Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "Polar transmitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
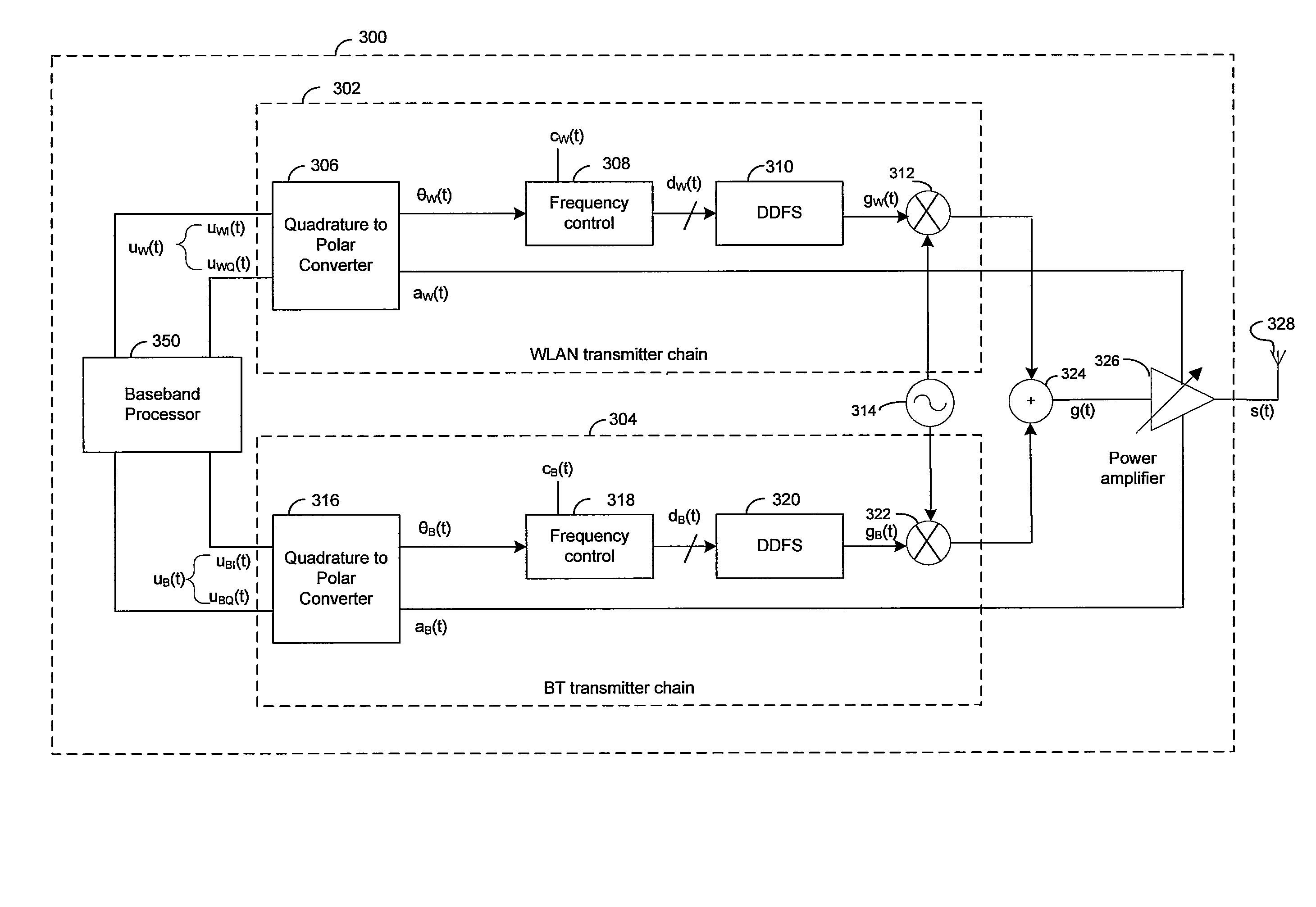
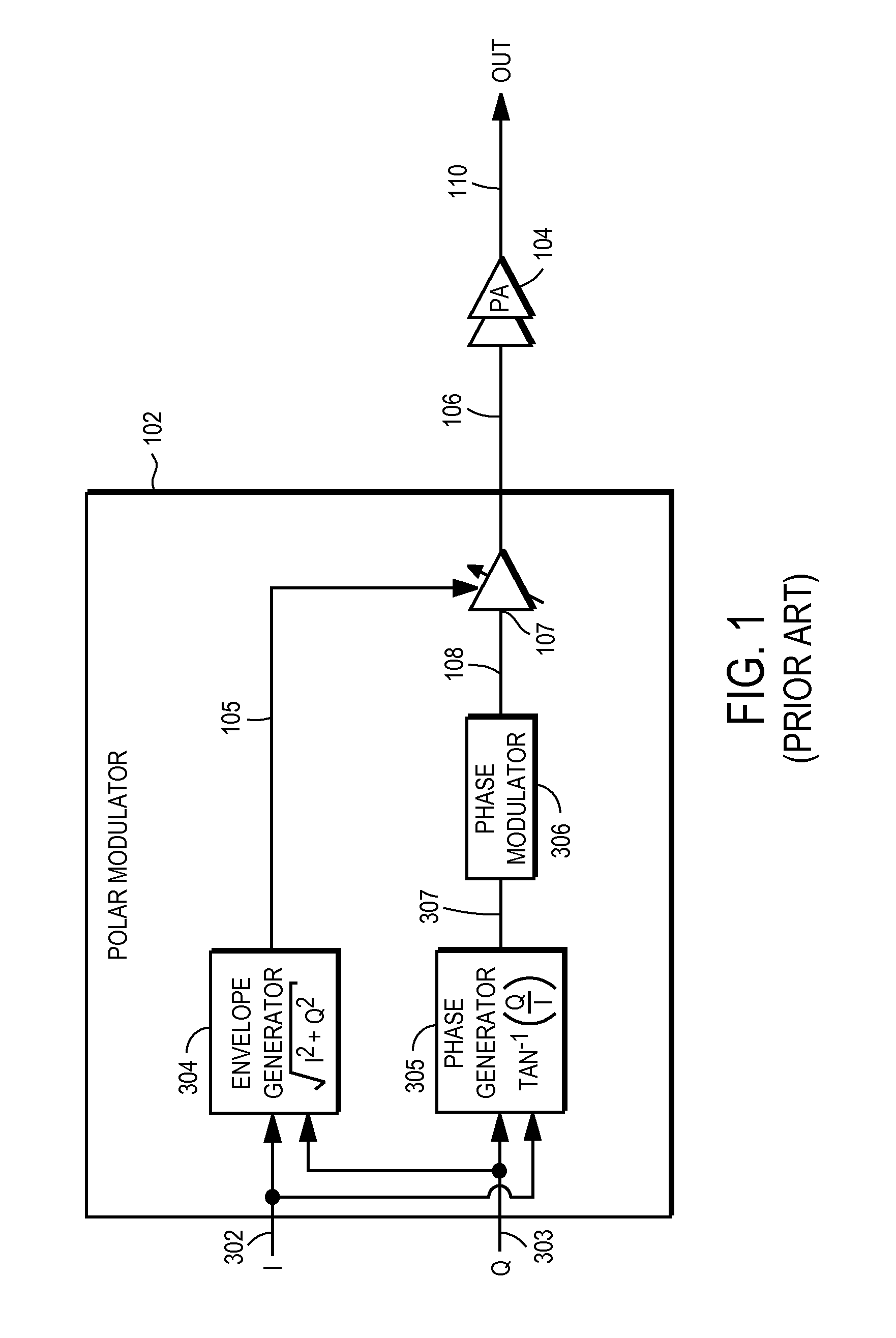
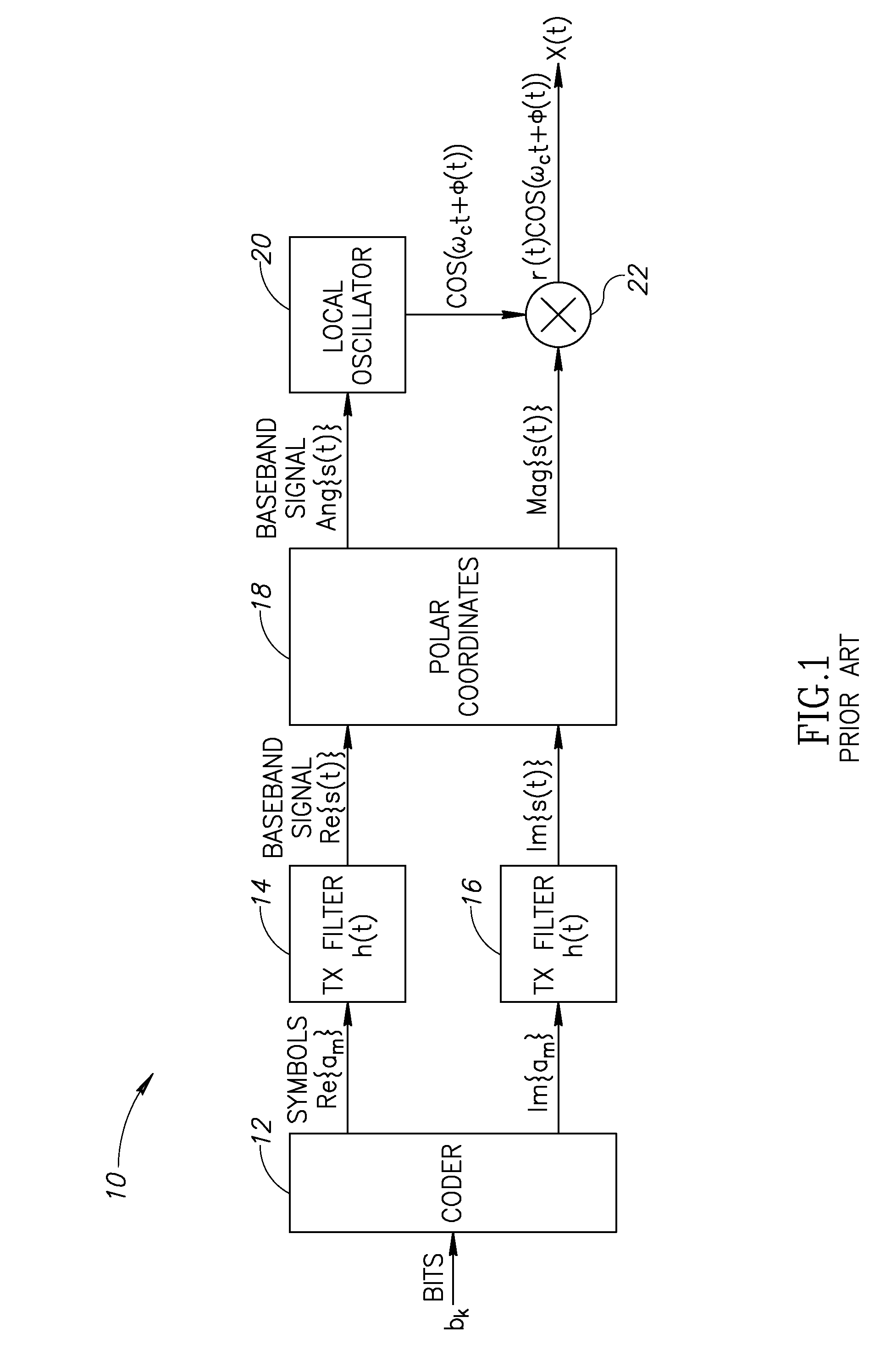
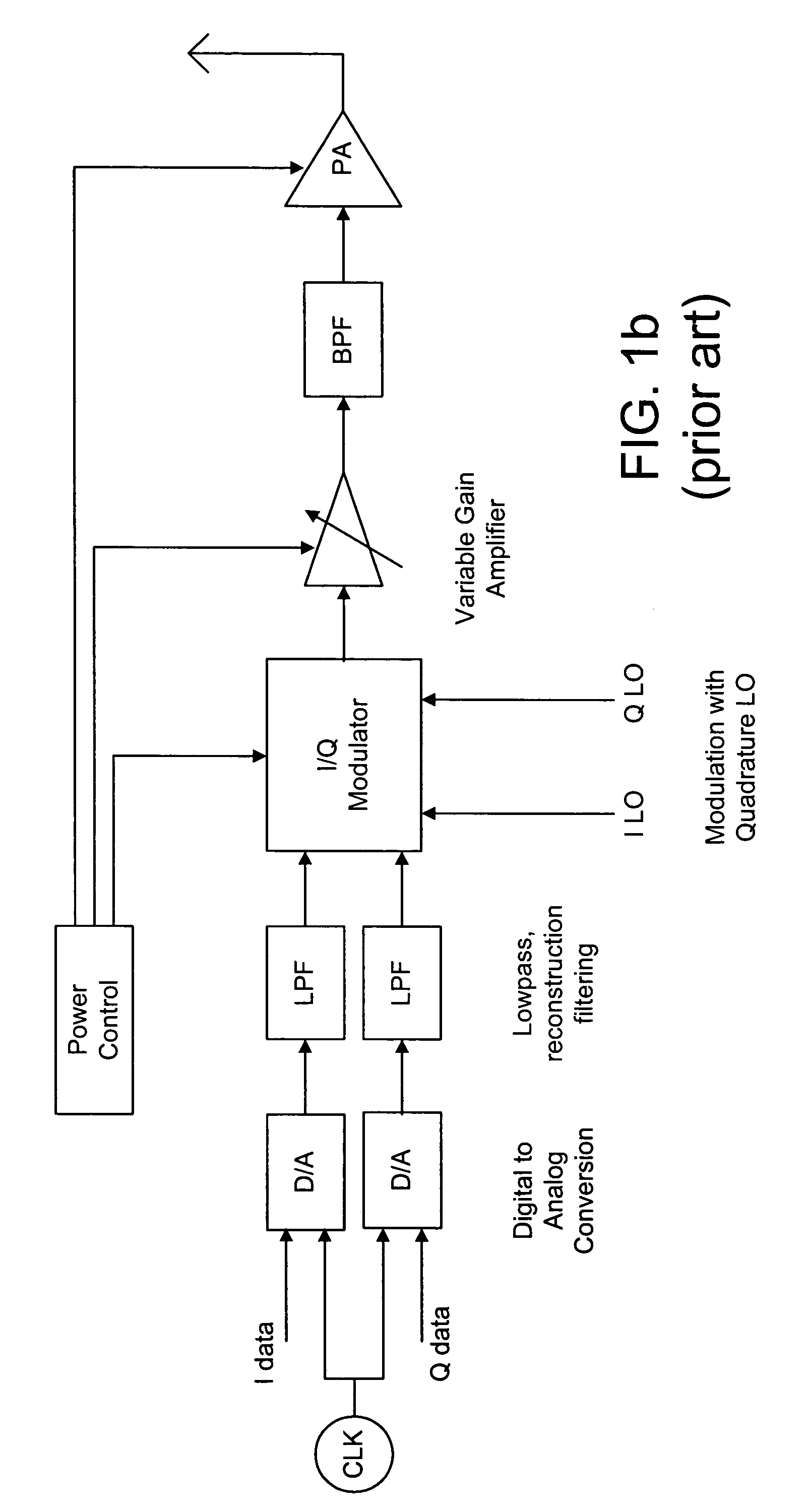
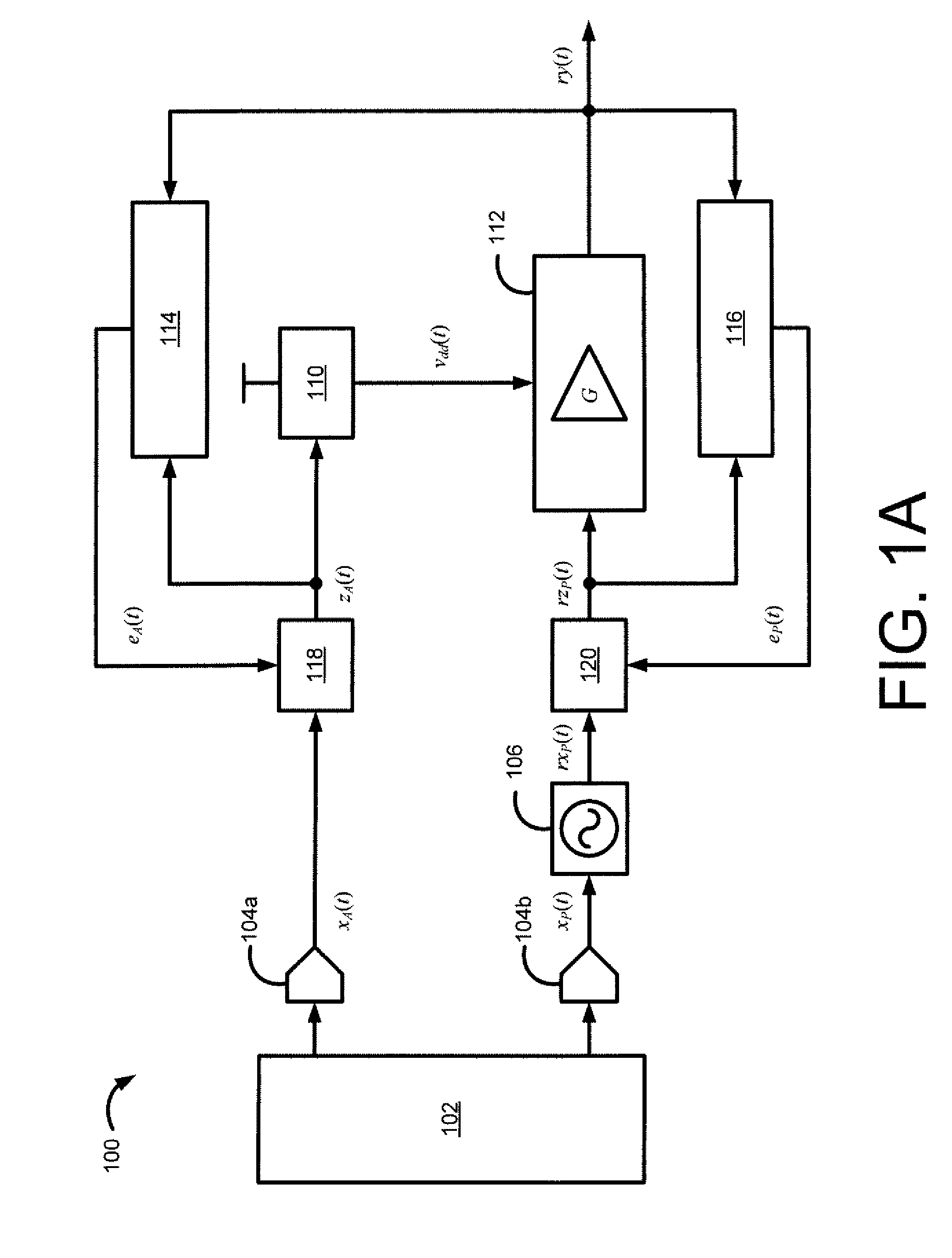
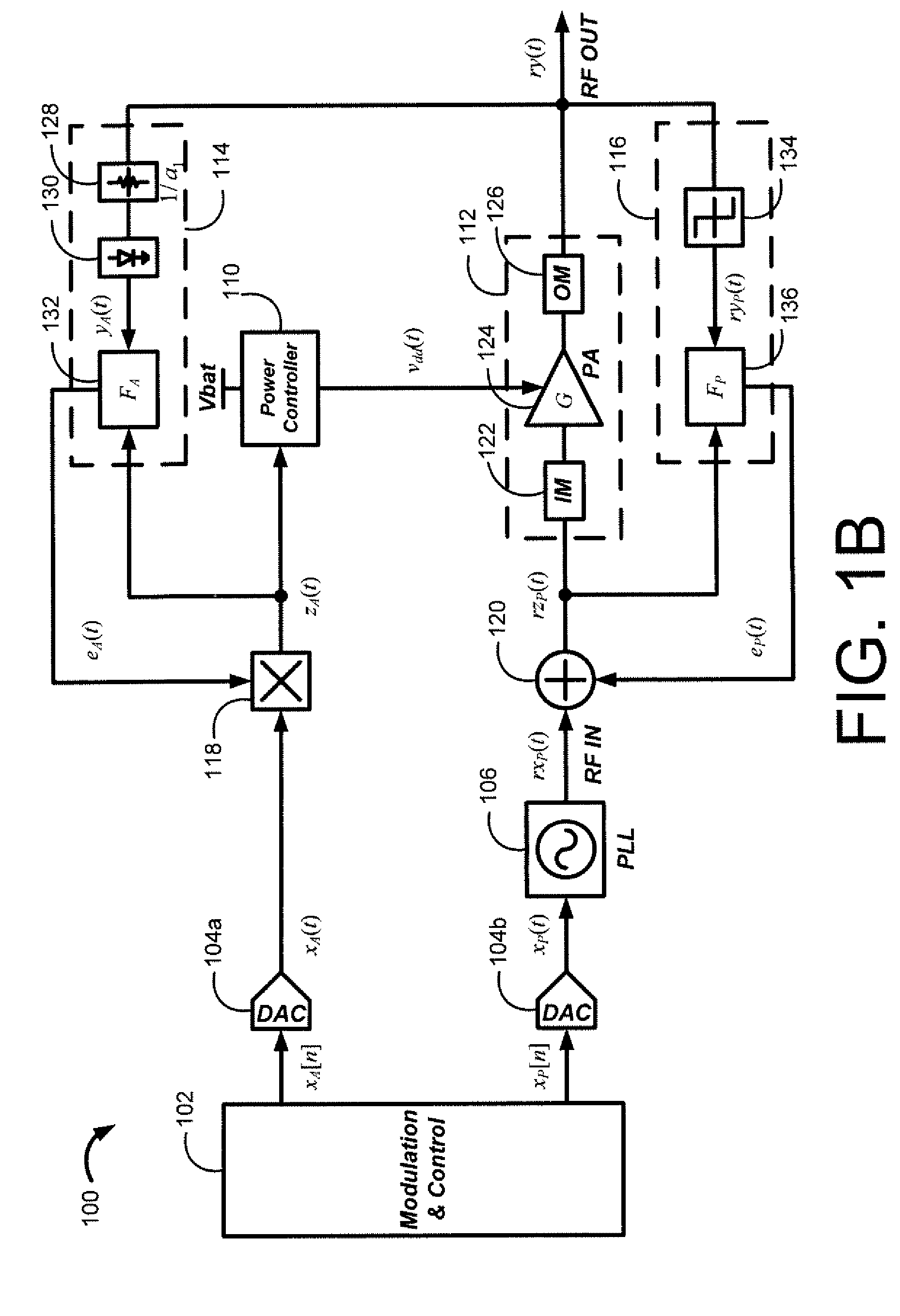
Method and system for a wideband polar transmitter
InactiveUS8036308B2Modulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsWireless communication protocolIntermediate frequency
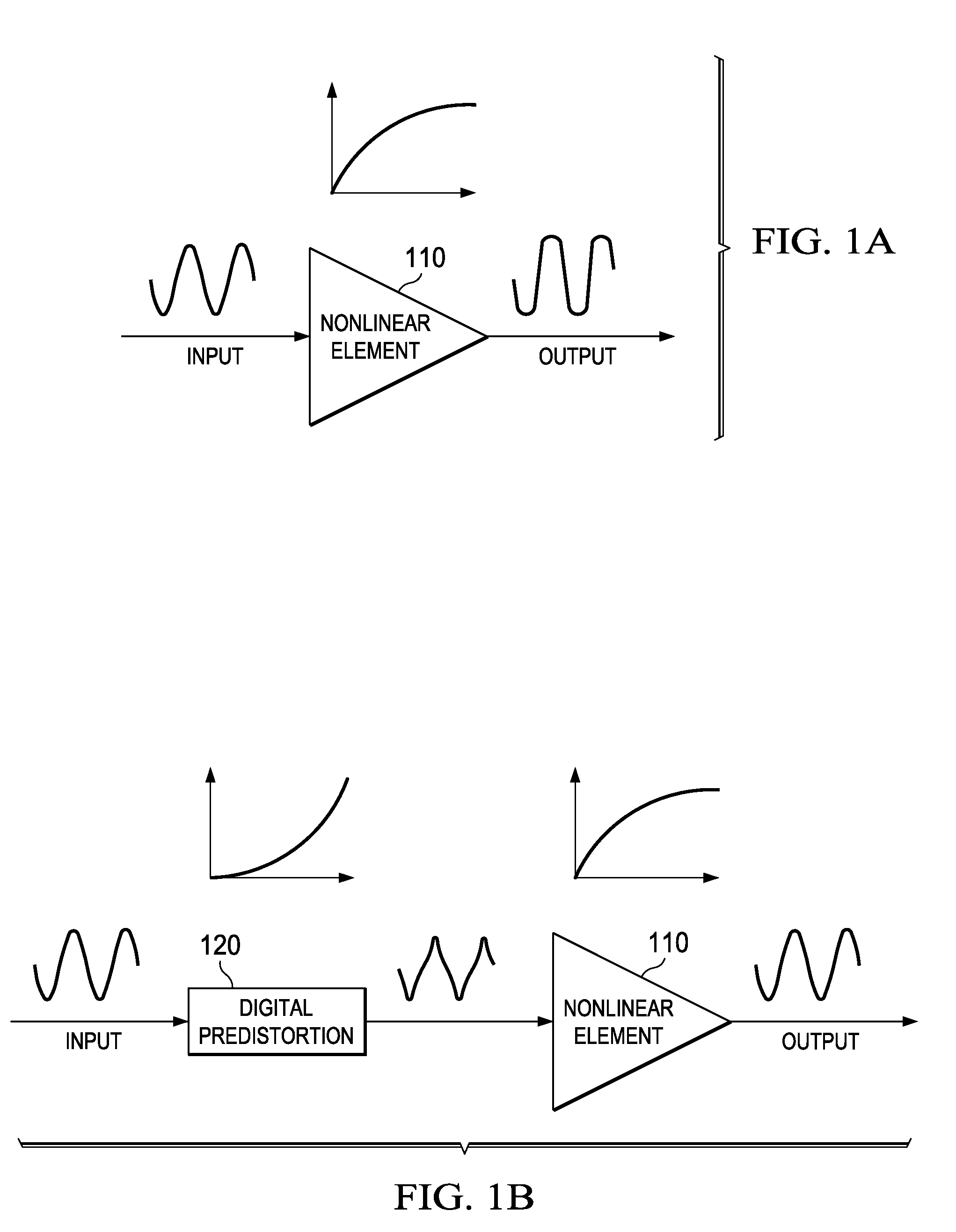
Certain aspects of a method and system for a wideband polar transmitter may be disclosed. Aspects of the method may include polar modulating a plurality of signals by generating a plurality of modulated intermediate frequency (IF) signals corresponding to each of a plurality of wireless communication protocols within a transmitter that handles the plurality of wireless communication protocols. The generated plurality of modulated IF signals may be upconverted to a plurality of radio frequency (RF) signals. The plurality of RF signals may be combined and the combined plurality of RF signals may be amplitude modulated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
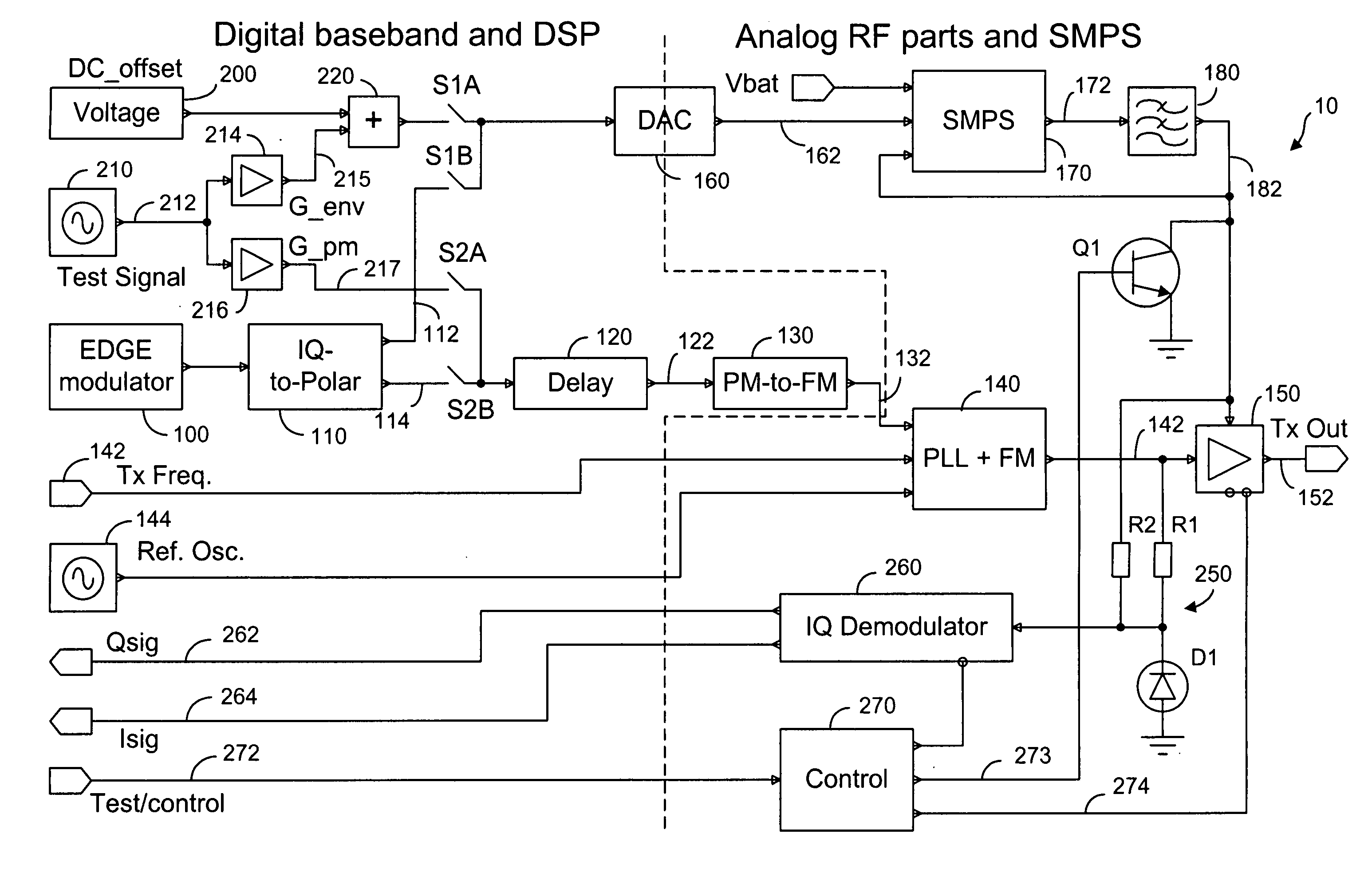
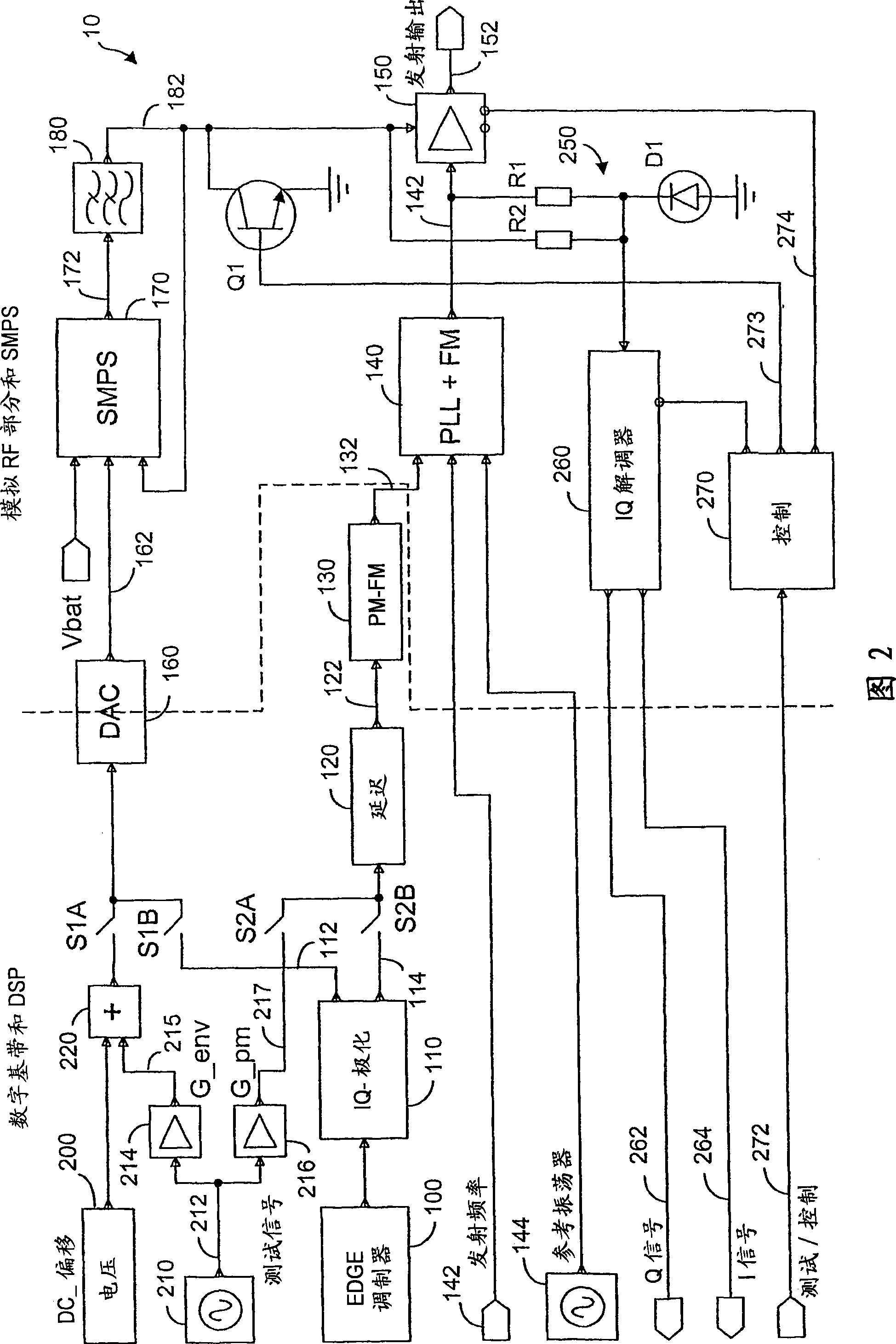
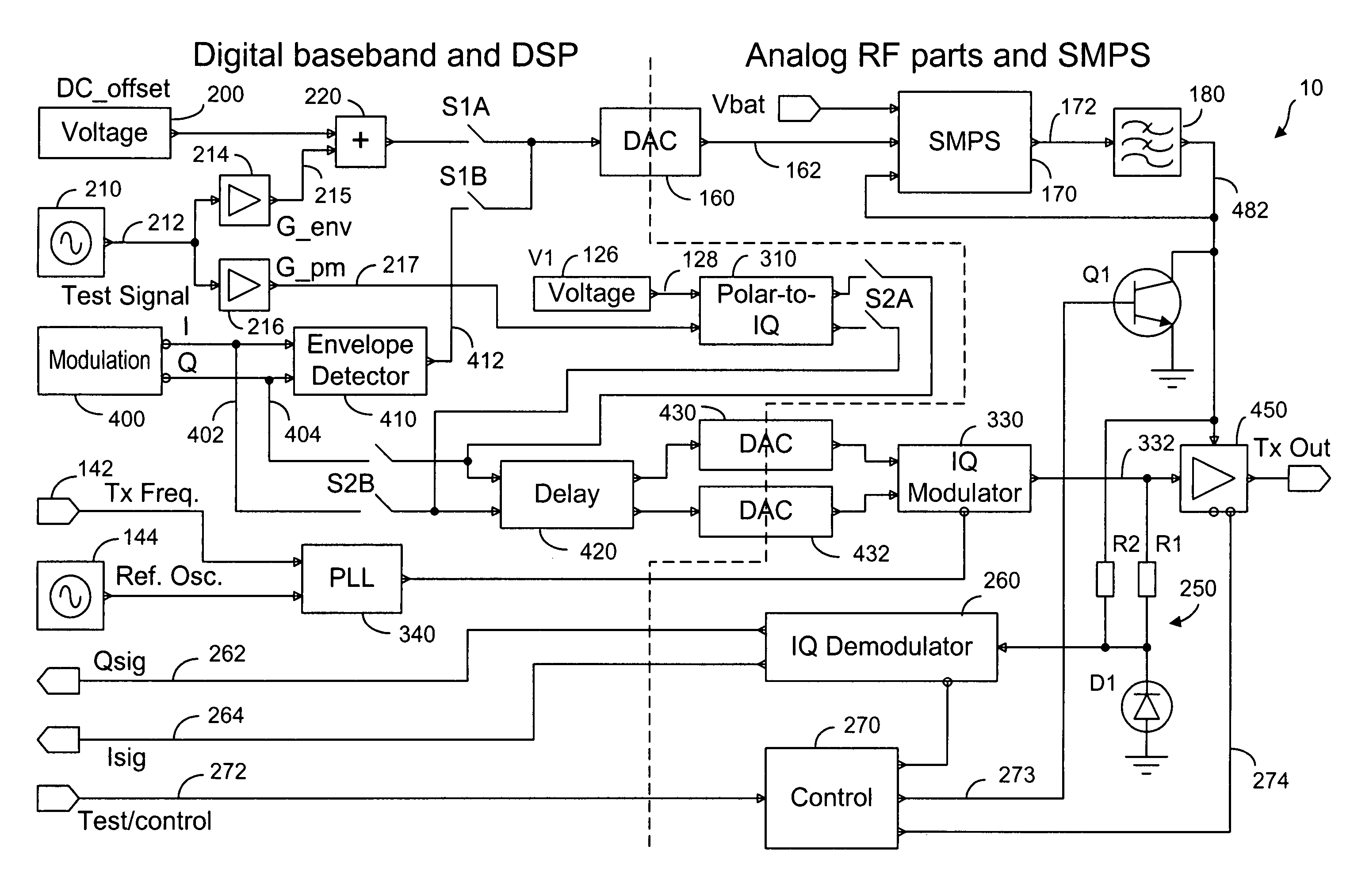
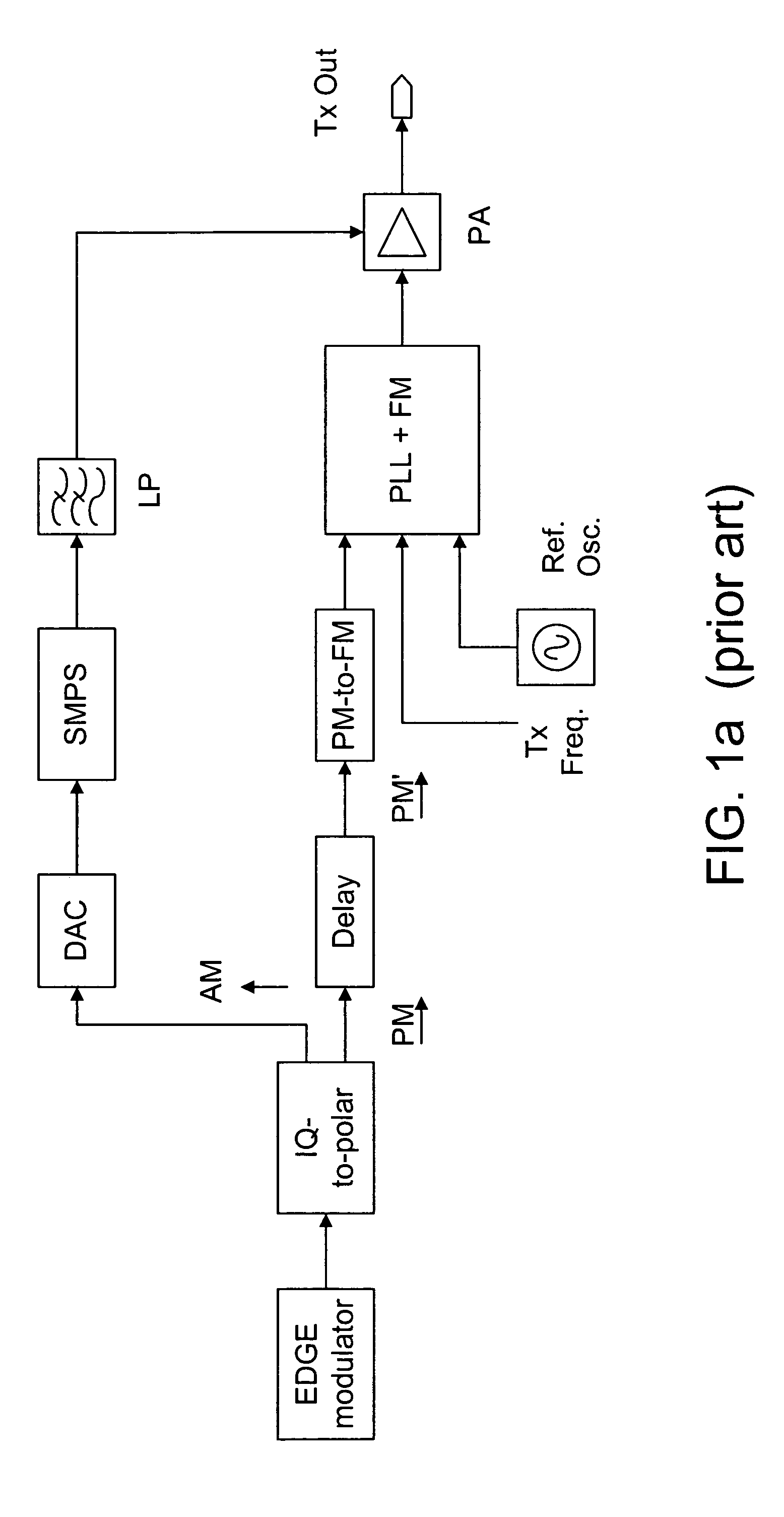
Method and system for transmitter envelope delay calibration
ActiveUS20070183532A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersPropagation delayTransceiver
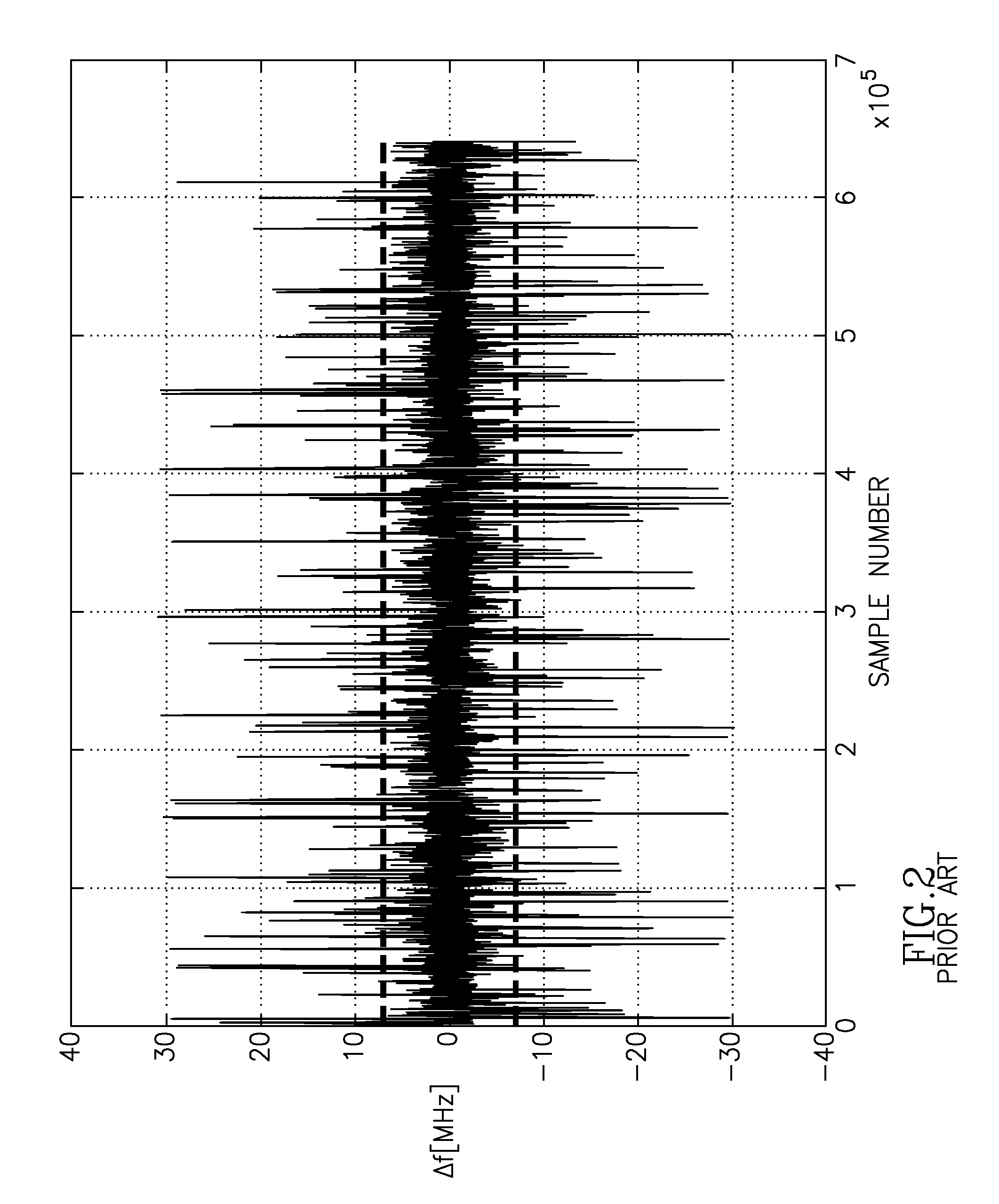
A test signal comprising a periodic waveform, such as a triangular waveform and sawtooth waveform, is used for propagation delay matching in a transceiver front-end. The test signal is separately fed to the envelope path and the RF path. At the power amplifier stage, a phase modulator is used to obtain the envelope signal and the phase modulated RF signal for demodulation by an IQ demodulator. At the output end of the IQ demodulator, the I-signal is measured while the delay block is adjusted in order to vary the propagation delay. When the propagation delay matching is correct, the peak-to-peak value of the I-signal is a minimum. Preferably, during calibration using the test signal, the transmitter RF power amplifier is disabled so that no spurious signals will be sent. The transmitter can be an EDGE polar transmitter, a non-EDGE transmitter or a EER polar transmitter.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Power amplifier controller with polar transmitter
ActiveUS7783269B2Reduce glitchesImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Power Amplifier Controller With Polar Transmitter
ActiveUS20100311365A1Reduce phase distortionMinimize the differenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
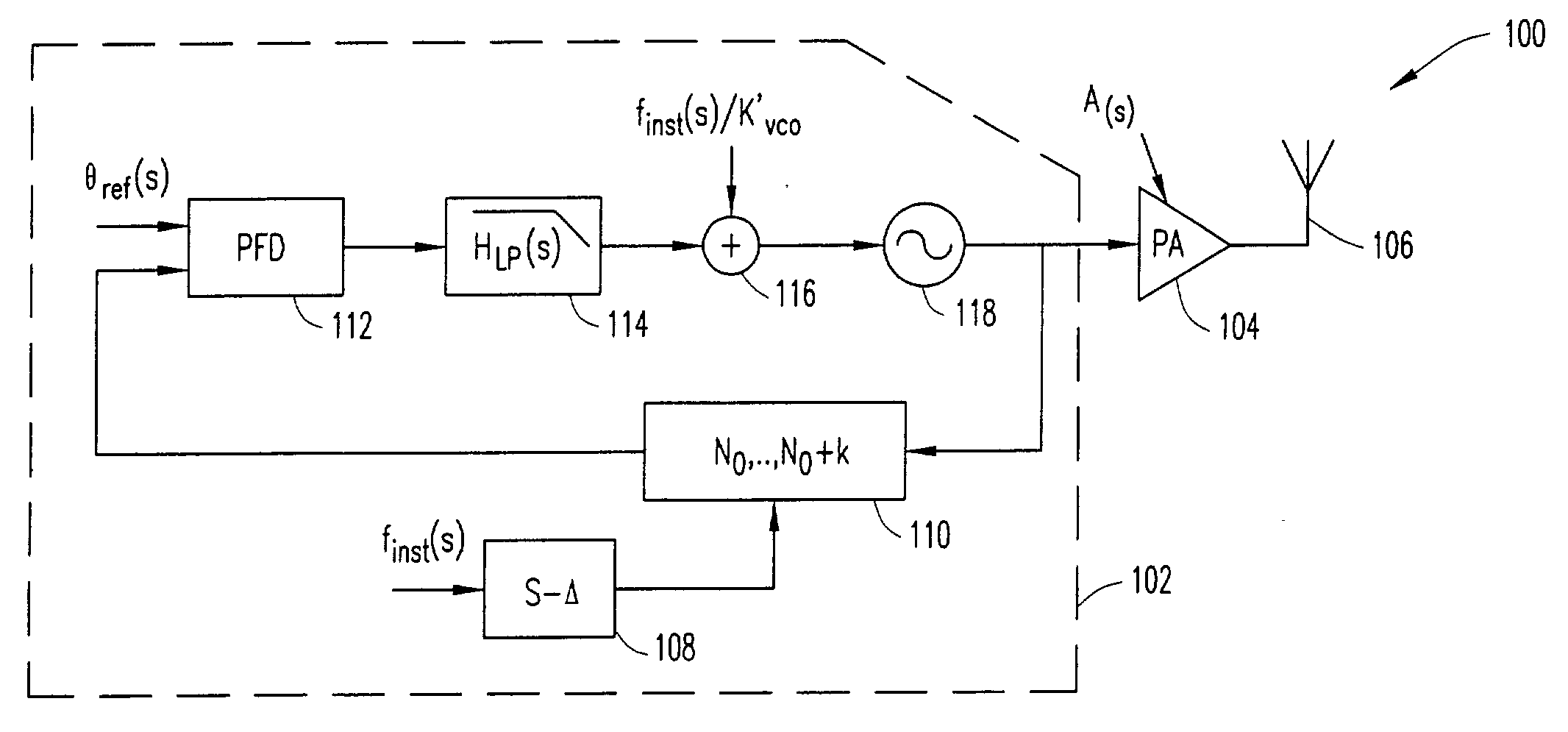
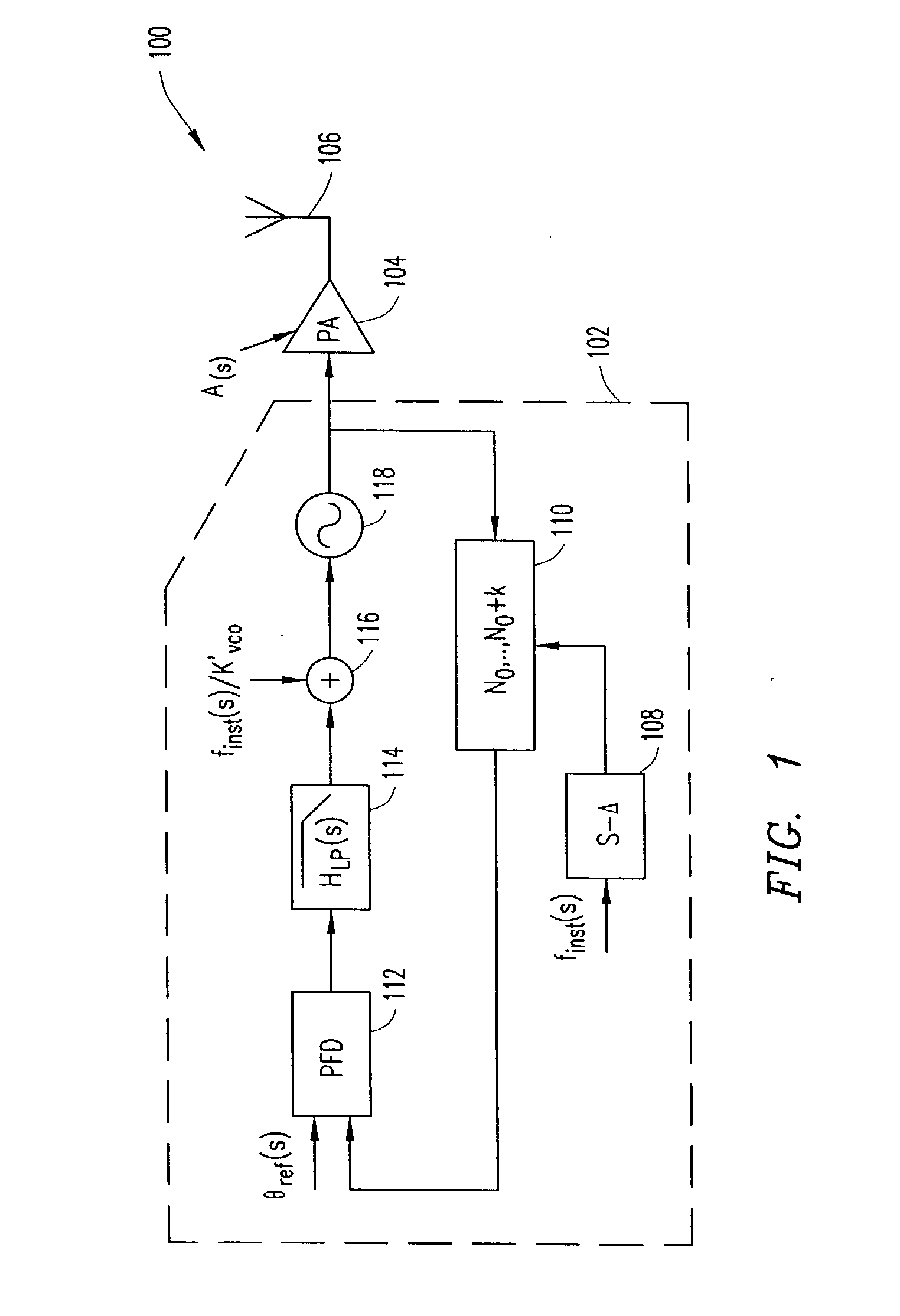
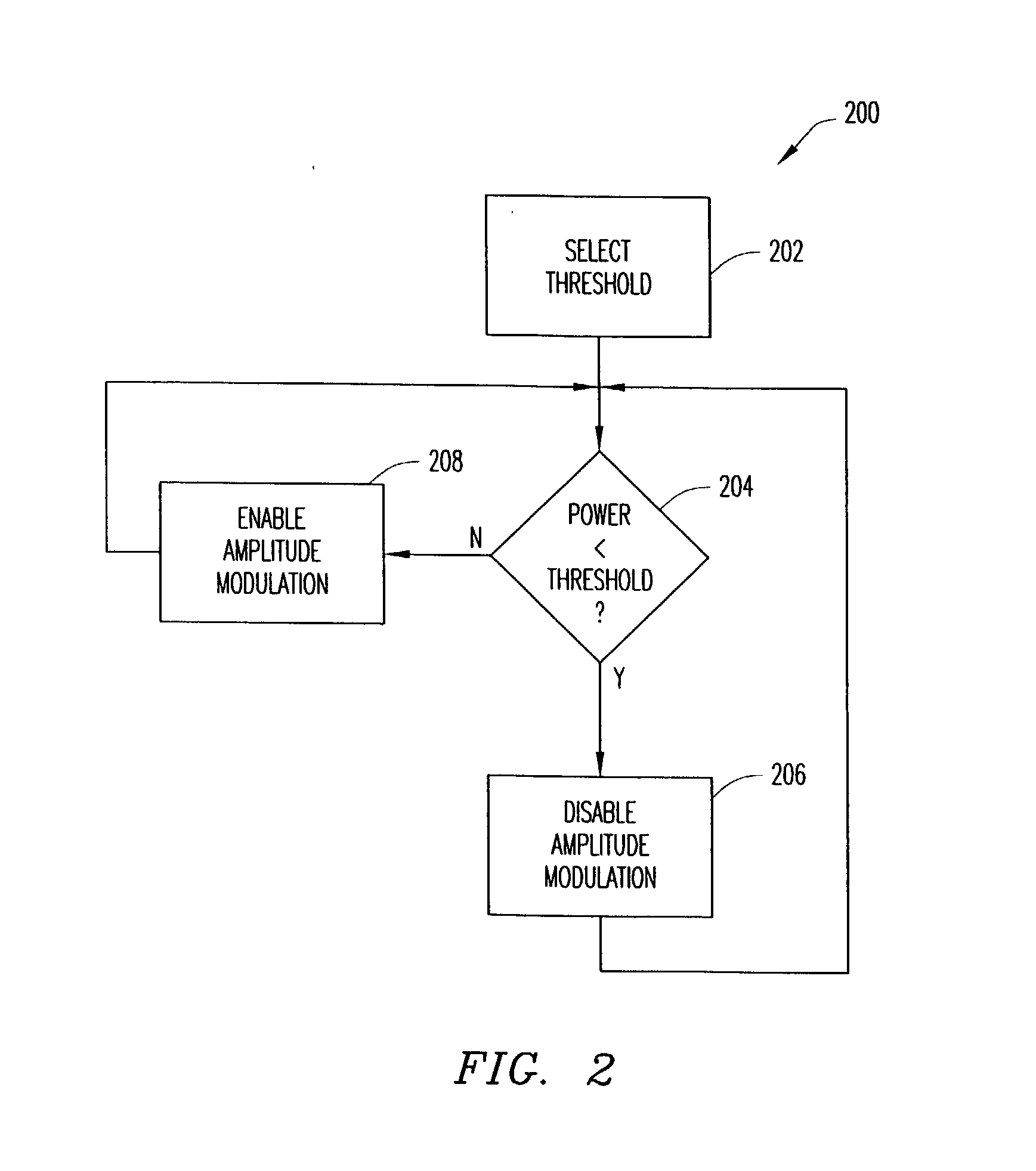
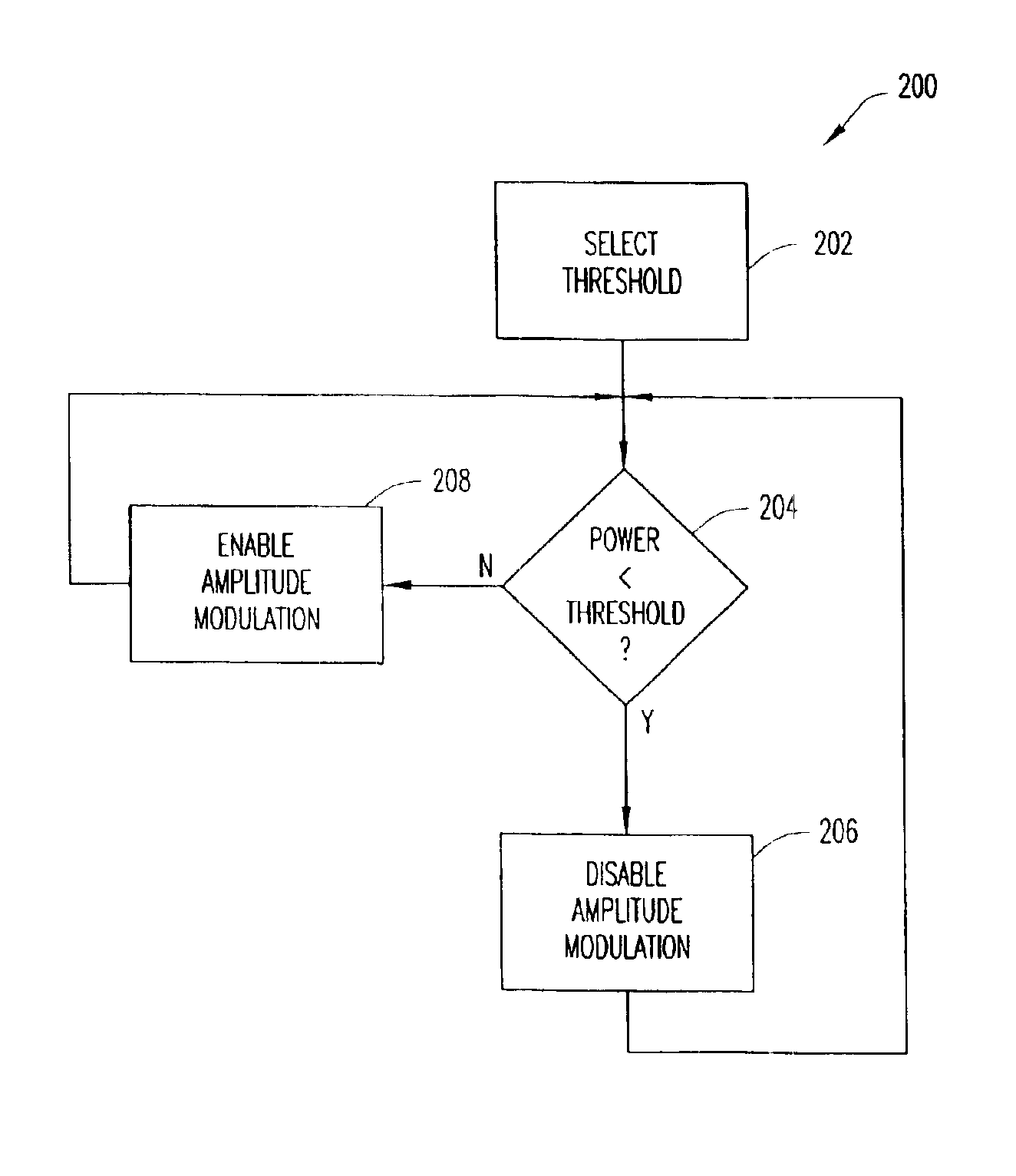
Method and apparatus for reducing dynamic range of a power amplifier
ActiveUS20040192369A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierPolar transmitter
An output-power threshold is selected such that one or more signal requirements is not outside a pre-determined range when output power of a polar transmitter is less than the output-power threshold. A determination is made whether the output power is less than the threshold. In response to a determination that the output power is less than the threshold, amplitude modulation of a polar signal transmitted by the polar transmitter is disabled. When the output power meets or exceeds the output-power threshold, the polar signal transmitted by the polar transmitter is both amplitude and phase modulated.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
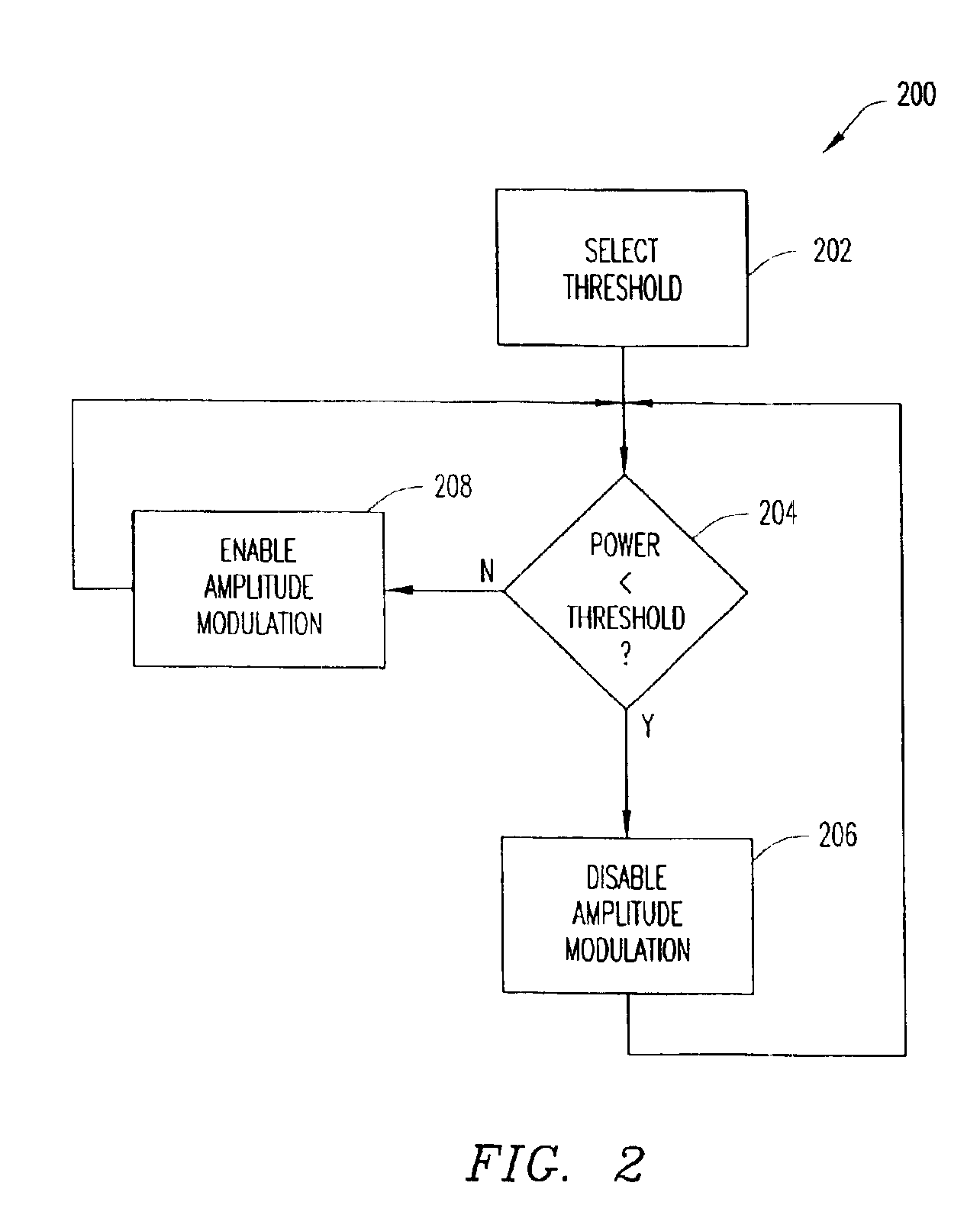
Method and apparatus for reducing dynamic range of a power amplifier
InactiveUS6892057B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
An output-power threshold is selected such that one or more signal requirements is not outside a pre-determined range when output power of a polar transmitter is less than the output-power threshold. A determination is made whether the output power is less than the threshold. In response to a determination that the output power is less than the threshold, amplitude modulation of a polar signal transmitted by the polar transmitter is disabled. When the output power meets or exceeds the output-power threshold, the polar signal transmitted by the polar transmitter is both amplitude and phase modulated.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for transmitter envelope delay calibration
InactiveCN101379695ASimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersPropagation delayTransceiver
A test signal comprising a periodic waveform, such as a triangular waveform and sawtooth waveform, is used for propagation delay matching in a transceiver front-end. The test signal is separately fed to the envelope path and the RF path. At the power amplifier stage, a phase modulator is used to obtain the envelope signal and the phase modulated RF signal for demodulation by an IQ demodulator. At the output end of the IQ demodulator, the I-signal is measured while the delay block is adjusted in order to vary the propagation delay. When the propagation delay matching is correct, the peak-to-peak value of the I-signal is a minimum. Preferably, during calibration using the test signal, the transmitter RF power amplifier is disabled so that no spurious signals will be sent. The transmitter can be an EDGE polar transmitter, a non-EDGE transmitter or a EER polar transmitter.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Methods and apparatus for dynamically compensating for DC offset drift and other pvt-related signal variations in polar transmitters
ActiveUS20100120384A1Reduce computing loadEasy CalibrationResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsPolar transmitterSignal characteristic
Methods and apparatus for dynamically compensating for signal variations in communications transmitters employing switch-mode PAs. An exemplary method includes first identifying a predetermined signal characteristic in an input signal applied to an input of a switch-mode PA. A modulated signal produced at the output of the switch-mode PA containing the identified signal characteristic is then sampled at approximately the same time the identified signal characteristic appears at the output of the switch-mode PA, to generate a digital sample representing an actual value of the identified signal characteristic. An error signal representing the extent to which the actual value deviates from an expected value is then generated. Finally, the DC level and / or gain of the input signal to the switch-mode PA is modified to reduce the error. By reducing the error in this manner, signal variations that adversely affect the accuracy of the switch-mode PA output signal are dynamically compensated for.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
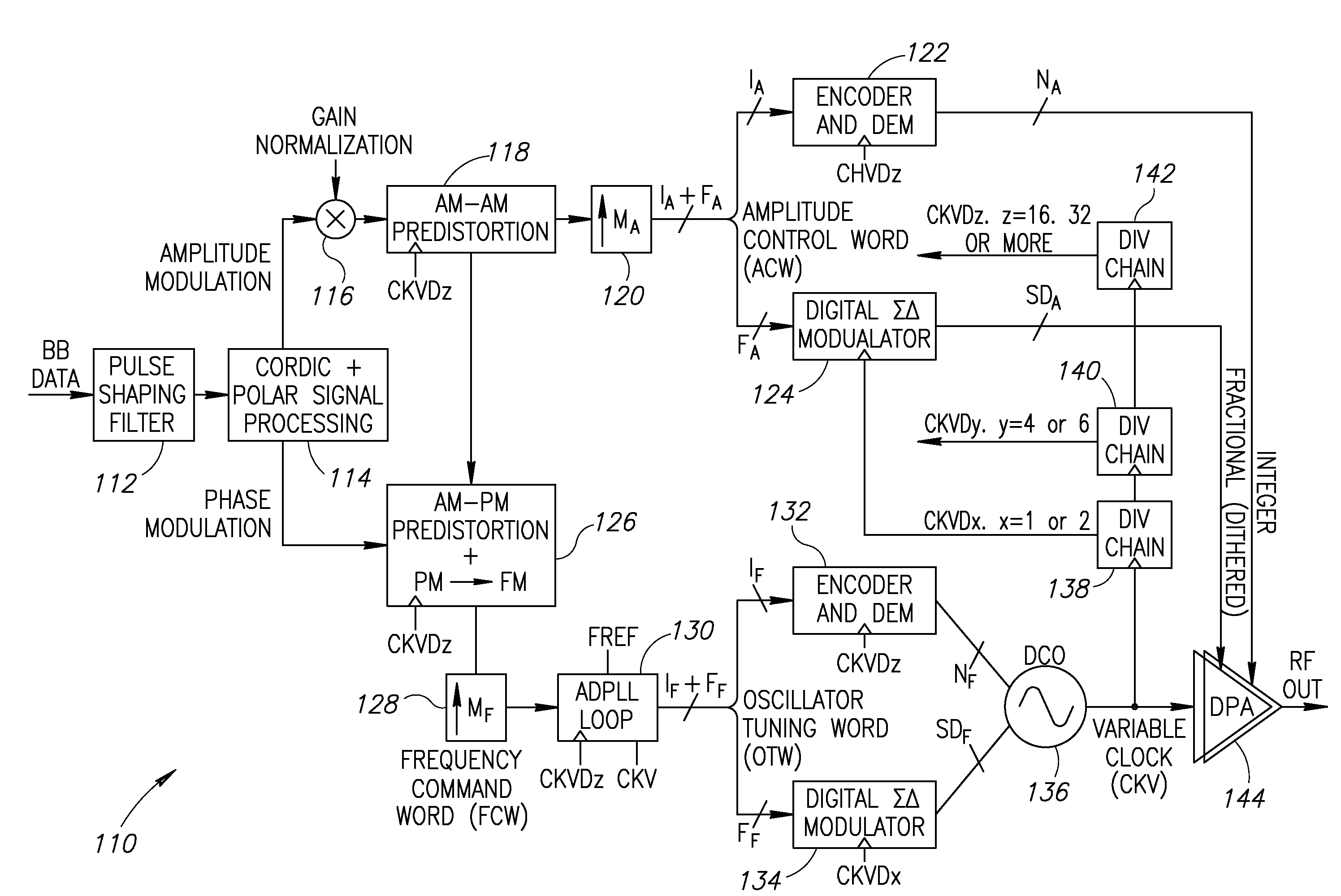
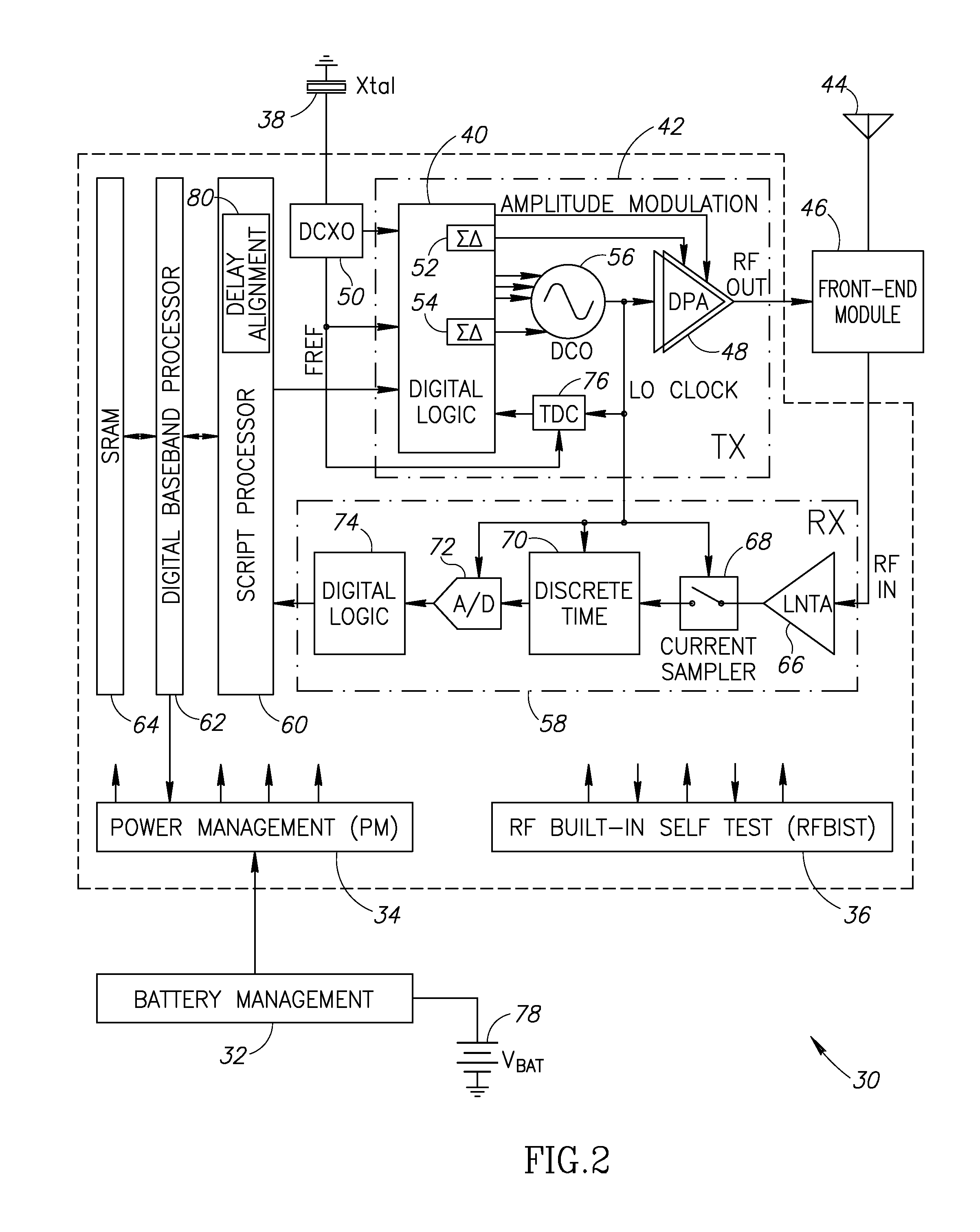
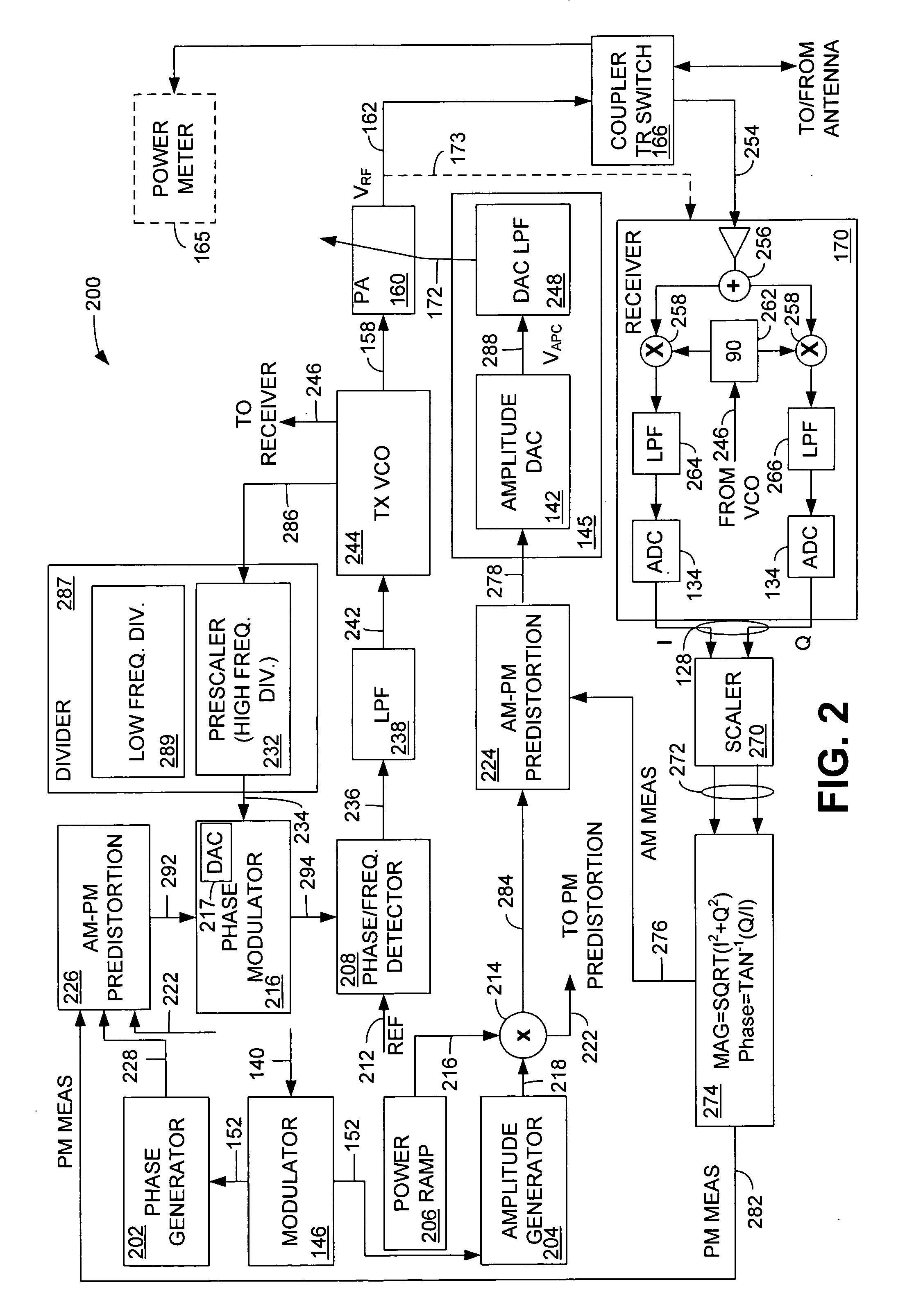
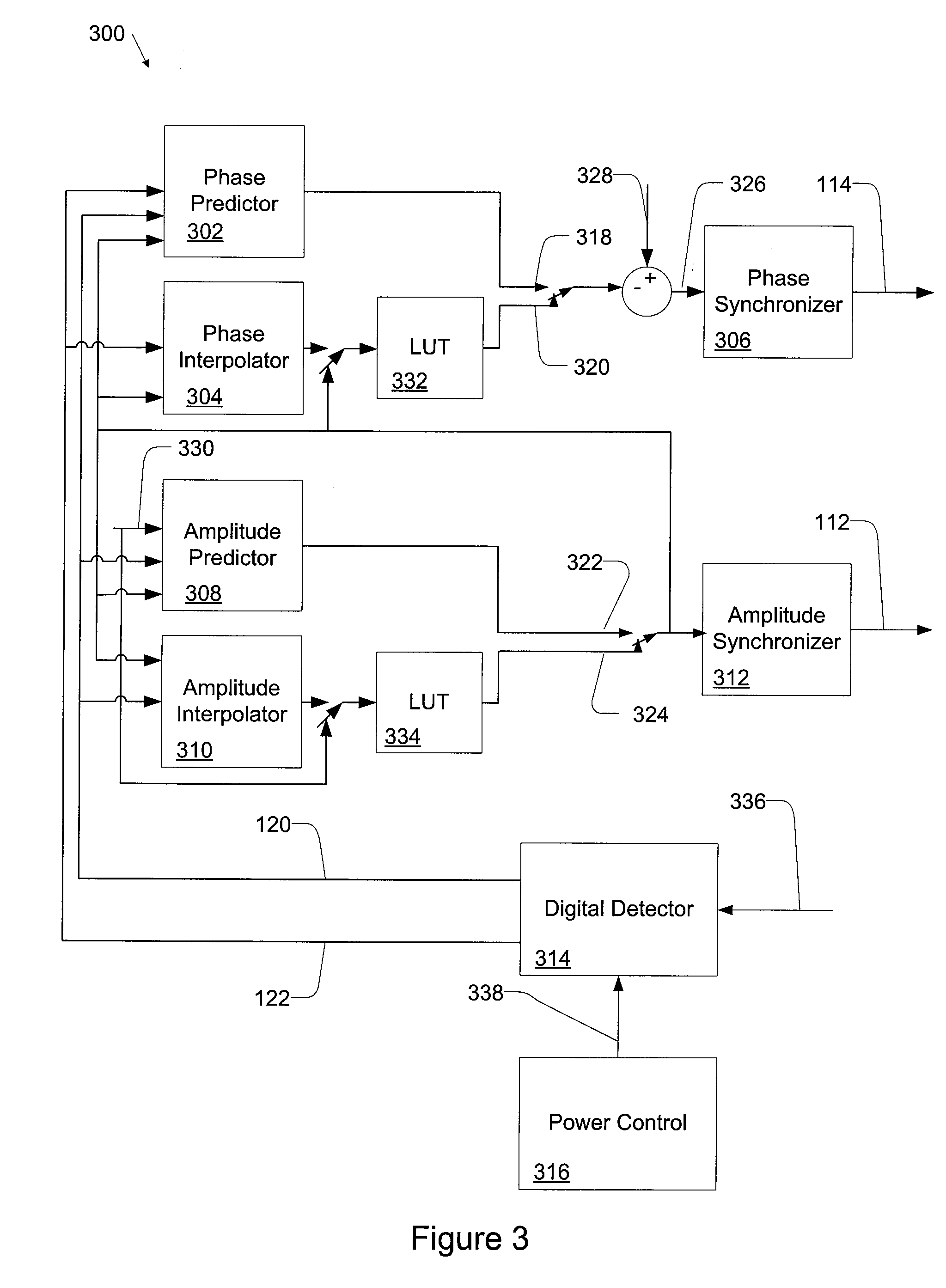
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS20070189417A1Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierNanosecond
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
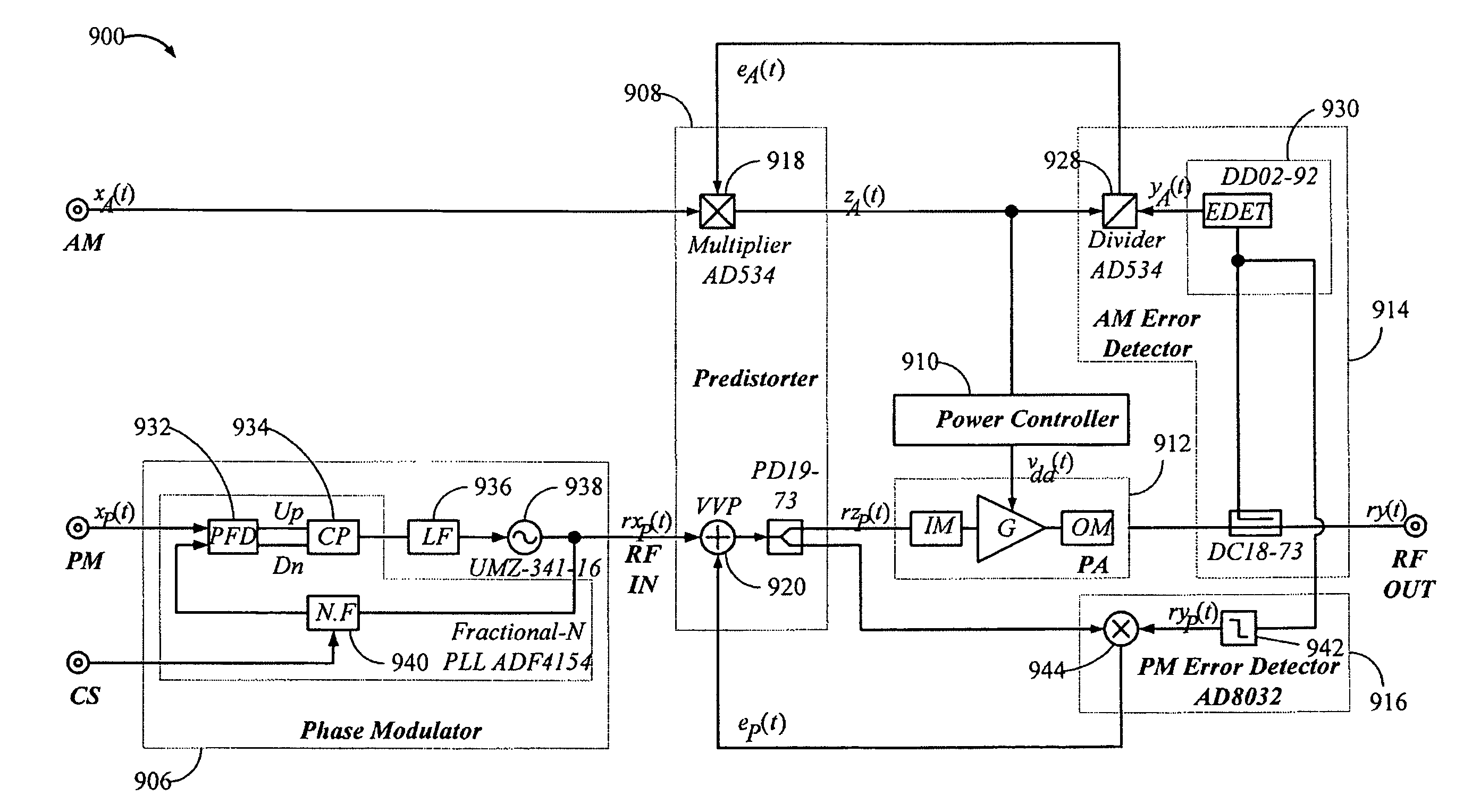
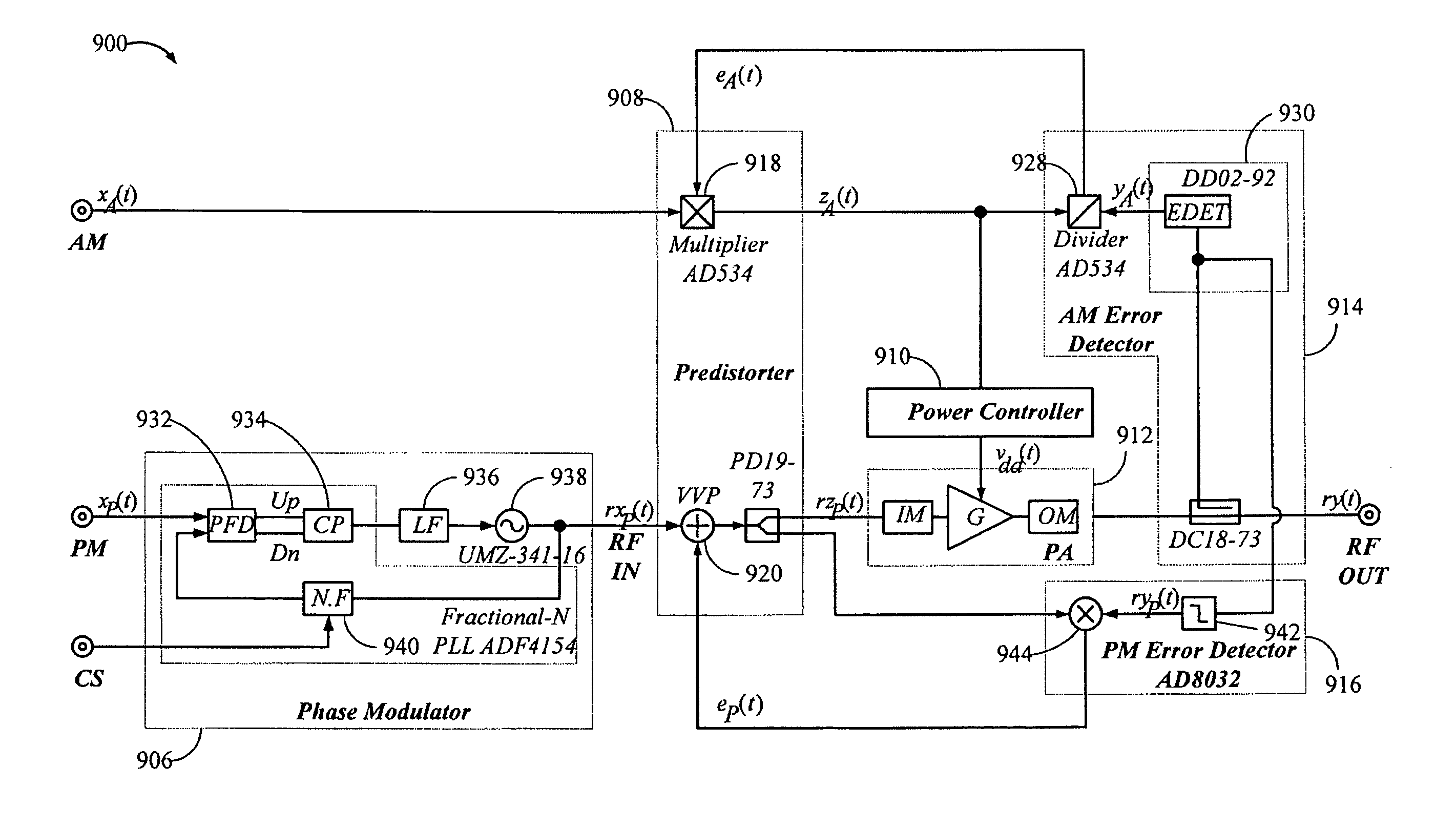
Open loop polar transmitter having on-chip calibration
InactiveUS20070129025A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersPolar transmitterPredistortion
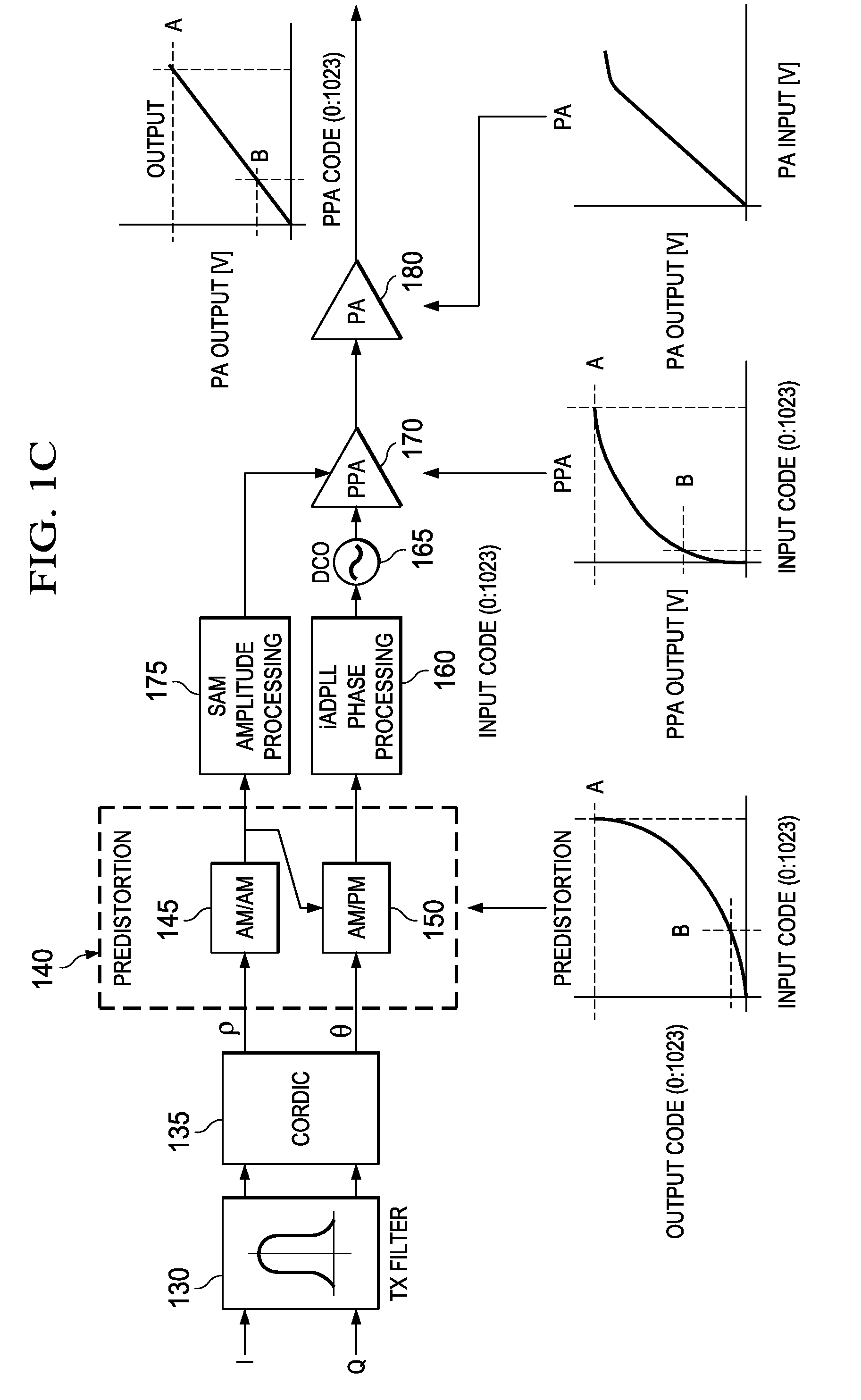
An on-chip calibration system comprises a transmitter, a receiver, a phase and amplitude determination element configured to determine amplitude and phase characteristics of an output signal generated in the transmitter, the signal representing transmitter characteristics, an amplitude comparison element configured to compare the signal representing transmitter characteristics with a desired amplitude signal and generate an amplitude compensation signal, an AM predistortion element configured to modify an ideal AM signal with the amplitude compensation signal, a phase comparison element configured to compare the signal representing transmitter characteristics with a desired phase signal and generate a phase compensation signal, and a PM predistortion element configured to modify an ideal phase signal with the phase compensation signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for linear polar transmitters
InactiveUS7860466B2High bandwidthResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierPolar transmitter
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing a linear polar transmitter. The systems and methods may include generating an input amplitude signal and an input phase signal, where the input amplitude signal and the input phase signal are orthogonal components of an input signal, and where the input amplitude signal and the input phase signal are generated on respective first and second signal paths. The systems and methods may also include processing the input amplitude signal along the first signal path using an amplitude error signal to generate a predistorted amplitude signal, and processing the input phase signal along the second signal path using an phase error signal to generate a predistorted phase signal. The systems and methods may also include providing the predistorted amplitude signal along the first signal path and the predistorted phase signal along the second signal path to a power amplifier to generate an output signal, where the amplitude error signal is generated from a comparison of at least an amplitude portion of the output signal with the predistorted amplitude signal and where the phase error signal is generated from a comparison of at least a phase portion of the output signal with the predistorted phase signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Bandwidth reduction mechanism for polar modulation
ActiveUS20090258612A1Reducing polar modulation bandwidthDegradation of modulation bandwidthSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumPhase bandwidth
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of reducing phase and amplitude modulation bandwidth in polar transmitters. The bandwidth reduction mechanism of the present invention effectively reduces the phase modulation bandwidth of the polar modulation performed in the transmitter by modifying the zero-crossing trajectories in the IQ domain. This significantly reduces the phase modulation bandwidth while still meeting the output spectrum and error vector magnitude (EVM) requirements of the particular modern wideband wireless standard, such as 3G WCDMA, etc. The mechanism detects a zero crossing or a near zero crossing within a predetermined threshold of the origin and an offset vector is generated that when added to the input TX IQ data, shifts the trajectory to avoid the origin thus reducing the resultant polar modulation amplitude and phase bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Polar transmitter with digital to RF converter
InactiveUS20050190854A1Resonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierLinearity
A polar transmitter, operable in linear mode or switched mode, uses a conversion module to convert baseband signals into amplitude data and phase data. The phase data is used to phase modulate a carrier frequency in a RF conversion module. The module comprises a plurality of parallel unit cells, each being a mixer cell type converter having a differential data switch section connected in series to a differential LO-switch pair. The differential LO-switch is connected in series to a current source. Each unit cell is adapted to receive a signal through an input end. In switched mode, the phase-modulated carrier frequency is amplitude modulated by the amplitude data through the supply voltage to a power amplifier. In linear mode, amplitude data is conveyed to the input end of the unit cells for modulating the phase-modulated carrier frequency in the conversion module.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Mitigation of RF Oscillator Pulling through Adjustable Phase Shifting
InactiveUS20100283665A1Wave based measurement systemsSubstation equipmentVibration amplitudeSelf interference
A digitally controlled mechanism for the minimization of the self-interference caused by an amplitude modulated signal generated within a polar transmitter to the oscillator circuit, where the carrier of that transmitter is created. A digitally controlled delay between the circuit where the signal is generated and the circuit where it is amplitude-modulated allows adjustment of the delay or phase-shift between the aggressing and victim signals. The optimal delay that is to be introduced in the path is determined, and a corresponding control word is generated to arrive at the selected delay / phase-shift.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
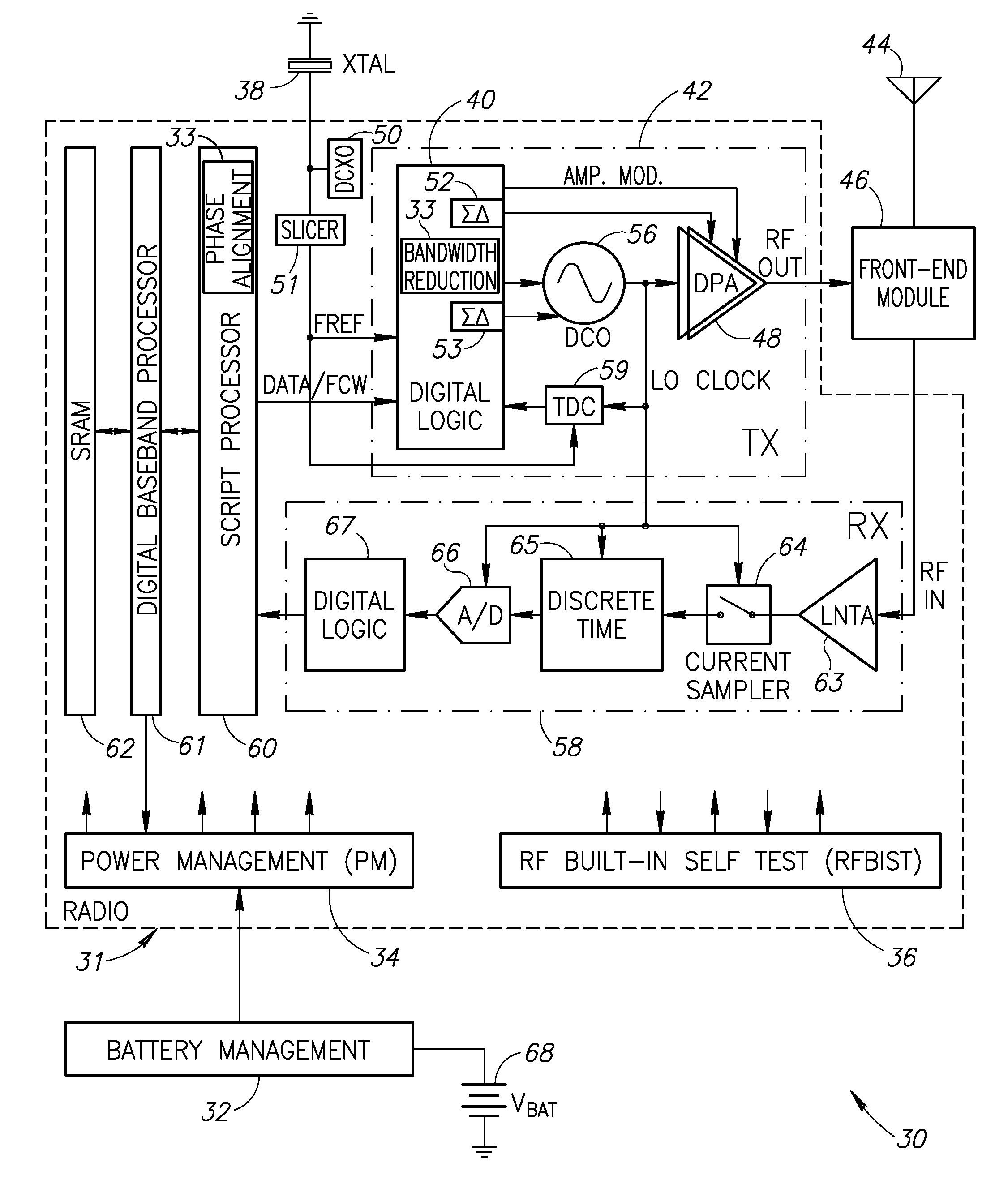
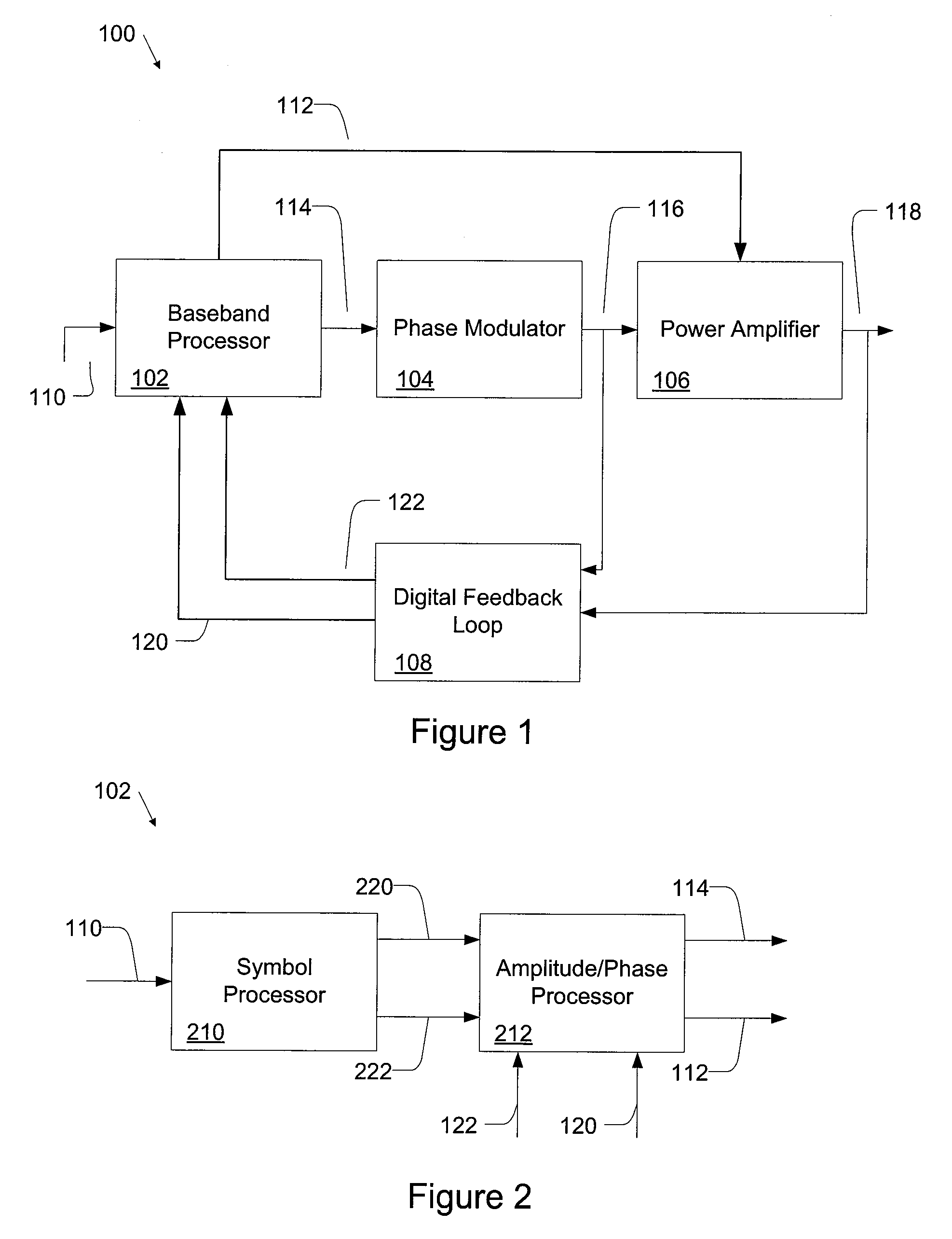
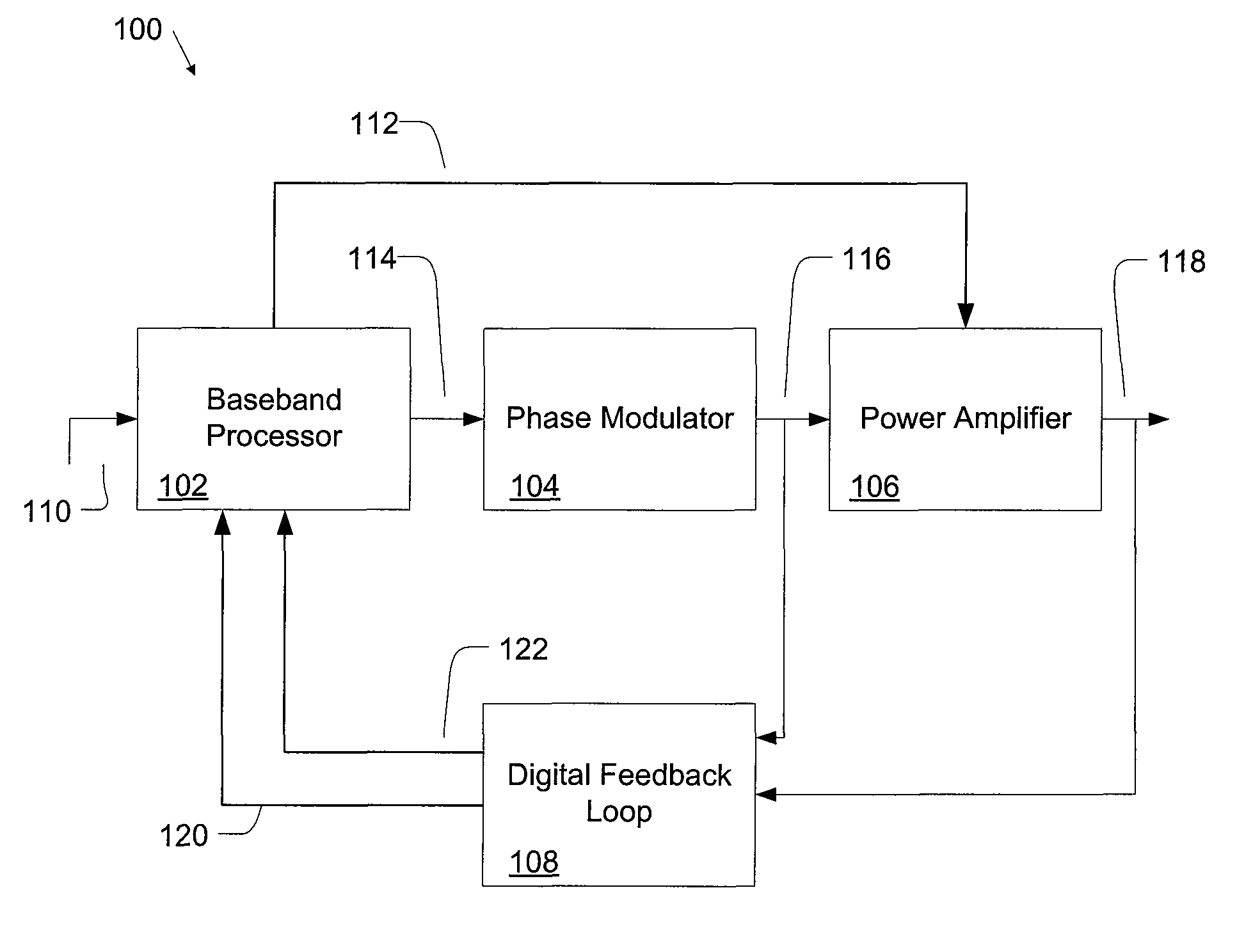
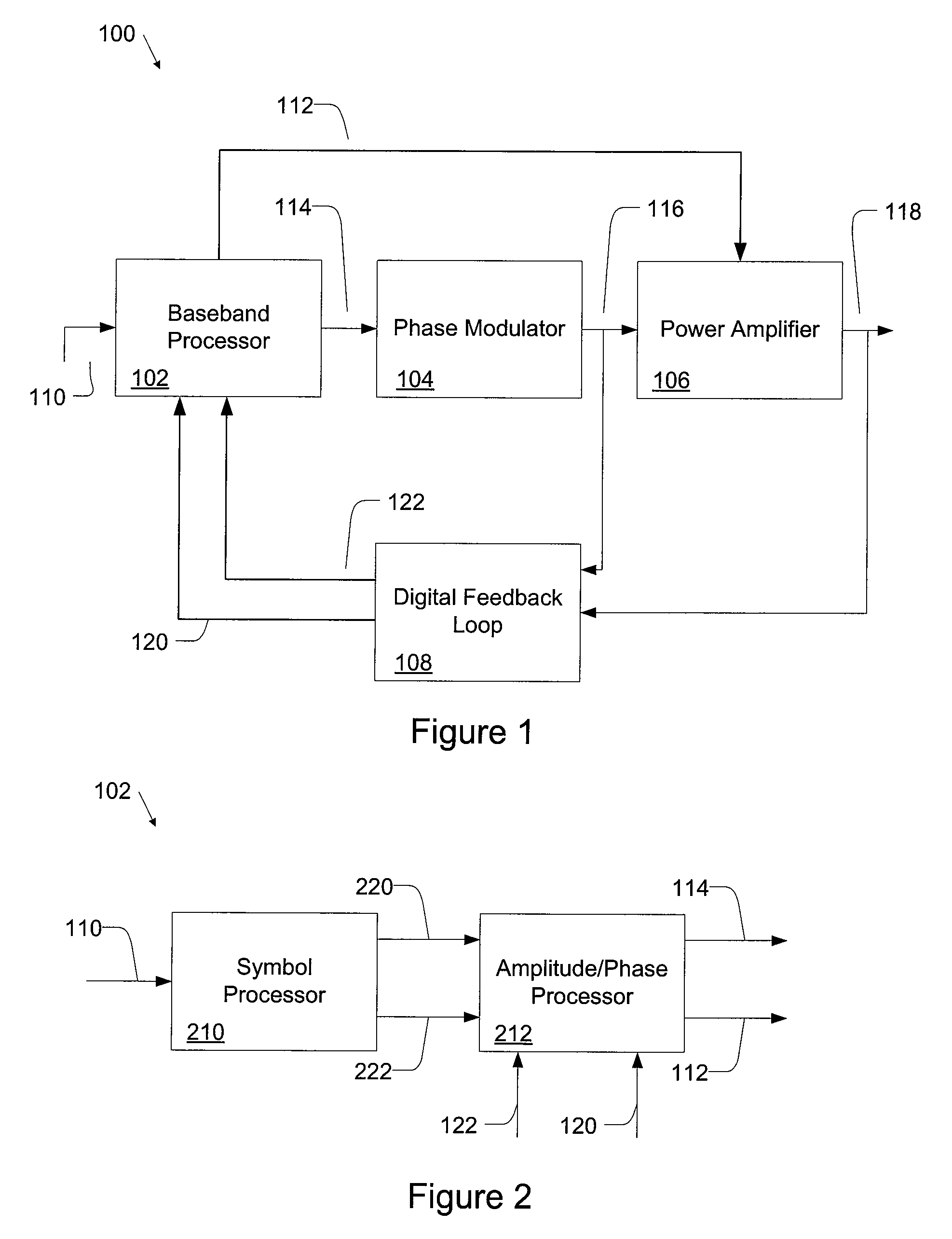
Digital Polar Transmitter
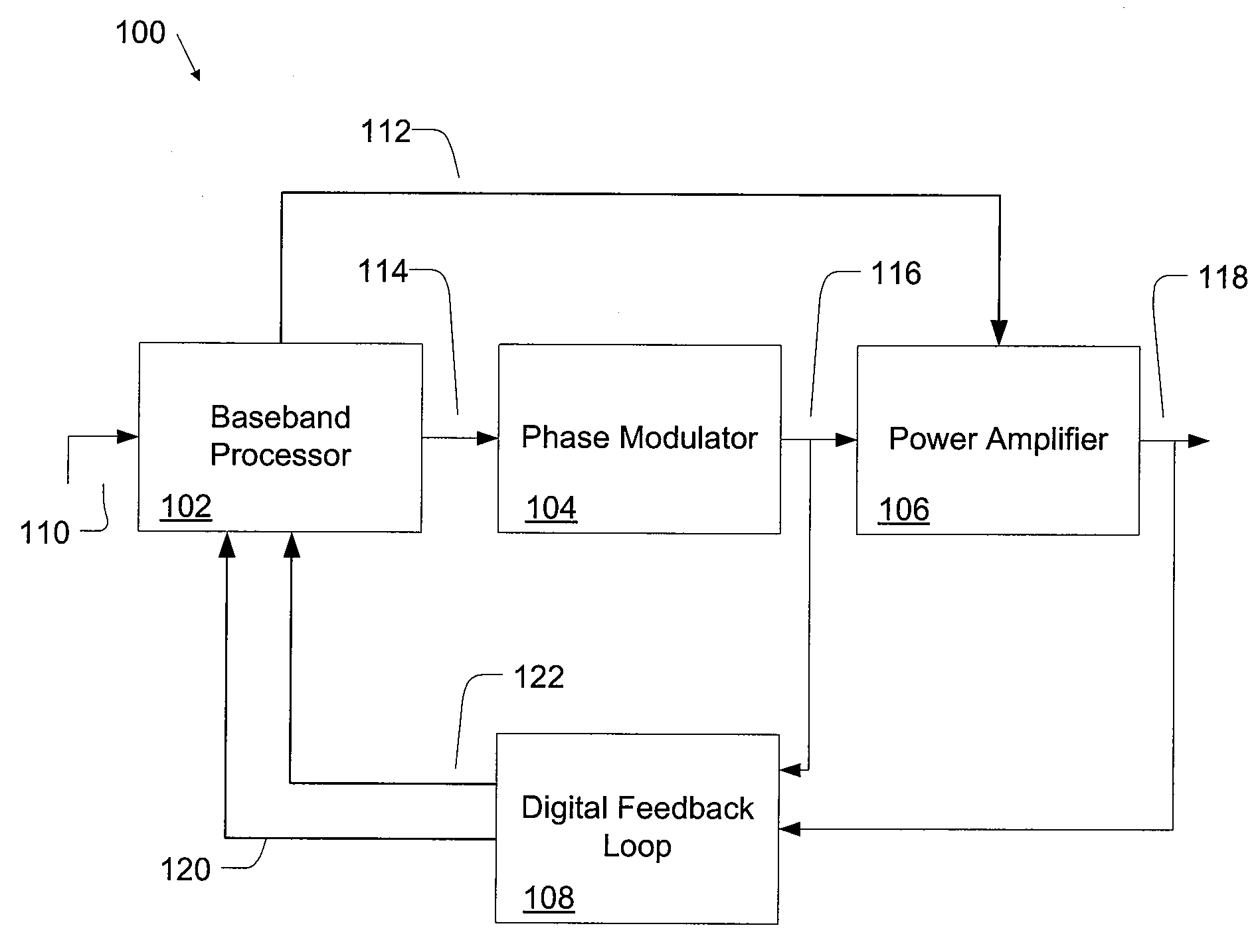
ActiveUS20080225984A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAudio power amplifierDigital feedback
A digital polar transmitter includes a baseband processor configured to receive an input signal and to convert the input signal into a baseband amplitude component and a baseband phase component. The transmitter also includes a phase modulator in communication with the baseband processor. The phase modulator is configured to modulate an RF carrier signal based on the phase component and to generate a phase-modulated RF carrier signal. A power amplifier is provided in communication with the baseband processor and the phase modulator. The power amplifier is configured to amplify the phase-modulated RF carrier signal based on the baseband amplitude component and to generate an amplified RF signal. The transmitter also includes a digital feedback loop in communication with the power amplifier and the baseband processor. The digital feedback loop is configured to detect the amplified RF signal and to provide a digital amplitude feedback signal and a detected phase feedback signal to the baseband processor.
Owner:EAGLE TECH LLC
Polar transmitter with digital to RF converter
InactiveUS7424064B2Resonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierLocal oscillator
A polar transmitter, operable in linear mode or switched mode, uses a conversion module to convert baseband signals into amplitude data and phase data. The phase data is used to phase modulate a carrier frequency in a radio frequency conversion module. The module comprises a plurality of parallel unit cells, each being a mixer cell type converter having a differential data switch section connected in series to a differential local oscillator-switch pair. The differential local oscillator-switch is connected in series to a current source. Each unit cell is adapted to receive a signal through an input end. In switched mode, the phase-modulated carrier frequency is amplitude modulated by the amplitude data through the supply voltage to a power amplifier. In linear mode, amplitude data is conveyed to the input end of the unit cells for modulating the phase-modulated carrier frequency in the conversion module.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
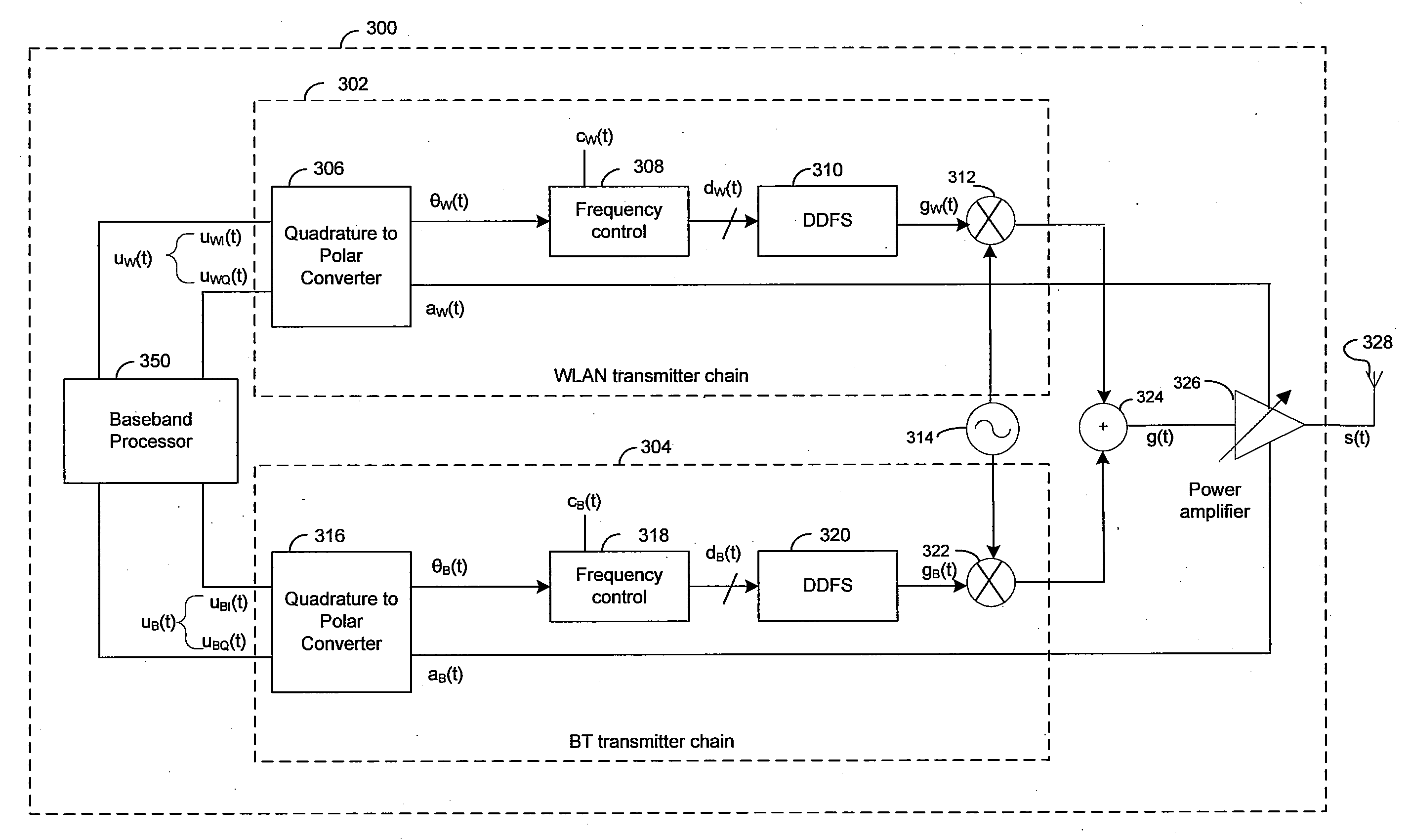
Method and System for a Wideband Polar Transmitter
InactiveUS20080205549A1Modulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsWireless communication protocolIntermediate frequency
Certain aspects of a method and system for a wideband polar transmitter may be disclosed. Aspects of the method may include polar modulating a plurality of signals by generating a plurality of modulated intermediate frequency (IF) signals corresponding to each of a plurality of wireless communication protocols within a transmitter that handles the plurality of wireless communication protocols. The generated plurality of modulated IF signals may be upconverted to a plurality of radio frequency (RF) signals. The plurality of RF signals may be combined and the combined plurality of RF signals may be amplitude modulated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Adaptive digital predistortion for polar transmitter
ActiveUS20180287569A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersRadio frequency signalLookup table
Owner:INNOPHASE
Systems, Methods, and Apparatuses for Linear Polar Transmitters
InactiveUS20070298734A1High bandwidthResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierLinearity
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing a linear polar transmitter. The systems and methods may include generating an input amplitude signal and an input phase signal, where the input amplitude signal and the input phase signal are orthogonal components of an input signal, and where the input amplitude signal and the input phase signal are generated on respective first and second signal paths. The systems and methods may also include processing the input amplitude signal along the first signal path using an amplitude error signal to generate a predistorted amplitude signal, and processing the input phase signal along the second signal path using an phase error signal to generate a predistorted phase signal. The systems and methods may also include providing the predistorted amplitude signal along the first signal path and the predistorted phase signal along the second signal path to a power amplifier to generate an output signal, where the amplitude error signal is generated from a comparison of at least an amplitude portion of the output signal with the predistorted amplitude signal and where the phase error signal is generated from a comparison of at least a phase portion of the output signal with the predistorted phase signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS7817747B2Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSynchronisation receiversNanosecondAudio power amplifier
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and system for transmitter envelope delay calibration
ActiveUS7522676B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersPropagation delayTransceiver
A test signal comprising a periodic waveform, such as a triangular waveform and sawtooth waveform, is used for propagation delay matching in a transceiver front-end. The test signal is separately fed to the envelope path and the RF path. At the power amplifier stage, a phase modulator is used to obtain the envelope signal and the phase modulated RF signal for demodulation by an IQ demodulator. At the output end of the IQ demodulator, the I-signal is measured while the delay block is adjusted in order to vary the propagation delay. When the propagation delay matching is correct, the peak-to-peak value of the I-signal is a minimum. Preferably, during calibration using the test signal, the transmitter RF power amplifier is disabled so that no spurious signals will be sent. The transmitter can be an EDGE polar transmitter, a non-EDGE transmitter or a EER polar transmitter.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Spectral emission shaping sigma delta modulator for wireless applications
ActiveUS20060203922A1Resonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
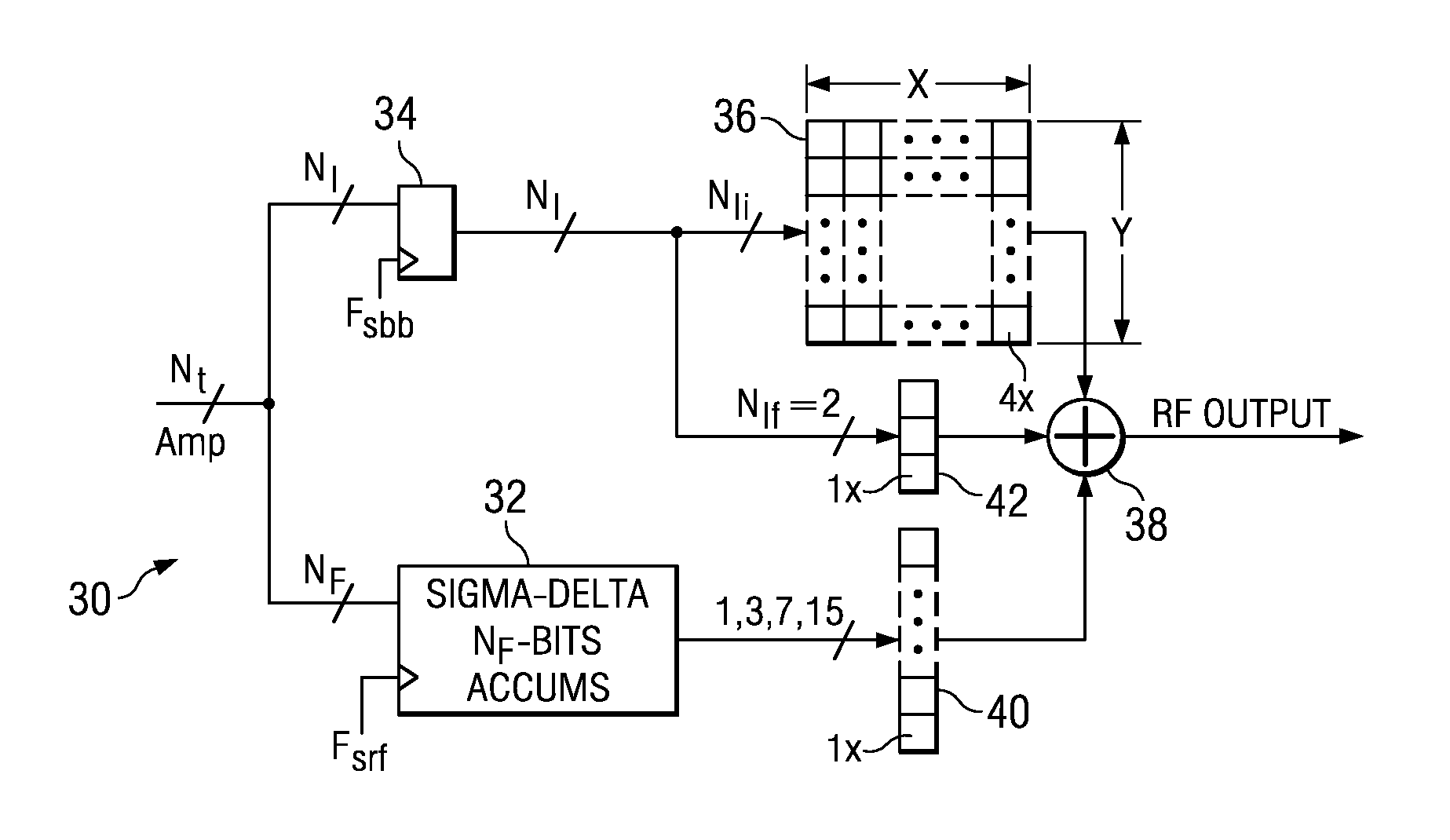
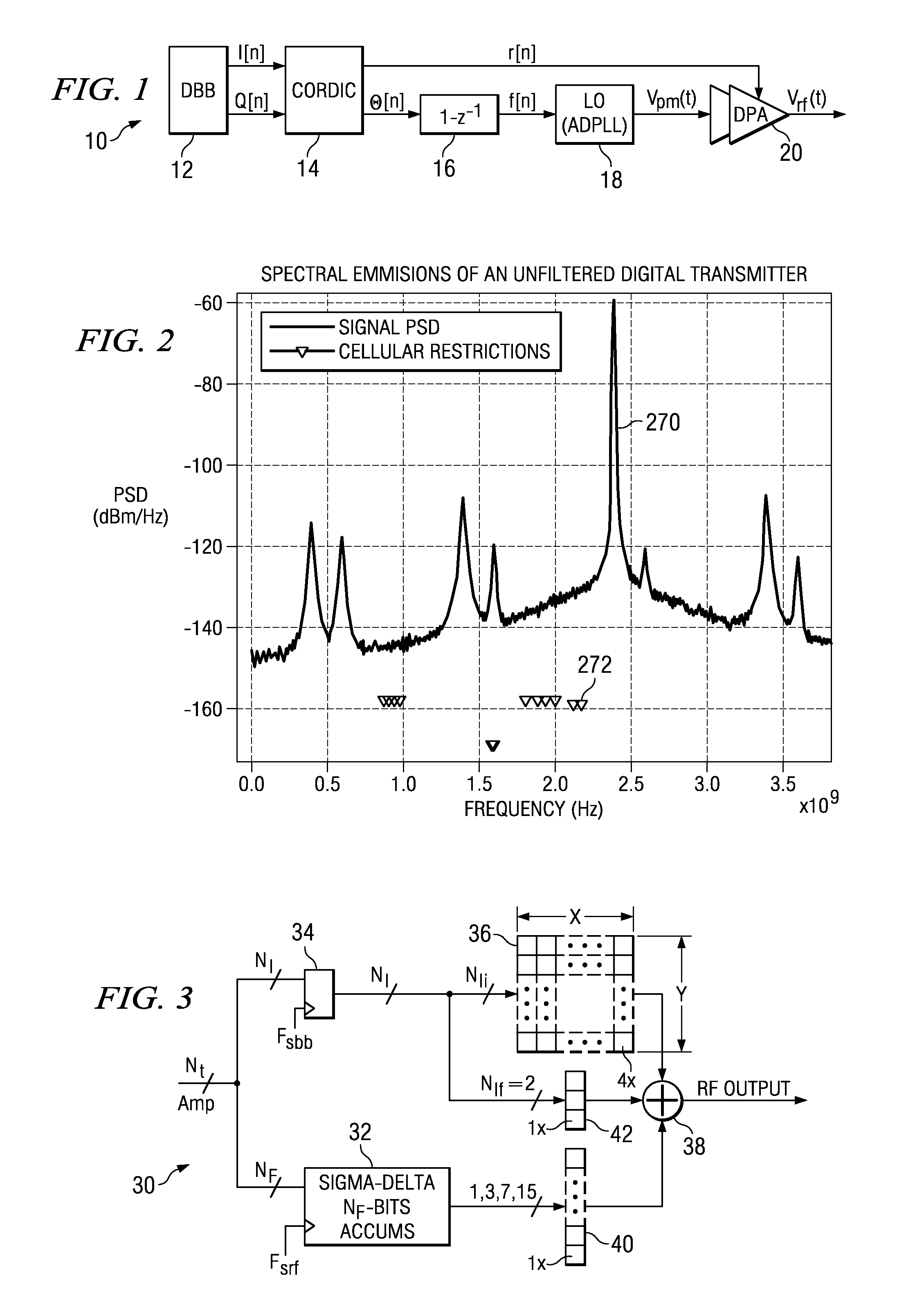
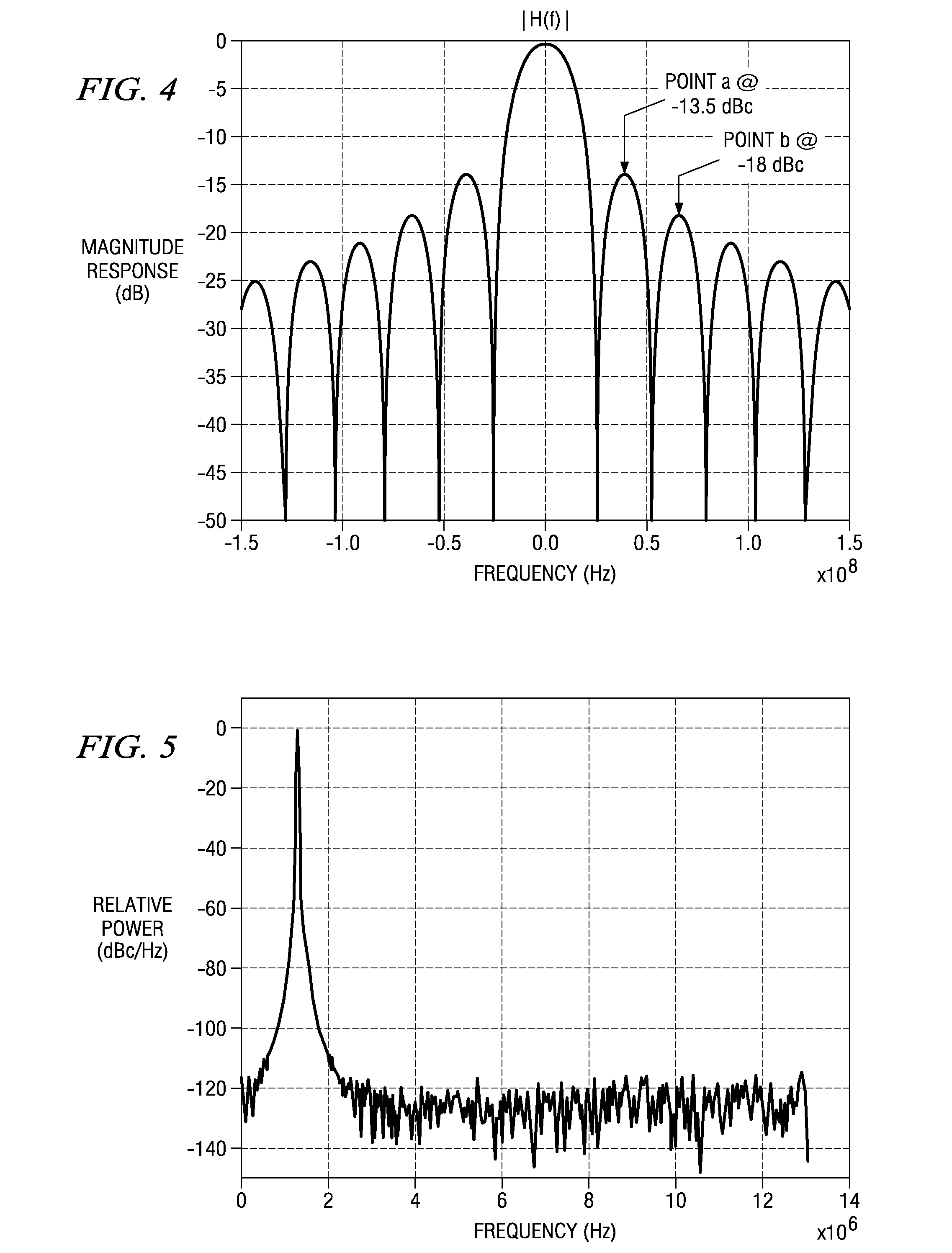
A novel sigma delta amplitude modulator having a noise transfer function adapted to shift quantization noise outside at least one frequency band of interest. In one embodiment, the sigma delta amplitude modulator includes a programmable order low pass stage. In a second embodiment, the sigma delta amplitude modulator incorporates comb filtering wherein each comb filter comprises a plurality of fingers to permit greater programmability in the frequency location of notches. A polar transmitter incorporating the sigma delta amplitude modulator is presented that shapes the spectral emissions of the digitally-controlled power amplifier such that they are significantly and sufficiently attenuated in one or more desired frequency bands.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS8009765B2Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionDigital feedbackAudio power amplifier
A digital polar transmitter includes a baseband processor configured to receive an input signal and to convert the input signal into a baseband amplitude component and a baseband phase component. The transmitter also includes a phase modulator in communication with the baseband processor. The phase modulator is configured to modulate an RF carrier signal based on the phase component and to generate a phase-modulated RF carrier signal. A power amplifier is provided in communication with the baseband processor and the phase modulator. The power amplifier is configured to amplify the phase-modulated RF carrier signal based on the baseband amplitude component and to generate an amplified RF signal. The transmitter also includes a digital feedback loop in communication with the power amplifier and the baseband processor. The digital feedback loop is configured to detect the amplified RF signal and to provide a digital amplitude feedback signal and a detected phase feedback signal to the baseband processor.
Owner:EAGLE TECH LLC
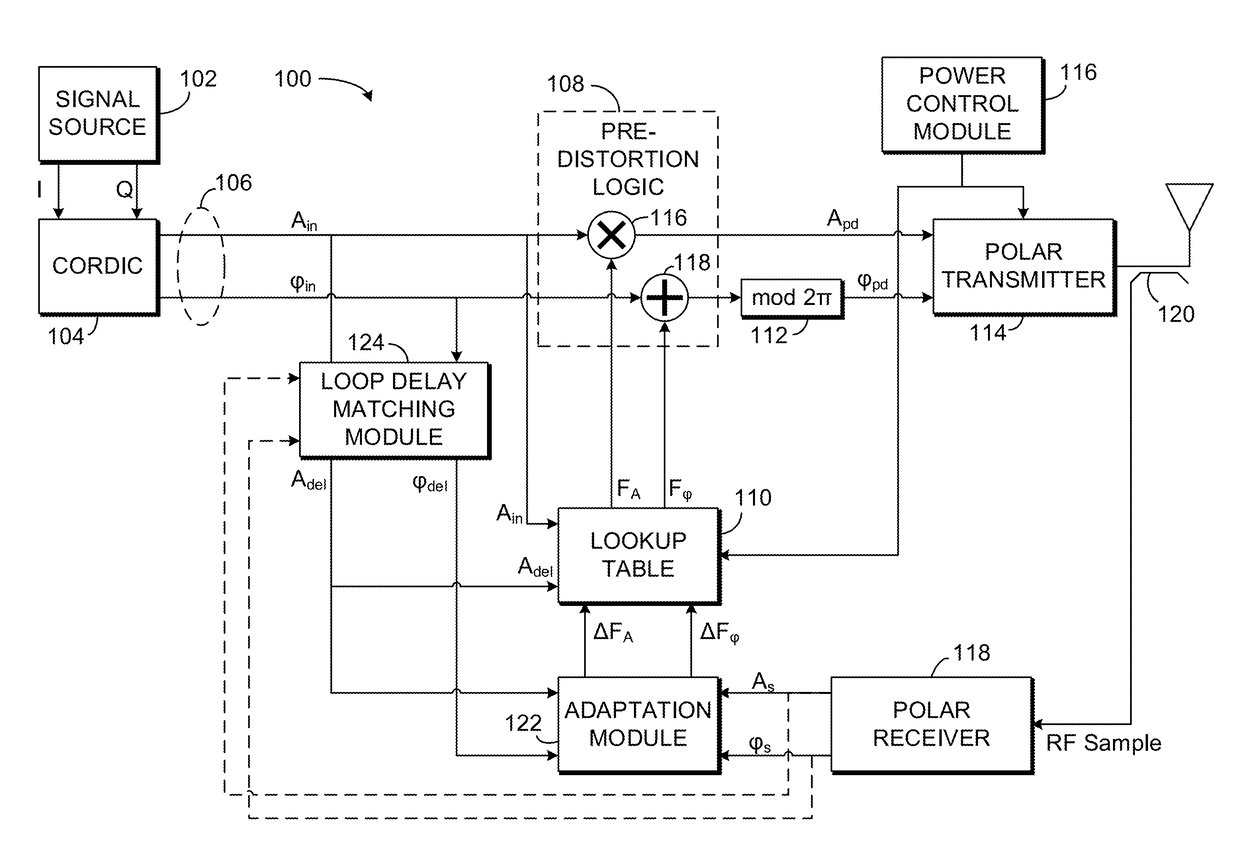
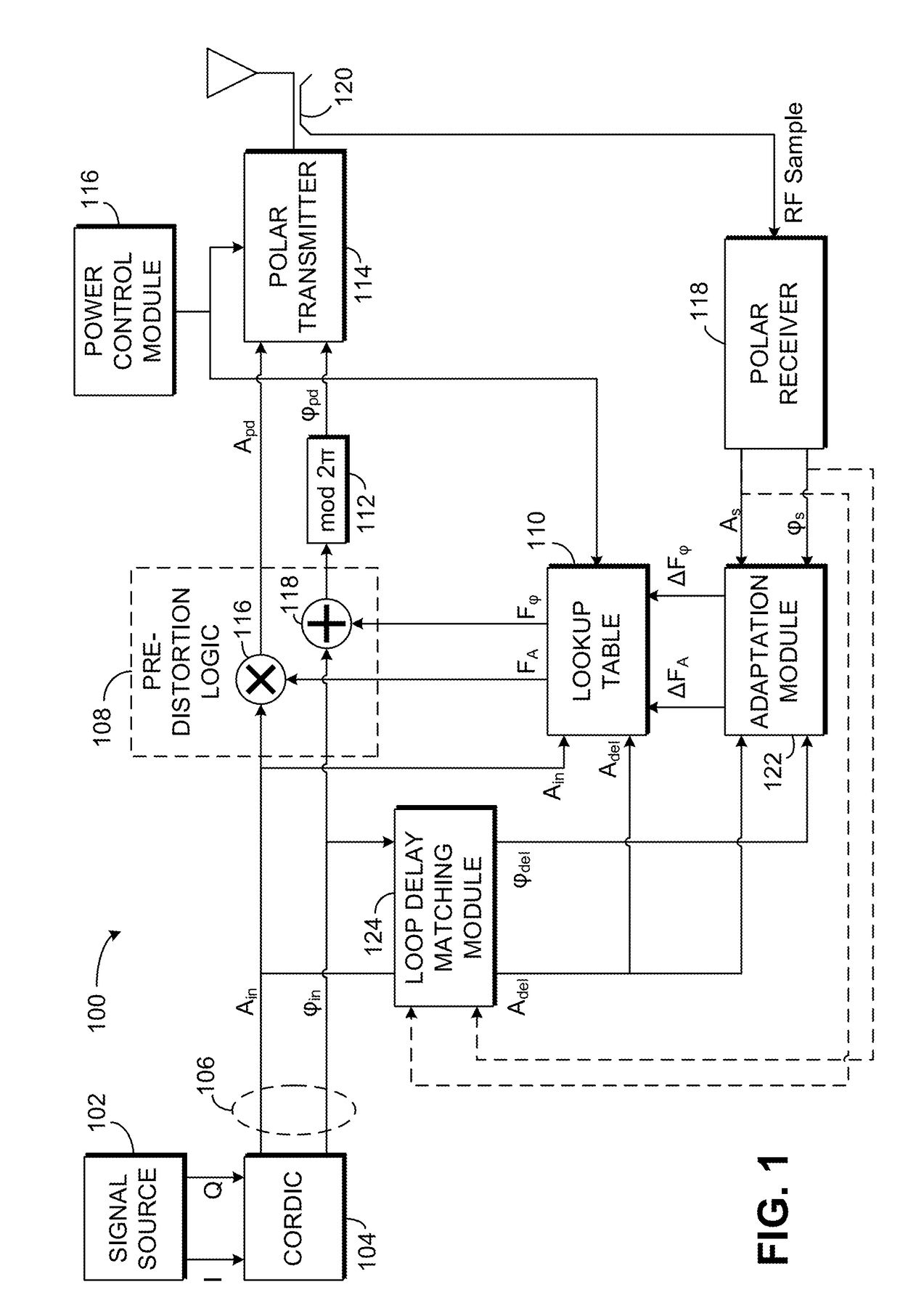
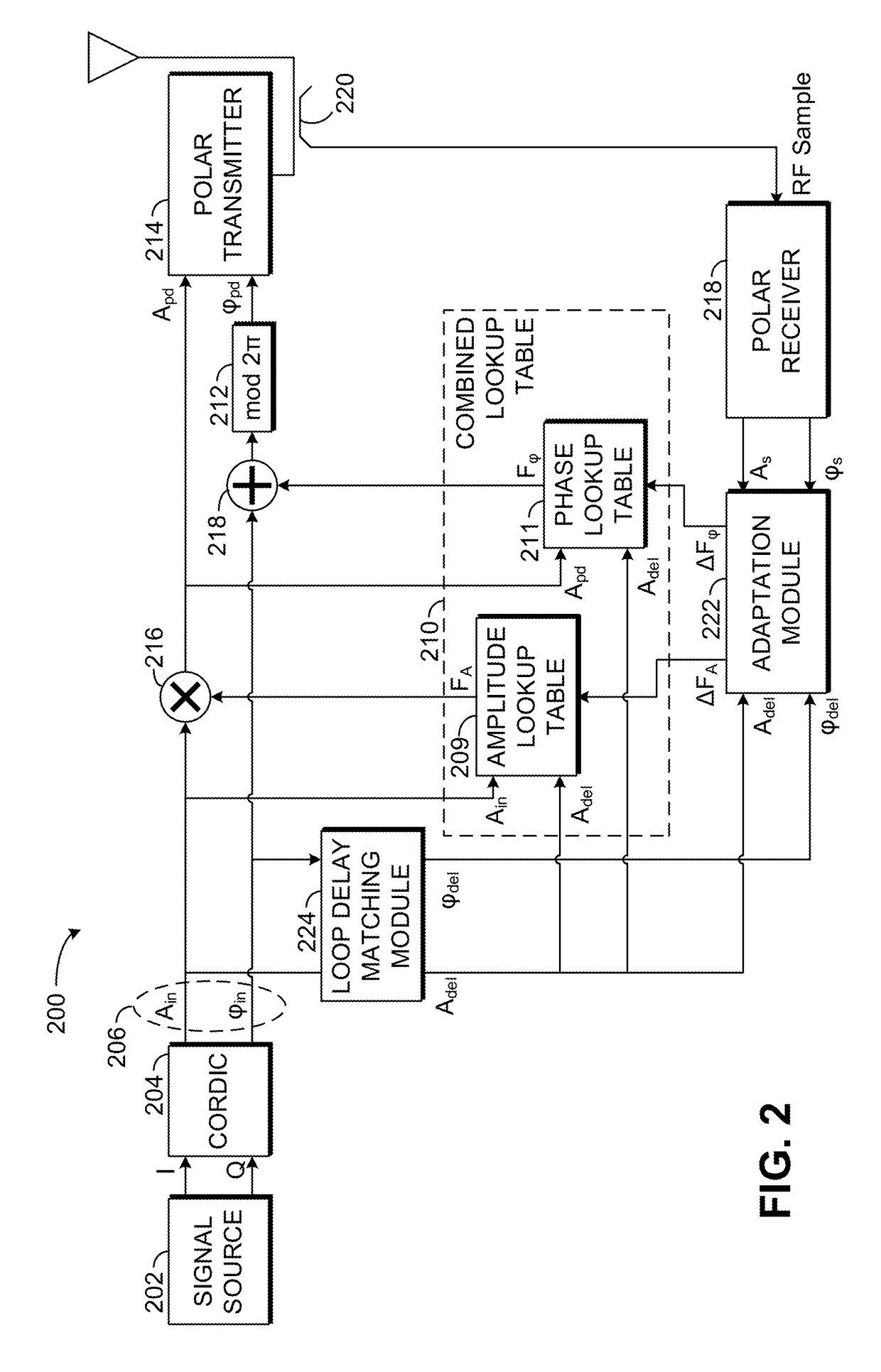
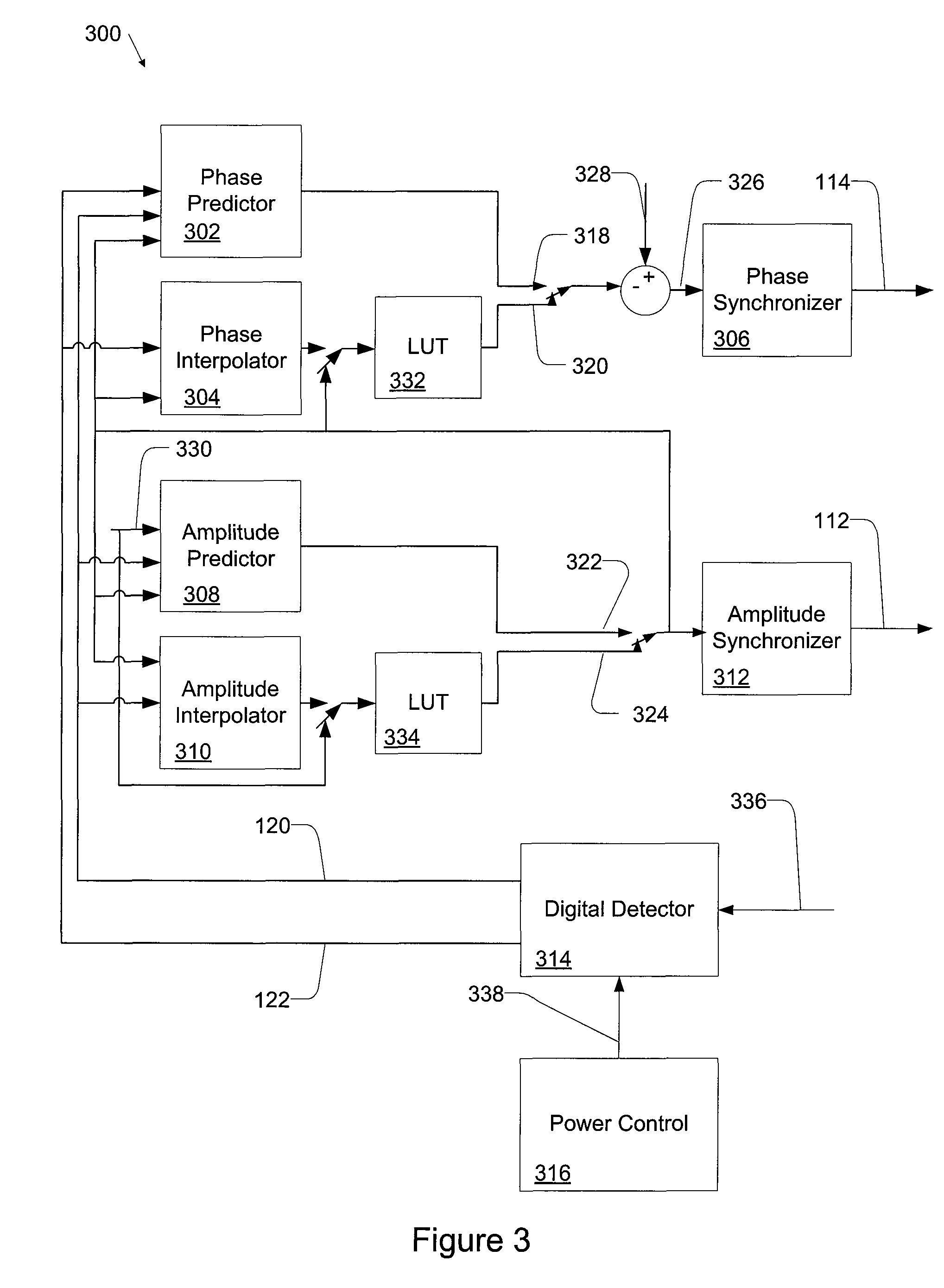
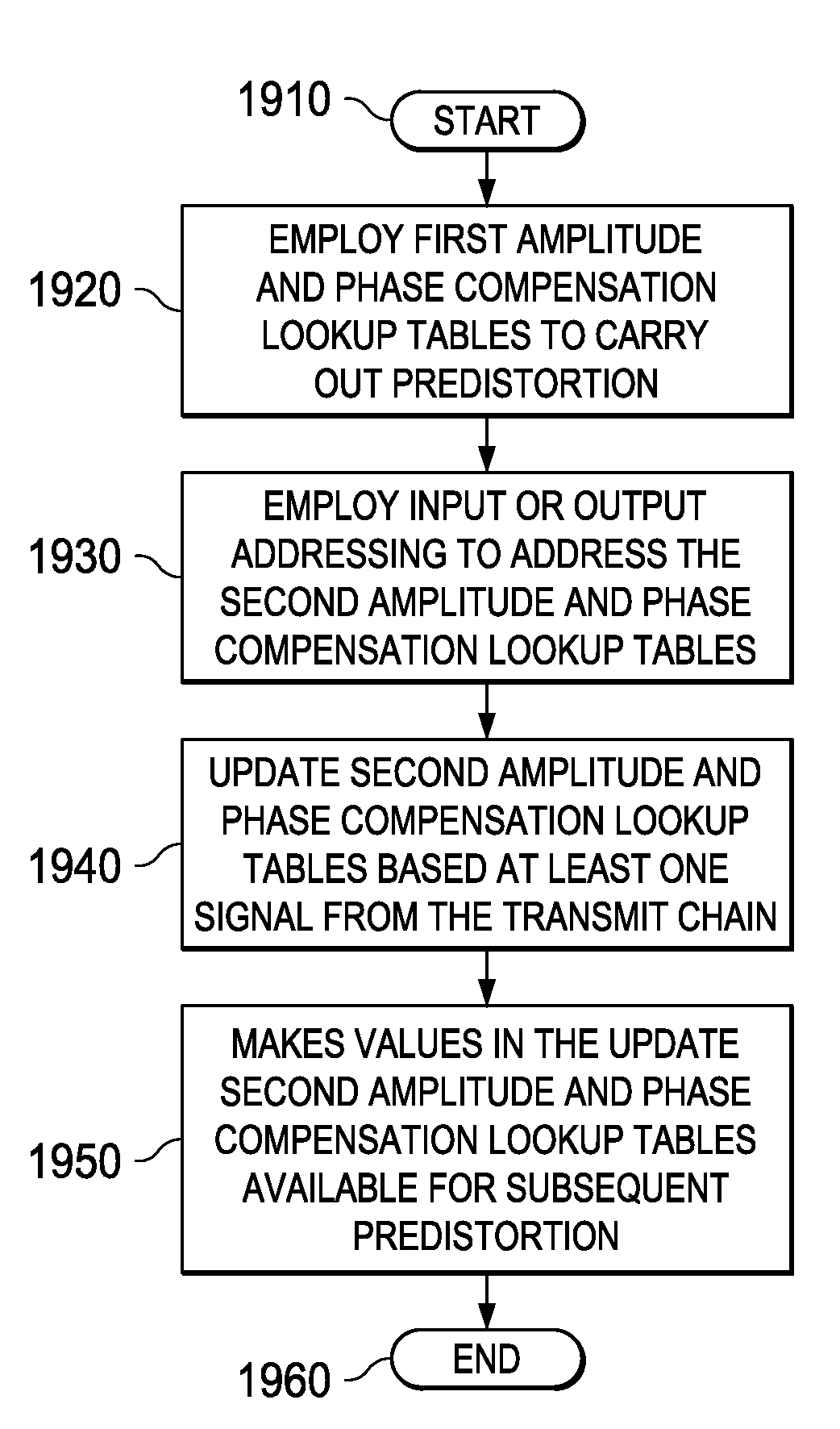
Apparatus and Method for Adaptive Polar Transmitter Linearization and Wireless Transmitter Employing the Same
ActiveUS20090054000A1Reduce the differenceSecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringLookup table
A polar transmitter and a method of linearizing a polar transmitter. In one embodiment, the transmitter includes: (1) a transmit chain having a predistorter configured to employ first amplitude and phase compensation lookup tables to carry out predistortion in the transmit chain, (2) a receiver coupled to the transmit chain and (3) predistortion compensation circuitry associated with the receiver and configured to update second amplitude and phase compensation lookup tables associated therewith based on at least one signal from the transmit chain, the values in the updated second amplitude and phase compensation lookup tables thereby available for subsequent predistortion.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
RF Amplifier with Digital Filter for Polar Transmitter
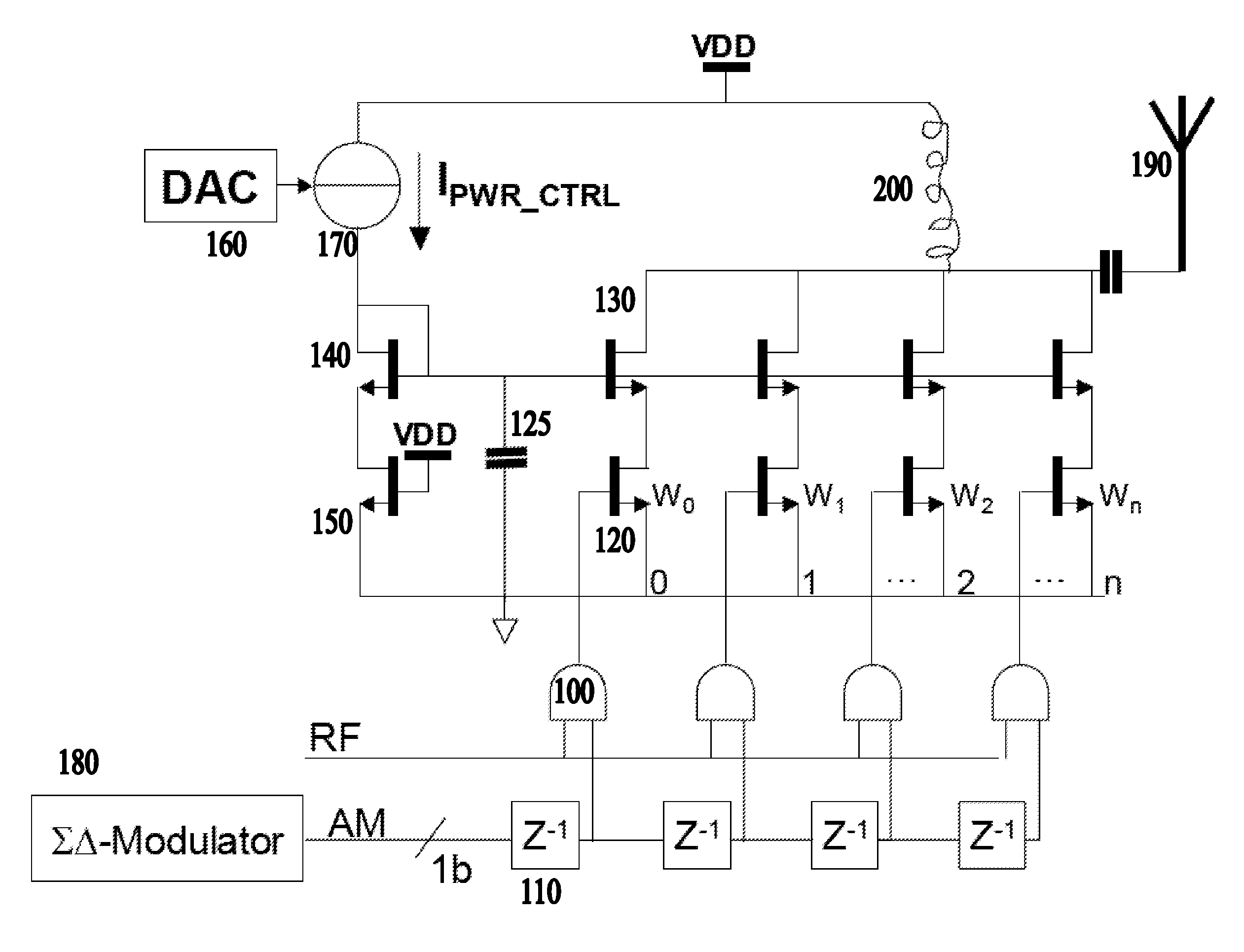
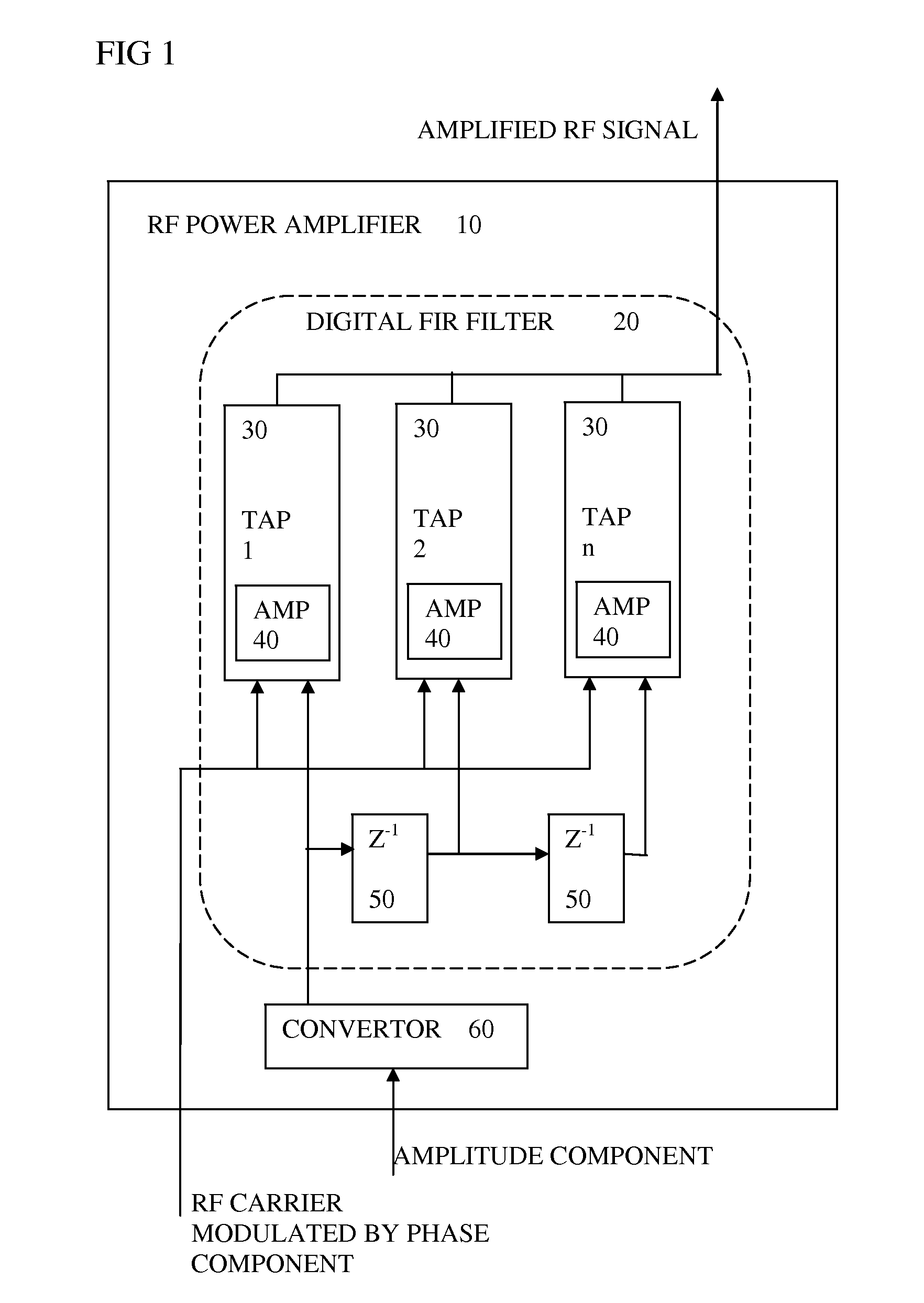
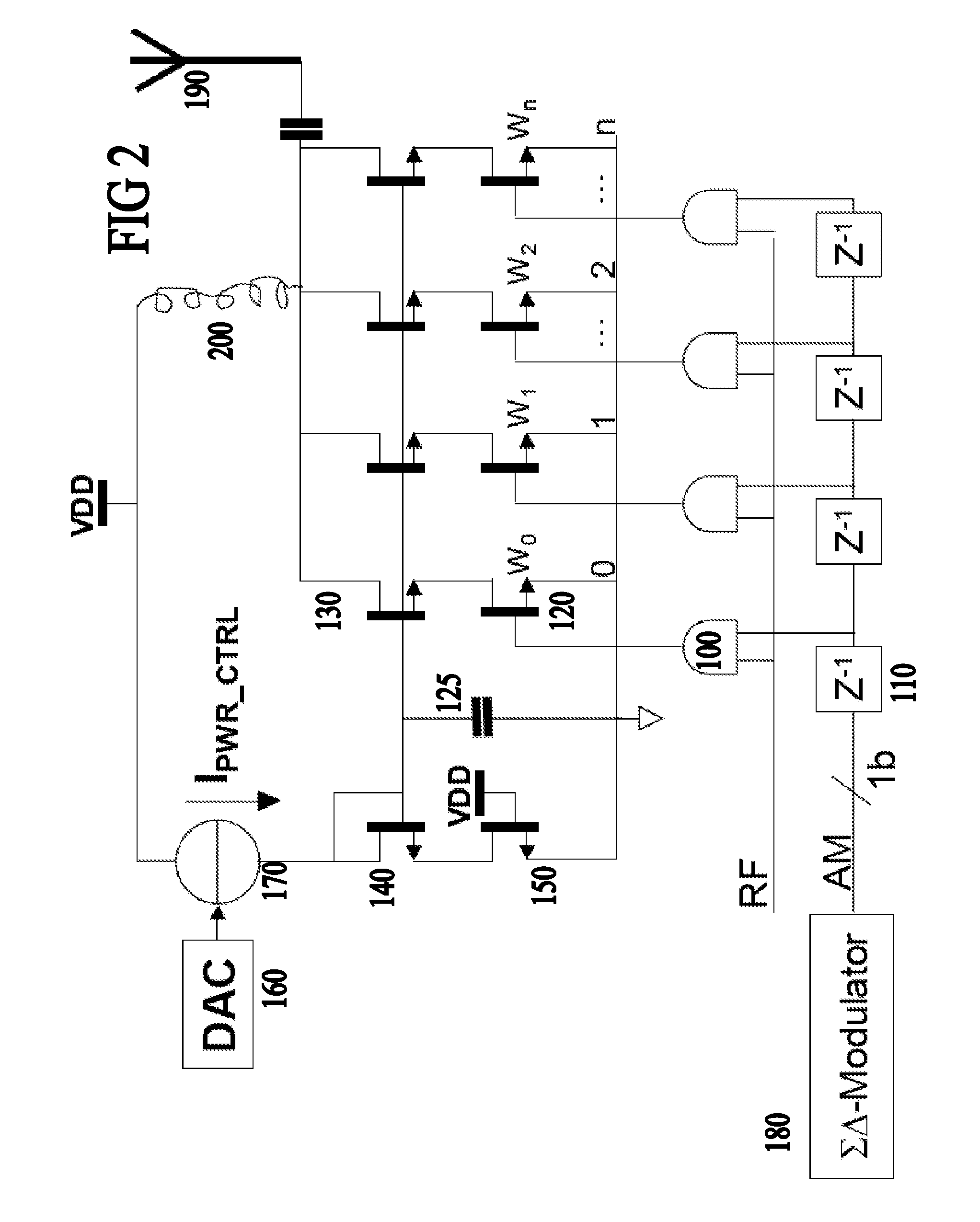
An RF power amplifier for a polar transmitter converts an amplitude component signal into a 1-bit digital amplitude signal, which is fed to a digital finite impulse response filter. Successive taps of the filter each have an RF amplification stage arranged to amplify successively delayed versions of the 1-bit digital amplitude signal, the amplifying being according to a respective tap coefficient, and according to the RF carrier modulated by the phase component. The filter is arranged to combine the outputs of the taps to provide the amplified RF signal. The power amplifier uses a one bit stream which therefore has only two states (2 values), thus achieving linearity in principle. Device mismatch between taps does not lead to non-linearity or distortion.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Polar transmitter
InactiveCN102291154AAchieving High Efficiency AmplificationAddressing Polar Coordinate Performance DeteriorationTransmissionTime domainTime delays
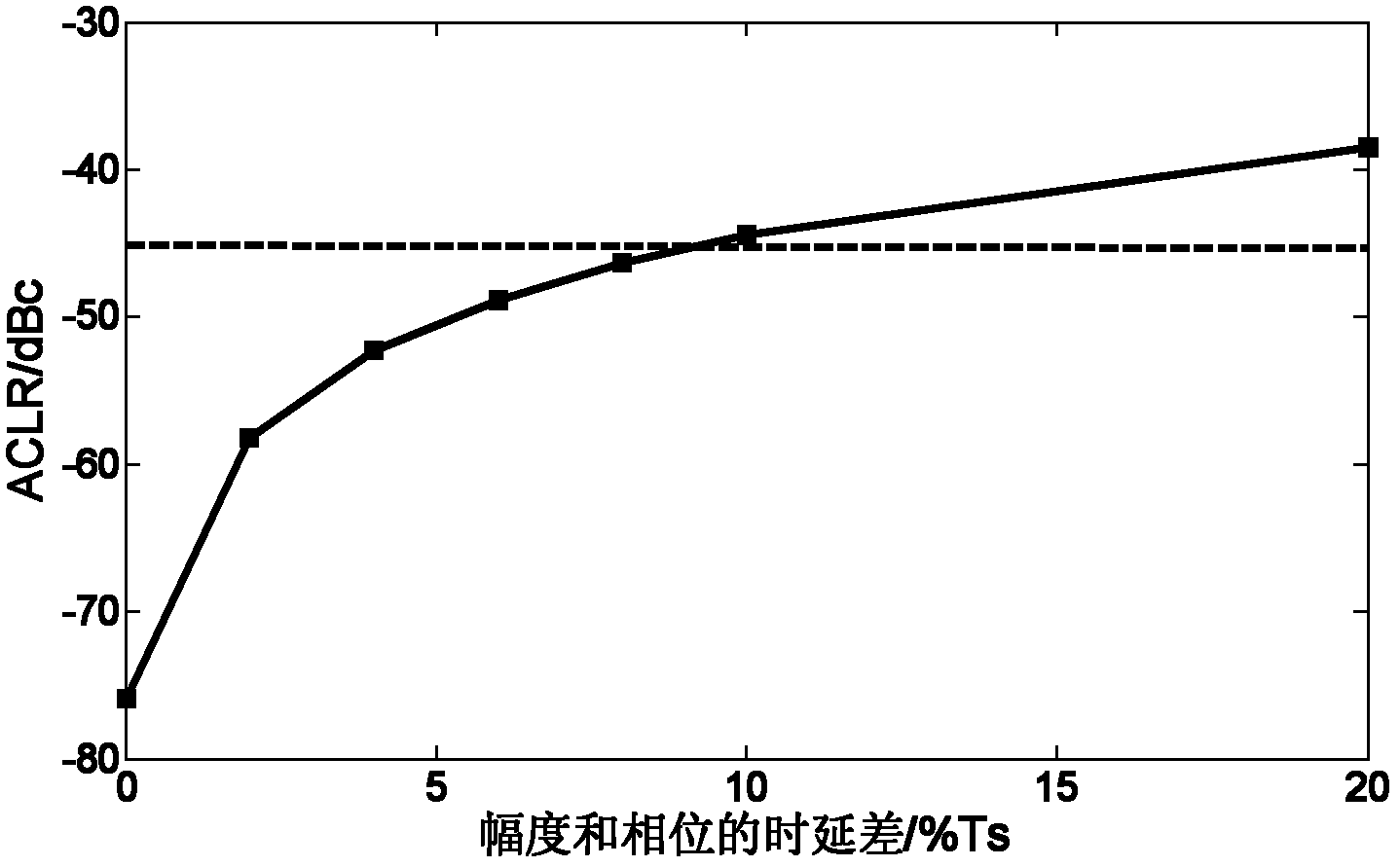
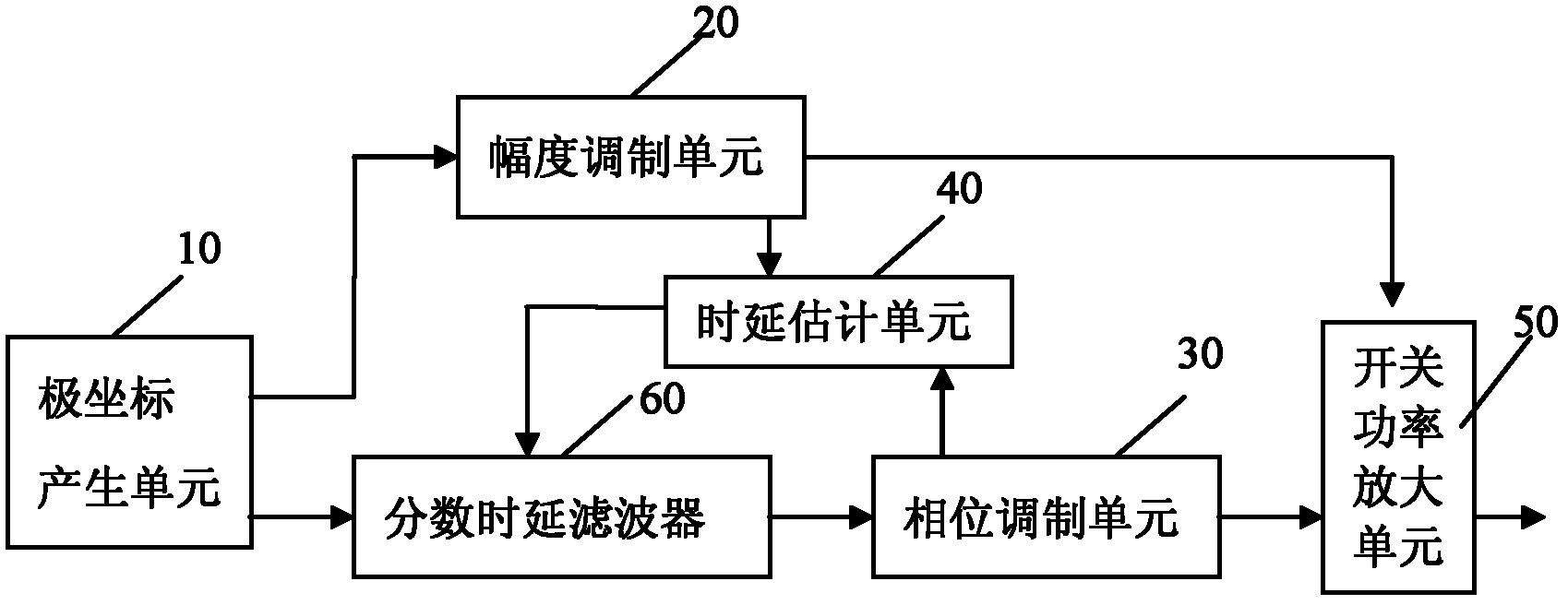
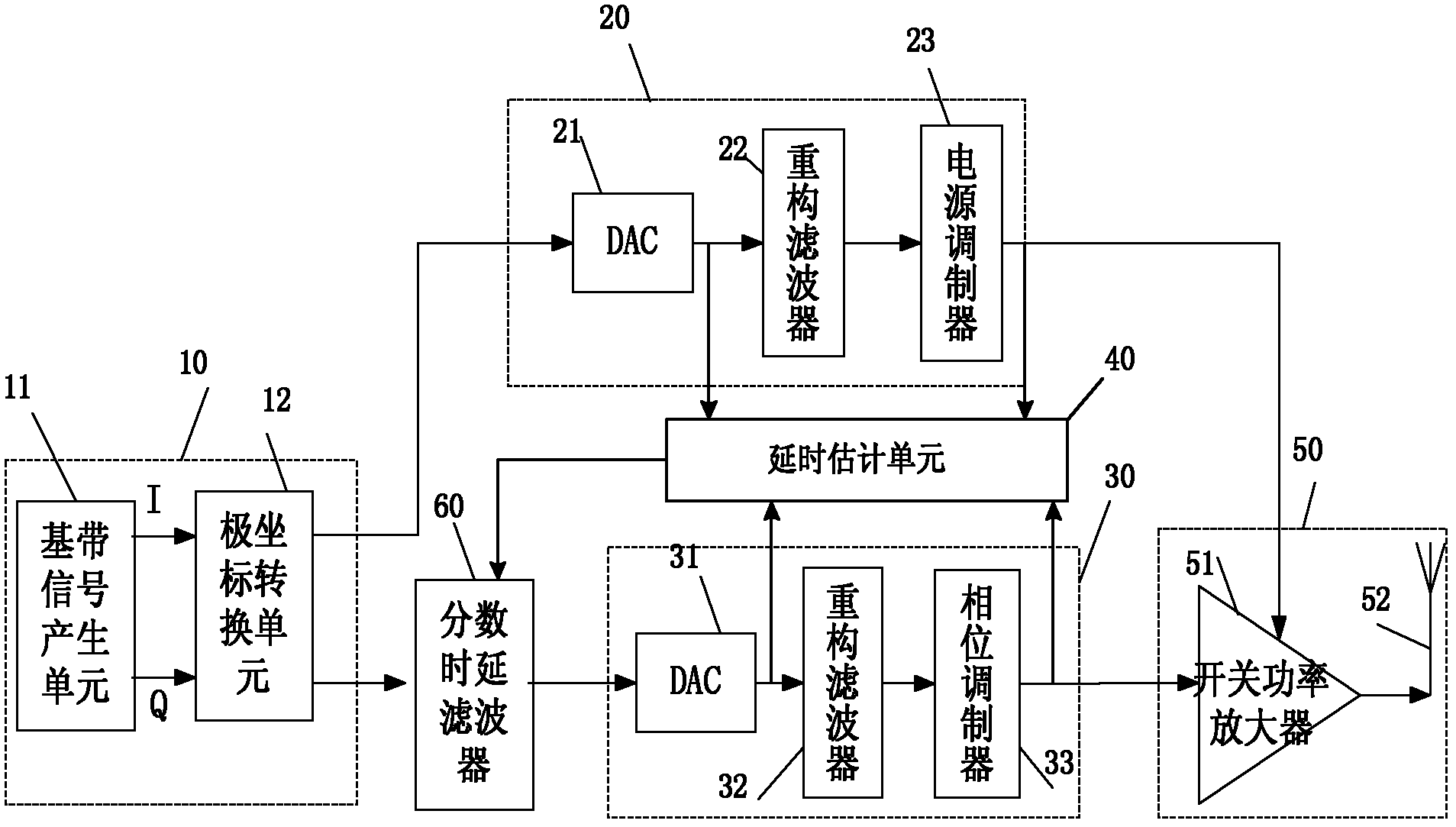
The invention provides a polar coordinate transmitter, which can meet the requirement of high speed rate at a low-speed clock frequency, i.e., compensate for integer time delay and fraction time delay under the condition of not increasing the sampling rate. The polar coordinate transmitter comprises a polar coordinate generating unit, an amplitude modulating unit, a phase modulating unit, a switch power amplifying unit, a time delay estimating unit and a variable fraction time delay filter, wherein the time delay estimating unit is used for estimating integer time delays of a phase channel and an amplitude channel on a time domain respectively, compensating for the integer time delays, estimating fraction time delays of the phase channel and the amplitude channel on a frequency domain respectively, adding an integer time delay error and a fraction time delay error between the phase channel and the amplitude channel to obtain a time delay error, and setting the variable fraction time delay filter according to the obtained time delay error; and the variable fraction time delay filter is used for performing time delay on a signal input into the phase channel and compensating for the time delay error between the phase channel and the amplitude channel.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Frequency synthesizer and polar transmitter having the same
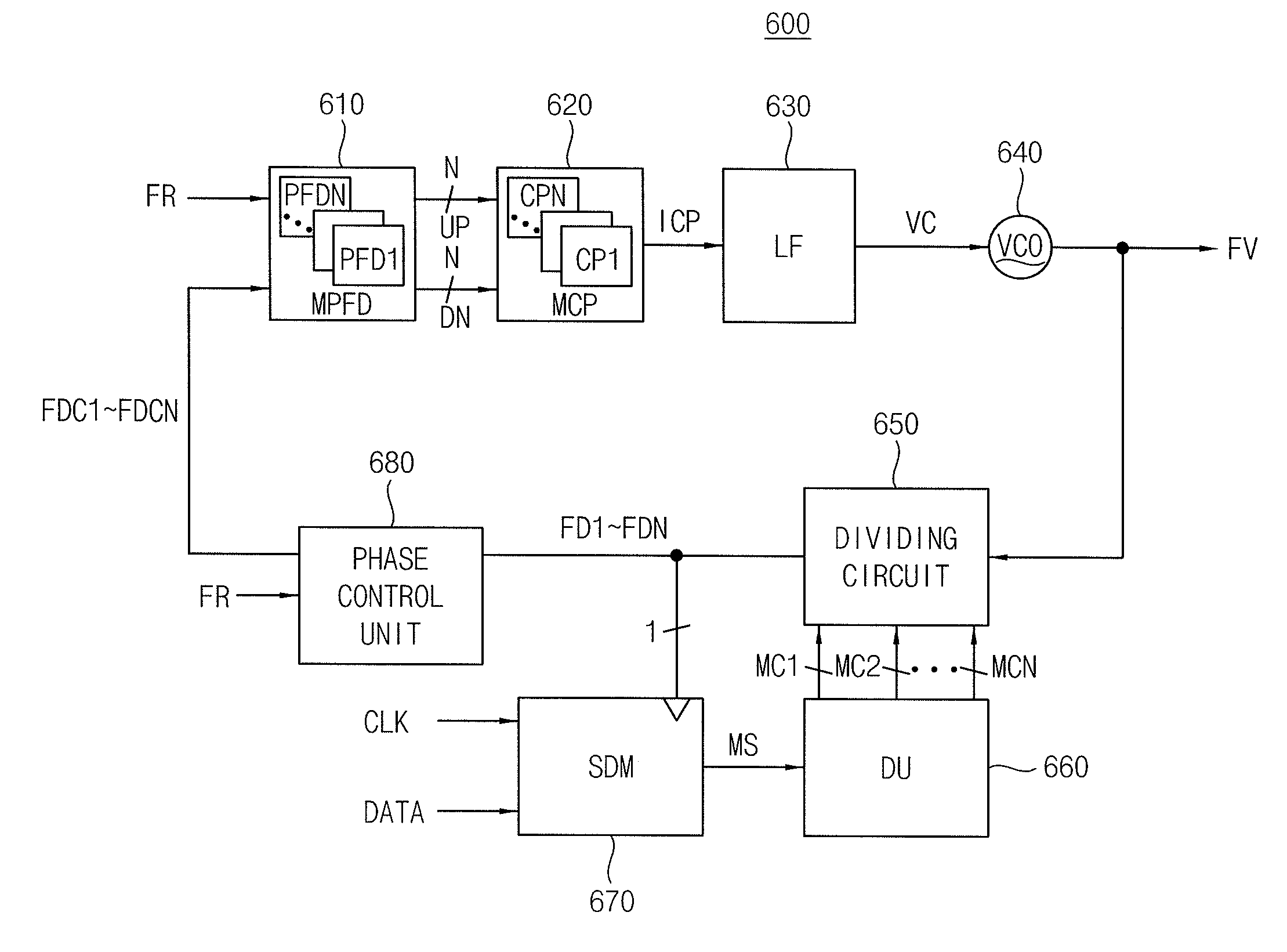
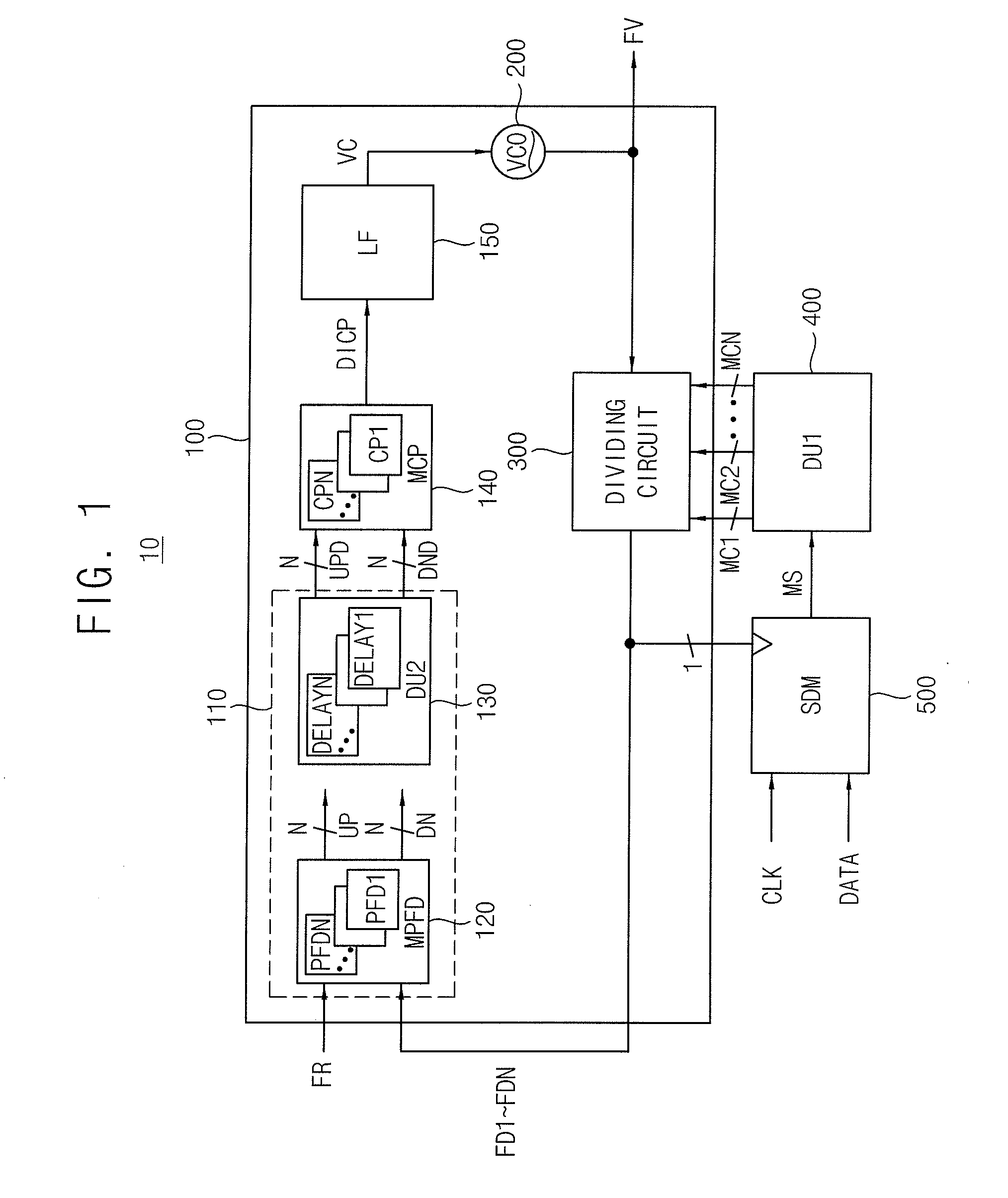
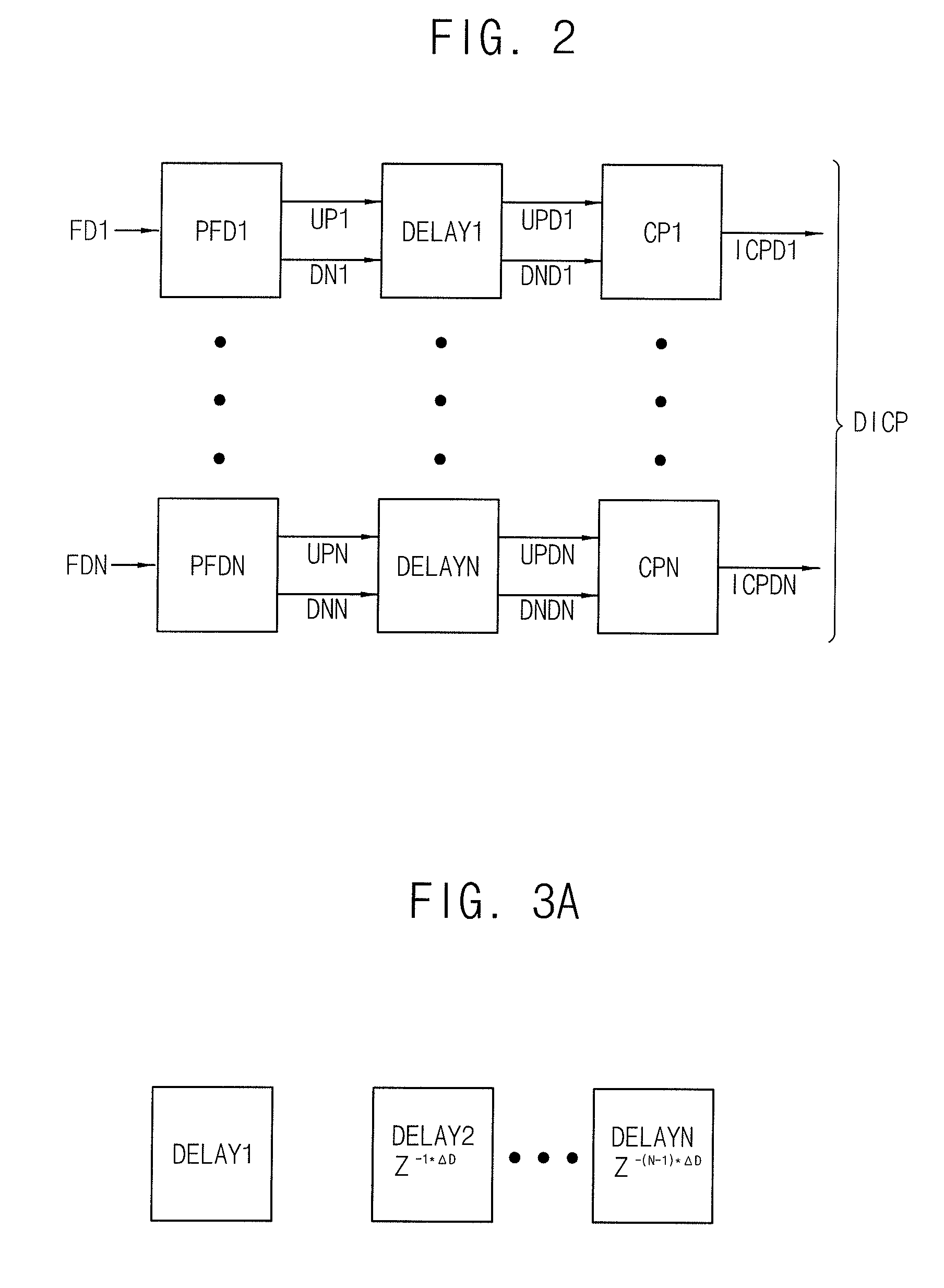
InactiveUS20100329388A1Avoid problemsModulation transferencePulse automatic controlLoop filterPhase detector
A frequency synthesizer includes a distributed phase detector circuit, a multiple charge pump, a loop filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator and a dividing circuit. The distributed phase detector circuit delays an up signal and a down signal to generate a delayed up signal and a delayed down signal. The multiple charge pump generates a distributed current signal including a plurality of current pulse signals. Each of the current pulse signal is based on each bit of the delayed up signal and the delayed down signal. The loop filter filters the distributed current signal to generate a control voltage. The voltage-controlled oscillator generates an oscillation frequency signal based on the control voltage. The dividing circuit divides the oscillation frequency signal to generate a plurality of division frequency signals in response to a plurality of control signals, where the frequency signals are fedback to the distributed phase detector circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
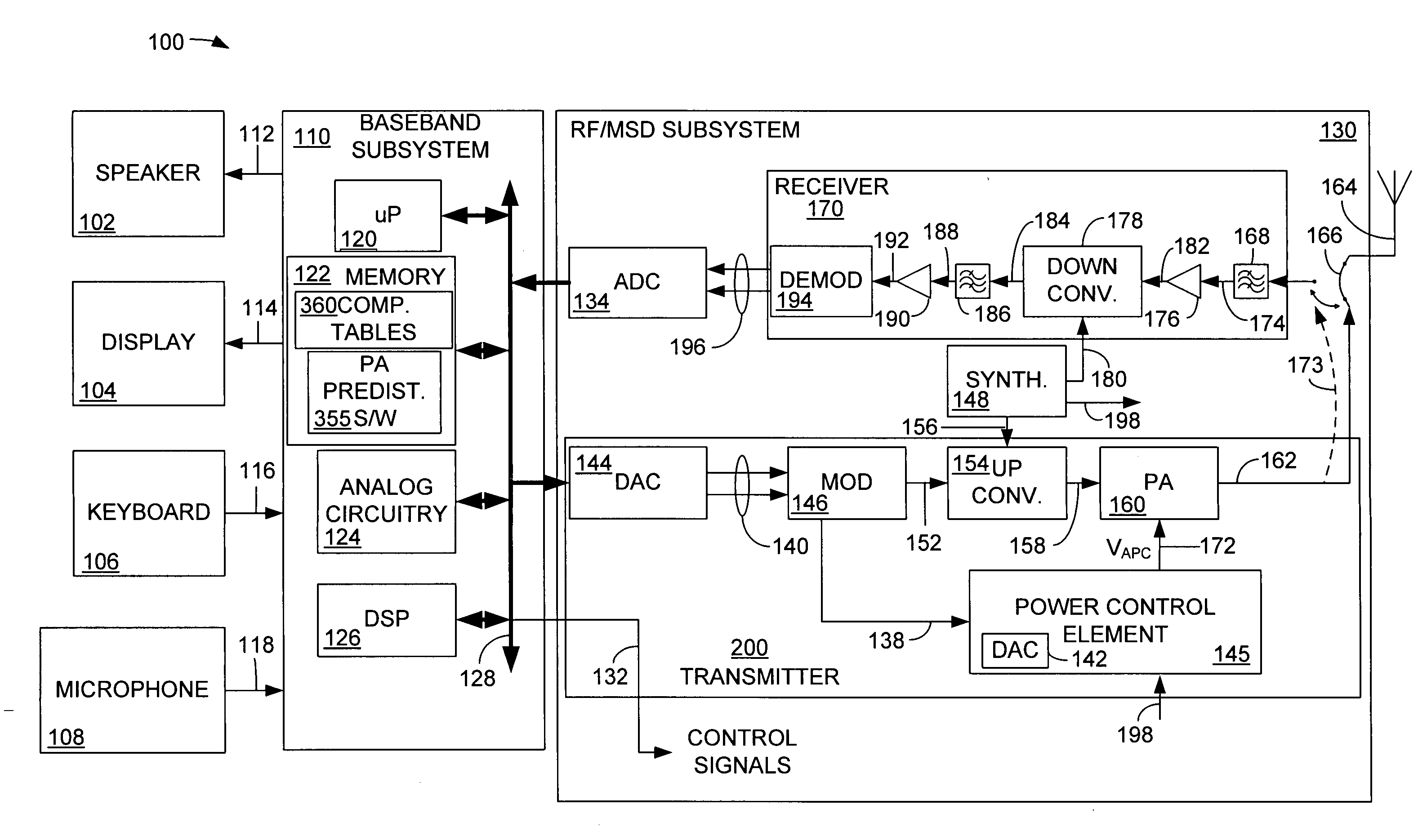
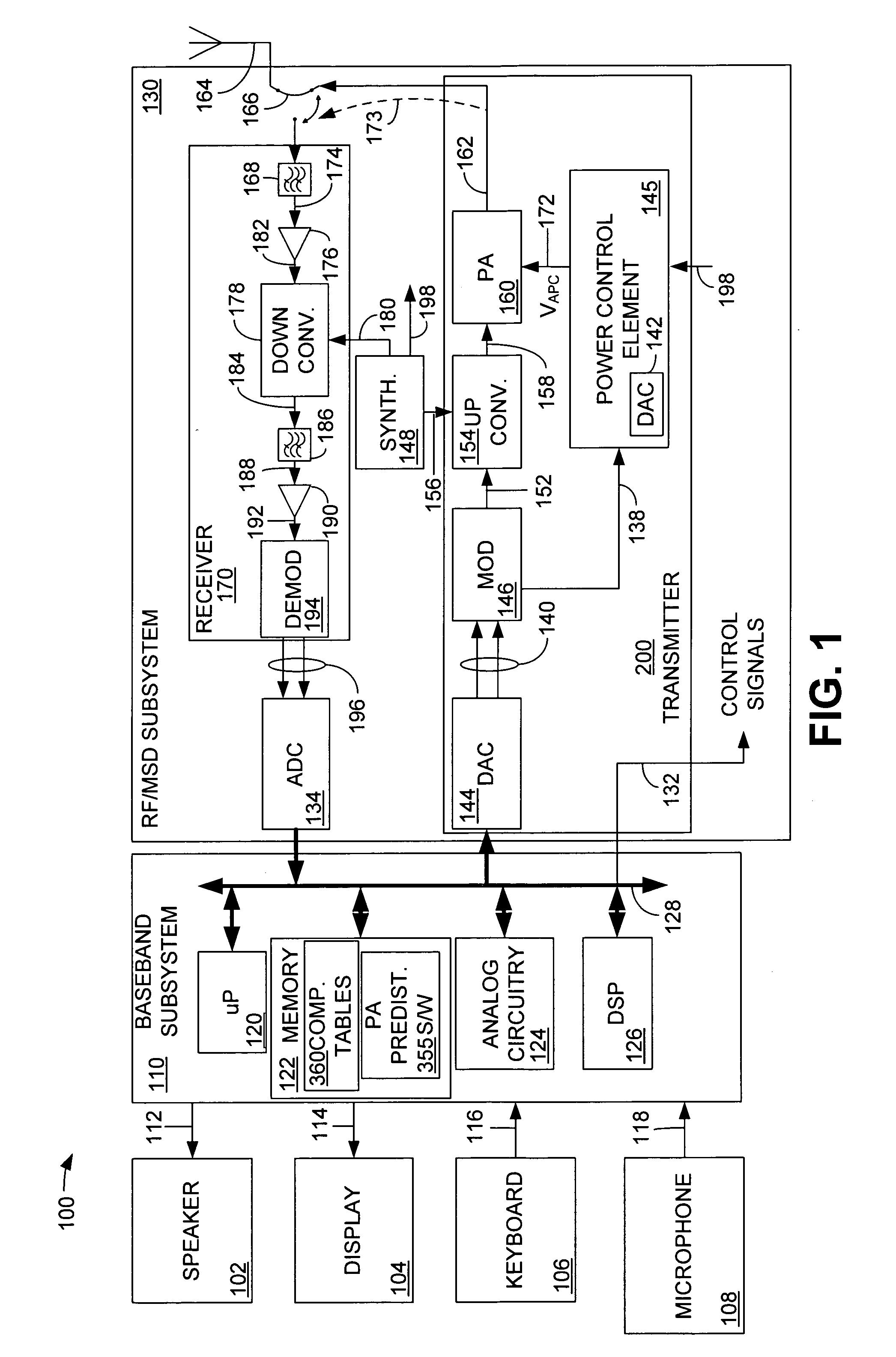
Methods and apparatuses for transmission power control in a wireless communication system
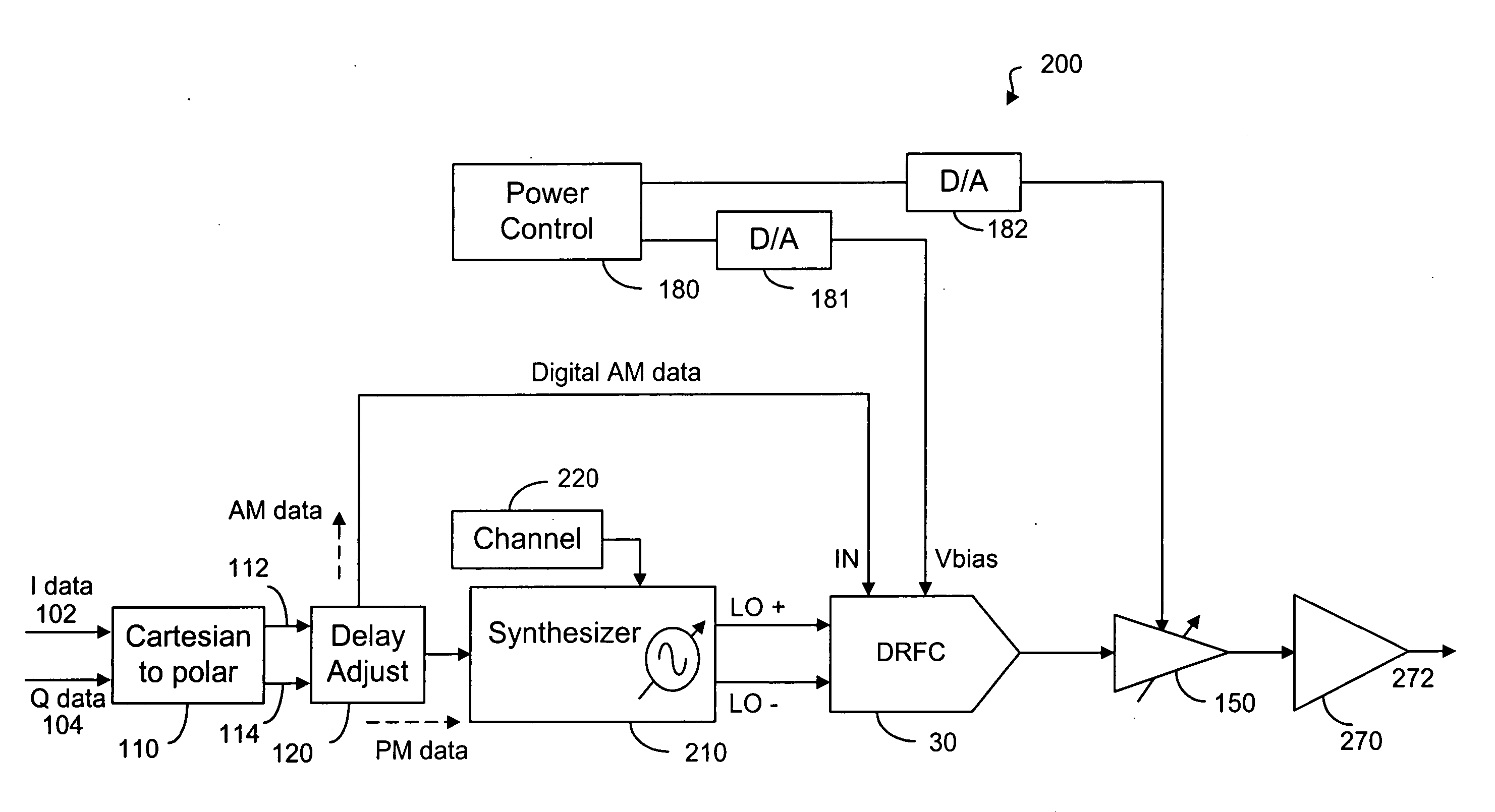
The invention includes methods for transmission power control in a wireless communication system. The method includes receiving at least one input parameter indicative of a transmission power level, generating a control parameter based on the at least one parameter and regulating an output transmission power level of a wireless terminal based on the control parameter. The invention further includes transmission power control methods for a digital polar transmitter.
Owner:PINE VALLEY INVESTMENTS INC
Adaptive delay alignment in polar transmitters
ActiveUS8126409B2Reduce degradationResonant long antennasModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierWave shape
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Polar transmitter using binary phase shift key (BPSK) modulation method
InactiveUS20070298732A1Simple circuit structureHigh speed machiningPhase-modulated carrier systemsMultiple carrier systemsPhase shiftedCarrier signal
A polar transmitter using a binary phase shift key (BPSK) method includes a data dividing unit which divides input data into an amplitude component and a phase component, a frequency synthesizer which produces an I value of a passband having a phase component of an I signal and a Q value of a passband having a phase component of a Q signal, a polar modulation circuit for the I signal which produces an I carrier wave to the I signal using the amplitude component from the data dividing unit and the I value from the frequency synthesizer, a polar modulation circuit for the Q signal which produces a Q carrier wave to the Q signal using the amplitude component and the Q value, and a carrier wave producing unit which combines the I carrier wave and the Q carrier wave thus to produce a carrier wave.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com