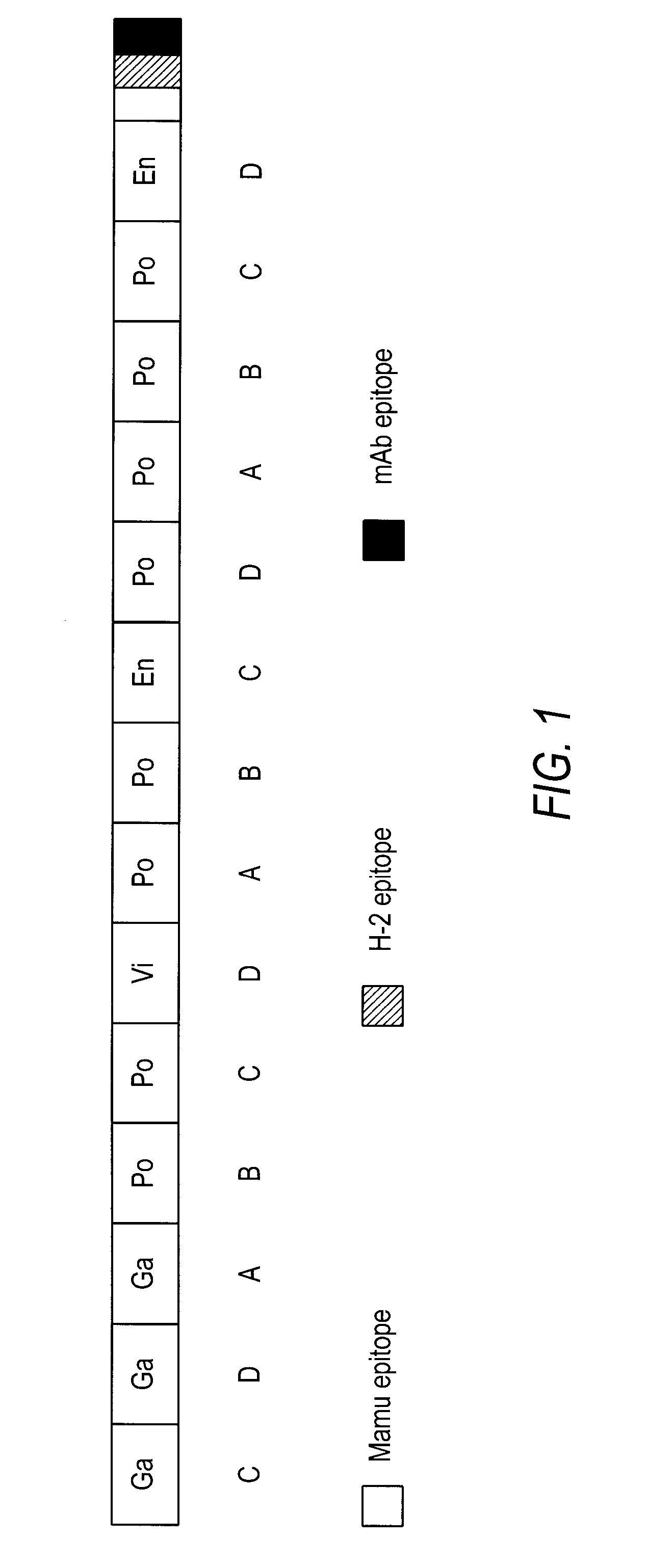
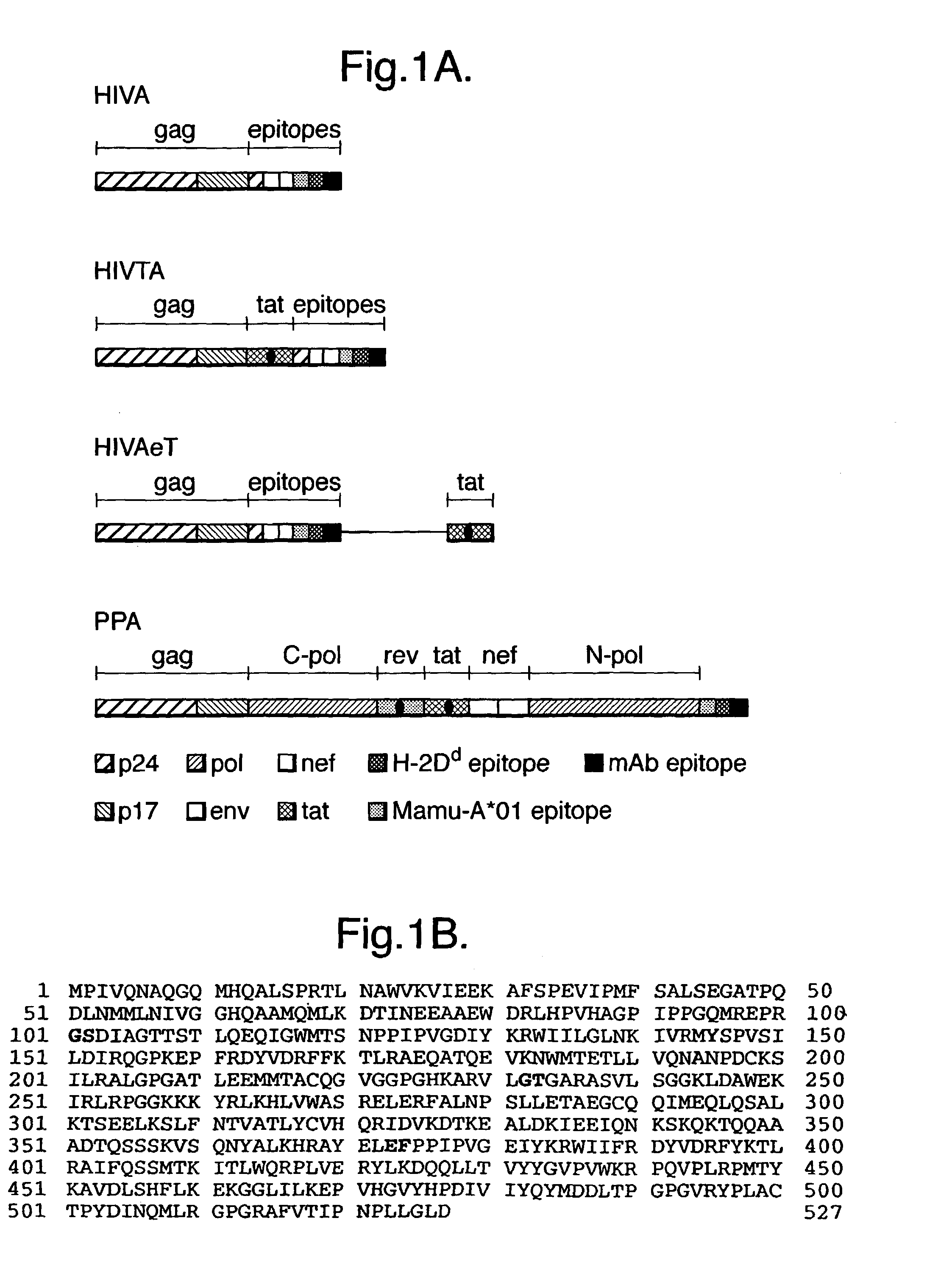
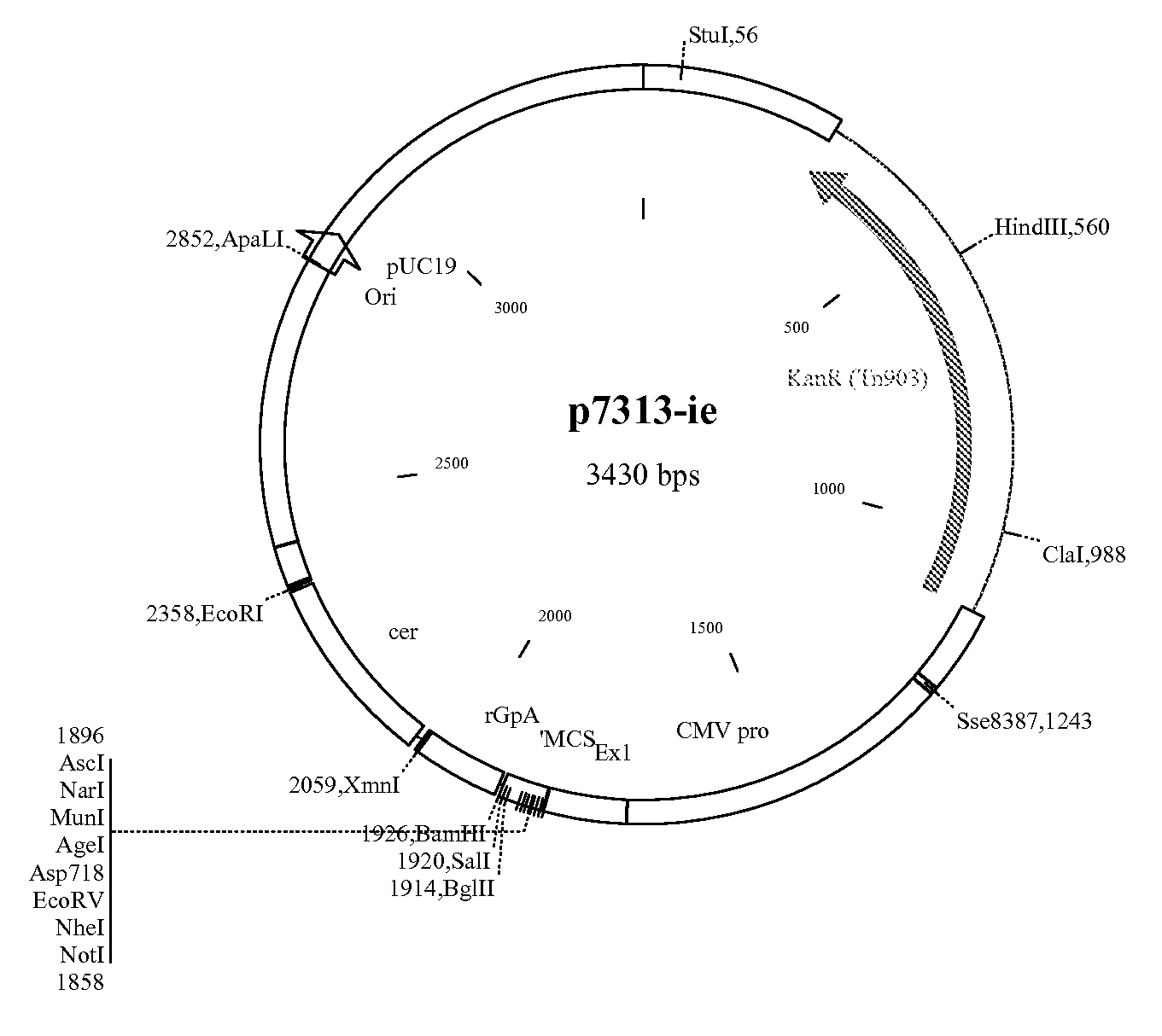
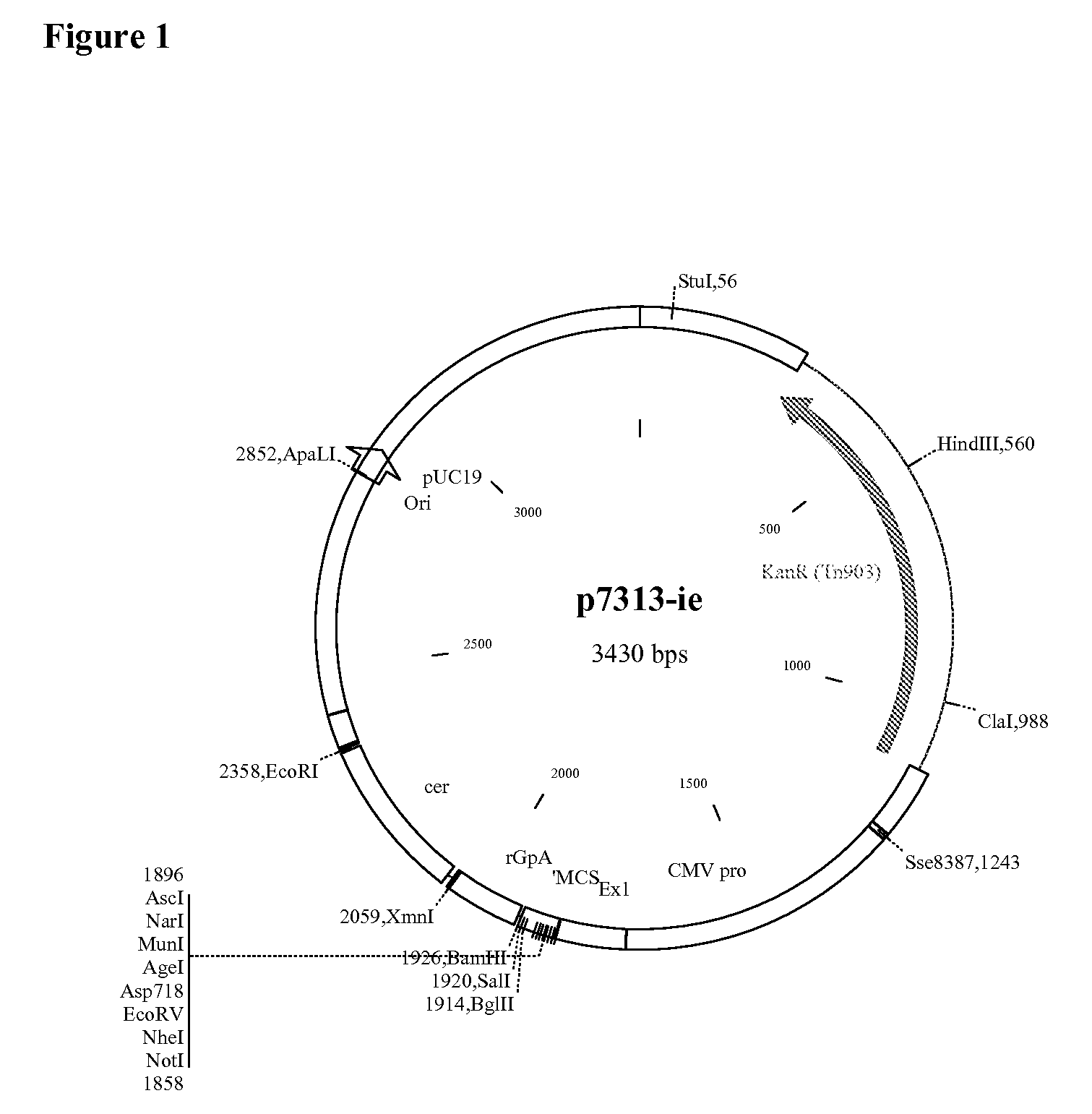
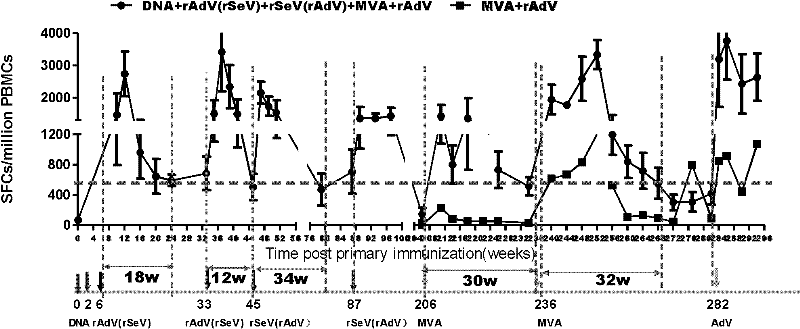
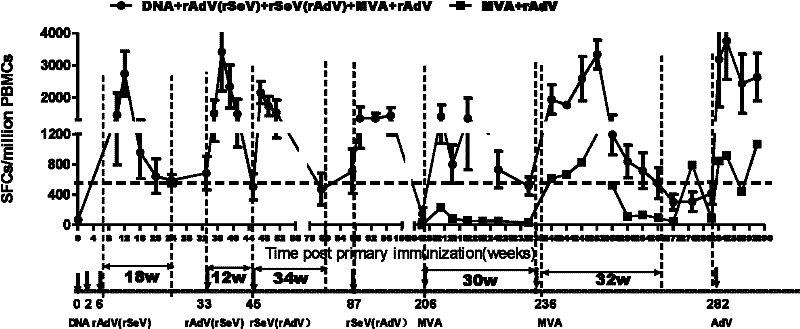
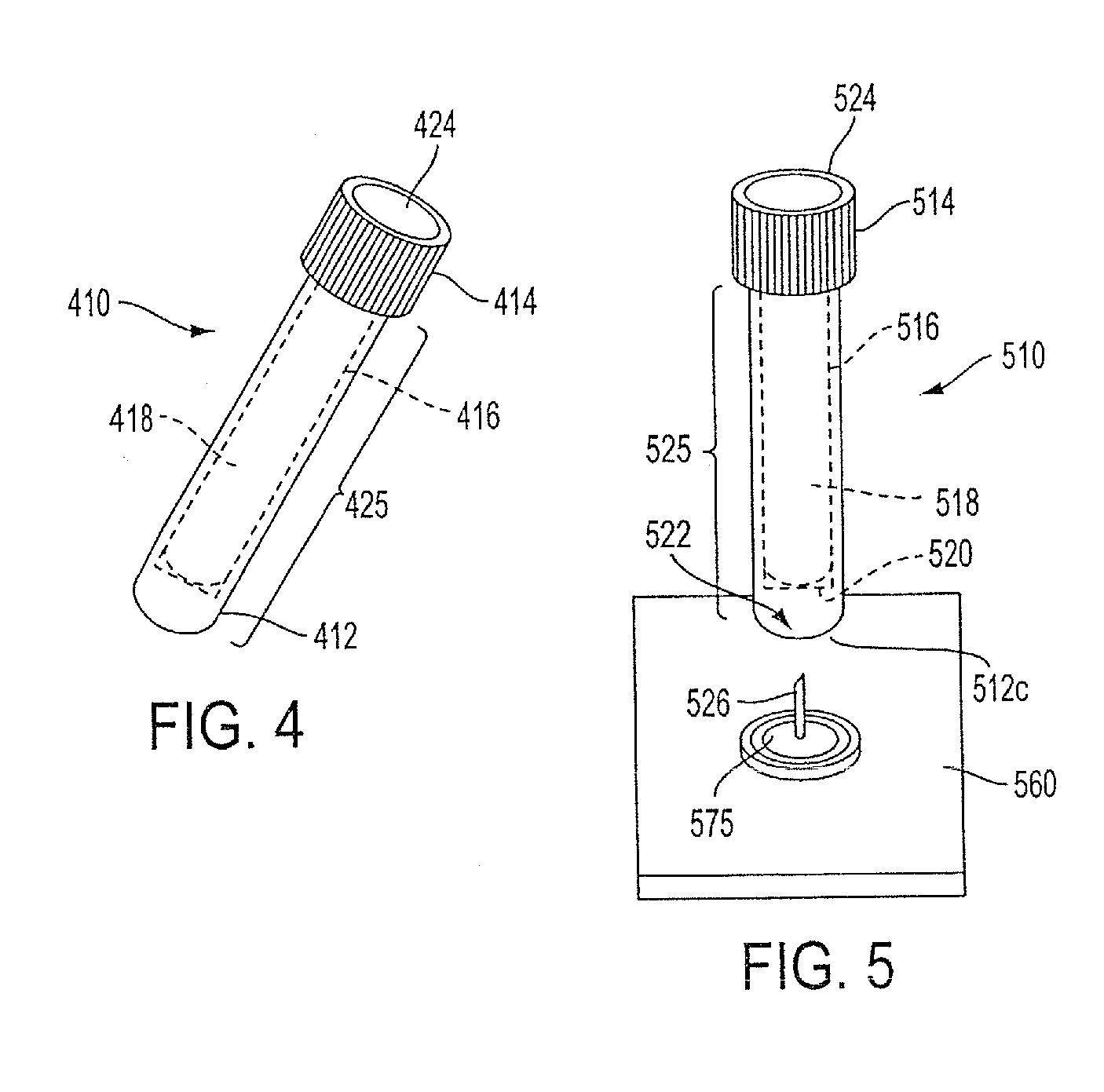
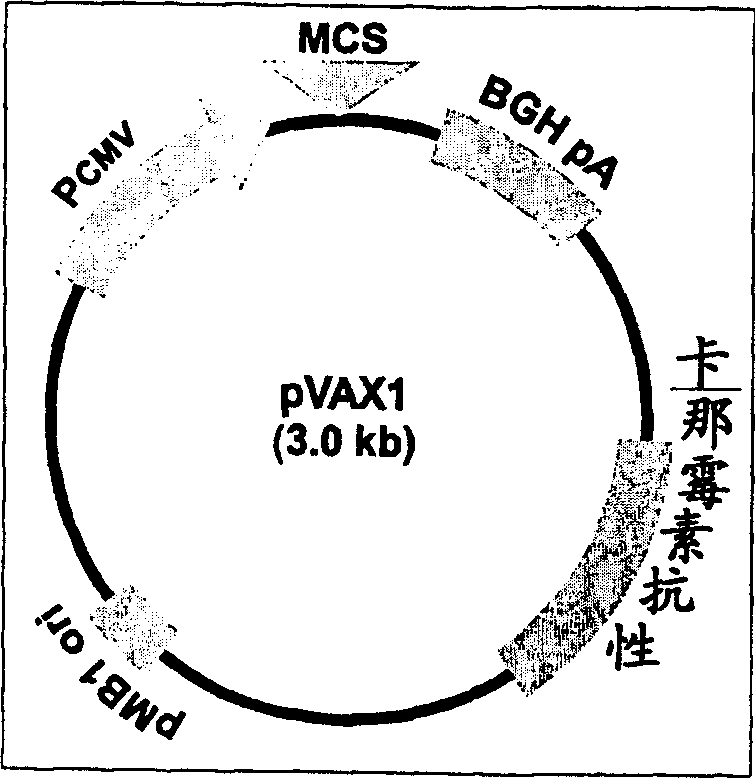
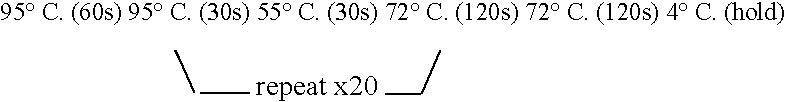Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
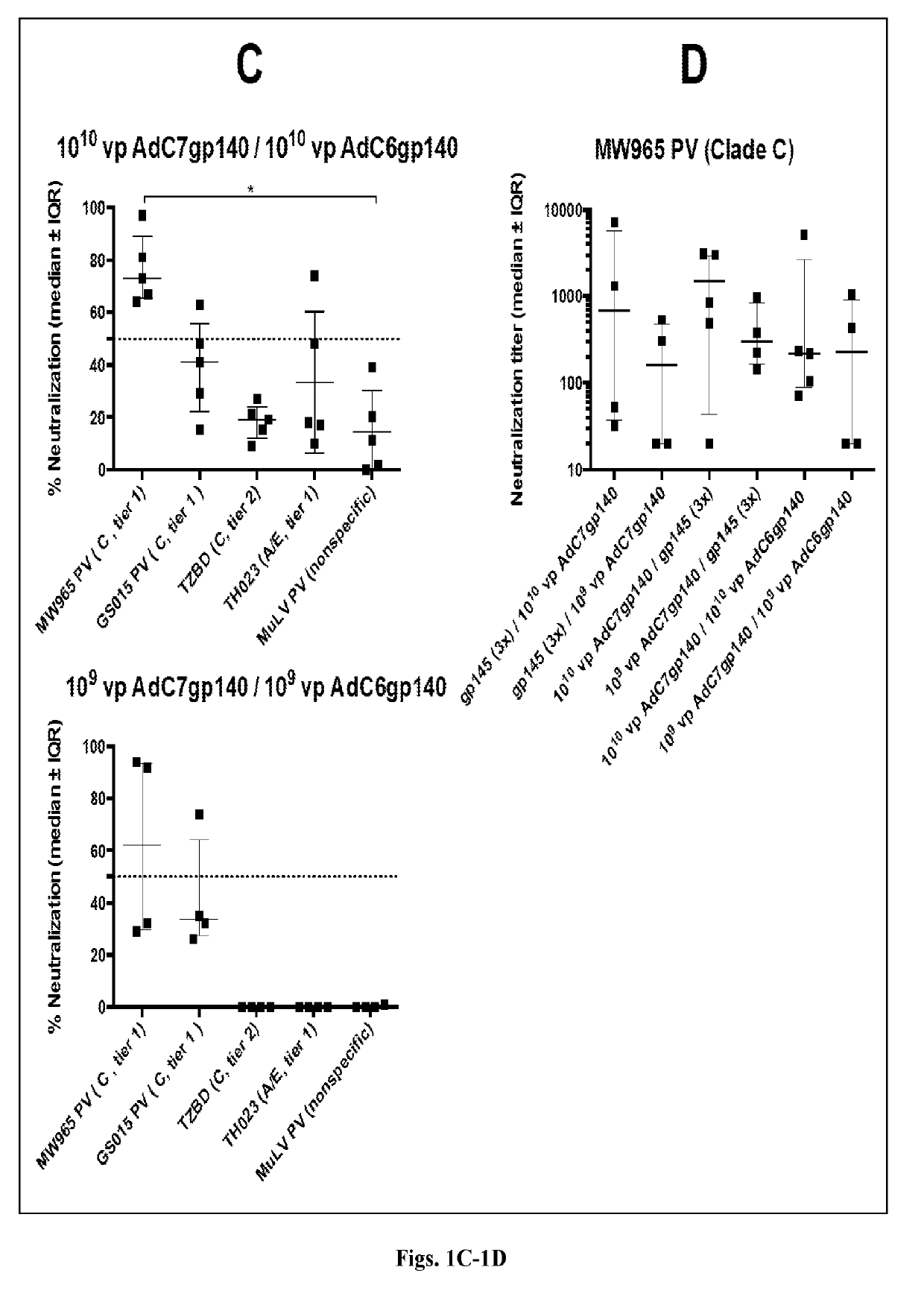
45 results about "HIV Proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HIV has several major genes coding for structural proteins that are found in all retroviruses as well as several nonstructural ("accessory") genes unique to HIV. The HIV genome contains nine genes that encode fifteen viral proteins.
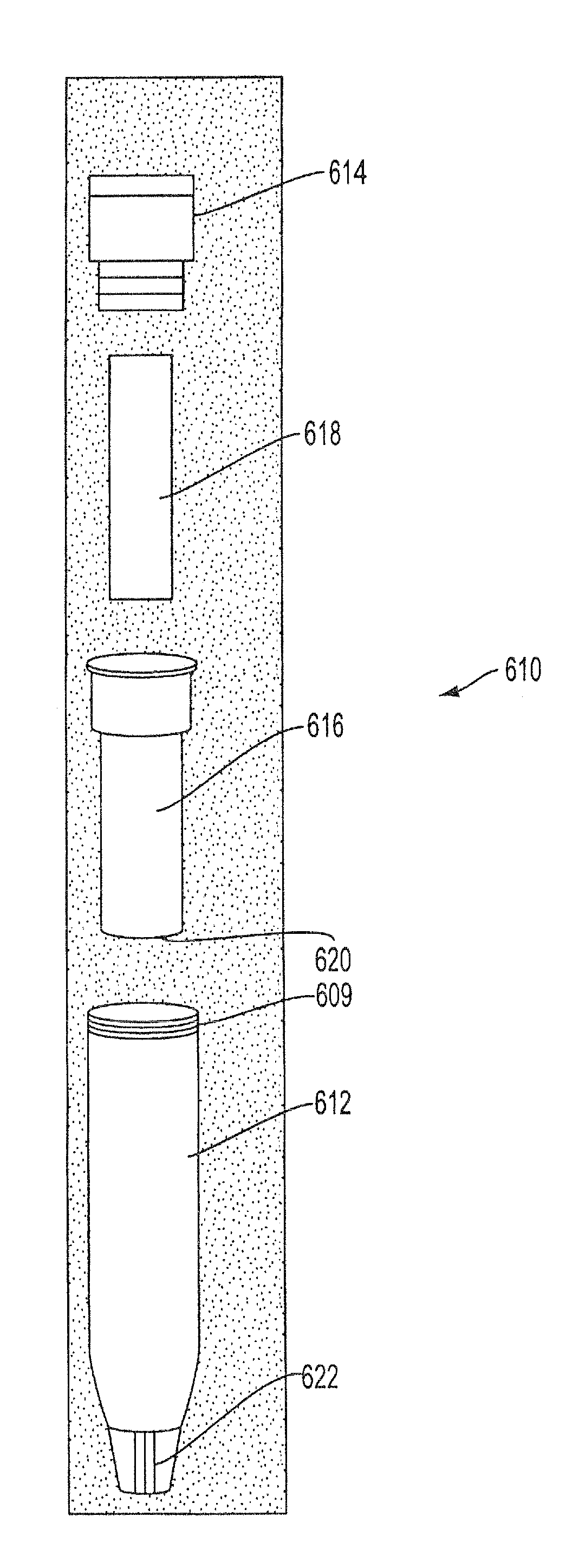
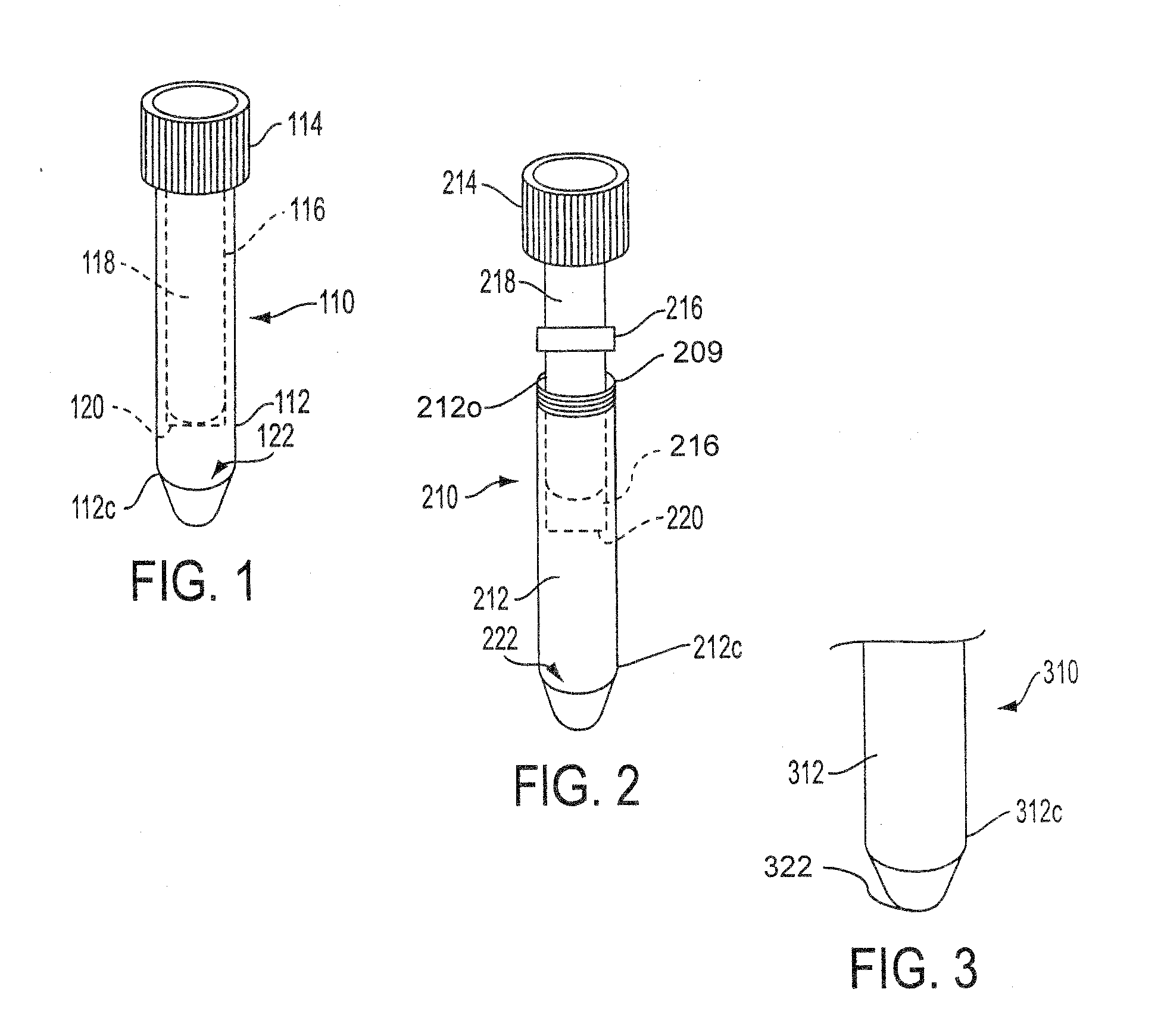
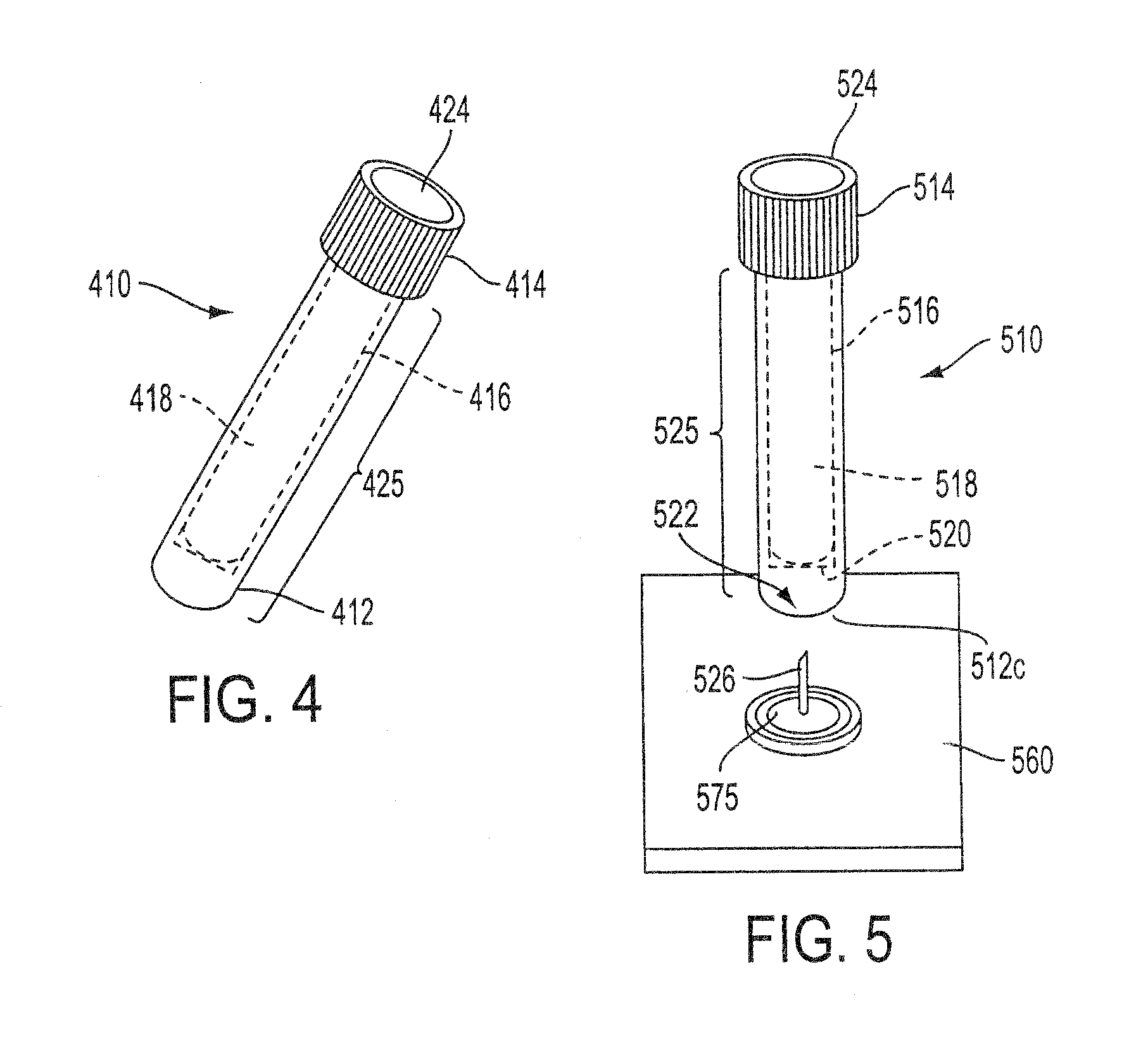
Sample Collection System and Method for Use Thereof
A sample collection system capable of collecting, storing and dispensing a liquid sample is disclosed. The collection system includes a collector composed of a material which has the unique ability to express constituents of interest at levels which are much more concentrated than their levels in the fluid samples from which they are expressed, where the expressed highly concentrated sample can then be used with modern rapid screening / testing protocols, such as solid phase assays, to test for the constituents of interest. Thus, it is now possible to obtain analytes of interest, such as the HIV protein antibodies, from saliva samples at concentrations that are detectable with systems and / or devices that are typically utilized only for blood serum or plasma testing. The collector is sized and shaped to fit within a recovery container, which, in turn, is sized and shaped to fit within a collection tube. The recovery container includes an aperture which does not permit passage of fluid under ambient conditions, but facilitates transfer thereof when subjected to pressure. An optional channel within the collection tube facilitates dispensing of the sample for further processing.
Owner:ARONOWITZ JACK L
Vaccine
InactiveUS7655235B2Reduce and prevent glycosylationGlycosylation can be reduced and preventedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesDNA vaccinationHeterologous
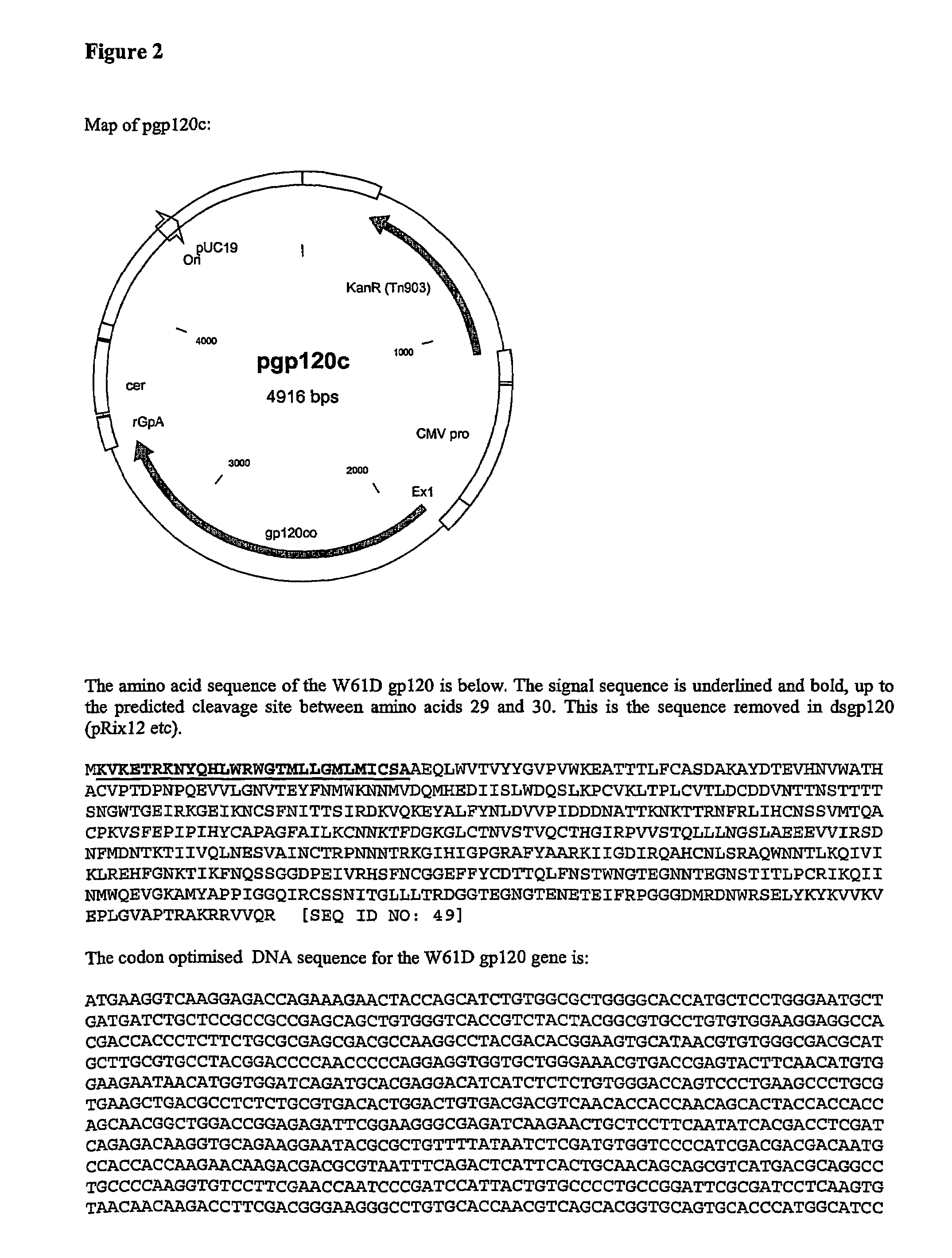
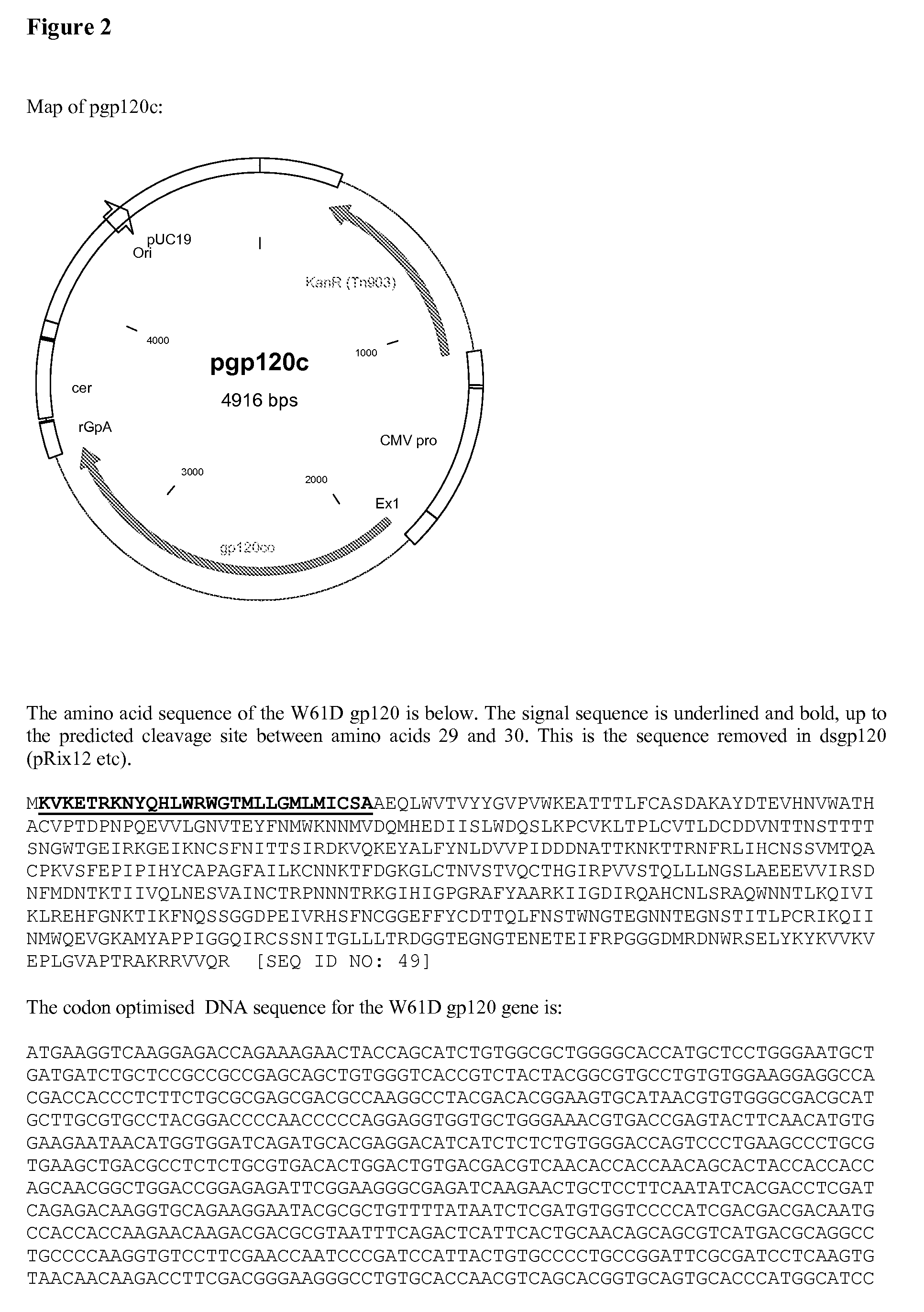
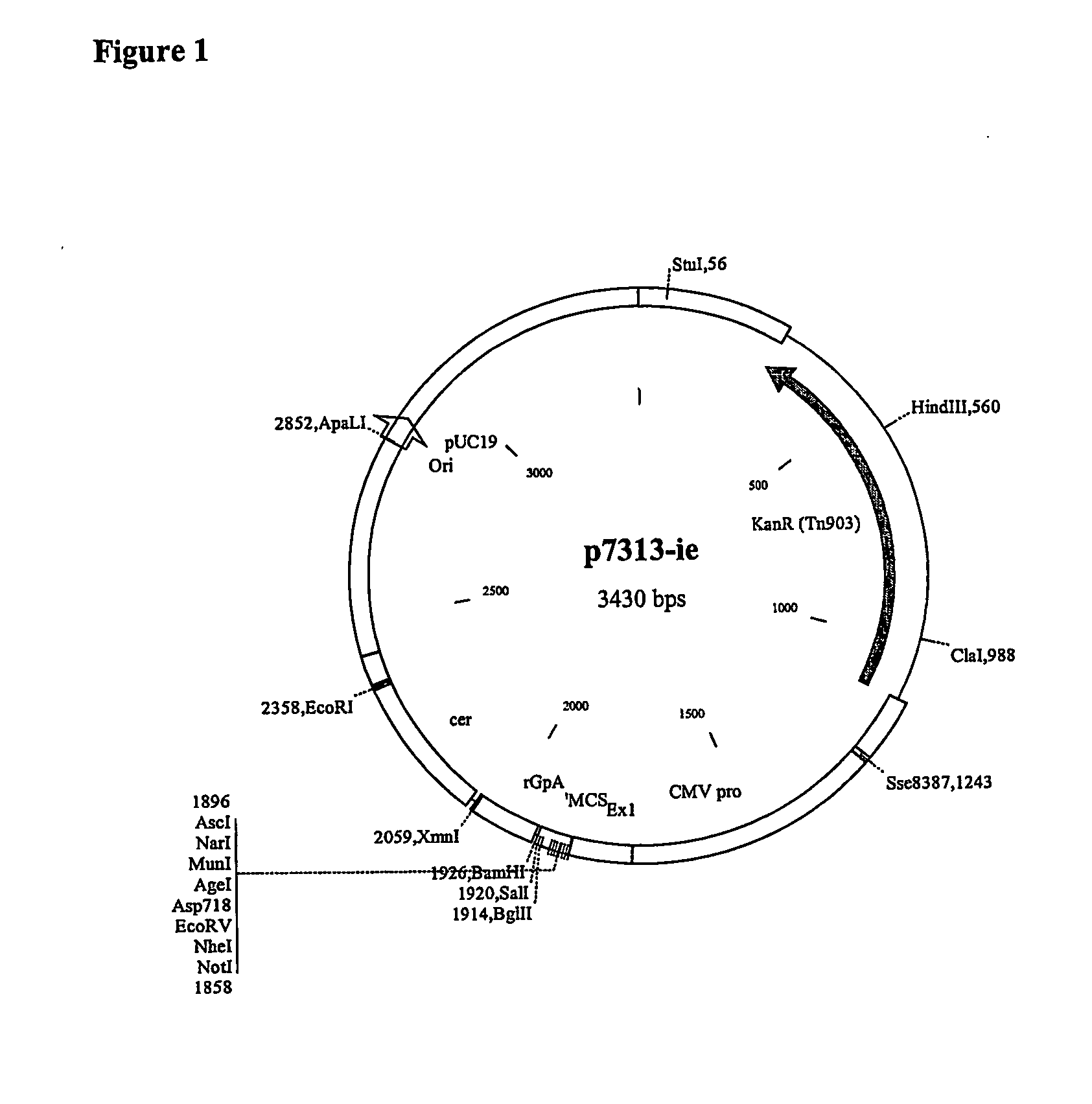
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative, which is non-glycosylated when expressed in a mammalian target cell, operably linked to a heterologous promoter. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule, such as gp120 or gp140 or gp160, lacks a functional secretion signal. It may be fused to additional HIV proteins such as Nef, Gag, RT or Tat.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
Sample Collection System and Method for Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100089181A1Small shapeSmall sizeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteSaliva sample
A sample collection system capable of collecting, storing and dispensing a liquid sample is disclosed. The collection system includes a collector composed of a material which has the unique ability to express constituents of interest at levels which are much more concentrated than their levels in the fluid samples from which they are expressed, where the expressed highly concentrated sample can then be used with modern rapid screening / testing protocols, such as solid phase assays, to test for the constituents of interest. Thus, it is now possible to obtain analytes of interest, such as the HIV protein antibodies, from saliva samples at concentrations that are representative of that found in serum or plasma. The collector is sized and shaped to fit within a recovery container, which, in turn, is sized and shaped to fit within a collection tube. The recovery container includes an aperture which does not permit passage of fluid under ambient conditions, but facilitates transfer thereof when subjected to pressure. An optional channel within the collection tube facilitates dispensing of the sample for further processing.
Owner:ARONOWITZ JACK L
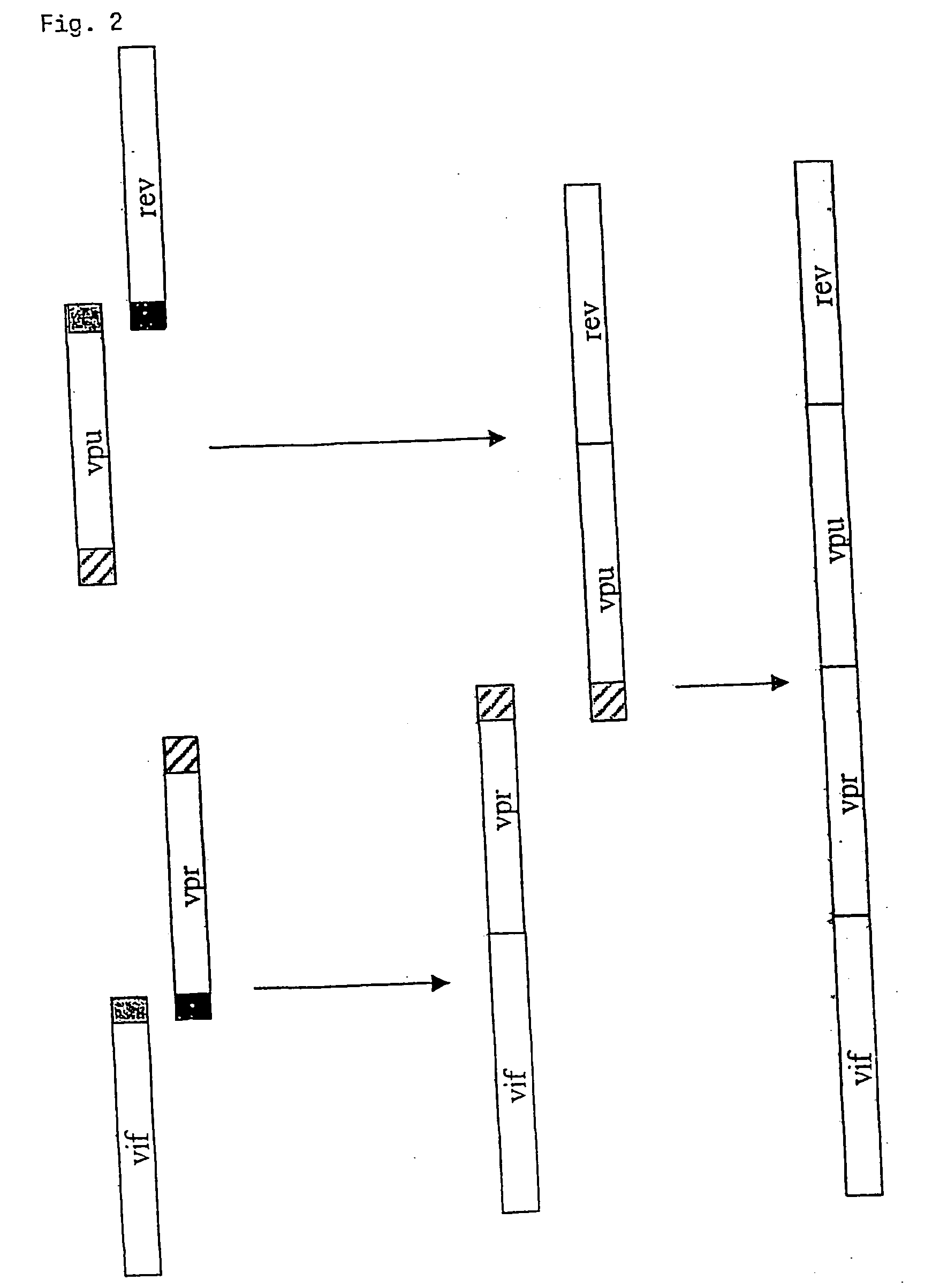
Fusion proteins of HIV regulatory/accessory proteins
InactiveUS20060257974A1Promote infectionDecreased and even no transactivation and interactionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesHIV ProteinsProteinase activity
Nucleic acids are disclosed encoding fusion proteins comprising the amino acid sequence of at least four non-attenuated HIV proteins selected from the group consisting of Vif, Vpr, Vpu, Vpx, Rev, Tat, and Nef, wherein the fusion protein does not contain a specific cleavage sequence for a cellular protease. Also disclosed are vectors comprising the nucleic acids and methods of preparing the fusion protein by transfecting a host cell with the nucleic acids or with the vectors containing the nucleic acids, expressing the fusion proteins, and recovering the fusion proteins.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Live vaccine for human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7189402B1Bacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSalmonella wienHIV Proteins
The present invention discloses development of a model live vaccine for HIV, using an attenuated strain of Salmonella engineered to surface express specific HIV proteins and testing of this vaccine in mice. There are provided two recombinant plasmids, containing the Lpp-OmpA genes required for surface exposure, followed by the genes for the HIV-1 proteins, Reverse Transcriptase or Transactivating protein (Tat). These plasmids are electroporated into an attenuated strain of Salmonella, and antigen expression is verified. These live vaccines are then used to orally inoculate mice and the vaccinated mice are tested for fecal IgA response and helper T cell response specific for the HIV antigens.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Hivcon: an HIV immunogen and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080089901A1Elicit immune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHIV ProteinsA-DNA
The present invention provides artificial fusion proteins (AFPs) designed to elicit an anti-HIV immune response, as well as nucleic acid molecules and expression vectors encoding those proteins. The AFPs of the invention may comprise domains from various HIV proteins, such as Gag, Pol, Vif, and Env proteins, which are partial sequences. HIVCON is an AFP in which the HIV domains are from several HIV clade consensus sequences and which optionally contains additional domains which may be useful, for example, in monitoring expression levels or laboratory animal immune responses. Other aspects of the invention may include compositions and methods for inducing an anti-HIV immune response in a subject, preferably with a DNA prime-MVA boost strategy, and to induce a cell-mediated immune response.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
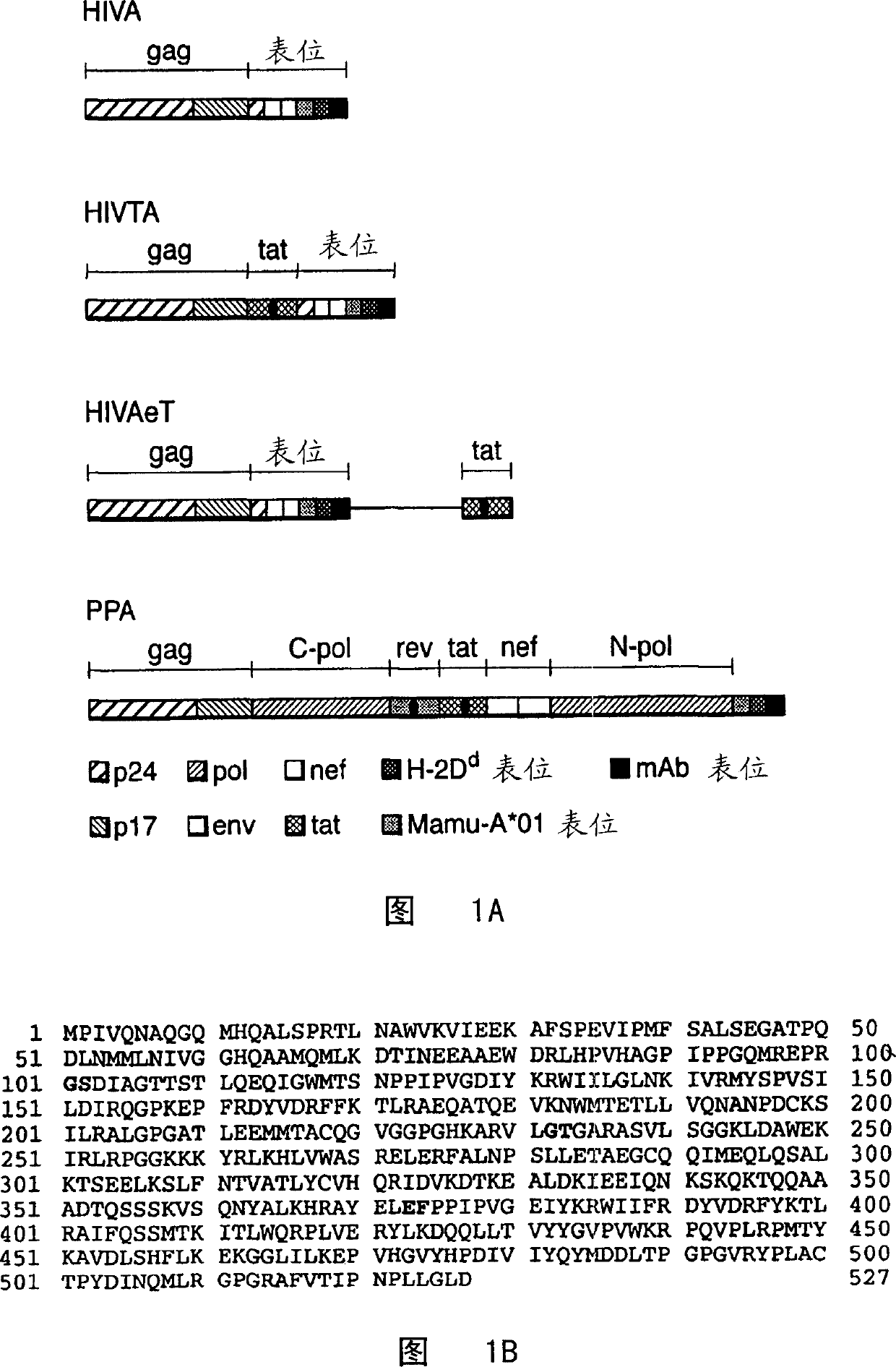
Chimeric human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immunogens comprising GAG P24-P17 fused to multiple cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitopes
InactiveUS7993651B2Improve presentation efficiencyPrevent myristylationBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCtl epitopeHIV Proteins
Disclosed is an immunogen in sterile form suitable for administration to a human subject, the immunogen comprising: at least a portion of the gag protein of HIV, said gag protein being from an HIV clade or having a consensus sequence for one or more HIV clades, and comprising at least parts of p17 and p24; and a synthetic polypeptide comprising a plurality of amino acid sequences, each sequence comprising a human CTL epitope of an HIV protein, and wherein a plurality of HIV proteins are represented in the synthetic polypeptide, said CTL epitopes being selected to stimulate an immune response to one or more HIV clades of interest.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL +2
Vaccine
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative fused to an additional HIV protein selected from a non-structural protein or capsid protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative thereof. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is gp120 and preferred fusions include one or more of HIV Nef, Gag, RT or Tat. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is non-glycosylated in mammalian cells.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
Generation of a broad t-cell response in humans against HIV
InactiveUS20120135032A1Reduce riskPromote infectionViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsHIV ProteinsVaccinia
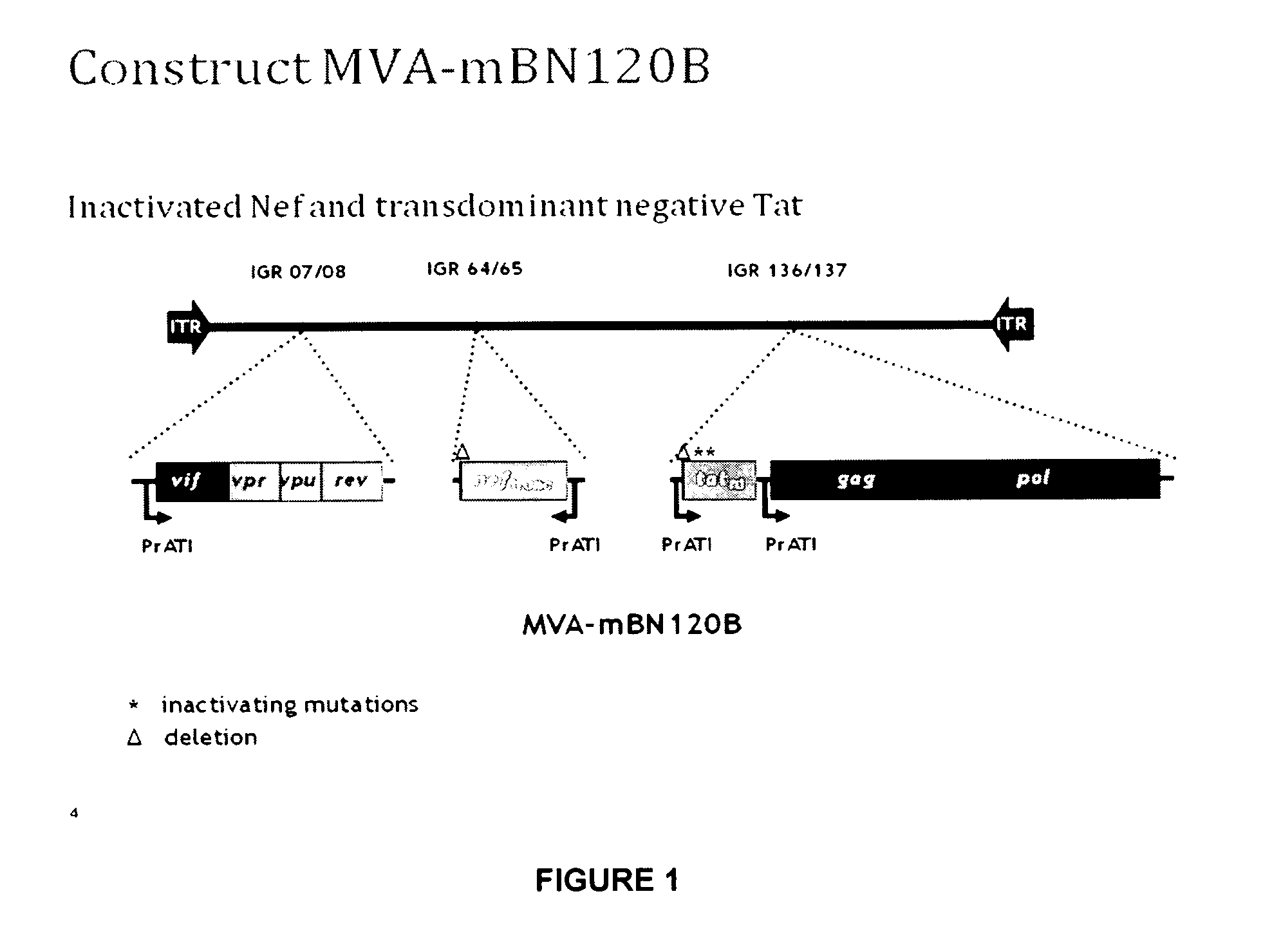
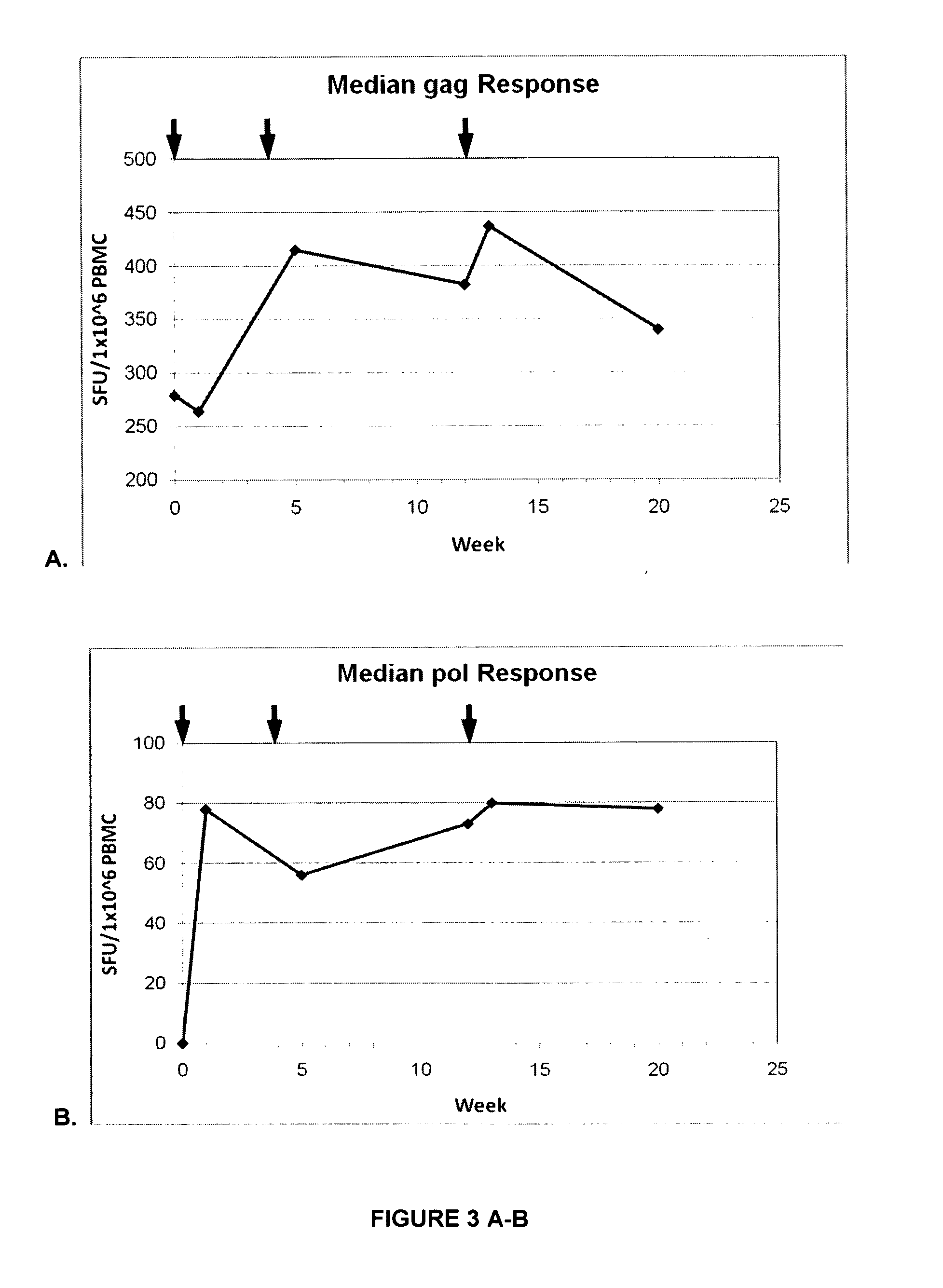
The present invention relates to a recombinant Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) comprising in the viral genome one or more expression cassettes for the expression of HIV proteins selected from Gag, Pol, Tat, Vif, Vpu, Vpr, Rev and Nef or a part or a derivative thereof or selected from Gag, Pol, Vpu, Vpr, Rev and Nef or a part or a derivative thereof for use as medicament or vaccine and its use for the treatment and / or prevention of HIV infections and AIDS.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Vaccine
InactiveUS20070042977A1Reduce and prevent glycosylationGlycosylation can be reduced and preventedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationHeterologous
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative, which is non-glycosylated when expressed in a mammalian target cell, operably linked to a heterologous promoter. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule, such as gp120 or gp140 or gp160, lacks a functional secretion signal. It may be fused to additional HIV proteins such as Nef, Gag, RT or Tat.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
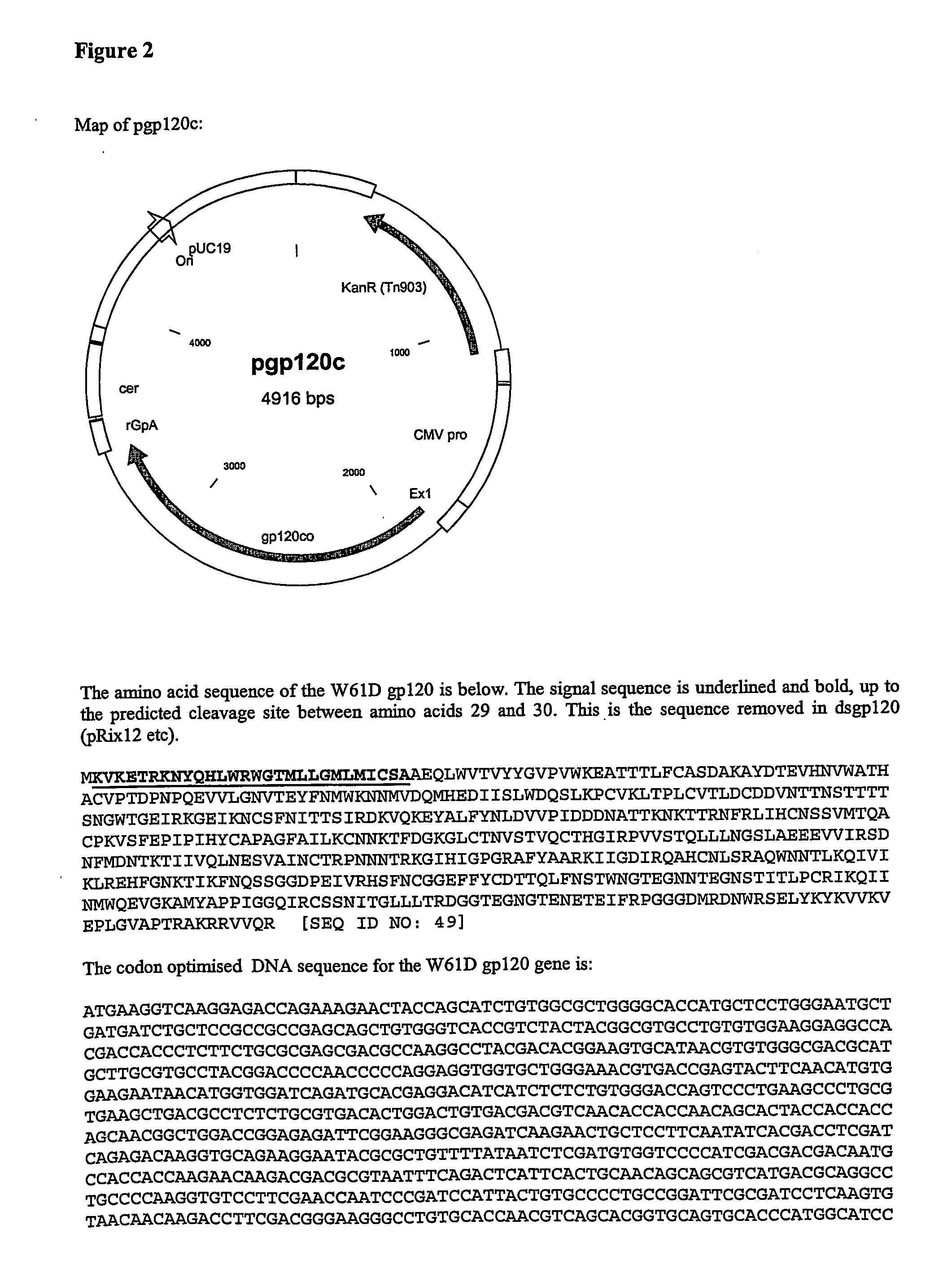
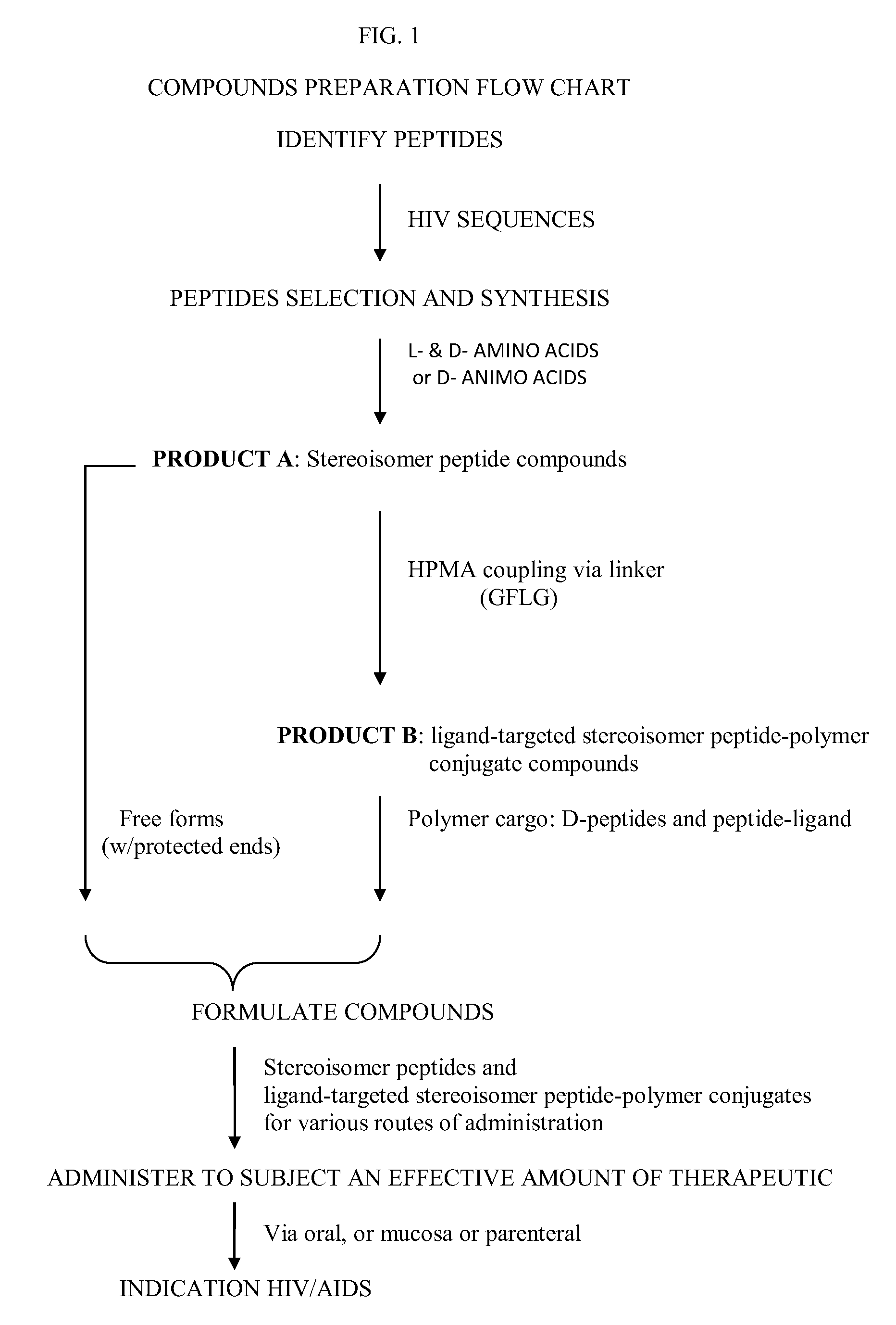
Stereoisomer Peptides and Their Polymer Conjugates for HIV Disease
InactiveUS20110014222A1Extended shelf lifeLong half-lifePeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHIV Proteins
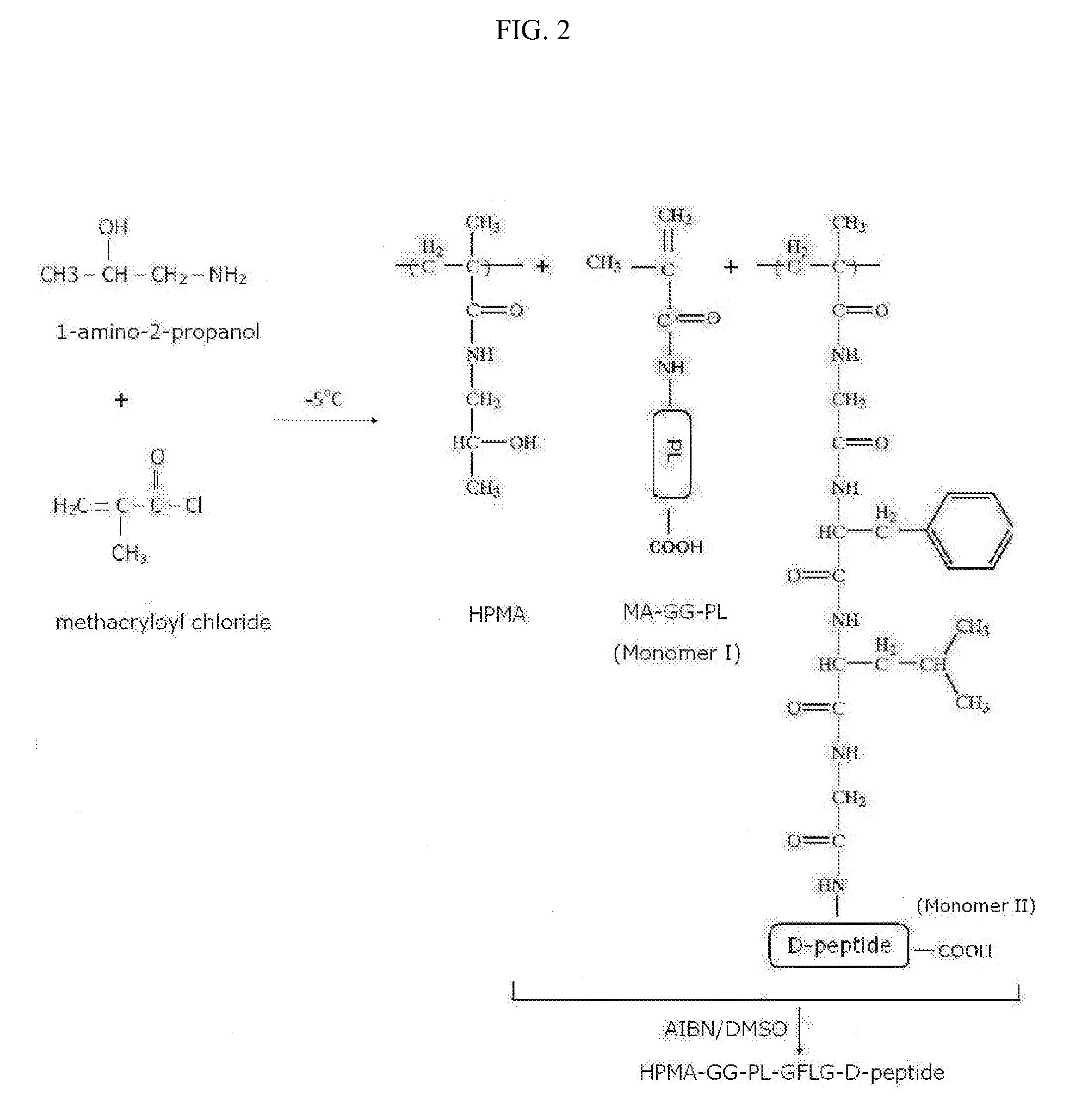
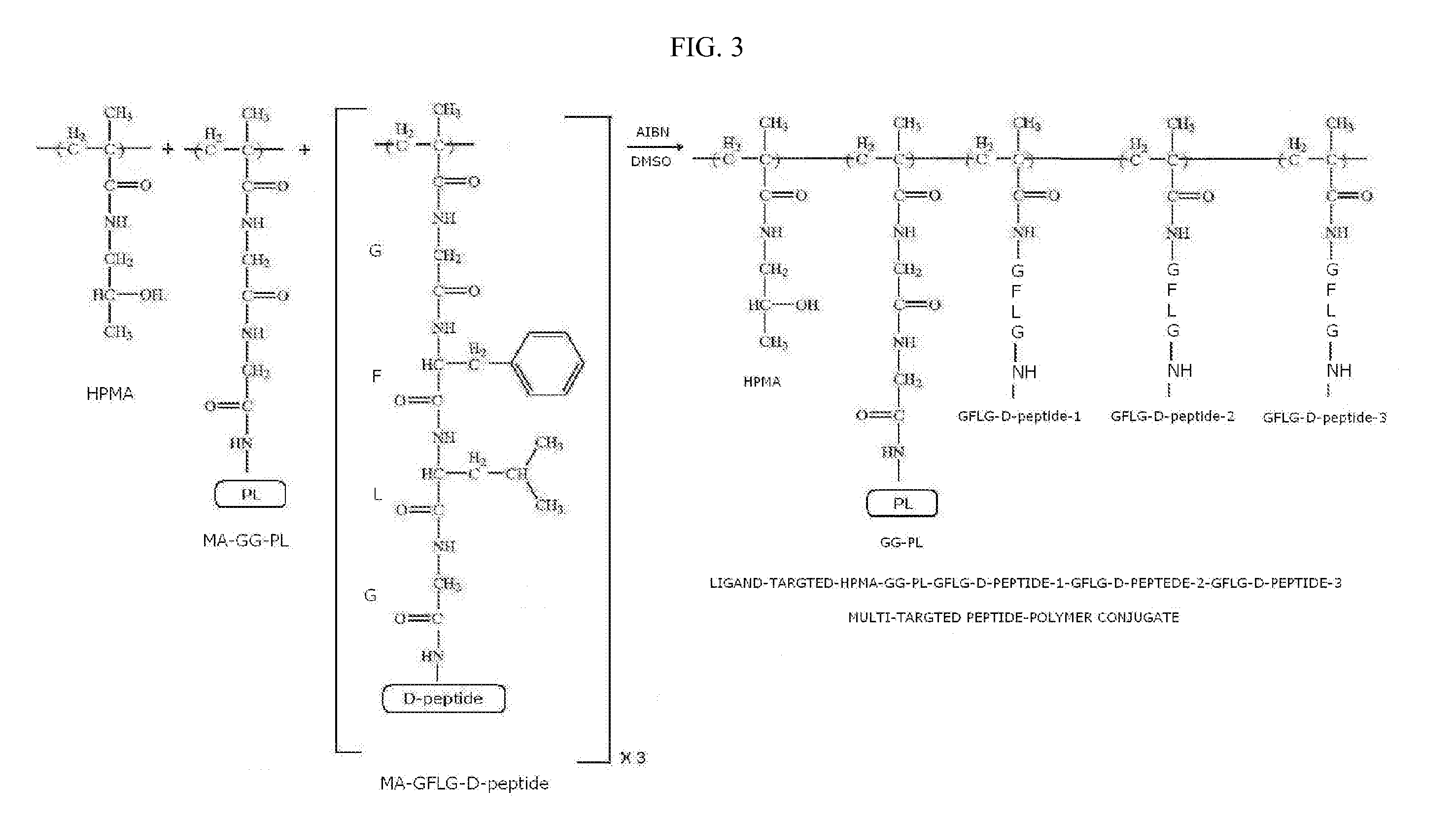
The invention relates to a library of 298 peptides useful for formulating a novel therapeutic HIV vaccine. The peptide sequences were selected on the basis of calibration of molecular structure properties of HIV-1 or host cell proteins. A mixture of D- and L-amino acids or all D-amino acids are used to synthesize the stereoisomer peptides for the purpose of increasing their stability. The peptides are expected to have the ability to potently inhibit functioning of proteins important for HIV infection. A plural of the peptides are conjugated together with a biocompatible polymer, preferably HPMA to further increase stability and solubility, decrease drug toxicity, and potentially evade multidrug resistance and exert cooperative effect, since some peptides are the ligands for host proteins such as integrin, trombospondin, VEGFR and LEDGF which can bring the therapeutic peptides to the target cells and therefore help disrupt the interactions between the host proteins and the HIV proteins.
Owner:GONZALEZ LUCIA IRENE
Immunogens for hiv vaccine
InactiveUS20060094017A1Low transmission rateLower Level RequirementsViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHIV ProteinsVaccination
Peptidyl sequences, called mimotopes, are disclosed which mimic the binding site of the broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody, 2G12, specific for the HIV protein gp120. The mimotopes are identified from a chimeric protein III (pIII) phage display library, each phage containing an additional random 15 amino acids near the N-terminus of pIII. Immunological conjugates of HIV-specific mimotopes that are useful for vaccination against HIV infection are disclosed. Methods for using the mimotopes and their immunological conjugates as part of an HIV vaccine regime, as well as diagnostic tools to perform viral assays, are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Improvments in or relating to immune responses to HIV
Disclosed is an immunogen in sterile form suitable for administration to a human subject, the immunogen comprising: at least a portion of the gag protein of HIV, said gag protein being from an HIV clade or having a consensus sequence for one or more HIV clades, and comprising at least parts of p17 and p24; and a synthetic polypeptide comprising a plurality of amino acid sequences, each sequence comprising a human CTL epitope of an HIV protein, and wherein a plurality of HIV proteins are represented in the synthetic polypeptide, said CTL epitopes being selected to stimulate an immune response to one or more HIV clades of interest.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL +2
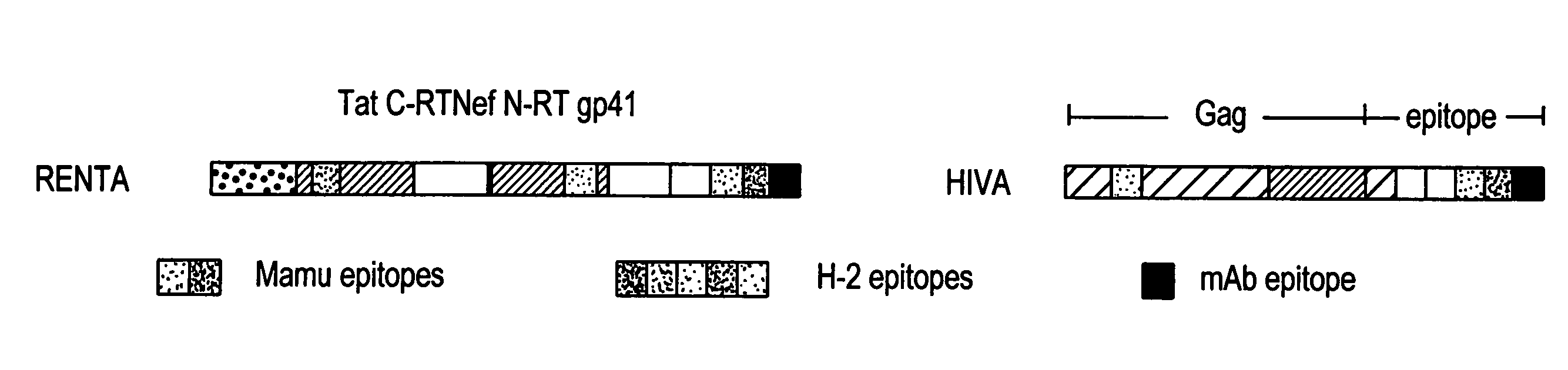
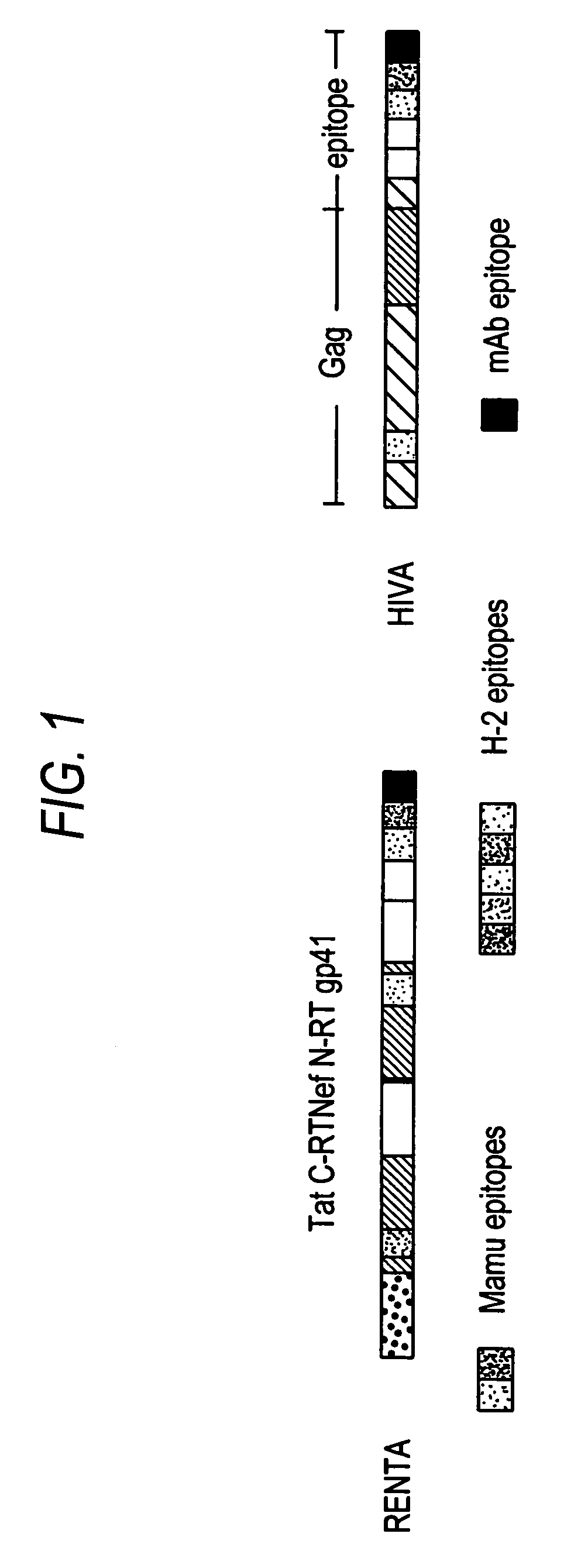
Renta: an HIV immunogen and uses thereof
The present invention provides artificial fusion proteins (AFPs) designed to elicit an anti-HIV immune response, as well as nucleic acid molecules and expression vectors encoding those proteins. The AFPs of the invention may comprise domains from various HIV proteins, including Reverse Trancriptase (RT), Env (gp41), Nef and Tat proteins, as well as at least one HIV CTL epitope associated with long-term, non-progression to AIDS; these domains are biologically-inactivated for one or more of the normal activity of those proteins or are partial protein sequences (and similarly biologically-inactivated). RENTA is an AFP in which the HIV domains are from an HIV Clade A consensus sequence and contains additional domains, useful for example, in monitoring expression levels or laboratory animal immune responses. Such domains are optionally included in the AFPs. Other aspects of the invention may include compositions for and methods of inducing an anti-HIV immune response in a subject, preferably using a DNA prime-MVA boost strategy, and preferably to induce a cell-mediated immune response.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL TECHNOLOGY
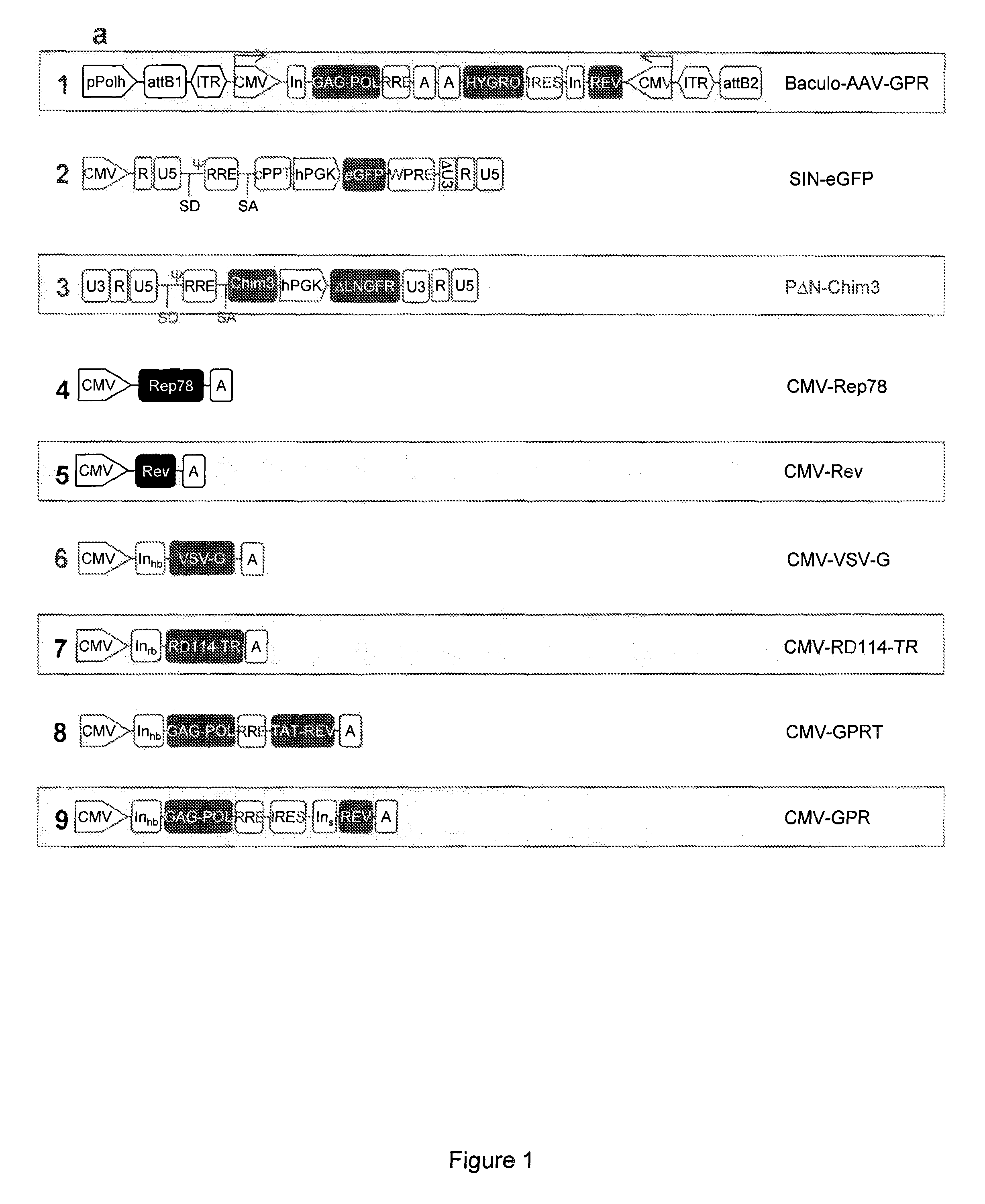
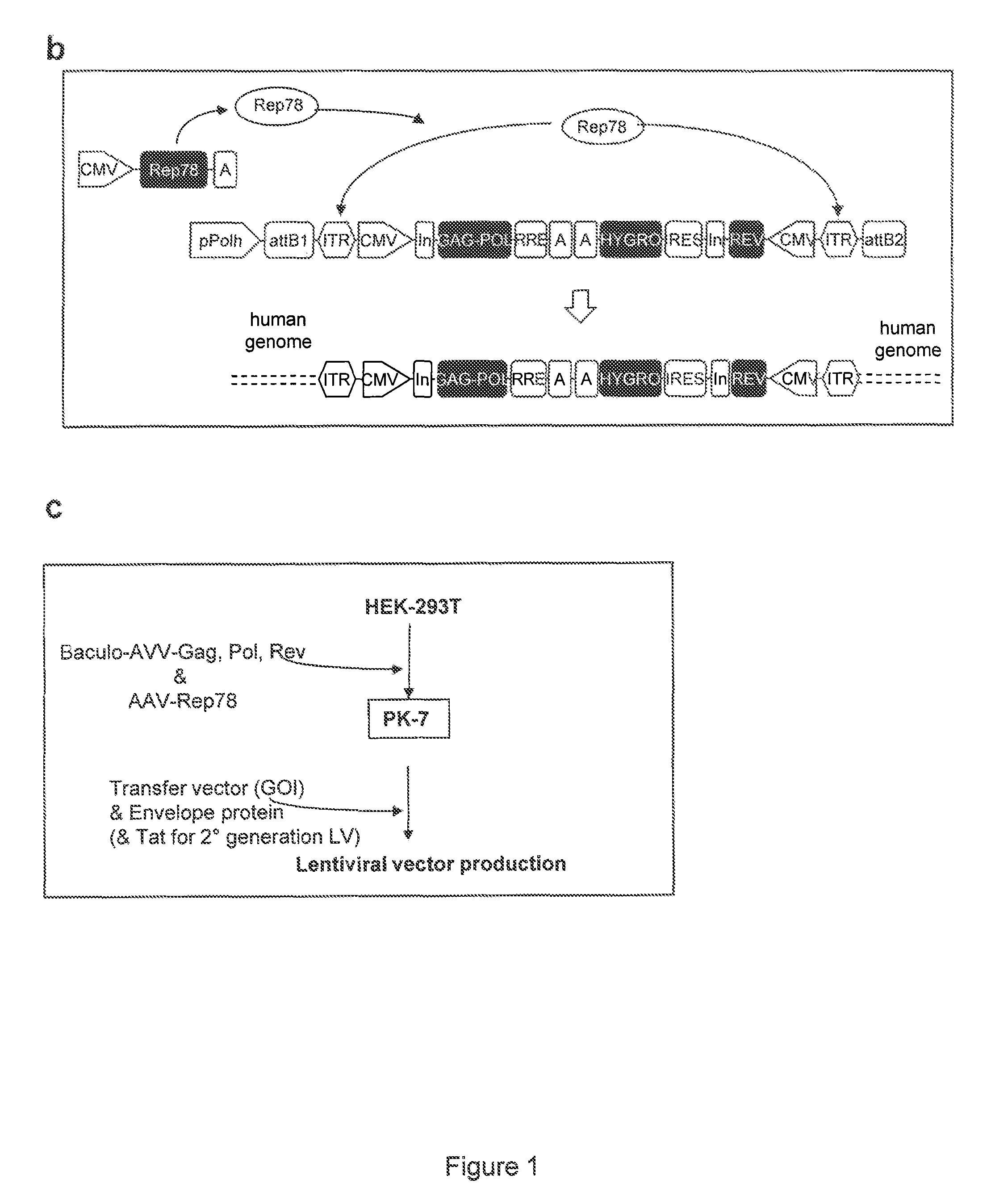
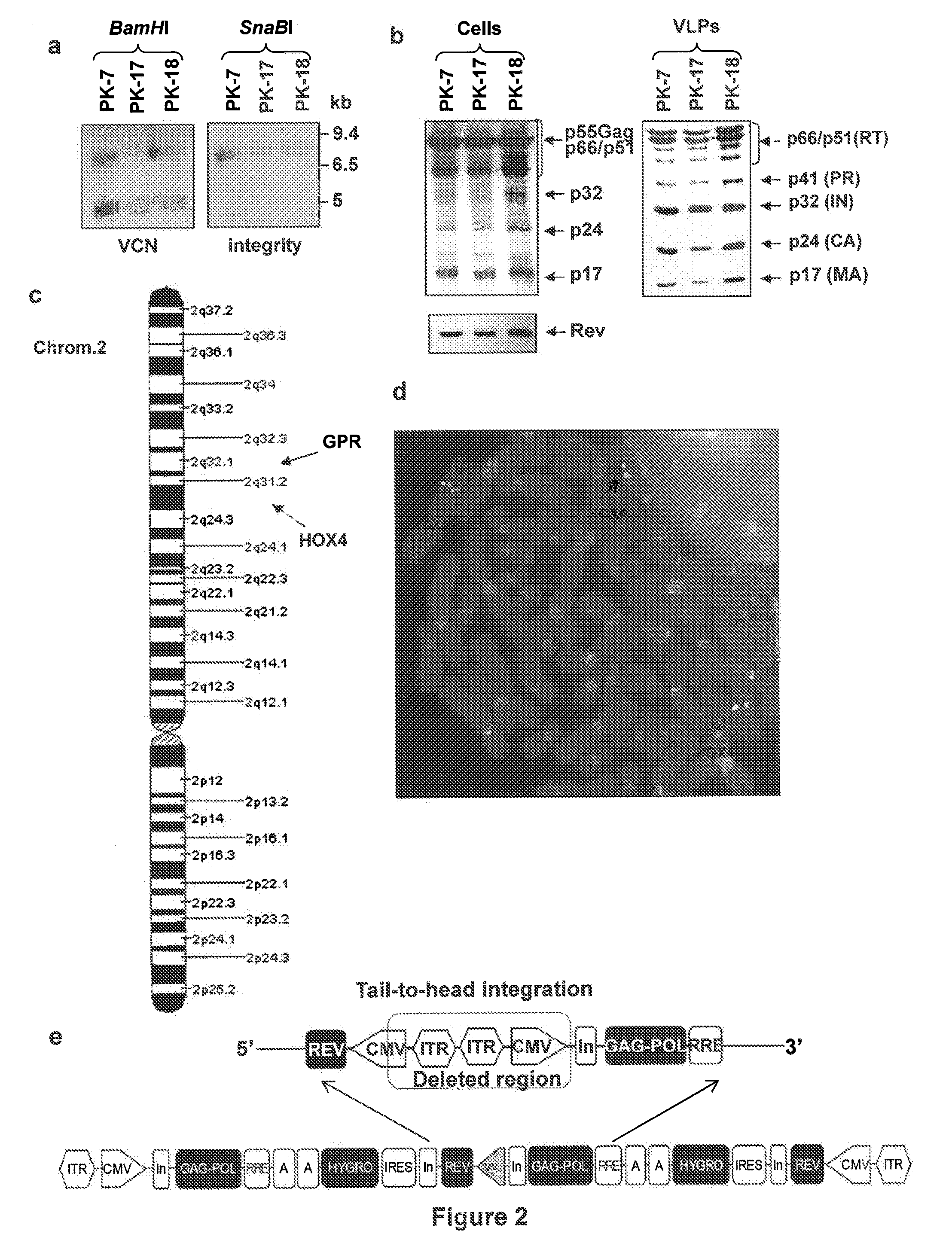
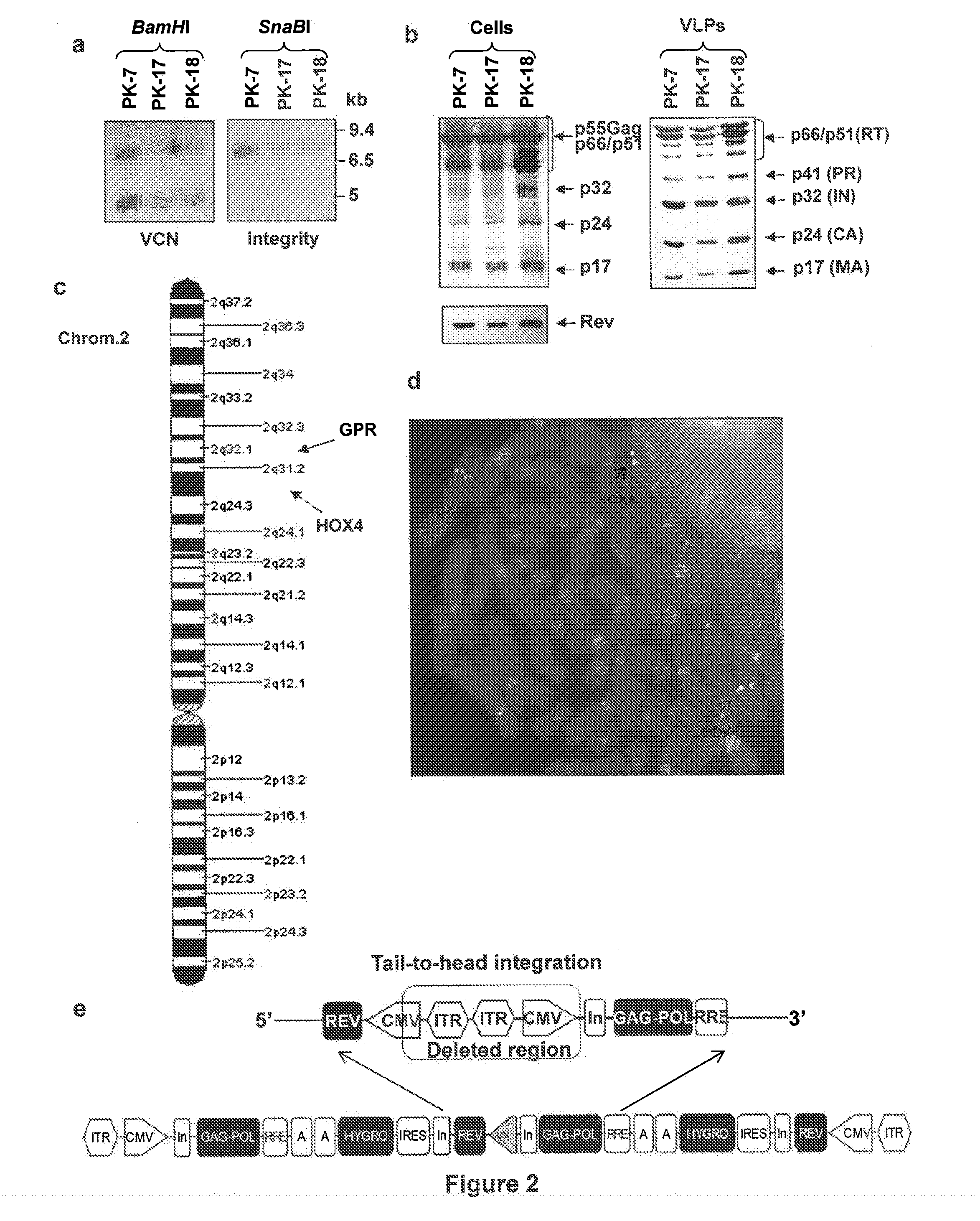
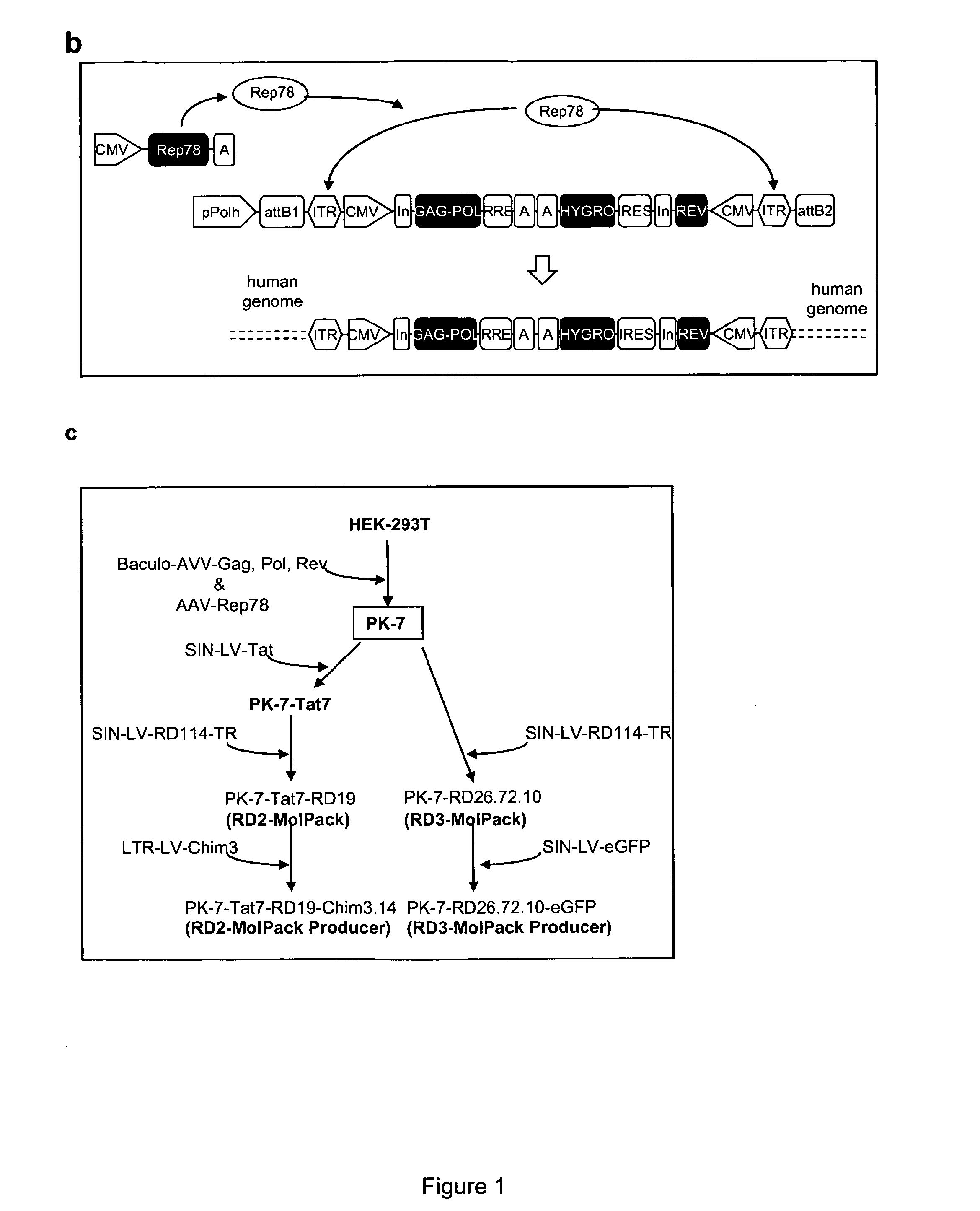
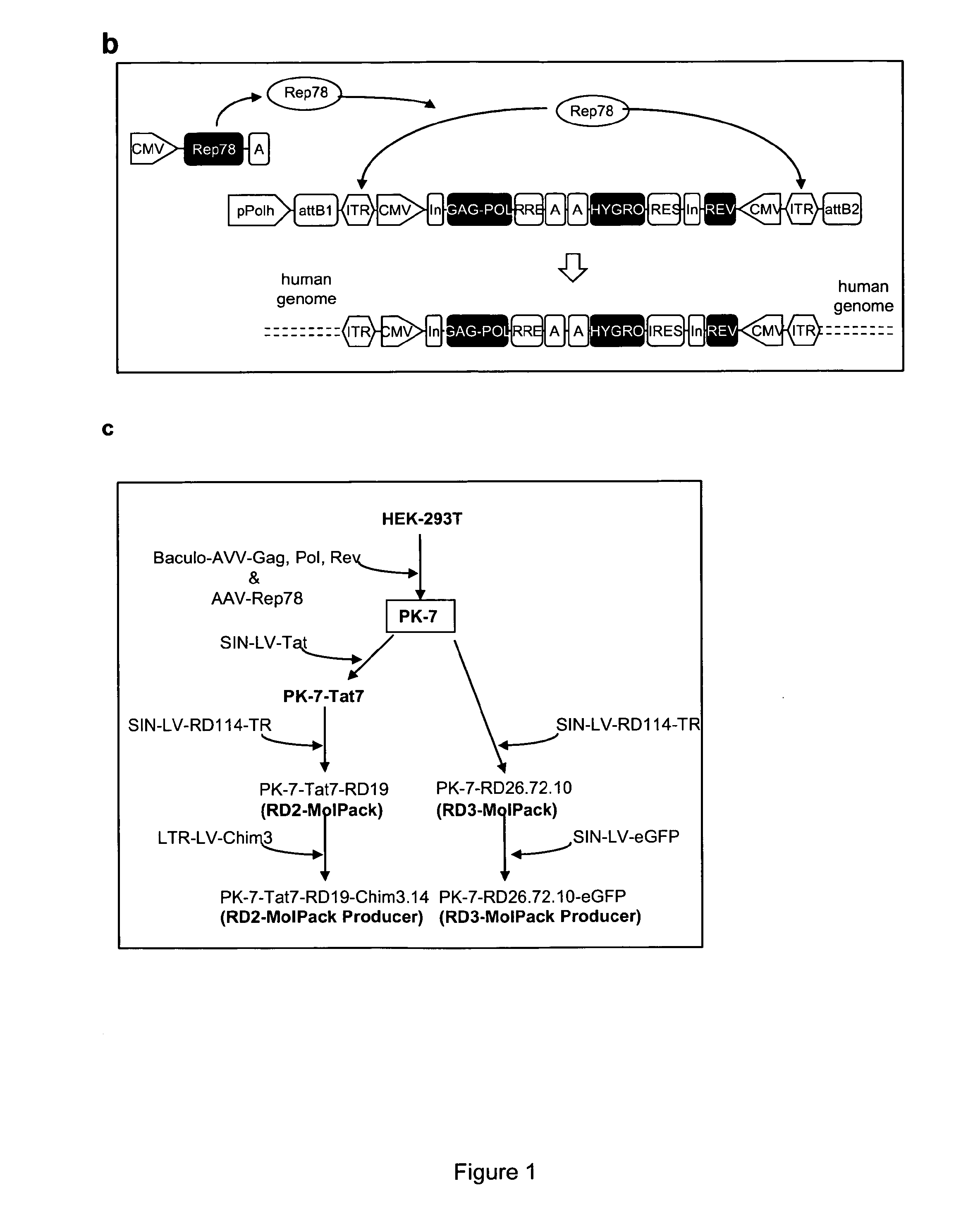
Semi-stable production of lentiviral vectors
ActiveUS9133481B2Stable integrationStably and effectively engineerVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsHIV ProteinsHybrid system
The present invention provides a new semi-stable packaging cell line and a method to produce lentiviral vectors (LV), using the semi-stable packaging cell line. New methods and packaging cell lines of the invention are generated using a baculo-AAV hybrid system for stable expression of structural and regulatory lentiviral proteins, such system comprising a baculoviral backbone containing an integration cassette flanked by AAV ITRs, in combination with a plasmid encoding rep protein. This system allows to obtain a stable integration of the structural and regulatory HIV-1 proteins gag / pol and rev. The system allows to obtain a cell line including the structural and regulatory HIV proteins gag / pol and rev, to be used for a semi-stable LV production.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
HIV-Env gene DNA allosteric recombinant envelope protein antigen immune response anti HIV experiment and method
InactiveCN101021539AEfficient removalIncrease variabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHIV ProteinsClinical trial
This invention is called: the experiment and method of the protein envelope which is allosteric restructuring of the HIV-Env gene DNA and its antigenic immunity responsive HIV. It relates to the domain of life sciences and medicine sciences. It is confirmed that gp120 of the HIV protein envelope or the gp160 of the antigenic vaccine combines with cell CD4+ that can induce the infirm immunogen of the alloantigen of the immune tolerant receptor CD4 and can not induce the HIV to infect the immune response of the parasitifer. It can also eliminate the multi-clone group of hill of the wild virus which is of fast copy the initial infection virus, high variability and sequence diversity. This invention can develop the non-spark human tolerant immunity HIV vaccine of the protein envelope which is allosteric restructuring of the HIV-Env gene DNA, the HIV preventive vaccine that can provide the scientific basis of the direct animal experiment and direct clinical trial of human being. It also provides the enforceable anti-HIV cell model, rodent model, non-human Primates model and the research program of human clinical trial.
Owner:叶新新
Multivalent HIV Vaccine Boost Compositions and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20190382453A1Increasing CD4+ T cell responsesIncreased susceptibilityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesHIV ProteinsRegimen
Compositions and methods of use are provided to boost a primed immune response to HIV. More specifically, the present invention relates to vaccine compositions comprising an HIV-protein boost or an MVA-expressed Env protein and methods of use. Exemplary HIV proteins for protein boosts include proteins such as gp120 proteins B.63521Δ11mutC and full-length single chain (FLSC), which has been modified to stabilize a CD4-induced Env structure. Exemplary MVAs expressing secreted Methods of administration and dosing regimens are also provided.
Owner:GEOVAX INC
Sequential and repeated application of four or more HIV vector gene vaccines
ActiveCN102258779AIncrease sequential useInduce cross immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHIV ProteinsVector vaccine
The invention relates to a sequential and repeated application strategy of four or more HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) vector gene vaccines, capable of maintaining high-level specific immune response for a long time. The combined AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) vaccine for preventing and / or treating AIDS is capable of activating broad-spectrum anti-AIDS virus cellular immune response, and is composed of four or more AIDS vaccines. The different AIDS vaccines can contain the same HIV protein gene, one kind of AIDS vaccine is inoculated once, and each kind of vaccine can be inoculated twice continuously. After the four or more kinds of different vector vaccines are sequentially applied, the vector vaccines can be repeatedly and sequentially applied.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Sample collection system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20130158431A1Small apertureTested easily and noninvasively and reliablyPreparing sample for investigationPharmaceutical containersHIV ProteinsAnalyte
A sample collection system capable of collecting, storing and dispensing a liquid sample is disclosed. The collection system includes a collector composed of a material which has the unique ability to express constituents of interest at levels which are more concentrated than their levels in the fluid samples from which they are expressed, where the expressed highly concentrated sample can then be used with modern rapid screening / testing protocols, such as solid phase assays, to test for the constituents of interest. Thus, it is now possible to obtain analytes of interest, such as the HIV protein antibodies, from saliva samples at concentrations that are representative of that found in serum or plasma. The collector is sized and shaped to fit within a recovery container, which, in turn, is sized and shaped to fit within a collection tube. The recovery container includes an aperture which does not permit passage of fluid under ambient conditions, but facilitates transfer thereof when subject to pressure. An optional channel within the collection tube facilitates dispensing of the sample for further processing.
Owner:ARONOWITZ JACK L
Immune method and composition for HIV-1
The present invention relates to nucleic acid and attenuated vaccinia vectors for prophylactic use against HIV infection, as well as methods of eliciting immune responses in subjects susceptible to HIV infection. The prophylactic vaccine regimen of the invention involves immunological priming with an inoculum comprising two novel DNA vectors, followed by boosting with a Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) recombinant viral vector expressing the corresponding HIV proteins.
Owner:AARON DIAMOND AIDS RES CT
Anti-SERINC5 antibody and application thereof
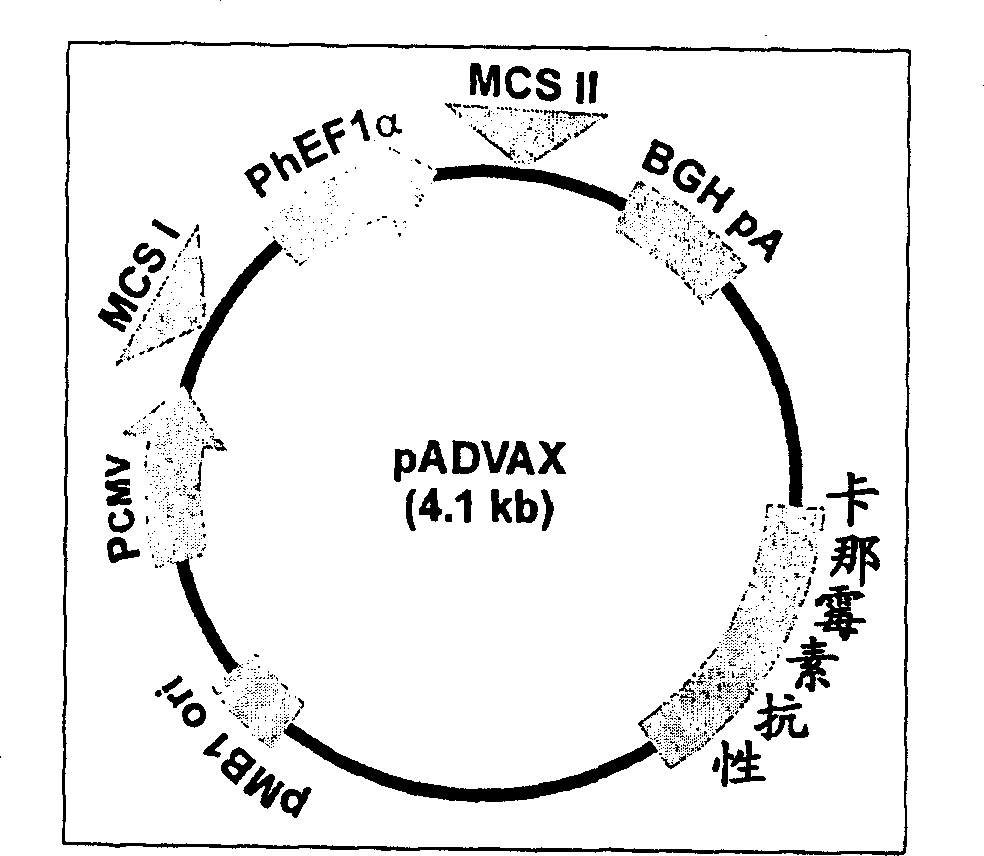
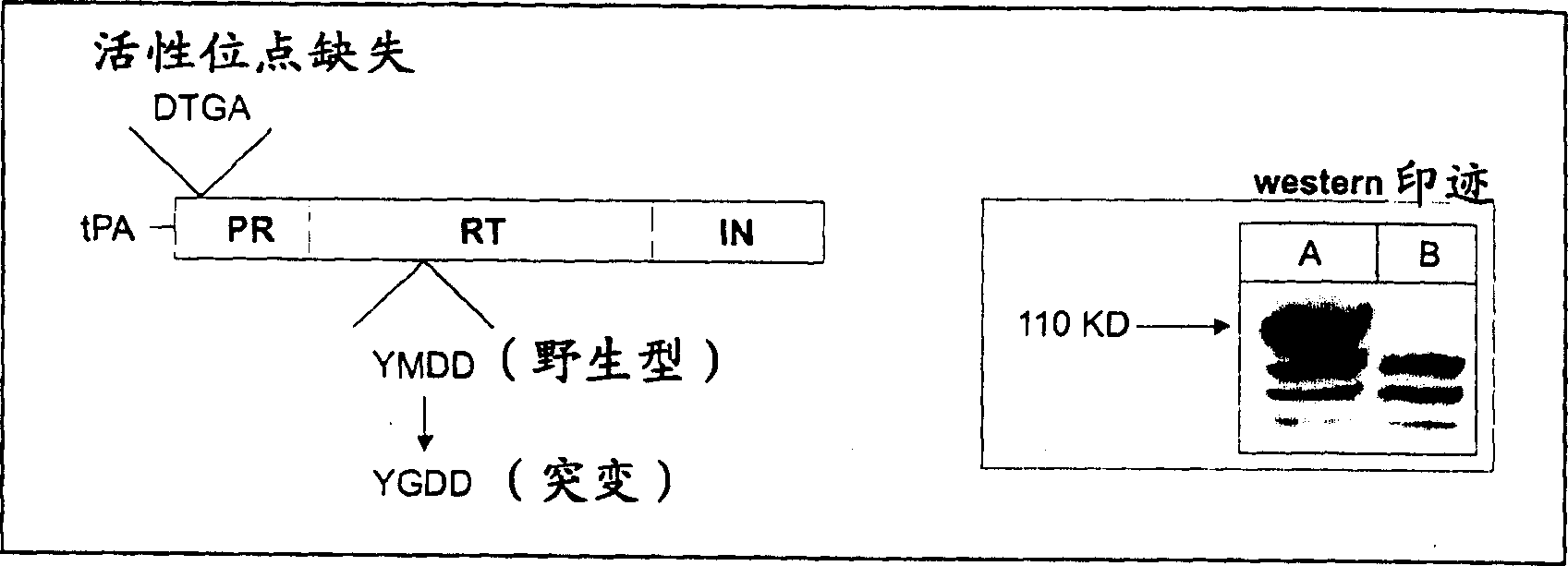
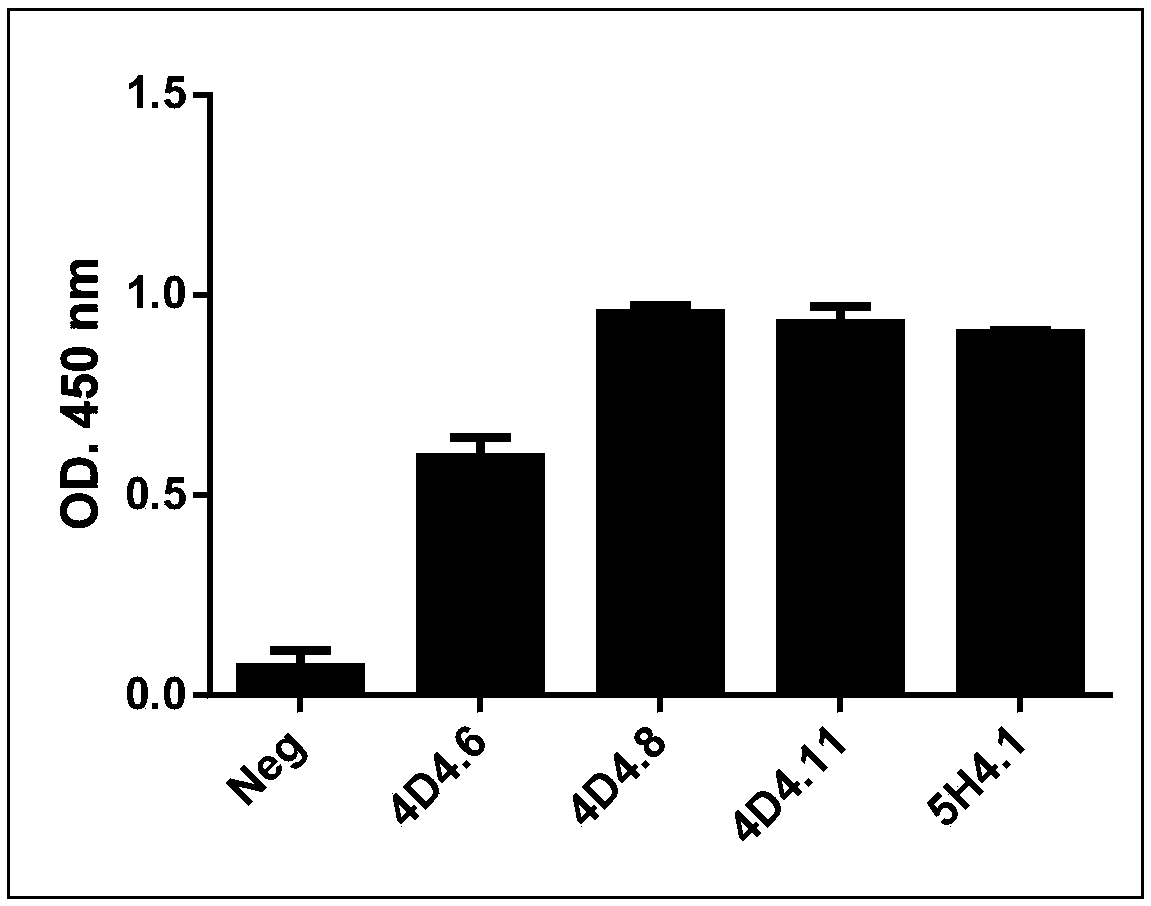
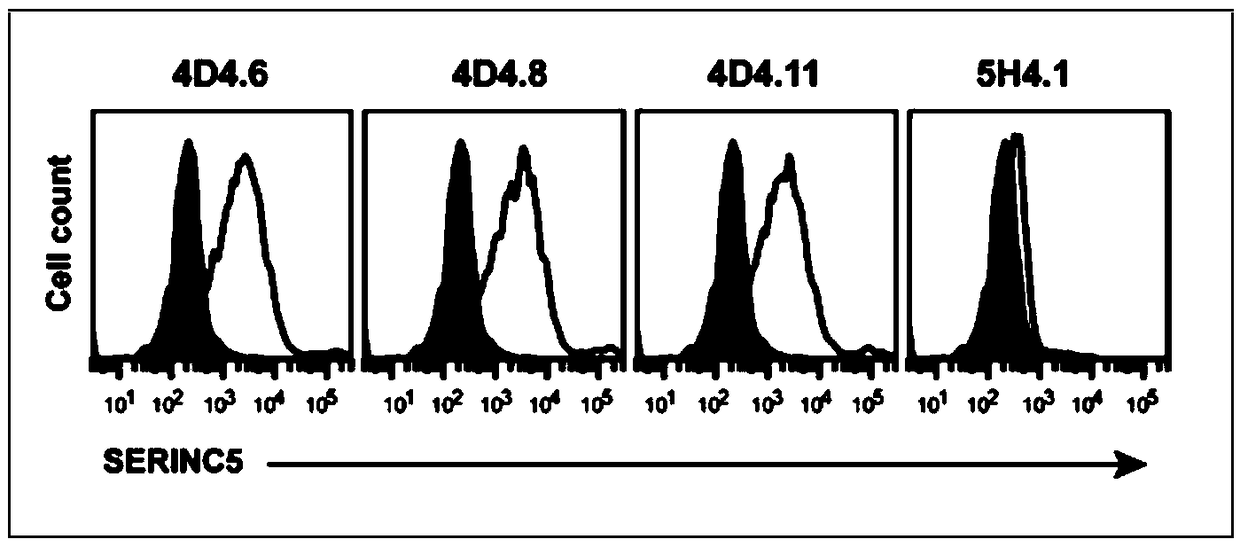
ActiveCN108929382APromote research progressBiologically activeImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHybrid cell preparationHIV ProteinsAntiviral mechanism
The invention relates to an anti-SERINC5 antibody and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an anti-SERINC5 antibody and functional fragment, a nucleotide, a carrier, a monoclonalantibody, a kit and application thereof in detection of SERINC5 protein or polypeptide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:9. At the same time, the invention also provides a preparation method of the monoclonalantibody and a preparation method of a monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line. The antibody and functional fragment prepared by the method provided by the invention can be effectively used for reaction with SERINC5 protein, like flow cytometry detection of SERINC5 molecules on cell surfaces and SERINC5 expressed in combination with cells, study of virus amplification mechanism, etc., thus providing an effective research tool for studying the antiviral mechanism of SERINC5, being conducive to accelerating the research progress in the field, and providing a new idea for further development ofnovel HIV protein Nef targeted AIDS drugs.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Semi-Stable Production of Lentiviral Vectors
ActiveUS20130164840A1Stable integrationStably and effectively engineerArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsHIV ProteinsHybrid system
The present invention provides a new semi-stable packaging cell line and a method to produce lentiviral vectors (LV), using the semi-stable packaging cell line. New methods and packaging cell lines of the invention are generated using a baculo-AAV hybrid system for stable expression of structural and regulatory lentiviral proteins, such system comprising a baculoviral backbone containing an integration cassette flanked by AAV ITRs, in combination with a plasmid encoding rep protein. This system allows to obtain a stable integration of the structural and regulatory HIV-1 proteins gag / pol and rev. The system allows to obtain a cell line including the structural and regulatory HIV proteins gag / pol and rev, to be used for a semi-stable LV production.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
Sample collection system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20140302617A1Small apertureRaise the concentration levelWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationHIV ProteinsAnalyte
A sample collection system capable of collecting, storing and dispensing a liquid sample is disclosed. The collection system includes a collector composed of a material which has the unique ability to express constituents of interest at levels which are much more concentrated than their levels in the fluid samples from which they are expressed, where the expressed highly concentrated sample can then be used with modern rapid screening / testing protocols, such as solid phase assays, to test for the constituents of interest. Thus, it is now possible to obtain analytes of interest, such as the HIV protein antibodies, from saliva samples at concentrations that are detectable with systems and / or devices that are typically utilized only for blood serum or plasma testing. The collector is sized and shaped to fit within a recovery container, which, in turn, is sized and shaped to fit within a collection tube. The recovery container includes an aperture which does not permit passage of fluid under ambient conditions, but facilitates transfer thereof when subjected to pressure. An optional channel within the collection tube facilitates dispensing of the sample for further processing.
Owner:ARONOWITZ JACK L
Vaccine
InactiveUS20060142221A1Reduce removalReduce and prevent glycosylationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationHIV Proteins
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative fused to an additional HIV protein selected from a non-structural protein or capsid protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative thereof. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is gp120 and preferred fusions include one or more of HIV Nef, Gag, RT or Tat. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is non-glycosylated in mammalian cells.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Methods of inducing an immune response against HIV by administering immunogenic peptides obtained from protease cleavage sites
Instead of generating immune responses to several HIV proteins and risk over activating more CD4+ T cells (easy targets for HIV-1 infection) as current candidate vaccines try to do, a lower magnitude, narrowly focused, well maintained virus specific CD8+ T cell response to multiple subtypes should destroy and eliminate a few founder viruses without inducing inflammatory responses that may activate more CD4+ T cells and provide more targets for HIV-1 virus infection. Specifically, described herein is a method that focuses the immune response to the 12 protease cleavage sites.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
HLA-restricted cytotoxic T-Lymphocytevaccine for prevention of HIV infection
InactiveUS20020172688A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsHIV ProteinsDendritic cell
An improved method of inducing protective immunity to the Human Immunodeficiency Virus through isolating a person's antigen-presenting cells from blood, then pulsing these cells with short peptides that bind the person's Class I Major Histocompatibility Complex Types and correspond to conserved segments of the HIV structural and functional genes. These pulsed dendritic cells are then injected intravenously, where they will travel to lymph tissue and prime HIV-specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. The immune system is then activated by injecting the person with a weakened arbovirus, Chikungunya. The interferons and other immune-activating chemicals induced by the virus will stimulate creation of billions of killer cells that recognize HIV proteins, allowing for rapid mobilization of memory immune cells to contain and eliminate any subsequent infection with the HIV virus. The vaccine is custom-designed to each person and uses no HIV virus for safety purposes. It is understood that the examples an embodiments described herein are for illustrative purposes only and various changes or modifications in light thereof will be suggested to persons skilled in the art and are to be included within the spirit and purview of this application and scope of the appended claims.
Owner:LYDAY BRUCE
Multivalent HIV vaccine boost compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS11098086B2Increasing CD4+ T cell responsesIncreased susceptibilityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesDosing regimenHIV Proteins
Compositions and methods of use are provided to boost a primed immune response to HIV. More specifically, the present invention relates to vaccine compositions comprising an HIV-protein boost or an MVA-expressed Env protein and methods of use. Exemplary HIV proteins for protein boosts include proteins such as gp120 proteins B.63521Δ11mutC and full-length single chain (FLSC), which has been modified to stabilize a CD4-induced Env structure. Exemplary MVAs expressing secreted Methods of administration and dosing regimens are also provided.
Owner:GEOVAX INC
Compositions and methods of replication deficient adenoviral vectors for vaccine applications
ActiveUS20190167813A1Elicit immune responseViral antigen ingredientsGenetic therapy composition manufactureHIV ProteinsCentral Memory T-Cell
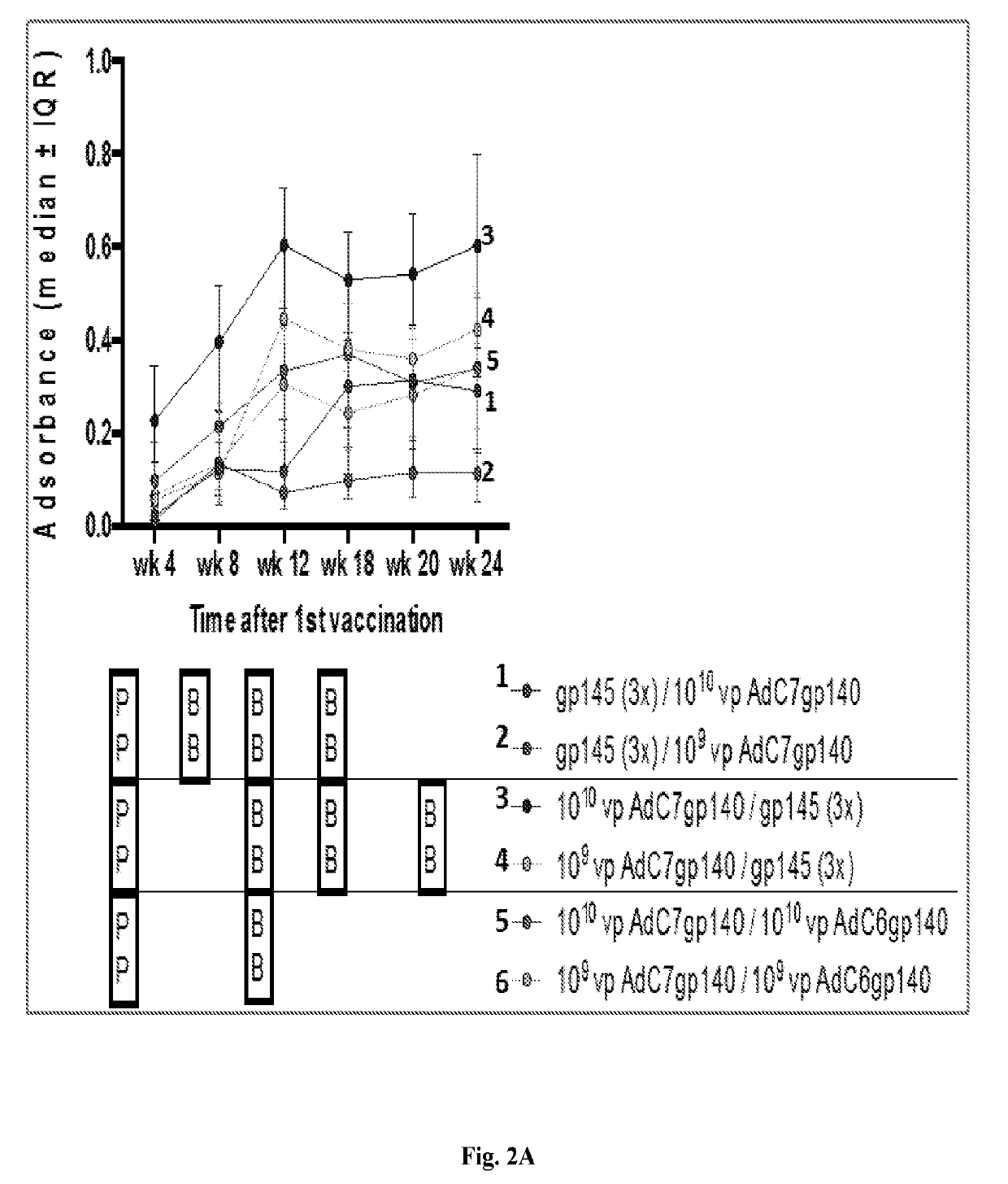
The invention includes compositions and methods of generating a chimpanzee-derived adenovirus AdC6 or AdC7 vector vaccine comprising a deletion of E1, a deletion of E3 ORF3, ORF4, ORF5, ORF6, and ORF7 and a sequence encoding HIV protein gp140, gp160 or Gag, methods of treating and / or preventing or immunizing against HIV and methods of inducing an effector T cell, memory T cell and B cell immune response in a mammal administered the composition produced thereby. Furthermore, the invention encompasses a pharmaceutical composition for vaccinating a mammal as well as a protein expression system.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY
Stable Production of Lentiviral Vectors
ActiveUS20140051125A1Stable integration of HIV-Stably and effectively engineerPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesHIV ProteinsHybrid system
The present invention provides new stable packaging cell lines and producer cell lines as well as methods to obtain them, and a new method to produce lentiviral vectors using such cell lines. New methods and packaging cell lines of the invention are generated using a baculo-AAV hybrid system for stable expression of structural and regulatory lentiviral proteins, such system comprising a baculoviral backbone containing an integration cassette flanked by AAV ITR, in combination with a plasmid encoding rep protein. This system allows to obtain a stable integration of the structural and regulatory HIV-1 proteins gag / pol and rev. The system allows to obtain a first intermediate including only the structural and regulatory HIV proteins gag / pol and rev, to be used as starting point to obtain stable packaging cell lines as well as producer cell lines.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
Stable production of lentiviral vectors
ActiveUS9441245B2Stable integration of HIV-Stably and effectively engineerPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesHIV ProteinsHybrid system
The present invention provides new stable packaging cell lines and producer cell lines as well as methods to obtain them, and a new method to produce lentiviral vectors using such cell lines. New methods and packaging cell lines of the invention are generated using a baculo-AAV hybrid system for stable expression of structural and regulatory lentiviral proteins, such system comprising a baculoviral backbone containing an integration cassette flanked by AAV ITR, in combination with a plasmid encoding rep protein. This system allows to obtain a stable integration of the structural and regulatory HIV-1 proteins gag / pol and rev. The system allows to obtain a first intermediate including only the structural and regulatory HIV proteins gag / pol and rev, to be used as starting point to obtain stable packaging cell lines as well as producer cell lines.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com