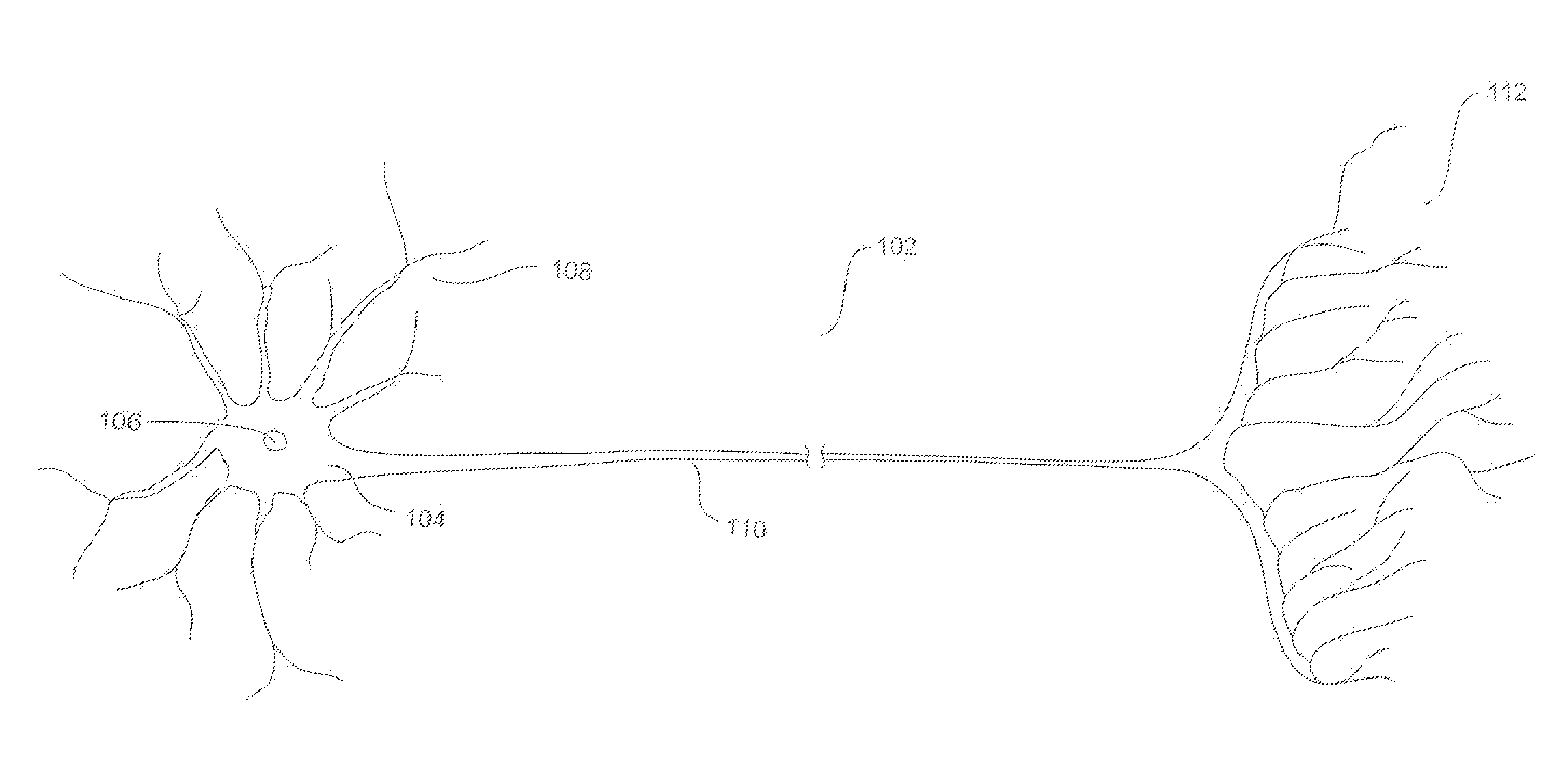Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Neuromorphic circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuromorphic Circuit
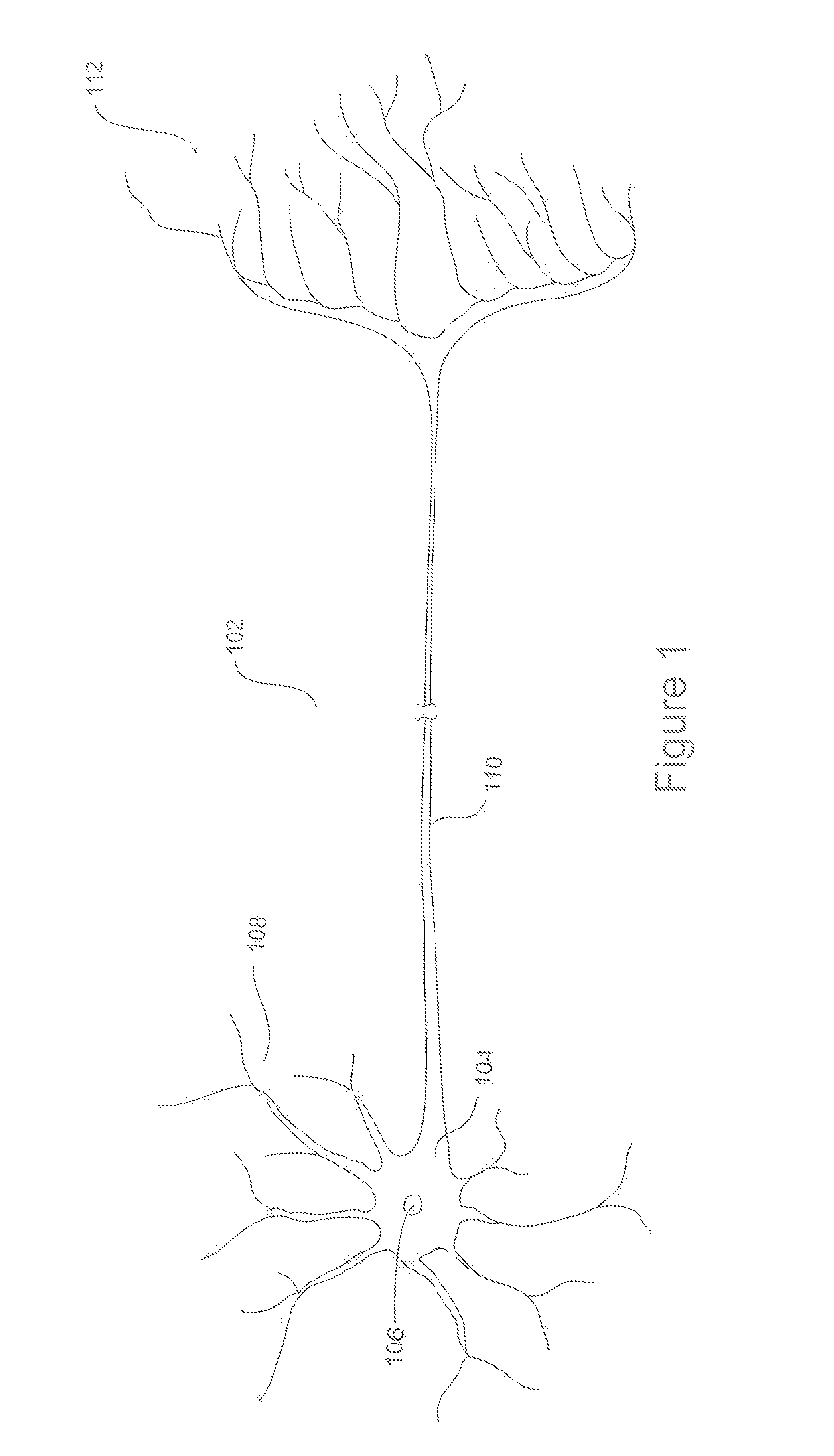
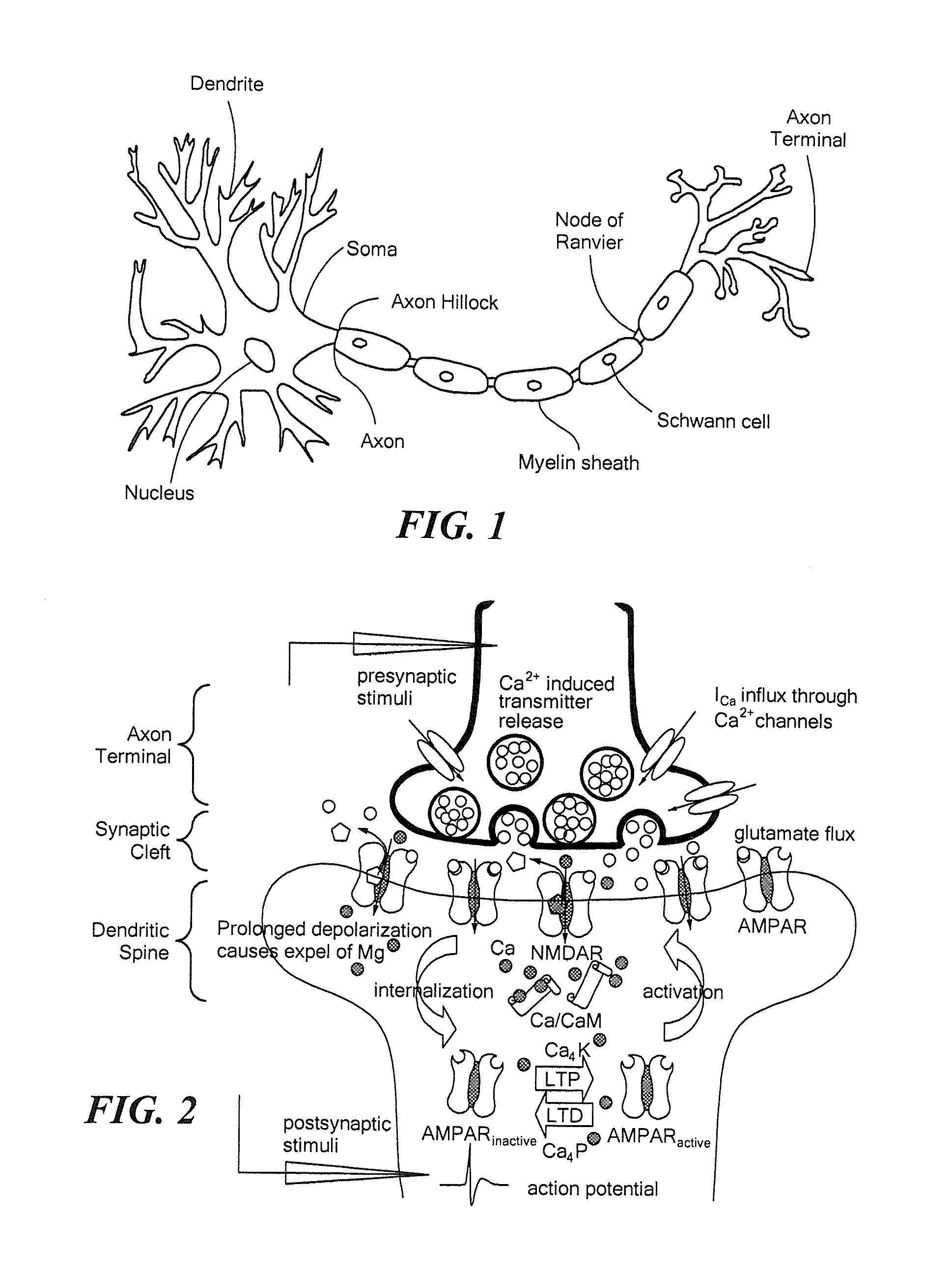
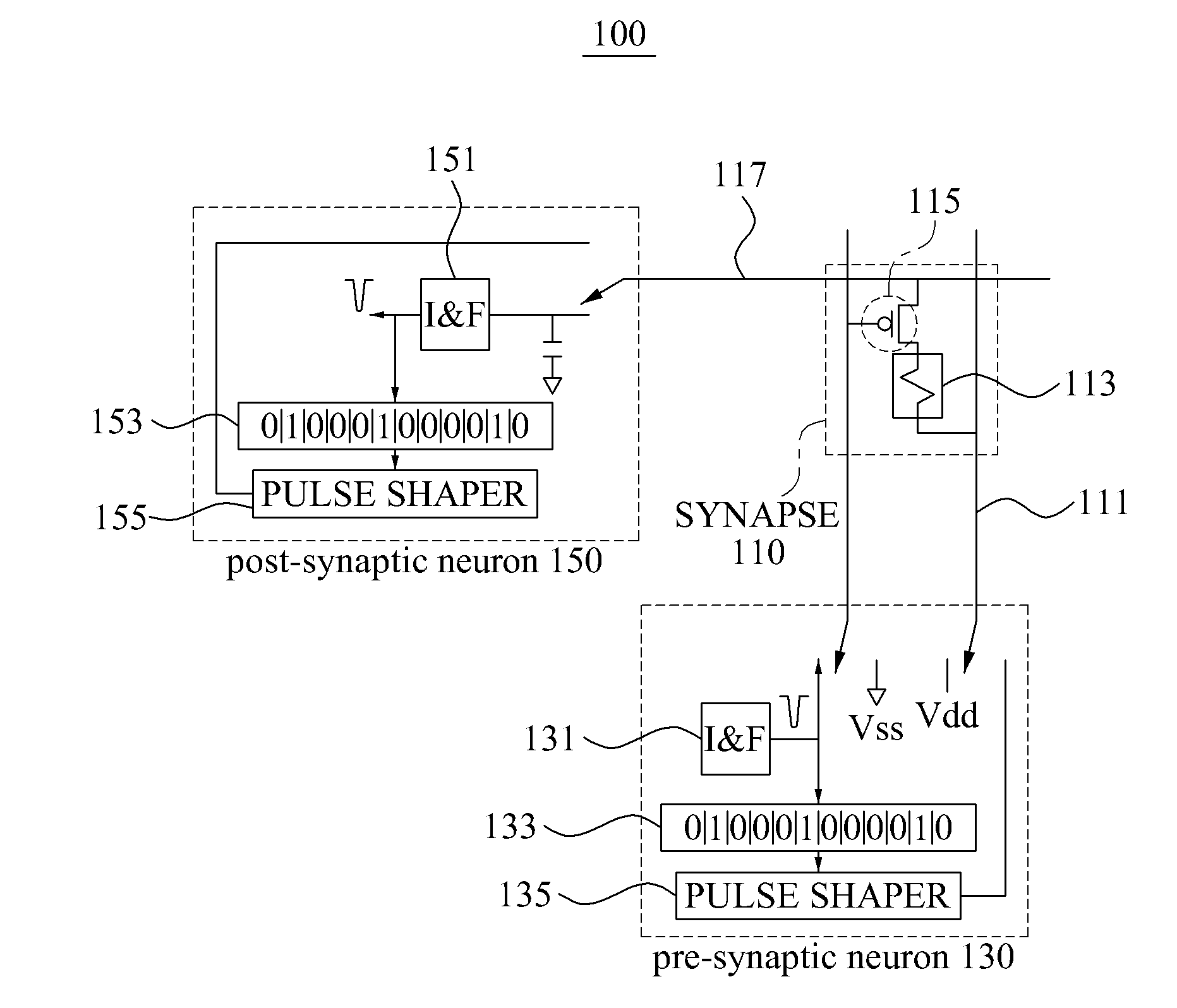
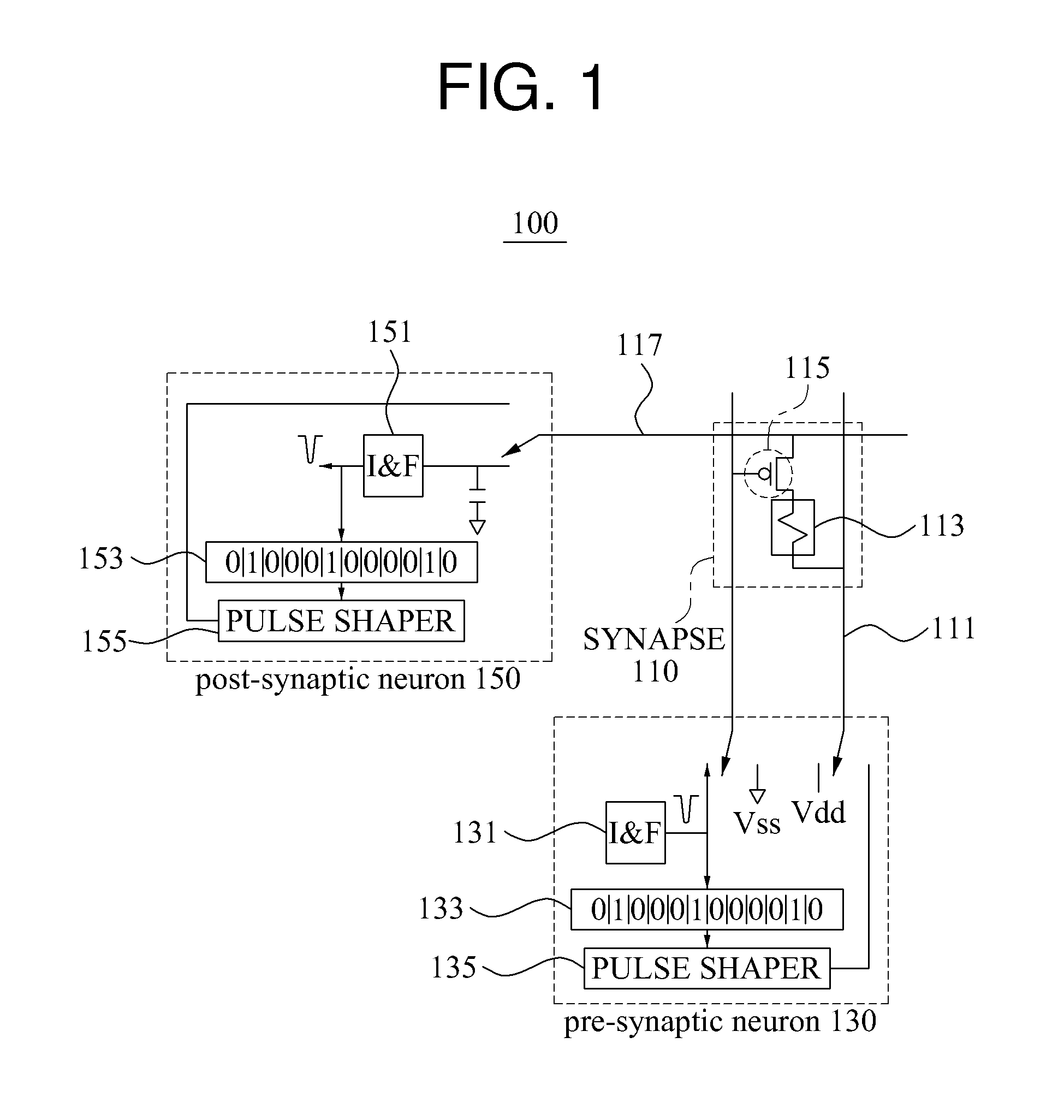
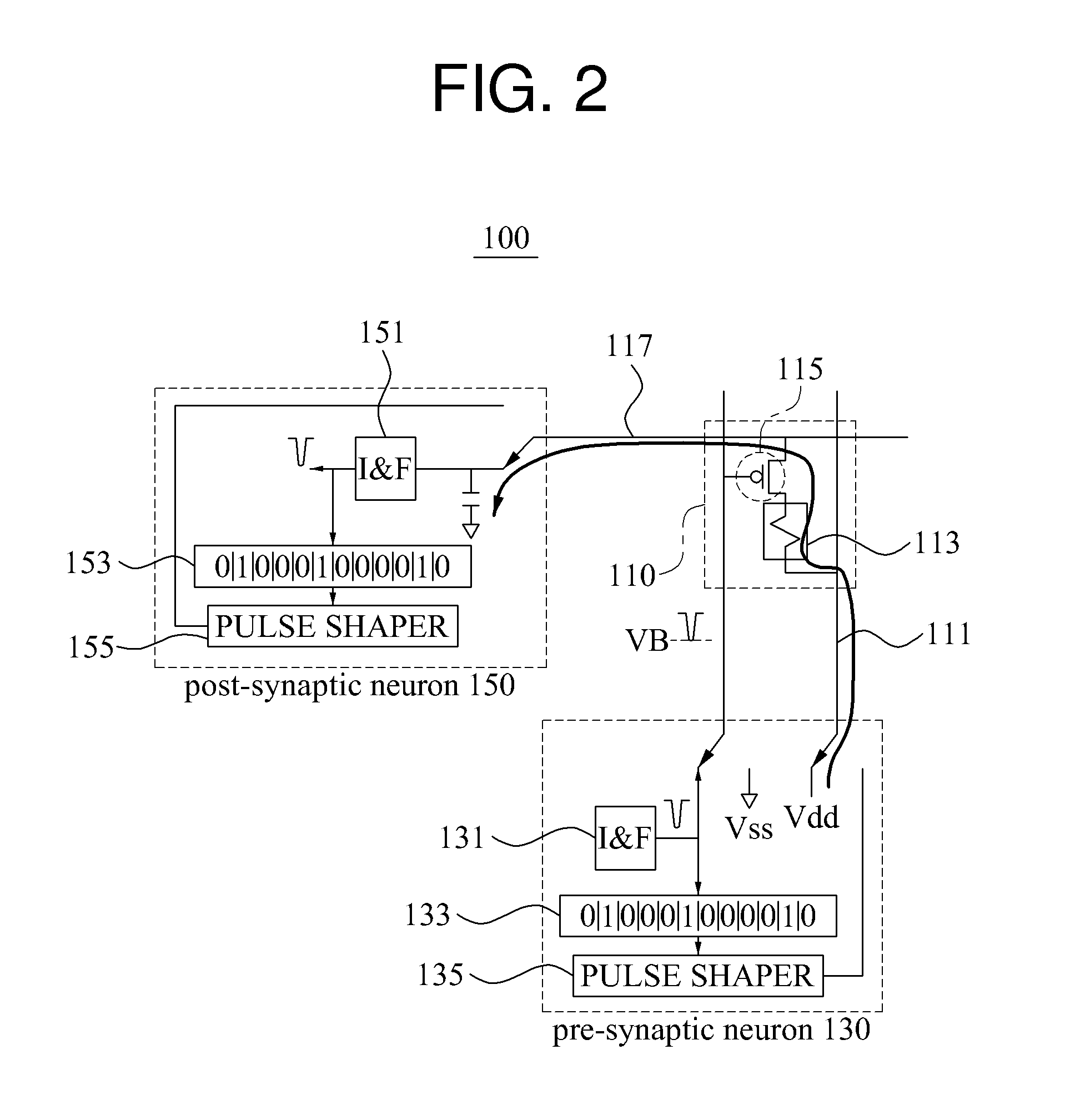
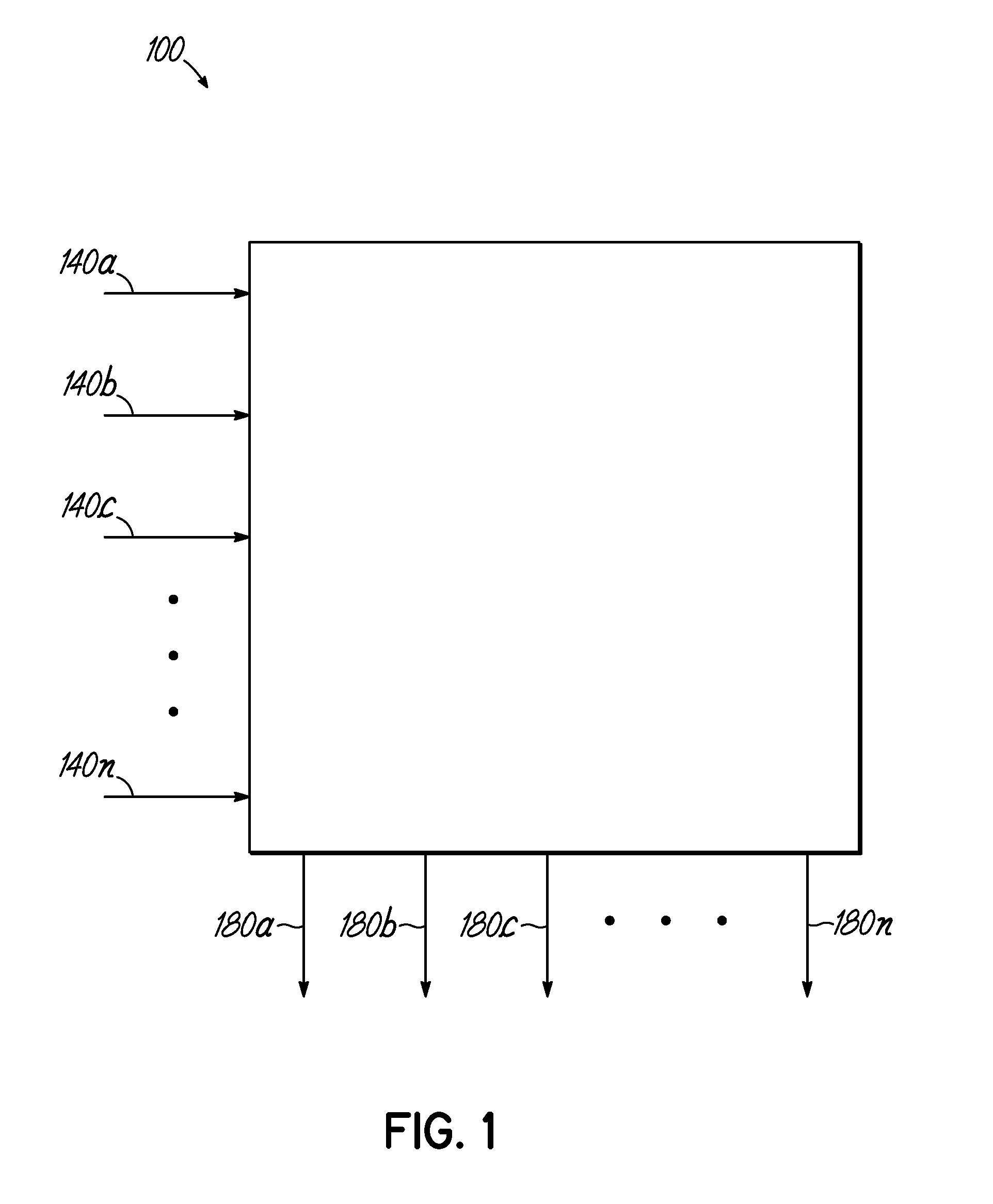
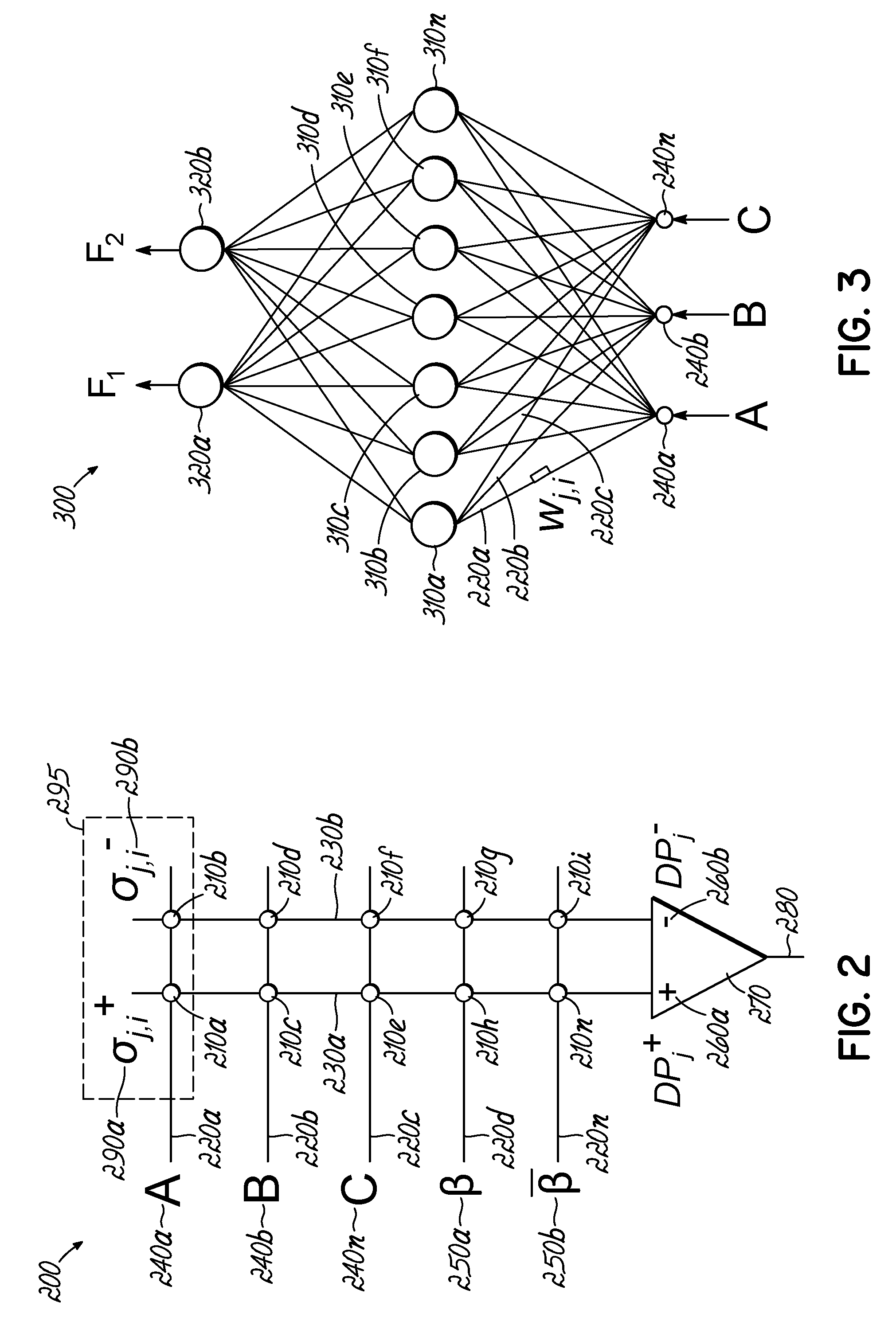
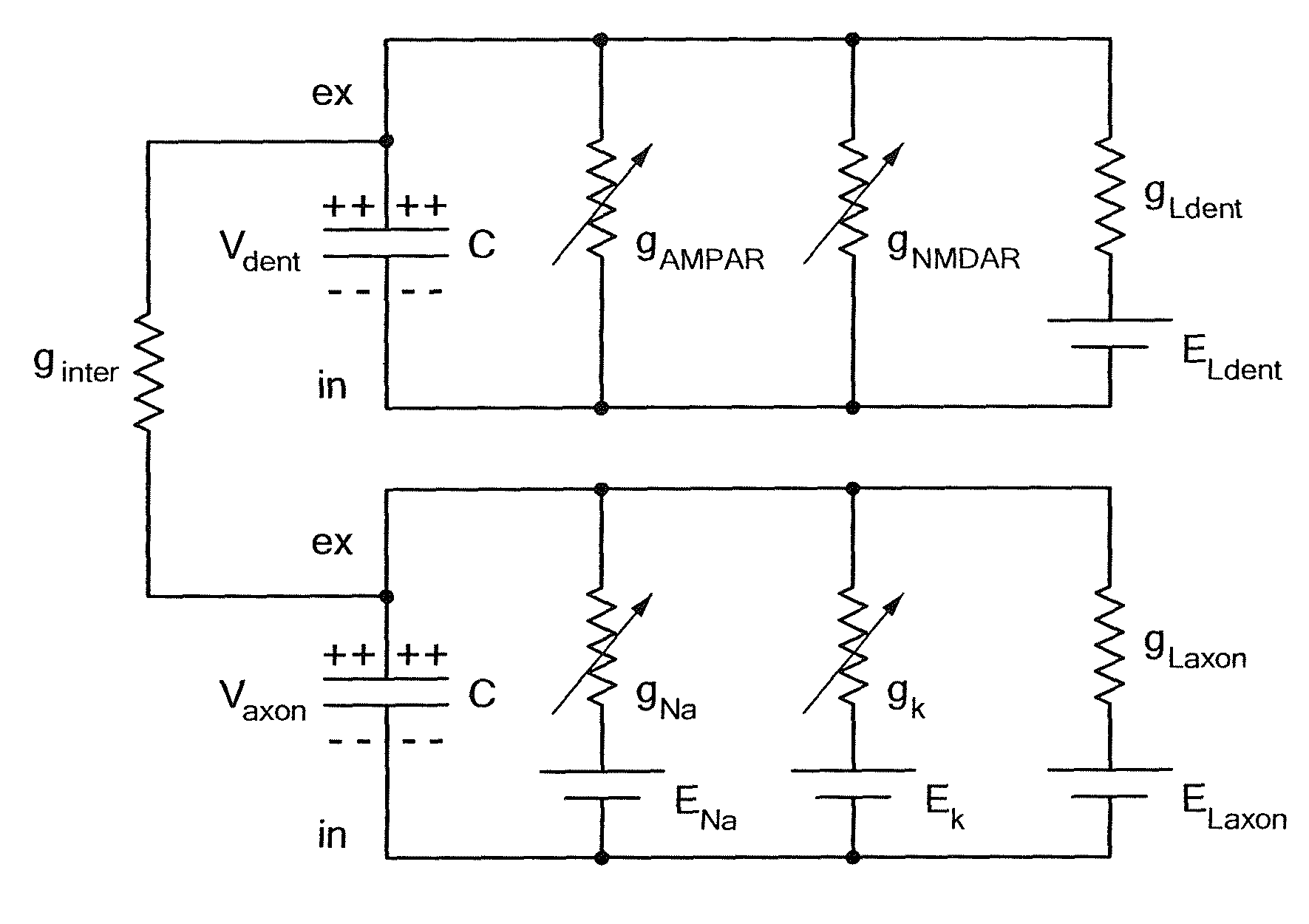
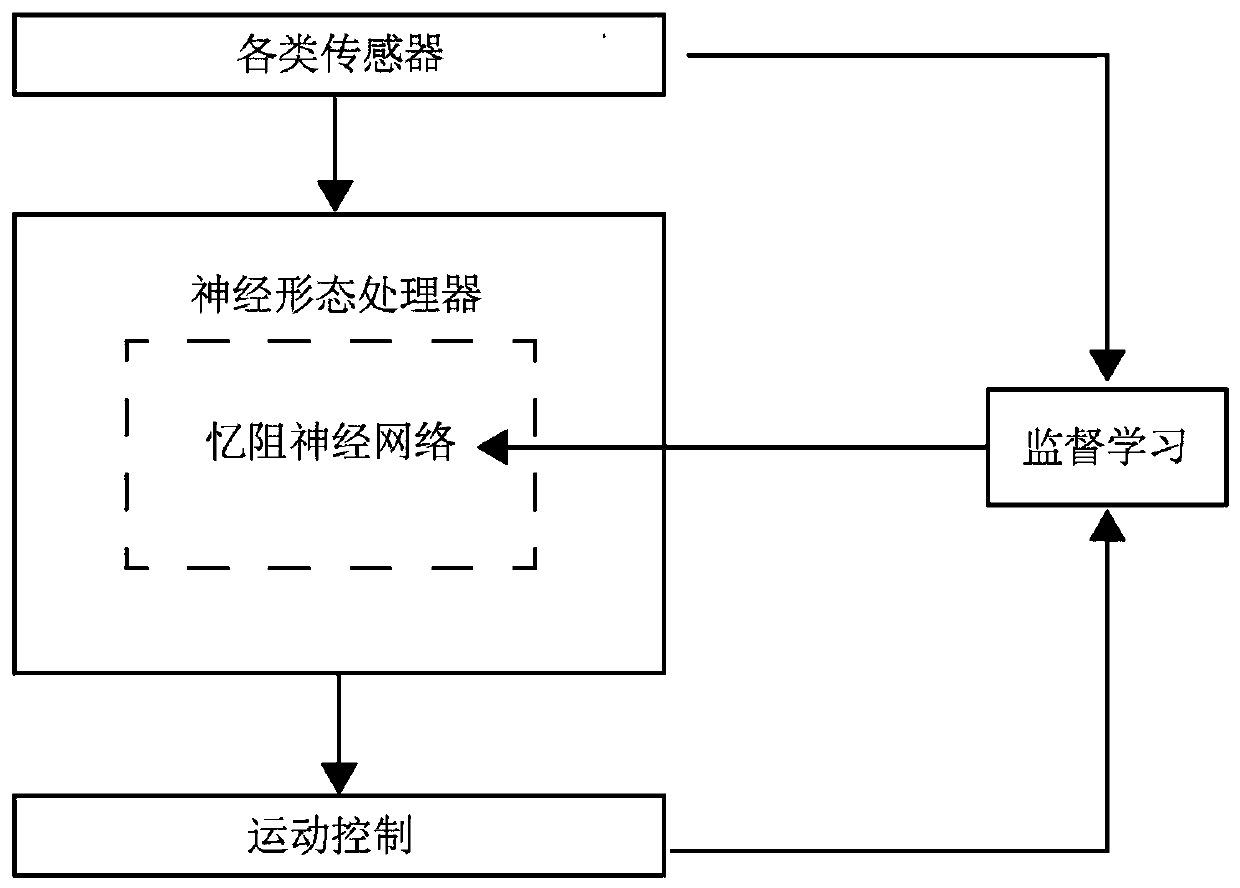
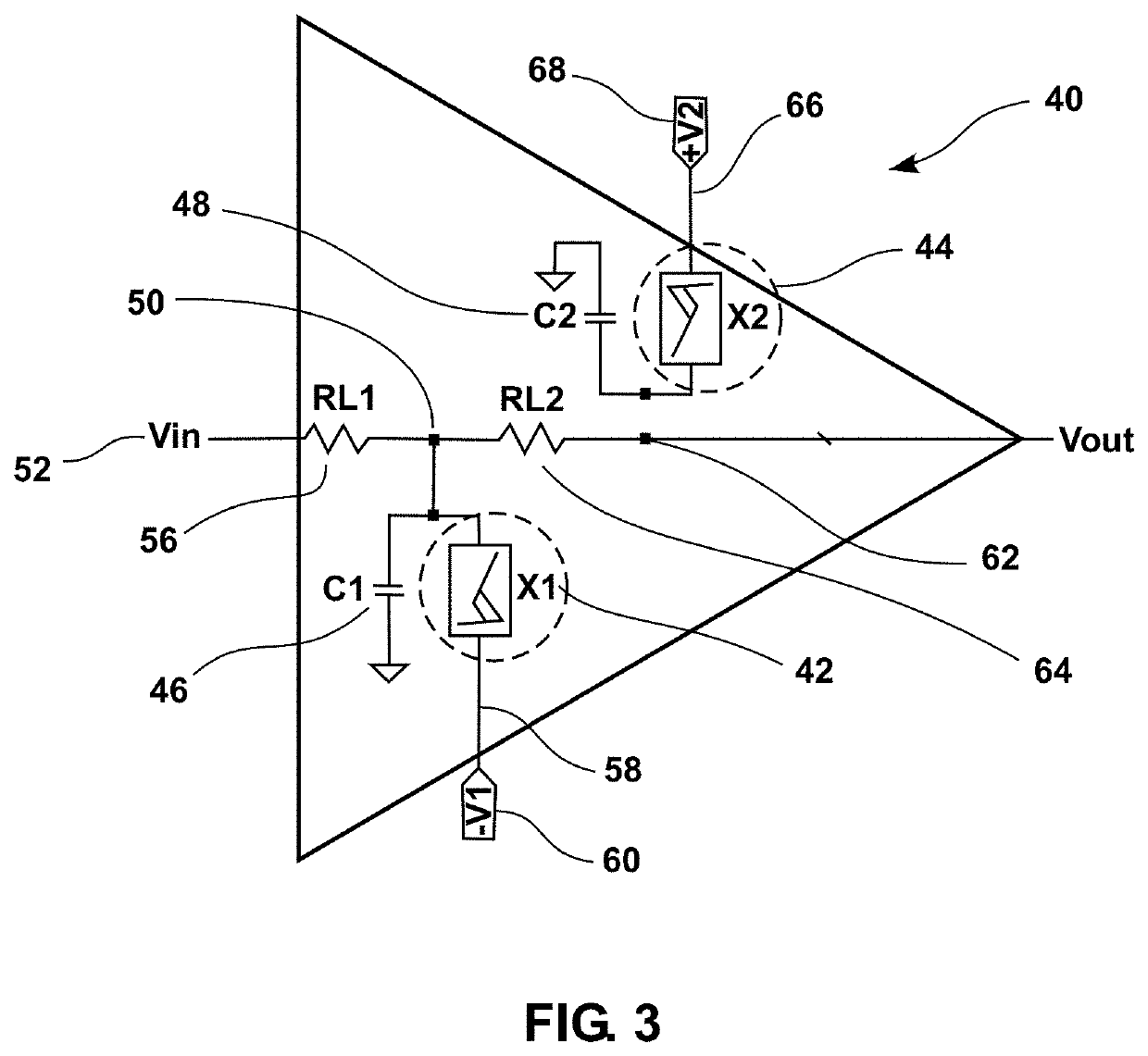
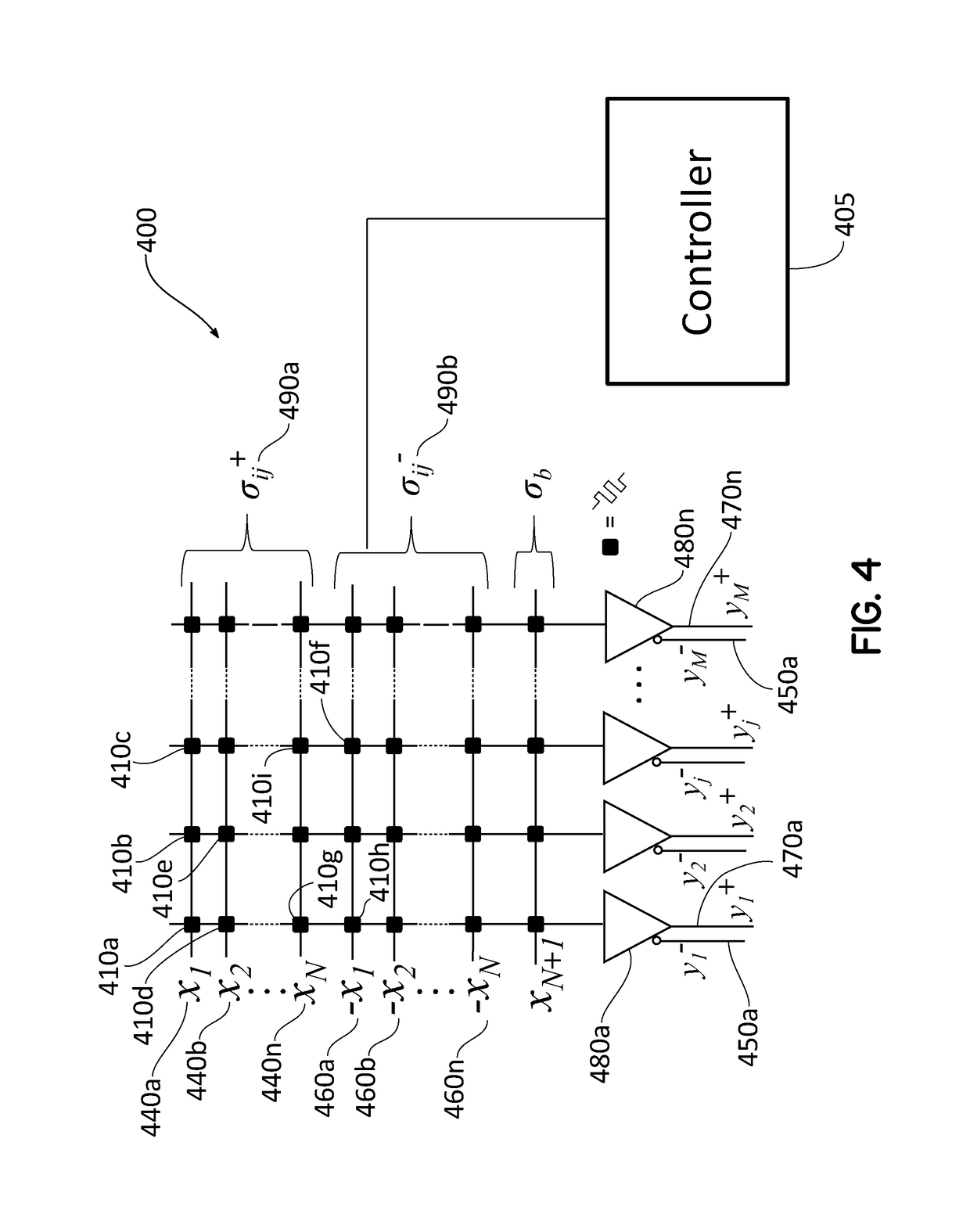
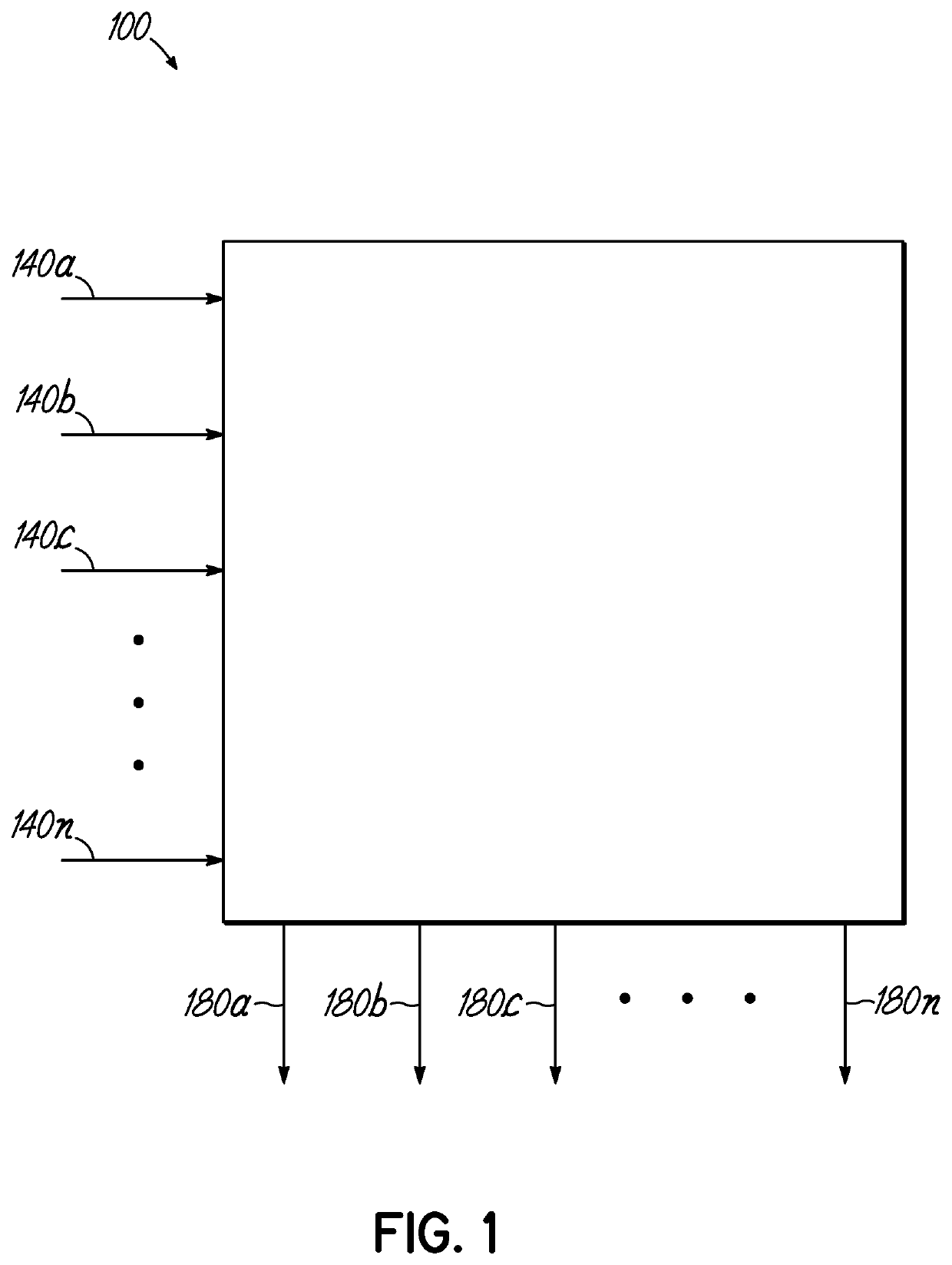
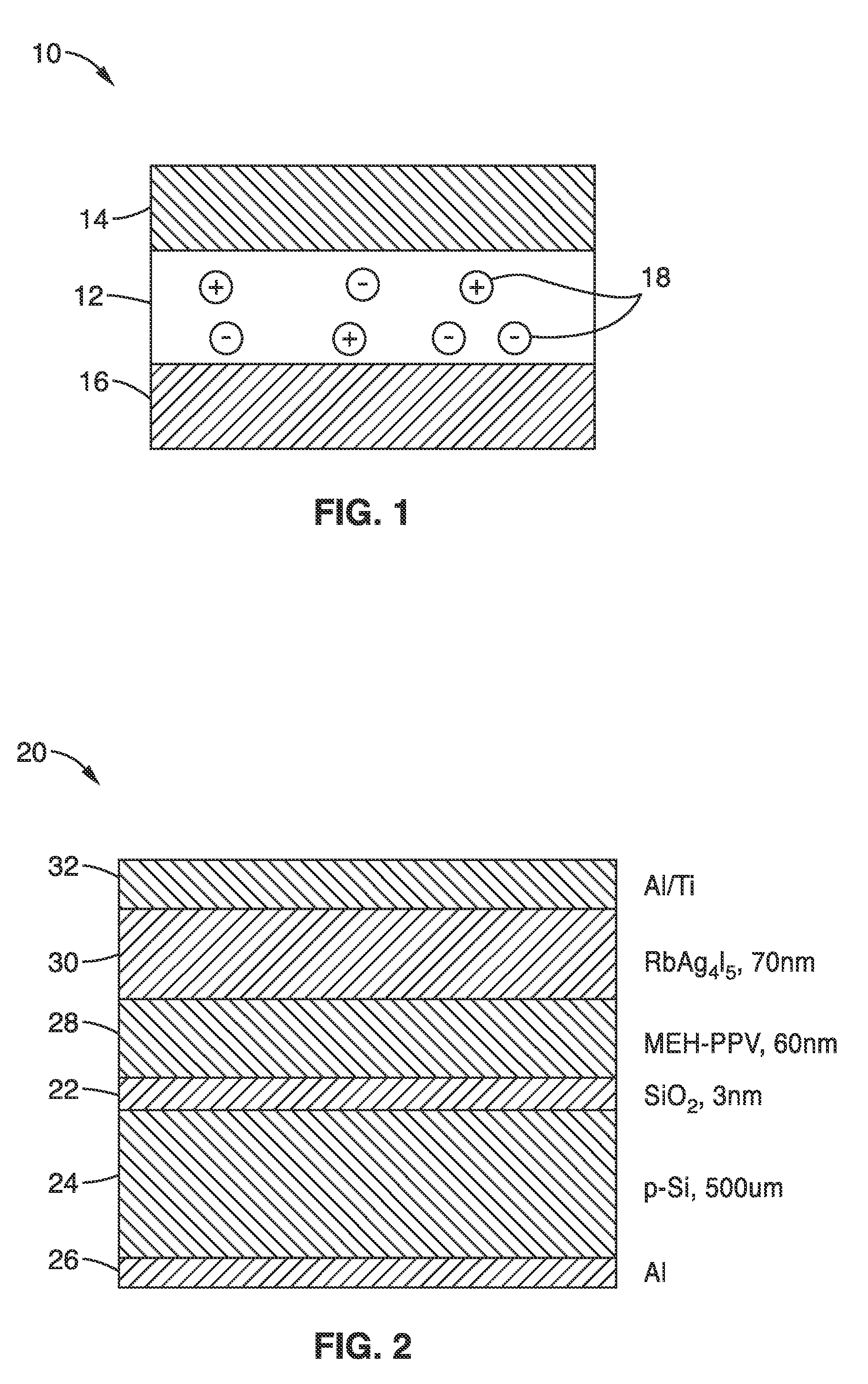
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to neuromorphic circuits containing two or more internal neuron computational units. Each internal neuron computational unit includes a synchronization-signal input for receiving a synchronizing signal, at least one input for receiving input signals, and at least one output for transmitting an output signal. A memristive synapse connects an output signal line carrying output signals from a first set of one or more internal neurons to an input signal line that carries signals to a second set of one or more internal neurons.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Circuits and Methods Representative of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity of Neurons
InactiveUS20110137843A1Digital computer detailsNeural architecturesSynapseSpike-timing-dependent plasticity
A neuromorphic circuit performs functions representative of spiking timing dependent plasticity of a synapse.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE +1
Analog neuromorphic circuits for dot-product operation implementing resistive memories
ActiveUS20180018559A1Digital storagePhysical realisationElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
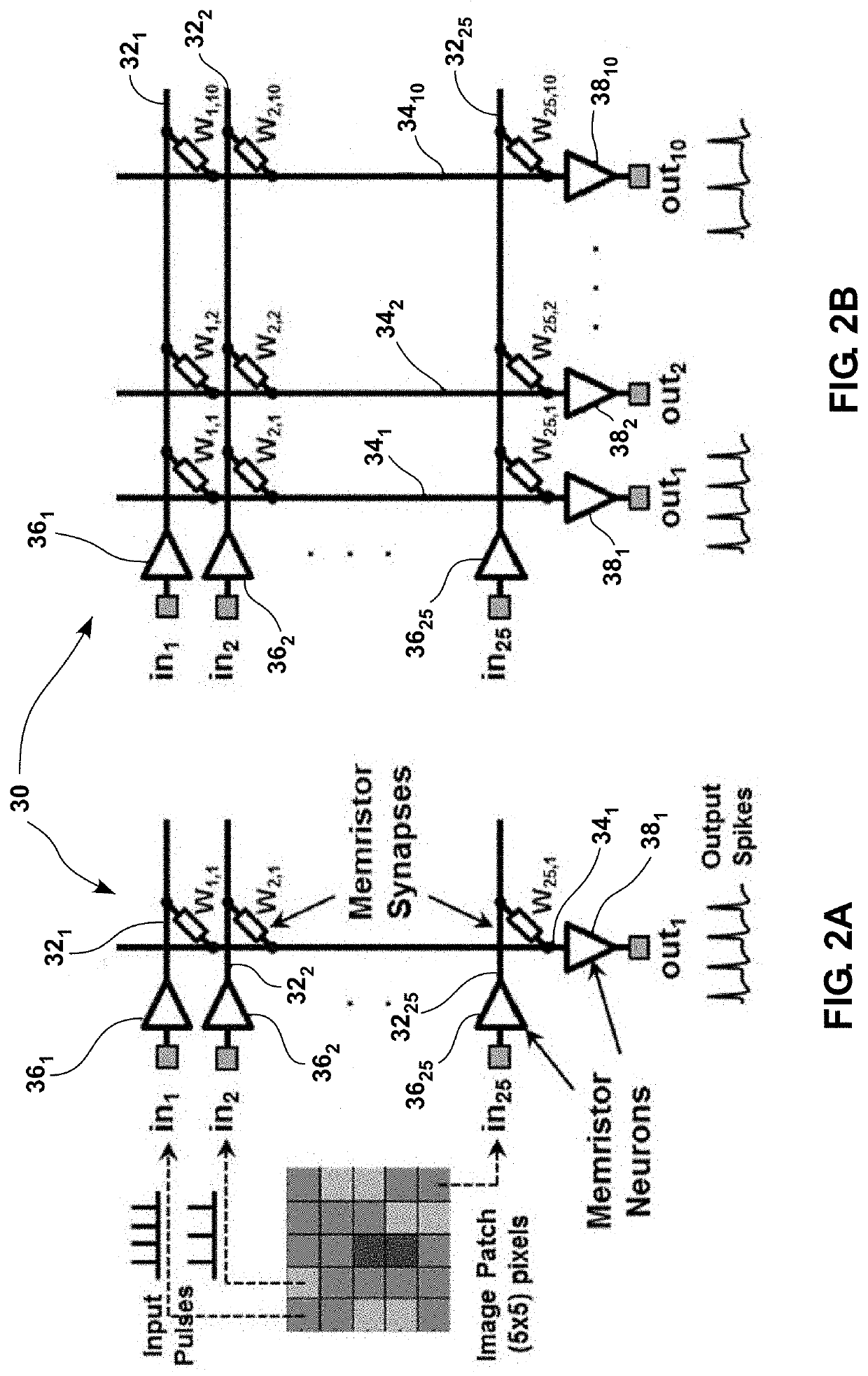
An analog neuromorphic circuit is disclosed having resistive memories that provide a resistance to each corresponding input voltage signal. Input voltages are applied to the analog neuromorphic circuit. Each input voltage represents a vector value that is a non-binary value included in a vector that is incorporated into a dot-product operation with weighted matrix values included in a weighted matrix. A controller pairs each resistive memory with another resistive memory. The controller converts each pair of resistance values to a single non-binary value. Each single non-binary value is mapped to a weighted matrix value included in the weighted matrix that is incorporated into the dot-product operation with the vector values included in the vector. The controller generates dot-product operation values from the dot-product operation with the vector and the weighted matrix where each dot-product operation is a non-binary value.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Neuromorphic circuit
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Synapse for function cell of spike timing dependent plasticity (STDP), function cell of stdp, and neuromorphic circuit using function cell of stdp
ActiveUS20120317063A1Synaptic weight can be decreasedReduce resistanceDigital computer detailsDigital storageSpike-timing-dependent plasticityNeuromorphic circuits
A synapse for a spike timing dependent (STDP) function cell includes a memory device having a variable resistance, such as a memristor, and a transistor connected to the memory device. A channel of the memory device is connected in series with a channel of the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
On-chip training of memristor crossbar neuromorphic processing systems
An analog neuromorphic circuit is disclosed having resistive memories that provide a resistance to an input voltage signal as the input voltage signal propagates through the resistive memories generating a first output voltage signal and to provide a resistance to a first error signal that propagates through the resistive memories generating a second output voltage signal. A comparator generates the first error signal that is representative of a difference between the first output voltage signal and the desired output signal and generates the first error signal so that the first error signal propagates back through the plurality of resistive memories. A resistance adjuster adjusts a resistance value associated with each resistive memory based on the first error signal and the second output voltage signal to decrease the difference between the first output voltage signal and the desired output signal.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
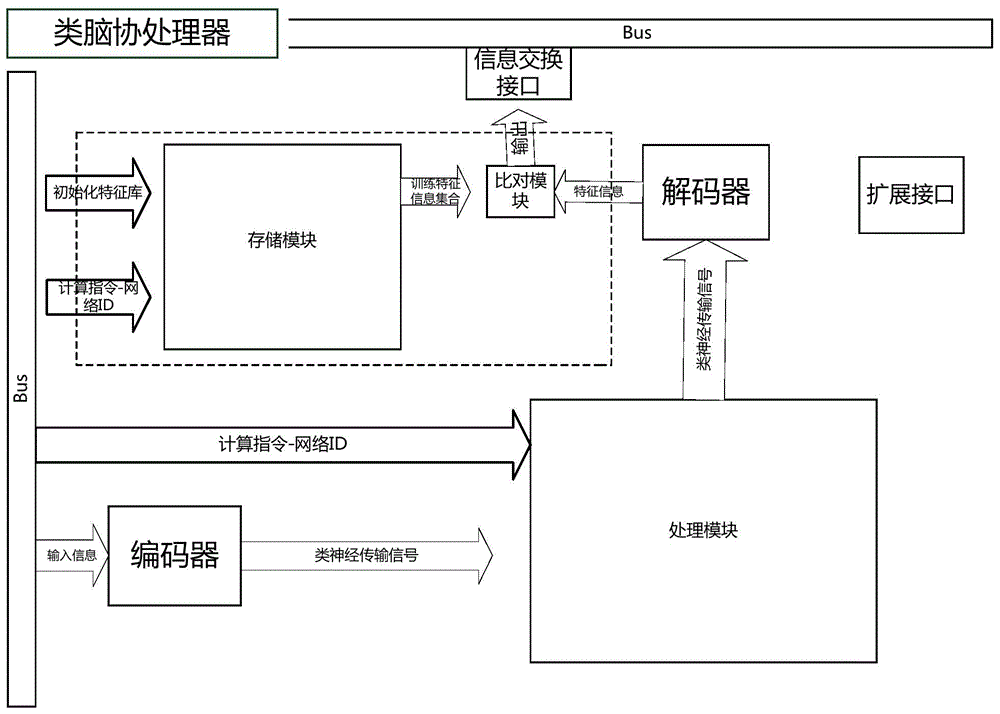
Brain-like coprocessor based on neuromorphic circuit
ActiveCN104809498AImprove work efficiencyAchieving AdaptivenessBiological modelsFault toleranceProgramming complexity
The invention provides a brain-like coprocessor based on a neuromorphic circuit. The brain-like coprocessor comprises a storage module storing training characteristic information, a processing module of the neuromorphic circuit based on a hierarchical structure, an encoder and a decoder which are respectively connected with the input end and the output end of the processing module, and a comparison module which is respectively connected with the output end of the storage module and the output end of the decoder. The storage module of the brain-like coprocessor comprises a training characteristic database and / or a configurable training characteristic database. The processing module comprises a solidification function network module and / or a configurable function network module and has a quite good expansion capability. According to the invention, the brain-like coprocessor employs a distributed storage and parallel cooperative processing mode, is especially suitable for processing non-formal problems and unstructured information and can also process formal problems and structured information, such that the speed of a computer in processing such problems as brain-like calculation, artificial intelligence and the like is substantially accelerated, the energy consumption is reduced, the fault tolerance capability is greatly improved, the programming complexity is reduced, and the computer performance is enhanced.
Owner:LYNXI TECH CO LTD
Analog neuromorphic circuit implemented using resistive memories
An analog neuromorphic circuit is disclosed, having input voltages applied to a plurality of inputs of the analog neuromorphic circuit. The circuit also includes a plurality of resistive memories that provide a resistance to each input voltage applied to each of the inputs so that each input voltage is multiplied in parallel by the corresponding resistance of each corresponding resistive memory to generate a corresponding current for each input voltage and each corresponding current is added in parallel. The circuit also includes at least one output signal that is generated from each of the input voltages multiplied in parallel with each of the corresponding currents for each of the input voltages added in parallel. The multiplying of each input voltage with each corresponding resistance is executed simultaneously with adding each corresponding current for each input voltage.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
Circuits and methods representative of spike timing dependent plasticity of neurons
InactiveUS8600919B2Digital computer detailsNeural architecturesSynapseSpike-timing-dependent plasticity
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE +1
Low-power-consumption nerve synapse thin film transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110416312AImprove performanceReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingState of artGate dielectric
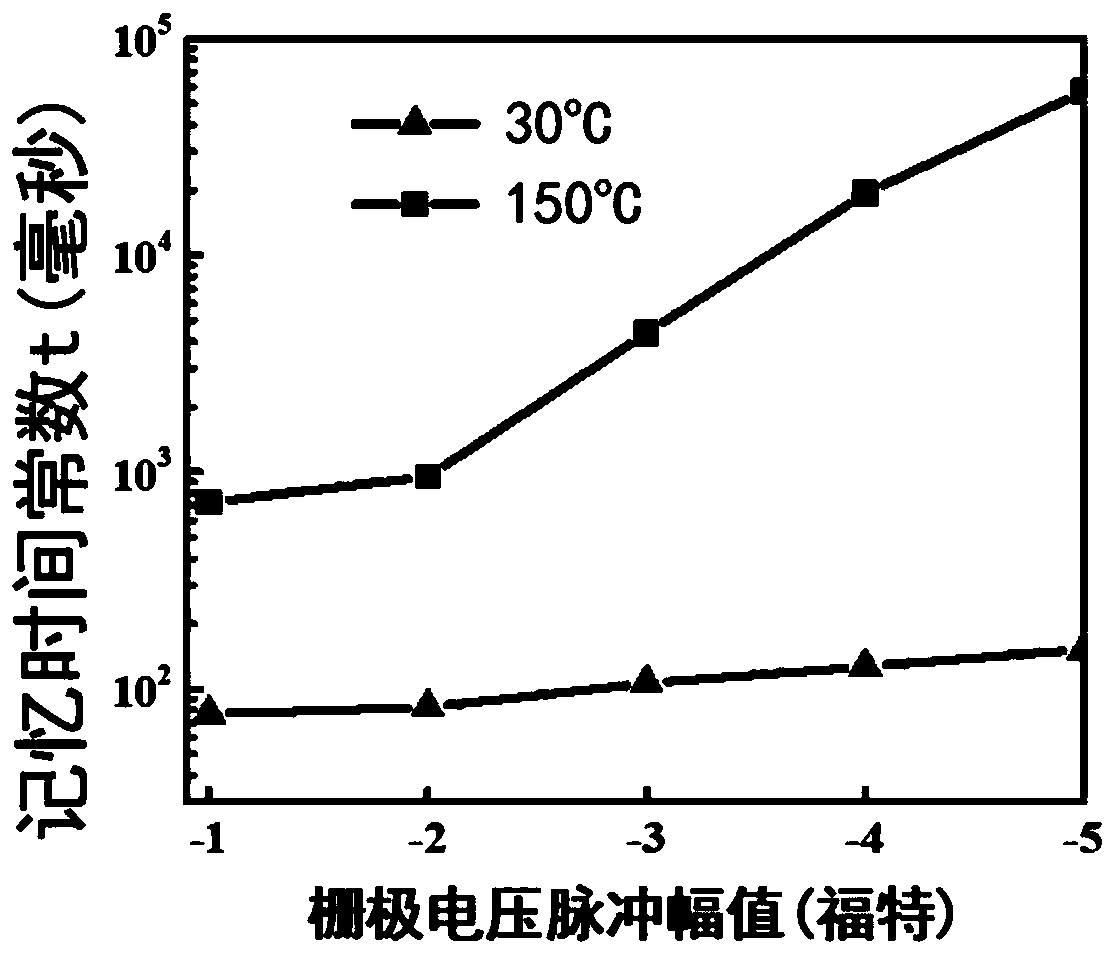
The invention relates to a low-power-consumption neural synapse thin film transistor and a preparation method thereof. The transistor structurally comprises a back gate electrode, a gate dielectric layer, a conductive channel and a source-source electrode from bottom to top in sequence. The source-drain electrode is arranged on the upper surface of the gate dielectric layer, and the conductive channels are located on the upper surface and two sides of the source-drain electrode; channels are formed on the upper surface of the source-drain electrode. Compared with the prior art, the transistorhas ultra-low power consumption at a normal focus level; the adjustable memory time from milliseconds to thousands of seconds can be realized at different dielectric layer preparation temperatures; meanwhile, the stability of the transistor is greatly improved due to the use of a full-inorganic material; the flexibility and synaptic performance of the transistor can be used for flexible electronics and large-scale neuromorphic circuit systems.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Analog neuromorphic circuit implemented using resistive memories
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Memory capacitor made from field configurable ion-doped materials
InactiveUS20110108952A1Consumes low amountConsume energySolid-state devicesCapacitorsDopantCapacitance
A memory capacitor based on a field configurable ion-doped polymer is reported. The device can be dynamically and reversibly programmed to analog capacitances with low-voltage (<5 V) pulses. After the device is programmed to a specific value, its capacitance remains nonvolatile. The field configurable capacitance is attributed to the modification of ionic dopant concentrations in the polymer. The ion and dipole concentrations in the ion conductive layer can be modified when the voltage biases applied to the electrodes exceeds a threshold value and can operate as a conventional capacitor when a voltage less than the threshold value is applied. The ion conductive layer will remain at a stable value after the device is modified without applying external voltage. The device has a nonvolatile memory function even when the external voltage is turned off. The memory capacitors may be used for analog memory, nonlinear analog and neuromorphic circuits.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Synapse for function cell of spike timing dependent plasticity (STDP), function cell of STDP, and neuromorphic circuit using function cell of STDP
ActiveUS9087302B2Reduce weightReduce resistanceDigital computer detailsDigital storageSpike-timing-dependent plasticityNeuromorphic circuits
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Robot control system and method based on memristor intersection array
ActiveCN110842915AImprove battery lifeReduce power consumptionProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical realisationControl signalNeural network nn
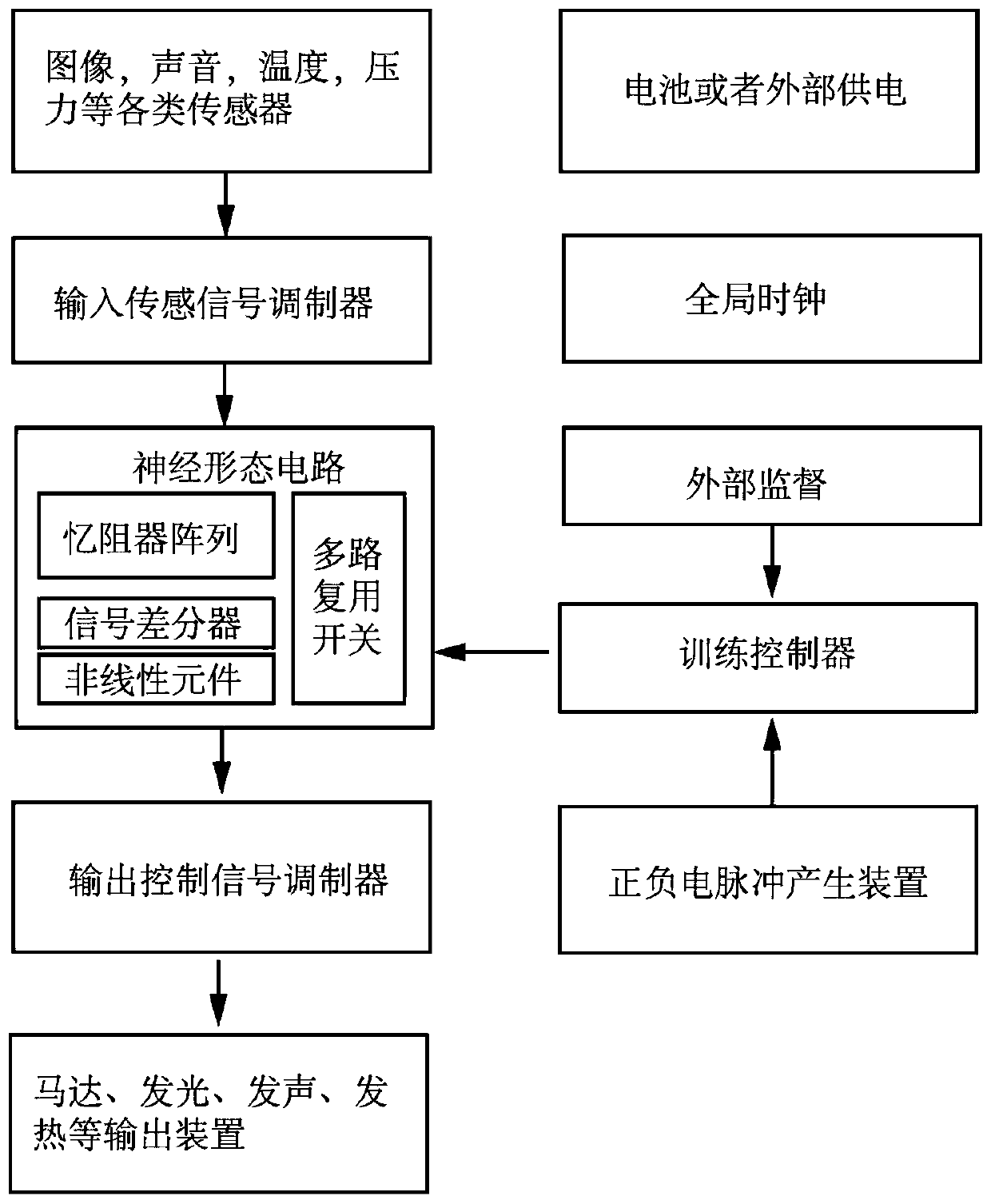
The invention discloses a robot control system and method based on a memristor intersection array. The system involves a sensor group, an input sensing signal modulator, a neuromorphic circuit, an output control signal modulator, an output device, an external supervision module and a training controller; and control of a robot is performed by the neuromorphic circuit, and the main part of the neuromorphic circuit is the memristor intersection array with a fully connected neural network structure. A differential amplification circuit and a multiplexing switch in the neuromorphic circuit are connected to the memristor intersection array, an input signal vector is multiplied with a weight matrix stored in the memristor intersection array, and then one or more analog output signals are obtained through the differential amplification circuit. According to the robot control system and method, the memristor neuromorphic circuit is used for reducing the power consumption of an existing robot control system in performing neural network operation; and memristors are directly used for simulating the weight in a biological neural network, the complexity is effectively reduced, and the responsespeed is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
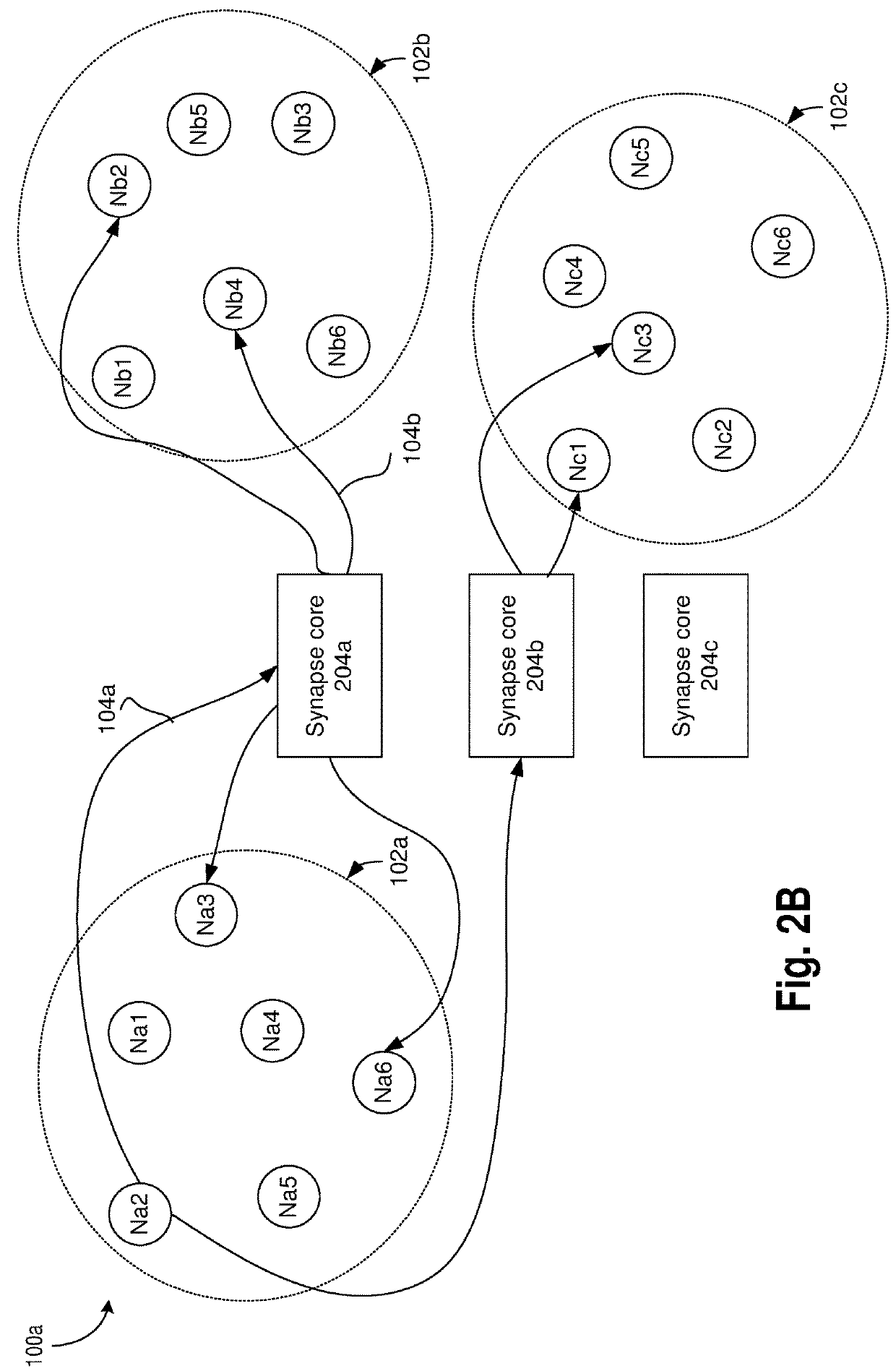
Neuromorphic circuits for storing and generating connectivity information
A neuromorphic computing system is provided which comprises: a synapse core; and a pre-synaptic neuron, a first post-synaptic neuron, and a second post-synaptic neuron coupled to the synaptic core, wherein the synapse core is to: receive a request from the pre-synaptic neuron, generate, in response to the request, a first address of the first post-synaptic neuron and a second address of the second post-synaptic neuron, wherein the first address and the second address are not stored in the synapse core prior to receiving the request.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Transistorless all-memristor neuromorphic circuits for in-memory computing
PendingUS20200356847A1Digital data processing detailsSolid-state devicesVoltage spikeElectrical conductor
A circuit for multiplying a number N of first operands each by a corresponding second operand, and for adding the products of the multiplications, with N≥2; the circuit comprising: N input conductors; N programmable conductance circuits connected each between one of the input conductors and at least one output conductor; each programmable conductance circuit being arranged to be programmable at a value depending in a known manner from one of the first operands; each input conductor being arranged to receive from an input circuit an input train of voltage spikes having a spike rate that derives in a known manner from one of the second operands; and at least one output circuit arranged to generate an output train of voltage spikes having a spike rate that derives in a known manner from a sum over time of the spikes received on the at least one output conductor.
Owner:HRL LAB
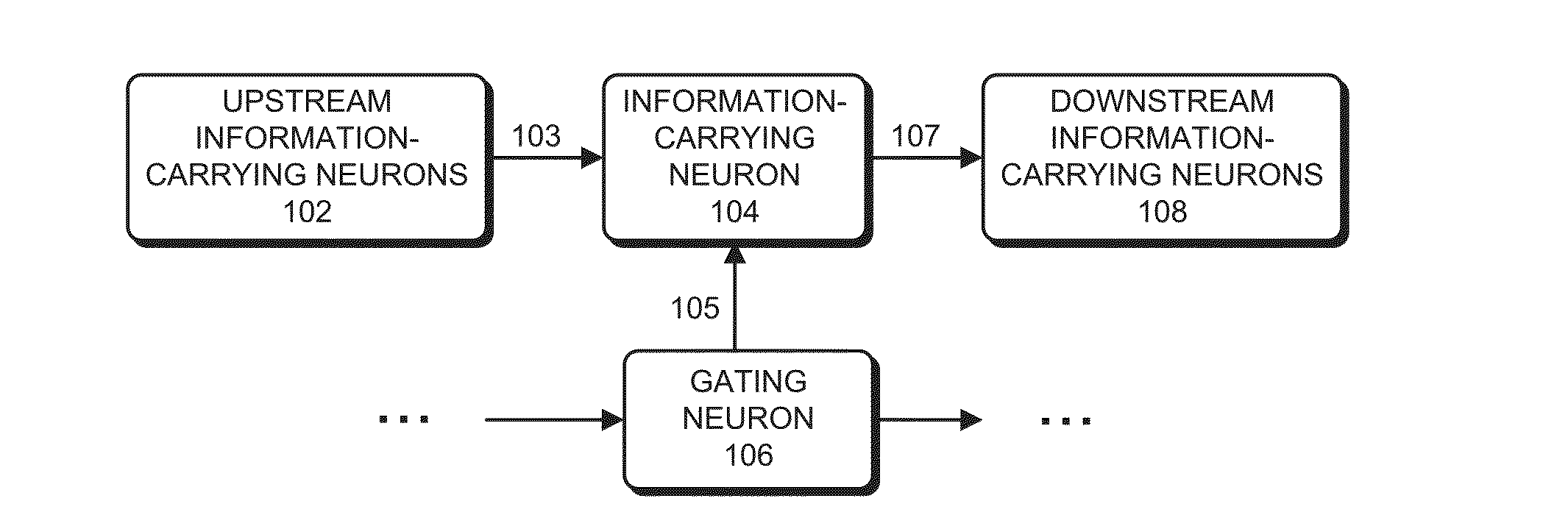
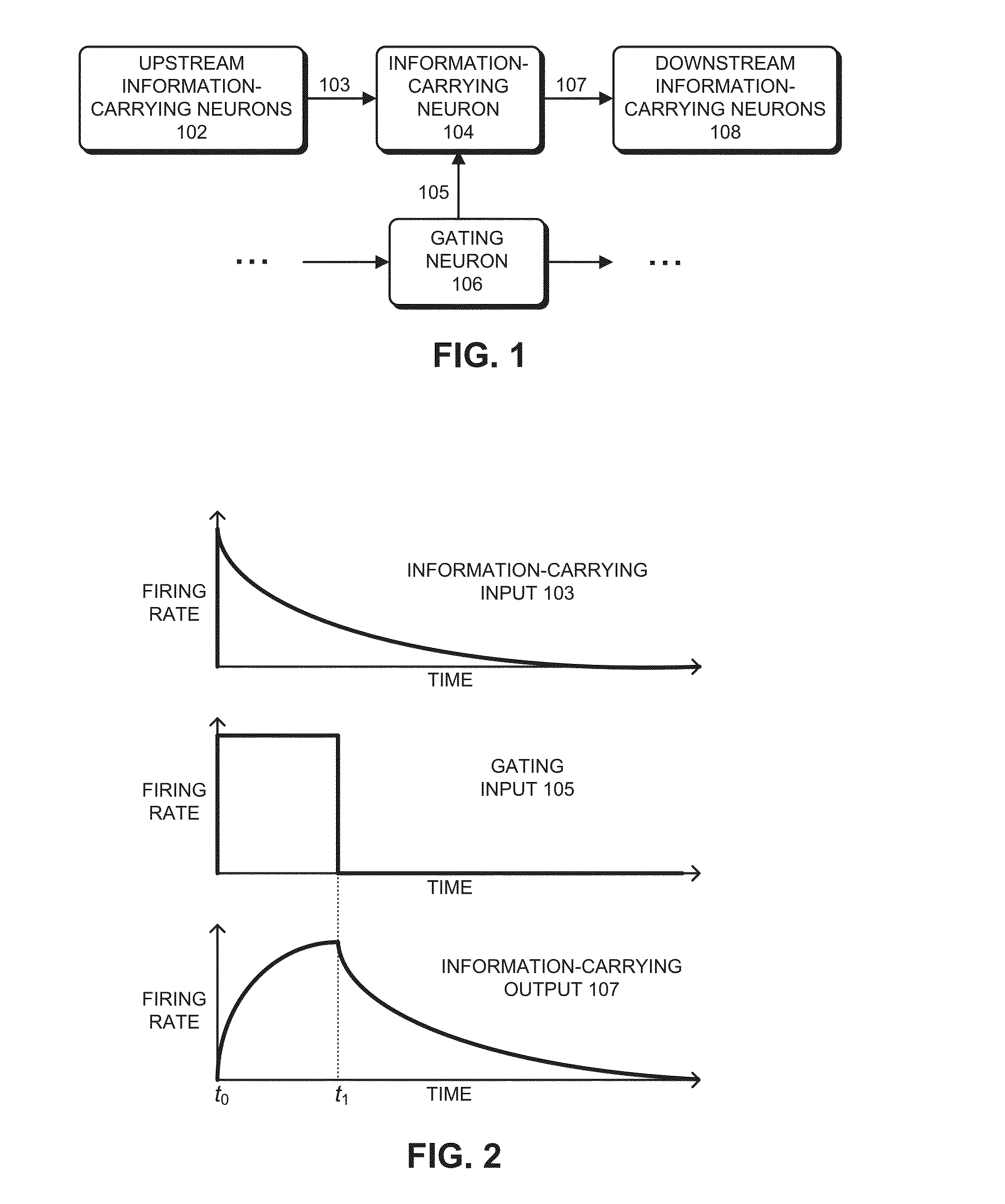
Neuromorphic circuit that facilitates information routing and processing
ActiveUS20160098630A1Digital computer detailsDigital dataArtificial intelligenceNeuromorphic circuits
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system that selectively propagates information through a neuromorphic circuit comprising a set of interconnected neurons. During operation, a neuron in the set of neurons receives information-carrying current pulses from one or more upstream information-carrying neurons, wherein the information-carrying current pulses are insufficient to cause the neuron to generate output current pulses. The neuron also receives selectively generated gating current pulses from one or more gating neurons, wherein the gating current pulses cause a neural voltage of the neuron to approach a firing threshold. In this way, concurrently received information-carrying current pulses combine with the gating current pulses to cause the neural voltage to exceed the firing threshold, which causes the neuron to generate output current pulses that propagate to downstream neurons.
Owner:UNIVERSTIY OF CALIFORNIA
Neuromorphic architecture with multiple coupled neurons using internal state neuron information
ActiveUS20170372194A1Improve performanceImprove abilitiesNeural architecturesPhysical realisationPhase changeNeuron
This invention relates to an apparatus, system, and method for computing with neuromorphic circuit architectures that have neurons with interconnected internal state information. The interconnected internal state information allows the neurons to enable or strengthen the input to other neurons. Furthermore, neuron internal state information provides insights on the characteristics of the input data that can be used to enhance the performance of the neuromorphic system. The neuromorphic system can be implemented with an artificial phase-change-based neurons.
Owner:IBM CORP
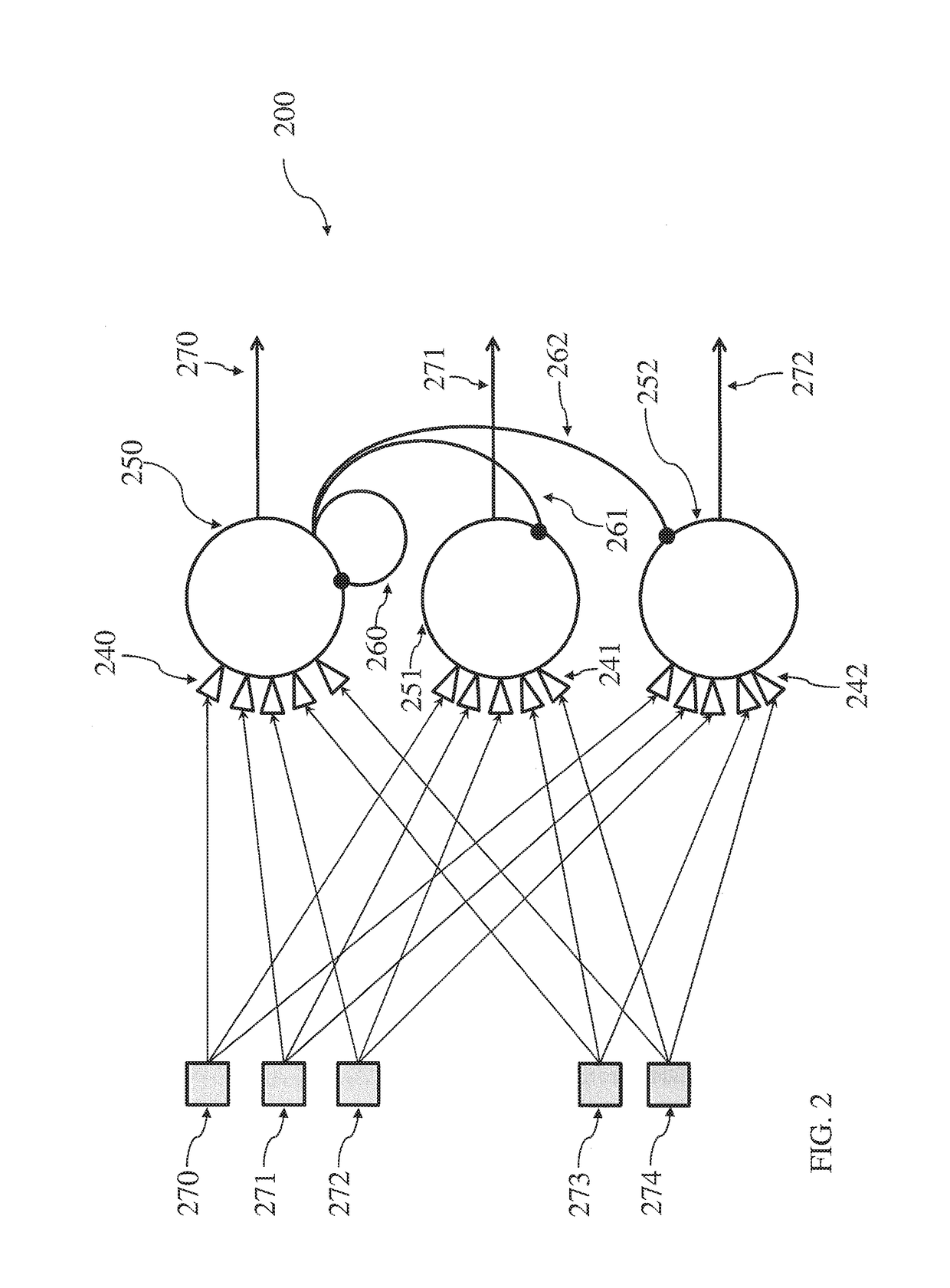
Electronic circuit with neuromorphic architecture
ActiveUS9171248B2Improve architectureImprove operationDigital computer detailsDigital dataElectrical conductorSynaptic weight
Neuromorphic circuits are multi-cell networks configured to imitate the behavior of biological neural networks. A neuromorphic circuit is provided which comprises a network of neurons each identified by a neuron address in the network, each neuron being able to receive and process at least one input signal and then later emit on an output of the neuron a signal representing an event which occurs inside the neuron, and a programmable memory composed of elementary memories each associated with a respective neuron. The elementary memory, which is a memory of post-synaptic addresses and weights, comprises an activation input linked by a conductor to the output of the associated neuron to directly receive an event signal emitted by this neuron without passing through an address encoder or decoder. The post-synaptic addresses extracted from an elementary memory activated by a neuron are applied, with associated synaptic weights, as inputs to the neural network.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Linearly weight updatable CMOS synaptic array without cell location dependence
A neuromorphic circuit, chip, and method are provided. The neuromorphic circuit includes a crossbar synaptic array cell. The crossbar synaptic array cell includes a Complimentary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) transistor having an on-resistance controlled by a gate voltage of the CMOS transistor to update a weight of the crossbar synaptic array cell. The neuromorphic circuit further includes a set of row-lines respectively connecting the synaptic array cell in series to a plurality of pre-synaptic neurons at first ends thereof. The neuromorphic circuit also includes a set of column-lines respectively connecting the synaptic array cell in series to a plurality of post-synaptic neurons at second ends thereof. The gate voltage of the CMOS transistor is controlled by performing a charge sharing technique that updates the weight of the crossbar synaptic array cell using non-overlapping pulses on control lines that are aligned with the set of row lines and the set of column lines.
Owner:IBM CORP
Analog neuromorphic circuits for dot-product operation implementing resistive memories
An analog neuromorphic circuit is disclosed having resistive memories that provide a resistance to each corresponding input voltage signal. Input voltages are applied to the analog neuromorphic circuit. Each input voltage represents a vector value that is a non-binary value included in a vector that is incorporated into a dot-product operation with weighted matrix values included in a weighted matrix. A controller pairs each resistive memory with another resistive memory. The controller converts each pair of resistance values to a single non-binary value. Each single non-binary value is mapped to a weighted matrix value included in the weighted matrix that is incorporated into the dot-product operation with the vector values included in the vector. The controller generates dot-product operation values from the dot-product operation with the vector and the weighted matrix where each dot-product operation is a non-binary value.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Semiconductor device including ferroelectric material, neuromorphic circuit including the semiconductor device, and neuromorphic computing apparatus including the neuromorphic circuit
PendingUS20210036024A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialHemt circuits
A semiconductor device includes a first transistor including a first channel layer of a first conductivity type, a second transistor provided in parallel with the first transistor and including a second channel layer of a second conductivity type, and a third transistor stacked on the first and second transistors. The third transistor may include a gate insulating film including a ferroelectric material. The third transistor may include third channel layer and a gate electrode that are spaced apart from each other in a thickness direction with the gate insulating film therebetween.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
On-chip training of memristor crossbar neuromorphic processing systems
An analog neuromorphic circuit is disclosed having resistive memories that provide a resistance to an input voltage signal as the input voltage signal propagates through the resistive memories generating a first output voltage signal and to provide a resistance to a first error signal that propagates through the resistive memories generating a second output voltage signal. A comparator generates the first error signal that is representative of a difference between the first output voltage signal and the desired output signal and generates the first error signal so that the first error signal propagates back through the plurality of resistive memories. A resistance adjuster adjusts a resistance value associated with each resistive memory based on the first error signal and the second output voltage signal to decrease the difference between the first output voltage signal and the desired output signal.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Scalable refresh for asymmetric non-volatile memory-based neuromorphic circuits
A computer-implemented method is provided for refreshing cells in a Non-Volatile Memory (NVM)-based neuromorphic circuit wherein synapses are each composed of a respective cell pair formed from a respective Gp cell and a respective Gm cell of the cells. The method includes randomly selecting multiple neurons and reading a conductance of any of the synapses connected to the multiple neurons. The method further includes selecting any of the synapses connected to the selected multiple neurons for which the Gm conductance has reached a maximum conductance. The method also includes resetting the Gp cell and Gm cell of the selected synapses, and setting, at most, one of the Gp cell and Gm cell of each of the selected synapses to recover an effective total weight of each of the selected synapses.
Owner:IBM CORP
Neuromorphic circuit, neuromorphic array learning method, and program
PendingUS20210312272A1Stable executionFast convergenceDigital storageNeural architecturesComputer hardwareControl cell
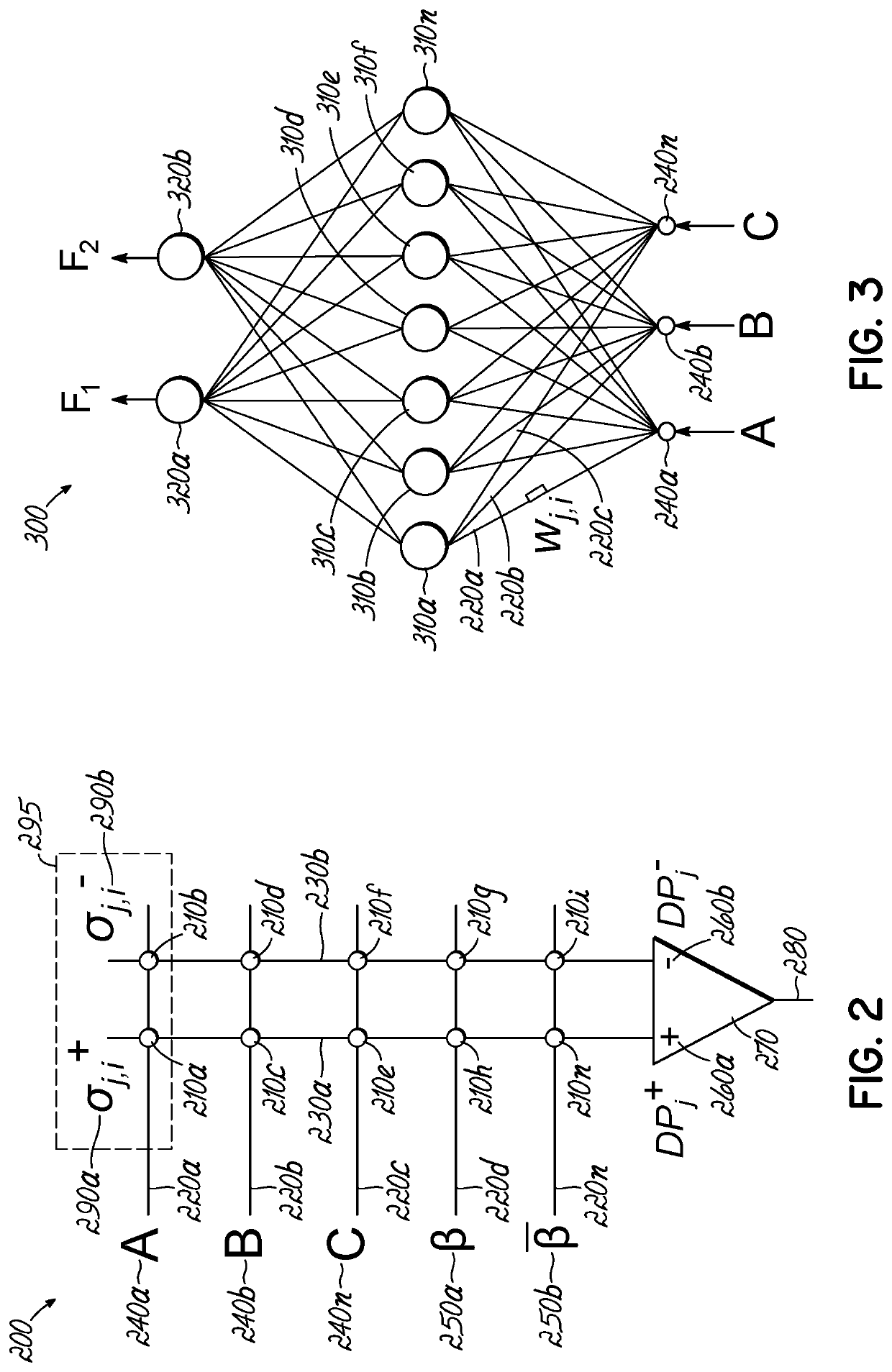
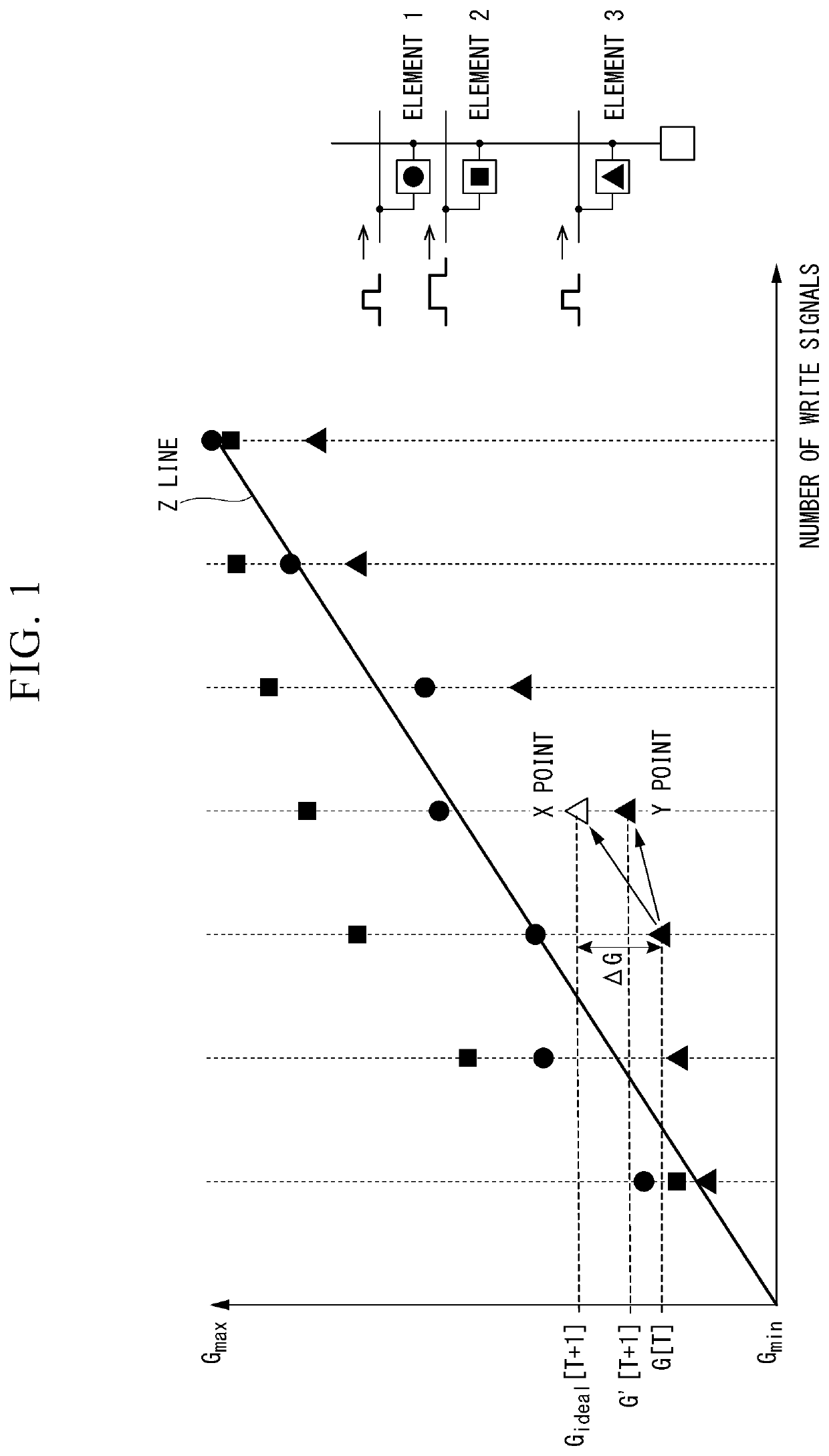
A control device of an array including neuromorphic elements that multiply a signal by a weight corresponding to a value of a variable characteristic is provided with a control unit which calculates update amounts of element conductances in a neuromorphic array on the basis of weight update amounts from a learning algorithm, and, after applying a write signal for changing conductances in the neuromorphic array, selects certain elements with reference to a predetermined threshold value and applies an additional write signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Memory capacitor made from field configurable ion-doped materials
A memory capacitor based on a field configurable ion-doped polymer is reported. The device can be dynamically and reversibly programmed to analog capacitances with low-voltage (<5 V) pulses. After the device is programmed to a specific value, its capacitance remains nonvolatile. The field configurable capacitance is attributed to the modification of ionic dopant concentrations in the polymer. The ion and dipole concentrations in the ion conductive layer can be modified when the voltage biases applied to the electrodes exceeds a threshold value and can operate as a conventional capacitor when a voltage less than the threshold value is applied. The ion conductive layer will remain at a stable value after the device is modified without applying external voltage. The device has a nonvolatile memory function even when the external voltage is turned off. The memory capacitors may be used for analog memory, nonlinear analog and neuromorphic circuits.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
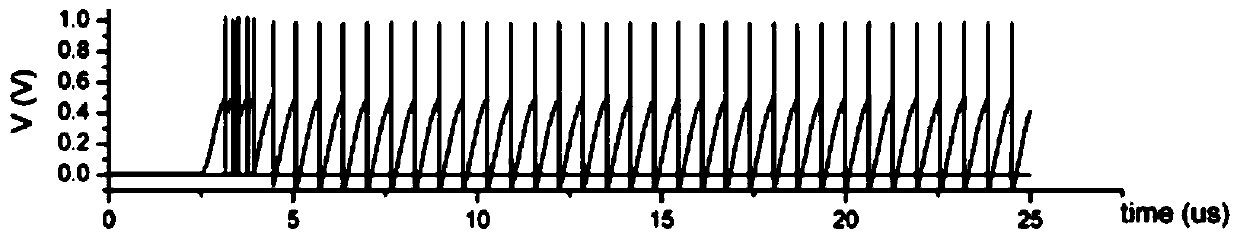
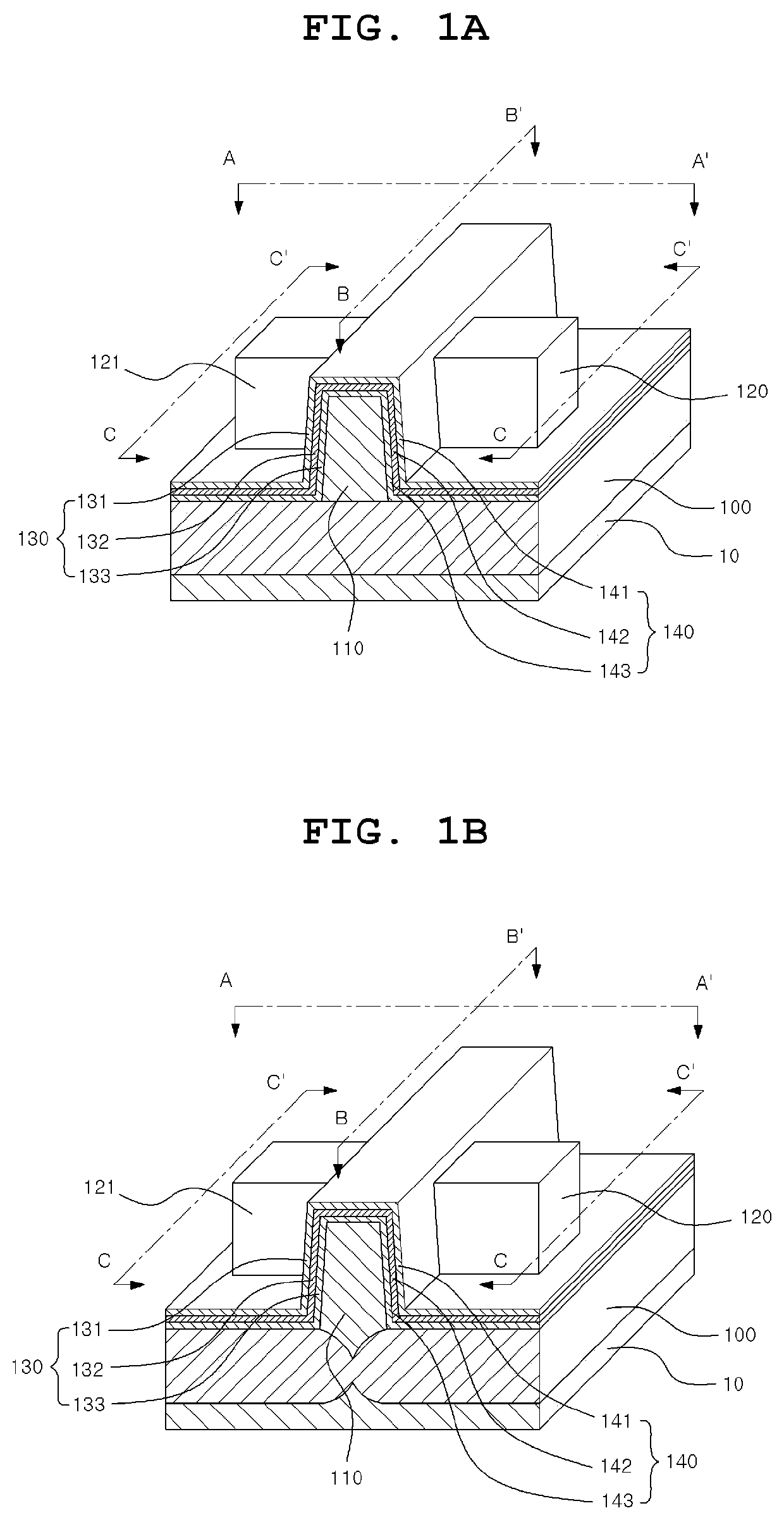
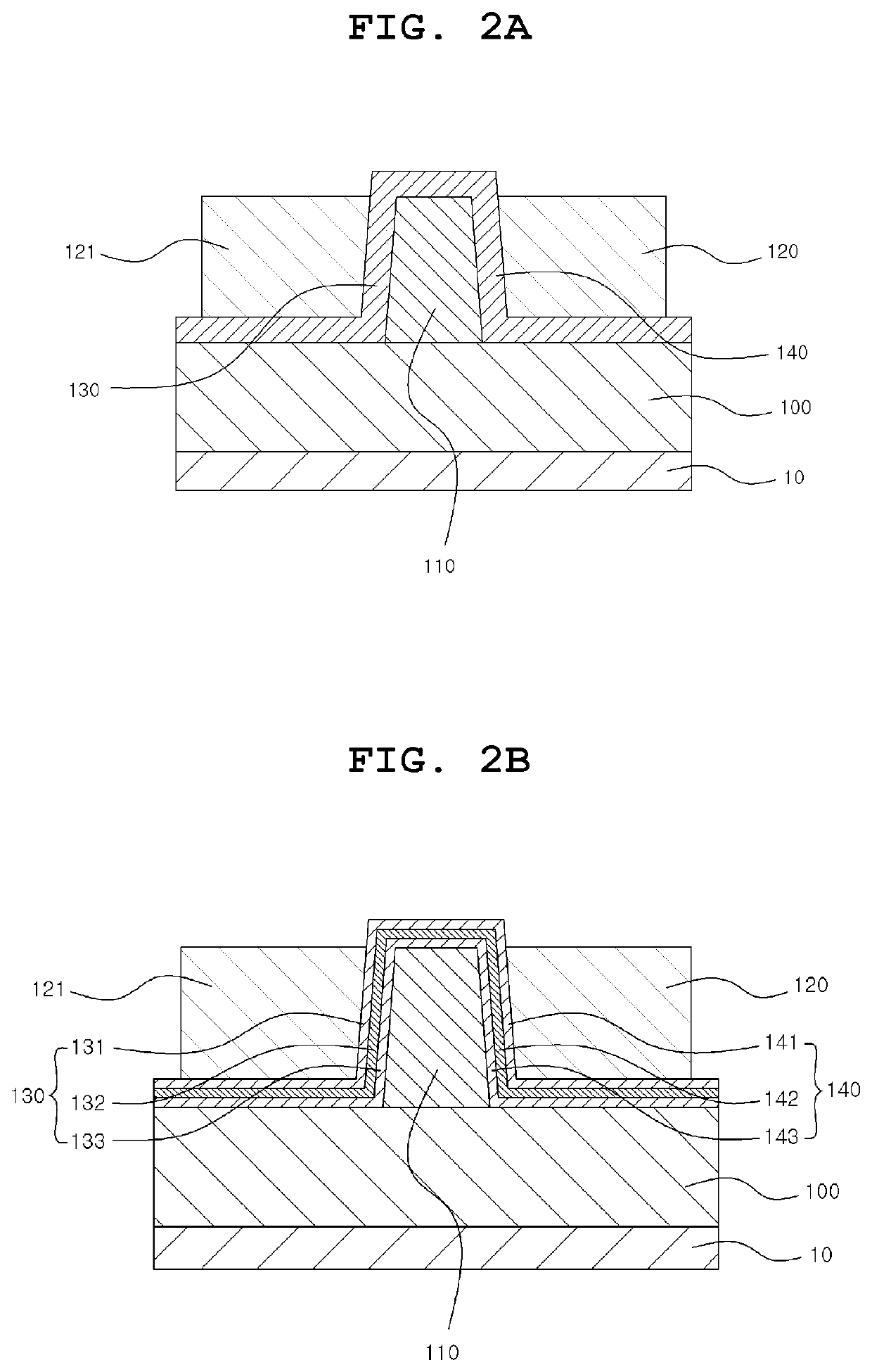
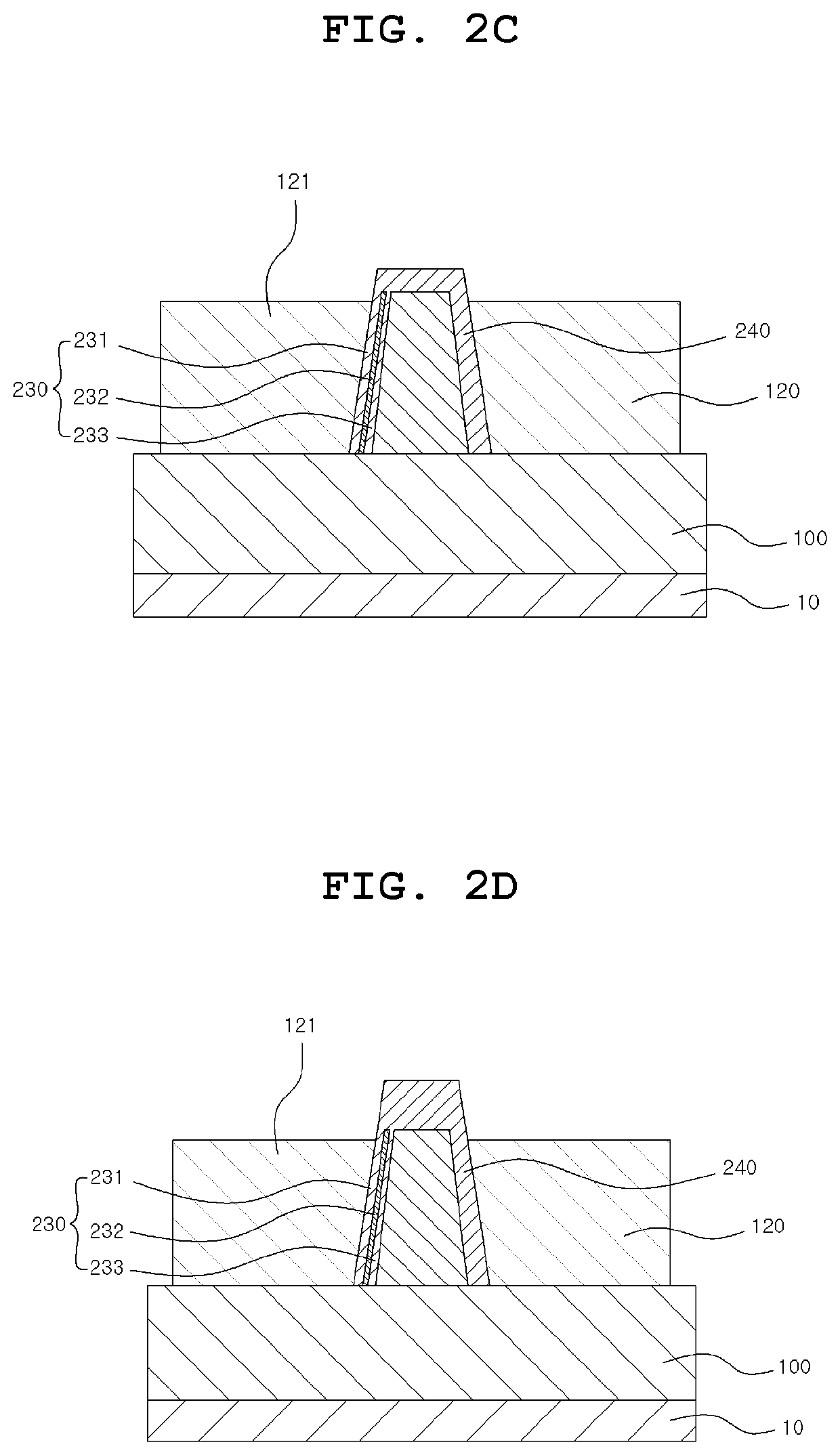
Neuromorphic devices and circuits
ActiveUS20170352750A1Function increaseImprove reliabilityTransistorThyristorNeuromorphic circuitsDumbbell shaped
Provided are a neuromorphic device and a neuromorphic circuit using the neuromorphic device. The neuromorphic device is configured to include a first semiconductor region formed on a substrate in a wall shape or a dumbbell shape; first, second, third, and fourth doped regions sequentially formed in the first semiconductor region; first and second gate insulating film stacks disposed on the respective side surfaces of the second doped region; first and second gate electrodes respectively disposed on the respective side surfaces of the second doped region; the first and second gate electrodes disposed on the respective side surface of the second doped region, the first and second gate electrodes being electrically insulated from the second doped, region by the first and second gate insulating film stacks; and first and second electrodes electrically connected to the first and fourth doped regions, respectively.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Neuromorphic circuit
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to neuromorphic circuits containing two or more internal neuron computational units. Each internal neuron computational unit includes a synchronization-signal input for receiving a synchronizing signal, at least one input for receiving input signals, and at least one output for transmitting an output signal. A memristive synapse connects an output signal line carrying output signals from a first set of one or more internal neurons to an input signal line that carries signals to a second set of one or more internal neurons.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Neuronal circuits and neuromorphic circuits
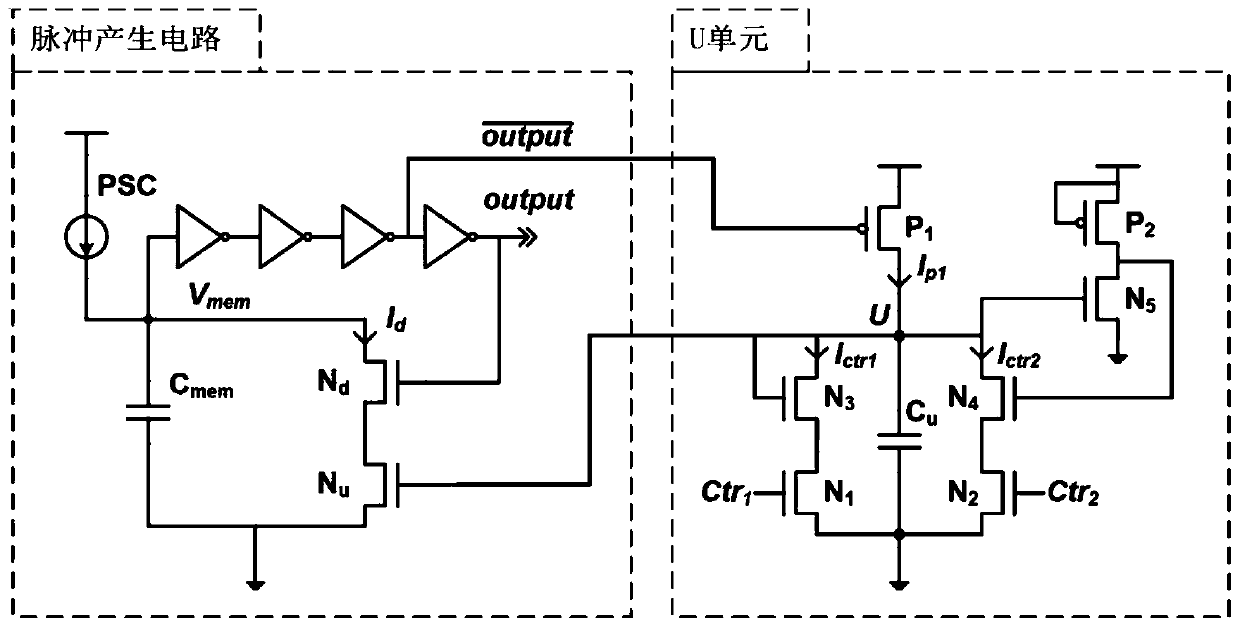
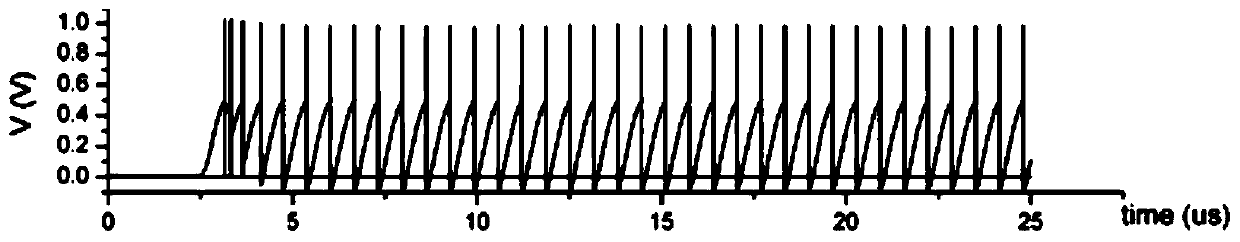
ActiveCN107194463BReduce power consumptionOvercoming sensitivityPhysical realisationPower flowEngineering
The present invention relates to a neuron circuit and a neuromorphic circuit, the neuron circuit includes a pulse generating circuit and a U unit connected to the control terminal of the pulse generating circuit; the pulse generating circuit is used to convert the input current into a pulse sequence , the U unit is used to control the excitation mode and pulse interval of the pulse generated by the pulse generating circuit. The neuron circuit and the neuromorphic circuit provided by the present invention use the U unit to control the pulse generation circuit to achieve different biological characteristics without using any bias voltage. The method realizes different biological characteristics, avoids the sensitivity of the circuit itself to the fluctuation of process, voltage and temperature, and makes the circuit easier to realize; at the same time, there is no normally open path in the circuit, so that the circuit consumes less power.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Neuromorphic devices and circuits
Provided are a neuromorphic device and a neuromorphic circuit using the neuromorphic device. The neuromorphic device is configured to include a first semiconductor region formed on a substrate in a wall shape or a dumbbell shape; first, second, third, and fourth doped regions sequentially formed in the first semiconductor region; first and second gate insulating film stacks disposed on the respective side surfaces of the second doped region; first and second gate electrodes respectively disposed on the respective side surfaces of the second doped region; the first and second gate electrodes disposed on the respective side surface of the second doped region, the first and second gate electrodes being electrically insulated from the second doped, region by the first and second gate insulating film stacks; and first and second electrodes electrically connected to the first and fourth doped regions, respectively.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com