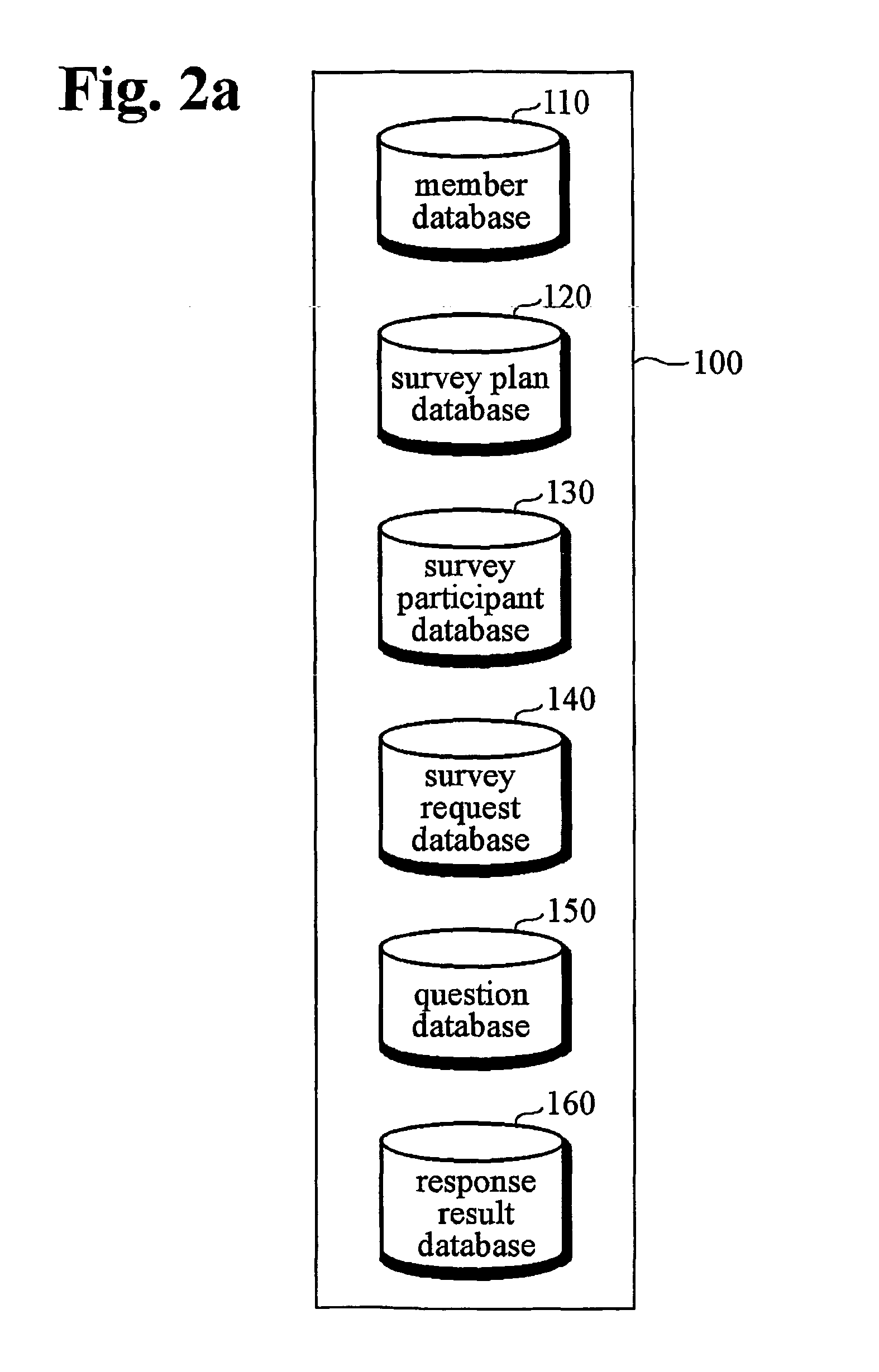
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
366 results about "Survey result" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The presentation of survey results is an integral part of survey research because it is the path towards communicating the results to the appropriate individuals, organizations or government agencies that can take action regarding the results of the survey. Presenting survey results involves the introduction and background...
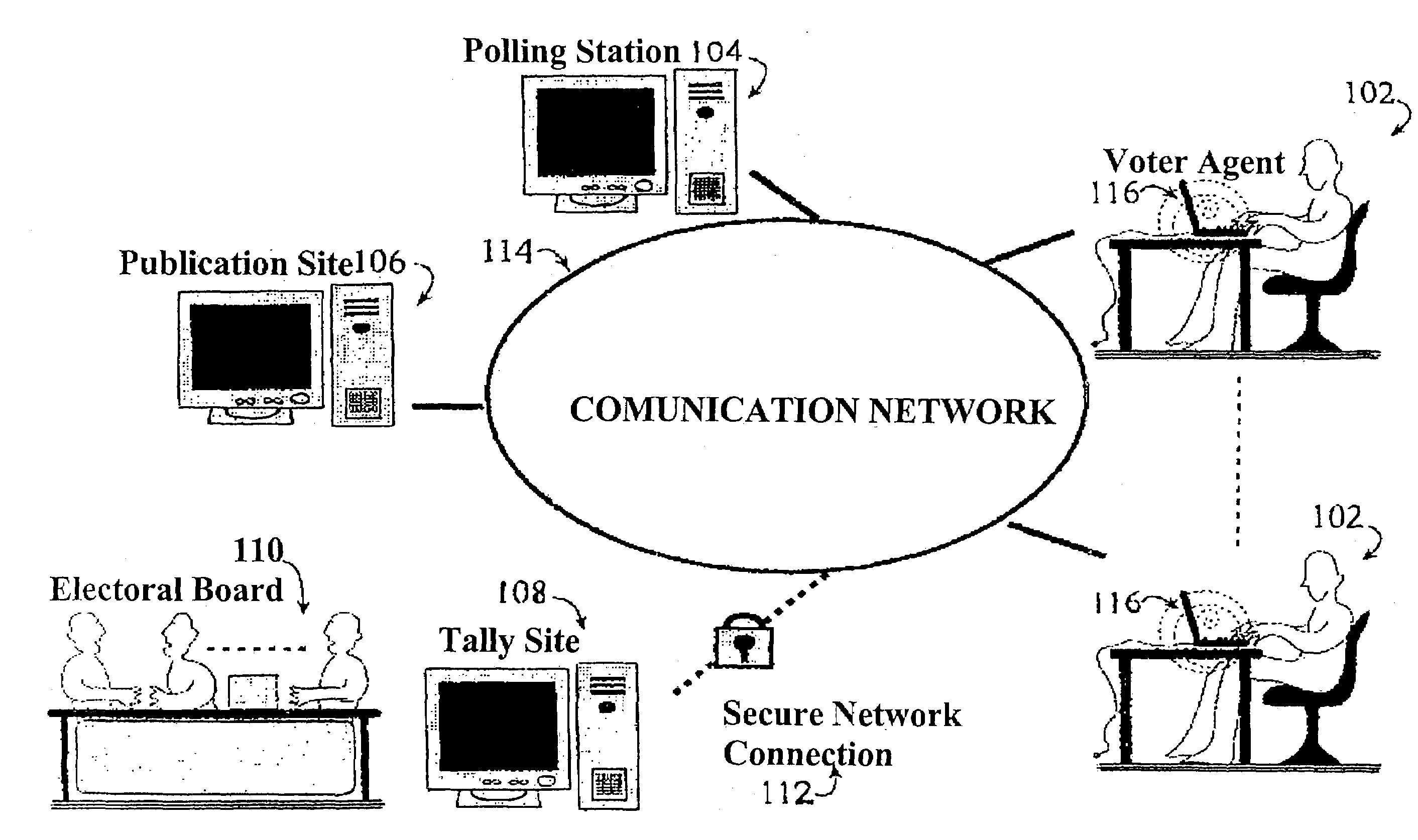
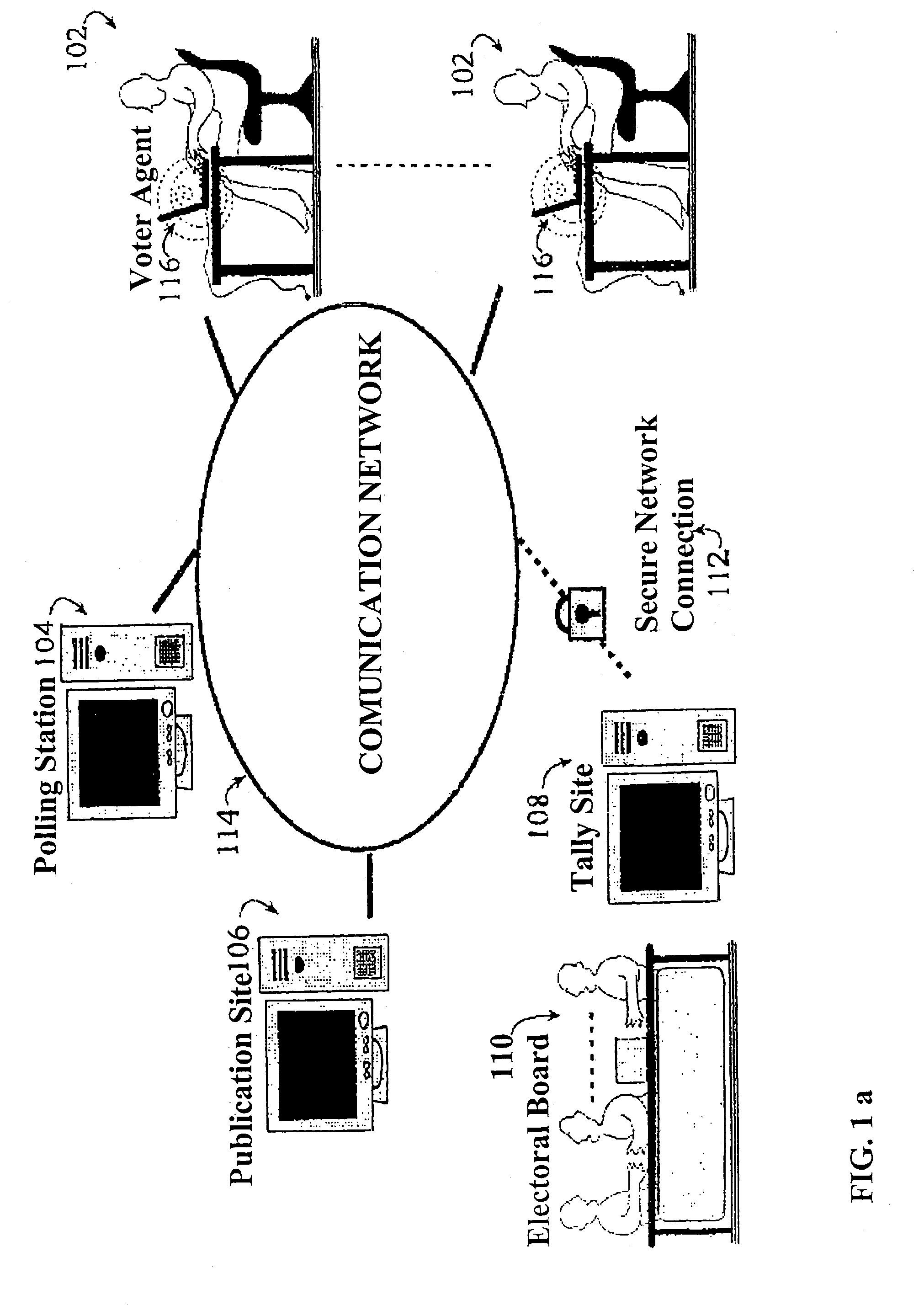
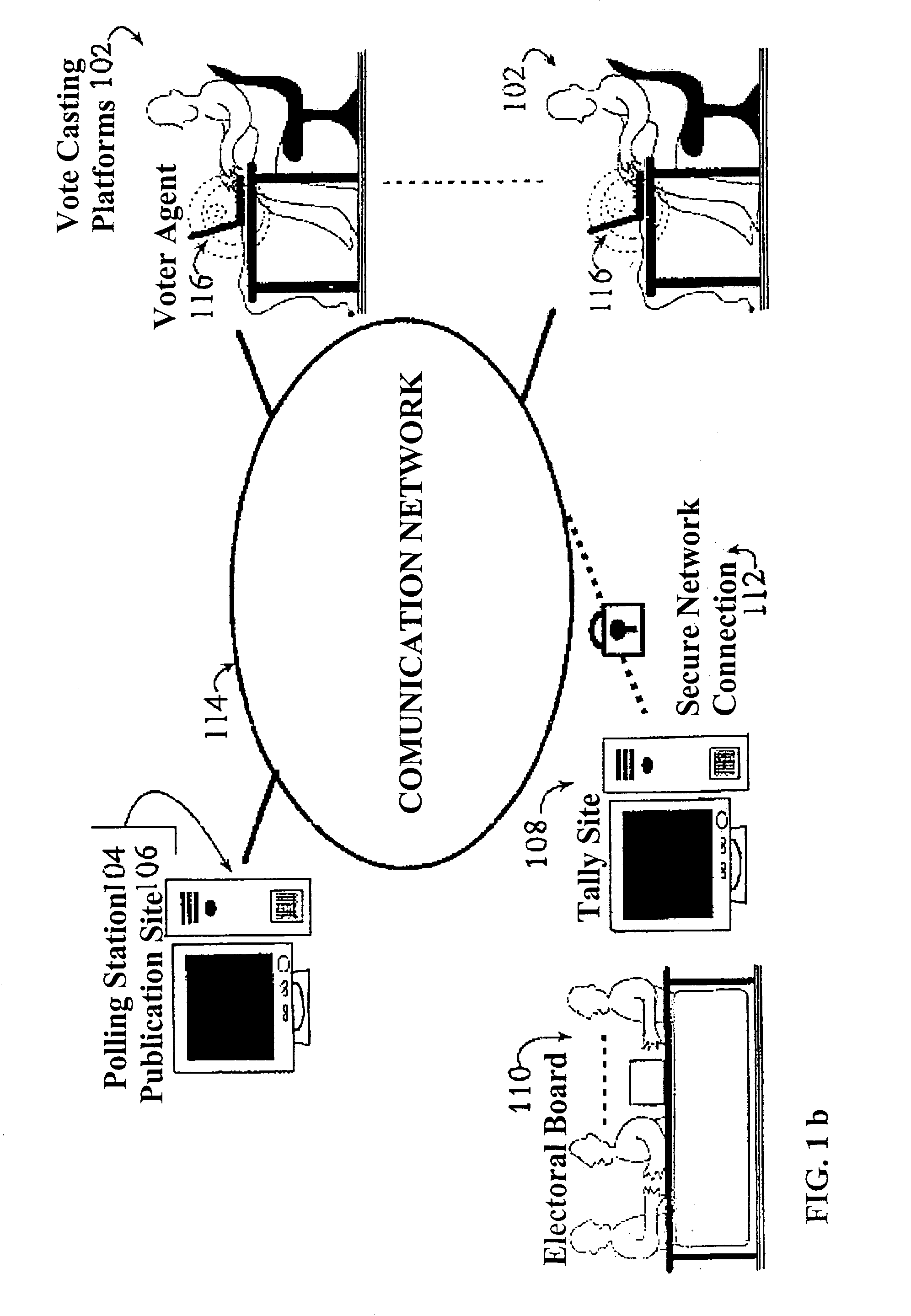
Secure remote electronic voting system and cryptographic protocols and computer programs employed
InactiveUS7260552B2Minimizing confidence levelHindering voters coercionVoting apparatusError detection/correctionCryptographic protocolSurvey result
The method employs interrelated cryptographic processes and protocols to provide reliability to vote casting, ballots recount, and verification of vote or poll results. These cryptographic processes and protocols jointly constitute a cryptographic voting scheme capable of meeting the specific reliability requirements of an electronic voting where voters remotely cast their votes. These reliability requirements include voter authentication and privacy; accurate results, the impossibility of coercion and sale of votes, verifying the final results and, if necessary, the secrecy of intermediate results before completing the vote or poll. The cryptographic voting method minimizes the confidence level to be placed on any of the electronic voting individual party and participants.
Owner:SCYTL ELECTION TECH SL
Analytical survey system
Owner:SAP AG
System and method for gathering consumer feedback
An electronic system and method for gathering consumer feedback and reporting the feedback. The system and method provides an incentive for engaging the consumer to register and answer a survey. The registration information and answers provided are compiled into a database and may be formatted into reports. The gathering of the feedback and the reporting may be done in real-time. Information from the survey may be used to communicate or market to targeted users. Thus, the present invention relates to an electronic system and method for achieving registration, gathering consumer feedback via a survey, and communicating or marketing to targeted users based on survey results.
Owner:AXALTO INC +1
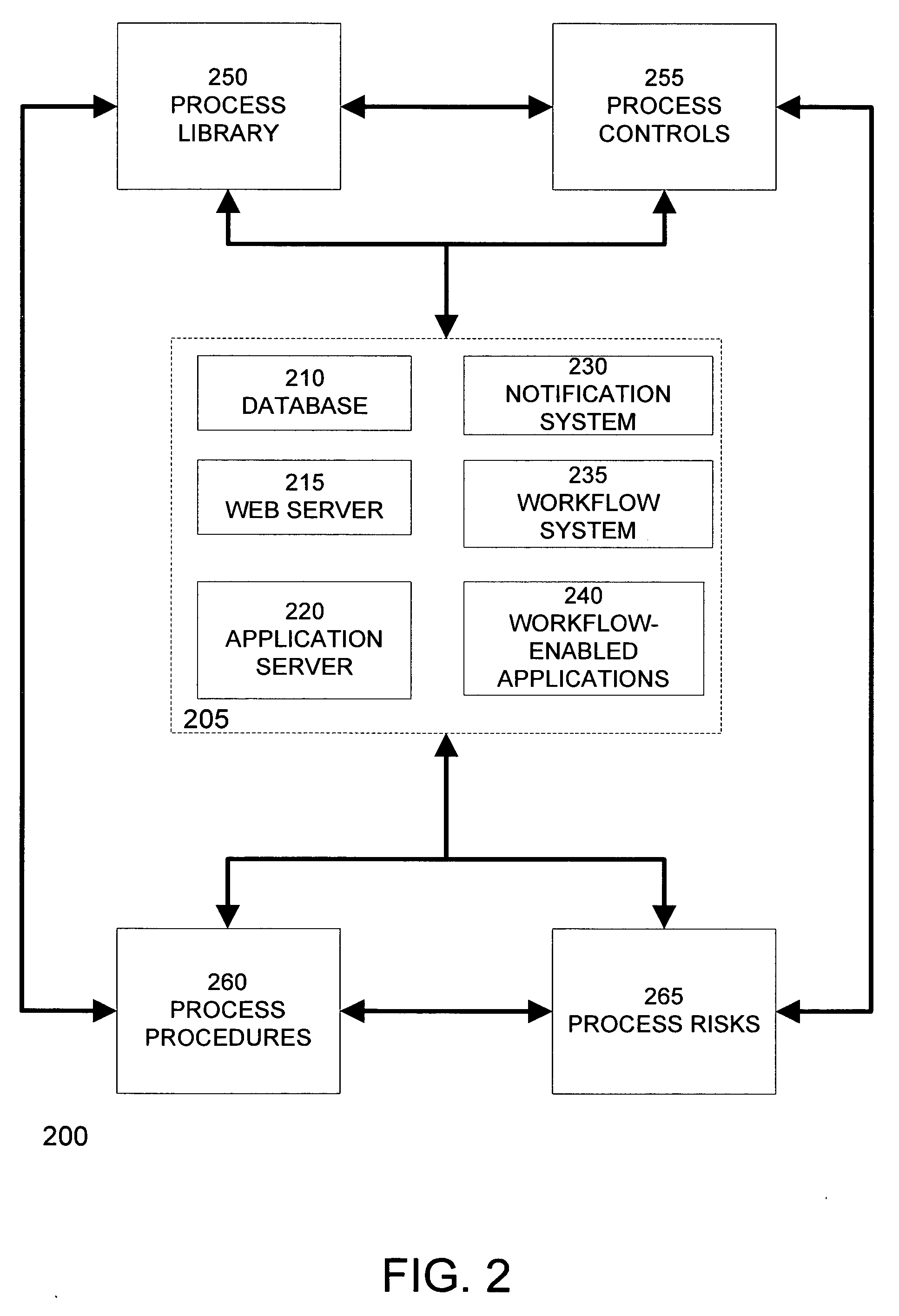
Survey based risk assessment for processes, entities and enterprise
An audit system creates, deploys, and analyzes surveys to perform risk assessment. Surveys can be associated with one or more contexts, which include an enterprise, an organization, a business process, a risk, a control, or any combination thereof. The audit system generates survey questionnaires for a context automatically using a question library that associates questions with one or more contexts. Using the process library and the associated sets of process risks and process controls, the audit system can automatically determine the set of individuals that should participate in the survey. The audit system can then distribute survey questionnaires to the set of individuals and collect the survey results. Survey results can be aggregated to create risk assessments detailing the perceived risks to the survey context. Additionally, survey results and risk assessments can be saved for future reference or to document an enterprise's good-faith efforts to comply with its legal obligations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
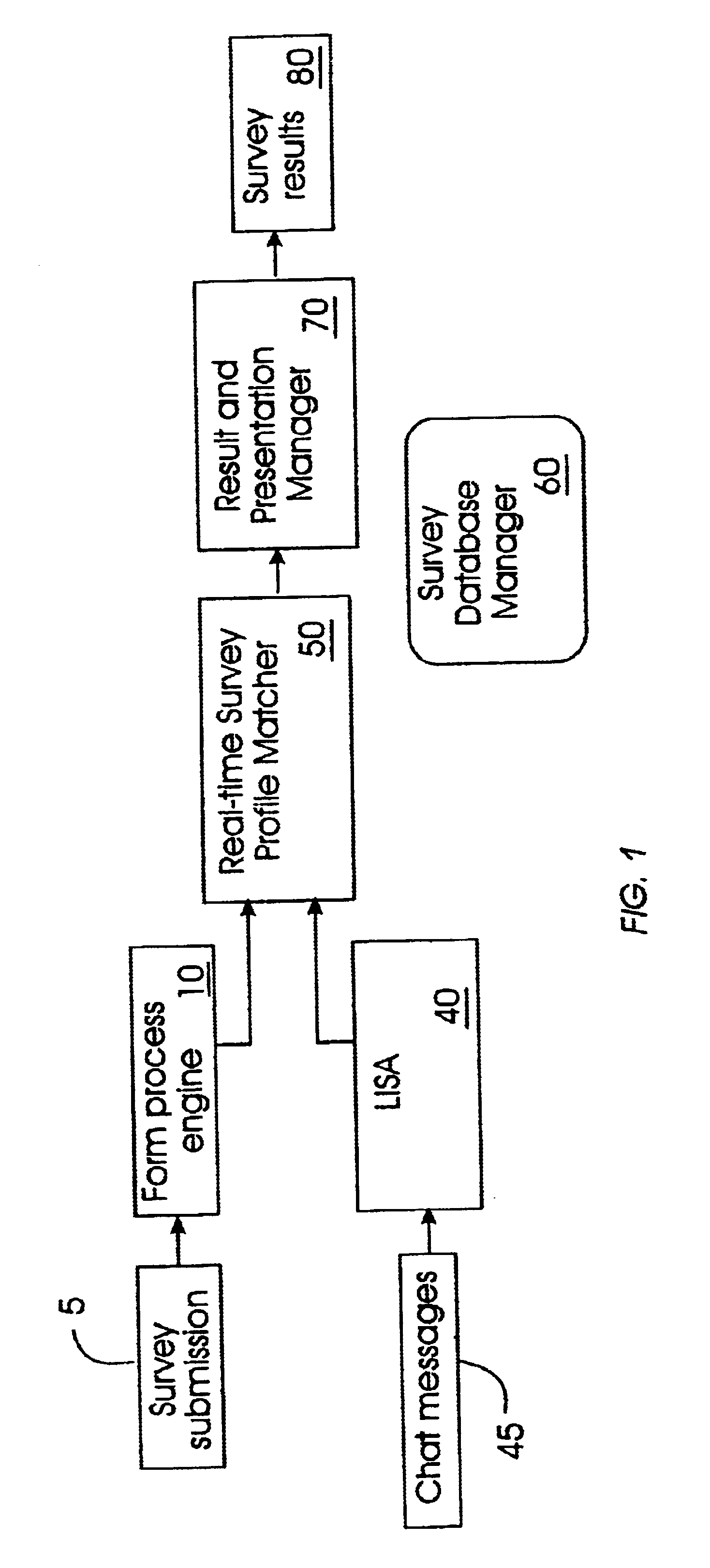
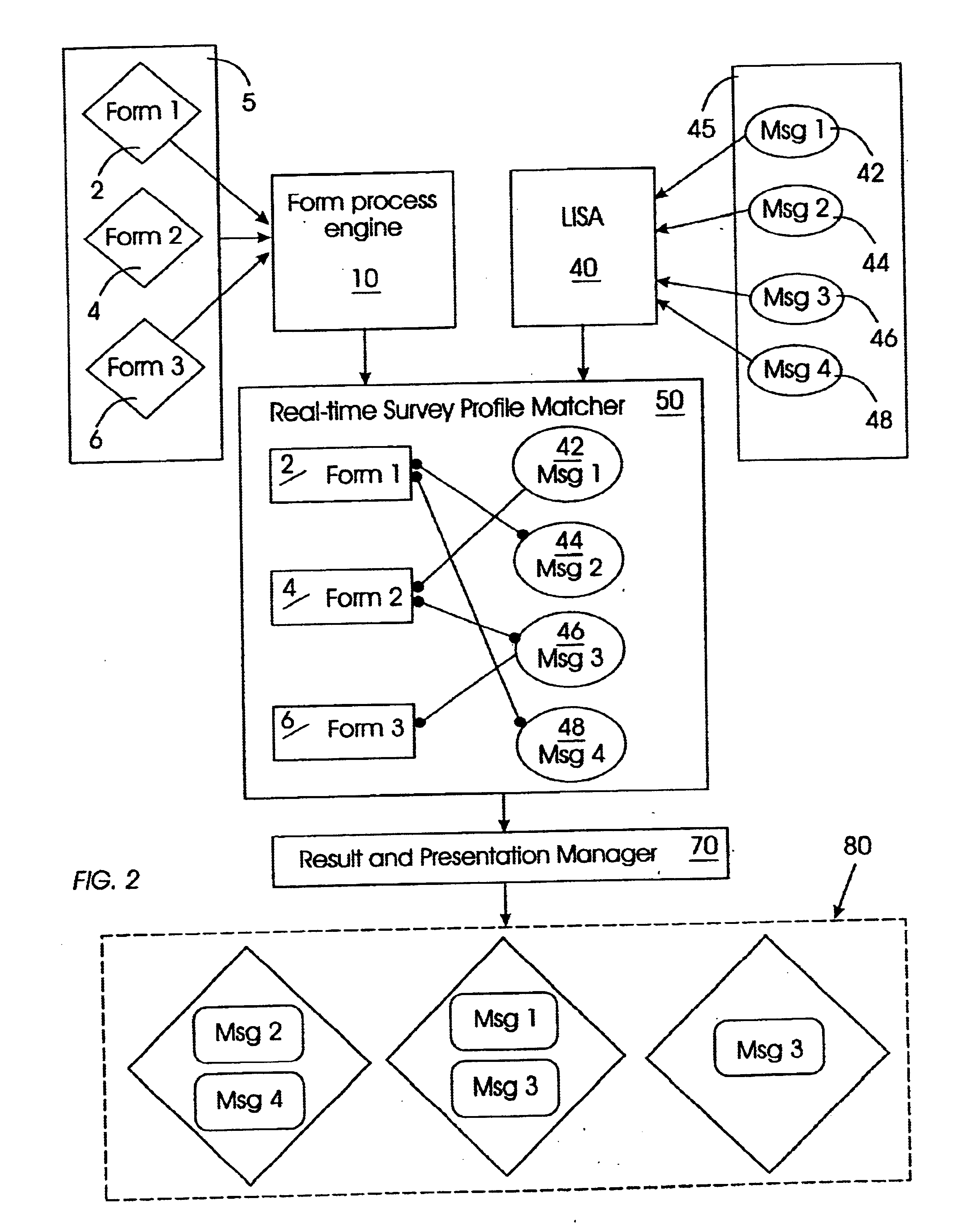
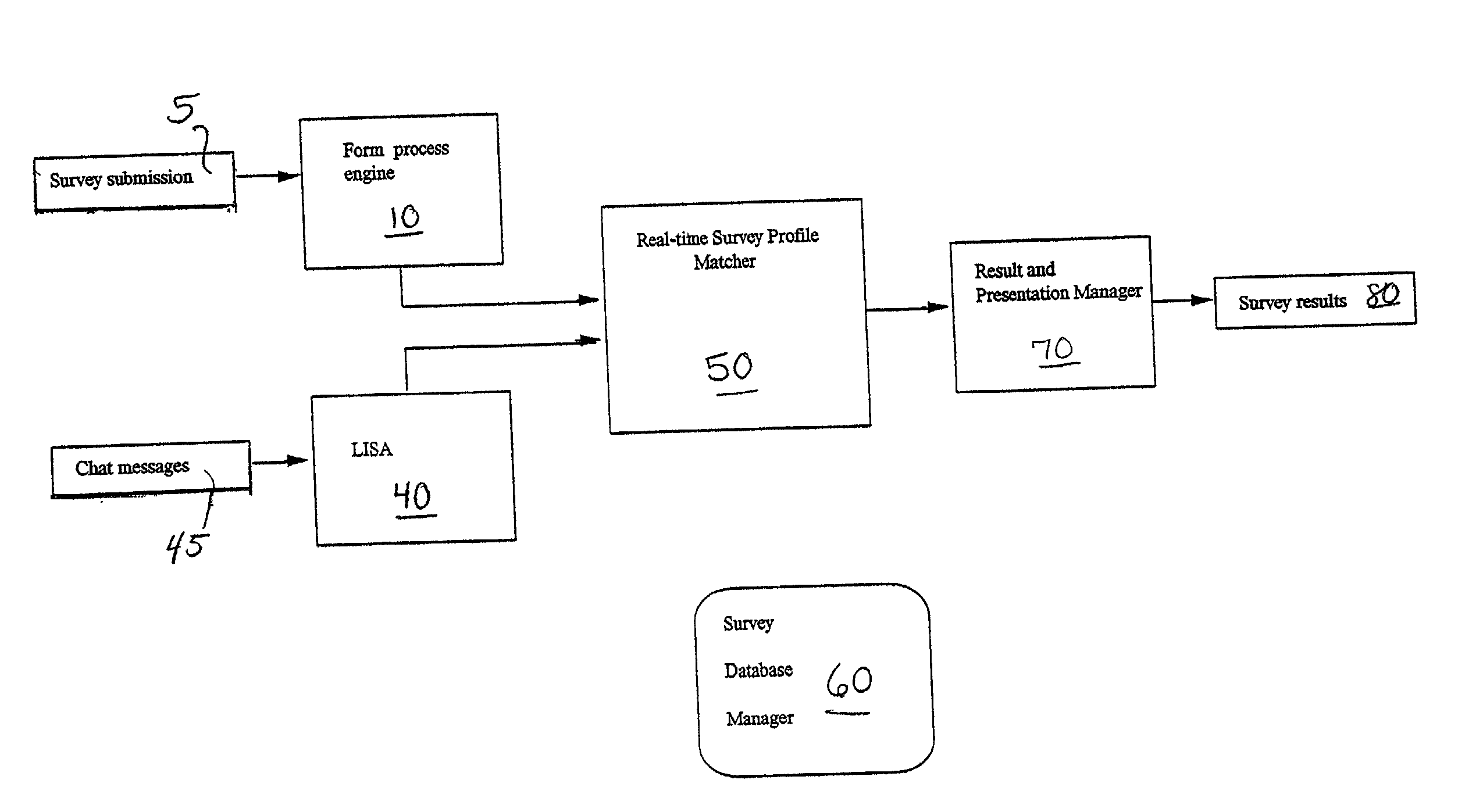
System and method for automatically conducting and managing surveys based on real-time information analysis
InactiveUS6912521B2Special service for subscribersSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTime informationService Interface for Real Time Information
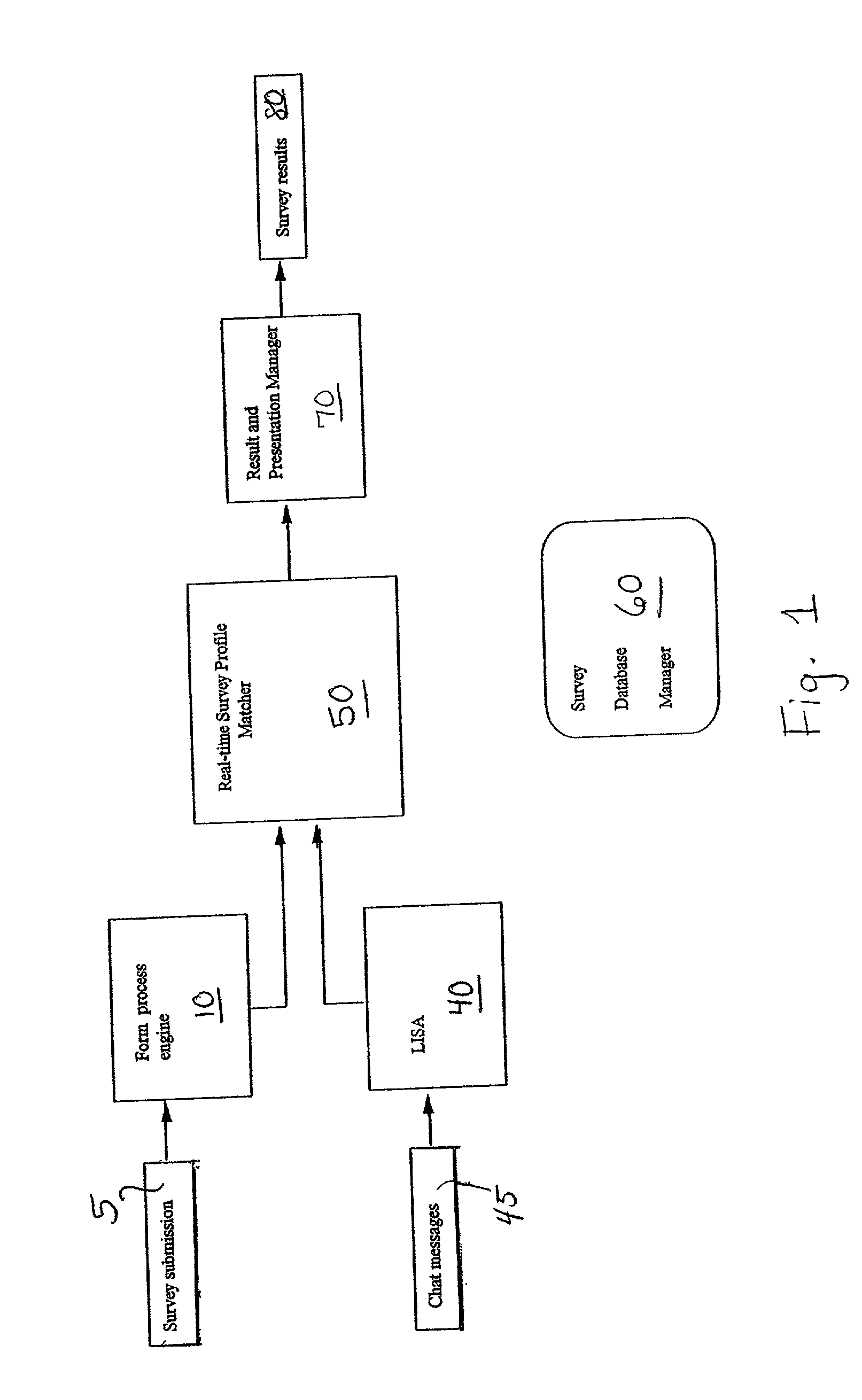
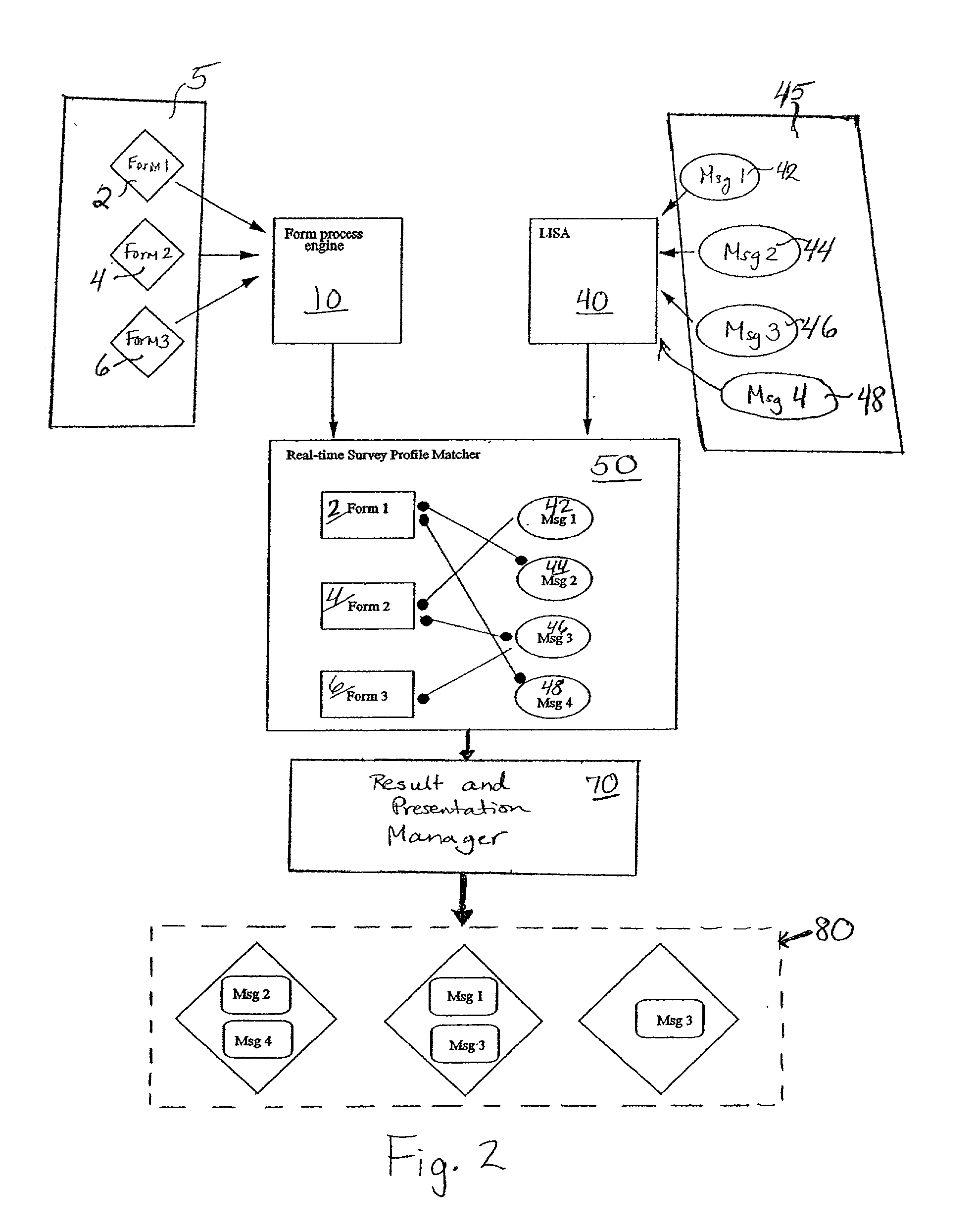
The present invention provides a system and technique for initiating, conducting, and managing real-time surveys, in the context of a real-time discourse, such as Internet chat, to provide dynamic, real-time survey results. A surveyor initiates a survey by filling out an electronic form which is processed and submitted to a sorting component of the invention. The invention imposes an additional layer of functionality upon a Live Information Selection and Analysis tool which gathers, summarizes, and indexes chat messages in a real-time discourse. The sorting component matches the collected real-time chat messages from the LISA tool with correlating submitted survey queries to provide raw real-time survey results which are converted into a viewable format for submission to the surveyor. The present invention makes it possible to initiate, conduct, and manage multiple surveys simultaneously to provide accurate, dynamic, real-time survey results within the context of a real-time discourse.
Owner:BEIJING PIANRUOJINGHONG TECH CO LTD
System and method for automatically conducting and managing surveys based on real-time information analysis
InactiveUS20020188777A1Easily initiatingFacilitate conductionDigital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersTime informationService Interface for Real Time Information
The present invention provides a system and technique for initiating, conducting, and managing real-time surveys, in the context of a real-time discourse, such as Internet chat, to provide dynamic, real-time survey results. A surveyor initiates a survey by filling out an electronic form which is processed and submitted to a sorting component of the invention. The invention imposes an additional layer of functionality upon a Live Information Selection and Analysis tool which gathers, summarizes, and indexes chat messages in a real-time discourse. The sorting component matches the collected real-time chat messages from the LISA tool with correlating submitted survey queries to provide raw real-time survey results which are converted into a viewable format for submission to the surveyor. The present invention makes it possible to initiate, conduct, and manage multiple surveys simultaneously to provide accurate, dynamic, real-time survey results within the context of a real-time discourse.
Owner:AWEMANE LTD
Method for respondent-based real-time survey
Owner:KIM JEONG UK
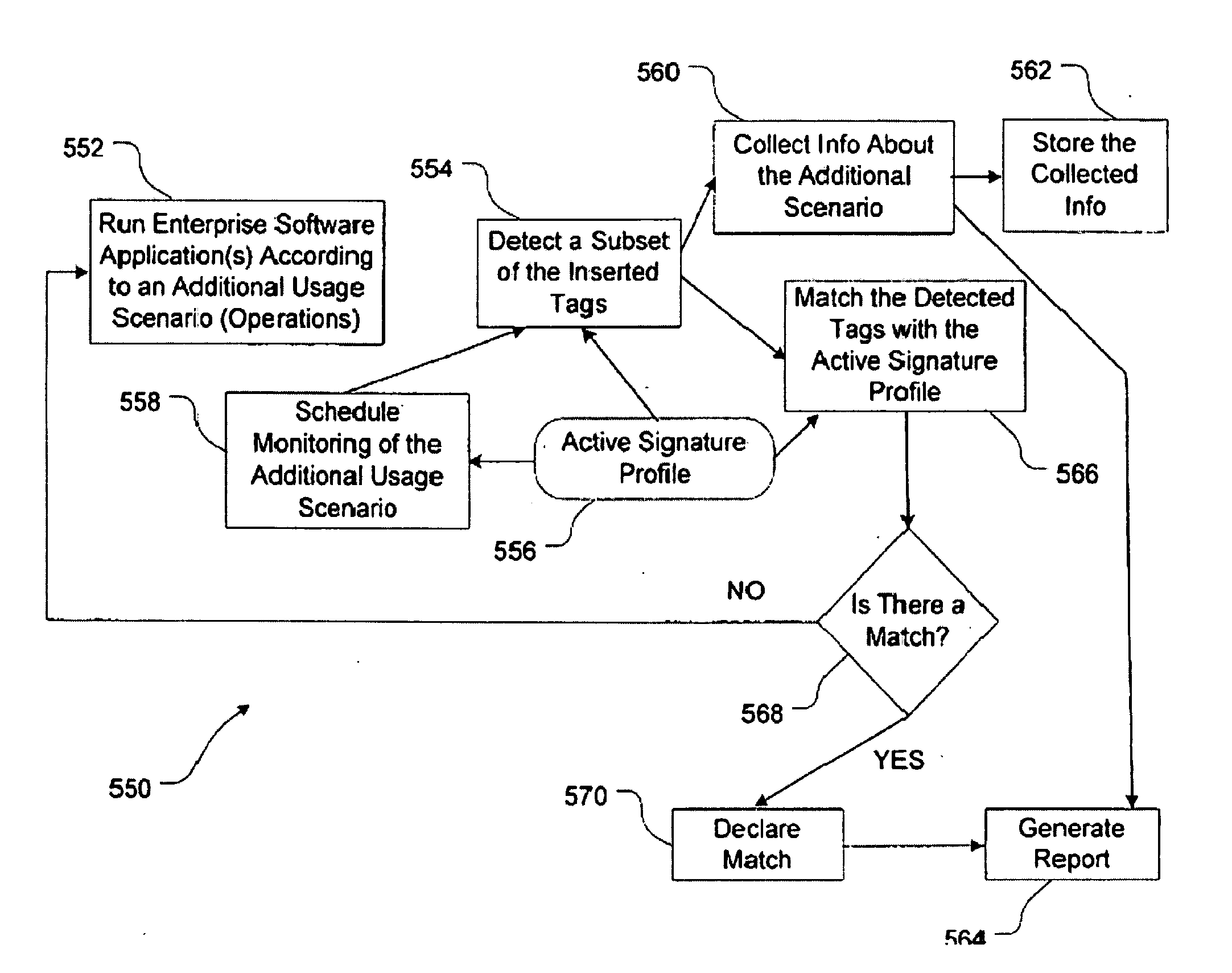
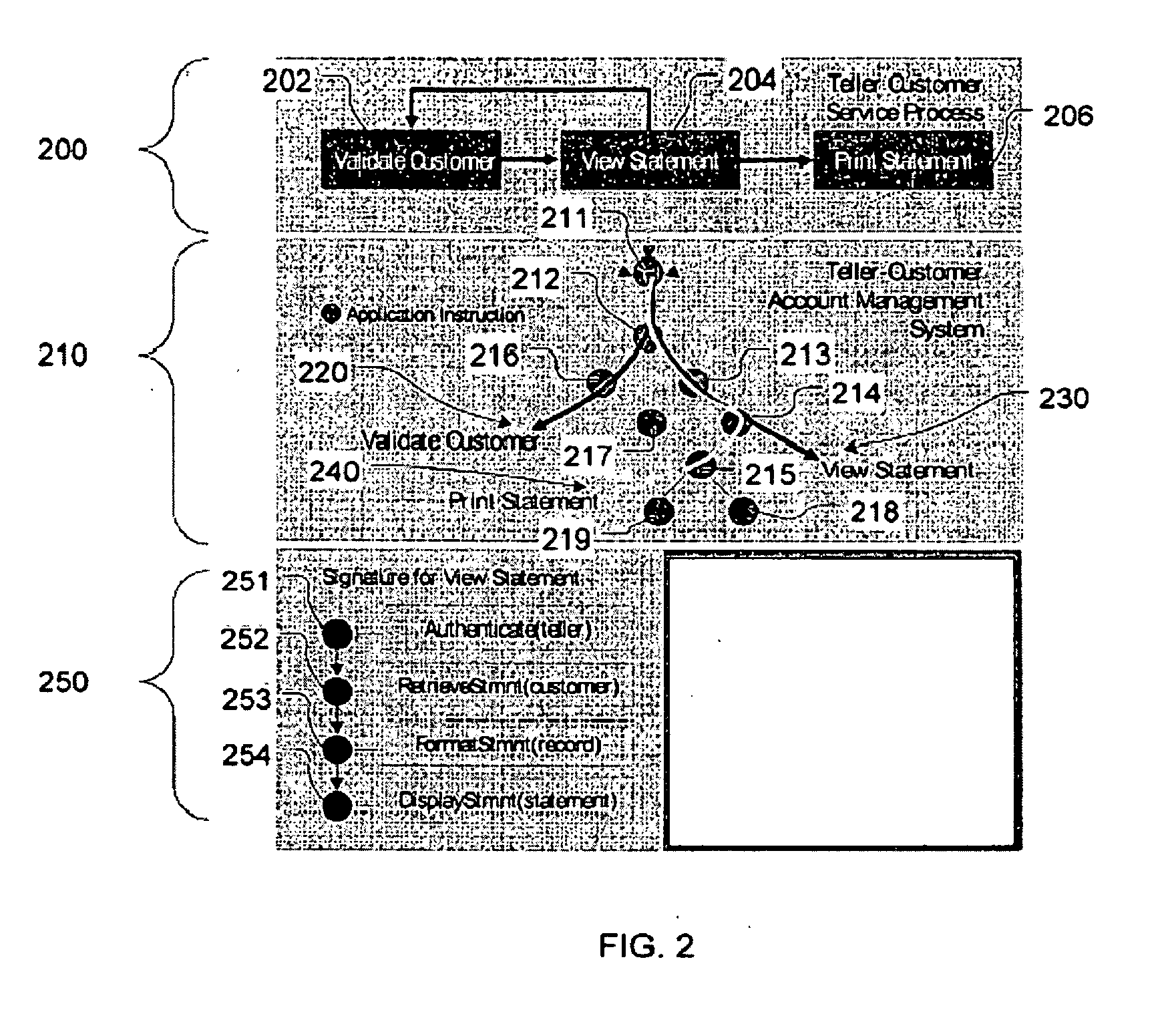
Systems and methods for monitoring and detecting fraudulent uses of business applications
ActiveUS20070073743A1Facilitates efficient accessEasy to processFinanceError detection/correctionSurvey resultData mining
A systems and methods are described detect fraud in existing logs of raw data. There can be several disparate logs, each including data of disparate data types and generated by different and possibly unrelated software enterprise applications. The fraud management system aggregates and organizes the raw log data, archives the data in a manner that facilitates efficient access and processing of the data, allows for investigation of potentially fraudulent usage scenarios, and uses the results of the investigation to identify patterns of data that correspond to correspond to high risk usage scenarios and / or process steps. In subsequent processing, archived data can be compared against the identified patterns corresponding to high risk usage scenarios to detect matches, and the invention thereby automatically detects high risk usage scenarios and issues appropriate alerts and reports.
Owner:FIS FINANCIAL COMPLIANCE SOLUTIONS
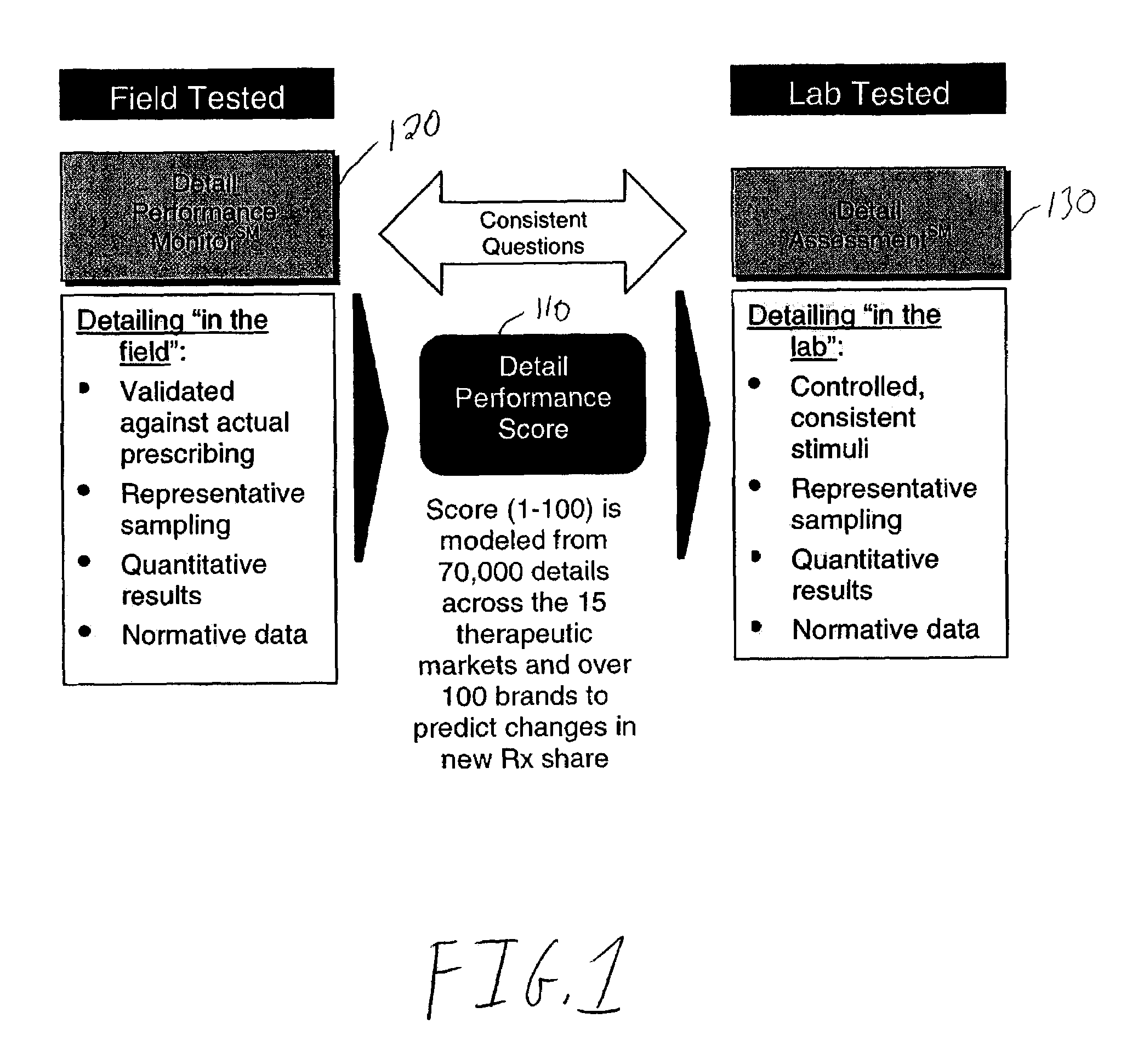
Method and system for analyzing the effectiveness of marketing strategies
InactiveUS7080027B2Eliminate in-person testing variabilityApproximating actual environmentMarket predictionsBroadcast information monitoringCombined useSurvey result
A method and system for analyzing a “detail” (the use of promotional materials in combination with a sales pitch), measures the effectiveness of a sales presentation and its ability to drive market share through a standardized, quantitative evaluation of the entire sale presentation and its related components. The method includes administering a two, different surveys. The first survey, the Detail Performance Monitor survey, comprises an “in the field” test of how respondents are responding to various marketing strategies by tracking subsequent behavioral data of the respondents and comparing the behavioral data to the survey results. The second survey, the Detail Assessment survey, comprises an “in the lab” test of how various marketing strategies affect respondent attitude towards a product by comparing respondent attitude before and after presentation of a simulated “detail” that represents the marketing strategy.
Owner:TARGETRX
Ranking system using instant post-transaction surveying of transaction judges
After a telecommunications interaction apparently concludes between first and second parties to the interaction, an automated means for detecting the termination of the interaction jumps in and presents at least one of the parties with an opportunity to participate in a survey (an instant survey) relating to the just-terminated interaction. In one embodiment, the interaction is between a prospective consumer and a lead buyer (or an agent of the buyer) and the instant survey queries the buyer or agent regarding immediate impressions of the quality of the purchased lead that brought the prospective consumer and the lead buyer (or agent) into contact with one another. In one embodiment, results of instant surveys feed into a ranking system that ranks the quality of leads provided through a specific sponsor and remuneration to the sponsor is automatically adjusted according to instant survey results collected for that sponsor.
Owner:LEADPOINT
Systems and methods for creating and maintaining a market intelligence portal
Systems and methods for creating and maintaining a market intelligence portal. Using automated data processing techniques, a market intelligence campaign is defined and executed to determine the most productive approach for marketing new products in a particular market segment. A key component of the systems and methods is identifying key opinion leaders who are deemed by their peers to be influential in a particular therapy space through surveying techniques. In addition to opinion leader information obtained through surveying, external data sources are used to create a detailed profile for each opinion leader identified through surveying. Social network mapping and other analysis is performed on the profiles. The survey results, profiles and social network diagrams are stored electronically on a network portal. An interactive dashboard interface to the portal is created so that the data can be accessed and visualized remotely, preferably using a web browser interface. One or more data streams are used to self-update the data as new data relevant to the campaign and / or the opinion leader profiles is available. The various systems and methods may have particular utility to pharmaceutical companies trying to gain market acceptance of new drug therapies.
Owner:PROLINK SERVICES
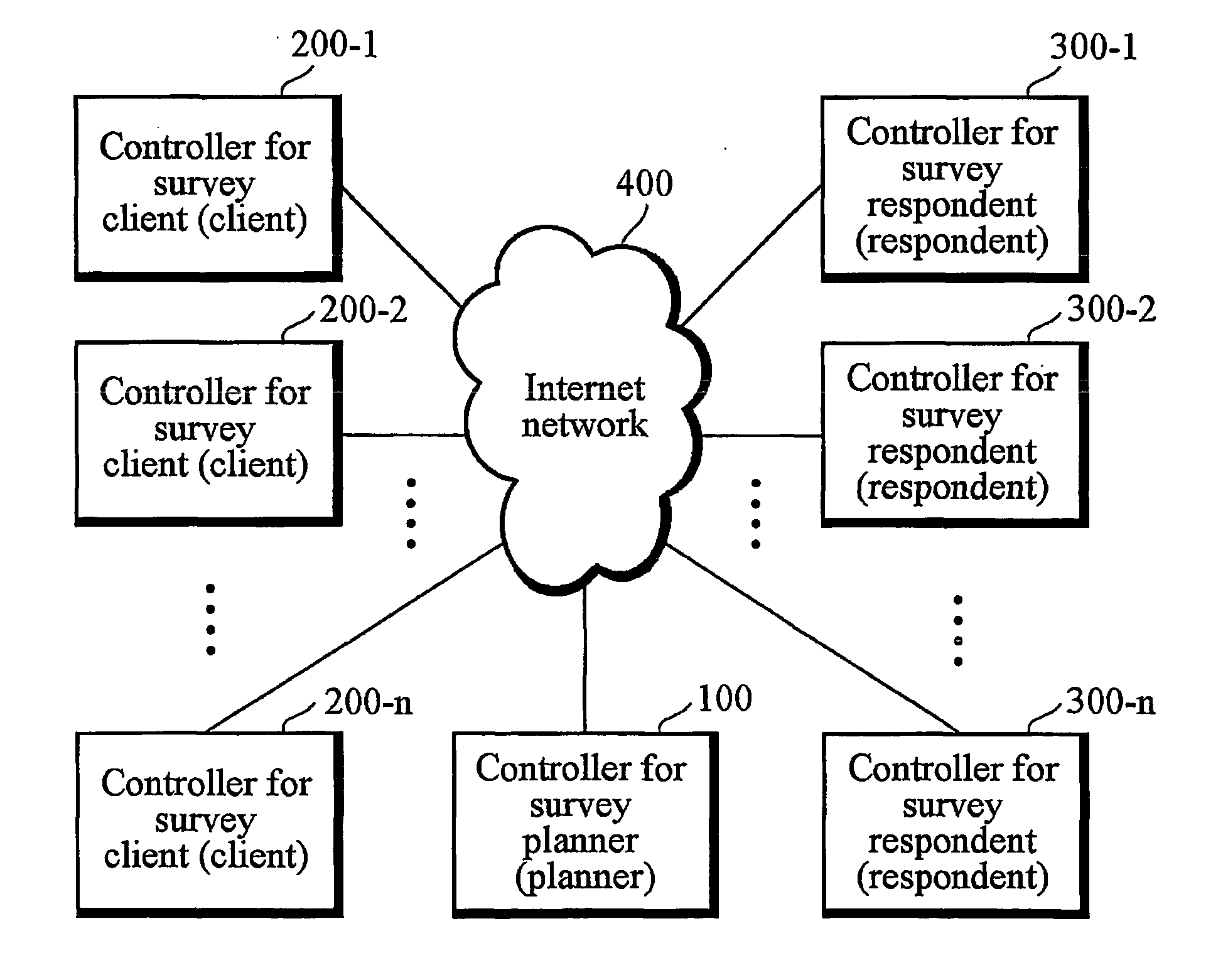
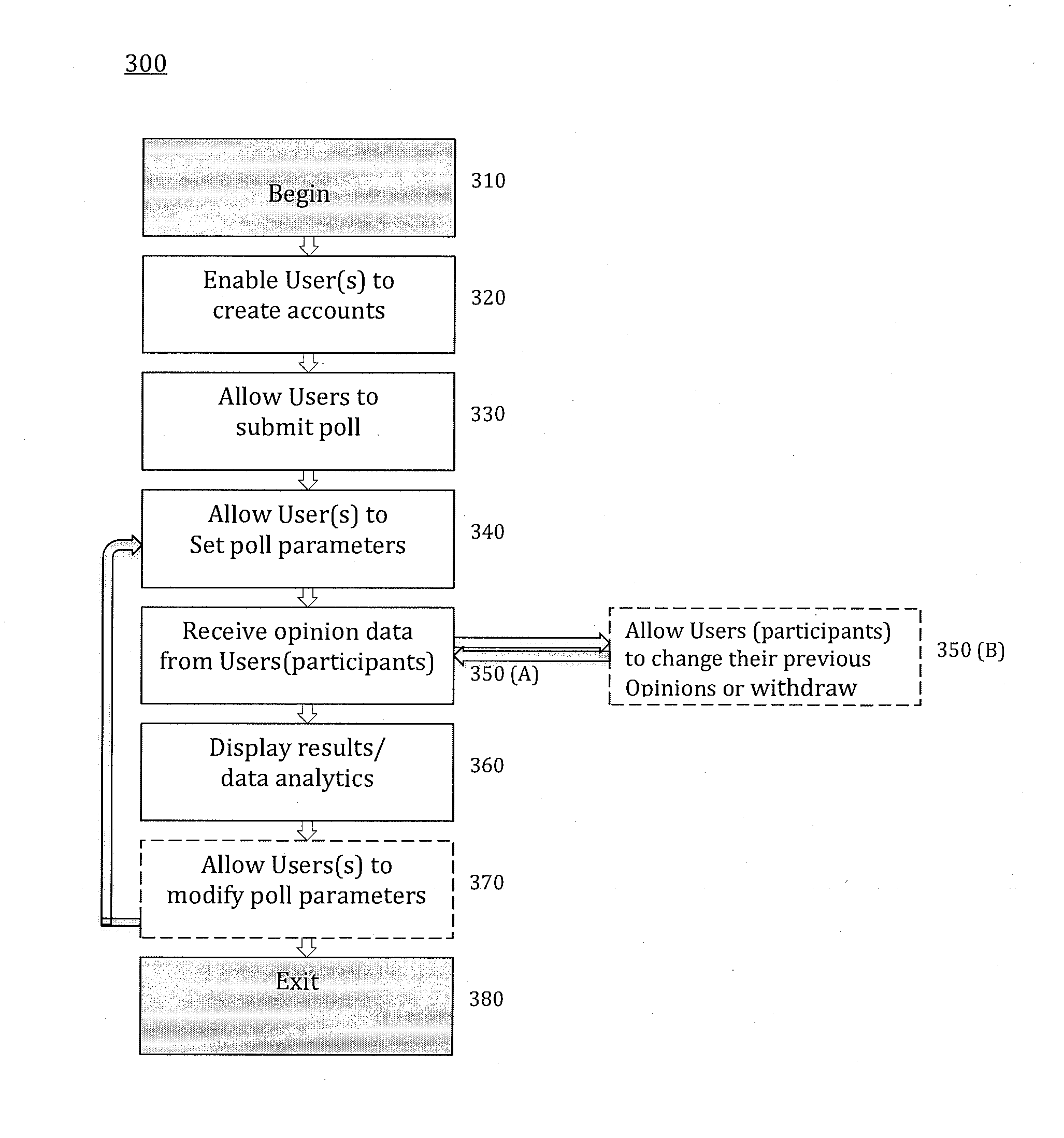
System of poll initiation and data collection through a global computer/communication network and methods thereof
A computer-implemented method of public opinion poll initiation and public opinion data collection for using non-deterministic mathematical models (e.g. chaos model), independent of third parties involvement (e.g., campaign managers, marketers, pollsters, etc.) is provided. In exemplary embodiments, the method may comprise receiving a post and an instruction for public opinion poll from a first user; initiating the public opinion poll and displaying it to a second user(s) / the public, receiving an initial answer to the public opinion poll from the second user(s); generating results of the public opinion poll based on the initial answer; receiving an alternative answer(s) from the second user(s) if wished by the second users, updating the results of the public opinion poll based on the alternative answer(s); and displaying a real-time feed of the public opinion poll results, the real-time feed updated when public opinion poll answers are entered or changed by a user.
Owner:GOLD ZARA A +1
Design and Analysis of Customer Feedback Surveys
Owner:VERINT AMERICAS
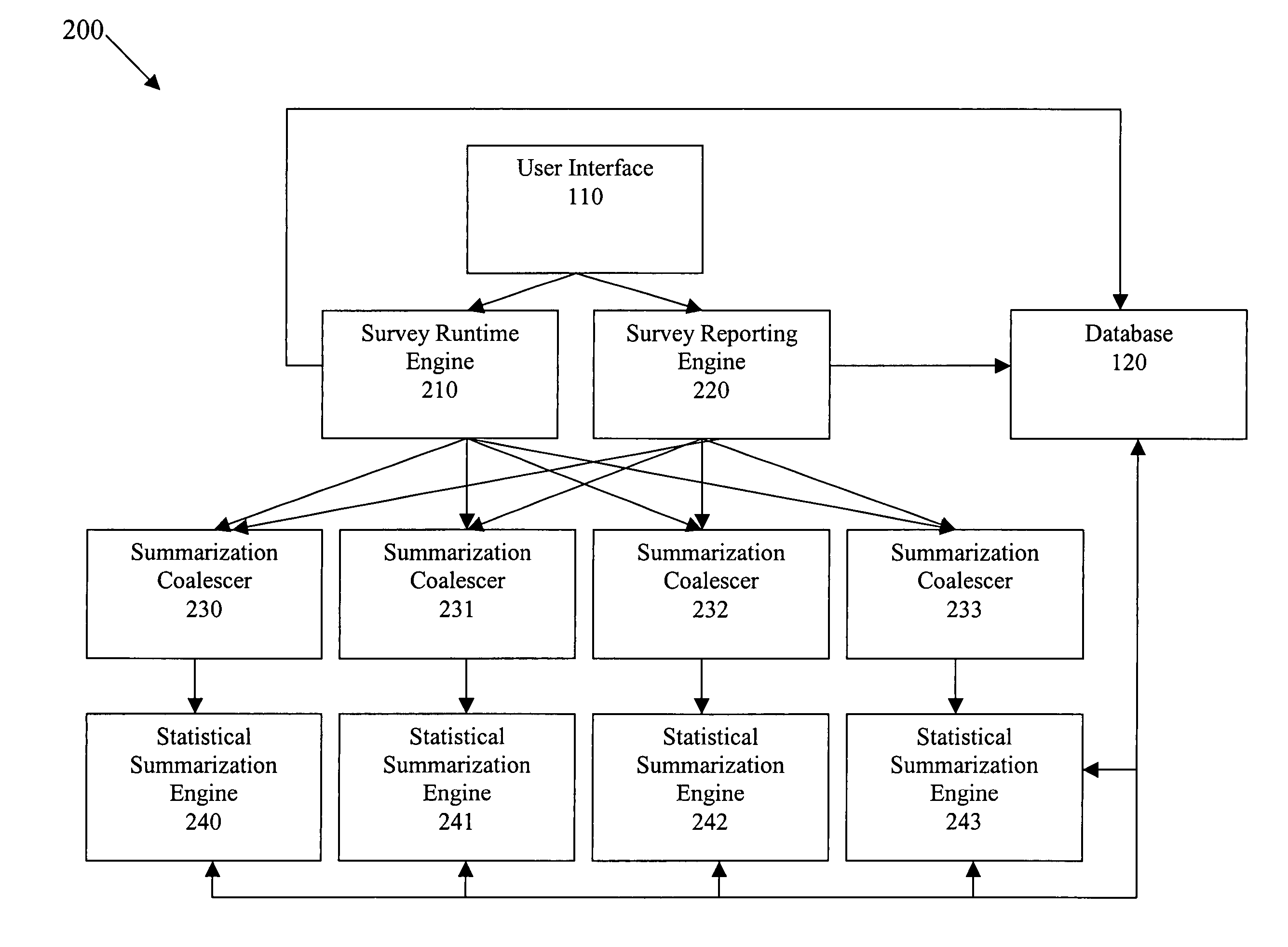
Method and apparatus for survey processing
InactiveUS7418496B2Efficient processingNatural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsGeneral purposeLexical rule
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for improved, real-time survey data processing and analysis. Certain embodiments use distributed computing techniques to perform statistical calculations for survey data, such as general purpose and multi-rater feedback data. Certain embodiments use a matrix structure coupled with hash tables for efficient processing of survey statistics across an entire survey. Certain embodiments use a criteria parser based on externally definable lexical rules to determine which survey responses belong to which groups. Certain embodiments allow coalescing of summarization requests between summarization servers to allow for peak performance across any number of surveys. Certain embodiments provide a scalable, adaptable survey processing system and method that processes survey results in real time, allowing for immediate feedback during the survey process.
Owner:PG CIQ INC
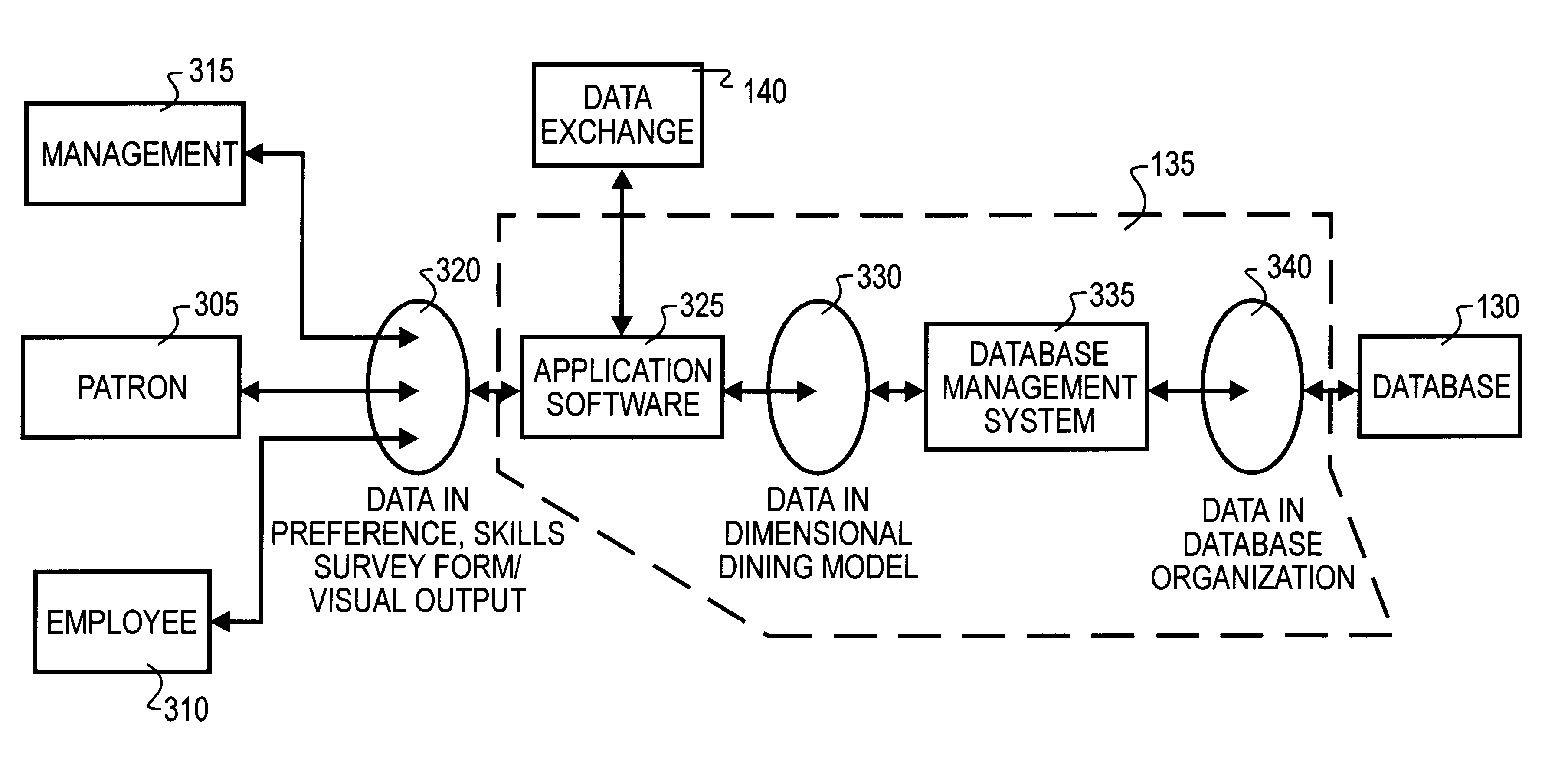
Dimensional dining restaurant management system
InactiveUS6301564B1Easy to createFacilitates conscious selectionMarketingSurvey resultApplication software
Apparatus and method for mass producing a unique dining experience for each individual diner within a group of patrons includes computers, applications software, models and databases. Through various alternative input mechanisms, each individual patron's preferences will be surveyed, and the results of the surveys are stored within the database. Staff and management of an establishment are also surveyed regarding various personal and facilities capabilities and assets. The preference surveys may be quite basic in nature, but with more detailed surveys a more elaborate model may be generated. Based upon the preference survey results, a dining event is developed that groups patrons according to areas of agreement among surveys, while simultaneously tailoring unique events or decor based upon the preference survey results that are not common among the patrons. The dining event is prepared for, including training of staff and management, and the dining event is then staged. During the event, an off-site person will most preferably provide monitor and provide feedback to the staff and management, and subsequent to the event further evaluation will occur. Based upon the event results and evaluation, the database and model may be updated. Electronic devices may form a part of the apparatus, and in this case will most preferably be controlled by computerized components to perform appropriately according to the stored model of the event. As a result of the differences in preferences, skills and assets of all participants, no two dining events will be identical. However, each dining event is designed and prepared according to pre-established models to fulfill each of the needs and expectations of each individual patron while simultaneously capitalizing on the strengths and talents of a staff and facility. Simultaneously, the managerial burden of maintaining a single atmosphere within an establishment is relieved, and patrons are offered unexpected, but consistently high-quality, dining experiences.
Owner:HALVERSON HELENA B
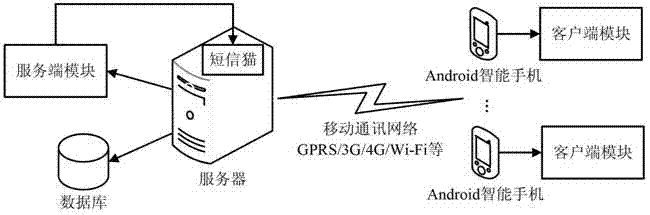
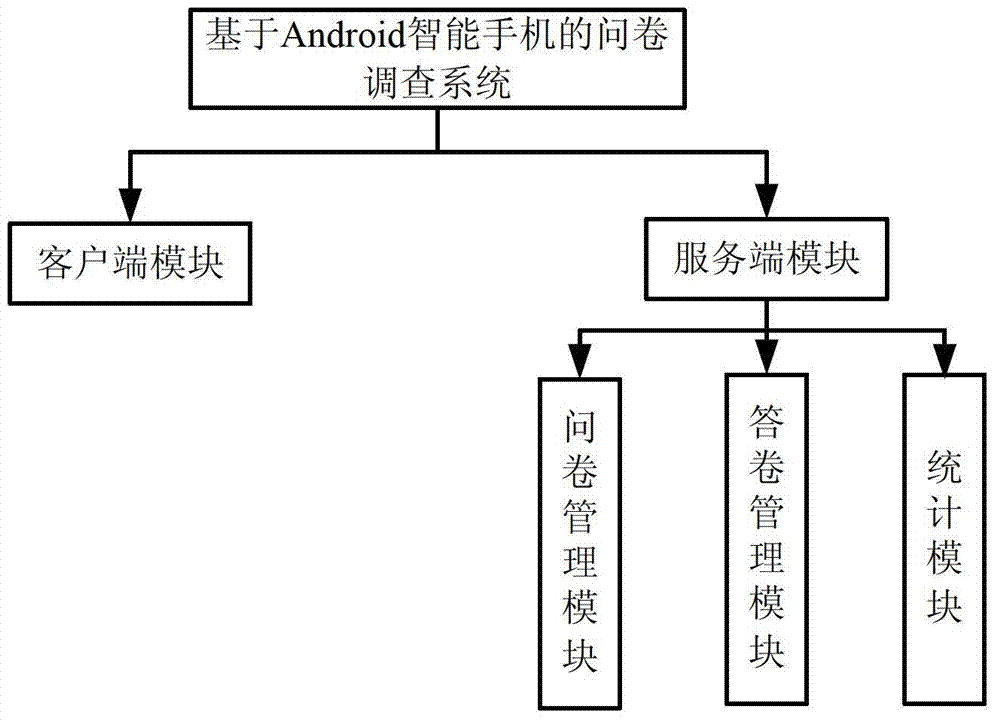
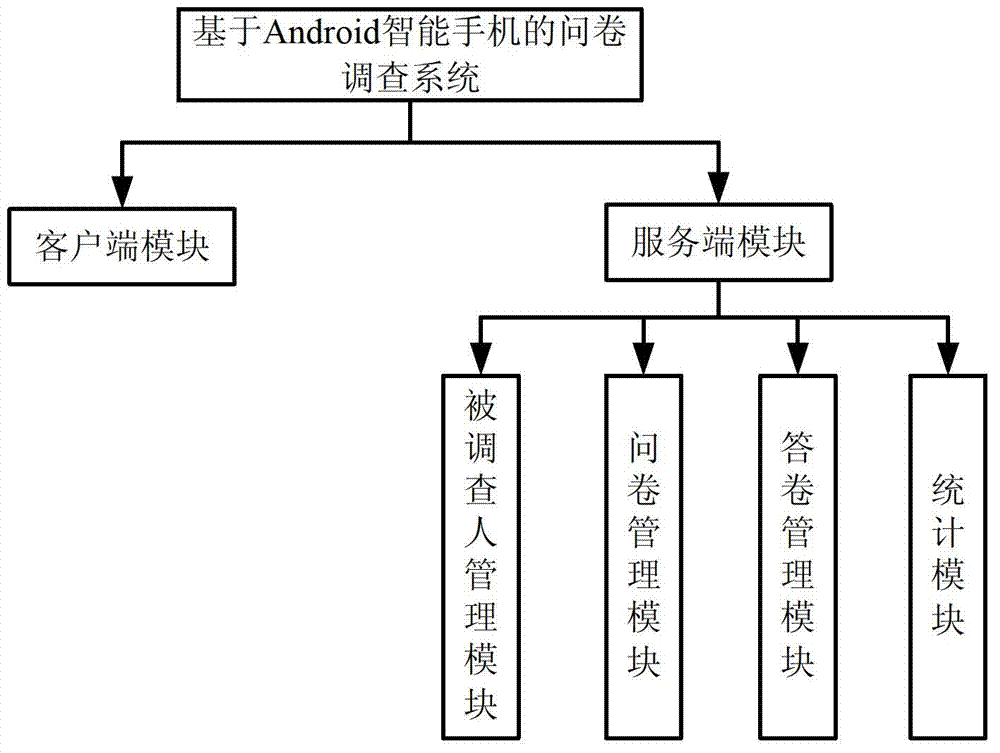
Questionnaire survey system on basis of intelligent mobile communication equipment and method thereof
InactiveCN102789606AComplete and true reflectionImprove investigation efficiencyOffice automationTransmissionSurvey resultComputer module
The invention relates to a questionnaire survey system on basis of intelligent mobile communication equipment, which comprises more than one intelligent mobile communication equipment and more than one server, wherein a client module is mounted in the intelligent mobile communication equipment and is used for realizing the recording of a questionnaire, participating in questionnaire survey and requesting for inquiring a statistical result of a survey answer sheet; a server module is mounted in the server; the server module comprises a questionnaire management module, an answer sheet management module and a statistic module; the server module is used for realizing the storage, starting and ending of the questionnaire survey, the checking and storage of the answer sheet and the statistics of the answer sheet; the questionnaire contains more than one question; each question is corresponding to more than one optional answer; the optional answer corresponding to each question can be autonomously added by an inquired person; and the client module is in data communication with the server module through a mobile communication network. The invention also provides a questionnaire survey method on the basis of the intelligent mobile communication equipment. According to the questionnaire survey method provided by the invention, a survey result is truly reflected and the survey is quick and convenient.
Owner:ZHUHAI ZAIZHOU SOFTWARE TECH
Recording equipment and recording method
InactiveUS20050276567A1Increase storage capacityEasy to processTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingSurvey resultOperating system
If programs are always recorded according to a decision that is made-based on the user preferences survey results or specific categories and user's recording instruction, the user will lose the opportunity to view programs of categories other than the user preferences. Further, if the entire viewable broadcast is recorded without any selection, a problem arises that there are required greatly increased storage capacity and greatly increased capacity of processing the bit rate required for the recording. According to the present invention, a rate converter is provided for changing a bit rate for each channel, the history of programs that have been viewed by the user is recorded as the usage history, the usage tendency of the user is extracted from the usage history with an agent, a decision is made as to whether the program selected for each channel matches the usage tendency of the user, and in case of matching the program is recorded on the recording medium without varying a bit rate allowing the high-quality video to be maintained, whereas when the selected program does not match the usage tendency of the user, the program is recorded on the recording medium upon conversion to a lower bit rate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
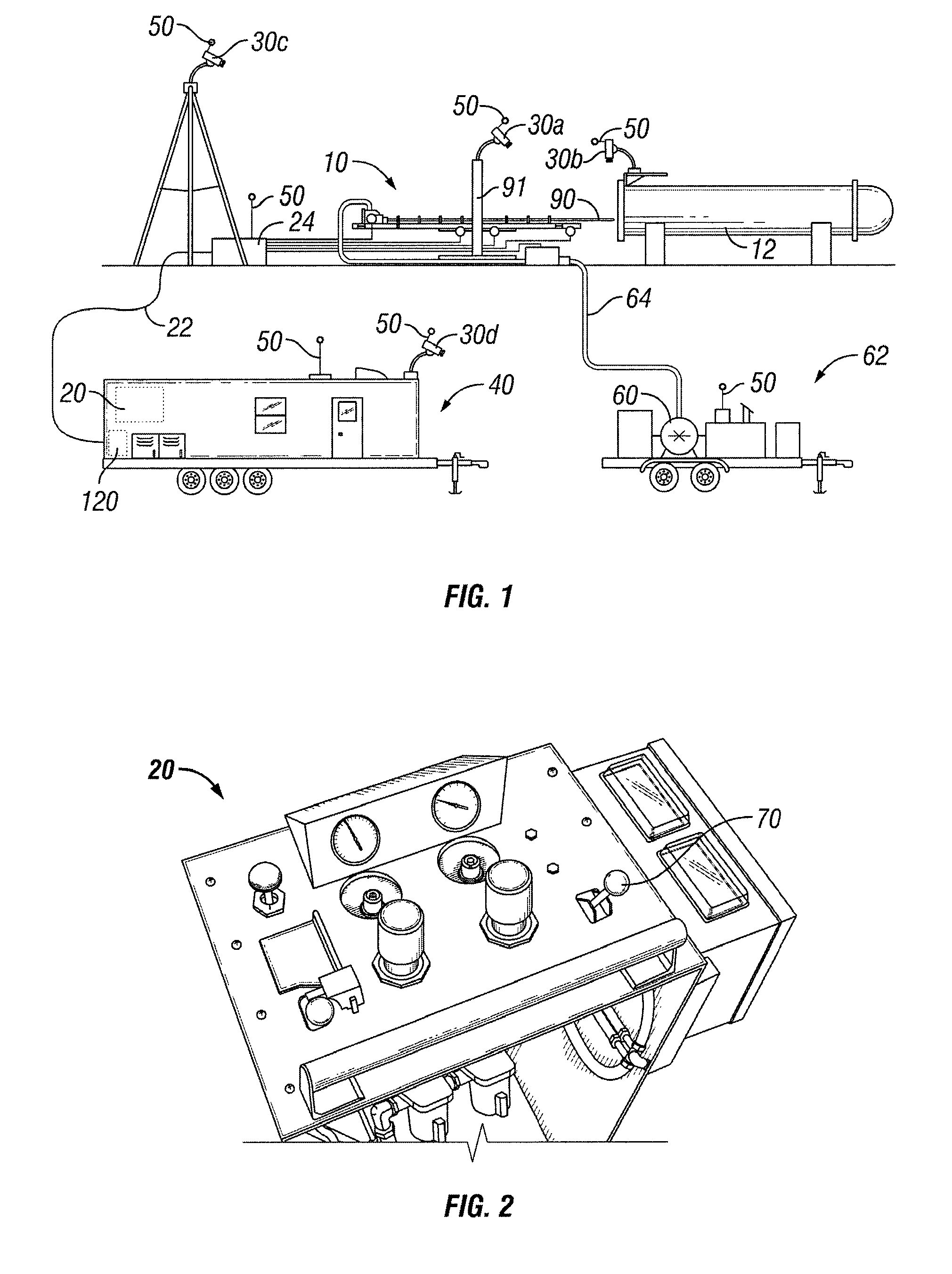
Automated heat exchanger tube cleaning assembly and system
ActiveUS20090255557A1Clean effectHollow article cleaningVehicle position/course/altitude controlSurvey resultThree dimensional measurement
An automated heat exchanger tube cleaning assembly and system are provided. The present system can automatically (without ongoing human intervention) survey the tube sheet of a heat exchanger in three-dimensions, convert and record the survey results as a digital file in three-dimensions, and then, according to sequential parameters input via custom software, automatically coordinate via computer one or more cleaning devices to effect the cleaning of each desired tube of the heat exchanger.
Owner:HYDROCHEM
Automated heat exchanger tube cleaning assembly and system
ActiveUS8057607B2Hollow article cleaningVehicle position/course/altitude controlThree dimensional measurementSurvey result
An automated heat exchanger tube cleaning assembly and system are provided. The present system can automatically (without ongoing human intervention) survey the tube sheet of a heat exchanger in three-dimensions, convert and record the survey results as a digital file in three-dimensions, and then, according to sequential parameters input via custom software, automatically coordinate via computer one or more cleaning devices to effect the cleaning of each desired tube of the heat exchanger.
Owner:HYDROCHEM
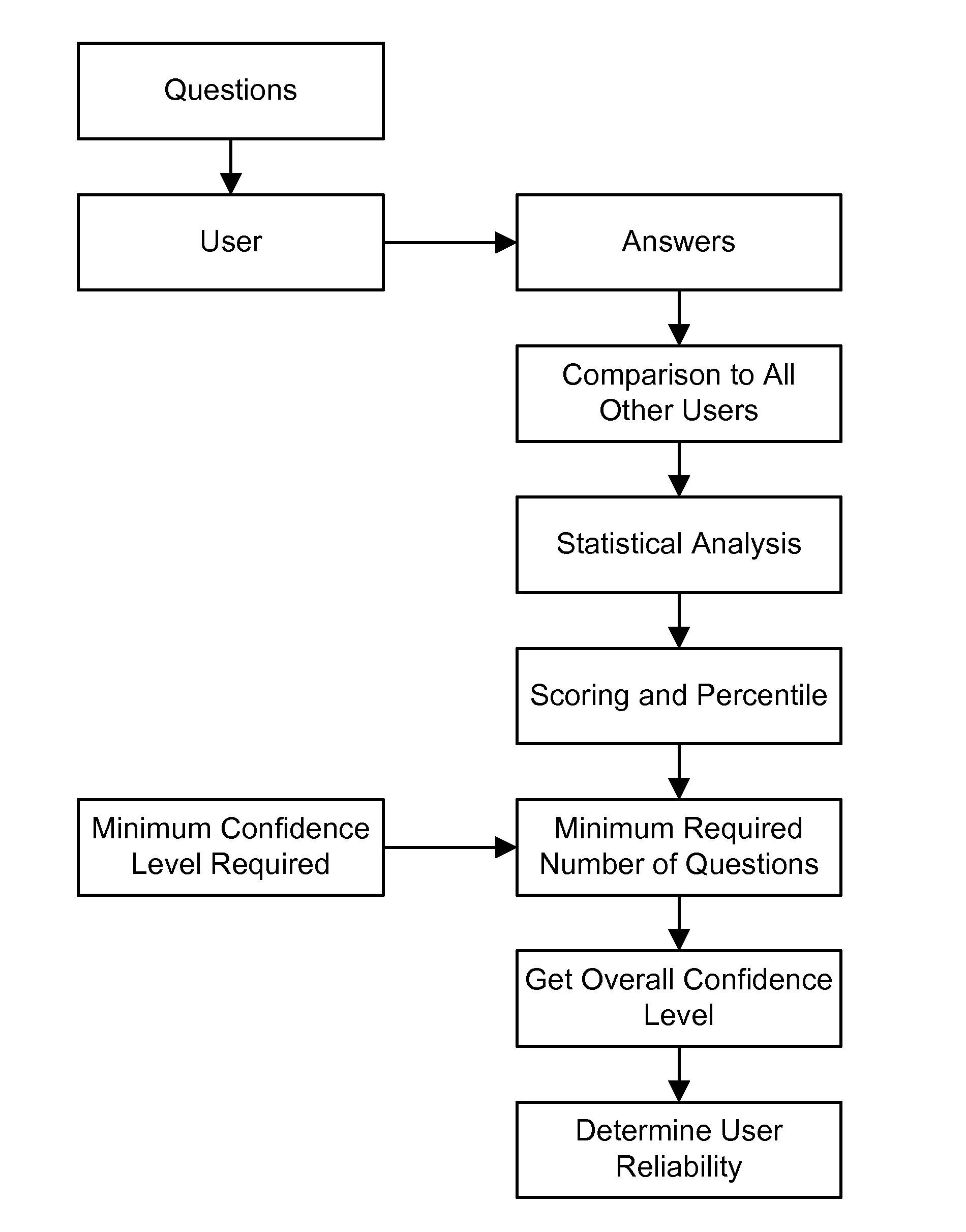
Method and System for Improving the Truthfulness, Reliability, and Segmentation of Opinion Research Panels
InactiveUS20110145043A1Increase valueQuality improvementMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsDemographic dataSurvey result
An example relates to survey analysis, survey panel members analysis, accuracy metrics, reliability analysis, and statistical analysis, to come up with confidence levels, and get an overall reliability of survey panel members, based on a score and percentile, and give incentives to the panel members, based on their reliability scores, to encourage them to be more reliable and truthful in the surveys, including their background and their demographics, increasing the values of the survey results drastically. In addition, this covers many separate embodiments: methods for improving and “incentivizing” truthful behavior in consumer panels; using Trustscore to measure and reward consistency and truthfulness; tag surveys to segment panels; and Doublecheck'd as a tool, to utilize the best responses through asking panel members twice (or more) with the same survey, and only including results from the members who answer the same both (or more) times.
Owner:HANDEL DAVID BRIAN
System and method for large scale survey analysis
InactiveUS8005712B2Computer-assisted medical data acquisitionElectrical appliancesOriginal dataSurvey result
Disclosed herein is a method of analyzing large scale survey results comprising obtaining a sparse data set representing a subset of an original data set comprising a plurality of individuals' responses to a plurality of questions, wherein the sparse data set comprises less than ninety percent of the responses in the original data set; analyzing the sparse data set using a general diagnostic model; and obtaining estimated person parameters using the general diagnostic model.
Owner:EDUCATIONAL TESTING SERVICE
Method for optimizing charging path of electric automobile based on user travel rules
ActiveCN108981736AGuaranteed charging experienceIncrease motivationInstruments for road network navigationInternal combustion piston enginesPersonalizationTraffic network
The invention discloses a method for optimizing a charging path of an electric automobile based on user travel rules. The method comprises the following steps: (1) counting the owner travel characteristic; (2) performing data acquisition, wherein the data comprises data related to the electric automobile travel characteristic as well as data of charging stations and road congestion conditions; (3)establishing a traffic network, namely establishing a regional traffic network comprising nodes and two-way edges; (4) performing data analysis and processing, namely counting habitual charging stations and charging time of the owner, generating corresponding travel links, and correcting the analytical result according to the survey results in the (1); (5) establishing an electric automobile charging path optimization model; and (6) selecting the optimal charging requirement guided traveling path integrating the charging time, traveling path and cost for owner preference from the multiple travel links by utilizing the electric automobile charging path optimization model. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the travel path corresponding to the travel requirements is provided for the user by fully considering the regional historical circumstances and user charging habits, the defect that the real-time path planning system has harsh requirements on communication hardwarefacilities is overcome, and the charging path is personalized.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +4
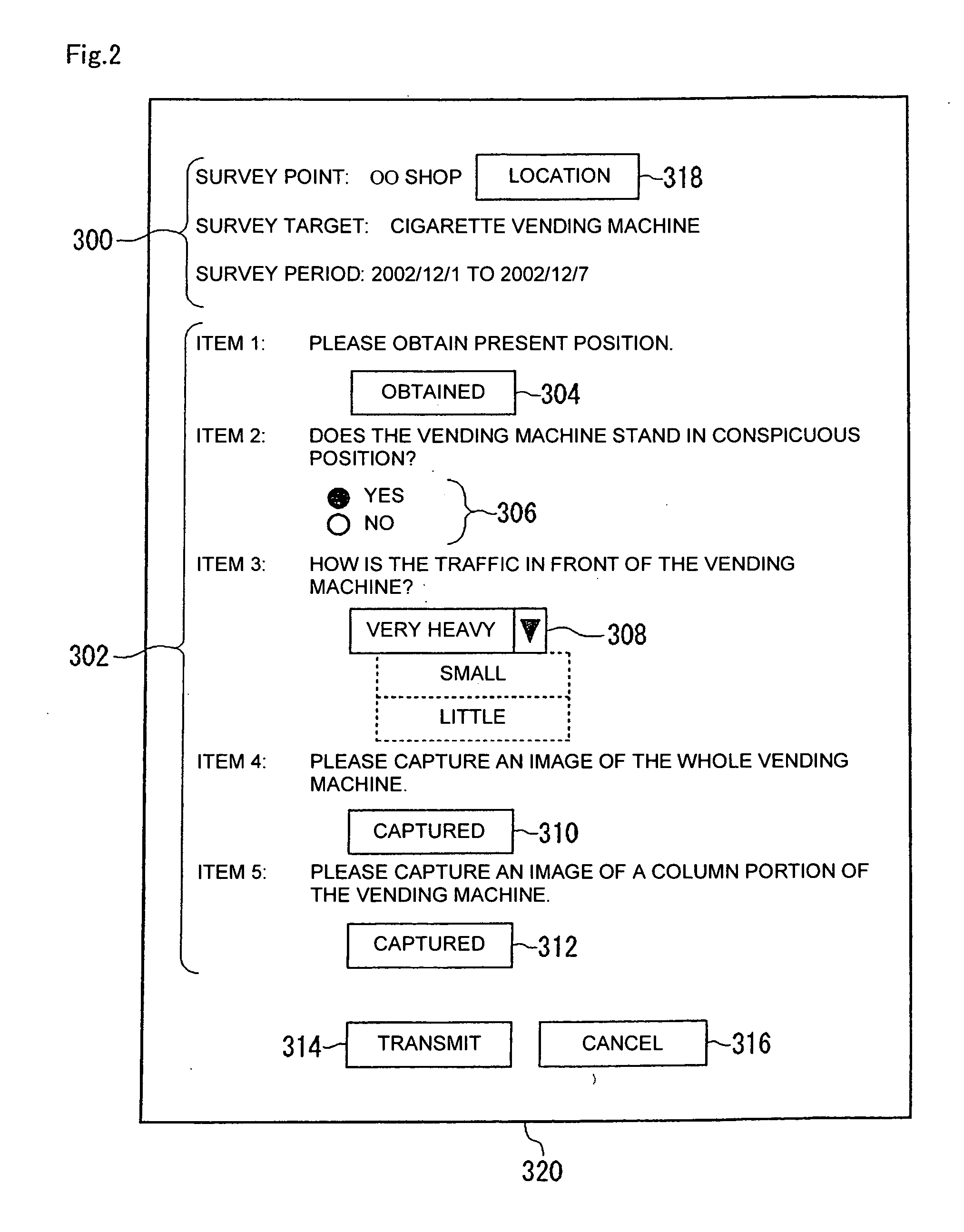
Analyzing system, analyzing method using the same, and system for collecting survey results for use in anlysis
InactiveUS20070141976A1Improve analysis qualityImprove reliabilityMarket predictionsRegistering/indicating time of eventsTerminal equipmentSurvey result
A surveyor carries a terminal device 200 and travels to a survey point preliminarily instructed. The surveyor obtains survey position information by using a GPS unit in the terminal device 200 at the survey point. The surveyor also photographs an object of a survey by using a camera in the terminal device 200 at the survey point. After completion of a series of surveys, the surveyor transmits survey results including the survey position information to an analyzing apparatus 100 by using the terminal device 200. The analyzing apparatus 100 determines reliability by using survey position information included in the survey results and carries out a predetermined analysis by using a survey result of high reliability. Consequently, a survey result of low reliability can be eliminated from objects to be analyzed.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
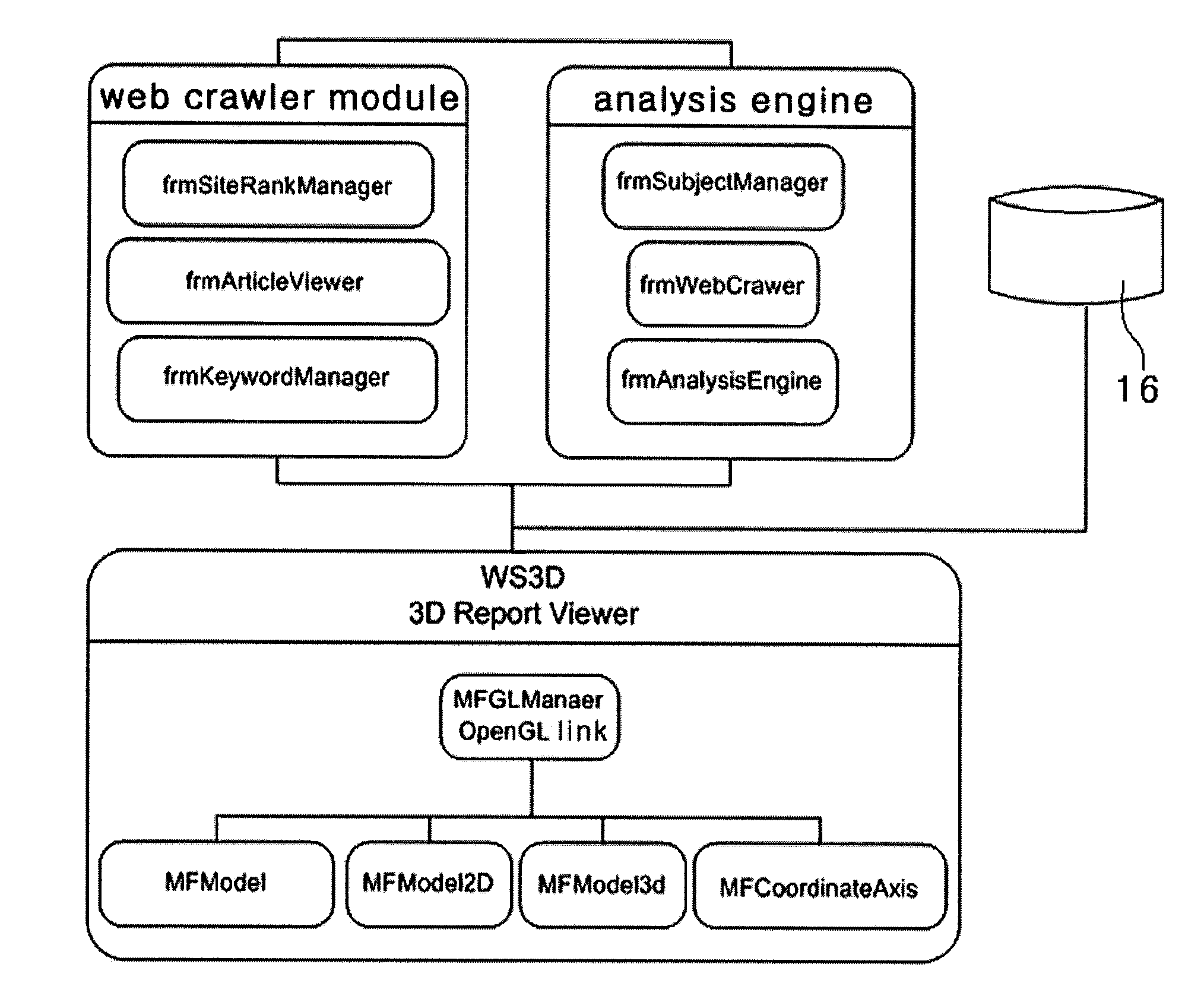
3D visualization system for web survey
InactiveUS20100153372A1Easy to understandImprove abilitiesWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsFixed starsReal-time web
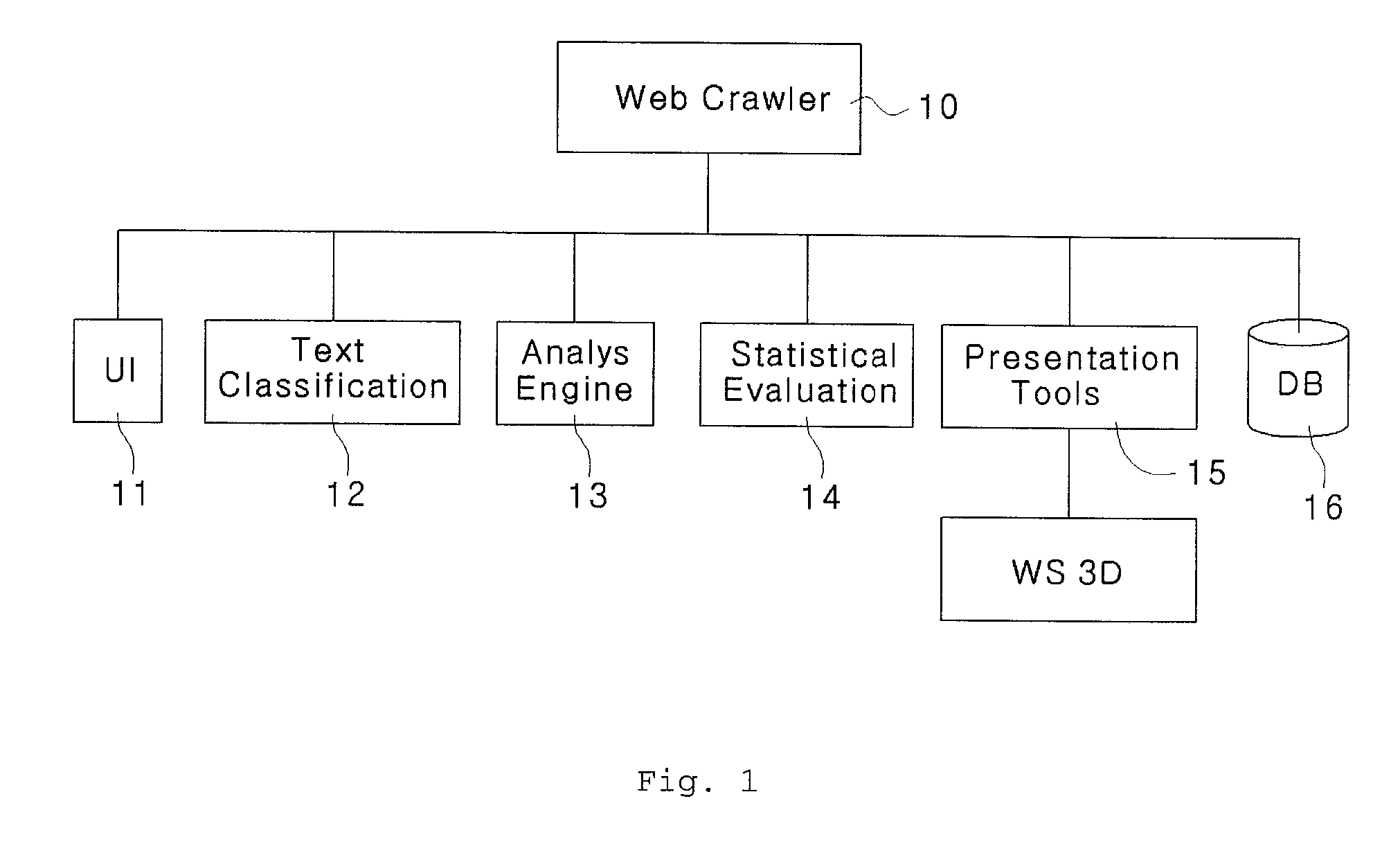
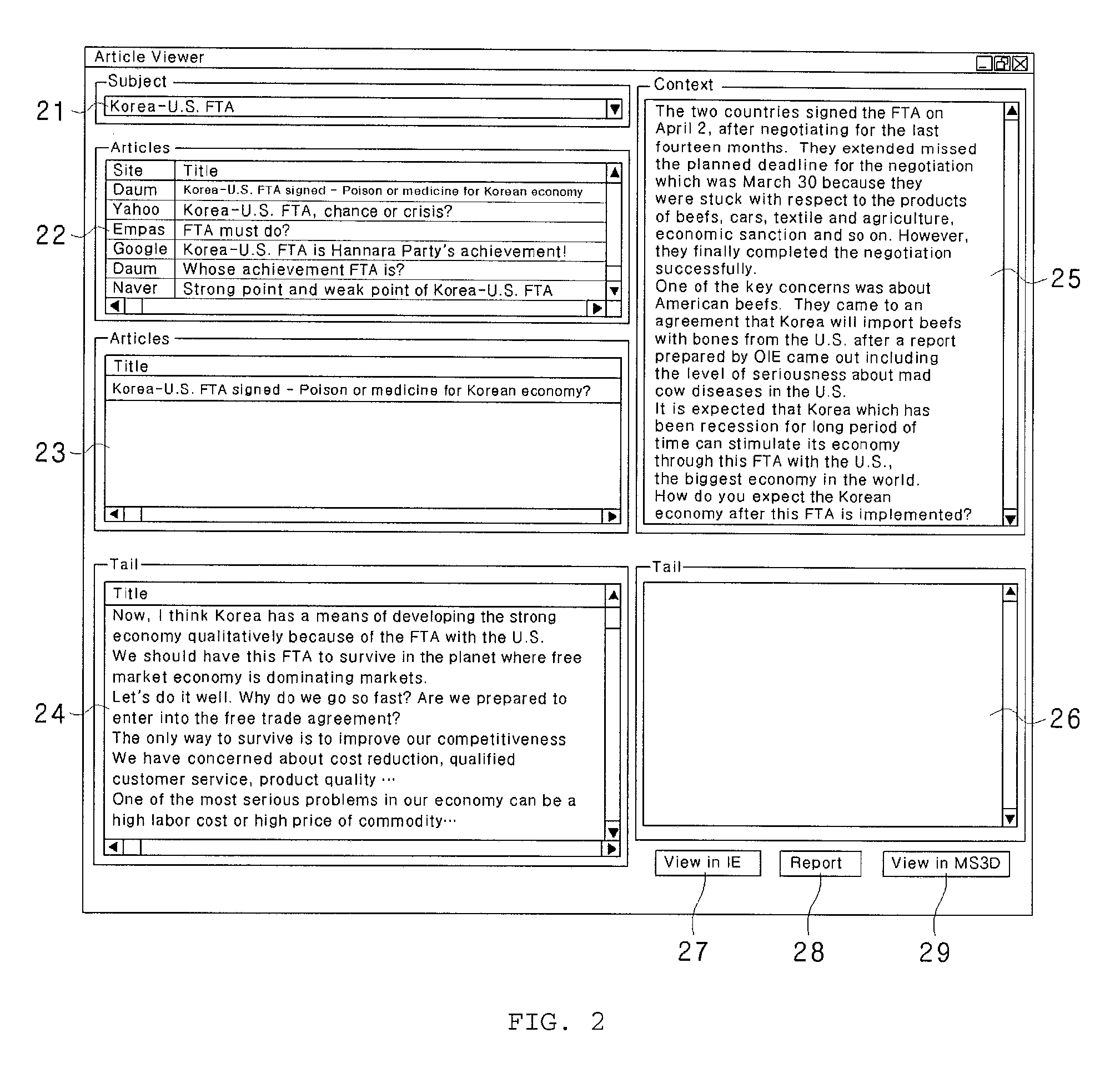
The present disclosure relates to a three-dimensional visualization system for internet-based web surveys which can collect in real time web articles about specific companies, products or public figures from specific websites, blogs or knowledge-search web pages, process and analyze collected articles and display survey results with a planetary system having a three-dimensional fixed star and planets such that the user can understand easily and accurately the survey results. The system can include a user interface, a database server configured to store collection conditions, a web crawler module a text classification module, an analysis engine module, a statistical evaluation module, and store rate values of the web articles and a presentation tool configured to display three-dimensional graphics of the rate values of the web articles stored in the statistical evaluation module symbolizing a planetary system having a fixed star and planets.
Owner:KIM SEA WOO
Method and system for improving the quality of service and care in a healthcare organization
InactiveUS20070179805A1Quality improvementData processing applicationsDiagnostic recording/measuringQuality of serviceNursing care quality
A method for improving the quality of healthcare, efficiency, and patient satisfaction procedures is provided. The method includes conducting at least a first survey of patients regarding care provided before, during, and after a procedure, wherein the survey focuses on benchmarks identified as being relevant to quality of care. The method further includes entering the results of the first survey into a database configured to store the results, reviewing the results of the first survey to determine the quality of care provided during the procedure, identifying incidences of poor quality of care, and comparing the results of the first survey with results of surveys taken from other patients to recognize patterns of poor quality of care. The method further includes addressing the incidences of poor quality of care by developing methods to address the recognized incidences of poor quality of care.
Owner:SOUTHEAST ANESTHESIOLOGY CONSULTANTS P A A NC
Health condition monitoring method and system and storage media
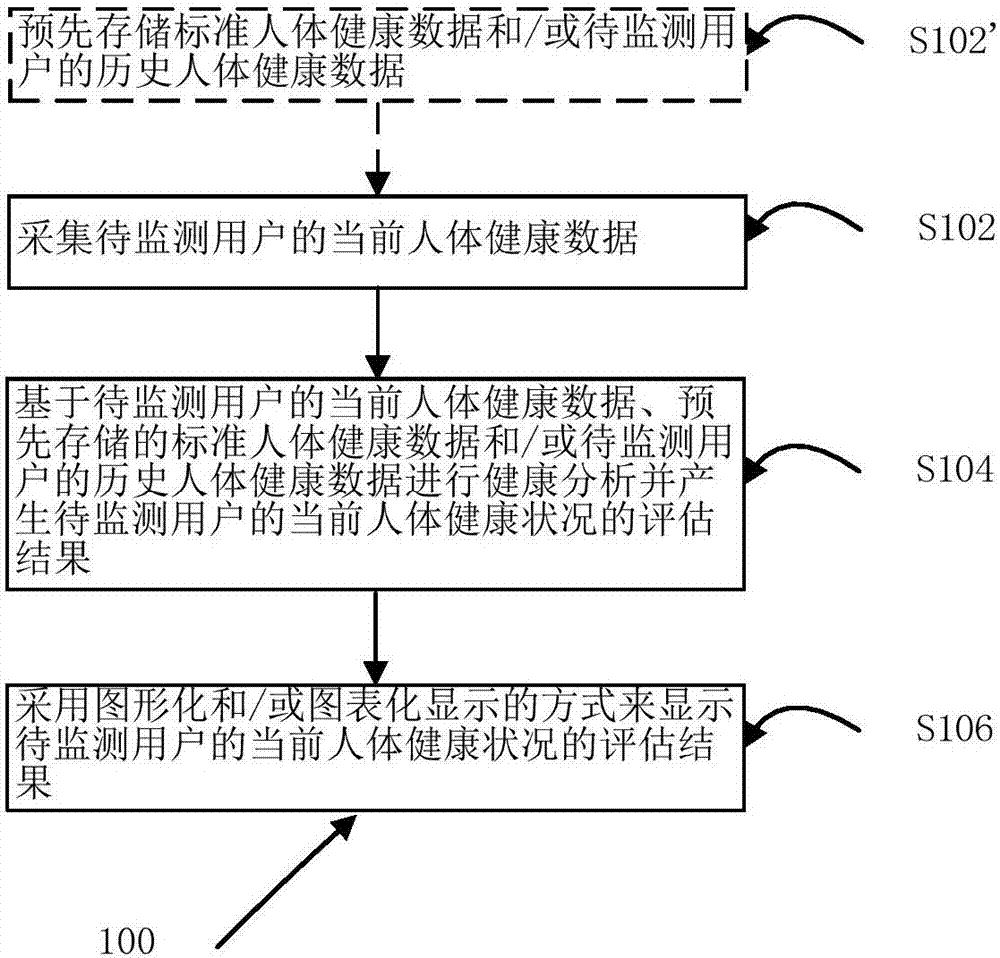
InactiveCN107194174ASmooth communicationConcise and easy-to-understand display of health statusSpecial data processing applicationsWestern medicineSurvey result
The invention discloses a health condition monitoring method and system and storage media. The method comprises the following steps that: collecting the current human body health data of a user to be monitored, wherein the current human body health data comprises a health and living condition questionnaire survey result, a traditional Chinese and western medicine professional medical examination result, an exercise physique examination result and a mentality and character test result, and the traditional Chinese and western medicine professional medical examination result comprises a traditional Chinese and western medicine clinic examination result and a traditional Chinese meridian and collateral examination result; on the basis of the current human body health data of a user to be monitored, pre-stored standard human body health data and / or the historical human body health data of the user to be monitored, carrying out health analysis, and generating the assessment result of the current human body health situation of the user to be monitored; and adopting a graphical and / or chart display way to display the assessment result of the current human body health situation of the user to be monitored. The simple assessment result which is easy in understanding is given.
Owner:白胜西
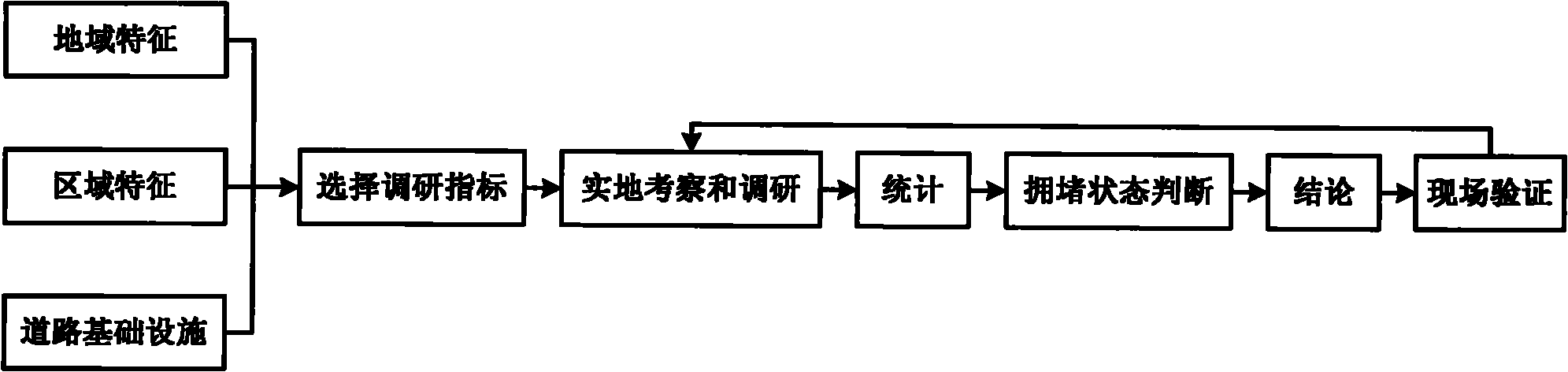
Simple urban road congestion statistic evaluation method
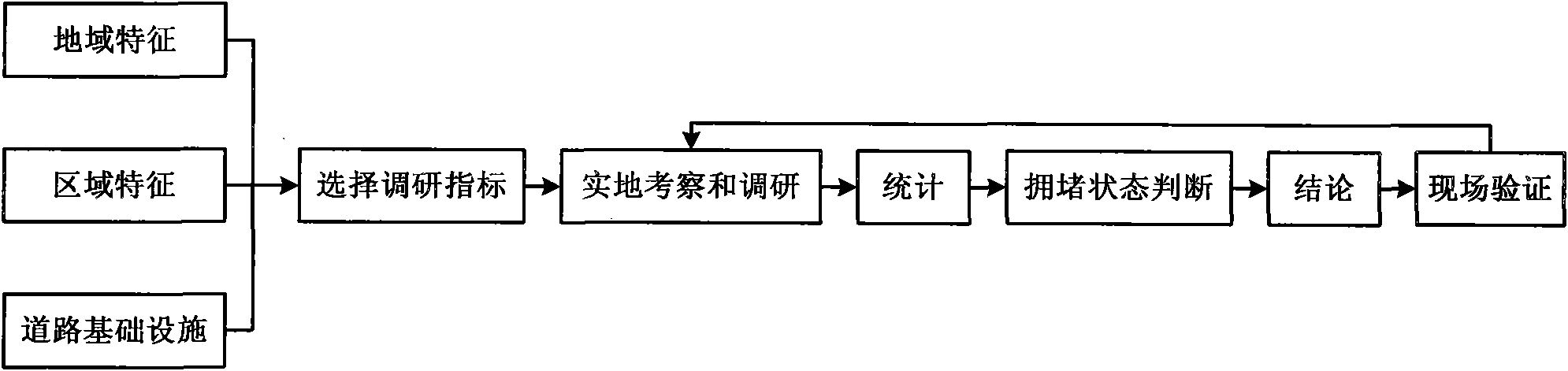
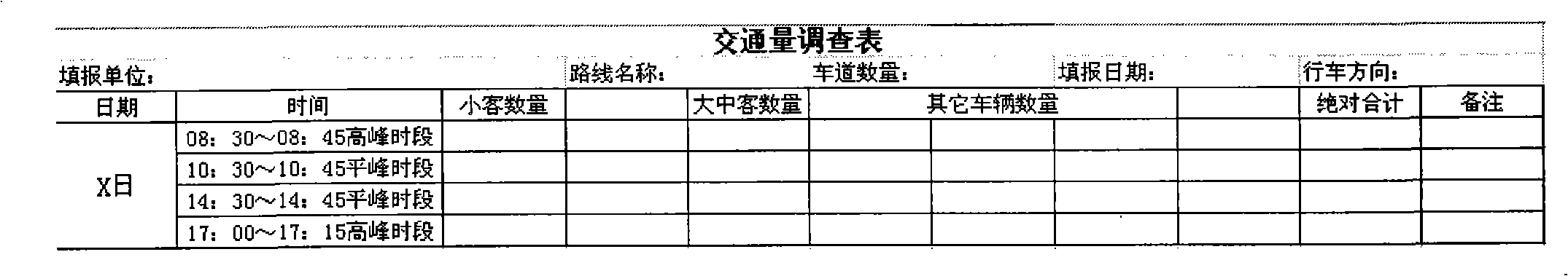
InactiveCN101872544AQuickly determine the level of congestionConform to the lumped propertyRoadwaysRoad vehicles traffic controlSurvey resultTraffic flow
The invention relates to a simple urban road congestion statistic evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) classifying according to the regional feature, the local feature and the scale and facility of roads; (2) selecting the traffic volume survey indicator related with the features obtained in the step (1), from the common urban traffic volume survey indicators; (3) performing a traffic volume survey according to the survey indicator selected by the step (2) so as to judge the urban road congestion; (4) performing field statistics to the same road section in one peak period; (5) comparing the statistical data obtained in the step (4) with the data obtained in the step (3) to find the difference; (6) adjusting the survey result obtained in the step (3) according to the data difference obtained in the step (5) to obtain final data; and (7) according to the final data obtained in the step (6), dividing the congestion of the urban road to be evaluated to five types, namely complete unimpeding, little congestion, some congestion, standard congestion and severe congestion; and obtaining the evaluation result. By using the method, the congestion level of the road section can be fast determined and the method corresponds to the lumped characteristic of the traffic flow.
Owner:JIANGSU TRANSPORTATION RES INST CO LTD
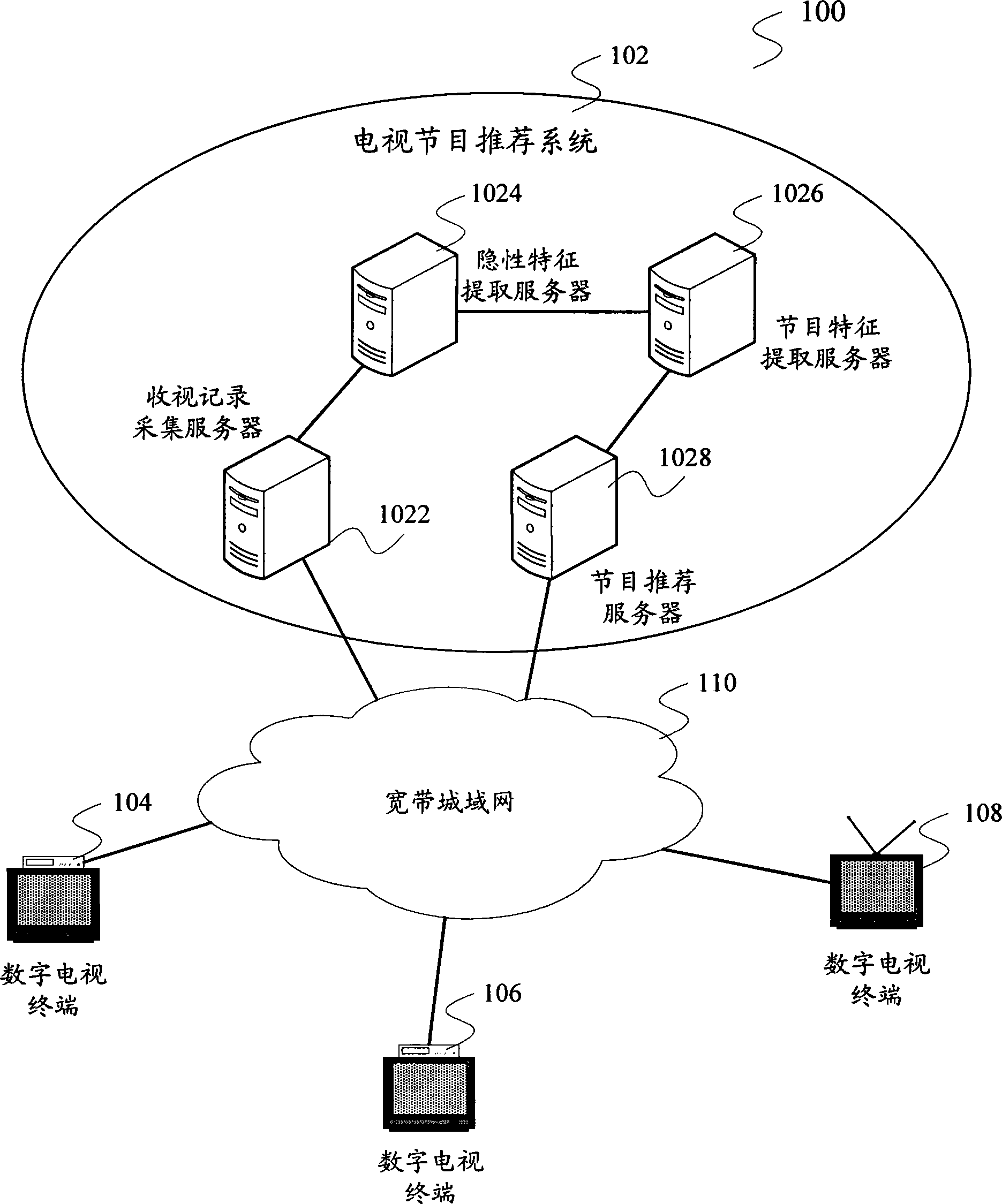
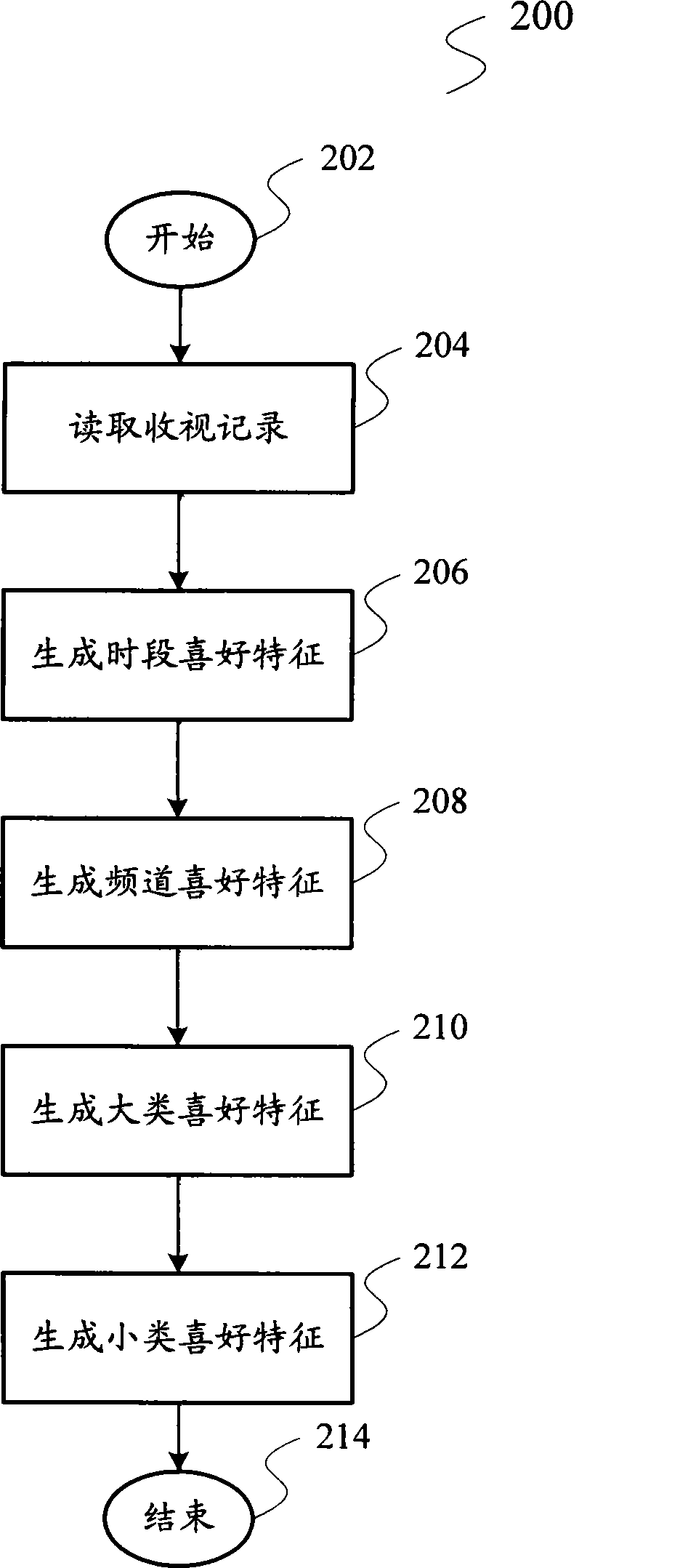
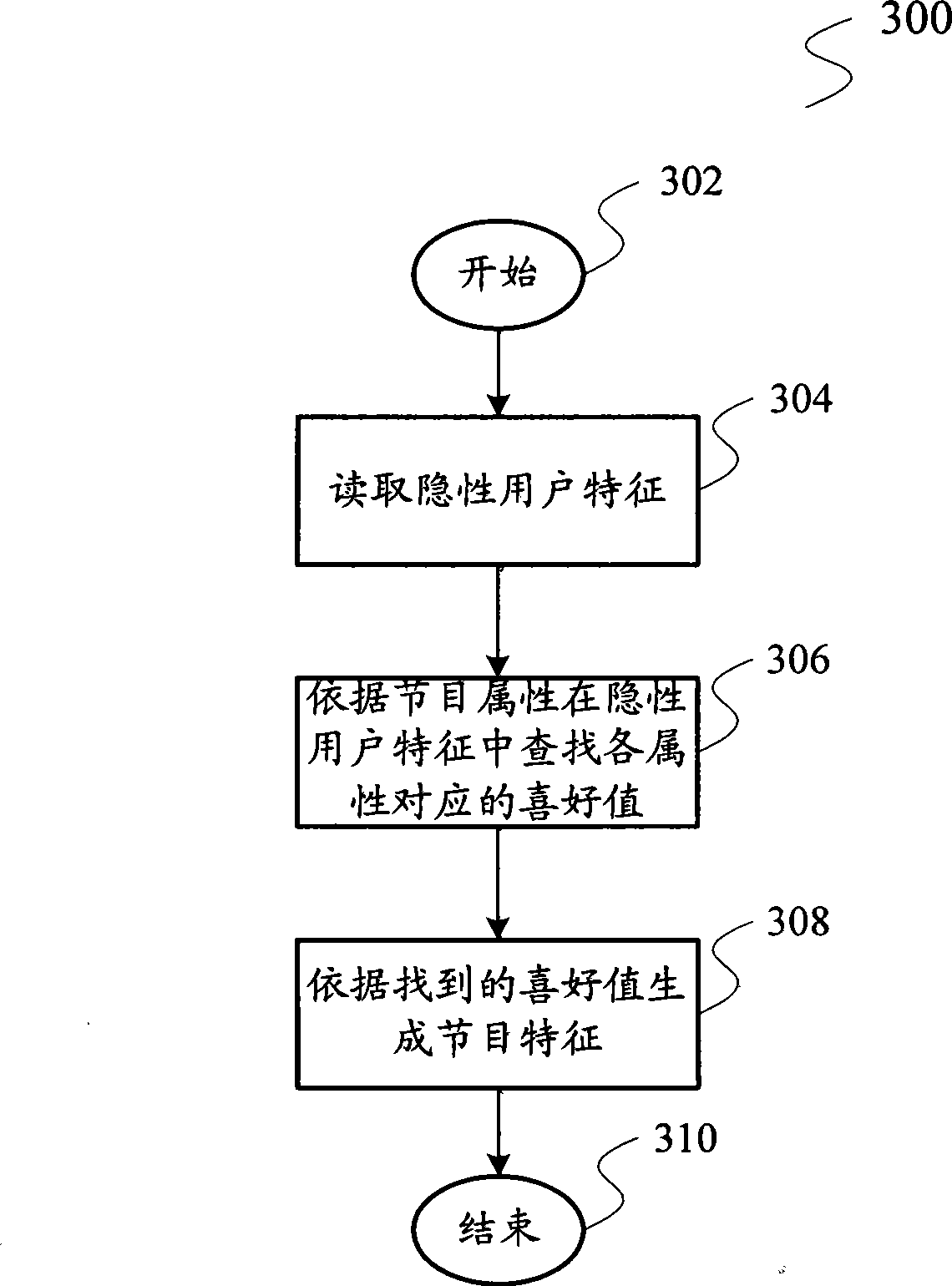
Hidden customer characteristic extracting method and television program recommendation method and system
ActiveCN101383942AMeet actual needsNo human intervention requiredAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMarketingFeature extractionSurvey result
The invention relates to a television program recommendation technology, and provides an implicit user characteristic extraction method, a television program recommendation method and a system thereof aiming at the defects existing in the prior art that survey results are not accurate enough and easily overdue and the task is heavy when the user characteristics are obtained by the questionnaire survey method. The implicit user characteristic extraction method comprises the steps of collecting user reception records and extracting the implicit user characteristics containing a plurality of favorite characteristics from the collected reception records. The invention also provides a television program recommendation method and a system thereof. The whole proposal of the invention is completed automatically without the manual interference, so the labor is greatly saved. Extracting the user characteristics according to the user reception records can update the user characteristics regularly along with the reception records, and the reception records are full, accurate and impersonal, so the particularity and the accuracy of the extracted results can be ensured. Integrally comparing the similarity of the program characteristics and the user characteristics from a plurality of angles enables the recommended television programs to coincide with the practical needs of the user.
Owner:SHENZHEN TOPWAY VIDEO COMM
Questionnaire generation method, server and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN108428152ARealize automatic generationRealize generation intelligenceMarket predictionsText processingApplication serverSurvey result
The invention discloses a questionnaire generation method. The method comprises steps: survey demand information is received, and questionnaires are generated according to the survey demand information; the questionnaires are distributed to preset target users, wherein the preset target users are users whose behavior logs or historical survey records are matched with the survey demand information;questionnaire filling results returned by the preset target users are collected; and the questionnaire filling results are summarized, the summarized questionnaire filling results are subjected to consensus analysis, and questionnaire filling results after summarizing are outputted. The invention also provides an application server and a computer readable storage medium. According to the questionnaire generation method, the application server and the computer readable storage medium, the questionnaires can be generated automatically according to the received survey demand information, the operation is simple and convenient, a lot of manpower and material resources can be saved, and the survey result effectiveness can be greatly improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
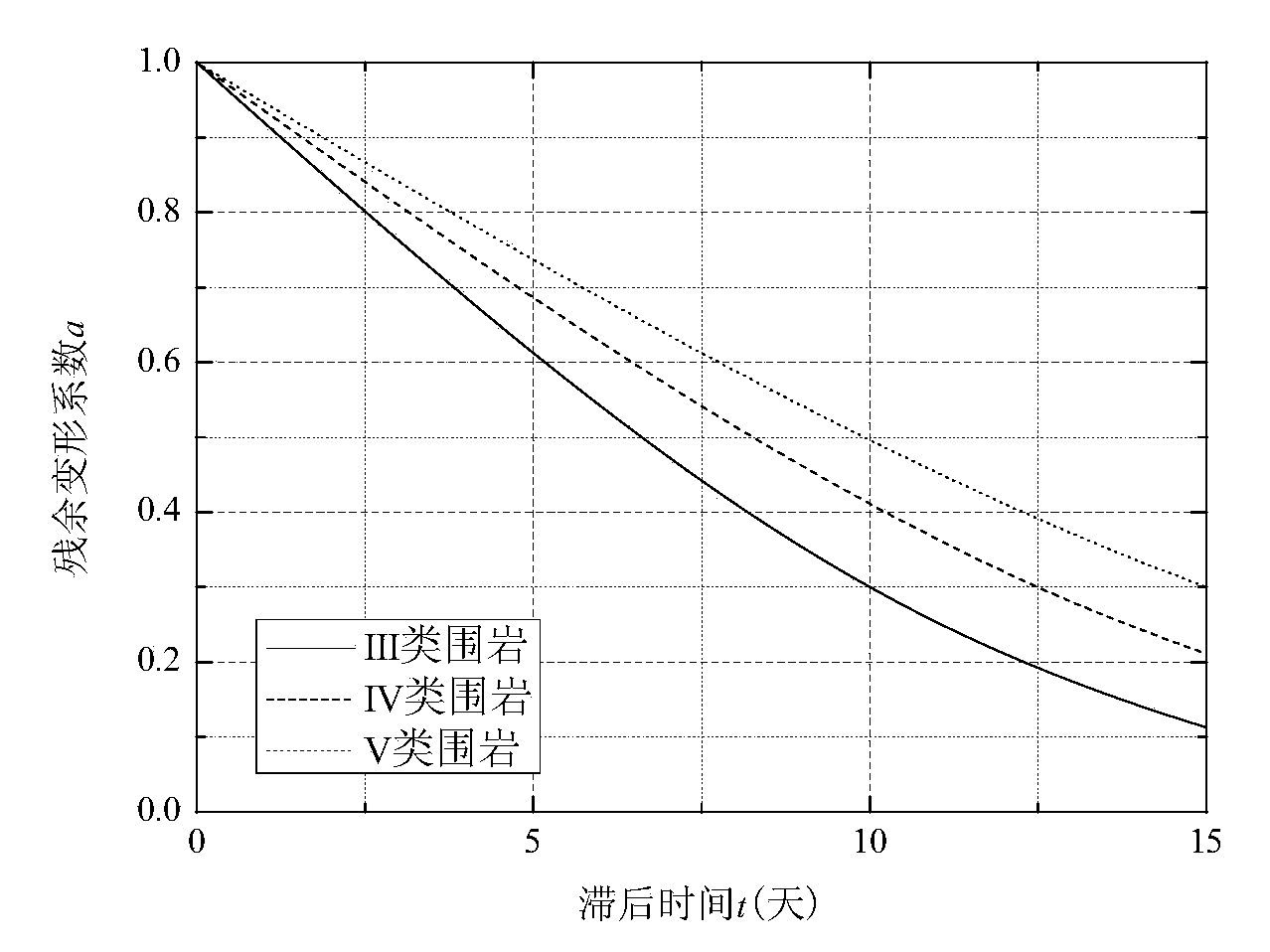
Surrounding rock deformation early-warning construction method for small-diameter tunnel full-section excavation
The invention discloses a surrounding rock deformation early-warning construction method for small-diameter tunnel full-section excavation. The surrounding rock deformation early-warning construction method for small-diameter tunnel full-section excavation comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out the earlier-stage geological survey and rock core sampling, finding out the position and the trend of a joint fissure of the terrane, determining parameters of surrounding rock through soil tests, classifying the surrounding rock and summarizing the types of the surrounding rock to form a list, and determining the design of the multipoint displacement meter installation scheme according to the results of the geological survey; (2) carrying out tunnel excavation and installation of multipoint displacement meters; (3) carrying out the middle-stage geological survey; (4) recording the installation time of the multipoint displacement meters; (5) determining a surrounding rock deformation early-warning value; (6) carrying out observation recording on data of the multipoint displacement meters, and determining remediation treatment measures of the dangerous section.
Owner:浙江广川工程咨询有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com