Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
177results about How to "Reduce data rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
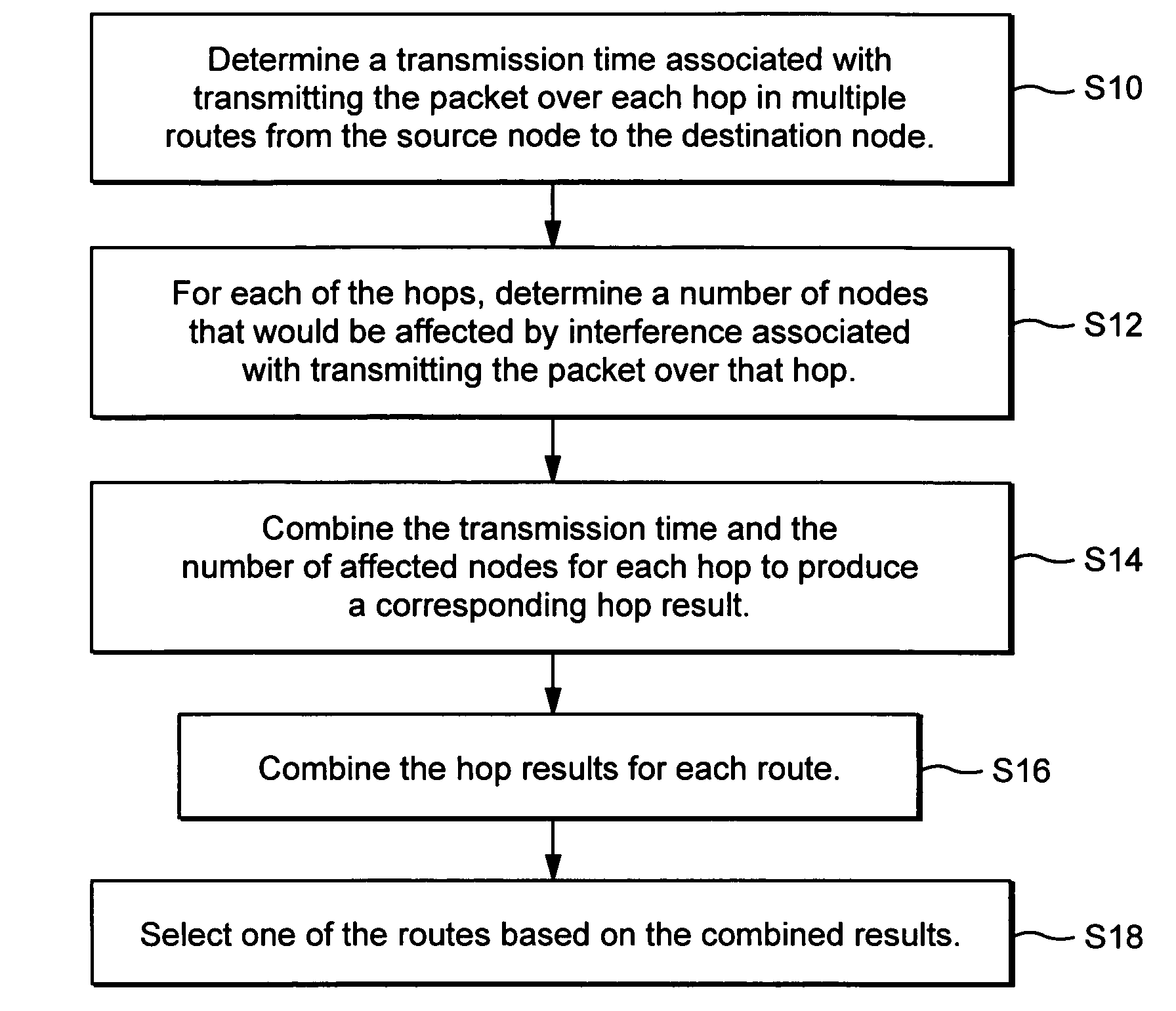
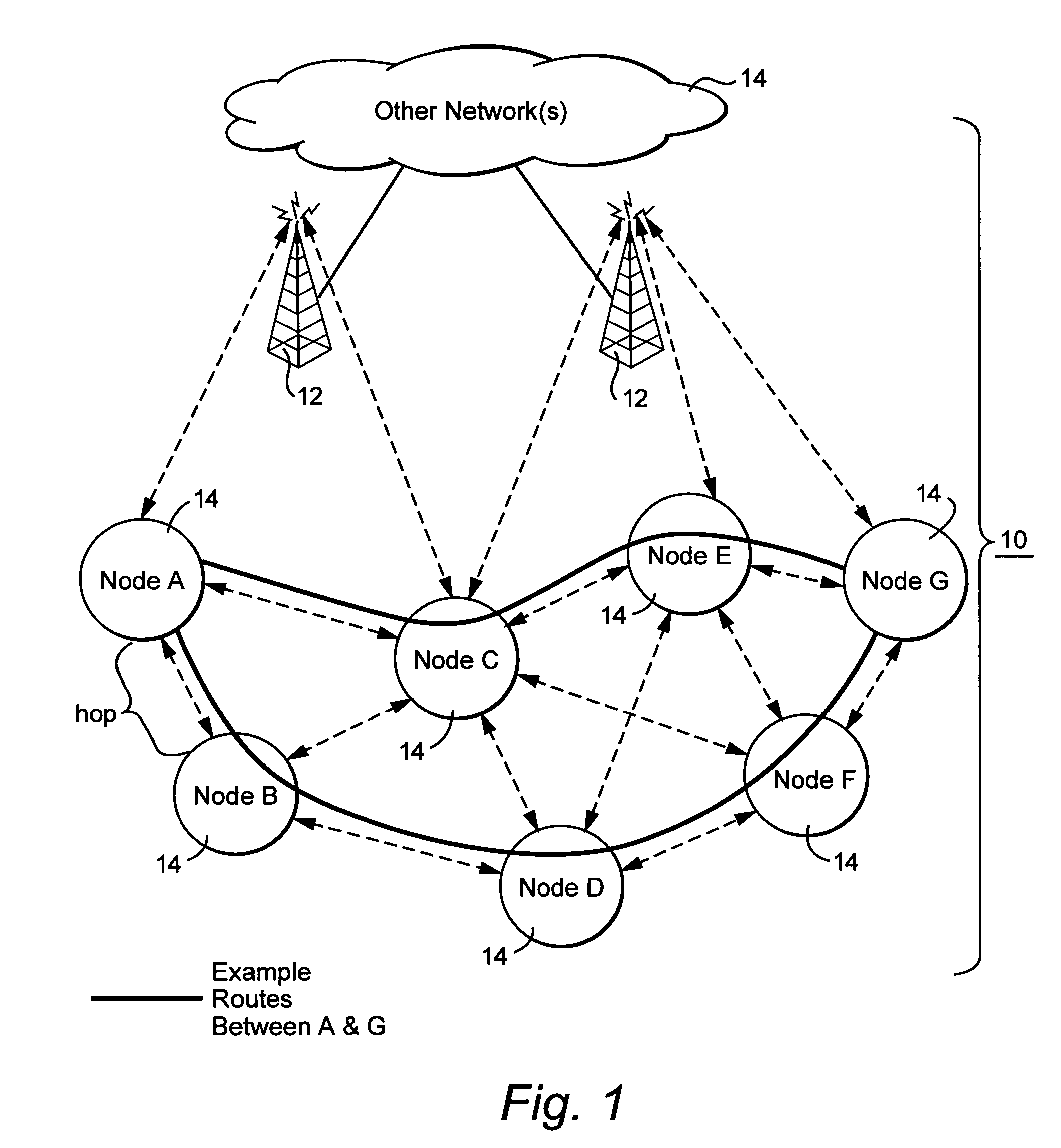
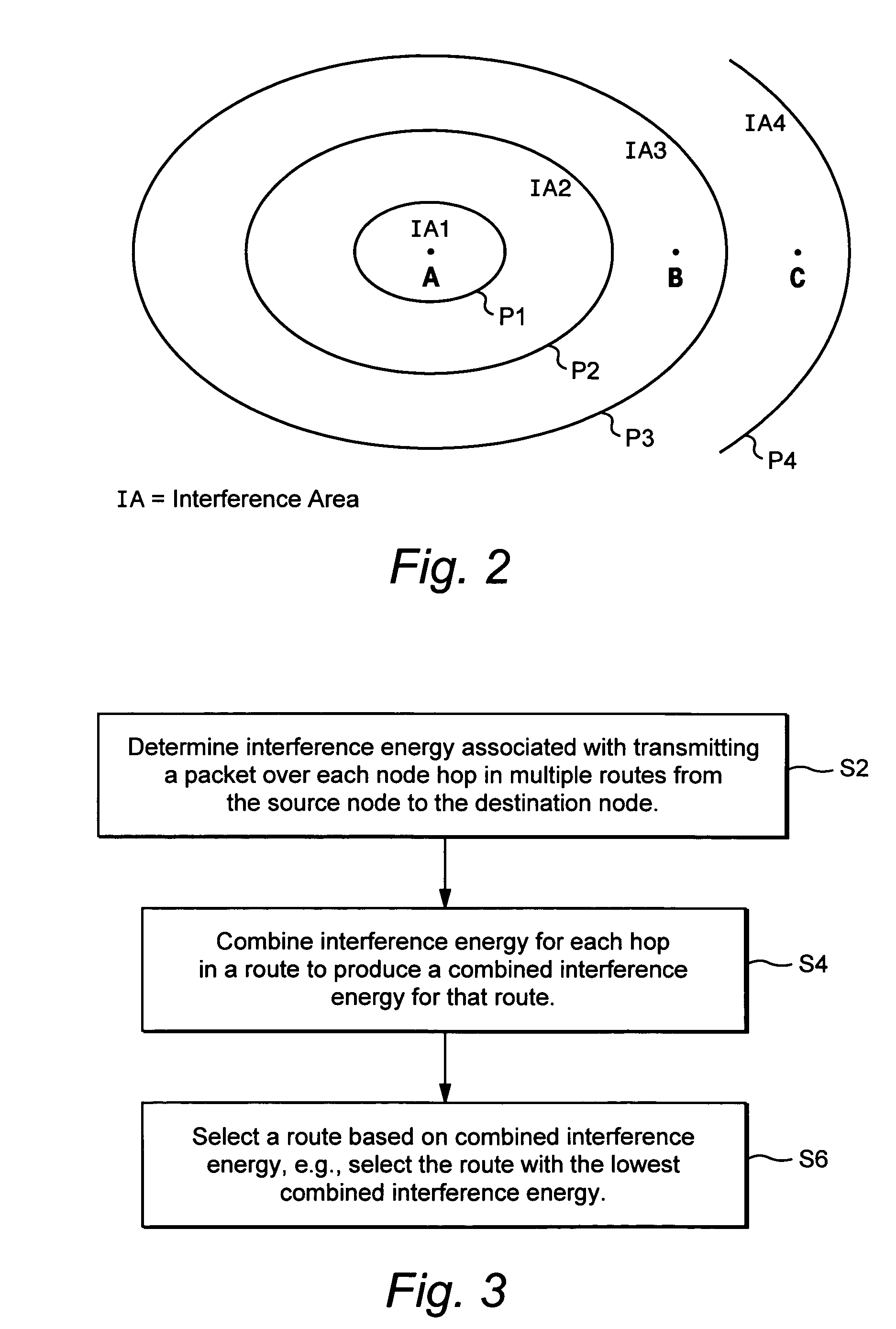
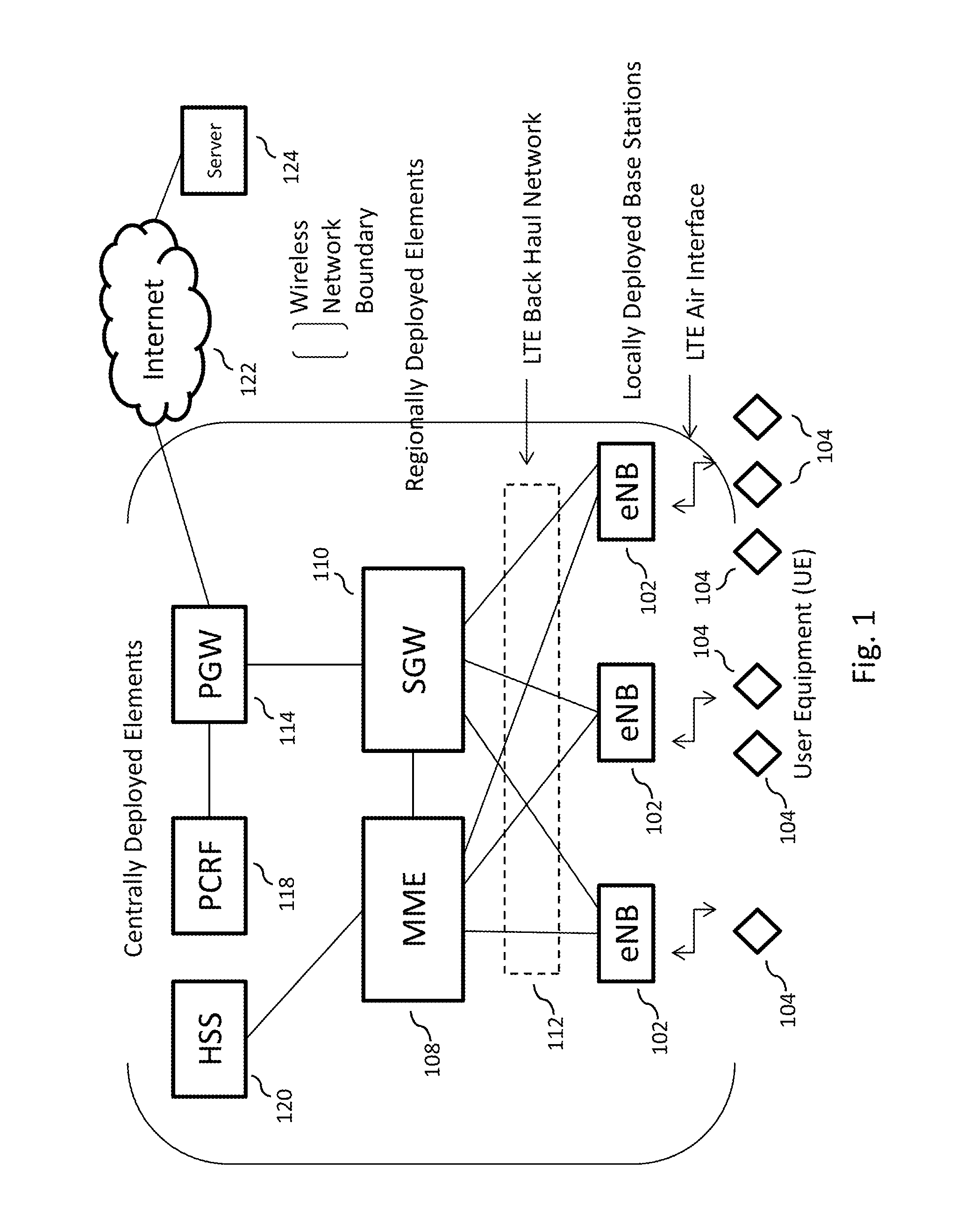
Interference-based routing in a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS7554998B2Low costReduce data rateEnergy efficient ICTError preventionComputer networkWireless mesh network
Route selection through a wireless mesh network between a source node and a destination node is based on minimizing generated interference in order to increase the capacity of the network. An interference energy associated with transmitting a packet over each hop in multiple routes from the source node to the destination node is determined. The interference energy for each hop is combined to generate a combined interference energy for each route. One of the routes is selected based on the combined interference energy determined for each route.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS20010036810A1Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS6785510B2Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
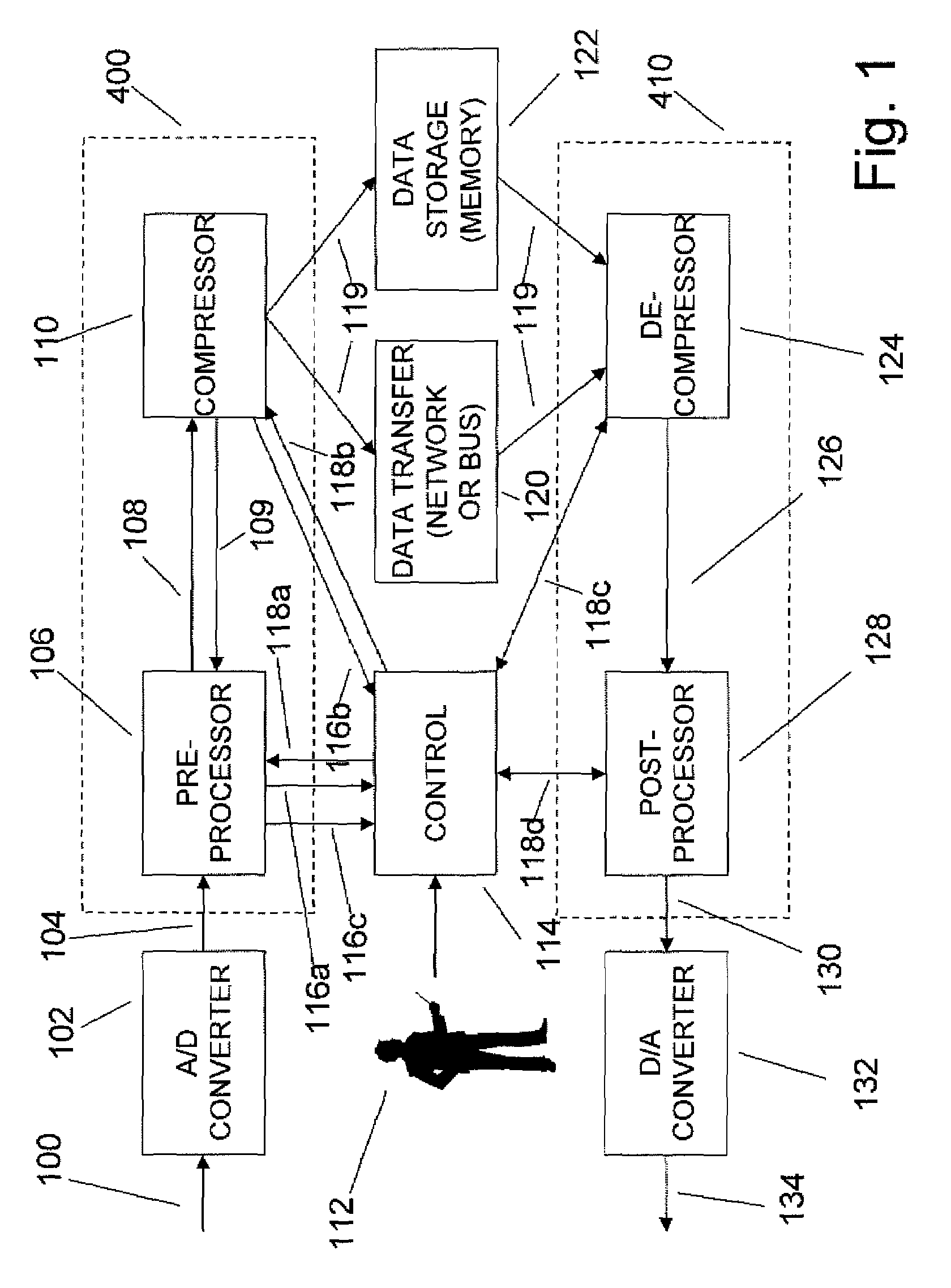
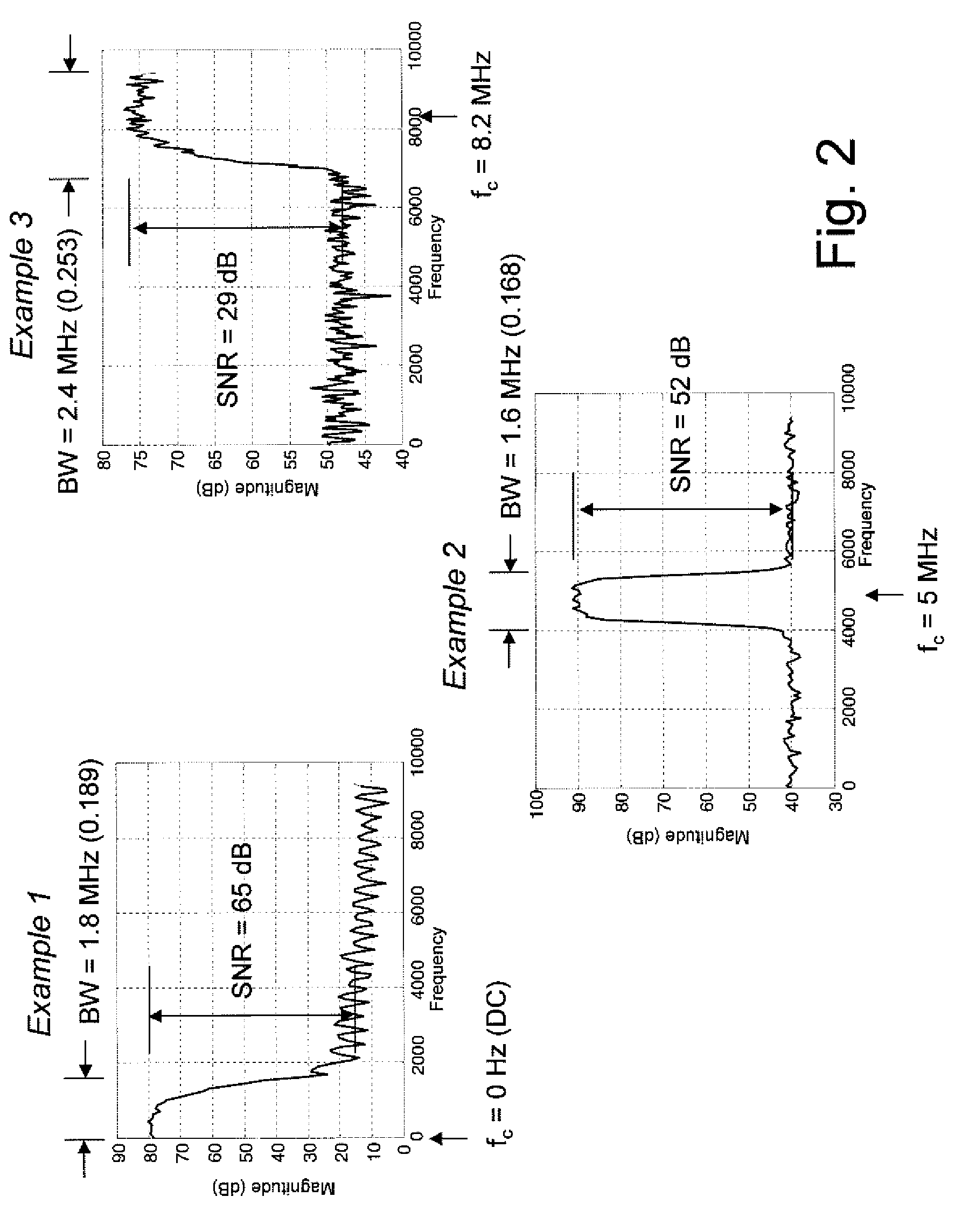
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
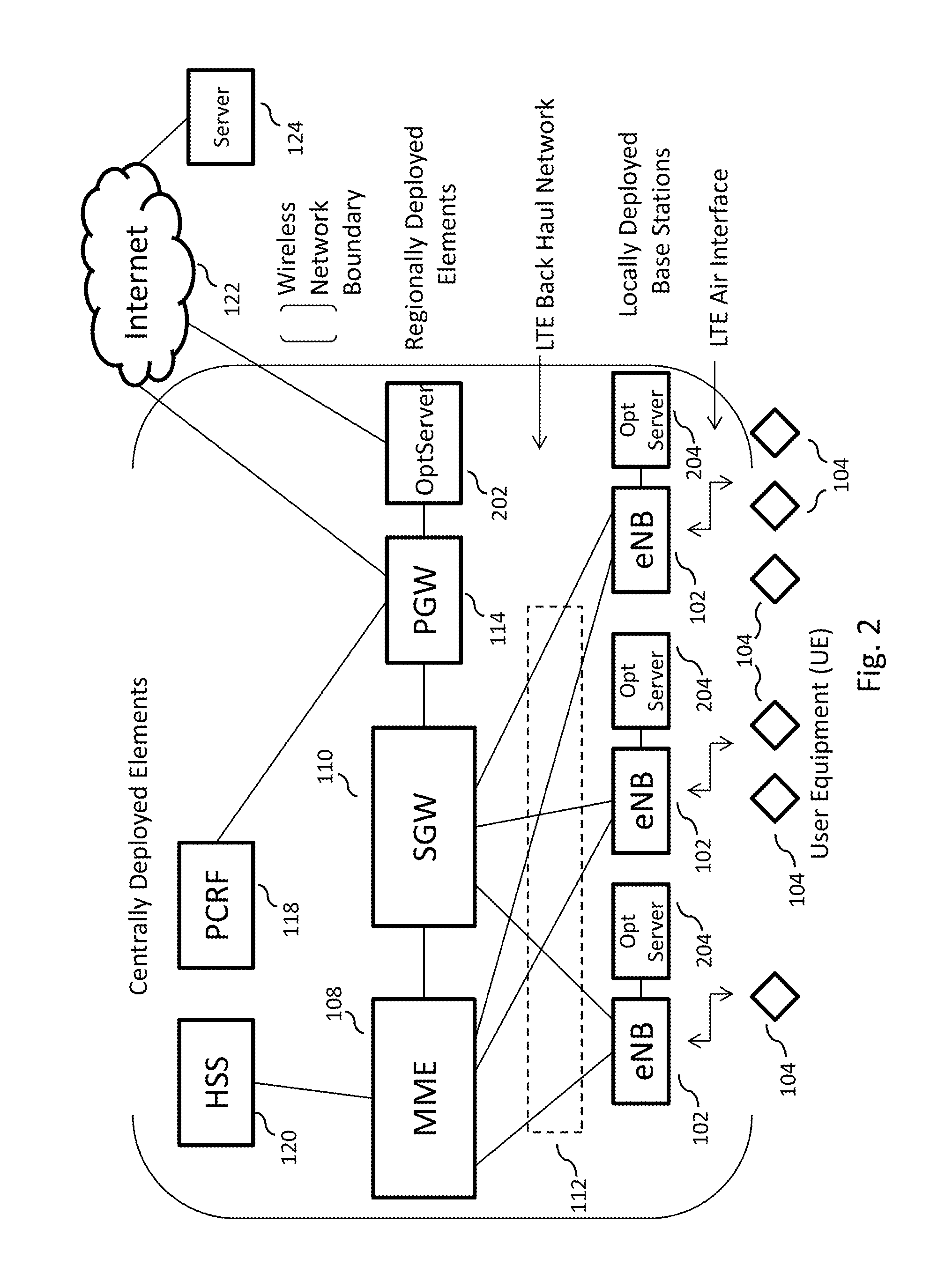
Telecommunication networks
ActiveUS20120064908A1High resolutionIncrease volumeAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkTelecommunications network
A mobile telecommunications network includes a core and a radio access network having a radio for wireless communication with mobile terminals registered with the network, wherein the radio access network includes a controller operable to control the use of network resources by the mobile terminals. The controller may include an application programming interface, API, which provides a consistent interface to a multiplicity of applications hosted on the control mean. The controller may be provided at an access node site and / or a gateway site.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
Telecommunication networks
ActiveUS8639260B2Increase volumeReduce the amount requiredAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkTelecommunications network
A mobile telecommunications network includes a core and a radio access network having a radio for wireless communication with mobile terminals registered with the network, wherein the radio access network includes a controller operable to control the use of network resources by the mobile terminals. The controller may include an application programming interface, API, which provides a consistent interface to a multiplicity of applications hosted on the control mean. The controller may be provided at an access node site and / or a gateway site.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
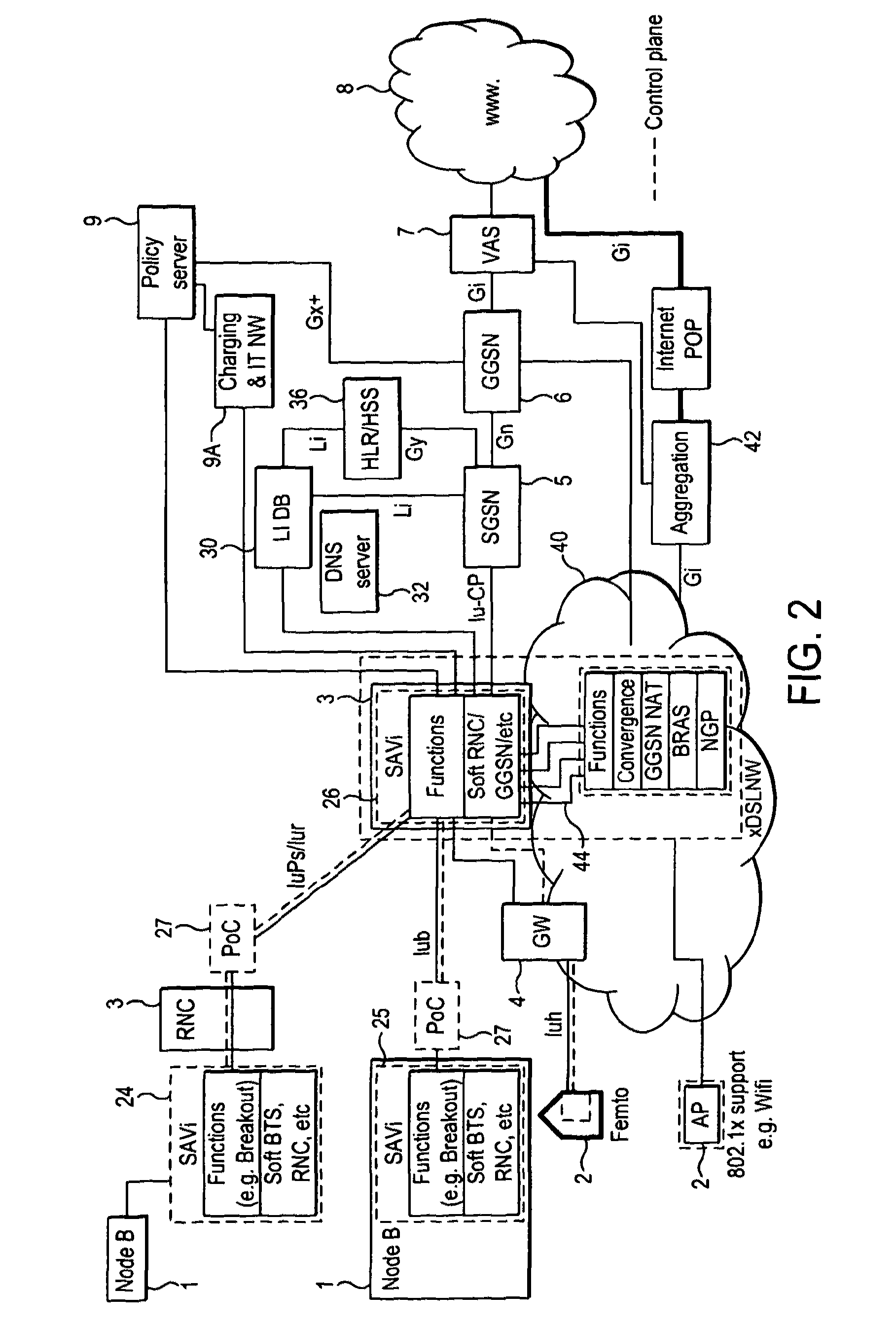
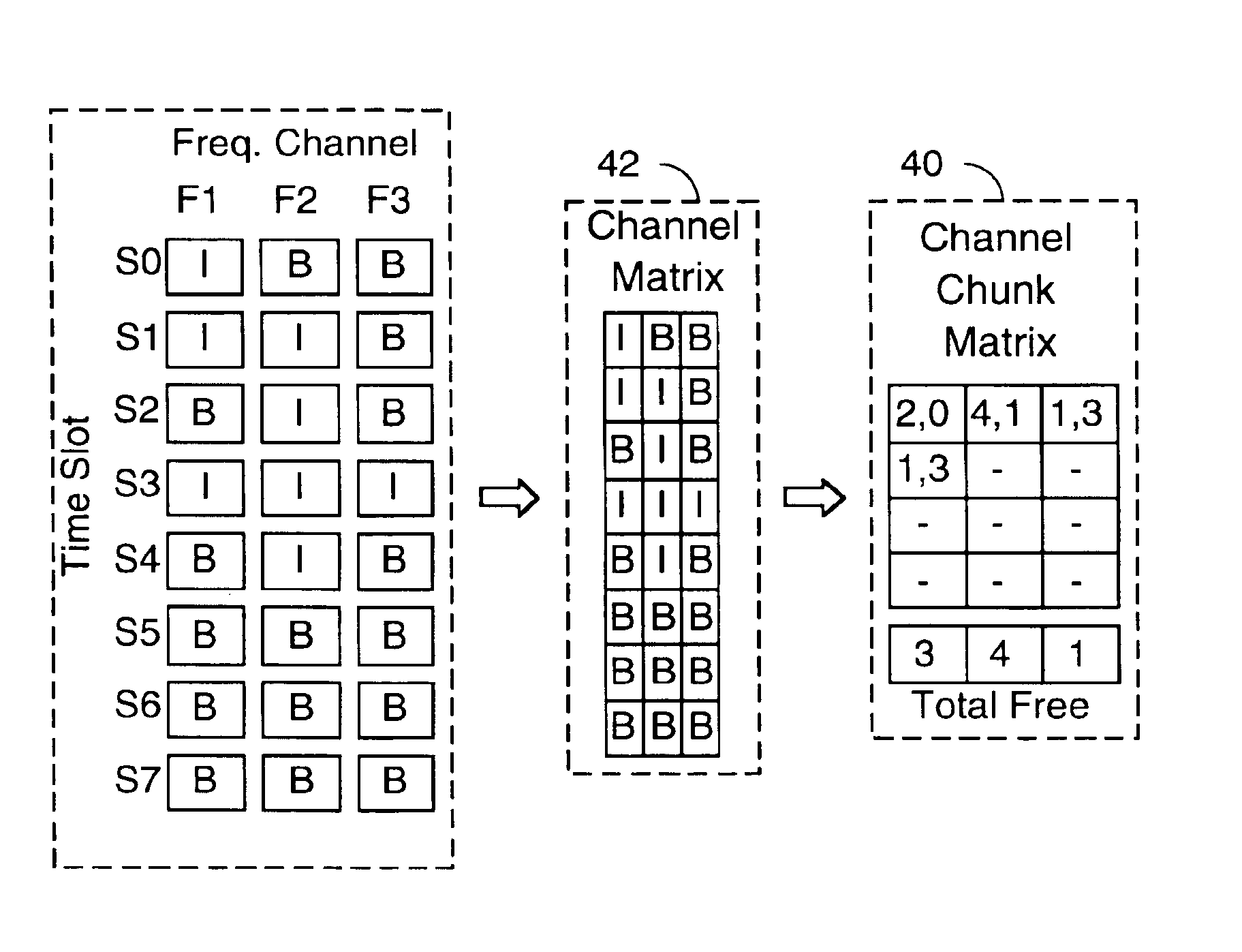
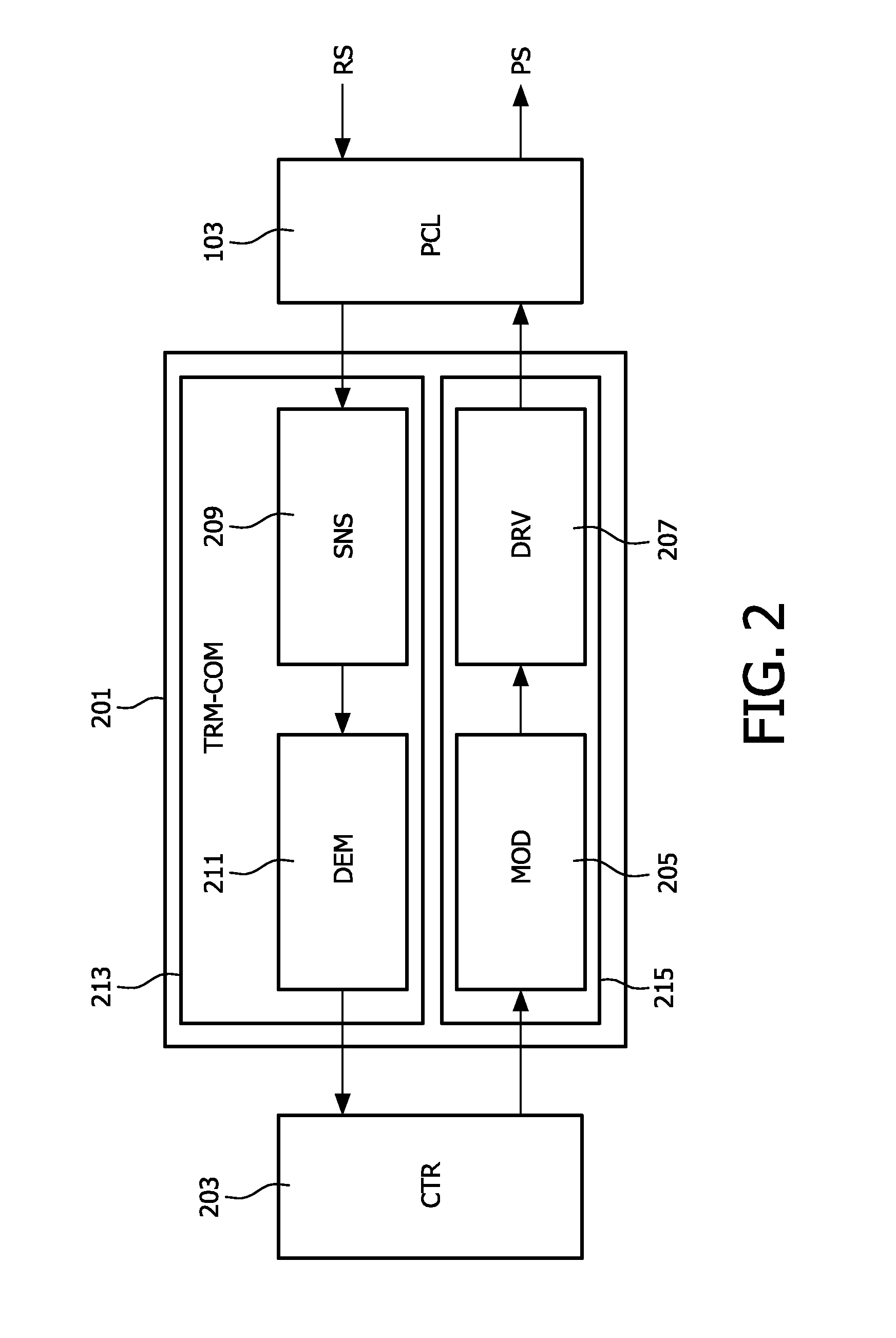
Dynamic resource allocation and media access control for a wireless ATM network
InactiveUS6895248B1Increase data rateLong rangeNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex communicationWireless mesh networkTelecommunications
A resource allocation method for use in a wireless ATM network comprises receiving on a wireless signaling channel a request for access to a shared frequency-time sliced wireless medium. A channel matrix is then searched for a set of available frequency-time slots. The channel matrix represents a time frame within the shared frequency-time sliced wireless medium, and is used to keep track of resource allocation in the time-frequency sliced medium. The set of available time-slots is then allocated if the allocation does not violate a frequency switching constraint, and if the set of available frequency-time slots contains a number of slots no smaller than a requested number of slots. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the searching step uses a greedy resource allocation strategy to search a channel-chunk matrix comprising a list of contiguous chunks of available time slots in each frequency of the shared frequency-time sliced wireless medium. The greedy resource allocation strategy comprises the following successive allocation steps: searching for a single contiguous set of available time slots in a single frequency, where the size of the set of available slots is equal to the requested size [60]; searching for a single contiguous set of available time slots in a single frequency, where the size of the set of available slots is greater than the requested size [64]; searching for separate chunks of available time slots in a single frequency [66]; and searching for separate chunks of available time slots in multiple frequencies [68]. Each allocation step comprises checking whether the allocation violates a frequency switching constraint.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
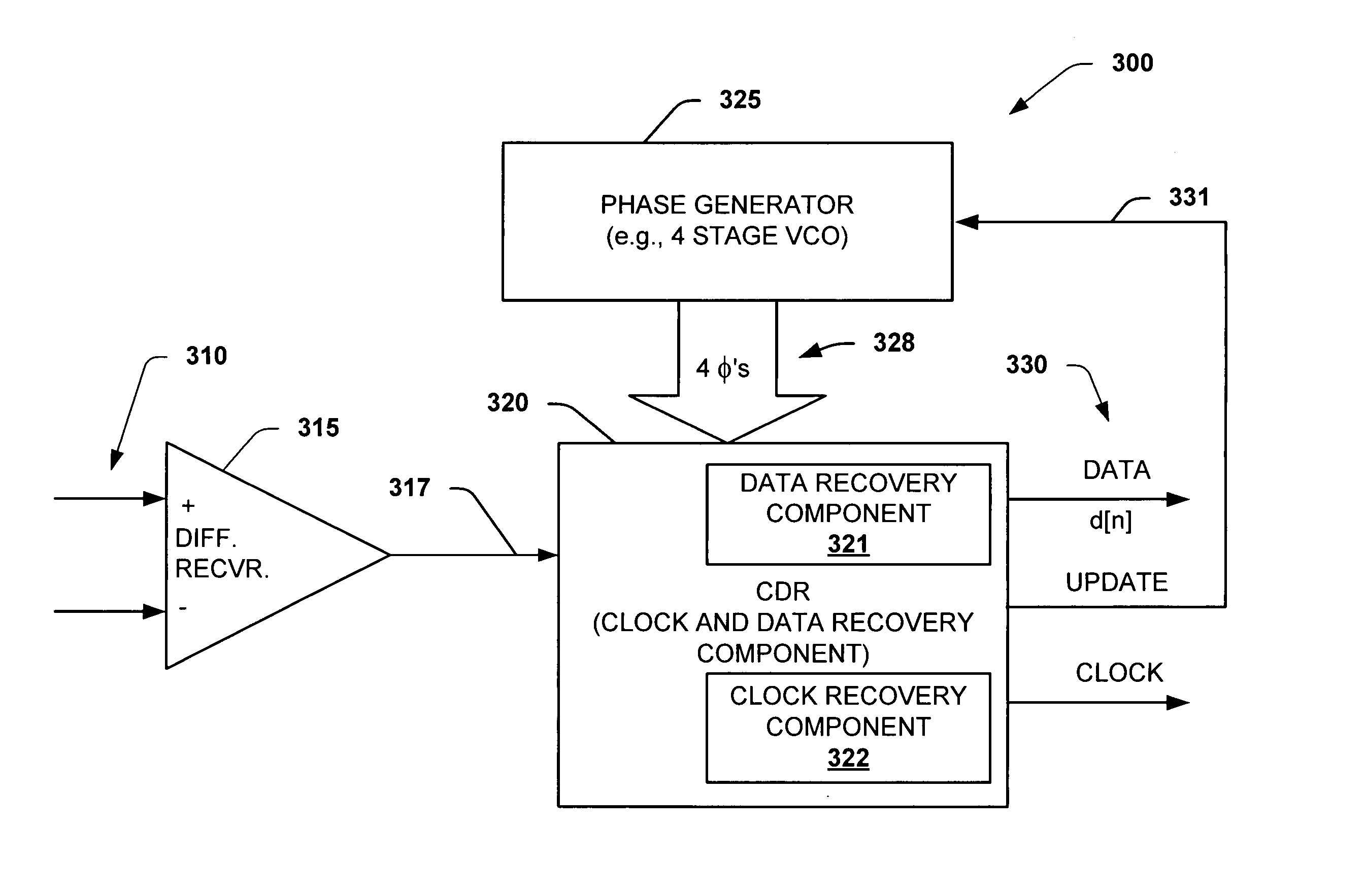
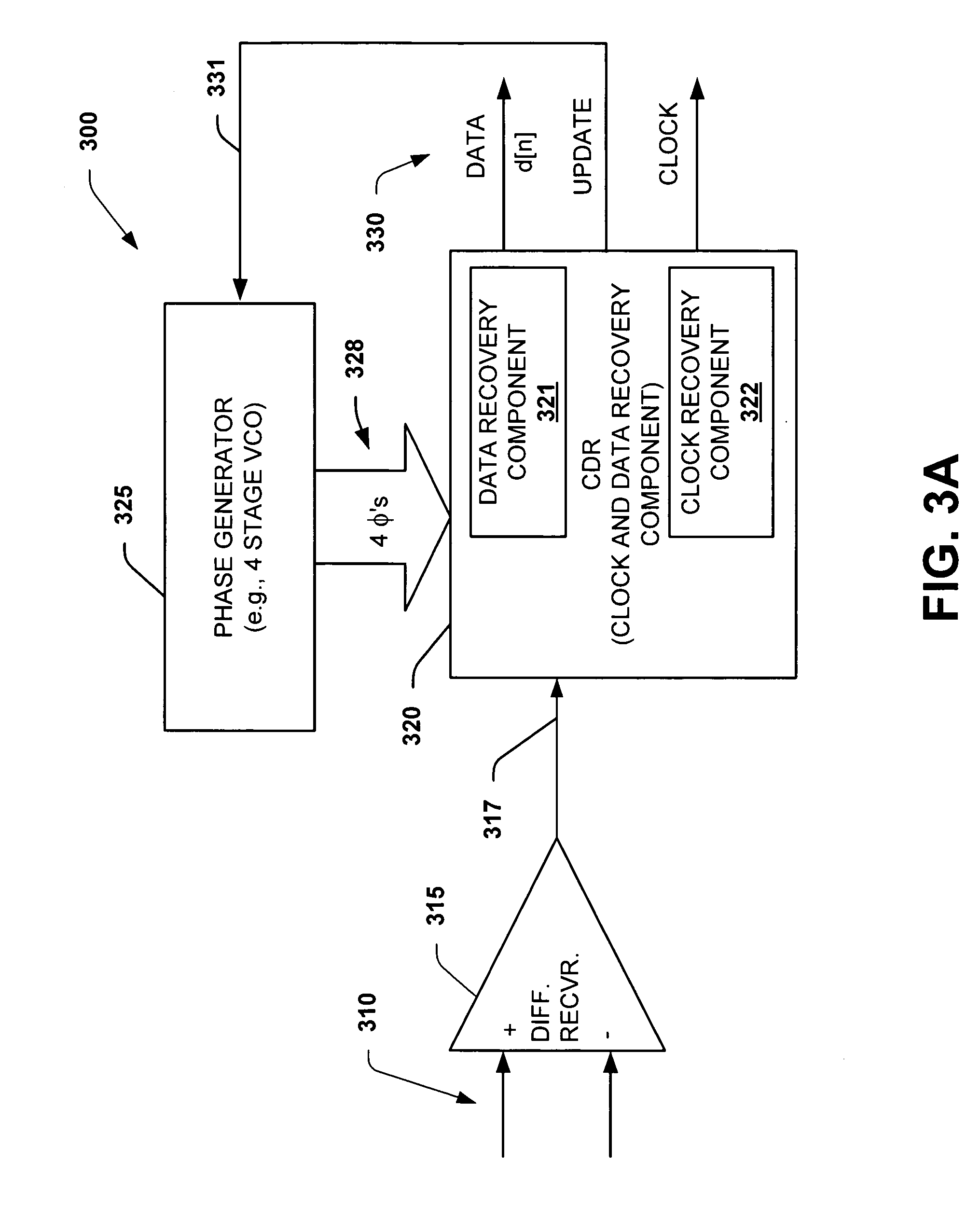
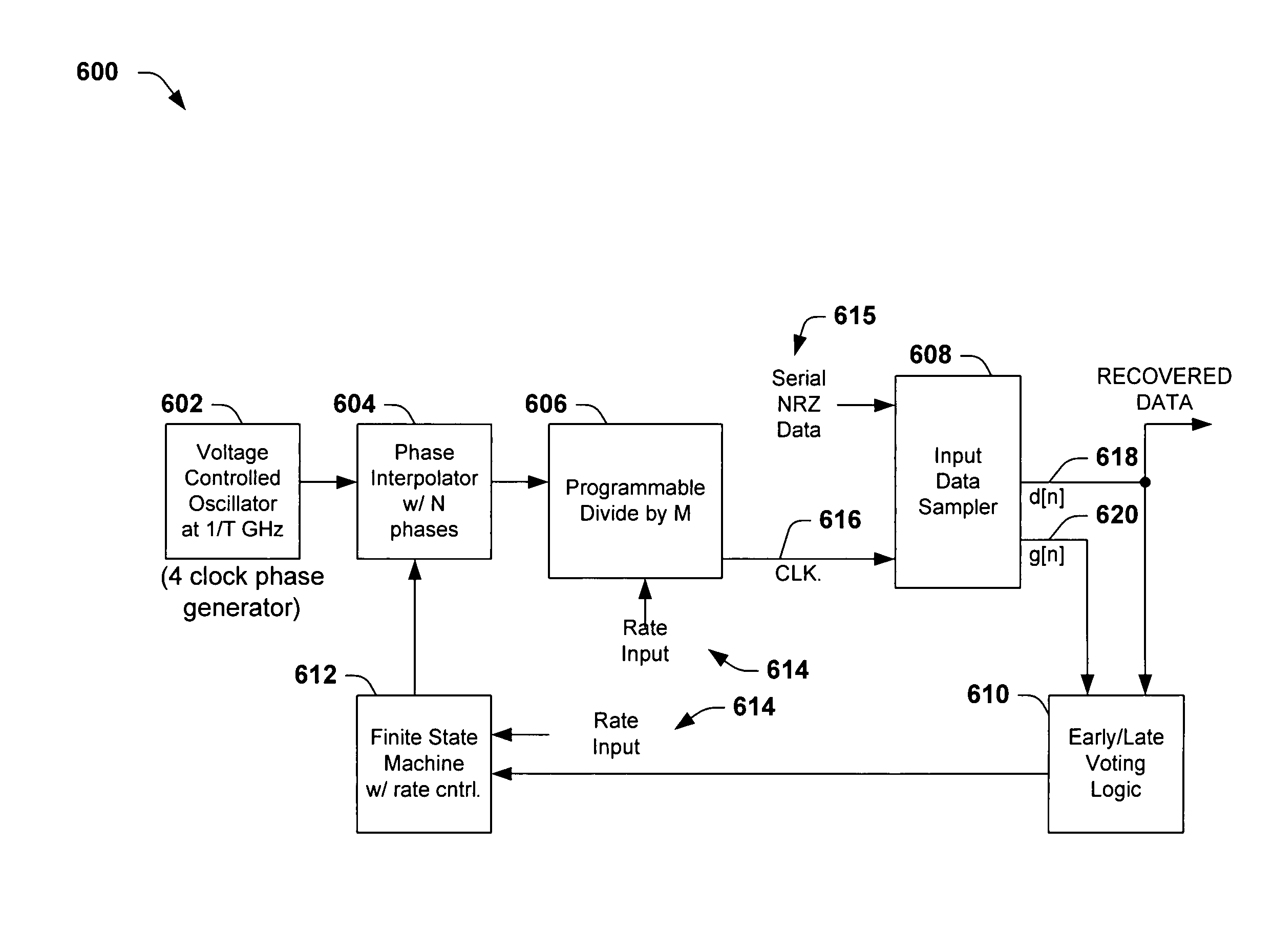
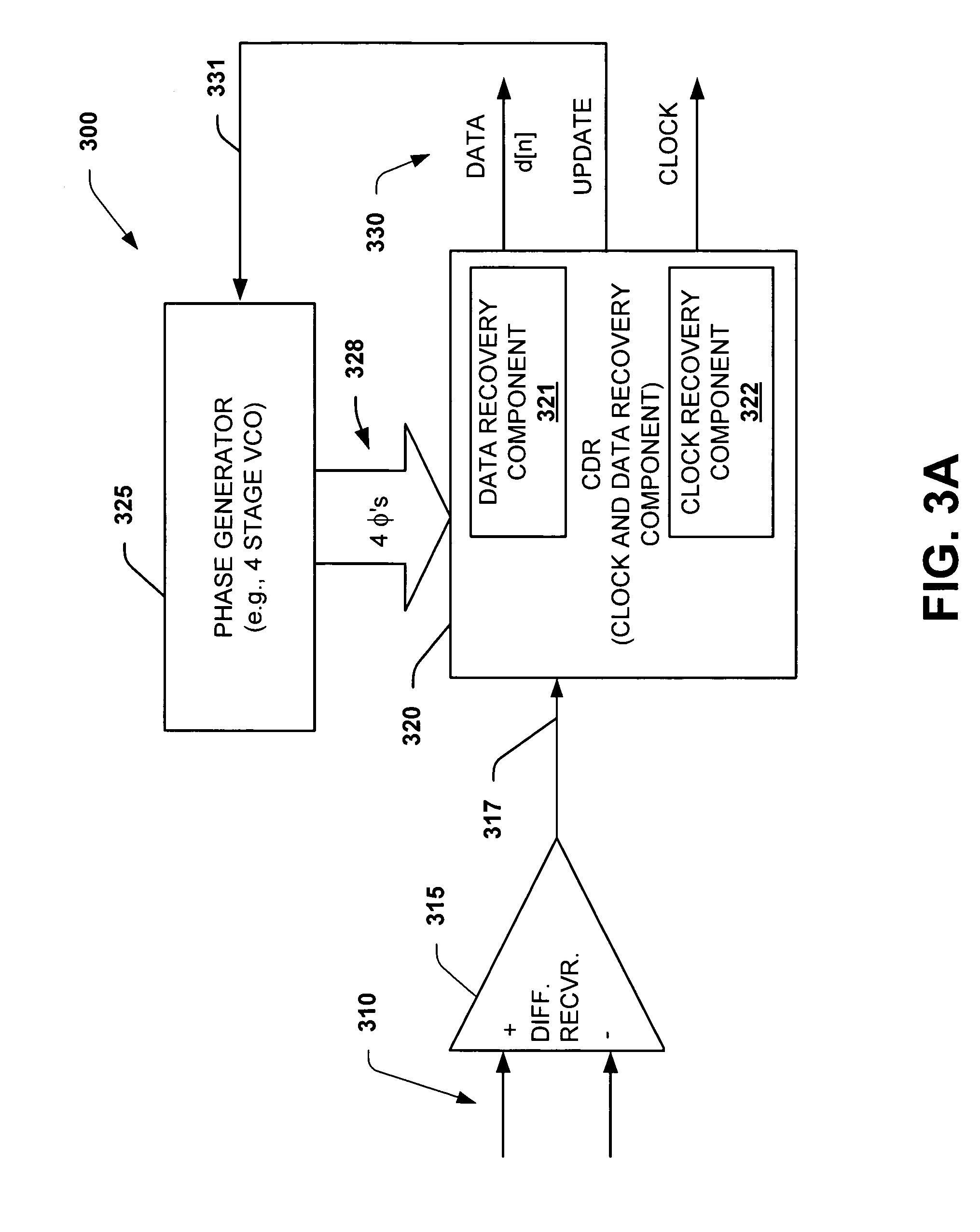
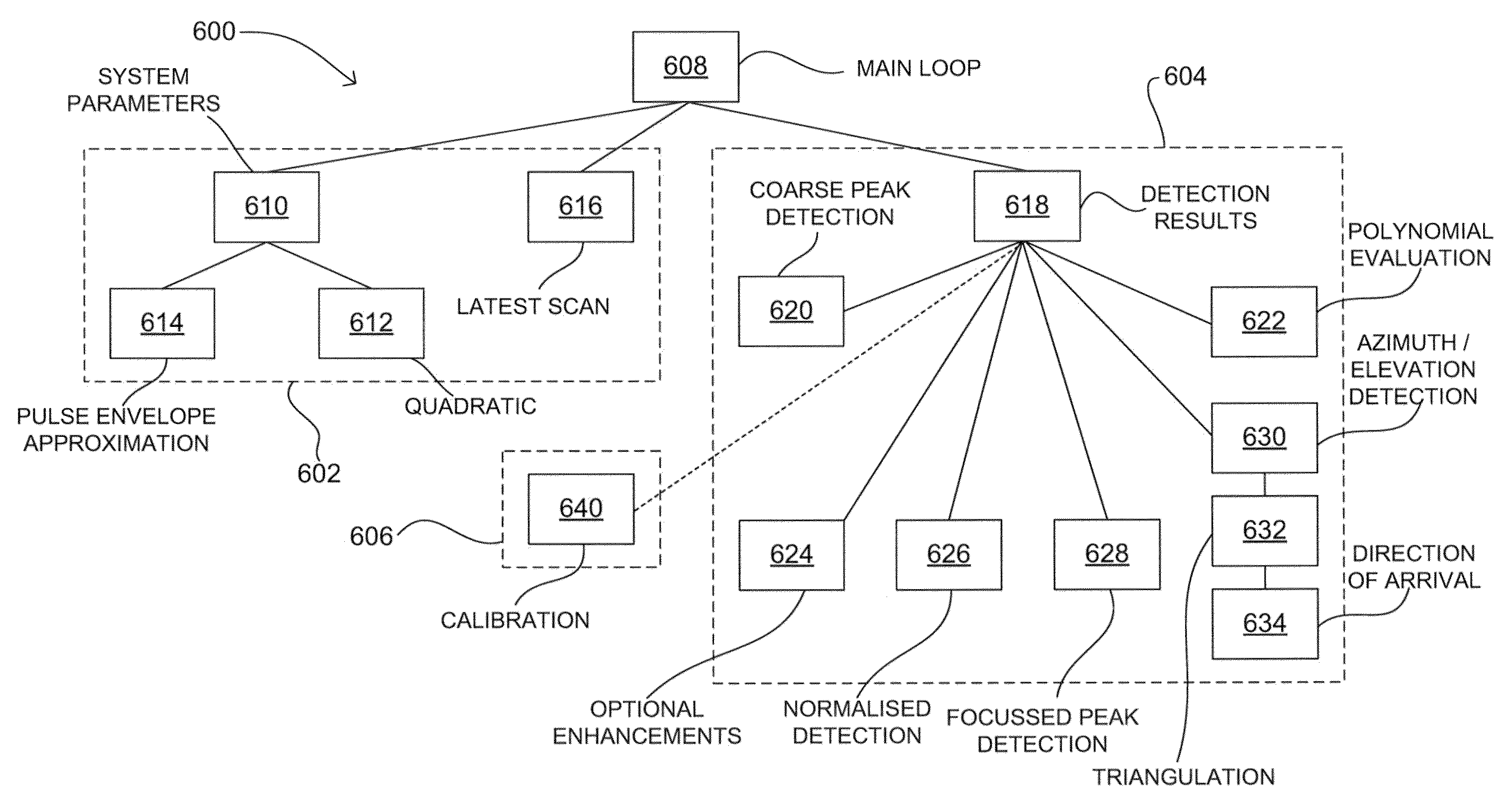
Interpolator based clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit with digitally programmable BW and tracking capability
ActiveUS20050180536A1High bandwidthLower latencyPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase correctionData stream
The present invention facilitates clock and data recovery (330,716 / 718) for serial data streams (317,715) by providing a mechanism that can be employed to maintain a fixed tracking capability of an interpolator based CDR circuit (300,700) at multiple data rates (e.g., 800). The present invention further provides a wide data rate range CDR circuit (300,700), yet uses an interpolator design optimized for a fixed frequency. The invention employs a rate programmable divider circuit (606,656,706) that operates over a wide range of clock and data rates (e.g., 800) to provide various phase correction step sizes (e.g., 800) at a fixed VCO clock frequency. The divider (606,656,706) and a finite state machine (FSM) (612,662,712) of the exemplary CDR circuit (600,650,700) are manually programmed based on the data rate (614,667). Alternately, the data rate may be detected from a recovered serial data stream (718) during CDR operations (on-the-fly) utilizing a frequency detection circuit (725) to automatically program the divider (706) and FSM (712) to provide CDR circuit operation at the nearest base clock rate (716).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
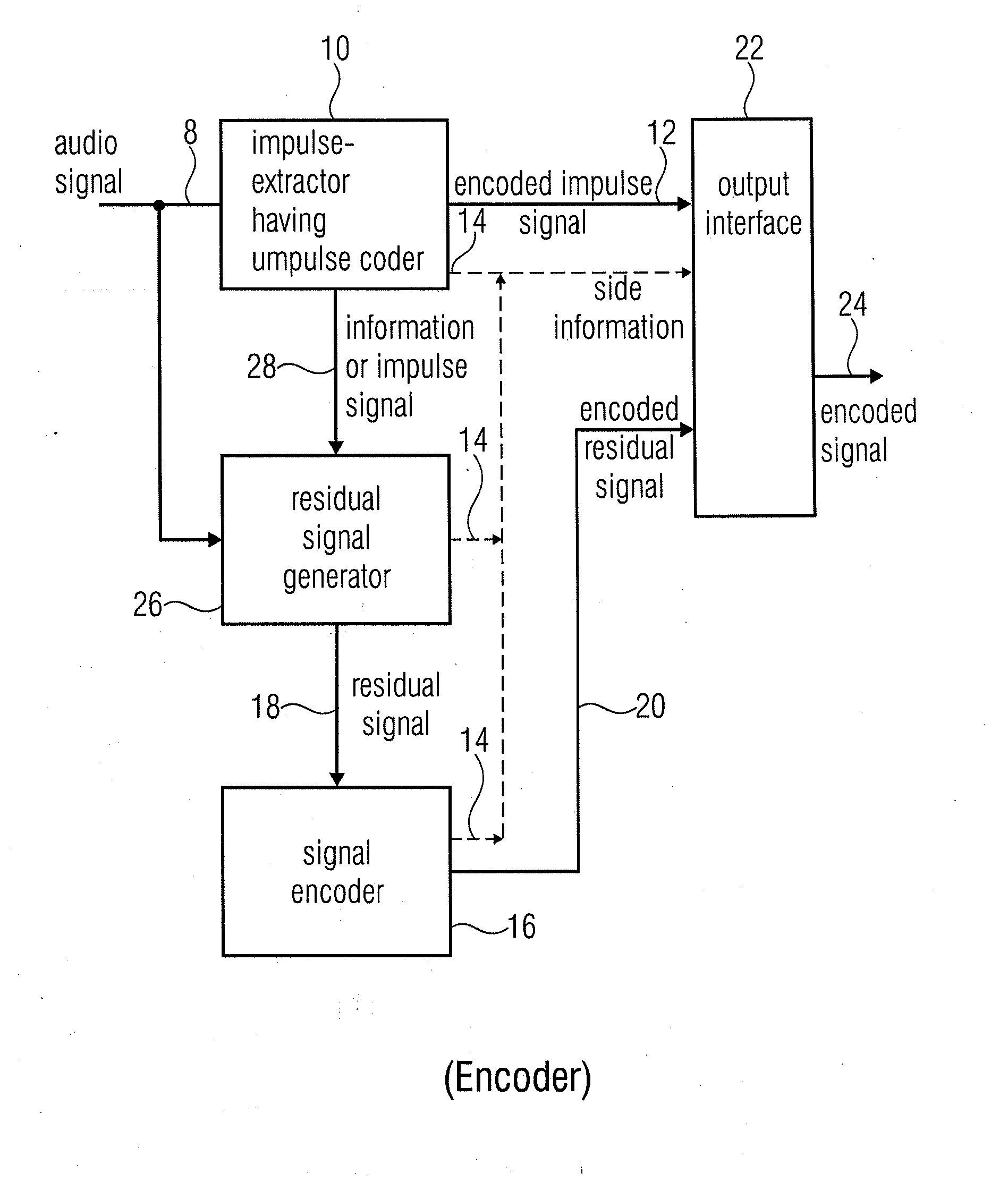
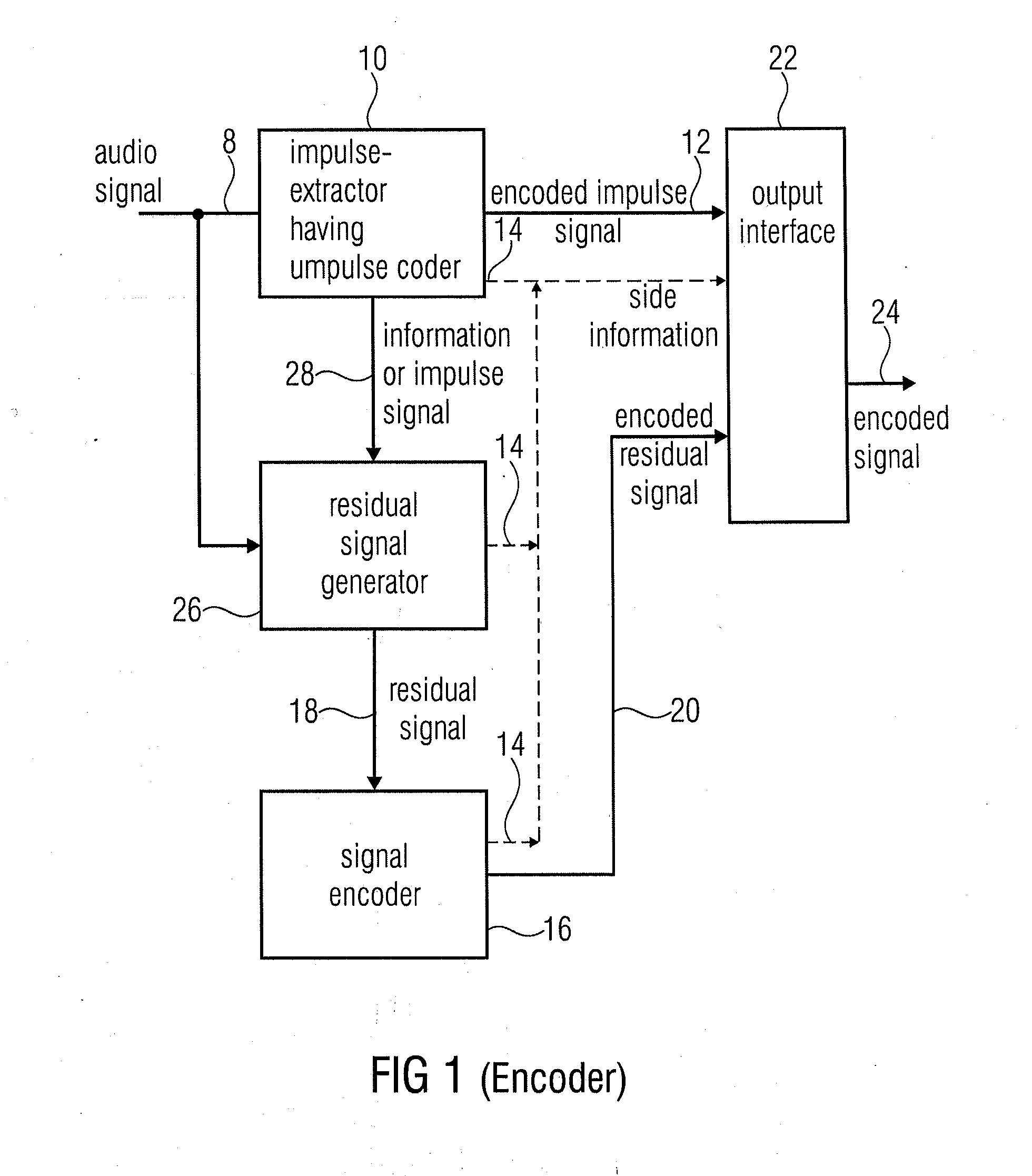
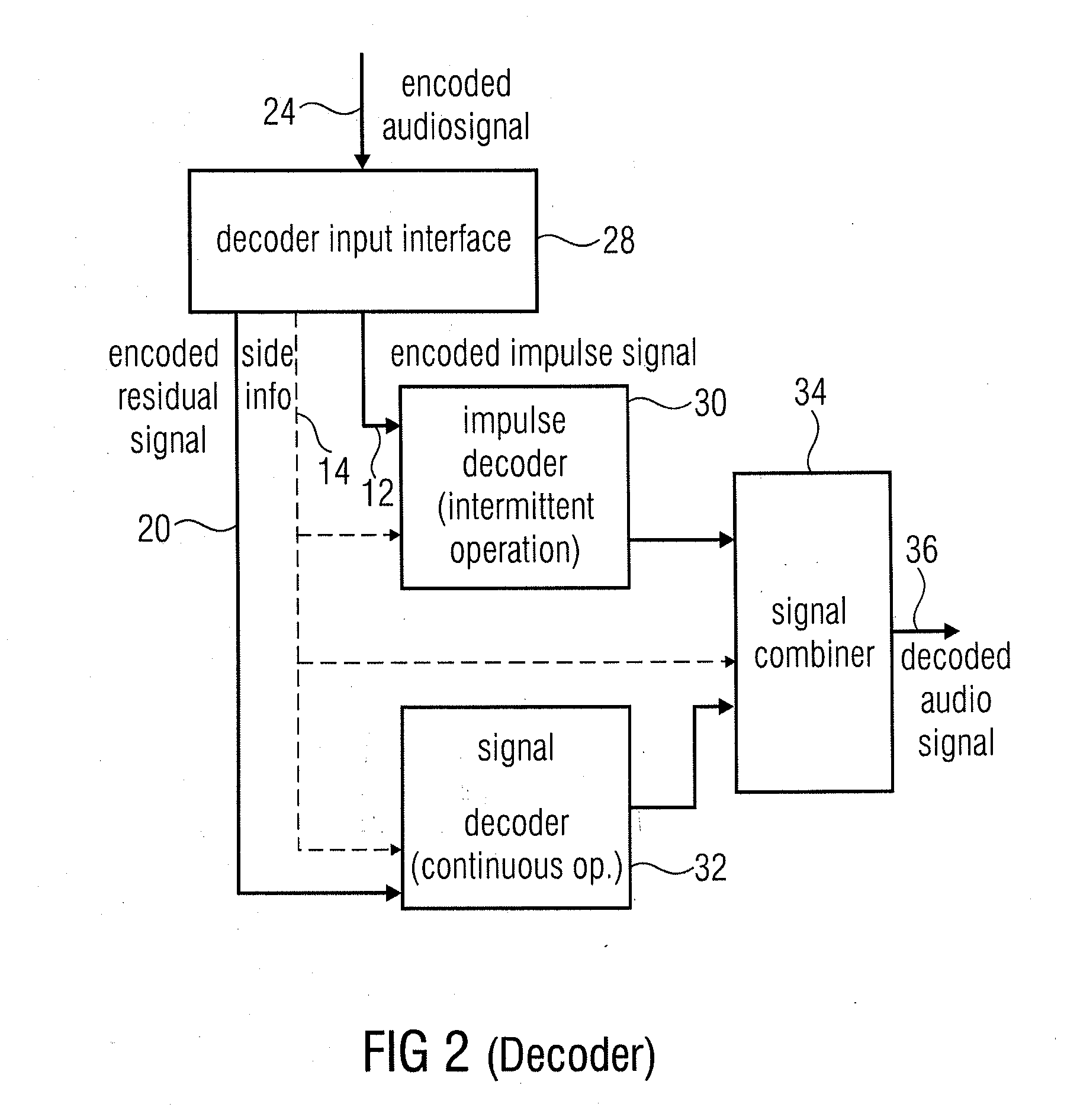
Audio encoder for encoding an audio signal having an impulse-like portion and stationary portion, encoding methods, decoder, decoding method, and encoding audio signal
ActiveUS20100262420A1Reduce data rateImprove efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsAudio signal flow
An audio encoder for encoding an audio signal includes an impulse extractor for extracting an impulse-like portion from the audio signal. This impulse-like portion is encoded and forwarded to an output interface. Furthermore, the audio encoder includes a signal encoder which encodes a residual signal derived from the original audio signal so that the impulse-like portion is reduced or eliminated in the residual audio signal. The output interface forwards both, the encoded signals, i.e., the encoded impulse signal and the encoded residual signal for transmission or storage. On the decoder-side, both signal portions are separately decoded and then combined to obtain a decoded audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
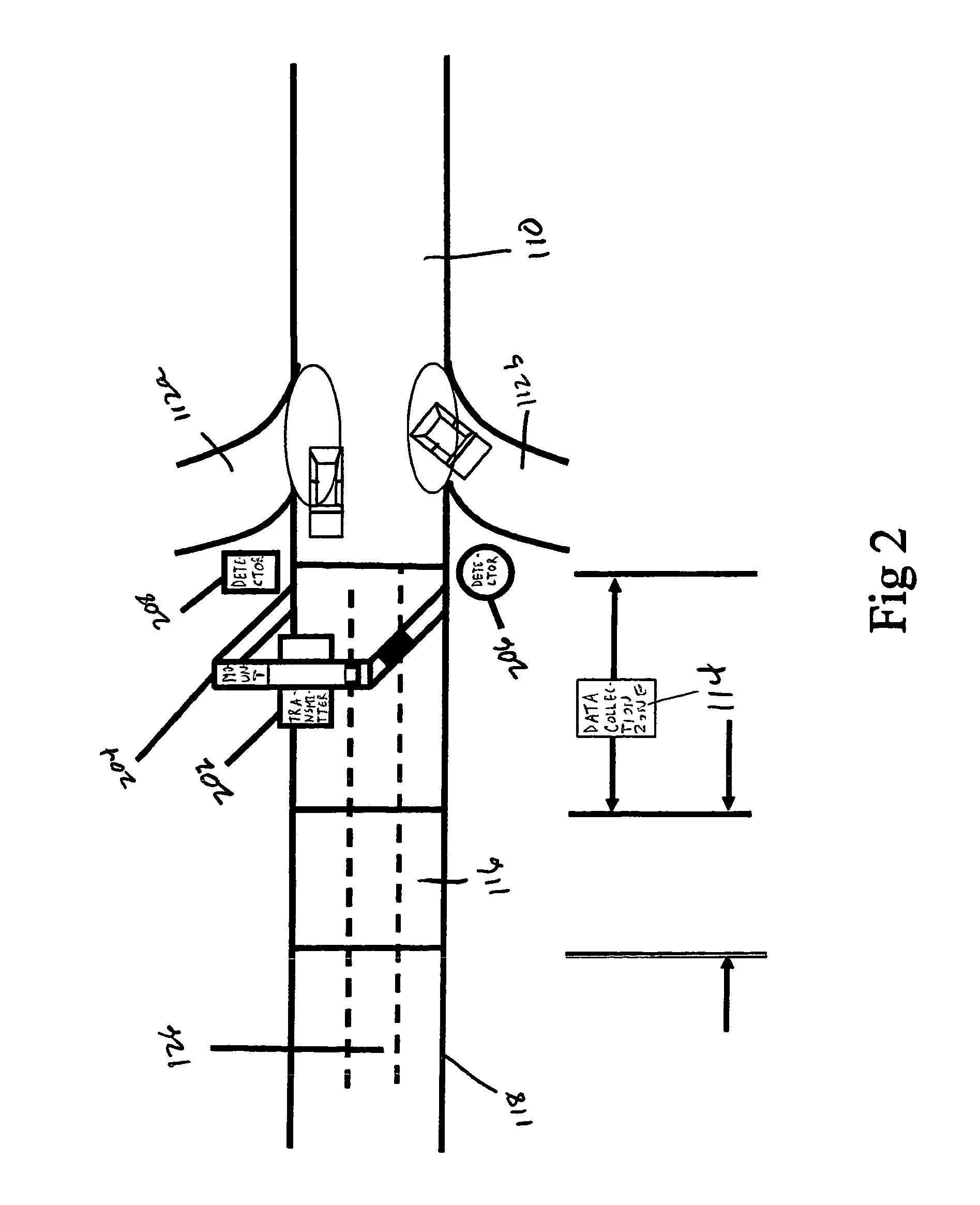
Vehicle passenger authorization system
InactiveUS6958676B1Avoiding vehicle accidentsEasy to measureElectric signal transmission systemsTicket-issuing apparatusAutomatic controlEngineering
A system for authorizing vehicle and passenger entry into a secure area while the vehicle is moving is disclosed. The vehicle passenger authorization system verifies the identity of the vehicle and its occupants while the vehicle is moving, thereby eliminating the need for the vehicle to stop as it approaches a secure area. Vehicle imaging technology is used to identify the vehicle. Biometric technology is used to confirm the identity of the occupants of the vehicle. By combining the biometric information of the occupants with the vehicle identification, an efficient and safe means for automatically controlling the flow of traffic into secured areas is disclosed.
Owner:S T S
Coherent probe and optical service channel systems and methods for optical networks
ActiveUS20130236169A1Reduce data rateTransmission monitoringOptical multiplexMonitoring systemEngineering
The present disclosure provides dynamic performance monitoring systems and methods for optical networks to ascertain optical network health in a flexible and accurate manner. The present invention introduces accurate estimations for optical channel performance characteristics based either on existing channels or with a dynamic optical probe configured to measure characteristics on unequipped wavelengths. Advantageously, the dynamic performance monitoring systems and methods introduce the ability to determine physical layer viability in addition to logical layer viability.
Owner:CIENA
Method and system for automatic classification of objects
InactiveUS20090184865A1Less demanding as to processing powerReliable classificationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThree-dimensional object recognitionContour matchingAlgorithm
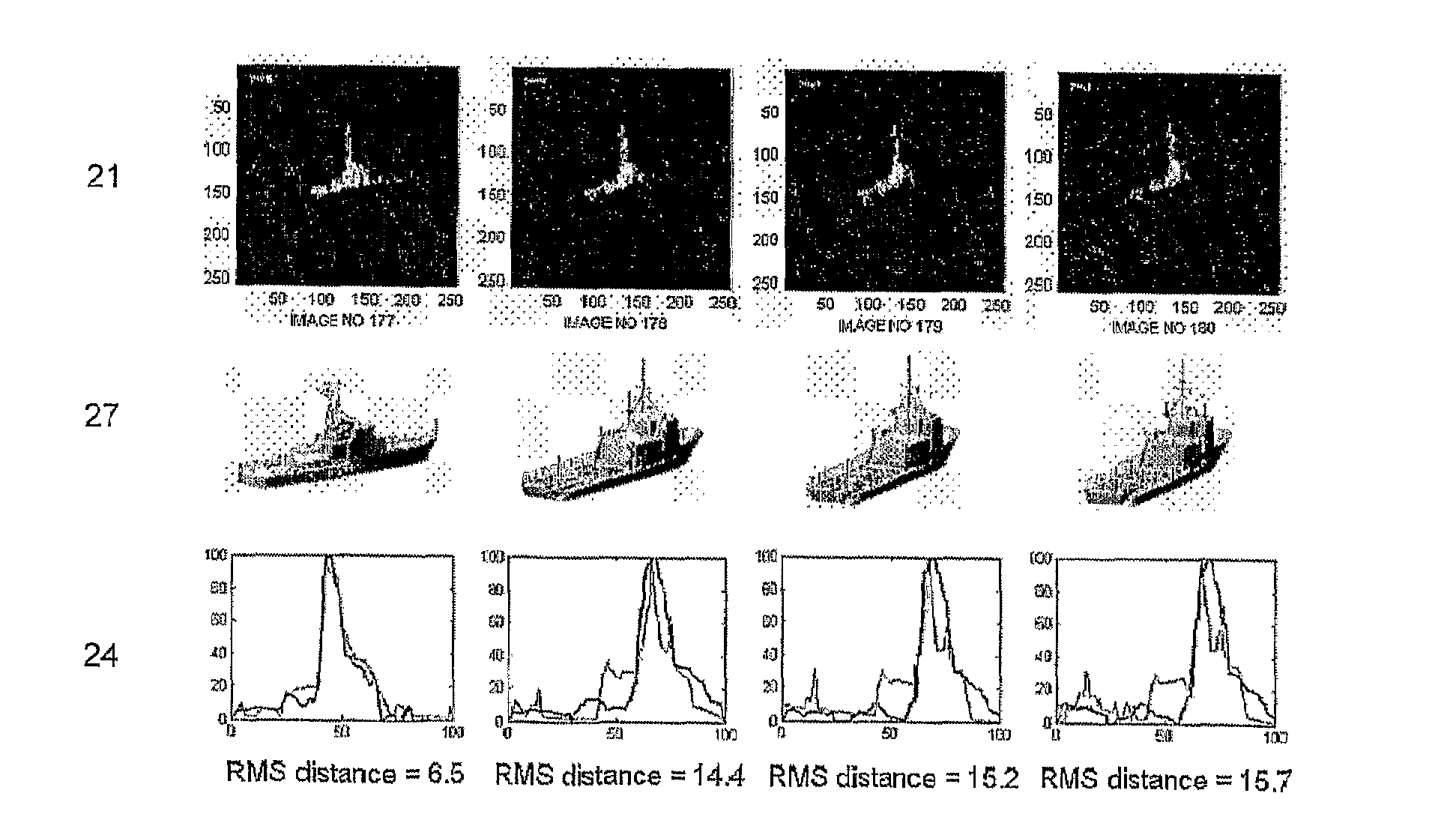
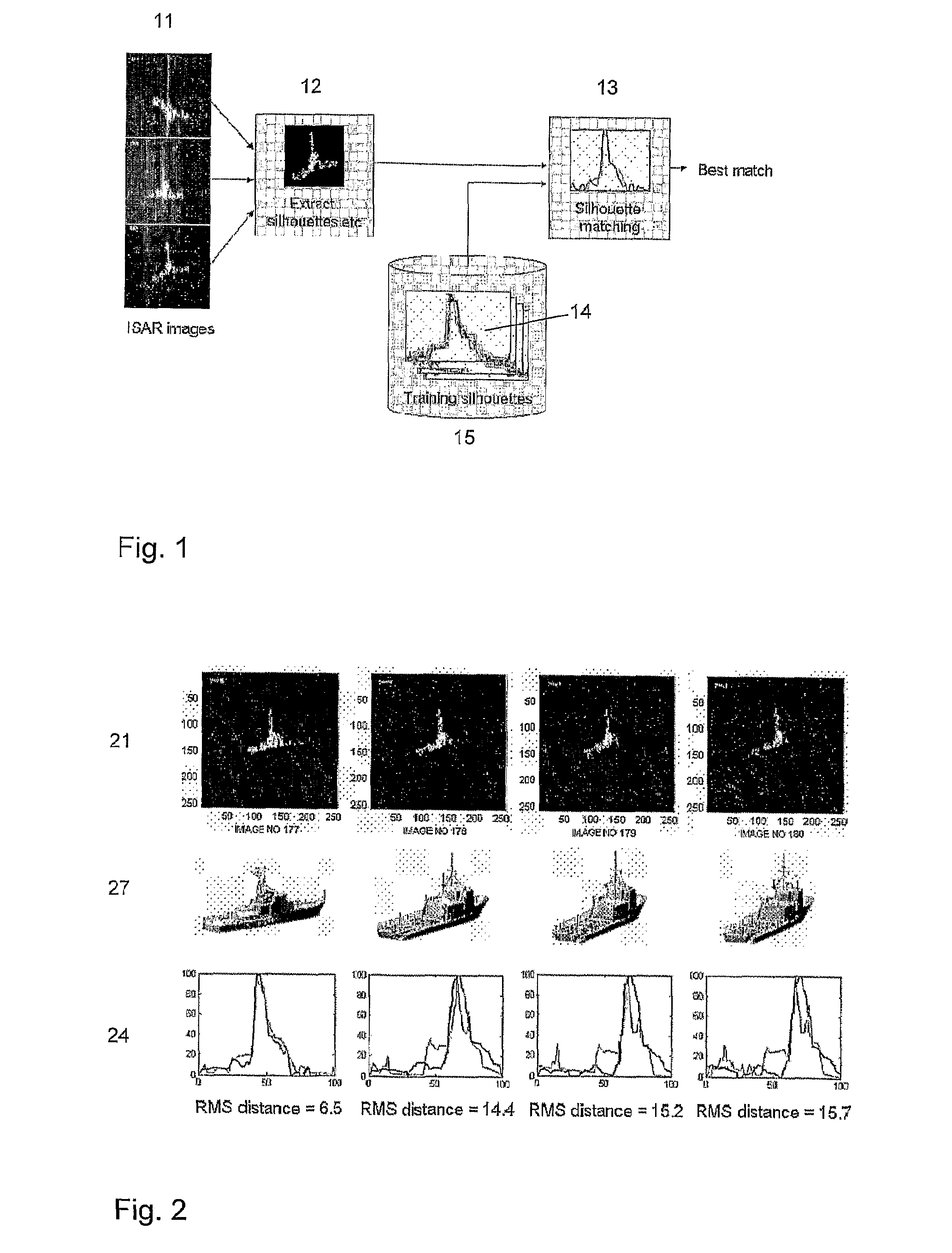
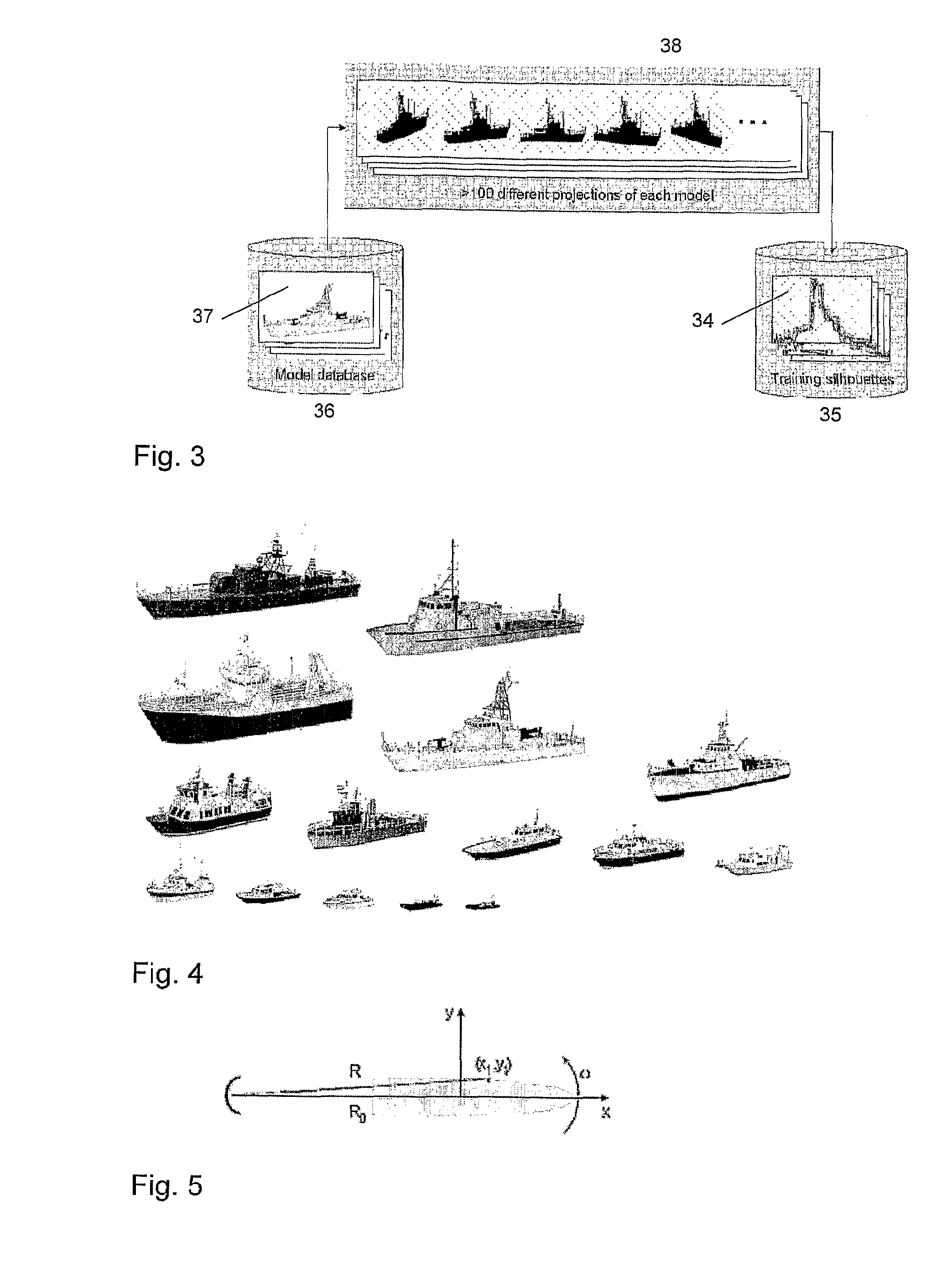
A new method has been developed as an attempt to improve speed and robustness of existing ISAR classification methods. The new method produces a set of silhouettes of possible models in a 3D model database. The set of silhouettes of each model views the model from various viewing angles, as the target dimensions will vary as it is viewed from different angles. The silhouettes are stored as a training set. Classification is done by comparing the silhouette of the target with the set of silhouettes in the training set. The silhouettes are calculated prior to the silhouette matching.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
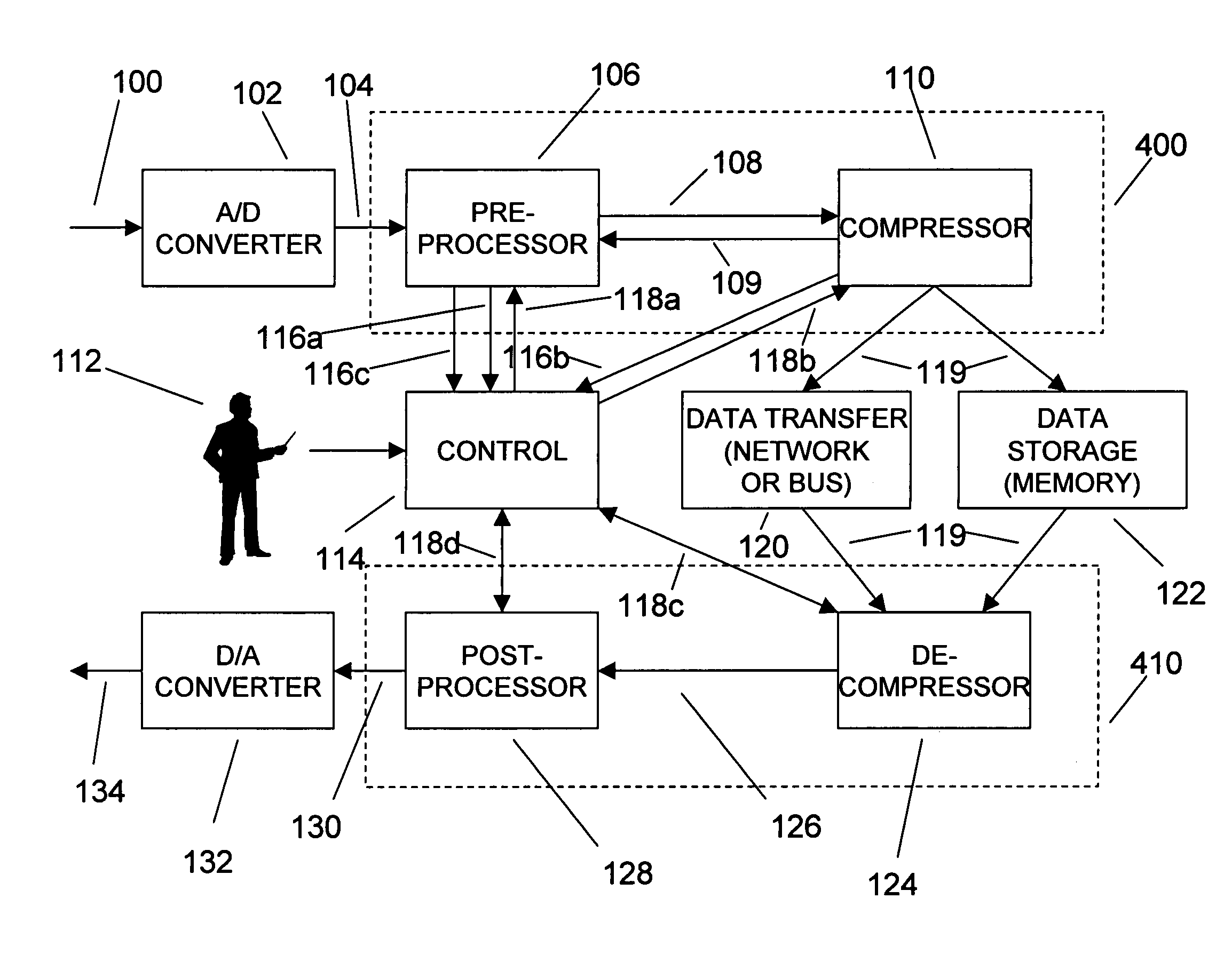
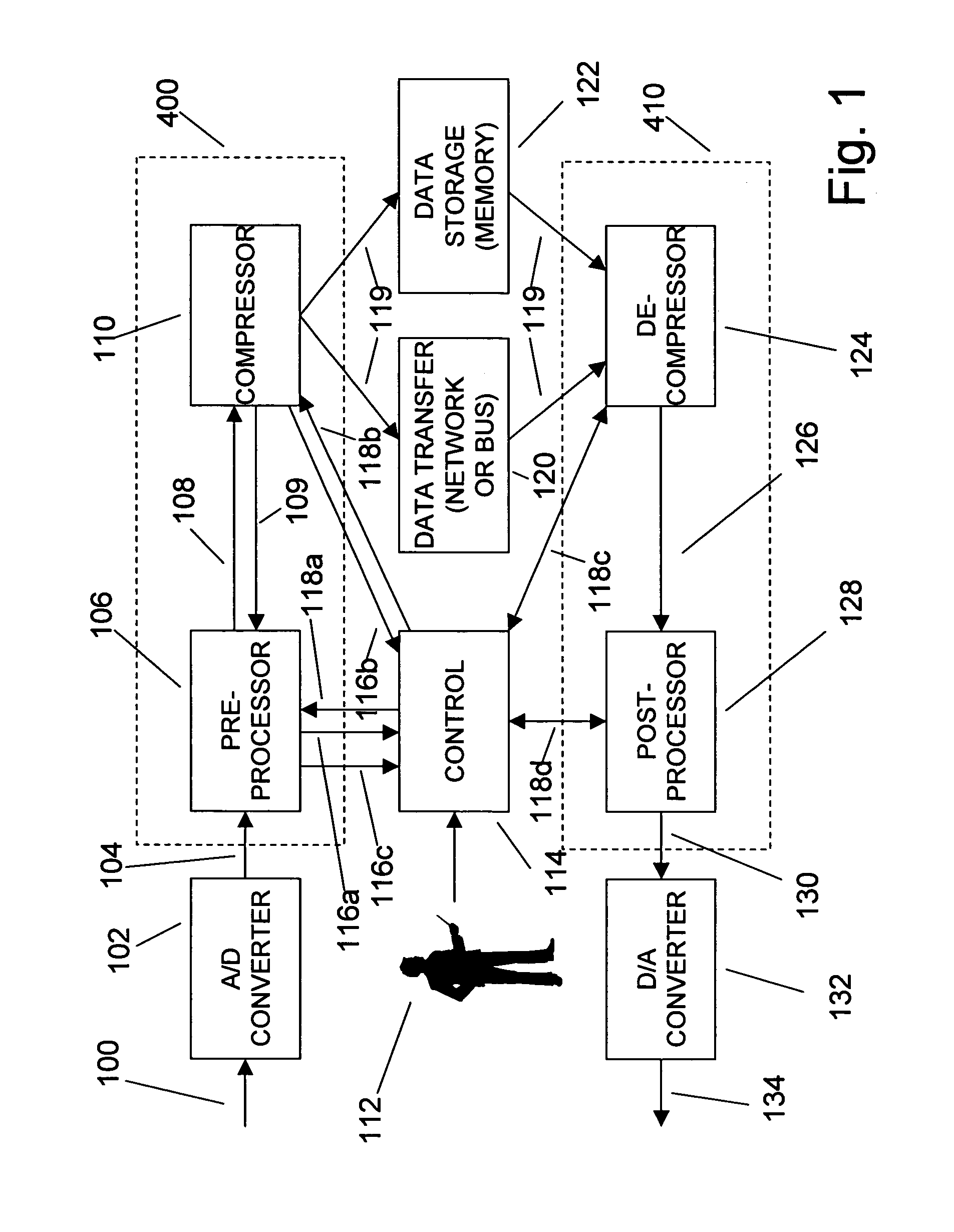
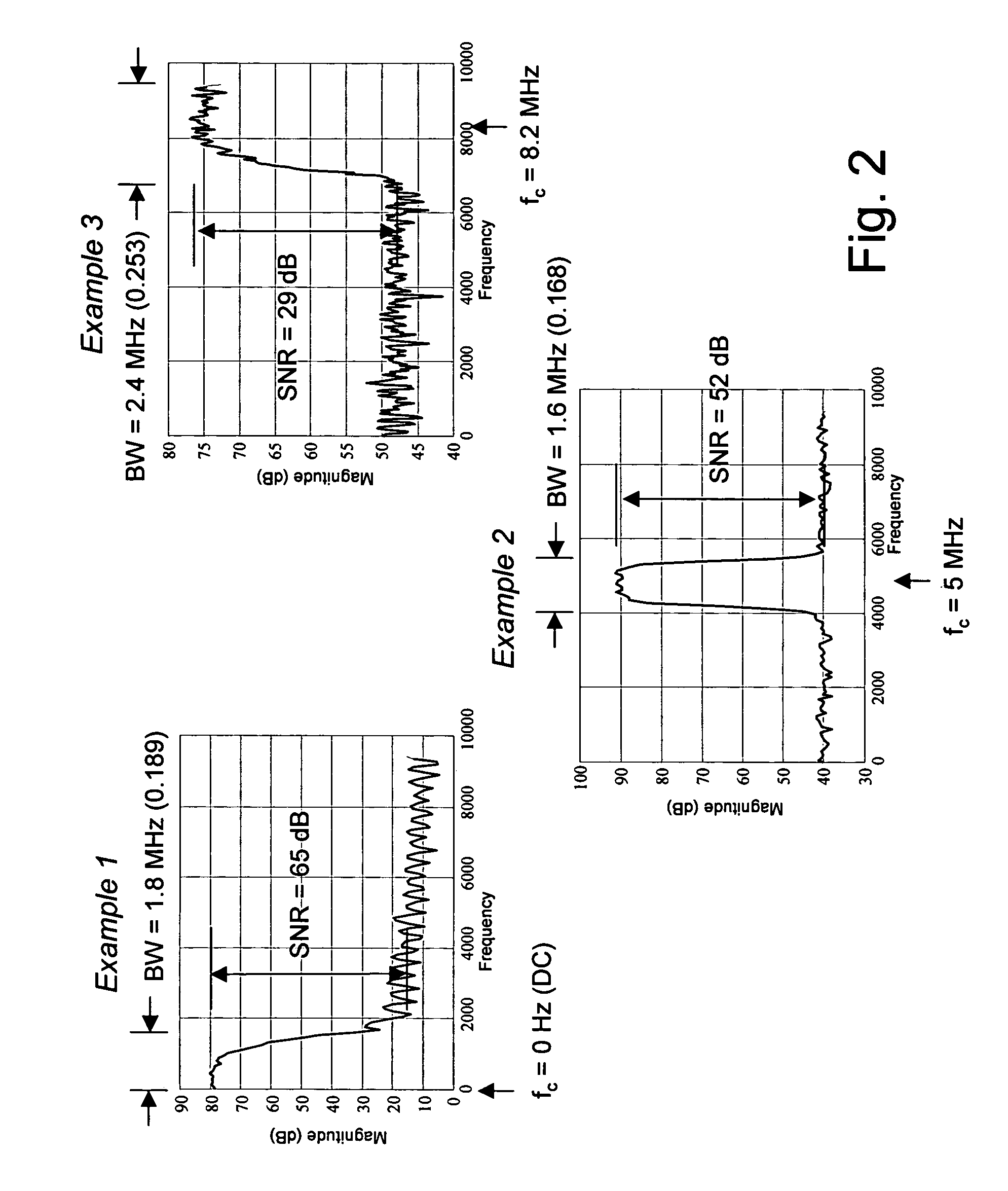
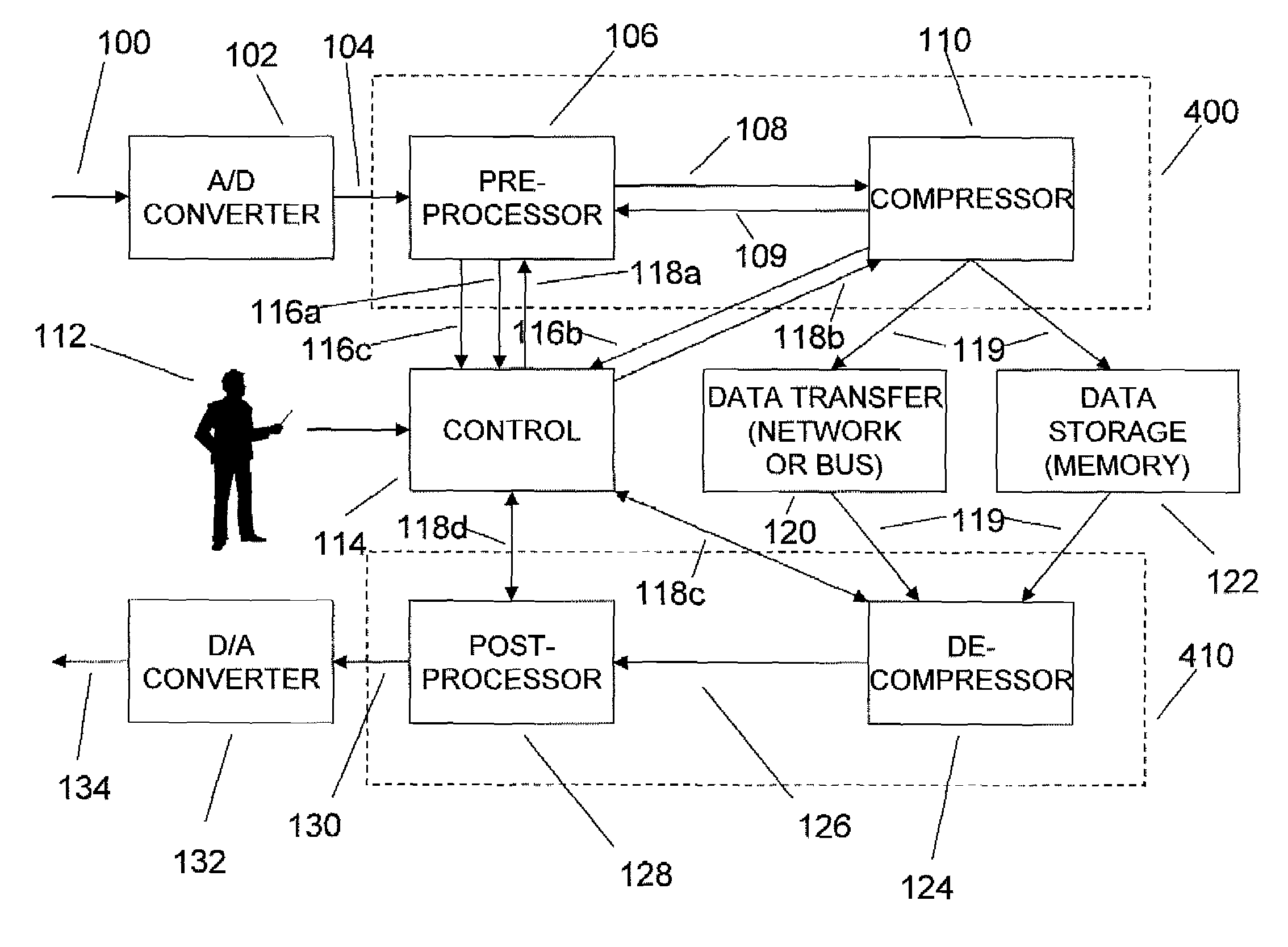
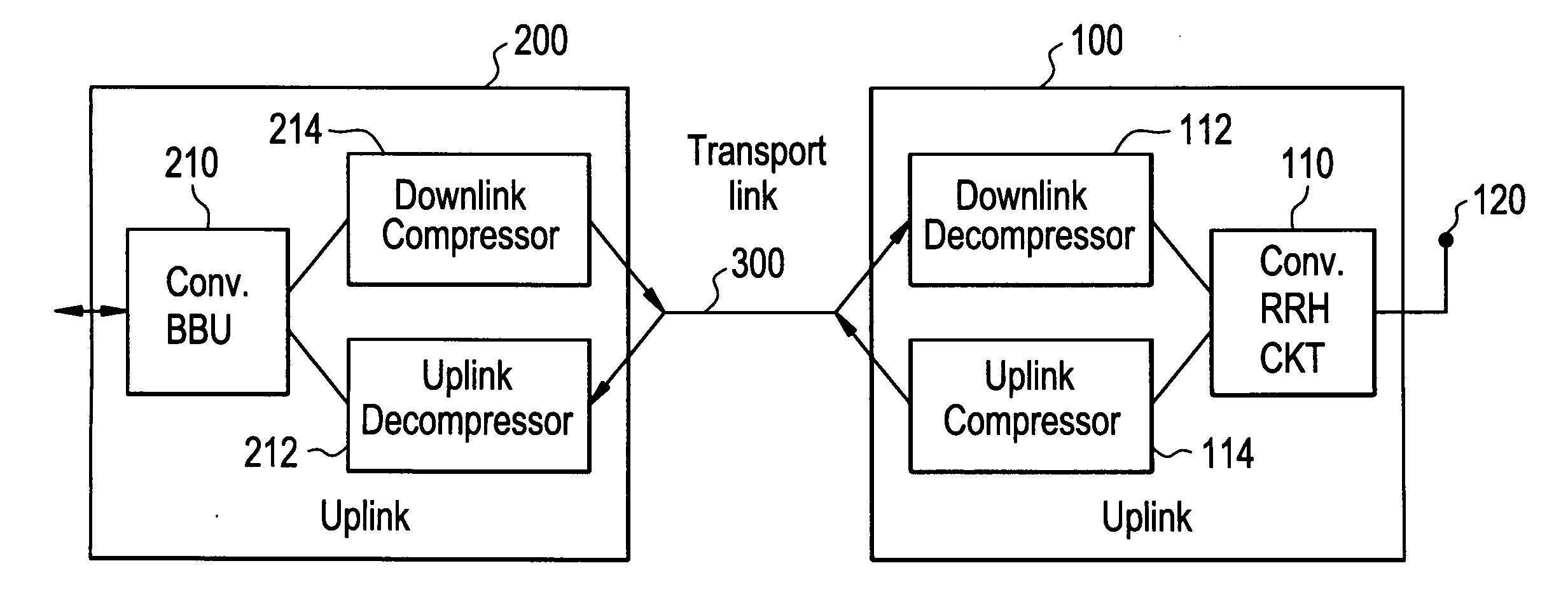
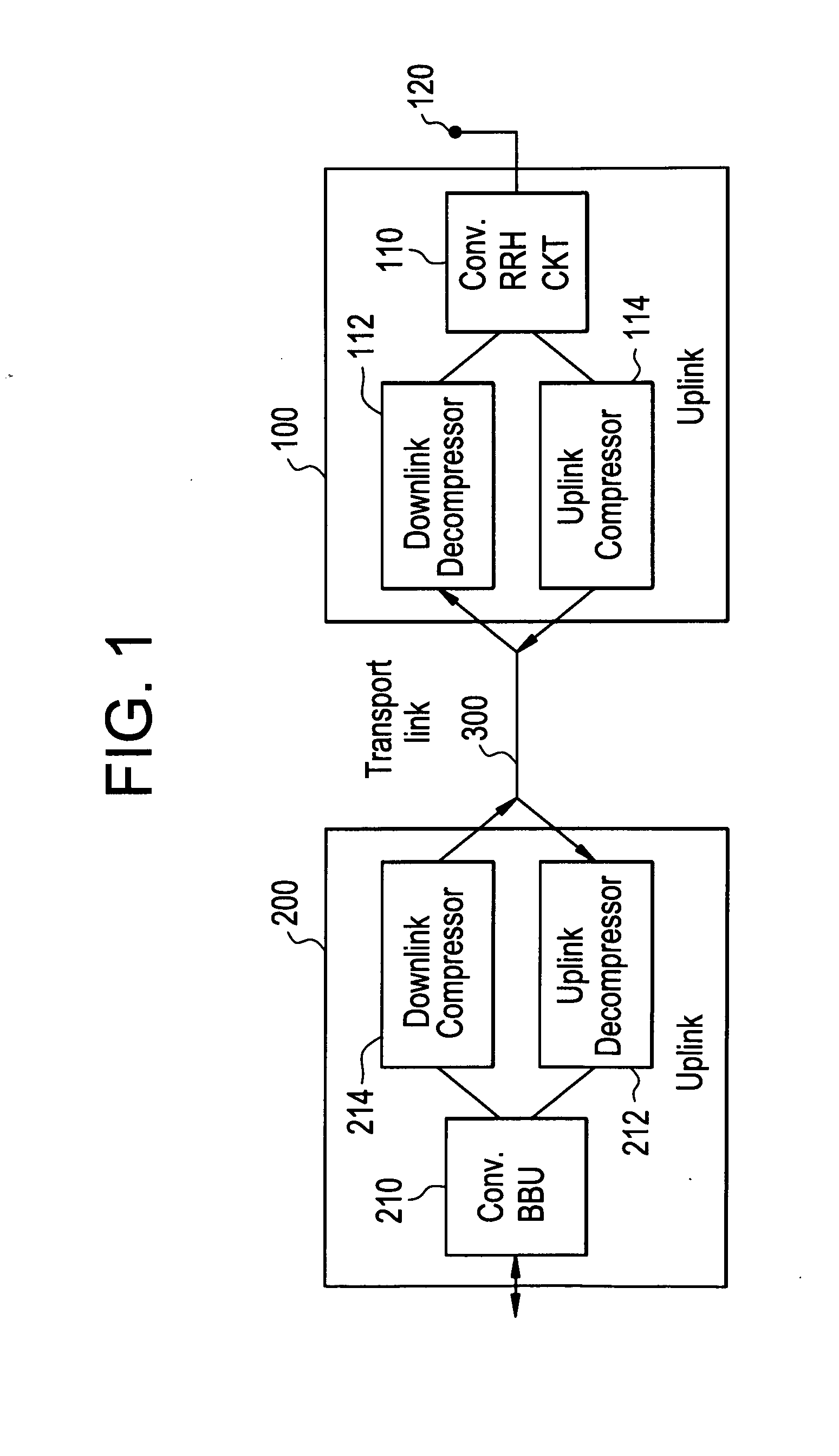
Enhanced data converters using compression and decompression
An enhancement that reduces the digital interface rate of analog-to-digital (A / D) and digital-to-analog (D / A) converters through the use of compression and decompression is described. Improved A / D converters compressing a sampled version of an A / D converter's analog input signal in real time, thereby significantly decreasing the required bit rate of the A / D converter's digital interface. Similarly, improved D / A converters decrease the required bit rate of the D / A converter's digital interface. D / A converters include a decompressor that decompresses the D / A converter's compressed digital input in real time, prior to conversion to an analog output signal.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
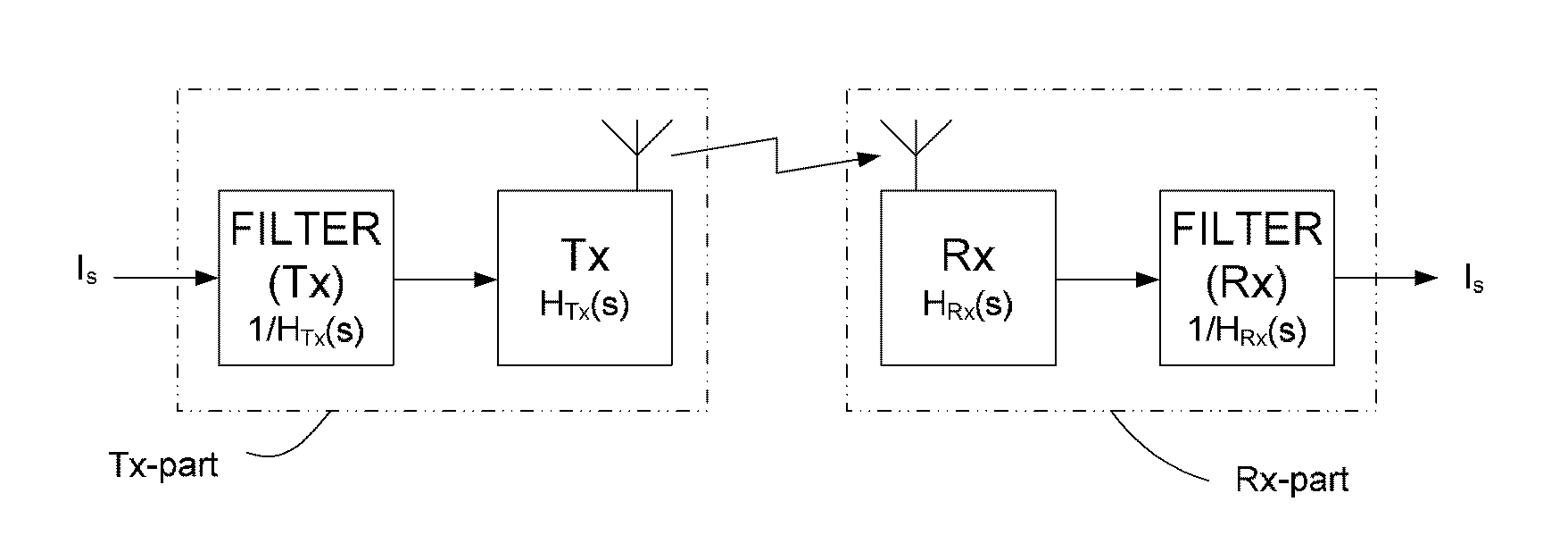
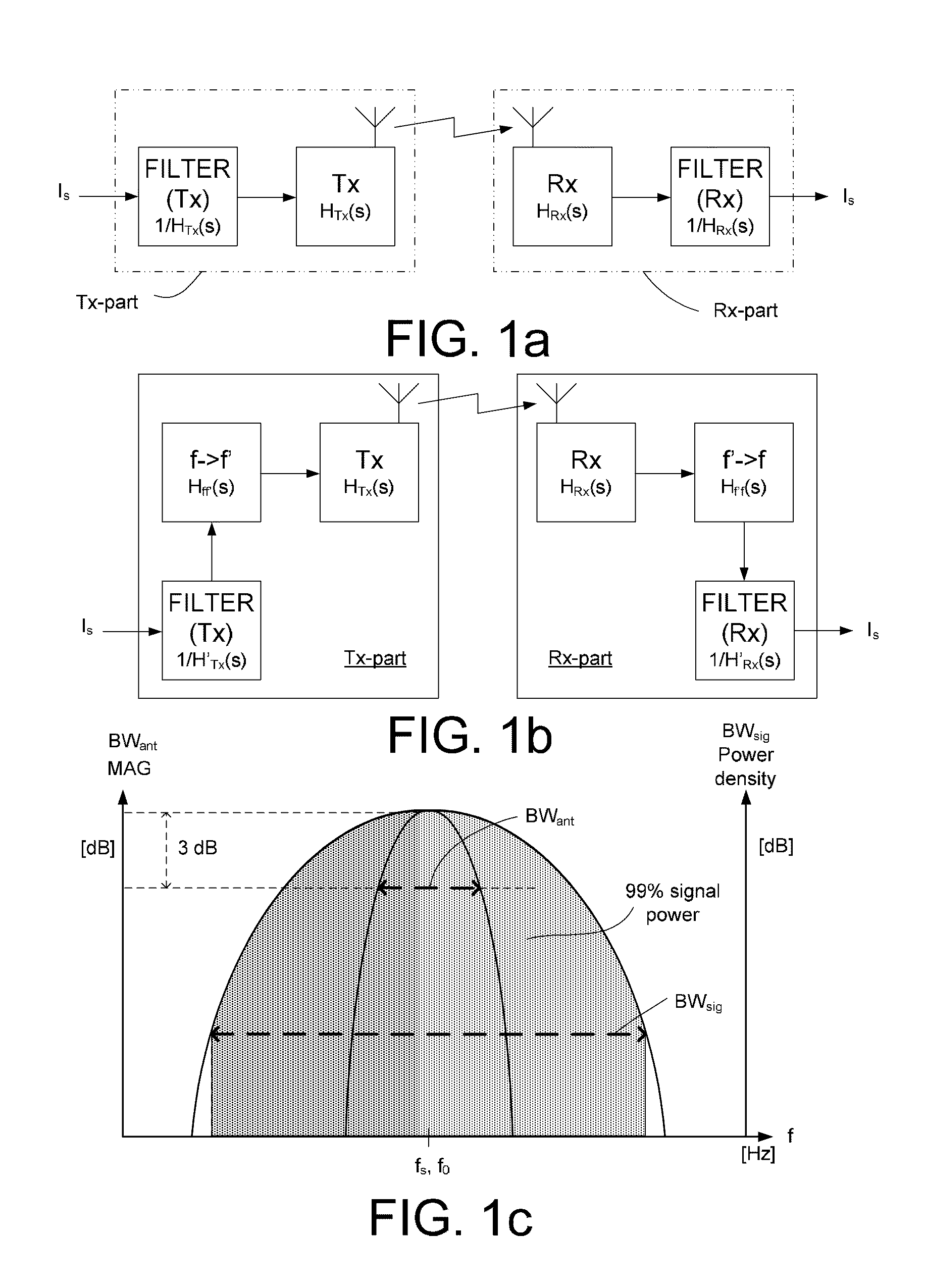
Wireless communication system with a modulation bandwidth comparable to or exceeding the bandwidth of the transmitter and/or receiver antennas
ActiveUS20110222621A1Enhanced advantageReducing BWantError preventionModulated-carrier systemsModulation bandwidthCommunications system
A wireless communication system includes a) a first device having a transmitter part with a Tx-antenna for transmitting an electrical signal having a signal bandwidth BWsig and b) a second device having a receiver part with an Rx-antenna for receiving the transmitted electromagnetic signal. At least one of the Tx- and Rx-antennas is a narrowband antenna having an antenna bandwidth BWant, wherein the Tx- and / or Rx-antenna bandwidths fulfil the relation BWant=k·BWsig. The system is adapted to provide that k is smaller than 1.25, and the antenna bandwidth BWant is defined as the −3 dB bandwidth of the loaded antenna when it is connected to the communication system, and the signal bandwidth BWsig is defined as the bandwidth within which 99% of the desired signal power is located.
Owner:OTICON
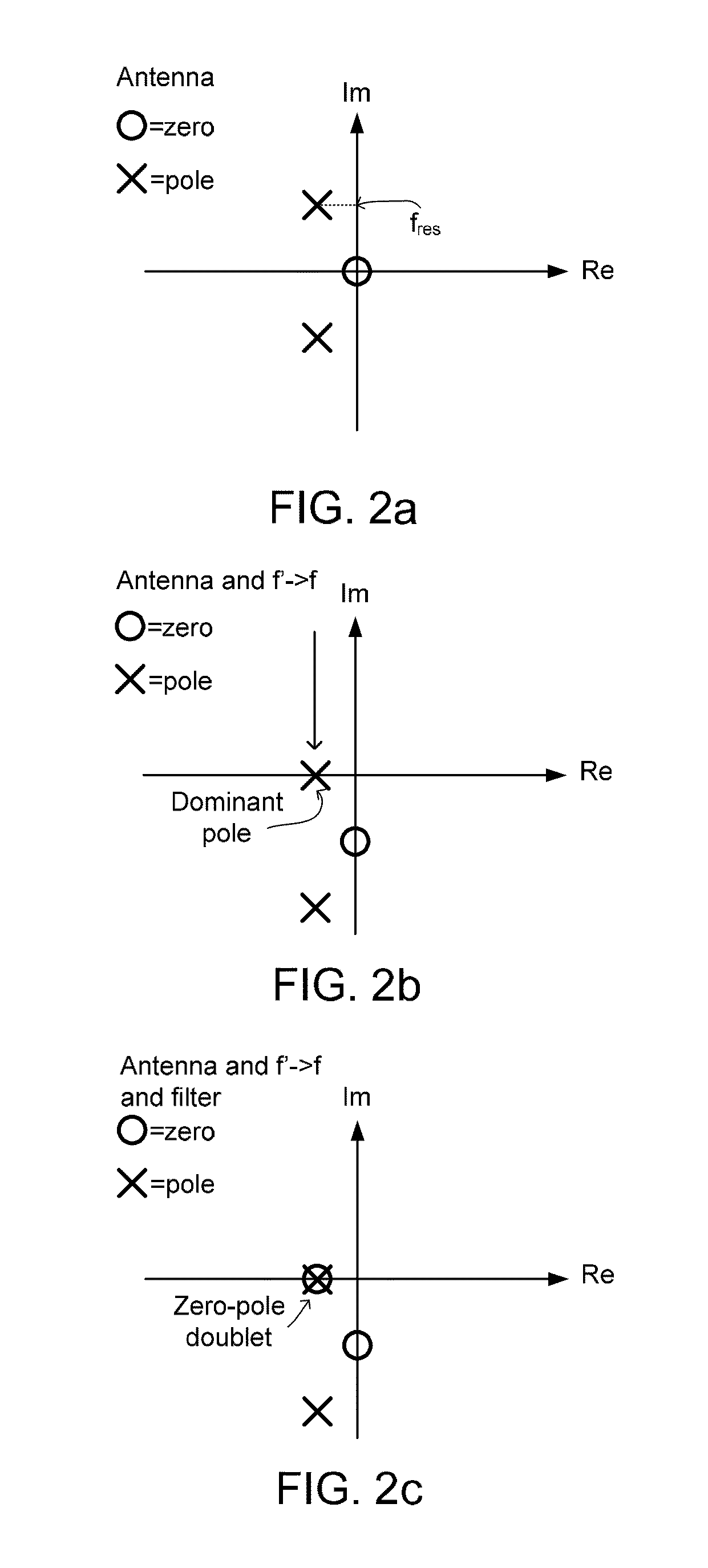
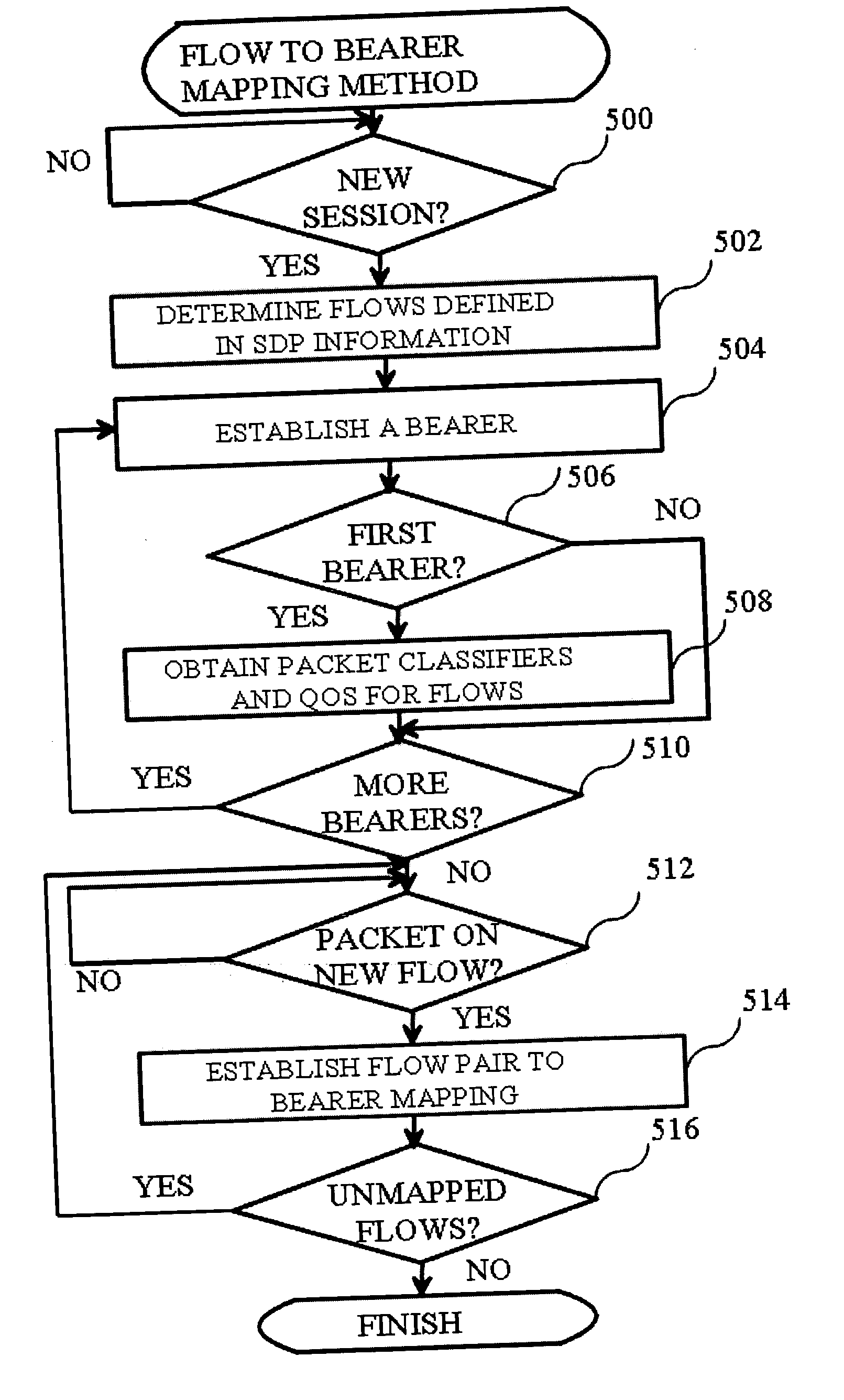
Method for the mapping of packet flows to bearers in a communication system
ActiveUS20070147244A1Reduce data rateError preventionTransmission systemsReal-time computingPacket classification
The invention relates to a method for the mapping of packet flows onto bearers in a communication system. The establishment of a session between a terminal and a remote terminal is initiated. Information on the session and packet flows associated with it is received to a second network node. A first network node obtains from the second network node one or two packet classifiers for each of the packet flows. At least a first bearer belonging to the bearers is established between the terminal and the first network node. A packet associated with the first bearer is received in the first network node. The packet is matched with the one or two packet classifiers associated with each of the packet flows to determine a first packet flow among the packet flows. A mapping is established between the first packet flow and the first bearer in the first network node.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Interpolator based clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit with digitally programmable BW and tracking capability
ActiveUS7315596B2Easy to operateWide data rate rangePulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase correctionData stream
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
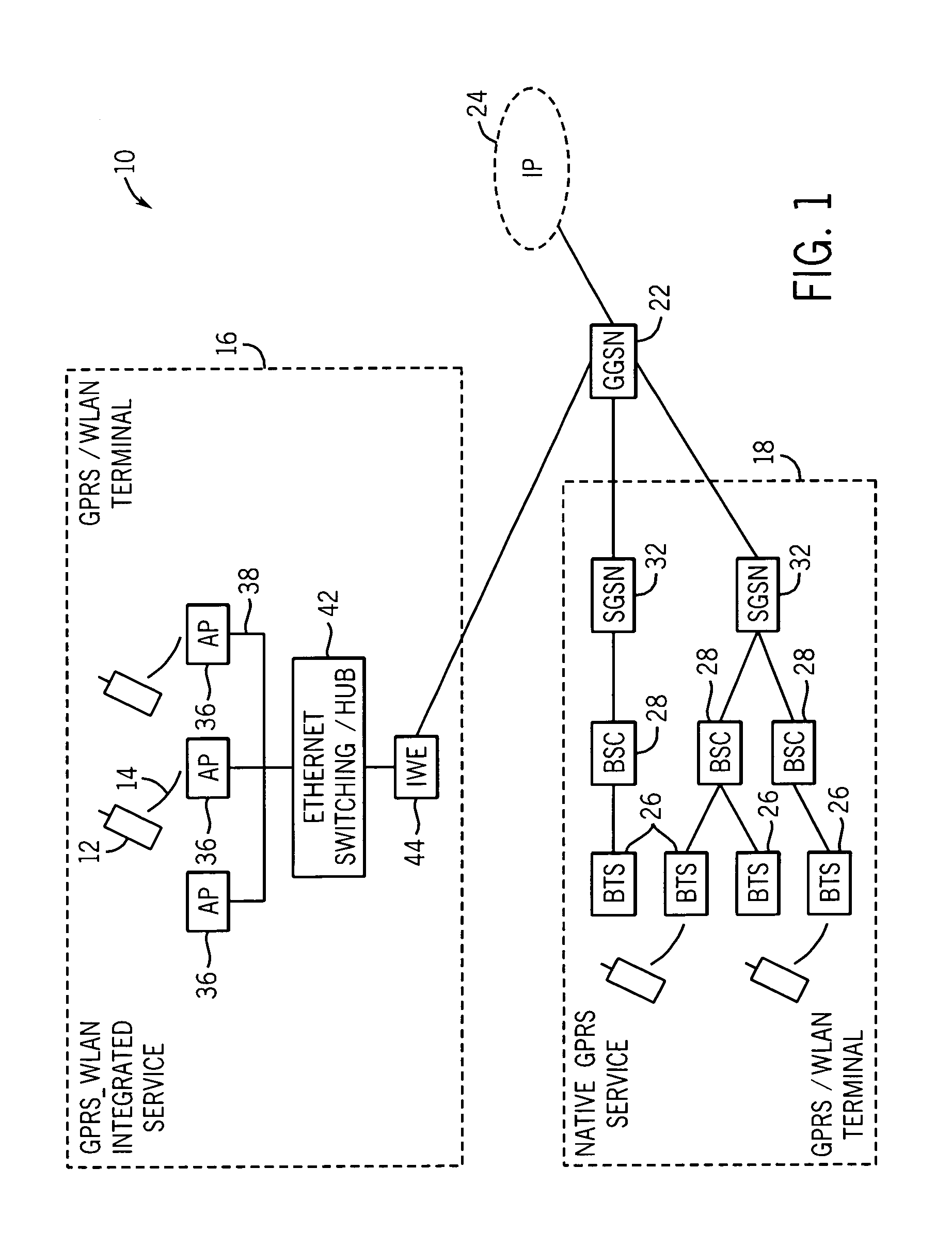
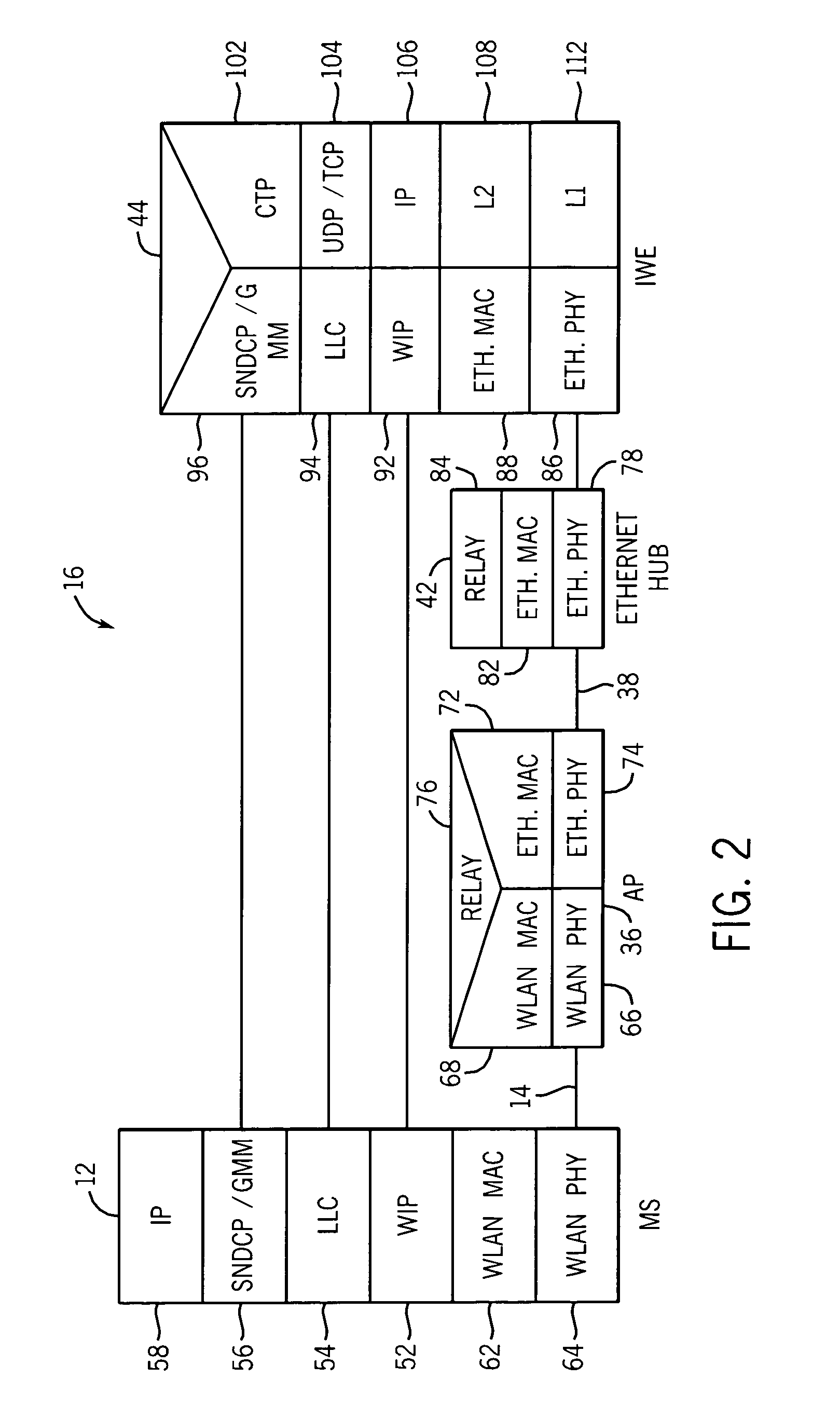
Apparatus, and associated method, for integrating operation of packet radio communication systems
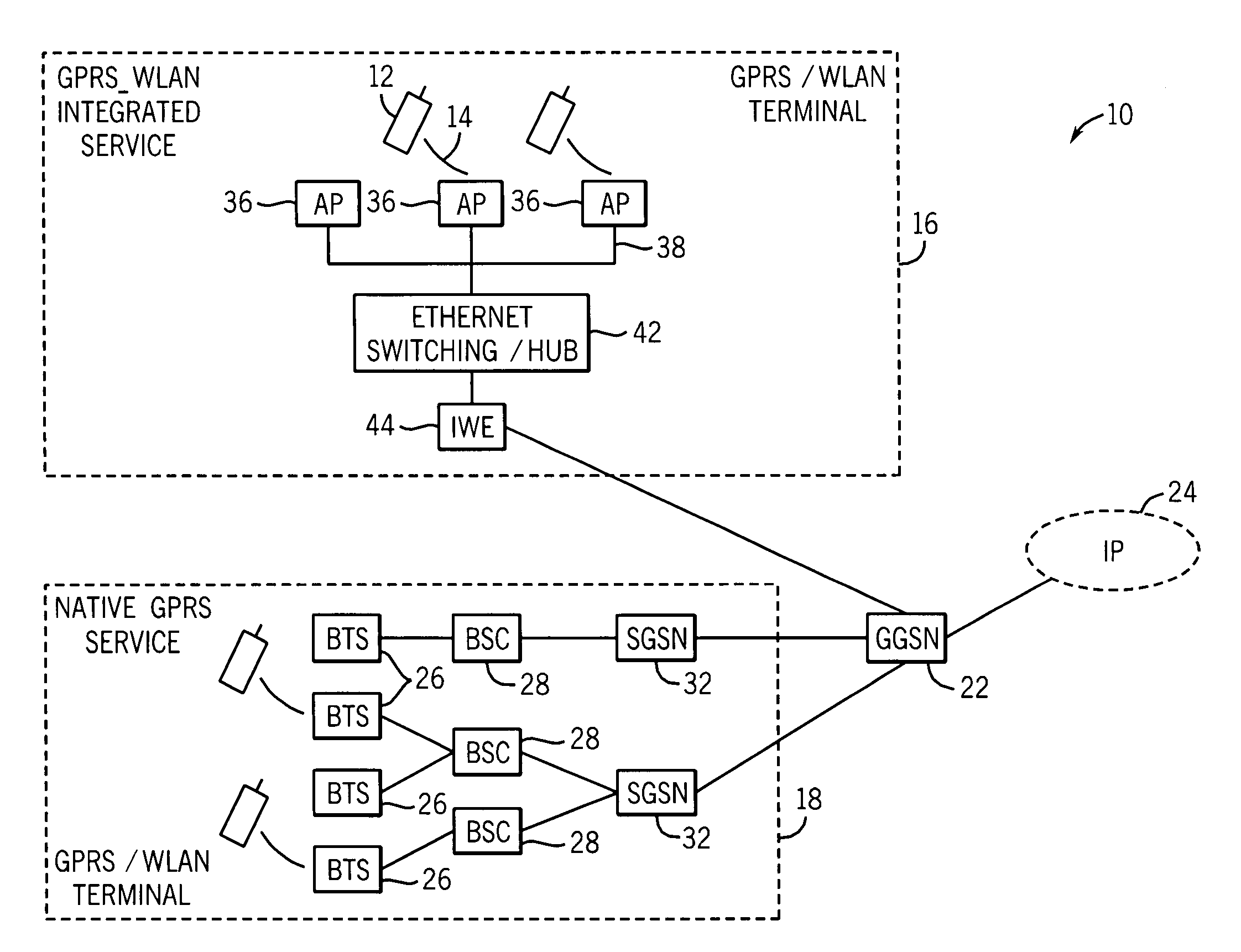
InactiveUS7099339B1Faster data rateImprove security levelNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationCommunications systemIntegrated systems
Apparatus, and an associated method, forms an integrated packet radio communication system. An integrated system is formed of portions of a GPRS system as well as portions of a WLAN system, such as that defined in the IEEE 802.11 standard. A WIP (WLAN Integrated Protocol) layer is defined, functionally positioned between upper-level, GPRS layers and lower-level, WLAN layers. Advantages of a GPRS system as well as advantages of the WLAN system are maintained in the integrated system.
Owner:RPX CORP
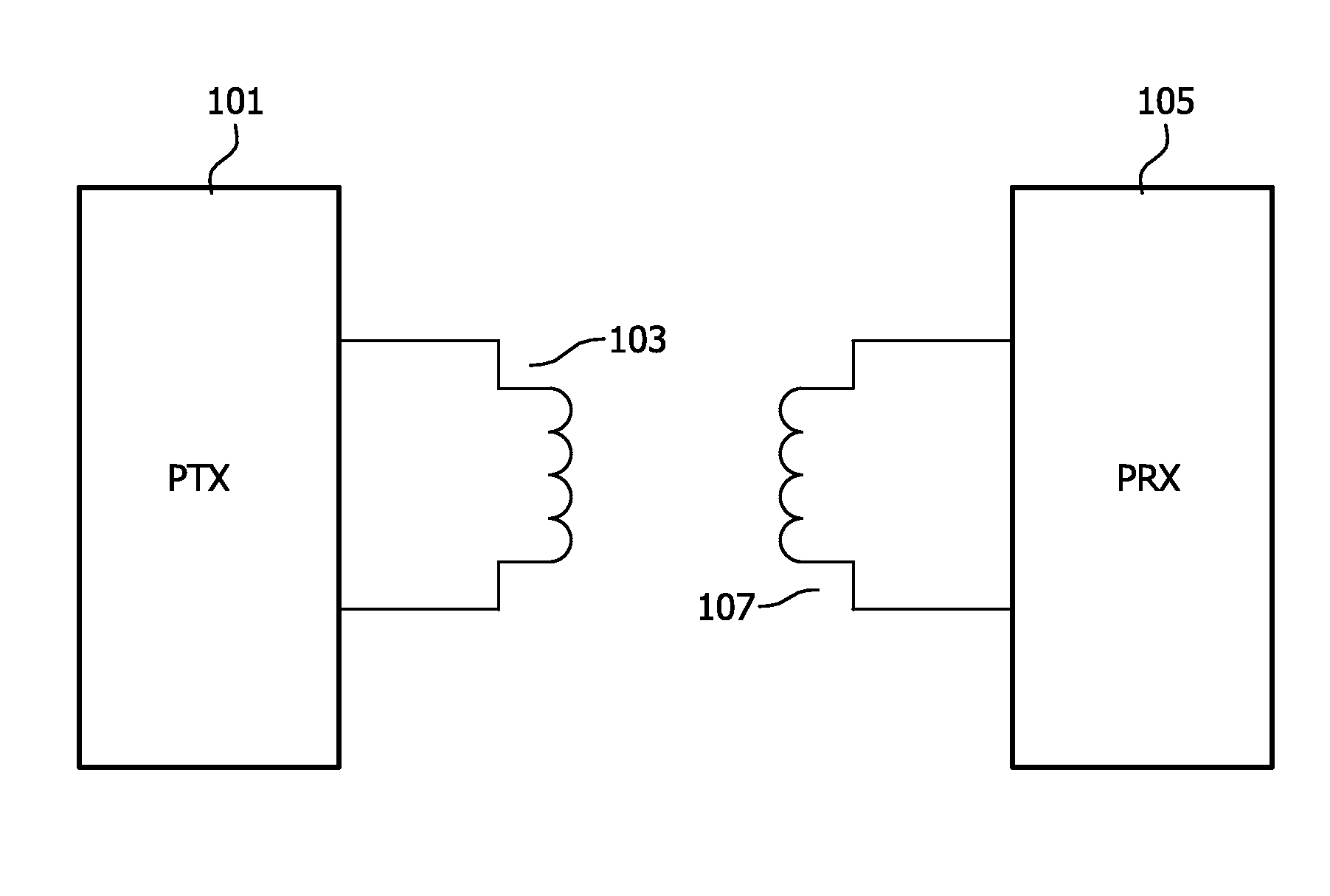
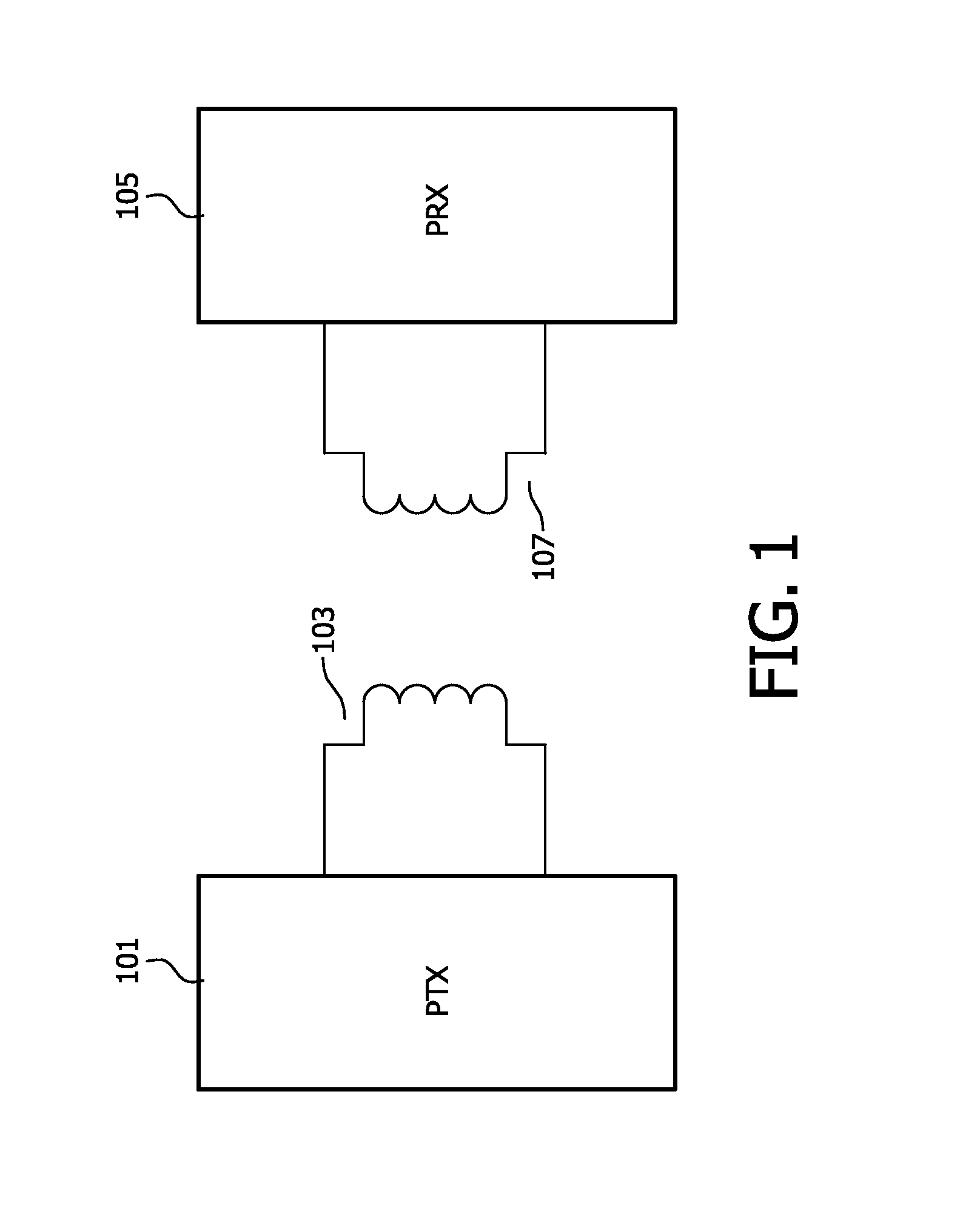
Wireless inductive power transfer
ActiveUS20150155918A1Reduce complexityCommunication time is longNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionTransfer system
An inductive power transfer system comprises a power transmitter (101) and a power receiver (105). The power transmission system supports two-way communications. The power receiver (105) first initiates a mandatory configuration phase by transmitting a signal strength package and the power transmitter and receiver then operates (505, 507) the mandatory configuration phase wherein a first set of power transfer operating parameters are selected for the power transmitter (101) and the power receiver (105). The power receiver (105) subsequently transmits (509) a request to enter a negotiation phase and the power transmitter (101) acknowledges (511) the request by transmitting an acknowledgement. It then enters the negotiation phase. The power receiver (105) enters the negotiation phase in response to receiving the acknowledgment message. The power receiver (105) and power transmitter (101) then determines (513, 515) a second set of operating parameters by performing the negotiation phase. The approach is particularly suitable for a Qi power transfer system.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
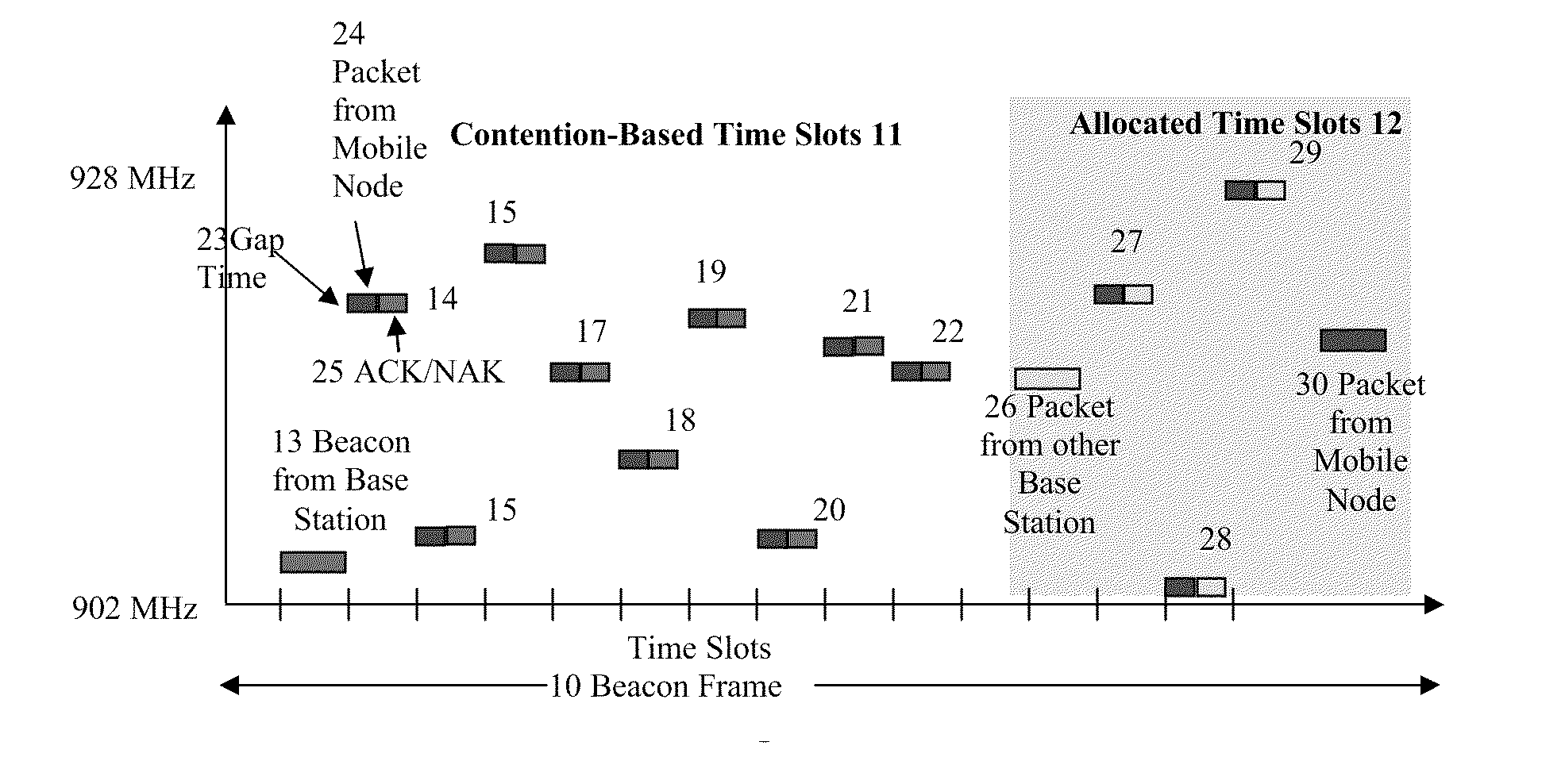
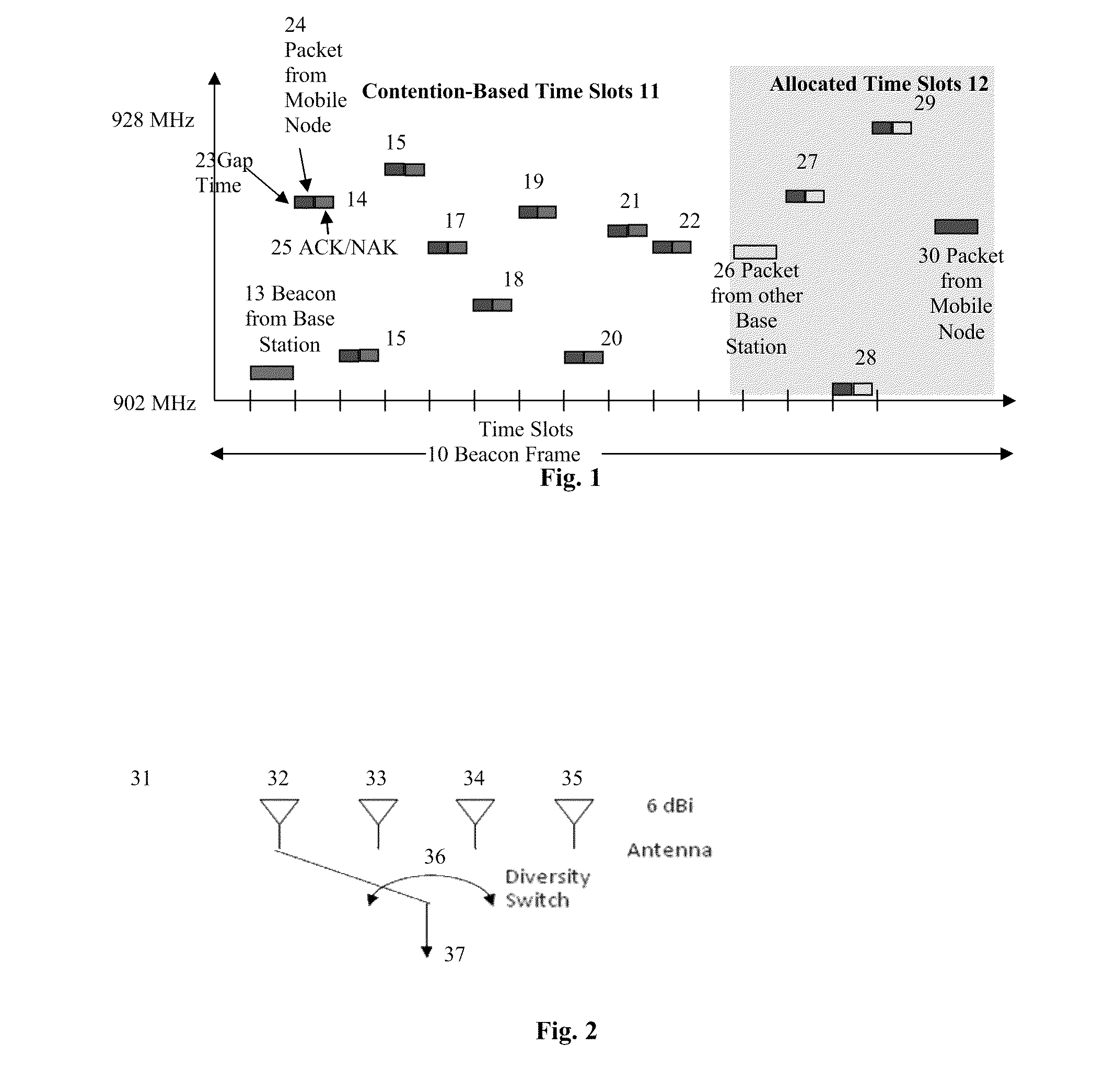
Method and apparatus for low cost, long range, power efficient, wireless system with enhanced functionality
ActiveUS20110176464A1Save battery powerLong power save statePower managementTransmission systemsSleep timePower efficient
The present invention provides a method and system for establishing a highly mobile, long range secure wireless network with dynamic topologies and near full connectivity with acceptable latency using low cost, low power, compact and lightweight devices. One aspect of the system deals with a highly mobile network with dynamic network topologies and a time varying wireless medium that has neither absolute nor readily observable boundaries outside of which radio nodes are known to be unable to receive network frames, although the desirable open field boundary is 1 mile in radius from a base station node. A synchronous frequency hopping technique is used with mobile nodes that can become slave base station nodes to a master base station node to increase the effective range of the master base station without increasing the transmit power. Furthermore, the use of adjustable sleep times for the mobile nodes, as well as a novel clock calibration method, provides a substantial range increase with acceptable battery size and system latency.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Method And Apparatus For Signal Compression And Decompression
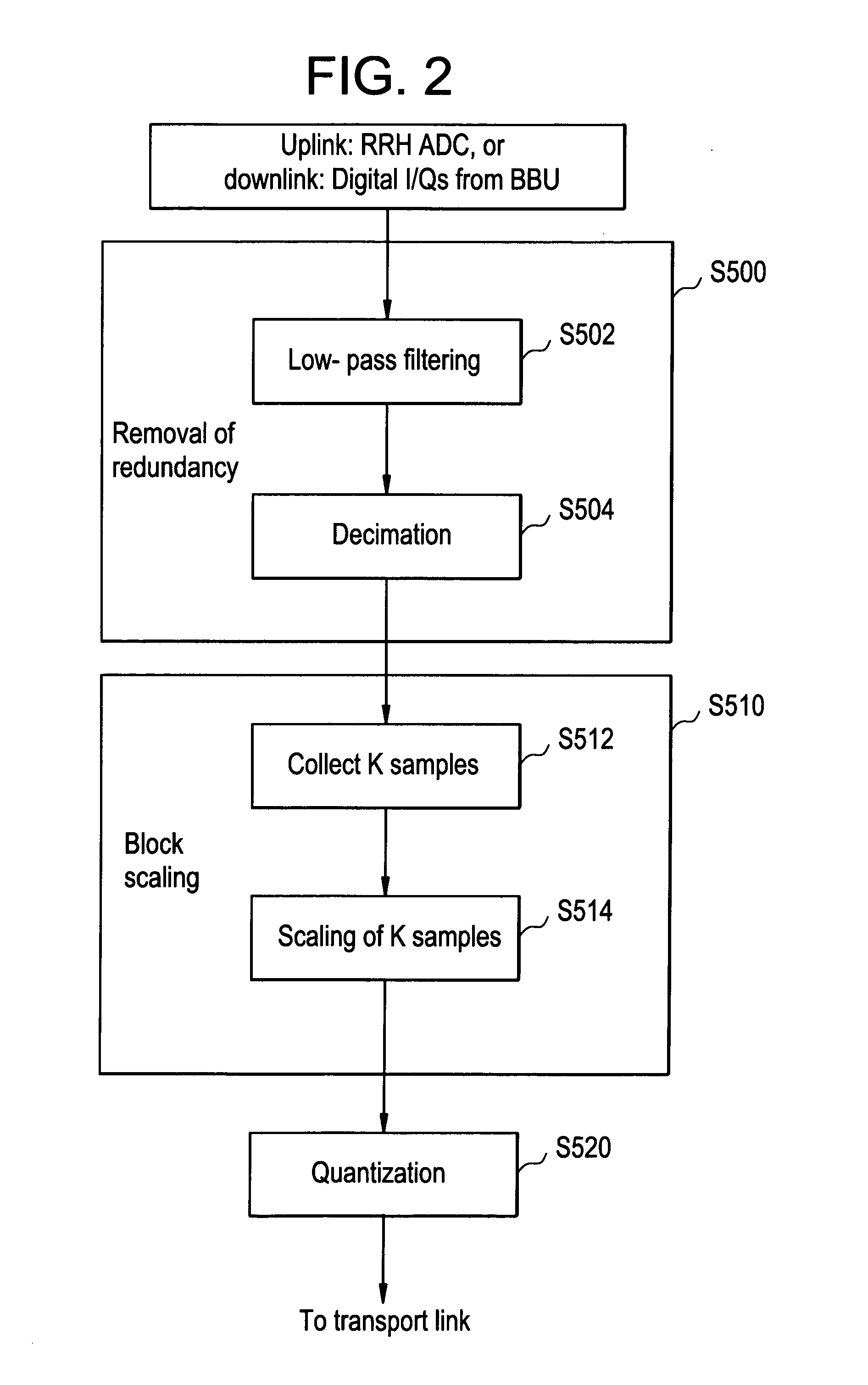
ActiveUS20120207206A1Low data rateReduce data rateCode conversionMultiple carrier systemsDigital radioComputer science
In one embodiment, the method of compressing a digital signal includes reducing redundancies in the digital signal, scaling a block of samples output from the reducing step by a scaling factor, and quantizing the scaled samples to produce compressed samples. The digital signal being compressed may be a digital radio frequency signal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Efficient reduction of inter-cell interference using RF agile beam forming techniques
ActiveUS20140010129A1Low data rateExperienceTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexCell to cell communicationData rate
In embodiments of the present disclosure improved capabilities are described for reducing inter-cell interference in a large area broadband LTE wireless network utilizing RF agile beam forming antennas, where the reduced inter-cell interference is realized by arranging the sets of rotating RF beams in each cell such that adjacent RF beam sub-areas in the same or in different cells are not illuminated at the same time. The reduction in inter-cell interference results in reduced interference noise for users located near the edges of cells, thereby allowing them to be assigned higher data rates. Also, the same set of sub-carriers can be assigned by adjacent cells to users located in the RF beam sub-areas at the cell boundaries, thereby allowing the complete set of LTE sub-carriers to be assigned to any user at any time, without requiring additional cell-to-cell communications.
Owner:ALL PURPOSE NETWORKS INC
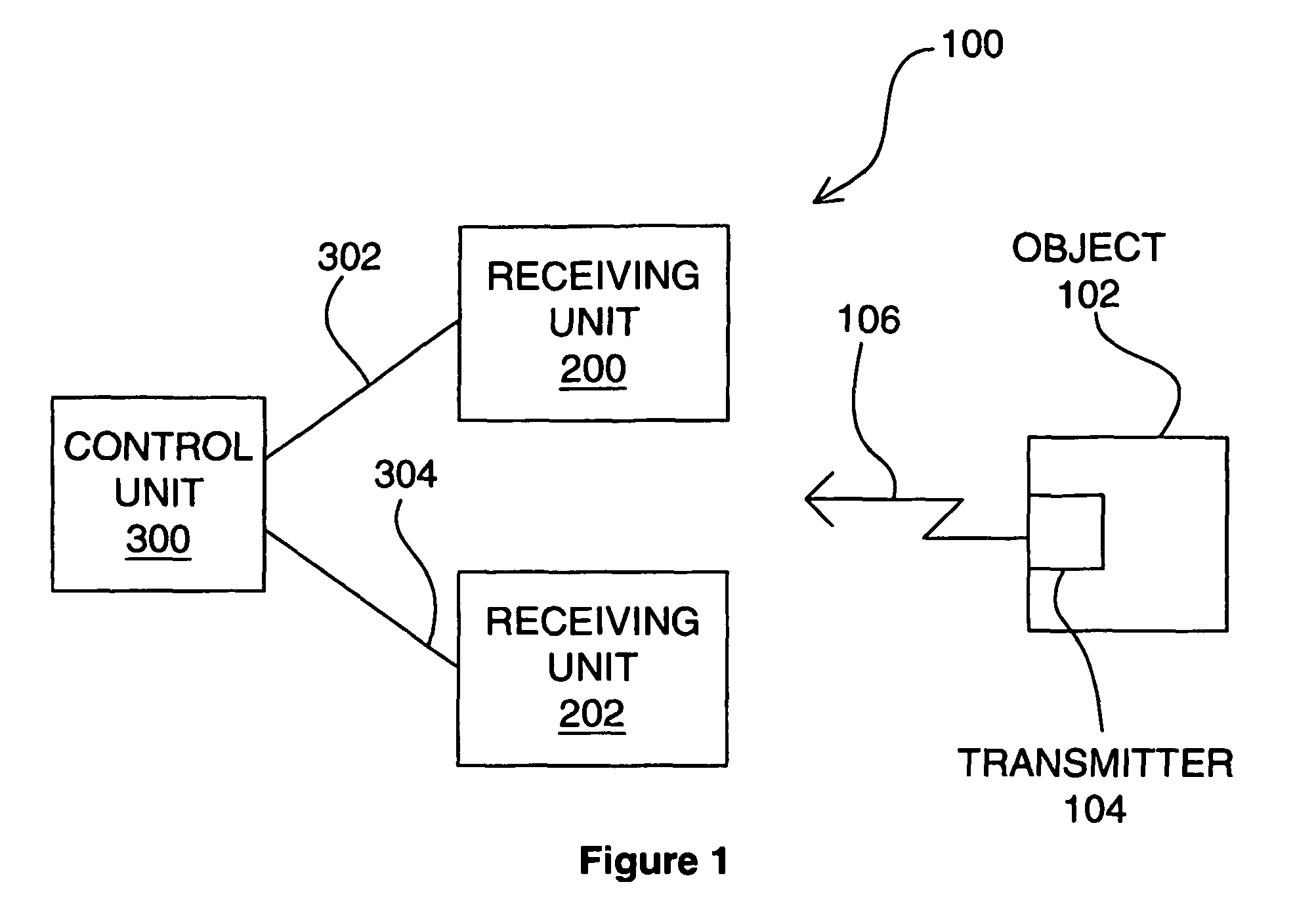
Determining positional information
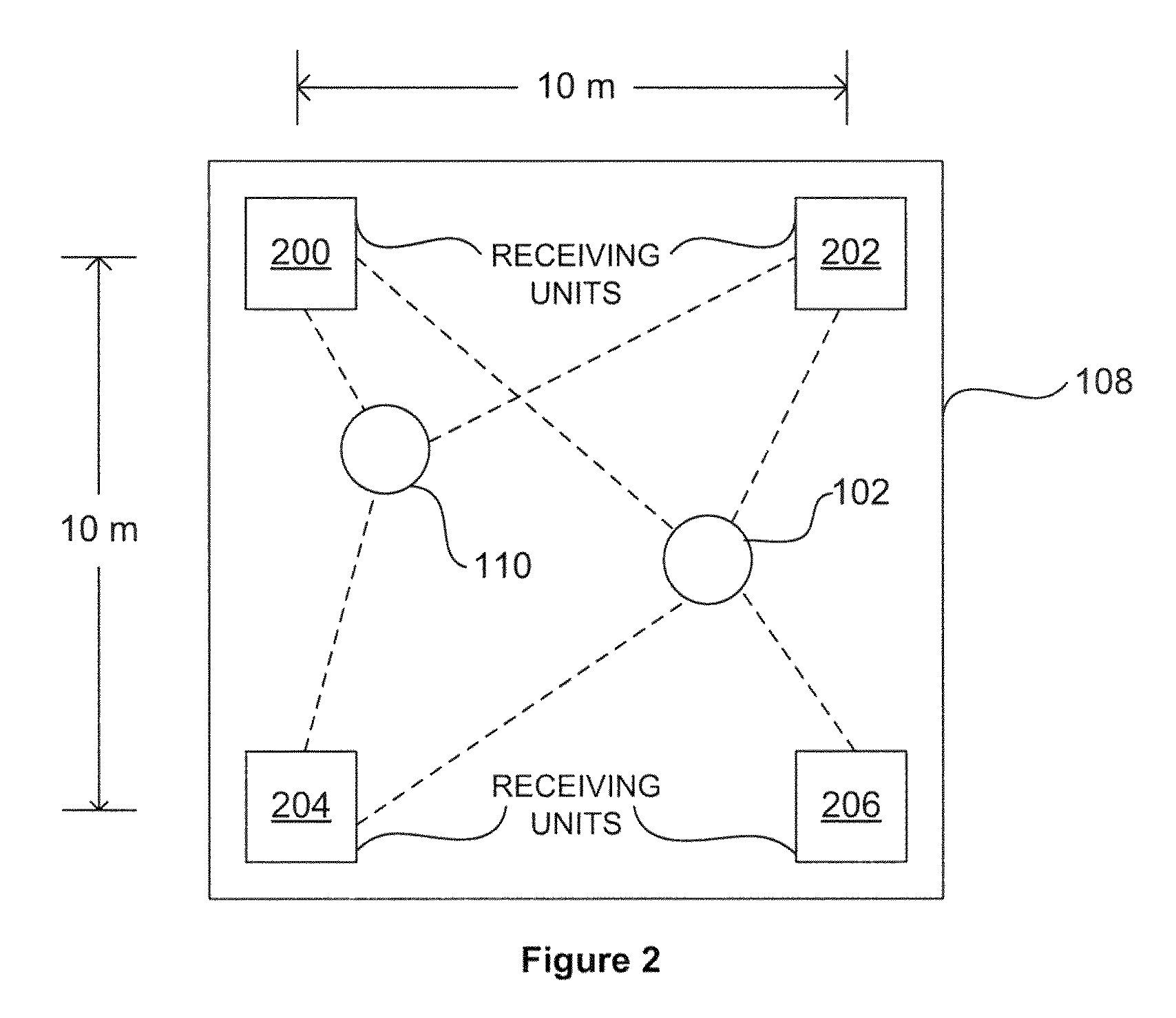
ActiveUS7750841B2Reduce data rateLow data rateDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringSignal production
Apparatus for determining positional information relating to an object, comprising: means for receiving, comprising a plurality of receiving elements; detection means for detecting signals received at the receiving elements and for generating output signals representative of the received signals; and processing means operable to apply, for each receiving element, a process to the output signal generated from the signal received at that receiving element separately from any output signal generated from a signal received at any other receiving element, so as to obtain a respective value of a parameter representative of the signal received at that receiving element, the processing means being further operable to compare the values of the parameter thus obtained so as to, obtain positional information relating to the object.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
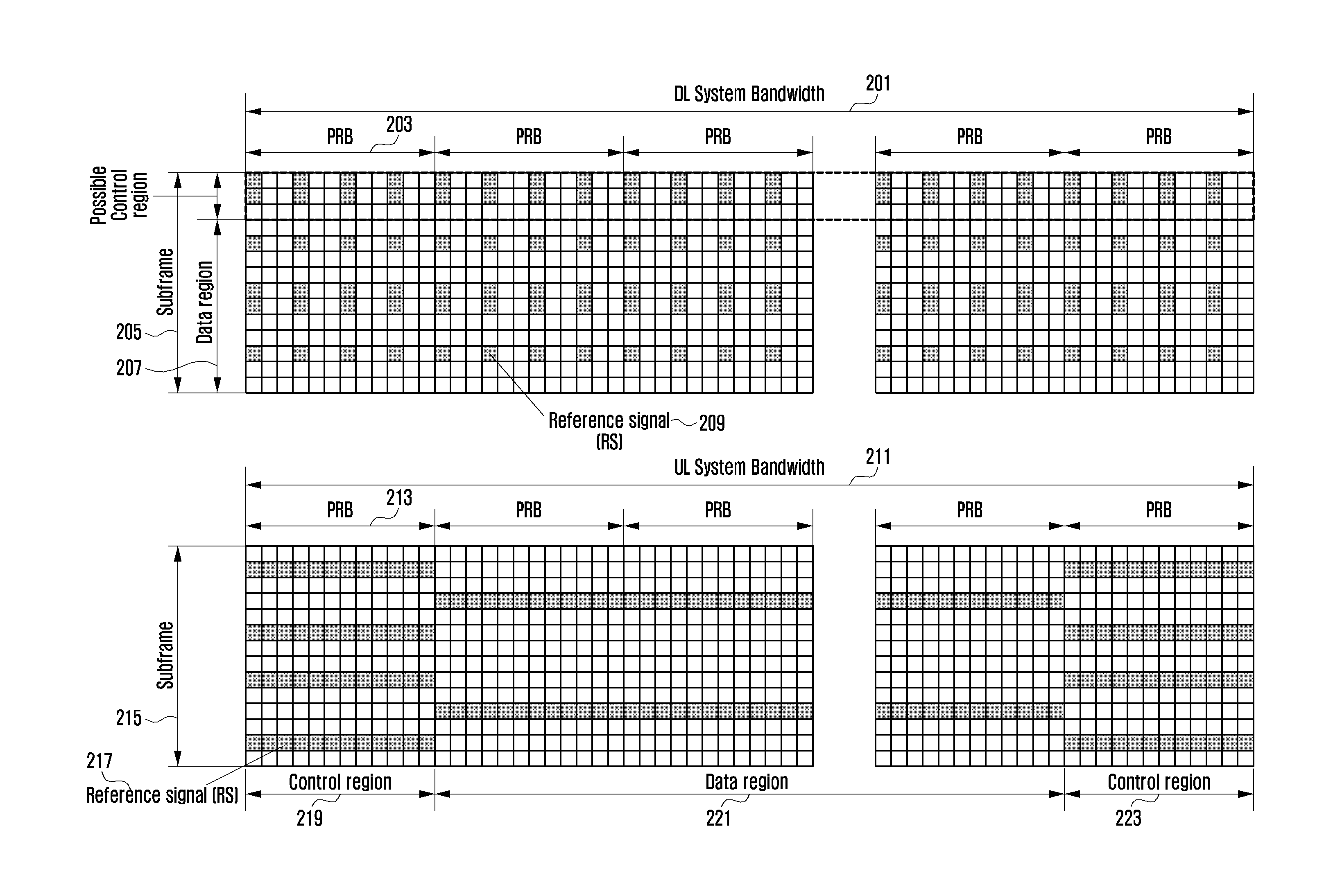
Method and apparatus for resource allocation in multi-carrier wireless system
ActiveUS20130114533A1Narrow bandwidthMaintain compatibilityTransmission path divisionRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemLow data rate
A method and apparatus for resource allocation in a multi-carrier wireless communication system enables transmission using smaller resource units and achieves efficient transmission of data channels with very low data rates, scheduling a greater number of user equipments without additional control channel overhead while maintaining compatibility with the resource allocation scheme of legacy user equipments. Thus, one cell controls a larger number of user equipments. In addition, as multiple user equipments are scheduled using a single control channel, resource efficiency is increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
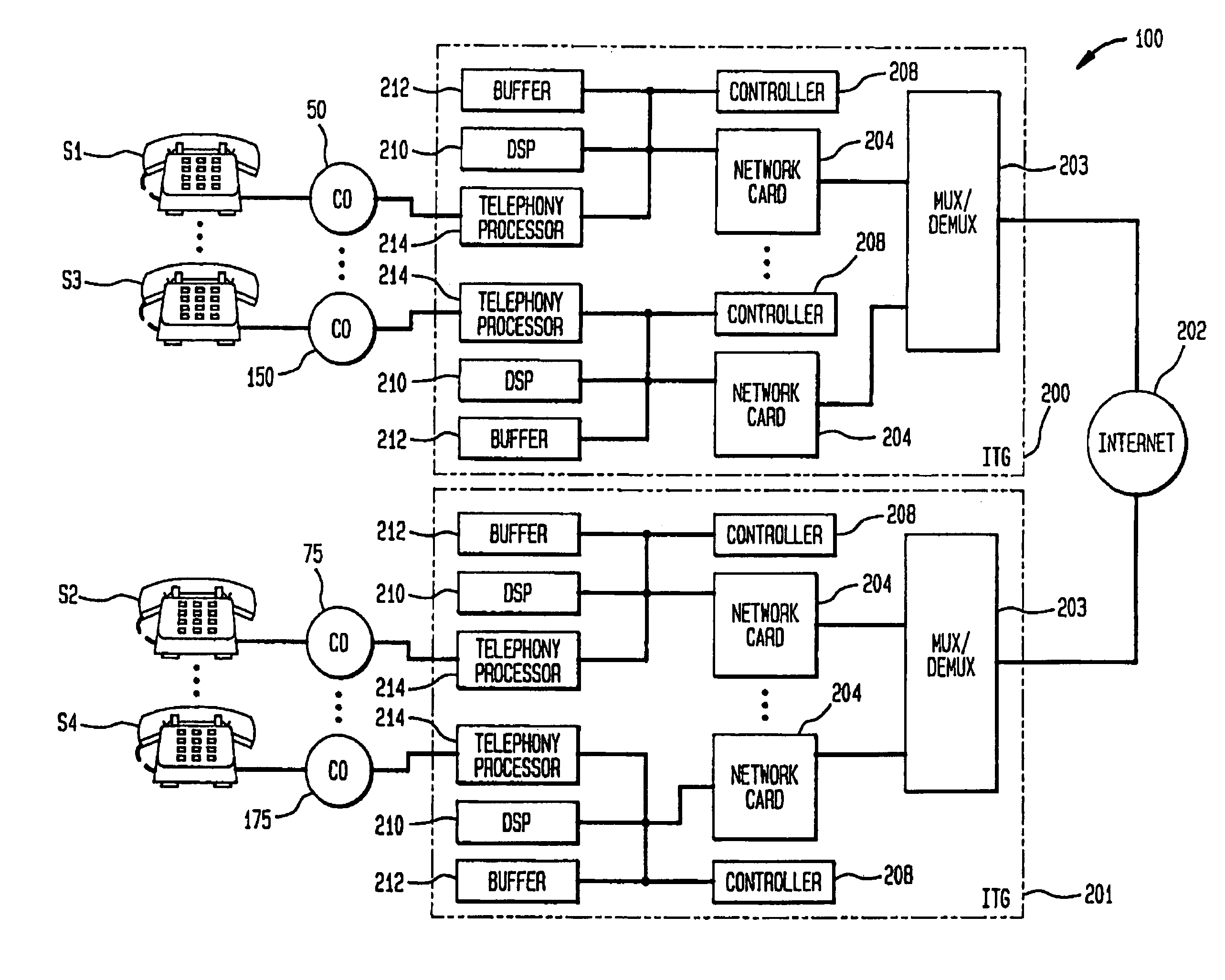
Methods and apparatus for providing voice communications through a packet network
InactiveUS7170887B2Improve efficiencyImprove abilitiesInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVoice communicationThe Internet
A communications system multiplexes voice communications signals onto one or more transport level connections established through a packetized network, such as the Internet. The invention supports the use of variable-length packets and accommodates variable jitter. The system conforms to real time protocol (RTP) and employs internet telephone gateways (ITGs) to bind users to channel identifiers, to indicate payload type and length, to provide channel identification and time stamps, and to indicate cessation and resumption of voice traffic from a particular user through use of, for example, marker bits.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
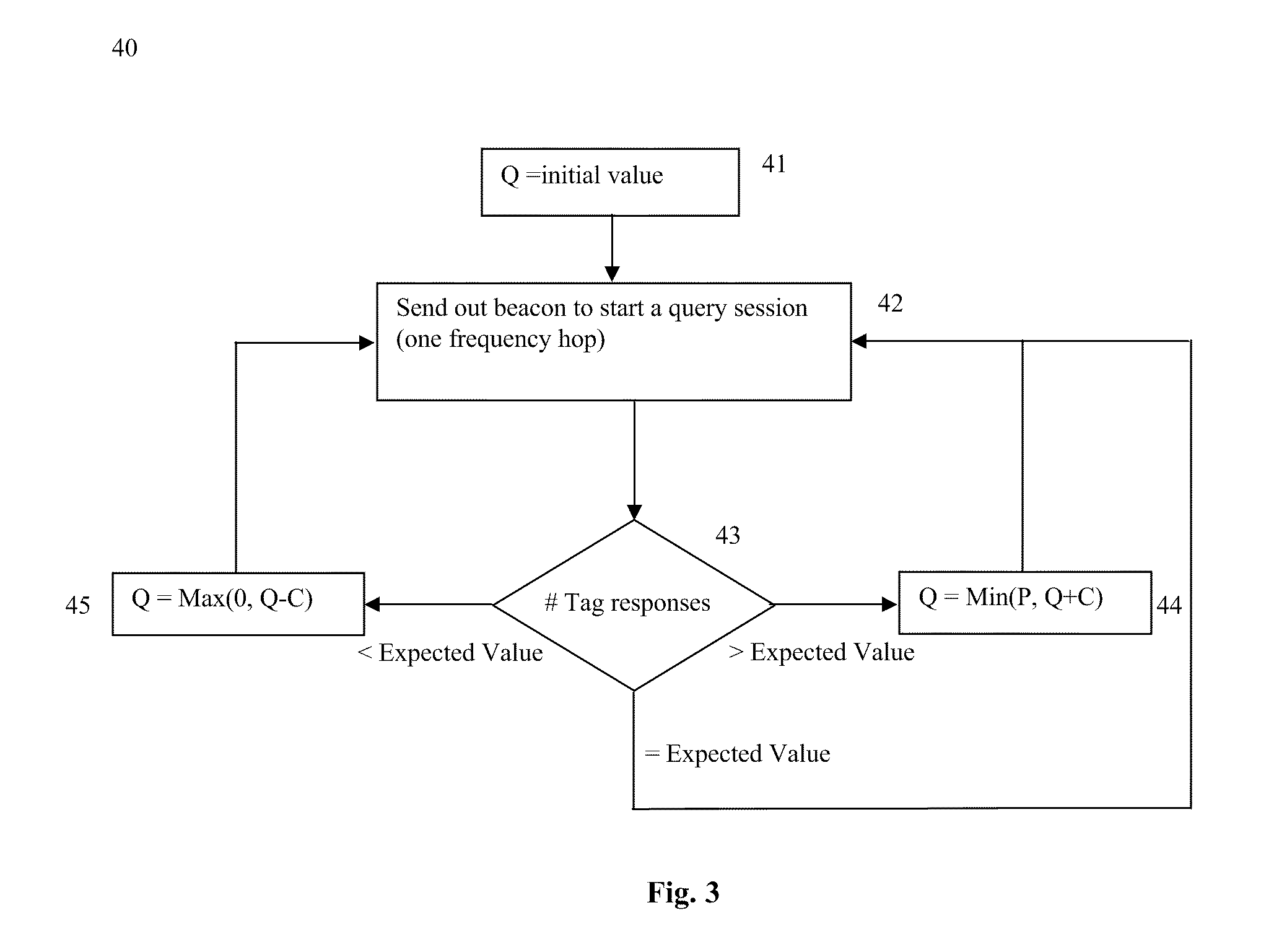
Devices and methods for fast catching signal in high dynamic satellite navigation receiving machine
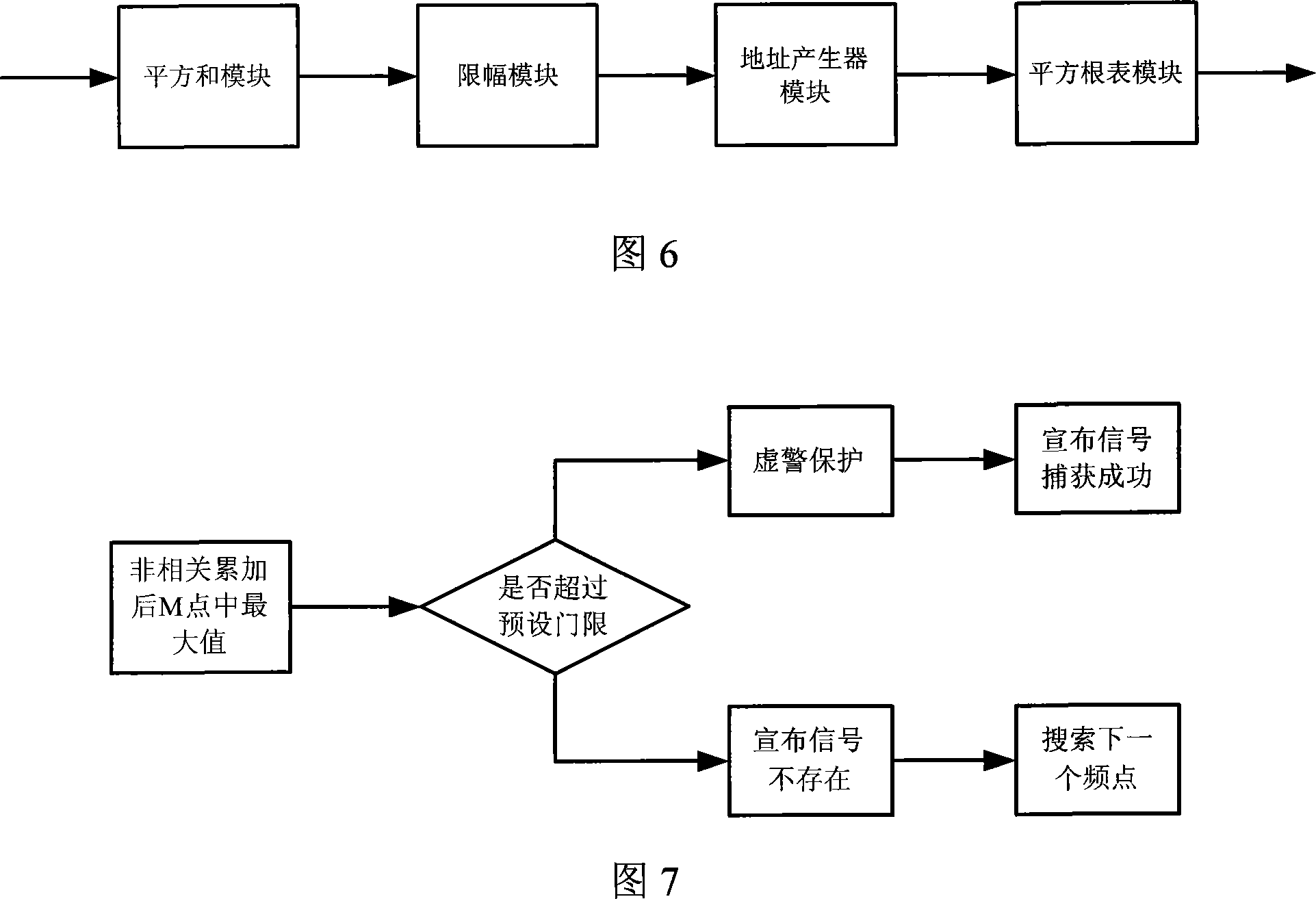
InactiveCN101082664AReduce complexityGuaranteed stabilityBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency changerSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
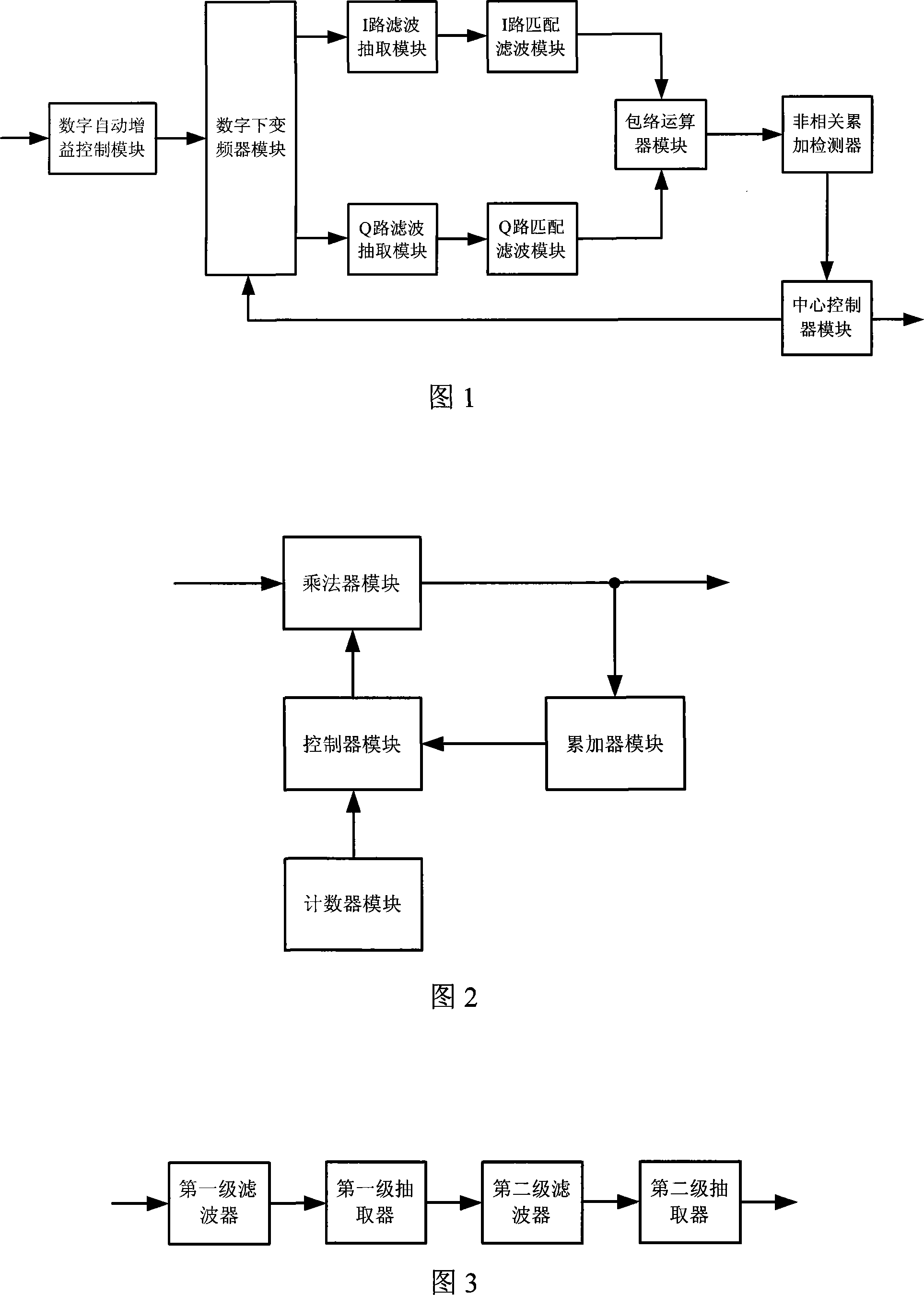
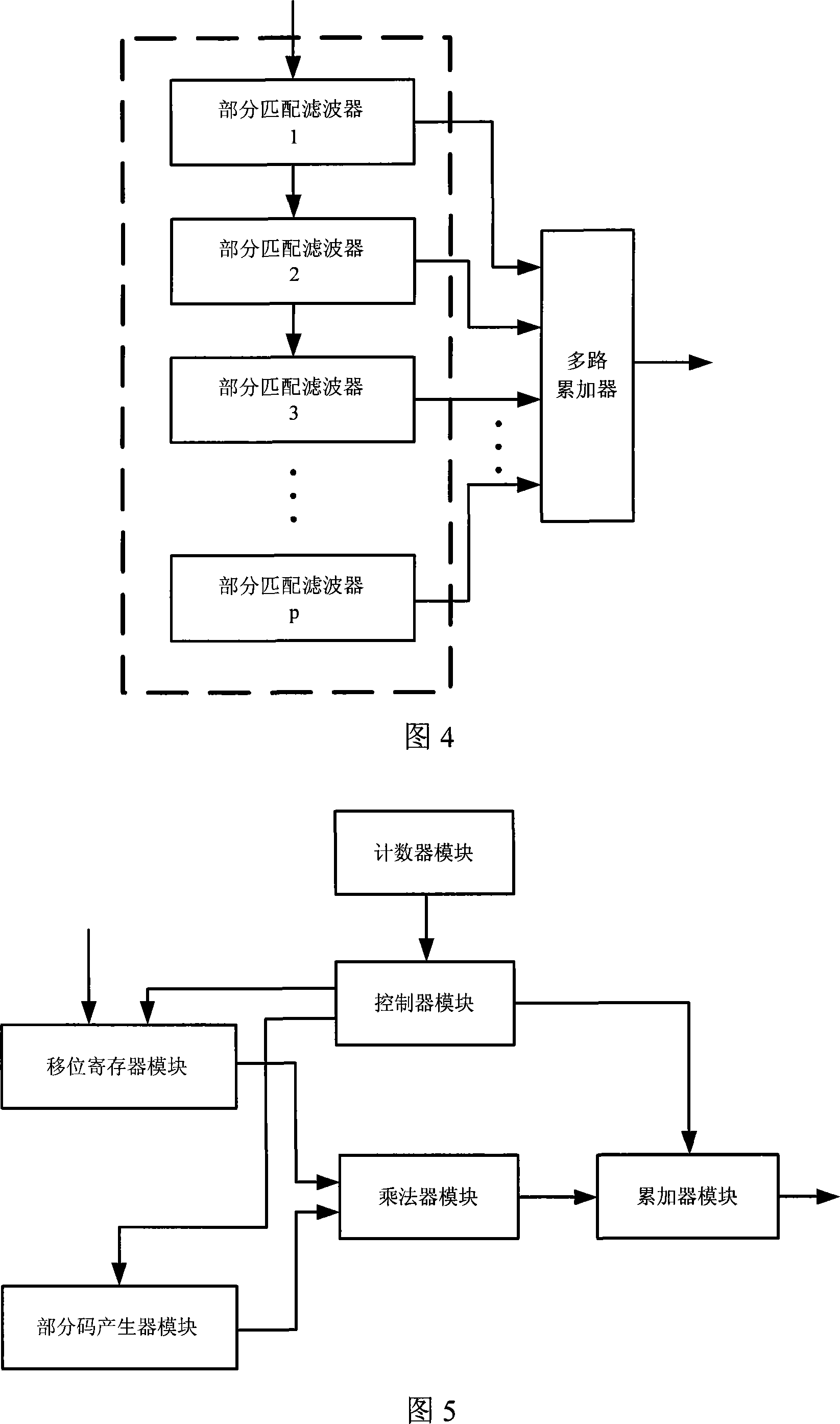
The invention discloses a signal rapid-capturing device and method in the high-dynamic satellite navigational receiver based on segmented mated filter, which comprises the following parts: frequency converter, low-pass filter, extractor, segmented mated filter, envelope calculator, incoherent signal accumulated tester and central controller, wherein the mated filter searches the entire code phase within time T in relative to integral, which obtains a relative result of all code phases under one Doppler frequency deviation to improve signal-to-noise ratio through incoherent signal accumulated tester, in order to judge whether the signal exists; the central frequency is changed by frequency converter to do frequency shaft stepping research. The invention can transmit two-dimensional research on the traditional code phase and Doppler frequency deviation into one-dimensional research on the Doppler frequency deviation, which improves the capture speed of signal greatly to save hardware resource through the design of the segmented mated filter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
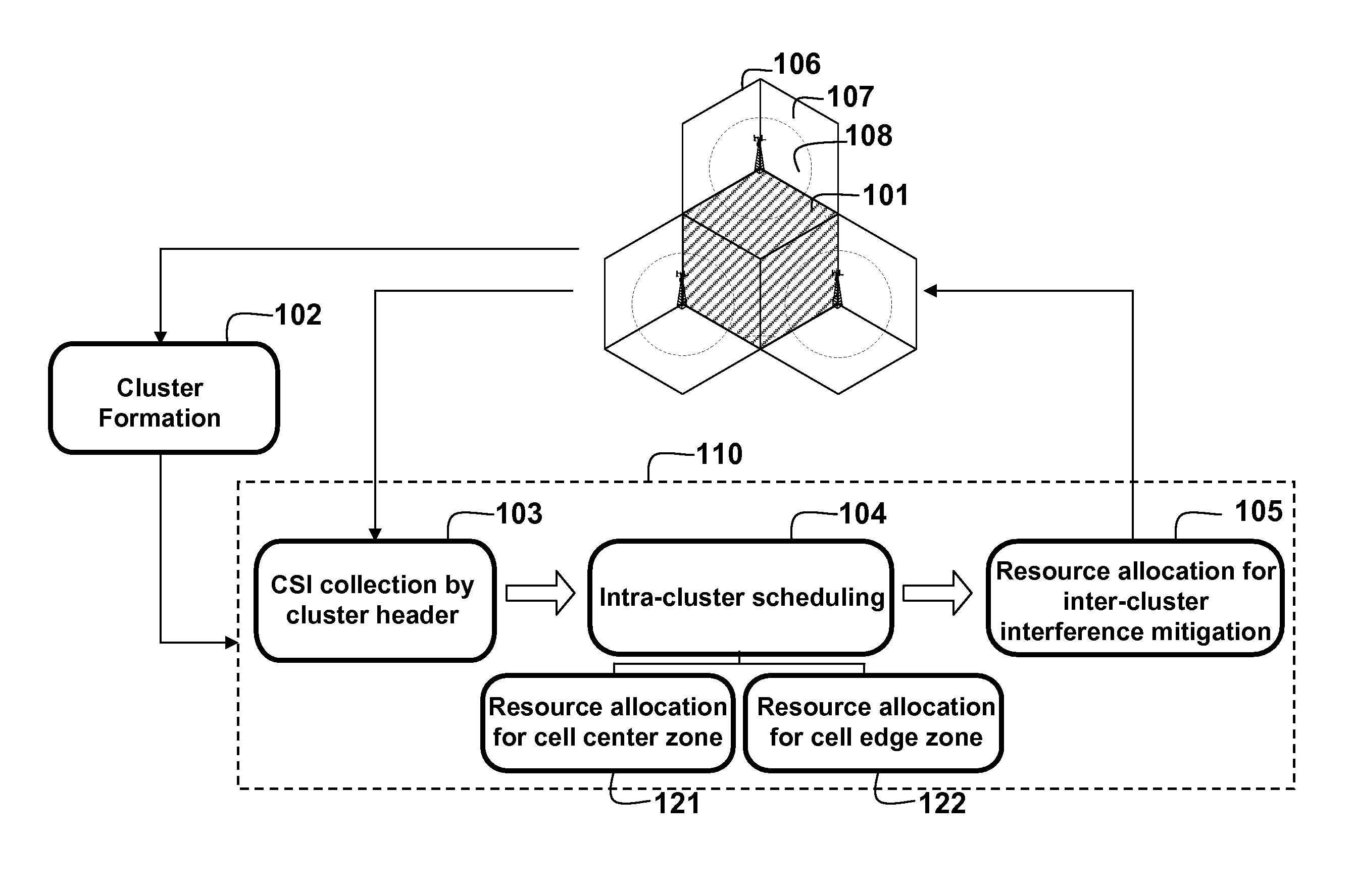
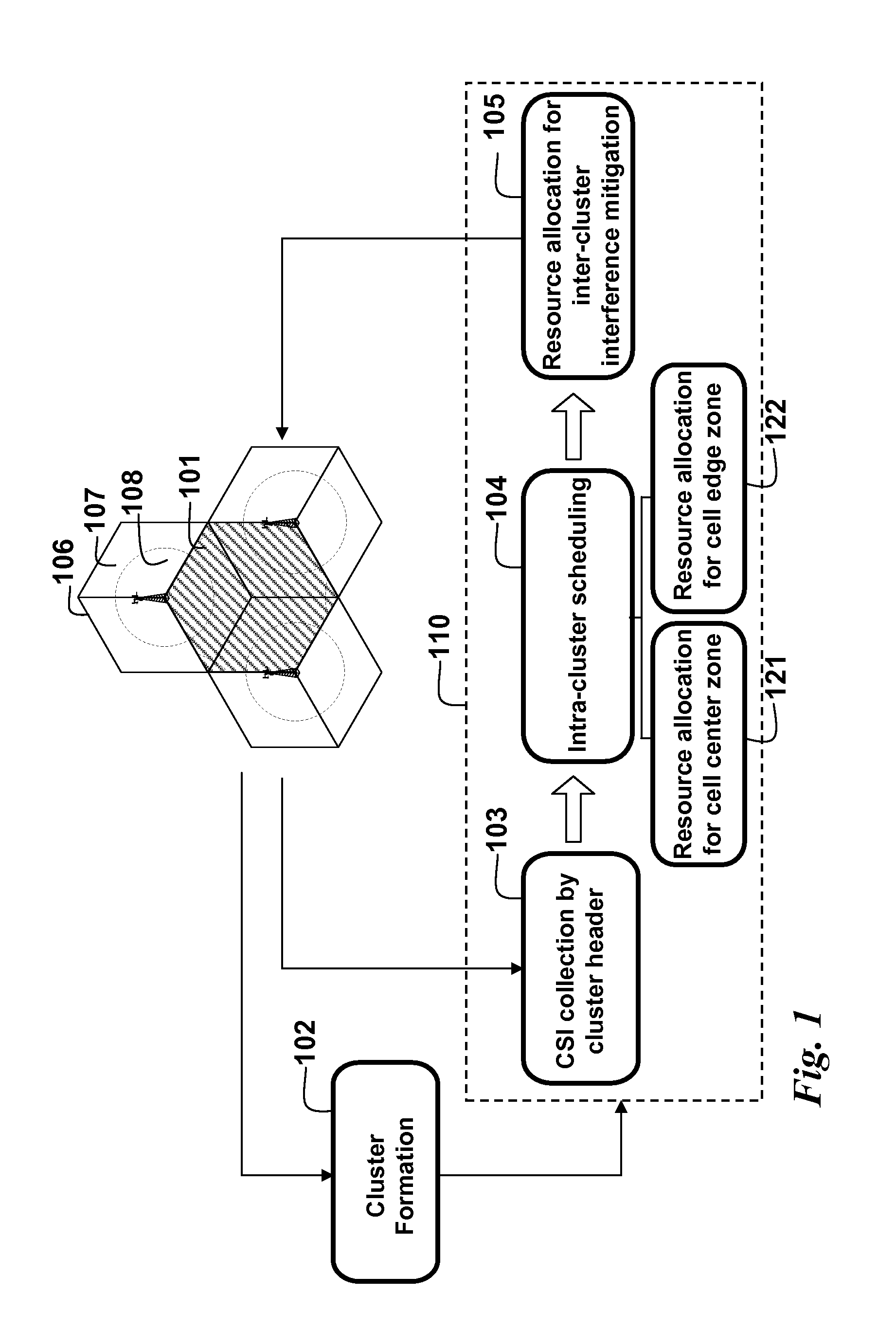
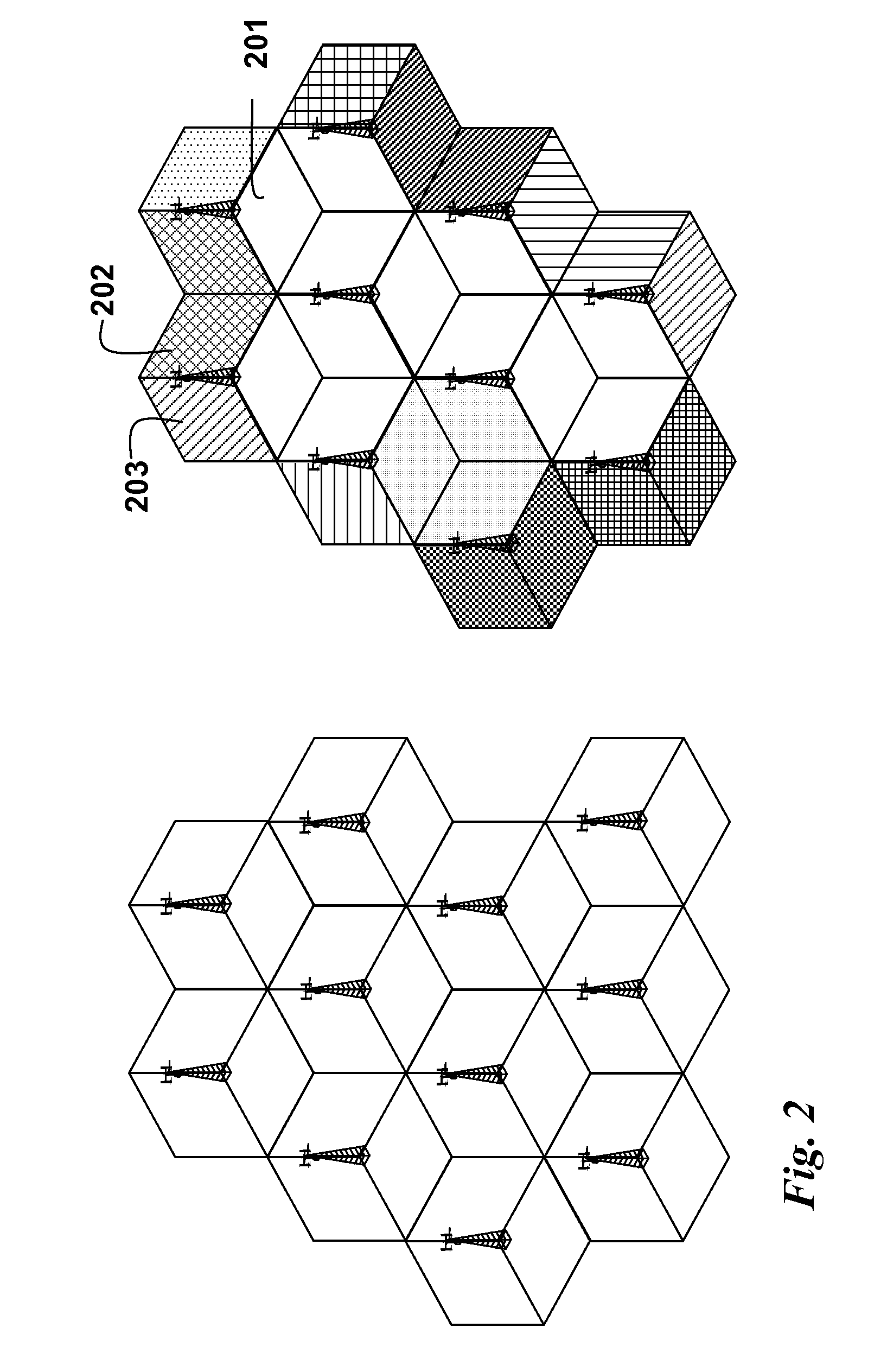
Clustering Based Resource Allocation in Multi-Cell OFDMA Networks
InactiveUS20100214997A1Interference can be avoided and reducedImprove performanceWireless commuication servicesNetwork planningOverlap zoneResource block
A method allocates resource in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) network, including a set of Base Stations (BSs) and a set of Mobile Stations (MSs) for each BS. OFDMA frame are constructed as multiple resource blocks, and each resource block contains symbols transmitted on different subcarriers. A cluster is formed from adjacent sectors of different neighboring cells to jointly optimize the resource allocation in multiple frames, and three non-overlap zones are sequentially identified in cluster: cell center zone, cell edge zone, and cluster corner zone. Resource allocation includes intra-cluster proportional fair scheduling and inter-cluster interference mitigation. Intra-cluster scheduling further includes resource allocation for cell center zone and resource allocation for cell edge zone.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Apparatus and methods for dynamic spectrum allocation in satellite communications
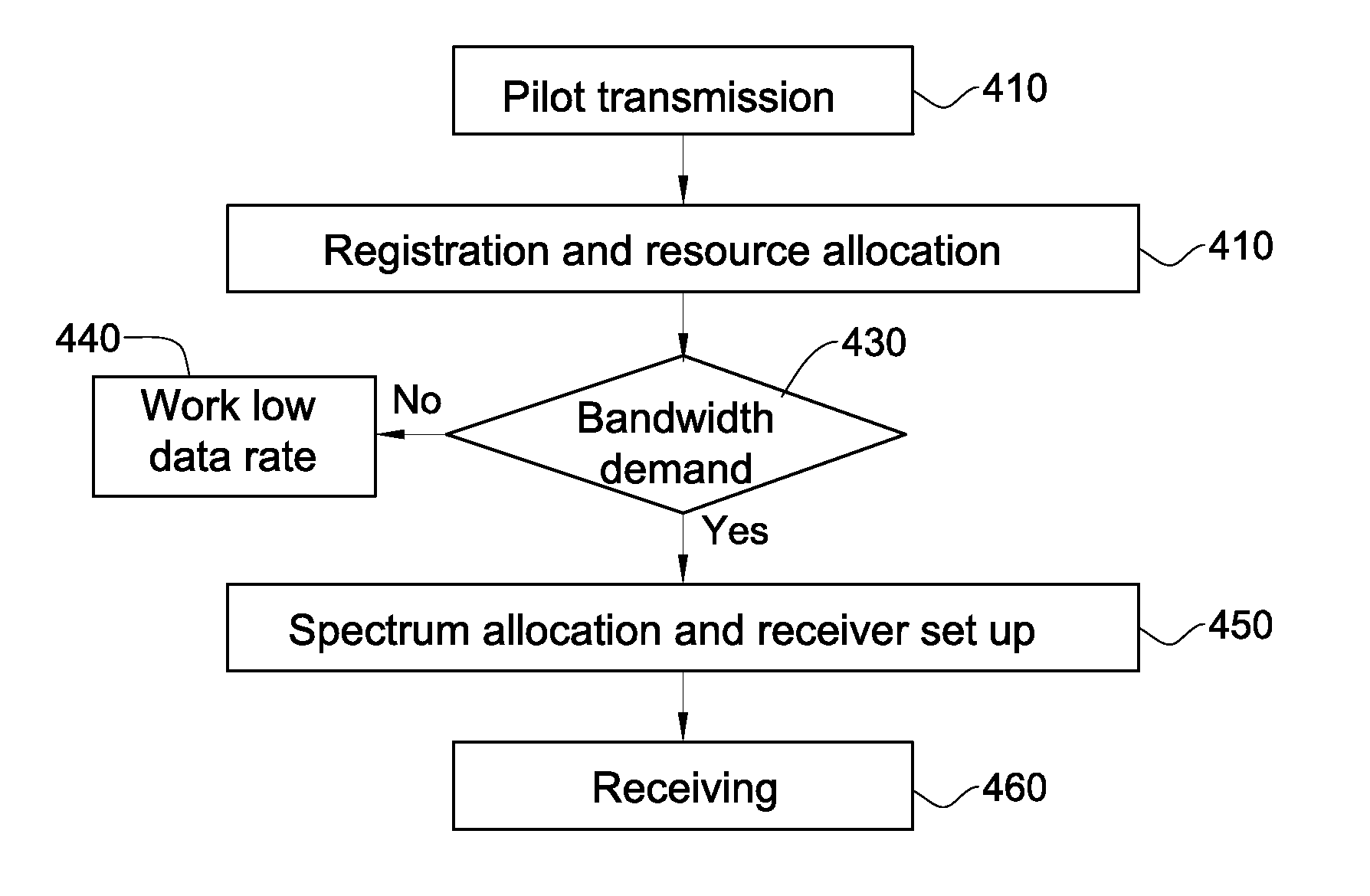
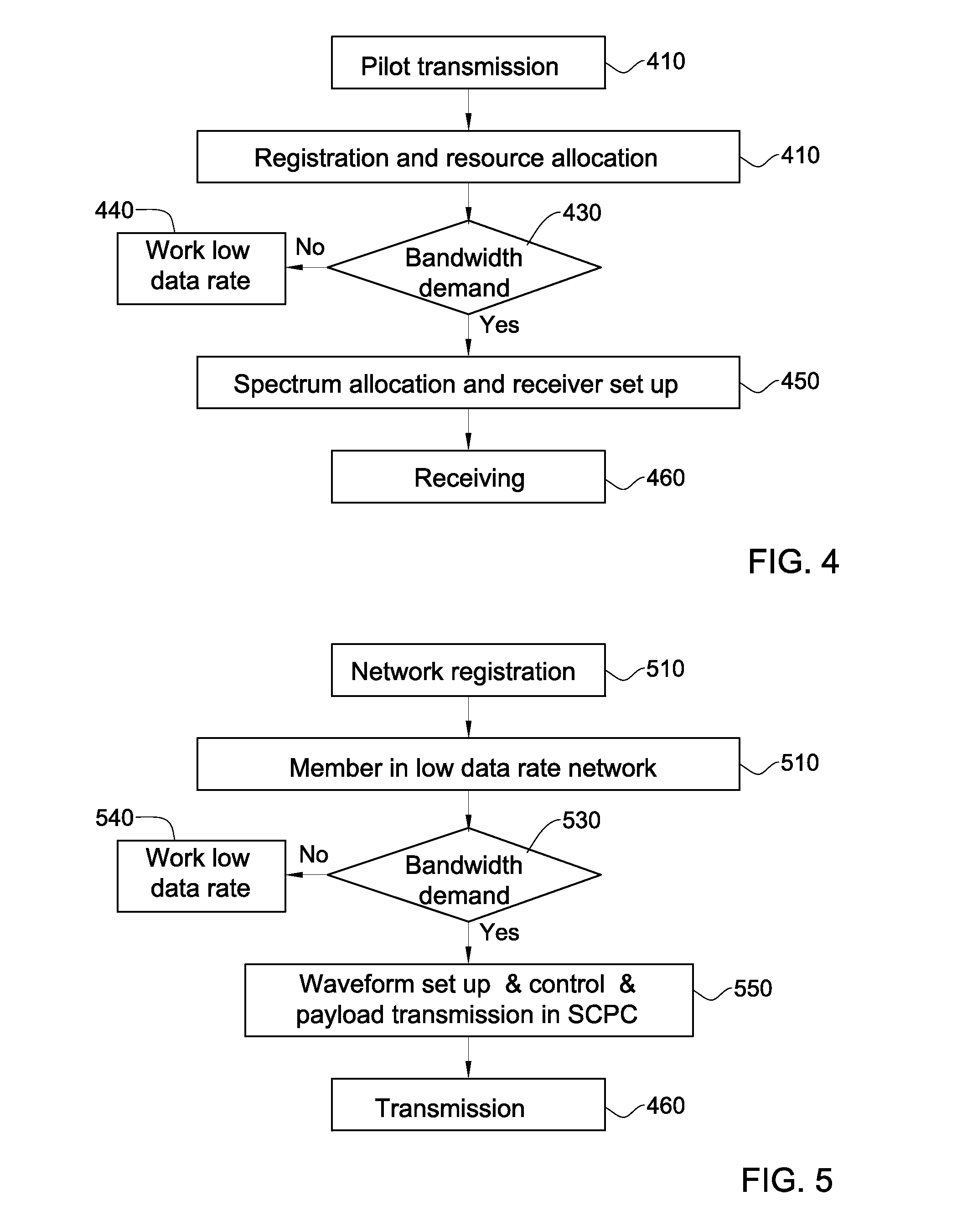
ActiveUS9246576B2Improve throughputReduce data rateNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A communication system including Satellite Communication apparatus providing communication services to at least a first set of communicants, the first set of communicants including a first plurality of communicants, wherein the communication services are provided to each of the communicants in accordance with a spectrum allocation corresponding thereto, thereby to define a first plurality of spectrum allocations apportioning a first predefined spectrum portion among the first set of communicants; and Dynamic Spectrum Allocations apparatus operative to dynamically modify at least one spectrum allocation corresponding to at least one of the first plurality of communicants without exceeding the spectrum portion.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
Dynamic Configuration of a Flexible Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing PHY Transport Data Frame
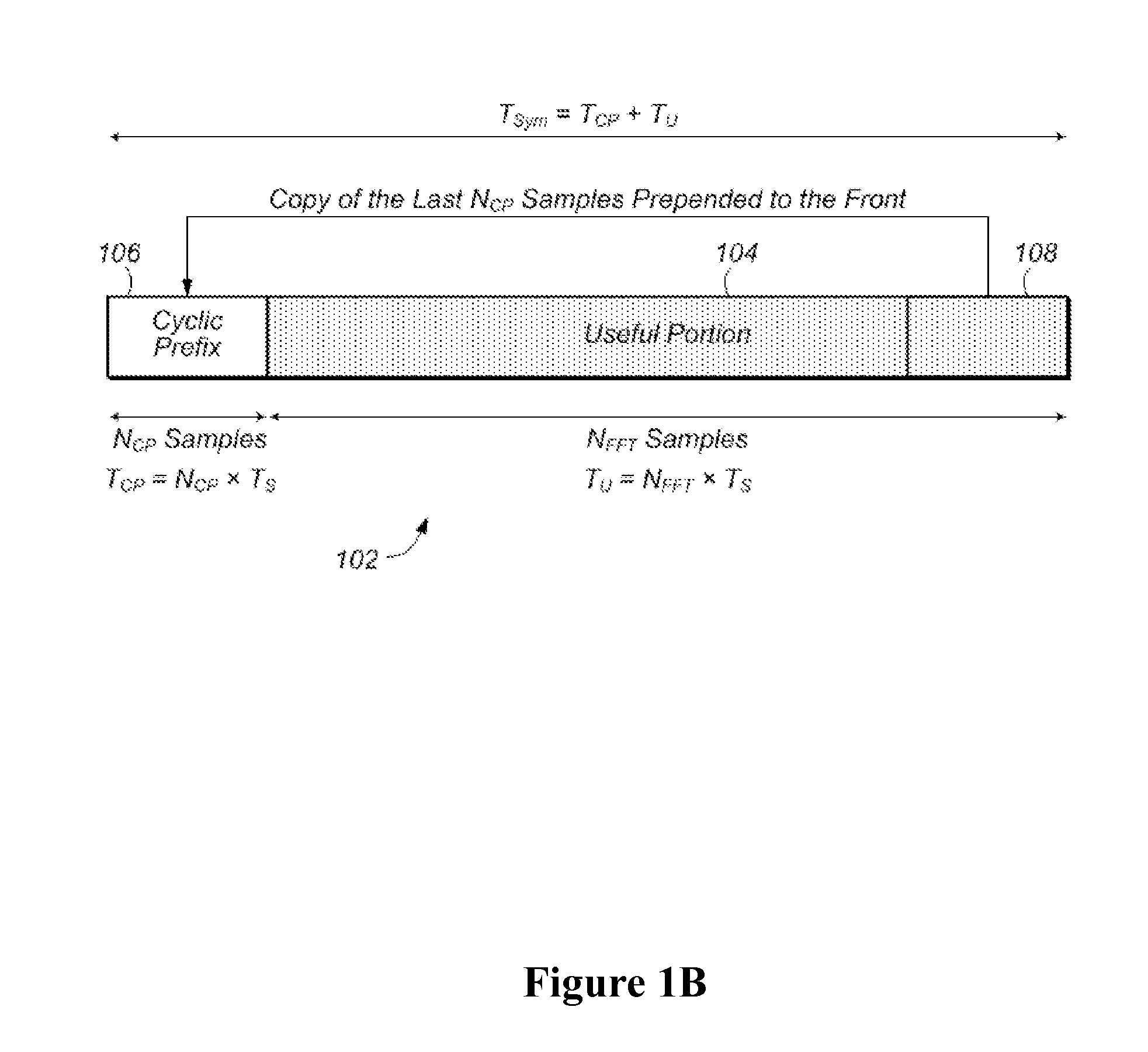
ActiveUS20160043830A1Increase flexibilityIncrease data rateError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDelay spreadUser device
A base station may generate and transmit a transport stream including a sequence of frames. A frame may include a plurality of partitions, where each partition includes a corresponding set of OFDM symbols. For each partition, the OFDM symbols in that partition may have a corresponding cyclic prefix size and a corresponding FFT size, allowing different partitions to be targeted for different collections of user devices, e.g., user devices having different expected values of maximum delay spread and / or different ranges of mobility. The base station may also dynamically re-configure the sample rate of each frame, allowing further resolution in control of subcarrier spacing. By allowing the cyclic prefixes of different OFDM symbols to have different lengths, it is feasible to construct a frame that conforms to a set payload duration and has arbitrary values of cyclic prefix size per partition and FFT size per partition. The partitions may be multiplexed in time and / or frequency.
Owner:ONE MEDIA LLC
Systems and Methods For Scalably Encoding and Decoding Data
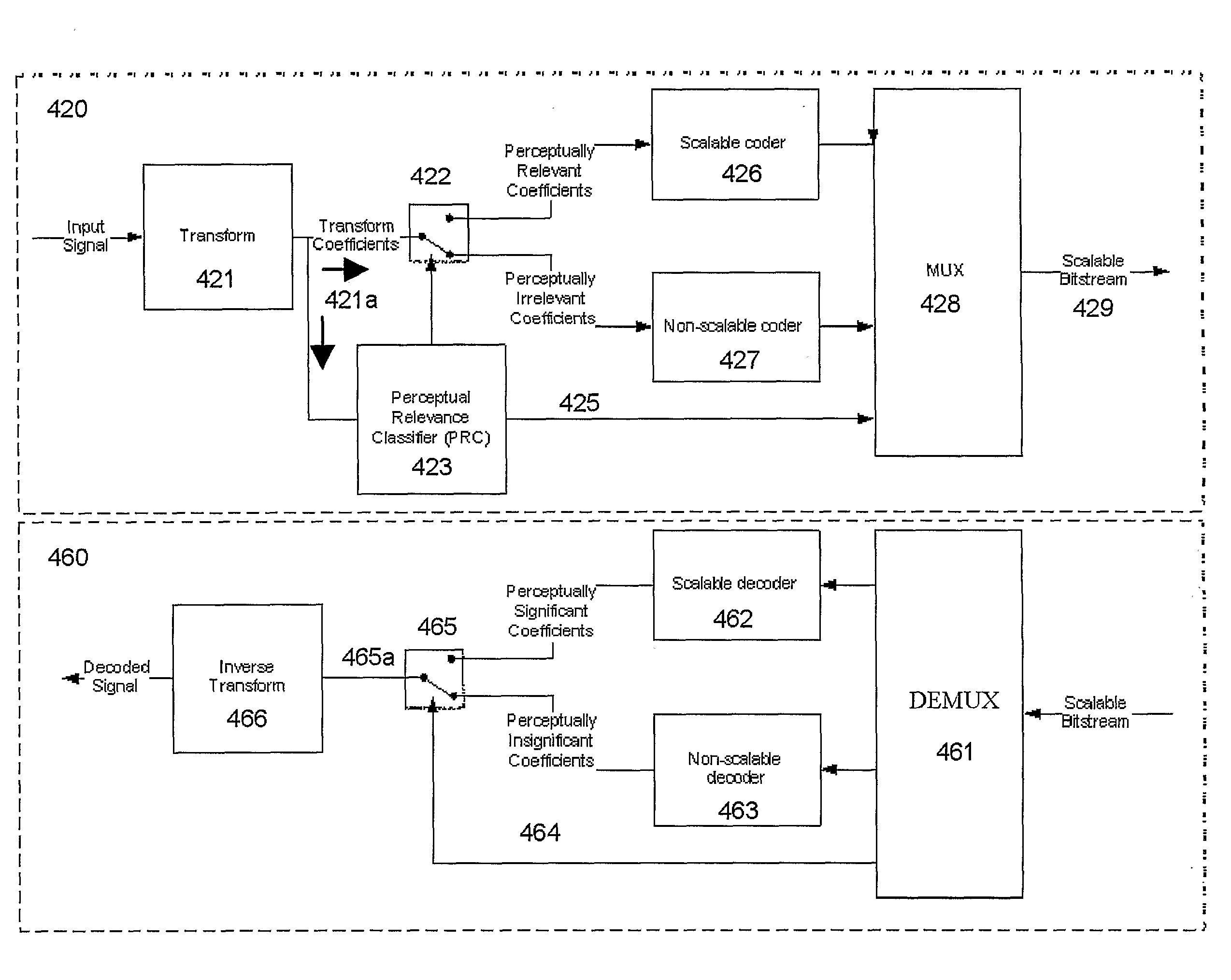
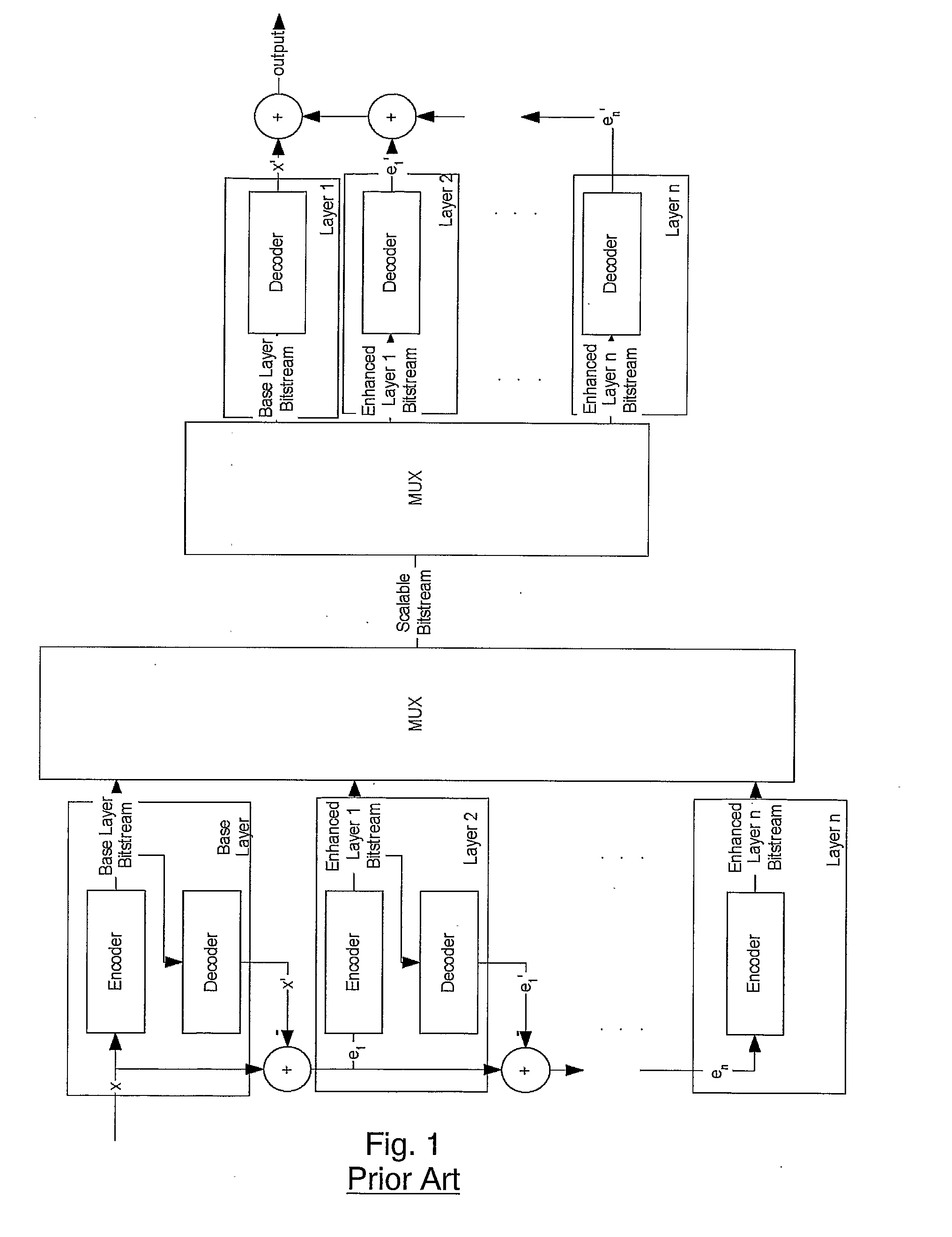
ActiveUS20110001642A1Optimize data processingEasily truncatedAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsData streamData system
Systems and methods for scalably encoding and decoding coded data are presented. One exemplary method for scalably coding data includes classifying, based upon at least one predetermined criteria, each of the plurality of data received as either (i) perceptually relevant data or (ii) perceptually irrelevant data. The perceptually relevant data is scalably coded, and the perceptually irrelevant data is non-scalably coded. Subsequently, the scalably coded perceptually relevant data and the non-scalably coded perceptually irrelevant are combined into a coded data stream for transmission.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
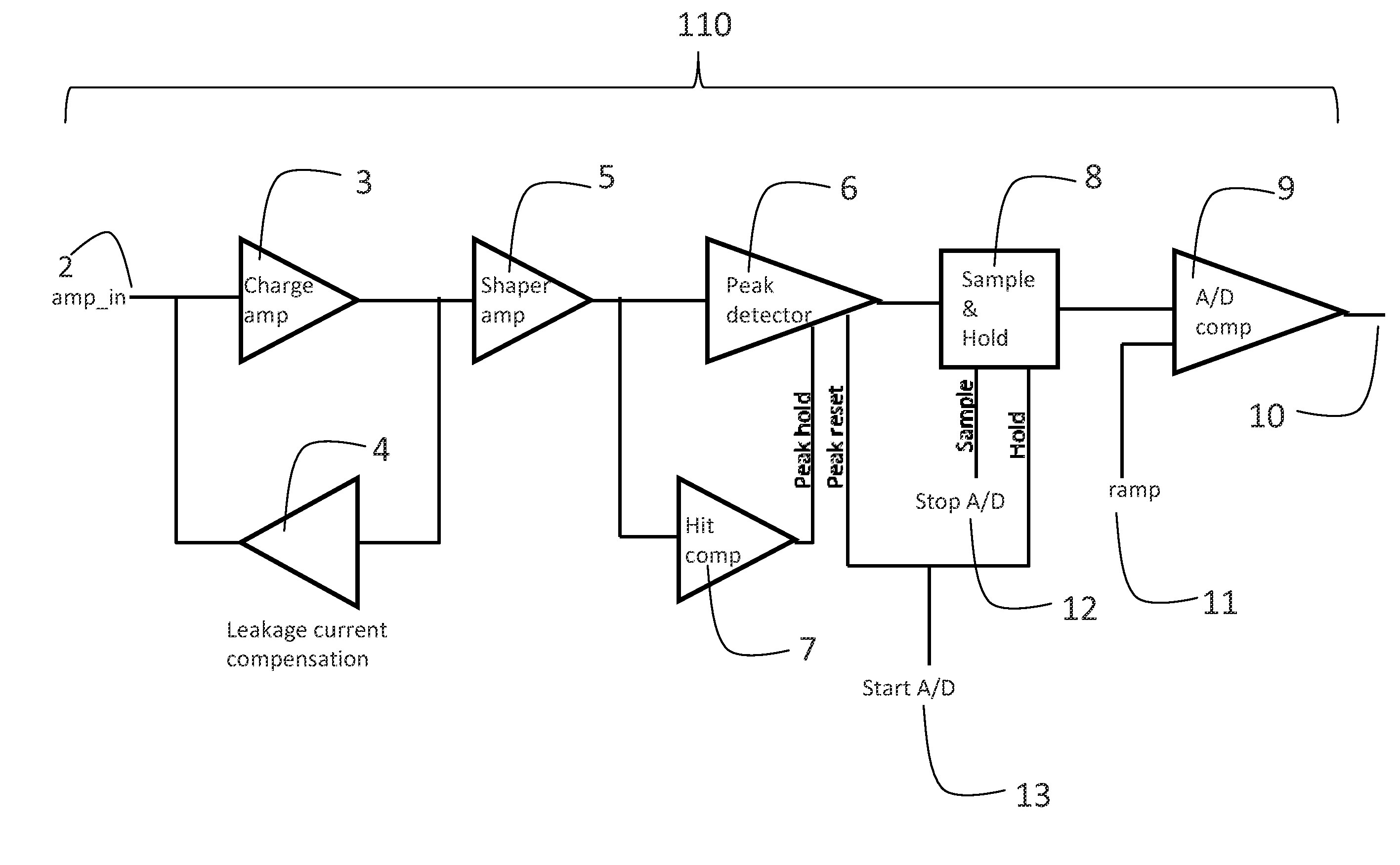
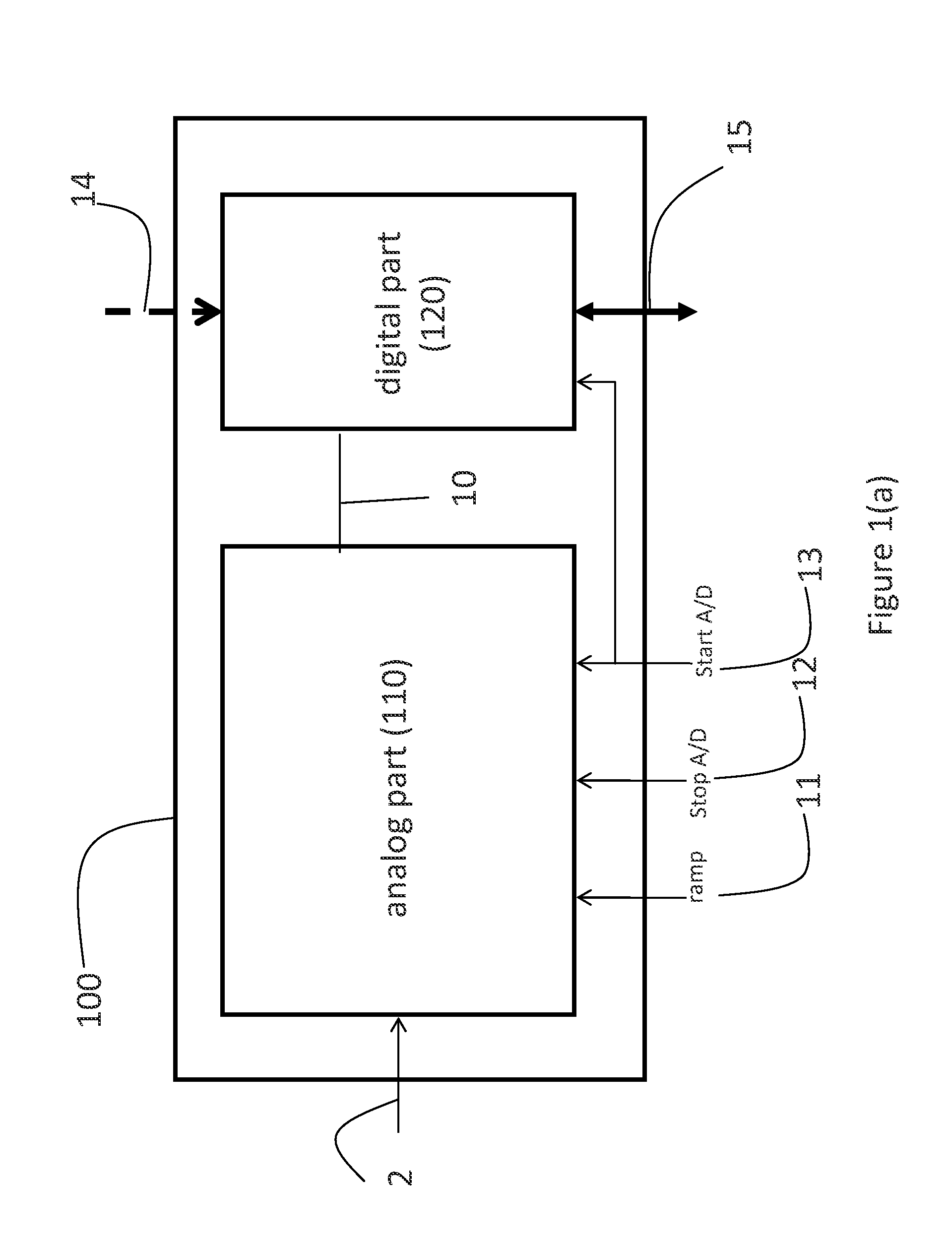
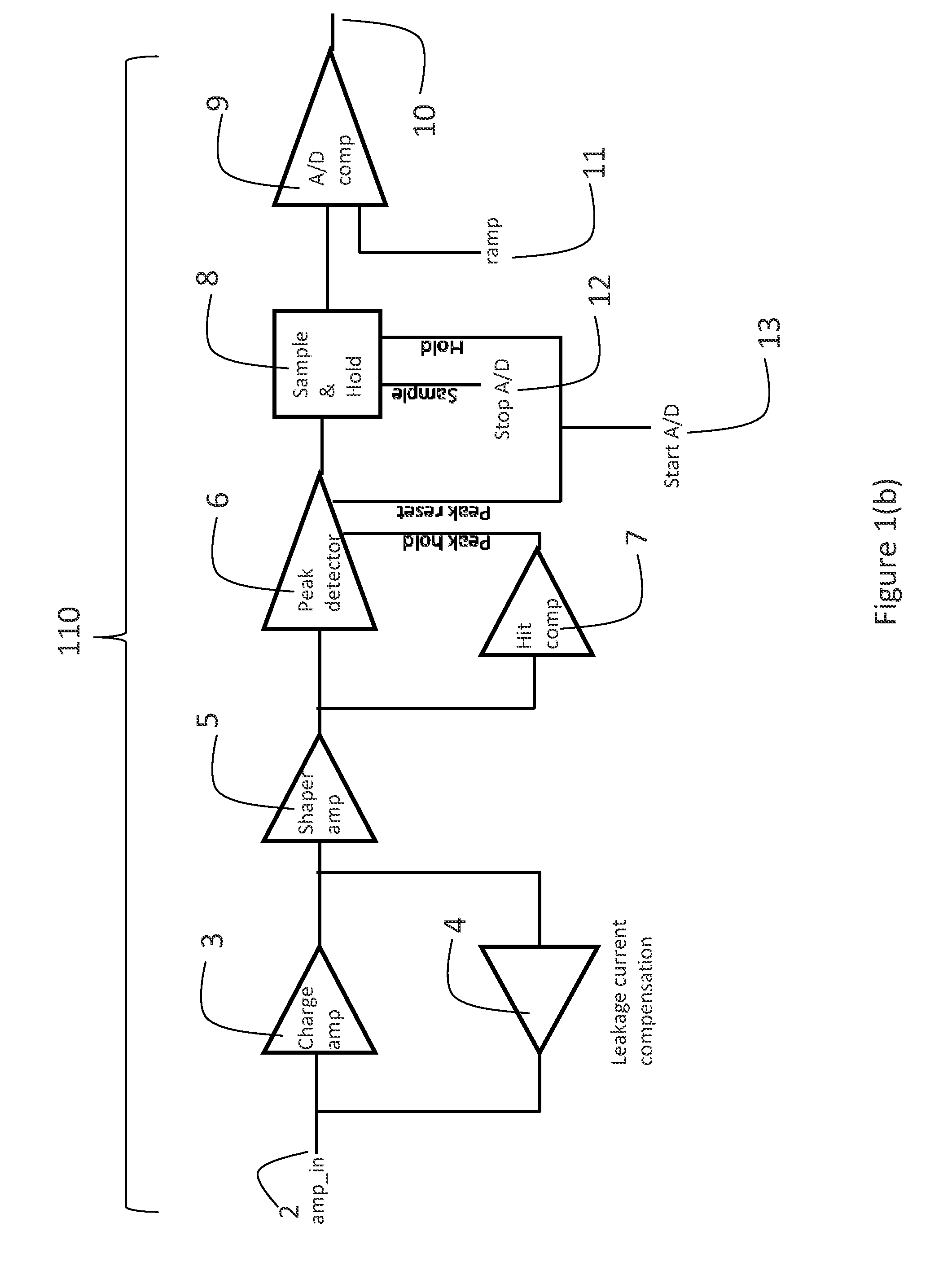
Photon/energy identifying x-ray and gamma ray imaging device ("pid") with a two dimensional array of pixels and system therefrom
ActiveUS20120280131A1Reduce the amount of dataReduce data rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSoft x rayDigital signal processing
An photon (energy) identifying radiation imaging device, for imaging x-ray, gamma ray and charged radiation in medical, dental and industrial applications. The imaging device includes a detector substrate and a readout substrate. The detector substrate has a plurality of detector pixels and the readout substrate has a plurality of corresponding pixel readout circuits. Each pixel readout circuit has circuitry for processing an input analog signal and also has one or more buffers for temporarily storing values corresponding to the signal of at least two individual incoming radiation events. The readout substrate includes a digital controller having digital processing units for carrying out off-pixel digital signal processing and data / rate reduction prior to readout.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com