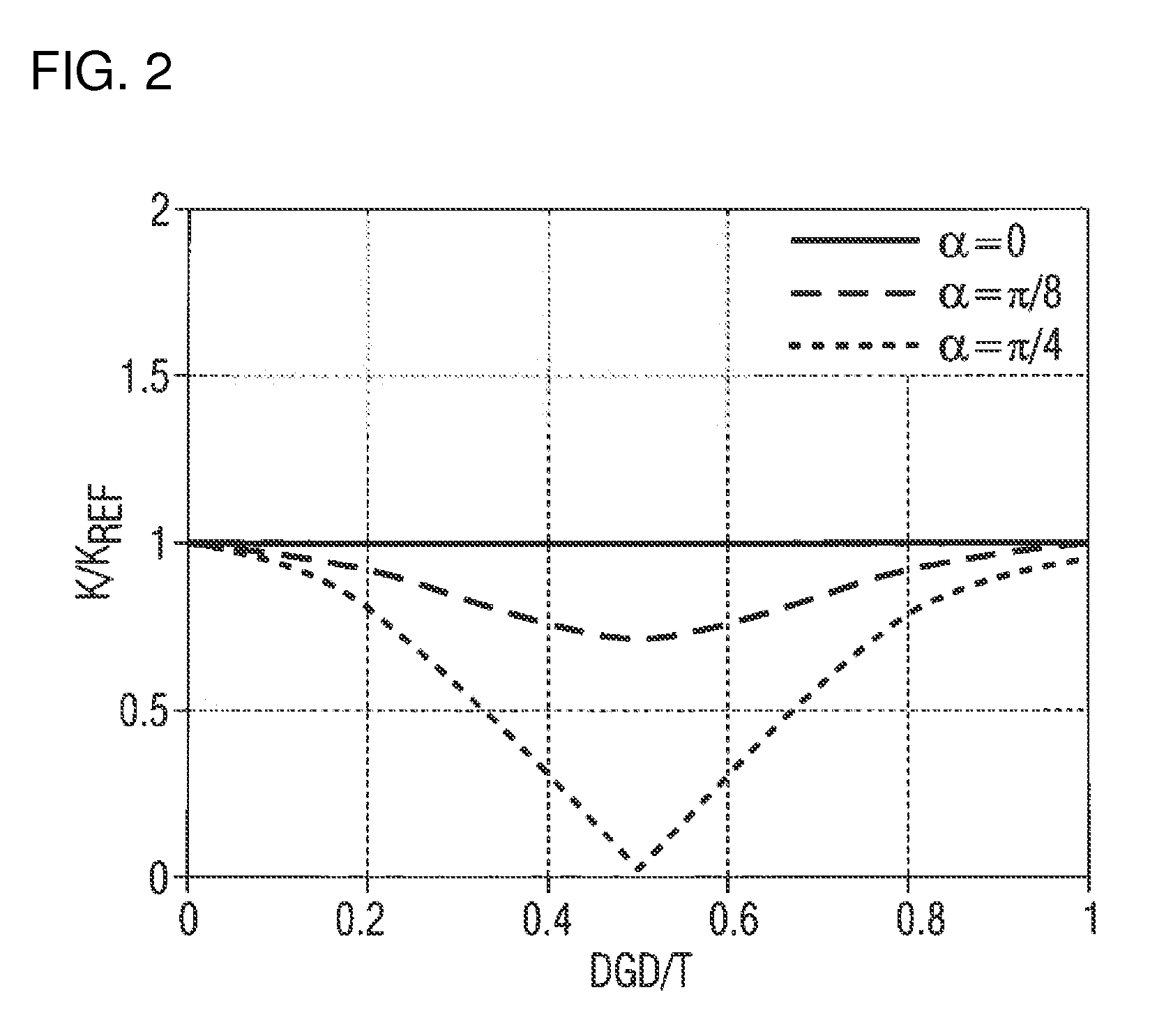
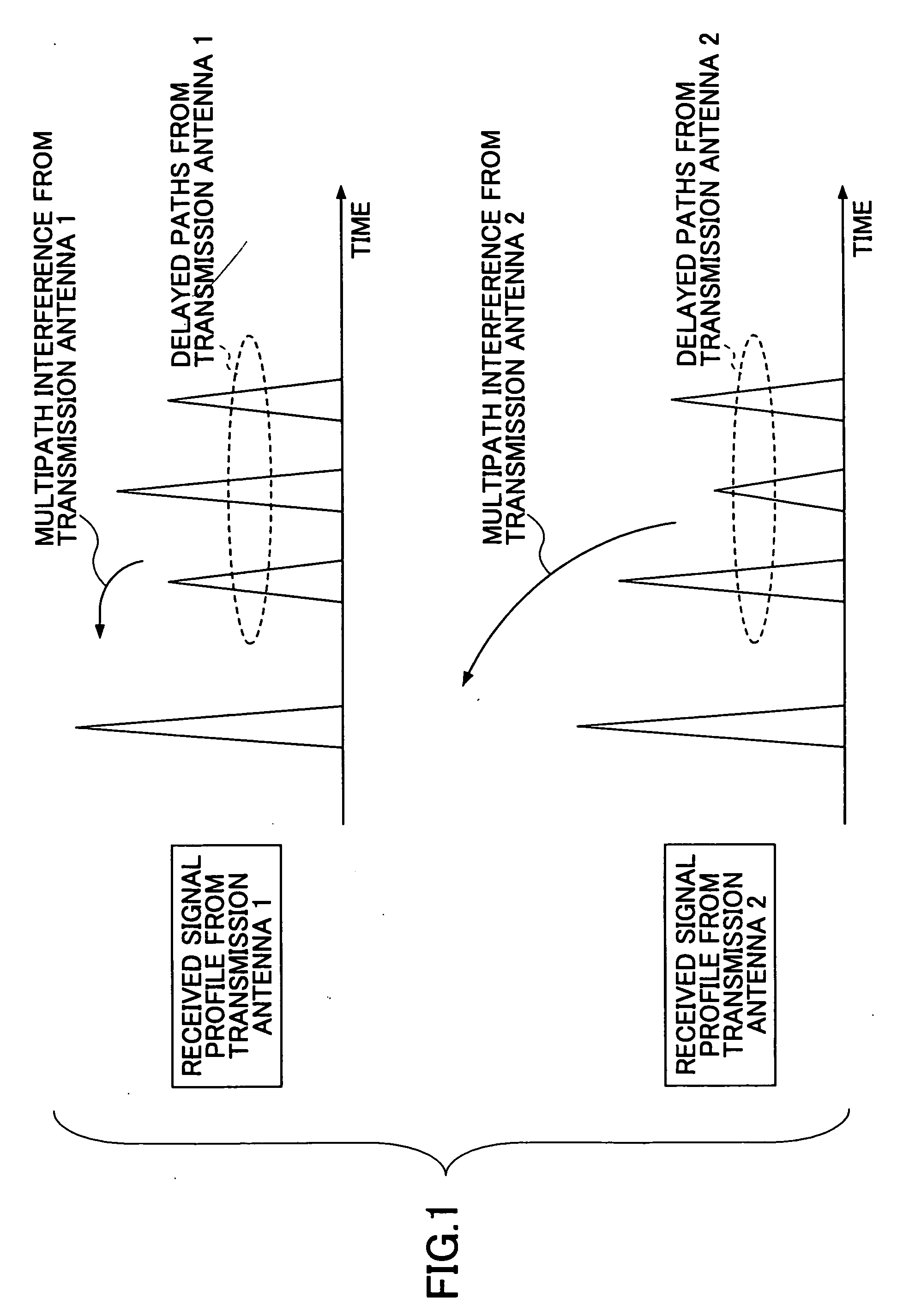
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
471results about "Synchronisation receivers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
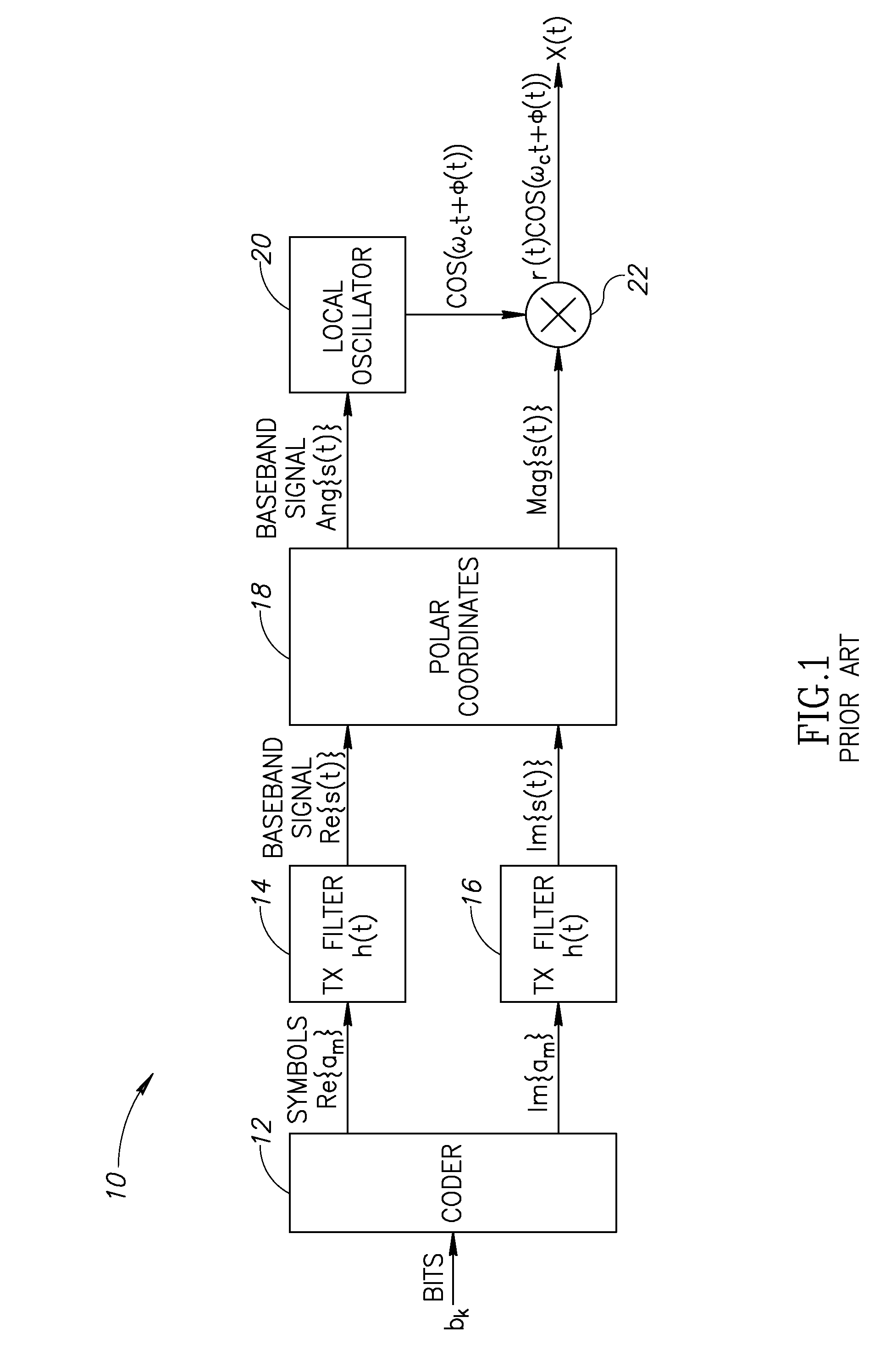
Communication control apparatus and method
ActiveUS7158488B2Easy to identifyEasy to set upElectrophonic musical instrumentsLaser detailsNetwork packetExecution control
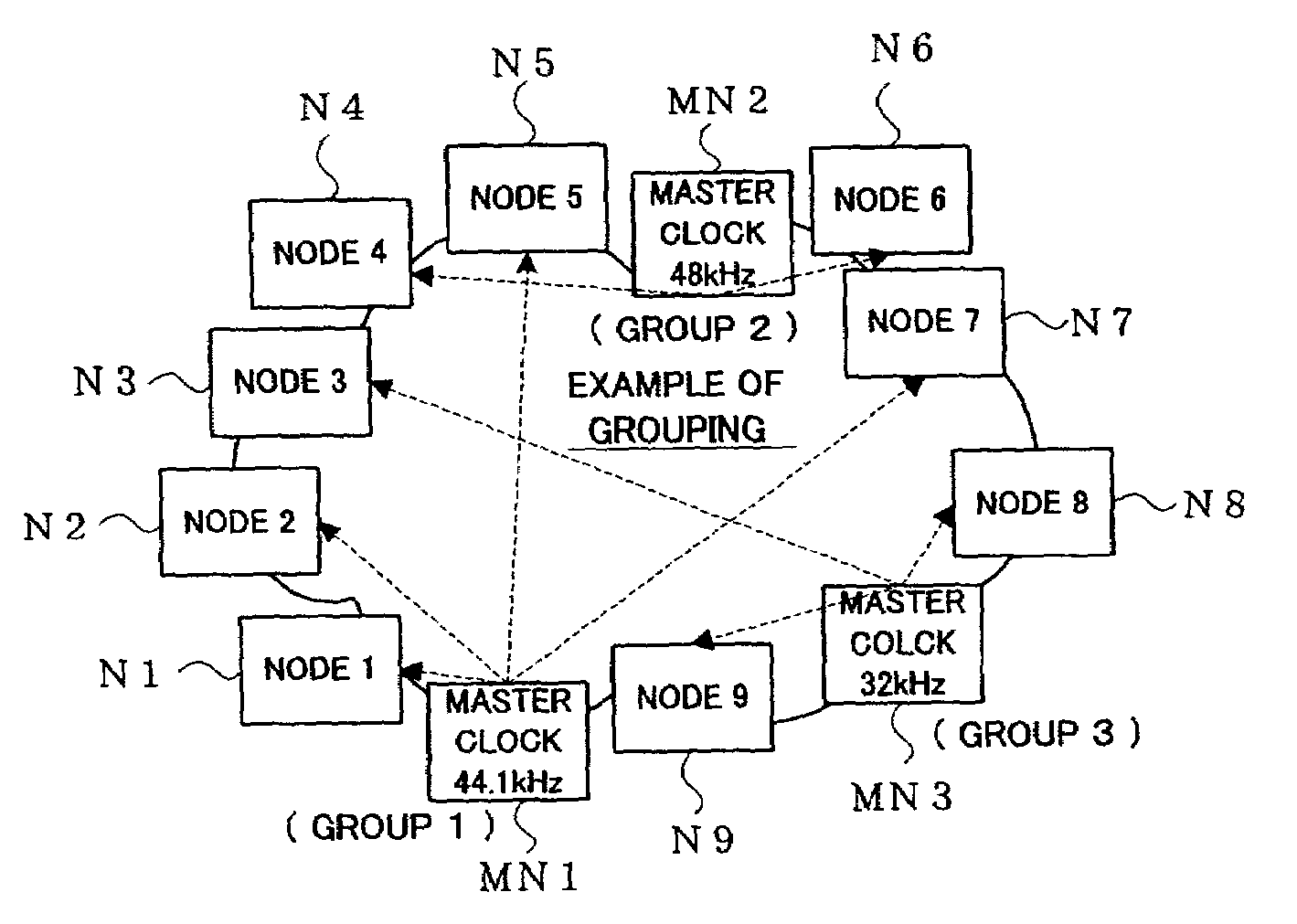
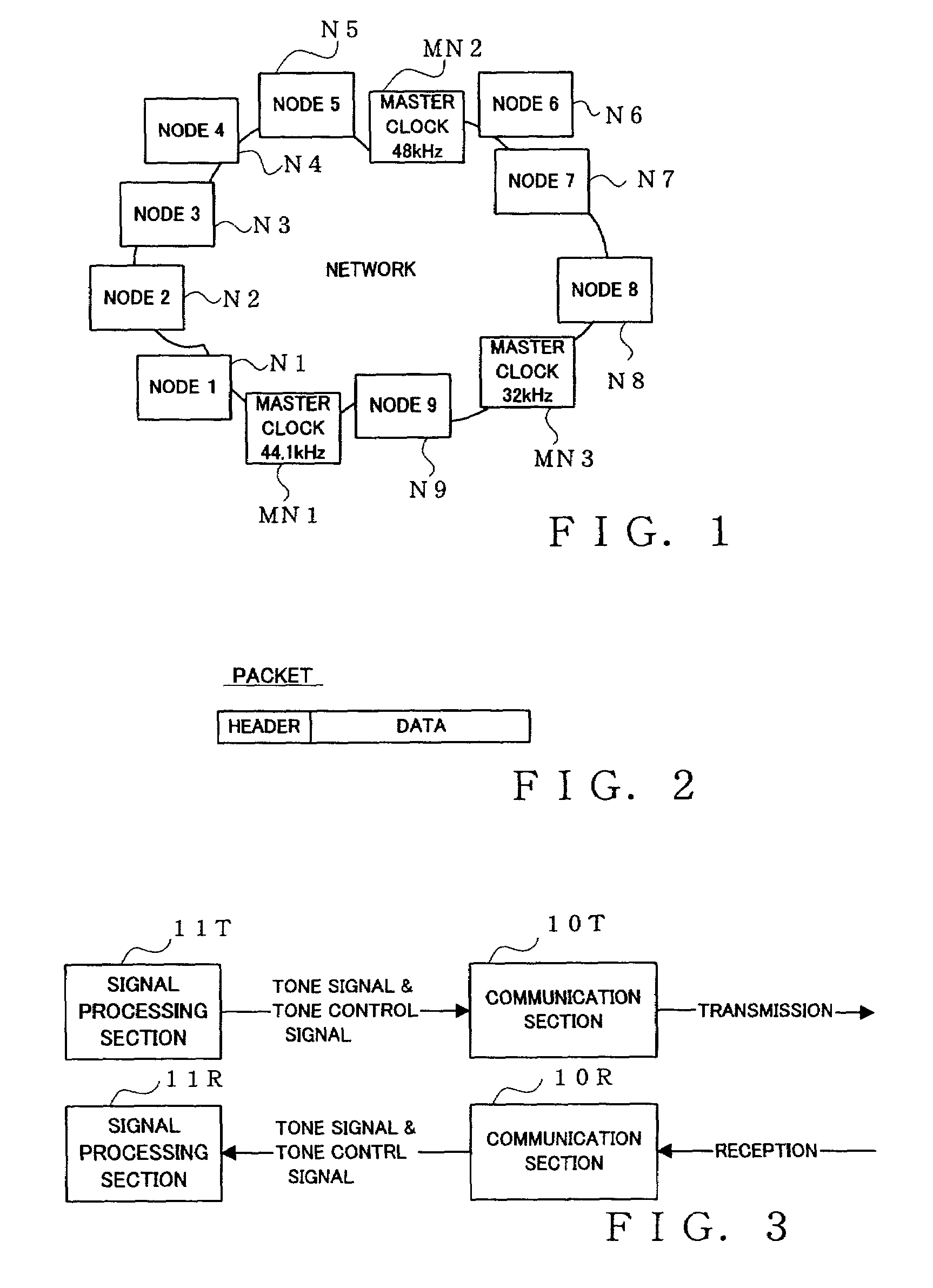
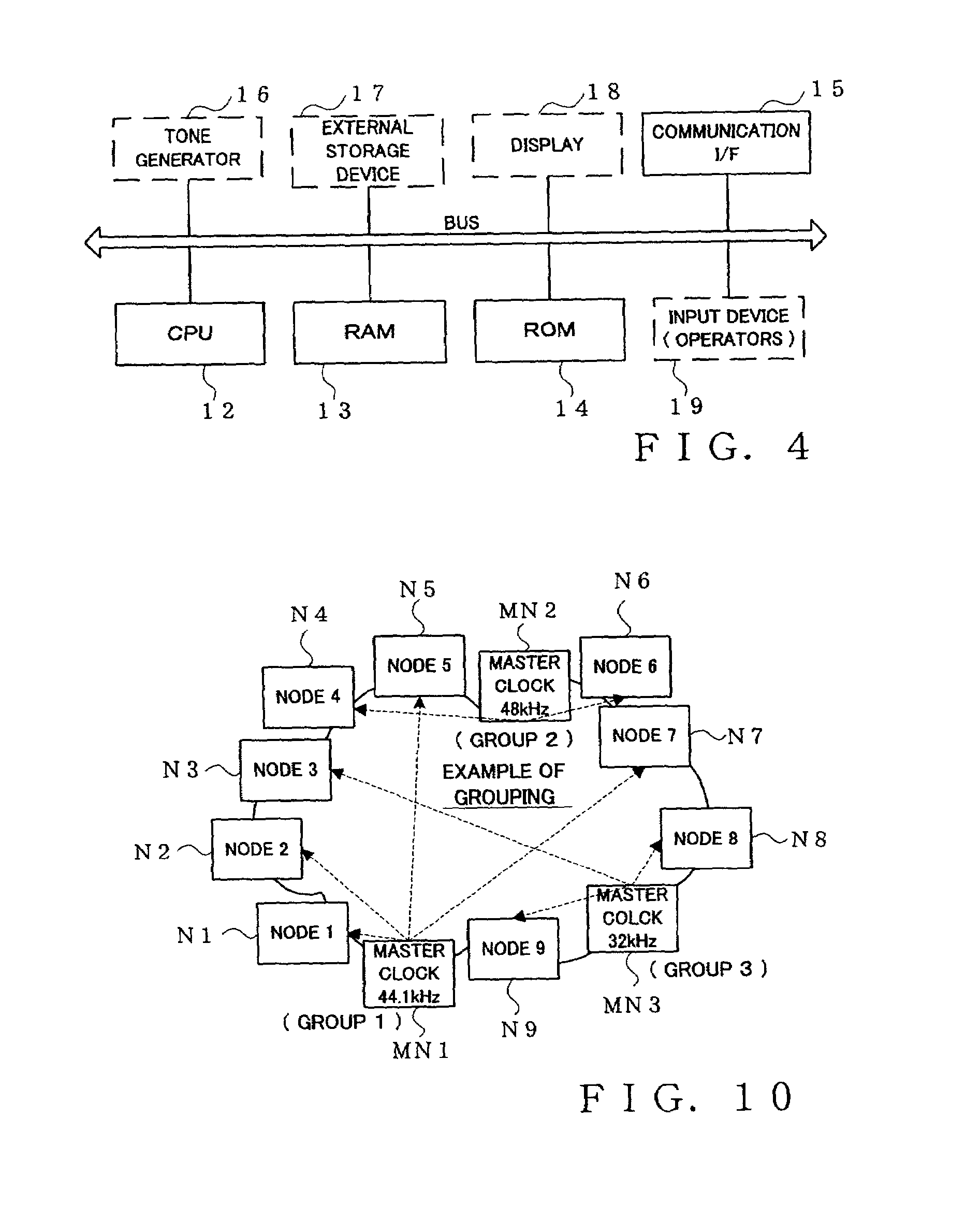
One or more nodes on a communication network are selected and set as one node group. In each of the nodes, group identification information representing the node group to which the node belongs is stored in advance. The group identification information is attached to the header of a data packet to be transmitted, so that nodes constituting a node group that should commonly receive data can be readily identified by comparing the group identification information imparted to the transmitted data packet and the group identification information stored in each receiving node. Given node can choose to become a node of a particular function, such as a clock master node, in which case control is performed to delete, from the node group, a node having so far played the role of the node of the particular function in such a manner that there exists only one node of the particular function per node group.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
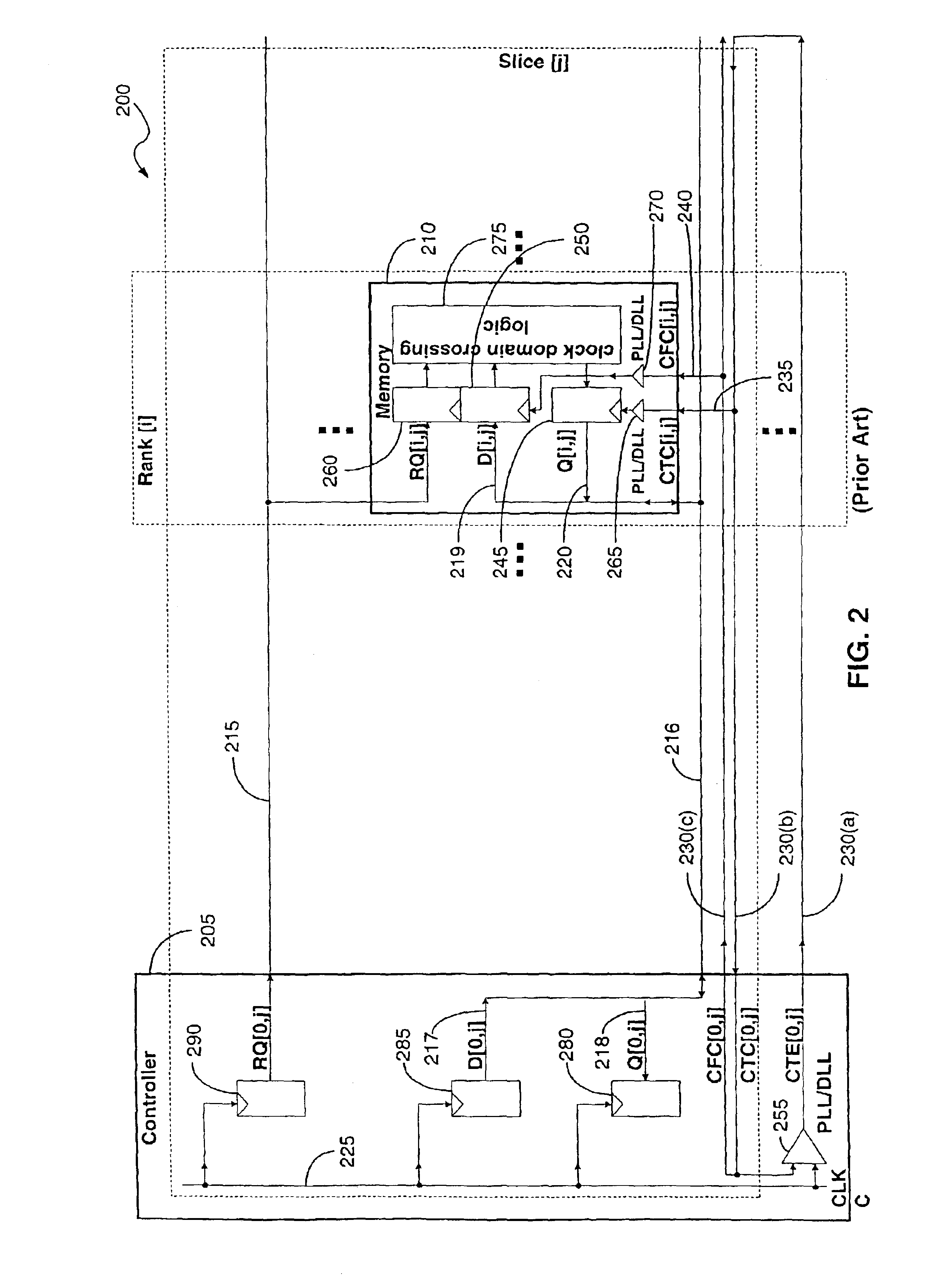
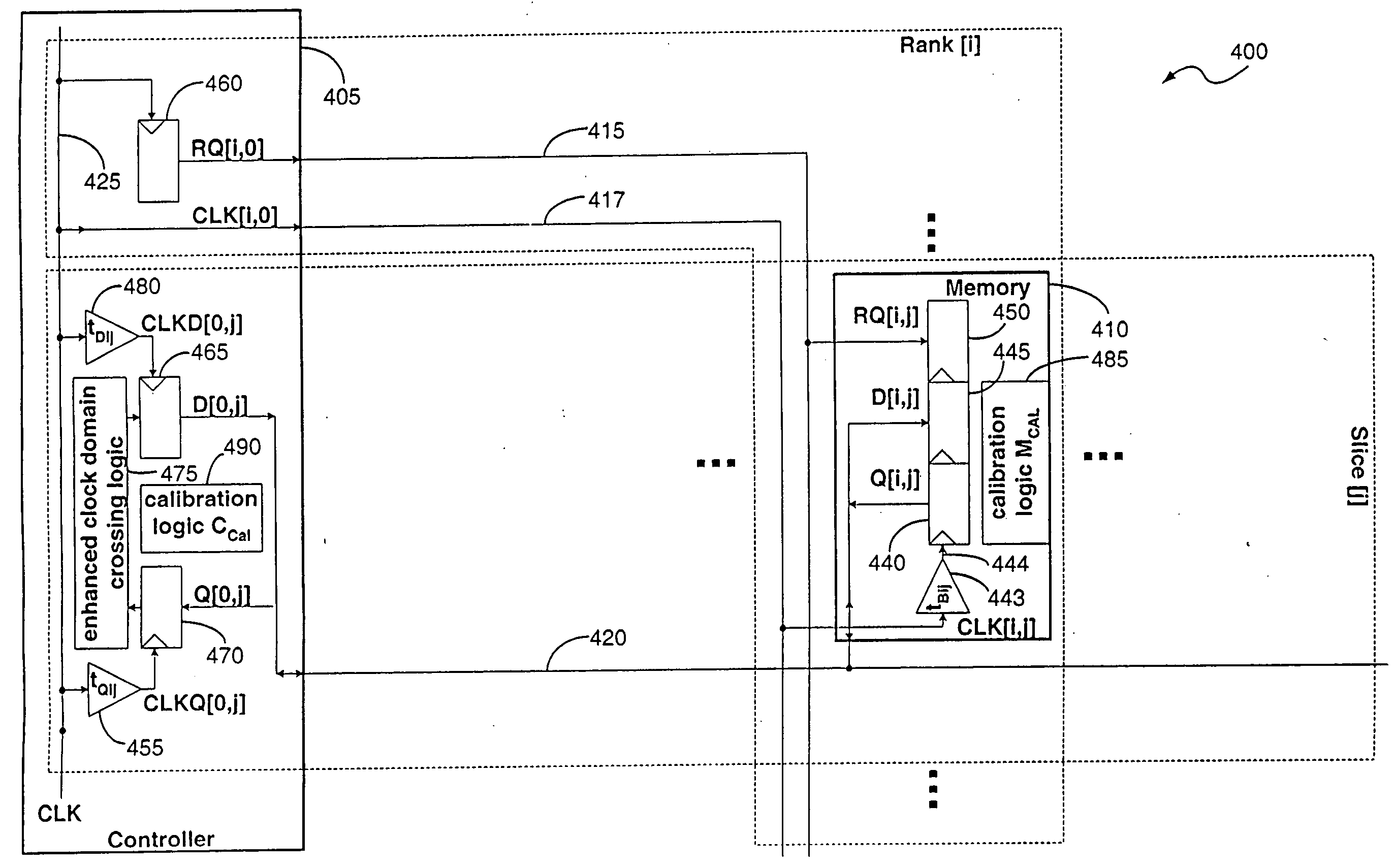
Timing calibration apparatus and method for a memory device signaling system
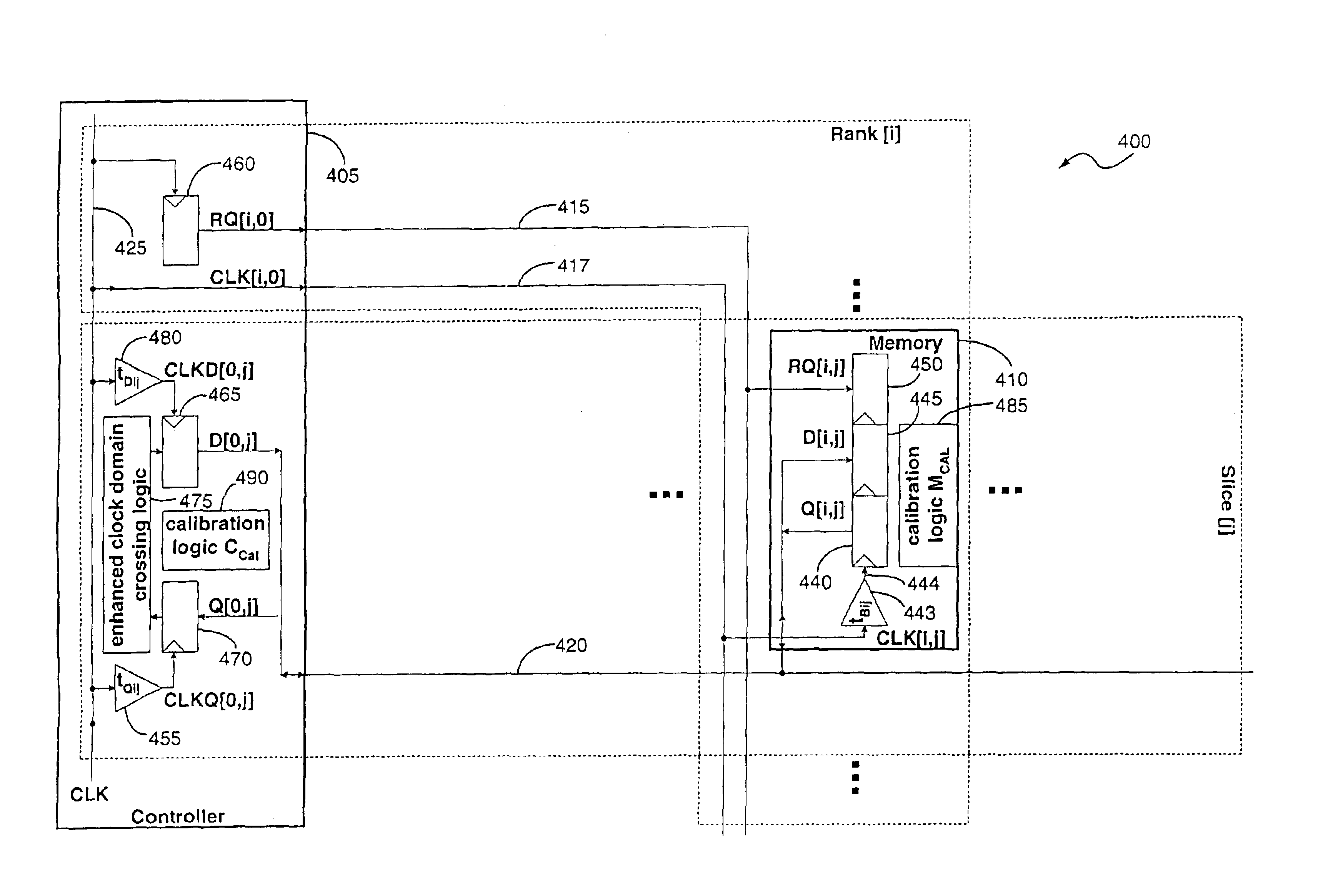
A memory system includes a memory controller and a memory component coupled to each other. An interface of the memory component is configured to receive a first signal from the memory controller with read request information, retrieve the read data information from the memory core in response to the request information, and transmit to the memory controller a second signal containing the read data information. The read data information includes read data symbols, where the average duration of the read data symbols, measured at the interface, defines a symbol time interval. A first external access time is measured at the interface between a first read request and read data transmitted by the interface in response to the first read request. A second external access time interval is measured at the interface between a second read request and read data transmitted by the interface in response to the second read request. The difference between the first external access time and the second external access time is greater than one-half of the symbol time interval.
Owner:RAMPART ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
Memory device signaling system and method with independent timing calibration for parallel signal paths
InactiveUS20050132158A1Error detection/correctionSolid-state devicesMemory controllerSignaling system
A memory system includes a memory controller and a memory component coupled to each other. The memory controller includes an interface to receive a first signal and a second signal from the memory component, wherein the first signal comprises a first symbol and the second signal comprises a second symbol. A first circuit of the memory controller receives the first signal by sampling the first symbol using a first timing offset relative to a reference clock signal, and a second circuit of the memory controller receives the second signal by sampling the second symbol using a second timing offset relative to the reference clock signal. The first timing offset is independent of the second timing offset.
Owner:RAMPART ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
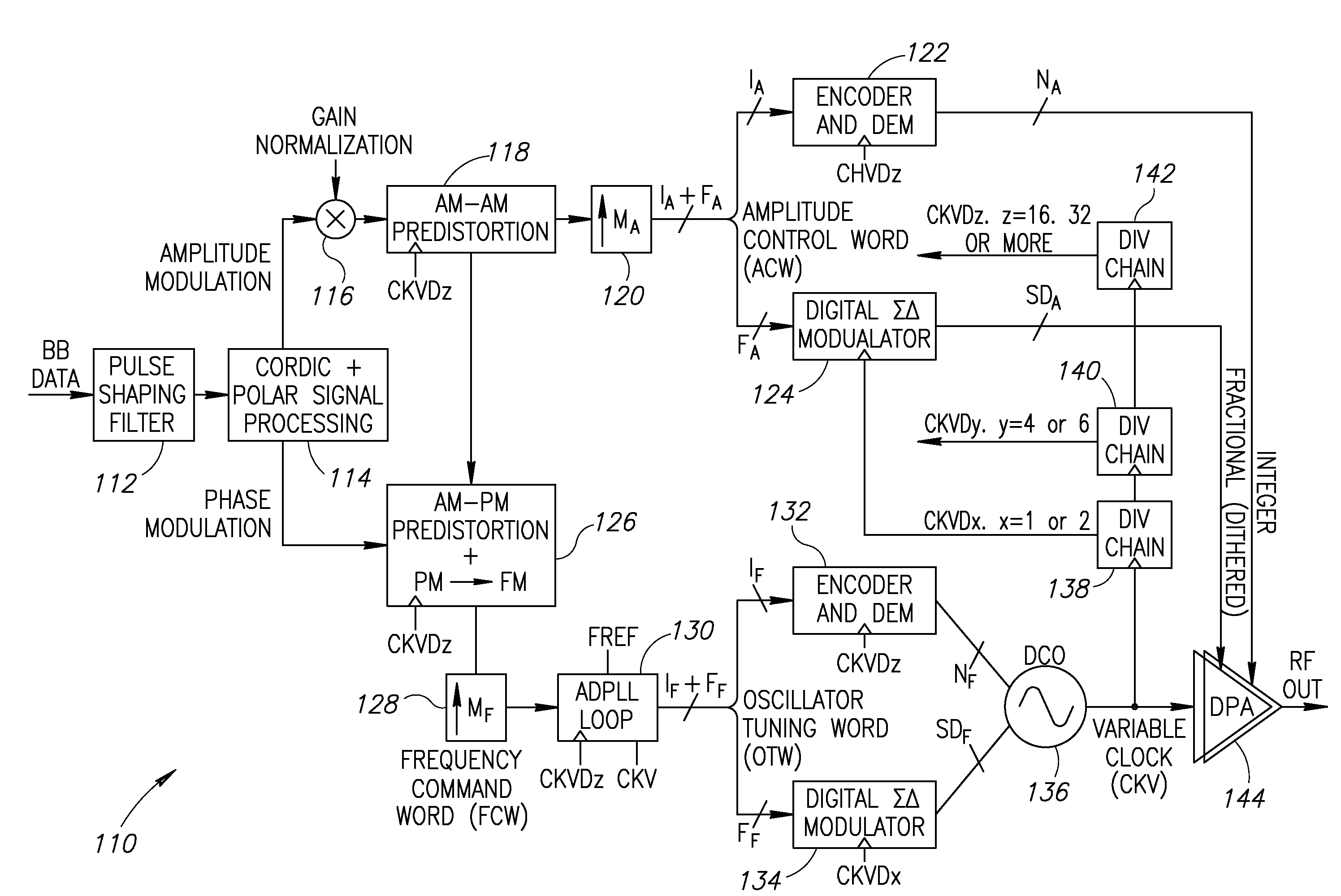
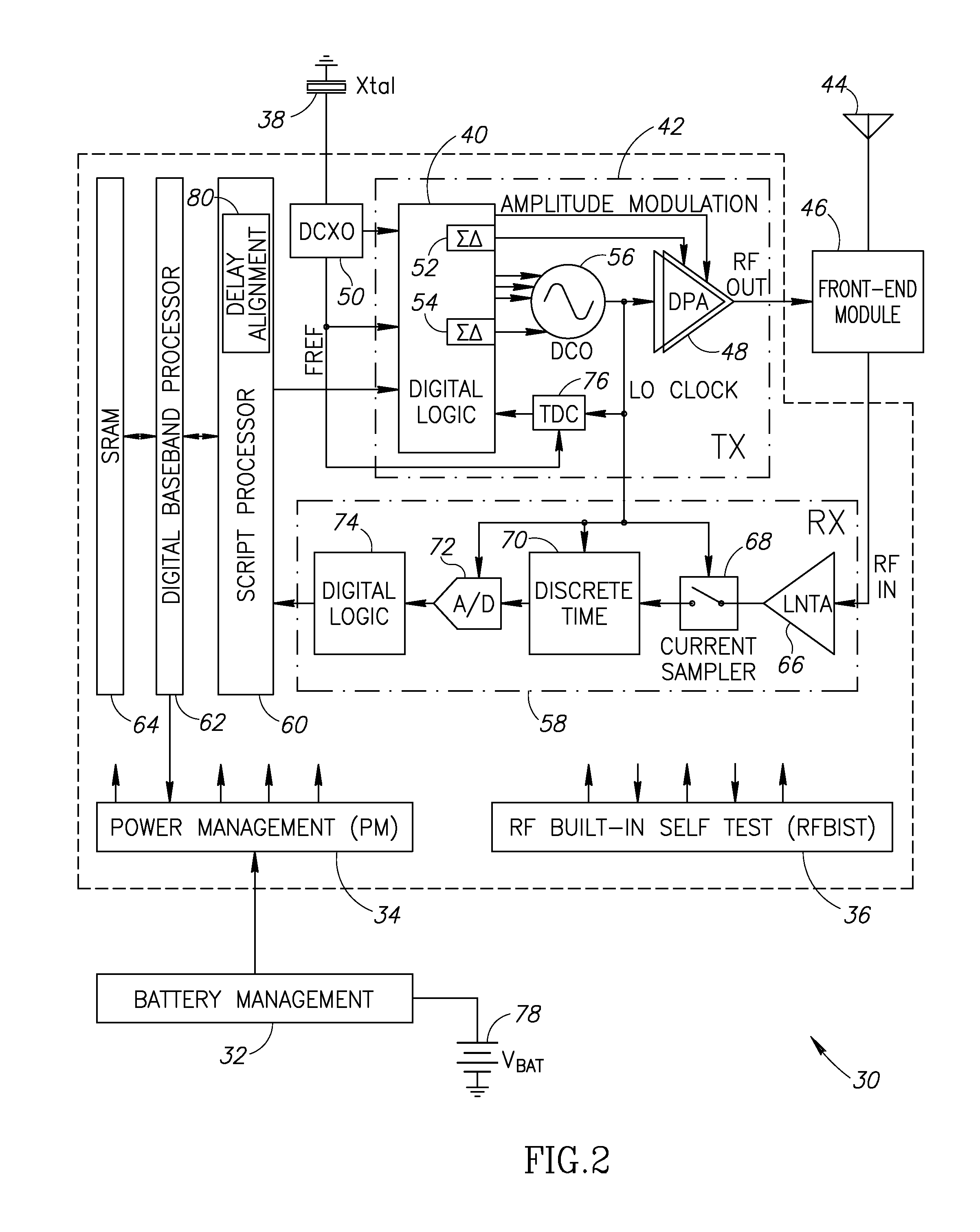
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS20070189417A1Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierNanosecond
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
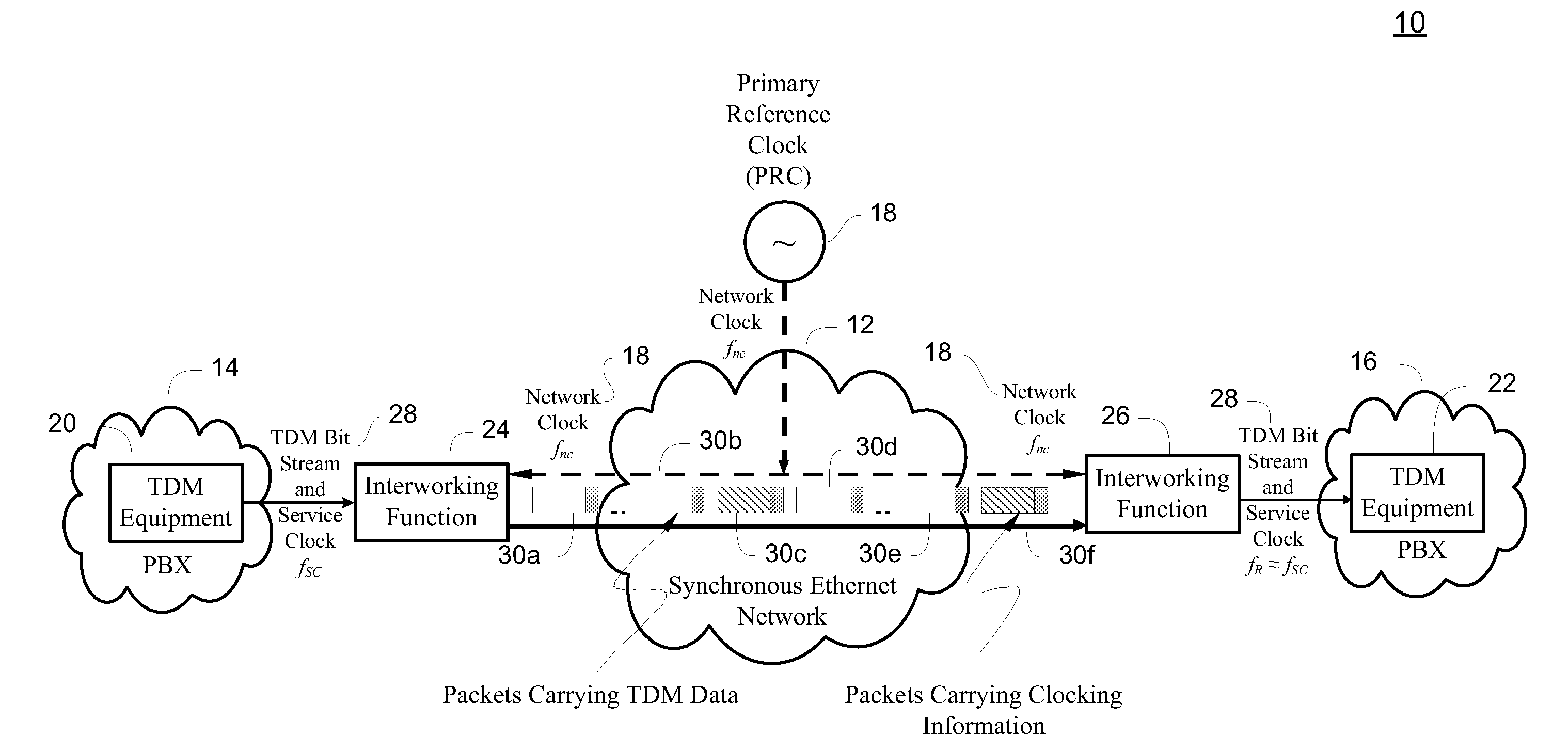
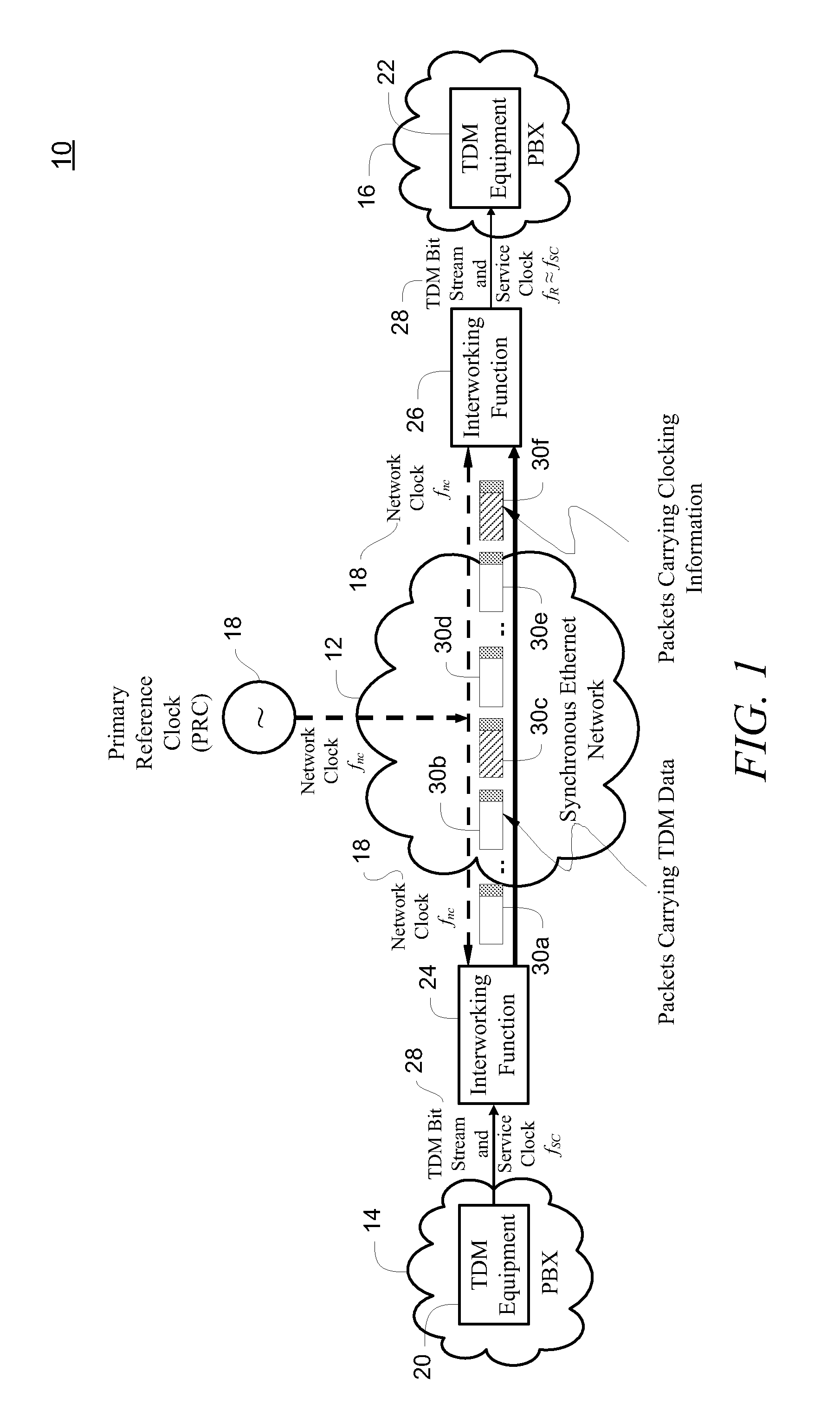
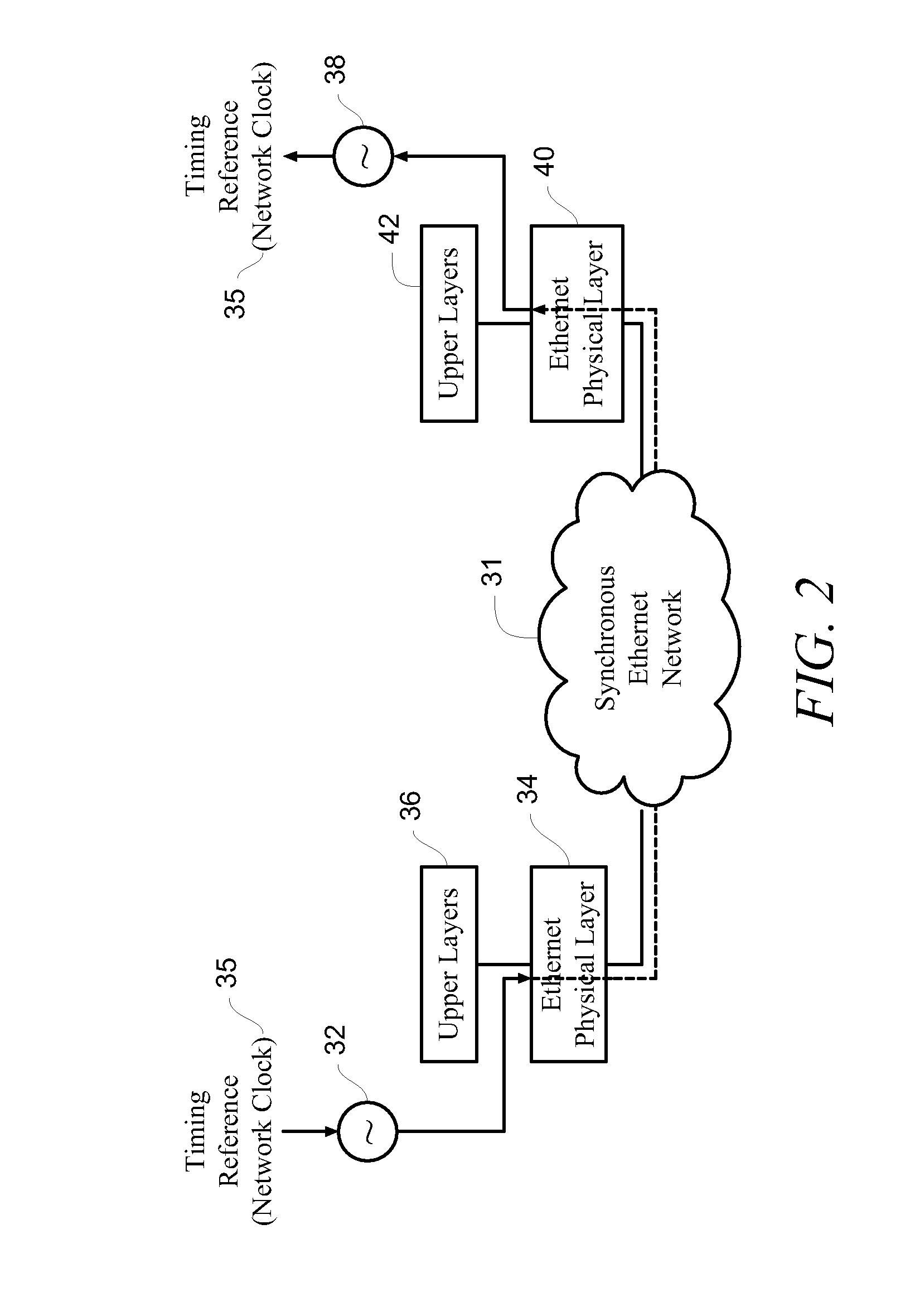
Differential timing transfer over synchronous ethernet using digital frequency generators and control word signaling
InactiveUS20100118894A1Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsReal-time computingBackplane
A method, system and master service interface transfer differential timing over a packet network. The transmitting service interface receives a service clock and is coupled to a receiving service interface through a network backplane. A primary reference clock is provided to time the network backplane. The primary reference clock and the service clock are used to synthesize a copy of the service clock connected to the transmitting service interface. A first control word containing an error differential between the service clock and the synthesized copy of the service clock is generated and transmitted through the network backplane via a packet. The first control word, together with the primary reference clock, is used to recreate the service clock for timing the receiving service interface.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
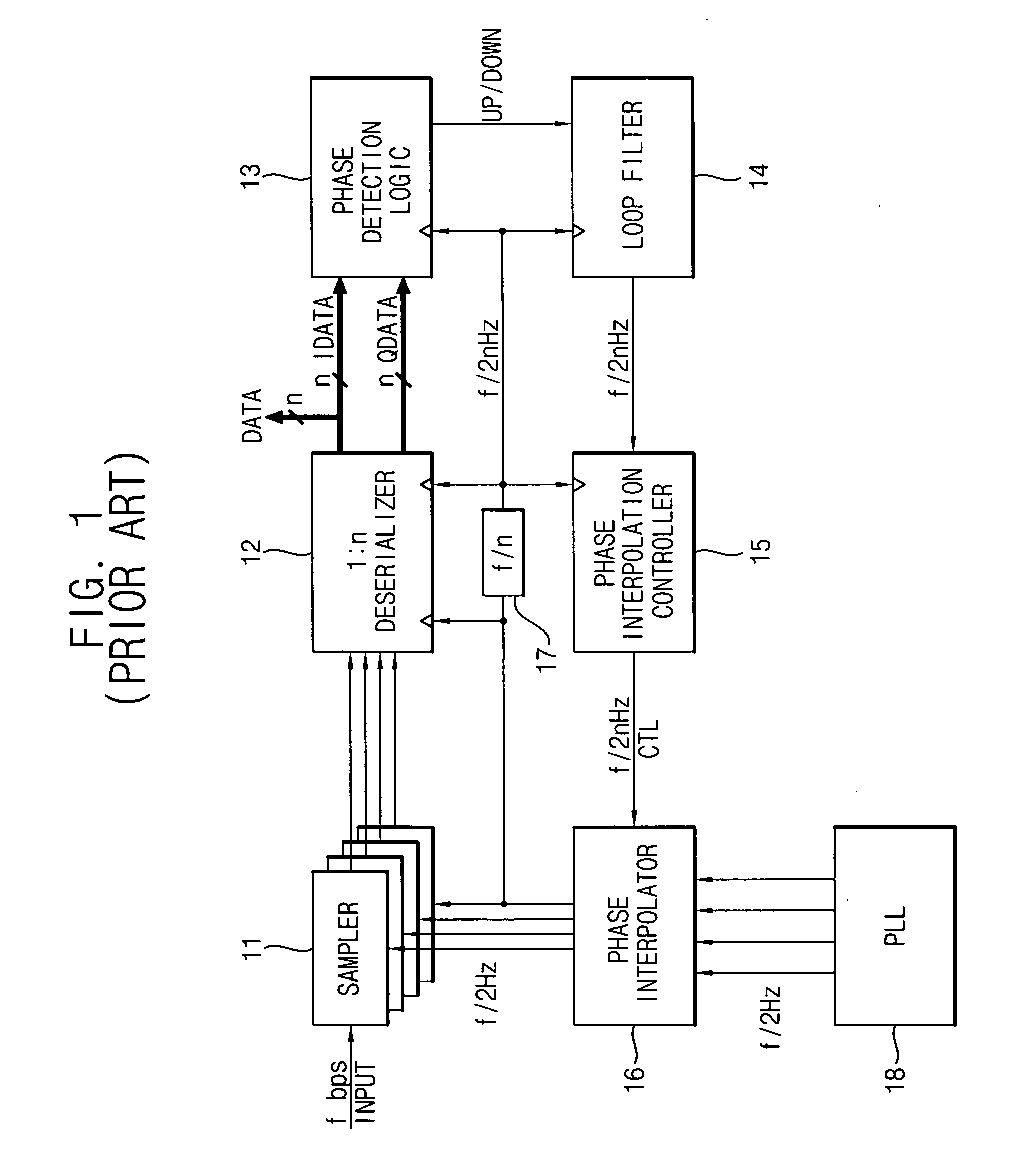
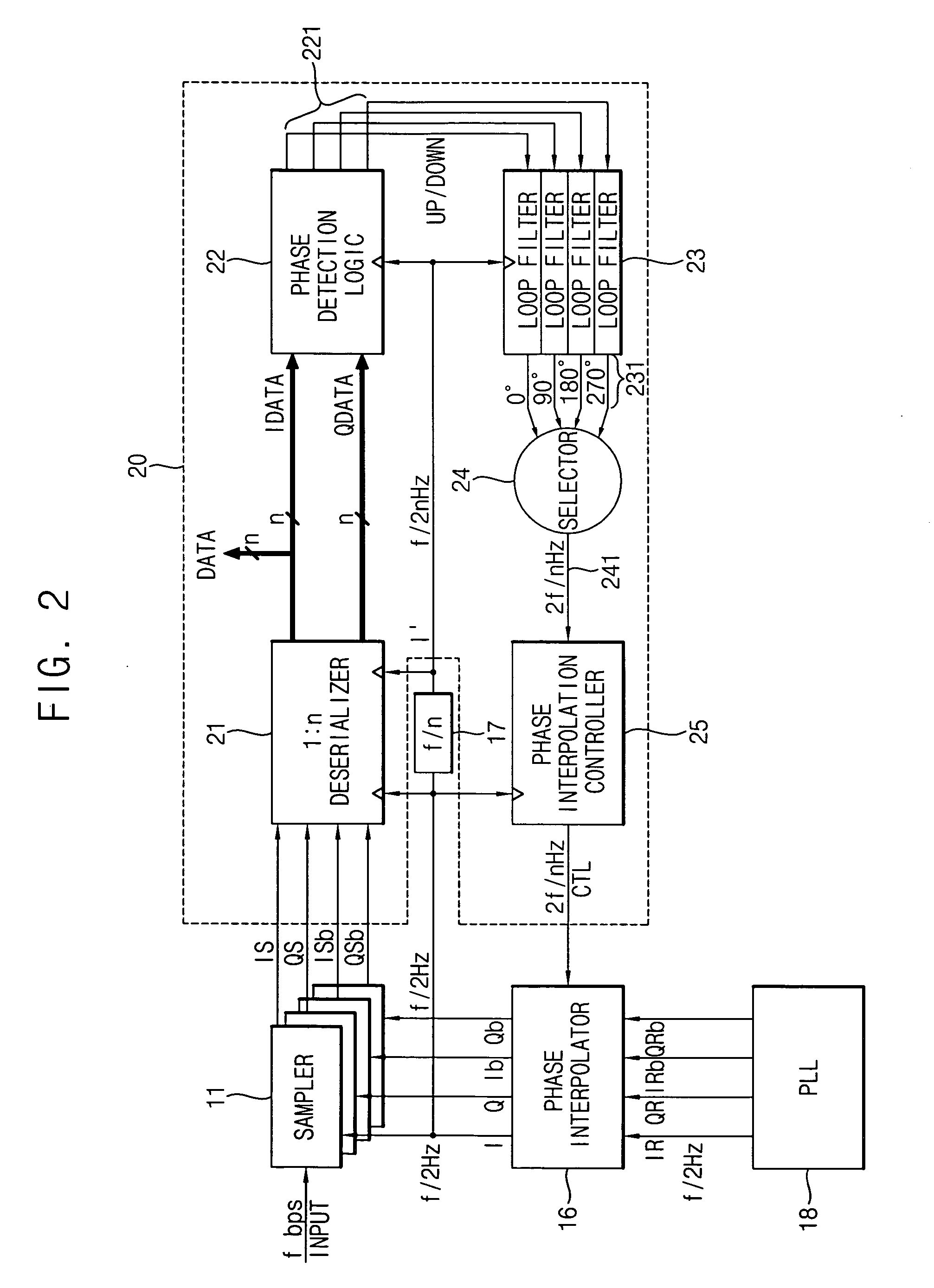
Clock and data recovery circuit having wide phase margin
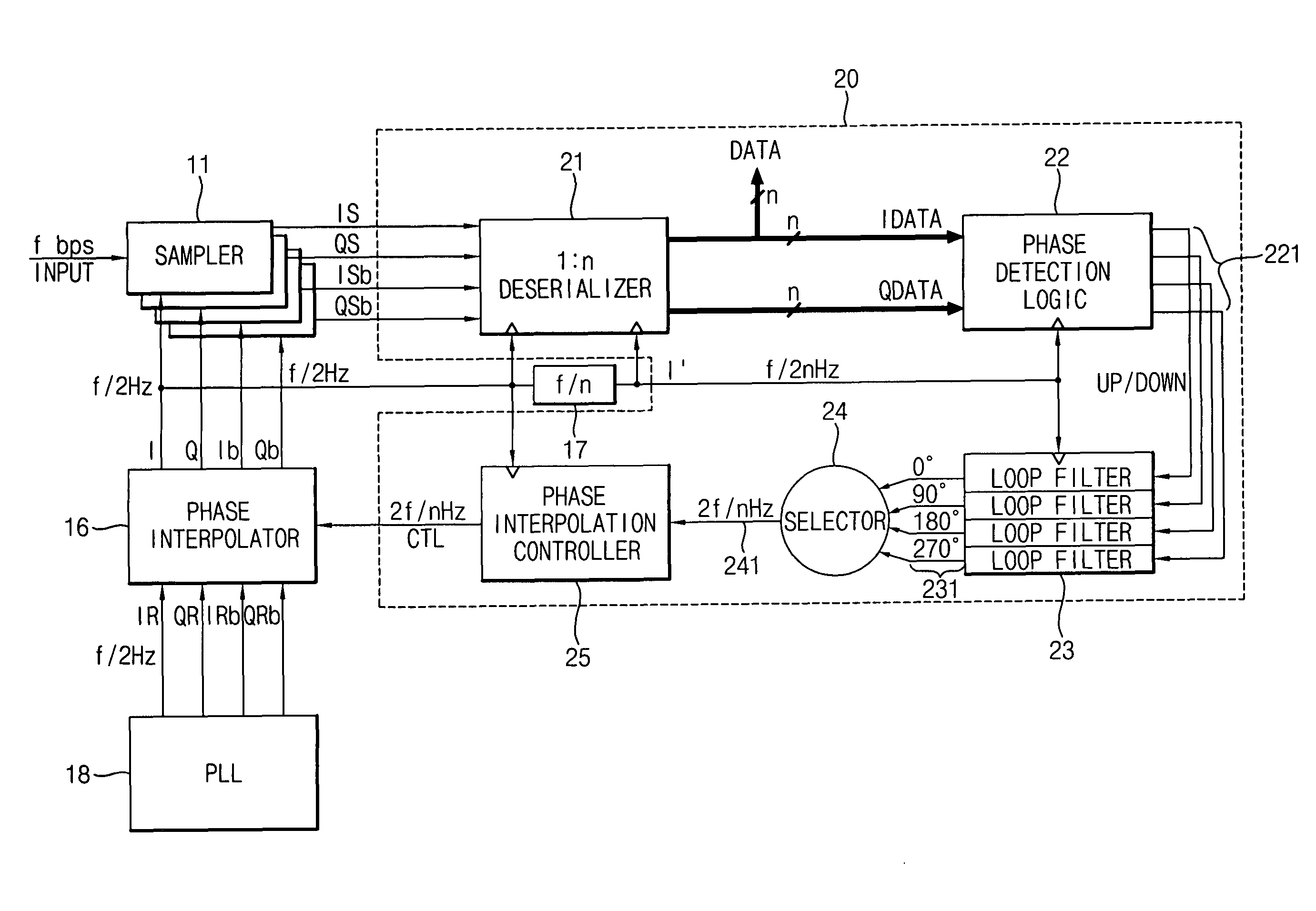
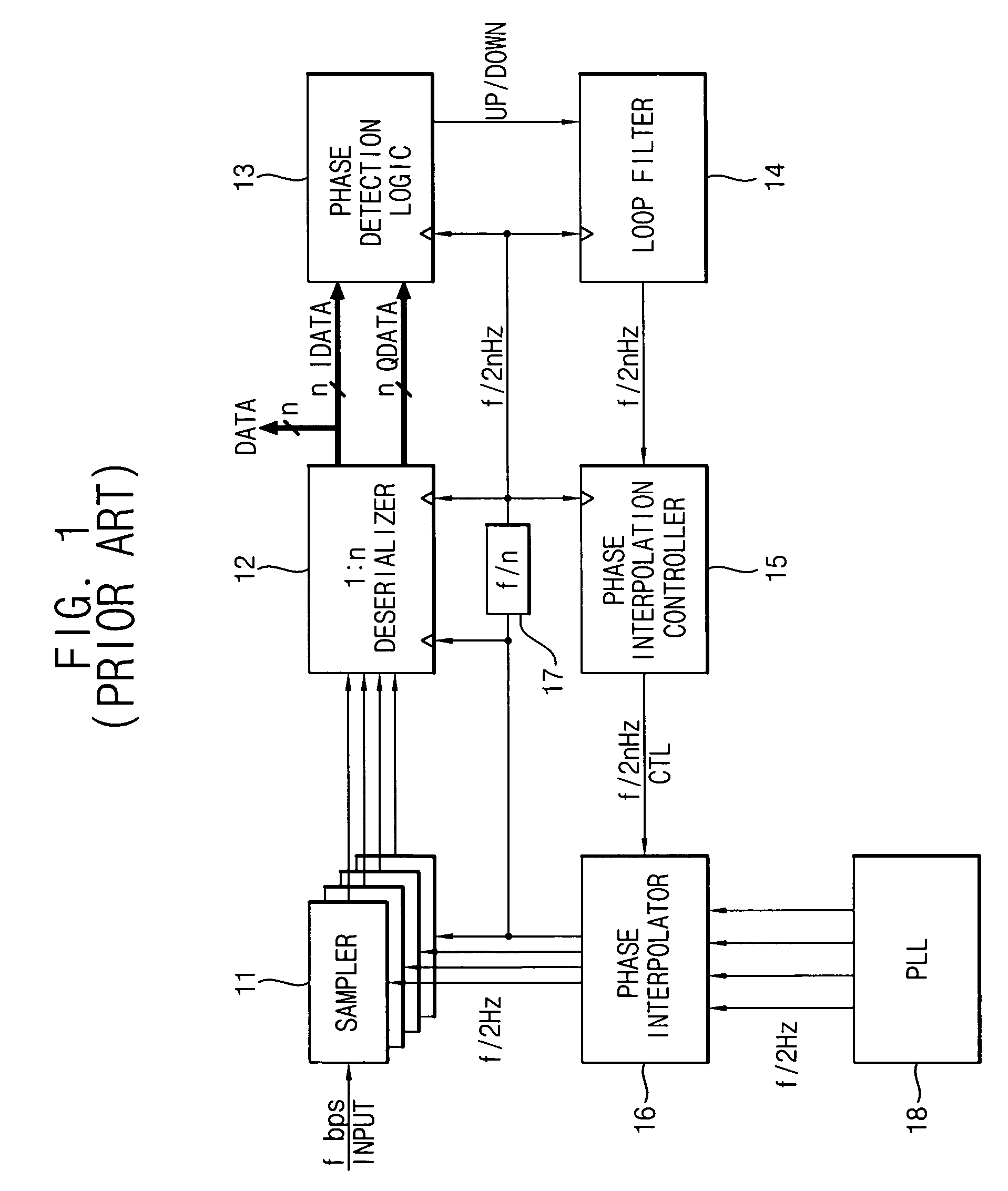
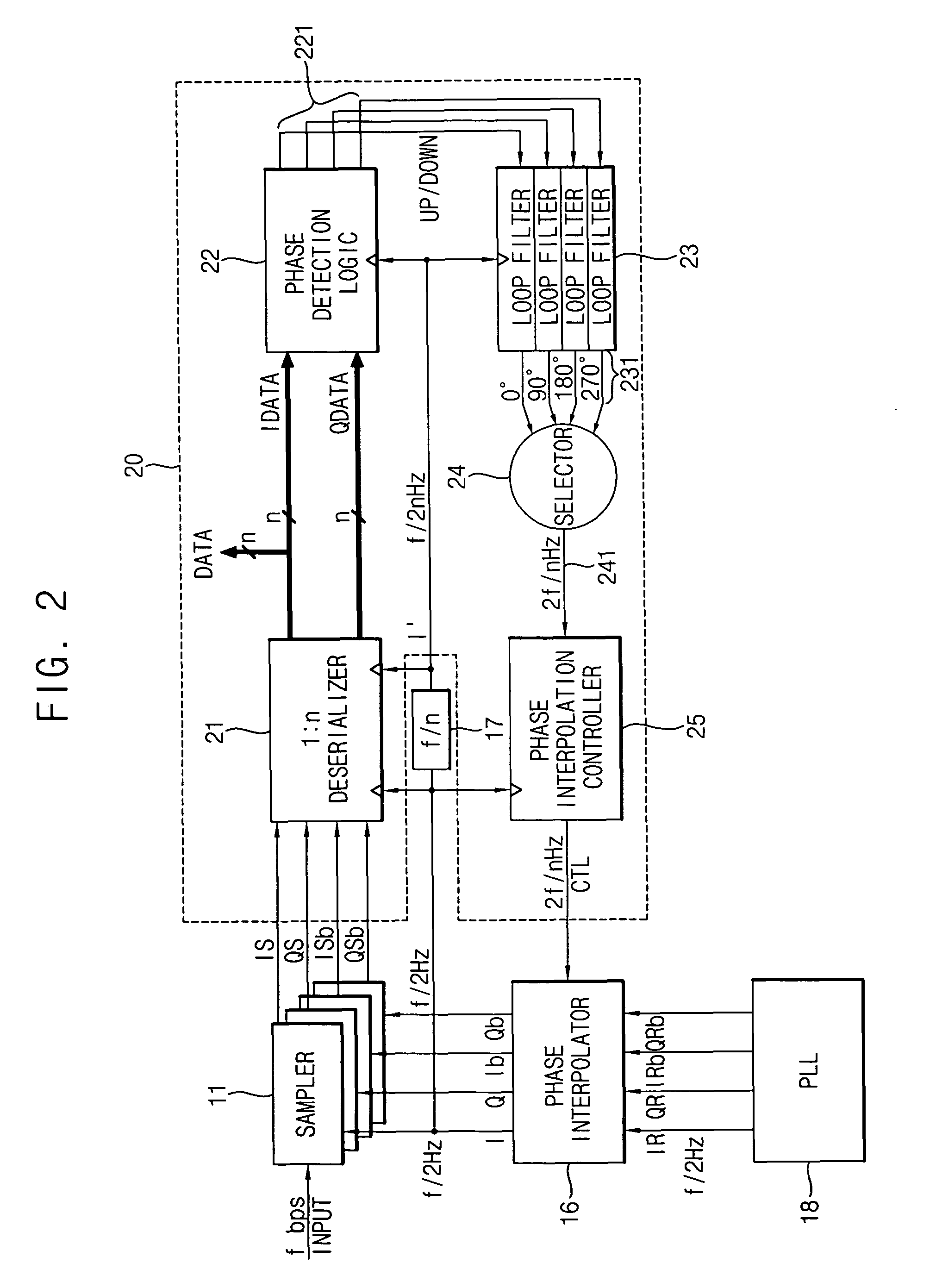
InactiveUS20070047683A1Wide phase marginIncrease speedPulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversSerial samplingPhase control
A clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit includes a sampler, a CDR loop and a phase interpolator. The sampler samples serial data in response to a recovery clock signal to generate a serial sampling pulse. The CDR loop transforms the serial sampling pulse into parallel data, generates a plurality of phase signals with a first speed based on the parallel data, and generates a phase control signal with a second speed higher than the first speed based on the plurality of phase signals. The phase interpolator generates the recovery clock signal by controlling a phase of a reference clock signal in response to the phase control signal. Therefore, the CDR circuit may recover data and a clock with a relatively high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
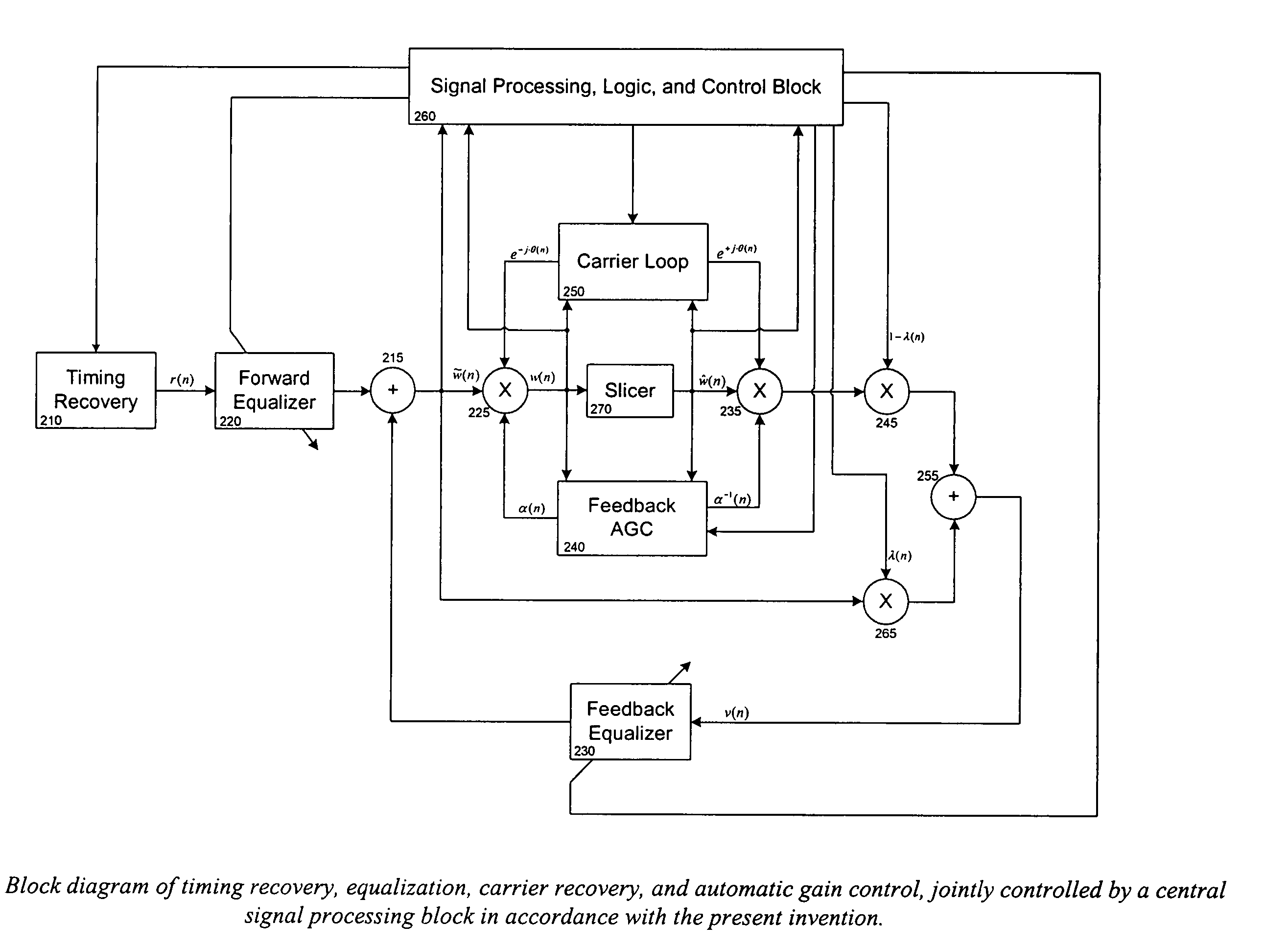
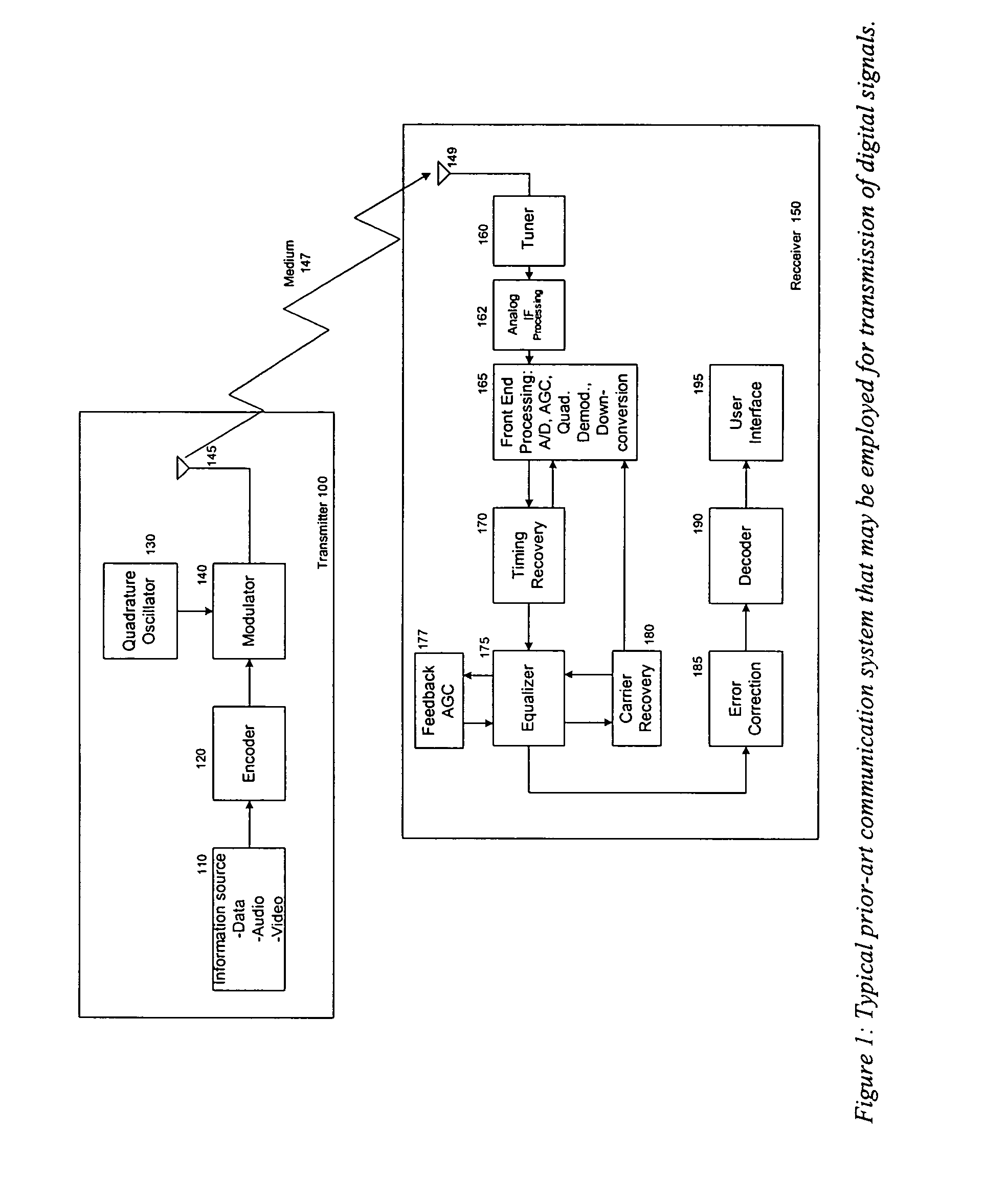
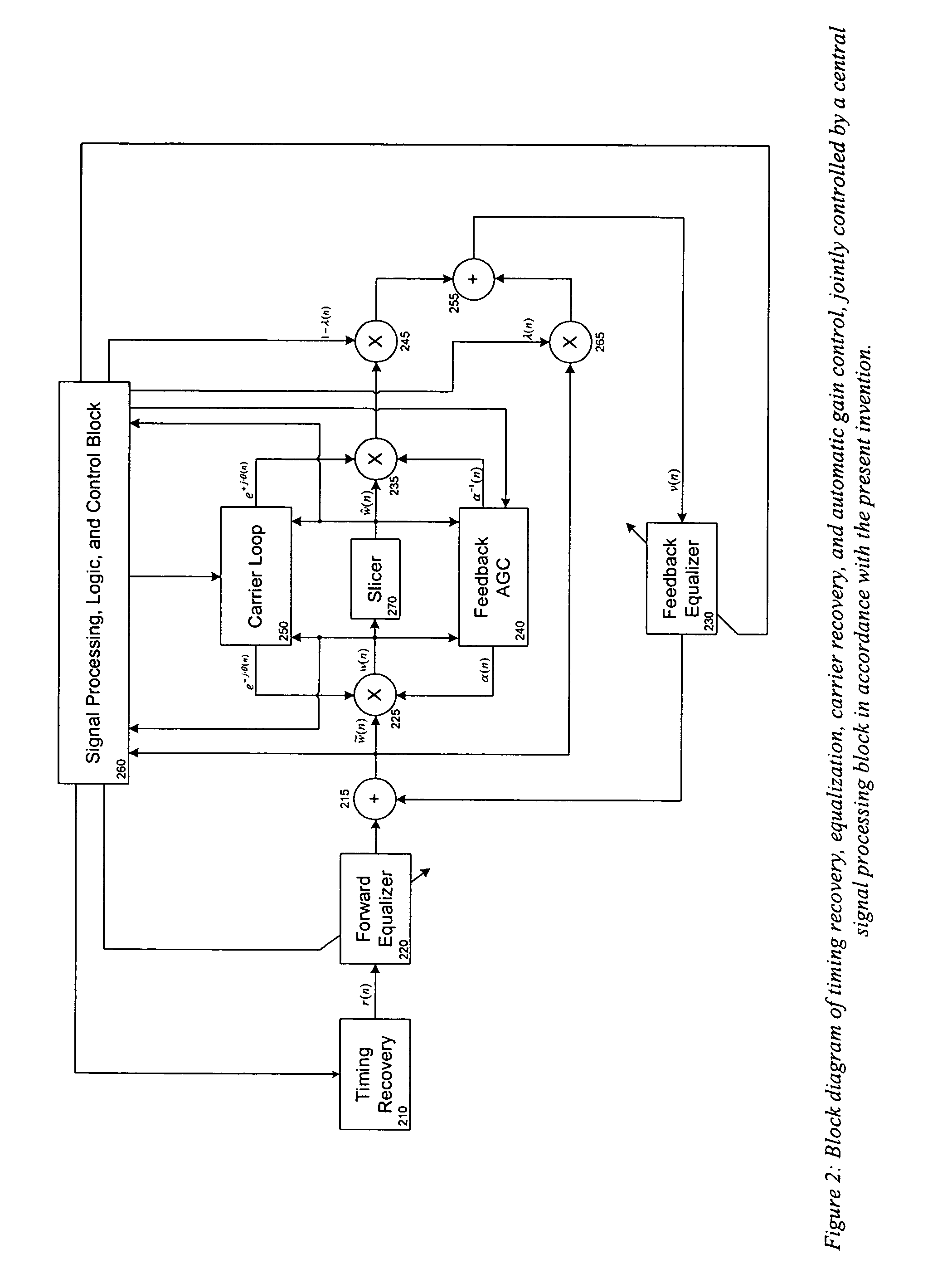
Joint, adaptive control of equalization, synchronization, and gain in a digital communications receiver
ActiveUS20040190649A1Quick and robust gain compensationCompensation can be slowPulse automatic controlGain controlSignal qualityEqualization
Various aspects and embodiments of the present invention derive statistics of received signal quality and use these statistics to jointly control operation of timing recovery, carrier recovery, automatic gain control, and equalization functions.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Synchronous device and method in narrowband wireless communication terminal
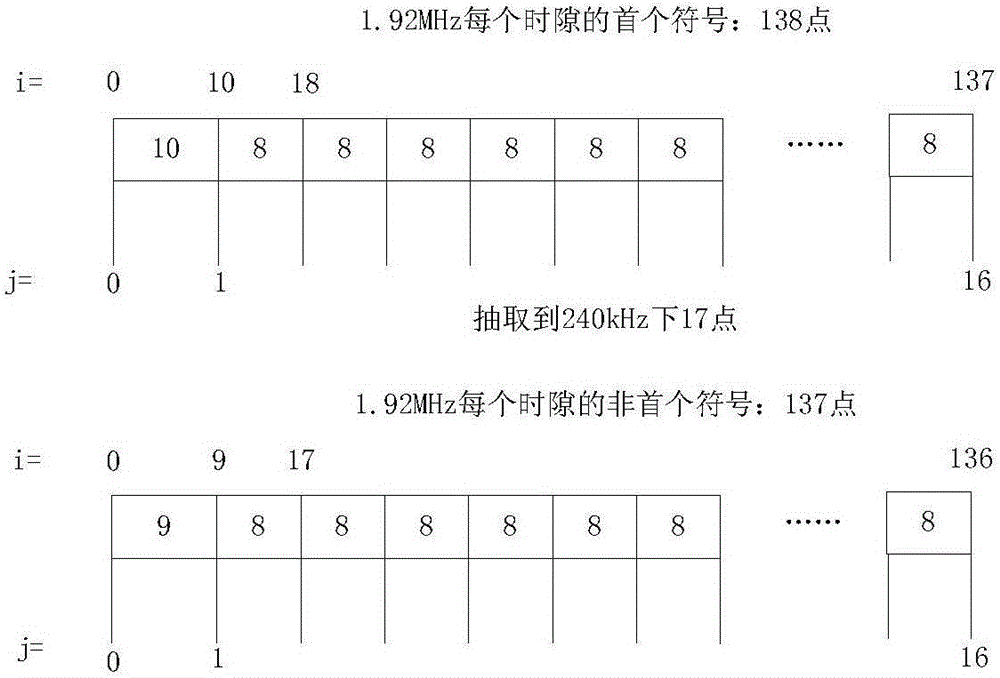
ActiveCN106656453AImprove performanceImprove the performance of anti-large frequency deviationCarrier regulationSynchronisation receiversTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
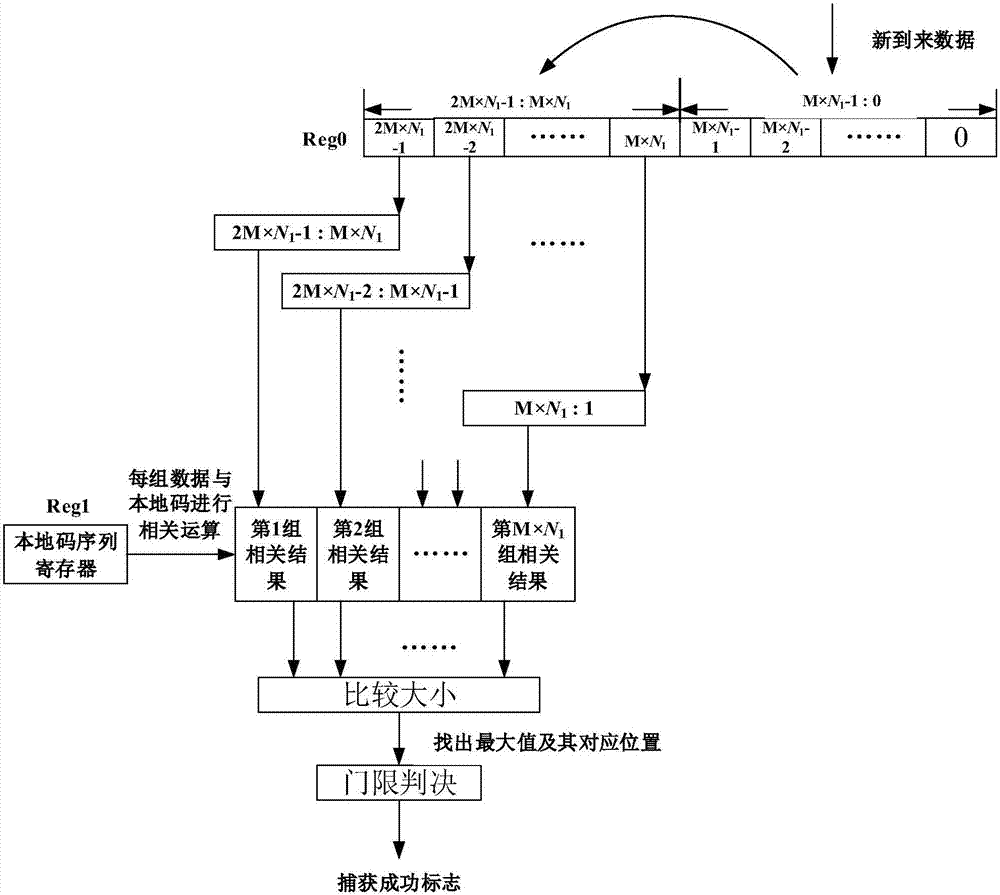
The invention discloses a synchronous detection device applied to a narrowband wireless communication system terminal. The device comprises a down-sampling module, a sliding autocorrelation module and a difference cross-correlation module. A received 1.92 MHz time-domain signal is subjected to down sampling to a 240 kHz signal through the down-sampling module in terms of OFDM symbol time periods and a fixed down-sampling pattern. Through the sliding autocorrelation module, sampling point data in a 10 ms wireless frame processing window is moved bit by bit as an initial position t, date of which the length is eleven OFDM symbol time periods is taken as a sliding window, and the eleven groups of sample points in the sliding window are correlatively accumulated at intervals of two groups. Through the difference cross-correlation module, an obtained primary synchronizing sequence is subjected to differencing to form two approximately equal parts and is correlatively accumulated with a main synchronizing sequence generated locally. According to the invention, by employing the synchronous detection device, main synchronizing signals are detected well in the narrowband-wireless-communication-system application scenario in which the signal-to-noise ratio is low and the frequency deviation is large, and the implementation complexity is low so that the low-cost requirement of the narrowband wireless communication terminal is met.
Owner:浙江芯科物联科技股份有限公司
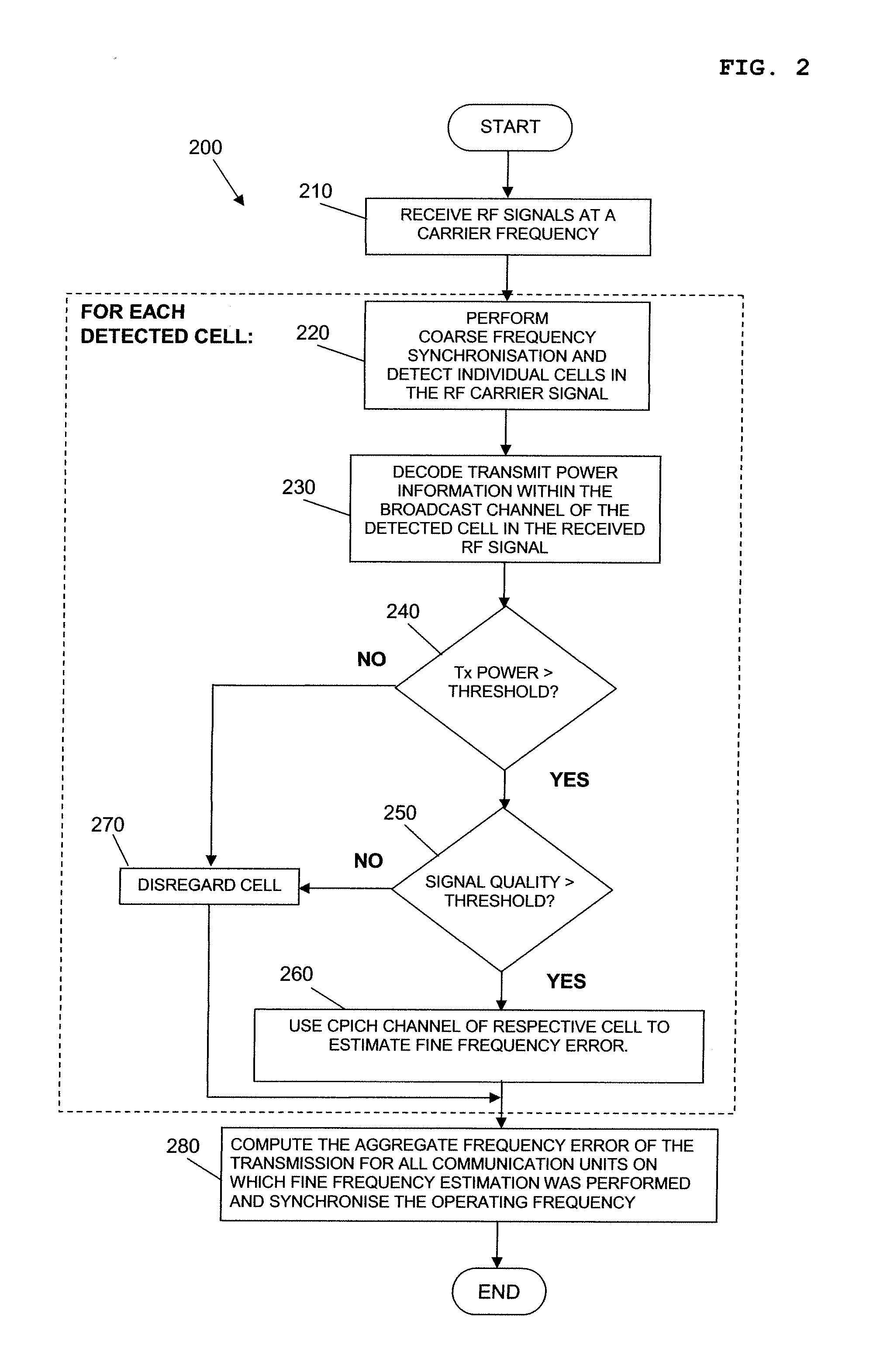
Communication unit and method for selective frequency synchronization in a cellular communication network
ActiveUS20110275402A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunication unitTransmitted power
A communication unit comprises a receiver for receiving radio frequency (RF) signals from at least one wireless serving communication unit, and signal processing logic module arranged to decode information within the received RF signals is the at least one wireless serving communication unit. The signal processing logic module is further arranged to decode transmit power information in a received RF signal from the at least one wireless serving communication unit, and determine from the decoded transmit power information whether a transmission from the at least one wireless serving communication unit is suitable for use as a timing reference. If it is determined that the transmission from the at least one wireless serving communication unit is suitable for use as a timing reference, the communication unit synchronises an operating frequency to the received RF signal of the at least one wireless serving communication unit.
Owner:IP ACCESS LTD
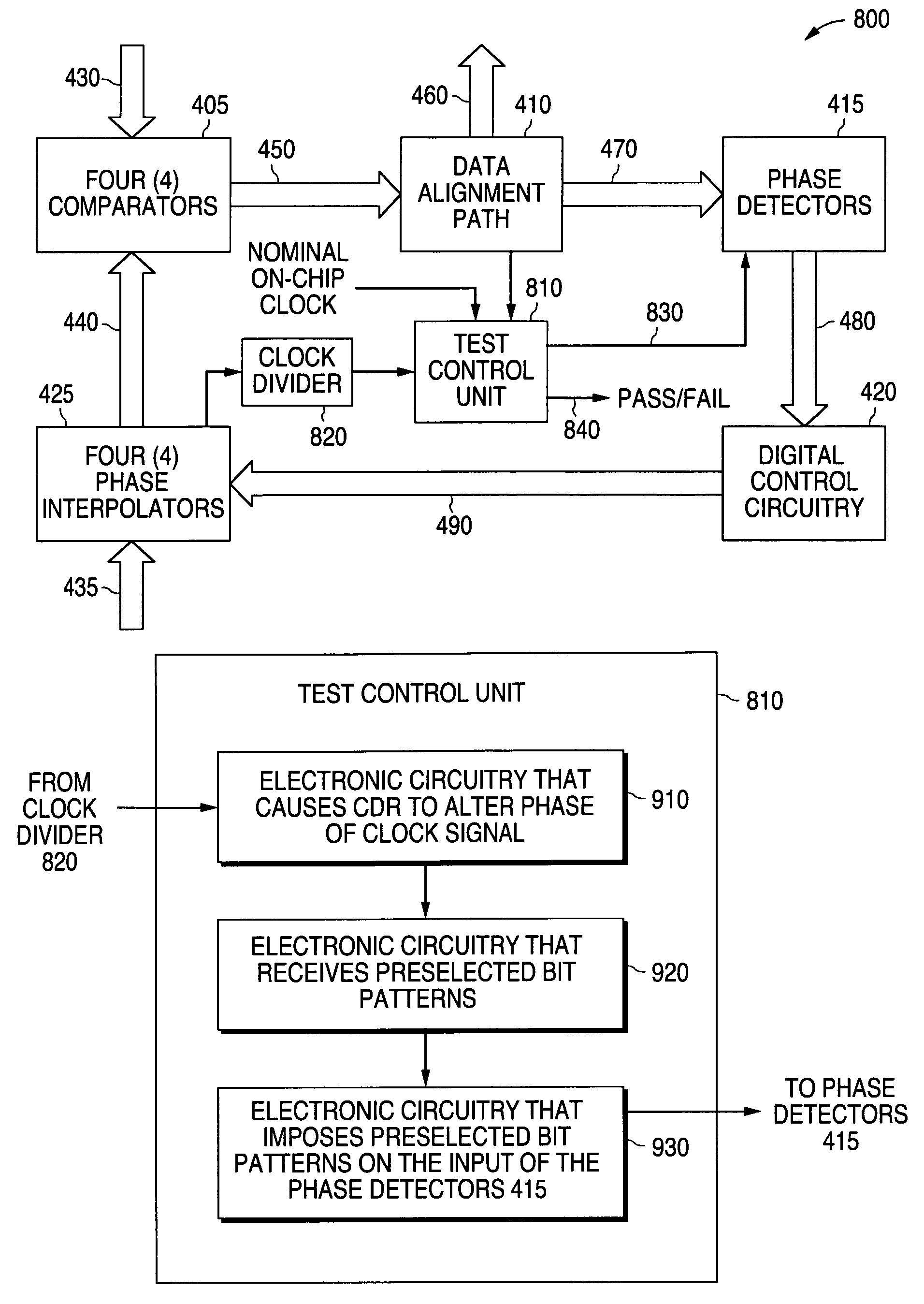
System and method for providing a clock and data recovery circuit with a self test capability
ActiveUS7555091B1Reduce amountIncreases manufacturing profit marginCorrect operation testingPulse automatic controlTest statusDigital control
A system and method is disclosed for providing a clock and data recovery circuit with a self test capability. A test control unit is provided that causes the clock and data recovery circuit to continuously alter a phase of an interpolated clock signal. A user selects a preselected bit pattern that causes the digital control circuitry of the clock and data recovery circuit to advance or retard the phase of the interpolated clock signal. The test control unit compares the advanced or retarded phase of the interpolated clock signal with a reference clock signal to determine a frequency difference between the two clock signals. The test control unit uses the frequency difference to determine the test status of the clock and data recovery circuit.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Peer-to-peer network and node of a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20190089716A1Simple processImprove tamper resistanceSynchronisation receiversTime-division multiplexDistributed computingPeer-to-peer
The invention relates to a peer-to-peer network having at least one first node with a first clock module and part of a peer-to-peer application. Also included is at least one second node with a second clock module and part of the peer-to-peer application. At least one communication connection between the first node and the second node is establishable. The first node comprises at least one first synchronization clock module. The second node comprises at least one second synchronization clock module. At least the first synchronization clock module is configured to transmit at least one first synchronization clock message to the second synchronization clock module via the communication connection, the second synchronization clock module is configured to synchronize the clock signal of the second clock module to the clock signal of the first clock module based on synchronization information included in the first synchronization clock message.
Owner:INNOGY INNOVATION GMBH
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS7817747B2Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSynchronisation receiversNanosecondAudio power amplifier
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
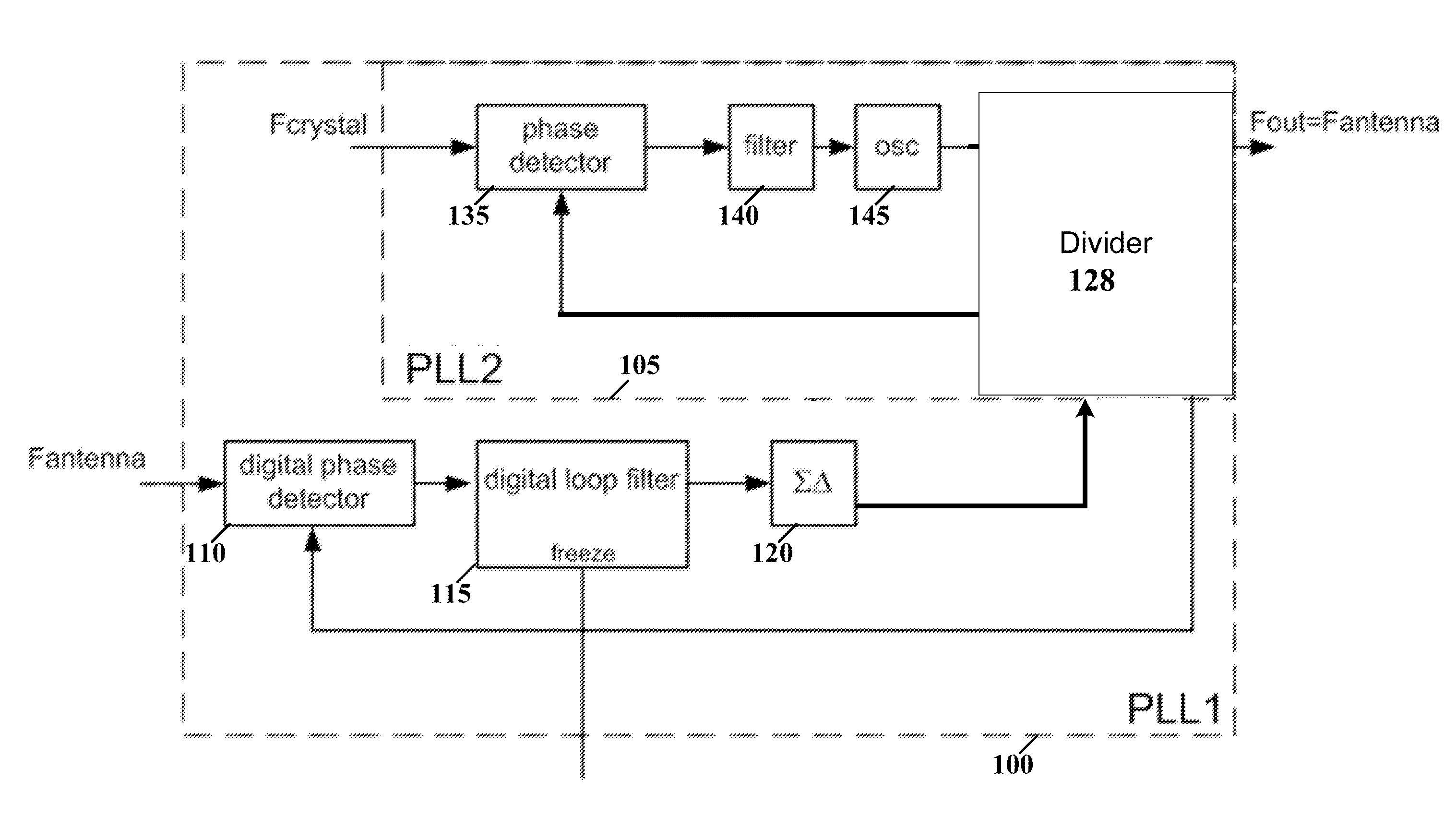
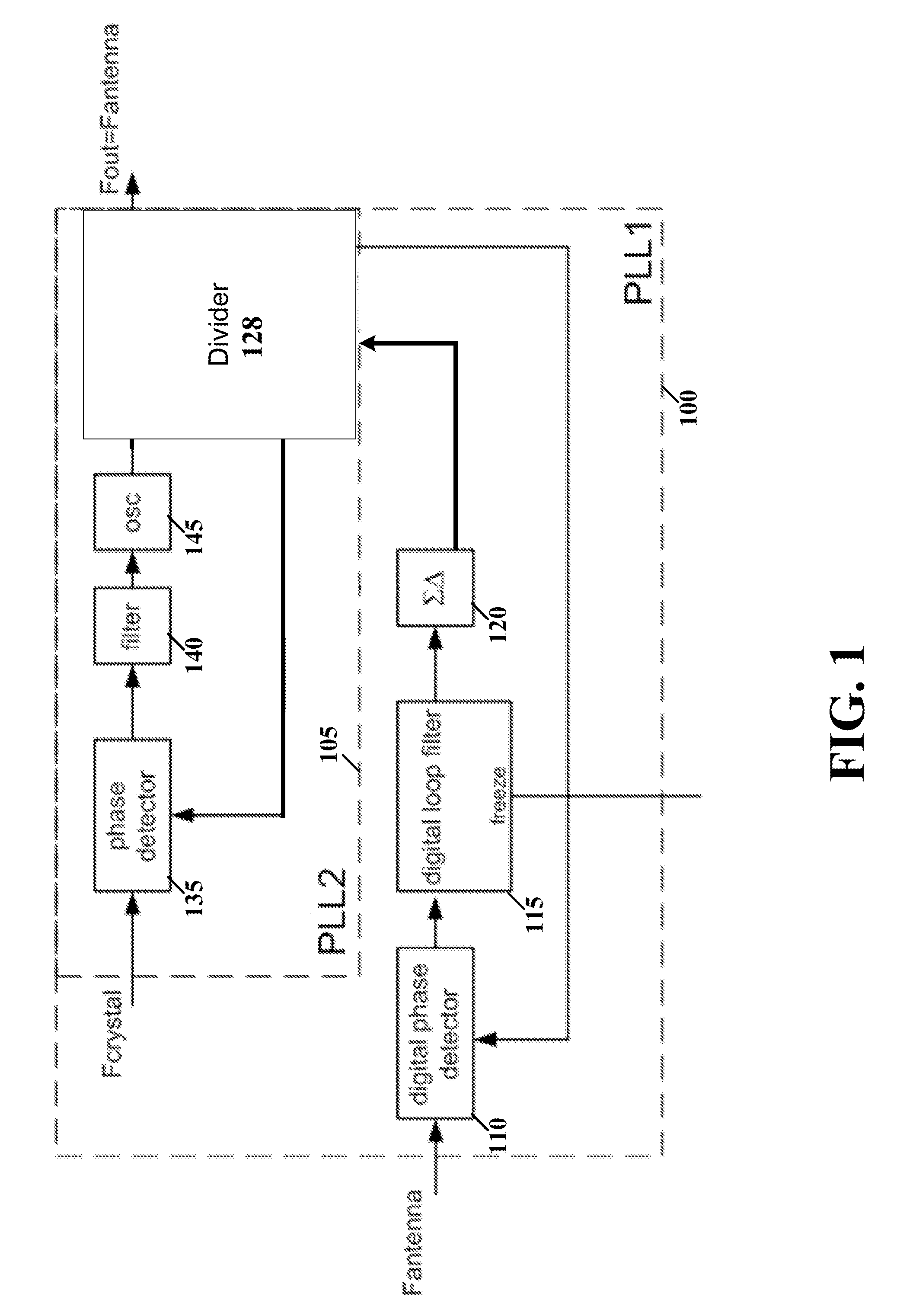
Clock synchronizer for aligning remote devices
ActiveUS20150063517A1Poor signal qualityPulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversControl signalCarrier signal
Various aspects of the present disclosure are directed apparatuses and methods including a first phase locked loop (PLL) circuit and a second PLL circuit. The first PLL circuit receives a carrier signal that is transmitted over a communications channel from a non-synchronous device, and generates a PLL-PLL control signal. The second PLL circuit receives a stable reference-oscillation signal, and, in response to the PLL-PLL control signal indicating a frequency offset, adjusts a fractional divider ratio of the second PLL circuit. The first PLL circuit and the second PLL circuit are configured to produce an output frequency signal that is synchronous to the carrier signal.
Owner:NXP BV
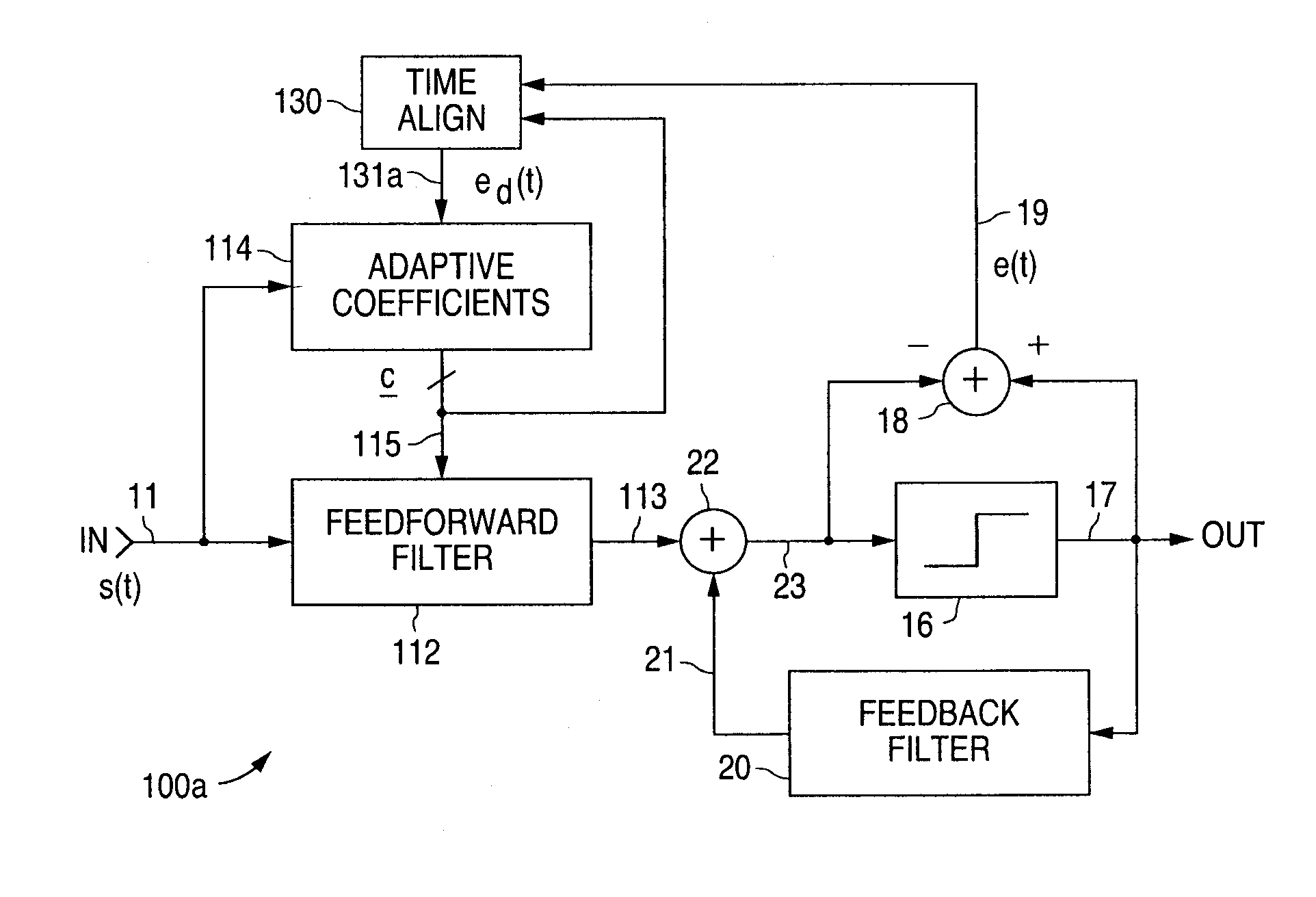
Adaptive signal equalizer with adaptive error timing and precursor/postcursor configuration control
InactiveUS20070230557A1Substantial avoidance of “driftingEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksAdaptive filterData signal
An adaptive signal equalizer with a feedforward filter in which the feedback error signal and corresponding incoming data signal are dynamically aligned in time using signal interpolation, and further, to control the precursor / postcursor filter taps configuration, thereby producing more adaptive filter tap coefficient signals for significantly improved and robust signal equalization.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Differential simultaneous bi-directional receiver
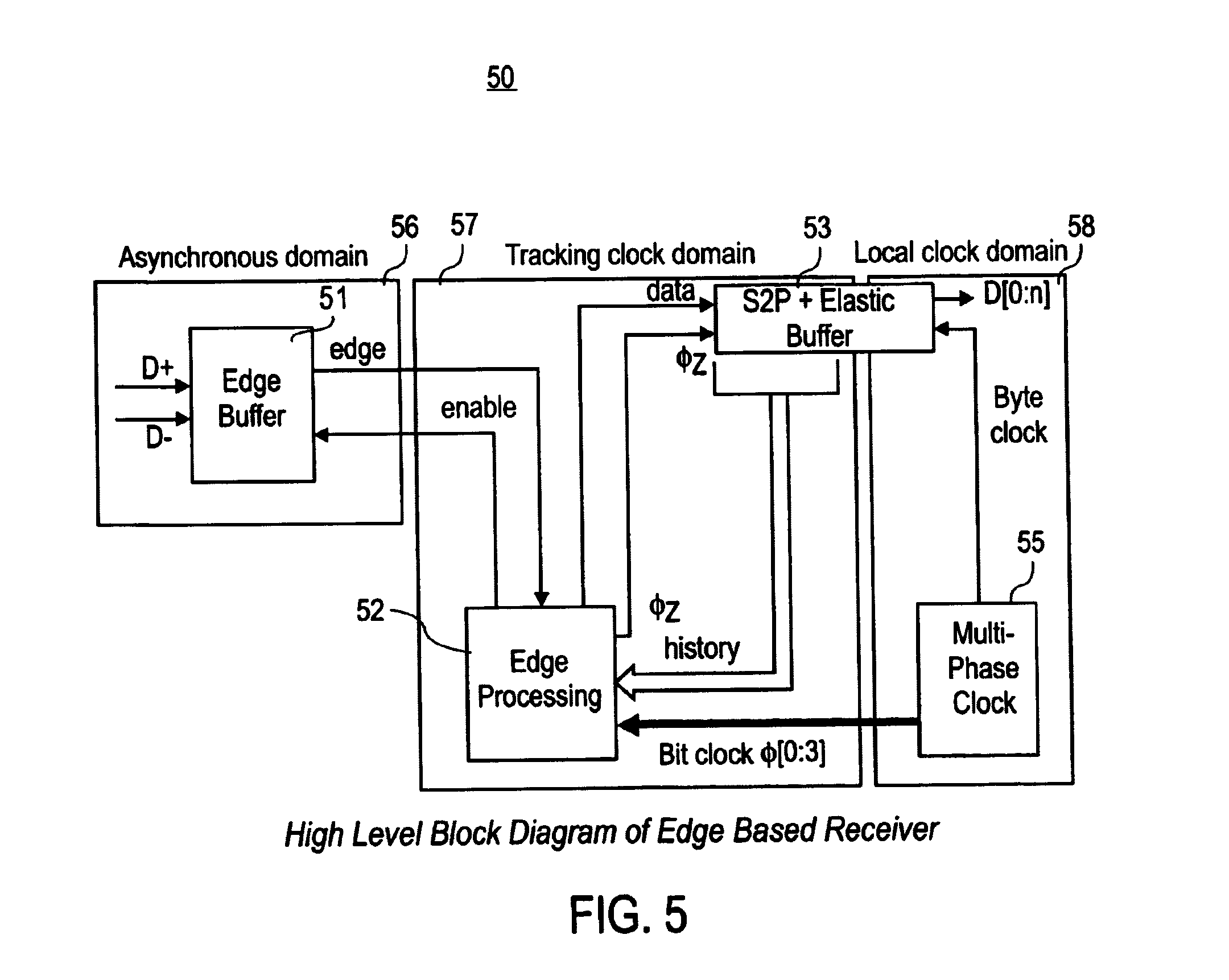
When signaling over cables or other media having significant return impedance, it is generally more efficient to use two conductors to carry two simultaneous bi-directional signals differentially, rather than utilizing unidirectional communications. Bi-directional communications increases the aggregate bandwidth of a pair of conductors. A conversion circuit converts unidirectional signaling between an edge-based receiver and a transmitter to simultaneous differential bi-directional signaling. A receiver for receiving data includes an edge processor operative to make decisions using edges of a received data stream and a communication circuit coupled to the edge processor. The communication circuit is operative to convert communications with the edge processor from a first format, such as unidirectional signaling, to a second format, such as differential bi-directional signaling.
Owner:INTEL CORP
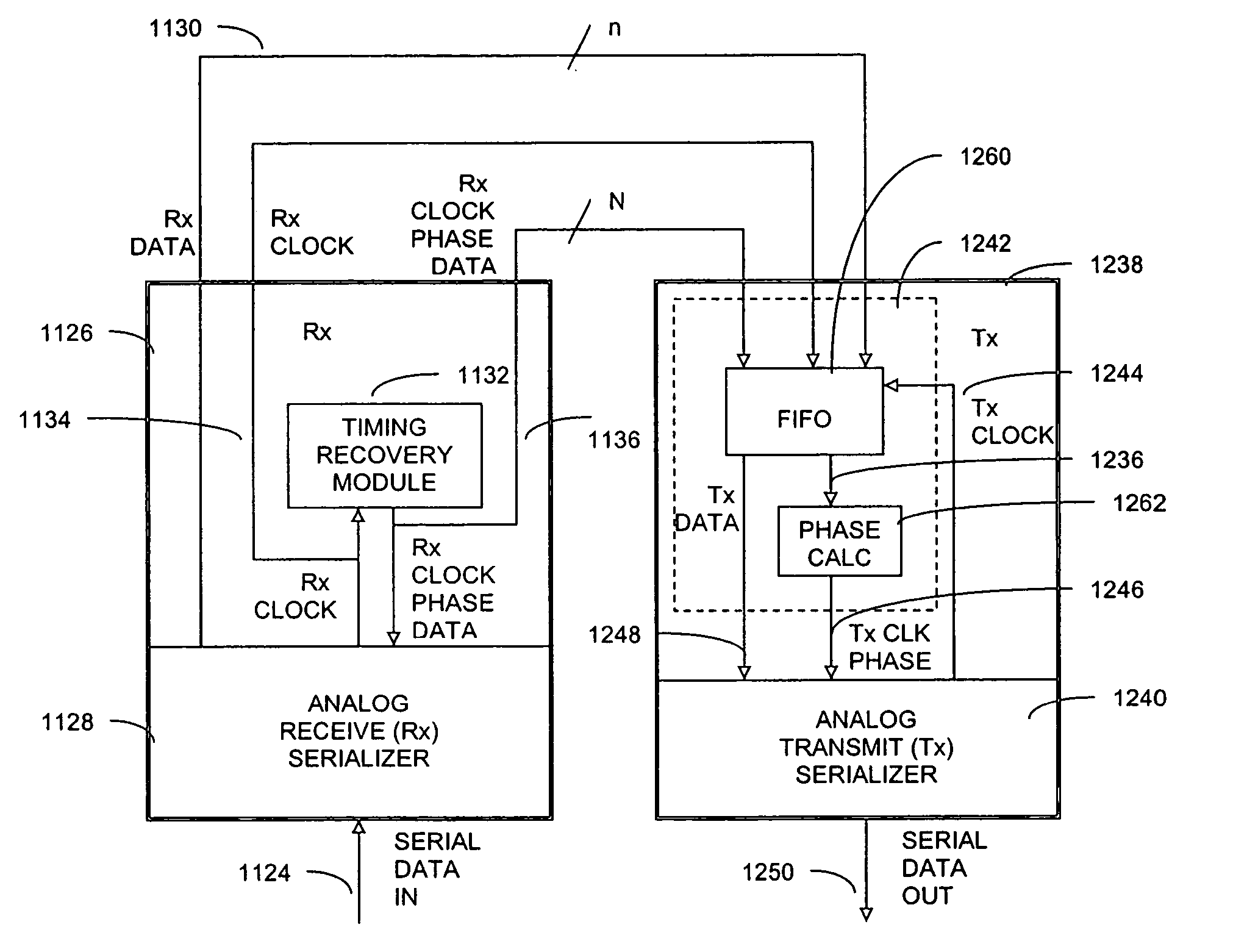
System and method of phase-locking a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase
ActiveUS20050169417A1Parallel/series conversionSynchronisation information channelsPhase differenceTransmission channel
Systems and methods for synchronizing a receive clock signal phase with a transmit clock signal phase are presented. A system includes a receiving channel and a transmitting channel, wherein the transmitting channel synchronizes a transmit clock signal phase with a receive clock signal phase based on receive clock signal phase data. A method includes storing a previous receive clock signal phase of a receiving channel and identifying a current receive clock signal phase of the receiving channel. The method further includes determining a phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase, and identifying a direction of the phase difference between the previous receive clock signal phase and the current receive clock signal phase. The method further includes adjusting a previous transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel to a current transmit clock signal phase of the transmitting channel based on the phase difference and direction.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
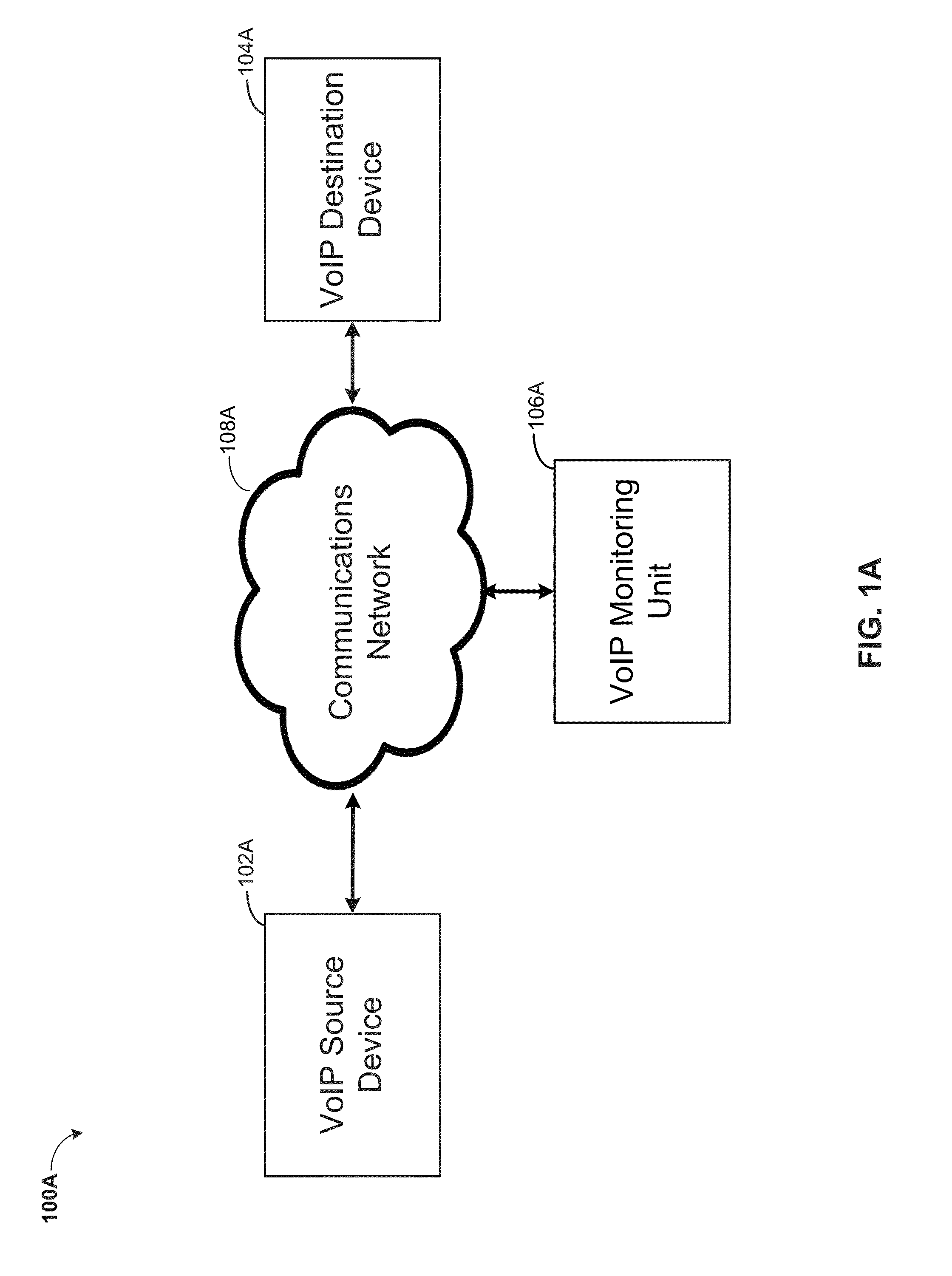
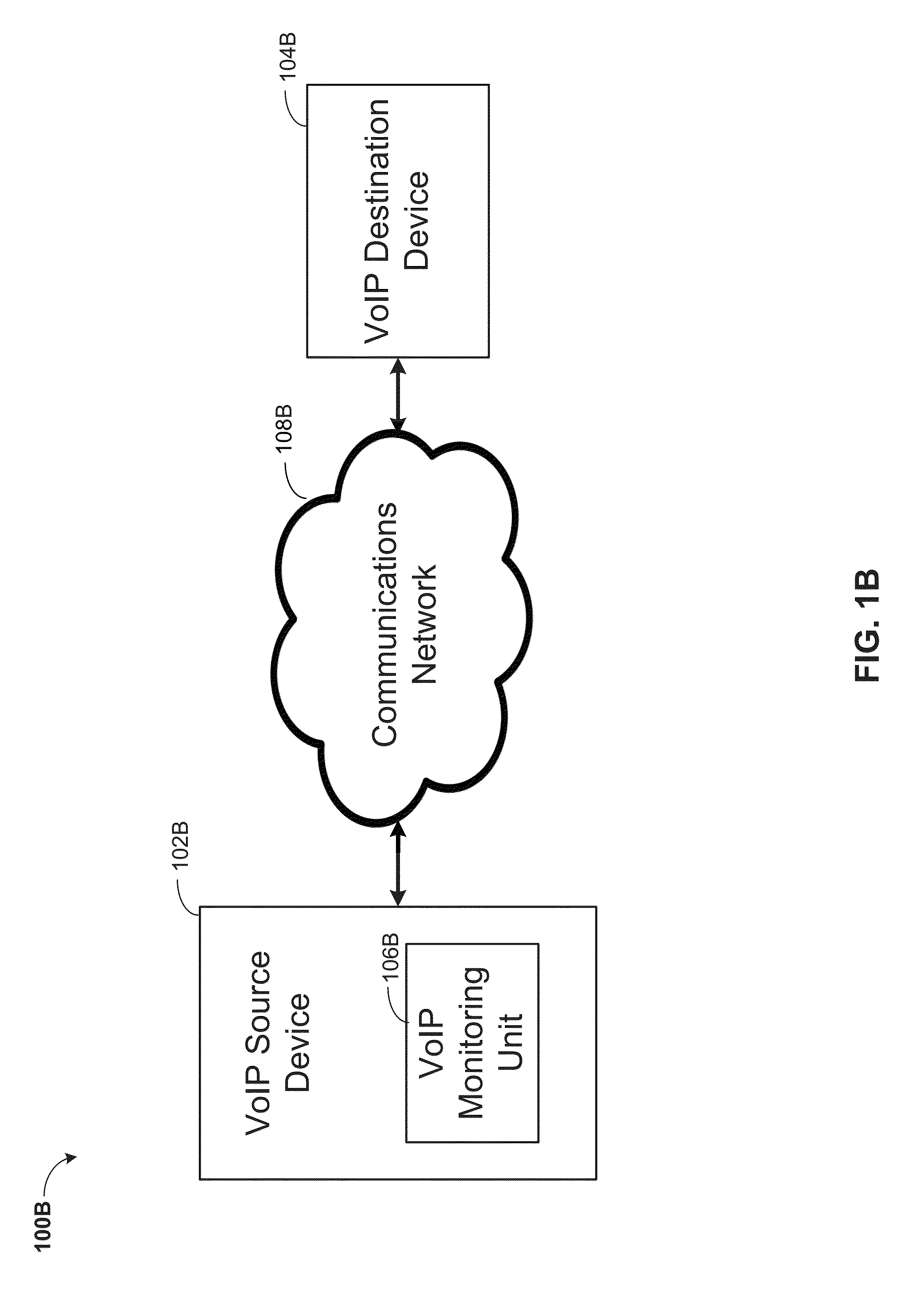
MONITORING VOICE OVER INTERNET PROTOCOL (VoIP) QUALITY DURING AN ONGOING CALL
InactiveUS20160028881A1Improve monitoring qualityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareTTEthernet
A method for calculating a mean opinion score (MOS) during an ongoing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) call is provided. The method may include determining a time delay between a VoIP source and a VoIP destination connected by a communications network. A start recording message is sent from the VoIP source to the VoIP destination. A first recorded call sample from the VoIP source and a second recorded call sample from the VoIP destination are generated, whereby the first and the second recorded call sample are generated with a recording delay value corresponding the determined time delay for synchronizing the first and the second recorded call sample. Using an intrusive call quality measurement, a first MOS value is calculated based on the first and the second recorded call sample. Using a non-intrusive call quality measurement, a second MOS value is calculated based on the first MOS value.
Owner:IBM CORP
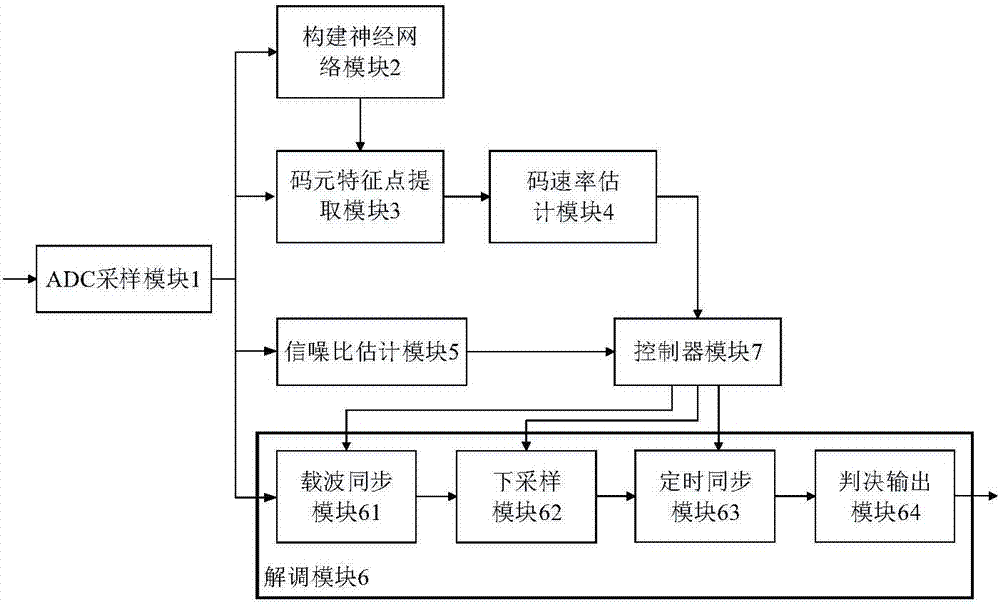
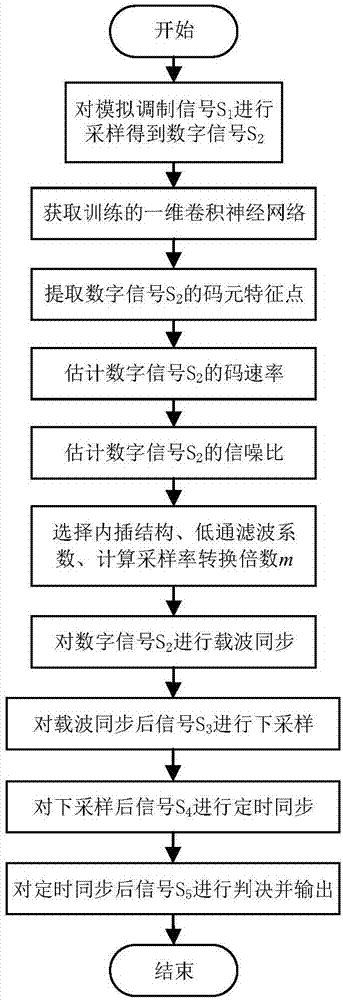
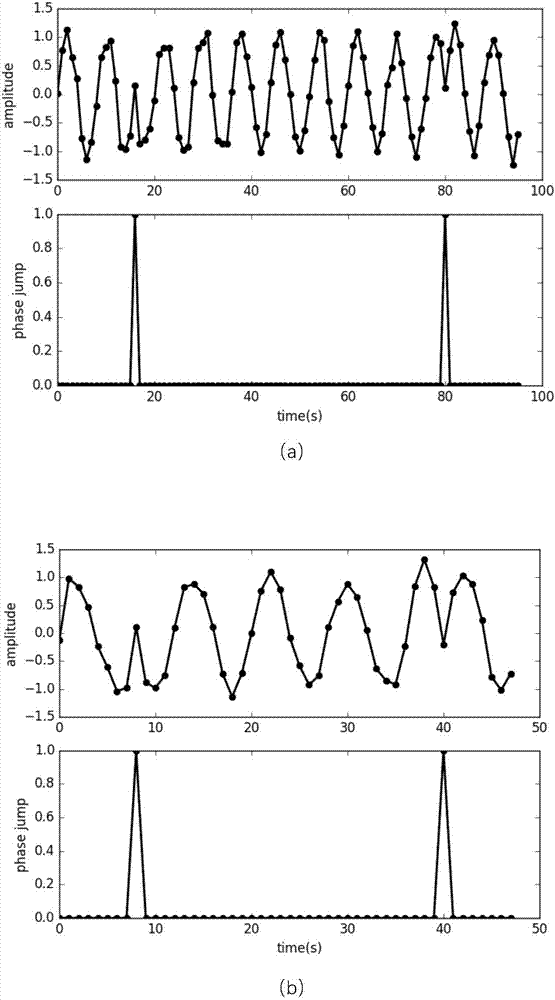
Multi-gear code rate adaptive demodulation system and method based on neural network
ActiveCN106936742AReduce complexityRealize adaptive demodulationCarrier regulationSynchronisation receiversSample rate conversionLow-pass filter
The invention provides a multi-gear code rate adaptive demodulation system and method based on a neural network so as to solve the technical problems of high complexity of realization of an existing multi-gear code rate adaptive demodulation system and large computation amount of a demodulation method. In the demodulation system, an ADC sampling module samples an analog modulation signal; a code element feature point extraction module carries out detection on phase jump points of the sampled signal by utilizing a one-dimensional convolution neural network trained by a neural network construction module; a code rate estimation module estimates code rate of the sampled signal according to the detection result; a signal-to-noise ratio estimation module estimates signal-to-noise ratio of the sampled signal; a controller module selects low-pass filter coefficients and an interpolation structure of a demodulation module according to the code rate estimation result and the signal-to-noise ratio estimation result, and calculates sampling rate conversion ratio of the demodulation module; and finally, the demodulation module carries out demodulation on the sampled signal according to the selected low-pass filter coefficients and the interpolation structure as well as the calculated sampling rate conversion ratio.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radio apparatus
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Audio transmission delay measuring method and system
ActiveCN104125022ASolve technical problems with inaccurate calculationsPrevent echoSynchronisation receiversSynchronisation transmittersTransmission delayCodebook
The invention discloses an audio transmission delay measuring method and system. The method comprises performing synchronization operation on transmission of an original audio codebook to be measured between a transmitting end and a receiving end to obtain the transmission starting indicating information, the transmission ending indicating information, the receiving starting indicating information and the receiving ending indicating information of the original audio codebook; enabling the transmitting end to respond to the transmission starting indicating information and transmit the original audio codebook to be measured to the receiving end and to respond to the transmission ending indicating information and stop transmitting the original audio codebook to the receiving end, and enabling the receiving end to respond to the receiving starting indicating information and collect the original audio codebook transmitted by the transmitting end and to respond to the receiving ending indicating information and stop collecting the original audio codebook transmitted by the transmitting end; obtaining audio transmission delay according to the testing audio codebook collected by the receiving end and the original audio codebook prestored in the receiving end. The audio transmission delay measuring method and system solves the problem of inaccurate computation of audio transmission delay in the prior art.
Owner:TENCENT TECH CHENGDU
Clock recovery method and clock recovery arrangement for coherent polarization multiplex receivers
ActiveUS20120308234A1Quality improvementIncrease probabilityPolarisation multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansPhase detectorClock recovery
Component signal values are derived from component signals and fed to at least one fixed equalizer which generates equalizer output signals. The signals are fed to phase error detectors generating phase error signals. The phase error signals are combined with further phase error signals derived by further error detectors receiving signal values from further equalizers and / or the component signal values directly from sample units.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
Method and System for Pilot-Based Time Domain Phase Noise Mitigation for Coherent Receiver
A method for phase noise mitigation for a coherent receiver in either an OFDM or single carrier based transmission system including applying a frequency offset and coarse phase noise compensation based on a radio frequency RF tone or using a phase lock loop PLL m-th power procedure, responsive to a signal from a digital signal processed transmission with an added pilots signal over an optical system, applying fine phase noise compensation based on comparison of the pilots signal in a time domain, removing the pilots, and demodulating the remaining pilotless signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
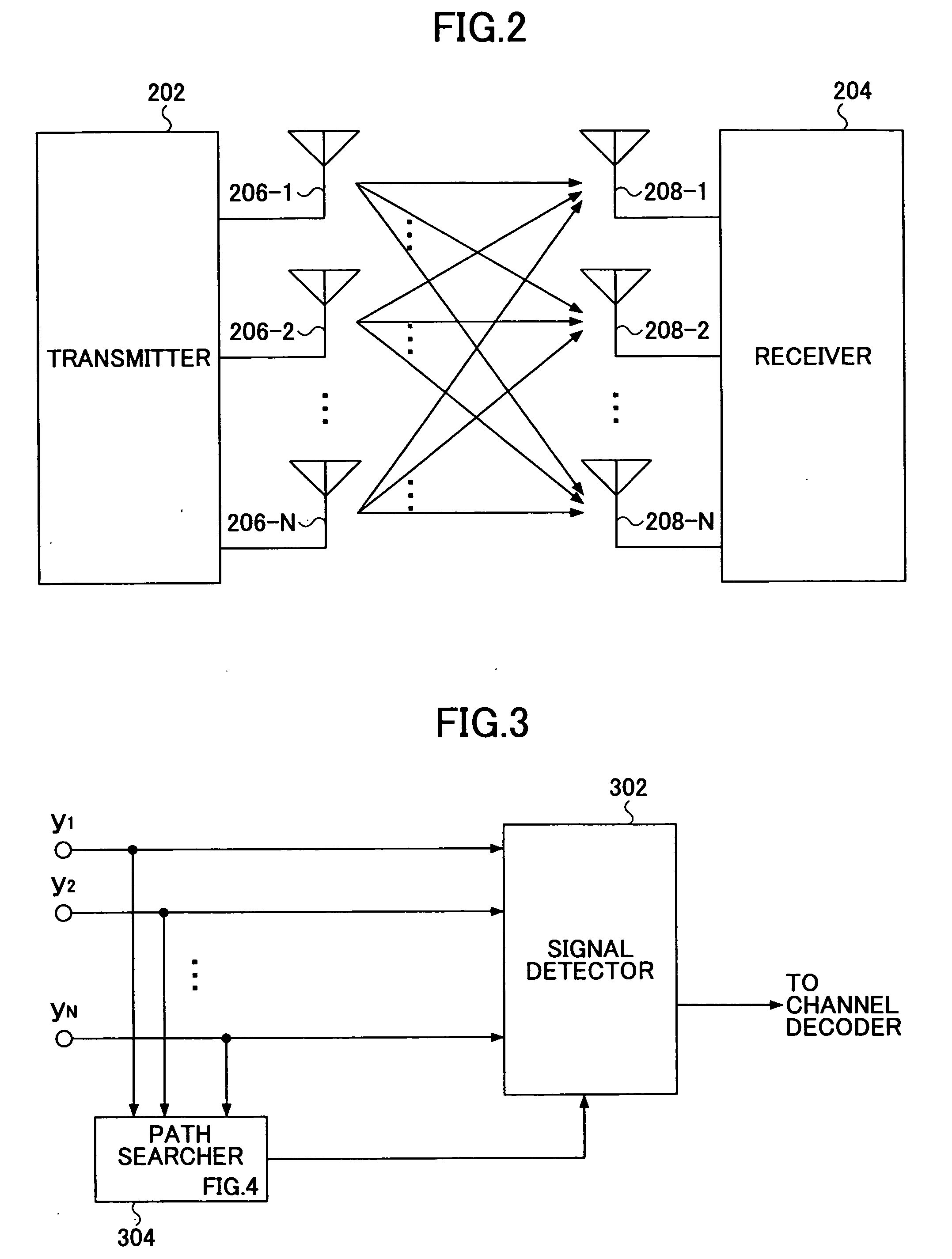
Path searcher and path searching method
InactiveUS20050255819A1Accurate detectionAccurate and reliable detectionSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPower delay profileEngineering
A path searcher (304) used in a receiver includes a power delay profile generating unit (402) configured to generate a power delay profile based on a signal received by the receiver, a sidelobe generating unit (406) configured to identify a sidelobe component of a path contained in the power delay profile based on a response characteristic of a band-limiting filter of the receiver, a sidelobe removing unit (407) configured to remove the sidelobe component from the power delay profile to produce a corrected power delay profile, and a path timing detection unit (408) configured to detect a path timing based on the corrected power delay profile.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
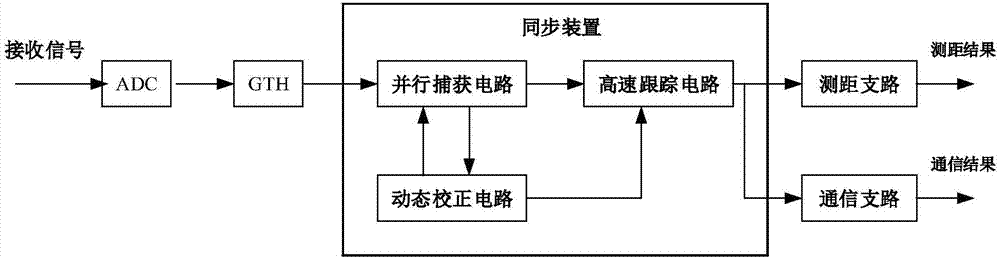
Synchronizer, synchronization method and high-speed receiver by using synchronizer
ActiveCN107425953AReduce processing burdenLow timing requirementsSynchronisation error correctionSynchronisation receiversTransceiverParallel computing
The present invention provides a synchronizer of a laser communication distance measurement integration system, a synchronization method of a laser communication distance measurement integration system and a high-speed receiver by using the synchronizer. The high-speed receiver receives high-speed signals, an analog-digital converter (ADC) is used for sampling of the high-speed signals, the sampling data is sent into a Gigabit transceiver (GTH) to perform serial-parallel conversion, and the high-speed serial data is converted to multi-path parallel data with low rate; the parallel data is sent into the synchronizer for signal synchronization, the parallel data is subjected to steps such as parallel data frame capture, dynamic correction, high-speed phase-locked loop tracking and the like in the synchronizer so as to complete accurate synchronization of the high-speed signals through the receiver; and moreover, on the basis of the accurate synchronization of the signals, and a distance measurement result and communication data can be solved out through the distance measurement branch and the communication branch of the receiver. The clock load is reduced and the complexity of the hardware realization is effectively reduced while ensuring the accurate synchronization of signals and accurate distance measurement and communication result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
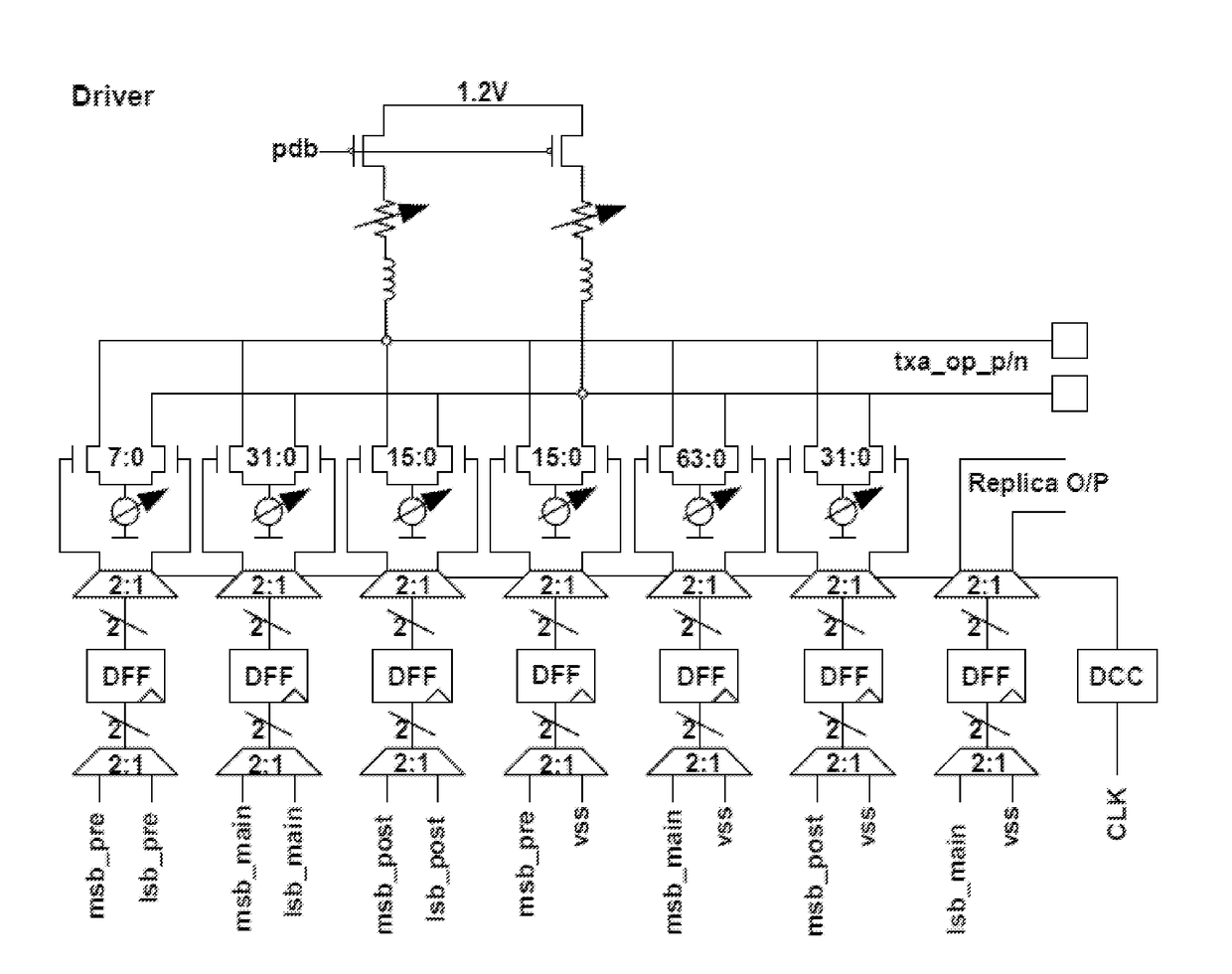
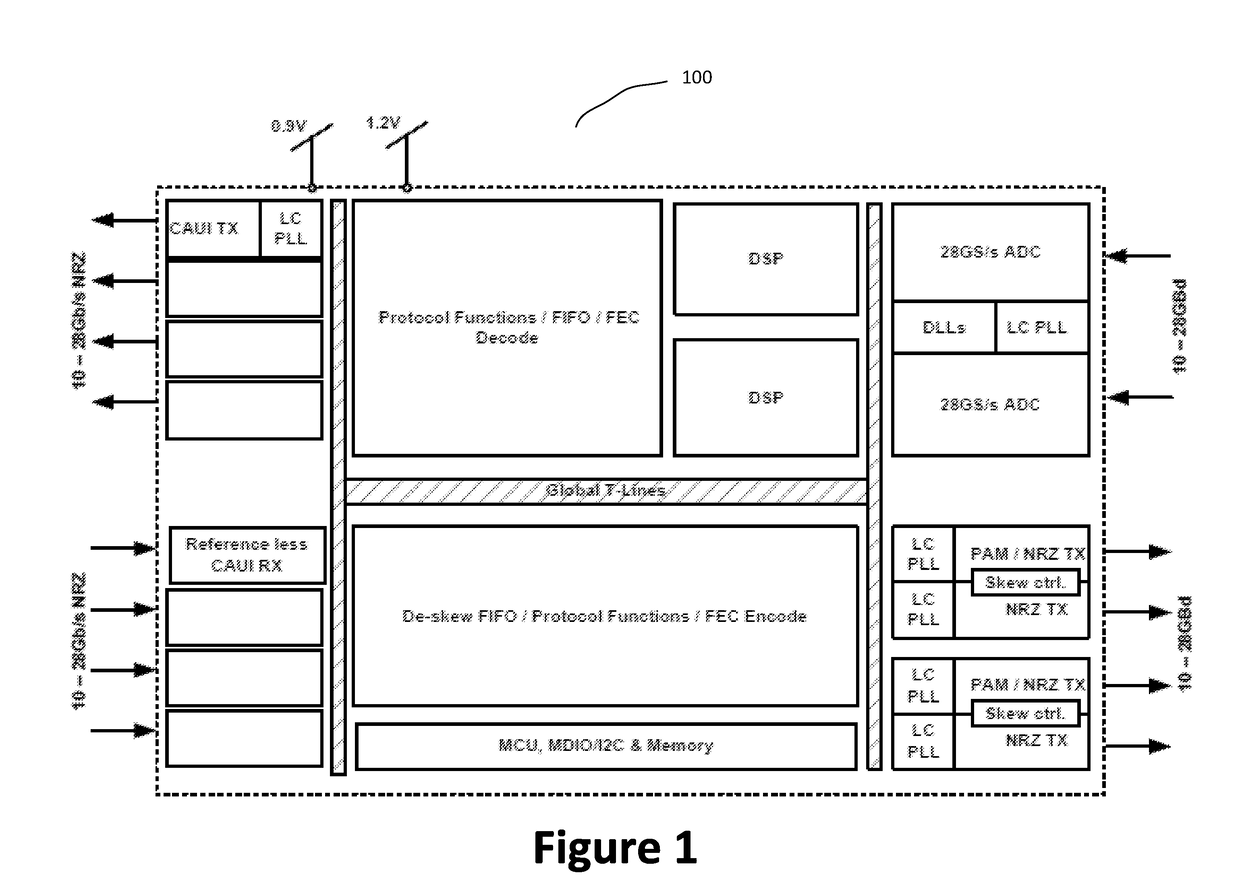
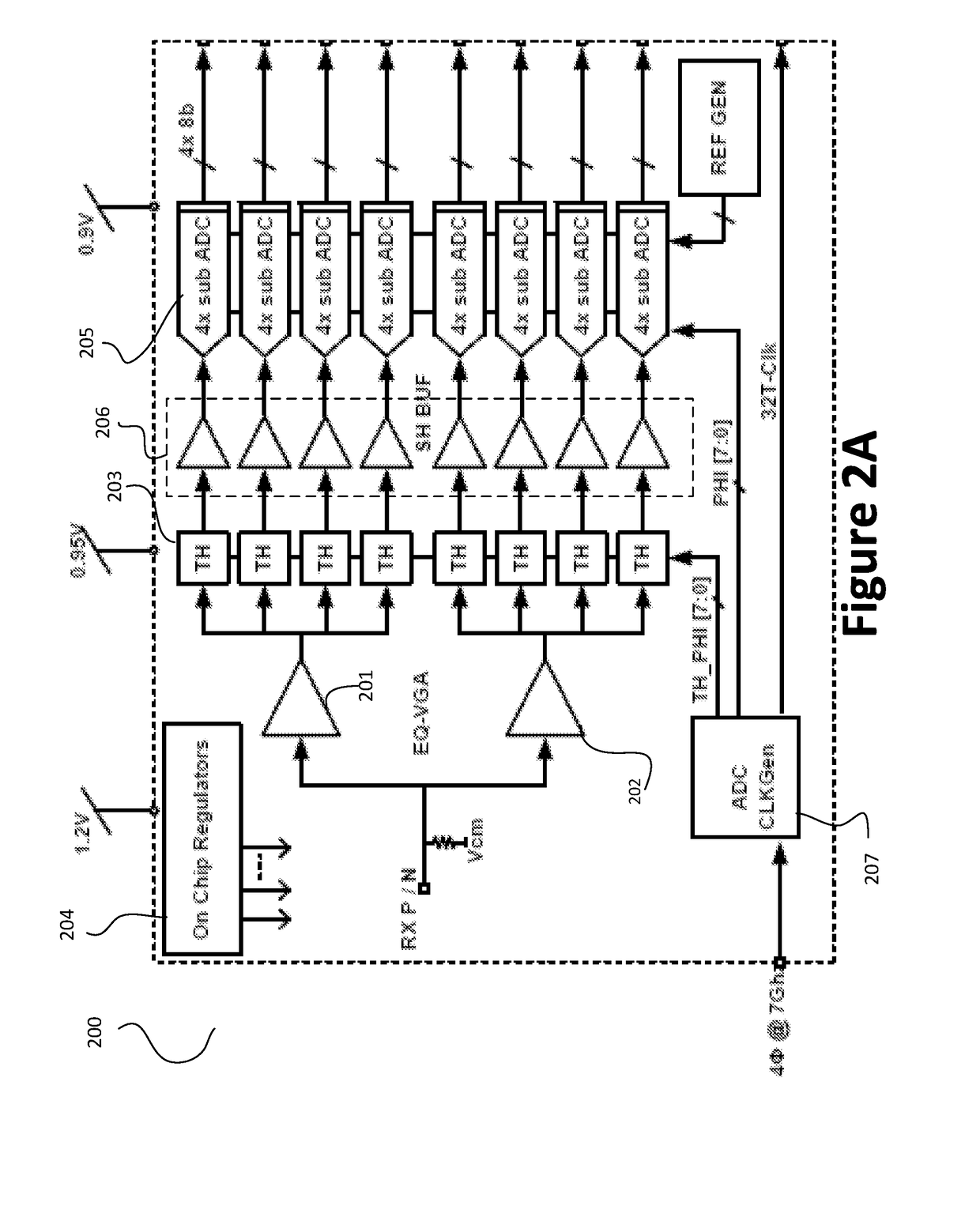
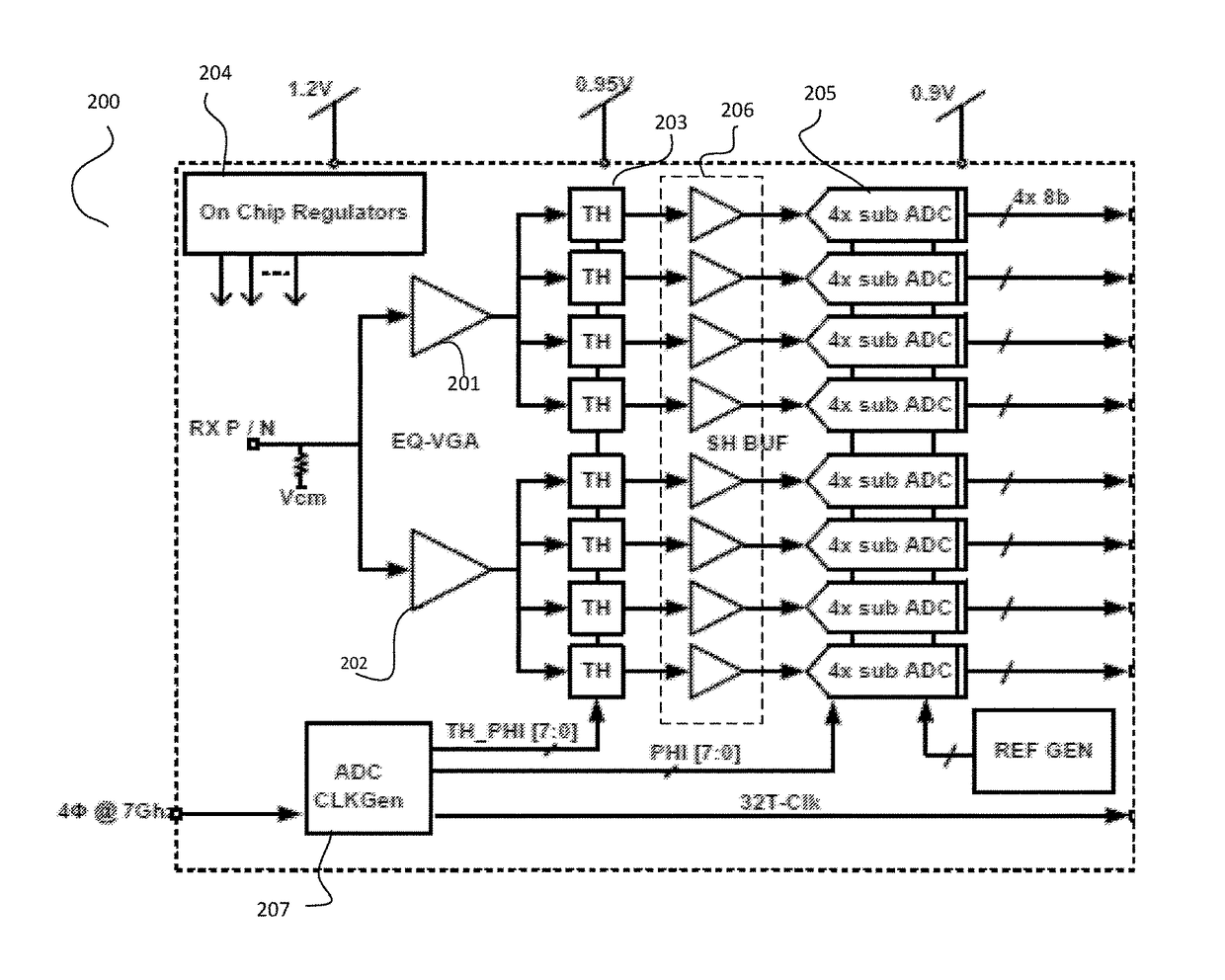
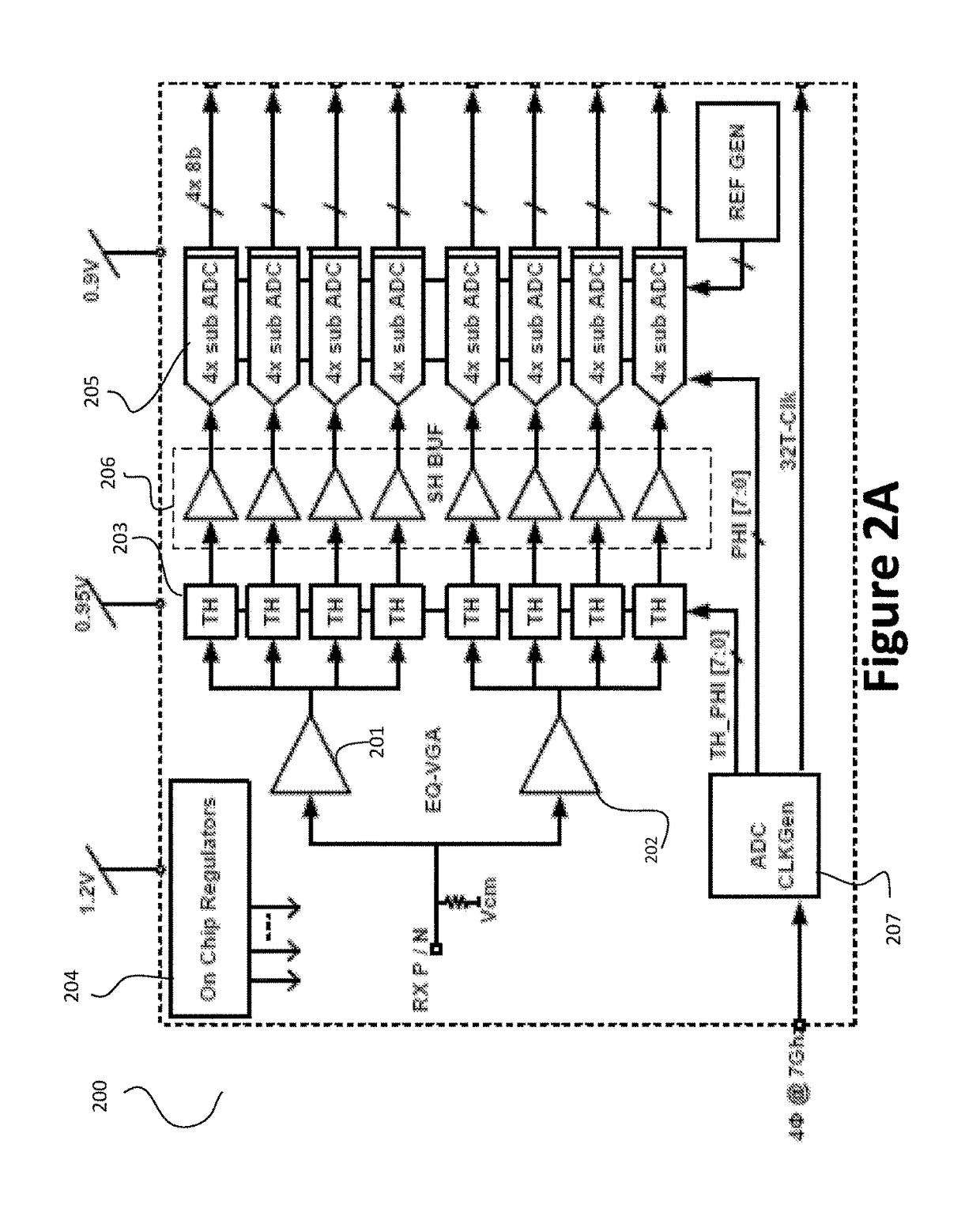
Pam4 transceivers for high-speed communication
ActiveUS20170257168A1Reduce power consumptionReduce noisePulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversAudio power amplifierTransceiver
The present invention is directed to data communication. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention provide a transceiver that processes an incoming data stream and generates a recovered clock signal based on the incoming data stream. The transceiver includes a voltage gain amplifier that also performs equalization and provides a driving signal to track and hold circuits that hold the incoming data stream, which is stored by shift and holder buffer circuits. Analog to digital conversion is then performed on the buffer data by a plurality of ADC circuits. Various DSP functions are then performed over the converted data. The converted data are then encoded and transmitted in a PAM format. There are other embodiments as well.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Clock and data recovery circuit having wide phase margin
InactiveUS7961830B2Increase speedReduce errorsPulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversSerial samplingPhase control
A clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit includes a sampler, a CDR loop and a phase interpolator. The sampler samples serial data in response to a recovery clock signal to generate a serial sampling pulse. The CDR loop transforms the serial sampling pulse into parallel data, generates a plurality of phase signals with a first speed based on the parallel data, and generates a phase control signal with a second speed higher than the first speed based on the plurality of phase signals. The phase interpolator generates the recovery clock signal by controlling a phase of a reference clock signal in response to the phase control signal. Therefore, the CDR circuit may recover data and a clock with a relatively high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for measuring and correcting multi-wire skew
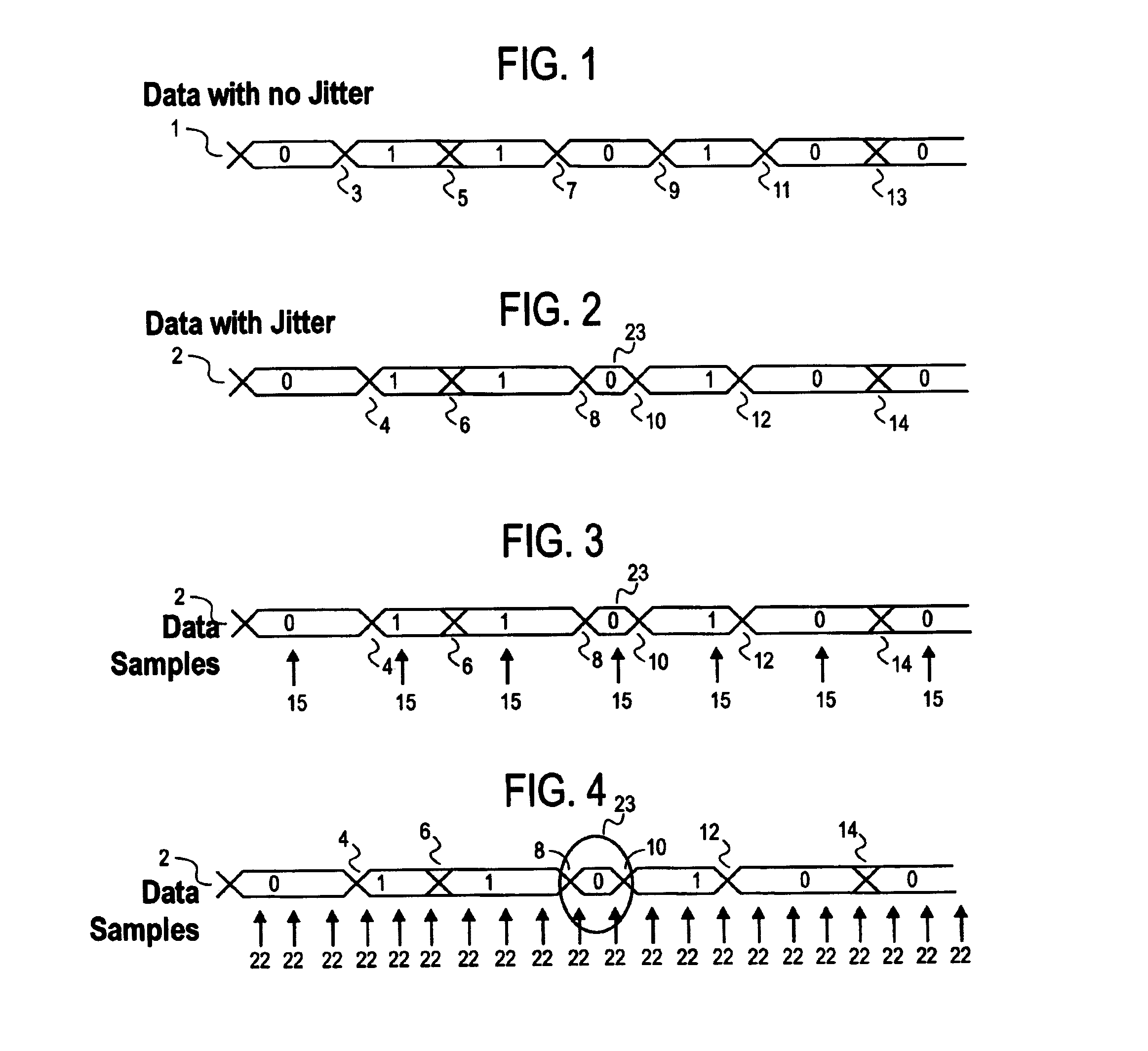
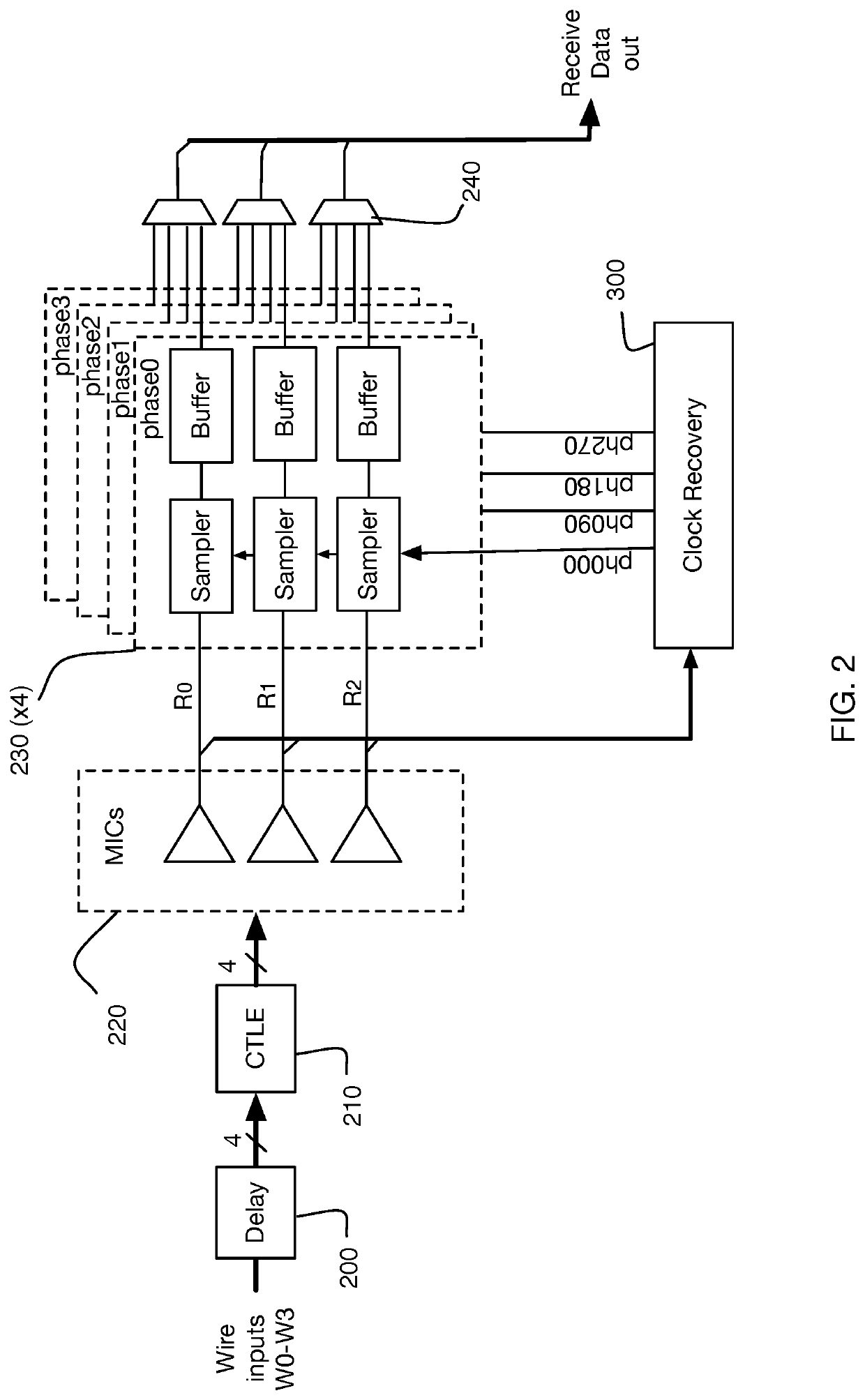
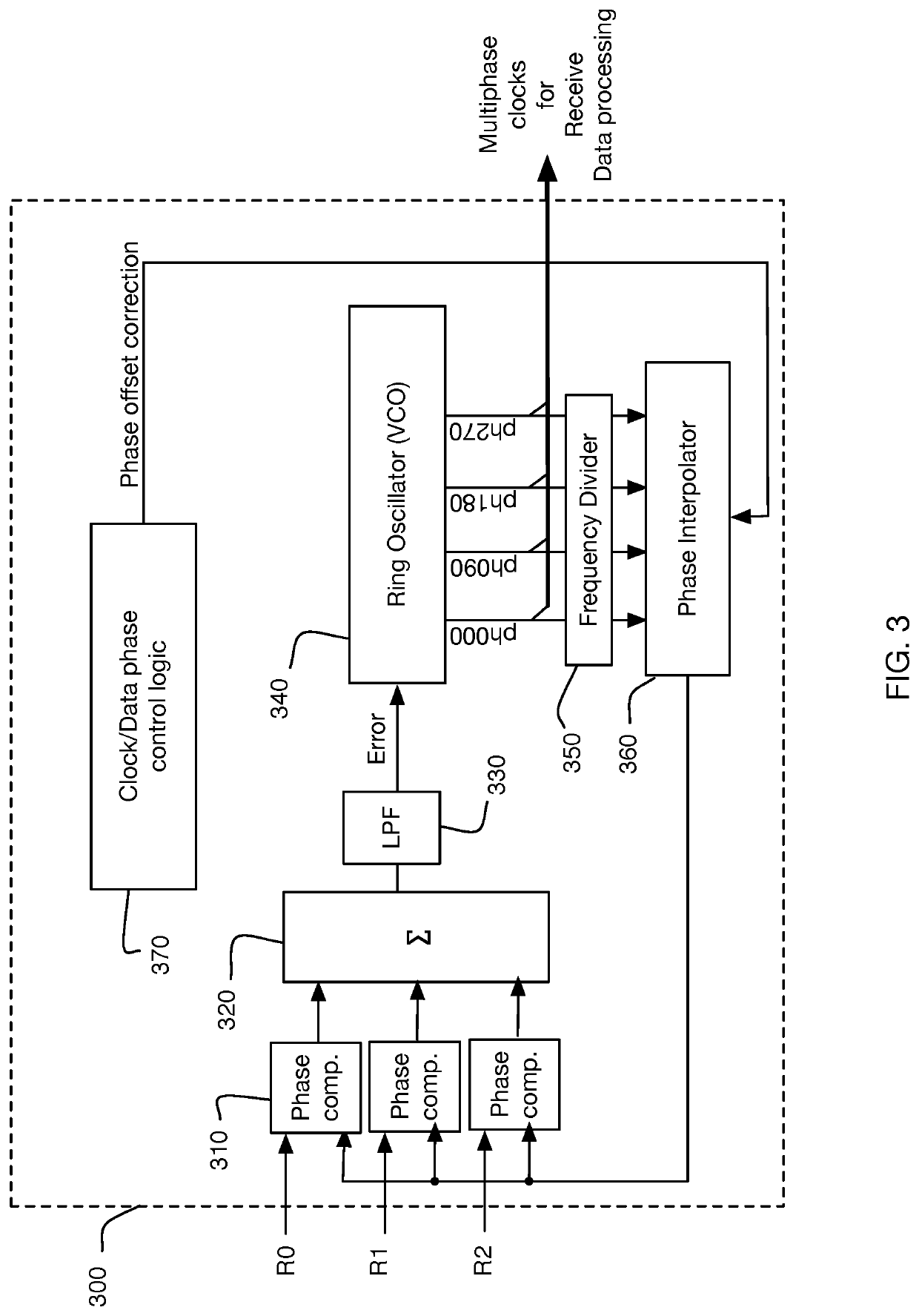
ActiveUS20200313841A1Reliable detectionAccurate interpretationChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation error correctionData signalSkew
Generating, during a first and second signaling interval, an aggregated data signal by forming a linear combination of wire signals received in parallel from wires of a multi-wire bus, wherein at least some of the wire signals undergo a signal level transition during the first and second signaling interval; measuring a signal skew characteristic of the aggregated data signal; and, generating wire-specific skew offset metrics, each wire-specific skew offset metric based on the signal skew characteristic.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
PAM4 transceivers for high-speed communication
ActiveUS9847839B2Reduce errorsReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlSynchronisation receiversData streamTransceiver
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
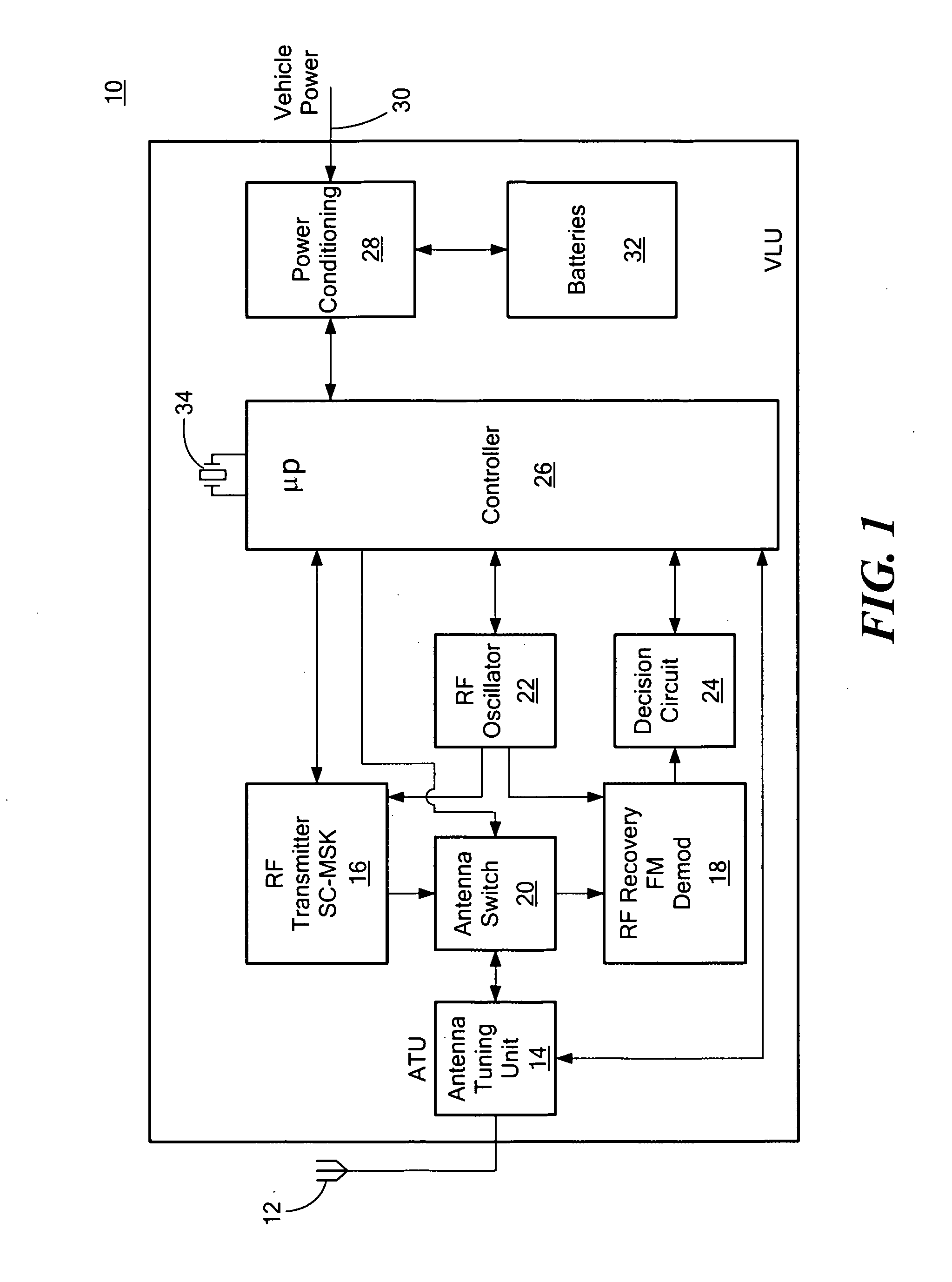
Synchronization system and method for achieving low power battery operation of a vehicle locating unit in a stolen vehicle recovery system which receives periodic transmissions
ActiveUS20110098015A1Reduced Power RequirementsEnabling synchronizationPower managementSynchronisation arrangementPower batteryRadio reception
Synchronization for achieving low power battery operation of a vehicle locating unit in a stolen vehicle recovery system whose radio receiver receives periodic transmissions, includes receiving periodic transmissions; turning on a radio receiver for a limited time to detect an expected message; if an expected message is not found, turning off the receiver and turning it on again after a time asynchronous with the transmission period; and after finding an expected message, waiting for the period of the transmissions less the length of an expected message and then looking for a synchronization symbol in the expected message and synchronizing subsequent actuation of the receiver using that synchronization symbol.
Owner:CALAMP WIRELESS NETWORKS
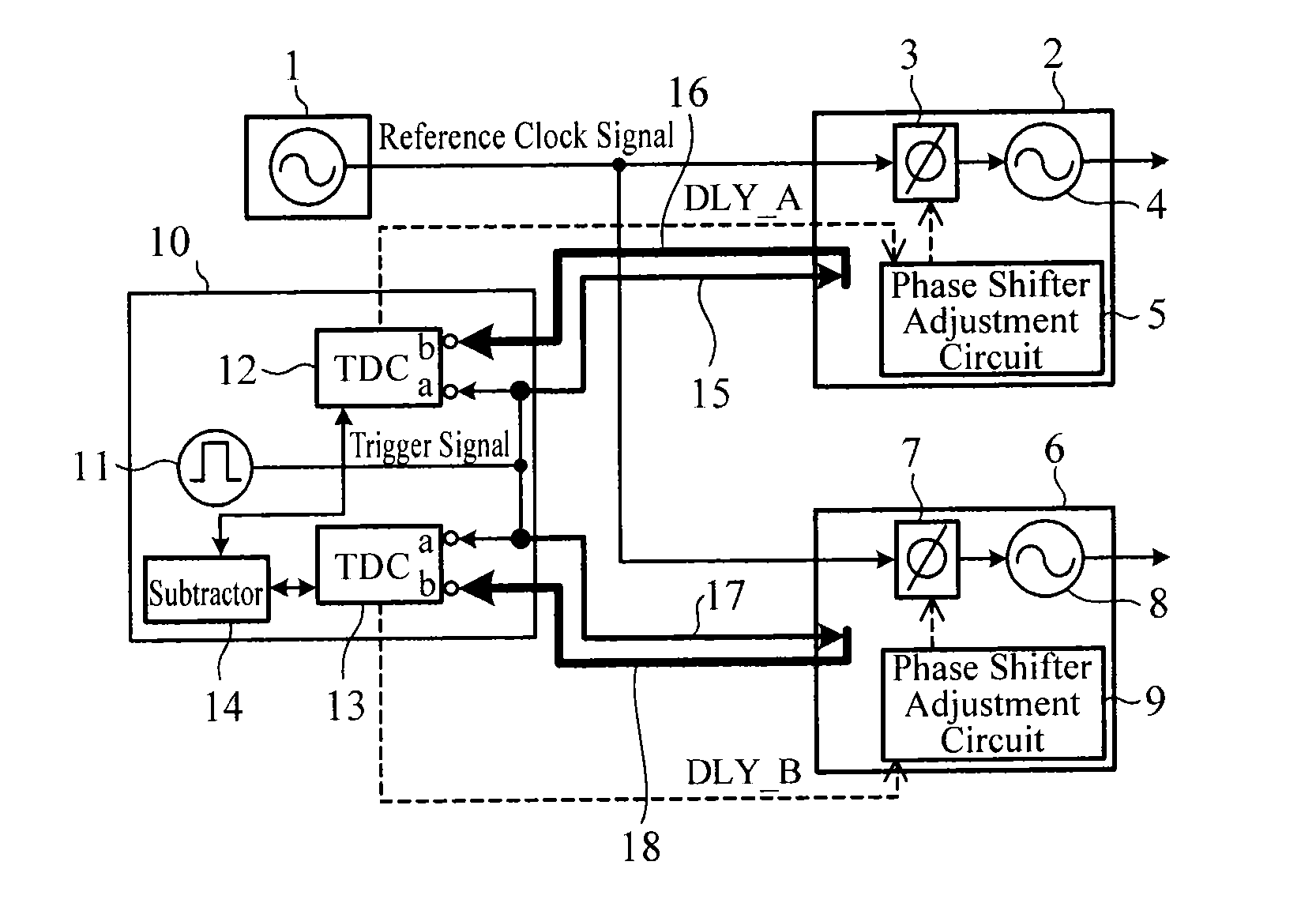
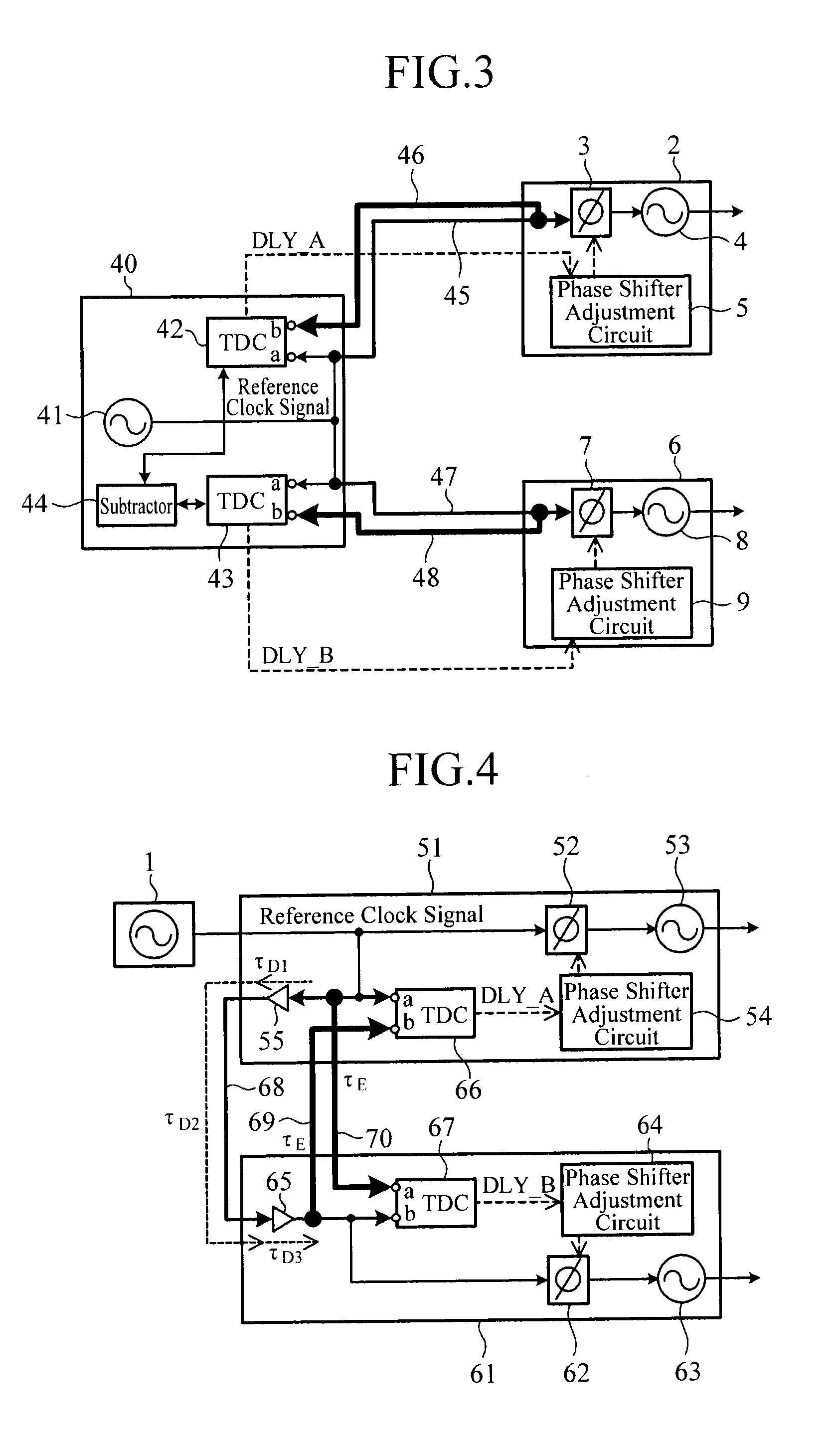
Signal source synchronization circuit
ActiveUS20130287155A1Improve accuracySynchronisation receiversSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlDelayed timeSignal source
A signal source synchronization circuit includes: a first TDC circuit that measures a first path delay time which is a time difference between an input time of a trigger signal to a first input terminal and an input time of the trigger signal to a second input terminal; and a second TDC circuit that measures a second path delay time which is a time difference between an input time of the trigger signal to a first input terminal and an input time of the trigger signal to a second input terminal, wherein a first phase shifter adjustment circuit sets a phase adjustment amount corresponding to the first path delay time in a first phase shifter, and a second phase shifter adjustment circuit sets a phase adjustment amount corresponding to the second path delay time in a second phase shifter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com