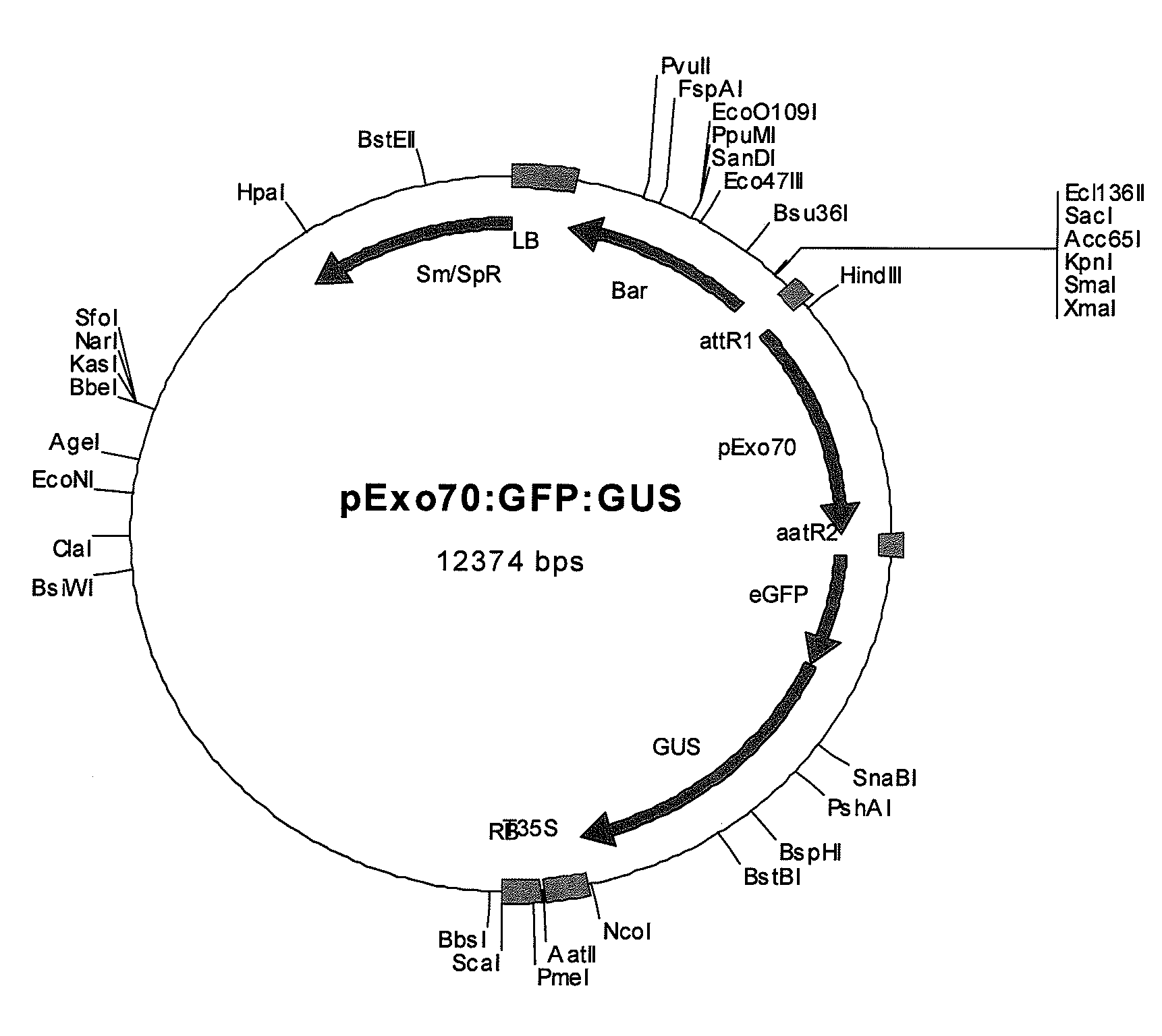
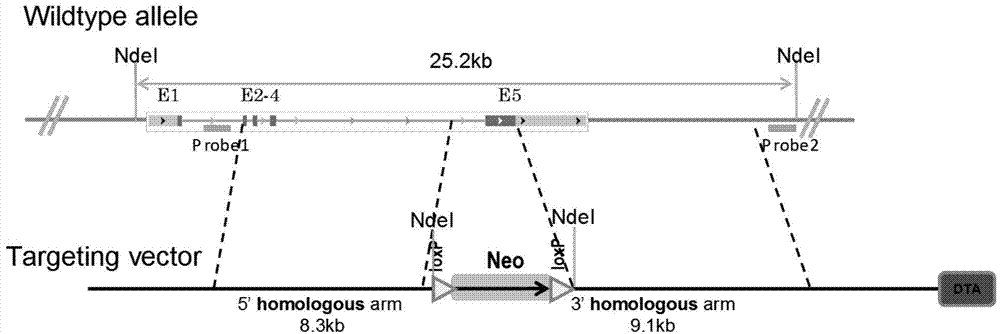
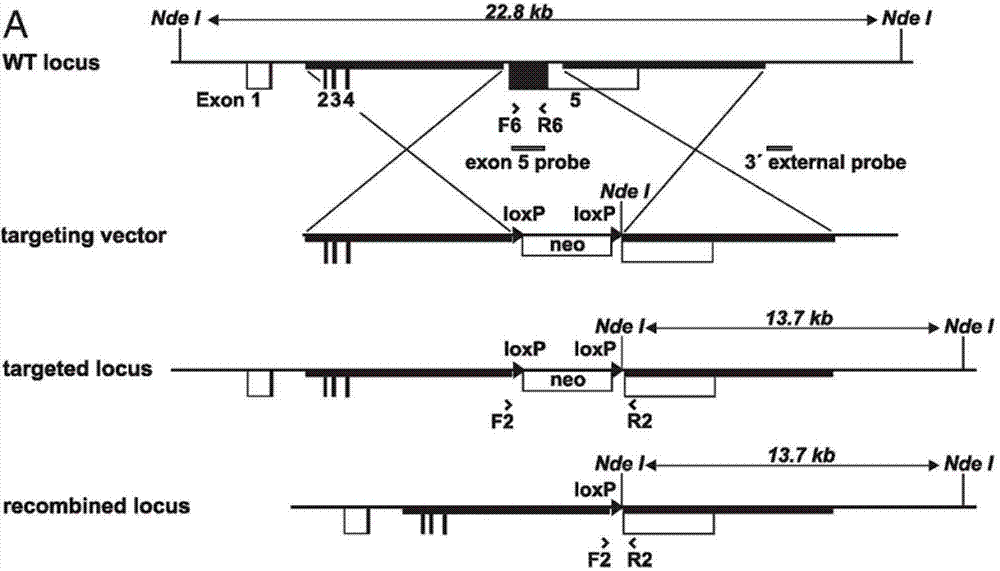
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
177 results about "Embryo cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
[edit on Wikidata] An embryo is an early stage of development of a multicellular diploid eukaryotic organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, an embryo develops from a zygote, the single cell resulting from the fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell.
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
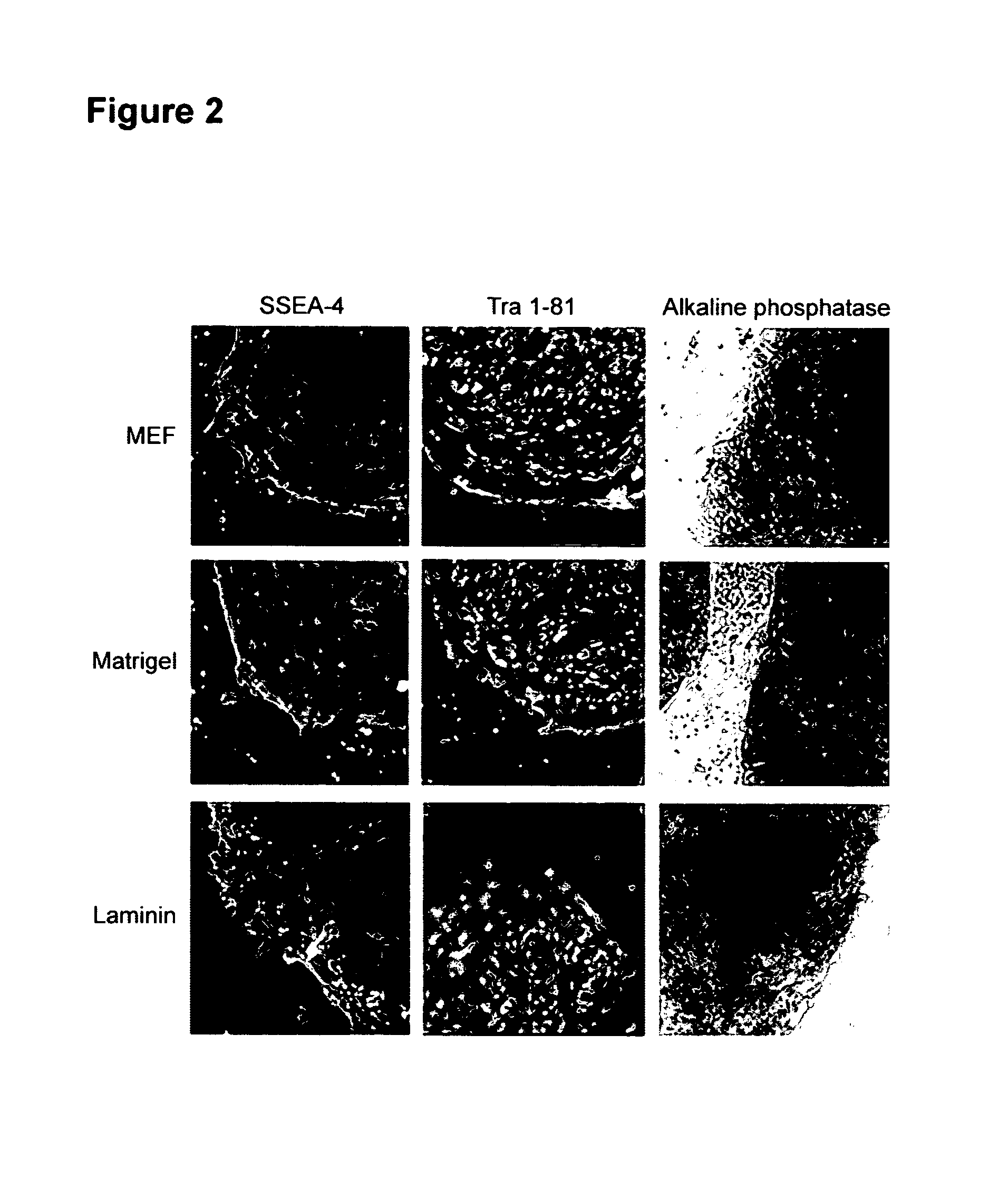
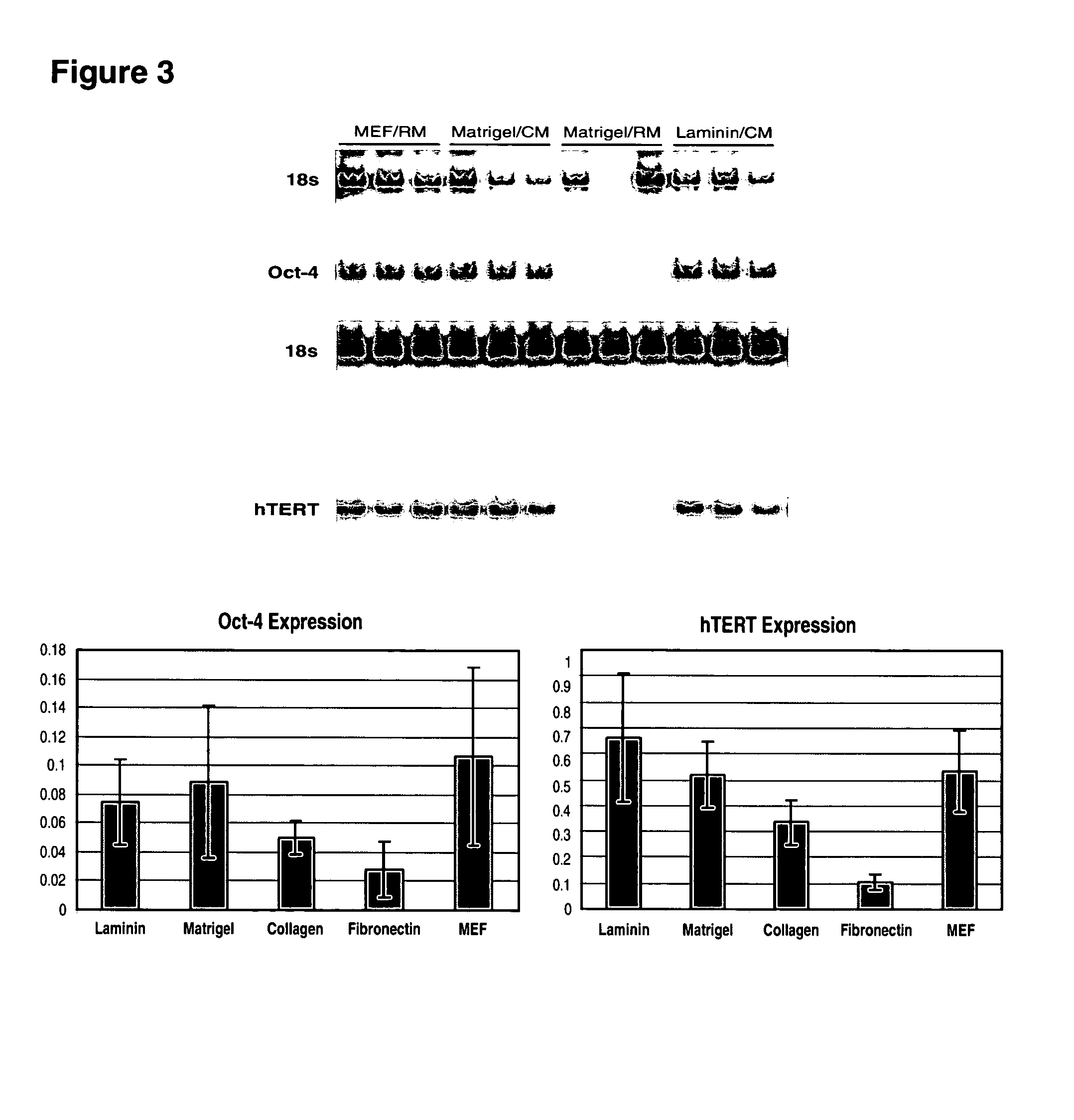
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Immunomodulatory properties of multipotent adult progenitor cells and uses thereof
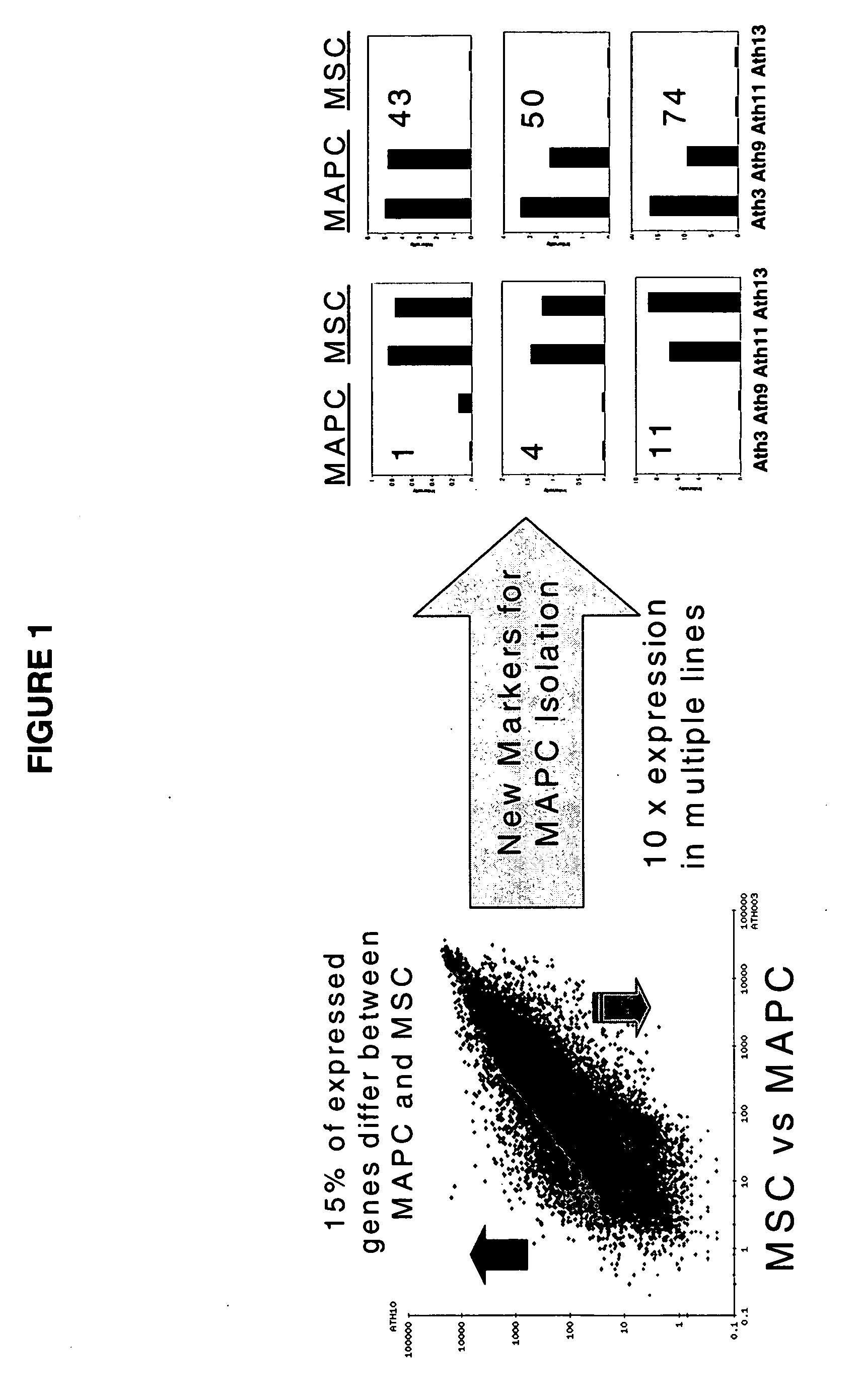
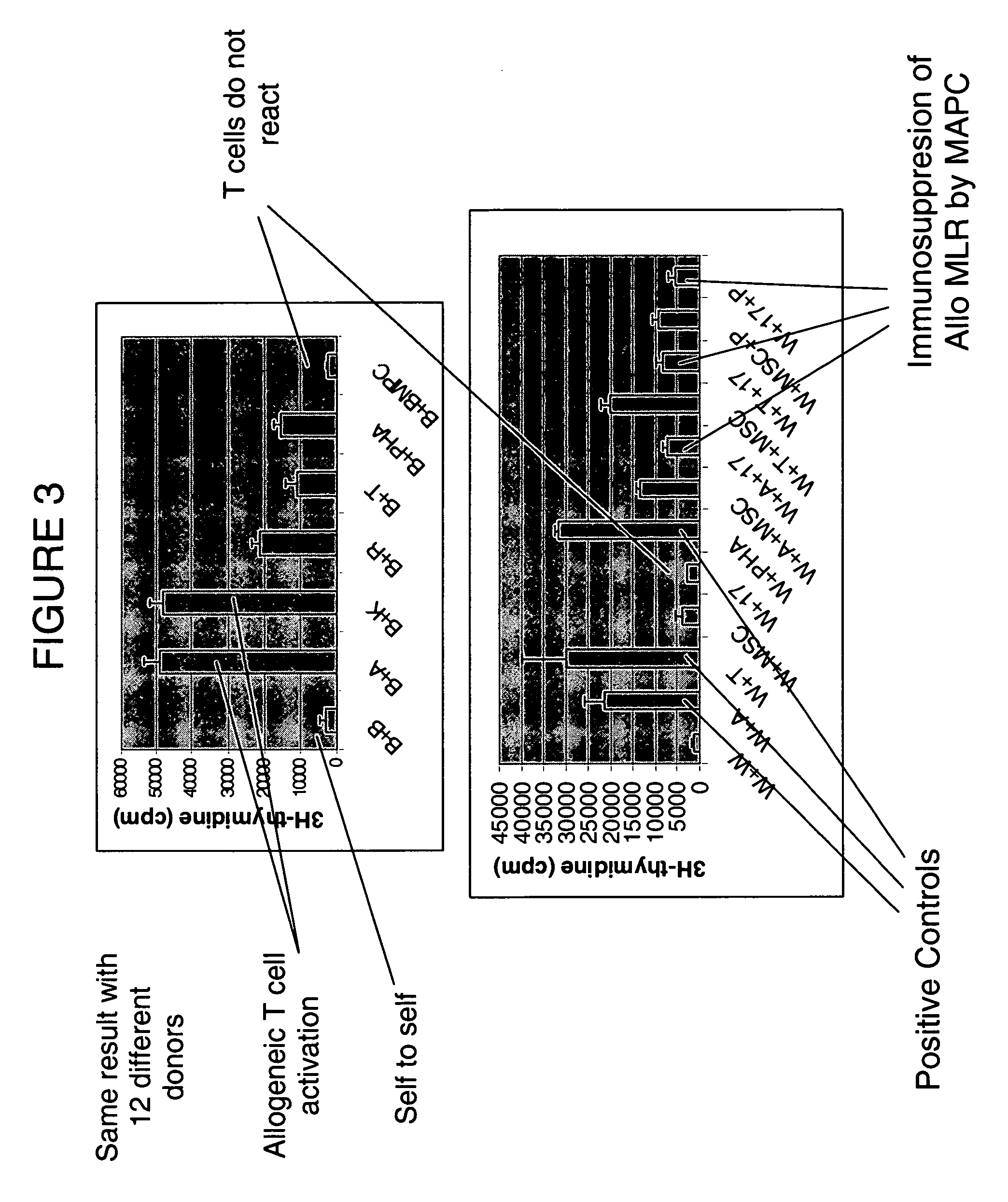
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
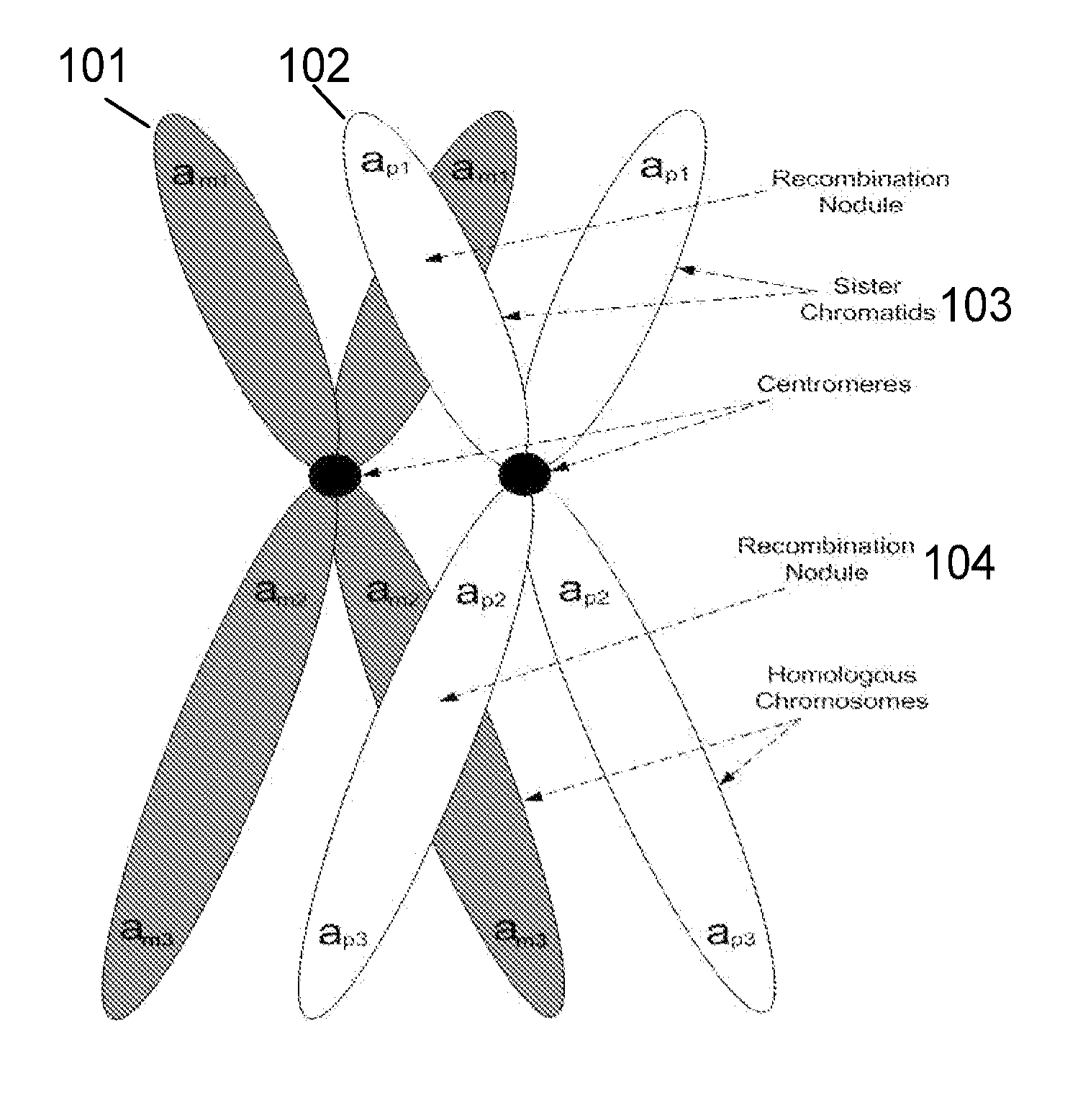
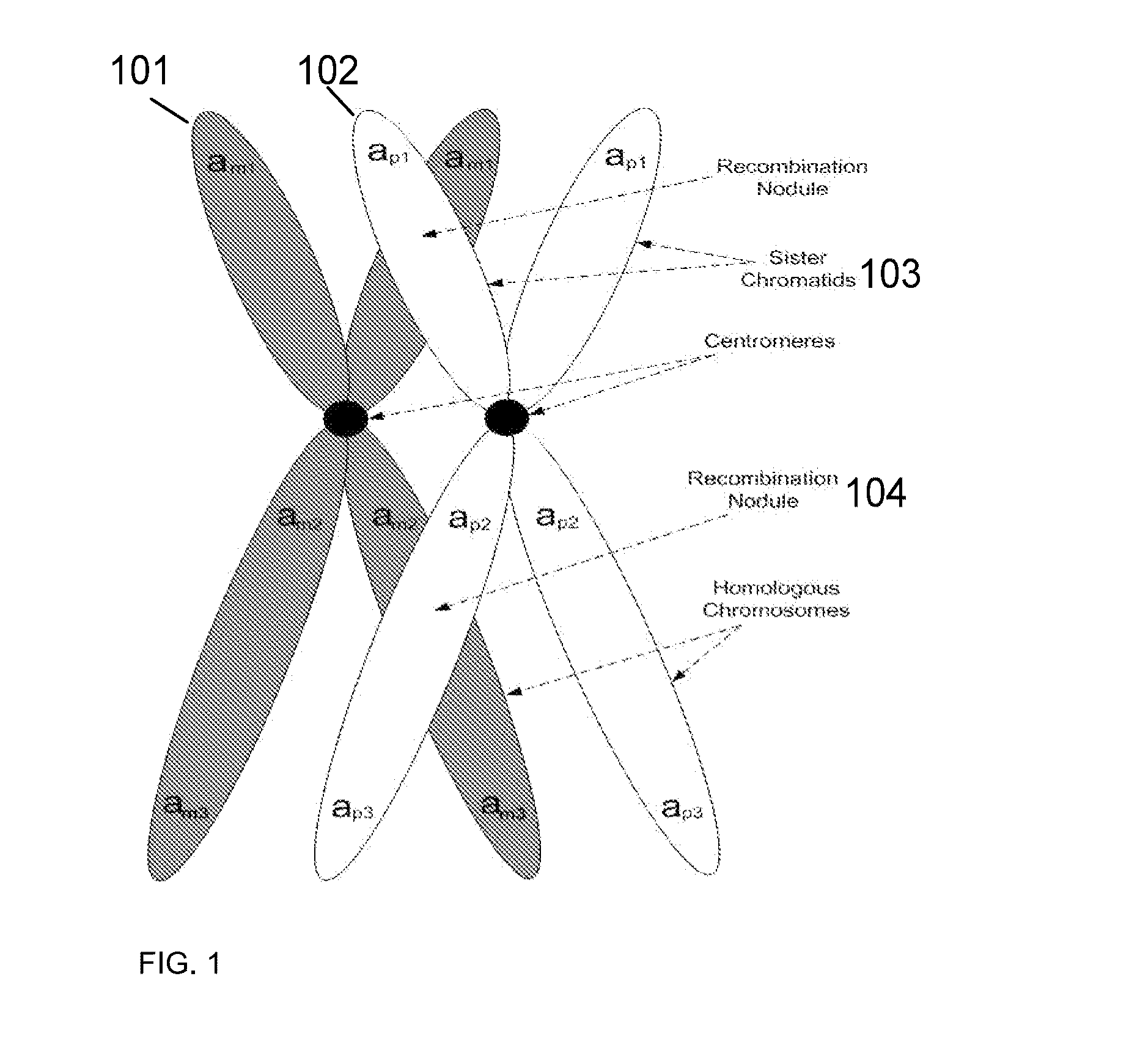
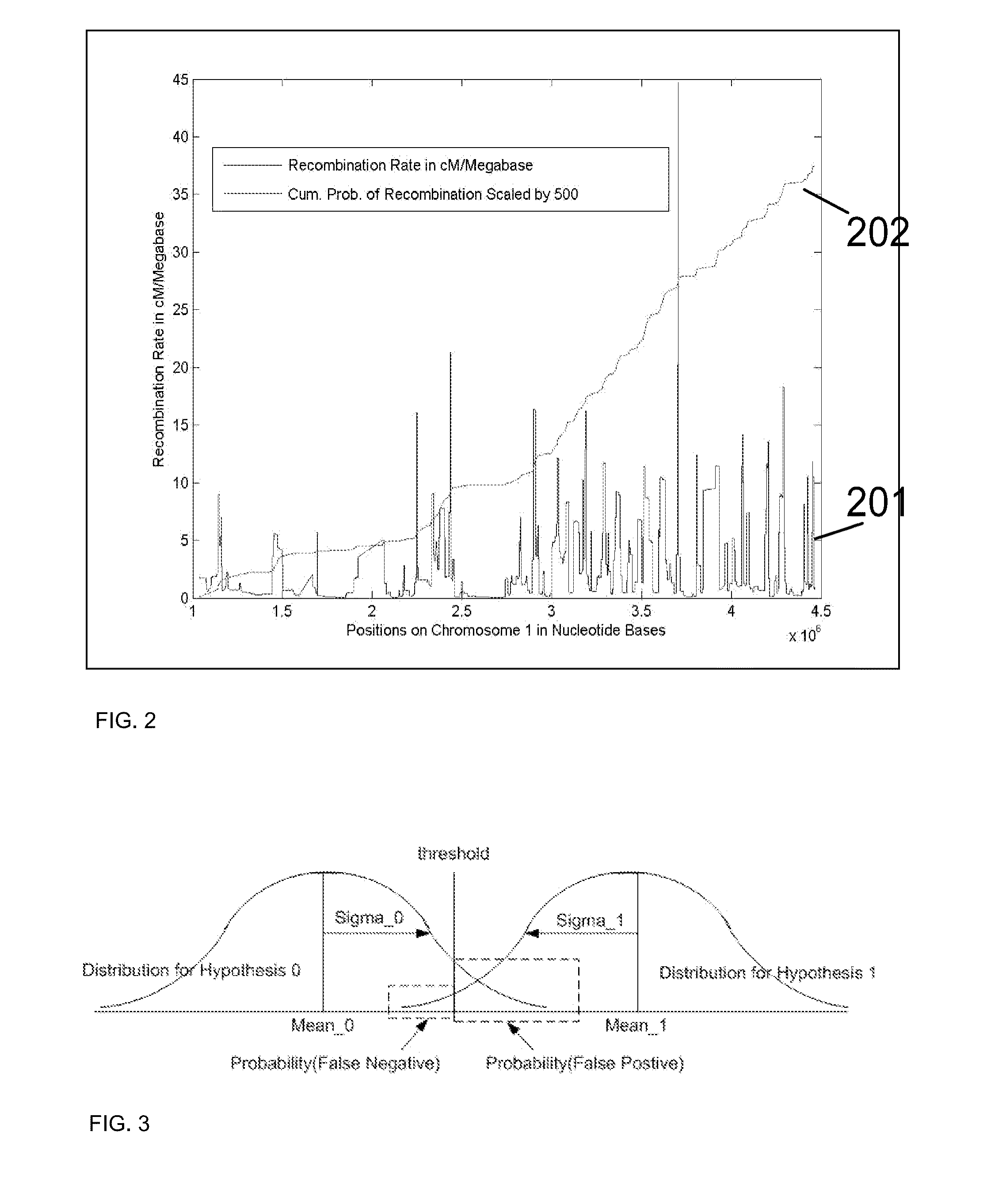
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
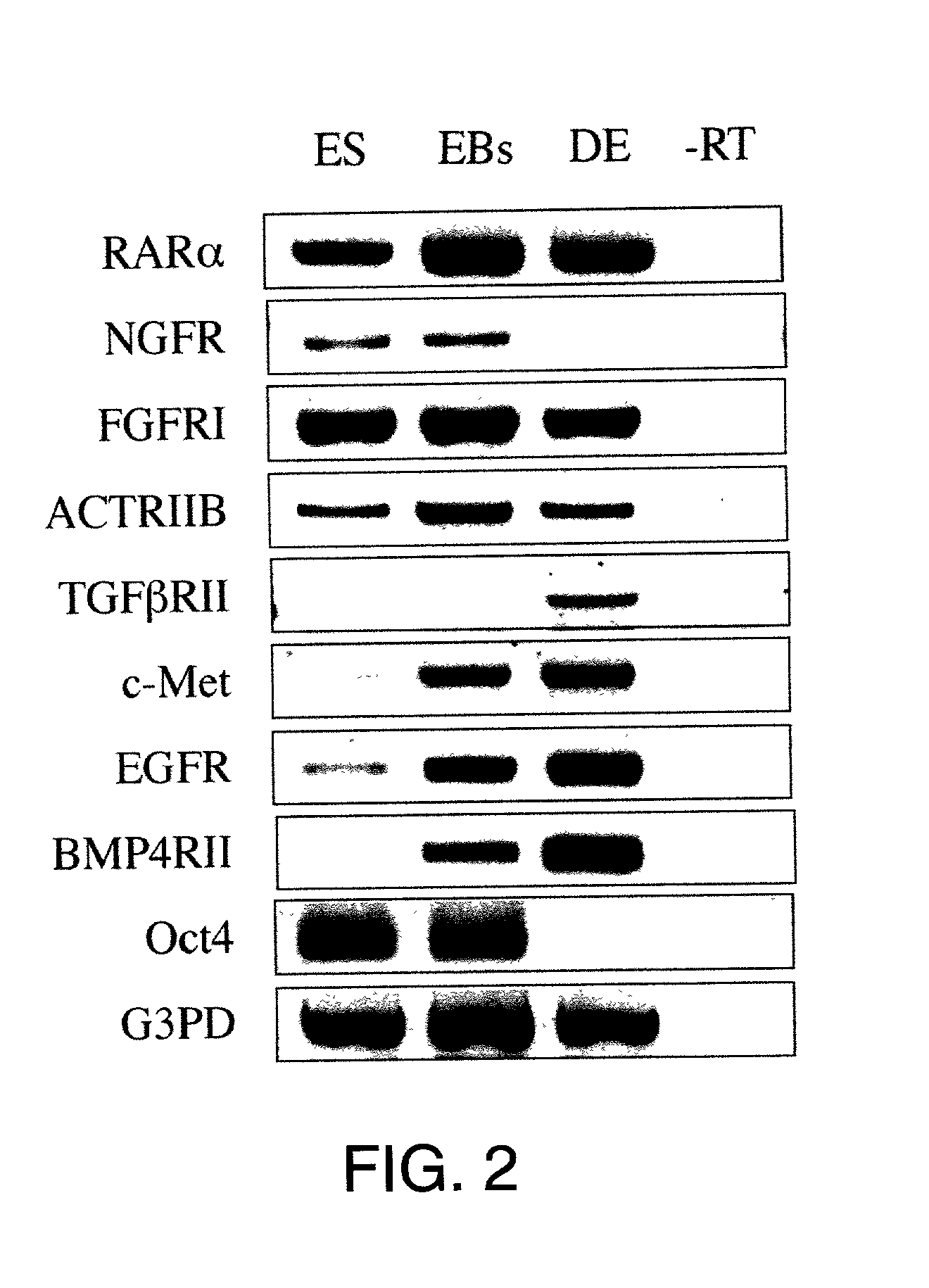
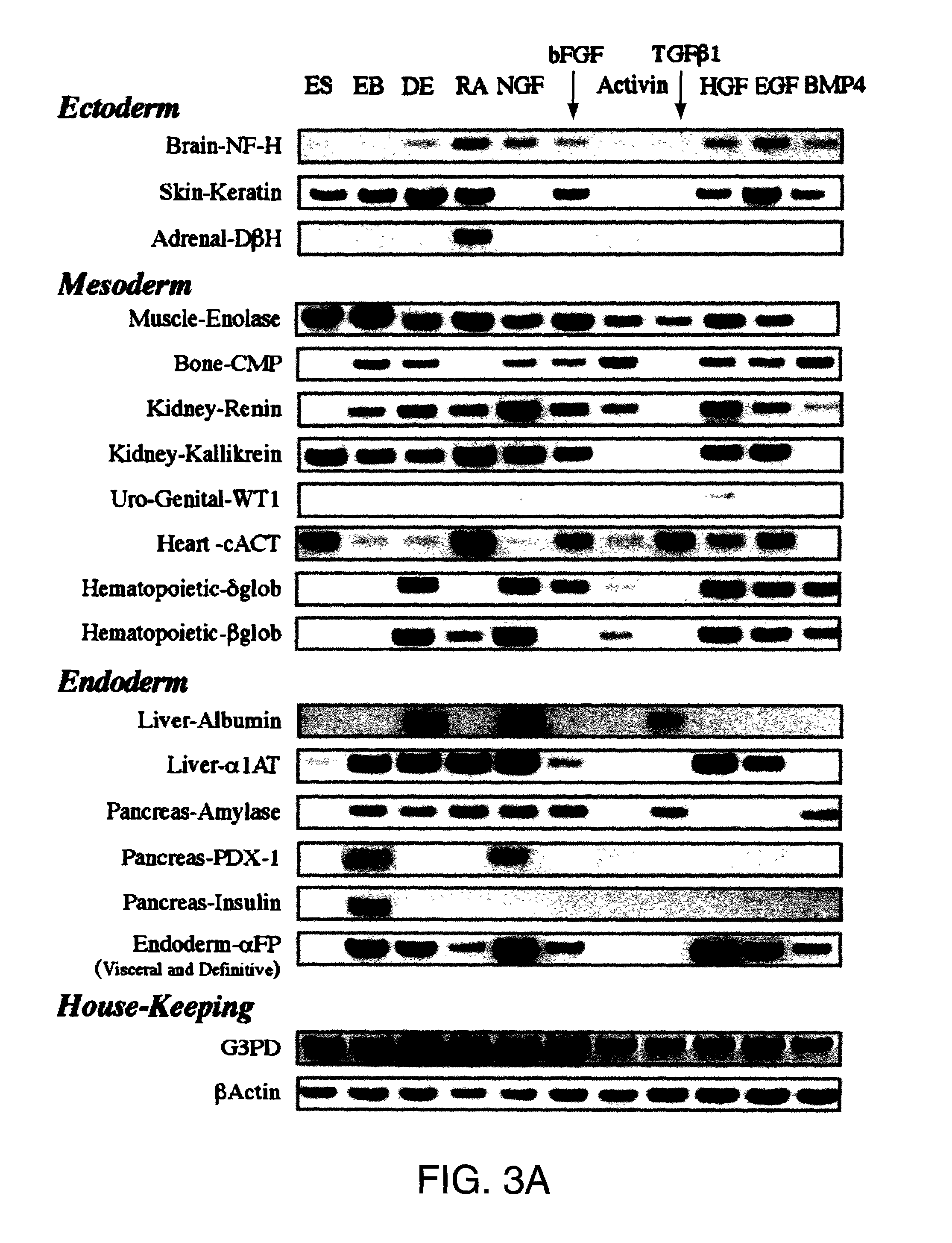
Directed differentiation of embryonic cells
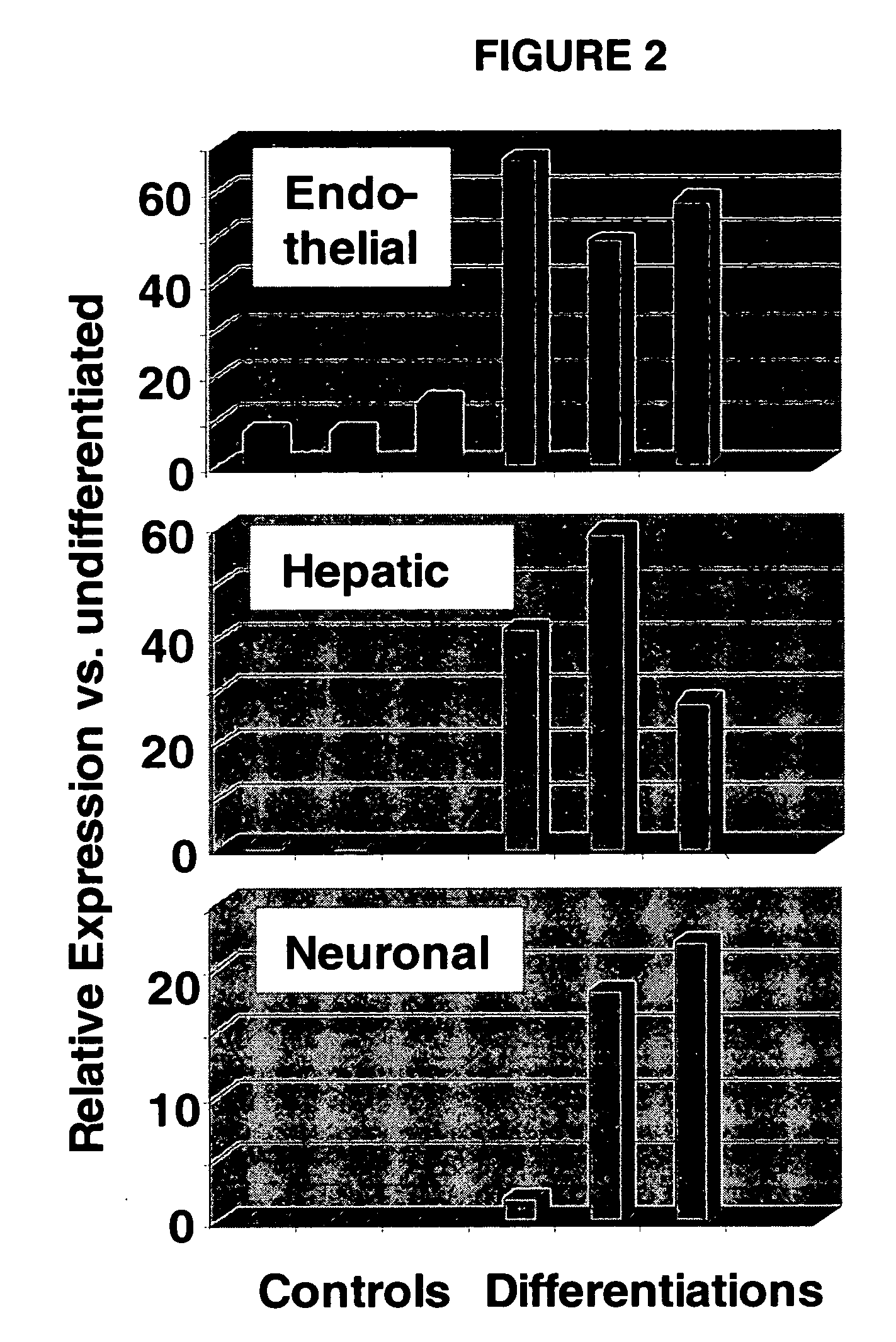
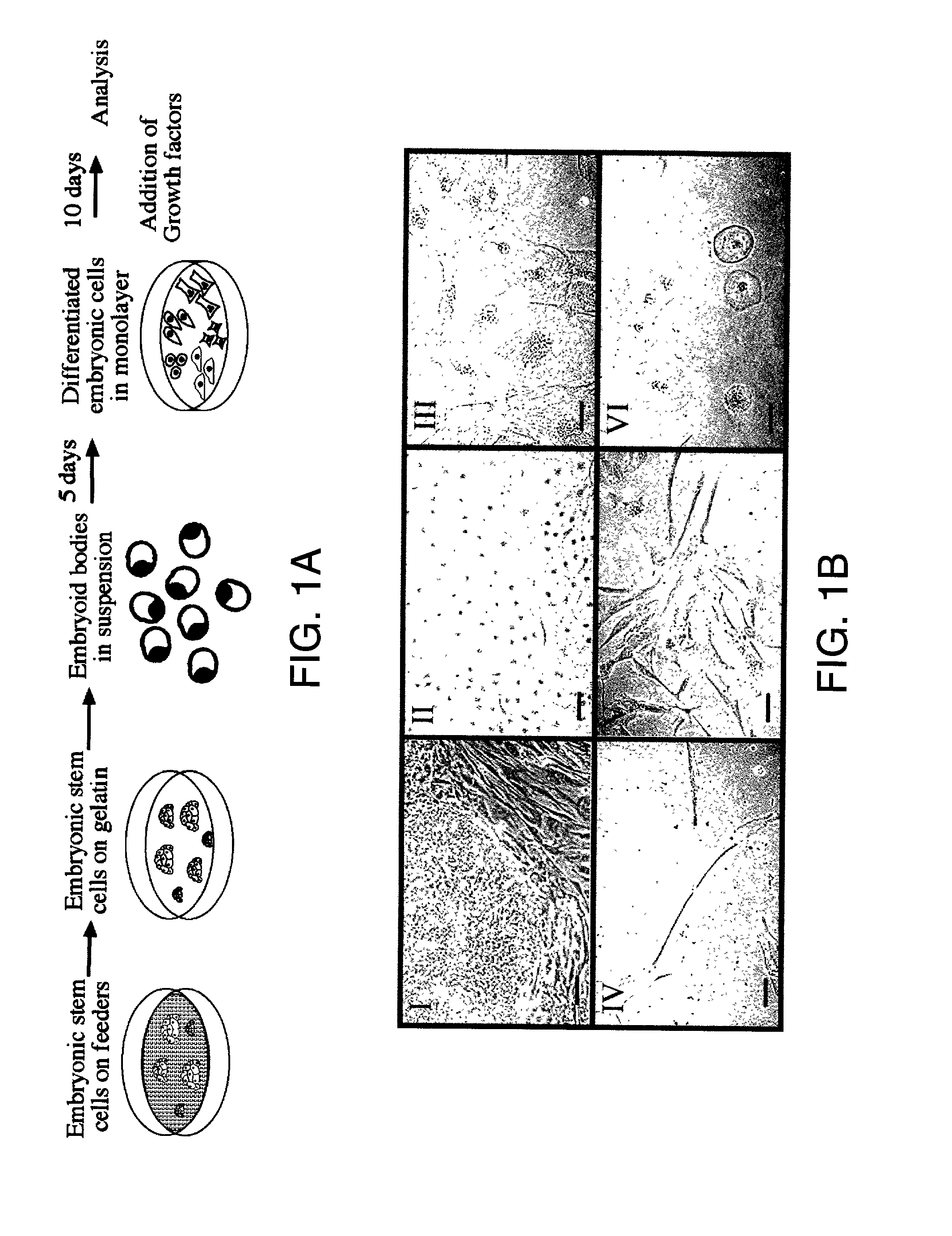
Methods are described for mapping a pathway of differentiation of a population of embryonic cells which includes exposing the cells to an exogenous factor and measuring gene expression products that are characteristic of a particular cell type or lineage. Directing differentiation of human embryonic cells relies on dissociated embryoid bodies which are then exposed to one or more exogenous factors to enrich a culture for a particular cell type. The differentiated cells may be used for treating a medical condition in a human. Kits for determining differentiation pathways and screening exogenous factors for their utility in differentiation are provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
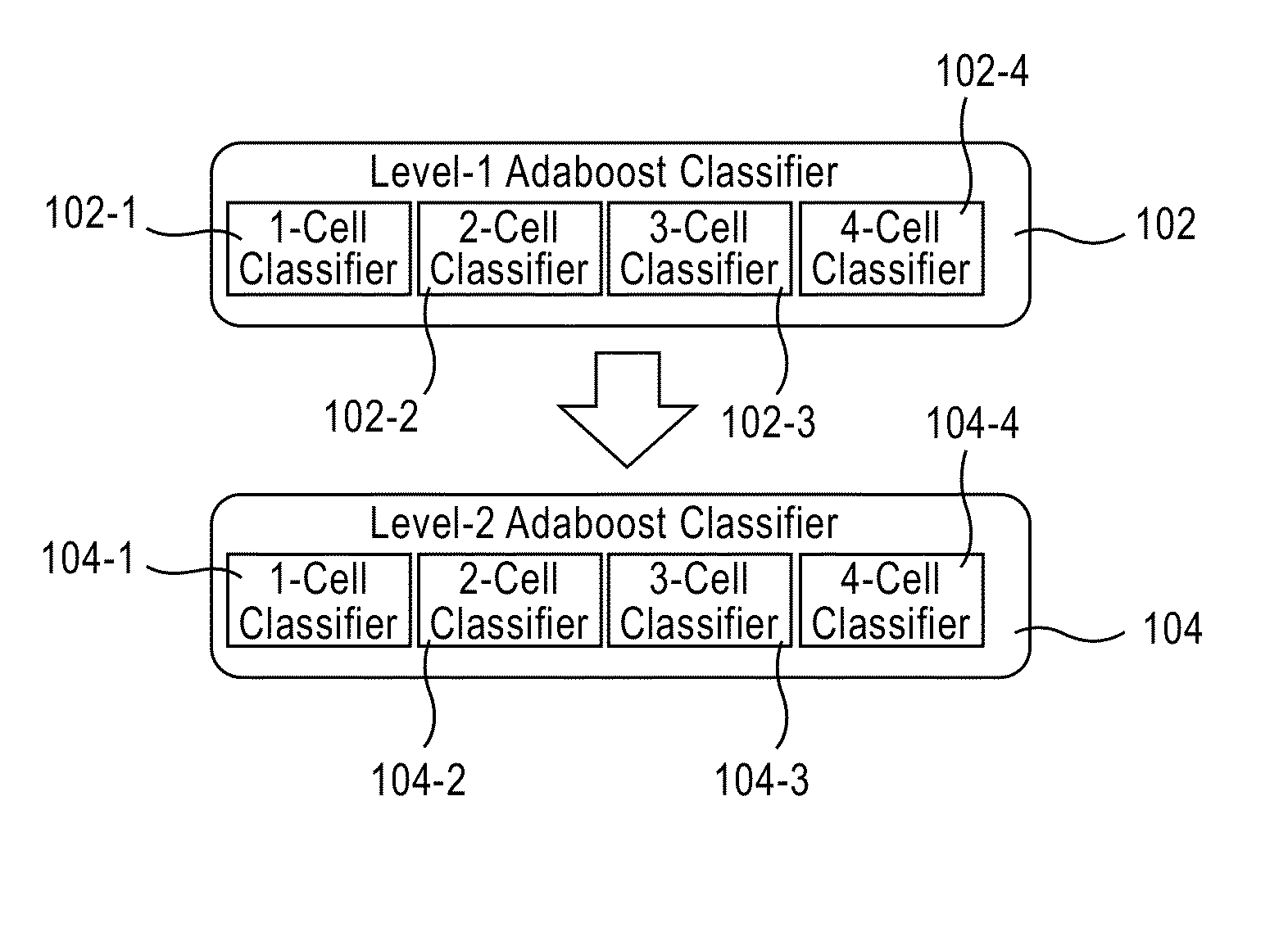
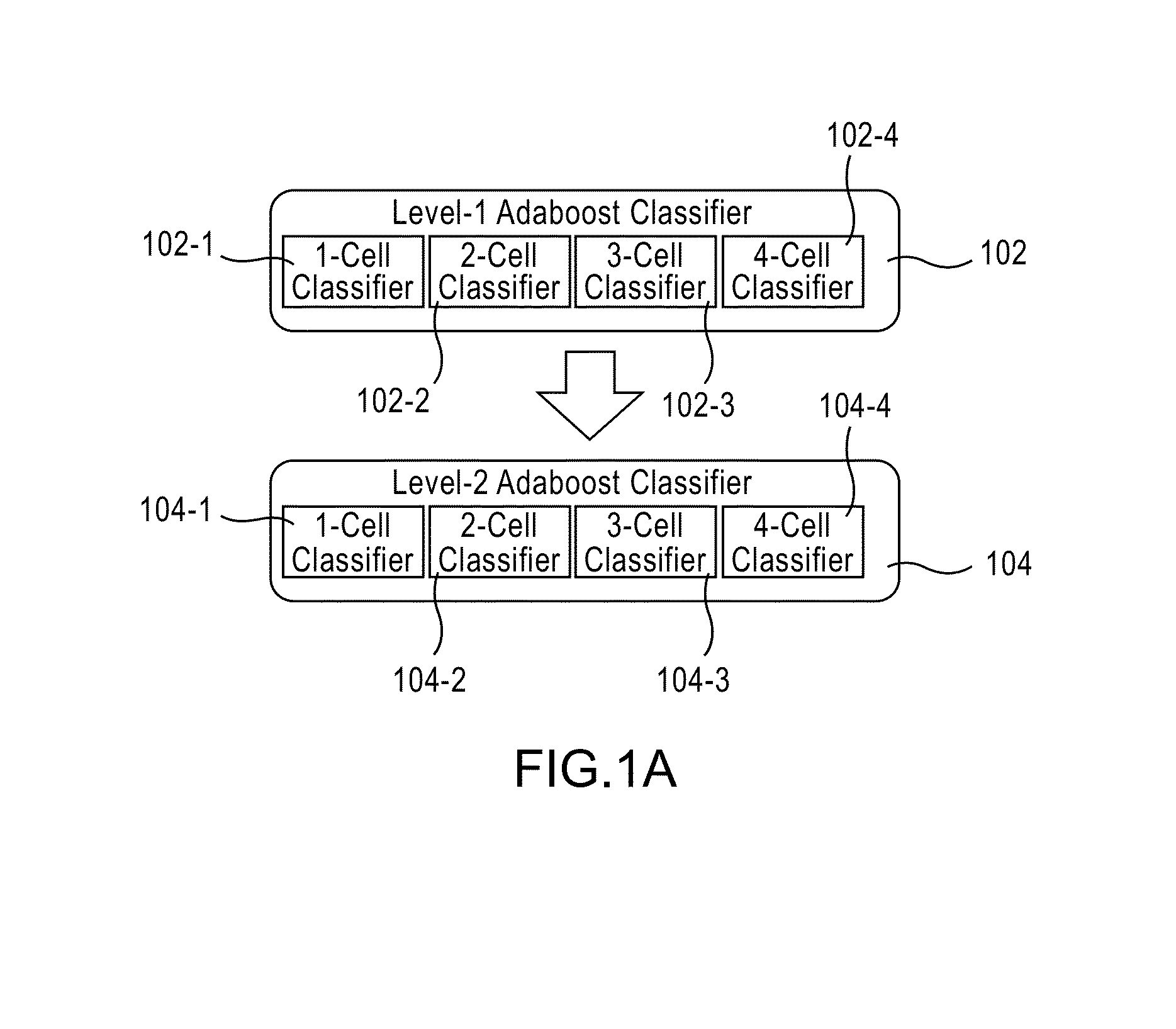
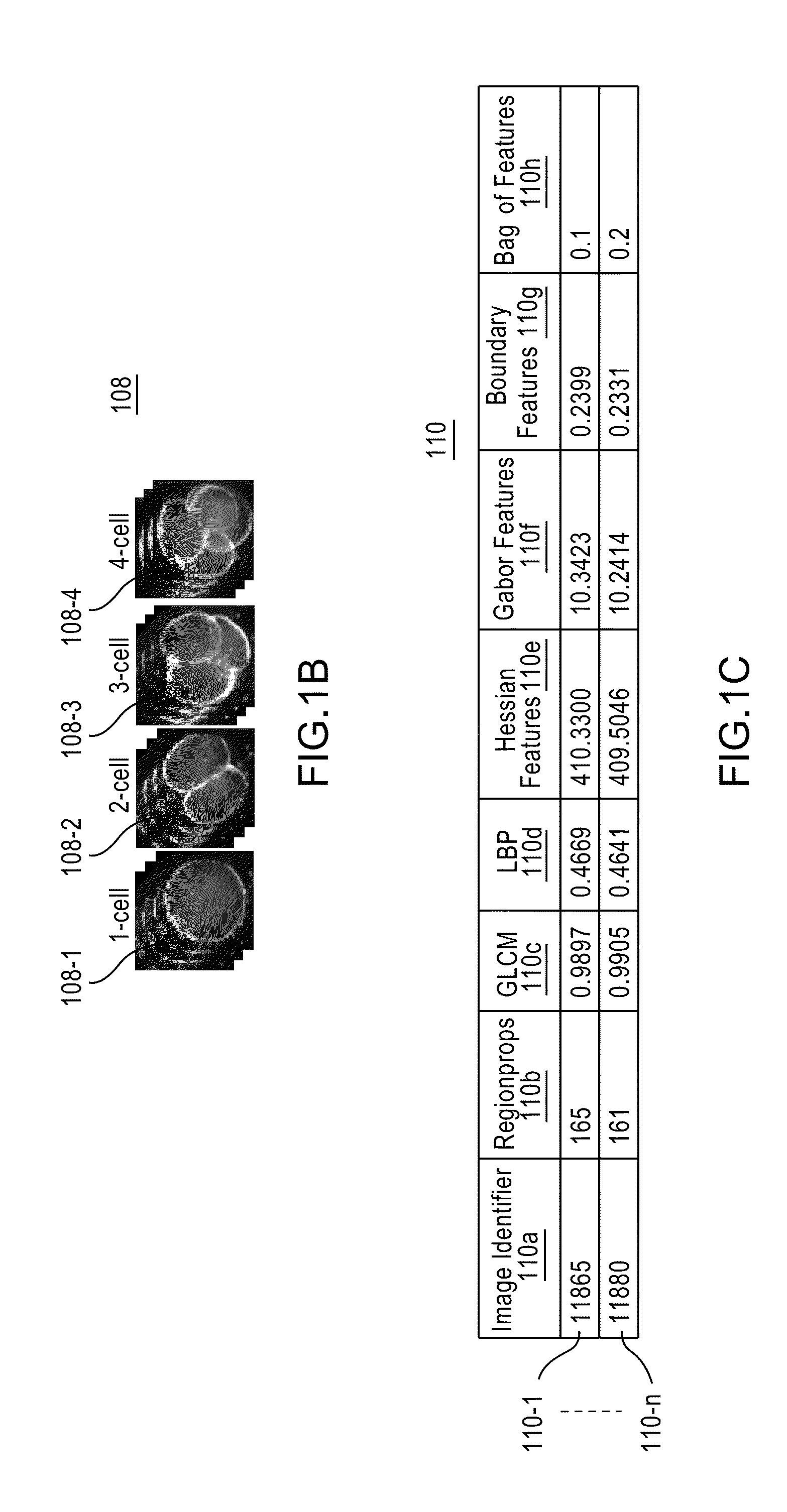
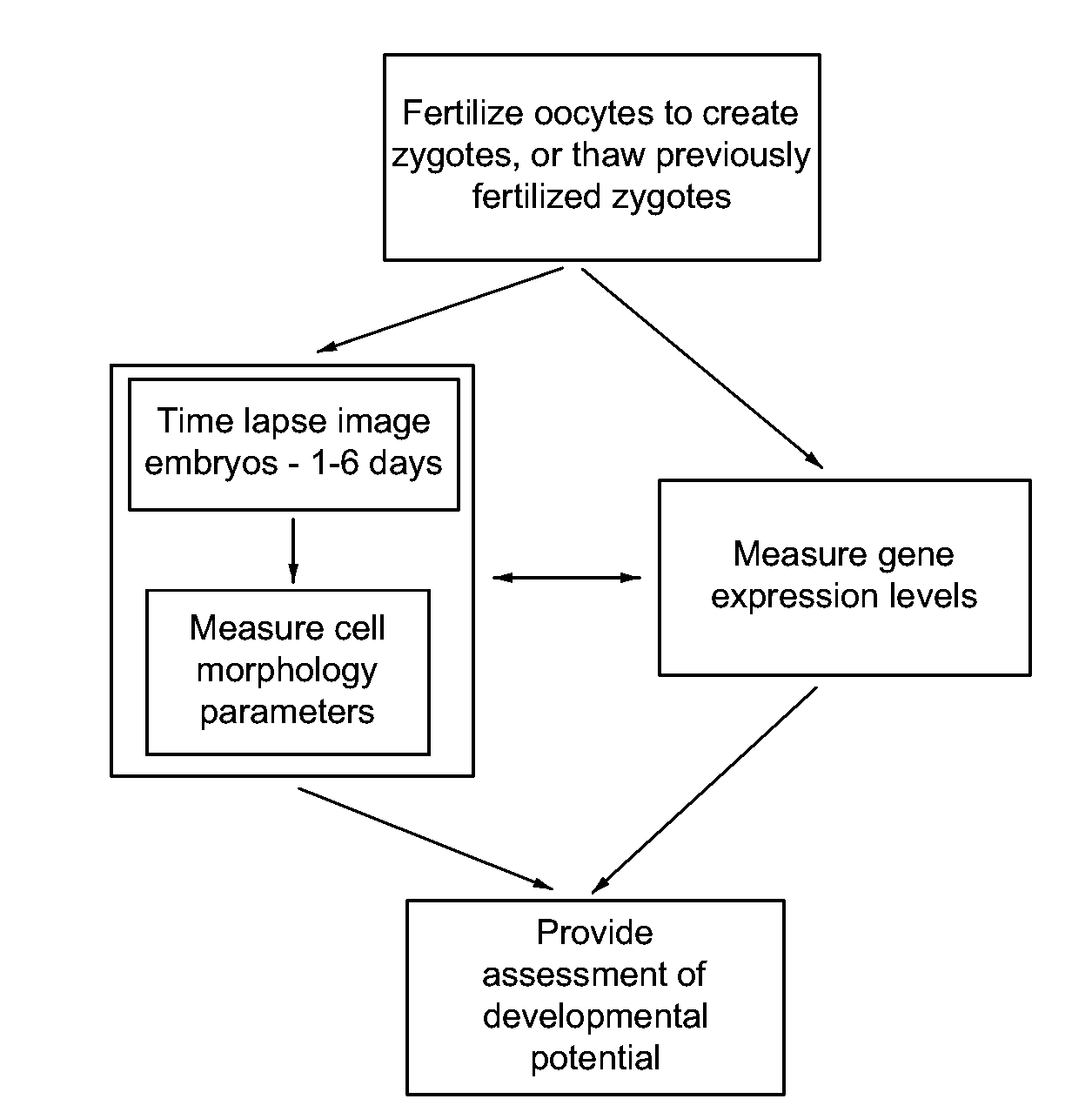
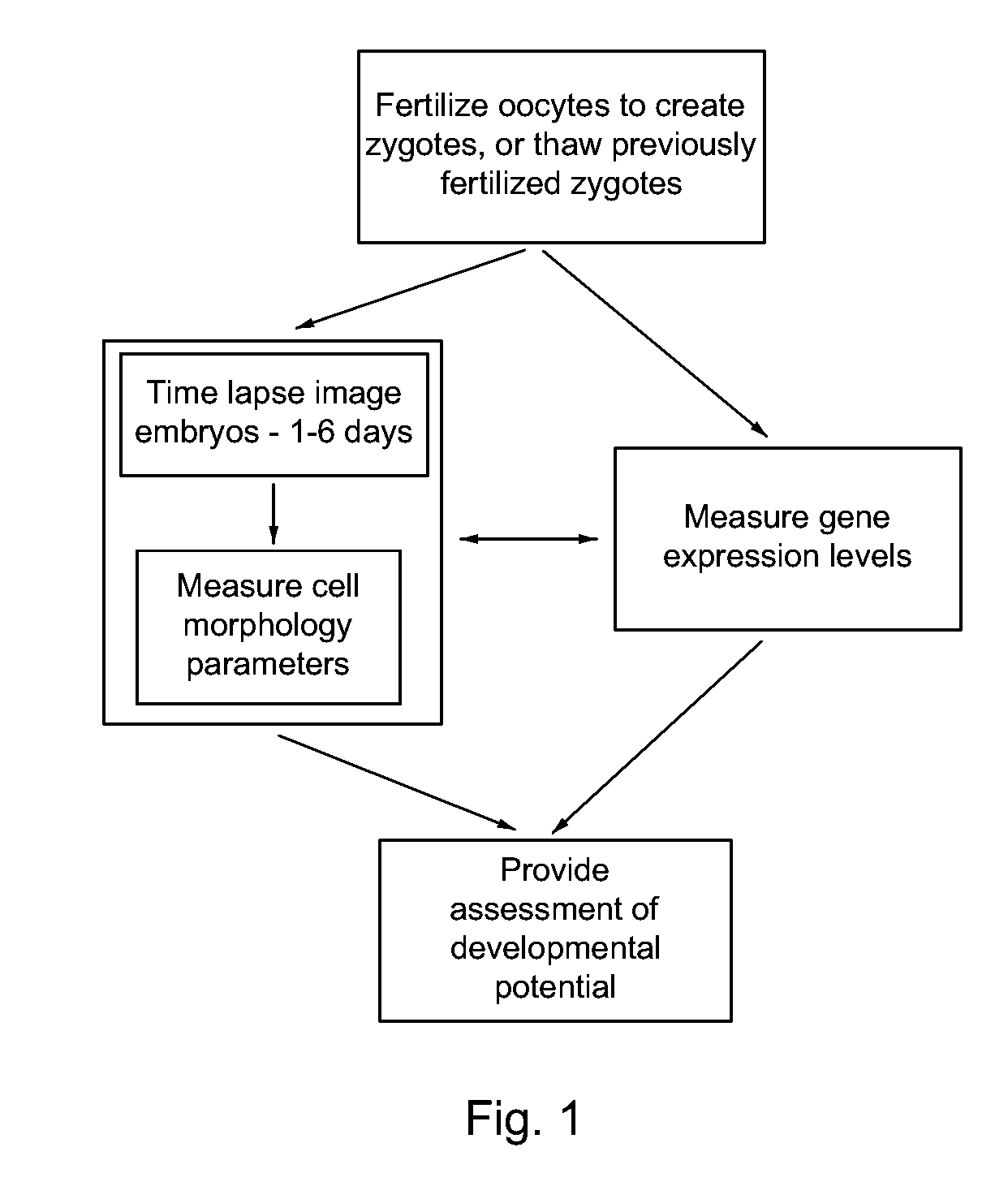
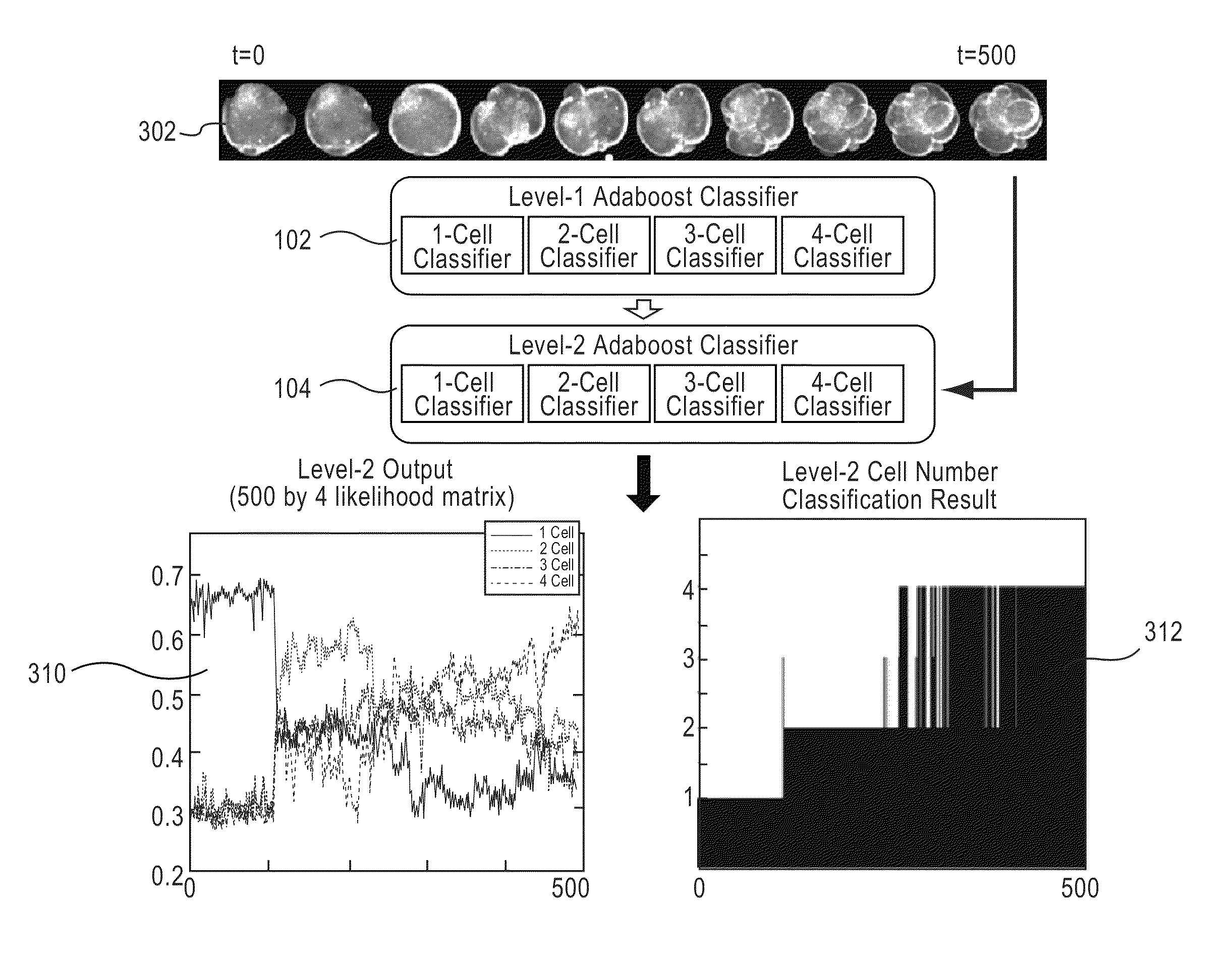
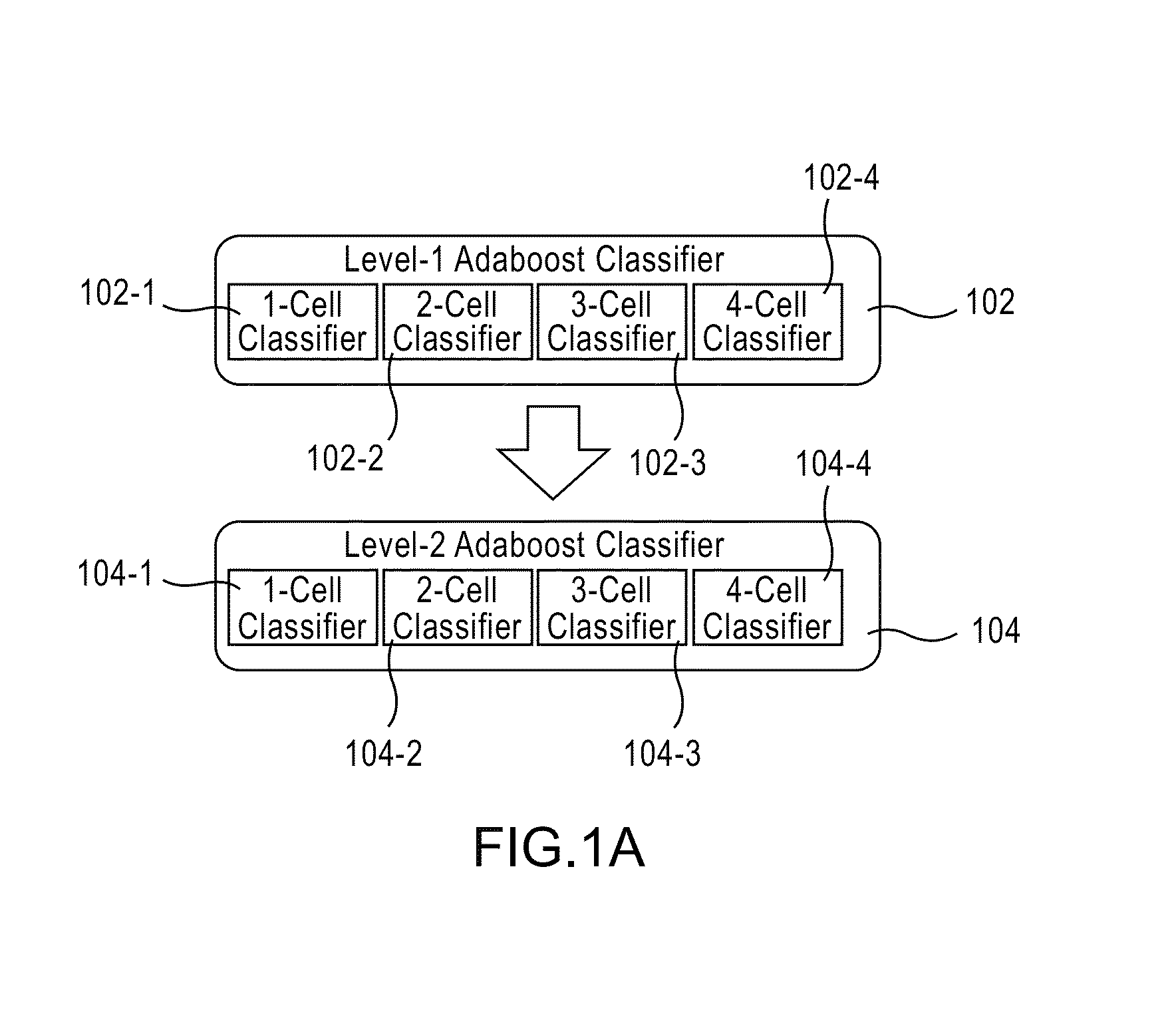
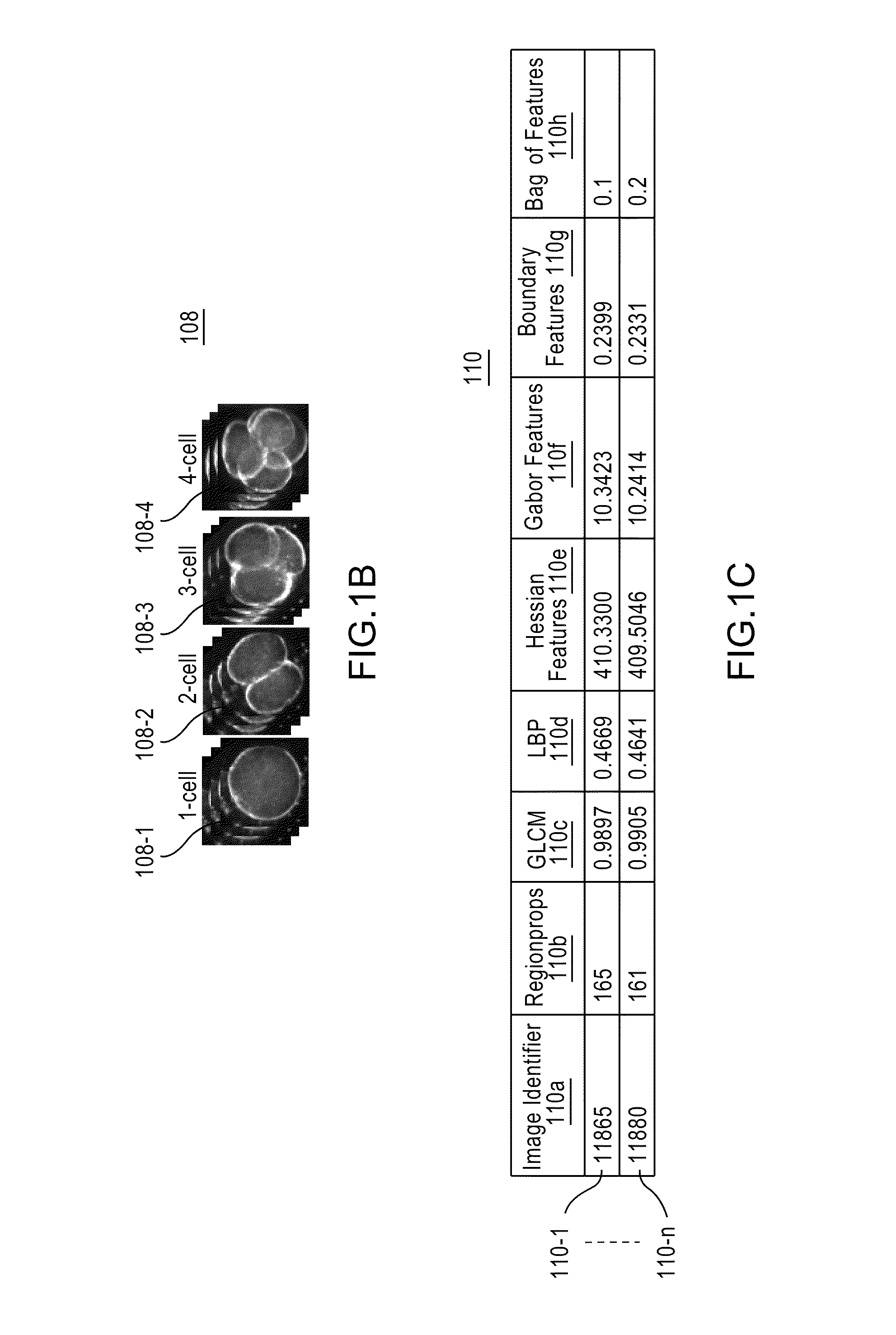
Apparatus, method, and system for image-based human embryo cell classification
Apparatuses, methods, and systems for automated cell classification, embryo ranking, and / or embryo categorization are provided. An apparatus includes a classification module configured to apply classifiers to images of one or more cells to determine, for each image, a classification probability associated with each classifier. Each classifier is associated with a distinct first number of cells, and is configured to determine the classification probability for each image based on cell features including one or more machine learned cell features. The classification probability indicates an estimated likelihood that the distinct first number of cells is shown in each image. The classification module is further configured to classify each image as showing a second number of cells based on the distinct first number of cells and the classification probabilities associated therewith. The classification module is implemented in at least one of a memory or a processing device.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
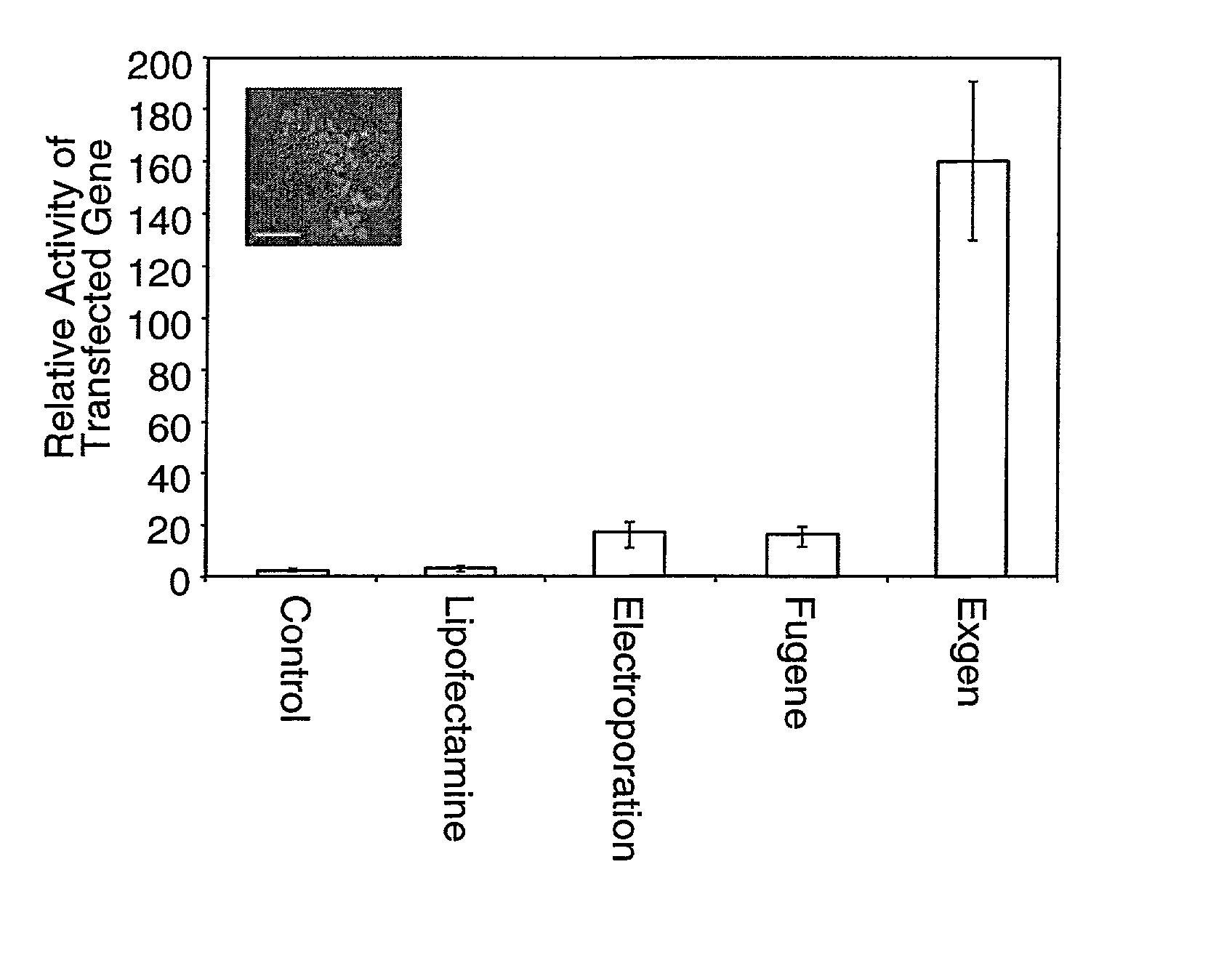
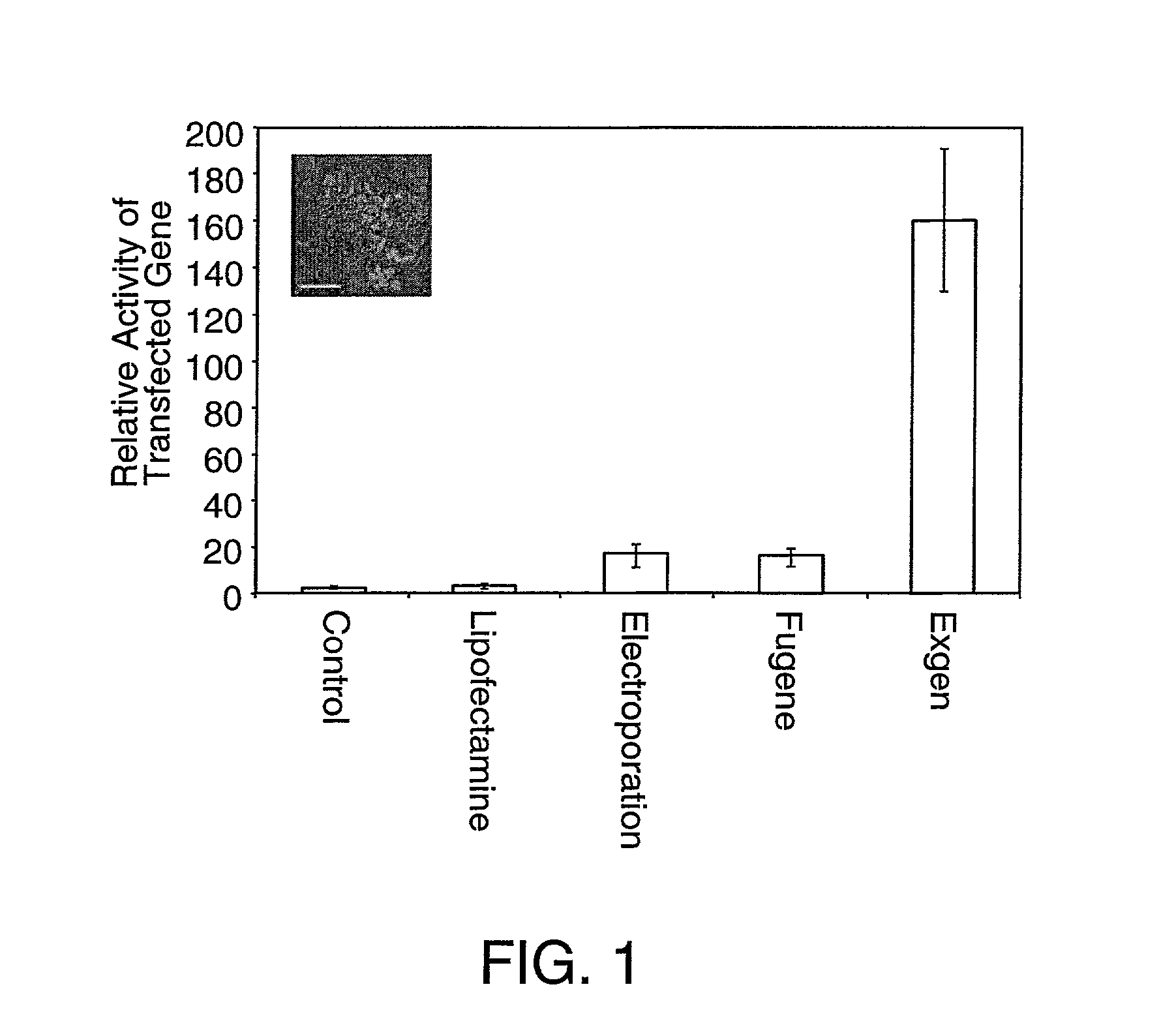
Transfection of human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20020127715A1Nervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsGene Expression AlterationGenetic Materials
Methods are provided for altering gene expression in a population of human embryonic cells that include introducing a gene expression altering sequence into cells the cells retaining their pluripotent character, for purifying pluripotent embryonic stem cells from a heterogeneous population of cells, and for treating a human suffering from a deficiency of a selected cell type. Reagent cell populations are further provided for supplying material for transplantation consisting essentially of pluripotent human embryonic stem cells modified by foreign genetic material.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Non-invasive prenatal genetic diagnosis using transcervical cells
InactiveUS20050181429A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPrenatal diagnosisStaining
A non-invasive, risk-free method of prenatal diagnosis is provided. According to the method of the present invention transcervical specimens are subjected to trophoblast-specific immuno-staining followed by FISH, PRINS, Q-FISH and / or MCB analyses and / or other DNA-based genetic analysis in order to determine fetal gender and / or identify chromosomal and / or DNA abnormalities in a fetus. Also provided is a method of in situ chromosomal, DNA and / or RNA analysis of a prestained specimen by incubating the prestained specimen in ammonium hydroxide. Also provided is a method of identifying embryonic cells according to a nucleus / cytoplasm ratio of at least 1:1 and the presence of at least variably condensed chromatin.
Owner:MONALIZA MEDICAL
Immunomodulatory Properties of Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells and Uses Thereof
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Imaging and evaluating embryos, oocytes, and stem cells
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Chimeric Avian-Based Screening System Containing Mammalian Grafts
ActiveUS20090064349A1The process is convenient and fastConvenient and efficient systemCompound screeningVirusesMammalModel system
The present invention relates to animal model systems comprising a chimera between an avian embryo and a mammalian organism. Specifically, chimeric model systems comprising normal, diseased or genetically transformed mammalian cells and tissues transplanted into avian embryos, and uses thereof for in vivo testing of drugs and therapeutic modalities are disclosed.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
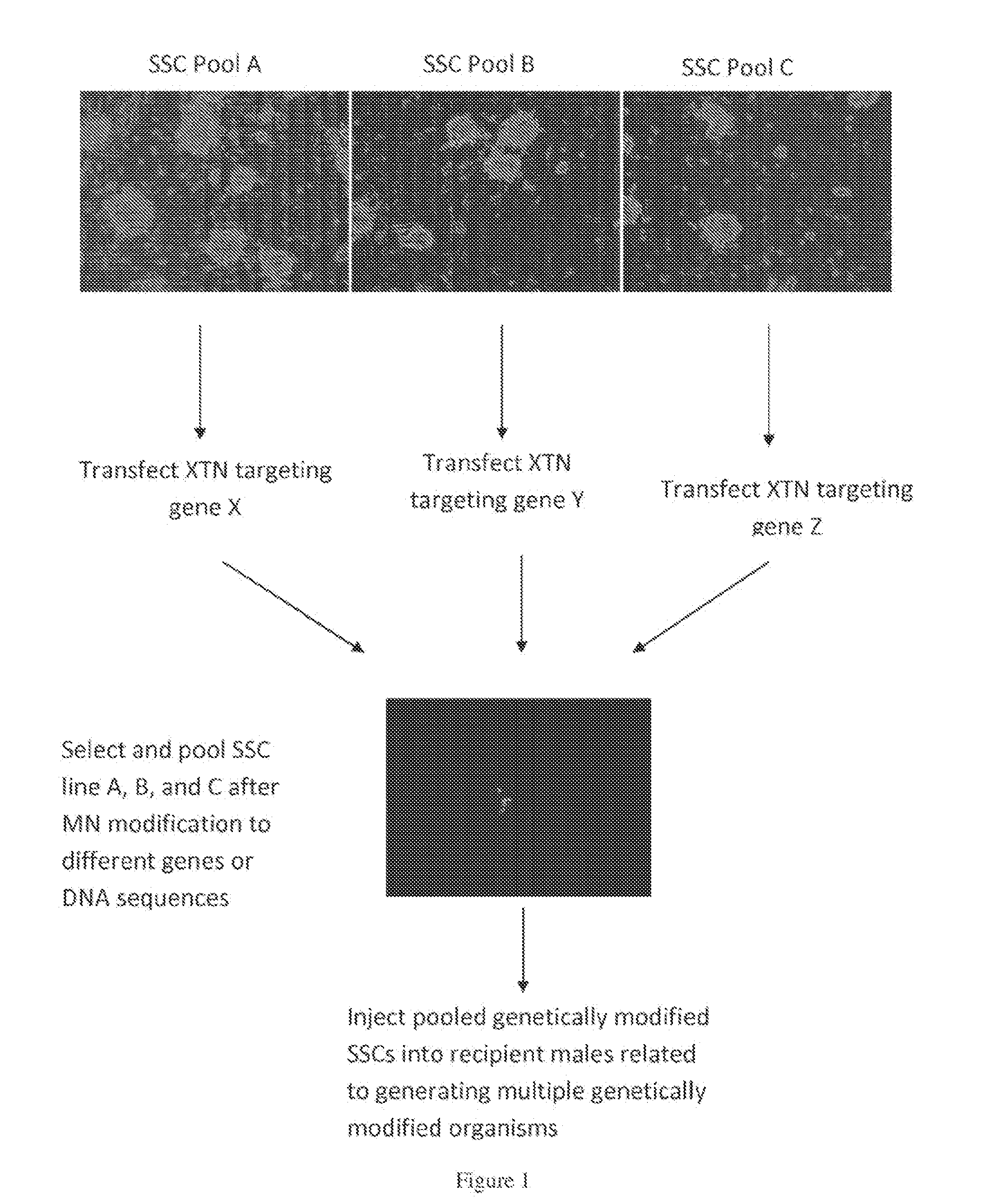
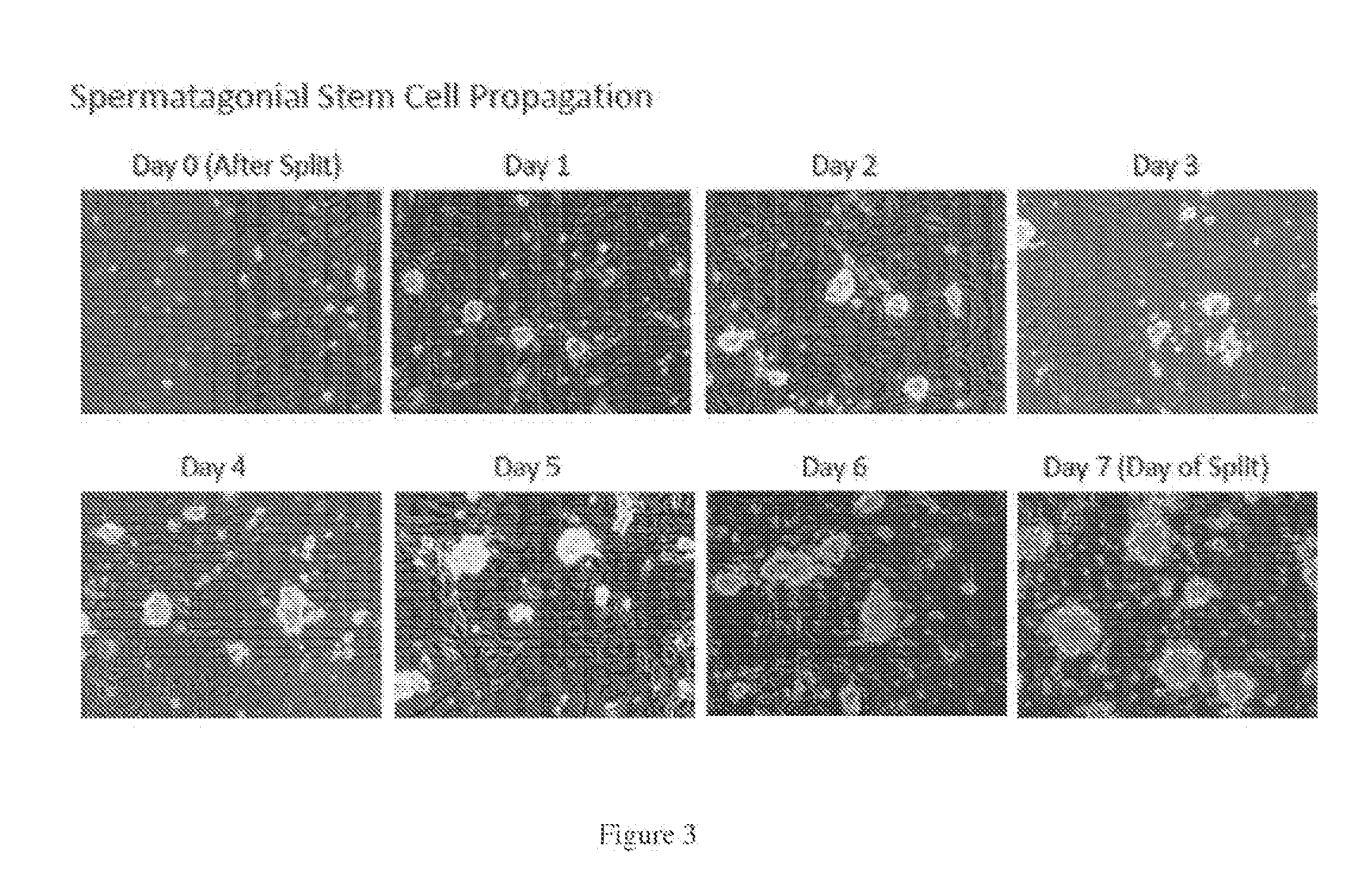
Methods for site-specific genetic modification in stem cells using xanthomonas tal nucleases (XTN) for the creation of model organisms
InactiveUS20140201858A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousXanthomonas campestris
The invention relates to organisms and compositions comprising one or more stem cells or one or more embryos, wherein the one or more stem cells or one or more embryos comprise one or more of the following mutations: (i) a deletion mutation; (ii) a knockout mutation; and / or (iii) an addition of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence; wherein the one or more mutations of (i), (ii), and / or (iii) are site-specific mutations caused by a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease (XTN). The invention also relates to method of mutating an embryo, iPS cell, stem cell, or more particularly a spermatogonial stem cell by exposing the nucleic acid sequence contained within such embryos or cell with a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease.
Owner:TRANSPOSAGEN BIOPHARM +1
Selection of embryo of test tube baby through sequencing by single cell genome of polar body or embryo
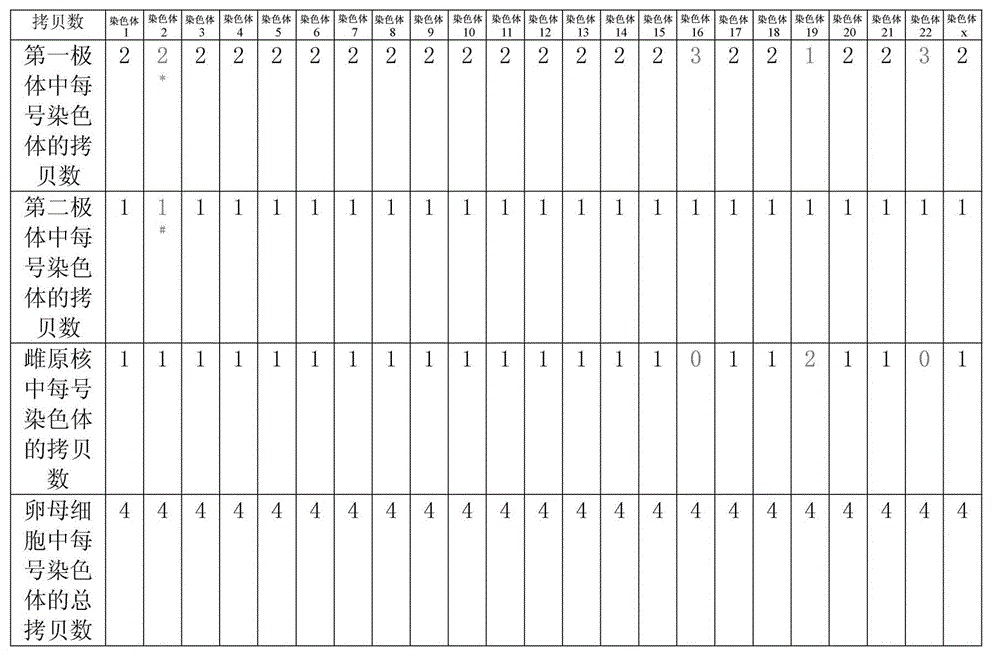
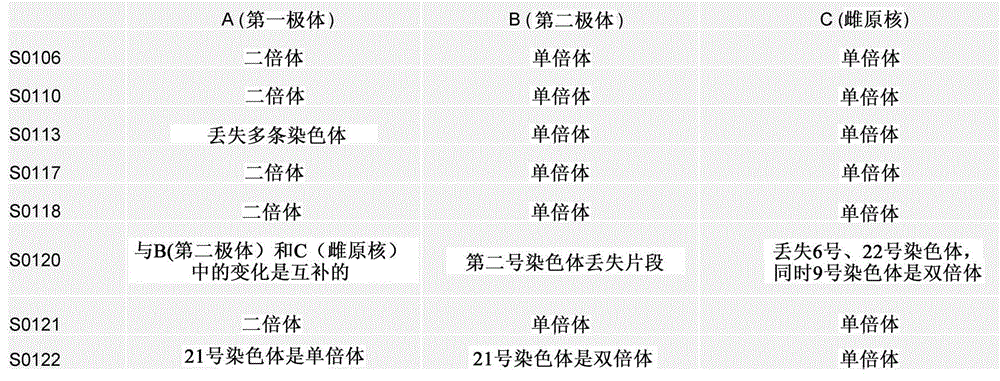
Disclosed is a method for using a first polar body and a second polar body as well as a single-cell embryo to carry out whole-genome non-exponential amplification and high-throughput genome sequencing, so as to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis for genetic disease and testing for pathogenic genes causing repeated miscarriages. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining oocytes and embryos, and carrying out separation and genome amplification of first and second polar bodies and single-cell embryos; (2) establishing a genome sequencing library and sequencing, and carrying out bioinformatic analysis of the genome to obtain a gene spectrum and information concerning the number of copies of chromosomes and fragments thereof; (3) determining the chromosome ploidy of the polar bodies and embryos as well as information concerning defects, replication and point mutation in the chromosome fragments; (4) selecting normal or suitable embryos for implantation.
Owner:HARVARD UNIV +2
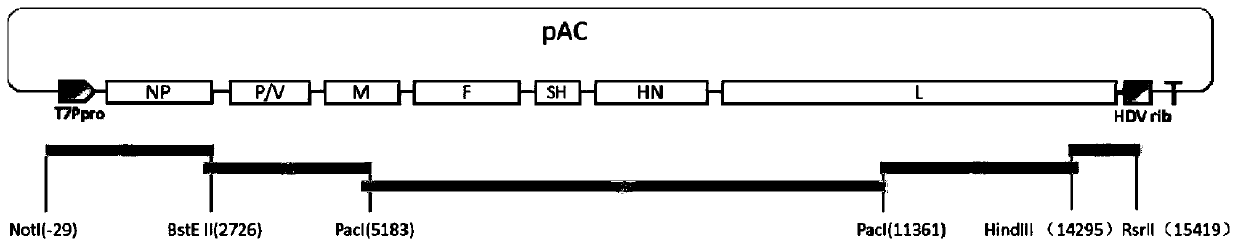
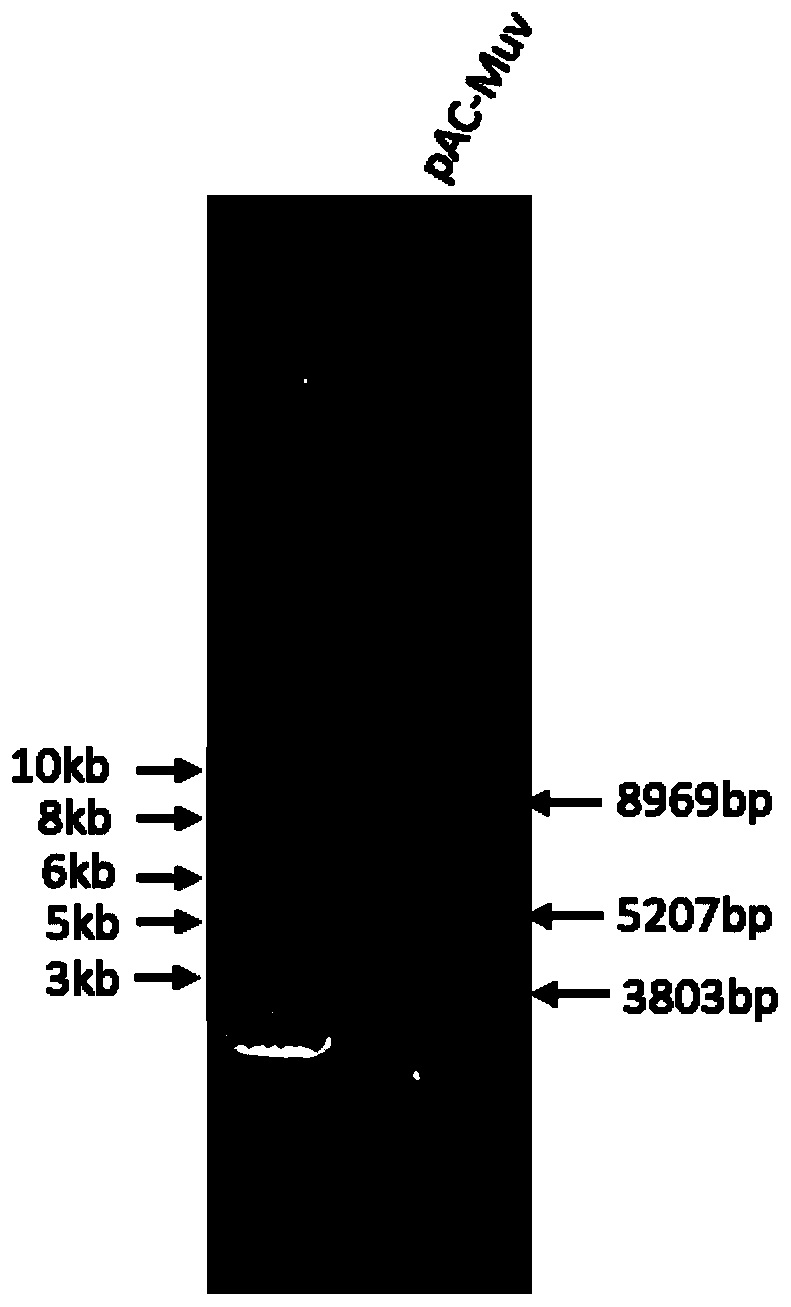
F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain and the attenuated strain is a mumps virus QS-F-SH2 with an accession number of CCTCC NO: V201950. The invention also provides a vaccine composition containing the F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as an active ingredient and a preparation method thereof. The mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain disclosed by the invention can match the F type mumps virus predominantly popular in China, and the level of the mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain is equivalent to that of the current vaccine strain in the aspects of growth characteristics, immunogenicity, neurotoxicity and the like.In addition, the mumps virus genetic engineering attenuated strain screened by the invention can be stably produced in chick embryo cells, and the safety is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING CELL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Method for pig in-vitro fertilization and embryo transplantation
The invention discloses a method for pig in-vitro fertilization and embryo transplantation, which comprises the following steps: oocyte preparation; sperm capacitation; adjustment of sperm concentration through adding sperm receiving fluid and capacitation through placing the adjusted mixture into an incubator; in-vitro fertilization and in-vitro oosperm culture; and embryo transplantation which adopts an embryo transplantation tube for transplantation. The method for pig in-vitro fertilization and embryo transplantation provided by the invention can be operated simply, the in-vitro fertilization and embryo transplantation can be realized without surgery, no damage can be caused to the pig, the success rate is high, the cost is low, and the method has great significance for promotion of pig in-vitro fertilization, pig cloning and transgenic embryo research and production.
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD +1
Infectious bursal virus and method for propagating bursal virus with chicken embryo cell line and bioreactor to prepare inactivated vaccine and combined vaccine
InactiveCN102260649AImprove adaptabilityImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesTGE VACCINEEmbryo cell
The invention relates to an infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) HQ strain CGMCC NO.4935 and a preparation method of inactivated vaccines and combined vaccines for infectious bursal disease (IBD). The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out chain amplification on cell seeds; (2) adding cell growth-promoting liquid into a sterilized bioreactor, and inoculating cells for preparing vaccines for suspension culture; (3) replacing maintenance liquid containing an IBDV strain when cells are of the maximum density, and continuing to culture; (4) collecting viruses in time, and measuring virus titer; and (5) inactivating virus liquid, and preparing inactivated vaccines and combined vaccines thereof for the IBD according to different proportions. The method provided by the invention increases the cell density, improves the virus titer, improves the vaccine titer, reduces the side reaction, reduces the labor intensity, lowers the production cost, improves the controllability of production processes, and ensures the uniformity and stability of product quality. The produced inactivated vaccines and combined vaccines thereof for the IBD have the advantagesof good safety and high immune efficiency and have a complete protective effect on the IBDV attack.
Owner:POULTRY DISEASE RES INST OF HENAN AGRI UNIV
Preparation method and application of tissue slice for observing temporal-spatial distribution of early embryo development in vivo
InactiveCN102944456AObservation continuityEasy to observe continuityPreparing sample for investigationCooking & bakingFluorescence
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a tissue slice for observing temporal-spatial distribution of early embryo development in vivo. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 4% paraformaldehyde fixing, upward gradient ethanol dehydration, wax dipping, embedding, serial section, baking, dewaxing and downward gradient ethanol rehydration are performed in sequence on oviducts or uterine tissues which contain mice embryos in every period, and finally, after haematoxylin-eosin staining is performed on the tissues in the slice, neutral gum is used for sealing the slice, or after immunofluorescence histochemical staining is performed on the slice, a fluorescence resistant quenching sealing agent is used for sealing the slice. The tissue slice disclosed by the invention can be used for manufacturing a map of early mice embryo development and detecting the expression of Crb3 in the mice embryos in every period of development in vivo. The preparation method has the advantages that positions of all organs in the embryos can be relatively fixed, so that the position change of embryo cells in a genital tract and the continuity of embryo development can be conveniently observed, the structure is clear, and the tissue slice is convenient to store.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Male trait inducer and induction method for pelodiscus sinensis in embryonic periods
ActiveCN102988986AIncrease humidityResidue reductionOrganic active ingredientsSexual disorderAdjuvantMale trait
The invention relates to a male trait induction method for pelodiscus sinensis in embryonic periods. The male trait inducer is characterized in that through dissolving an aromatase inhibitor and an adjuvant into alcohol with the purity of 92-98%, the inducer with an aromatase inhibitor concentration of 50-150 mu g / mu l and an adjuvant concentration of 50-150 mu g / mu l is obtained; and the adjuvant is selected from testosterone, methyltestosterone or testosterone propionate. According to the induction method provided by the invention, the male induction rate can be more than 95% just through spraying the inducer two times at the sex determination key time point in embryonic development, and meanwhile, the normal development and low drug residues of pelodiscus sinensis gonads are ensured; and the induction method provided by the invention is easy to operate, low in cost, and remarkable in economic benefit, thereby being a sex control technology which is worthy of popularization in the existing pelodiscus sinensis breeding.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Apparatus, method, and system for image-based human embryo cell classification
Apparatuses, methods, and systems for automated cell classification, embryo ranking, and / or embryo categorization are provided. An apparatus includes a classification module configured to apply classifiers to images of one or more cells to determine, for each image, a classification probability associated with each classifier. Each classifier is associated with a distinct first number of cells, and is configured to determine the classification probability for each image based on cell features including one or more machine learned cell features. The classification probability indicates an estimated likelihood that the distinct first number of cells is shown in each image. The classification module is further configured to classify each image as showing a second number of cells based on the distinct first number of cells and the classification probabilities associated therewith. The classification module is implemented in at least one of a memory or a processing device.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
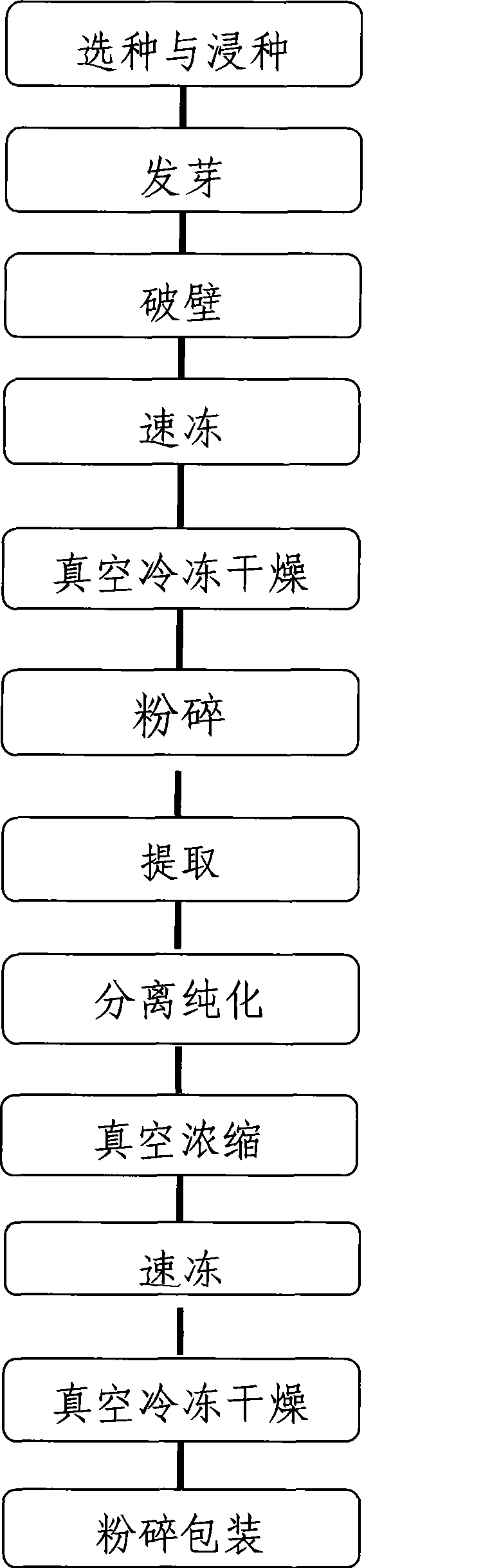
Preparation method of buckwheat germ rutin capsule
InactiveCN101385782AIncreased rutin contentPromote absorptionSugar derivativesImmunological disordersPolygonum fagopyrumAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for preparing a buckwheat germ rutin capsule. The method comprises the following steps: a. seed selecting and seed soaking; b. germinating; c. pulping; d. quick freezing; e. vacuum freeze drying; f. crushing and packaging; g. extracting; h. separating and purifying; h. vacuum concentration; i. quick freezing; k. vacuum freeze drying; and l. crushing and packaging. In the invention, the raw material buckwheat sprouts until the whole embryo cells thereof break walls and is micronized, and then is made into buckwheat germ powder by extracting with a solvent, purifying by macroporous adsorbing resin, quick freezing, vacuum freeze drying, and finally refined into the buckwheat germ rutin capsule. The buckwheat germ rutin capsule has the faint scent of the buckwheat germ, and the contents of the flavonoid and mineral substance in the capsule amino acid, rutin and the like are higher than those of the common buckwheat seed powder, so that the buckwheat germ rutin capsule has enhanced activities of nutrient components and is easily absorbed by human body.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
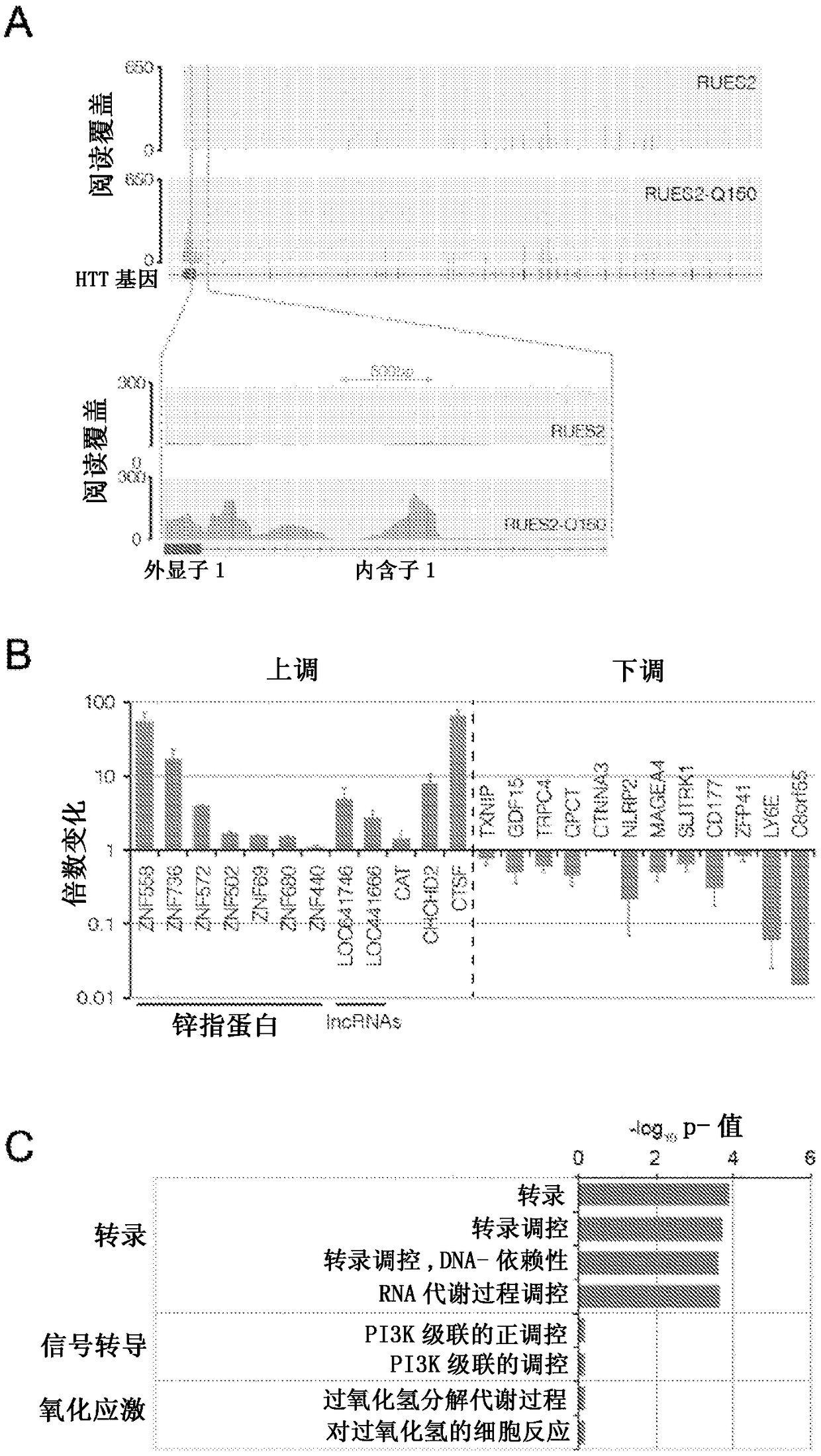
Embryonic cell-based therapeutic candidate screening systems, models for huntington's disease and uses thereof
Compositions and methods disclosed concern an isogenic population of in vitro human embryonic stem cells comprising a disease form of the Huntingtin gene (HTT) at the endogenous HTT gene locus in thegenome of the cell; wherein the disease form of the HTT gene comprises a polyQ repeat of at least 40 glutamines at the N-terminus of the Huntingtin protein (HTT). The cell lines of the disclosure comprise genetically-defined alterations made in the endogenous HTT gene that recapitulate Huntington's Disease in humans. Furthermore, the cell lines have isogenic controls that share a similar genetic background. Differentiating cell lines committed to a neuronal fate and fully differentiated cell lines are also provided and they also display phenotypic abnormalities associated with the length of the polyQ repeat of the HTT gene. These cell lines are used as screening tools in drug discovery and development to identify substances that fully or partially revert these phenotype abnormalities.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
In-vitro maturation culture method for oocyte of mouse and method for establishing parthenogenetic embryonic stem cell line
InactiveCN101735978ASimple ingredientsLow costMicroorganism based processesEmbryonic cellsStem cell lineBiological activation
The invention discloses an in-vitro maturation culture method for an oocyte mouse and a method for establishing a parthenogenetic embryonic stem cell line. In the in-vitro maturation culture method, an immature oocyte is cultured in a basic culture solution in which the HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and PMSG (pregnant mare serum gonadotropin) are added, and the maturation rate of the oocyte can reach more than 83 percent. In the method for establishing a parthenogenetic embryonic stem cell line, the parthenogenetic activation culture development is carried out on the mouse oocyte after in-vitro maturation culture to obtain the embryonic stem cell line; a hepatocyte obtained by the method has no immunogenicity, is simultaneously equivalent to a stem cell derived from a fertilized embryo on totipotency and has guiding significance for utilizing in-vitro maturation of the immature oocyte of a human and separating parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells. Aiming at the current conditionsof human ovum donation shortage, great discarding of clinical immature oocytes by an assisted reproductive technology, and the like, the two methods are combined to lay the foundation for developing and utilizing the in-vitro maturation culture of the immature oocyte of people and further researching the parthenogenetic embryo by utilizing an in-vitro mature ovum and separating the embryonic stemcells.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Cloning using donor nuclei from differentiated fetal and adult cells
InactiveUS20020010949A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orBiocideNervous disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
Vessel for vitrification-cryopreservation in liquid, kit provided with vessel and tube for receiving same, and method for vitrification-cryopreservation in liquid
InactiveUS20190141986A1Easy to operateReduce harmAnalysis material containersBiological substance pretreatmentsVitrificationEngineering
A vessel is provided for cryopreservation by vitrification for use in the cryopreservation by vitrification of cells or embryos. The cells or embryos are retained by a retaining part of the vessel and has recesses on the retaining part to store the cells or embryos therein. The vessel for cryopreservation by vitrification in a liquid cryogen has holes in the walls which make up the recesses which do not allow the cells or embryos to pass through the walls, but which do allow vitrification solution to pass therethrough. A kit is also provided which includes the vessel and a tube for storing the vessel. A method for cryopreservation by vitrification in a liquid cryogen is also provided.
Owner:INUI MEDICAL LTD
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I polypeptide and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Method Of Producing Haploid And Doubled Haploid Plant Embryos, And Embryos, Plants, Progeny, Cells, Tissues And Seeds Obtainable By Method
The invention relates to a method for producing haploid plant embryos, comprising providing microspores or pollen that comprise cell division inducing molecules; pollinating an embryo sac cell, in particular an egg cell, of the plant of which the haploid embryo is to be made with the microspores or pollen; allowing the microspores or pollen to discharge the cell division inducing molecules in or in the vicinity of the embryo sac cell, in particular the egg cell, to trigger division thereof to obtain a haploid plant embryo. When doubled haploid plant embryos are to be produced doubling of the chromosome number takes place at a certain stage after pollination, in particular during cell division or after obtaining the embryo. The invention further relates to the embryos thus obtained, plants regenerated therefrom and progeny thereof.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Method for preparing non-human mammal with iGb3S gene knockout and applications
The invention relates to the field of preparing gene knockout animal models, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a non-human mammal with iGb3S gene knockout and applications. The method includes: separating an iGb3S gene from genome DNA, amplifying through a long-chain RCR method to obtain a homologous arm, compositing with an antibiotic resistance gene to construct a targeting vector, transferring the targeting vector into an embryonic cell, injecting the recombinant embryonic cell into a surrogate animal embryo, transplanting the embryo into a pseudopregnancy animal, mating with an normal animal, subjecting the obtained chimera animals to genotype verification, screening the chimera animal with positive gene knockout and success gene knockout, further mating with wild type animals to obtain F1 heterozygotes, mating the F1 heterozygotes to obtain a homozygote animal with both two chromosomes being deleted, and establishing to obtain a gene knockout animal population.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
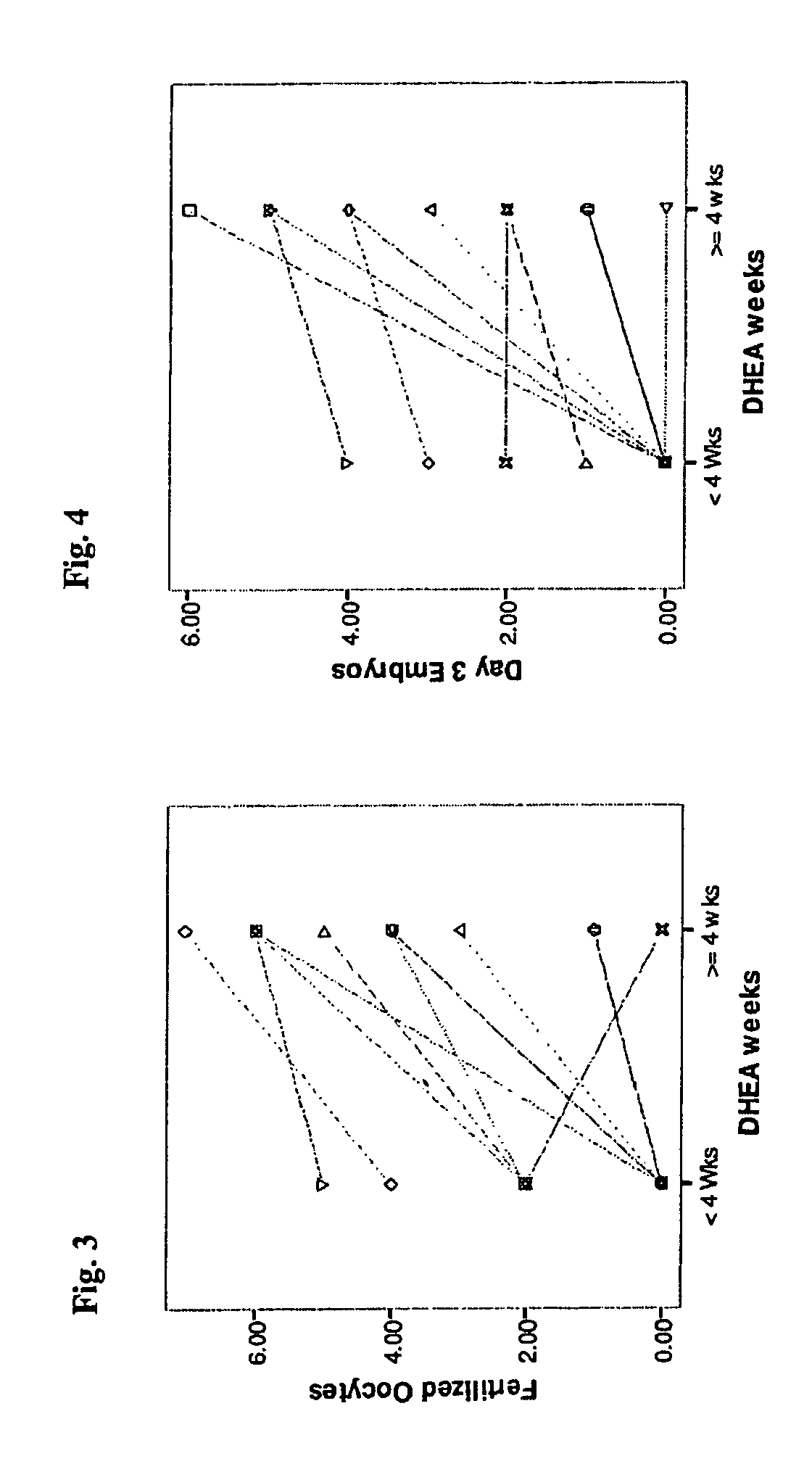
Method of improving cumulative embryo score and quantity of fertilized oocytes, increasing euploidy rate and of normalizing ovarian function using an androgen such as dehydroepiandrosterone
A method of improving cumulative embryo score may comprise administering an androgen to a human female, for example, DHEA, for at least about four consecutive months followed by harvesting and fertilizing oocytes and forming embryos. Between about 50 mg and about 100 mg of DHEA may be administered to a human female per day. Moreover, a method of increasing the quantity of fertilized oocytes in one cycle of in vitro fertilization may comprise administering an androgen to a human female for at least about four consecutive months, harvesting and fertilizing the oocytes. Furthermore, a method of increasing the quantity of day 3 embryos from one cycle of in vitro fertilization may comprise administering an androgen for at least about four consecutive months, harvesting and fertilizing the oocytes and forming day 3 embryos. A method of normalizing ovarian DHEA also may include administering an androgen for at least about four consecutive months. A method of increasing the euploidy rate in embryos may include administering an androgen for at least about four consecutive weeks.
Owner:AMERICAN INFERTILITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com