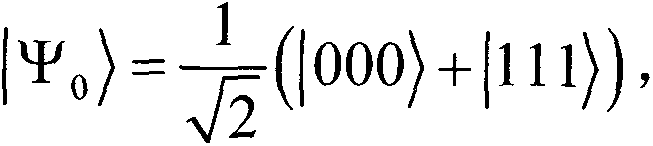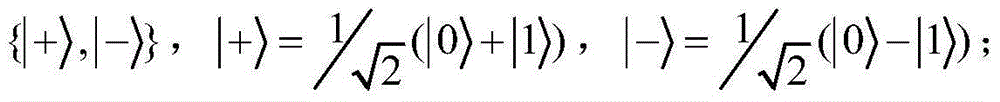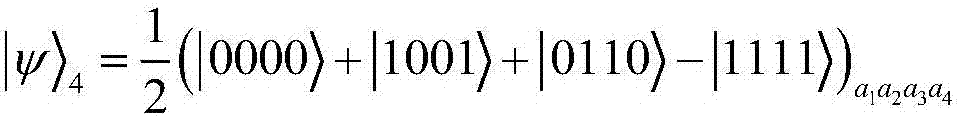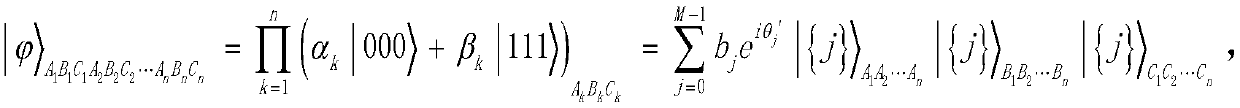Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Alice and Bob" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alice and Bob are fictional characters commonly used as placeholder names in cryptology, as well as science and engineering literature. The Alice and Bob characters were invented by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in their 1978 paper "A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems." Subsequently, they have become common archetypes in many scientific and engineering fields, such as quantum cryptography, game theory and physics. As the use of Alice and Bob became more widespread, additional characters were added, each with a particular meaning. These characters do not have to refer to humans; they refer to generic agents which might be different computers or even different programs running on a single computer.
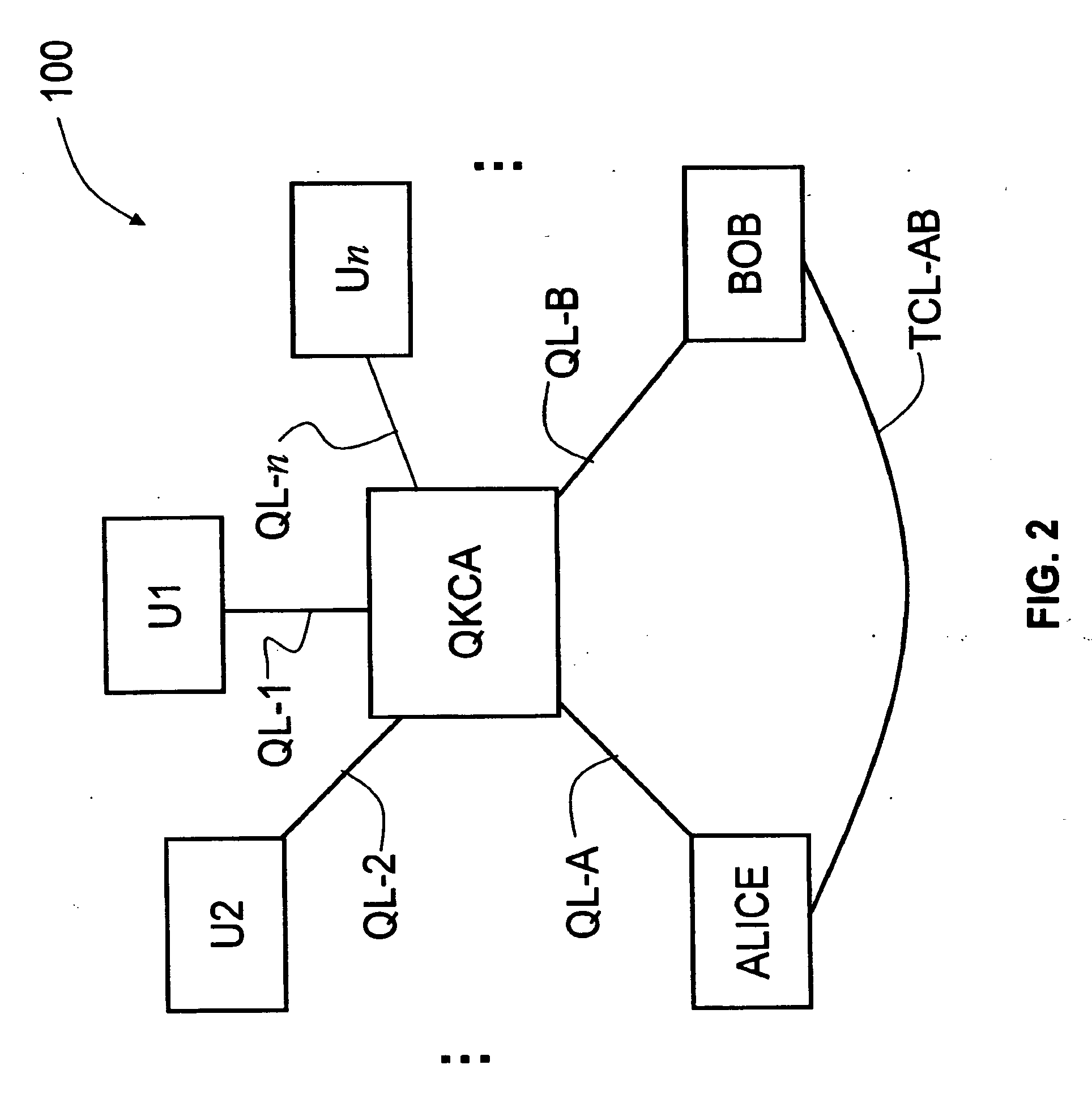
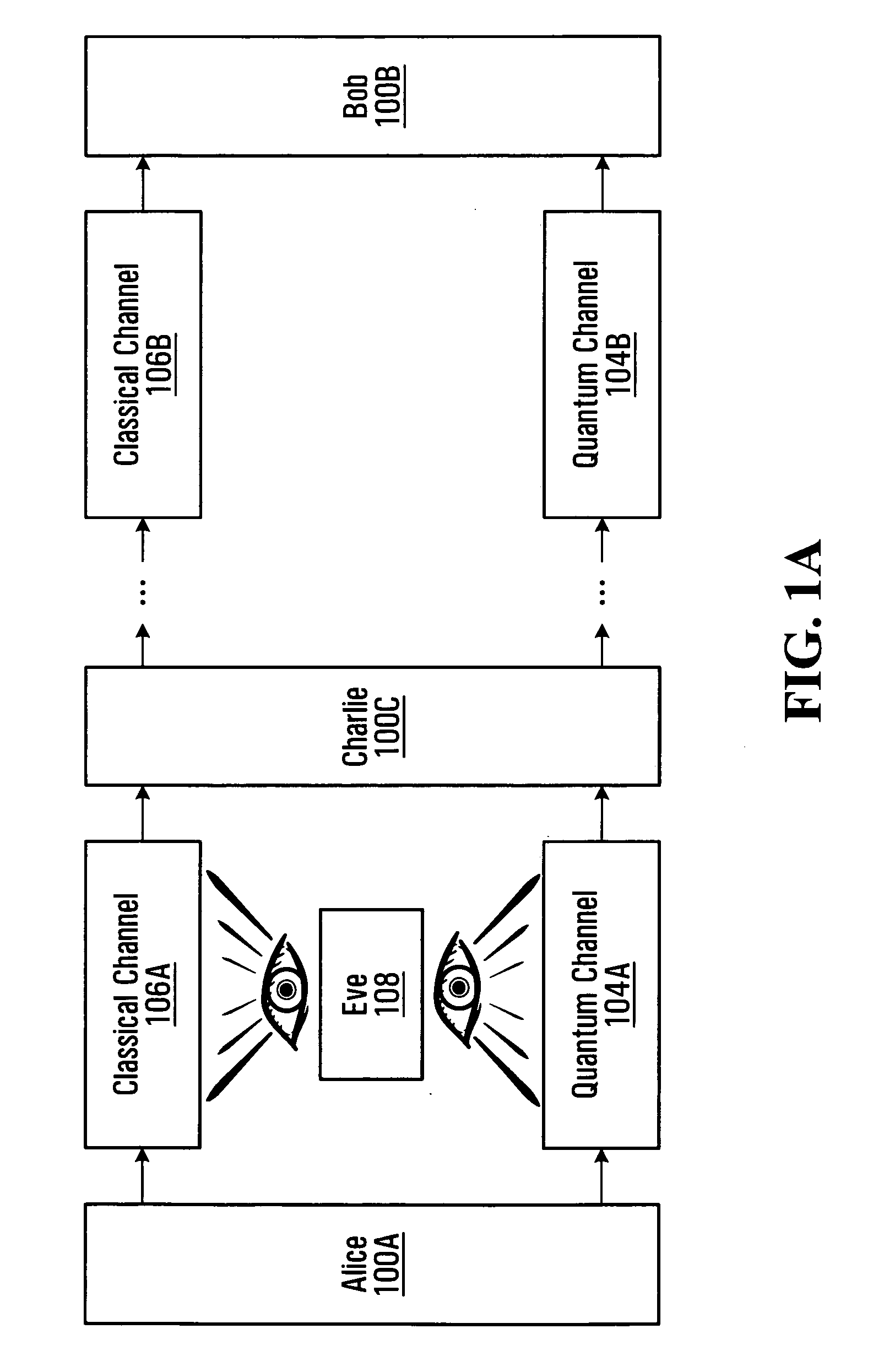
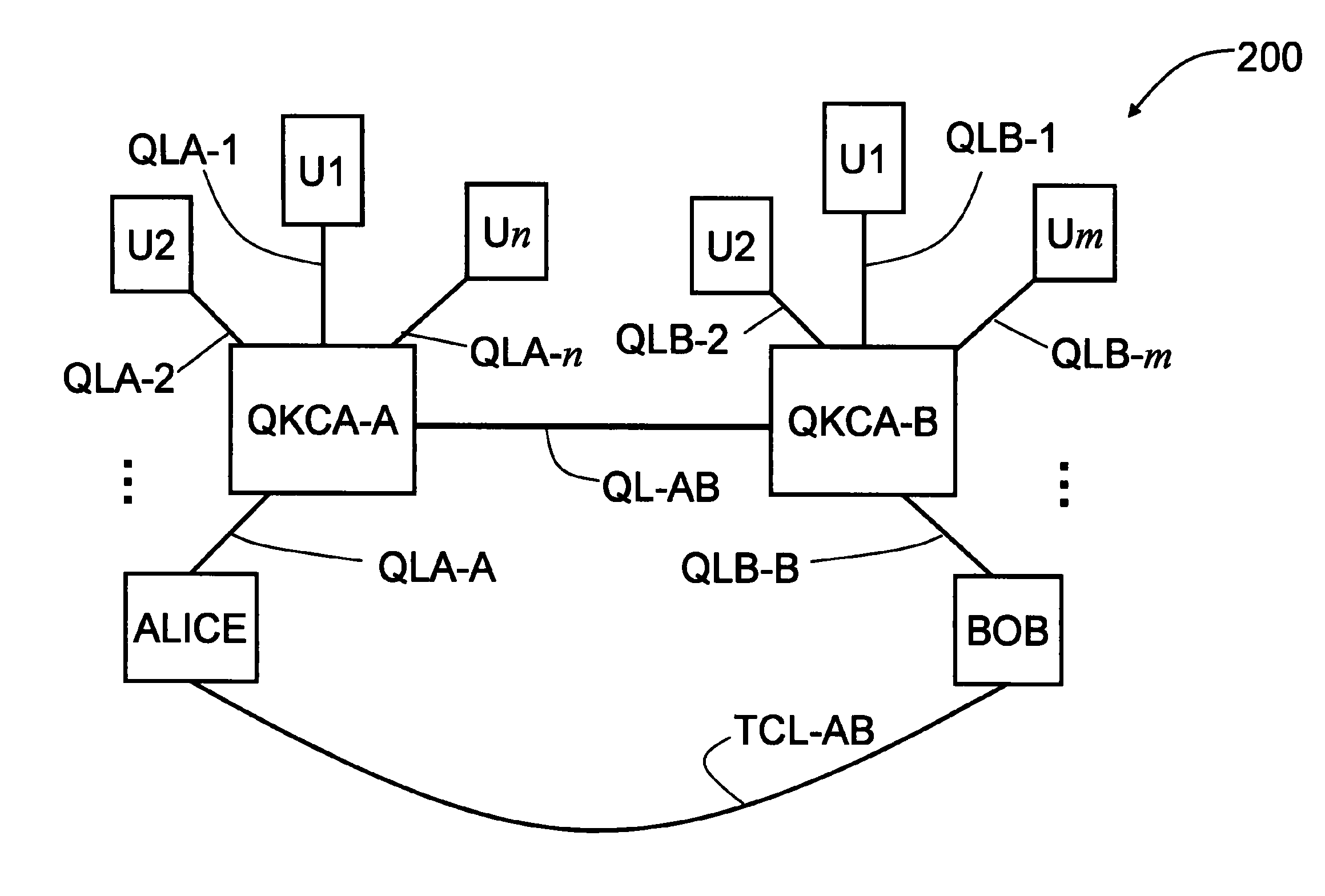
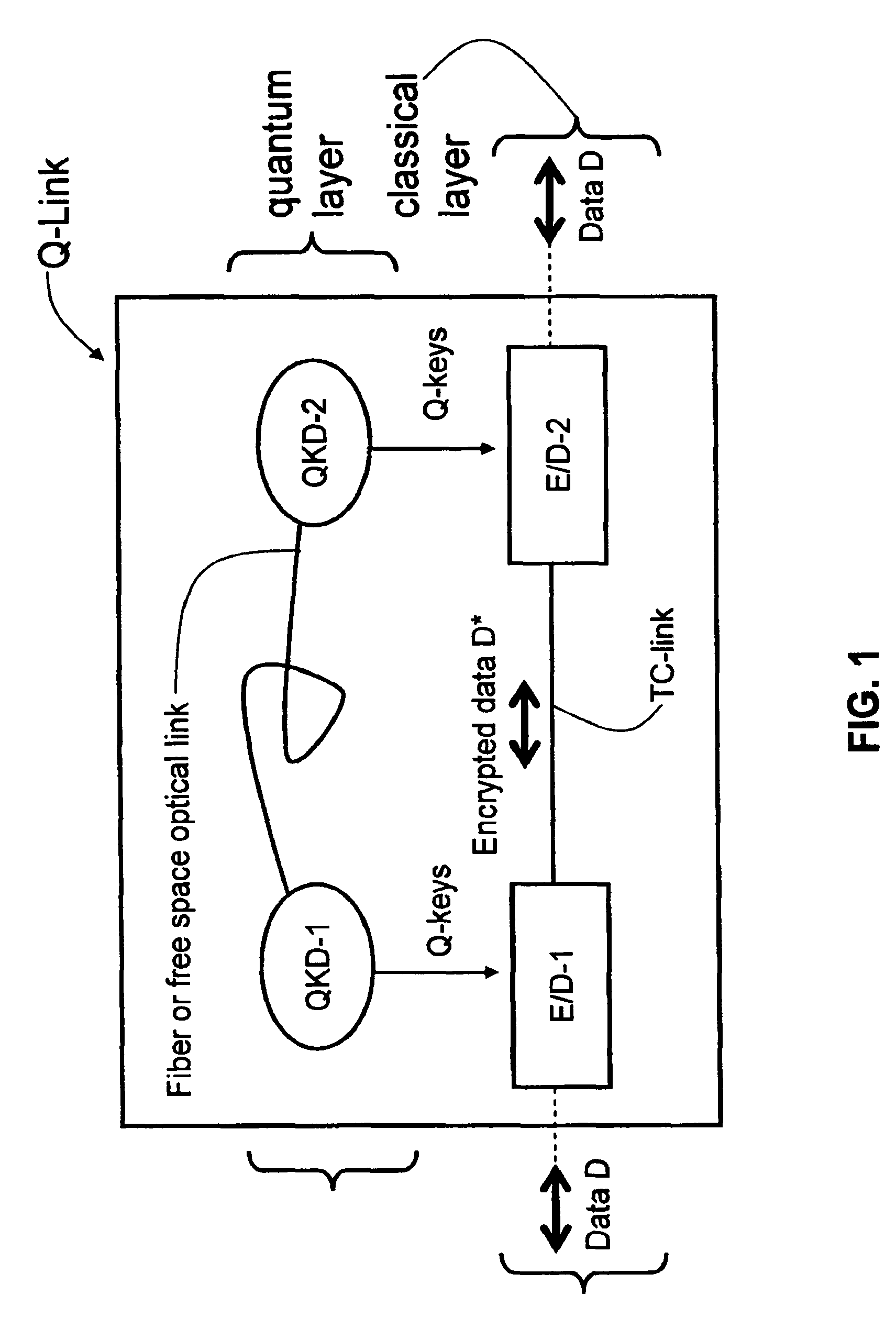
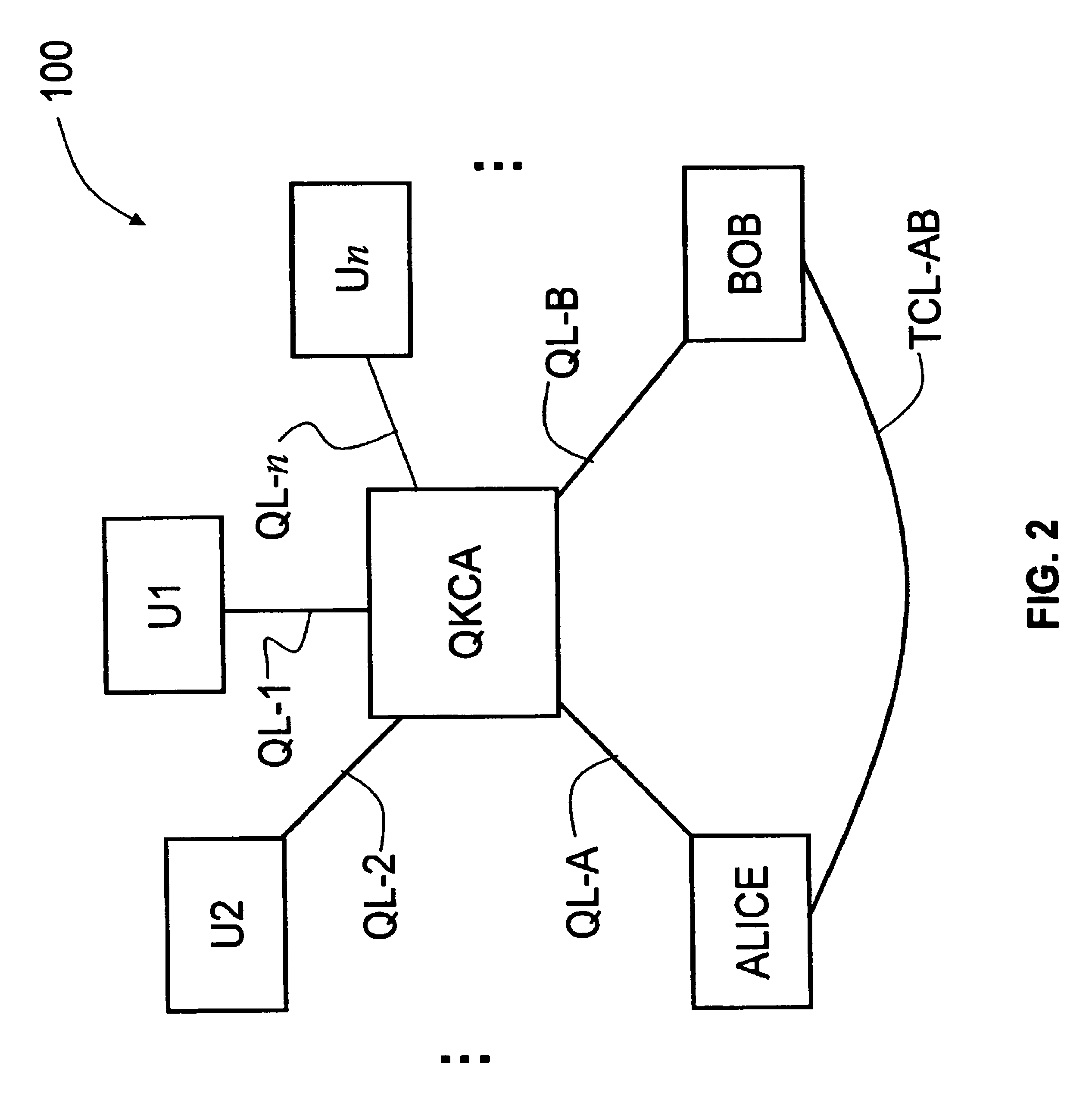
Key Management and User Authentication for Quantum Cryptography Networks
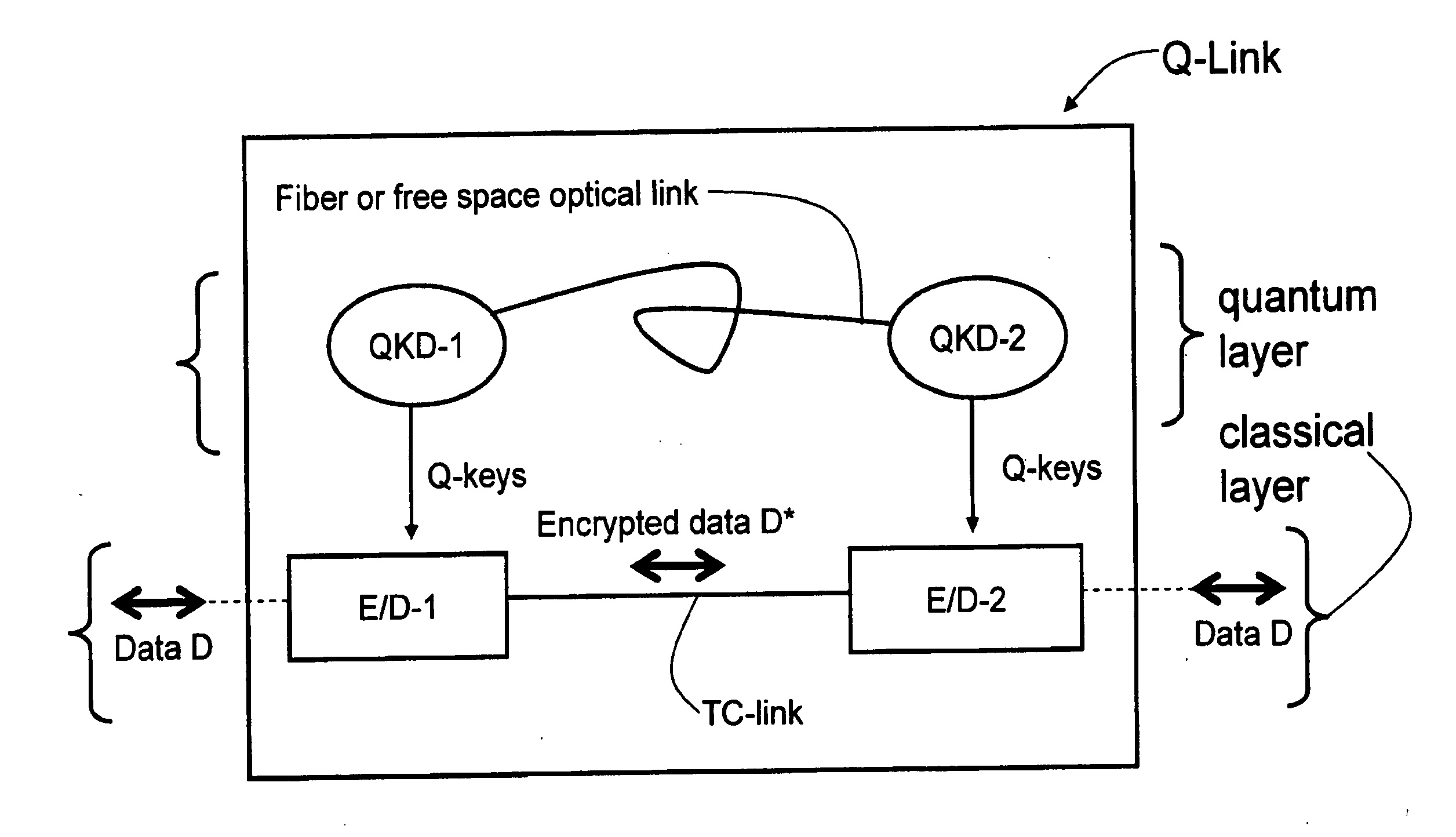
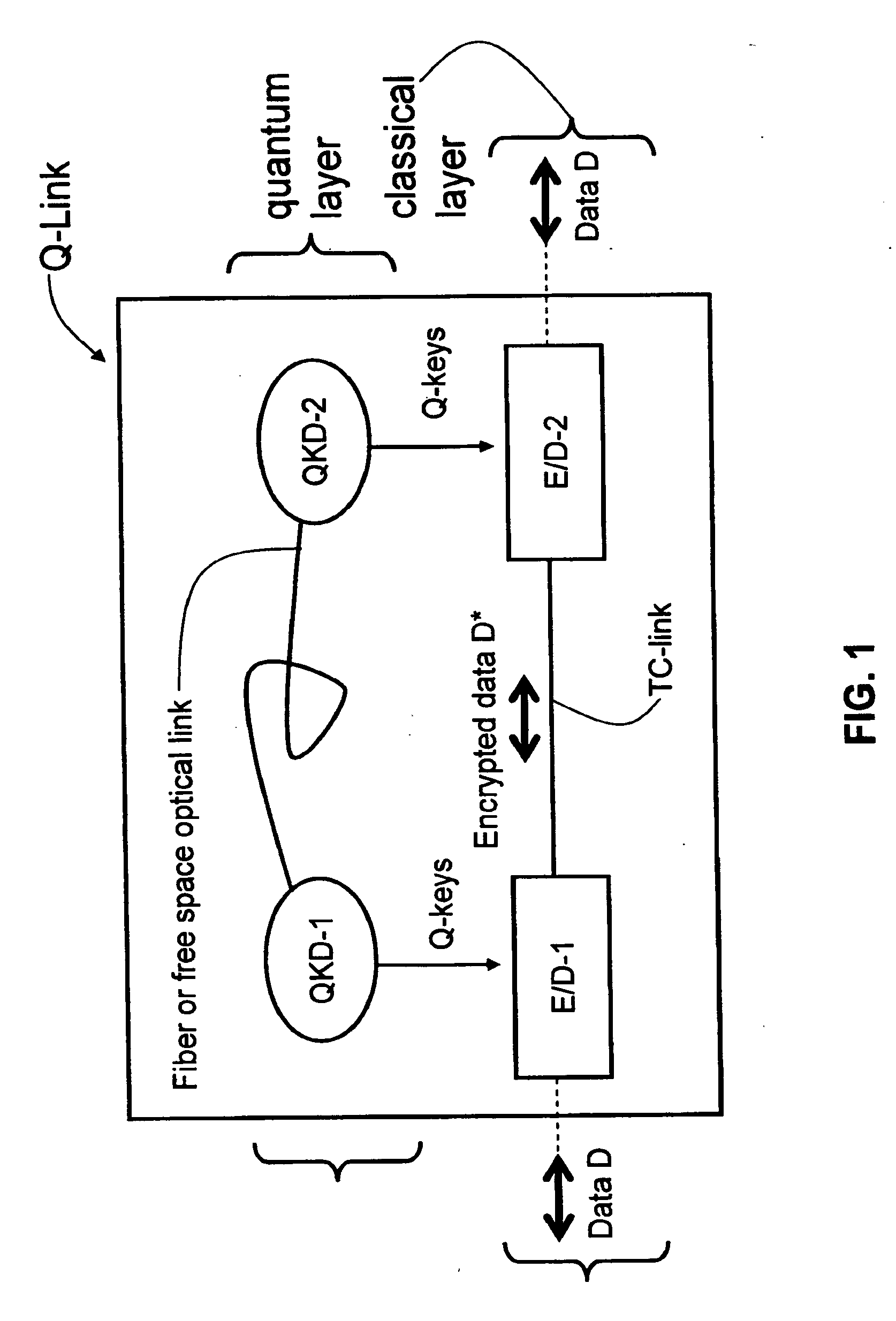
ActiveUS20090175452A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesAlice and BobTelecommunications link
Key management and user authentication systems and methods for quantum cryptography networks that allow for users securely communicate over a traditional communication link (TC-link). The method includes securely linking a centralized quantum key certificate authority (QKCA) to each network user via respective secure quantum links or “Q-links” that encrypt and decrypt data based on quantum keys (“Q-keys”). When two users (Alice and Bob) wish to communicate, the QKCA sends a set of true random bits (R) to each user over the respective Q-links. They then use R as a key to encode and decode data they send to each other over the TC-link.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
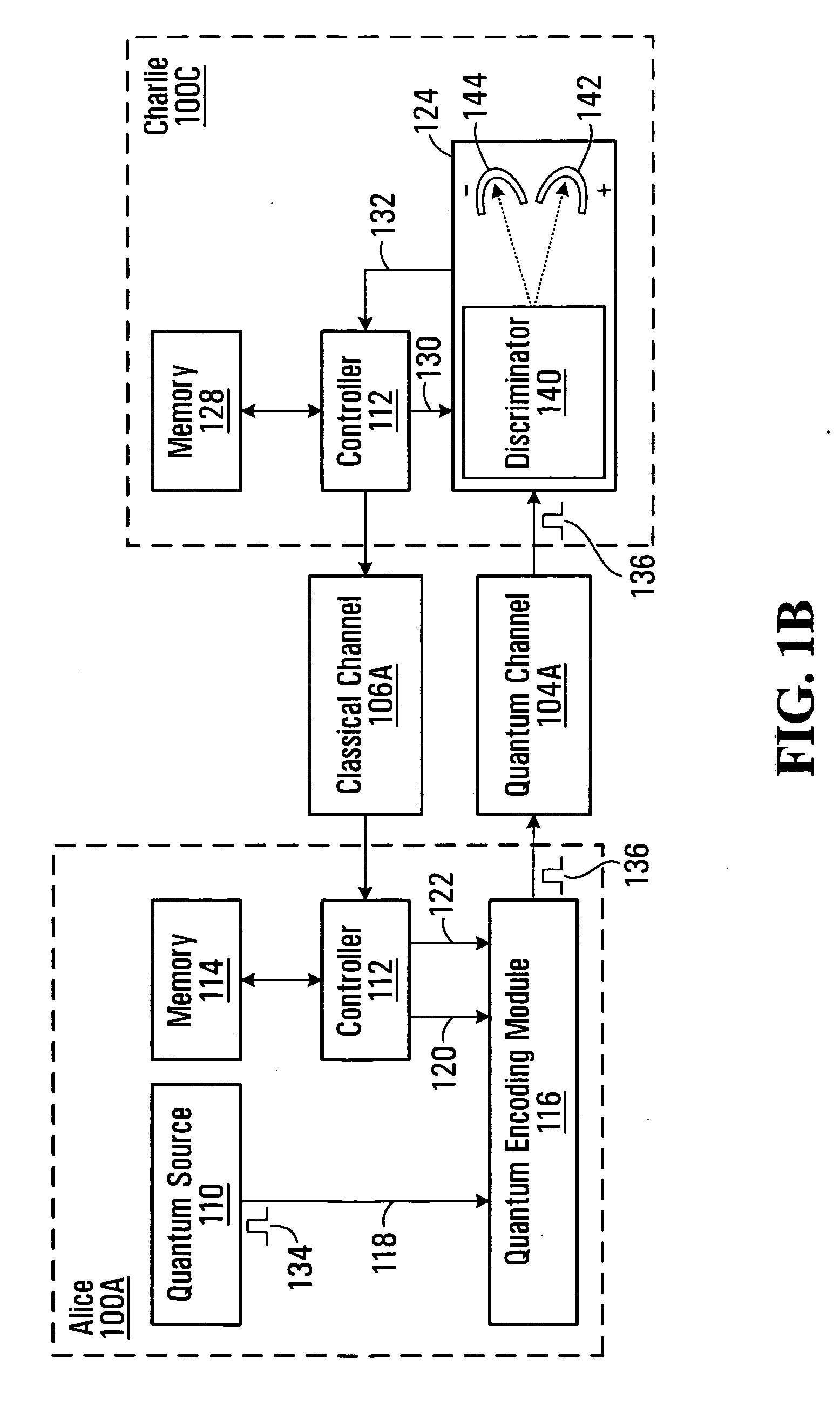
Methods and systems for communicating over a quantum channel
Alice generates a sequence of key bits forming an initial cryptographic key. Alice then uses the sequence of key bits and a sequence of cipher bits to control respective control parameters of a quantum encoding process applied to a sequence of quantum pulses, where the sequence of cipher bits used is known to Bob. Alice then releases the encoded pulses towards Bob over a quantum channel. Bob uses the previously agreed-upon sequence of cipher bits to control a control parameter, such as the quantum basis, of a quantum detection process applied to the pulses received from Alice, thus producing a detection outcome for each received pulse. Bob then derives a final cryptographic key from the detection outcomes. Because the cipher bits used to select the quantum bases used by both Alice and Bob are known by both parties, the method allows the final cryptographic key to be distributed with full basis alignment compared to 50% for BB84, thus allowing efficient quantum key distribution over multiple hops.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
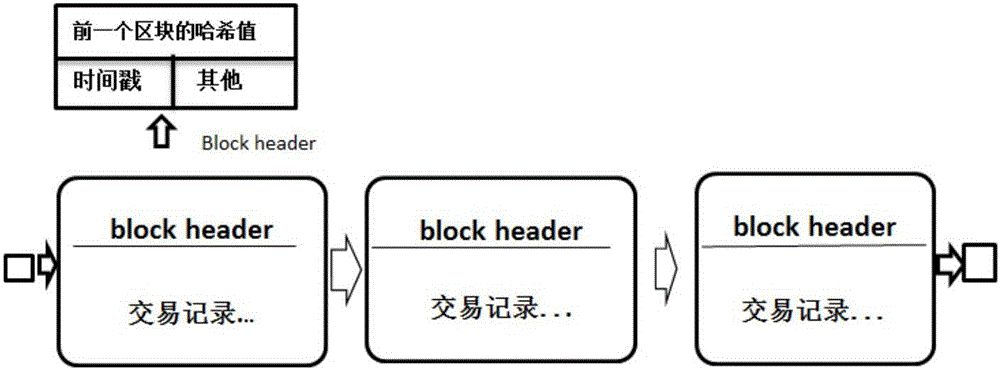
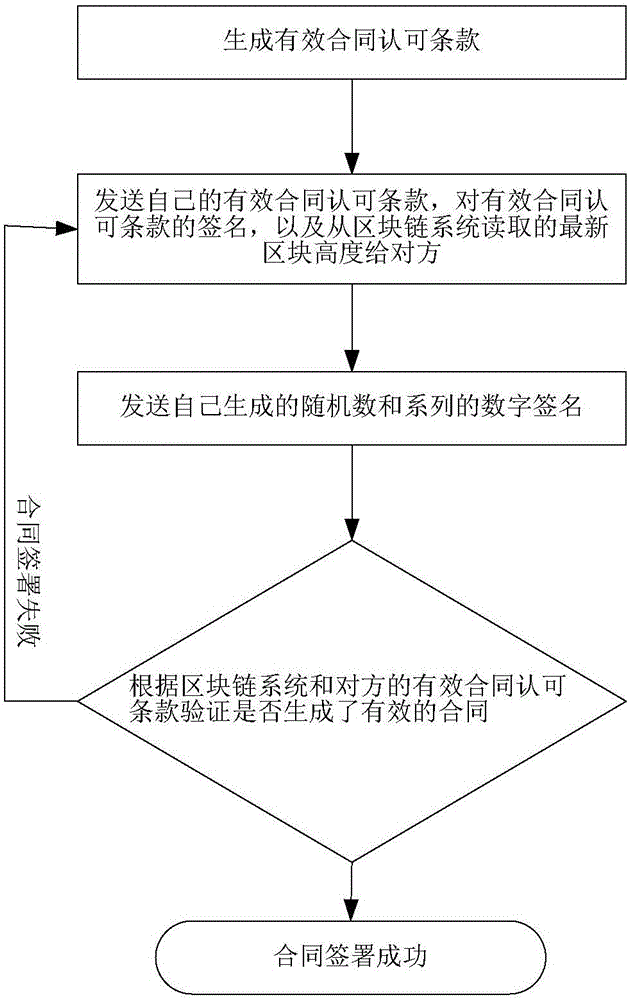
Fair contract signing method based on block chain
InactiveCN106504008AEasy to deployCustomer relationshipUser identity/authority verificationAlice and BobThird party
The invention relates to a fair contract signing method based on a block chain. The fair contract signing method based on a block chain relates to two user entities Alice and Bob, and a block chain system. The fair contract signing method based on a block chain includes the steps: 1) Alice and Bob respectively generate the respective valid contract admitted clauses PAA and PAB; 2) Alice and Bob exchange the respective valid contract admitted clauses PAA and PAB, the respective signature for the valid contract admitted clauses, and the respective block height BHA and BHB read from the block chain system; and 3) Alice and Bob exchange the respective generated randomized number and digital signature, and verifies whether a valid contract is generated according to the block chain system and the valid contract admitted clauses of the opposite party, and if not valid, the steps from the step 2 need to be executed again, or the steps are completed. As the fair contract signing method based on a block chain does not need a trusted third party and does not need perform any expansion on the block chain system, thus being able to fairly complete contract signing for both parties, and solves the problem that the prior art needs a trusted third party for contract signing or cannot satisfy the fairness requirement or needs modifying the block chain system, in the background technology.
Owner:深圳市数峰科技有限公司
Quantum secret splitting based on non-orthogonal multi-particle states
Systems and methods for quantum secret splitting based on non-orthogonal multi-particle states are disclosed. The method includes preparing at a sender (“Charlie”) two qubits each of which can be in one of two non-orthogonal states and distributing the qubits to respective parties Alice and Bob. The method also includes measuring at Alice the state of the qubit she receives by a projective measurement so that the measurement result is either 0 or 1, and at Bob measuring the state of the qubit he receives such that the measurement result is either 0, 1 or ƒ, wherein ƒ represents a failure by Bob to properly measure the qubit state. The method also includes communicating between Alice, Bob and Charlie the outcome of their respective measurements so as to deduce the state of the qubits sent to Alice and Bob.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Qkd stations with fast optical switches and qkd systems using same
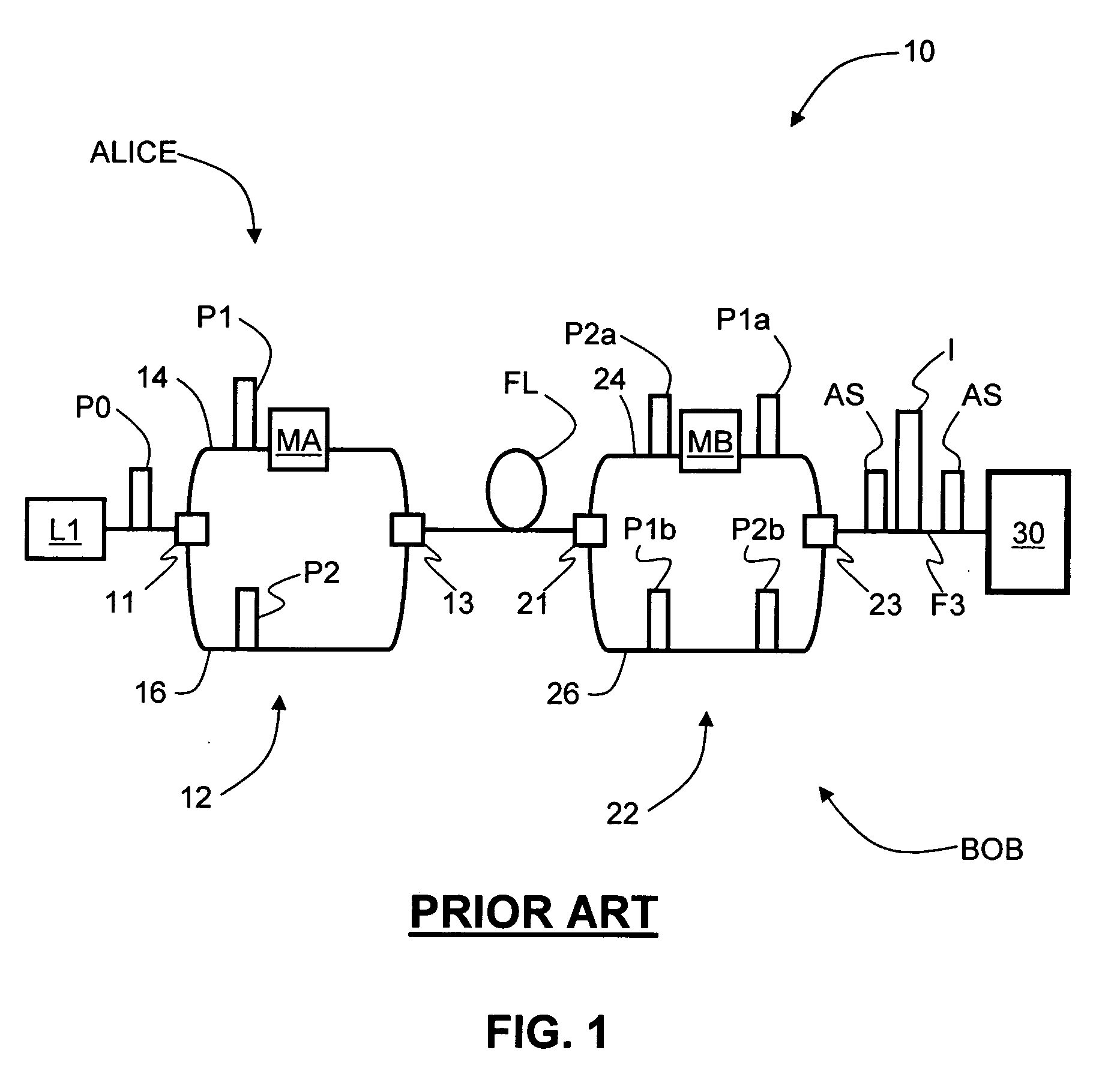
InactiveUS20090180615A1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationAlice and BobFiber
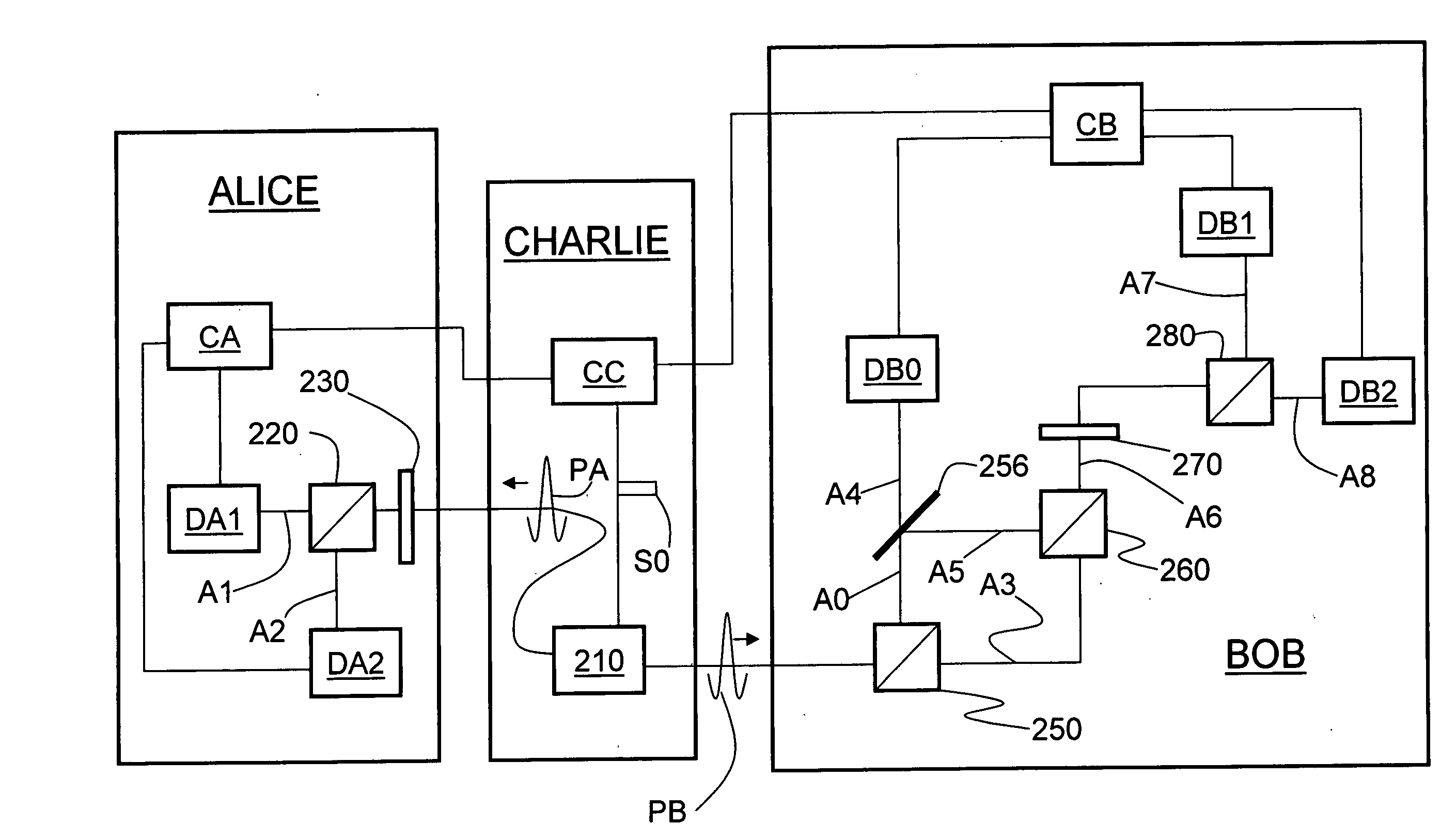
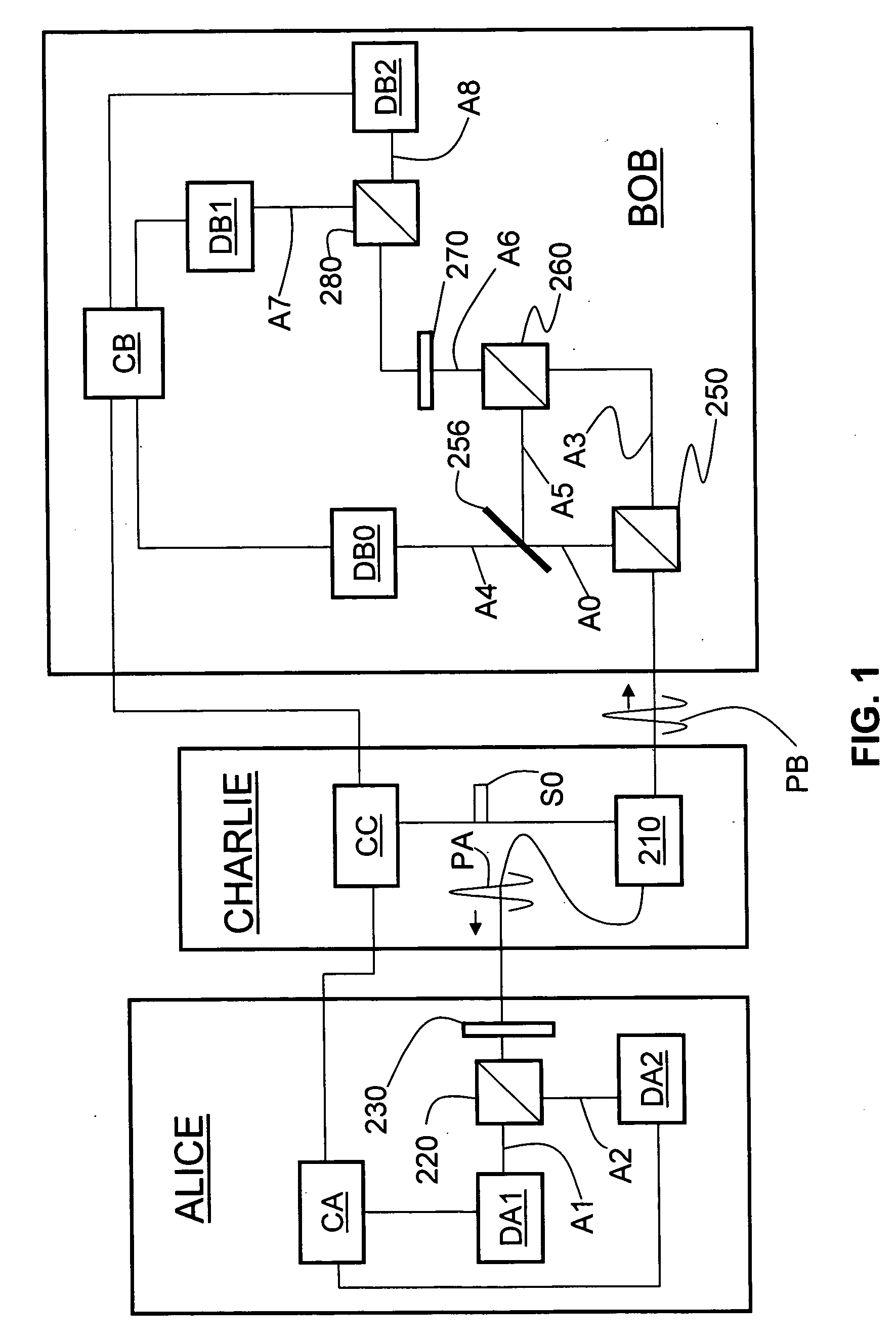
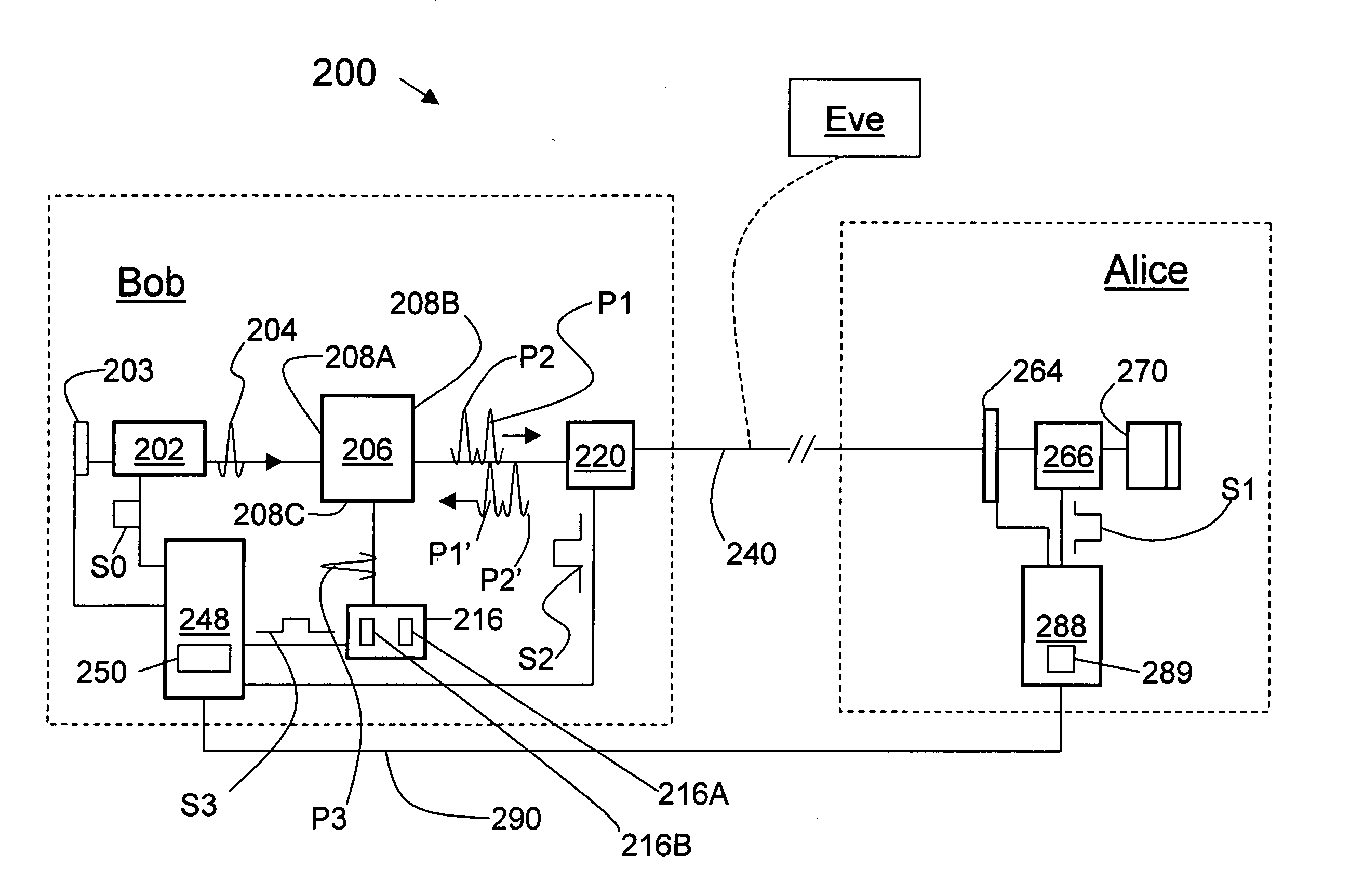
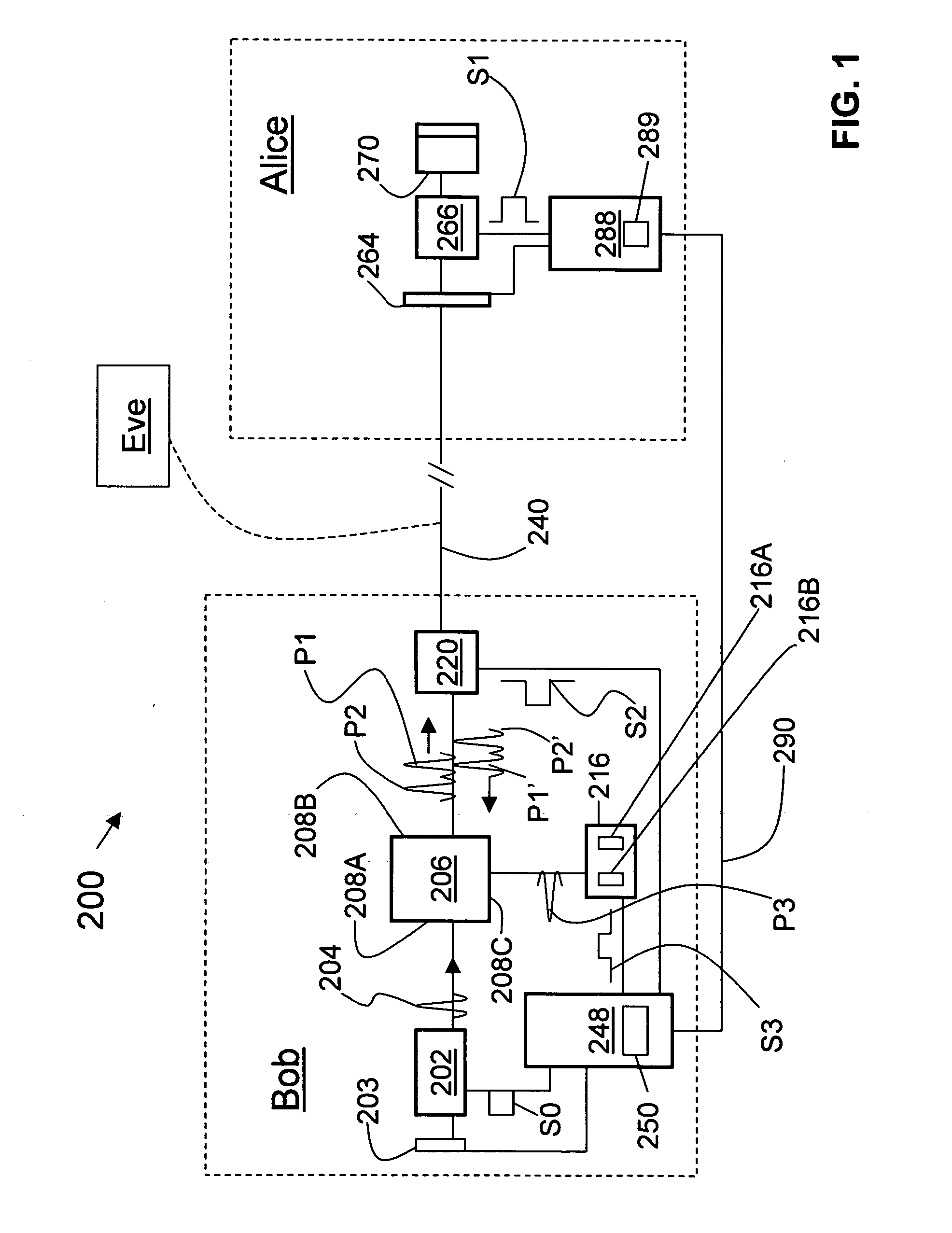
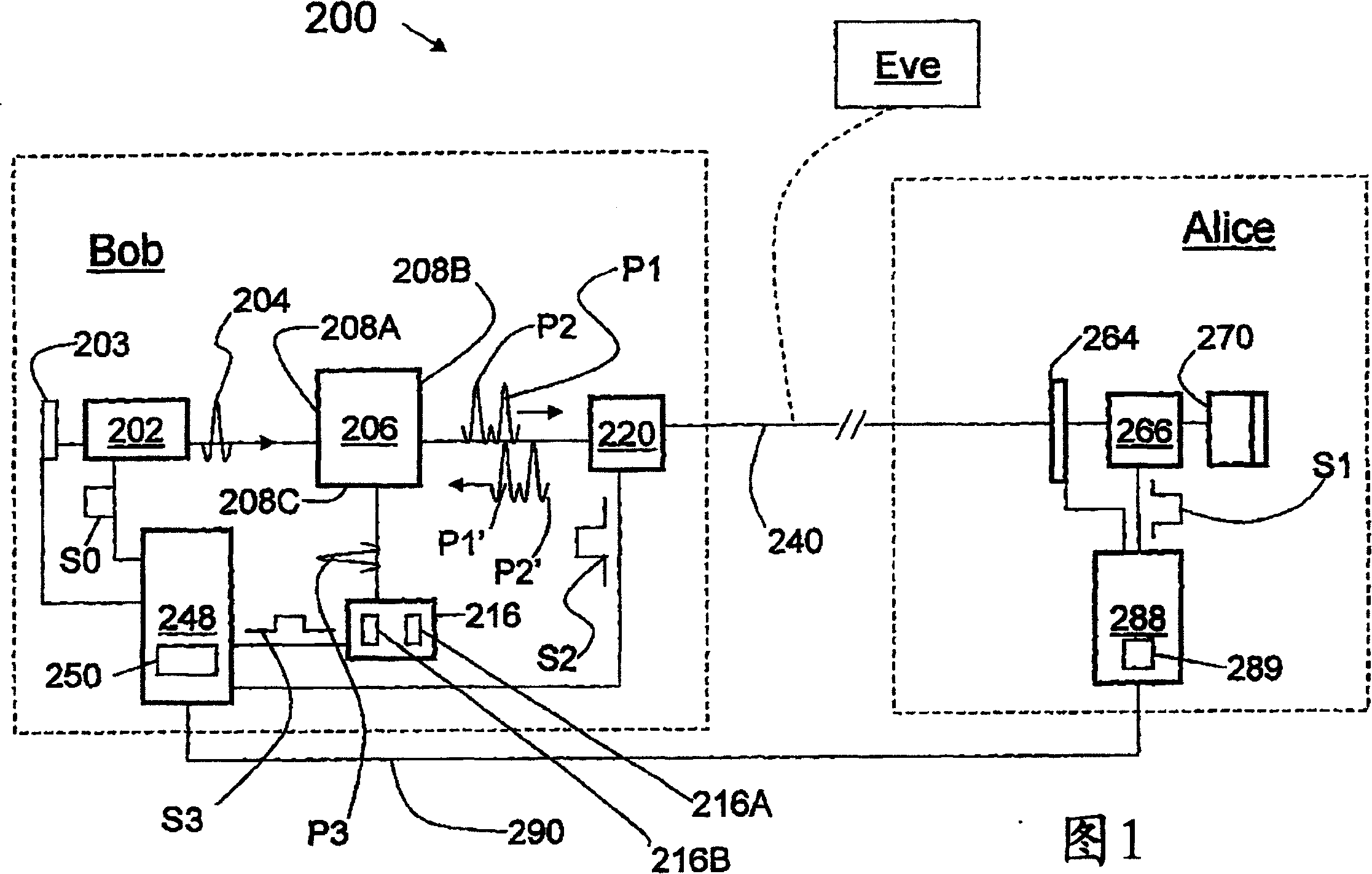
The quantum key distribution (QKD) systems (200, 300, 400) of the invention includes first and second QKD stations (Alice and Bob) according to the present invention, wherein either one or both QKD stations include fast optical switches (120, 220, 310, 320). Each fast optical switch is respectively optically coupled to two different round-trip optical paths (OP1 and OP2 at Alice, OP3 and OP4 at Bob) of different length that define respective optical path differences OPDA and OPDB, wherein OPDA=OPDB. By switching the fast optical switches using timed switching signals (S1-S3 at Alice, S4-S6 at Bob) from their corresponding controllers (CA at Alice, CB at Bob), the quantum signals—which can be single-photon or weak-coherent pulses—can be generated from a single optical pulse (112), randomly selectively encoded while traversing the optical paths in Alice and Bob, and then interfered and measured (detected) at Bob. The QKD system has less loss as compared to conventional fiber-based QKD systems because it omits at least some of the beamsplitters in conventional QKD systems.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Entanglement-Based Qkd System With Active Phase Tracking
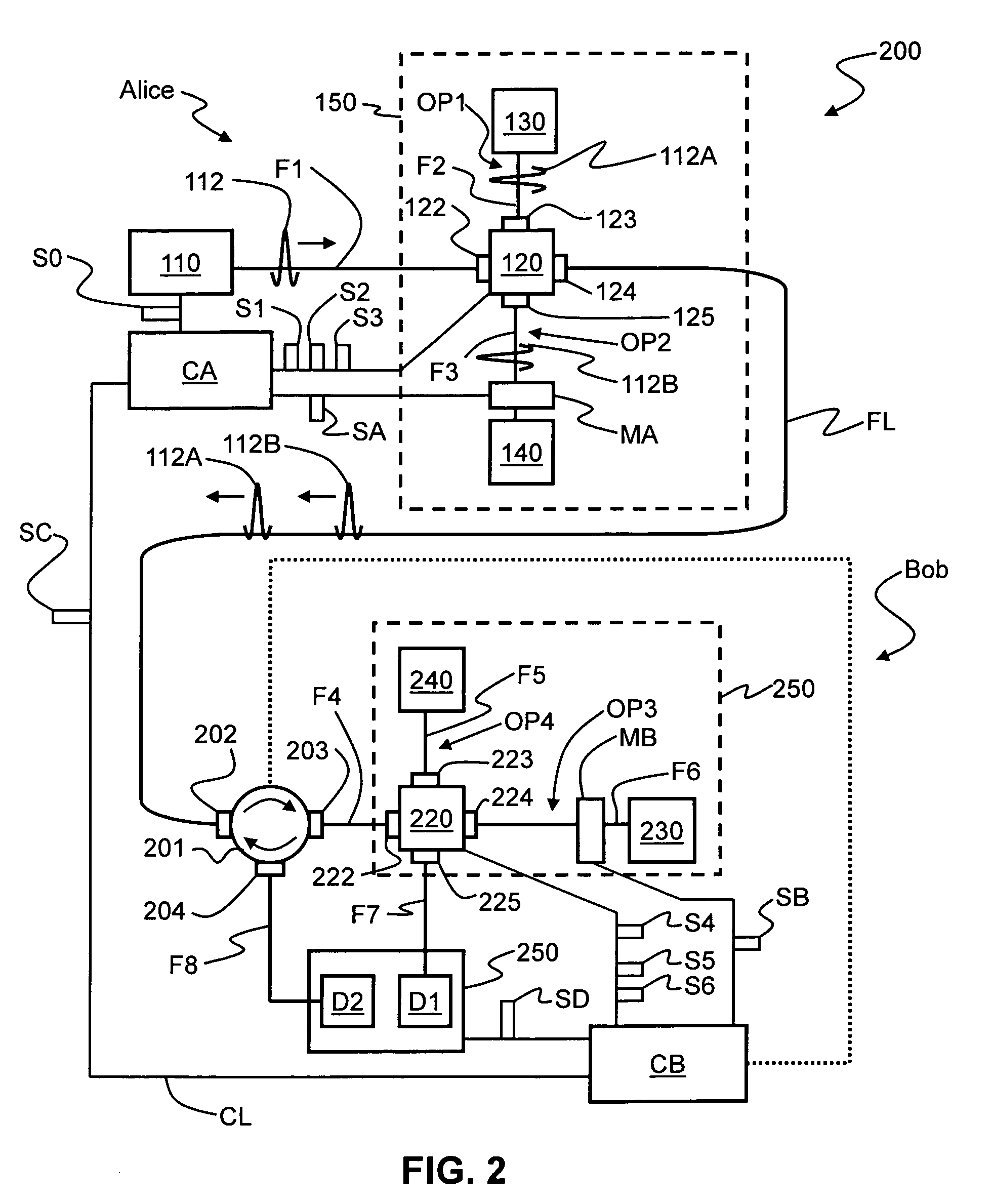
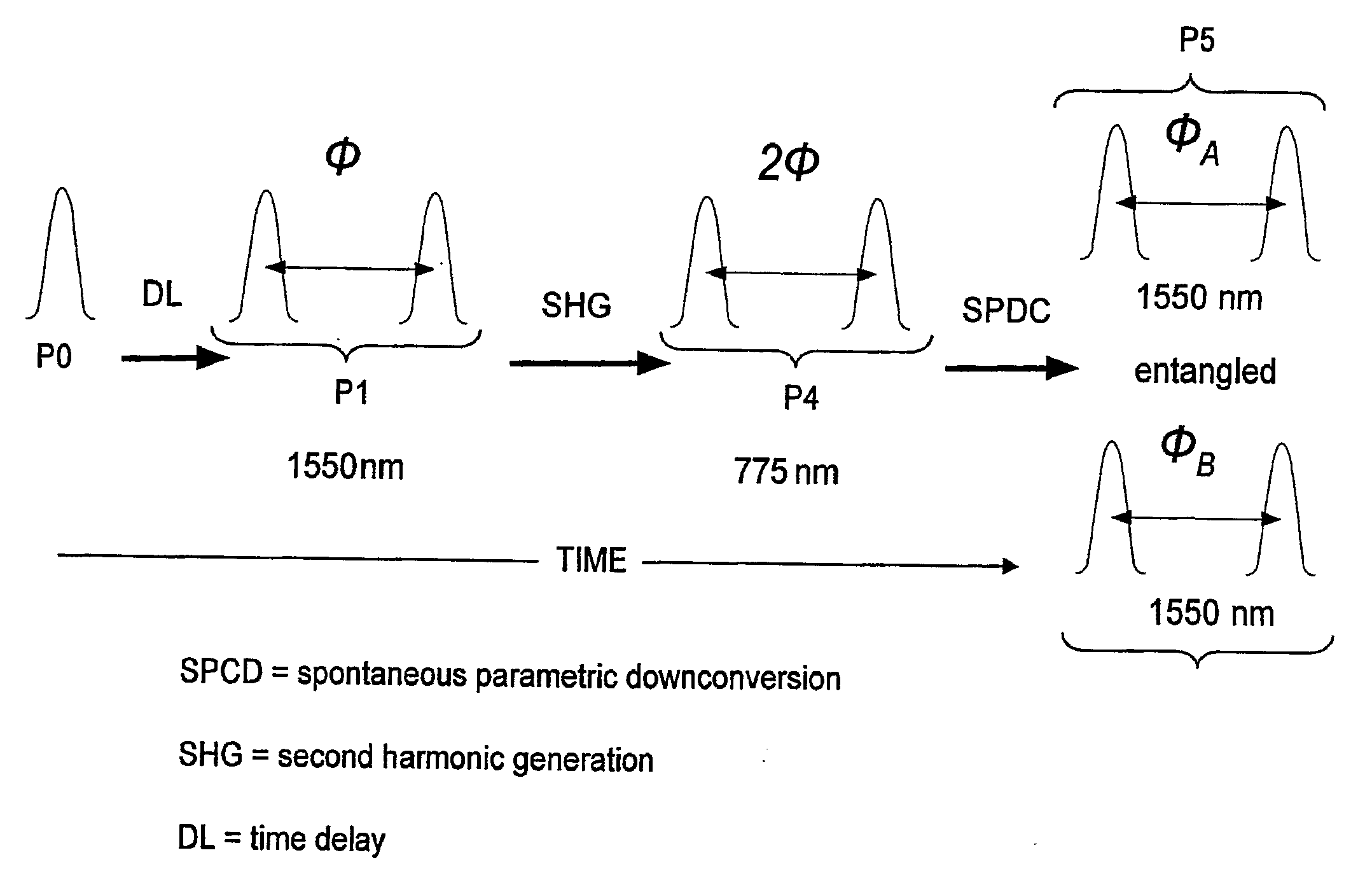
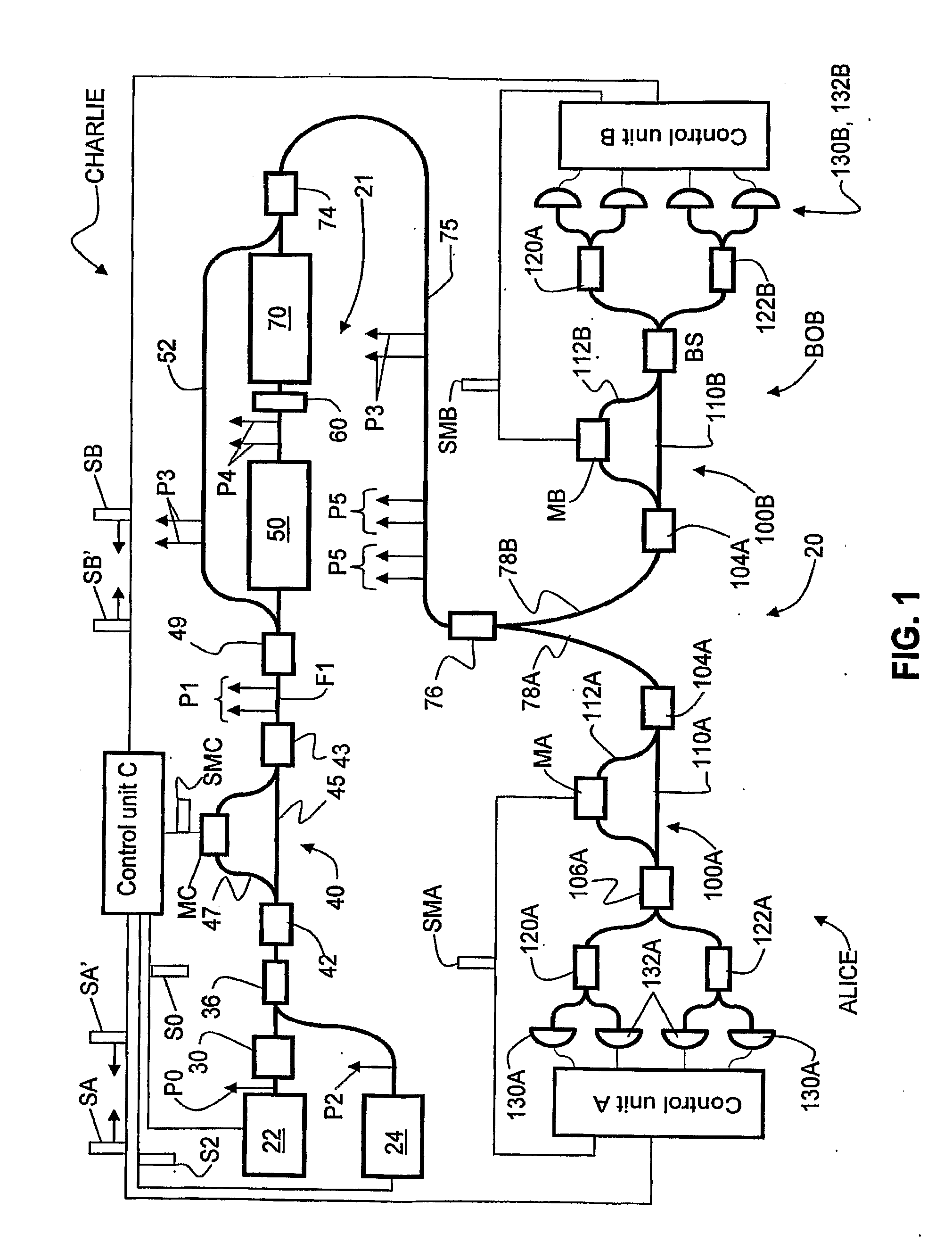
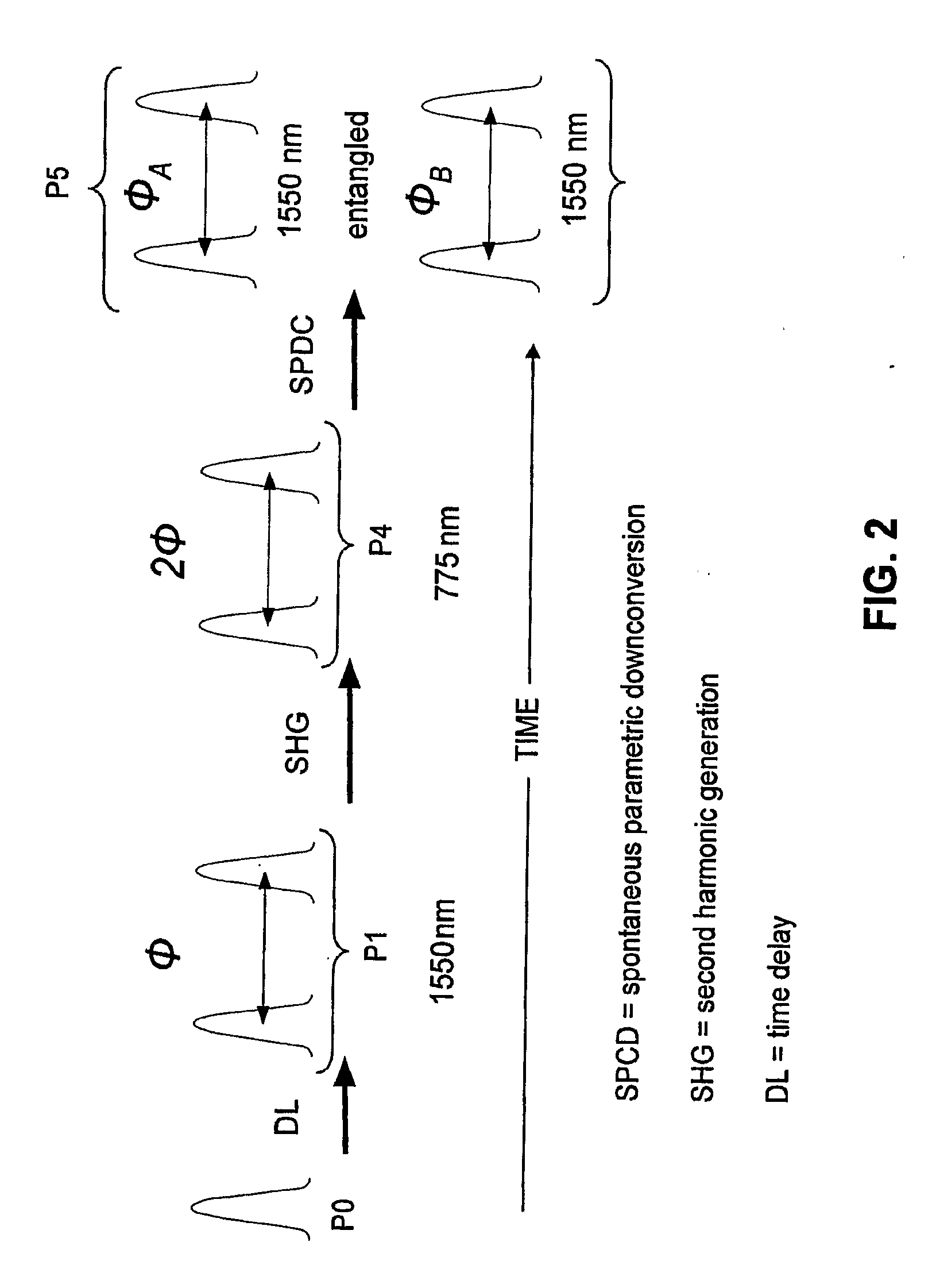
ActiveUS20090022322A1Cost-effectiveEffective lightingKey distribution for secure communicationUsing optical meansAlice and BobPhase correction
Entanglement-based QKD systems and methods with active phase tracking and stabilization are disclosed. The method includes generating in an initial state-preparation stage (Charlie) pairs of coherent photons (P1) at a first wavelength. Second harmonic generation and spontaneous parametric downconversion are used to generate entangled pairs of photons (P5) having the first wavelength—State detection stages (Alice and Bob) optically coupled to Charlie receive respective entangled photons from Charlie. The relative phase delays of the entangled photons are tracked using reference optical signals (P3) generated by Charlie and having the same wavelength as the entangled photons. Classical detectors (132A, 132B) detect the reference signals while single-photon detectors (130A, 130B) and a control unit (control unit C) generates an phase-correction signal that maintains the relative phases of the three phase delay loops (40, 100A,100B ) via adjustable phase-delay elements (MA, MB).
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
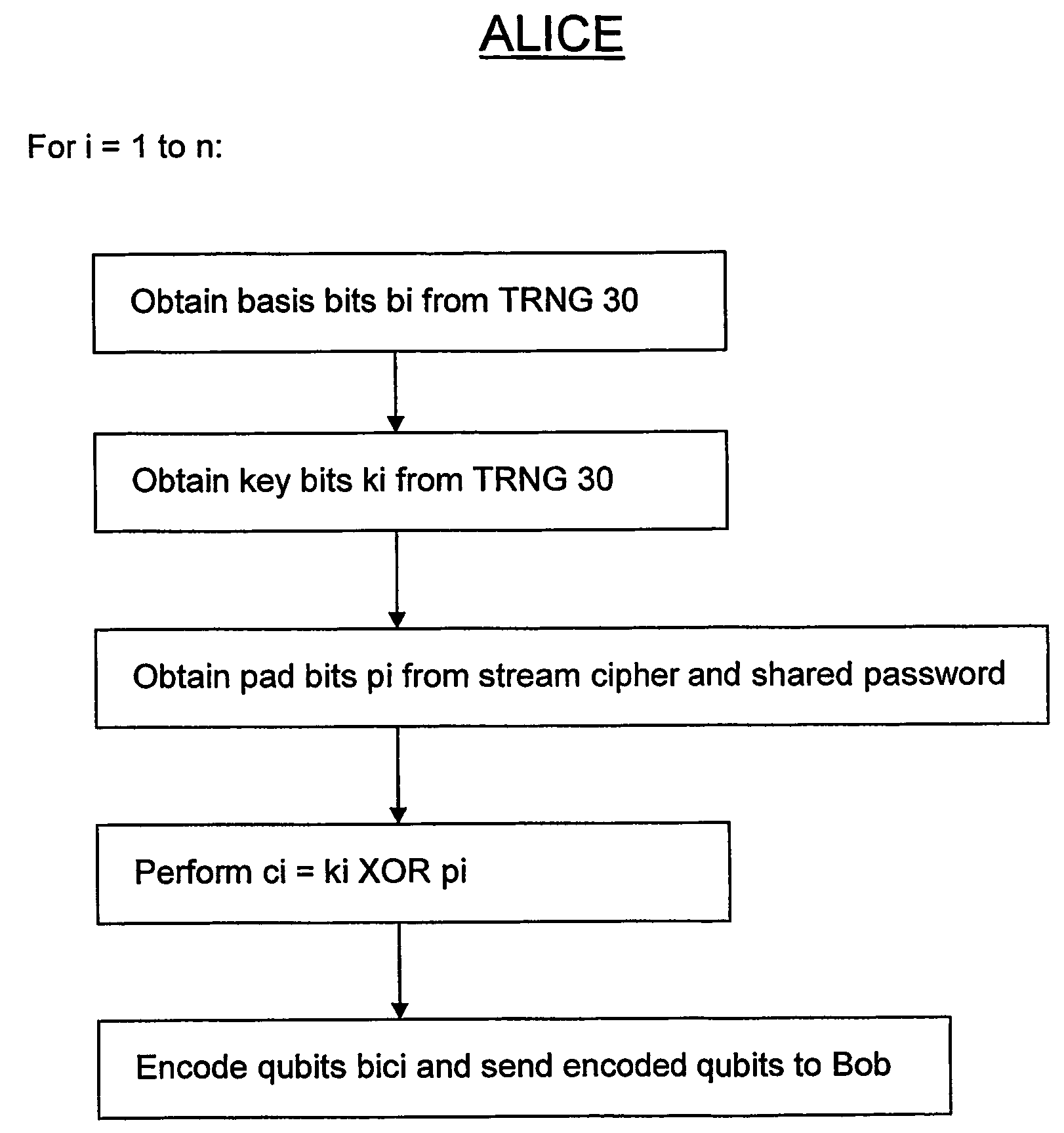
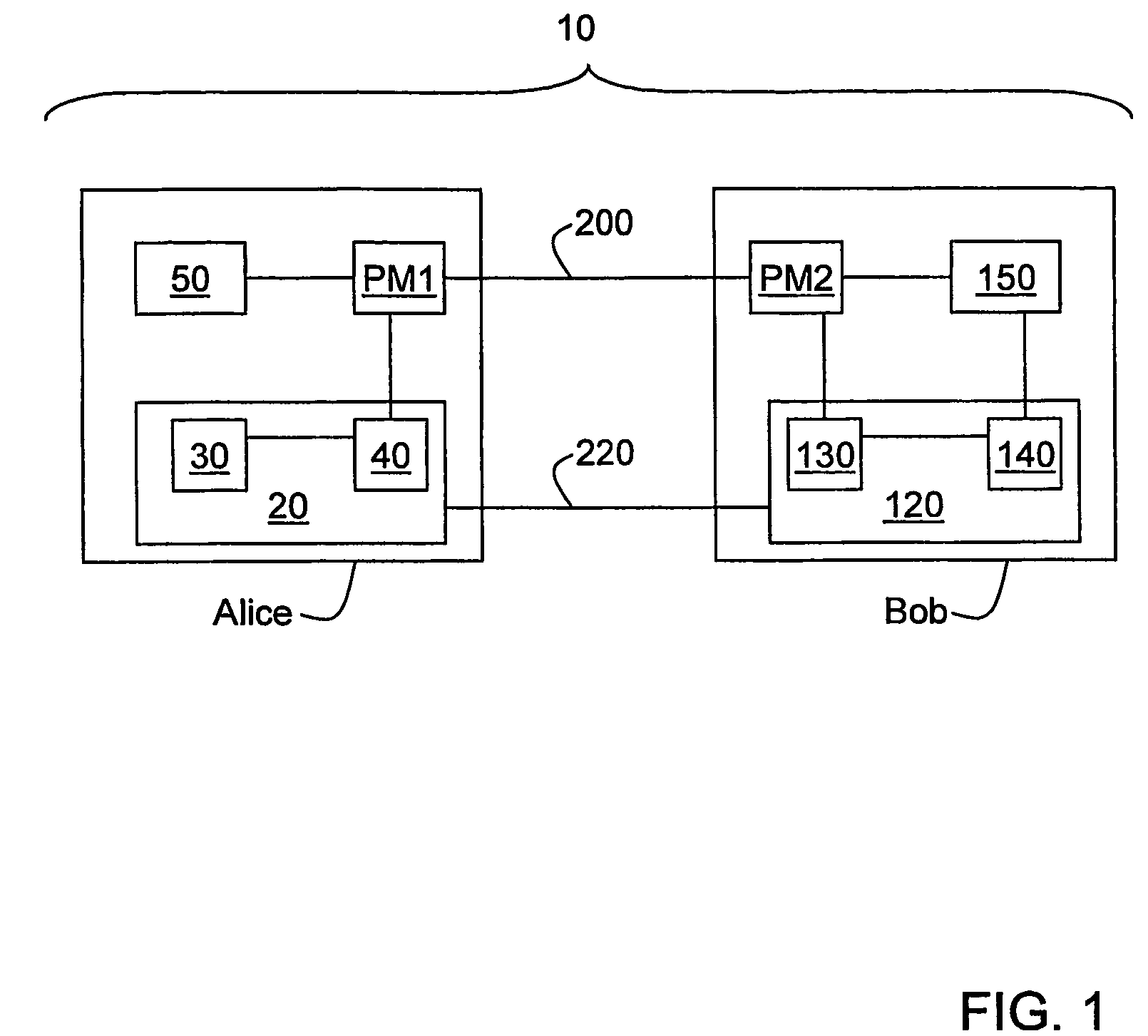
Qkd with classical bit encryption
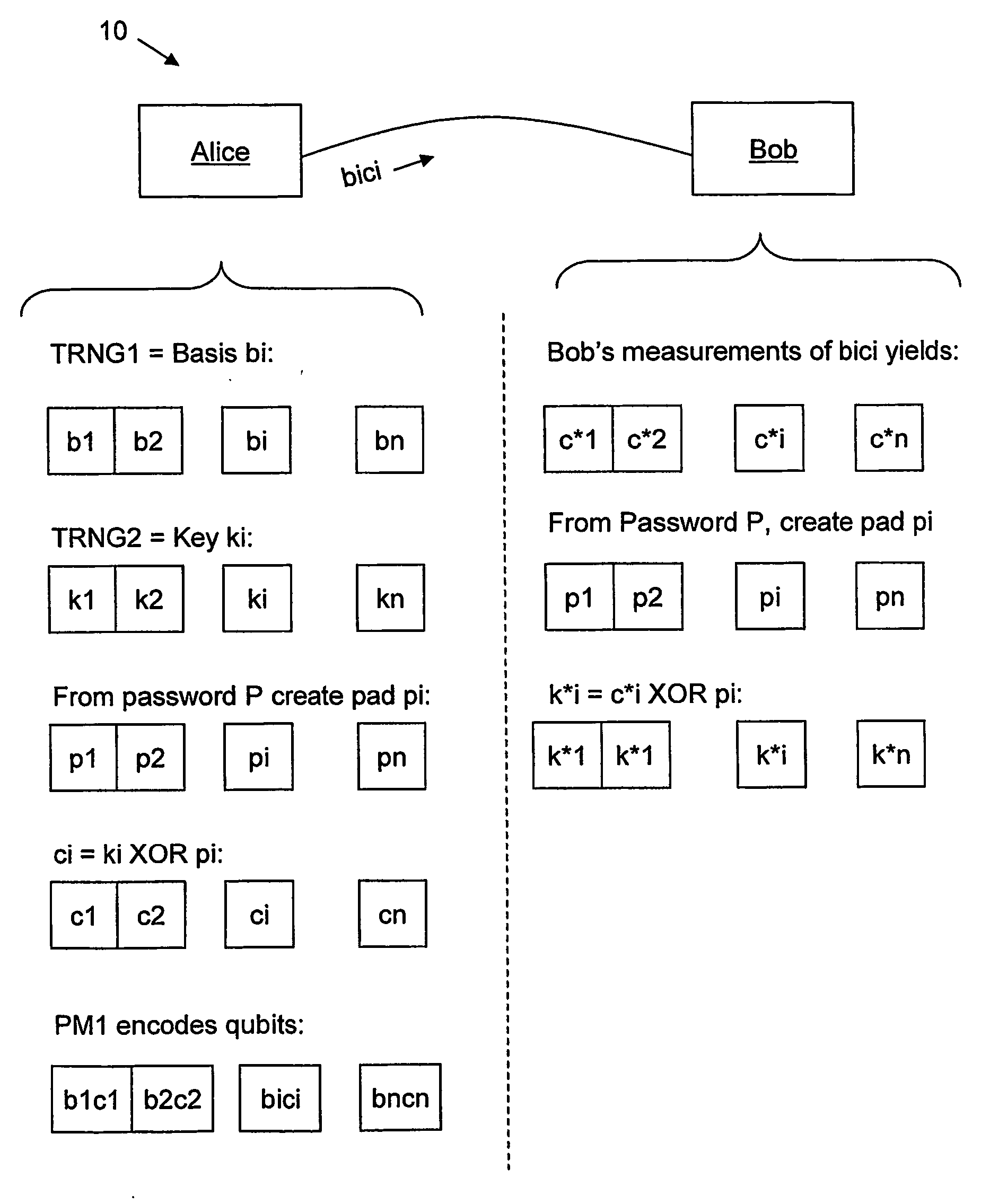
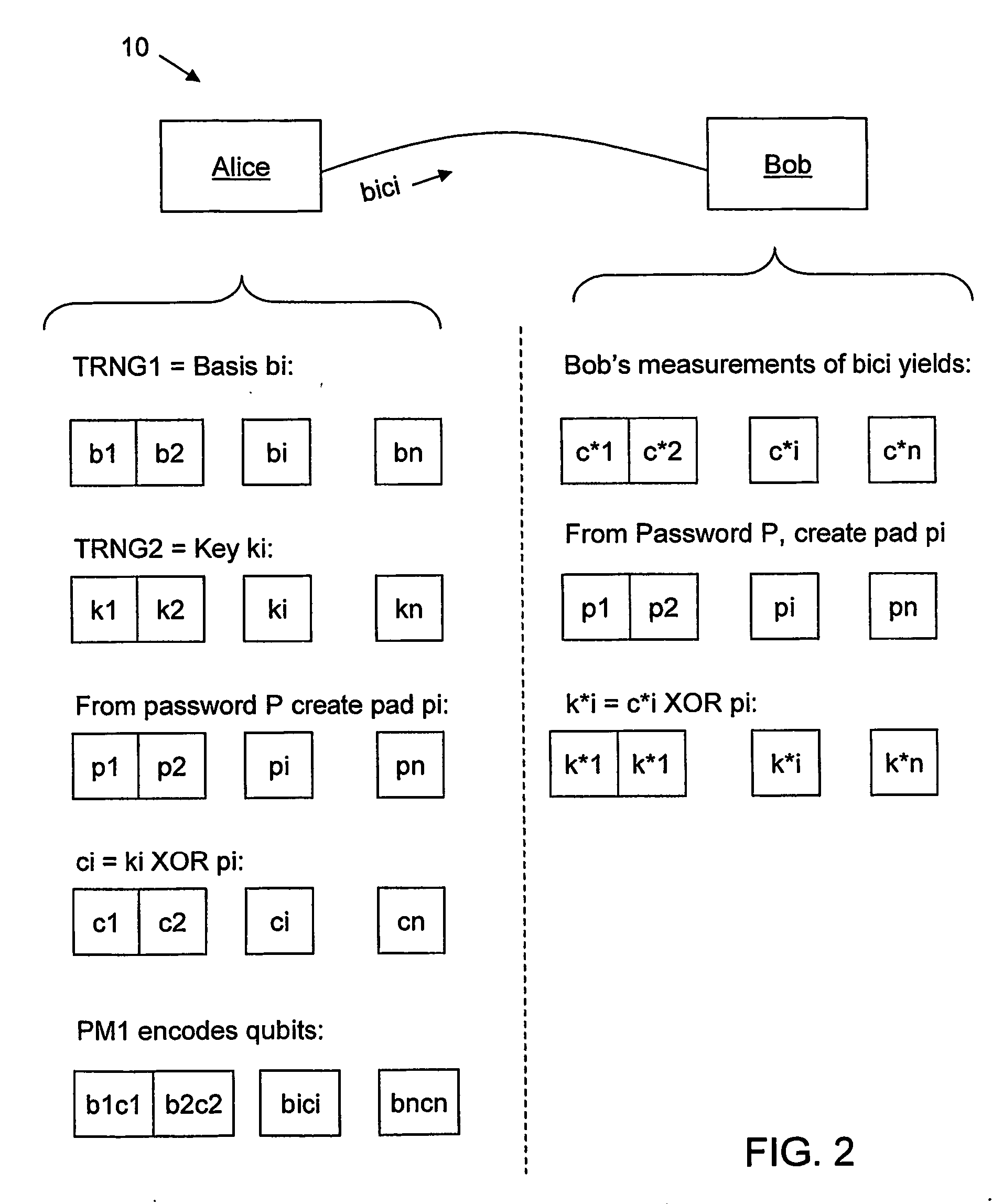
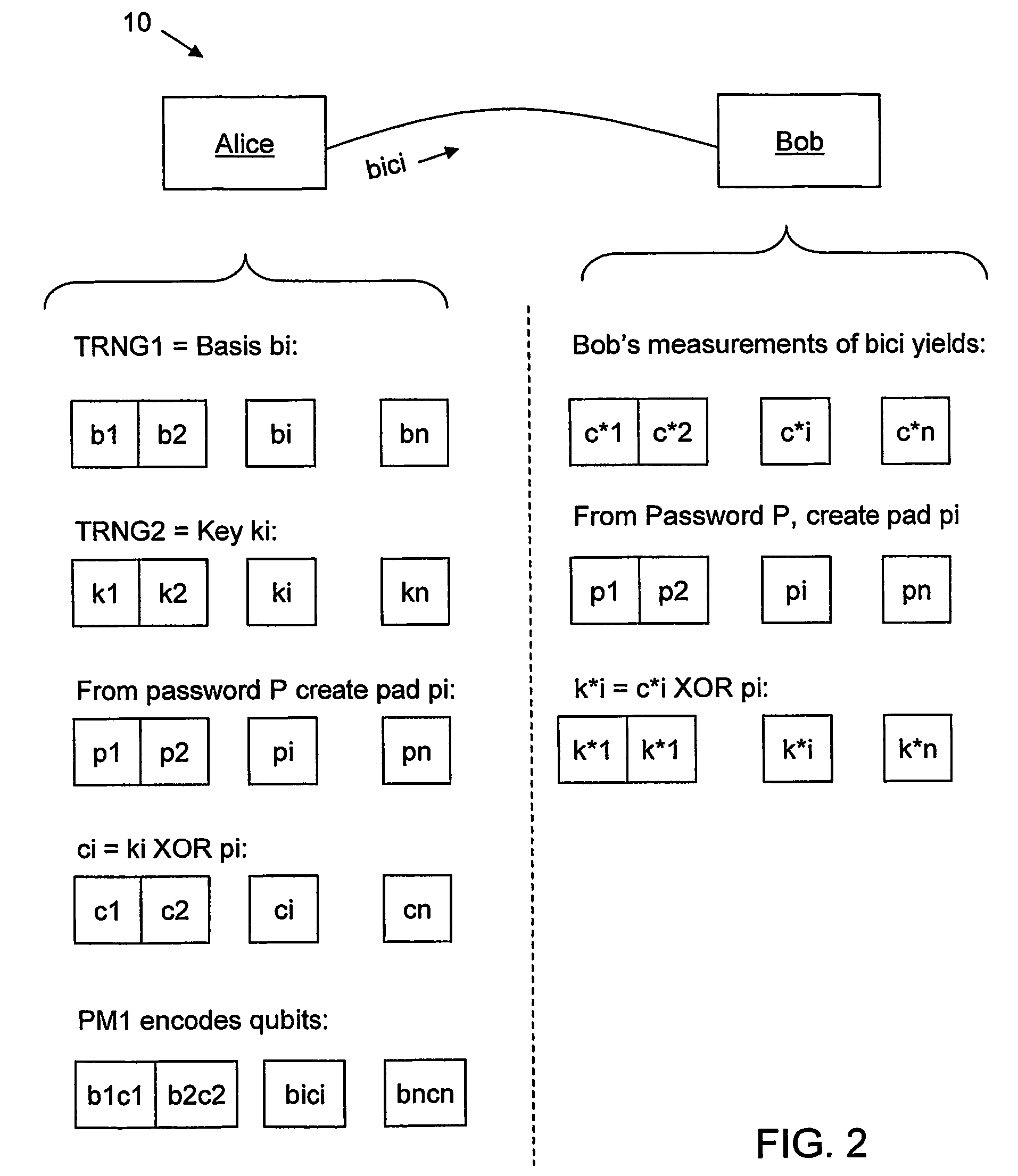
InactiveUS20070140495A1Key distribution for secure communicationData stream serial/continuous modificationComputer hardwareAlice and Bob
A method for enhancing the security of a quantum key distribution (QKD) system having QKD stations Alice and Bob. The method includes encrypting key bits generated by a true random number generator (TRNG) and sent to a polarization or phase modulator to encode weak optical pulses as qubits to be shared between Alice and Bob. Key bit encryption is achieved by using a shared password and a stream cipher. Bob obtains at least a subset of the original key bits used by Alice by utilizing the same stream cipher and the shared password.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Information leakage-free bidirectional quantum secure direct communication protocol based on any two gigahertz (GHZ) state/entanglement exchange result collection codes
ActiveCN103338187APrevent leakageIncrease capacityTransmissionAlice and BobQuantum secure direct communication
At present, information leakage is a serious security threat to bidirectional quantum secure direct communication (BQSDC). The invention provides an information leakage-free bidirectional quantum secure direct communication protocol based on any two gigahertz (GHZ) state / entanglement exchange result collection codes. In the information leakage-free bidirectional quantum secure direct communication protocol, two remote legitimate communication sides, namely, Alice and Bob can exchange their respective secret information without concern on information disclosure required. According to the protocol, a shared secret gigahertz (GHZ) state is utilized to overcome the problem of information disclosure. The shared secret gigahertz (GHZ) state has the following functions in a bidirectional communication process that: on the one hand, the shared secret gigahertz (GHZ) state makes Bob known a configured initial state, and on the other hand, the shared secret gigahertz (GHZ) state can be used by Bob so that Bob can encode secret information; and further, the protocol can transmit six-bit secret information per communication round. Compared with an existing BQSDC protocol, the protocol of the invention has the following advantages that: the protocol can overcome the problem of information disclosure; and on the other hand, the capacity of the protocol can achieve six bit per communication round.
Owner:浙江海宁经编产业园区开发有限公司
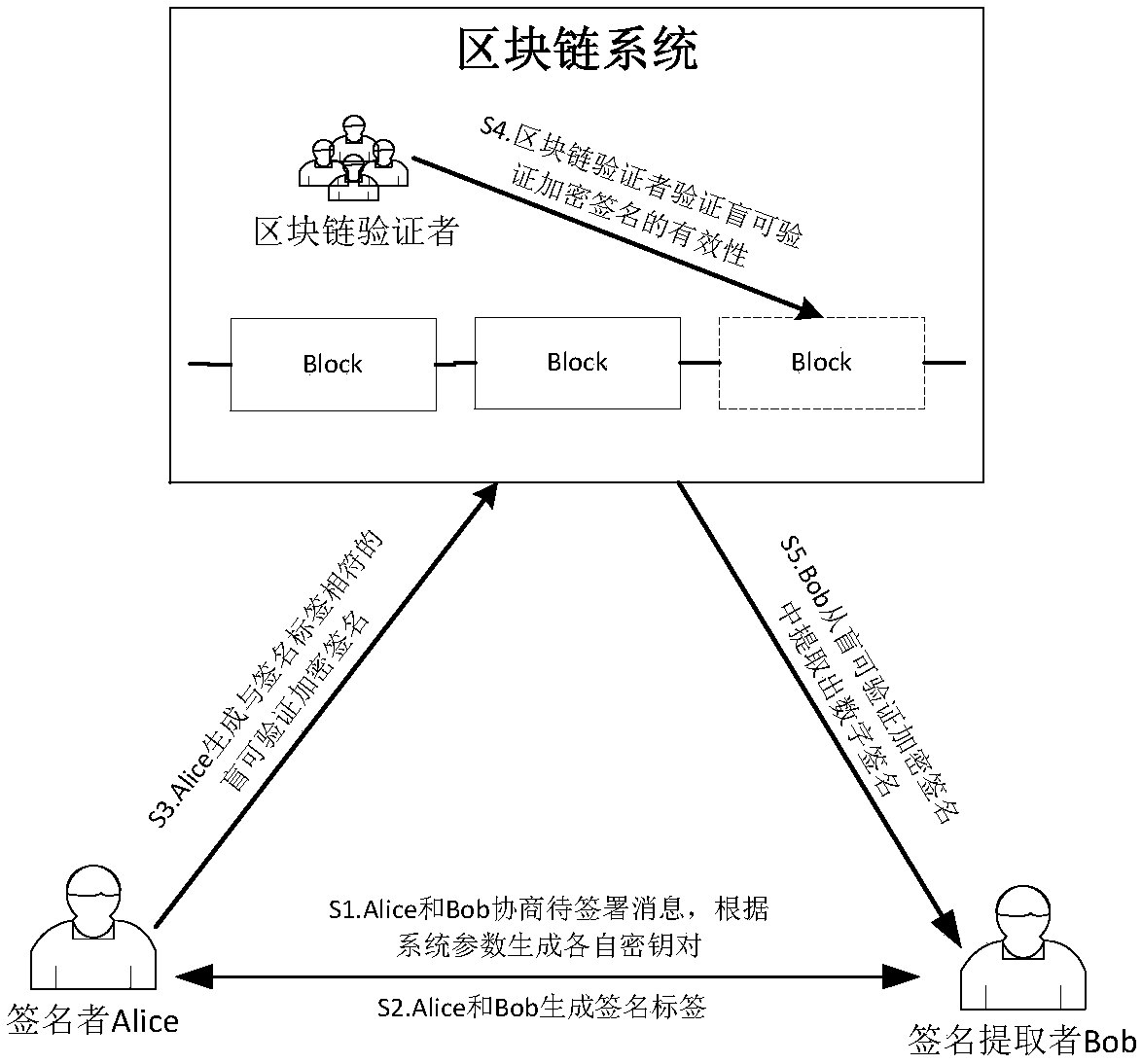
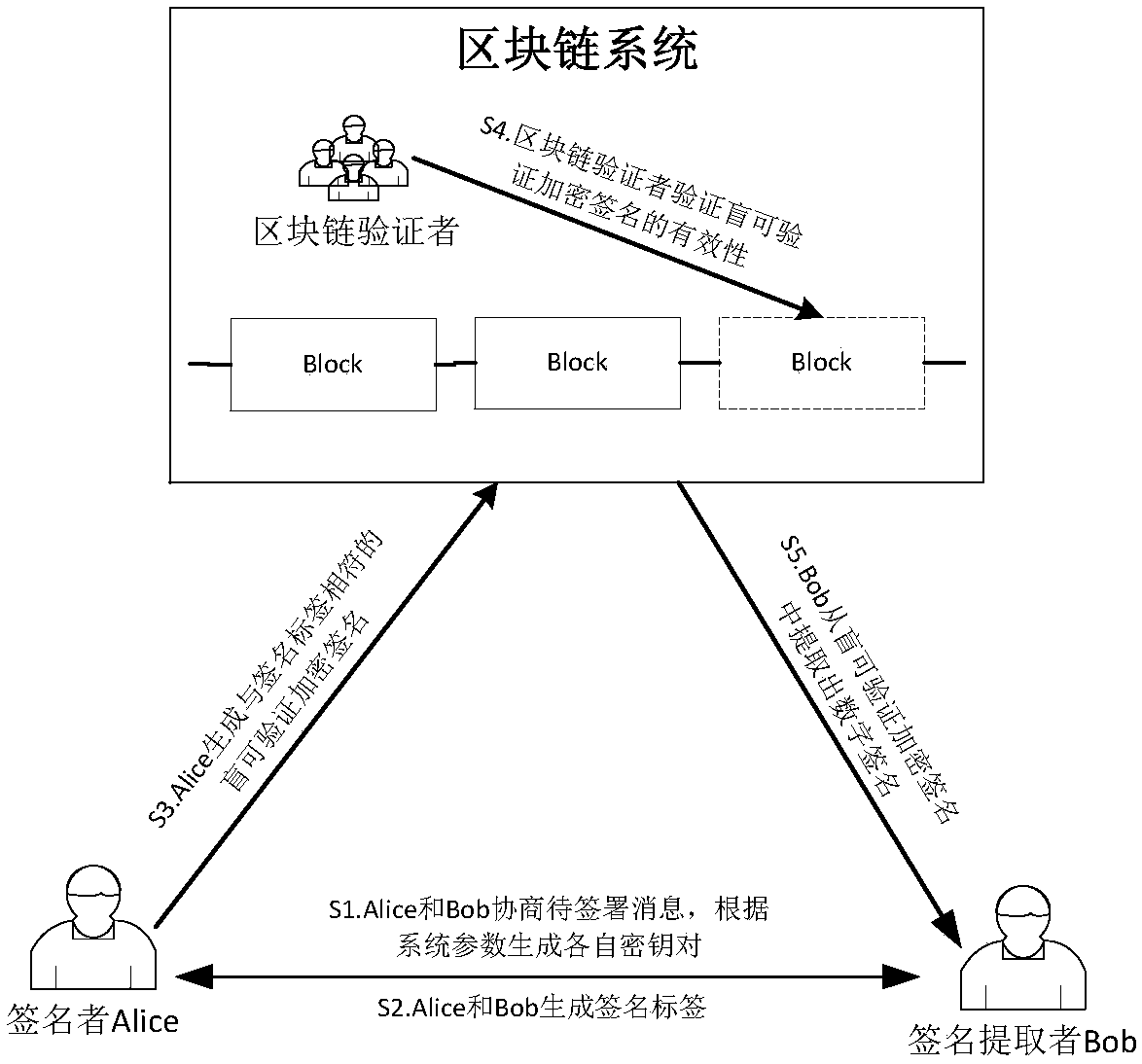
Blind verifiable cryptographic signature method based on block chain
InactiveCN107040383APrivacy protectionPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlice and BobDigital signature
The invention relates to a blind verifiable cryptographic signature method based on a block chain. The method includes three parties: a signer Alice, a signature extractor Bob, and a block chain verifier. The method is implemented in the following steps: Alice and Bob negotiate a message to be signed and generate their own key pairs respectively according to system parameters; Alice and Bob generate signature tags; Alice generates a blind verifiable cryptographic signature that matches the signature tag; the block chain verifier verifies the validity of the cryptographic verifiable cryptographic signature; and Bob extracts a digital signature from the blind verifiable cryptographic signature. The method can be used to construct a fair digital signature exchange protocol that protects privacy in a public block chain environment. The method blindens the public key information of the signer so that a node on a block chain cannot obtain the real digital signature and the public key of the signer aside from verifying the validity of the signature, and the privacy protection for the signer is achieved.
Owner:深圳市数峰科技有限公司
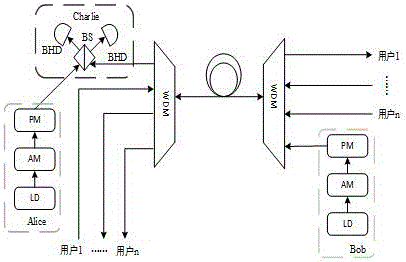
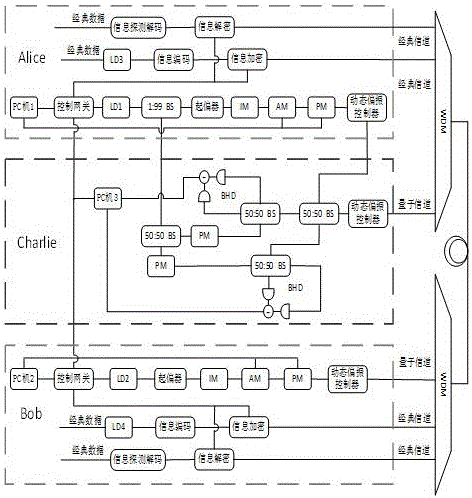
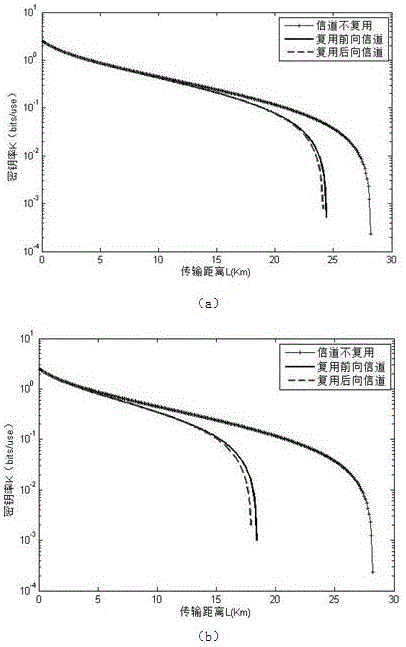
Quantum key distribution system and method based on continuous variable measurement equipment independence
InactiveCN106685658AObvious advantage of metropolitan area networkKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobKey generation
The invention provides a quantum key distribution system and method based on continuous variable measurement equipment independence. The quantum key distribution system comprises a sender Alice and a receiver Bob, and is characterized in that the receiver Bob is connected with a balance homodyne detector BHD through a wavelength division multiplexer WDM; the sender Alice is connected with the balance homodyne detector BHD at Alice and Bob ends; after a continuous wave laser device (LD) passes through an intensity modulator (IM), light pulse is formed by attenuation; Gaussian-modulation encoding of a coherent state is finished after the light pulse is processed by an amplitude modulator (AM) and a phase modulator (PM) under the control of a random number generated by a PC (Personal Computer) machine; then a result is sent to a third party Charlie; generated noises have relatively small influences on the system; influences on a safety key generation speed of the system, caused by forward transmission and backward transmission of a channel can be ignored; and advantages of a metropolitan area network based on a CV-MDIQKD quantum cryptography communication system are very obvious, and a foundation can be laid for commercialized and networked application in the future.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol free of information leakage
Bi-directional quantum secure direct communication aims at enabling two legal communication parties to exchange secret information of each other simultaneously. The invention provides a controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol free of information leakage. In the protocol, two legal communication parties Alice and Bob are controlled by a controller Charlie to achieve exchange of the secret information of each other without information leakage. The protocol utilizes measuring relevancy after entanglement swapping of 3 Bell states to solve an information leakage problem. In addition, the protocol only uses the Bell states as quantum resources, only Bell measuring is required to be conducted, and the controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol is convenient to achieve.
Owner:浙江海宁经编产业园区开发有限公司
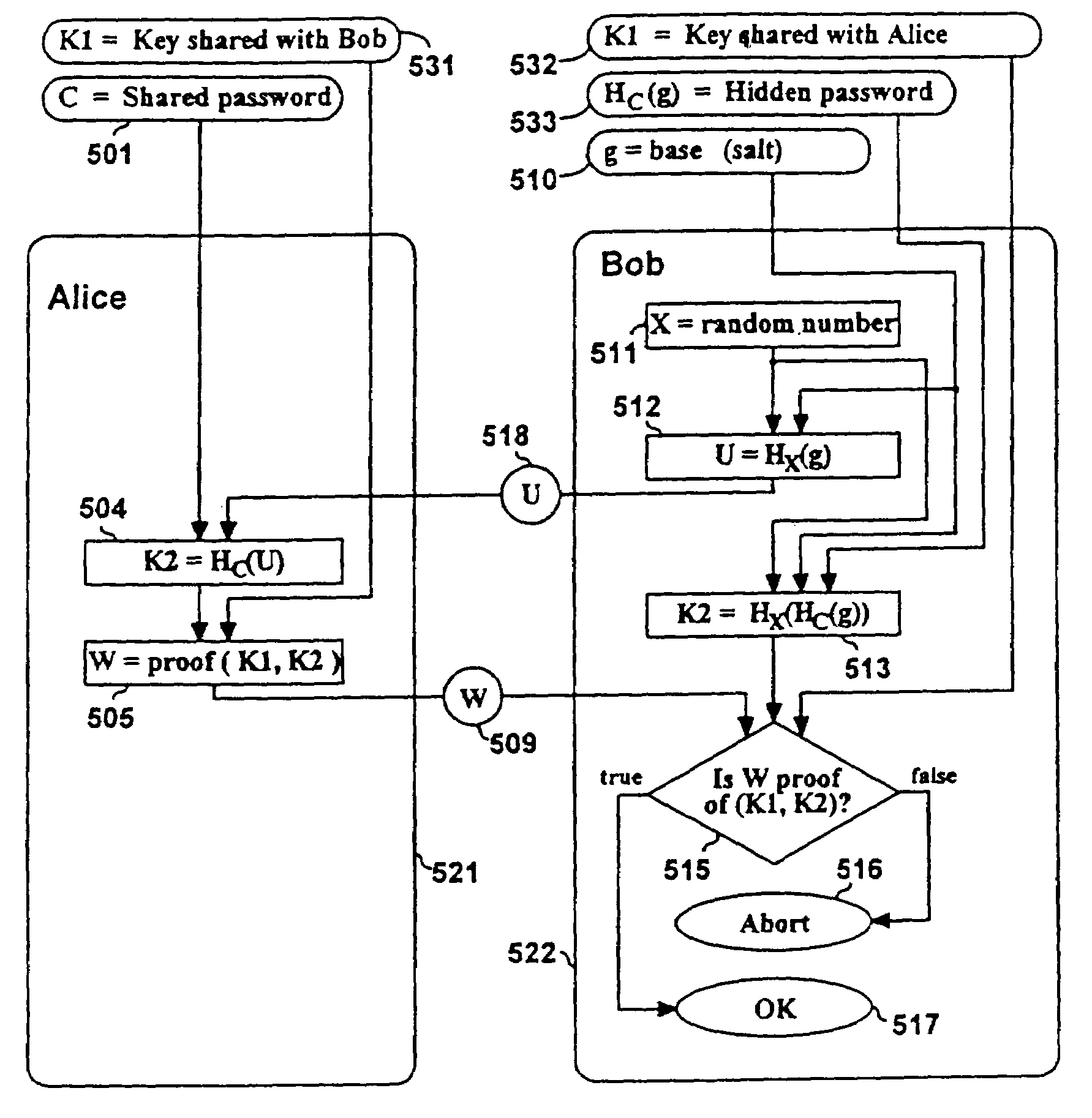
Cryptographic methods for remote authentication
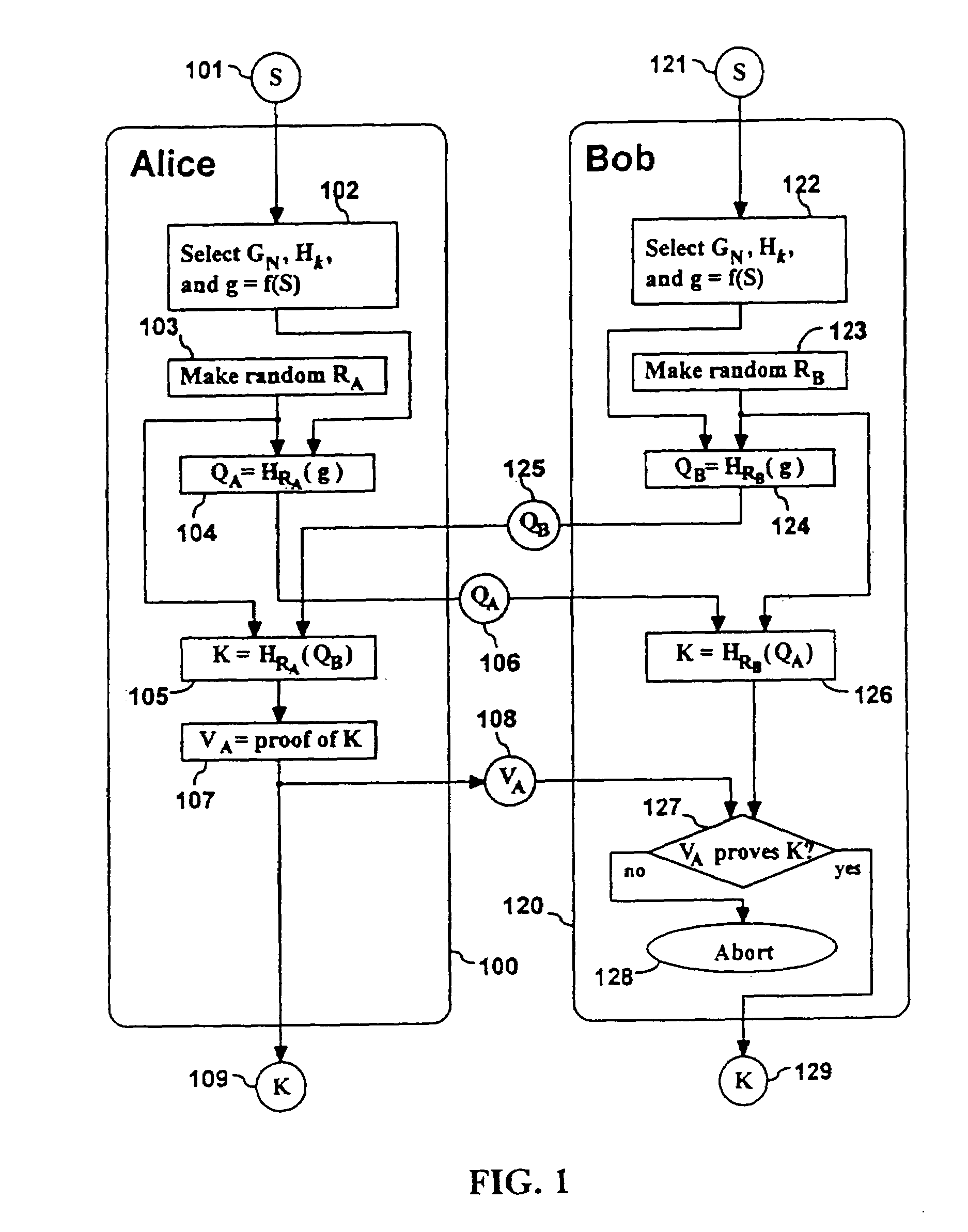
InactiveUS7010692B2Prevent replay attacksImprove the immunityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationAlice and BobKey exchange
Methods are described for two parties to use a small shared secret (S) to mutually authenticate one another other over an insecure network. The methods are secure against off-line dictionary attack and incorporate an otherwise unauthenticated public key distribution system. One embodiment uses two computers Alice and Bob, and a Diffie-Hellman exponential key exchange in a large prime-order finite group. Both parties choose the same generator of the group (g) as a function of S. Alice chooses a random number RA, and sends gR<sub2>A < / sub2>to Bob. Bob chooses a random RB, sends gR<sub2>B < / sub2>to Alice. Both compute a shared key K=g(R<sub2>A< / sub2>R<sub2>B< / sub2>). Each party insures that K is a generator of the group, verifies that the other knows K, and then uses K as an authenticated key. Constraints are described to prevent passive and active attacks. An extension is described where Alice proves knowledge of S to Bob who knows only a one-way transformation of S. These methods establish a secure, authenticated network session using only an easily memorized password.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
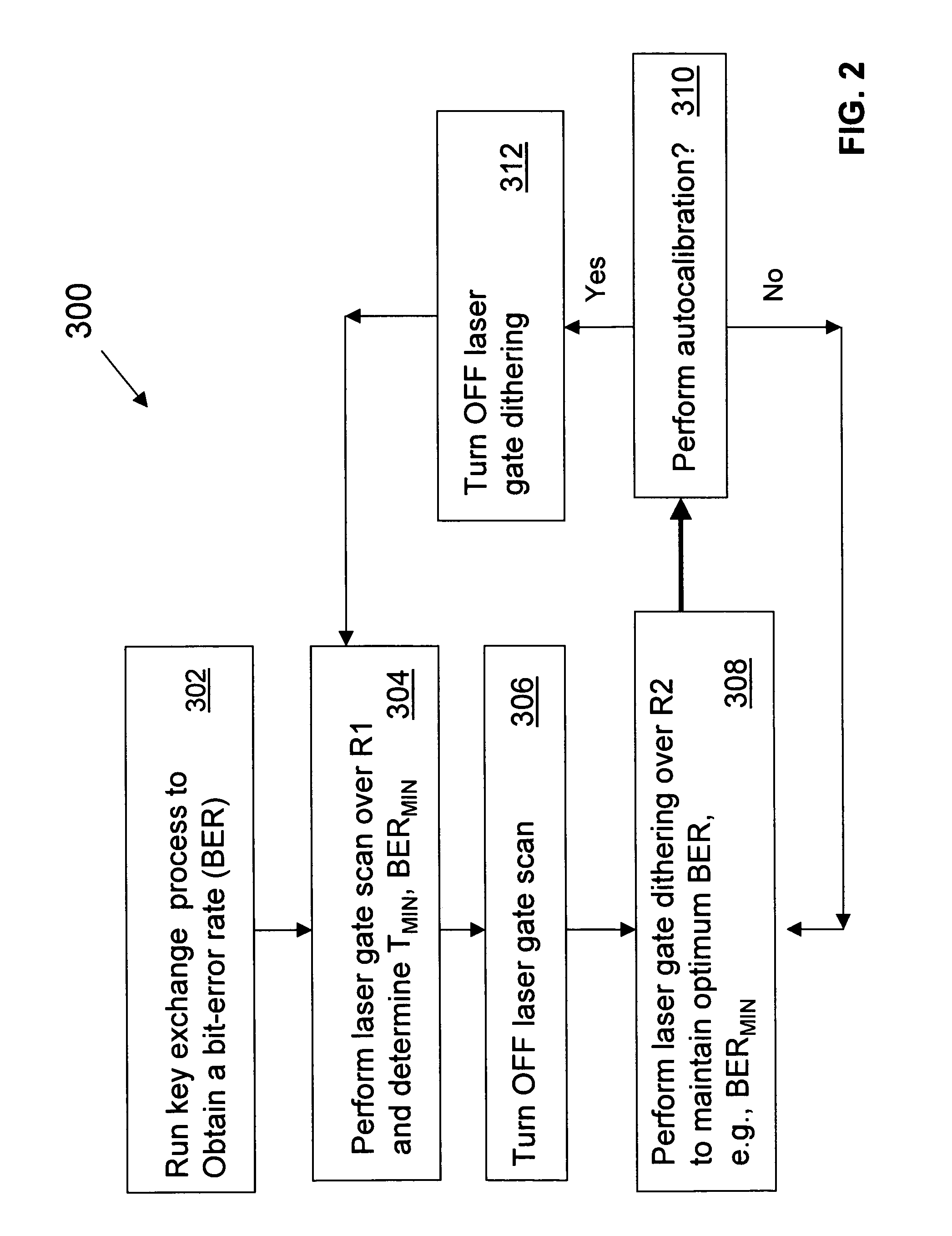
QKD system laser autocalibration based on bit-error rate
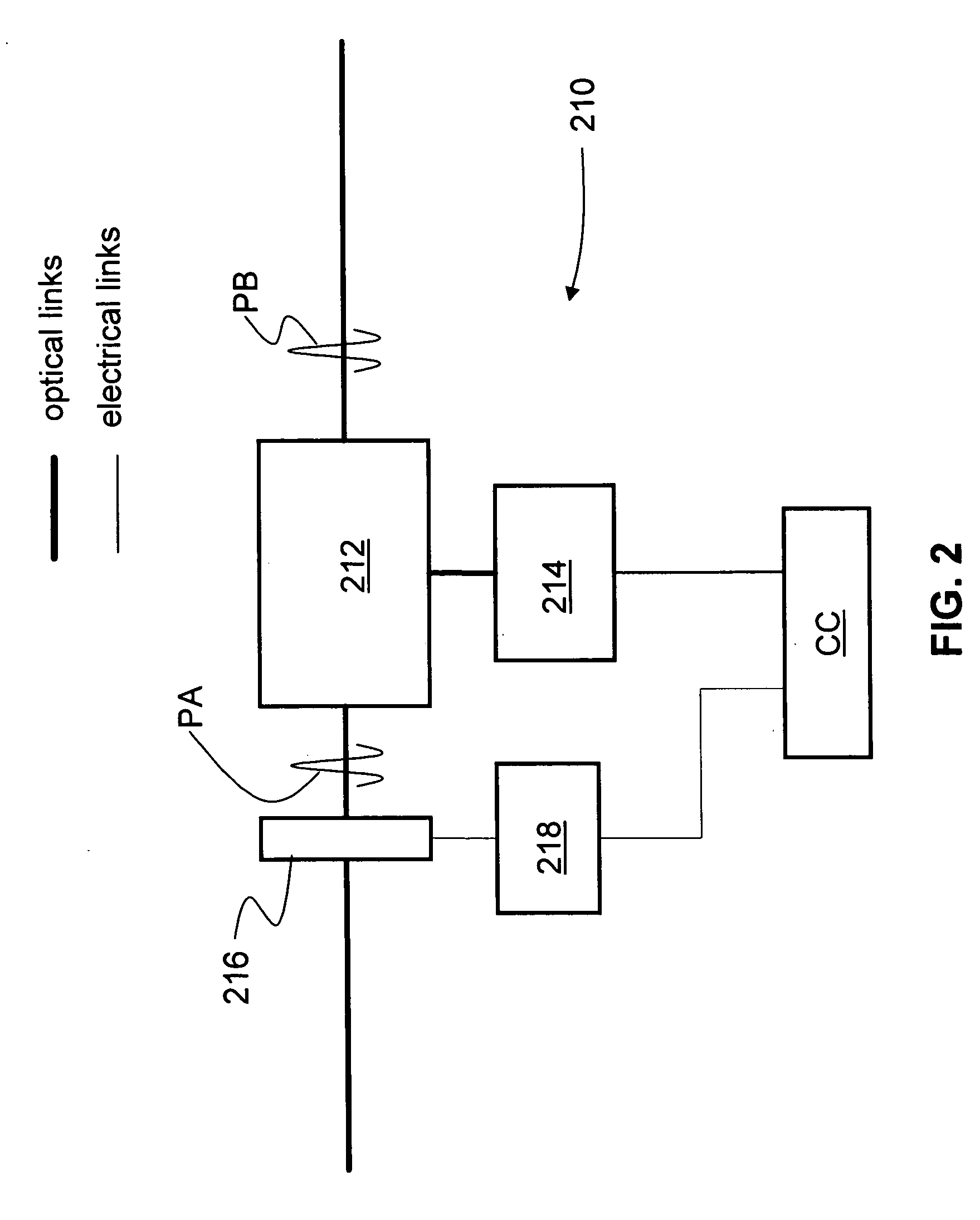
ActiveUS20060239463A1Improve system performanceKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationAlice and BobOptoelectronics
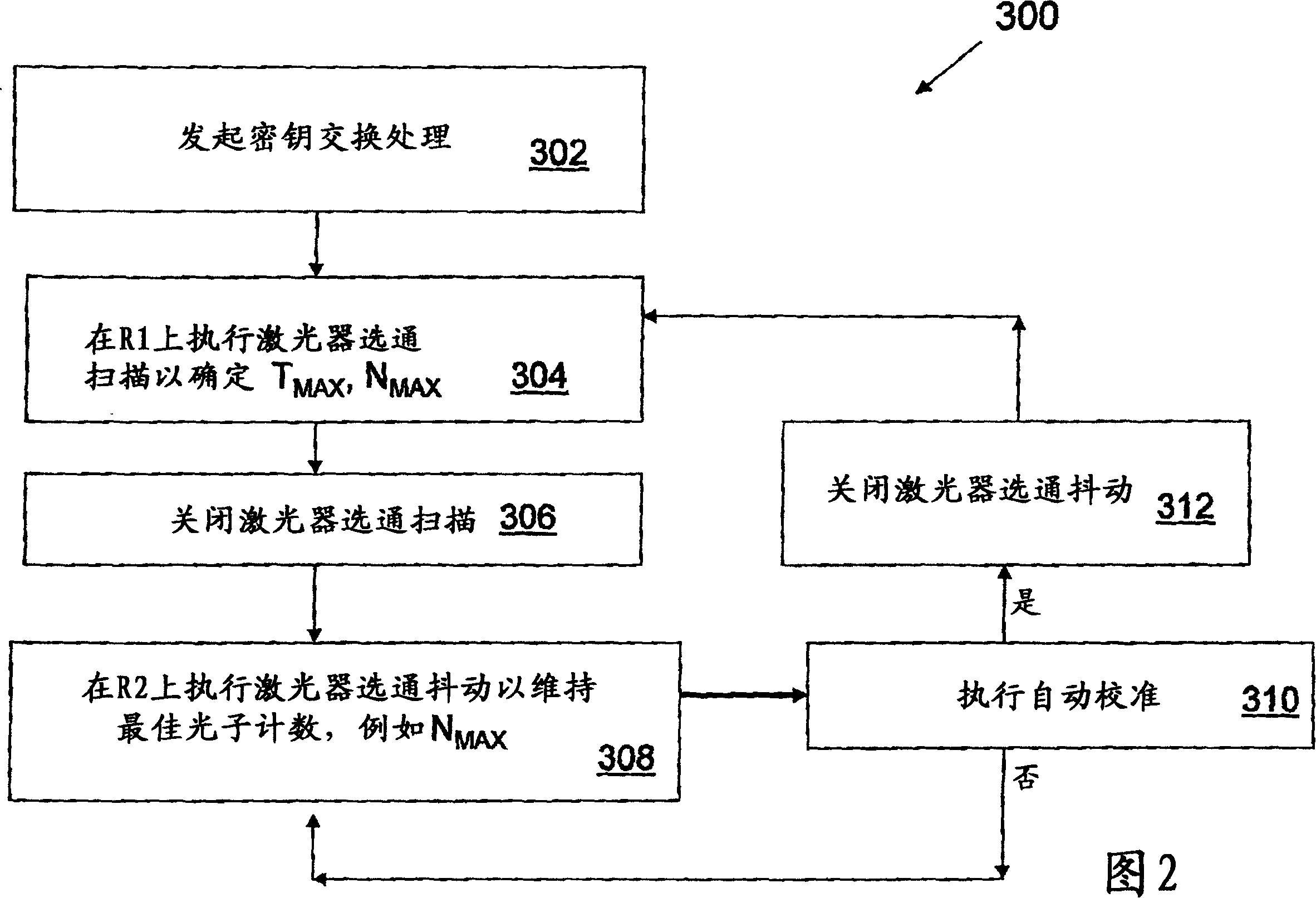
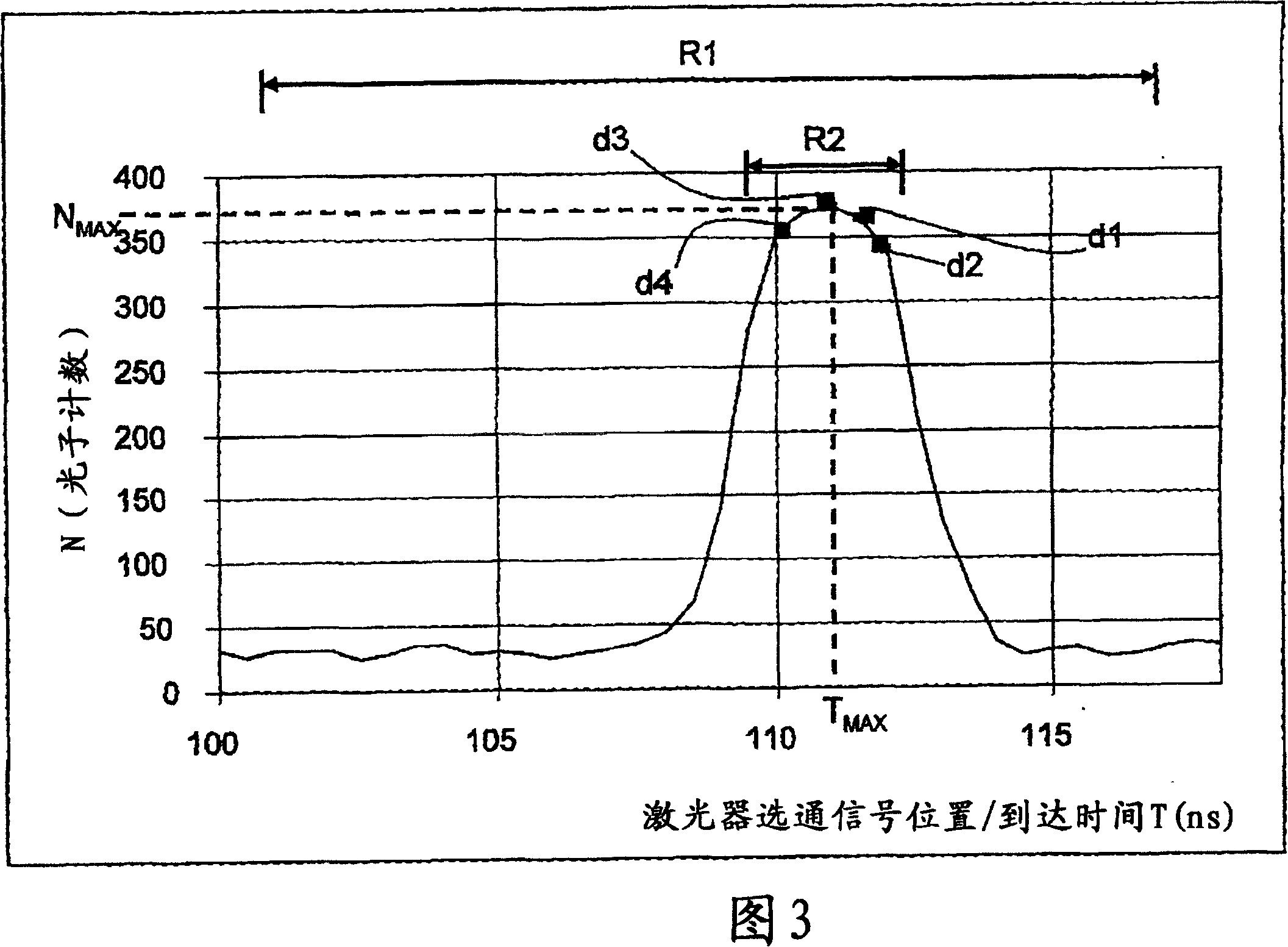
A method of autocalibrating the timing of the laser (202) in a quantum key distribution (QKD) system (200) is disclosed. Laser (202) generates photon signals (204) in response to a laser gating signal (S0) from a controller (248). The method includes first performing a laser gate scan (304) to establish the optimum arrival time (TMIN) of the laser gating signal corresponding to an optimum (e.g., minimum) bit-error rate BER (e.g., BERMIN) when exchanging photon signals between encoding stations (Alice and Bob) of the QKD system. Once the optimum laser gating signal arrival time (TMIN) is determined, the laser gate scan is terminated (306) and a laser gate dither process (308) is initiated. The laser gate dither involves varying the arrival time (T) of the laser gating signal around the optimum value of the arrival time TMIN. The laser gate dither provides minor adjustments to the laser gating signal arrival time to ensure that the system operates at or near the optimum BER.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
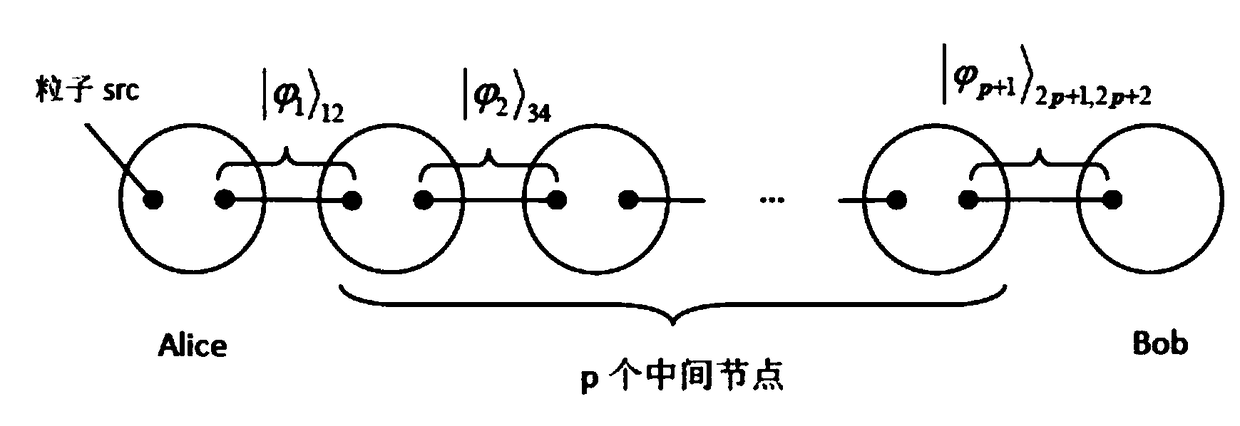
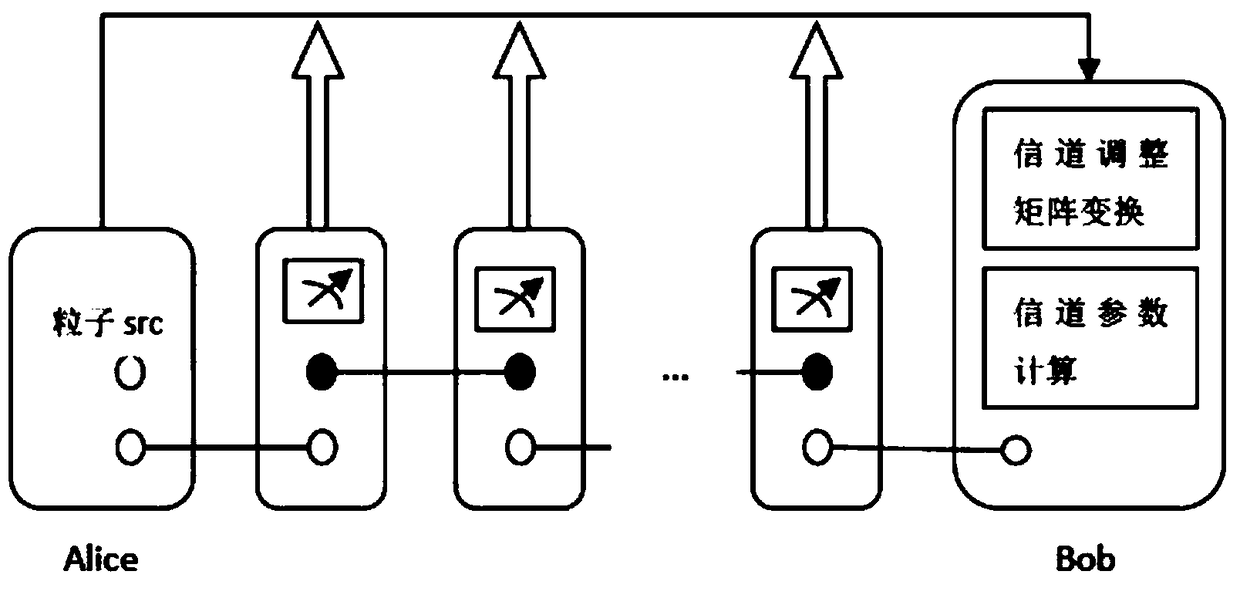
Multi-hop lossless teleportation method based on non-maximum entangled chain channel
ActiveCN109379183AWill not cause lossImprove transmission efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobQuantum entanglement
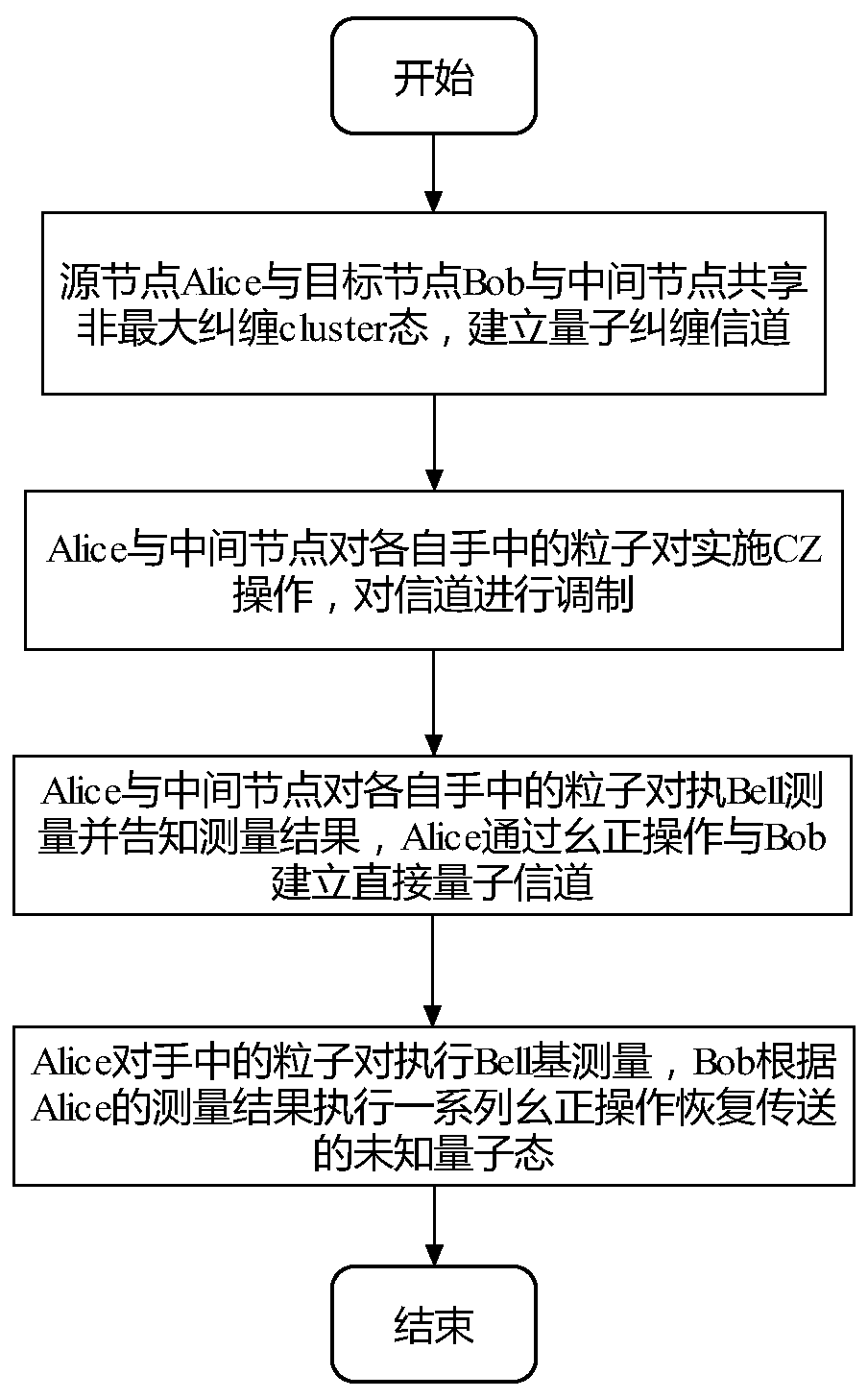
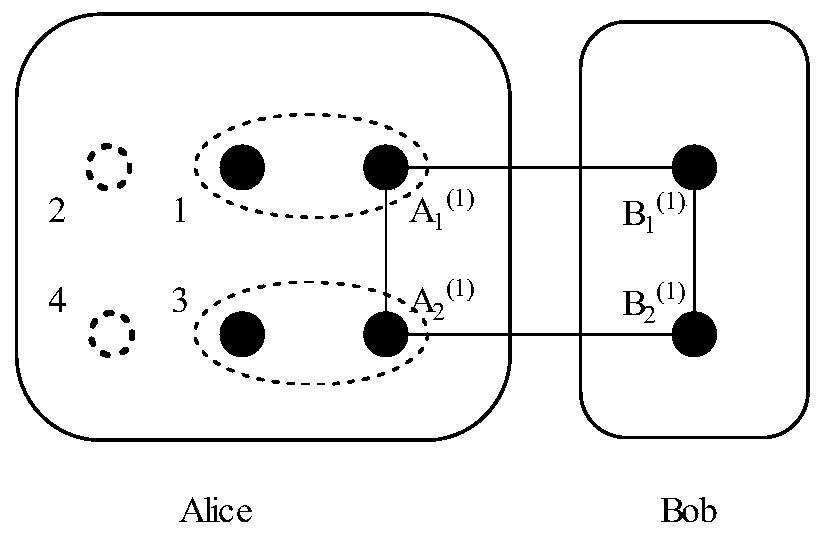
The invention relates to a multi-hop lossless teleportation method based on a non-maximum entangled chain channel. Alice and Bob, which do not directly share a quantum entanglement pair at the beginning, continuously carry out entanglement exchange through the help of p middle nodes; finally, a quantum entanglement channel is constructed; and the multi-hop teleportation process of the sender Alicetransmitting a single-particle multi-energy level unknown quantum state to the receiver Bob is completed. The method in the invention uses the non-maximum entangled chain channel; even the sender andthe receiver do not directly share the quantum entanglement pair, the quantum state information can be still transmitted between both the sides; and the requirement for constructing a complex quantumcommunication network can be satisfied; in the multi-hop lossless teleportation system in the invention, if the teleportation process is successfully executed, the information receiver Bob can obtainthe transmitted quantum state information; if the teleportation process fails, the information sender Alice can restore the transmitted unknown quantum state information; and the unknown quantum state information is not lost.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG INST OF IND TECH SOOCHOW UNIV +1
Quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state
ActiveCN105227301AHigh qubit efficiencyResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobComputer hardware
The invention discloses a quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state, comprising the following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob randomly generate respective classical keys; step 2, Alice prepares the GHZ state and divides all particles into sequences, inserts decoy photons into one of the sequences and then transmits the sequence to Bob; step 3, Bob measures the decoy photons, Alice calculates an error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 4 is executed, otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 4, Alice and Bob respectively perform measurement and obtain the measurement result of each other; step 5, Alice executes unitary transformation and obtains a new sequence, and Alice transits the sequence with the inserted decoy photons to Bob; step 6, Bob measures the decoy photons, and Alice calculates the error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 7 is executed, and otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 7, Alice calculates a shared key of both sides; step 8, Bob generates the shared key. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state can resist participant attack, outside attack and Trojan horse attack. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is safe in both a noiseless quantum channel and a quantum noisy channel. Moreover, quantum bit efficiency of the quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is higher than the existing protocols.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Controlled quantum security direct communication method based on four particle cluster states
ActiveCN107222307AMaintain entanglementLong cycleKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobQuantum secure direct communication
The invention discloses a controlled quantum security direct communication method based on four particle cluster states. Alice and Bob respectively serve as a legal information sender and a legal information receiver during a quantum communication process, and Charlie serves as a credible scheme control party; information security is achieved by randomly inserting a single photon to perform measurement-based comparison detection, and communication starts after security detection; Alice uniformly divides the prepared four particle cluster states into two groups, after being subjected to an XOR operation with a pseudorandom sequence, the sent information is encoded on the two particles reserved by Alice via unitary transformation. Alice performs Bell-based measurement on reserved particles, and sends measurement information to Bob, and Bob recovers the original sequence via an initial state sent by Charlie after the measurement information is compared. The four particle cluster states used by the method has good entanglement, connectivity and damage resistance, only the receiver Bob in the method gets the permission of the controller Charlie, Bob can recover the original information, so that the information can be effectively prevented from being attacked during a transmission process, and an implementation process is simple.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
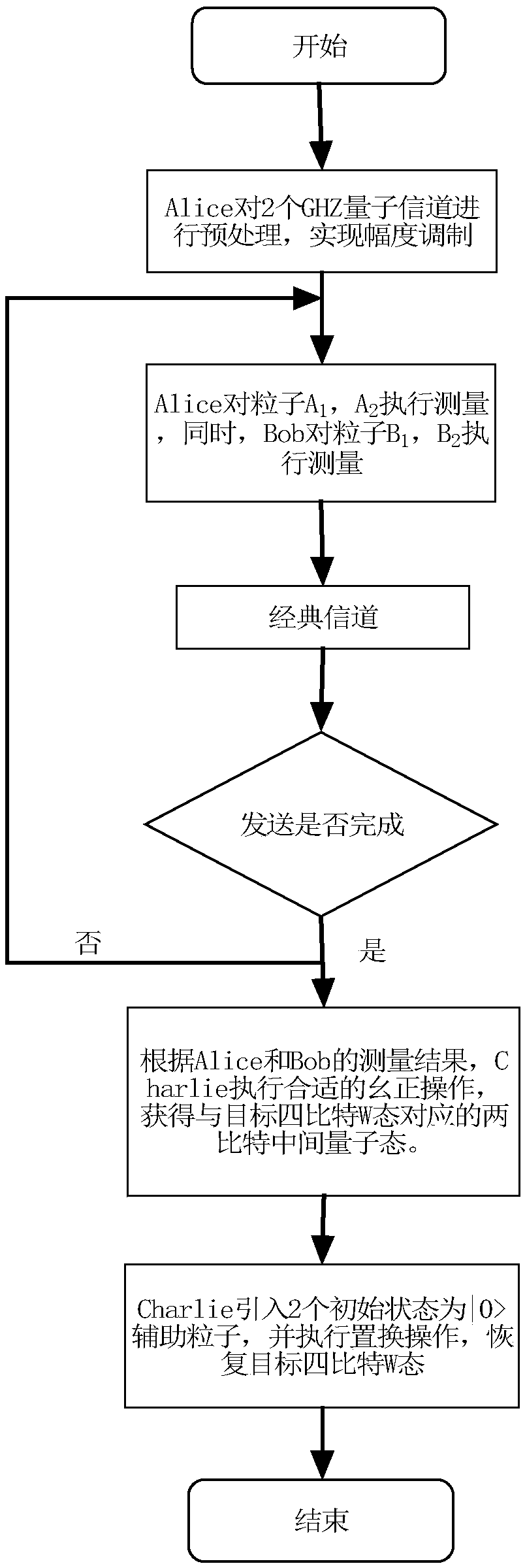
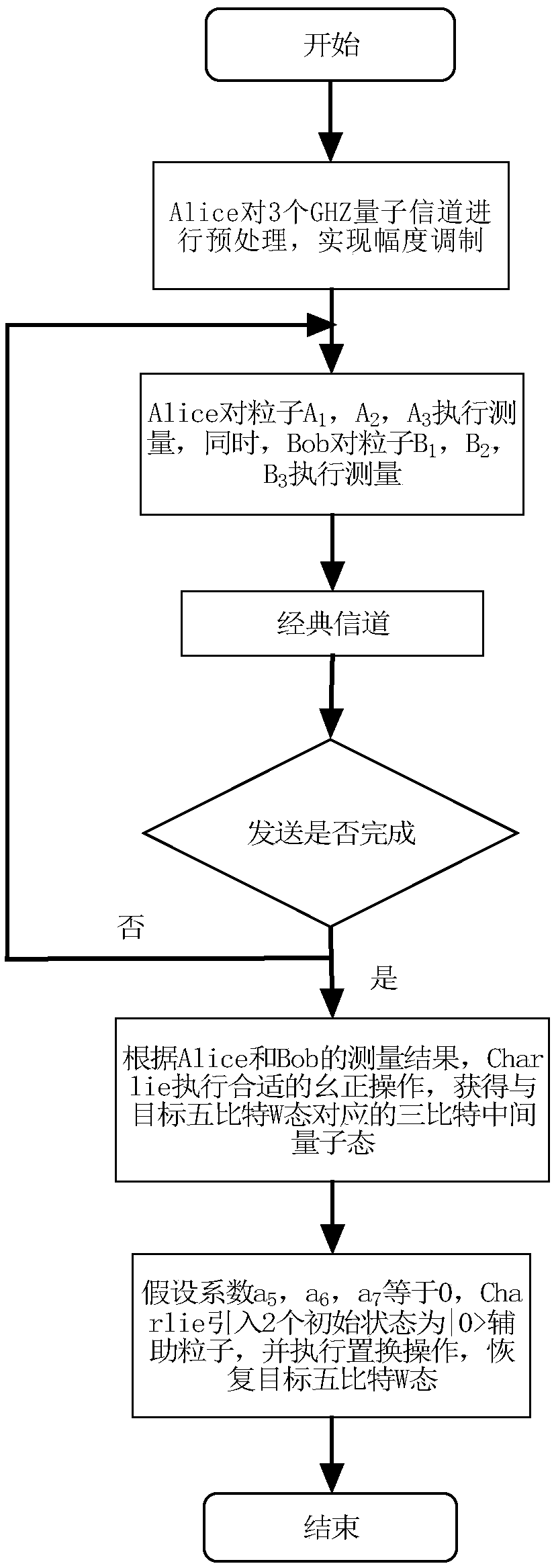
GHZ-state-based joint remote M-bit W state preparation method
ActiveCN108540236APrevent leakageReduce consumptionPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobMedicine
The invention relates to a GHZ-state-based joint remote M-bit W state preparation method, which is designed to utilize least quantum channel resources. The method comprises the following steps that: two senders, namely, Alice and Bob as well as one receiver, namely, Charlie remotely prepare an M-bit W state, the three parties only need to share [log<2>M] GHZ channels, and the sender, namely, Alicepreprocesses a quantum communication channel according to amplitude information of the W state; the two senders, namely, Alice and Bob respectively construct corresponding measurement bases accordingto partial phase information of the W state to be prepared, measure own particles, and send measurement results to the receiver, namely, Charlie; the receiver, namely, Charlie performs a unitary operation on owned particles according to the measurement results of the two senders, namely, Alice and Bob to obtain an intermediate quantum state corresponding to a target W state; and the receiver, namely, Charlie introduces auxiliary particles, performs a corresponding substitution operation, and recovers a target M-bit W state. Through adoption of the method, information leakage can be avoided, and the consumption of quantum resources is reduced effectively.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Differential non-Gauss operation radioactivity continuous variable quantum key distribution method
InactiveCN103746799AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobCommunications system
The invention discloses a differential non-Gauss operation radioactivity continuous variable quantum key distribution method. A trusted third party Fred prepares a dual-mode vacuum compression state which is marked as rho[ab] by use of a laser generator, a photon undergoes beam dividing of the dual-mode vacuum compression state rho[ab] and then undergoes double-mode unitary transformation Uab<^> to commonly generate a double-mode vacuum compression state phi>a0b0, at the moment, the output modes of the photon are respectively marked as a0 and b0, photon subtraction operation is used to realize non-Gauss operation to respectively obtain a mode a1 and a mode b1, when Alice and Bob receive photon output modes a2 and b2 transmitted by a noise channel, a heterodyne detector is utilized to perform detection for secret negotiation and error correction, and finally, a secret key is extracted and obtained for data encryption. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: non-Gauss modulation is realized at a source by use of a photon number distinguishing detector, and the security of secret key transmission in a quantum communication system is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
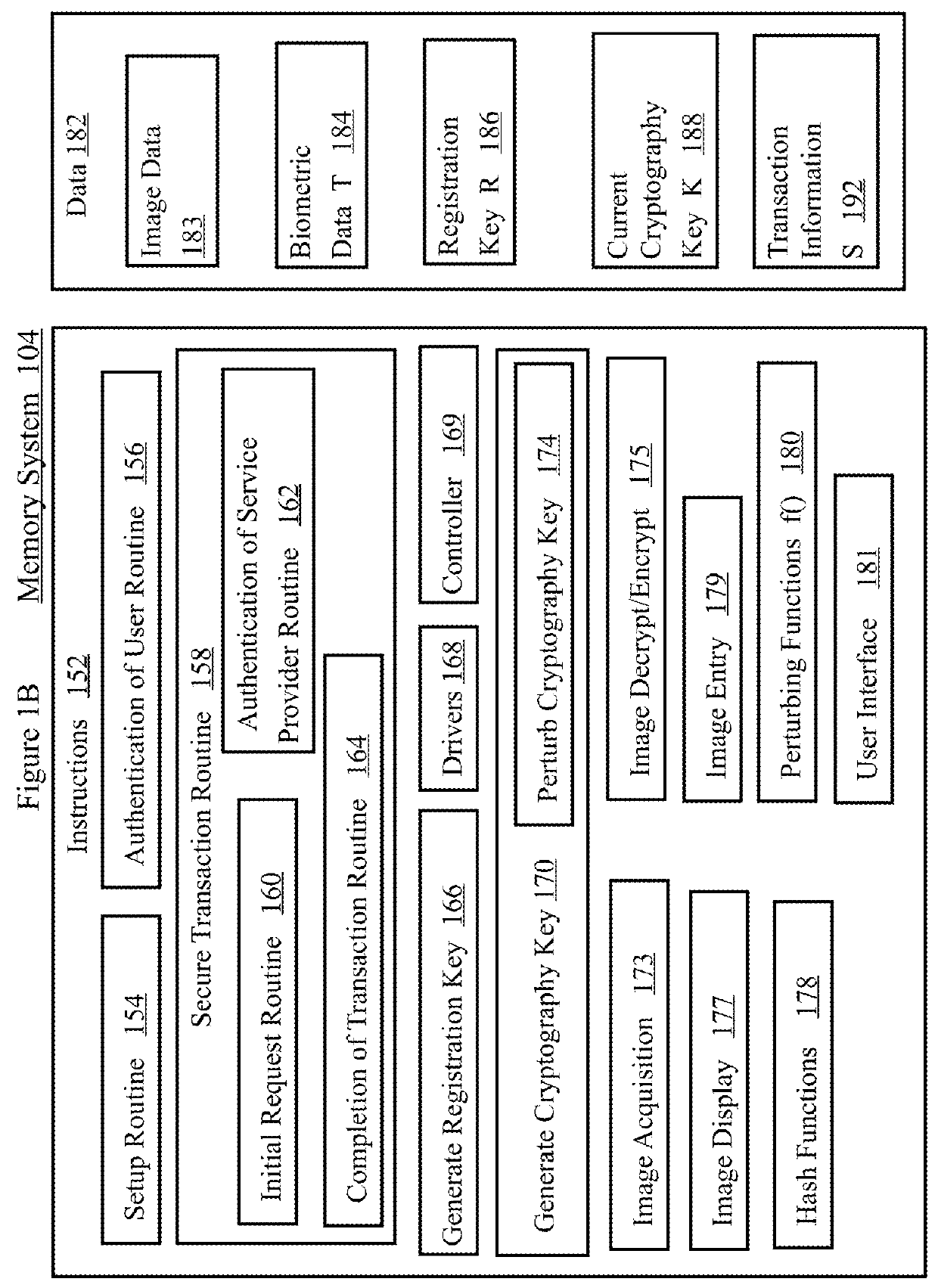
Visual image authentication
ActiveUS20160034682A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsAlice and BobKey exchange
Methods and systems described herein perform a secure transaction. A display presents images that are difficult for malware to recognize but a person can recognize. In at least one embodiment, a person communicates transaction information using visual images received from the service provider system. In at least one embodiment, a universal identifier is represented by images recognizable by a person, but difficult for malware to recognize.In some embodiments, methods and systems are provided for determining whether to grant access, by generating and displaying visual images on a screen that the user can recognize. In an embodiment, a person presses ones finger(s) on the screen to select images as a method for authenticating and protecting communication from malware.In at least one embodiment, quantum randomness helps unpredictably vary the image location, generate noise in the image, or change the shape or texture of the image.In some embodiments, visual image authentication helps Alice and Bob detect if Eve has launched a man-in-the-middle attack on their key exchange.
Owner:FISKE SOFTWARE
QKD with classical bit encryption
InactiveUS7620182B2Key distribution for secure communicationData stream serial/continuous modificationAlice and BobPassword
A method for enhancing the security of a quantum key distribution (QKD) system having QKD stations Alice and Bob. The method includes encrypting key bits generated by a true random number generator (TRNG) and sent to a polarization or phase modulator to encode weak optical pulses as qubits to be shared between Alice and Bob. Key bit encryption is achieved by using a shared password and a stream cipher. Bob obtains at least a subset of the original key bits used by Alice by utilizing the same stream cipher and the shared password.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Four-particle GHZ state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol
ActiveCN105245331AHigh qubit efficiencyResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobSerial code
The invention discloses a four-particle GHZ state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol. The protocol includes the following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob randomly generate respective classic keys and negotiate on functions; step 2, Alice selects n four-particle GHZ combination and separation sequences, and randomly inserts decoy photons into three sequences and transmits the new sequences to Bob; step 3, Bob measures the decoy photons, and Alice calculates an error rate; step 4, Alice executes CNOT operation on every three corresponding particles with the same serial numbers in the sequences by twice; step 5, Alice executes unitary transformation so as to obtain new sequences, and selects out the decoy photons and inserts the decoy photons into the sequences and transmits the sequences to Bob; step 6, Bob measures the decoy photons; Alice compares measurement results and calculates an error rate, and step 7 is executed if the error rate is low, otherwise, the method returns to step 2; step 7, Alice generates a shared key; and step 8, Bob generates a shared key. With the four-particle GHZ state two-party quantum key agreement protocol of the invention adopted, existing participant attacks and the external attacks can be resisted. The quantum bit efficiency of the protocol is much higher than that of an existing protocol.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
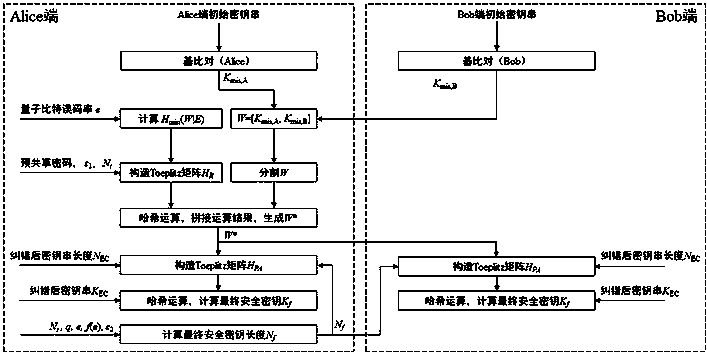
Verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution
ActiveCN108599934AMeet security needsEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobLower limit
The invention discloses a verifiable and secure privacy amplification method based on quantum key distribution. The method comprises the steps of S1, generating an initial random number string W, respectively generating random number strings K<mis,A> and K<mis,B> by two communication parties (Alice and Bob) in a base comparison process of quantum key distribution, and combining the two random number strings into a random number string W=[<Kmis,A>, K<mis,B>] by the Alice; S2, verifying randomness, after an error correction phase of the quantum key distribution is finished, estimating the minimum entropy lower limit of the W relative to an attacker Eve, wherein H<min>(W|E) is greater than or equal to 1-H<2>(e); S3, calculating a final secure key length N<f>; S4, extracting a perfect random string W*, through adoption of a partial pre-shared secure key of the two communication parties, constructing a Toeplitz matrix H<R>, and extracting the perfect random number string W* from the W according to the H<R>; S5, negotiating a universal hash function H<PA> through a public channel according to the W*; and S6, respectively carrying out hash operation on error corrected key strings by the two communication parties according to the H<PA>, and generating a final secure key. The method has the advantages of verifiability, security, easy realization and simplification of quantum key distribution system design and realization.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
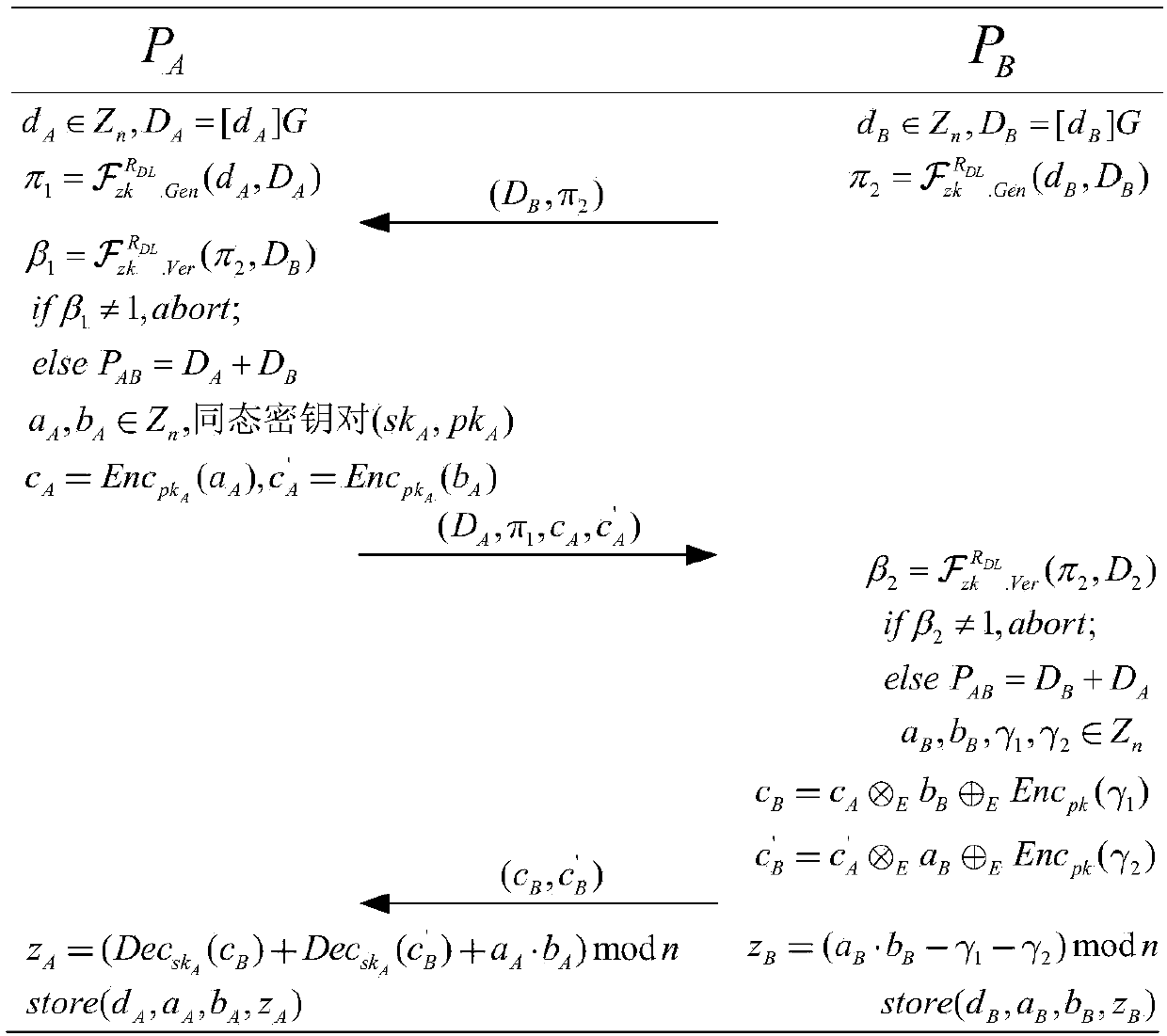
ECDSA digital signature method based on two-party collaboration
ActiveCN109639439ASafe and efficient collaborative signatureImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlice and BobDigital signature
The invention discloses an ECDSA digital signature method based on two-party collaboration. The method comprises the following steps: step 1), respectively generating corresponding signature public and private key pairs and other parameters by a signature party Alice and a signature party Bob participating in the collaborative signature; and step 2), collaboratively completing ECDSA signature by Alice and Bob, and finally outputting the signature (r,s). According to the ECDSA digital signature method based on the two-party collaboration provided by the invention, under the premise of ensuringthe security and the correctness, a signature process does not introduce high-overhead password operations such as homomorphic encryption, oblivious transfer and the like, so that a signature scheme achieves a good balance between the communication overhead and the computation overhead, and therefore the performance is remarkably superior to that of all existing ECDSA two-party collaborative digital signature methods.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Key management and user authentication for quantum cryptography networks
ActiveUS8340298B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAlice and BobTelecommunications link
Key management and user authentication systems and methods for quantum cryptography networks that allow for users securely communicate over a traditional communication link (TC-link). The method includes securely linking a centralized quantum key certificate authority (QKCA) to each network user via respective secure quantum links or “Q-links” that encrypt and decrypt data based on quantum keys (“Q-keys”). When two users (Alice and Bob) wish to communicate, the QKCA sends a set of true random bits (R) to each user over the respective Q-links. They then use R as a key to encode and decode data they send to each other over the TC-link.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
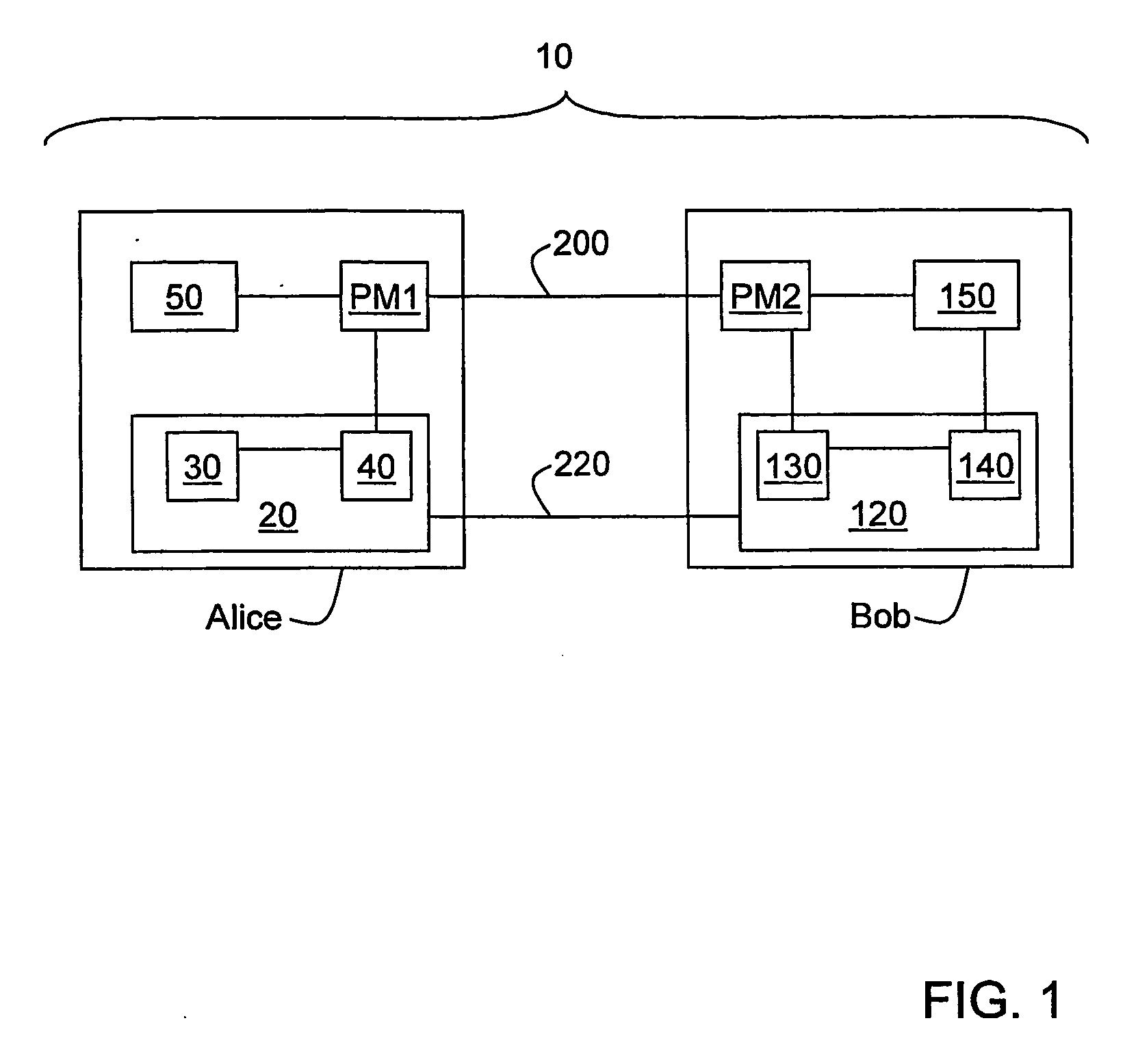
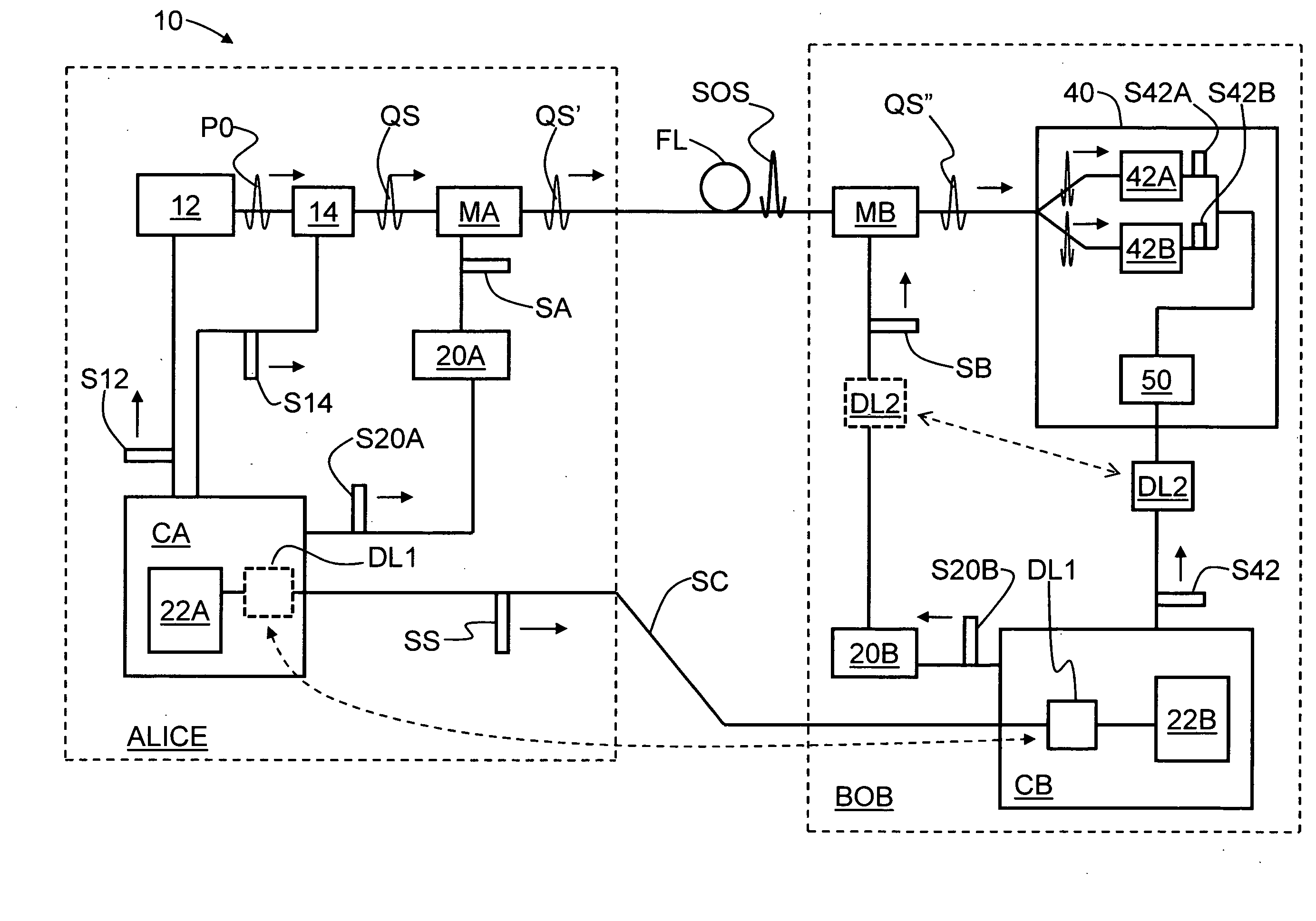
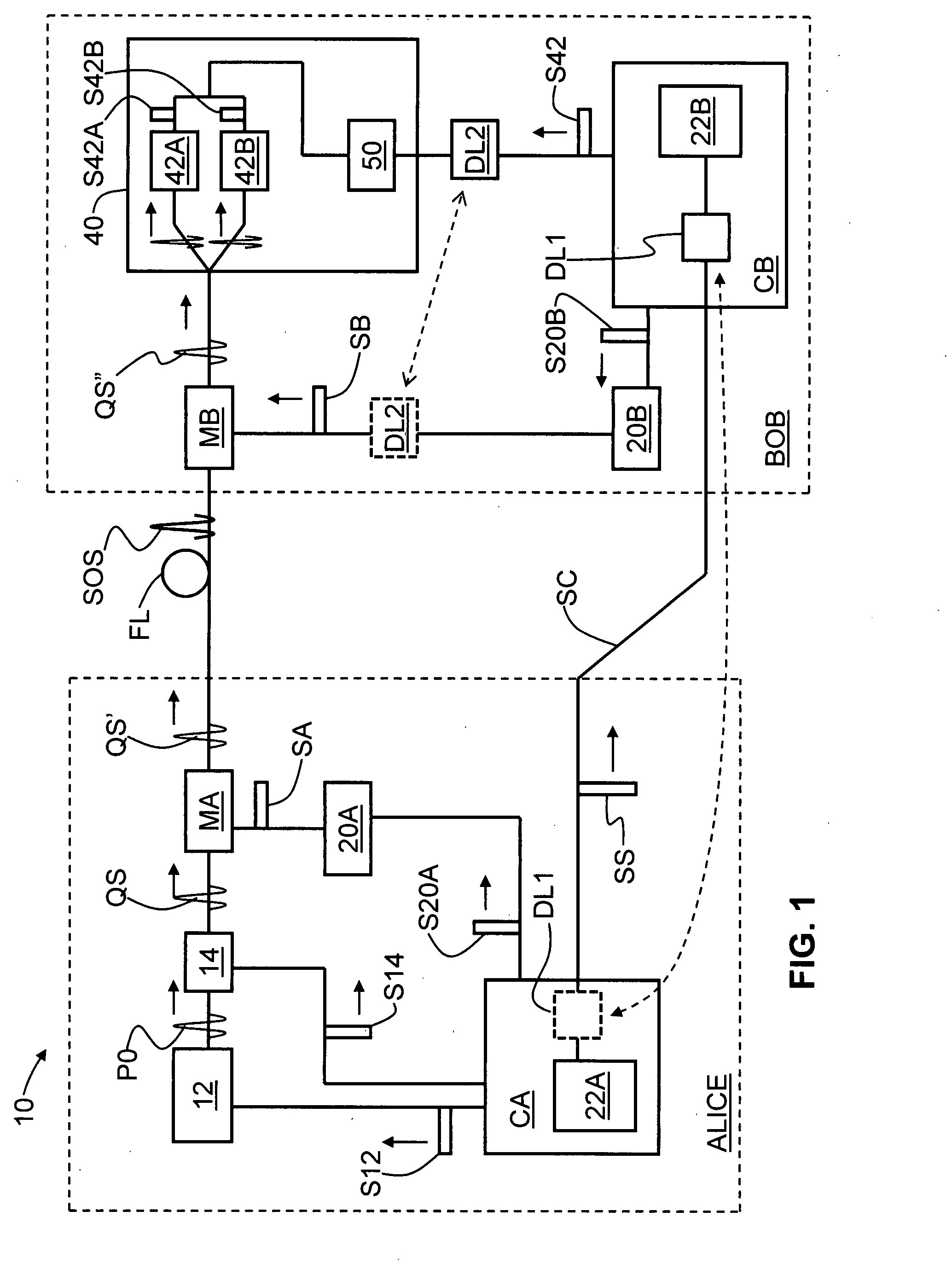
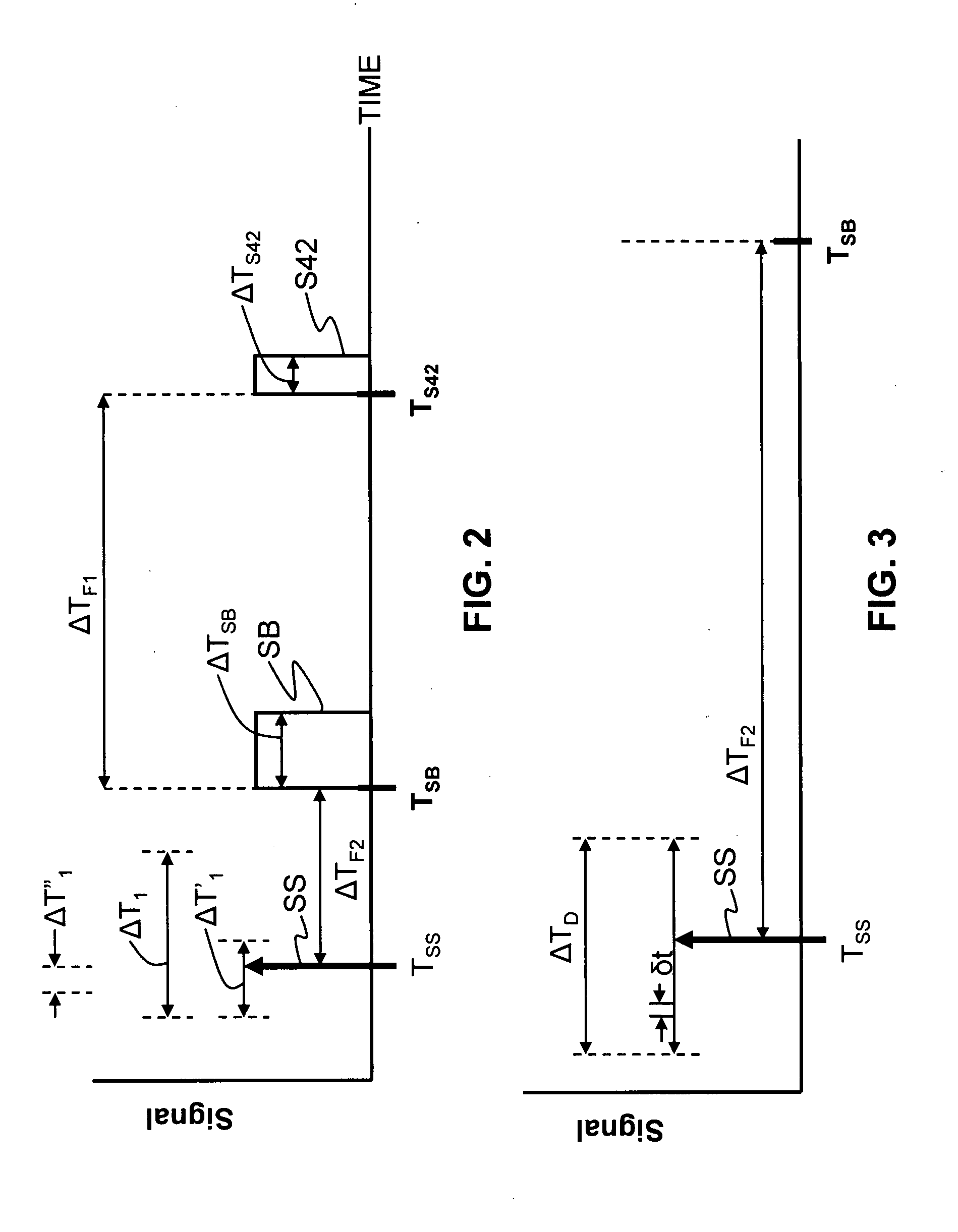
QKD system with common-mode dithering
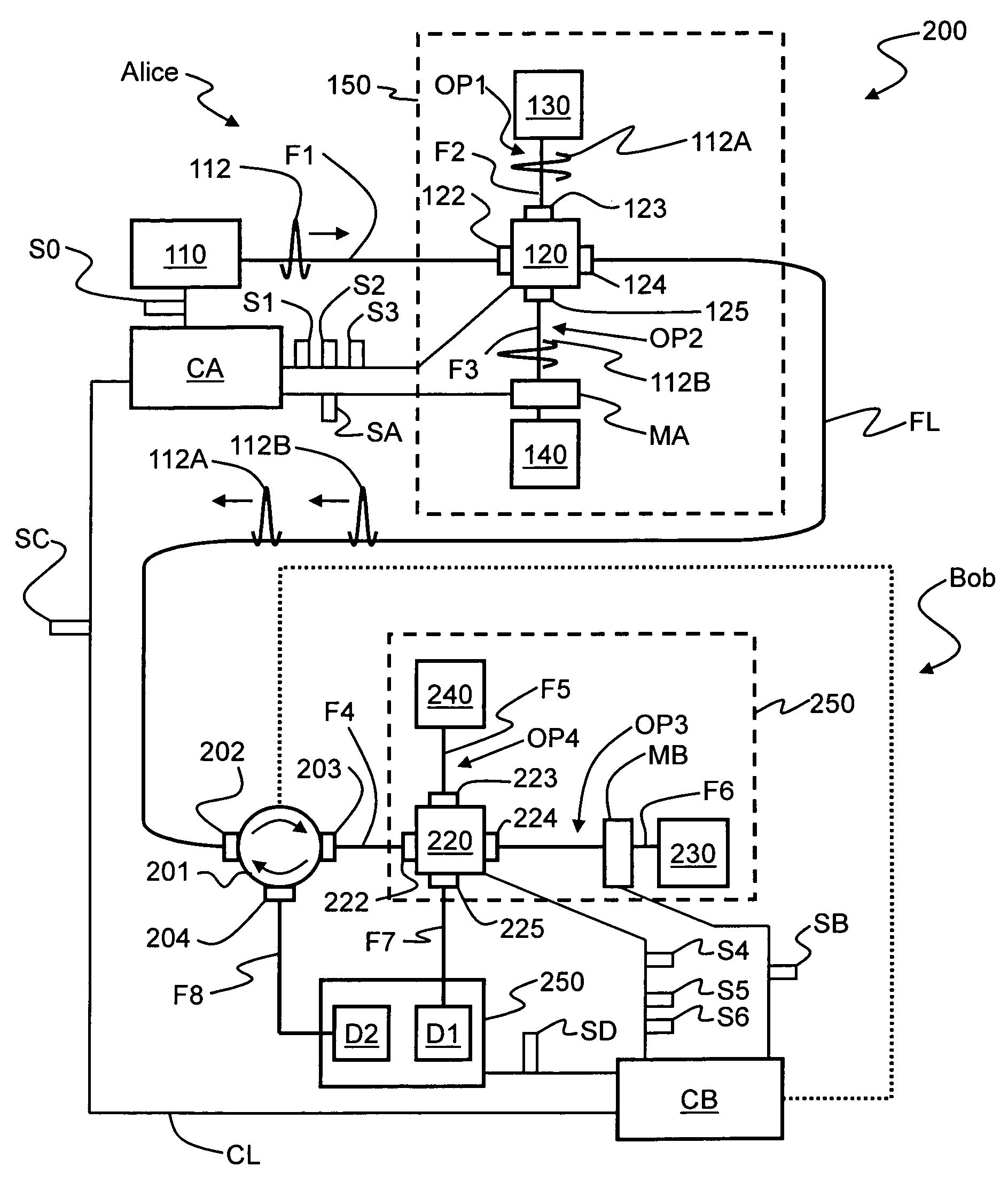
ActiveUS20090022326A1Key distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobSignal timing
A QKD system (10) having two QKD stations (Alice and Bob) optically coupled by an optical fiber link (FL), wherein Bob includes a variable timing delay arranged between Bob's controller (CB) and modulator (MB) or detector unit (40). A set-up and calibration procedure is performed wherein delay DL2 is adjusted until the timings for the modulator and detector unit (TSB and TS42, respectively) are established. Delay DL2 is then fixed so that the detector unit and modulator operate in a common timing mode that is not changed if the synchronization signal is changed. The timing TSS of the synchronization (sync) signals (SS) sent from Alice to Bob is adjusted to arrive at optimum system performance. Once the QKD system is in operation, because the sync signal can drift, the sync signal timing TSS is dithered maintain optimum QKD system performance. Since the modulator and detector unit timing is tied together, dithering the sync signal also dithers the modulator and detector unit together in a “common mode,” rather than varying the timing of each of these elements separately.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
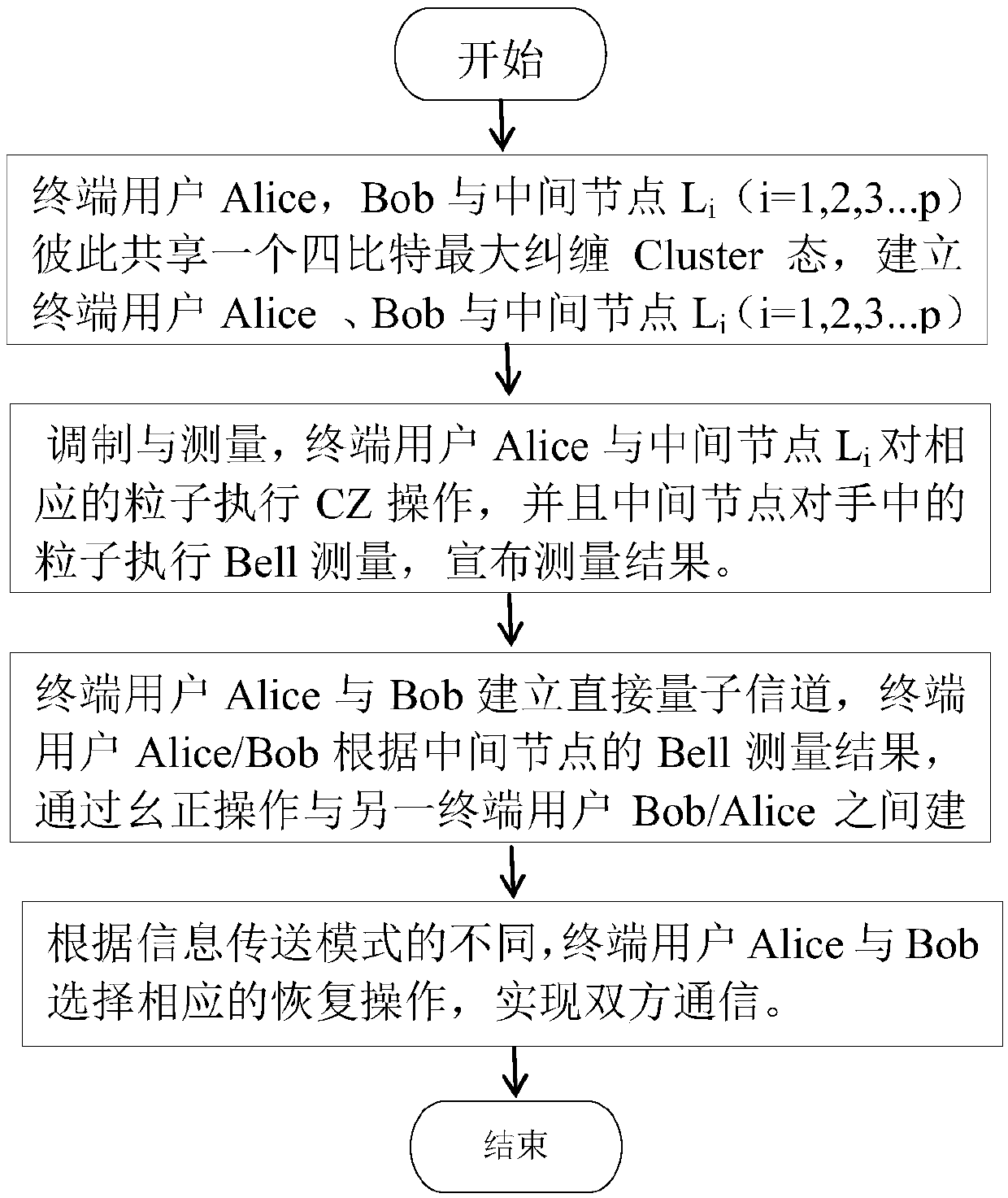
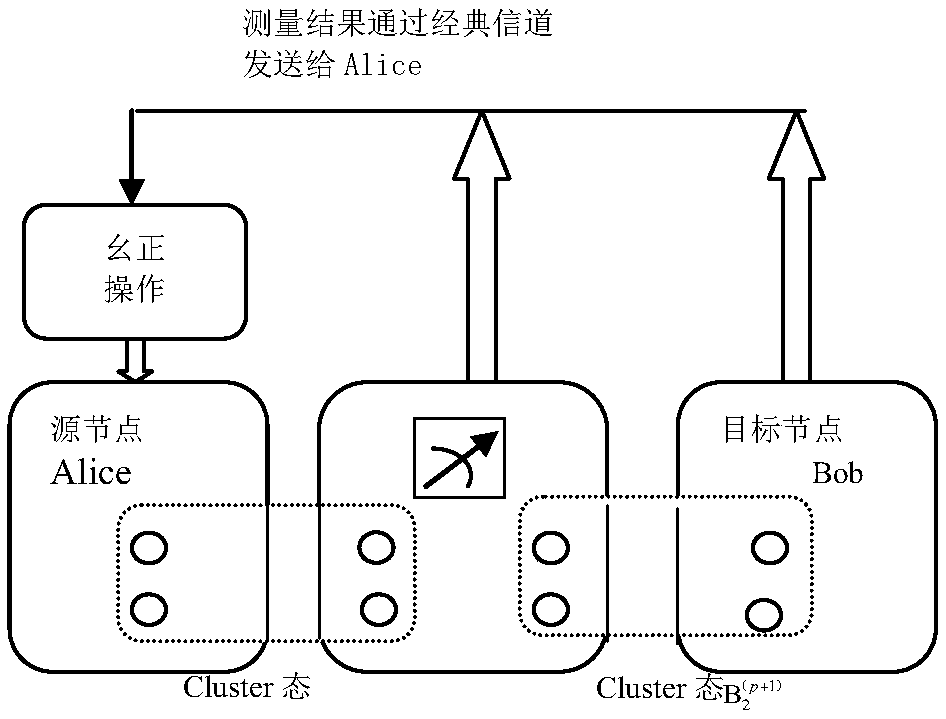
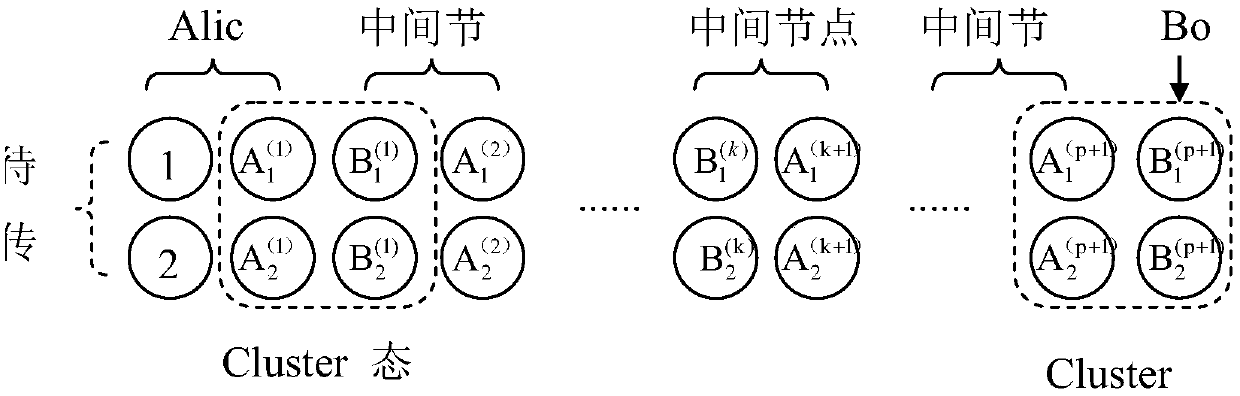
Remote teleportation method based on four-bit Cluster state
InactiveCN108900254AImprove transmission efficiencySolving the problem of long-distance long-distance quantum communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobNetwork termination
The invention discloses a remote teleportation method based on a four-bit Cluster state. For network terminal users Alice and Bob, through help of an intermediate node, communication between a networkterminal Alice and the other terminal user Bob is completed. The method comprises the four steps that 1, the four-bit most entangled Cluster state is shared by the terminal users Alice, Bob and the intermediate node Li (i=1, 2, 3, ..., p), and a quantum entanglement channel of the terminal users Alice and Bob and the intermediate node Li (i=1, 2, 3, ..., p) is built; 2, modulation and measurementare conducted, wherein CZ operation is conducted on corresponding particles by the terminal user Alice and the intermediate node Li, moreover, Bell measurement is conducted on the particles in handsby the intermediate node, and measurement results are announced; 3, a direct quantum channel between the terminal user Alice / Bob and the other terminal user Bob / Alice is built according to the Bell measurement results of the intermediate node through unitary operation; 4, according to difference of information transferring modes, the terminal users Alice and Bob choose corresponding restoring operation according to the Bell measurement results of each other to achieve intercommunication.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Two-party quantum key negotiation protocol based on three-particle GHZ state
ActiveCN105490804AFair establishmentSecure and confidential communicationKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareAlice and Bob
The present invention discloses a two-party quantum key negotiation protocol based on a three-particle GHZ state, comprising the following steps: step 1: Alice and Bob negotiate codes of quantum states; step 2: Alice prepares n+q GHZ states and divides all the particles into sequences; Alice sends a sequence SC to Bob; step 3: Bob selects and measures q sample particle(s); Alice selects measurement bases to measure corresponding particles; Bob calculates an error rate; and if the error rate is low, step 4 is performed, otherwise step 2 is performed; step 4: Alice performs a Bell measurement on two particles with the same sequence number in the sequences; Bob performs X-base measurement on the particles in the sequences; and Alice and Bob respectively obtain the same shared key according to measurement results and the codes of the quantum states. According to the present invention, the two-party quantum key negotiation protocol can resist existing participant attacks and external attacks as well as Trojan horse attacks, is safe in noiseless quantum channels and quantum noise channels, and can achieve a relatively high quantum bit efficiency.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Laser autocalibration for QKD systems
InactiveCN1954541AKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobOptoelectronics
A method of autocalibrating a quantum key distribution (QKD) system (200) is disclosed. The QKD system includes a laser ((202) that generates photon signals in response to a laser gating signal (S0) from a controller (248). The method includes first performing a laser gate scan (304) to establish the optimum arrival time (TMAX) of the laser gating signal corresponding to an optimum-e.g., a maximum number of photon counts (NMAX)-from a single-photon detector (SPD) unit (216) in the QKD system when exchanging photon signals between encoding stations (Alice and Bob) of the QKD system. Once the optimal laser gating signal arrival time (TMAX) is determined, the laser gate scan is terminated and a laser gate dither process (308) is initiated. The laser dither involves varying the arrival time (T) of the laser gating signal around the optimum value of the arrival time TMAX. The laser gate dither provides minor adjustments to the laser gating signal arrival time to ensure that the SPD unit produces an optimum (e.g., maximum) number of photon counts.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Four-particle cluster state multi-hop stealth transfer method based on non-maximum entanglement cluster state
ActiveCN110572219AImprove transmission efficiencySolving the problem of long-distance long-distance quantum communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobInformation transmission
The invention discloses a four-particle cluster state multi-hop stealth transfer method based on a non-maximum entanglement cluster state. A source node Alice and a target node Bob realize long-distance quantum communication between Alice and Bob through the help of an intermediate node. The method mainly comprises four steps that (1) a source node Alice, a target node Bob and an intermediate nodeshare a non-maximum entanglement cluster state, and a quantum entanglement channel is established; (2) Alice and an intermediate node carry out CZ operation on particle pairs in hands of the Alice and the intermediate node, and modulate a channel; (3) the Alice and the intermediate node perform Bell measurement on the particle pairs in their hands and inform the measurement result, and the Aliceestablishes a direct quantum channel with the Bob through unitary operation; and (4) the Alice performs Bell-based measurement on the particle pairs in the hand, and Bob performs a series of unitary operations according to the measurement result of the Alice to obtain a transmitted unknown quantum state. The information transmission efficiency is high, the long-distance remote quantum communication problem can be solved through the help of the intermediate nodes, and the requirement for constructing a complex quantum communication network can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Cross-medium equipment-independent and discrete modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system
ActiveCN111130780AImprove security levelWill not irrelevantly affectKey distribution for secure communicationCommunications securityAlice and Bob
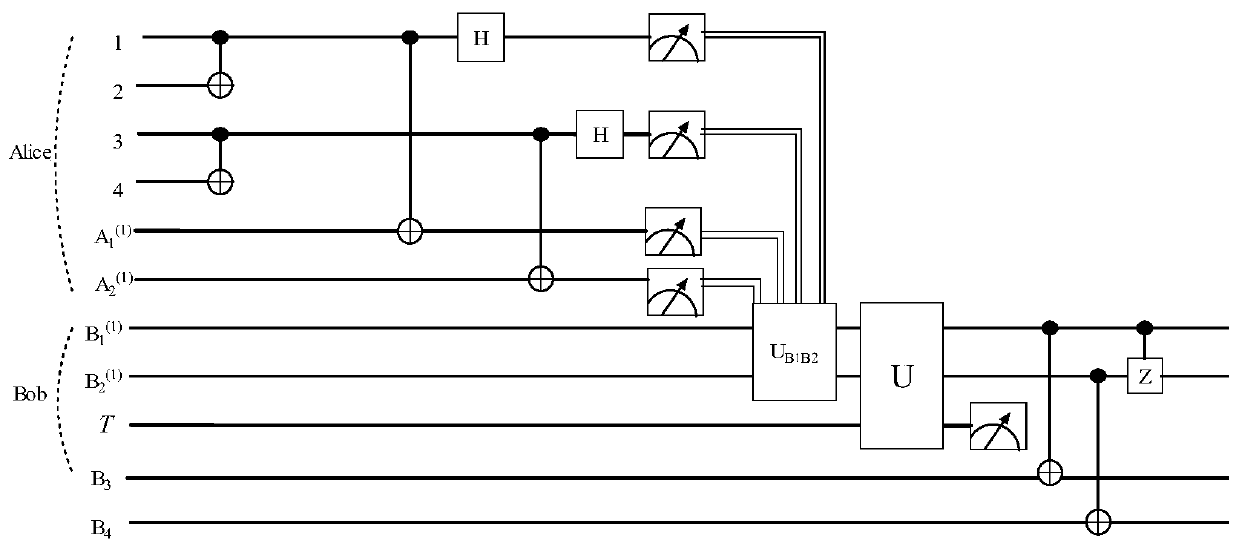
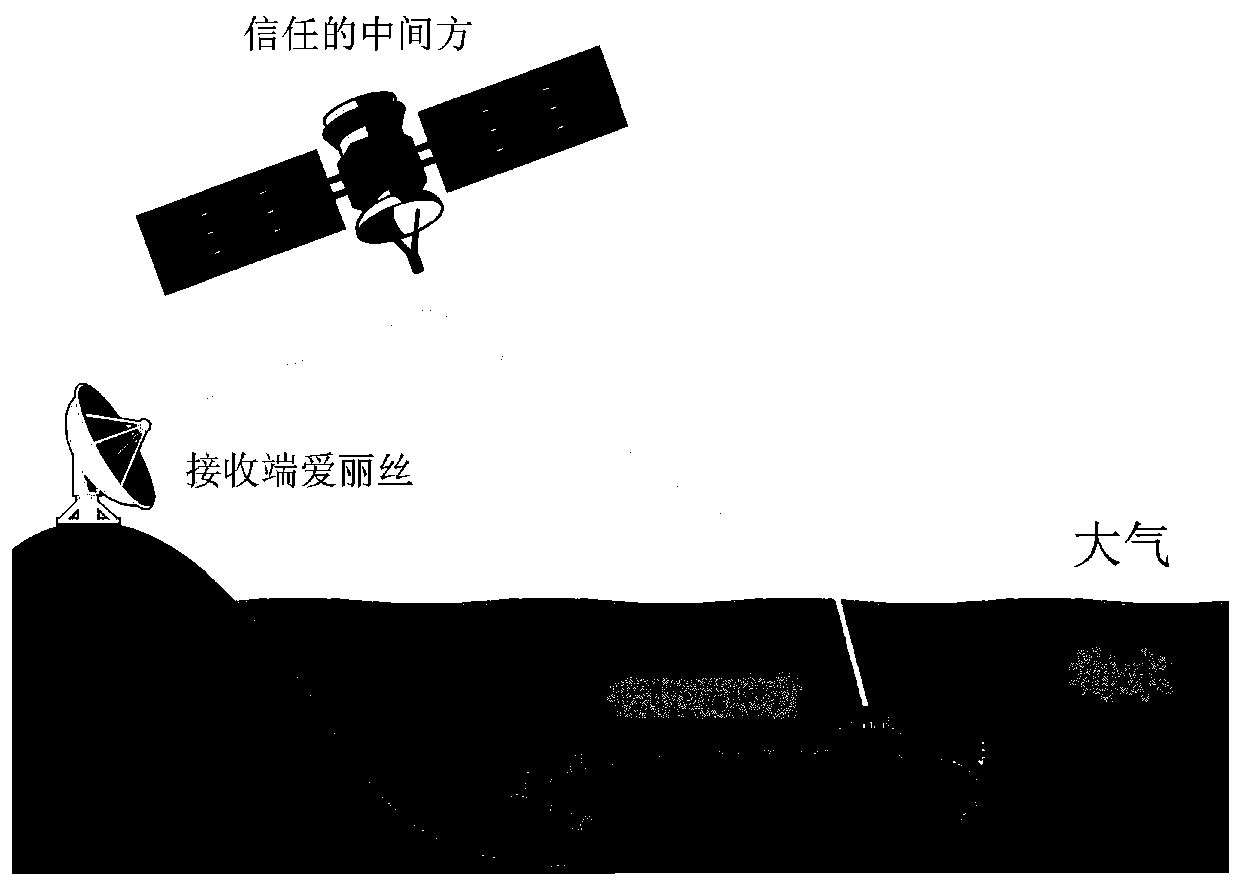
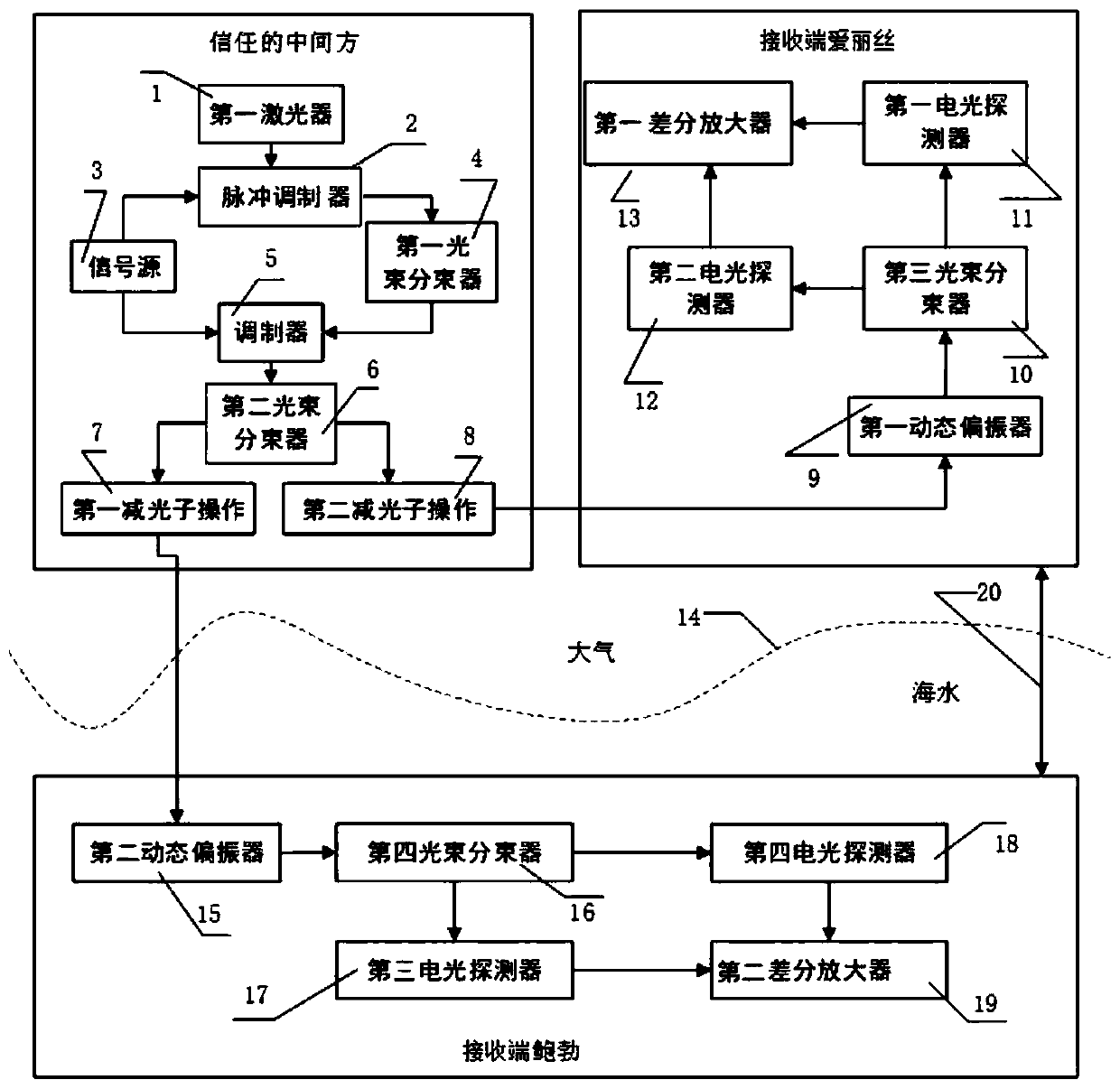
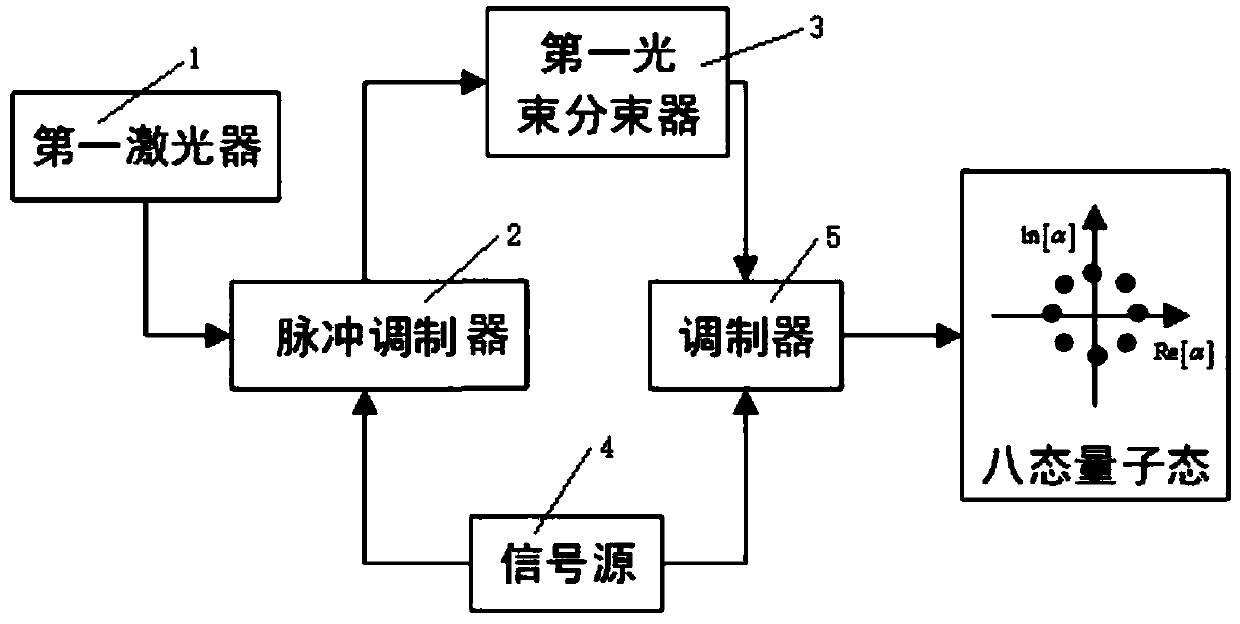
The invention discloses a cross-medium equipment-independent and discrete modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system. An eight-state quantum state is prepared by a trusted intermediate party through discrete modulation, the eight-state quantum state is sent to Alice and Bob after photon subtraction, Alice and Bob perform demodulation and homodyne detection on the received quantum state respectively, and a security key is established within an effective distance. According to the invention, a continuous variable quantum key distribution technology in a free space is improved, and the quantum state is prepared and sent by the trusted intermediate party, so that the system has equipment independence, and the communication security is ensured; the photon subtraction operation can improve the entanglement degree between the quanta so as to improve the transmission distance; the homodyne detection can effectively filter the interference of the outside on the optical signal, and the detection result can be well obtained even if the optical signal is influenced to a certain extent. The scheme is oriented to equipment independence under an air-water channel, discrete modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution is utilized, and more practicability is brought to free space communication of quanta.
Owner:WUXI TAIHU UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com