Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
336 results about "Matrix pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Is a term which is normally associated with factor analysis where the factor pattern matrix is a matrix of regression-like weights that indicate the composition of the manifest variable with respect to the factors involved.
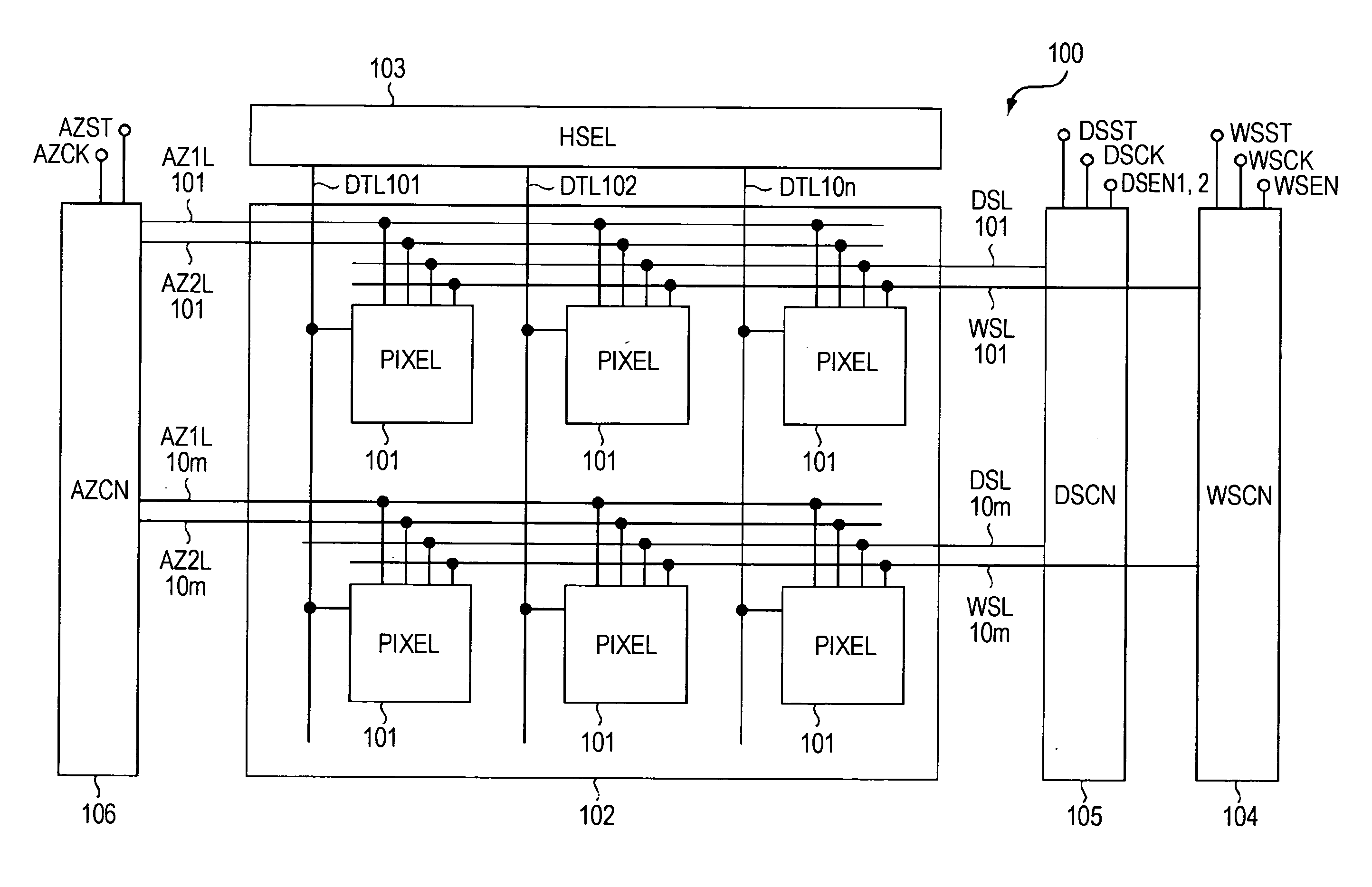
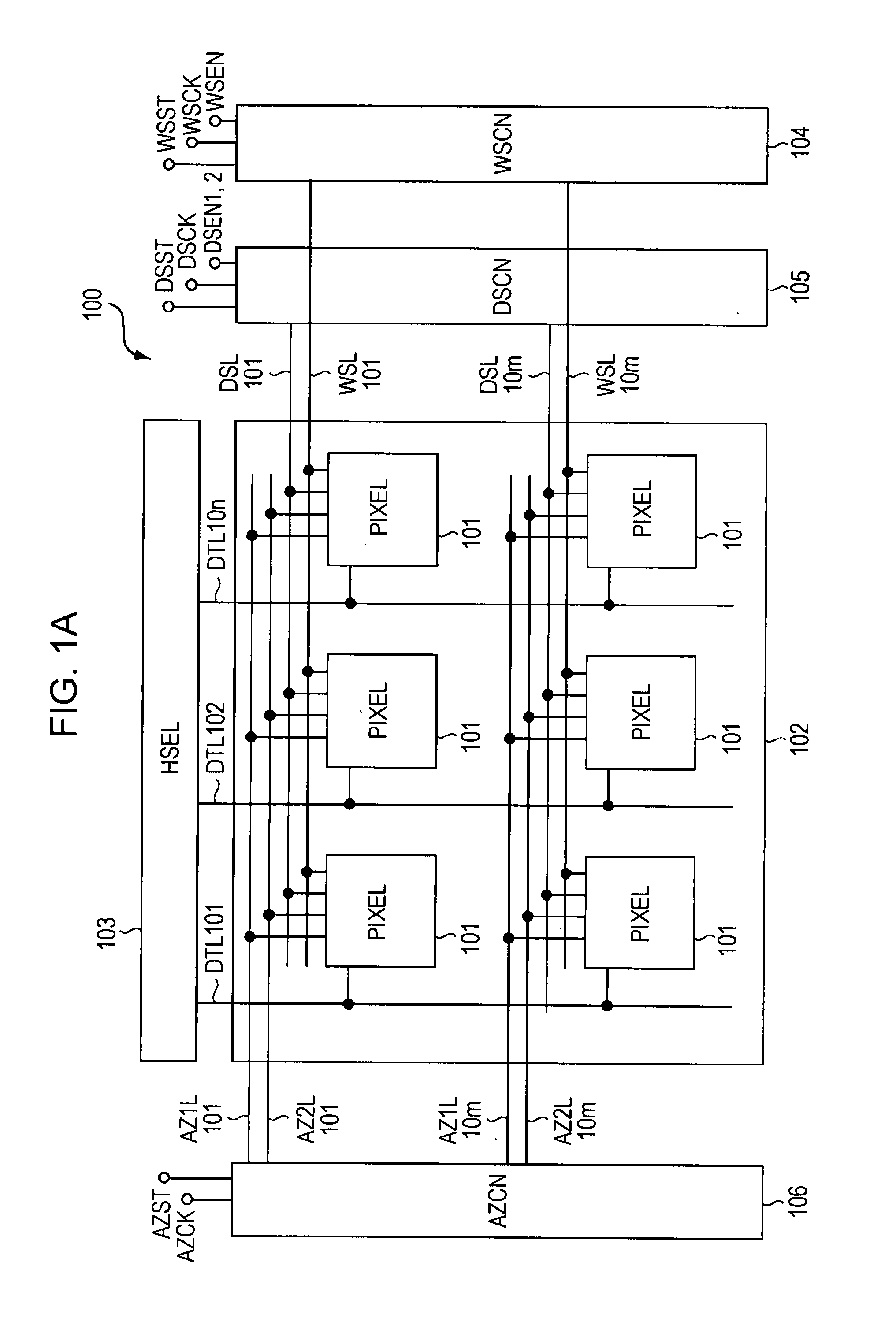
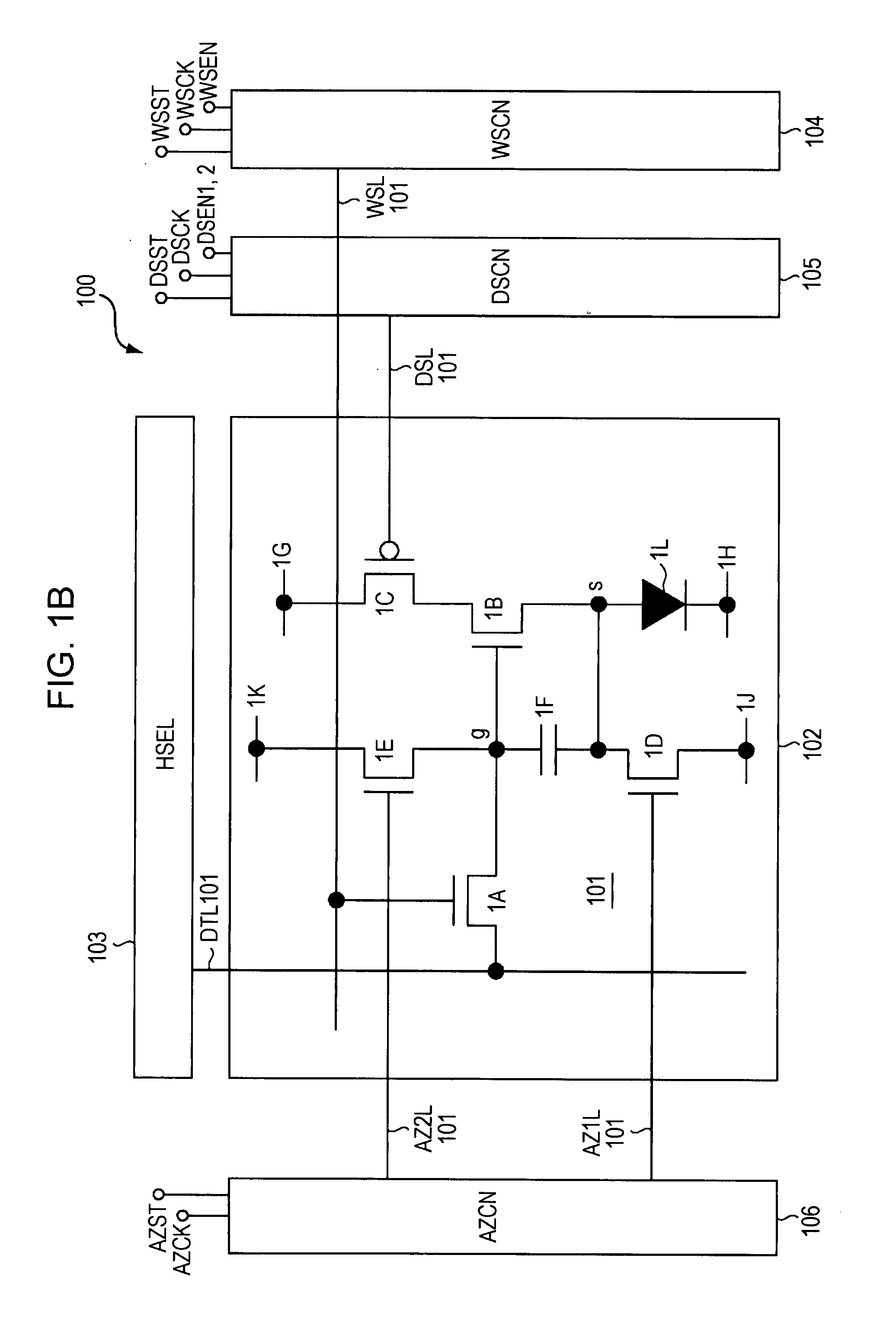
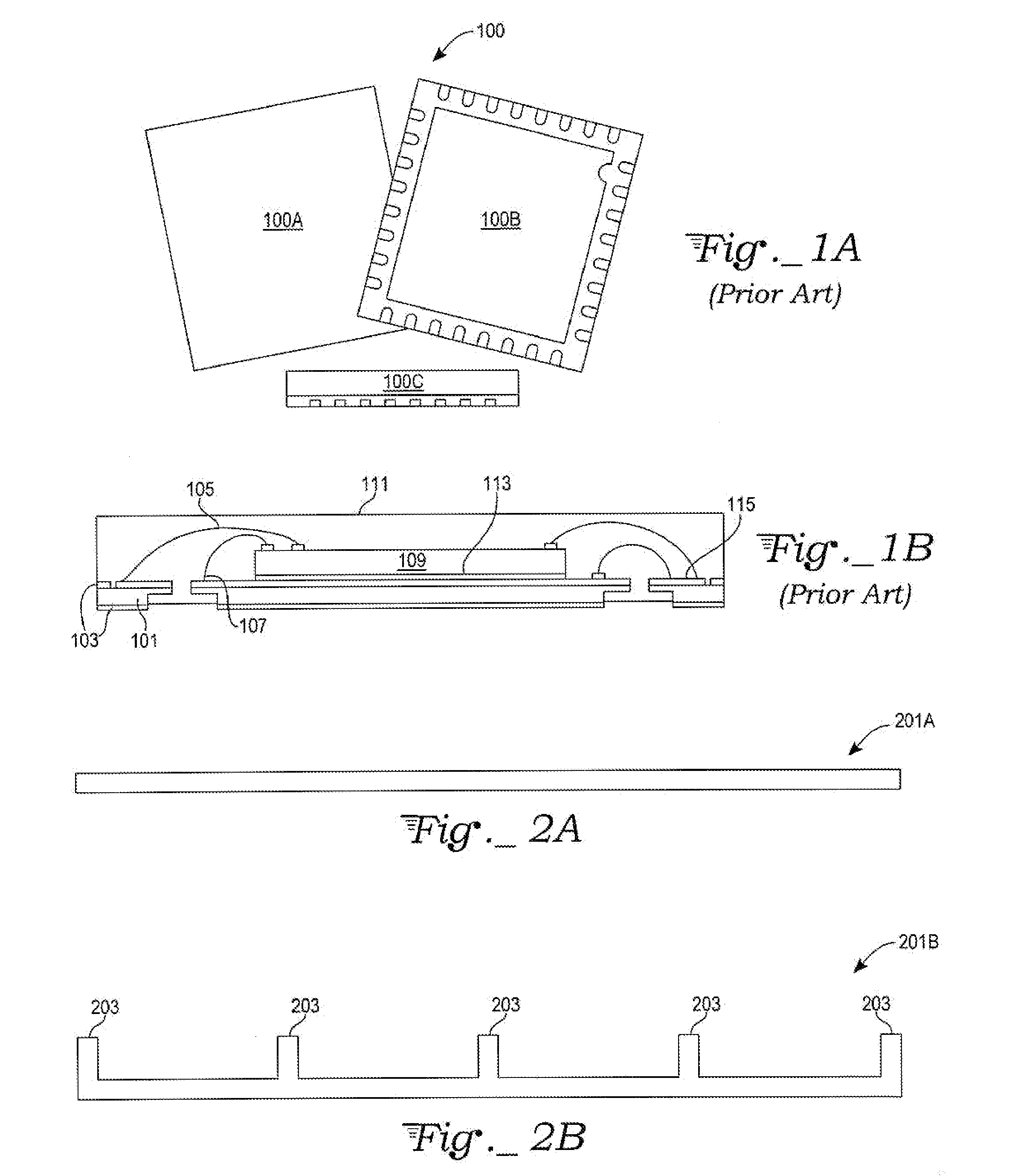
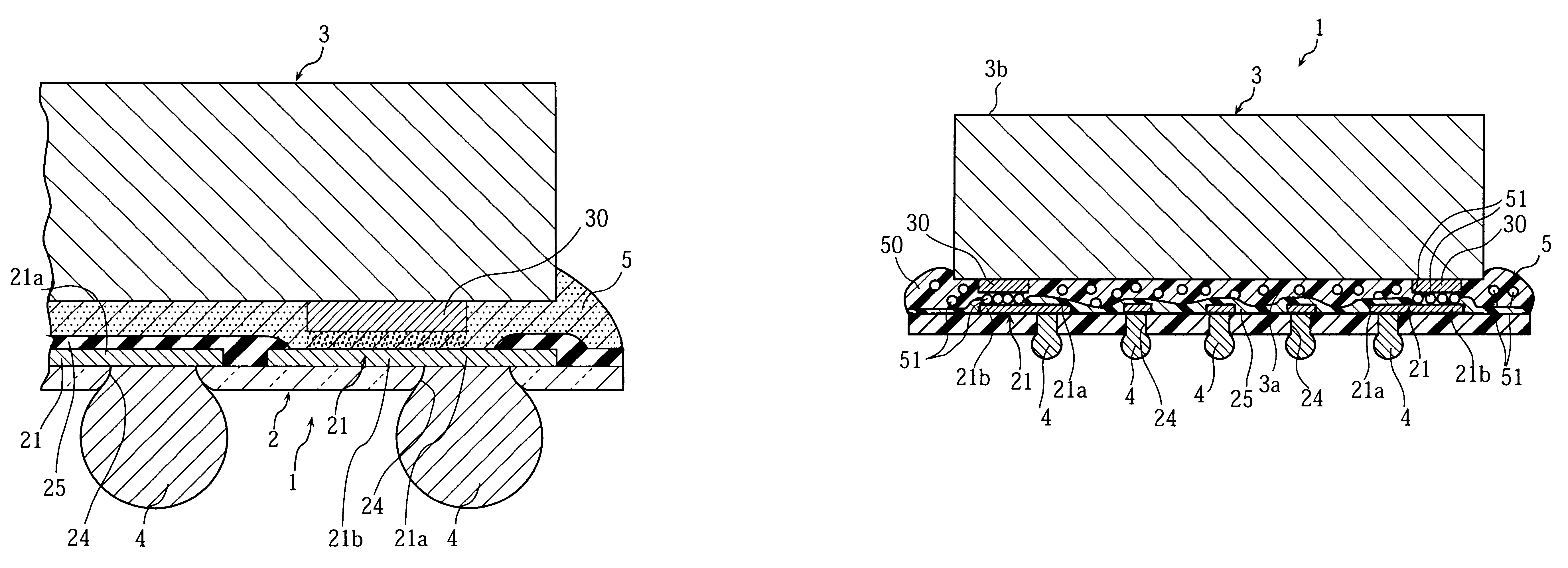
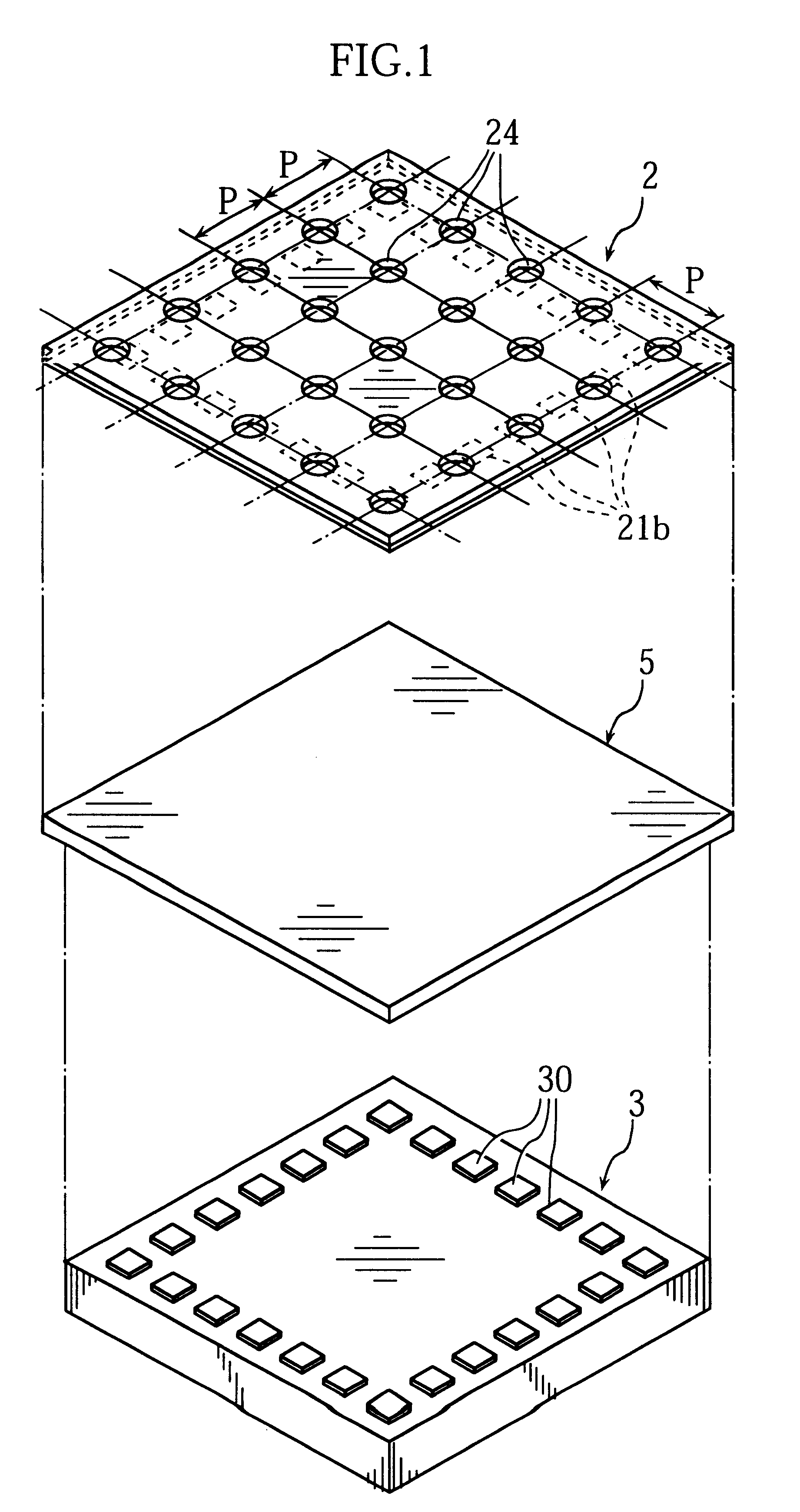
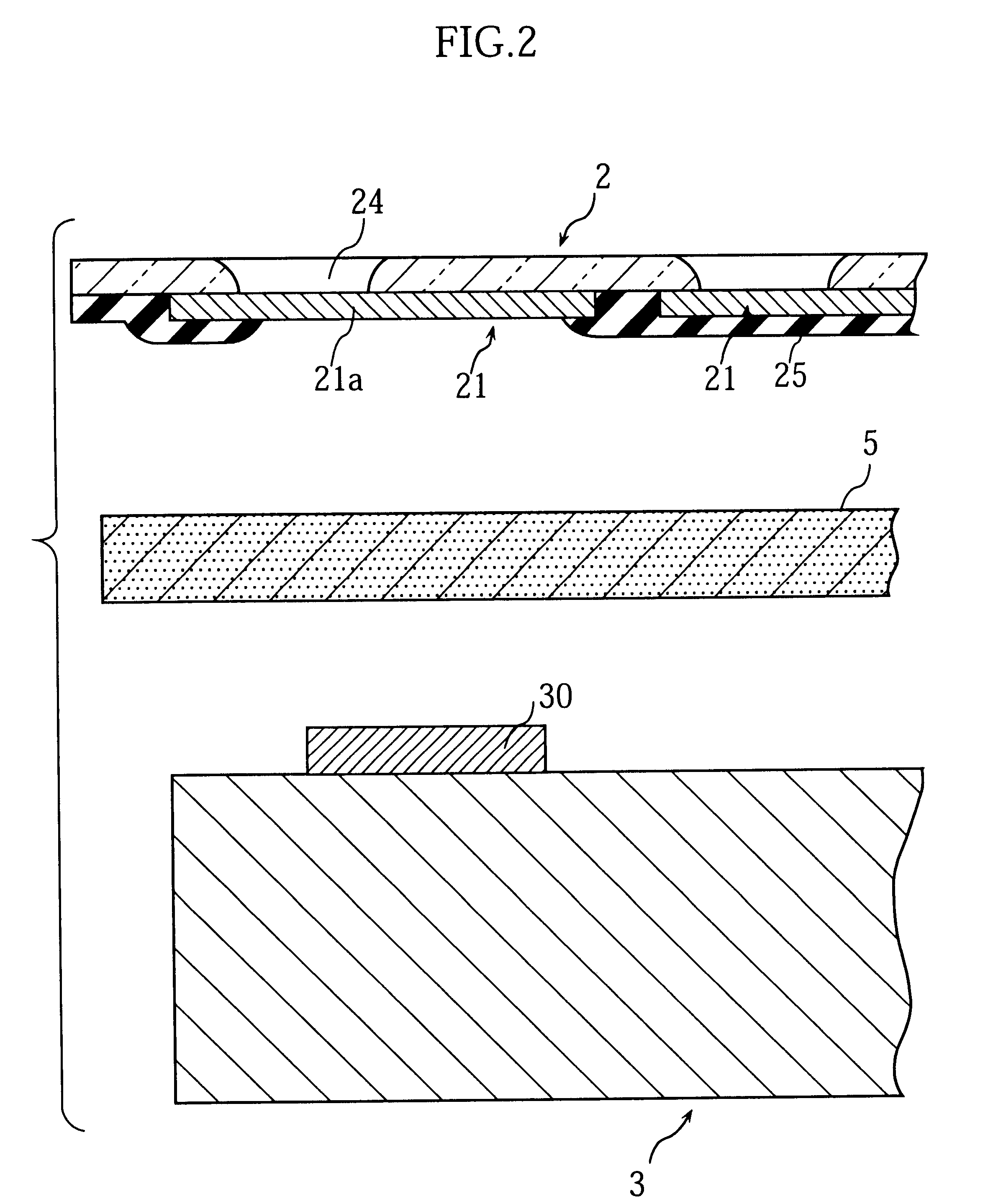
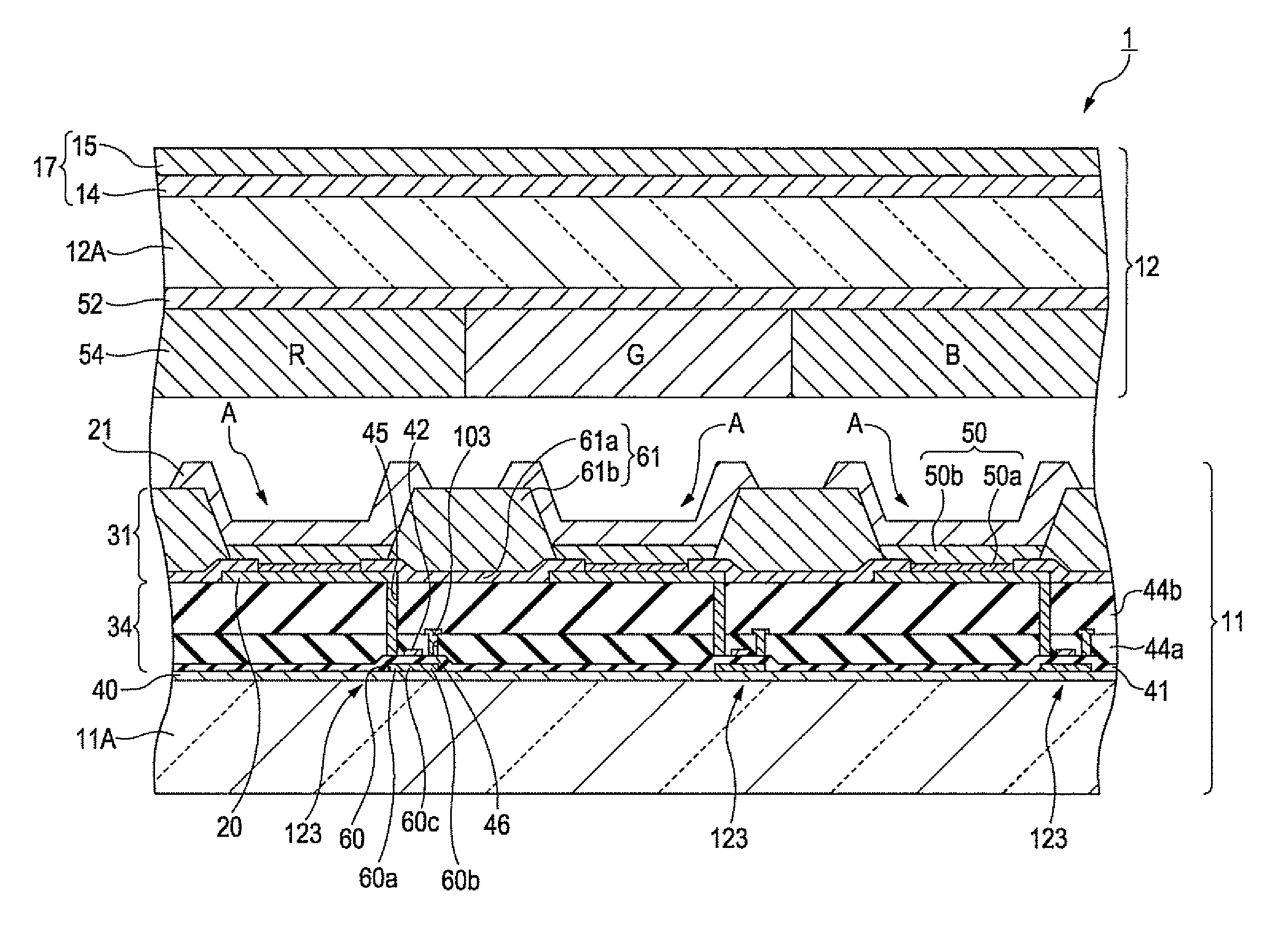
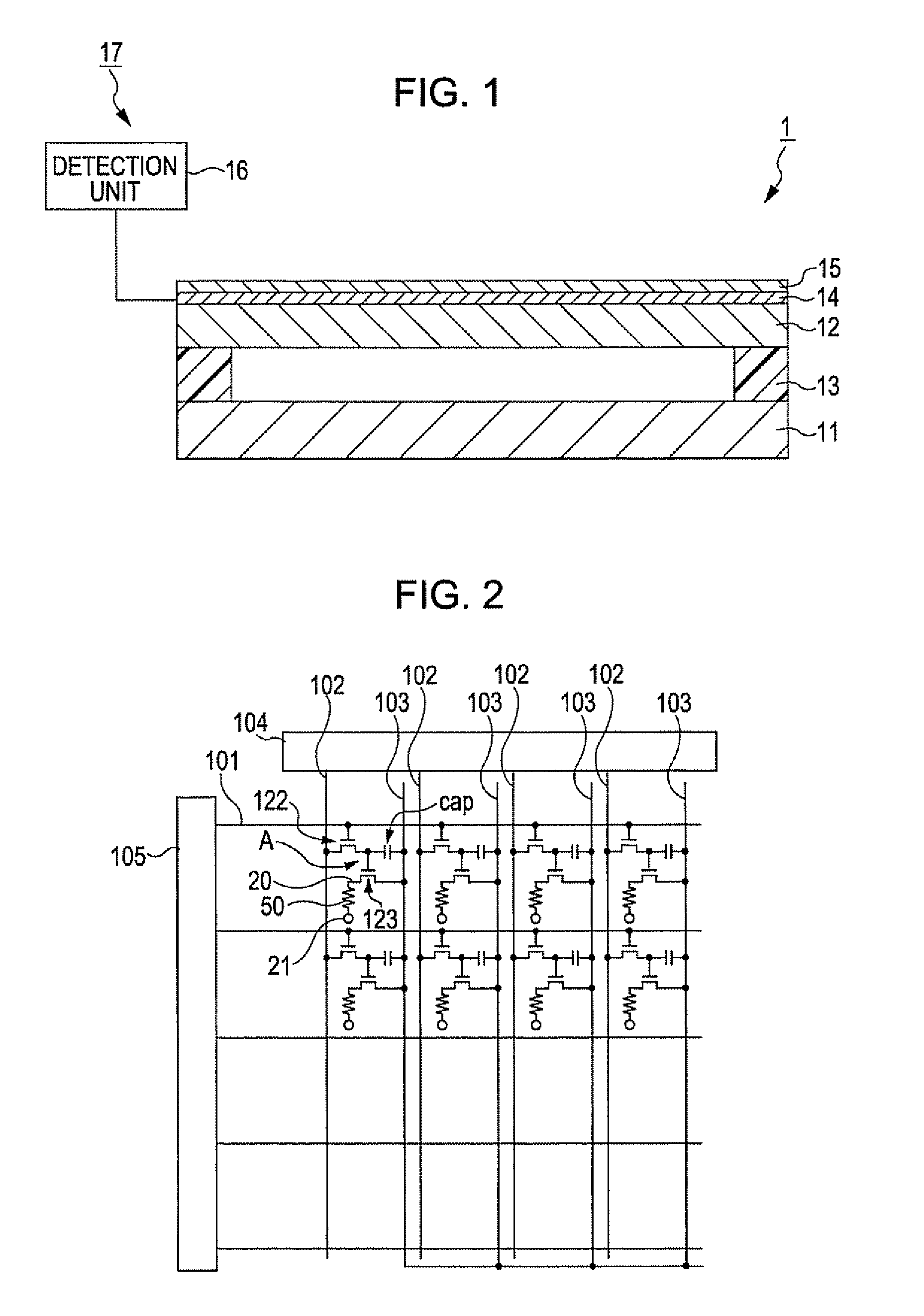
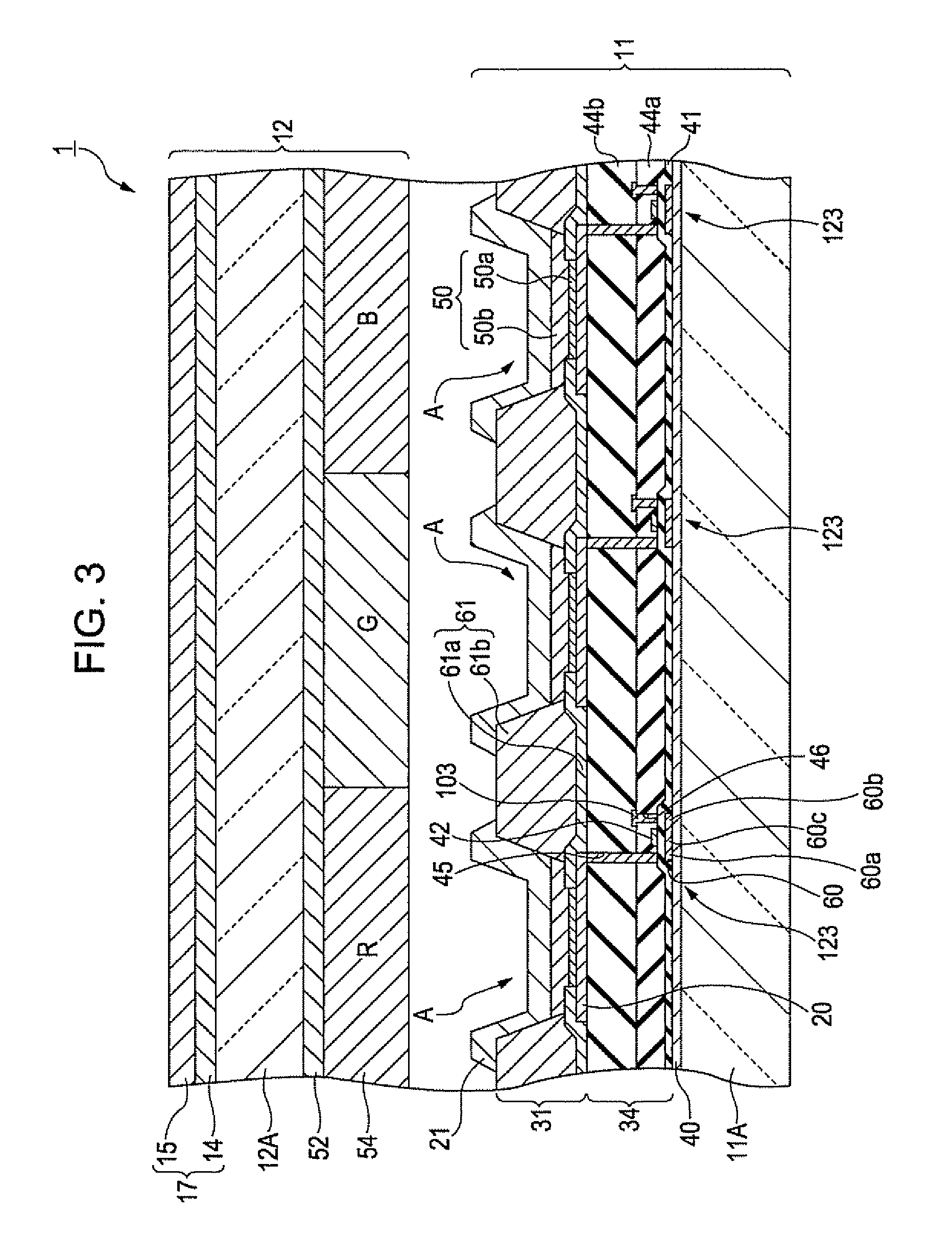
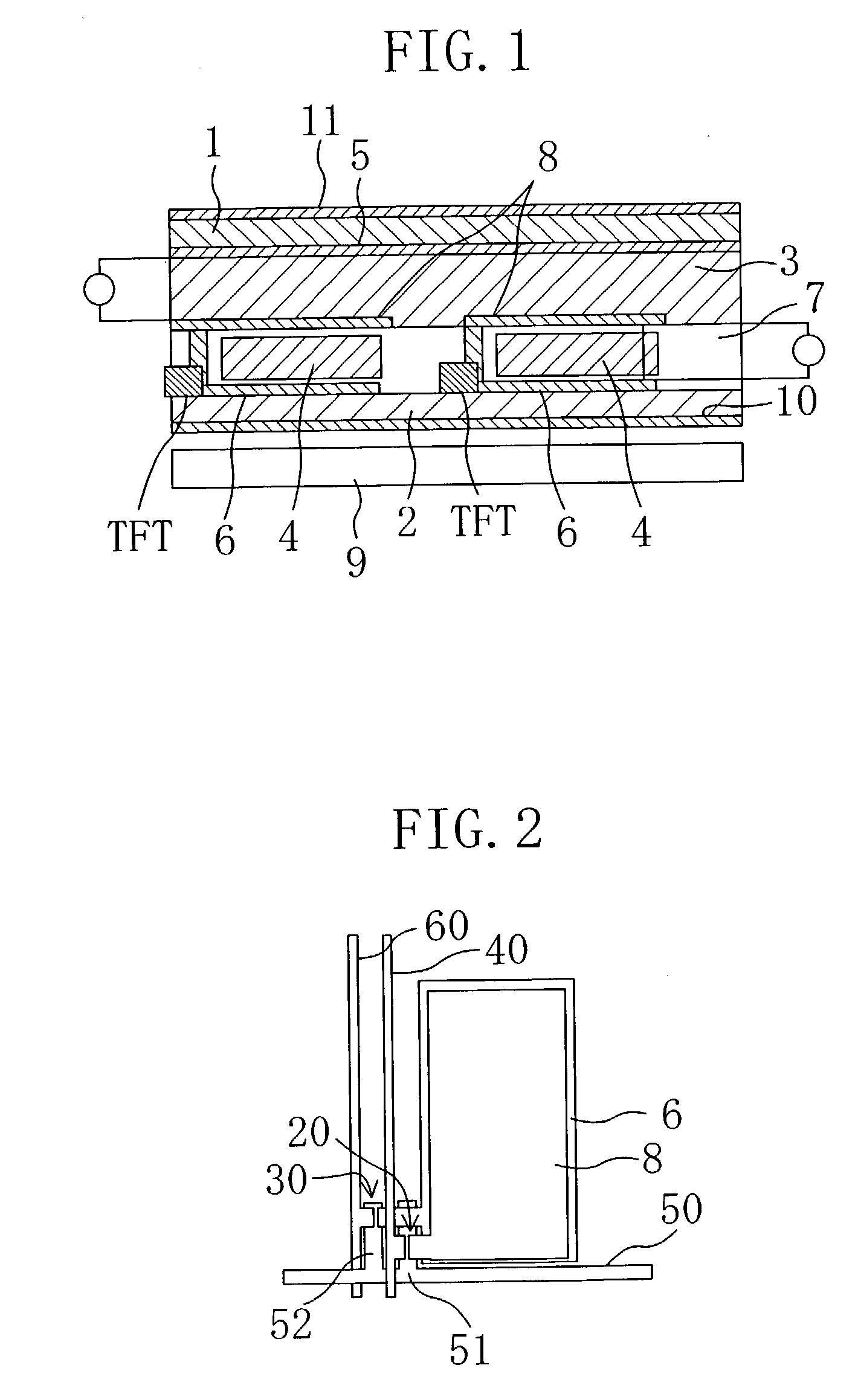
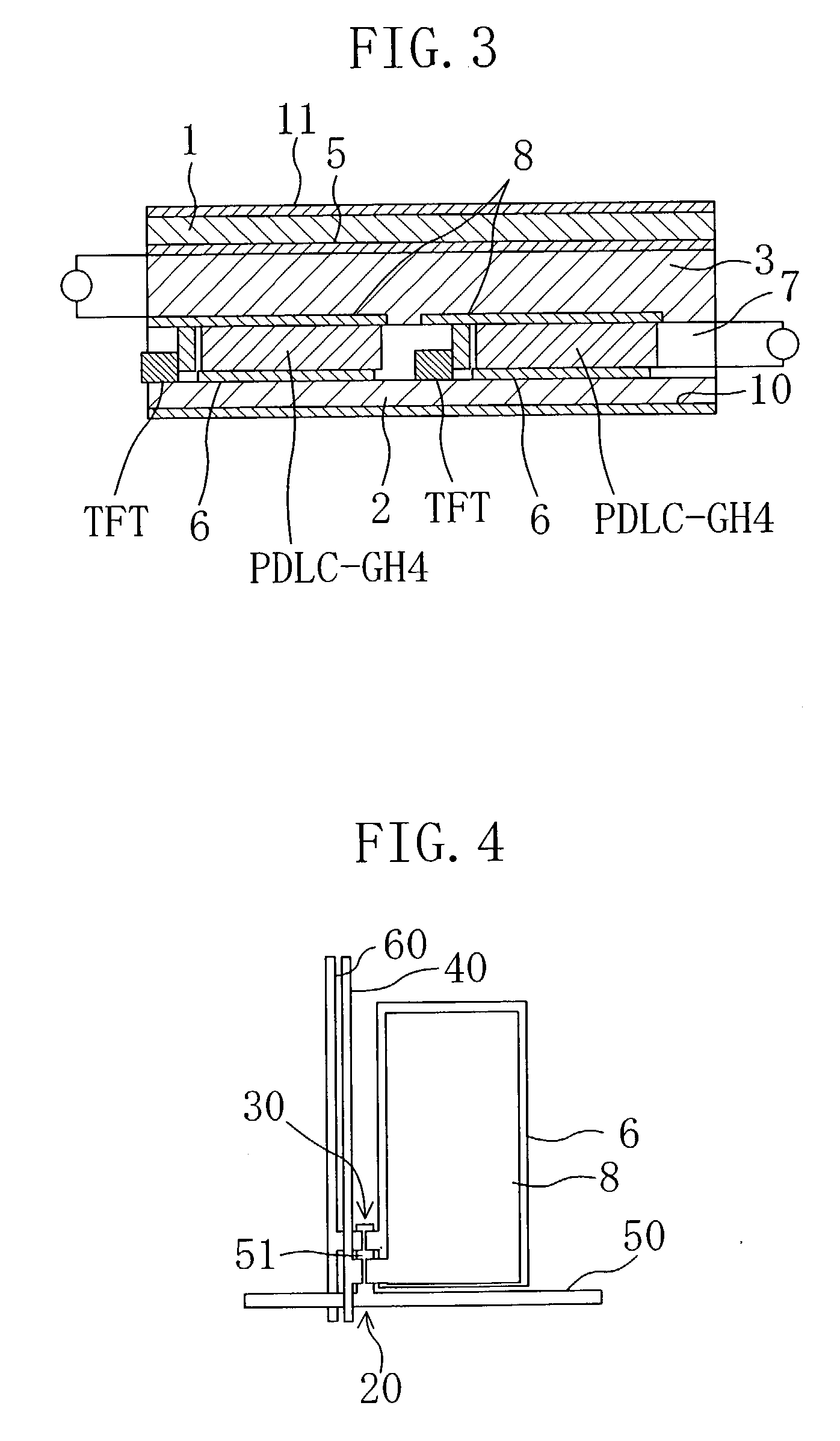
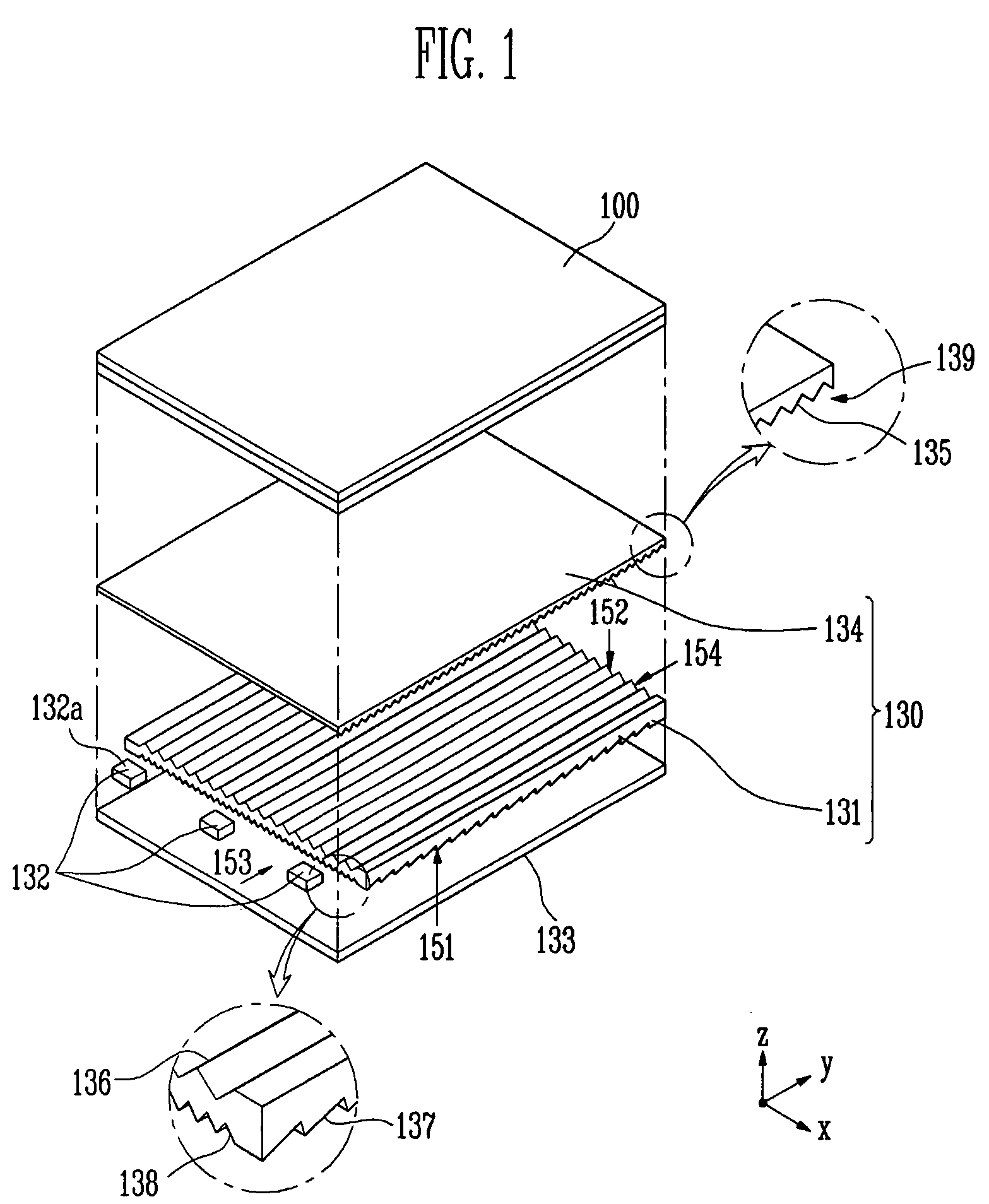
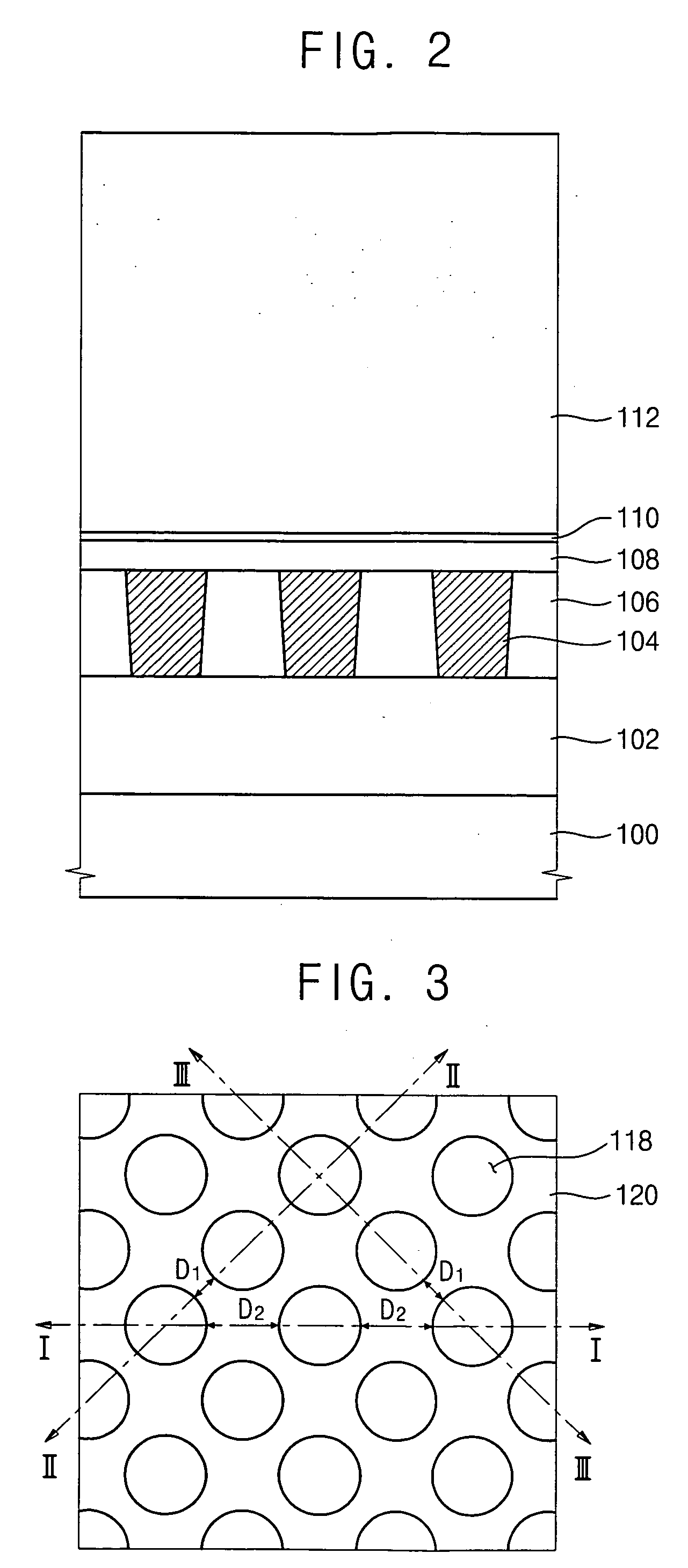
Display device, method for driving the same, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20080111766A1Influence on image quality in a display deviceCorrection of mobilityElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
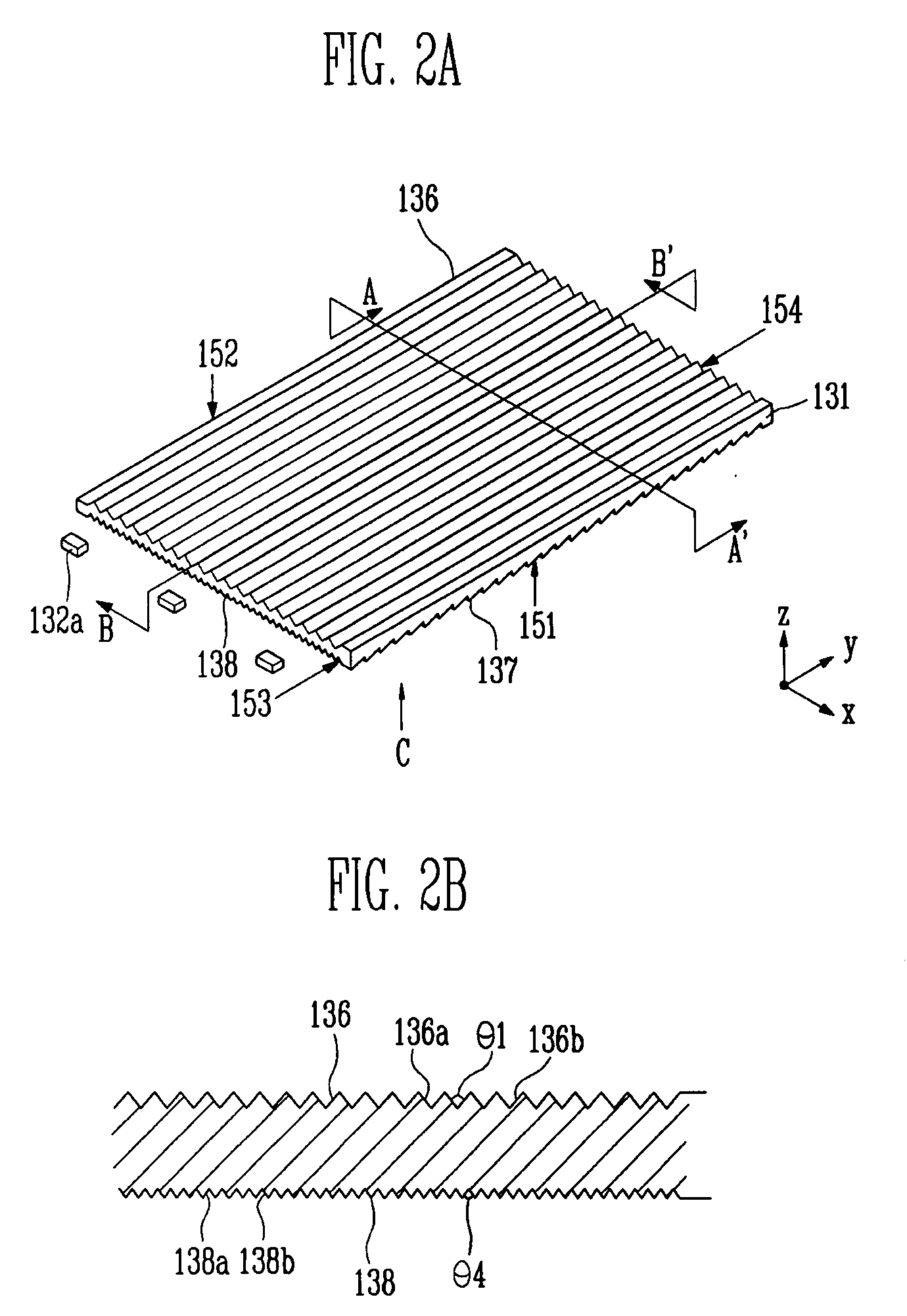
A display device includes a pixel array unit and a peripheral circuit unit. The pixel array unit includes first scanning lines arranged in rows; second scanning lines arranged in rows; signal lines arranged in columns; and pixels arranged in a matrix pattern at intersections of the scanning lines and the signal lines. The peripheral circuit unit includes a first scanner to supply first control pulses to the first scanning lines; a second scanner to supply second control pulses to the second scanning lines; and a signal driver to supply video signals to the signal lines. Each of the pixels includes at least a sampling transistor; a driving transistor; an emission time controlling transistor; a holding capacitance; and a light-emitting element.
Owner:SONY CORP
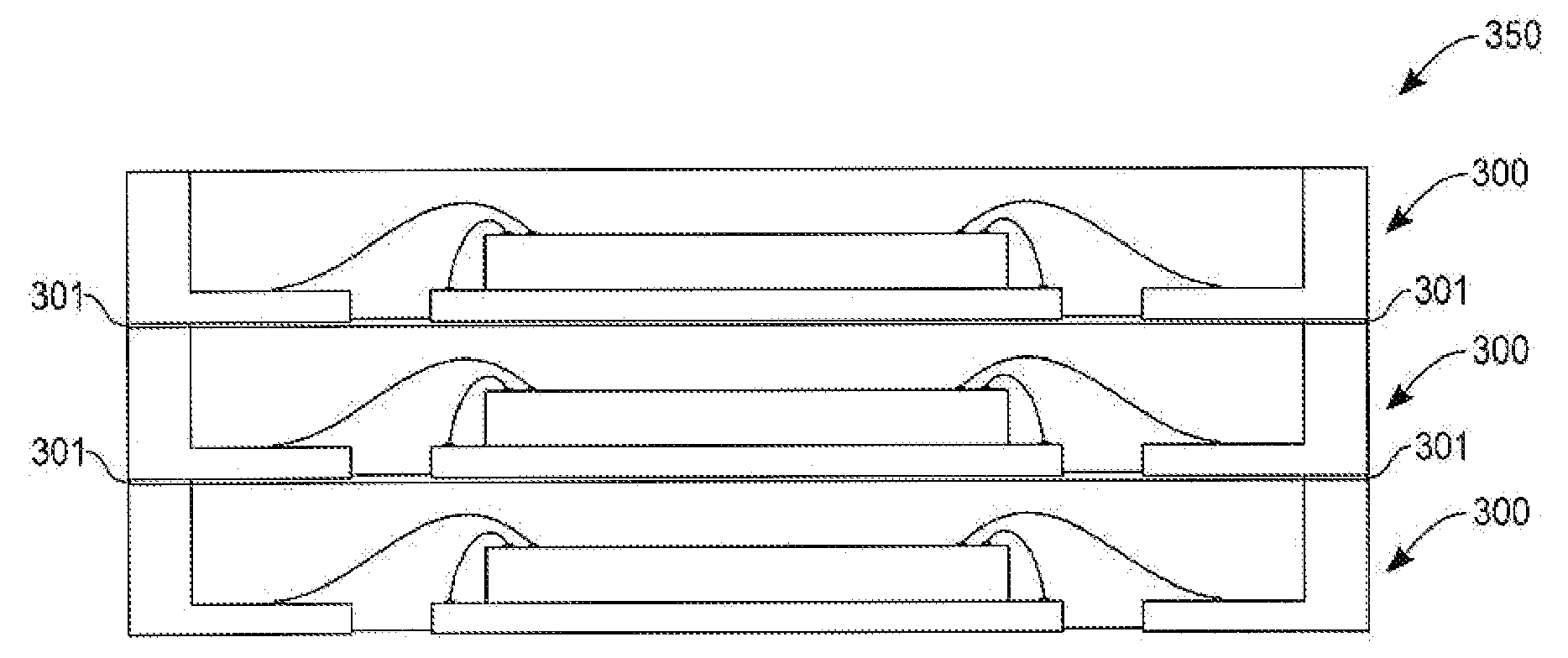
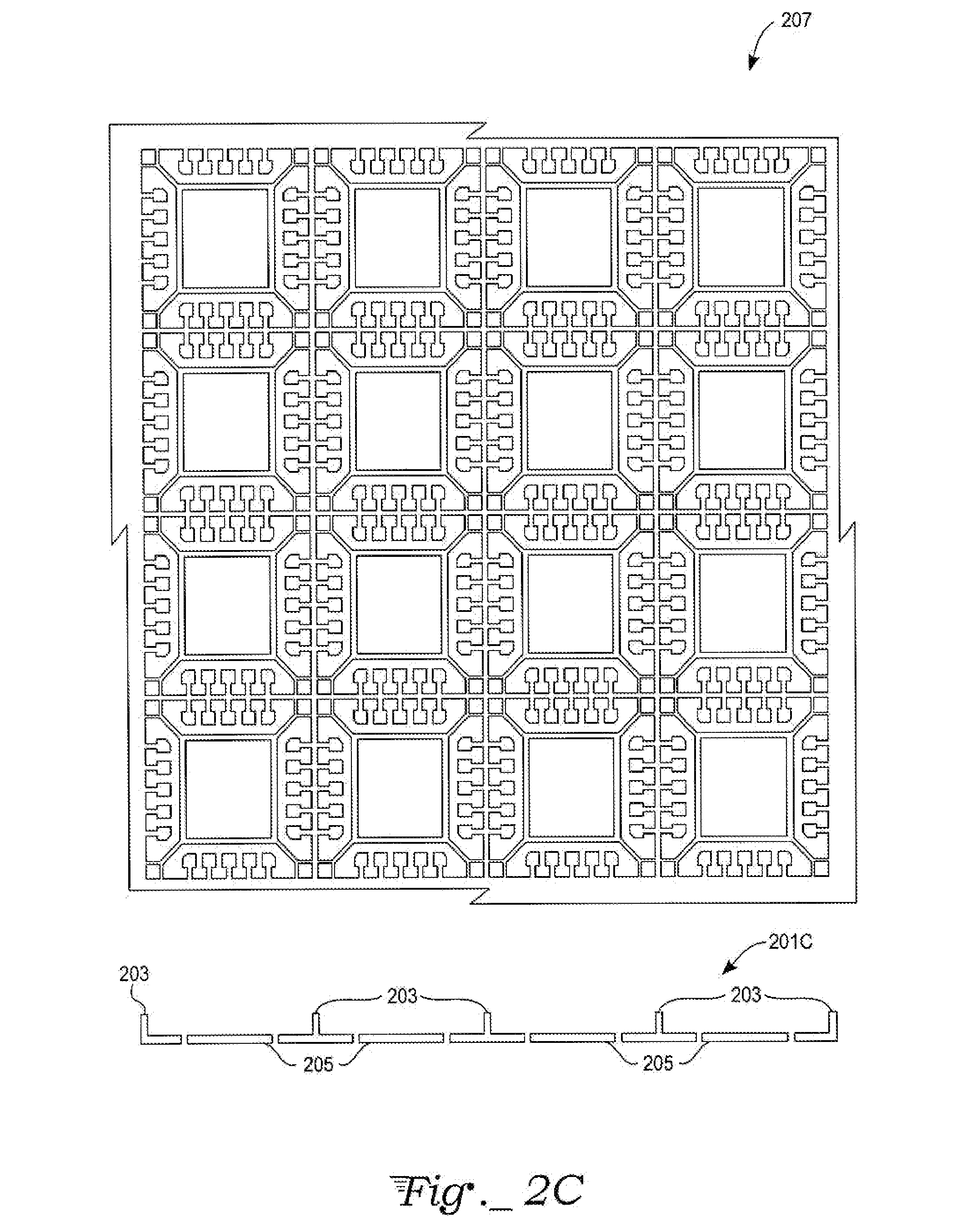
Stackable packages for three-dimensional packaging of semiconductor dice
ActiveUS20080048308A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor package
An apparatus and a method for packaging semiconductor devices. The apparatus includes a substrate strip component of a leadless three-dimensional stackable semiconductor package having mounting contacts on, for example, four peripheral edges. The substrate strip may either be fabricated for mounting a single electrical component (e.g., an integrated circuit die) or a plurality of substrate strips may be laid out in an X-Y matrix pattern which may later be singulated into individual package strip for leadless packages. Three-dimensional stacking is achieved by a bonding area on an uppermost portion of the sidewall. The sidewall of the strip is high enough to enclose an encapsulant covering a later mounted integrated circuit die and associated bonding wires.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Matrix substrate, liquid-crystal device incorporating the matrix substrate, and display device incorporating the liquid-crystal device
InactiveUS6127998AReduce chip sizeReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
A matrix substrate comprises a plurality of pixel electrodes arrayed in a matrix pattern, a plurality of switching elements connected to the pixel electrodes, a plurality of signal lines for supplying video signals to the plurality of switching elements, a plurality of scanning lines for supplying scanning signals to the plurality of switching elements, a horizontal driving circuit for supplying the video signals to the plurality of signal lines, and a vertical driving circuit for supplying the scanning signals to the plurality of scanning lines, wherein the horizontal driving circuit is comprised of a dynamic type circuit and the vertical driving circuit is comprised of a static type circuit.
Owner:CANON KK
Electrical connector for use in transmitting a signal
InactiveUS6971916B2Reduce generationPrevent degradationElectrically conductive connectionsTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical connectorGround plate
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Semiconductor device and method for making the same
InactiveUS6204564B1Reduce thicknessReduce weightSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor device comprising a film substrate and a semiconductor chip bonded to an upper surface of the film substrate is provided. The semiconductor chip has a main surface formed with a plurality of terminal pads. The film substrate has a lower surface formed with a plurality of external terminal portions in a matrix pattern, and an upper surface formed with a plurality of wiring patterns for respectively connecting with the external terminal portions. The wiring patterns formed in the upper surface of the film substrate are respectively connected to the terminal pads formed on the main surface of the semiconductor chip.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
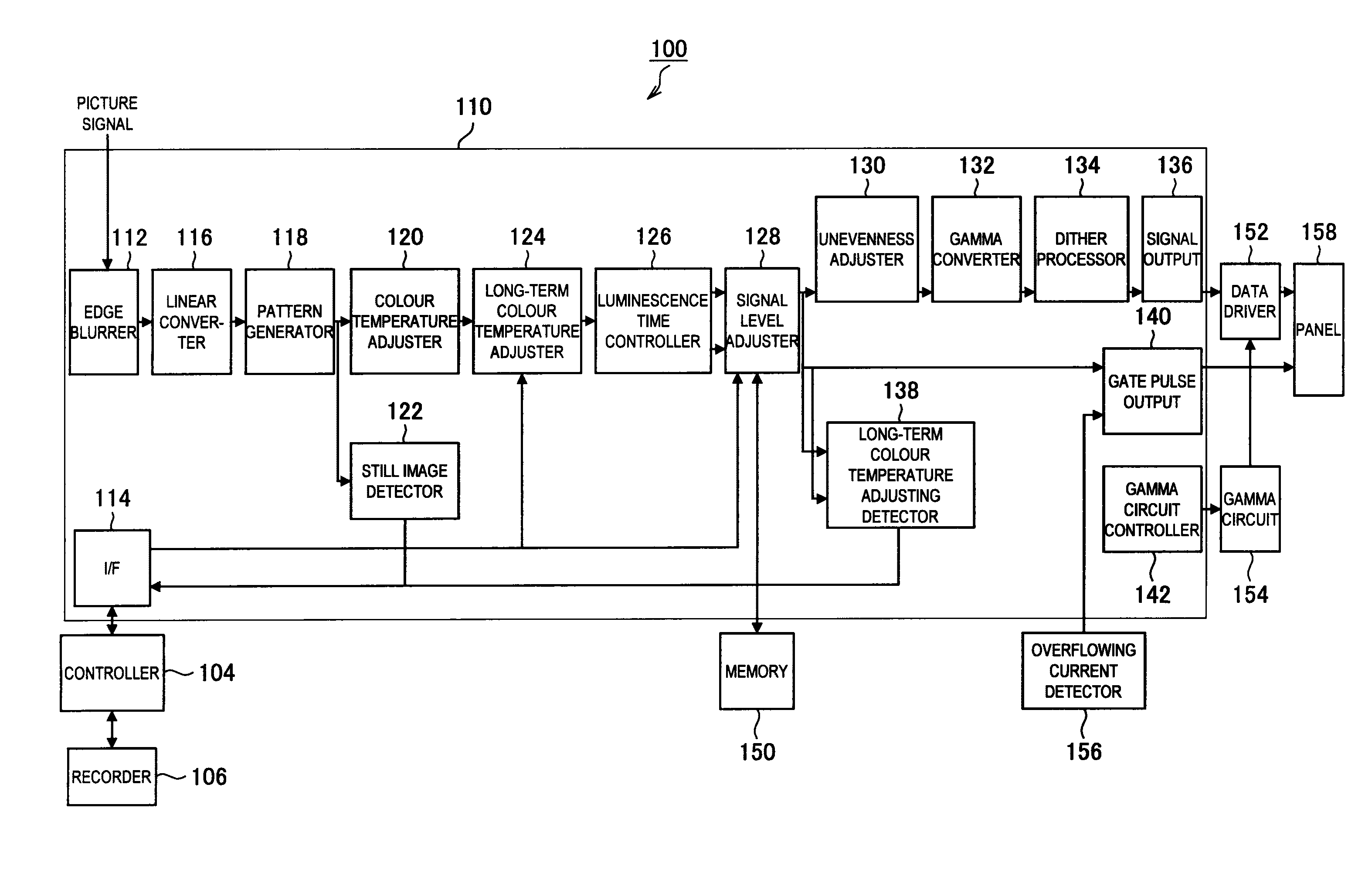
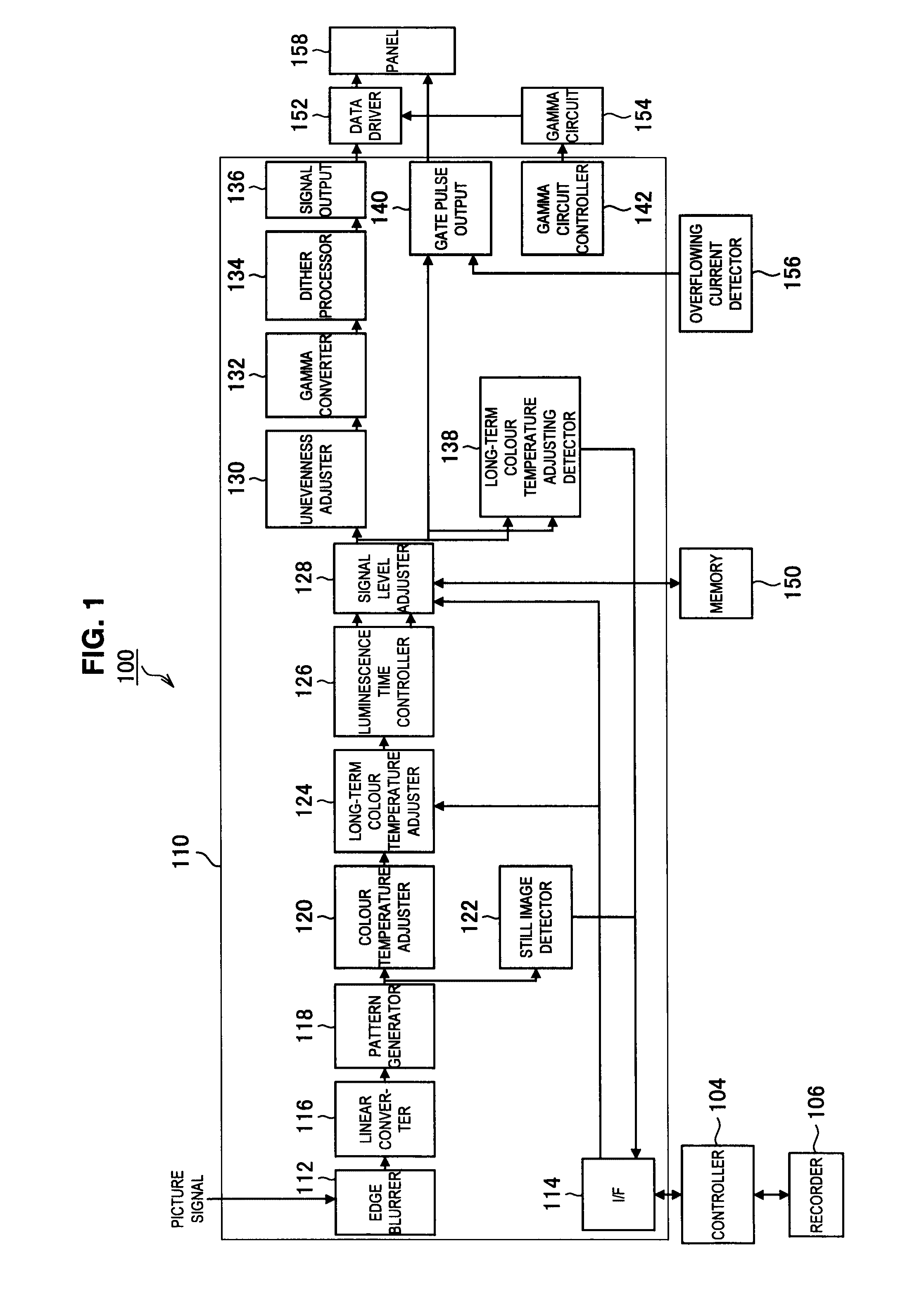
Display device, picture signal processing method, and program
ActiveUS20100328359A1Inhibit currentImprove display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer science
Provided is a display device including a display unit having luminescence elements that individually becomes luminous depending on a current amount. The luminescence elements are arranged in a matrix pattern. The display device comprises a luminescence amount regulator for setting a reference duty for regulating a luminescence amount per unit time for each of the luminescence elements, according to picture information of an input picture signal, and also comprises an adjuster for adjusting, based on the reference duty, an effective duty regulating a luminous time for which the luminescence elements become luminous within a unit time, so that the effective duty is within a predetermined range, and for adjusting a gain of the picture signal, so that a luminescence amount regulated with the effective duty and with the gain of the picture signal equals to the luminescence amount regulated with the reference duty.
Owner:JOLED INC
Transmission/reflection type color liquid crystal display device
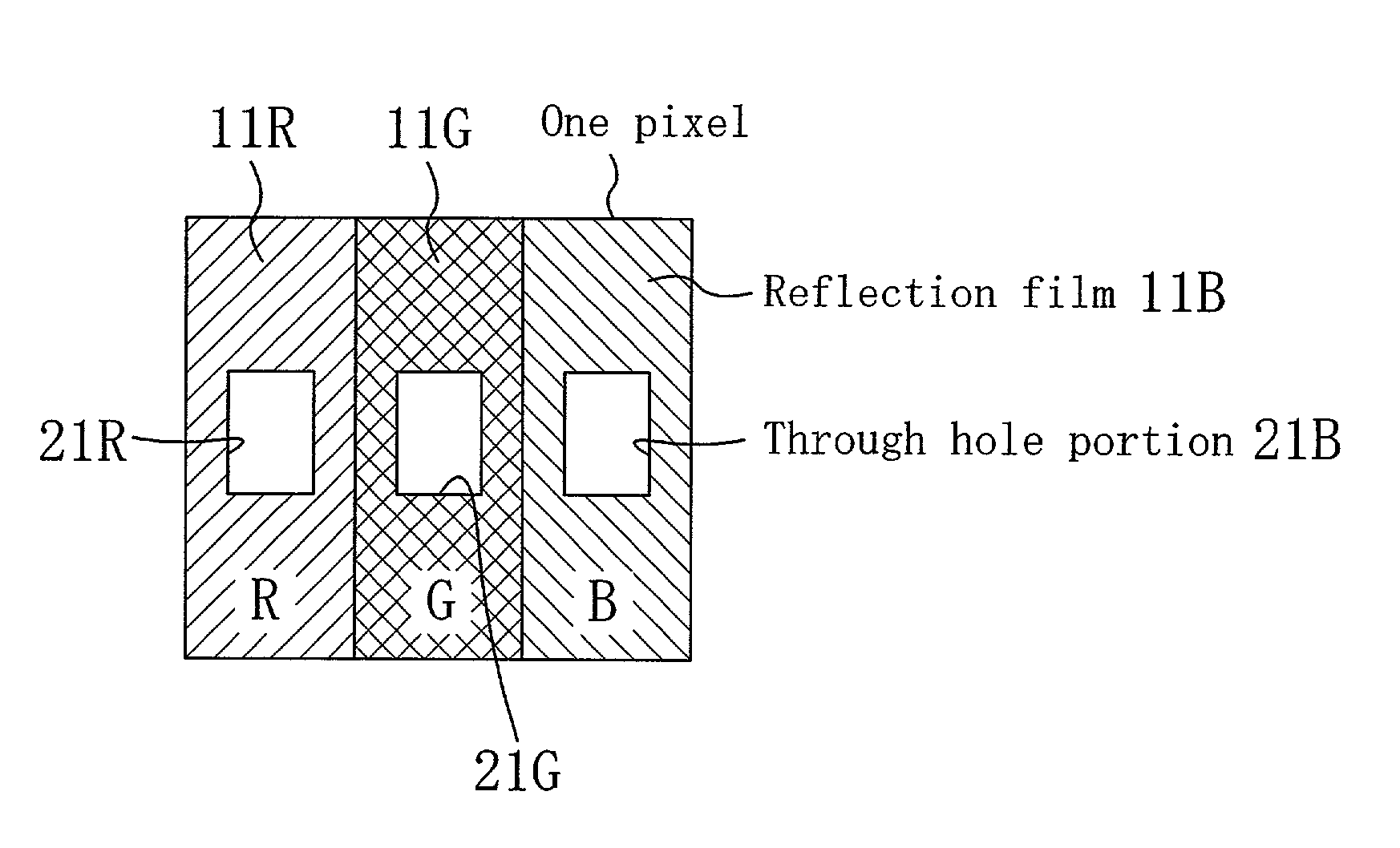
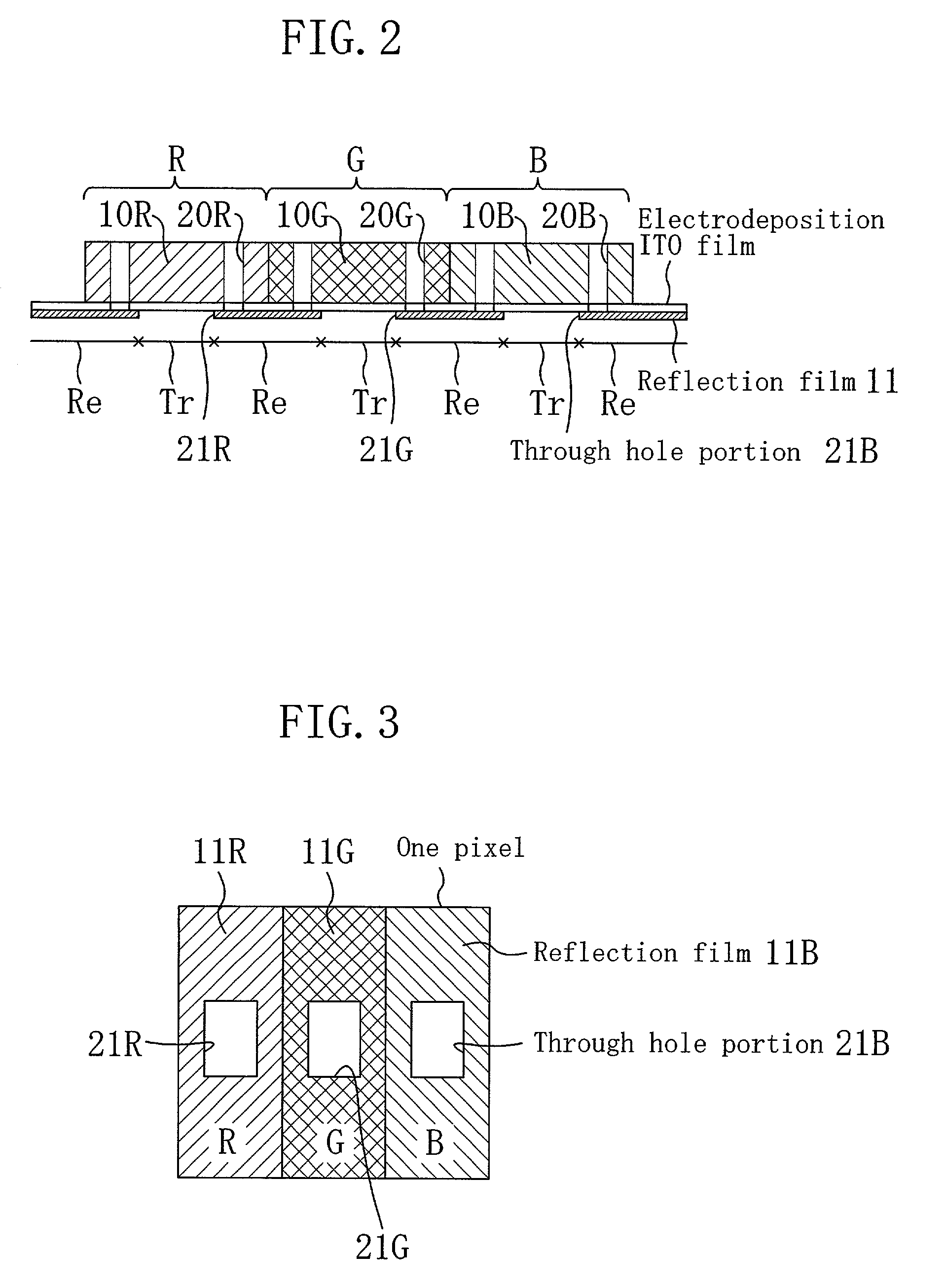
InactiveUS6885418B2High color purityDisplay brightNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayMatrix pattern
A liquid crystal display device, including: a first substrate; a second substrate; opposing the first substrate; a liquid crystal layer interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate; a reflection film formed on one side of the second substrate that is closer to the liquid crystal layer; and a color filter formed on the reflection film, wherein: a plurality of pixel regions are arranged in a matrix pattern, each of the pixel regions including a reflection region where light coming from the first substrate side is reflected by the reflection film back to the first substrate side, and a transmission region where light coming from the second substrate side is transmitted to the first substrate side; and the color filter includes an opening in the reflection region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic Electroluminescence Device Having Input Function and Electronic Apparatus
ActiveUS20080211394A1Avoid contactImprove detection accuracyDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical conductorOptoelectronics
The invention provides an organic electroluminescence device having an input function, including: an element substrate that has a light-emitting layer sandwiched between a positive electrode and negative electrode in each of a plurality of sub pixel regions that are arrayed in a matrix pattern; a sealing substrate that seals the element substrate; and a touch panel section that is provided at the outer-surface side of the sealing substrate. In such a configuration of the organic electroluminescence device having an input function according to an aspect of the invention, the negative electrode is formed on an individual basis so as to correspond to the display color of each of the sub pixel regions; and the sealing substrate has a shield conductor that is formed on the element-substrate side of the sealing substrate, the shield conductor having a fixed potential.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Light modulating device
InactiveUS20030184692A1Full-color displayHigh-resolution displayOptical filtersNon-linear opticsControl layerOptoelectronics
A light modulating device includes: a first substrate on which a first electrode layer and a light amount control layer are deposited in this order; a second substrate on which a second electrode layer and a color filter layer are deposited in this order, the second substrate opposing the first substrate; and a third electrode layer interposed between the light amount control layer and the color filter layer, wherein a plurality of picture elements are defined in a matrix pattern by the first electrode layer and the third electrode layer. An amount of light transmitted through the light amount control layer is electrically controlled by the first electrode layer and the third electrode layer. A colored / uncolored state of the color filter layer is electrically controlled by the second electrode layer and the third electrode layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
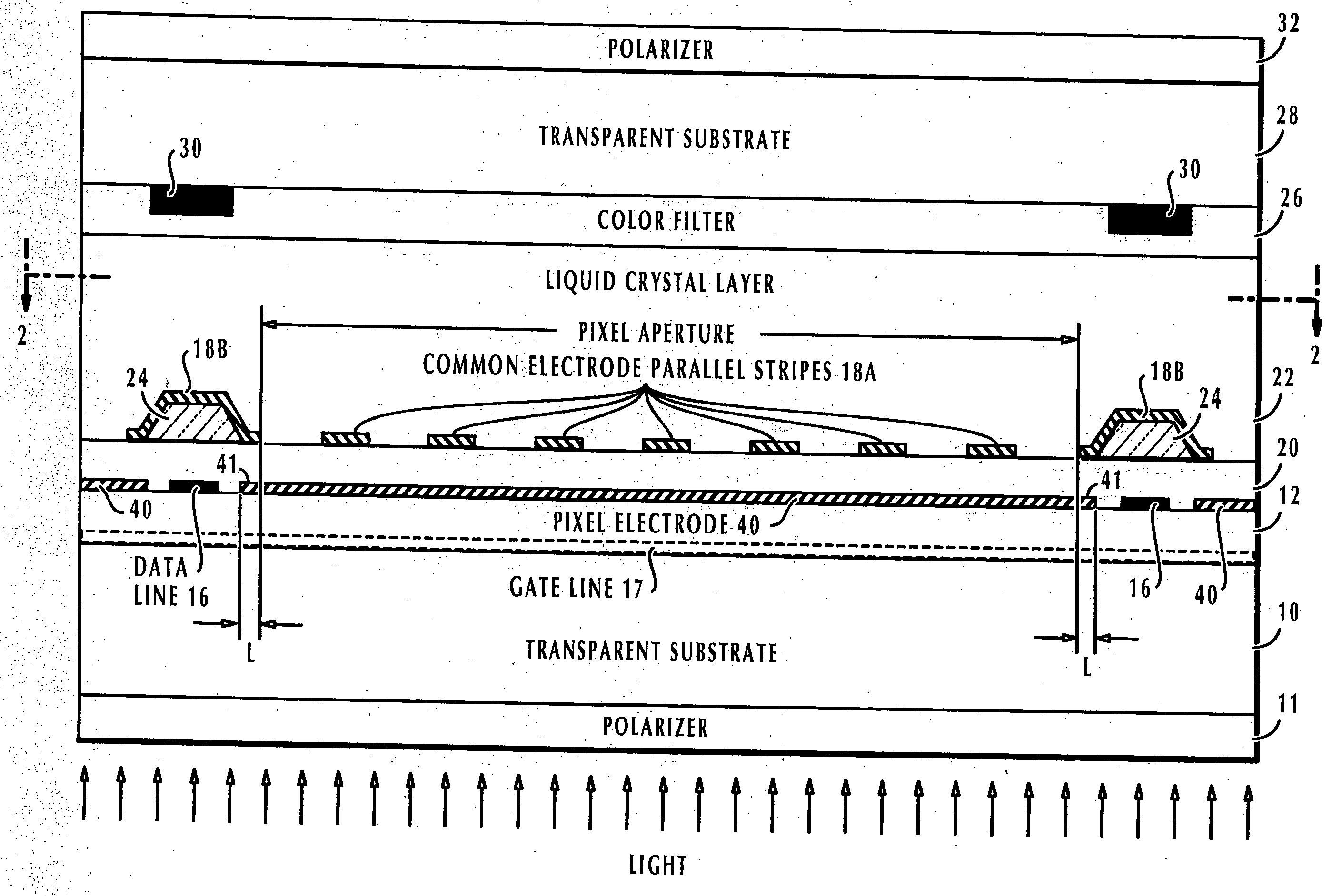
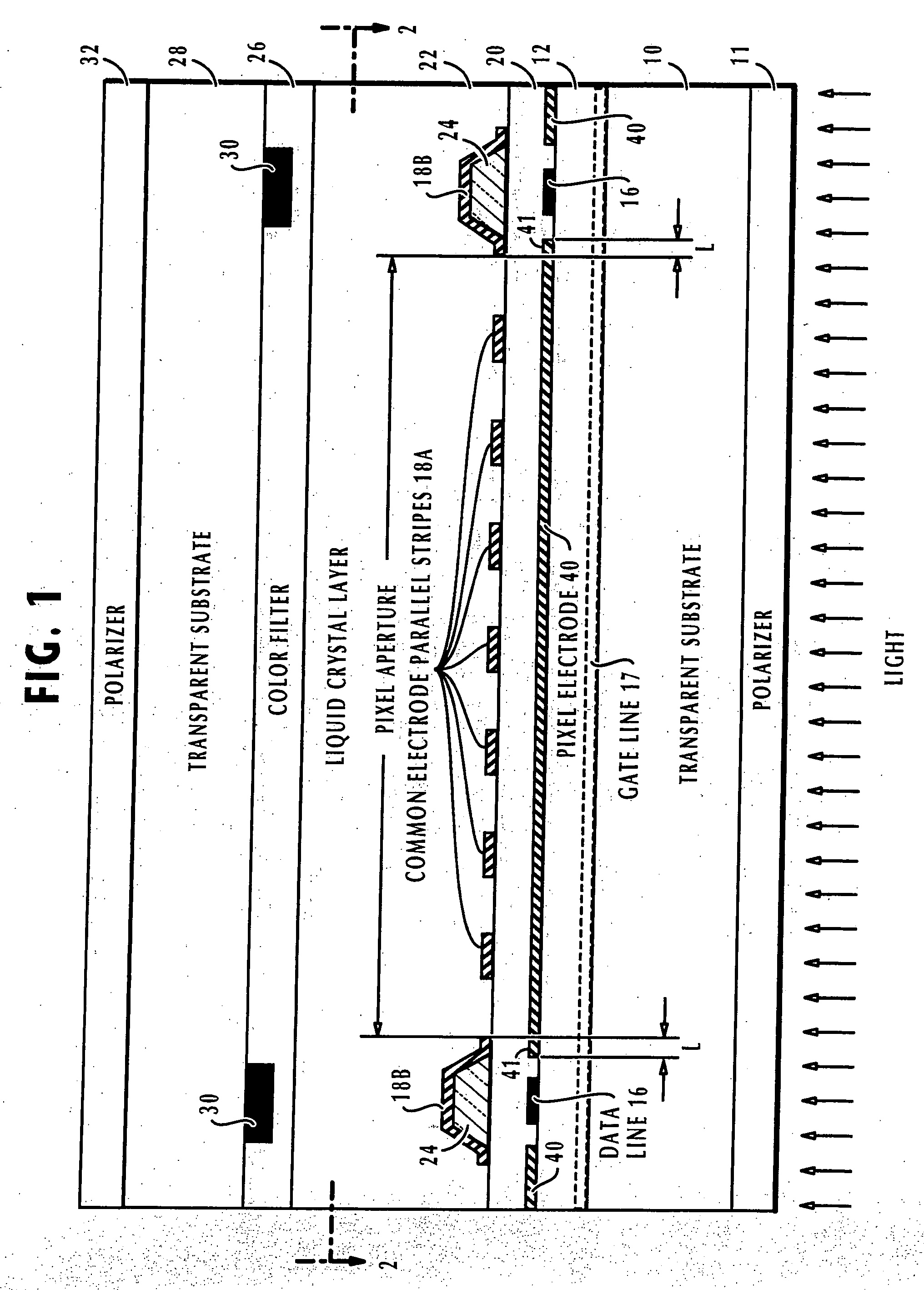
High aperture ratio in-plane switching mode active matrix liquid crystal display unit
ActiveUS20070273819A1Increase opening ratioNon-linear opticsActive-matrix liquid-crystal displayAperture ratio
In a liquid crystal display unit where a matrix pattern of pixels are defined by gate lines and crosswise data lines, transparent pixel electrodes are formed on the same layer as the data lines and corresponding transparent common electrodes are formed above the transparent pixel electrodes. On the common electrodes the liquid crystal layer is provided. In the aperture of each pixel, the common electrode has a pattern of parallel stripe portions and a peripheral portion outside of the aperture for shielding the field of the corresponding data line. Each pixel electrode cooperates with that parallel stripe portions of the corresponding common electrode to produce inner fringe fields along such parallel stripe portions and has portions that overlap the peripheral portions of the common electrode to produce peripheral fringe fields so that liquid-crystal cells can be uniformly in-plane switched by the inner fringe fields as well as by the peripheral fringe fields.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Material(s)/content(s) management method and apparatus
Volumetric enclosure(s) provides methods and / or apparatus for teaching, generating and deriving supply chain efficiency improvement. Prime Manifold Enclosure(s) methods and / or apparatus provide for deriving and generating efficiency by volumetric displacement and volumetric replacement of dissimilar material(s) and volumetric displacement and volumetric replacement of material having dissimilar origin. Prime Manifold Enclosure(s) interposed for cooperative coaptaion and flow path communication / continuity between gradient matrix flow paths for volumetrically displacing and volumetrically replacing dissimilar materials, and volumetrically displacing and volumetrically replacing of materials of dissimilar origin. In process flow continuity embodying volumetric displacement and replacement of distinct materials of distinct origin interposing manifolds comprising materials having rigid, and / or, semi-rigid, and / or, semi-flexible, and / or flexible characteristics are disclosed for ingressing and egressing fluent materials along gradient flow matrix patterns.
Owner:MEDINDICA PAK
Transmission/reflection type color liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20020126238A1Desirable color reproducibilityIncrease the area ratioNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayMatrix pattern
A liquid crystal display device, including: a first substrate; a second substrate; opposing the first substrate; a liquid crystal layer interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate; a reflection film formed on one side of the second substrate that is closer to the liquid crystal layer; and a color filter formed on the reflection film, wherein: a plurality of pixel regions are arranged in a matrix pattern, each of the pixel regions including a reflection region where light coming from the first substrate side is reflected by the reflection film back to the first substrate side, and a transmission region where light coming from the second substrate side is transmitted to the first substrate side; and the color filter includes an opening in the reflection region.
Owner:SHARP KK
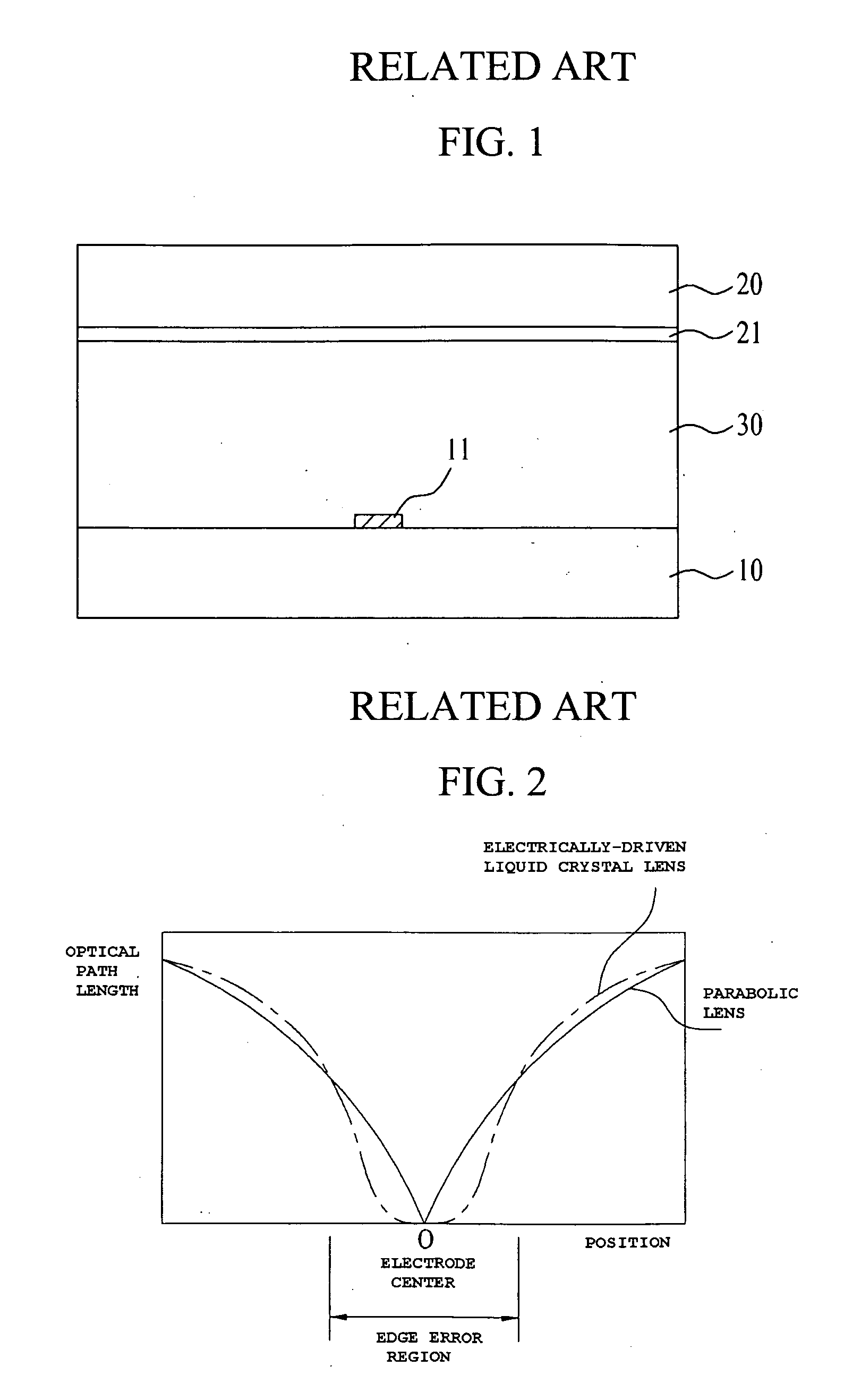
Electrically-driven liquid crystal lens and stereoscopic display device using the same
InactiveUS20090015738A1Widen perspectiveReduce crosstalkNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDisplay deviceImage signal
An liquid crystal lens for improving a viewing angle and reducing crosstalk caused at the center of an electrode in a multi-view stereoscopic display fashion using an increased number of views per a viewing zone, and a stereoscopic display device using the same are disclosed. The display device includes a display panel having a plurality of sub-pixels in a matrix pattern to emit a 2-dimensional image signal, and an electrically-driven liquid crystal lens located at an upper surface of the display panel and including lens regions having a crosswise width equal to “m”, a multiple of a crosswise width of a single sub-pixel and a lengthwise width equal to “n”, a multiple of a lengthwise width of the sub-pixel, the lens regions of one line being shifted more than the lens regions of a following line by a distance “a” when viewed from a column direction.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Polarization control optical space switch
The present invention is directed to an optical space switch accommodating a plurality of input light paths and output light paths. The optical space switch comprises a plurality of polarization control optical switches, each consisting essentially of: polarization control means having elements, one for each input light path, for rotating through 90 DEG the polarizing direction of light information incident from each input light path or otherwise retaining the polarizing direction thereof for output; and a light path routing element for routing the light path for the light information output from the polarization control means in accordance with the polarizing direction of the light information. These polarization control optical switches are arranged in a matrix pattern or coupled in cascade to implement a polarization control optical space switch.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
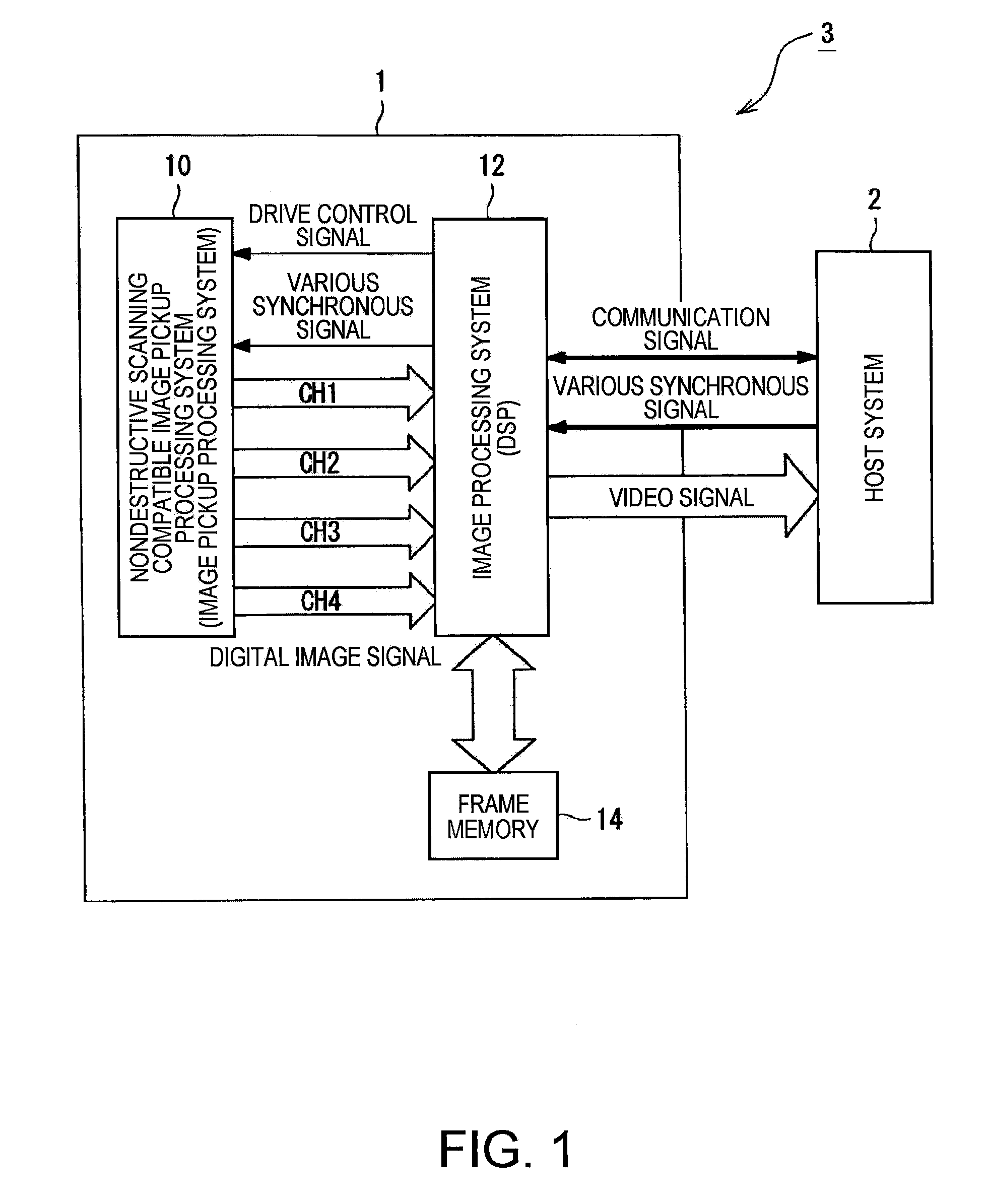
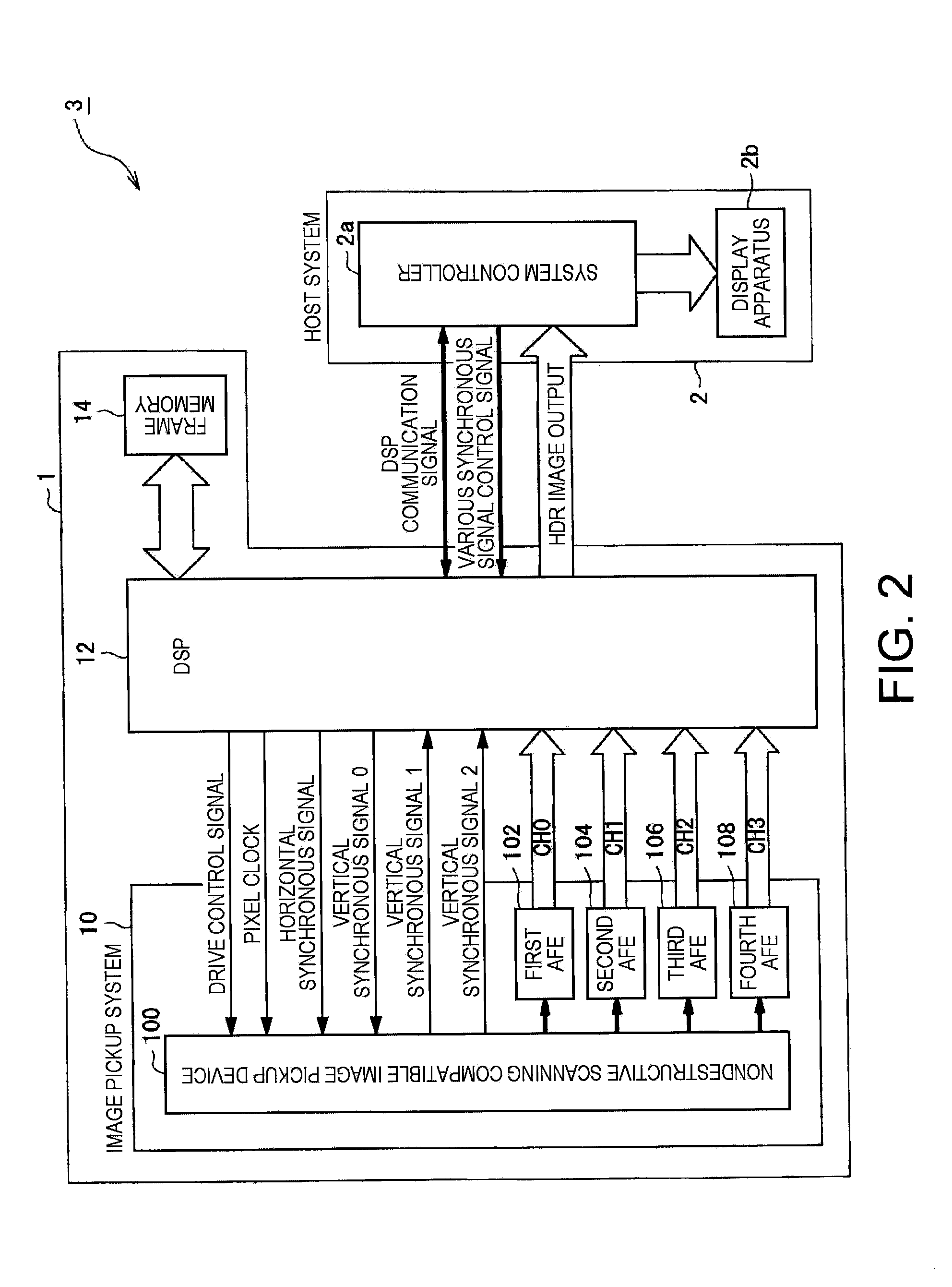
Image pickup device and image pickup apparatus
InactiveCN101072303ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectronic shutterImaging processing
An image pickup device having a photoelectric conversion unit having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged in a matrix pattern for converting exposed light into electric charges and accumulating the same and an electronic shutter function for controlling the exposure time for each frame including: a first reader for reading out electric charges exposed during a standard exposure time from respective pixels including the photoelectric conversion elements in the exposed area of the photoelectric conversion unit in a destructive read-out method; a second reader for reading out electric charges exposed during a short exposure time, which is an exposure time shorter than the standard exposure time, from the respective pixels including the photoelectric conversion elements during the same exposure period as the first reader in a nondestructive read-out method; and a saturation predictor for predicting whether or not the amounts of accumulated electric charges in the respective pixels being exposed during the standard exposure time are saturated on the basis of a non-standard exposure pixel data including the electric charges being exposed during the short exposure time, which are read out by the second reader.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Frontlight unit for enhancing illumination of a reflective display
InactiveUS8596846B2Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityCosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsPhase shiftedRidge waveguides
The frontlight illumination system is intended for enhancing illumination of a reflective display having pixels arranged in a matrix pattern and using monochromatic laser lights as light sources. The unit contains a network of light-distributing planar ridge waveguides with holograms arranged in a matrix pattern that corresponds to the matrix pattern of the reflective display. The light-distributing holograms of the system are formed on opposite sides of each core of respective light-distributing planar ridge waveguides. Neighboring holograms located on opposite sides of the core are combined into pairs and are arranged on each core in positions at which they interact with a predetermined phase shift that doubles the intensity of light directed to the reflective display and extinguishes light directed to the external surface.
Owner:VELIKOV LEONID MR +1
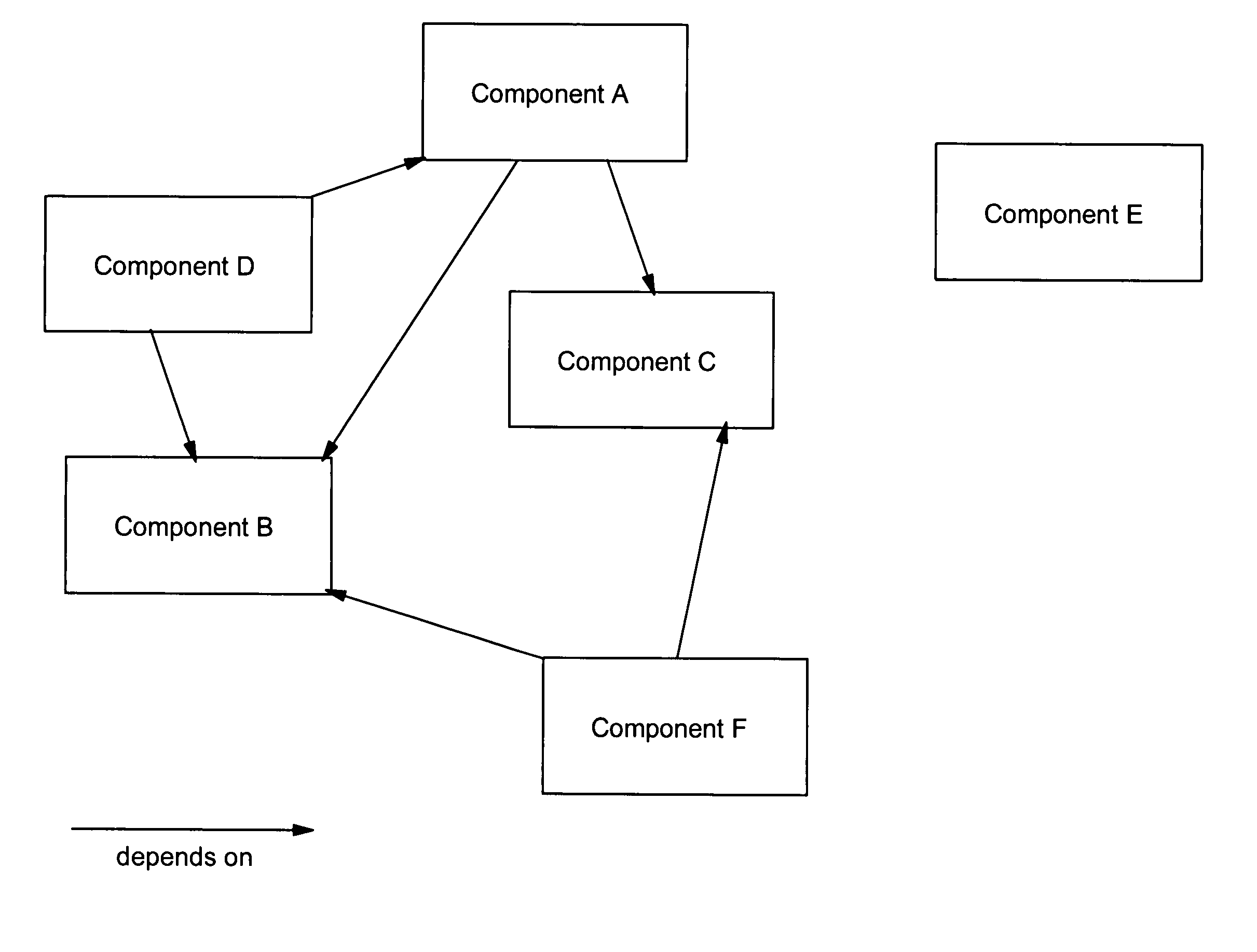
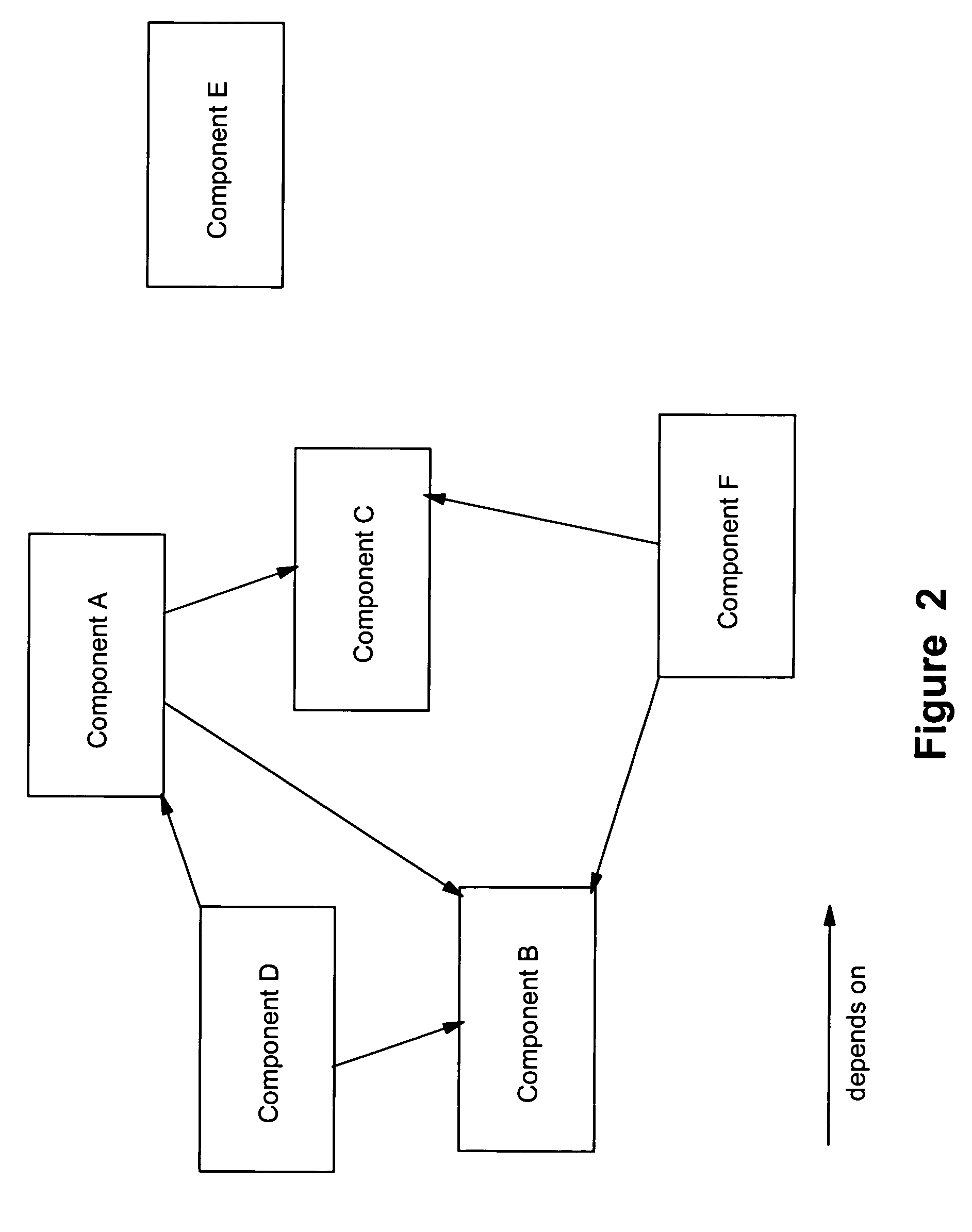
Matrix pattern match techniques for uninstalling multiple dependent components
InactiveUS20050289513A1Safely uninstalledRapid determinationProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsData processing systemParallel computing
There is disclosed a data processing system-implemented method, system and an article of manufacture for tracking software component dependencies among a set of multiple dependent software components of an application. In one aspect there is means for creating an n-dimensional matrix of predefined size in which is established a first dimension to represent the software components and a second dimension to represent the cross component dependencies. Next there is placed in each cell a value indicating an absence or a presence of a software component dependency within the set of multiple dependent software components of the application to create a software component dependency matrix. In a second aspect for uninstalling multiple dependent software components for a selected application from a computer system one then obtains the software component dependency matrix for the selected application. Next there is determined a candidate software component from the software component dependency matrix for removal. Next follows the process of uninstalling the candidate software component from the computer system and updating the software component dependency matrix to reflect removal of the candidate software component. The process of determining, uninstalling, and updating is repeated until all multiple dependent software components for the selected application have been uninstalled from the computer system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Light guide member and backlight unit including light guide member
ActiveUS20080008434A1Thinner and lightOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsLight guideEngineering
A light guide member for guiding light incident thereon from a light source, the light guide member including a plurality of the first grooves extending along a first direction on a first side of the light guide member, a plurality of second grooves extending along a second direction on the first side of the light guide member, the first direction may cross the second direction such that the first grooves and the second grooves may form a matrix pattern on the first side of the light guide member, wherein a polygonal shaped projection is formed between every two adjacent ones of the second grooves and a corresponding two adjacent ones of the first grooves.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Display device and color filter substrate
InactiveUS20120147314A1Increase the aperture ratioAperture ratio of a display deviceElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMatrix patternDisplay device
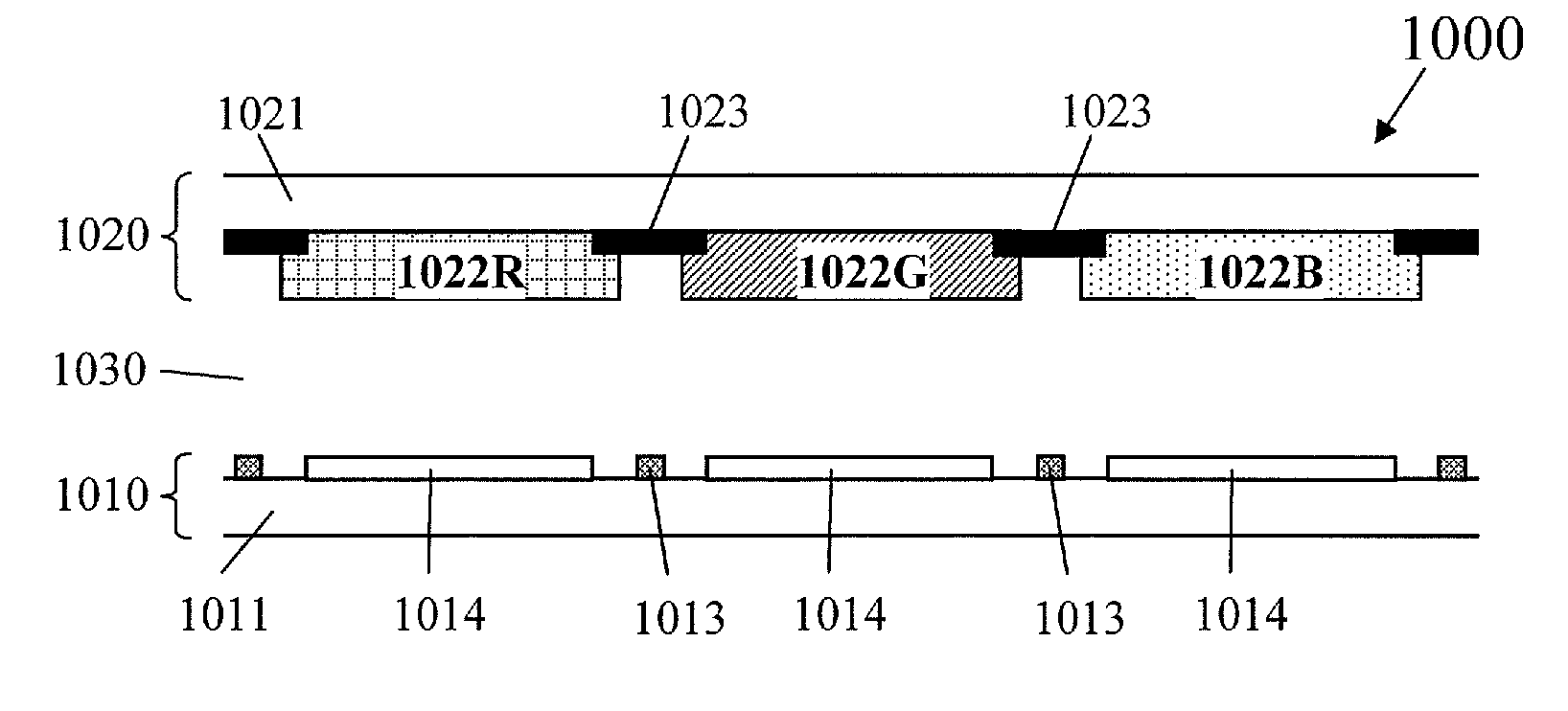
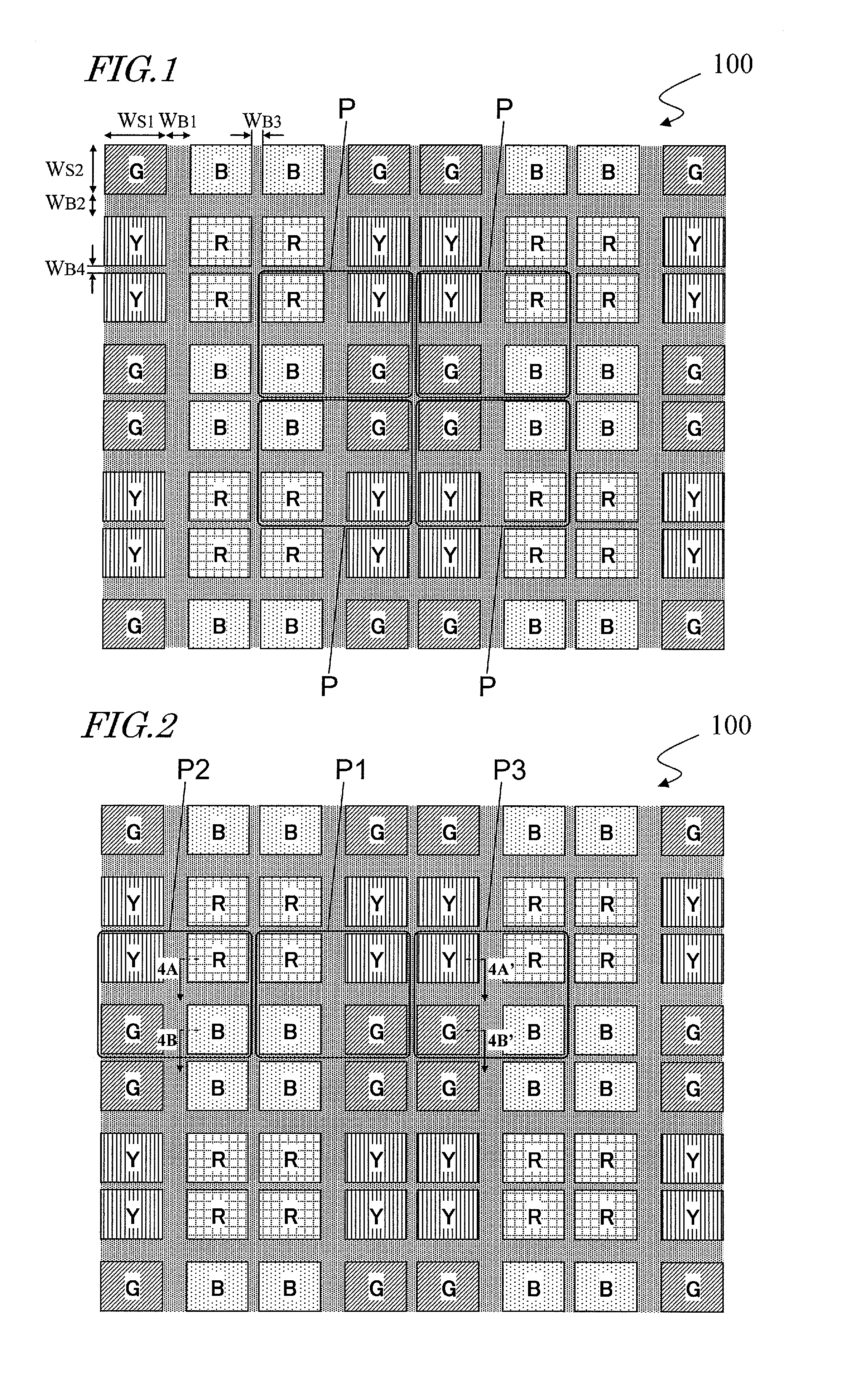
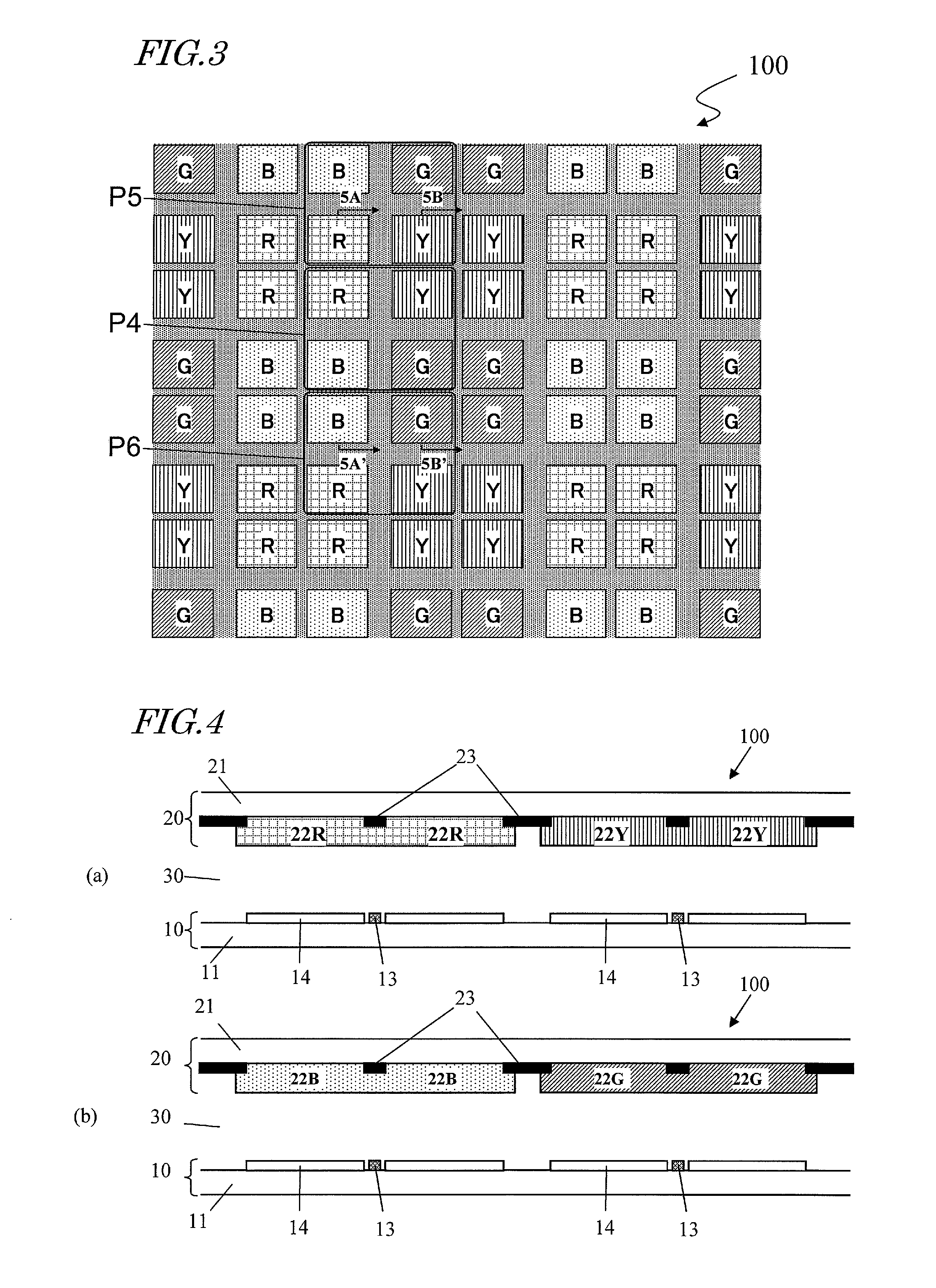
The display device (100) of this invention has pixels (P) arranged in columns and rows to form a matrix pattern. Each pixel (P) is defined by subpixels (R, G, B, Y) arranged in m columns and n rows (where n and m are integers and n and m≧2) to form a matrix pattern and that include first, second, third and fourth subpixels (R, B, Y, G) representing first, second, third and fourth colors, respectively. In three arbitrary pixels (P) arranged in line in one of row and column directions, if the central one of the three is called a first pixel (P1) and the other two second and third pixels (P2, P3), the arrangement of the subpixels (R, G, B, Y) in the first pixel (P1) is different from that of the subpixels (R, G, B, Y) in the second and third pixels (P2, P3). The first subpixels (R) of the first and second pixels (P1, P2) are adjacent to each other, so are their second subpixels (B). The third subpixels (Y) of the first and third pixels (P1, P3) are adjacent to each other, so are their fourth subpixels (G). According to the present invention, a display device, of which each pixel is defined by four or more subpixels, can have its aperture ratio increased.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display and method for manufacturing display
ActiveUS20100171120A1High light sensitivityHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay devicePhotoelectric conversion
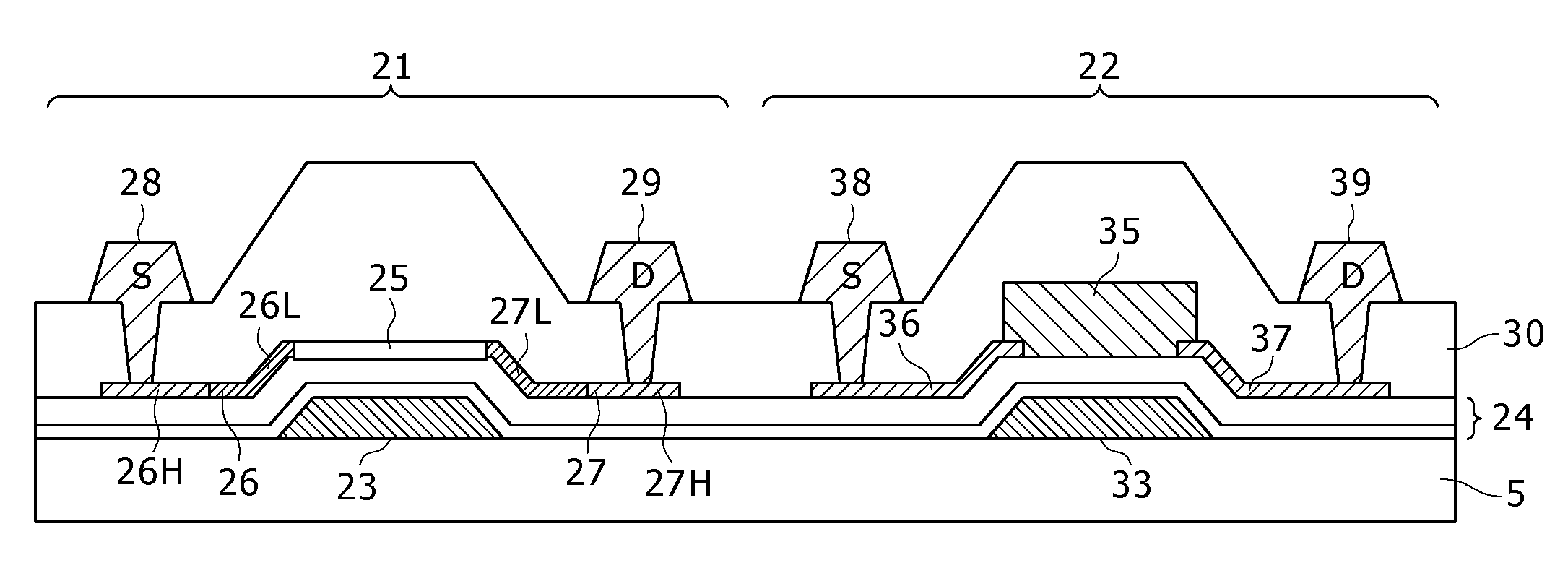
In the case of forming switching elements and light sensor elements over the same substrate, an increase in the film thickness of active layers in an attempt to enhance the sensitivity of the light sensor elements would adversely affect the characteristics of the switching elements (TFTs). In a configuration of a display in which a channel layer 25 for constituting thin film transistors to form the switching elements for pixels and a photoelectric conversion layer 35 for constituting the light sensor elements are provided over a gate insulating film 24 on a glass substrate 5 to be provided with a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix pattern, the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed to be thicker than the channel layer 25, and / or the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed of a material different from the material for the channel layer 25, whereby the light absorption coefficient of the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is made to be higher than that of the channel layer 25.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
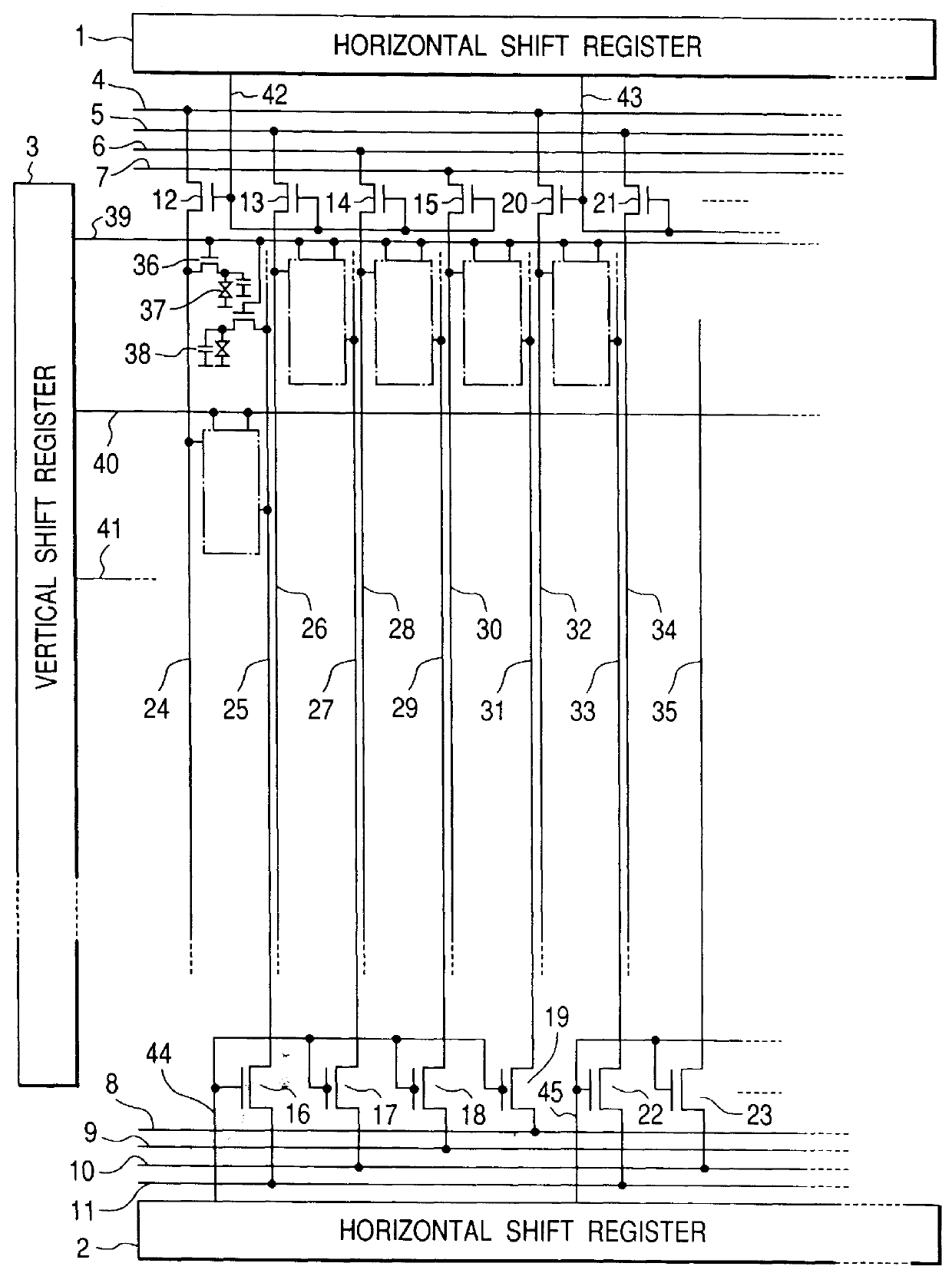
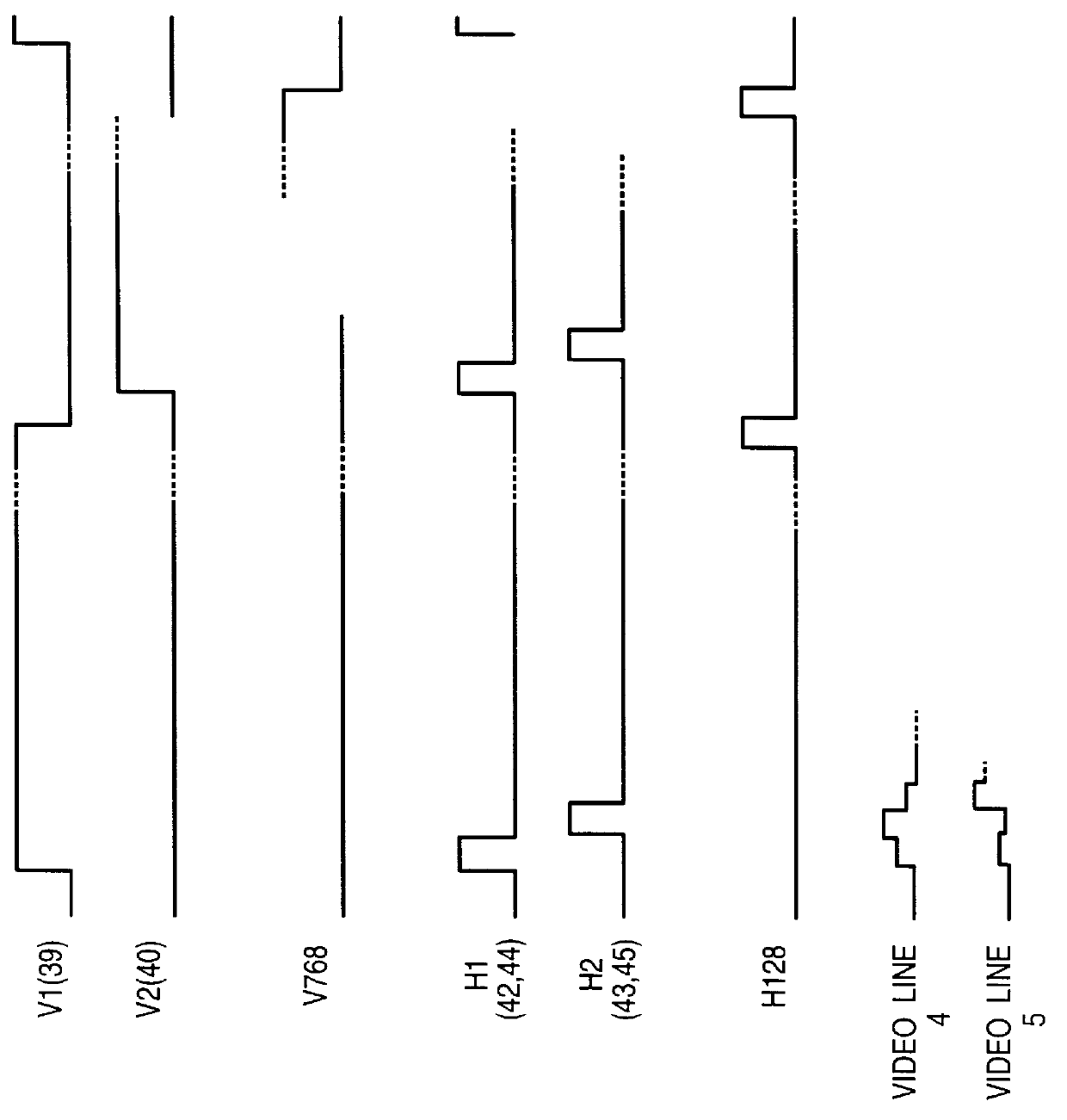
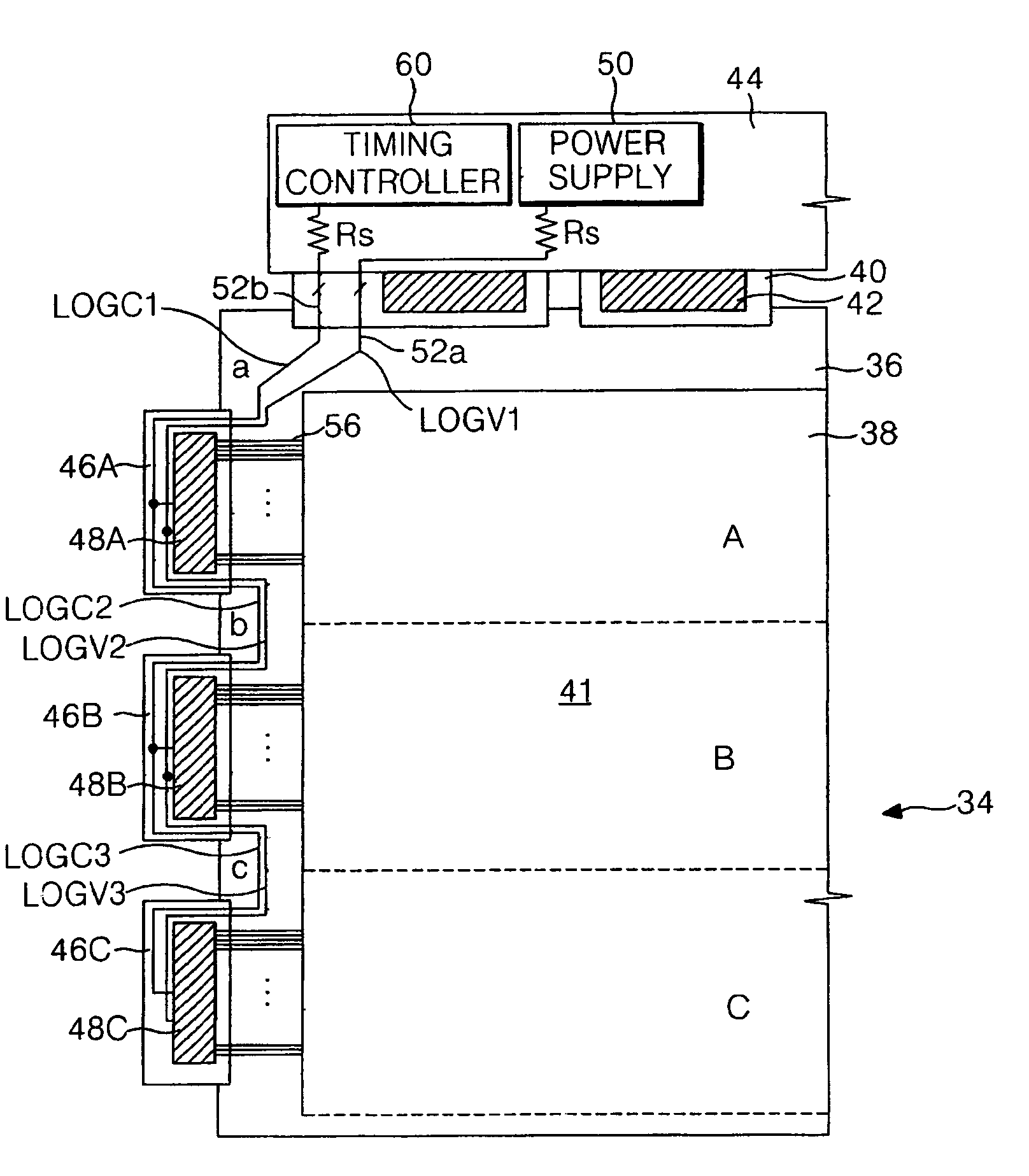
Active matrix display device, video signal processing device, method of driving the active matrix display device, method of processing signal, computer program executed for driving the active matrix display device, and storage medium storing the computer program
InactiveUS7071930B2Increased complexityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
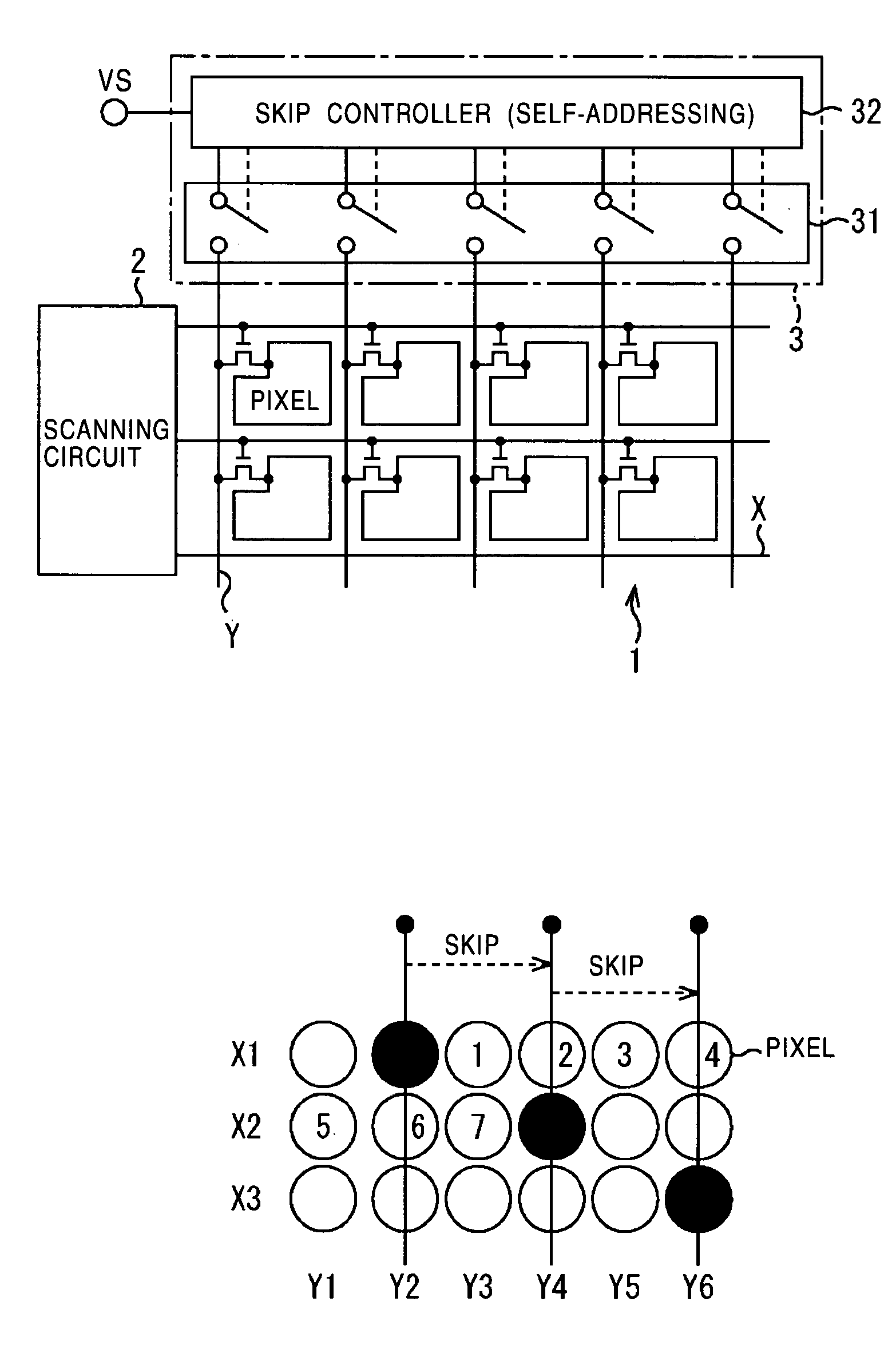
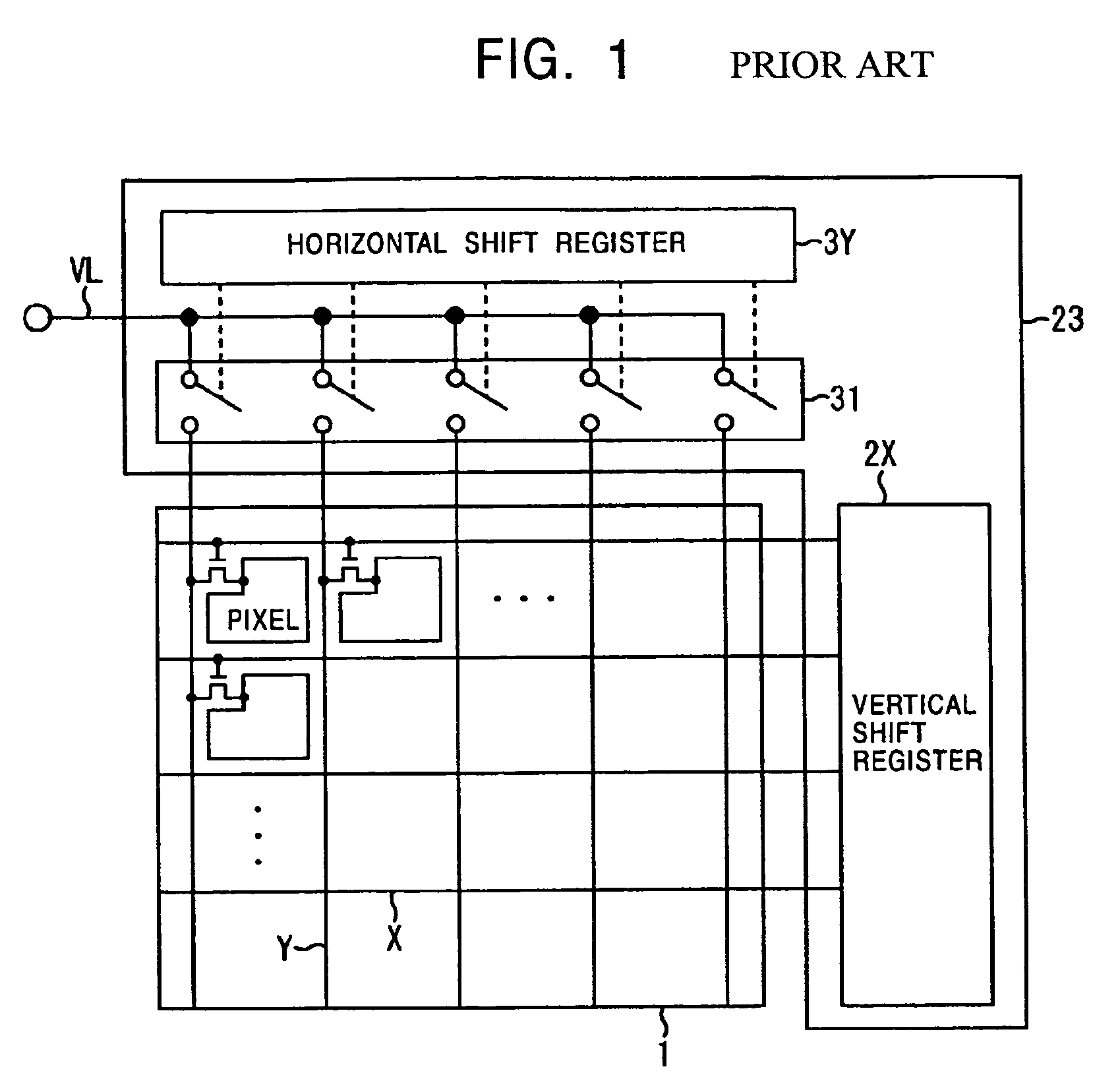
An active matrix display device includes a pixel array unit having pixels arranged in a matrix pattern, a scanning circuit which sequentially selects pixels in unit of rows, and a signal circuit which receives a video signal containing serial dot data corresponding to each pixel and which writes the dot data into a selected pixel. The signal circuit receives a video signal which includes dot data corresponding to pixels to be rewritten but does not include dot data corresponding to pixels not to be rewritten and which includes skip data defining a skip amount. The signal circuit sequentially processes the dot data and skip data so as to write the corresponding dot data into pixels to be rewritten by skipping pixels not to be rewritten based on the skip data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20100103339A1Improve display qualityLow costStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsFormation matrixLiquid-crystal display
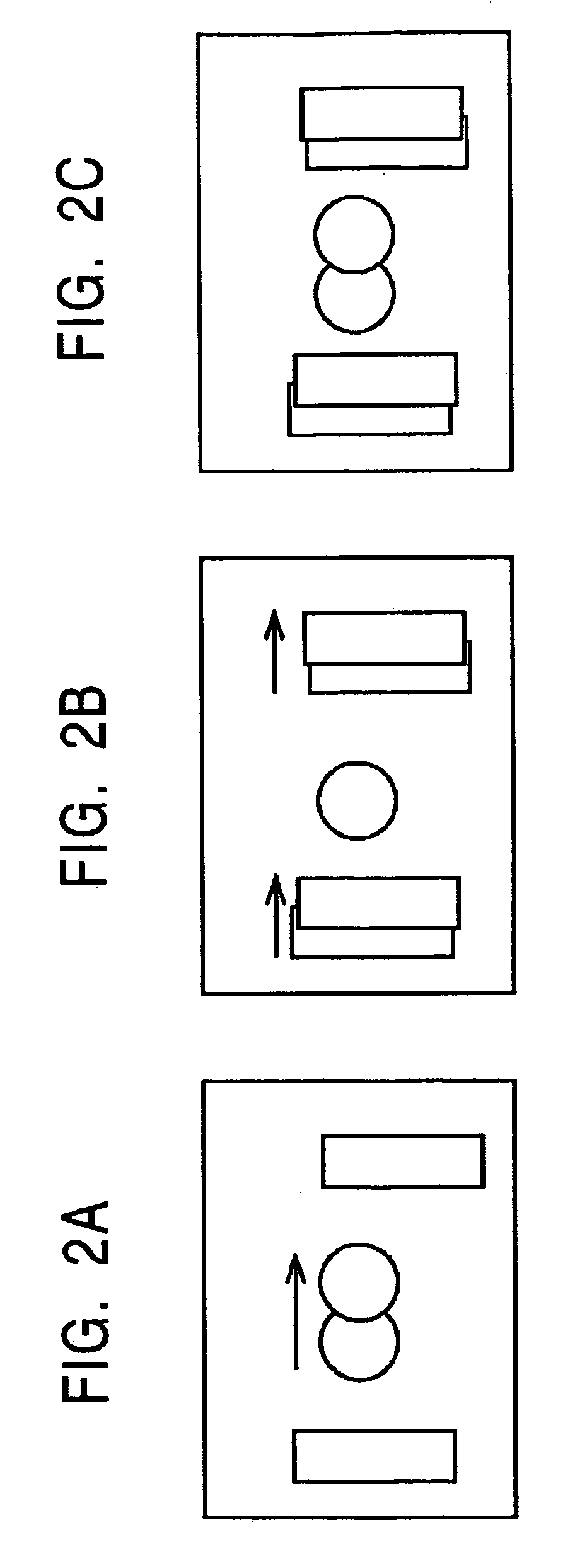
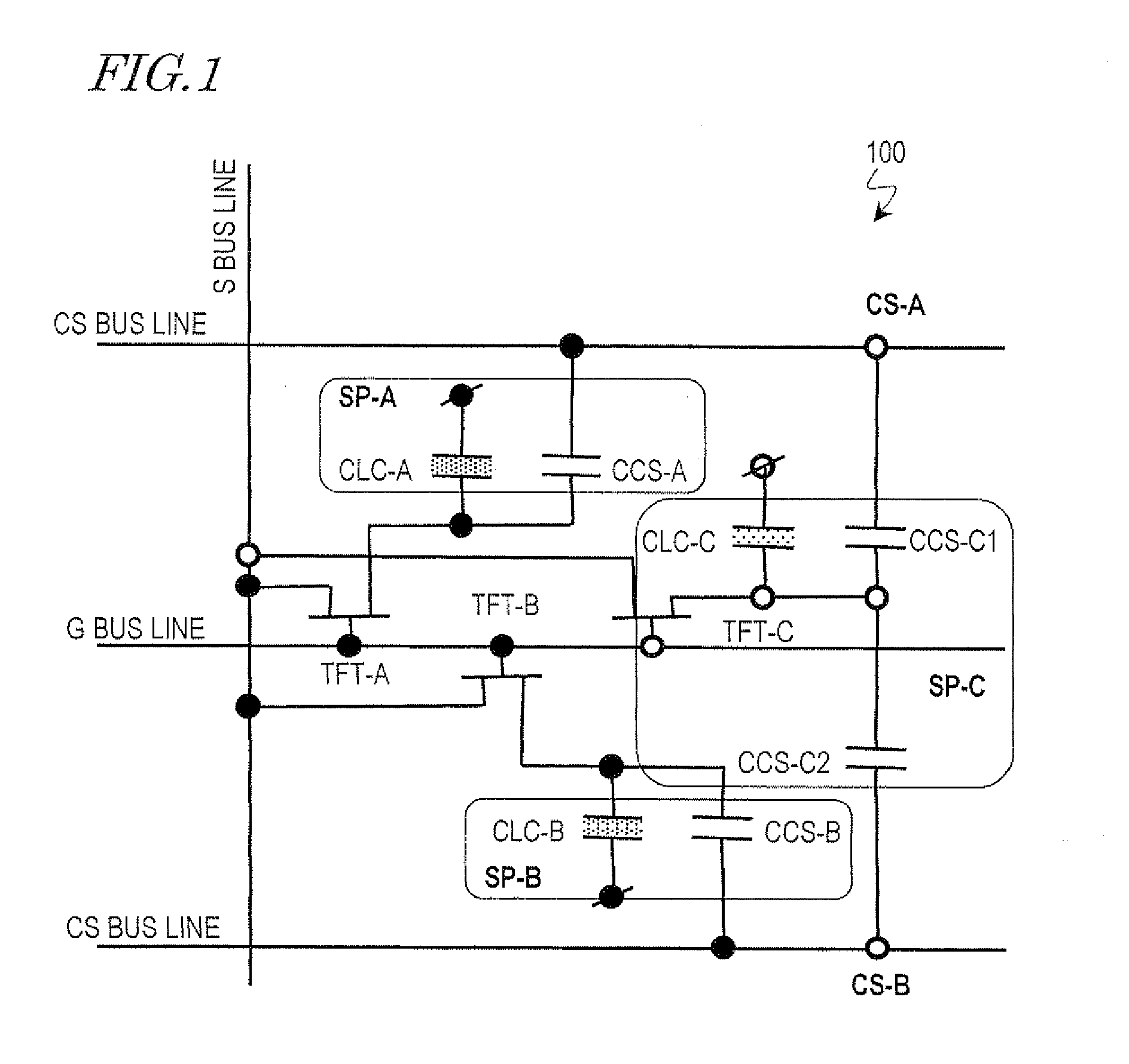
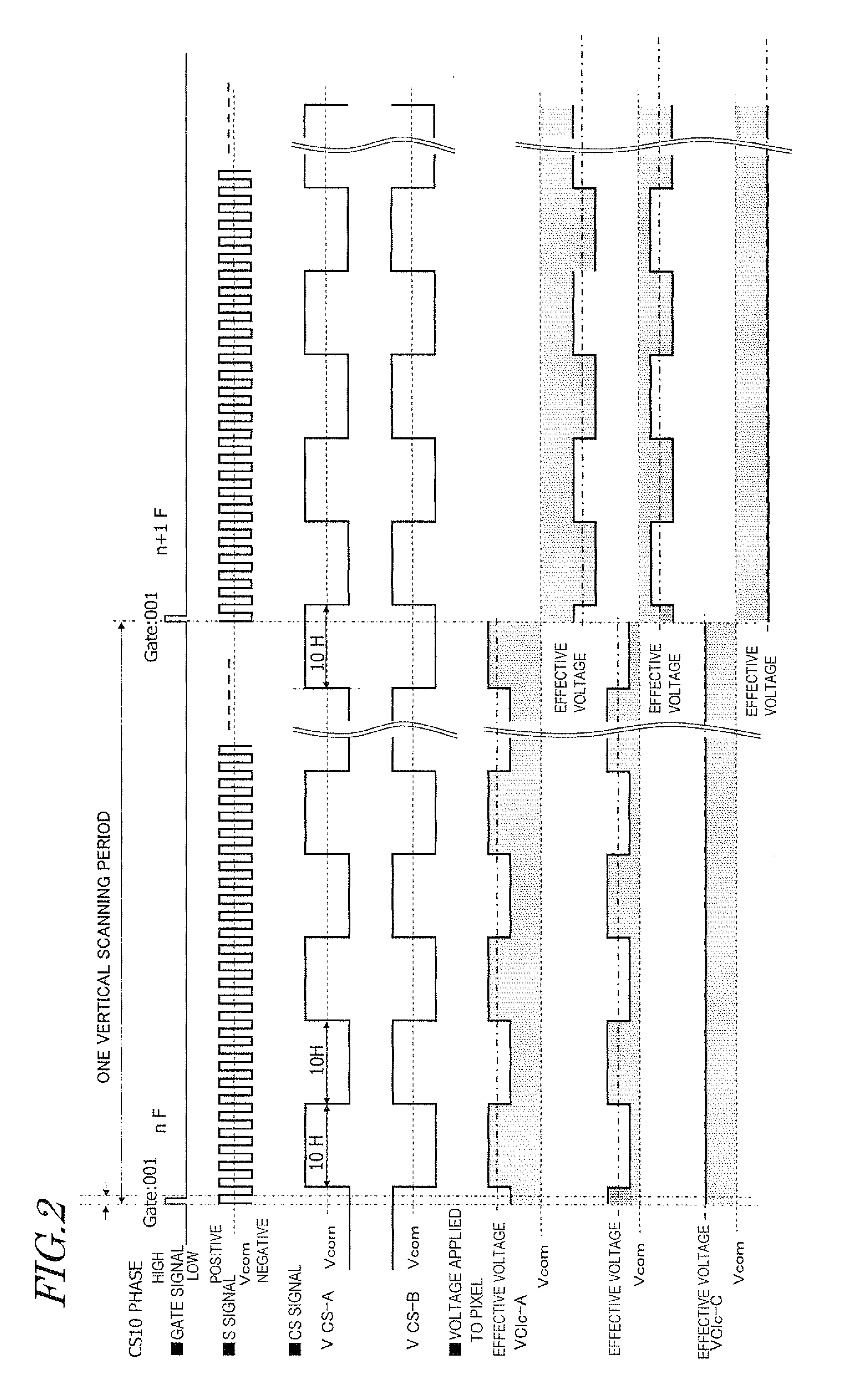
A liquid crystal display device according to the present invention includes: a plurality of pixels that are arranged in rows and columns so as to form a matrix pattern; and TFTs (TFT-A, TFT-B and TFT-C), source bus lines, gate bus lines and CS bus lines (CS-A and CS-B), which are associated with the respective pixels. Each pixel includes at least three subpixels (SP-A, SP-B and SP-C) with liquid crystal capacitors that are able to retain mutually different voltages. By supplying a signal (CS-A or CS-B) that makes two of the at least three subpixels display mutually different luminances at least at a certain grayscale tone from the source, gate and CS bus lines to each pixel, the at least three subpixels are able to display mutually different luminances.
Owner:SHARP KK
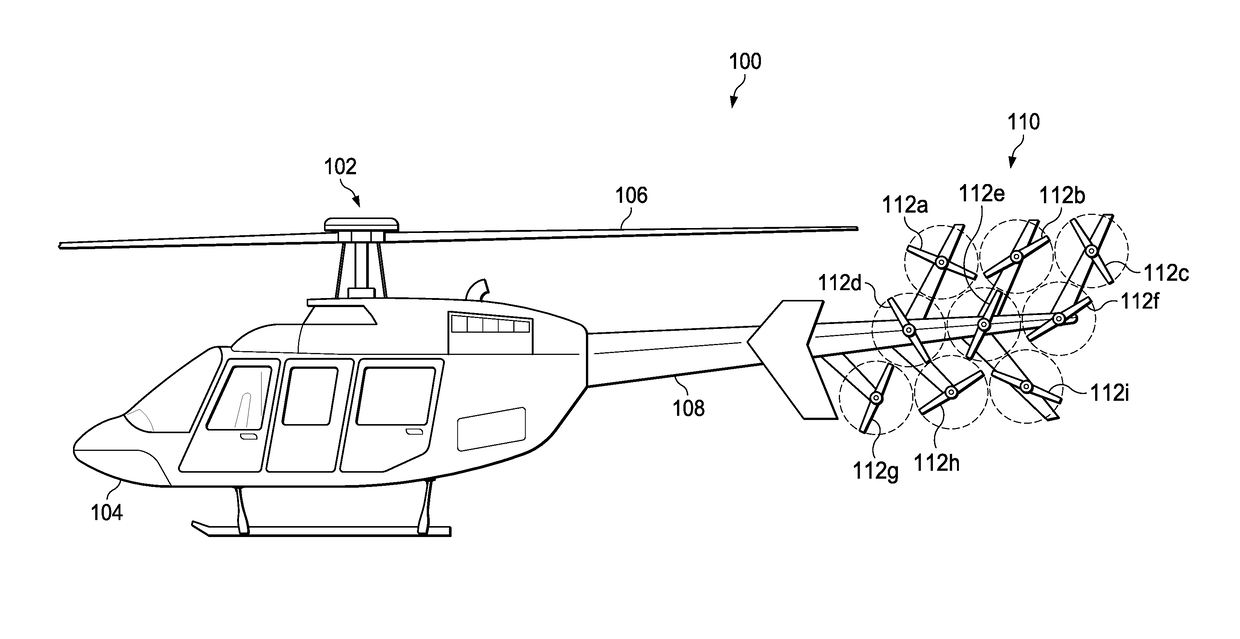
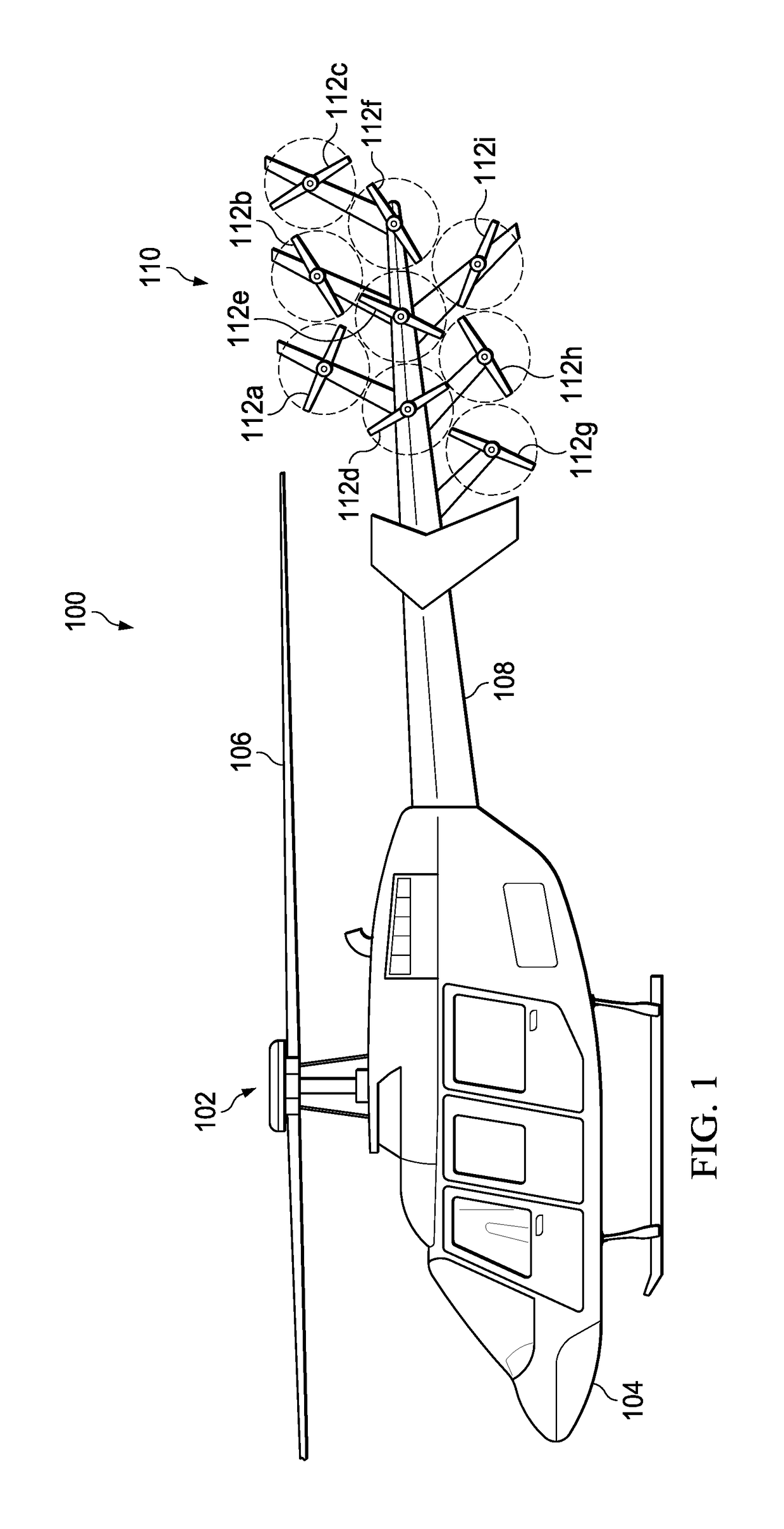
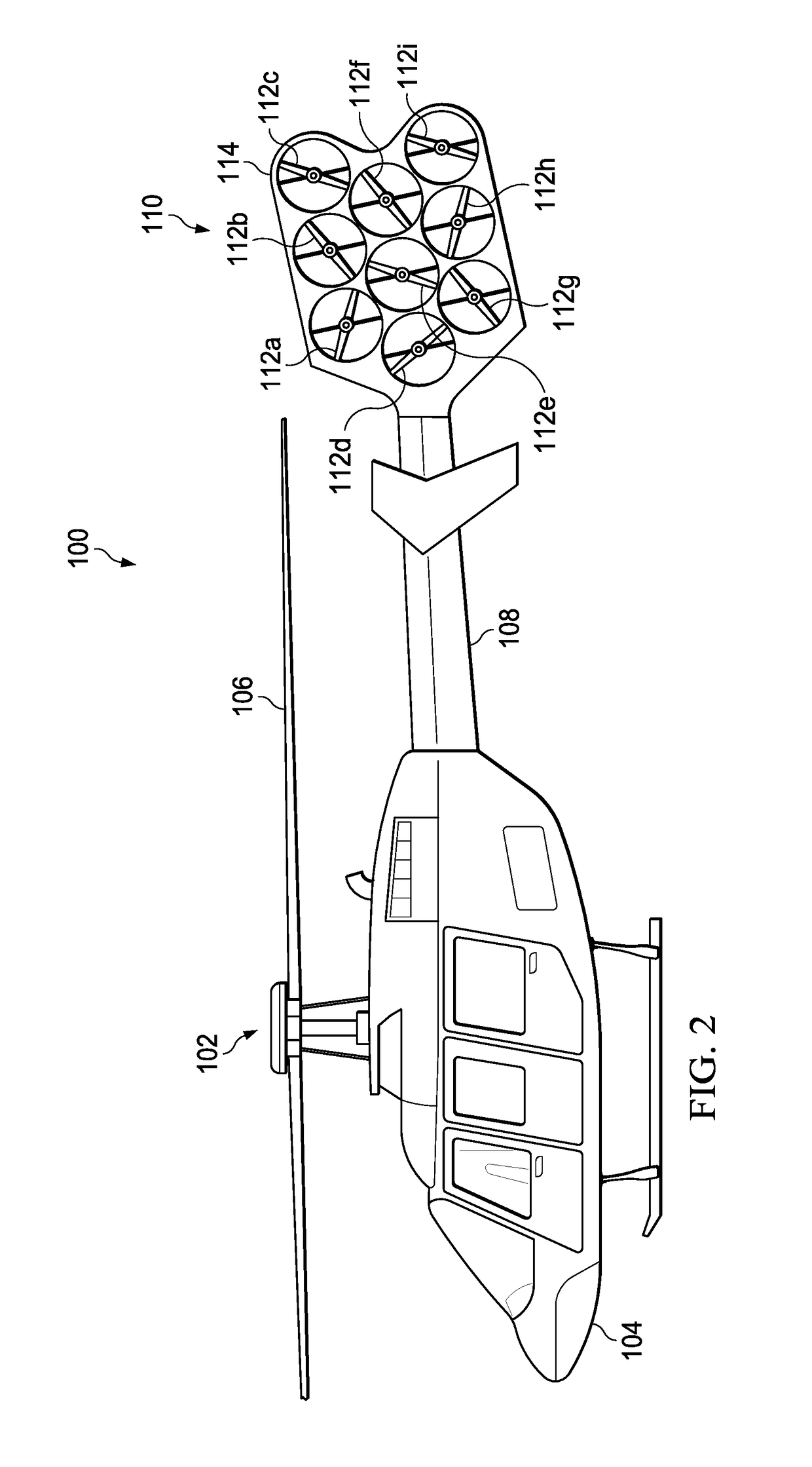
Anti-torque control using matrix of fixed blade pitch motor modules
ActiveUS20170349274A1Eliminate torqueReduce torqueActive noise reduction systemAttitude controlElectric machineComputer module
The present invention includes an a plurality of first variable speed motors arranged in a first matrix pattern and mounted on a tail boom of the helicopter; one or more fixed pitch blades attached to each of the plurality of first variable speed motors; and wherein a speed of one or more of the plurality of first variable speed motors is varied to provide an anti-torque thrust.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Image pickup device and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20070268396A1High precisionImage quality of the wide dynamic range image is improvedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectronic shutterPhotoelectric conversion
An image pickup device having a photoelectric conversion unit having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements arranged in a matrix pattern for converting exposed light into electric charges and accumulating the same and an electronic shutter function for controlling the exposure time for each frame including: a first reader for reading out electric charges exposed during a standard exposure time from respective pixels including the photoelectric conversion elements in the exposed area of the photoelectric conversion unit in a destructive read-out method; a second reader for reading out electric charges exposed during a short exposure time, which is an exposure time shorter than the standard exposure time, from the respective pixels including the photoelectric conversion elements during the same exposure period as the first reader in a nondestructive read-out method; and a saturation predictor for predicting whether or not the amounts of accumulated electric charges in the respective pixels being exposed during the standard exposure time are saturated on the basis of a non-standard exposure pixel data including the electric charges being exposed during the short exposure time, which are read out by the second reader.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
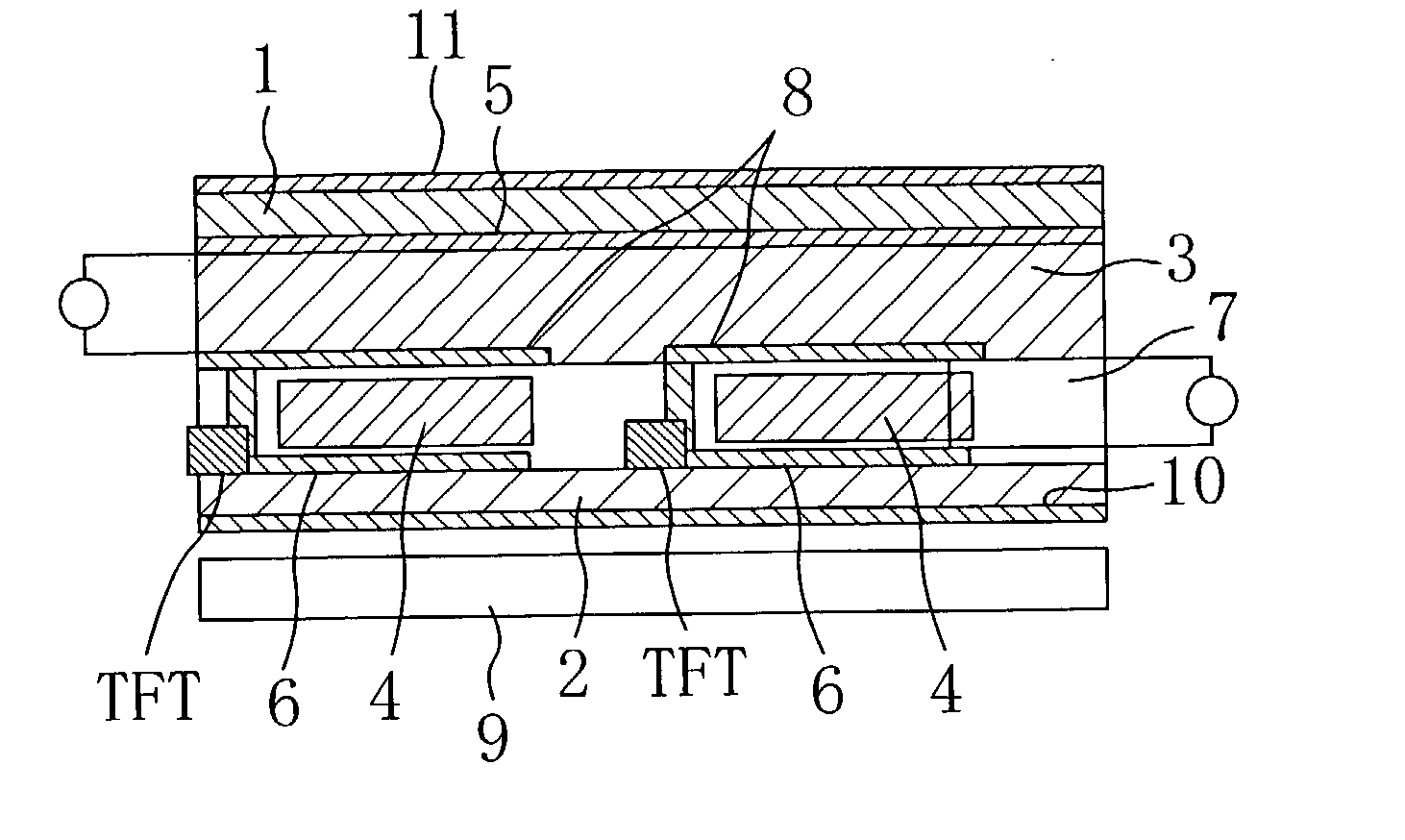
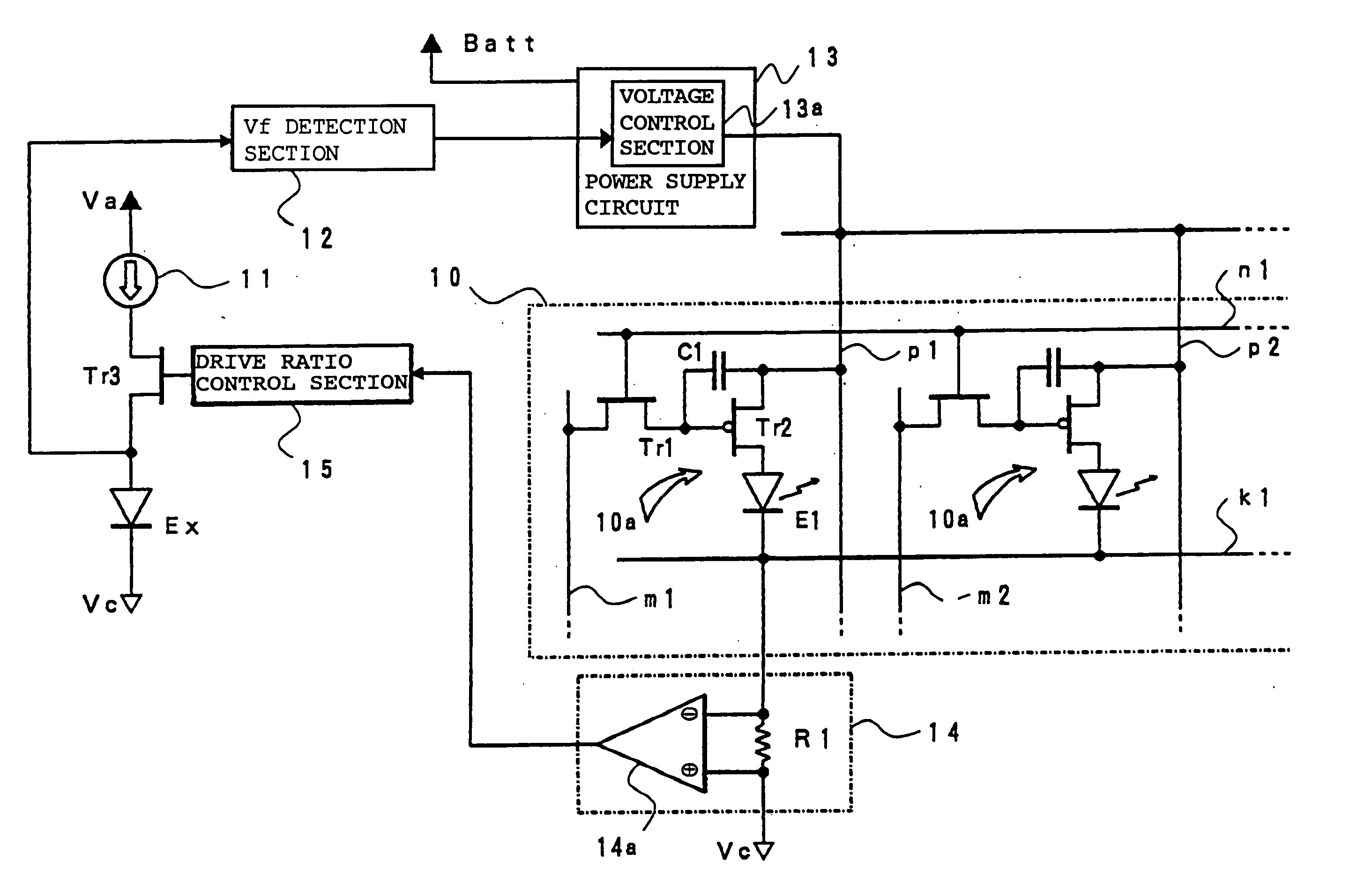
Drive device of light emitting display panel
InactiveUS20060055631A1Improve utilization efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringCurrent consumption
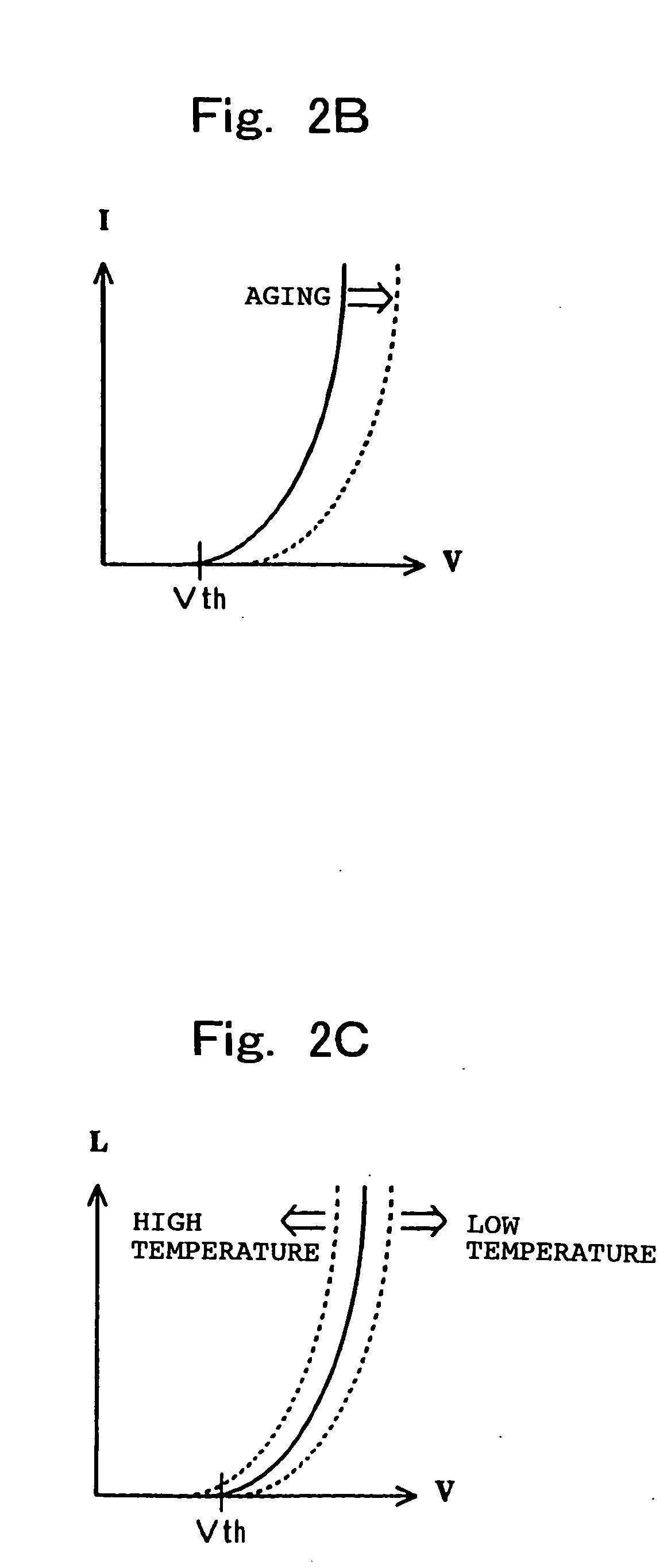
In a light emitting display panel 10, a large number of light emitting display pixels 10a are arranged in a matrix pattern, and a monitoring element Ex is provided therein which can extract a voltage which corresponds to the forward voltage of EL elements E1 on the display panel. By a signal from a current consumption detection section 14 which detects current consumption in the light emitting display panel 10, a drive ratio control section 15 performs ON / OFF control of a transistor Tr3 which is connected in series to the monitoring element Ex to control current provided from a constant current circuit. Thus, progression rates of agings of the monitoring element Ex and the EL elements E1 arranged in the display panel can be controlled to roughly coincide with each other, and a power loss generated in a light emission drive transistor Tr2 in each pixel 10a can be restrained as much as possible.
Owner:TOHOKU PIONEER CORP
Large EL panel and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS6967114B2Avoid smallHigh resolutionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSurface plateMatrix pattern
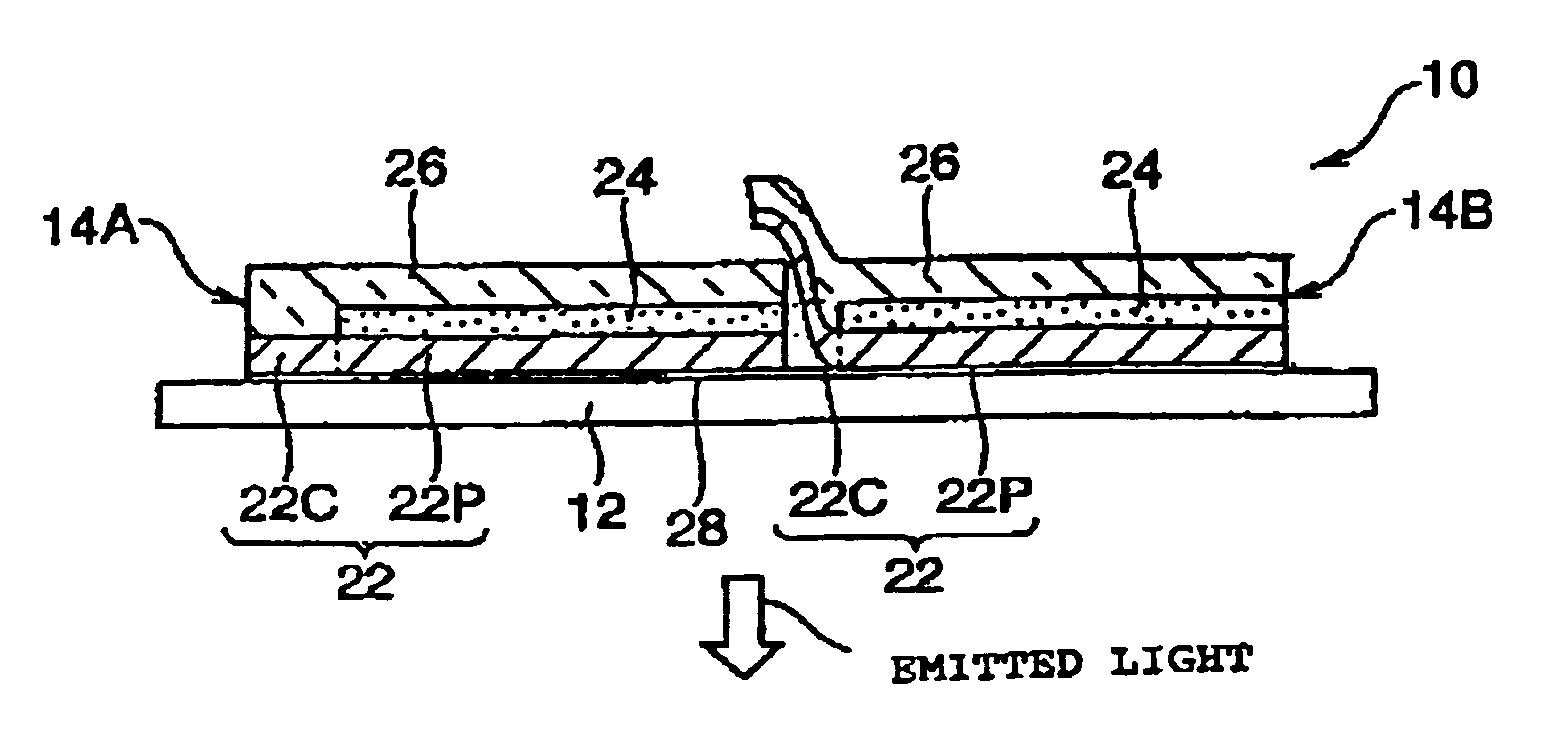
A manufacturing method is disclosed for a large EL panel in which a plurality of EL display panels are used. Each of said plurality of EL display panels are constructed of an EL display device and a sub-transparent substrate. The EL display device includes a base layer over which a luminescent material is applied, an electrode layer which is laminated on one side of said base layer, and a TFT layer including a circuit section. The circuit section of a TFT layer is disposed behind an adjacent EL display device. Thus, the EL display devices appear to be unified, forming a large EL display panel. In addition, in the case of in which a plurality of EL display devices are arranged in a matrix pattern, pitch between the pixels provided in the pixel section of the TFT array is maintained constant.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Thin film transistor array substrate, manufacturing method thereof, and mask
ActiveUS20060186411A1Reduce manufacturing costIncrease productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A thin film transistor array substrate including a gate pattern having a gate electrode, a gate line connected to the gate electrode, and a gate pad connected to the gate line, a source / drain pattern having a source electrode, a drain electrode, a data line connected to the source electrode, and a data pad connected to the data line, a gate insulating pattern formed along a matrix pattern including the gate pattern and the source / drain pattern except for a pixel area, a semiconductor pattern formed on the gate insulating pattern having a same pattern as the gate insulating pattern and partially removed at a thin film transistor area and the gate line area, and a transparent electrode pattern having a pixel electrode formed at the pixel area and connected to the drain electrode, a gate pad protective electrode formed on the gate pad, and a data pad protective electrode formed on the data pad.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device package
InactiveUS20120187564A1Good effectImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDifferential signalingSemiconductor package
A semiconductor device or semiconductor device package for transmitting a plurality of differential signals, the reliability of which hardly deteriorates. The semiconductor device is an area array semiconductor device in which a plurality of lands (external terminals) including a plurality of lands for transmitting a plurality of differential signals are arrayed in a matrix pattern in the back surface of a wiring substrate. Some of the lands are located in the outermost periphery of the matrix pattern. Some others of the lands are located inward of the outermost periphery of the matrix pattern and in rows next to the outermost periphery. The spacing between lands in a second region between the lands located in the rows next to the outermost periphery and the side surface of the wiring substrate is larger than in a first region in the outermost periphery.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of forming a capacitor for a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060046382A1Improve structural stabilityLow heat budgetSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
In an embodiment, a method of forming a capacitor for a semiconductor device of which structural stability is improved is shown. Cylindrical storage electrodes are formed in a matrix pattern on a substrate that includes an insulation interlayer having contacts therein so that a mold layer surrounds the cylindrical storage electrodes. Sacrificial plugs are formed with a cap within these electrodes. A stabilizing layer is formed on the etched mold layer and the cylindrical storage electrode by partially etching the mold layer. The stabilizing layer is etched until the sacrificial plug is exposed, thereby forming a spacer. While the sacrificial plug and the mold layer are fully removed, the spacer is partially removed, thereby forming a stabilizing member for supporting neighboring storage electrodes adjacent to each other. Accordingly, a structural stability of the capacitor is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS7224353B2Avoid Brightness DifferencesCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsHigh resistanceLine resistance
A liquid crystal display and a method of driving the same is capable of for preventing a difference in brightness from occurring between horizontal line blocks. A liquid crystal display includes a liquid crystal display panel having liquid crystal cells arranged in a matrix pattern; at least one integrated circuit for driving the liquid crystal display panel; a supply line commonly connected to the at least one integrated circuit for applying drive signals to the at least one integrated circuit; and a signal-limiting part formed at an input terminal of the supply line, wherein the supply line has a higher resistance than the sum of the line resistances of the entire supply line.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com