Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Lossless compression algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
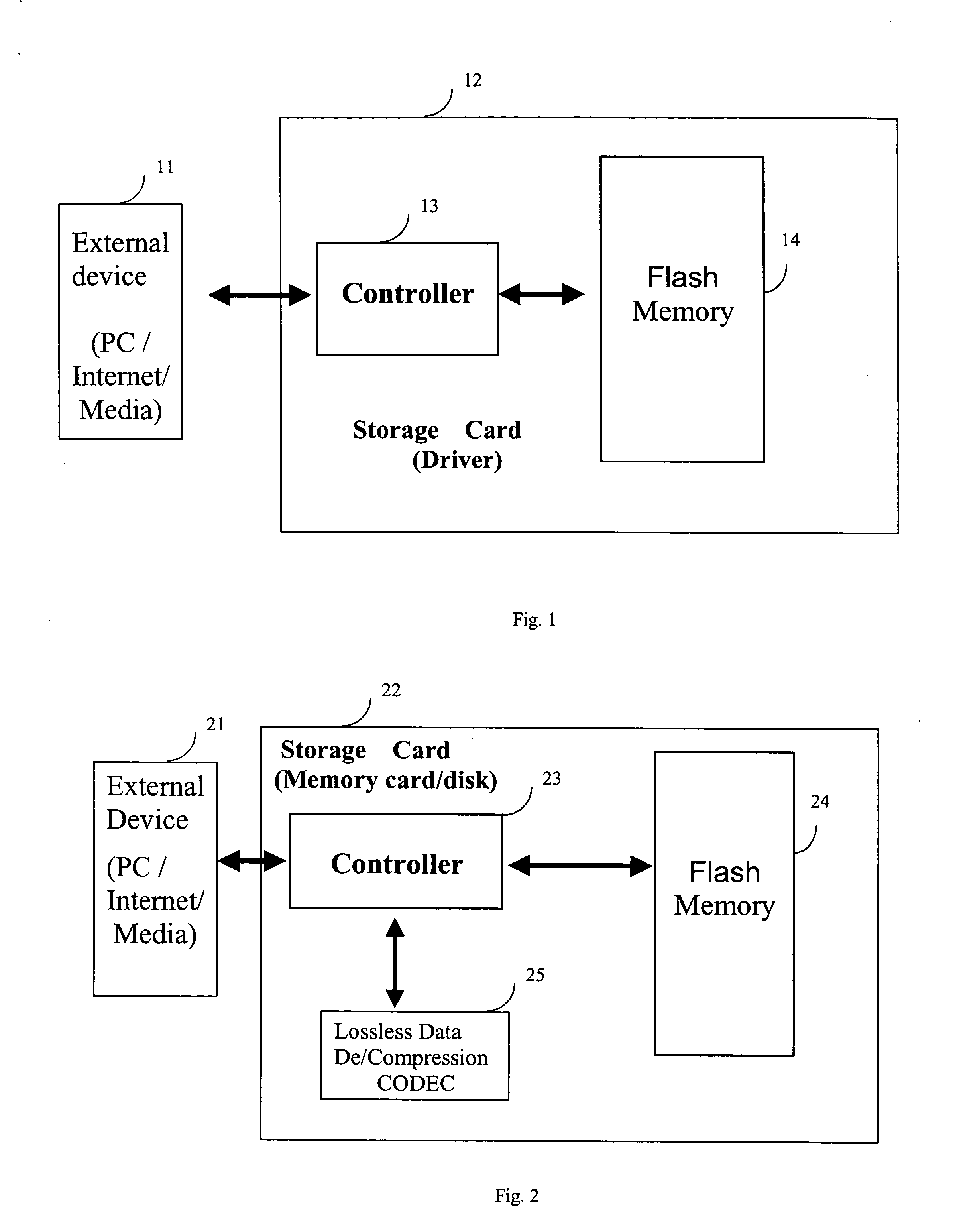
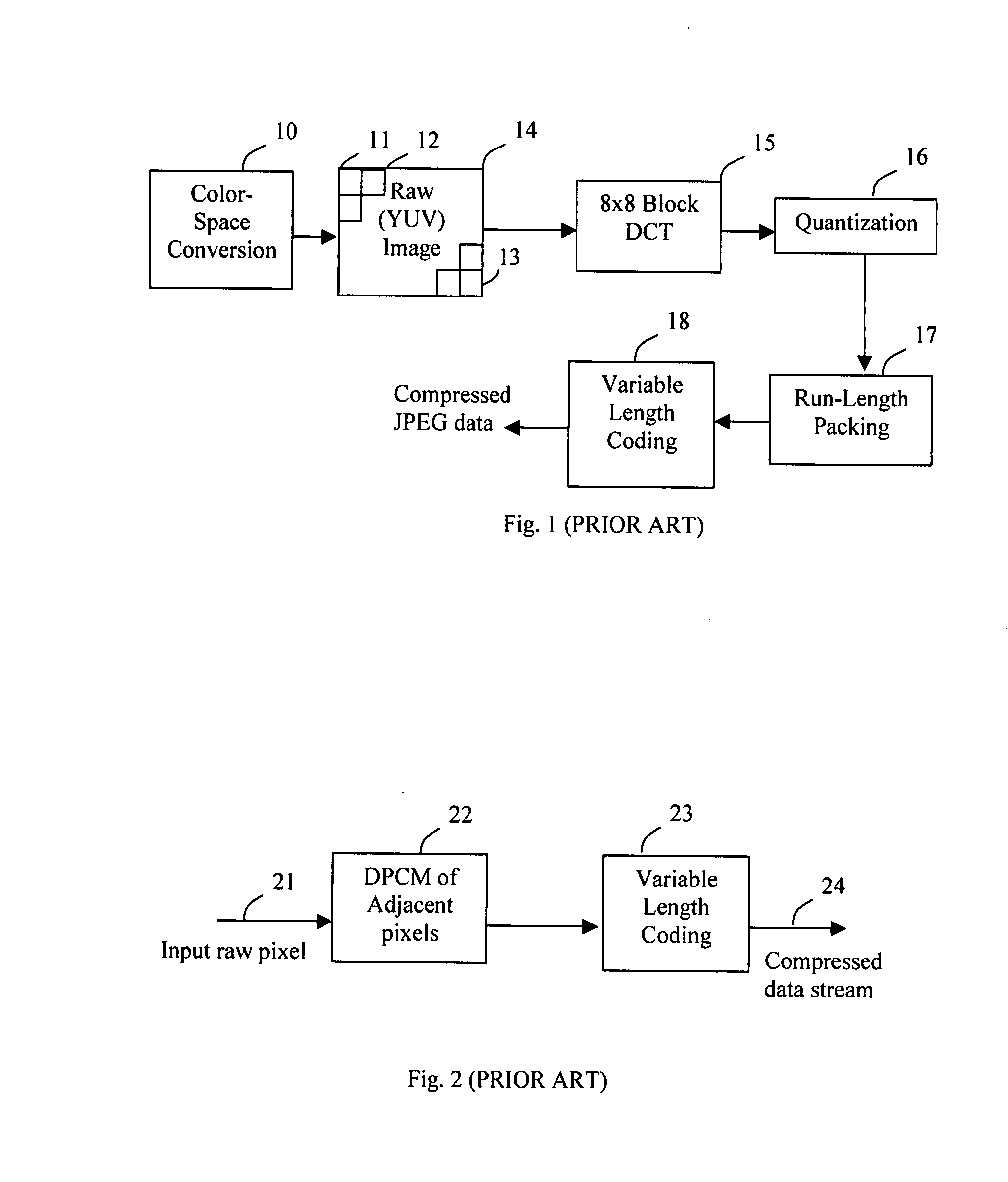
A lossless compression algorithm compresses data such that it can be decompressed to achieve exactly what was given before compression. The opposite would be a lossy compression algorithm. Lossy compression can remove data from a file.
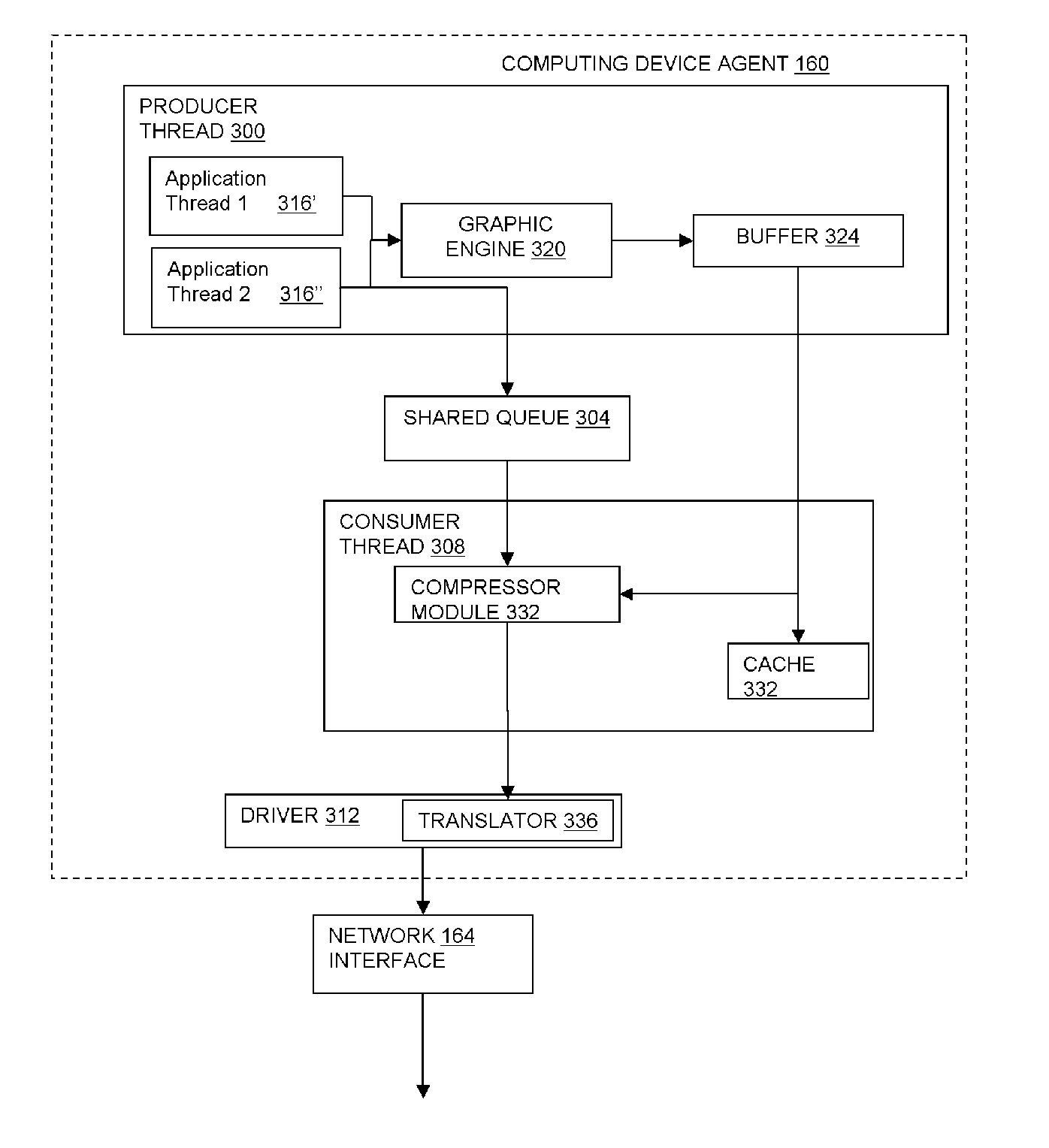
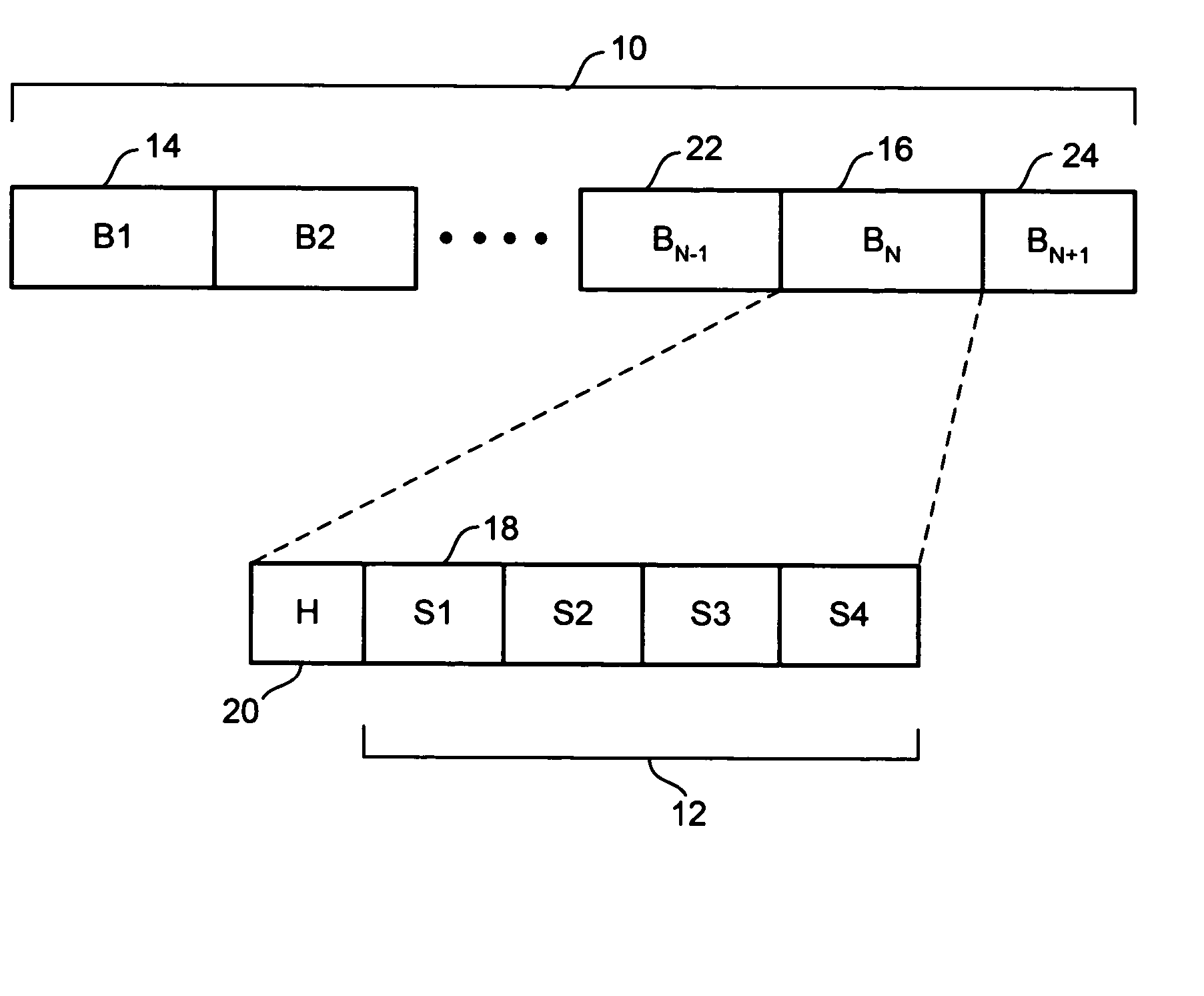
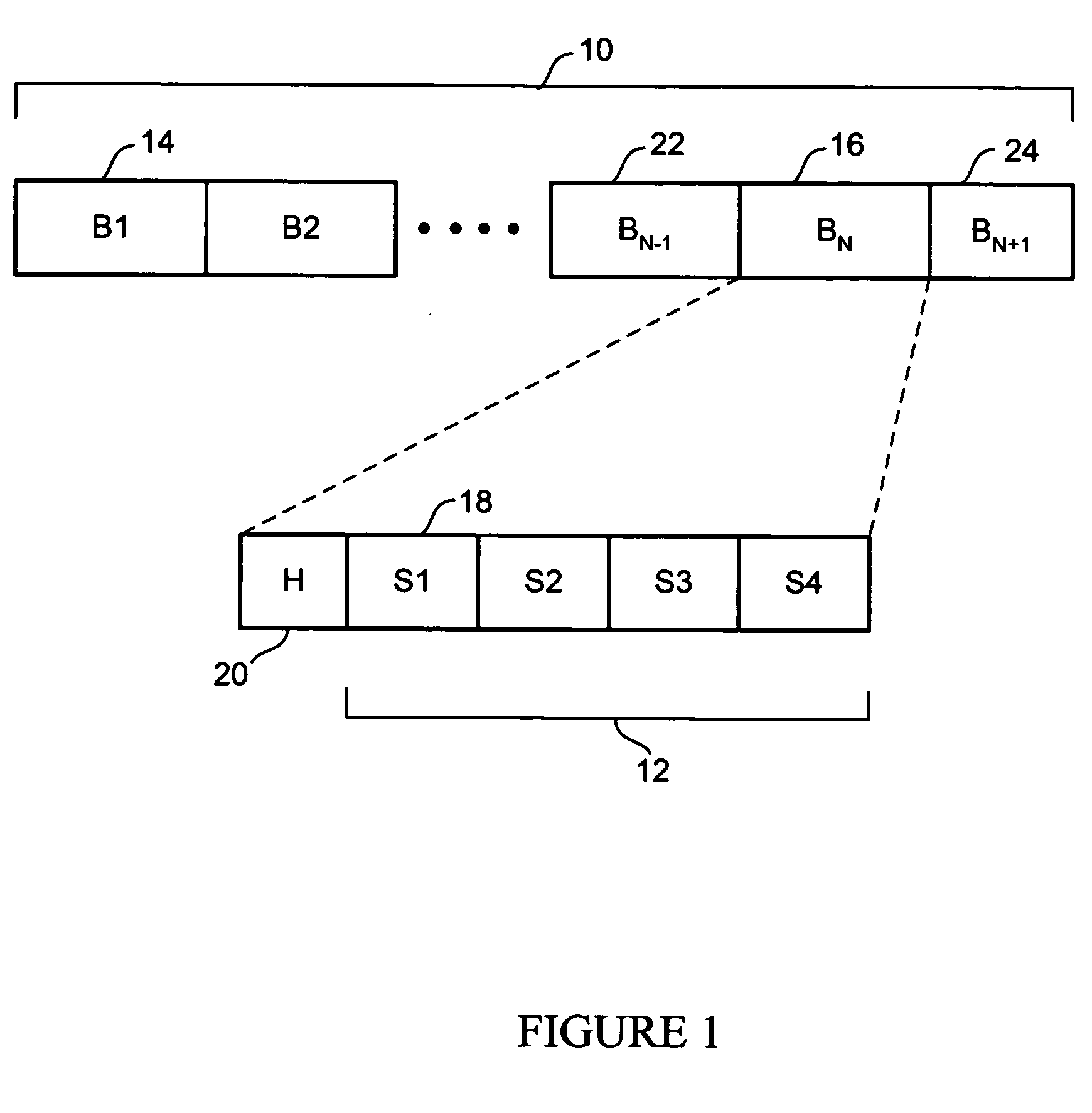
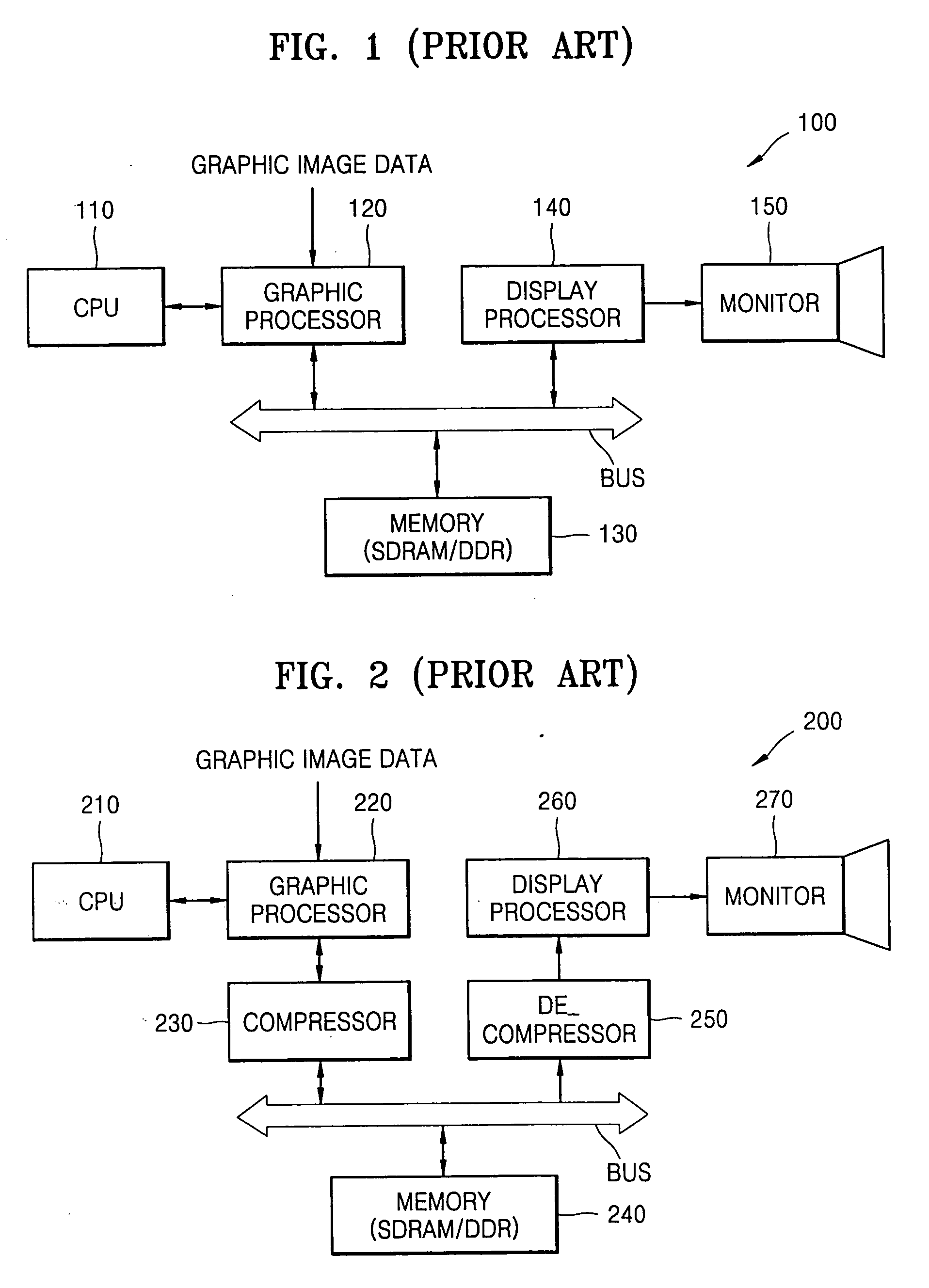
A method and apparatus for updating a graphical display in a distributed processing environment using compression
ActiveUS20060203007A1Database updatingGeometric image transformationGraphicsLossless compression algorithm
A system and method for updating a remote display unit that communicates with a computing system are described. The method includes accessing display update information from an update queue that stores drawing commands issued by an application executing on the computing system, caching the display update information, applying a lossy compression algorithm to the display update information to create a lossy display update, and transmitting the lossy update to the remote display. The method also includes applying a lossless compression algorithm to the display update information in the cache to create a lossless display update and transmitting the lossless display update a predetermined of time after transmitting the lossy update.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
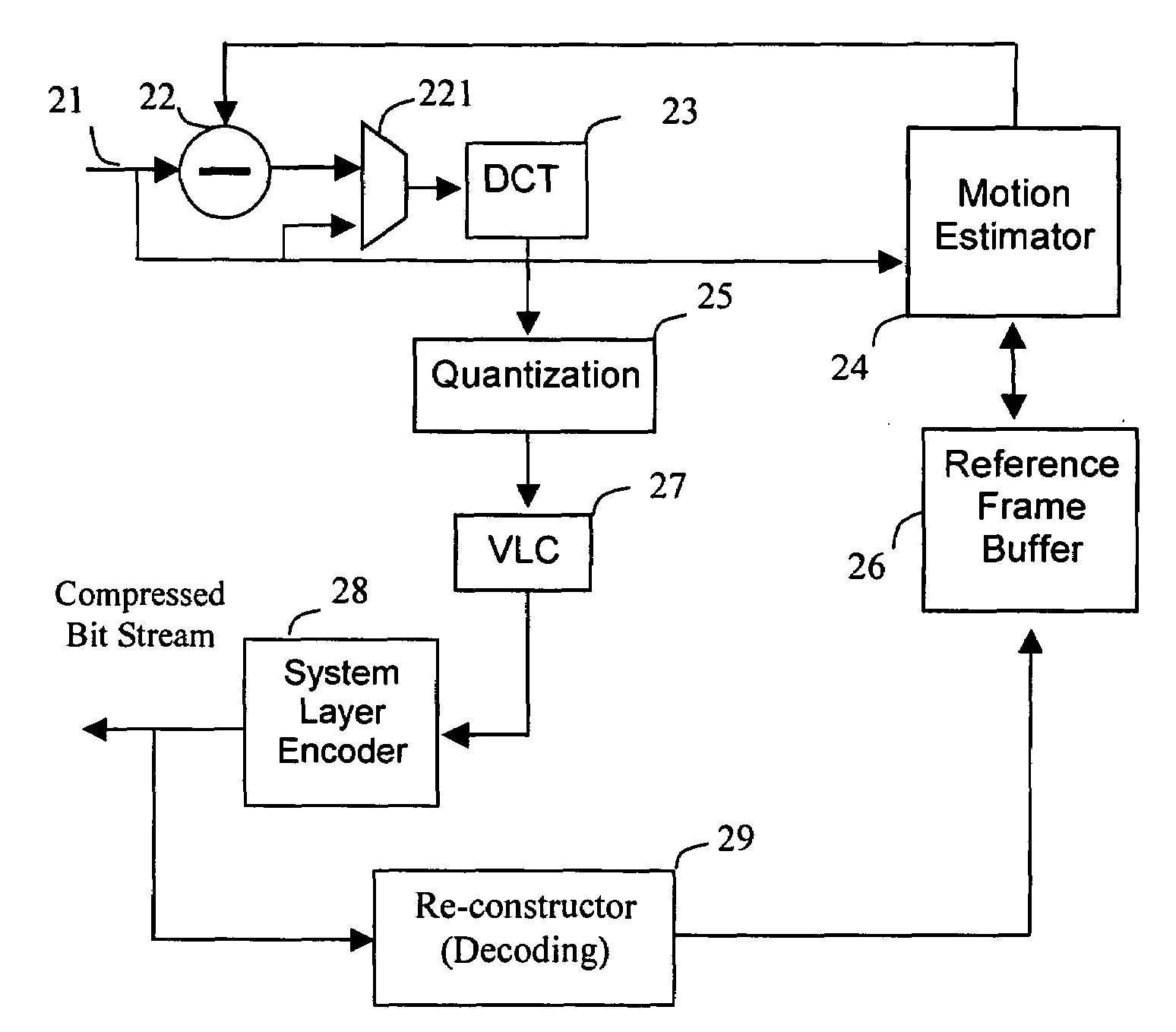
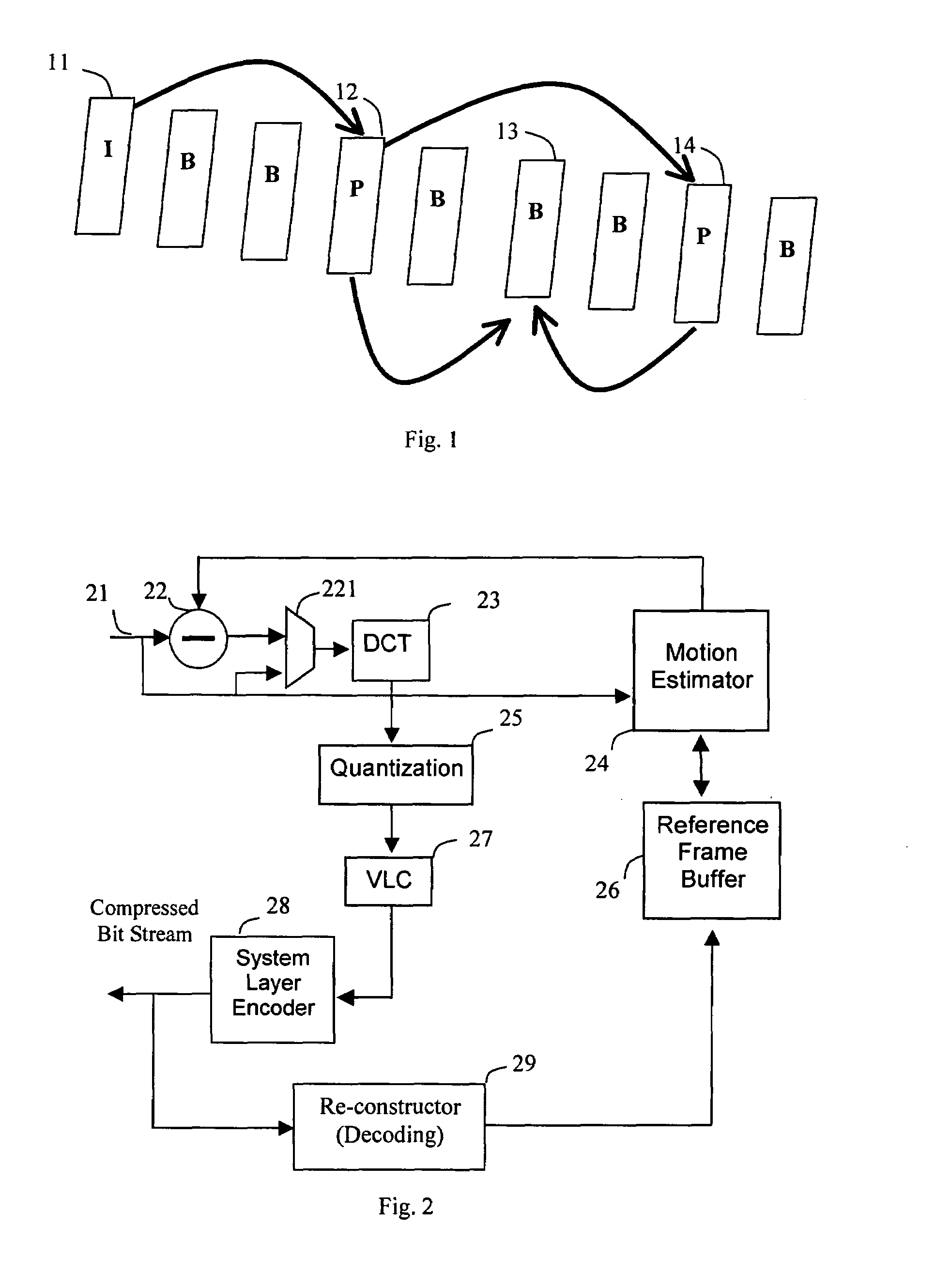
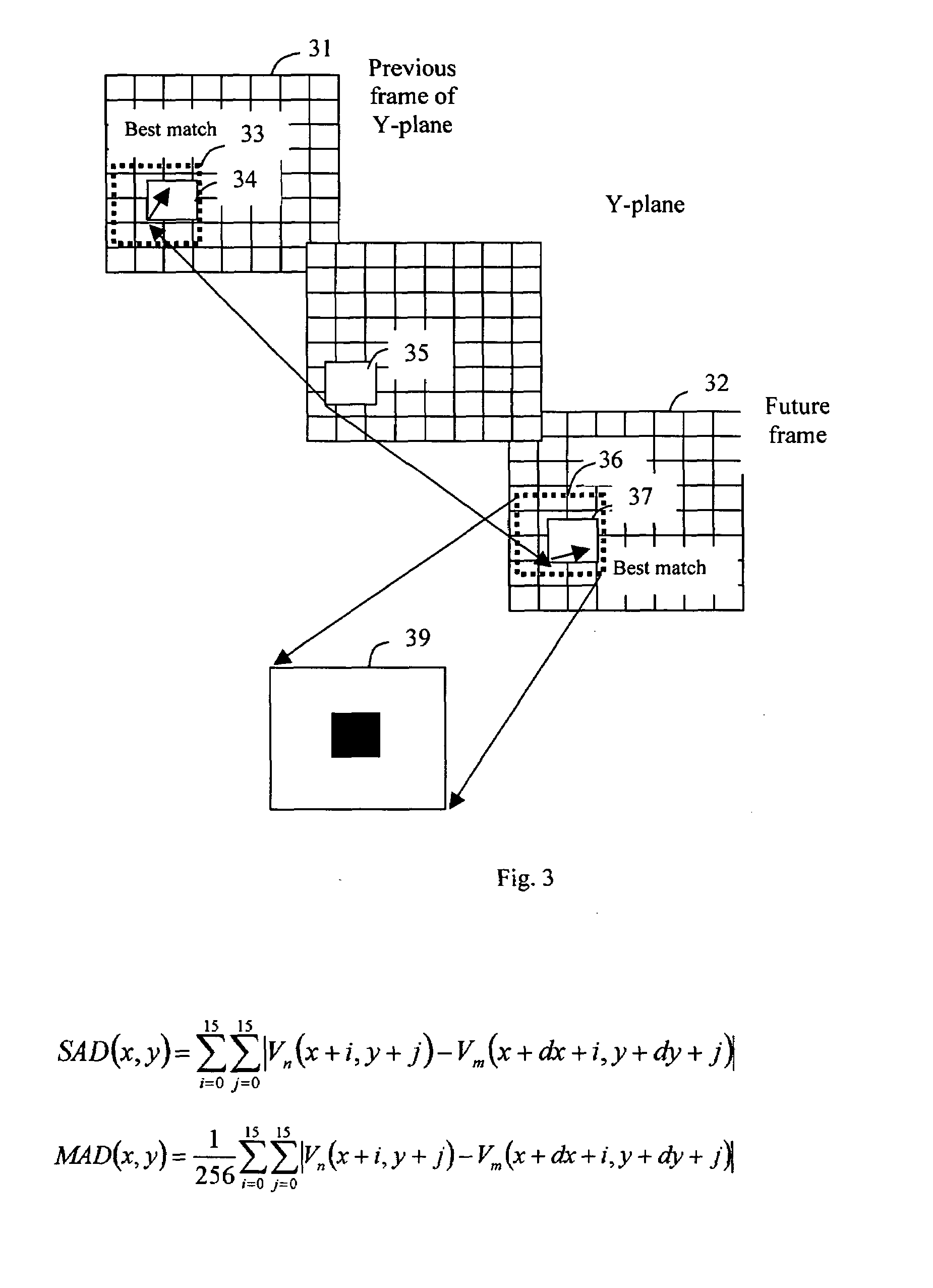
Method of digital video reference frame compression
ActiveUS20080170626A1High complexityAccelerated programColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoLossless compression algorithm
The digital video referencing frame image is compressed block by block by applying lossless compression algorithm to pixel components with full length, or 1 bit, 2 bits, 3 bits or 4 bits LSB bits truncation. If a sub-block has high complexity which results in more than 3 bits error for most pixel components, a transfer algorithm with quantization and VLC coding is applied to compress this sub-block. Should the complexity is higher than a threshold or at least one sub-block having error of more than 3 bits for most pixel components, truncating 1 LSB bit of sub-block with simple pattern to save more bits to be allocate to code the sub-block with highest complex pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
Lossless compression algorithm for hyperspectral data
InactiveUS20090018801A1Improve the level ofSmall sizeCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionSatellite dataData set
Lossless compression techniques provide efficient compression of hyperspectral satellite data. The present invention combines the advantages of a clustering with linear modeling. A number of visualizations are presented, which help clarify why the approach of the present invention is particularly effective on this dataset. At each stage, the algorithm achieves an efficient grouping of the data points around a relatively small number of lines in a very large dimensional data space. The parametrization of these lines is very efficient, which leads to efficient descriptions of data points. The method of the present invention yields compression ratios that compare favorably with what is currently achievable by other approaches.
Owner:SEC OF COMMERCE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
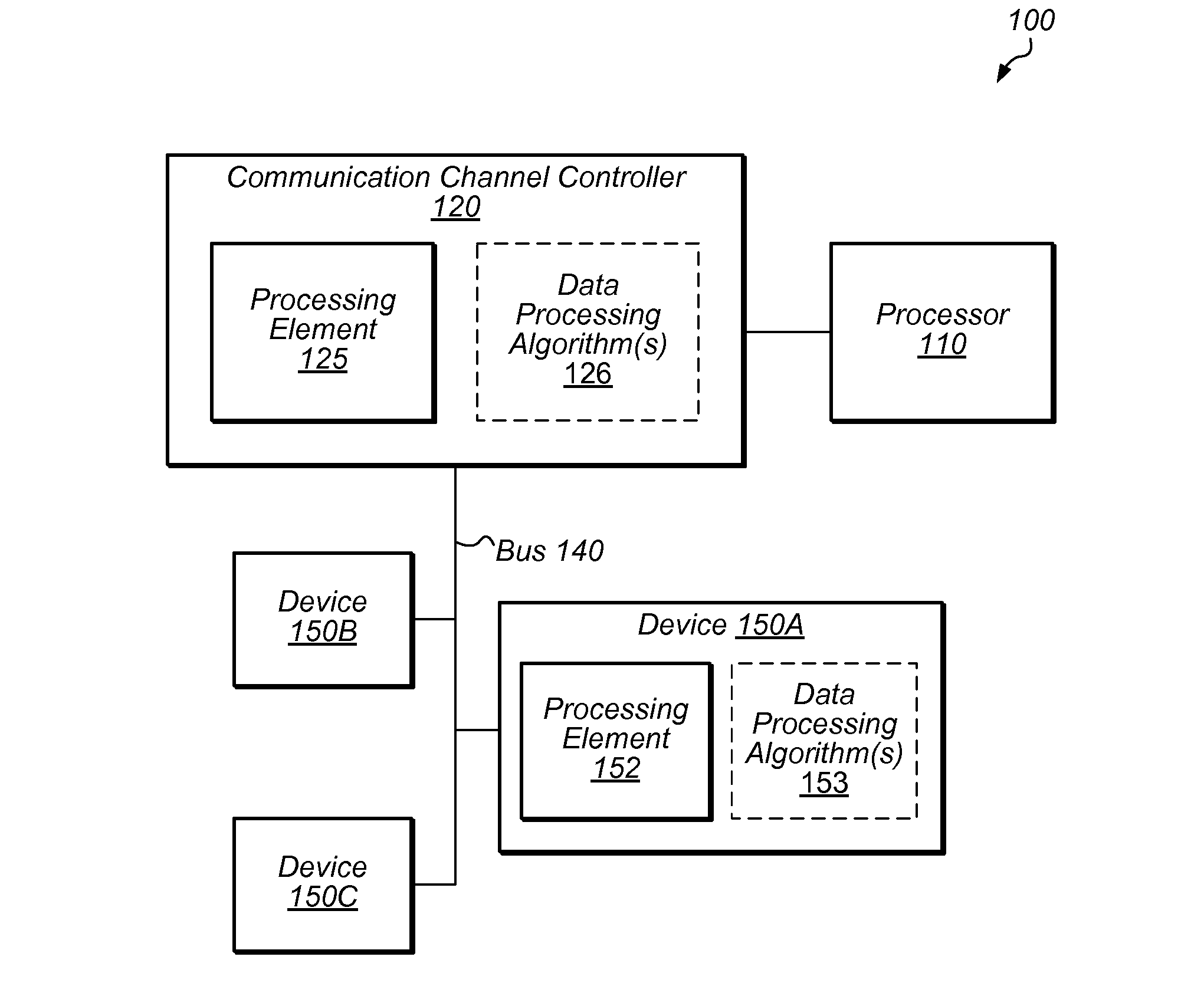
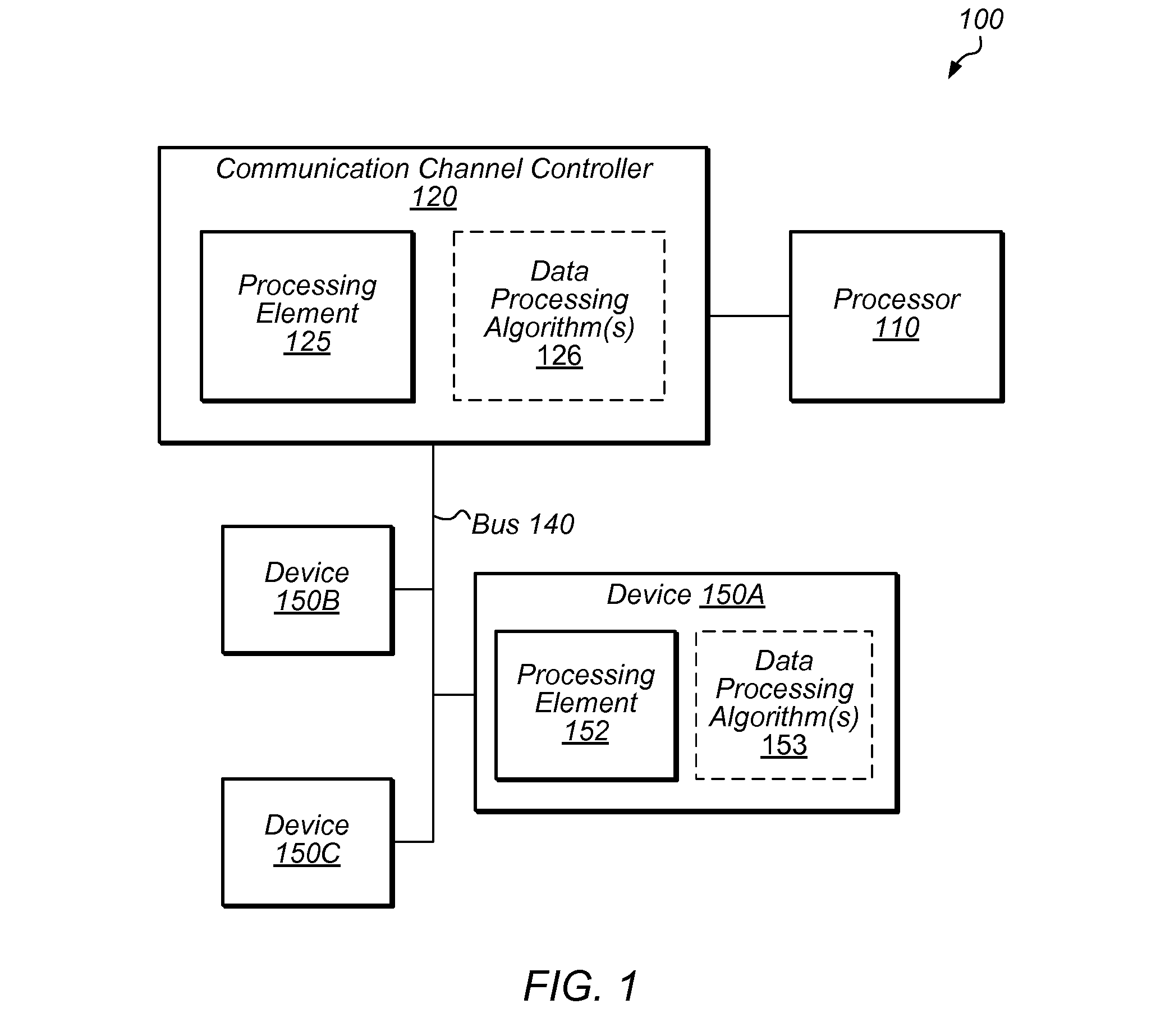
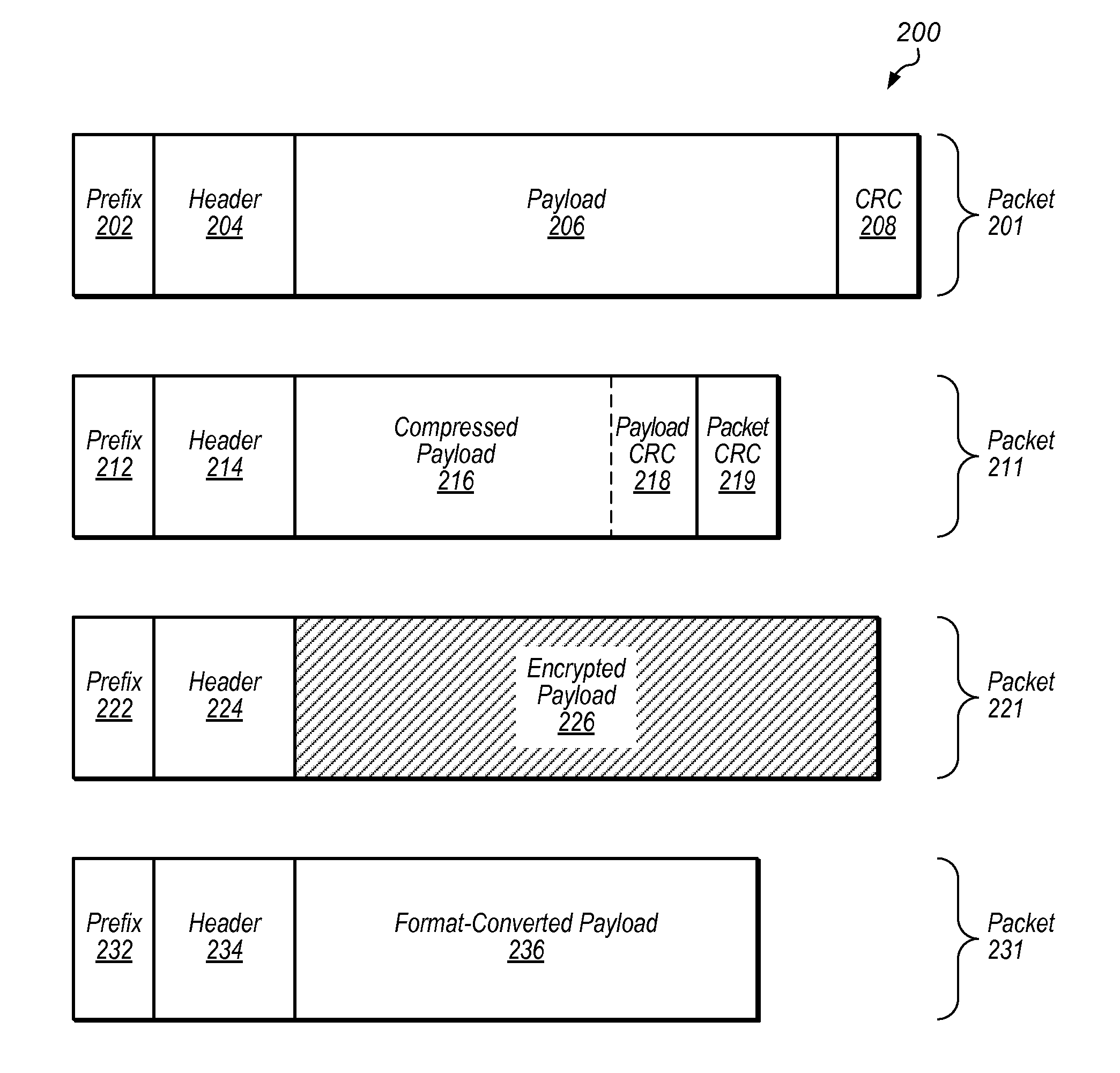
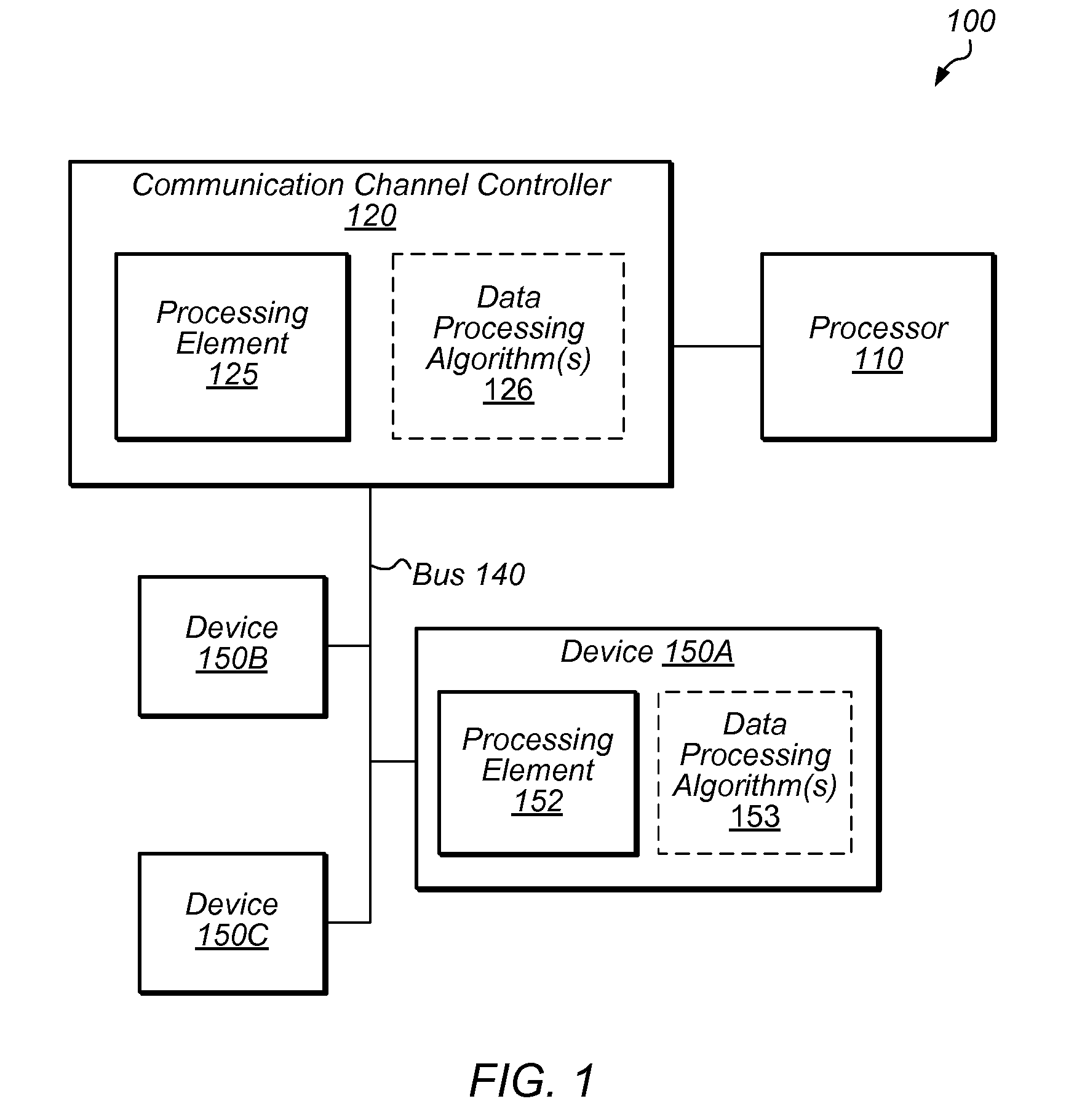
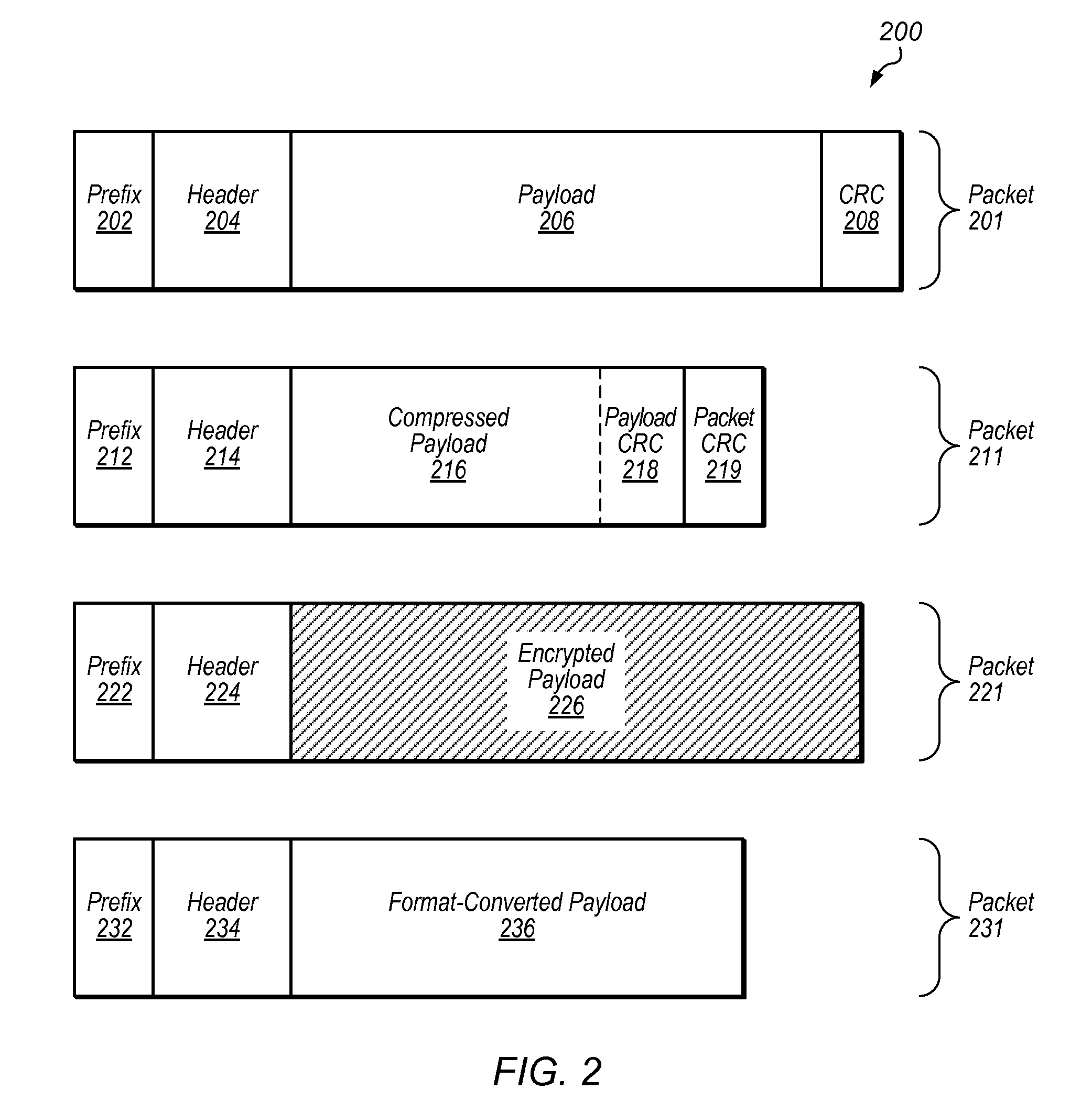
Data modification for device communication channel packets
ActiveUS20130054850A1Time-division multiplexData switching networksLossless compression algorithmTelecommunications link
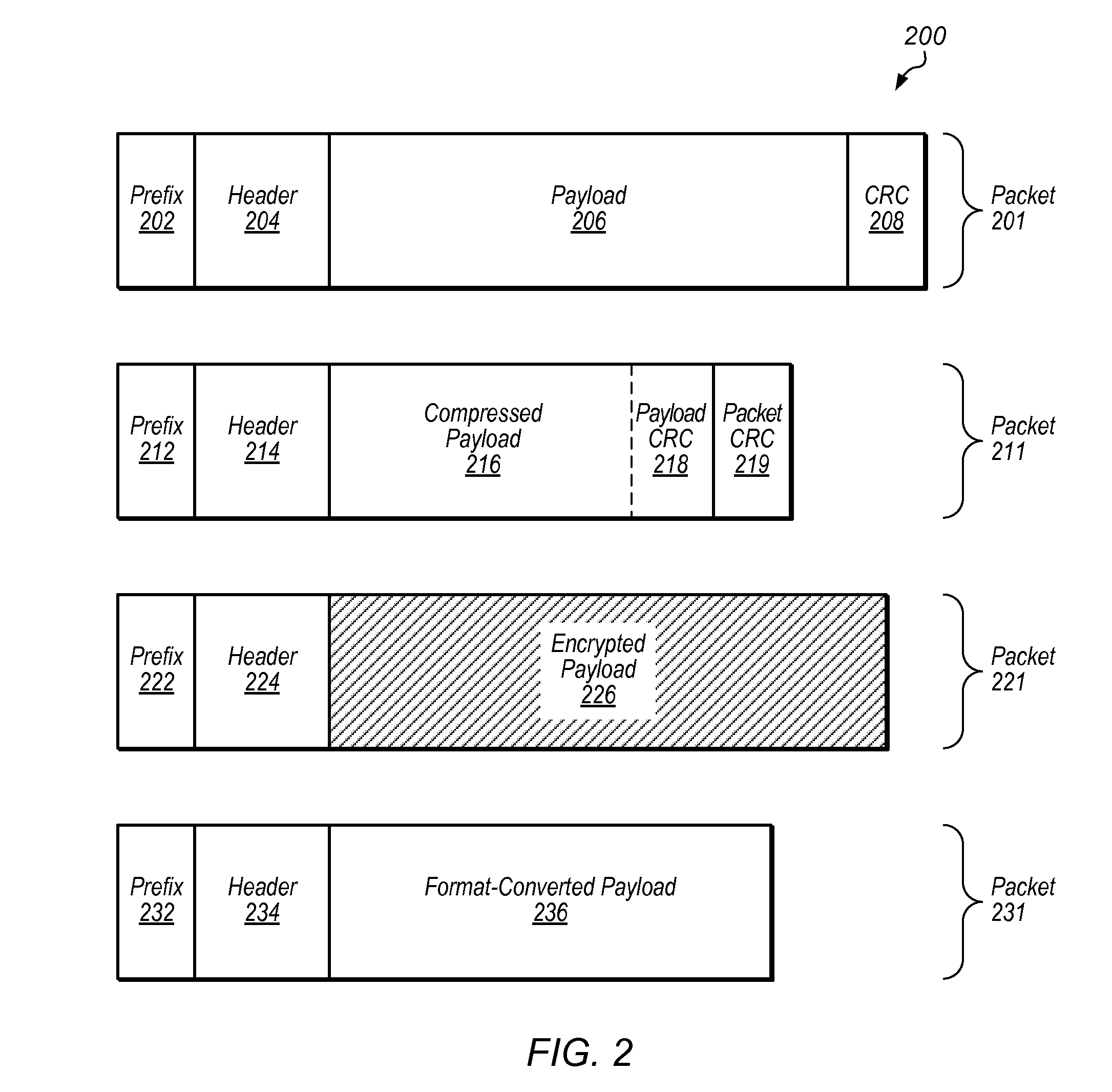
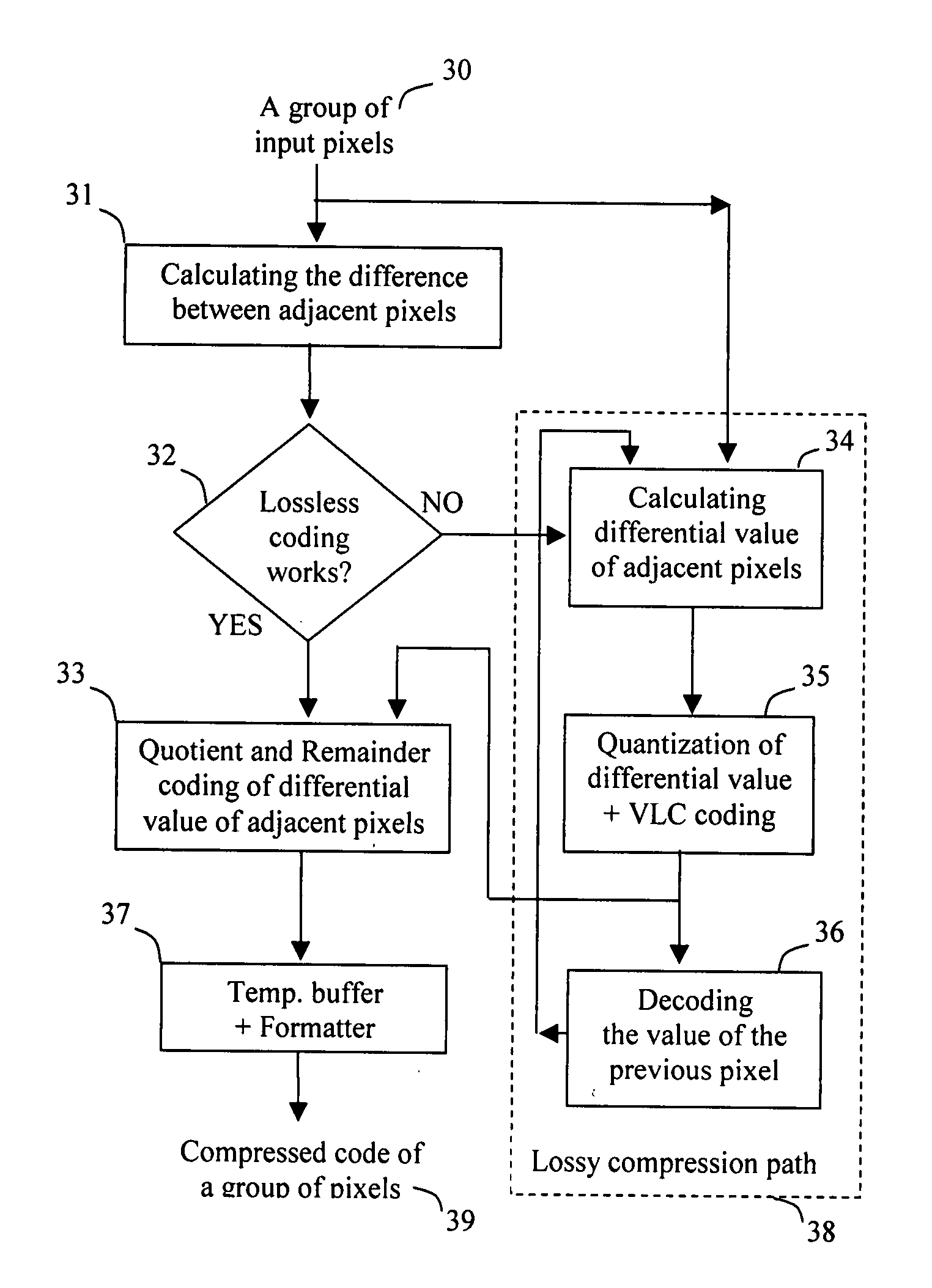
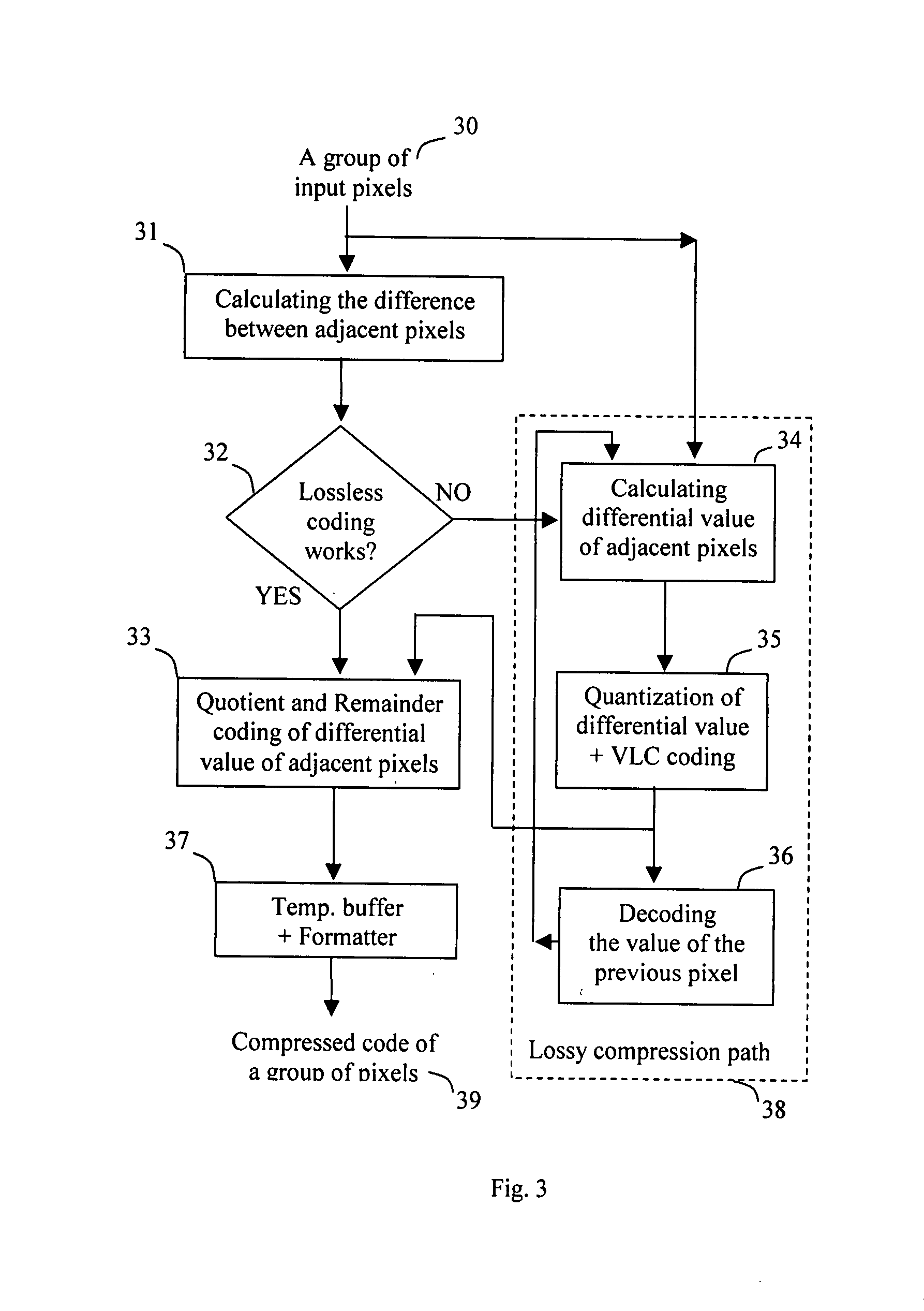
Techniques are disclosed relating to modifying packet data to be sent across a communication link and / or bus. Data may be modified in accordance with one or more data processing algorithms, and according to the capabilities of a destination device to receive such modified data. Lossless compression algorithms may be used on data in order to achieve a higher effective bandwidth over a particular bus or link. Encryption algorithms may be used, as well as data format conversion algorithms. One or more processing elements of a communication channel controller or other structure within a computing device may be used to modify packet data, which may be in PCI-Express format in some embodiments. A packet prefix or header may be used to store an indication of what algorithm(s) has been used to modify packet data so that a destination device can process packets accordingly.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
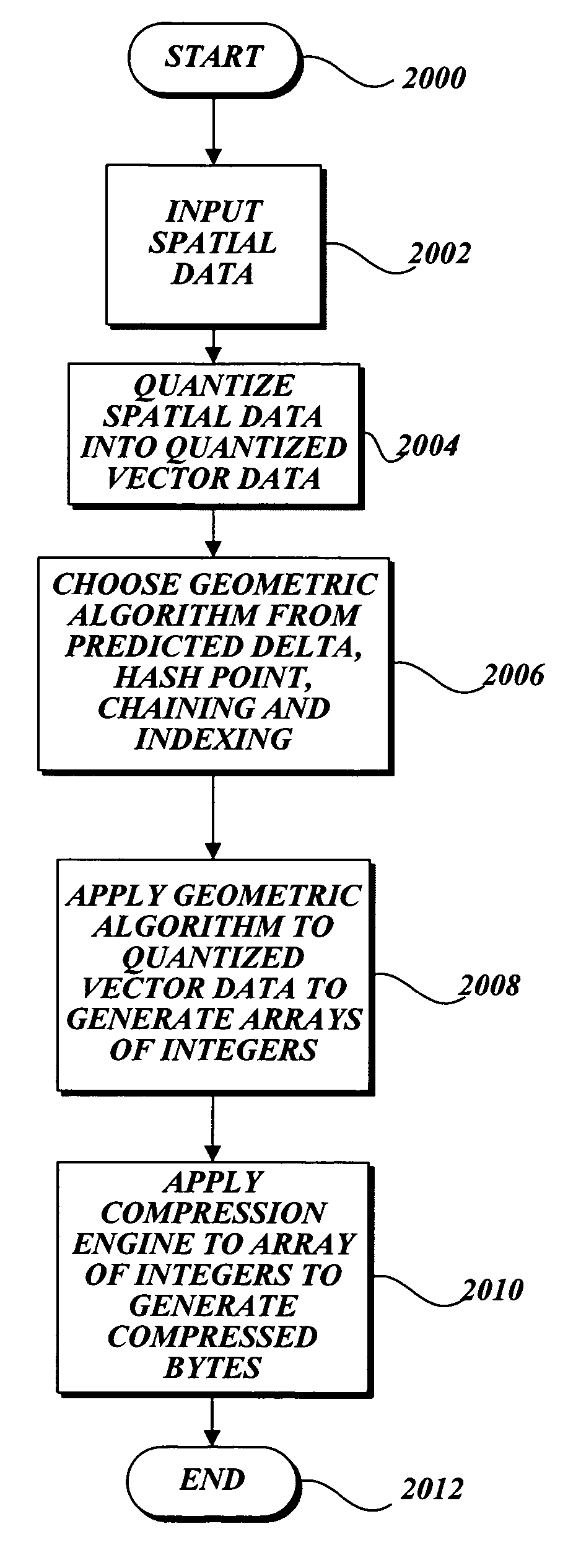
Lossless compression algorithms for spatial data
InactiveUS20060215923A1Loss of fidelityCompression can be losslessCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingLossless compression algorithmData mining
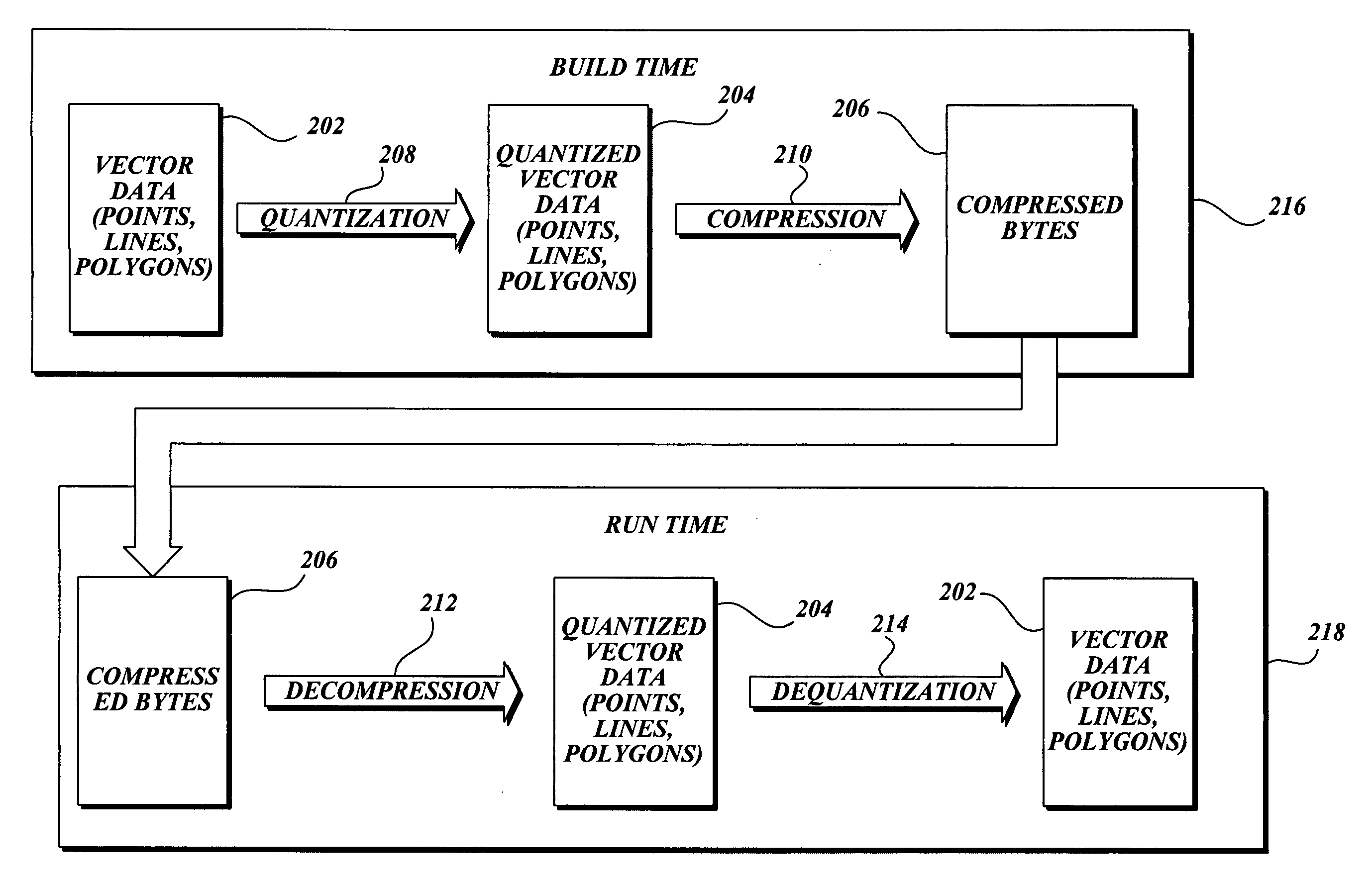
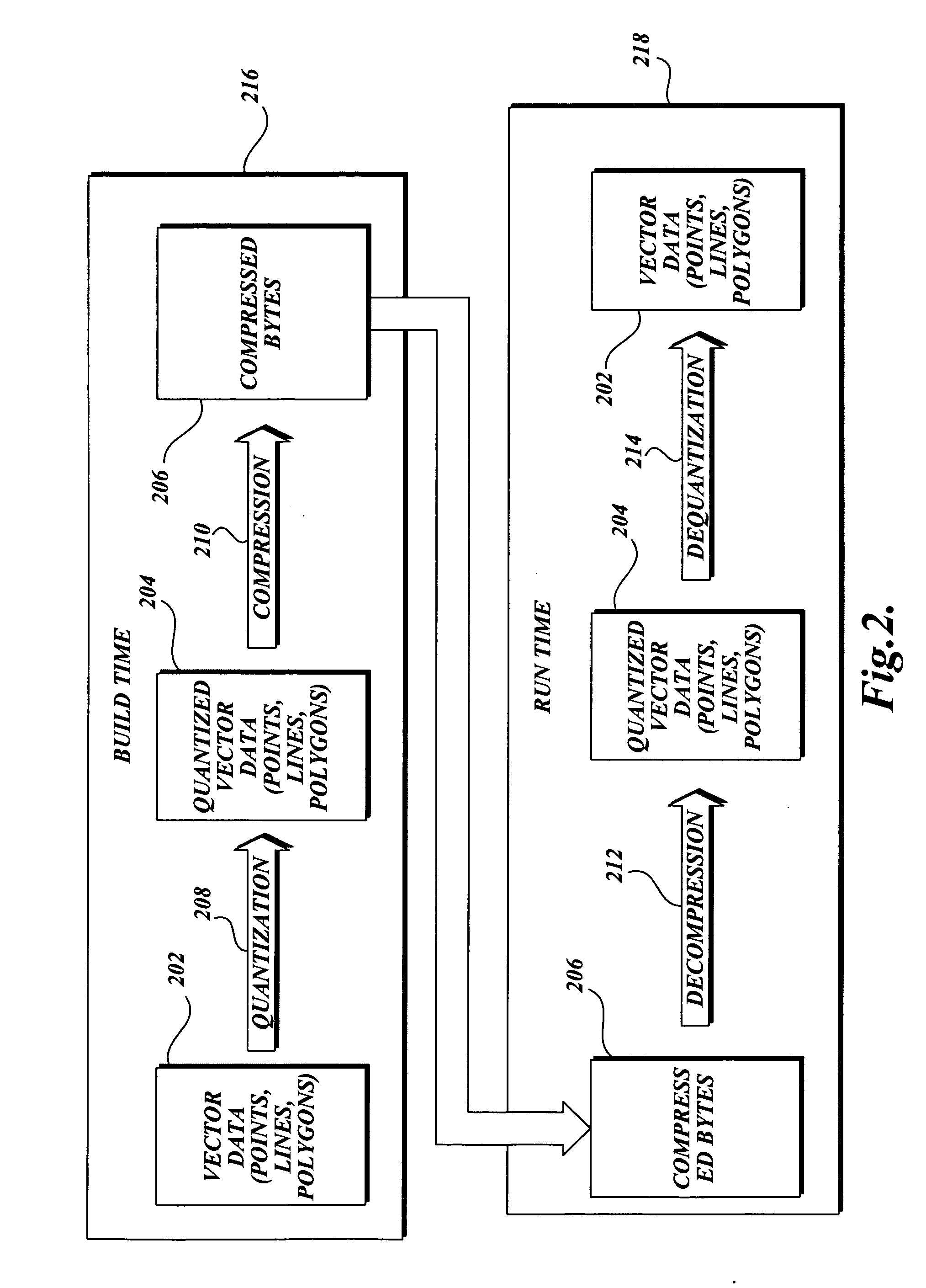
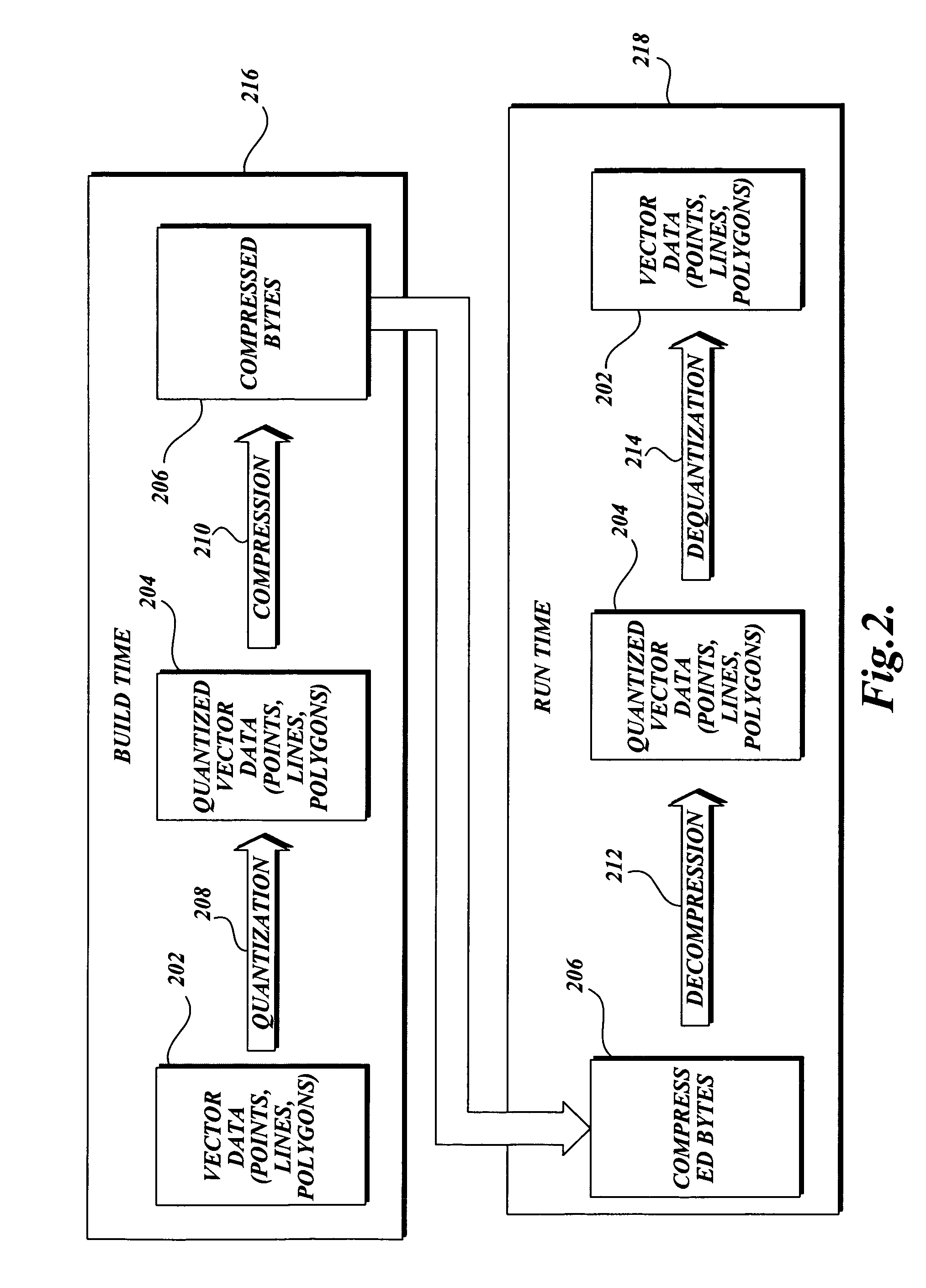
The present invention is related to routines for the processing of quantized vector data into one or more arrays of integers whose values are closer to zero than the integers in the quantized vector data. The arrays are input to a compression engine resulting in compressed bytes of data that may be transferred to a computing device for the decompression of the data. The quantized vector data can include vertices expressed as a pair of integer values that may represent geometric, spatial elements, such as points, interconnected lines (polylines), and polygons. These geometric objects may be representative of information on a map. The compressed bytes may be grouped according to grids, wherein each grid represents a distinct geographic area of a map, so that a consumer can store and decompress only the portion of the map data which is of interest.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
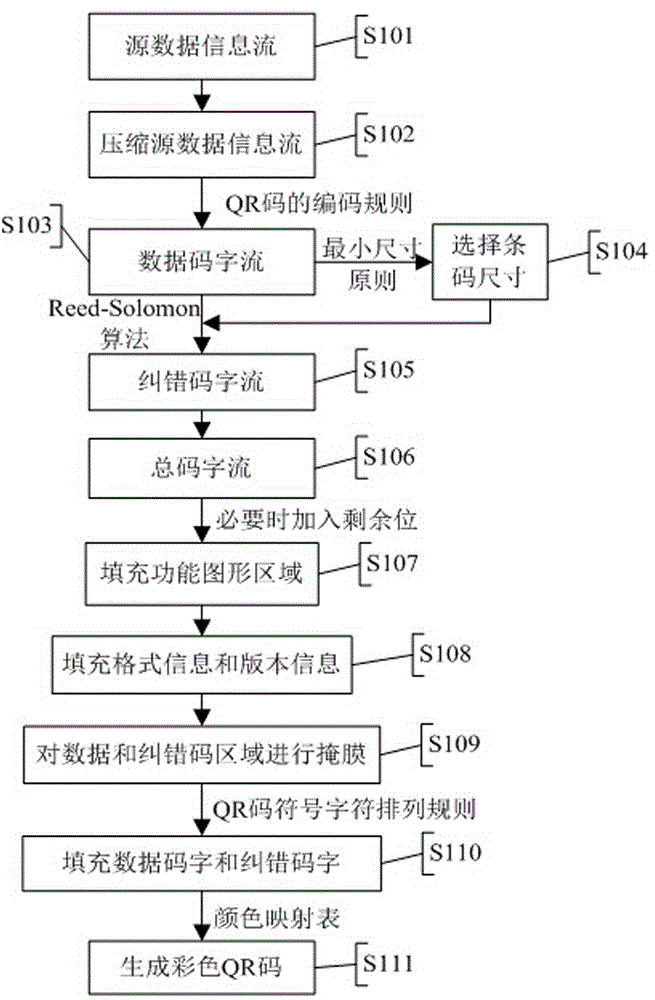
Method of encoding/decoding color QR code
ActiveCN104899630AIncrease capacityIncrease data capacityRecord carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationPattern recognitionData capacity
This invitation discloses a method of encoding / decoding a color QR (Quick Response) code. The method maintains the reliability and robustness of a standard black and white QR code, and employs a lossless compression algorithm to make the data capacity of a color QR code much larger than the data capacity of other colored two-dimensional code of a same kind. In addition, encoding colors are not required to be the most distant from each other in an RGB color space in order to enhance color resolution. A process of encoding / decoding a color QR code does not require color space transfer, i.e., color information loss can be avoided. Color QR cod decoding has no special requirements for ambient lighting, and does not need to utilize reference colors as a palette, thereby greatly reducing computational complexity, and obtaining 100% decoding accuracy.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Reducing context memory requirements in a multi-tasking system
InactiveUS20050240380A1Reduce memory requirementsReduce context memory requirementCode conversionSpecial data processing applicationsLossless compression algorithmPrefix header
A process for reducing the context memory requirements in a processing system is provided by a generic, lossless, compression algorithm applied to multiple tasks or multiple instances running on any type of processor. The process includes dividing data in a task of a multi-tasking system into blocks with each block containing the same number of words. For the data in each task, a word in a block having a maximum number of significant bits is determined, a packing width to the block of said maximum number of significant bits is assigned, and the least significant bits of each word in the block into a packed block of the packing width multiplied by a total number of words in the block is encoded with a lossless compression algorithm. A prefix header at the beginning of each packed block to represent a change in the packing width from the packed block from a packing width of a previous packed block is also provided.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
Data modification for device communication channel packets
ActiveUS8832331B2Time-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsLossless compression algorithmTelecommunications link
Techniques are disclosed relating to modifying packet data to be sent across a communication link and / or bus. Data may be modified in accordance with one or more data processing algorithms, and according to the capabilities of a destination device to receive such modified data. Lossless compression algorithms may be used on data in order to achieve a higher effective bandwidth over a particular bus or link. Encryption algorithms may be used, as well as data format conversion algorithms. One or more processing elements of a communication channel controller or other structure within a computing device may be used to modify packet data, which may be in PCI-Express format in some embodiments. A packet prefix or header may be used to store an indication of what algorithm(s) has been used to modify packet data so that a destination device can process packets accordingly.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
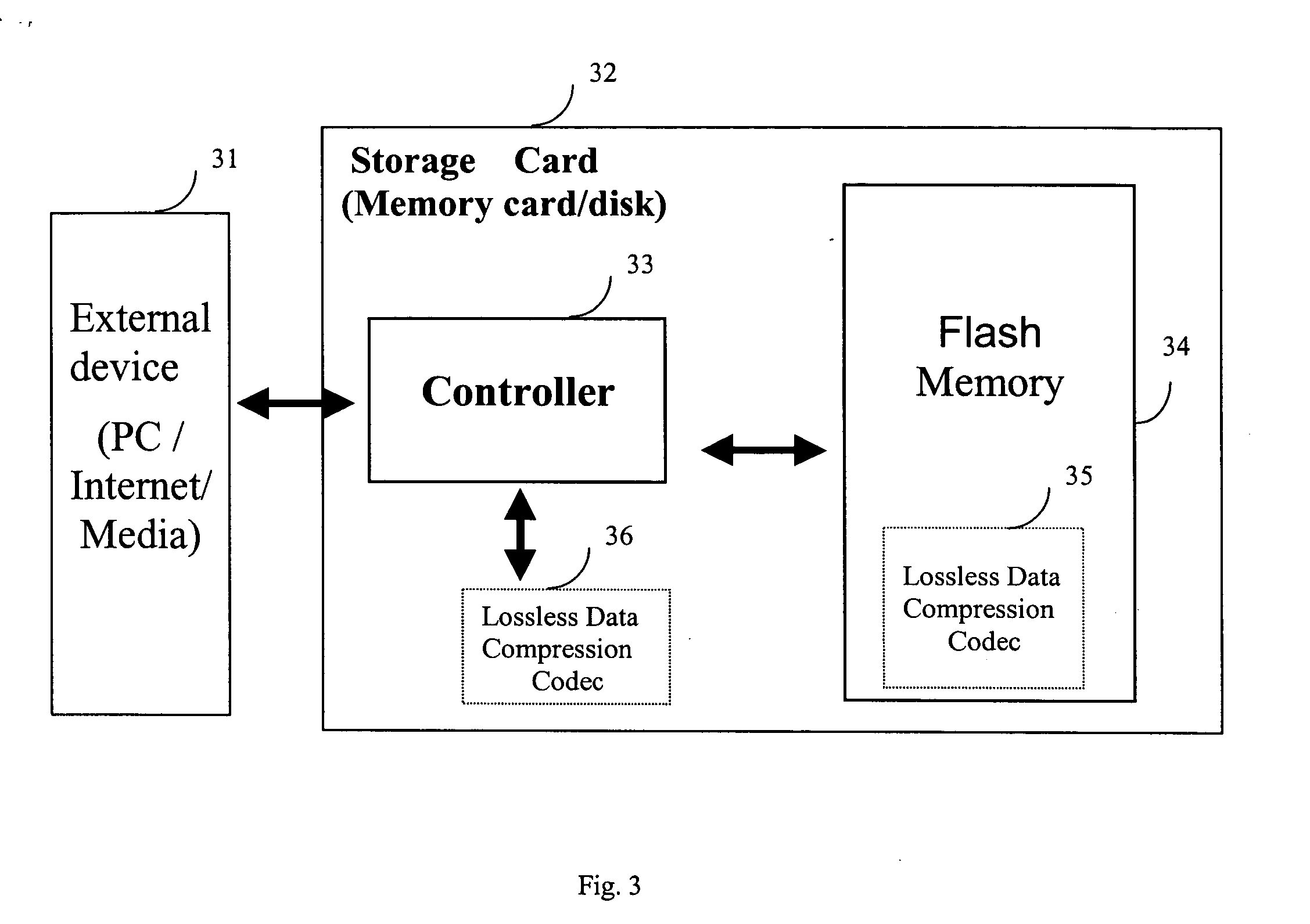
Lossless compression method and apparatus for data storage and transmission
InactiveUS20060010151A1Reduce data volumeImproves performance of data transmission dataCode conversionSpecial data processing applicationsLossless compression algorithmData stream
The present invention provides method and apparatus of a lossless data compression to reduce the amount of data to be transmitted or to be saved into a storage device. In the VLSI implementation, a data path module combined with some state machines support multiple formats of data file and to execute the function of the lossless data compression. The amount of the program data of a File System is reduced by a lossless compression method before it is saved into the storage device and to be recovered to execute the function of a File System. Before transmission, the data file compressed by the lossless compression algorithm coupled with the corresponding decompression code will be packed into a data stream and the receiving node will recover the data file by executing the decompression code.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
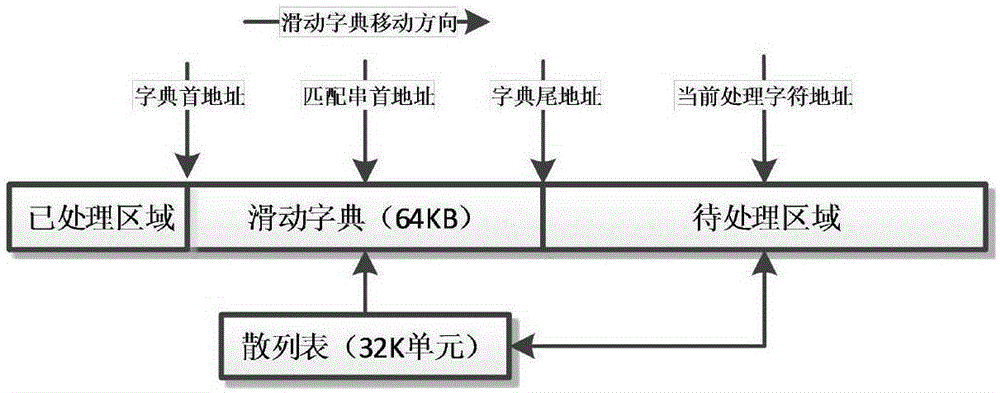
Hardware realizing system for improved LZ4 compression algorithm
The invention discloses a hardware realizing system for an improved LZ4 compression algorithm. The speed is higher than the processing speed of a current existing LZ series lossless compression algorithm, and the improved LZ4 compression algorithm is suitable for high-bandwidth data compression occasions. According to the realizing method for the improved LZ4 compression algorithm, a method for full-range word-for-word hash is adopted, and the defect that in an original LZ4 algorithm, hash table recording is not carried out in matched character strings is overcome. The invention further discloses the hardware realizing system for realizing the algorithm, a hardware circuit is utilized for realizing the improved LZ4 compression algorithm, and the maximum performance of the compression algorithm can be brought into play. The compression speed is higher than that of the current existing LZ series lossless compression algorithm, and possibility is provided for using LZ compression algorithm in the high-bandwidth data processing process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for compressing and uncompressing image based on color classification and cluster
ActiveCN103458242AReduce lossesSmall amount of calculationTelevision systemsPattern recognitionLossless compression algorithm
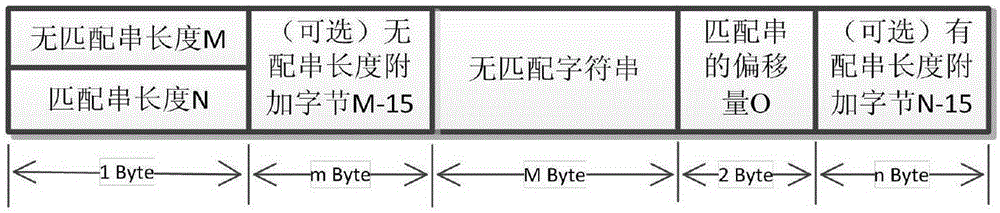
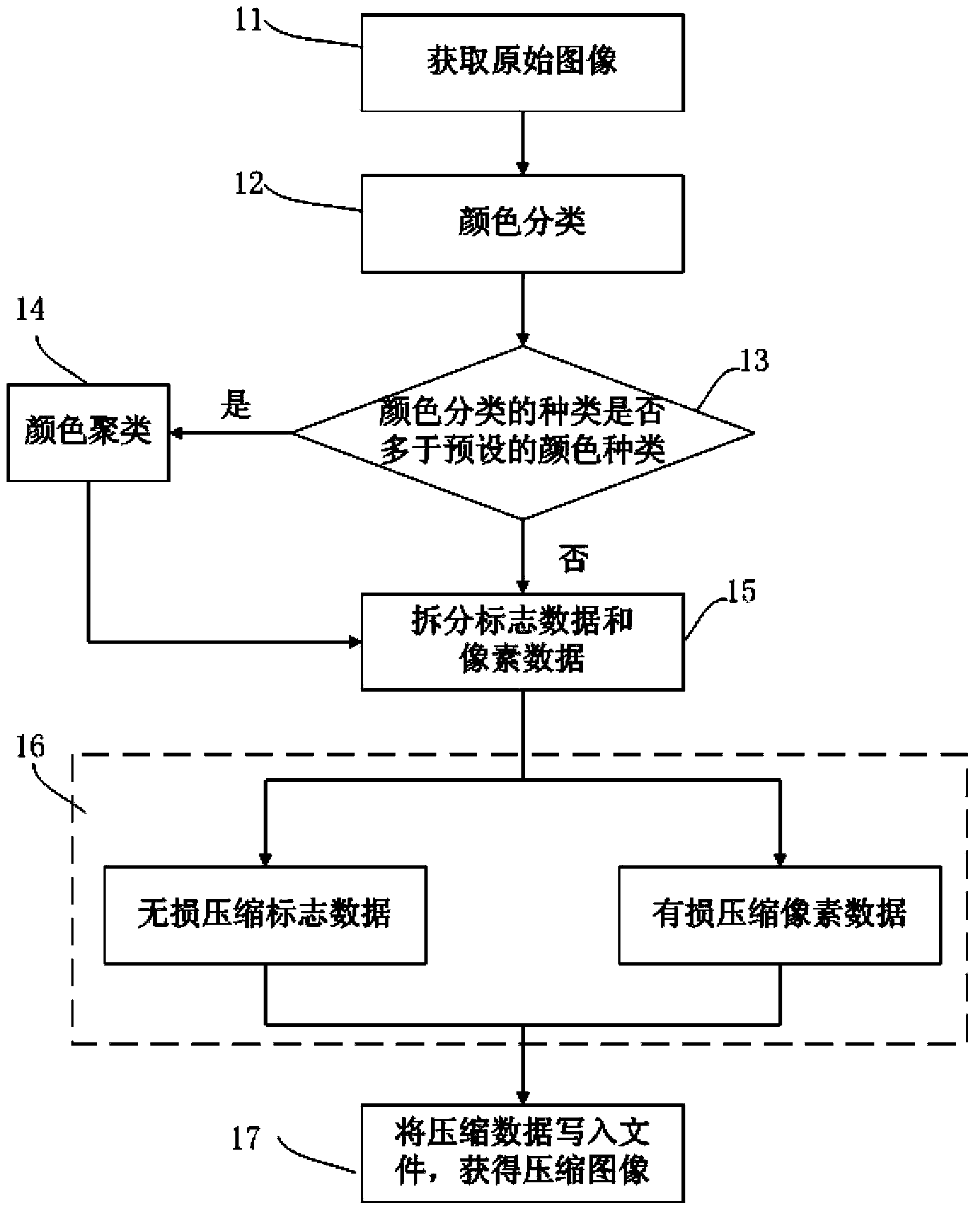
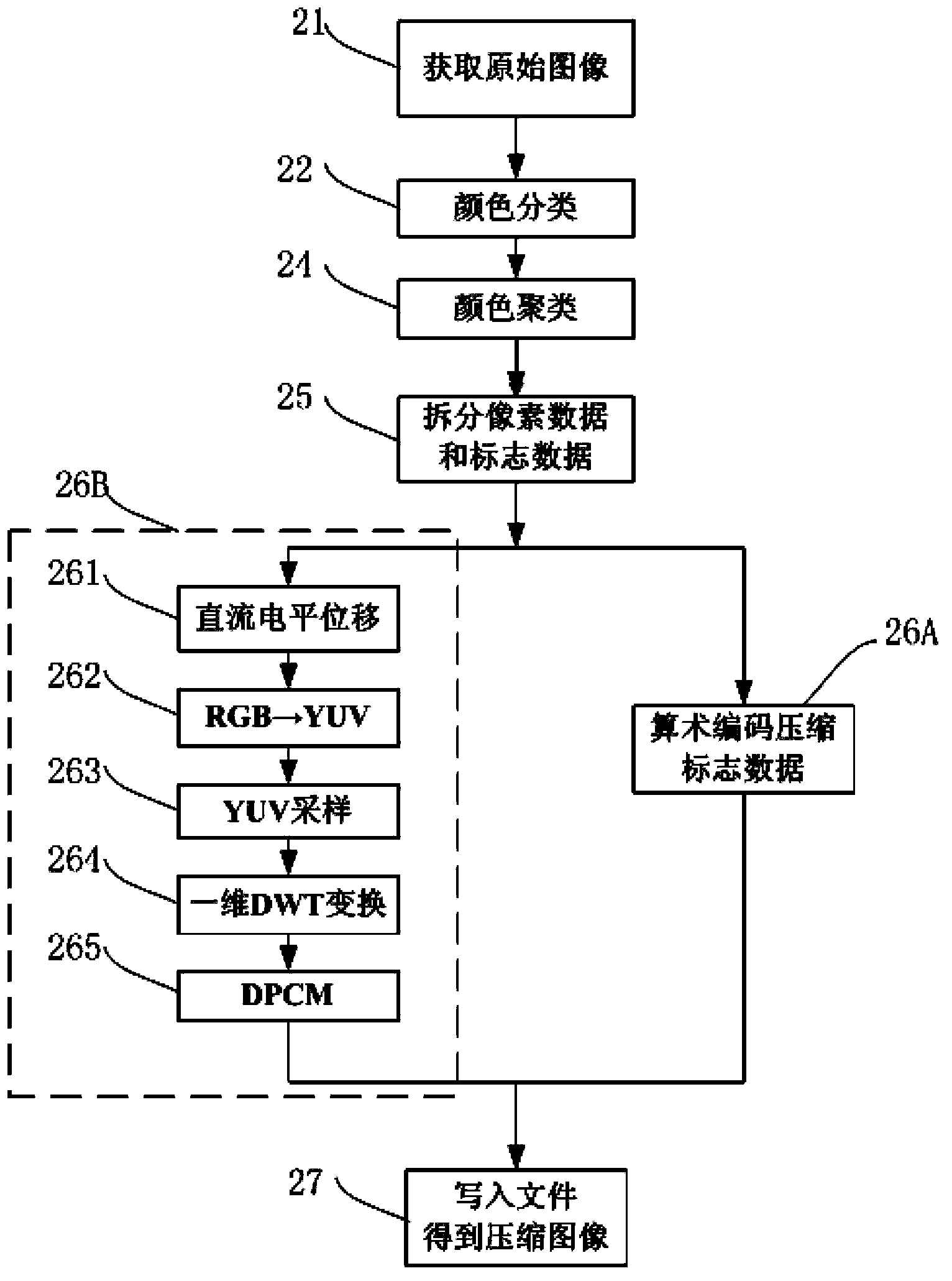
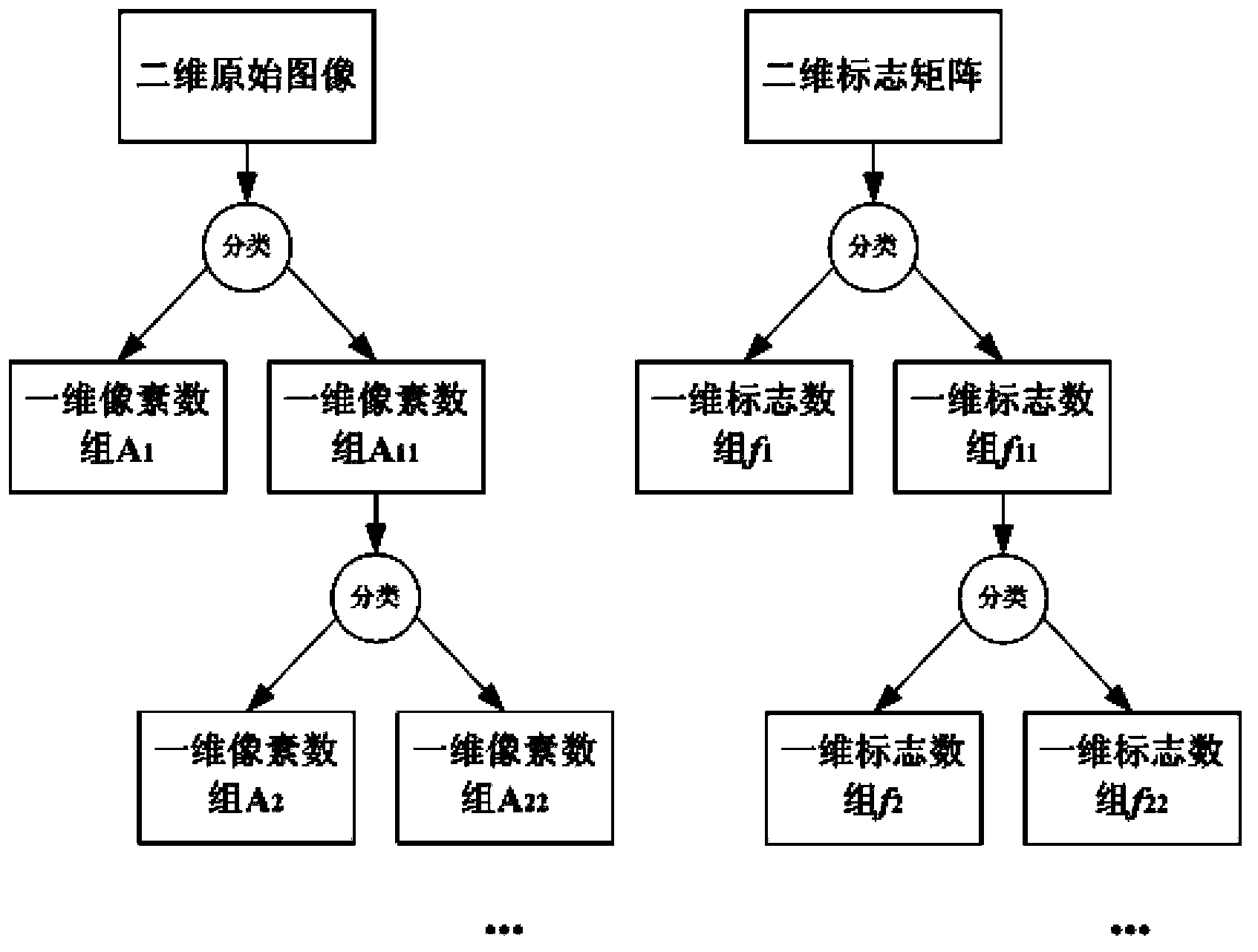
The invention discloses a method for compressing and uncompressing an image based on color classification and cluster. The method for compressing the image comprises the step of acquiring an original image and establishing a sign matrix for the original image; the step of classifying colors of the original image; the step of judging the number of types of the classified colors is larger than the number of the types of preset colors or not, wherein if yes, the excessive colors in color classification are clustered; the step of splitting pixel data and sign data of the original image according to the types of the color classification; the step of compressing the sign data based on the lossless compression algorithm and compressing the pixel data based on the loss algorithm; the step of writing compressed data into a file according to the preset sequence to obtain a compressed image. According to the method, the information of the colors of the image is classified and clustered, the lossless compression algorithm and the loss algorithm are combined, and the purpose of compressing the image at a high speed in a high-quality and high compression ratio is achieved.
Owner:京北方信息技术股份有限公司
Method of high quality digital image compression
InactiveUS20080193028A1Reduce computing timeImprove image qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationLossless compression algorithmAlgorithm
This image compression applies a lossless compression algorithm and a lossy compression algorithm to code the differential value of the adjacent pixels. If lossy algorithm is selected, it codes the differential value of the present pixel and the reconstructed previous pixel. In quantizing the differential value of adjacent pixel components, a variable range of interval of value is predetermined with smaller interval range in values closer to “0” and larger interval range farer from “0”. The region with less mean variance, less quantization error will be allowed and the region with larger mean variance, more quantization error is allowed
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
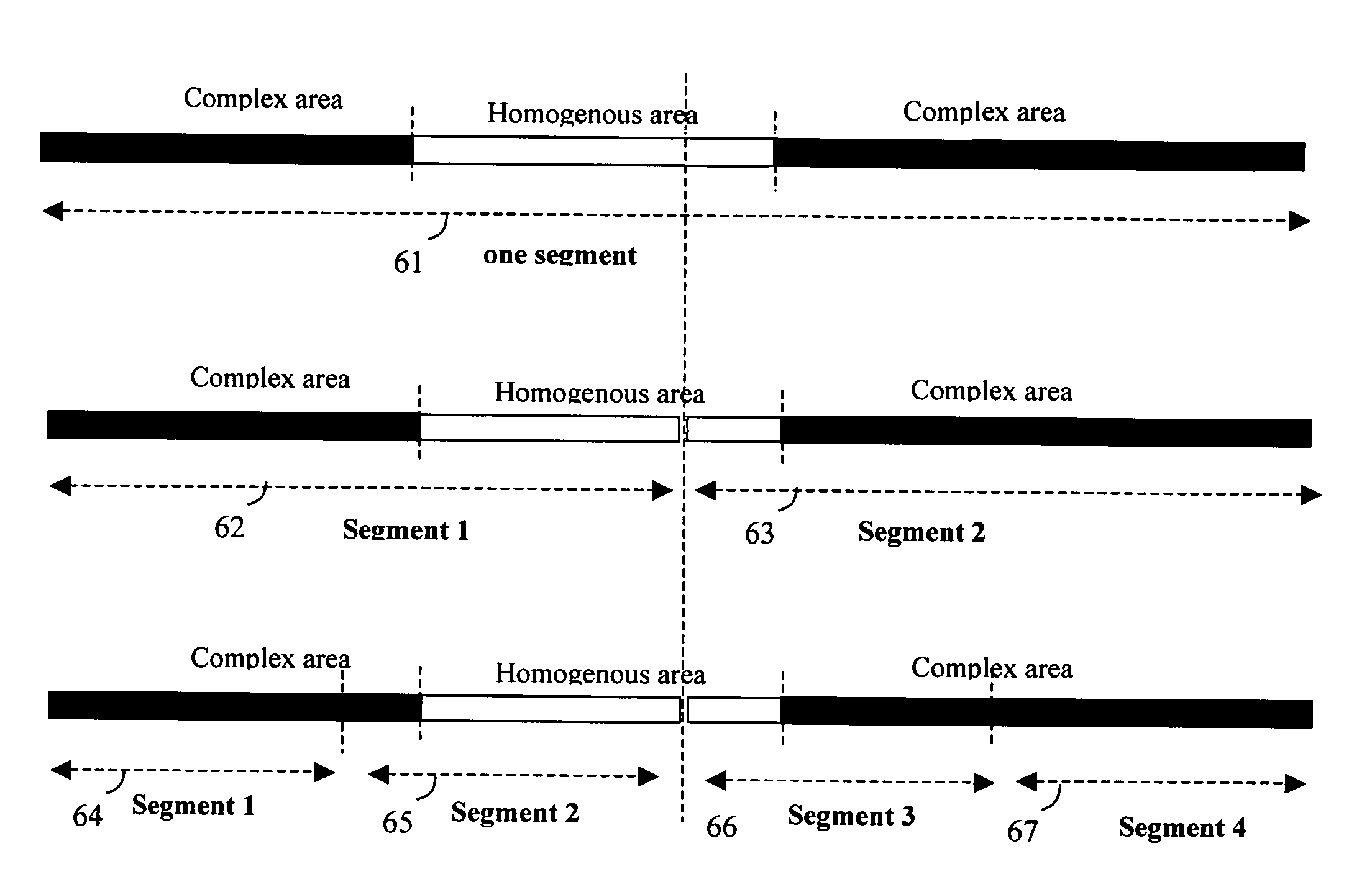
Method of image frame compression
InactiveUS20080175475A1Reduce memory densityAccelerated programCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationLossless compression algorithmAlgorithm
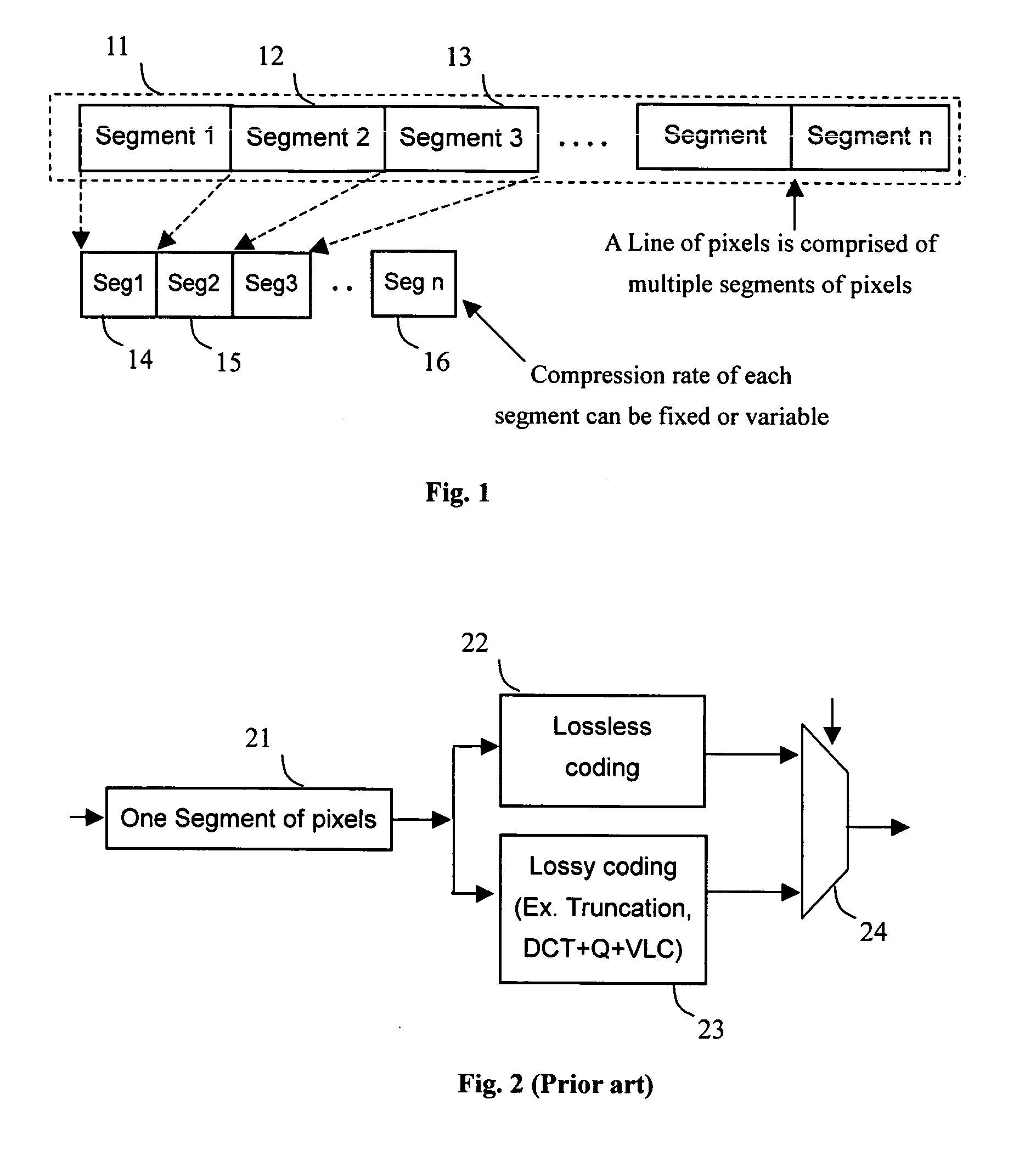
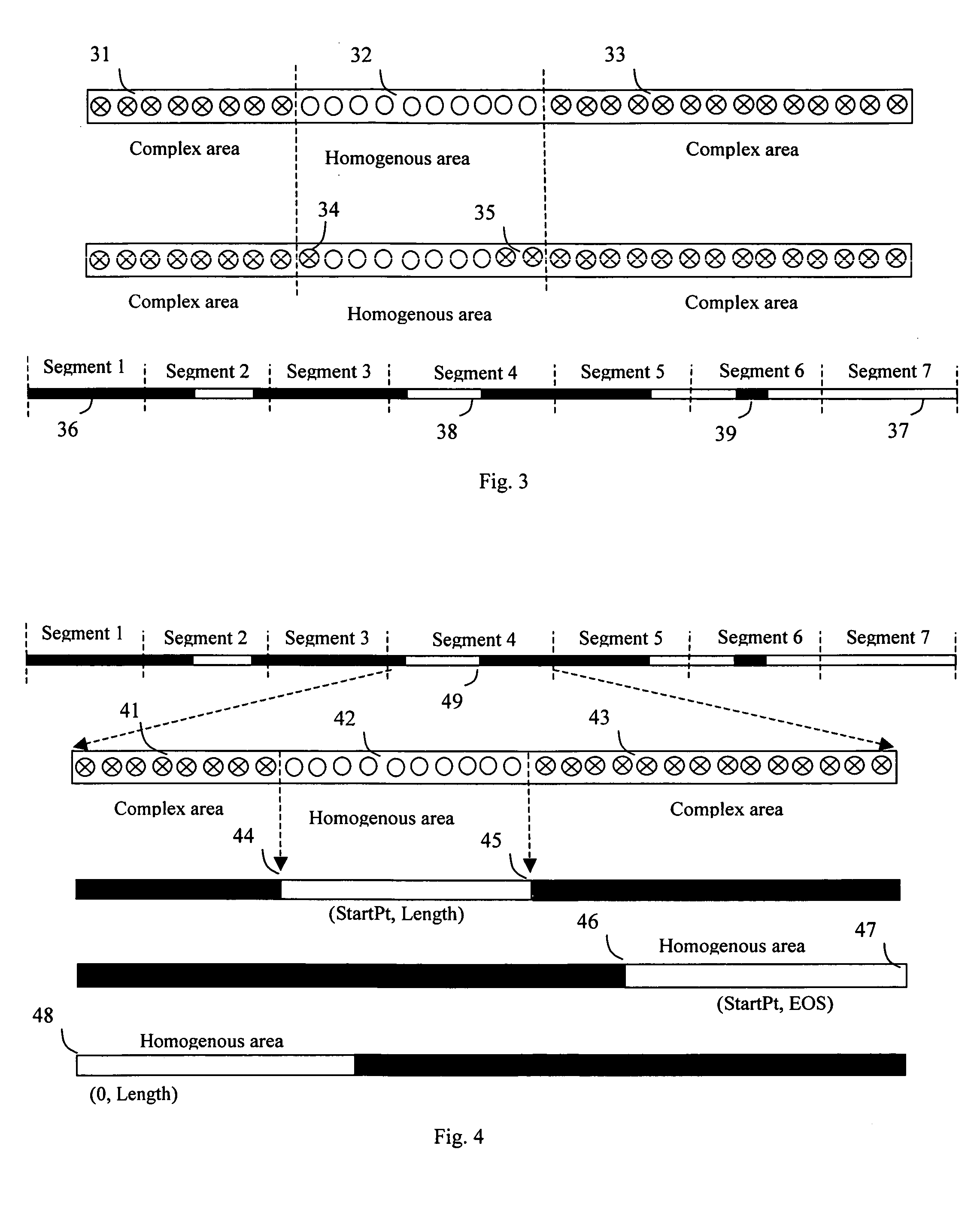
An image frame is compressed segment by segment by applying a lossless compression algorithm to the segment of pixels with simple pattern and a lossy algorithm to the segment with complex pattern. A segment comprising at least one homogenous area and one complex area will be compressed separately by assigning a lossless compression algorithm to compress the homogenous area and a lossly algorithm to compress the complex area. Another mechanism of partitioning a segment into multiple sub-segments with each sub-segment being compressed by one compression algorithm also helps in reducing the error in the homogenous area.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
Novel chaos-based image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm
ActiveCN105704500AEnsure safetyLarge key spaceTelevision systemsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsLossless compression algorithmData compression ratio
The invention discloses an image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm based on multiple kinds of chaos, which belongs to the technical field of multimedia information safety. In view of high safety requirements of the image lossless compression algorithm SPIHT, an image lossless compression encryption joint algorithm based on multiple kinds of chaos is designed. The algorithm is designed to generate an encryption pseudo random sequence which is safer and is not easy to be broken, a wavelet transform coefficient matrix is encrypted in a mode of design local diffusion and overall scrambling, and during an SPIHT coding process, and multiple turns of encryption are carried out on a sorting scanning part. Theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the algorithm of the invention has the advantages that the encryption speed is quick; the safety is high; influences on a compression ratio are few; an image file can be kept to be lossless; and the application prospect and the practical value are wide.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Method of software version upgrade and terminal and system
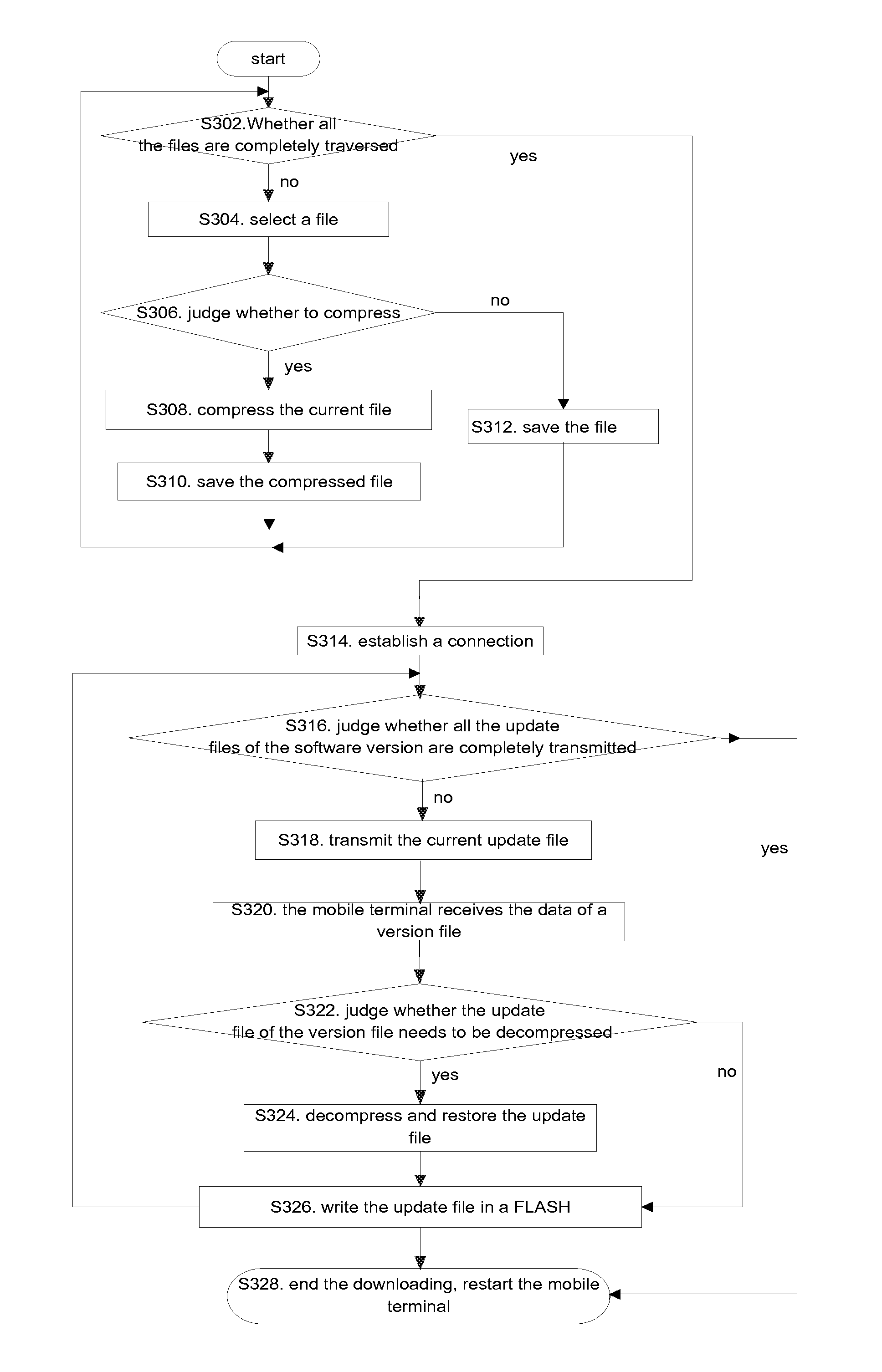
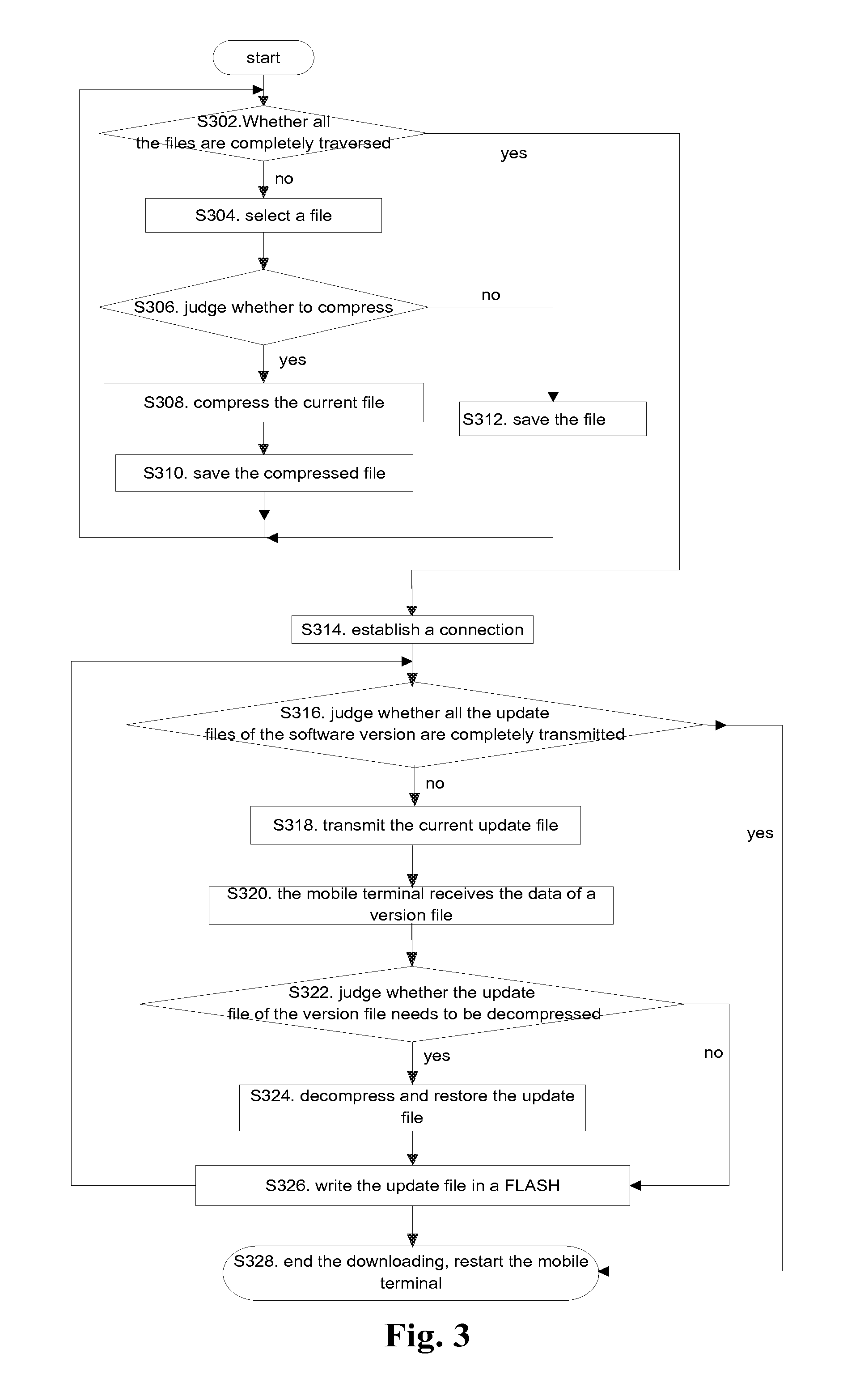
InactiveCN101984405AReduce upgrade timeFast and secure upgrade processProgram loading/initiatingSoftware deploymentLossless compression algorithmFirst pass yield
Owner:ZTE CORP
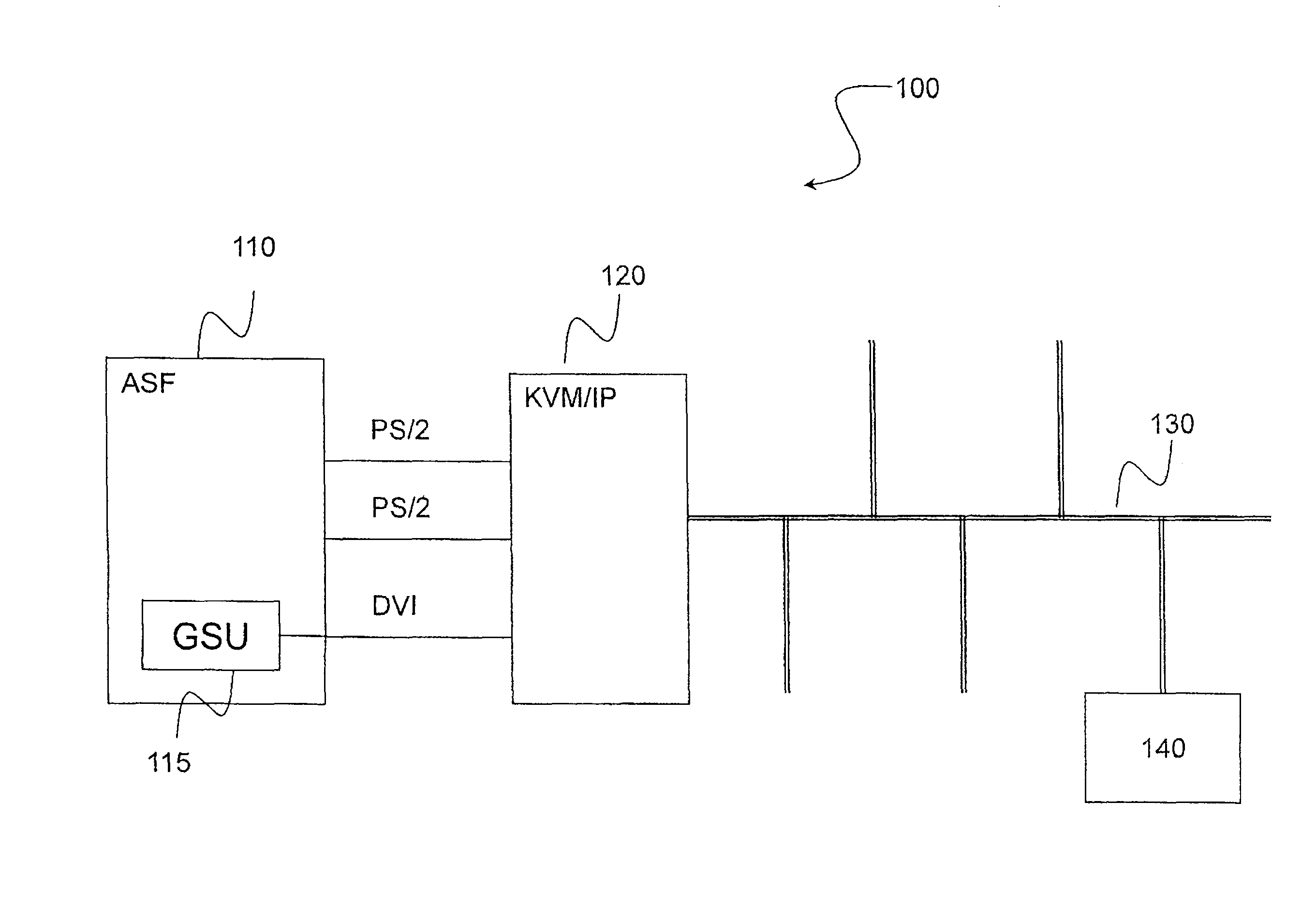
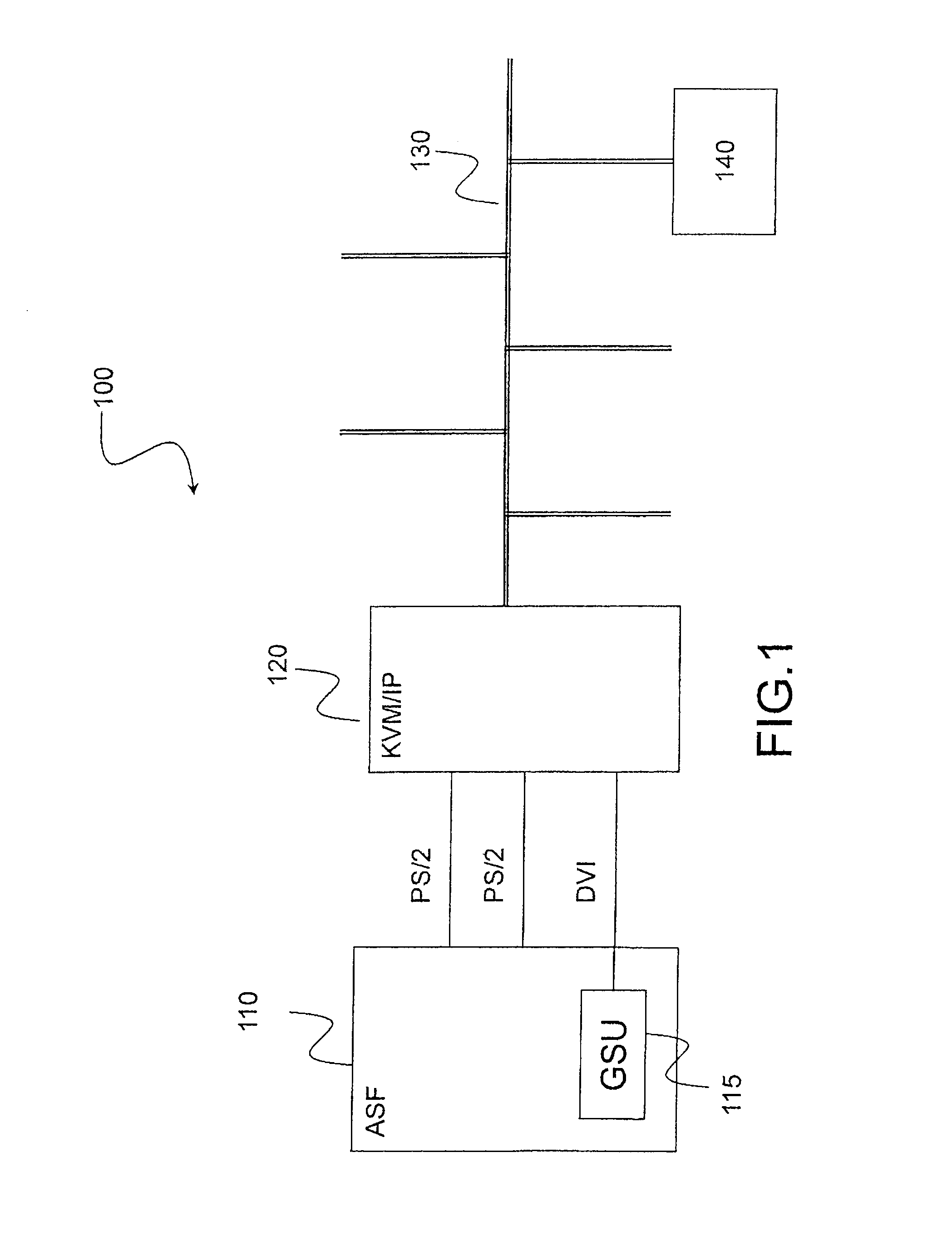
Computer maintenance system for an aircraft with remote terminal
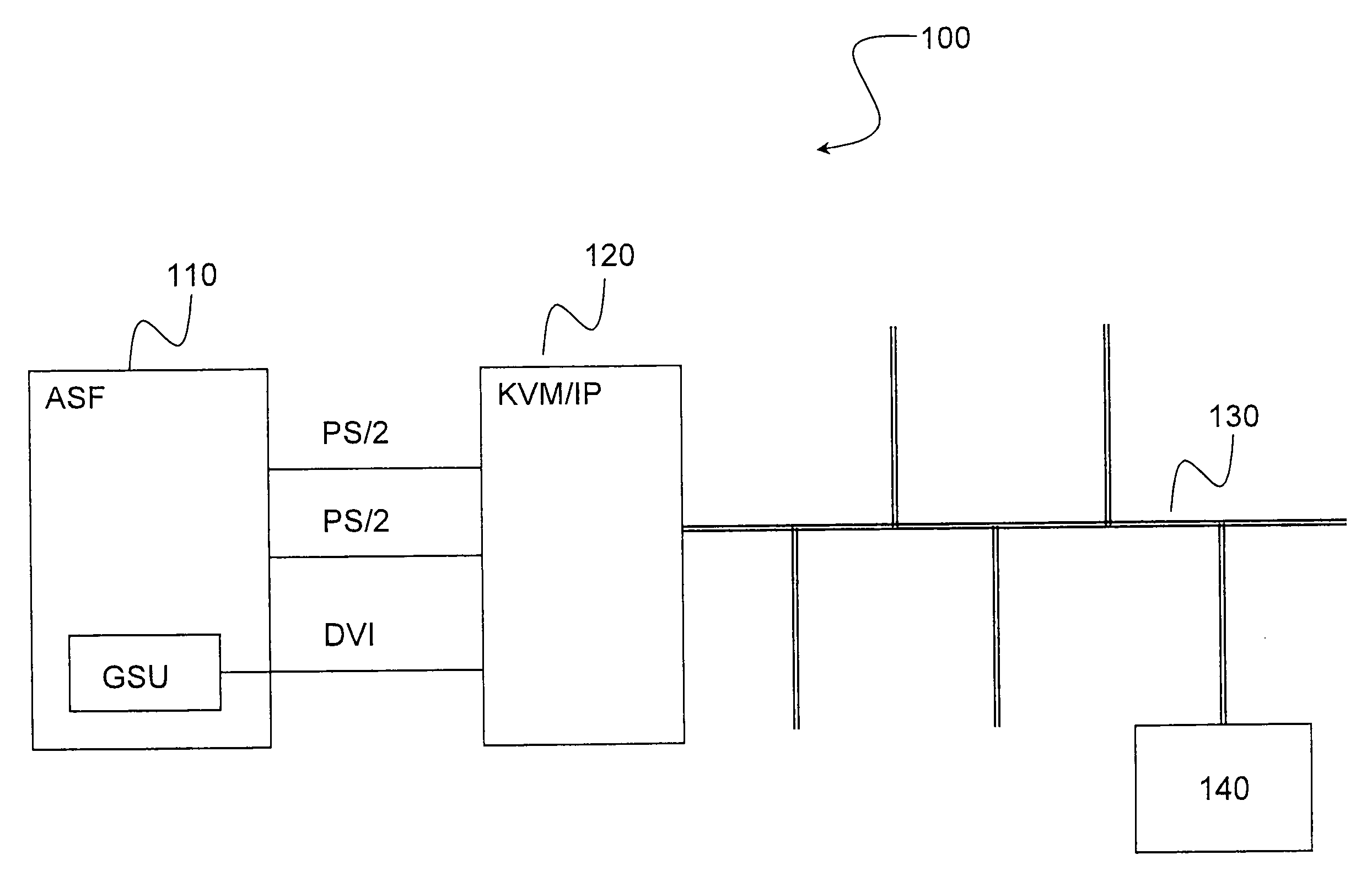
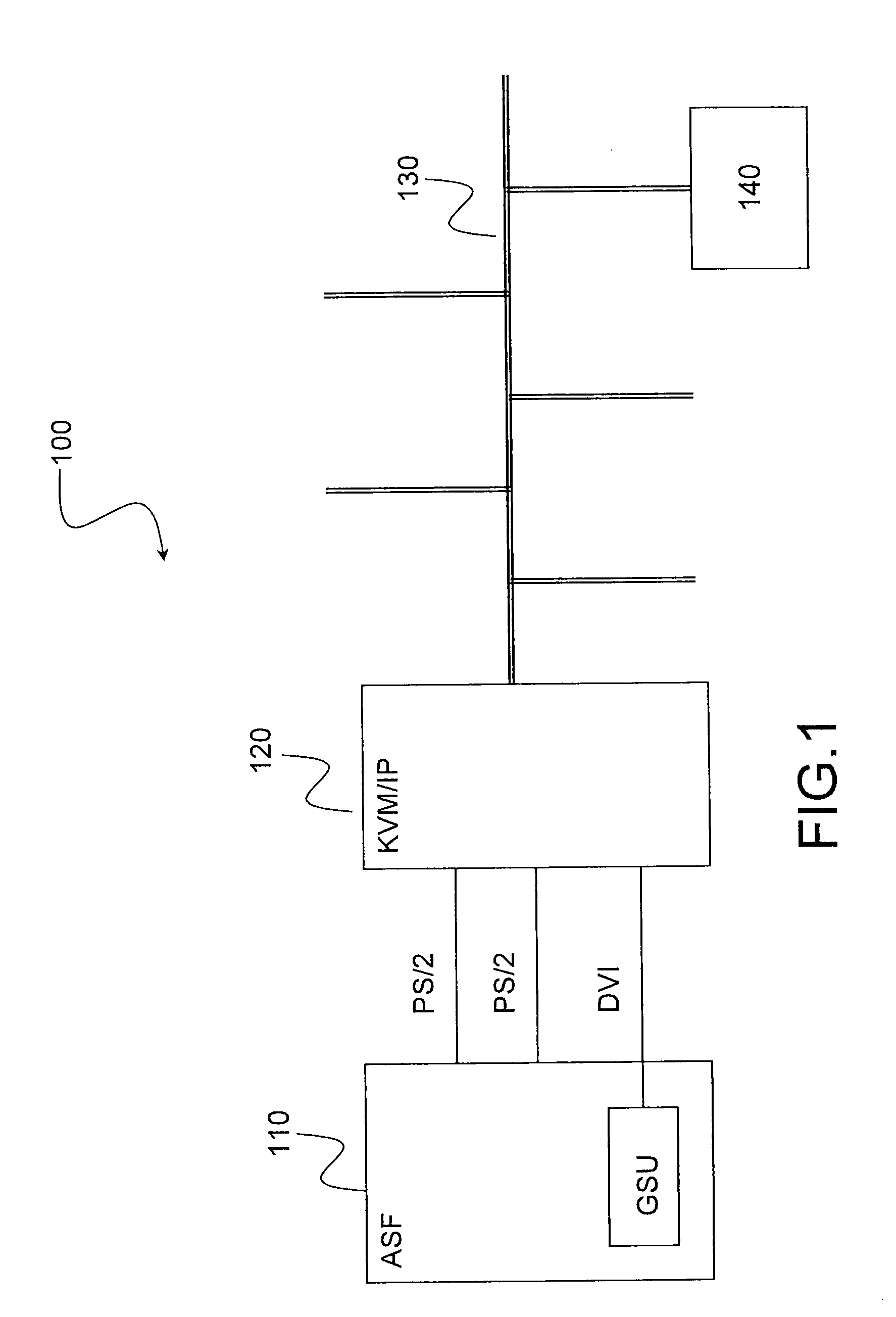
ActiveUS20090319099A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLossless compression algorithmKVM switch
The present invention relates to a computer maintenance system for an aircraft comprising a server hosting maintenance software and at least one access terminal. The system comprises a KVM switch over IP linked to said server. The terminal is adapted to connect to said switch by means of a TCP / IP connection and hosts a client application. Symmetrically, the switch hosts a server application, said applications being suitable for implementing a protocol for remotely accessing a video frame buffer. Each video frame is transmitted from the server application to the client application in the form of bitmap image data, uncompressed or else compressed by a lossless compression algorithm.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
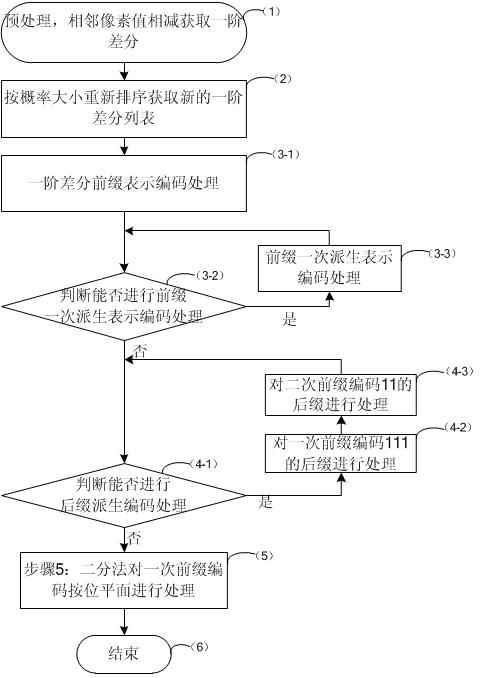
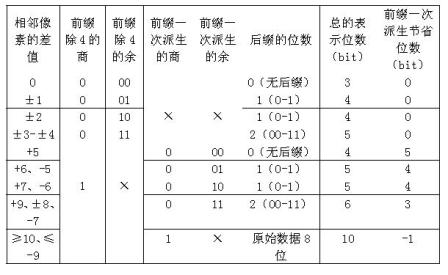
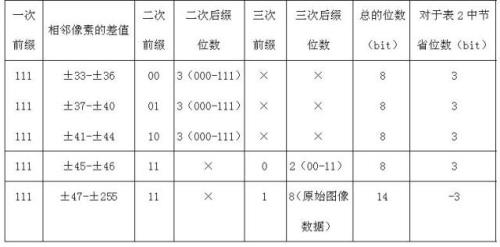
First-order difference prefix notation coding method for lossless compression of image data
InactiveCN102014283AReduce computational complexitySimple codingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationLossless compression algorithmComputation complexity
The invention discloses a first-order difference prefix notation coding method for the lossless compression of image data, which comprises the following steps of: 1, pre-processing original image data to obtain first-order differences between adjacent pixel values; 2, counting the probabilities of occurrence of each first-order difference, and re-sequencing the first-order differences from higher probabilities to lower probabilities to obtain new first-order differences; 3, performing first-order difference prefix notation coding processing on the new first-order differences obtained by the step 2 to obtain a prefix code table and a suffix code table; 4, performing order-reduction processing on suffix codes in the step 3 by adopting a suffix derivation method; and 5, performing coding processing on primary prefix codes in the step 4 according to bit planes by adopting dichotomy. The method ensures relatively lower computational complexity, simple coding, high coding and decoding efficiency remarkably higher than that of JPEG2000, and no need of adopting special compression and decompression chips, and compared with a conventional lossless compression algorithm, remarkably increases a compression ratio to be equivalent to that of the international standard JPEG2000.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
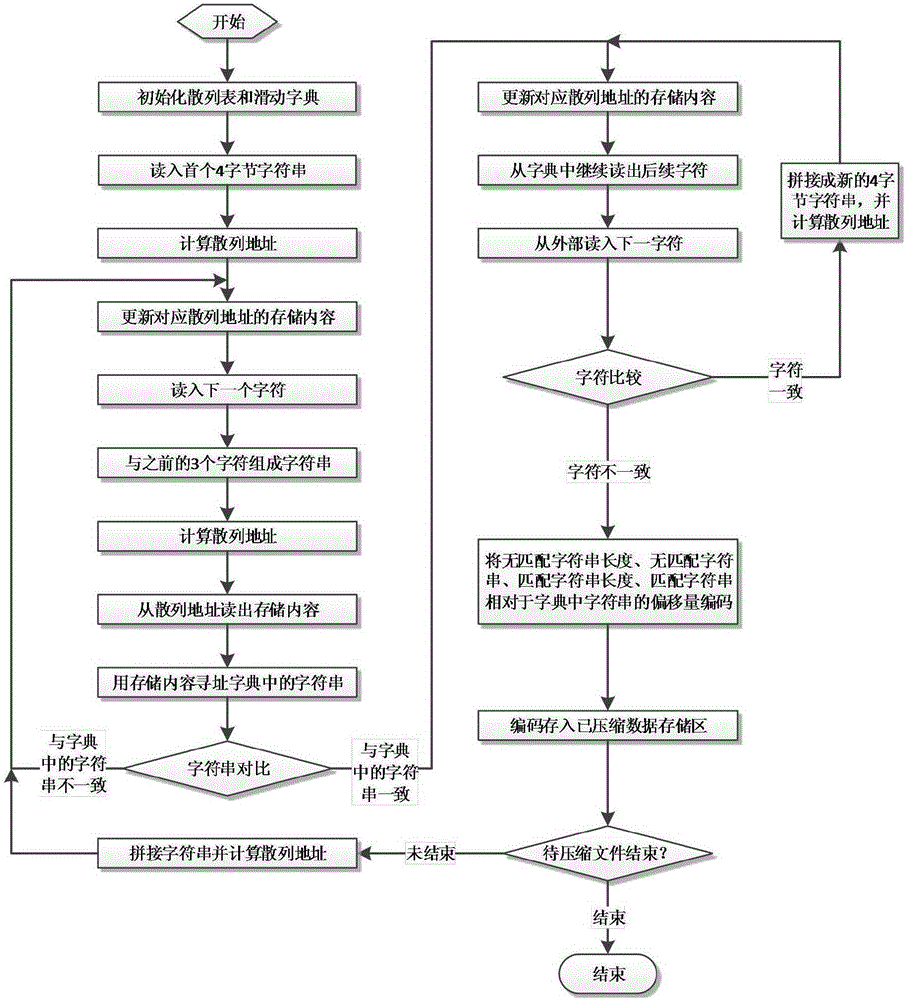
Configurable data compression system based on hardware
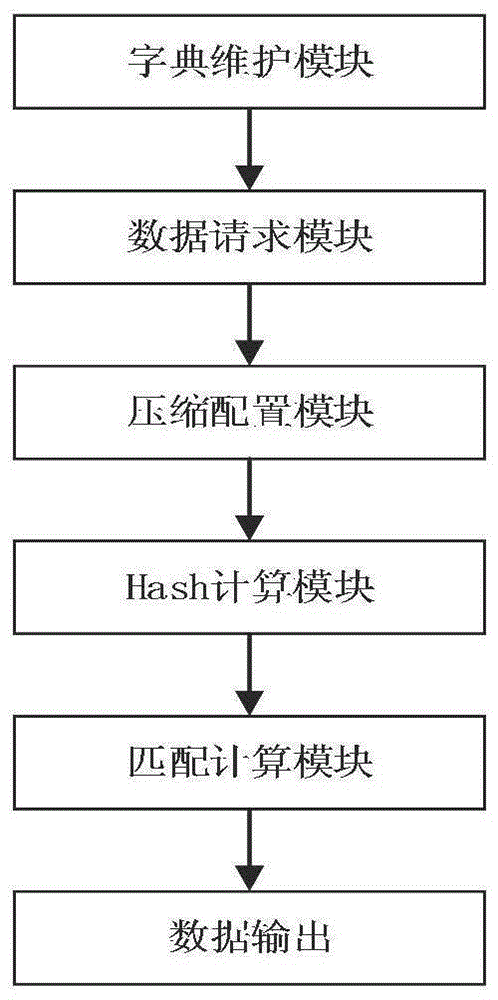
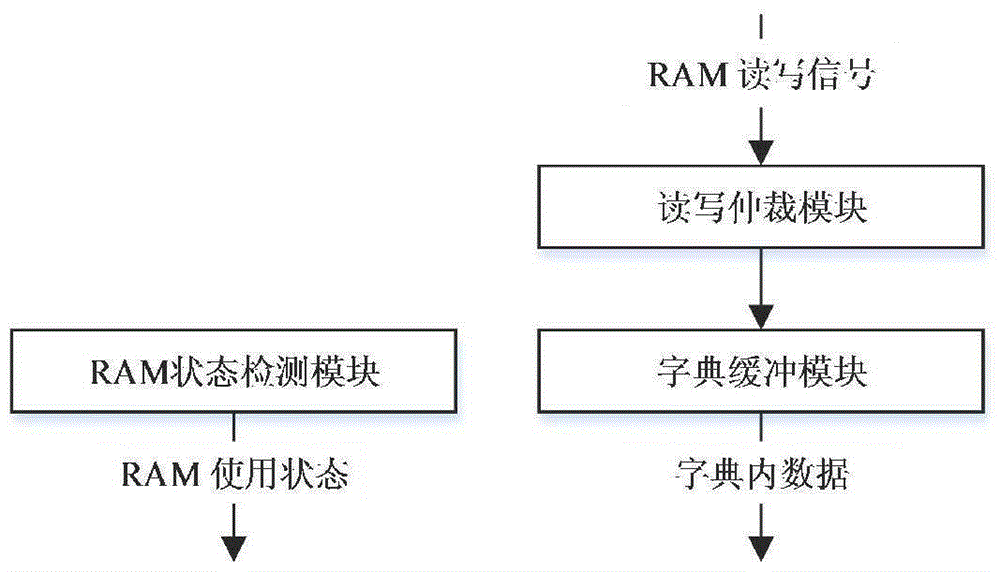
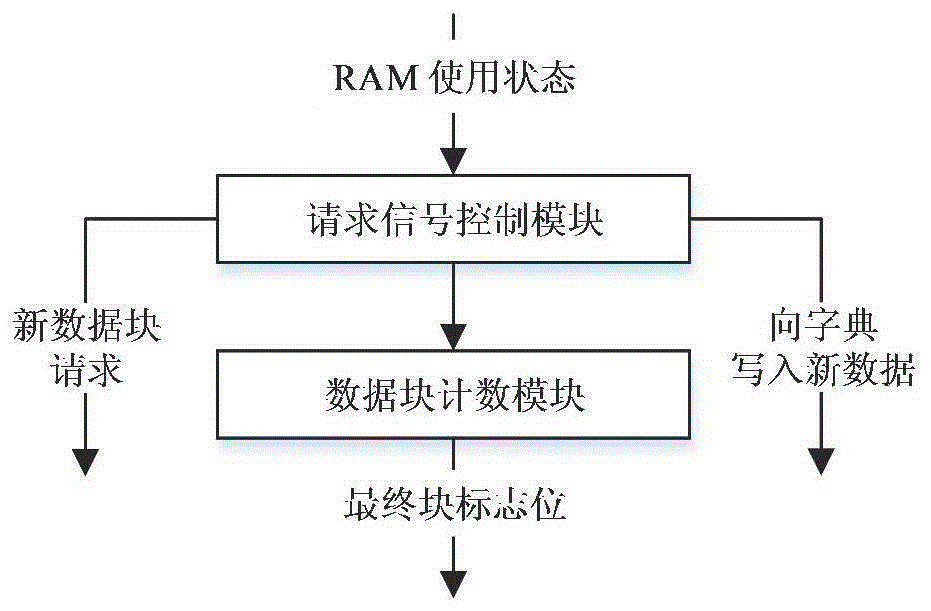
ActiveCN105183557AImprove the efficiency of data compression processingGuaranteed continuous readResource allocationCode conversionLossless compression algorithmProgrammable logic device
The present invention discloses a configurable data compression system based on hardware. The configurable data compression system comprises a dictionary maintenance module, a data request module, a data compression module and a data output module. By using the configurable data compression system disclosed by the present invention, a data compression function is realized by using a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the data compression system is realized by adding related modules communicated with a PC, and the efficiency of data compression process is greatly improved by adopting a LZ77 lossless compression algorithm and designing a reasonable hardware circuit structure according to the algorithm. In addition, the degree of preference to compression ratio and compression rate in an LZ77 compression process can be adjusted according to different compression levels. Further, the result of data compression can be coded differently to form compressed files with different formats, thereby realizing compatibility between hardware and software.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Graphic image data compressor and method of compressing graphic image data
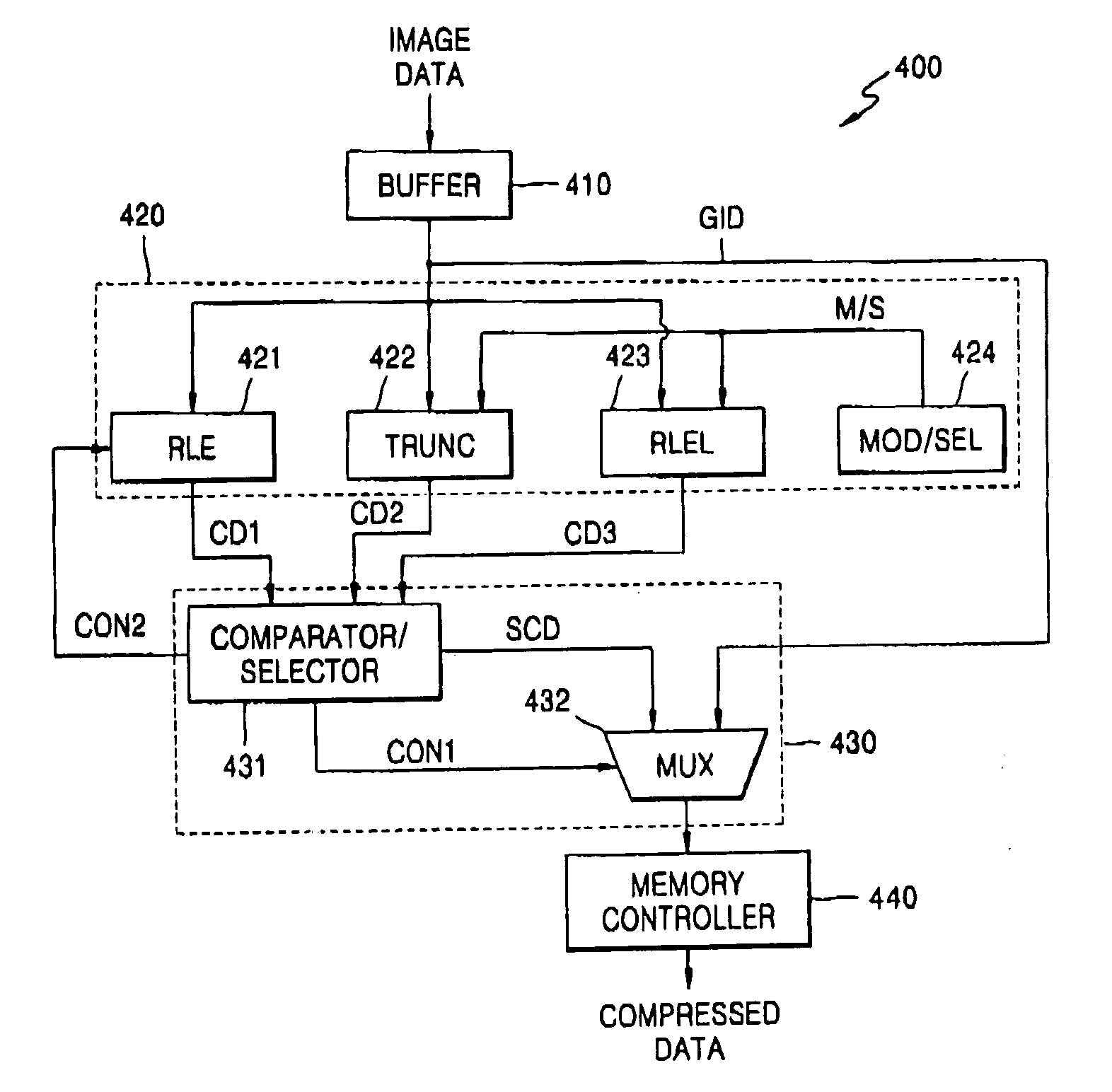
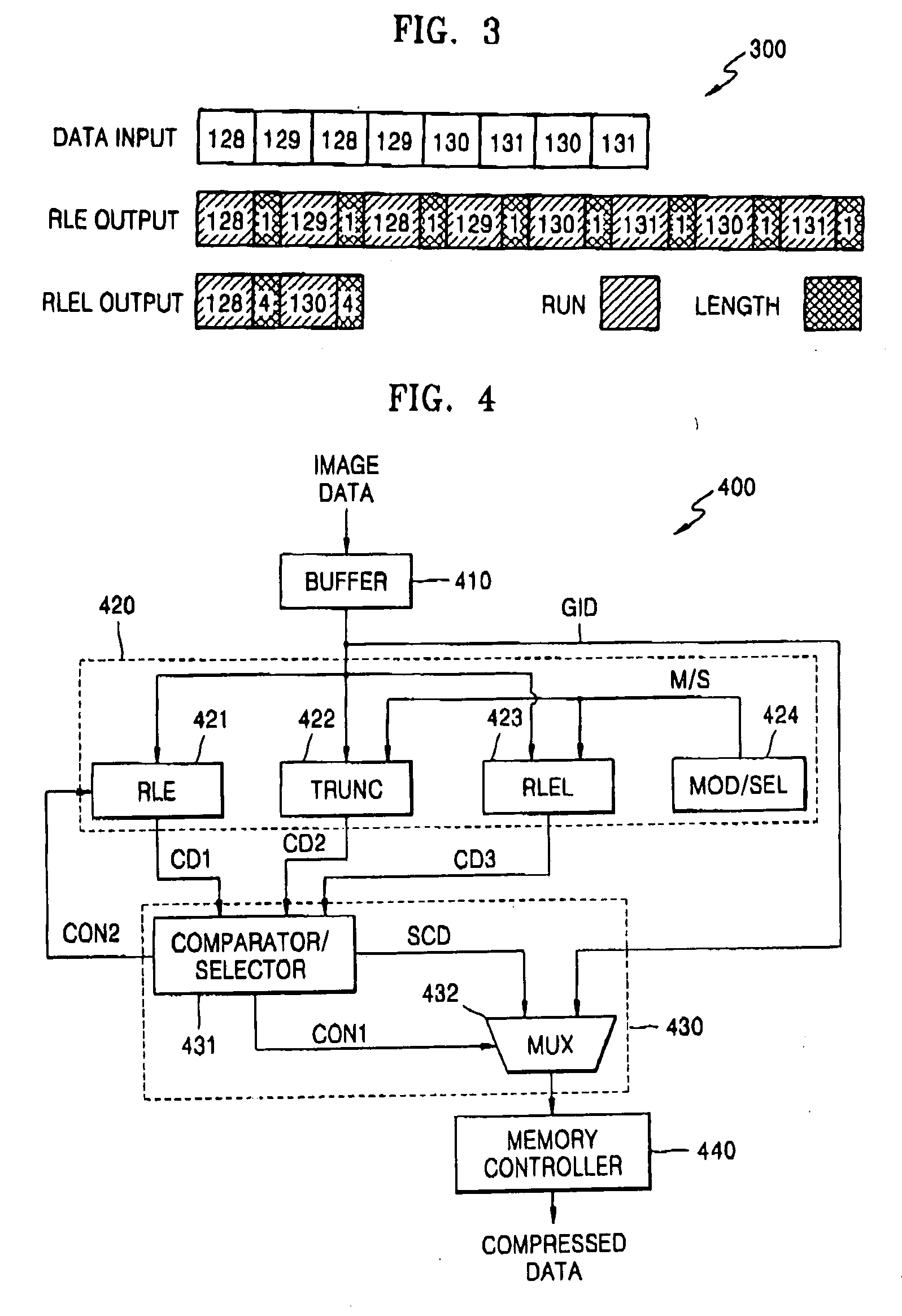
InactiveUS20060159358A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationGraphicsLossless compression algorithm
Provided are a graphic image data compressor that provides a complete image instead of an erroneous image when graphic image data fails to be compressed to satisfy its bandwidth and a method of compressing graphic image data using the same, where the graphic image data compressor includes a compression block for compressing received graphic image data using a loss compression algorithm and a lossless compression algorithm and controlling an amount of loss data in the loss and lossless compression algorithms, and a compressed data determination block for comparing a compression rate of data compressed according to the loss and lossless compression algorithms with an established compression rate, selecting optimum compressed data, and determining to output the selected compressed data or the graphic image data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for compression of generalized sensor data
ActiveUS20140091953A1Code conversionDigital video signal modificationLossless compression algorithmComputer vision
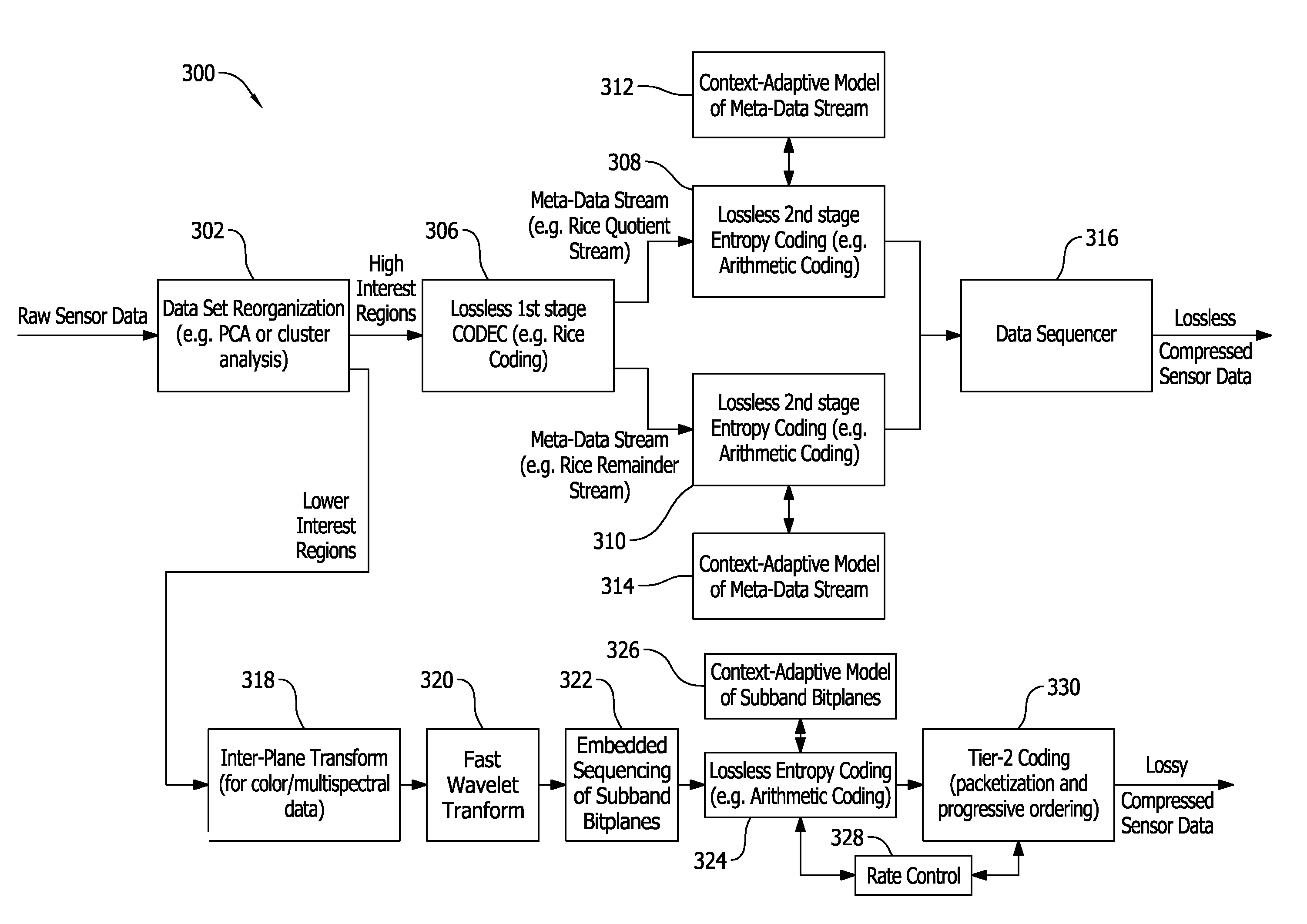
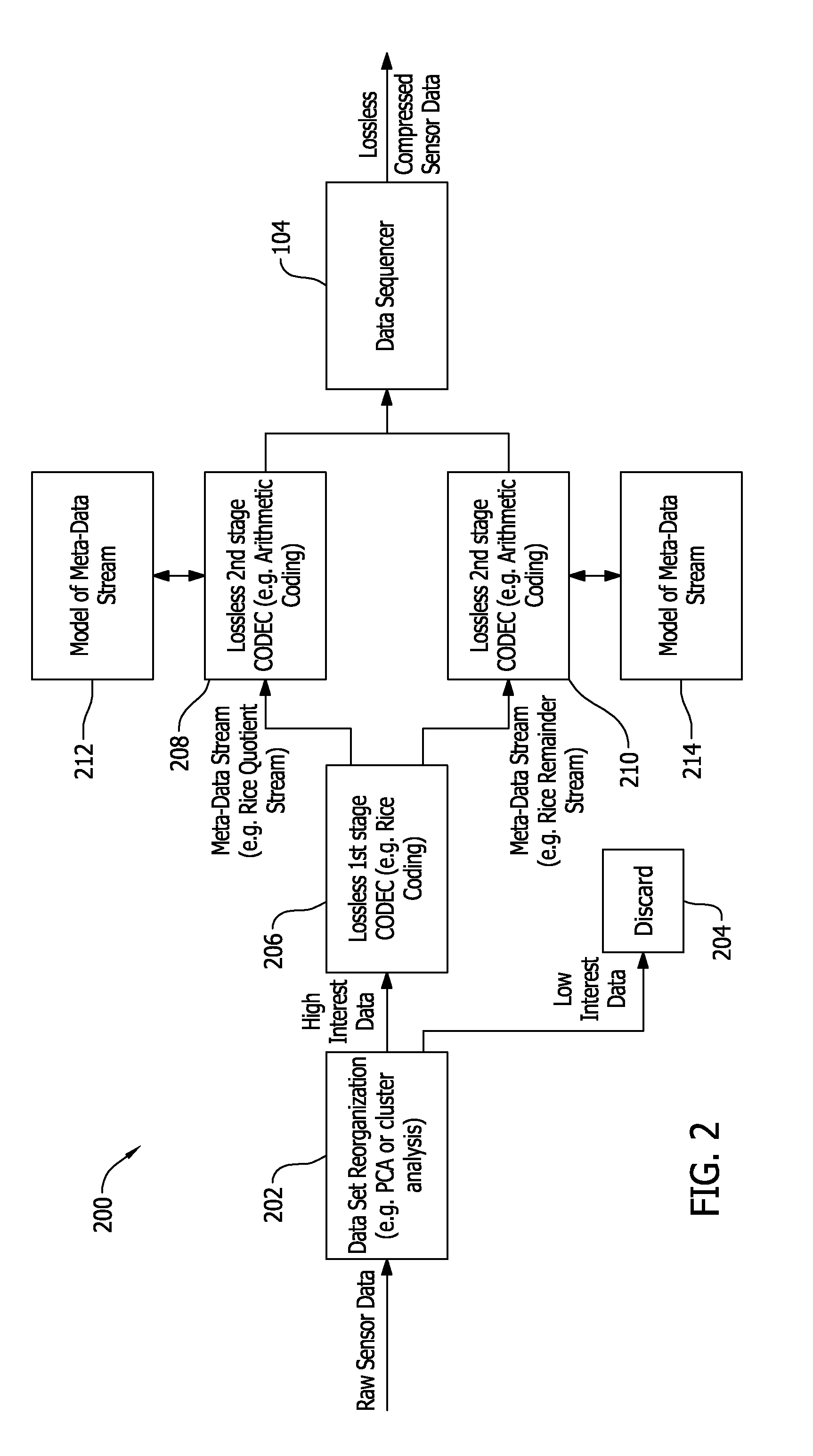
Methods and apparatus for compression of generalized sensor data are described. One example method for use in compression of generalized sensor data at a first location for transmission to a second location includes analyzing the sensor data to identify high interest data and low interest data, and compressing the high interest data with a lossless compression algorithm.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method for ink or handwriting compression
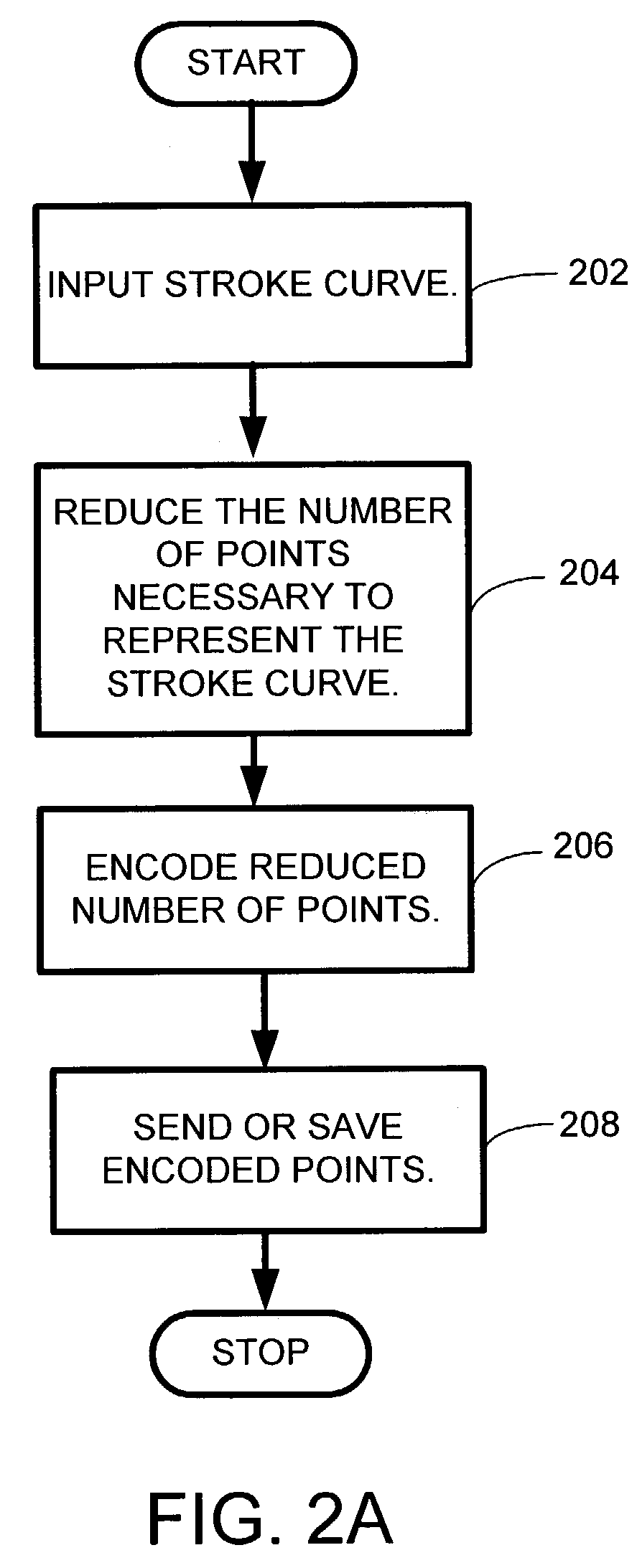
ActiveUS7302106B2Reduce the amount requiredSmall appearanceInput/output for user-computer interactionDrawing from basic elementsHandwritingLossless compression algorithm
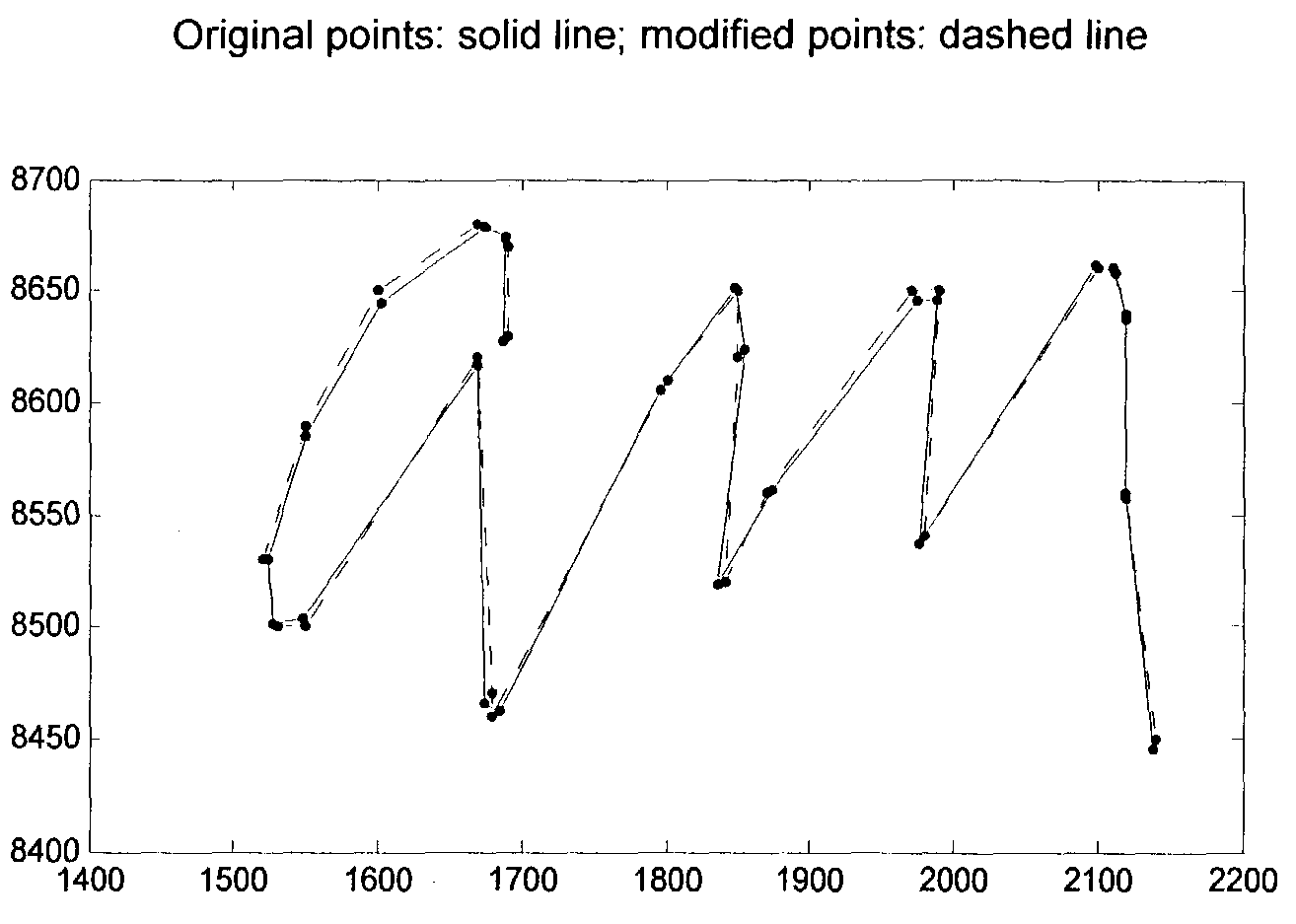
A system and method for compressing digital pen stroke data utilizing curve simplification. Digital pen stroke images (ink images) generate a relatively large amount of data to preserve the ink image generated on a device. Current ink compression algorithms utilize lossless compression algorithm that have limited success. The invention provides a lossy compression algorithm to reduce the amount of data required to store and transmit ink data. The invention utilizes a two-part algorithm to reduce and compress the number of data points representing the ink data. The invention also utilizes curve splines to reconstruct and smooth the lossy ink data image.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
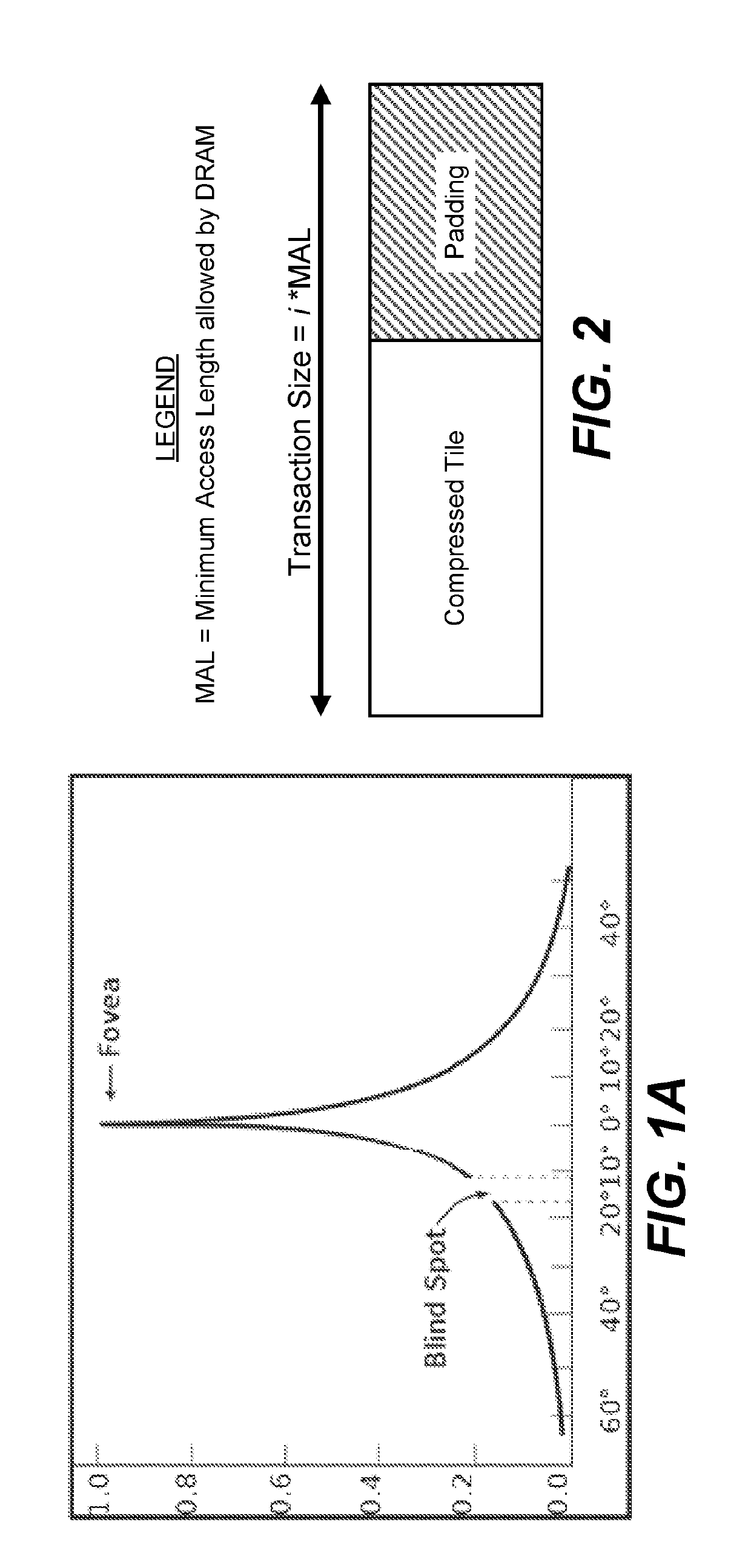
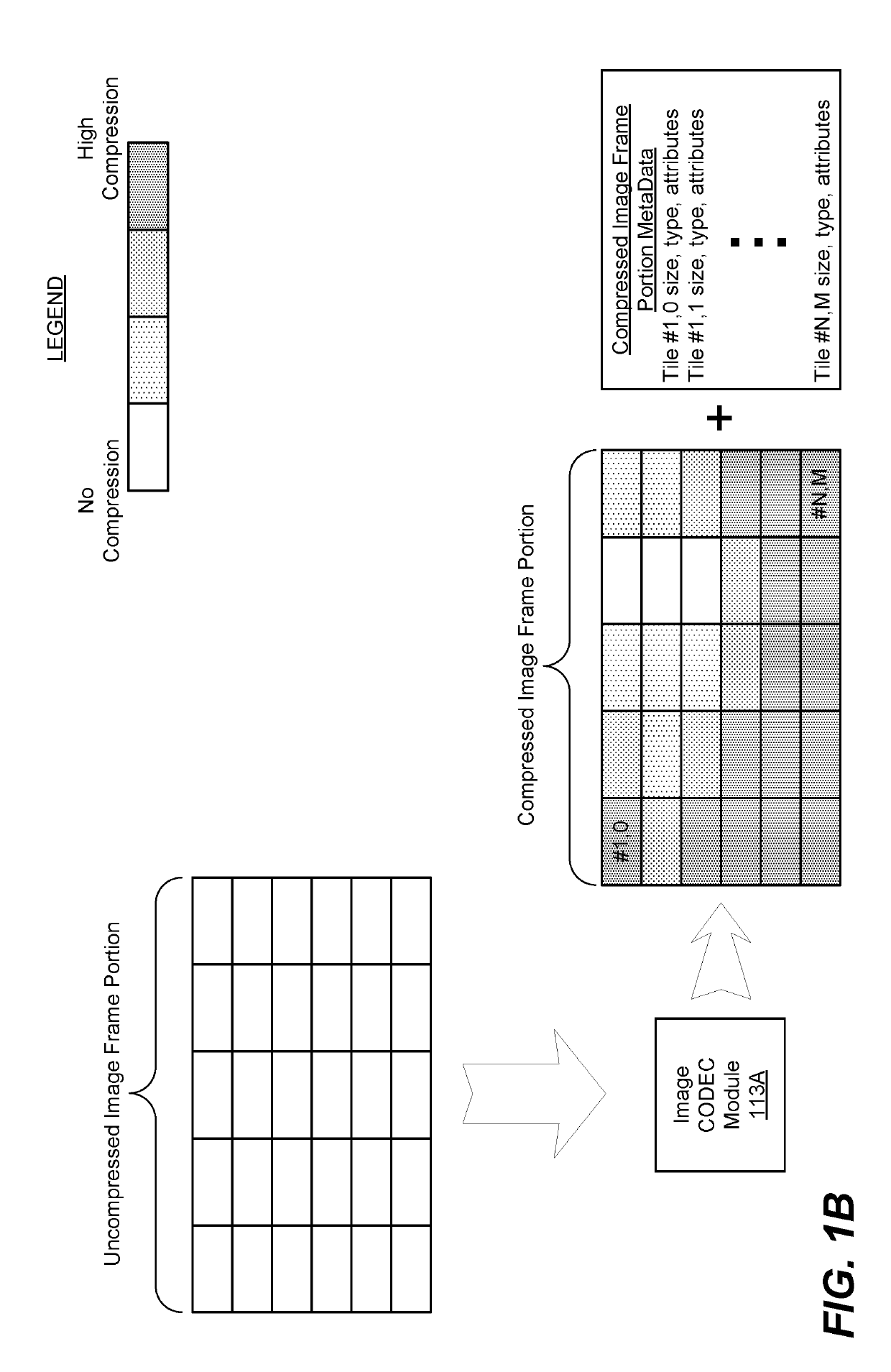
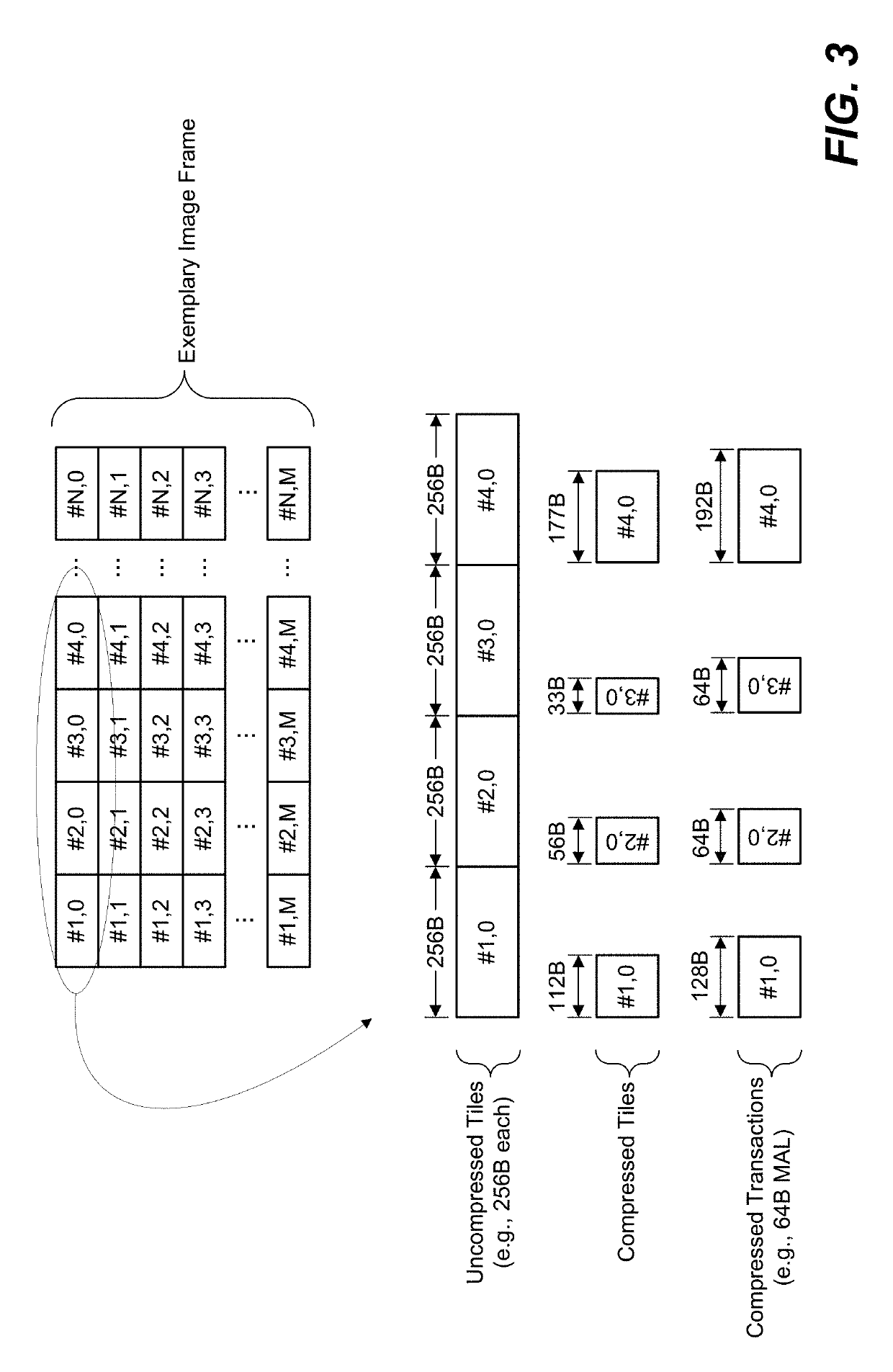
System and method for foveated compression of image frames in a system on a chip
ActiveUS20190110053A1Increase the compression factorCompression can be losslessMemory architecture accessing/allocationTelevision system detailsFixation pointLossless compression algorithm
An exemplary method for intelligent compression uses a foveated-compression approach. First, the location of a fixation point within an image frame is determined. Next, the image frame is sectored into two or more sectors such that one of the two or more sectors is designated as a fixation sector and the remaining sectors are designated as foveation sectors. A sector may be defined by one or more tiles within the image frame. The fixation sector includes the particular tile that contains the fixation point and is compressed according to a lossless compression algorithm. The foveation sectors are compressed according to lossy compression algorithms. As the locations of foveation sectors increase in angular distance from the location of the fixation sector, a compression factor may be increased.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Computer maintenance system for an aircraft with remote terminal
ActiveUS8165732B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLossless compression algorithmKVM switch
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Lossless compression algorithms for spatial data
InactiveUS7668386B2Loss of fidelityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingArray data structureLossless compression algorithm
The present invention is related to routines for the processing of quantized vector data into one or more arrays of integers whose values are closer to zero than the integers in the quantized vector data. The arrays are input to a compression engine resulting in compressed bytes of data that may be transferred to a computing device for the decompression of the data. The quantized vector data can include vertices expressed as a pair of integer values that may represent geometric, spatial elements, such as points, interconnected lines (polylines), and polygons. These geometric objects may be representative of information on a map. The compressed bytes may be grouped according to grids, wherein each grid represents a distinct geographic area of a map, so that a consumer can store and decompress only the portion of the map data which is of interest.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method, terminal and system for upgrading software version
InactiveUS20130167133A1Keep for a long timeReduce transmissionProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsLossless compression algorithmData transmission
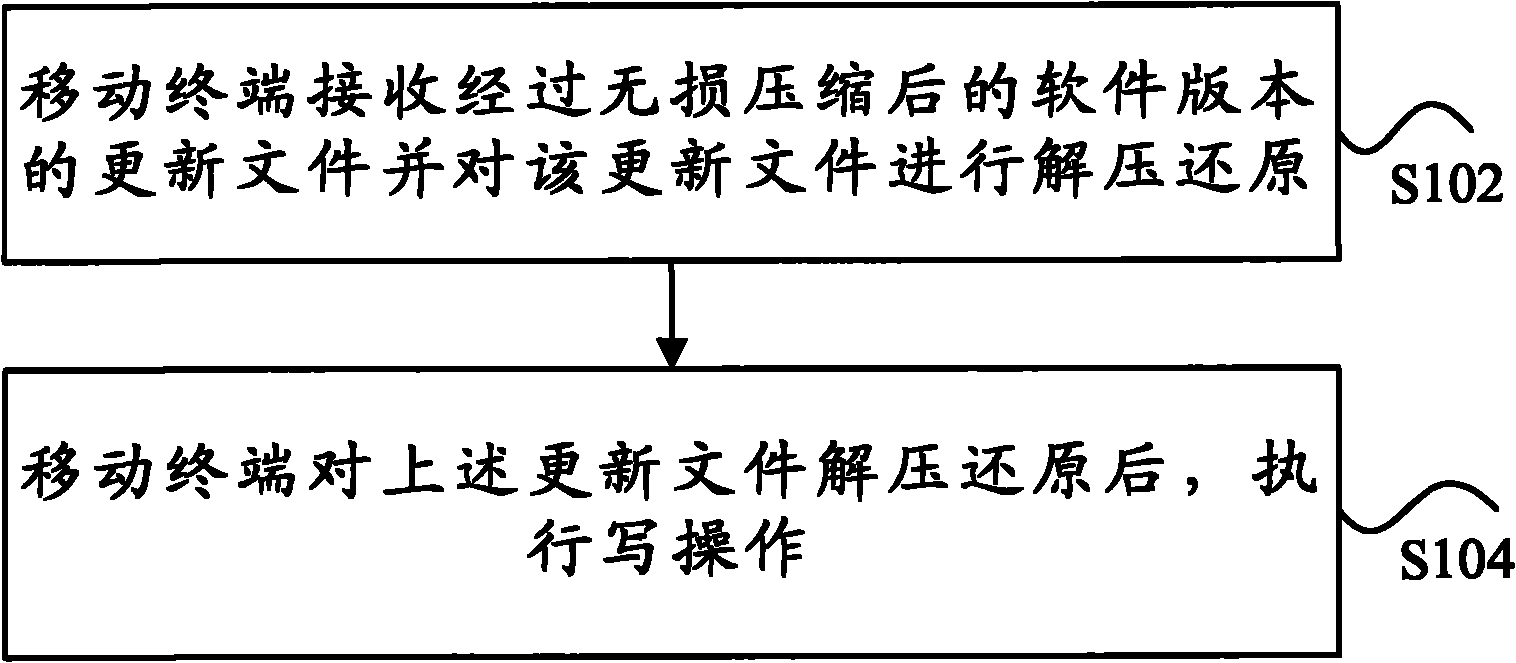
The present invention discloses a method for upgrading a software version, which is applied to a mobile terminal, and the method comprises: a mobile terminal receiving a losslessly-compressed update file of a software version, and decompressing and restoring the update file; and the mobile terminal performing writing operation after the update file is decompressed and restored. The present invention further provides a mobile terminal and a system based on the method. Through the present solution, the update file of the software version of the mobile terminal is losslessly compressed by a lossless compression algorithm to solve the problems of very long downloading time and low downloading direct through rate in the related arts where the update file of the software version is directly downloaded and upgraded, therefore, the data transmission volume is reduced, the upgrade time of the mobile terminal is effectively reduced, and the mobile terminal can complete the upgrade process fast and securely, thus the upgrading and downloading efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
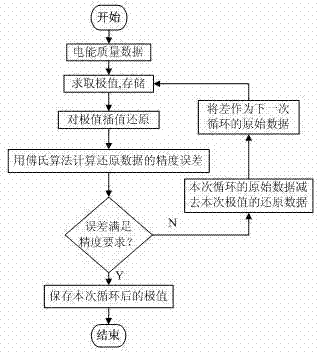
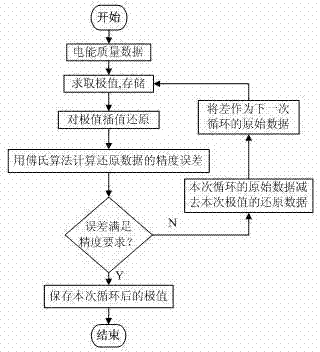
Real-time power quality data compression algorithm
ActiveCN102394657AEfficient compressionImprove real-time performanceCode conversionPower qualityLossless compression algorithm
The invention provides a real-time power quality data compression algorithm, namely an integrated extremum method which comprises an extremum method and an LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch) lossless compression algorithm. The data sampled by a power quality monitoring device for a long time at a high speed in an on-line mode is firstly subjected to real-time loss compression by the extremum method and then subjected to lossless compression and storage, and is uploaded to a power quality data center regularly; and the data is decompressed and reduced to valid data meeting error and accuracy requirements in the power quality data center. The algorithm provided by the invention realizes real-time high-efficiency compression of the power quality sampling data, is simple, and has good timeliness and wide engineering application prospects.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD
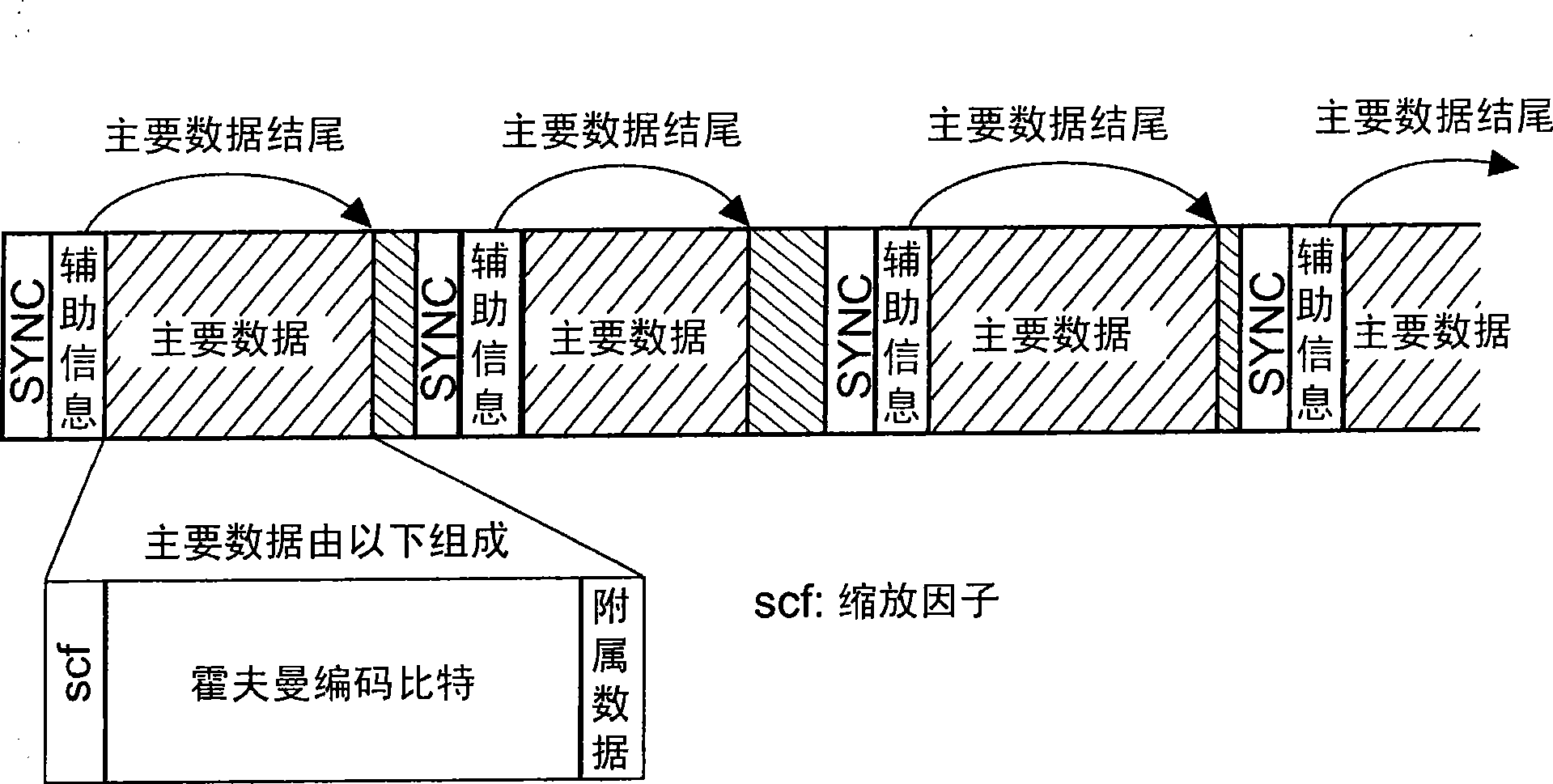
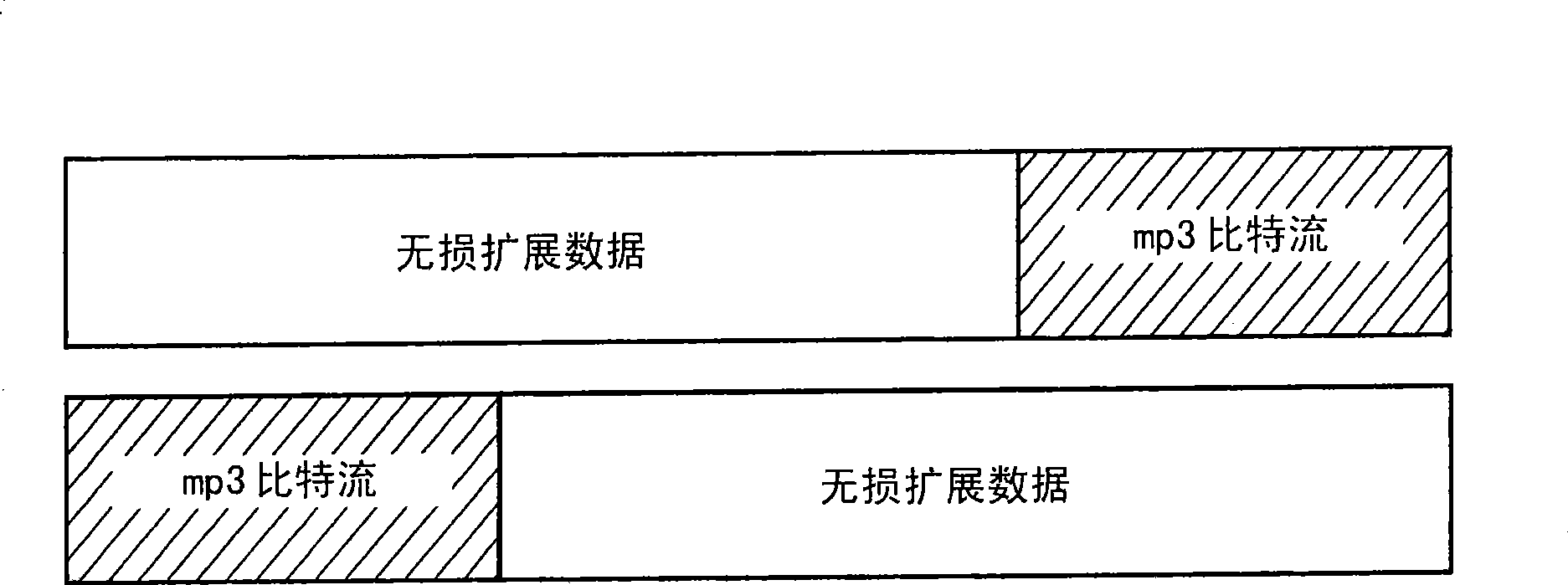
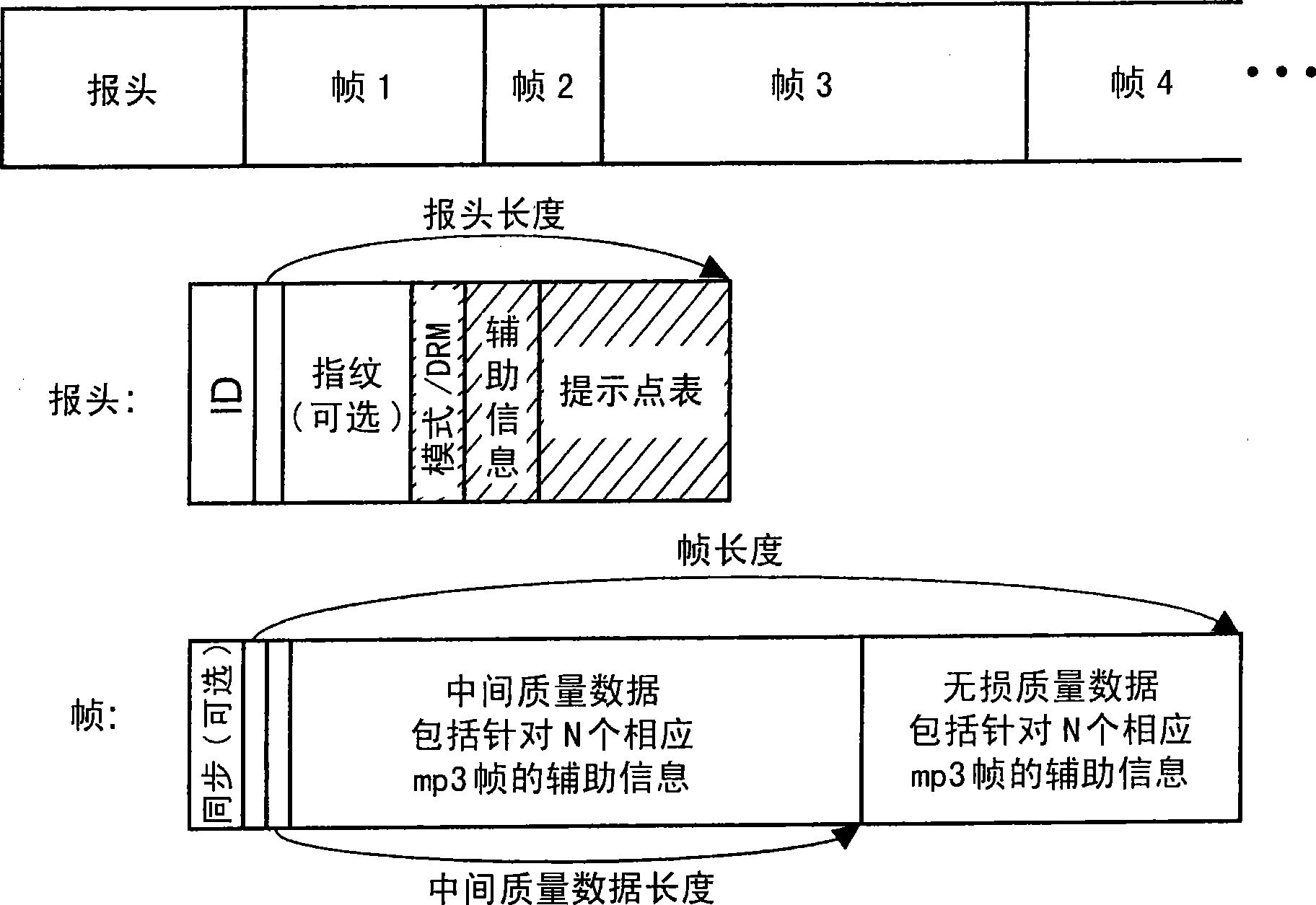
Audio bitstream data structure arrangement of a lossy encoded signal together with lossless encoded extension data for said signal
Lossless compression algorithms can only exploit redundancies of the original audio signal to reduce the data rate, but not irrelevancies as identified by psycho-acoustics. Lossless audio coding schemes apply a filter or transform for decorrelation and then encode the transformed signal. The encoded bit stream comprises the parameters of the transform or filter, and the lossless representation of the transformed signal. However, in case of lossy based lossless coding the additional amount of information exceeds the amount of data for the base layer by a multiple of the base layer data amount. Therefore the additional data cannot be packed completely into the base layer data stream e.g. as ancillary data. The at least two data streams resulting from the combination of lossy coding format with a lossless coding extension are the base layer containing the lossy coding information and the enhancement data stream for rebuilding the mathematically lossless original input signal. Furthermore several intermediate quality layers are possible. However, these data streams are not independent from each other. Every higher layer depends on the lower layers and can only be reasonably decoded in combination with these lower layers. According to the invention, a special combination of one-time header information with repeated header information in a block structure is used, which kind of combination depends on the type of application. Assignment information data identify the different parts or layers of the lossless format belonging to one input signal. Synchronisation data are used to combine the different data streams or parts or layers to a single lossless or intermediate output signal. These features are used in a file format and in a streaming format.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
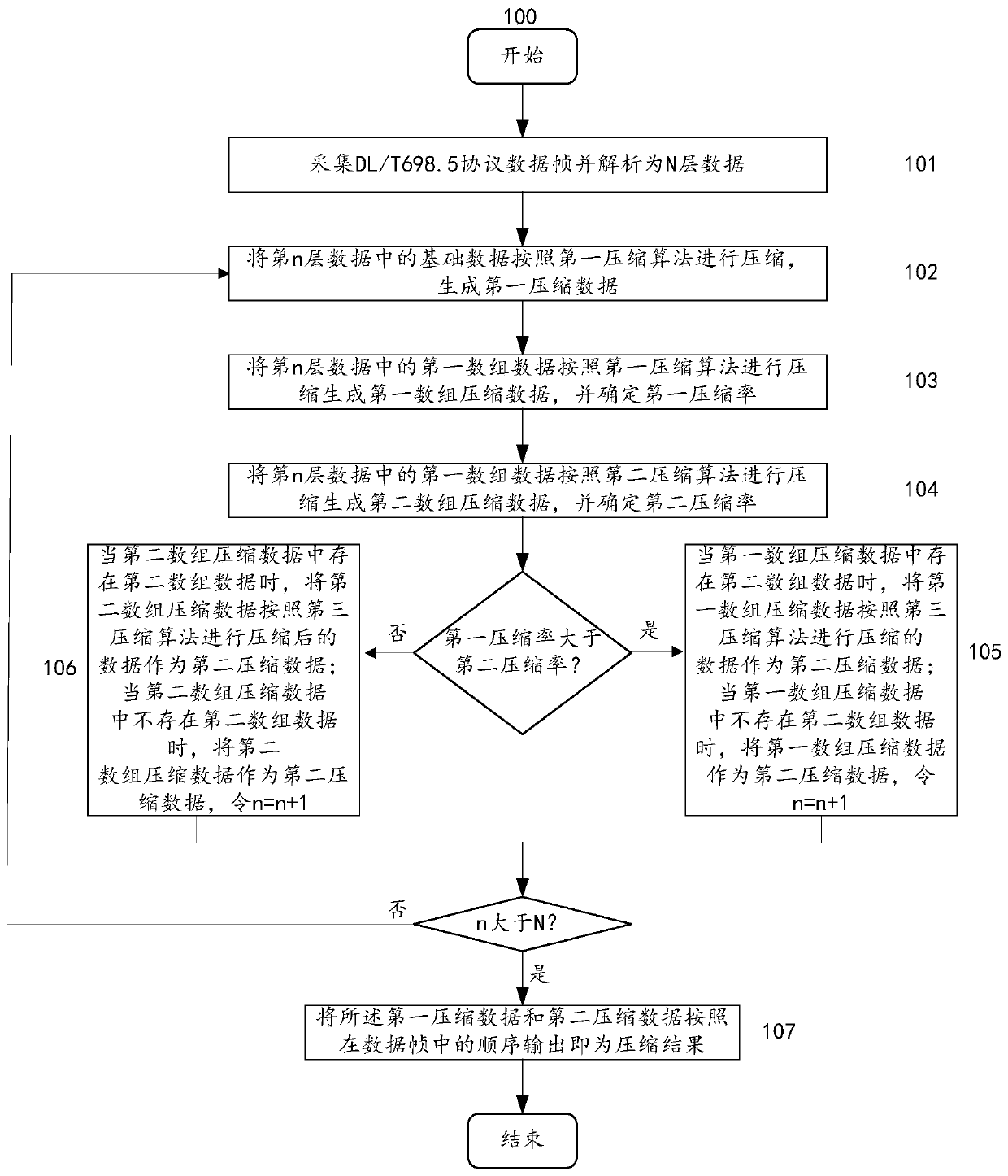
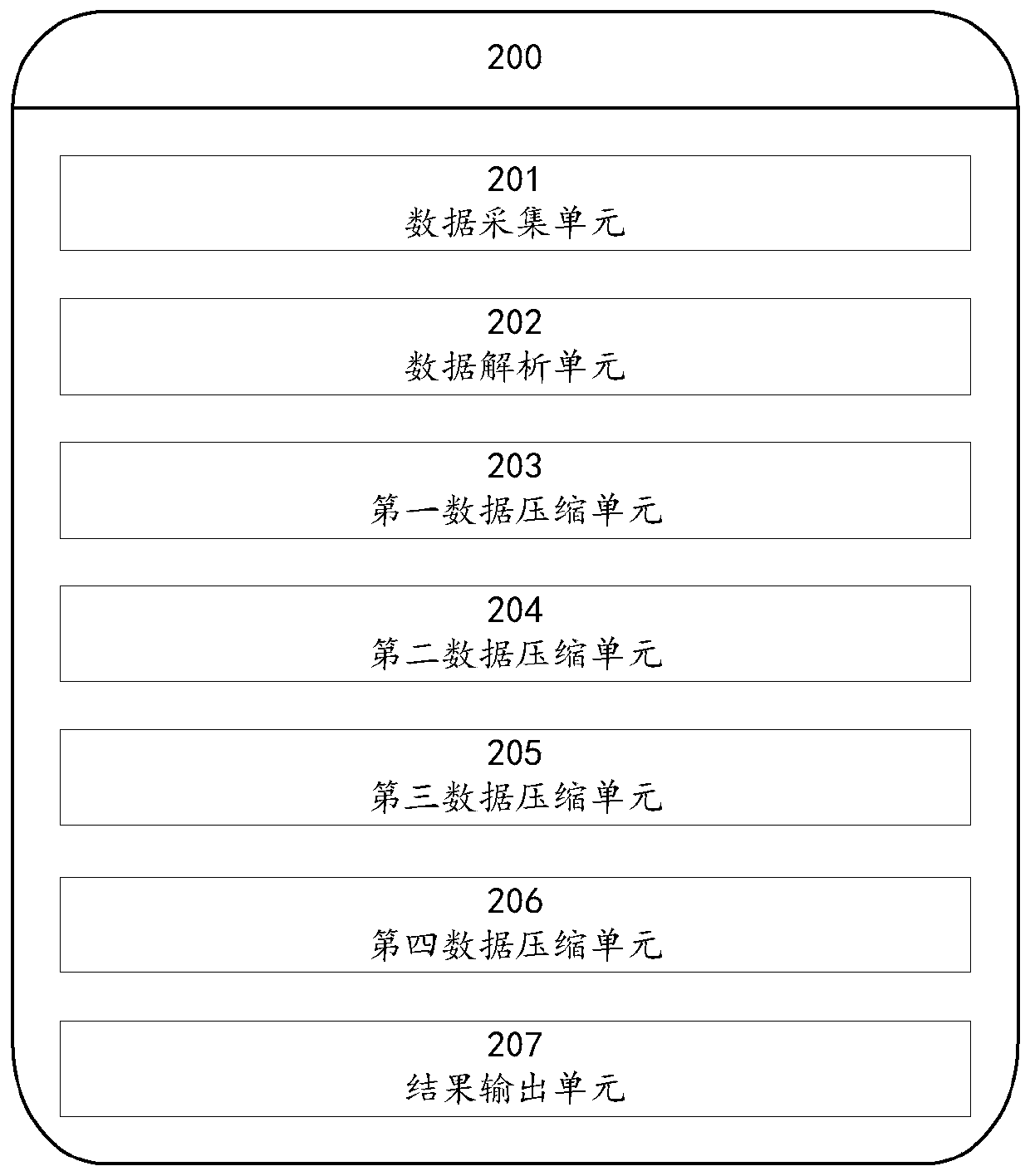
Data frame compression method and system based on DL/T698.45 protocol
ActiveCN110535846AImprove execution efficiencyTransmissionLossless compression algorithmArray data structure
The invention provides a data frame compression method and system based on a DL / T698.45 protocol. According to the method and the system, acquired data frames are analyzed and layered; the data in each layer is compressed by adopting different compression algorithms according to types; wherein the basic data adopts a first compression algorithm; for different data type compression bytes, for firstarray data which cannot be compressed by array elements, a second compression algorithm is adopted, the data types of the array elements are extracted to serve as array element types, and for secondarray data which have the same array elements and can be compressed, only one group of array elements are reserved by defining the compression array types. The data frame compression method and systembased on the DL / T698.45 protocol are simple in compression algorithm and high in execution efficiency, not only have the characteristic of being compressed again through a universal compression algorithm, but also retain the characteristic that data frames are easy to analyze, and are an efficient lossless compression algorithm.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Data lossless compression transmission method suitable for geophysical exploration
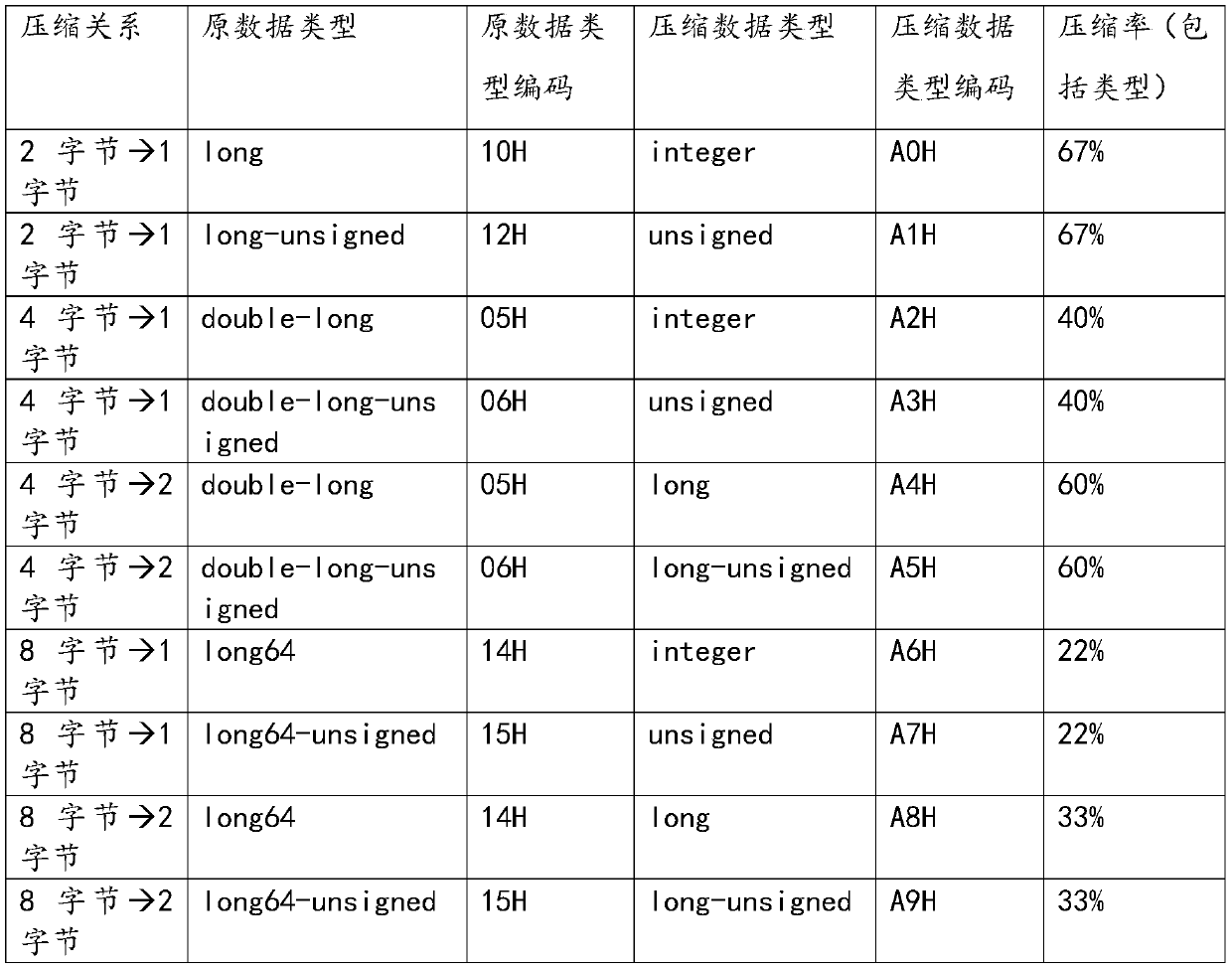
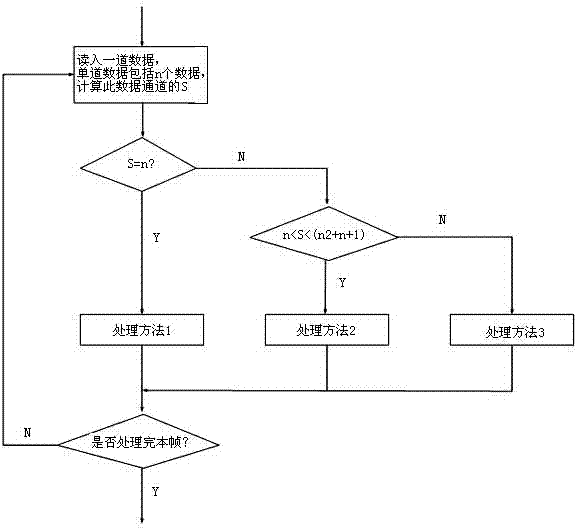
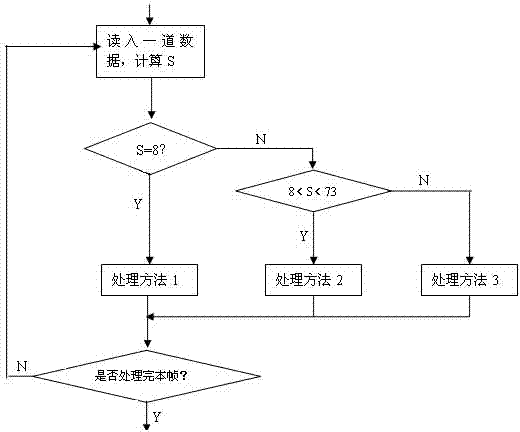
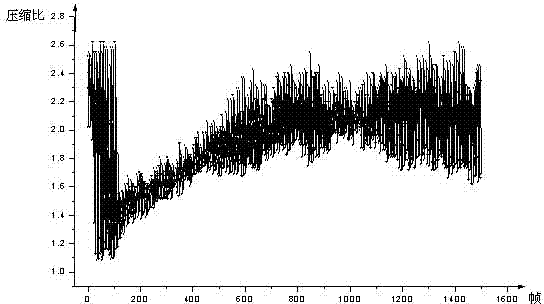
ActiveCN103197343AReduce data volumeImprove stabilitySeismic signal transmissionLossless compression algorithmDead time
The invention discloses a data lossless compression transmission method suitable for geophysical exploration. The data lossless compression method suitable for the geophysical exploration comprises the following steps: carrying out framing of sampling values of multiple sampling points, carrying out calculation of a variable S of data inside each channel in a frame according to a data lossless compression algorithm, then carrying out transmission of the compressed data finally according to the S selection compression processing method. The data lossless compression transmission method suitable for the geophysical exploration greatly reduces requirements of a system to the message transmission rate, reduces system design complexity, and increases system stability and manufacturing and maintenance cost of the system; in addition, the data lossless compression transmission method suitable for the geophysical exploration can effectively reduce data transmission time under the same data rate, and further reduces system dead time.
Owner:HEFEI GUOWEI ELECTRONICS
Improved train control system security data interaction method
ActiveCN110267266AIncrease the lengthMake up for loopholesNetwork traffic/resource managementEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesOccupancy rateTransceiver
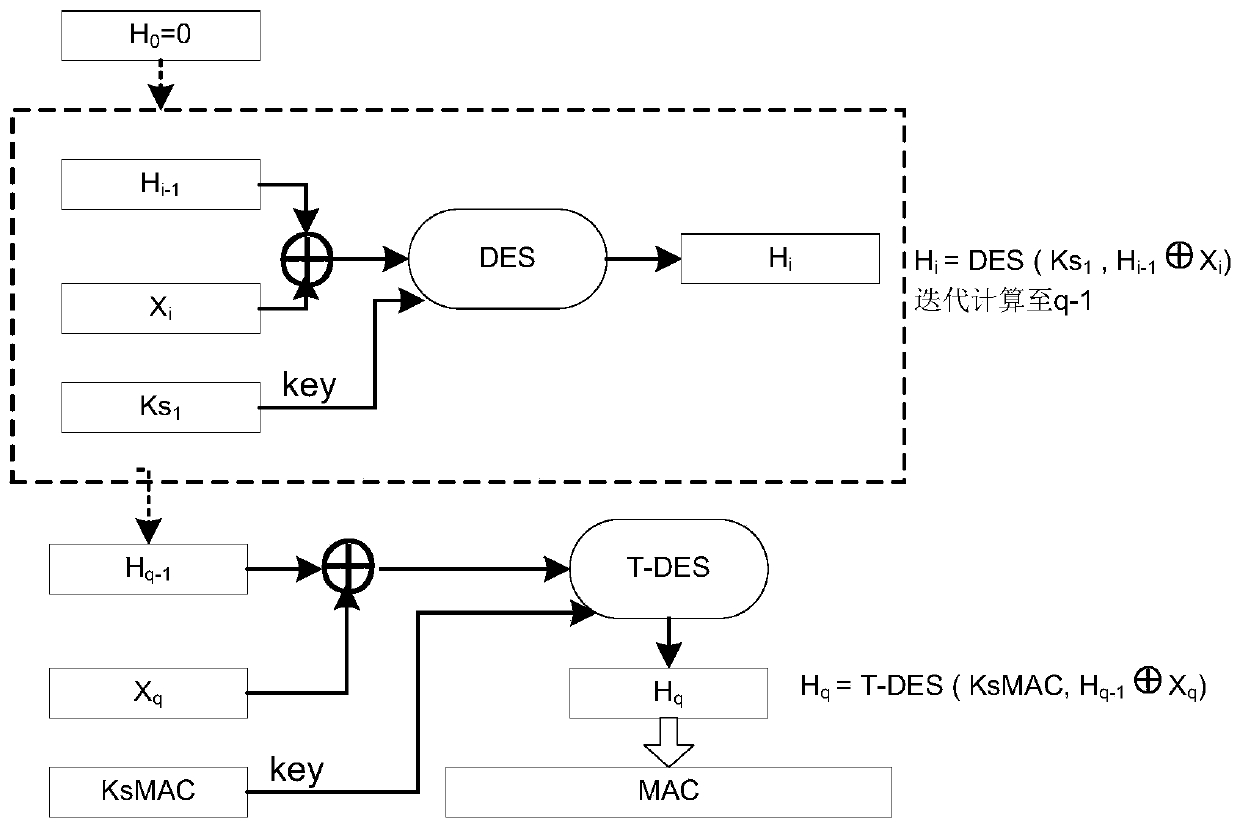
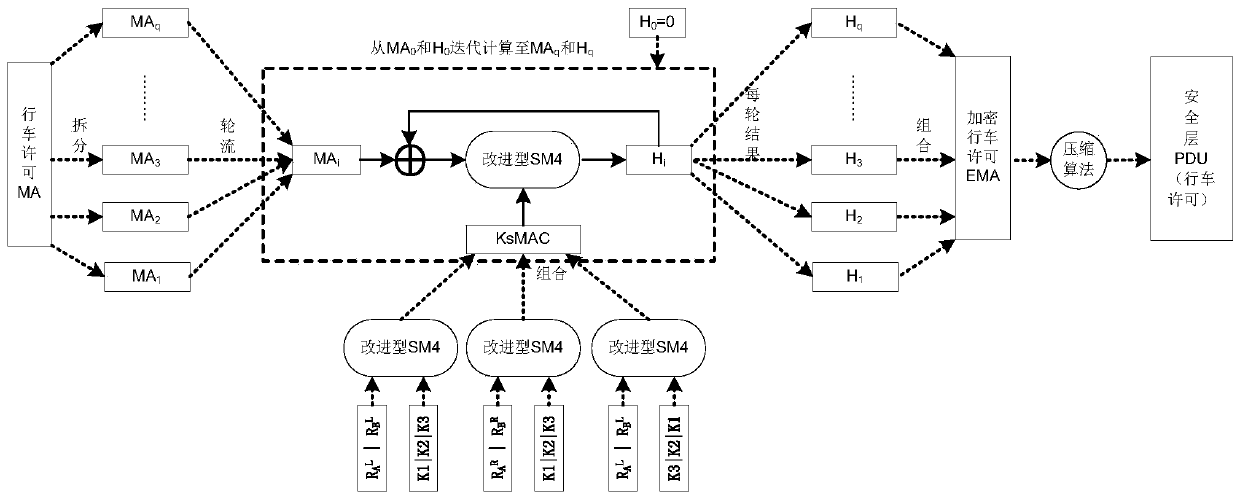
The invention discloses an improved train control system secure data interaction method, which comprises the following steps of: expanding the shared key of a data transceiver and the length of a random number generated and shared by the transceiver, and calculating a session key with an increased key length by matching with a corresponding SM4 algorithm; dividing the security data X of the train control system into blocks according to N bits, using a data block and a full text of a session key as input in each round, performing iterative computation by using a corresponding SM4 algorithm, and generating an N-bit operation result Hi corresponding to the corresponding data block; regarding the operation result Hi as encrypted data of the corresponding data block, and covering the corresponding data block, so that the security encryption of the security data X of the train control system is realized; and selecting a corresponding lossless compression algorithm according to the type of the train control system security data, performing data lossless compression on the full-text encrypted train control system security data X, and sending the compressed data X to a receiver. According to the method, the data security is greatly improved, and meanwhile, the occupancy rate of wireless resources is reduced.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com