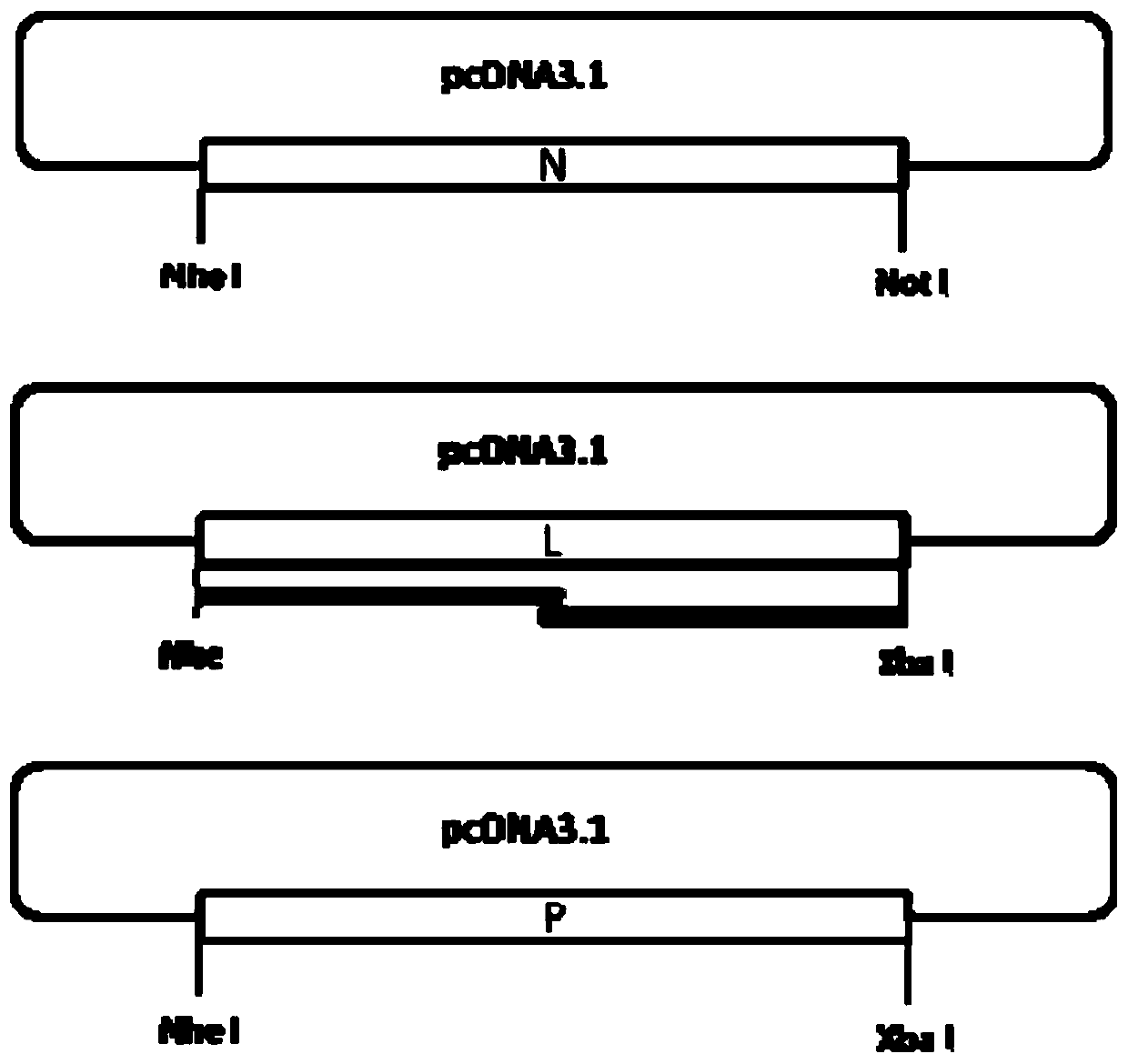
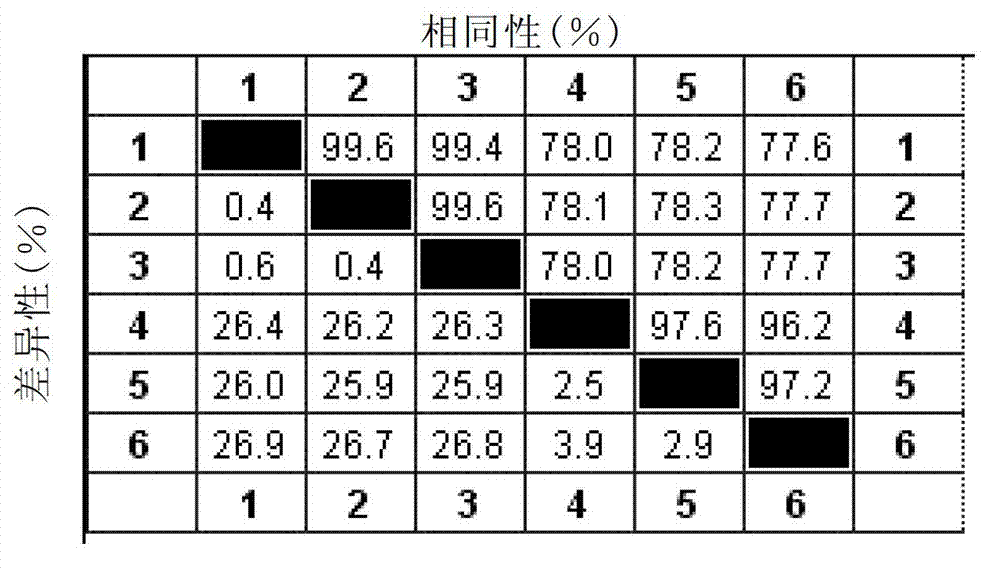
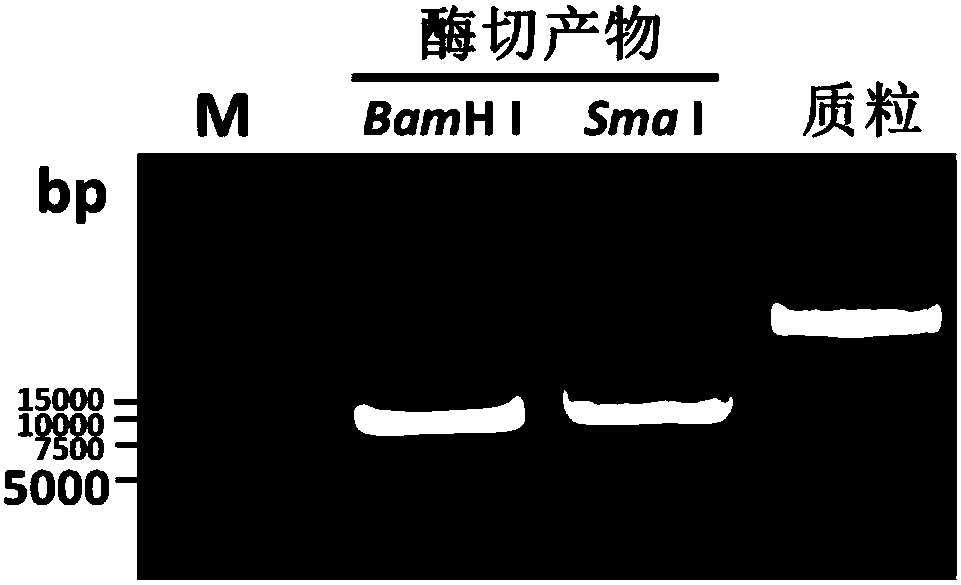
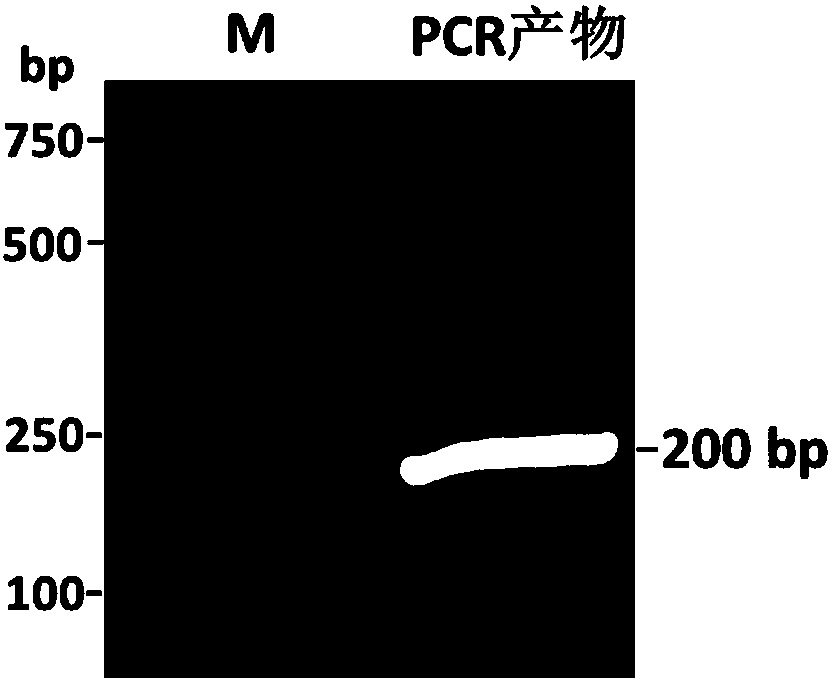
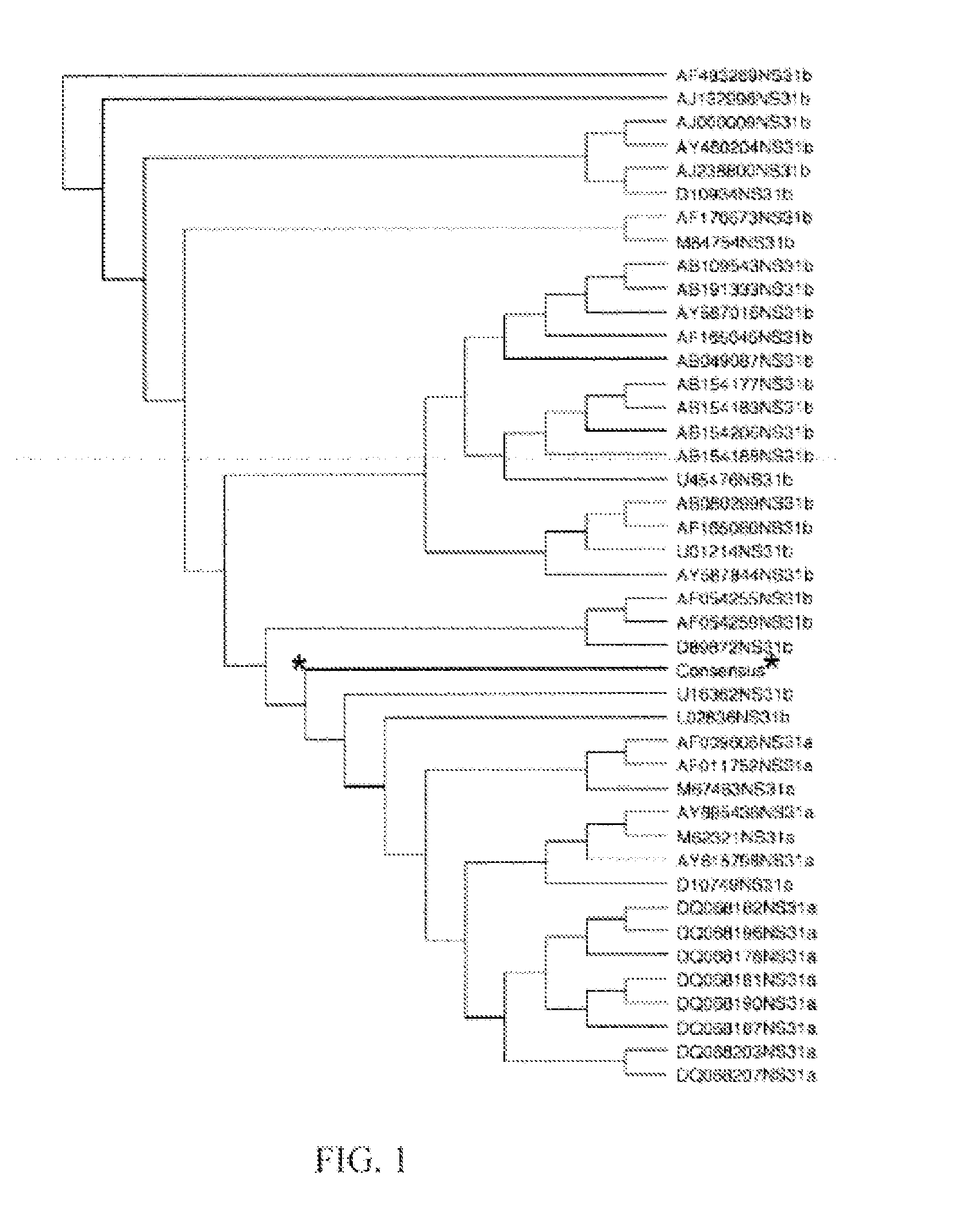
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
579 results about "Attenuated vaccine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An attenuated vaccine is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable (or "live"). Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the virus (inactivated vaccine).
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
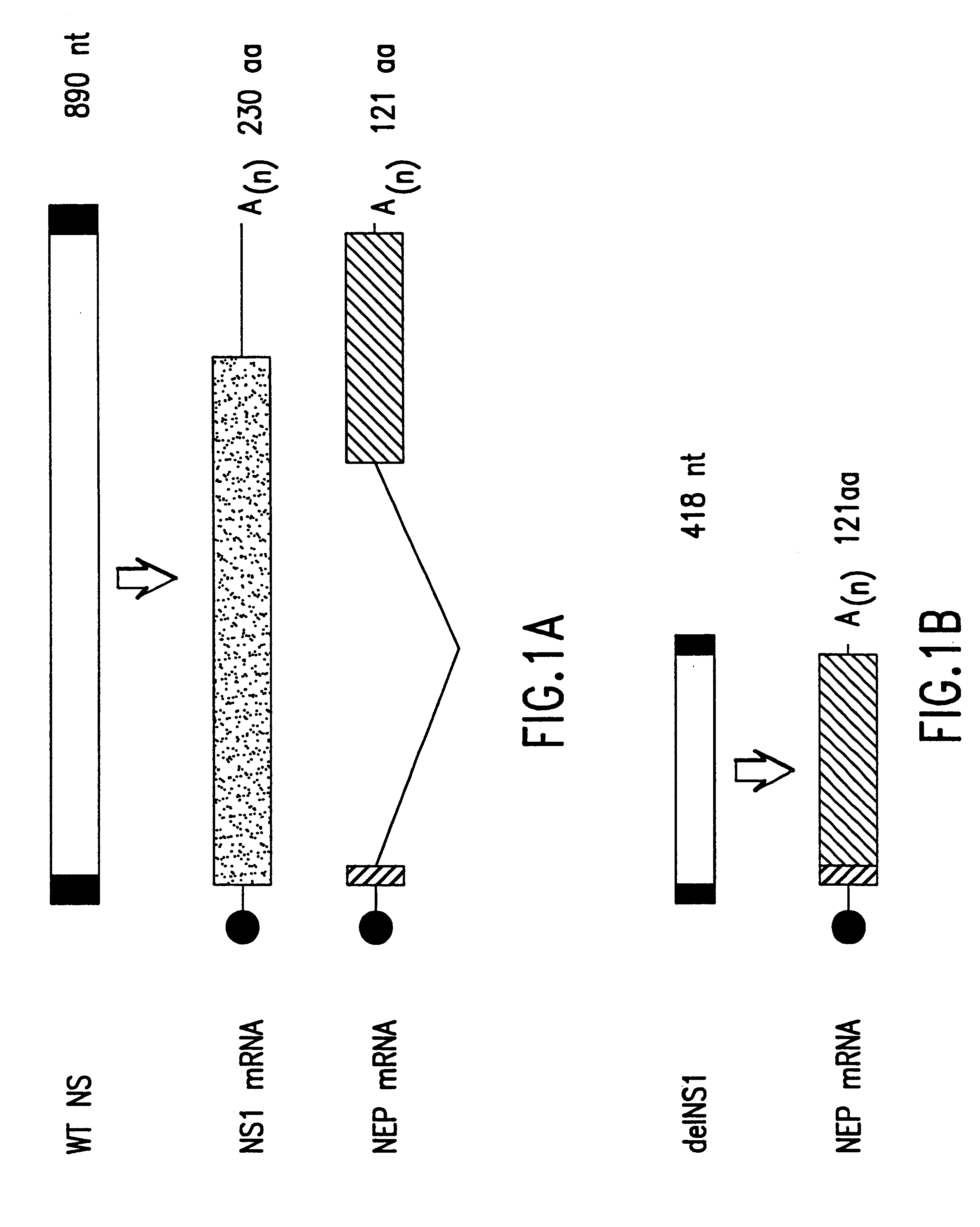
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Methods and Compositions for Stabilization of a Virus Vaccine
InactiveUS20110243988A1Improve stabilityReduce pressureBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsRoom temperatureAttenuated vaccine
This invention provides compositions and methods for stabilizing a live attenuated virus in dried formulations. In particular, compositions and methods of preparing a dried vaccine are provided that stabilize the viability of live vaccines such as measles and adenovirus at room temperature.
Owner:ARIDIS PHARMA INC
Attenuated Pasteurella piscicida vaccine for fish
Live-attenuated vaccines against Edwardsiella ictaluri or against Pasteurella piscicida are disclosed. Both vaccines are incapable of reversion to virulence, because both are made by deletion mutations in the aroA gene, the purA gene, or both. These vaccines may be used not only to vaccinate fish against Edwardsiella ictaluri or Pasteurela piscicida, but also to serve as vectors to present antigens from other pathogens to the fish, thereby serving as vaccines against other pathogens as well, with no risk of infection by reversion to the virulent form of the pathogen in which the antigen occurs naturally.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
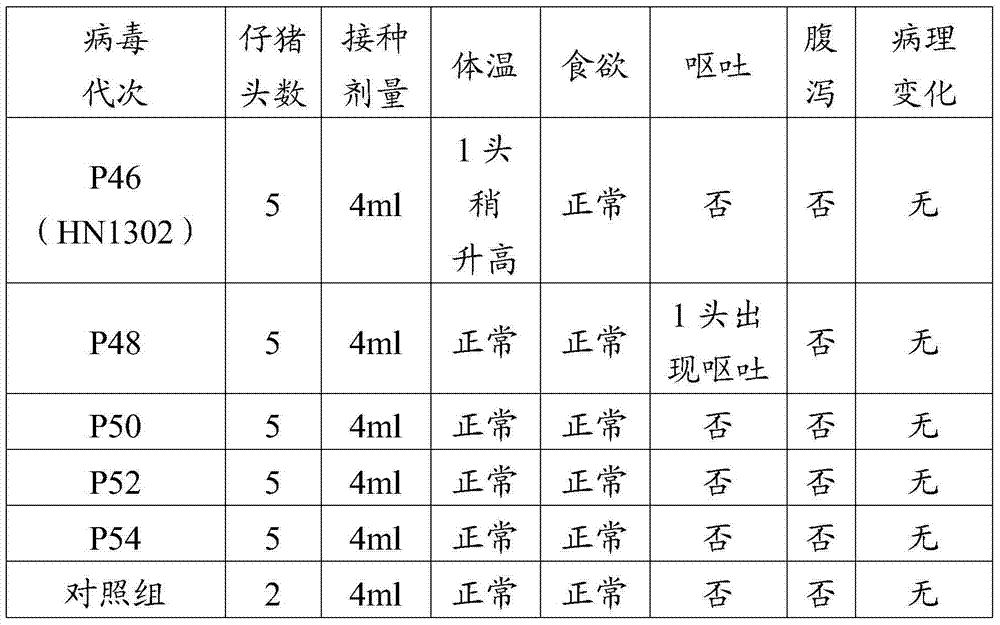
Porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain, attenuated vaccine strain thereof and application thereof
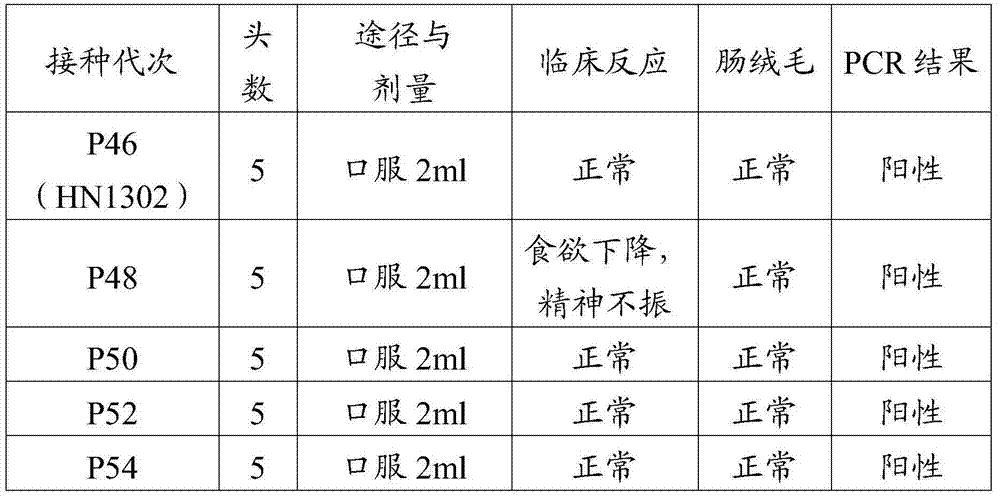
The invention discloses a porcine epizootic diarrhea virus strain (HN1301) and an attenuated vaccine strain (HN1302) attenuated by passage of the porcine epizootic diarrhea virus. The attenuated vaccine strain of the porcine epizootic diarrhea virus is assigned the accession number CCTCC-V201342. The attenuated vaccine strain (HN1302) is good in safety, is strong in immune protective capability and is high in immune efficacy.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
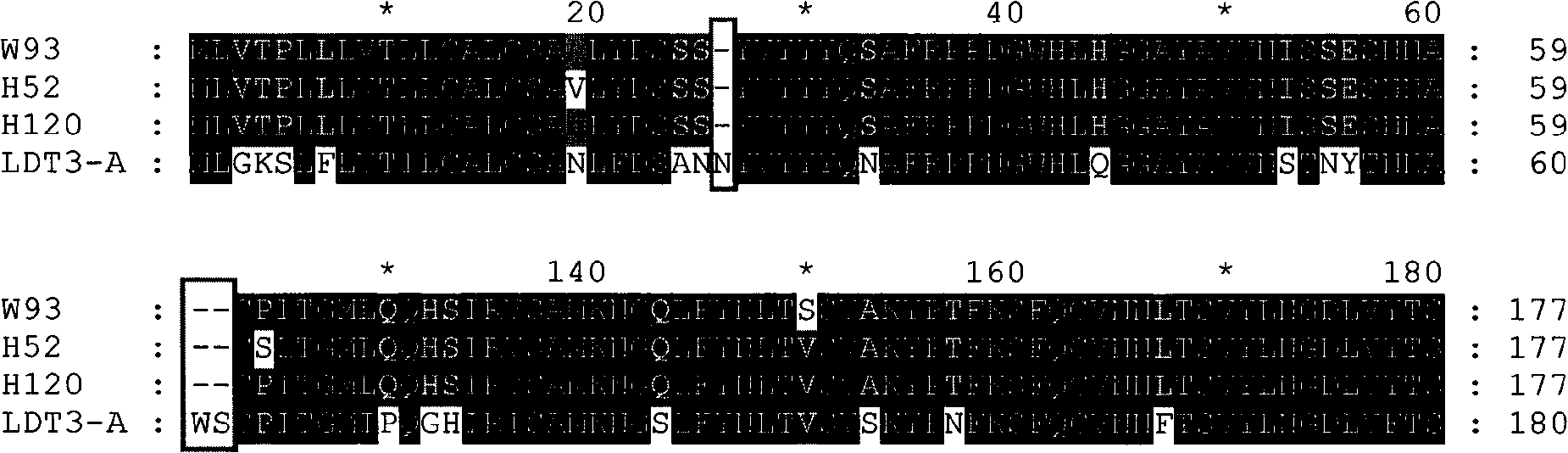
Chicken infectivity bronchitis virus attenuated vaccine strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101514334AImprove securityNo side effectsInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesInfectious bronchitisMicroorganism
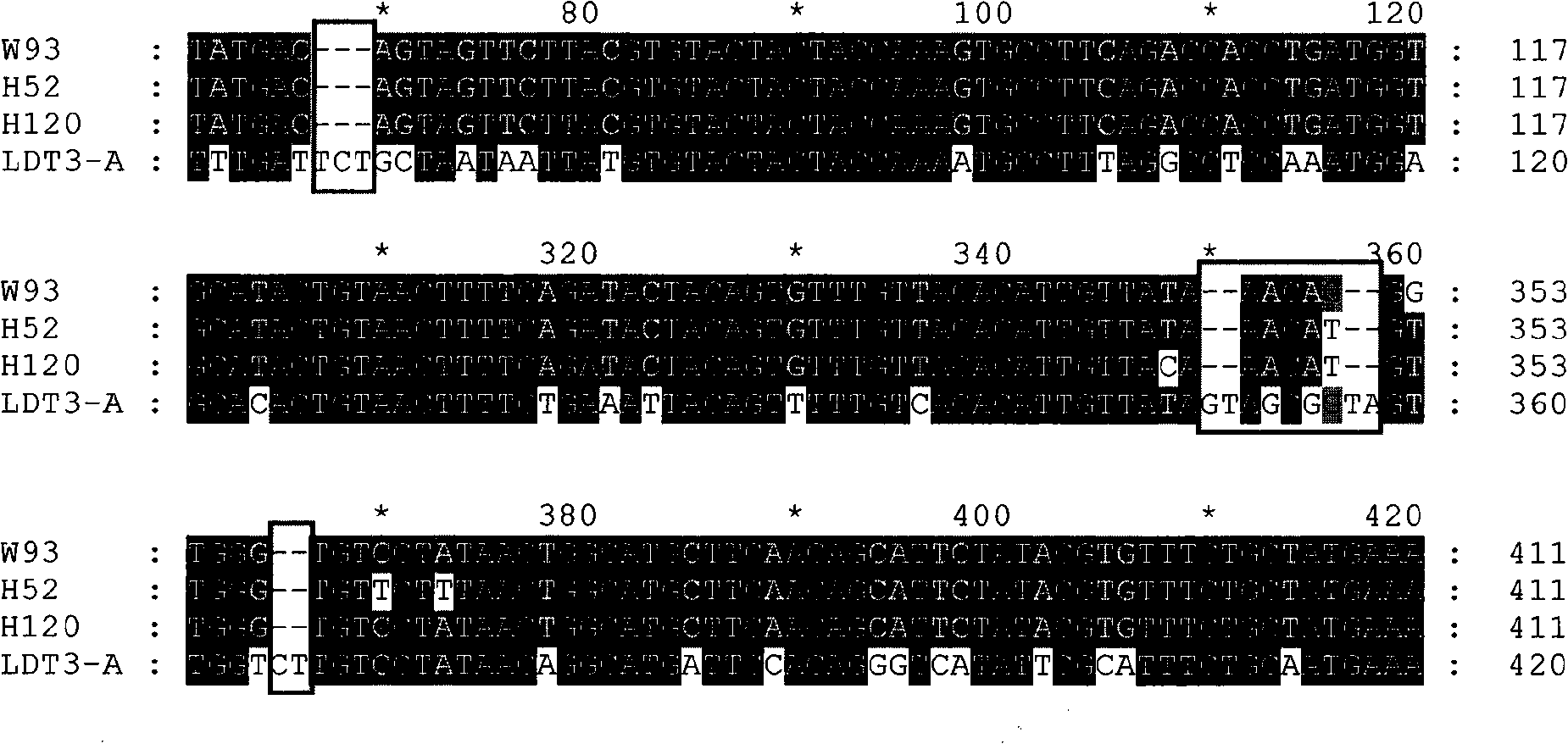
The invention discloses a infectivity bronchitis attenuated vaccine strain LDT3-A strain, and discloses application and application effect thereof in preventing and curing chicken infectivity bronchitis. The microorganism accession number of the attenuated vaccine strain is CGMCC-2902. The attenuated vaccine strain of the present invention has good safety and good immunization protection effect to the chicken infectivity bronchitis. The attenuated strain can be prepared into single vaccine or combined vaccine for preventing or curing infectivity bronchitis virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Avian influenza virus live attenuated vaccine and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110150912A1Poor replicationLess virulentSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaHeterologousDonor strain
Described in this application are attenuated strains of avian influenza virus containing temperature sensitive mutations in addition to a genetic tag in the PB1 gene. The attenuated viruses are useful as avian and mammalian vaccine for protective immunity against homologous and heterologous lethal challenges with influenza virus. A genetically modified avian influenza virus backbone is described which can be used as a master donor strain for the generation of live attenuated vaccines for epidemic and pandemic influenza.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
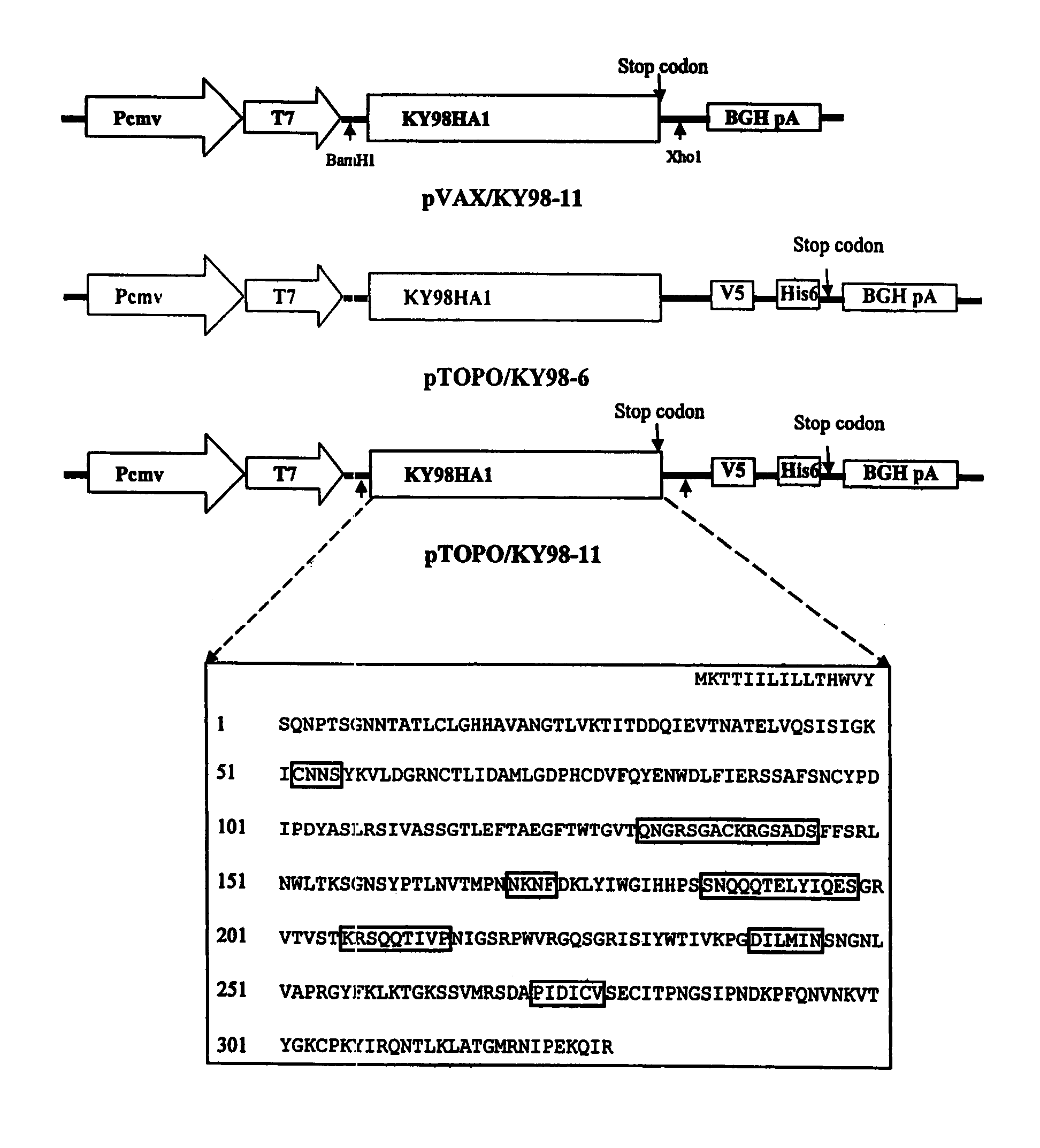
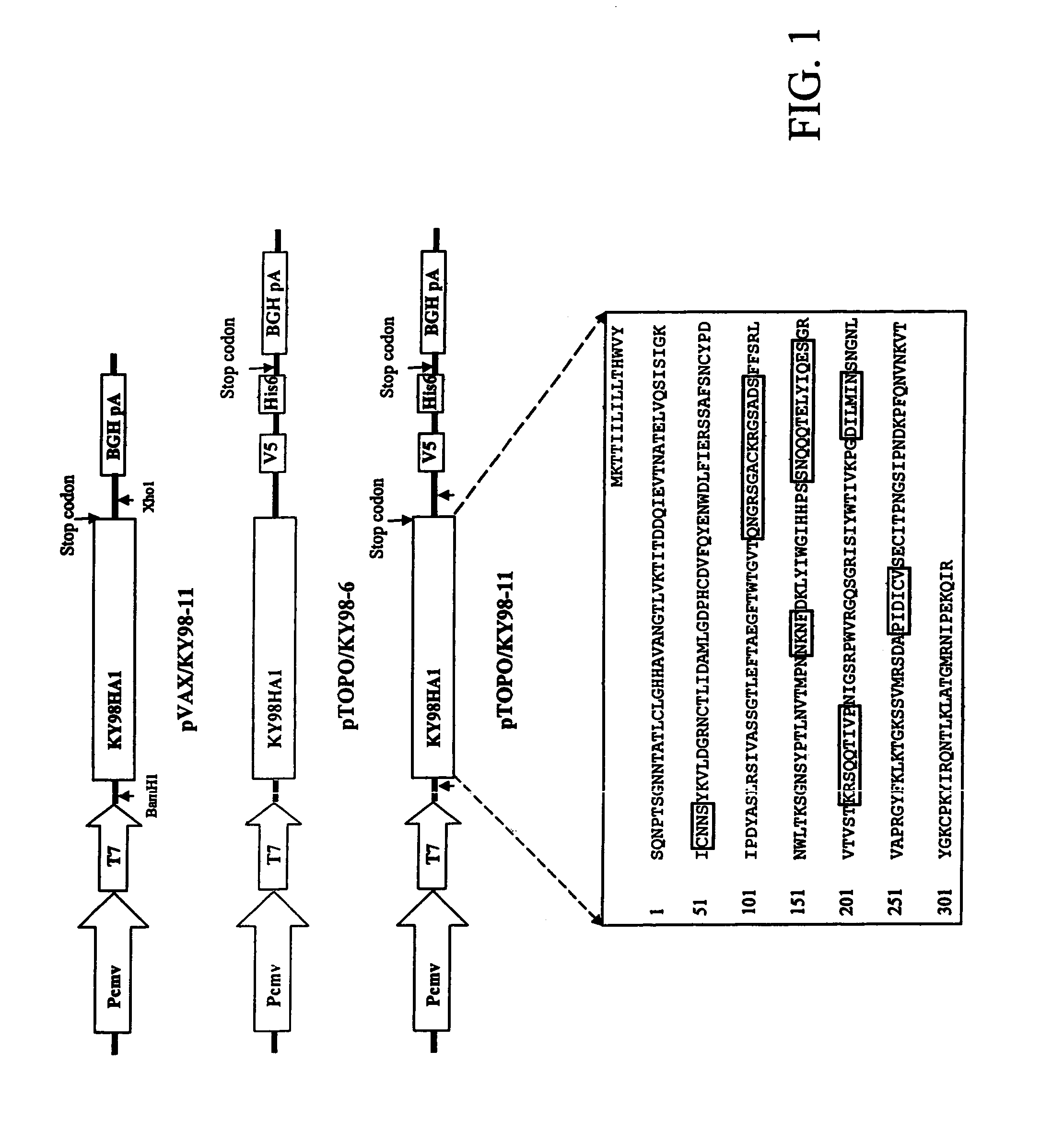
DNA vaccine expressing HA1 of equine-2 influenza virus
InactiveUS7244435B2Reduce riskReduce dosageSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininA-DNA
The invention is for a DNA vaccine expressing the hemagglutinin (HA1) gene of equine-2 influenza virus. By engineering a stop codon within HA1, expression of HA1 is ensured. By encapsulation of the DNA vaccine in liposome and by intranasal inoculation, it is sufficient to elicit protective immunity at a significantly lower dosage compared to a DNA vaccine expressing the full length HA gene. Lower dosage reduces the risk of induction of anti-DNA antibodies. Intranasal inoculation directly to the respiratory epithelial cells reduces the risk of DNA integration. The inventive vaccine is advantageous over current inactivated or live attenuated vaccines, as updating of the vaccine requires only the replacement of the encoding sequence with the new virus.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Virus velogen strain for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, attenuated vaccine strain thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN101280292AImprove securityNo side effectsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMicroorganism
The invention discloses a virulent strain HuN4 for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, and an attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 (the collection number of microorganism: CGMCC No.2484) attenuated because of virulent strain HuN4 passage, and also discloses the application of the attenuated vaccine strain in preventing or curing the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease, which belongs to the biomedical field. The attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 can be prepared into single-vaccine or combined strain (live vaccine or inactivated vaccine), can effectively prevent or cure the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease, and also can be prepared into diagnostic reagent for the highly pathogenic blue-ear disease diagnosis. The attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112 of the invention has the advantages of good security and high protection efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Use of flavivirus for the expression of protein epitopes and development of new live attenuated vaccine virus to immunize against flavivirus and other infectious agents
InactiveUS20060159704A1Stable expressionSafe and effectiveSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesEpitopeSpecific immunity
The present invention relates to a vaccine against infections caused by flavivirus. More particularly to the use of the YF vaccine virus (17D) to express at the level of its envelope, protein epitopes from other pathogens which will elicit a specific immune response to the parental pathogen.
Owner:FUNDACAO OSWALDO CRUZ FIOCRUZ
Genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and application thereof
ActiveCN102250843AMeet the differential diagnosisEasy to solveViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). The attenuated vaccine strain comprises a genomic nucleic acid of a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus attenuated vaccine strain HuN4-F112; the HuN4-F112 genome includes a mutation in a genetic region for coding an Nsp2 protein, and the mutation is as follows: a nucleotide sequence for coding a Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to a lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 480-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein; or the nucleotide sequence for coding the Newcastle disease virus NP protein is inserted to the lacking region of a nucleotide sequence for coding 508-532-site amino acid of the Nsp2 protein. The invention also discloses an application of the genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain. The genetic engineering marked attenuated vaccine strain of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus provided by the invention not only can provide completely safe immune protection to resist high-pathogenicity PRRSV after the porcine is immunized, but also can effectively distinguish the immunized porcine of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccine with the naturally infected porcine of the field virus.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing live vaccines of hog cholera and product thereof
InactiveCN101879311ASmall batch-to-batch quality varianceStable production processInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsVaccine ProductionFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for preparing live vaccines of hog cholera and a product thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing porcine passage cell lines; (2) inoculating the porcine passage cell lines with live vaccine production seed viruses of the hog cholera to obtain attenuated vaccine strains of the hog cholera; (3) performing virus multiplication on the attenuated vaccine strains of the hog cholera; (4) measuring the virus titer of multiplication virus suspension by adopting an immunofluorescence method; and (5) adding a freeze-drying protective agent and antibiotics into the virus suspension which is detected to be qualified for vaccine matching and freeze-drying. The preparation method has the advantages of producing the live vaccines of the hog cholera by using the cell lines so as to achieve small quality differences among batches and the characteristics of simple and stable process, easy operation, high yield, low cost, the feasibility and extendibility of industrial production and the like, and measuring the virus titer of the multiplication virus suspension by adopting the immunofluorescence method so as to achieve sensitive, fast, specific and accurate detection, high repeatability and reliable results. The live vaccines of the hog cholera prepared by the method can completely protect pigs from the attacks of violent hog cholera viruses.
Owner:武华
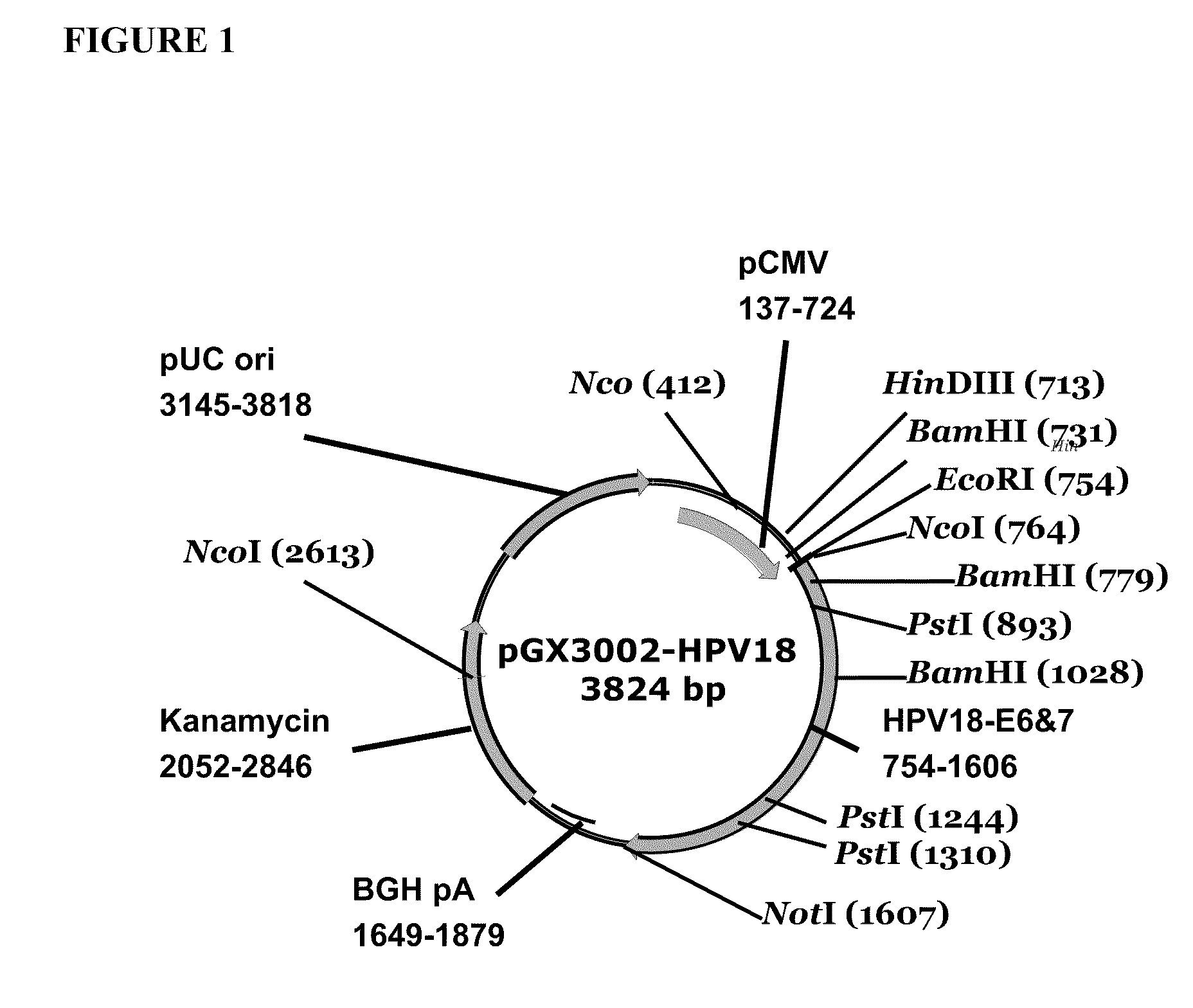
Vaccines for human papilloma virus and methods for using the same
ActiveUS20100189730A1Improved immunogenic targetImproved immunogenic targetsSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsRecombinant vaccinesAttenuated vaccine
Improved anti-HPV immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them are disclosed. Immunogens disclosed include those having consensus HPV 18 E6 and E7. Pharmaceutical composition, recombinant vaccines comprising and live attenuated vaccines are disclosed as well methods of inducing an immune response in an individual against HPV are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome
ActiveCN103397018ARealize fixed-point transformationQuick insertRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationFreeze thawingRecombinant virus
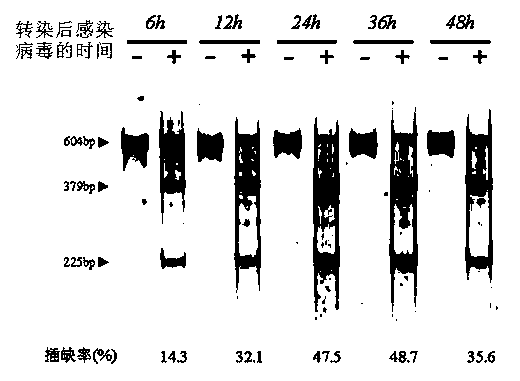
The invention provides a site-directed modification method for DNA viral genome, and the problems in the prior art are solved that induction of site-directed mutagenesis of DNA viral genome is difficult, the operation of inserting an exogenous fragment is complex, and recombination rate is lower. The site-directed modification method comprises: transfecting cells by a plasmid carrying a nuclease system, infecting by a virus, after the cells show pathological changes, collecting the cells with pathological changes, performing freeze-thaw or ultrasonic processing, and centrifuging, separating the liquid supernatant to obtain a progeny virus. The site-directed modification method is capable of realizing applications to screening of virus attenuated vaccine strains, construction of viral genetic carriers and an oncolytic virus, research on virus function sequences, and the like; during modification of the viral genome, the method helps to improve mutagenesis efficiency, accurately control DNA virus for genome site-directed mutagenesis and specific gene knockout, simplify operation steps of inserting the DNA virus carrier by an exogenous gene, and improve efficiency that the exogenous gene is integrated to the viral genome, so that the work of screening high-flux recombination viruses is convenient to conduct.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
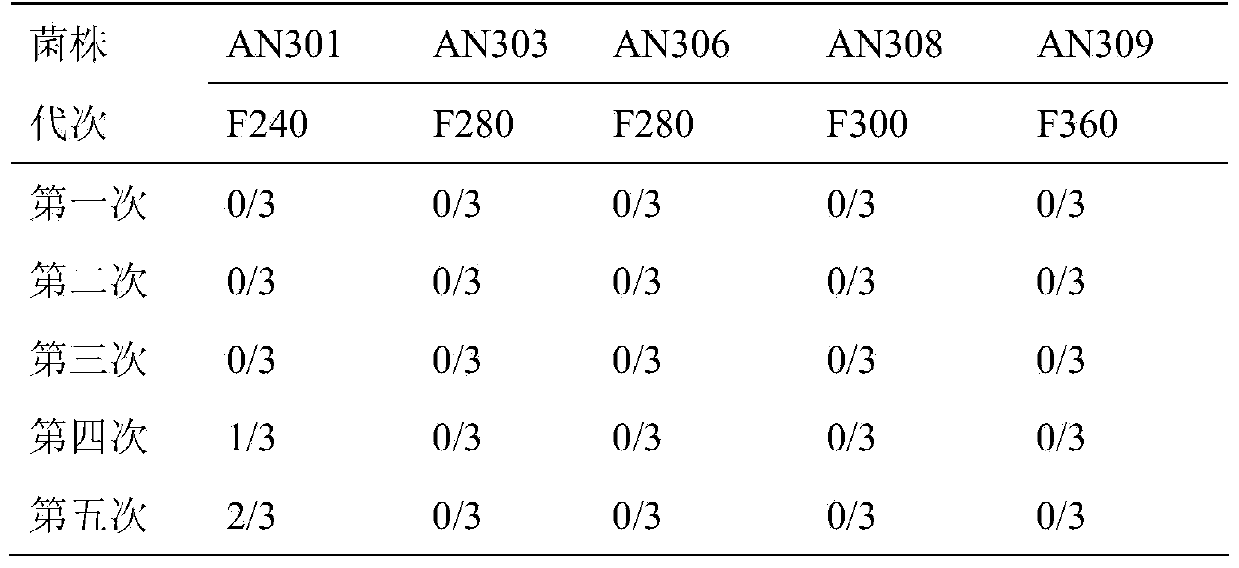
Pig mycoplasma pneumonia live attenuated vaccine and application thereof
ActiveCN103740625AAvoid infectionSimple and fast operationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantPneumonia mrsa
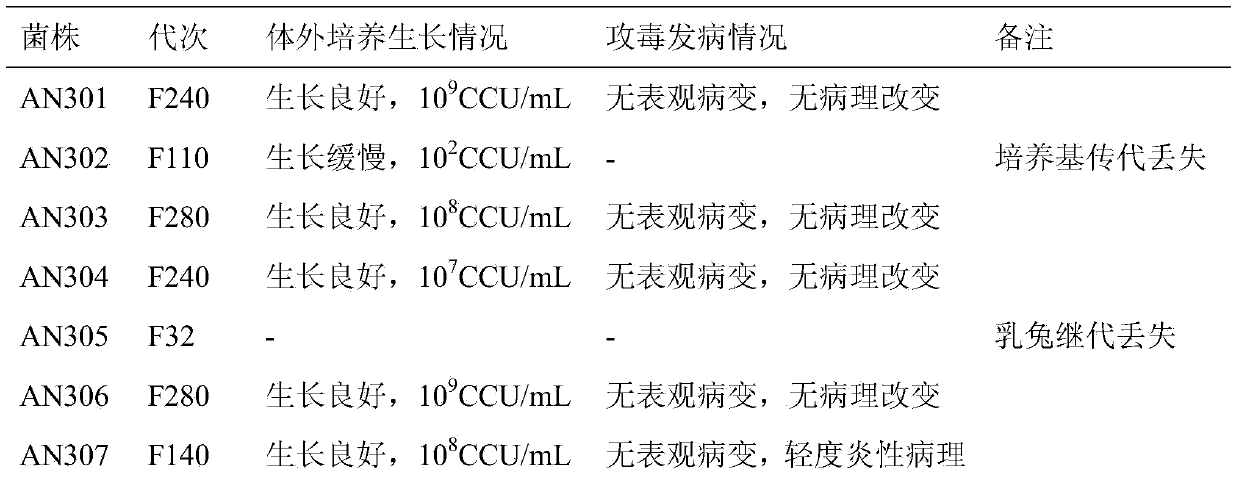
The invention discloses a pig mycoplasma pneumonia live attenuated vaccine and application thereof. A pig lung disease material infected by typical pig mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and not infected by other pathogens is screened and then is subcultured to the 100th generation through the lung of a baby rabbit, then pig mycoplasma hyopneumoniae strains are separated and are continuously subcultured through a culture medium; meanwhile, the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae AN306 is obtained through screening of a plurality of strains, and the preservation number of the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae AN306 is CCTCC M2012431. The invention also relates to a pig mycoplasma pneumonia live vaccine preparation based on the preparation of the attenuated vaccine strain. The pig mycoplasma pneumonia live vaccine preparation comprises a live attenuated vaccine strain, a pharmaceutically acceotable carrier or auxiliary ingredient and an adjuvant, and further comprises immunogens of other pathogens. The pig mycoplasma pneumonia live vaccine disclosed by the invention can be immunized in multiple ways and can enable animals to gain protection ability for resisting pig mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain and the attenuated strain is a mumps virus QS-F-SH2 with an accession number of CCTCC NO: V201950. The invention also provides a vaccine composition containing the F genotype mumps virus attenuated strain as an active ingredient and a preparation method thereof. The mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain disclosed by the invention can match the F type mumps virus predominantly popular in China, and the level of the mumps virus attenuated vaccine strain is equivalent to that of the current vaccine strain in the aspects of growth characteristics, immunogenicity, neurotoxicity and the like.In addition, the mumps virus genetic engineering attenuated strain screened by the invention can be stably produced in chick embryo cells, and the safety is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING CELL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome bivalence recombinant adenovirus vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101380468AImmediately exert cellular immune functionNot pathogenicViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsEukaryotic plasmidsAttenuated vaccine
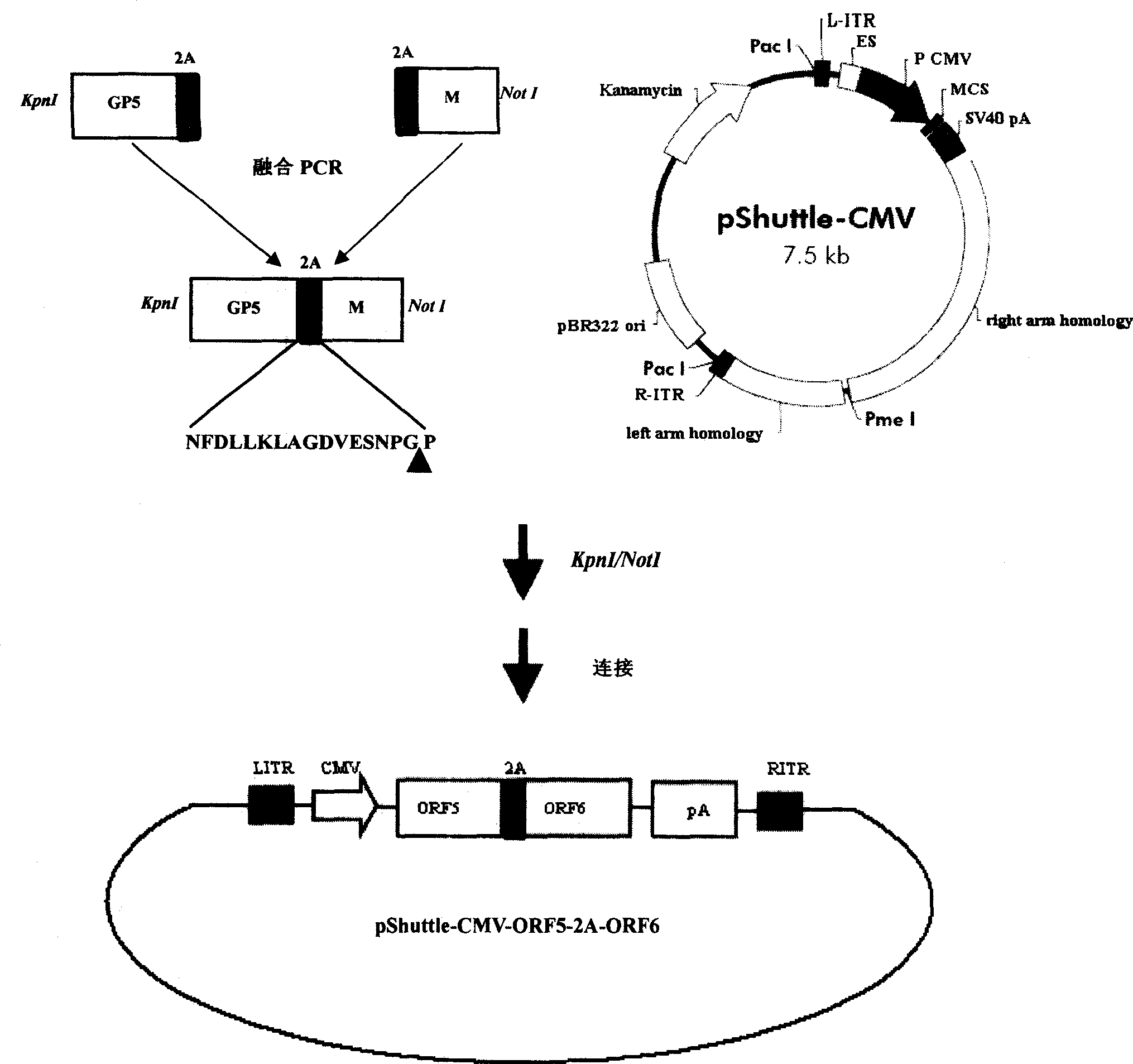
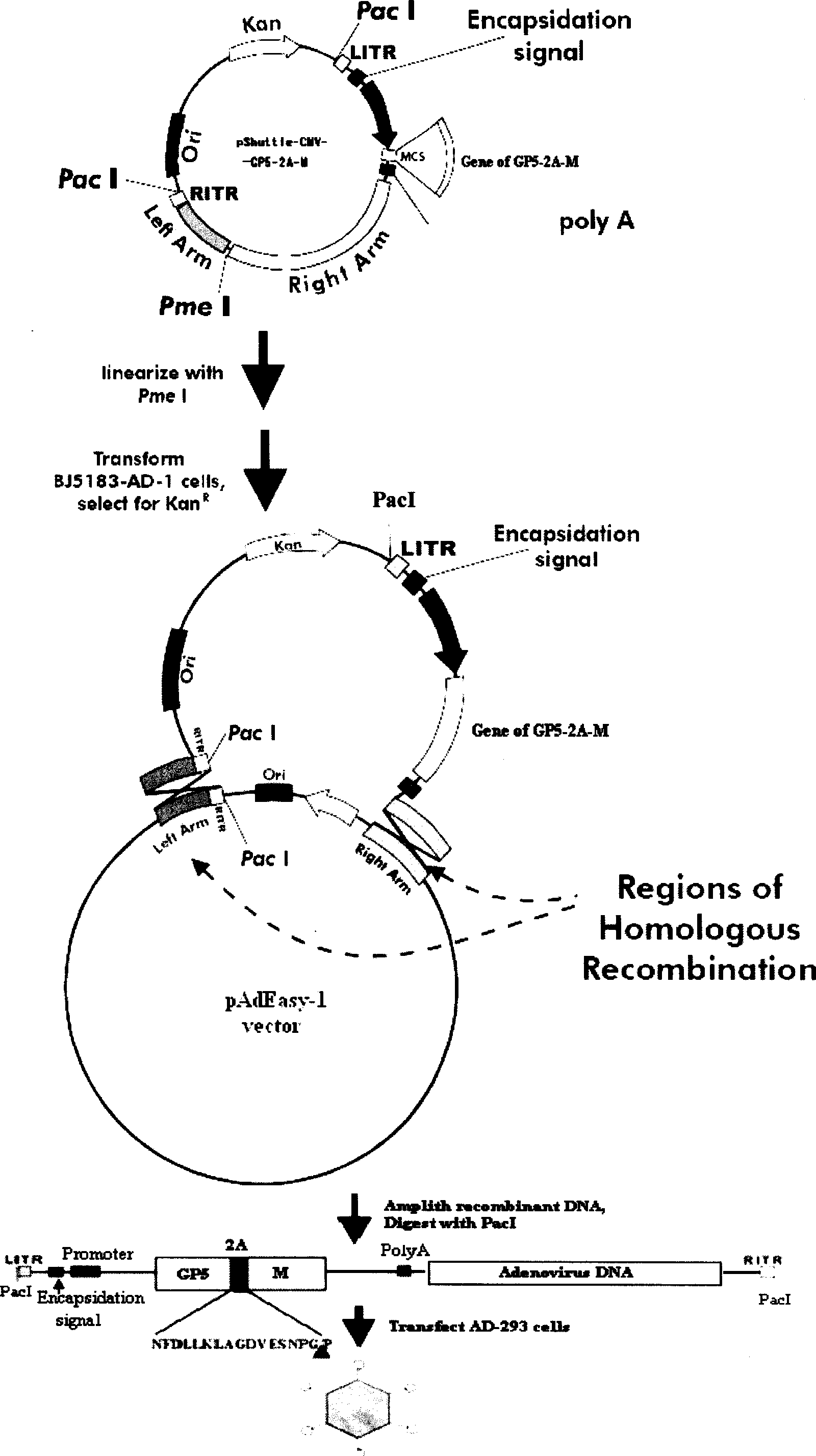
The invention discloses a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome divalent recombination adenovirus vaccine and the preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to the technical field of biological vaccine preparation. The vaccine can be prepared by the following steps: a GP5-2A-M fusion protein gene can be constructed by inserting an FMDV2A gene with self craking between PRRSV GP5 and M protein; homologous recombination is carried out on the GP5-2A-M fusion protein gene and adenovirus backbone plasmid pAdEasy-1; recombination adenovirus rAd-GP5-2A-M is prepared by restriction enzyme and HEK-293A cells transfection, and the divalent recombination adenovirus vaccine is prepared by the technology and the steps such as purification, amplification, and the like. After expression, the aggregate protein GP5-2A-M constructed by the invention is self cracked into GP5 and M protein, as well as exerts the viral neutralization of GP5 and the immune function of the M protein; the vaccine has stable titer with the virulent valence being 10<10.43>TCID<50> / 1.0ml, as well as has both the duplication characteristic of a routine attenuated vaccine and the safety of an inactivated vaccine; the divalent recombination adenovirus vaccine can be popularized in and applied to the control work of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Attenuated vaccine strain for avian infectious bronchitis virus and application thereof
InactiveCN102851257AImprove securityInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesInfectious bronchitisFowl
The method relates to an attenuated vaccine strain for avian infectious bronchitis virus and application thereof. According to the invention, avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is attenuated, so as to successfully obtain an IBV attenuated strain CCTCC.V201232 and a derivative virus strain thereof. The attenuated strain and derivative virus strain provided by the invention can be used in preparation of a vaccine composition for prevention of infectious bronchitis. Experiments show that the attenuated strain and vaccine composition provided by the invention can be inoculated to immature birds, so as to effectively activate immune system in the birds and well prevent avian infectious bronchitis.
Owner:SHANGHAI QISHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Tobacco PDS gene fragment-containing cucumber mosaic virus RNA2 attenuated mutant type plasmid vector and application thereof
ActiveCN108486148AMeet basic requirementsSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesNicotiana tabacumPlasmid Vector
The invention discloses a tobacco PDS gene fragment-containing cucumber mosaic virus RNA2 attenuated mutant type plasmid vector and application thereof. The plasmid vector contains a CMVFny strain RNA2 complete sequence, and a tobacco PDS gene 199bp fragment is inserted behind a 2a protein termination codon. The plasmid vector and a wild CMVFny RNA1 and wild CMVFny RNA3-containing plasmid are inoculated to nicotiana benthamiana through an agrobacterium infiltration method, so that weakly pathogenic symptoms can be displayed, and the capacity of inducing gene silencing can be judged with nakedeyes without depending on an instrument; great convenience is provided for deep researches on attenuated vaccines.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hcv vaccines and methods for using the same
ActiveUS20120034256A1Improved immunogenic targetOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseRecombinant vaccinesAttenuated vaccine
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA +1
Kit for distinguishing and diagnosing capripox field virus infection, preparation and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102183643AEasy to purifyEasy to manufactureDepsipeptidesFermentationCapripox virusAttenuated vaccine
The invention discloses an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) antibody detection kit for distinguishing and diagnosing capripox field virus infection. The indirect ELISA antibody detection kit for distinguishing and diagnosing capripox field virus infection, disclosed by the invention, is internally provided with a coated antigen ELISA antibody detection board and an ELIAS secondary antibody, wherein the coated antigen is a mixture of a recombination capripox virus ORF95 protein and an ORF103 protein. The recombination proteins of ORF95 and ORF103, adopted by the invention, are convenient to prepare and purify in large quantities. The kit disclosed by the invention has a strong specificity, can effectively exclude the interference of the capripox attenuated-vaccine immunity, and specifically detects the capripox field virus infection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Canine distemper attenuated vaccine strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101914503ACharacteristics of typical paramyxovirionsImproving immunogenicityInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCanine distemper virus CDV
The invention discloses a canine distemper attenuated vaccine strain and application thereof. In the invention, passing and cloning are performed on a separated canine distemper virulent strain to culture the canine distemper attenuated vaccine strain, and the microorganism collection number is CGMCC No.3810. The canine distemper attenuated vaccine strain of the invention can provide better protection for the canines suffering homological virulent attack, has perfect immunogenicity and can provide relatively good immune protection for the canines infected with the canine distemper virus. The attenuated vaccine strain can be prepared into single vaccine or united vaccine (live vaccine or inactivated vaccine) and can effectively prevent or cure the canine distemper. The attenuated vaccine strain of the invention has the advantages of stable transmissibility, lasting immunity, good effect, safety, reliability, long storage time and the like.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Lentogenic CH60 strain of duck virual hepatitis virus and attenuated live vaccine thereof
ActiveCN103103163AImprove securityImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsDuck viral hepatitisAttenuated vaccine
The invention discloses a lentogenic CH60 strain of duck virual hepatitis virus. The lentogenic CH60 strain of the duck virual hepatitis virus is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University in China; and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: V201248. As the strain of duck virus hepatitis attenuated vaccine, the lentogenic CH60 strain of duck virual hepatitis virus provided by the invention is good in security and good in immunogenicity.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
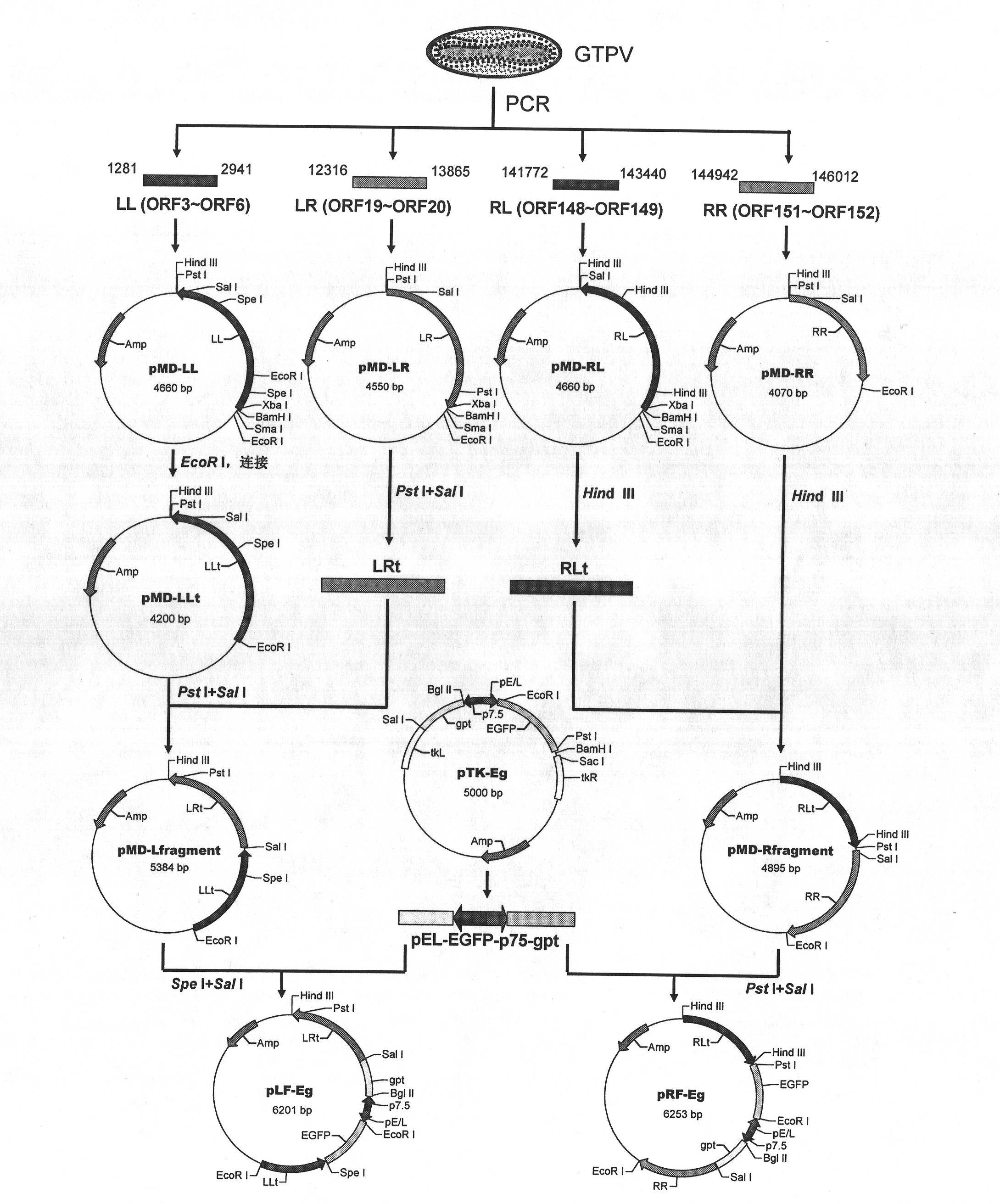
Method for screening non-essential regions for replication of goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same
InactiveCN102174508AImprove securitySmall virulent effectsViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodTransfer vector
The invention relates to a method for screening non-essential regions for replication of a goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same. The method comprises the steps of amplifying two-end gene segments of any two regions of a goat pox virus gene by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; then, inserting an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene and a xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (gpt) gene expression cassette into the segments; establishing two universal transfer vectors of the goat pox virus; and acquiring a recombinant virus expressing an exogenous gene stably from the transfer vectors, thereby determining the selected regions to be non-essential regions for replication of the goat pox virus, wherein each universal transfer vector contains one unique restriction enzyme cutting site Sal I and allows gene expression cassettes of other items to insert in. The recombinant virus obtained by means of the two universal transfer vectors provided by the invention not only has a growth performance similar to a parent virus, but also has better safety because a plurality of toxicity related genes in a genome are knocked out in an orientation way, and has the potential to be developed into an attenuated vaccine strain for gene engineering.
Owner:广西壮族自治区动物疫病预防控制中心
Mink canine distemper-parvovirus enteritis bigeminal live vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104383530APrevention of parvovirus enteritisAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsDiseaseMink
The invention discloses a mink canine distemper-parvovirus enteritis bigeminal live vaccine as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The bigeminal live vaccine comprises the effective constituents of a mink parvovirus attenuated vaccine strain MEVB-F61 and a mink canine distemper attenuated vaccine strain CDV3-CL, wherein the artificially-attenuated mink parvovirus attenuated vaccine strain MEVB-F61 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number of the mink parvovirus attenuated vaccine strain MEVB-F61 is CGMCC No.9560. Safety testing results show that no any adverse effect is realized when the mink is inoculated with the bigeminal live vaccine; an effect test result shows that after inoculation of the single-dose bigeminal live vaccine, the minks are prevented from attach of high toxicity for detecting canine distemper virus and parvovirus, so that minks are protected. The bigeminal live vaccine provided by the invention can simultaneously prevent two diseases of mink canine distemper and mink parvovirus enteritis, that two diseases are prevented through an injection of the bigeminal live vaccine is realized, and the bigeminal live vaccine has a wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
Attenuated vaccine strain of VII type new castle disease virus with mutated L gene and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104962526AHigh titerGenetically stableMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesAntigenDisease
The invention relates to an attenuated vaccine strain of a VII type new castle disease virus with a mutated L gene which is produced by reverse genetic operation technology and a preparation method thereof, and the invention belongs to the fields of biological products and biological technology. The virulence of the attenuated vaccine strain of the VII type new castle disease virus with the mutated L gene is obviously decreased, simultaneously the attenuated vaccine strain has the characteristics of high titer, stable heritability and high matching with the antigen of the epidemic virus according to the chicken embryo experiment; the preparation method is suitable for large scale production of vaccines, and is used for producing vaccines; compared with the conventional vaccines (gene I and gene II types), the attenuated vaccine strain of the VII type new castle disease virus with the mutated L gene has wide application prospects in the aspects of morbidity and epidemic control of new castle disease.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Attenuated strain of Leishmania
Differentially expressed Leishmania genes and proteins are described. One differentially expressed gene (A2) is expressed at significantly elevated levels (more than about 10 fold higher) in the amastigote stage of the life cycle when the Leishmania organism is present in macrophages than in the free promastigote stage. The A2 gene encodes a 22 kD protein (A2 protein) that is recognized by kala-azar convalescent serum and has amino acid sequence homology with an S-antigen of Plasmodium falcilparum Vietnamese isolate VI. Differentially expressed Leishmania genes and proteins have utility as vaccines, diagnostic reagents, as tools for the generation of immunological reagents and the generation of attenuated variants of Leishmania.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Avian influenza virus live attenuated vaccine and uses thereof
Described in this application are attenuated strains of avian influenza virus containing temperature sensitive mutations in addition to a genetic tag in the PB1 gene. The attenuated viruses are useful as avian and mammalian vaccine for protective immunity against homologous and heterologous lethal challenges with influenza virus. A genetically modified avian influenza virus backbone is described which can be used as a master donor strain for the generation of live attenuated vaccines for epidemic and pandemic influenza.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Vaccine strains of infectious clones of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) and application thereof
ActiveCN101984061AEasy to solveEasy to controlViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHighly pathogenicAttenuated vaccine
The invention discloses an artificially cloned attenuated vaccine strains. The vaccine strains are strains cloned from attenuated vaccine strains HuN4-F112 of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), and marked restriction enzyme sites are introduced in the structural protein gene sequences of the strains. The invention also discloses a recombinant vector which comprises a full-length gene cDNA sequence of the attenuated vaccine strains HuN4-F112 of the highly pathogenic PRRSV. The 5'-end of the full-length gene cDNA sequence is additionally provided witha transcription promoter and the full-length gene cDNA sequence is internally introduced with the marked restriction enzyme sites. The artificially cloned attenuated vaccine strains of the invention can not only provide completely safe immune protection for resistance of an immune pig to the highly pathogenic PRRSV, but also effectively distinguish an immune pig of the PRRSV from a naturally infectious pig of the PRRSV, thus being beneficial to preventing and controlling the highly pathogenic PRRSV.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Live vaccine for human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7189402B1Bacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSalmonella wienHIV Proteins
The present invention discloses development of a model live vaccine for HIV, using an attenuated strain of Salmonella engineered to surface express specific HIV proteins and testing of this vaccine in mice. There are provided two recombinant plasmids, containing the Lpp-OmpA genes required for surface exposure, followed by the genes for the HIV-1 proteins, Reverse Transcriptase or Transactivating protein (Tat). These plasmids are electroporated into an attenuated strain of Salmonella, and antigen expression is verified. These live vaccines are then used to orally inoculate mice and the vaccinated mice are tested for fecal IgA response and helper T cell response specific for the HIV antigens.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Method for producing pseudorabies attenuated vaccine by using bioreactor and pseudorabies attenuated vaccine product
ActiveCN101695572AImprove immune efficiencyIncrease growth densityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVaccine ProductionAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a method for producing a pseudorabies attenuated vaccine by using a bioreactor and a pseudorabies attenuated vaccine product. After being sterilized, the bioreactor and a micro carrier are inoculated with cells for producing the vaccine, and a cell growth medium is added for culture. A maintenance medium containing attenuated strains of pseudorabies viruses are inoculated into the bioreactor to continue culturing the cells. 2 to 3 days after virus inoculation, cell culture virus liquid is obtained and added with a stabilizer and antibiotics, and the cell culture virus liquid is refrigerated and dried under vacuum to obtain the pseudorabies attenuated vaccine. In the method, the cell density and virus concentration are improved greatly, the titer of the vaccine is improved, the side reactions, labor intensity and product cost are reduced, the monitoring performance of vaccine production is improved and uniform and stable product quality is guaranteed. The pseudorabies attenuated vaccine produced by the method has high safety, immune efficacy and good immune and protective effect against the attack by the virulent pseudorabies viruses.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com