Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1085results about "Monocomponent copolyesters artificial filament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isosorbide containing polyesters and methods for making same
InactiveUS6063464AHigher inherent viscosityInherent viscosityBottlesSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterDiol
A polyester polymer and method for making the polyester, wherein the polyester is prepared by (1) combining in a reactor a monomer containing a diacid moiety; a monomer comprising a diol moiety; and a monomer containing an isosorbide moiety; with a condensation catalyst suitable for condensing aromatic diacids and diols; and (2) heating the monomers and catalyst to polymerize the monomers to yield a polyester having an inherent viscosity of at least about 0.15 dL / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20080311815A1Reduce blockingReduce fusionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceSlurry
A water non-dispersible polymer microfiber is provided comprising at least one water non-dispersible polymer wherein the water non-dispersible polymer microfiber has an equivalent diameter of less than 5 microns and length of less than 25 millimeters. A process for producing water non-dispersible polymer microfibers is also provided, the process comprising: a) cutting a multicomponent fiber into cut multicomponent fibers; b) contacting a fiber-containing feedstock with water to produce a fiber mix slurry; wherein the fiber-containing feedstock comprises cut multicomponent fibers; c) heating the fiber mix slurry to produce a heated fiber mix slurry; d) optionally, mixing the fiber mix slurry in a shearing zone; e) removing at least a portion of the sulfopolyester from the multicomponent fiber to produce a slurry mixture comprising a sulfopolyester dispersion and water non-dispersible polymer microfibers; and f) separating the water non-dispersible polymer microfibers from the slurry mixture. A process for producing a nonwoven article is also provided.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Biodegradable polyesters
InactiveUS6120895AMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsFiberPolymer science
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 04908 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 17, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 17, 1999 PCT Filed Sep. 19, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 12242 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1998Biodegradable polyesters based on A) 95-99.99 mol % of at least one polyester A containing as monomeric building blocks of an acid component comprising a11) 20-95 mol % of at least one aliphatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acid or its ester-forming derivative and a12) 5-80 mol % of at least one aromatic dicarboxylic acid or its ester-forming derivative and at least one dihydroxy compound or at least one amino alcohol or their mixtures, and B) 0.01-5 mol % of a mixture comprising mono-, bi-, tri-, tetra- and higher-nuclear isocyanurates or corresponding compounds containing two, three or four functional groups capable of reacting with the end groups of polyester A, or mixtures of the isocyanurates and the corresponding compounds, as well as molding compositions comprising said polyesters, their manufacture and their use in the manufacture of moldings, filsm, fibers and coatings.
Owner:BASF AG
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyhydroxyalkanoate medical textiles and fibers
ActiveUS8034270B2Easy to operateProlonged strength retentionSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterFiber
Absorbable polyester fibers, braids, and surgical meshes with prolonged strength retention have been developed. These devices are preferably derived from biocompatible copolymers or homopolymers of 4-hydroxybutyrate. These devices provide a wider range of in vivo strength retention properties than are currently available, and could offer additional benefits such as anti-adhesion properties, reduced risks of infection or other post-operative problems resulting from absorption and eventual elimination of the device, and competitive cost. The devices may also be particularly suitable for use in pediatric populations where their absorption should not hinder growth, and provide in all patient populations wound healing with long-term mechanical stability. The devices may additionally be combined with autologous, allogenic and / or xenogenic tissues to provide implants with improved mechanical, biological and handling properties.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Copolyesters and fibrous materials formed therefrom
InactiveUS20020132960A1Deep dyeabilityGood printabilityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesCelluloseFiber
This invention relates to binary blends of cellulose esters and aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters, cellulose esters and aliphatic polyesters as well as ternary blends of cellulose esters and / or aliphatic polyesters and / or aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters and / or polymeric compounds as well as fibers, nonwovens, molded objects, and films prepared therefrom.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
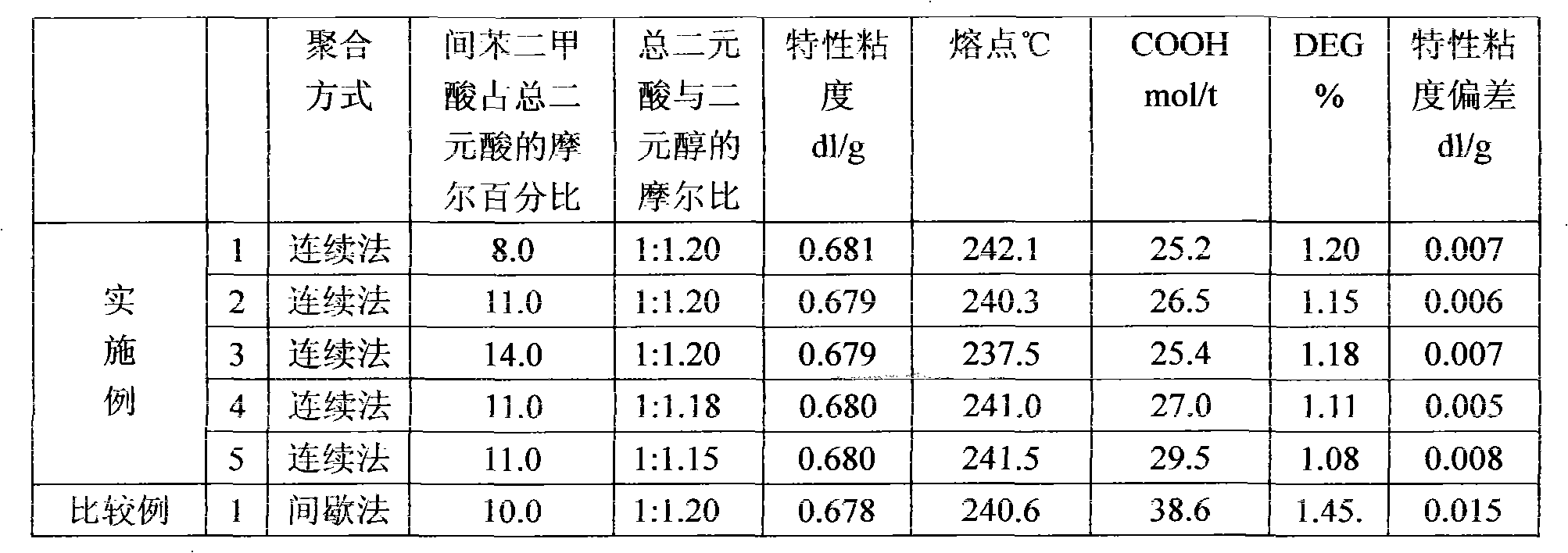
Copolyester as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102030893AImprove dyeing effectLow investment costMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentDisperse dyeSide chain
The invention discloses copolyester and a preparation method and application thereof. The copolyester comprises binary acid components and binary alcohol components, wherein in the binary acid components, the content of the terephthalic acid structural unit is more than 90mol%; and in the binary alcohol components, the content of the ethylene glycol structural unit is 70-99mol%, and the content of the aliphatic dihydric alcohol structural unit which contains side chains and less than 6 carbon atoms is 1-30mol%. The copolyester also comprises a polyethylene glycol structural unit. Because the aliphatic dihydric alcohol structural unit which contains side chains and less than 6 carbon atoms and the polyethylene glycol structural unit are added to the copolyester, the copolyester can be made into fiber with the known method, and the fiber can be made into fabric. The prepared finished product has good dyeing property on disperse dye at normal temperature and pressure, thus the high equipment investment and operation cost resulted from high-temperature and high-pressure dying can be reduced.
Owner:TORAY FIBER RES INST(CHINA) CO LTD
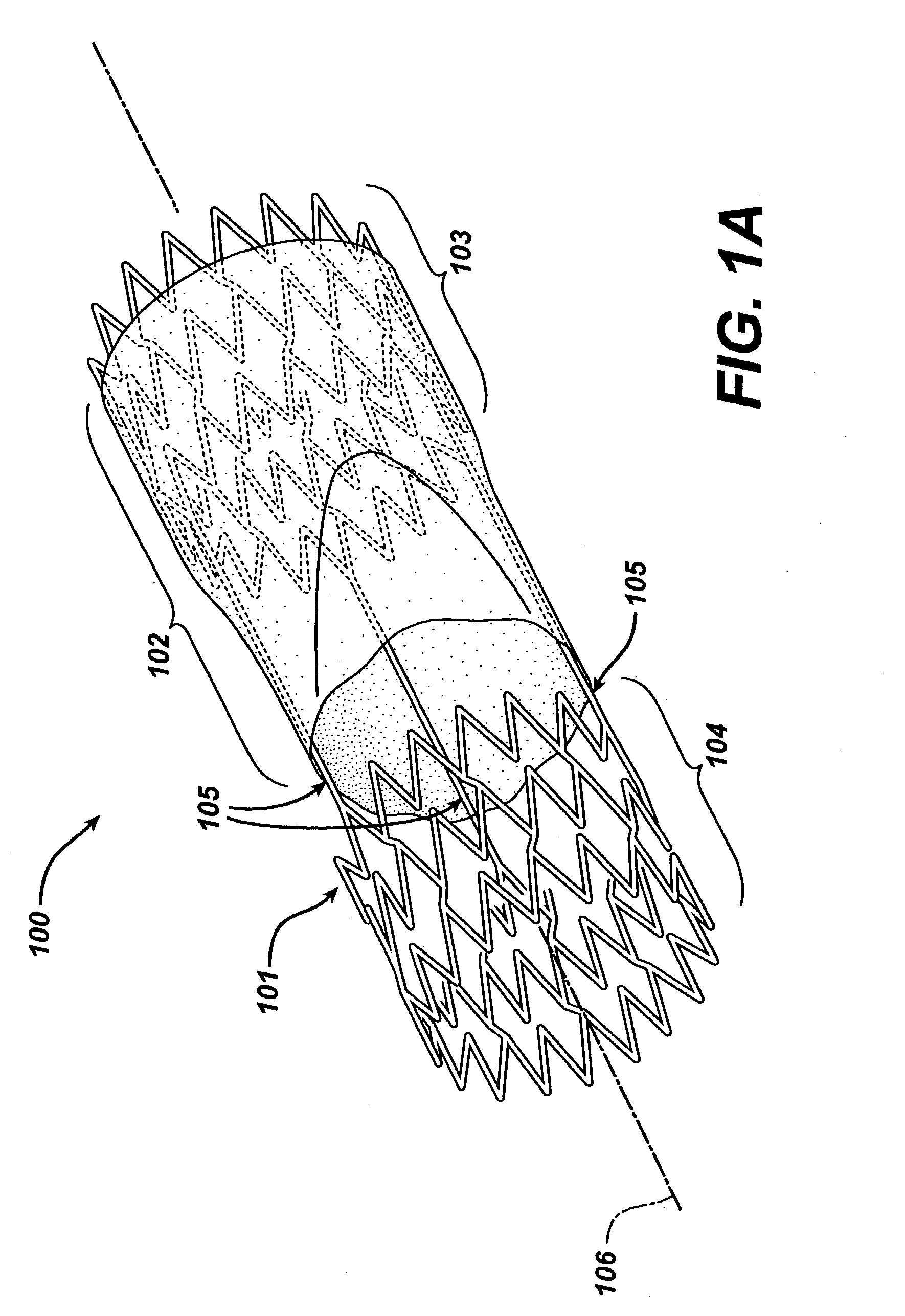
Method of forming a tubular membrane on a structural frame
The present invention relates to a medical device and method of forming the medical device. In particular, the present invention relates to a medical device having a tubular membrane structure over a radially expandable structural frame, and to a method of forming the tubular membrane on the radially expandable structural frame. In one aspect, a structural frame is placed over a spinning mandrel and a fiber is electro-statically spun over at least a portion of the structural frame forming a membrane. A transfer sheath may be used between the mandrel and structural frame to prevent the electro-statically spun fiber from adhering to the mandrel. In another aspect, a first membrane is spun over the mandrel before the structural frame is placed over the mandrel. In this aspect, at least a portion of the structural frame is sandwiched between the membranes. The membrane or membranes and structural frame form a fiber spun frame assembly. The fiber spun frame assembly may be coated with an elastic polymer. In addition, the membrane or membranes may go through some post processing to achieve desired characteristics or configurations.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Polyether ester elastomer comprising polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and trimethylene ester hard segment
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Porous fiber
InactiveUS7097904B2Good color propertiesMaintain good propertiesFilament/thread formingNanotechnologyMetallurgyNanopore
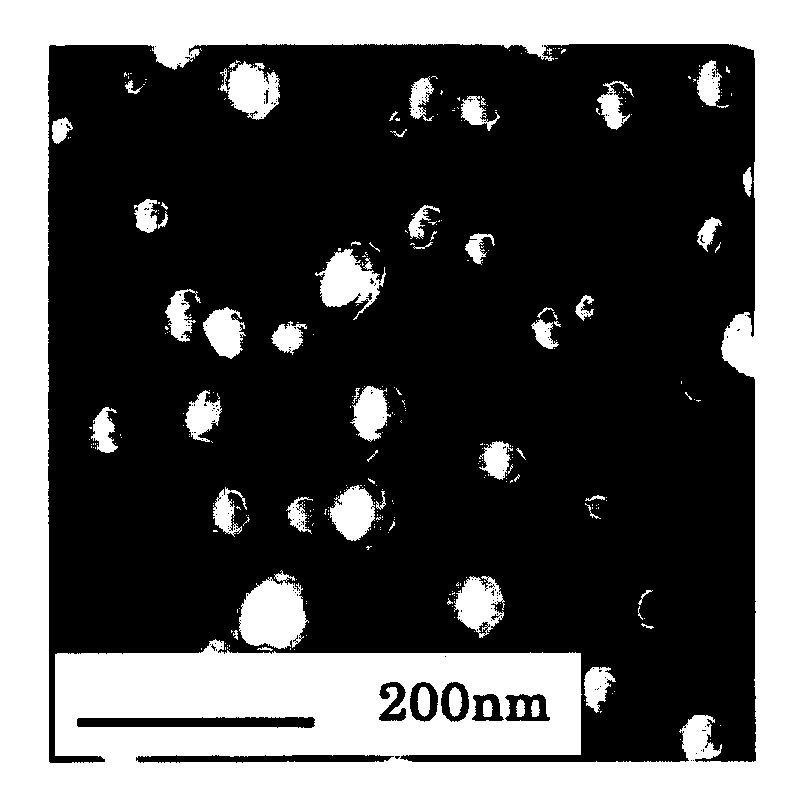
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Disclosed are water-dispersible fibers derived from sulfopolyesters having a Tg of at least 25° C. The fibers may contain a single sulfopolyester or a blend of a sulfopolyester with a water-dispersible or water-nondispersible polymer. Also disclosed are multicomponent fibers comprising a water dispersible sulfopolyester having a Tg of at least 57° C. and a water non-dispersible polymer. The multicomponent fibers may be used to produce microdenier fibers. Fibrous articles may be produced from the water-dispersible fibers, multicomponent fibers, and microdenier fibers. The fibrous articles include water-dispersible and microdenier nonwoven webs, fabrics, and multilayered articles such as wipes, gauze, tissue, diapers, panty liners, sanitary napkins, bandages, and surgical dressings. Also disclosed is a process for water-dispersible fibers, nonwoven fabrics, and microdenier webs. The fibers and fibrous articles have further applications in flushable personal care and cleaning products, disposable protective outerwear, and laminating binders.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Polyester DTY fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108385186AHigh molecular weightNarrow molecular weightSpinning head liquid feederFilament/thread formingFiberThermal insulation
The invention relates to polyester DTY fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: metering a modified polyester melt, extruding, cooling, oiling, and winding to preparethe polyester POY fiber. According to the present invention, during the cooling, the longitudinal height is maintained, and the cross section area of the slow cooling chamber is increased while the plate surface temperature of the spinning plate is maintained by using the thermal insulation method; the material of the fiber is the modified polyester, the molecular chain of the modified polyester comprises a terephthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment and a diol chain segment having the branched chain, the structure formula of the diol chain segment having the branched chain is defined in the specification, R1 and R2 are respectively and independently selected from straight chain alkylidene with a carbon atom number of 1-3, R3 is selected from alkyl with a carbon atomnumber of 1-5, and R4 is selected from alkyl with a carbon atom number of 2-5; the chromatic aberration [delta]E of the prepared fiber is less than 0.200; and the preparation process is simple and reasonable, and the obtained fiber has excellent performance.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Process of preparing PDT copolyester fiber
InactiveCN101046007ASpinning high speedHigh speed spinning equipmentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberAlcohol
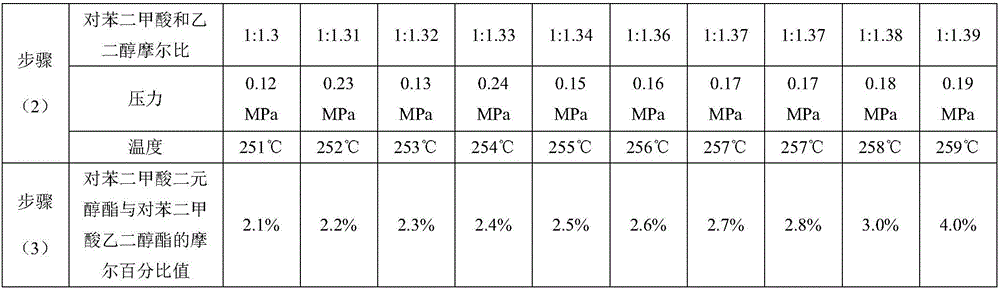
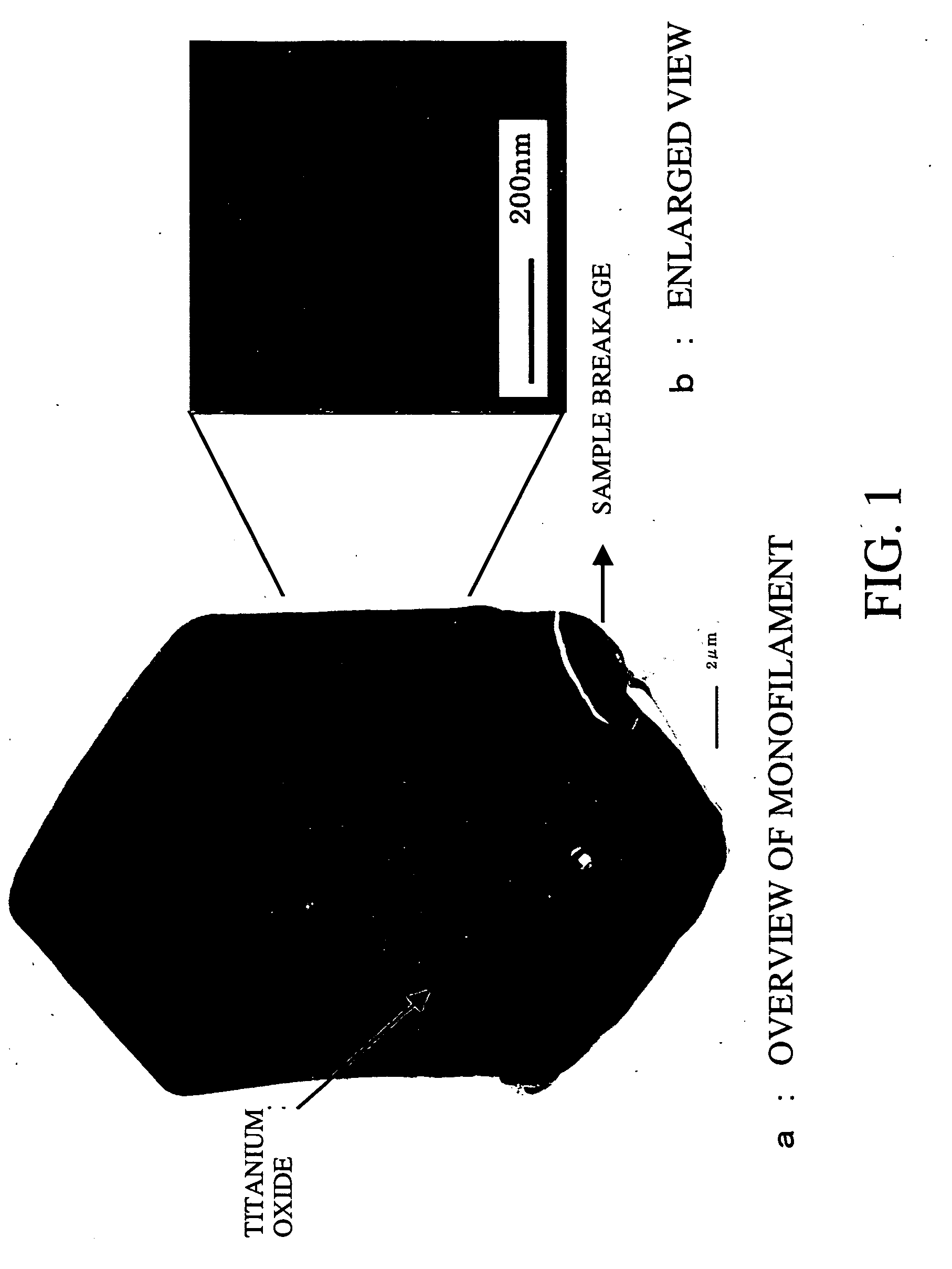
The process of preparing PDT copolyester fiber includes the following steps: 1. saccharifying and catalytically hydrogenating corn starch to prepare sorbitol, catalytically hydrogenating to prepare multicomponent mixed alcohol, and fractionating in a fractionating tower at 182-212 deg.c to obtain corn-base ethylene glycol product of 89-99 % content and with ethylene glycol as main component and other diols; 2. detecting the contents of component diols in the ethylene glycol product and adding insufficient components for content fluctuation controlled within 10-30 %; and 3. adding nanometer titania in 0.05-1 wt% into the corn-base ethylene glycol product, and copolymerizing together with terephthalic acid at 280-288 deg.c for 5-7 hr to prepare PDT copolyester. The process is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
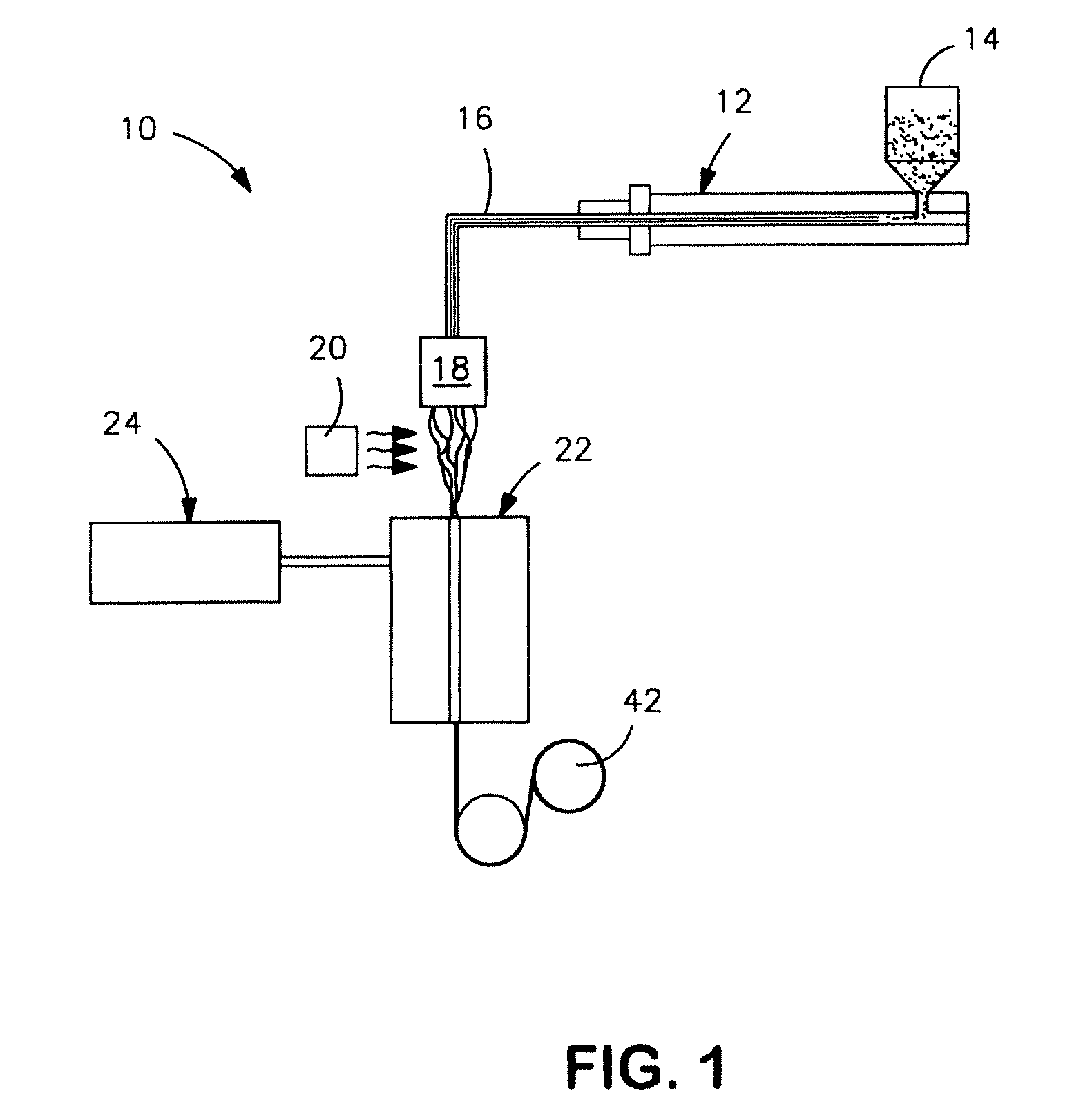
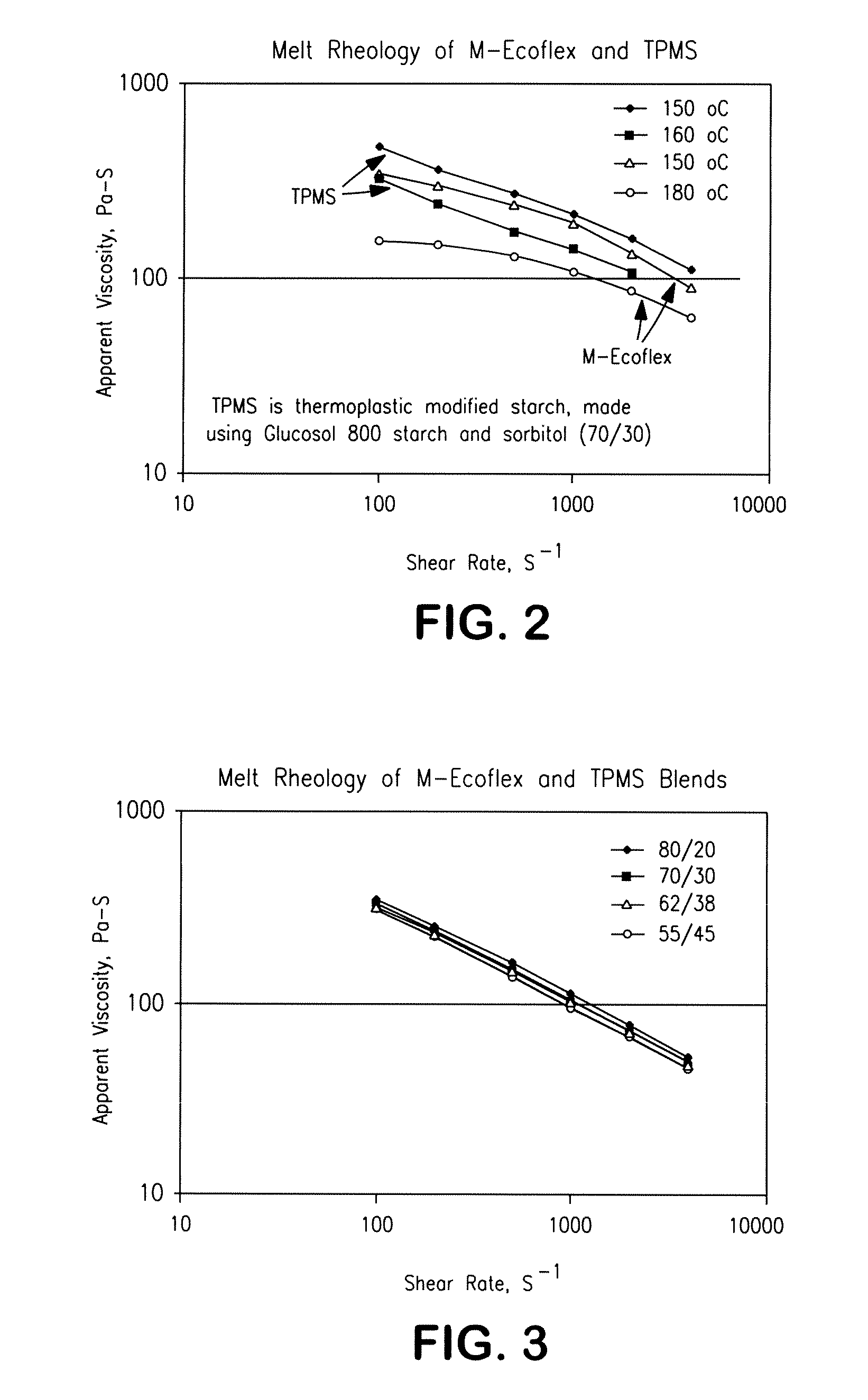
Fibers Formed from a Blend of a Modified Aliphatic-Aromatic Copolyester and Thermoplastic Starch
ActiveUS20090305592A1Ceramic shaping apparatusMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberAlcohol
A fiber formed from a thermoplastic composition that contains a thermoplastic starch and an aliphatic-aromatic copolyester is provided. The copolyester enhances the strength of the starch-containing fibers and also facilitates the ability of the starch to be melt processed. Due to its relatively low melting point, the aliphatic-aromatic copolyester may also be extruded with the thermoplastic starch at a temperature that is low enough to avoid substantial removal of the moisture found in the starch. Furthermore, the aliphatic-aromatic copolyester is also modified with an alcohol so that it contains one or more hydroxyalkyl or alkyl terminal groups. By selectively controlling the conditions of the alcoholysis reaction (e.g., alcohol and copolymer concentrations, temperature, etc.), the resulting modified aliphatic-aromatic copolyester may have a molecular weight that is relatively low. Such low molecular weight polymers have the combination of a higher melt flow index and lower apparent viscosity, which is useful in a wide variety of fiber forming applications, such as in the meltblowing of nonwoven webs.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method for manufacturing yarn for vessel stent
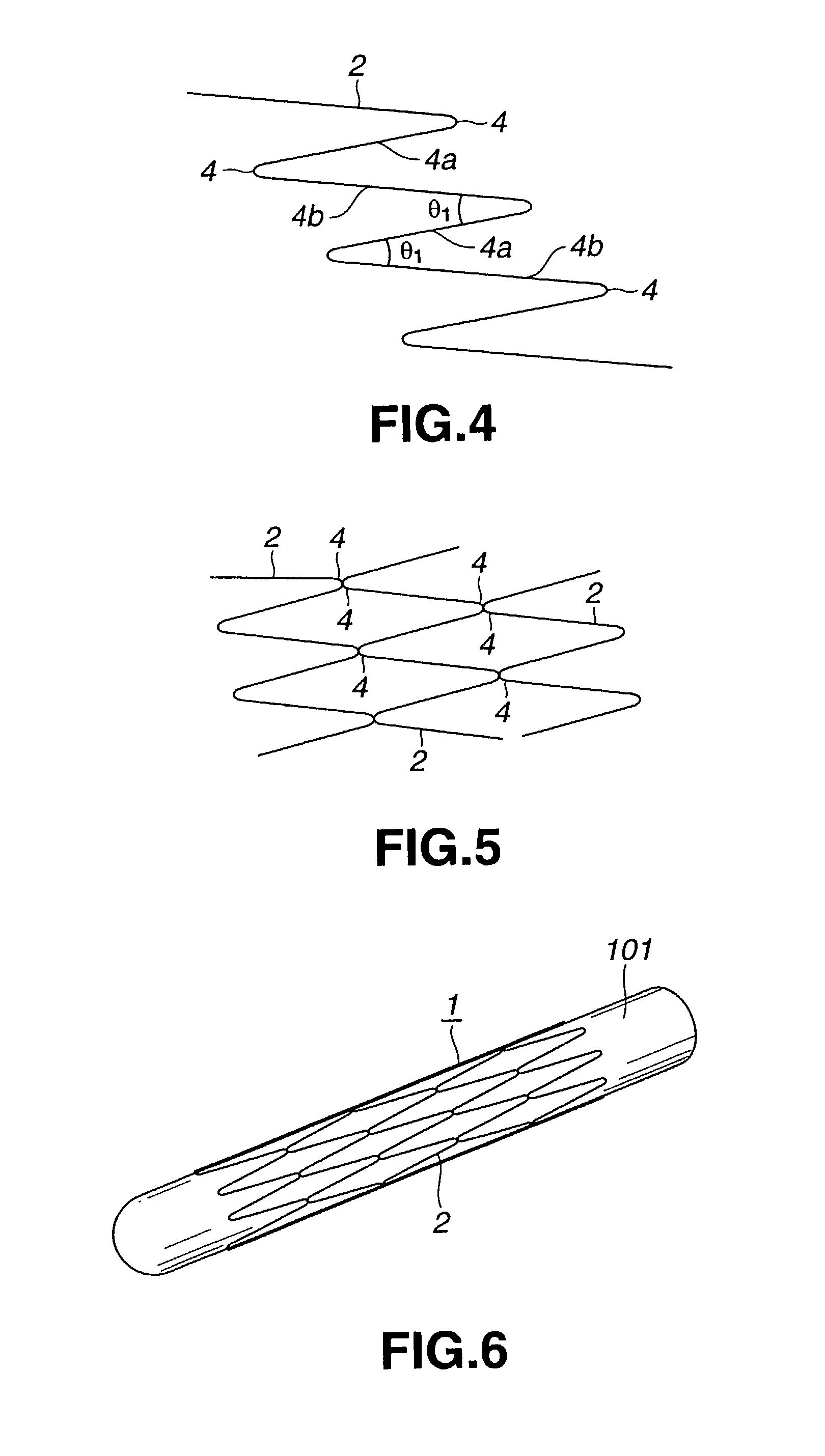
A stent for a vessel implanted in the vessel of the living body including a main body portion of the stent formed into a tube by a yarn formed of a biodegradable polymer exhibiting a shape memory function. The main body portion of the stent is shape-memorized to a size that can be inplanted in the vessel. The main body portion of the stent is implanted in the vessel of the living body as it is contracted in diameter by an external force, and is enlarged in diameter by being heated with the temperature of the living body. The main body portion of the stent is formed by winding a yarn formed of a biodegradable polymer in a tube form as the yarn is bent in a zigzag design. The main body portion of the stent is enlarged or contracted in diameter with the bends of the yarn as the displacing portions.
Owner:IGAKI IRYO SEKKEI
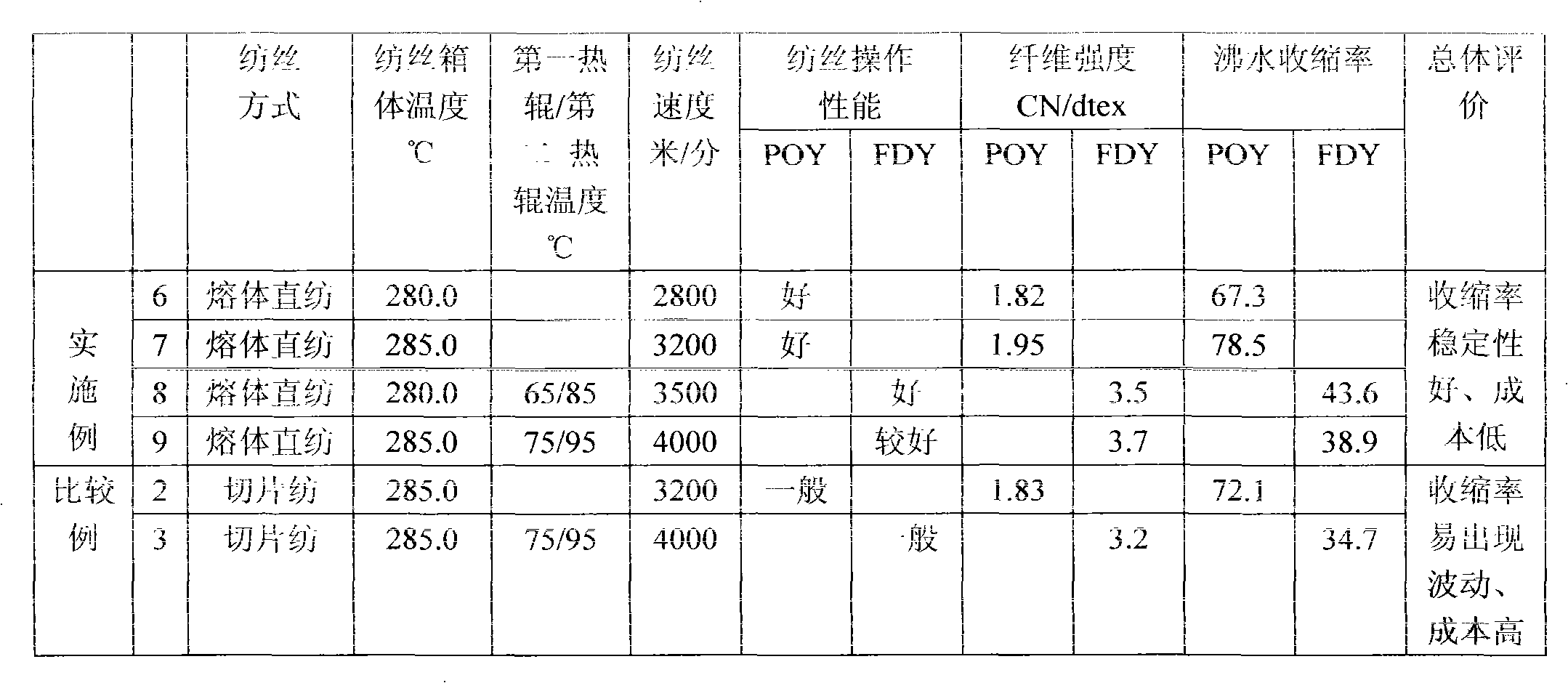
Method for preparing continuous polymerization directly-spun high-shrinkage polyester filaments
InactiveCN101787583AShrinkage stableShort processSpinning head liquid feederMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentYarnFiber
The invention discloses a method for preparing continuous polymerization directly-spun high-shrinkage polyester filaments, which comprises a process for preparing continuous polymerization modified copolyester melt and a process for preparing directly-spun cation-dyeable high-shrinkage polyester filaments. In the process for preparing the continuous polymerization modified copolyester melt, purified terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and glycol monomers are taken as raw materials to prepare the modified copolyester melt; and the copolyester melt directly passes through a melt conveying piping equipment, and is metered, extruded, blown to be cooled, drawn for heat shaping, and wound to prepare one of high-shrinkage polyester preoriented yarns and high-shrinkage polyester drawn yarns. The method has the advantages of short flow, less working procedures, reasonable process, stable melt quality, and good spinning performance; and the prepared high-shrinkage fibers have good shrinkage stability and even dyeing, and the production cost is reduced obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
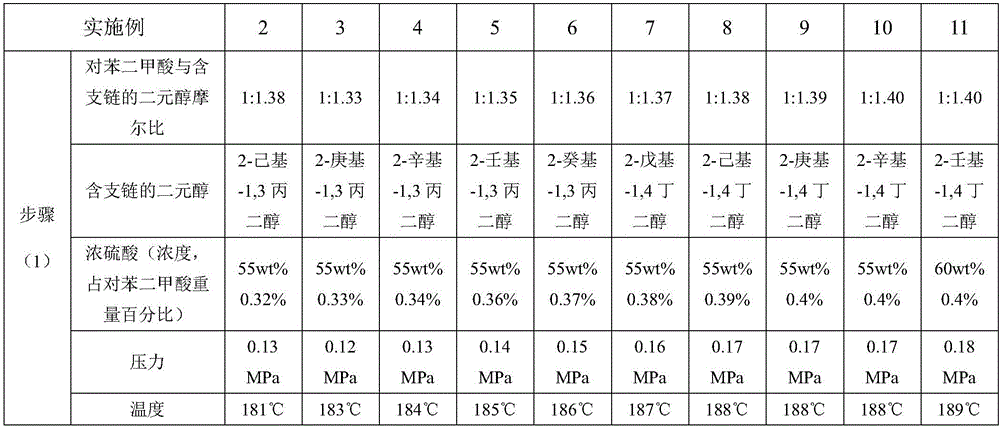
Polyester fibres and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106367835AImprove dyeing effectEasy to processSpinnerette packsMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentSlurryLow vacuum
The invention relates to polyester fibres and a preparation method thereof. The raw material of the polyester fibres is modified polyester which consists of a terephthalic acid chain segment, an ethylene glycol chain segment and a branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol chain segment. The preparation method of the polyester fibres comprises the following steps: performing esterification reaction on terephthalic acid and branched chain-containing dihydric alcohol under the catalysis of concentrated sulphuric acid to obtain terephthalic acid dihydric alcohol ester; then, preparing the terephthalic acid and the ethylene glycol into slurry, and performing the esterification reaction on the slurry to obtain the terephthalic acid ethylene glycol ester; finally, stirring and mixing the terephthalic acid dihydric alcohol ester and the terephthalic acid ethylene glycol ester, and performing condensation polymerization in a low vacuum stage and a high vacuum stage under the action of a catalyst and a stabilizing agent to obtain modified polyester; metering, extruding, cooling, oiling, stretching, heat-setting and winding the polyester to prepare the polyester fibres. The increasing amplitude of the spatial gaps of the polyester fibres is much higher than that of branched chain-free polyester fibres at the same temperature, which is beneficial to the degree of micro particles, such as a dye, that enter the polyester; the dyeing rate is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Porous fiber
ActiveUS20050260911A1Good color propertiesExcellent moisture adsorptionWarp knittingCeramic shaping apparatusMetallurgyNanopore
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Preparation method for moisture-absorbing and flame-retardant polyester fiber
InactiveCN103012765AGood hygroscopicityImprove flame retardant performanceMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberMoisture
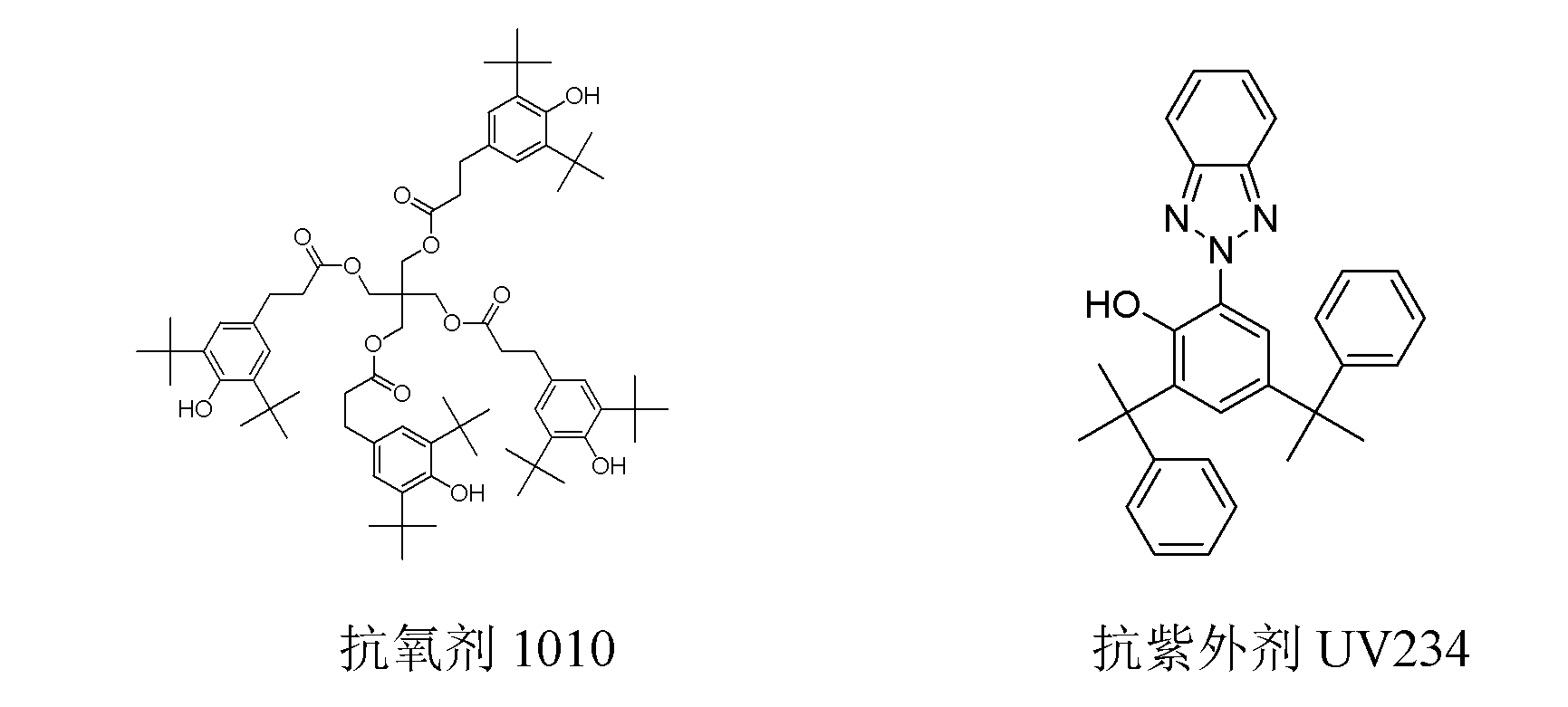
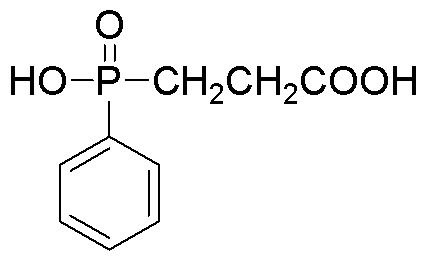
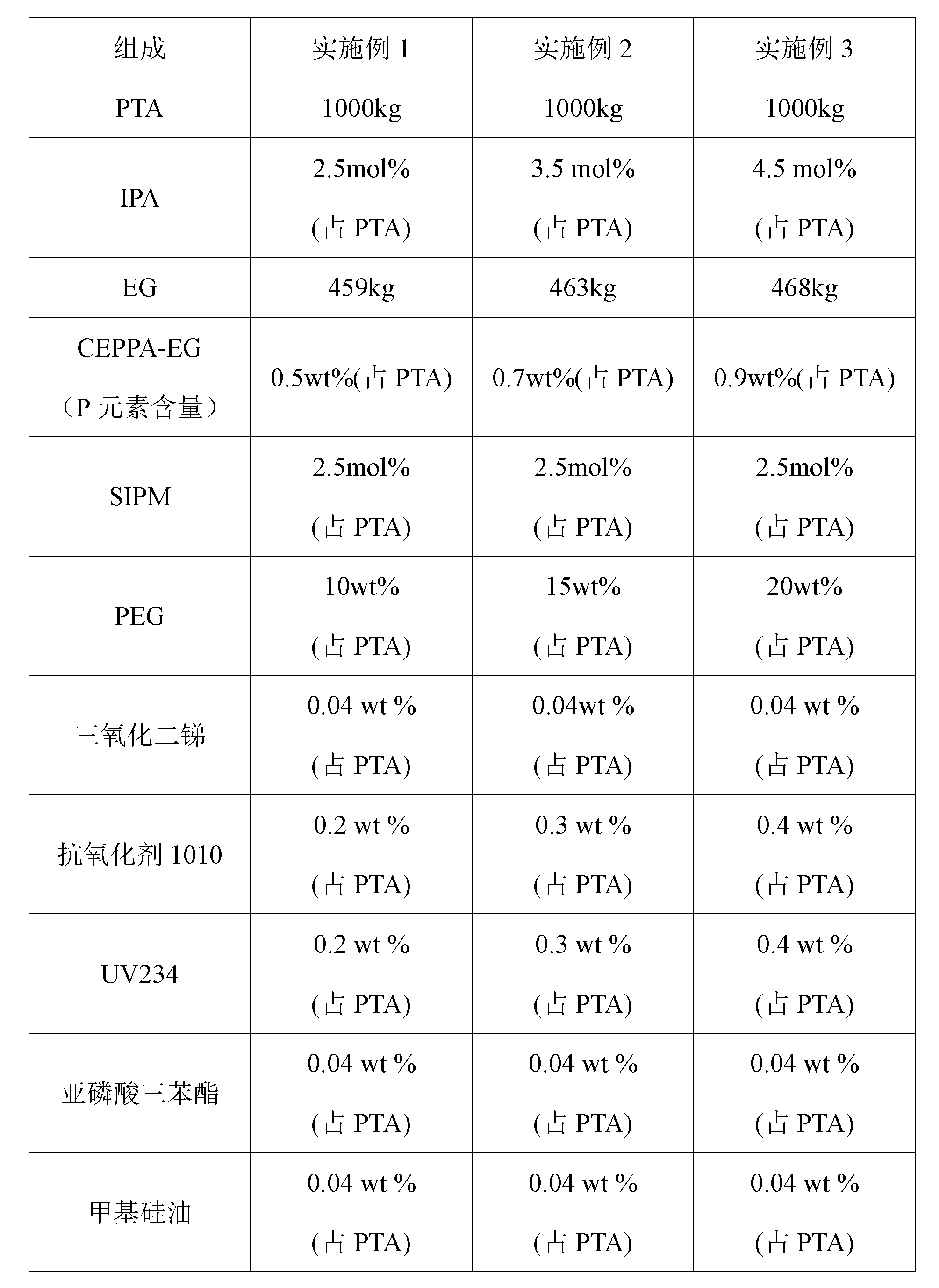
The invention provides moisture-absorbing and flame-retardant copolyester, which comprises terephthalic acid (PTA), other aromatic dicarboxylic acid or ester derivatives, aliphatic diol containing C2 to C6 atoms, a phosphorus flame retardant, moisture-adsorption group containing monomers, copolymer which is polymerized by flexible-chain monomers and contains ether bonds, a heat stabilizer and an anti-oxidation and uvioresistant additive. The textile fabric, which is prepared by spinning the synthesized moisture-absorbing and flame-retardant copolyester, has favorable moisture-absorbing and flame-retardant functions, and greatly improves the wearing comfort and safety flame retardancy of the polyester fabric.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF CLOTHING TECHNOLOGY
Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20110168625A1Reduces blocking and fusionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceSlurry
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Low-melting-point copolyester and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101338023AIncrease exerciseLow melting pointMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
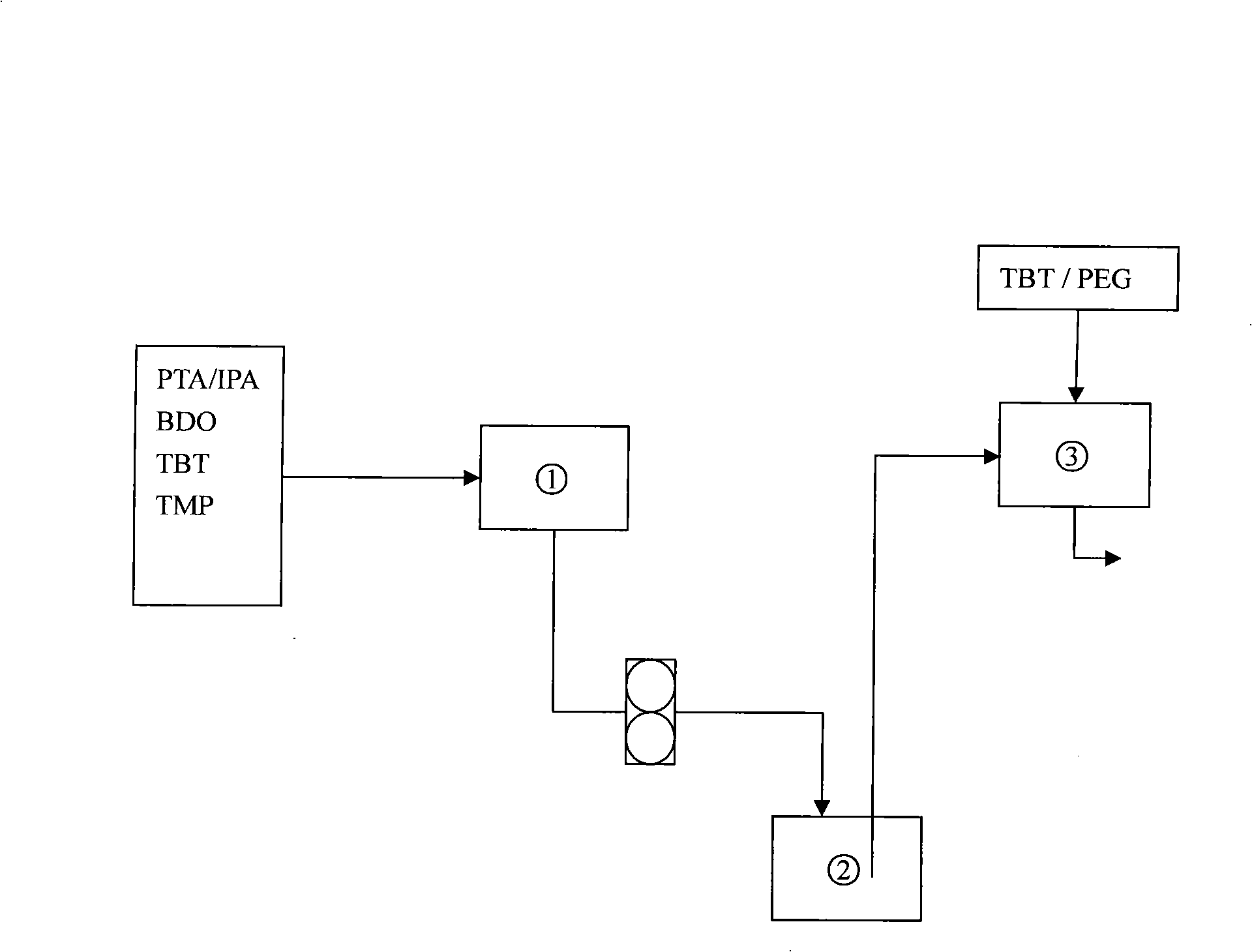
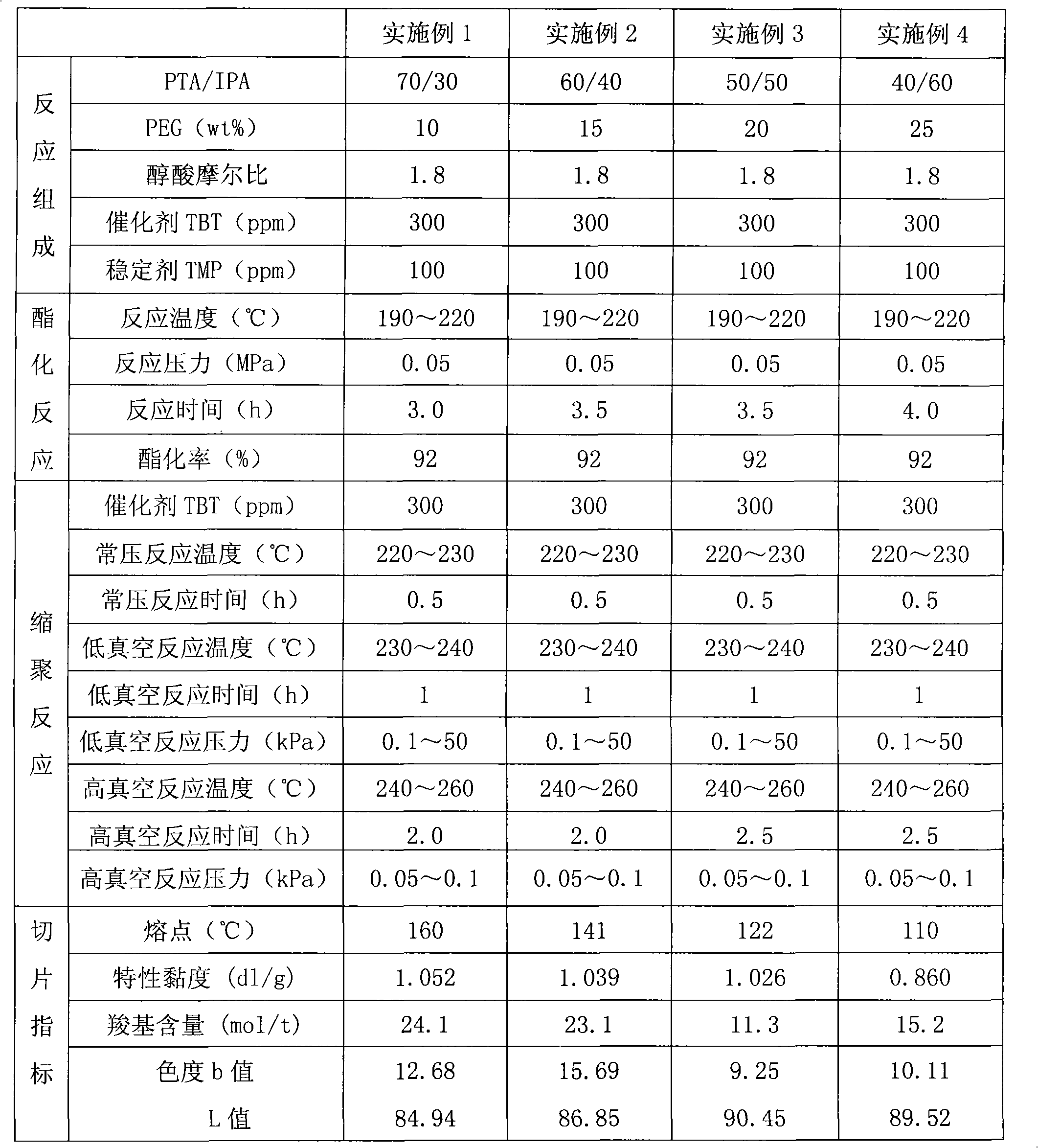
The invention relates to low melting point copolyester and a preparation method thereof. The low melting point copolyester is made from the following monomers followed by the esterification reaction and the polycondensation reaction: (a) terephthalic acid (PTA) and isophthalic acid (IPA), (b) 1, 4- butanediol (BDO) and (c) polyethylene glycol 600 to 6000 (PEG); wherein, in the a component, the feeding mass ratio of the terephthalic acid and the isophthalic acid is between 80 to 20 : 20 to 80; in the c component, the feeding weight ratio of polyethylene glycol is 1 to 30 percent based on the a; the molar ratio of the a and the b is 1:1.5 to 2.3. The preparation method comprises an esterifcation stage and a polycondensation stage. The copolyester has the characteristics of low melting point, good crystallization property, high intrinsic viscosity and difficult adhesion of particles, and is suitable for spinning the filament, the staple fibers and the non-woven fabrics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Side chain-containing aliphatic diol modified copolyester section and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101613466ANo itchingReduce crystallinityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates a side chain-containing aliphatic diol modified copolyester section and a preparation method thereof; the section is copolymerized by terephthalic acid, ethanediol, m-benzene dicarboxylic acid diethyl ester-5-sodium sulfonate or potassium sulfonate and side chain-containing aliphatic diol and is synthesized in a semicontinuous polymerzation device. The copolyester section of the invention can be dyed to dark color with cationic dye at room temperature and normal pressure; the crystallization property and the glass state temperature of the copolyester are reduced so that the prepared fibre has extremely soft hand feeling; the manufacturing process has no special demand on devices and the cost is low so that the preparation method is applicable to industrialized production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
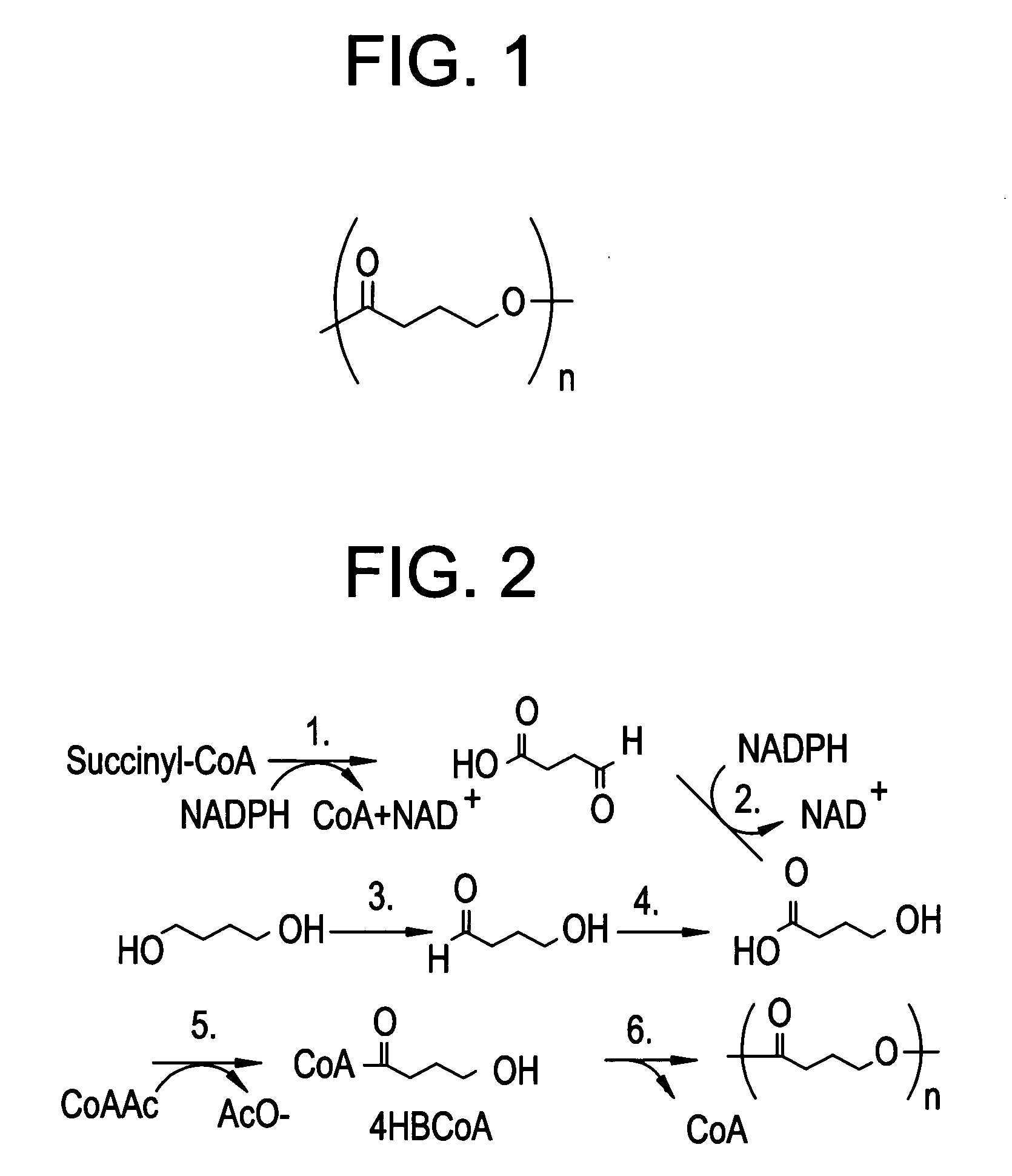
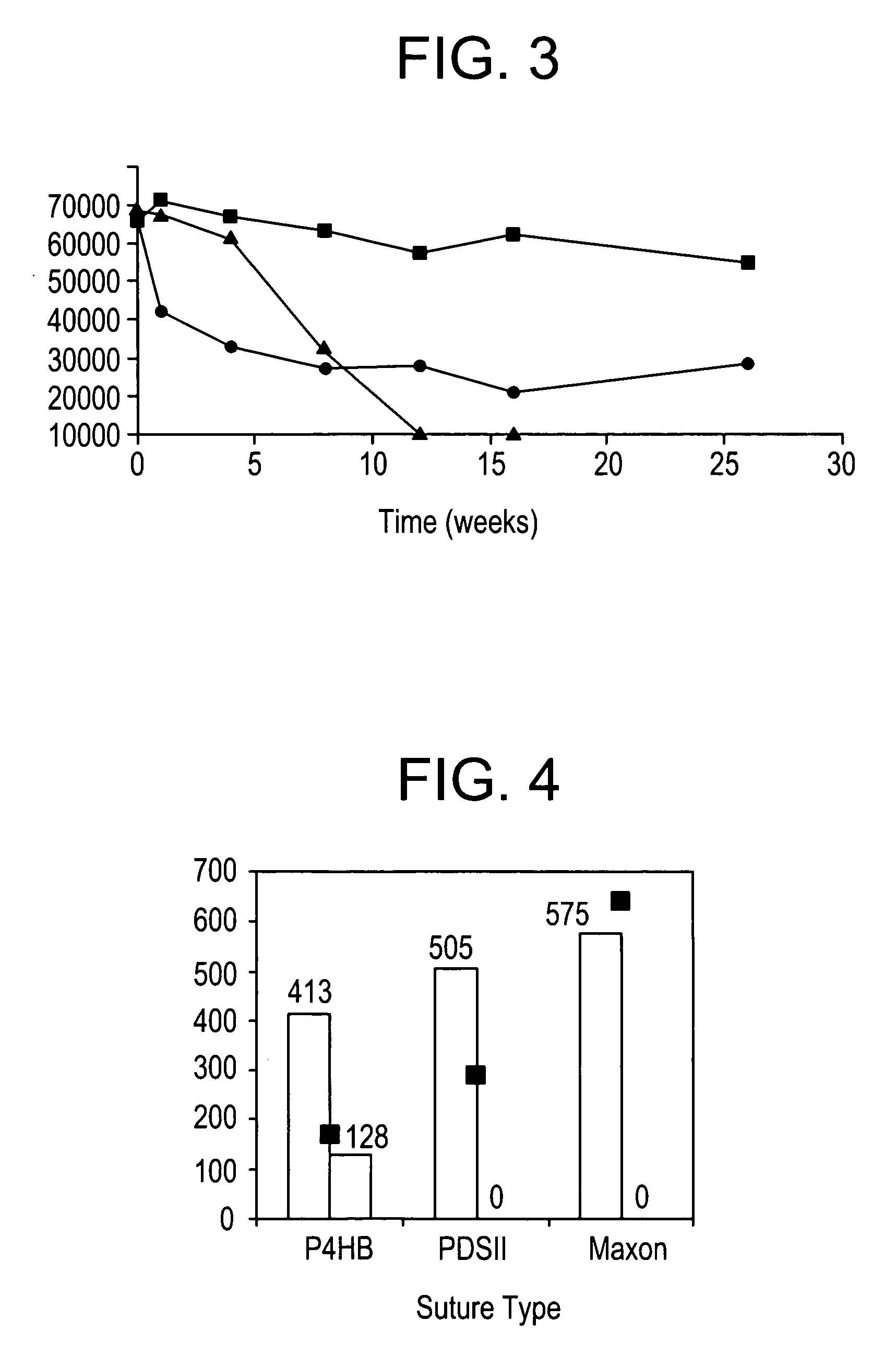
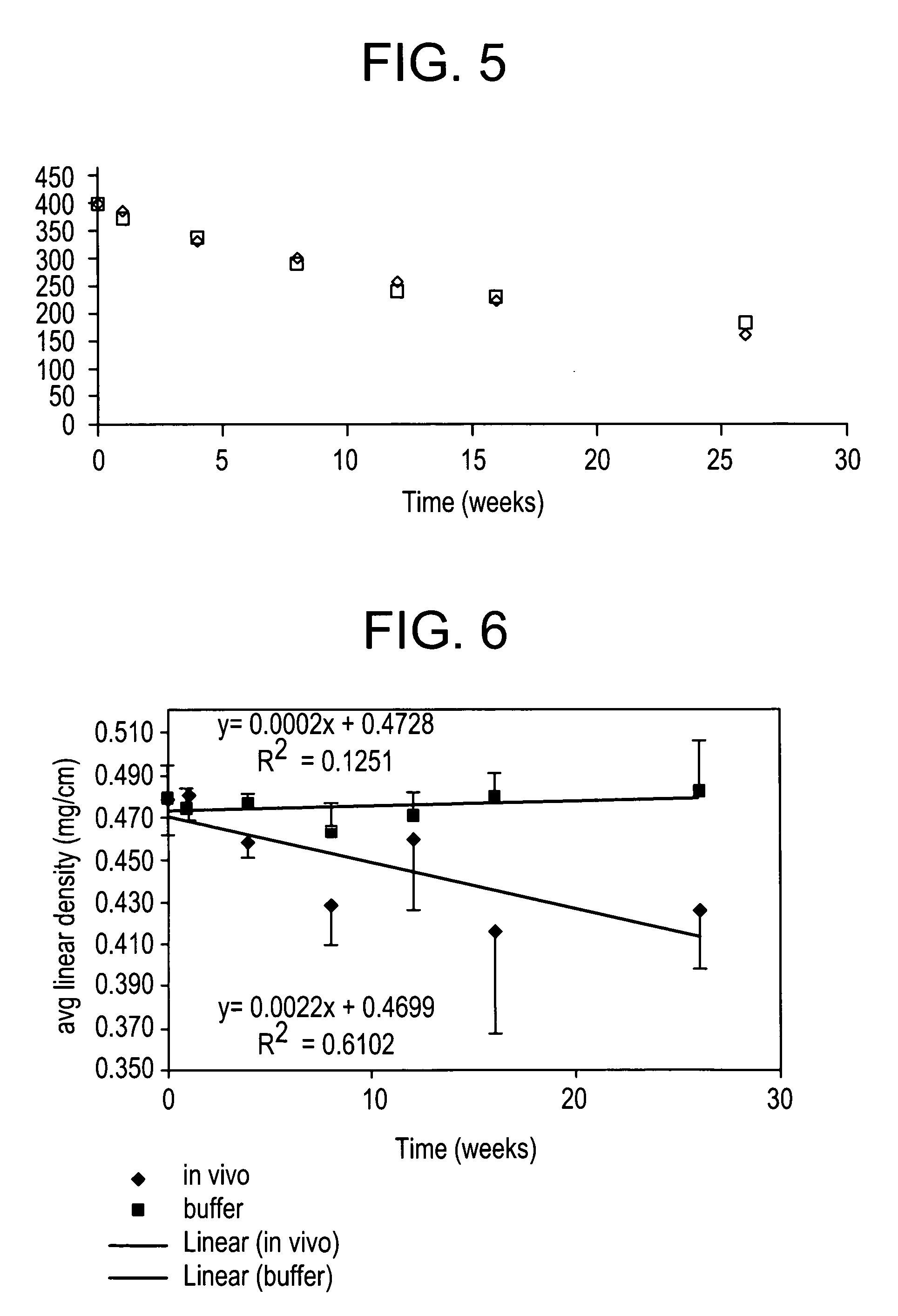
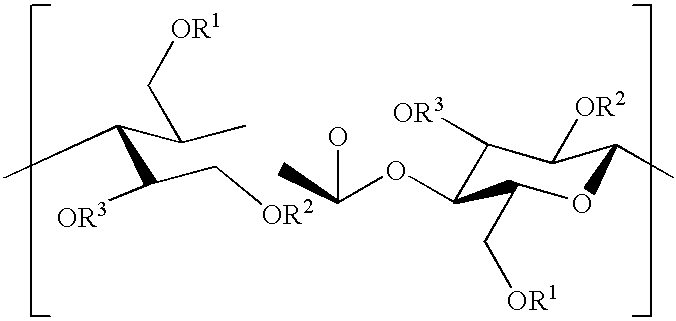
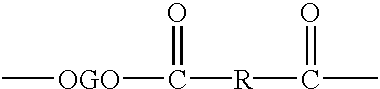
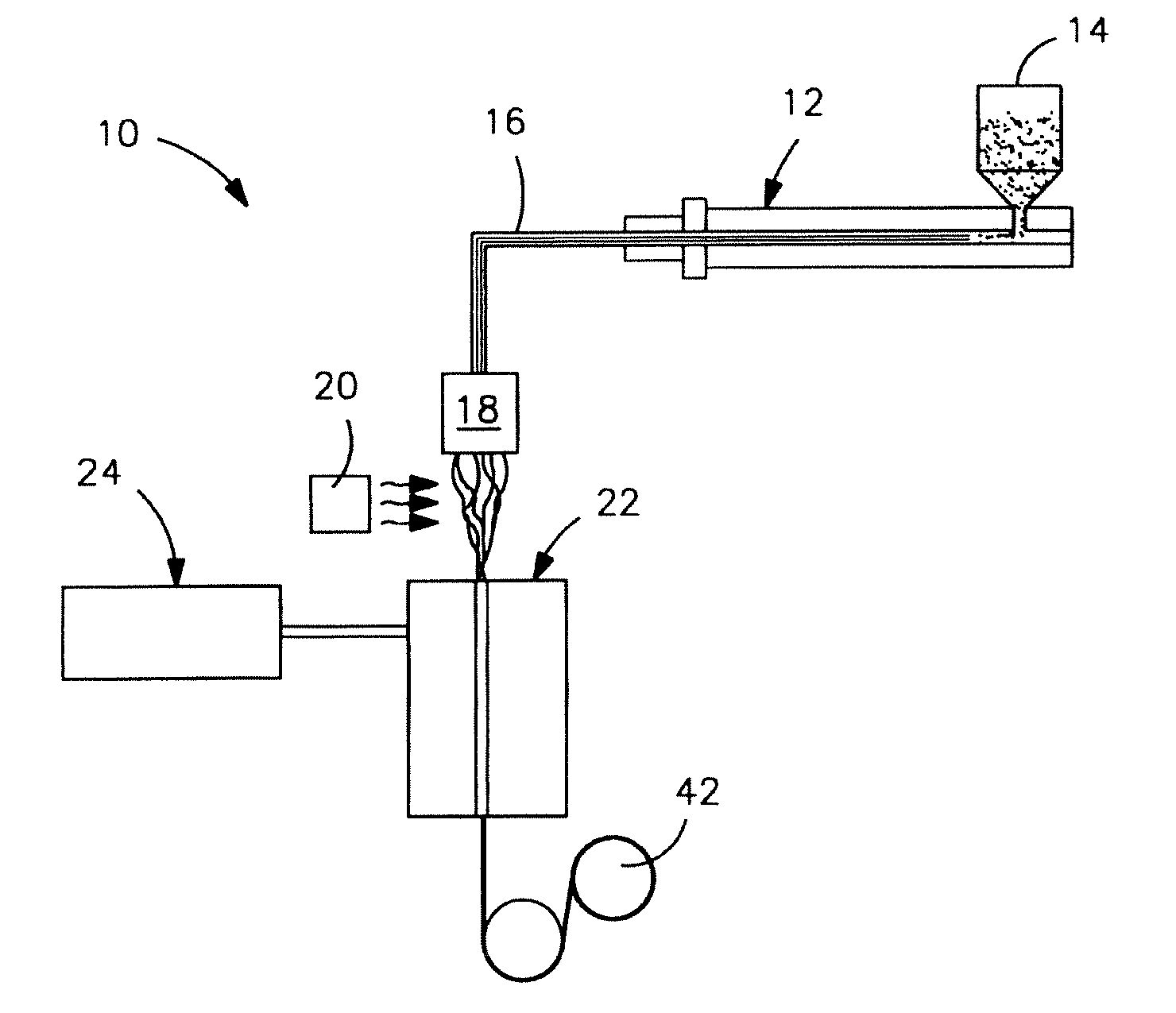
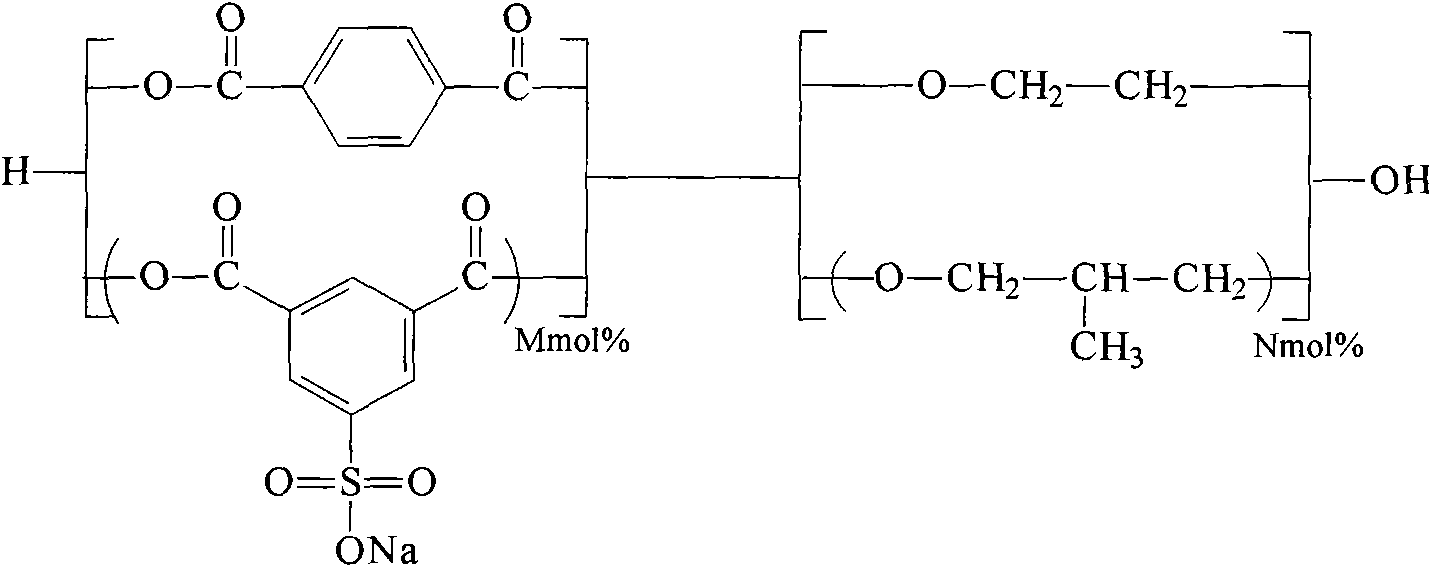
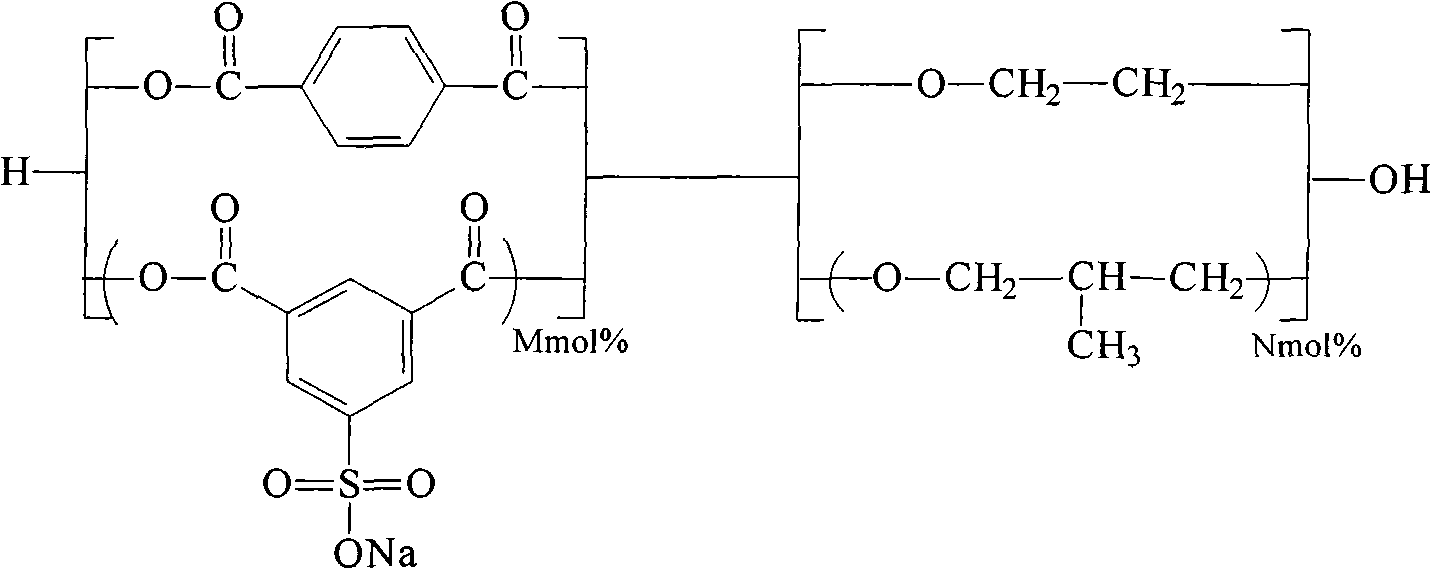
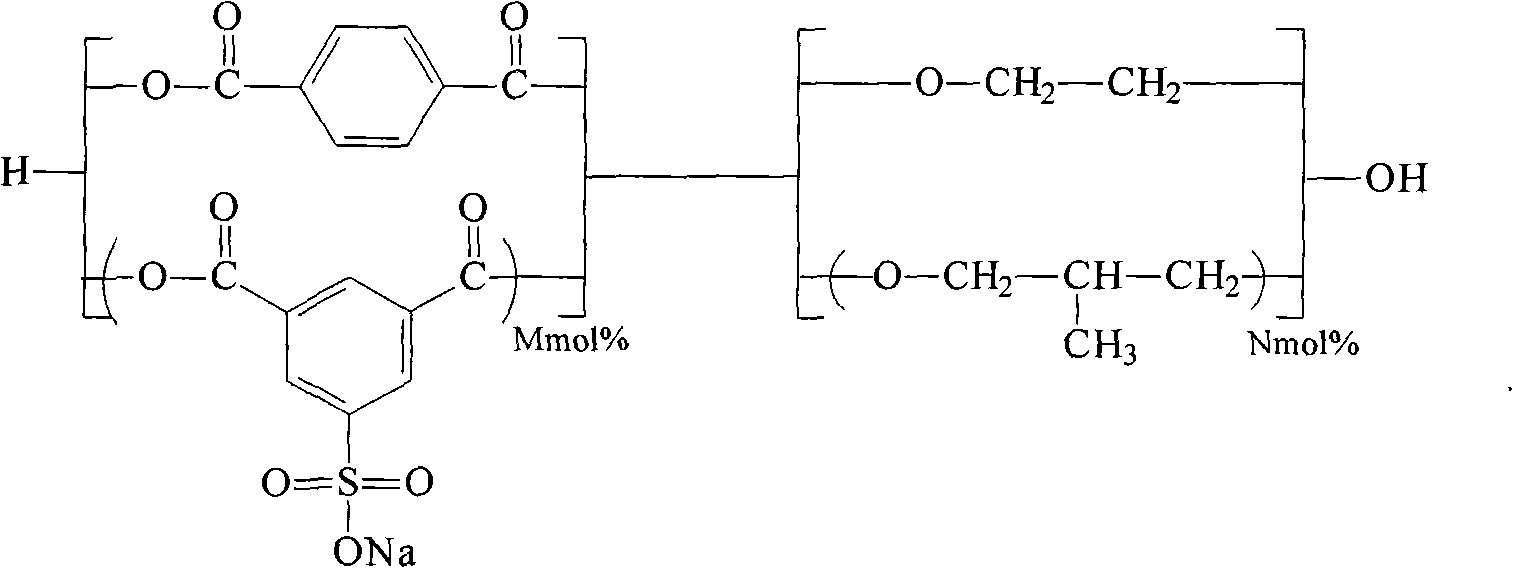
Shaped articles comprising poly[(trimethylene-co-dianhydrosugar ester) dicarboxylate] or poly(trimethylene-co-dianhydro-dicarboxylate with improved stability
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Regenerated terylene filament and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102505175AAvoid pollutionAvoid exhaustionPlastic recyclingMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentPolyesterEnvironmental resistance
The invention provides regenerated terylene filament, which has higher mechanical properties and is prepared by depolymerizing waste polyester with polyol as a solvent. The PET (Polyethyleneglycol Terephthalate) granules are depolymerized in a homogeneous state by optimizing the solvent, pressure, temperature, time, catalyst and parameter conditions as well as controlling the pressure and temperature, so as to improve the depolymerization reaction rate. A composite catalyst is adopted, thus the ratio of the solvent to waste polyester is strictly controlled, the polyol consumption is reduced, the process economy is improved, the generation of diethylene glycol is reduced, and the quality and spinnability of the regenerated polyester are improved. The depolymerization rate of the polyester and the mechanical properties of the regenerated terylene filament are improved by adding a third component, thus the mechanical properties of the prepared regenerated terylene filament achieve the properties of the conventional terylene filament. The preparation method is simple, economical and environmentally friendly and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:江苏芮邦科技有限公司
Multi-hole polyester fiber DTY (draw textured yarn) and preparation method thereof
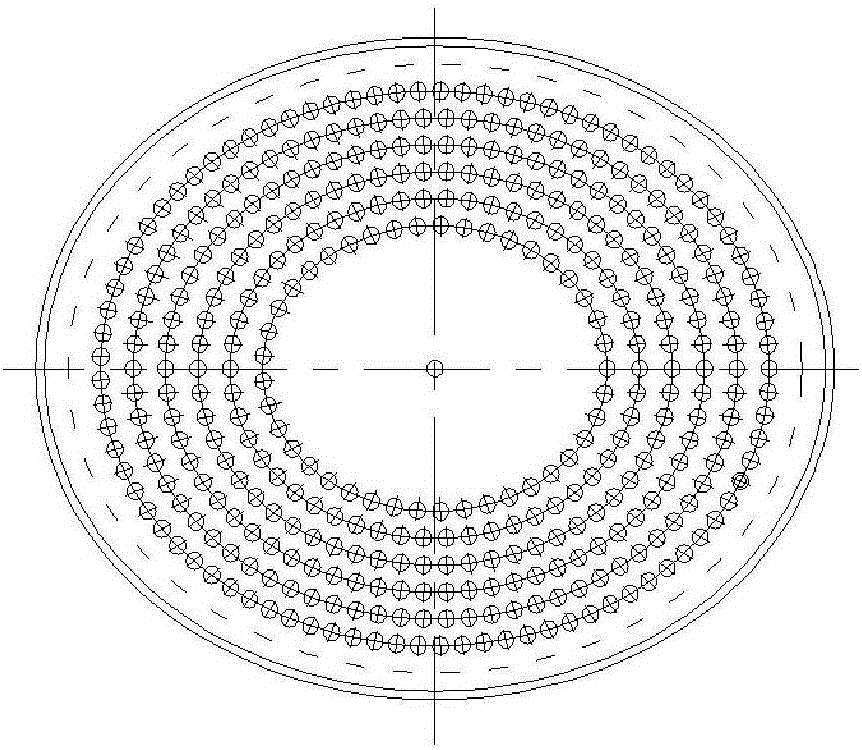
ActiveCN106283253AIncreased access to polyester interiorImprove cooling effectSpinnerette packsMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberYarn
The invention relates to a multi-hole polyester fiber DTY (draw textured yarn) and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, modified polyester is spun to prepare the multi-hole polyester fiber DTY by the aid of a multi-hole spinneret plate; spinneret holes in the multi-hole spinneret plate are elliptically arrayed, namely, the hole centers of the spinneret holes are positioned on concentric ellipses, the concentric ellipses are series ellipses, long axes of the all ellipses are collinear, short axes of the all ellipses are collinear, the modified polyester is used for preparing a POY (polyester pre-oriented yarn) and then further processed to obtain the multi-hole polyester fiber DTY. A preparation method of the modified polyester includes the steps: performing reaction for terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol to prepare terephthalic acid ethylene glycol ester; adding the terephthalic acid and dihydric alcohol with branching chains, and performing reaction for mixture to prepare terephthalic acid dihydric alcohol ester; continuing to react to obtain the modified polyester. According to the method, prepared fibers are excellent in performance, the deviation ratio of linear density of the DTY is smaller than or equal to 2.0%, a breaking strength CV (variation coefficient) value is smaller than or equal to 4.0%, a breaking elongation CV value is smaller than or equal to 8.0%, and a CV value of crimping shrinkage rate is smaller than or equal to 8.0%.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Aliphatic-aromatic polyesters, and articles made therefrom
Sulfonated aliphatic-aromatic polyester compositions having improved thermal properties, and articles such as films, coatings and laminates, produced from the sulfonated aliphatic-aromatic polyester compositions, are provided. Some of the films are biocompostable. Films made from the sulfonated aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters can be used to make shaped articles, such as sheets, thermoformed containers, and coatings for, for example, films and other substrates. The sulfonated aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters are produced from a mixture of aromatic dicarboxylic acids, aliphatic dicarboxylic acids, certain glycols, and components containing alkali metal or alkaline earth metal sulfonate groups, such as a metal 5-sulfoisophthalic acid derivative.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Production technique of three-dimensional curly hollow polyester staple fibers
InactiveCN102517675AQuality assuranceLow costFilament forming substance formingHollow filament manufacturePolyesterDrum drying
The invention discloses a production technique of three-dimensional curly hollow polyester staple fibers, wherein the production technique comprises the steps of: utilizing regenerative PET material as raw material; sequentially performing the following procedures to obtain a finished product: pre-treating, drum drying, melting spinning, cooling forming, winding, stretching, curling, oiling, cutting and heat setting, wherein the drum drying duration is 9.5-10.5 h, a spinneret plate in the melting spinning procedure is three-dimensional hollow helical, the cross section of a spinneret orifice is a sealed space formed by sealing the circular arcs of two concentric circles, the temperatures of the threaded rod of a threaded rod extruding machine and the box body of a spinning box are 265-275 DEG C; a circular air blowing asymmetrical cooling forming mode is utilized, the circular blowing blast temperature is 20-24 DEG C, and the circular blowing wind speed is 4.7-5.7 m / s; the total stretching fold is 2.5-2.7 folds, the main curling pressure of a curling wheel is 0.05-0.1 MPa, and no backpressure exists; the heat setting temperature is 175-180 DEG C, and the heat setting duration is 10-14 min. The production technique of the invention has the advantages of saving the cost and protecting the environment, and the prepared finished product not only has good three-dimensional configuration and bulkiness, but also has better thermal stability.
Owner:HANGZHOU BEST CHEM FIBER
Polyhydroxyalkanoates fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101538750AArrange straight and neatHigh crystallinityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a fiber and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a degradable fiber and a preparation method thereof. The fiber contains polyhydroxyalkanoates, and the preparation method thereof comprises the steps of melting and extruding a base material, obtaining a sample band, cold-stretching or pre-stretching the sample band, quenching, performing isothermal crystallization and the like. The fiber disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good biocompatibility, biodegradability, high strength and / or good toughness.
Owner:TIANJIN GREENBIO MATERIAL CO LTD +1
Method for continuously preparing modified polyester
ActiveCN101735430AEvenly dispersedExtended stayMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolymer scienceEsterification reaction
The invention relates to a method for continuously preparing modified polyester, comprising the following steps: conveying PET AND EG to an esterification autoclave from a feed port for esterification reaction, so as to obtain terephthalic acid ethylene glycol low polymer; then inputting the low polymer melt to a polycondensation autoclave through a pipeline for polymerization reaction with SIPM or multi-simplexes and addition agent, thus obtaining modified polyester melt and then carrying out granulation or direct spinning; wherein the two ends of the pipeline are respectively connected with the esterification autoclave and the polycondensation autoclave, when the low polymer melt flows through the pipeline, ethylene glycol solution of the SIPM or multi-simplexes and addition agent are added to the pipeline and mixed evenly with the low polymer melt in the pipeline, meanwhile the later-stage esterification reaction is carried out, and the mixture enters the polycondensation autoclave for polymerization reaction. With the method of the invention adopted, continuous industrialized production is realized, production cost is greatly reduced; in addition the SIPM or multi-simplexes with special groups are evenly distributed on the backbone of the polyester, as a result, high quality modified polyester products can be obtained for sure in the later stage.
Owner:SHANGHAI JUYOU CHEM ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



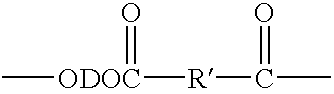
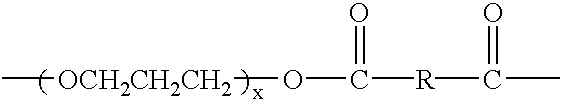
![Shaped articles comprising poly[(trimethylene-co-dianhydrosugar ester) dicarboxylate] or poly(trimethylene-co-dianhydro-dicarboxylate with improved stability Shaped articles comprising poly[(trimethylene-co-dianhydrosugar ester) dicarboxylate] or poly(trimethylene-co-dianhydro-dicarboxylate with improved stability](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1e8ba9a2-bf32-45bc-af03-5458a231dcfc/US07052764-20060530-D00001.png)
![Shaped articles comprising poly[(trimethylene-co-dianhydrosugar ester) dicarboxylate] or poly(trimethylene-co-dianhydro-dicarboxylate with improved stability Shaped articles comprising poly[(trimethylene-co-dianhydrosugar ester) dicarboxylate] or poly(trimethylene-co-dianhydro-dicarboxylate with improved stability](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/1e8ba9a2-bf32-45bc-af03-5458a231dcfc/US07052764-20060530-C00001.png)