Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1113 results about "Crystal plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
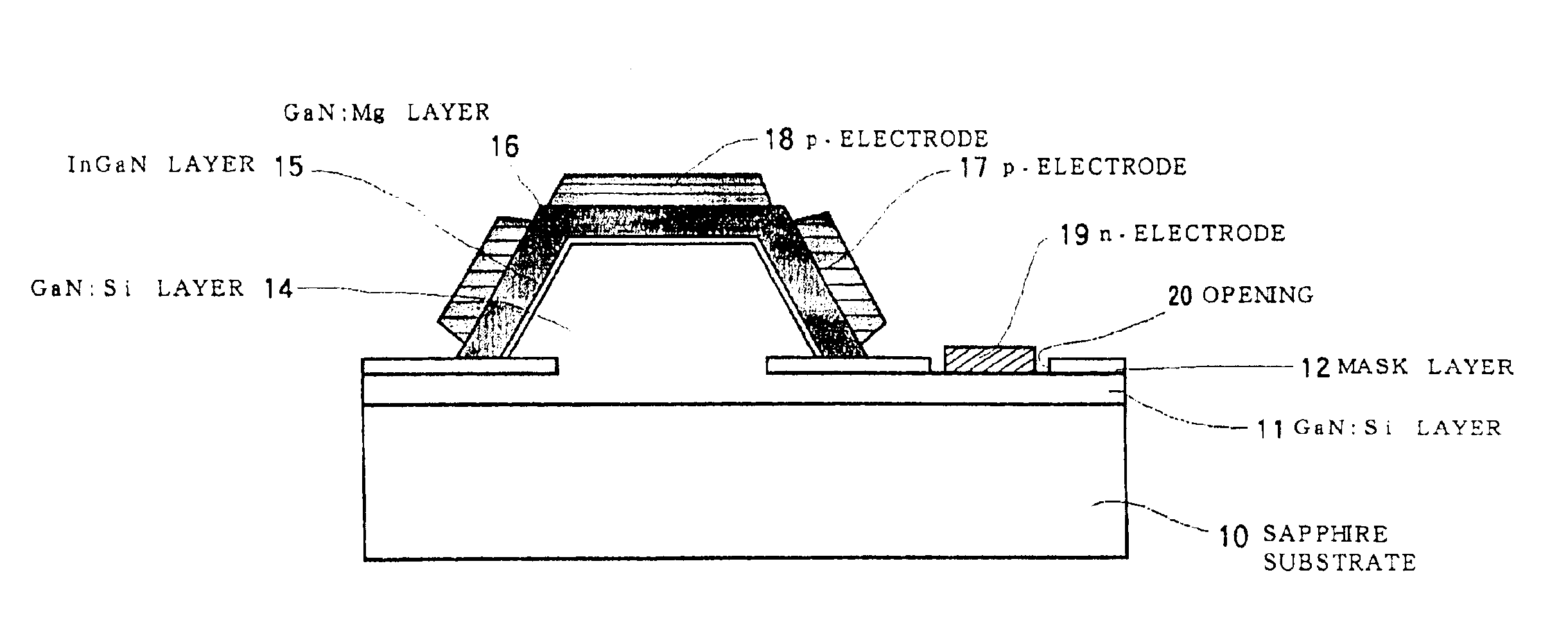
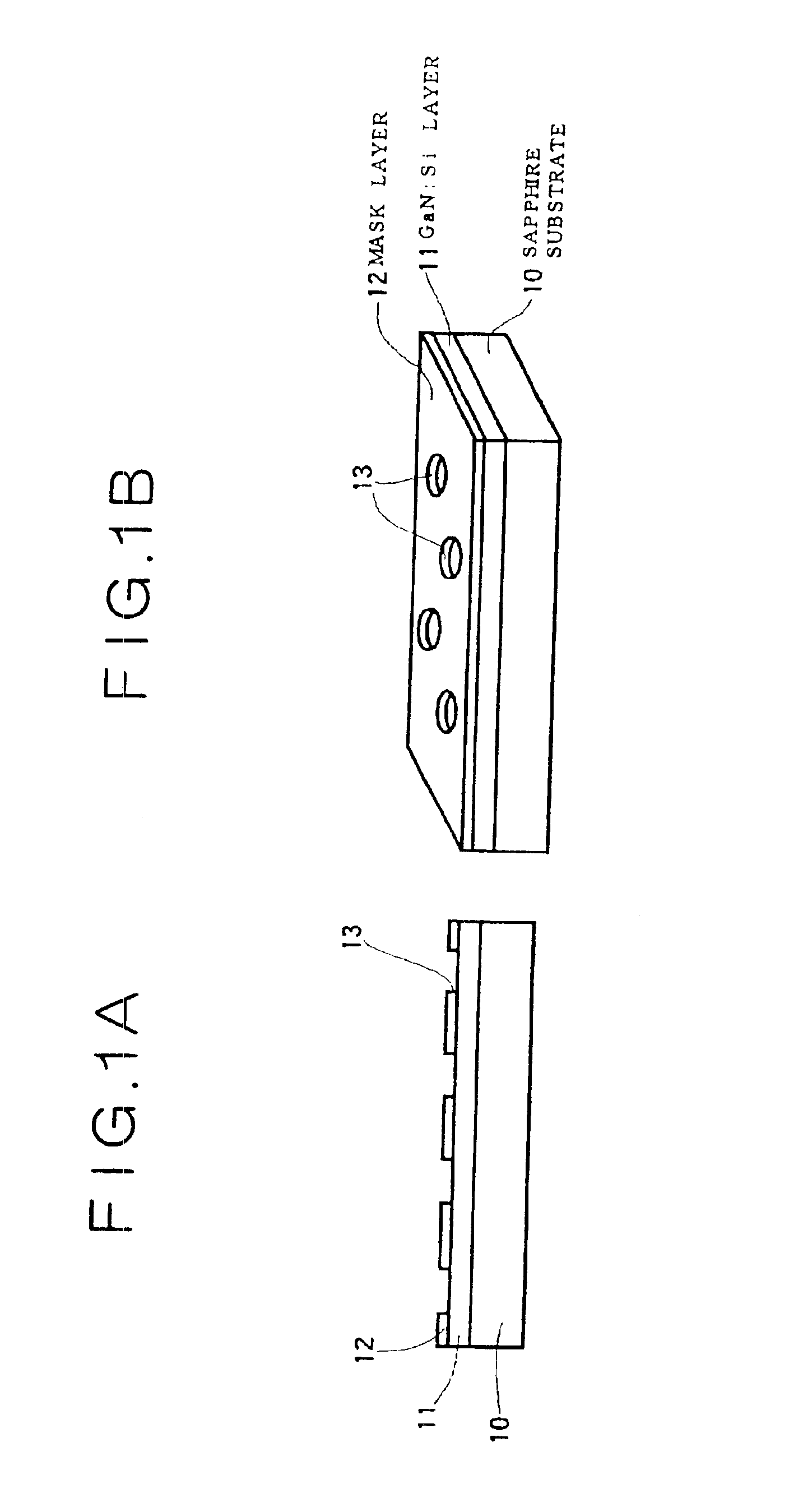
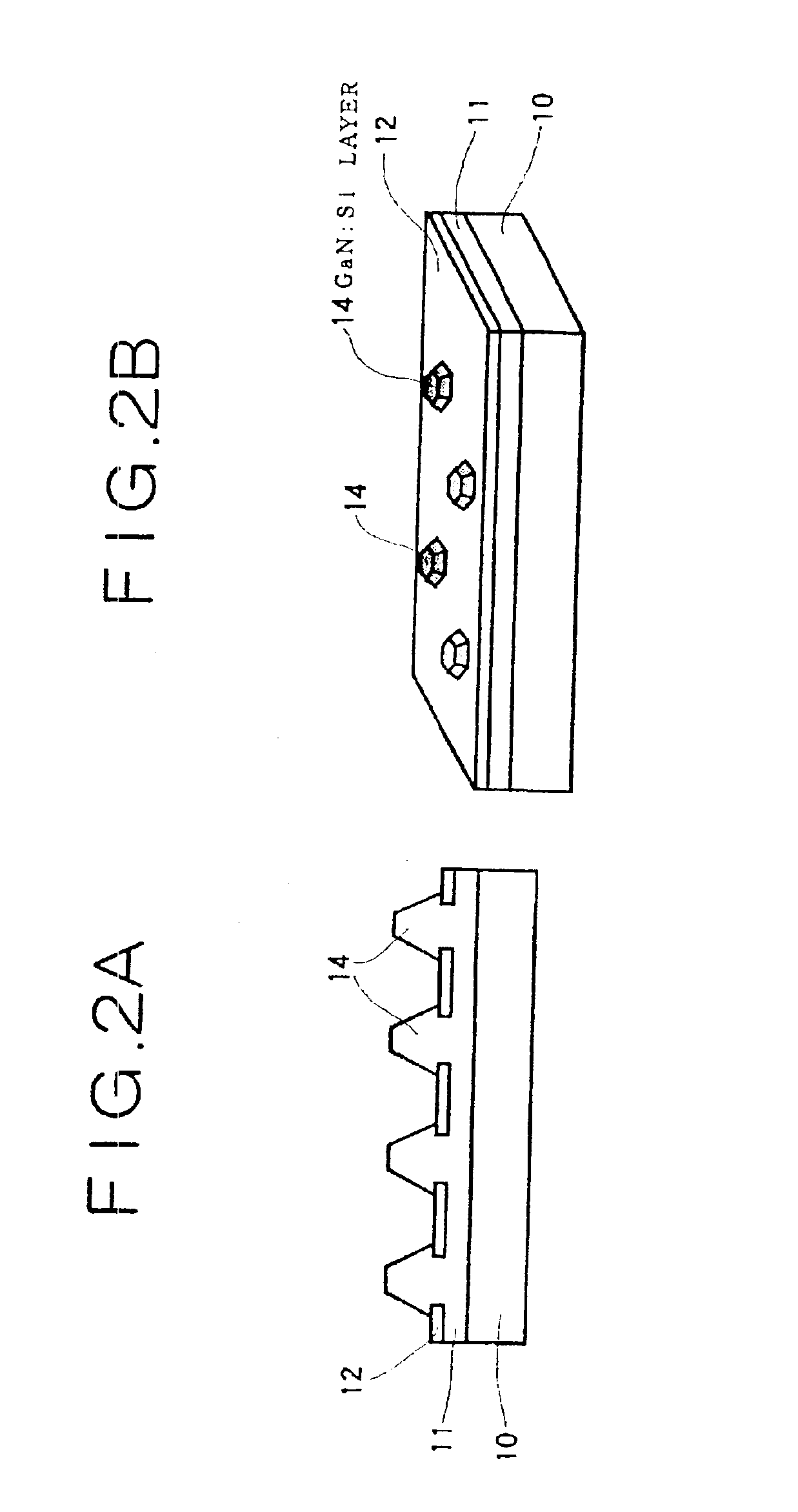
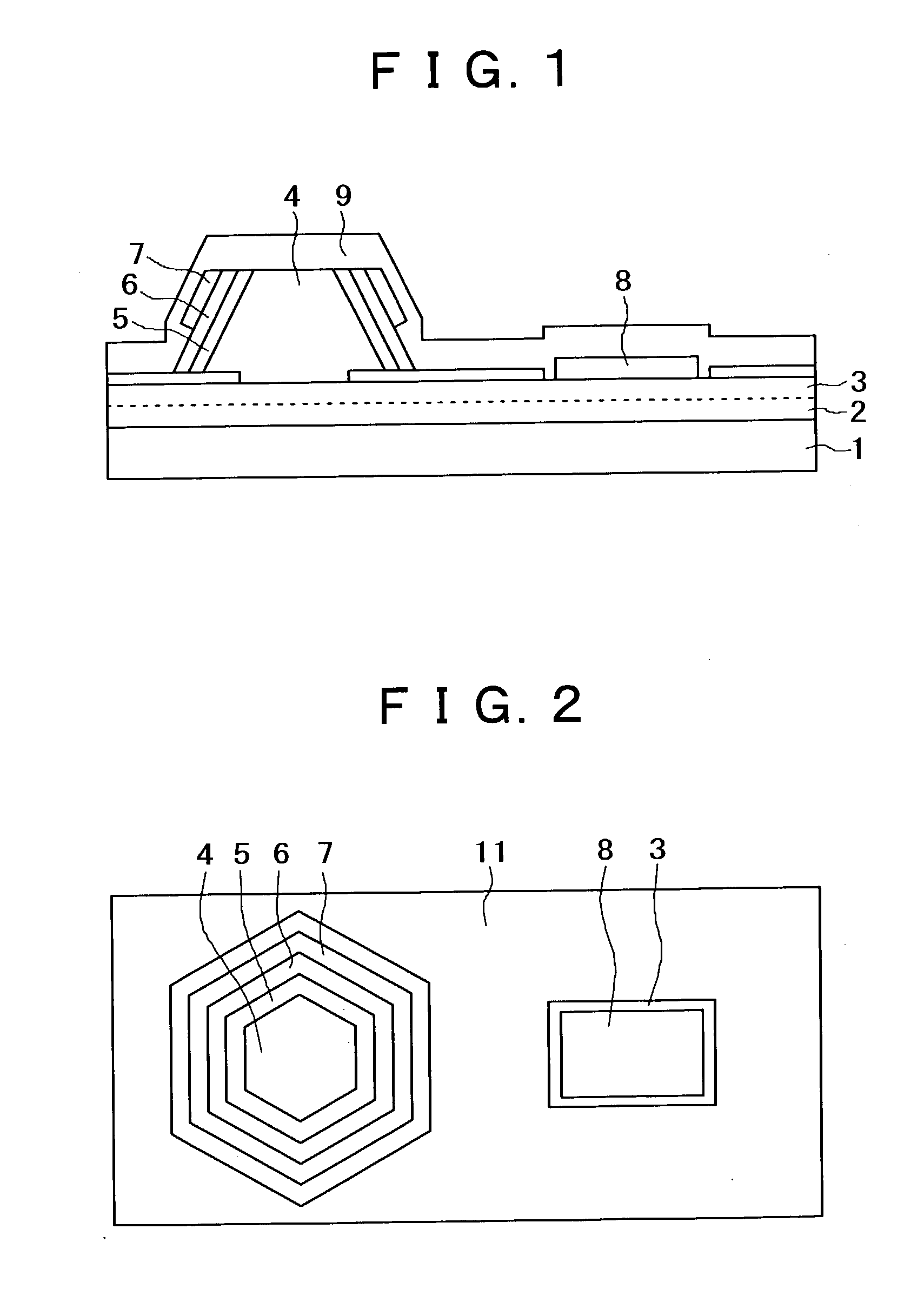
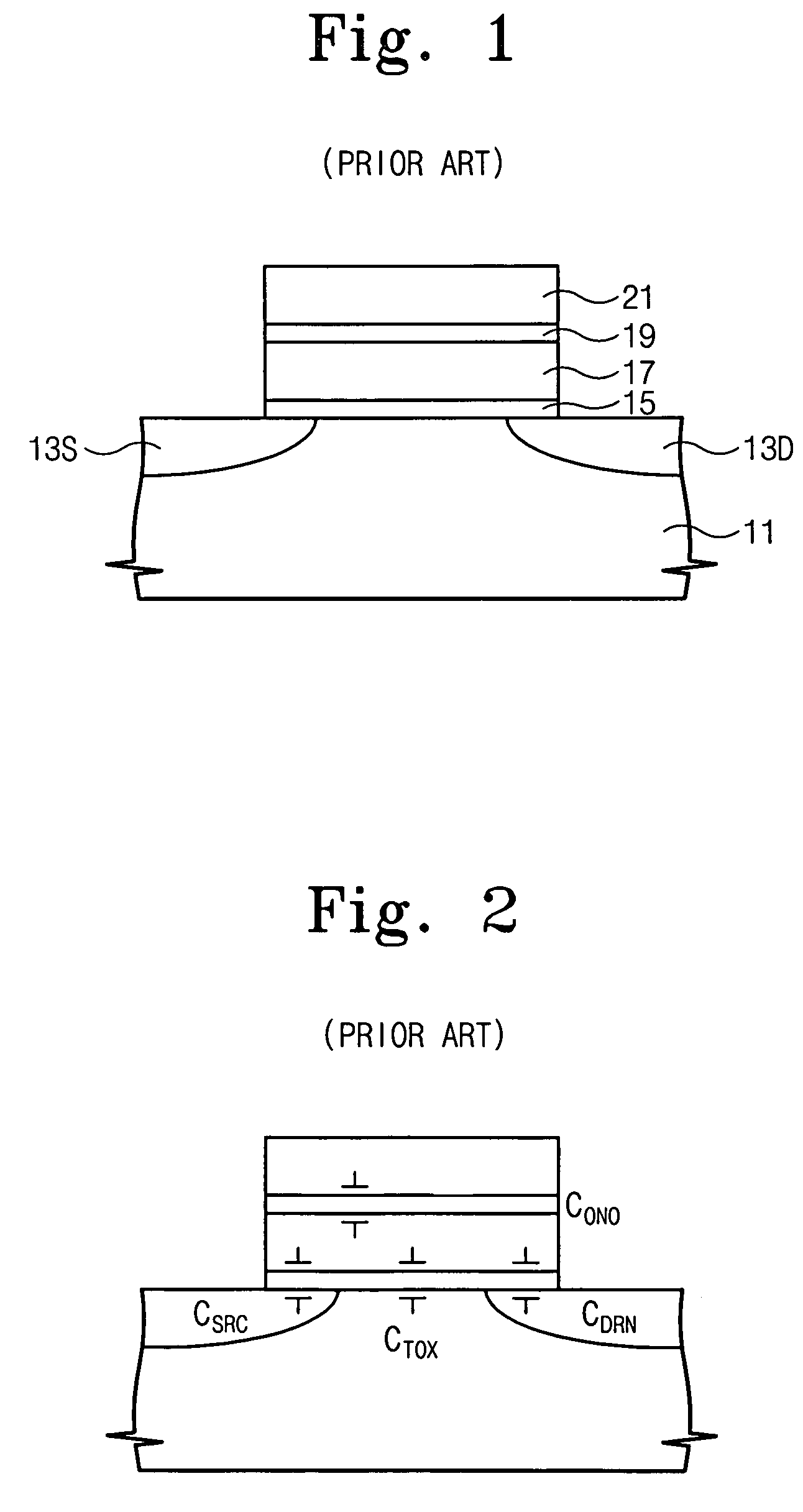
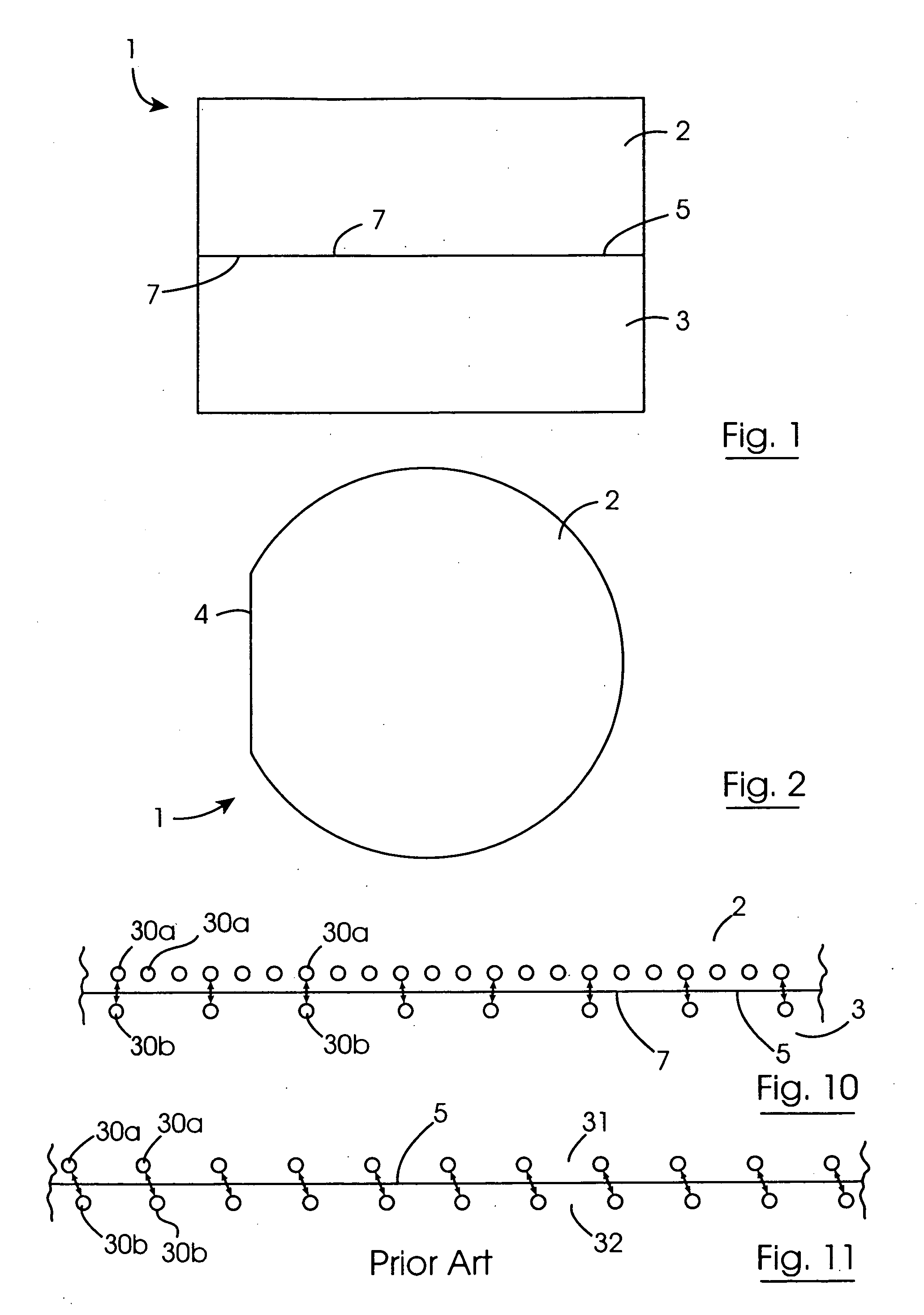
Semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS7087932B2Well formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal planeCrystallinity
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS6967353B2Improve luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal planeActive layer
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a crystal layer formed on a substrate, the crystal layer having a tilt crystal plane tilted from the principal plane of the substrate, and a first conductive type layer, an active layer, and a second conductive type layer, which are formed on the crystal layer in such a manner as to extend within planes parallel to the tilt crystal plane, wherein the device has a shape formed by removing the apex and its vicinity of the stacked layer structure formed on the substrate. Such a semiconductor light emitting device is excellent in luminous efficiency even if the device has a three-dimensional device structure. The present invention also provides a method of fabricating the above semiconductor light emitting device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flash memory device using semiconductor fin and method thereof
ActiveUS20060044915A1Improve scalabilityProgramming and erasing efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling ratioEngineering
A flash memory device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor fin including a top surface and a side surface originated from different crystal planes. The flash memory device comprises: insulating layers having different thicknesses formed on a side surface and a top surface of the semiconductor fin, a storage electrode, a gate insulating layer and a control gate electrode sequentially formed on the insulating layers. A thin insulating layer enables charges to be injected or emitted through it, and a thick insulating layer increases a coupling ratio. Accordingly, it is possible to increase an efficiency of a programming or an erase operation of a flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
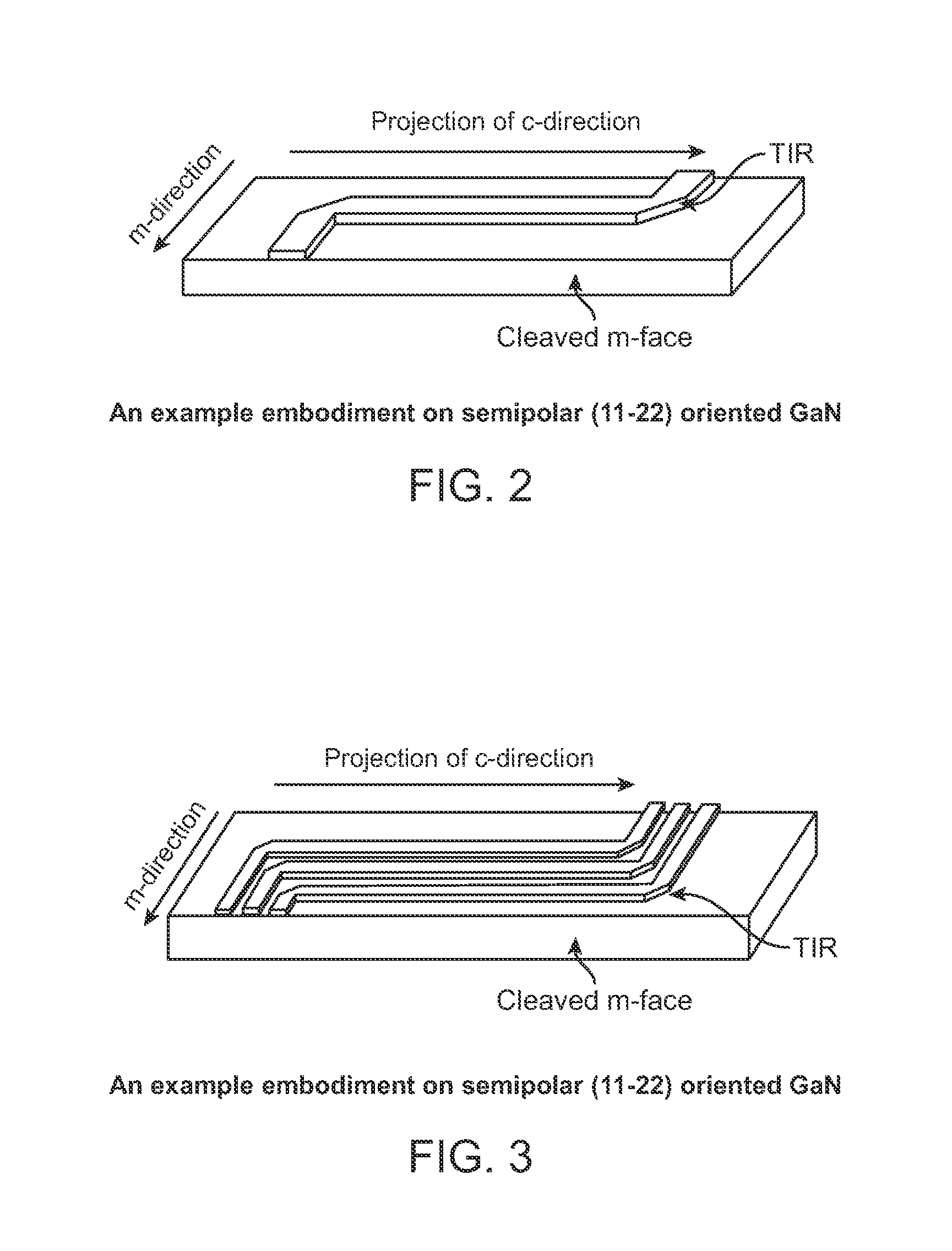
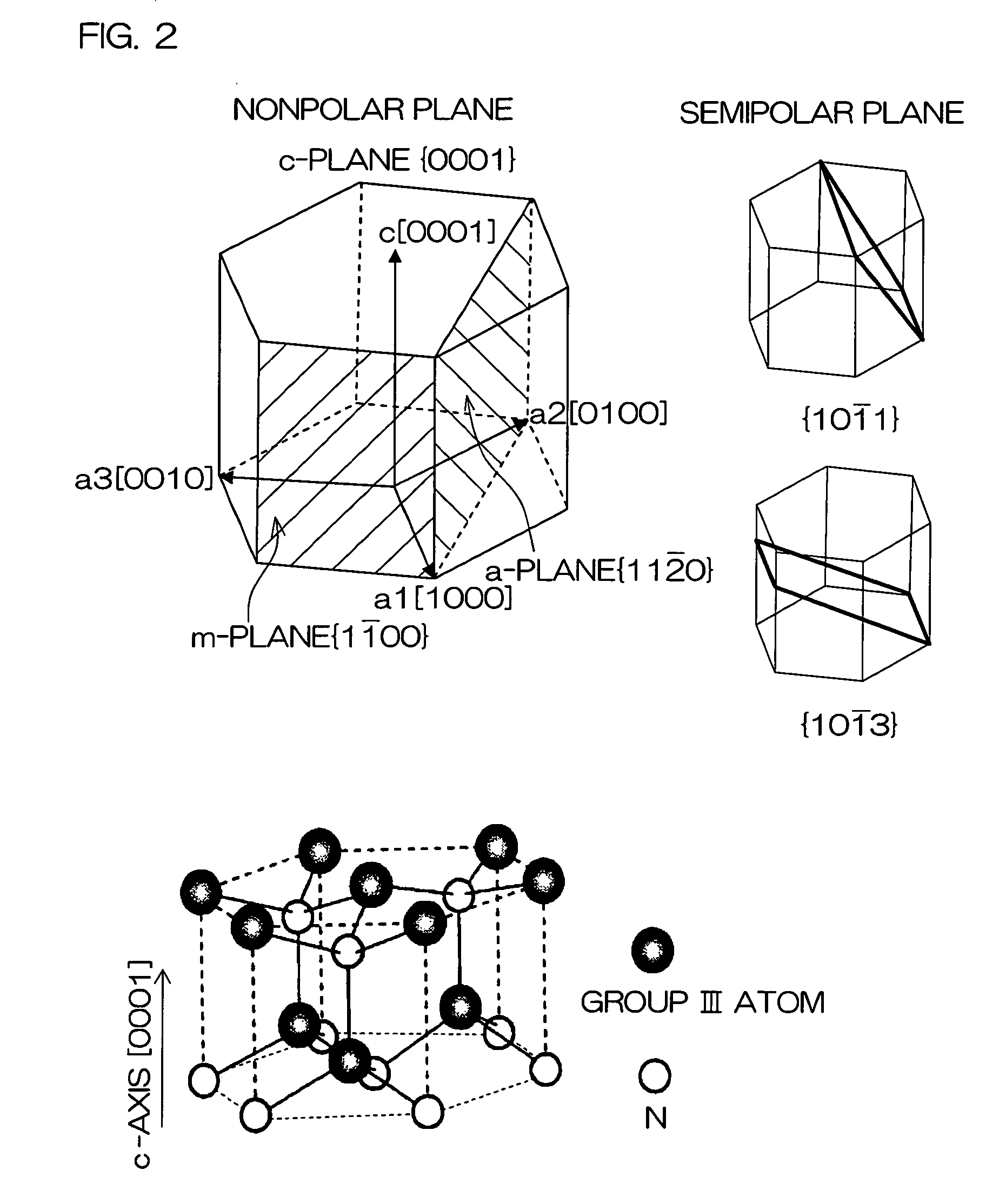
Semi-polar iii-nitride optoelectronic devices on m-plane substrates with miscuts less than +/-15 degrees in the c-direction
ActiveUS20110216795A1QCSE induced dependentIncrease oscillator strengthOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCrystal planeNitride
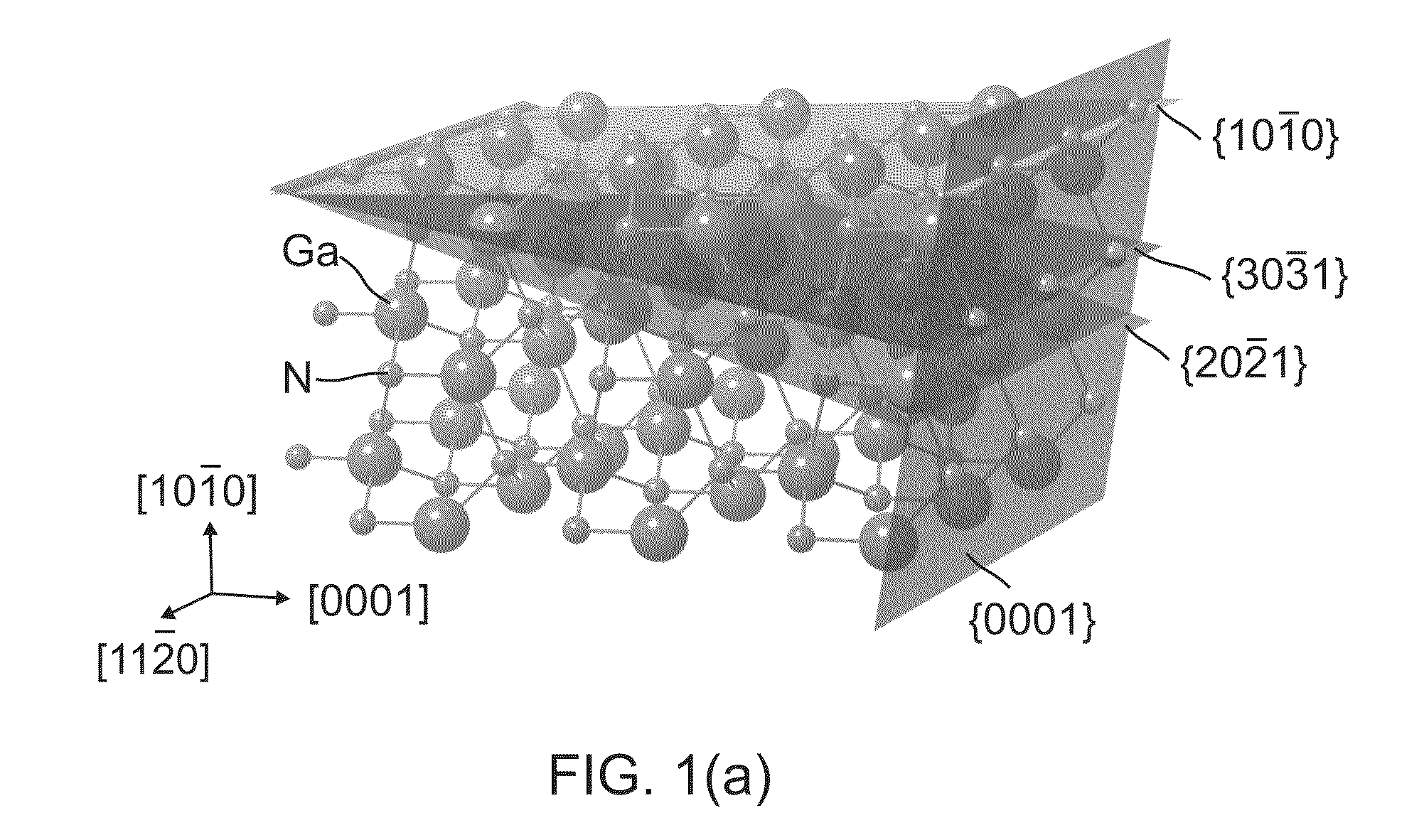
An optoelectronic device grown on a miscut of GaN, wherein the miscut comprises a semi-polar GaN crystal plane (of the GaN) miscut x degrees from an m-plane of the GaN and in a c-direction of the GaN, where −15<x<−1 and 1<x<15 degrees.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
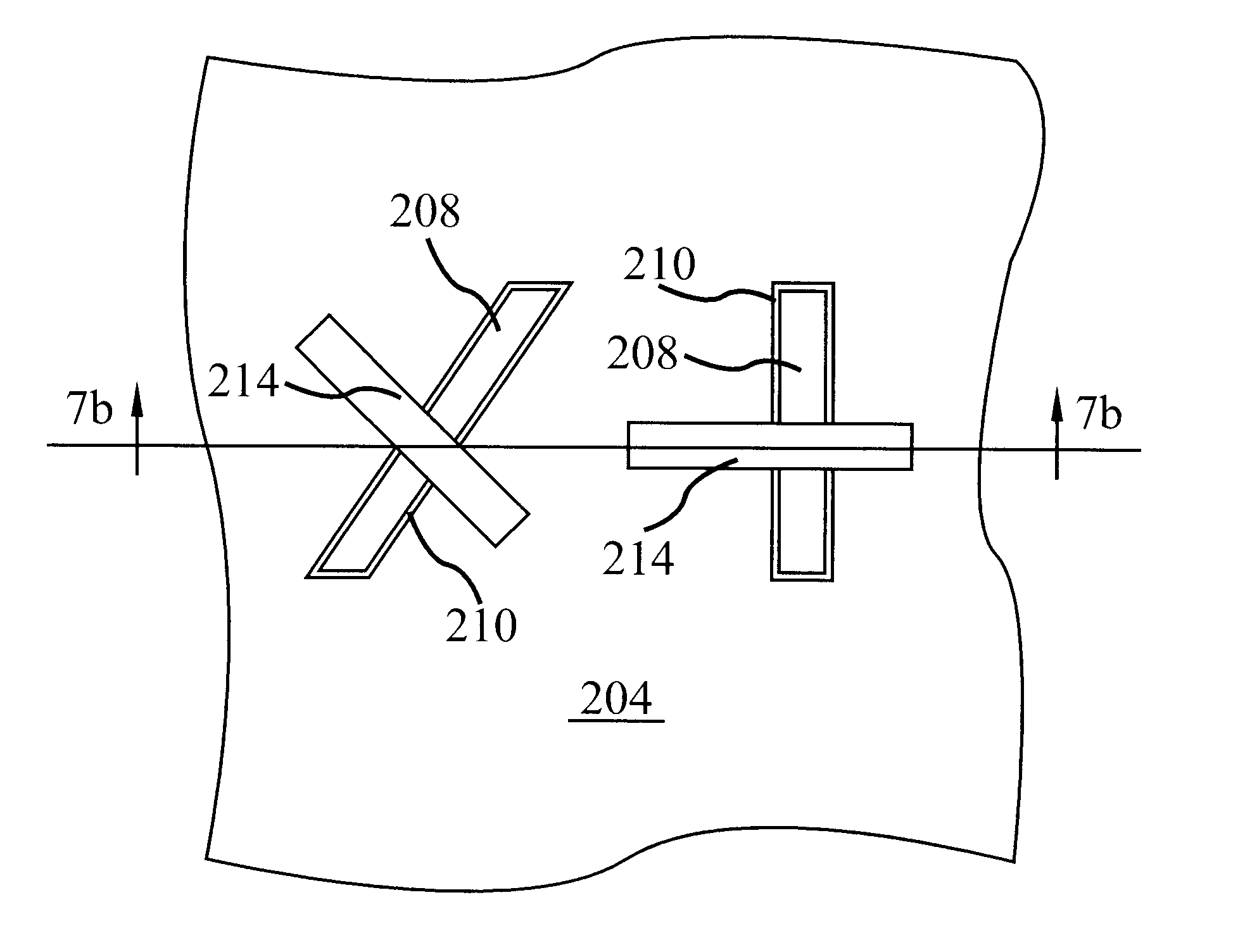
SRAM layout for relaxing mechanical stress in shallow trench isolation technology and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6117722ARelieve pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCrystal plane
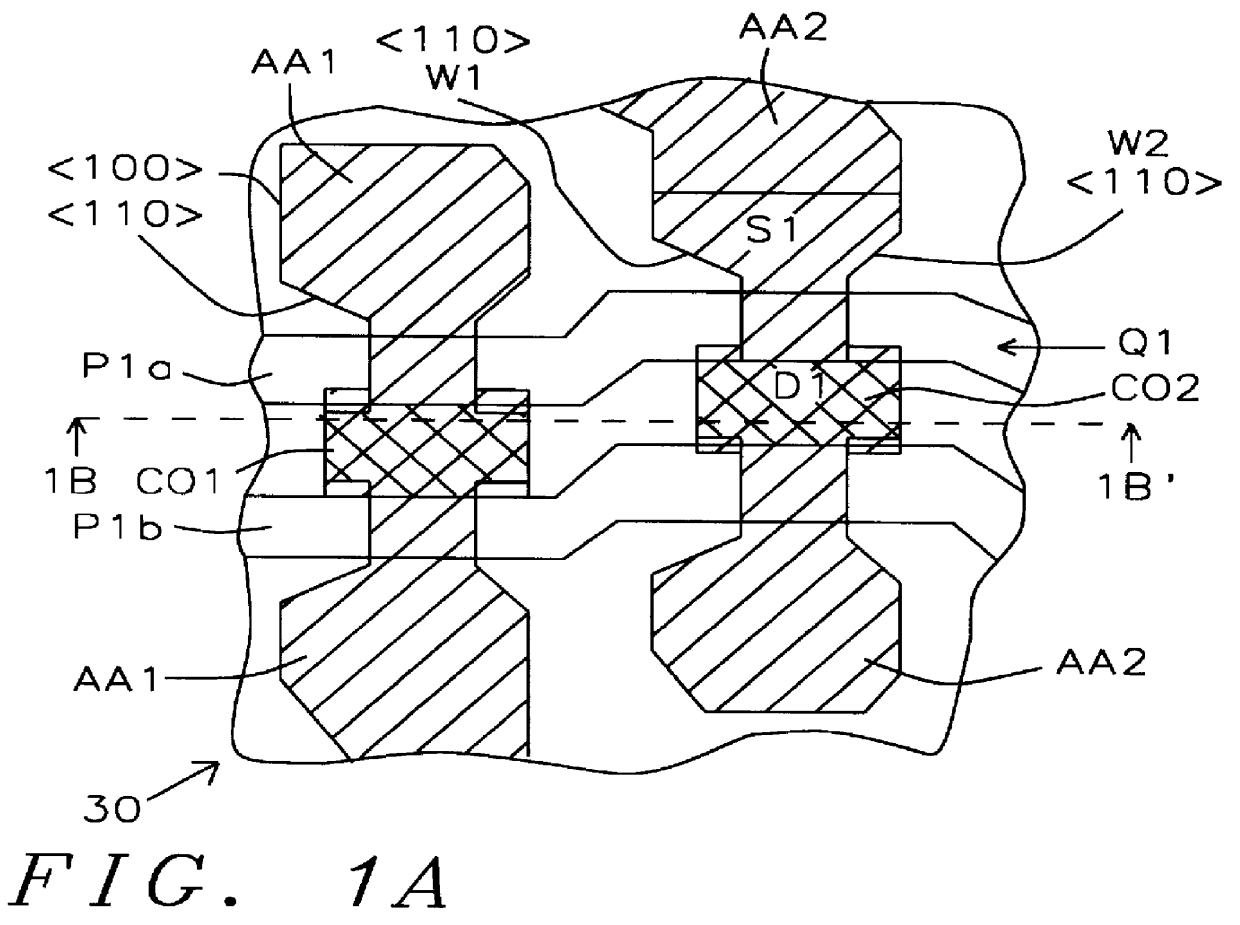
An SRAM device has STI regions separated by mesas and doped regions including source / drain regions, active areas, wordline conductors and contacts in a semiconductor substrate is made with a source region has 90 DEG transitions in critical locations. Form a dielectric layer above the active areas. Form the wordline conductors above the active areas transverse to the active areas. The source and drain regions of a pass gate transistor are on the opposite sides of a wordline conductor. Form the sidewalls along the <100> crystal plane. Form the contacts extending down through to the dielectric layer to the mesas. Substrate stress is reduced because the large active area region formed in the substrate assures that the contacts are formed on the <100> surfaces of the mesas are in contact with the mesas formed on the substrate and that the <110> surfaces of the silicon of the mesas are shielded from the contacts.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Flash memory device using semiconductor fin and method thereof
ActiveUS7285820B2Improve scalabilityProgramming and erasing efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesCoupling ratioCrystal plane
A flash memory device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor fin including a top surface and a side surface originated from different crystal planes. The flash memory device comprises: insulating layers having different thicknesses formed on a side surface and a top surface of the semiconductor fin, a storage electrode, a gate insulating layer and a control gate electrode sequentially formed on the insulating layers. A thin insulating layer enables charges to be injected or emitted through it, and a thick insulating layer increases a coupling ratio. Accordingly, it is possible to increase an efficiency of a programming or an erase operation of a flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting diode element and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20090159870A1Reduce probabilityFacilitate light extractionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTotal internal reflectionCrystal plane
The present invention discloses a light emitting diode (LED) element and a method for fabricating the same, which can promote light extraction efficiency of LED, wherein a substrate is etched to obtain basins with inclined natural crystal planes, and an LED epitaxial structure is selectively formed inside the basin. Thereby, an LED element having several inclines is obtained. Via the inclines, the probability of total internal reflection is reduced, and the light extraction efficiency of LED is promoted.
Owner:TEKCORE CO LTD
Perovskite-based thin film structures on miscut semiconductor substrates
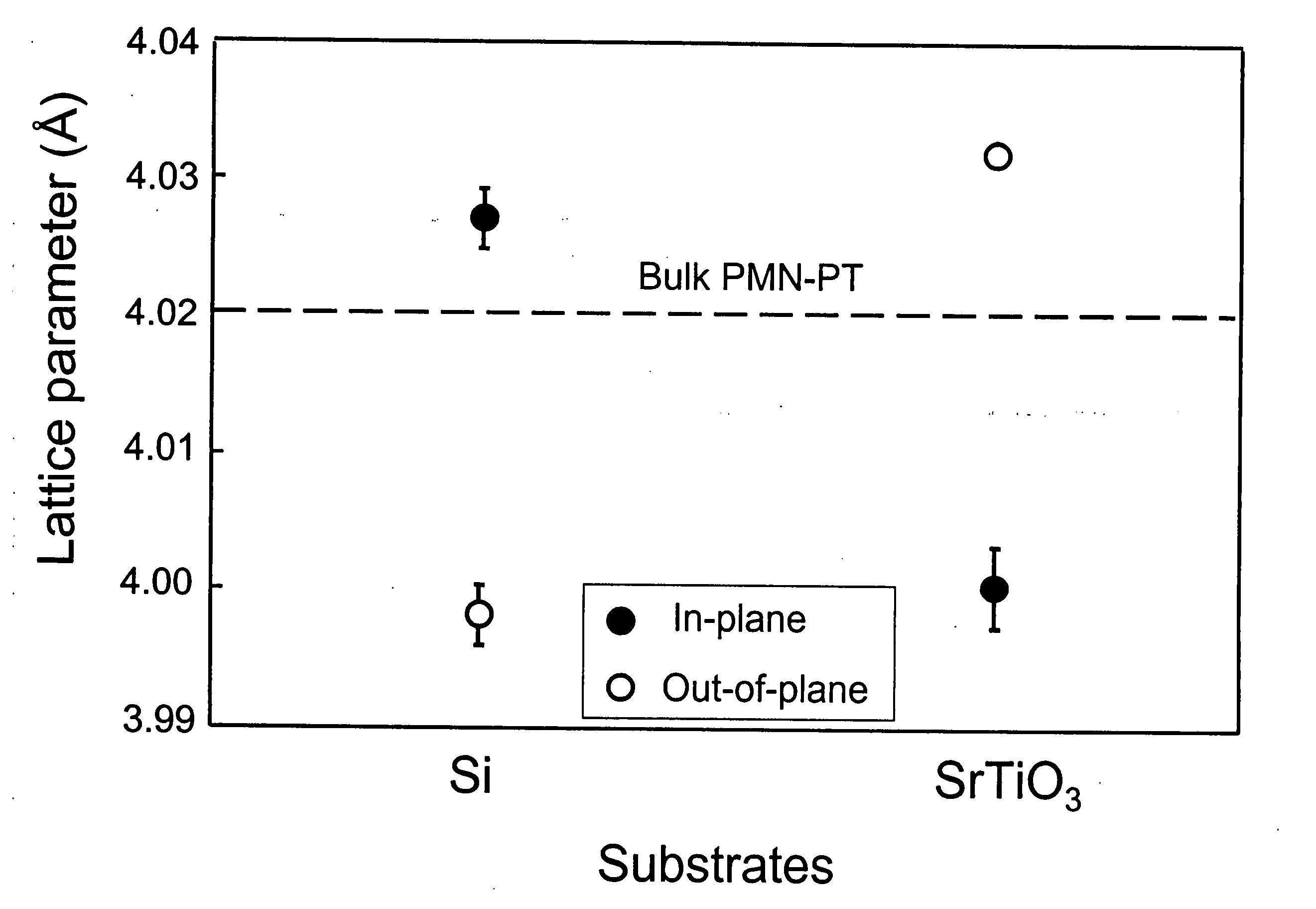
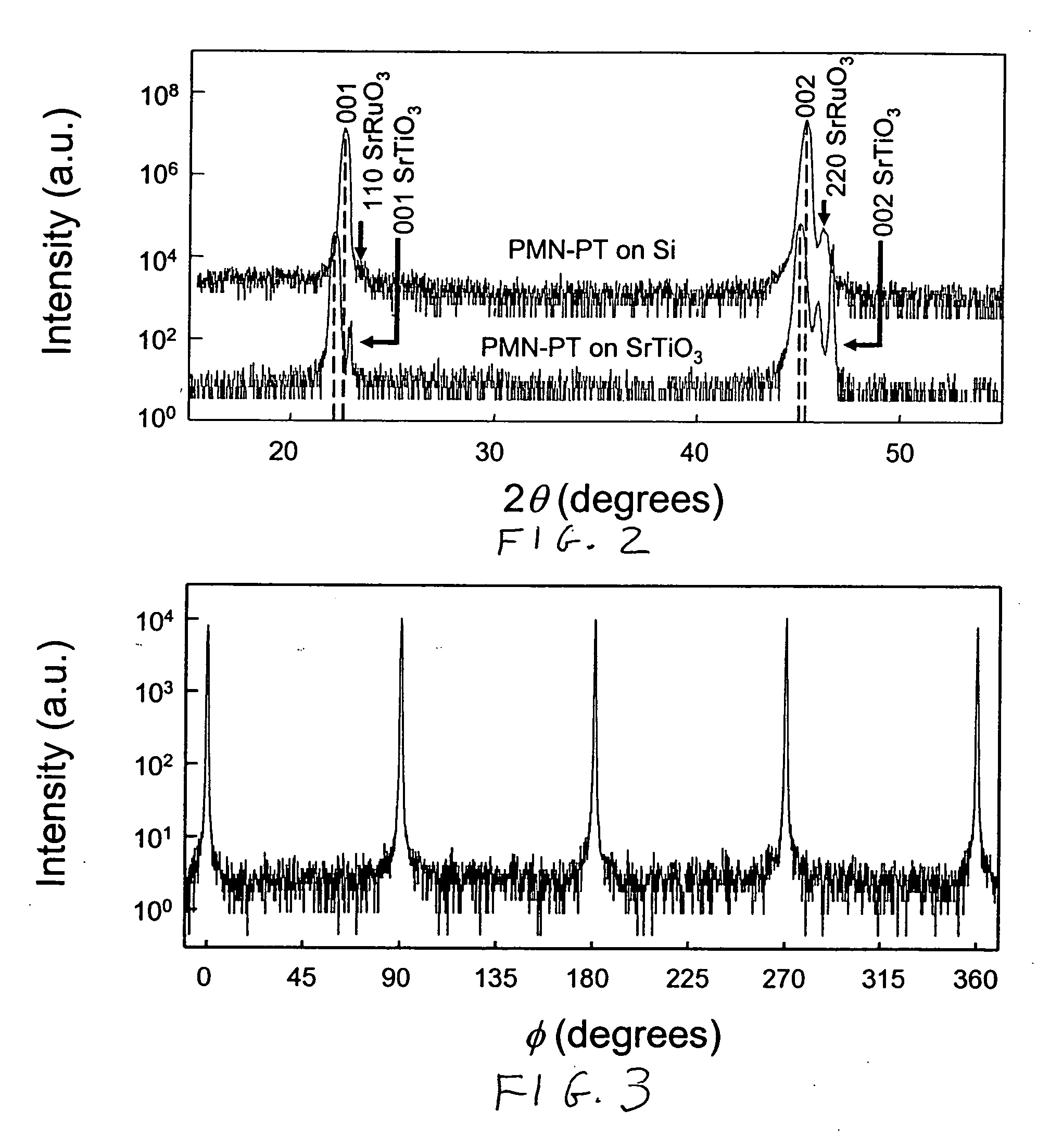
InactiveUS20060288928A1Quality improvementGood metallic behaviorPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesCrystal structureCrystal plane
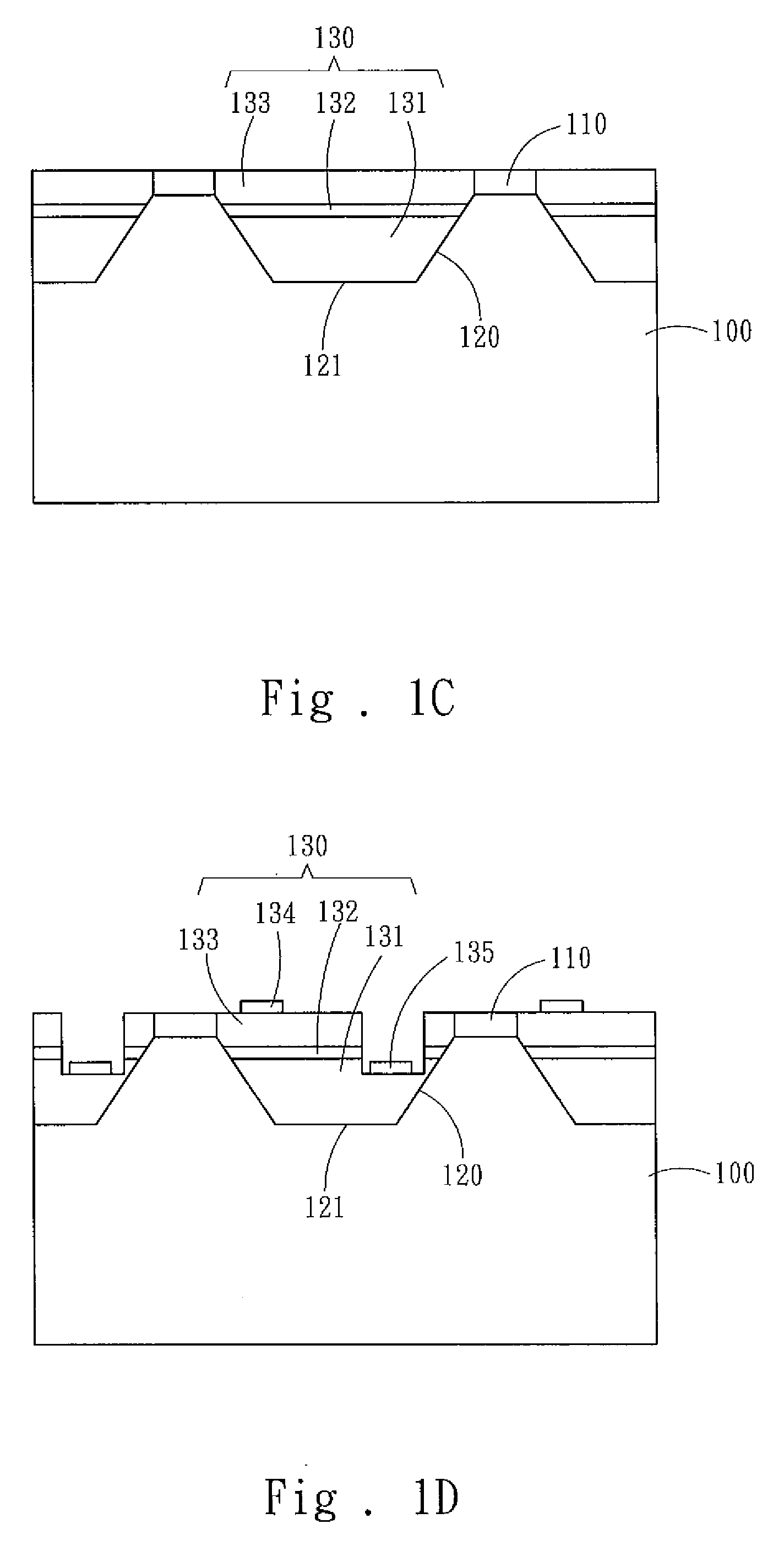
A perovskite-based thin film structure includes a semiconductor substrate layer, such as a crystalline silicon layer, having a top surface cut at an angle to the (001) crystal plane of the crystalline silicon. A perovskite seed layer is epitaxially grown on the top surface of the substrate layer. An overlayer of perovskite material is epitaxially grown above the seed layer. In some embodiments the perovskite overlayer is a piezoelectric layer grown to a thickness of at least 0.5 μm and having a substantially pure perovskite crystal structure, preferably substantially free of pyrochlore phase, resulting in large improvements in piezoelectric characteristics as compared to conventional thin film piezoelectric materials.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
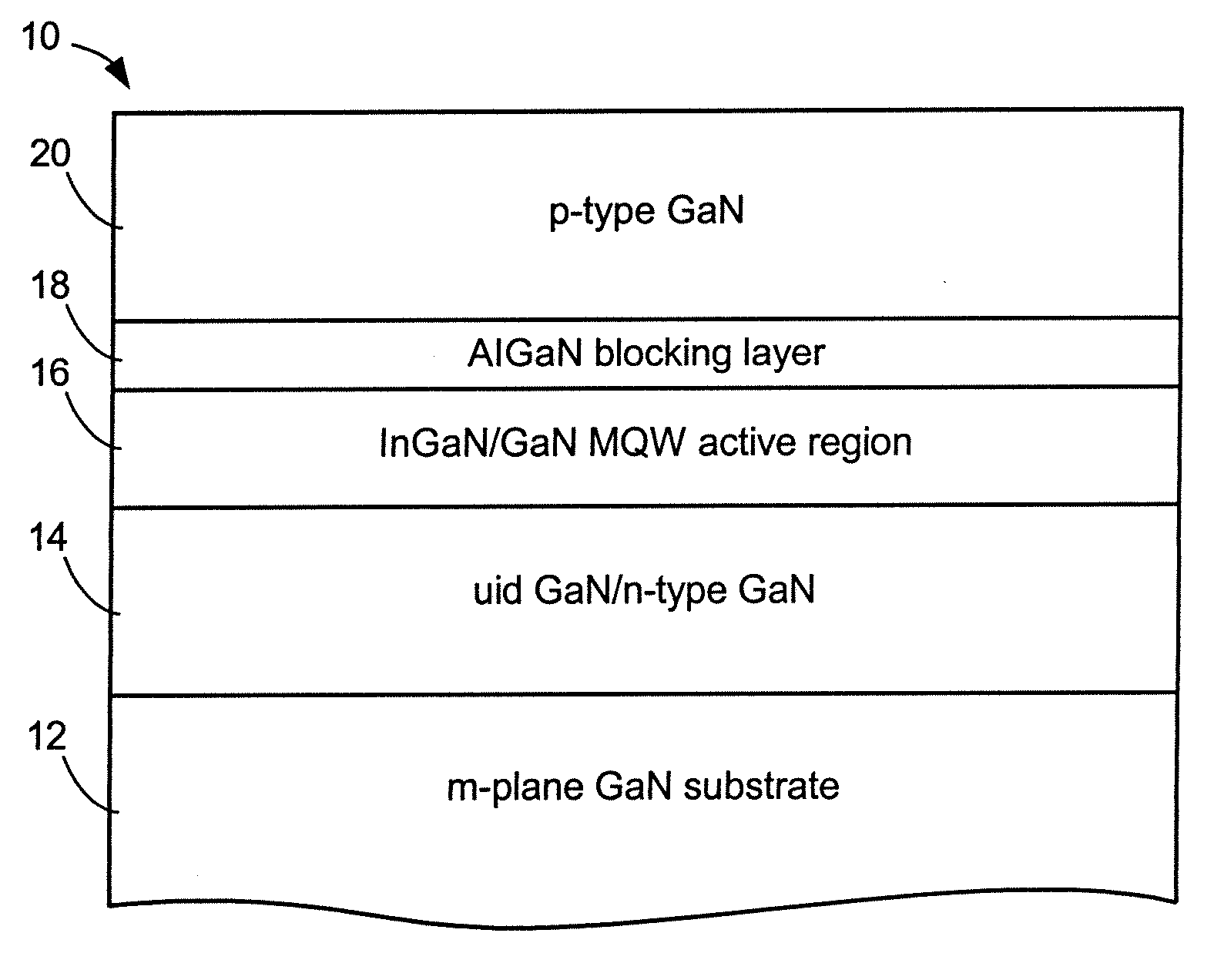
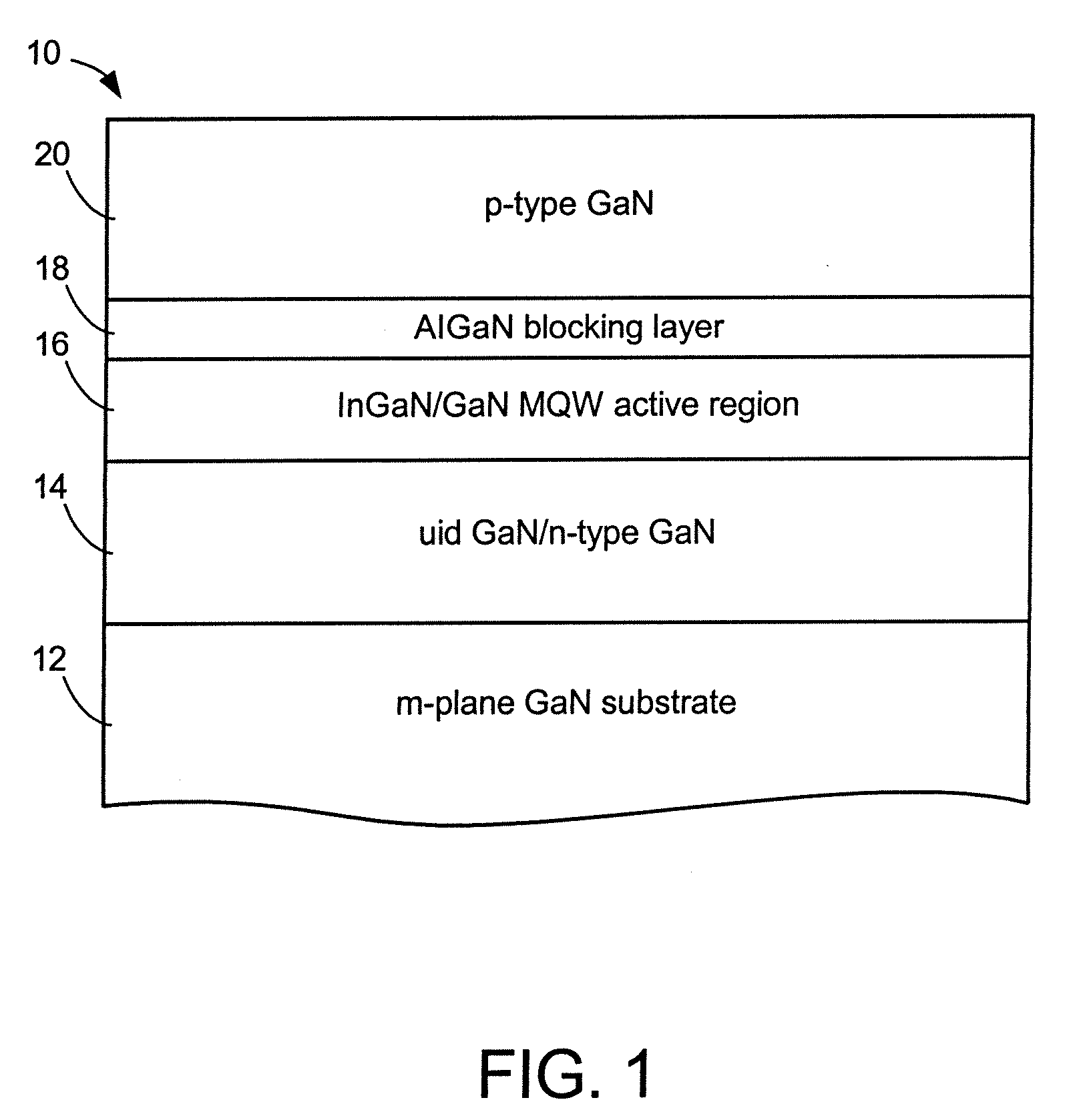
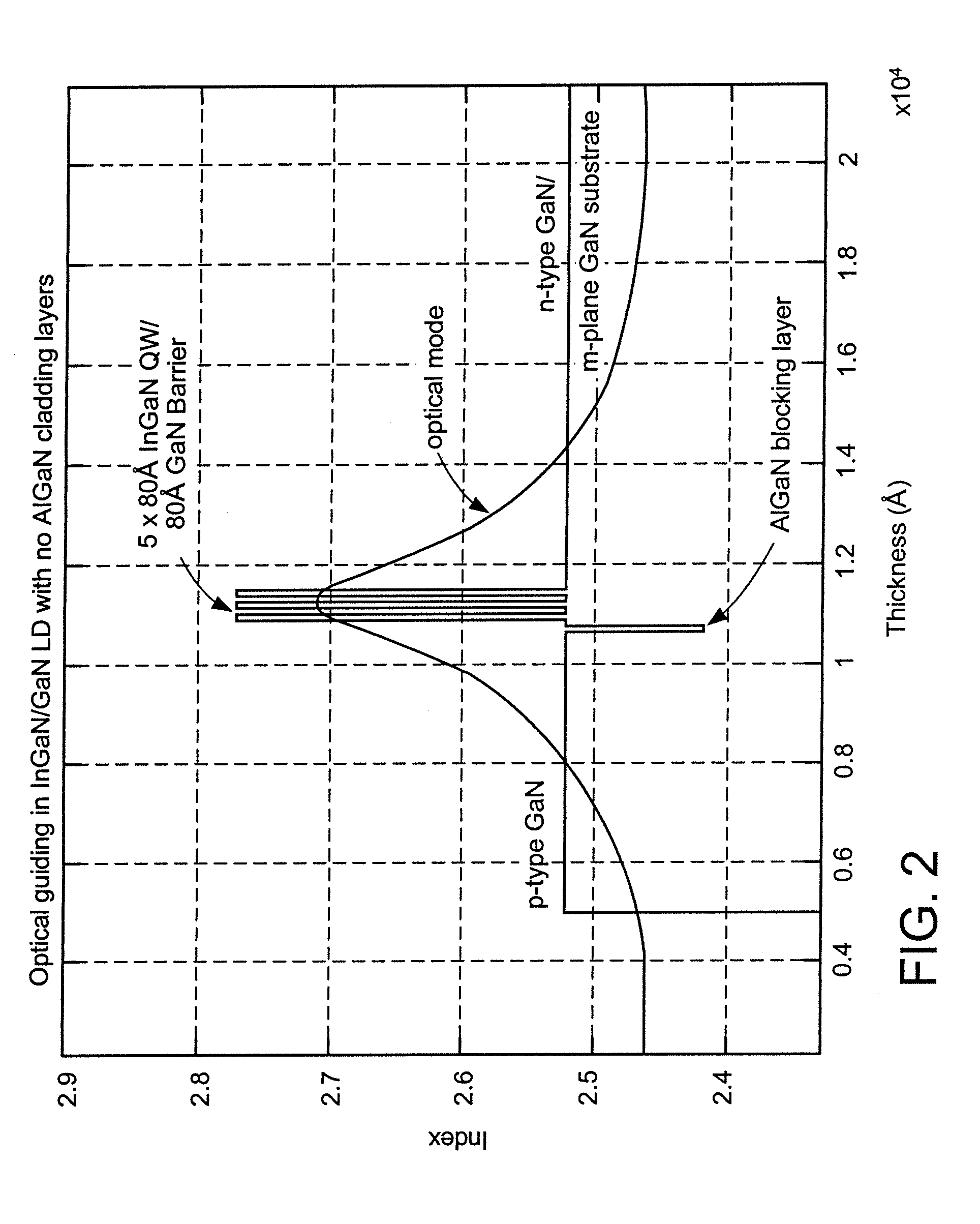
Al(x)Ga(1-x)N-CLADDING-FREE NONPOLAR III-NITRIDE BASED LASER DIODES AND LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
ActiveUS20080191192A1Effective limitSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsQuantum wellCrystal plane
A method for fabricating AlxGa1-xN-cladding-free nonpolar III-nitride based laser diodes or light emitting diodes. Due to the absence of polarization fields in the nonpolar crystal planes, these nonpolar devices have thick quantum wells that function as an optical waveguide to effectively confine the optical mode to the active region and eliminate the need for Al-containing waveguide cladding layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
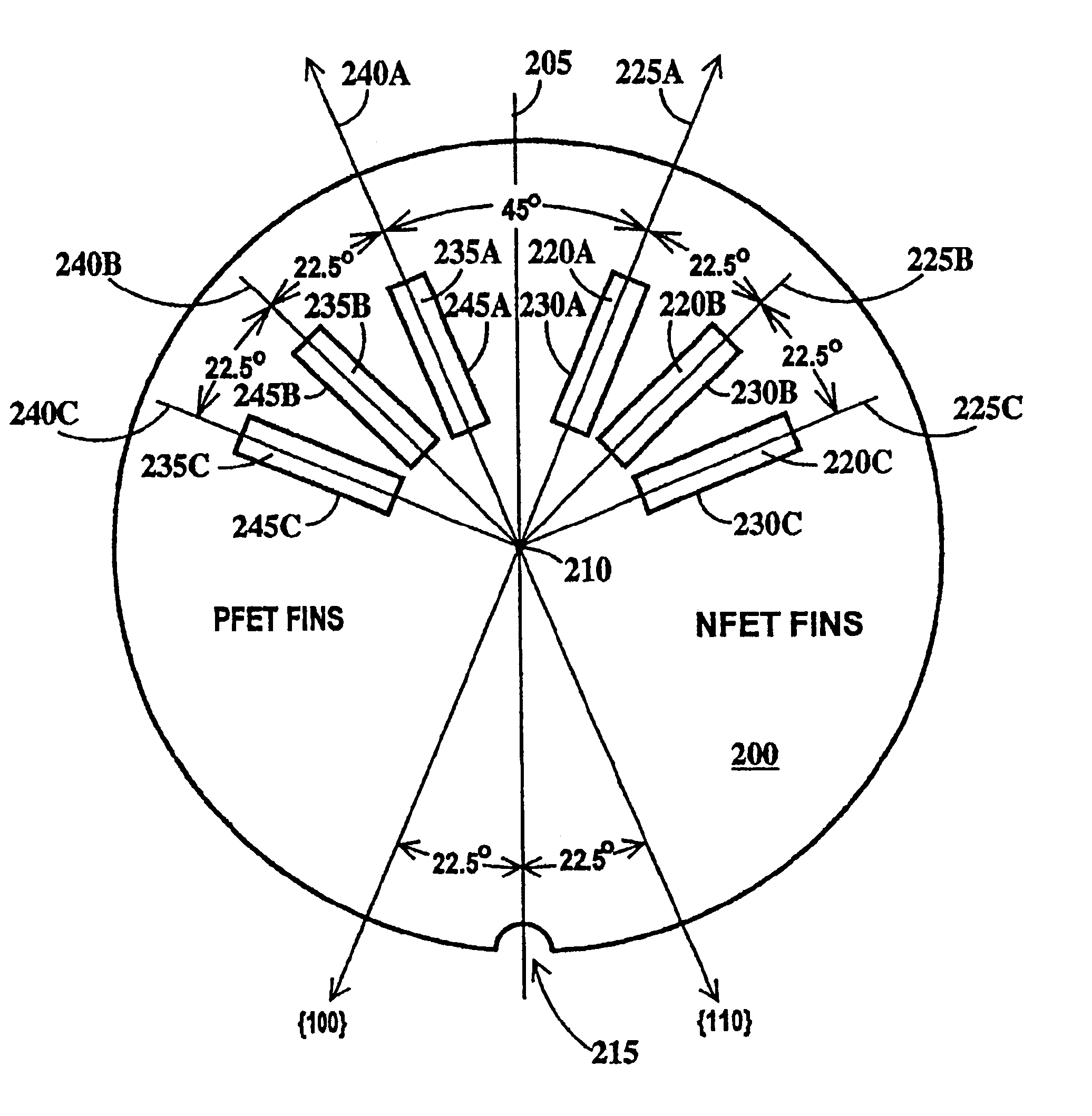
FinFET SRAM cell with chevron FinFET logic
An electronic device, and SRAM and a method of forming the electronic device and SRAM. The semiconductor device including: a pass gate transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a first direction and having a first majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of the fin body; a pull down latch transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a second direction and having a second majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of thc fin body; a pull up latch transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a third direction and having a third majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of the fin body; and CMOS chevron logic circuits, wherein crystal planes of each fin body and of CMOS transistor of the chevron logic are co-aligned.
Owner:IBM CORP
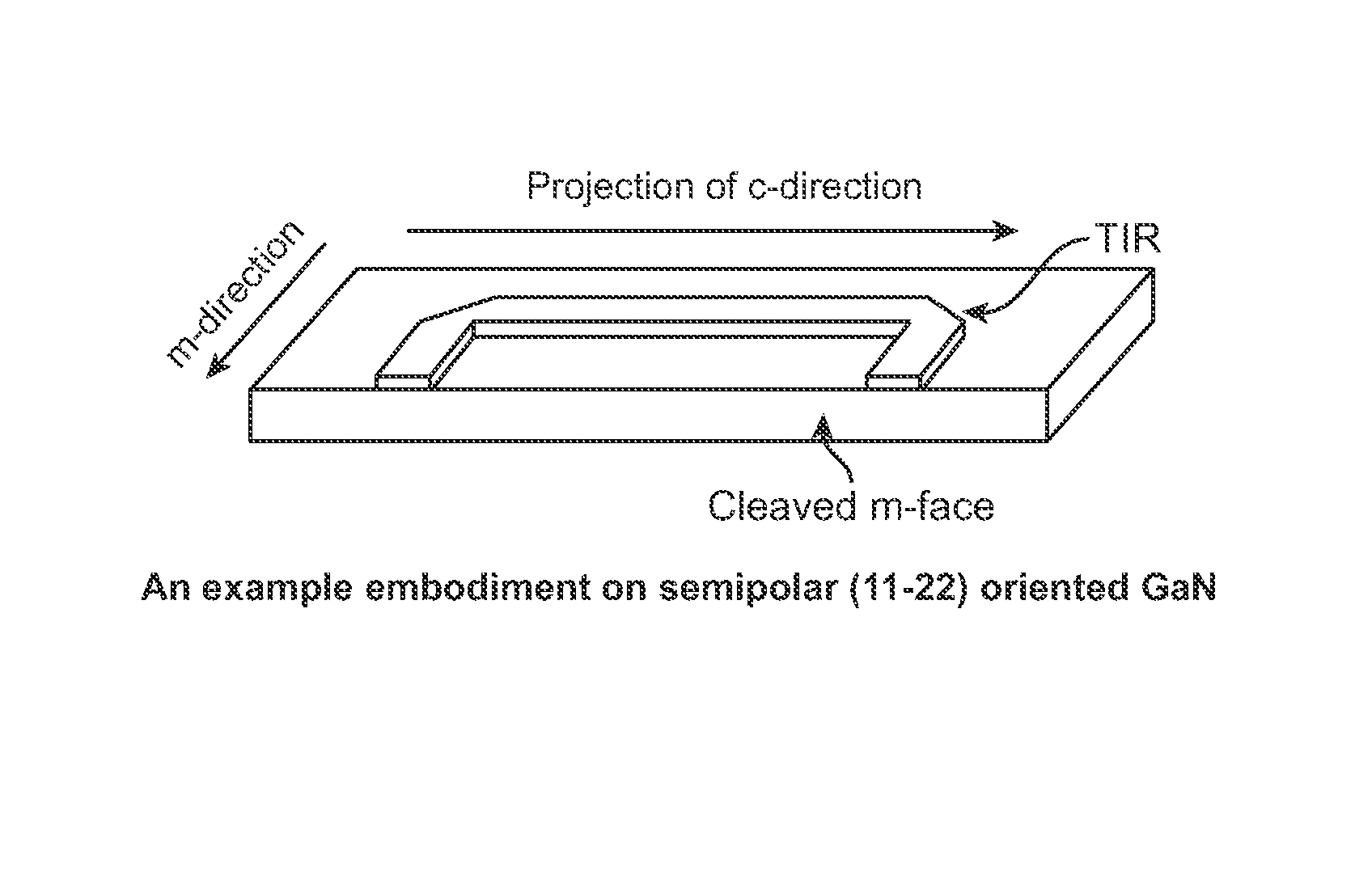
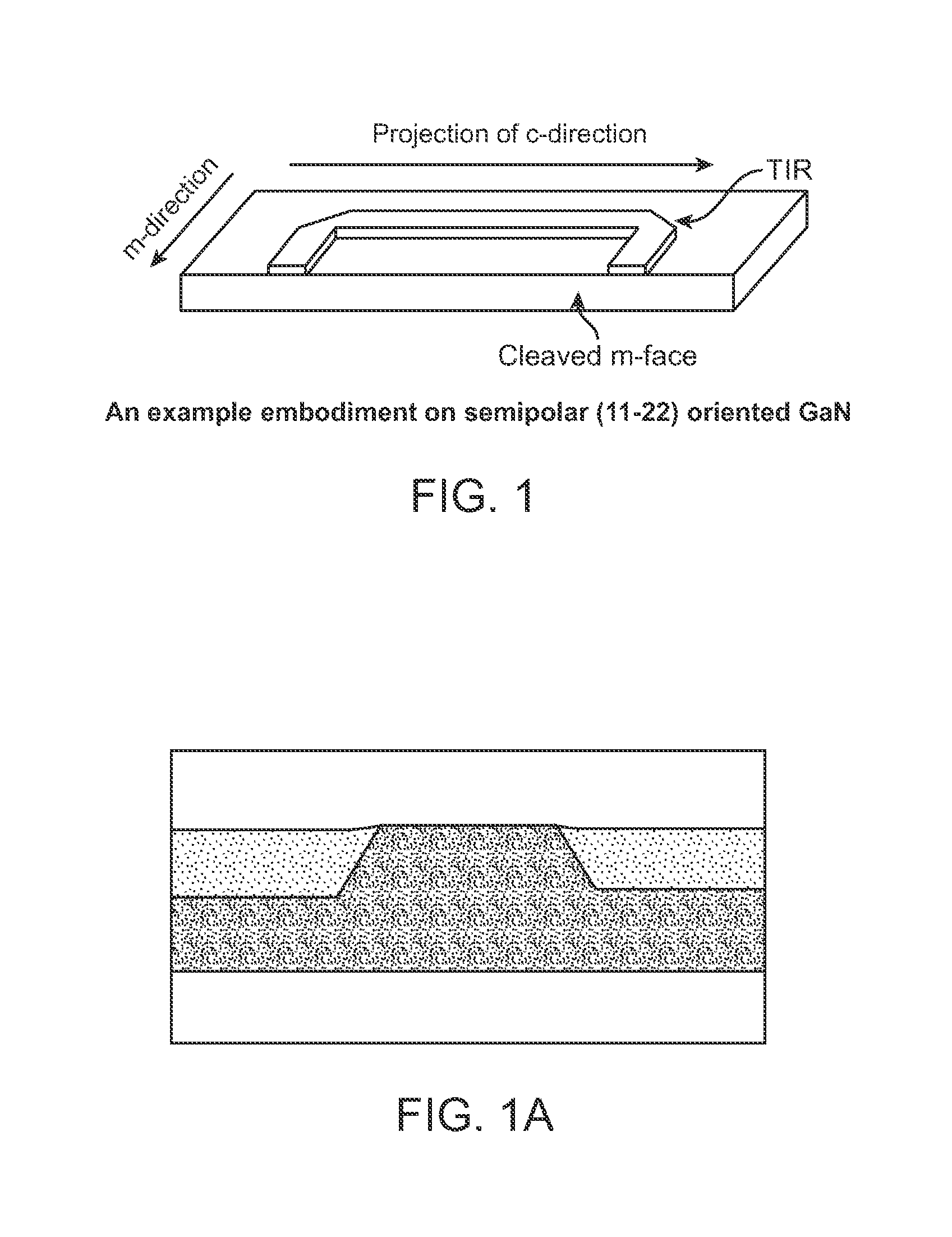
Integrated total internal reflectors for high-gain laser diodes with high quality cleaved facets on nonpolar/semipolar GaN substrates
ActiveUS8259769B1High yieldWell formedOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionTotal internal reflectionCrystal plane
A laser diode device operable at a one or more wavelength ranges. The device has a first waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first gain characteristic and a first direction. In a specific embodiment, the first waveguide has a first end and a second end and a first length defined between the first end and the second end. The device has a second waveguide provided on a non-polar or semipolar crystal plane of gallium containing material. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a second gain characteristic and a second direction. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has a first end, a second end, and a second length defined between the first end and the second end. In a specific embodiment, the second waveguide has the first end being coupled to the first end of the first waveguide. The second length is in a different direction from the second length. In a specific embodiment, the device has a cleaved region provided on the second end of the second waveguide, the cleaved region being perpendicular to the second direction of the second waveguide.
Owner:KAAI +1
Multiple-plane FinFET CMOS
InactiveUS6657259B2Improve mobilityReduced carrier mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSCurrent channel
The present invention provides FinFETs on the same substrate utilizing various crystal planes for FET current channels in order to optimize mobility and / or to reduce mobility. An embodiment of the present invention provides a substrate having a surface oriented on a first crystal plane that enables subsequent crystal planes for channels to be utilized. A first transistor is also provided having a first fin body. The first fin body has a sidewall forming a first channel, the sidewall oriented on a second crystal plane to provide a first carrier mobility. A second transistor is also provided having a second fin body. The second fin body has a sidewall forming a second channel, the sidewall oriented on a third crystal plane to provide a second carrier mobility that is different from the first carrier mobility.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
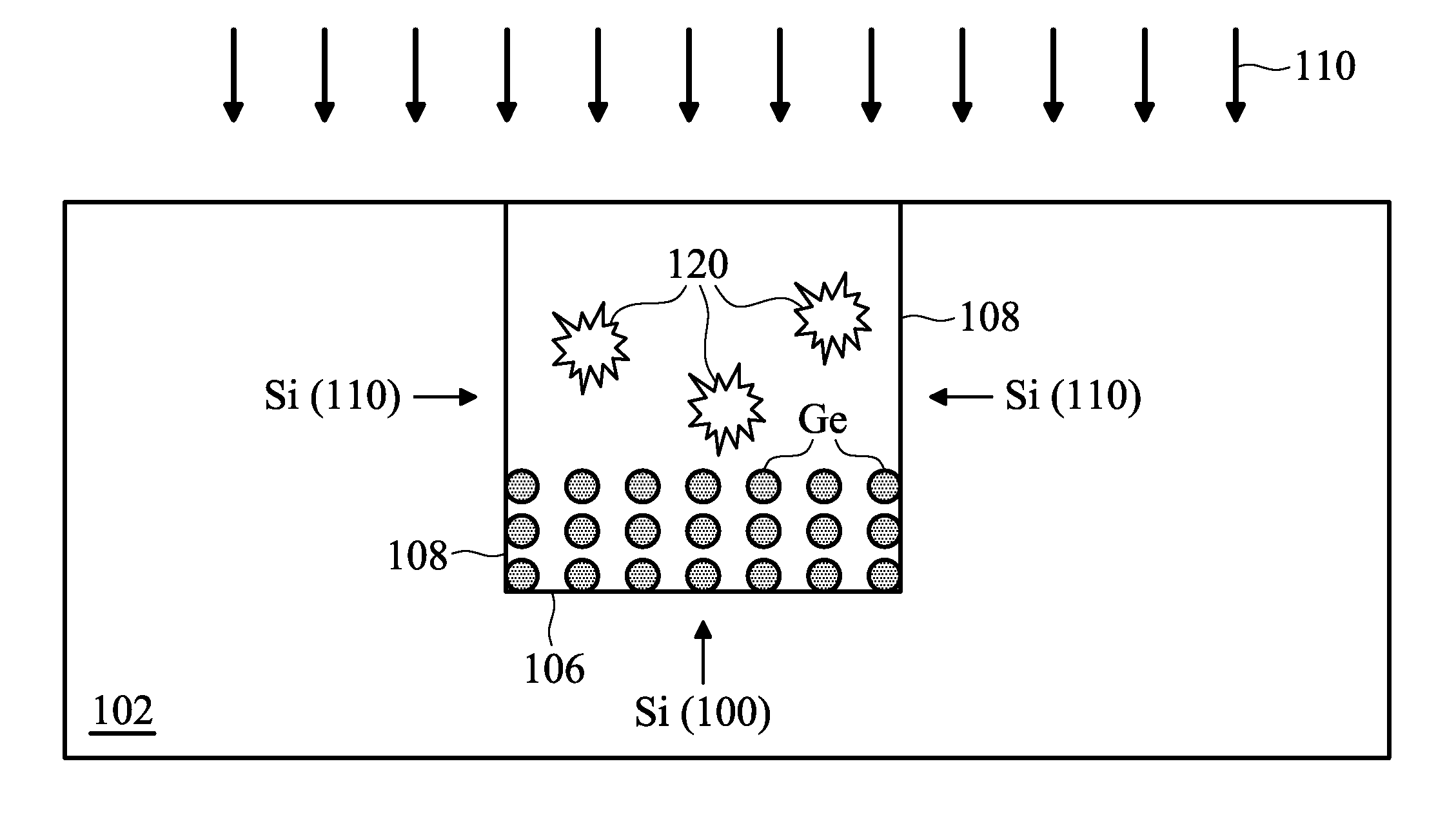
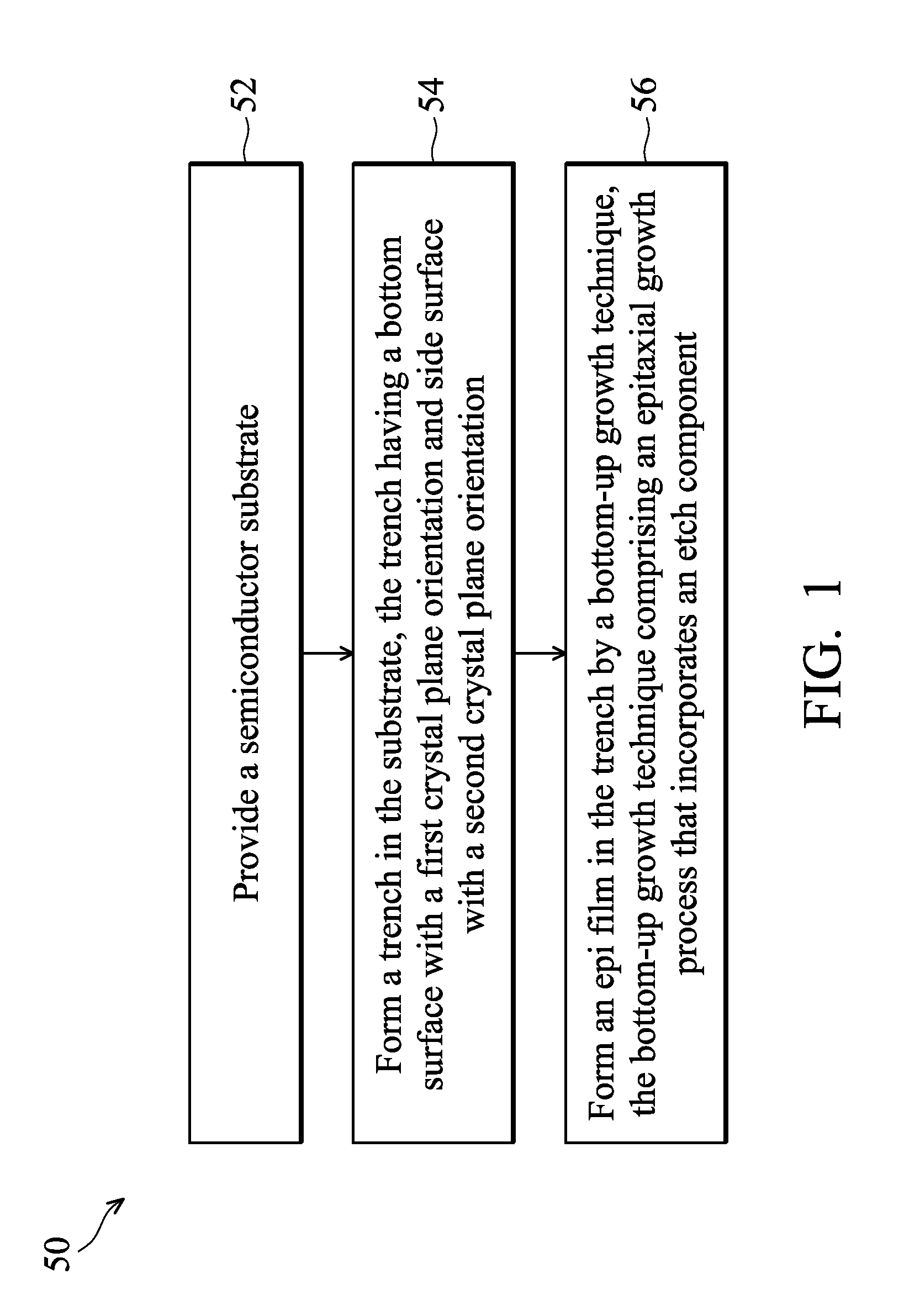
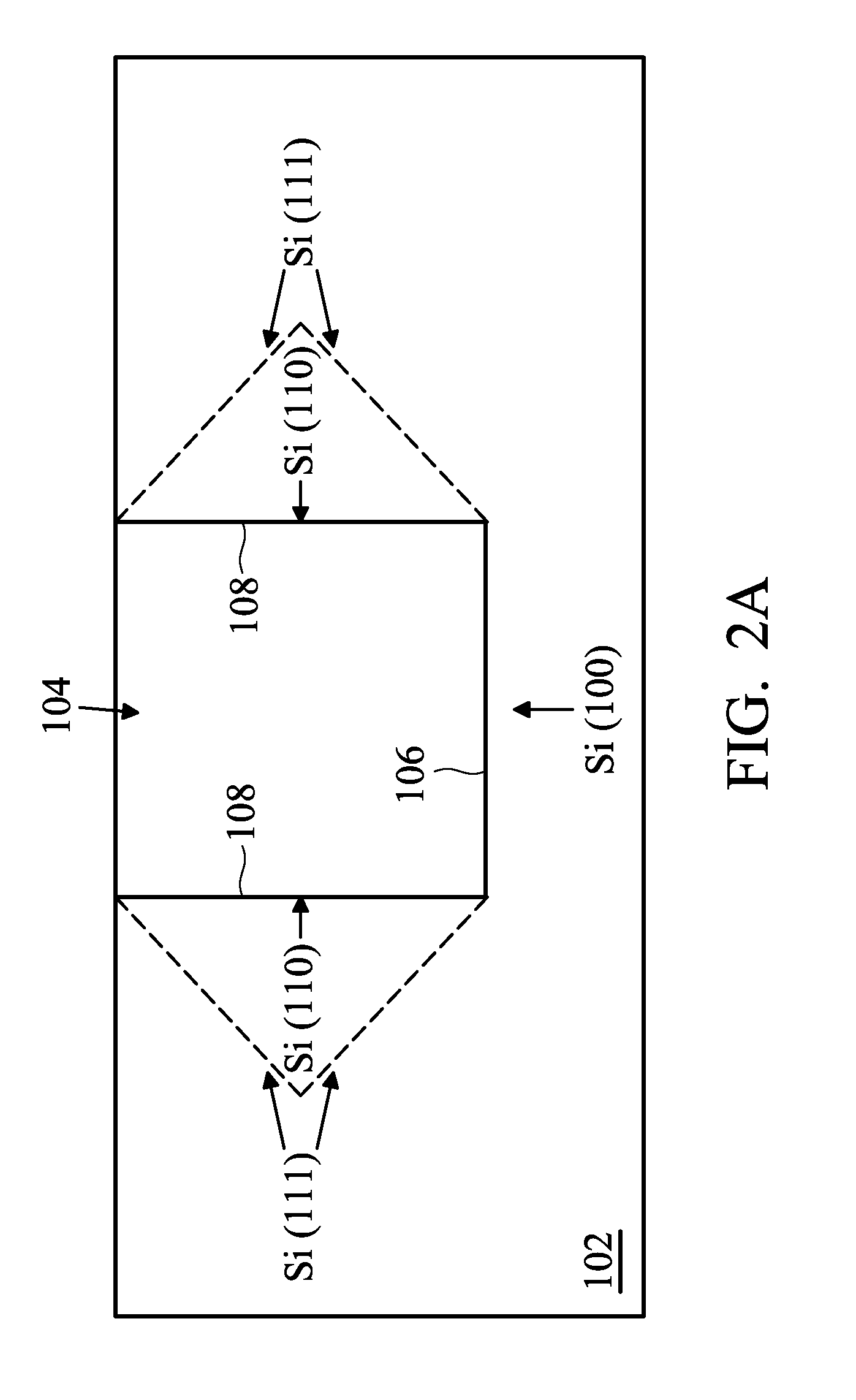
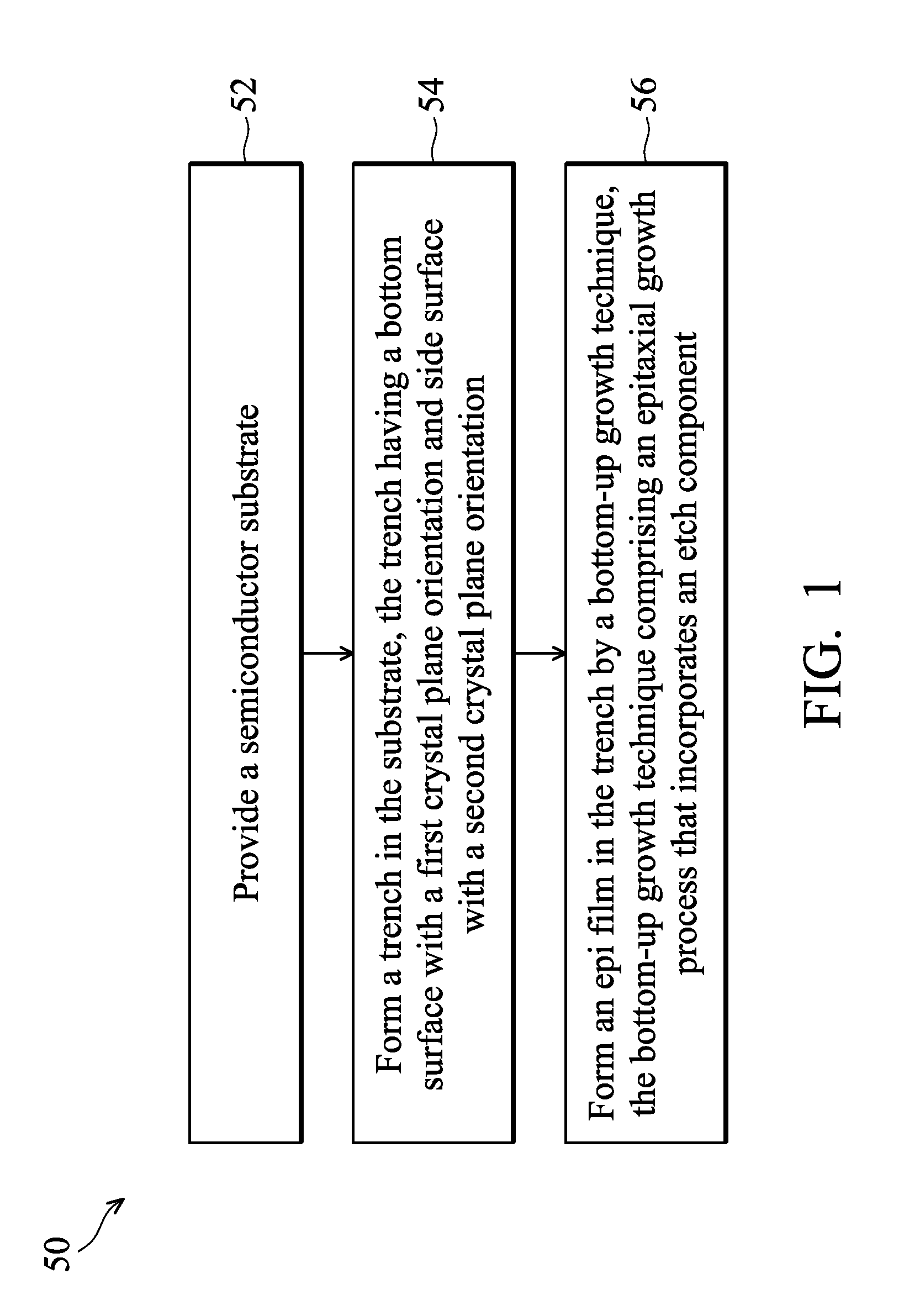
Method of forming epi film in substrate trench
ActiveUS8415718B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCrystal plane
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
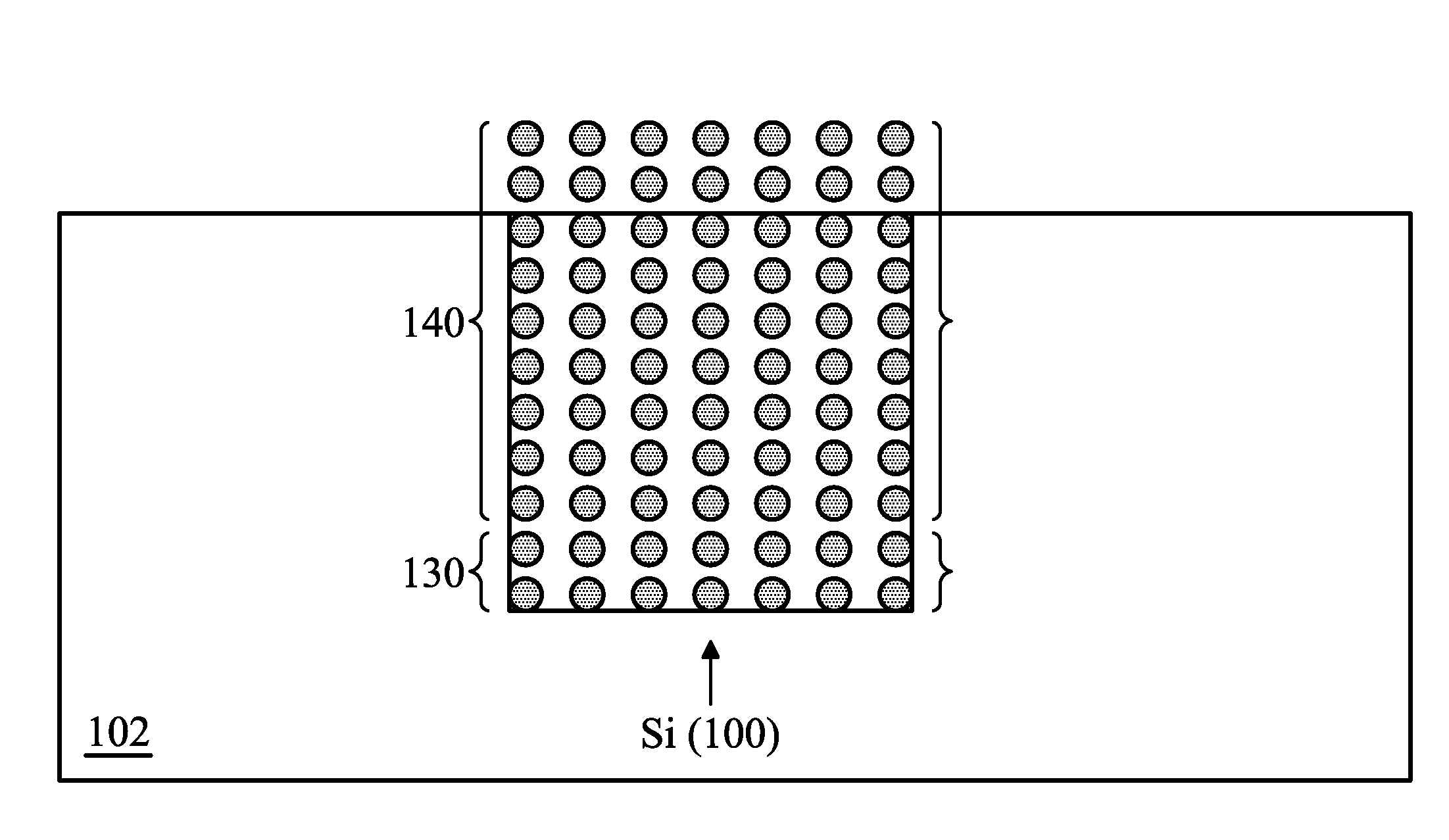
Semiconductor structure and a method of forming the same
ActiveUS8350273B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
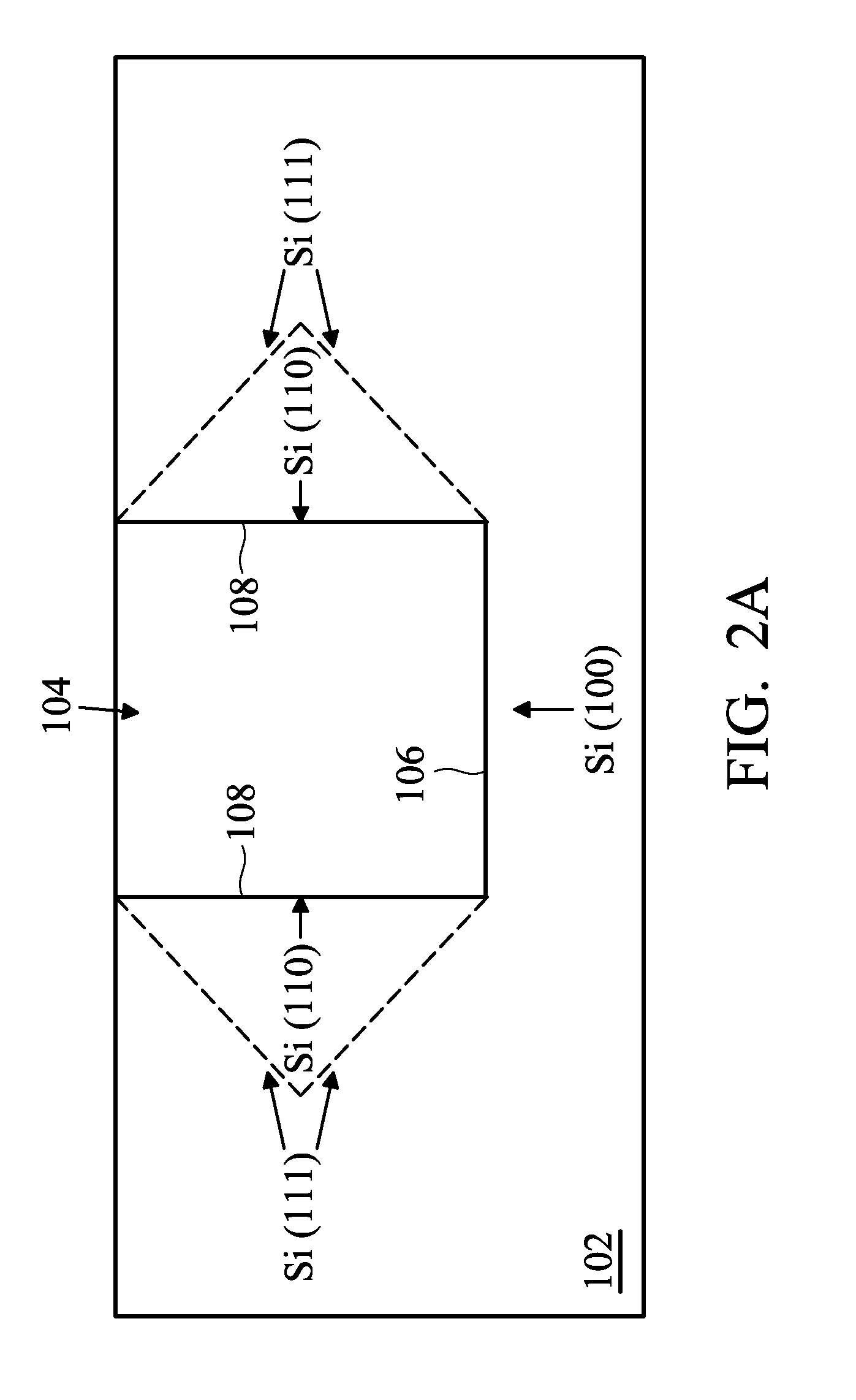
Some embodiments show a semiconductor structure including a substrate with a {100} crystal surface plane which includes a plurality of adjacent structured regions at a top side of the substrate. The plurality of adjacent structured regions includes adjacent substrate surfaces with {111} crystal planes and a III-V semiconductor material layer above the top side of the substrate. A semiconductor device region includes at least one semiconductor device structure. The semiconductor device region is arranged above the plurality of adjacent structured regions at the top side of the substrate.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
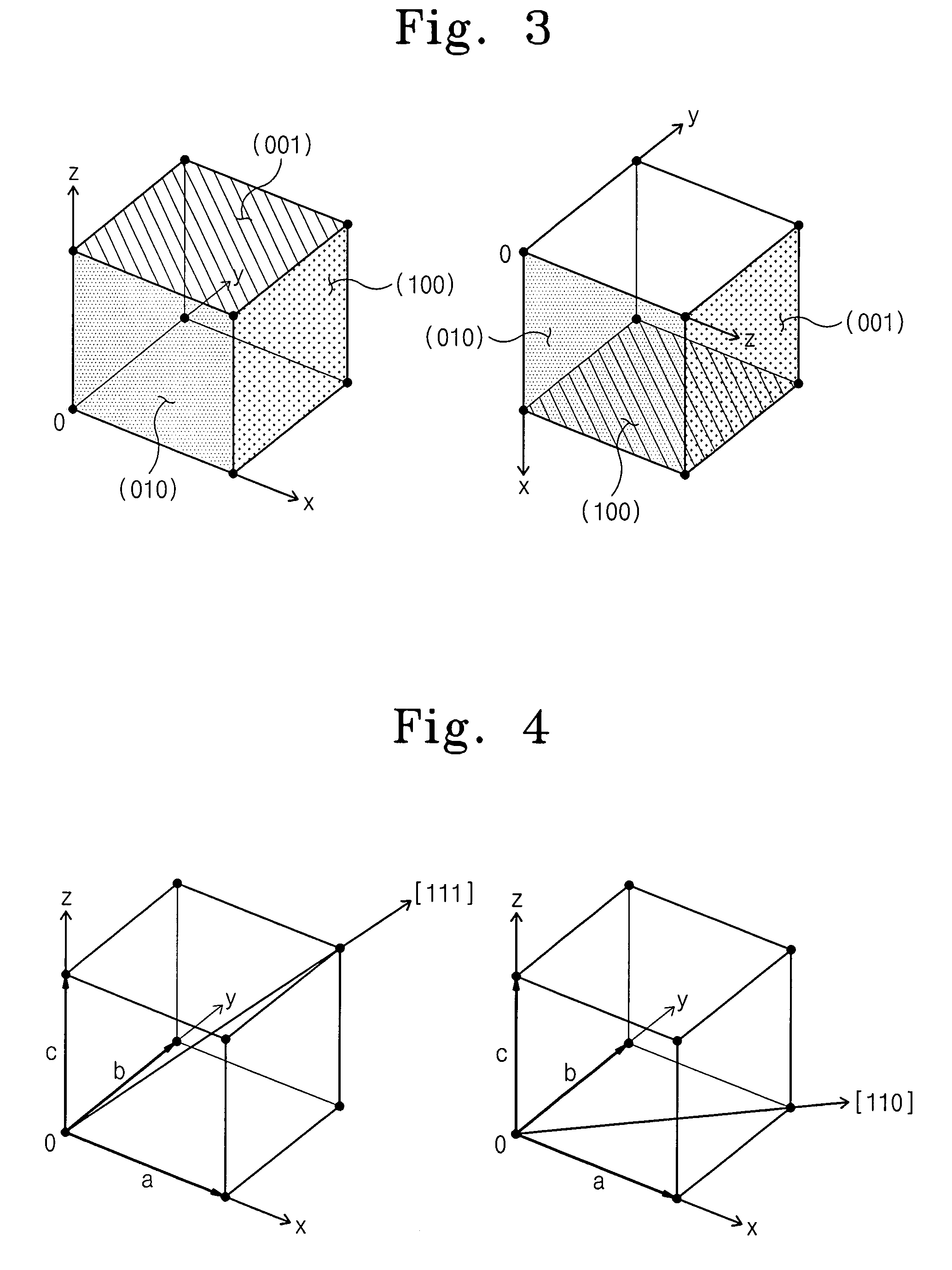
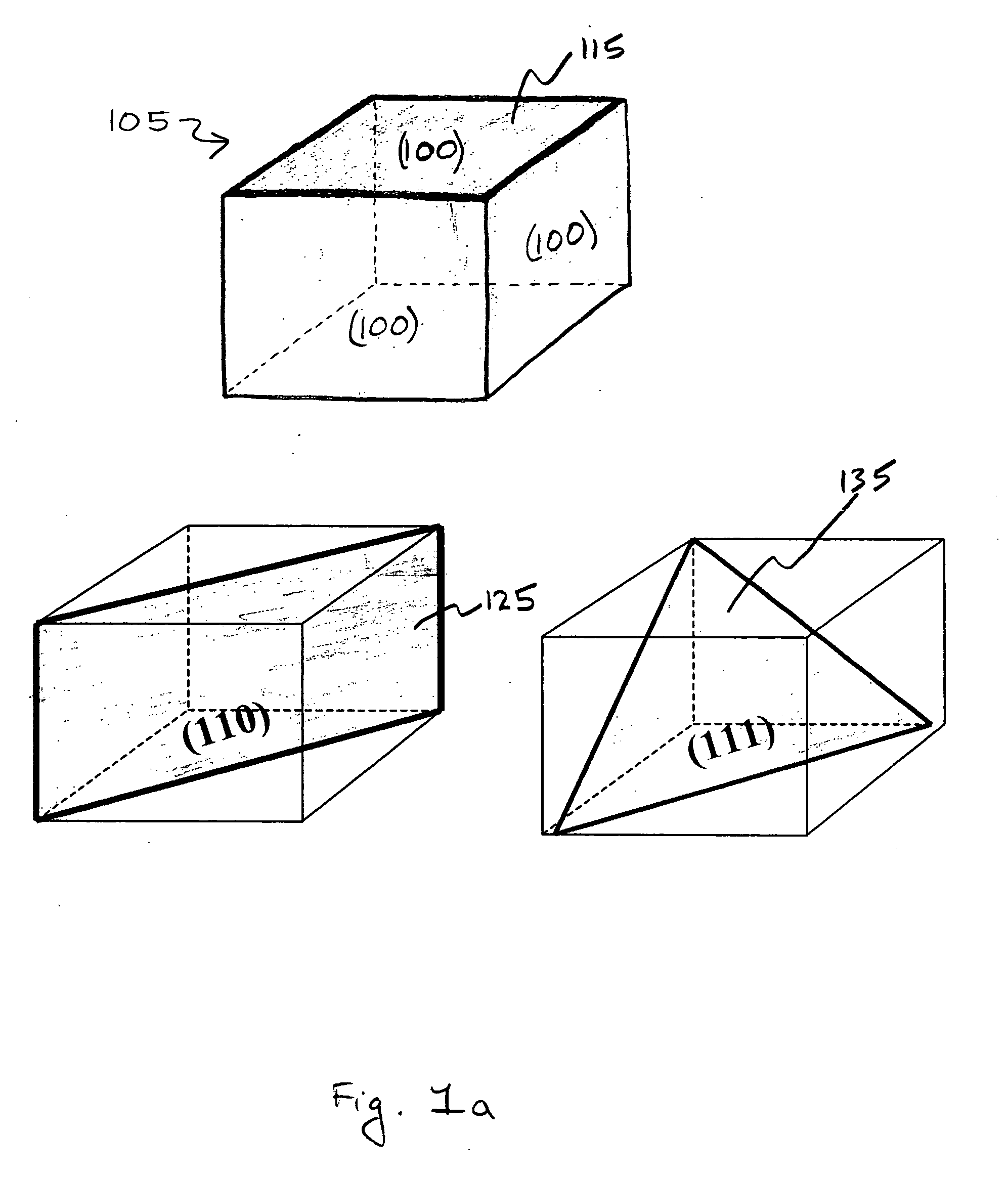
Semiconductor wafers with non-standard crystal orientations and methods of manufacturing the same
The crystal orientations of monocrystalline semiconductor wafers may be varied by four parameters. The first parameter is the type of crystal seed used to grow the monocrystalline semiconductor ingot from which the wafers are cut. The second parameter is the angle at which the wafer is sliced from the ingot. The third parameter is the crystal plane towards which the wafer is cut. And, the fourth parameter is the position of the orientation indication feature that is used to align the wafer during processing. Different combinations of these parameters provide variations of non-standard crystal orientations of monocrystalline semiconductor wafers and semiconductor-on-insulator substrates such as silicon-on-insulator.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20090095973A1Good ohmic contactOptical wave guidanceNanoopticsCrystal planeLight emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device has a device body made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane. In the device body, a contact portion with an n-type electrode includes a crystal plane different from the major surface. For example, the contact portion may include a corrugated surface. More specifically, the contact portion may include a region having a plurality of protrusions parallel to a polar plane formed in a striped manner.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
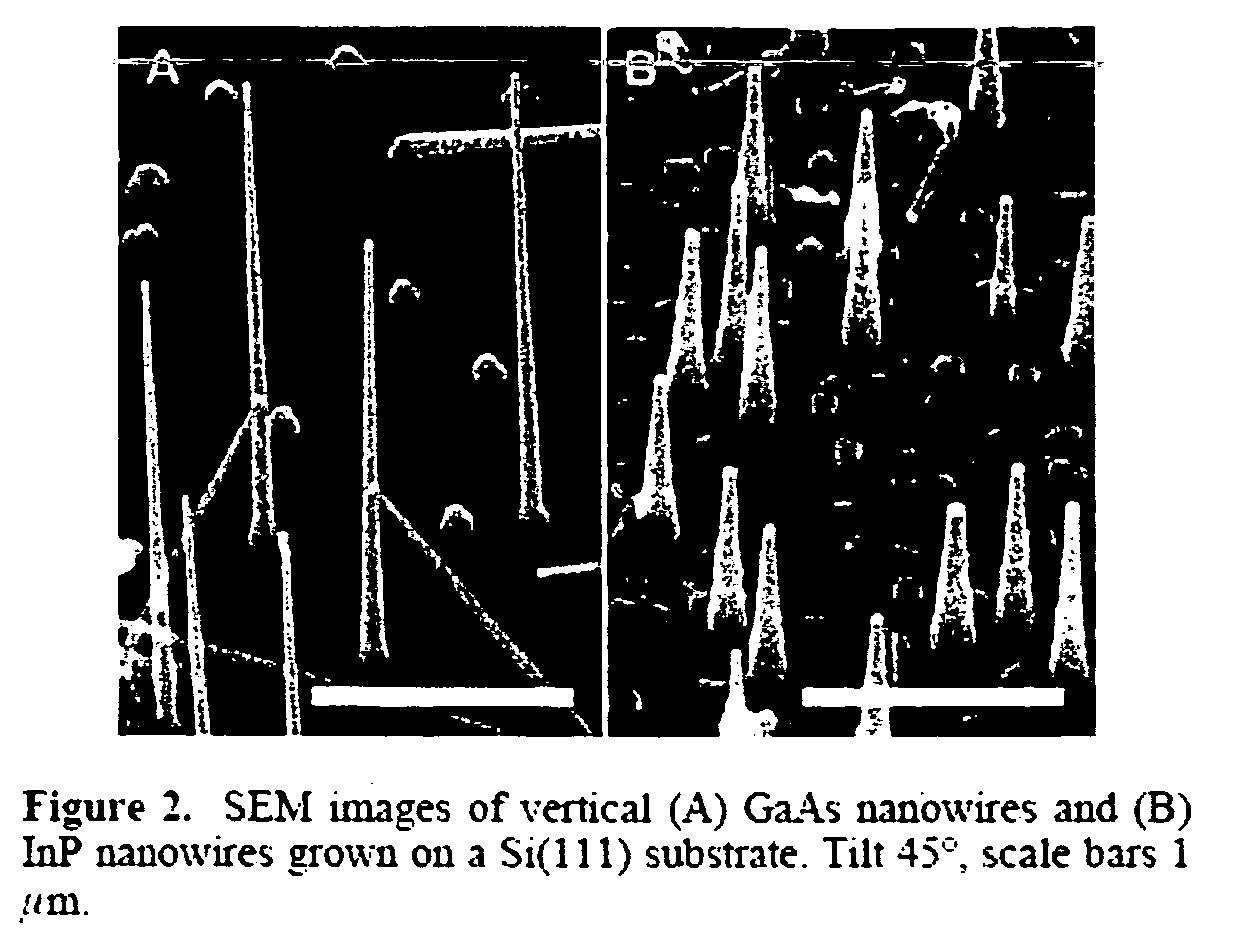
Formation of nanowhiskers on a substrate of dissimilar material
InactiveUS20060125056A1Improve reliabilityEfficient implementationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthHeterojunctionThermal energy
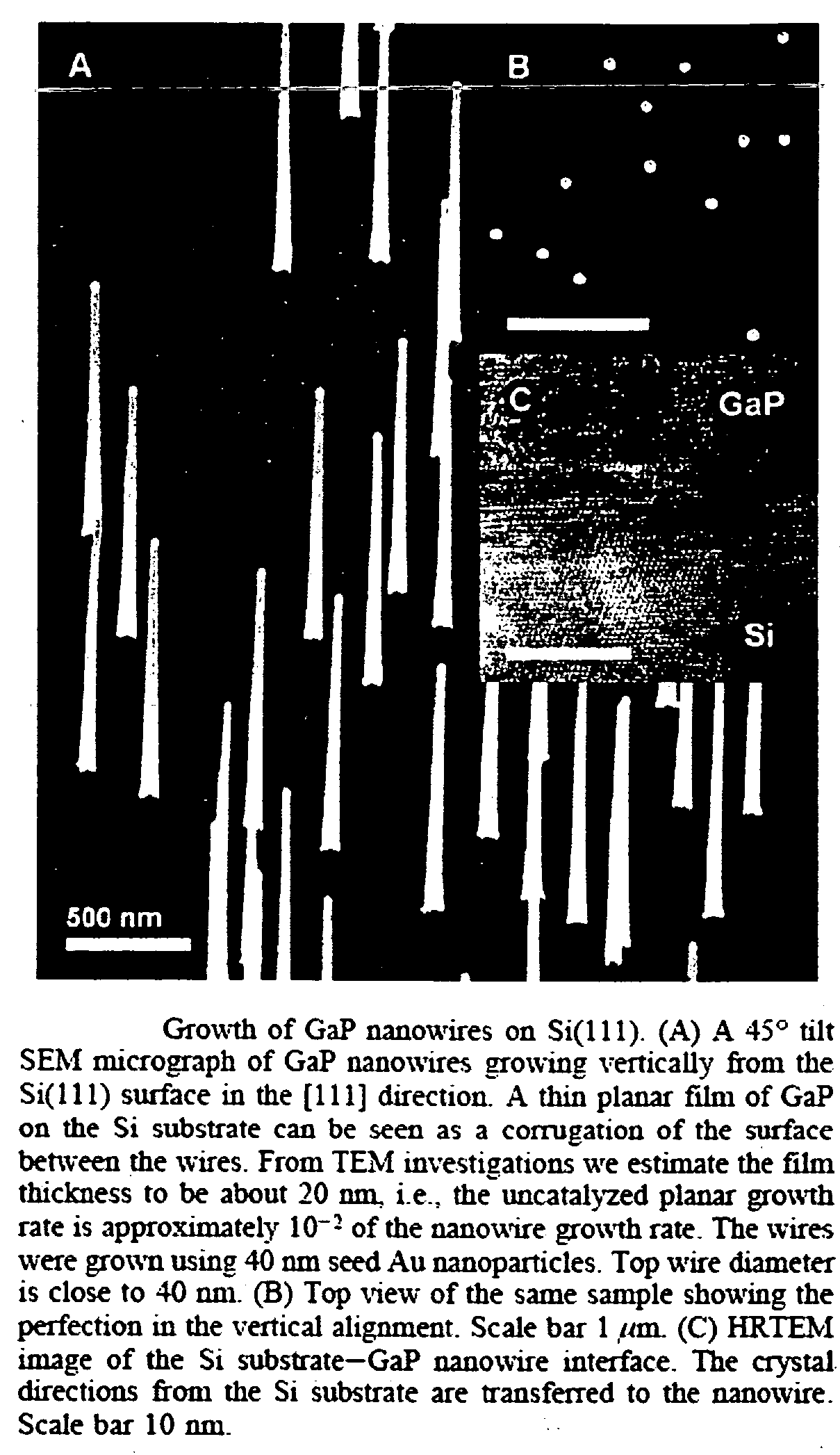
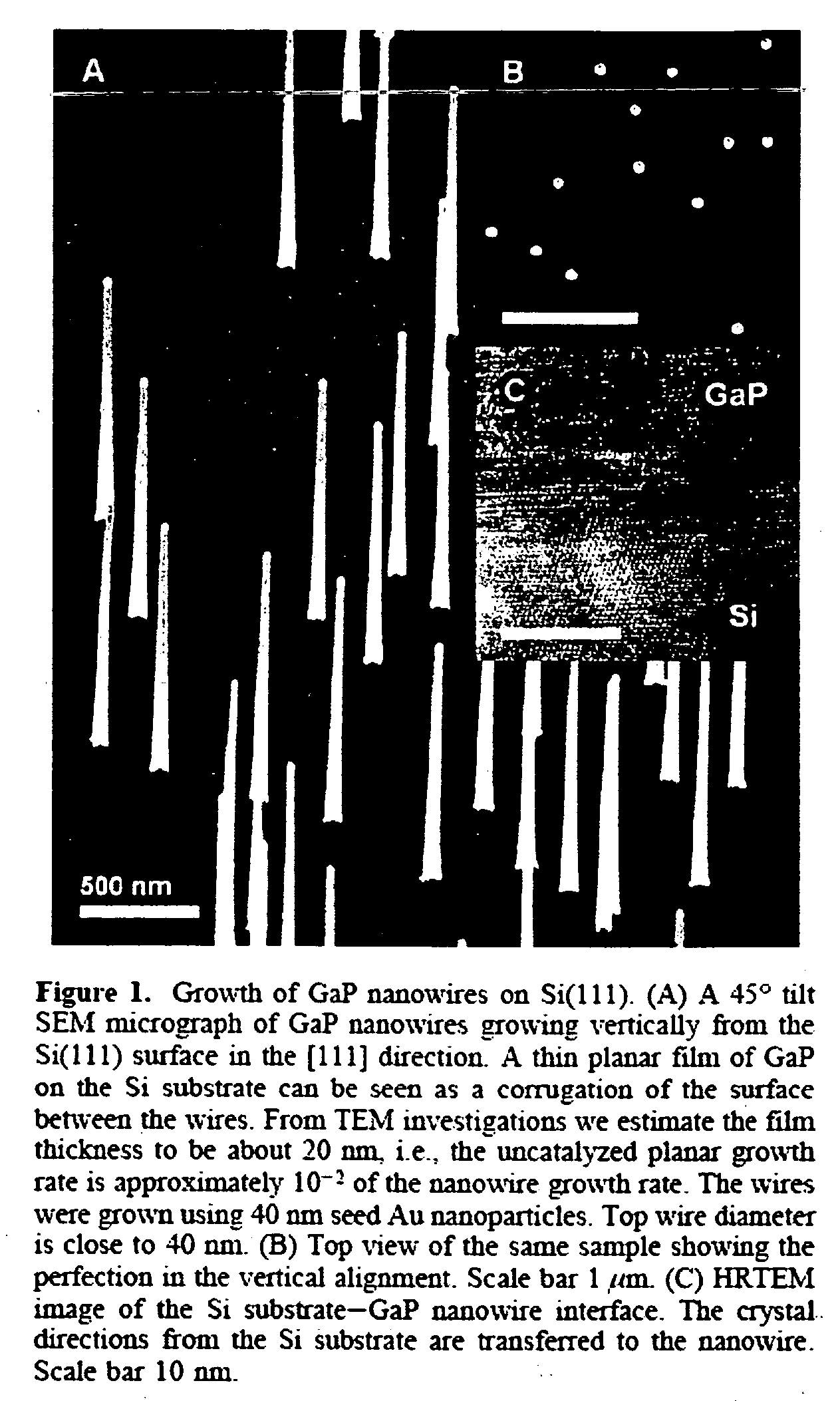
A method for forming a nanowhisker of, e.g., a III-V semiconductor material on a silicon substrate, comprises: preparing a surface of the silicon substrate with measures including passivating the substrate surface by HF etching, so that the substrate surface is essentially atomically flat. Catalytic particles on the substrate surface are deposited from an aerosol; the substrate is annealed; and gases for a MOVPE process are introduced into the atmosphere surrounding the substrate, so that nanowhiskers are grown by the VLS mechanism. In the grown nanowhisker, the crystal directions of the substrate are transferred to the epitaxial crystal planes at the base of the nanowhisker and adjacent the substrate surface. A segment of an optically active material may be formed within the nanowhisker and bounded by heterojunctions so as to create a quantum well wherein the height of the quantum well is much greater than the thermal energy at room temperature, whereby the luminescence properties of the segment remain constant without quenching from cryogenic temperatures up to room temperature.
Owner:QUNANO
Nitride semiconductor laser device and nitride semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050224783A1Excellent characteristicsProlong lifeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndiumCrystal plane
A nitride semiconductor laser device comprises, on a principle face of a nitride semiconductor substrate: a nitride semiconductor layer having a first conductivity type; an active layer comprising indium, and a nitride semiconductor layer having a second conductivity type that is different from said first conductivity type, and on the surface of which is formed a stripe ridge; said principal face of said nitride semiconductor substrate having an off angle a (θa) with respect to a reference crystal plane, in at least a direction substantially parallel to said stripe ridge.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Semiconductor structure and method of fabricating the semiconductor structure
ActiveUS20100207172A1High carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSManufacturing technology
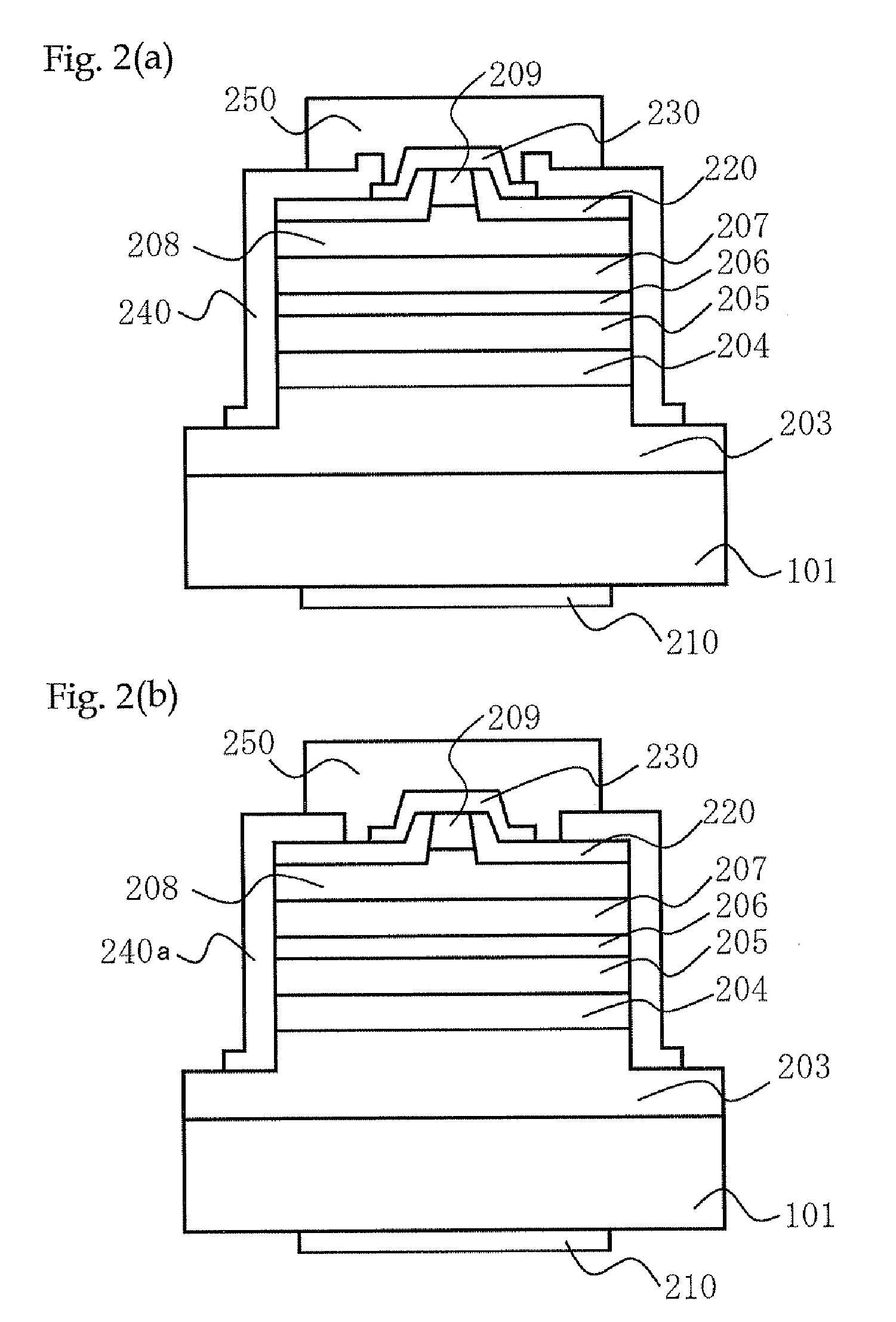
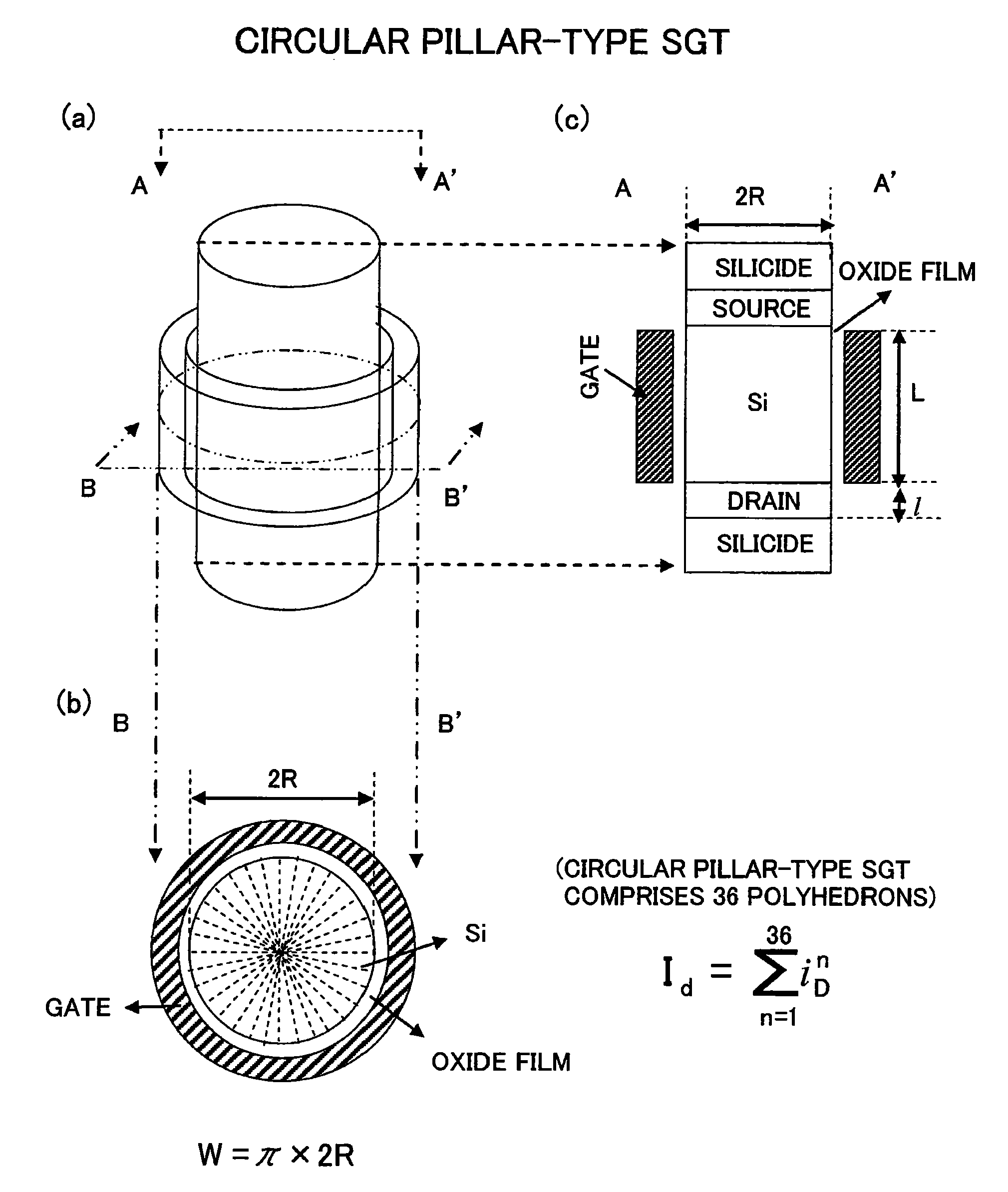
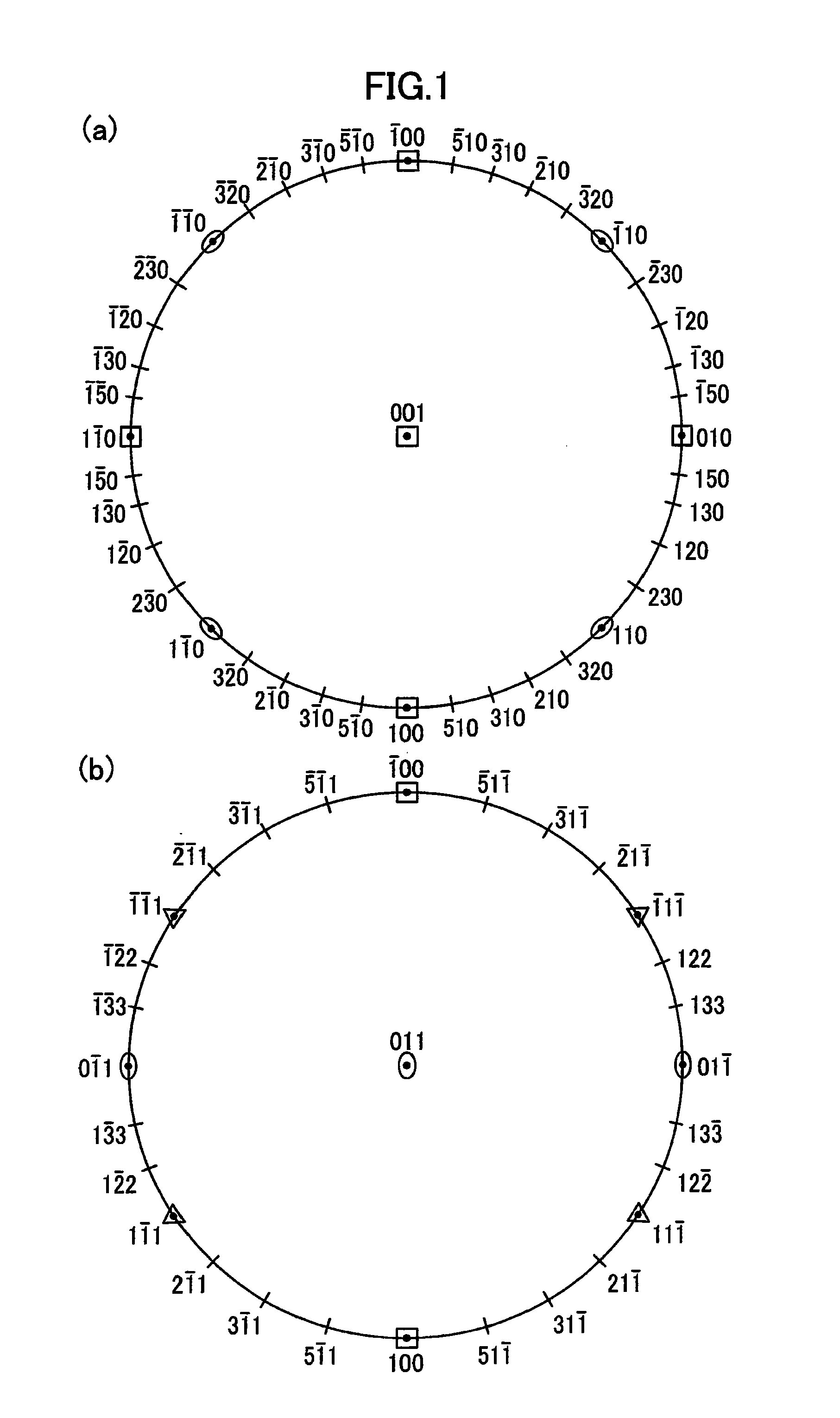
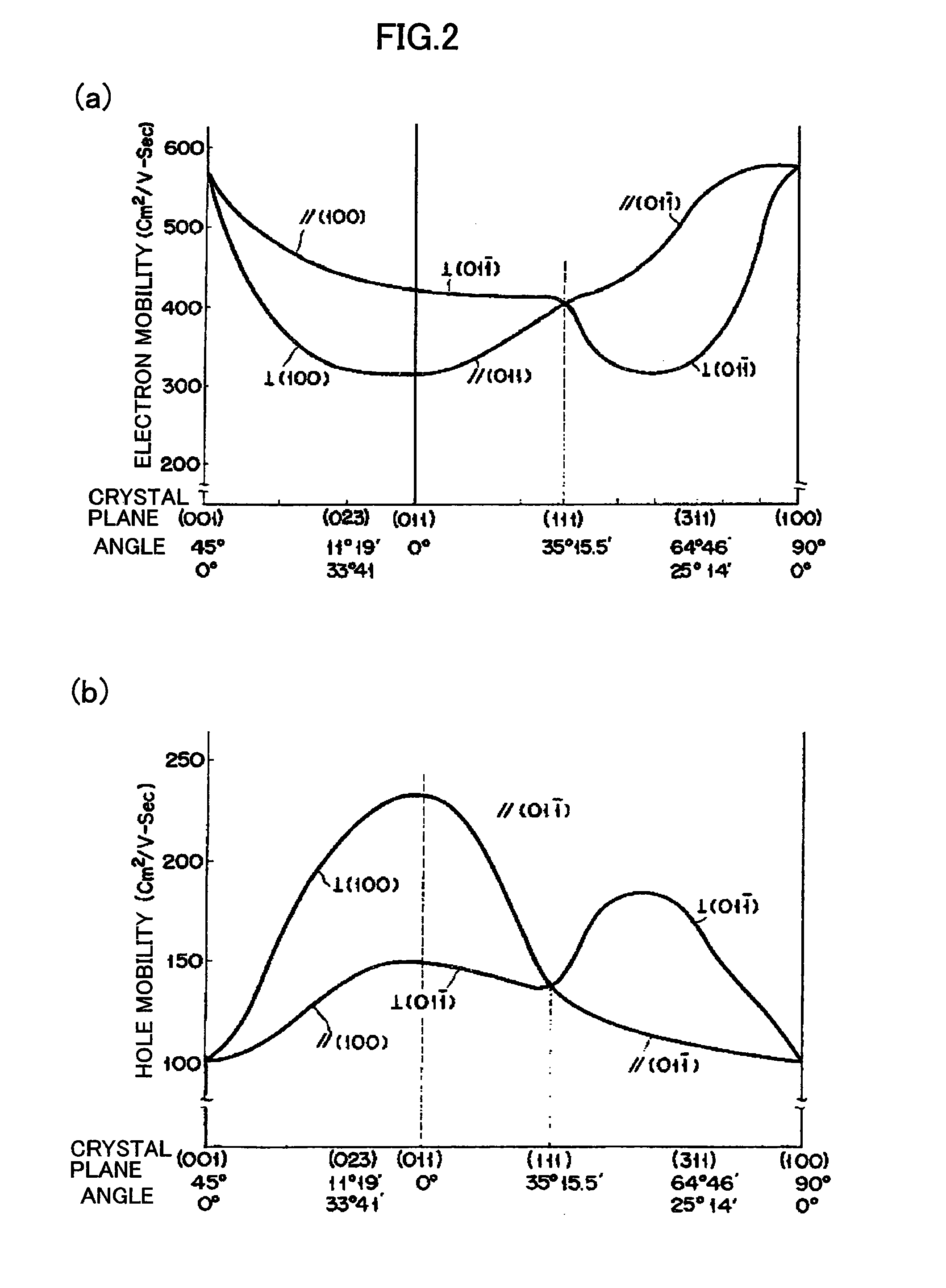
In contrast to a conventional planar CMOS technique in design and fabrication for a field-effect transistor (FET), the present invention provides an SGT CMOS device formed on a conventional substrate using various crystal planes in association with a channel type and a pillar shape of an FET, without a need for a complicated device fabrication process. Further, differently from a design technique of changing a surface orientation in each planar FET, the present invention is designed to change a surface orientation in each SGT to achieve improvement in carrier mobility. Thus, a plurality of SGTs having various crystal planes can be formed on a common substrate to achieve a plurality of different carrier mobilities so as to obtain desired performance.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Grain oriented ceramics and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060006360A1Excellent piezoelectric propertiesEnvironment safetyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyCeramicsAlkaline earth metalCrystal plane
To provide a grain oriented ceramic capable of exerting excellent piezoelectric properties, a production method thereof, and a piezoelectric material, a dielectric material, a thermoelectric conversion element and an ion conducting element each using the grain oriented ceramic, there is provided a grain oriented ceramic comprising, as the main phase, an isotropic perovskite-type compound which is represented by formula (1): {Lix(K1−yNay)1−x}(Nb1−z−wTazSbw)O3 in which x, y, z and w are in respective composition ranges of 0≦x≦0.2, 0≦y≦1, 0≦z≦0.4, 0≦w≦0.2 and x+z+w>0. The main phase comprises a polycrystalline body containing from 0.0001 to 0.15 mol of any one or more additional element selected from metal elements, semimetal elements, transition metal elements, noble metal elements and alkaline earth metal elements belonging to Groups 2 to 15 of the Periodic Table, per mol of the compound represented by formula (1). A specific crystal plane of each crystal grain constituting said polycrystalline body is oriented.
Owner:DENSO CORP
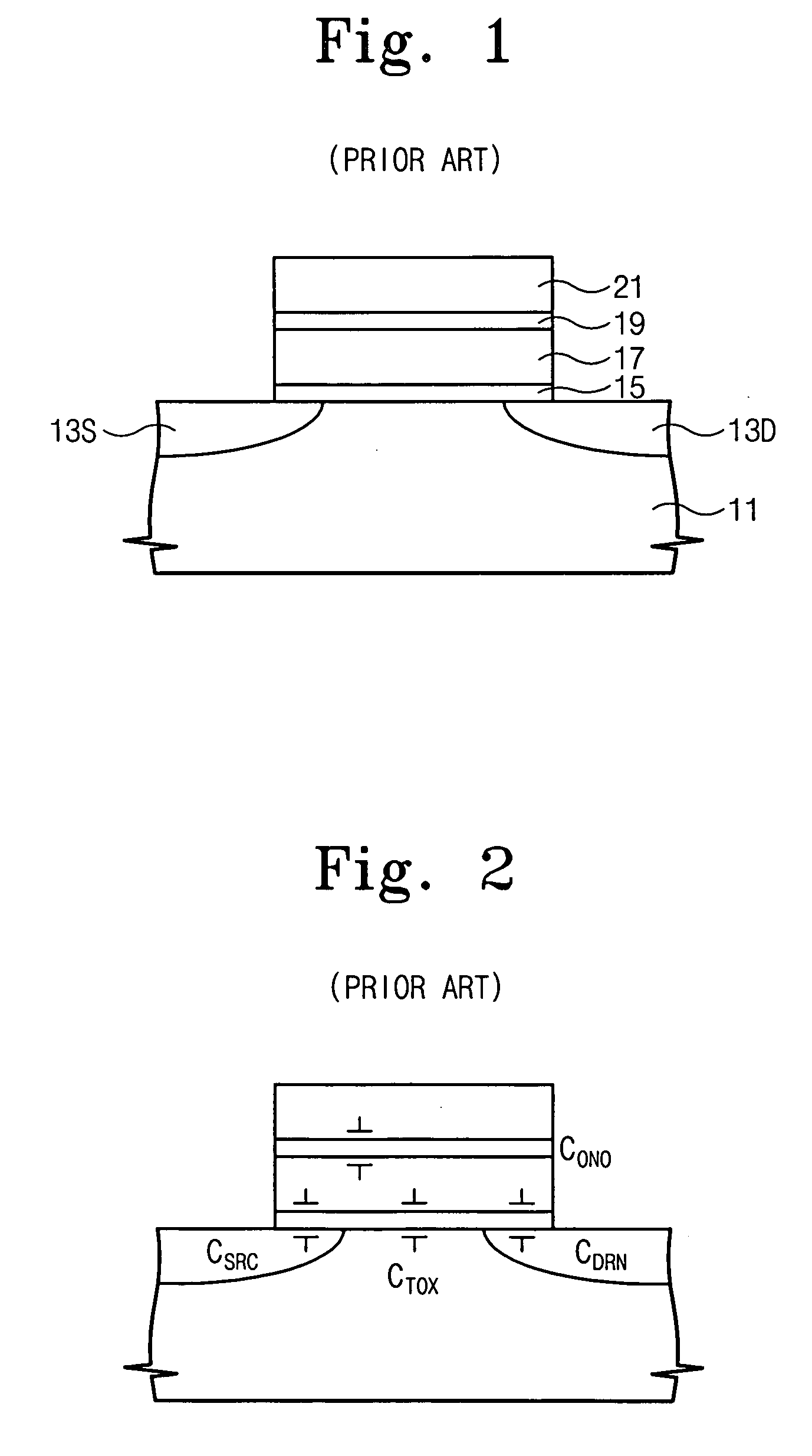
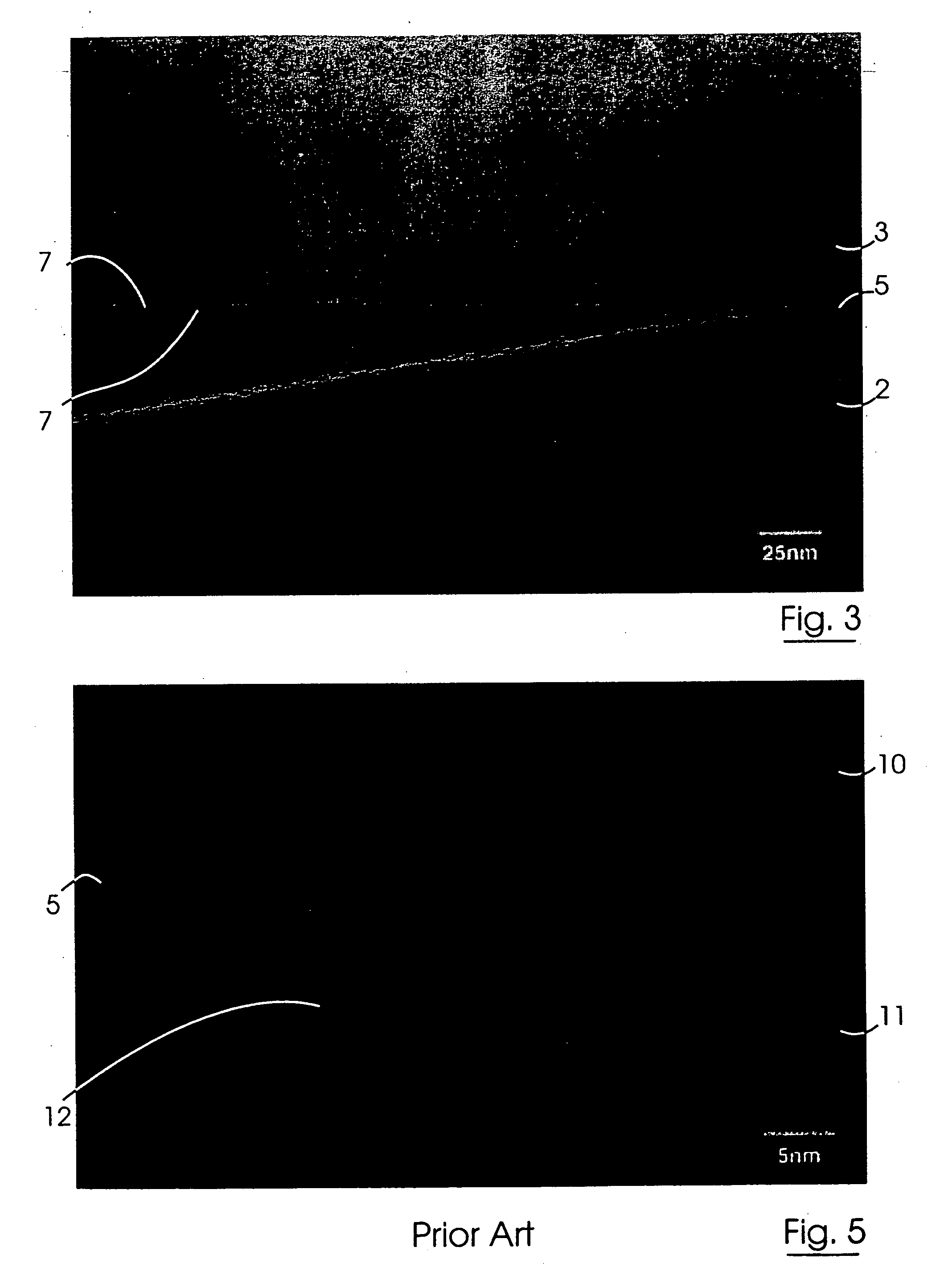
Semiconductor device, method of manufacturing the same, and method of evaluating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050285203A1Thickness of gate be reducedReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCrystal planeSilicon
A semiconductor device has: a silicon (semiconductor) substrate; a gate insulating film and a gate electrode, which are formed on the silicon substrate in this order; and source / drain material layers formed in recesses (holes) in the silicon substrate, the recesses being located beside the gate electrode. Here, each of side surfaces of the recesses, which are closer to the gate electrode, is constituted of at least one crystal plane of the silicon substrate.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor device, semiconductor device production method, and substrate for the semiconductor device
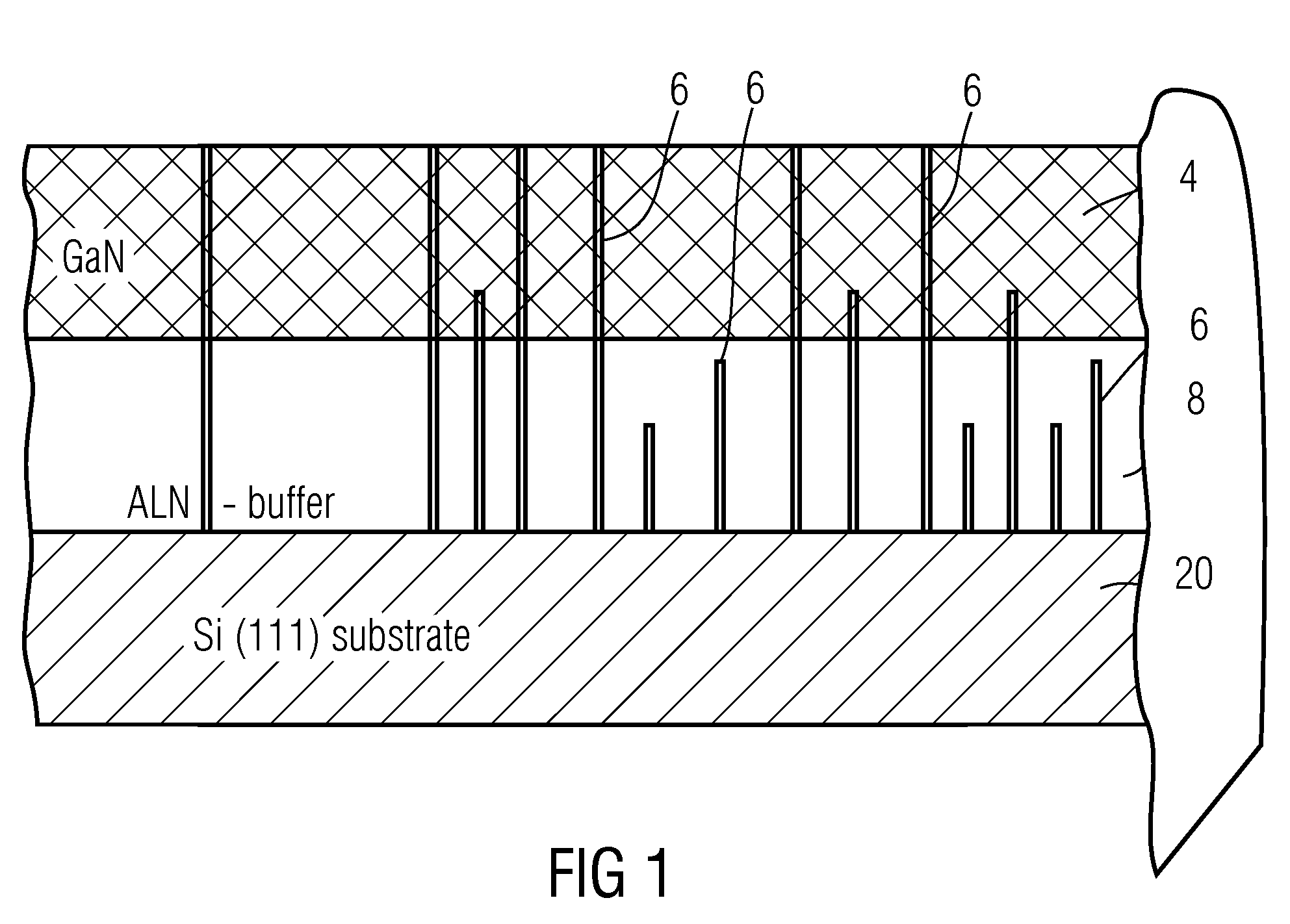
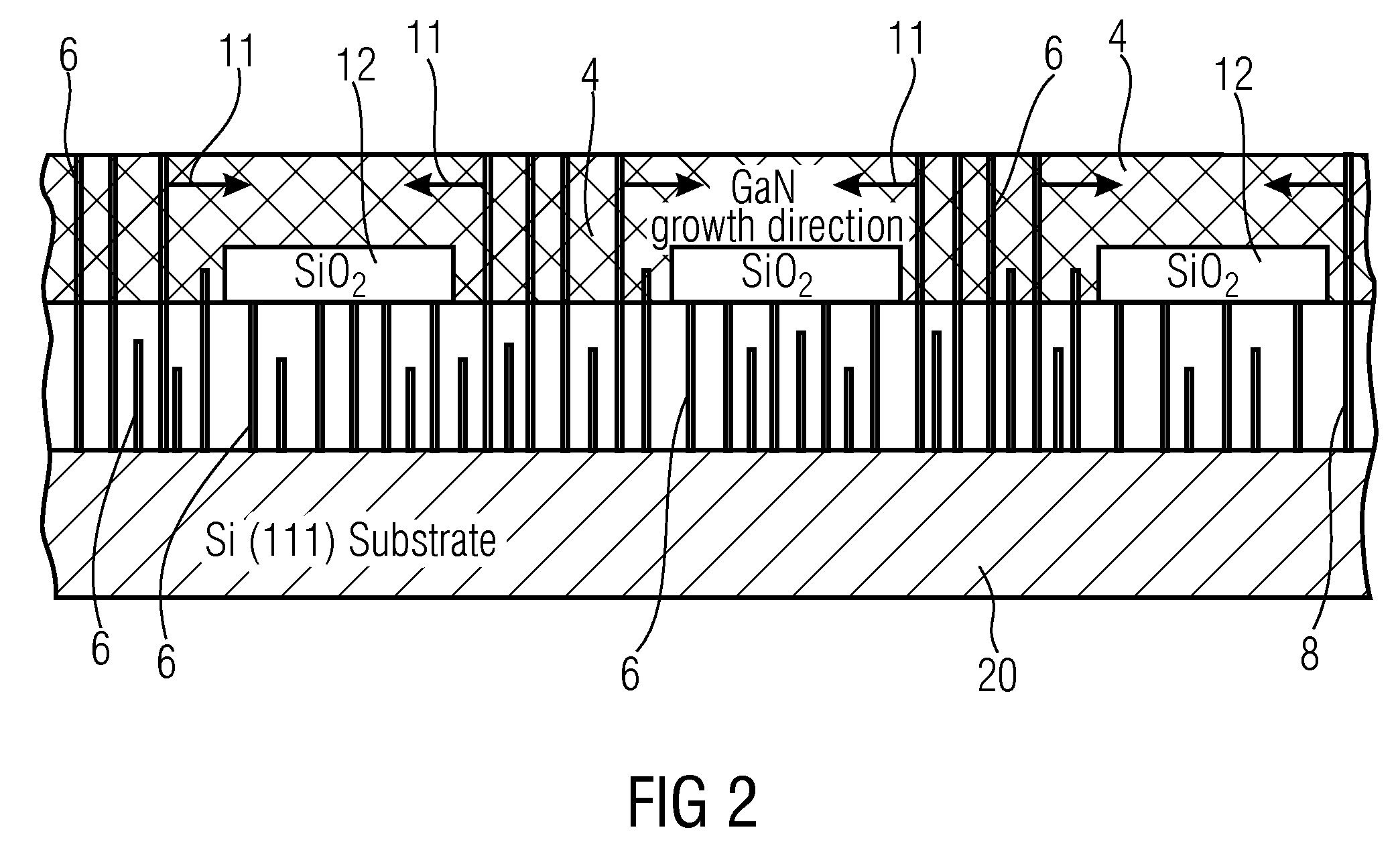
InactiveUS20060084245A1Good surface smoothnessHigh crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCrystal planeGallium nitride
A semiconductor device production method includes the steps of: forming a linear gallium nitride stripe pattern on a major surface of a substrate, the major surface of the substrate being offset from a predetermined crystal plane by offset angles of 0.1 degree to 0.5 degrees respectively defined with respect to a first crystal axis and a second crystal axis parallel to the predetermined crystal plane, the linear gallium nitride stripe pattern extending along the first crystal axis; and growing a gallium nitride compound semiconductor crystal along the predetermined crystal plane by selective lateral epitaxial growth to form a gallium nitride compound semiconductor layer on the major surface of the substrate formed with the gallium nitride stripe pattern. The first crystal axis and the second crystal axis may be perpendicular to each other. The substrate may be a sapphire substrate, a silicon carbide substrate, an aluminum nitride substrate or a gallium nitride substrate. In this case, the predetermined crystal plane is preferably a C-plane.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
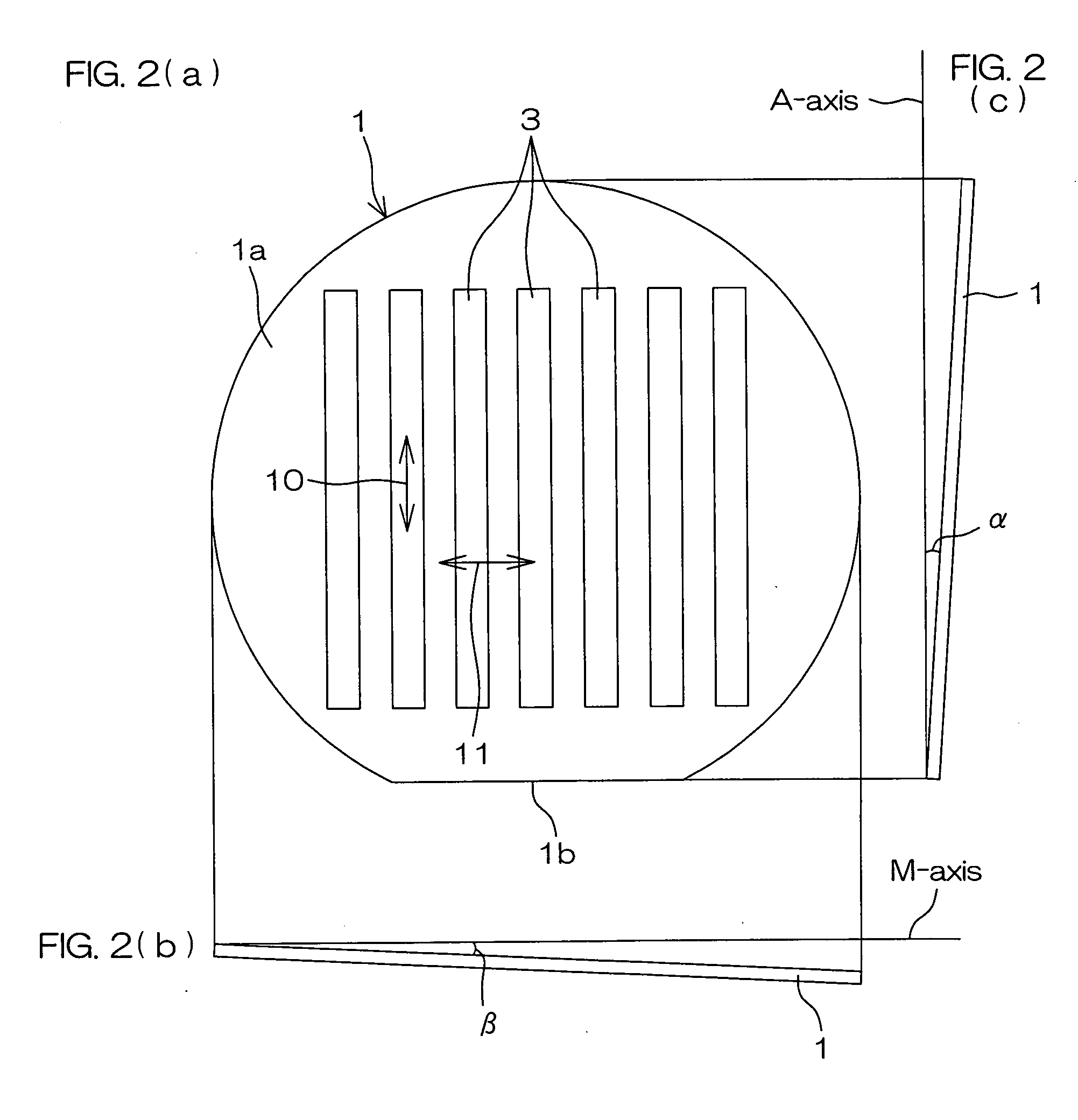
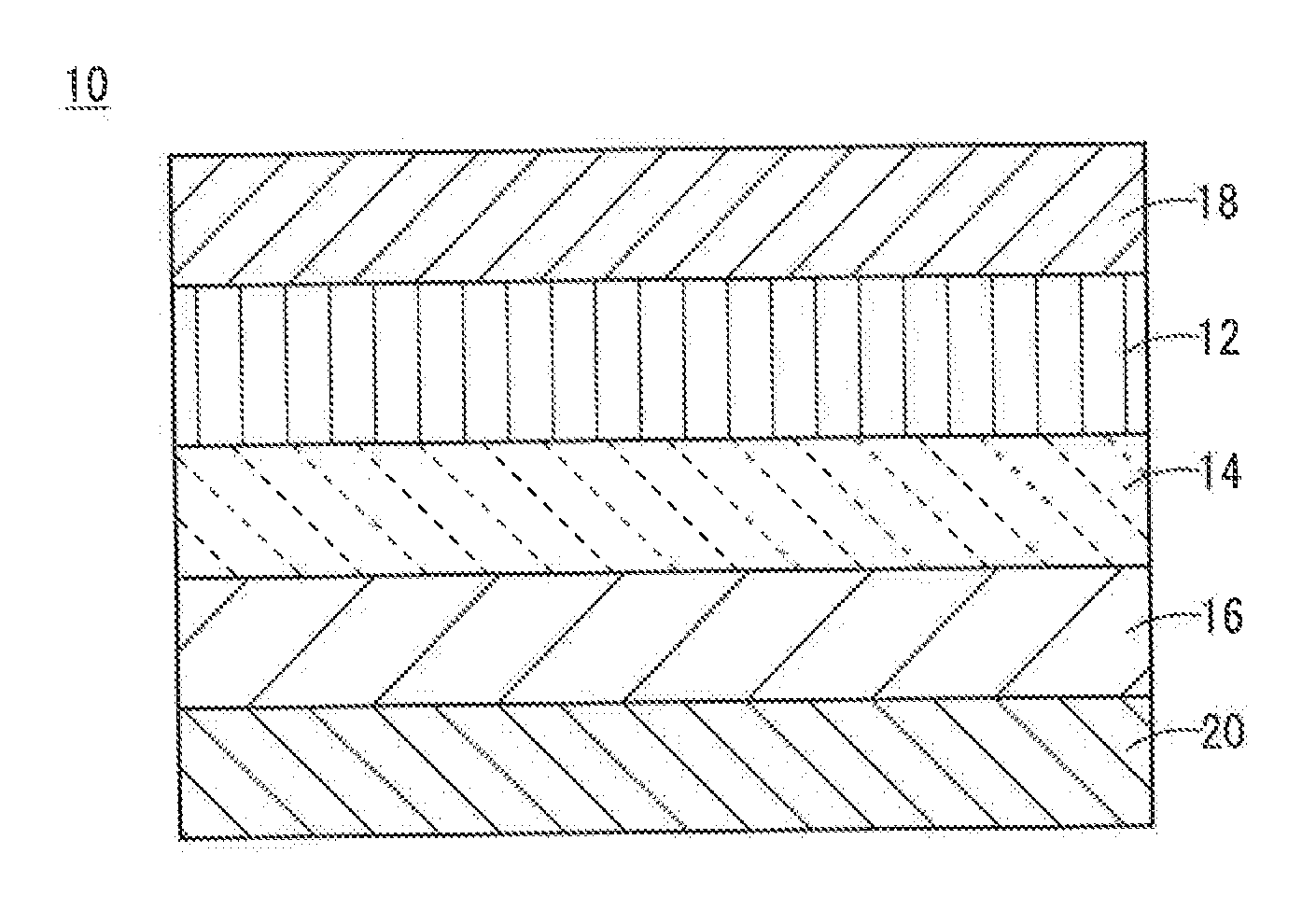
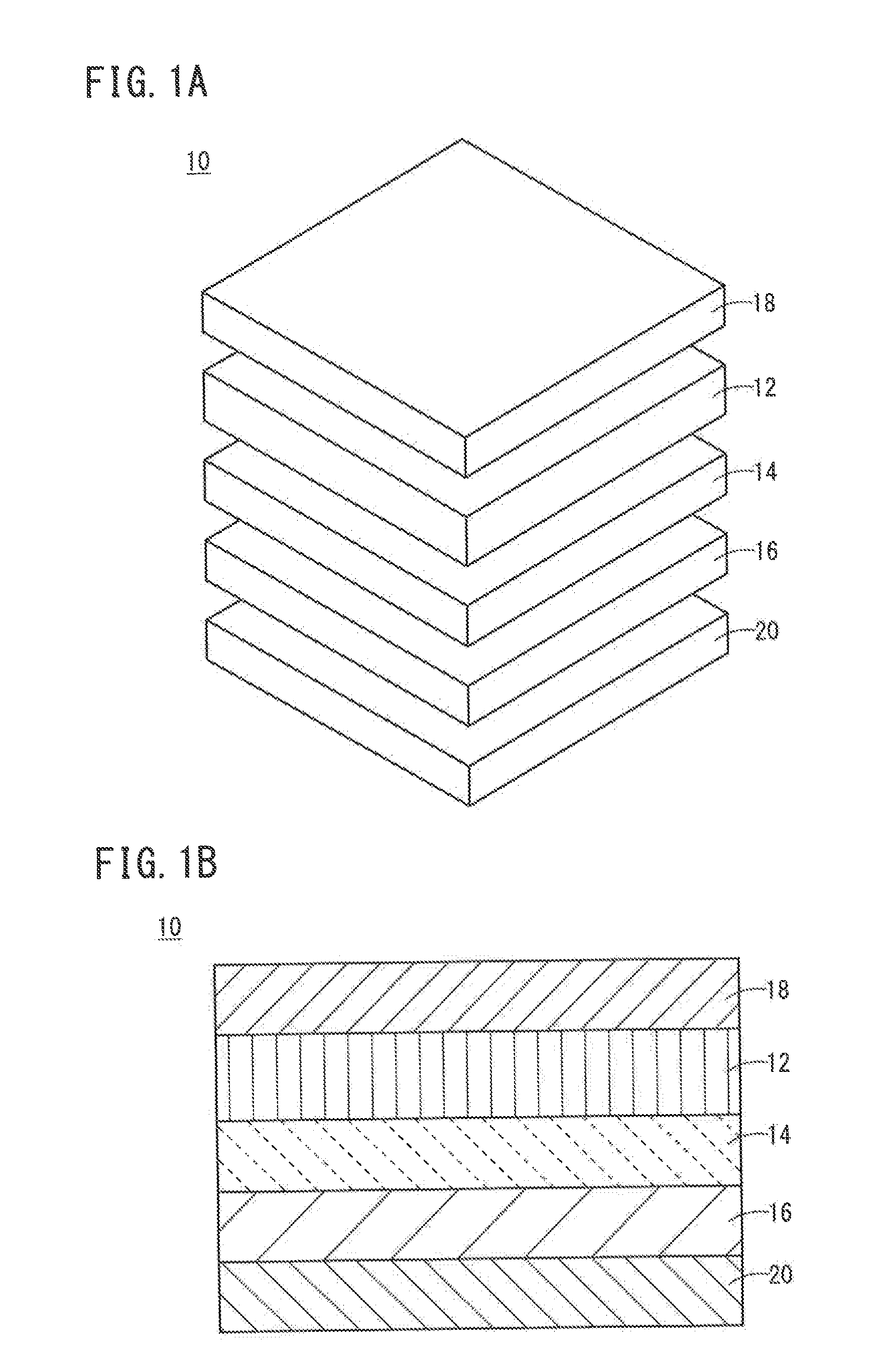
All-Solid-State Cell
InactiveUS20150037688A1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsIncrease capacitySolid electrolytesElectrode thermal treatmentAll solid stateCrystal plane
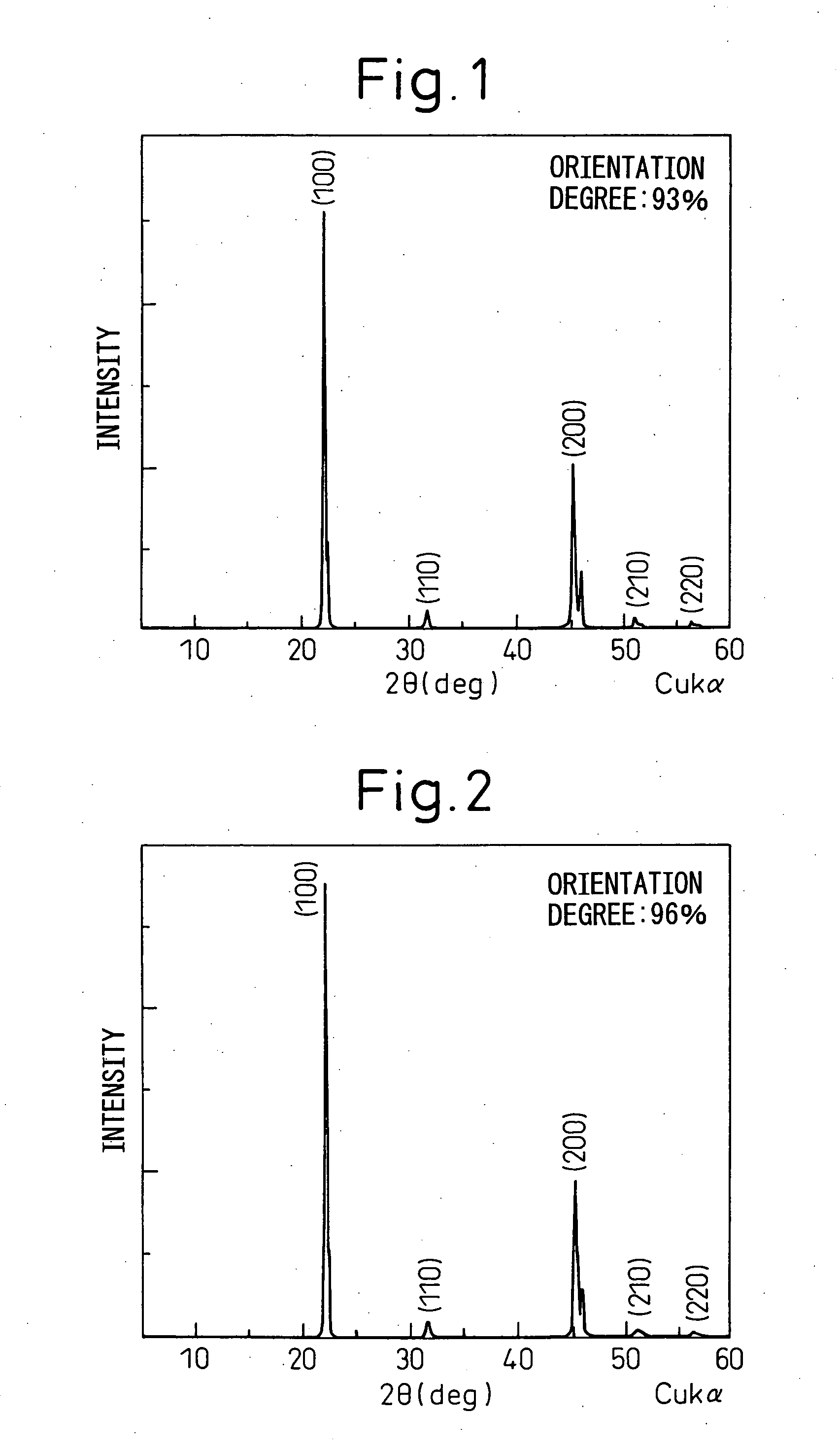
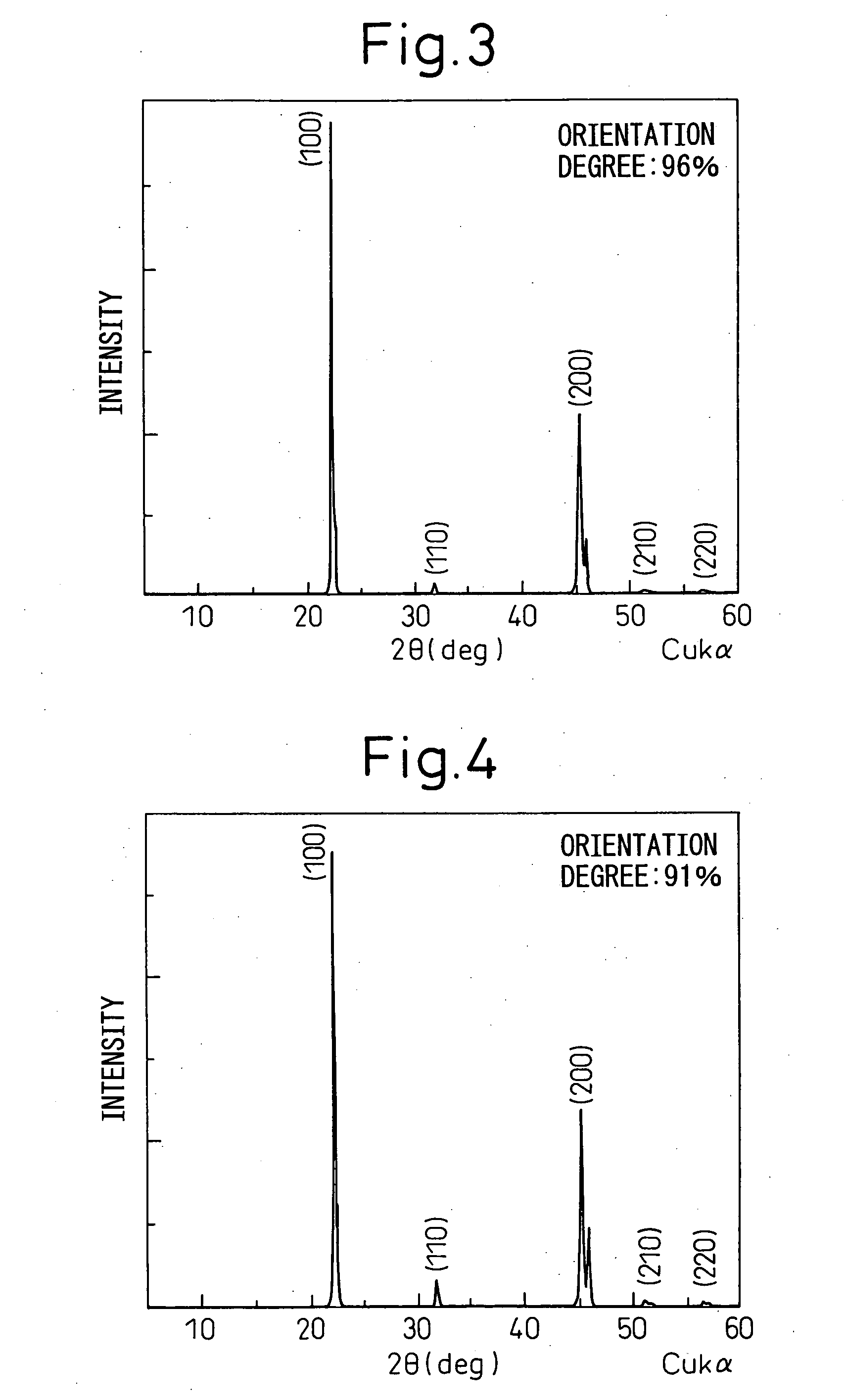
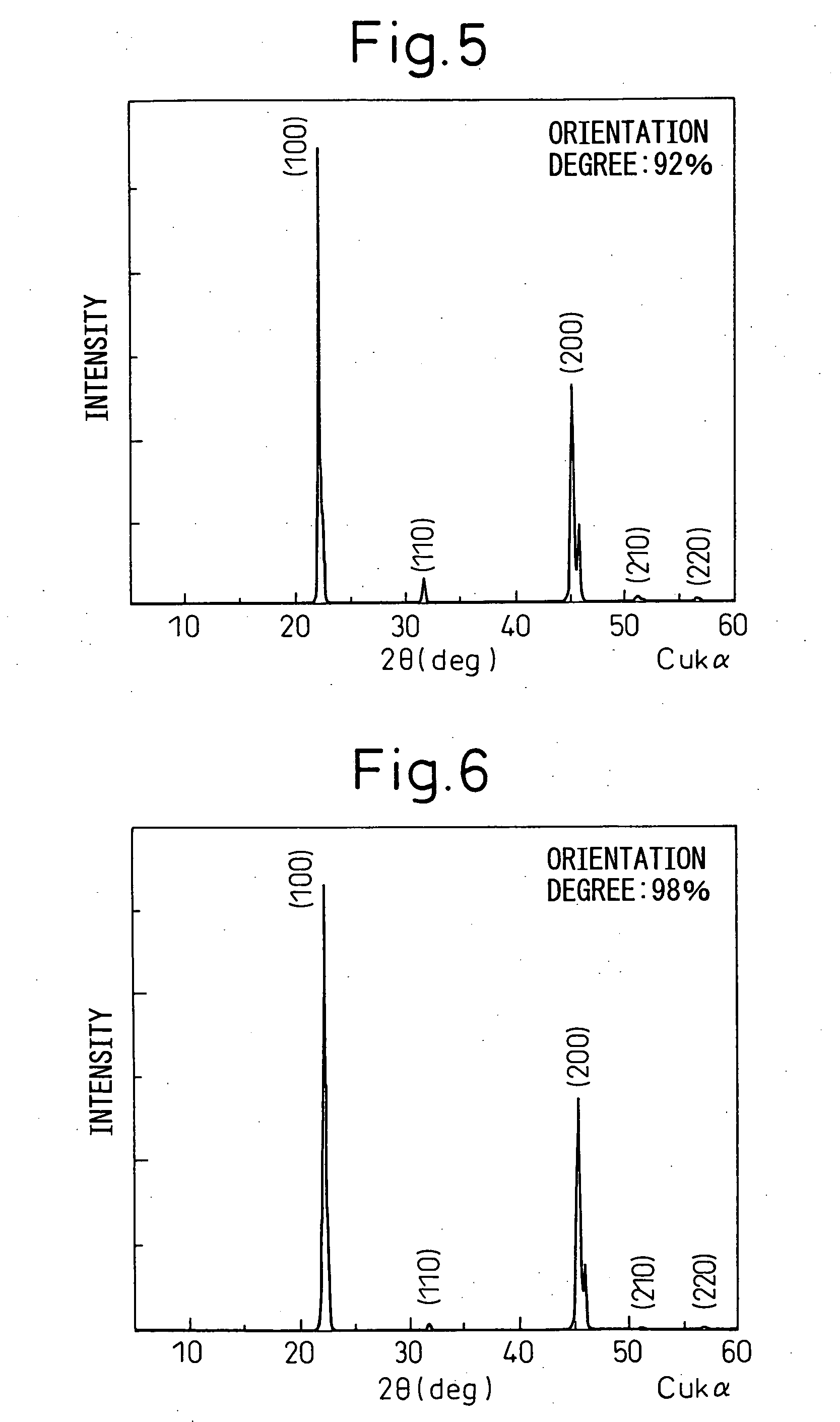
An all-solid-state cell contains at least a positive electrode layer, a solid electrolyte layer, and a negative electrode layer, which are arranged in a stack. The positive electrode layer contains only a positive electrode active material, and a predetermined crystal plane of the positive electrode active material is oriented in a direction of lithium ion conduction. The negative electrode layer contains a carbonaceous material, and the volume ratio of the carbonaceous material to the negative electrode layer is 70% or greater.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
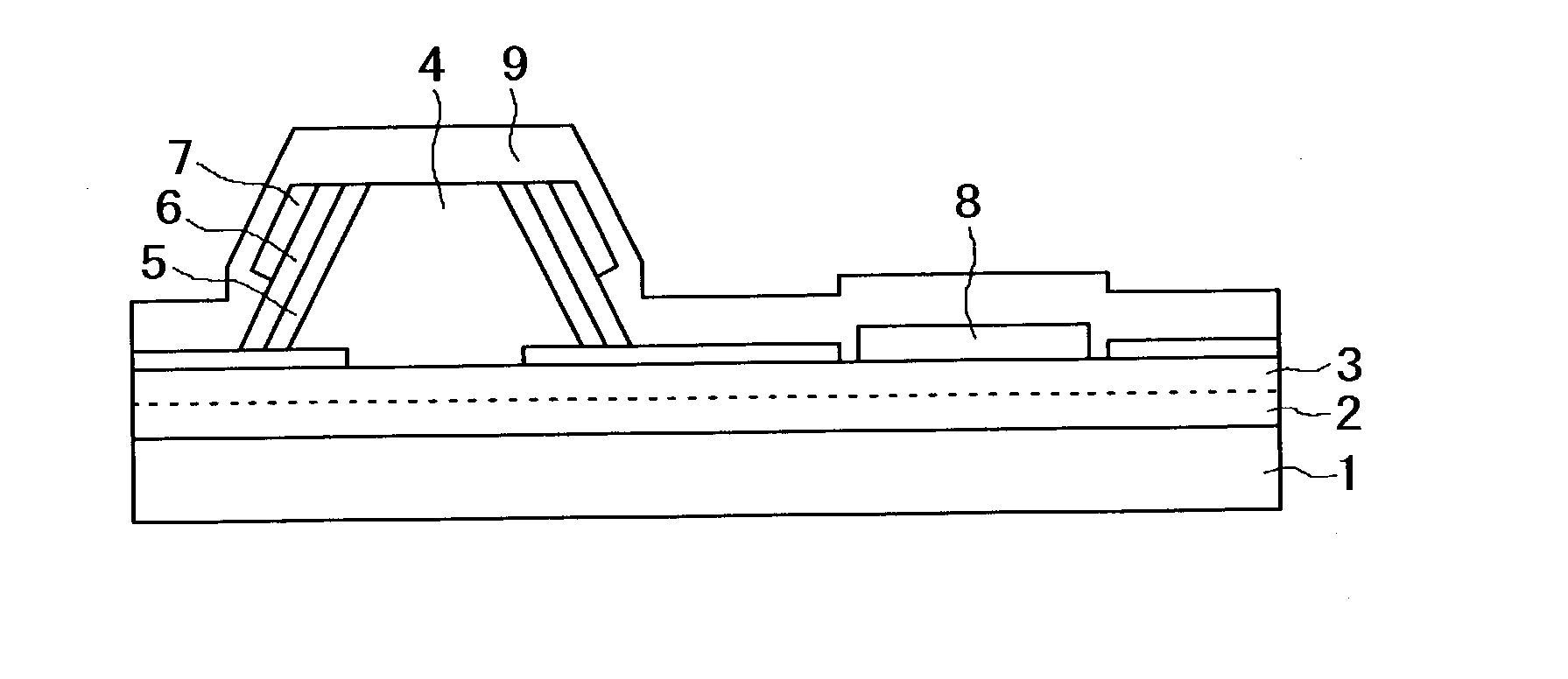
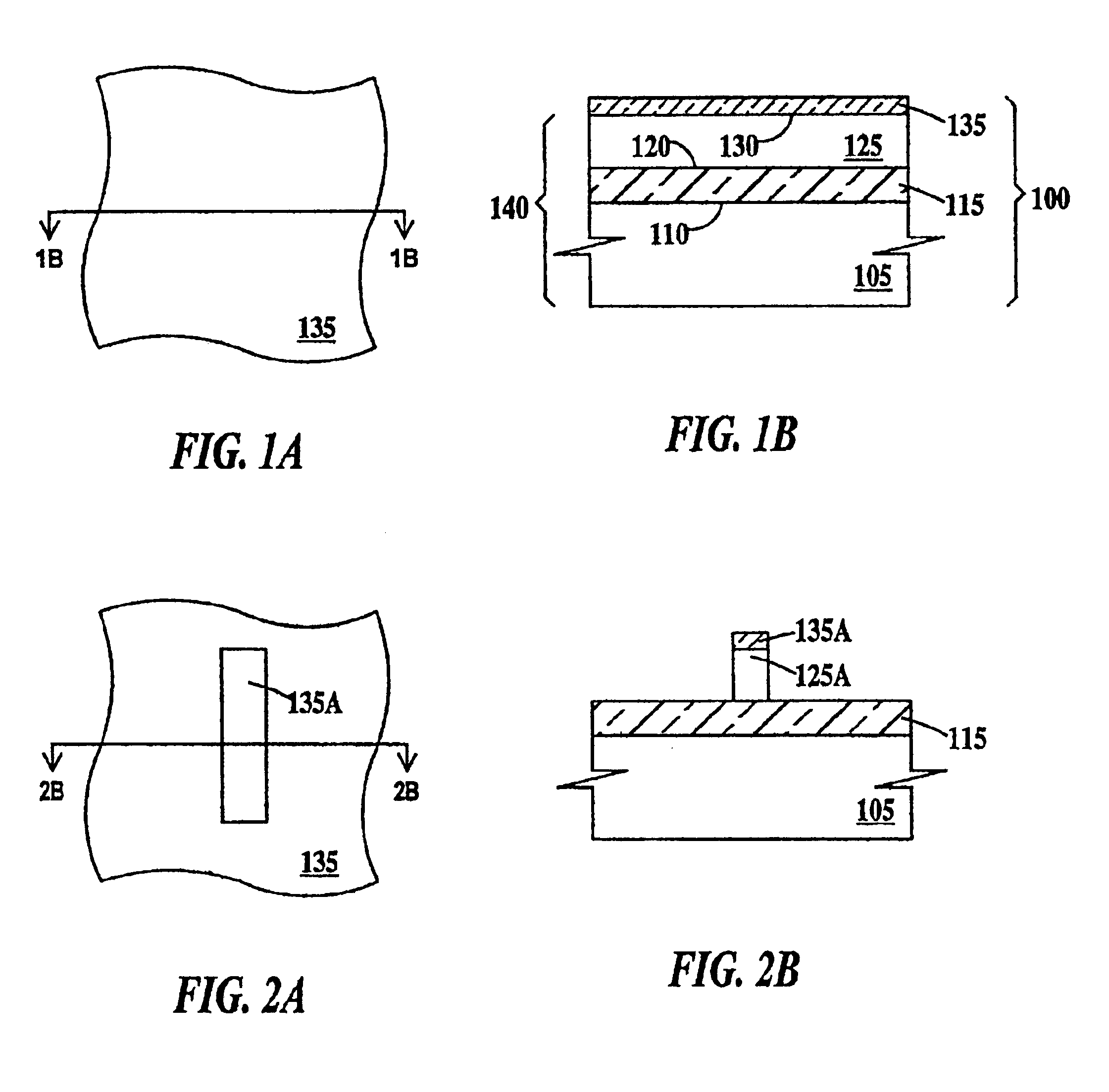
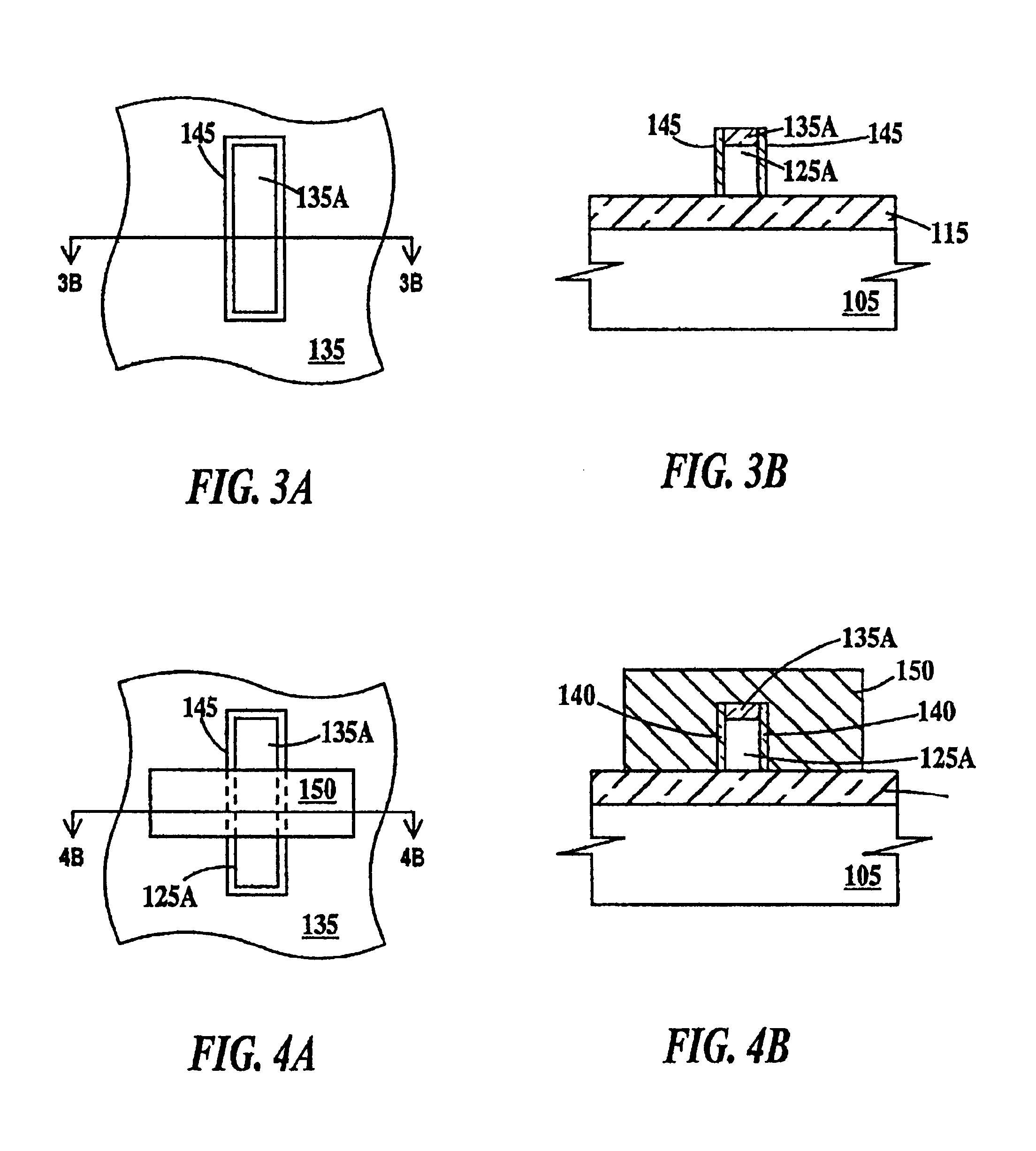
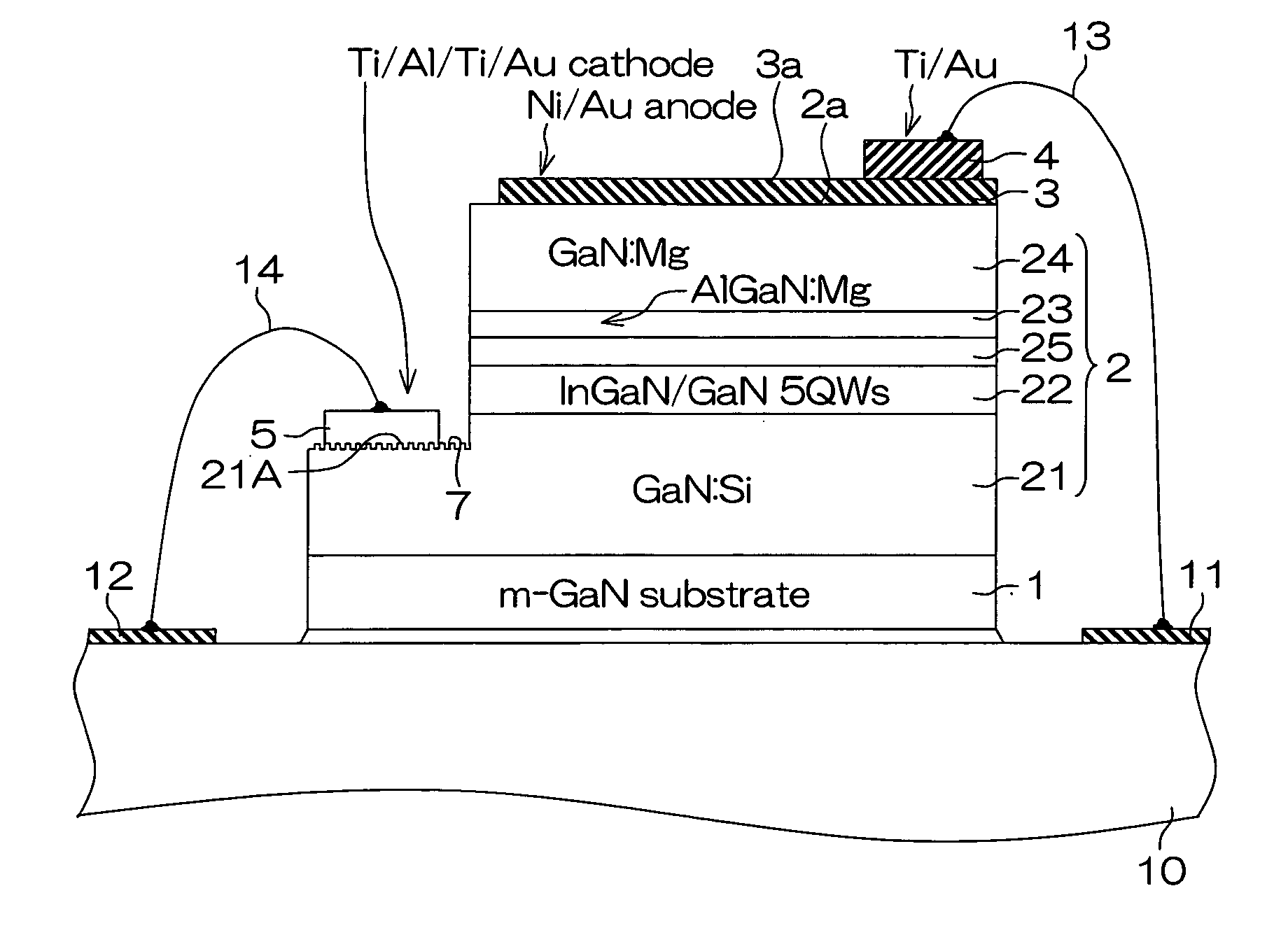
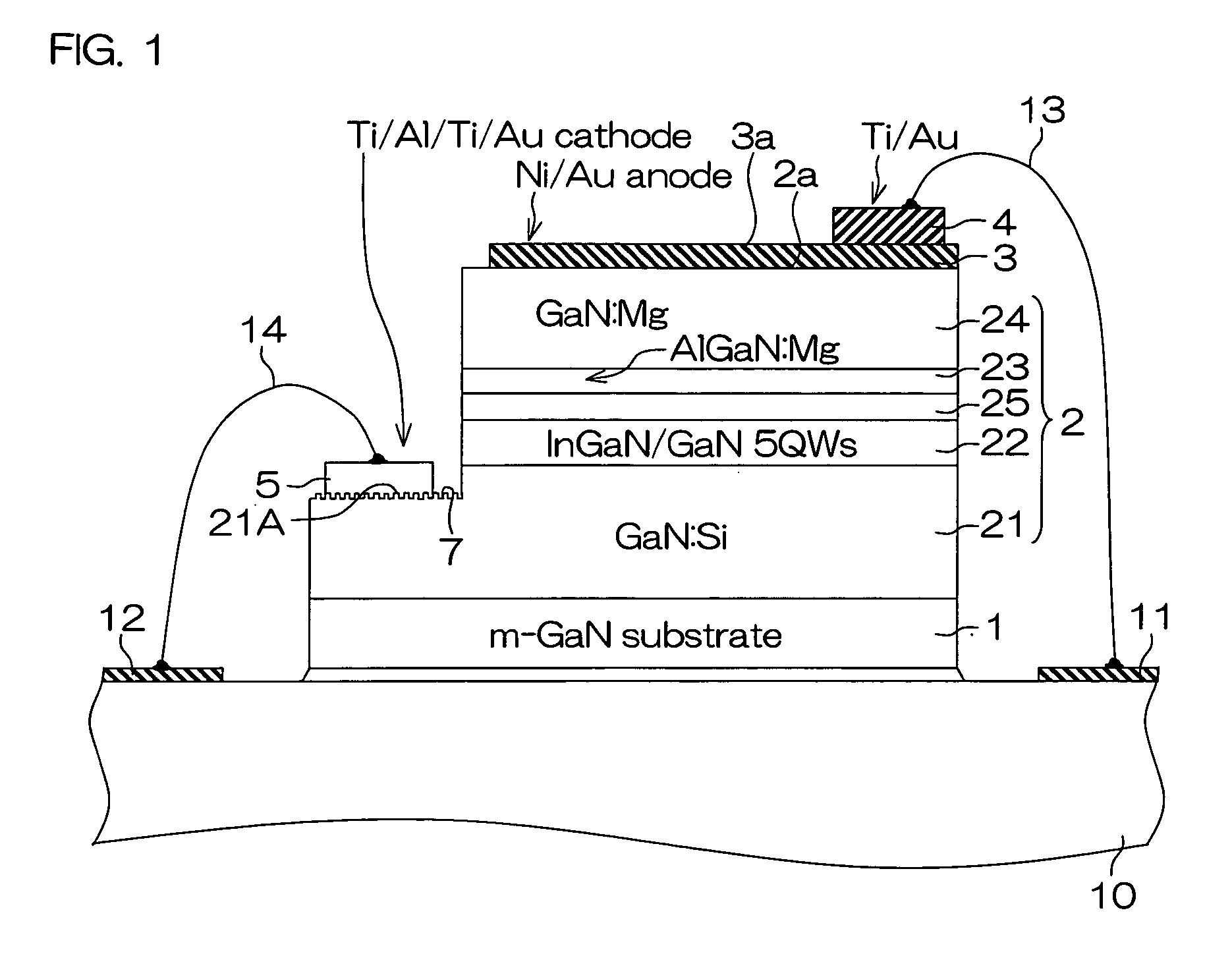
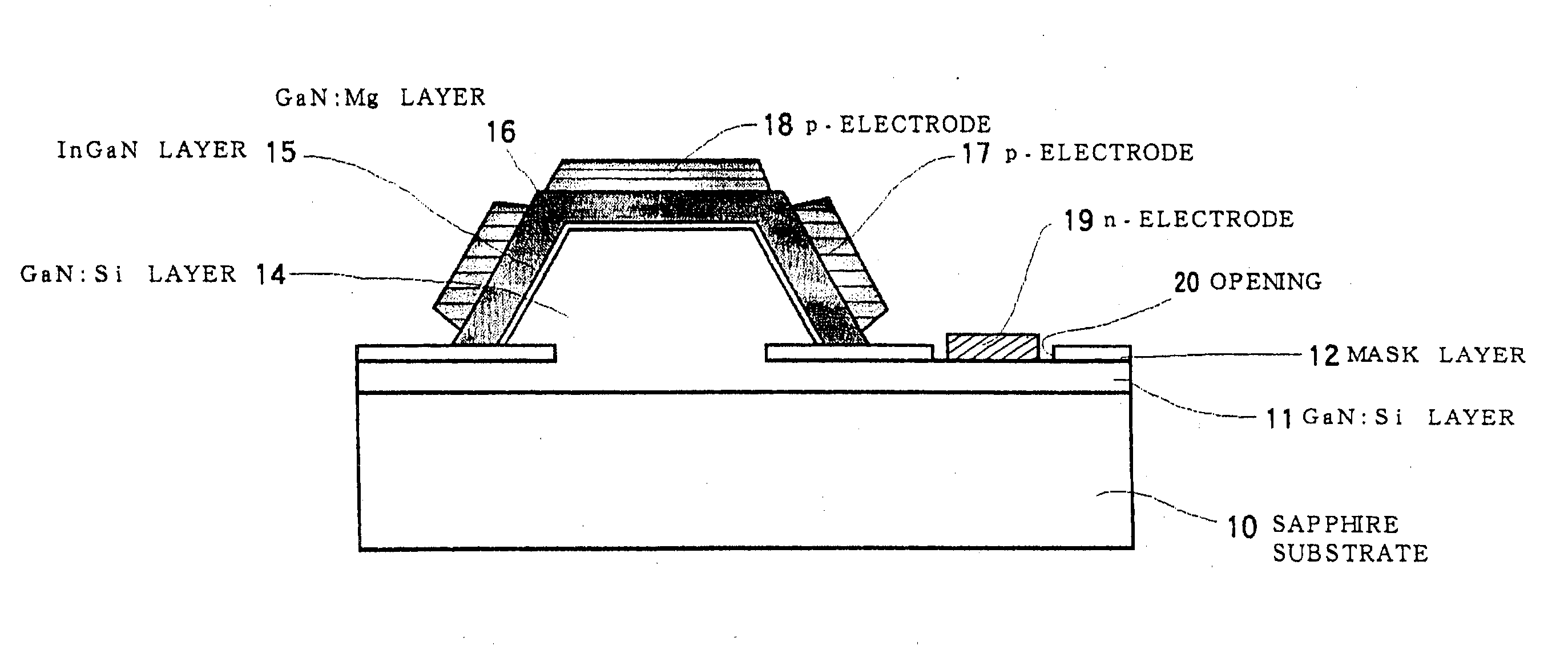
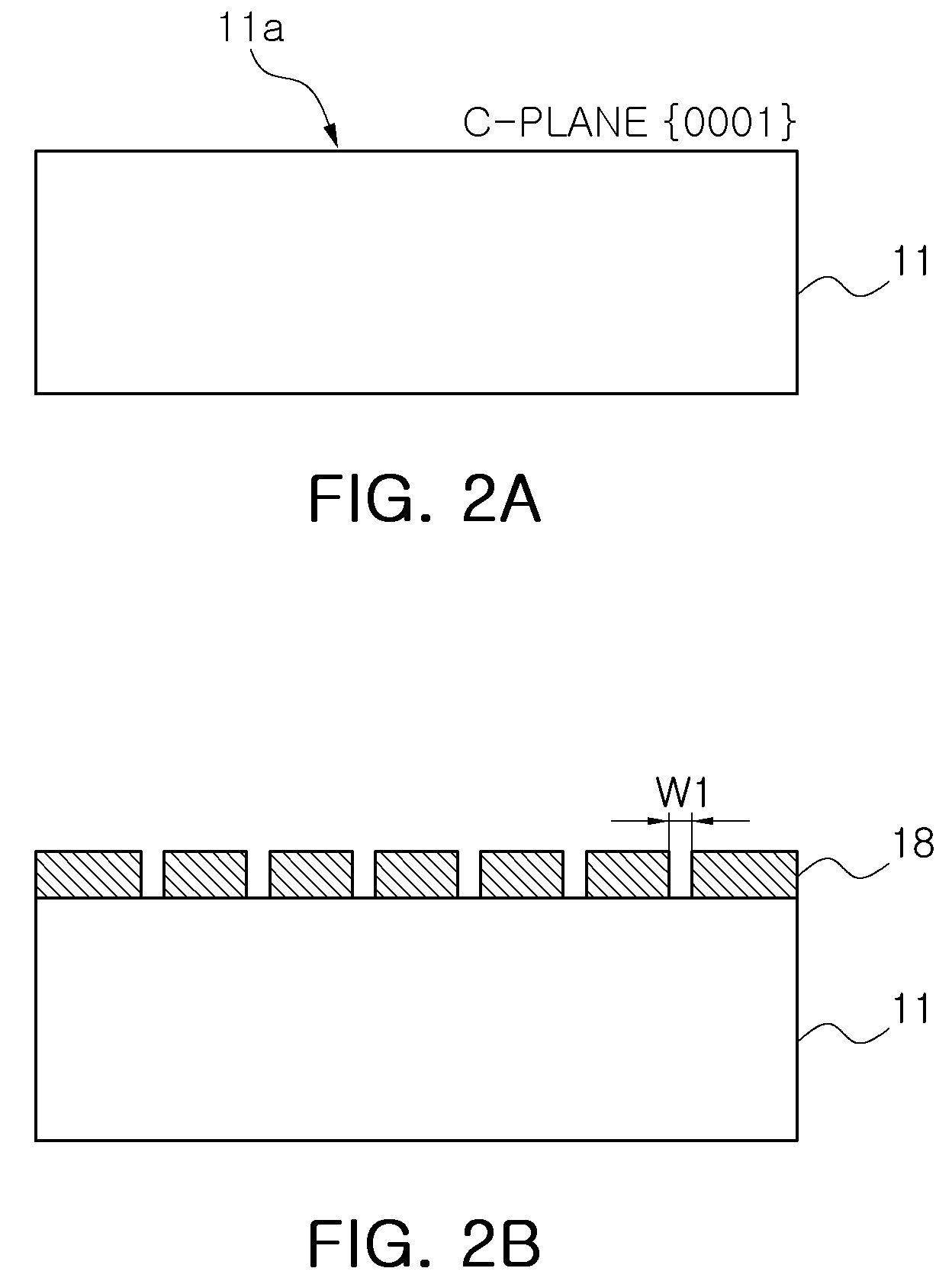
Semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor light-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS20030107047A1Easily feasibleReduce lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyCrystal plane
A semiconductor light-emitting element having a structure that does not complicate a fabrication process, can be formed in high precision and does not invite any degradation of crystallinity is provided. A light-emitting element is formed, which includes a selective crystal growth layer formed by selectively growing a compound semiconductor of a Wurtzite type, and a clad layer of a first conduction type, an active layer and a clad layer of a second conduction type, which are formed on the selective crystal growth layer wherein the active layer is formed so that the active layer extends in parallel to different crystal planes, the active layer is larger in size than a diffusion length of a constituent atom of a mixed crystal, or the active layer has a difference in at least one of a composition and a thickness thereof, thereby forming the active layer having a plurality of light-emitting wavelength region whose emission wavelengths differ from one another. The element is so arranged that an electric current or currents are chargeable into the plurality of light-emitting wavelength regions. Because of the structure based on the selective growth, it is realized that the band gap energy varies within the same active layer, thereby forming an element or device in high precision without complicating a fabrication process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
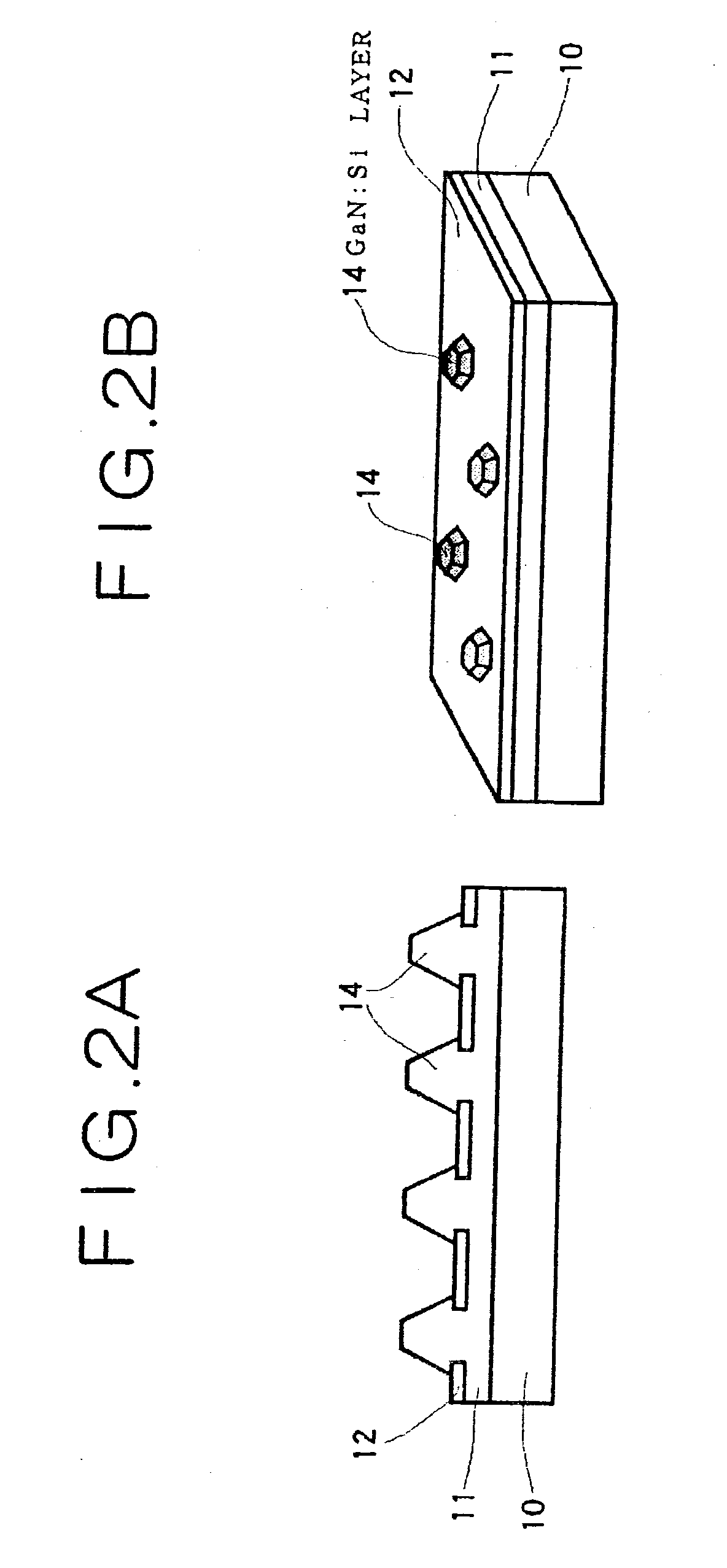
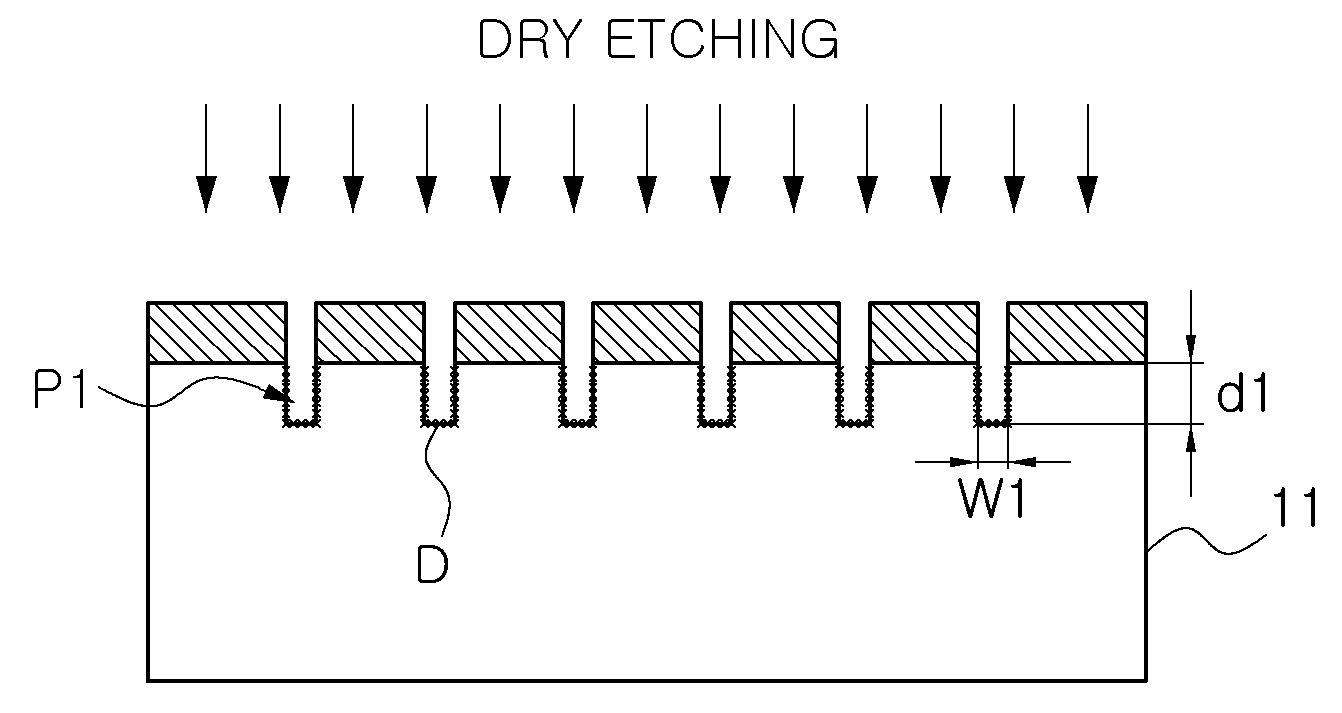
Method of forming fine patterns and manufacturing semiconductor light emitting device using the same
ActiveUS20090087994A1Area minimizationImprove light outputDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal structureEngineering
A method of forming a fine pattern begins with providing a c-plane hexagonal semiconductor crystal. A mask having a predetermined pattern is formed on the semiconductor crystal. The semiconductor crystal is dry-etched by using the mask to form a first fine pattern on the semiconductor crystal. The semiconductor crystal including the first fine pattern is wet-etched to expand the first fine pattern in a horizontal direction to form a second fine pattern. The second fine pattern obtained in the wet-etching the semiconductor crystal has a bottom surface and a sidewall that have unique crystal planes, respectively. The present fine-pattern forming process can be advantageously applied to a semiconductor light emitting device, particularly, to a phonic crystal structure required to have fine patterns or a structure using a surface plasmon resonance principle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
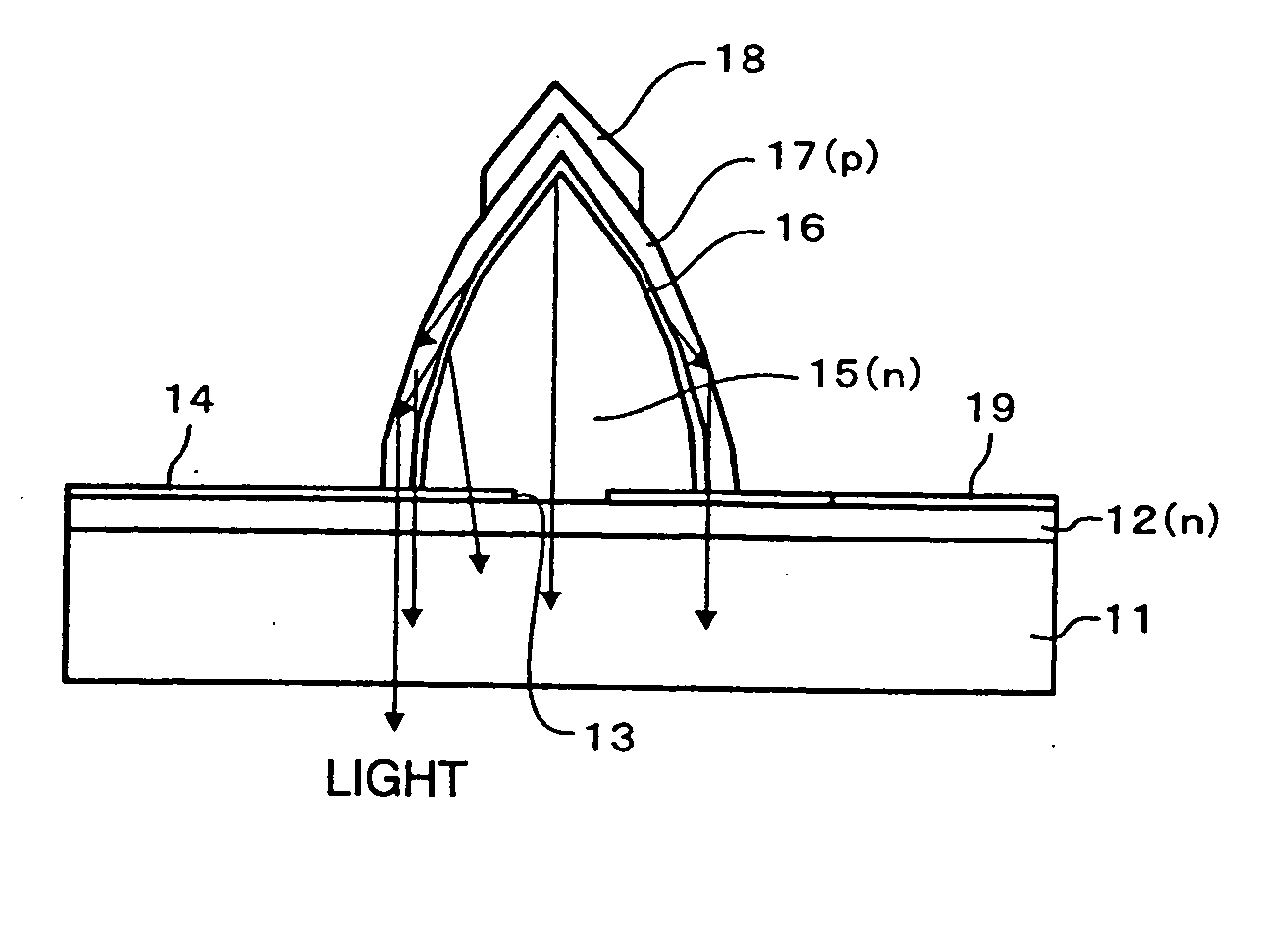
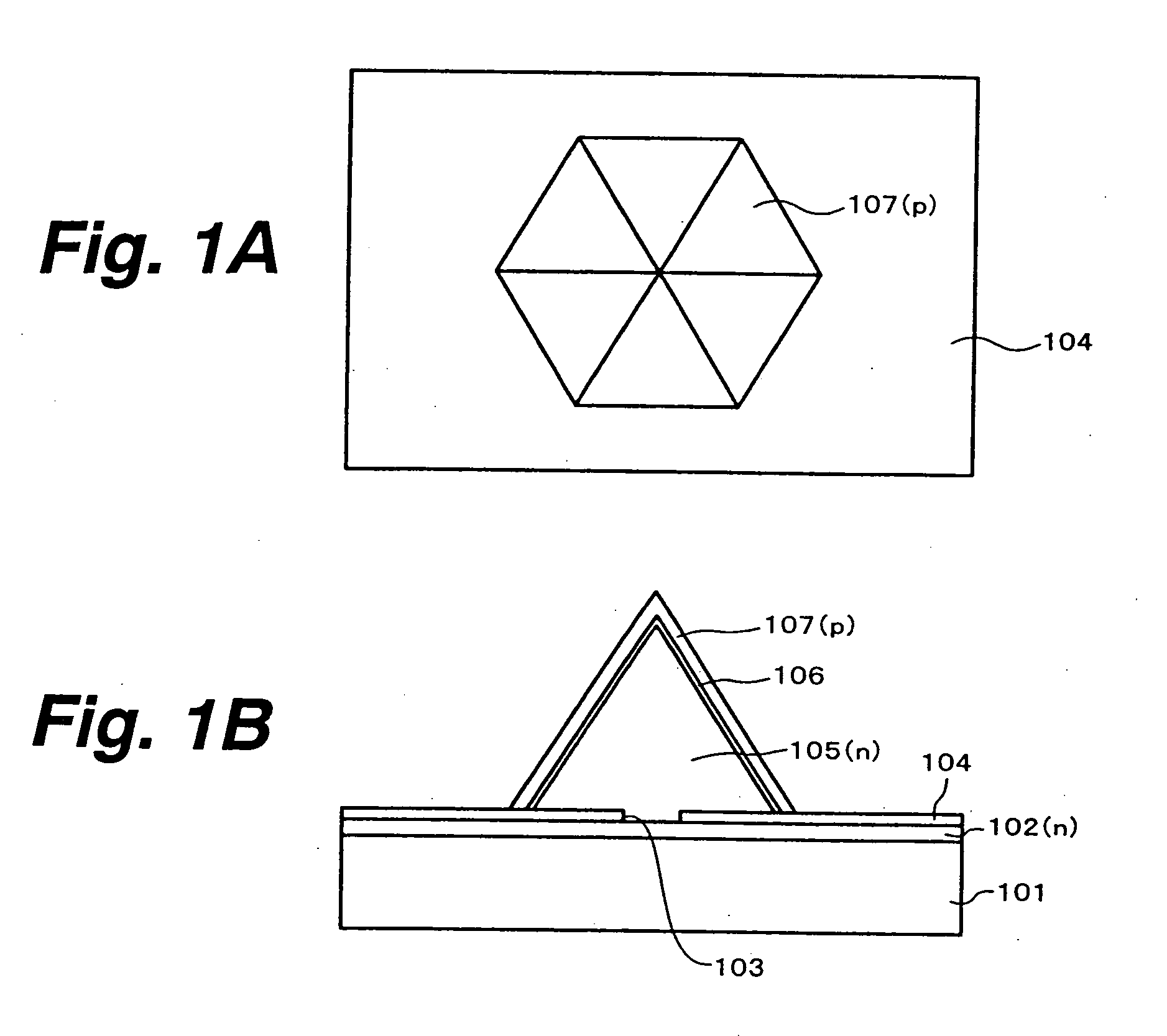
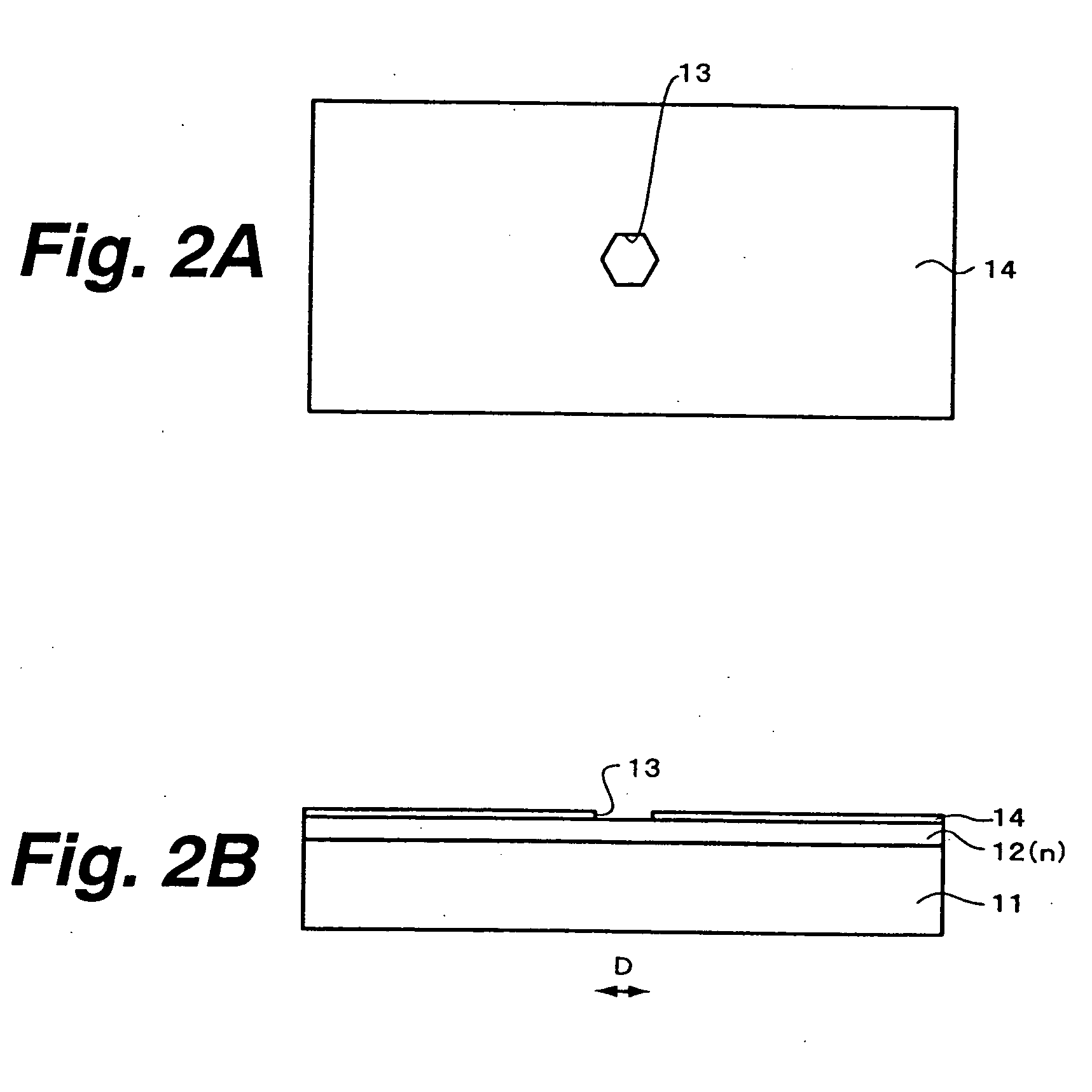
Semiconductor light emitting element and method for manufacturing same, integrated semiconductor light-emitting device and method for manufacturing same, image display and method for manufacturing same, and illuminating device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050145865A1Small sizeLess subjectWater treatment parameter controlFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesDisplay deviceCrystal plane
A semiconductor light emitting element, manufacturing method thereof, integrated semiconductor light emitting device, manufacturing method thereof, illuminating device, and manufacturing method thereof are provided. An n-type GaN layer is grown on a sapphire substrate, and a growth mask of SiN, for example, is formed thereon. On the n-type GaN layer exposed through an opening in the growth mask, a six-sided steeple-shaped n-type GaN layer is selectively grown, which has inclined crystal planes each composed of a plurality of crystal planes inclined from the major surface of the sapphire substrate by different angles of inclination to exhibit a convex plane as a whole. On the n-type GaN layer, an active layer and a p-type GaN layer are grown to make a light emitting element structure. Thereafter, a p-side electrode and an n-side electrode are formed.
Owner:SONY CORP
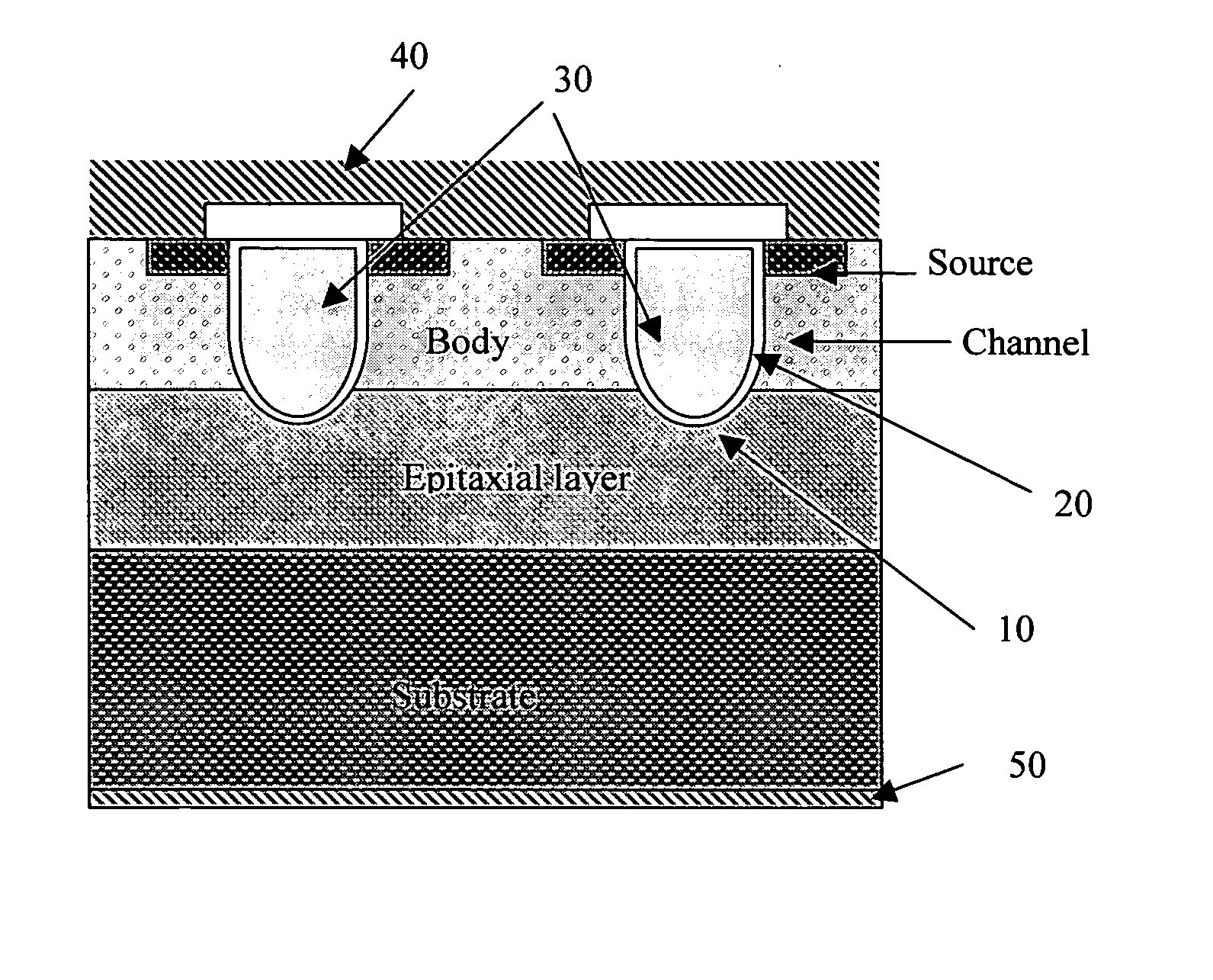
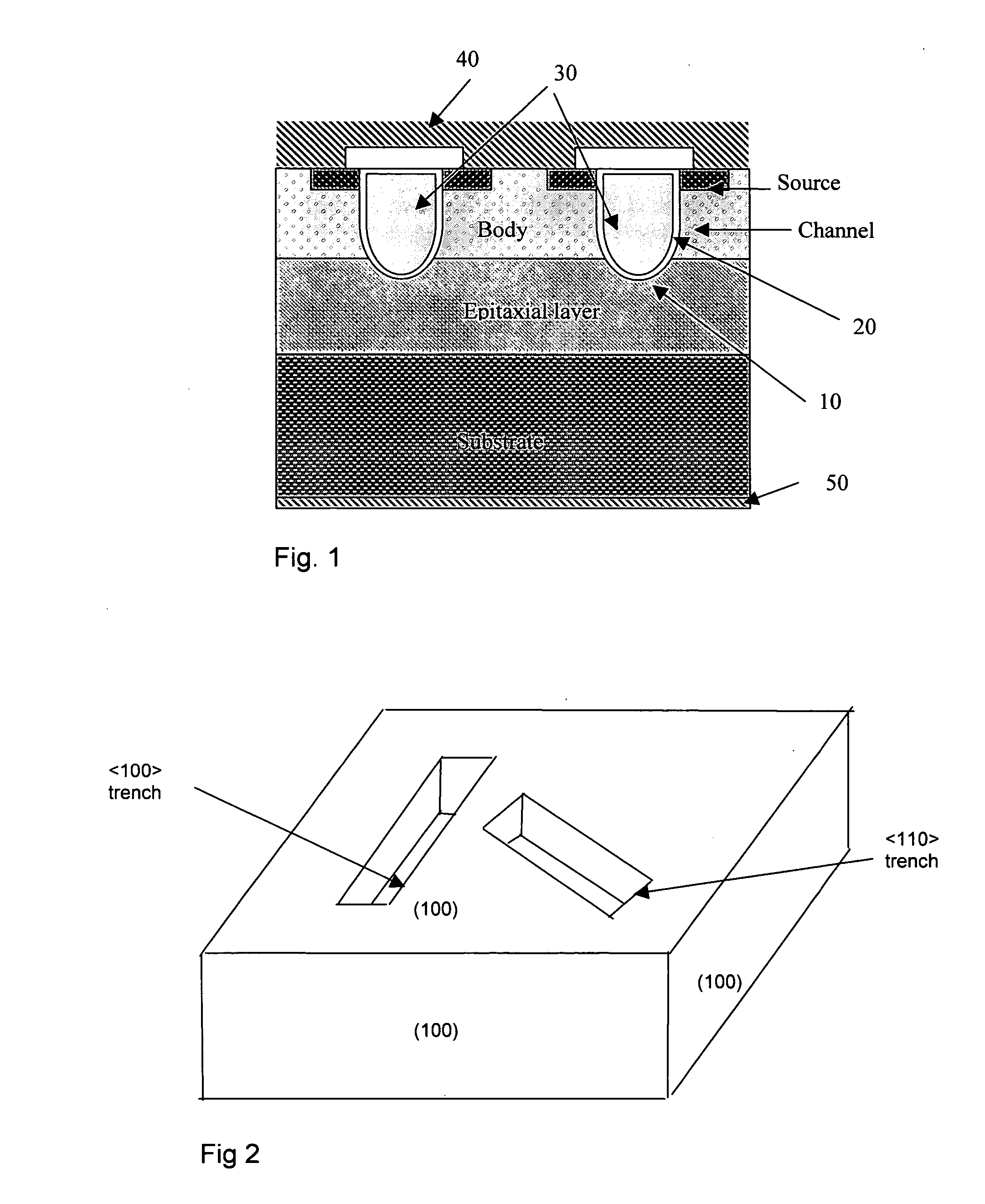
Trenched MOSFETS with part of the device formed on a (110) crystal plane
InactiveUS20060108635A1Overcome limitationsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMOSFETManufacturing technology
This invention discloses an improved MOSFET devices manufactured with a trenched gate by forming part of the trench on a (110) crystal orientation of a semiconductor substrate. The trench is covering with a dielectric oxide layer along the sidewalls and the bottom surface or the termination of the trench formed along different crystal orientations of the semiconductor substrate. Special manufacturing processes such as oxide annealing process, special mask or SOG processes are implemented to overcome the limitations of the non-uniform dielectric layer growth.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
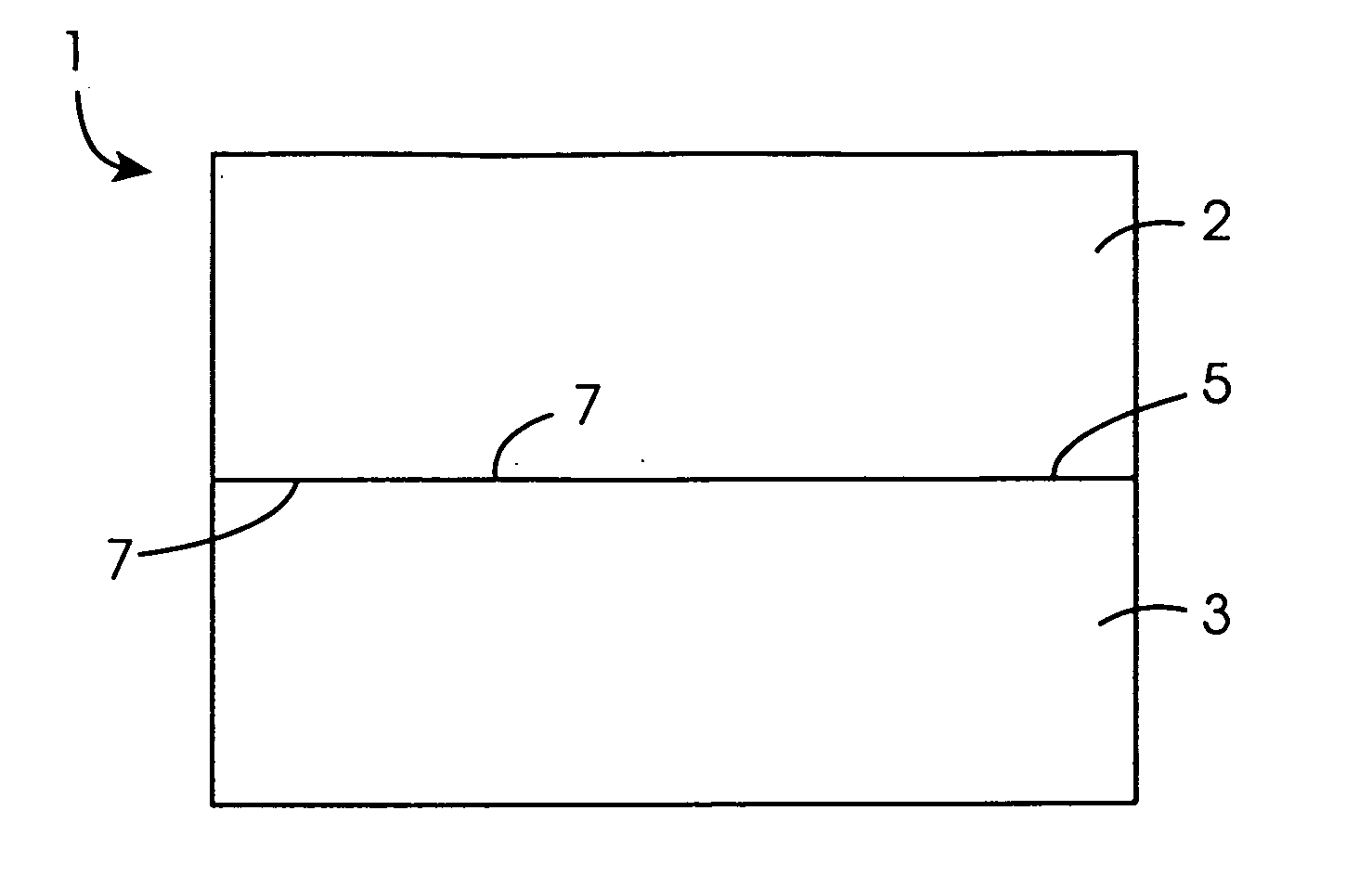
Method for direct bonding two silicon wafers for minimising interfacial oxide and stresses at the bond interface, and an SOI structure
InactiveUS20040087109A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterfacial oxideBond interface
A semiconductor substrate (1) comprises first and second silicon wafers (2,3) directly bonded together with interfacial oxide and interfacial stresses minimised along a bond interface (5), which is defined by bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3). Interfacial oxide is minimised by selecting the first and second wafers (2,3) to be of relatively low oxygen content, well below the limit of solid solubility of oxygen in the wafers. In order to minimise interfacial stresses, the first and second wafers are selected to have respective different crystal plane orientations. The bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are polished and cleaned, and are subsequently dried in a nitrogen atmosphere. Immediately upon being dried, the bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are abutted together and the wafers (2,3) are subjected to a preliminary anneal at a temperature of at least 400° C. for a time period of a few hours. As soon as possible after the preliminary anneal, and preferably, within forty-eight hours of the preliminary anneal, the first and second wafers (2,3) are fusion bonded at a bond anneal temperature of approximately 1,150° C. for a time period of approximately three hours. The preliminary anneal may be omitted if fusion bonding at the bond anneal temperature is carried out within approximately six hours of the wafers (2,3) being abutted together. An SOI structure (50) may subsequently be prepared from the semiconductor structure (1) which forms a substrate layer (52) supported on a handle layer (55) with a buried insulating layer (57) between the substrate layer (52) and the handle layer (55).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method of forming epi film in substrate trench
ActiveUS20110101421A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCrystal plane
The present disclosure provides a method of fabricating a semiconductor device that includes providing a semiconductor substrate, forming a trench in the substrate, where a bottom surface of the trench has a first crystal plane orientation and a side surface of the trench has a second crystal plane orientation, and epitaxially (epi) growing a semiconductor material in the trench. The epi process utilizes an etch component. A first growth rate on the first crystal plane orientation is different from a second growth rate on the second crystal plane orientation.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
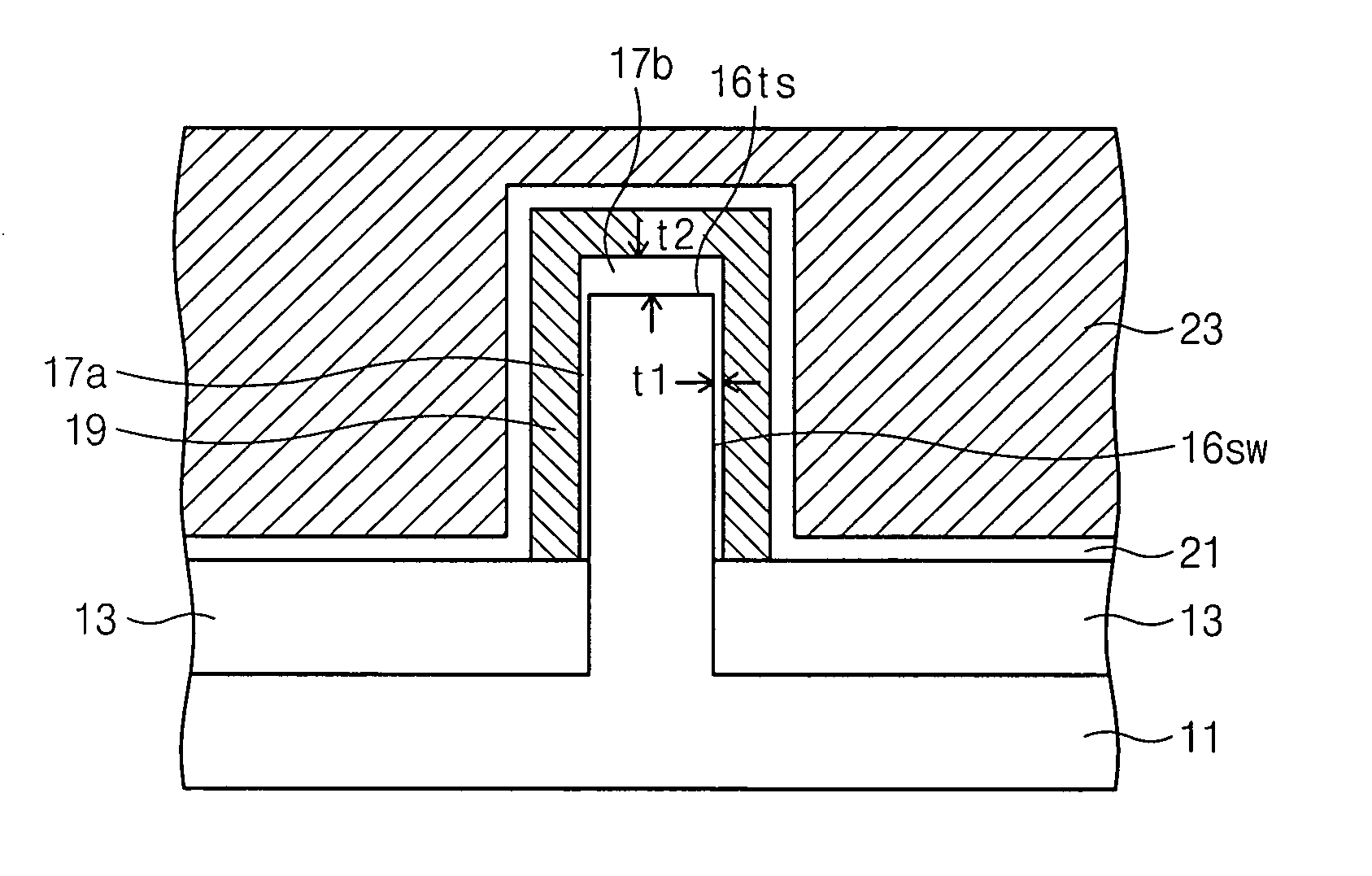
FinFET and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080135888A1Overcome problemsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricCrystal plane
A FinFET may include a semiconductor fin having a top surface and a sidewall having different crystal planes. A gate dielectric layer on the top surface and on the sidewall has different thicknesses. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric layer across the top surface and sidewall of the semiconductor fin.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com