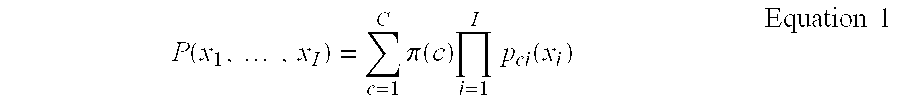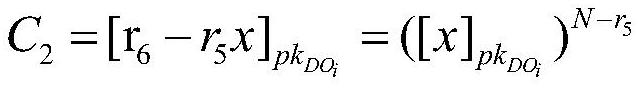Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Sparse data sets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
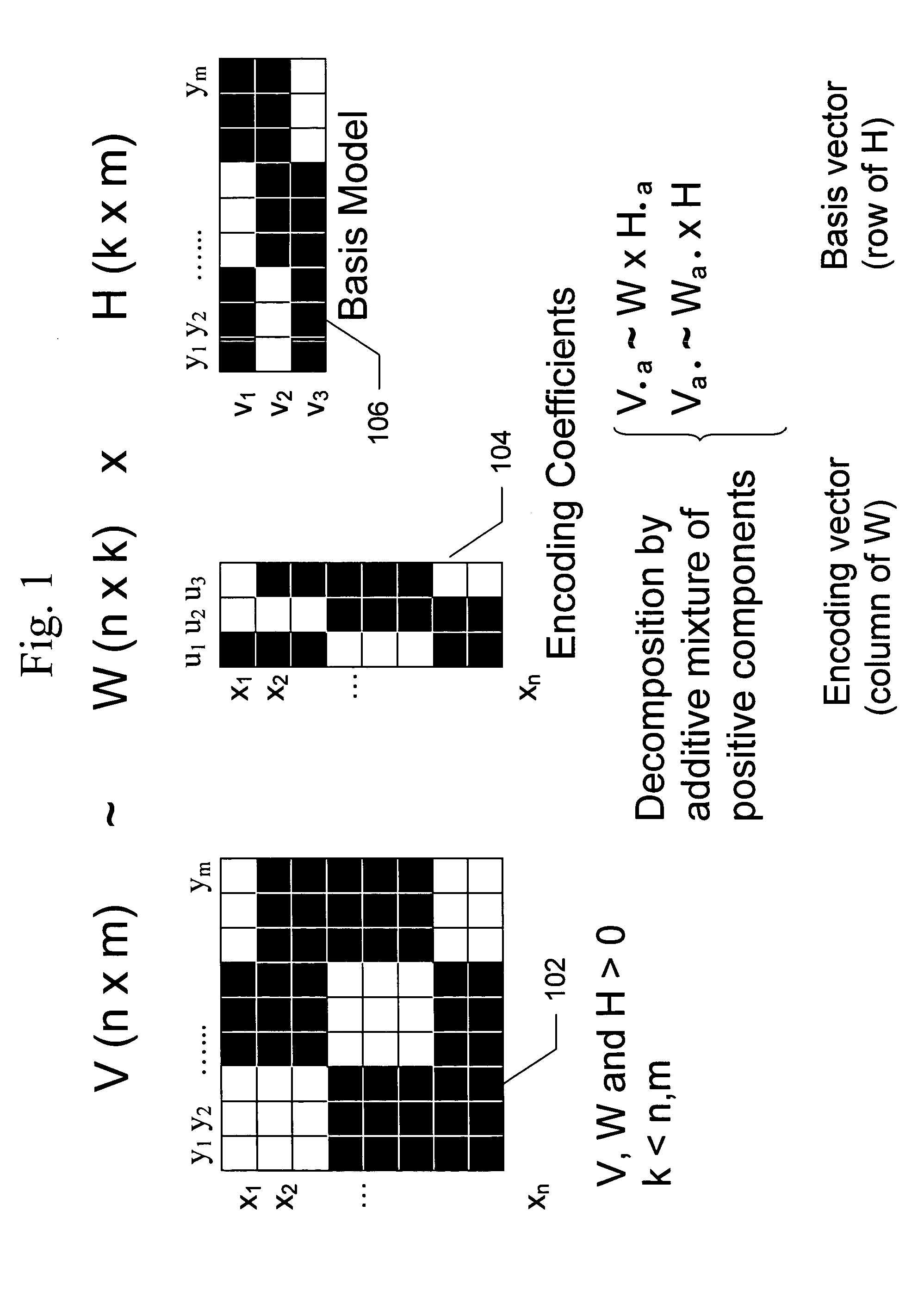
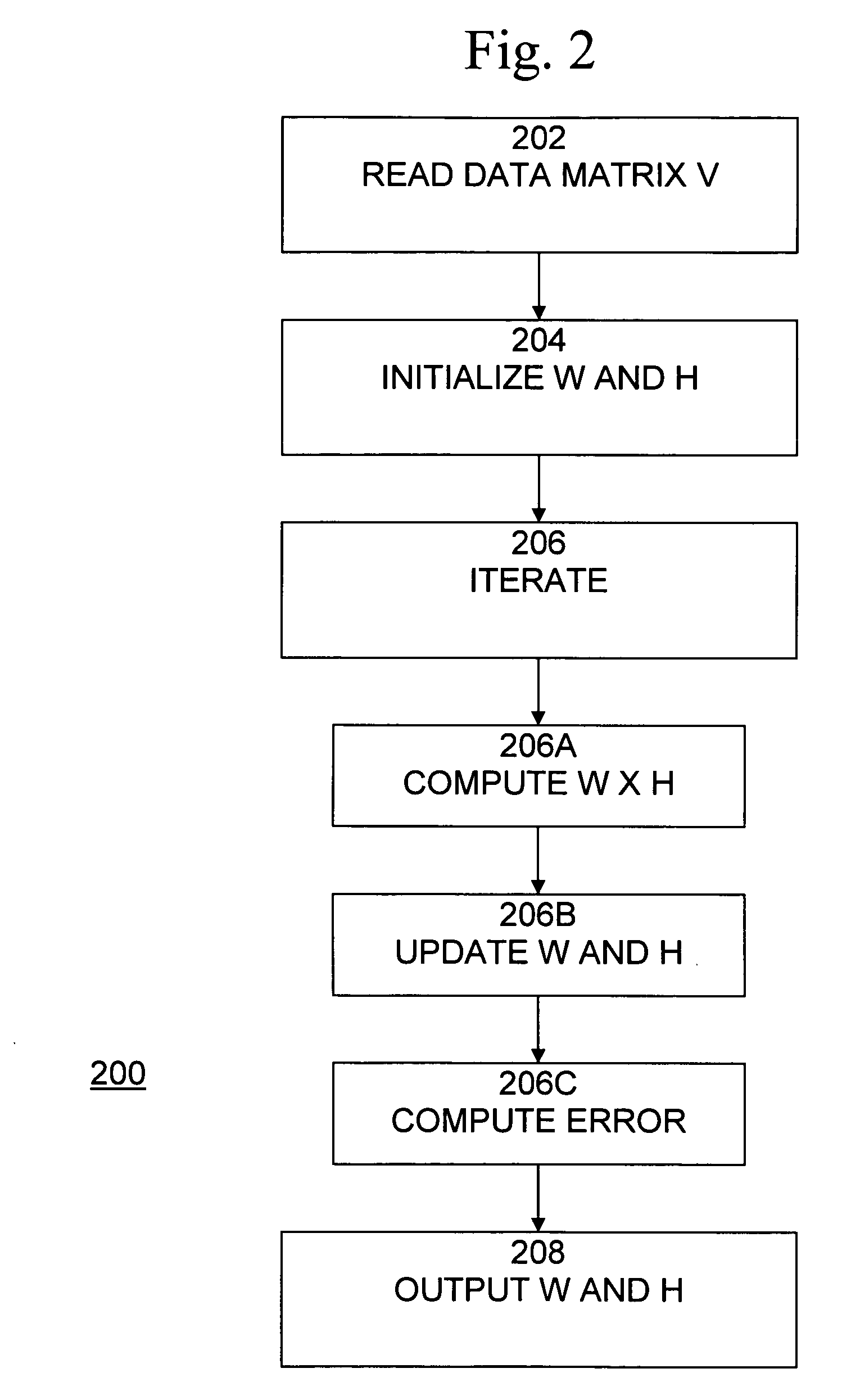
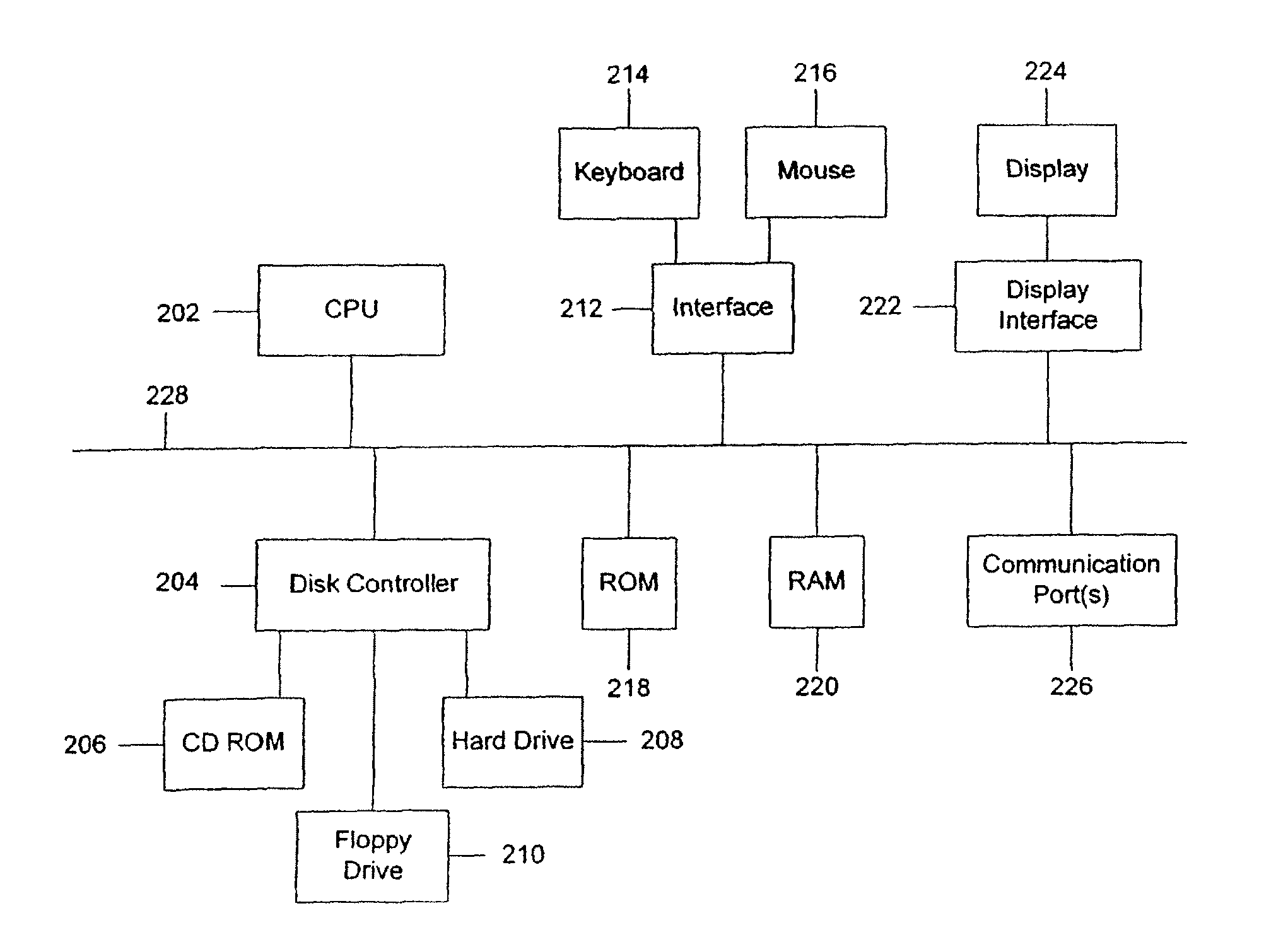
Non-negative matrix factorization from the data in the multi-dimensional data table using the specification and to store metadata representing the built relational database management system
ActiveUS7734652B2High indexDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesRelational database management systemMultidimensional data
An implementation of NMF functionality integrated into a relational database management system provides the capability to apply NMF to relational datasets and to sparse datasets. A database management system comprises a multi-dimensional data table operable to store data and a processing unit operable to perform non-negative matrix factorization on data stored in the multi-dimensional data table and to generate a plurality of data tables, each data table being smaller than the multi-dimensional data table and having reduced dimensionality relative to the multi-dimensional data table. The multi-dimensional data table may be a relational data table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
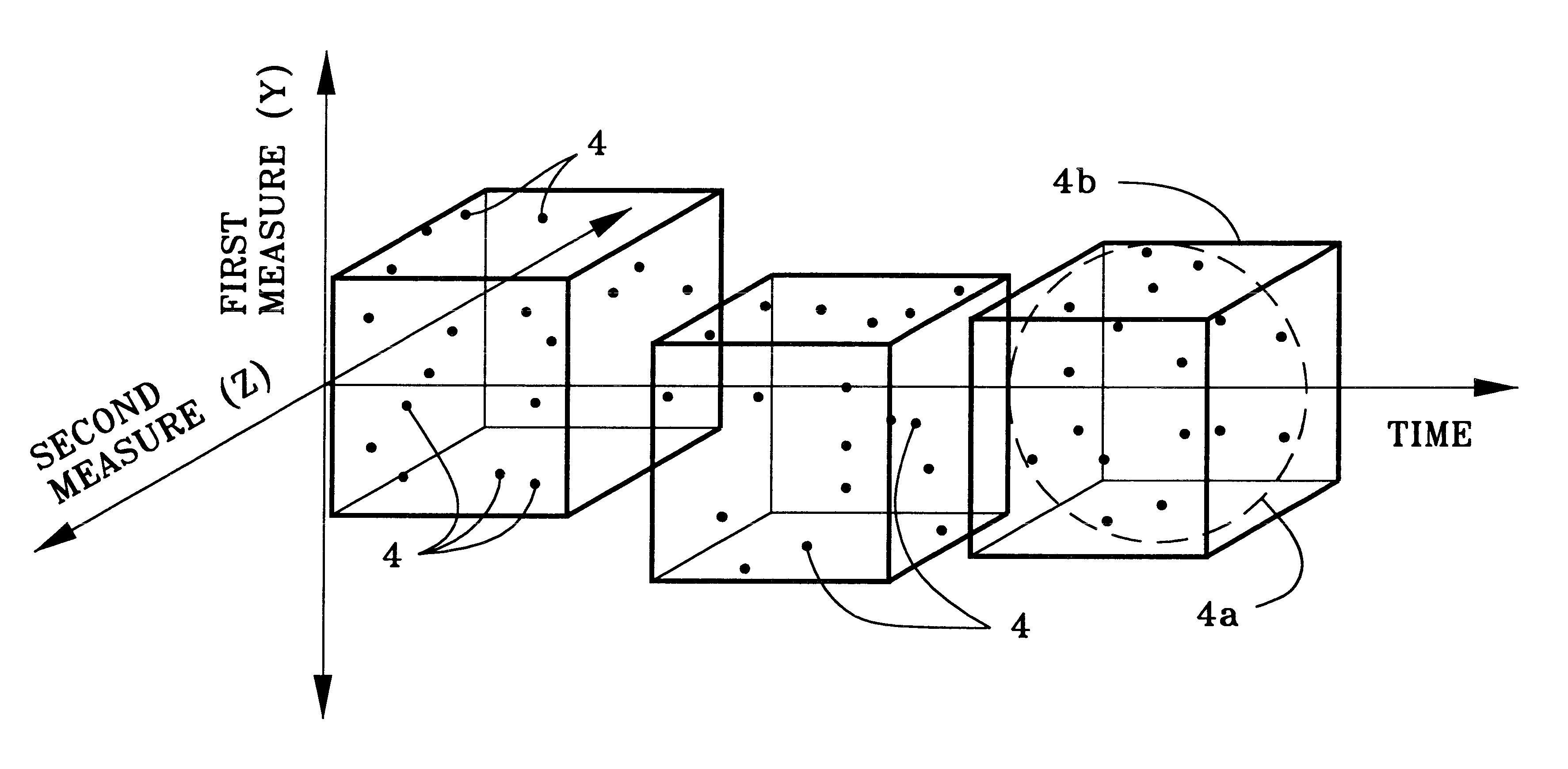
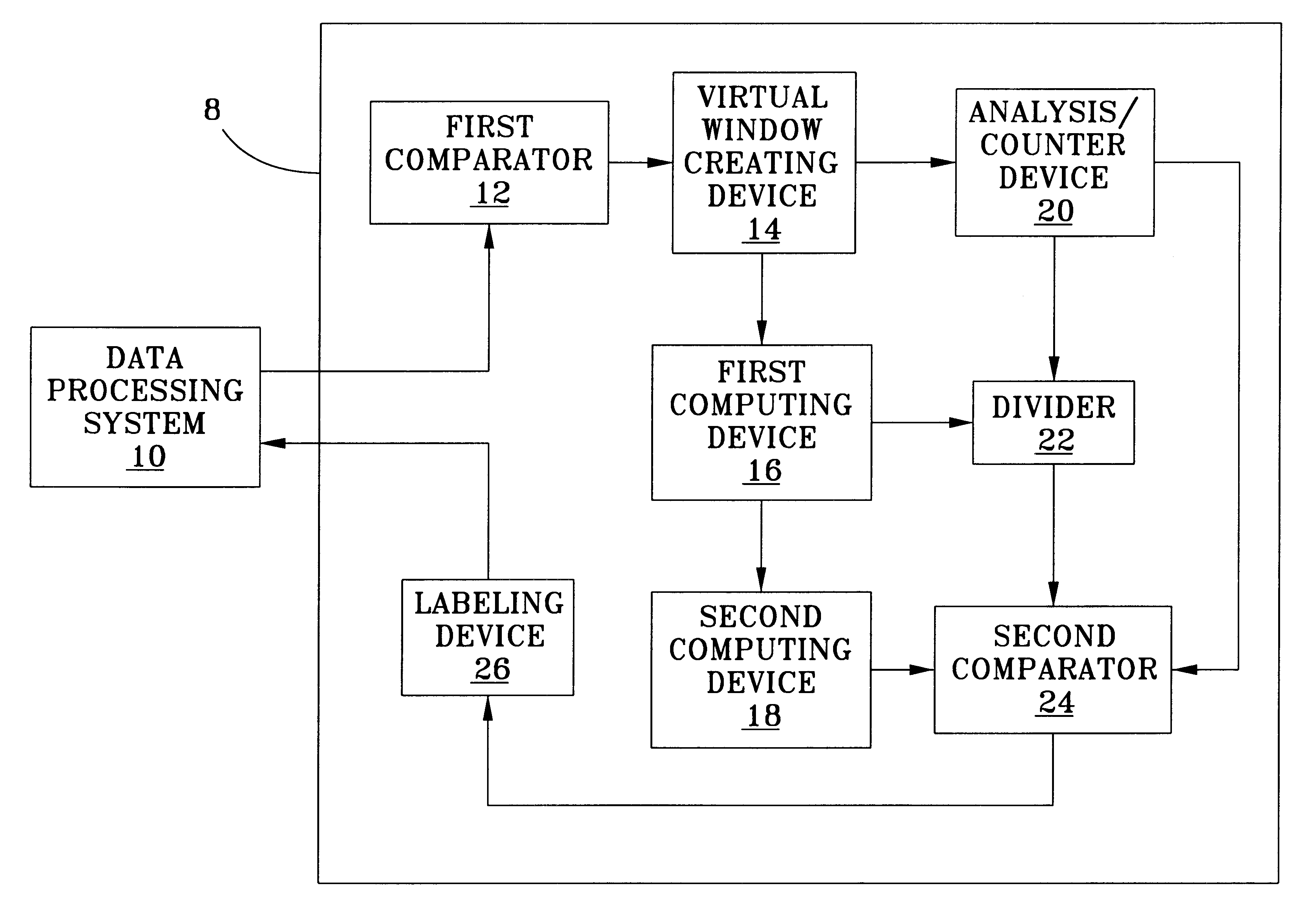
System and apparatus for the detection of randomness in three dimensional time series distributions made up of sparse data sets
InactiveUS6466516B1High sensitivityAppropriate detectionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionDigital computer detailsData processing systemComputer science
A method and apparatus are provided for automatically characterizing the spatial arrangement among the data points of a three-dimensional time series distribution in a data processing system wherein the classification of said time series distribution is required. The method and apparatus utilize grids in Cartesian coordinates to determine (1) the number of cubes in the grids containing at least one input data point of the time series distribution; (2) the expected number of cubes which would contain at least one data point in a random distribution in said grids; and (3) an upper and lower probability of false alarm above and below said expected value utilizing a discrete binomial probability relationship in order to analyze the randomness characteristic of the input time series distribution. A labeling device also is provided to label the time series distribution as either random or nonrandom, and / or random or nonrandom within what probability, prior to its output from the invention to the remainder of the data processing system for further analysis.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System and method for large scale survey analysis
InactiveUS8005712B2Computer-assisted medical data acquisitionElectrical appliancesOriginal dataSurvey result
Disclosed herein is a method of analyzing large scale survey results comprising obtaining a sparse data set representing a subset of an original data set comprising a plurality of individuals' responses to a plurality of questions, wherein the sparse data set comprises less than ninety percent of the responses in the original data set; analyzing the sparse data set using a general diagnostic model; and obtaining estimated person parameters using the general diagnostic model.
Owner:EDUCATIONAL TESTING SERVICE
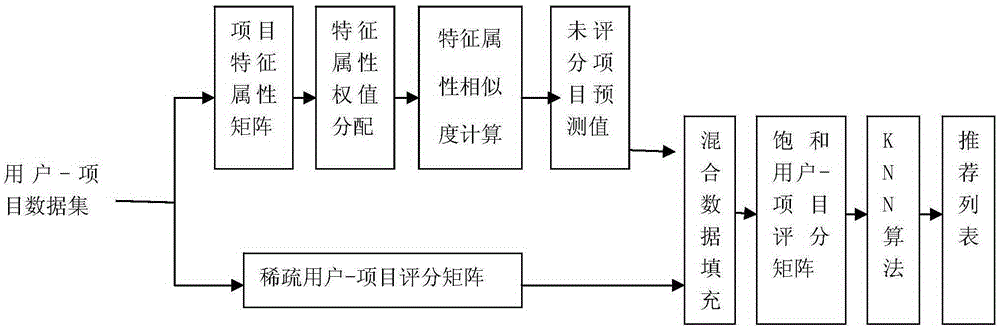
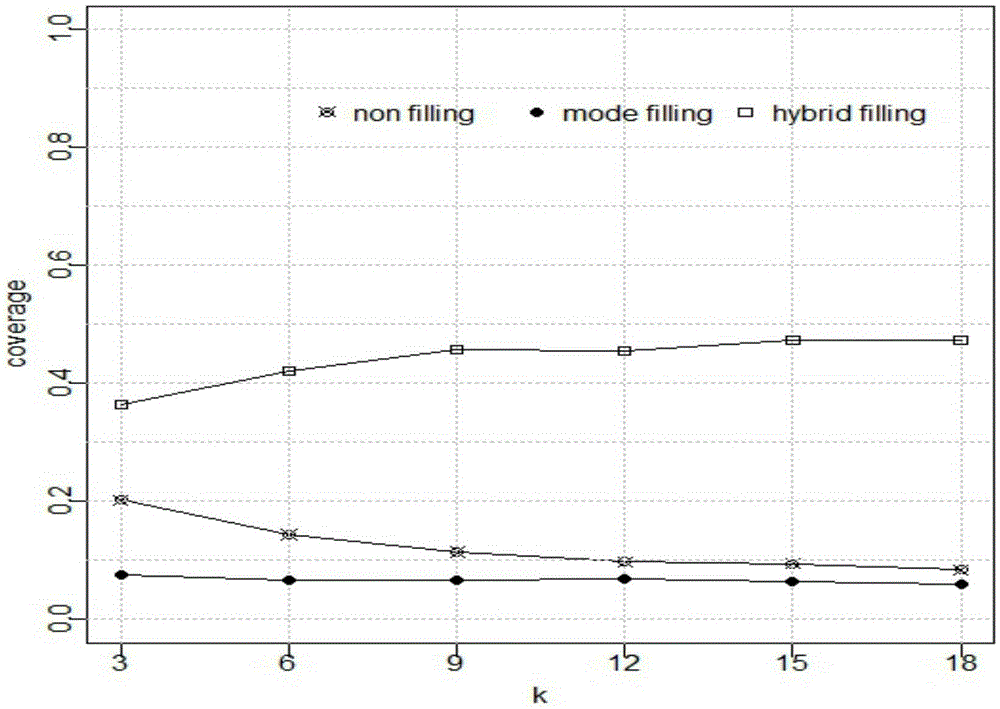
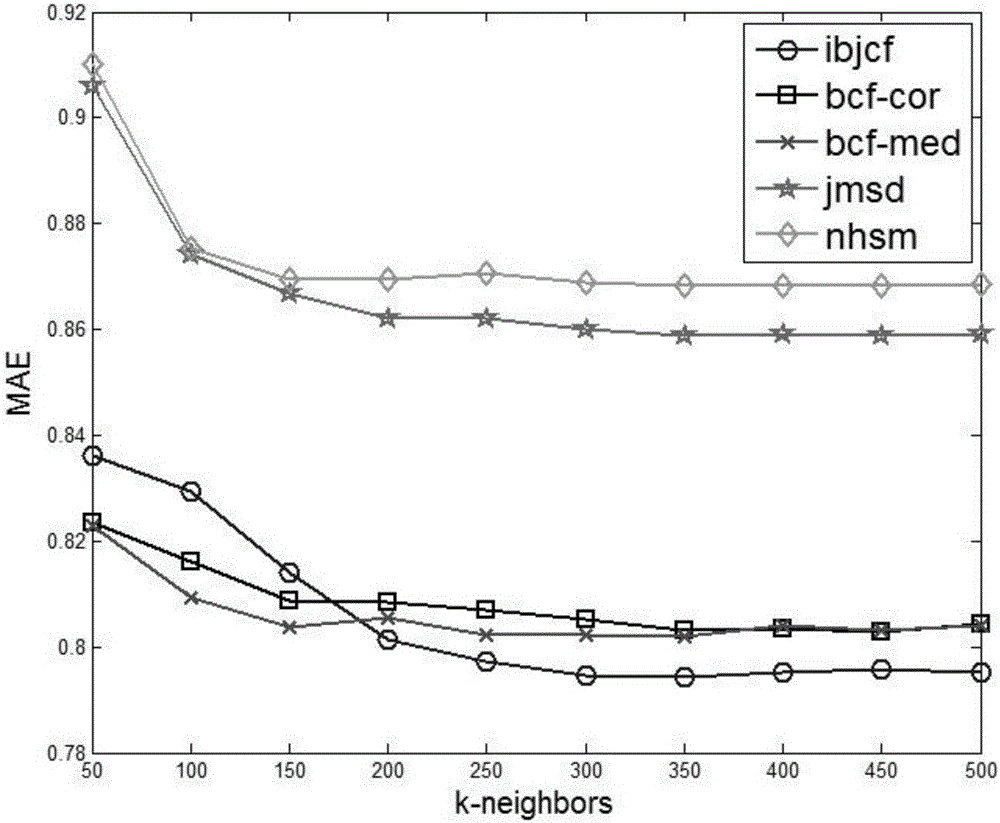
Sparse data preprocessing based collaborative filtering recommendation method
InactiveCN105354330ASolve the problem of consistent scoringMulti-valueSpecial data processing applicationsData miningComputer science
The invention discloses a sparse data preprocessing based collaborative filtering recommendation method. The method is carried out based on information of a project; firstly, characteristic attribute information of the project is introduced, and different weights are allocated to each characteristic attribute; the similarity of the characteristic attributes among projects is calculated; the score on non-graded projects from users is predicted initially; then hybrid filling preprocessing is preformed on the non-graded projects in a spare data set to enable the sparse users and project data matrix to be fully saturated. The problems of low recommendation precision and low recommendation coverage caused by that the sparse data are not processed or fixed values are adopted for filling in the conventional method are effectively solved by the sparse data preprocessing based collaborative filtering recommendation method provided by the invention, so that the recommendation performance of a recommendation system based on the sparse data preprocessing based collaborative filtering recommendation method is well improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A user similarity-based sparse data collaborative filtering recommendation method
InactiveCN106021329AGlobal similarity is accurateImprove recommendation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsUser needsPattern recognition
The invention provides a user similarity-based sparse data collaborative filtering recommendation method and mainly aims to solves the problems in the prior art that the calculation of the values of similarity between users is in accurate for sparse data and further the recommendation quality is influenced. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a sparse matrix for item scores from users; (2) calculating the overall situation similarity between any two items; (3) calculating the local similarity between any two user scores; (4) calculating the similarity between any two users; (5) predicting scores; (6) generating a recommendation list; (7) completing collaborative filtering item recommendation for all the users. Experimental simulation results show that for sparse data sets, the method has the advantages of guaranteeing higher accuracy of the similarity between users, improving the recommendation quality and better meeting user requirements compared with conventional collaborative filtering recommendation methods.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
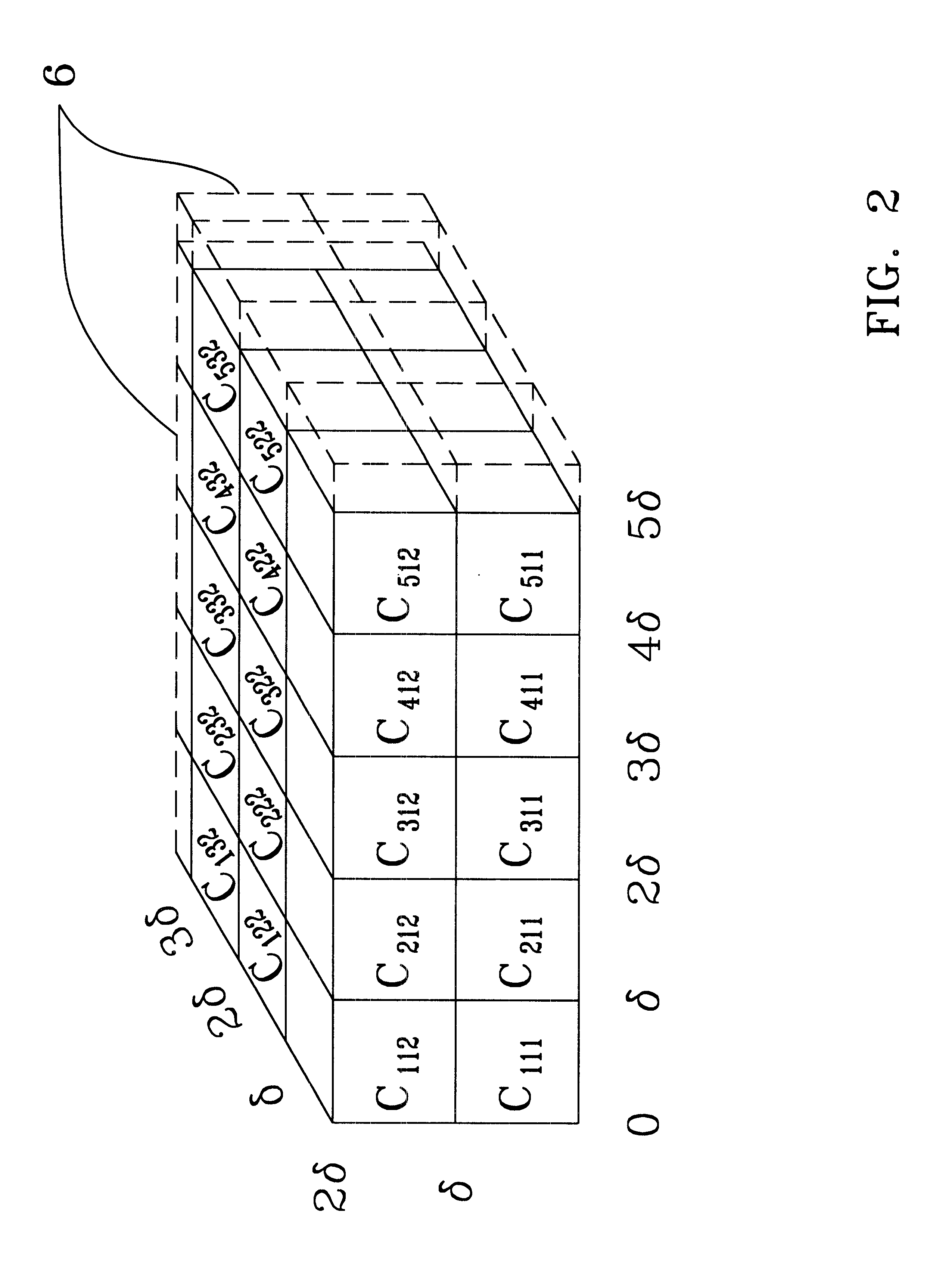
System and apparatus for the detection of randomness in time series distributions made up of sparse data sets
InactiveUS6397234B1High sensitivityAppropriate detectionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData processing systemComputer science
A method and apparatus are provided for automatically characterizing the spatial arrangement among the data points of a time series distribution in a data processing system wherein the classification of said time series distribution is required. The method and apparatus utilize a grid in Cartesian coordinates to determine (1) the number of cells in the grid containing at least-one input data point of the time series distribution; (2) the expected number of cells which would contain at least one data point in a random distribution in said grid; and (3) an upper and lower probability of false alarm above and below said expected value utilizing a discrete binomial probability relationship in order to analyze the randomness characteristic of the input time series distribution. A labeling device also is provided to label the time series distribution as either random or nonrandom, and / or random or nonrandom.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
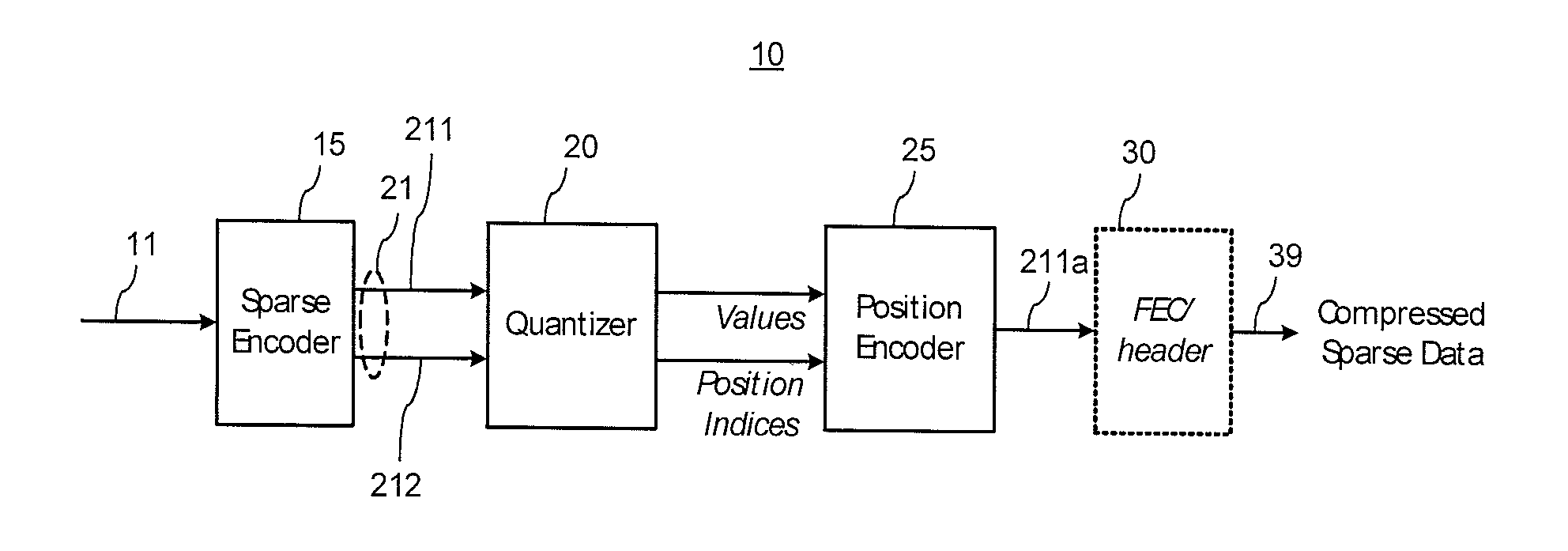
Sparse data compression
The invention relates to compressing of sparse data sets contains sequences of data values and position information therefor. The position information may be in the form of position indices defining active positions of the data values in a sparse vector of length N. The position information is encoded into the data values by adjusting one or more of the data values within a pre-defined tolerance range, so that a pre-defined mapping function of the data values and their positions is close to a target value. In one embodiment, the mapping function is defined using a sub-set of N filler values which elements are used to fill empty positions in the input sparse data vector. At the decoder, the correct data positions are identified by searching though possible sub-sets of filler values.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Backdoor attack method of video analysis neural network model
ActiveCN111260059AIncrease success rateReduce distractionsMathematical modelsInternal combustion piston enginesNoise (video)Algorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of neural network security, and particularly relates to a backdoor attack method of a video analysis neural network model. For more severe backdoor attackimplementation environments such as a high sample dimension, a high frame resolution and a sparse data set of a video, a video backdoor pollution sample construction framework is used for carrying outbackdoor attack on a video analysis neural network model. The video backdoor pollution sample construction framework comprises three parts: a task-oriented model high-sensitivity video backdoor modegeneration algorithm, a feature fuzzy model low-sensitivity anti-noise video sample generation algorithm and a pollution sample generation and attack algorithm; gradient information is introduced fromtwo aspects of a backdoor mode and an original sample to establish association between an attack target value and the backdoor mode. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high attack success rate, high secrecy, good robustness, good expansibility and the like, and has very good generalization in a video analysis neural network model.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
K-anonymous privacy protection method adopting density-based partition
InactiveCN107292195AHigh similarityReduce lossesCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data protectionOriginal dataTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a k-anonymous privacy protection method adopting density-based partition, namely, a DBTP-MDAV (density-based twice partition-MDAV) method, and relates to the technical field of anonymous privacy protection. The method comprises the steps of firstly performing primary division on an original data set by using a density-based method to obtain aggregated clusters with relatively high tuple similarity; and secondly, performing secondary division on the aggregated clusters by using a classic micro-aggregation method, thereby enabling the data set to reach optimal k partition and reducing information loss of an anonymous process. Through a large amount of experiments, the proposed DBTP-MDAV method can effectively reduce the information loss of the anonymous process and improve the availability of the released data set. The method has remarkable advantages for performing anonymous processing on a sparse data set.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
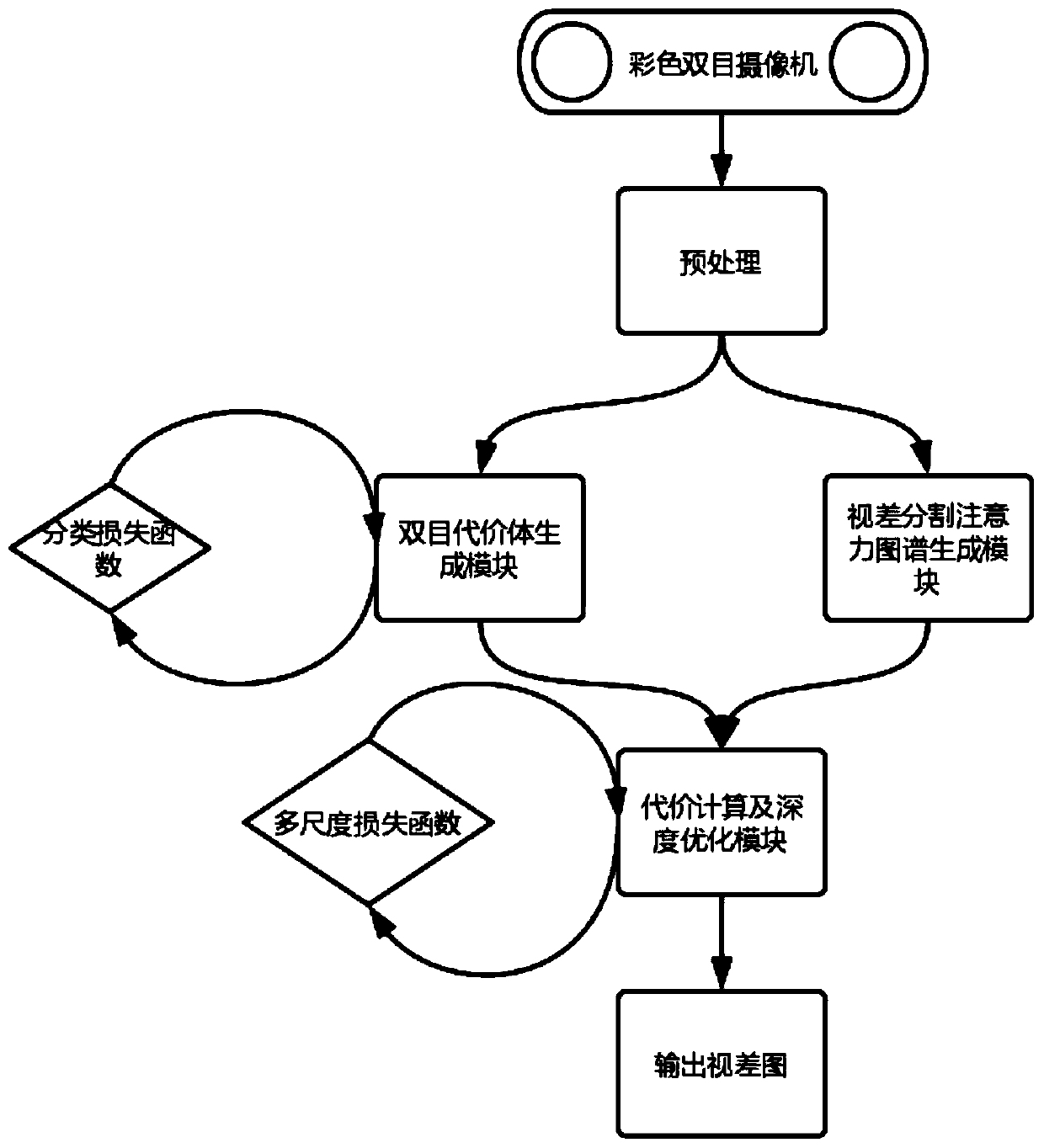
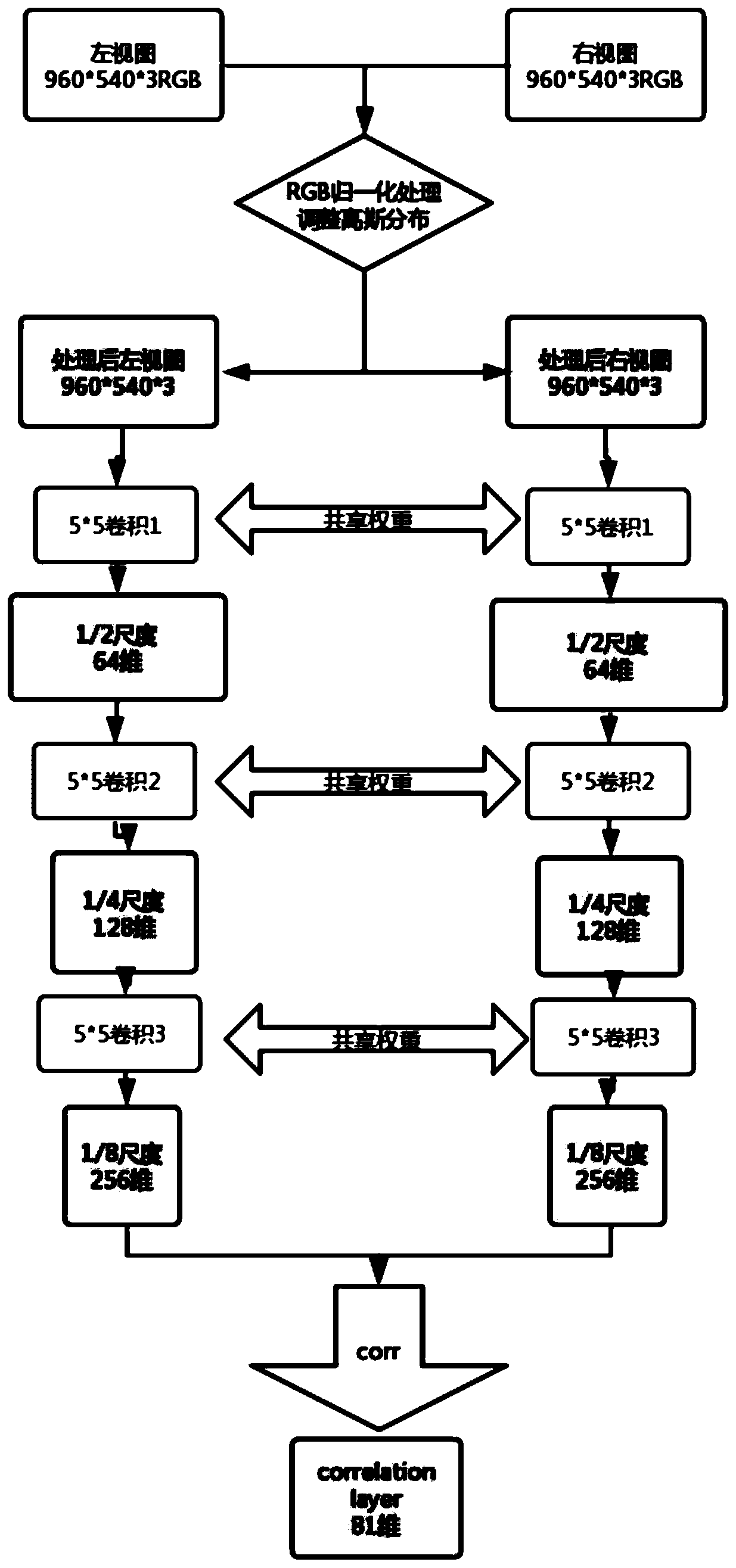
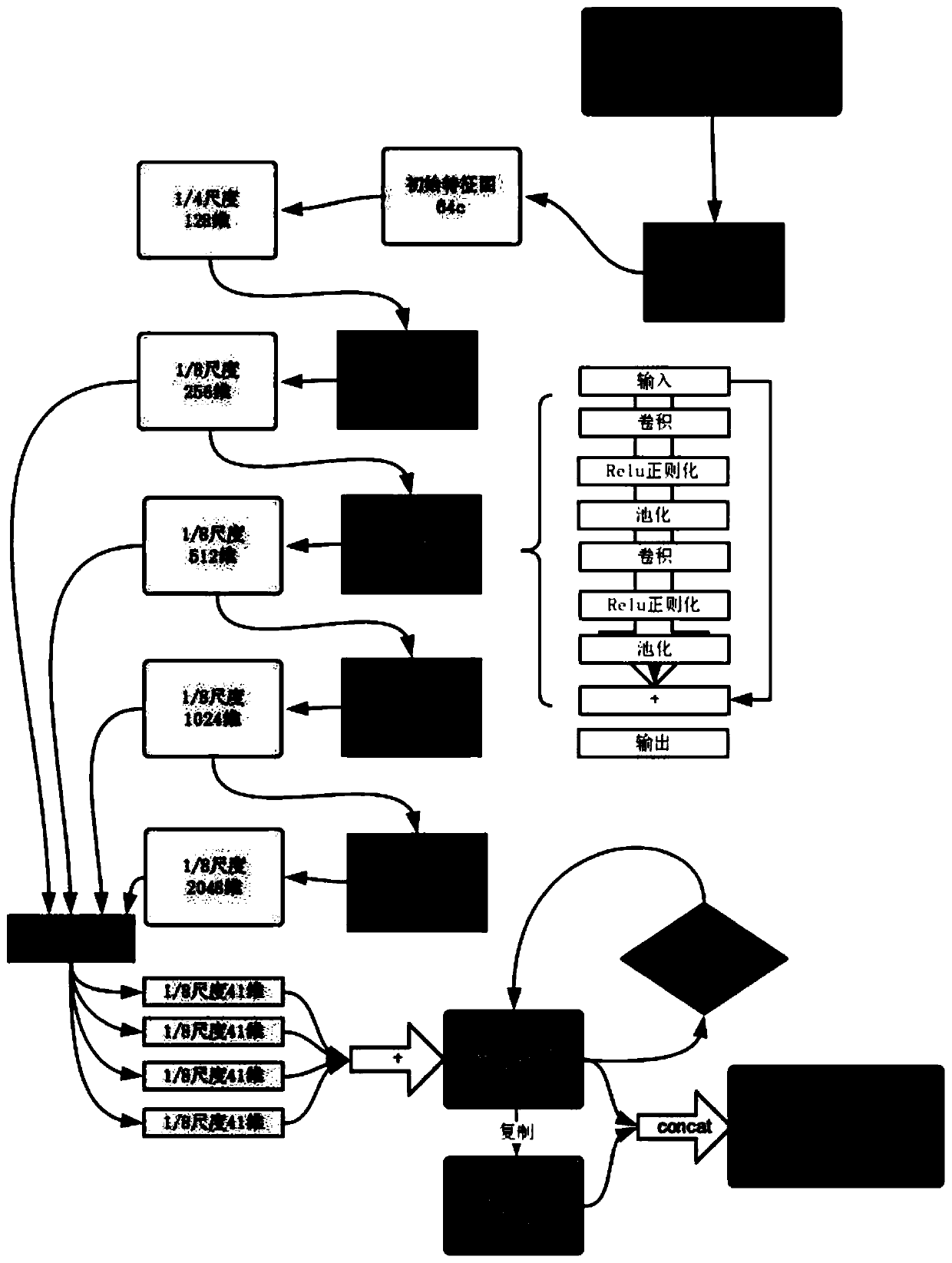
Binocular parallax estimation method introducing attention map
ActiveCN111259945AReduce mismatchOptimizing Deep Learning MethodsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesParallaxComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a binocular parallax estimation method introducing an attention map, and particularly relates to a method for obtaining global information, generating an attention map and guiding binocular parallax estimation by using deep learning data learning capability. According to the attention map provided by the invention, the global features and semantic structures of an image arebetter extracted by leading out independent branches, the obtained attention map acts on the cost in a weighted mode to play a role in matching and guiding, and it is ensured that regions with the same semantic structure have parallax in smooth distribution. Meanwhile, the invention provides a strategy for fine adjustment based on sparse labels. Different supervision strategies are adopted in different fine adjustment stages, the optimal effect of the method can be achieved on a sparse data set through reconstruction error guidance, sparse correction and smooth constraint optimization, and the problem that the effect of a label-free area is poor is solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
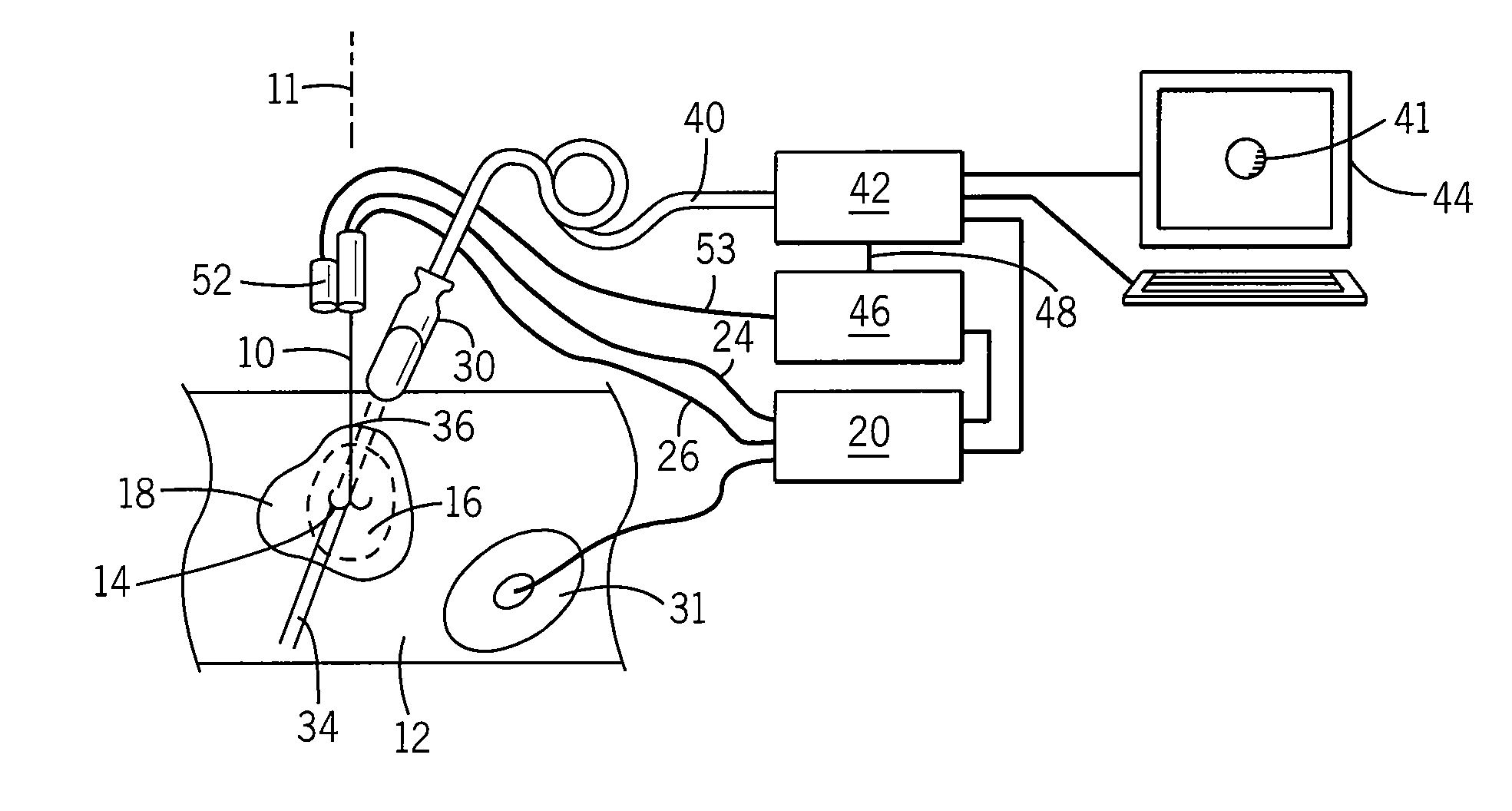
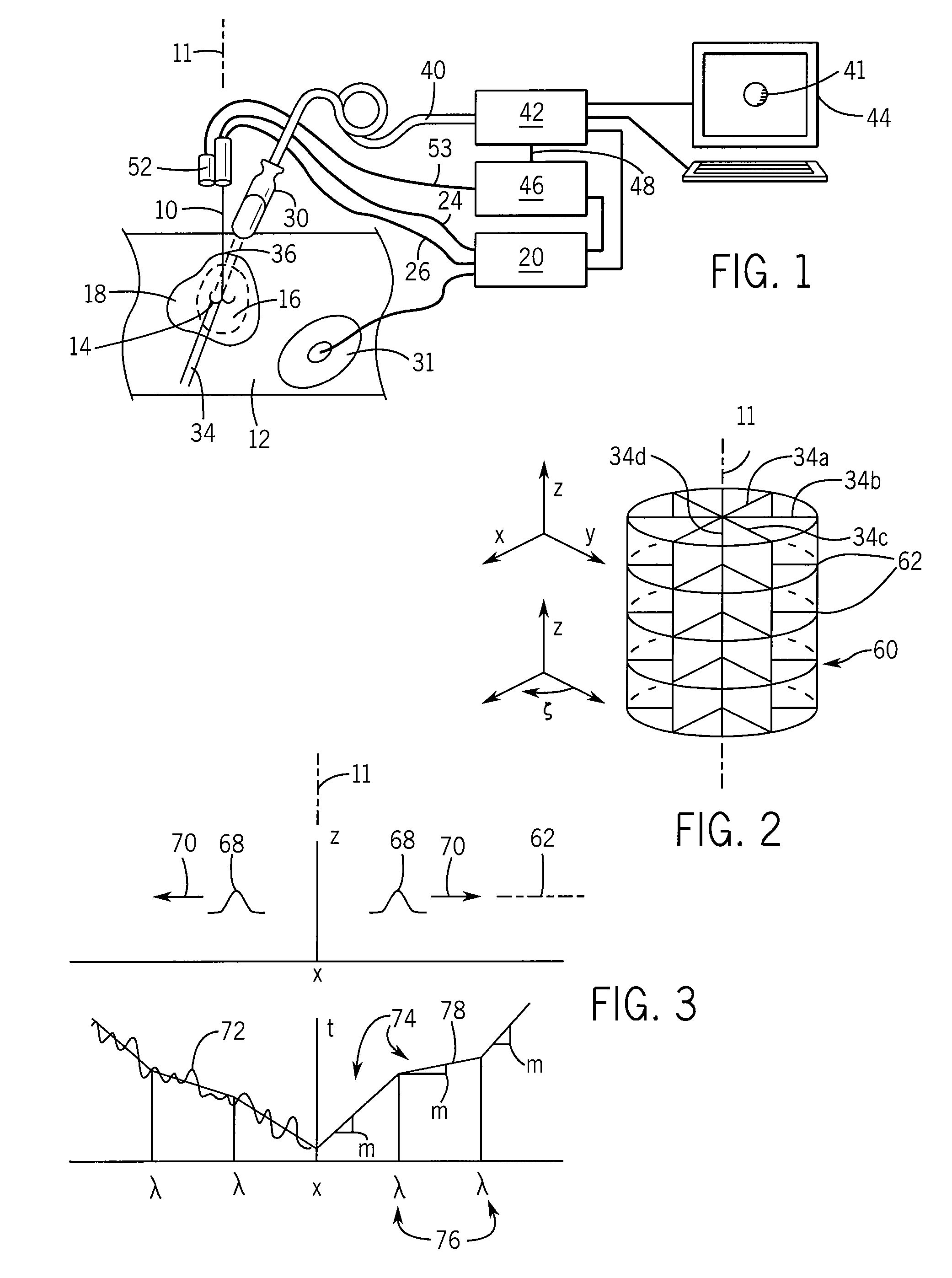
Method and Apparatus for Rapid Acquisition of Elasticity Data in Three Dimensions
ActiveUS20140243668A1Reduce data collectionEasy accessBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionIn planeComputer science
High-speed three-dimensional reconstruction of elasticity data is obtained by acquiring a sparse set of data in planes sharing a common axis line and angularly arrayed about the axis line. The axis line may be an RF ablation probe and the reconstruction may enforce a circumferential smoothness in the reconstruction about the probe, as is compatible with an ablation volume.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
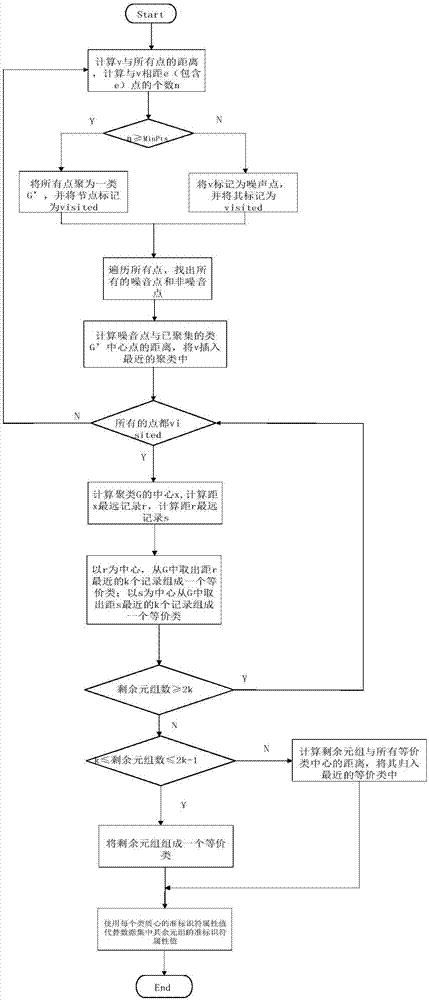
A feature selection method for clustering algorithm based on density clustering
PendingCN109543775AEasy to handleImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmFeature set
The invention discloses a feature selection method for a clustering algorithm based on density clustering. the method includes the following steps: a. Supposing that the data set D contains M instances and N features, then there is a feature set F=,, ..., fN composed of N features; normalizing the data set D to obtain The data set D ', and then using the Euclidean distance as the similarity measure between the features in the data set D' to construct the similarity matrix between the features. B. Using DBSCAN algorithm to cluster the features of similarity matrix, and dividing the features into three categories: core features, boundary features and atypical features; (c) after that feature clustering is completed, using the feature selection algorithm to select an n-dimensional feature subset F ', where n <= N, and (shown in the description) guarantees the least redundancy between features in the feature subset F '. The method has the characteristics of high accuracy, low calculation cost and strong processing ability of massive data and sparse data sets.
Owner:贵州联科卫信科技有限公司
Image recognition method for efficient GPU training model based on wide model sparse data set
ActiveCN110929627AEasy to handleImprove abilitiesCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention discloses an image recognition method for an efficient GPU training model based on a wide model sparse data set, and the method comprises the steps: converting pixels of an image into vectors, and carrying out the training and classification of the vectors; establishing a machine learning training method CuWide; enabling the cuWide to adopt a flow pipeline with a replication strategy, an importance cache, column-oriented storage and multi-flow technology. GPU is utilized and a large number of sparse data sets are used for efficiently training the image recognition prediction widemodel, the image recognition prediction wide model is deployed and trained on the GPU, the method is excellent in performance in the aspect of training large-scale wide models, and the image recognition efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Sparse data compression
InactiveUS8711015B2Code conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to compressing of sparse data sets contains sequences of data values and position information therefor. The position information may be in the form of position indices defining active positions of the data values in a sparse vector of length N. The position information is encoded into the data values by adjusting one or more of the data values within a pre-defined tolerance range, so that a pre-defined mapping function of the data values and their positions is close to a target value. In one embodiment, the mapping function is defined using a sub-set of N filler values which elements are used to fill empty positions in the input sparse data vector. At the decoder, the correct data positions are identified by searching though possible sub-sets of filler values.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
System and method for large scale survey analysis
ActiveUS20080021576A1Computer-assisted medical data acquisitionElectrical appliancesOriginal dataSurvey result
Disclosed herein is a method of analyzing large scale survey results comprising obtaining a sparse data set representing a subset of an original data set comprising a plurality of individuals' responses to a plurality of questions, wherein the sparse data set comprises less than ninety percent of the responses in the original data set; analyzing the sparse data set using a general diagnostic model; and obtaining estimated person parameters using the general diagnostic model.
Owner:EDUCATIONAL TESTING SERVICE
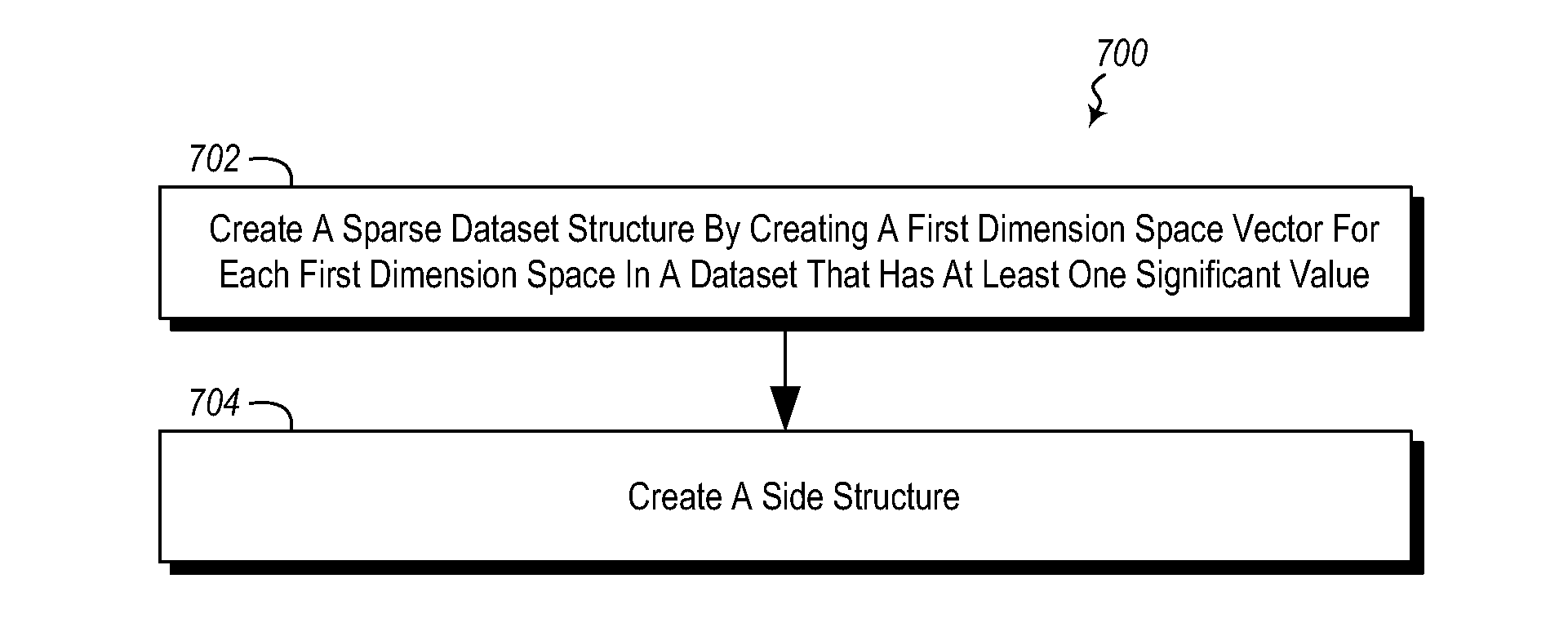
Sparse datatable data structure
ActiveUS20150317334A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureEntry point
A sparse dataset structure is created by creating column vectors for one or more columns in a dataset that have at least one significant value. Each column vector includes data values for columns of the dataset. Each column vector that is a sparse column vector includes a look-up index array and a value array. Entries in the look-up index array represent columns. The value array includes values for a row in a column. Each entry in the value array points to a row entry in the look-up index array. A side structure includes a row index and a column index. The row index includes a location for an entry for each row where entries point to a location in the column index that identifies a column that has a first significant entry for a row. Alternatively a sparse dataset could be constructed with sparse rows.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
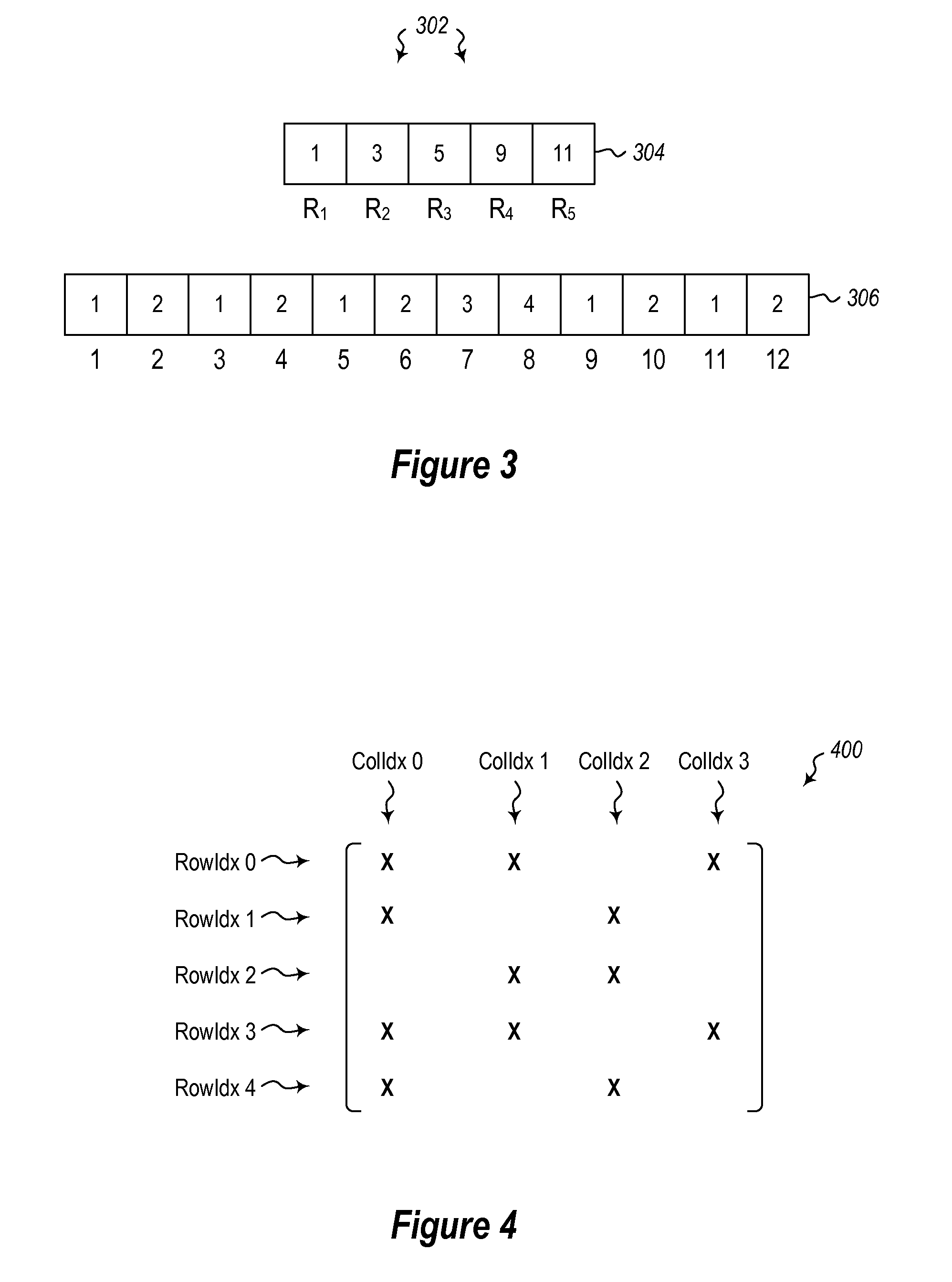
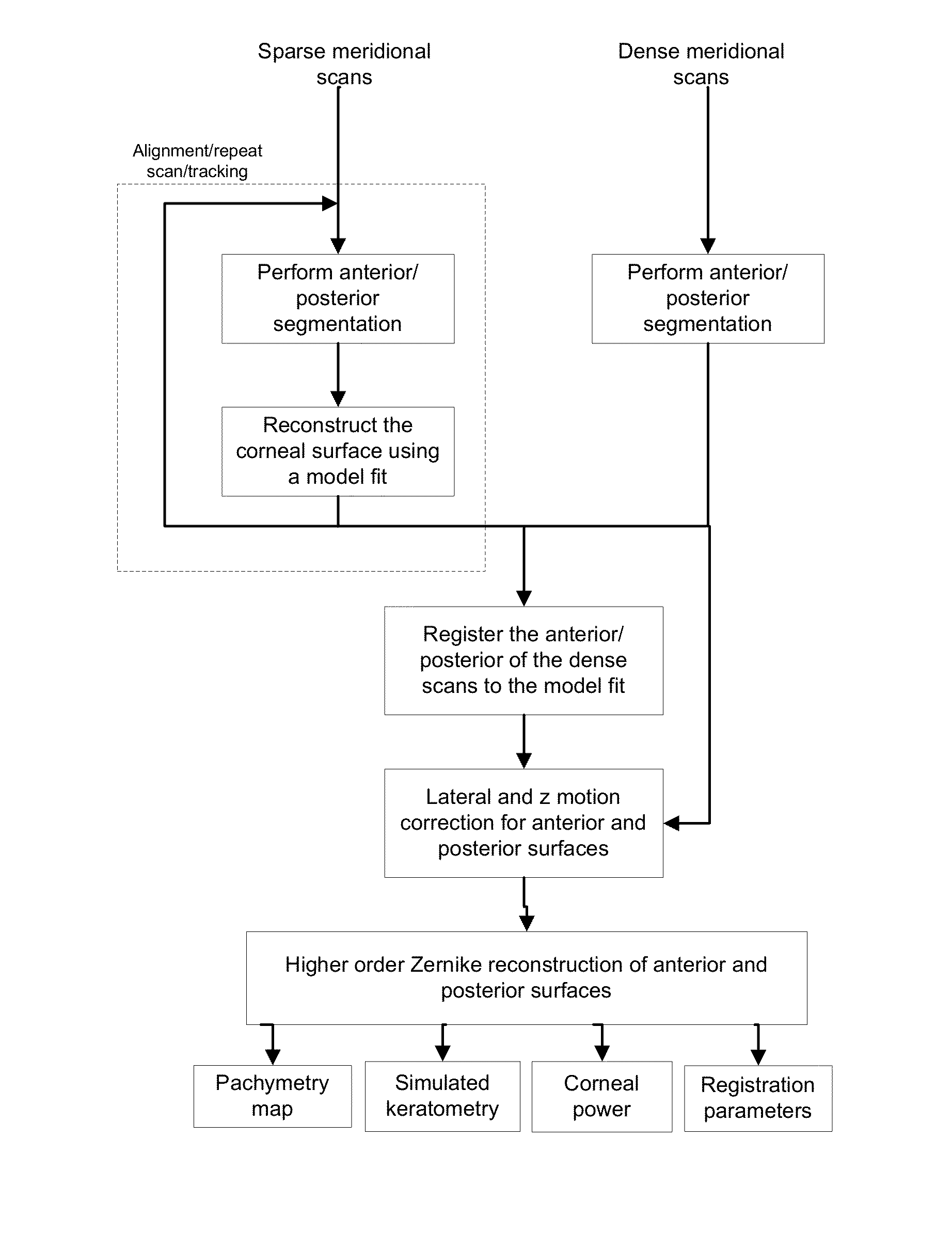
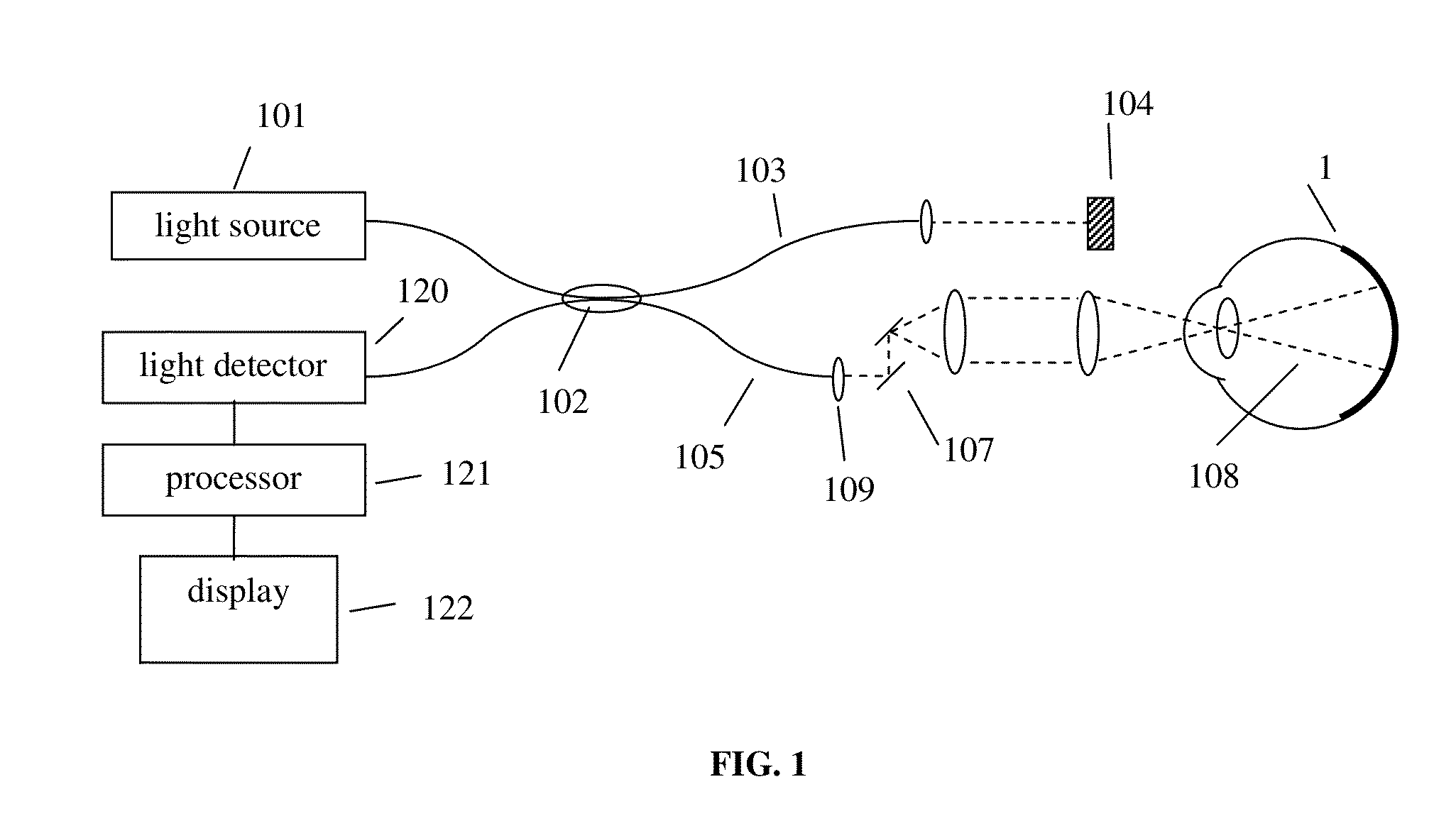
Systems and methods for enhanced accuracy in OCT imaging of the cornea
ActiveUS9101294B2Improve accuracyScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansCorneal surfaceData acquisition
Systems and methods for enhanced accuracy in optical coherence tomography imaging of the cornea are presented, including approaches for more accurate corneal surface modeling, pachymetry maps, keratometric values, and corneal power. These methods involve new scan patterns, an eye tracking mechanism for transverse motion feedback, and advanced motion correction algorithms. In one embodiment the methods comprise acquiring a first sparse set of data, using that data to create a corneal surface model, and then using the model to register a second set of denser data acquisition. This second set of data is used to create a more accurate, motion-corrected model of the cornea, from which pachymetry maps, keratometric values, and corneal power information can be generated. In addition, methods are presented for determining simulated keratometry values from optical coherence tomography data, and for better tracking and registration by using both rotation about three axes and the corneal apex.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
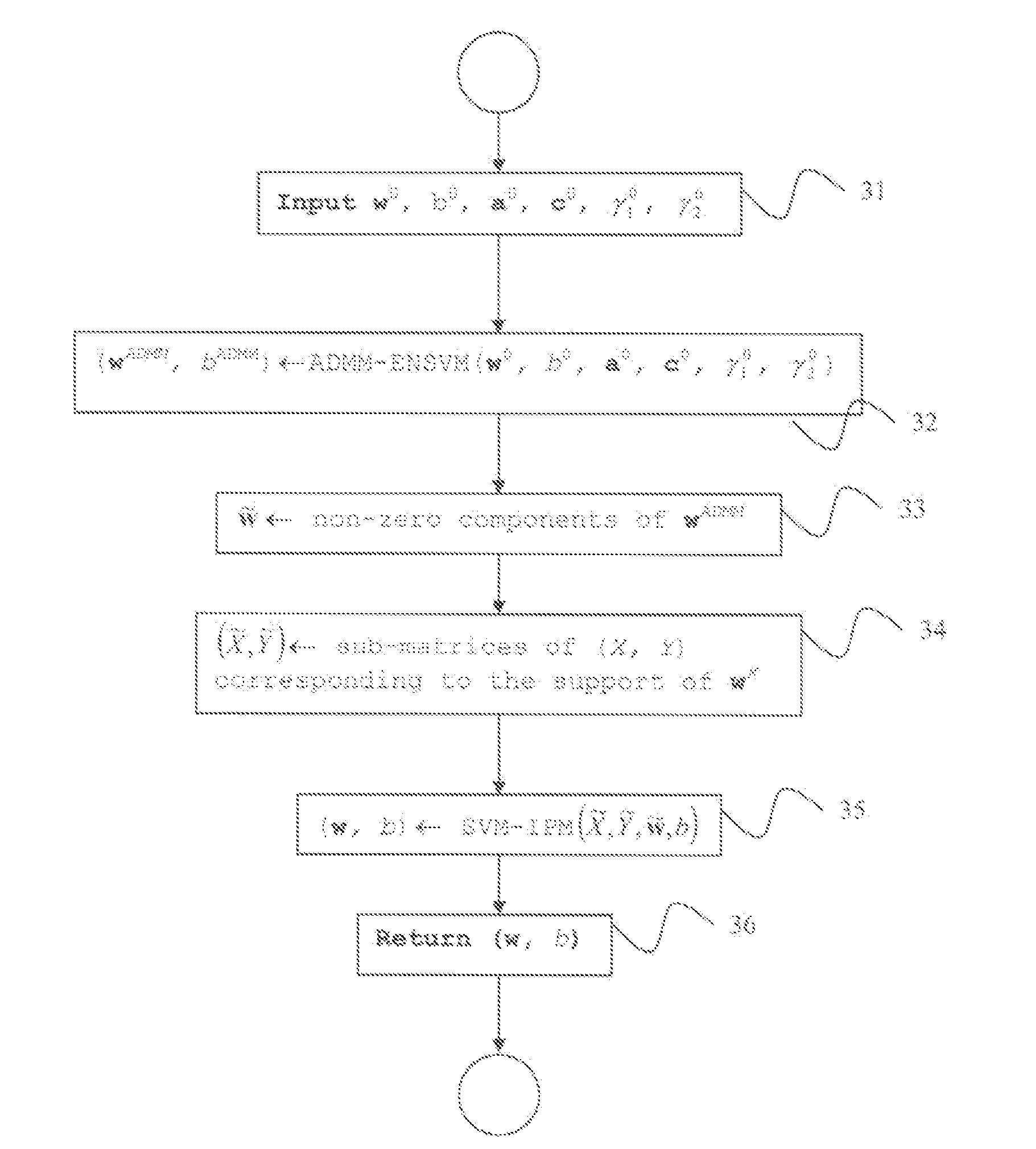
Hybrid interior-point alternating directions algorithm for support vector machines and feature selection
ActiveUS8719194B2Improve accuracyAdd dimensionKernel methodsDigital computer detailsAlgorithmFeature selection
Owner:SIEMENS AG
An update generation method of fuzzy concept lattice
PendingCN109086381AConsistent resultImprove update efficiencyFuzzy logic based systemsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a method for generating a complete fuzzy concept lattice, in particular to a lattice updating method for fuzzy concepts based on an integration technology, which uses the integration scheme between two fuzzy concept lattices to solve the problem of L-Fuzzy Concept Lattice Renewal. The invention does not need to regenerate the complete L from the updated data set. Fuzzy concept lattice, and the original fuzzy concept lattice before updating is used in the generation of new fuzzy concept lattice, which avoids the waste of resources and improves the Updating efficiency ofL-fuzzy concept lattice. The invention avoids regenerating the fuzzy concept lattice from the updated formal background, and updates the original fuzzy concept lattice by using the update data, so the update efficiency is greatly improved. Especially for sparse dataset and small truth degree set, the update efficiency is improved obviously.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
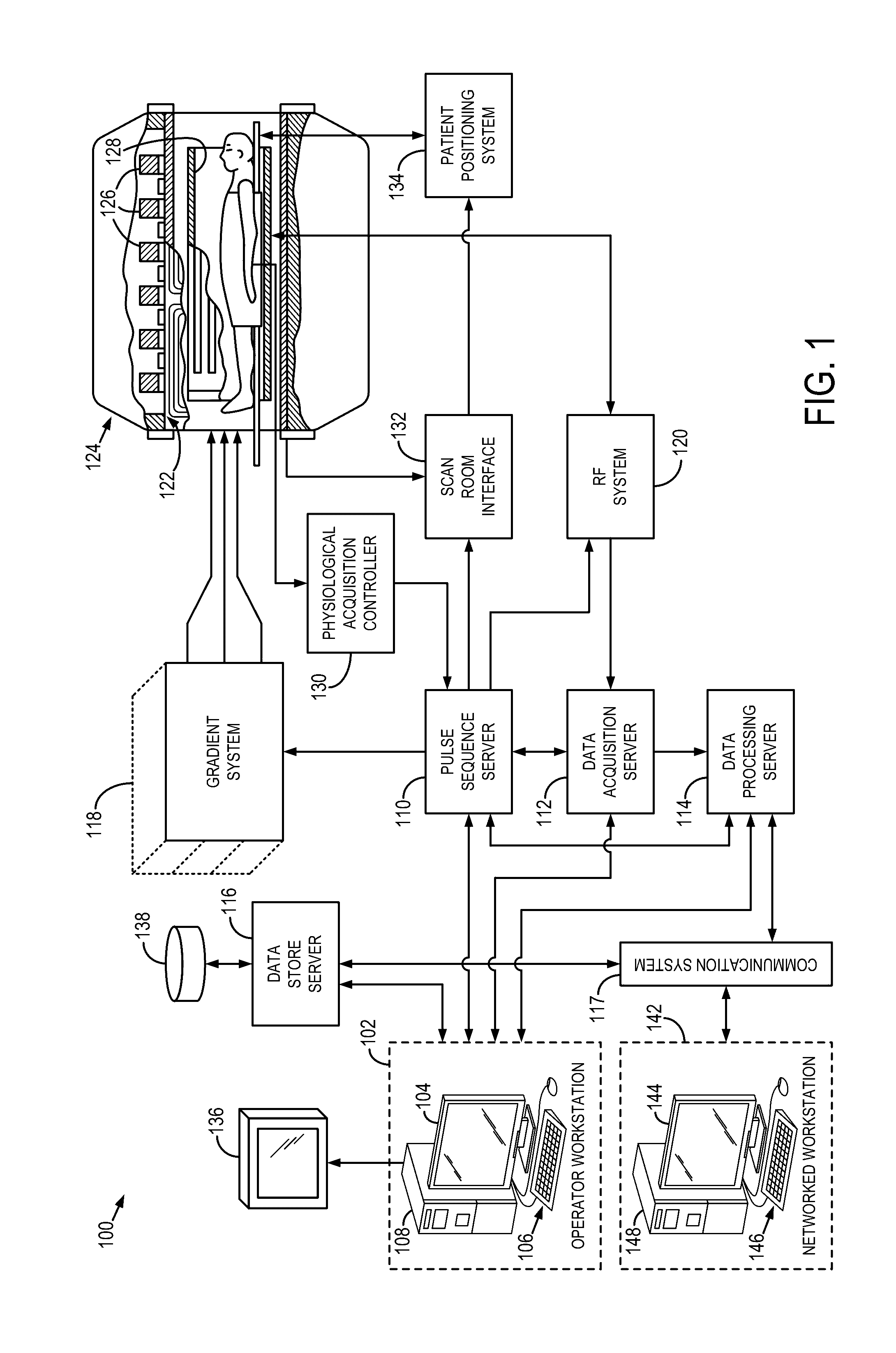
System and method for imaging of vascular structures using non-contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
A system and method is provided for acquiring a medical image of a portion of a vascular structure of a subject using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. At least one radio frequency (RF) saturation pulse is applied to a selected region of a subject that is free of exogenous contrast agents using the MRI system to saturate spins of all tissues within the selected region. A delay time is selected to allow an inflow of unsaturated vascular spins that are free of influence from exogenous contrast agent into the selected region through vascular structures within the selected region. A sparse dataset is formed from a series of spatially-encoded views from the selected region using an undersampled radial k-space trajectory in which the center of k-space is sampled for each view in the series of spatially-encoded views. An image of the vascular structures within the selected region is reconstructed from the sparse dataset.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST
Sparse Datatable Data Structure
ActiveUS20160299926A1Special data processing applicationsDatabase design/maintainanceArray data structureEntry point
A sparse dataset structure is created by creating column vectors for one or more columns in a dataset that have at least one significant value. Each column vector includes data values for columns of the dataset. Each column vector that is a sparse column vector includes a look-up index array and a value array. Entries in the look-up index array represent columns. The value array includes values for a row in a column. Each entry in the value array points to a row entry in the look-up index array. A side structure includes a row index and a column index. The row index includes a location for an entry for each row where entries point to a location in the column index that identifies a column that has a first significant entry for a row. Alternatively a sparse dataset could be constructed with sparse rows.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
APP risk assessment method and device based on factorization machine and electronic equipment
The invention discloses an APP risk assessment method and device based on a factorization machine, and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining APP installation list information of a mobile terminal associated with a user; extracting APP features and APP combination features according to the APP installation list information; performing one-hot coding on the APP features and the APP combination features to obtain one-hot coding features associated with the user; and inputting the one-hot coding features into a trained machine learning model, and calculating a risk score of the user. According to the invention, the one-hot coding characteristics converted from the APP installation list information of the user mobile terminal are substituted into the preset machine learning model for training; the method and device are simple to operate and easy to implement, the accuracy of an assessed credit risk result is high, meanwhile, the contribution degree to the creditrisk when multiple feature combinations exist can be assessed under the condition of a sparse data set, the stability is good, in the aspects of modeling and feature maintenance, the input manpower issmall, resources are saved, and the effect is remarkable.
Owner:上海淇毓信息科技有限公司
Systems and/or methods for machine-learning based data correction and completion in sparse datasets
PendingUS20210357706A1ConfidenceRelational databasesCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning basedRecordset
Certain example embodiments herein relate to techniques for automatically correcting and completing data in sparse datasets. Records in the dataset are divided into groups with properties having similar values. For each group, one or more properties of the records therein that is / are to be ignored is / are identified, based on record distances relative to the records in the group, and distances among values for each of the properties of the records in the respective group. The records in the groups are further divided into sub-groups without regard to the one or more properties that is / are to be ignored. The sub-groups include a smaller and more cohesive set of records. For each sub-group: based on the records therein, predicted values to be applied to values identified as being empty but needing to be filled in are determined; and those predicted values are applied. The corrected / completed dataset is provided as output.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
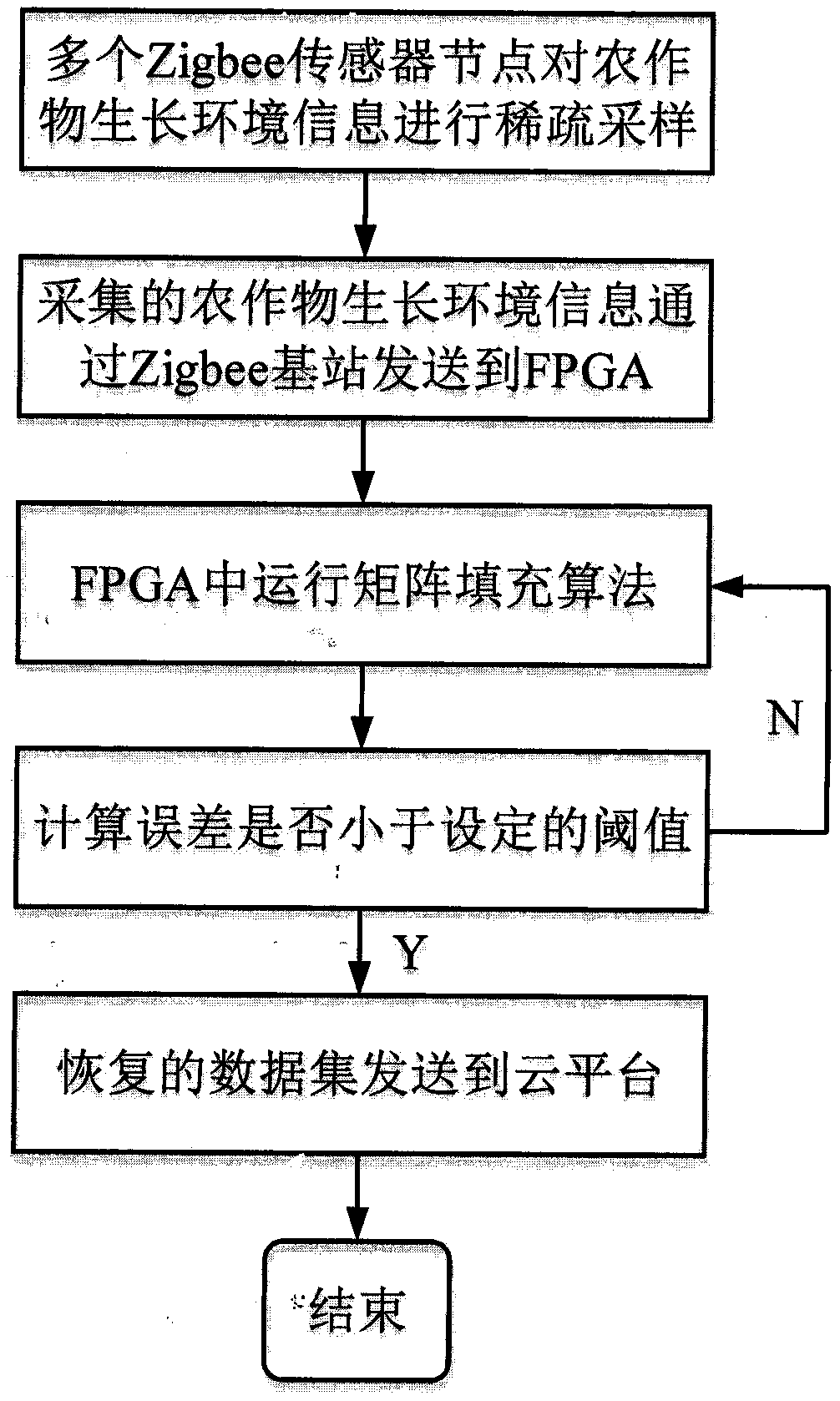
WSN crop growth environment information sparse acquisition and transmission method based on NB-IoT and FPGA
InactiveCN110022541ARealize collection and acquisitionReduce collection frequencyPower managementParticular environment based servicesLine sensorAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a wireless sensor network (WSN) crop growth environment information sparse acquisition and transmission method based on NB-IoT and FPGA and applied to smart agriculture. The method mainly comprises the steps that crop growth environment information is collected in a sparse sampling mode through Zigbee wireless sensor nodes; the collected sparse data information is sent to an FPGA core control end, and a matrix filling algorithm is executed in the FPGA to fill the sparse data set matrix; data recovered to be complete is sent to the cloud platform end in the NB-IoT mannerand is displayed at the cloud end, so that the functions of collecting, transmitting and monitoring the crop growth environment information are finally realized. According to the invention, a sparsesampling theory is applied to the wireless sensor network, and a matrix filling algorithm is realized by hardware, so that lower power consumption of sensor nodes and higher data recovery speed can beensured.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Recommendation method and system of efficient data analysis
InactiveCN106202106AImprove experienceImprove conversion rateSpecial data processing applicationsLinear methodsAlgorithm optimization
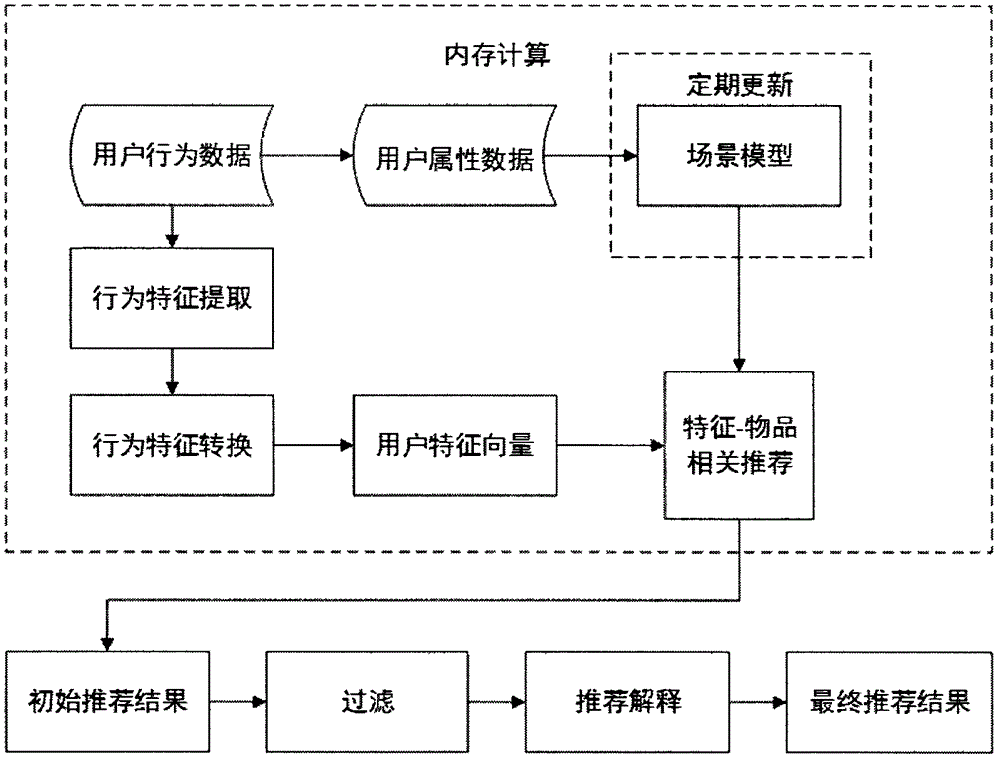
The invention relates to a recommendation method and system of efficient data analysis. Specifically, the synchronous real-time recommendation of a scene perception recommendation algorithm is realized through a grading module, a scene optimization module and a big data operation module. A scene model is introduced to correct a sparse linear method, and a recommendation engine based on memory calculation is imported, so that recommendation efficiency is greatly improved. Meanwhile, the problems of the algorithm optimization of a sparse data set and recommendation result abduction are solved. The system can be applied to the real-time recommendation of supermarket consumption. Compared with existing off-line recommendation, the system is characterized in that a user can timely receive relevant recommendations after selecting or purchasing corresponding products, and therefore, a conversion rate brought by the recommendation system is greatly improved. A scene model is imported to cause the user to obtain accurate recommendations under the certain scene under different scenes, and user experience is improved.
Owner:盛玲
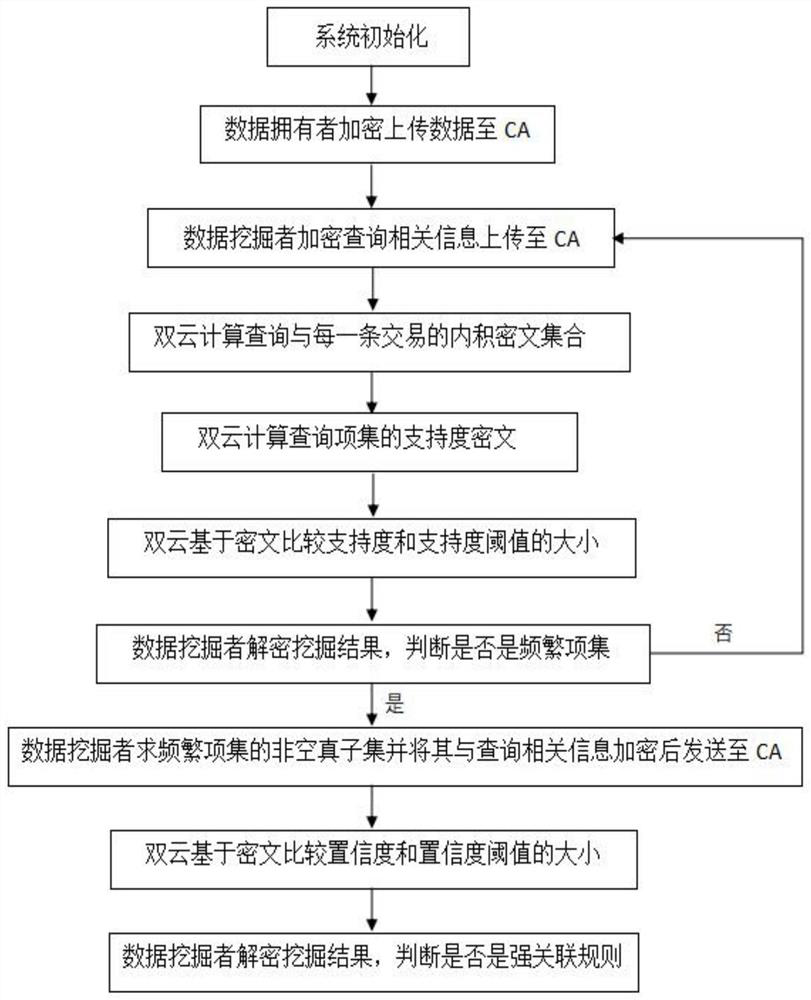
Privacy protection association rule mining method based on sparse data set
ActiveCN112966281AWeaken decryption abilityAvoid security issuesDigital data information retrievalDigital data protectionCiphertextTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a privacy protection association rule mining method based on a sparse data set, and mainly solves the problems that an existing mining method needs to introduce additional calculation overhead and privacy leakage. The scheme comprises the following steps: 1) initializing a system; 2) enabling the data owner to encrypt the uploaded data; 3) enabling a data miner to encrypt, upload and query; 4) performing double-cloud calculation on an inner product ciphertext set of query and transaction, and calculating a support degree ciphertext of query; 5) comparing the support degree with a support degree threshold value by the double-cloud security; (6) enabling the data miner to decrypt the mining result, judge whether the mining result is a frequent item set or not, solve a non-empty proper subset of the frequent item set, and querying, encrypting and uploading the non-empty proper subset and the query; 7) comparing the confidence coefficient with a confidence coefficient threshold value by the double-cloud security; and 8) enabling the data miner to decrypt the mining result and judge whether the mining result belongs to the strong association rule. According to the invention, the risk of privacy disclosure is reduced, and higher privacy protection requirements can be met; and meanwhile, the mining calculation efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for predicting network service quality
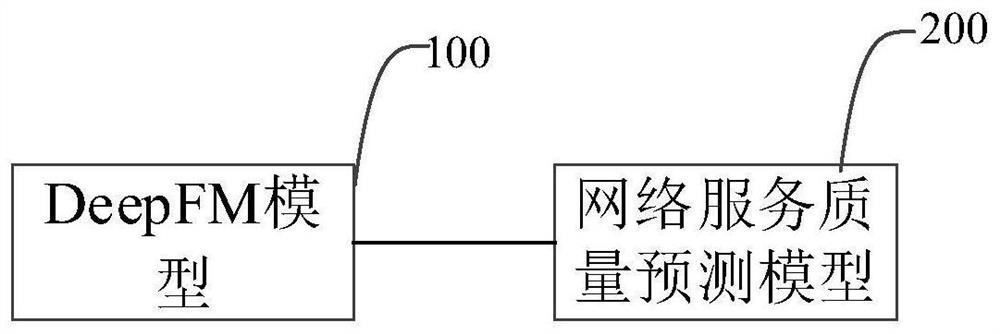
PendingCN113762737ASmall scaleReduce operation and maintenance loadCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesQos quality of serviceData pack
The invention discloses a network service quality prediction method and system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining user data and service data, inputting the user data and the service data into a trained network service quality prediction model, and obtaining a network service quality prediction result, wherein the trained network service quality prediction model is obtained by training different sample data and corresponding soft labels, the sample data comprises user training data and service training data, and the soft label is prediction data output by the trained DeepFM model after the sample data is input. According to the method, the DeepFM model is adopted, manual feature combination is not needed, a sparse data set can be processed, the prediction data output by the trained DeepFM model after the sample data is input serves as the soft label to train the network service quality prediction model, the scale of the network service quality prediction model is reduced, and the operation and maintenance load is relieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Scalable configurable universal full spectrum cyber process that utilizes measure points from sensor observation-derived representations or analytically rich sparse data sets for making cyber determinations regarding or utilizing sensor observations or sensor observations subjects
ActiveUS20180336400A1Simple, concise and efficientDetermination is accurate and reliableCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringInformation representation
A scalable configurable universal full spectrum cyber process that utilizes measure points from sensor observation-derived representations or analytically rich sparse data sets for making selected cyber determinations regarding or utilizing sensor observations or sensor observation subjects. Utilizing necessary cyber resources and predetermined criteria for making selected cyber determinations regarding or utilizing the sensor observation or at least one sensor observation subject, the disclosed cyber process employs the use of measure points for accurately or reliably locating selected analytically rich indicators from sensor observation-derived representations, wherein appropriate informational representations or measurements regarding or utilizing the selected analytically rich indicators, the measure points or the sensor observation are assigned and stored in analytically rich sparse data sets where they may be utilized by the cyber process for making, in real time or at any time thereafter, selected cyber determinations regarding or utilizing sensor observations or sensor observation subjects.
Owner:ARONSON JEFFRY DAVID
Personal identification information positioning identification method based on static pollution
PendingCN114357250AAccurate location extractionAvoid false positivesOther databases indexingOther databases queryingGraph theoreticInternet traffic
The invention relates to a personal identification information positioning identification method based on static pollution, and belongs to the technical field of network information security. According to the method, input personal identification information is used as shared information, the flow behavior of the shared information in data is utilized, the incidence relation between different service-positions is found, an information flow graph is constructed, and the personal identification information is positioned and extracted by utilizing a traversal algorithm of a graph theory. According to the method, the personal identification information is automatically and accurately positioned and extracted according to the input infection value. According to the method, the problem of accurately positioning and extracting the personal identification information in the network flow data, particularly under the large-scale network flow data, is effectively solved, meanwhile, the false alarm caused by excessive pollution is overcome, the large-scale sparse data set can be automatically marked, and manual intervention and crowdsourcing feedback are avoided.
Owner:YANAN UNIV
System and method for detection of noise in sparse data sets with edge-corrected measurements
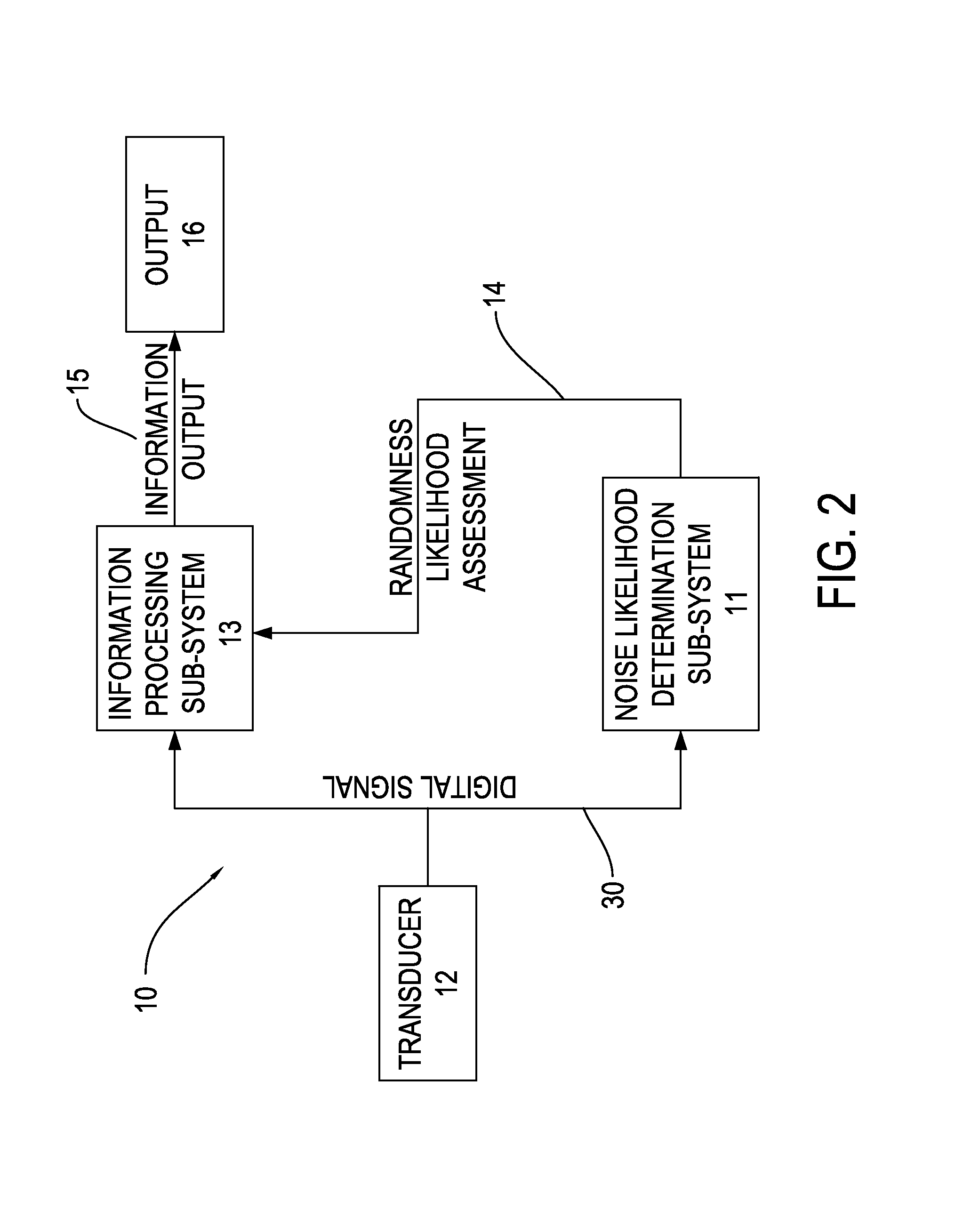
InactiveUS8837566B1Increase probabilityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCorrect operation testingInformation processingNear neighbor
A signal processing system and method includes a transducer for receiving an analog signal having a random component and possibly an information component. The analog signal is converted into a digital signal having sample points. A nearest-neighbor calculation component calculates the expected average nearest neighbor distance between the sample points, the actual average distance and an error value. These values are corrected for edge effects. A first randomness assessment compares the actual average distance against the expected average distance with the standard error value. A second randomness assessment compares actual repeated values in the digital signal against expected repeated values. An information processing system continues processing the signal if the assessments indicate the possibility of an information component.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com