Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Oblivious transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, an oblivious transfer (OT) protocol is a type of protocol in which a sender transfers one of potentially many pieces of information to a receiver, but remains oblivious as to what piece (if any) has been transferred.
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
ActiveUS20050259817A1Data processing applicationsPublic key for secure communicationOblivious transferData mining
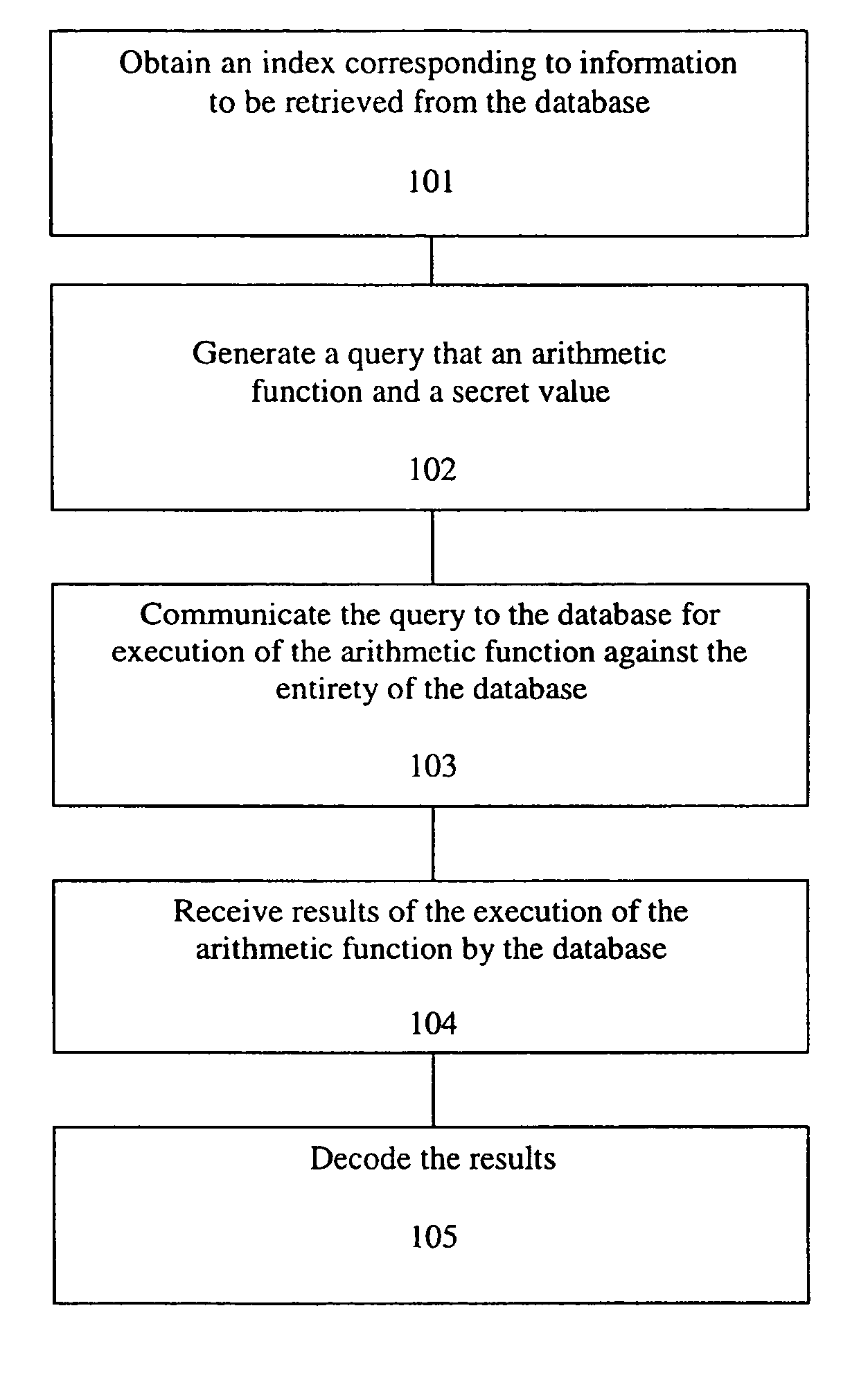
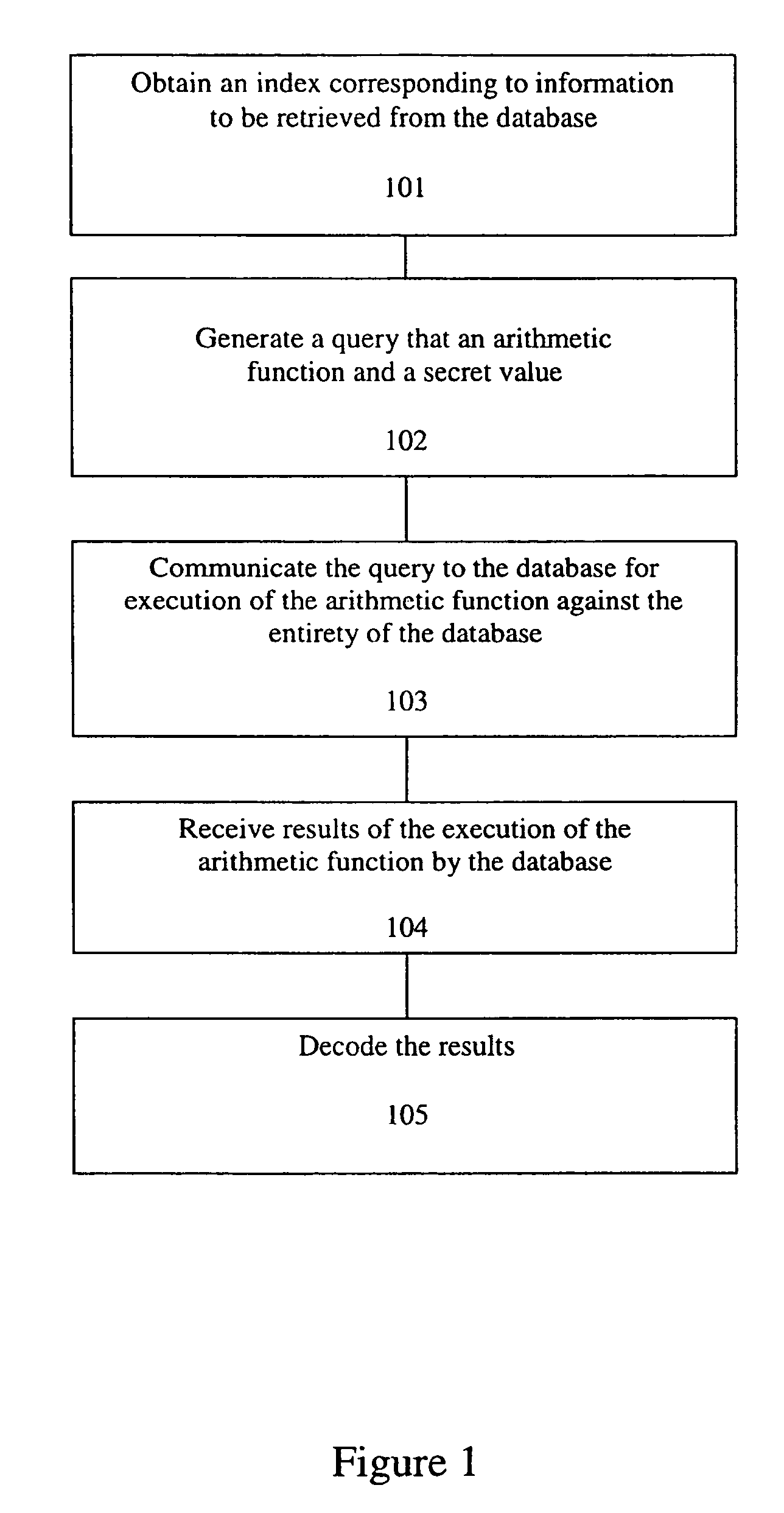
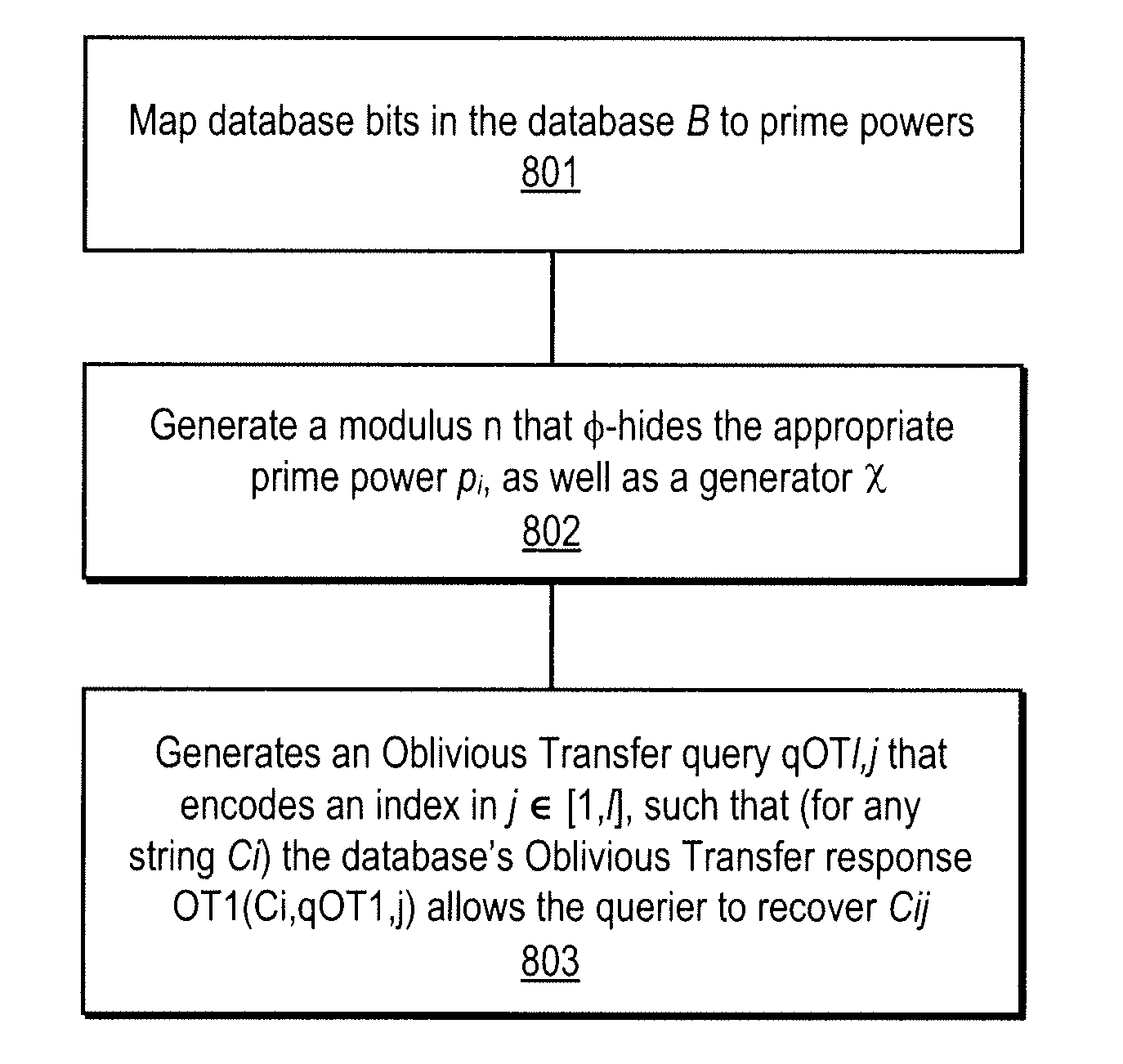
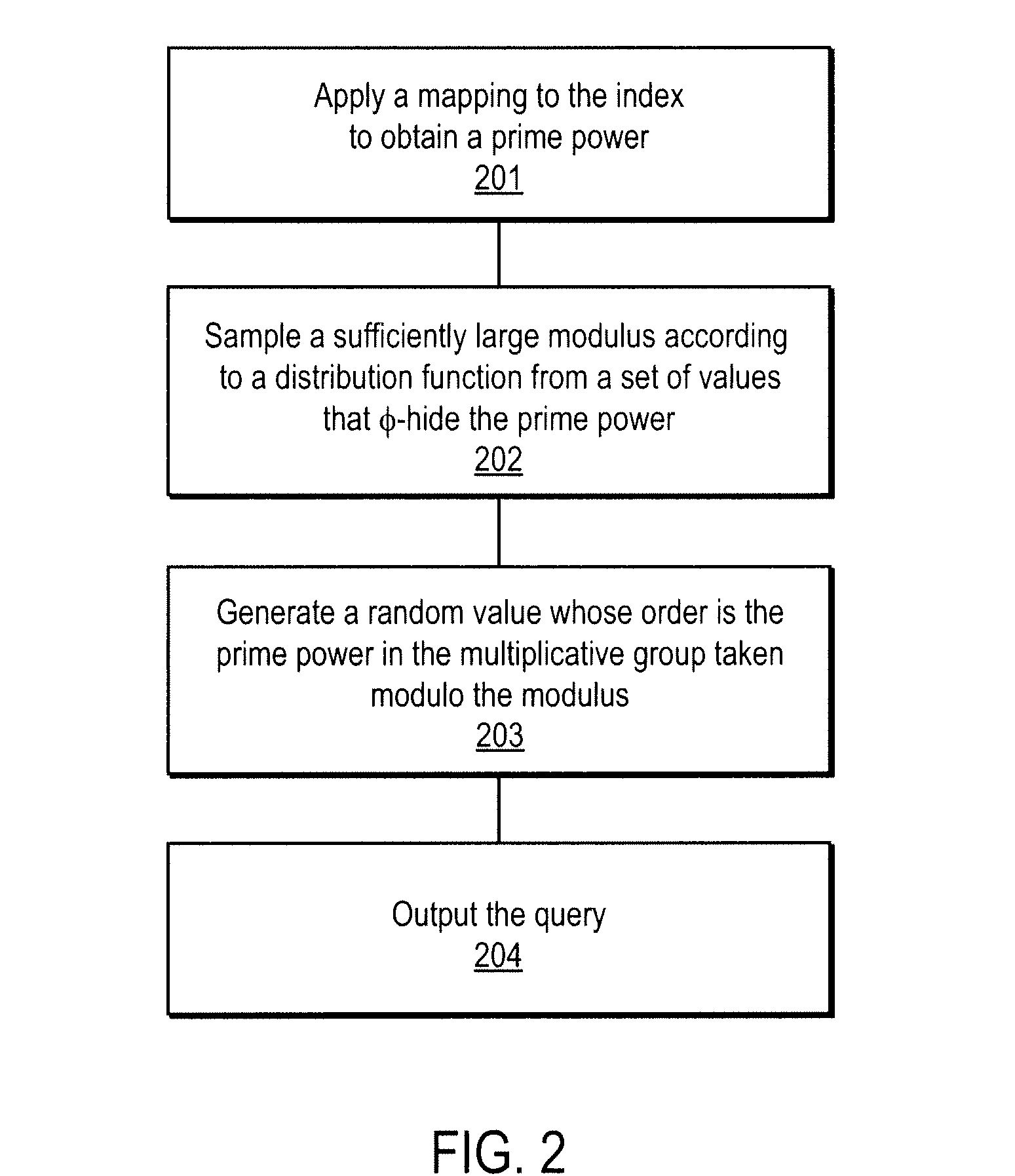
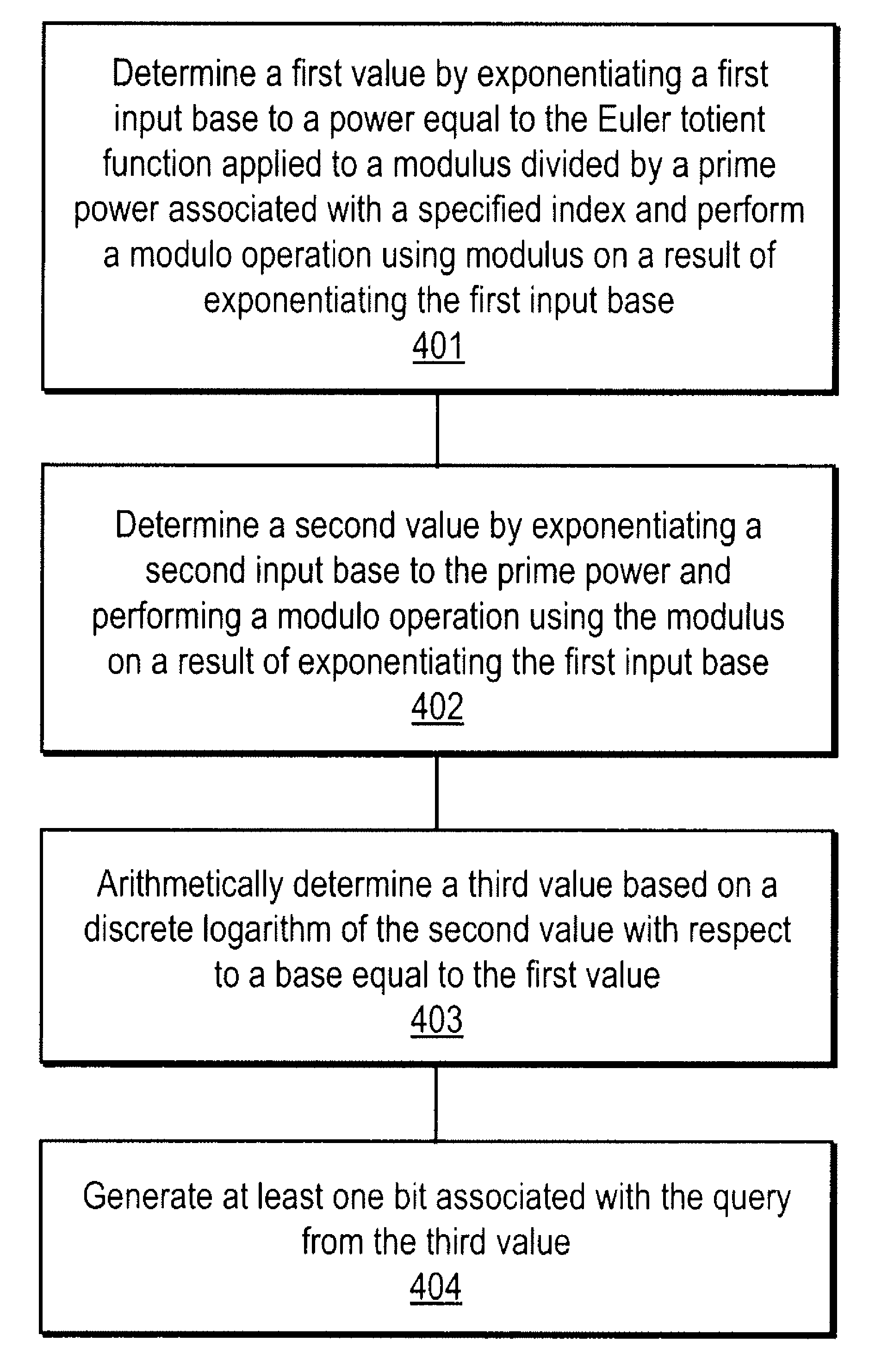
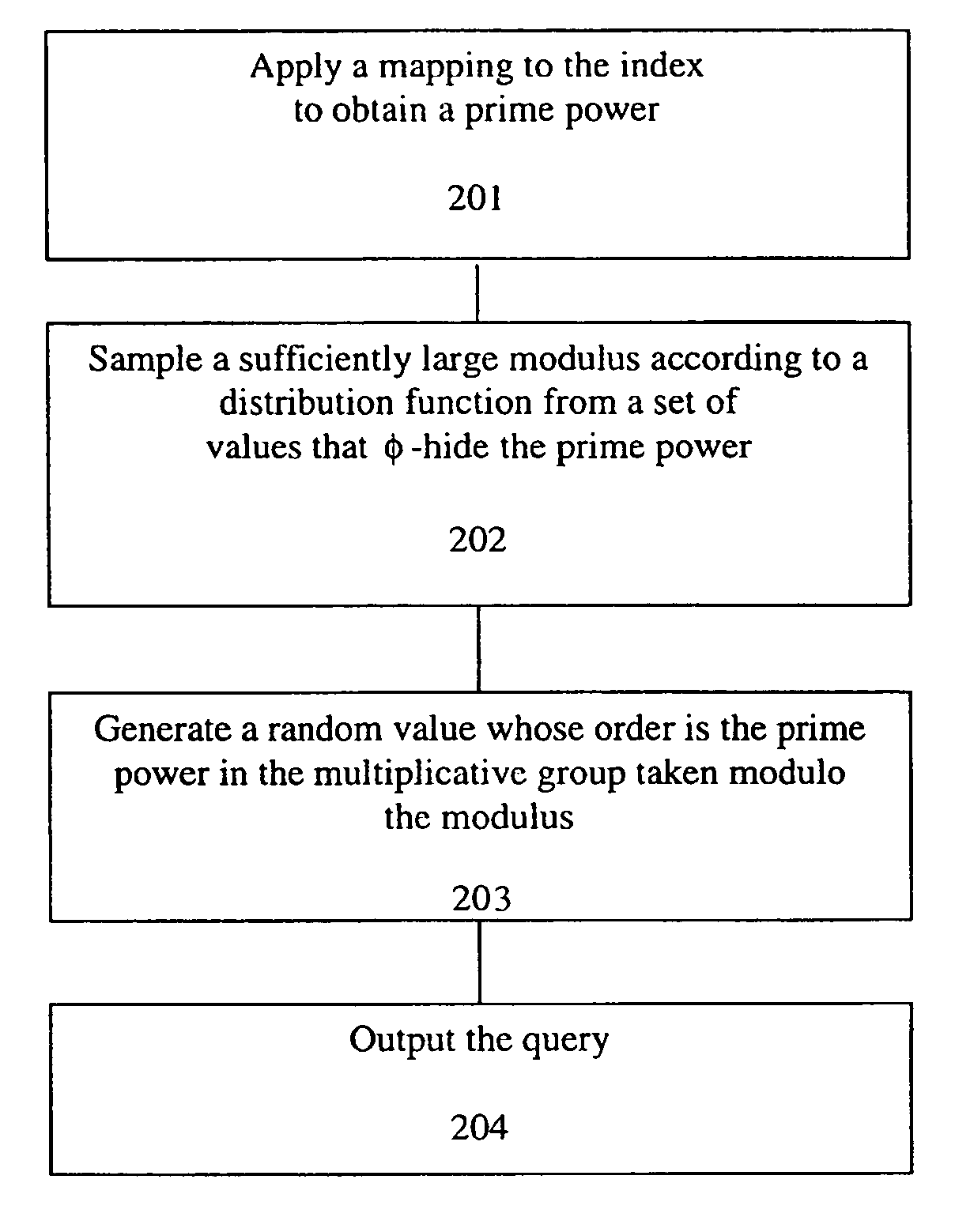
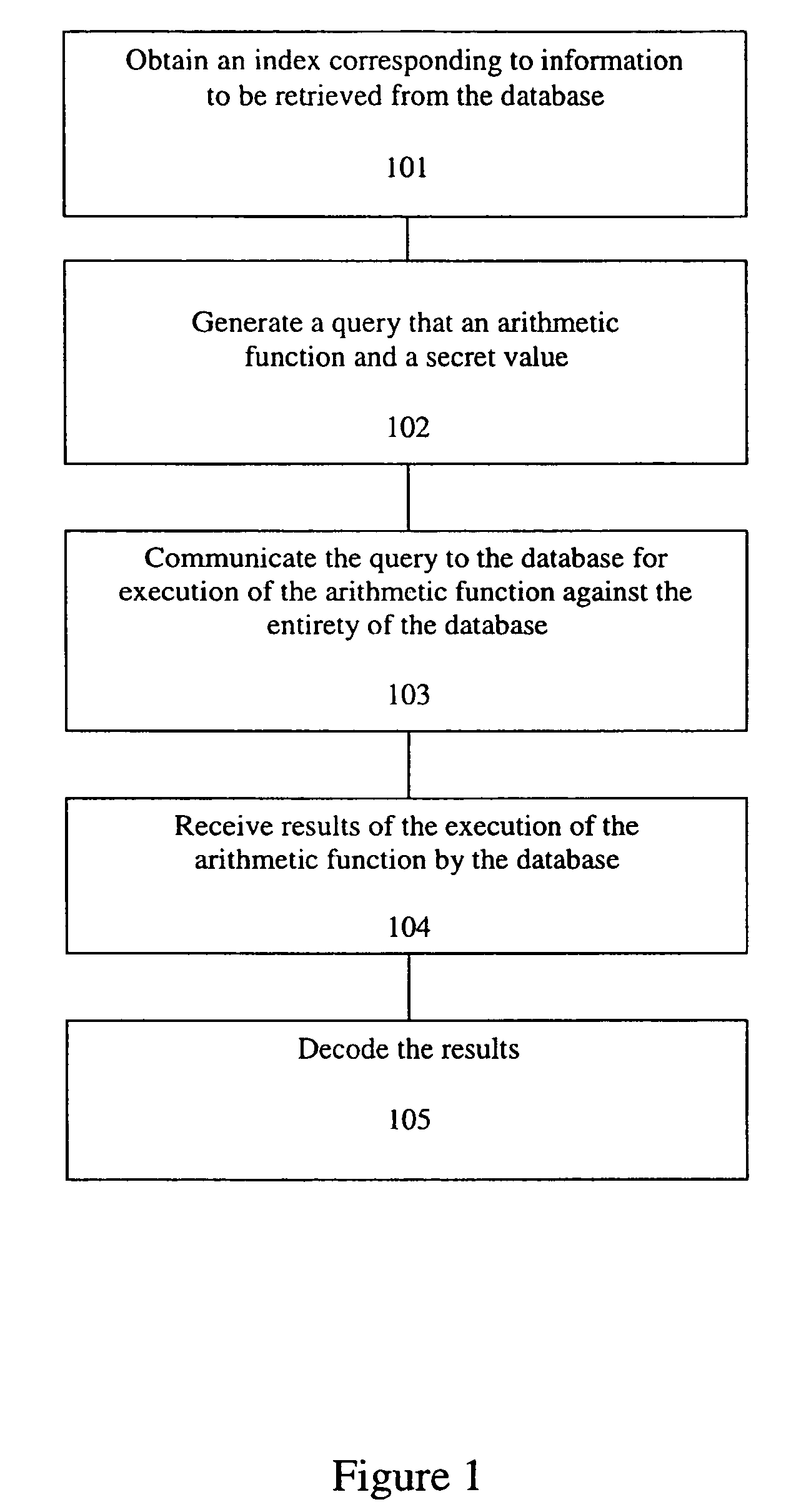
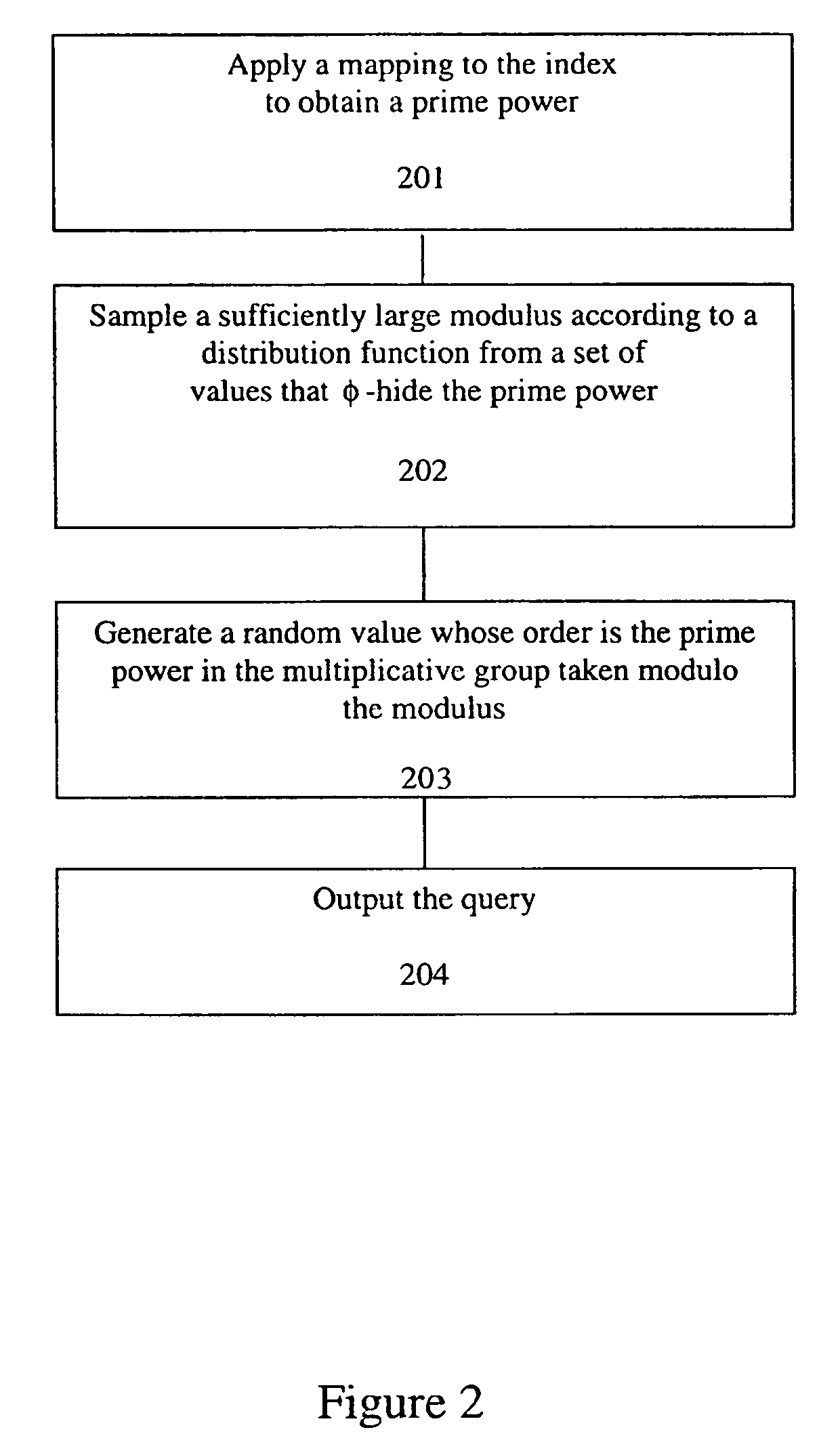
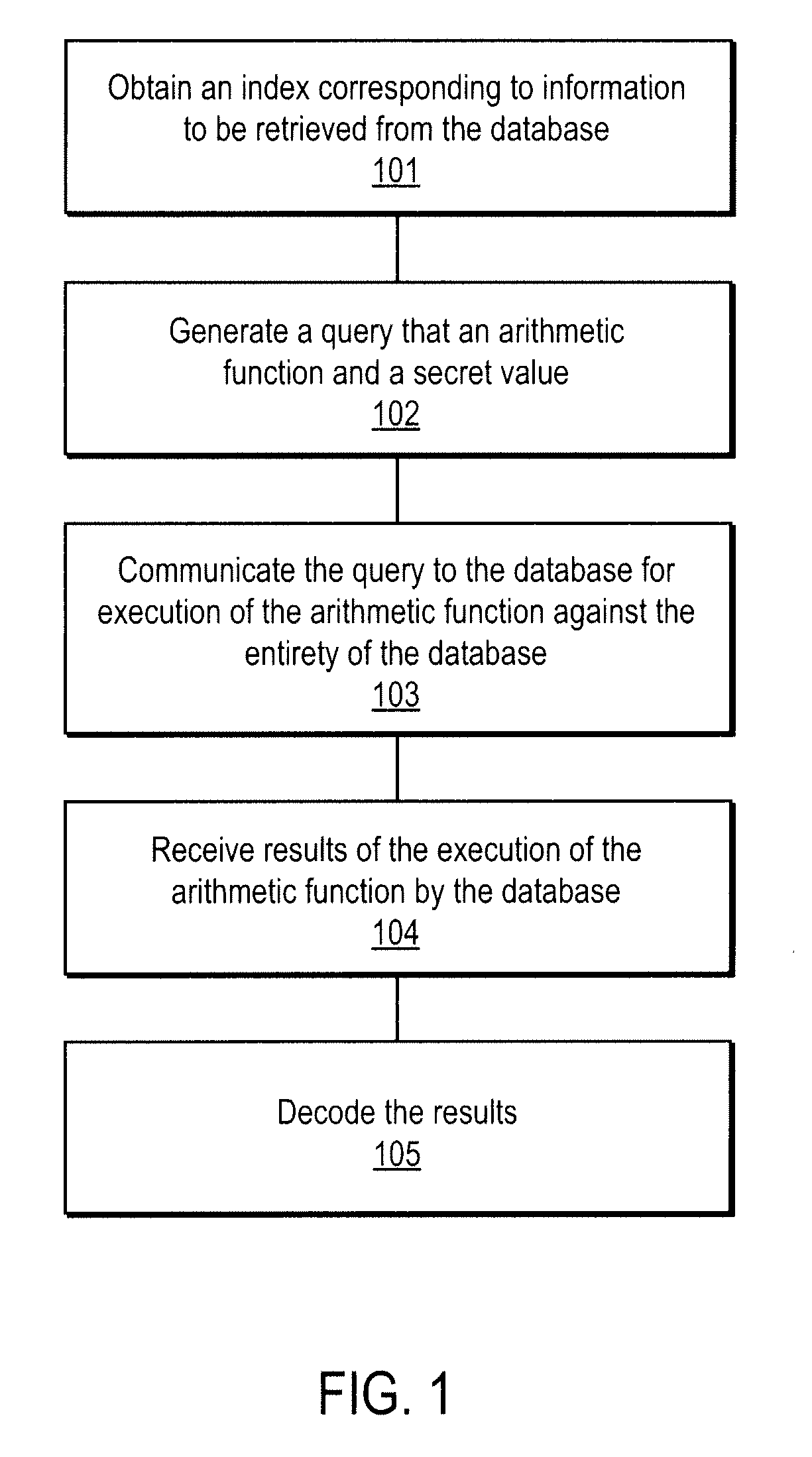
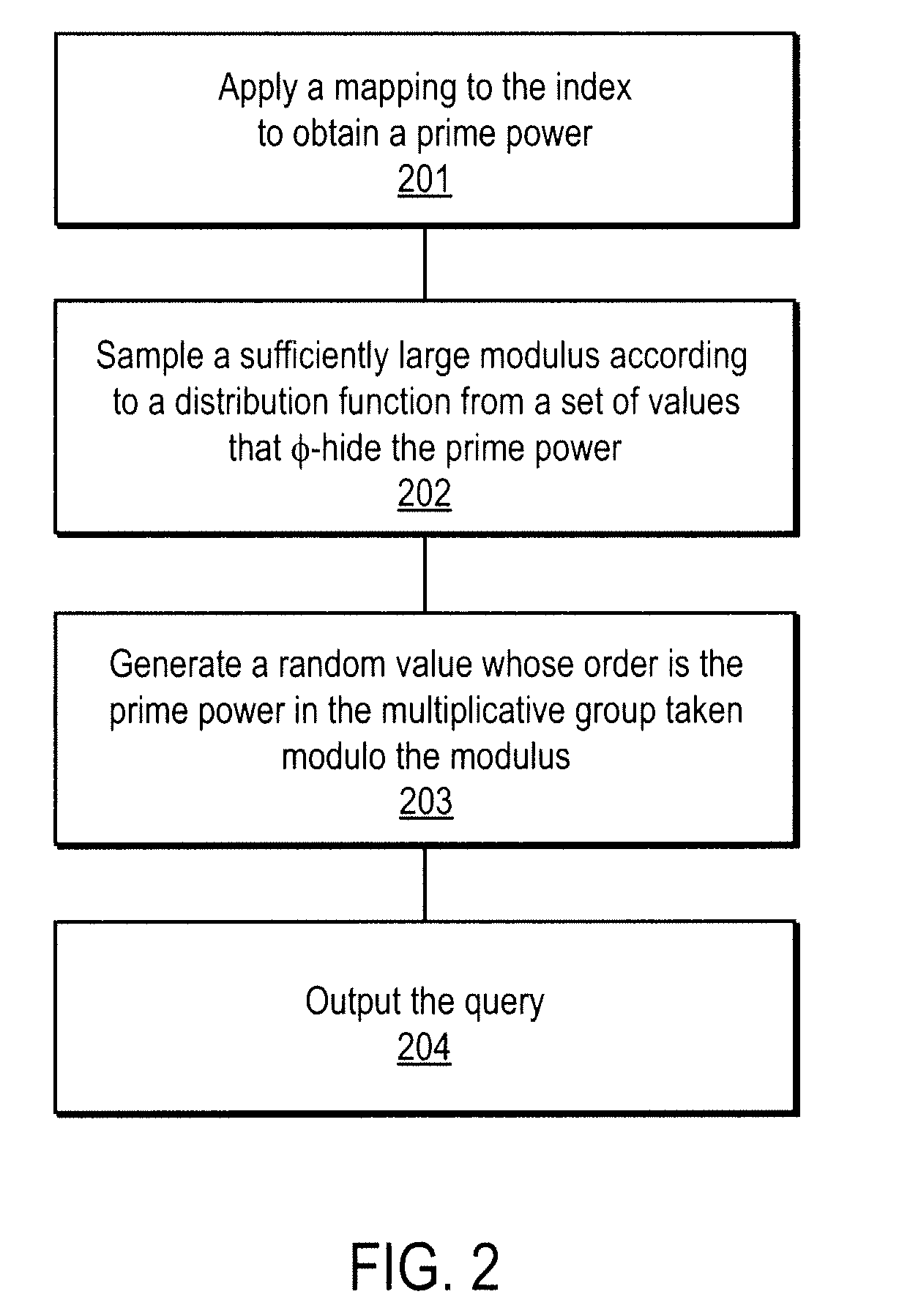
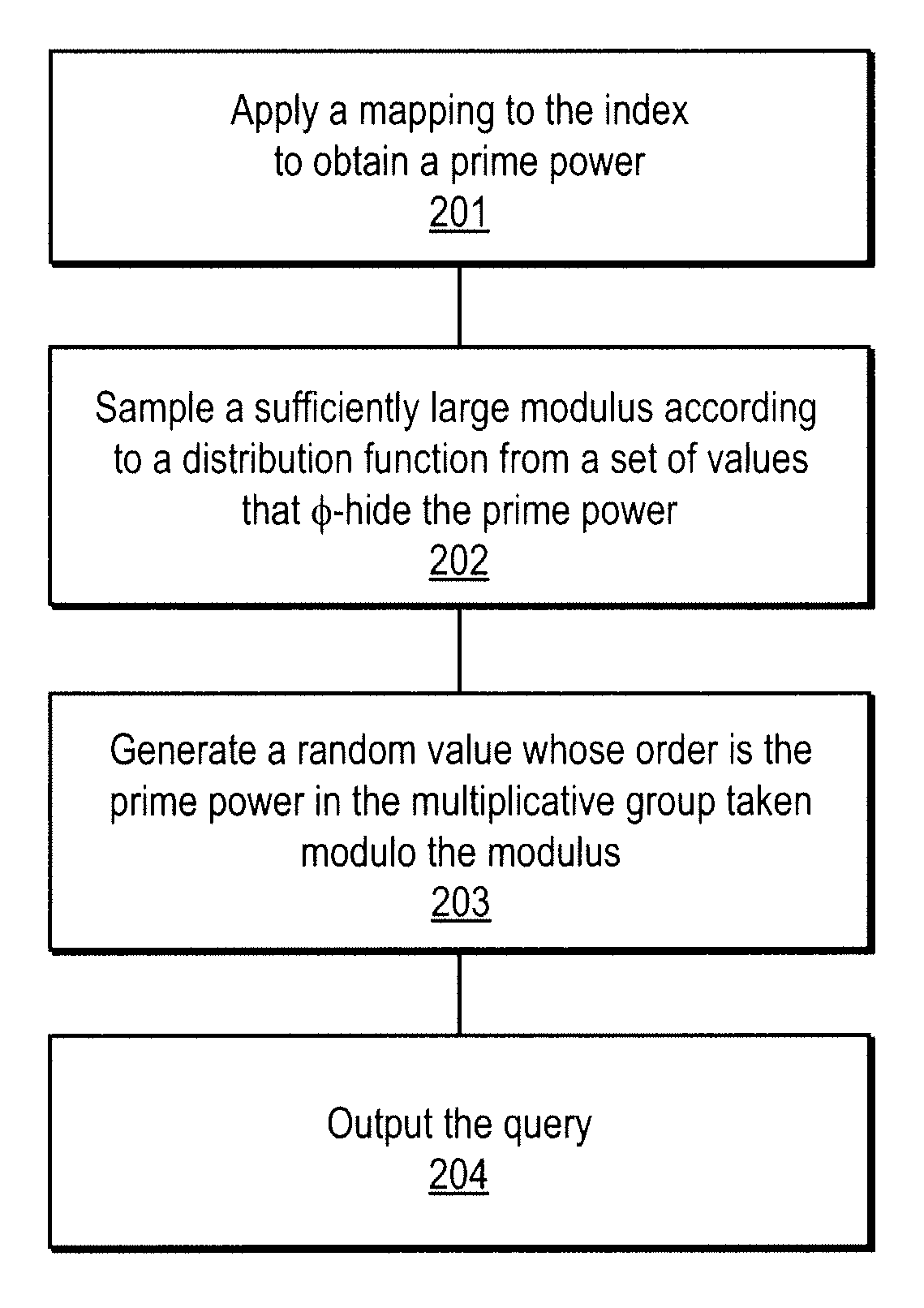
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
InactiveUS20090193033A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsOblivious transferData mining
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
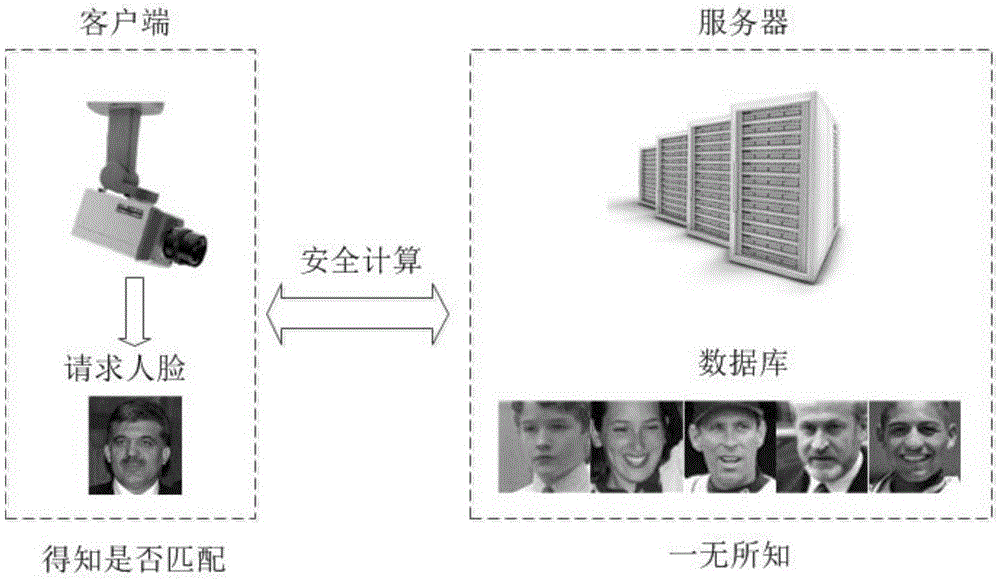
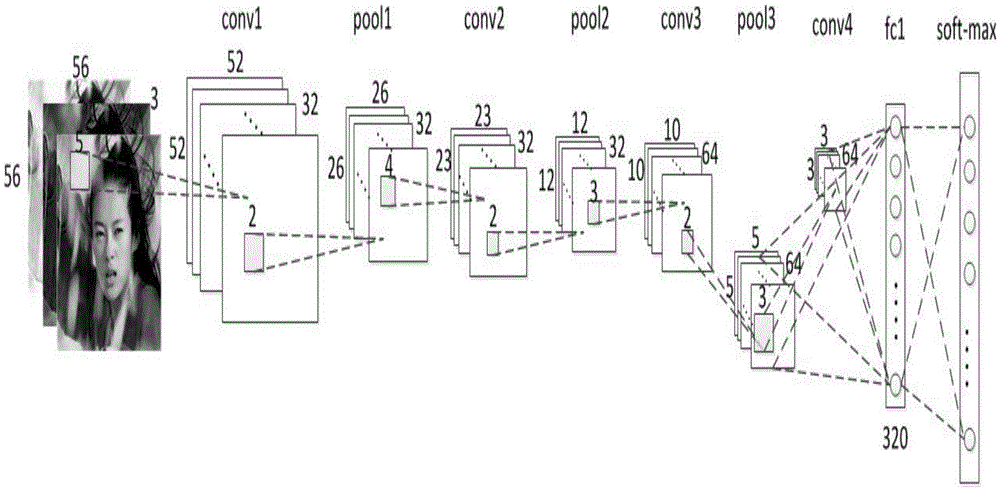
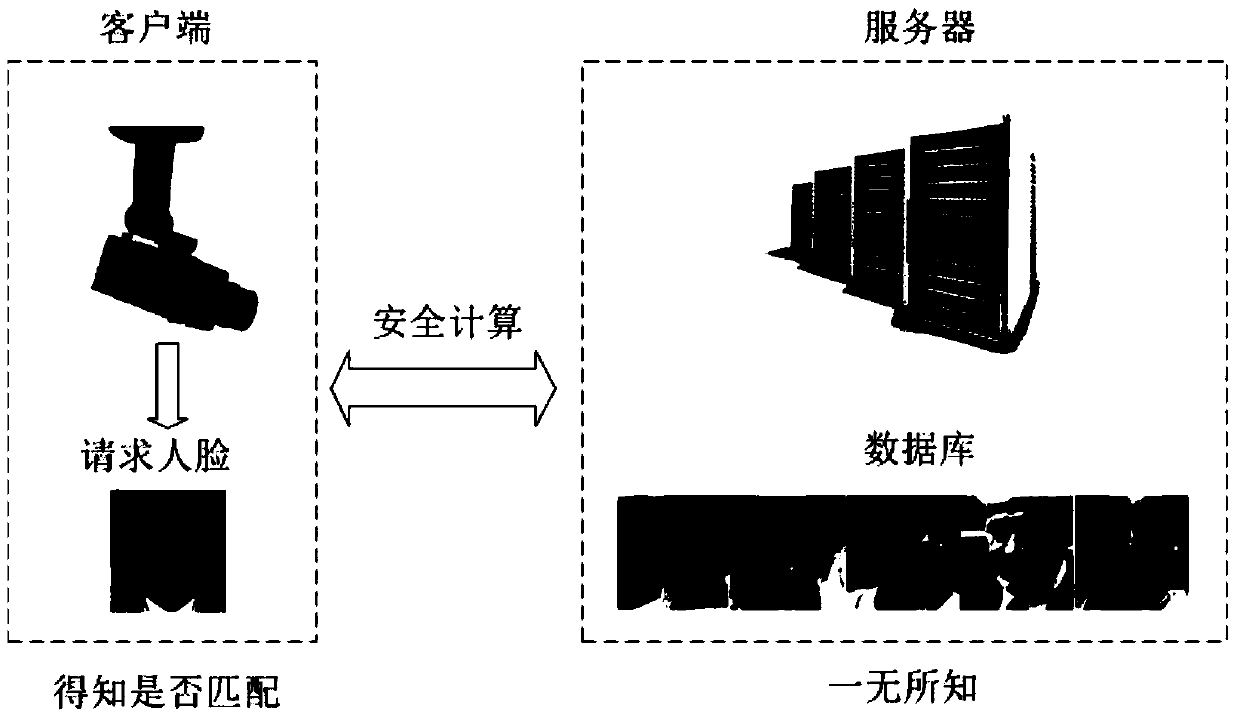
Design method of safety face verification system based on CNN (convolutional neural network) feature extractor
ActiveCN105631296AImprove authentication accuracyImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionCiphertextOblivious transfer
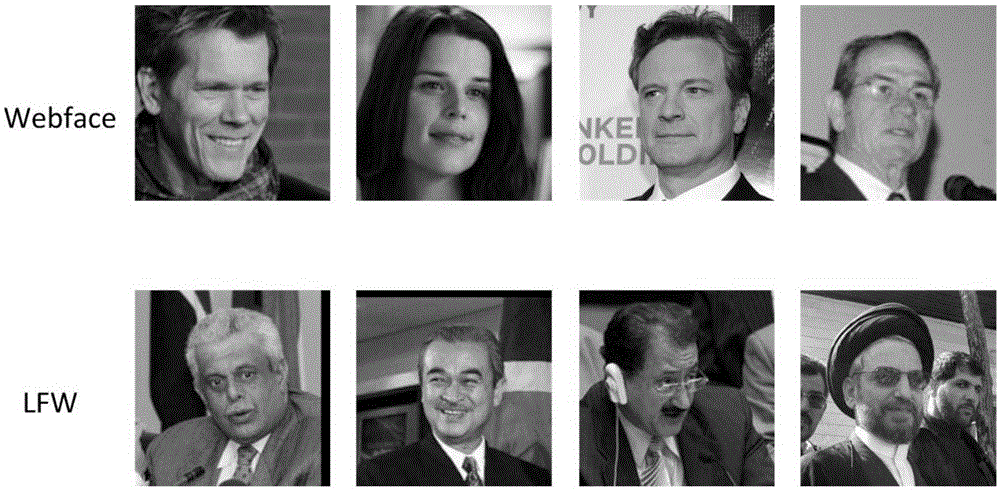
The invention provides a design method of a safety face verification system based on a CNN (convolutional neural network) feature extractor, belongs to the field of biological feature identification, and particularly relates to a method of utilizing the CNN to extract face features and using a Paillier algorithm and an oblivious transfer technique to encrypt. Compared with the SCiFi (secure computation of face identification) system, the method has the advantages that the manually extracted feature is converted into the CNN self-learning feature, and the CNN self-learning feature is performed with binarization to remove the noise effect, so that the identification accuracy is higher; the testing identification rate is 91.48% on a view 2 of an LFW (labeled face wild) base; in the whole identification process, a server will not obtain any feature information of a requester, and only receive the feature ciphertext information, but not decrypt; a client only obtains whether the identification is passed or not, and does not know the other information, including hamming distance; one face picture is expressed by the 320bit feature, and compared with the SCiFi system, the feature data volume is decreased by 2 / 3, so that the consumption time of encrypting and identification is low, and the real-time performance is high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
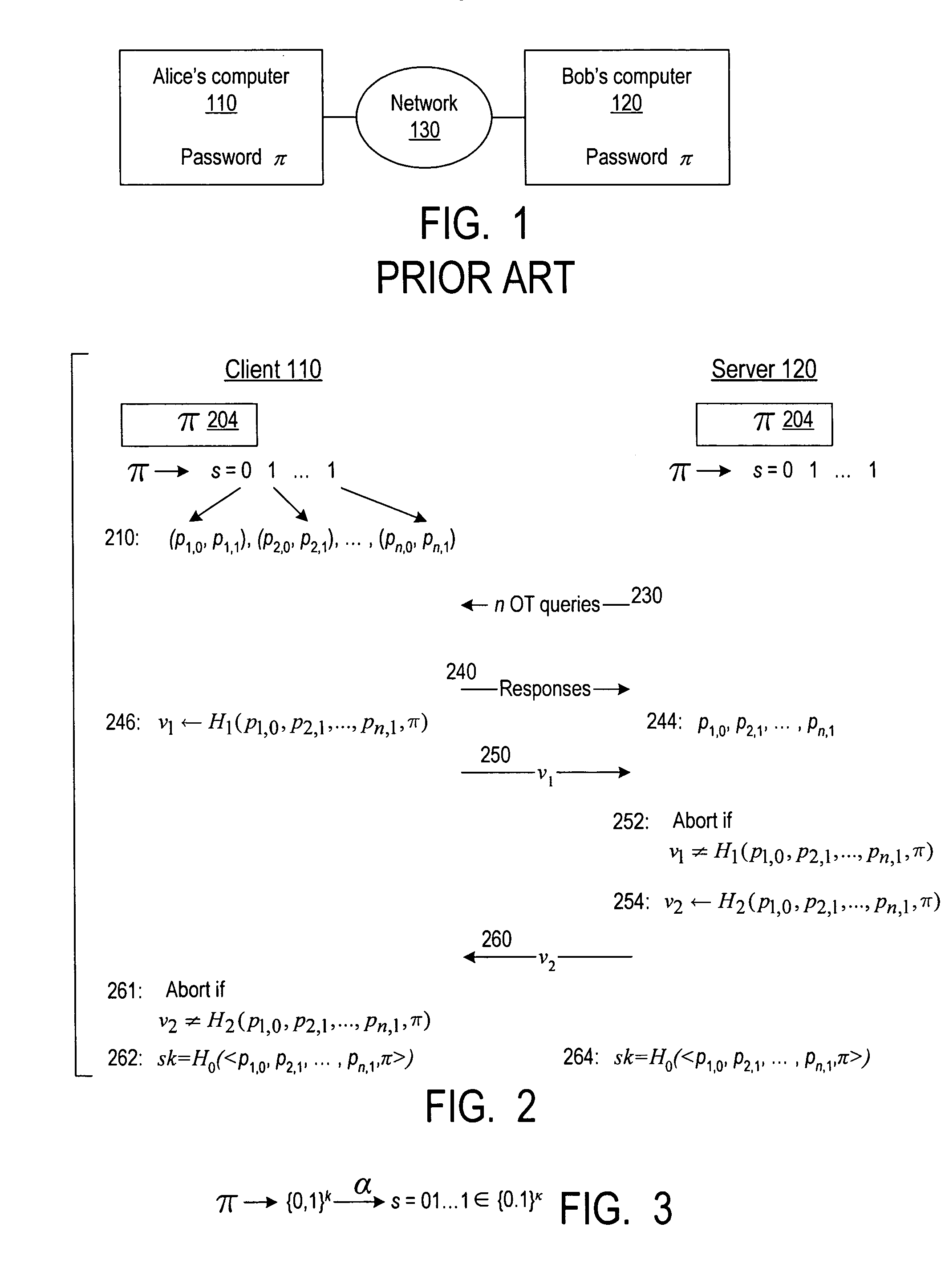
Cryptographic authentication and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, including, but not limited to, password authenticated key exchange (PAKE)
ActiveUS20060291661A1Improve efficiencySmall probabilityUser identity/authority verificationTransmission protocolAlgorithm
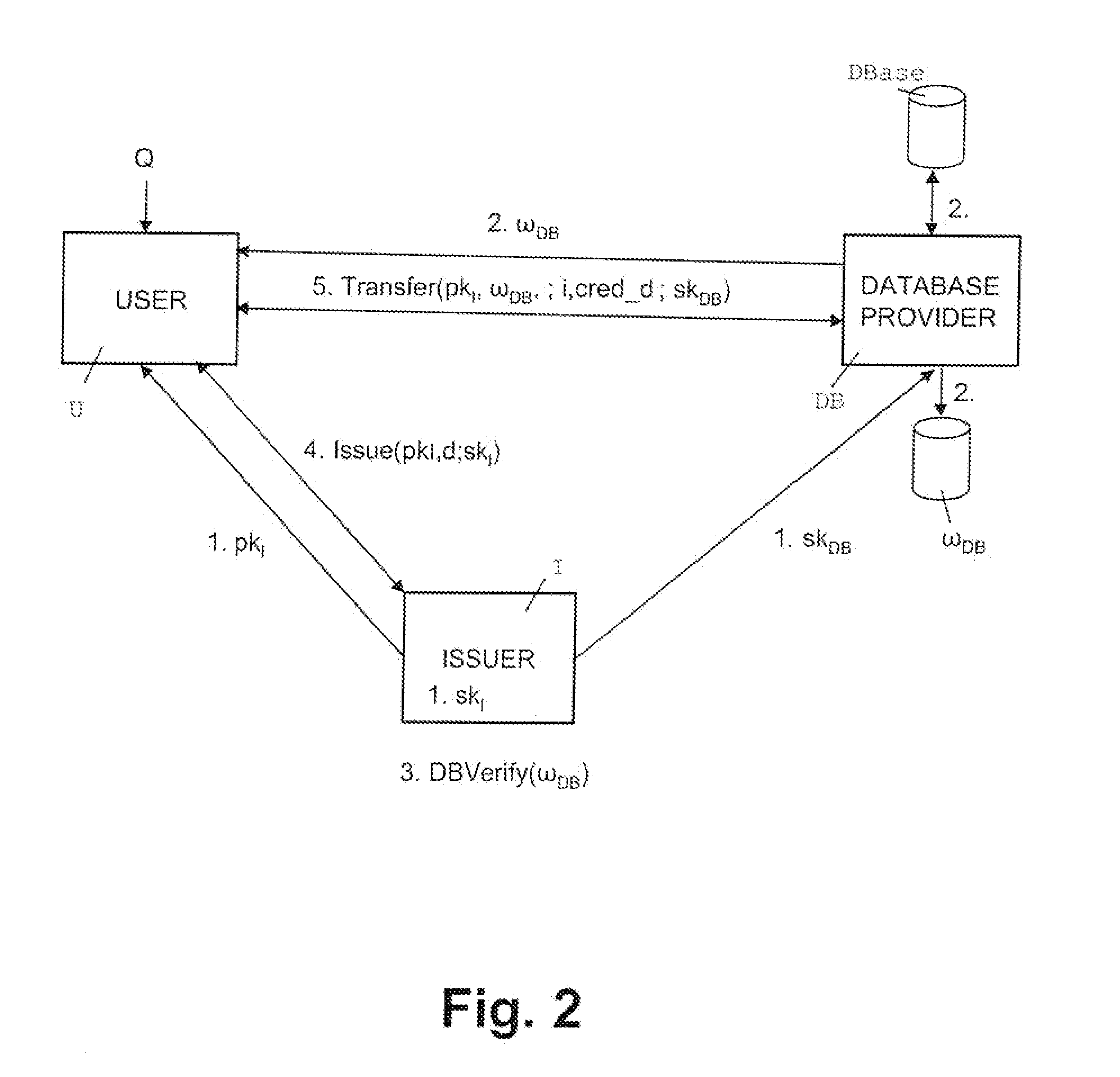
A server (120) uses a password (π) to construct a multiplicative group (ZN*) with a (hidden) smooth order subgroup (<x′>), where the group order (Pπ) depends on the password. The client (110) uses its knowledge of the password to generate a root extraction problem instance (z) in the group and to generate data (y) allowing the server to construct a discrete logarithm problem instance (y′) in the subgroup. The server uses its knowledge of the group order to solve the root extraction problem, and solves the discrete logarithm problem efficiently by leveraging the smoothness of the subgroup. A shared key (sk) can be computed as a function of the solutions to the discrete logarithm and root extraction problem instances. In some embodiments, in an oblivious transfer protocol, the server queries the client (at 230) for data whose position in a database (210) is defined by the password. The client provides (240) such data without knowing the data position associated with the server's query. The client obtains the data position independently from the password. The data positions and / or the respective data are used for authentication and shared secret key generation. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
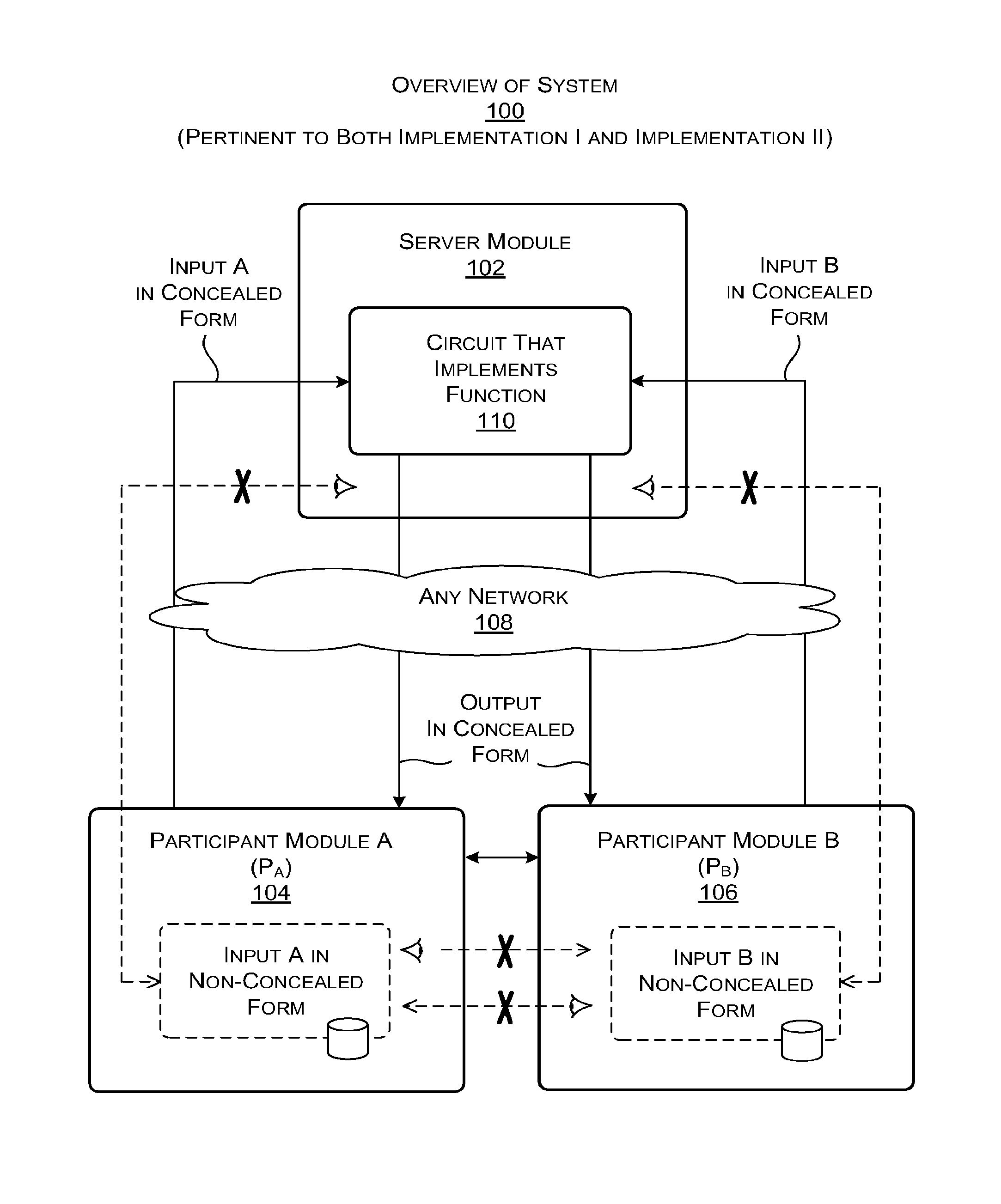
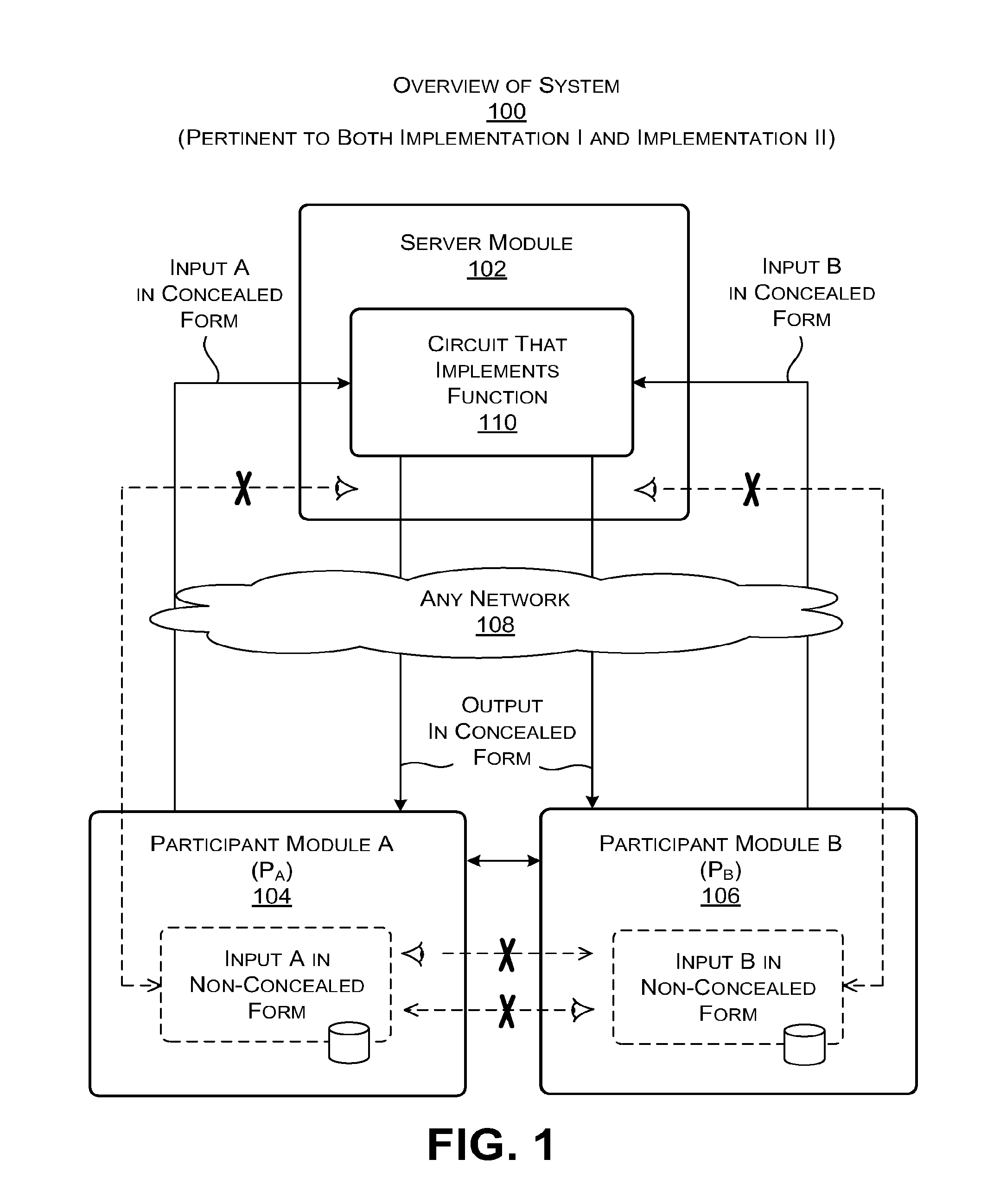
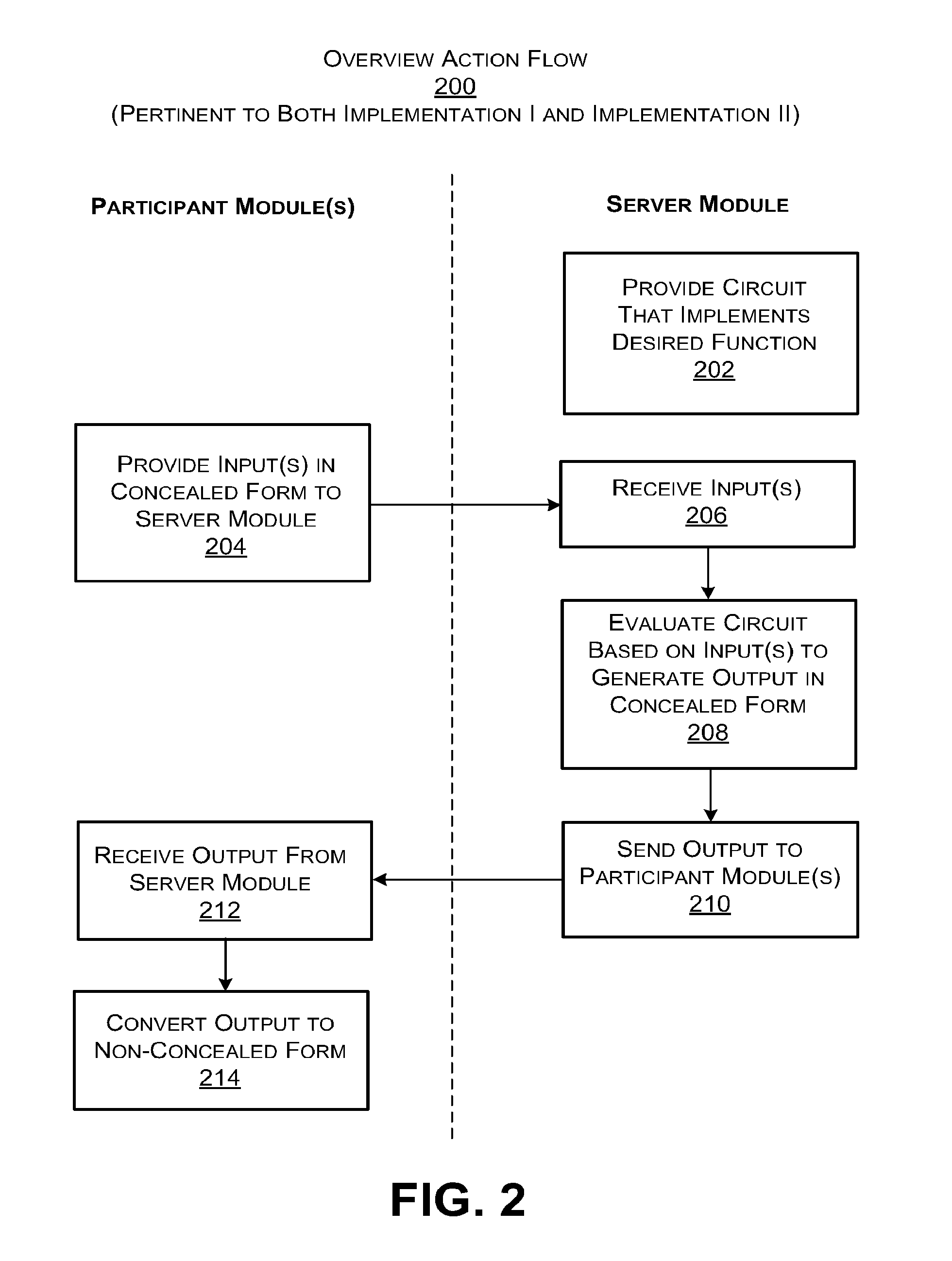
Secure computation using a server module
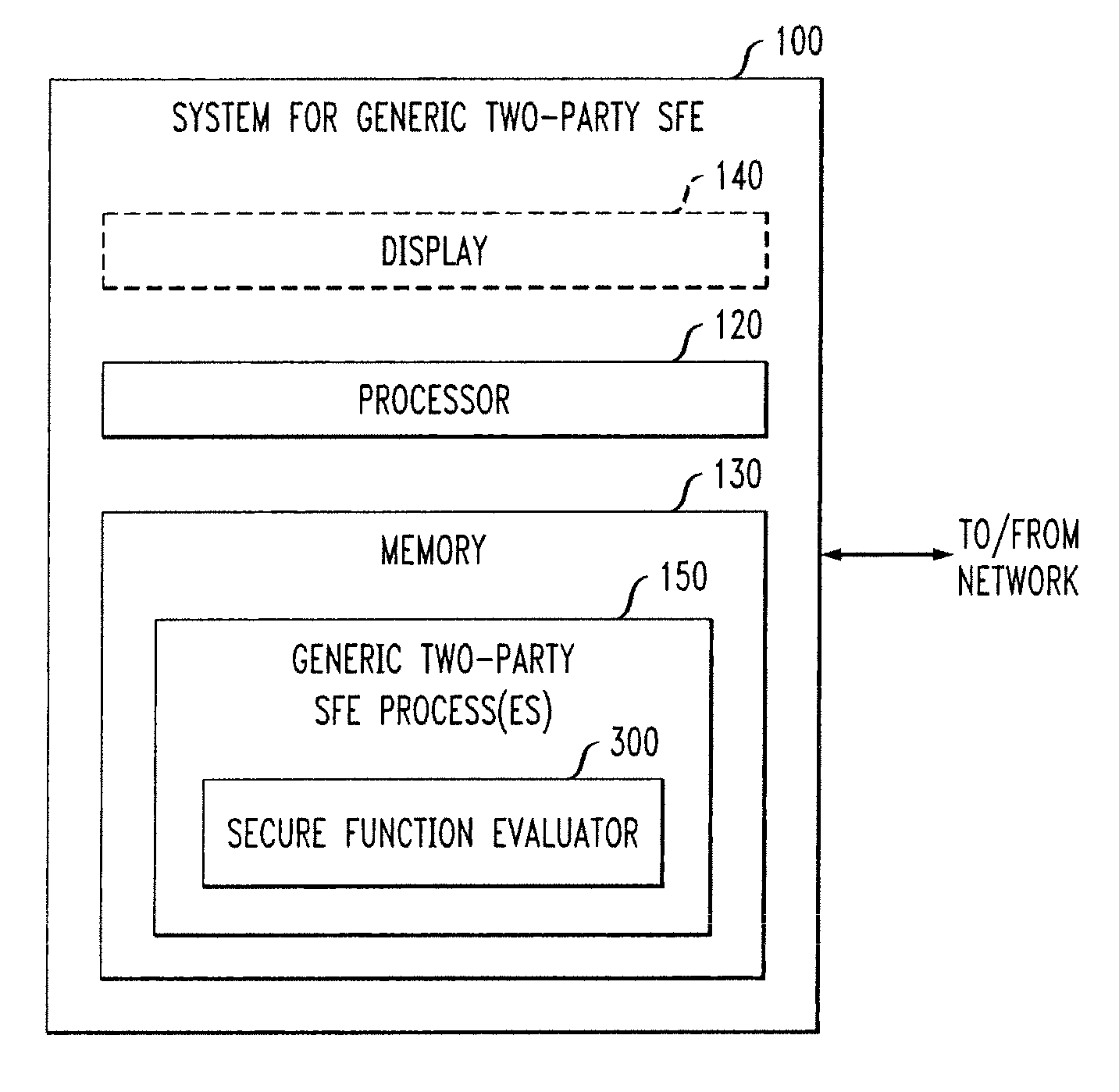
ActiveUS20160044003A1Utilize processing powerReduce processing burdenKey distribution for secure communicationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionBoolean circuitComputer hardware
A server module evaluates a circuit based on concealed inputs provided by respective participant modules, to provide a concealed output. By virtue of this approach, no party to the transaction (including the sever module) discovers any other party's non-concealed inputs. In a first implementation, the server module evaluates a garbled Boolean circuit. This implementation also uses a three-way oblivious transfer technique to provide a concealed input from one of the participant modules to the serer module. In a second implementation, the server module evaluates an arithmetic circuit based on ciphertexts that have been produced using a fully homomorphic encryption technique. This implementation modifies multiplication operations that are performed in the evaluation of the arithmetic circuit by a modifier factor; this removes bounds placed on the number of the multiplication operations that can be performed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
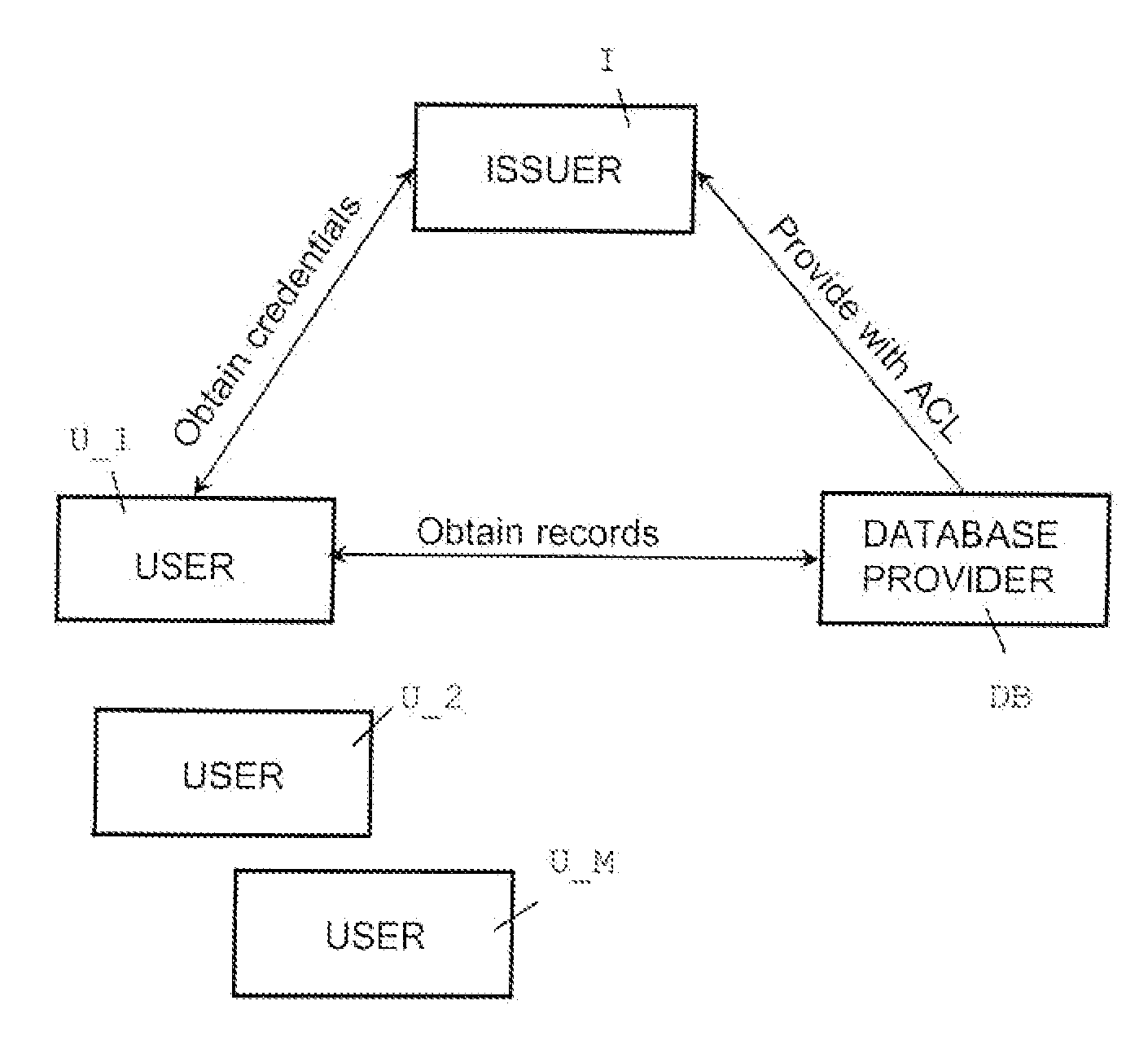
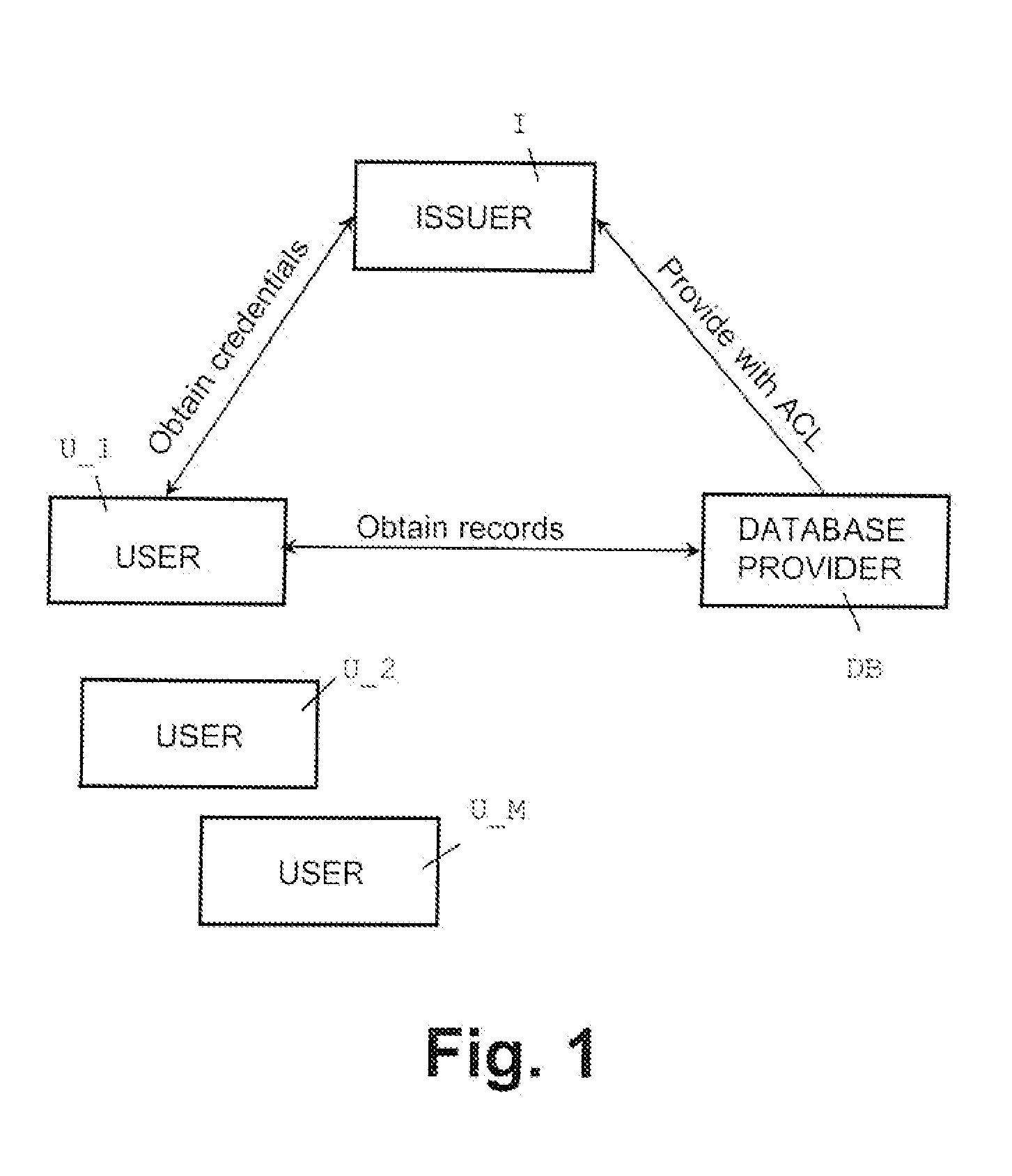
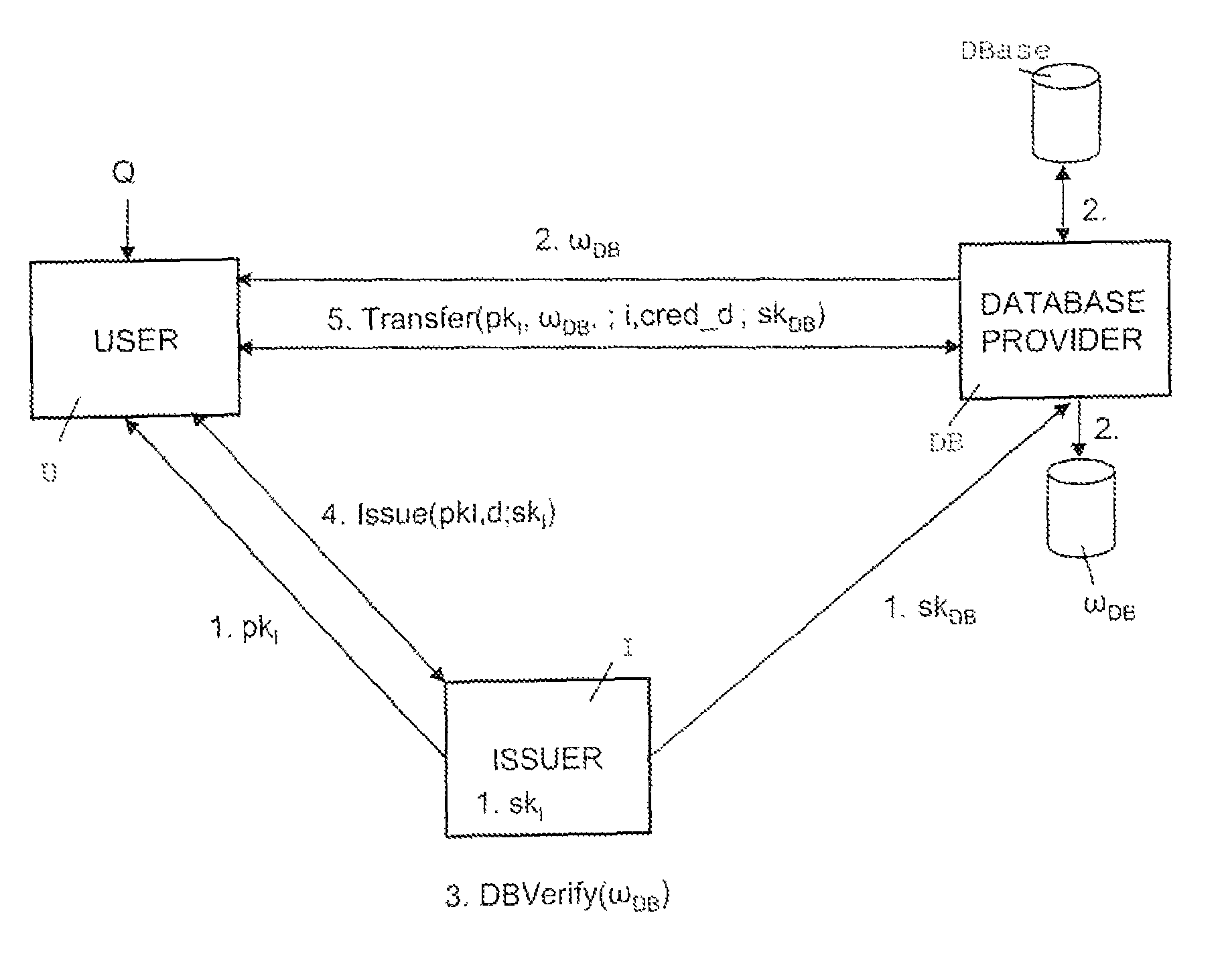
Oblivious transfer with hidden access control lists
InactiveUS20120063593A1Computer security arrangementsSecuring communicationOblivious transferVLAN access control list
A method, apparatus, and a computer readable storage medium having computer readable instructions to carry out the steps of the method for anonymous access to a database. Each record of the database has different access control permissions (e.g. attributes, roles, or rights). The method allows users to access the database record while the database does not learn who queries a record. The database does not know which record is being queried: (i) the access control list of that record or (ii) whether a user's attempt to access a record had been successful. The user can only obtain a single record per query and only those records for which he has the correct permissions. The user does not learn any other information about the database structure and the access control lists other than whether he was granted access to the queried record, and if so, the content of the record.
Owner:IBM CORP
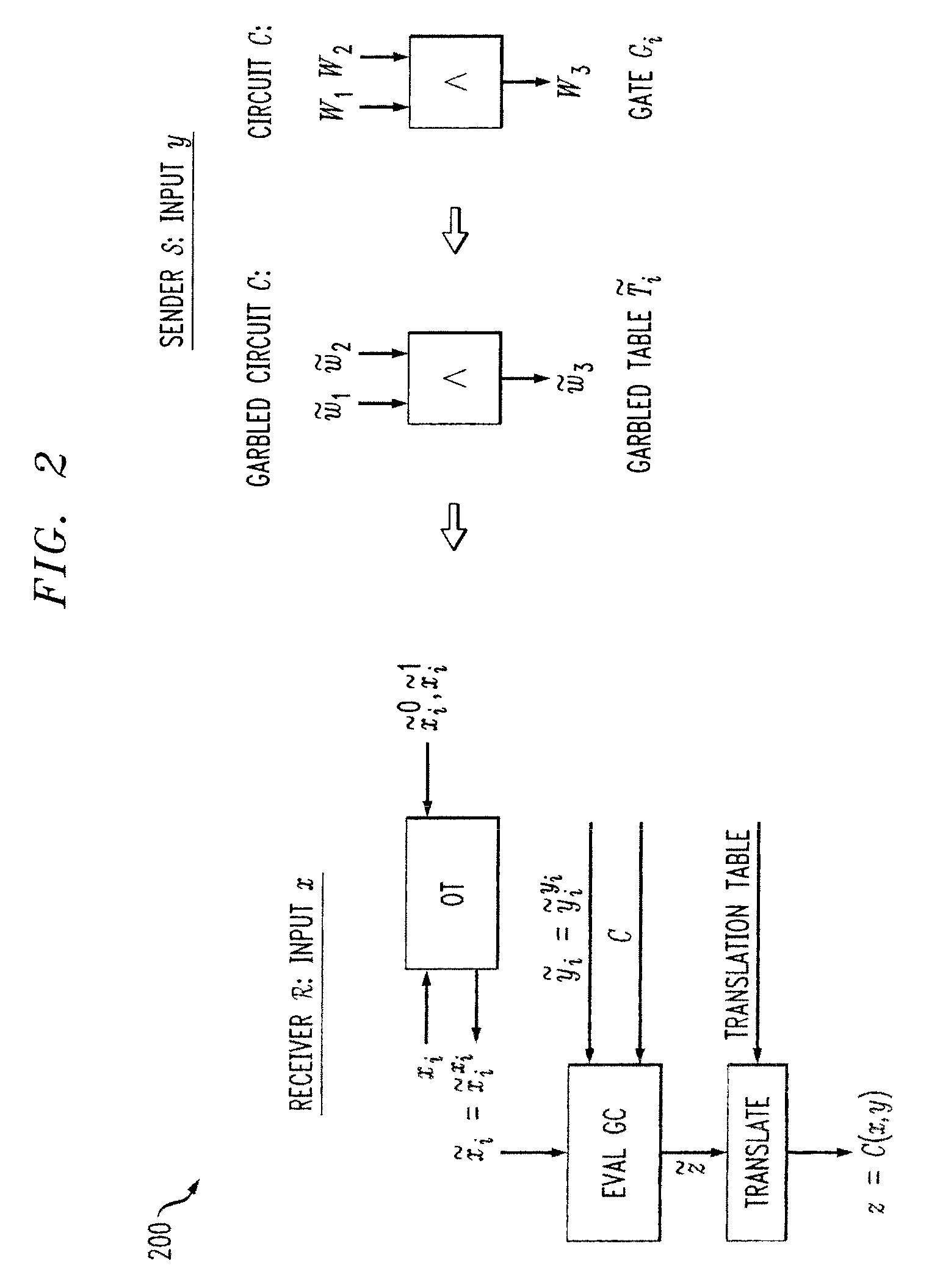
Secure function evaluation for a covert client and a semi-honest server using string selection oblivious transfer
ActiveUS20140040614A1Computer security arrangementsCoding/ciphering apparatusOblivious transferComputer engineering
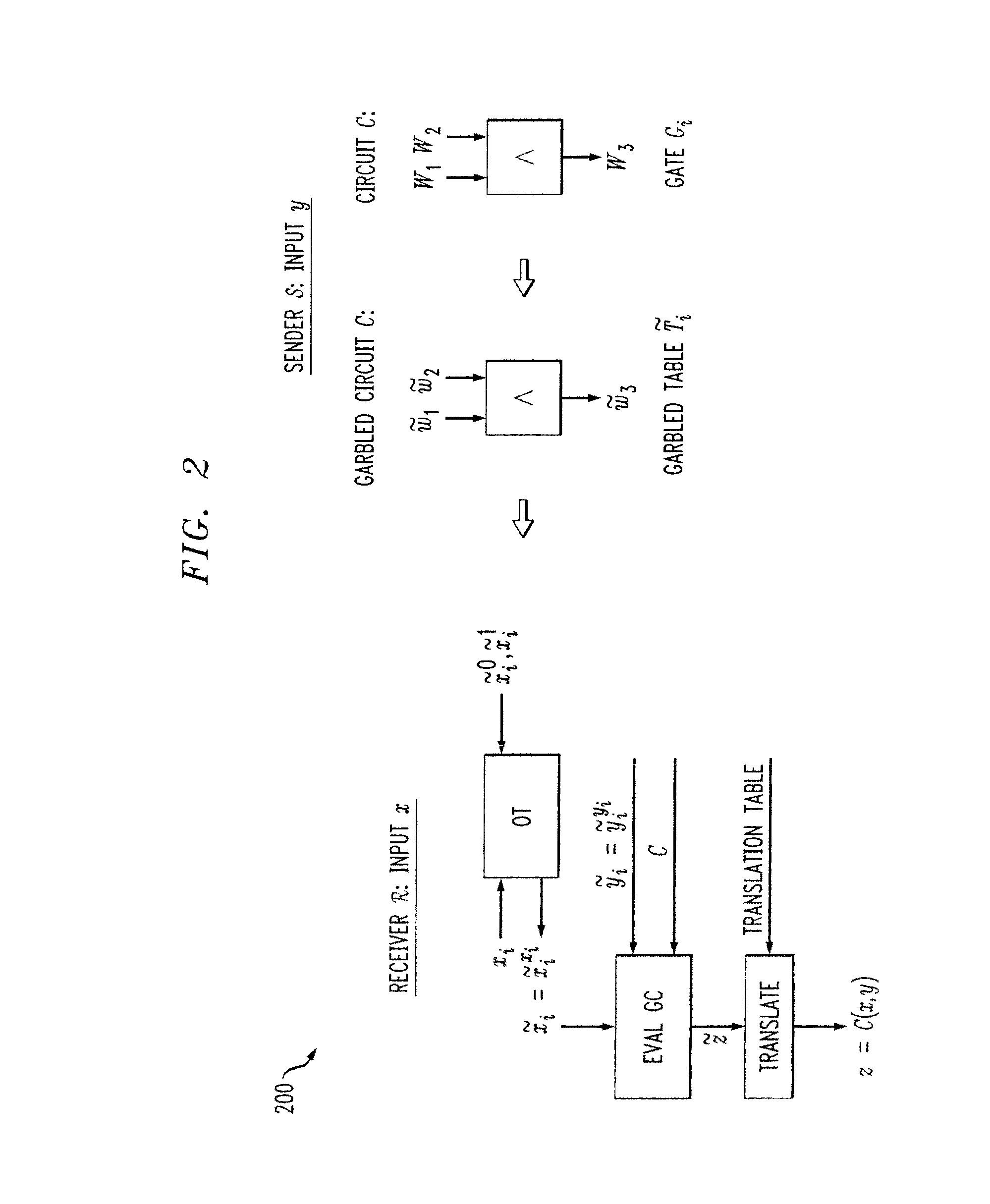
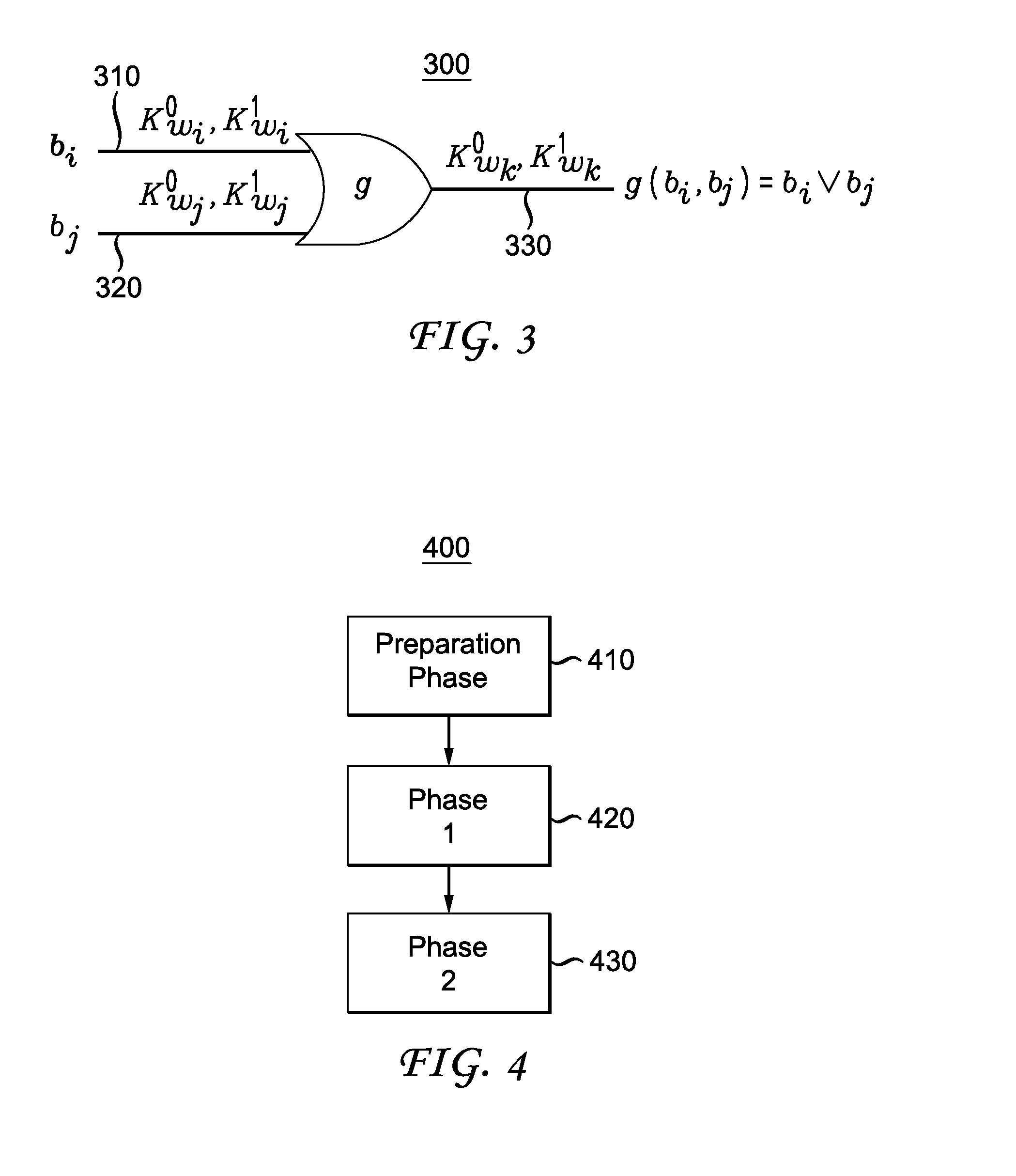
Methods and apparatus are provided for secure function evaluation for a covert client and a semi-honest server using string selection oblivious transfer. An information-theoretic version of a garbled circuit C is sliced into a sequence of shallow circuits C1, . . . Cn,that are evaluated. Consider any wire wj of C that is an output wire of Ci, and is an input wire of Ci+1. When a slice Ci is evaluated, Ci's 1-bit wire key for wj is computed by the evaluator, and then used, via string selection oblivious transfer (SOT), to obtain the wire key for the corresponding input wire of Ci+1. This process repeats until C's output wire keys are computed by the evaluator. The 1-bit wire keys of the output wires of the slice are randomly assigned to wire values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Privacy-preserving ridge regression using masks
InactiveUS20150381349A1Avoid decryptionFast linearUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringPrivacy preservingOblivious transfer
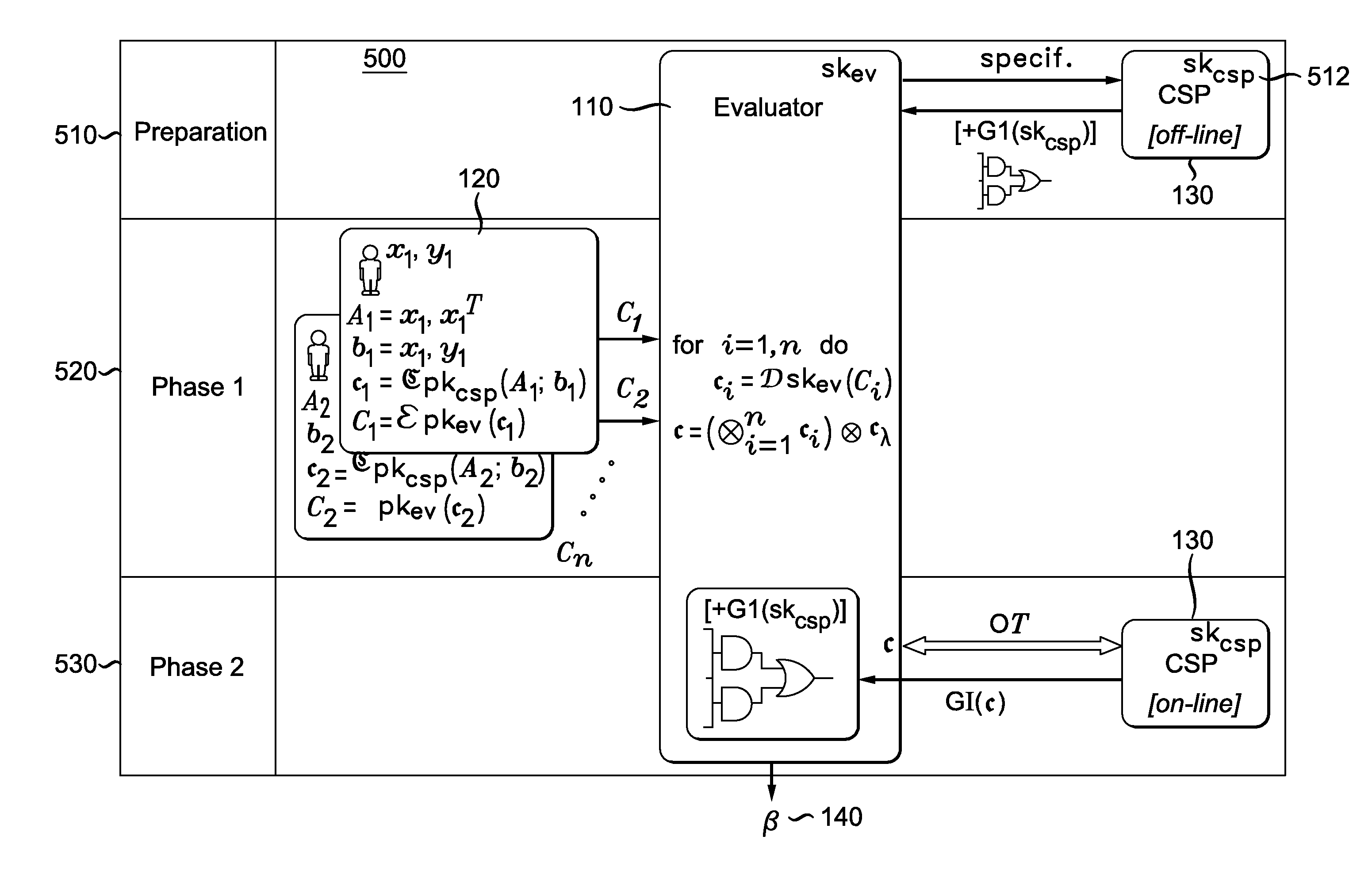
A method and system for privacy-preserving ridge regression using masks is provided. The method includes the steps of requesting a garbled circuit from a crypto service provider, collecting data from multiple users that has been formatted and encrypted using homomorphic encryption, summing the data that has been formatted and encrypted using homomorphic encryption, applying prepared masks to the summed data, receiving garbled inputs corresponding to prepared mask from the crypto service provider using oblivious transfer, and evaluating the garbled circuit from the crypto service provider using the garbled inputs and masked data.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
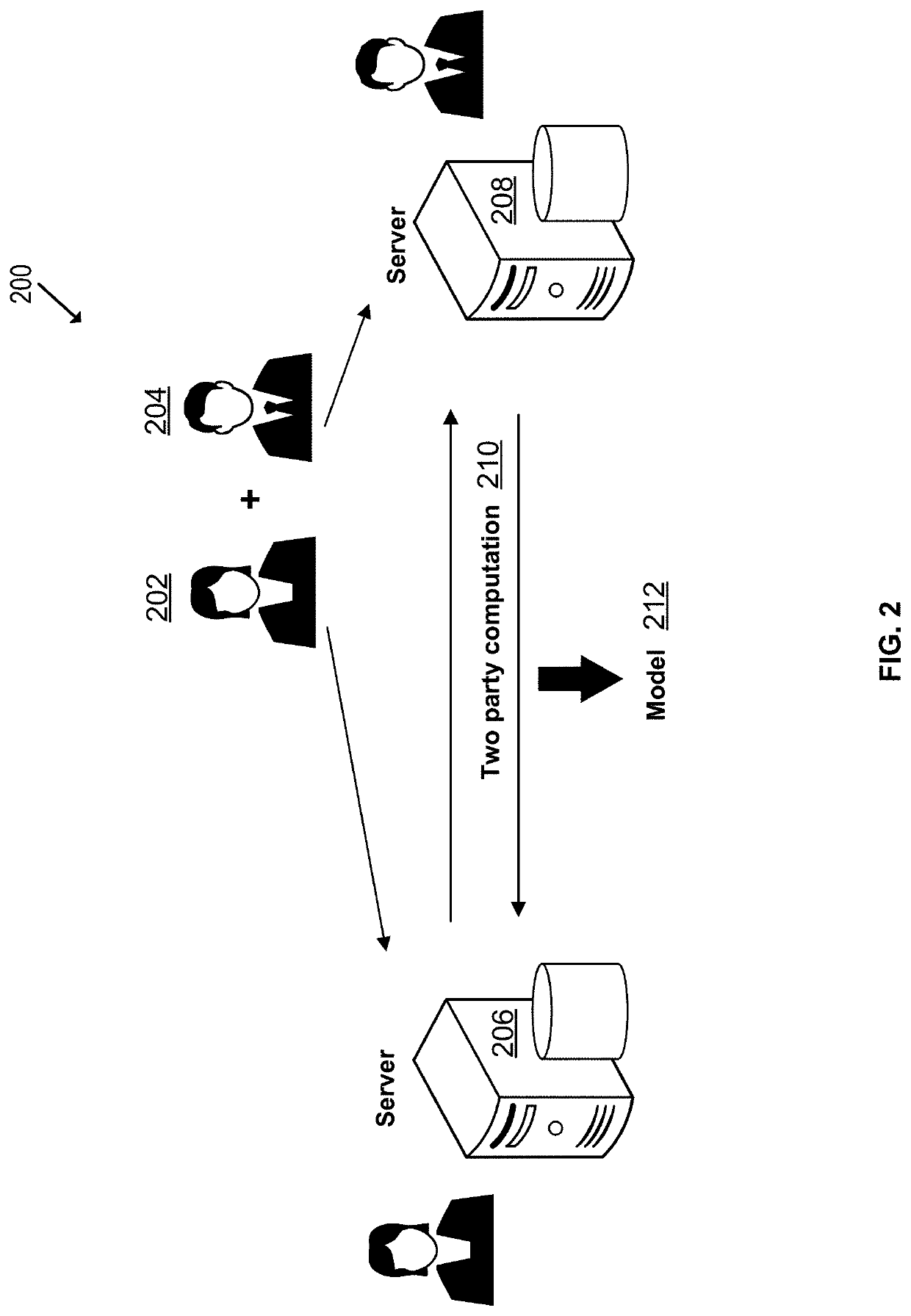
Privacy-preserving machine learning in the three-server model
ActiveUS20210209247A1Efficient executionDigital data protectionCombat sportsTransmission protocolEngineering
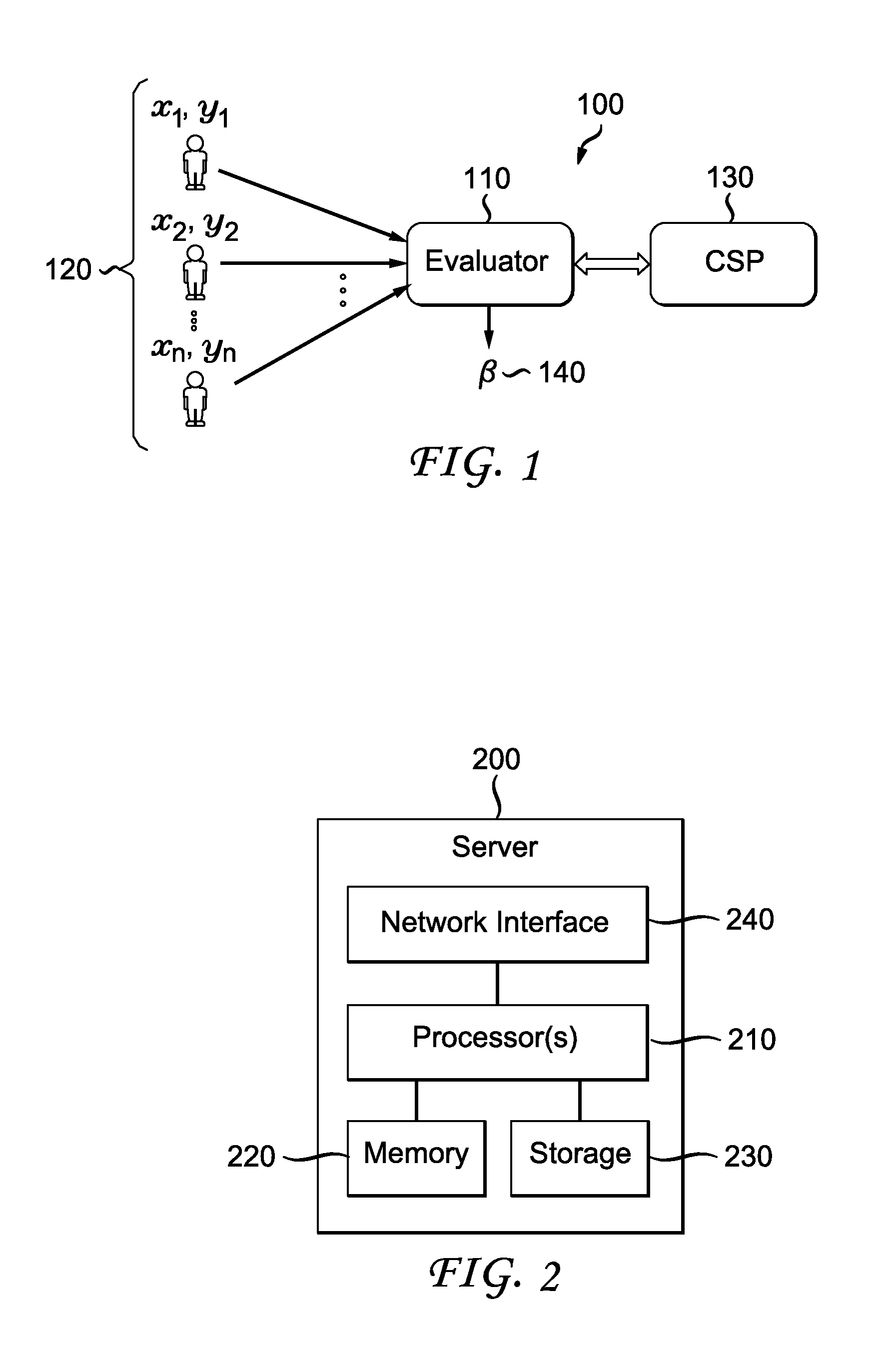
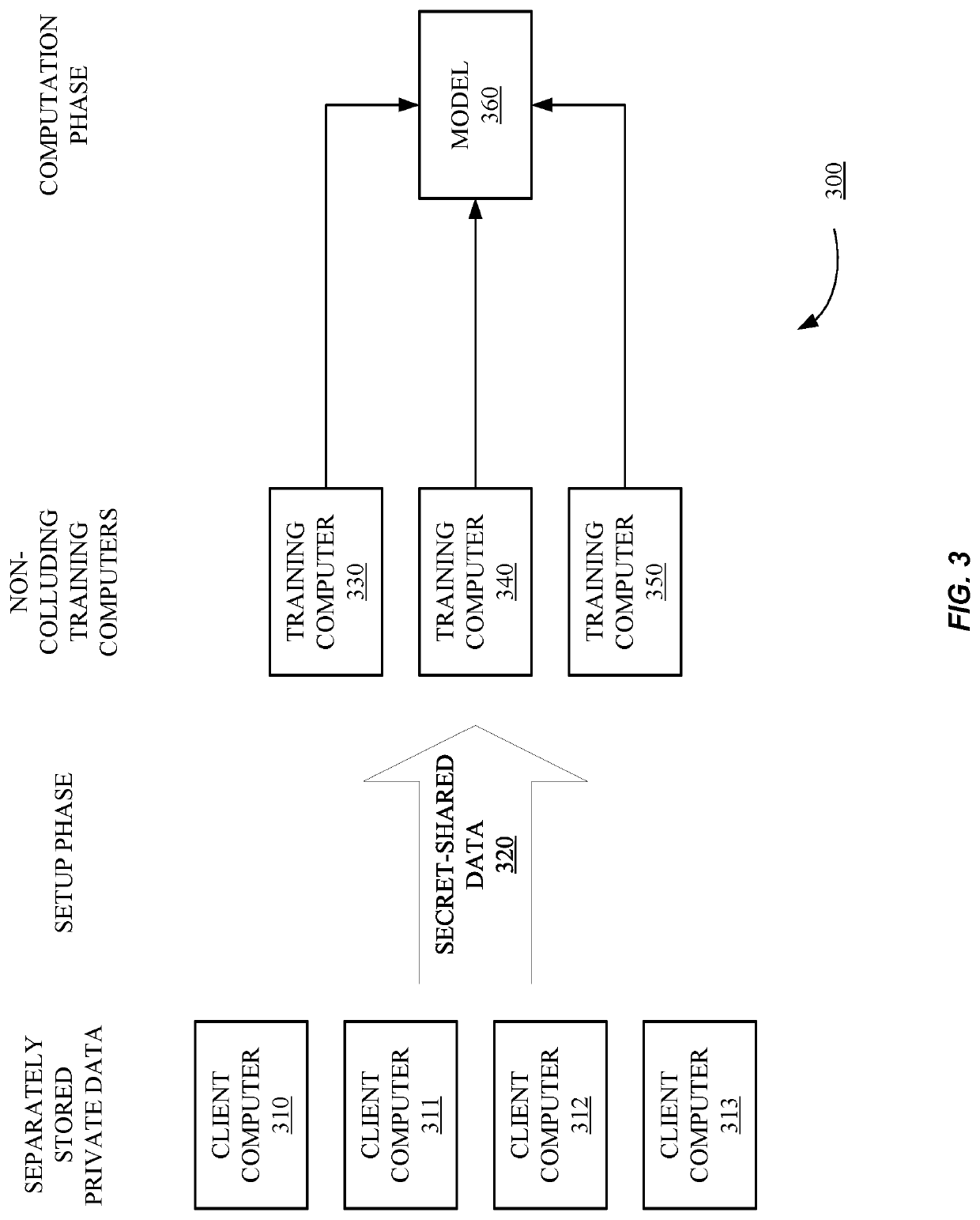
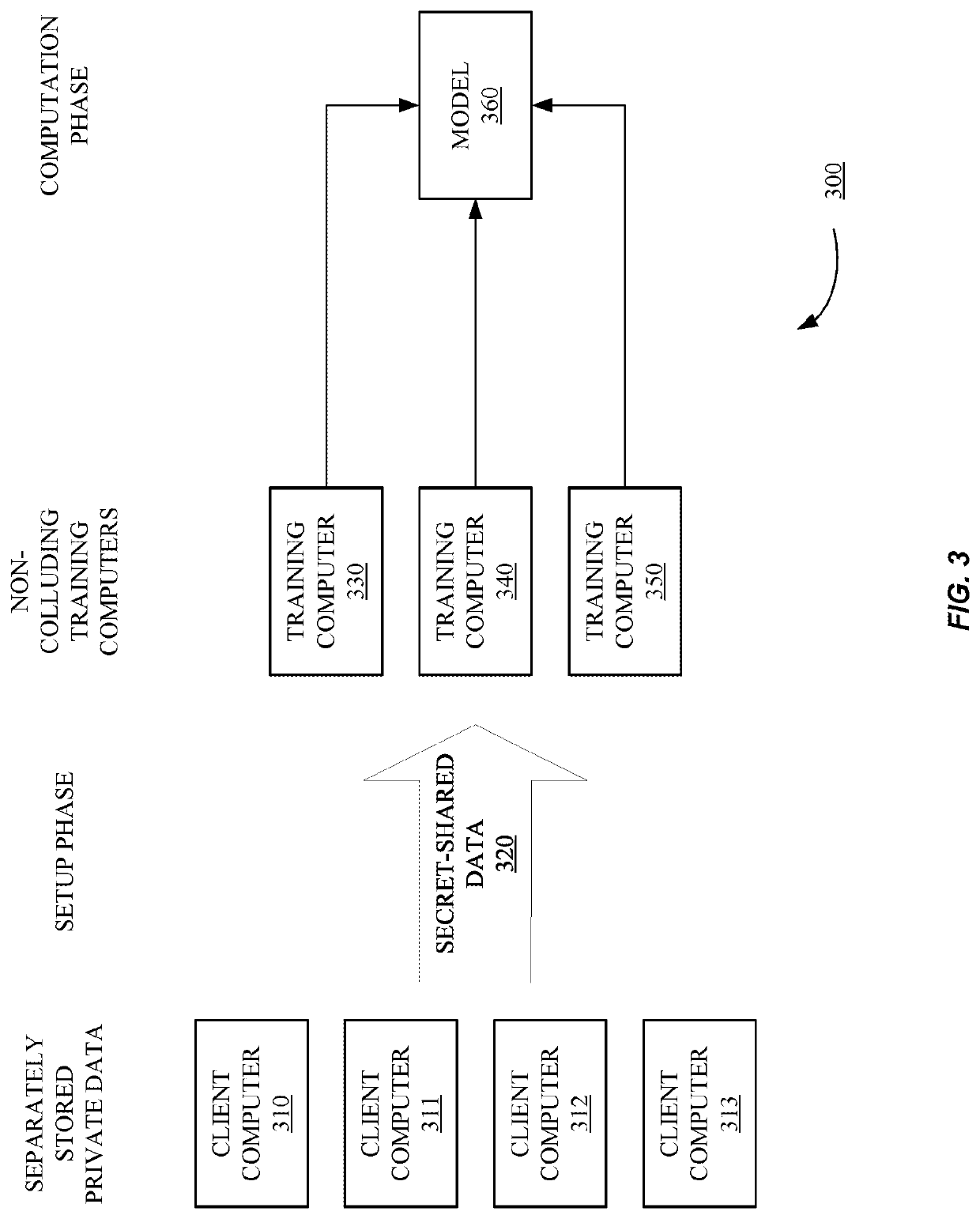
Methods and systems according to embodiments of the invention provide for a framework for privacy-preserving machine learning which can be used to obtain solutions for training linear regression, logistic regression and neural network models. Embodiments of the invention are in a three-server model, wherein data owners secret-share their data among three servers who train and evaluate models on the joint data using three-party computation (3PC). Embodiments of the invention provide for efficient conversions between arithmetic, binary, and Yao 3PC, as well as techniques for fixed-point multiplication and truncation of shared decimal values. Embodiments also provide customized protocols for evaluating polynomial piecewise functions and a three-party oblivious transfer protocol.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
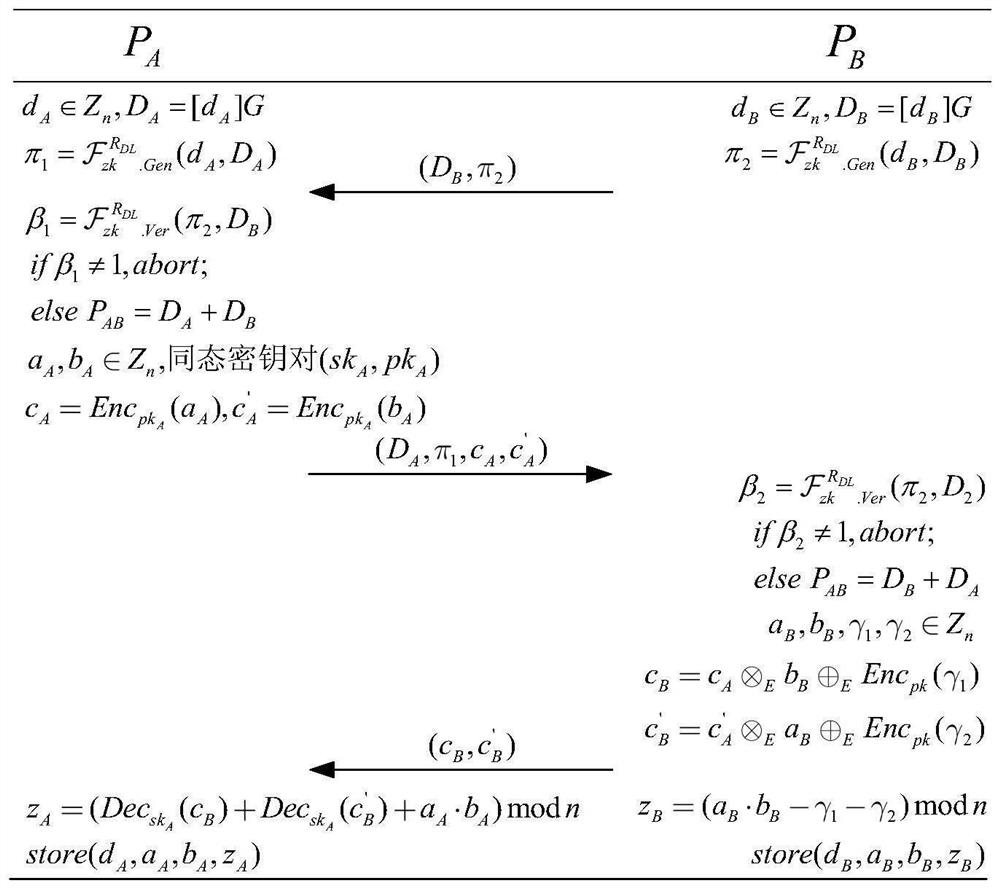
ECDSA digital signature method based on two-party collaboration
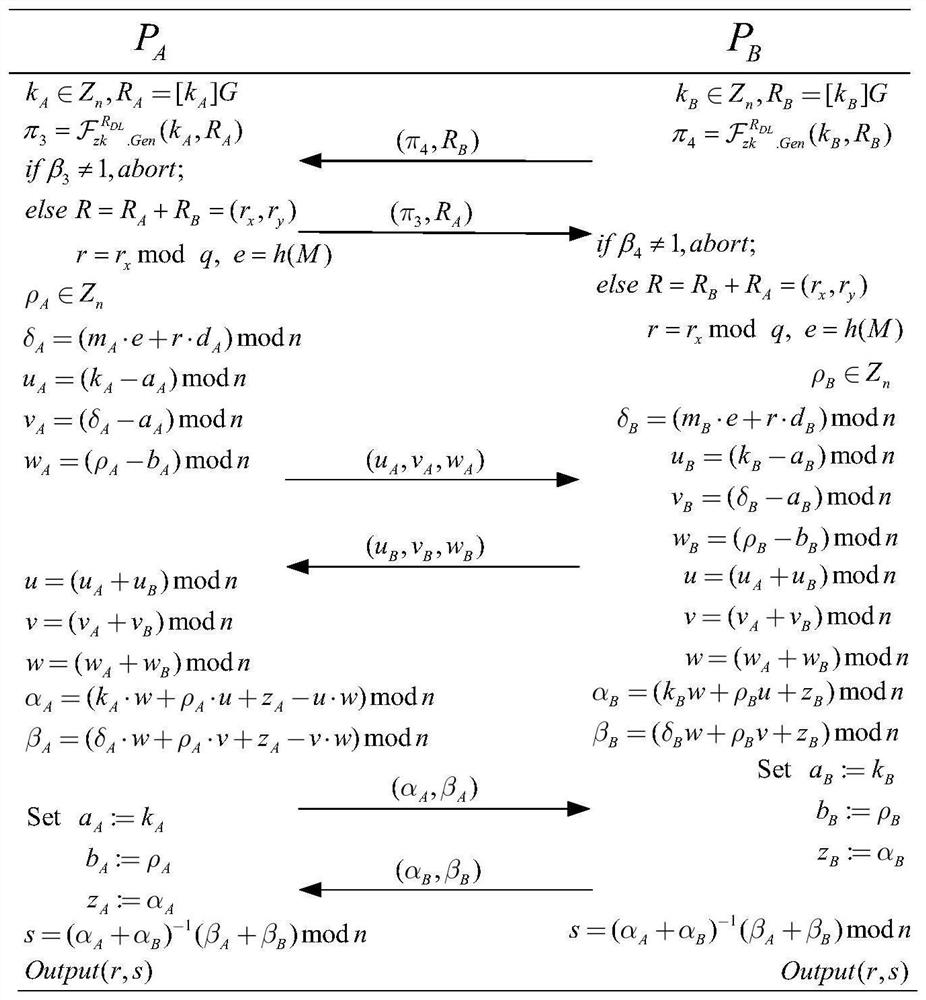
ActiveCN109639439ASafe and efficient collaborative signatureImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlice and BobDigital signature
The invention discloses an ECDSA digital signature method based on two-party collaboration. The method comprises the following steps: step 1), respectively generating corresponding signature public and private key pairs and other parameters by a signature party Alice and a signature party Bob participating in the collaborative signature; and step 2), collaboratively completing ECDSA signature by Alice and Bob, and finally outputting the signature (r,s). According to the ECDSA digital signature method based on the two-party collaboration provided by the invention, under the premise of ensuringthe security and the correctness, a signature process does not introduce high-overhead password operations such as homomorphic encryption, oblivious transfer and the like, so that a signature scheme achieves a good balance between the communication overhead and the computation overhead, and therefore the performance is remarkably superior to that of all existing ECDSA two-party collaborative digital signature methods.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Fast oblivious transfers
ActiveUS20200259800A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRandom oracleKey exchange
Systems, methods, and computing device readable media for implementing fast oblivious transfer between two computing devices may improve data security and computational efficiency. The various aspects may use random oracles with or without key agreements to improve the security of oblivious transfer key exchanges. Some techniques may include public / private key strategies for oblivious transfer, while other techniques may use key agreements to achieve simultaneous and efficient cryptographic key exchange.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Privacy-preserving machine learning in the three-server model
PendingUS20220092216A1Efficient executionDigital data protectionMachine learningTransmission protocolEngineering
Methods and systems according to embodiments of the invention provide for a framework for privacy-preserving machine learning which can be used to obtain solutions for training linear regression, logistic regression and neural network models. Embodiments of the invention are in a three-server model, wherein data owners secret-share their data among three servers who train and evaluate models on the joint data using three-party computation (3PC). Embodiments of the invention provide for efficient conversions between arithmetic, binary, and Yao 3PC, as well as techniques for fixed-point multiplication and truncation of shared decimal values. Embodiments also provide customized protocols for evaluating polynomial piecewise functions and a three-party oblivious transfer protocol.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
ActiveUS7620625B2Data processing applicationsPublic key for secure communicationOblivious transferData mining
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Social recommendation method based on oblivious transfer
InactiveCN105677701AImprove securityAdaptableSpecial data processing applicationsOblivious transferData value
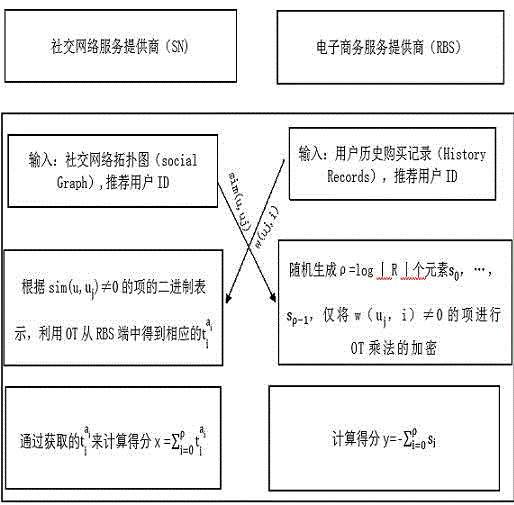
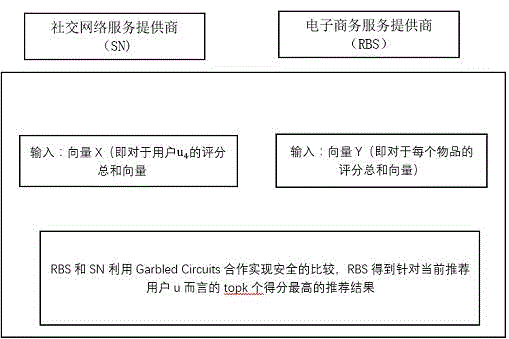
The present invention discloses a social recommendation method based on oblivious transfer, which comprises the following steps that (1) an SN terminal and an RBS terminal share data distribution conditions of user historic behavior recording matrixes to each other, and the two terminals only calculate items of sim(u, u<j>) is not equal to 0 and w(u<j>, i) is not equal to 0 (only the data distribution conditions are shared by the two terminals, and data value information of the two terminals are not involved); (2) the two terminals respectively complete recommendation score calculation of articles by utilization of the OT multiplication protocol, and the RBS and the SN cannot presume data of the other one only according to the owned calculation scores; (3) the recommendation scores of the articles are secretly shared by the RBS and the SN in an addition sum manner; and (4) a recommendation result is obtained by comparison. Through the mode, the social recommendation method based on the oblivious transfer is advantaged by extremely little calculation cost, extremely strong adaptability and extremely high efficiency, and promotion of the social recommendation method based on the oblivious transfer has wide market prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Secure Function Evaluation Between Semi-Honest Parties
ActiveUS20140040620A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOblivious transferComputer engineering
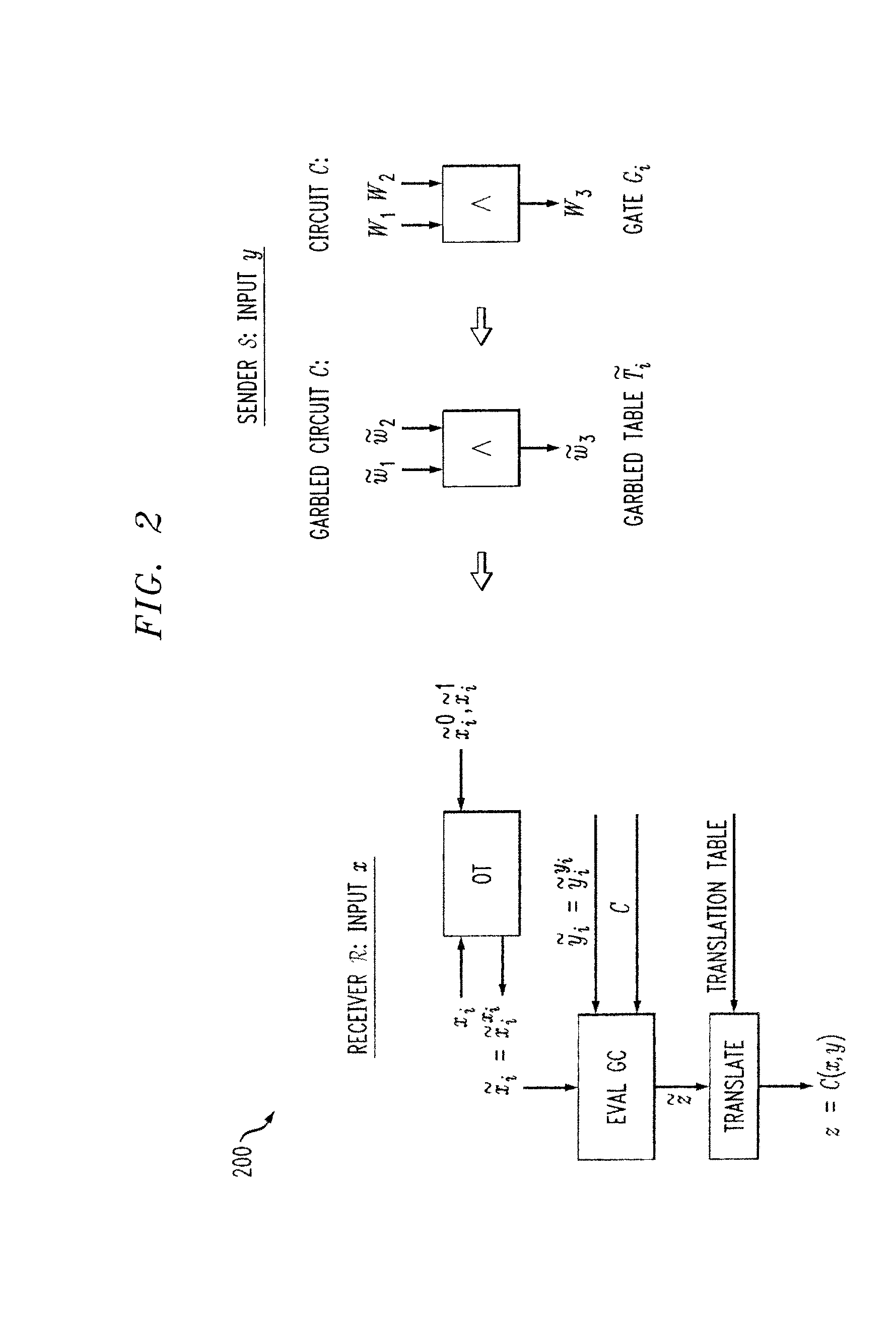
Methods and apparatus are provided for secure function evaluation between a semi-honest client and a semi-honest server using an information-theoretic version of garbled circuits (GC). An information-theoretic version of a garbled circuit C is sliced into a sequence of shallow circuits C1, . . . Cn, that are evaluated. Consider any wire wj of C that is an output wire of Ci, and is an input wire of Ci+1. When a slice Ci is evaluated, Ci's 1-bit wire key for wj is computed by the evaluator, and then used, via oblivious transfer (OT), to obtain the wire key for the corresponding input wire of Ci+1. This process repeats until C's output wire keys are computed by the evaluator. The 1-bit wire keys of the output wires of the slice are randomly assigned to wire values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
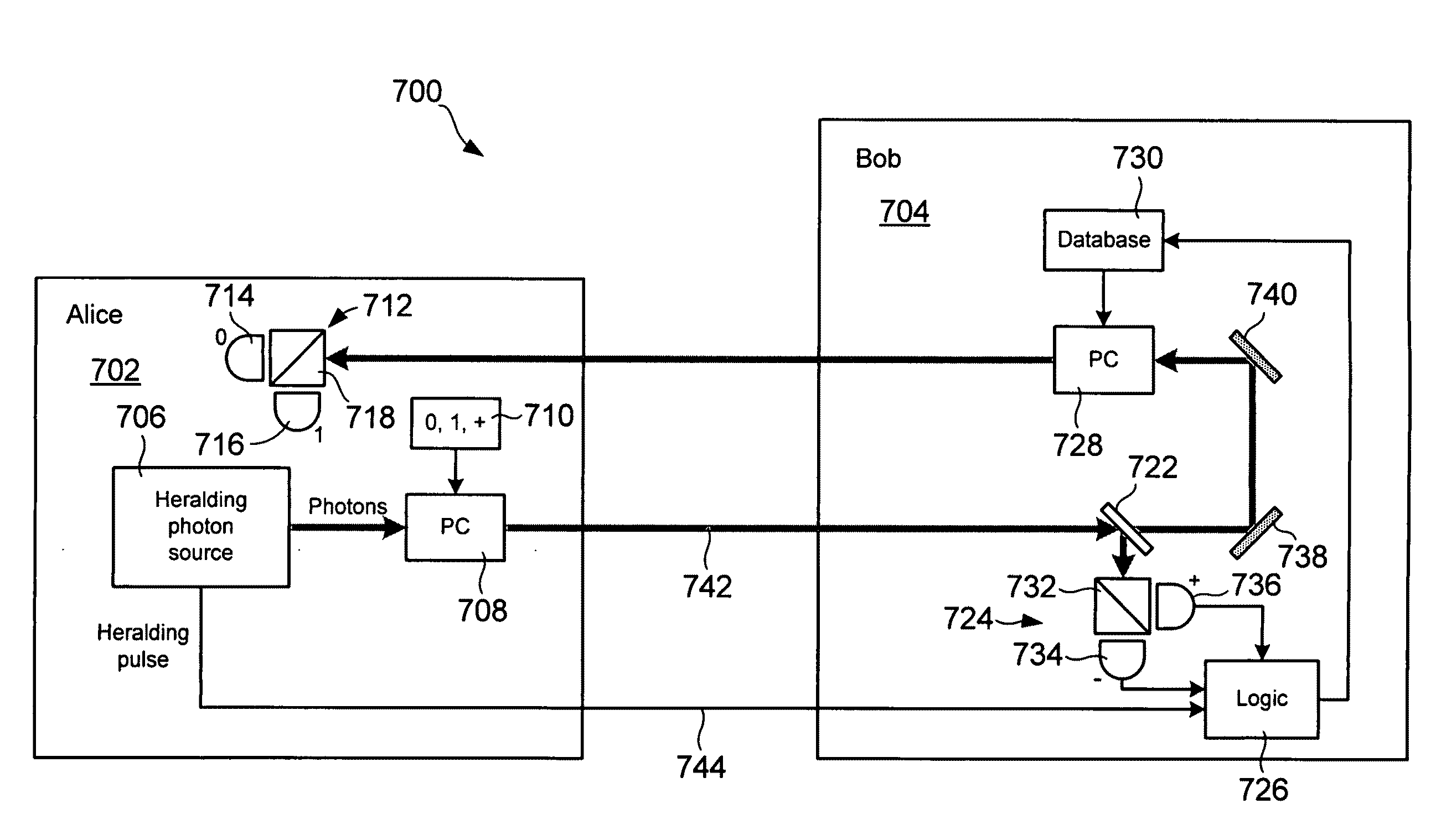
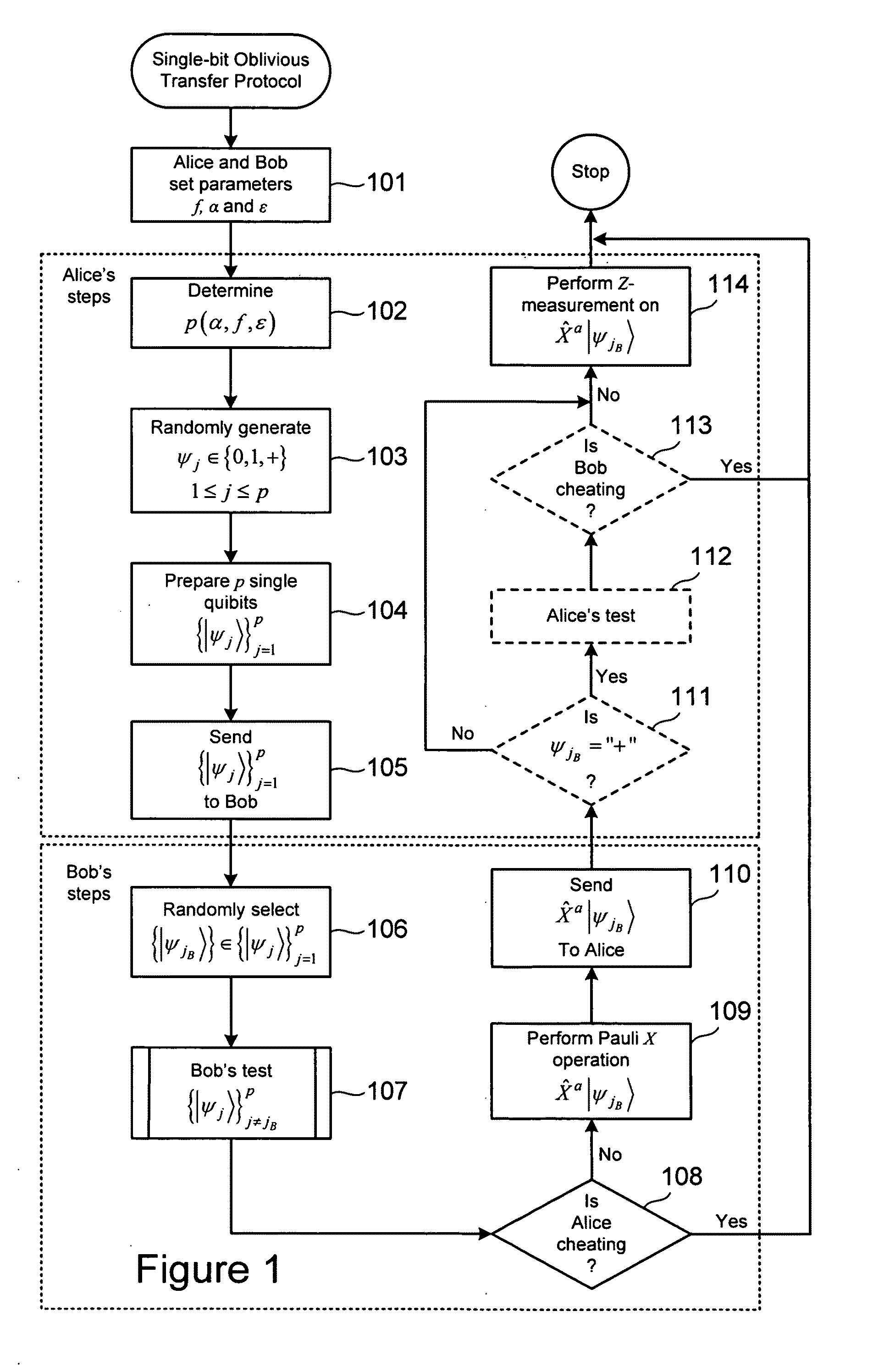
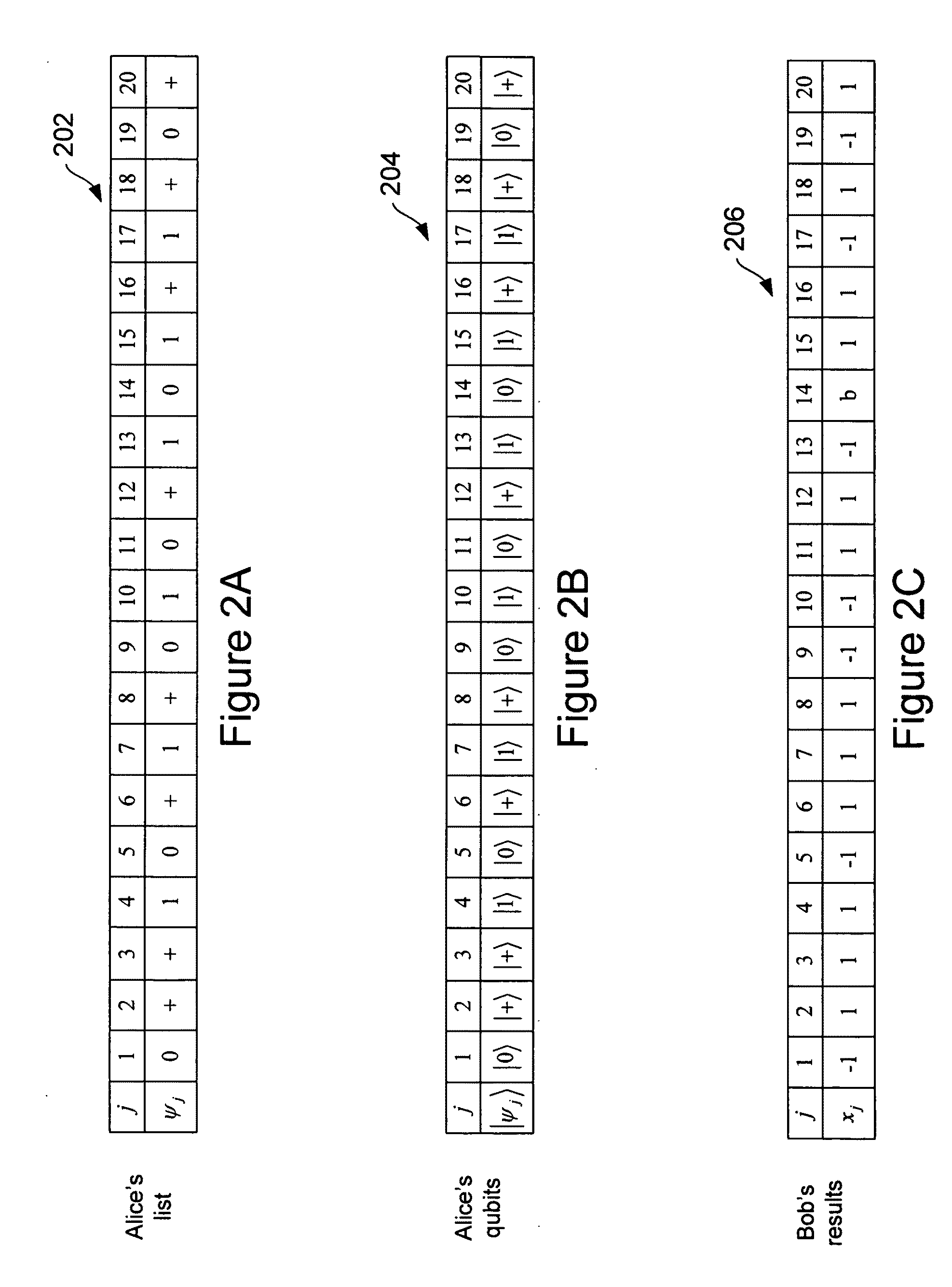
Quantum-based oblivious transfer and private data sampling protocols and systems for performing the same
ActiveUS20100094842A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTransmission protocolProtocol implementations
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to oblivious transfer protocols and to system for performing oblivious transfer. Embodiments of the present invention include a private data sampling protocol that is designed to balance the competing privacy interest of a database user and a database owner. Protocol embodiments enable the database user to obtain a fixed size random sample of the available data held by the database owner without the database owner learning which bits of data were accessed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Two-server privacy-preserving clustering
ActiveUS20210133587A1Improve efficiencyImprove scalabilityMathematical modelsRandom number generatorsExtensibilityEngineering
Described herein are systems and techniques for privacy-preserving unsupervised learning. The disclosed system and methods can enable separate computers, operated by separate entities, to perform unsupervised learning jointly based on a pool of their respective data, while preserving privacy. The system improves efficiency and scalability, while preserving privacy and avoids leaking a cluster identification. The system can jointly compute a secure distance via privacy-preserving multiplication of respective data values x and y from the computers based on a 1-out-of-N oblivious transfer (OT). In various embodiments, N may be 2, 4, or some other number of shares. A first computer can express its data value x in base-N. A second computer can form an ×N matrix comprising random numbers mi,0 and the remaining elements mi,j=(yjNi-mi,0) mod . The first computer can receive an output vector from the OT, having components mi=(yxi Ni-mi,0) mod .
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
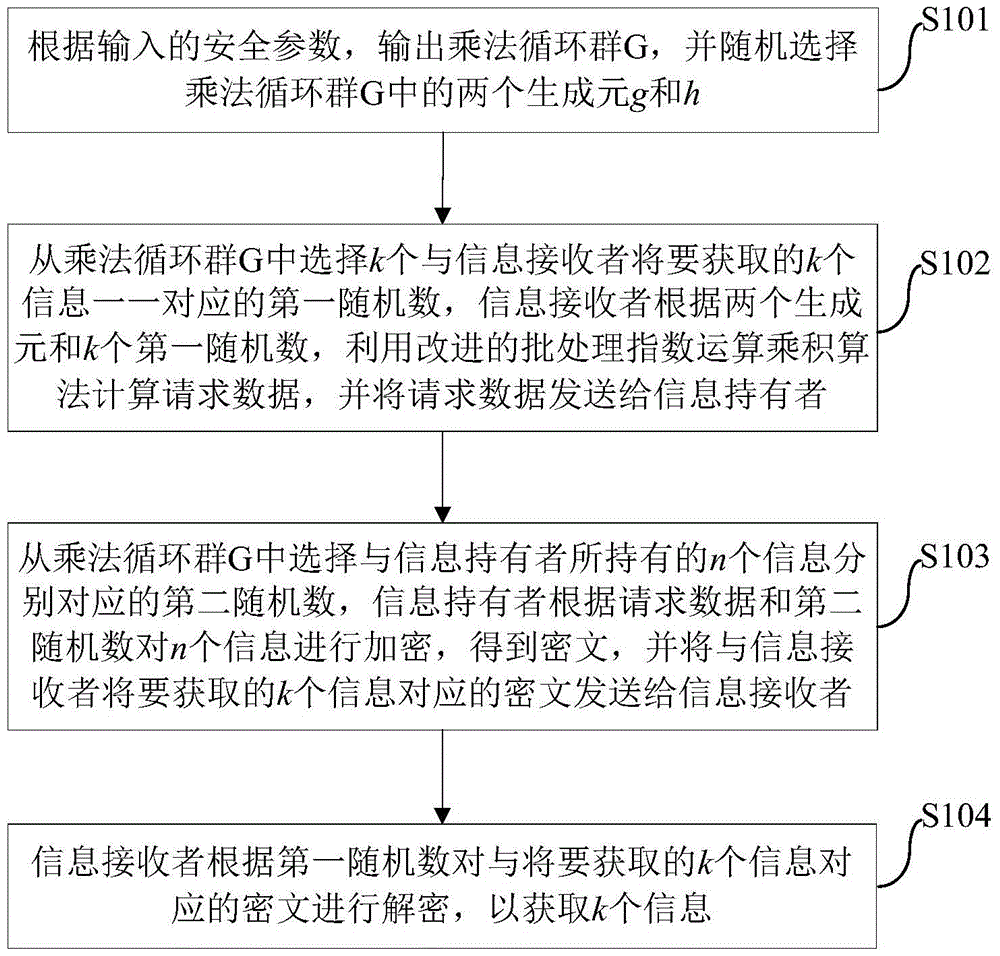
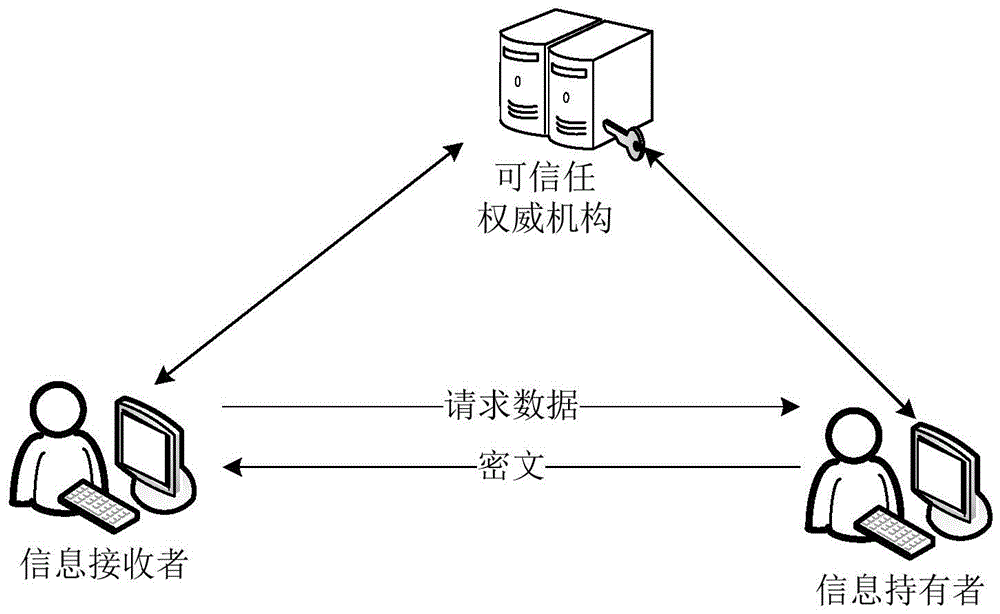
K out of n oblivious transfer method and system
ActiveCN105721140AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce computational overheadEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesBatch processingInformation transmission
The invention discloses a k out of n oblivious transfer method and system. The method comprises following steps of outputting a multiplication cyclic group G according to security parameters; randomly selecting two generation elements in the multiplication cyclic group G; selecting k first random numbers from the multiplication cyclic group G, wherein the first random numbers are in one to one correspondence with k pieces of information to be obtained by an information receiver; calculating request data by the information receiver by utilizing an improved batch processing exponent arithmetic product algorithm according to the two generation elements and the first random numbers; sending the request data to an information holder; selecting second random numbers corresponding to n pieces of information held by the information holder from the multiplication cyclic group G; encrypting the n pieces of information by the information holder according to the request data and the second random numbers, thus obtaining ciphertexts; sending the ciphertexts corresponding to the k pieces of information to the information receiver; and decrypting the ciphertexts by the information receiver according to the first random numbers, thus obtaining the k pieces of information. According to the method provided by the invention, the calculating cost can be reduced; and the information transmission efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Oblivious transfer with hidden access control lists
InactiveUS8577029B2Computer security arrangementsSecuring communicationData access controlOblivious transfer
A method, apparatus, and a computer readable storage medium having computer readable instructions to carry out the steps of the method for anonymous access to a database. Each record of the database has different access control permissions (e.g. attributes, roles, or rights). The method allows users to access the database record while the database does not learn who queries a record. The database does not know which record is being queried: (i) the access control list of that record or (ii) whether a user's attempt to access a record had been successful. The user can only obtain a single record per query and only those records for which he has the correct permissions. The user does not learn any other information about the database structure and the access control lists other than whether he was granted access to the queried record, and if so, the content of the record.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
InactiveUS20090190752A1Digital data processing detailsSecret communicationOblivious transferData mining
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
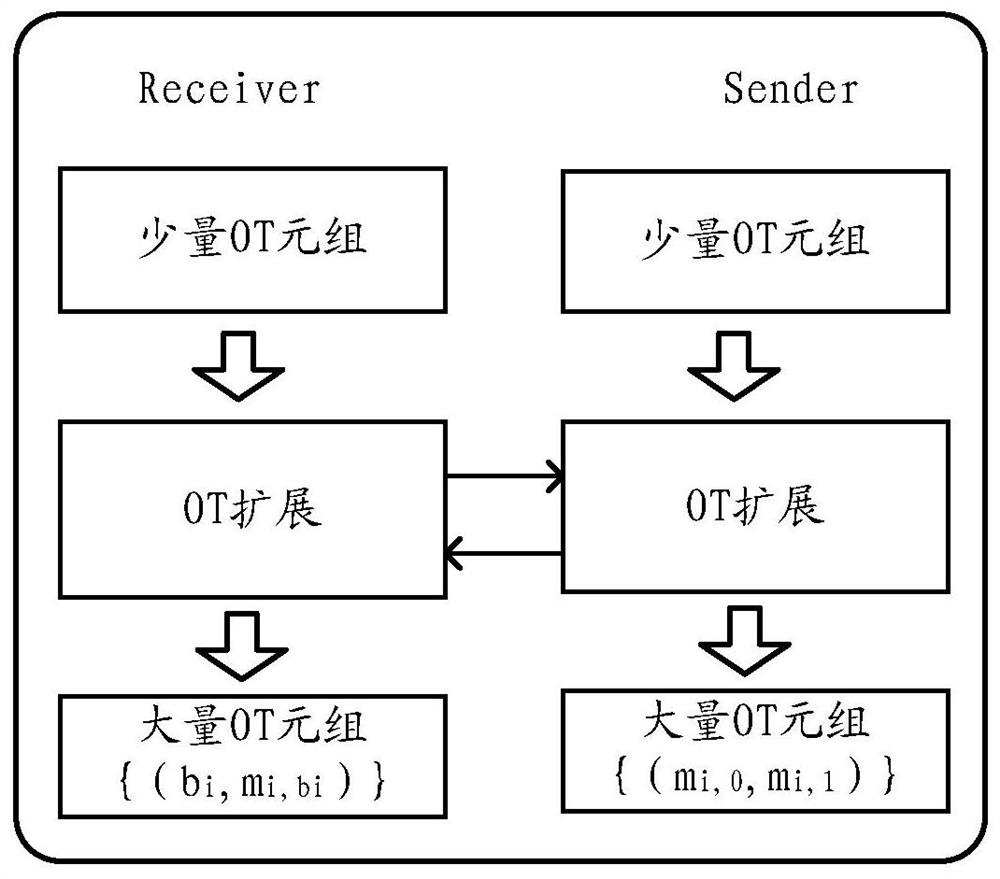
Data processing method and device for oblivious transfer (OT) extension protocol
ActiveCN112134682AImprove production efficiencyReduce communication costsSecuring communicationComputational scienceParallel computing
The embodiment of the invention provides a data processing method and device for an oblivious transfer (OT) extension protocol, and the method comprises the steps: executing, by an executor of the OTextension protocol, an OT protocol through another executor for a plurality of times, so as to obtain a first number of initial OT tuples; and then, extending the first number of initial OT tuples byusing a first OT extension algorithm with relatively high network consumption and relatively low calculation consumption to obtain a second number of OT tuples. and extending the second number of OT tuples again by using a second OT extension algorithm with relatively low network consumption and relatively high calculation consumption to obtain a target number of OT tuples.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Privacy protection method based on location service in scene of Internet of Things (IOT)
ActiveCN103037306BGuaranteed privacy and securityReduce security risksPayment architectureTransmissionPrivacy protectionOblivious transfer
Provided is a privacy protection method based on location service in a scene of the Internet of Things (IOT). The privacy protection method based on the location service in the scene of the IOT comprises two privacy protection schemes according to the characteristics on the basis of the location service and the privacy protection level, namely an absolute privacy query scheme for a quite high security level and a query privacy scheme for a quite low security level. Through analysis of application scenes, the secure multi-party computation technology is integrated into IOT location privacy protection, by utilization of technologies such as adding random numbers, using dot product properties, and carrying out homomorphic encryption and oblivious transfer protocols, a dot which is nearest to a query input location in a database to be queried is calculated and found out, different levels of protection measures are taken according to the different application scenes, and therefore the effect that the privacy of query input, query results and contents of the database to be queried is protected is achieved in the absolute privacy protection scheme, and the privacy of the query input and the query results is protected in the query privacy protection scheme.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for communication efficient private information retrieval and oblivious transfer
InactiveUS20090190751A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOblivious transferData mining
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for performing private retrieval of information from a database is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprising obtaining an index corresponding to information to be retrieved from the database and generating a query that does not reveal the index to the database. The query is an arithmetic function of the index and a secret value, wherein the arithmetic function includes a multiplication group specified by a modulus of a random value whose order is divisible by a prime power, such that the prime power is an order of the random value. The secret value is an arithmetic function of the index that comprises a factorization into prime numbers of the modulus. The method further comprises communicating the query to the database for execution of the arithmetic function against the entirety of the database.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Secure function evaluation for a covert client and a semi-honest server using string selection oblivious transfer
ActiveUS8990570B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOblivious transferComputer engineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for secure function evaluation for a covert client and a semi-honest server using string selection oblivious transfer. An information-theoretic version of a garbled circuit C is sliced into a sequence of shallow circuits C1, . . . Cn, that are evaluated. Consider any wire wj of C that is an output wire of Ci, and is an input wire of Ci+1. When a slice Ci is evaluated, Ci's 1-bit wire key for wj is computed by the evaluator, and then used, via string selection oblivious transfer (SOT), to obtain the wire key for the corresponding input wire of Ci+1. This process repeats until C's output wire keys are computed by the evaluator. The 1-bit wire keys of the output wires of the slice are randomly assigned to wire values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Secure function evaluation between semi-honest parties
ActiveUS8977855B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOblivious transferComputer engineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for secure function evaluation between a semi-honest client and a semi-honest server using an information-theoretic version of garbled circuits (GC). An information-theoretic version of a garbled circuit C is sliced into a sequence of shallow circuits C1, . . . Cn, that are evaluated. Consider any wire wj of C that is an output wire of Ci, and is an input wire of Ci+1. When a slice Ci is evaluated, Ci's 1-bit wire key for wj is computed by the evaluator, and then used, via oblivious transfer (OT), to obtain the wire key for the corresponding input wire of Ci+1. This process repeats until C's output wire keys are computed by the evaluator. The 1-bit wire keys of the output wires of the slice are randomly assigned to wire values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
An ecdsa digital signature method based on two-party collaboration
ActiveCN109639439BSafe and efficient collaborative signatureImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlice and BobDigital signature
The invention discloses an ECDSA digital signature method based on two-party collaboration. The method comprises the following steps: step 1), respectively generating corresponding signature public and private key pairs and other parameters by a signature party Alice and a signature party Bob participating in the collaborative signature; and step 2), collaboratively completing ECDSA signature by Alice and Bob, and finally outputting the signature (r,s). According to the ECDSA digital signature method based on the two-party collaboration provided by the invention, under the premise of ensuringthe security and the correctness, a signature process does not introduce high-overhead password operations such as homomorphic encryption, oblivious transfer and the like, so that a signature scheme achieves a good balance between the communication overhead and the computation overhead, and therefore the performance is remarkably superior to that of all existing ECDSA two-party collaborative digital signature methods.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A Design Method of Secure Face Authentication System Based on CNN Feature Extractor
ActiveCN105631296BImprove authentication accuracyImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionCiphertextFace verification
A design method for a secure face authentication system based on a CNN feature extractor belongs to the field of biometric identification, and specifically relates to a method for extracting face features using CNN and encrypting them with Paillier algorithm and inadvertent transmission protocol. Compared with the SCiFi system, the present invention replaces manually extracted features with features learned automatically by CNN, and performs binarization to remove the influence of noise, and has higher authentication accuracy. The test authentication rate on LFW library view2 is 91.48%. During the entire authentication process, the server will not know any characteristic information of the requester, and can only receive the characteristic ciphertext information but cannot decrypt it. The client only knows whether the authentication is passed, and knows nothing about other information including the Hamming distance. This system uses 320bit features to represent a face picture, and the amount of feature data is reduced by 2 / 3 compared with the SCiFi system, so the time-consuming encryption and authentication is low and the real-time performance is high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Data processing method, device and system for machine learning model
PendingCN113711247AEnsure safetyEnsure privacyDigital data protectionMachine learningTransmission protocolAlgorithm
The invention provides a data processing method, device and system for a machine learning model, that can transmit data of a data holder to a model holder by adopting an oblivious transfer protocol or a homomorphic encryption algorithm (102), and call a function for realizing comparison functionality by each level of a tree model (104), while ignoring a path choice of the data in the tree model. The oblivious transfer protocol or the homomorphic encryption algorithm is combined with the function for realizing comparison functionality, so as to guarantee that the model holder and the data holder do not reveal any information to each other, except a model output result, thereby ensuring the security and privacy of the data interaction.
Owner:SHANGHAI MATRIXELEMENTS TECH CO LTD +1
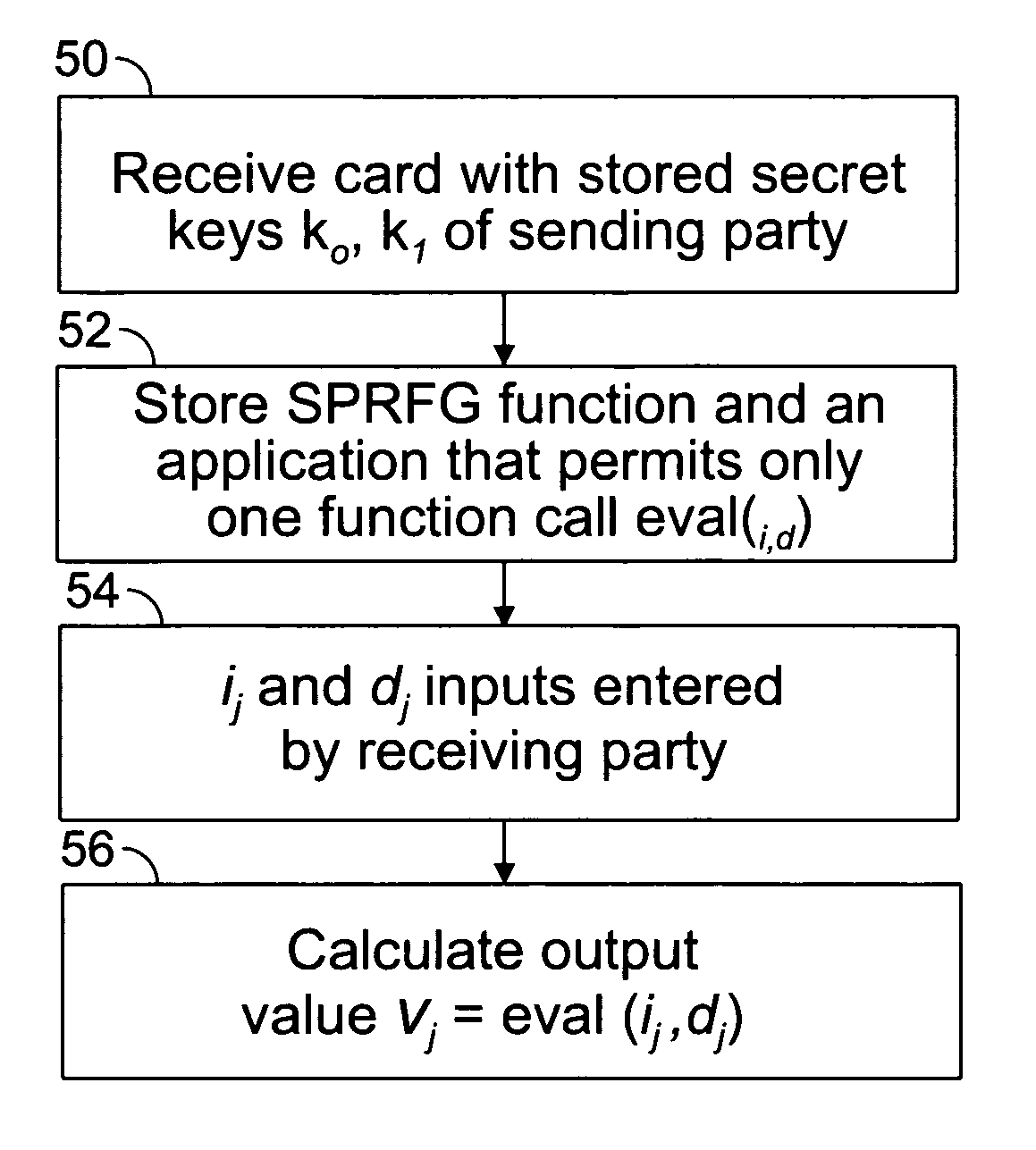
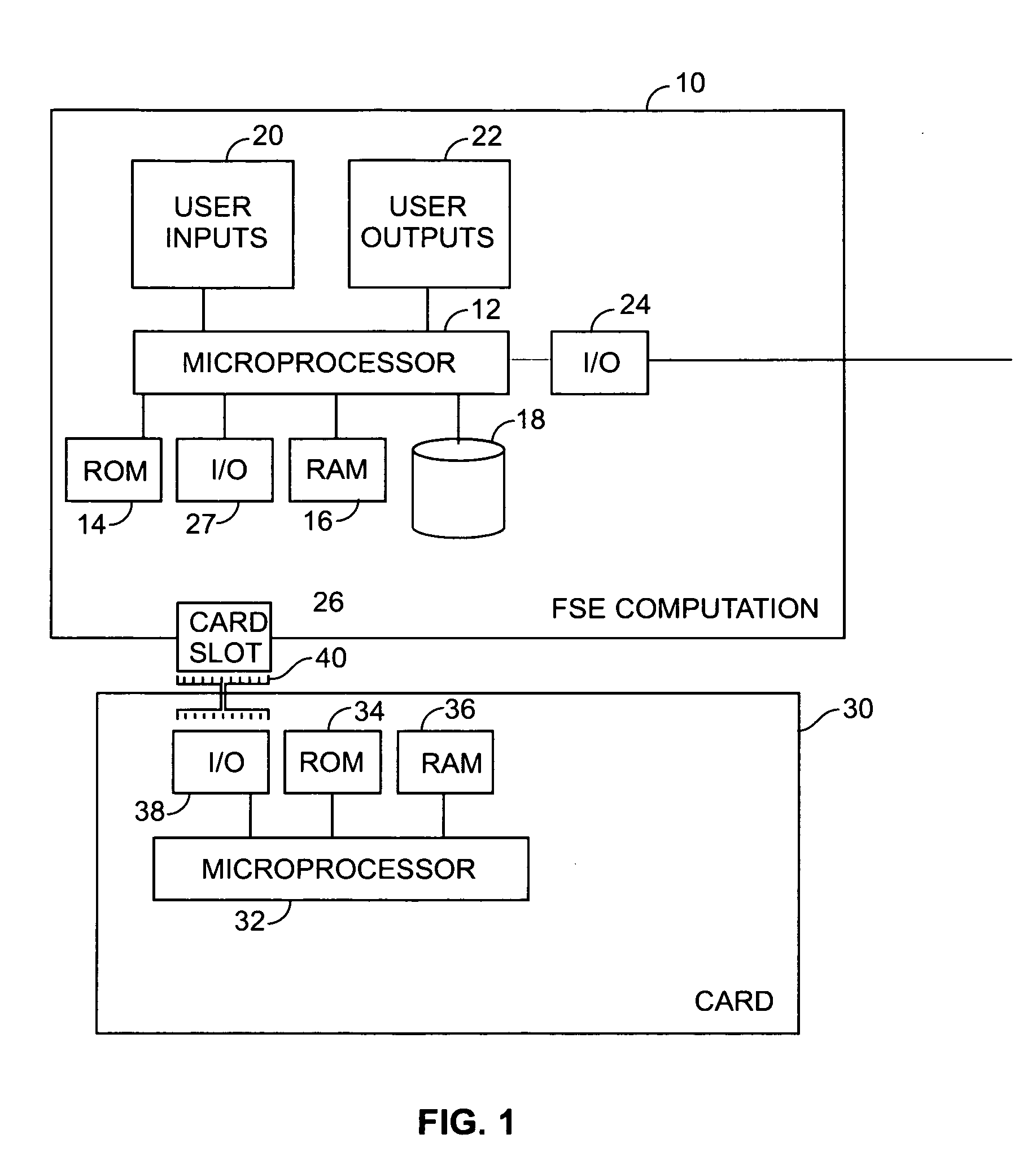
Method of efficient secure function evaluation using resettable tamper-resistant hardware tokens
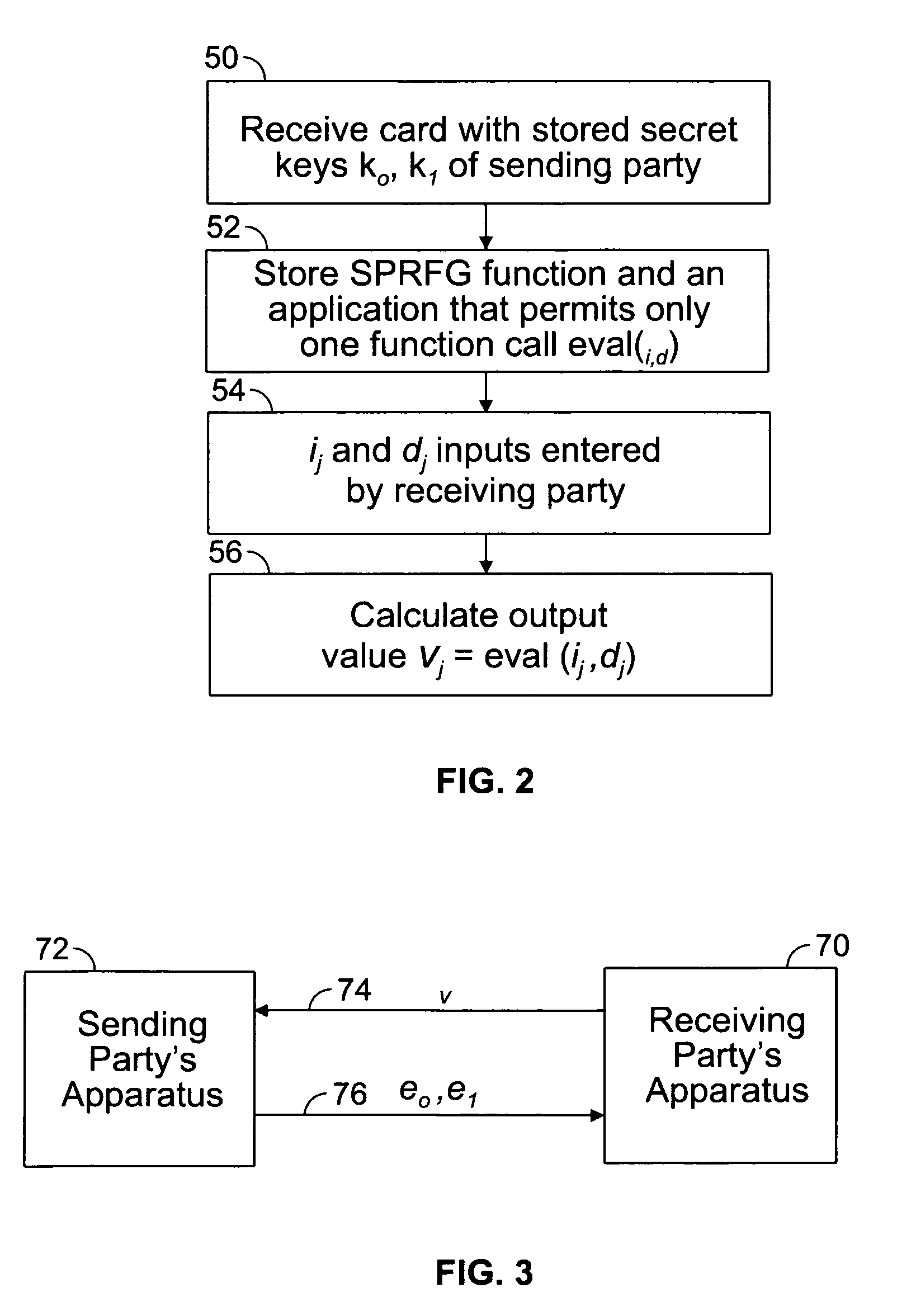
ActiveUS8923519B2Minimizes computational effortKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesOblivious transferComputer security
An embodiment of the present invention provides a computer implemented method for the transfer of private information of one user to another user—a primitive known as Oblivious Transfer. An output from a strong pseudorandom function generation (SPRFG) is calculated by a first user's computing module based on first and second parameters: the first parameter specifying one of two secret keys; the second parameter being a value selected within the domain of the SPRFG by the first user. The first user is prevented from reading or learning the stored two secret keys. The output is transmitted to a computer of a second user which generates first and second encrypted values that are each based on an inverse SPRFG calculation using the first and second secret keys, respectively, and corresponding private values of the second user. The encrypted values are sent to a first computer of the first user that calculates one of the private values using a mathematical computation based on the second parameter and the one of the first and second encrypted values that corresponds to the one of the first and second key used.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com