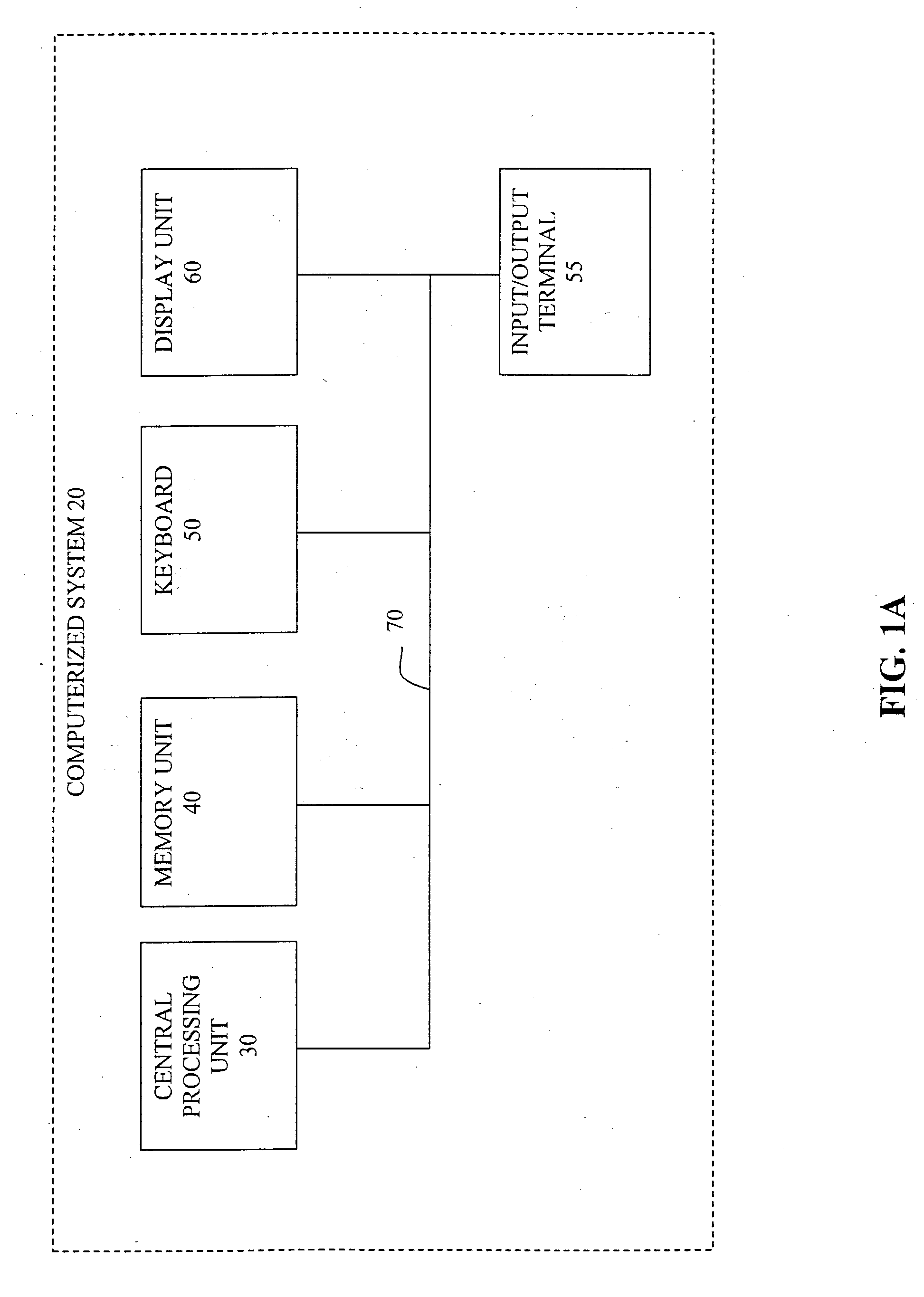
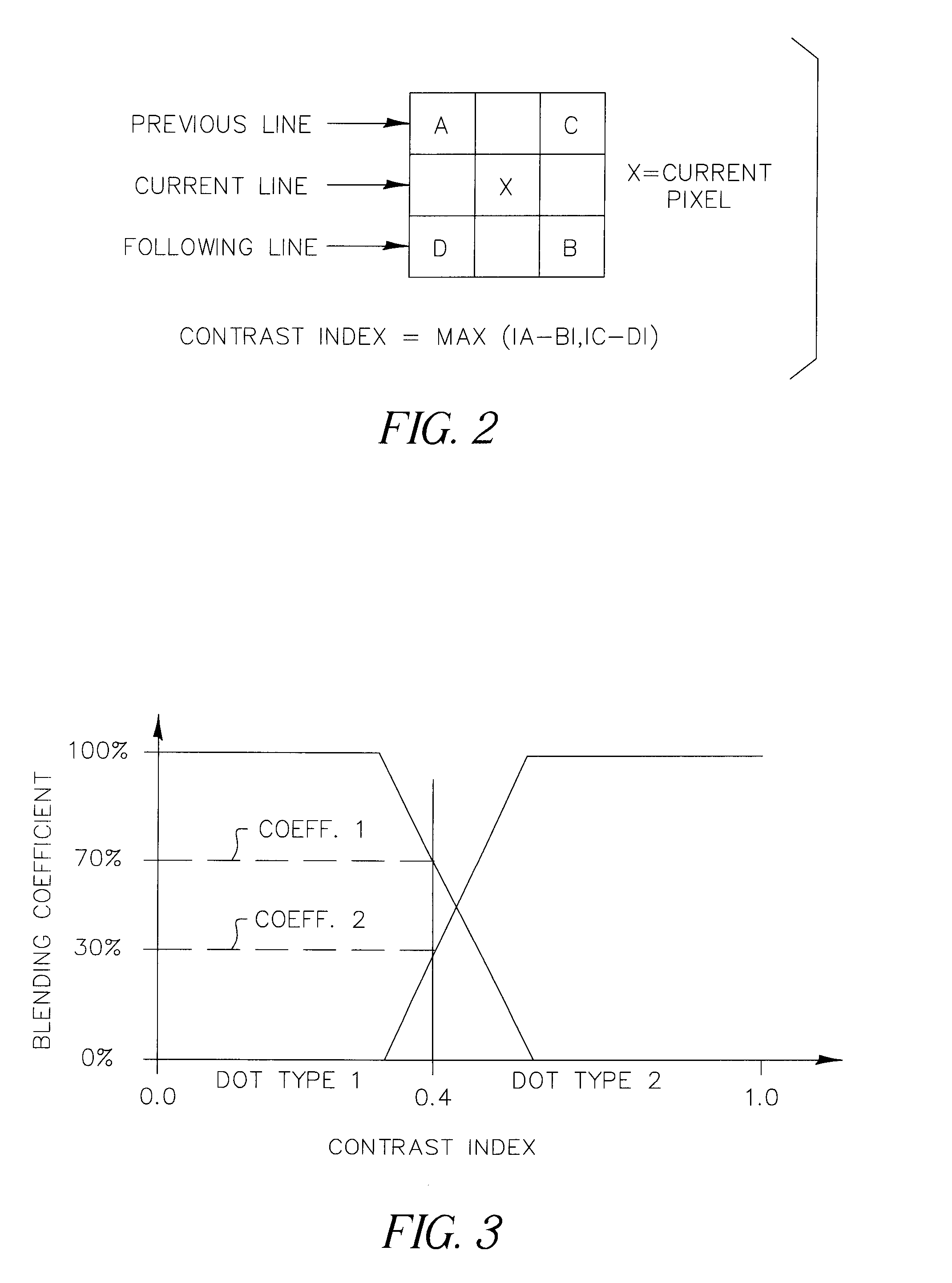Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
257 results about "Continuous tone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
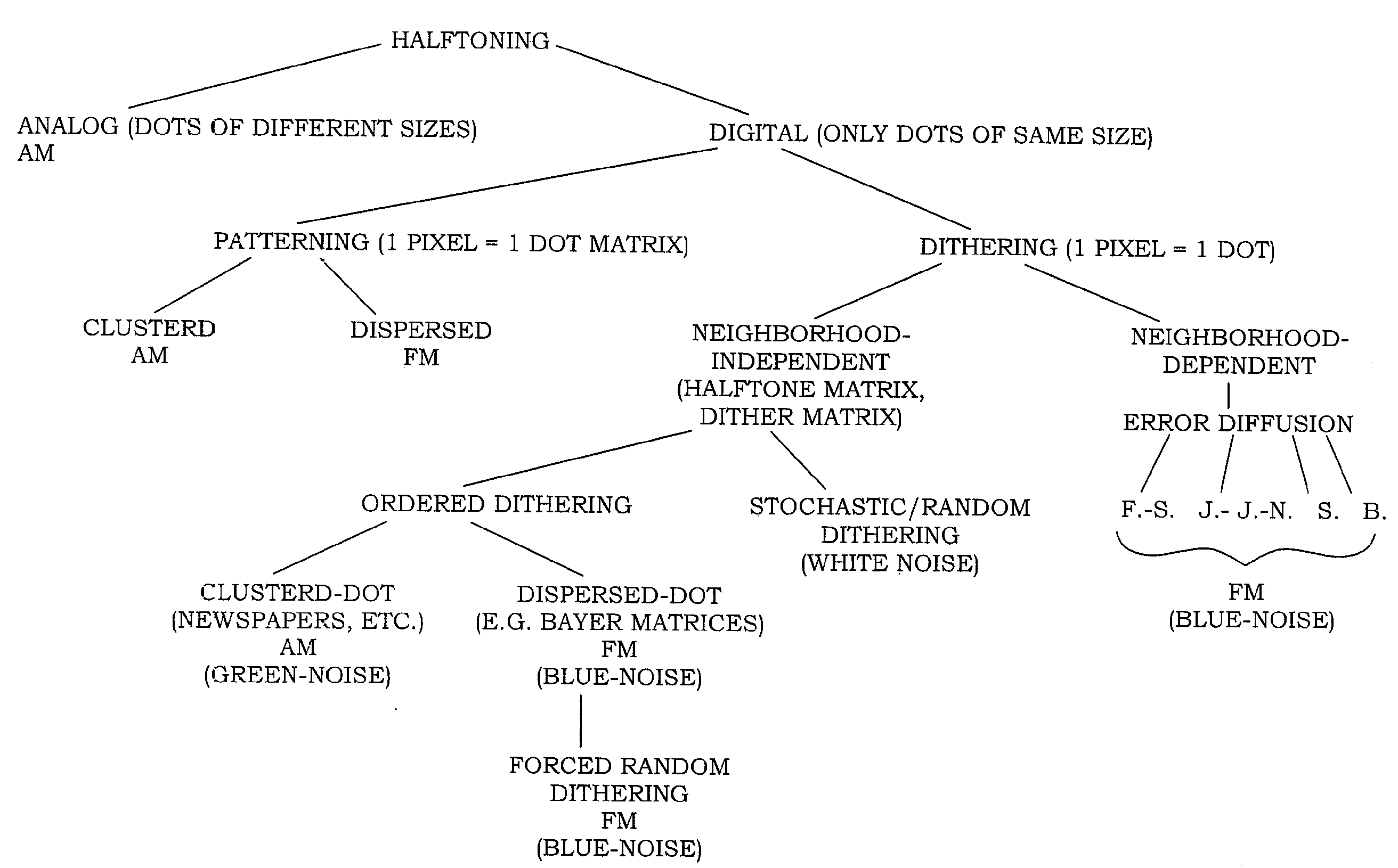
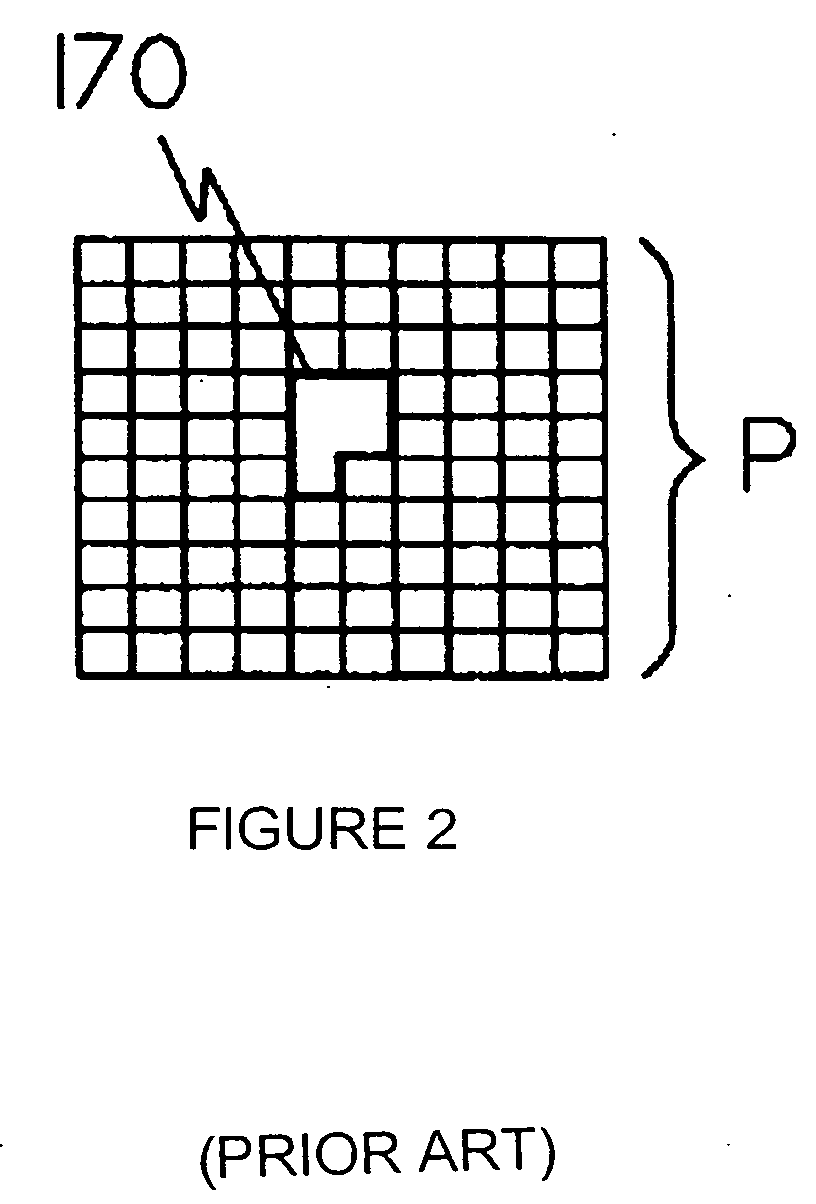
A continuous tone image (contone for short, or CT even shorter) is one where each color at any point in the image is reproduced as a single tone, and not as discrete halftones, such as one single color for monochromatic prints, or a combination of halftones for color prints.
Perceptual similarity image retrieval
InactiveUS7031555B2High degreeNoise insensitiveData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb serviceContinuous tone
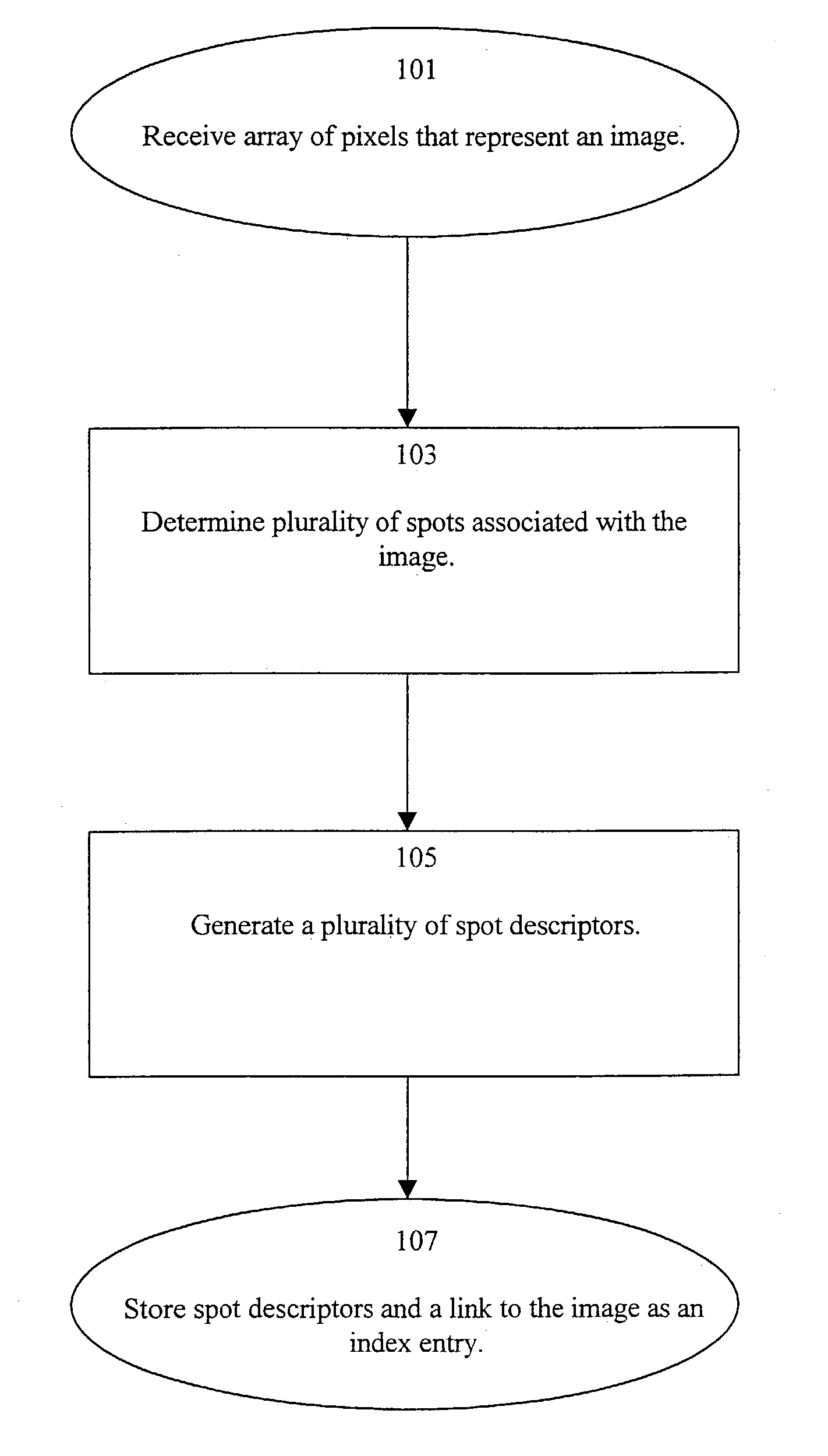
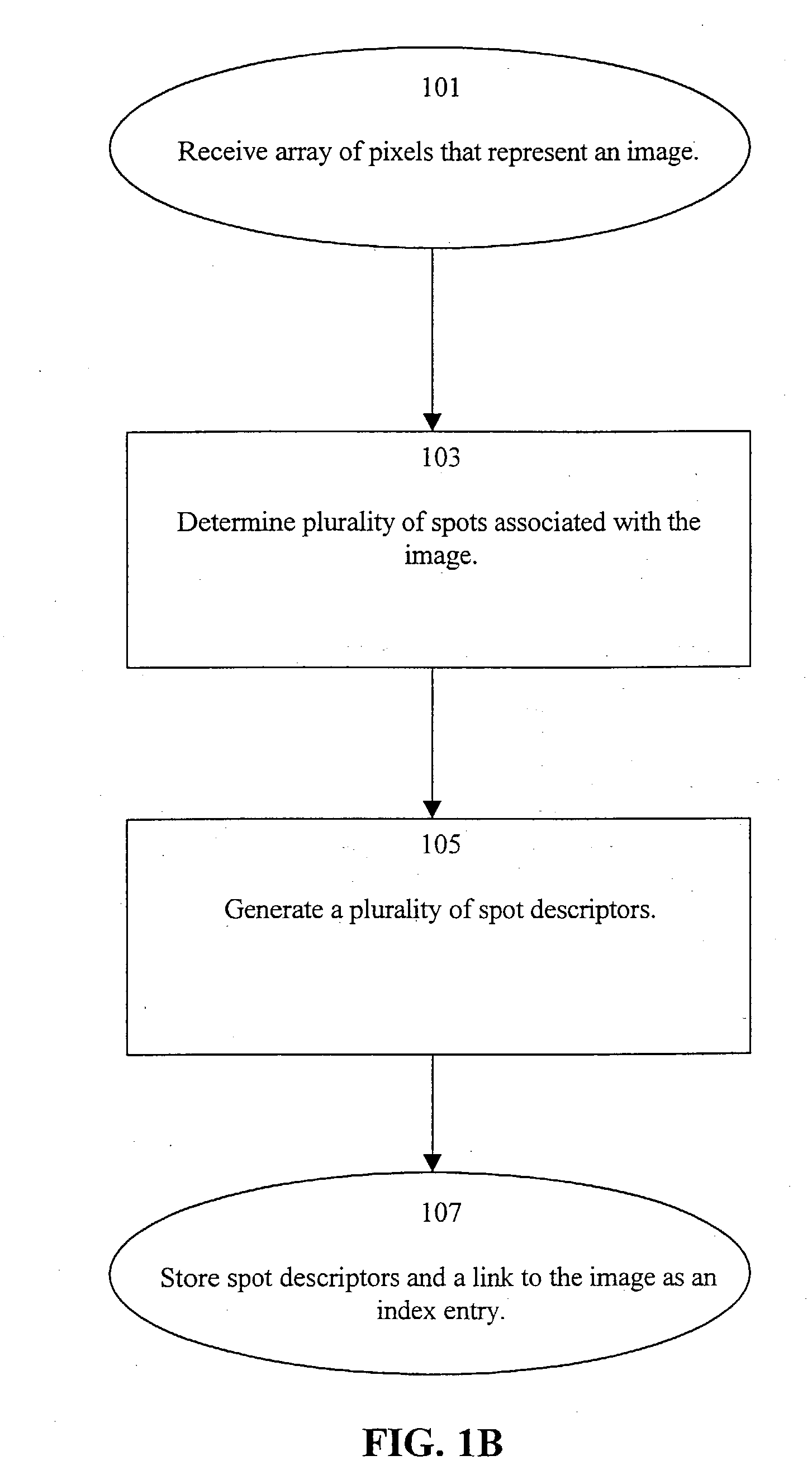
A system and method indexes an image database by partitioning an image thereof into a plurality of cells, combining the cells into intervals and then spots according to perceptual criteria, and generating a set of spot descriptors that characterize the perceptual features of the spots, such as their shape, color and relative position within the image. The shape preferably is a derivative of the coefficients of a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the perimeter trace of the spot. The set of spot descriptors forms as an index entry for the spot. This process repeated for the various images of the database. To search the index, a key comprising a set of spot descriptors for a query image is generated and compared according to a perceptual similarity metric to the entries of the index. The metric determines the perceptual similarity that the features of the query image match those of the indexed image. The search results are presented as a scored list of the indexed images. A wide variety of image types can be indexed and searched, including: bi-tonal, gray-scale, color, “real scene” originated, and artificially generated images. Continuous-tone “real scene” images such as digitized still pictures and video frames are of primary interest. There are stand alone and networked embodiments. A hybrid embodiment generates keys locally and performs image and index storage and perceptual comparison on a network or web server.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Weld characteristic communication system for a welding mask
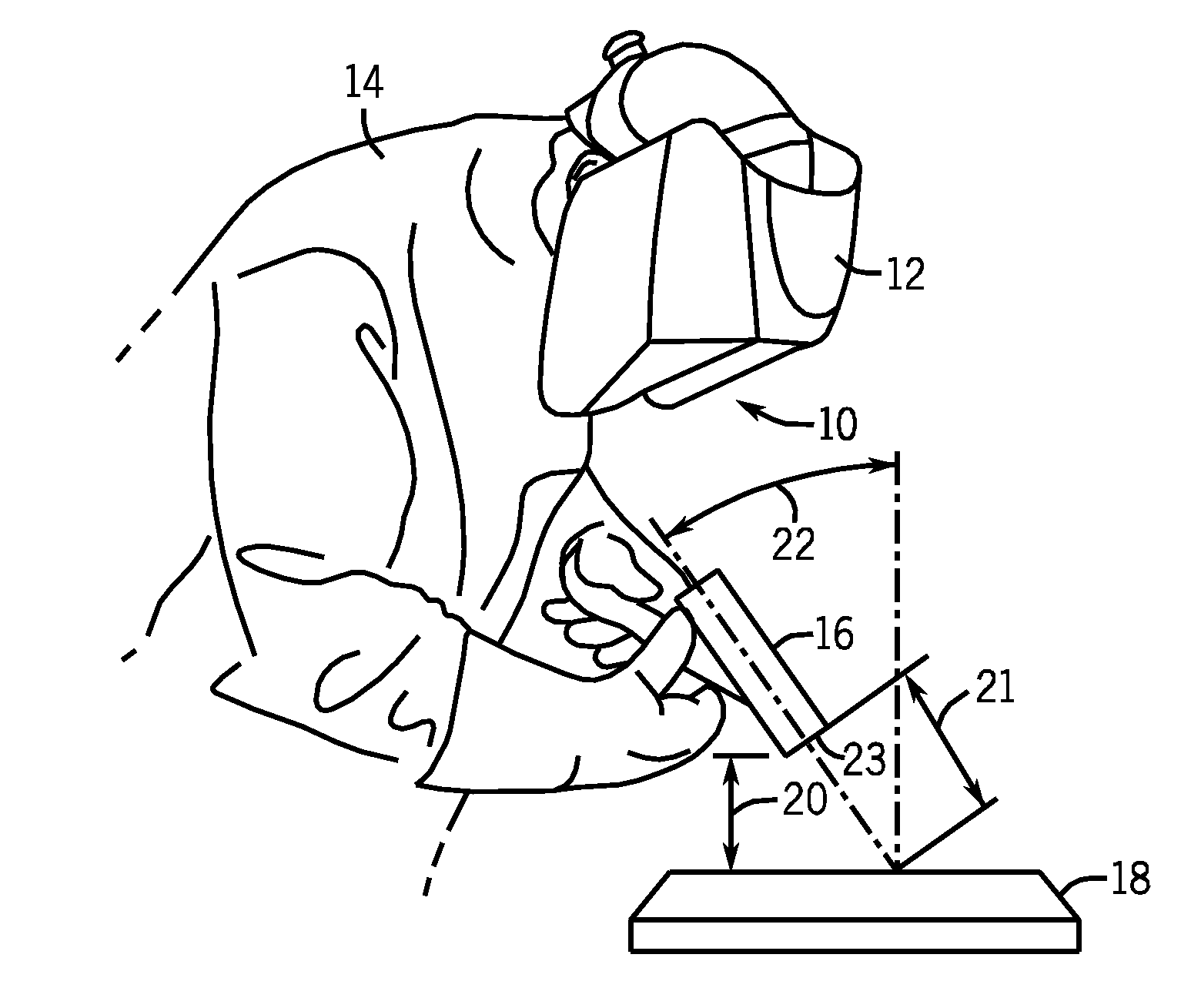
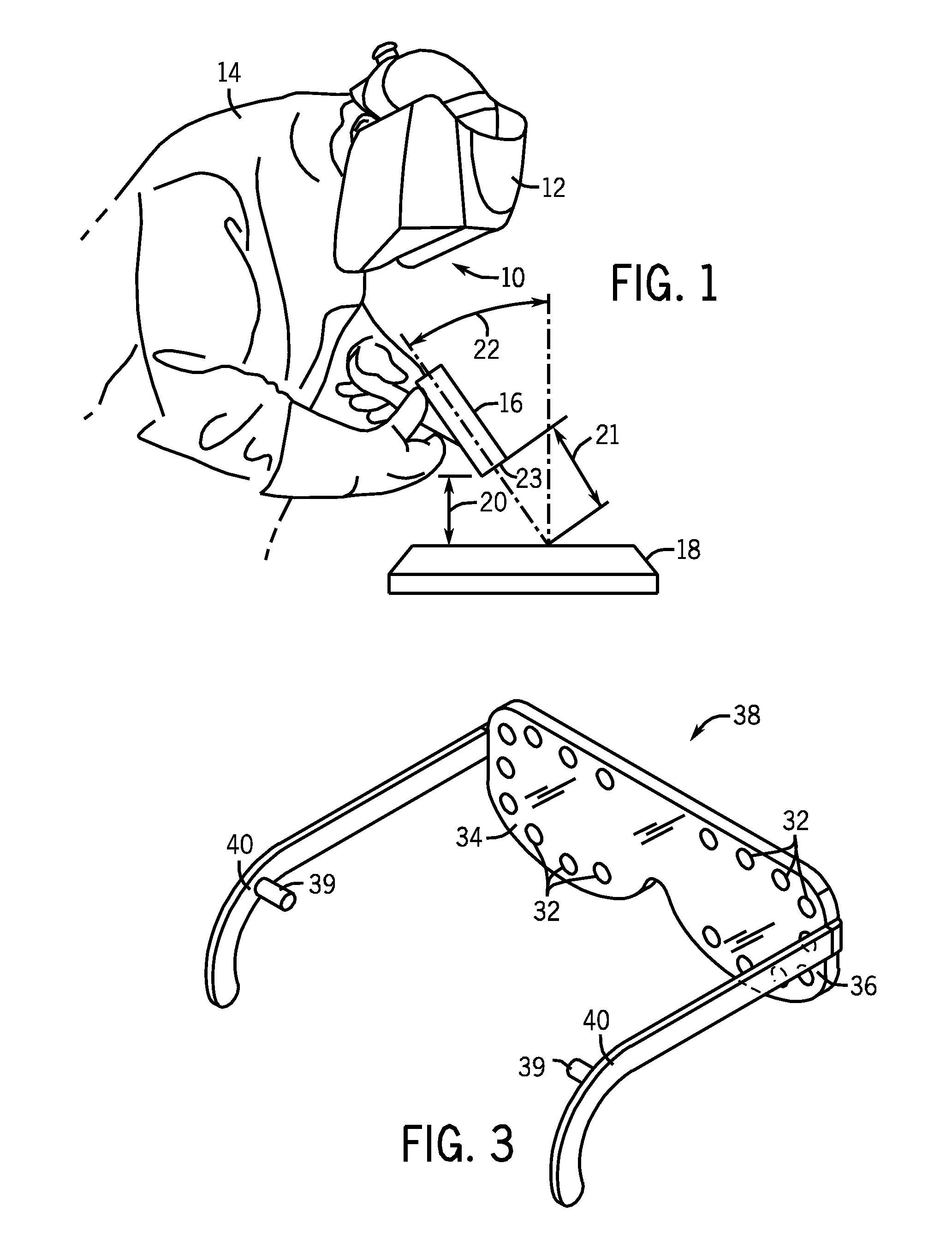
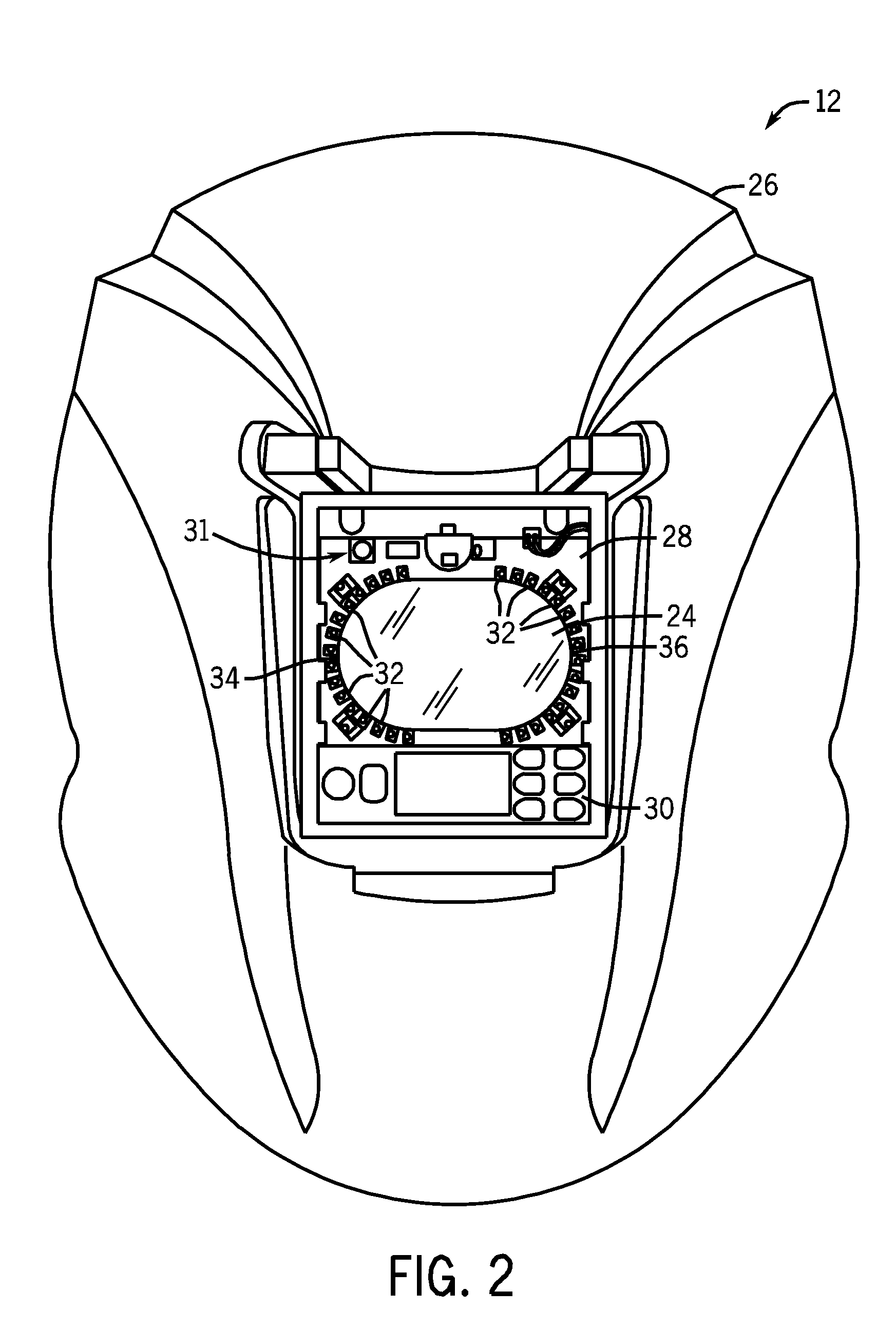
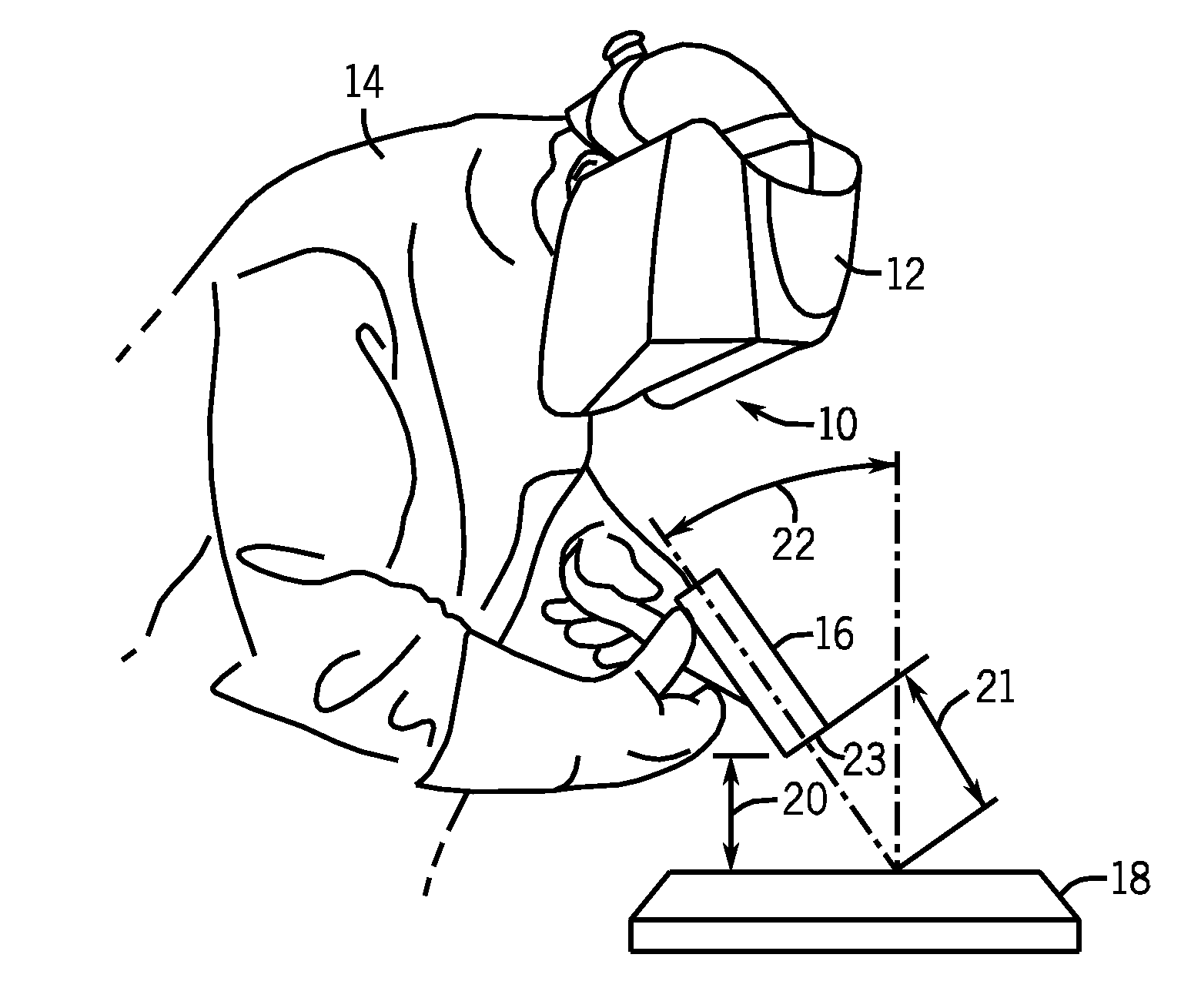
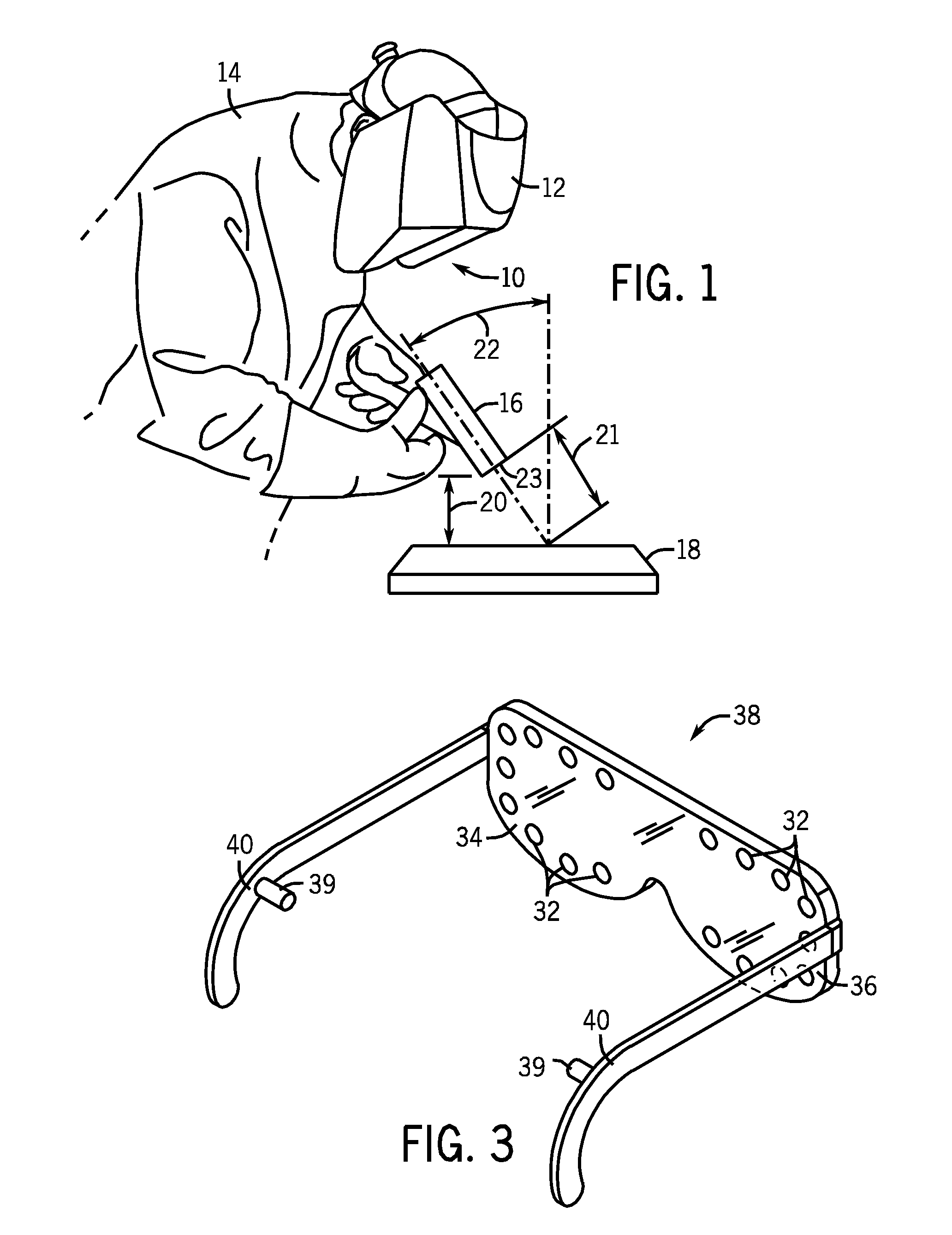
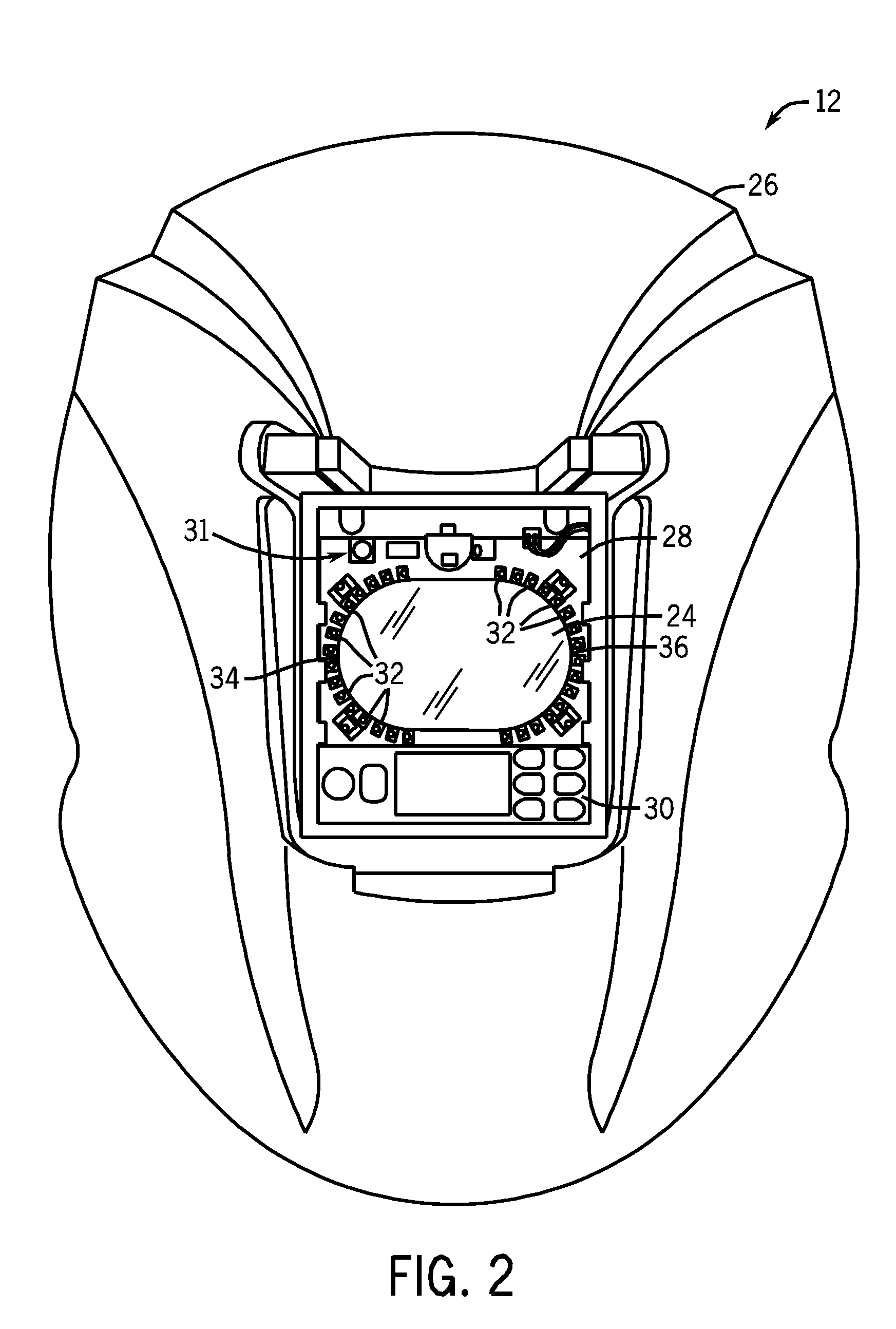
Methods and systems for transmitting a torch angle and / or a torch-to-workpiece distance error to a welding operator when these parameters are outside of a preset optimal range via real time visual and / or audio cues are provided. One embodiment of the present disclosure relates to weld characteristic communication via intuitive arrays of visual indicators located on the periphery of a lens, which indicate to the welding operator the direction and severity of the torch angle error. In one embodiment, audio cues, such as pulsed or continuous tones may be used to communicate torch-to-workpiece distance to the welding operator. In certain embodiments, vertical visual indicator arrays may be used to indicate additional weld or auxiliary information, such as battery charge state, torch speed and so forth, to the welding operator. All the components of the communication system may be located in or on the welding helmet or the components may be split between the helmet and a belt pack.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Perceptual similarity image retrieval
InactiveUS20030231806A1High degree of successInsensitive to irrelevant detailData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalWeb serviceContinuous tone
A system and method indexes an image database by partitioning an image thereof into a plurality of cells, combining the cells into intervals and then spots according to perceptual criteria, and generating a set of spot descriptors that characterize the perceptual features of the spots, such as their shape, color and relative position within the image. The shape preferably is a derivative of the coefficients of a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the perimeter trace of the spot. The set of spot descriptors forms as an index entry for the spot. This process repeated for the various images of the database. To search the index, a key comprising a set of spot descriptors for a query image is generated and compared according to a perceptual similarity metric to the entries of the index. The metric determines the perceptual similarity that the features of the query image match those of the indexed image. The search results are presented as a scored list of the indexed images. A wide variety of image types can be indexed and searched, including: bi-tonal, gray-scale, color, "real scene" originated, and artificially generated images. Continuous-tone "real scene" images such as digitized still pictures and video frames are of primary interest. There are stand alone and networked embodiments. A hybrid embodiment generates keys locally and performs image and index storage and perceptual comparison on a network or web server.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Weld characteristic communication system for a welding mask
Methods and systems for transmitting a torch angle and / or a torch-to-workpiece distance error to a welding operator when these parameters are outside of a preset optimal range via real time visual and / or audio cues are provided. One embodiment of the present disclosure relates to weld characteristic communication via intuitive arrays of visual indicators located on the periphery of a lens, which indicate to the welding operator the direction and severity of the torch angle error. In one embodiment, audio cues, such as pulsed or continuous tones may be used to communicate torch-to-workpiece distance to the welding operator. In certain embodiments, vertical visual indicator arrays may be used to indicate additional weld or auxiliary information, such as battery charge state, torch speed and so forth, to the welding operator. All the components of the communication system may be located in or on the welding helmet or the components may be split between the helmet and a belt pack.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Three-dimensional portrait photograph system and realizing method thereof
InactiveCN101082765AHard textureNew Visual EnjoymentPrintersProjectorsContinuous toneLaser engraving
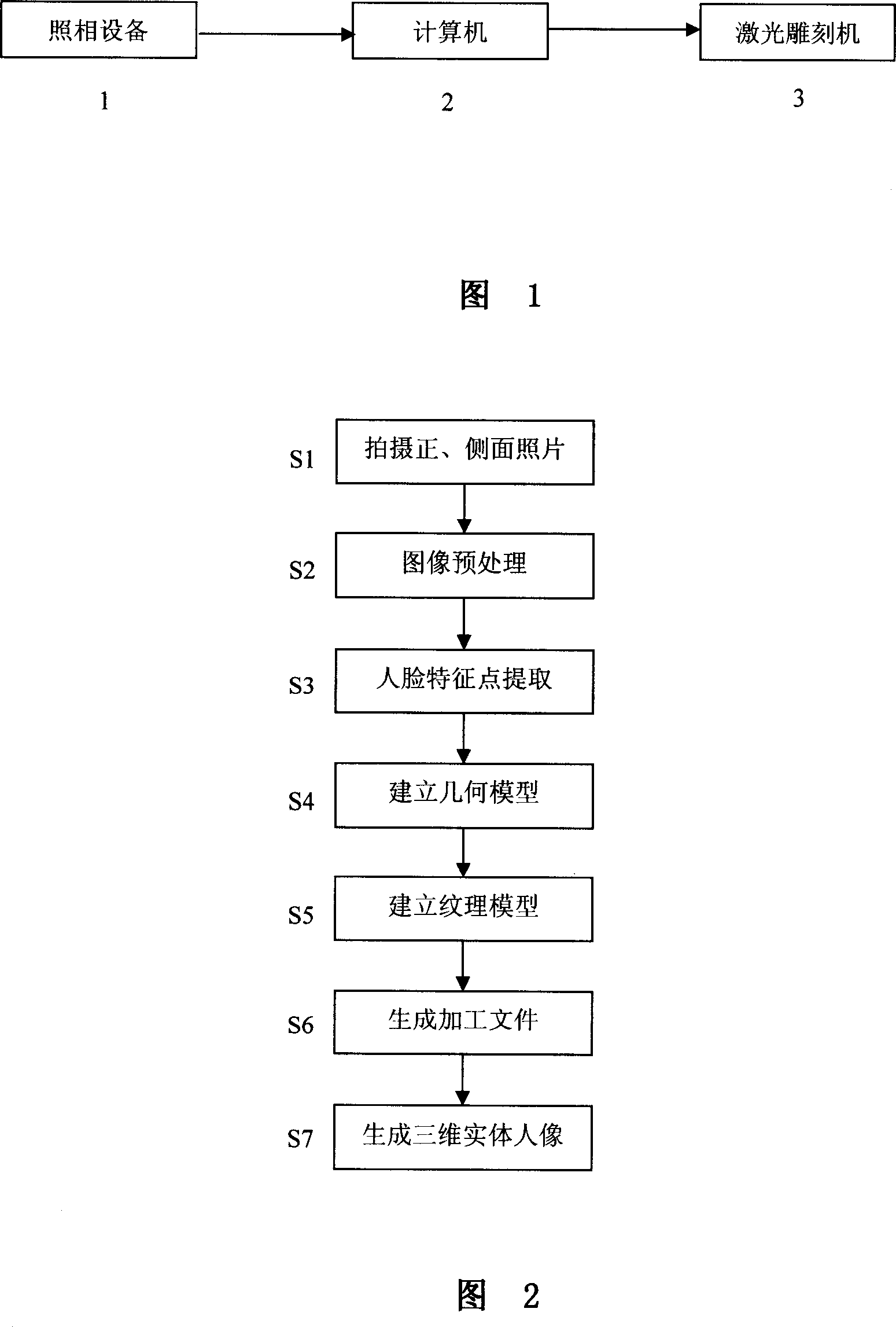
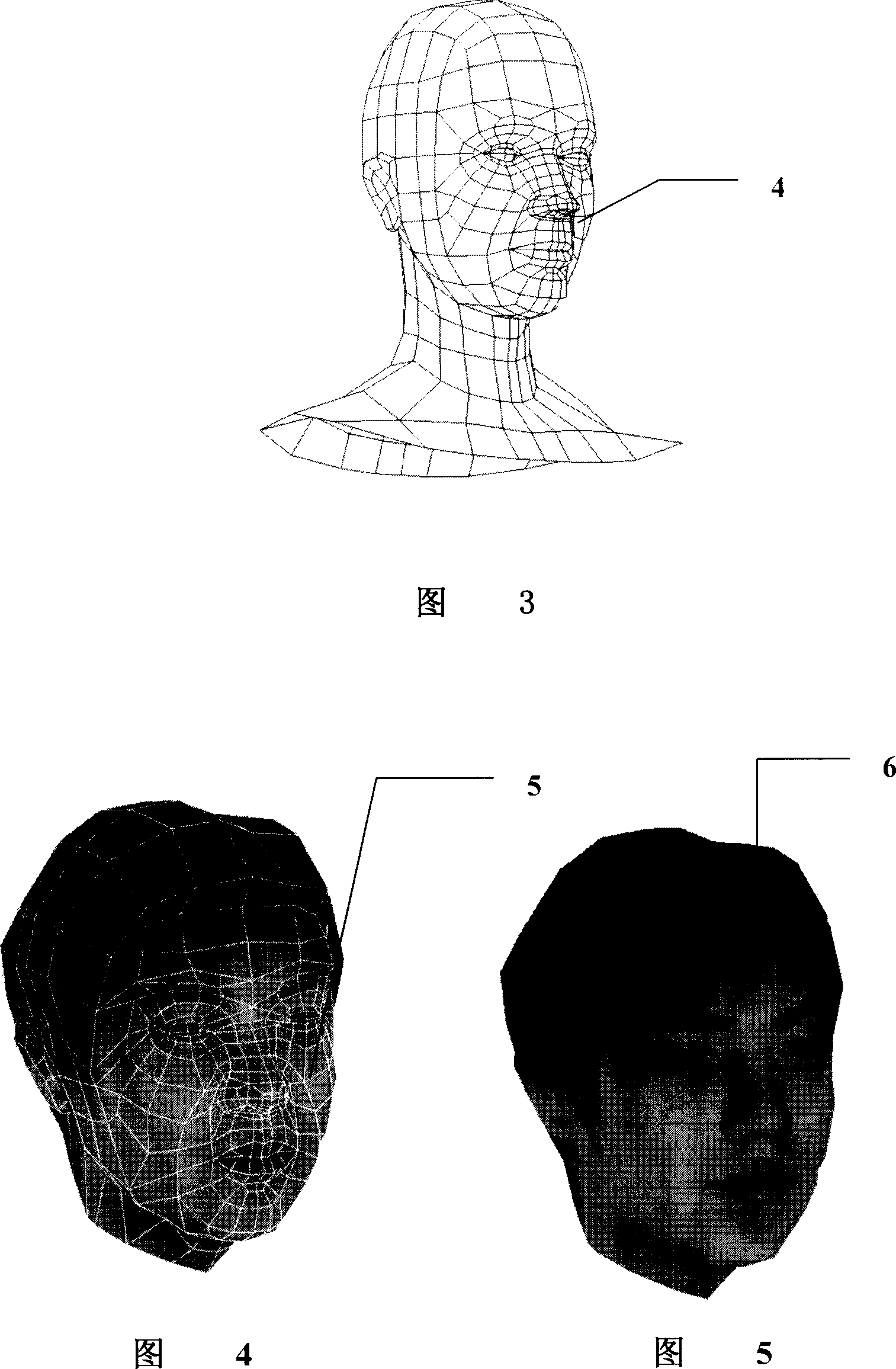
The invention discloses a three-dimensional portrait shooting system and realizing method, which comprises the following steps: using common camera to shoot positive and lateral photos of portrait; adopting computer visual algorism to acquire three-dimensional geometrical model of head; projecting the photo as texture on the three-dimensional mould according to the projecting relationship of photo and geometrical model; obtaining the three-dimensional portrait model with photo-grade true sense; using spatial semi-tone method to modulate the space of texture grey image continuously; printing binary image approaching three-dimensional image on the visual observing effect in the artificial crystal through laser carving machine; forming the three-dimensional entity head portrait with true sense.
Owner:高宏 +1
De-screening halftones using sigma filters
InactiveUS6947178B2Reduce degradationEasy to createImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageDigital imaging
A digital imaging system and method uses a two-stage sigma filter to de-screen color images. This filter does not assume any a priori knowledge about the screening process using to produce the halftone image. The two-stage sigma filter may therefore be used to convert color halftone images into continuous-tone images irrespective of the screening process used. The two-stage sigma filter may be constructed, or emulated in software, using an O (N) algorithm which performs smoothing and preserves edge information simultaneously in the Red / Green / Blue color space. This system and method outperforms conventional approaches which, for example, use a Gaussian blur, because it satisfies the dual criteria of completely eliminating halftone screens while preserving edge information. When combined with halftone segmentation techniques, a complete document processing algorithm for gray-scale and color documents is created.
Owner:RICOH KK
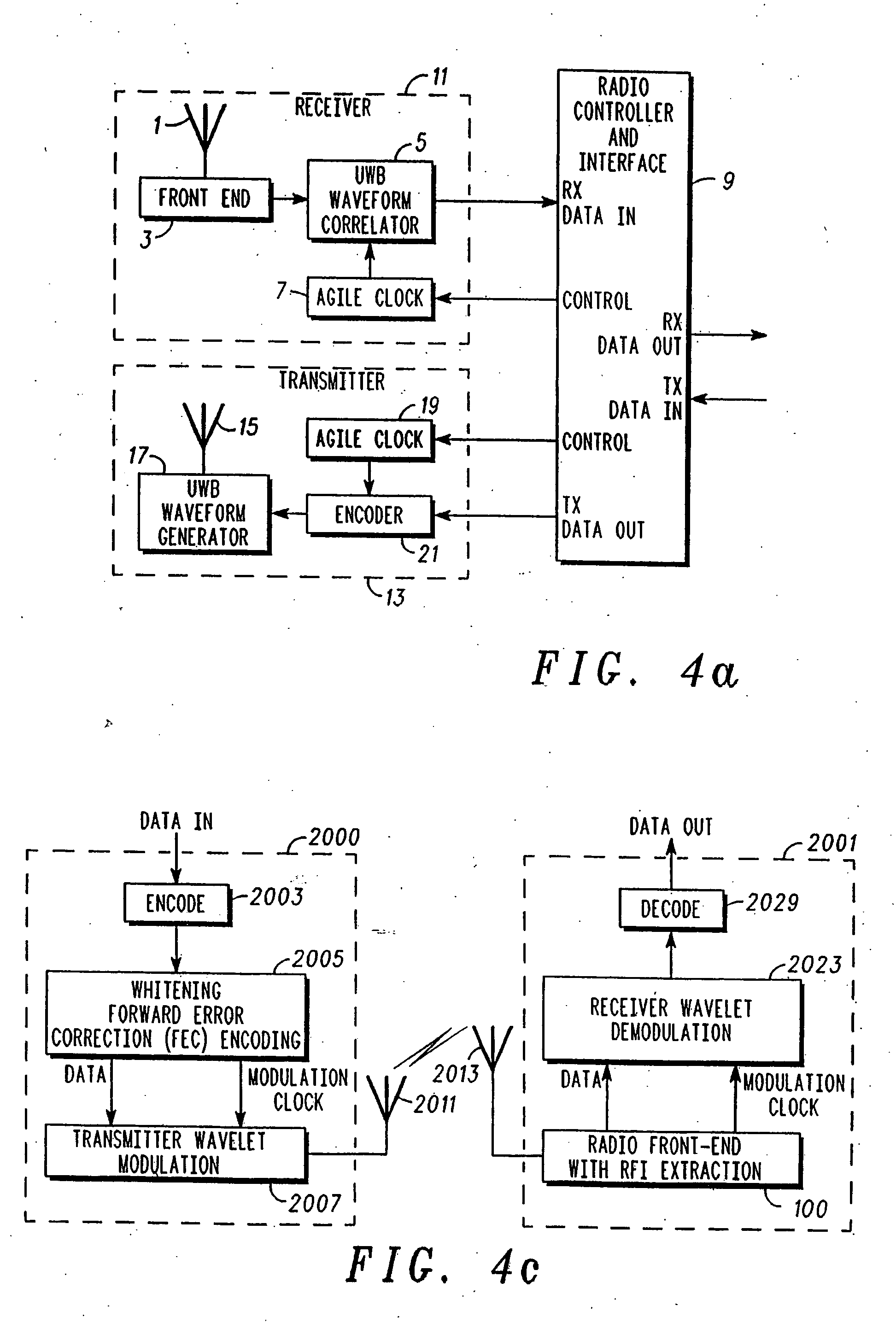
Analog signal separator for UWB versus narrowband signals
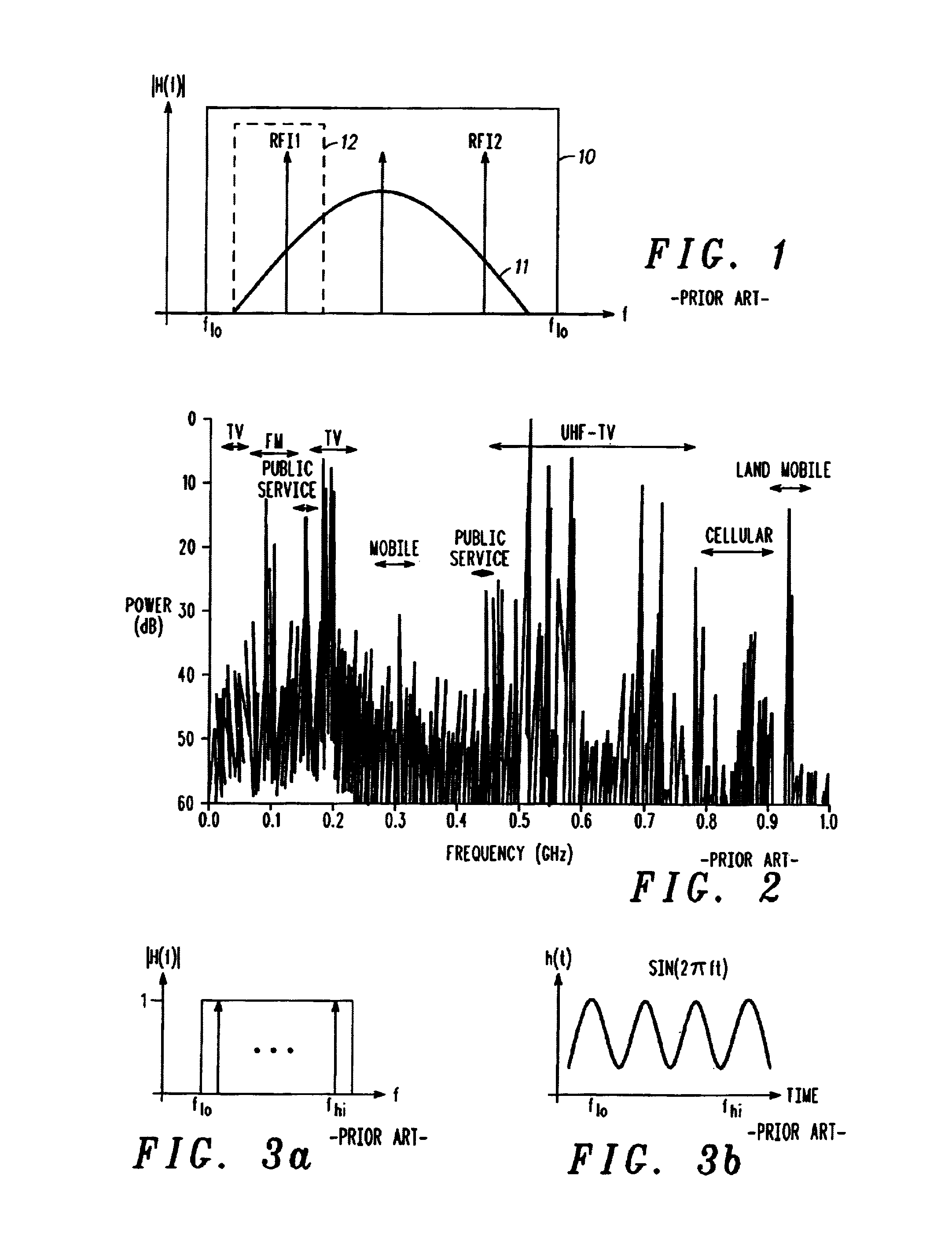
InactiveUS7006553B1Improve dynamic rangeAvoid saturationTyre partsTelevision system detailsFrequency spectrumContinuous tone
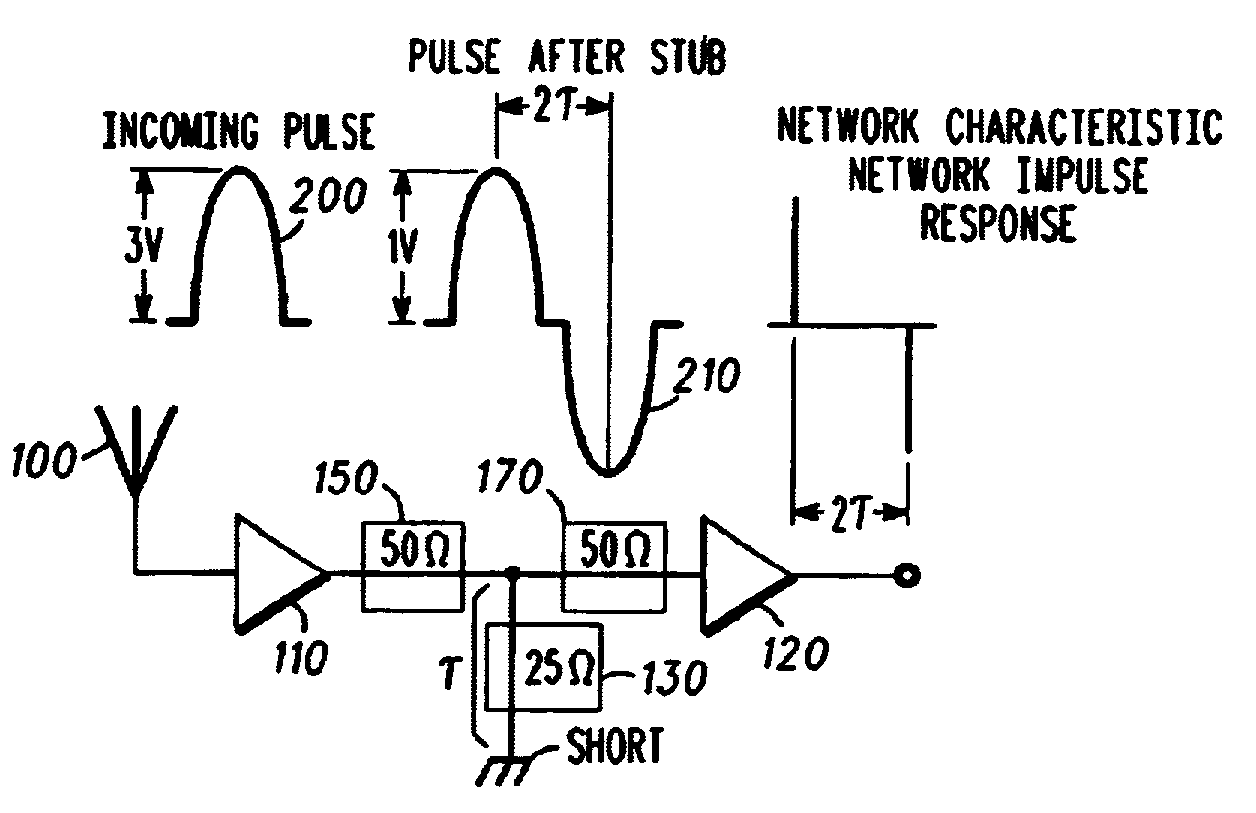
A system, method, and computer program product for removing “narrowband” interference from a broader spectrum containing a UWB signal, in a receiver of the UWB signal. The RFI is extracted from a broader spectrum to remove interference from the UWB signal, by employing an impulse response in a radio front-end of the UWB receiver that is matched with an incoming wavelet employed as part of a UWB signal to be received, matching the impulse response to the wavelet and its time-shifted and inverted versions, passing the wavelet unscathed through the receiver, and excising narrowband signals (continuous tones). Exemplary embodiments for the RFI extraction mechanism include a transmission line circuit, an active transmission line circuit, and an adaptable, controllable phase delay circuit.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
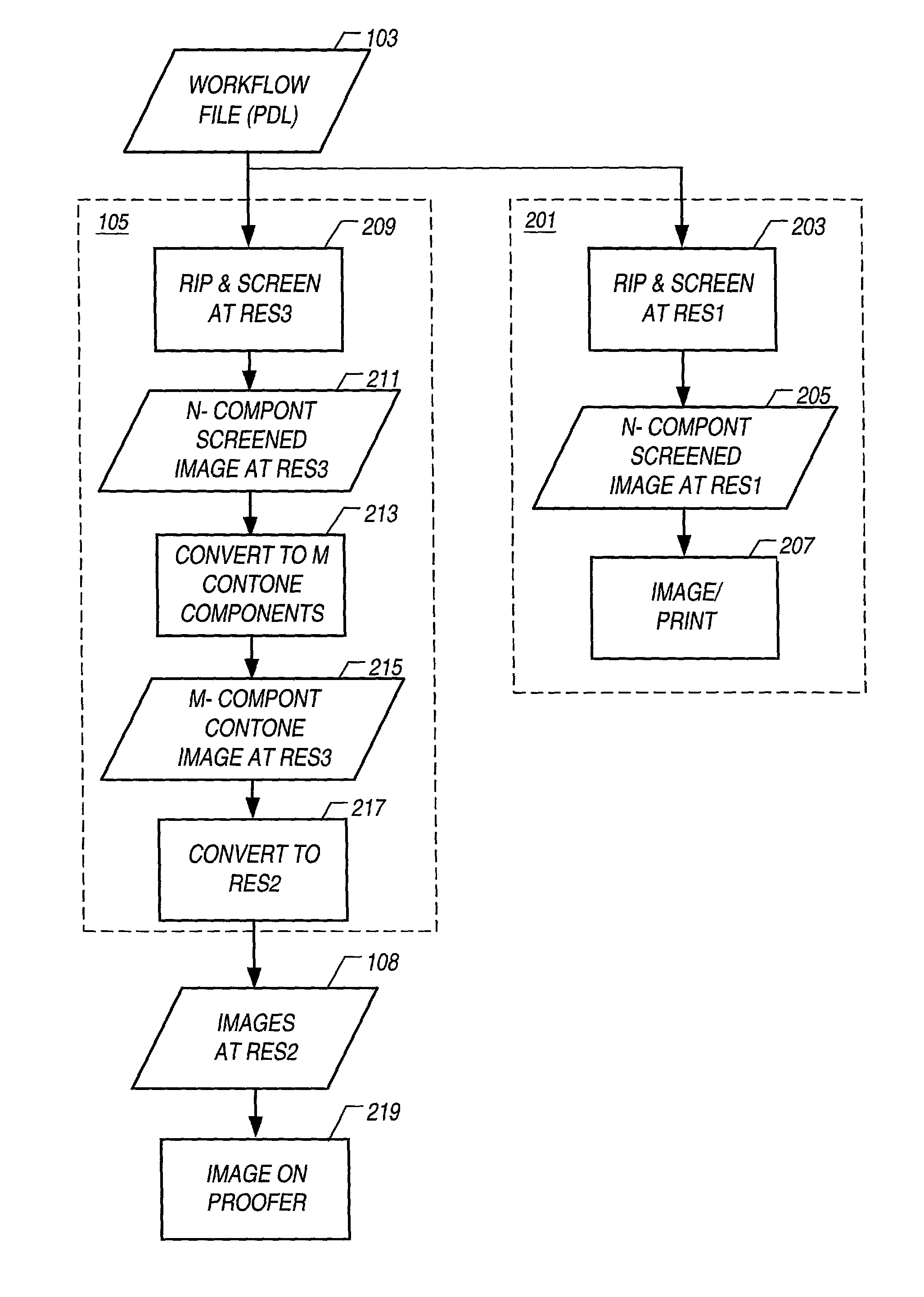
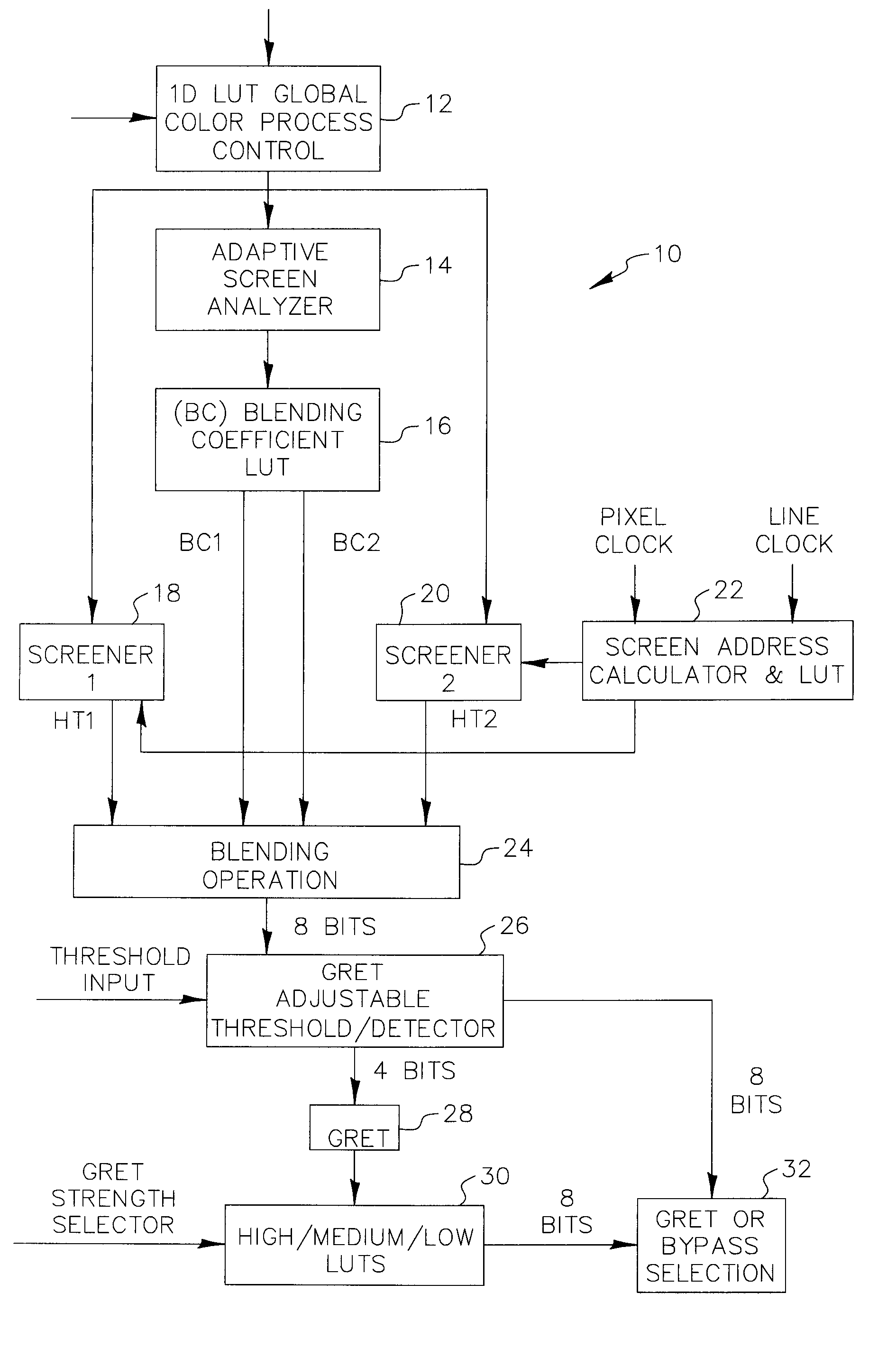
Proofing method, apparatus, and computer software product matching color and halftone screen properties
ActiveUS7068391B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsContinuous toneOutput device
A method, apparatus, and computer software product to reproduce an input image on a proofing device including accurately reproducing color substantially matching the screening properties of an imaging process that includes screening. The proofer may use a different number of colorants and / or different colorants than the printing colorants of the imaging process. The proofer also may be capable of continuous tone output or may be a screened output device. The proofer also may be a computer screen.
Owner:BARCO GRAPHICS
Printed page tag encoder
InactiveUS7070098B1Ease dot detection and decoding algorithmEasy to placeDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersComputer graphics (images)Continuous tone
A tag encoder for producing tags to be incorporated into a printed page is disclosed. The tag encoder has an input to receive a tag structure template, an input to receive fixed data bits, an input to receive variable data bit records and a tag generator outputting single bits depending on the position in the tag defined by the tag structure template and the fixed and variable data bits. The encoder has a redundancy encoder which utilizes Reed-Solomon encoding. The tag encoder is present in a printer. In addition to the tag encoder, the printer has a contone image decoder to decode compressed continuous tone image planes and a bi-level decoder to decode any compressed bi-level image plane in the compressed data. These decoded image planes are combined with the output of the tag encoder in a halftoner / compositor to produce a printed page carrying tagged areas. The tags are printed in ink which is invisible to the human eye. Such inks, could be IR or UV absorptive.
Owner:ZAMTEC
Multipass Printing
A multi-pass printing system and a corresponding method are provided for printing an image, which includes a plurality of continuous-tone values, based on halftone matrices having threshold values. The printed image is composed of sub-images, each of which includes dots printed in a respective pass. The sub-images present independent dot patterns at corresponding places. The printing system is arranged to obtain the sub-images by splitting the continuous-tone values into at least two pass values, an individual pass value indicating an intensity to be printed in a respective pass. Then, in one pass a first halftone matrix for printing the respective pass values, and in another pass one or more second halftone matrices are used, which are obtained by positionally shifting the threshold values of the first halftone matrix, for printing all pass values of the other pass, or at least those pass values above a highlight threshold.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
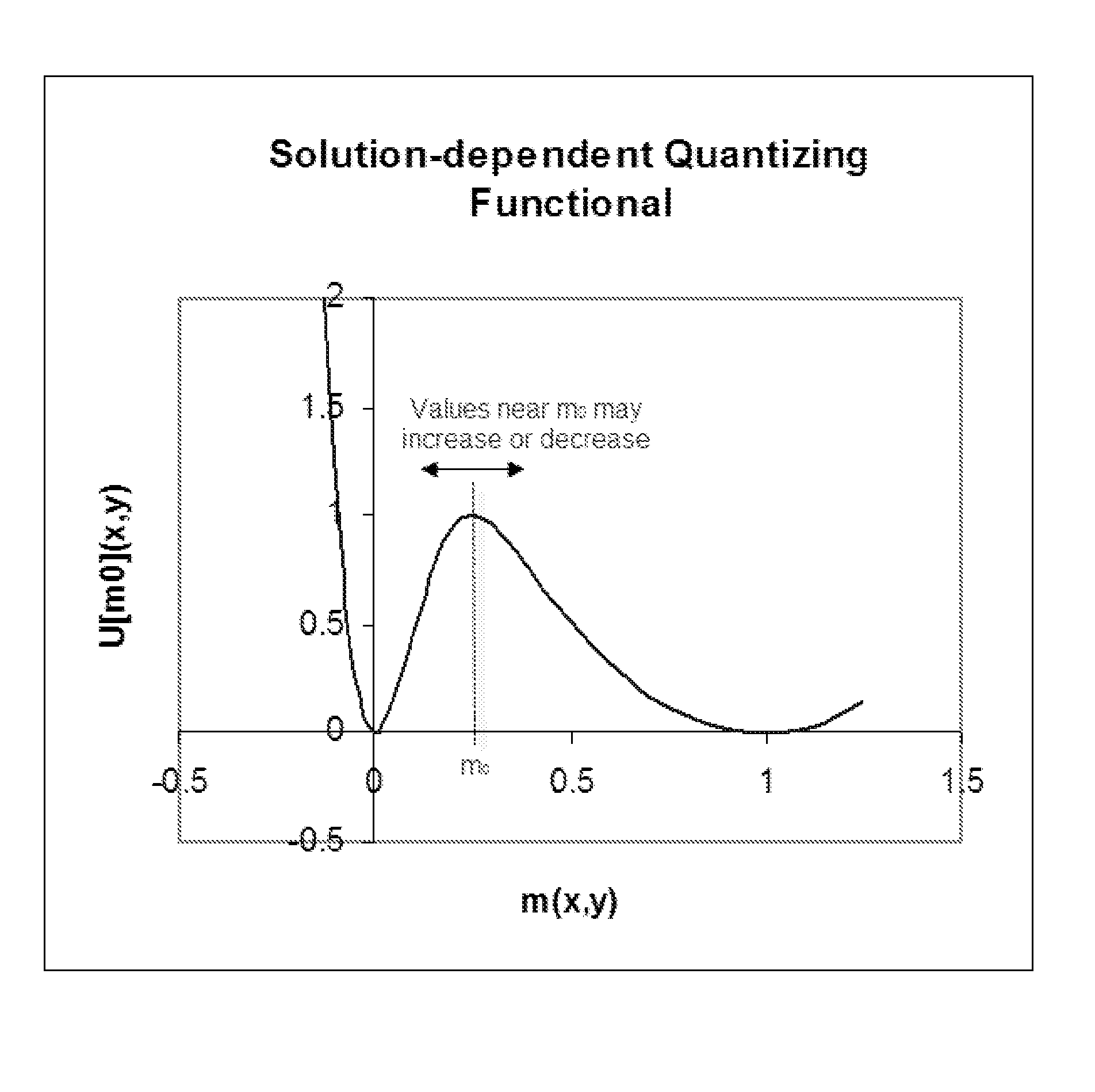
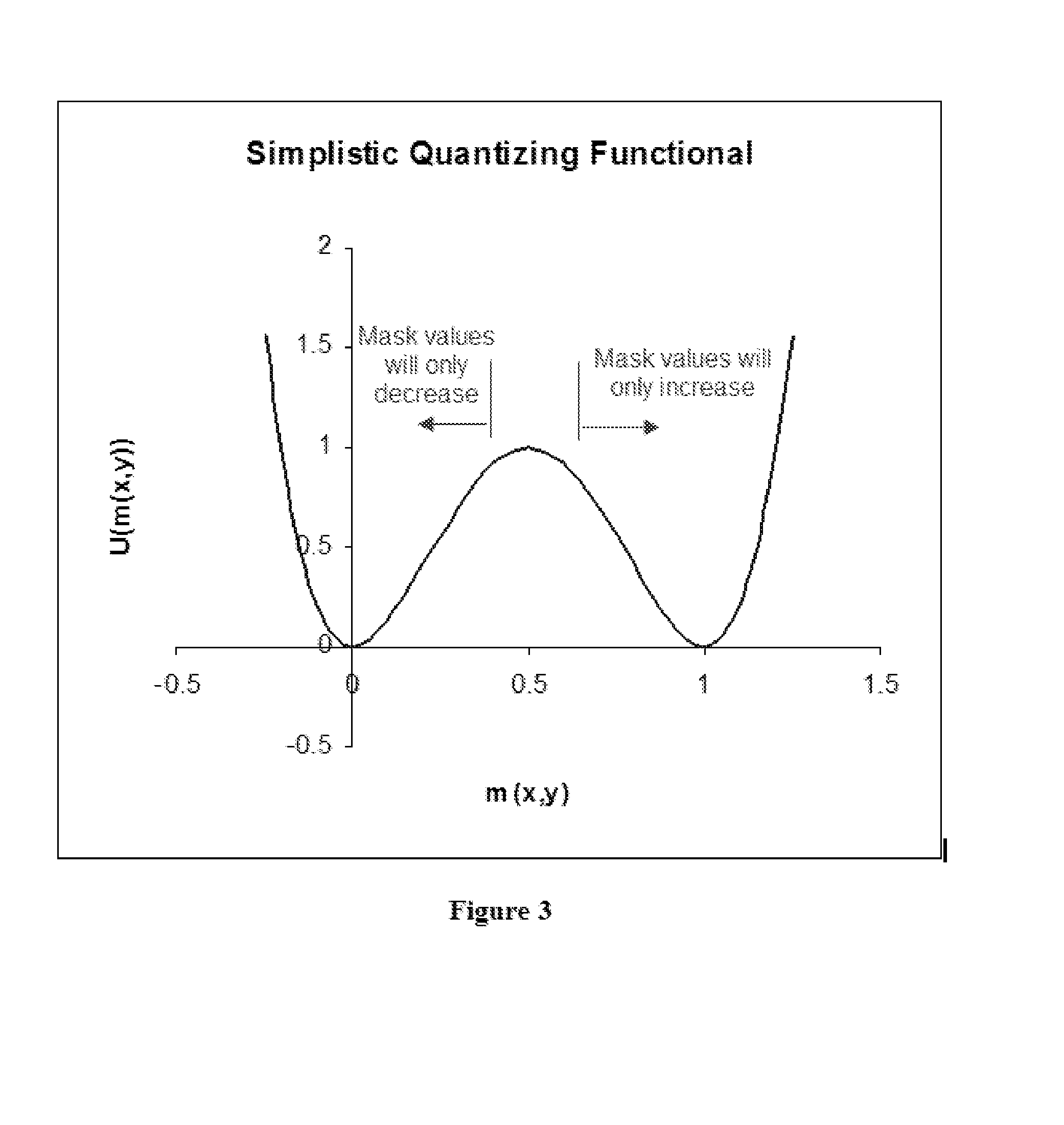
Solution-dependent regularization method for quantizing continuous-tone lithography masks
ActiveUS7716627B1Large fractionNatural language data processingCAD circuit designContinuous toneEngineering
In an electronic design automation technique for optical proximity correction, an optimized mask function that has values other than those allowed for a particular mask type, such as 0 and 1 for a chrome-on-glass binary mask, evolves it to a solution restricted to these values or narrow intervals near them. The technique “regularizes” the solution by mixing in a new cost functional that encourages the mask to assume the desired values. The mixing in may be done over one or more steps or even “quasistatically,” in which the total cost functional and the mask is brought from pure goodness-of-fit to the printed layout for given conditions to pure manufacturability by keeping the total cost functional minimized step-by-step. A goal of this gradual mixing-in is to do thermodynamically optimal work on the mask function to bring it to manufacturable values.
Owner:D2S
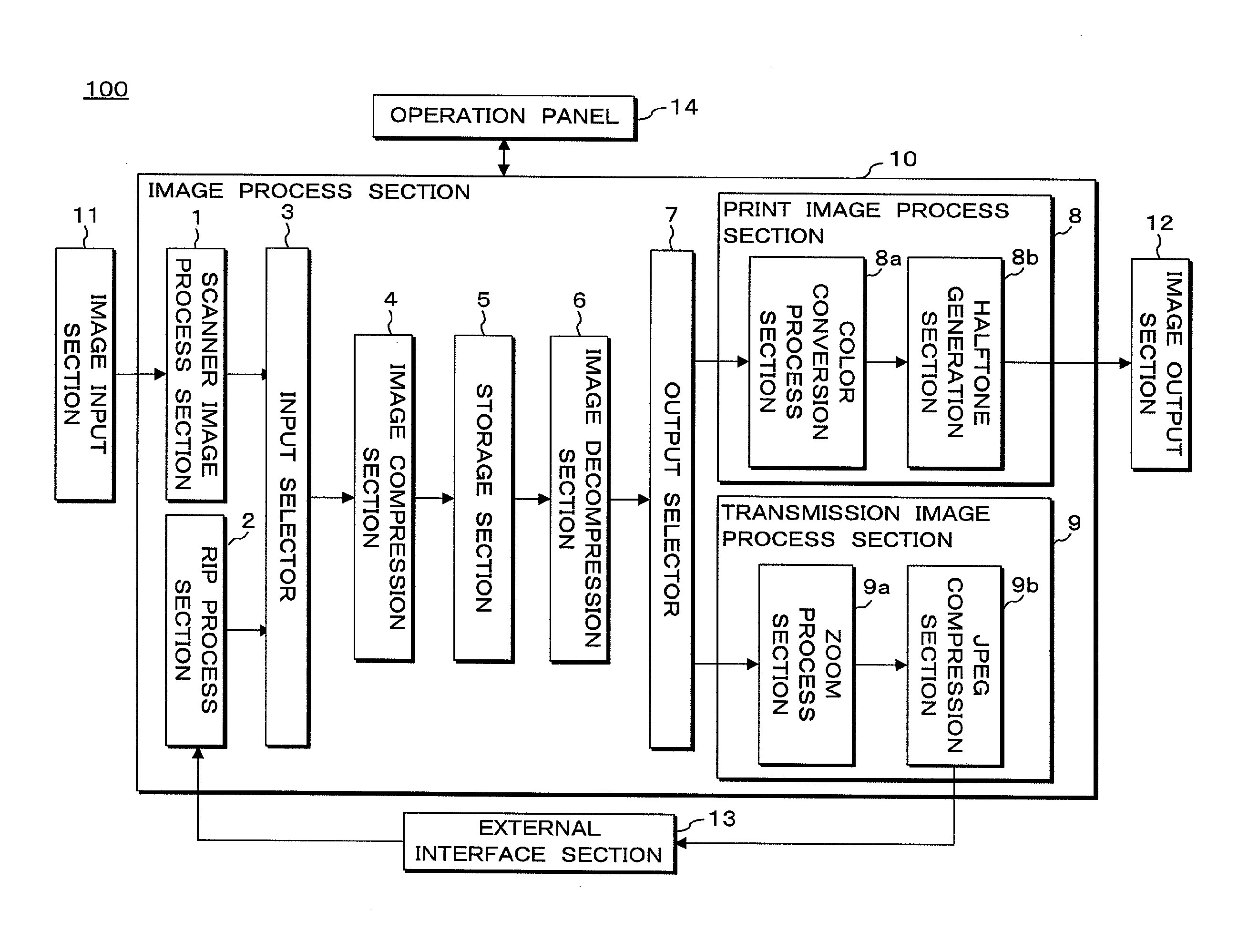
Image compressing apparatus, image compressing method, image decompressing apparatus, image decompressing method, image forming apparatus and recording meduim
ActiveUS20100329548A1Increase the compression ratioPerforming compression processCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationContinuous toneJPEG
When compressing continuous tone bit map image data, the image compression section of the image compressing apparatus segments the continuous tone bit map image data into bit map image data for lossy compression, index image data for lossless compression and bit map image data for lossless compression based on pixel identification information data. The lossy compression section of the image compression section performs lossy compression process according to the JPEG method for the bit map image data for lossy compression, and the first lossless compression section thereof performs lossless compression process according to the JBIG method for the index image data for lossless compression. Furthermore, the second lossless compression section thereof performs lossless compression process according to the JPEG-LS method for the bit map image data for lossless compression.
Owner:SHARP KK
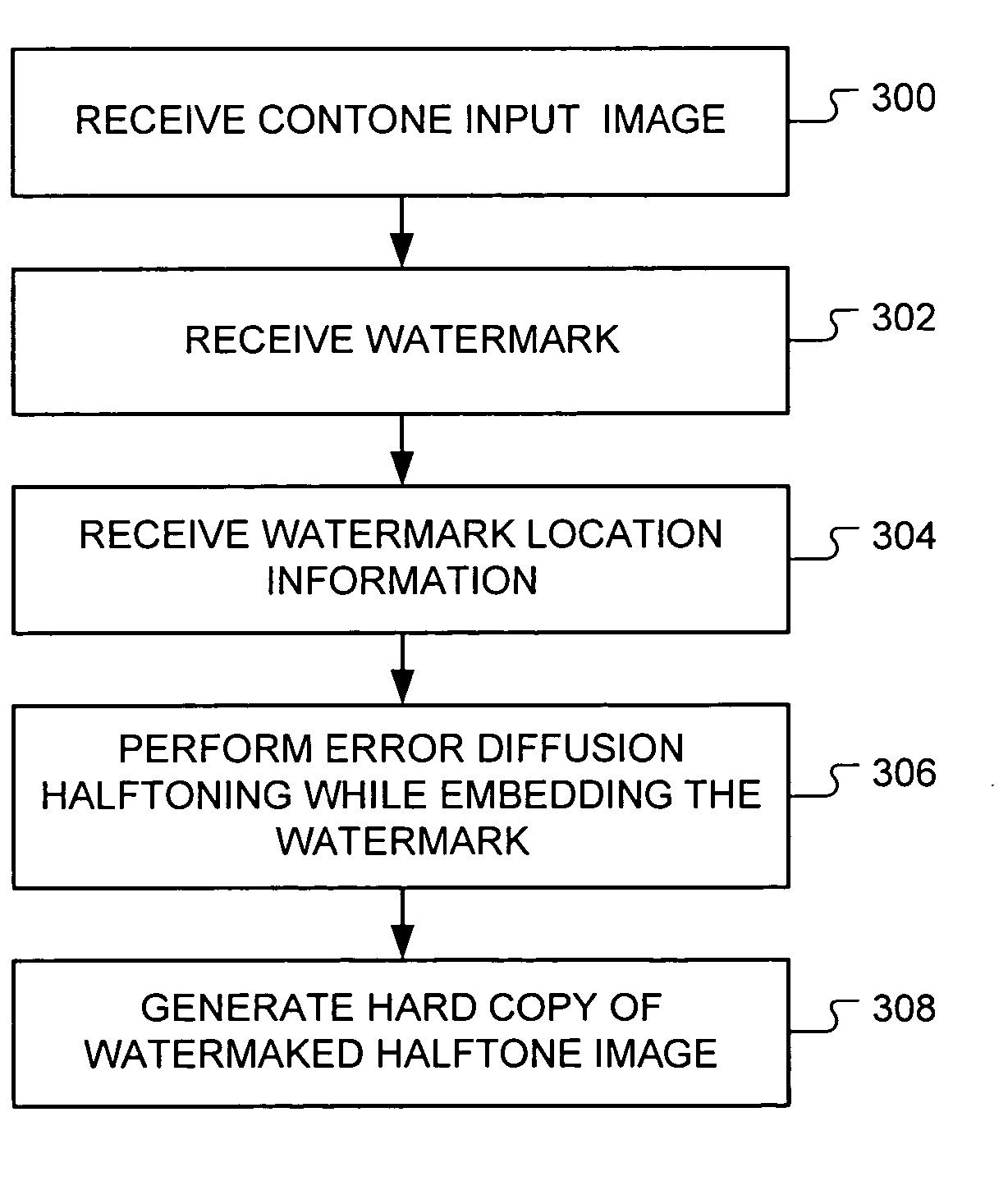
Error diffusion halftone watermarking
InactiveUS20050031160A1Other printing matterUser identity/authority verificationContinuous toneError diffusion
A watermarked halftone image is generated from a continuous tone image by performing error diffusion halftoning on the continuous tone image while adding a watermark to the halftone image during the halftoning. A location of the watermark in the halftone image may be based on prediction criteria. Error caused by adding the watermark may be diffused into the halftone image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Binary half tone photomasks and microscopic three-dimensional devices and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050118515A1Reduce areaNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusMicro structureThree dimensional microstructure
The present invention generally relates to improved binary half tone (“BHT”) photomasks and microscopic three-dimensional structures (e.g., MEMS, micro-optics, photonics, micro-structures and other three-dimensional, microscopic devices) made from such BHT photomasks. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for designing a BHT photomask layout, transferring the layout to a BHT photomask and fabricating three-dimensional microscopic structures using the BHT photomask designed by the method of the present invention. In this regard, the method of designing a BHT photomask layout comprises the steps of generating at least two pixels, dividing each of the pixels into sub-pixels having a variable length in a first axis and fixed length in a second axis, and arraying the pixels to form a pattern for transmitting light through the pixels so as to form a continuous tone, aerial light image. The sub-pixels' area should be smaller than the minimum resolution of an optical system of an exposure tool with which the binary half tone photomask is intended to be used. By using this method, it is possible to design a BHT photomask to have continuous gray levels such that the change in light intensity between each gray level is both finite and linear. As a result, when this BHT photomask is used to make a three-dimensional microscopic structure, it is possible to produce a smoother and more linear profile on the object being made.
Owner:PHOTRONICS INC
Pattern inspection method and apparatus, and pattern alignment method
InactiveCN1576782AEliminates the Effect of Density VariationsData processing applicationsImage analysisPattern recognitionContinuous tone
In a pattern inspection method, a master pattern serving as a reference and the continuous tone image of a pattern to be measured that is sensed by a camera are aligned. At least the position of a base in the continuous tone image of the pattern to be measured is detected on the basis of the master pattern. At least one threshold is set on the basis of the difference from at least the density value of the base. The continuous tone image of the pattern to be measured is binarized on the basis of the set threshold. The pattern to be measured is inspected by comparing the binarized pattern to be measured and the master pattern. A pattern inspection apparatus and alignment method are also disclosed.
Owner:NIPPON AVIONICS CO LTD
Progressive image coding
InactiveUS6031572AImprove visual qualityLow costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingImage transfer
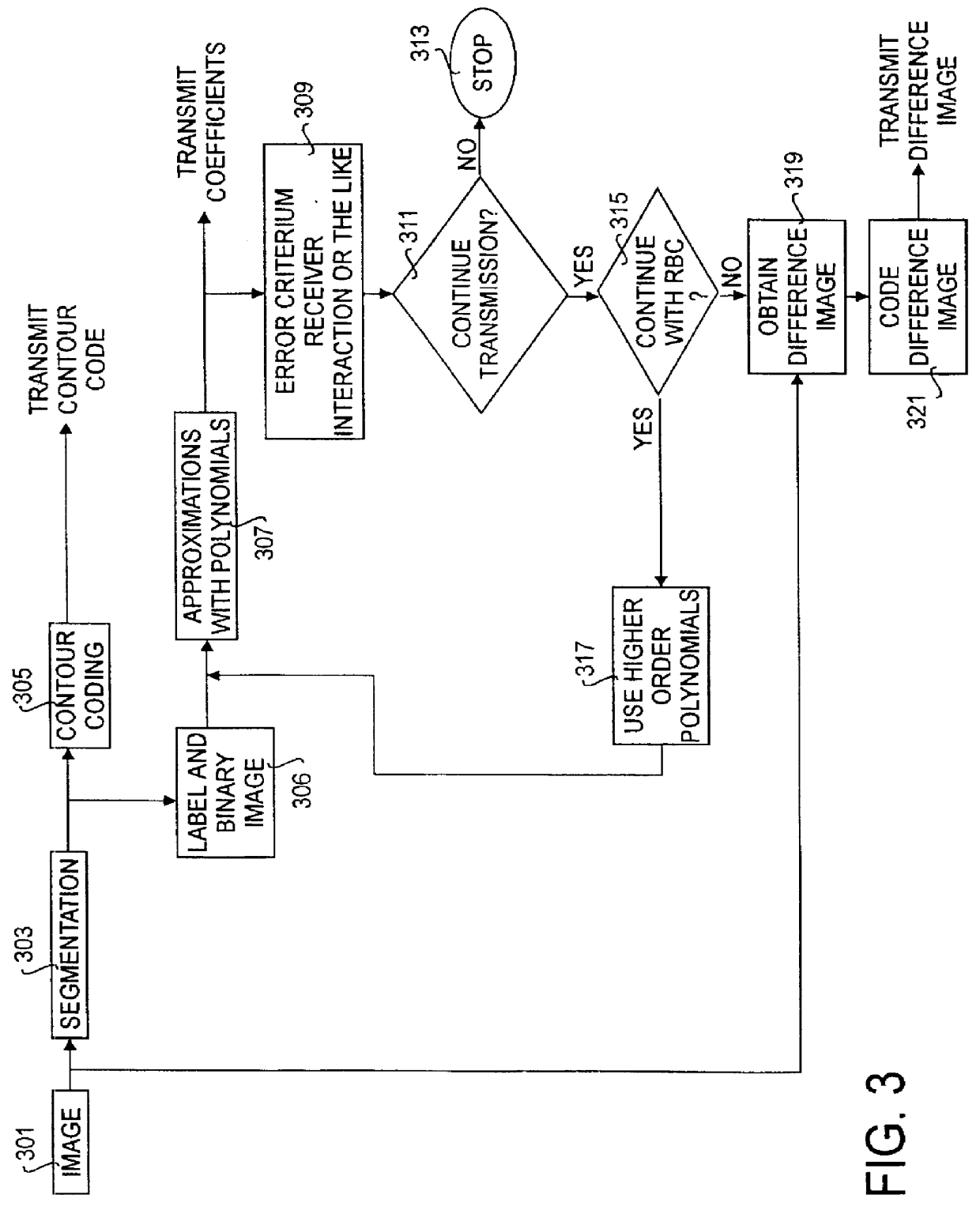
A method and a transmission system for use in coding and Progressive Image Transmission (PIT), in which the transmitter at the initial stages of the transmission uses a Region Based Coding (RBC) scheme (905) in order to provide the receiver with an image of good visual quality at a high compression ratio, which the RBC is known to be able to provide. At a later stage of the transmission, when the visual quality of the RBC image is no longer superior to other compression techniques such as JPEG, the PIT switches (903) use a continuous tone compressor (907) for the further transmission, without losing the information contained in the RBC image already transmitted. Also a hybrid RBC-DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) is used for further improving the performance of the transmission scheme, in which the image segmented by the RBC algorithm is divided into rectangular blocks, and those blocs that are fully contained inside a region of the segmented image are transmitted using predefined base functions such as DCT base functions. Also a method for video coding using a similar scheme is disclosed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
InactiveUS20050270582A1Improve accuracyQuality improvementImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingRadiology
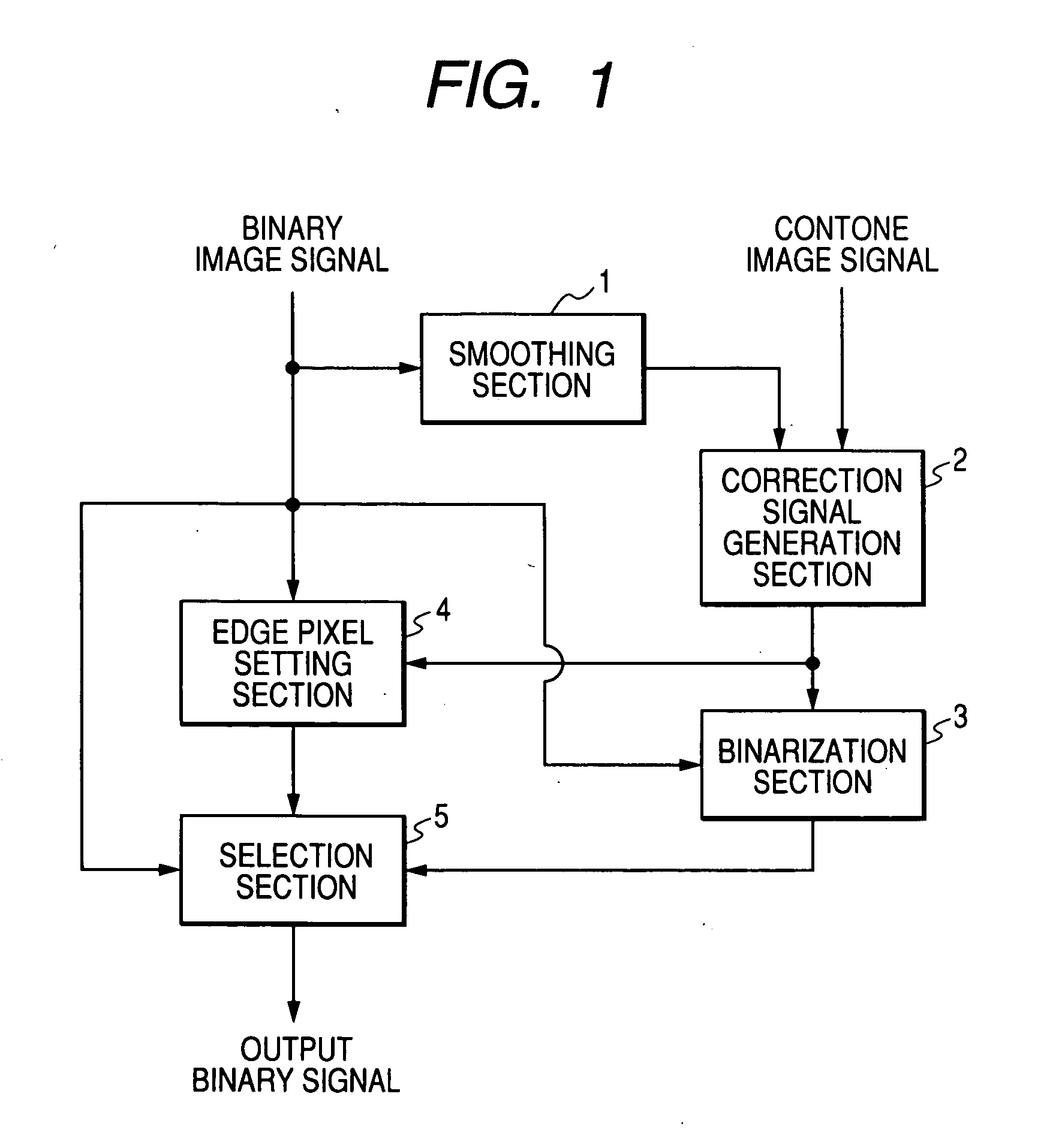
An image processing apparatus includes a correction data generation section, a binarization section, an edge pixel setting section, and a selection section. The correction data generation section generates correction data. The binarization section binarizes one of the correction data generated and contone image data that has been subjected to the one of color correction and density correction, to generate corrected binary data. The edge pixel setting section sets a pixel, in binary image data, assumed to be an edge as an edge pixel. The selection section selects, for the pixel set as the edge pixel, the corrected binary data and selects, for a pixel not being set as the edge pixel, the binary image data. The edge pixel setting section detects presence of the edge from the binary image data.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
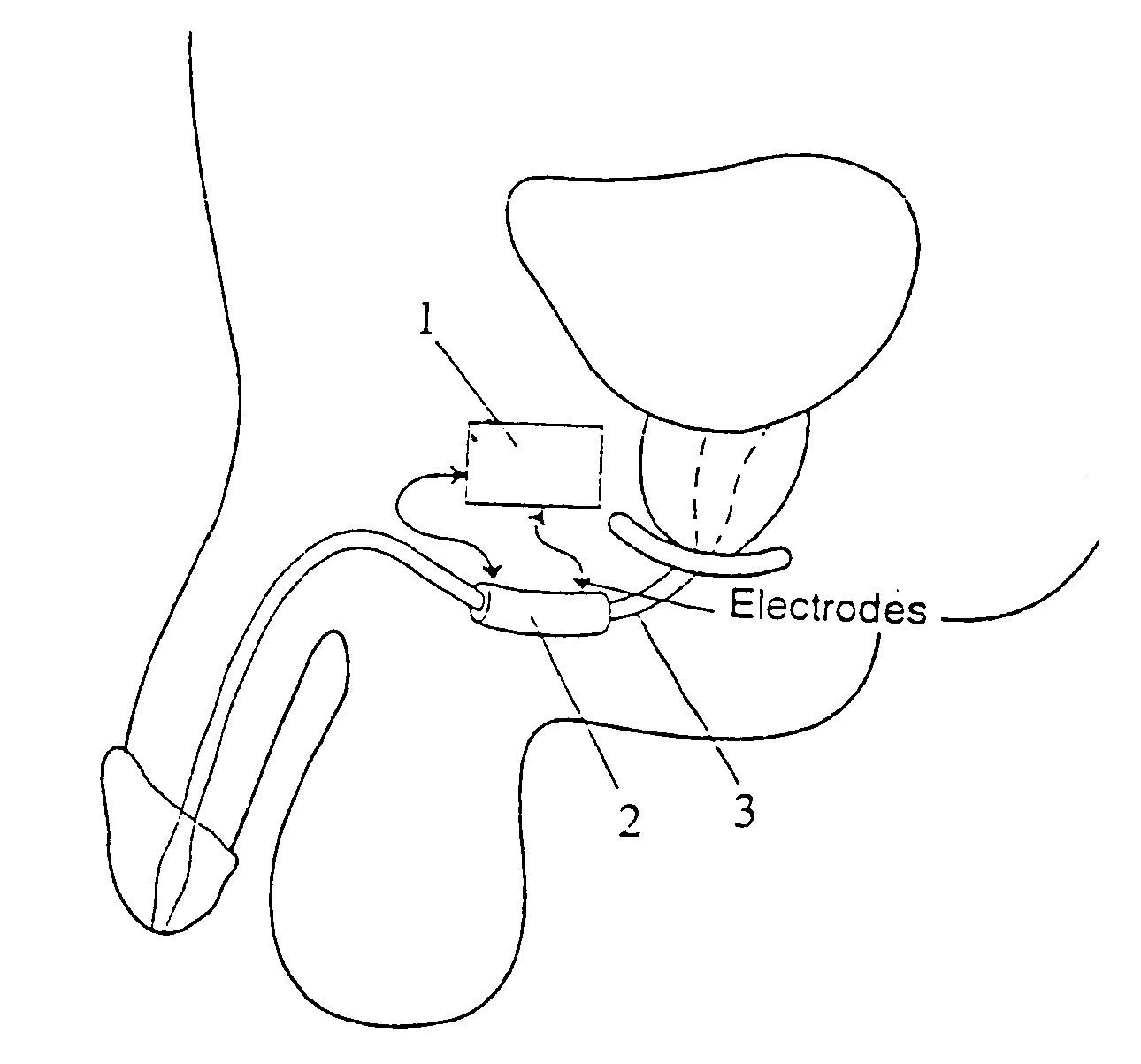
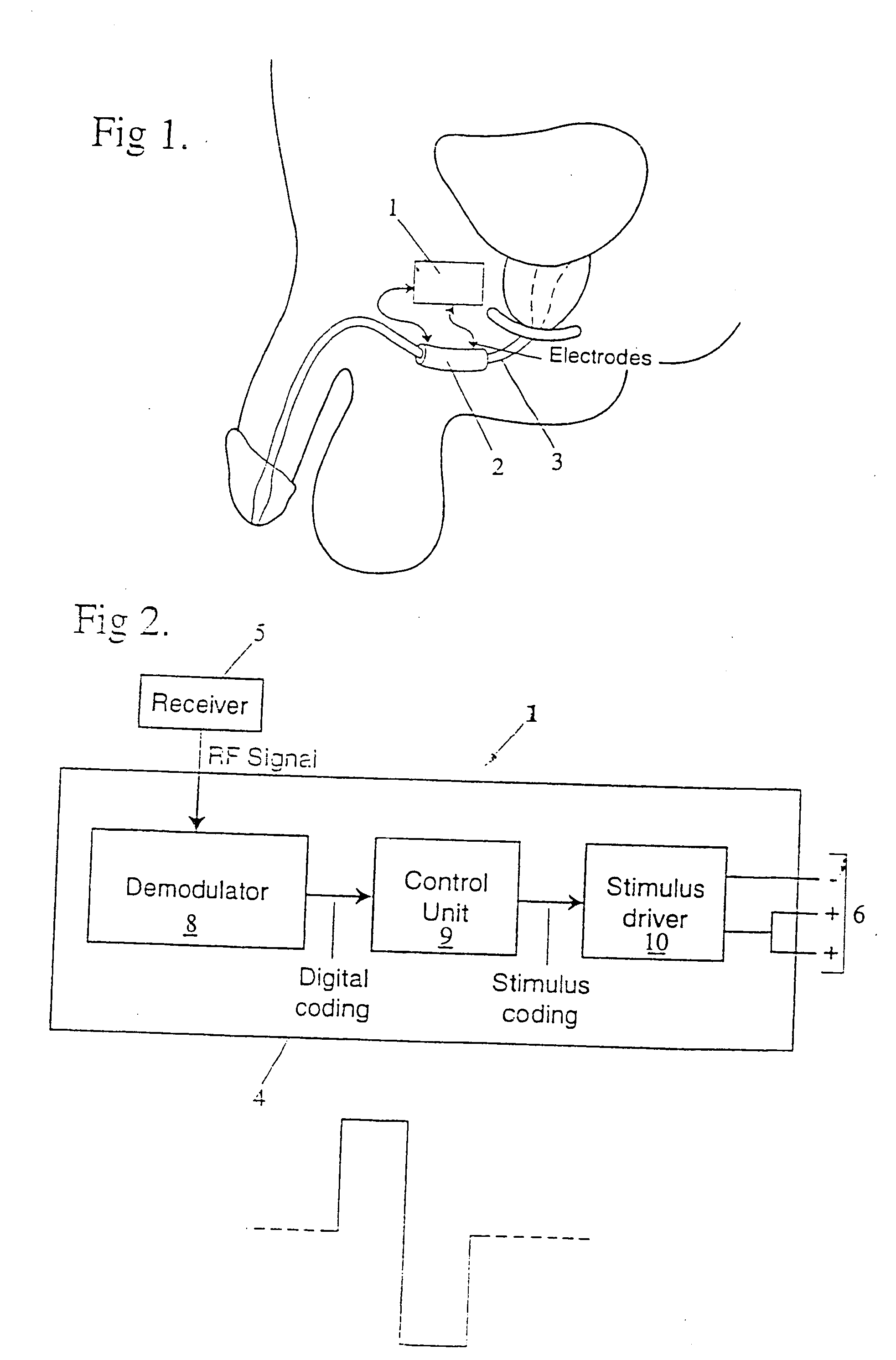
Method and apparatus for treating incontinence
InactiveUS20050119710A1Reduce power consumptionEasy to moveAnti-incontinence devicesInternal electrodesSmooth muscleSphincter
An improved method, system and arrangement for treatment of urinary incontinence is disclosed, in which a portion of innervated smooth muscle (2) is transplanted and disposed around the urethra to provide a urethral sphincter (2). Electrical stimulation, by an implanted stimulator (1), maintains continuous tone in the sphincter. A remote controller (7) permits the sphincter (2) to be allowed to relax, and hence permit urine to flow out of the bladder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Electrophotographic device, electrophotography, and process for preparing sheet bearing toner images
InactiveUS6256051B1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternLatent imageDot gain
The present invention can provide an electrophotographic apparatus and electrophotographic method which are less affected by dot gain, can realize smooth gray scale expression, are high in gray scale reproducibility, and are hard to generate moire.In an embodiment of the present invention, a continuous tone image is binarized by using the frequency modulation screening, to form a latent image free from the generation of moire and high in relative resolution. The latent image thus formed is developed using a liquid developer, to form a thin toner layer, for forming a toner image less in the generation of mechanical and optical dot gain.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, method for processing image, computer program, and recording medium
InactiveUS7518755B2Improving accuracy of discrimination and image quality of imageHigh discrimination accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging qualityContinuous tone
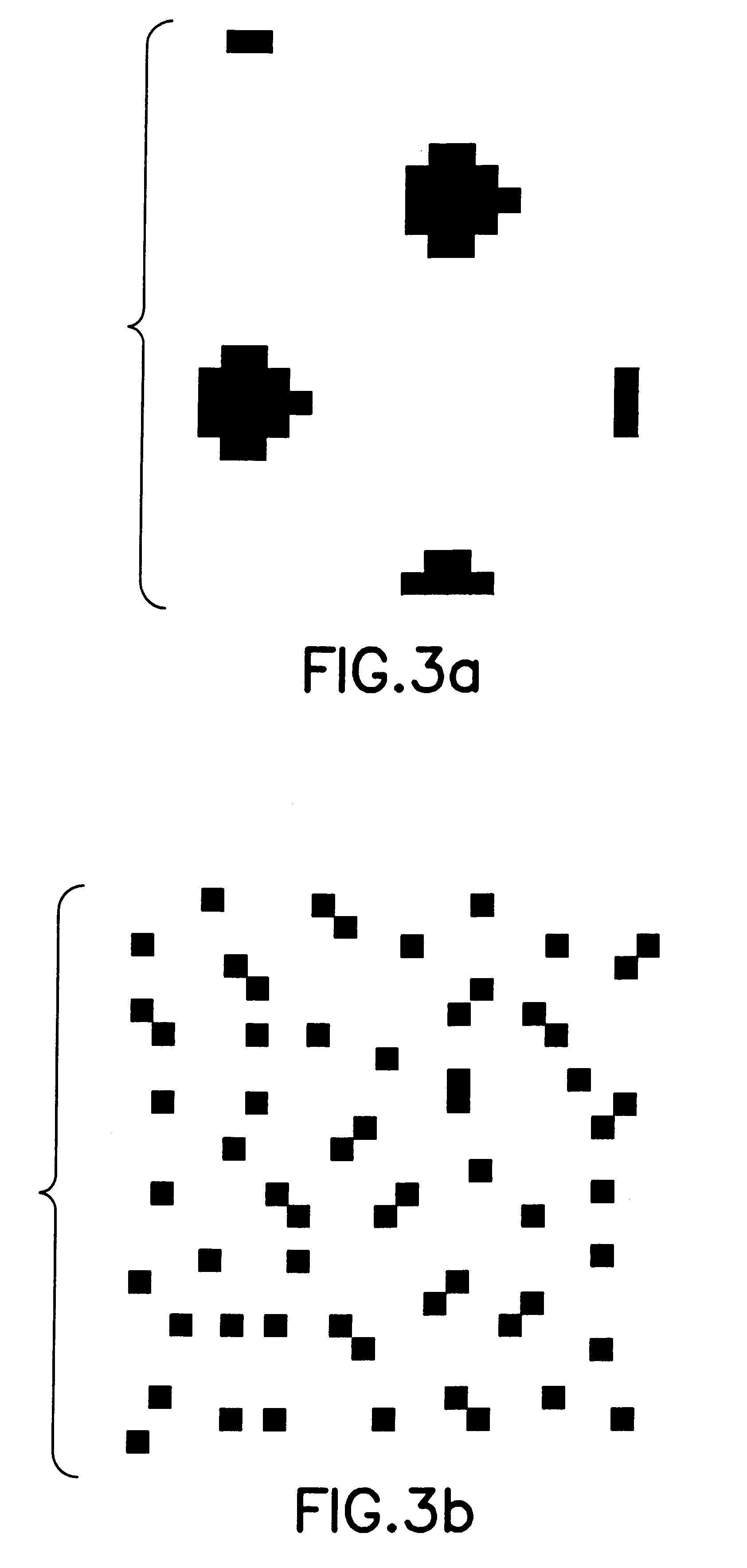
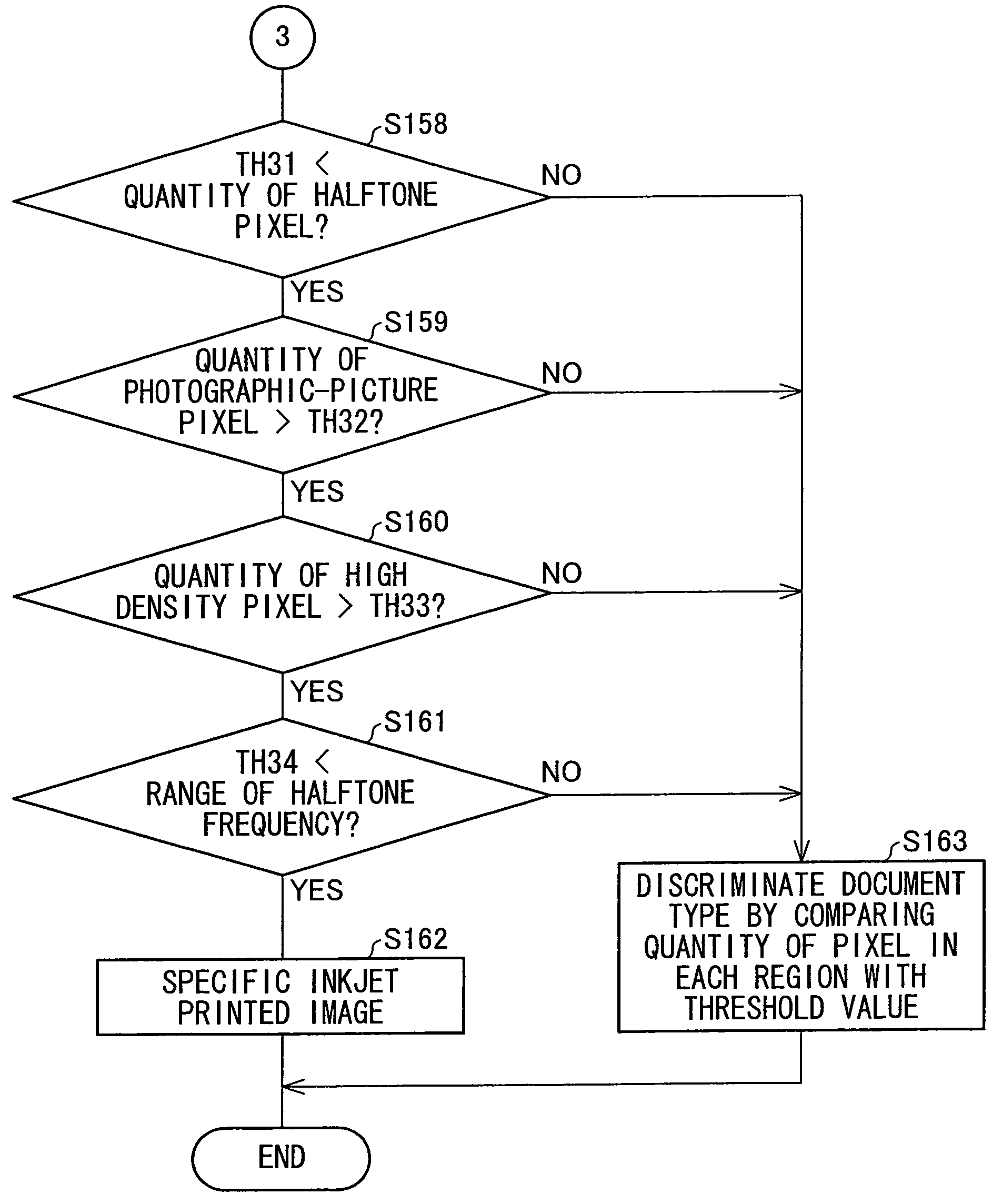
An image processing apparatus includes a document type automatic discrimination section that, based upon input image data read from a document, automatically discriminates a document type of the document. The document type automatic discrimination section, based upon plural types of parameters (quantity of halftone pixels, quantity of photographic-picture pixels, and quantity of high density pixels) obtained from plural types of characteristics (maximum density difference, total density busyness) extracted from the input image data and which parameters are used for discriminating a document type. A specific inkjet printed image whose output image data would not reach a standard level, if a process for a halftone reproduction region or a process for a continuous tone region were to be carried out on the input image data. This can improve the accuracy of document discrimination and the image quality of reproduced image.
Owner:SHARP KK
Color trapping on a halftoned bi-level bitmap
ActiveUS20100277770A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsContinuous toneOutput device
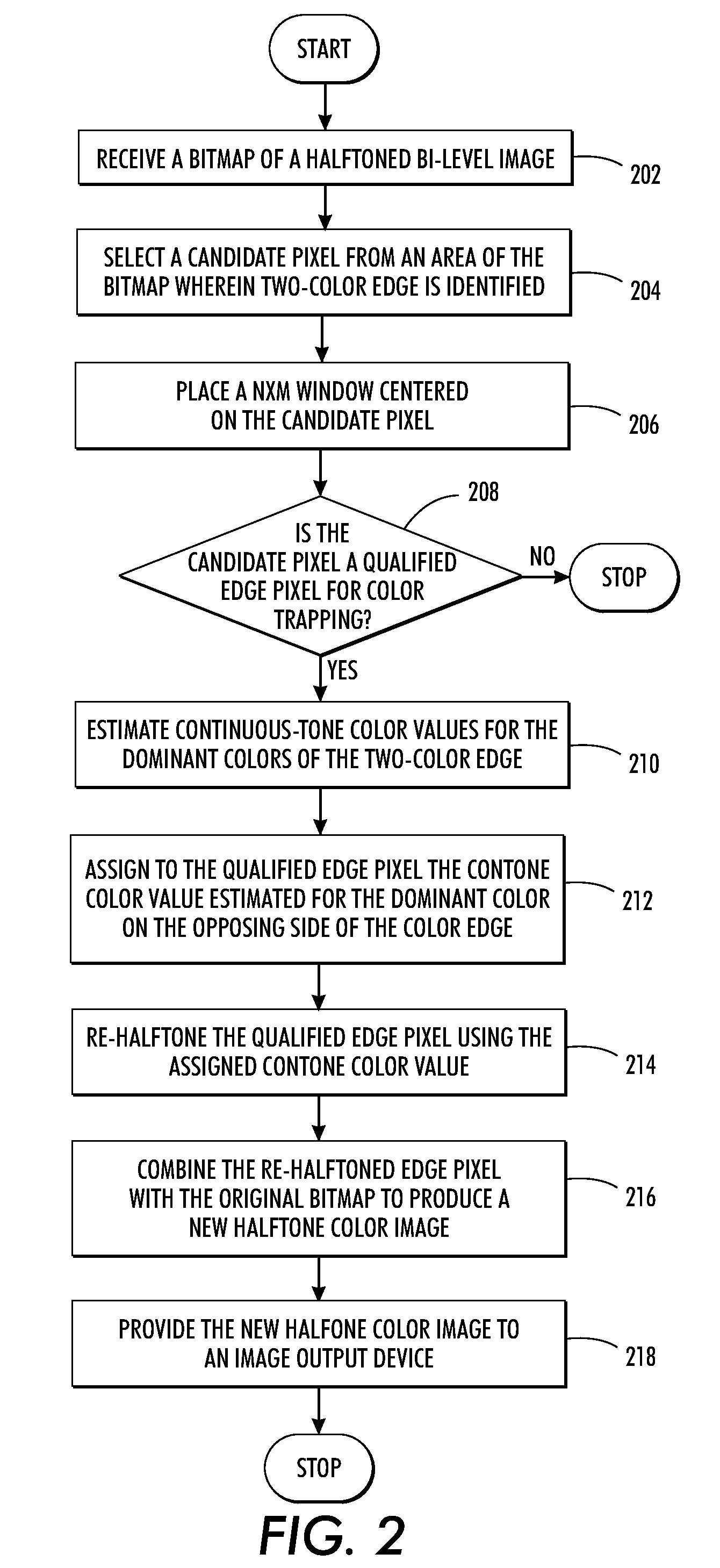
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for color trapping on halftoned bi-level bitmaps. Color edges are detected and edge pixels that need to be trapped are identified. The number of pixels qualified as edge pixels eligible for color trapping can be up to a pre-determined number of pixels away from the color edge. Estimates for the continuous-tone values are obtained for the dominant colors on each side of the two-color edge. The contone value of the dominant color on the opposing side of the two-color edge is assigned to the qualified edge pixels. Qualified edge pixels are re-halftoned using their assigned contone value so that halftones for one color are extended beyond the edge into the other color. The re-halftoned edge pixels are combined with the original bitmap to produce a new bitmap for the image. The new bitmap is then provided to an image output device.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Grayscale lithography of photo definable glass
InactiveUS20140272688A1Increased autofluorescenceBiofuelsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThree dimensional microstructureContinuous tone
A method for forming a three-dimensional microstructure includes providing a photosensitive glass substrate; exposing the photosensitive glass substrate to energy through a continuous tone, variable transmission photomask so as to form opaque portions in the photosensitive glass substrate, each of the opaque portions having one of a variety of depths extending through the entire thickness of the photosensitive glass substrate; and removing the opaque portions so as to form three-dimensional features in the photosensitive glass substrate.
Owner:PHOTRONICS INC
Analog signal separator for UWB versus narrowband signals
InactiveUS20060078038A1Suppresses unwanted in-band RFI without adversely affecting the reception of the intended UWB signalTyre partsOther chemical processesFrequency spectrumContinuous tone
A system, method, and computer program product for removing “narrowband” interference from a broader spectrum containing a UWB signal, in a receiver of the UWB signal. The RFI is extracted from a broader spectrum to remove interference from the UWB signal, by employing an impulse response in a radio front-end of the UWB receiver that is matched with an incoming wavelet employed as part of a UWB signal to be received, matching the impulse response to the wavelet and its time-shifted and inverted versions, passing the wavelet unscathed through the receiver, and excising narrowband signals (continuous tones). Exemplary embodiments for the RFI extraction mechanism include a transmission line circuit, an active transmission line circuit, and an adaptable, controllable phase delay circuit.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
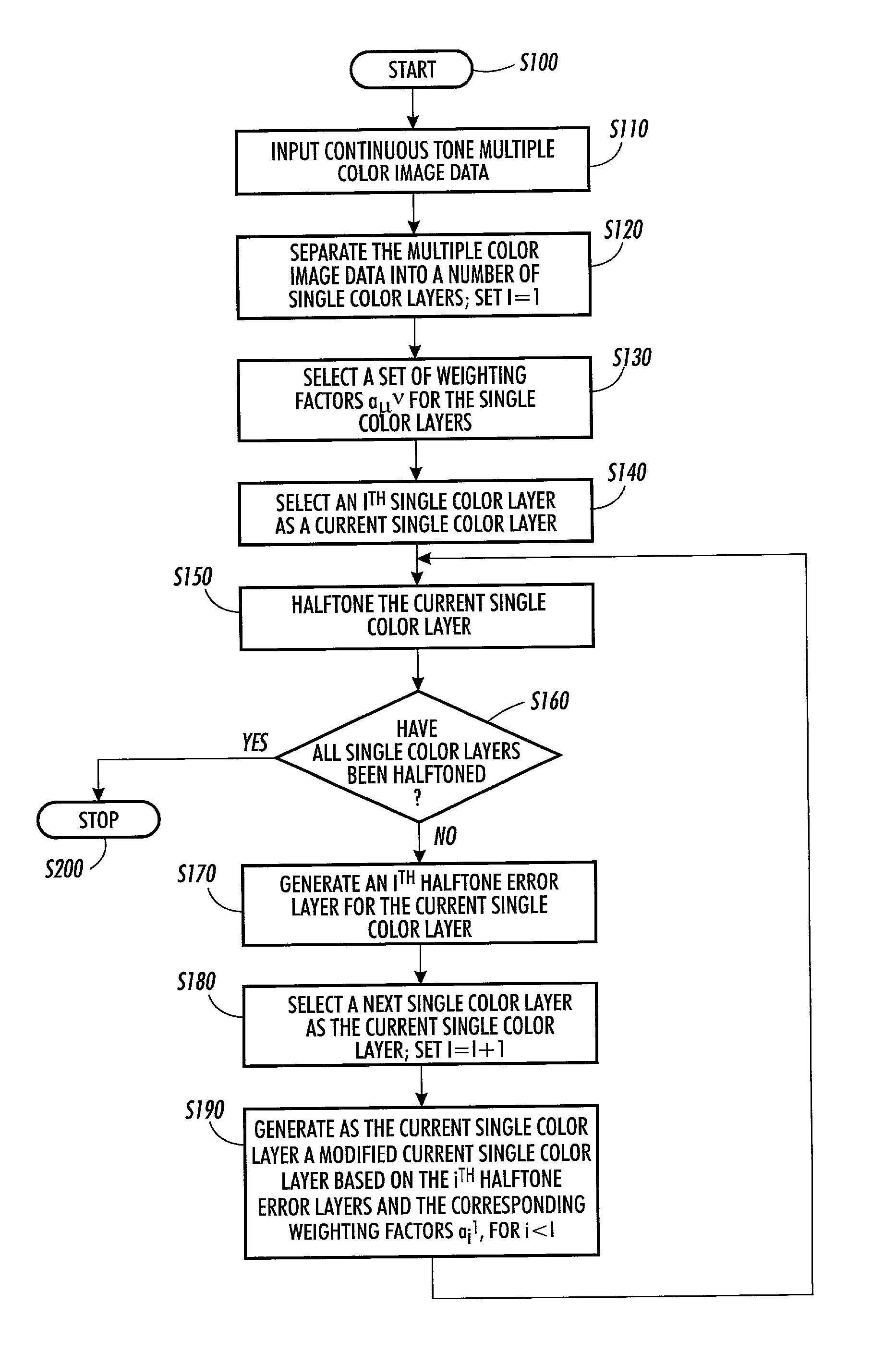
Systems and methods for halftoning multiple color separation layers by interlayer error diffusion
Error diffusion halftoning systems and methods propagate the error both within a color layer and between the color layer being halftoned and subsequent color layers yet to be halftoned. Threshold array halftoning systems and methods diffuse error to subsequent color layers after a color layer has been halftoned using a threshold array. A color continuous tone image is separated into color layers. A plurality of weighting factors are selected that control how error is diffused to subsequent color layers as each color layer is halftoned. A first color layer is halftoned using error diffusion or threshold array halftoning. An error layer is generated from the first halftoned color layer and the first color layer. A modified second continuous tone color layer is generated based on at least one error layer and the corresponding weighting factor. That modified second continuous tone color layer is then halftoned and the process is repeated.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Image recording apparatus and method providing personalized color enhancement
InactiveUS20070081205A1Image enhancementImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionPersonalization
An image processing method and system wherein an operator may provide adjustments to tweak color saturation of a particular color in an image. In the method and operation of the system a first signal representing color separation continuous tone gray level image data of pixels is provided as one input to a lookup table. An operator adjustable color tweaking input data second signal represents an adjustment in color saturation and is provided as a second input to the lookup table. In response to the first and second inputs a third signal representing adjustment in color saturation in accordance with the operator adjustable color tweaking input is output from the lookup table. Thereafter, data represented by the third signal is subject to a halftone process to generate halftone rendered gray level data values for the pixels.
Owner:TAI HWAI TZUU +1
Lossless Compression of Color Image Data Using Entropy Encoding
ActiveUS20090129691A1Reduce complexityCompression can be losslessColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionColor imageScan line
A method compresses a digital continuous tone image of pixels situated on scan lines. The method includes the steps of, for a current pixel to be encoded, said current pixel having an actual pixel value, predicting a predicted pixel value based on pixel values of at least one previously processed pixel from the same image, using a fixed rule, determining a difference parameter based on a difference value of said predicted pixel value and the actual pixel value of said current pixel to be encoded, and inspecting the difference parameter for existence of an uninterrupted series of highest order bits having a value equal to zero, removing at least part of said highest order zero bits, and, if a number of bits within predetermined limits remains, generating a compression code having a predetermined fixed length, said code indicating the number of remaining bits.
Owner:OCE TECH
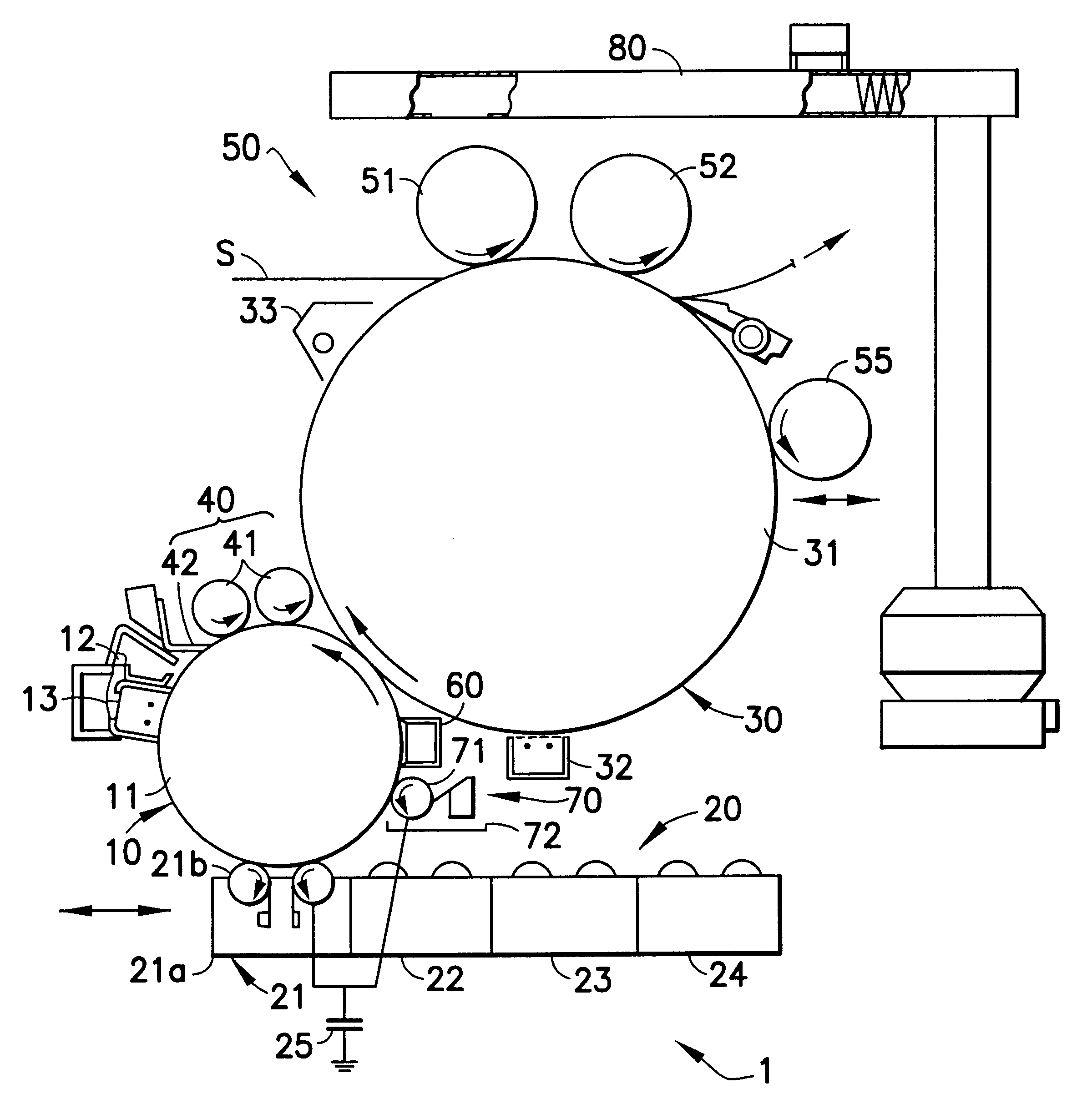
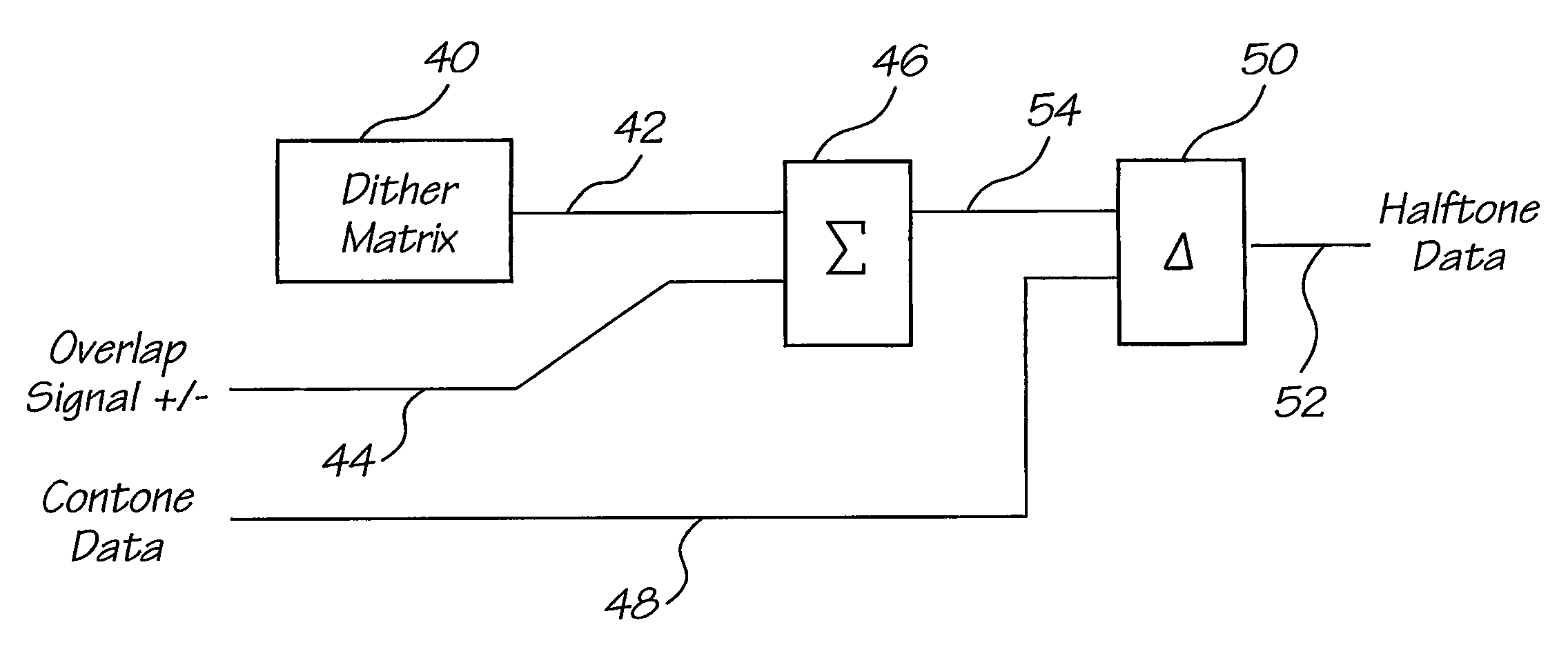
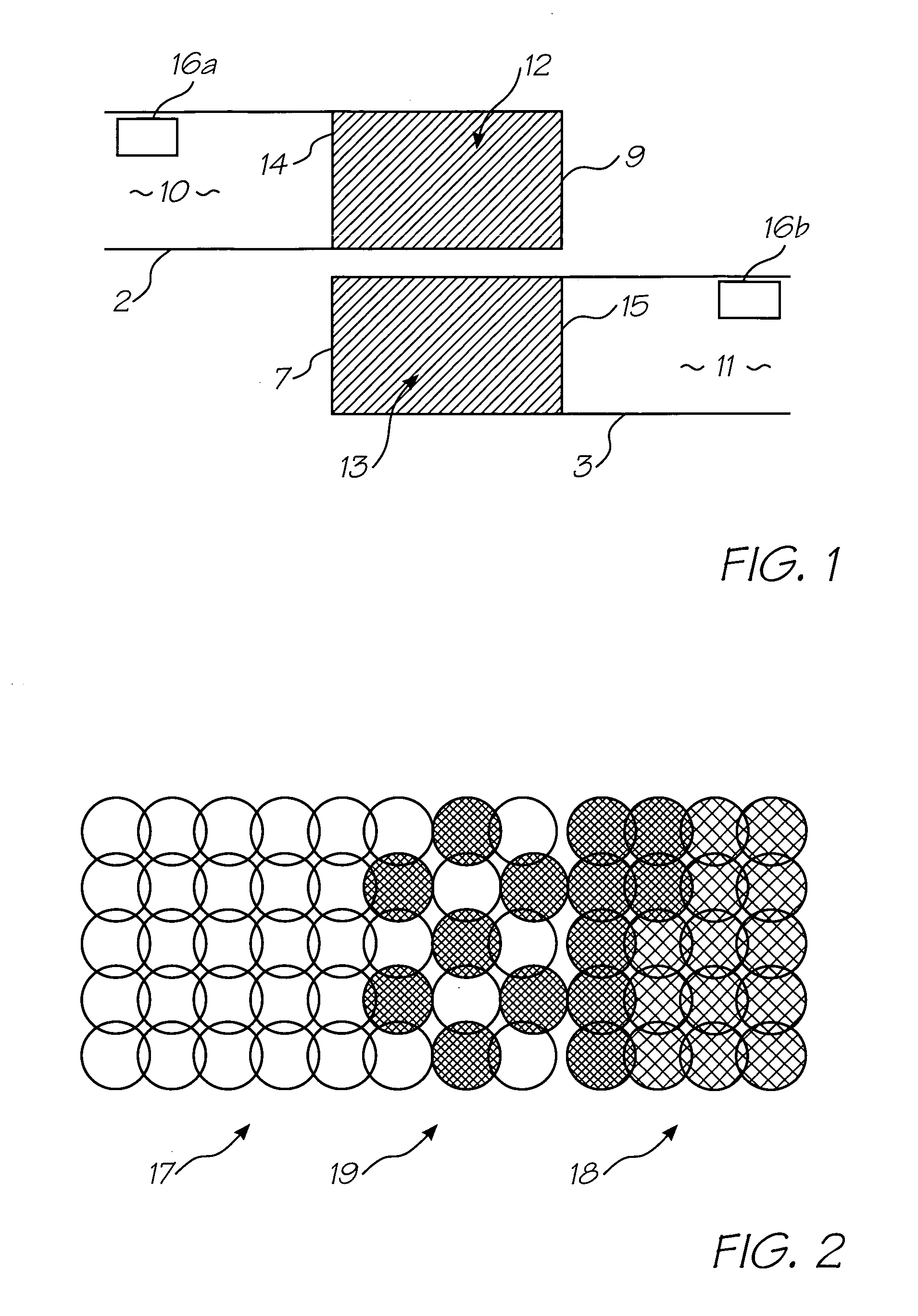
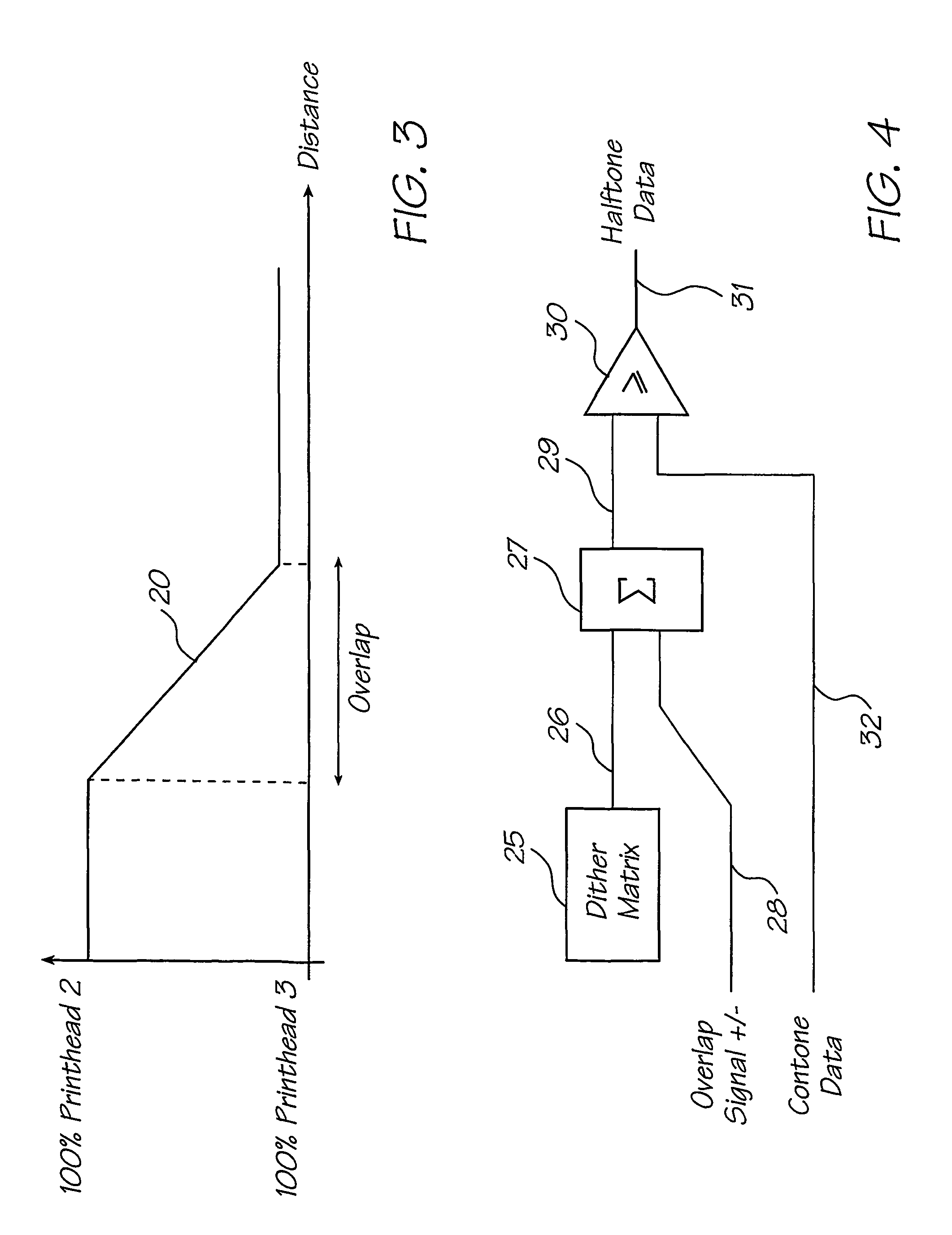
Method and apparatus for compensation for time varying nozzle misalignment in a drop on demand printhead
InactiveUS7201460B1Effective and convenient mannerProduce some attenuationOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationRelative displacementContinuous tone
A method and apparatus is provided for compensating for variable overlap between segments of a page width print head system to reduce visually perceptible artifacts due to misalignment of adjacent overlapped segments. One method employs a summator which sums a current dither value from a dither matrix with an overlap signal to provide an output value which is then compared in a comparator with an input continuous tone data value providing an output compensated dither value to control nozzles in the overlap region of the segments. Another method uses a software program to provide the compensated dither matrix. A sensor provides a measure of the degree of overlap of the segments to generate the overlap signal. The sensor may sense temperature or relative displacement of the segments. The degree of overlap may be determined for various temperatures and stored in a ROM.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
3+n layer mixed rater content (MRC) images and processing thereof
ActiveUS20110069885A1Character and pattern recognitionEditing/combining figures or textPattern recognitionContinuous tone
A method for processing image data includes using advantages of both a three-layer MRC model and an N-layer MRC model to create a new 3+N layer MRC model and to generate a 3+N layer MRC image. The method includes providing input image data; segmenting the input image data to generate: (i) a background layer representing the background and the pictorial attributes of the image data, (ii) one or more binary foreground layers, (iii) a selector layer, and (iv) a contone foreground layer representing the foreground attributes of the image data on the background layer; and integrating the background layer, the selector layer, the contone foreground layer, and the one or more binary foreground layers into a data structure having machine-readable information for storage in a memory device. Each binary foreground layer includes one or more pixel clusters representing text pixels of a particular color in the input image data.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Enhanced halftone screening method for the dry offset printing process
ActiveUS8400681B1Increase in print contrastIncrease in color vibrancyCylinder pressesDigitally marking record carriersContinuous toneScreening method
A method of file preparation, ripping and plate making for high end graphics printed on cylindrical products utilizing Dry Offset printing presses. While utilizing two inverse angle techniques and one fixed angle on the Black, with virtually unlimited color pluralities, encompassing a majority of all open areas of the common printing blanket without any ink overlap. The nesting of the halftone dots at even coarse line screen rulings eliminating a dot rosette pattern and creating a continuous tone appearance. Print contrast is increased to that of offset printing quality and ink contamination over the course of the run length is virtually eliminated. This current invention also increases the ability to print white with colors as opposed to needing white coating done in advanced to transparent plastics and metallic surfaces.
Owner:MORAVCIK GIRARD J
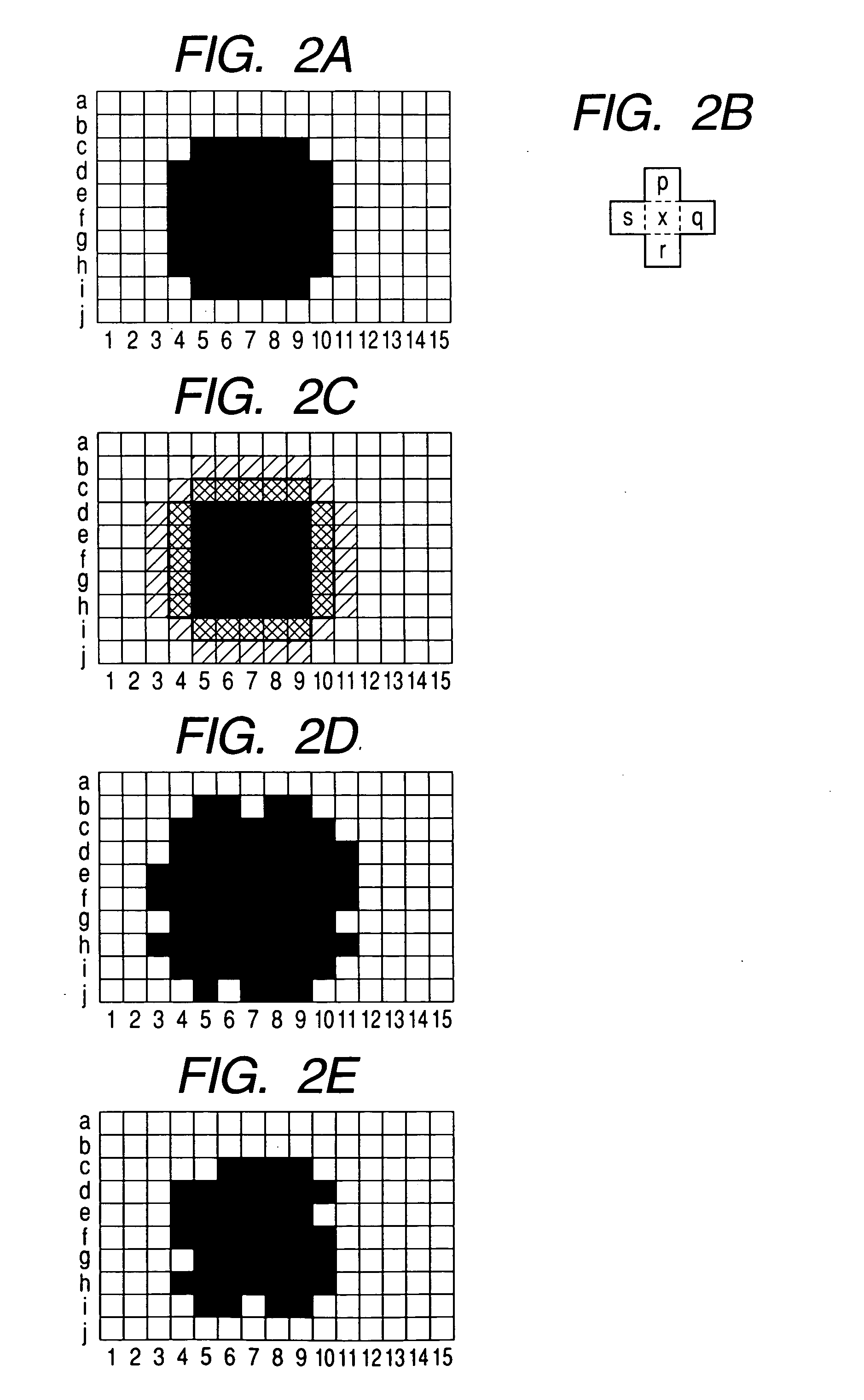
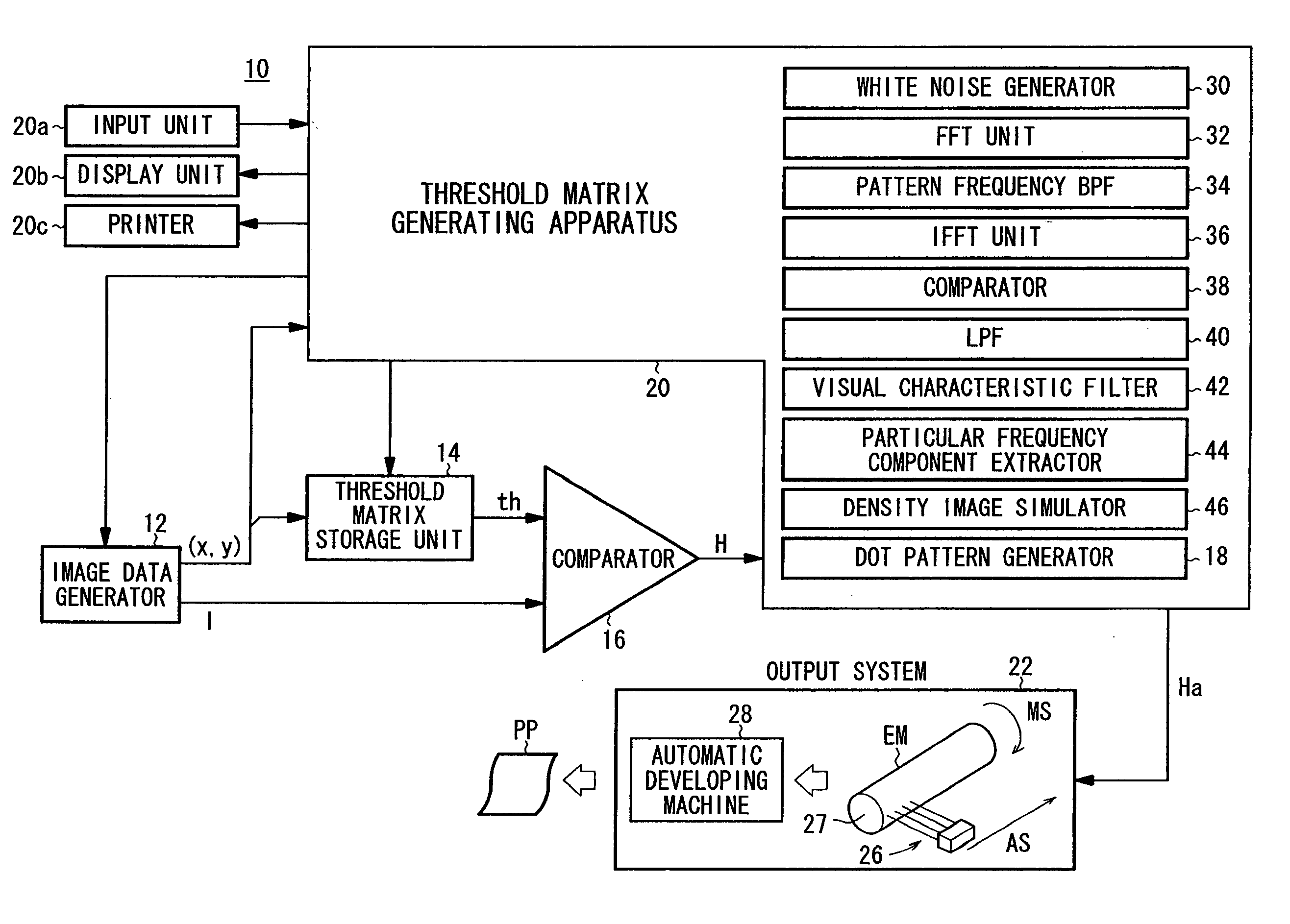
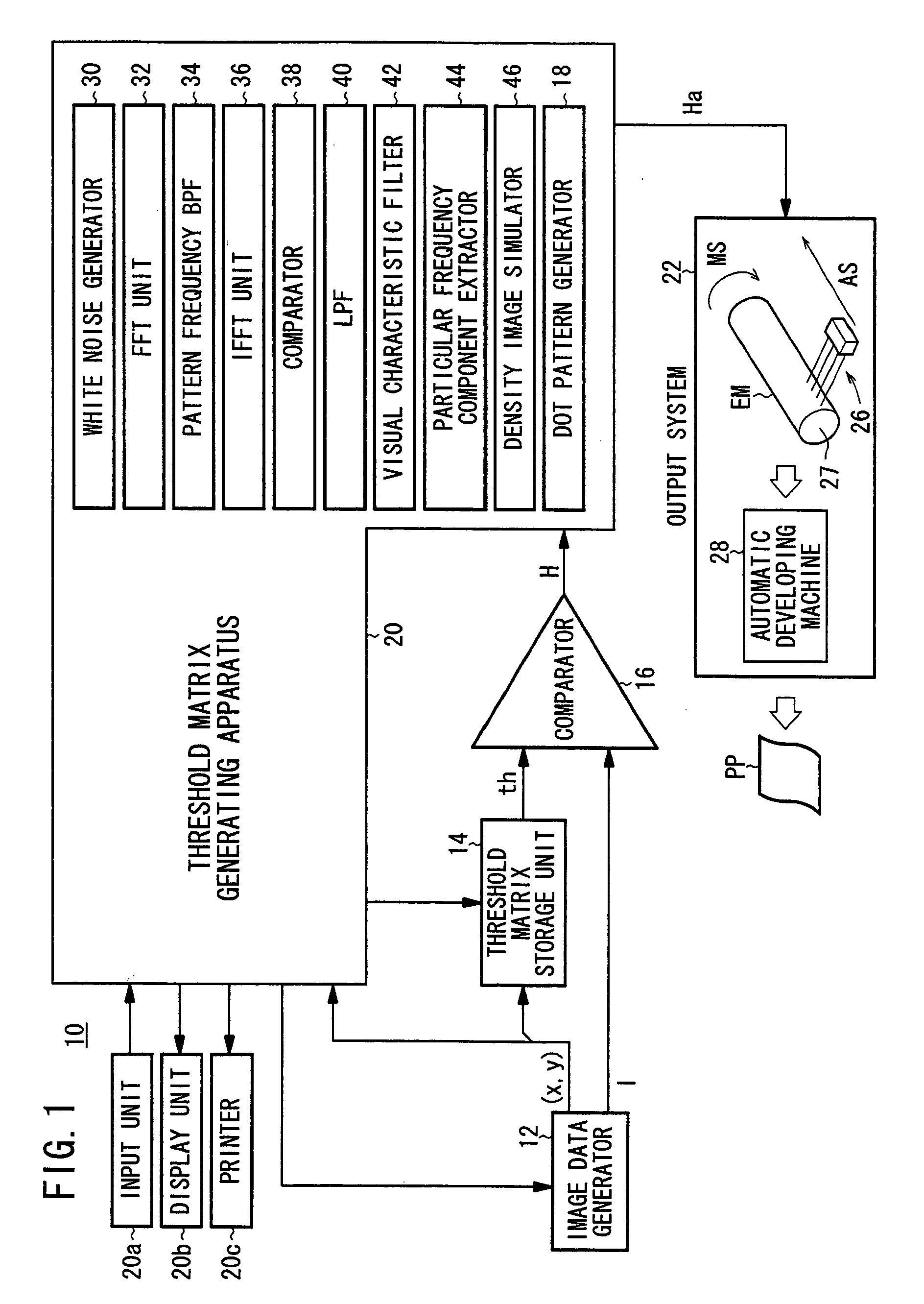
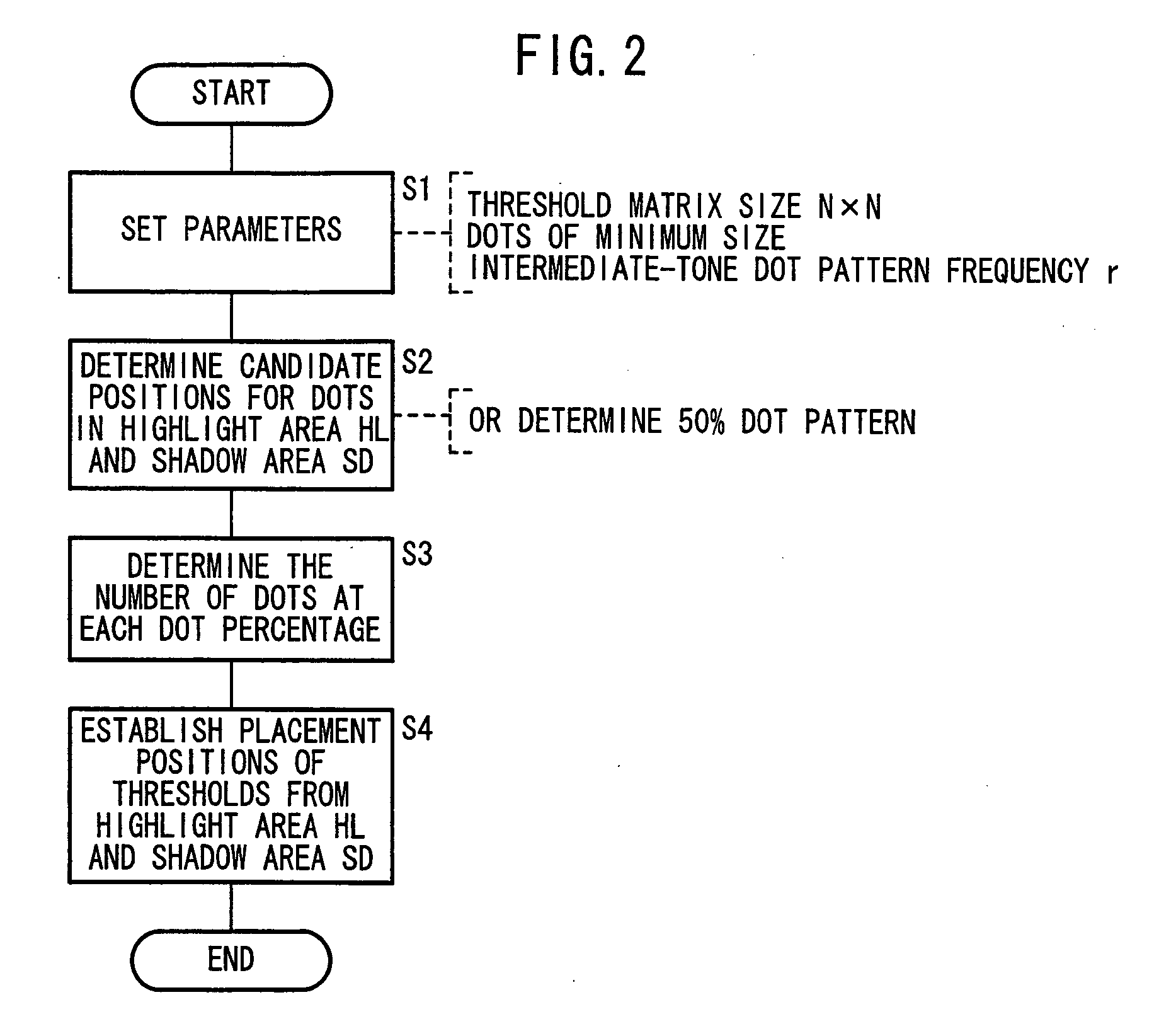
Threshold matrix, a method generating threshold matrix, and storage unit for storing threshold matrix as data
InactiveUS20050195442A1Solve the real problemReduce unevennessImage enhancementVisual presentationGraphicsDot matrix
A threshold matrix for converting a continuous-tone image into a dot pattern representing a binary image is generated. When the continuous-tone image whose pixel values correspond to a dot percentage of 50% is converted into a dot pattern by the threshold matrix, a graph is obtained by conversion from the dot pattern into frequency-domain data. Then, the intensity of the dot pattern at angles corresponding to at least a main scanning direction is weakened, so that a periphery length of the dot pattern in the main scanning direction can be short.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com