Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
219 results about "Maximum density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
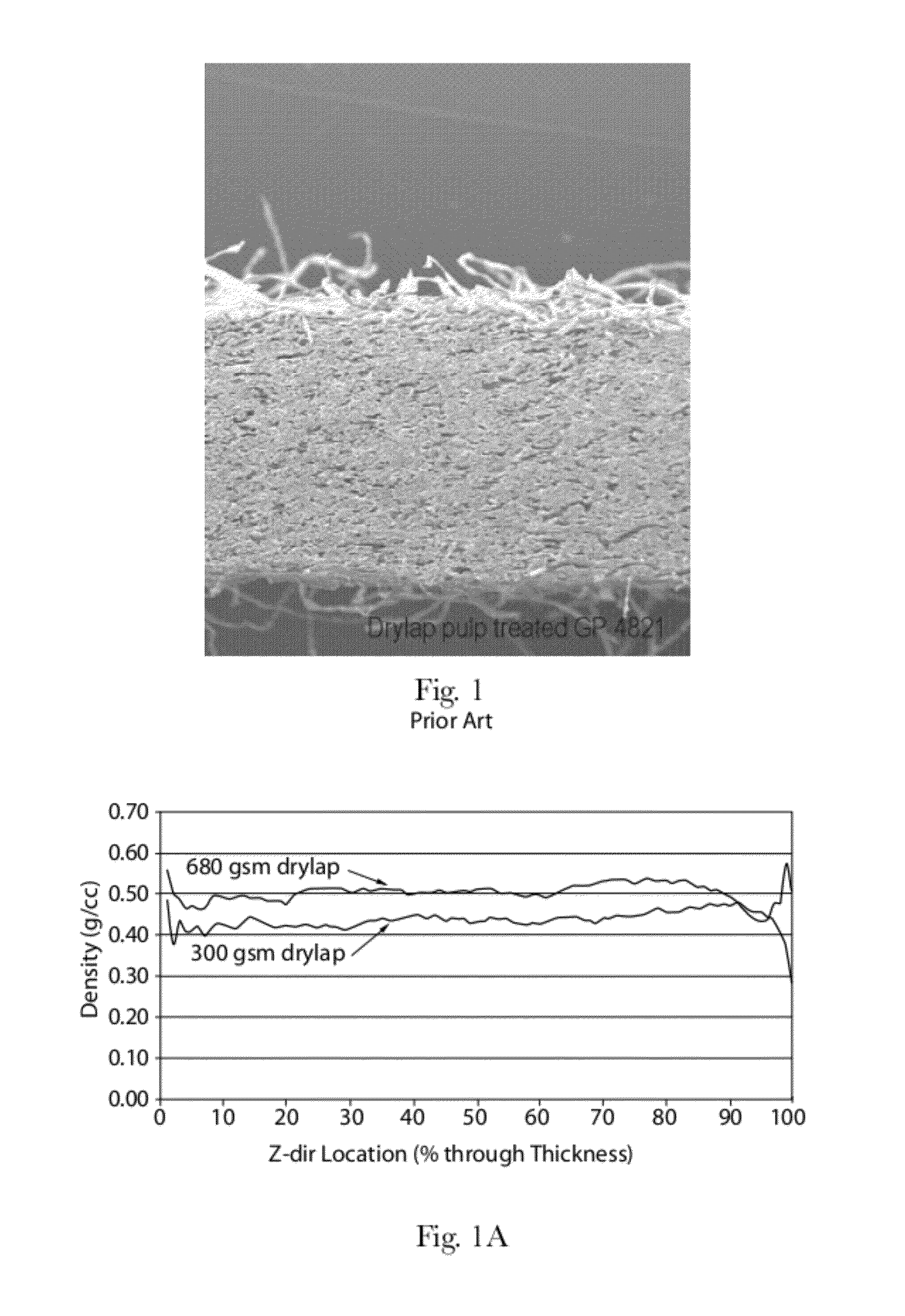
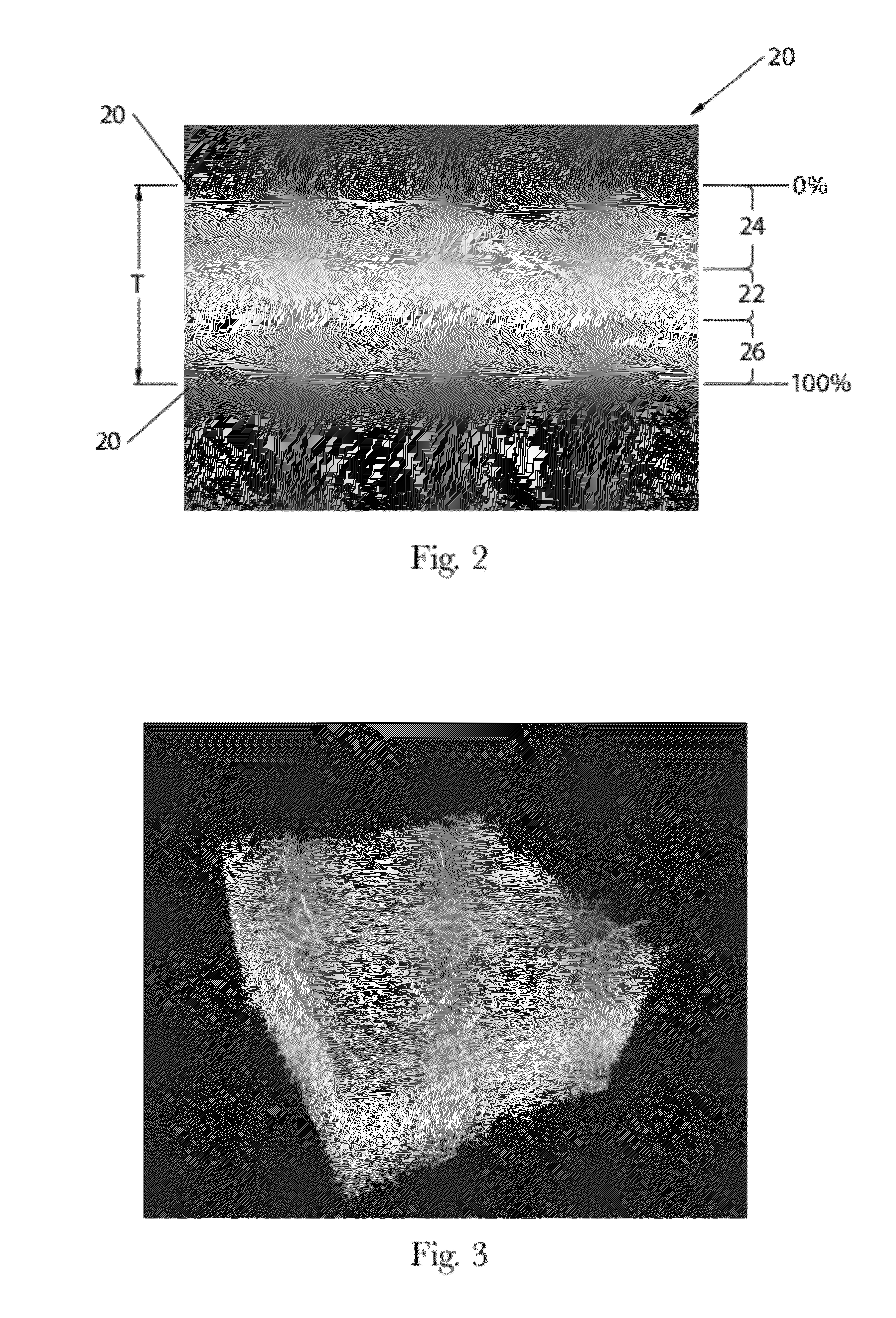
The maximum density of a substance is the highest attainable density of the substance under given conditions.
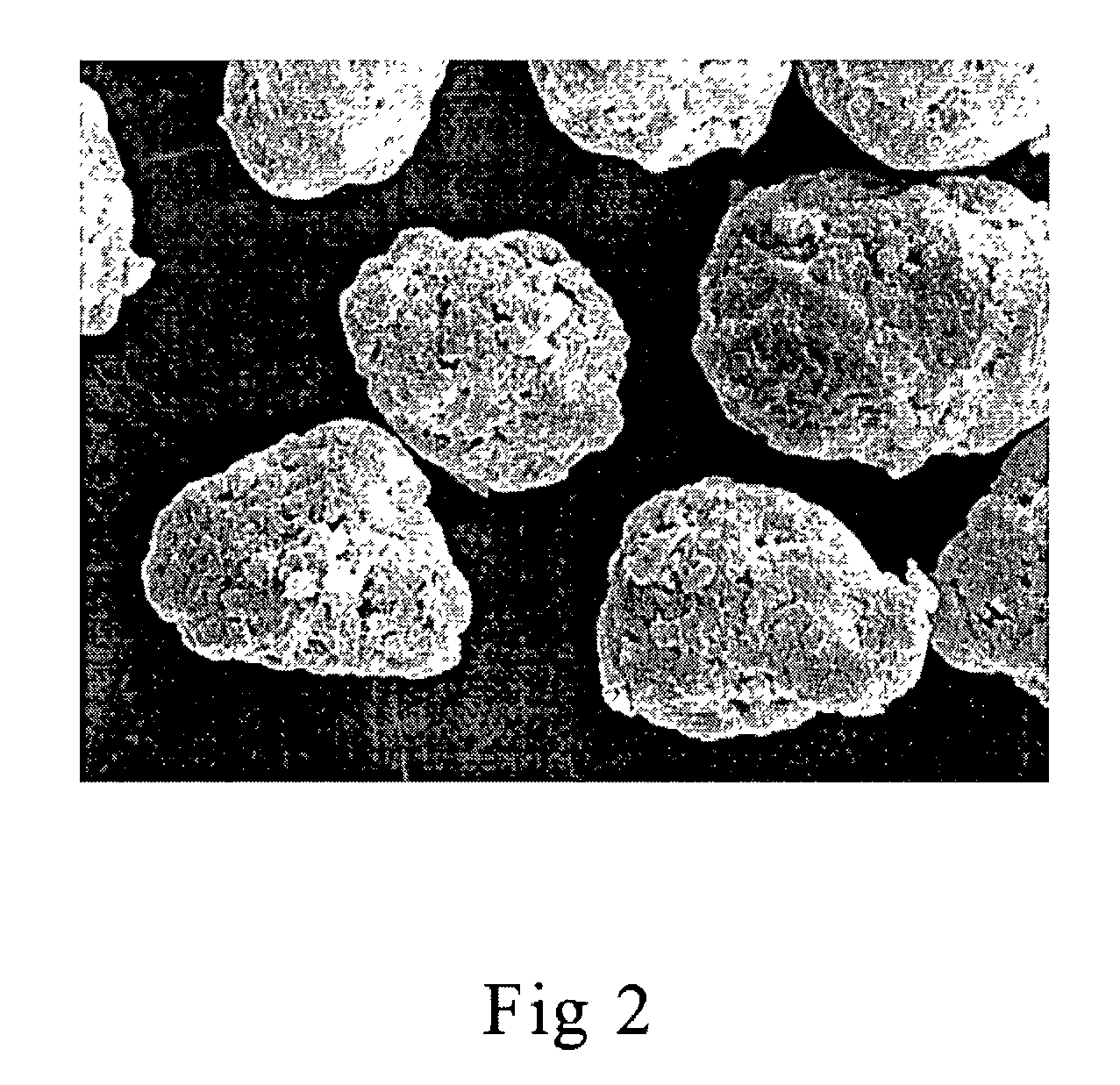
Gas porous polymer filter and methods of use
InactiveUS7112280B2Enhances bonding capabilityHigh densitySemi-permeable membranesIsotope separationPolymer scienceFiltration
The filtration device of the present invention relies on materials and methodologies that achieve the formation of a structural matrix that may later accommodate the addition of other adsorbent materials as opposed to merely binding adsorbent materials together through the use of compression and / or binder materials. The filter device of the present invention relies on (i) a unique method of processing to achieve maximum density of materials, (ii) a polymeric material having a distinct morphology and (iii) a very small micron diameter of the polymeric material to create uniformity. For example, in place of compression to increase density, the materials comprising the filtration device of the present invention are instead vibrated into a mold cavity. Thus, the methodology of the current invention optimizes how all of the materials comprising the filtration device fit together without compaction. The material being processed is vibrated as it is gradually poured into the mold. Once the mold cavity has been filled to a point where it will hold no more material, it is heated and then cooled. In place of an external binder, the structural material adheres to itself as it softens. This results in a tortuous path matrix of pores rather than an absolute pore barrier.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Liquid and gas porous plastic filter and methods of use
InactiveUS7112272B2Enhances bonding capabilityHigh densityMembrane filtersLoose filtering material filtersPolymer scienceFiltration
The filtration device of the present invention relies on materials and methodologies that achieve the formation of a structural matrix that may later accommodate the addition of other adsorbent materials as opposed to merely binding adsorbent materials together through the use of compression and / or binder materials. The filter device of the present invention relies on (i) a unique method of processing to achieve maximum density of materials, (ii) a polymeric material having a distinct morphology and (iii) a very small micron diameter of the polymeric material to create uniformity. For example, in place of compression to increase density, the materials comprising the filtration device of the present invention are instead vibrated into a mold cavity. Thus, the methodology of the current invention optimizes how all of the materials comprising the filtration device fit together without compaction. The material being processed is vibrated as it is gradually poured into the mold. Once the mold cavity has been filled to a point where it will hold no more material, it is heated and then cooled. In place of an external binder, the structural material adheres to itself as it softens. This results in a tortuous path matrix of pores rather than an absolute pore barrier.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
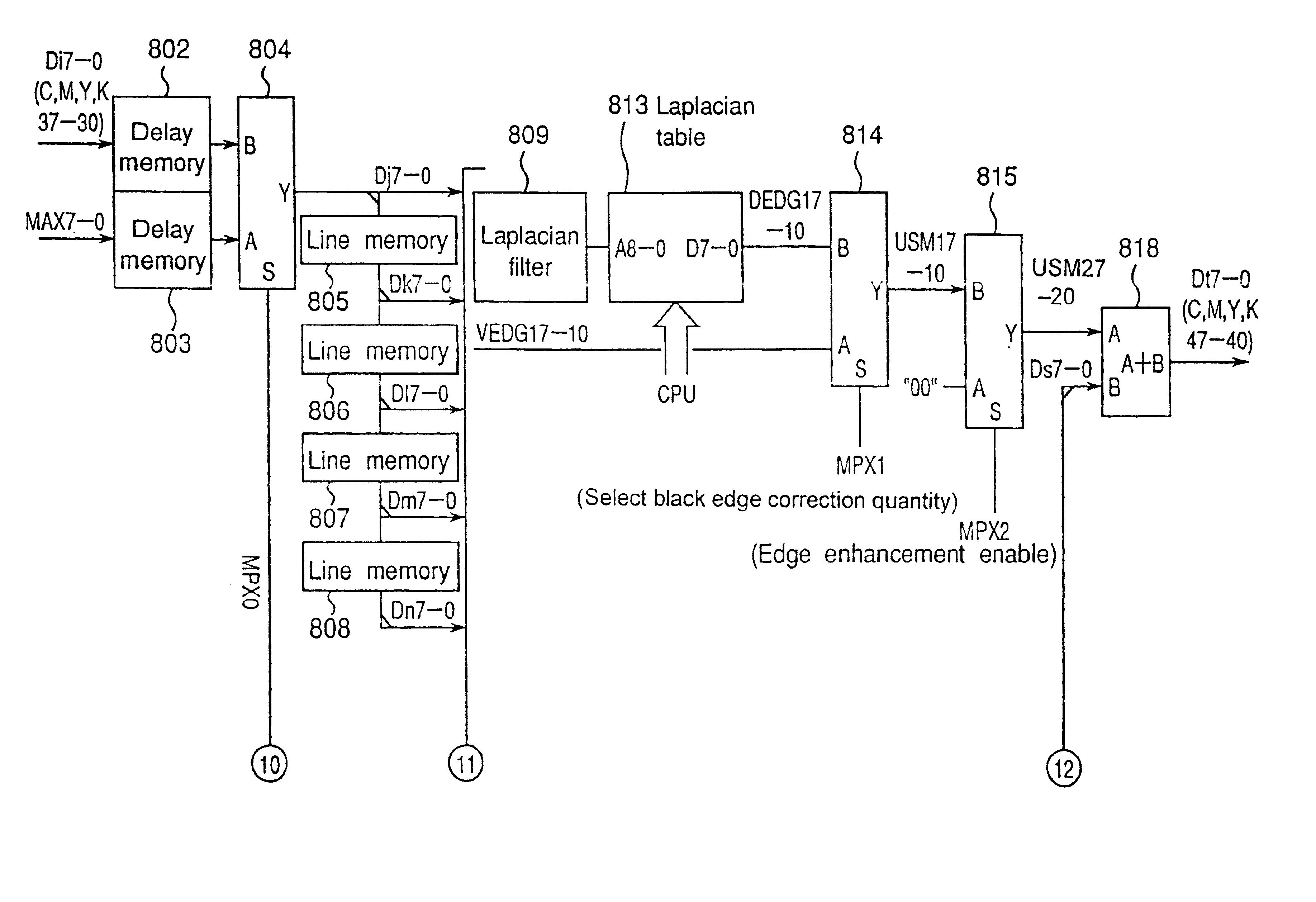
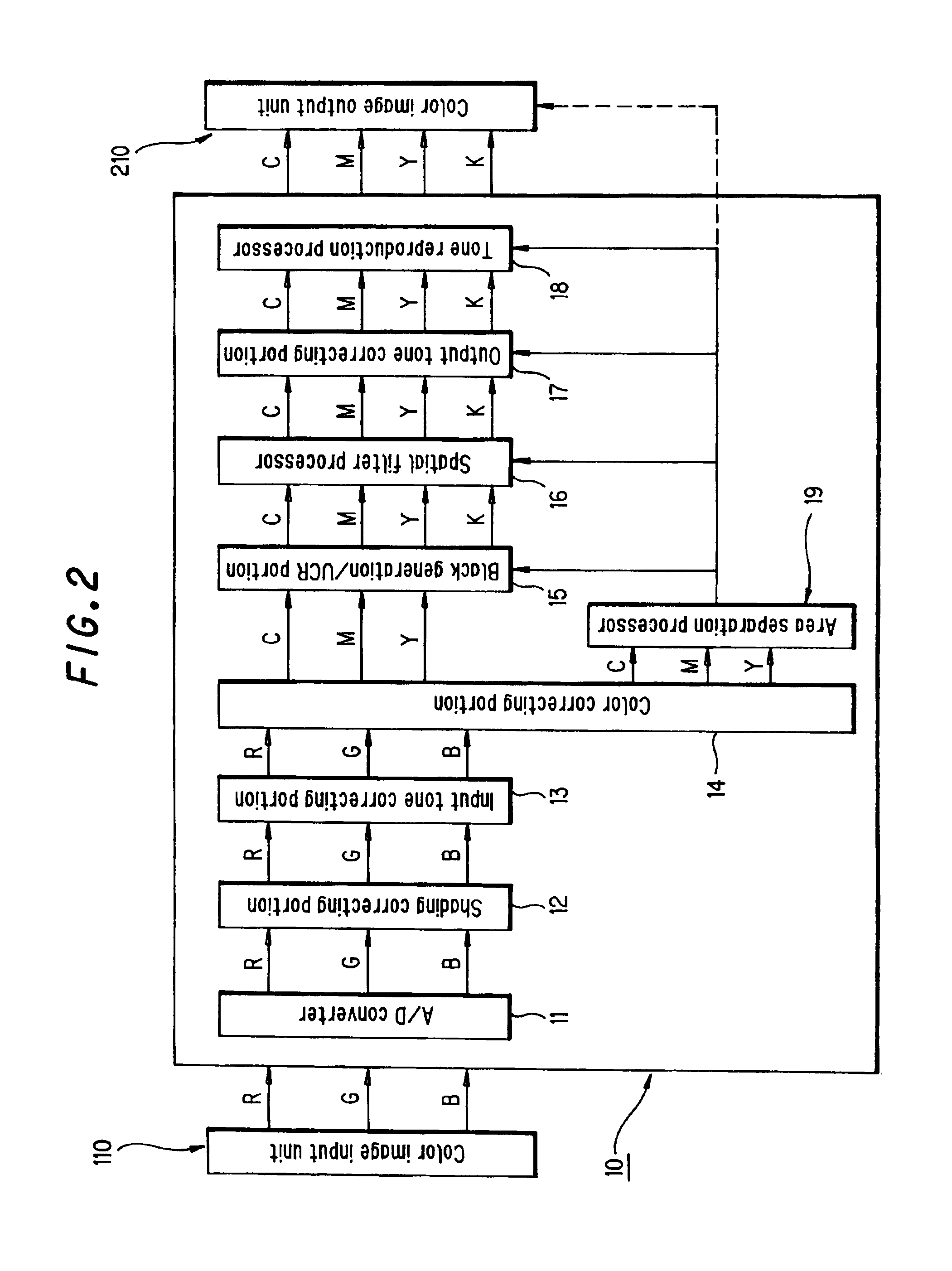
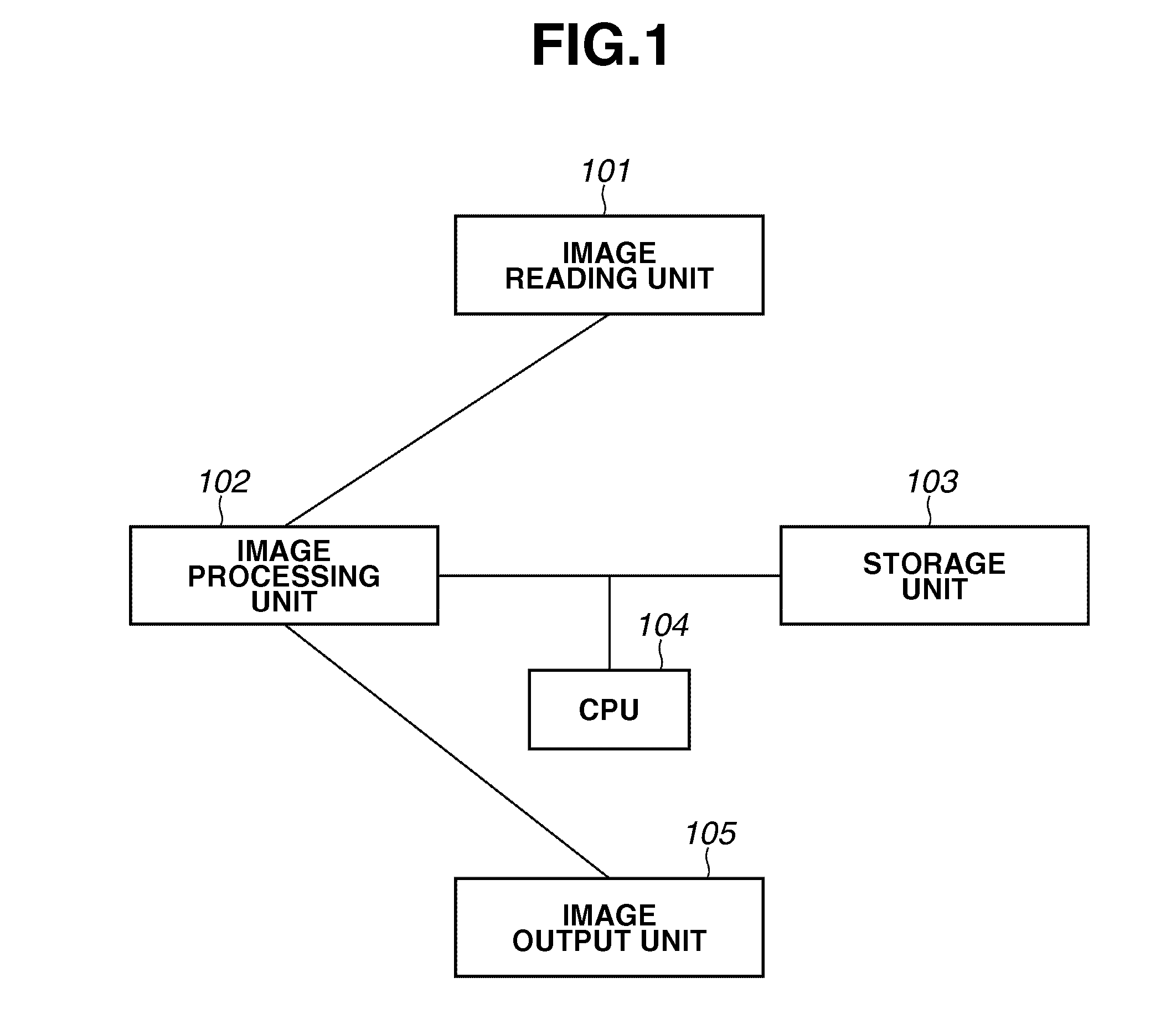
Method and apparatus for image processing, including processing for reproducing black character areas of color and monochromatic images
InactiveUS7079685B1Solve the lack of densityCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationColor imageImaging processing
In an image processor which converts color image data to image data of cyan, magenta, yellow and black necessary for forming an image, a black character edge is discriminated in R, G, B image data. The edge component in a black character area is deleted by narrowing on image data of cyan, magenta and yellow. Further, in a black character area, K data is replaced with maximum density data in the R, G, B data, and edge emphasis is performed on the substituted data. Then, reproducibility of a thin line portion in a character is improved largely.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
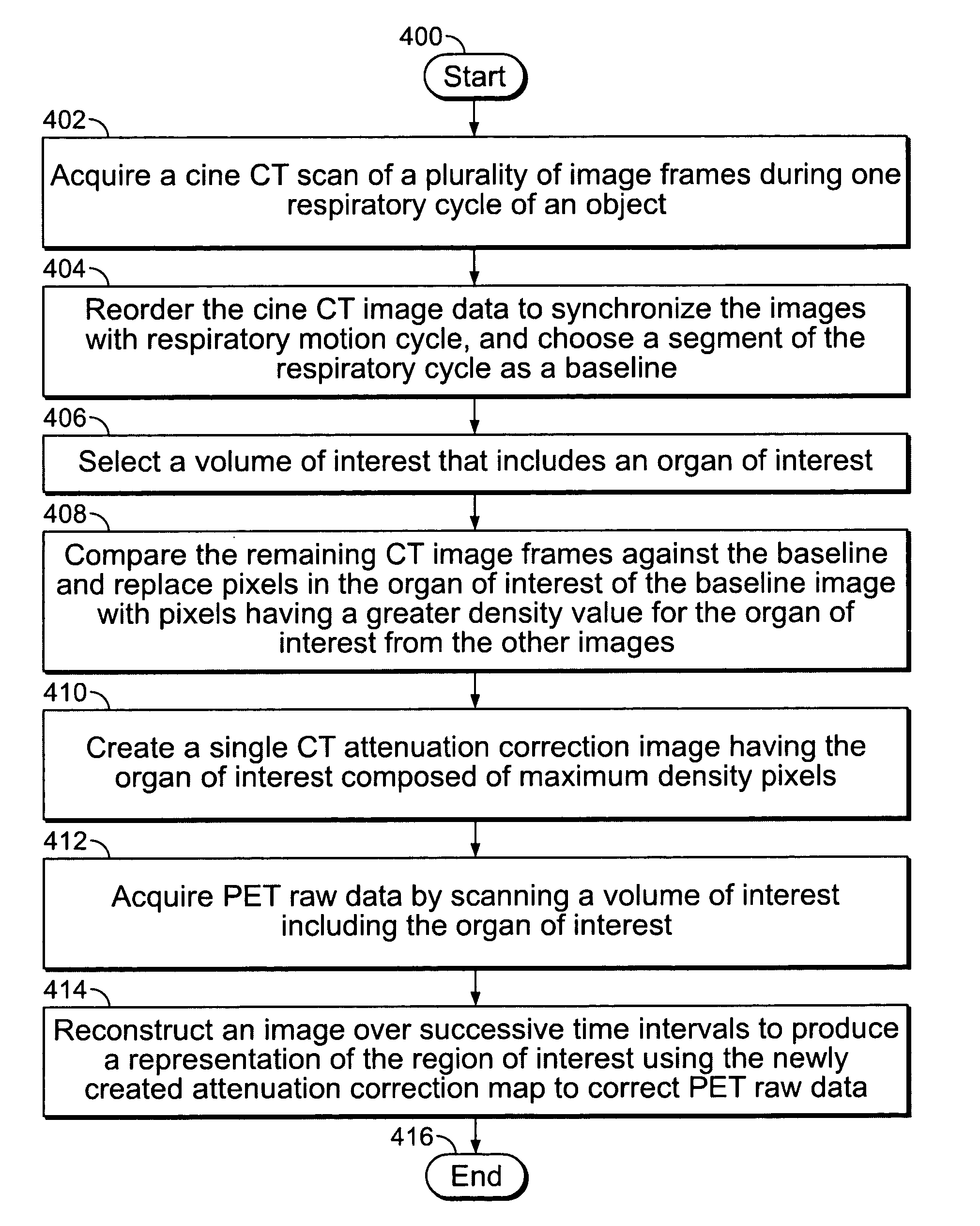
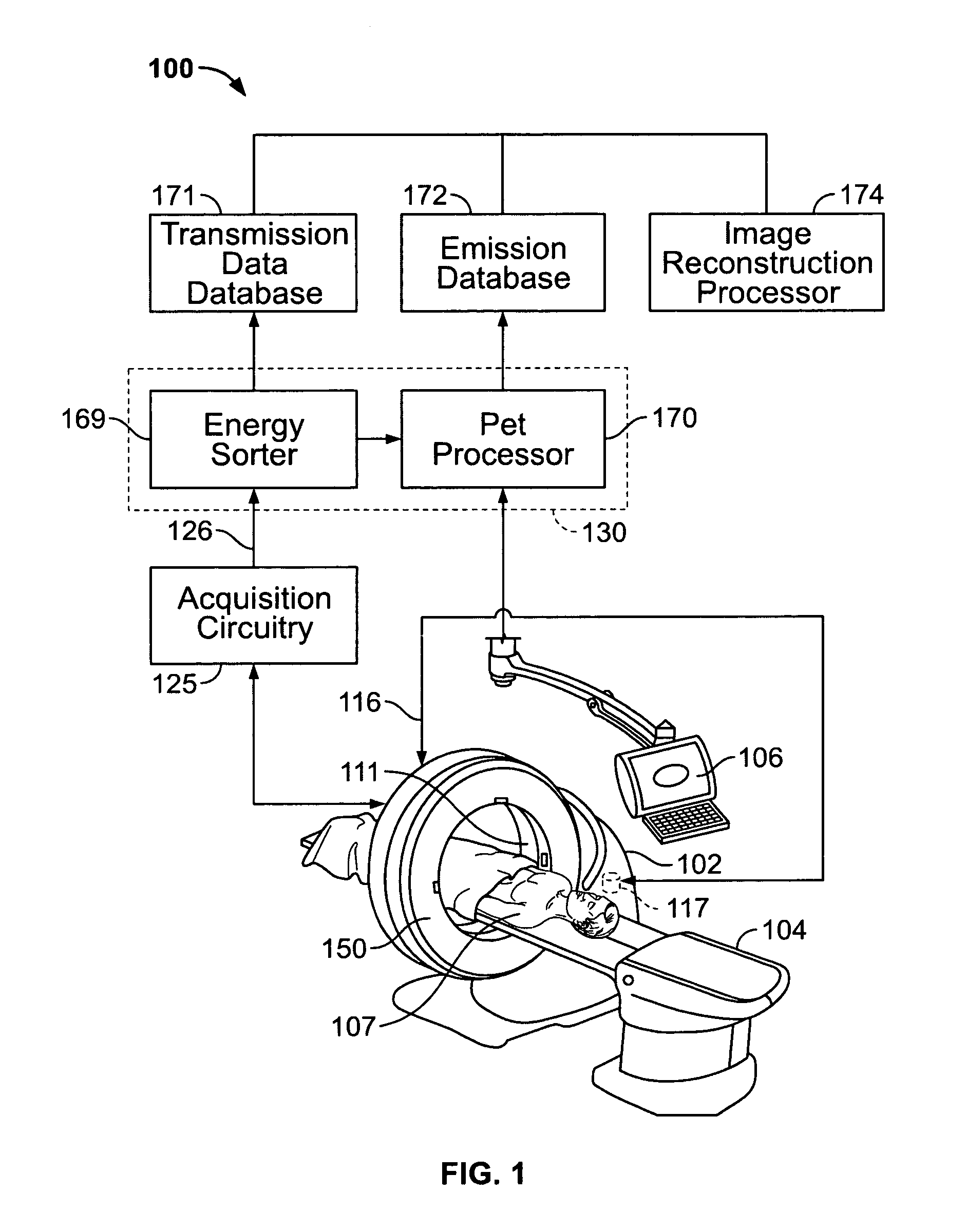
Methods and systems for attenuation correction in medical imaging
ActiveUS20080107229A1Area maximizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationTomography
Methods and systems for imaging a patient are provided. The method includes scanning a patient and acquiring a plurality of frames of cine computed tomography (CT) images during one complete respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, a method is provided that includes selecting an organ of interest in the cine CT data and selecting a value for each pixel in the organ of interest that represents the maximum density measurement. An attenuation corrected positron emission tomography (PET) image is constructed based on the maximization of the pixel intensity of the organ of interest in the CT attenuation correction map. Incorrect attenuation correction values for PET images can be avoided by utilizing the CT attenuation correction map.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Porous polymer water filter and methods of use in refrigeration
InactiveUS7169304B2Enhances bonding capabilityHigh densitySemi-permeable membranesLayered productsPolymer scienceFiltration
The filtration device of the present invention relies on materials and methodologies that achieve the formation of a structural matrix that may later accommodate the addition of other adsorbent materials as opposed to merely binding adsorbent materials together through the use of compression and / or binder materials. The filter device of the present invention relies on (i) a unique method of processing to achieve maximum density of materials, (ii) a polymeric material having a distinct morphology and (iii) a very small micron diameter of the polymeric material to create uniformity. For example, in place of compression to increase density, the materials comprising the filtration device of the present invention are instead vibrated into a mold cavity. Thus, the methodology of the current invention optimizes how all of the materials comprising the filtration device fit together without compaction. The material being processed is vibrated as it is gradually poured into the mold. Once the mold cavity has been filled to a point where it will hold no more material, it is heated and then cooled. In place of an external binder, the structural material adheres to itself as it softens. This results in a tortuous path matrix of pores rather than an absolute pore barrier.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Epitaxially coated semiconductor wafer and process for producing it
InactiveUS6899762B2Provide contaminationImprove flatnessPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAlcoholSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor wafer with a front surface and a back surface and an epitaxial layer of semiconducting material deposited on the front surface. In the semiconductor wafer, the epitaxial layer has a maximum local flatness value SFQRmax of less than or equal to 0.13 μm and a maximum density of 0.14 scattered light centers per cm2. The front surface of the semiconductor wafer, prior to the deposition of the epitaxial layer, has a surface roughness of 0.05 to 0.29 nm RMS, measured by AFM on a 1 μm×1 μm reference area. Furthermore, there is a process for producing the semiconductor wafer. The process includes the following process steps: (a) as a single polishing step, simultaneous polishing of the front surface and of the back surface of the semiconductor wafer between rotating polishing plates while an alkaline polishing slurry is being supplied, the semiconductor wafer lying in a cutout of a carrier whose thickness is dimensioned to be 2 to 20 μm less than the thickness of the semiconductor wafer after the latter has been polished; (b) simultaneous treatment of the front surface and of the back surface of the semiconductor wafer between rotating polishing plates while a liquid containing at least one polyhydric alcohol having 2 to 6 carbon atoms is being supplied; (c) cleaning and drying of the semiconductor wafer; and (d) deposition of the epitaxial layer on the front surface of the semiconductor wafer produced in accordance with steps (a) to (c).
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
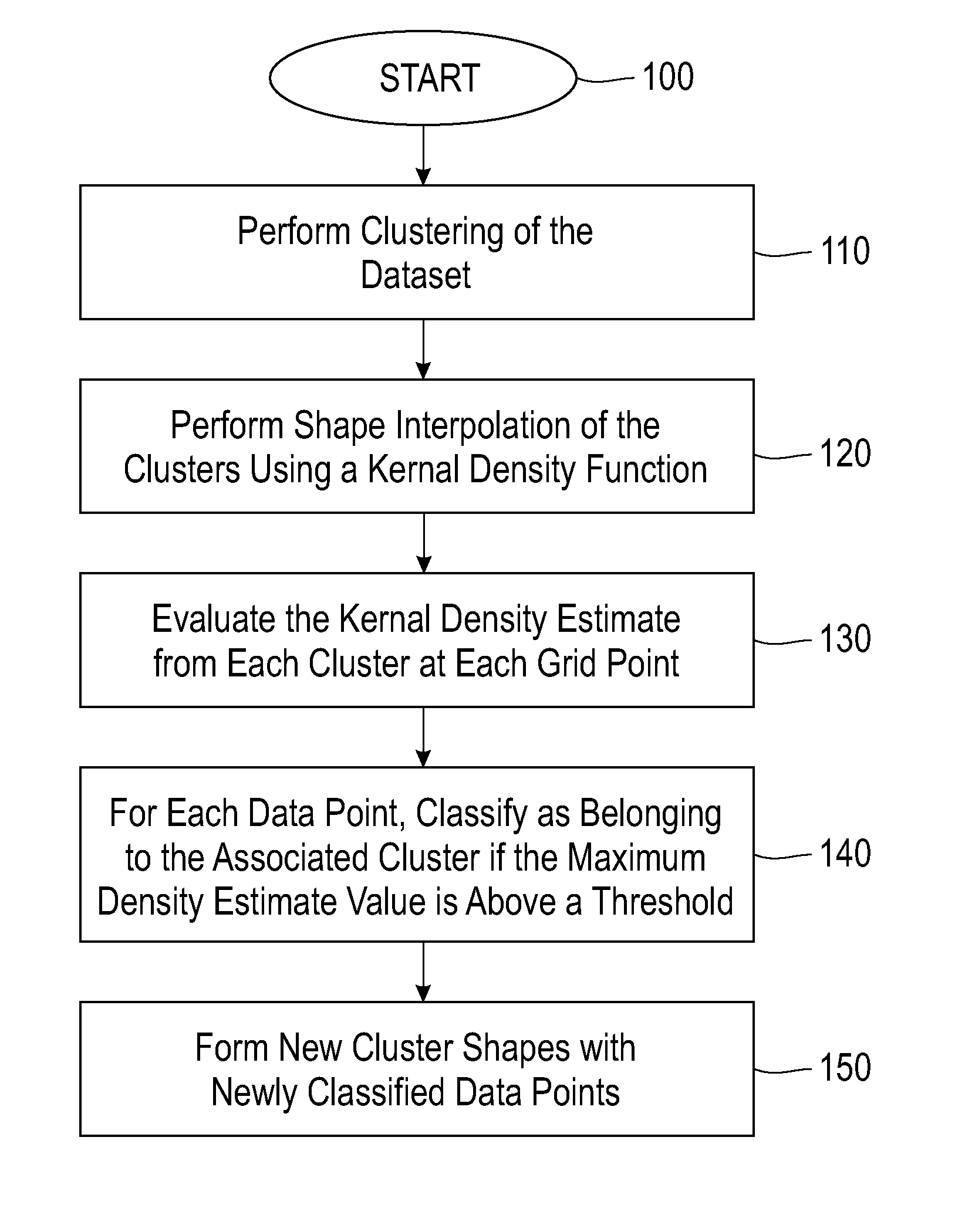
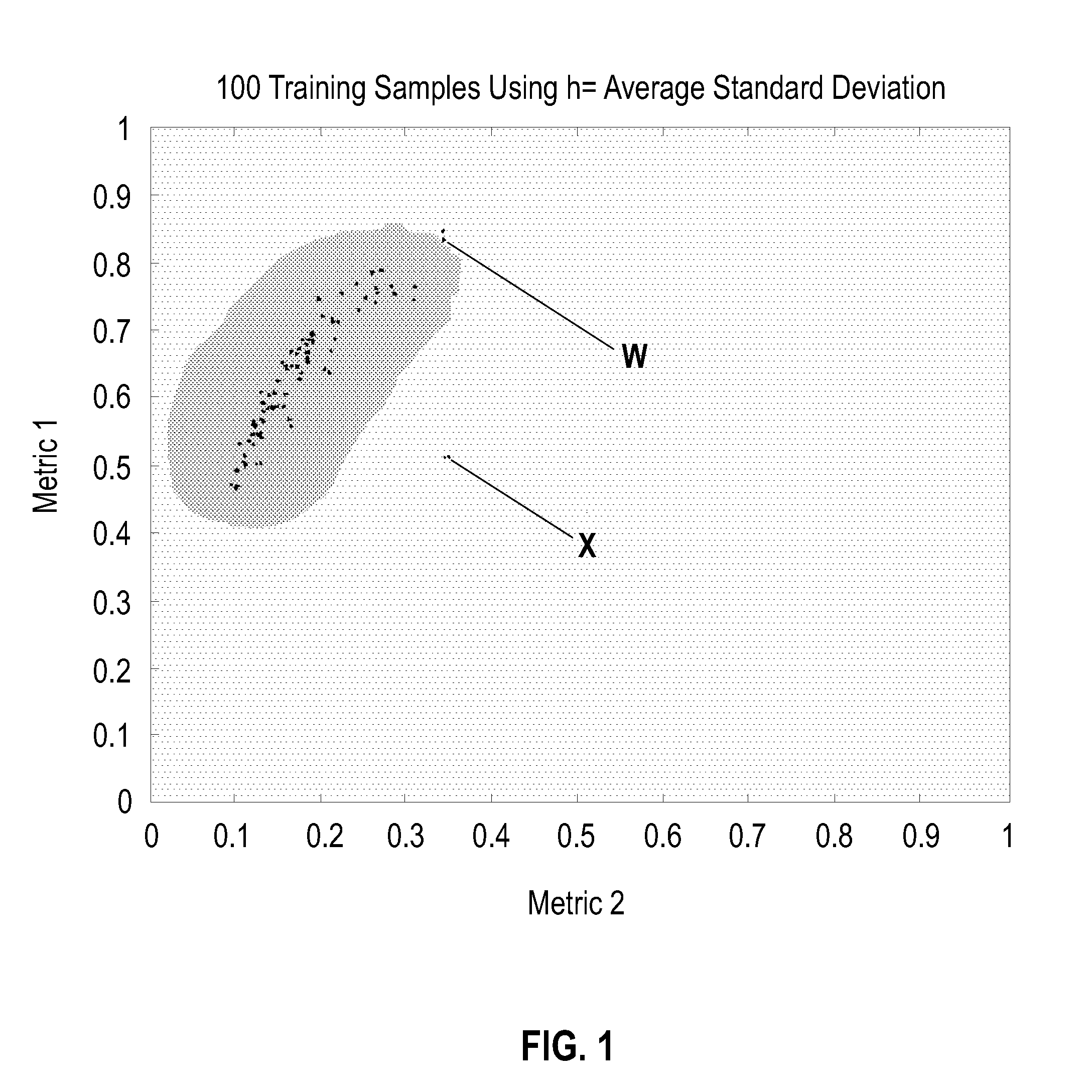
Method for data classification by kernel density shape interpolation of clusters
ActiveUS7412429B1Pointing accuratelyAccurate classificationKernel methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setImage resolution
A method for obtaining a shape interpolated representation of shapes of one or more clusters in an image of a dataset that has been clustered comprises generating a density estimate value of each grid point of a set of grid points sampled from the image at a specified resolution for each cluster in the image using a kernel density function; evaluating the density estimate value of each grid point for each cluster to identify a maximum density estimate value of each grid point and a cluster associated with the maximum density estimate value of each grid point; and adding each grid point for which the maximum density estimate value exceeds a specified threshold to the cluster associated with the maximum density estimate value for the grid point to form a shape interpolated representation of the one or more clusters.
Owner:SAP AG
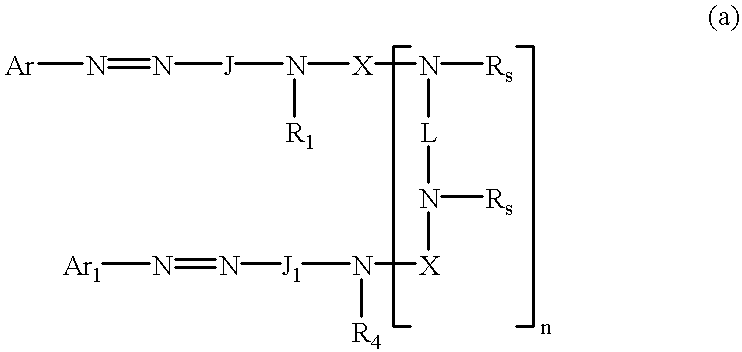
Fastening film system and assembly comprising a fastening film system and a substrate
The present invention relates to an assembly comprising a substrate bearing an adhesive layer and a multitude of discrete portions of a backing, said discrete portions of a backing being attached to the adhesive layer through one of the major surfaces of the backing and bearing on its exposed major surface opposite to the major surface attached to the adhesive layer, a plurality of male fastening elements capable of engaging with fibrous materials having a plurality of complementary female fastening elements, wherein the sum of the maximum densities of the discrete portions of the backing along the extension of the adhesive layer in the cross direction and in the machine direction, respectively, is at least 1 cm-1?, whereby the assembly releasably adheres to said fibrous material through a combination of a mechanical and an adhesive bonding mechanism.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
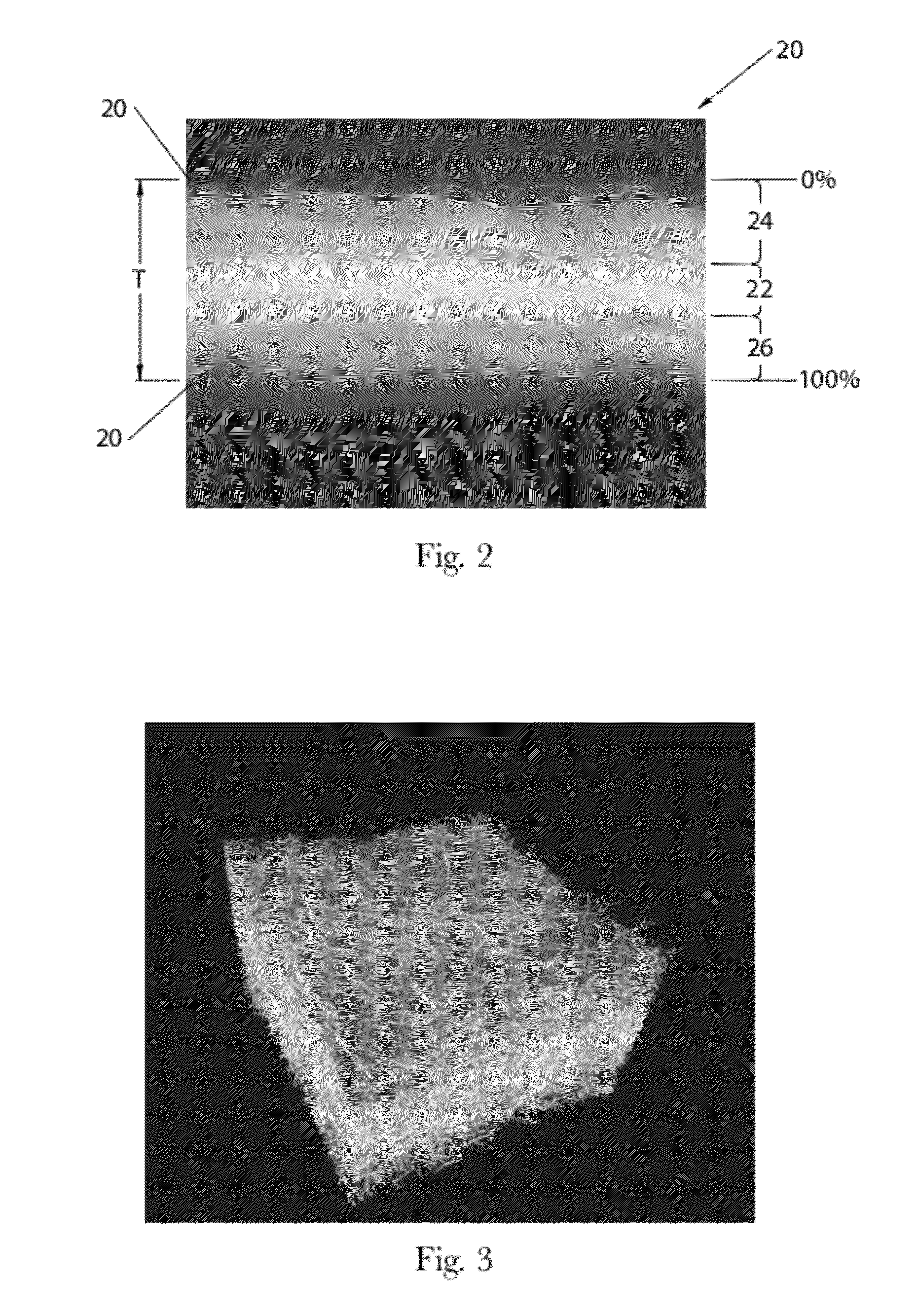
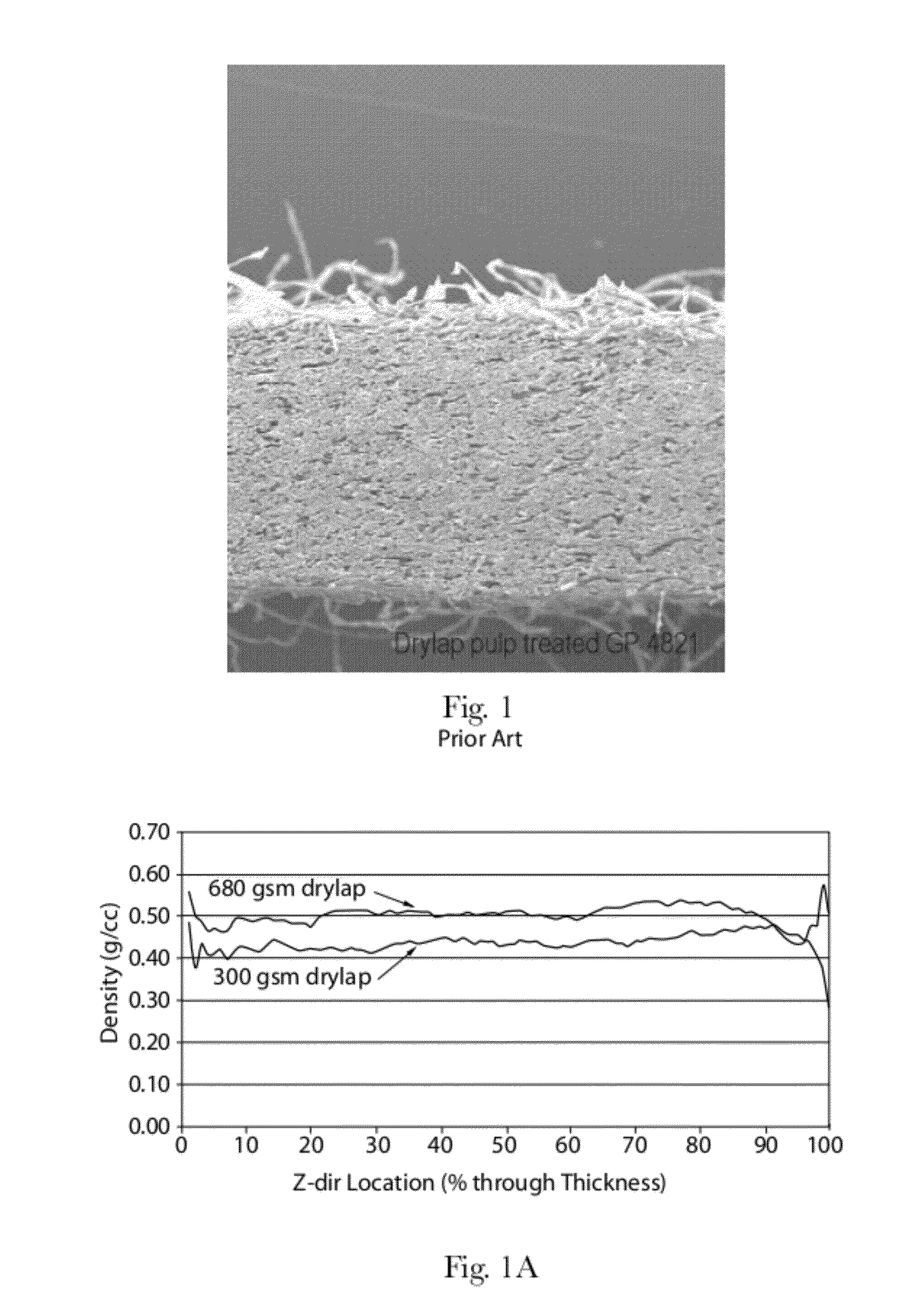
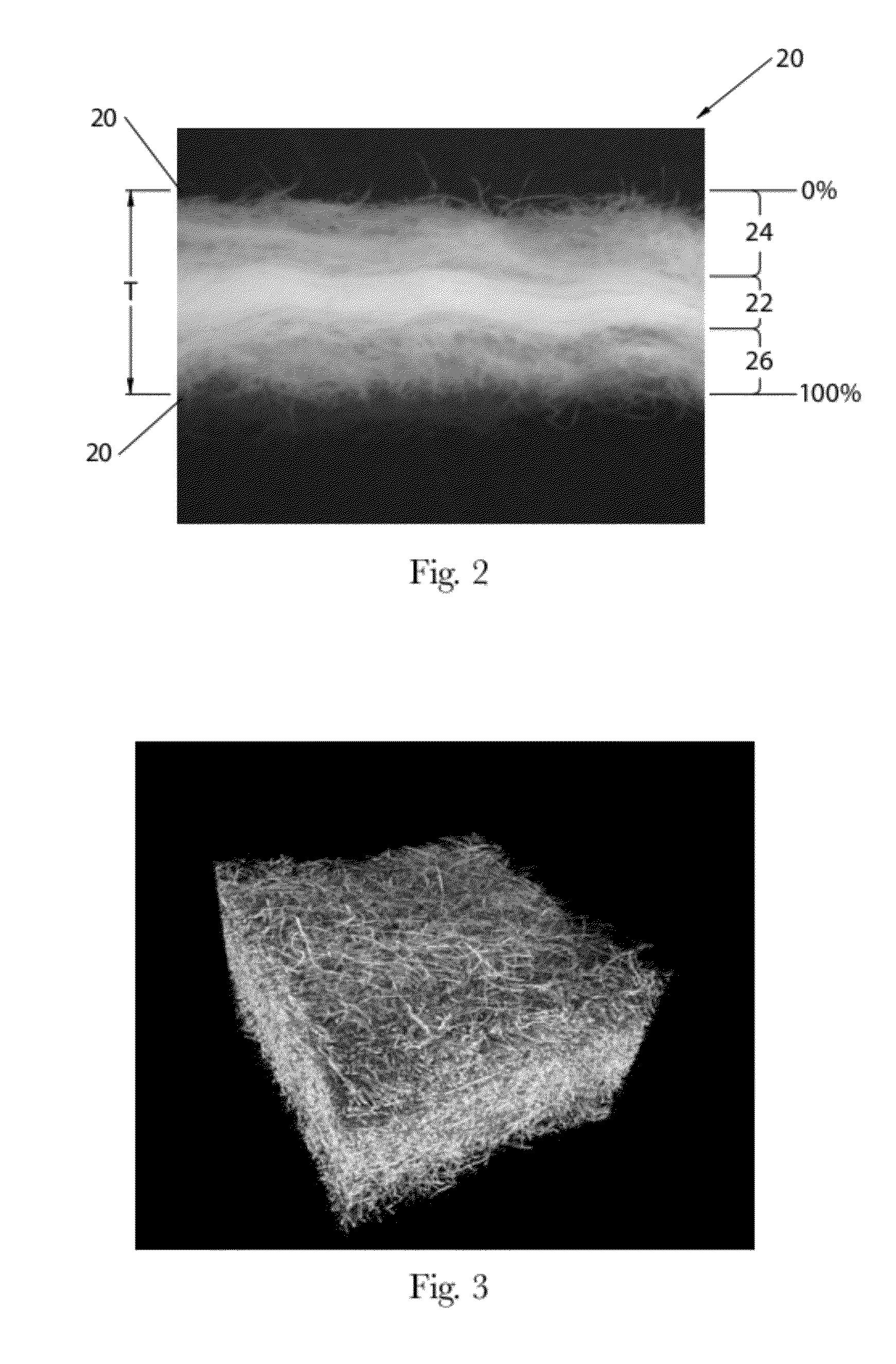
Methods of Making Absorbent Members Having Density Profile
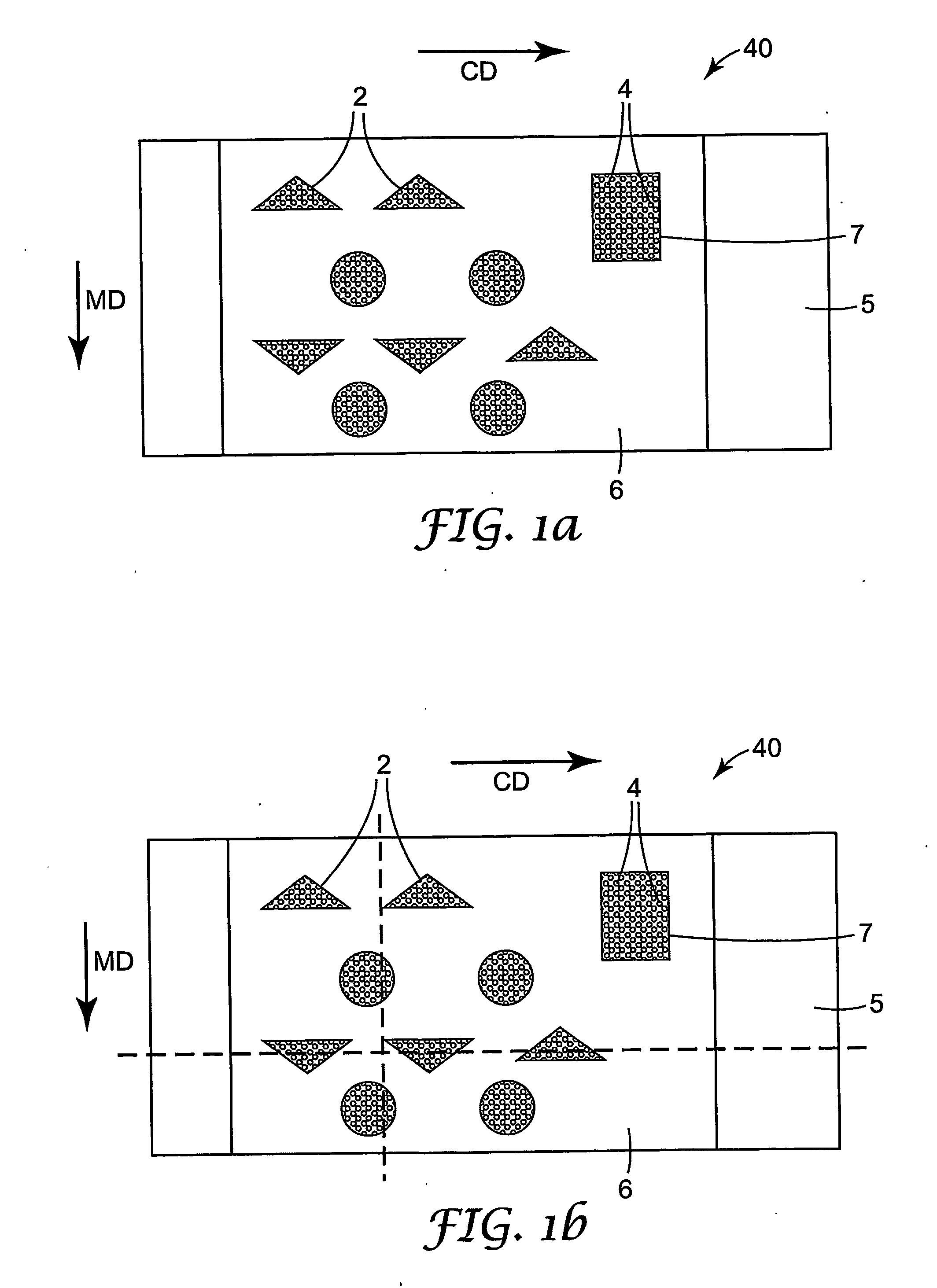
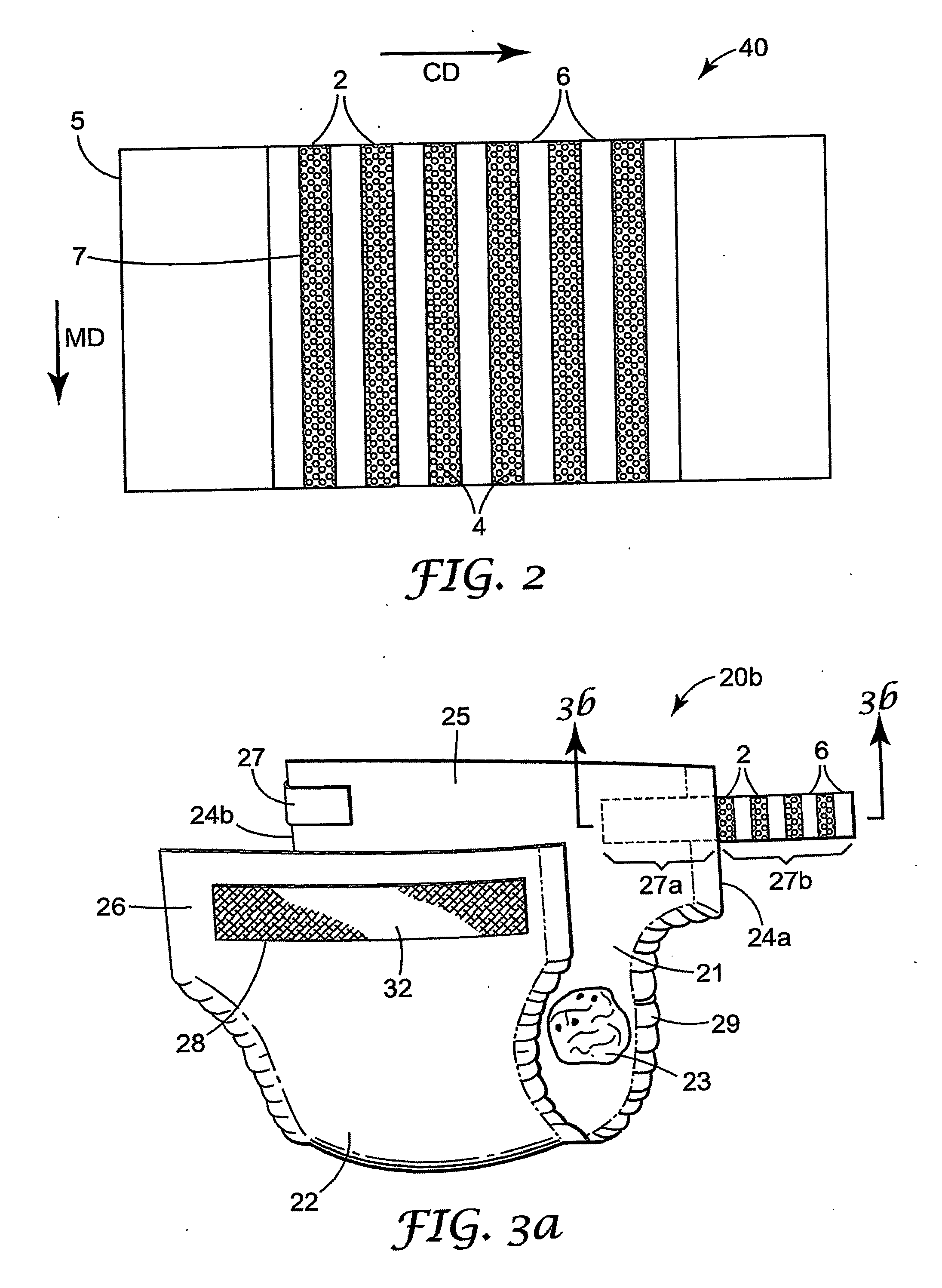
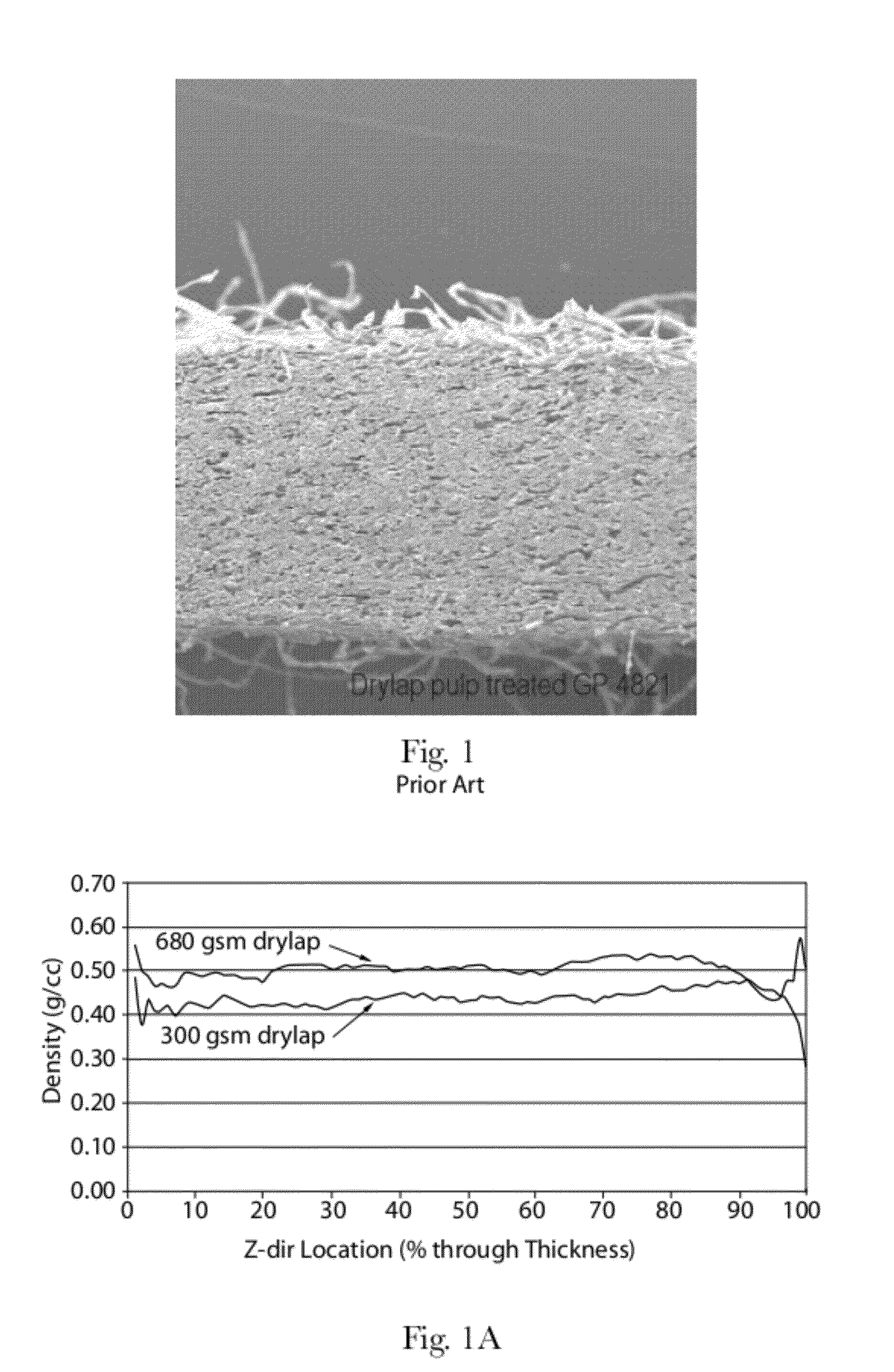
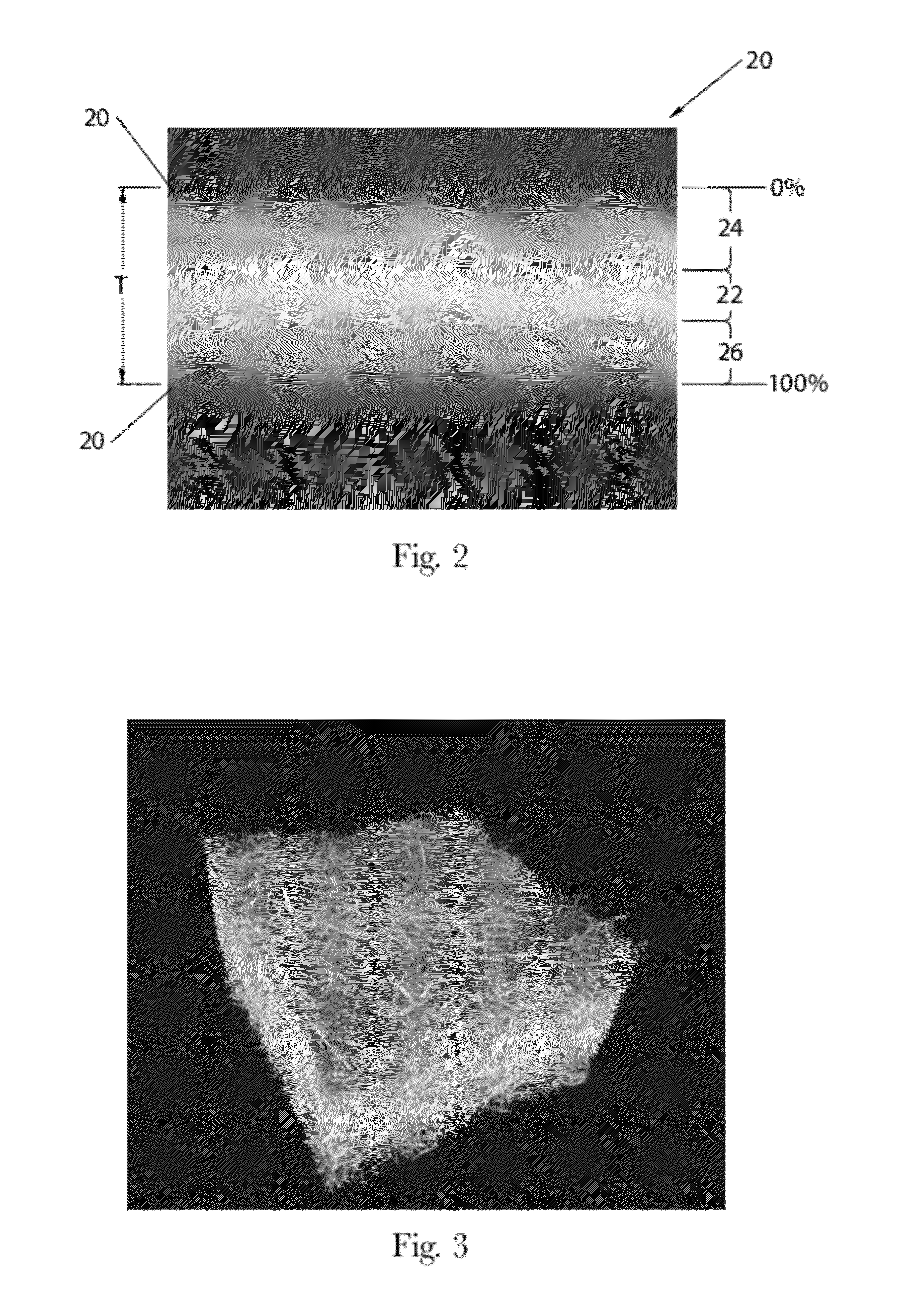
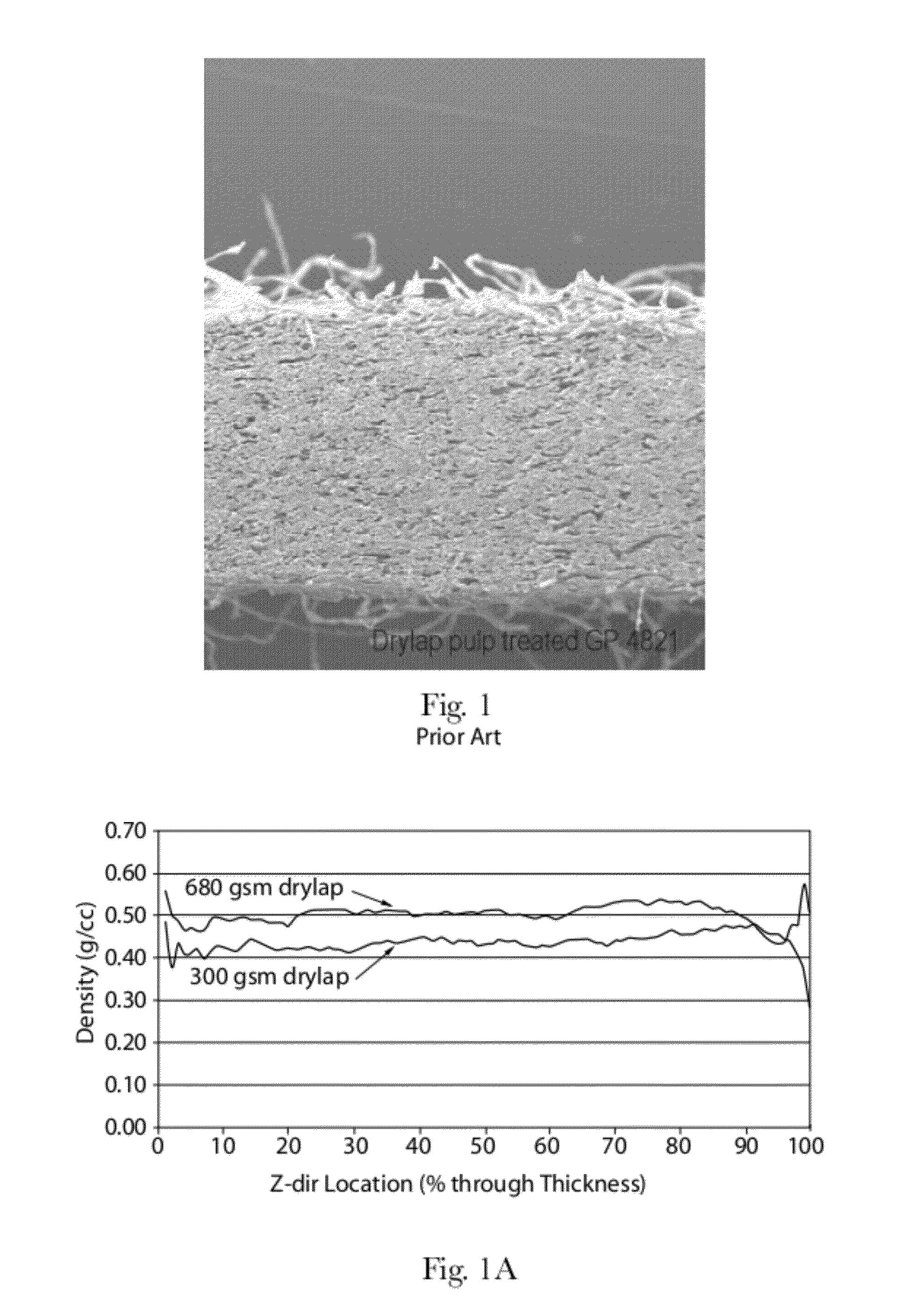
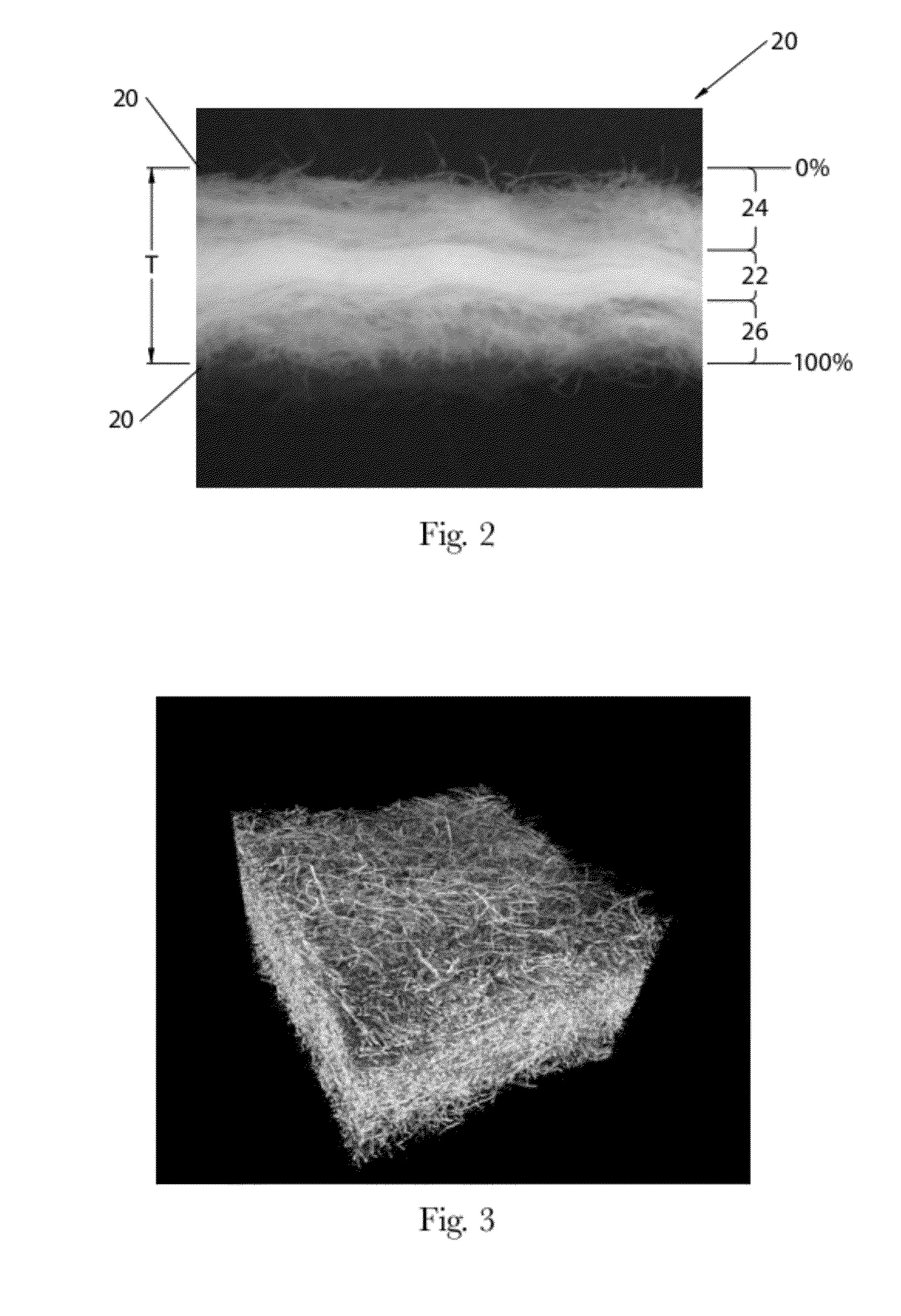
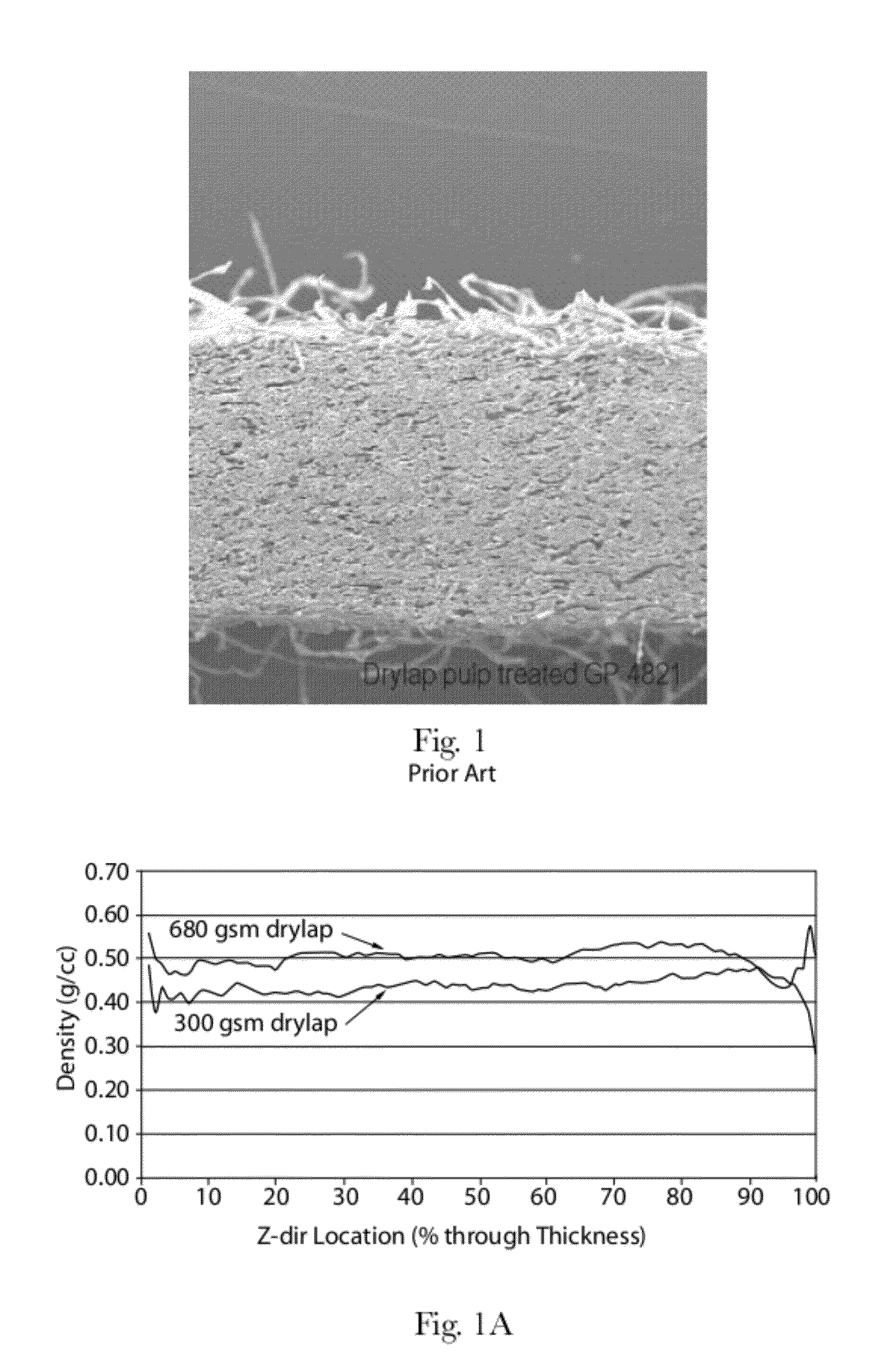
ActiveUS20120277710A1Weaken energyMechanical working/deformationMachine wet endMaximum densityMechanical engineering
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In one embodiment, the density profile is relatively centered through the thickness of the web and the maximum density of the web is located between about 35% and about 65% of the distance through the thickness of the web. In one embodiment, the method involves subjecting a precursor web to at least one cycle (or pass) through a mechanical deformation process. Typically, the method involves subjecting the precursor web to multiples cycles (or passes) through a mechanical deformation process.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
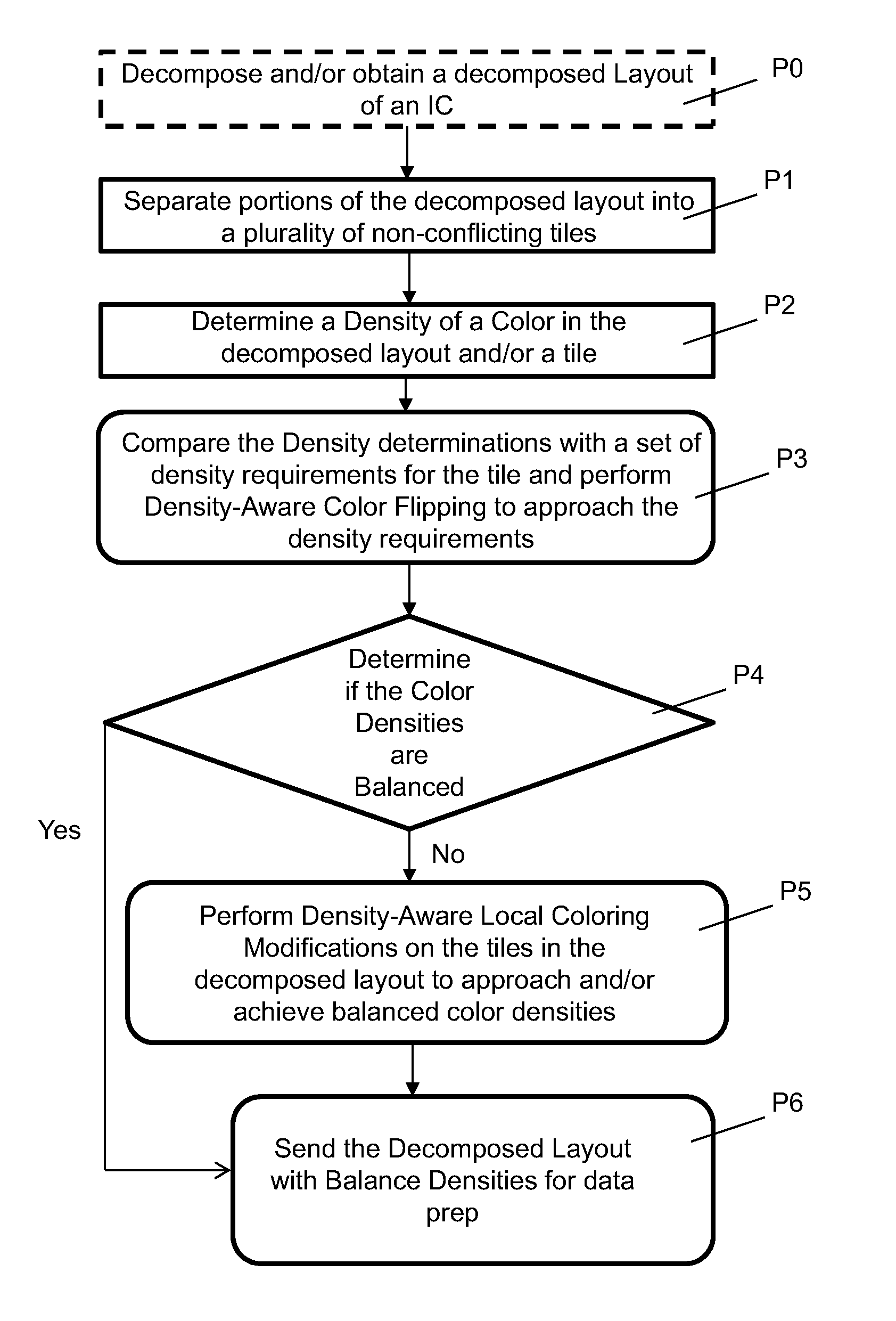
Method for post decomposition density balancing in integrated circuit layouts, related system and program product
ActiveUS8647893B1Programme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPattern recognitionMinimum density
Embodiments of the invention provide a method of modifying a decomposed integrated circuit (IC) layout. The method includes providing a decomposed IC layout, the decomposed IC layout including a set of colors; determining a density of each color in the decomposed IC layout, wherein each color includes a plurality of features formed by a related exposure; separating the decomposed IC layout into a set of tiles; determining a first color with a minimum density in one tile of the set of tiles and a second color with a maximum density in tile, the first color including a first set of first features and the second color including a first set of second features; and replacing the first set of second features on the tile with a second set of first features, and the first set of first features on the tile with a second set of second features.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Absorbent Members Having Skewed Density Profile
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In such an embodiment, the density profile of the fibrous web is skewed toward one of the surfaces of the fibrous web. In such embodiments, the maximum density of the web may be located outside of the central 30% zone of thickness of the web.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Methods of Making Absorbent Members Having Skewed Density Profile
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In one embodiment, the density profile of the fibrous web is skewed toward one of the surfaces of the fibrous web. In such embodiments, the maximum density of the web may be located outside of the central 30% zone of the thickness of the web. In one embodiment, the method involves subjecting a precursor web to at least one cycle (or pass) through a mechanical deformation process. Typically, the method involves subjecting the precursor web to multiples cycles (or passes) through a mechanical deformation process.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Methods of Making Absorbent Members Having Density Profile
InactiveUS20120277706A1Weaken energyLaminationLamination apparatusMaximum densityMechanical engineering
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In one embodiment, the density profile is relatively centered through the thickness of the web and the maximum density of the web is located between about 35% and about 65% of the distance through the thickness of the web. In one embodiment, the method involves subjecting a precursor web to at least one cycle (or pass) through a mechanical deformation process. Typically, the method involves subjecting the precursor web to multiples cycles (or passes) through a mechanical deformation process.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
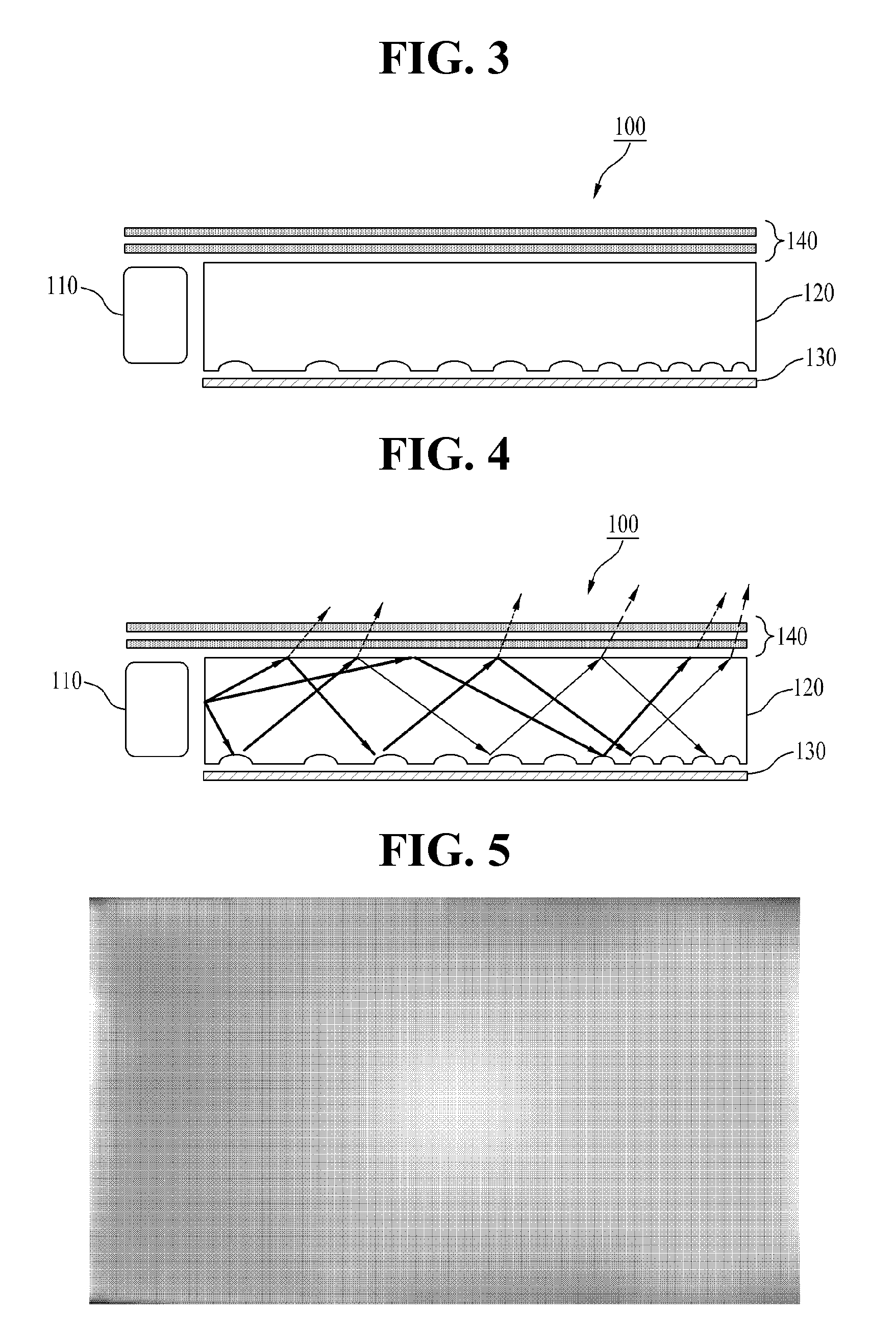
Light guide plate and backlight unit including the same
A light guide plate having a pattern to minimize generation of a dark zone and a backlight unit including the same are disclosed. The light guide plate includes an intaglio pattern consisting of recesses formed in a surface opposite to a light emitting surface thereof to have a cross section having major-axis and minor-axis diameters and depth, the recesses being spaced apart from one another in first and second directions by first and second distances respectively. The density of the intaglio pattern is directly proportional to the major-axis and minor-axis diameters and depth, and is inversely proportional to the first and second distances. The intaglio pattern has the minimum density in a first region adjacent to a light source, and the maximum density in a second region that is the maximum distance from the light source. A density ratio of the maximum density to the minimum density is 900.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Ink-jet recording method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS6341855B1High densityHigh imageMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsImage densityMaximum density
An ink-jet recording method capable of providing a record that has highly transmissible image density and a great maximum image density, a good tone and an excellent gradation. The ink-jet recording method uses different concentrations of black ink to make a graded record, wherein in addition to a set of inks employed for the graded recording, an ink containing a pigment or the like for increasing the maximum density after the recording on a recording medium is also applied to the recording medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and systems for attenuation correction in medical imaging
ActiveUS20080273780A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionVolumetric Mass DensityCompanion animal
Methods and systems for imaging a patient are provided. The method includes scanning a patient and acquiring a plurality of frames of cine computed tomography (CT) images during one complete respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, a method is provided that includes selecting a value for each pixel that represents the maximum density measurement for the pixel throughout the cine acquisition. In one embodiment, an attenuation correction image of a volume of interest is constructed by weighting a combination of the maximum pixel intensity value and an average pixel intensity value. Undesirable motion artifacts can be removed from positron emission tomography (PET) images by utilizing the CT attenuation correction image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Absorbent Members Having Density Profile
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In such an embodiment, the density profile may be relatively centered through the thickness of the web and the maximum density of the web is located between about 35% and about 65% of the distance through the thickness of the web.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Absorbent Members Having Skewed Density Profile
Absorbent members and methods of making the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the absorbent member is a unitary absorbent fibrous web having a density profile through its thickness. In such an embodiment, the density profile of the fibrous web is skewed toward one of the surfaces of the fibrous web. In such embodiments, the maximum density of the web may be located outside of the central 30% zone of thickness of the web.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Epitaxially coated semiconductor wafer and process for producing it
InactiveUS6995077B2Reduce the risk of fracturesHigh yieldPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWaferingCelsius Degree
A semiconductor wafer with a front surface and a back surface and an epitaxial layer of semiconducting material deposited on the front surface, wherein the surface of the epitaxial layer has a maximum density of 0.14 localized light scatterers per cm2 with a cross section of greater than or equal to 0.12 μm, and the front surface of the semiconductor wafer, prior to the deposition of the epitaxial layer, has a surface roughness of 0.05 to 0.29 nm RMS, measured by AFM on a 1 μm×1 μm reference area. There is also a process for producing a semiconductor wafer with a front surface and a back surface and an epitaxial layer of semiconducting material deposited on the front surface. The process includes the following: (a) a stock removal polishing step as the only polishing step; (b) cleaning and drying of the semiconductor wafer; (c) pretreatment of the front surface of the semiconductor wafer at a temperature of from 950 to 1250 degrees Celsius in an epitaxy reactor; and (d) deposition of the epitaxial layer on the front surface of the pretreated semiconductor wafer.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
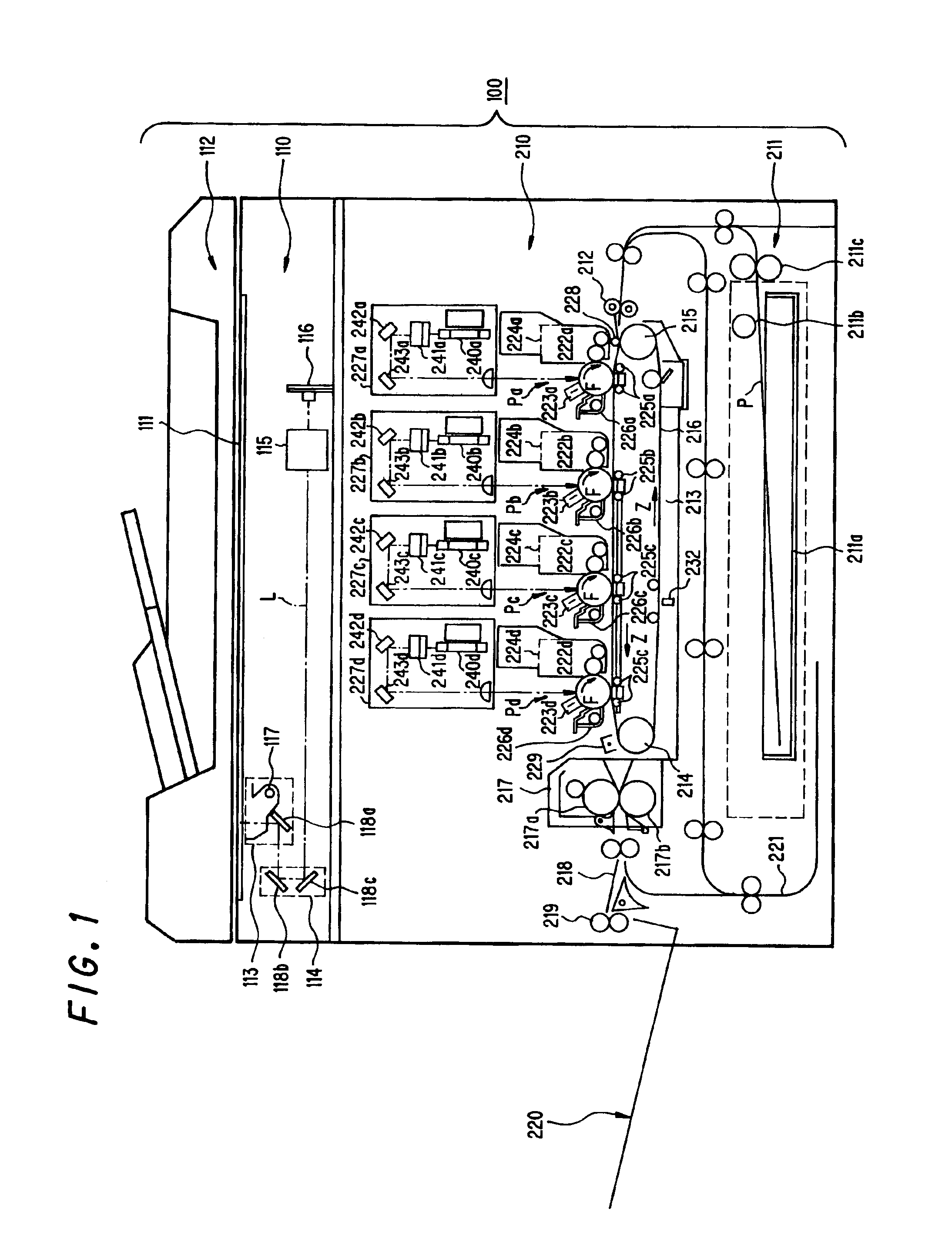
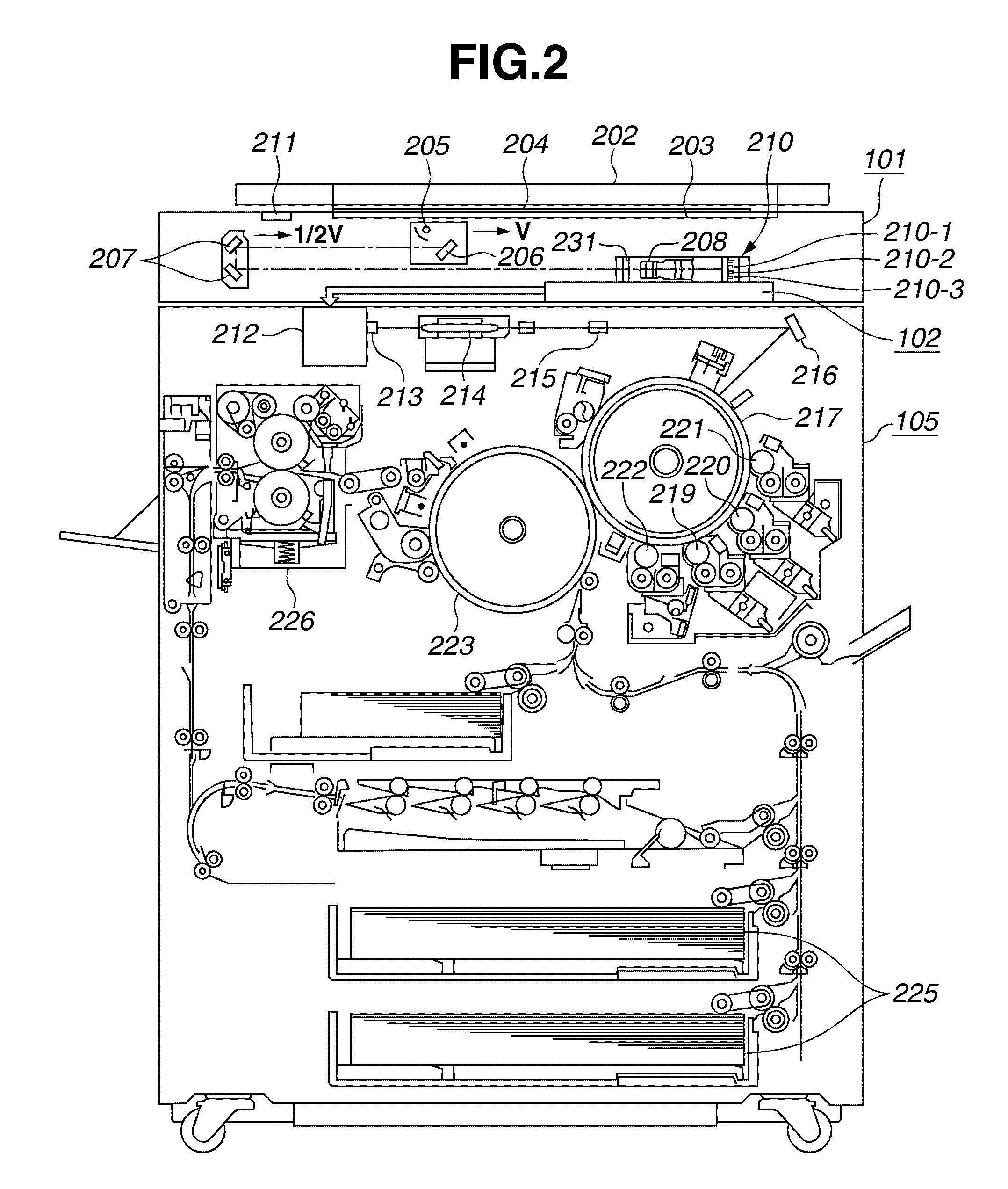
Image output device and test chart for the same
InactiveUS7130076B2High precision calibrationEasy to copyImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage resolutionOutput device
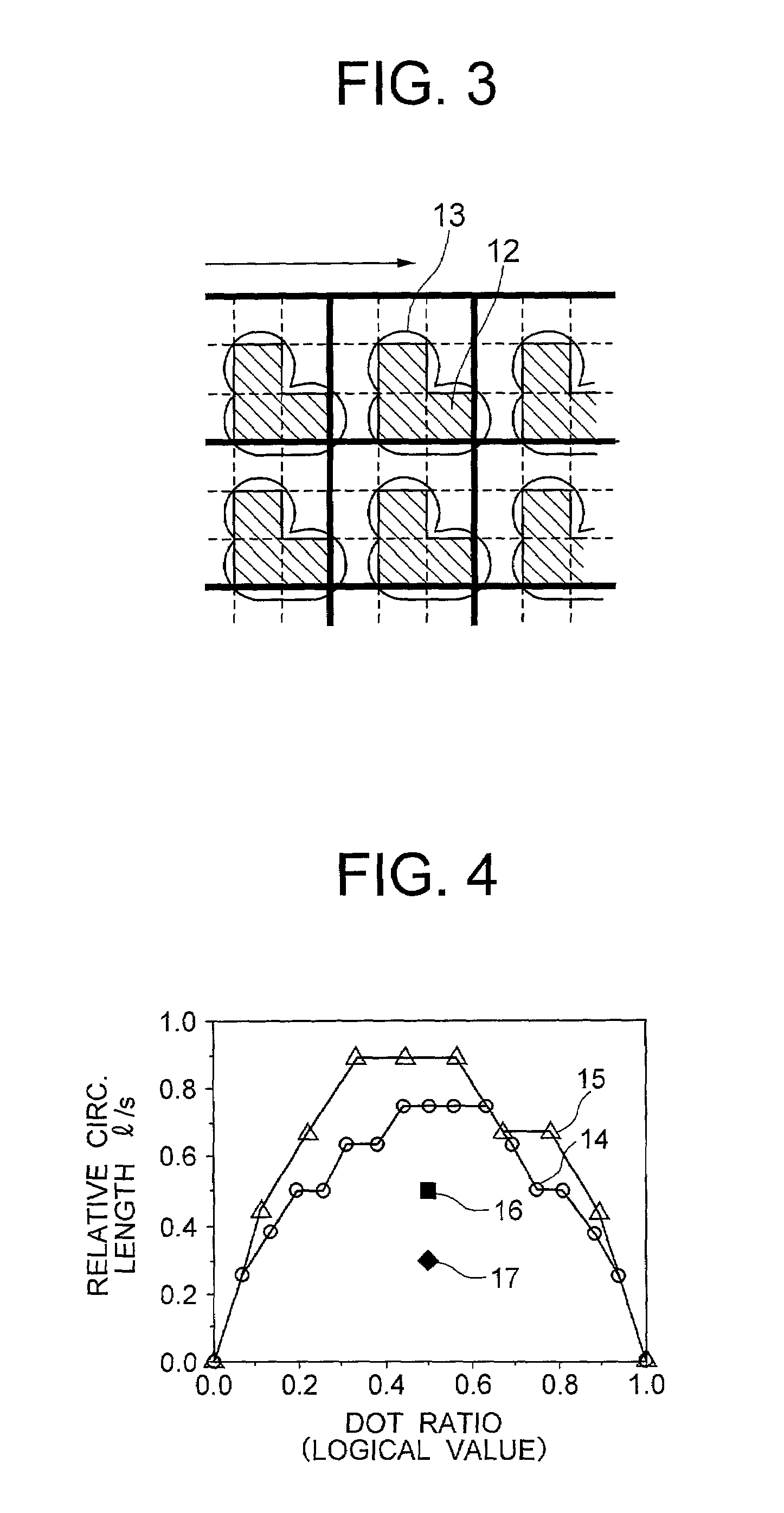
In an image output device a test chart 18 including tests charts 6 of each color is used, and a tone correction table is calculated. The test charts 6 are patterned in a checkered pattern, each including continuous areas 10 in which the tones increase in steps and reference areas 11 for comparison with the continuous areas 10. The reference areas 11 are formed of white ground of paper in a highlight proof part 7, a solid pattern with a maximum density in a shadow proof part 8, and halftone dot-concentrated or line screens with a lower resolution than in the continuous areas in a middle proof part 9. Tone correction values are calculated from characteristic values of the highlight, shadow and middle parts, obtained from visual data of the test chart 18.
Owner:RICOH PRINTING SYST
Image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, method for processing image, computer program, and recording medium
InactiveUS7518755B2Improving accuracy of discrimination and image quality of imageHigh discrimination accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging qualityContinuous tone
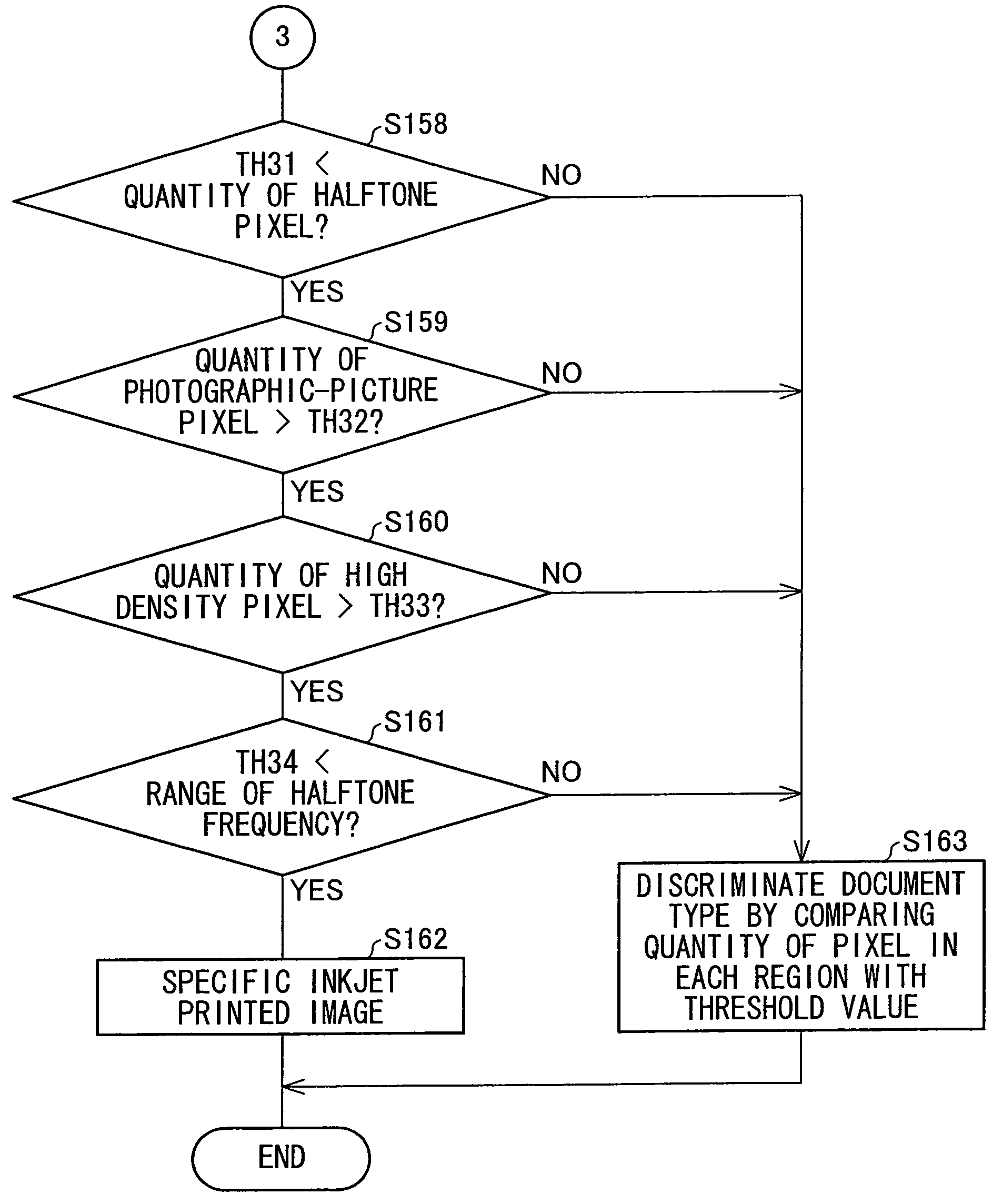
An image processing apparatus includes a document type automatic discrimination section that, based upon input image data read from a document, automatically discriminates a document type of the document. The document type automatic discrimination section, based upon plural types of parameters (quantity of halftone pixels, quantity of photographic-picture pixels, and quantity of high density pixels) obtained from plural types of characteristics (maximum density difference, total density busyness) extracted from the input image data and which parameters are used for discriminating a document type. A specific inkjet printed image whose output image data would not reach a standard level, if a process for a halftone reproduction region or a process for a continuous tone region were to be carried out on the input image data. This can improve the accuracy of document discrimination and the image quality of reproduced image.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for the production of an oxide ceramic shaped part and a part produced by such method
InactiveUS20050164045A1Low production costImprove aestheticsImpression capsWood working apparatusOxide ceramicPowder mixture
A method for producing an oxide ceramic shaped part includes pressing a powder provided with a binding material or a powder mixture of an oxide ceramic into a shaped part, pre-sintering the shaped part at substantially atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 600 to 1,300° C., and evacuating a closed container in which the pre-sintered shaped part is disposed with the shaped part having a maximum density of 10 to 90%. The container is at an absolute pressure of less than 40 mbar. Subsequently, an infiltration material is applied onto the shaped part via infiltration with the infiltration material operating to seal off the shaped part relative to the surrounding atmosphere. The length of time of the infiltration is preferably 1 to 10 minutes.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
ActiveUS6917446B2Excellent gradation representationVariation of error to periodic variation can be suppressedDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingPeak value
An image processing apparatus for quantizing image data indicative of a density gradation level of a constituent pixel of an image into a discrete value on the basis of quantization levels of a number smaller than the maximum density gradation level and not smaller than two. The apparatus comprises: an N-level / M-level quantization circuit for quantizing image data of an object pixel on an N-level basis or on an M-level basis; an error diffusion circuit for distributing an error generated through the N-level quantization or the M-level quantization to peripheral pixels around the object pixel; an N-level quantization threshold setting circuit for setting an N-level quantization threshold in a periodically variable manner; and a process setting circuit for causing the N-level / M-level quantization circuit to perform the M-level quantization for pixels adjacent to a pixel corresponding to either or both of a peak point and a saddle point in the periodic variation of the N-level quantization threshold and causing the N-level / M-level quantization circuit to perform the N-level quantization for pixels corresponding to the peak point and the saddle point.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
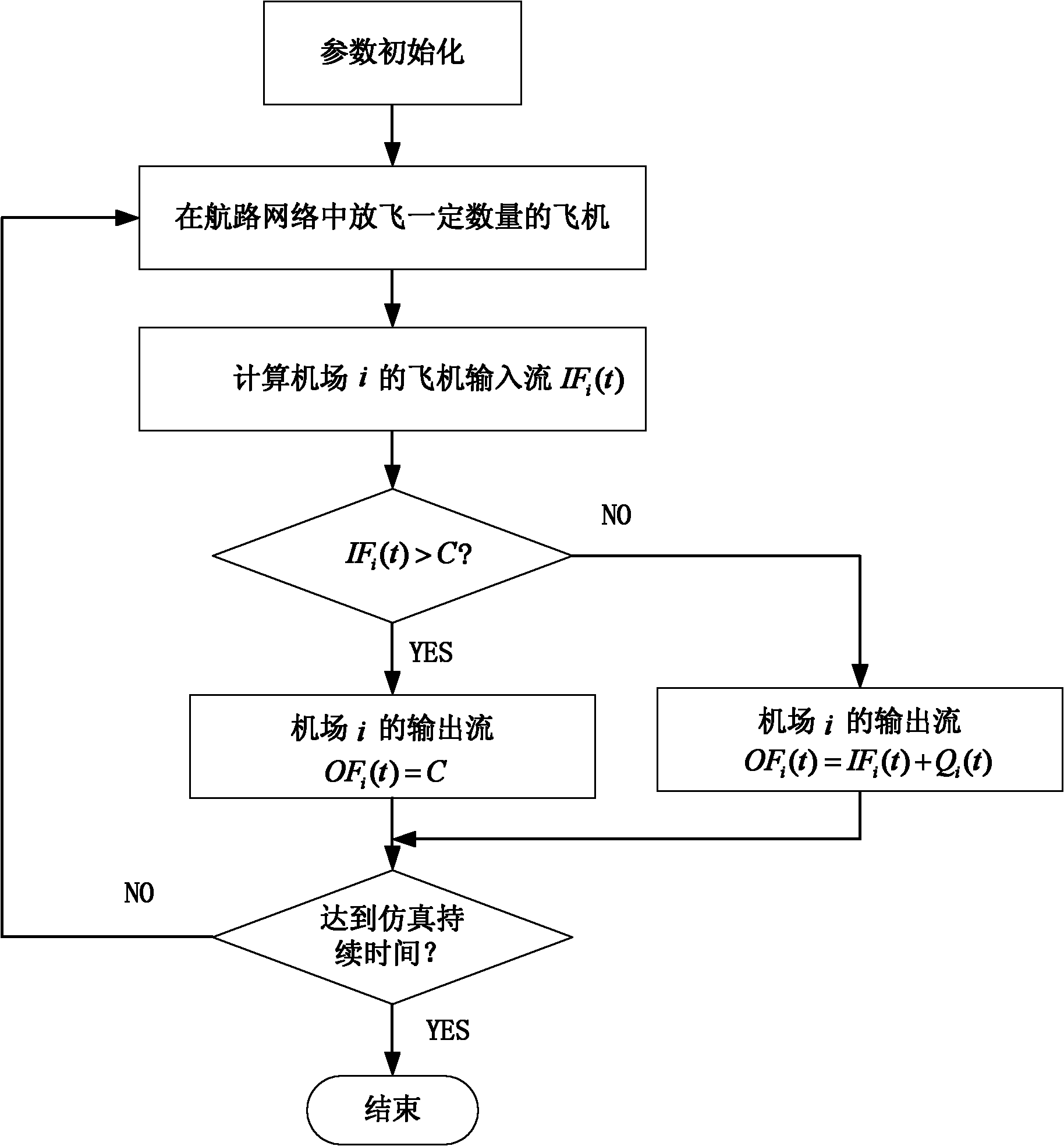
Method for optimizing layout of convergent points of air routes by introducing airspace capacity
The invention discloses a method for optimizing layout of convergent points of air routes by introducing airspace capacity. The method comprises the following specific implementation processes of: firstly, establishing a flowrate model of an air route network; secondly, determining the maximum density of scheduled flights bearable for the air route network according to the degree of crowdedness imposed to the air route network by different densities of the scheduled flights; and thirdly, carrying out the optimal layout of the convergent points of the air routes. The method puts forth the quantitative airspace capacity description method by establishing the traffic flowrate model for the air route network, constructs the multi-objective optimization model based on flight efficiency and theairspace capacity, and optimizes the positions of the convergent points of the air routes by adopting a multi-objective particle swarm algorithm. The method takes both the flight efficiency and the airspace capacity into consideration, and the obtained air route network can effectively postpone the occurrence of the airspace congestion under the circumstance of increasing of aviation flowrate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and systems for attenuation correction in medical imaging
ActiveUS7813783B2Area maximizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVolumetric Mass DensityCompanion animal
Methods and systems for imaging a patient are provided. The method includes scanning a patient and acquiring a plurality of frames of cine computed tomography (CT) images during one complete respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, a method is provided that includes selecting an organ of interest in the cine CT data and selecting a value for each pixel in the organ of interest that represents the maximum density measurement. An attenuation corrected positron emission tomography (PET) image is constructed based on the maximization of the pixel intensity of the organ of interest in the CT attenuation correction map. Incorrect attenuation correction values for PET images can be avoided by utilizing the CT attenuation correction map.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
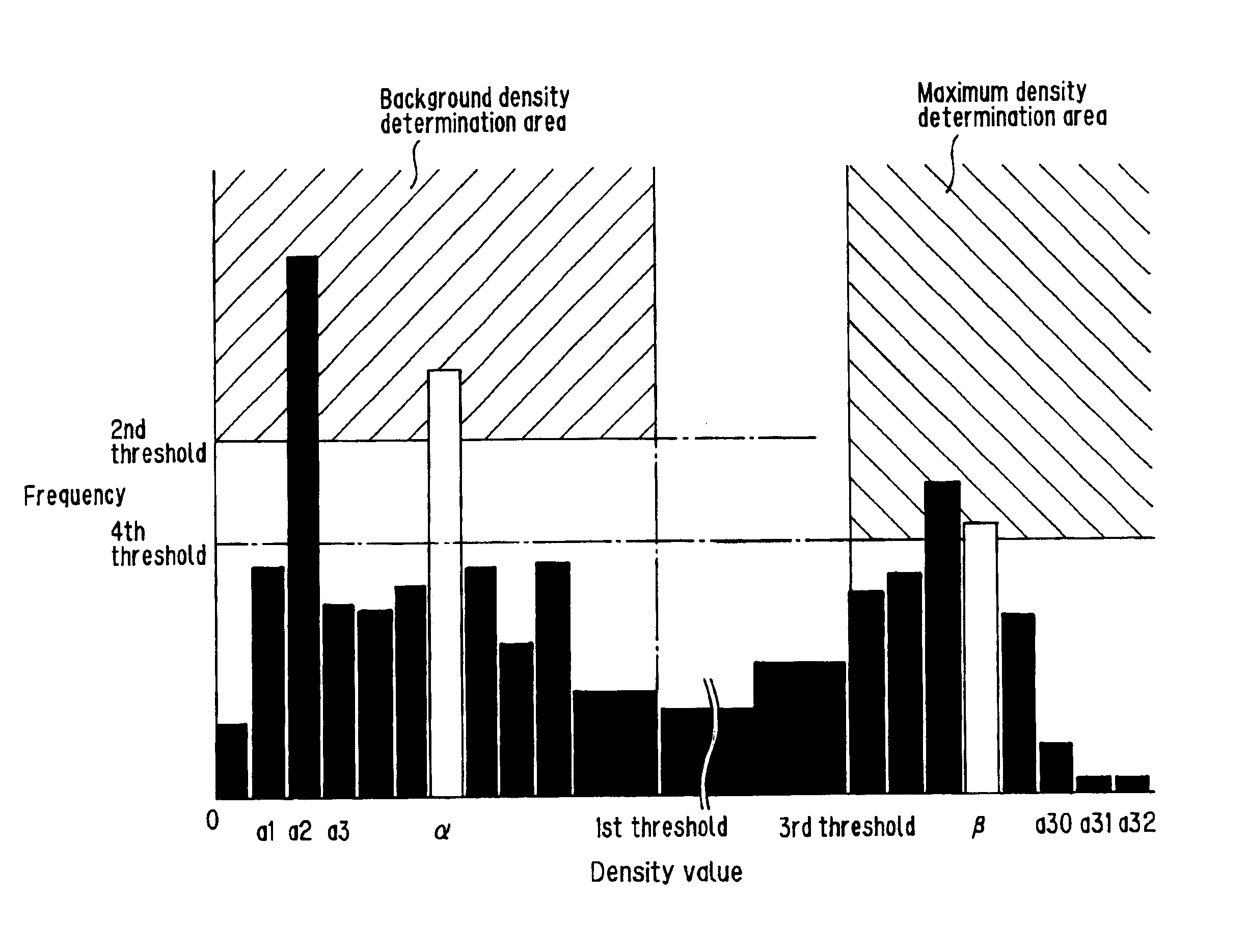
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS6917707B1Optimal density correctionOptimized tone processingImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingVolumetric Mass Density
A mono-color signal converter extracts a mono-color signal in terms of the CMY system from RGB signals. A histogram generator generates a density histogram based on the density of the pixels in the digital image. At the same time, based on the thresholds determined previously, determination areas for the background density and maximum density are formed. A density class extracting portion extracts the density class of the background density and the density class of the maximum density. Based on the result from the density class extracting portion, a density correction curve generator generates a density correction curve. When the density correction curve needs to be adjusted as desired, the starting point and end point of the density correction curve are renewed through a first correction value and second correction value setting portion. A signal converter converts the mono-color signal into the K-signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
Process control of electrophotographic device
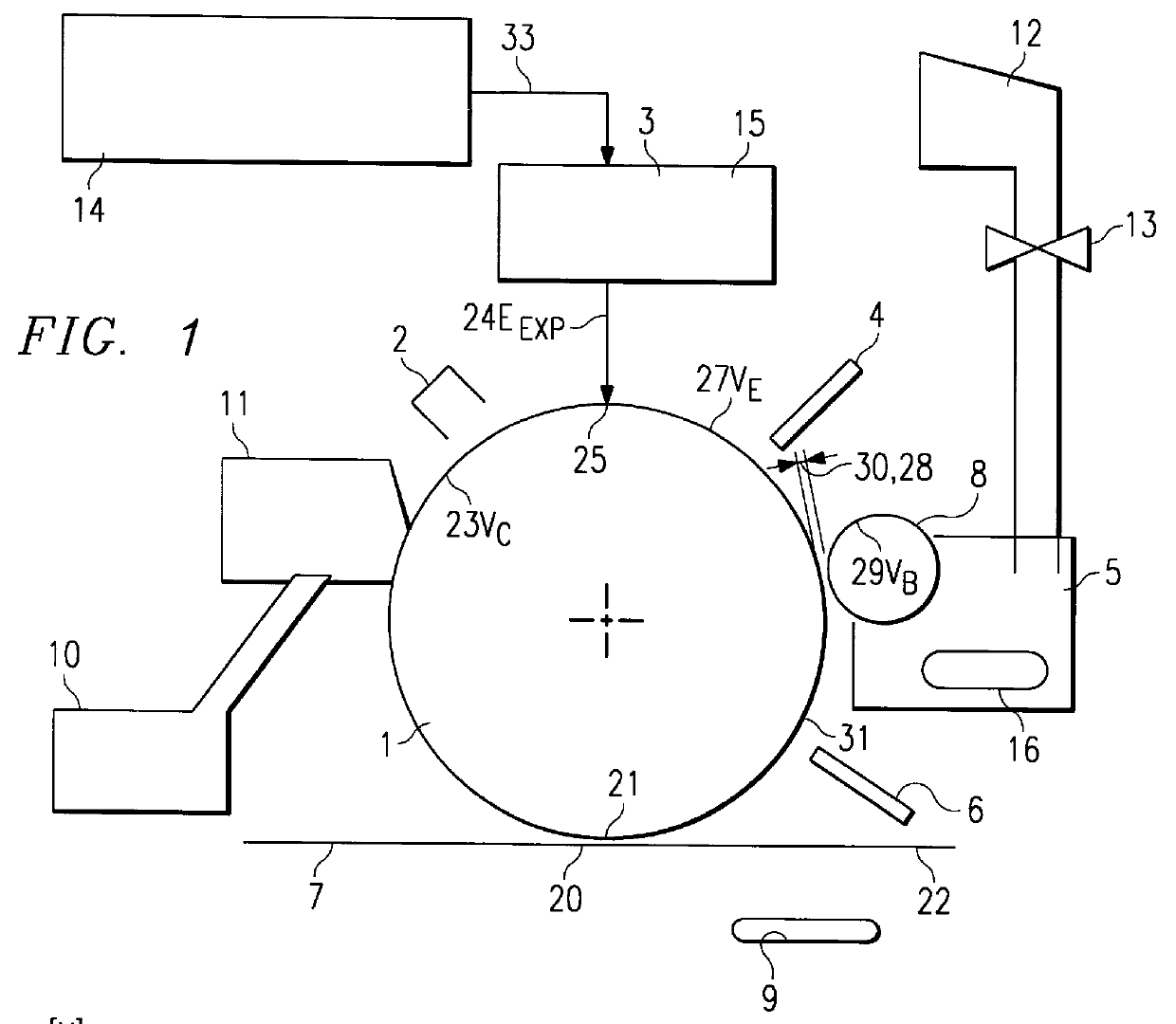
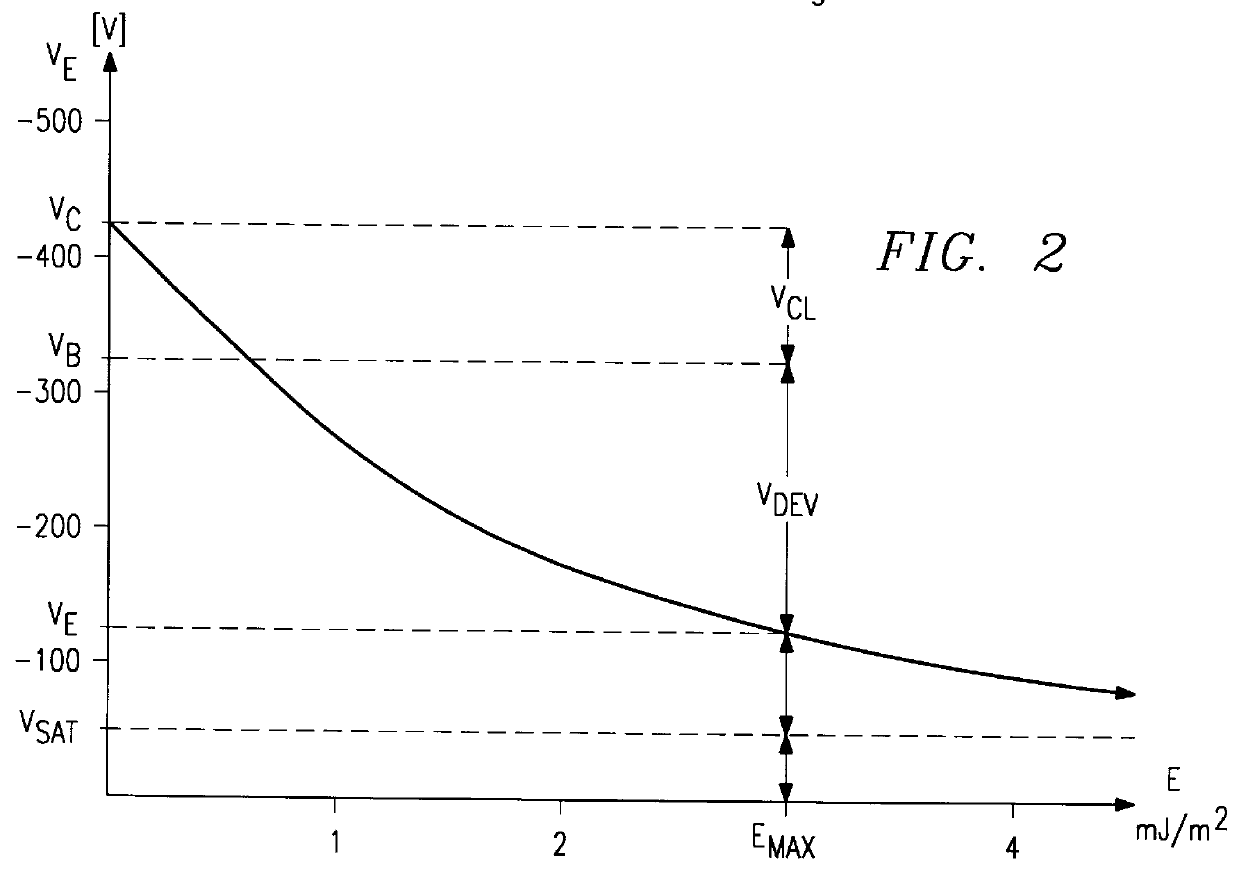
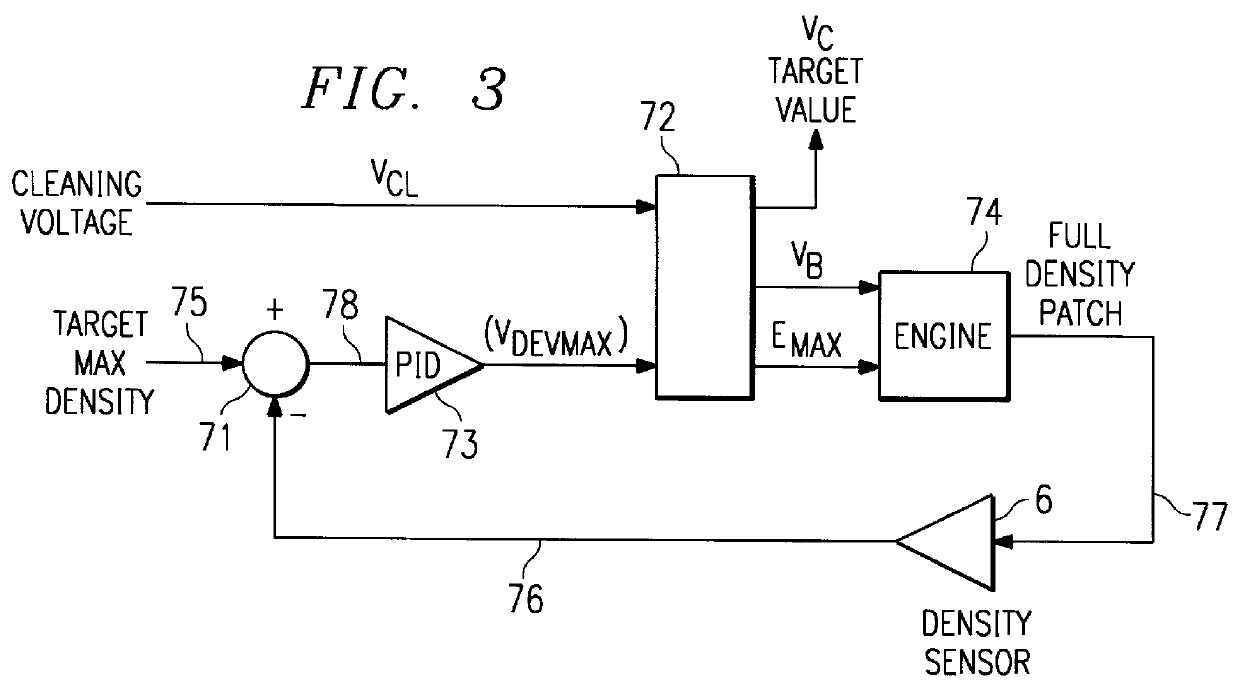
InactiveUS6034703AImproved tone scale linearityScale upElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternVolumetric Mass DensityMaximum density
A method is described to control the maximum density and the pixel profile of microdots produced by a binary or multilevel electrophotographic device. In various embodiments, from the maximum development potential. The working point of the device is established by imposing a relation between charge level, discharge level and saturation voltage level of the photosensitive element. This allows to achieve consistent output densities, irrespective of the environmental parameters, such as relative humidity and temperature.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC +1
Pixel-density augmentation and adjustment with minimum data, in an incremental printer
InactiveUS6690485B1Extended Density RangeAdd funImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPixel densityAnalysis data
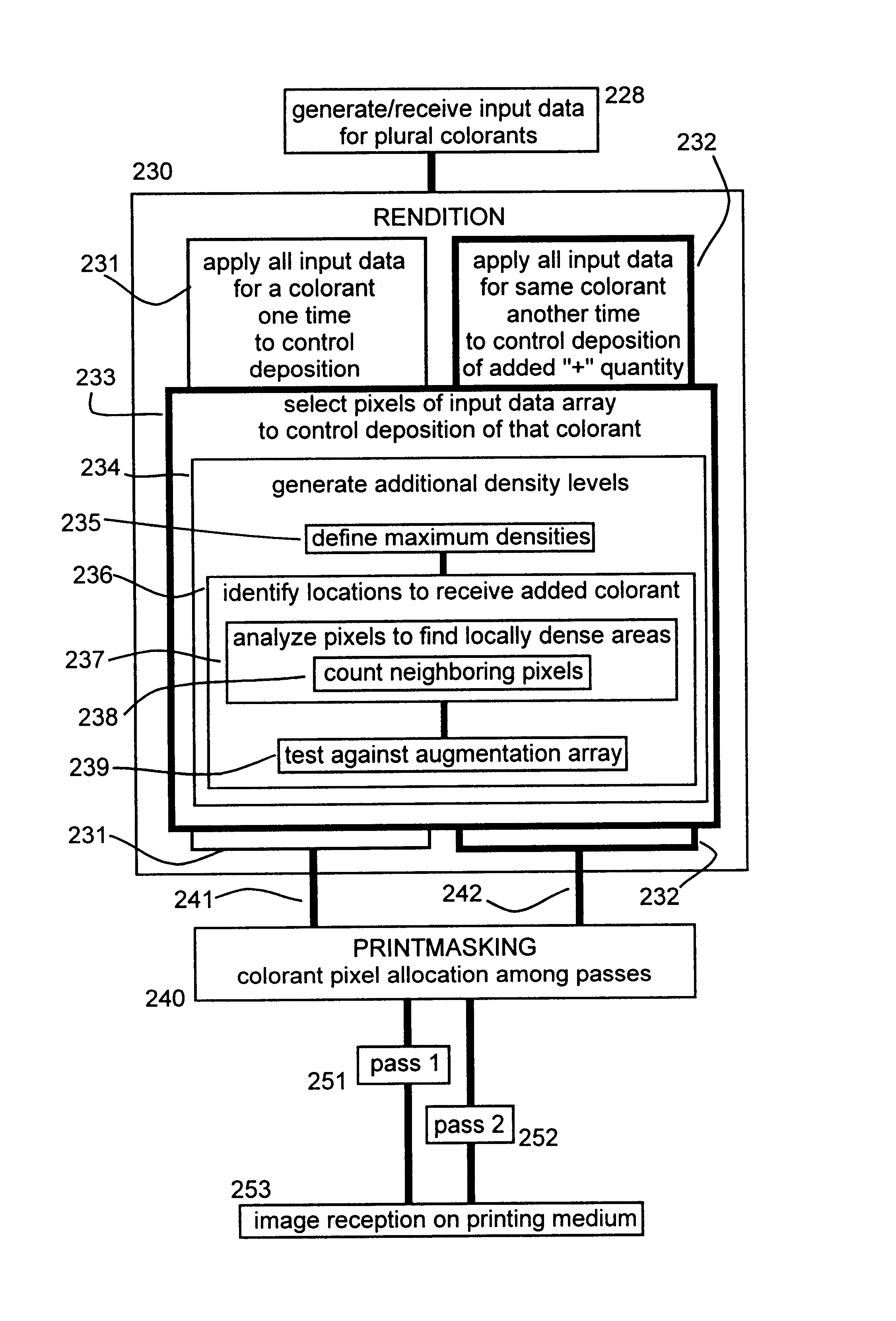
One invention form is a method using all input data for one or preferably plural colorants, one time to control colorant deposition in forming a pixel array on a printing medium, and at least one other time to control deposition of more of the same colorants. At least one "applying" includes choosing data-array pixels to deposit added colorant. The two data-usage times can be associated directly with depositing colorant in respective printer passes; or may be done at (or near) rendition, sending output data to printmasking for pass allocation. Selection preferably includes setting maximum density on the medium-and choosing locations for that density, best by analyzing data to find locally dense areas, e. g. counting neighboring pixels. Selecting also includes defining locations to receive particular density, and creating additional density levels based on densities in the data array. Another method form includes defining an augmentation array and applying it to control part of colorant deposition. Preferably also included is applying the original array to control other deposition of colorant. Applying the augmentation array preferably increases colorant deposition, relative to applying the original array, by less than 100% with non-linear response to data.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Image processing apparatus, method for processing image, and storage medium therefor
ActiveUS20120086987A1Reduce material usageElectrographic process apparatusVisual presentationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
A limit value of a recording material is determined based on a difference between a maximum density value of an image formed by an image forming unit and a maximum density value to be targeted by an image processing apparatus, and the amount of the recording material corresponding to the image data is controlled so as to be the determined limit value or below.
Owner:CANON KK
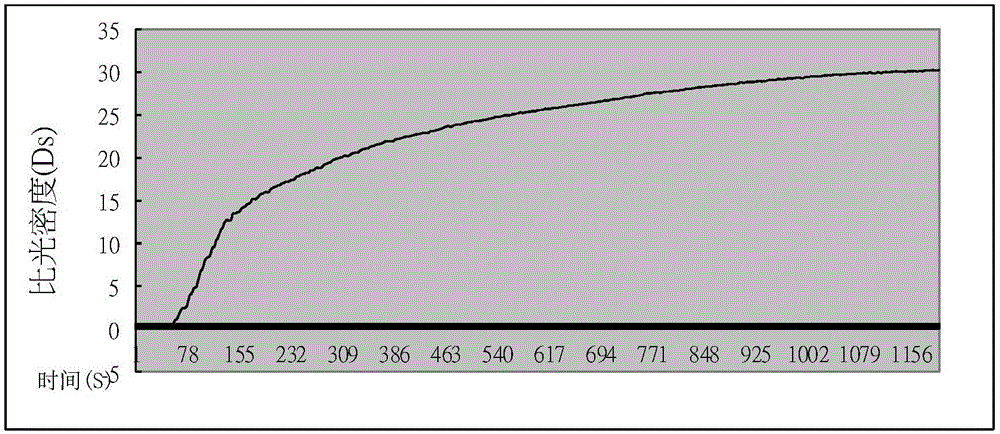
Intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The smoke inhibitor is a layered structural material formed by assembling a laminated sheet consisting of metal cations and interlayer anions, wherein a specific composition general formula of the smoke inhibitor is M<2+>1-xM<3+>x(OH)2(A<n->)n / 2.mH2O. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is prepared by adopting a one-step coprecipitation method or a clean hydrothermal reaction at one step; the preparation method is simple and practical; according to the obtained intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor, smoke inhibiting groups such as molybdate anions, an octamolybdate radical, a cuprate radical and a stannate radical are arranged at an interlayer, and smoke inhibiting elements such as iron and copper are introduced into the laminated sheet, so that a good carbon forming effect is realized, the smoke generating amount can be reduced, and the smoke inhibiting effect is synergically enhanced; meanwhile, a layered double hydroxide laminated sheet forms an alkaline porous substance at high temperature; the alkaline porous substance has greater specific surface area and can effectively adsorb smog; the prepared intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is applied to an ordinary rubber-plastic product and a high-temperature rubber-plastic product; the maximum density (Ds, max) at low additive amount (1phr) can be reduced by 87.3 percent; the intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is remarkable in smoke inhibiting effect and is a smoke inhibitor material with excellent performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com