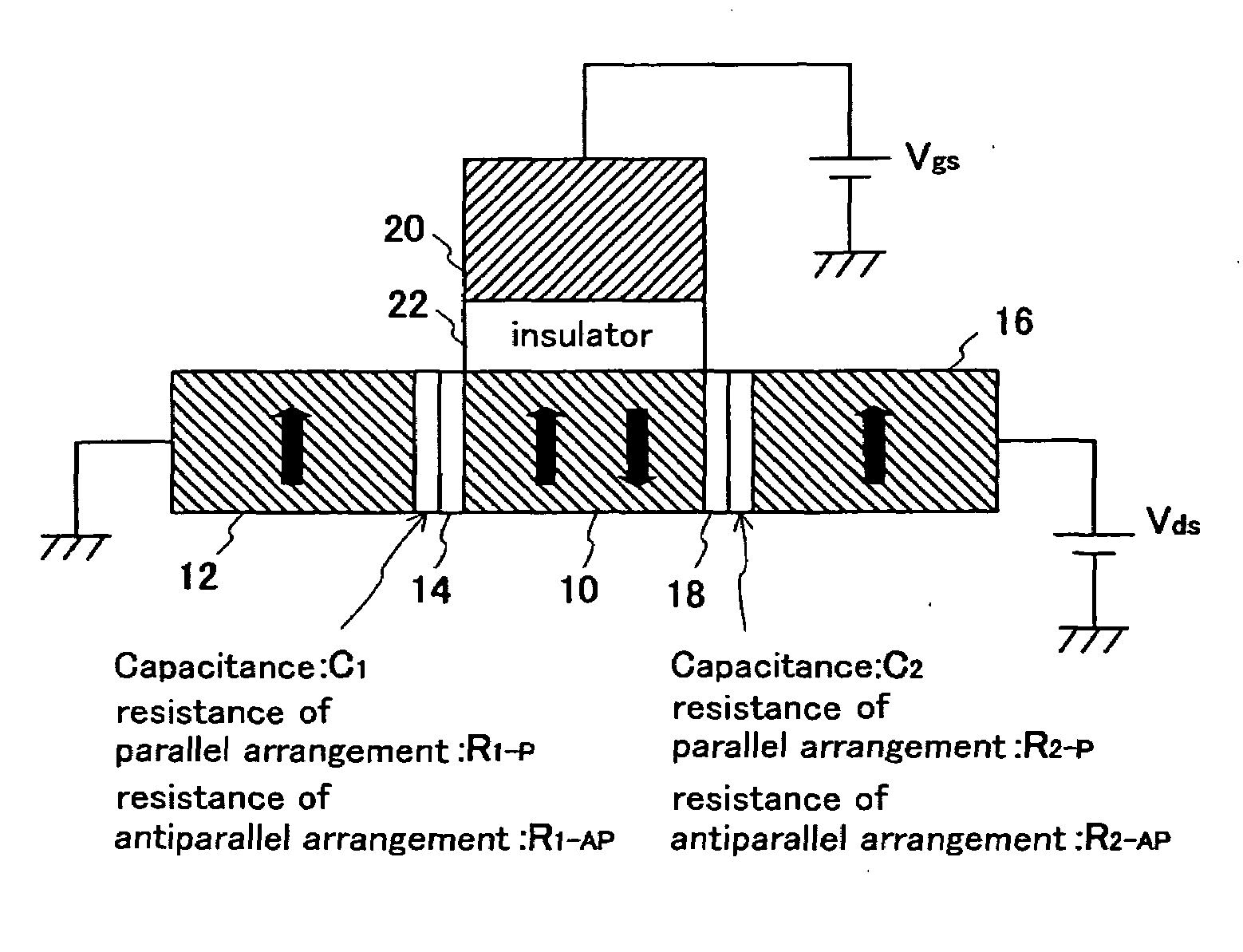
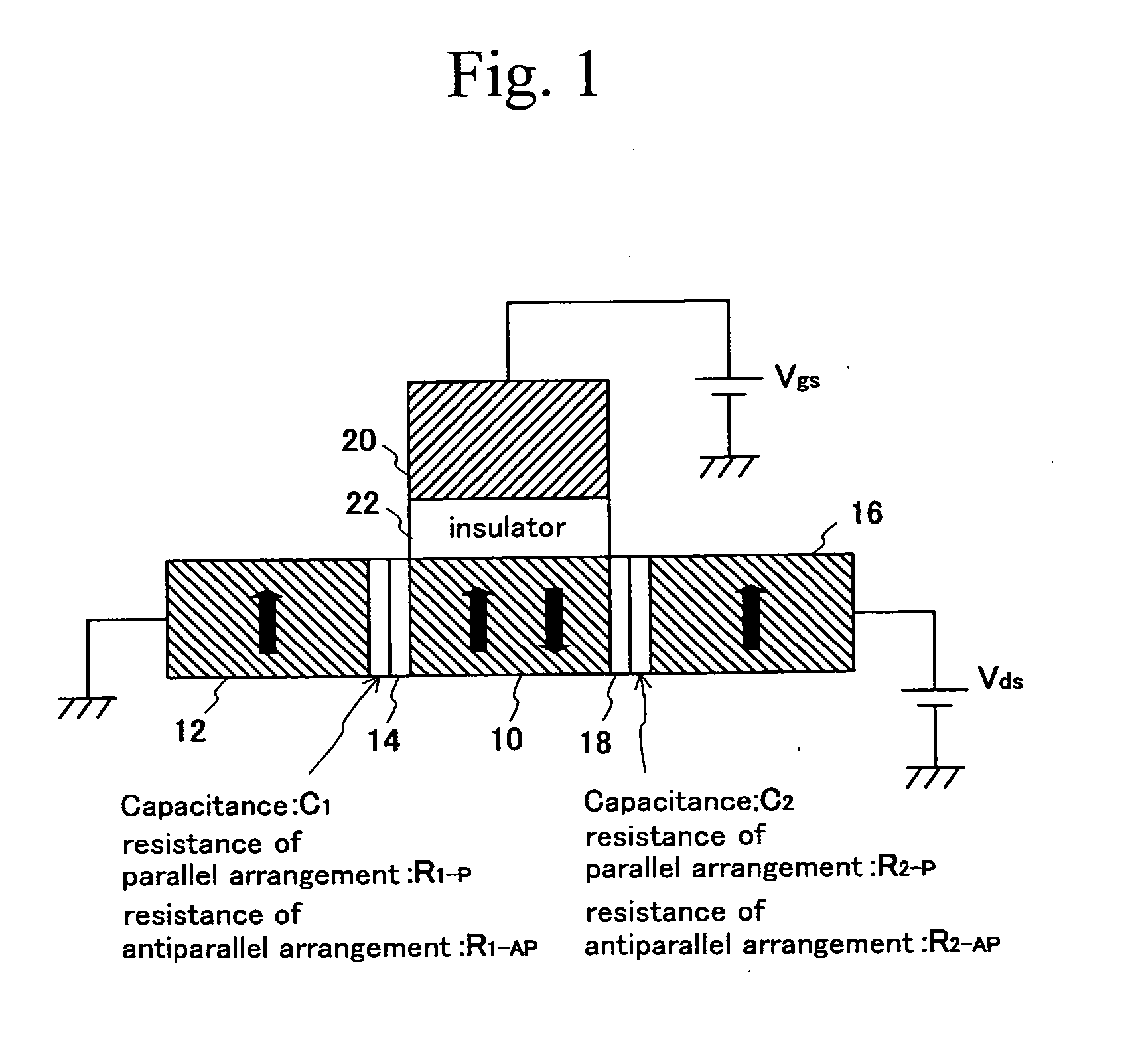
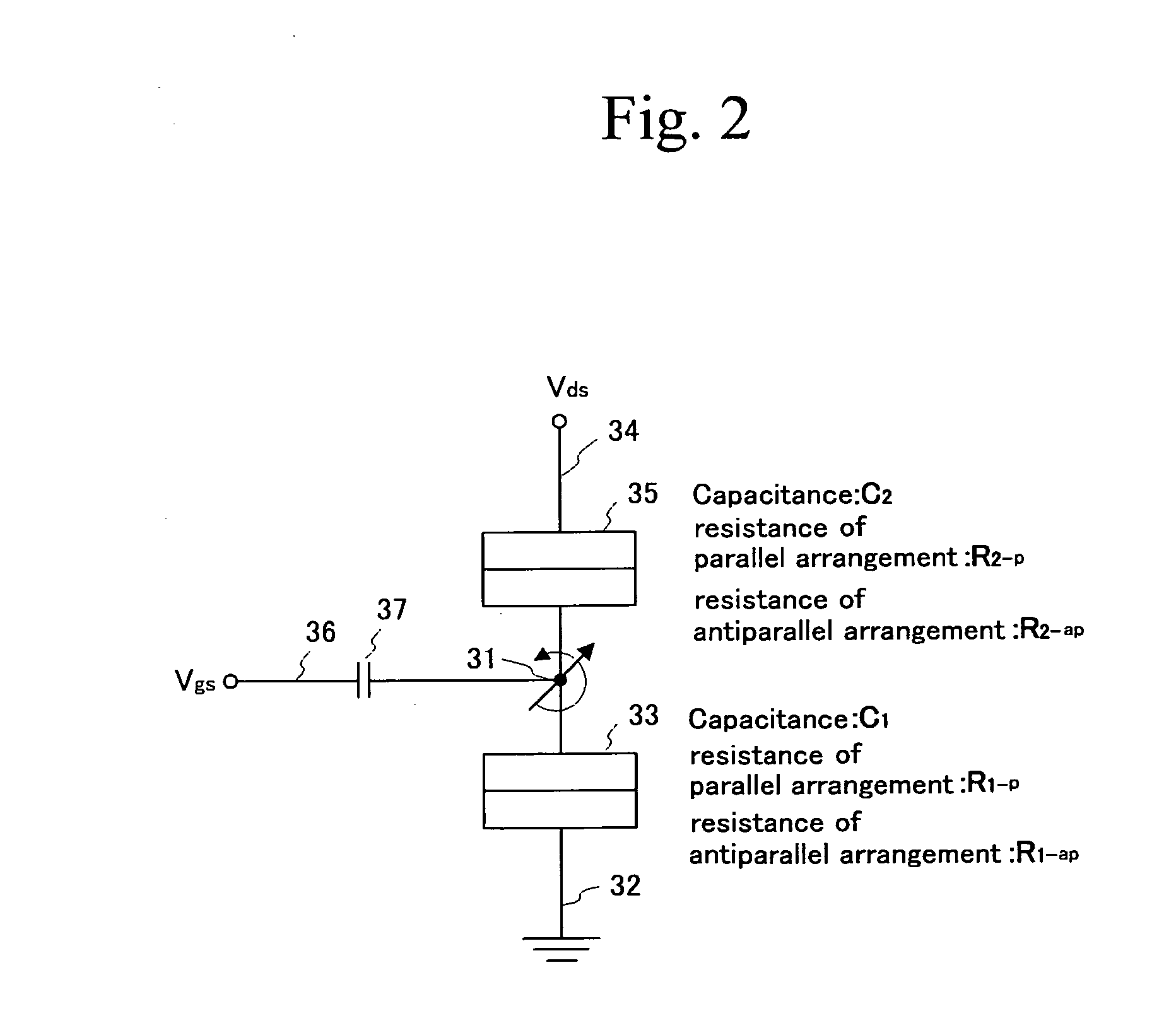
Spin transistor, programmable logic circuit, and magnetic memory
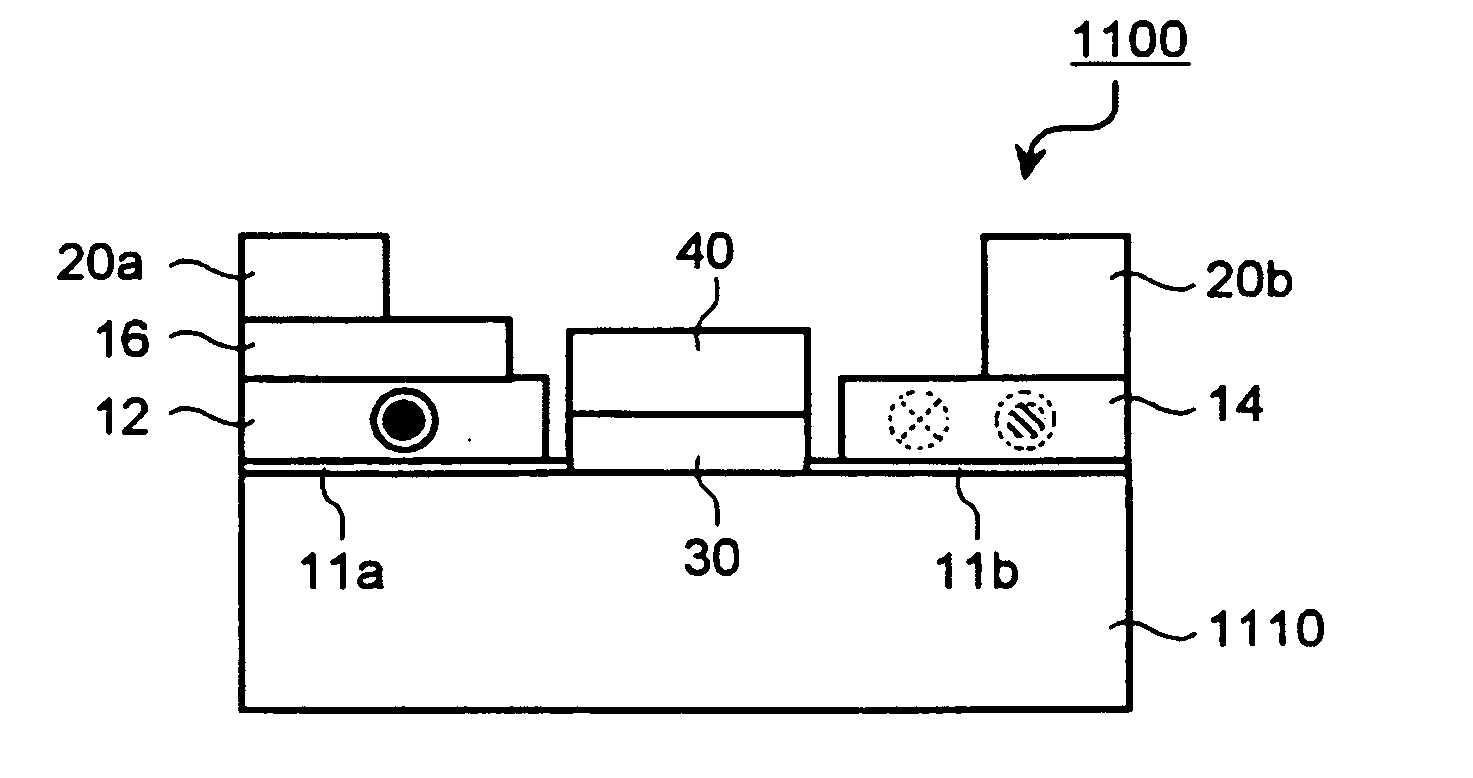
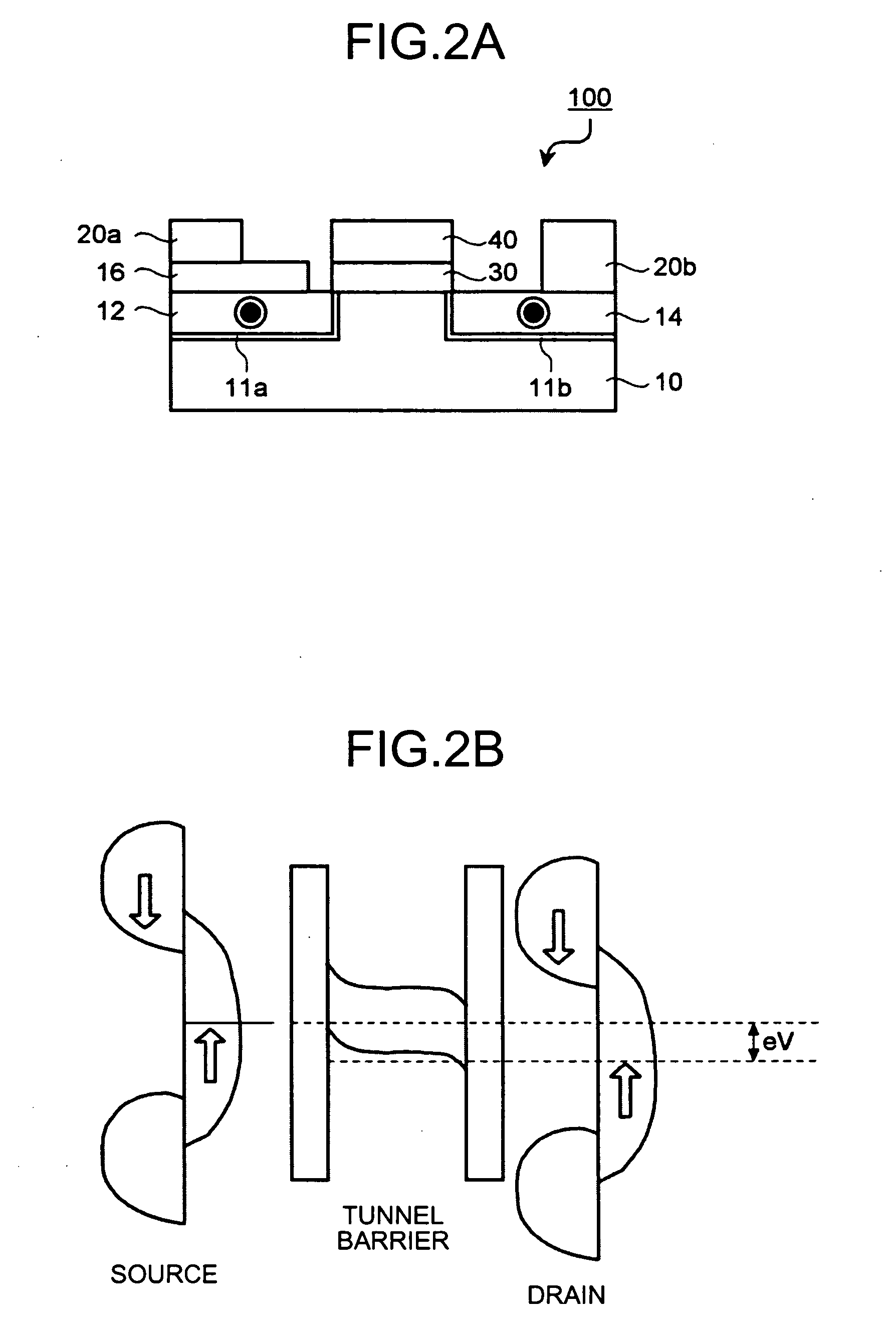
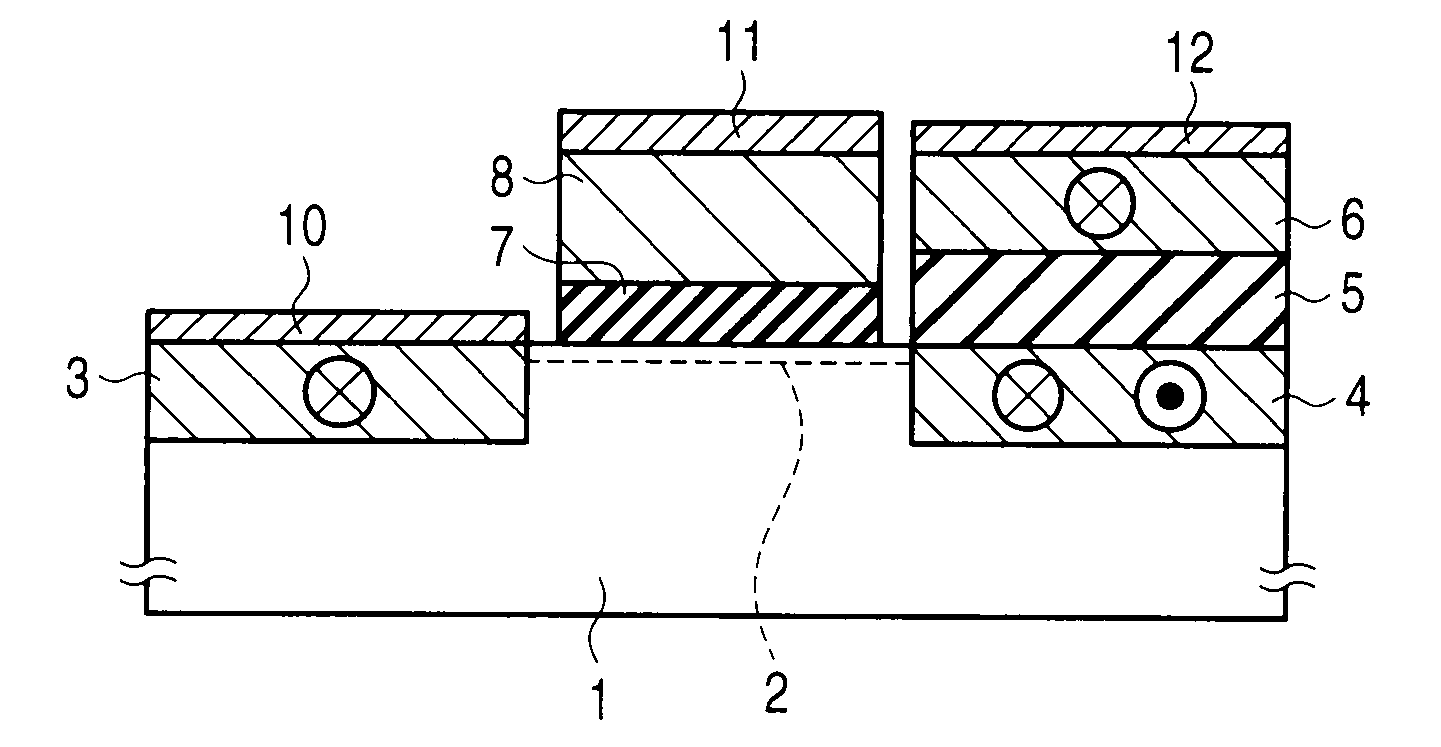
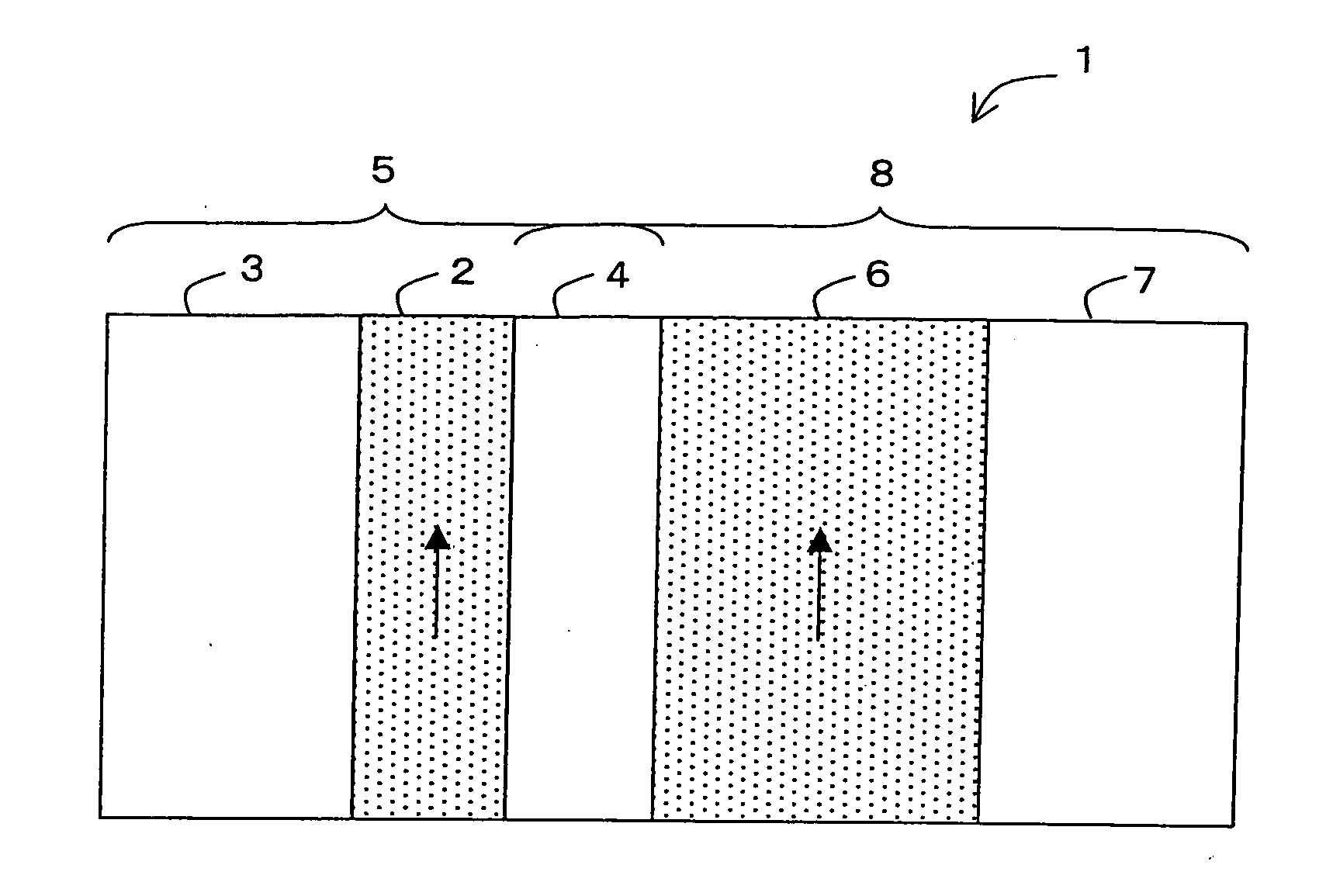
A spin transistor includes a first conductive layer that is made of a ferromagnetic material magnetized in a first direction, and functions as one of a source and a drain; a second conductive layer that is made of a ferromagnetic material magnetized in one of the first direction and a second direction that is antiparallel with respect to the first direction, and functions as the other one of the source and the drain. The spin transistor also includes a channel region that is located between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer, and introduces electron spin between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer; a gate electrode that is located above the channel region; and a tunnel barrier film that is located between the channel region and at least one of the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-magnetic semiconductor spin transistor
InactiveUS20050263751A1High sensitivityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesTunnel diodeDevice material
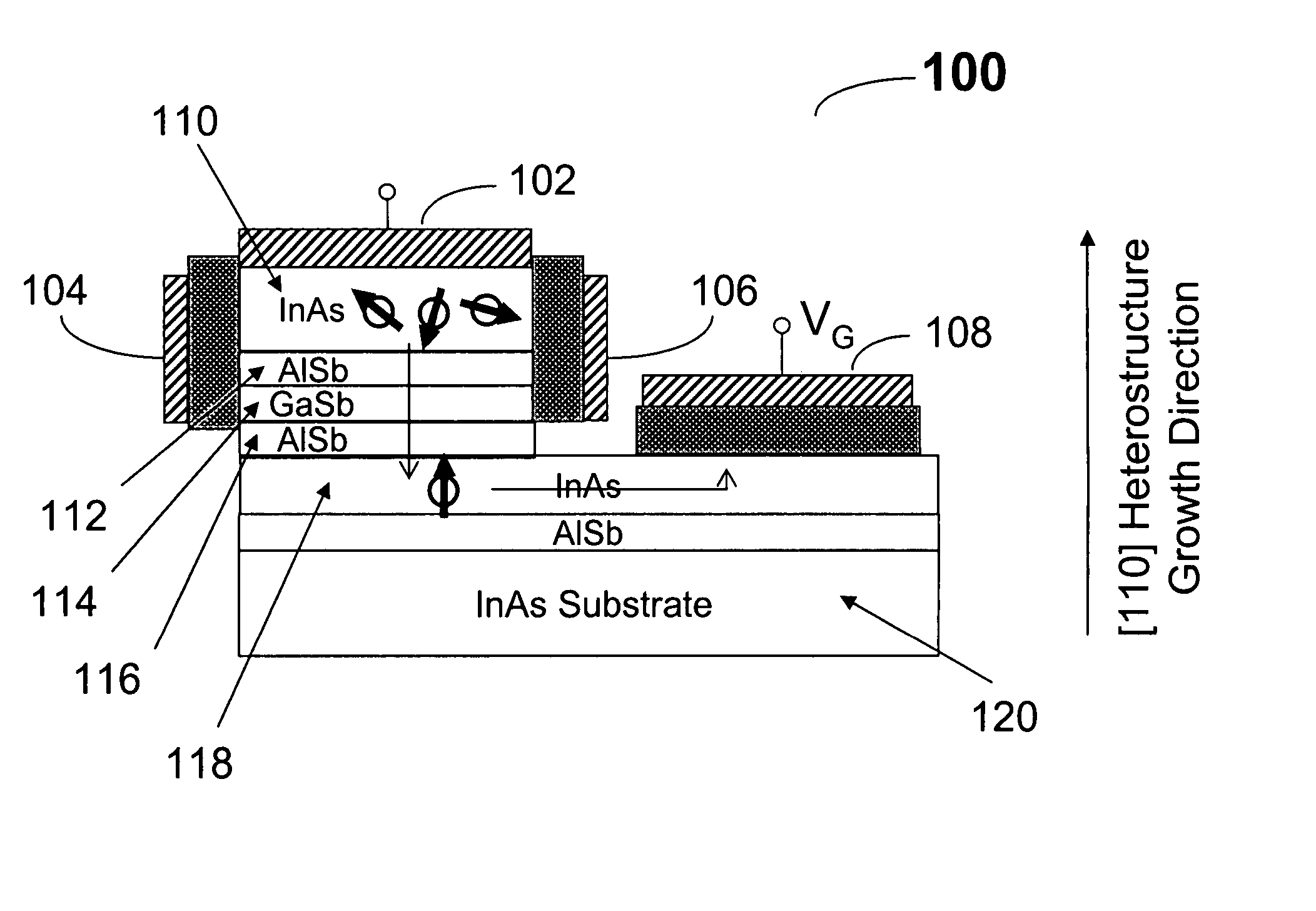
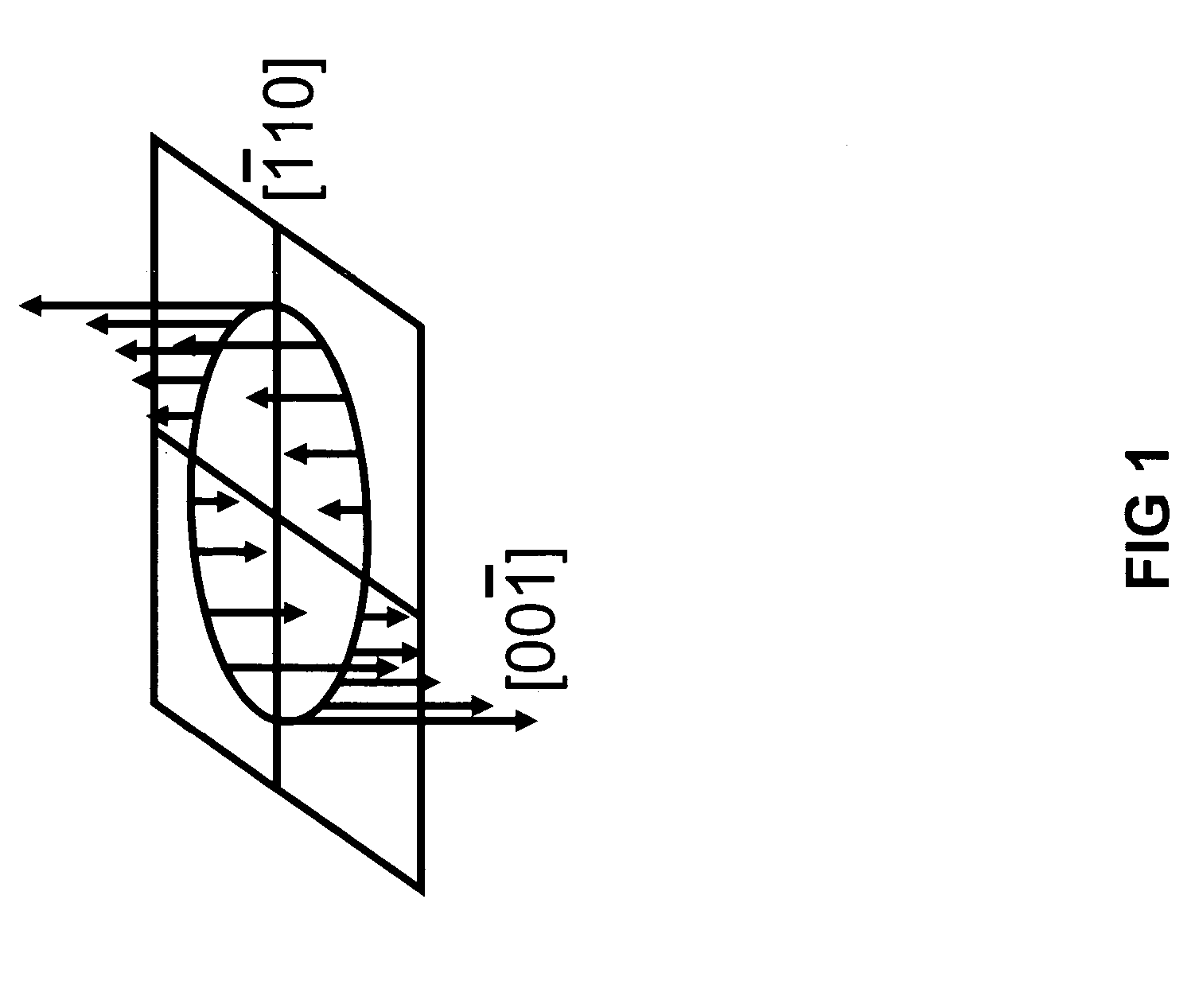
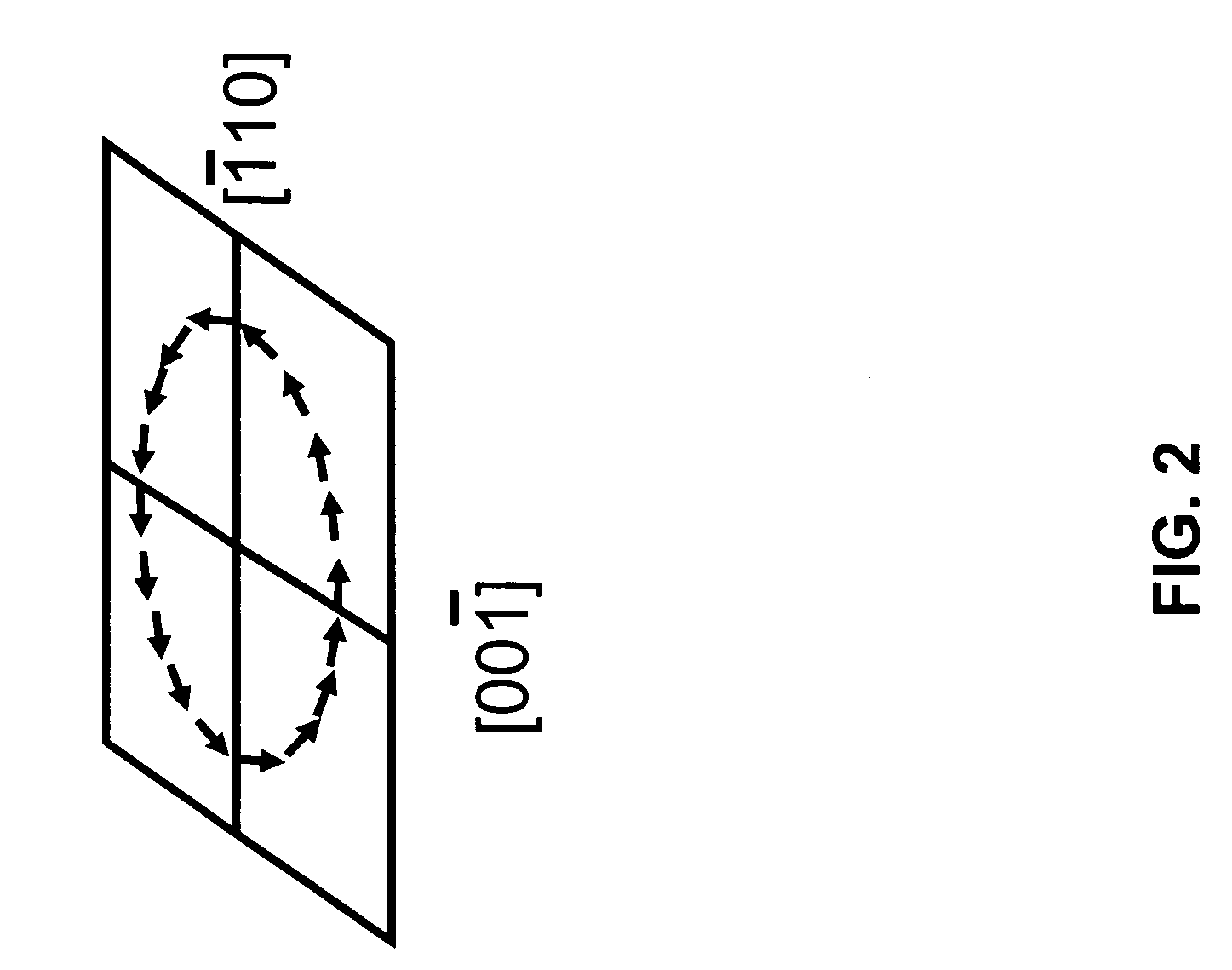
A nonmagnetic semiconductor device which may be utilized as a spin resonant tunnel diode (spin RTD) and spin transistor, in which low applied voltages and / or magnetic fields are used to control the characteristics of spin-polarized current flow. The nonmagnetic semiconductor device exploits the properties of bulk inversion asymmetry (BIA) in (110)-oriented quantum wells. The nonmagnetic semiconductor device may also be used as a nonmagnetic semiconductor spin valve and a magnetic field sensor. The spin transistor and spin valve may be applied to low-power and / or high-density and / or high-speed logic technologies. The magnetic field sensor may be applied to high-speed hard disk read heads. The spin RTD of the present invention would be useful for a plurality of semiconductor spintronic devices for spin injection and / or spin detection.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Magnetic tunnel junction
InactiveCN103531707ALower resistanceIncreased tunneling currentMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsStatic random-access memoryField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a magnetic tunnel junction of a spinel oxide potential barrier, and the application in device thereof. The potential barrier of the magnetic tunnel junction is made of spinel oxides. The tunnel junction may be of a single potential barrier structure or of a double potential barrier structure. The novel single potential barrier magnetic tunnel junction provided by the invention can be applied to a spintronic device and comprises a magneto-dependent sensor, a magnetic random access memory unit, a magnetic logic device unit, a spin transistor and a spin field effect transistor. According to the magnetic tunnel junction based on novel potential barriers, the mismatch degree between a potential barrier layer and a magnetic crystal lattice is quite small, while a high room temperature tunneling magneto-resistor ratio is maintained, the bias dependence feature is quite weak, and the breakdown voltage is improved.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spin transistor, programmable logic circuit, and magnetic memory
A spin transistor includes a first conductive layer that is made of a ferromagnetic material magnetized in a first direction, and functions as one of a source and a drain; a second conductive layer that is made of a ferromagnetic material magnetized in one of the first direction and a second direction that is antiparallel with respect to the first direction, and functions as the other one of the source and the drain. The spin transistor also includes a channel region that is located between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer, and introduces electron spin between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer; a gate electrode that is located above the channel region; and a tunnel barrier film that is located between the channel region and at least one of the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Spin transistor using spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field
ActiveUS20070059877A1Great spin-orbit coupling effectHigh electron mobilityNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingMagnetization
A spin transistor having wide ON / OFF operation margin and producing less noise is provided. The spin transistor includes a substrate having a channel, a source, a drain and a gate formed on the substrate. The source and the drain are formed to have magnetization directions perpendicular to the length direction of the channel. The ON / OFF operations of the spin transistor can be controlled by generating a spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field to have a direction parallel or anti-parallel to the magnetization directions of the source and the drain.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
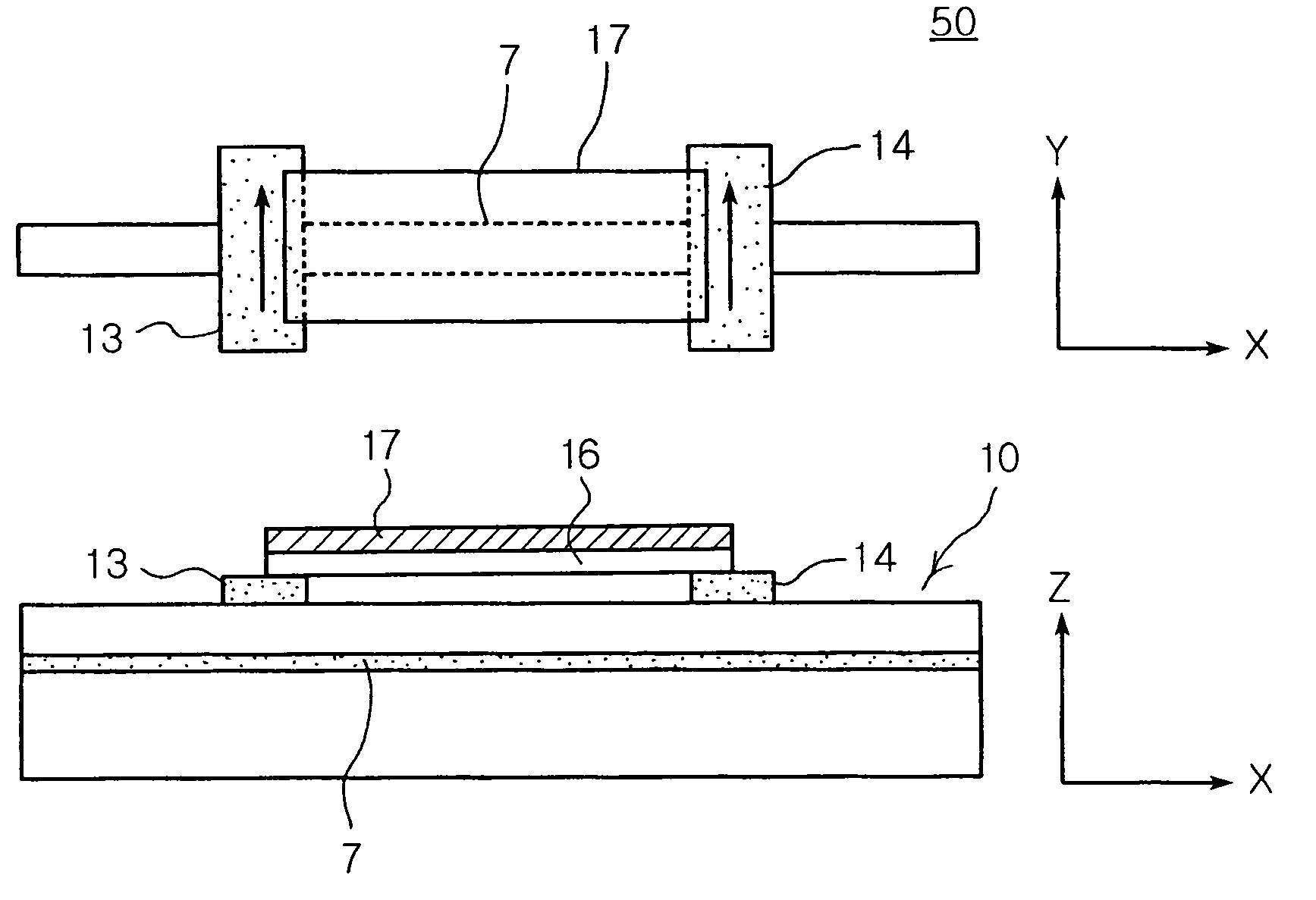
Complementary spin transistor logic circuit
ActiveUS20110279146A1Reduce power consumptionEasy to handleNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetizationHemt circuits
There is provided a complementary spin transistor logic circuit, including: a parallel spin transistor that includes a magnetized first source, a first drain magnetized in parallel with the magnetization direction of the first source, a first channel layer and a first gate electrode; and an anti-parallel spin transistor that includes a magnetized second source, a second drain magnetized in anti-parallel with the magnetization direction of the second source, a second channel layer and a second gate electrode, wherein the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are connected to a common input terminal.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
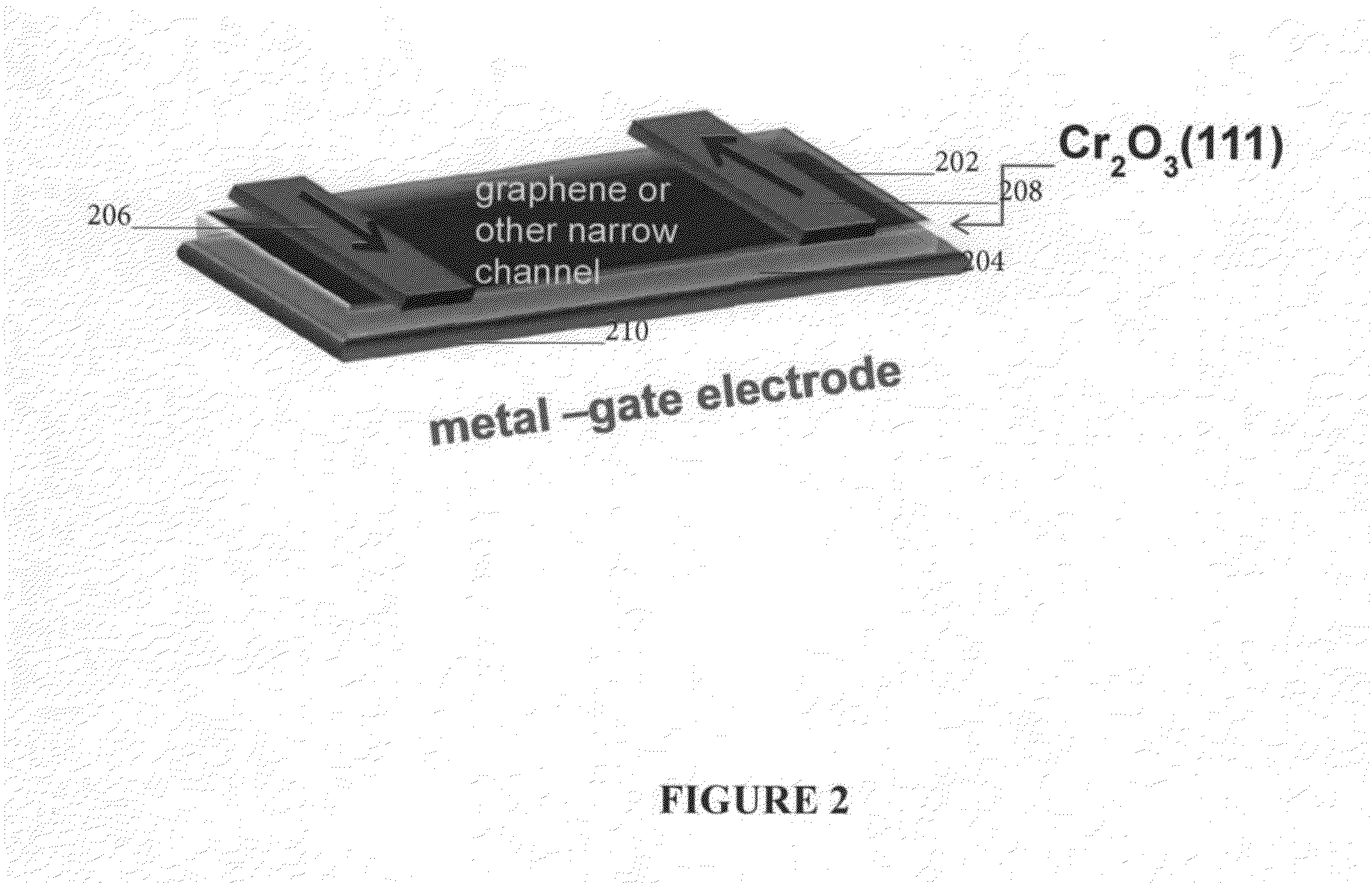
Magneto-Electric Voltage Controlled Spin Transistors
The invention relates to a magneto-electric spin-FET including a gate film of chromia and a thin film of a conductive channel material which may be graphene, InP, GaAs, GaSb, PbS, MoS2, WS2, MoSe2, WSe2 and mixtures thereof. The chromia, or other magneto-electric, and conduction channel material are in intimate contact along an interface there between. The resulting magneto-electric device may be voltage-controlled and provide non-volatile memory.
Owner:QUANTUM DEVICES +1
Spin Transistor Using Stray Magnetic Field
InactiveUS20080169492A1High spin transmission effectHigh transmission effectNanotechSolid-state devicesPhysicsSpin transistor
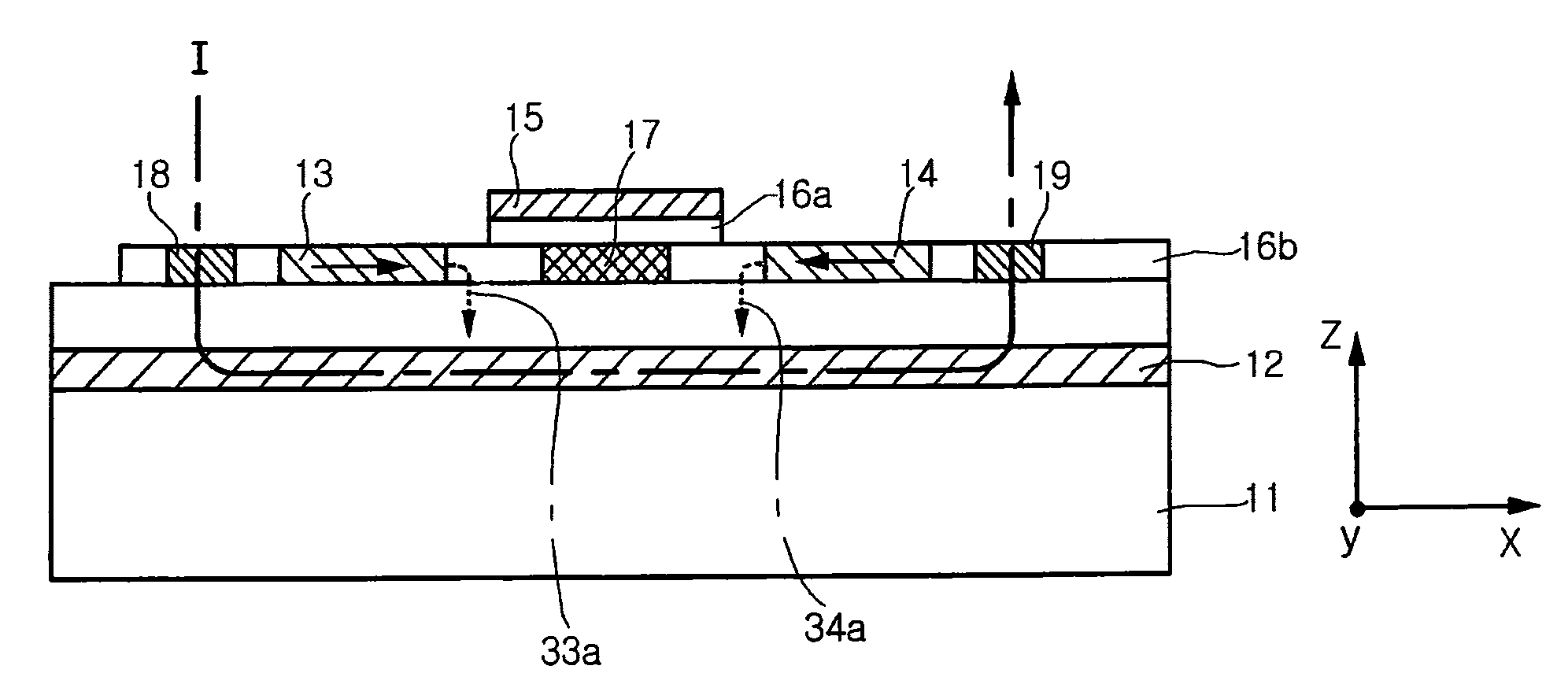
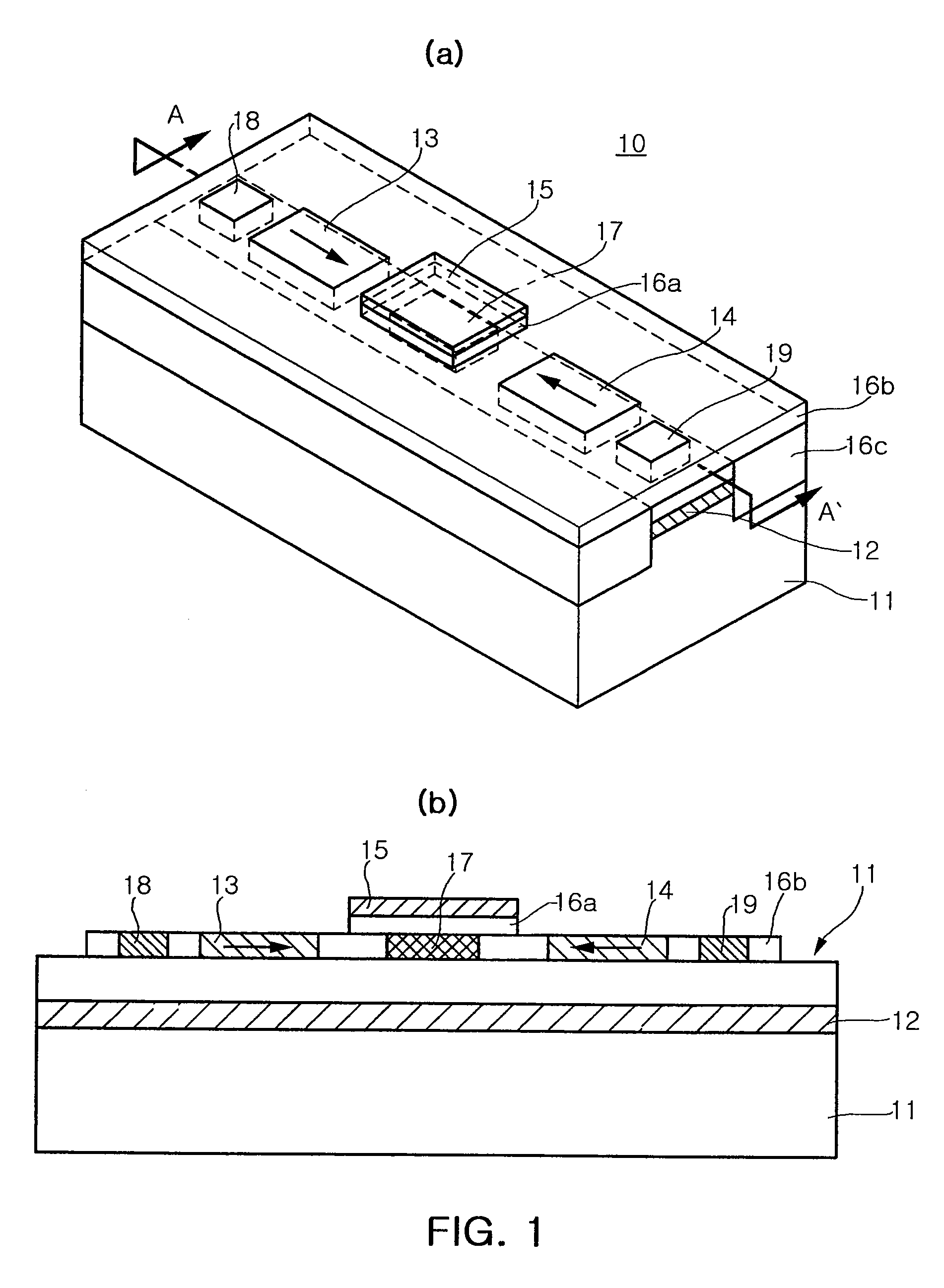
Disclosed herein is a spin transistor including: a semiconductor substrate having a channel layer formed therein; first and second electrodes which are formed to be spaced apart from each other on the substrate at a predetermined distance along a longitudinal direction of the channel layer; a source and drain which include magnetized ferromagnetic materials and are formed to be spaced apart form each other between the first electrode and the second electrode at a predetermined distance along the longitudinal direction of the channel layer; and a gate which is formed on the substrate between the source and the drain, and adjusts spin orientations of electrons passing through the channel layer, wherein the electrons passing through the channel layer are spin-aligned at a lower side of the source by a stray magnetic field of the source and spin-filtered at a lower side of the drain by a stray field of the drain.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic multilayer film with geometrical shape and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101221849AEasy to controlEasy to driveRecord information storageMagnetic film to substrate applicationMagnetic storageRandom access memory
The invention relates to a magnetic multiplayer film with geometric shape, comprising all layers of a magnetic multiplayer film unit deposited on a substrate, wherein the cross section of the magnetic multiplayer film unit is polygonal closing ring shaped, magnetic moments or magnetic fluxes of film layers with ferromagnetism in the magnetic multiplayer film unit become in a clockwise or counter clockwise closing state; the invention also comprises a metal core arranged on the geometric center of the polygonal closed ring shaped magnetic multiplayer film, wherein the cross section of the metal core is a corresponding polygon; the invention also relates to a magnetic storage made of the magnetic multiplayer film which comprises(or does not comprise) the metal core; in the invention, the closing shape magnetic multiplayer film is prepared based on the micro processing method; the closing with(or without) metal core polygonal closing ring shaped magnetic multiplayer film is widely applicable to devices which takes the magnetic multiplayer film such as magnetic random access memory, computer magnetic reading head, magneto-dependent sensor, magnetic logic device and self-rotation transistor, etc. as the core.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
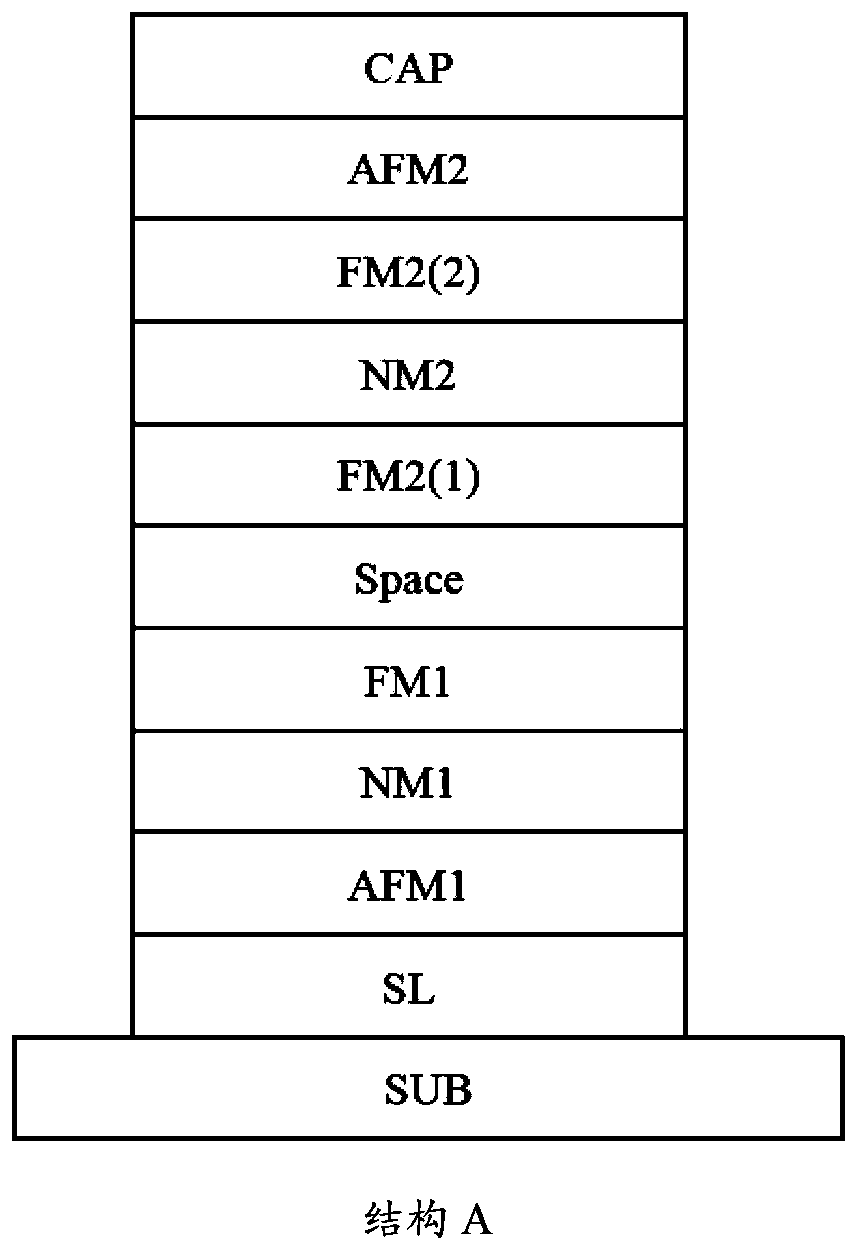
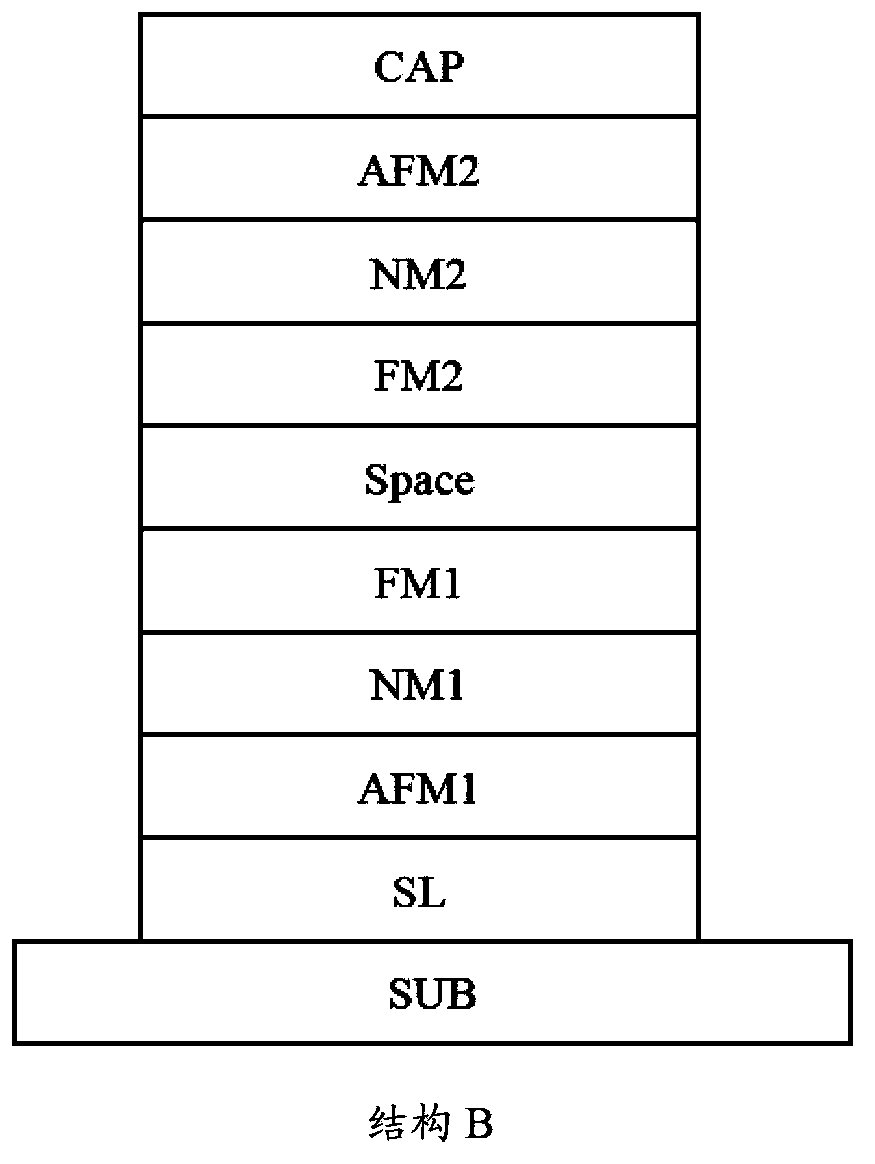
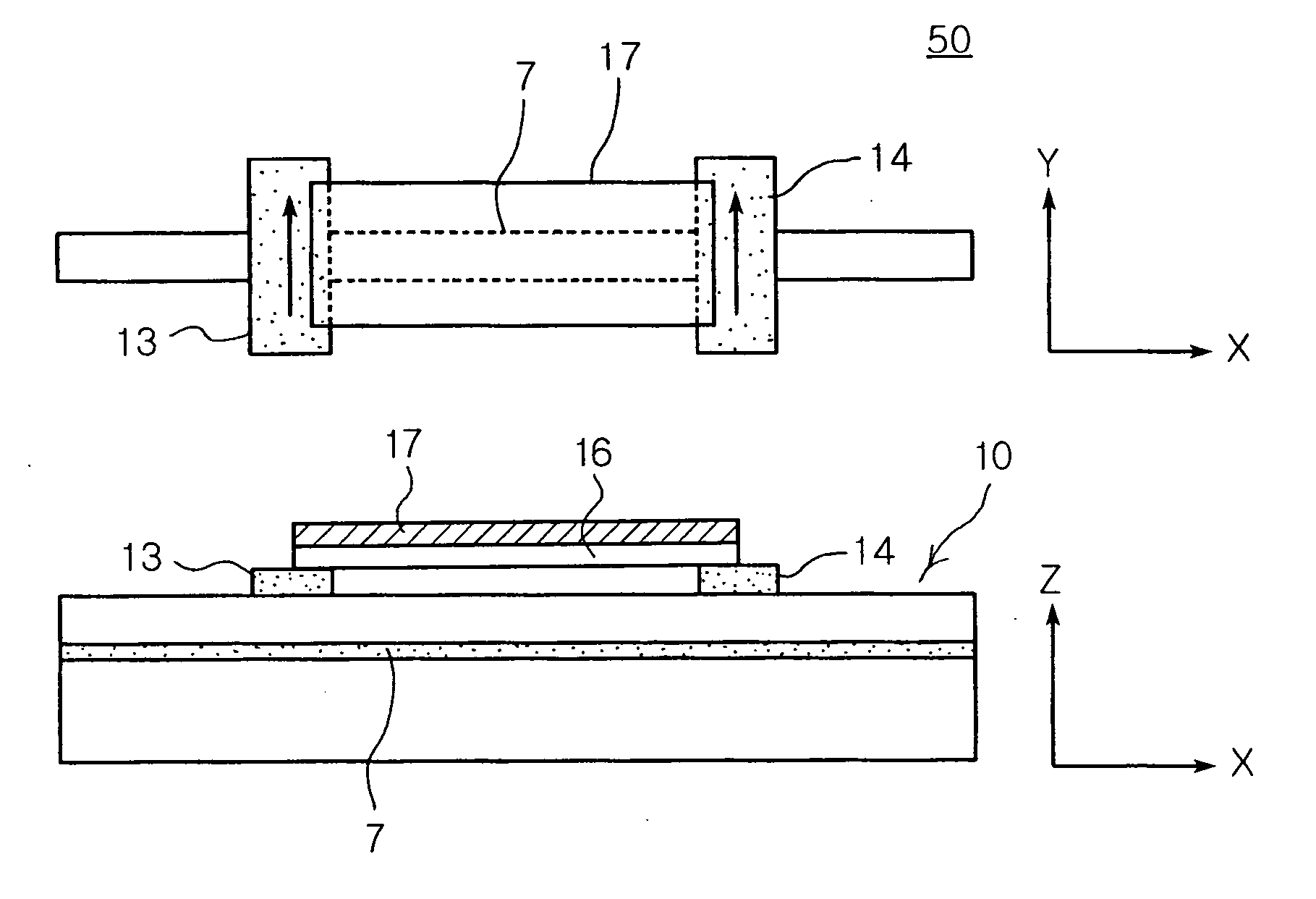
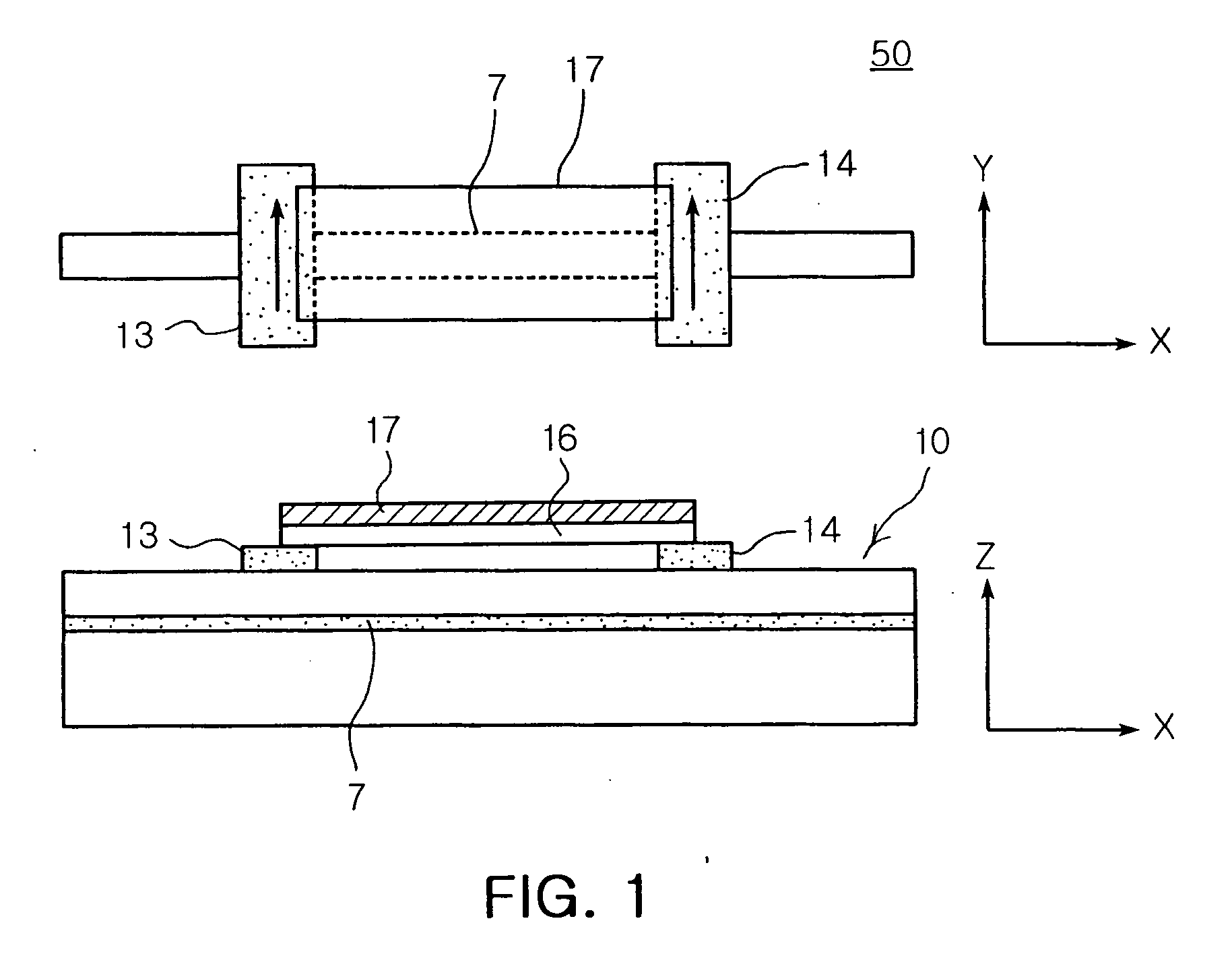
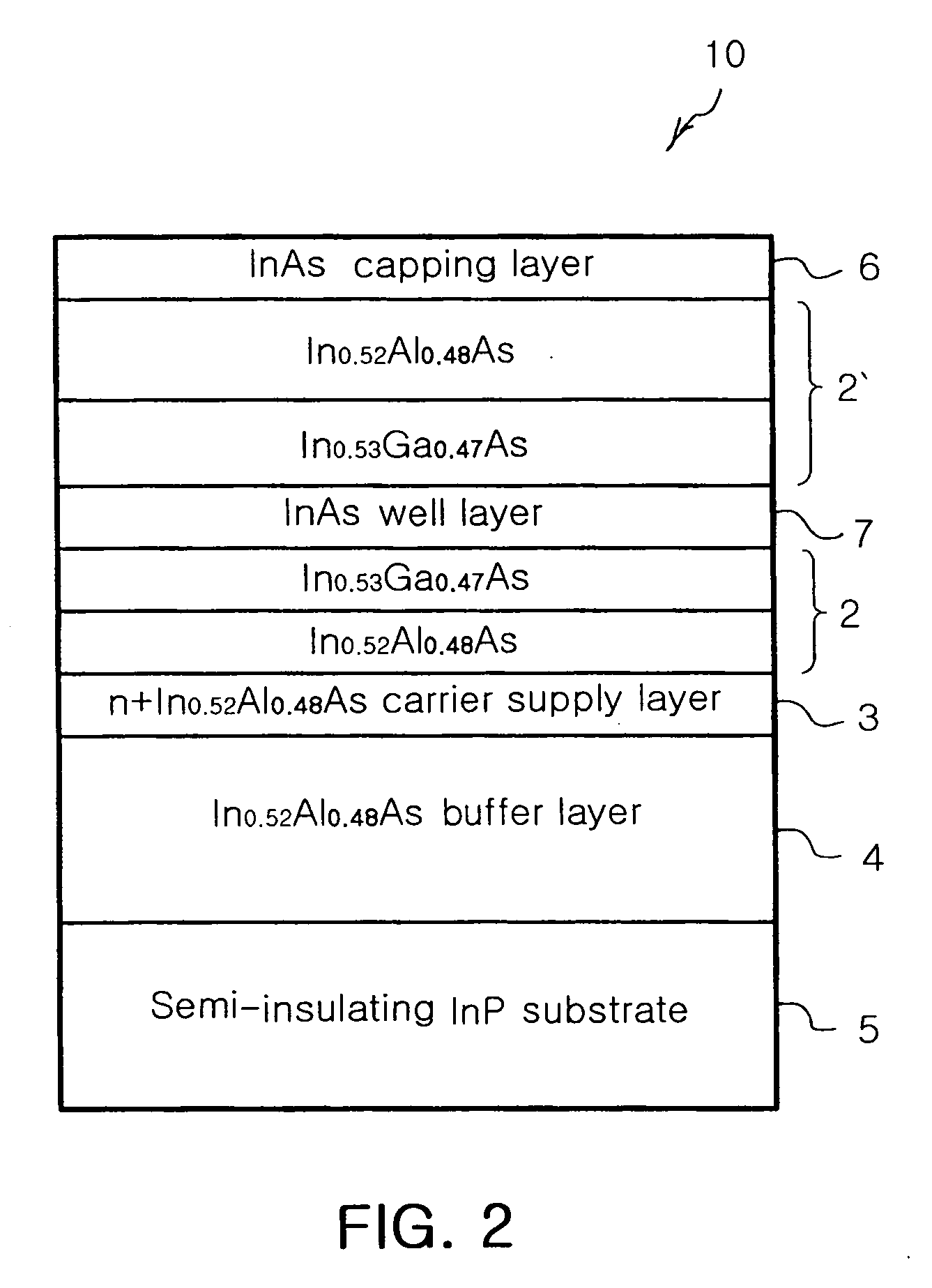
Spin memory and spin transistor
Certain embodiments provide a spin memory including a memory cell including a ferromagnetic stacked film that has a stacked structure in which a first ferromagnetic layer, a first nonmagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, a second nonmagnetic layer, and a third ferromagnetic layer are stacked in this order or reverse order, the third ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer being antiferromagnetically exchange-coupled via the second nonmagnetic layer. The ferromagnetic stacked film includes a current path in which a first and second write currents flow from the first ferromagnetic layer to the third ferromagnetic layer to write a first and second magnetization states into the first ferromagnetic layer respectively, and the second write current is higher than the first write current.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Spin transistor using stray magnetic field
Disclosed herein is a spin transistor including: a semiconductor substrate having a channel layer formed therein; first and second electrodes which are formed to be spaced apart from each other on the substrate at a predetermined distance along a longitudinal direction of the channel layer; a source and drain which include magnetized ferromagnetic materials and are formed to be spaced apart form each other between the first electrode and the second electrode at a predetermined distance along the longitudinal direction of the channel layer; and a gate which is formed on the substrate between the source and the drain, and adjusts spin orientations of electrons passing through the channel layer, wherein the electrons passing through the channel layer are spin-aligned at a lower side of the source by a stray magnetic field of the source and spin-filtered at a lower side of the drain by a stray field of the drain.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Spin transistor and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20090059659A1NanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic memoryMagnetization
A spin transistor includes a first ferromagnetic layer provided on a substrate and having an invariable magnetization direction, a second ferromagnetic layer provided on the substrate apart from the first ferromagnetic layer in a first direction, and having a variable magnetization direction, a plurality of projecting semiconductor layers provided on the substrate to extend in the first direction, and sandwiched between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer, a plurality of channel regions respectively provided in the projecting semiconductor layers, and a gate electrode provided on the channel regions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
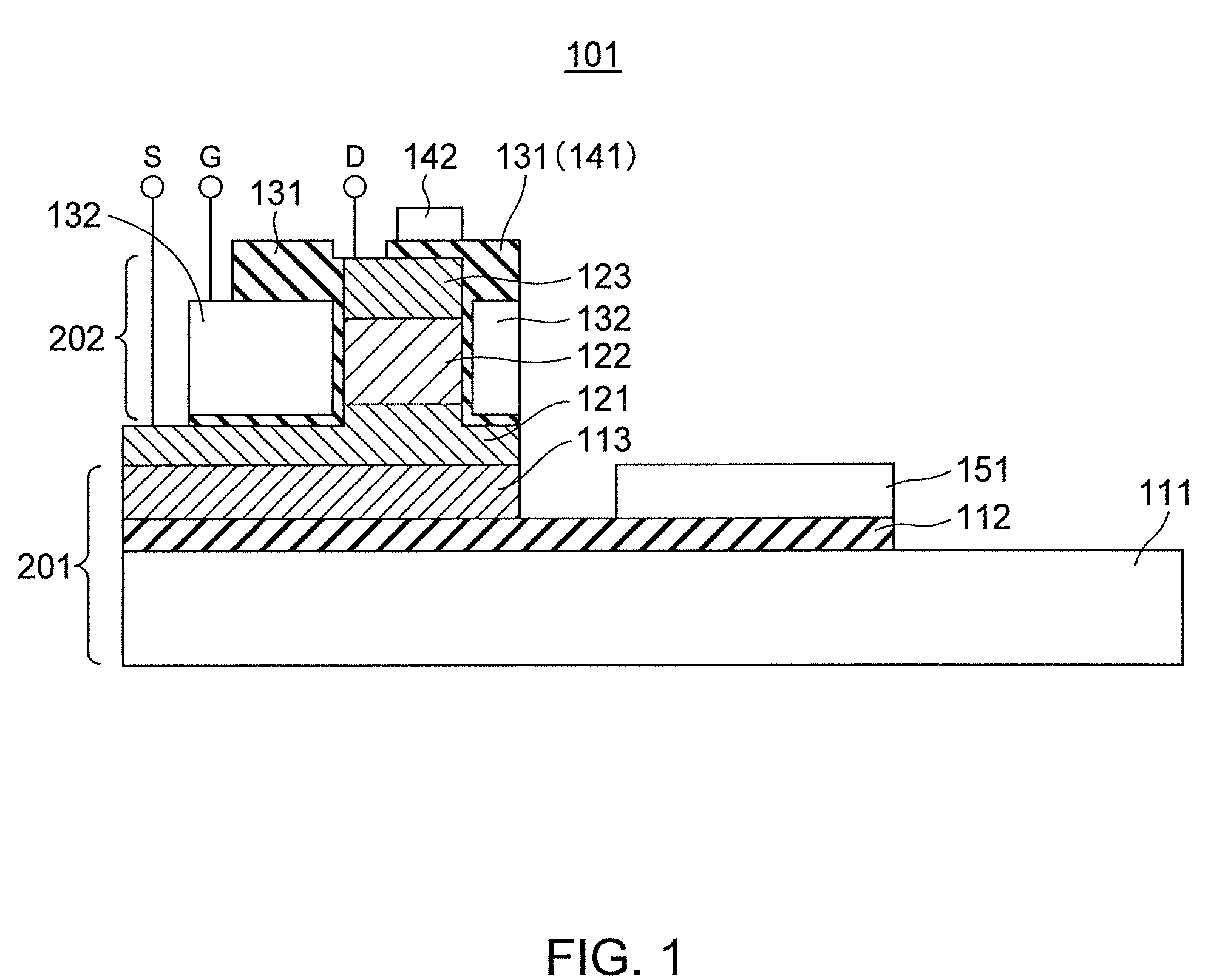
Spin transistor and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20090057793A1Increasing the thicknessReduce probabilityNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic reluctanceSemiconductor
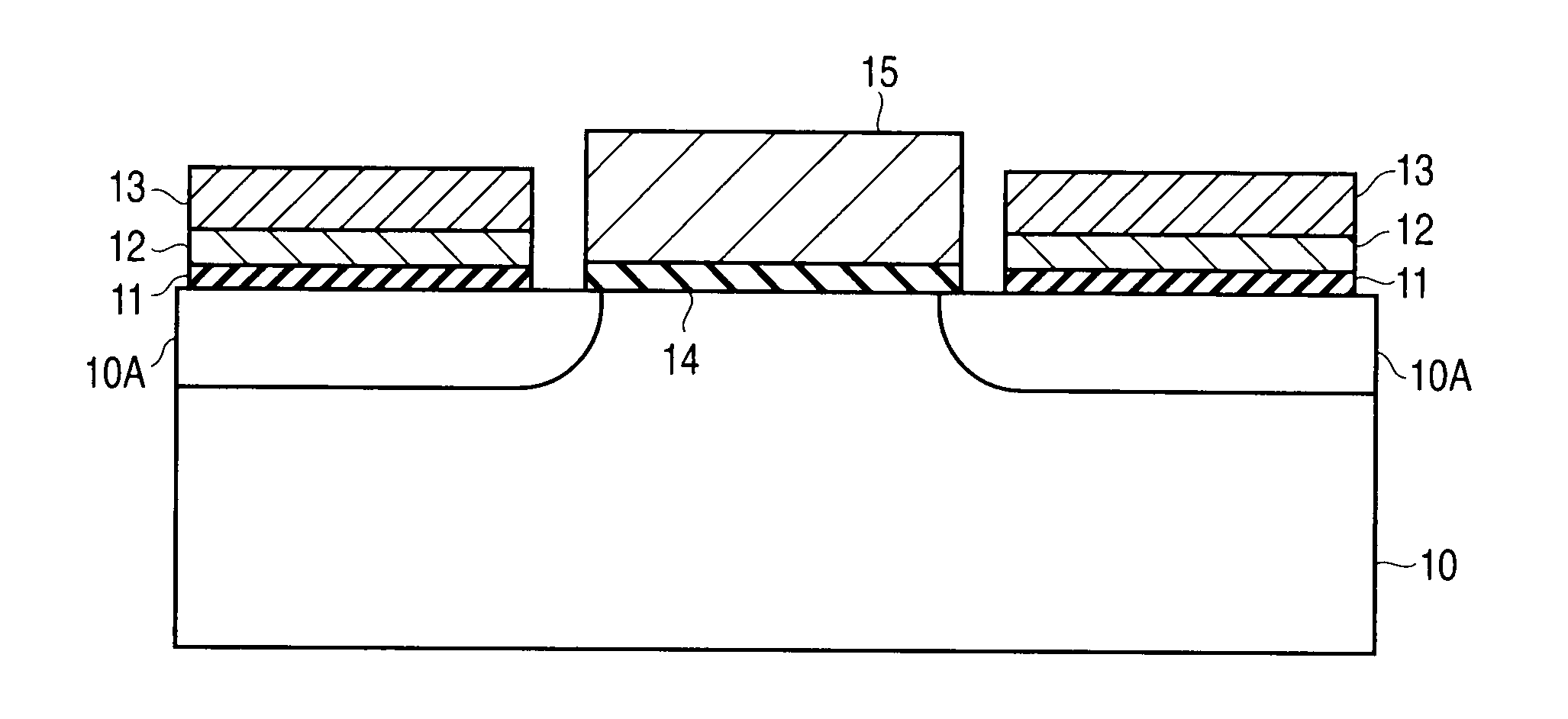
The spin transistor in accordance with the present invention comprises a magnetoresistive element having a fixed layer, a free layer, and a semiconductor layer provided between the fixed layer and free layer; a source electrode layer electrically connected to one end face in a laminating direction of the magnetoresistive element; a drain electrode layer electrically connected to the other end face in the laminating direction of the magnetoresistive element; and a gate electrode layer laterally adjacent to the semiconductor layer through a gate insulating layer provided on a side face of the semiconductor layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Spin Transistor Using Perpendicular Magnetization
InactiveUS20080308844A1Limited resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronTransistor
A spin transistor useful for device miniaturization and high-density integration is provided. The spin transistor includes: a semiconductor substrate including a channel layer; ferromagnetic source and drain disposed on the semiconductor substrate to be separated from each other and to be magnetized in a direction perpendicular to a surface of the channel layer; a gate formed on the semiconductor substrate between the source and the drain to adjust spins of electrons passing through the channel layer, wherein spin-polarized electrons are injected from the source to the channel layer, and the electrons injected into the channel layer pass though the channel layer and are injected into the drain, and wherein the spins of the electrons passing through the channel layer undergo precession due to a spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field according to a voltage of the gate.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Spin transistor, integrated circuit, and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20100072528A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageHigh energyMagnetic memory
A spin transistor includes a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, a semiconductor layer between the first and second ferromagnetic layers, and a gate electrode on or above a surface of the semiconductor layer, the surface being between the first and second ferromagnetic layers. The first ferromagnetic layer comprises a ferromagnet which has a first minority spin band located at a high energy side and a second minority spin band located at a low energy side, and has a Fermi level in an area of the high energy side higher than a middle of a gap between the first and second minority spin bands.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
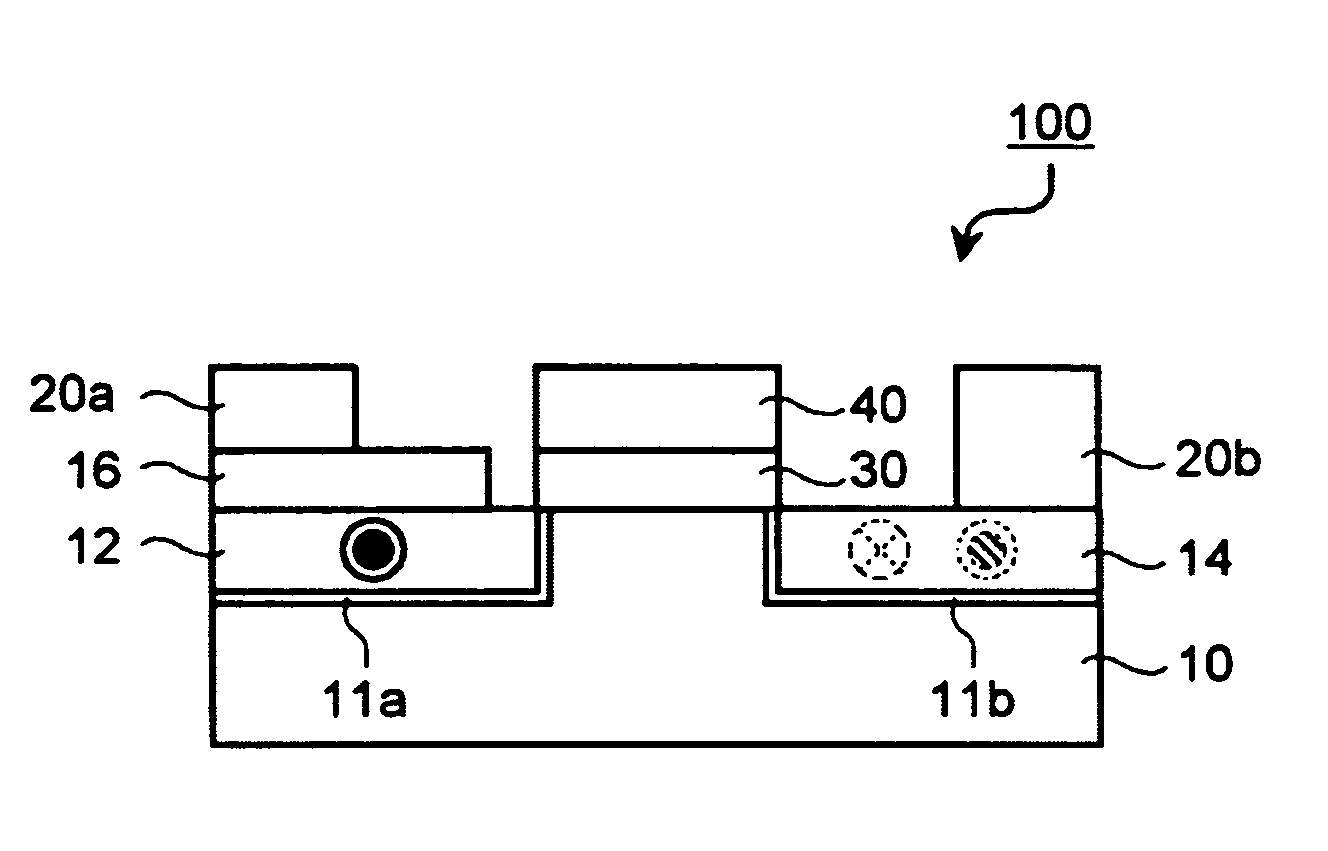
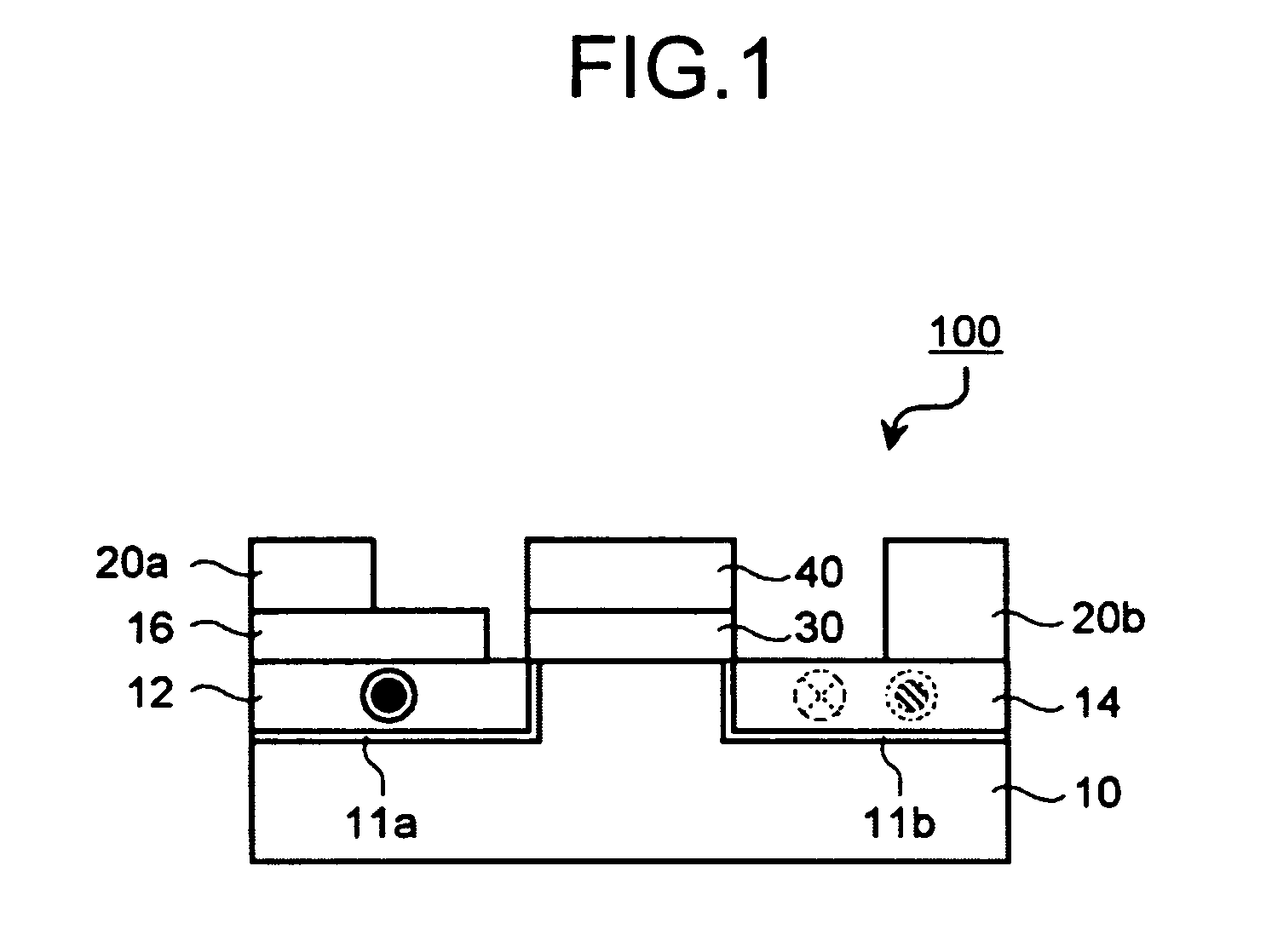
Vertical spin transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7629658B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin magnetic filmsSemiconductorSpin transistor
A vertical spin transistor according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a first source / drain layer including a layer formed of magnetic material; a protruding structure including, a channel layer formed on the first source / drain layer and including a layer formed of semiconductor, and a second source / drain layer formed on the channel layer and including a layer formed of magnetic material; a gate insulating film formed on a side of the channel layer; and a gate electrode formed on a surface of the gate insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Spin transistor using spin-filter effect and nonvolatile memory using spin transistor
InactiveUS20060043443A1Design freedomImprove the level ofTransistorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpinsSpin splitting
A spin transistor comprises a spin injector for injecting, from a first nonmagnetic electrode carriers with a spin parallel to a spin band forming the band edge of a first ferromagnetic barrier layer, to a second nonmagnetic electrode layer, as hot carriers. It also comprises a spin analyzer whereby, due to spin-splitting at the band edge of a second ferromagnetic barrier layer, the spin-polarized hot carriers are transported to a third nonmagnetic electrode when the direction of the spin of the carriers injected into the second nonmagnetic electrode is parallel to that of the spin of the spin band at the band edge of the second ferromagnetic barrier layer, whereas the hot carriers are not transported to the third nonmagnetic electrode in the case of antiparallel spin. A memory element is also provided that comprises such a spin transistor.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Stack having Heusler alloy, magnetoresistive element and spin transistor using the stack, and method of manufacturing the same
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Stack having heusler alloy, magnetoresistive element and spin transistor using the stack, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100072529A1Solid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMetallurgySpin transistor
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Spin Transistor Using Epitaxial Ferromagnet-Semiconductor Junction
InactiveUS20090152606A1MiniaturizationConducive to large scale integrationNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesMiniaturizationMagnetization
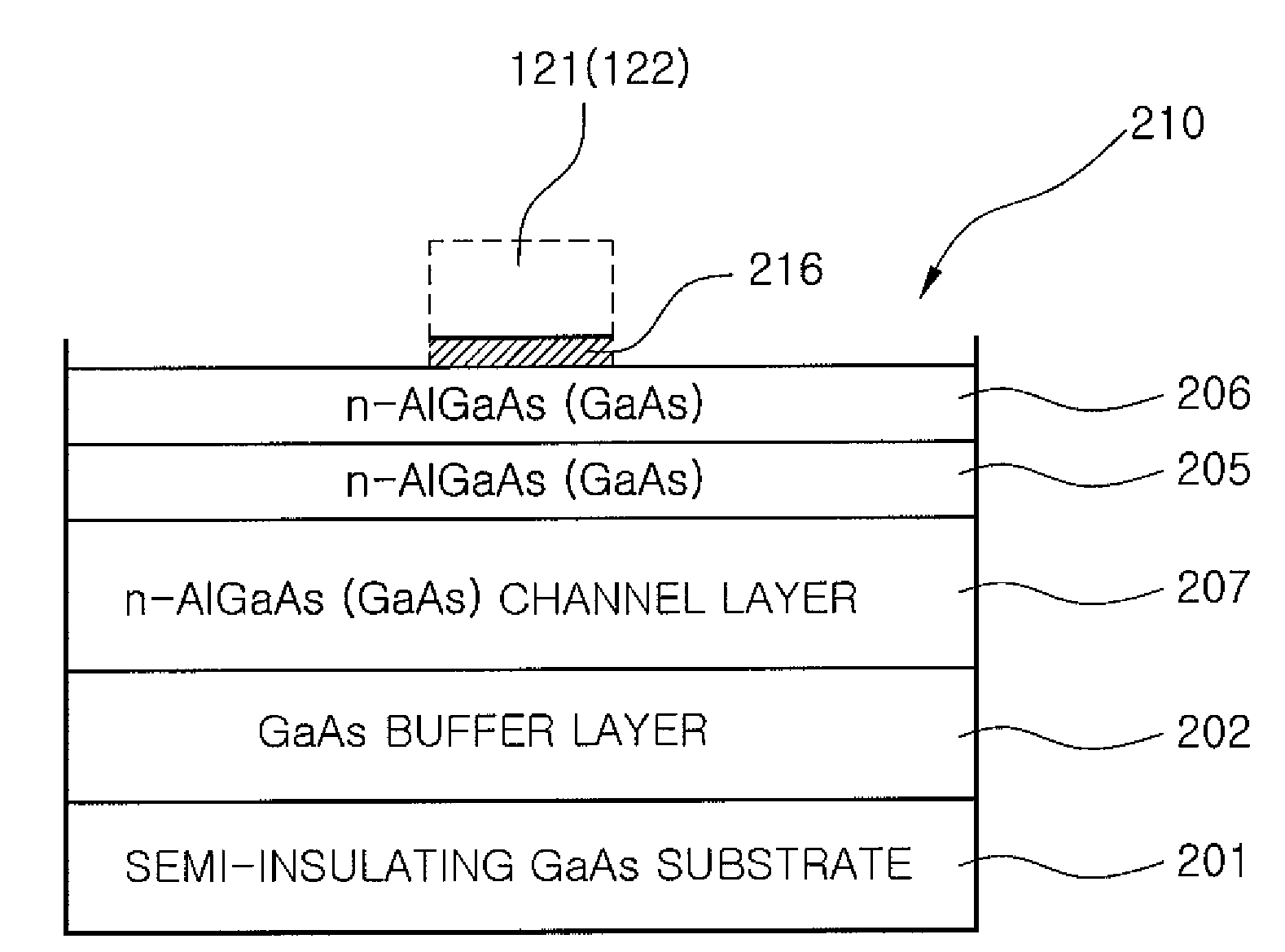
A spin transistor conducive to the miniaturization and large scale integration of devices, because a magnetization direction of a source and a drain is determined by a direction of the epitaxial growth of a ferromagnet. The spin transistor includes a semiconductor substrate having a channel layer formed thereinside; ferromagnetic source and drain epitaxially grown on the semiconductor substrate and magnetized in a longitudinal direction of the channel layer due to magnetocrystalline anisotropy—the source and drain being disposed spaced apart from each other in a channel direction and magnetized in the same direction—; and a gate disposed between the source and the drain to be insulated with the semiconductor substrate and formed on the semiconductor substrate to control the spin of electrons that are passed through the channel layer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
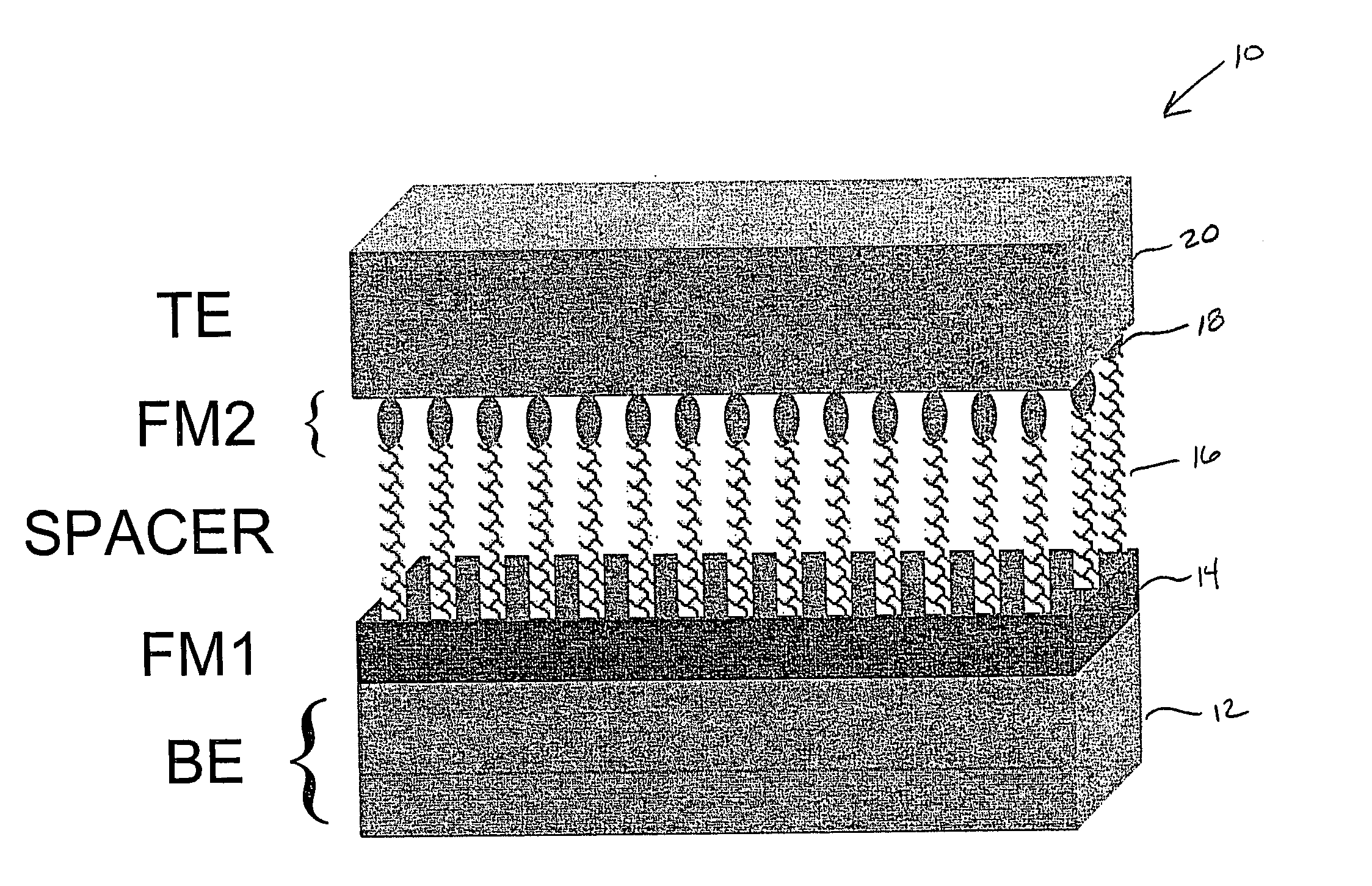
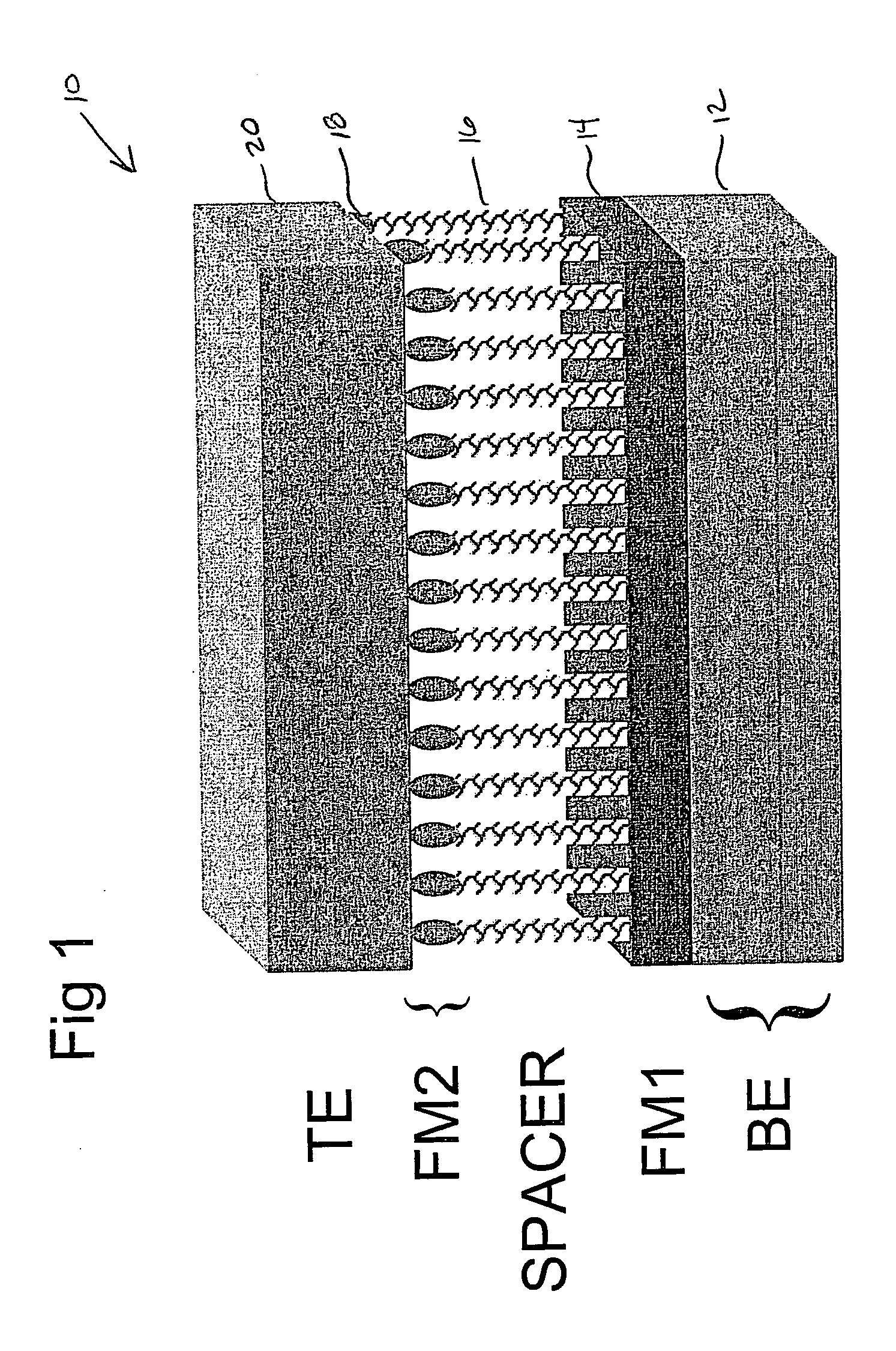
Spintronic device having a carbon nanotube array-based spacer layer and method of forming same
This invention relates to spintronic devices—and electronic devices comprising them, such as spin valves, spin tunnel junctions and spin transistors—which utilize a layer comprised of an array of aligned carbon nanontubes. A spintronic device includes, a bottom electrode, a first ferromagnetic layer, a CNT array, a second ferromagnetic layer and a top electrode.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Spin Transistors Employing a Piezoelectric Layer and Related Memory, Memory Systems, and Methods
ActiveUS20130299880A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsSpin transitionSpin channel
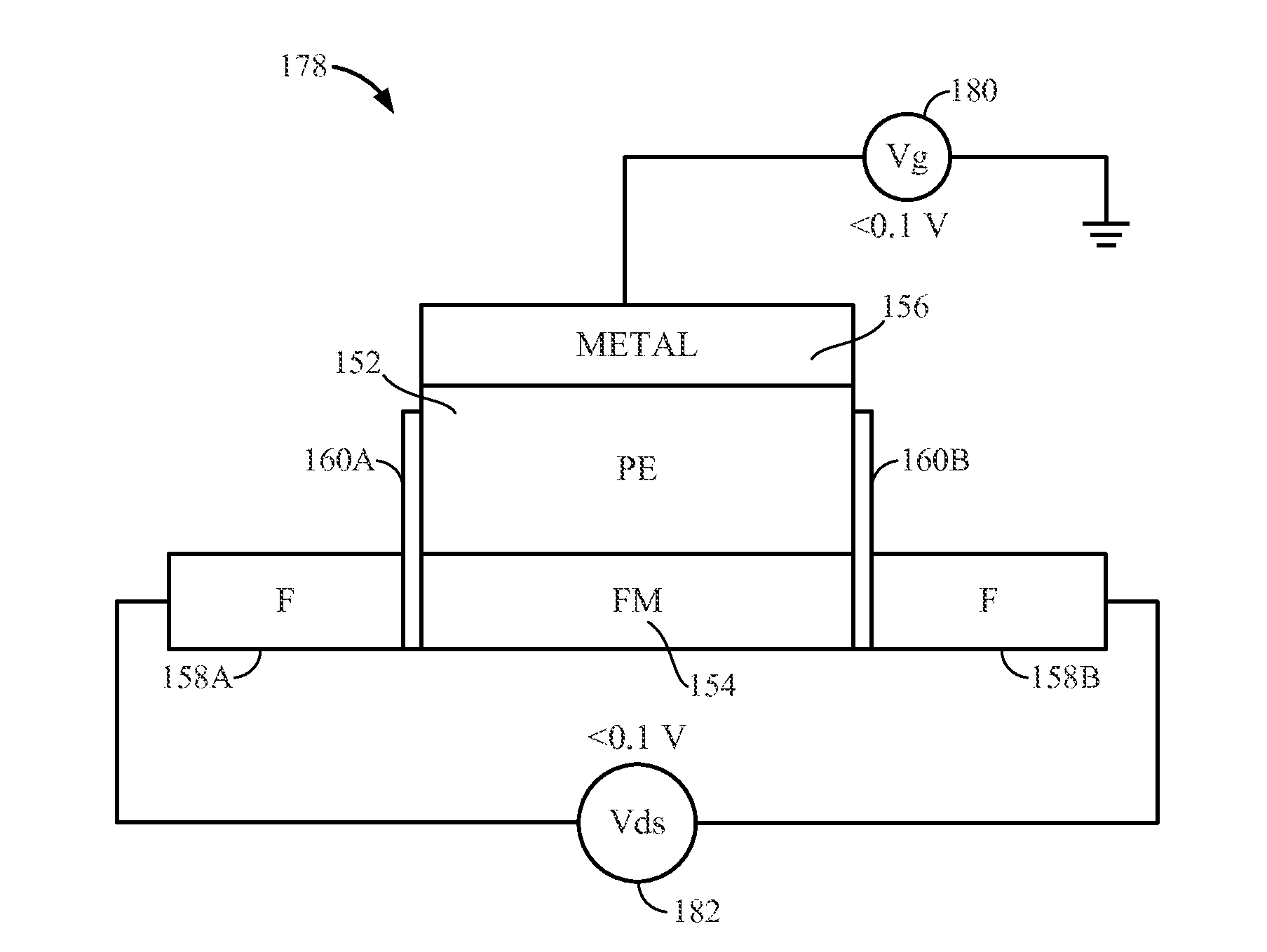
Spin transistors and related memory, memory systems, and methods are disclosed. A spin transistor is provided by at least two magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) with a shared multiferroic layer. The multiferroic layer is formed from a piezoelectric (PE) thin film over a ferromagnetic thin film (FM channel) with a metal electrode (metal). The ferromagnetic layer functions as the spin channel and the piezoelectric layer is used for transferring piezoelectric stress to control the spin state of the channel. The MTJ on one side of the shared layer forms a source and the MTJ on the other side is a drain for the spin transistor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Logic Circuit and Single-Electron Spin Transistor
InactiveUS20090039401A1Reduce areaSolve the large power consumptionNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle electronCapacitance
A logic circuit that can reconfigure its functions in a nonvolatile manner and a single-electron transistor to be used in the logic circuits are provided. The logic circuit has a single-electron spin transistor that includes: a source; a drain; an island that is provided between the source and the drain, and has tunnel junctions between the island and the source and drain; and a gate that is capacitively coupled to the island. In this logic circuit, at least one of the source, the drain, and the island includes a ferromagnetic material having a variable magnetization direction.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Spin transistor using spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field
ActiveUS7307299B2Wide ON/OFF operation marginBroad process margin for channel lengthNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingSpins
A spin transistor having wide ON / OFF operation margin and producing less noise is provided. The spin transistor includes a substrate having a channel, a source, a drain and a gate formed on the substrate. The source and the drain are formed to have magnetization directions perpendicular to the length direction of the channel. The ON / OFF operations of the spin transistor can be controlled by generating a spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field to have a direction parallel or anti-parallel to the magnetization directions of the source and the drain.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Three-terminal spin transistor magnetic random access memory and the method to make the same
InactiveUS20150364676A1Decrease switching energy barrierEasy to switchMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionDielectricEngineering
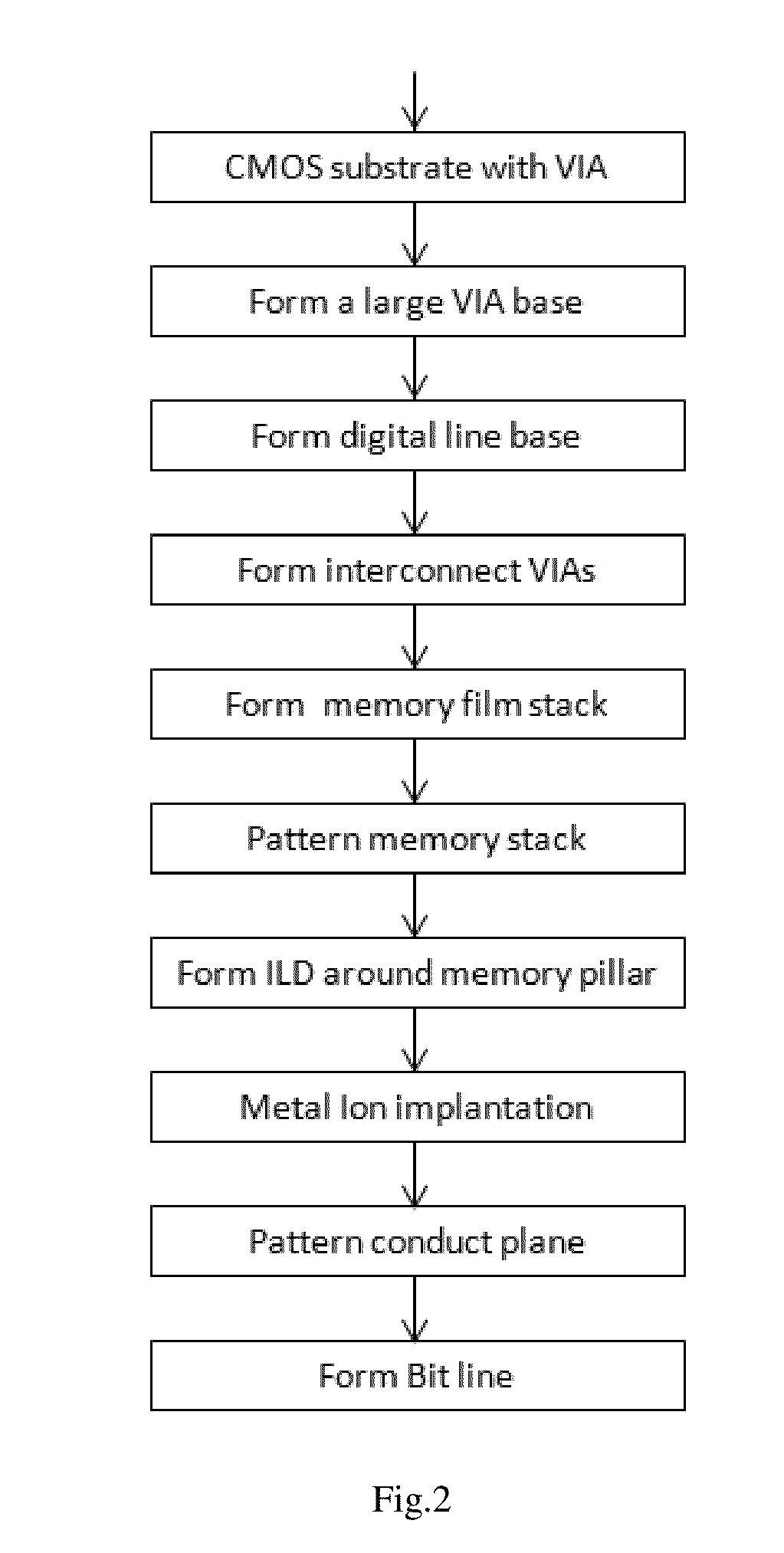
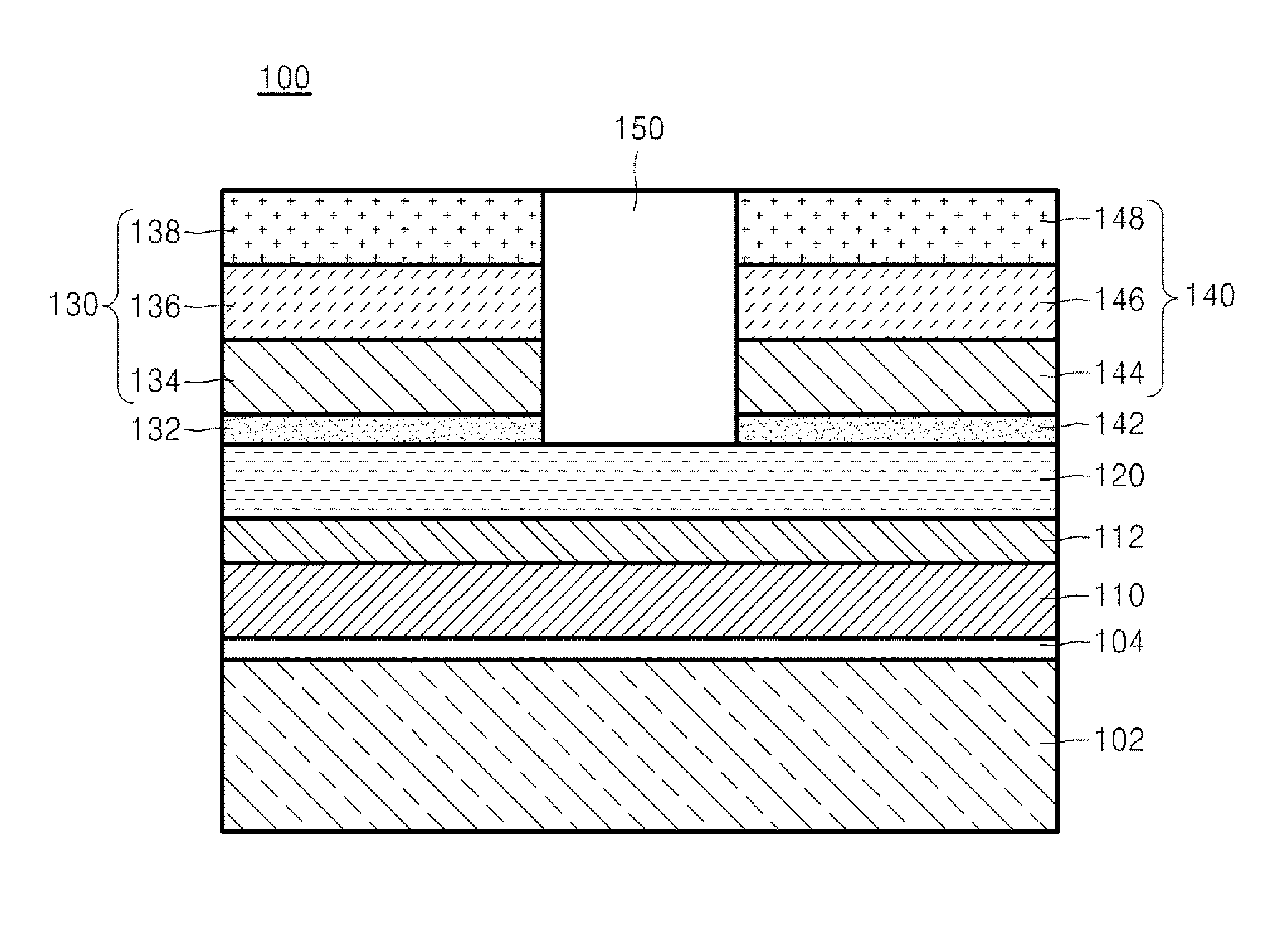
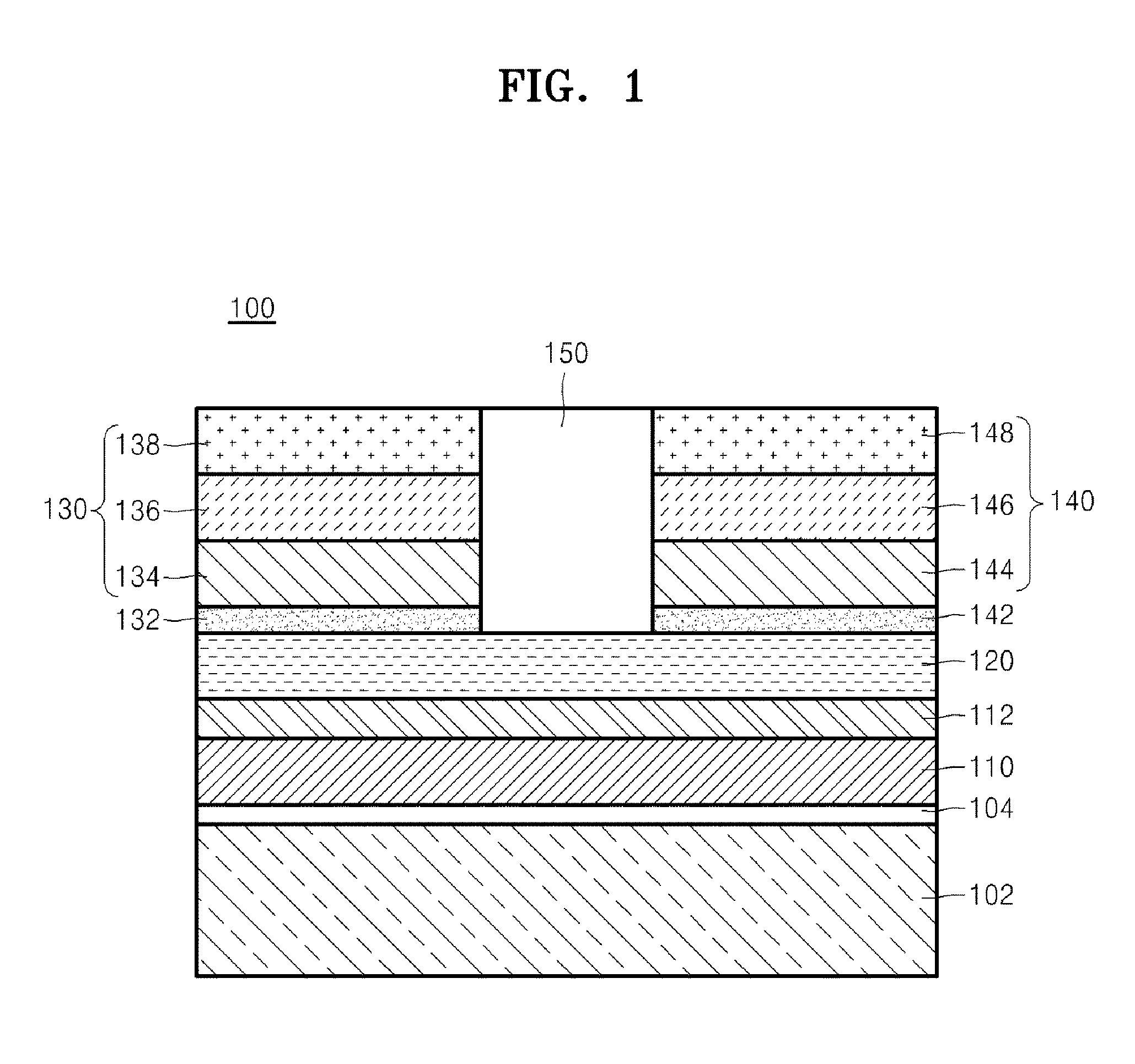
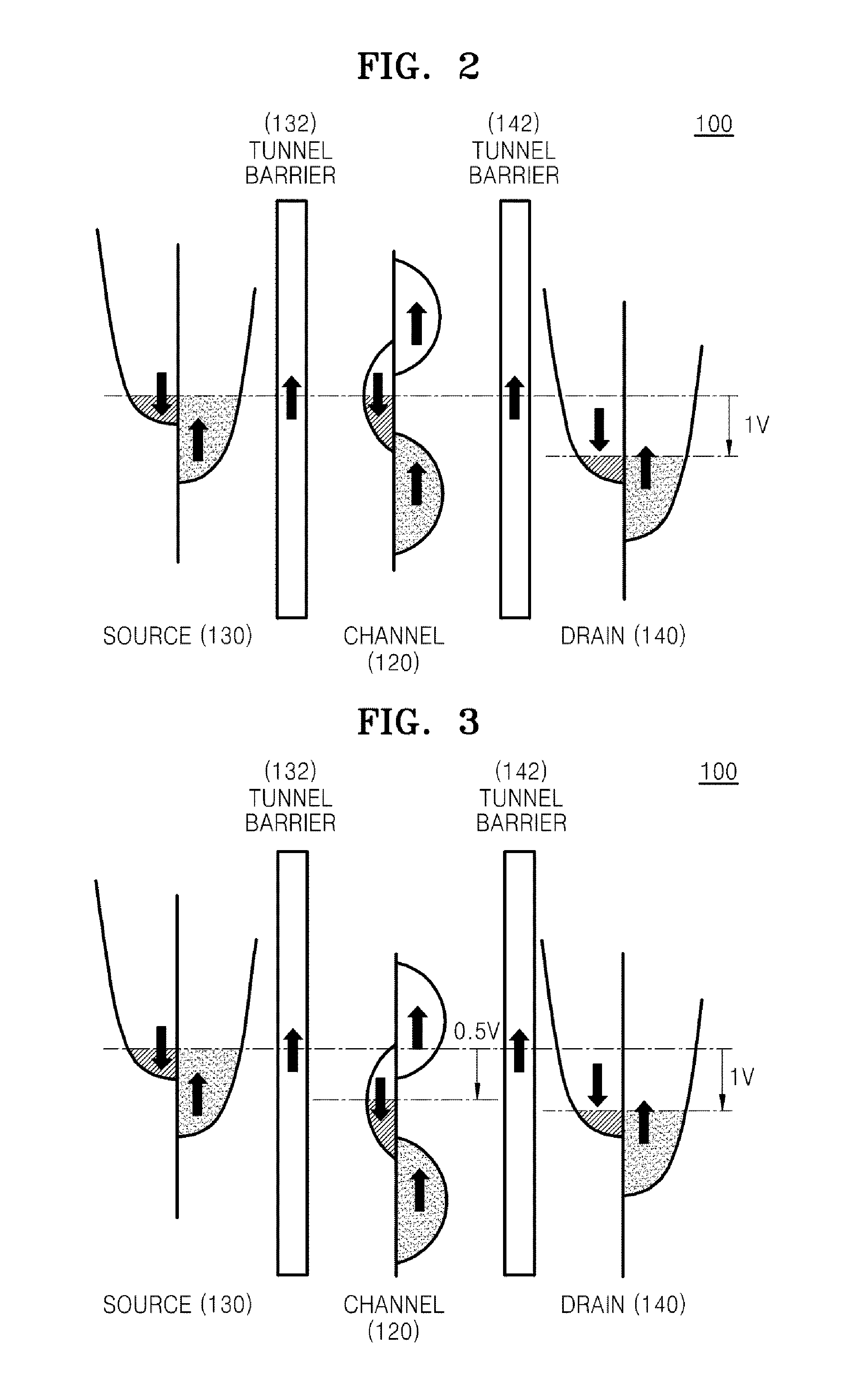
This invention is about a three-terminal spin transistor magnetic random access memory and the method to make it with a narrow foot print. The first terminal, a bit line, is connected to the top magnetic reference layer, and the second terminal is located at the middle memory layer which is connected to the underneath CMOS control circuit through VIA and the third one, a digital line, is a voltage gate with a narrow point underneath the memory layer across an insulating layer which is used to reduce the write current when it is turned on. The fabrication includes formation of a large VIA base, formation of digital line, formation of memory cell & VIA connection and formation of the top bit line. Dual photolithography patterning and hard mask etch are used to form the digital line pillar and small memory pillar. Oxygen plasma ion implantation is used to define an insulating region underneath the memory cell and metallic ion implantation is used to convert a buried dielectric VIA base outside the center memory pillar into an electric conductive path between middle memory cell and underneath CMOS device.
Owner:T3MEMORY
Spin transistor and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20100271112A1Increase charge mobilityReduce the amount requiredNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpinsSpin polarization
Disclosed are a spin transistor and a method of operating the spin transistor. The disclosed spin transistor includes a channel formed of a magnetic material selectively passing a spin-polarized electron having a specific direction, a source formed of a magnetic material, a drain, and a gate electrode. When a predetermined voltage is applied to the gate electrode, the channel selectively passes a spin-polarized electron having a specific direction and thus, the spin transistor is selectively turned on.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic multilayer film unit, preparation method and magnetic moment overturning method thereof
ActiveCN102082018AReduce power consumptionHighly integratedDigital storageMagnetic film to substrate applicationCommunication industryMiniaturization
The invention provides a magnetic multilayer film unit, comprising a magnetic multilayer film core unit and a magnetic moment control unit, wherein the magnetic multilayer film core unit comprises a free layer; the magnetic moment control unit comprises two conducting layers; and the free layer of the magnetic multilayer film core unit is positioned in an electric field formed by the two conducting layers. In addition, the invention also provides a corresponding preparation method and a magnetic moment overturning control method of the magnetic multilayer film unit. In the invention, the power consumption of the devices is greatly reduced, and the integration level of the devices can be improved; a preparation process and a semiconductor process are compatible so as to be beneficial to large-scale industrial production; and the magnetic multilayer film unit is beneficial to miniaturization of spintronic devices and has the advantage of radiation resistance. The magnetic multilayer film unit can be widely applied in the spintronic devices such as logic devices, nonvolatile storages, spinning transistors and various sensors and the like in the field of the future computer information communication industry. The invention is beneficial to widening of the application range of the spintronic devices.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-electron magnetic resistance structure and application thereof
ActiveCN101853918AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceDouble barrier
The invention discloses a single-electron magnetic resistance structure and application thereof, such as a spin diode, a spin transistor, a sensor, a magnetic random access memory and a magnetic logic device unit. A GMR (Giant Magnetic Resistance) quantum dot single-electron tunneling magnetic resistance structure comprises a substrate as well as a bottom conducting layer, a first barrier layer, a GMR magnetic quantum dot layer, a second barrier layer and a top conducting layer which are arranged on the substrate. A double-barrier magnetic quantum dot structure comprises a core film layer comprising a bottom electrode, a first barrier layer, a magnetic quantum dot layer, a second barrier layer and a top electrode from bottom to top. Due to the combination with a coulomb blockade effect and a tunneling magnetic resistance effect, the invention controls coulomb energy level resonant tunneling passing through quantum dots by utilizing an external magnetic field to improve tunneling magnetic resistance. The invention can effectively improve the tunneling magnetic resistance effect by utilizing a magnetic resistance design formed by coulomb blockade and improve the signal to noise ratio of device application, and simultaneously reduces tunneling current by utilizing single-electron tunneling, thereby reducing the power consumption of device application.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com