Computer-aided discrimination method for Parkinson's disease symptoms based on KINECT bone data
A computer-aided technology for Parkinson's disease, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as interference with normal walking posture, achieve the effect of ensuring accuracy, reducing complexity, and ensuring detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] 1. Implementation process
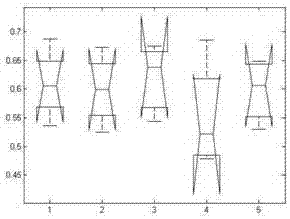
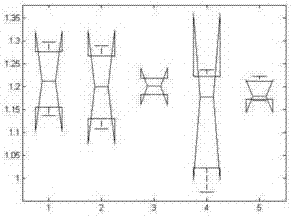
[0062] The main steps of the method provided by the present invention are as follows: obtain the bone point data of the whole body for a walk; carry out 'rlowess' filtering to the sequence of bone point coordinates changing with time, and ask for the instantaneous rate of change of each point, and calculate "unit stride" according to the instantaneous rate of change The lowest point" and the gait cycle, and then calculate the kinematic parameters, stride parameters and time parameters of the gait respectively. One-way analysis of variance was performed on the stride parameters to extract the normal sequence of the subjects walking. Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient for the stride length of the left and right feet, find the stride symmetry, compare the coefficient range of the patient, and judge whether it is a patient; standardize the acceleration sequence in the kinematic parameters to obtain the distribution sequence, and establ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com