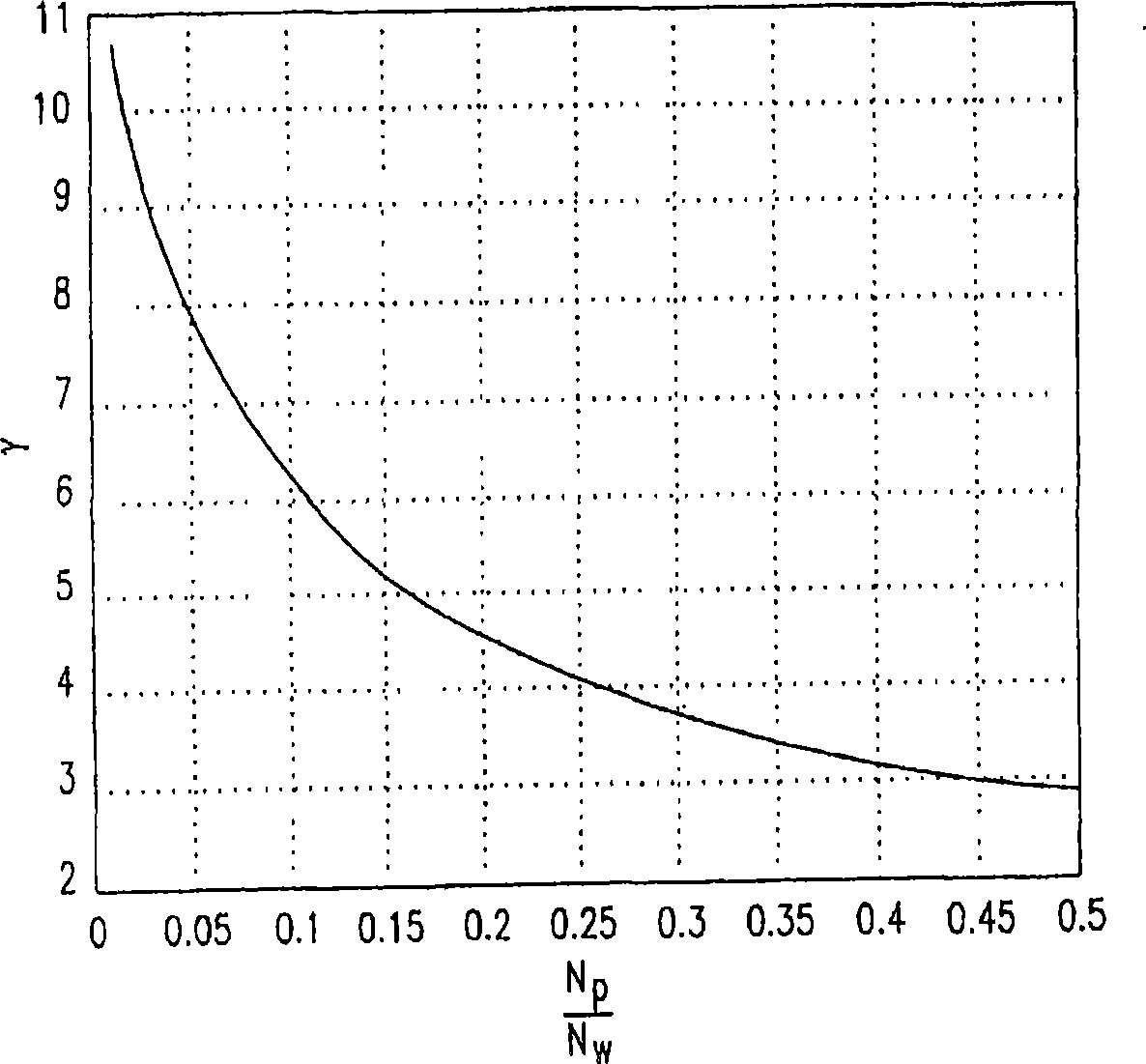
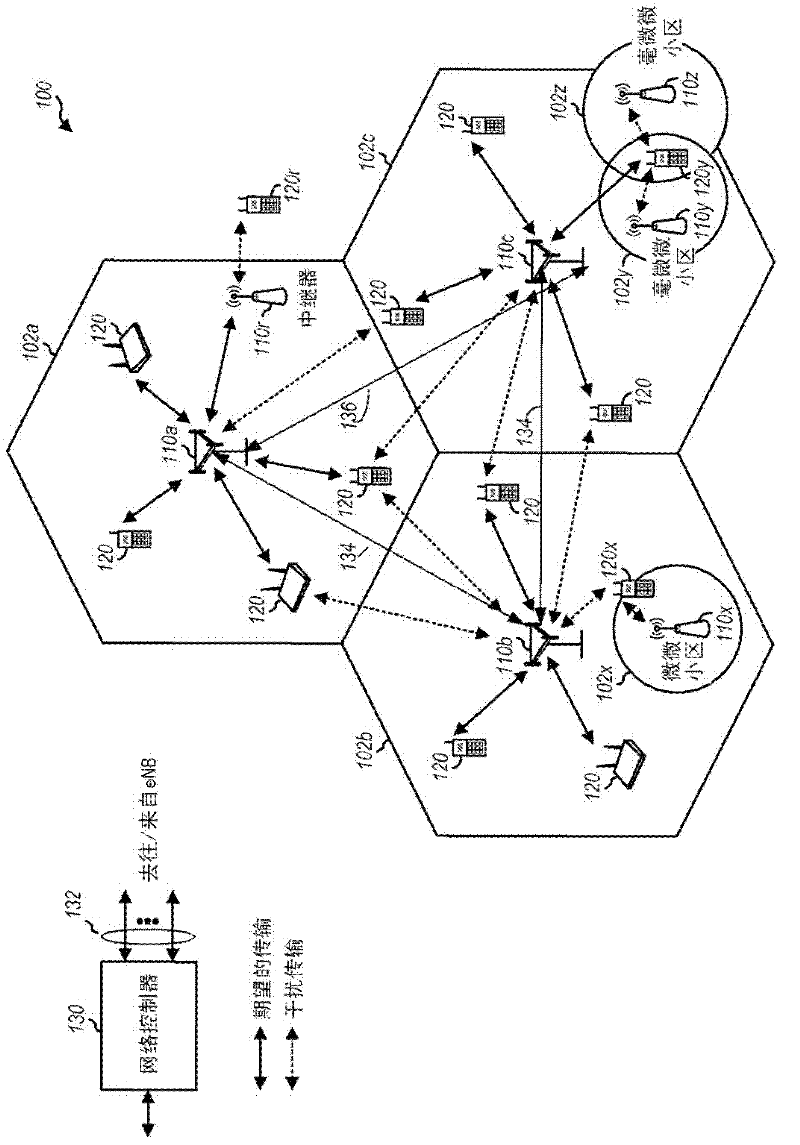
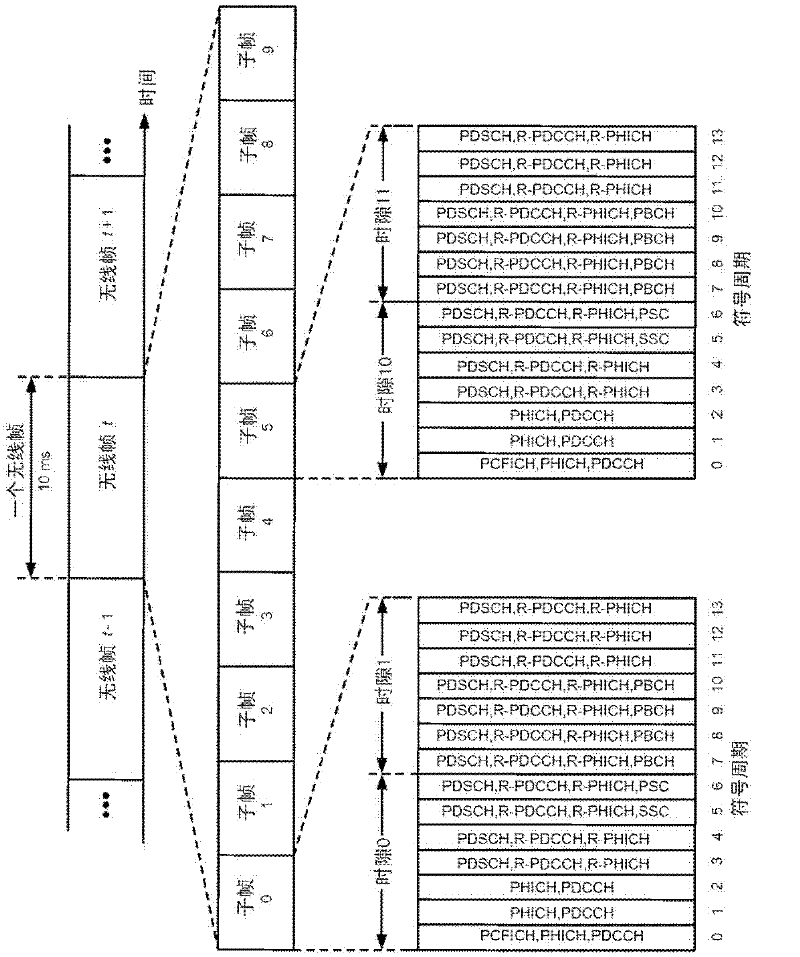
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Power delay profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
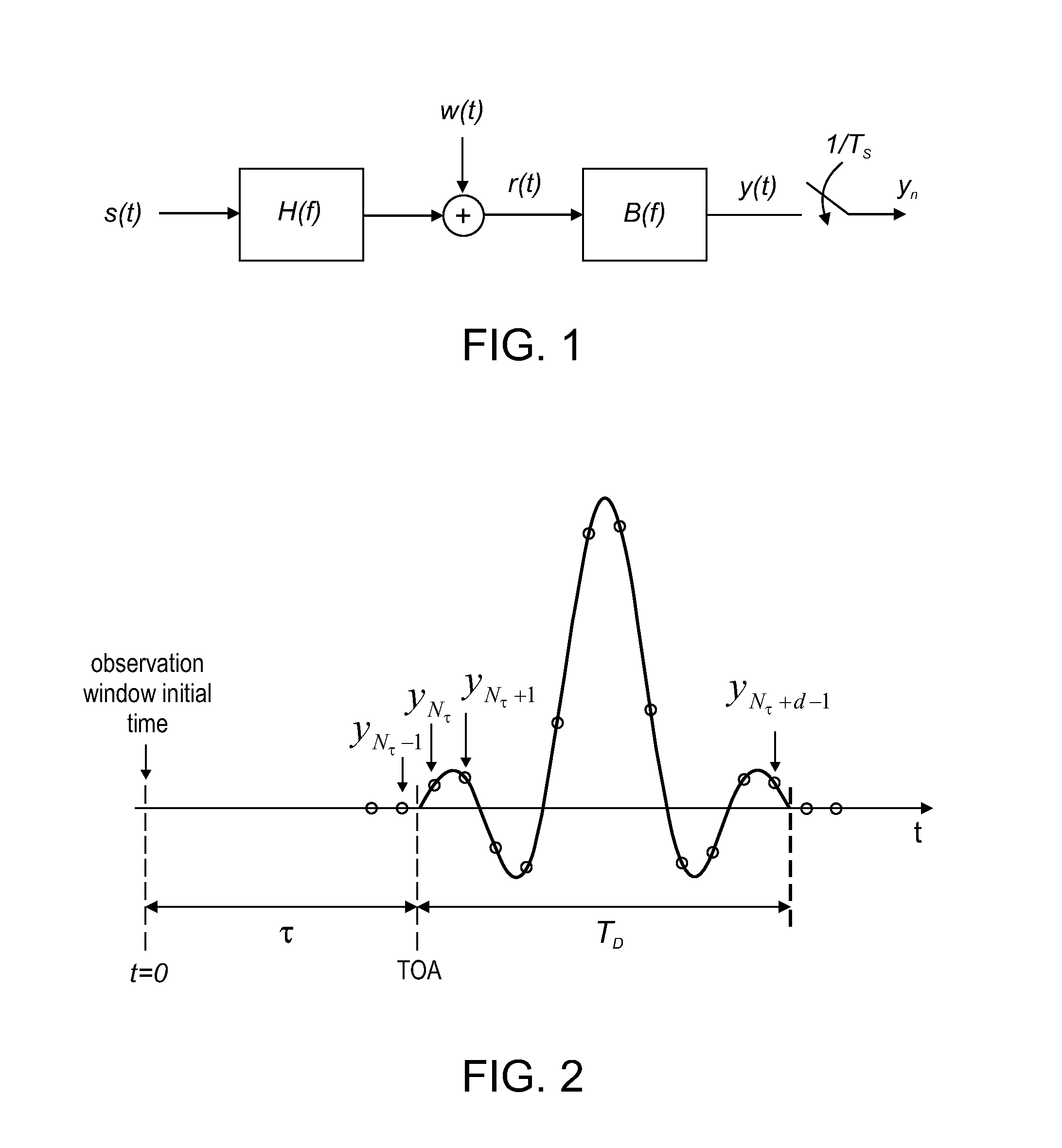
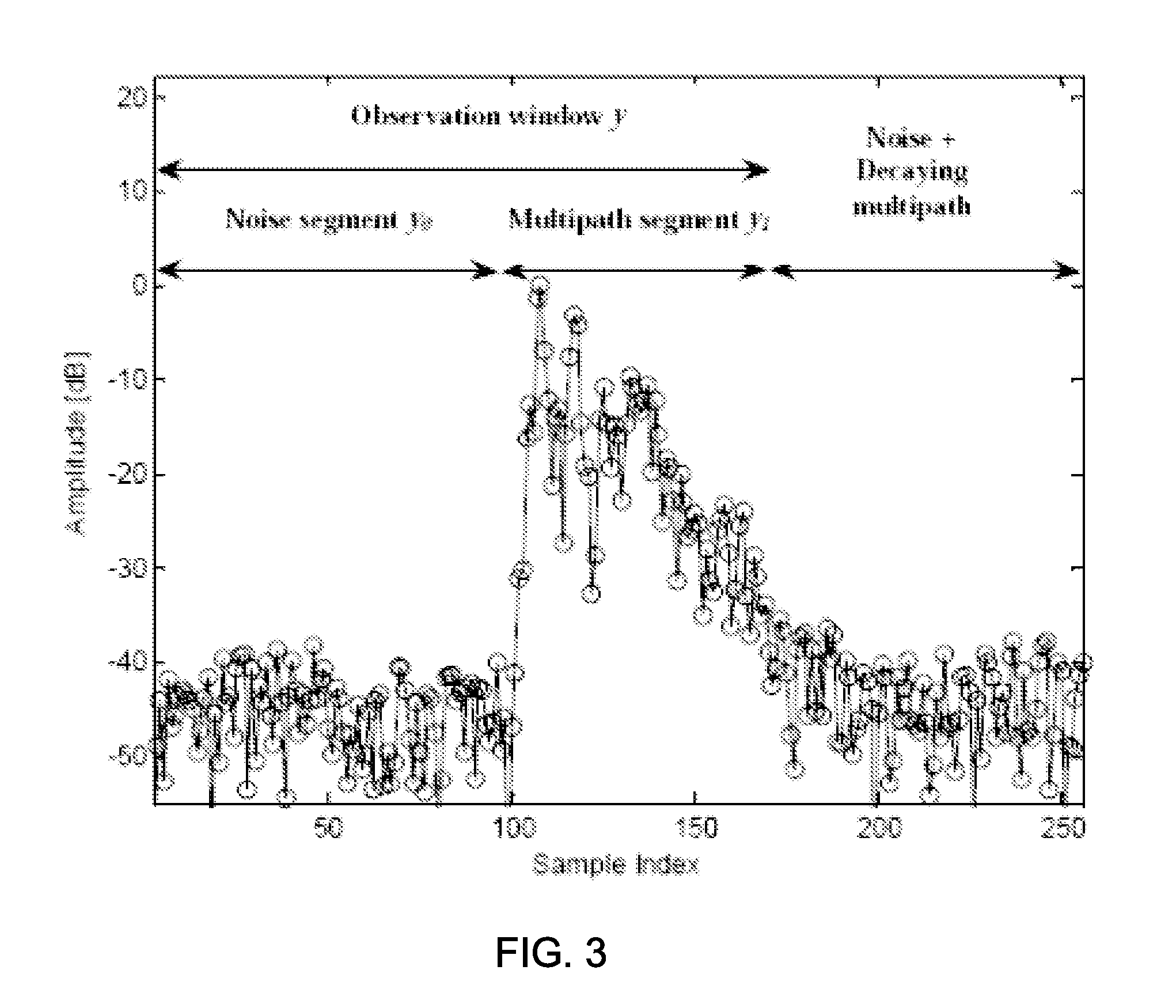
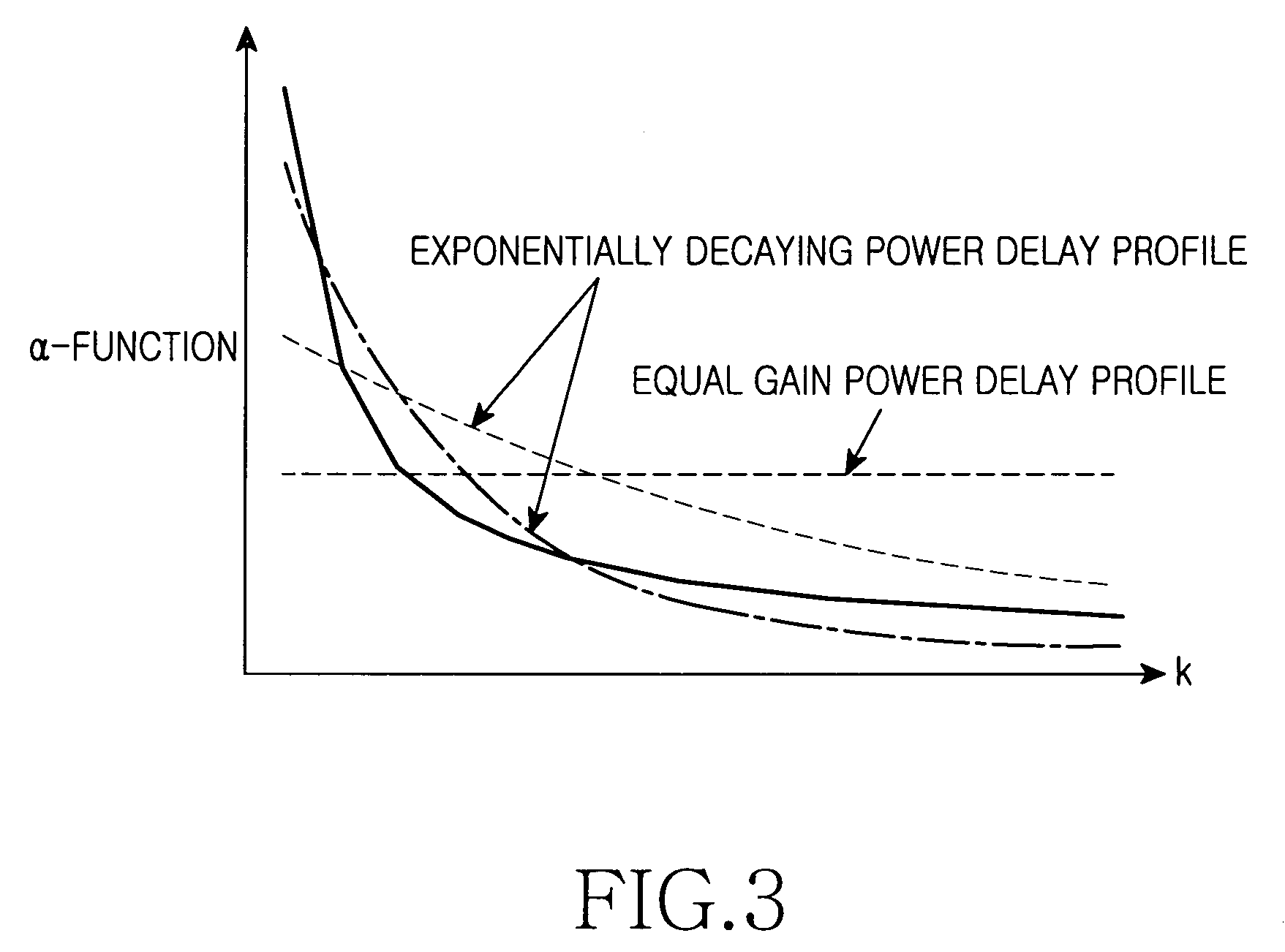
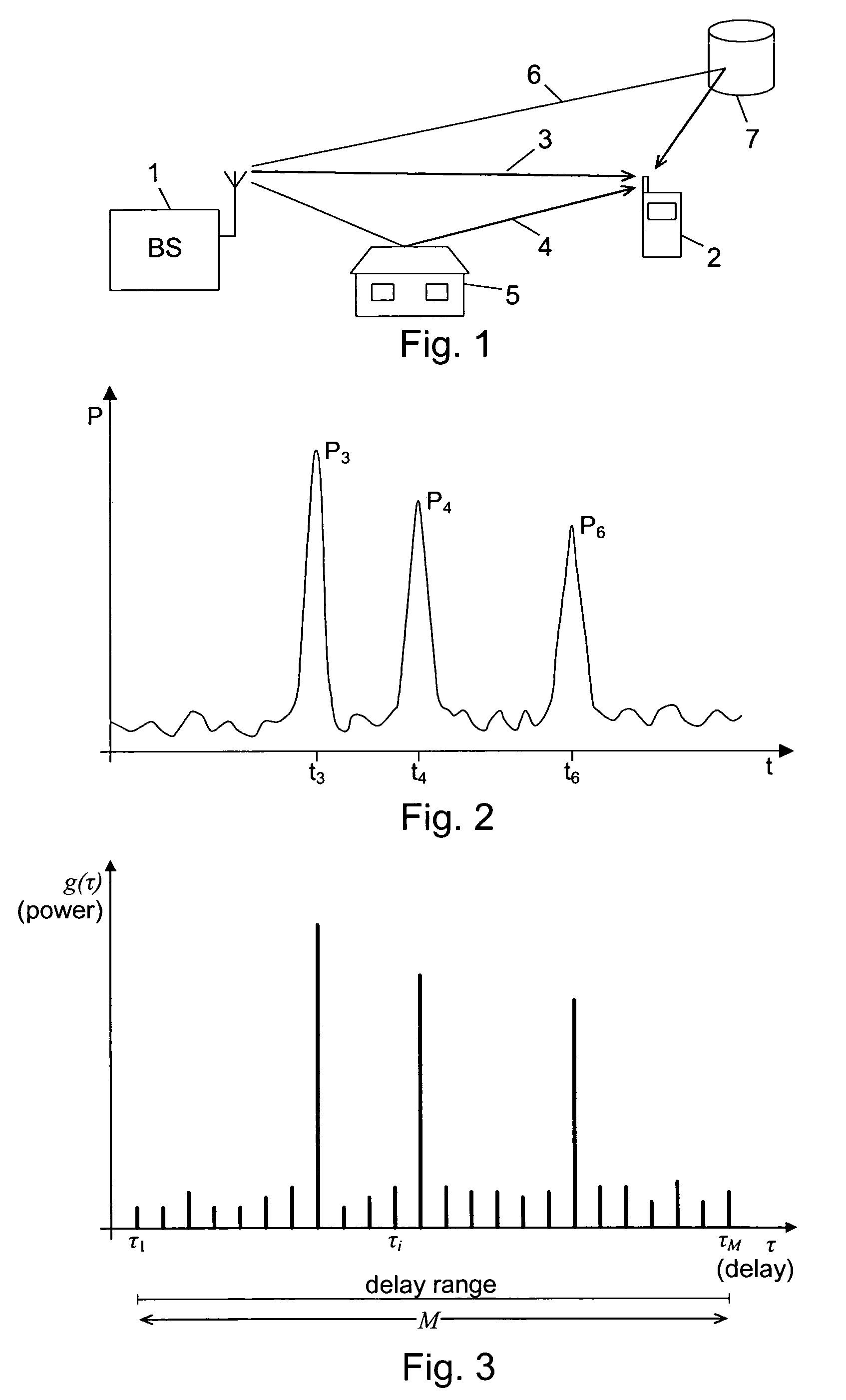
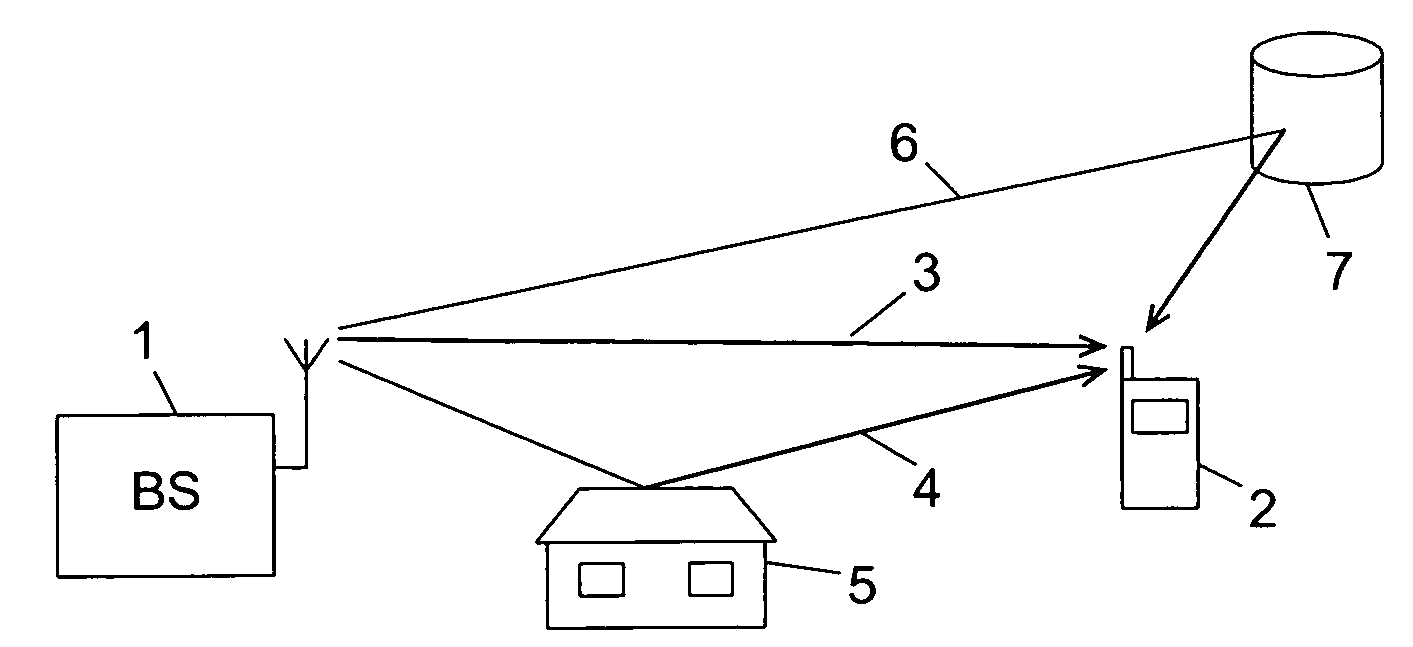
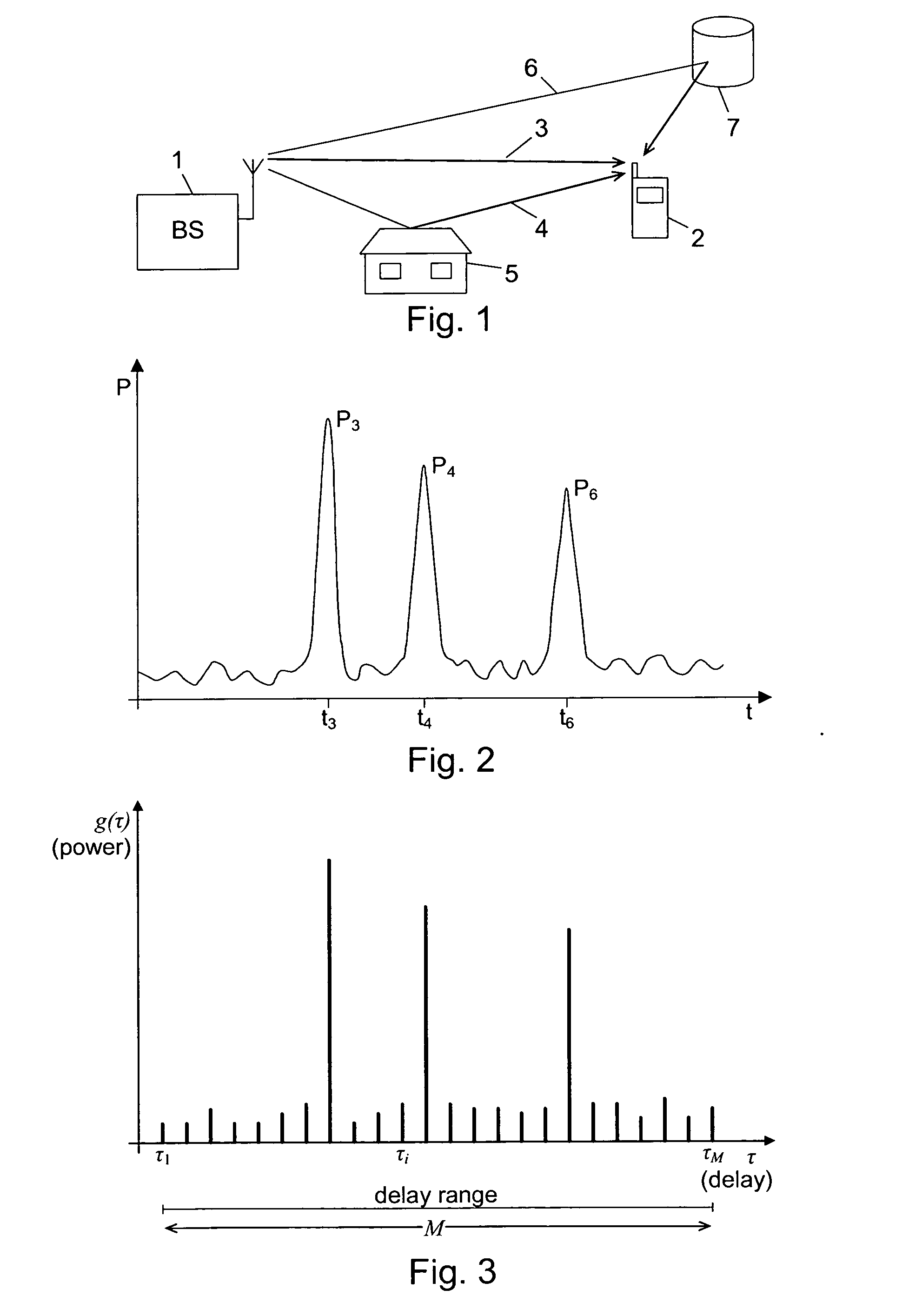
The power delay profile (PDP) gives the intensity of a signal received through a multipath channel as a function of time delay. The time delay is the difference in travel time between multipath arrivals. The abscissa is in units of time and the ordinate is usually in decibels. It is easily measured empirically and can be used to extract certain channel's parameters such as the delay spread. For Small Scale channel modeling, the power delay profile of the channel is found by taking the spatial average of the channel's baseband impulse response i.e. |hb(t,τ)|² over a local area.
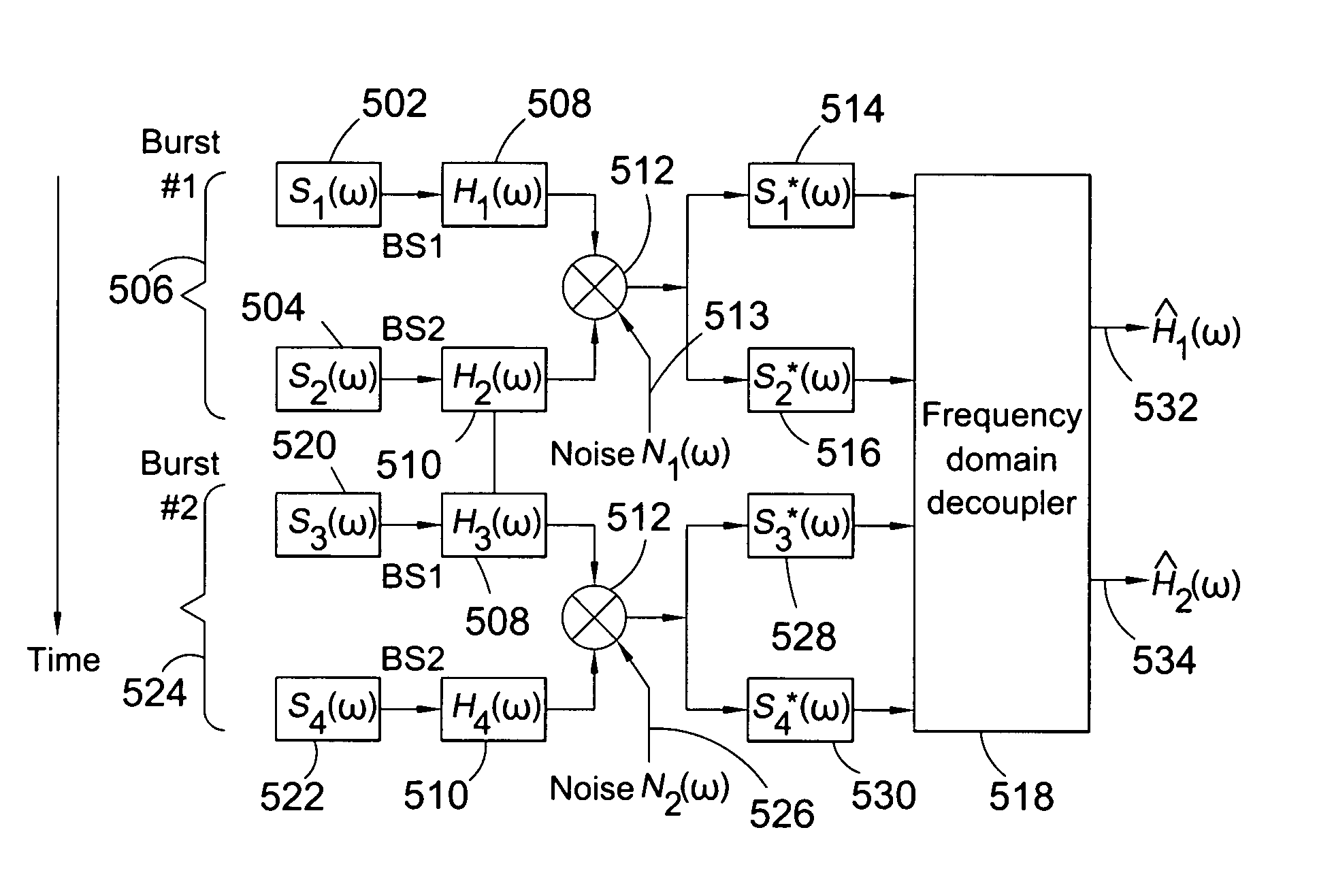
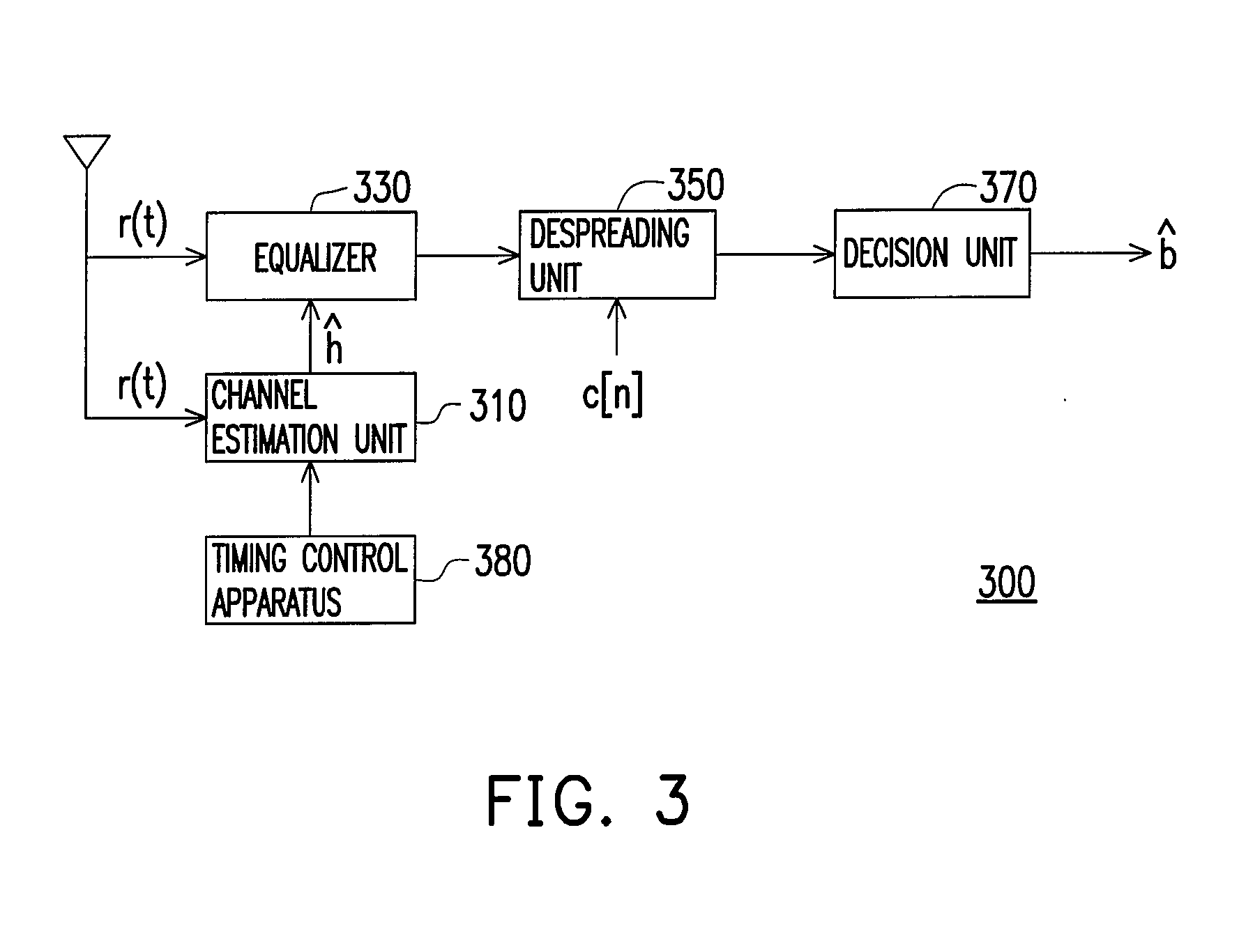
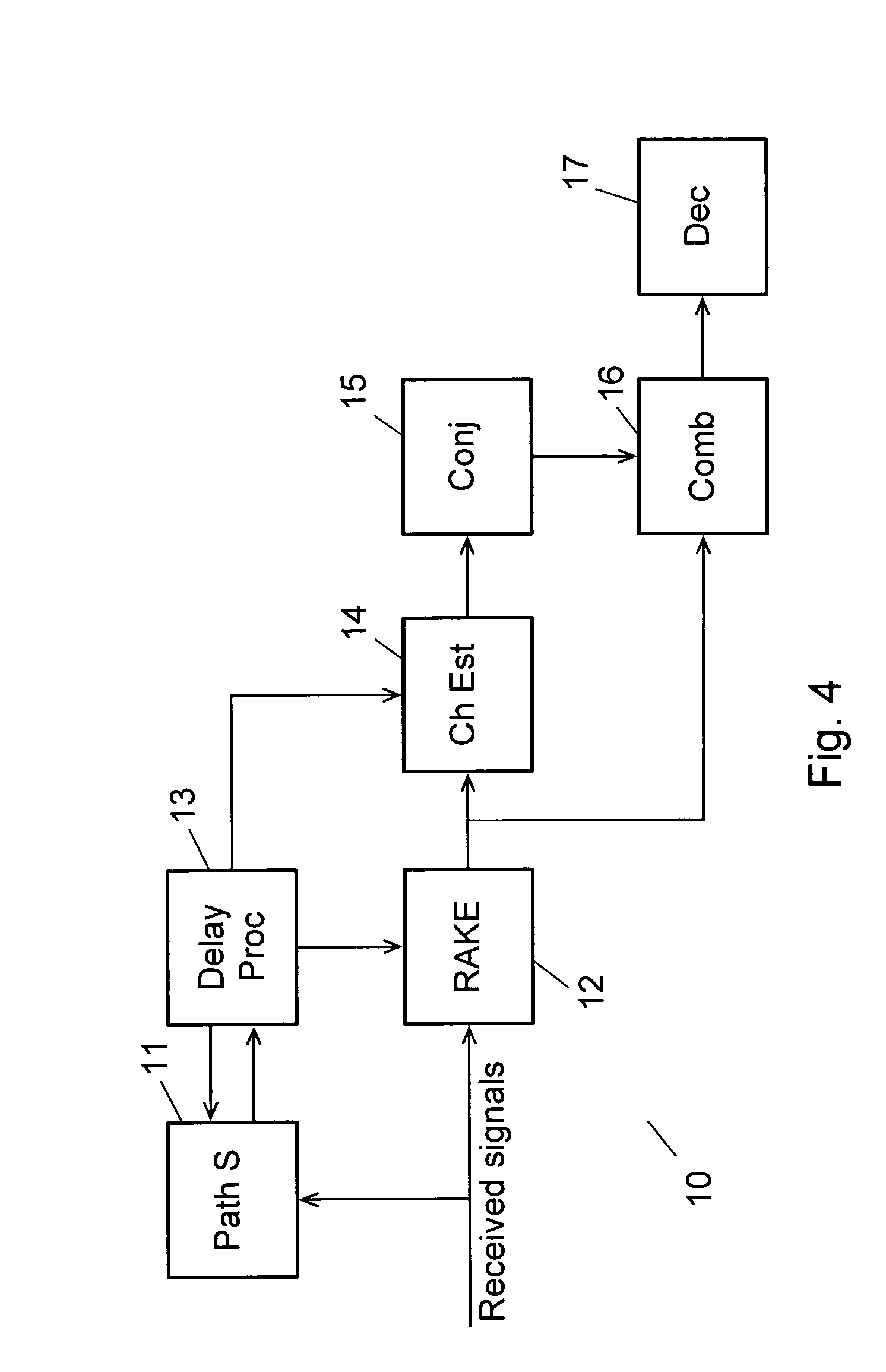
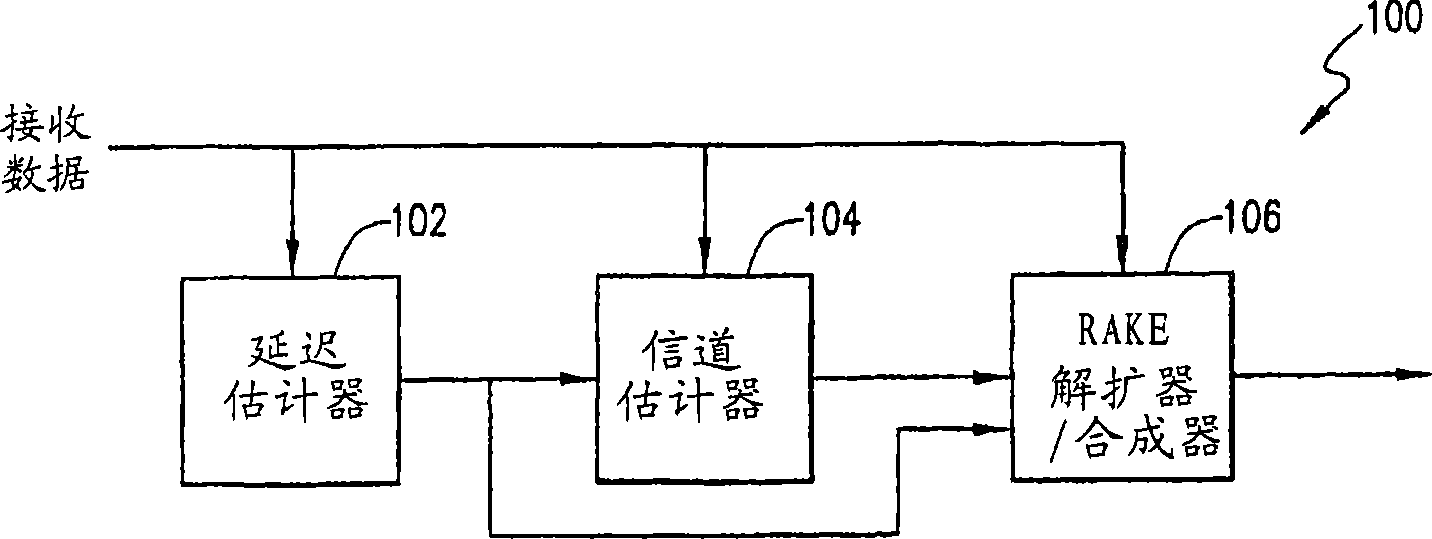
Communication system and methods of estimating channel impulse responses therein
InactiveUS7149239B2Improve interferenceImprove accuracySecret communicationChannel estimationTime transformationEngineering
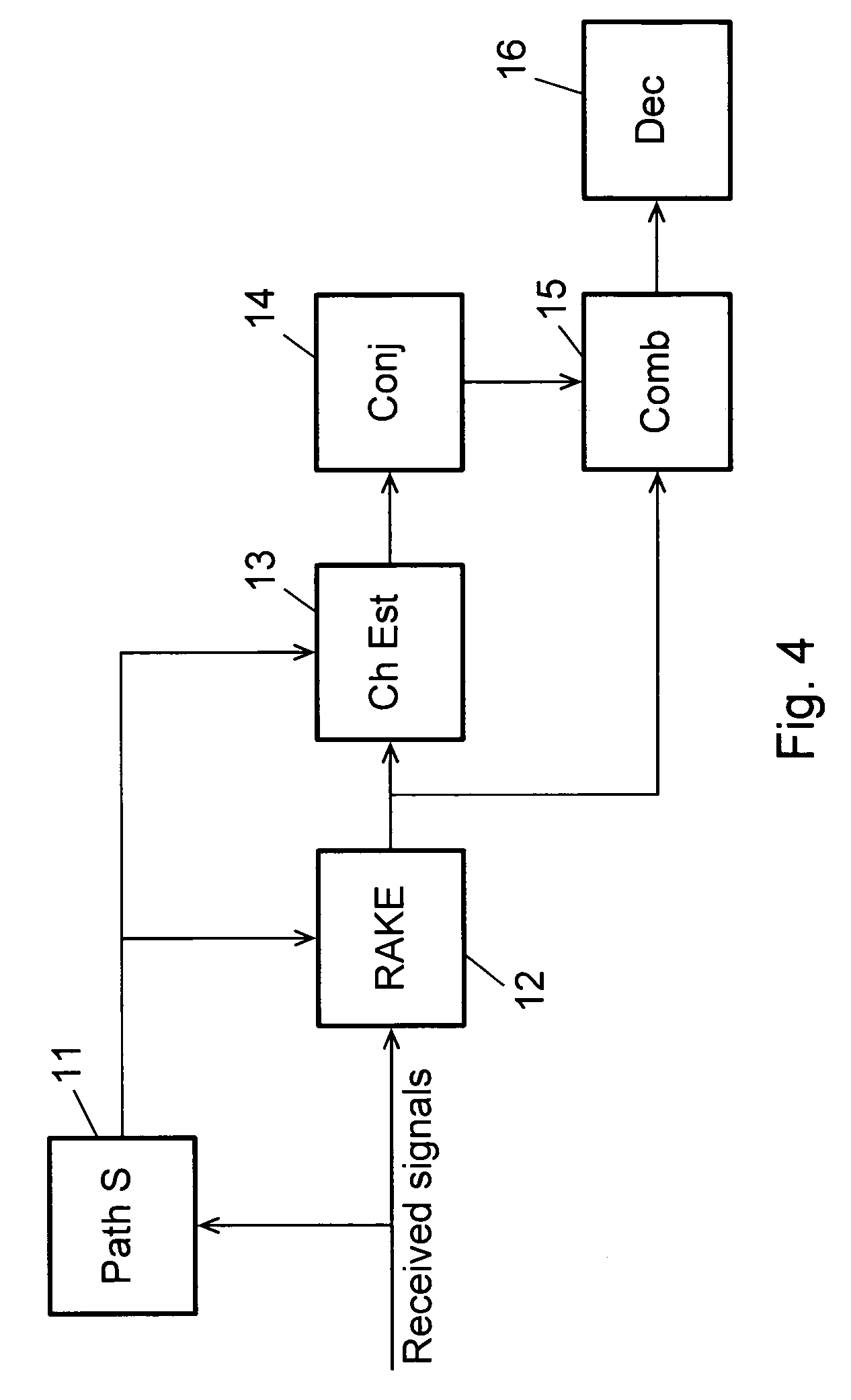
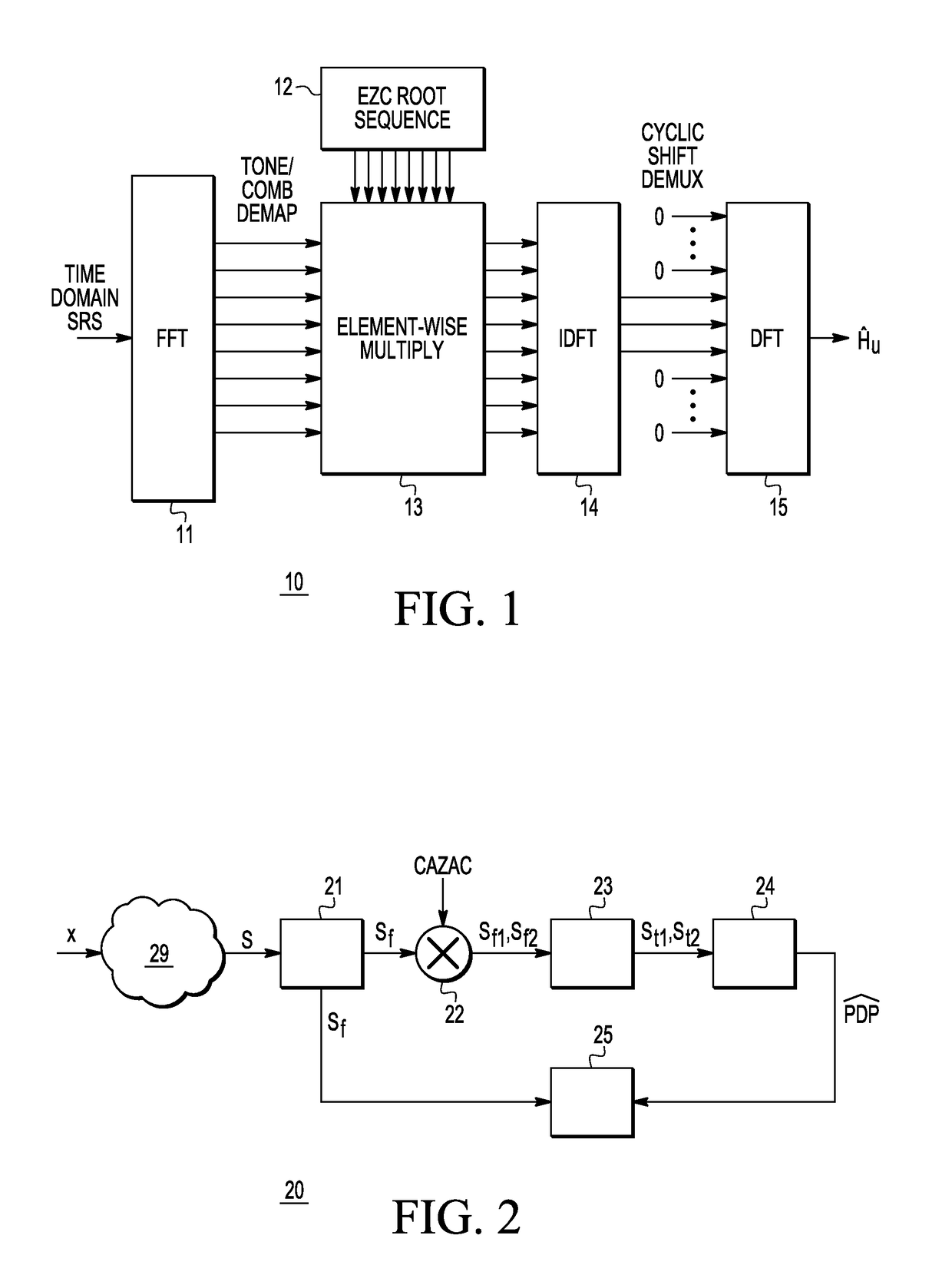
Multiple Steiner codes are transmitted as bursts from multiple base stations (182, 184, 186) having one or more transmit elements (174, 176, 178, 180), with successive bursts providing an extended training sequence for use in channel estimation at an addressed unit (172), such as a mobile handset. Accurate channel estimation is possible through the use of Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution (518) combined with frequency domain spatial decoupling matrices, with quasi-orthogonal pseudo-noise sequences (502, 504, 520, 522) allocated to base stations and their antenna elements. The use of Steiner codes to supplement Wiener frequency domain MMSE deconvolution and frequency domain spatial decoupling results in the possibility of allocating only a single training sequence to each base station provided that the training sequence is of sufficient length to encompass all multiple time-translated channel impulse responses (H). Estimates may be refined iteratively by minimising the MS error of demodulated pilot symbols. Estimates may also be refined by removing taps from the impulse response which are insignificant based on a relatively long-term power-delay profile for the channel.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
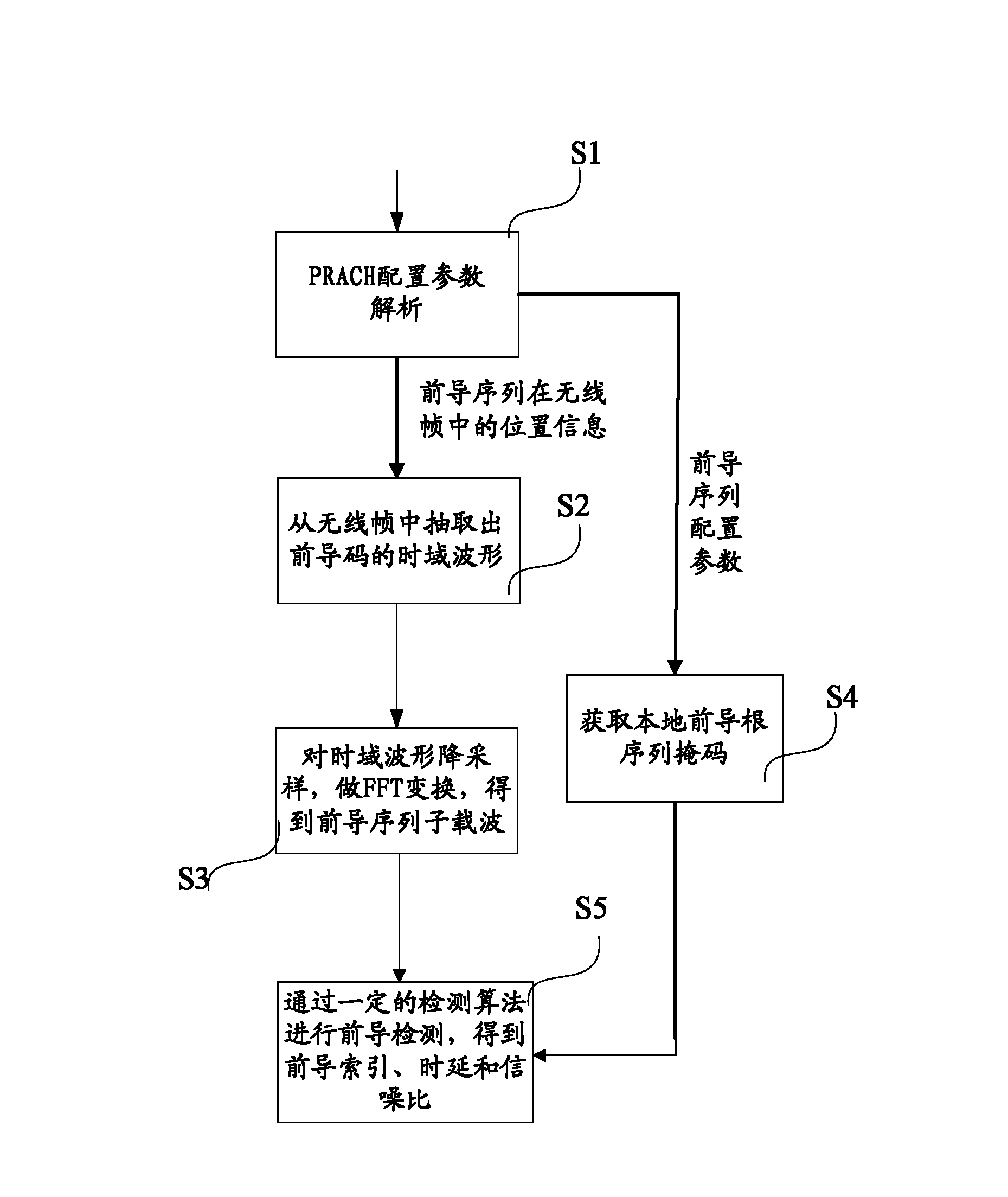
Leader sequence detection method and device for random access channel
ActiveCN102316601AReduce computationReduce complexityBaseband system detailsWireless communicationChannel powerTime delays
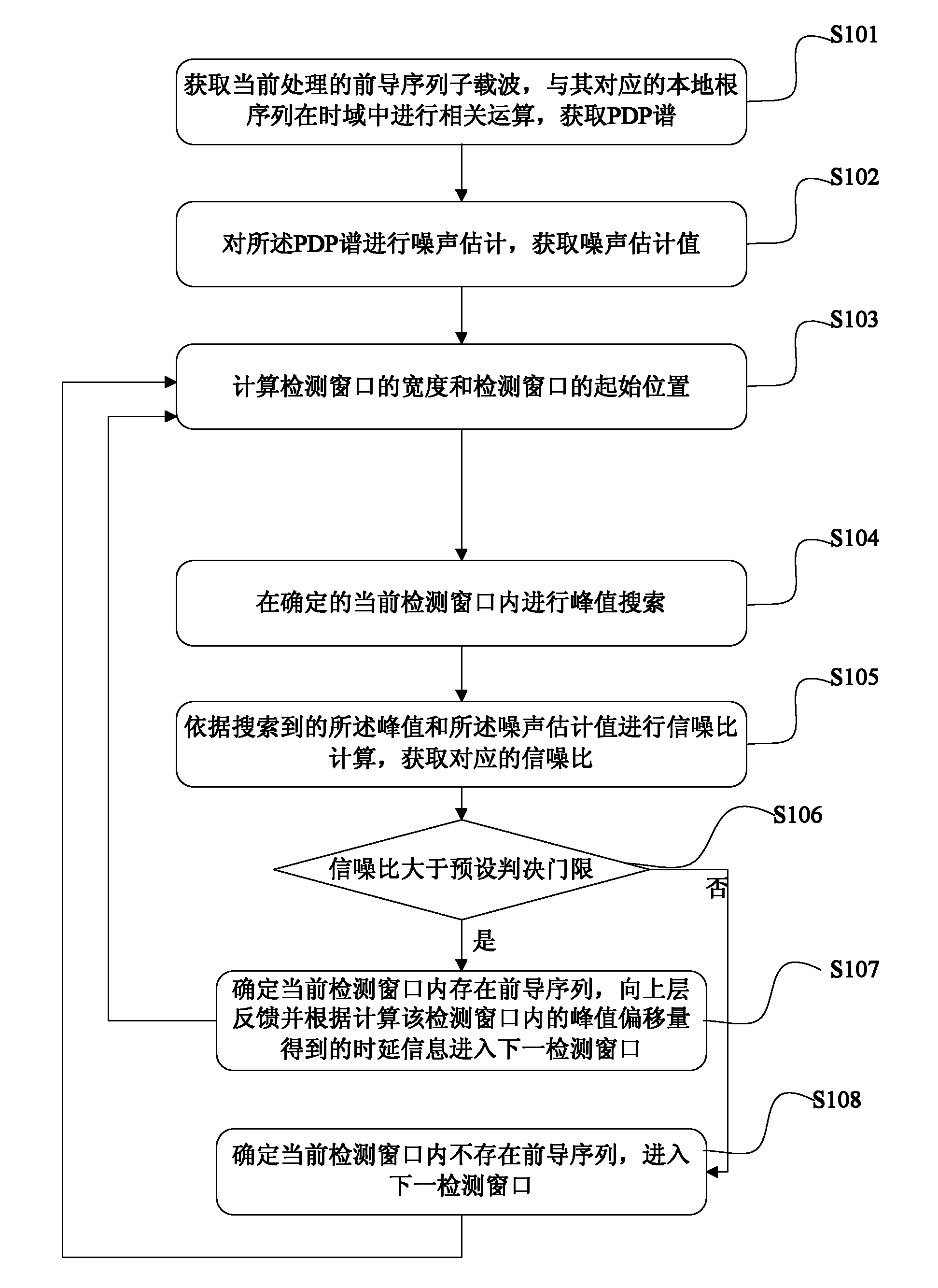
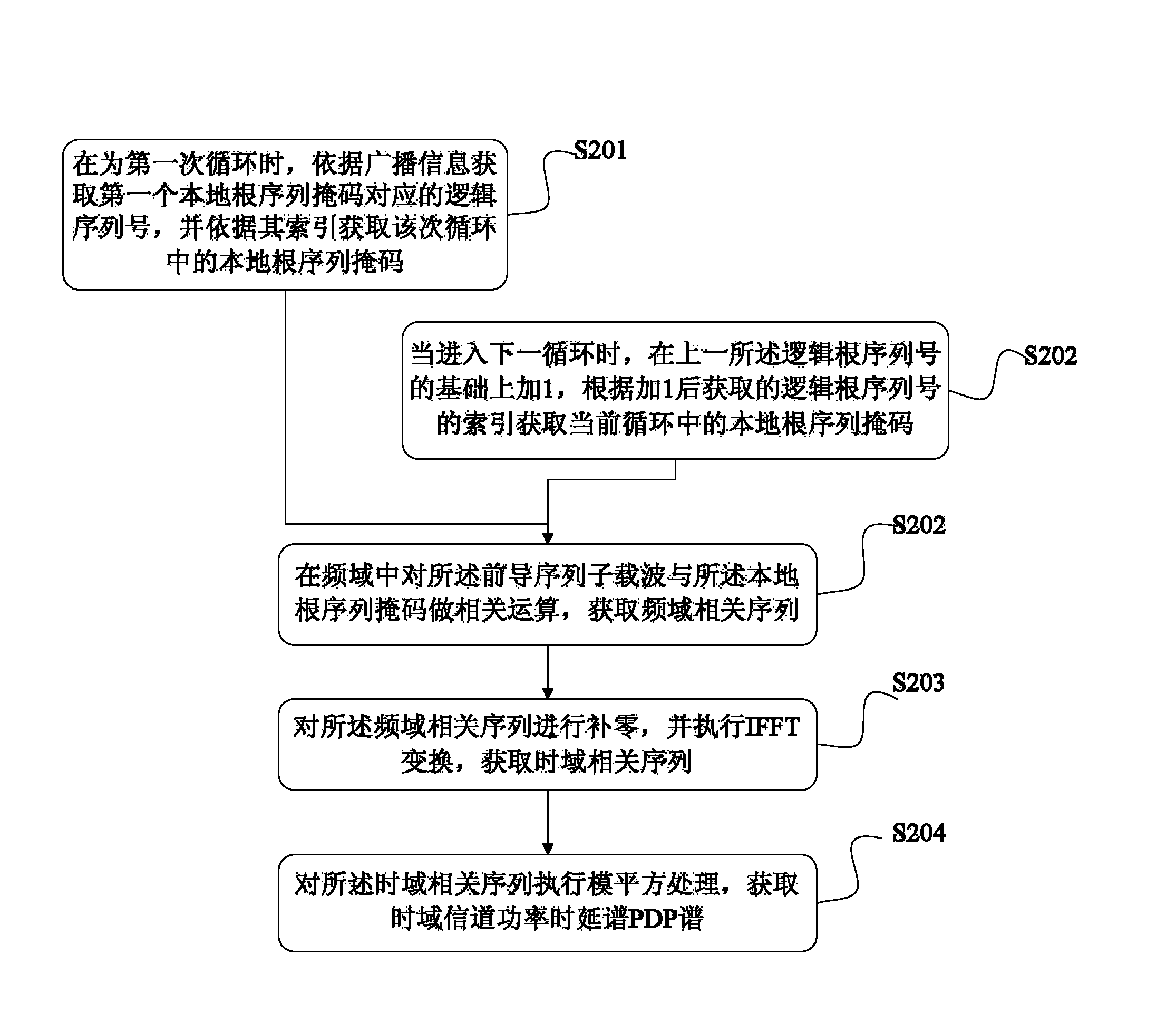
The invention discloses a leader sequence detection method and a device for a random access channel. The method comprises the following steps that: sub carrier waves of a leader sequence are extracted, the related operation is carried out with the corresponding local root sequence mask in the frequency domain to obtain the time domain channel power time delay spectrum power delay profile (PDP); the noise estimation is carried out on the PDP to obtain the noise estimation value; the width and an initial position of a detection window are calculated; the peak searching is carried out on the determined current detection window; the signal-to-noise calculation is carried out according to the searched peak and the noise estimation value to obtain the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio; and the signal-to-noise ratio and the judgment threshold are compared, and the detected leader sequence is determined in the current detection window when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than the judgment threshold. The leader sequence detection method the device have the advantages that the simplification processing is respectively carried out on the relative operation, noise estimation and signal-to-noise ratio operation processes in the detection process, so the goals of reducing the operation quantity in the leader sequence detection process and reducing the processing complexity are realized.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
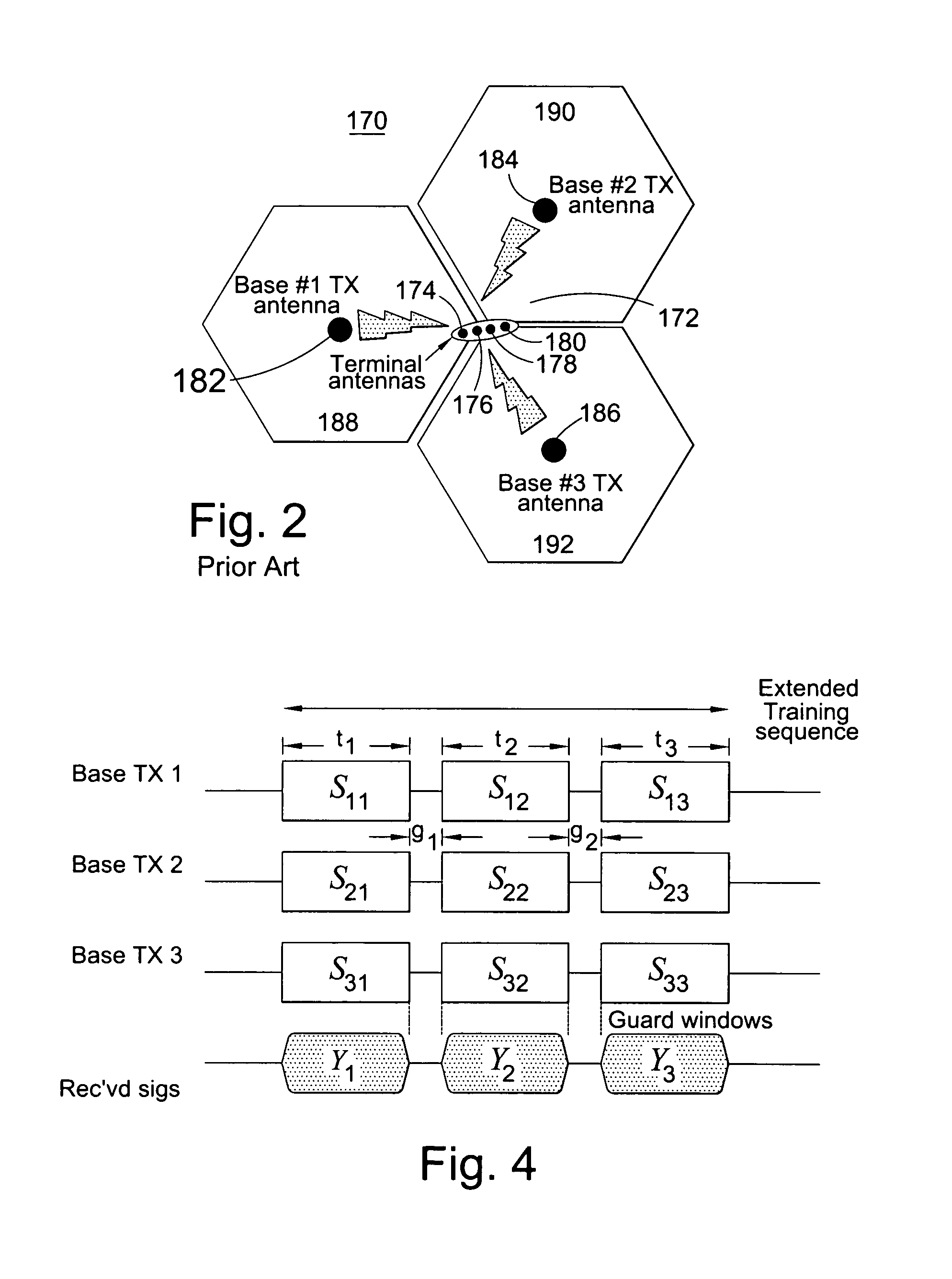
Method distinguishing line of sight (los) from non-line of sight (nlos) in cdma mobile communication system
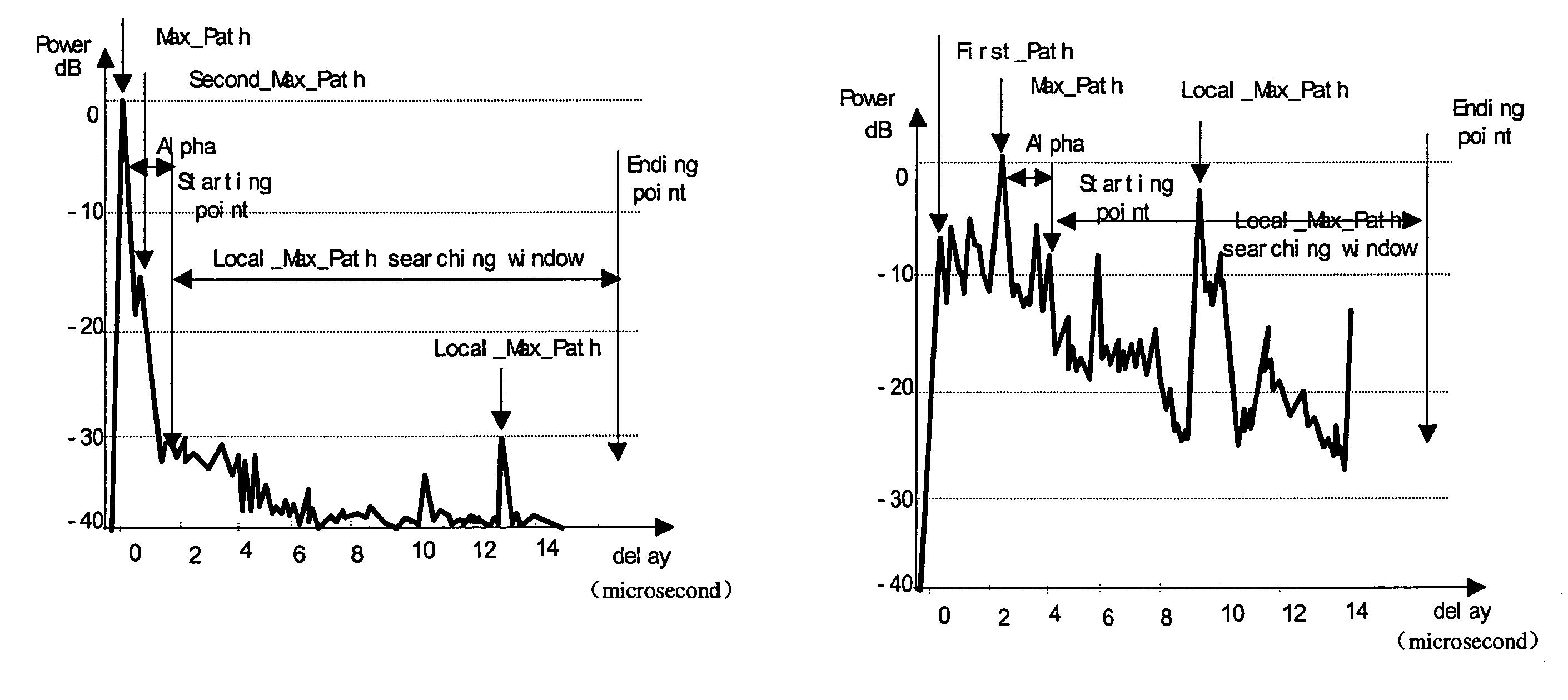
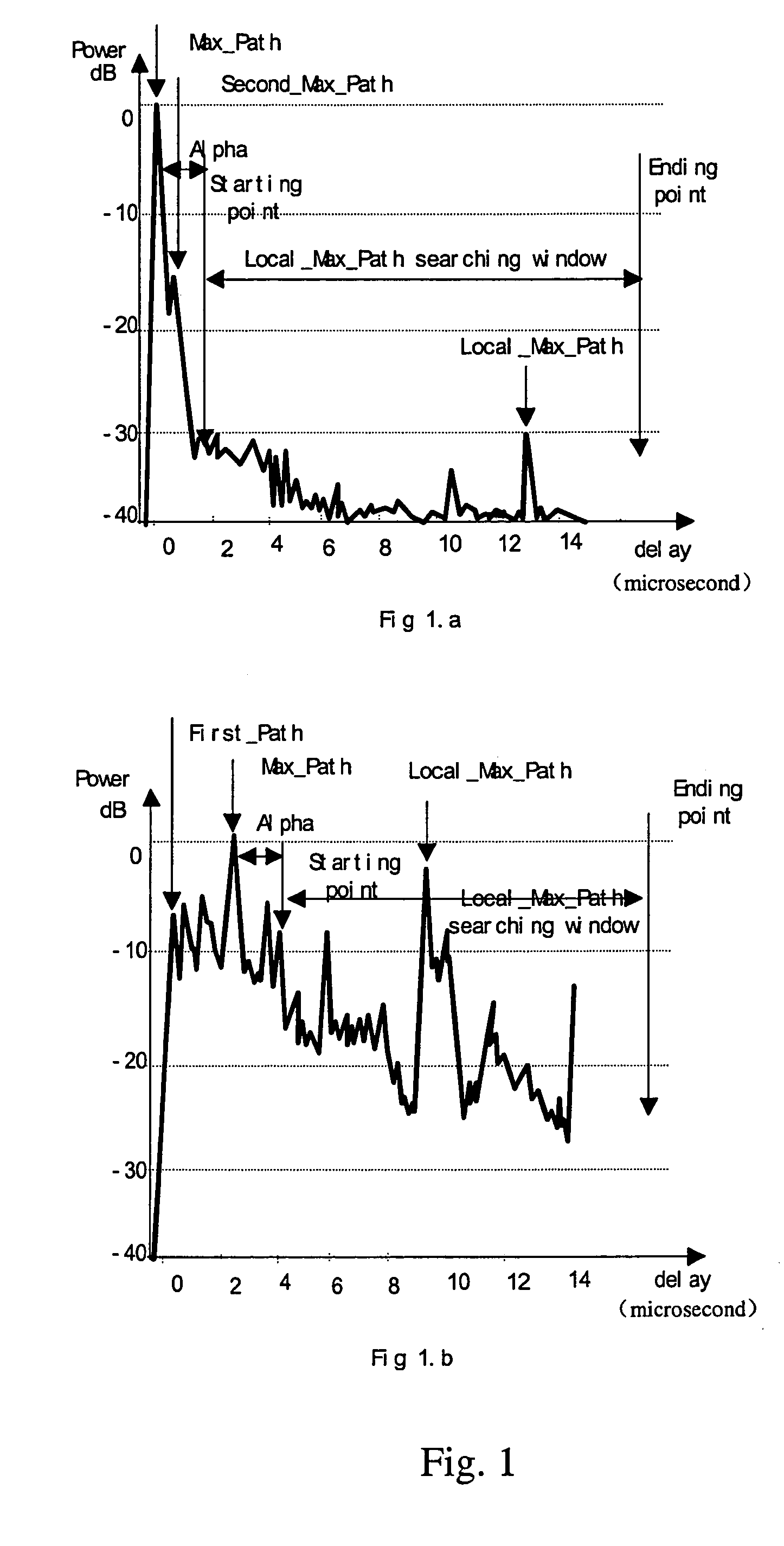
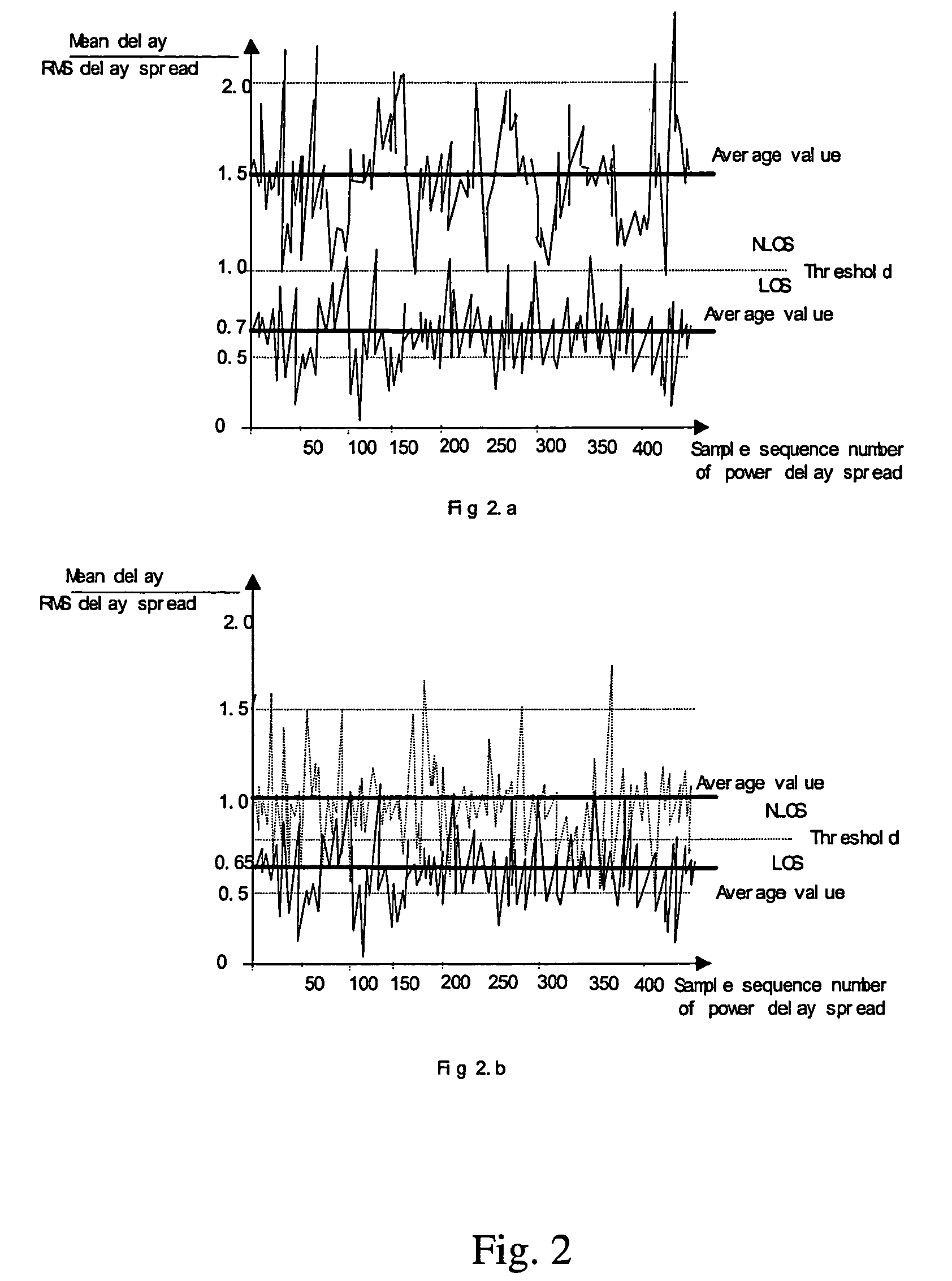
InactiveUS20050124368A1Effectively lead to differentiationHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPower delay profileDirect path
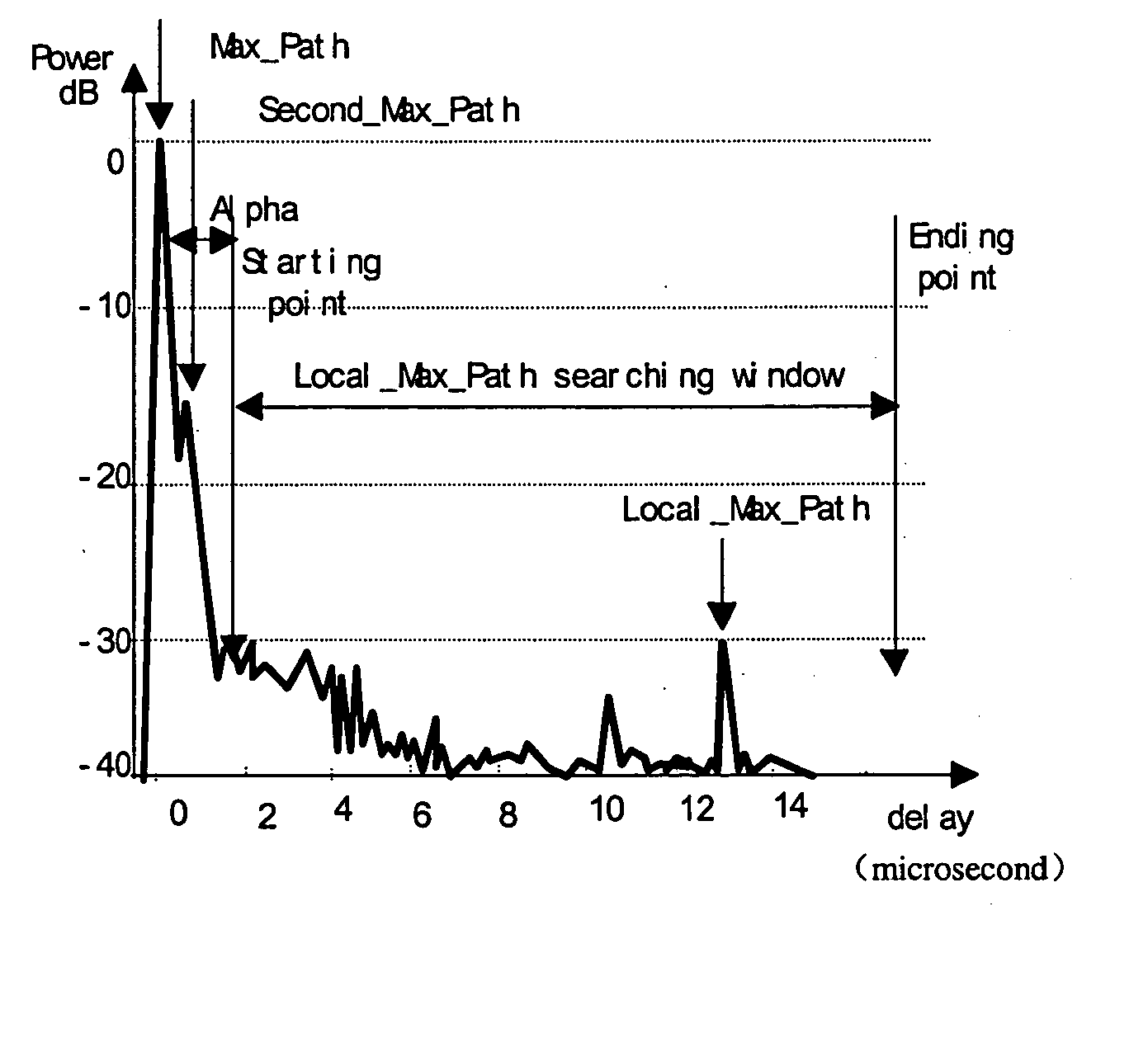
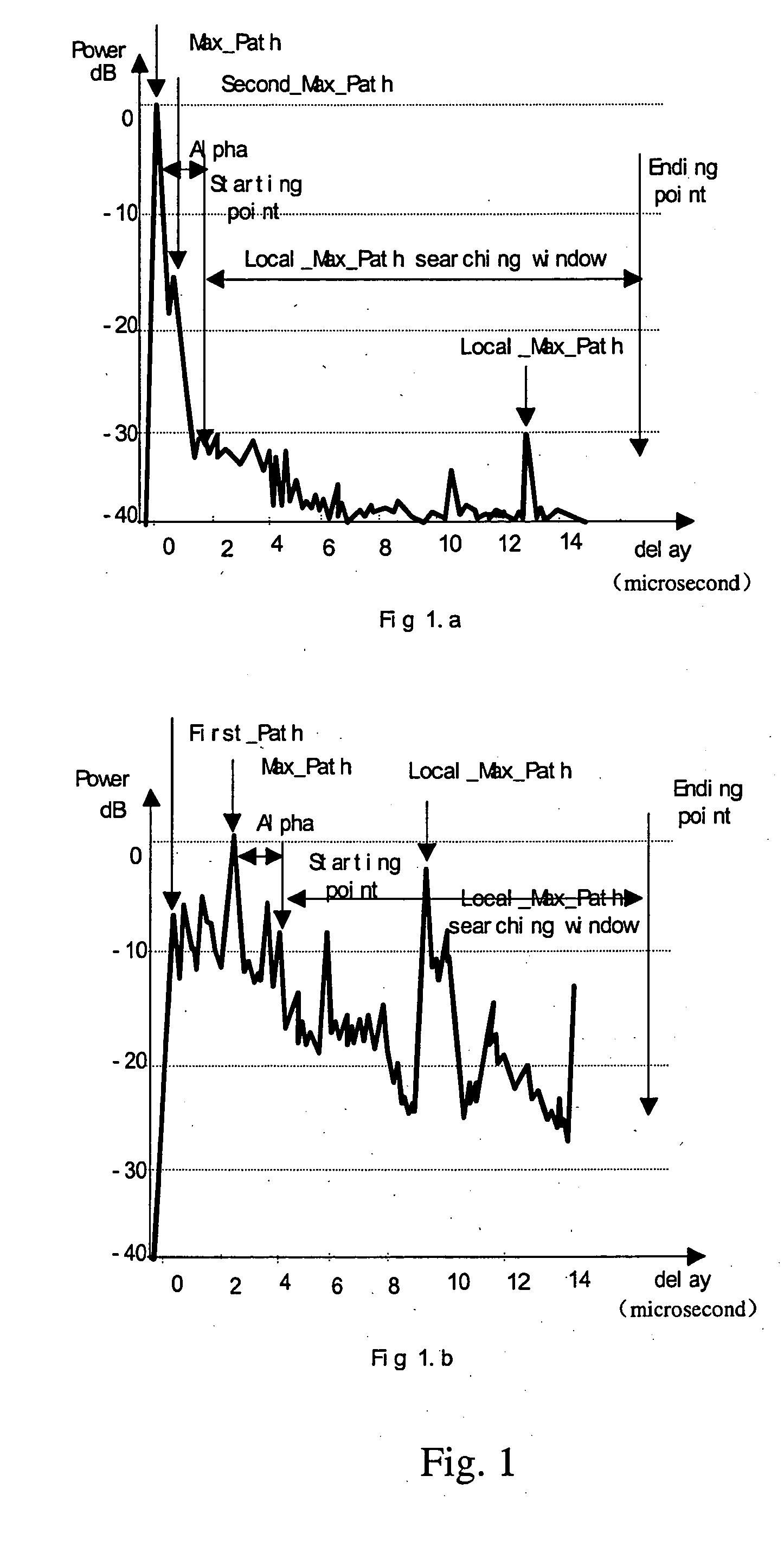
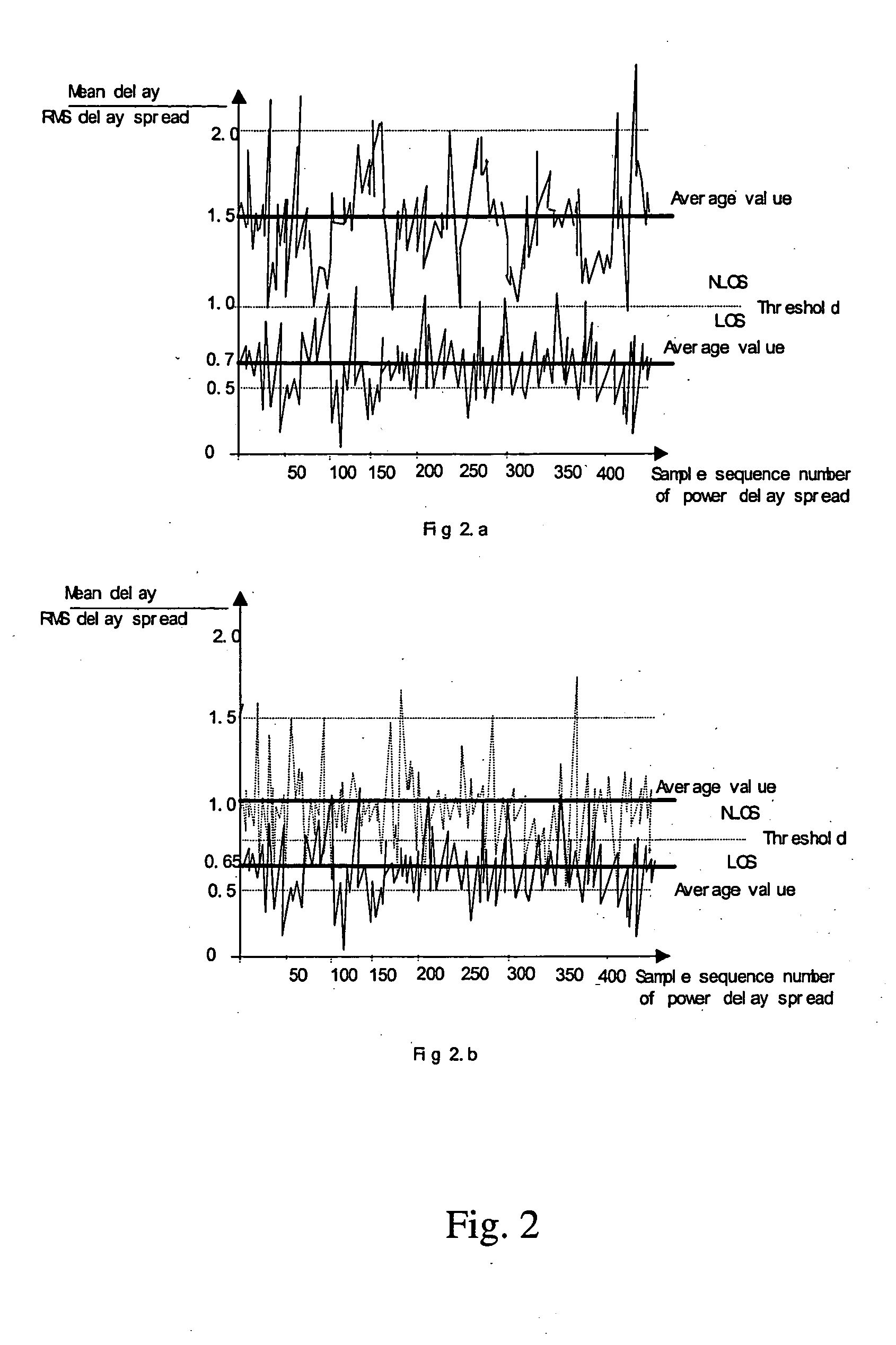
The invention discloses a method that identifies whether a channel is LOS or NLOS in a mobile communication system. After coherent accumulation and non-coherent accumulation have been made by the system, first the method takes power difference between the direct path and the non-direct path in a same power delay profile to identify a channel; and then the result is further determined by {overscore (τ)} / σ difference of a LOS channel and a NLOS channel (where {overscore (τ )}and σ is the mean delay and the RMS delay spread of a multipath power profile, respectively). A channel is determined as a LOS channel, if the power ratio of the Maximum Path to the Local Maximum Path is greater than a threshold K, and simultaneously the arrival time difference between the First Path and said Maximum Path is less than a time interval T; otherwise it is a NLOS channel. The method is easier to implement and compatible with the present mobile communication system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
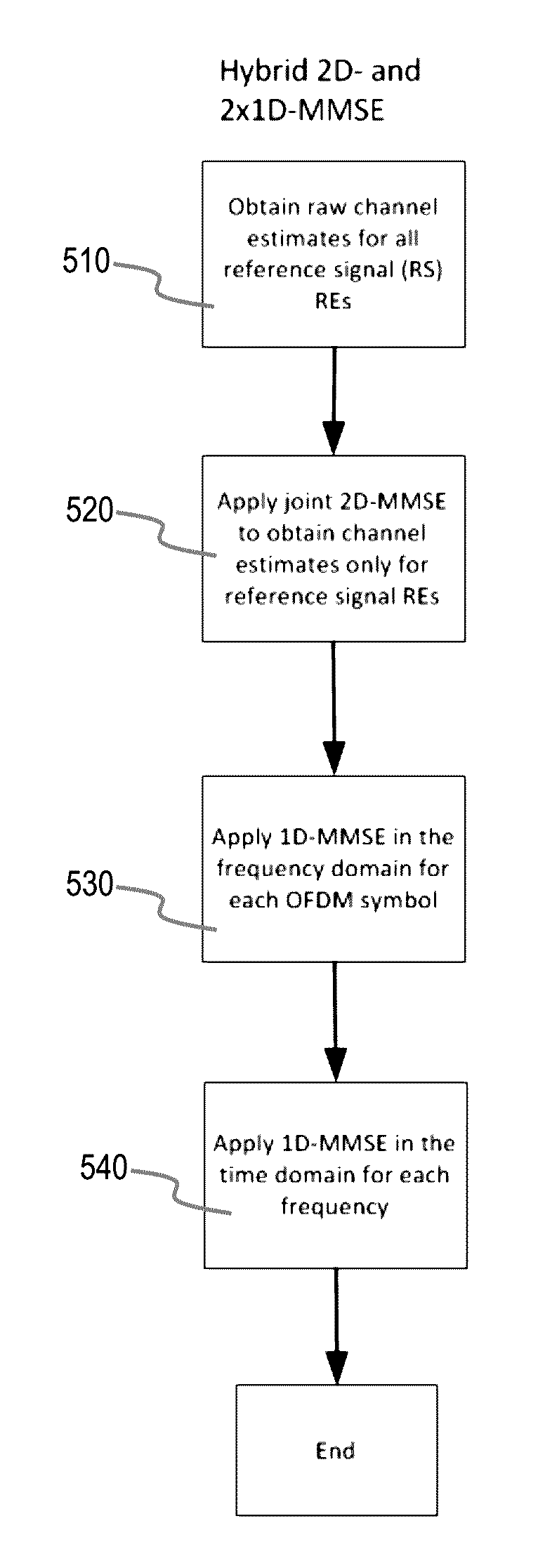
Method and apparatus for robust two-stage OFDM channel estimation
ActiveUS20150229493A1Improve accuracyLess complexError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for improved channel estimation in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system are discussed. In one example discussed herein, joint two-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (2D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed on any Resource Element (REs) containing a reference signal in a Resource Block (RB), one-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (1D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed in the frequency domain on each OFDM symbol in the RB, and then channel estimation is performed in the time domain on each frequency sub-carrier in the RB. In another example discussed herein, Power Delay Profiles (PDPs) and / or frequency correlations are calculated using minimax optimization and then stored in a Look-Up Table (LUT) indexed by estimated Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and the estimated maximum delay spread. A portable device could use such an LUT in MMSE calculations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for estimating position
ActiveUS20150282112A1Beacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationVIT signalsPower delay profile
A method of estimating a position of an object is disclosed. The method comprises receiving a plurality of signals transmitted between each of a respective plurality of reference stations of a known position and the object. The method further comprises, for each received signal: processing the signal using a matrix featuring a characteristic power delay profile and a characteristic signal waveform to provide a processed signal, and calculating a direct estimate of the position of the object based, at least in part, on the processed signals.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
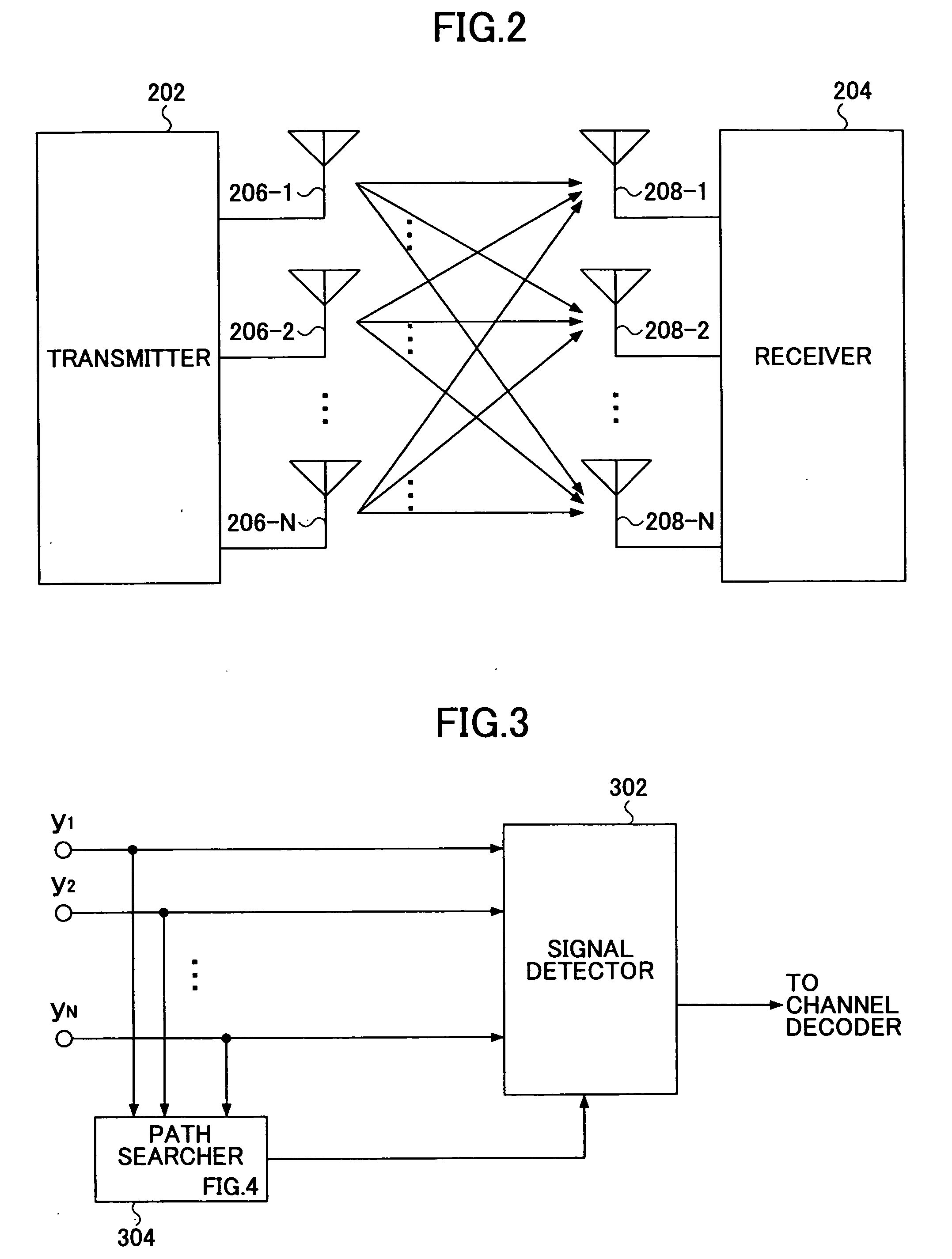
Path searcher and path searching method
InactiveUS20050255819A1Accurate detectionAccurate and reliable detectionSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPower delay profileEngineering
A path searcher (304) used in a receiver includes a power delay profile generating unit (402) configured to generate a power delay profile based on a signal received by the receiver, a sidelobe generating unit (406) configured to identify a sidelobe component of a path contained in the power delay profile based on a response characteristic of a band-limiting filter of the receiver, a sidelobe removing unit (407) configured to remove the sidelobe component from the power delay profile to produce a corrected power delay profile, and a path timing detection unit (408) configured to detect a path timing based on the corrected power delay profile.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and device for detecting common-frequency cells of LTE system
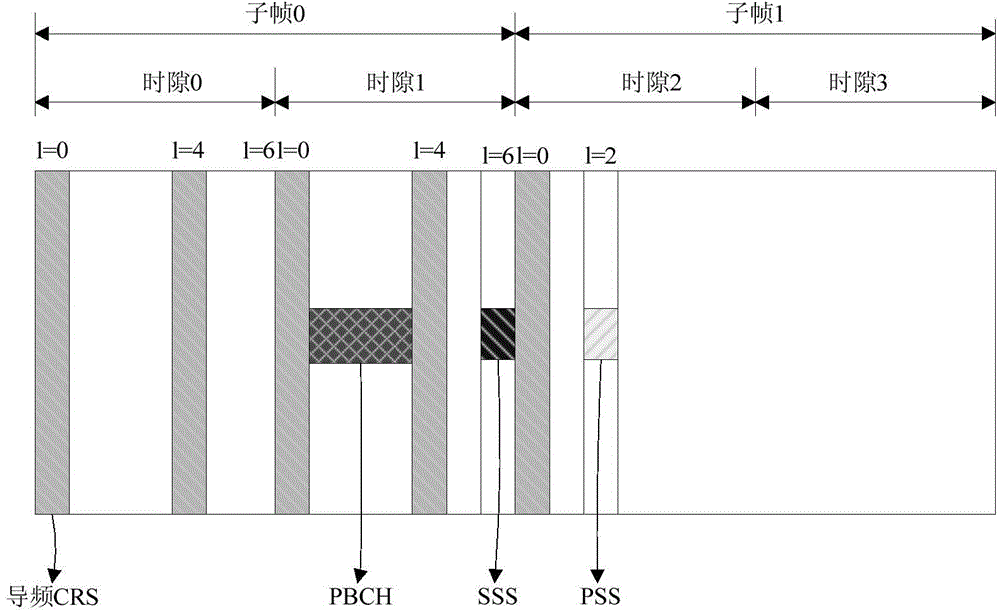
ActiveCN104378764AGood cross-correlationImprove accuracyNetwork planningTime domainPower delay profile
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for detecting common-frequency cells of an LTE system. The method comprises the steps that received first time domain data are segmented and transformed into a frequency domain, first correlation operation is carried out on each segment of data transformed to the frequency domain and a local reference primary synchronizing signal (PSS), a result of the first correlation operation is transformed back to a time domain, and second time domain data are obtained; power of all sampling points in the second time domain data is calculated, power delay profiles (PDP) of the sampling points are obtained, and peak mean ration (PMR) values of all the sampling points are calculated according to the power delay profiles (PDP); the primary synchronizing signal (PSS) and the synchronous position of the primary synchronizing signal (PSS) in a half frame are determined according to the point with the largest the peak mean ration (PMR) value; a secondary synchronizing signal (SSS) is determined according to the primary synchronizing signal (PSS) and the synchronous position of the primary synchronizing signal (PSS) in the half frame, and therefore the common-frequency cells are determined. The embodiment of the invention further discloses a device for detecting the common-frequency cells of the LTE system. The LTE common-frequency cells can be effectively detected, and the requirement for measuring the common-frequency cells, covered with a wireless network, of the existing LTE system can be met.
Owner:DATANG LINKTESTER TECH
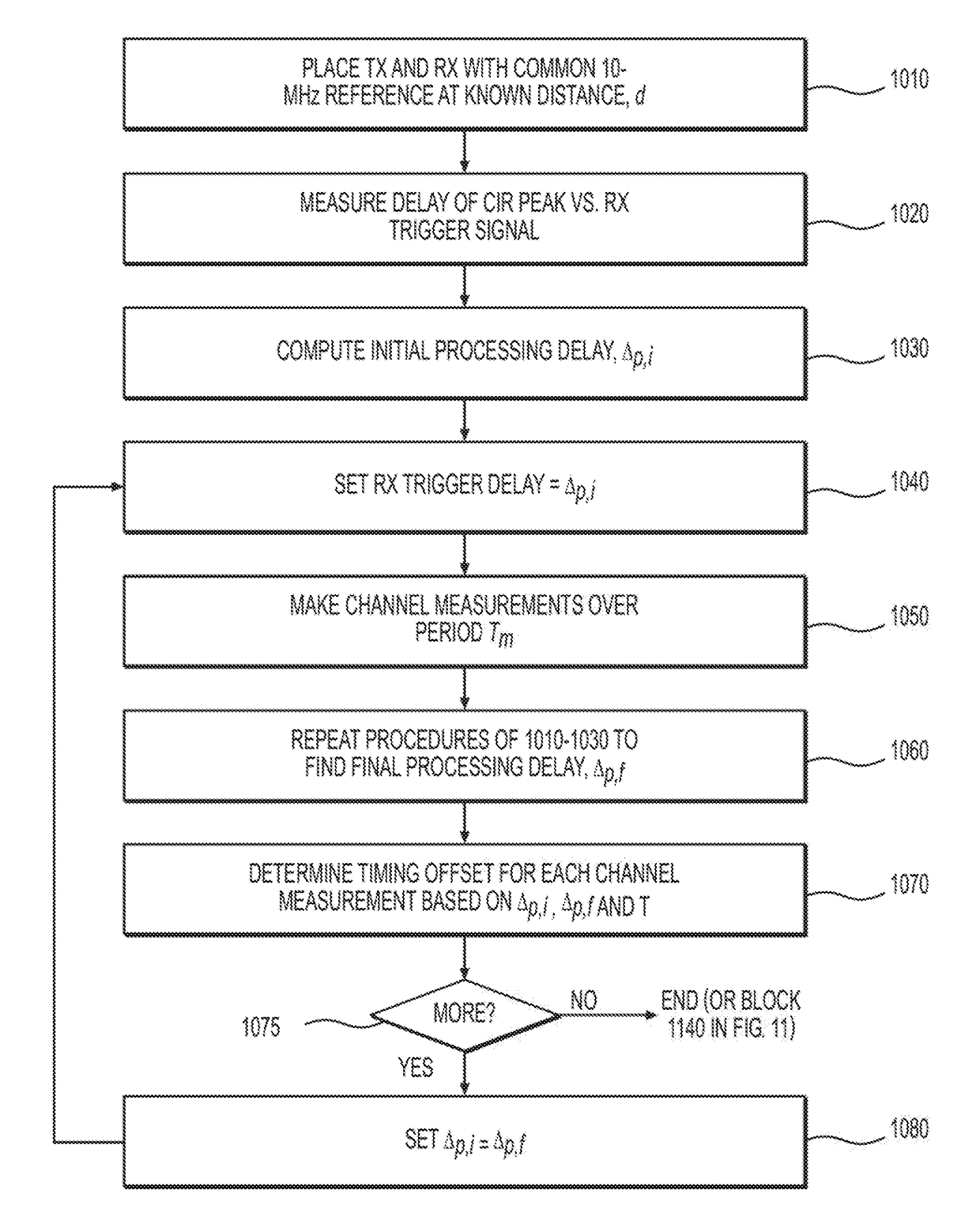
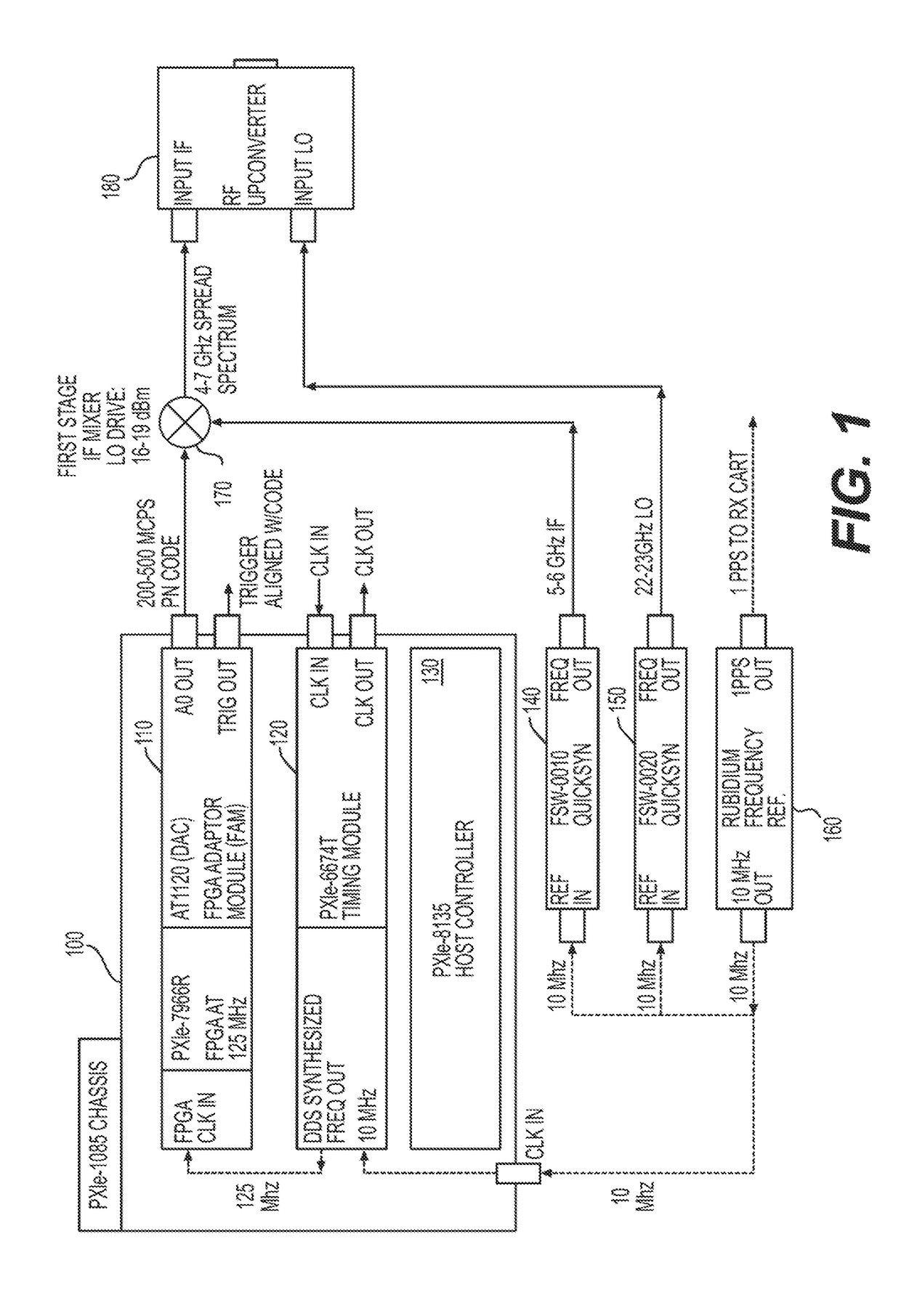
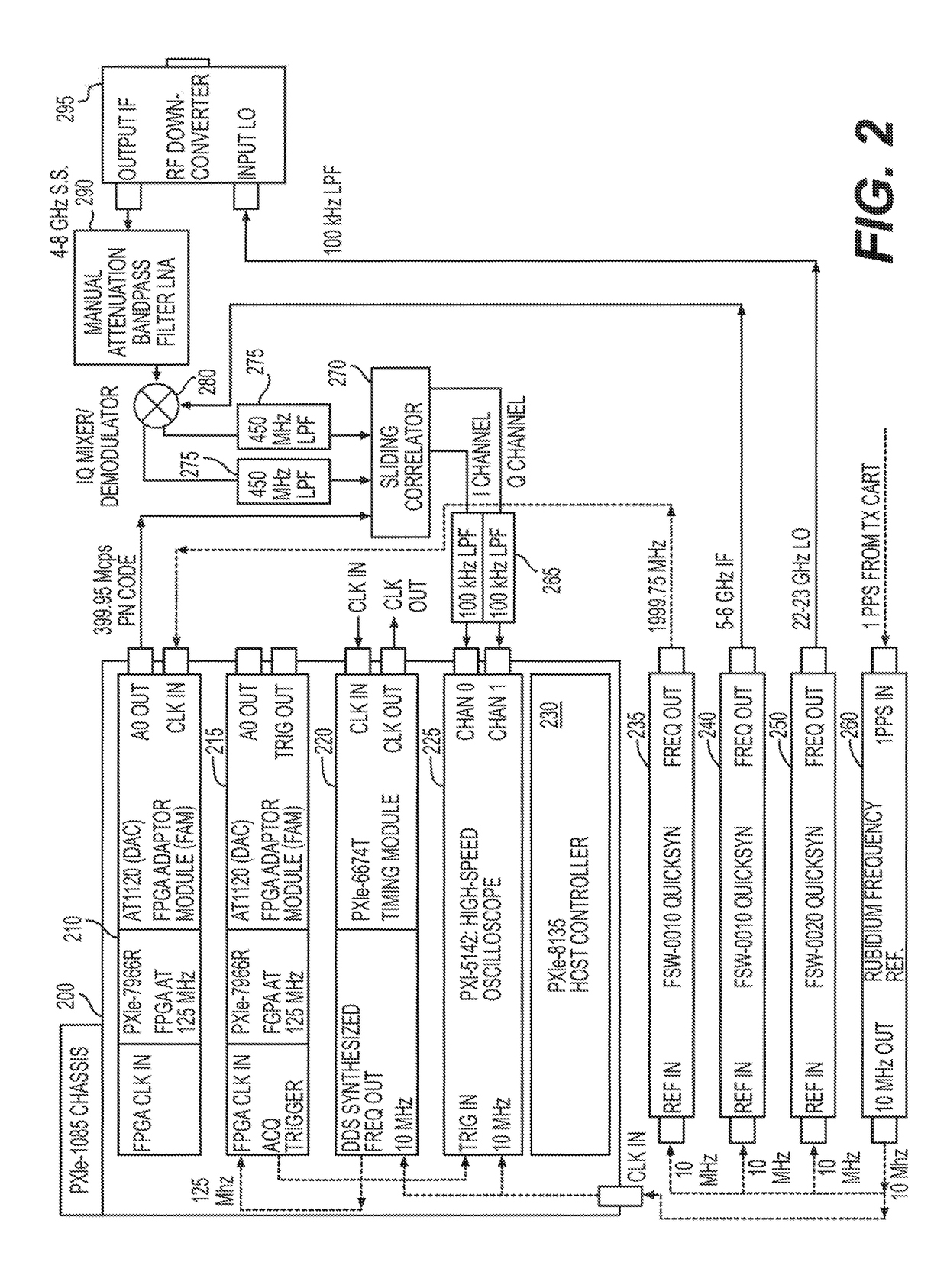
Systems, methods, and computer-accessible media for measuring or modeling a wideband, millimeter-wave channel and methods and systems for calibrating same
ActiveUS20180054294A1Transmitters monitoringSynchronisation arrangementChannel impulse responseChannel parameter
Exemplary systems and methods can be provided for measuring a parameter—e.g., channel impulse response and / or power delay profile—of a wideband, millimeter-wave (mmW) channel. The exemplary systems can include a receiver configured to receive a first signal from the channel, generate a second signal, and measure the parameter based on a comparison between the first and second signals; and a controller configured to determine first and second calibration of the system before and after measuring the parameter, and determine a correction for the parameter measurement based on the first and second calibrations. Exemplary methods can also be provided for calibrating a system for measuring the channel parameter. Such methods can be utilized for systems in which the TX and RX devices share a common frequency source and for systems in which the TX and RX devices have individual frequency sources that free-run during channel measurements.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Positioning of a path searcher window in a CDMA receiver
InactiveUS7715464B2Avoid detectionReduce complexityTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDigital radioPower delay profile
Multipath components of signals transmitted through time-varying digital radio channels are received with individual delays, and signals through a given channel comprise a code identifying that channel. A delay profile indicating a magnitude (Y) for delay values in a search window is calculated repetitively for known channels; the delays of multipath components for known channels estimated; a signal strength indicator calculated; and a search for new multipath components not already estimated performed at regular time intervals. When a new multipath component is found, its identification code is compared to the codes of the known channels. If the code of the new component is identical to the code of a known channel, a delay profile and a signal strength indicator is calculated for a window transposed to include the new multipath component. In this way as many multipath components as possible are included in the search window for a new cell.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
SNR estimation for sounding signals
InactiveUS20160173248A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionTime domainCommunications system
An OFDM receiving apparatus for SNR estimation of a sounding signal transmitted over a wide channel of a wireless communication system.The proposed apparatus brings improvements over conventional receiver for sounding signals by separately determining the noise power level and the signal power associated with the sounding signal. Namely, the noise power level is determined in the frequency domain based on a noise covariance matrix. Further, the sounding signal's power level is determined, in the time domain, based on power delay profile of the wide channel over which the sounding signal has been transmitted. Based on the proposed solution, required processing power, memory footprint and bus load is reduced in comparison the conventional receivers.A method and a computer program are also claimed.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Apparatus and method for acquiring synchronization in mobile communication system using OFDM scheme
InactiveUS7630463B2Minimal complexityMaximize log probability distribution functionError preventionSolid-state devicesSpecific functionPower delay profile
Disclosed is a method for acquiring synchronization in a mobile communication system using an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) scheme. The method includes modeling a power delay profile in time-varying frequency selective fading channel conditions by a specific function; detecting a log probability distribution function of a timing offset and a frequency offset in consideration of a correlation between a received signal and the received multi-path signal in the time-varying frequency selective fading channel conditions having the power delay profile modeled as the specific function; and estimating a timing offset and a frequency offset which maximize the log probability distribution function of the timing offset and the frequency offset.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
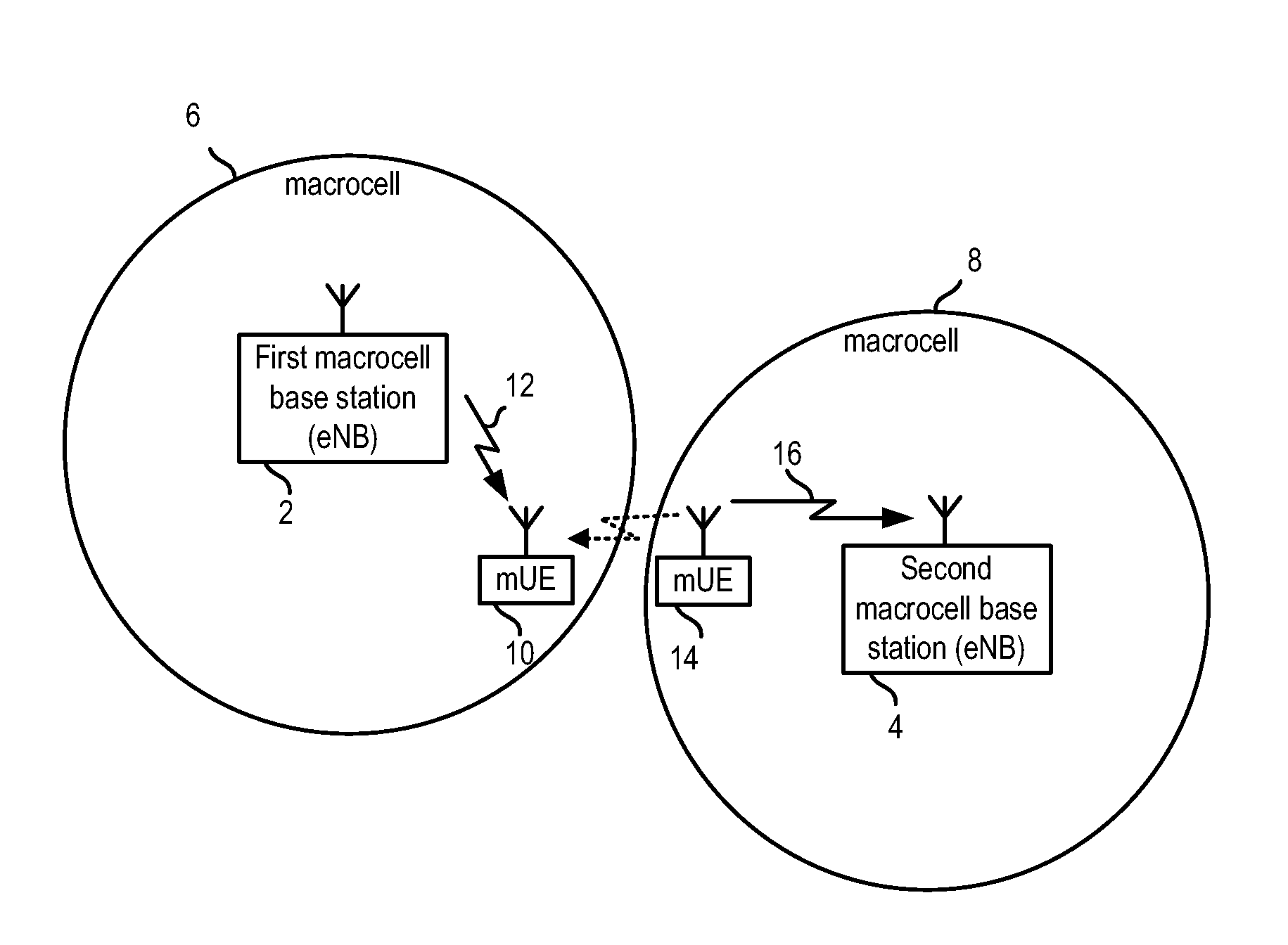
Femtocell base station synchronization
InactiveUS20130343372A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexPower delay profilePicocell
There is provided a method of refining a timing estimate used to synchronize a femtocell base station to a macrocell base station. The method in the femtocell base station comprises estimating a multipath power delay profile from signals received from the macrocell base station, detecting the earliest path in the multipath power delay profile and determining a correction to the timing estimate from the earliest path detected in the multipath power delay profile.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method distinguishing line of sight (LOS) from non-line of sight (NLOS) in CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7099640B2Effectively lead to differentiationHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemPower delay profile
The invention discloses a method that identifies whether a channel is LOS or NLOS in a mobile communication system. After coherent accumulation and non-coherent accumulation have been made by the system, first the method takes power difference between the direct path and the non-direct path in a same power delay profile to identify a channel; and then the result is further determined by {overscore (τ)} / σ difference of a LOS channel and a NLOS channel (where {overscore (τ)} and σ is the mean delay and the RMS delay spread of a multipath power profile, respectively). A channel is determined as a LOS channel, if the power ratio of the Maximum Path to the Local Maximum Path is greater than a threshold K, and simultaneously the arrival time difference between the First Path and said Maximum Path is less than a time interval T; otherwise it is a NLOS channel. The method is easier to implement and compatible with the present mobile communication system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Robust channel estimation for wireless systems
ActiveUS20090016455A1Avoid excessive delayLess sensitivity to noiseAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationCorrelation functionPower delay profile
The present invention relates to a method, apparatus, and computer program product, wherein frequency co-variances or correlations of a measured power delay profile or frequency correlation function are estimated at two different non-zero sub-carrier lags of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing channel. A ratio of squared magnitudes of the two estimated frequency co-variances is calculated and a delay spread or coherence bandwidth of said channel is estimated based on the calculated ratio.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
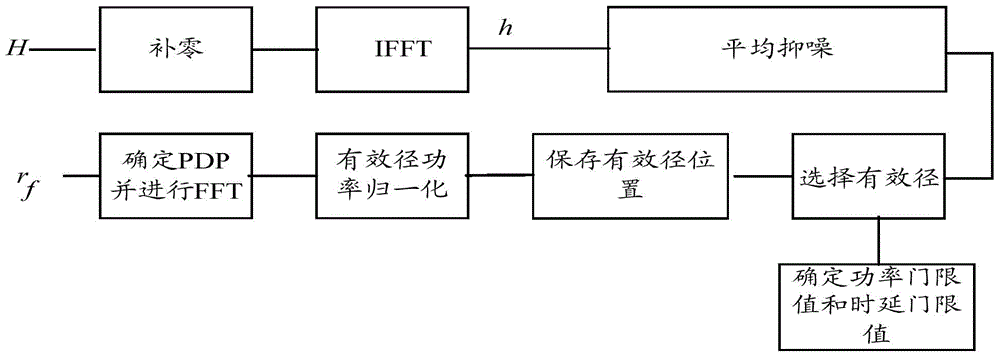
Power delay spectrum PDP estimation method and device
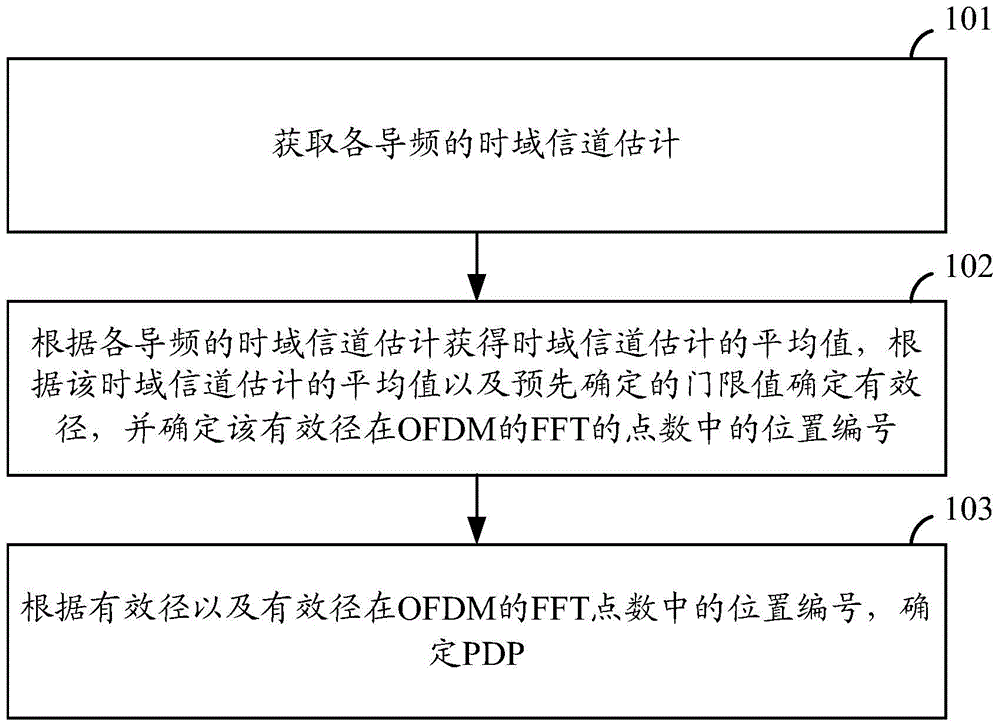
ActiveCN105024951AImprove estimation accuracyImprove accuracyBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainFast Fourier transform
Disclosed are a power delay profile (PDP) estimation method and device, used for improving accuracy of PDP estimation. The method comprises: acquiring time-domain channel estimates of pilots; obtaining an average time-domain channel estimate according to the time-domain channel estimates of the pilots, determining an effective path according to the average time-domain channel estimate and a preset threshold, and determining a position number of the effective path in the number of points of fast Fourier transform (FFT) for performing orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM); and determining a power delay profile (PDP) according to the effective path and the position number.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
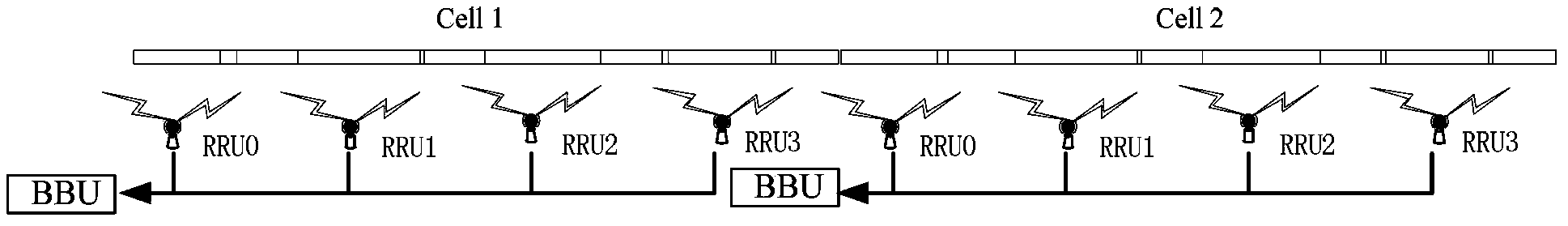
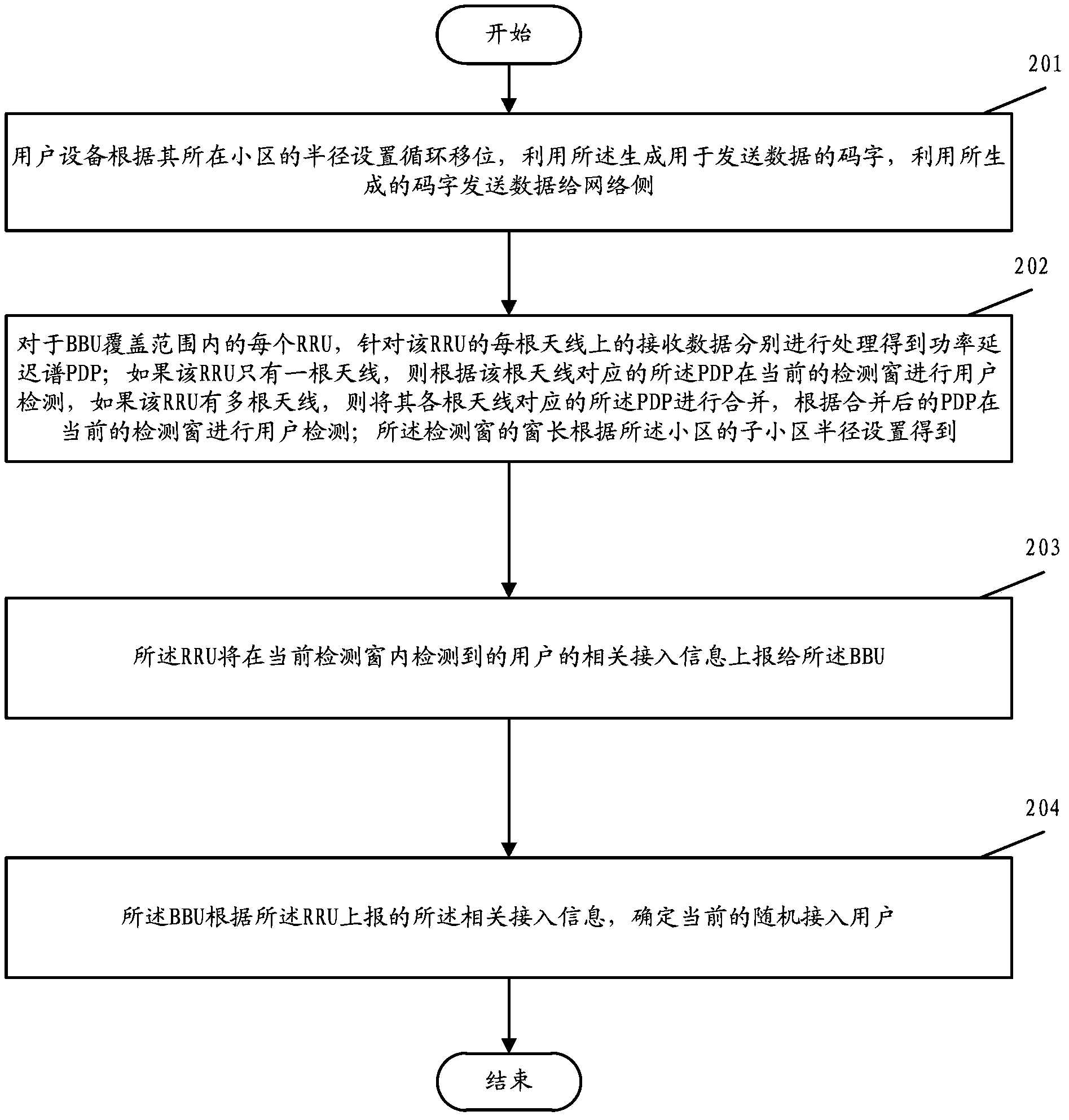
Random access method
InactiveCN104053244AReduce overheadSuppress false alarmsWireless communicationRandom access memoryPower delay profile
The application discloses a random access method. The method comprises the following steps that: user equipment (UE) sets a cyclic shift Ncs according to a cell radius, uses the Ncs to generate a code word, and sends the code word to a network side; for each RRU in a BBU coverage range, reception data of each antenna of the RRU are respectively processed to obtain a power delay profile (PDP); if the RRU only has one antenna, user detection is carried out at a current detection window according to the PDP of the antenna; and if the RRU has a plurality of antenna, PDPs of all antennas are combined and user detection is carried out at a current detection window according to the combined PDPs, wherein the length of the detection window is obtained by the cell radius; the RRU reports related access information of the user detected in the current detection window to the BBU; and the BBU determines a current random access user based on the related access information. According to the invention, the provided method is suitable for the distributed scene with one BBU and a plurality of RRUs.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
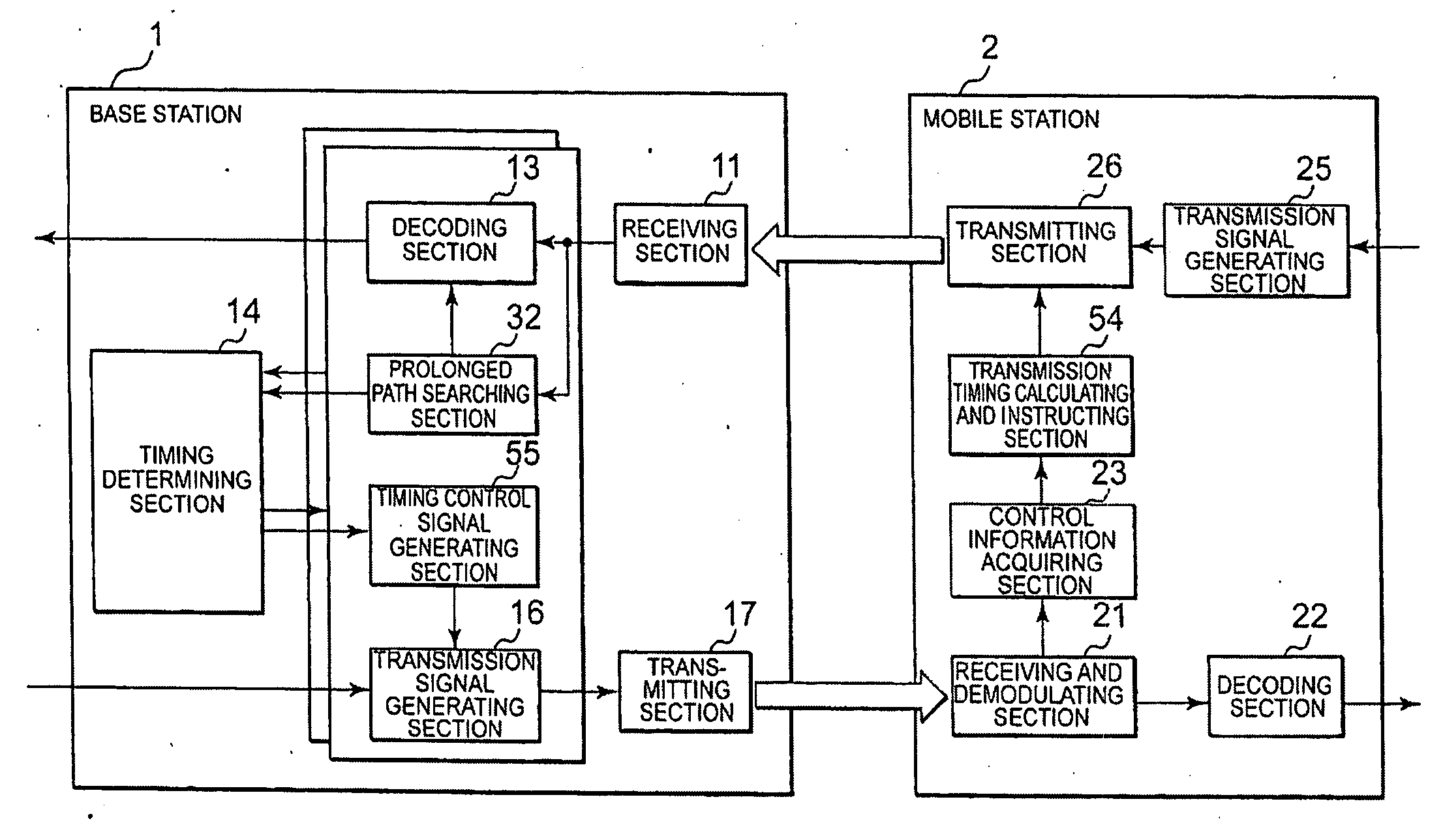
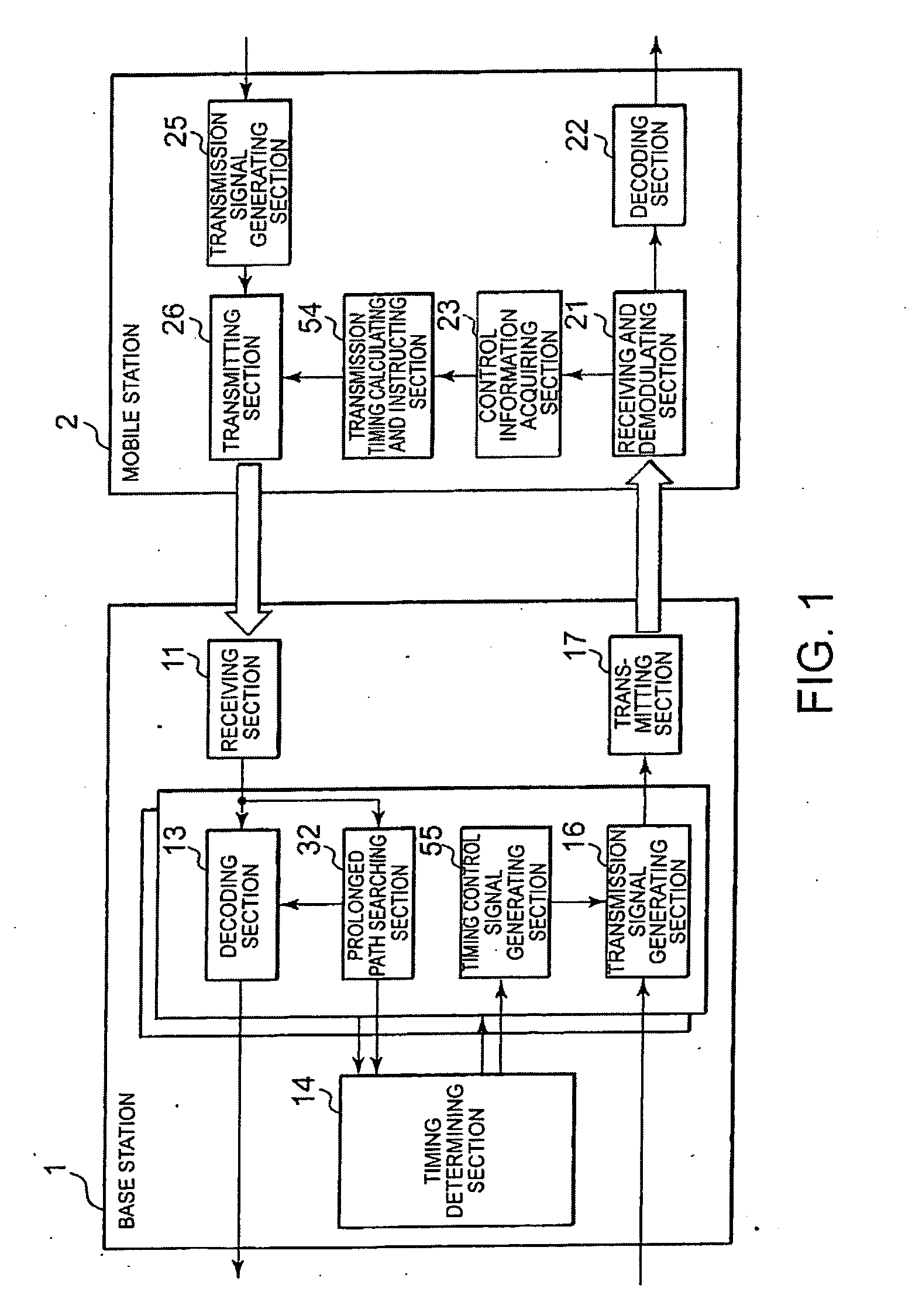
Transmission timing control system and method thereof, and base station using the same and mobile station
InactiveUS20100238906A1Limited resistanceImprove the immunitySynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexControl signalControl system
An adaptive transmission timing control system is provided in which a base station can correctly instruct a mobile station of a timing control signal indicating the amount of variation in transmission timing and a multipath situation can be estimated in the base station with accuracy. When control information for controlling transmission timing of an upstream signal of the mobile station is generated in the base station, the mobile station is notified of the control information in every frame of the upstream signal. Specifically, the control information is generated by determining the transmission timing using a power delay profile in which frames of the upstream signal are added and synthesized in every RTT (Round Trip Time) cycle of the upstream signal. This makes it possible to heighten resistance to an error in the timing control signal, and transmission timing control can be carried out correctly.
Owner:NEC CORP
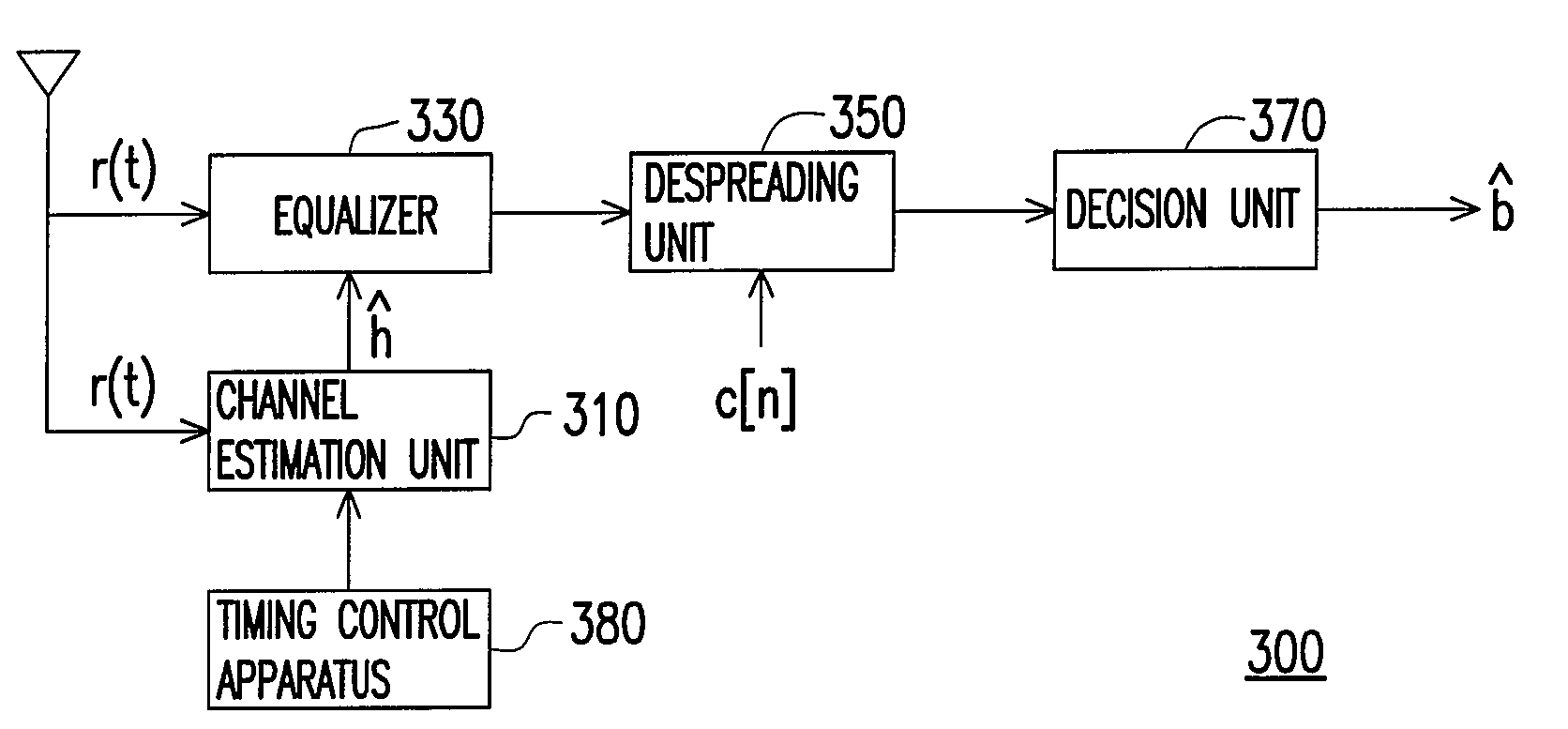
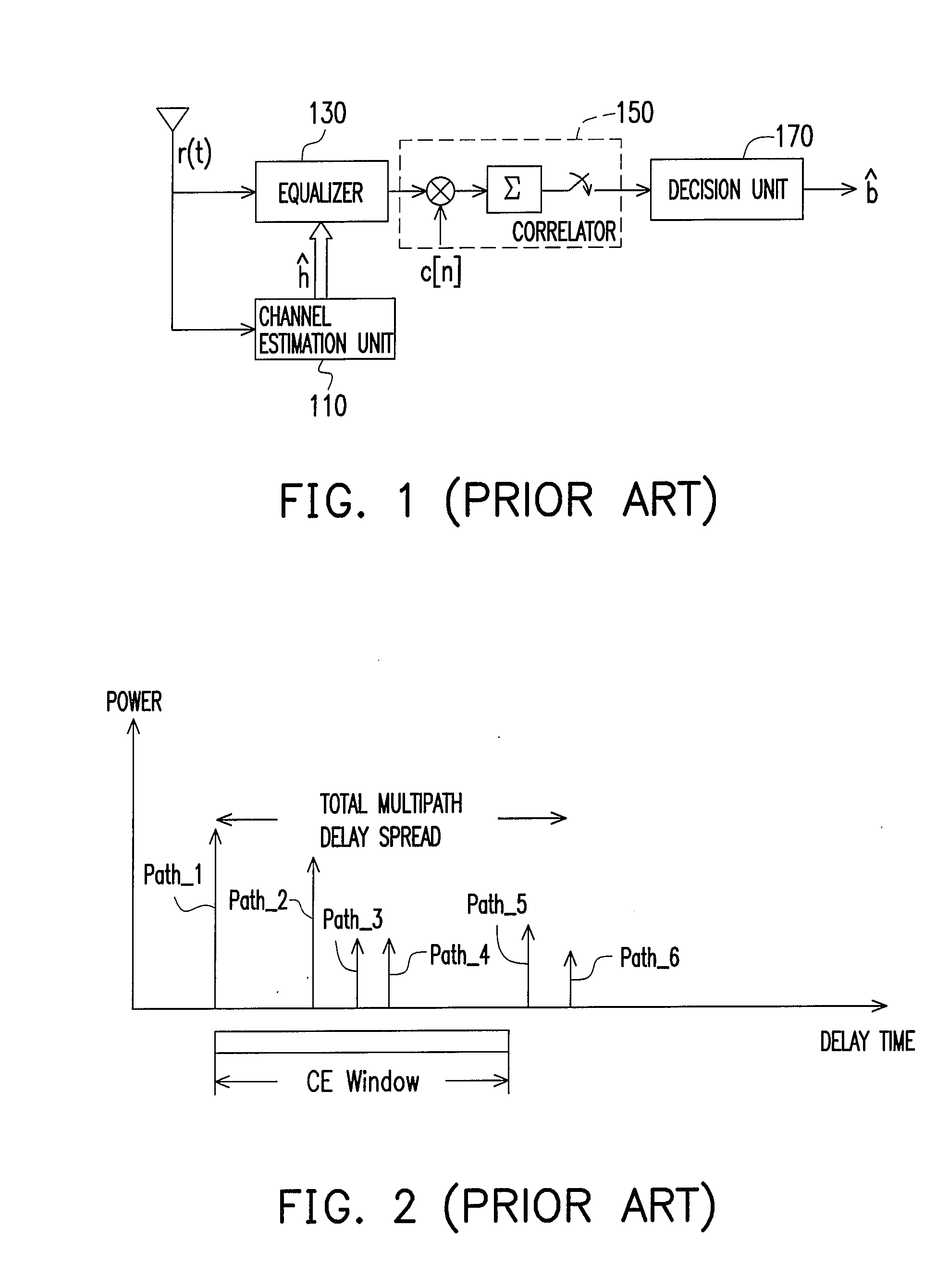
Method and an apparatus for timing control of channel estimation
ActiveUS20090103640A1Improve performanceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationChannel powerPower delay profile
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for timing control of channel estimation. The method includes: sequentially shifting a channel estimation window in a power-delay profile in a specific time interval to obtain a plurality of candidate segments; sequentially calculating a metric corresponding to the candidate segments according to the delay paths and the channel power contained in the candidate segments; among the metrics, finding out an optimal segment with the maximum metric and deciding a timing of channel estimation based on the optimal segment.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
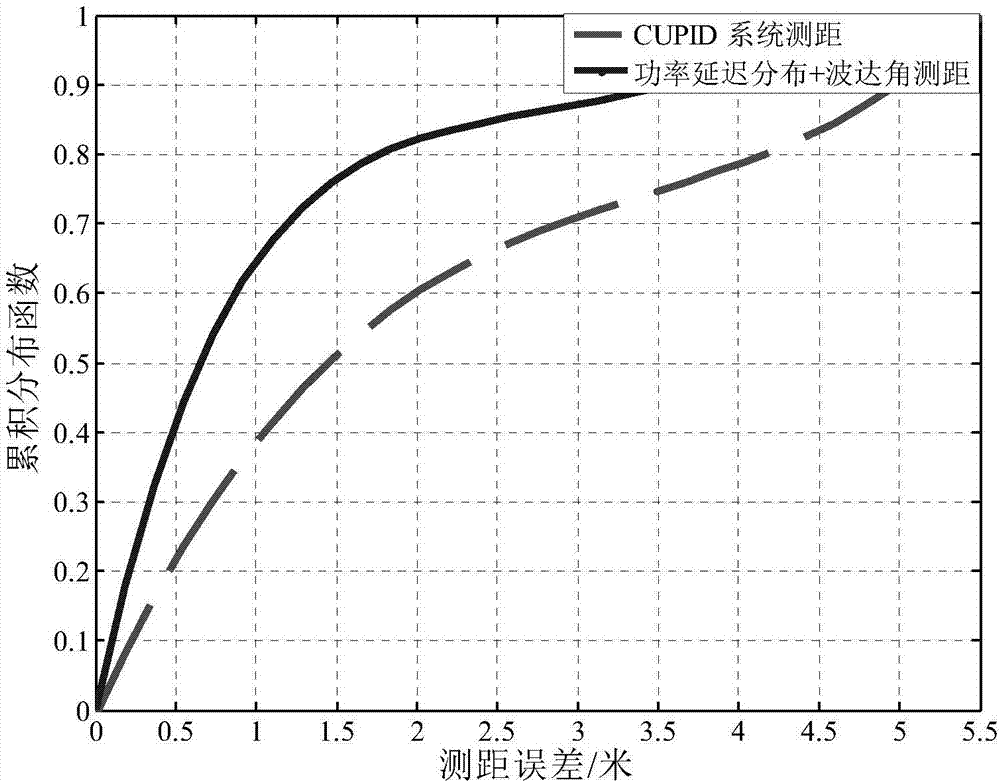
Single-node indoor positioning method based on power delay profile and direction of arrival distance measurement
InactiveCN107015196ASave manpower and material resourcesReduce positioning errorsPosition fixationChannel state informationSimulation
The invention relates to a single-node indoor positioning method based on power delay profile and direction of arrival distance measurement. The invention aims to solve defects that an existing fingerprint map positioning system is low in positioning accuracy, the positioning accuracy depends on the performance of an approximation algorithm, fingerprint map positioning need to deploy a lot of positioning nodes in a positioning environment and acquire a fingerprint map in advance, a lot of material resources and financial resources are consumed, and that the single node is large in positioning implementation error. The process of the single-node indoor positioning method comprises the steps that firstly, an indoor positioning system receiver acquires a group A of channel state information; secondly, phase information and amplitude information in the channel state information are acquired; thirdly, error elimination is performed on the phase information in the acquired channel state information by adopting an interpolation method; fourthly , the amplitude information and the error eliminated phase information are processed so as to acquired a transmission distance; and fifthly, the customer location is solved based on trilateral positioning according to the the transmission distance acquired in the step four. The single-node indoor positioning method is applied to the field of indoor positioning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Method and apparatus for robust two-stage OFDM channel estimation
ActiveUS9537678B2Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for improved channel estimation in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system are discussed. In one example discussed herein, joint two-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (2D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed on any Resource Element (REs) containing a reference signal in a Resource Block (RB), one-dimensional Minimum Mean-Square Error (1D-MMSE) channel estimation is performed in the frequency domain on each OFDM symbol in the RB, and then channel estimation is performed in the time domain on each frequency sub-carrier in the RB. In another example discussed herein, Power Delay Profiles (PDPs) and / or frequency correlations are calculated using minimax optimization and then stored in a Look-Up Table (LUT) indexed by estimated Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and the estimated maximum delay spread. A portable device could use such an LUT in MMSE calculations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Received communication signal processing methods and components for wireless communication equipment
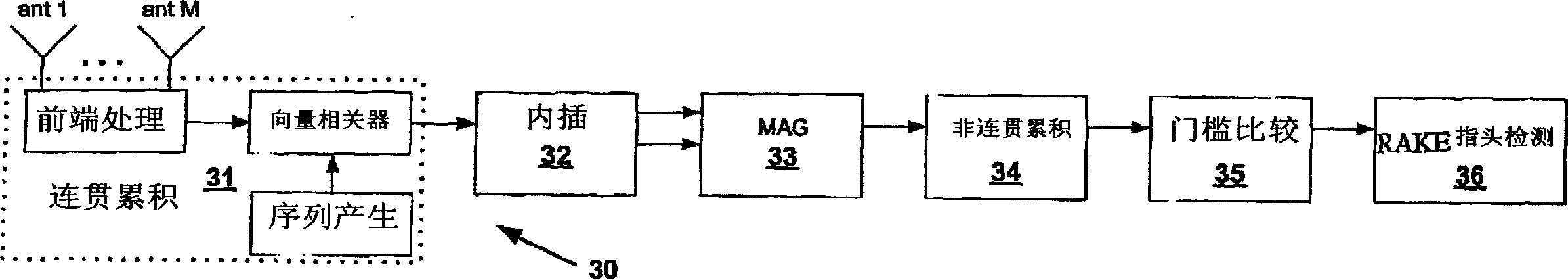
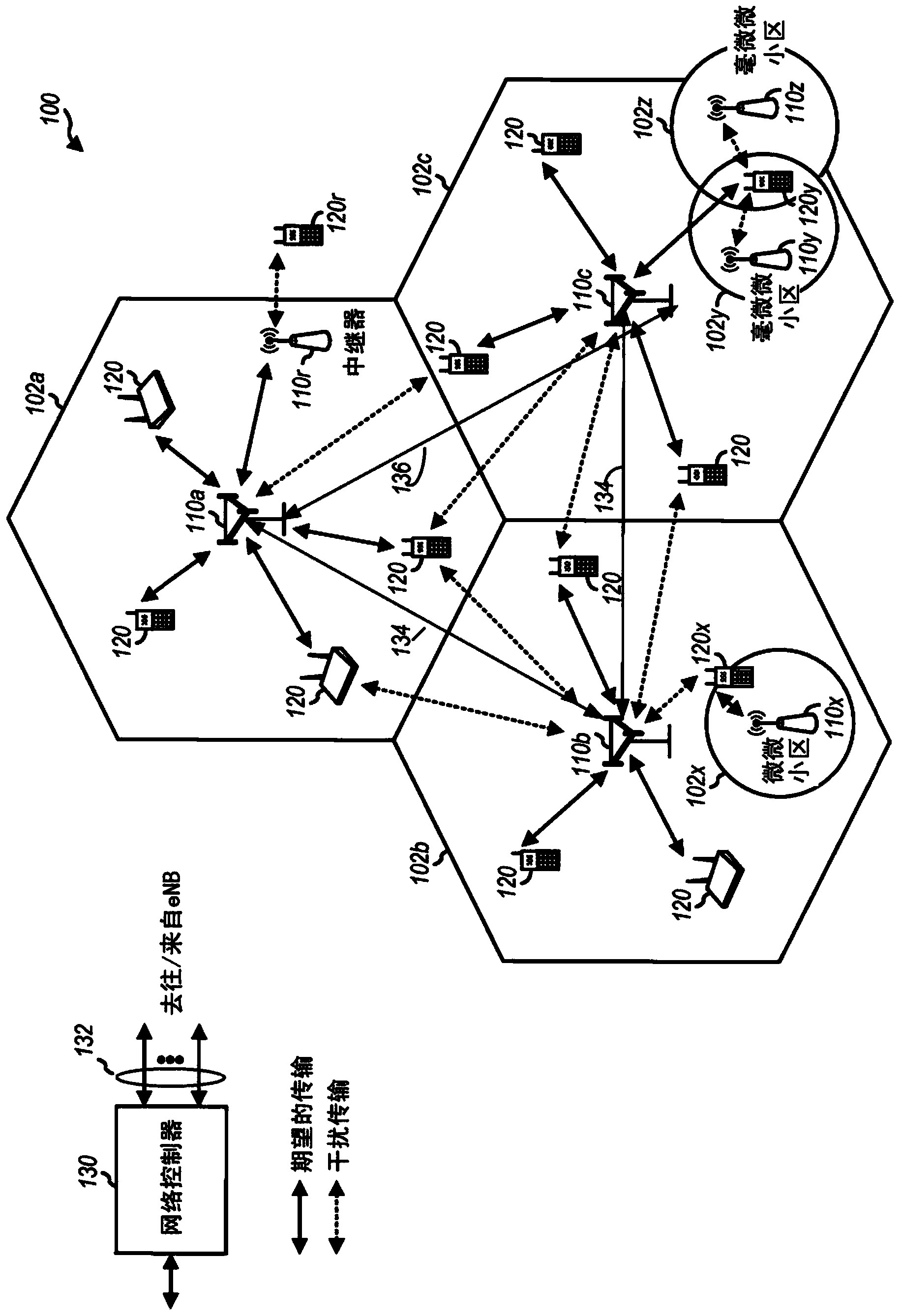
A wireless transmit receive unit (WTRU) and methods are used in a wireless communication system to process sampled received signals to establish and / or maintain wireless communications. A selectively controllable coherent accumulation unit produces power delay profiles. A selectively controllable post processing unit passes threshold qualified magnitude approximation values and PDP positions to a device such as a rake receiver to determine receive signal paths.
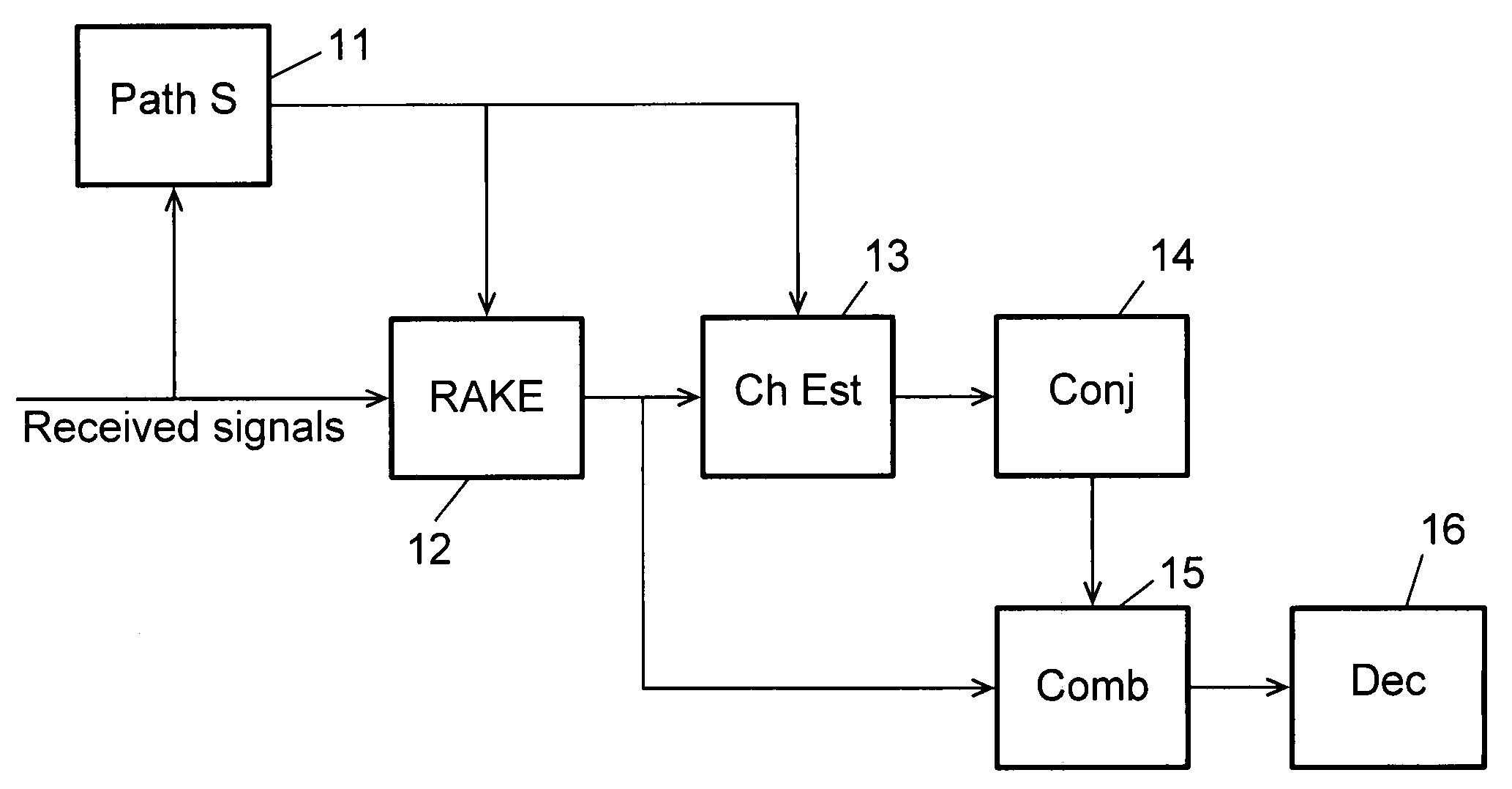
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Selecting Delay Values For a Rake Receiver
InactiveUS20080205556A1Save computing resourcesImprove abilitiesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationTime criticalPower delay profile
Multipath components of transmitted data symbols are received with individual delays and processed by a RAKE unit having a number of fingers. A delay profile is calculated, and delay values for peaks detected therein are determined. A number of peak delay values (P<SUB>A1< / SUB>, P<SUB>A3< / SUB>, P<SUB>A4< / SUB>, P<SUB>A5< / SUB>) representing the largest peaks for the profile are pre-selected, and for each of them a signal-to-interference ratio for delay values in an interval around the pre-selected peak delay value is calculated. In each interval the delay value having the highest signal-to-interference ratio is selected and provided to the RAKE unit with each selected delay being assigned to a RAKE finger. Hereby the ability to select correct and accurate path delays can be improved also in time critical processes, where filtering of the delay profiles over several frames is not possible, because quite accurate delay values can be provided shortly after wake-up of the receiver.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Selecting Delay Values for a RAKE Receiver
ActiveUS20090041163A1Without increasing the current consumption or the dye area requiredSolve the lack of resolutionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationImage resolutionPower delay profile
Multipath components of transmitted data symbols are received with individual delays and processed by a RAKE having a number of fingers. A delay profile indicating magnitudes for a first number of delay values is provided. Estimated magnitudes for a second number of delay values located between the first number of delay values are calculated by interpolation, and a combined delay profile is provided by combining the magnitudes for the first and second number of delay values. Delay values for peaks in the combined delay profile are determined, and a number of peak delay values (P1, P2, P) comprising the largest peak are selected from the combined delay profile. At least some of the selected peak delay values are provided to the RAKE and assigned to the fingers. This allows a reduction of current consumption and dye area, while still providing delay values with sufficient resolution for the RAKE.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of and apparatus for computation of unbiased power delay profile
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for path-seacher scheduling
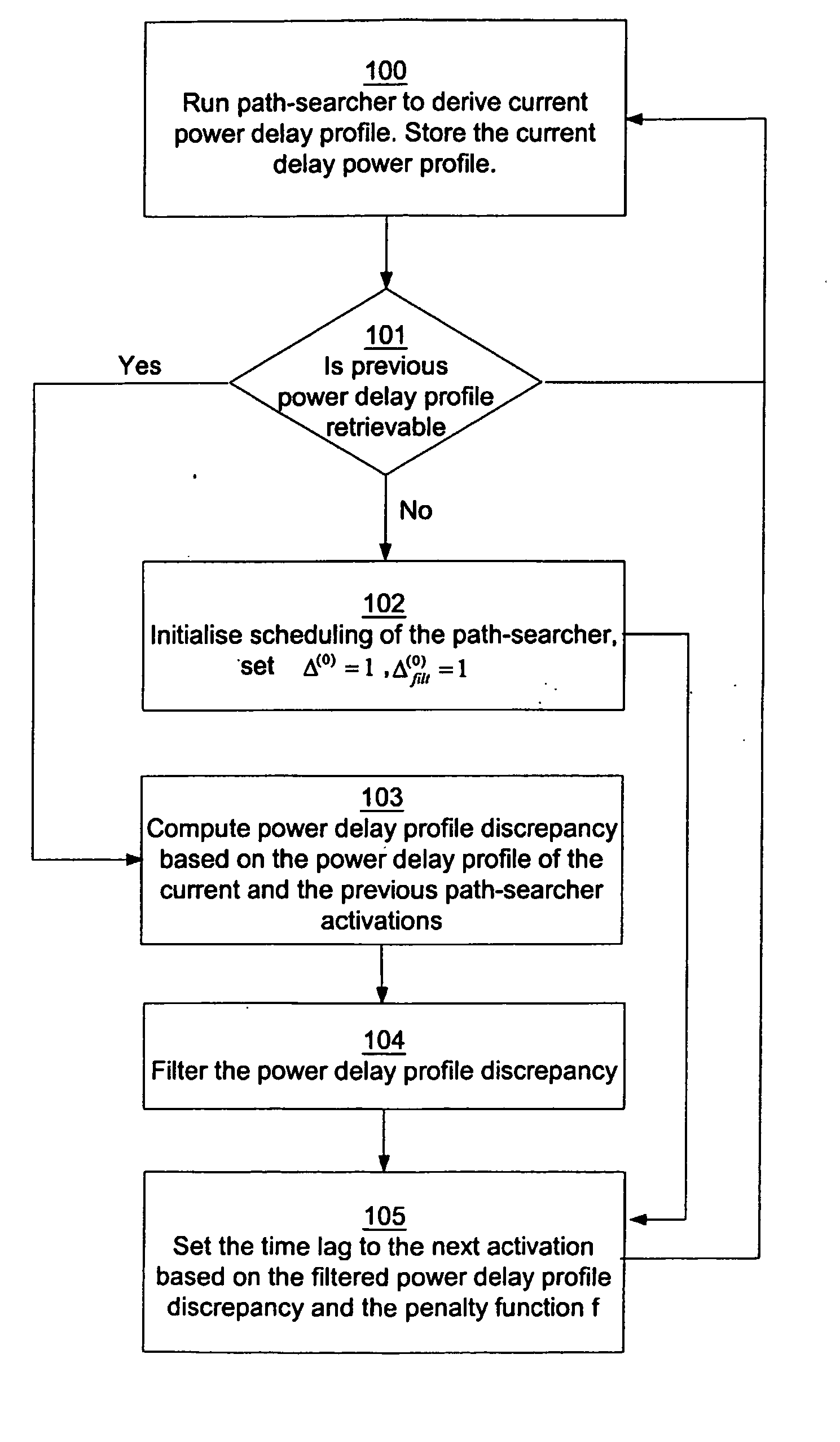
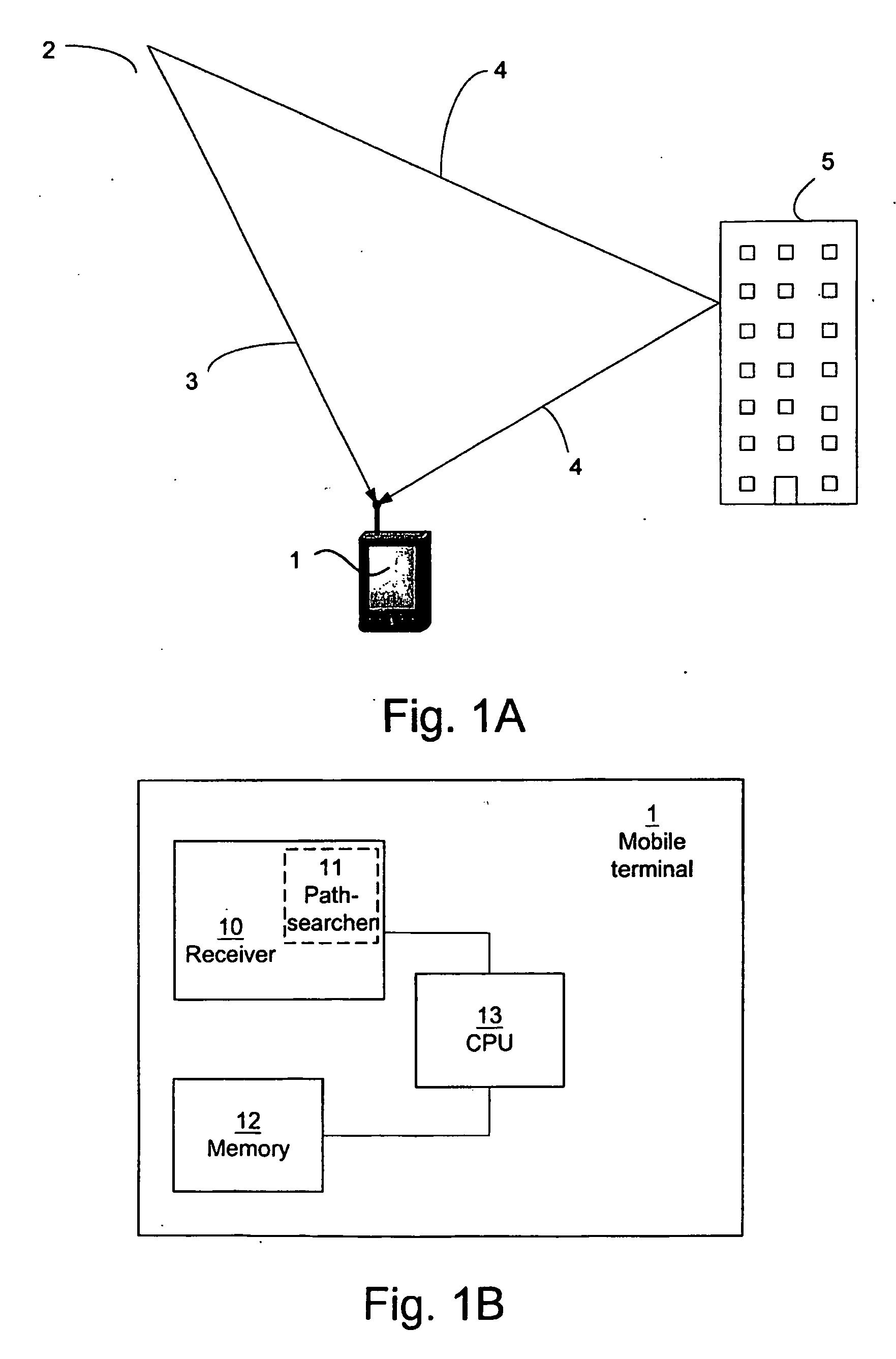
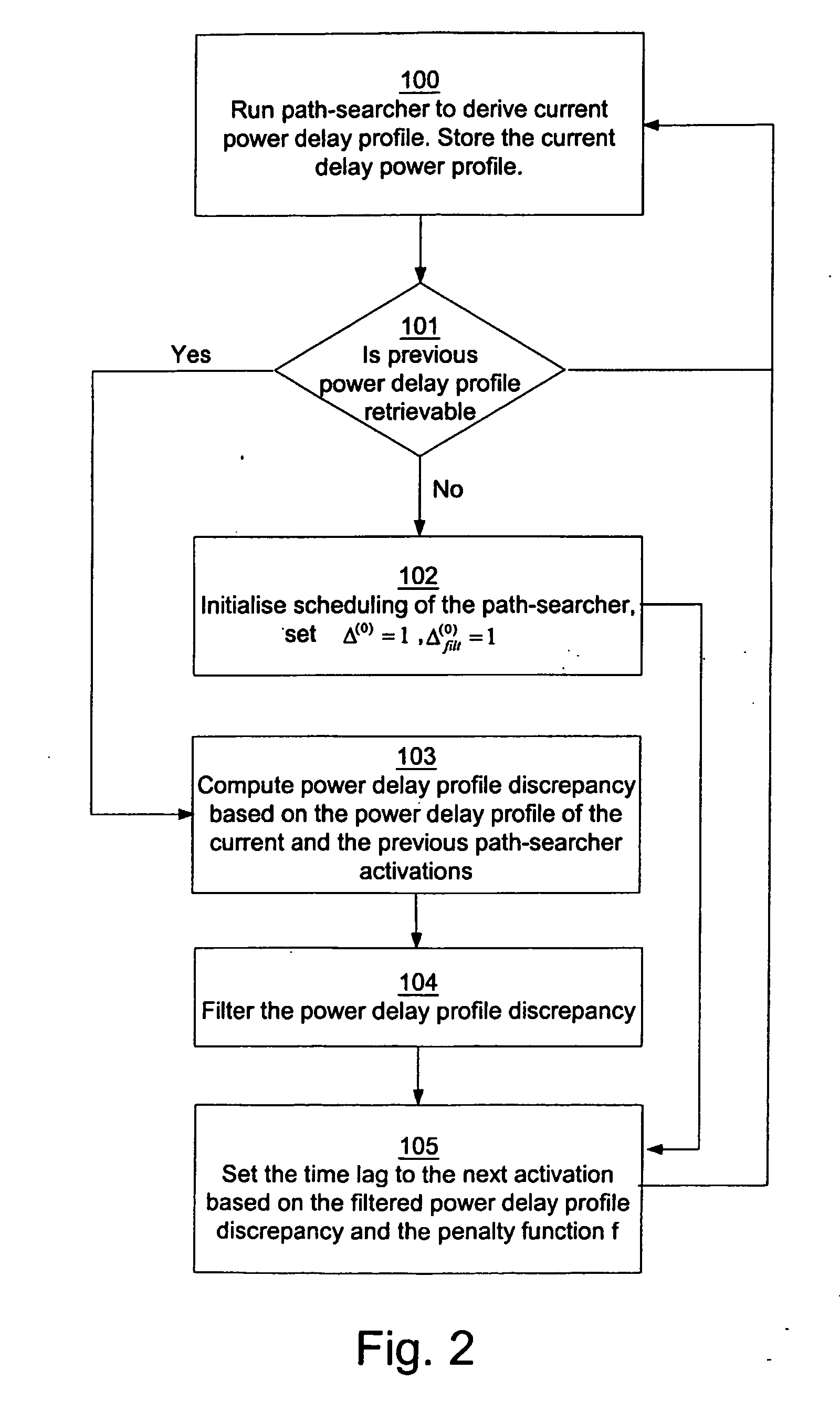
ActiveUS20050271122A1Reduce power consumptionTime lagPolarisation/directional diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionTime delaysPower delay profile
The invention describes a method for adaptively scheduling activation of a path-searcher for a mobile terminal (1) operative in a telecommunication system. The mobile terminal (1) is capable of receiving multi-path signals (3, 4) originating from a scattered signal from a transmitter of at least one base station (2) in said system. The time lag between consecutive path-searcher activations is according to the method determined based on a value of the power delay profile discrepancy between two consecutive power delay profiles. The power delay profiles are derived from at least a subset of the powers of signals (3, 4) received at different delays during the path-searcher activation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
SNR estimation for sounding signals
InactiveUS9641274B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCode division multiplexTime domainCommunications system
An OFDM receiving apparatus is provided for estimating a signal-to-noise ratio of a code-division multiplexed sounding signal transmitted over a wide channel of a wireless communication system. The apparatus separately determines the noise power level and the signal power associated with the sounding signal. Namely, the noise power level is determined in the frequency domain based on a noise covariance matrix. Further, the sounding signal's power level is determined, in the time domain, based on power delay profile of the wide channel over which the sounding signal has been transmitted.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Path searching circuit, path searching method, and path searching program in a CDMA communication system
InactiveUS20040184411A1Inaccurate detection signalFor signal receptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionPower addedPower delay profile
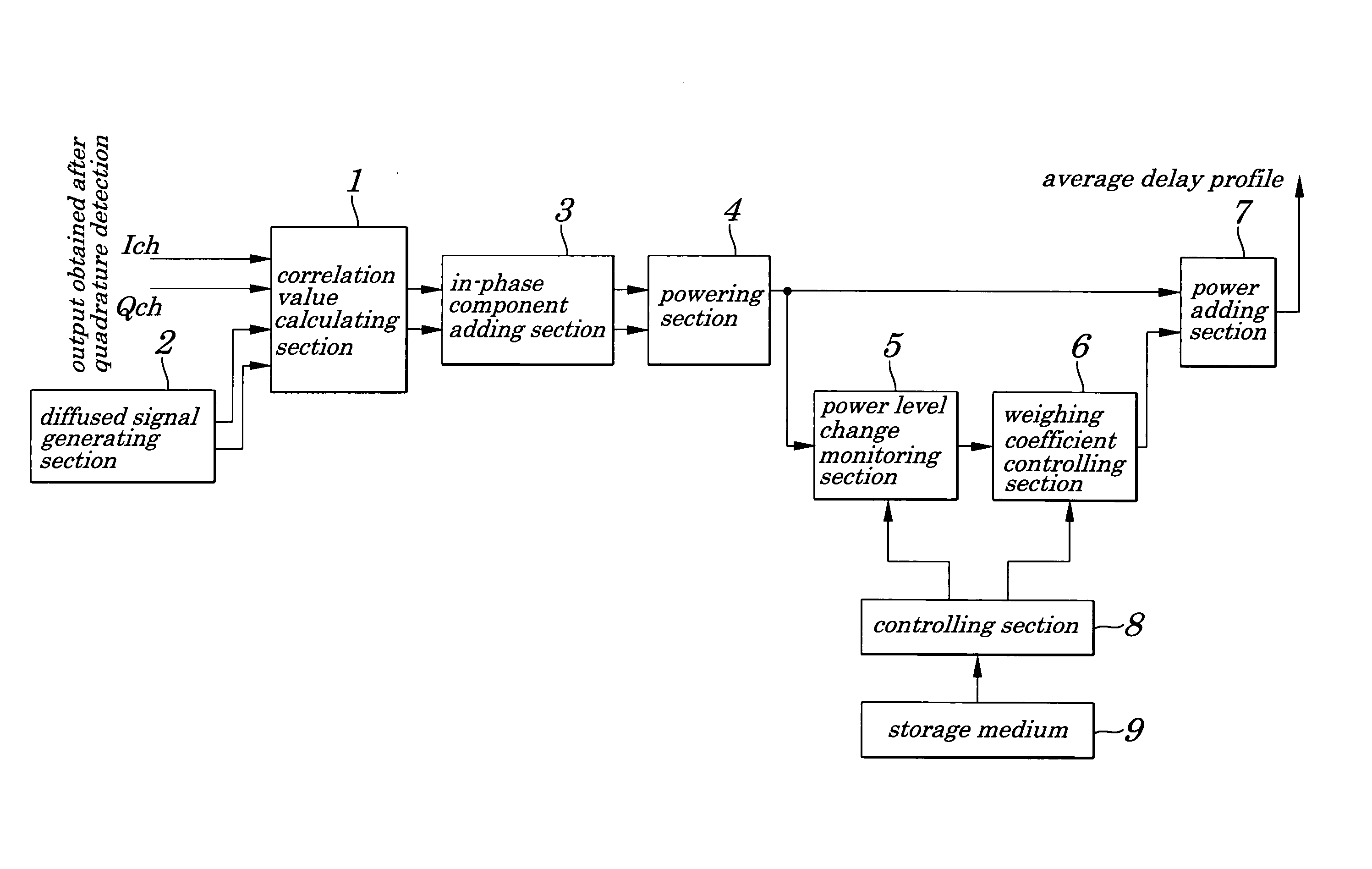
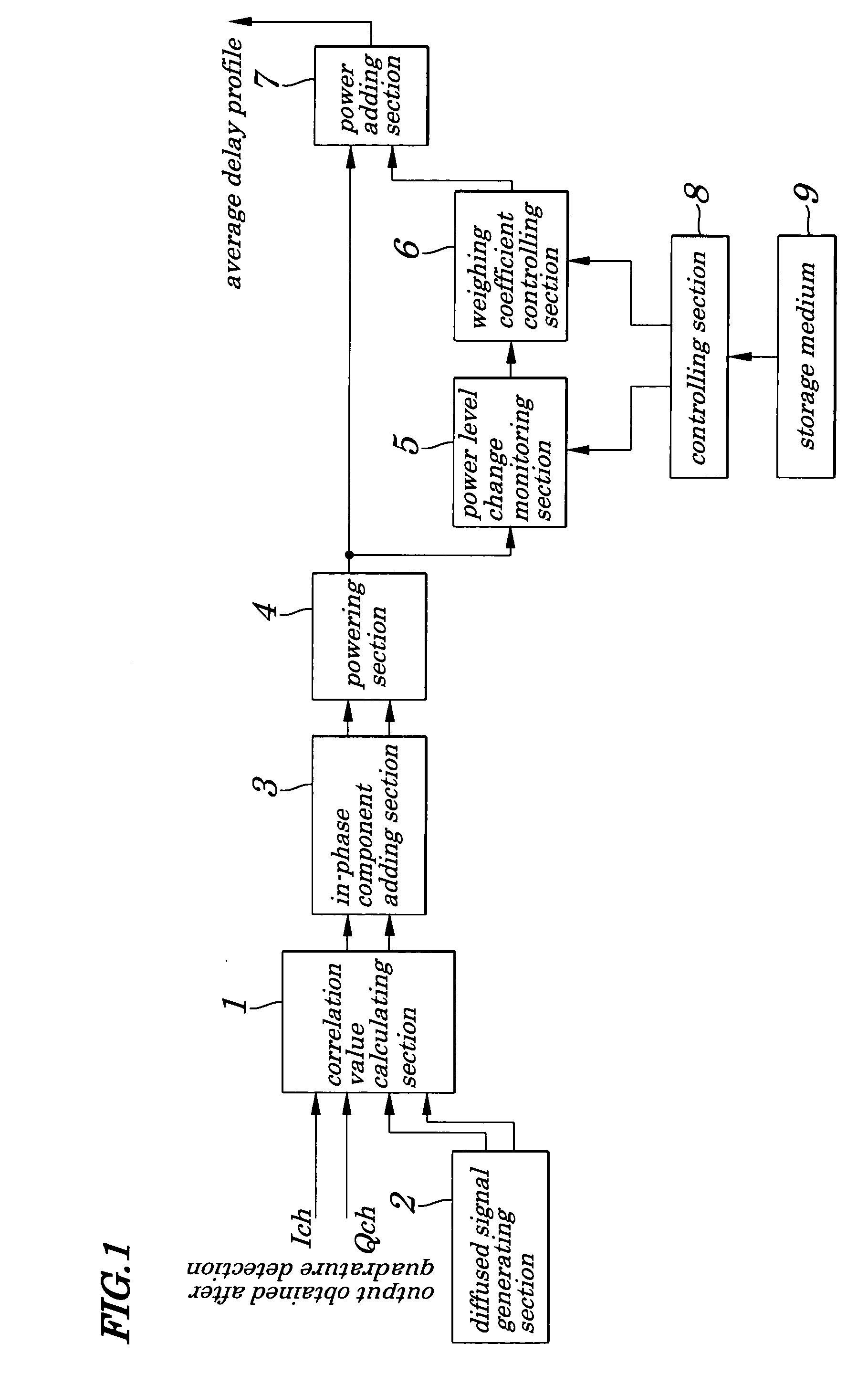
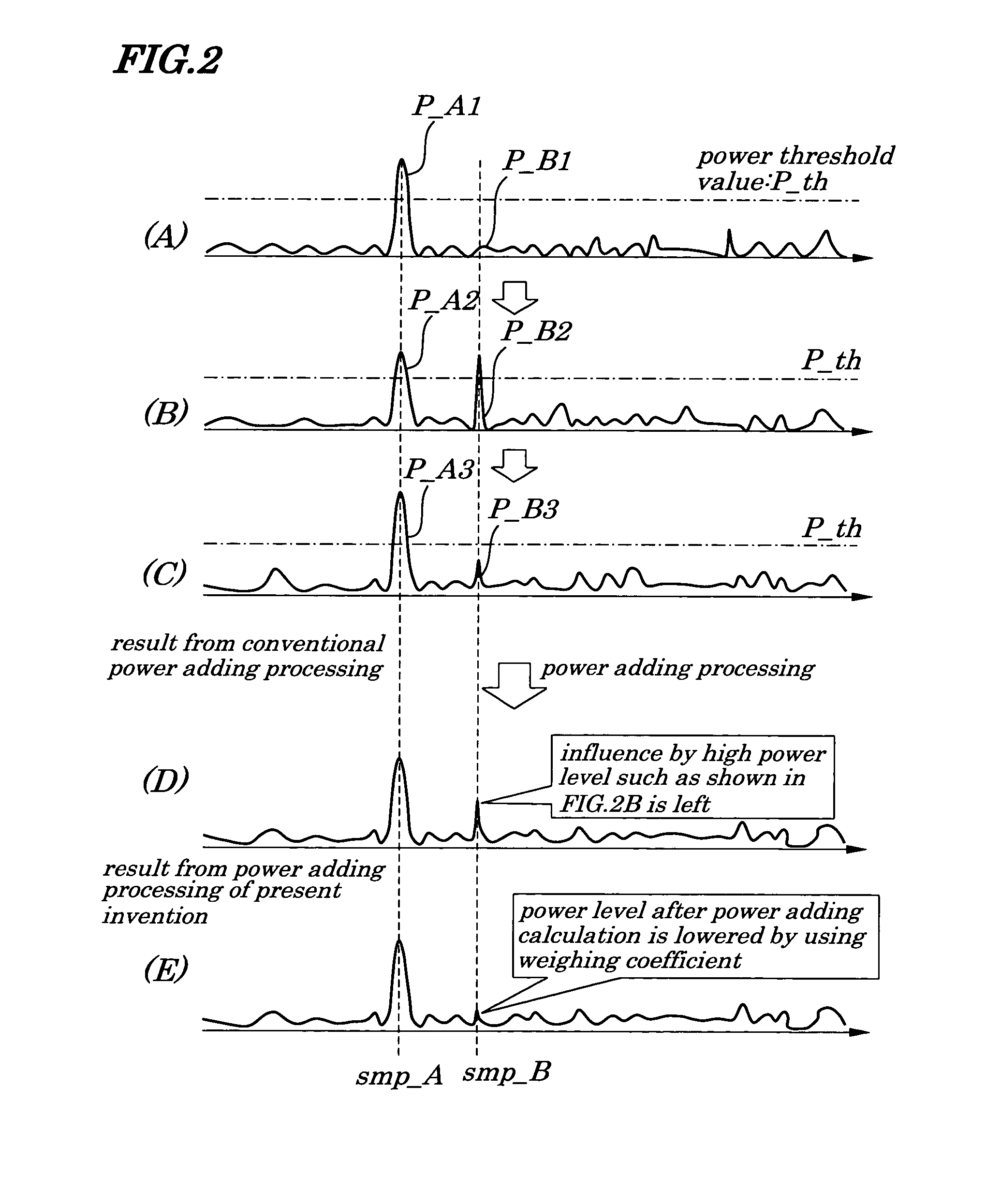
A path searching circuit is provided which is capable of searching a stable path. A power delay profile calculated by a powering section using an I component correlation value and a Q component correlation value is input to a power level change monitoring section, where a change in a power level is monitored at a sampling point for each of two or more delay profiles to be used for same power adding processing. With correct signal receiving path timing, stable high correlation values are observed, that is, it is observed that the received power level is small in change. On the other hand, with instantaneously high correlation values caused by noises, it is observed that the received power level is great in change. As a result, in the weighing coefficient controlling section, a weighing coefficient for correlation values providing a great change in a received power level is determined so that the received power level becomes low when power is added and so that weighing control is exercised.
Owner:NEC CORP
Time and frequency acquisition and tracking for ofdma wireless systems
InactiveCN103825626ASynchronisation arrangementDistributed allocationPower delay profileUser equipment
The present invention relates to time and frequency acquisition and tracking for OFDMA wireless systems. Obtaining a timing reference in wireless communication is facilitated when desiring to communicate with a weak serving base station (such as an evolved NodeB) in the presence of a stronger interfering base station. The user equipment (UE) may track a stronger interfering base station's timing, or the UE may track a timing that is derived by a composite power delay profile (PDP) from multiple base stations. The composite PDP may be constructed by adjusting individual base station PDPs according to a weighting scheme. The timing obtained in such a manner may be used for estimation of the channel of the interfering base station and cancelling interfering signals from the base station. It may also be used to estimate the channel of the serving base station after adding a backoff. The UE may track a stronger interfering base station's frequency, or the UE may track a composite frequency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
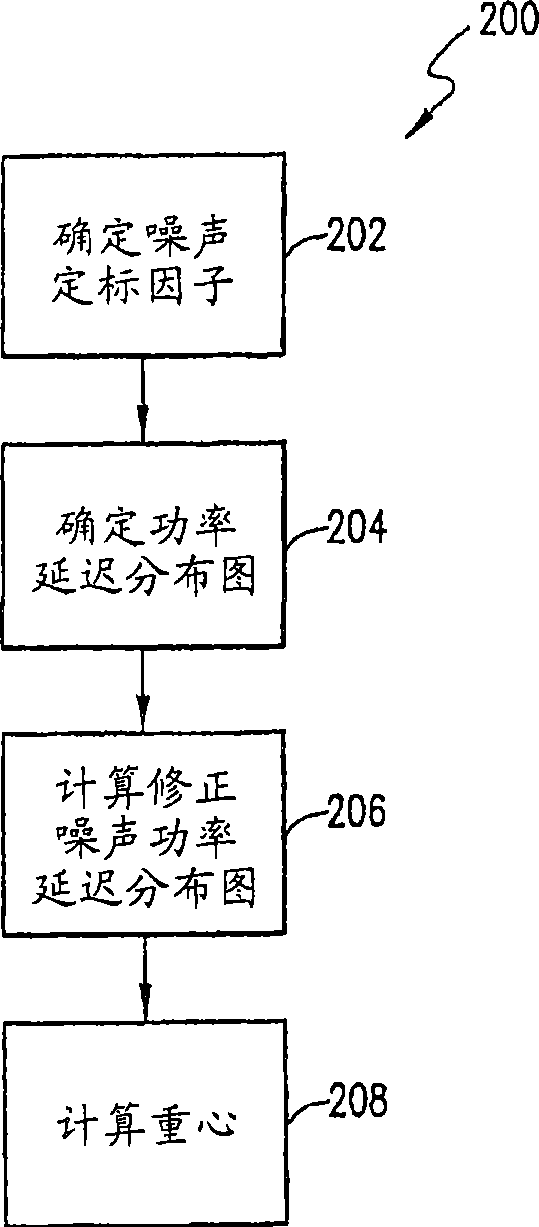
Method of and apparatus for computation of unbiased power delay profile
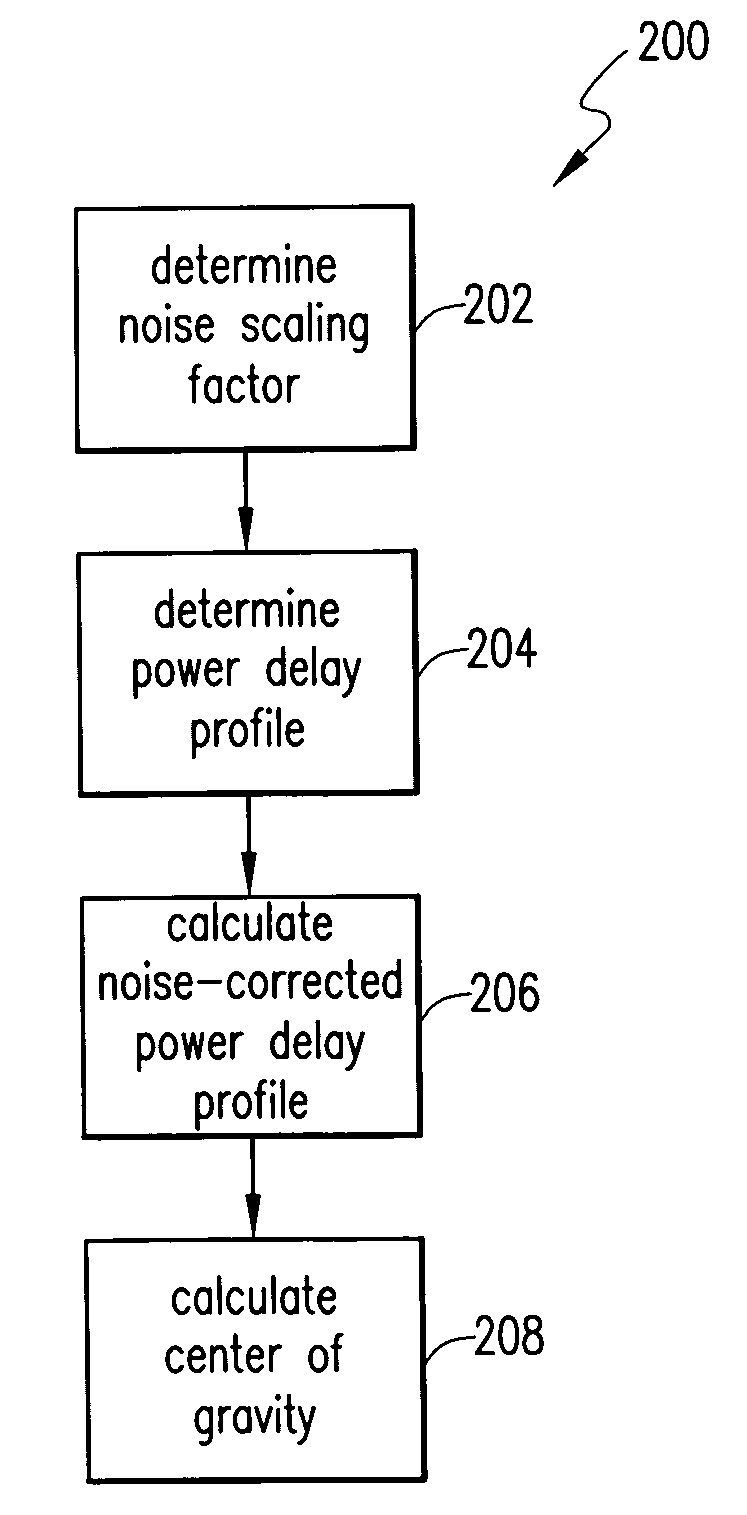
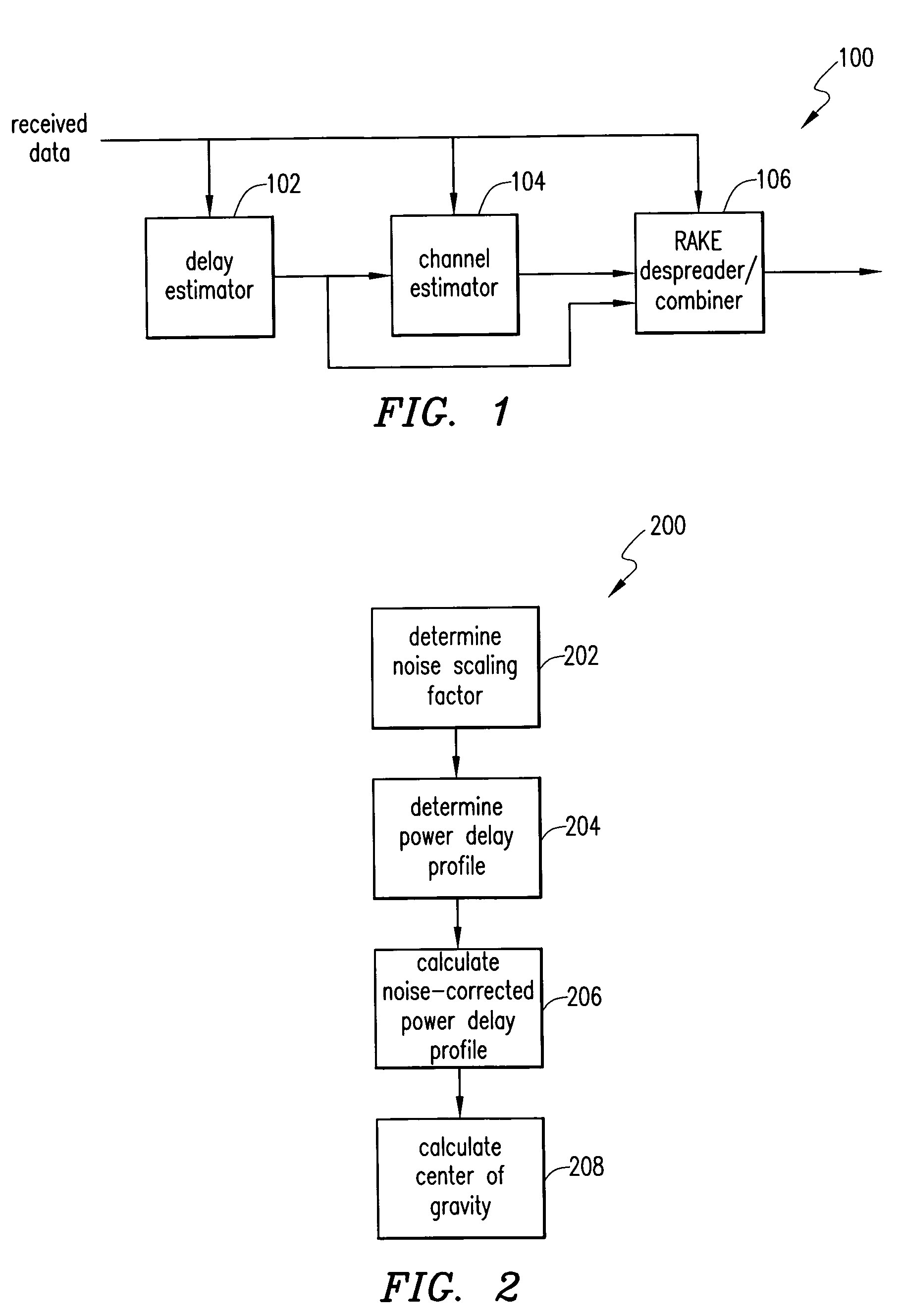
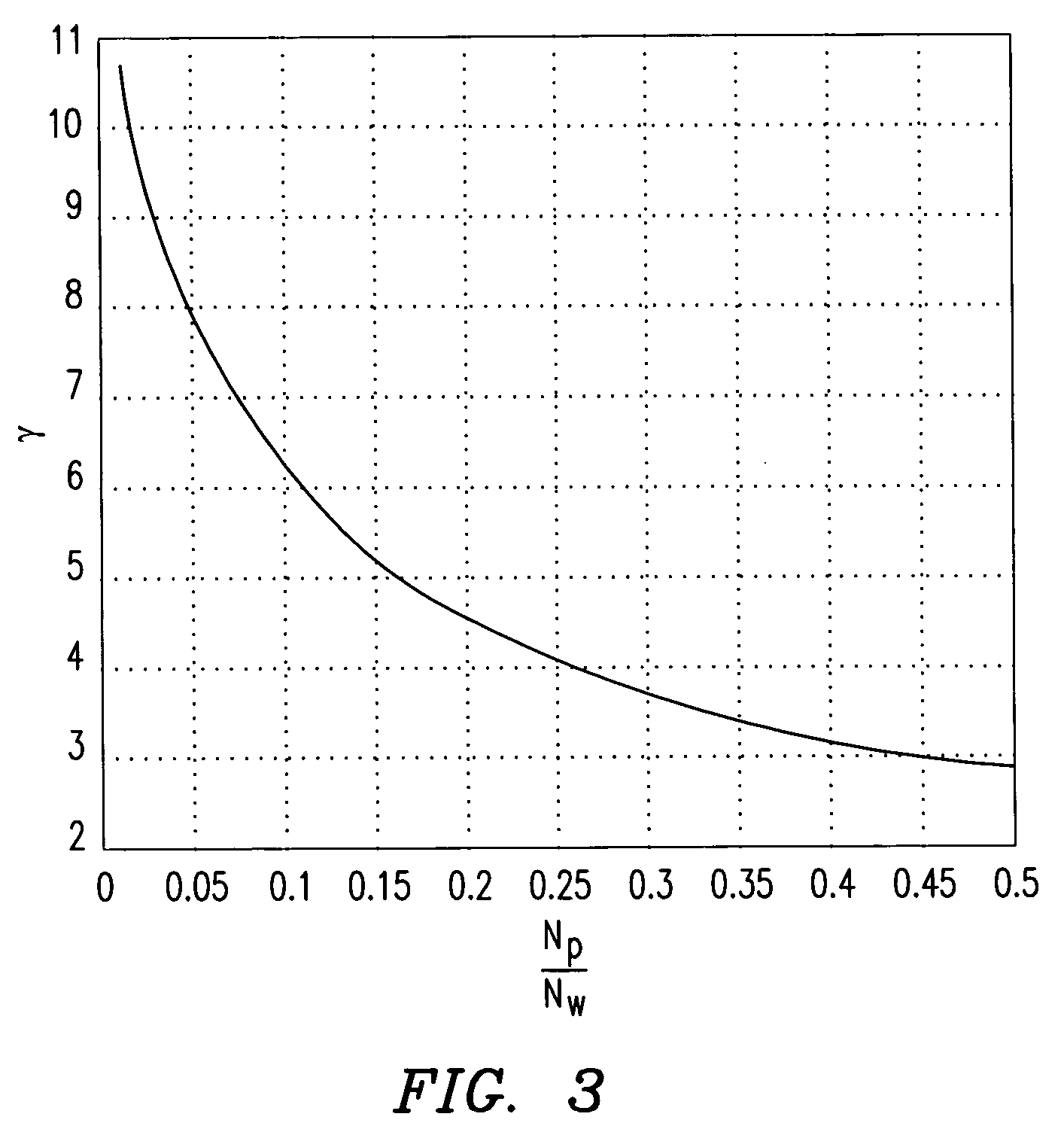
A method of determining a noise-corrected power delay profile includes determining a power delay profile and calculating a noise-corrected power delay profile. The step of calculating the noise-corrected power delay profile includes using a biased noise-floor power estimate, the power delay profile, and a noise-scaling factor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Time and frequency acquisition and tracking for ofdma wireless systems
InactiveCN102577144ASynchronisation arrangementDistributed allocationPower delay profileUser equipment
Obtaining a timing reference in wireless communication is facilitated when desiring to communicate with a weak serving base station (such as an evolved Node B) in the presence of a stronger interfering base station. The user equipment (UE) may track a stronger interfering base station's timing, or the UE may track a timing that is derived by a composite power delay profile (PDP) from multiple base stations. The composite PDP may be constructed by adjusting individual base station PDPs according to a weighting scheme. The timing obtained in such a manner may be used for estimation of the channel of the interfering base station and cancelling interfering signals from the base station. It may also be used to estimate the channel of the serving base station after adding a backoff. The UE may track a stronger interfering base station's frequency, or the UE may track a composite frequency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com