Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Multiprocessor architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
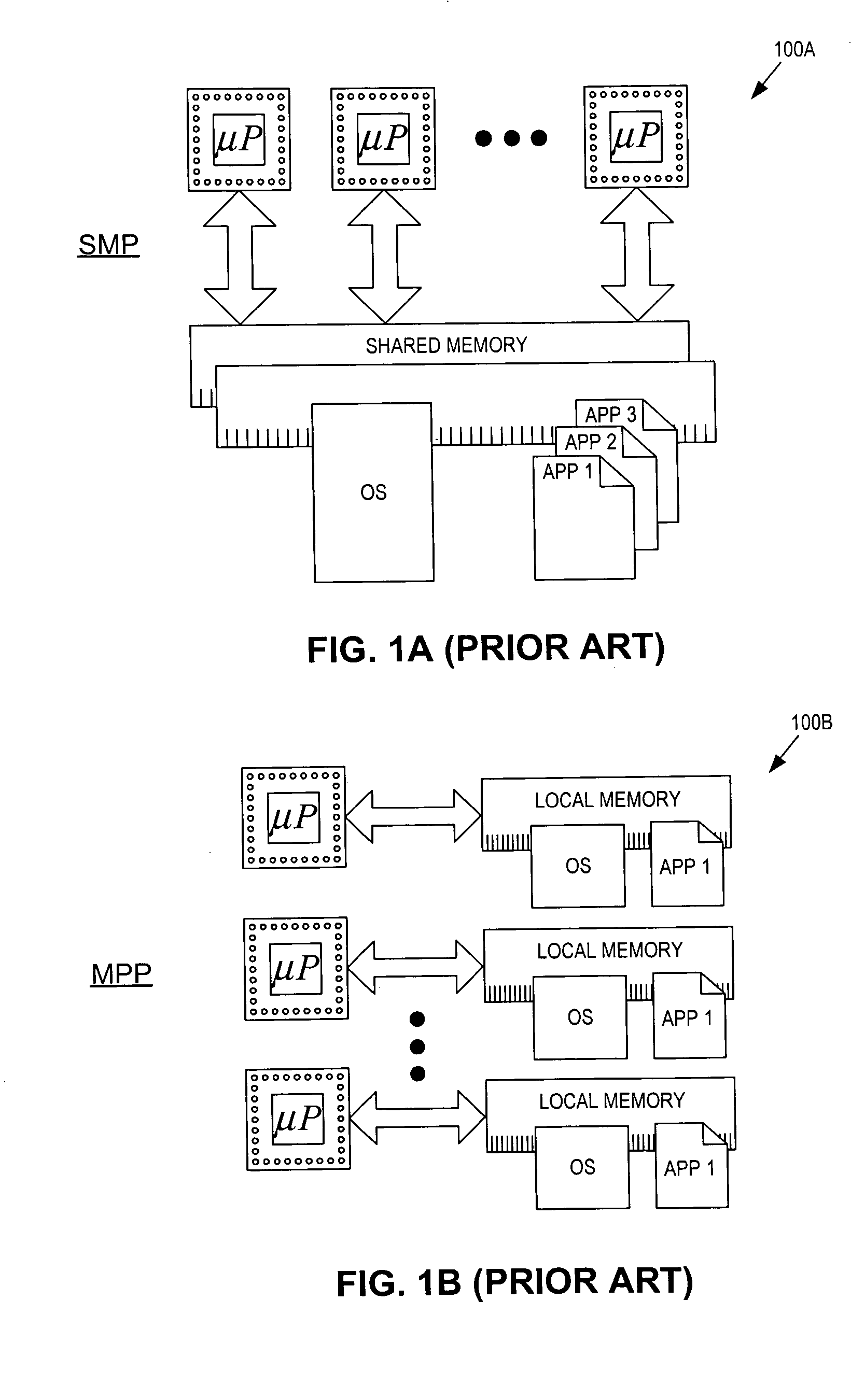
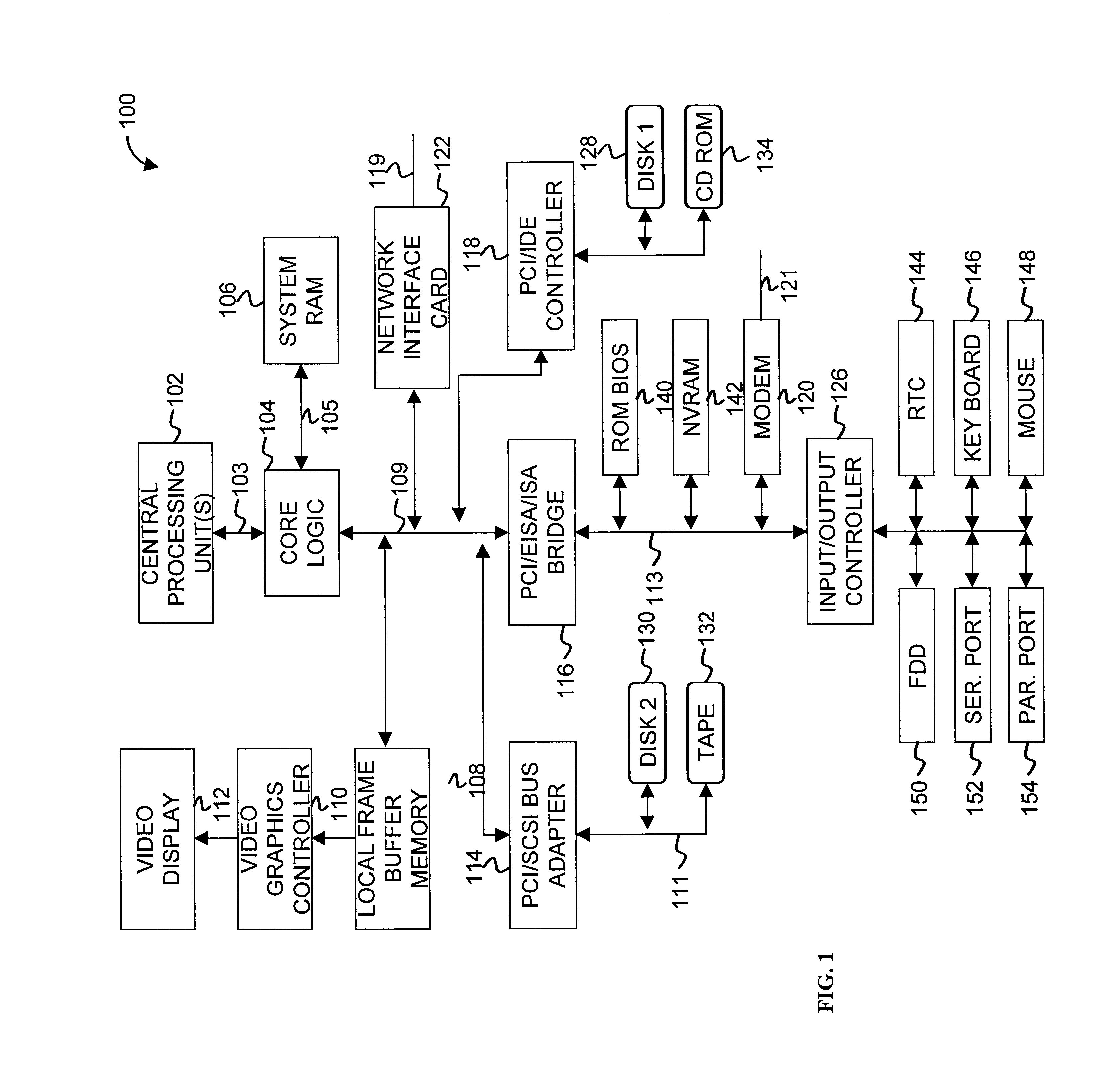
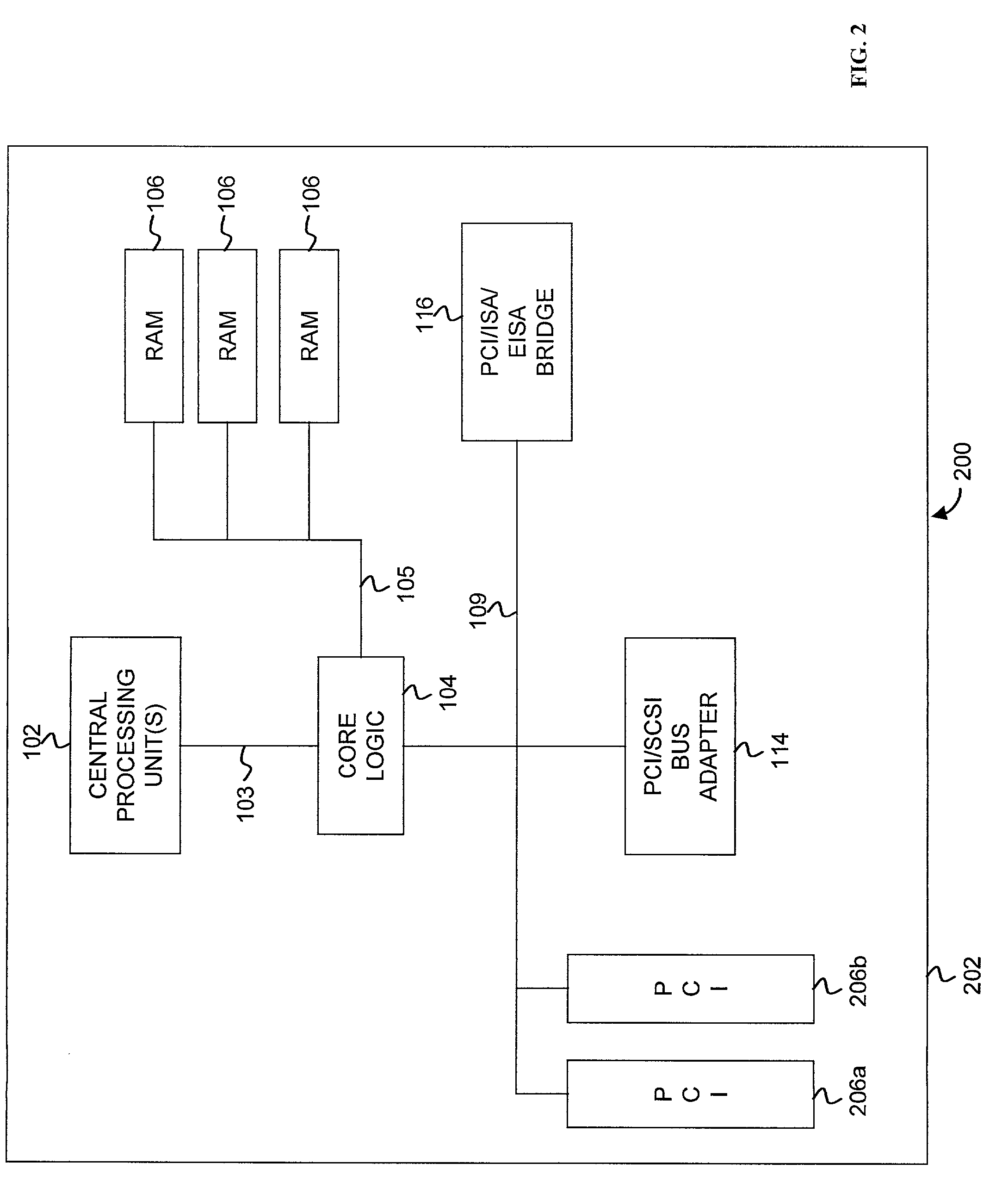
The MultiProcessor Specification (MPS) for the x86 architecture is an open standard describing enhancements to both operating systems and firmware, which will allow them to work with x86-compatible processors in a multi-processor configuration. MPS covers Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) architectures.
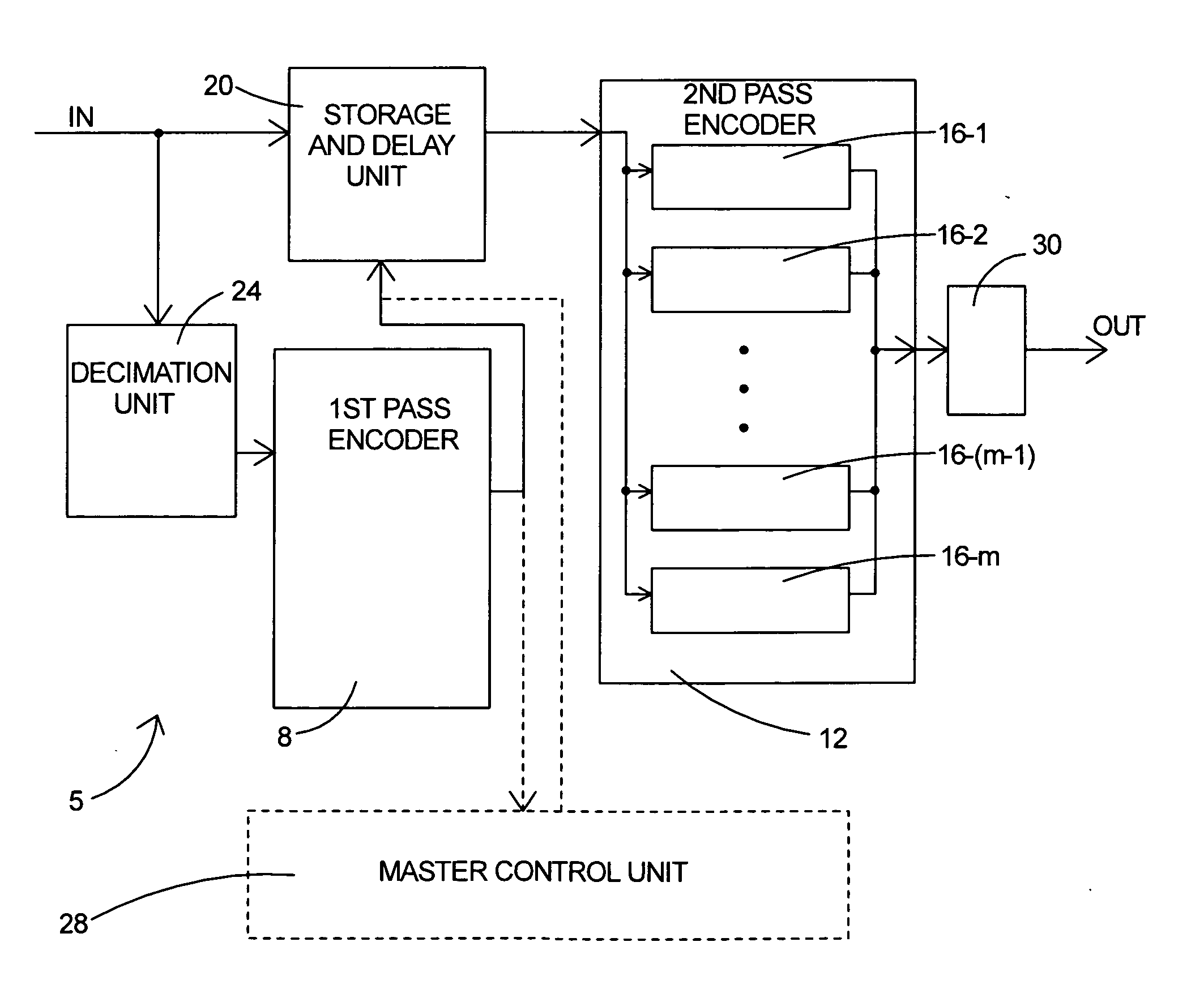
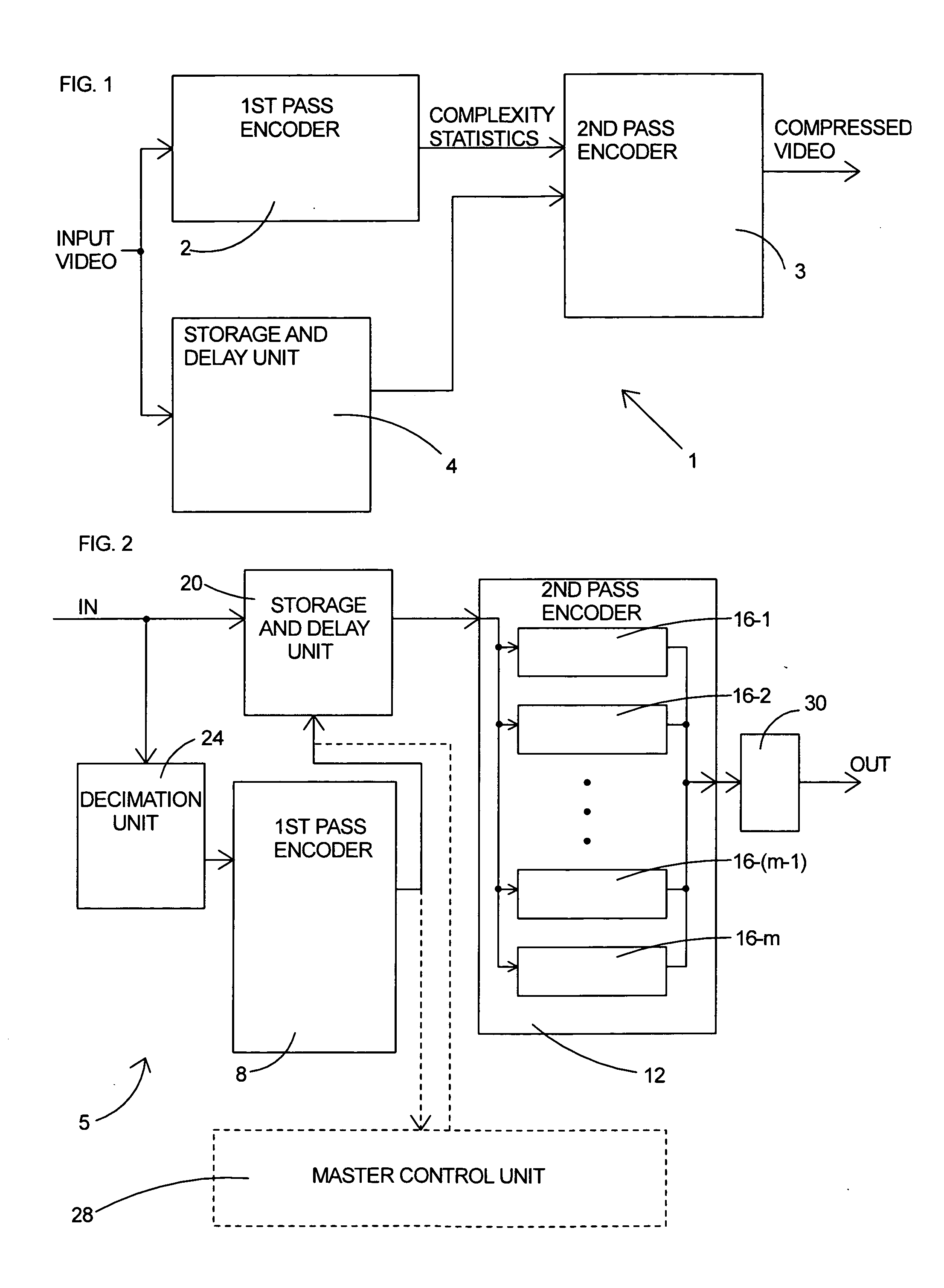
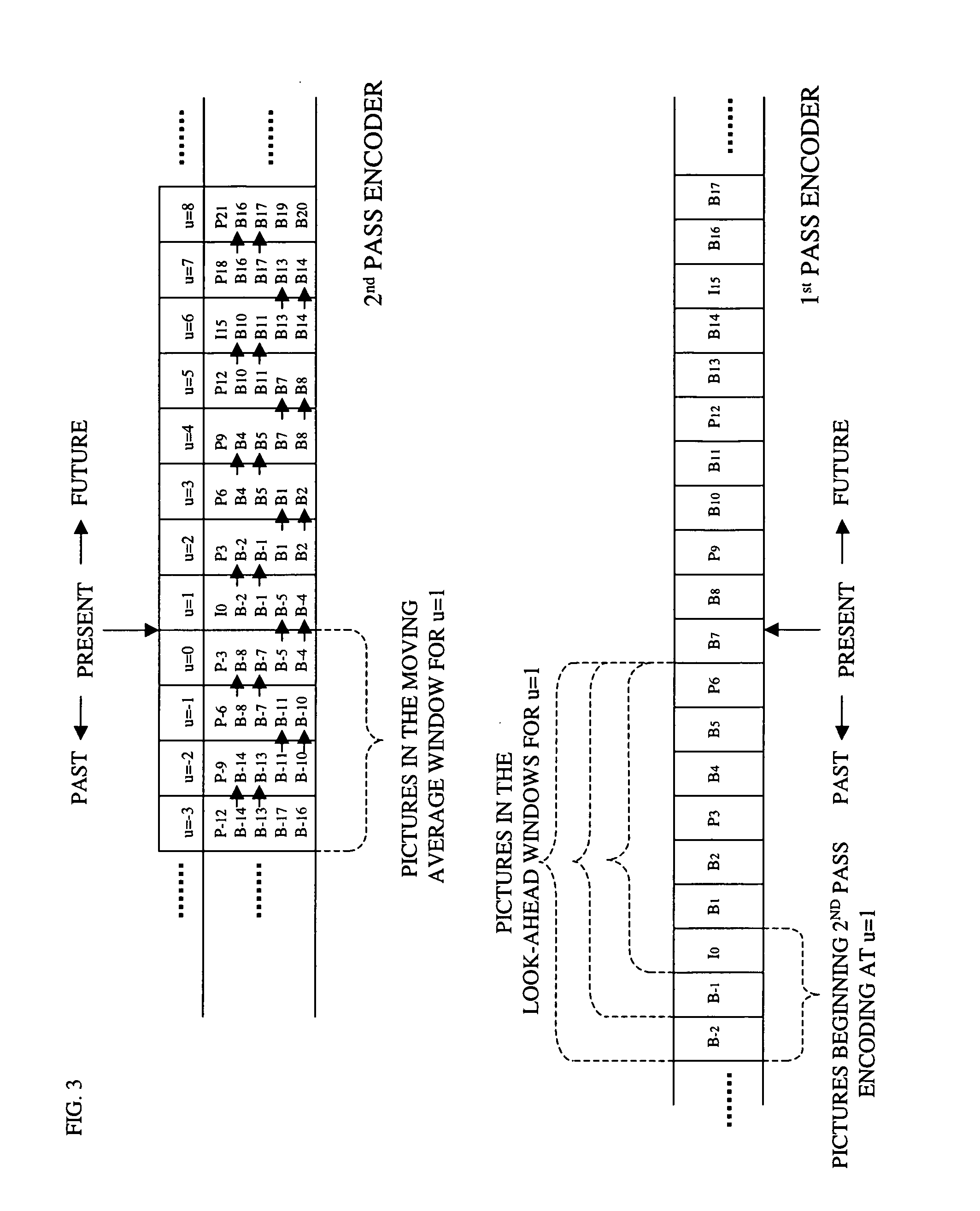
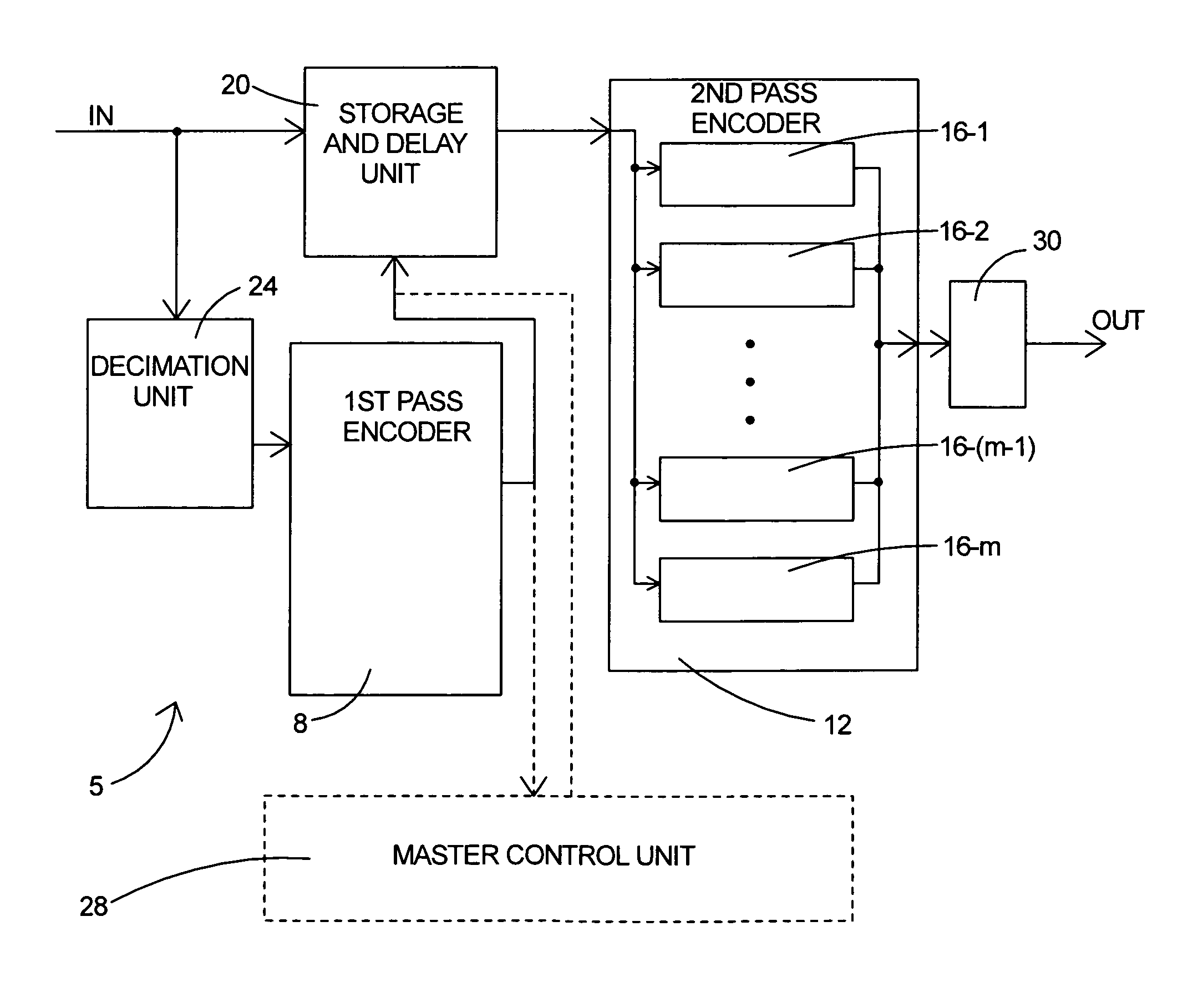
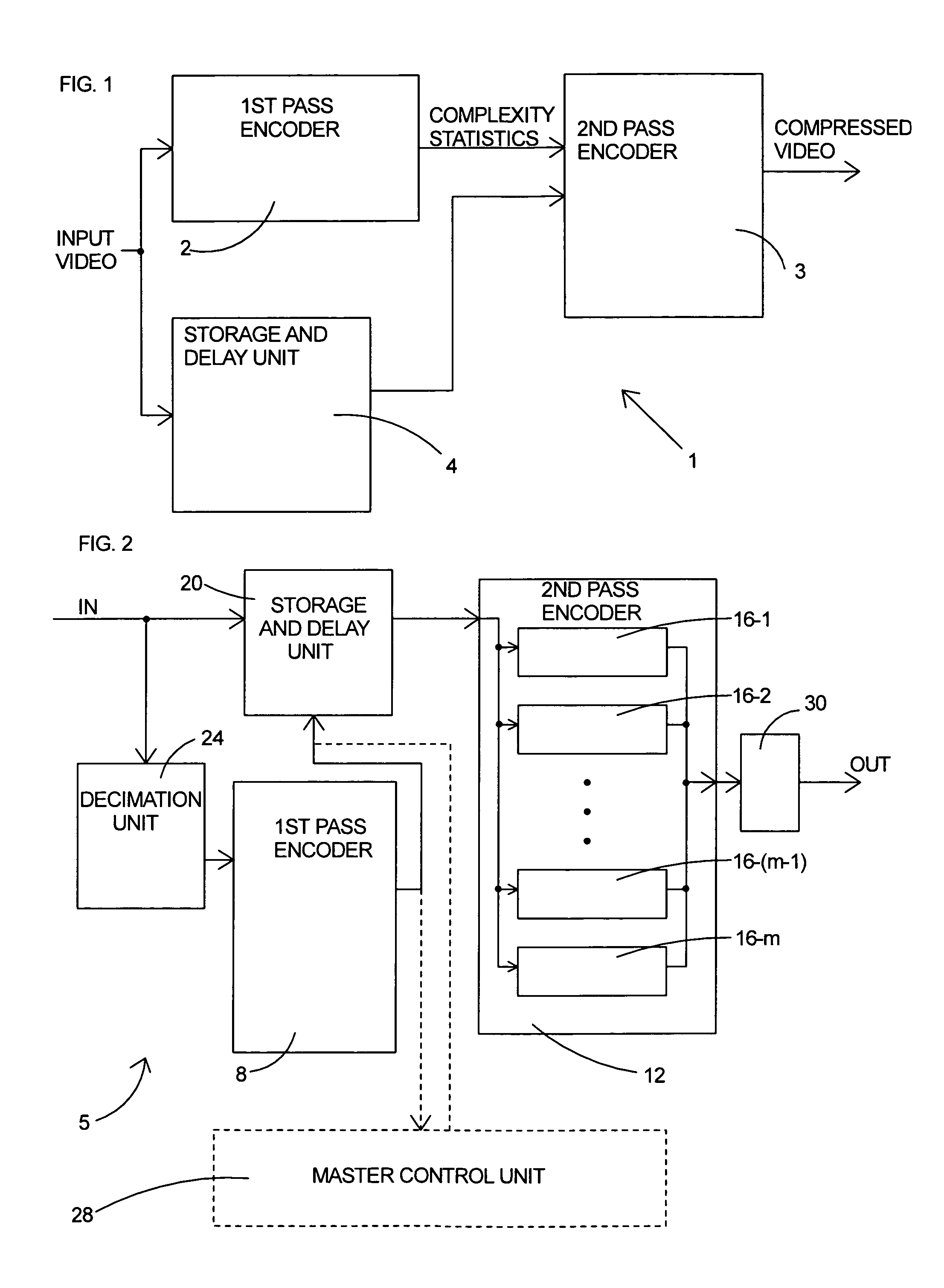
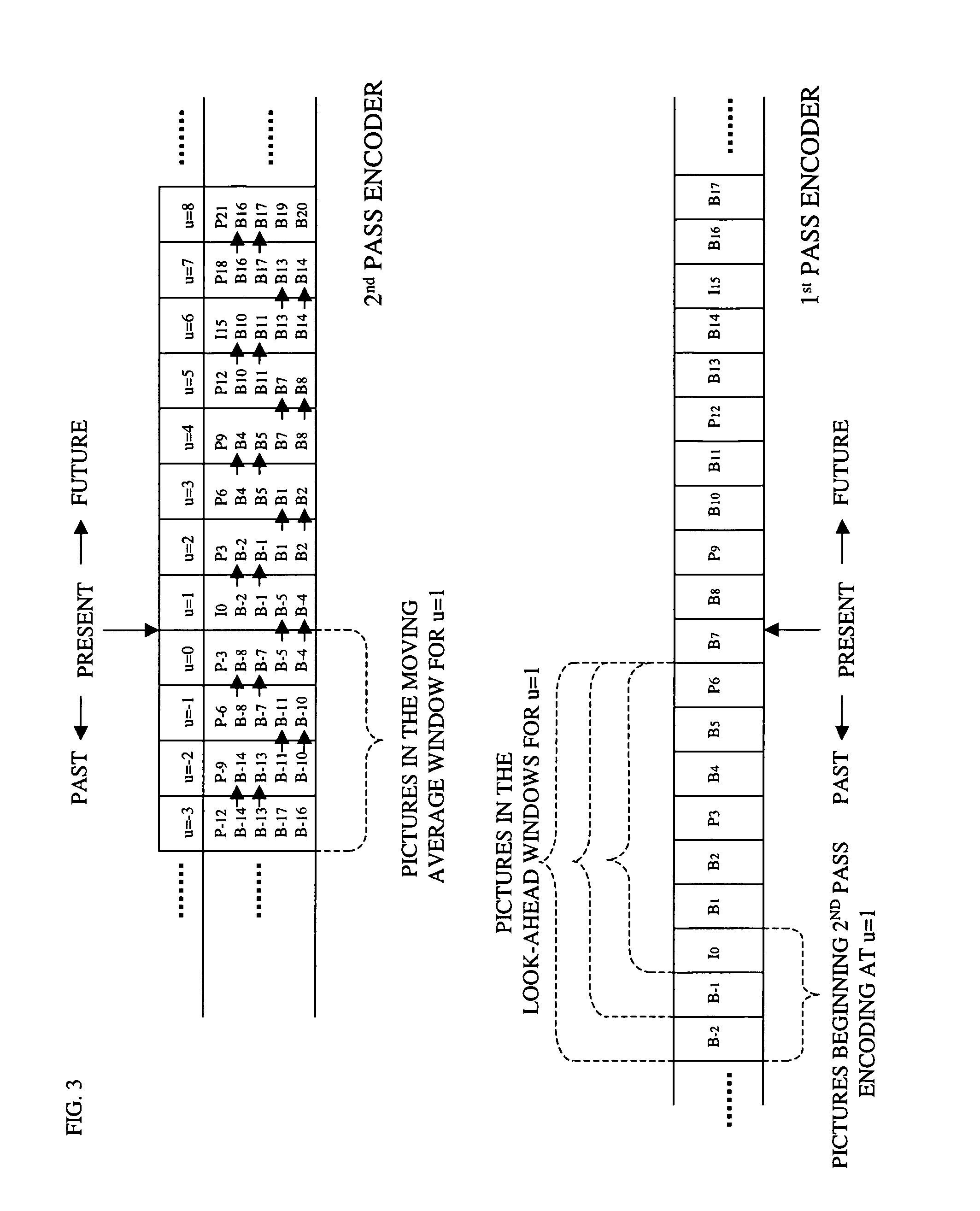
Parallel rate control for digital video encoder with multi-processor architecture and picture-based look-ahead window
ActiveUS20060126728A1Prevent underflowIncrease in sizeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMulti processor
A method of operating a multi-processor video encoder by determining a target size corresponding to a preferred number of bits to be used when creating an encoded version of a picture in a group of sequential pictures making up a video sequence. The method includes the steps of calculating a first degree of fullness of a coded picture buffer at a first time, operating on the first degree of fullness to return an estimated second degree of fullness of the coded picture buffer at a second time, and operating on the second degree of fullness to return an initial target sized for the picture. The first time corresponds to the most recent time an accurate degree of fullness of the coded picture buffer can be calculated and the second time occurs after the first time.
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
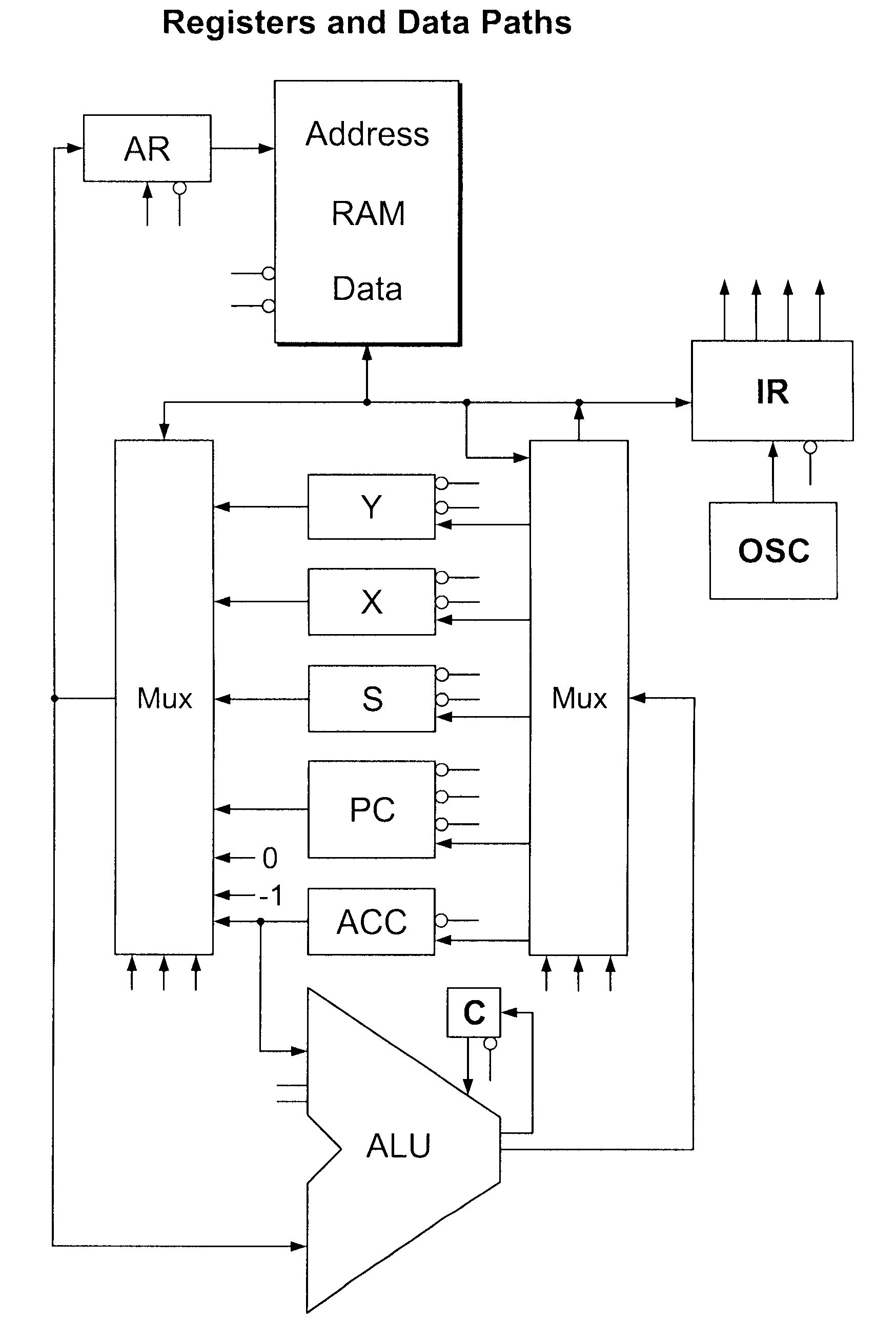
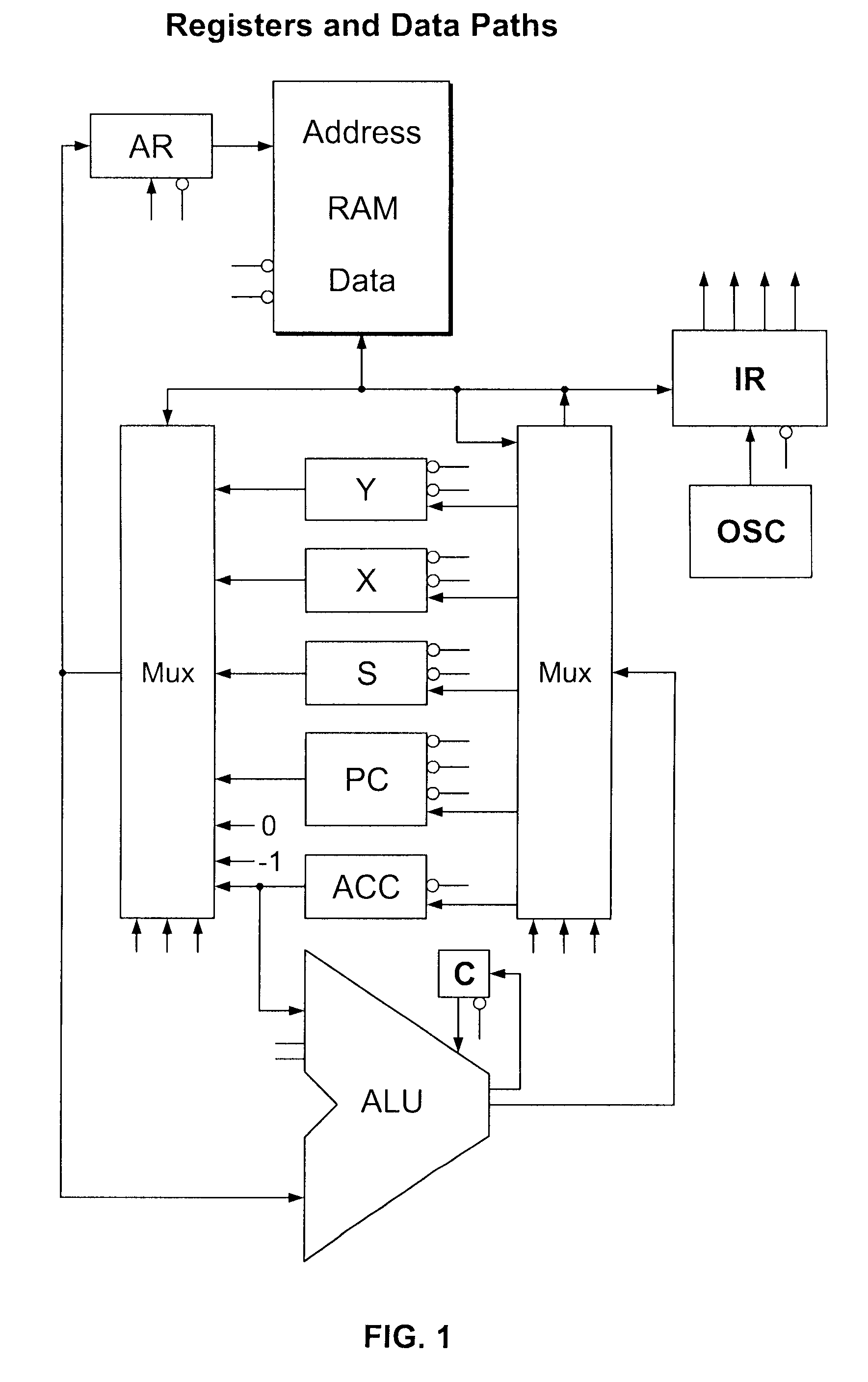
Object-oriented, parallel language, method of programming and multi-processor computer
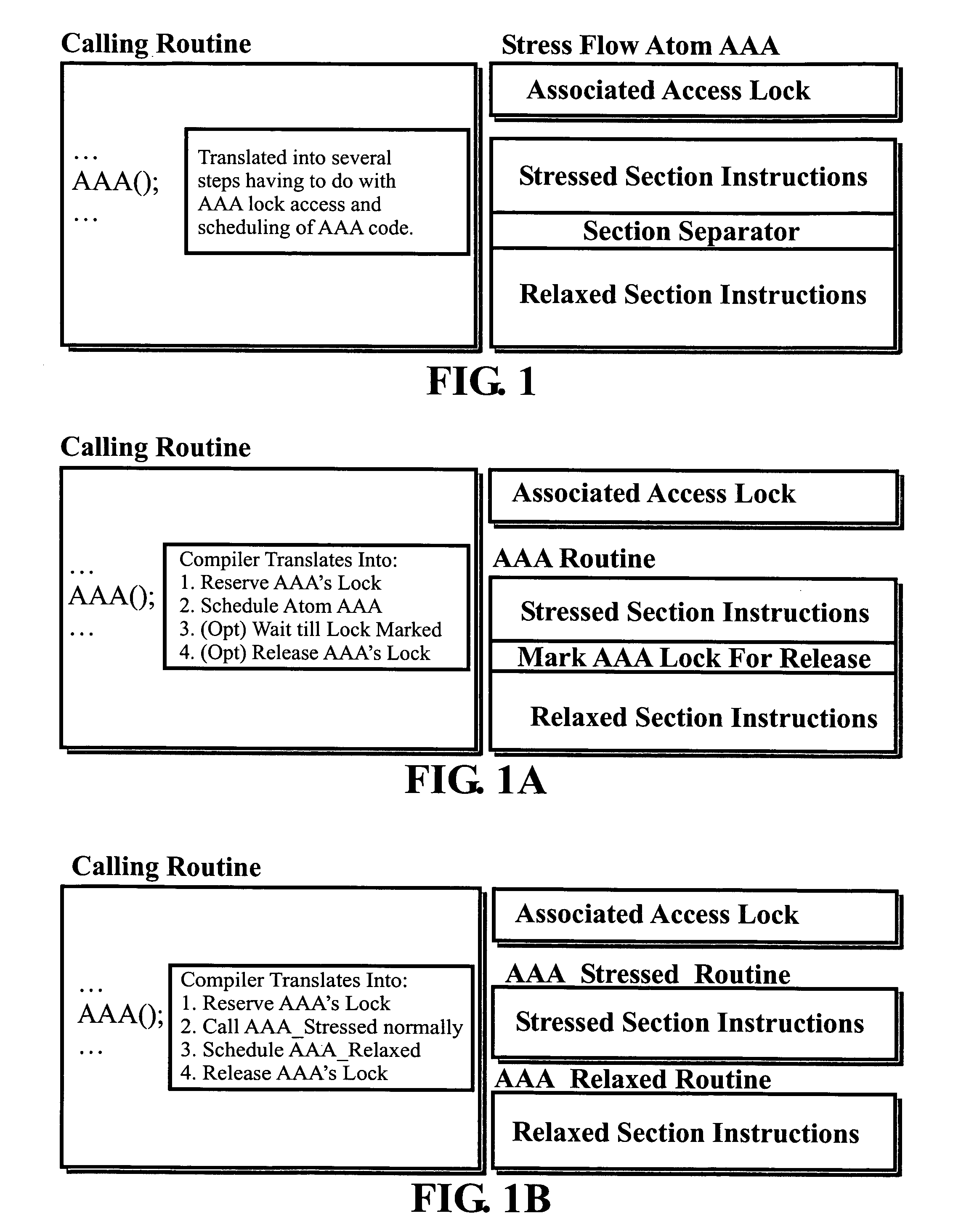
This invention relates to architecture and synchronization of multi-processor computing hardware. It establishes a new method of programming, process synchronization, and of computer construction, named stress-flow by the inventor, allowing benefits of both opposing legacy concepts of programming (namely of both data-flow and control flow) within one cohesive, powerful, object-oriented scheme. This invention also relates to construction of object-oriented, parallel computer languages, script and visual, together with compiler construction and method to write programs to be executed in fully parallel (or multi-processor) architectures, virtually parallel, and single-processor multitasking computer systems.
Owner:JANCZEWSKA NATALIA URSZULA +2
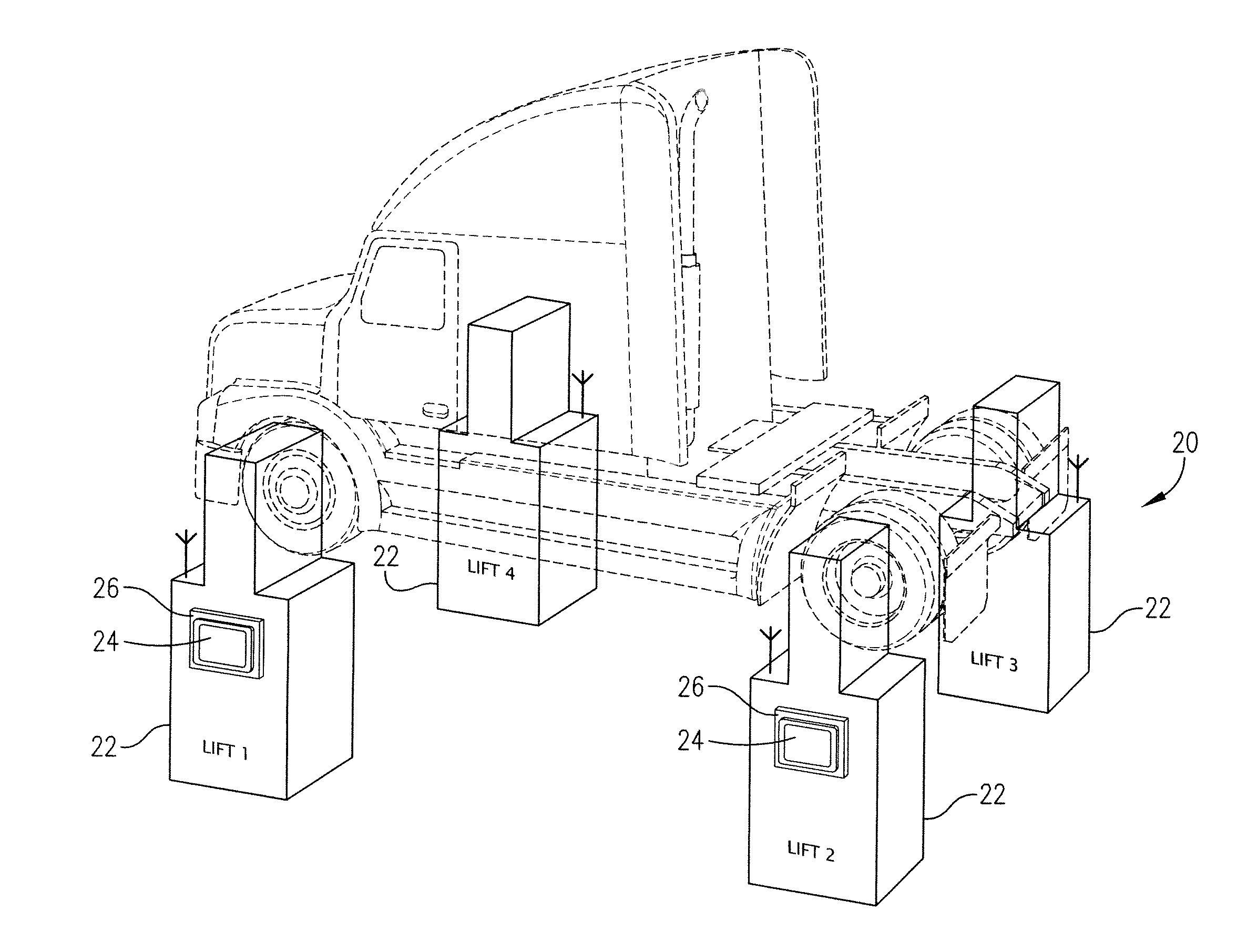
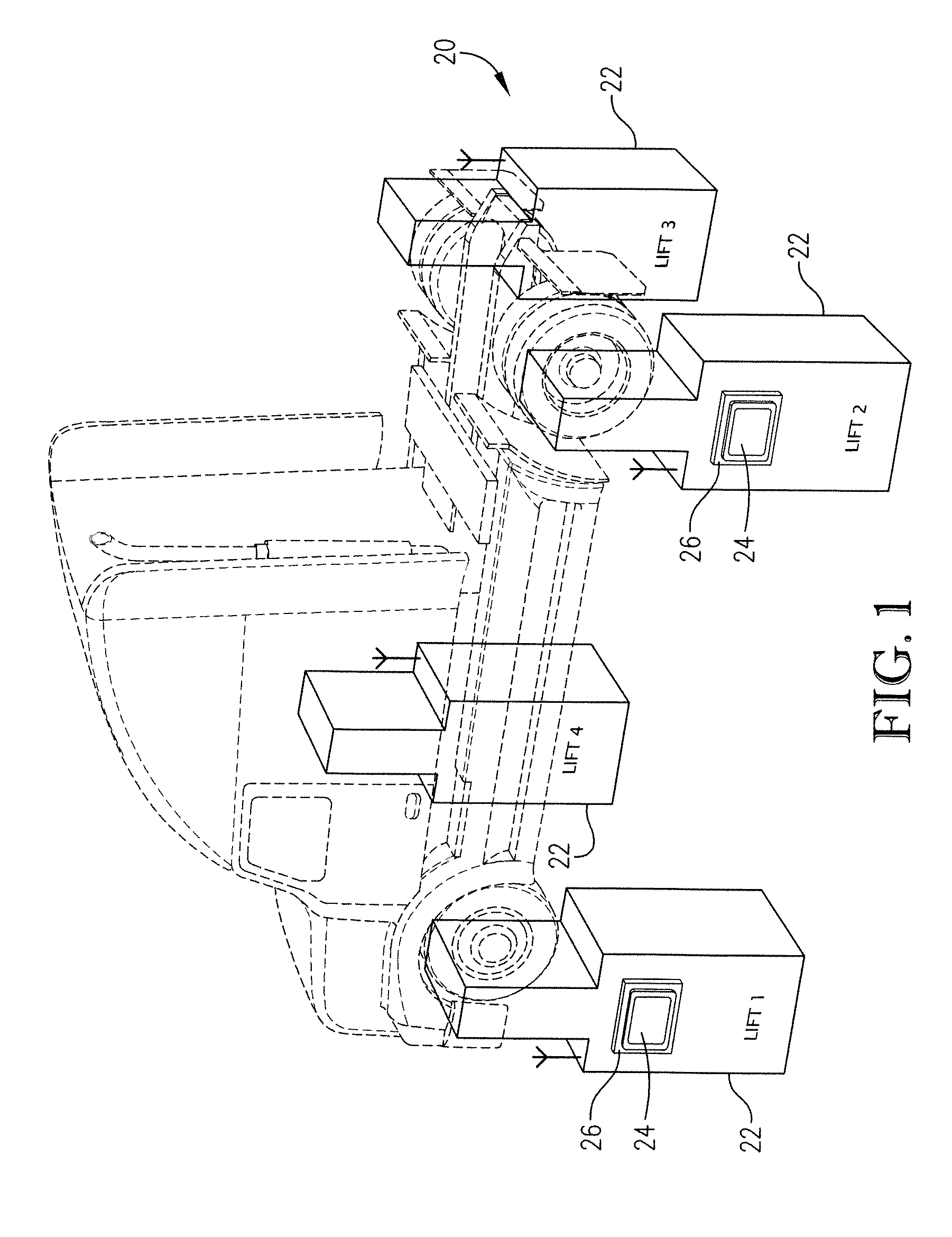
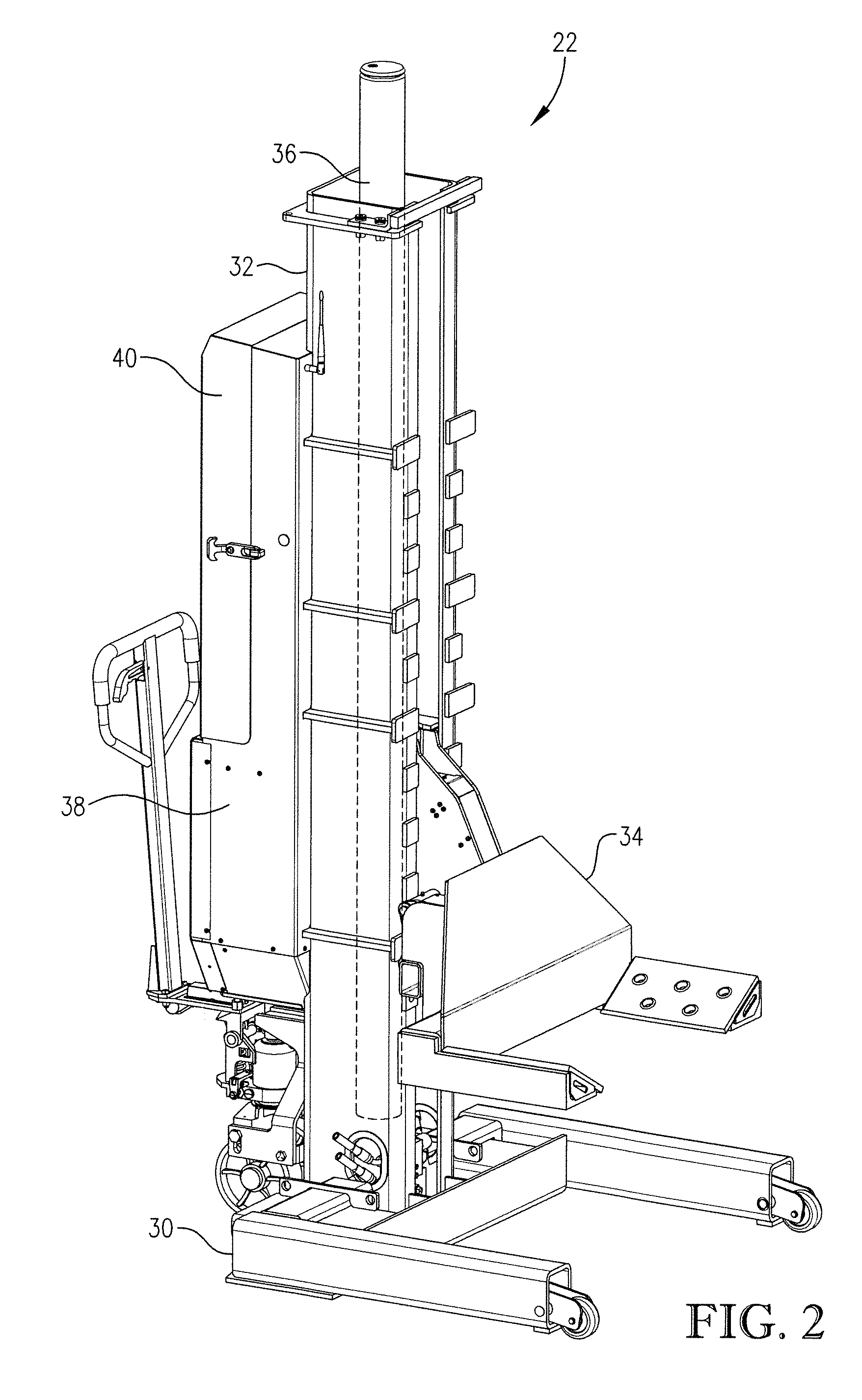
Wireless vehicle lift system with enhanced communication and control
Wireless portable vehicle lift system incorporating one or more enhanced communication and / or control features. The lift system can incorporate enhanced touch screen-enabled functionalities, enhanced multi-processor architectures, and / or enhanced emergency stop features.
Owner:GRAY MFG
Parallel rate control for digital video encoder with multi-processor architecture and picture-based look-ahead window
ActiveUS8054880B2Prevent underflowIncrease in sizeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMulti processor
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
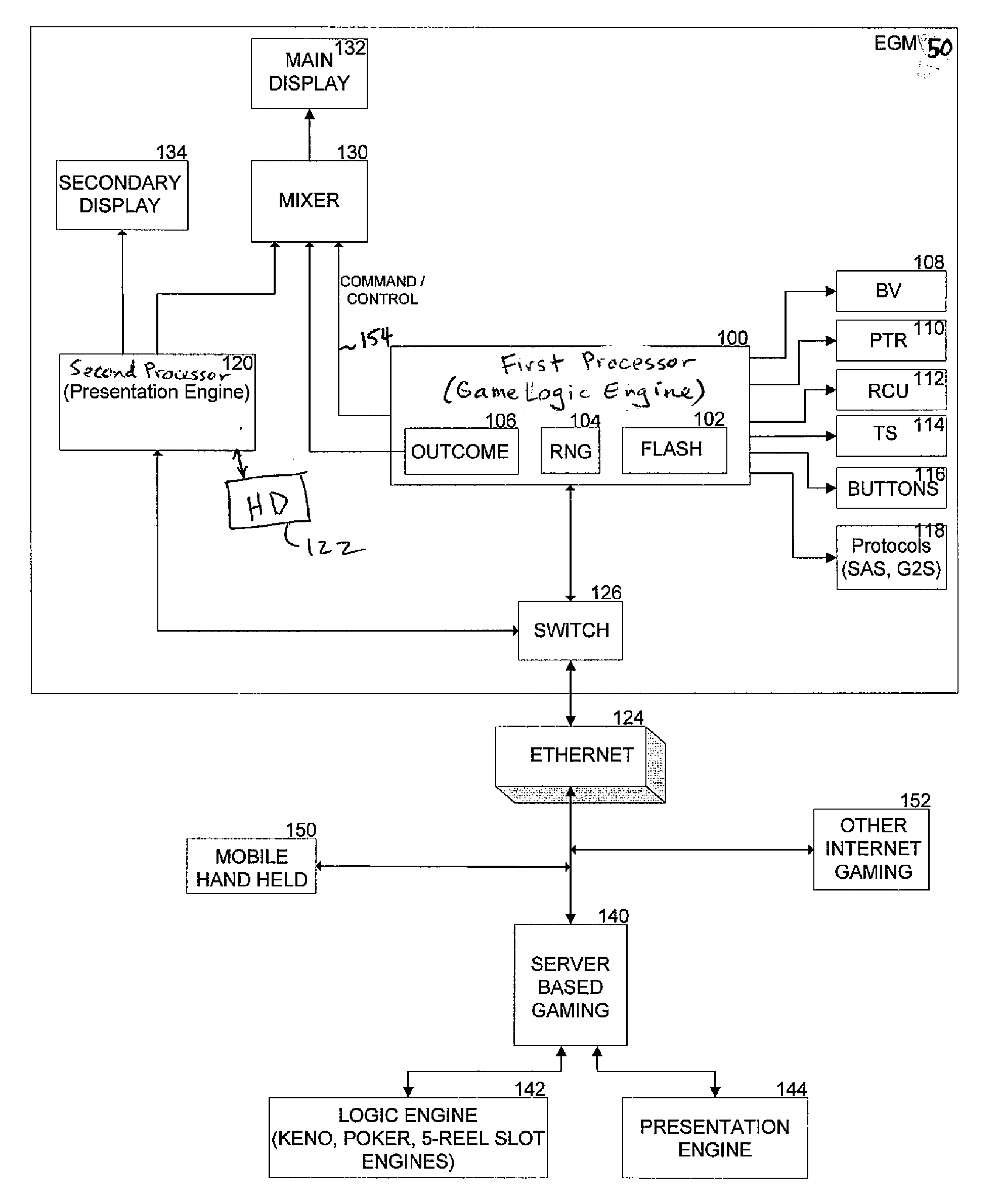
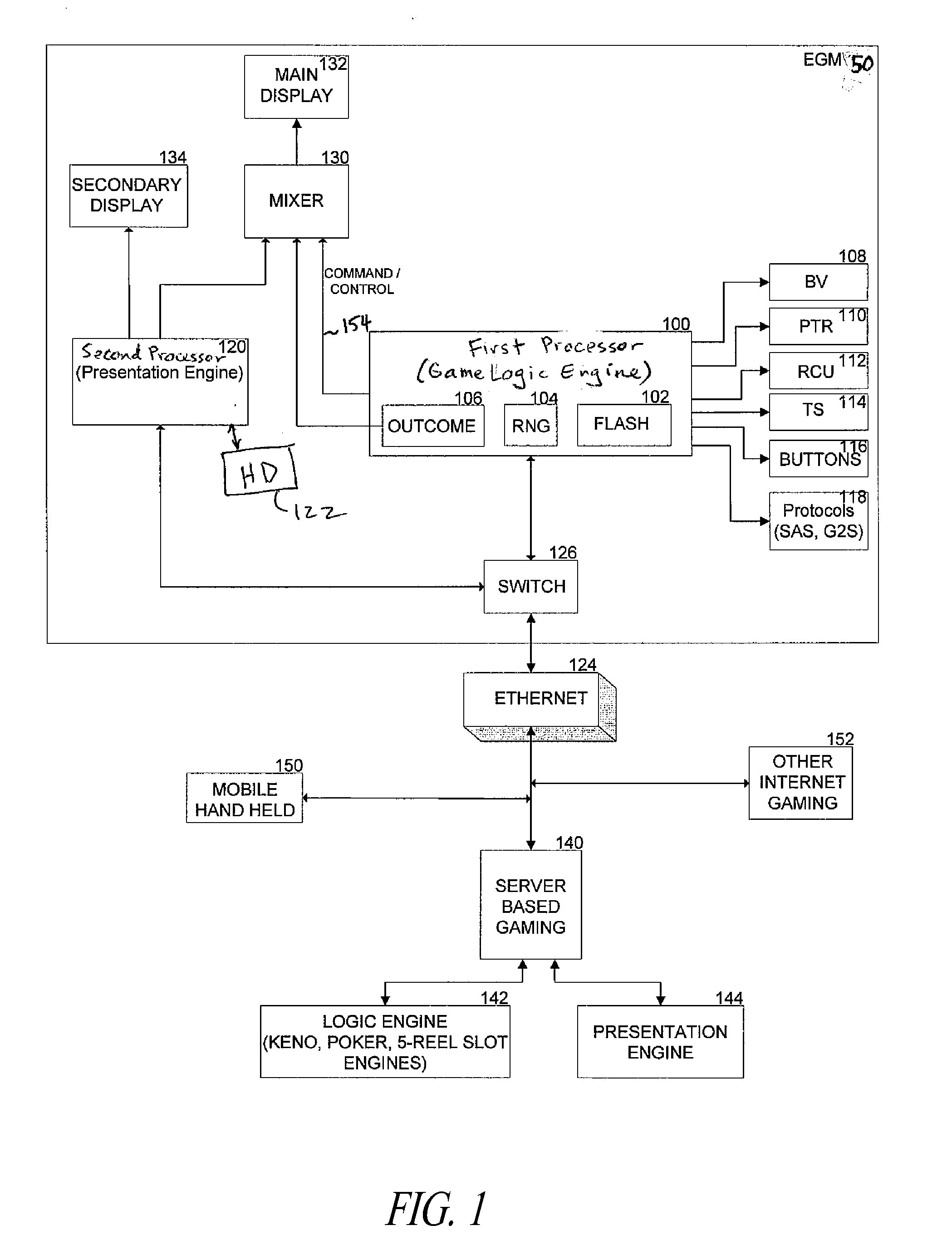
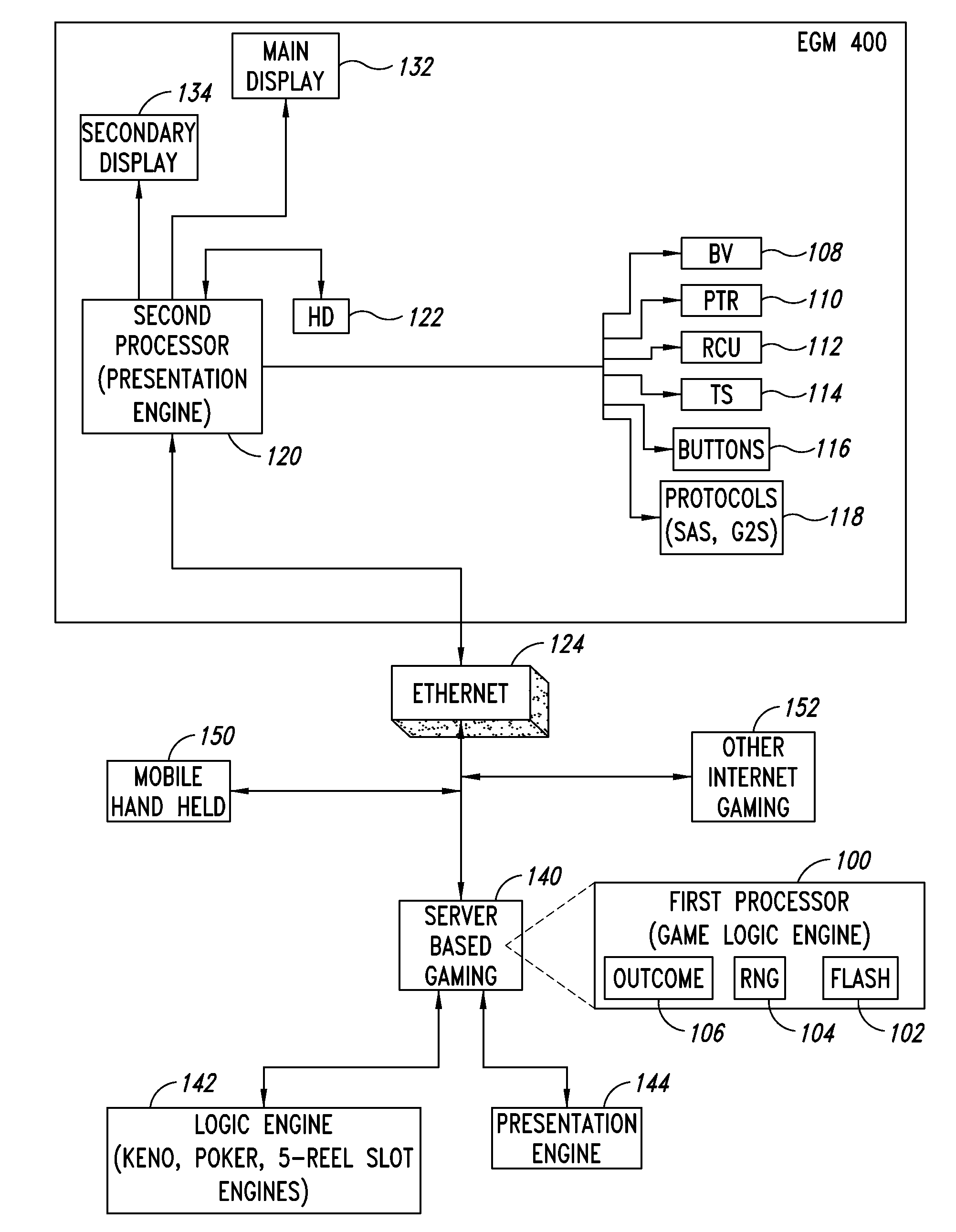
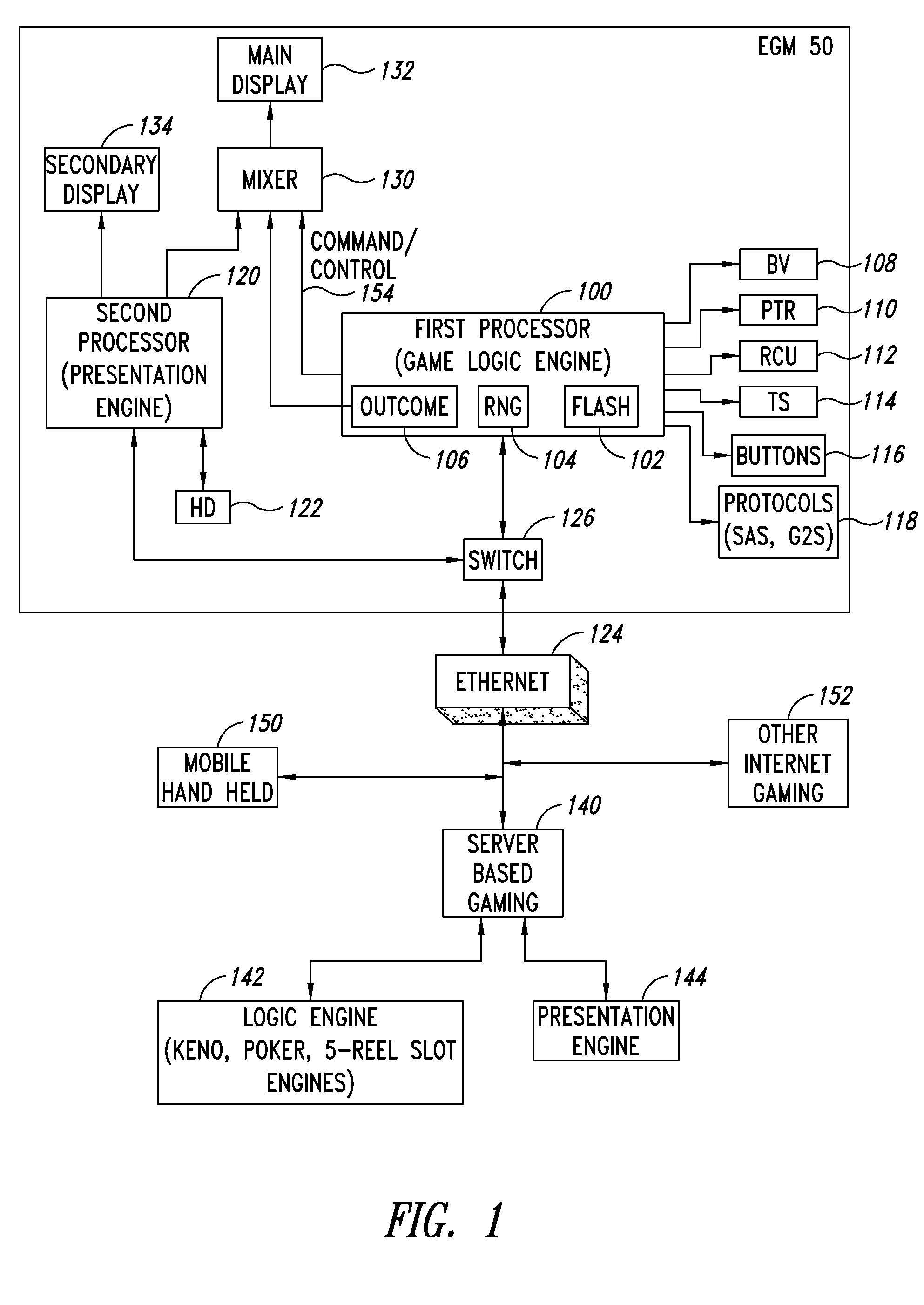
Apparatus, method, and system to provide a multiple processor architecture for server-based gaming
ActiveUS20100124990A1Multiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingComputer architectureMulti processor
An architecture for an electronic gaming machine (EGM) includes multiple processors that separate game logic from game presentation. The multi-processor architecture includes a dedicated game logic engine and a dedicated presentation engine. A first processor having the game logic engine is adapted to handle the input / output (I / O), peripherals, communications, accounting, critical gaming and other game logic, power hit tolerances, protocols to other systems, and other tasks related to operation of the EGM. A second processor is adapted to running a presentation engine. The second processor receives commands from the first processor to present game-oriented outcome and results.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Optical add/drop interconnect bus for multiprocessor architecture
InactiveUS7366368B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMulti processorEngineering
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing efficient data dependence tracking for multiprocessor architectures
InactiveUS20080162889A1Simple and efficientEasy to controlDigital computer detailsMemory systemsData dependenceMultiprocessor architecture
A system for tracking memory dependencies includes a speculative thread management unit, which uses a bit vector to record and encode addresses of memory access. The speculative thread management unit includes a hashing unit that partitions the addresses into a load hash set and a store hash set, a load hash set unit for storing the load hash set, a store hash set unit for storing the store hash set, and a data dependence checking unit that checks data dependence when a thread completes, by comparing a load hash set of the thread to a store hash set of other threads.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for SIMD processing using multiple queues
InactiveUS6898692B1Operational speed enhancementGeneral purpose stored program computerGraphicsMultilevel queue
A method of processing data relating to graphical primitives to be displayed on a display device using region-based SIMD multiprocessor architecture, has the shading and blending operations deferred until rasterization of the available graphical primitive data is completed. For example, the method may comprise the steps of: a) defining a data queue having a predetermined number of locations therein; b) receiving fragment information belonging to an image to be displayed by the pixel; c) determining whether the fragment information belongs to an opaque image or to a blended image; d) if the fragment information relates to a blended image, storing the fragment information on the next available location in the queue; e) if the fragment information relates to an opaque image, clearing the locations of the queue and storing the fragment information in the first location in the queue; f) repeating steps b) to e) for new fragment information until fragment information is stored in all the locations in the data queue or until no further fragment information is available; and g) processing in turn fragment information stored in the locations of the queue to produce respective pixel display values.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
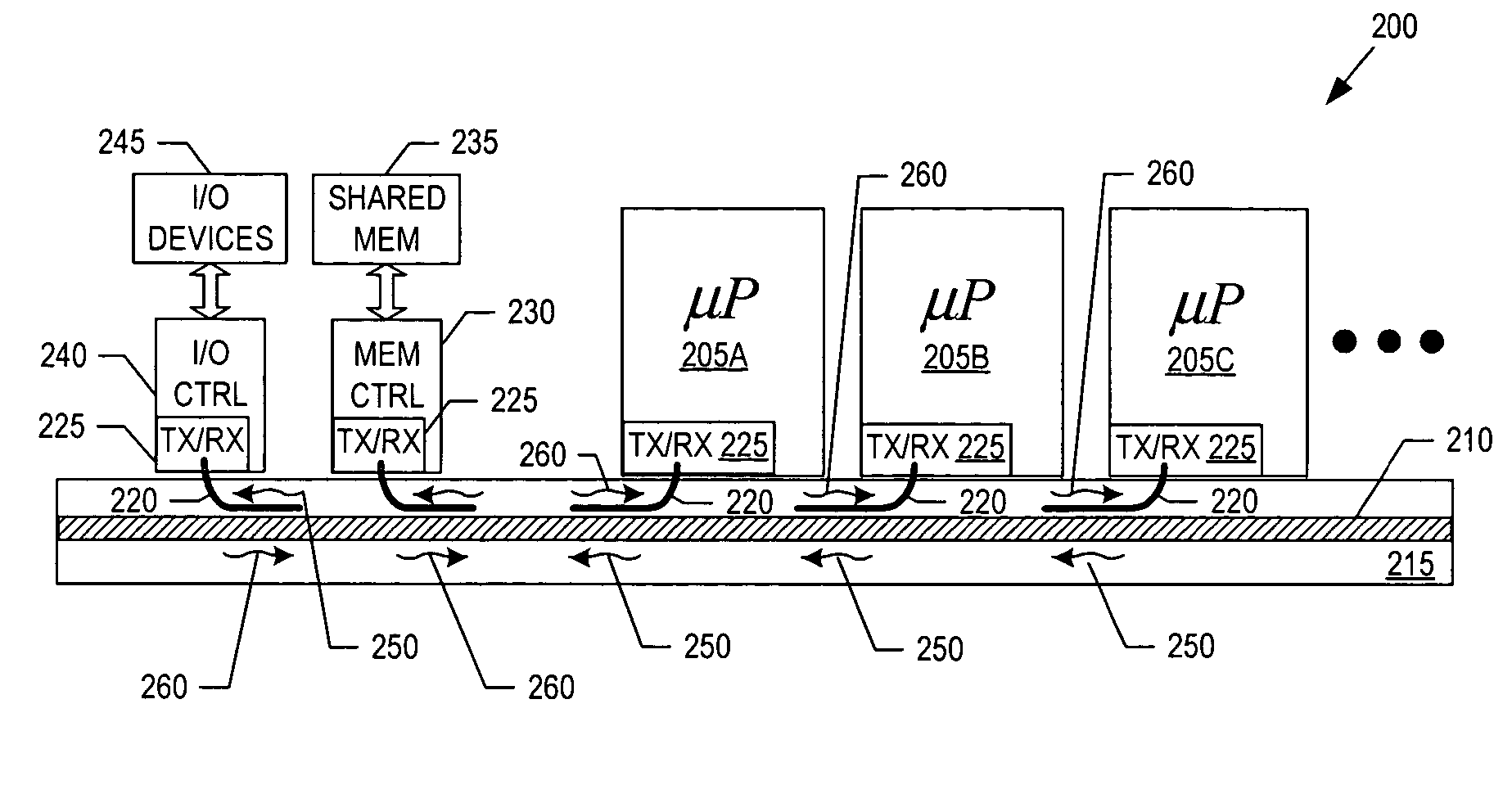
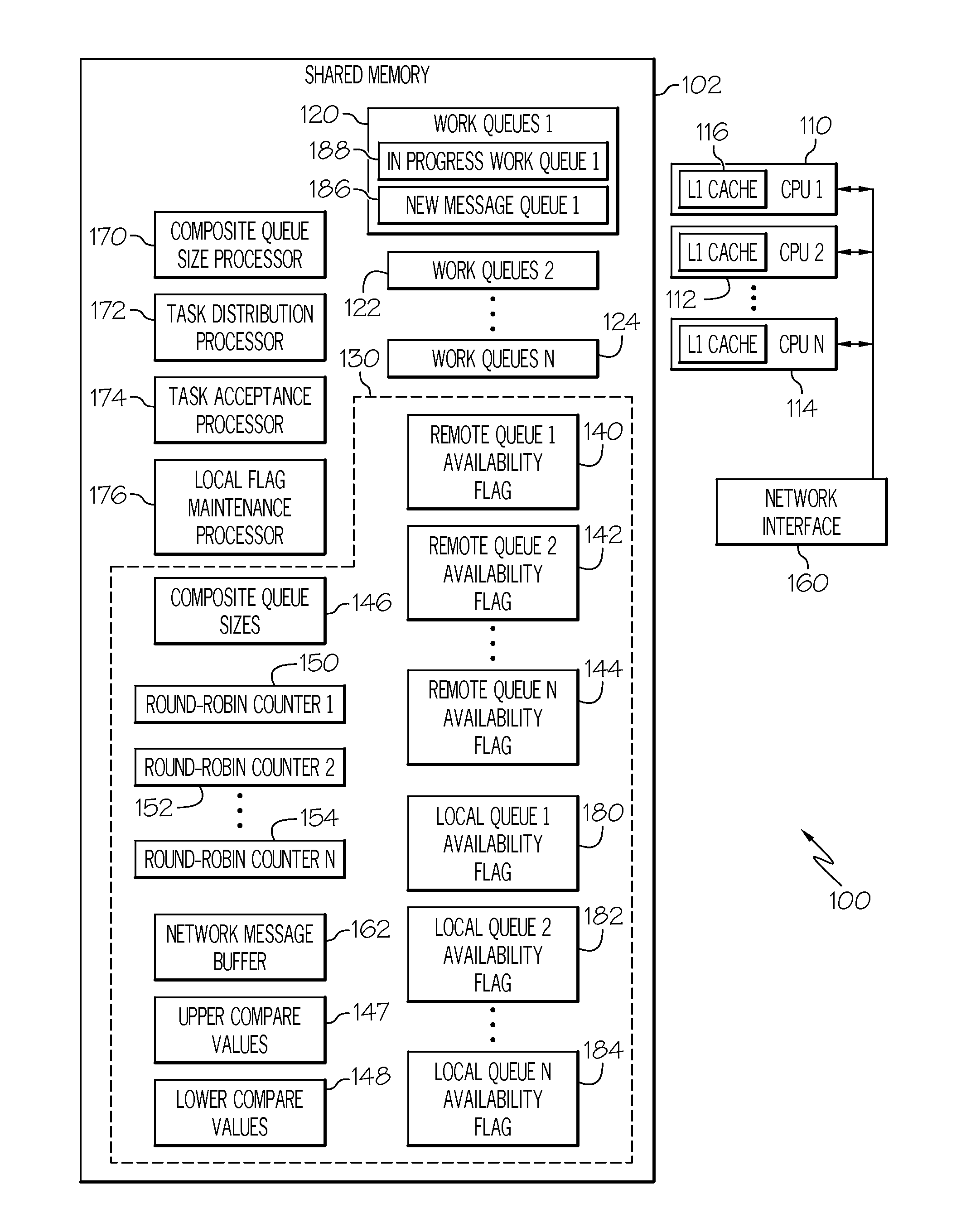
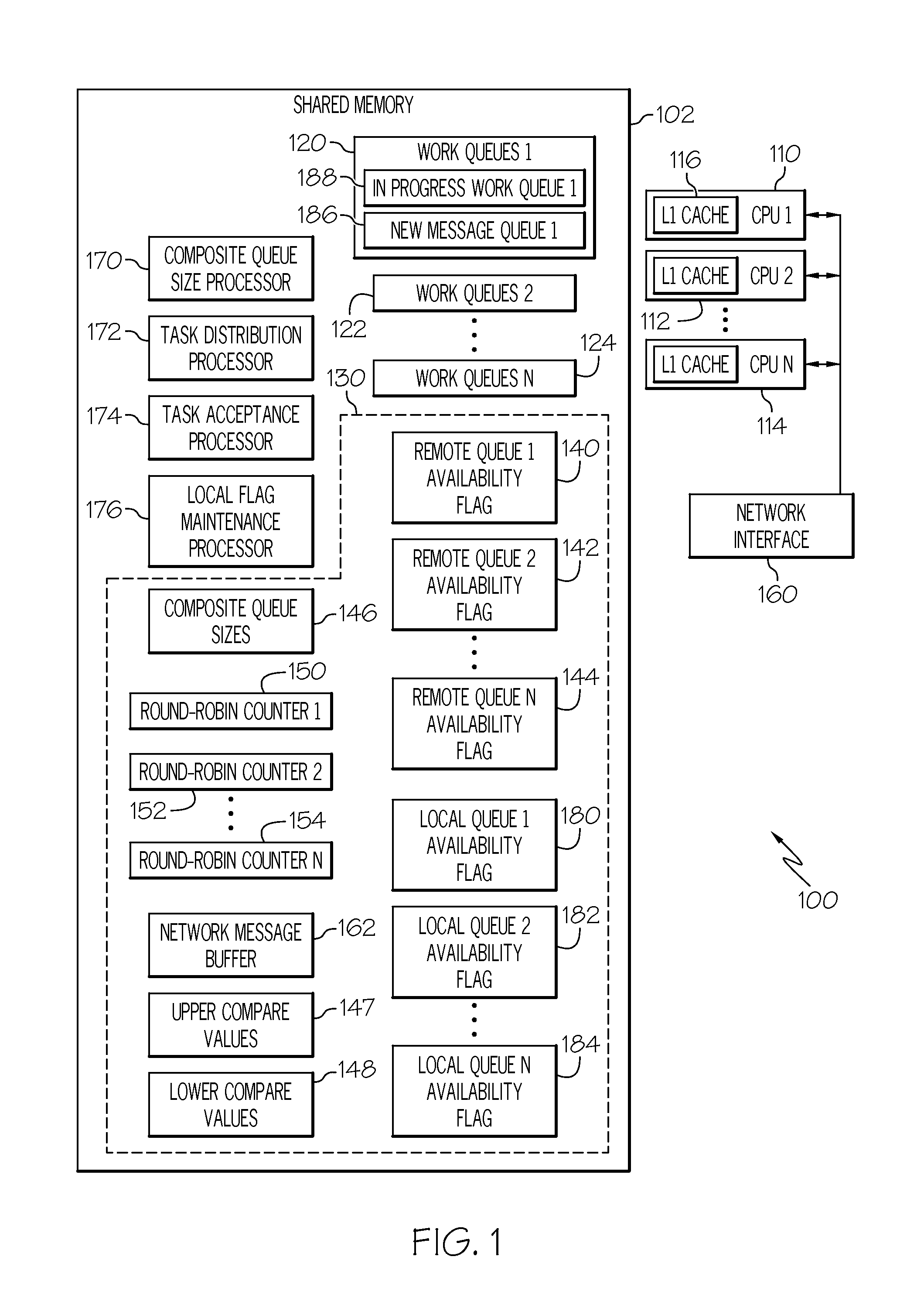
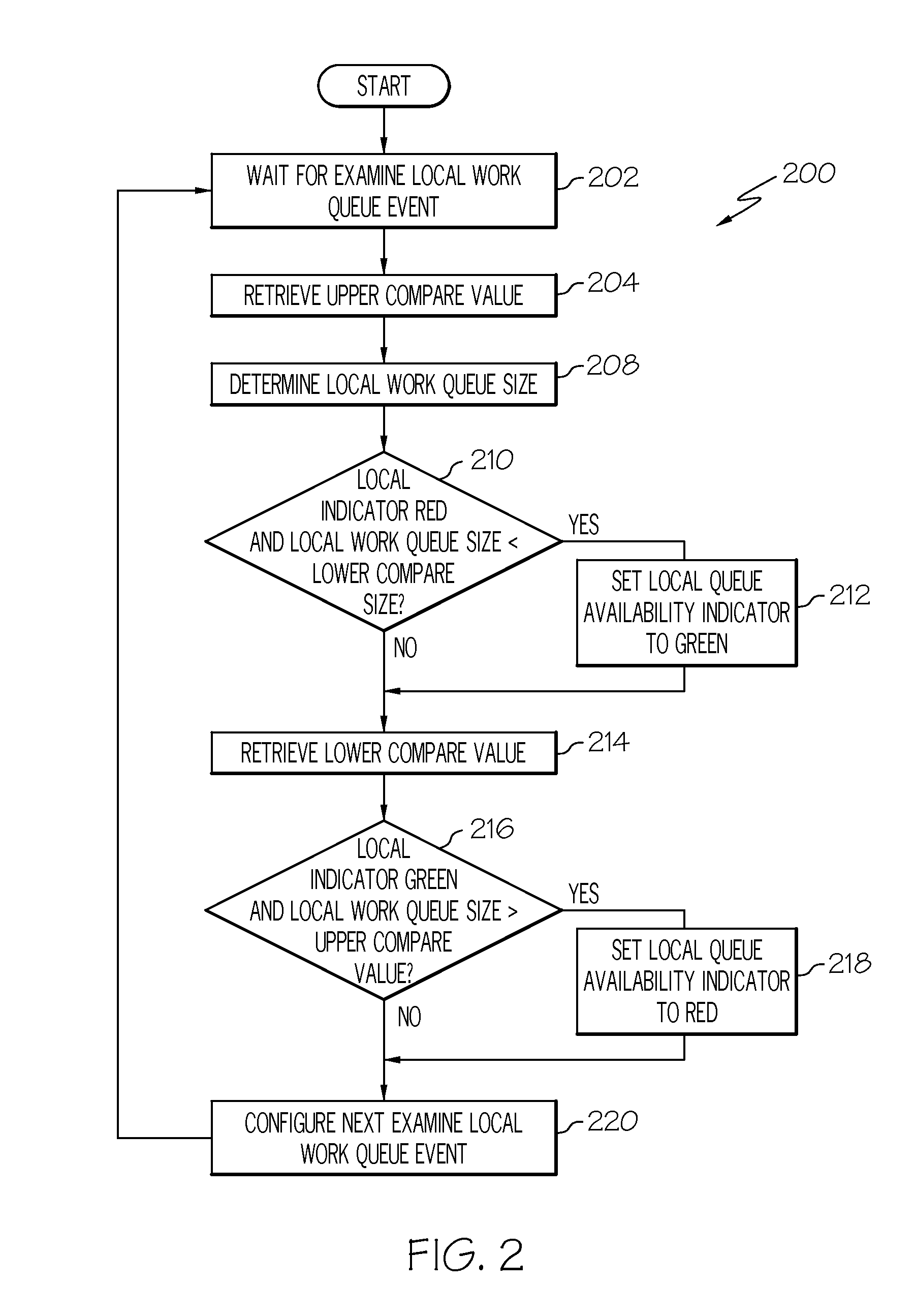
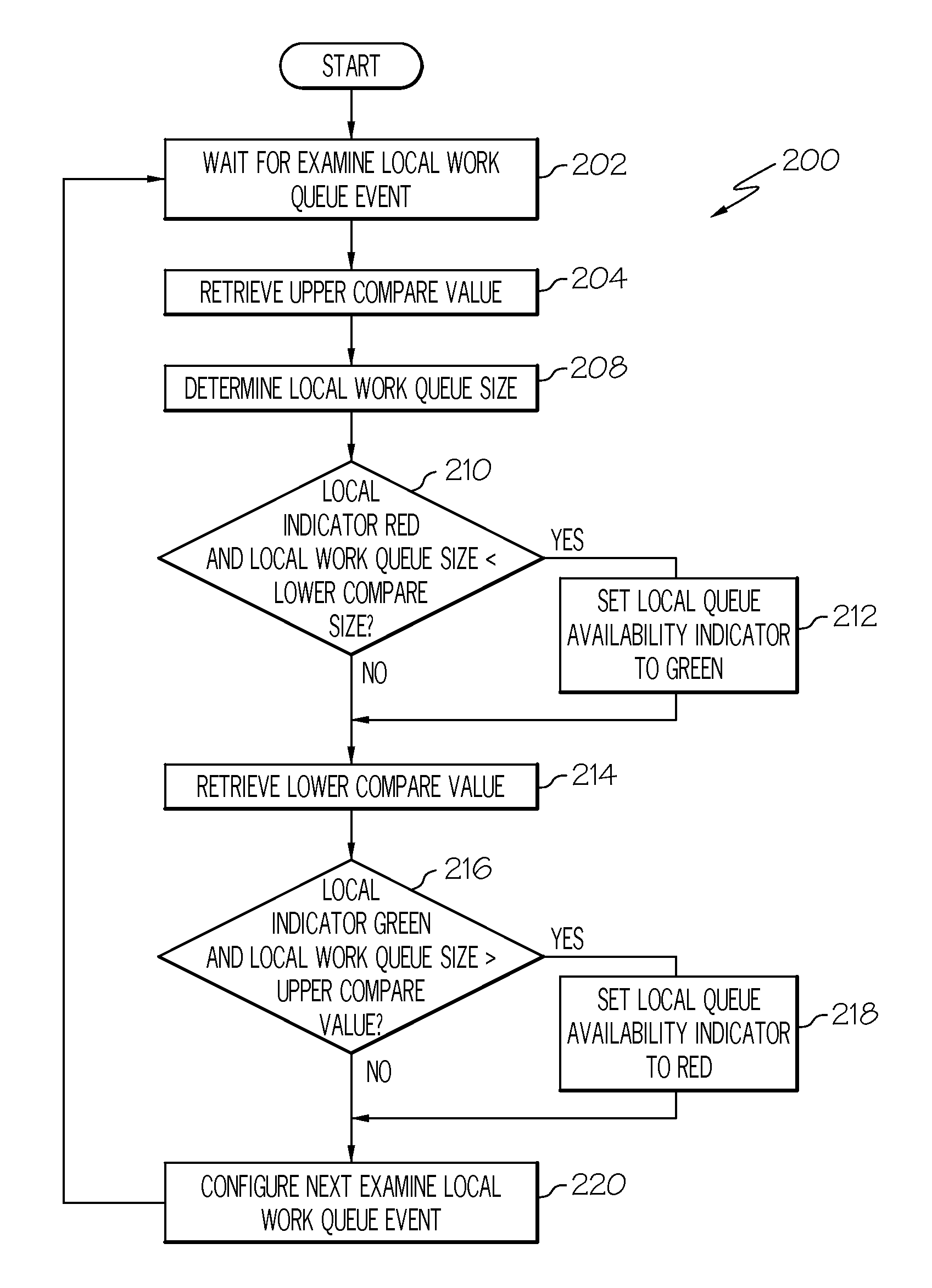
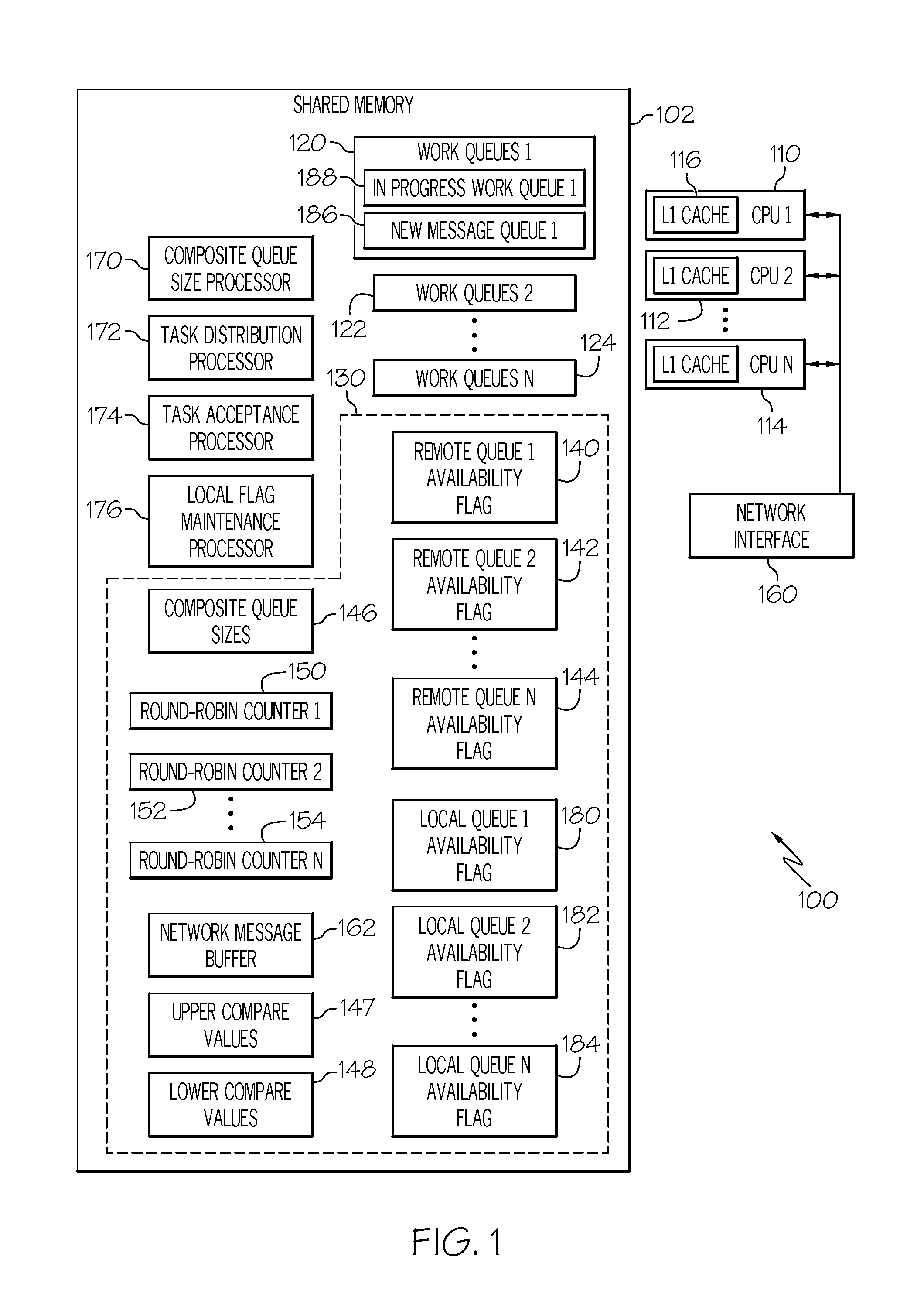
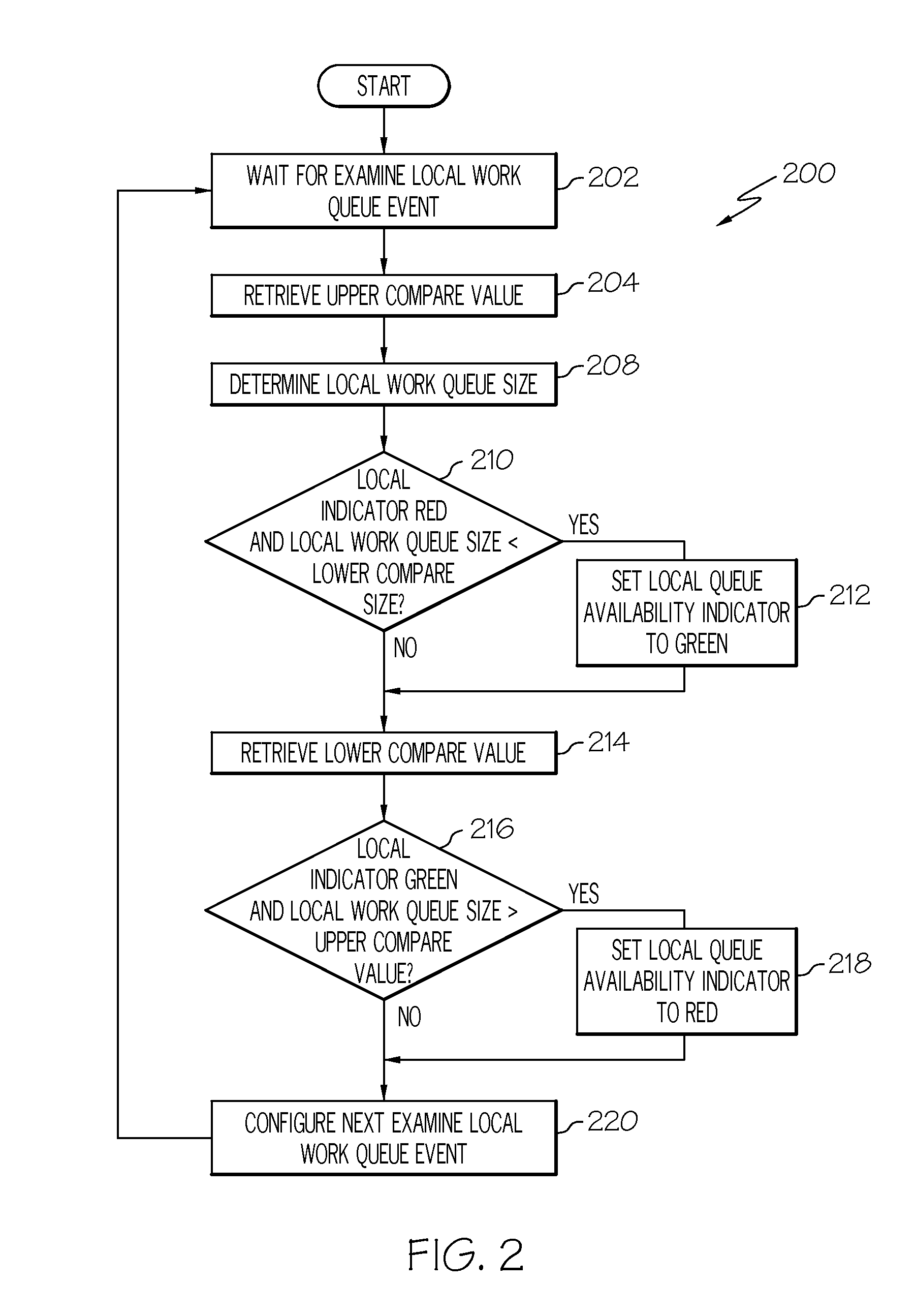
Work queue selection on a local processor within a multiple processor architecture
A method and system is disclosed for selecting a work queue associated with a processor within a multiple processor architecture to assign a new task. A local and a remote queue availability flag is maintained to indicate a relative size of work queues, in relationship to a mean queue size, for each processor in a multiple processor architecture. In determining to which processor to assign a task, the processor evaluates its own queue size by examining its local queue availability flag and evaluates other processor's queue sizes by examining their remote queue availability flags. The local queue availability flags are maintained asynchronously from task assignment. Remote flags are maintained at time of task assignment. The presented algorithm provides improved local processor queue size determinations in systems where task distribution processes execute with lower priorities that other tasks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optical add/drop interconnect bus for multiprocessor architecture
InactiveUS20050276604A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMulti processorOptical coupler
An optical bus interconnects two or more processors in a multiprocessor system. One or more electrical-to-optical (“E-O”) transmitters are optically coupled to the optical bus using optical couplers. The E-O transmitters receive electrical signals from the processors and convert the electrical signals to optical signals to be guided onto the optical bus. Optical-to-electrical (“O-E”) receivers are also coupled to the optical bus using the optical couplers. The O-E receivers receive optical signals from the optical bus and convert the optical signals to electrical signals for the processors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Thread optimized multiprocessor architecture
ActiveUS20070192568A1Increase computing speedImprove execution speedProgram control using stored programsInstruction analysisMulti processorComputer memory
In one aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors; wherein each of the processors is operable to process a de minimis instruction set, and wherein each of the processors comprises local caches dedicated to each of at least three specific registers in the processor. In another aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors, wherein each of the processors is operable to process an instruction set optimized for thread-level parallel processing.
Owner:BLANKENSHIP BETH
Securing CPU affinity in multiprocessor architectures
InactiveUS20090126006A1Limited abilityDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionMulti processorMultiprocessor architecture
In an embodiment of the present invention, the ability for a user or process to set or modify affinities is restricted in order to method for control a multi-processor environment. This may be accomplished by using a reference monitor that controls a process' capability to retrieve and set its or another process' affinity. This aids in the prevention of security breaches.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
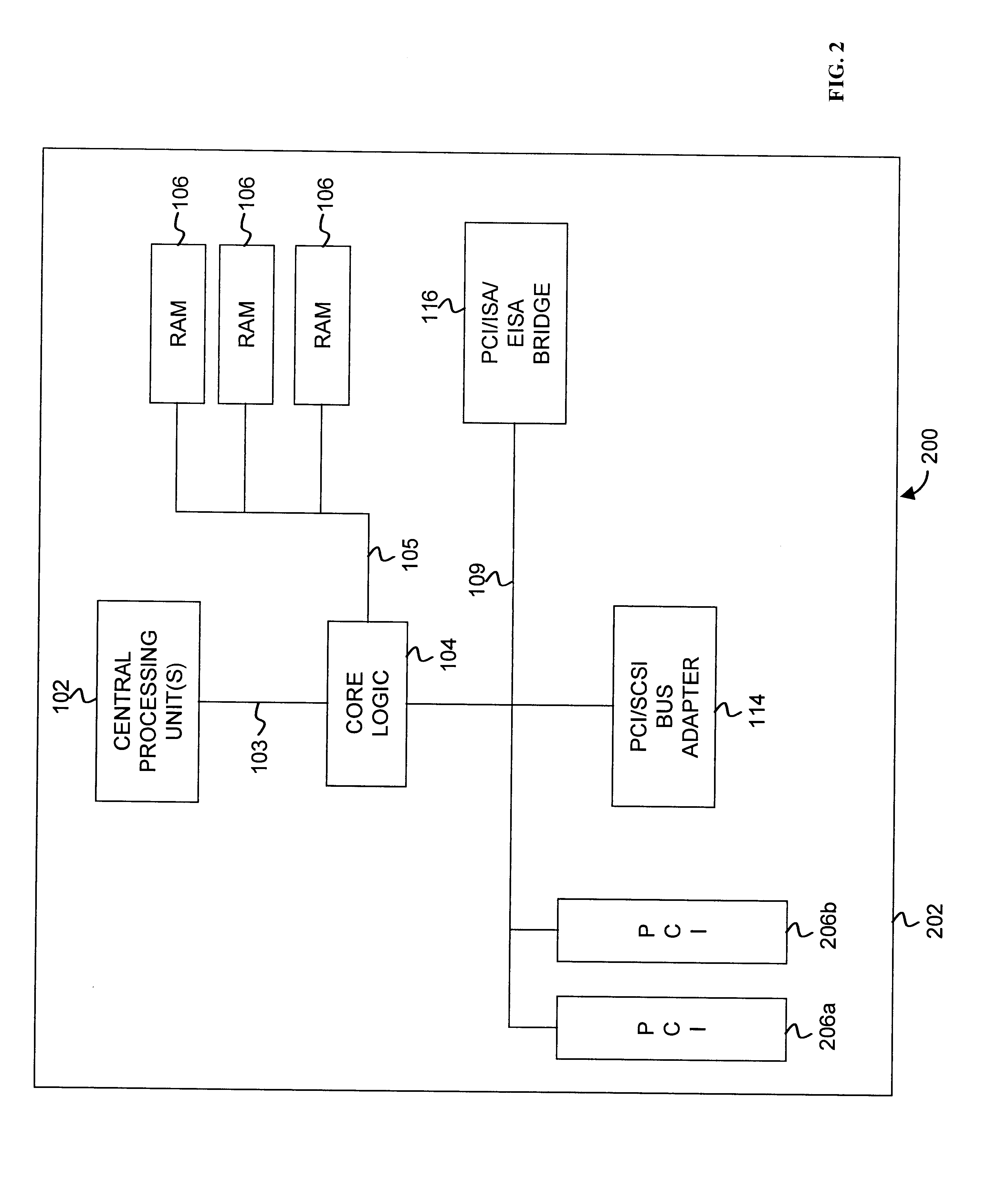
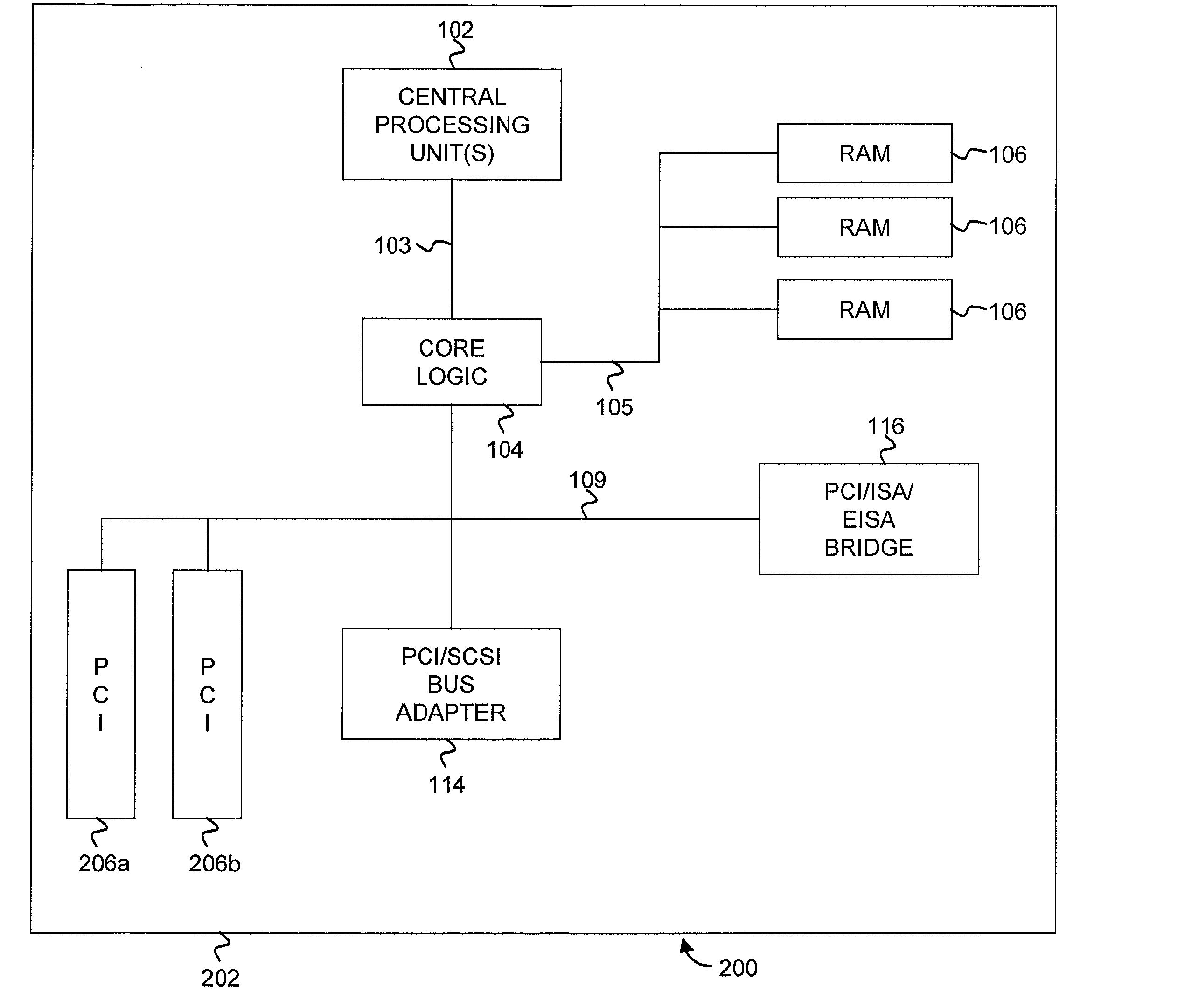
Priority transaction support on the PCI-X bus
InactiveUS6801970B2Multiprogramming arrangementsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingProcessing Instruction
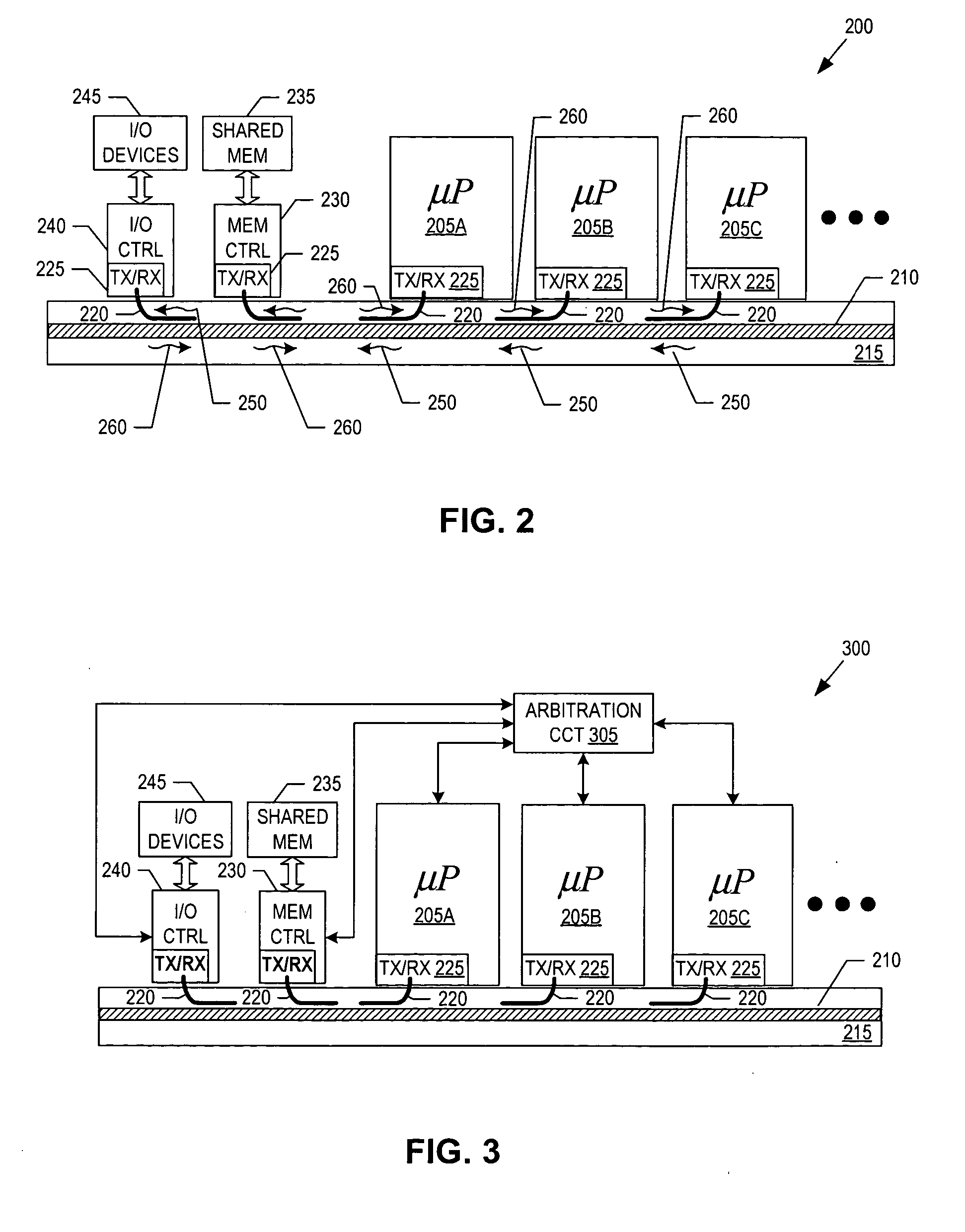
Support for indicating and controlling transaction priority on a PCI-X bus. Embodiments of the invention provide indicia that can be set to communicate to PCI-X-to-PCI-X bridges and Completer that a transaction should be handled specially and scheduled ahead of any other transaction not having their corresponding indicia set. A special handling instruction allows the priority transaction to be scheduled first or early. The indicia are implemented by setting a bit(s) in an unused portion of a PCI-X attribute field, or multiplexed with a used portion, to schedule the associated transaction as the priority transaction over other transactions that do not have their corresponding bit set. The present invention can be used for interrupt messaging, audio streams, video streams, isochronous transactions, or for high performance, low bandwidth control structures used for communication in a multiprocessor architecture across PCI-X.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
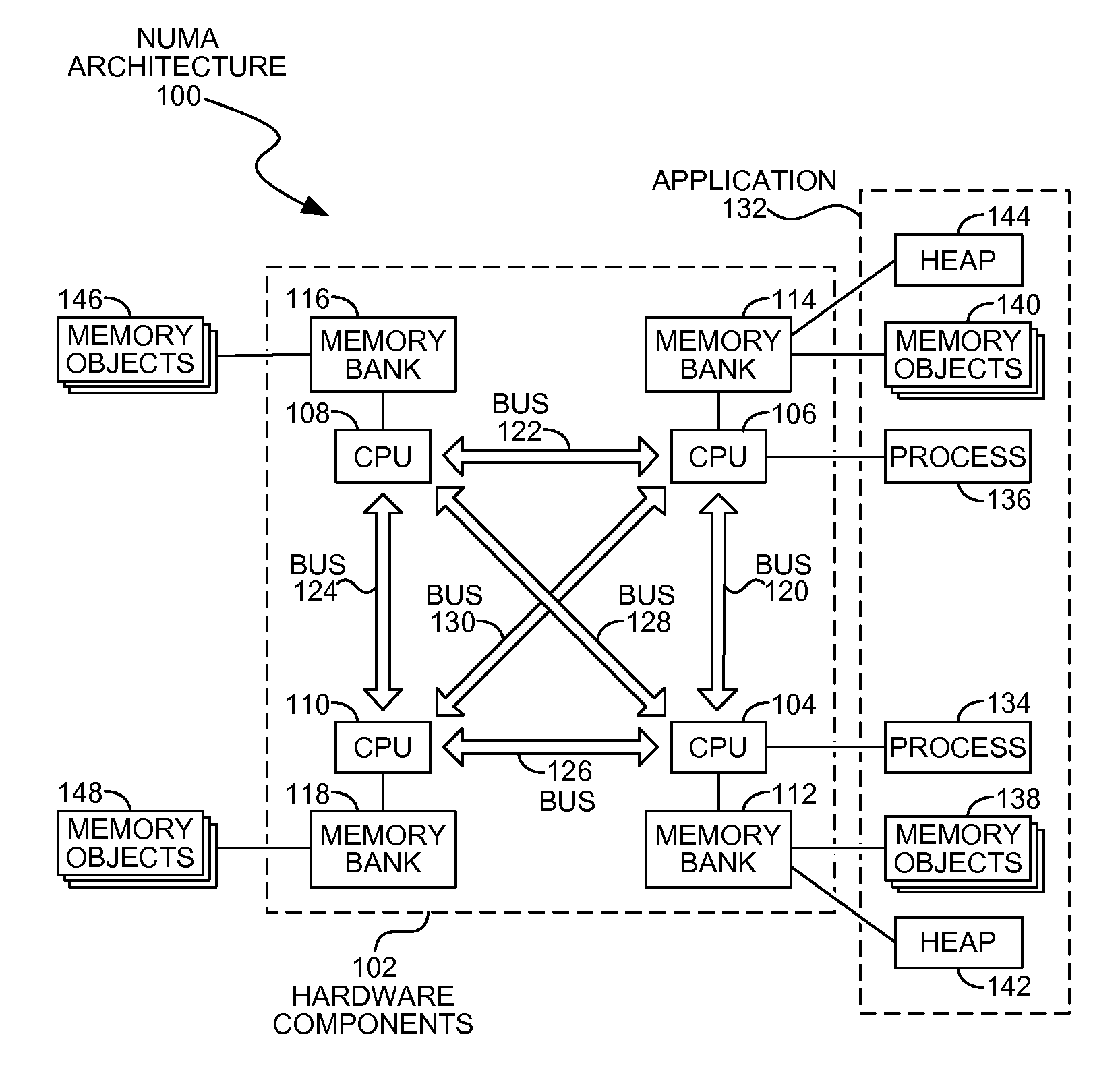
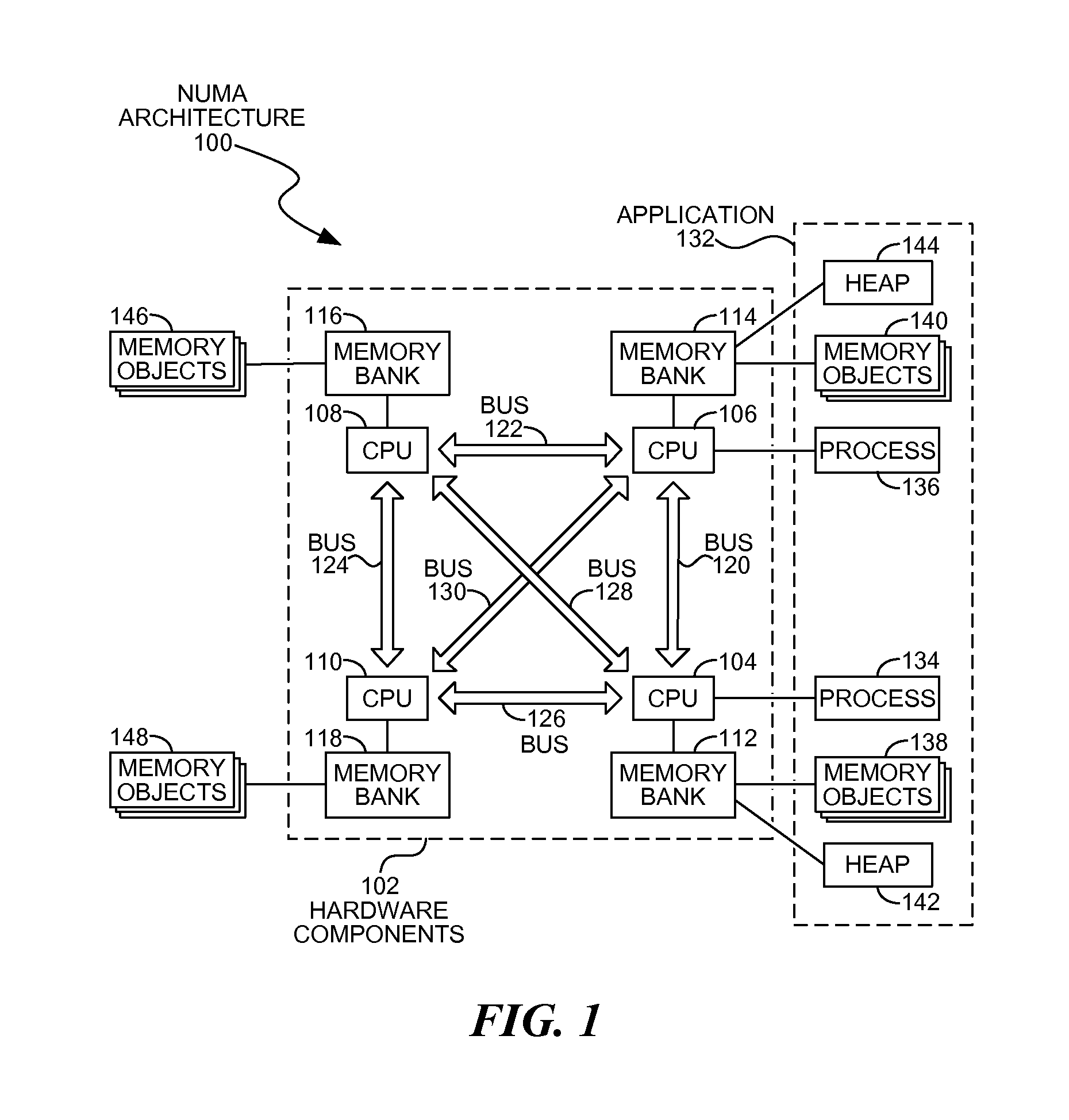
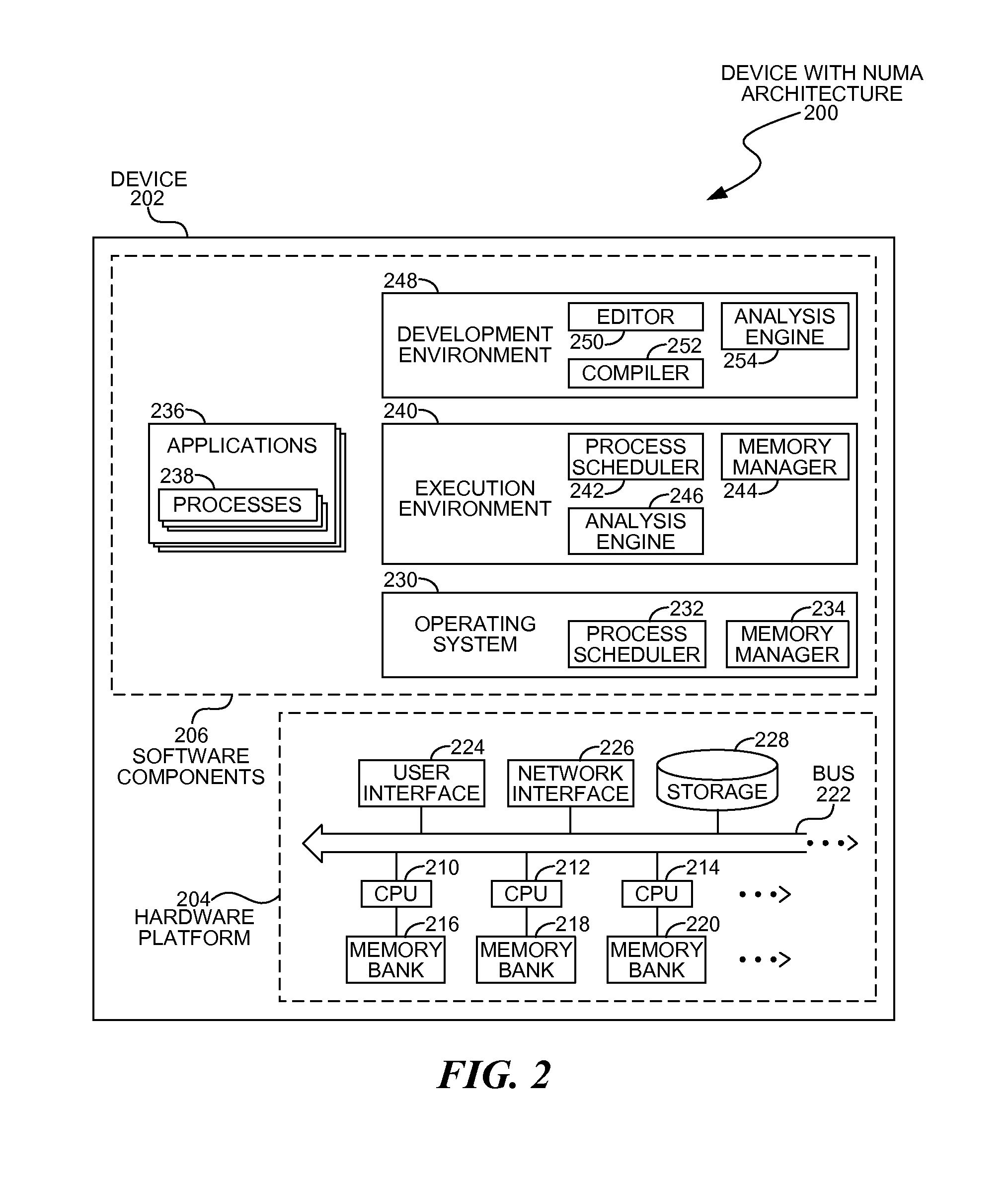
Allocating heaps in NUMA systems
InactiveUS8700838B2Well formedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHardware monitoringMemory bankParallel computing
Processes may be assigned heap memory within locally accessible memory banks in a multiple processor NUMA architecture system. A process scheduler may deploy a process on a specific processor and may assign the process heap memory from a memory bank associated with the selected processor. The process may be a functional process that may not change state of other memory objects, other than the input or output memory objects defined in the functional process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Thread Optimized Multiprocessor Architecture
ActiveUS20080320277A1Increase computing speedImprove execution speedSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsInstruction analysisMulti processorComputer memory
In one aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors; wherein each of the processors is operable to process a de minimis instruction set, and wherein each of the processors comprises local caches dedicated to each of at least three specific registers in the processor. In another aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors, wherein each of the processors is operable to process an instruction set optimized for thread-level parallel processing and wherein each processor accesses the internal data bus of the computer memory on the chip and the internal data bus is the width of one row of the memory.
Owner:BLANKENSHIP BETH
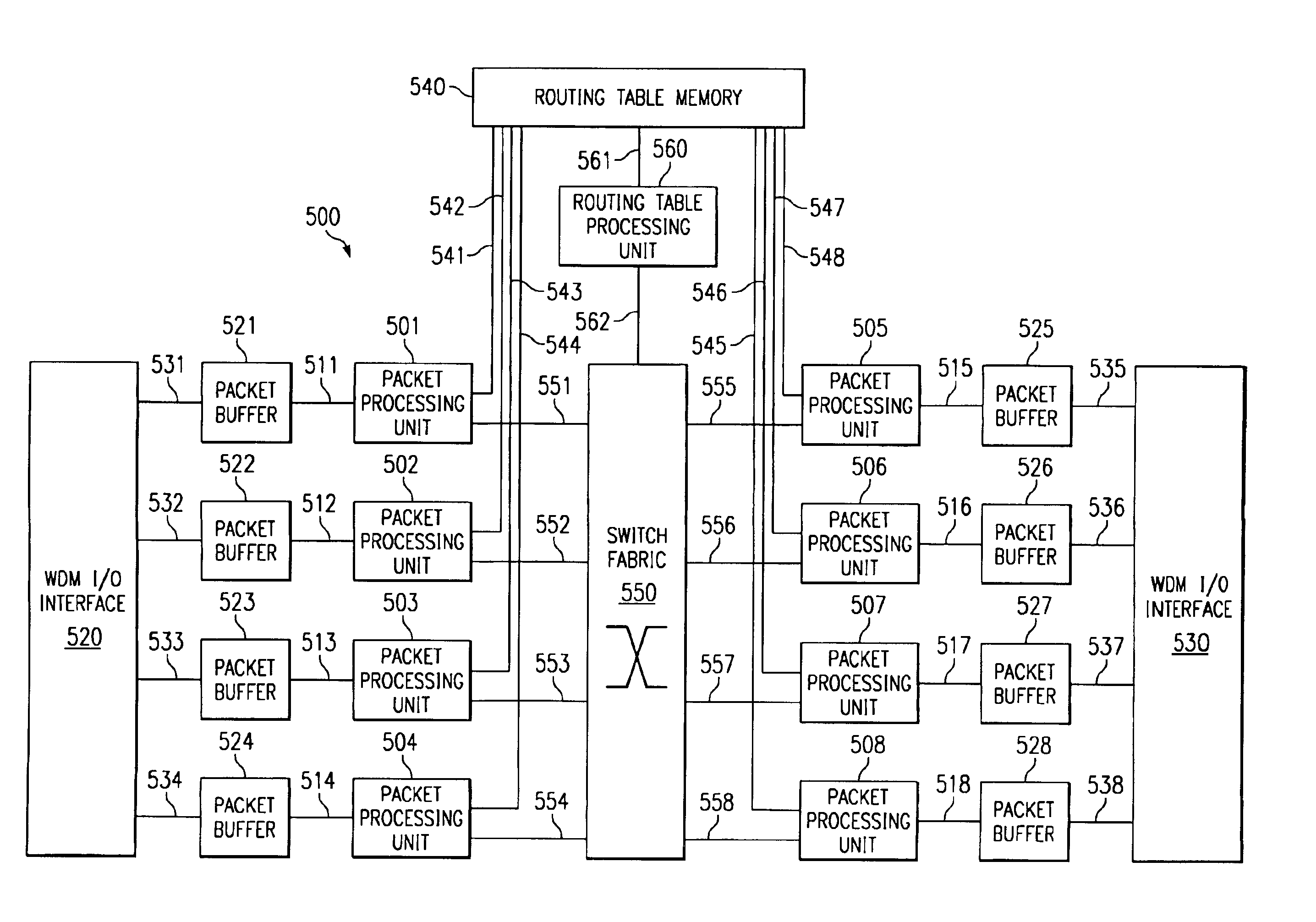
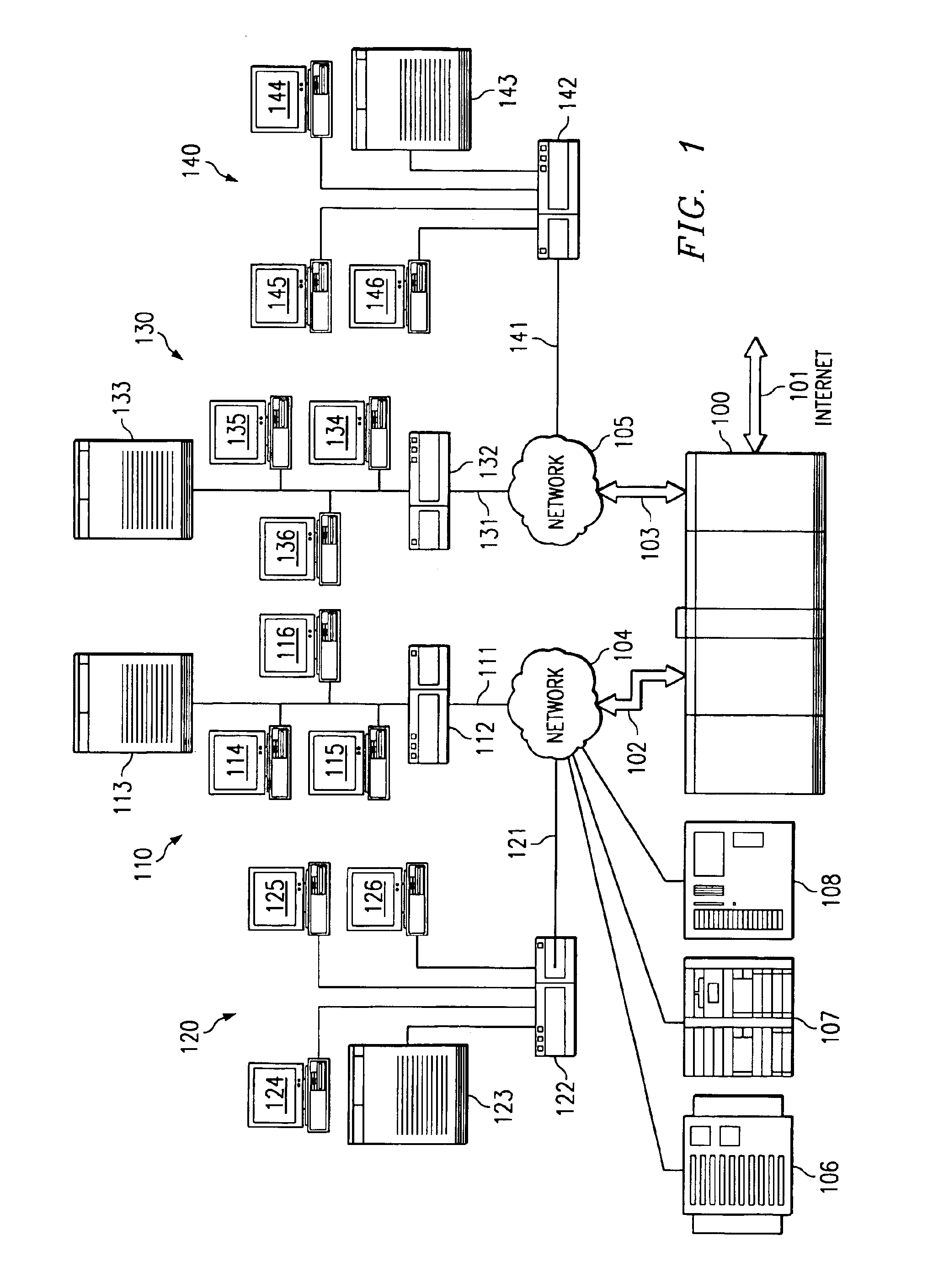
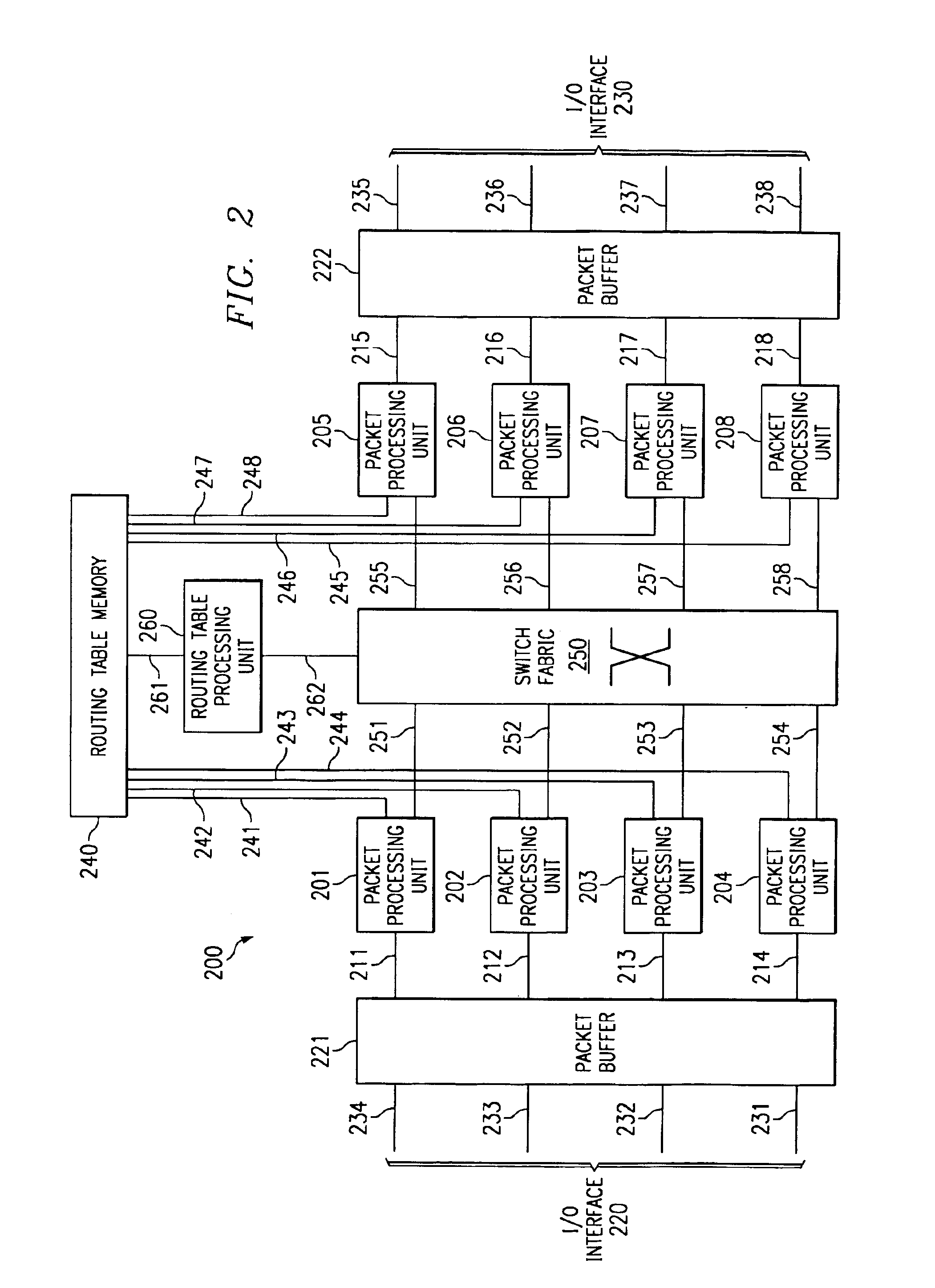
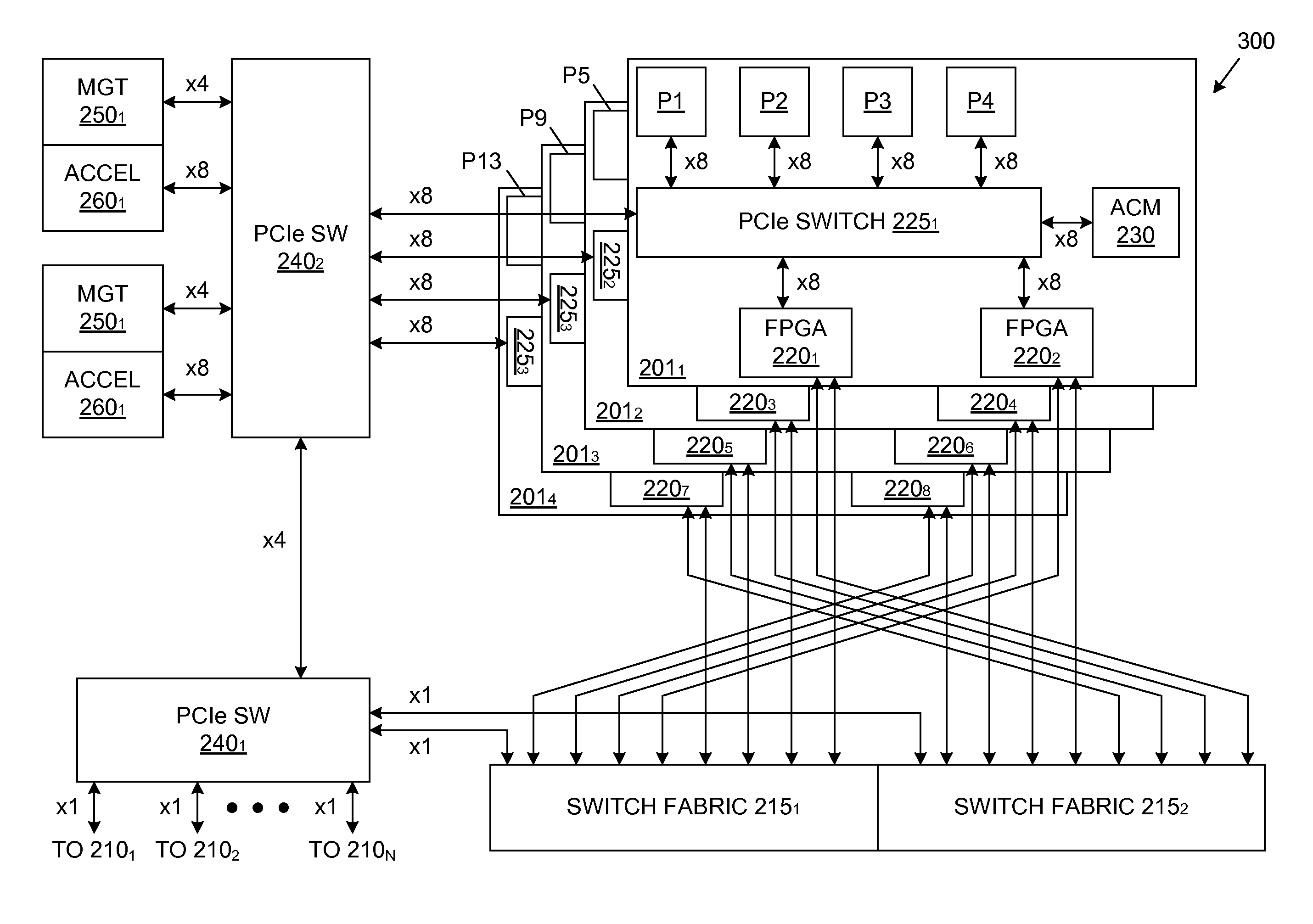
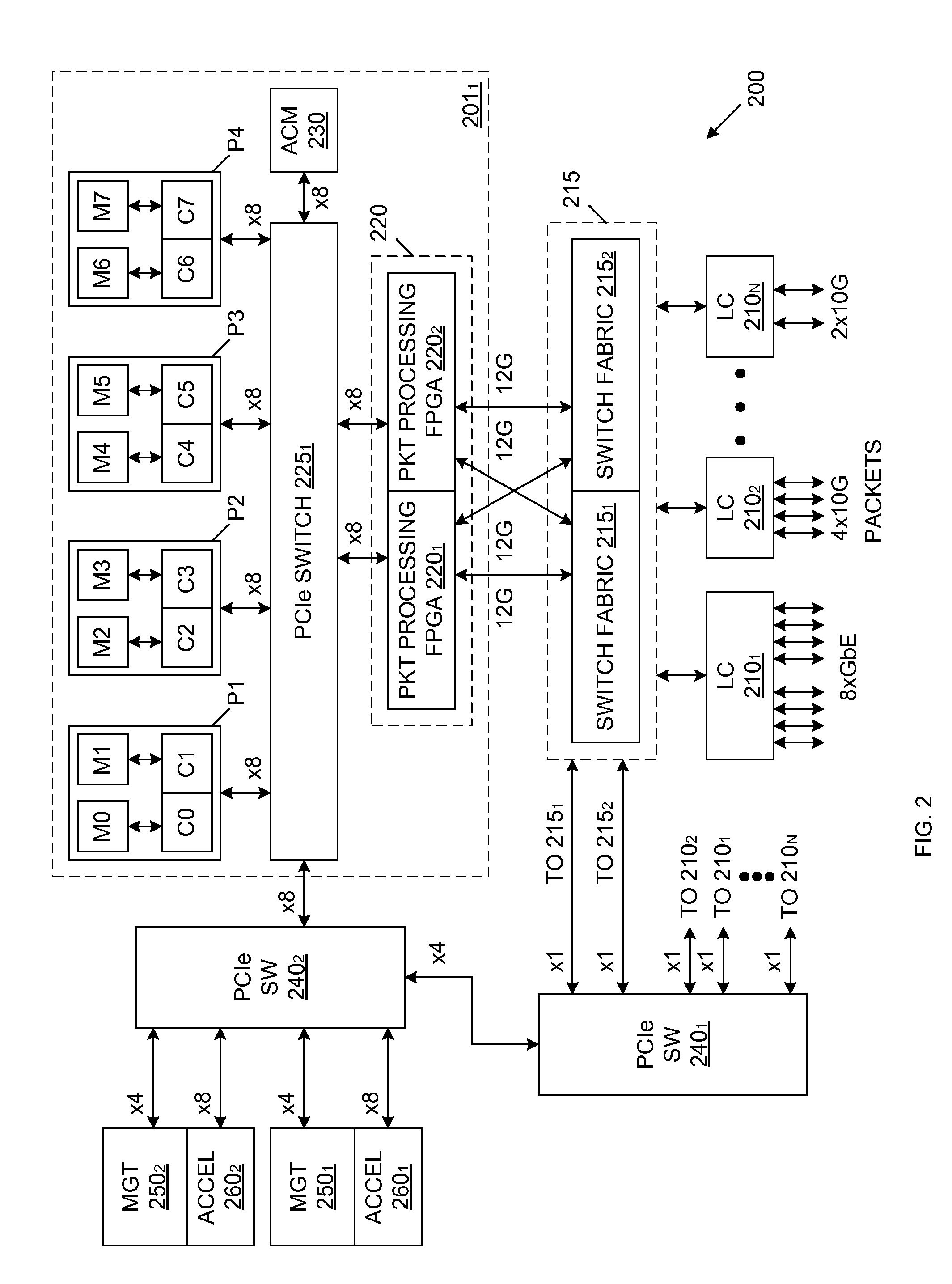
Method and apparatus for processing packets in a routing switch
A method, apparatus, and instructions for processing packets within a routing switch uses a multiprocessor architecture. The routing switch includes a switch fabric, a Routing Table Processing Unit, at least one packet buffer for queuing incoming and outgoing packets, at least one Packet Processing Unit, and a shared memory for storing a routing table. A Packet Processing Unit retrieves packets from a packet buffer memory, which may be a shared memory accessible to more than one of the Packet Processing Units depending upon the internal configuration of the components. The Packet Processing Unit categorizes the packets into routing information packets and data packets. The Packet Processing Unit forwards a routing information packet to a Routing Table Processing Unit and processes any other data packet by retrieving forwarding information from a routing table, updating the packet with the retrieved forwarding information, and forwarding the updated packet using a switch fabric connected to the Packet Processing Unit. A locking mechanism within the routing table memory provides synchronization between the activities of the various processing units. In response to receiving a routing information packet, the Routing Table Processing Unit locks a portion of the routing table, updates the locked portion of the routing table with information from the routing table information packet, and then unlocks the locked portion of the routing table. The Packet Processing Unit waits for a necessary portion of the routing table to be unlocked before retrieving any forwarding information. If more than one packet buffer memory is employed, the routing switch may be configured to support a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) enabled network such that each input / output interface receives packets over a particular wavelength and queues the packets within separate packet buffers.
Owner:CIENA
Priority transaction support on the PCI-X bus
InactiveUS20030065842A1Multiprogramming arrangementsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingProcessing Instruction
Support for indicating and controlling transaction priority on a PCI-X bus. Embodiments of the invention provide indicia that can be set to communicate to PCI-X-to-PCI-X bridges and Completer that a transaction should be handled specially and scheduled ahead of any other transaction not having their corresponding indicia set. A special handling instruction allows the priority transaction to be scheduled first or early. The indicia are implemented by setting a bit(s) in an unused portion of a PCI-X attribute field, or multiplexed with a used portion, to schedule the associated transaction as the priority transaction over other transactions that do not have their corresponding bit set. The present invention can be used for interrupt messaging, audio streams, video streams, isochronous transactions, or for high performance, low bandwidth control structures used for communication in a multiprocessor architecture across PCI-X.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
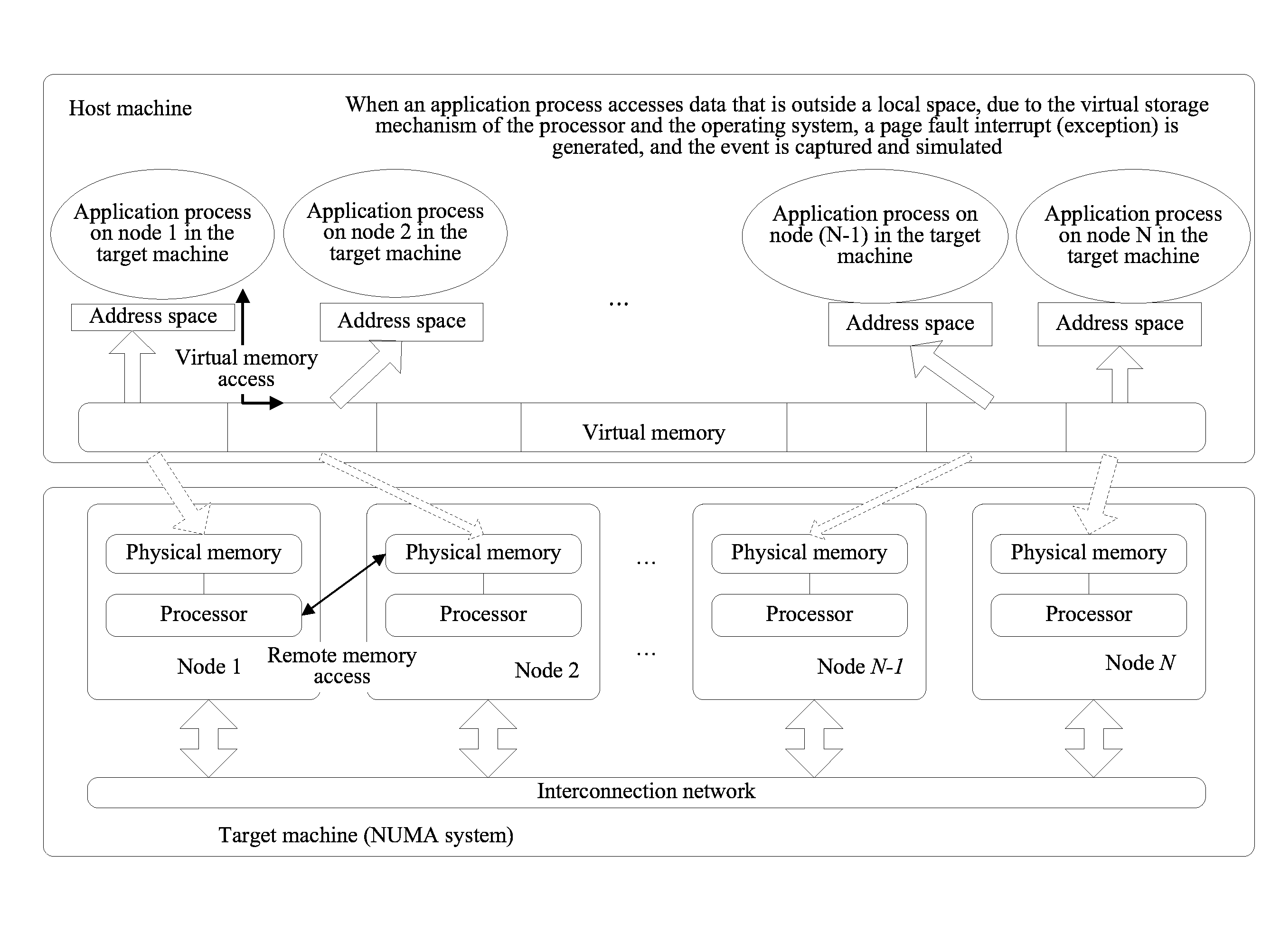
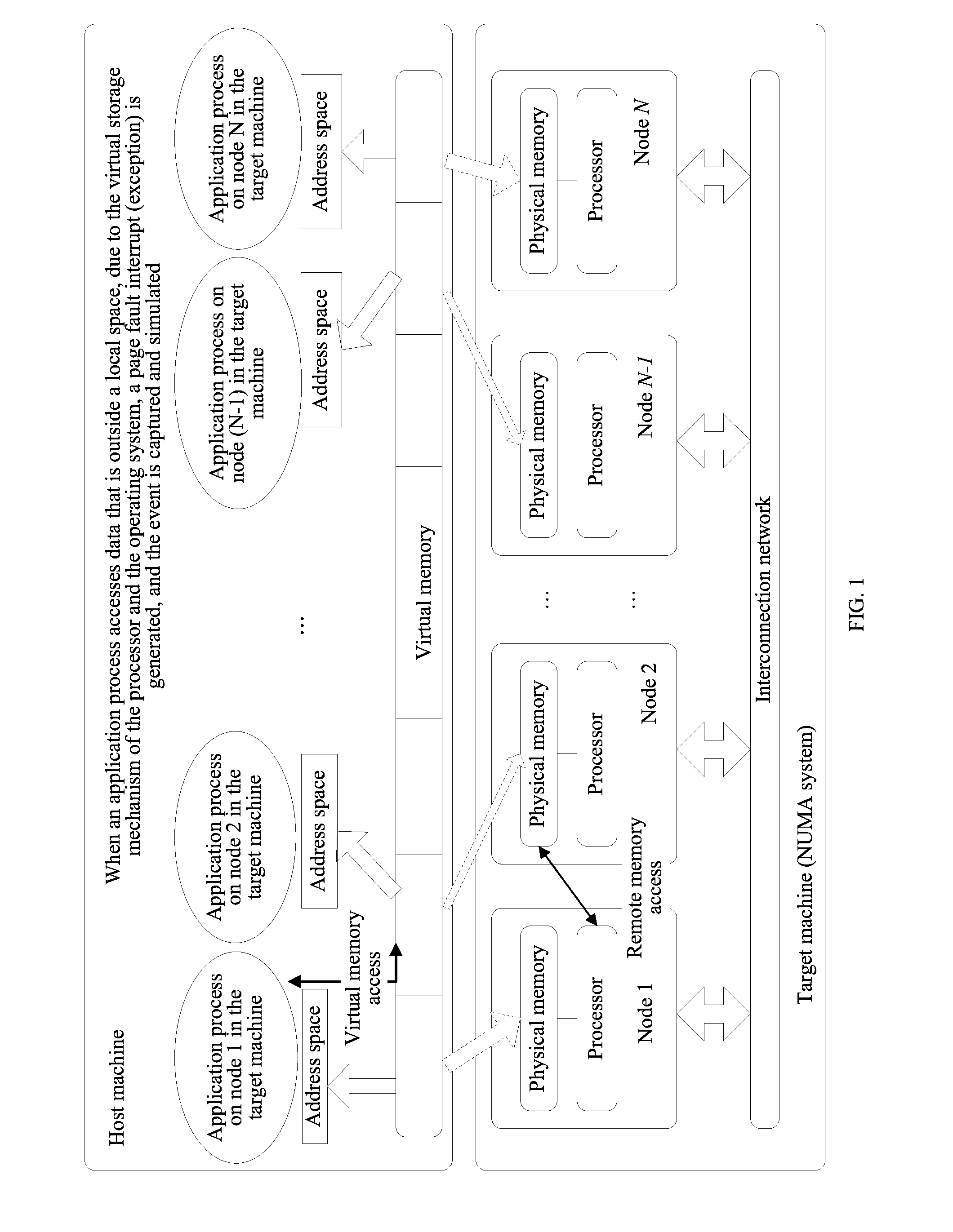
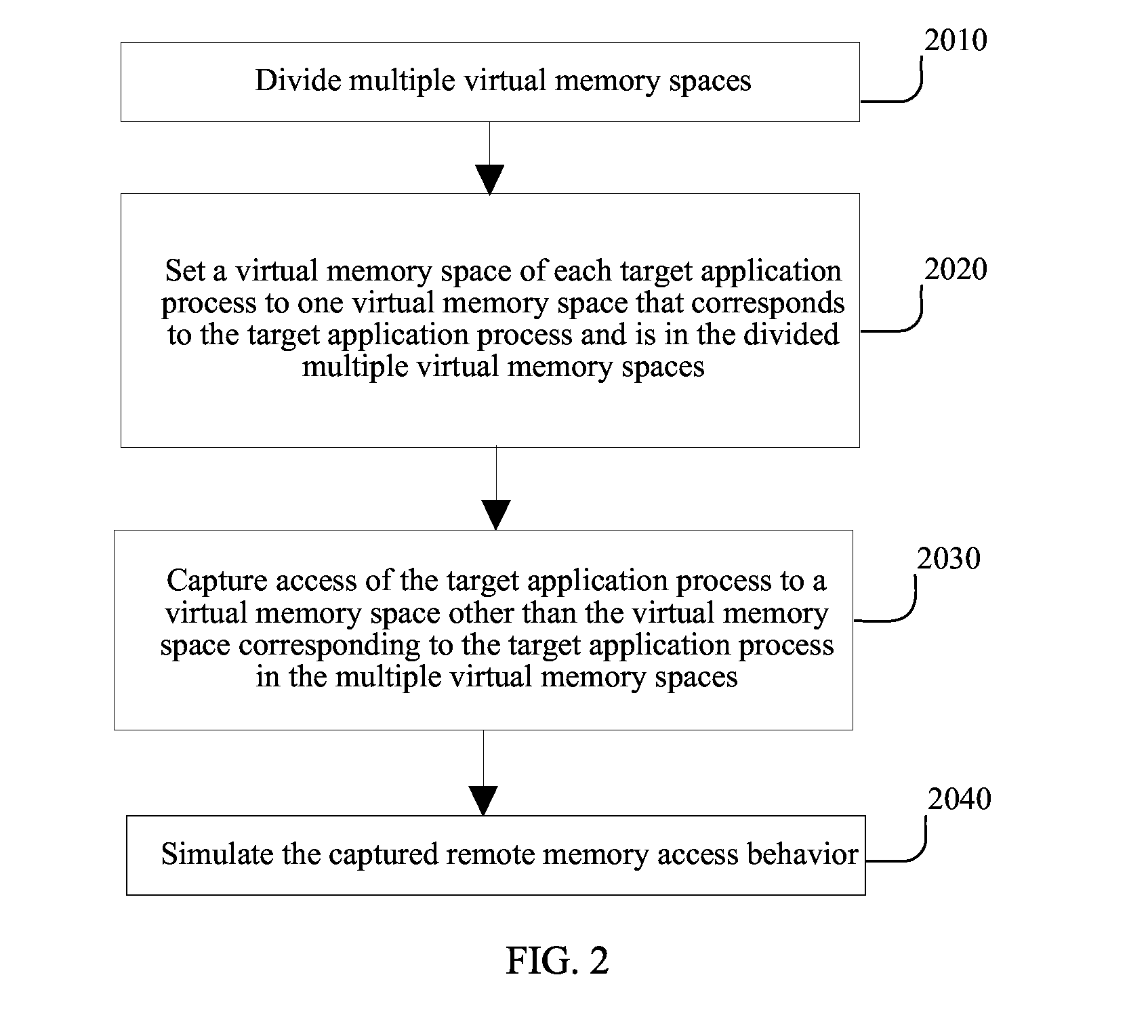
Method and Simulator for Simulating Multiprocessor Architecture Remote Memory Access
InactiveUS20130024646A1Improve efficiencySimplifies complex modeling procedureMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCAD circuit designVirtual memoryRemote memory access
A method for simulating remote memory access in a target machine on a host machine is disclosed. Multiple virtual memory spaces in the host machine are divided and a virtual address space of each target application process is set to one virtual memory space that corresponds to a target application process and is in the multiple virtual memory spaces. Access of the target application process is captured to a virtual memory space other than the virtual memory space corresponding to the target application process in the multiple virtual memory spaces.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Interleaved boot block to support multiple processor architectures and method of use
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Multi-processor soc system
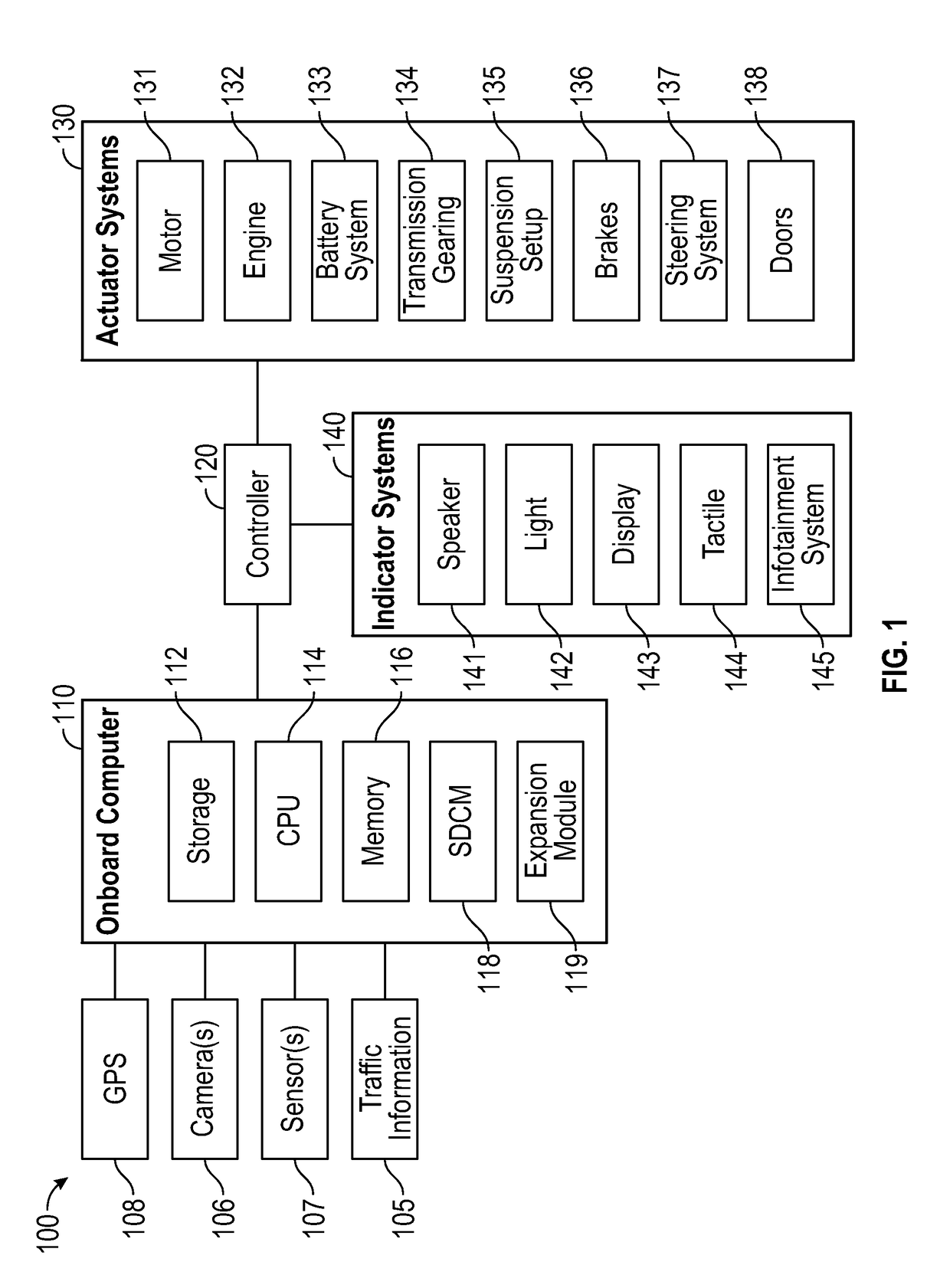
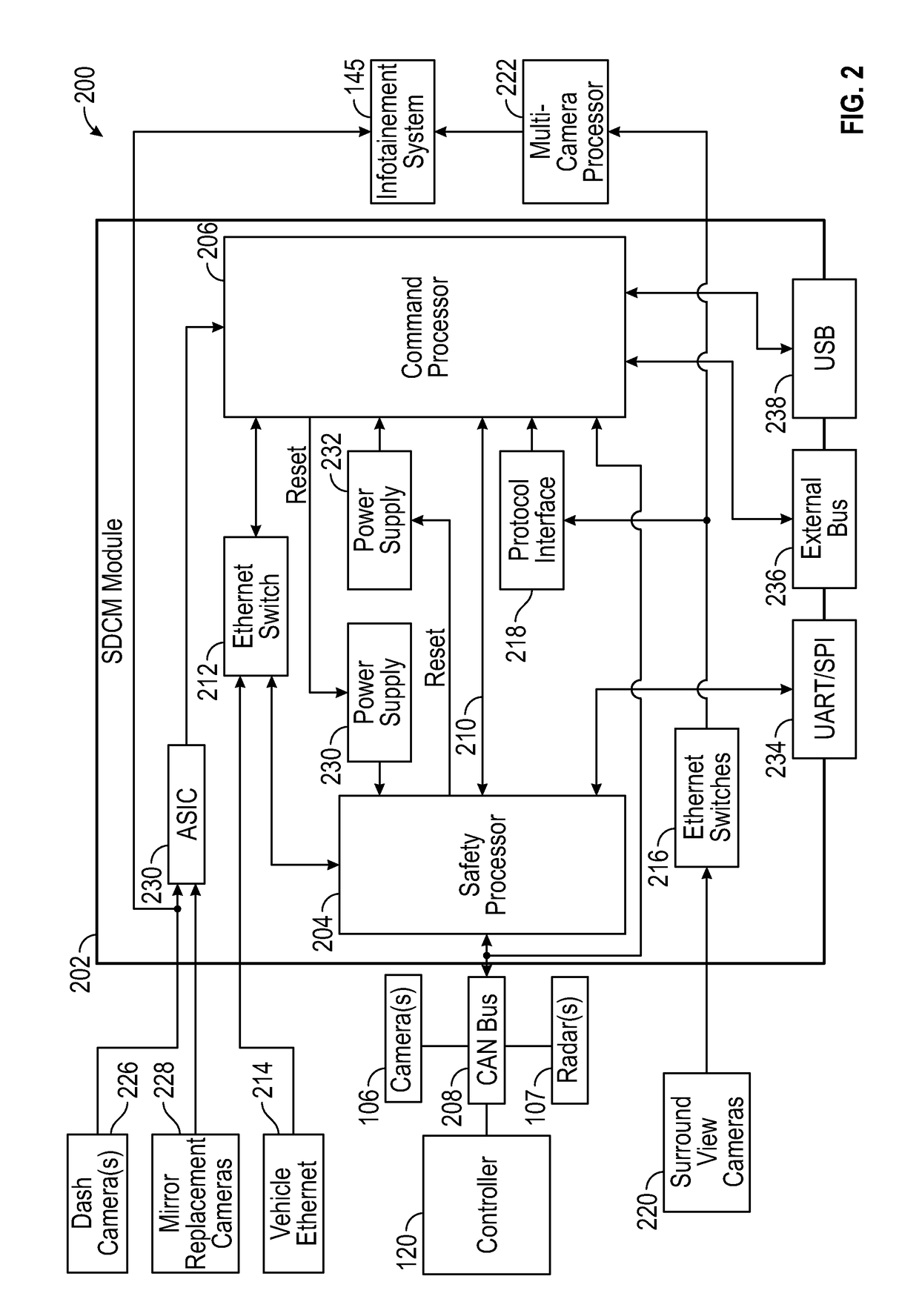
ActiveUS20180143633A1Reduce processing bottleneckReduce performanceAutonomous decision making processError detection/correctionMulti processorComputer module
A multi-processor architecture for automated driving systems can be used to improve performance and provide design flexibility. For example, a multi-processor architecture can be used to implement command generation and safety functionality in different processors. The command generation processor can be a high performing processor compared with the safety processor. The safety processor can verify the safety of commands output from the command generation processor and provide additional I / O channels that are typically absent on high performing processors. Additionally, processing of some sensor data can be moved to expansion modules with additional processors to reduce bottlenecks and provide design flexibility for systems with different sensing requirements.
Owner:FARADAY&FUTURE INC
Apparatus, method, and system to provide a multiple processor architecture for server-based gaming
ActiveUS8266213B2Multiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingComputer architectureMulti processor
An architecture for an electronic gaming machine (EGM) includes multiple processors that separate game logic from game presentation. The multi-processor architecture includes a dedicated game logic engine and a dedicated presentation engine. A first processor having the game logic engine is adapted to handle the input / output (I / O), peripherals, communications, accounting, critical gaming and other game logic, power hit tolerances, protocols to other systems, and other tasks related to operation of the EGM. A second processor is adapted to running a presentation engine. The second processor receives commands from the first processor to present game-oriented outcome and results.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Multi-processor architecture implementing a serial switch and method of operating same
ActiveUS8335884B2Easy to upgradeImprove processor performanceEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingMulti processorDatapath
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
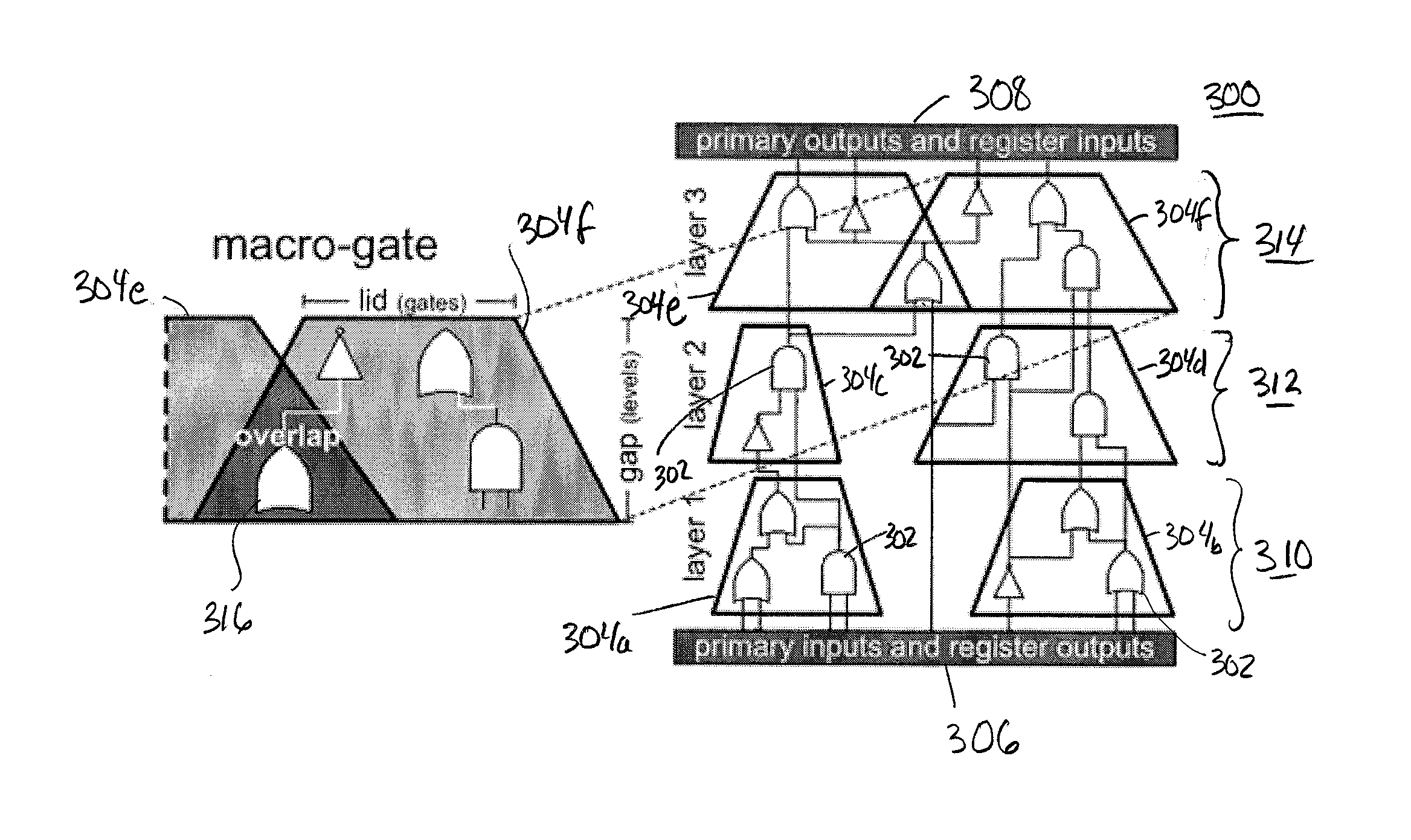
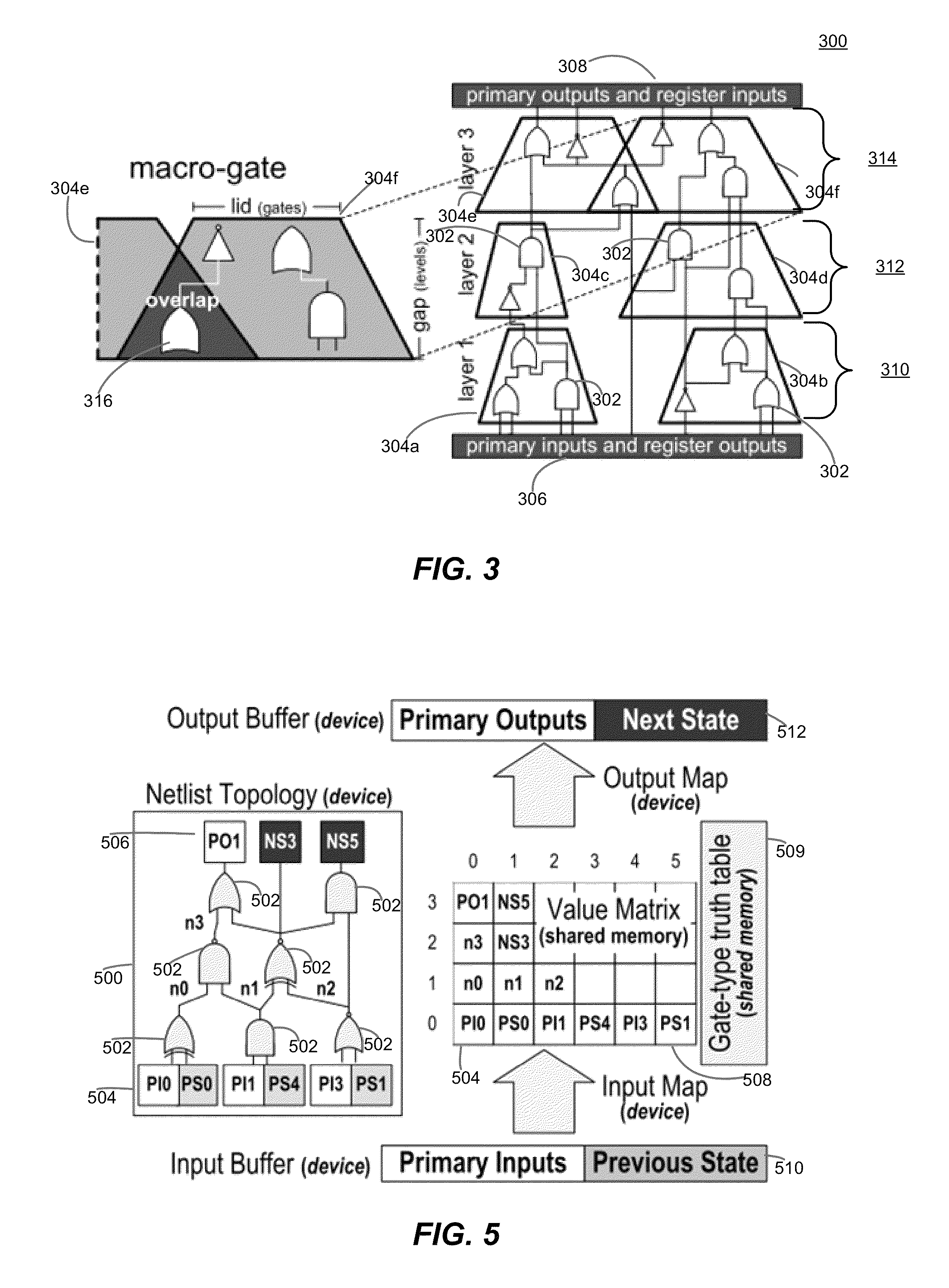
Gate-Level Logic Simulator Using Multiple Processor Architectures
ActiveUS20110257955A1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsSimd processorCluster group
Techniques for simulating operation of a connectivity level description of an integrated circuit design are provided, for example, to simulate logic elements expressed through a netlist description. The techniques utilize a host processor selectively partitioning and optimizing the descriptions of the integrated circuit design for efficient simulation on a parallel processor, more particularly a SIMD processor. The description may be segmented into cluster groups, for example macro-gates, formed of logic elements, where the cluster groups are sized for parallel simulation on the parallel processor. Simulation may occur in an oblivious as well as event-driven manner, depending on the implementation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Thread optimized multiprocessor architecture
ActiveUS8984256B2Increase computing speedImprove execution speedSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsInstruction analysisComputer memoryMultiprocessor architecture
In one aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors; wherein each of the processors is operable to process a de minimis instruction set, and wherein each of the processors comprises local caches dedicated to each of at least three specific registers in the processor. In another aspect, the invention comprises a system comprising: (a) a plurality of parallel processors on a single chip; and (b) computer memory located on the chip and accessible by each of the processors, wherein each of the processors is operable to process an instruction set optimized for thread-level parallel processing and wherein each processor accesses the internal data bus of the computer memory on the chip and the internal data bus is the width of one row of the memory.
Owner:BLANKENSHIP BETH
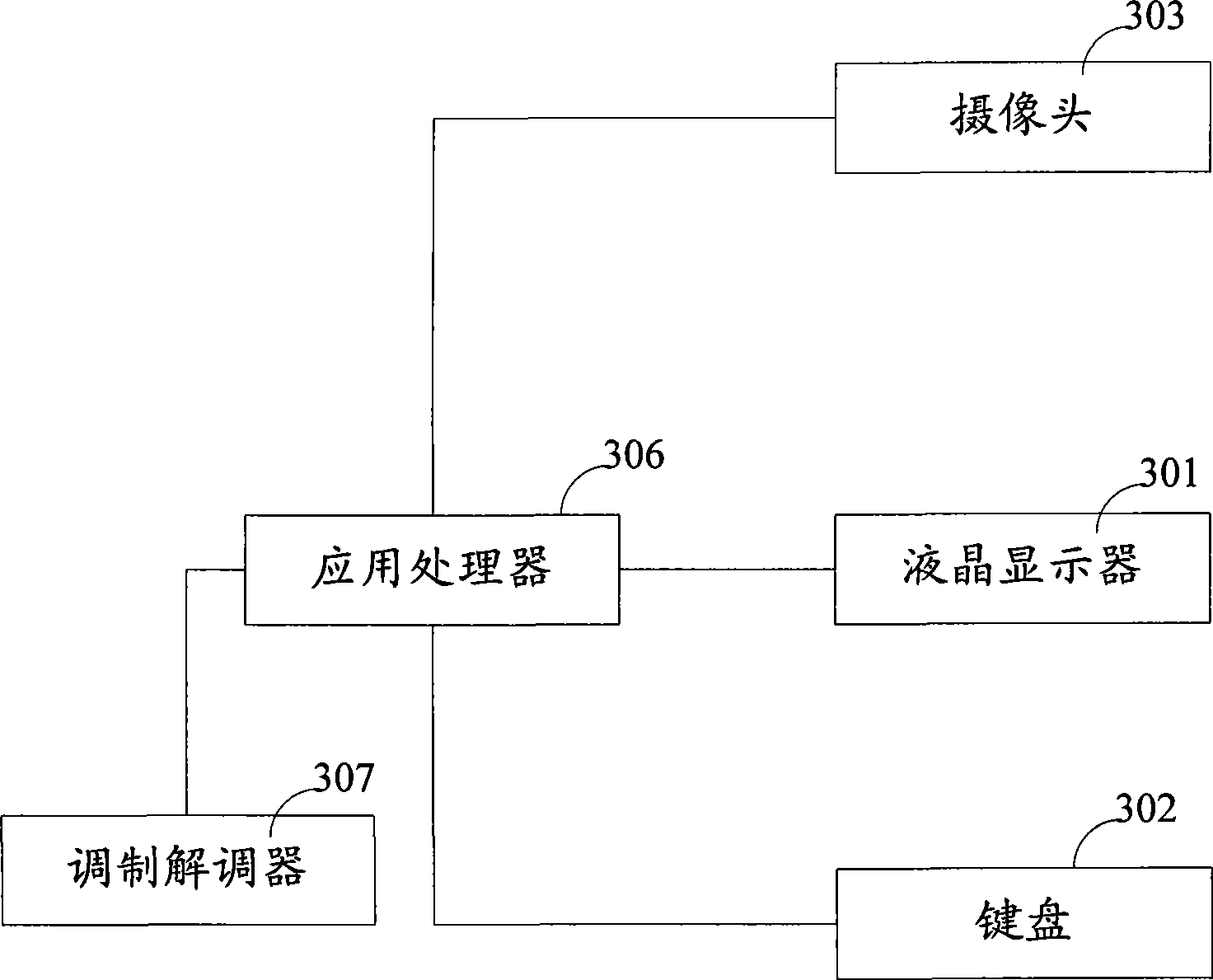
Method and terminal for processing information by multi processors
InactiveCN101441510AIncrease profitReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationInformation processingMulti processor
The invention provides a method and a terminal for realizing information processing by a multiprocessor. The method is applied to the terminal comprising at least two processor units, and the method at least comprises the following steps: generating an information processing request; previously calculating total power consumption of a system when each processor unit executes the information processing request respectively, according to predetermined algorithmic logic; and selecting the processor unit of which the total power consumption of the system is smaller than a threshold value to execute the information processing request. In the embodiment of the invention, the method has the advantages of reducing power consumption of the terminal with the multiprocessor architecture and improving utilization ratio of each processor in the terminal of the multiprocessor.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
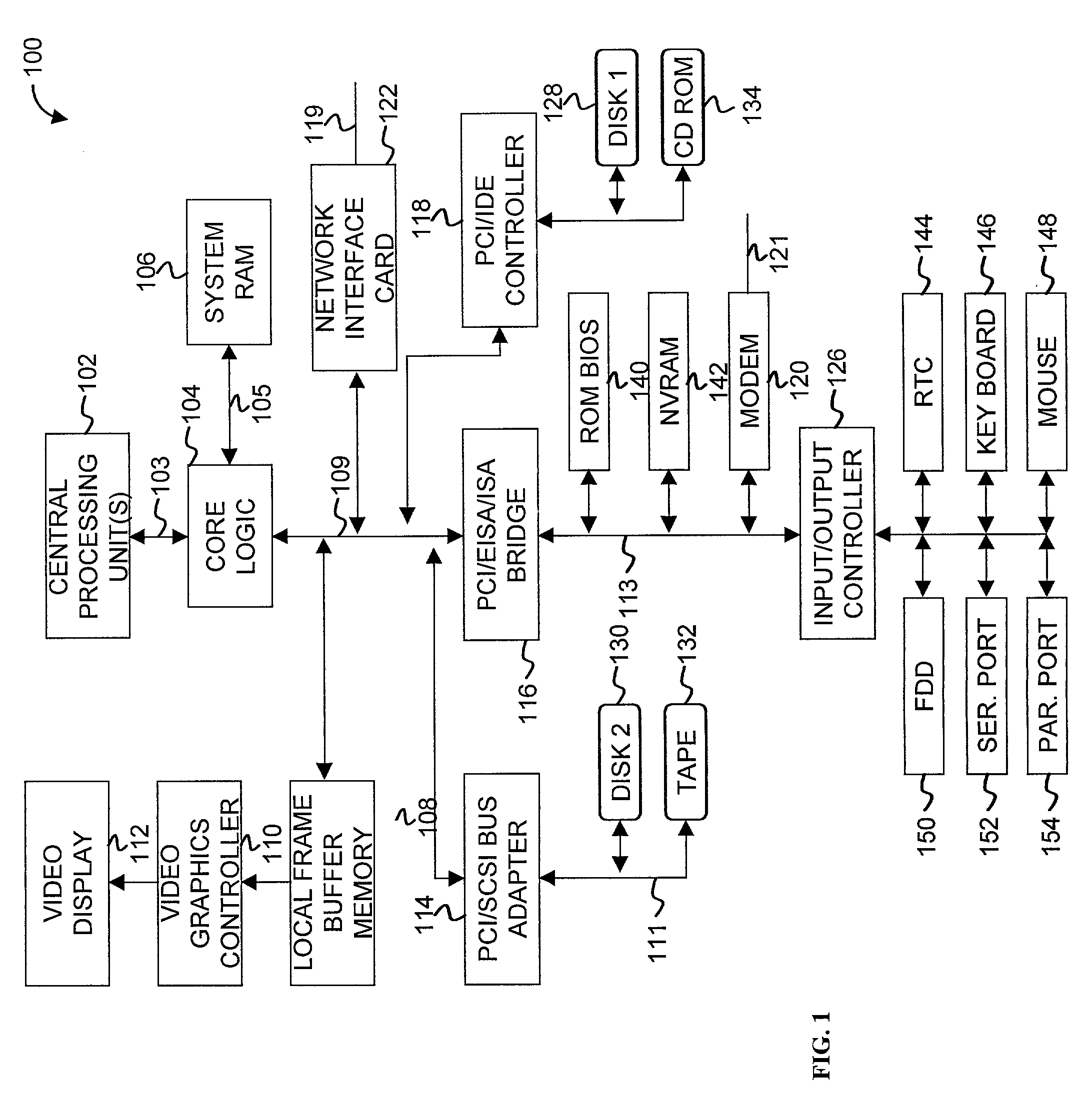
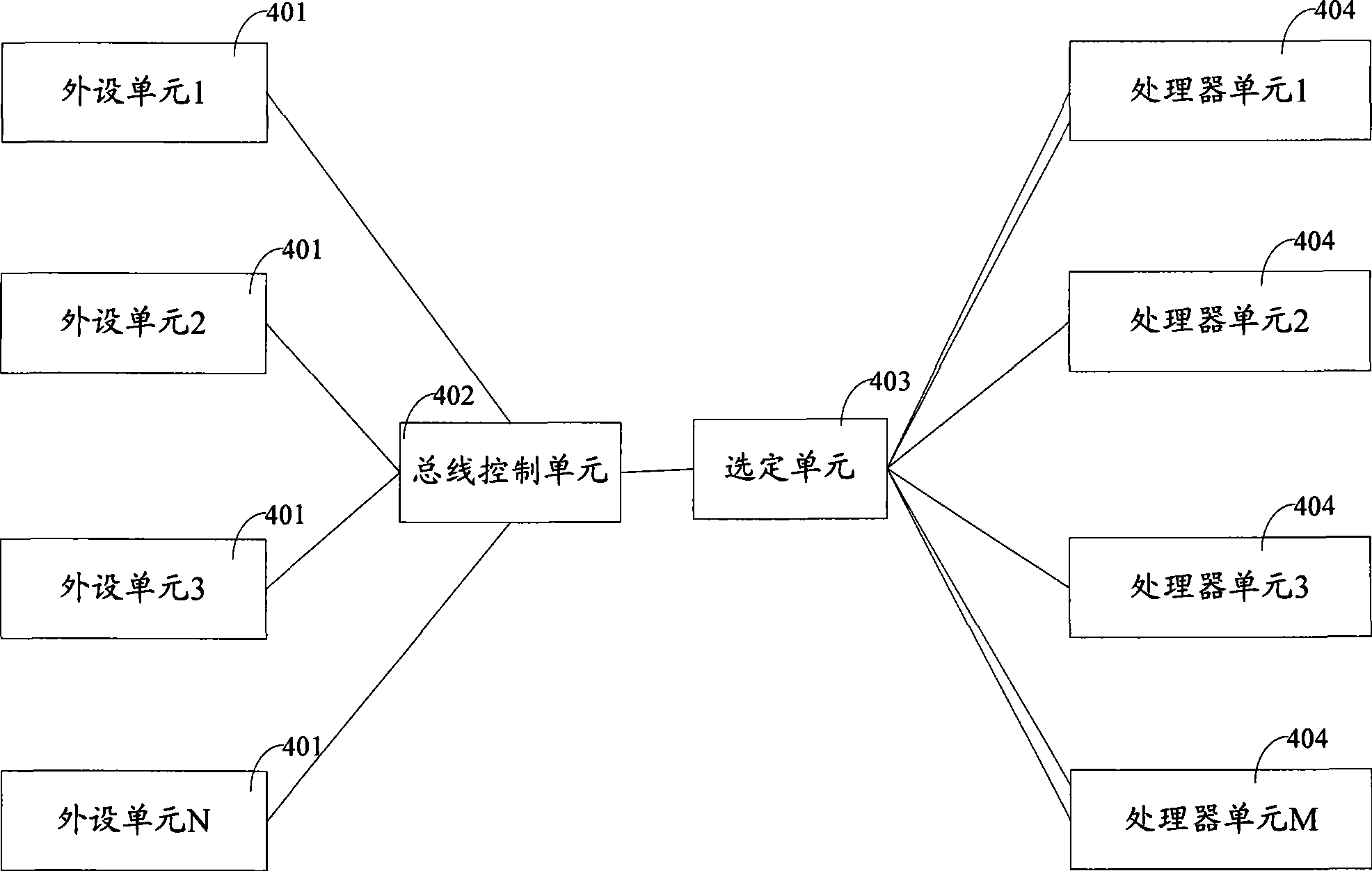
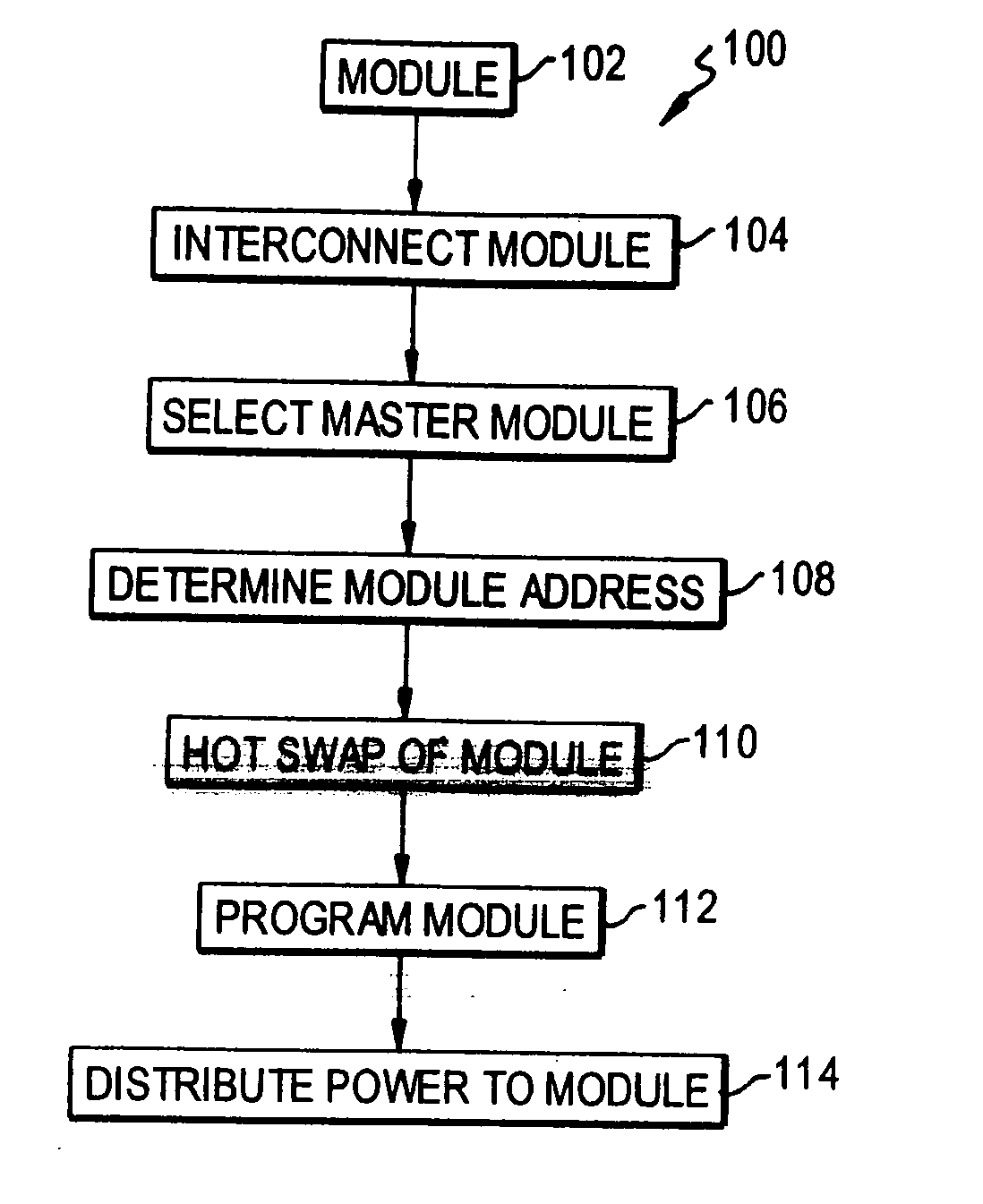
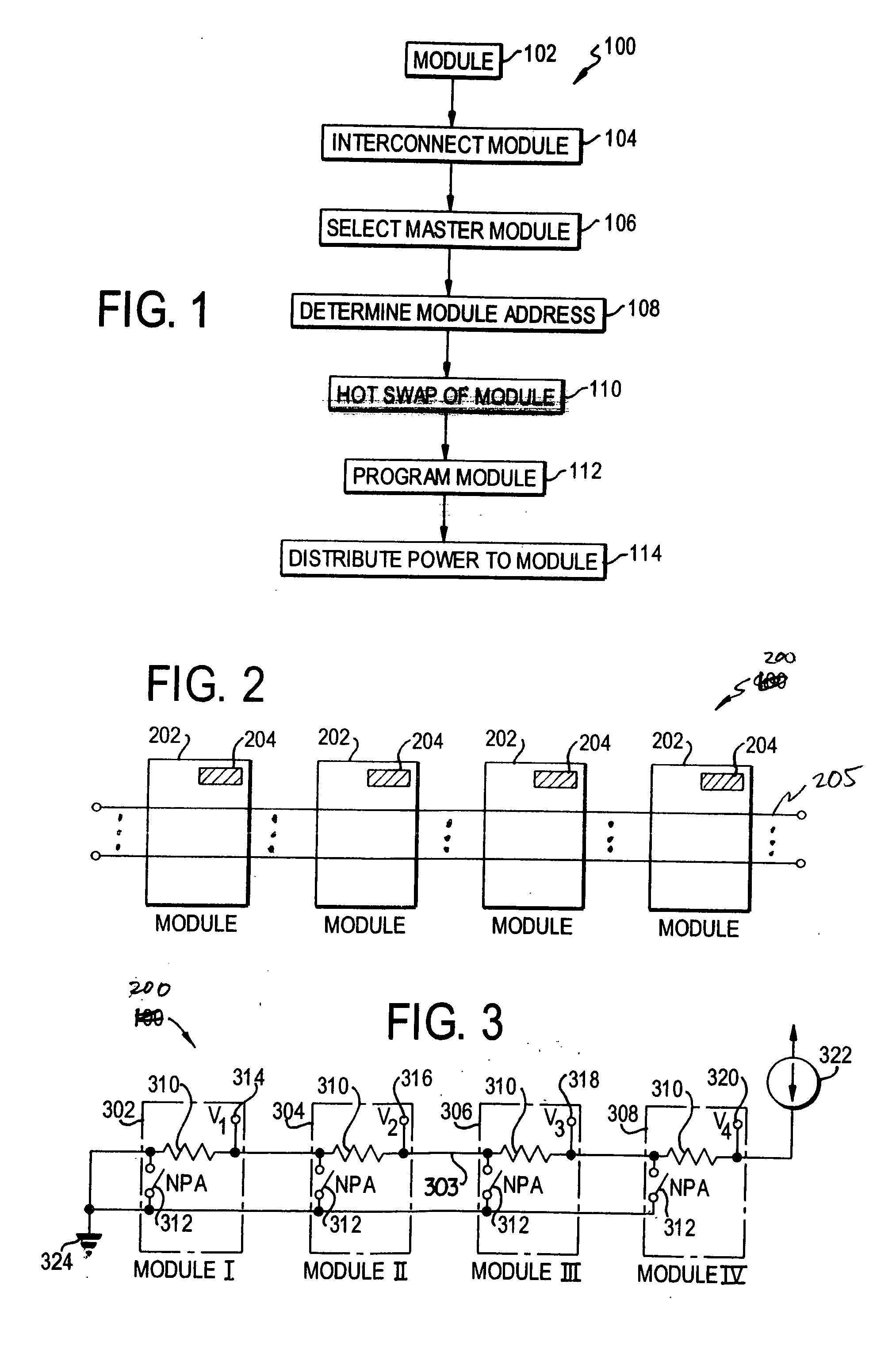
Modular programmable automation controller with multi-processor architecture
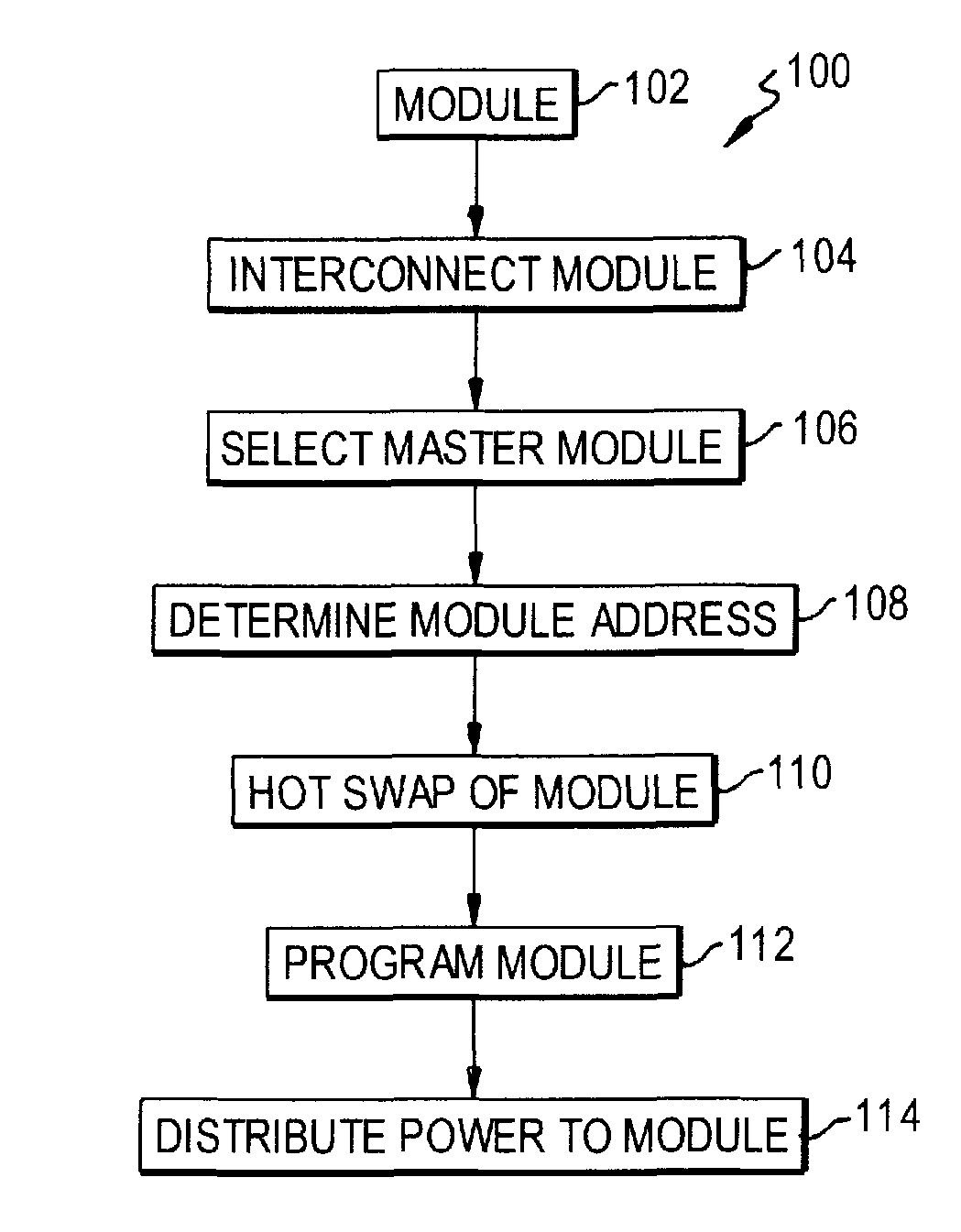
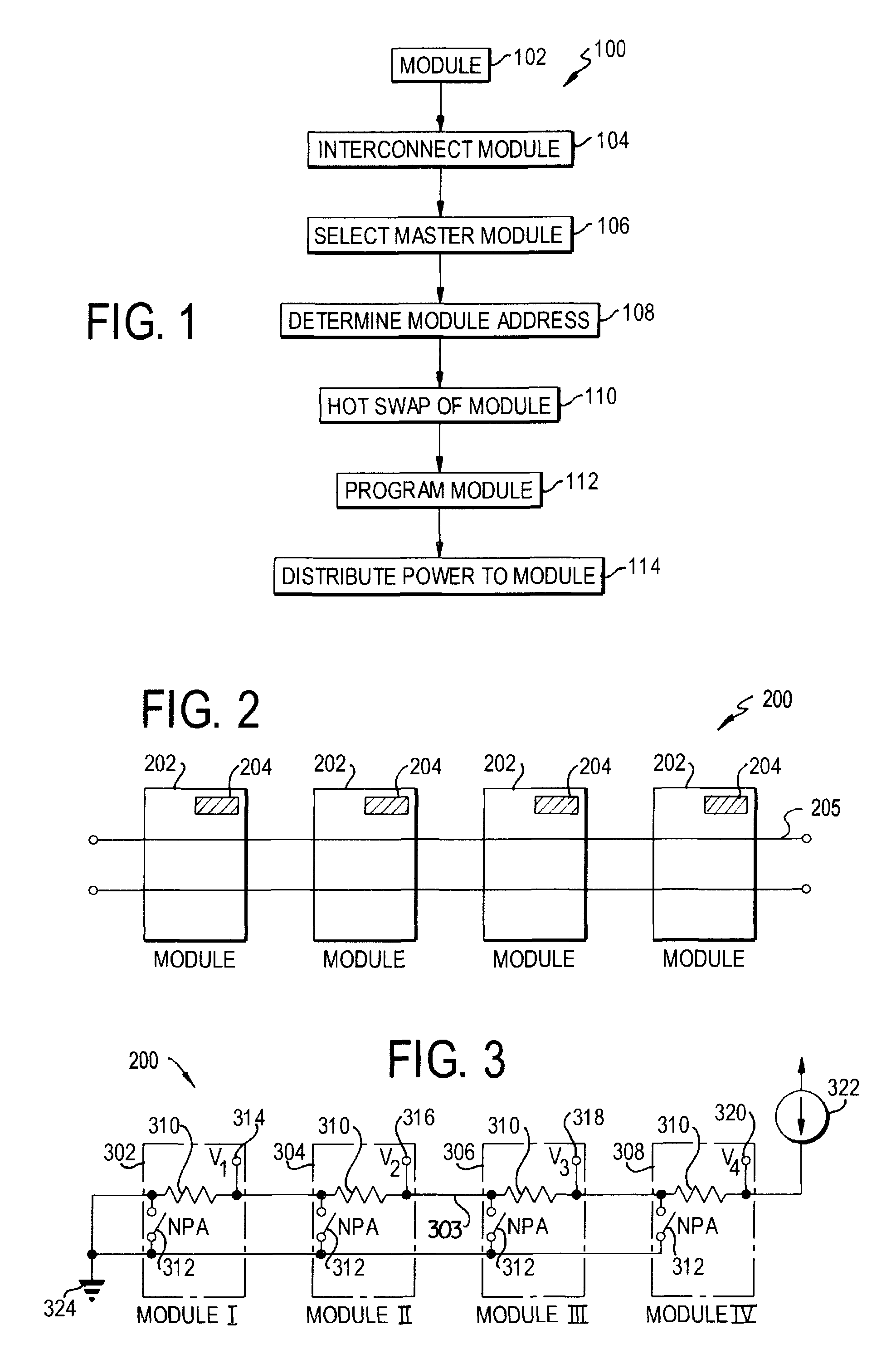
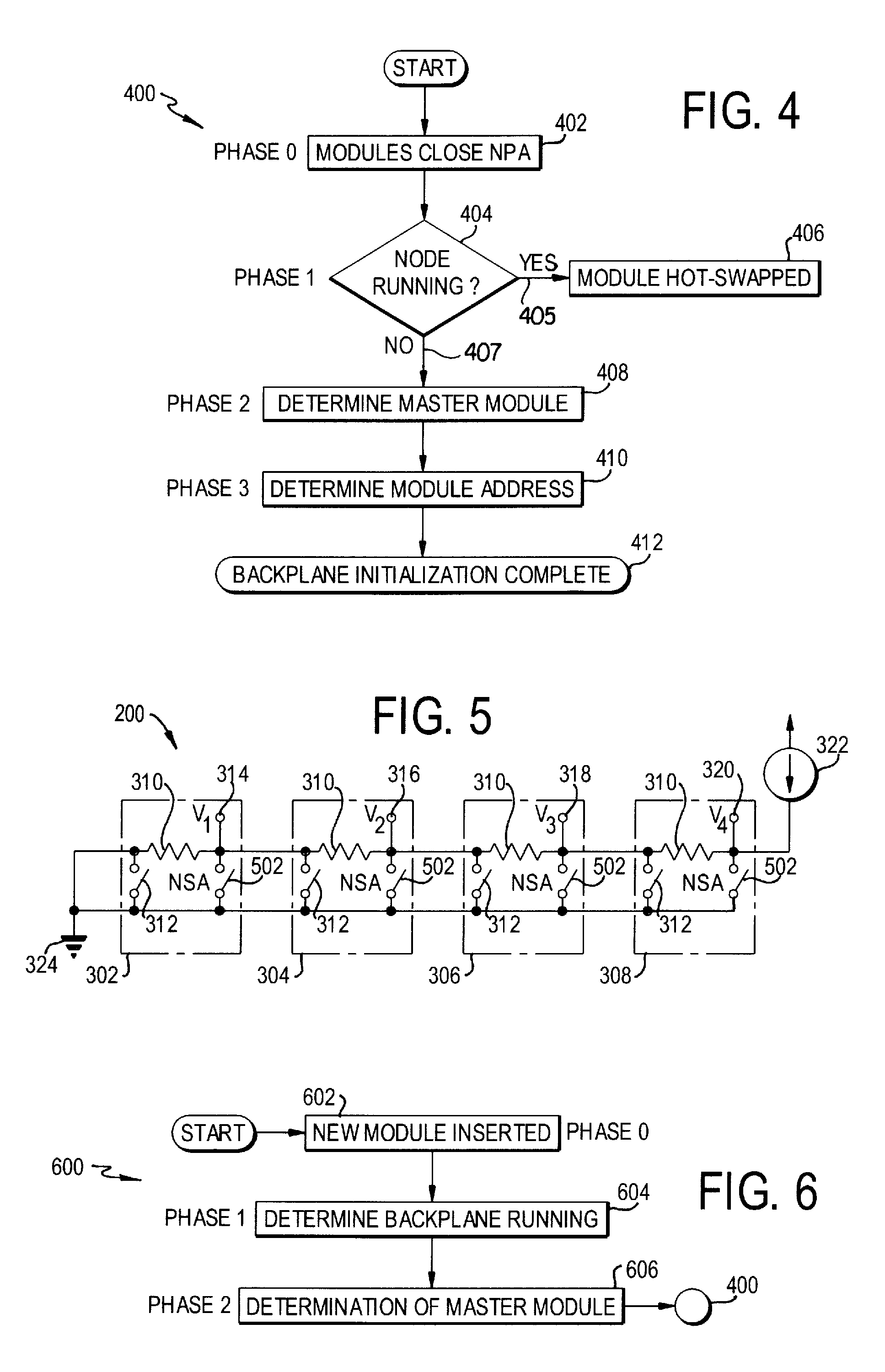
An apparatus and method for forming a control node in a programmable architecture, is disclosed. The node includes a plurality of user-programmable, microprocessor-based modules connected together. The modules are connected to create a parallel-processing environment with a selected functionality. Hot-swapping of the modules can be determined in the node. Power is distributed throughout the modules in the node. The modules may be automatically programmed to accommodate a target independent device.
Owner:FAIRMONT AUTOMATION
Work queue selection on a local processor within a multiple processor architecture
A method and system is disclosed for selecting a work queue associated with a processor within a multiple processor architecture to assign a new task. A local and a remote queue availability flag is maintained to indicate a relative size of work queues, in relationship to a mean queue size, for each processor in a multiple processor architecture. In determining to which processor to assign a task, the processor evaluates its own queue size by examining its local queue availability flag and evaluates other processor's queue sizes by examining their remote queue availability flags. The local queue availability flags are maintained asynchronously from task assignment. Remote flags are maintained at time of task assignment. The presented algorithm provides improved local processor queue size determinations in systems where task distribution processes execute with lower priorities that other tasks.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Modular programmable automation controller with multi-processor architecture
An apparatus and method for forming a control node in a programmable architecture, is disclosed. The node includes a plurality of user-programmable, microprocessor-based modules connected together. The modules are connected to create a parallel-processing environment with a selected functionality. Hot-swapping of the modules can be determined in the node. Power is distributed throughout the modules in the node. The modules may be automatically programmed to accommodate a target independent device.
Owner:FAIRMONT AUTOMATION
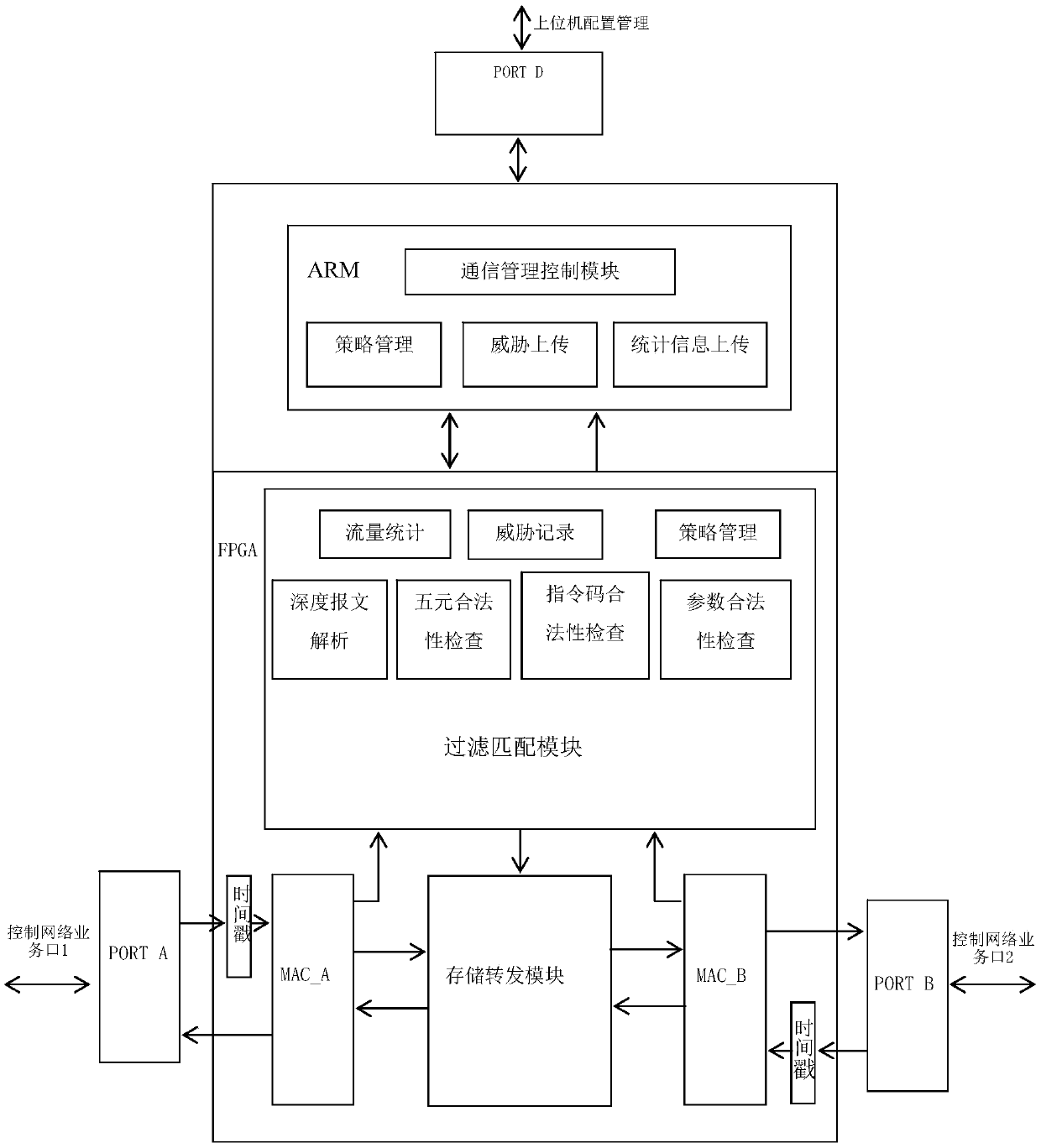
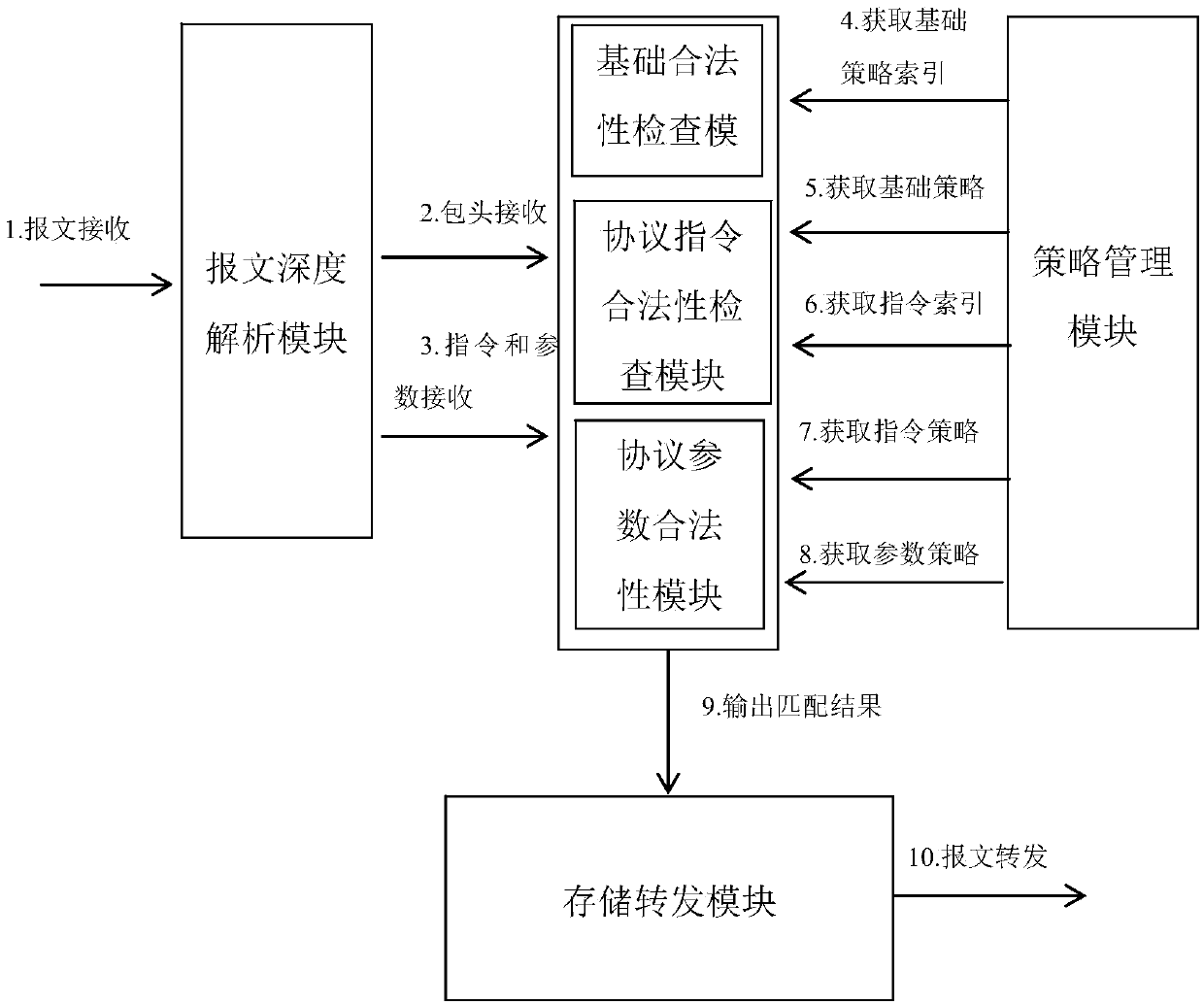
Firewall based on multiprocessor architecture
ActiveCN109558366AResist attackReduce security threatsMultiple digital computer combinationsPlatform integrity maintainanceService flowByte
A firewall based on a multiprocessor architecture comprises a main processor for processing a management flow of the firewall and a coprocessor which is used for carrying out parallel processing on the service flow of the firewall, and the main processor and the coprocessor are independent of each other and communicate with each other through a communication interface. The firewall provided by theinvention adopts a double-processor architecture, the two processors are independent of each other and are in limited communication through the communication interface, and when the main processor isattacked by a network or the main processor cannot work normally, the service processing unit of the coprocessor can still process the service flow normally. Compared with other industrial control firewalls, the firewall disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the reduced processing time reaches several orders of magnitudes, and the 100% throughput is achieved under the conditions of gigabit rate linear speed and 64-byte Ethernet message through the modules such as message deep analysis, basic strategy matching, industrial control protocol function code matching, industrial controlprotocol parameter matching, alarm information uploading and the like.
Owner:浙江国利网安科技有限公司
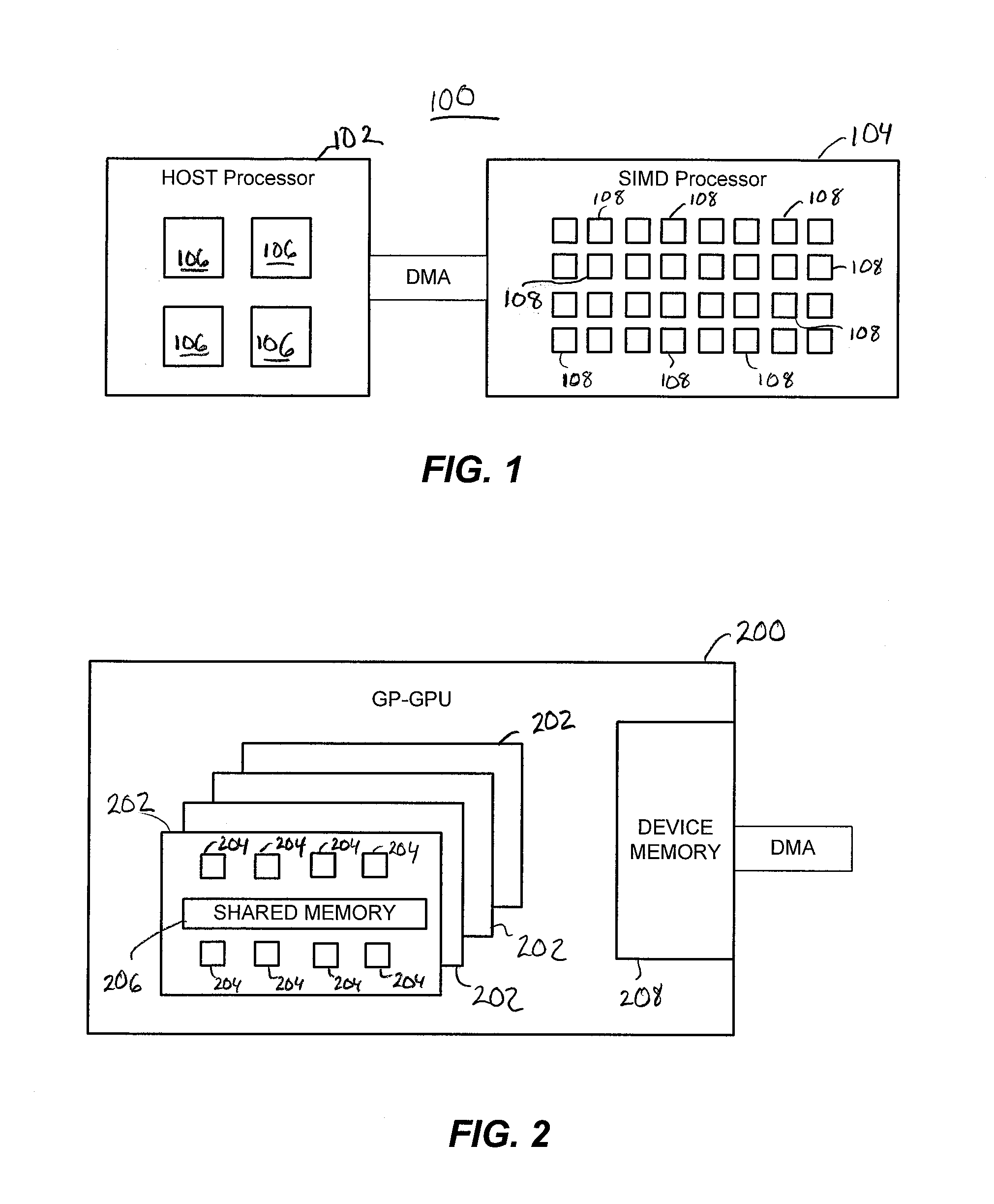
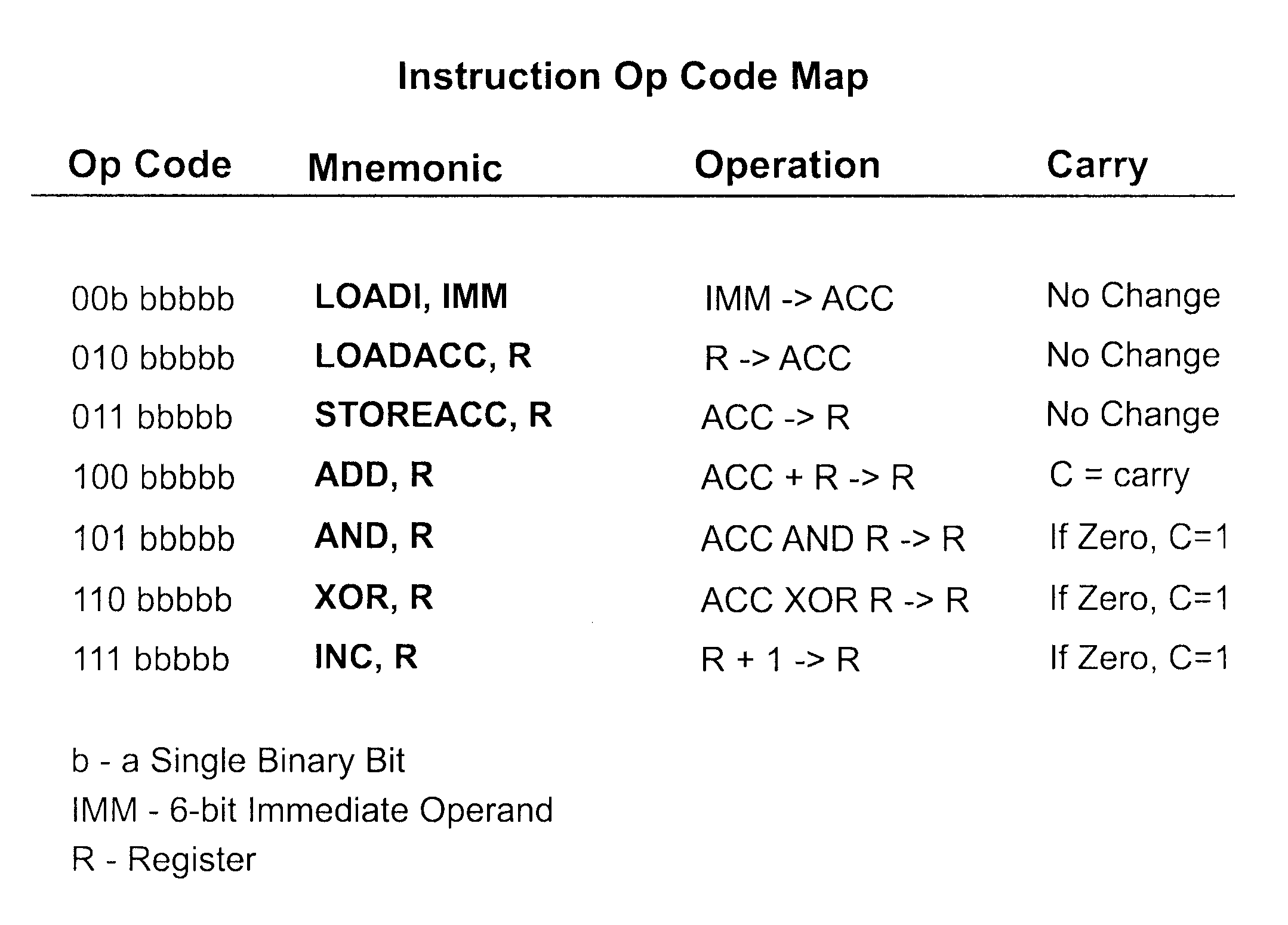
Gate-level logic simulator using multiple processor architectures
Techniques for simulating operation of a connectivity level description of an integrated circuit design are provided, for example, to simulate logic elements expressed through a netlist description. The techniques utilize a host processor selectively partitioning and optimizing the descriptions of the integrated circuit design for efficient simulation on a parallel processor, more particularly a SIMD processor. The description may be segmented into cluster groups, for example macro-gates, formed of logic elements, where the cluster groups are sized for parallel simulation on the parallel processor. Simulation may occur in an oblivious as well as event-driven manner, depending on the implementation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com