Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
569 results about "Database structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
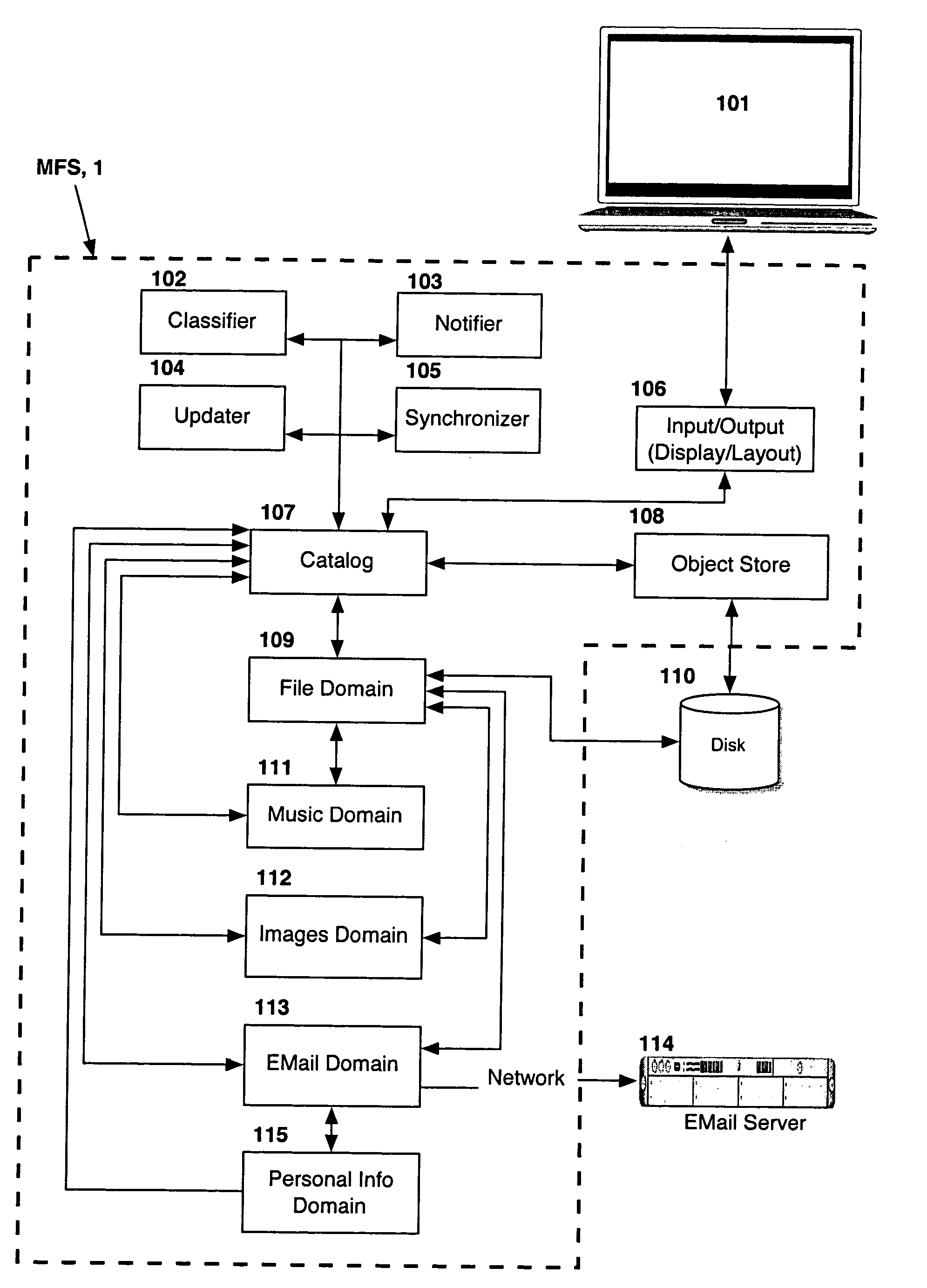
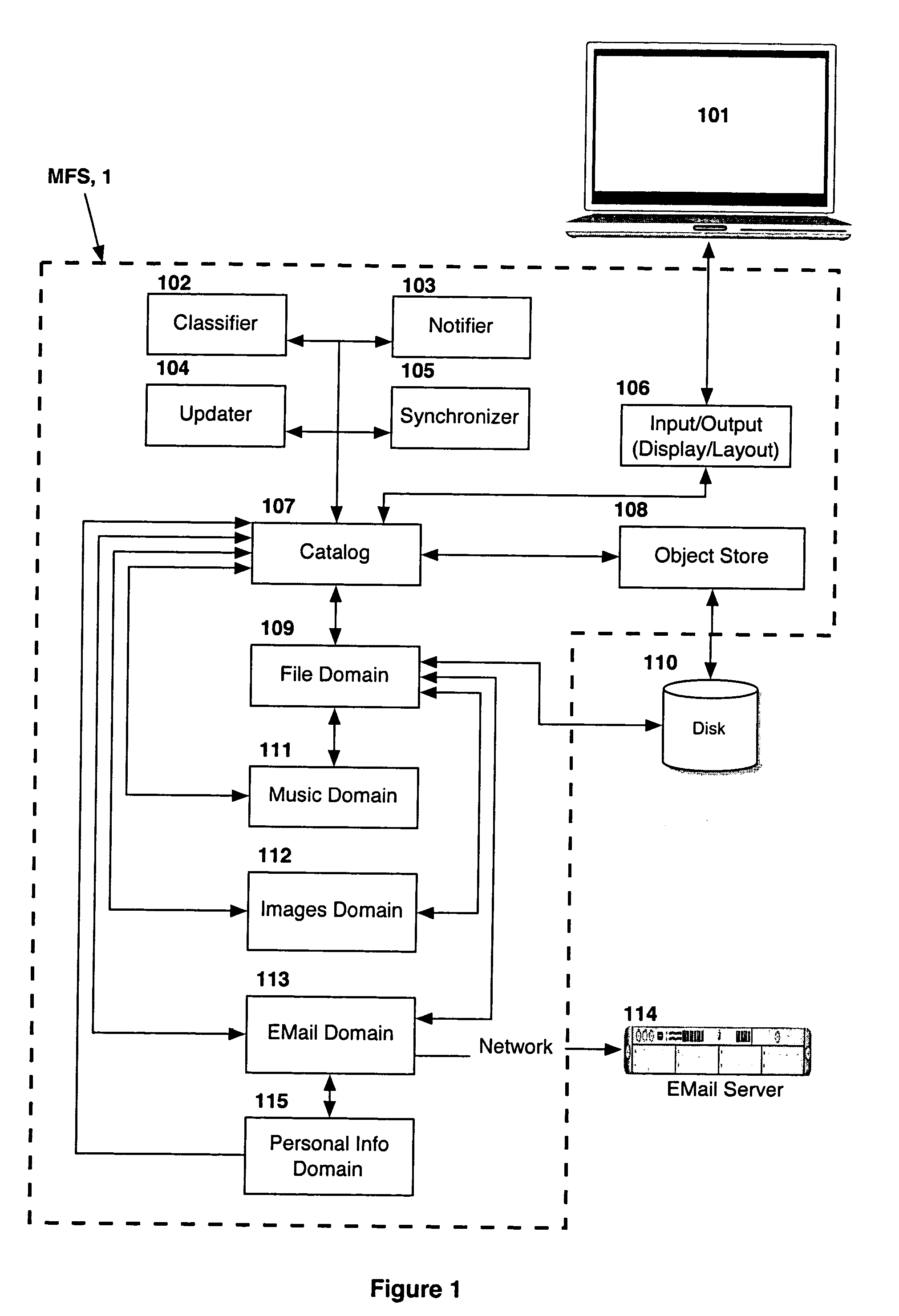
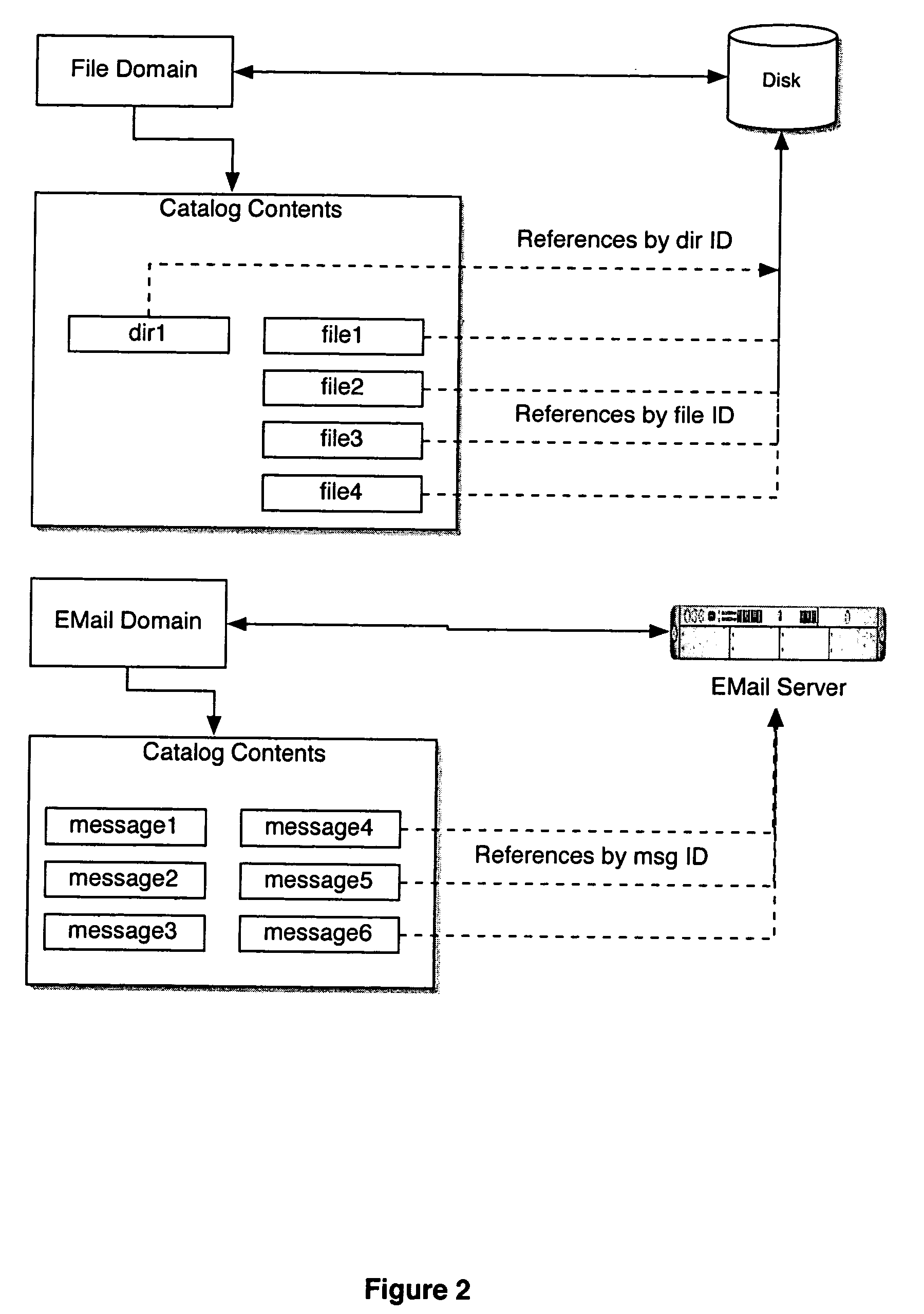
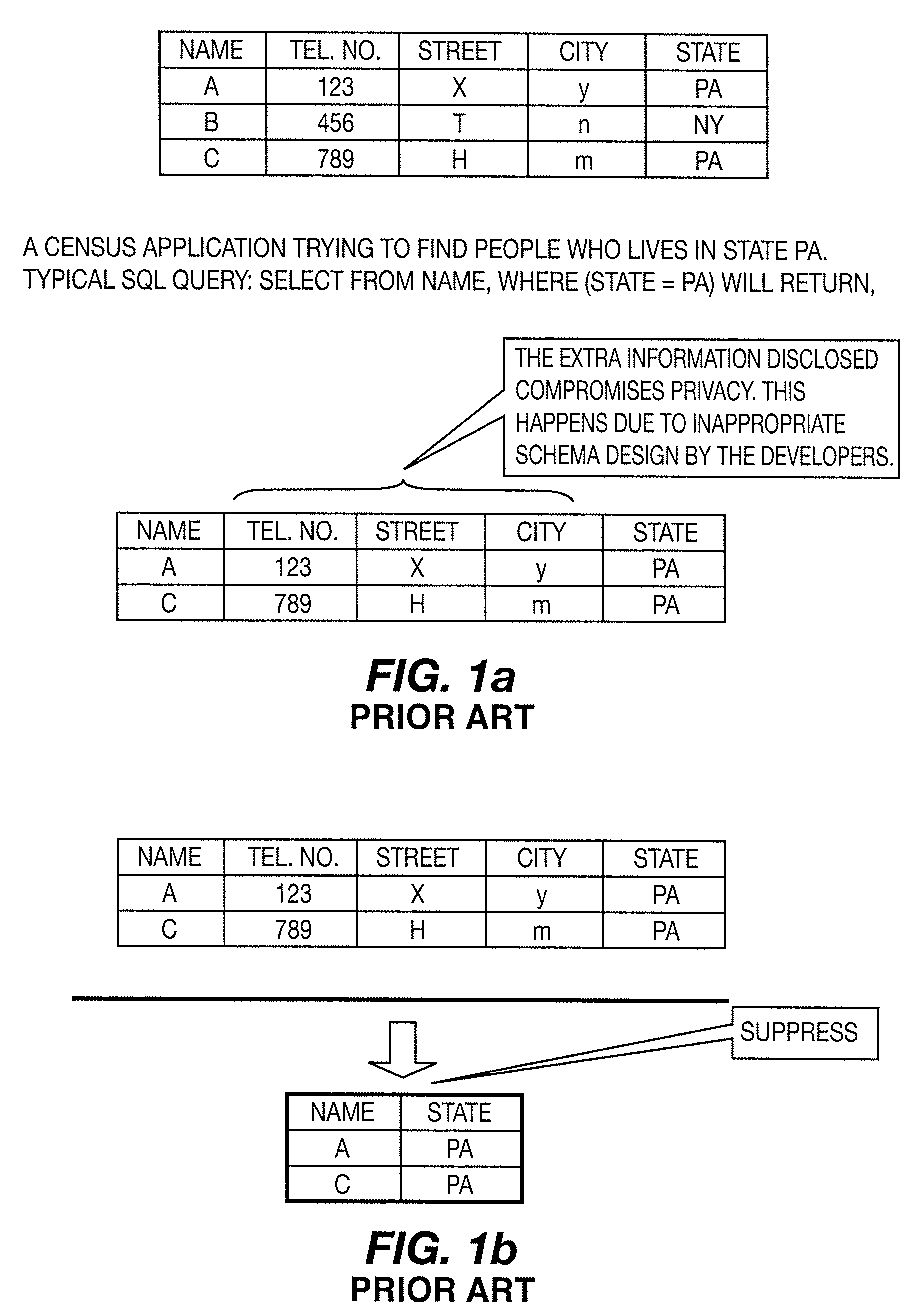
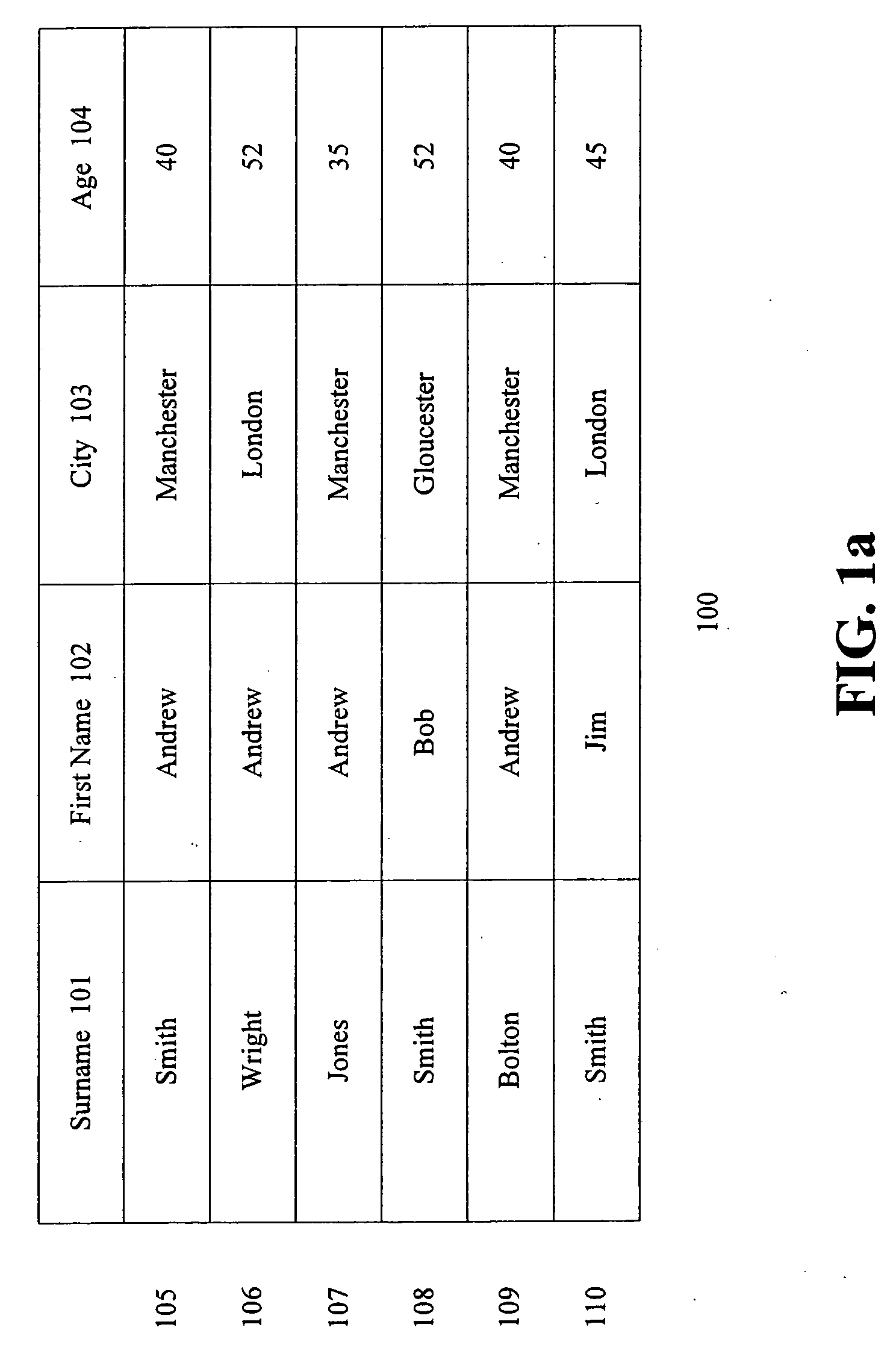
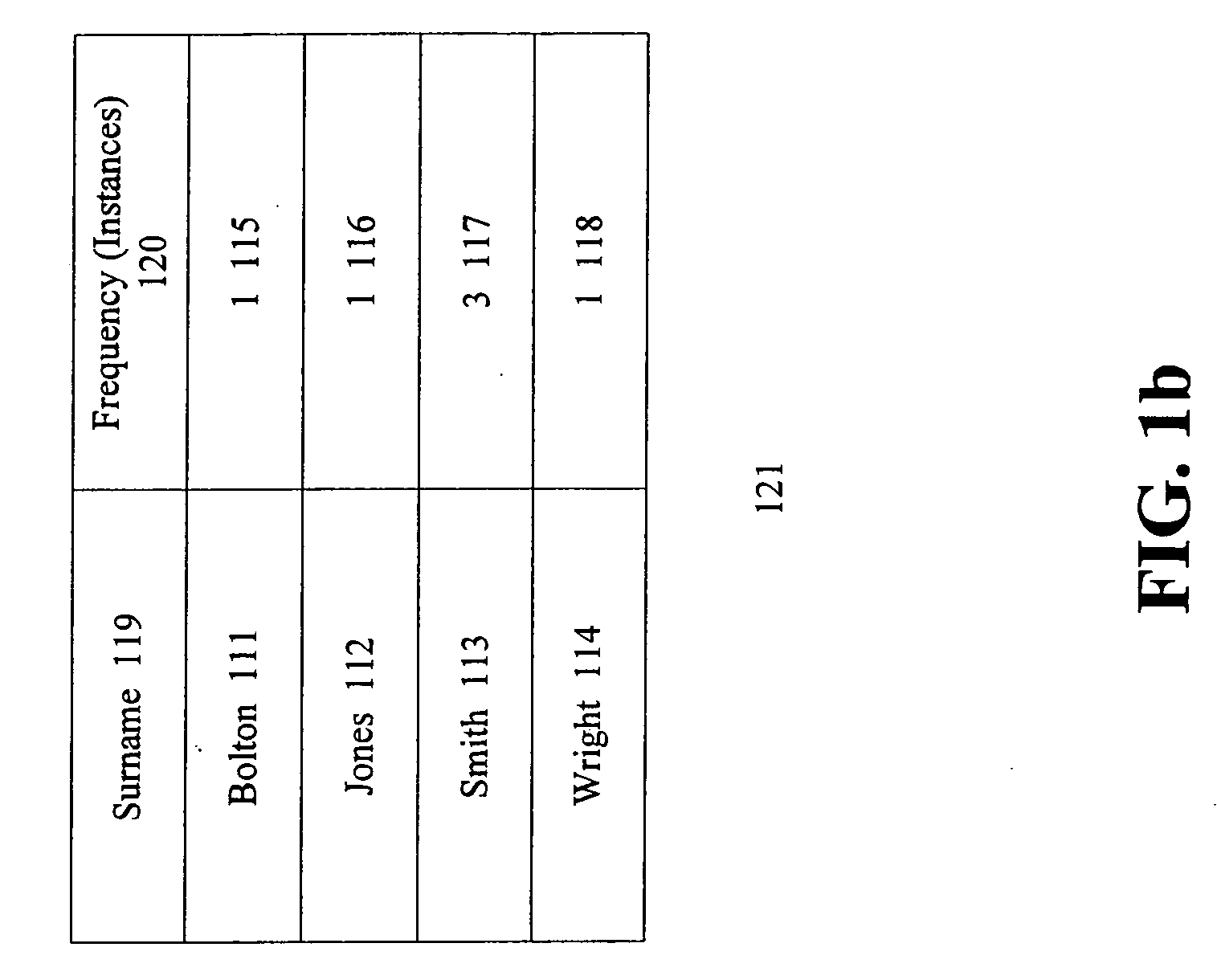
Database Structure A database is essentially an electronic filing system that houses a collection of information organized in such a way that allows a computer program to quickly find desired pieces of data.
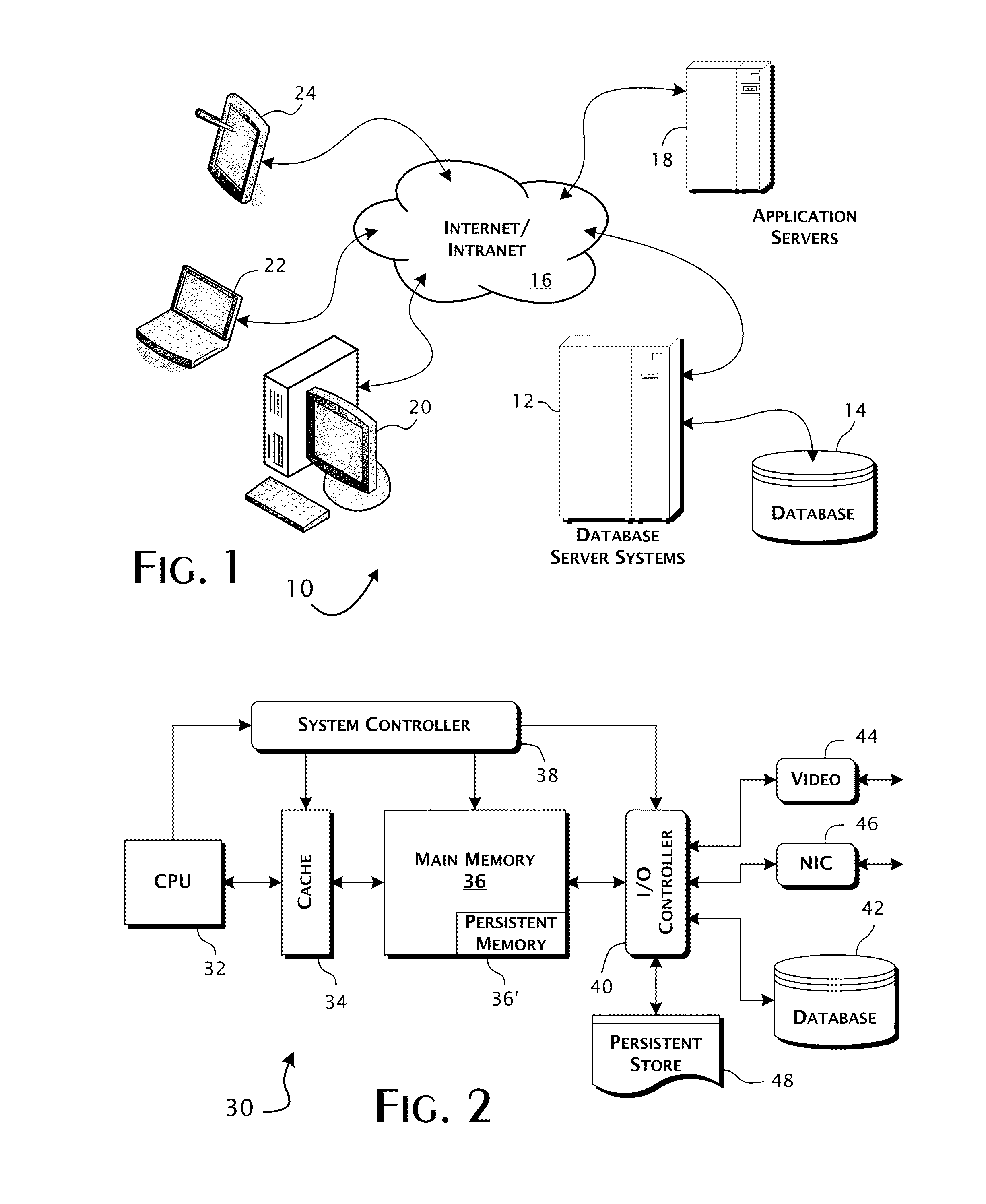
Computer system for automatic organization, indexing and viewing of information from multiple sources
ActiveUS7275063B2Facilitate communicationMultimedia data indexingFile access structuresPathPingSoftware system
Owner:EHIERARCHY LLC
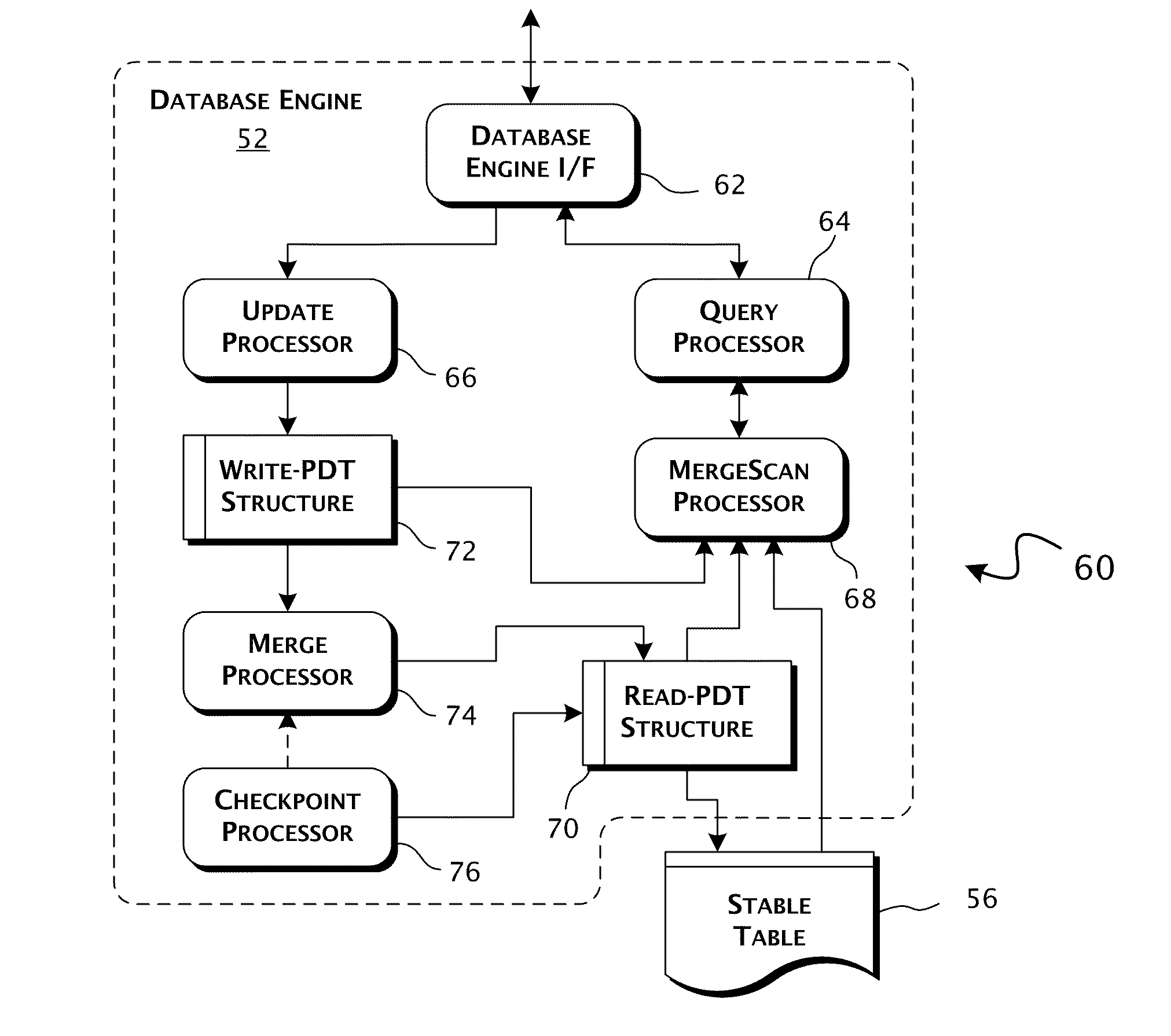
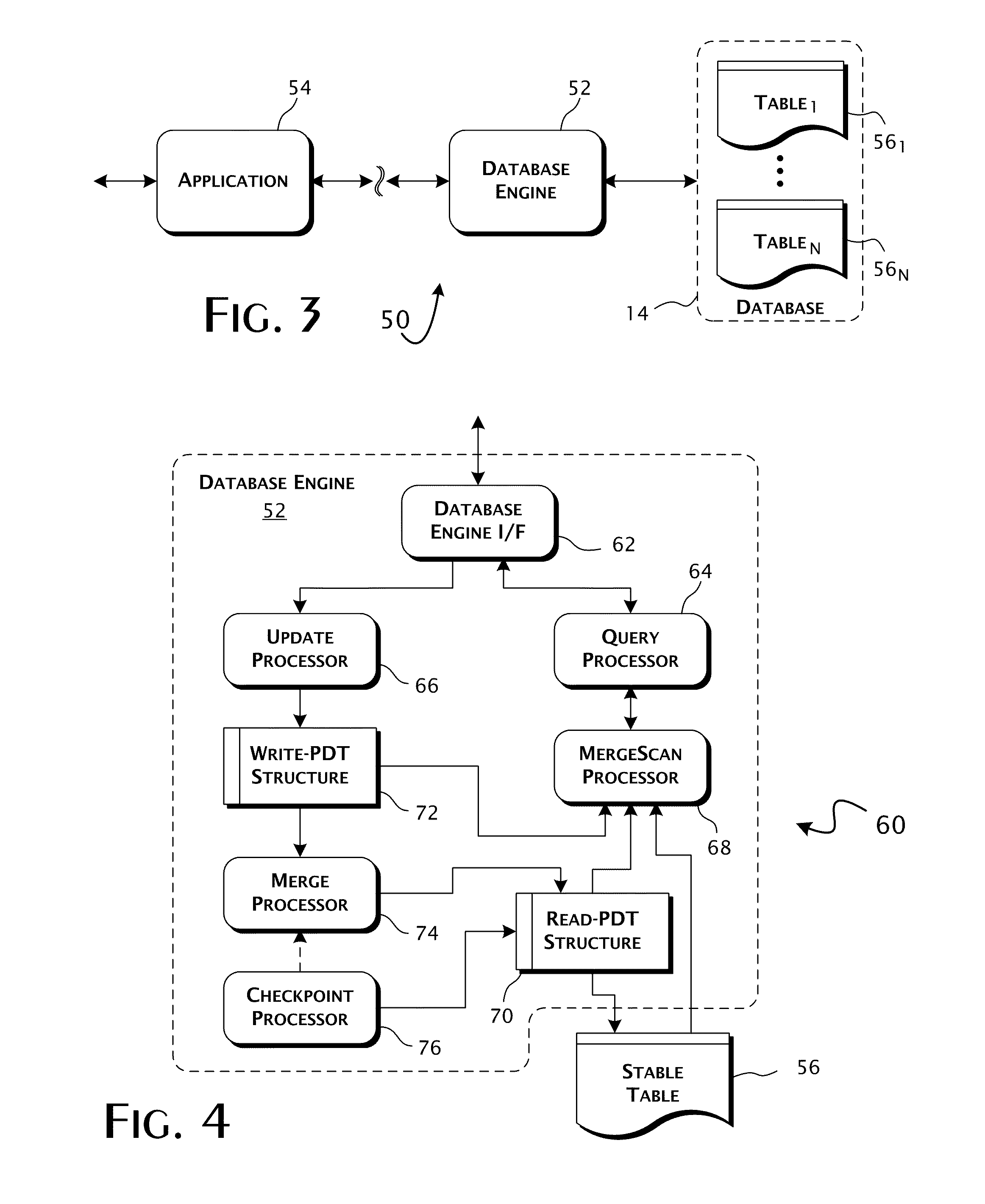
Column-store database architecture utilizing positional delta tree update system and methods
ActiveUS20100235335A1Minimize computationalFast operationDatabase updatingDigital data processing detailsDatabase machineTree (data structure)
A column-store database computer system responsive to database requests for the update and retrieval of data from within a stable data table providing for the storage of database tuples within a column-store organized database structure. A positional delta tree data structure is implemented in the memory space of the computer system and is operatively coupled in an update data transfer path between a database engine interface and the stable data table. The positional delta tree data structure includes a differential data storage layer operative to store differential update data values in positionally defined relative reference to database tuples stored by the stable data table.
Owner:ACTIAN CORP
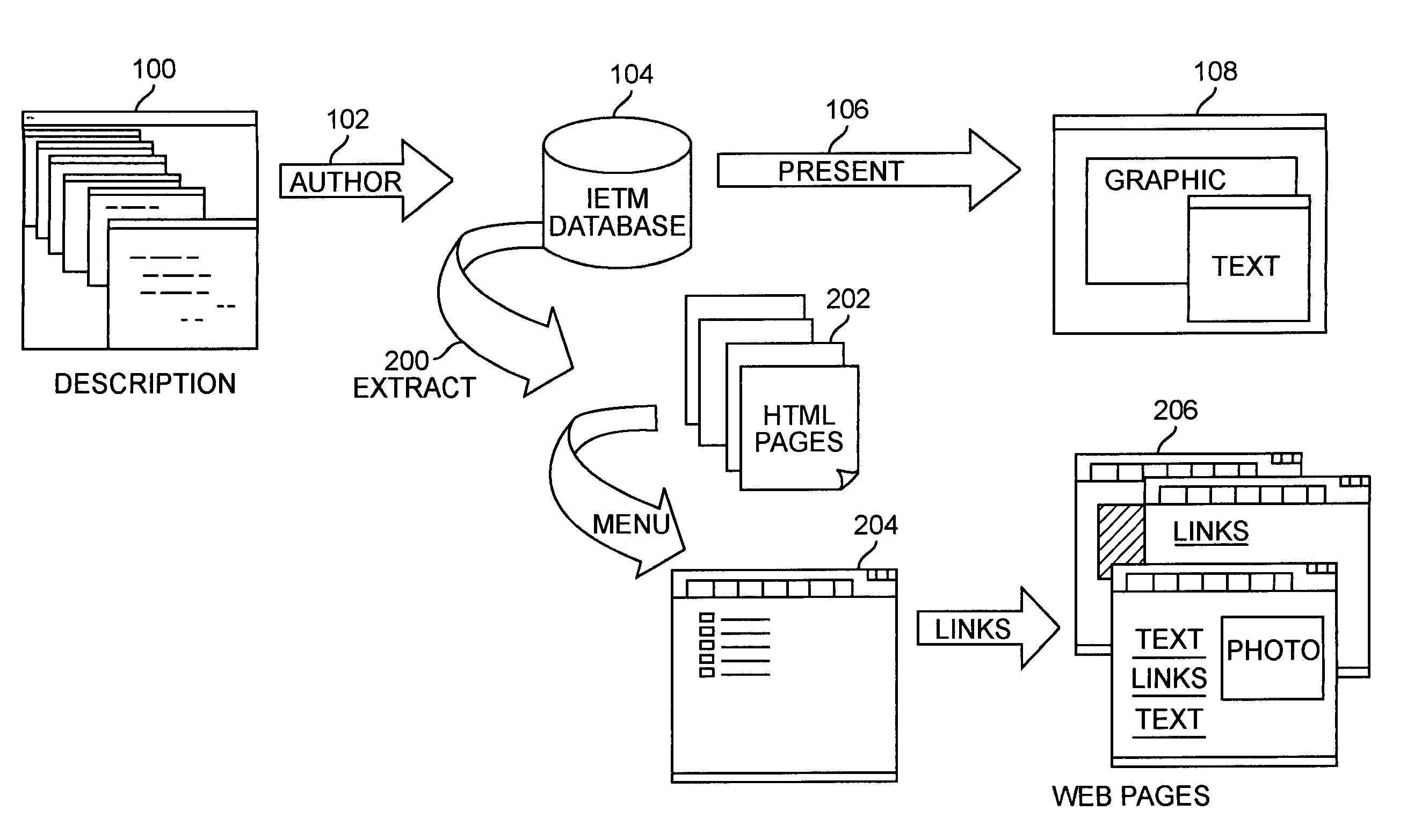
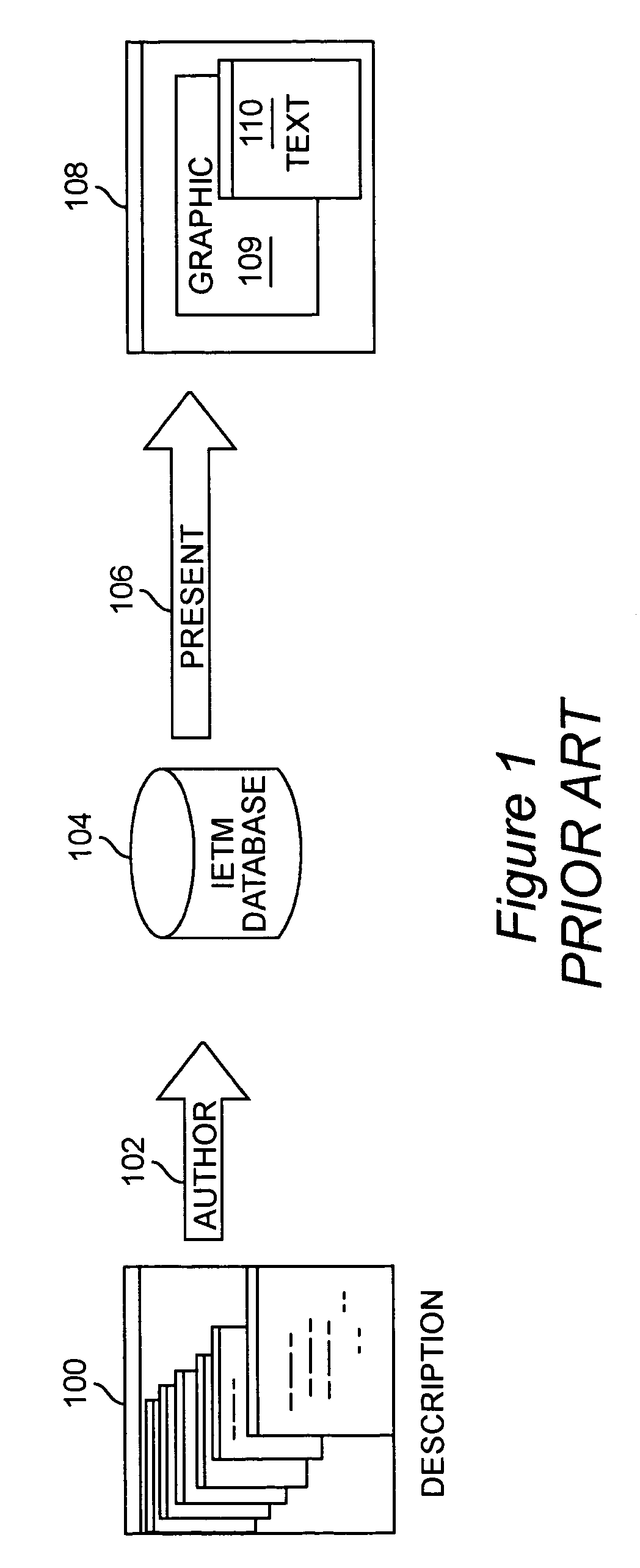
System and method for interactive electronic media extraction for web page generation
InactiveUS6961897B1Efficient updateExtend the life cycleDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingData warehouseRelational database
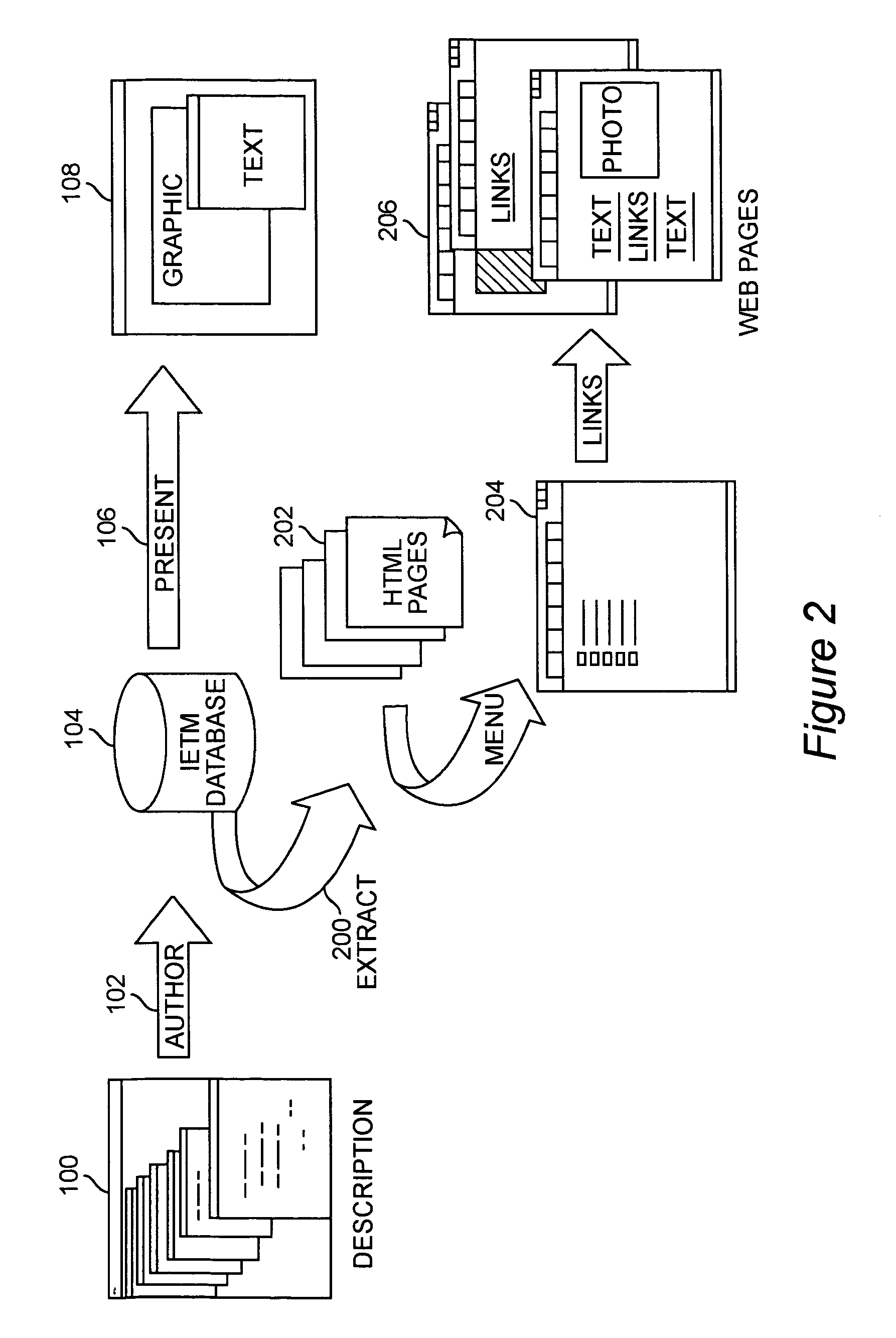
A system and method for parsing an electronic media database structure to produce tagged data that preserves the content, links, and electronic media structure. In particular, HyperText Markup Language (HTML) data is generated as an Interactive Electronic Technical Manual (IETM) (home page) linked into a relative structure of Web pages to support IETM deployment. An extraction process assesses the functionality associated with each node designated for presentation and builds a virtual Web, based on attributes stored in the IETM database. A series of Web pages with links that hierarchically presents IETM data at run time is produced. The method supports a data warehousing strategy that converts any data type eligible within the relational database. This expands support across multiple types of technical and engineering data. The preferred implementation utilizes a relative addressed pure HTML solution viewable in standard Web browsers. This open system implementation is cross platform and infrastructure independent, requiring no special server software. Retaining the hierarchical structure dictated by the relational database in HTML output enhances the supportability and maintainability of the Web implementation. Updates to this Web implementation can be incrementally applied within the hierarchy (small sections of data) or the entire logical sections of Web data.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for creating and operating an investable hedge fund index fund
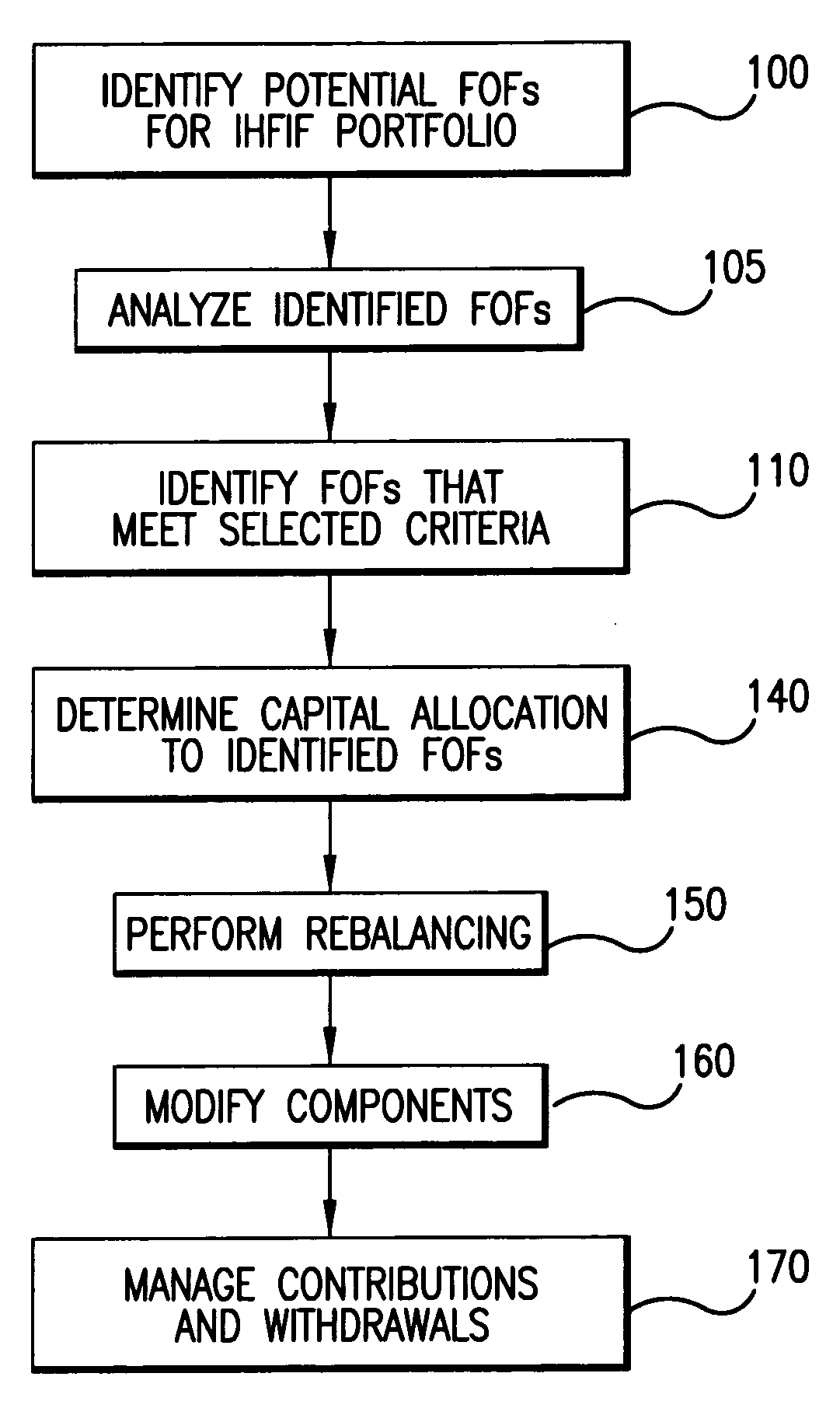
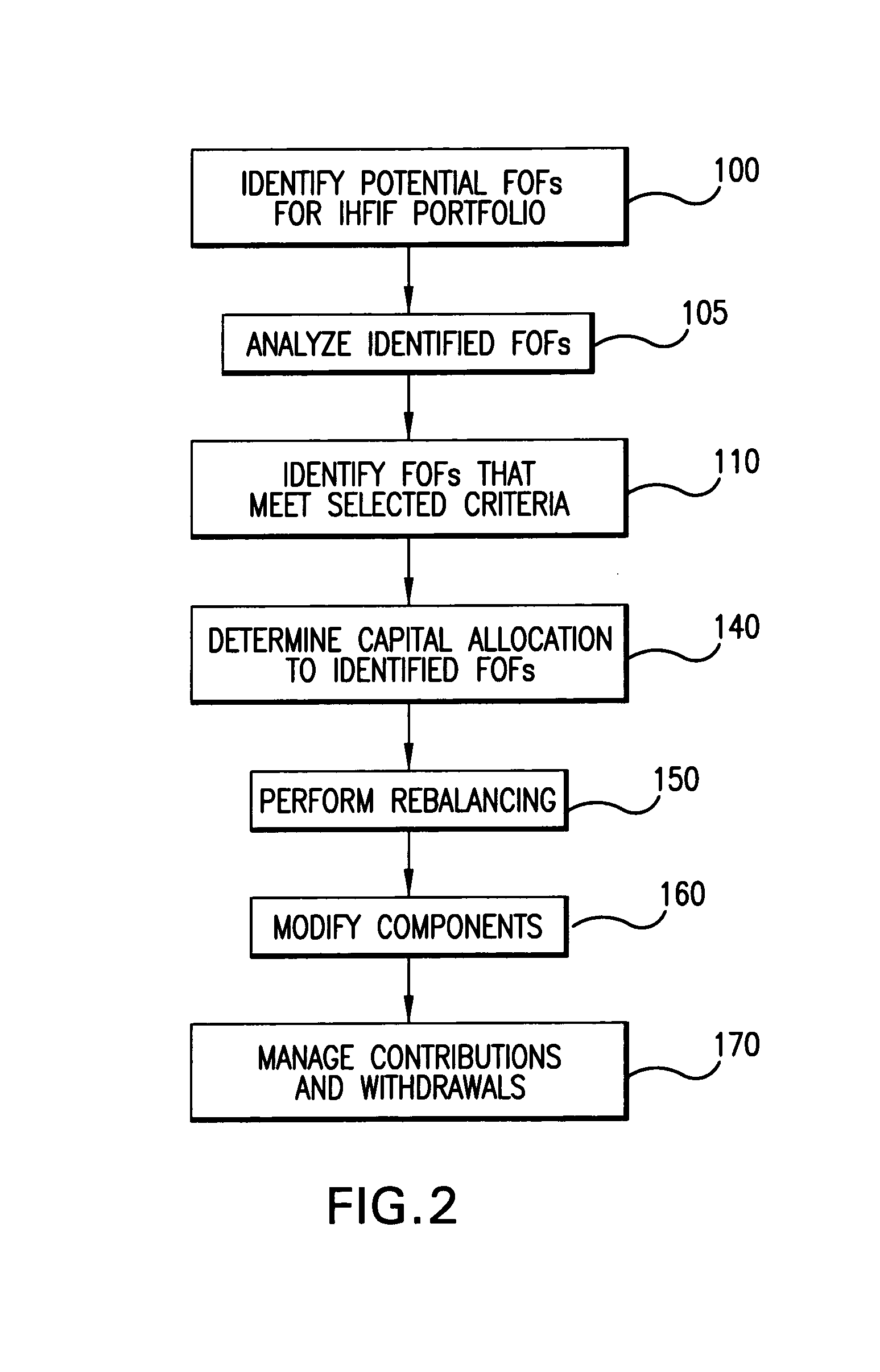
A preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises a method of creating and managing an index fund based on an index of funds of hedge funds, comprising steps of (a) identifying potential funds for an index of funds of hedge funds; (b) identifying which of the potential funds meet specific criteria selected so as to minimize biases comprising selection bias and survivorship bias; (c) creating an index by indexing funds identified as meeting the criteria; (d) acquiring a portfolio of funds in the index; and (e) allocating capital to funds in the portfolio.The invention also comprises software to perform the steps of the method described above. In particular, the invention comprises software wherein data regarding potential funds is stored in a database according to object role modeling. A preferred database structure is described.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
Hidden link dynamic key manager for use in computer systems with database structure for storage of encrypted data and method for storage and retrieval of encrypted data
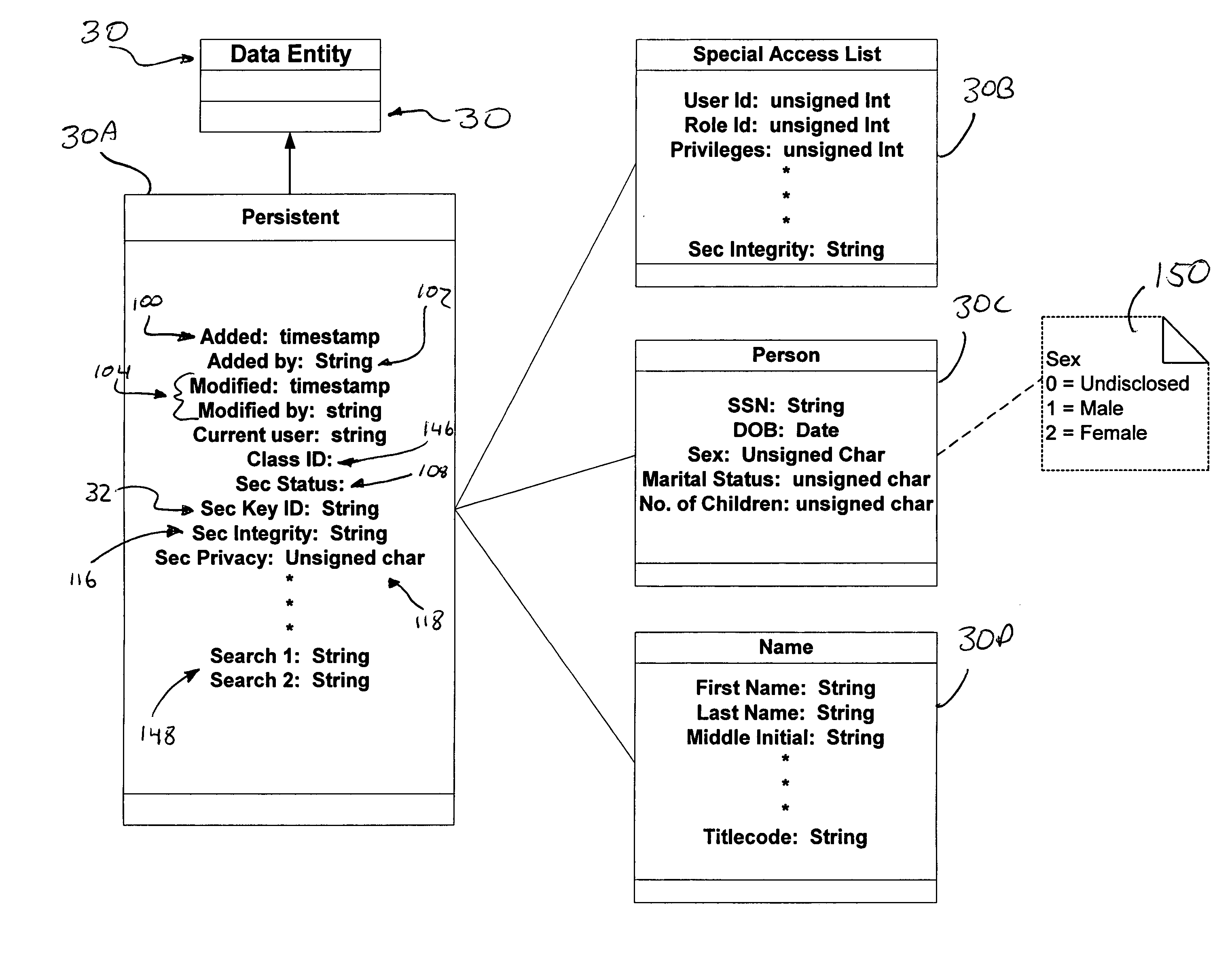
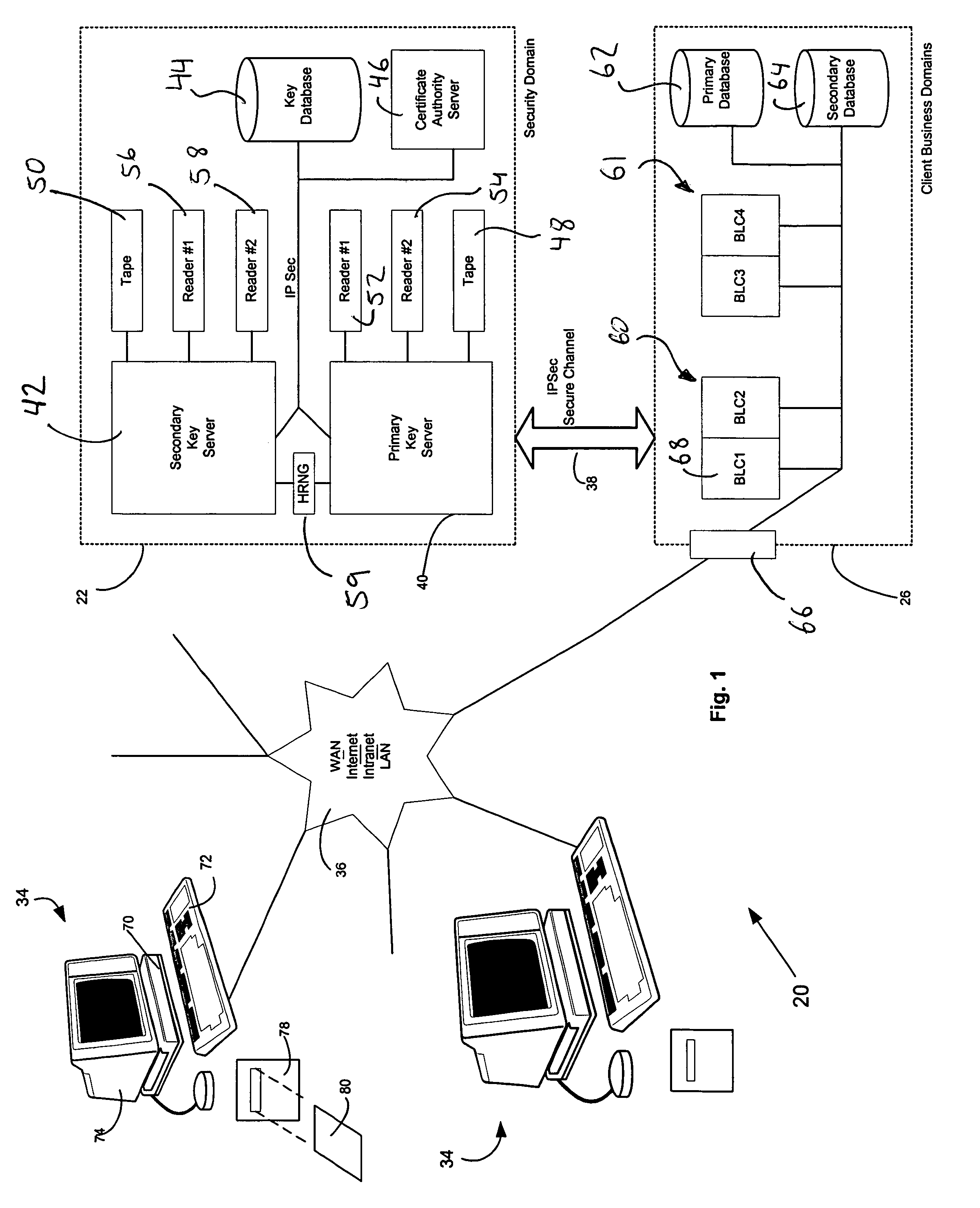
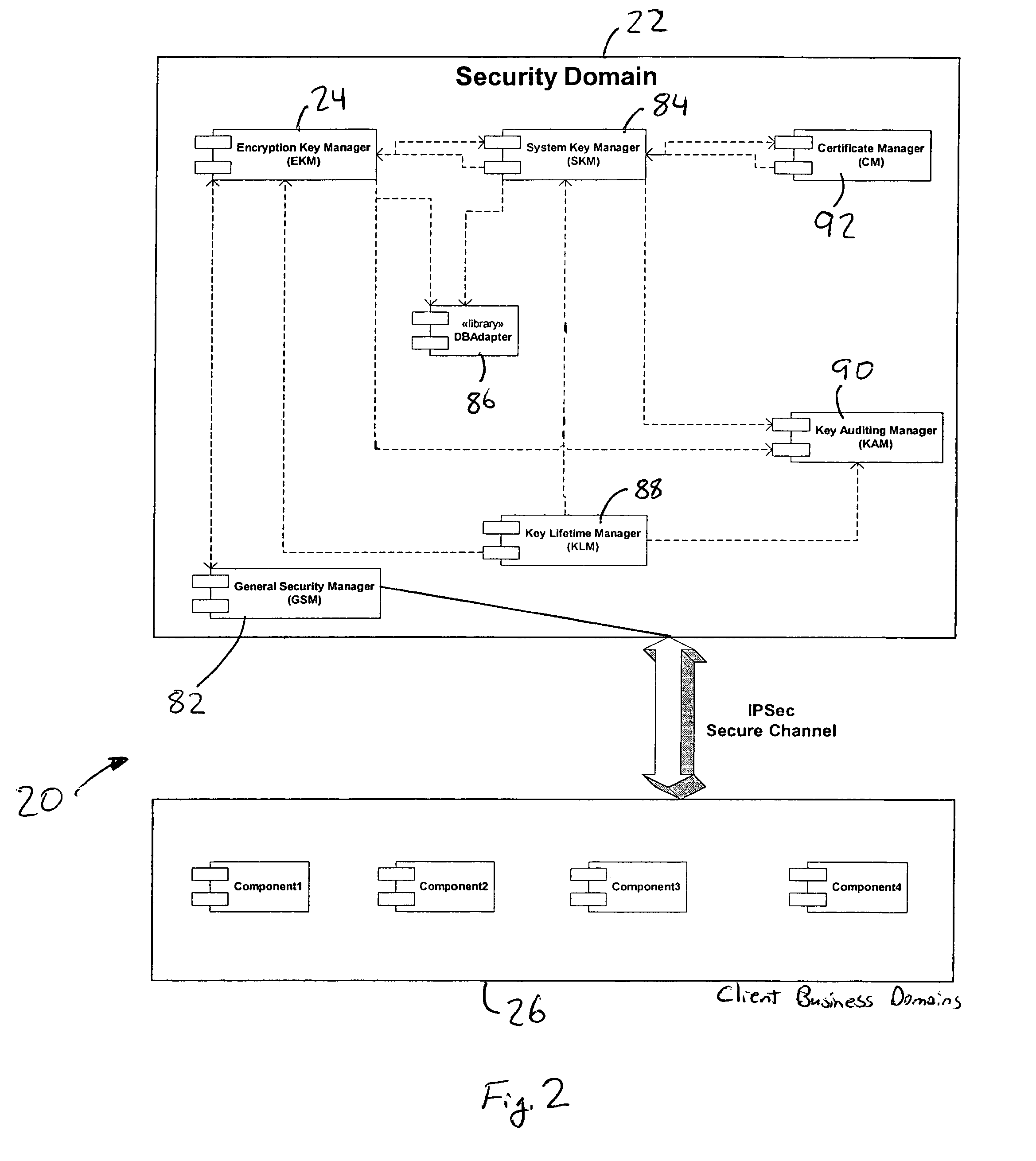
InactiveUS7362868B2Improve securityOpportunities decreaseMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer security arrangementsCommon nameSecurity domain
A computer system (20) having a security domain (22), at least one client business domain (26), and a plurality of client terminals (34) utilizes a hidden link dynamic key manager (24, 84) and a database structure that includes encrypted data entities (30C, 30D) and a security identification attribute (32) for storage of encrypted data. Methods for encrypting data and for storing, decrypting, and retrieving encrypted data operate on the computer system (20), which also includes an information database (62) and a key database (44). The key database (44) is isolated from the information database (62). The hidden link key manager is stored in the security domain (22) and includes a system key manager (84) operable to generate system keys with system key common names and an encryption key manager (24) operable to generate encryption keys having encryption key identifications. The key managers (24, 84) operate on a key server (40), which is mirrored by a secondary key server (42). A general security manager (82) also operates on the key server (40) to control access to the security domain (22). The security information attribute (32) is stored with a persistent data entity (30A) that is associated with the other encrypted data entities (30C, 30D) by a database schema. The encryption key identification (112) for the encryption key used to encrypt the data entities (30C, 30D) is encrypted by a system key and then stored as part of the security information attribute (32). The system key common name hash value (114) is also stored in the security information attribute (32). The information data entities (30) are stored on the information database (62), but the encryption key identification (153), encryption key (154), system key common name hash value (156, 157), and system key common name (158) are stored in the key database (44) inside the security domain (22). The system key itself is stored on a Smart Card reader (56) inside the security domain.
Owner:FARRUKH ABDALLAH DR +1
Data audit system
ActiveUS20050097149A1Digital data information retrievalComputer security arrangementsDatabase schemaCollections data
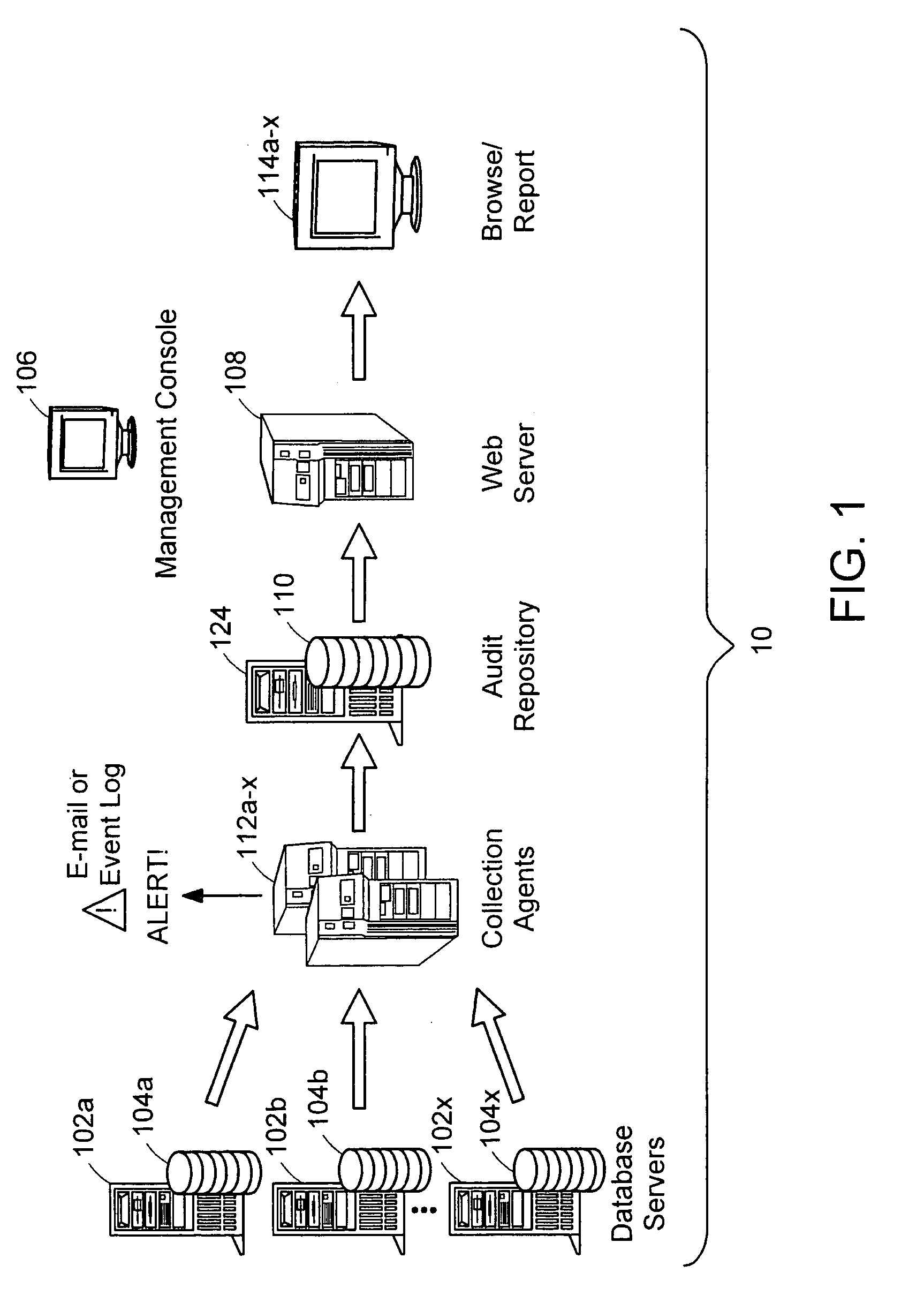
Described is a database audit system used to monitor, and optionally alert on database activity, providing a complete record of access to data and database structure. The data audit system may also provide an audit trail of data accesses and changes to database schema and permissions. A database audit may be performed by collecting data from database transaction logs and traces, exporting the collected data into a repository, and analyzing the data in the repository to create data audit reports and to provide data audit browsing capabilities.
Owner:BEYONDTRUST SOFTWARE INC
Database design for collection of medical instrument parameters
InactiveUS20080312953A1Data processing applicationsLocal control/monitoringUser interfaceWorld Wide Web
A method and system for maintaining medical items is provided. The system includes a medical database structure, a medical database utility configured to maintain medical database contents by organizing medical information into levels, and a user interface component configured to enable a user to access the medical database utility. The medical database utility provides a user with an ability to access the user's collections of settings in the medical database, the user's collection of settings maintained separately from settings accessible by other users. The method stores medical data items in a database configured with multiple levels of organization, establishes a logical relationship between medical data items at each level of organization, presents a user with available medical system choices at each level of organization, and enables the user to select from among the available medical system choices presented at each level of organization.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method for storing and sharing secure files based on blockchain
ActiveCN108462568AGuaranteed not to be tampered withIntegrity guaranteedKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPlaintextData library
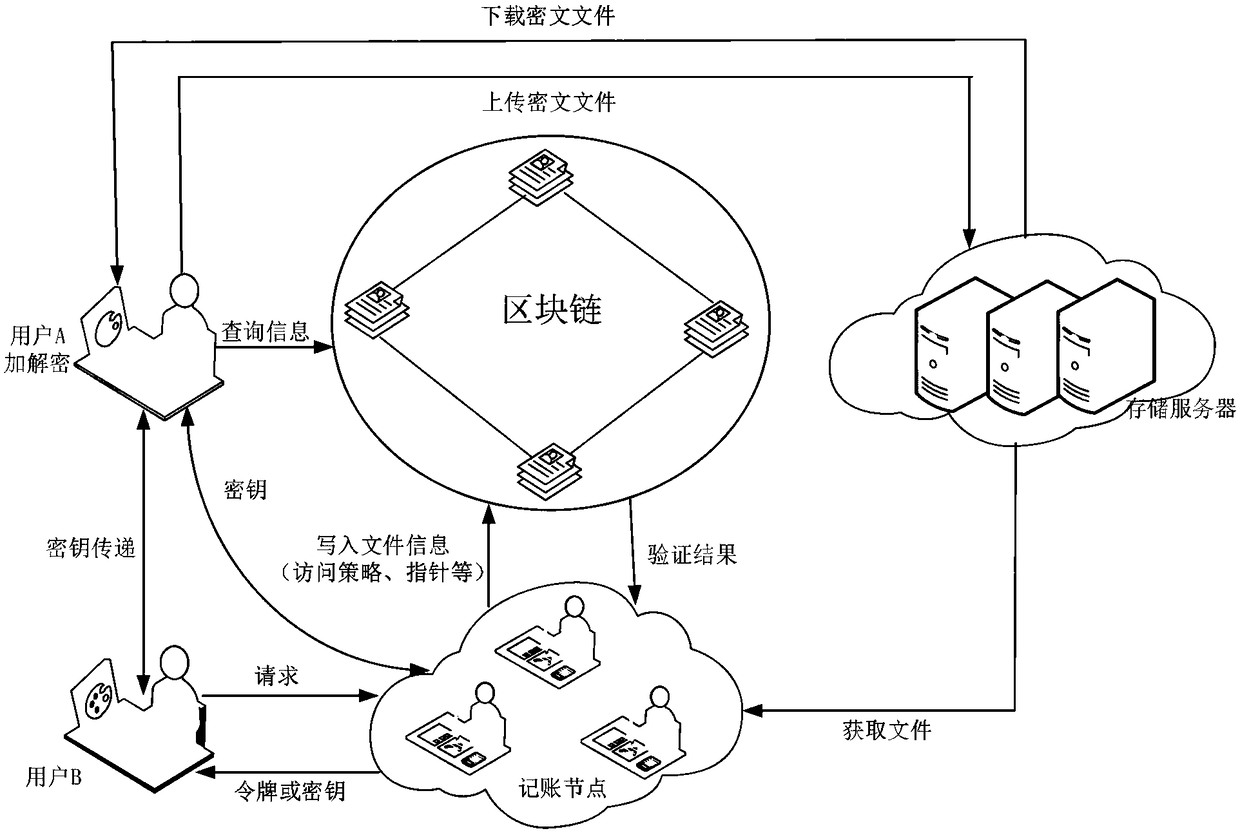
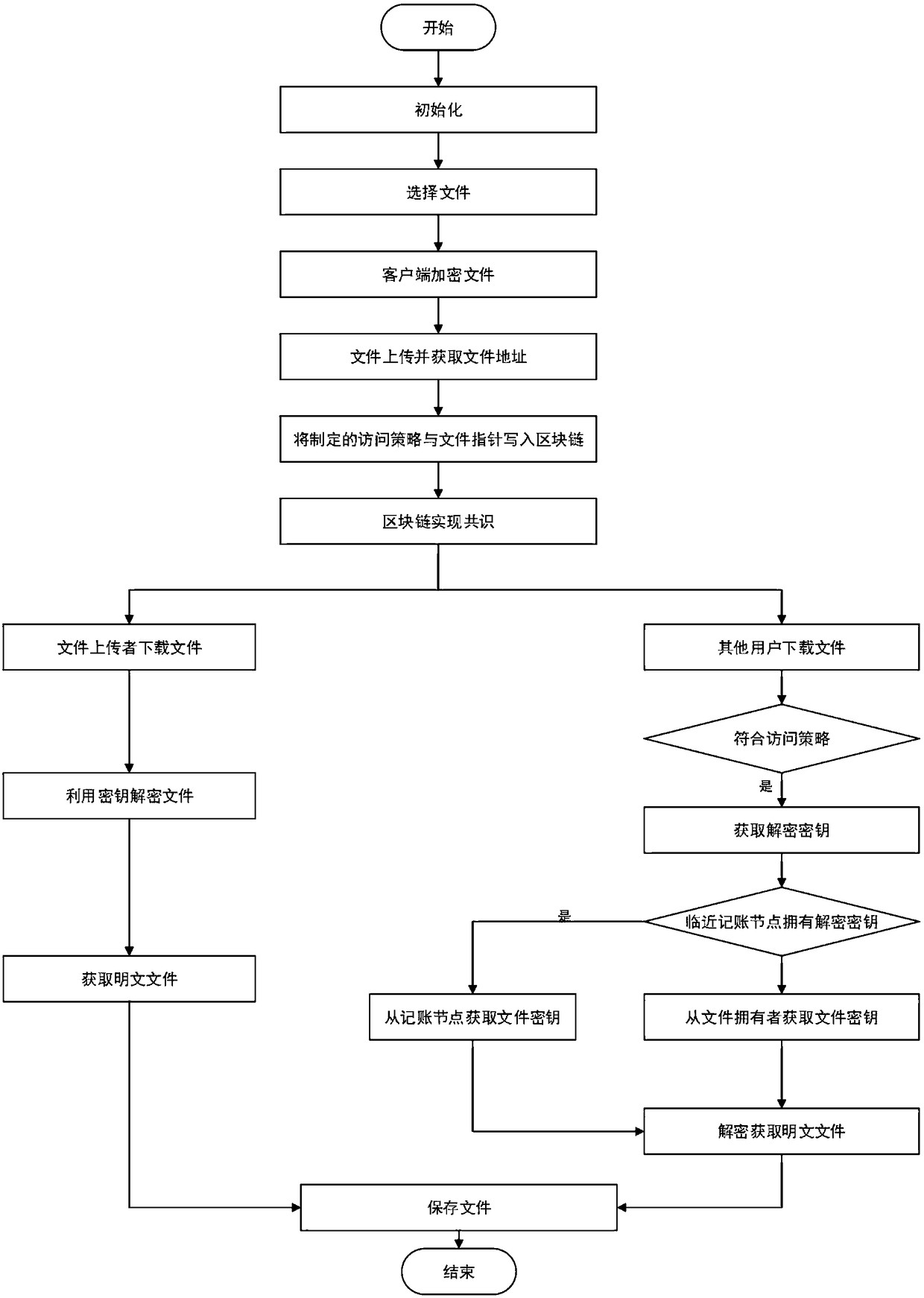
The invention belongs to the technical field of information retrieval and database structure, discloses a method for storing and sharing secure files based on a blockchain, and uses the blockchain technology to realize secure storage and sharing of files. A user encrypts and uploads the files to obtain a file pointer, and acquires the partial file as the excitation after the accounting node writesthe information such as the formulated access policy and the pointer into a blockchain account. And the other users may acquire a file key from the adjacent accounting node or the file owner after satisfying the access policy to decrypt the files so as to finally obtain a plaintext file. The invention ensures the security of the user data, and is simple and convenient for the user to use, and thepublic key cryptography technology makes the file more secure at the same time. The unchangeable modification progress of the blockchain account further ensures the complete availability of the files, enables the user to formulate different access strategies for different files, and enables full control of the files while sharing the same.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Workflow management system and method
InactiveUS20070208606A1Easy to editFacilitates economy of scale and processing efficiencyFinancePayment architectureStream managementSystems management
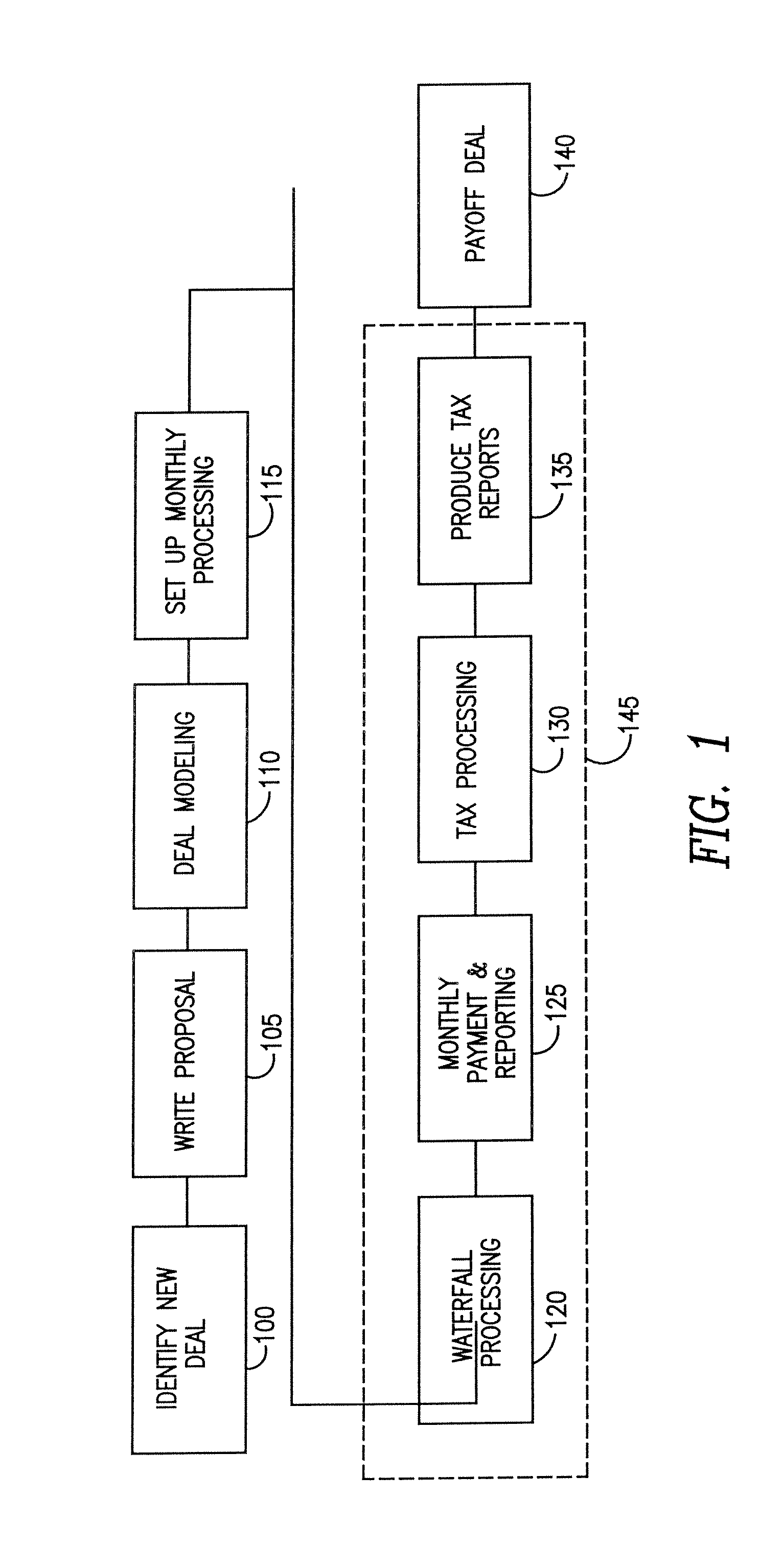
A computerized workflow management method and system to provide operational support for complex multi-step processes, having particular utility in supporting operations involving securitizations for which periodic valuation and distribution computations, disbursements and reporting must be set up and executed. The invention permits unification of manual operations and operations performed by legacy software, even if implemented with database structures different from the workflow management system, automated quality control, workflow status display and automatic updating of workflow status records. The method of workflow management involves creating an underlying database structure for recording the processing steps and other information required for each transaction, entering the necessary setup information by selection from lists of pre-stored information about processing functions, associated workflow events and milestones for the queues, mapping the data structures of the subsystem databases and the workflow management database to provide transparent interfacing and convenient manual entry of data were necessary, displaying for the user the workflow status of all transactions for which he or she is responsible, permitting menu driven initiation of required actions and automatically updating the database records for the universe of deals being managed by the system.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
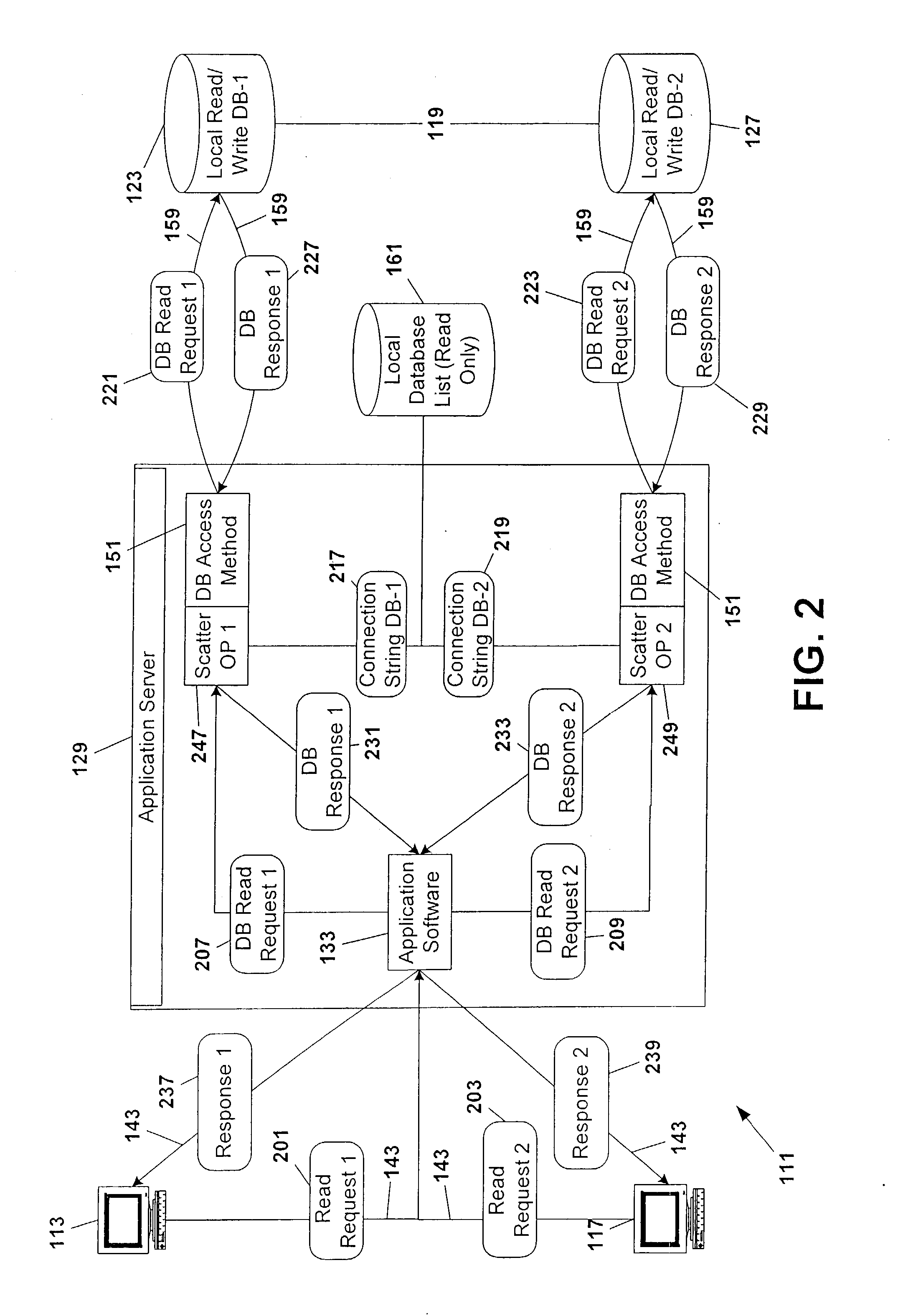
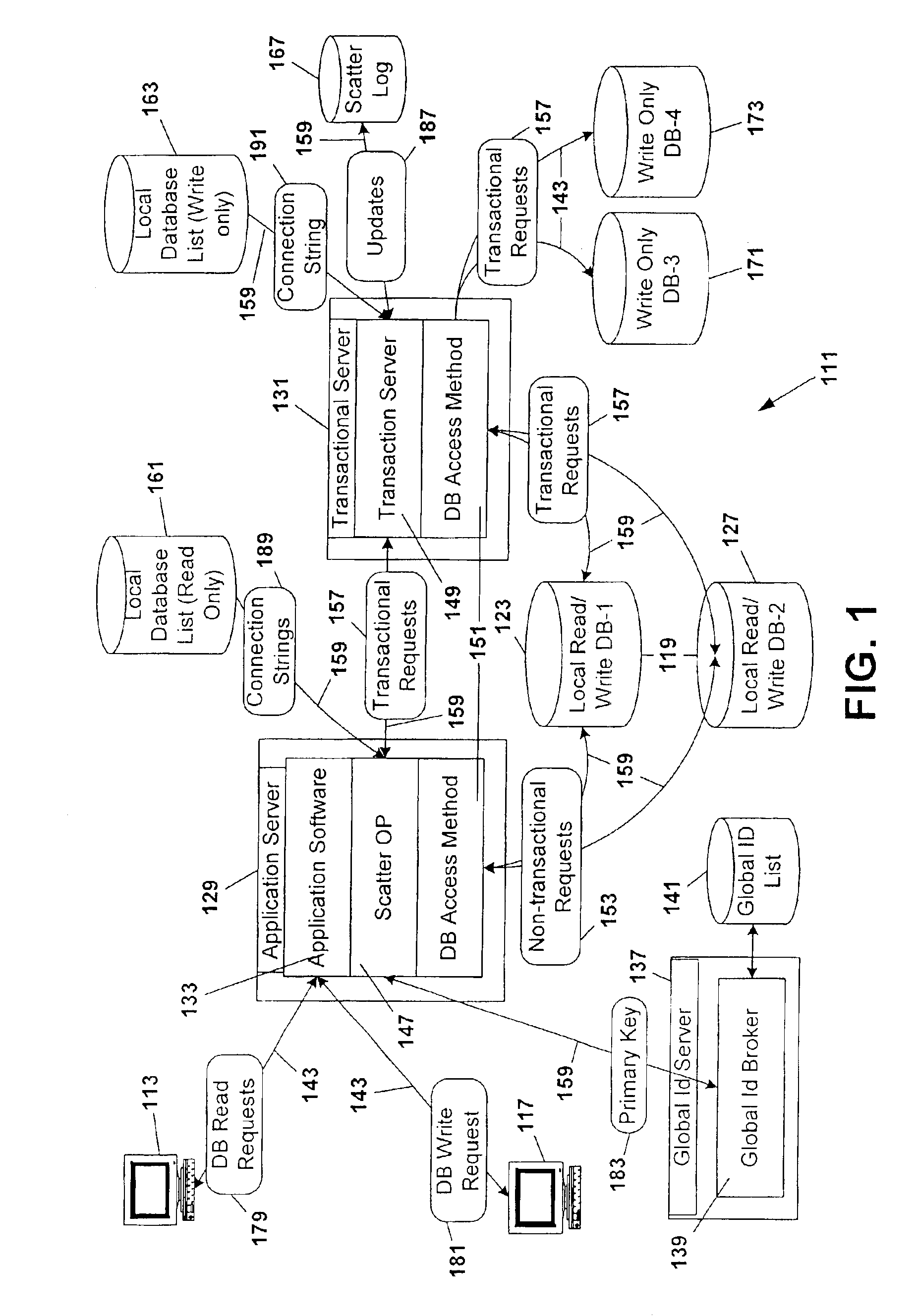
Database scattering system
InactiveUS20030212660A1Reduce needPermit scalabilityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalEngineeringNetwork data
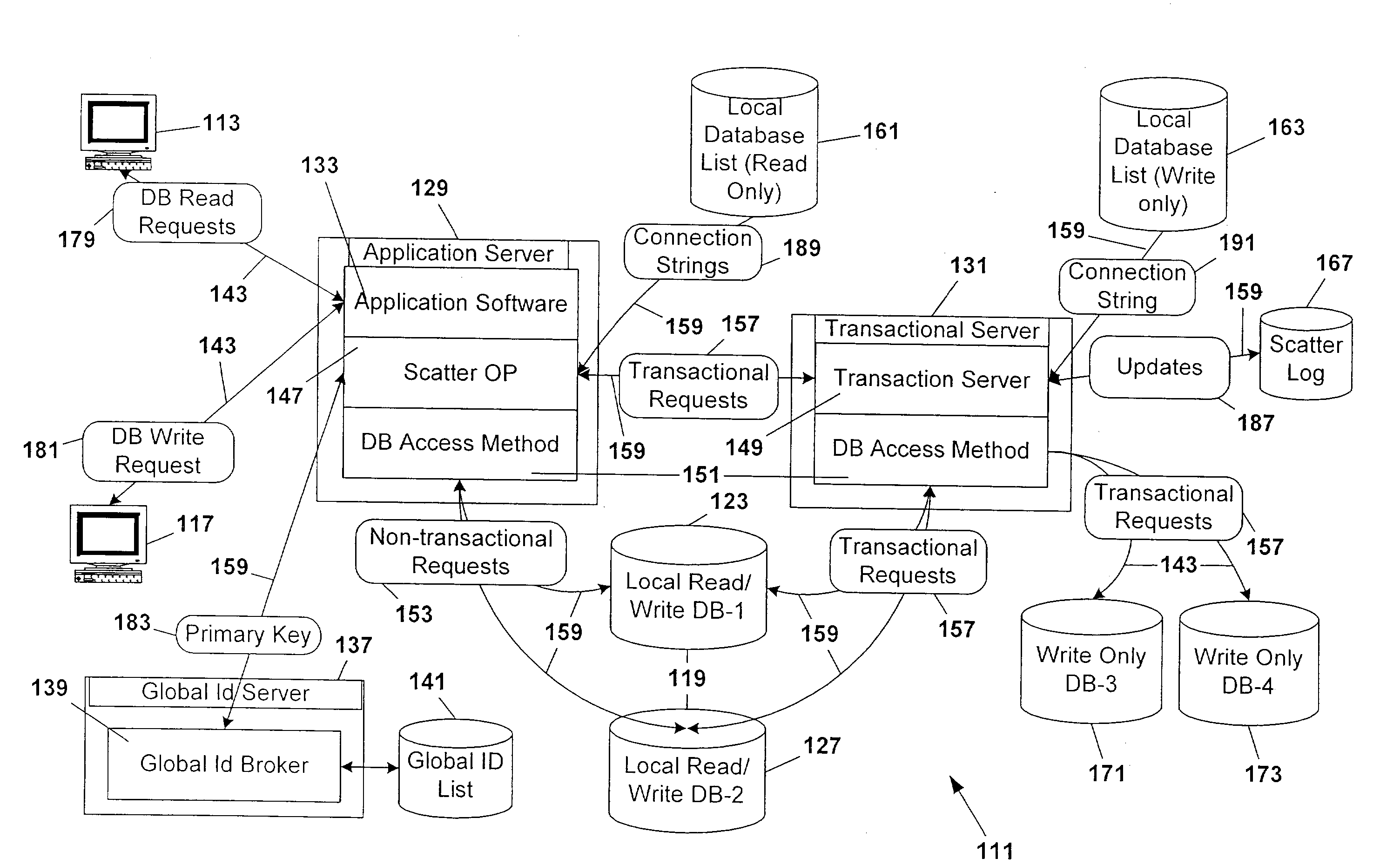
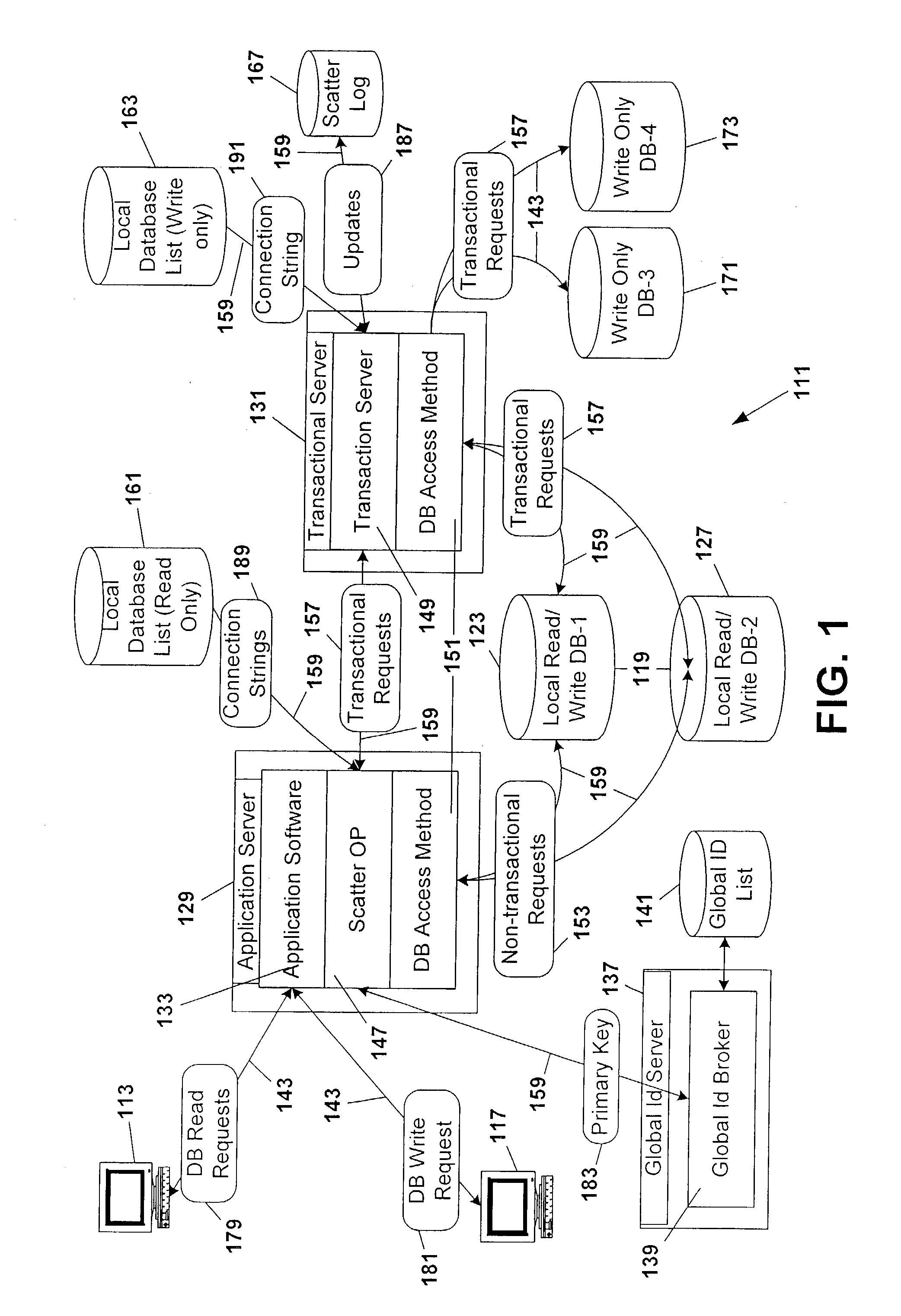
A computer system for providing load balancing and scalable access to a network database system by providing multiple database instances with each instance being substantially identical in data content, database structure, and primary key system. Requests from users are received by the system, examined to determine their nature as transactional or non-transactional and, in the case of non-transactional queries, scattered among the multiple database instances. Such scattering of queries permits multiple instances of the database to be serving responses to multiple users at substantially the same time. In the case of transactional queries, the system automatically propagates the transactional query to all instances of the database to maintain homogeneity.
Owner:ENTERPRISEDB
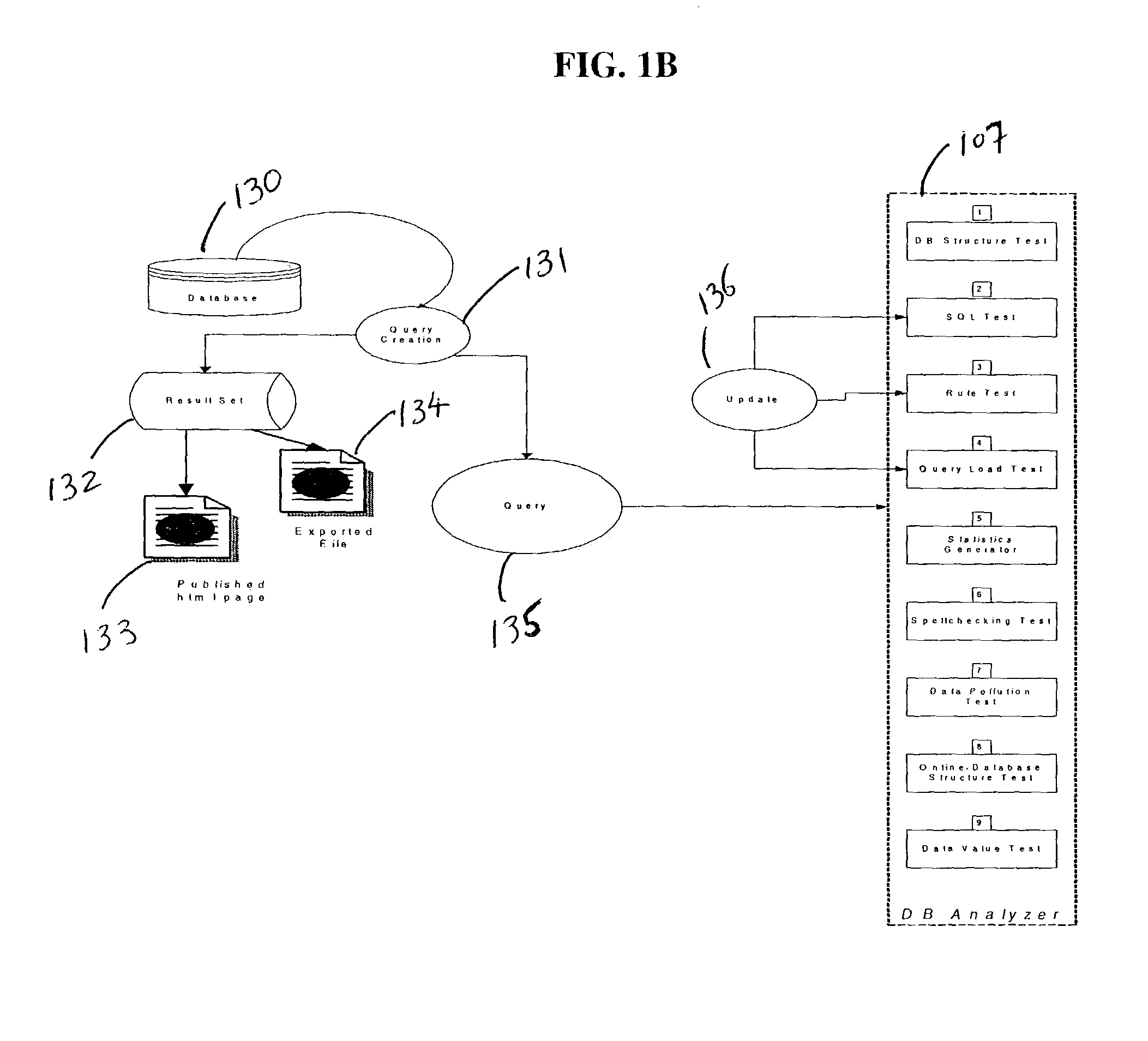
Method and system for testing data sources and database oriented software applications
InactiveUS7010546B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRegression testingAnalysis data
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and system for testing databases and database oriented applications through analyzing database contents and structure. The method and system provide a framework for various tests, which can be deployed against the database structure or contents. The system provides a set of ready to use tests, however, custom tests can also be written using system API. Tests used within the framework constitute test suits. Test suits can be used during database oriented application development process for regression testing, verifying newly added functionality, re-testing of existing and modified functionality, deploying new versions of an application. Test suits can also be used for database monitoring and database cleaning.
Owner:PARASOFT
System and method for comparing heterogeneous data sources
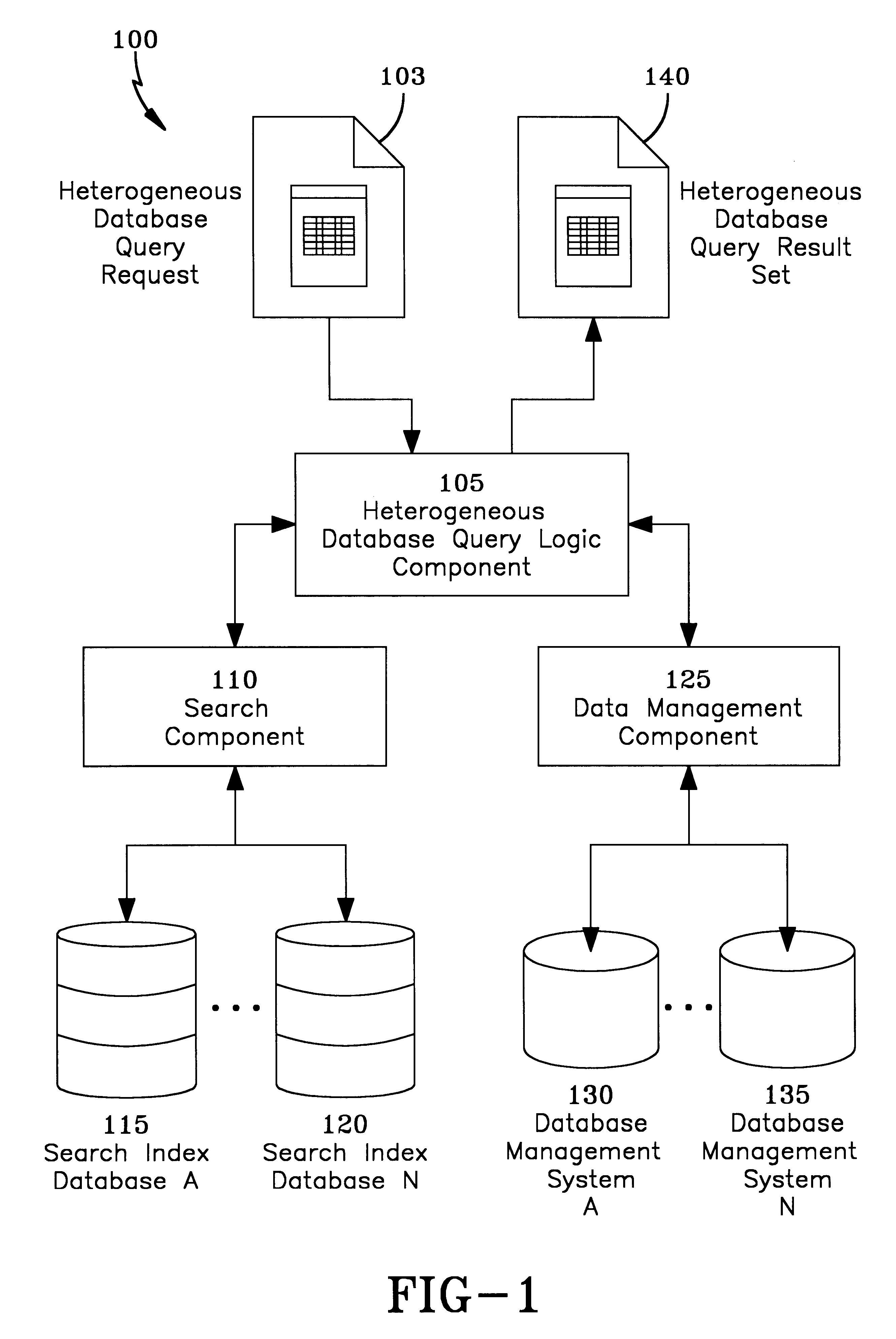
InactiveUS6839714B2Facilitate cross database searchingFew penaltyData processing applicationsDatabase management systemsData sourceInformation searching
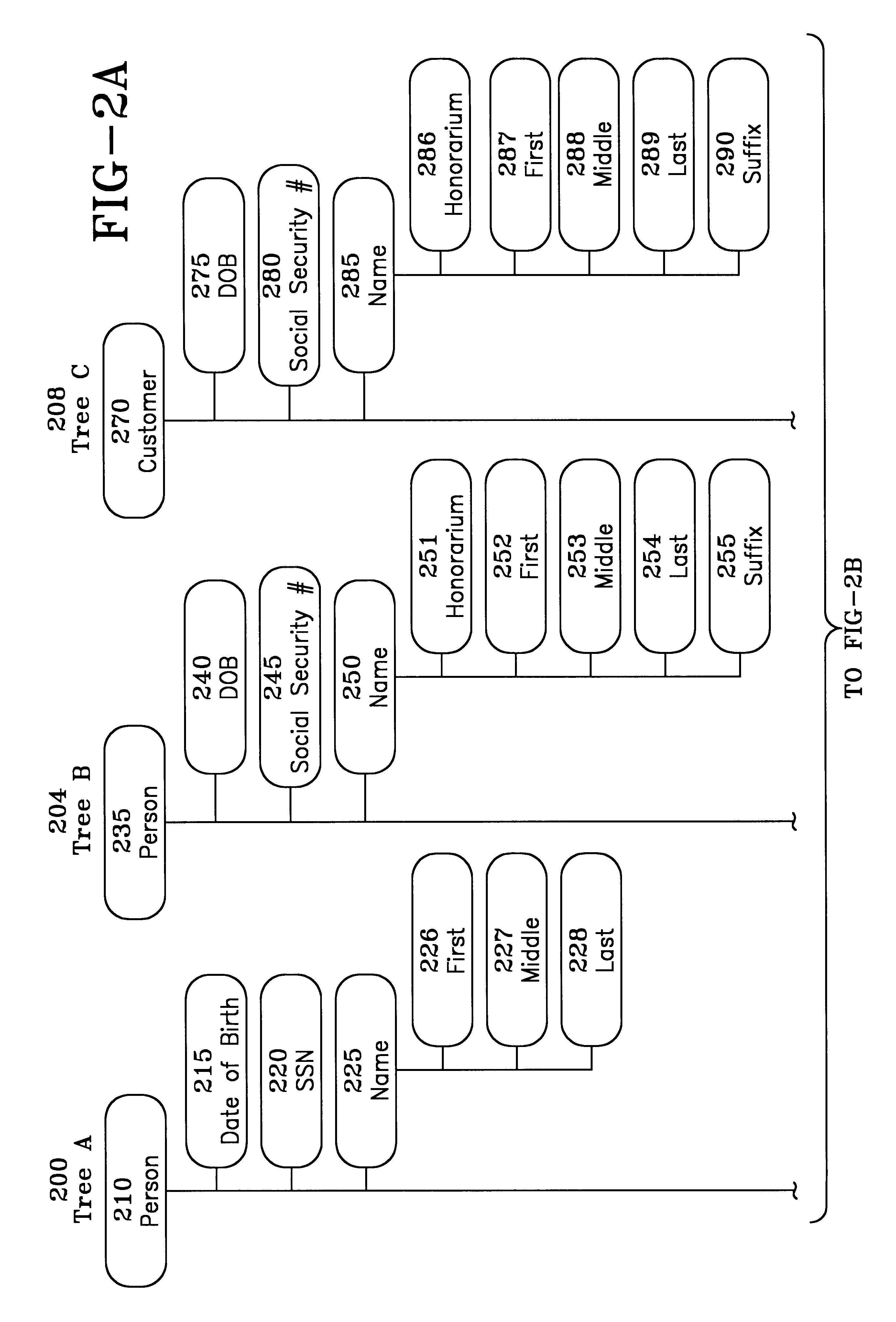
The present invention is a computer-implemented system and method that allows data in different databases to be shared without requiring the data to be remodeled to fit an existing data convention. The invention allows the comparison of two database structures, and facilitates the searching of information from one database to other databases, or from an external set of search criterion against a plurality of databases. The invention allows information to be exchanged from heterogeneous data sources, or database query sources without having to alter the structure of the data sources that are being searched. A number of techniques may be used to do this comparison and facilitate the cross database searching. Tree comparison methods, user defined mapping methods, the use of similarity comparisons to determine similar database structures and data are used to facilitate the cross database searching.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
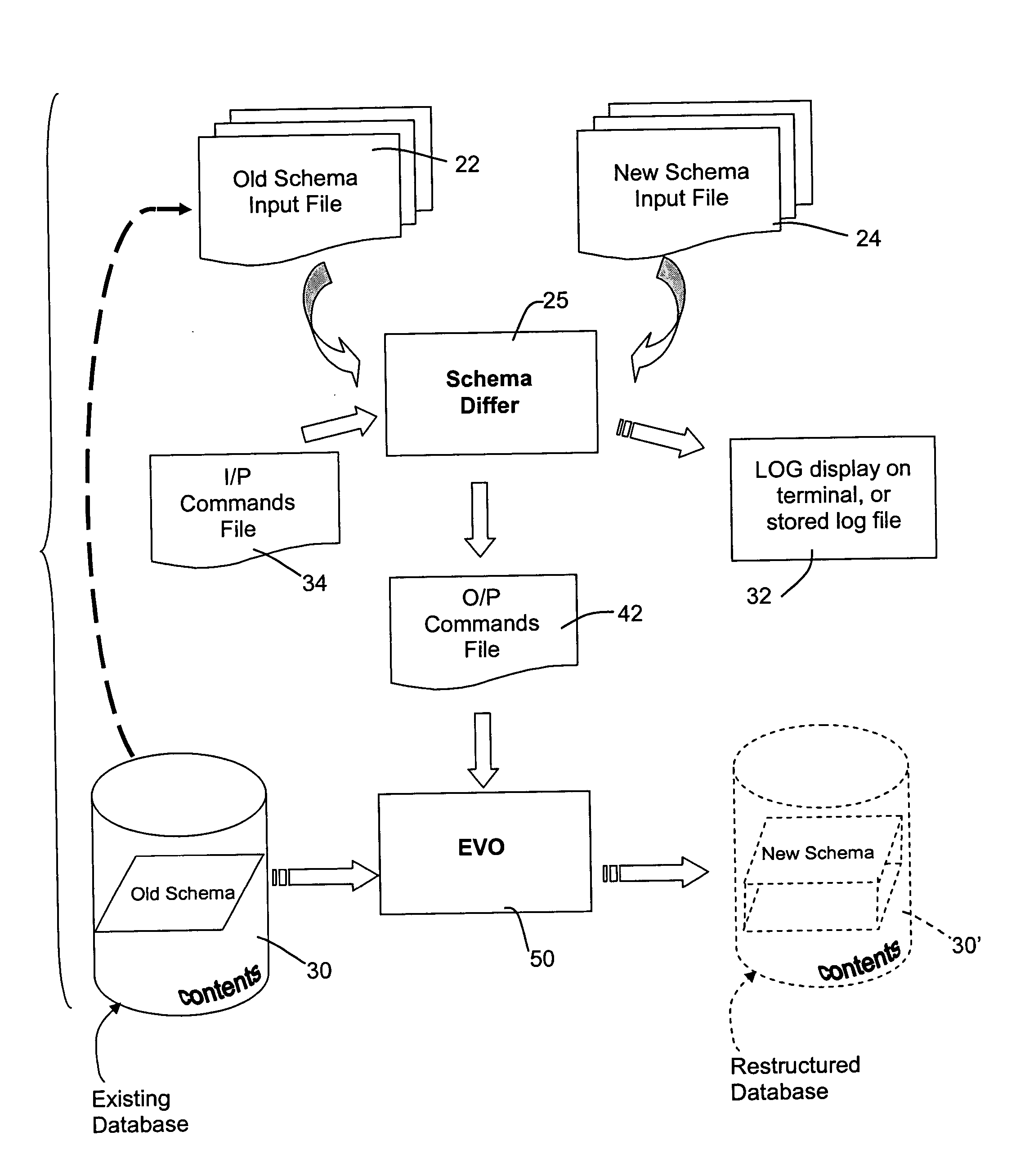
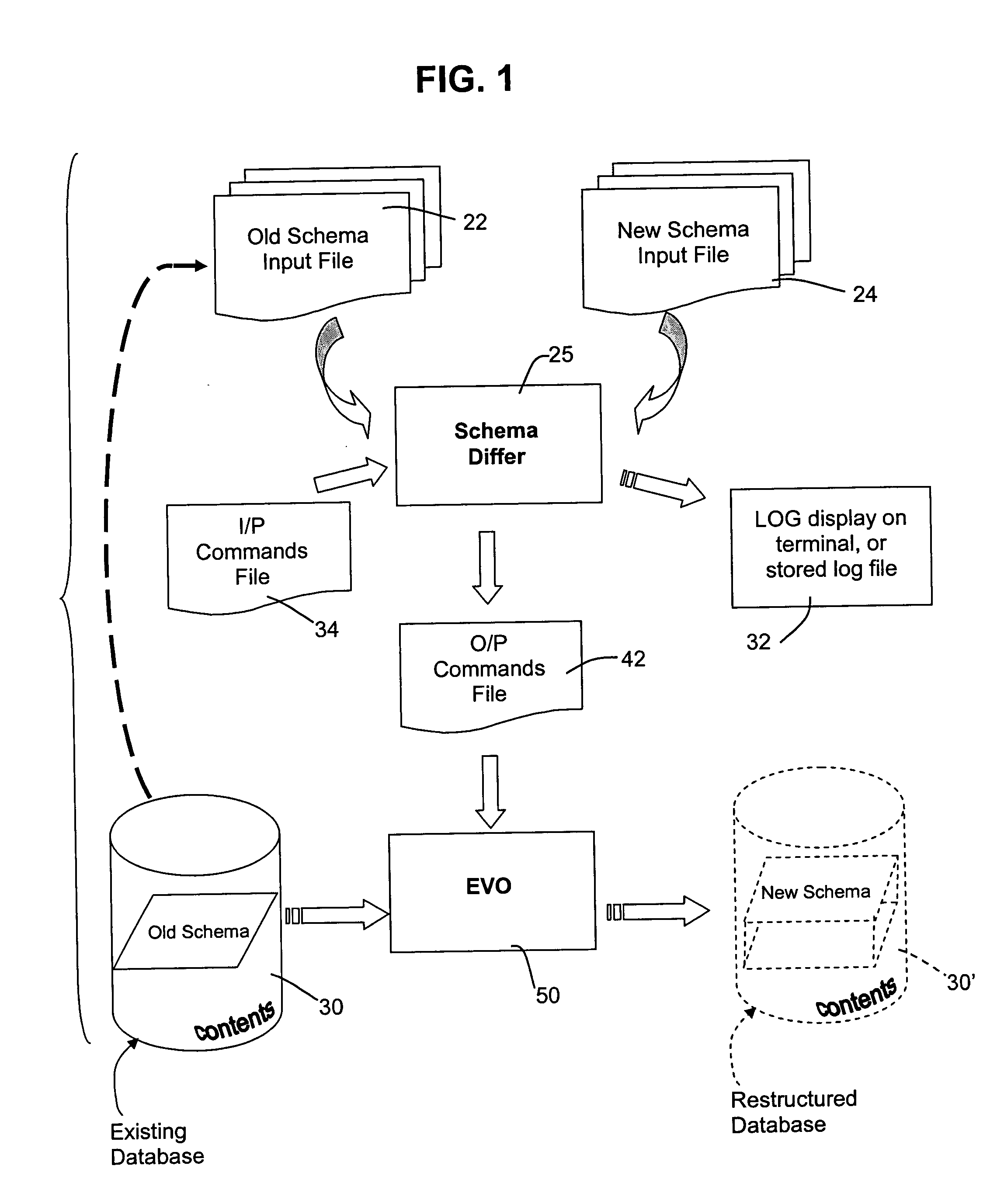
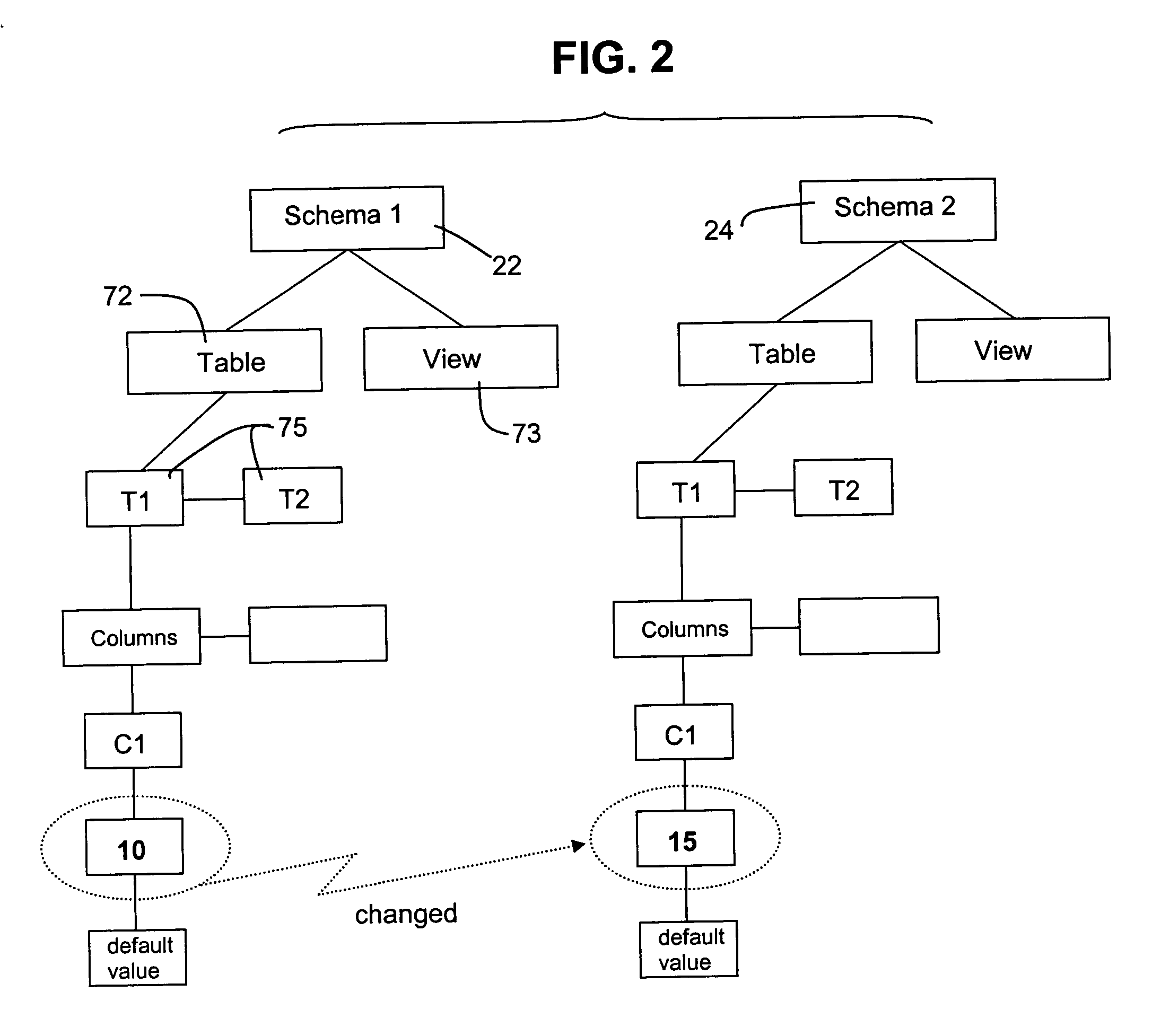
Method for automated database schema evolution
InactiveUS20050071359A1Easy to changeMinimal impactDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsSchema for Object-Oriented XMLAutomated database
A database structure of a sort defined by an access and query language that defines tables of variables having labels and field characteristics, such as ANSI structured query language (SQL), is modified by determining the structural differences between an existing schema and a new schema, independent of database contents. The differences are processed to generate commands that are then applied to evolve an existing database from the old schema or structure to the new one. This avoids the need to dump and restructure the contents of the old database for reload into an empty new database that has been prepared to meet the new schema.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Database scattering system
InactiveUS6898609B2Reduce needPermit scalabilityDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsComputerized systemData content
A computer system for providing load balancing and scalable access to a network database system by providing multiple database instances with each instance being substantially identical in data content, database structure, and primary key system. Requests from users are received by the system, examined to determine their nature as transactional or non-transactional and, in the case of non-transactional queries, scattered among the multiple database instances. Such scattering of queries permits multiple instances of the database to be serving responses to multiple users at substantially the same time. In the case of transactional queries, the system automatically propagates the transactional query to all instances of the database to maintain homogeneity.
Owner:ENTERPRISEDB
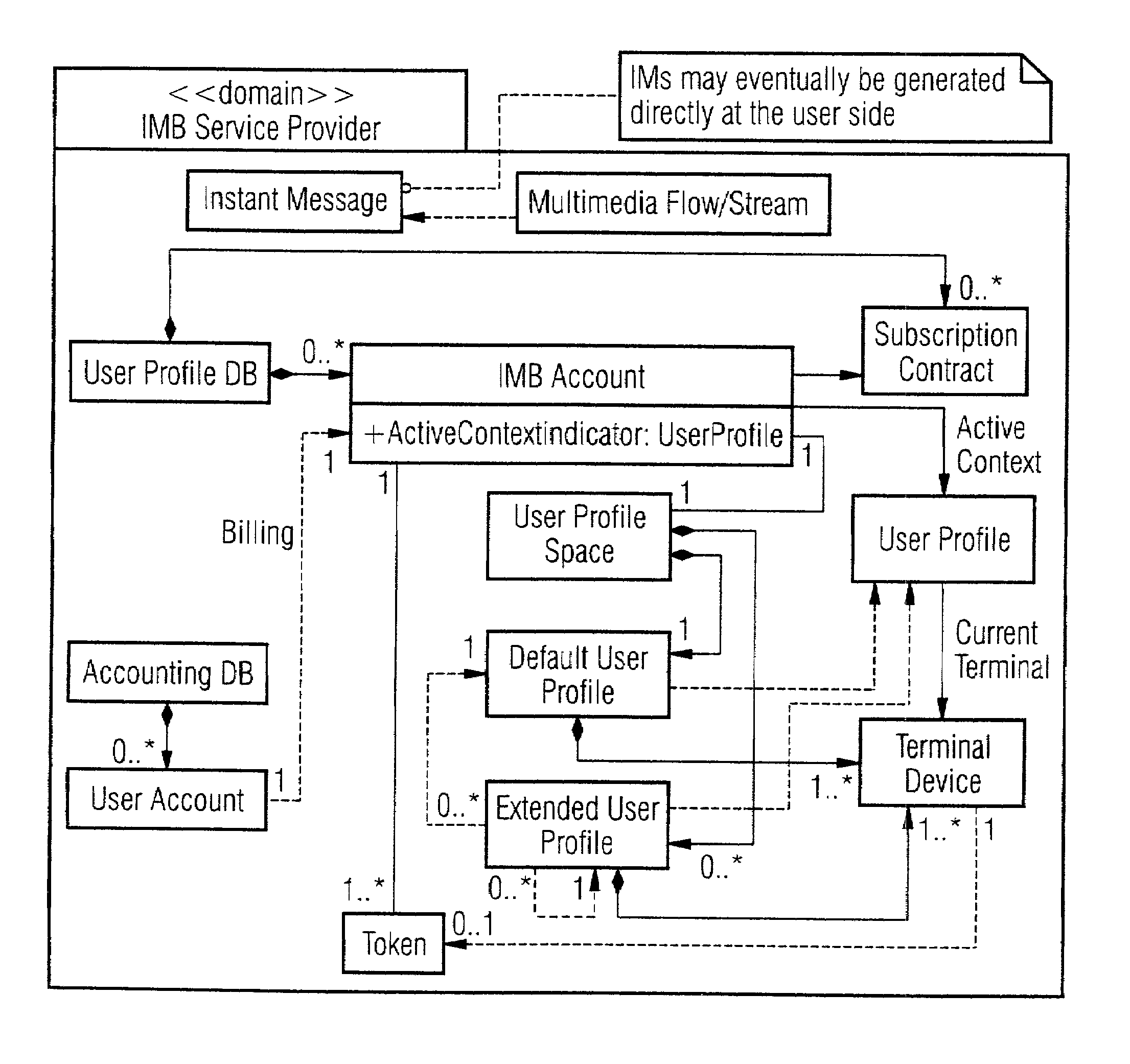
Management of user profile data
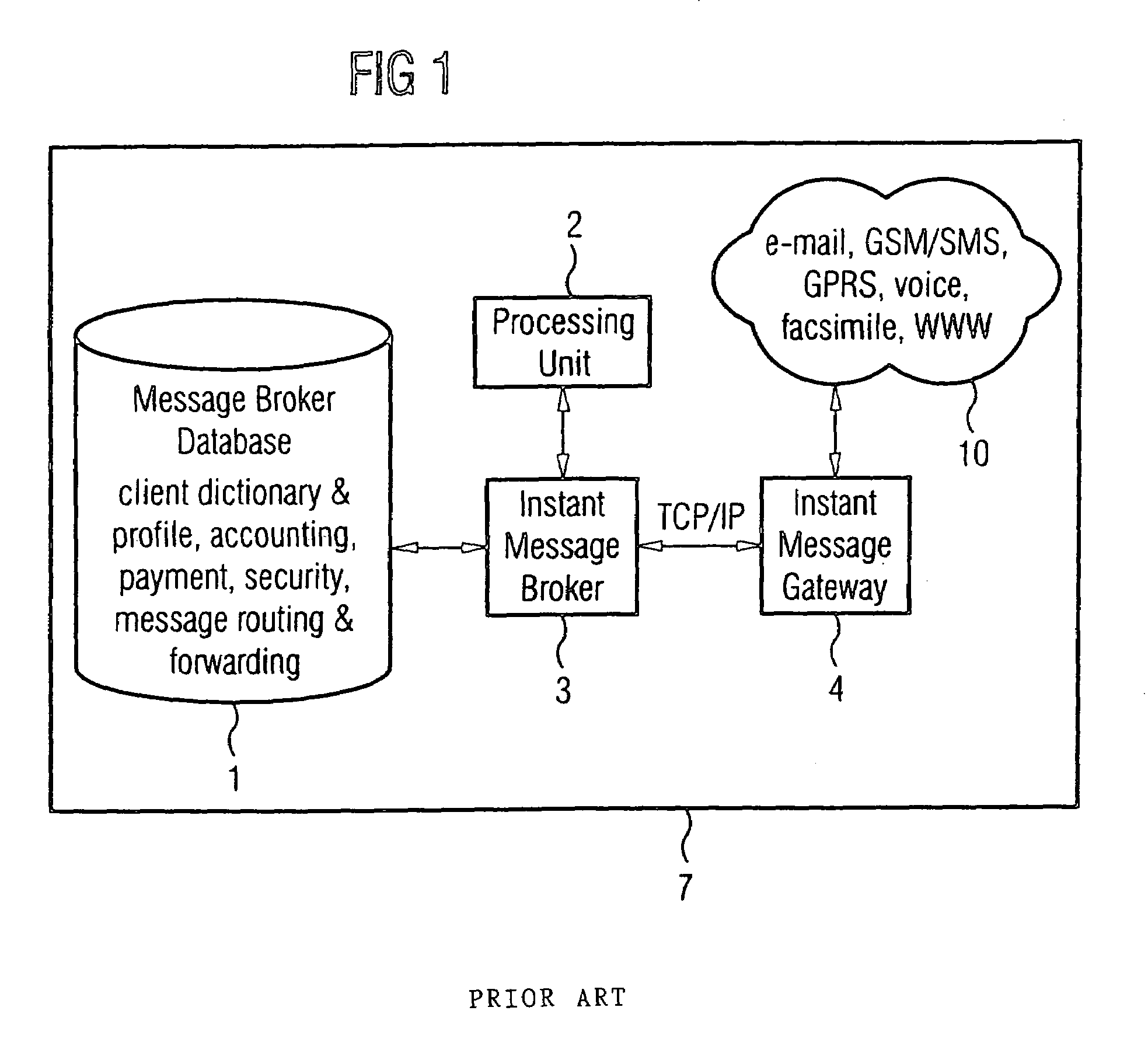
InactiveUS7181441B2Improve usabilityHigh-quality conversionData processing applicationsSpecial service for subscribersGeolocationHand held
The invention generally related to the field of mobile multimedia middle-ware, computer networking, distributed processing systems, data bases, hand-held computers and wireless communication. A method for conveniently managing user profile information in an unified instant messaging system (7) is proposed. This method operates on a data base structure, which accommodates in a flexible way subscribers' information. More specifically, this method takes into account the mutable characteristics of the environment where subscribers' devices (9) are operating: subscribers can in fact freely modify their personal user profiles (1) as situations change and / or as they move to different geographical locations.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
TV white space devices using structured databases
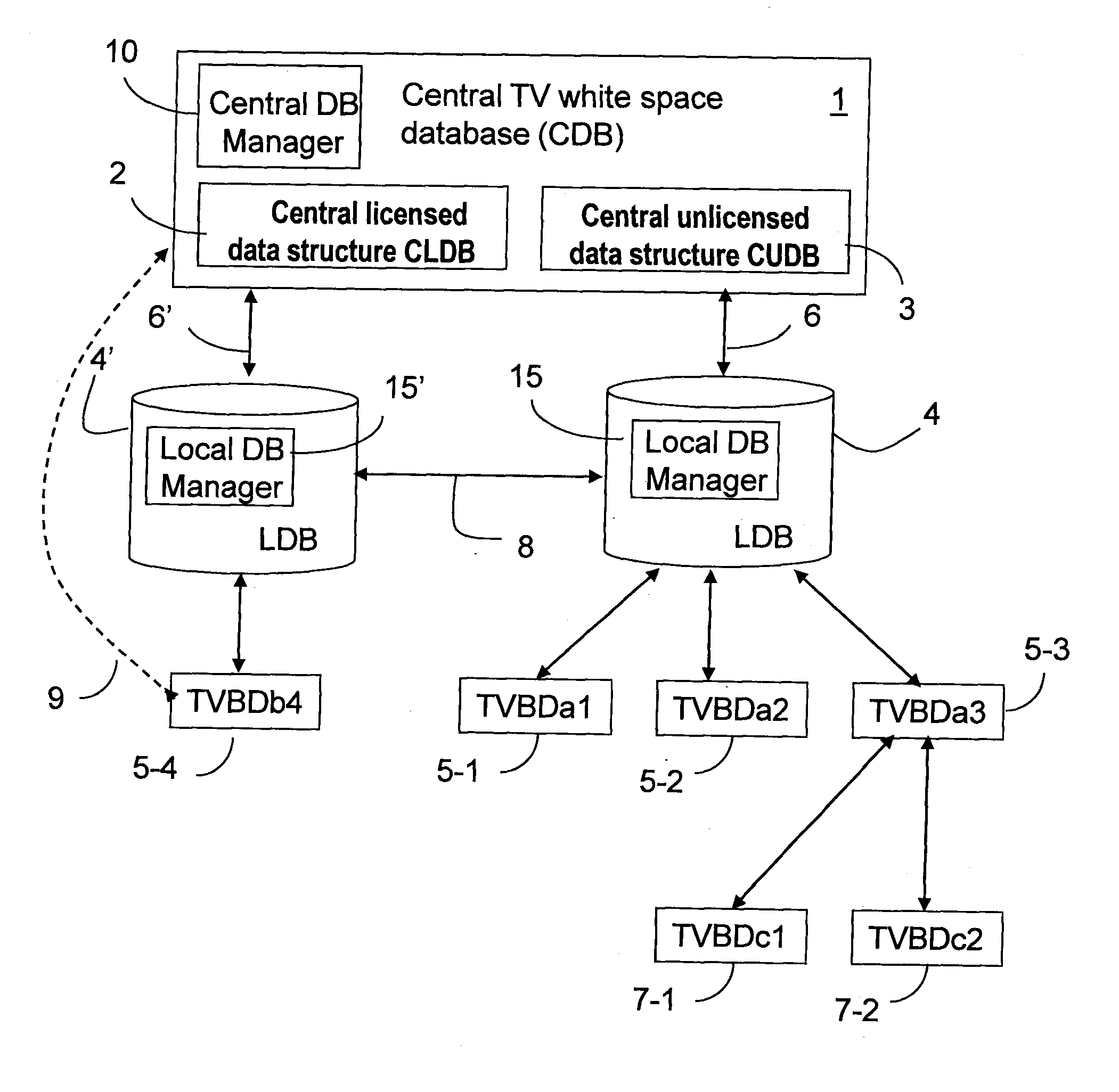
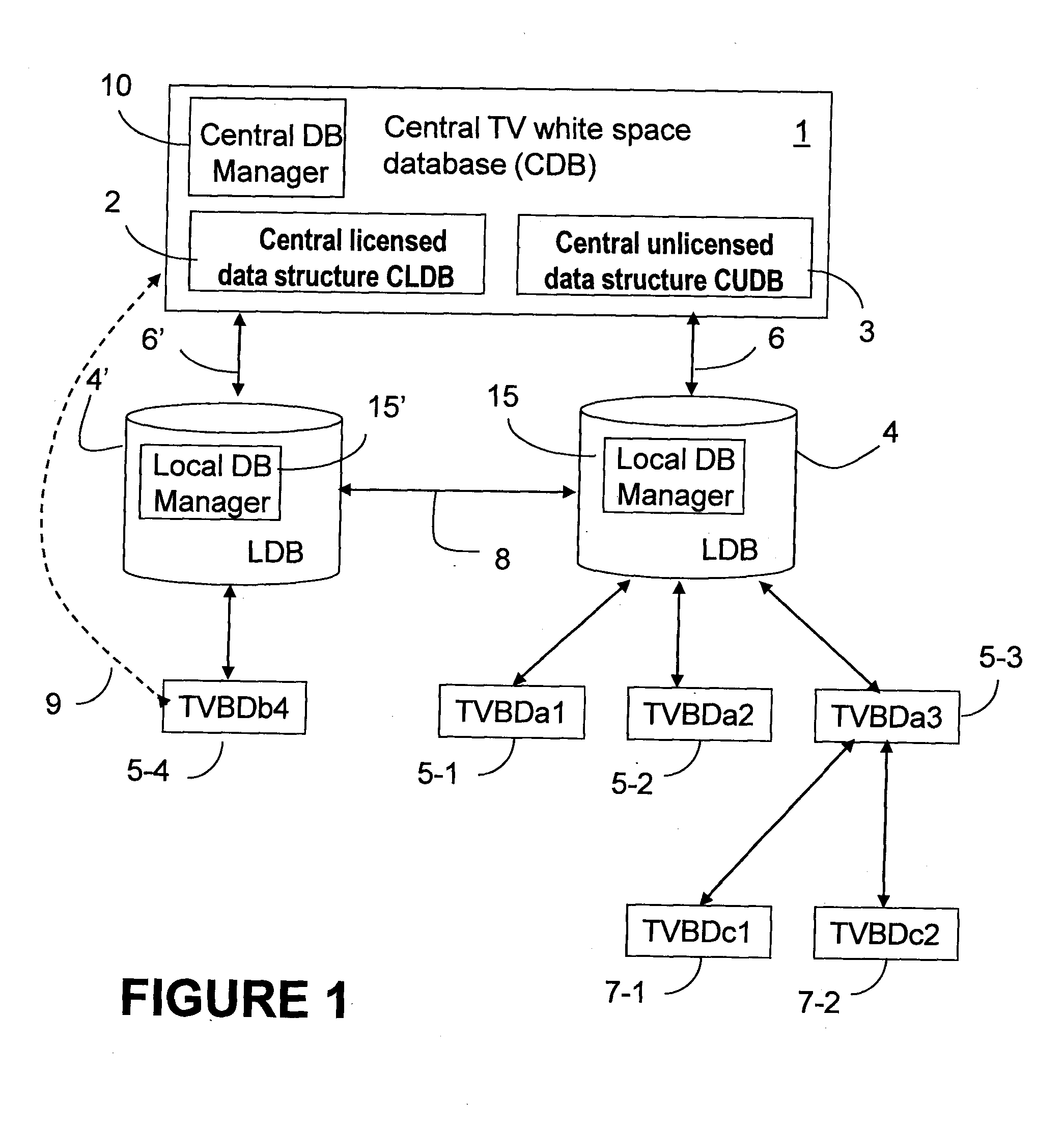
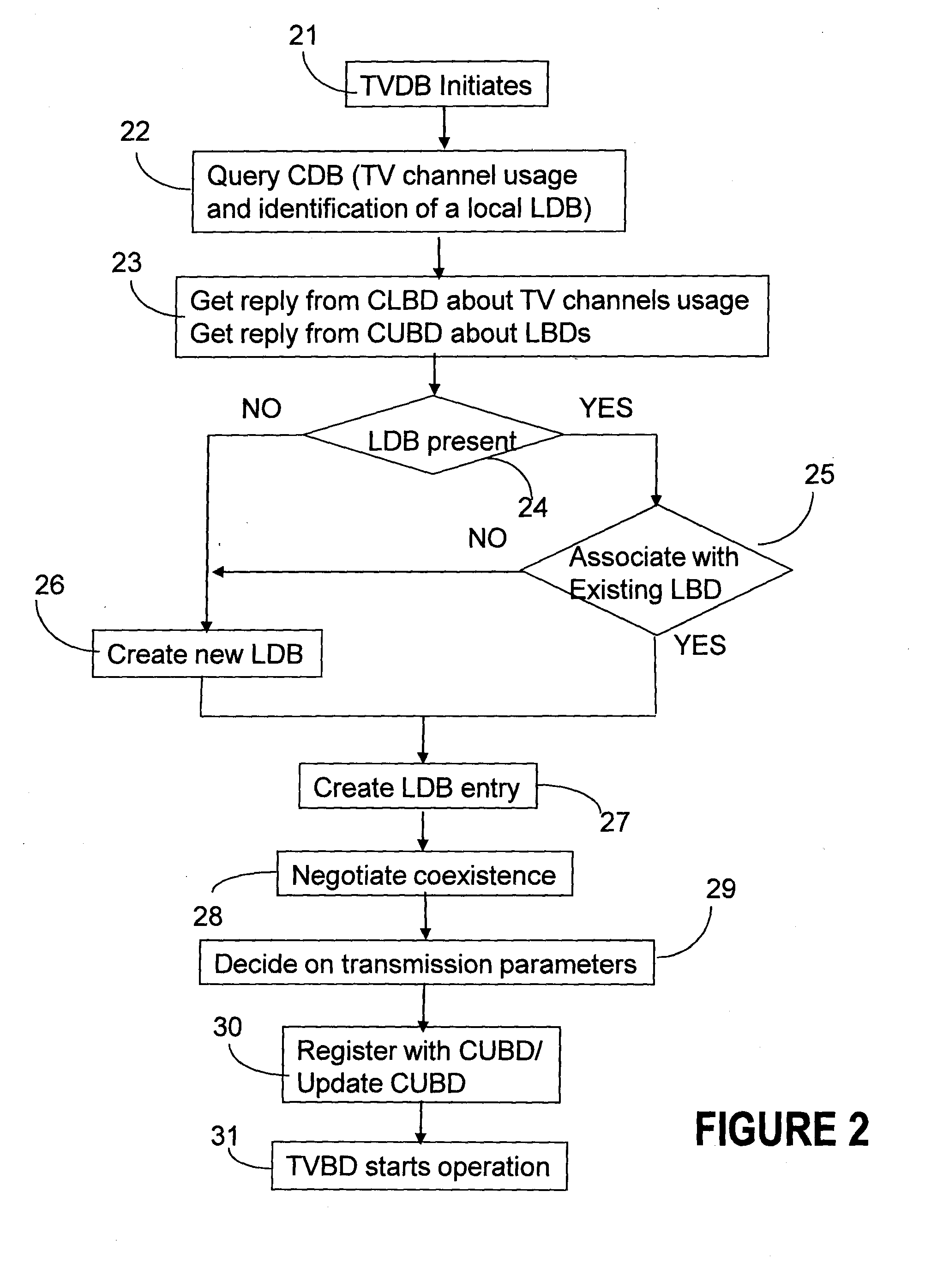
ActiveUS20130103684A1Improve protectionDatabase updatingNetwork traffic/resource managementElectric power transmissionFrequency spectrum
A two-level database structure for use by unlicensed TVBD devices operating in TV white space comprises a central database and local databases. The central database comprises two sub-database: the central licensed database which maintains information about all licensed TV devices and the central unlicensed database which maintains information about unlicensed wireless devices operating in TV spectrum. The local database is created by each TVBD device or TVBD network when it initiates and it stores information related to all transmitters in the local area including location, power transmission levels, operating schedule, sensing results, backup channel information. The local databases communicate with central database to query it about licensed usage of TV spectrum and register with central database. The local databases communicate with each other to exchange information about channel usage, sensing results, transmission patterns and other information that will allow the local databases to negotiate coexistence without central coordinator. The locally implemented negotiation prevents the overloading of the central database.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
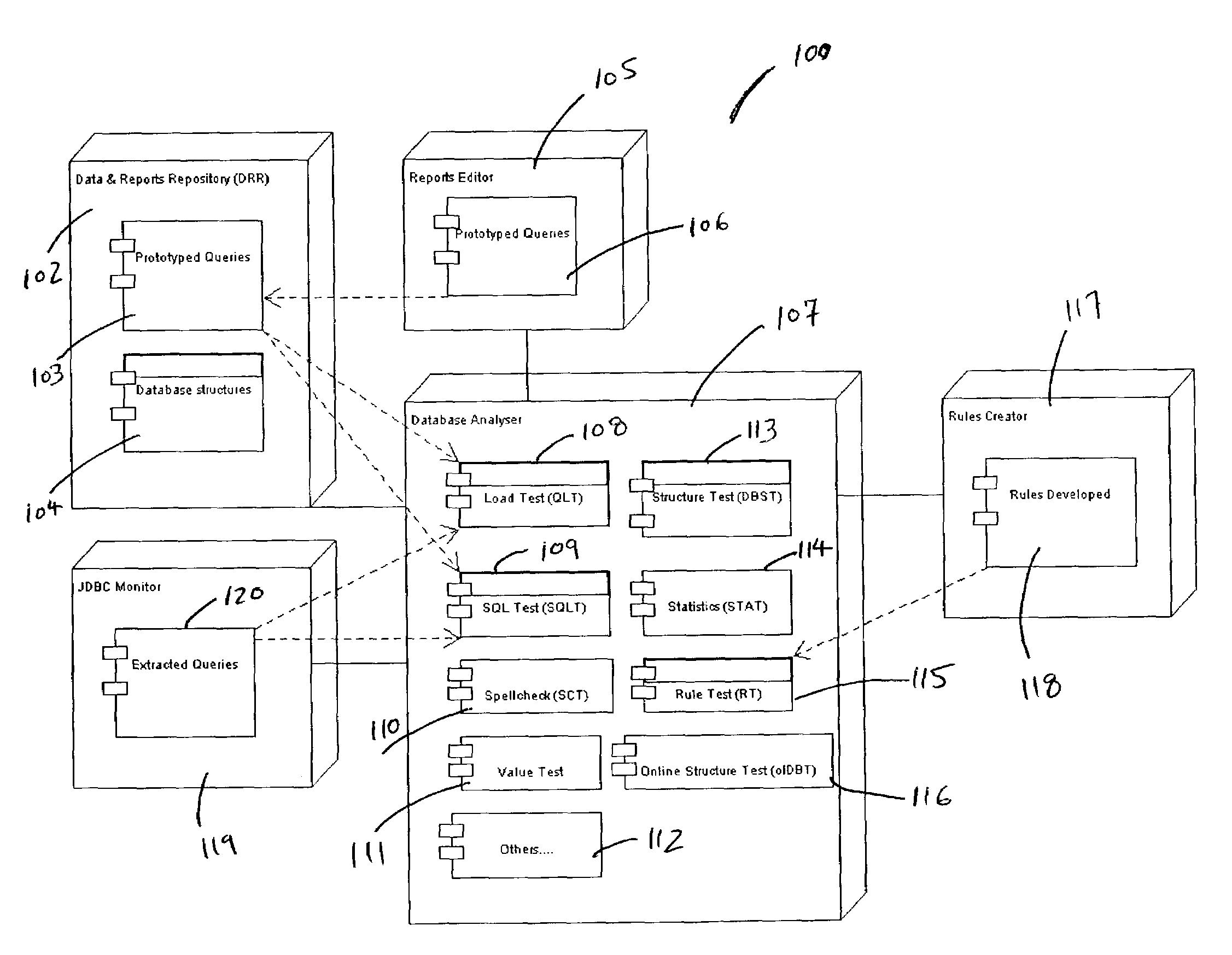
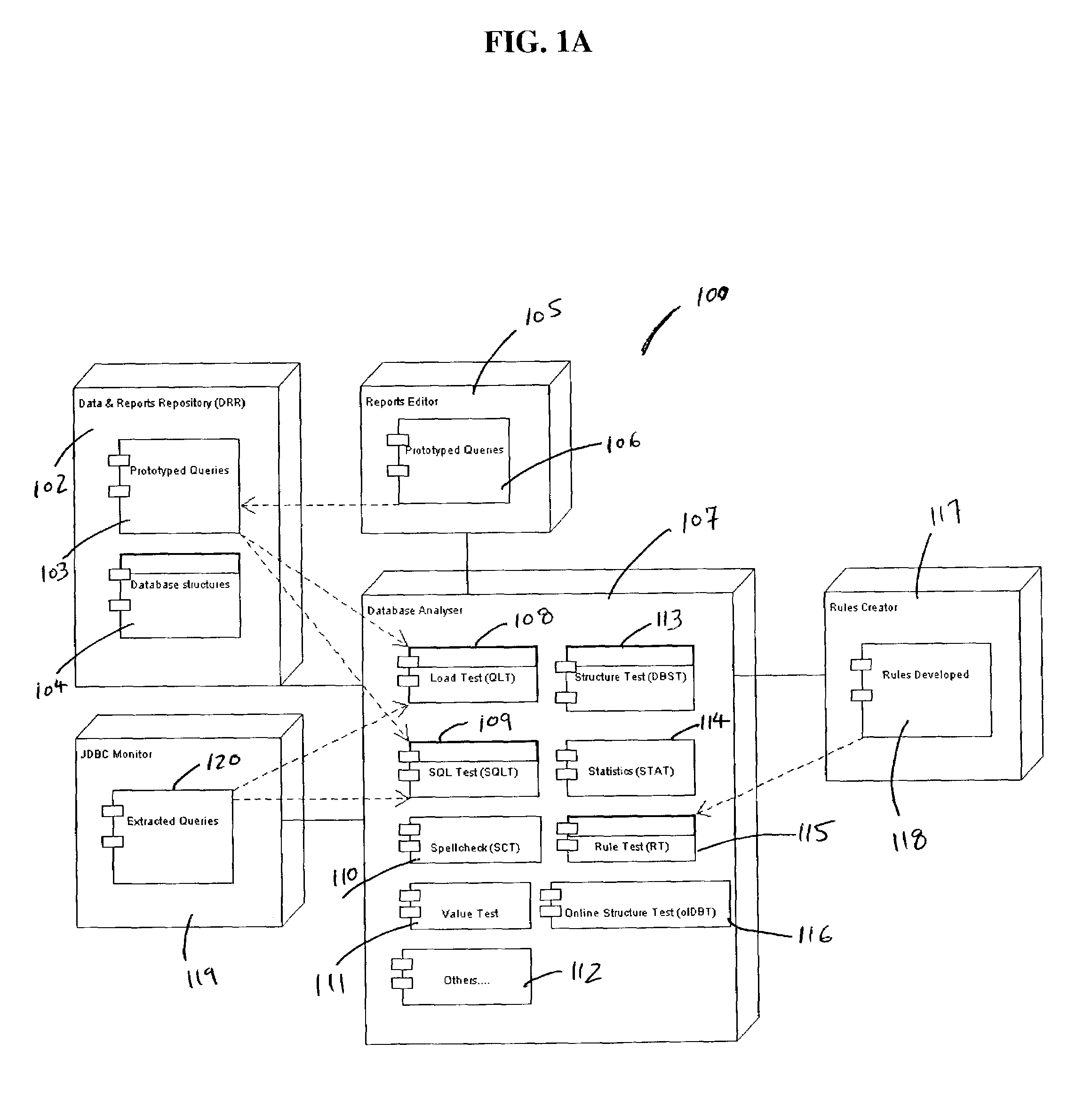
Techniques for database structure and management
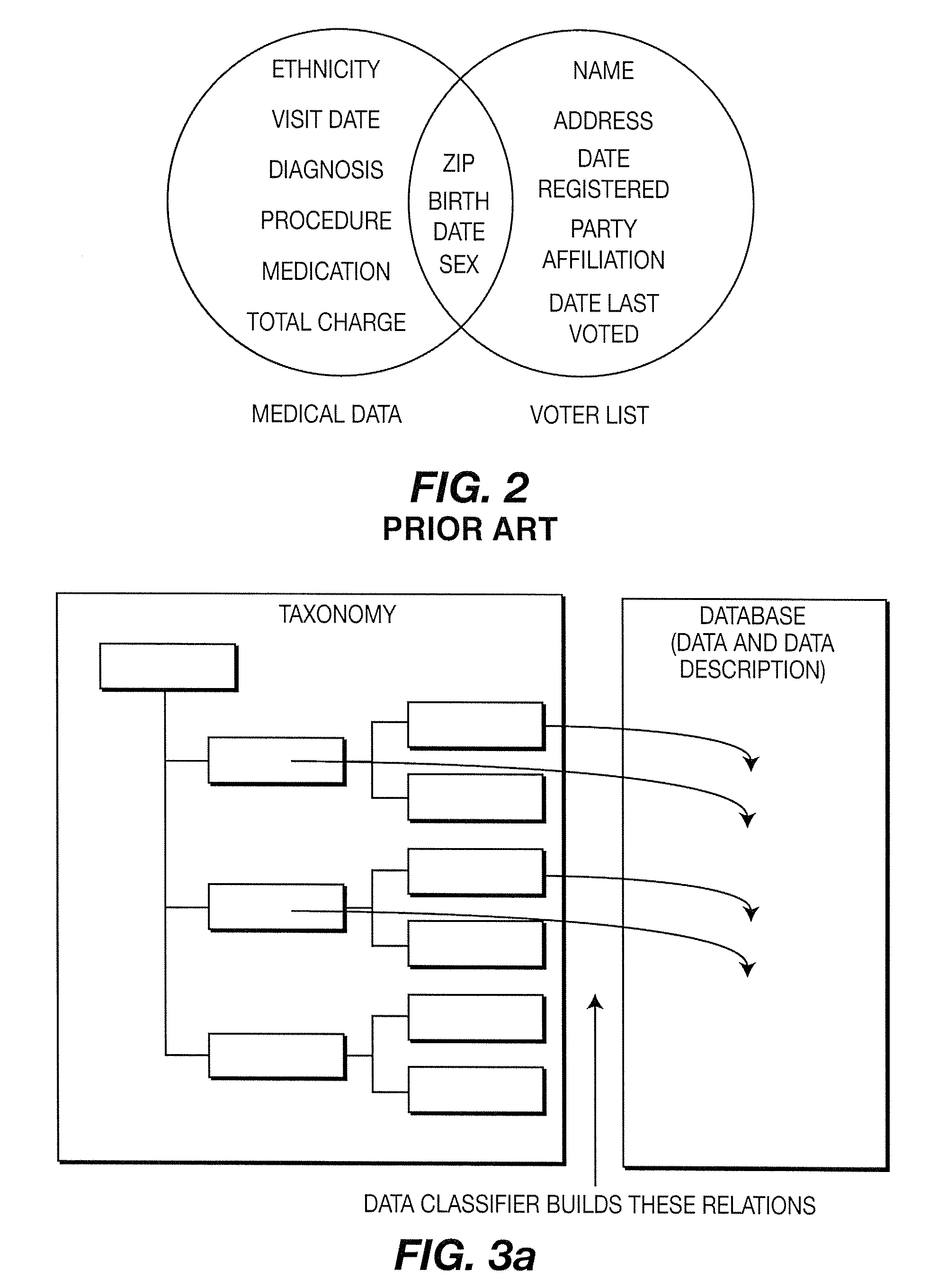
InactiveUS20080189250A1Efficient processingFacilitates seamless and organic handover of service and network accessDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDatabase structureUser agent
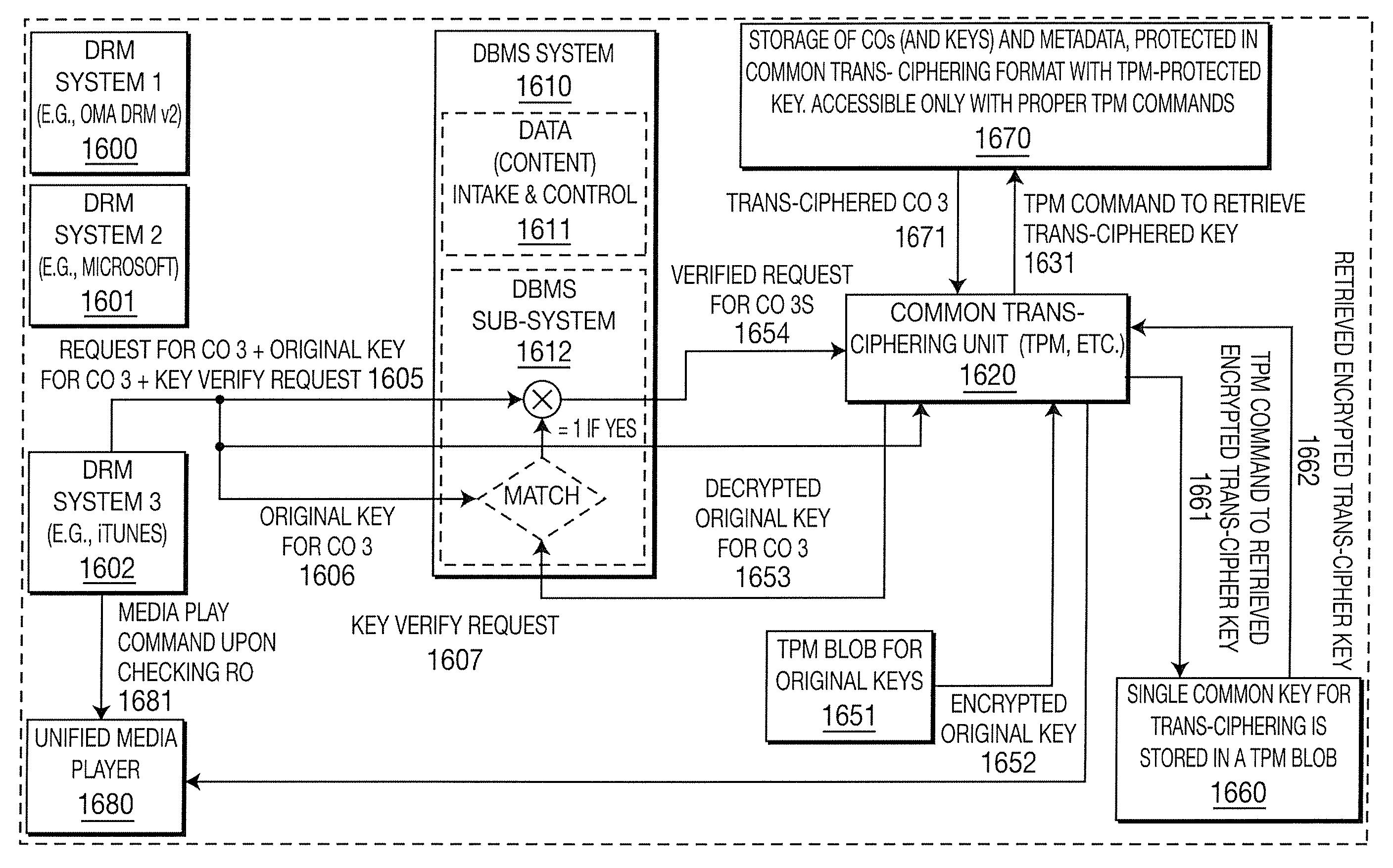
An embodiment is related to a database system for protecting data privacy and efficient organization of data. An enhanced database system comprises a DBMS, a data classifier, a database of applications and a rules and policy unit. The DBMS includes a query processor for processing a query from a user. The rules and policy unit outputs a pointer to a node within the data classification tree based on several criteria. In accordance with another embodiment, a DBMS residing within a communication network organizes data related to the ID of mobile users. In accordance with another embodiment, an enhanced database system comprises a DRM user agent and a DBMS. The DRM user agent receives a CO protected by DRM. The DBMS stores the CO and controls access to the CO based on restrictions specified in an RO associated with the CO.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
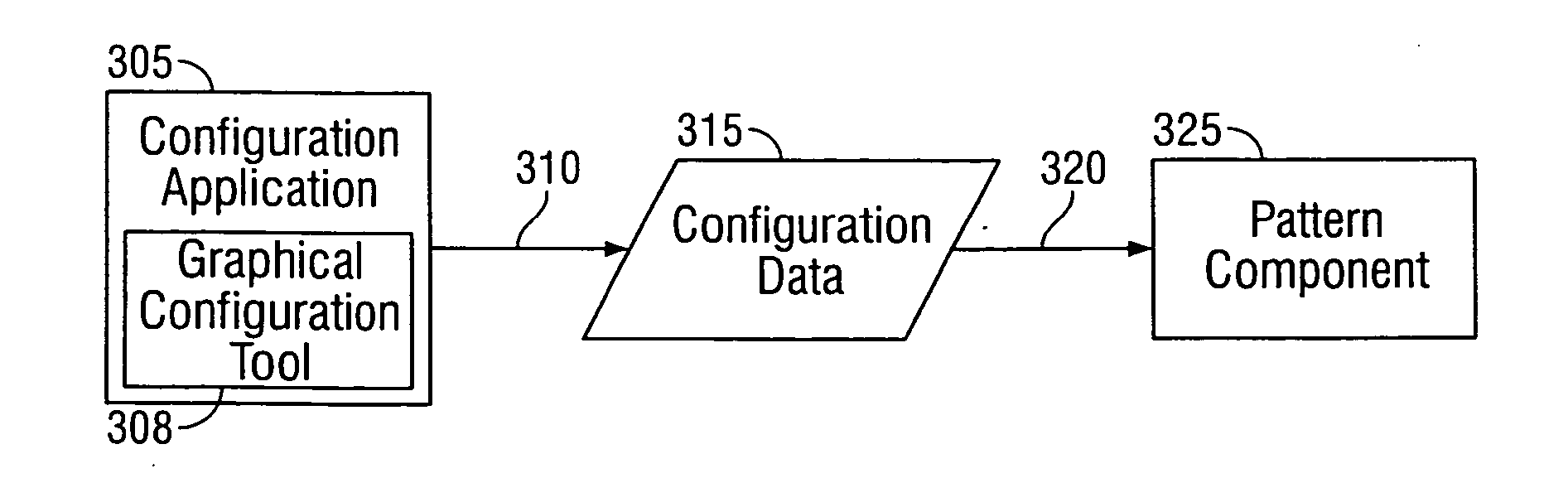
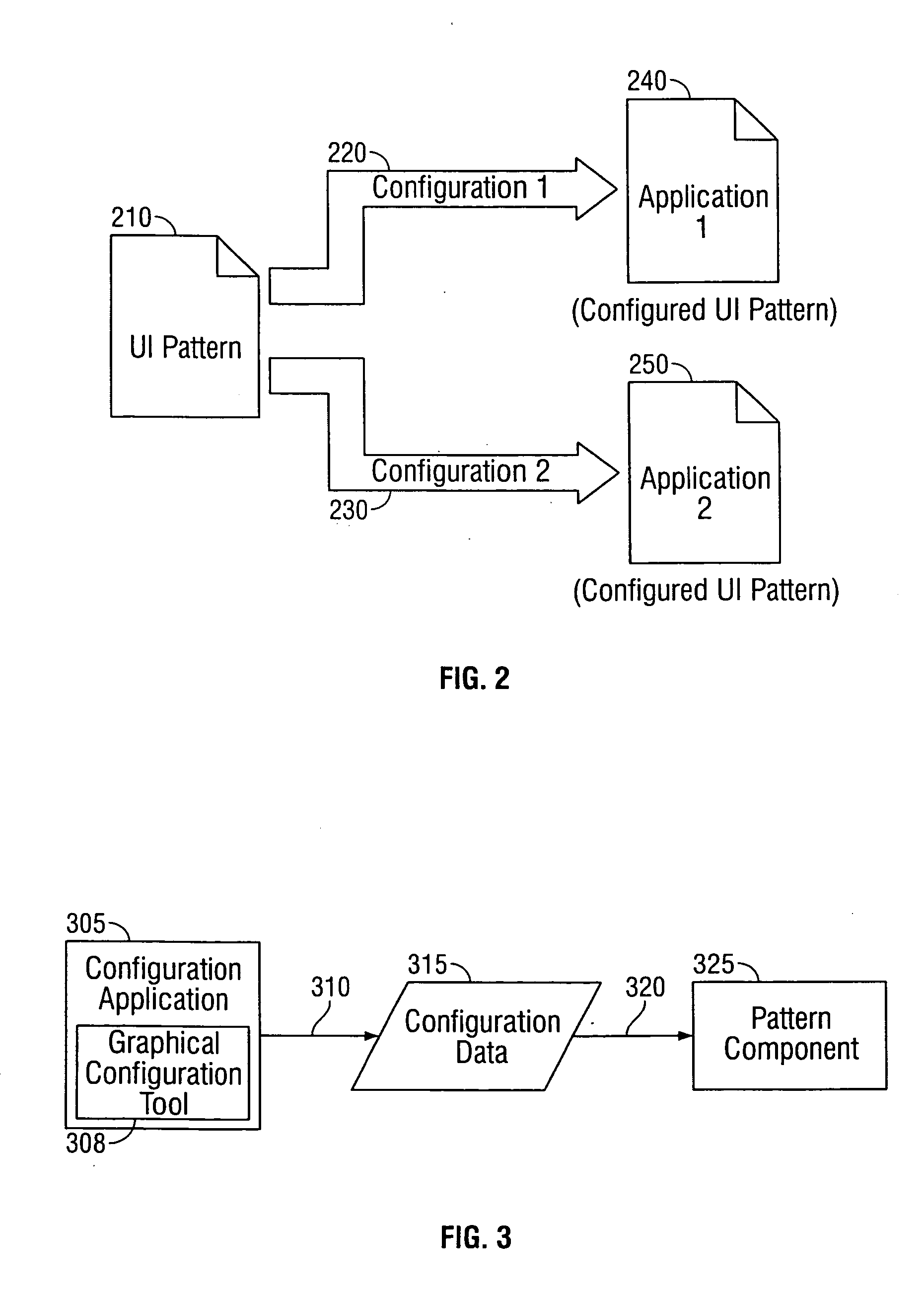
Developing applications using configurable patterns
ActiveUS20060075382A1Configure operationSimple processDigital data processing detailsVisual/graphical programmingApplication softwareQuery statement
Methods, systems, and computer program products, implementing techniques for developing applications using configurable patterns. The techniques include determining the functionality of a pre-existing application; selecting one or more patterns based on the functionality of the pre-existing application, and configuring the patterns so that the patterns execute similar functionality as the pre-existing application. The patterns comprise multiple pattern elements including prearranged user interface elements. The patterns specify predefined actions that can be performed using the user interface elements. The predefined actions match actions performed by the pre-existing application. Configuring the patterns includes importing database structure from a database used by the pre-existing application, generating a visual model of a query performed on the database by the pre-existing application, converting the visual model of a query into a query statement, and configuring the patterns to use the query statement.
Owner:SAP AG
Method and software for mobile data collection having managed workflow
InactiveUS20060288014A1Reduce data volumeOvercome excessive storage spaceDigital data processing detailsResourcesGps receiverMobile worker
A computerized method for collecting information on geo-spatially distributed assets. The method includes managed workflow so that work crews are automatically informed of the work that needs to be done and can report back to management when the work is completed. Mobile workers use a network-disconnected mobile computing device for data collection that includes a GPS receiver for use in generating a map showing the user's position in relation to the asset. An asset attribute database having a vertical database schema permits live-entry of the collected data without the need for confirmation, thereby speeding data entry and reducing the likelihood of data loss in the event of power failure, etc. The vertical database schema also permits data collection forms to be changed without updating the underlying database structure. The vertical database schema is converted to a relational database schema for management reporting purposes.
Owner:AGRIGIS
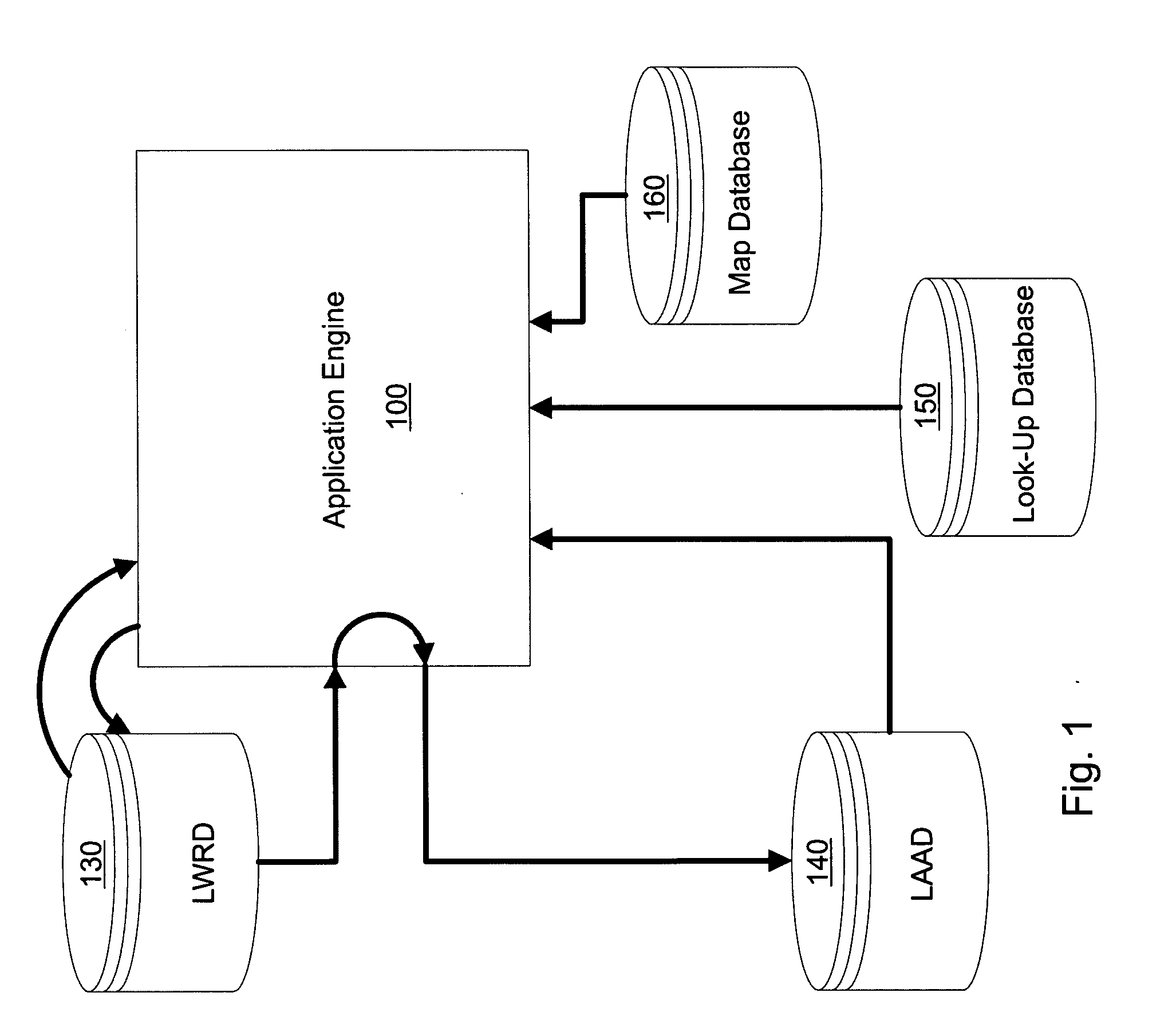
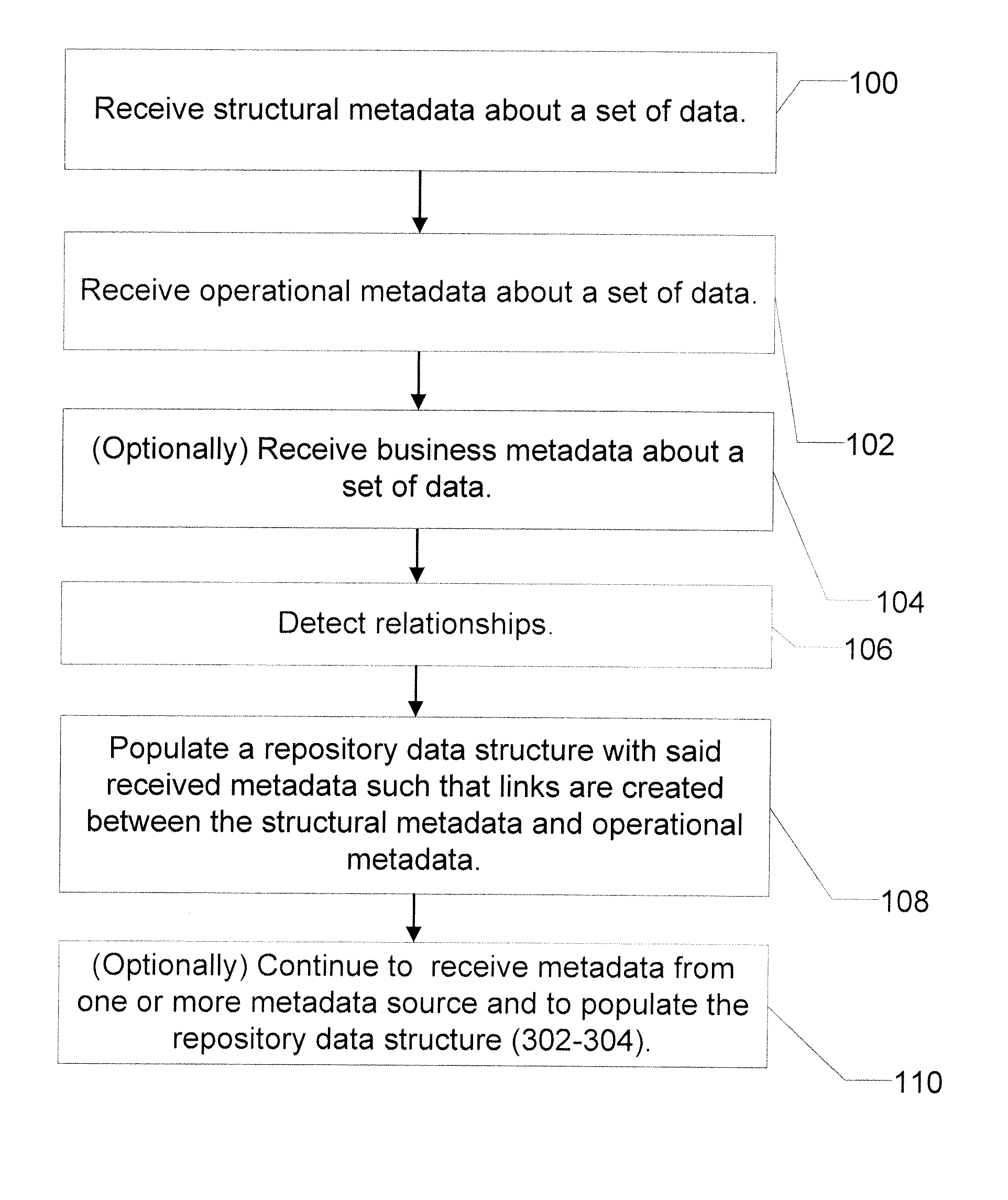
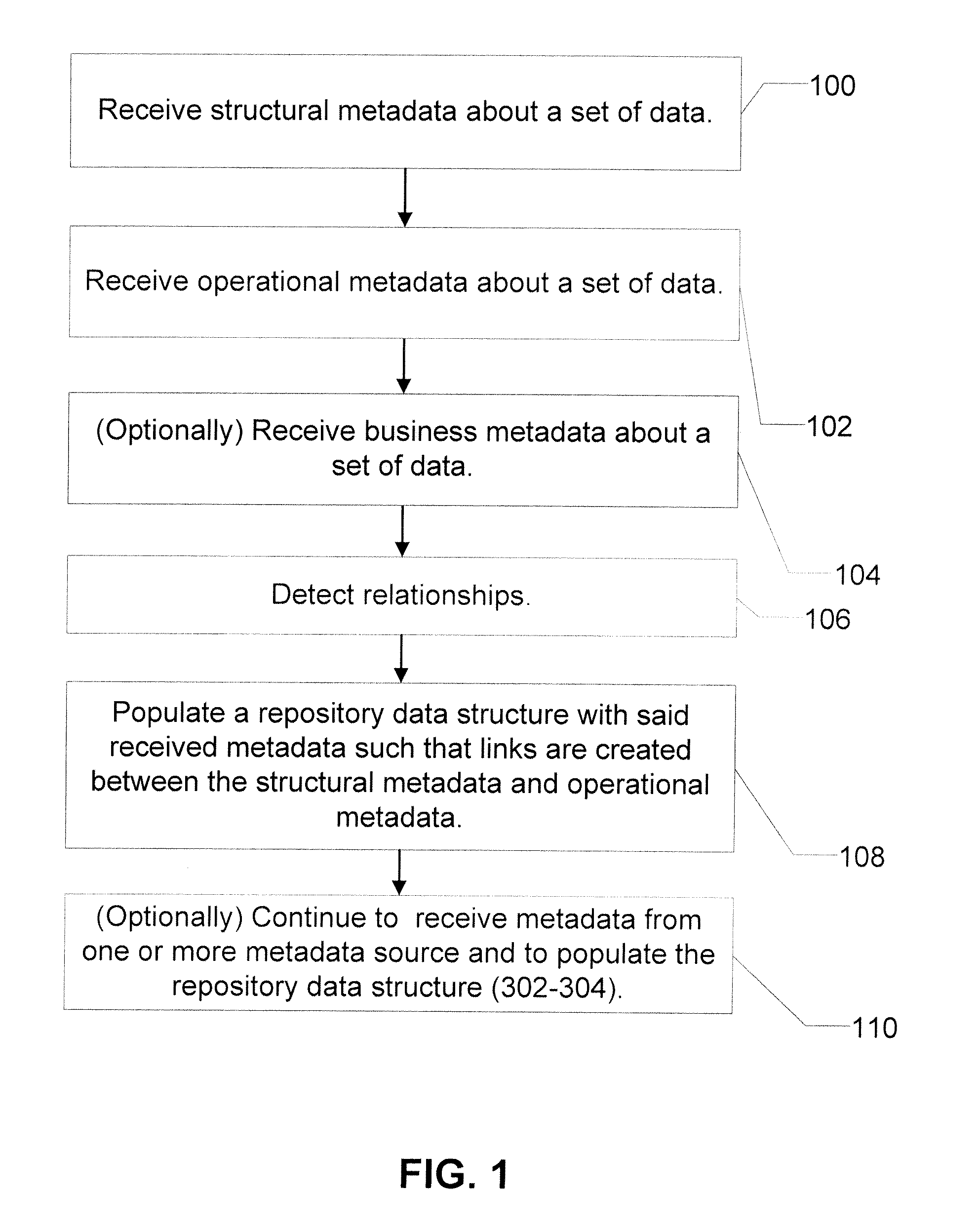
Apparatus and method for merging metadata within a repository
InactiveUS20070255741A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsLinked dataMetadata
A computer readable storage medium includes executable instructions to create a database structure that contains groups of linked data tables to store different types of metadata selected from Business Metadata, Structural Metadata and Operational Metadata. At least two different types of metadata are received. The database structure is populated with the at least two different types of metadata to form composite metadata.
Owner:BUSINESS OBJECTS DATA INTEGRATION
Model inventory manager
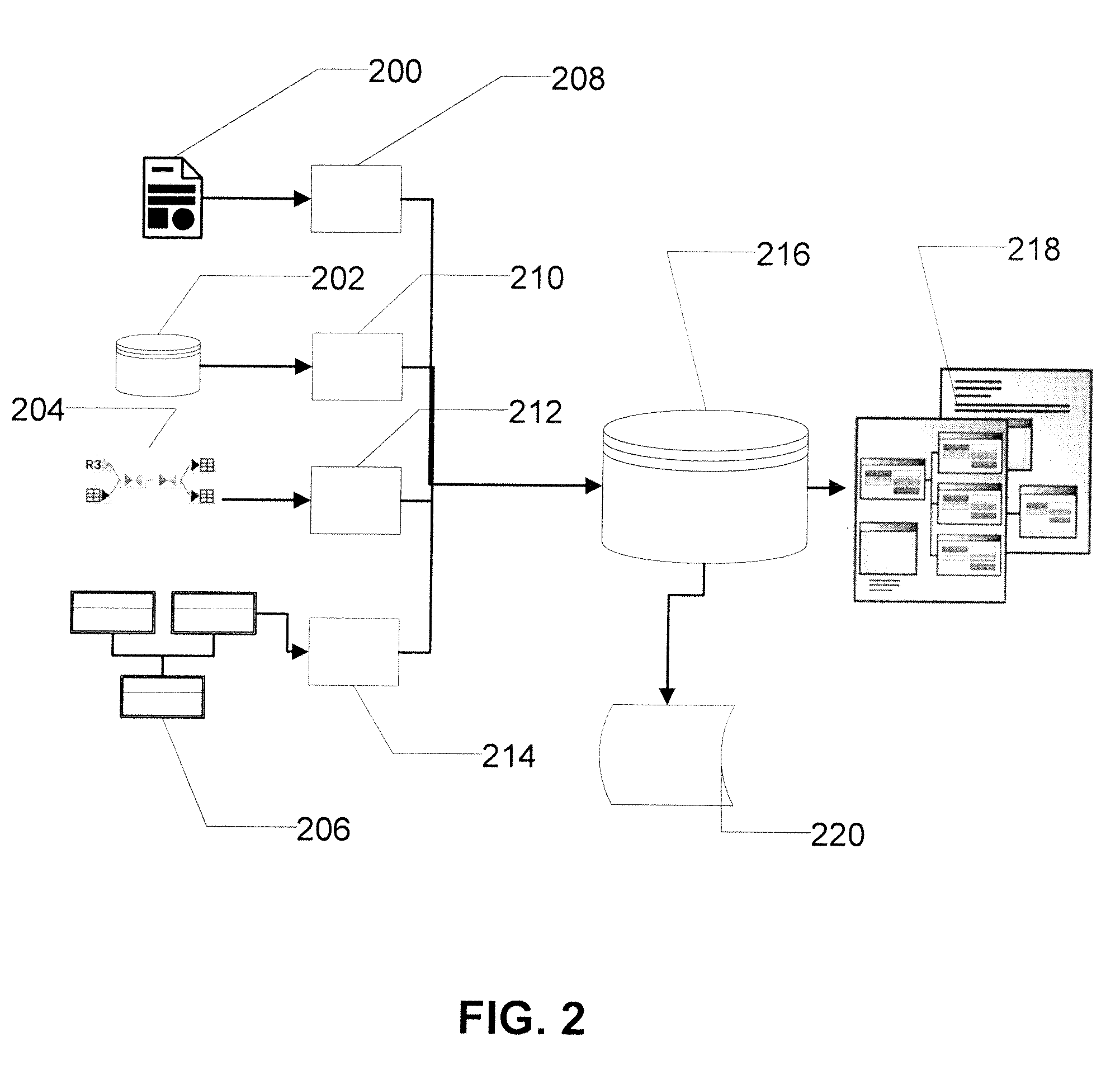
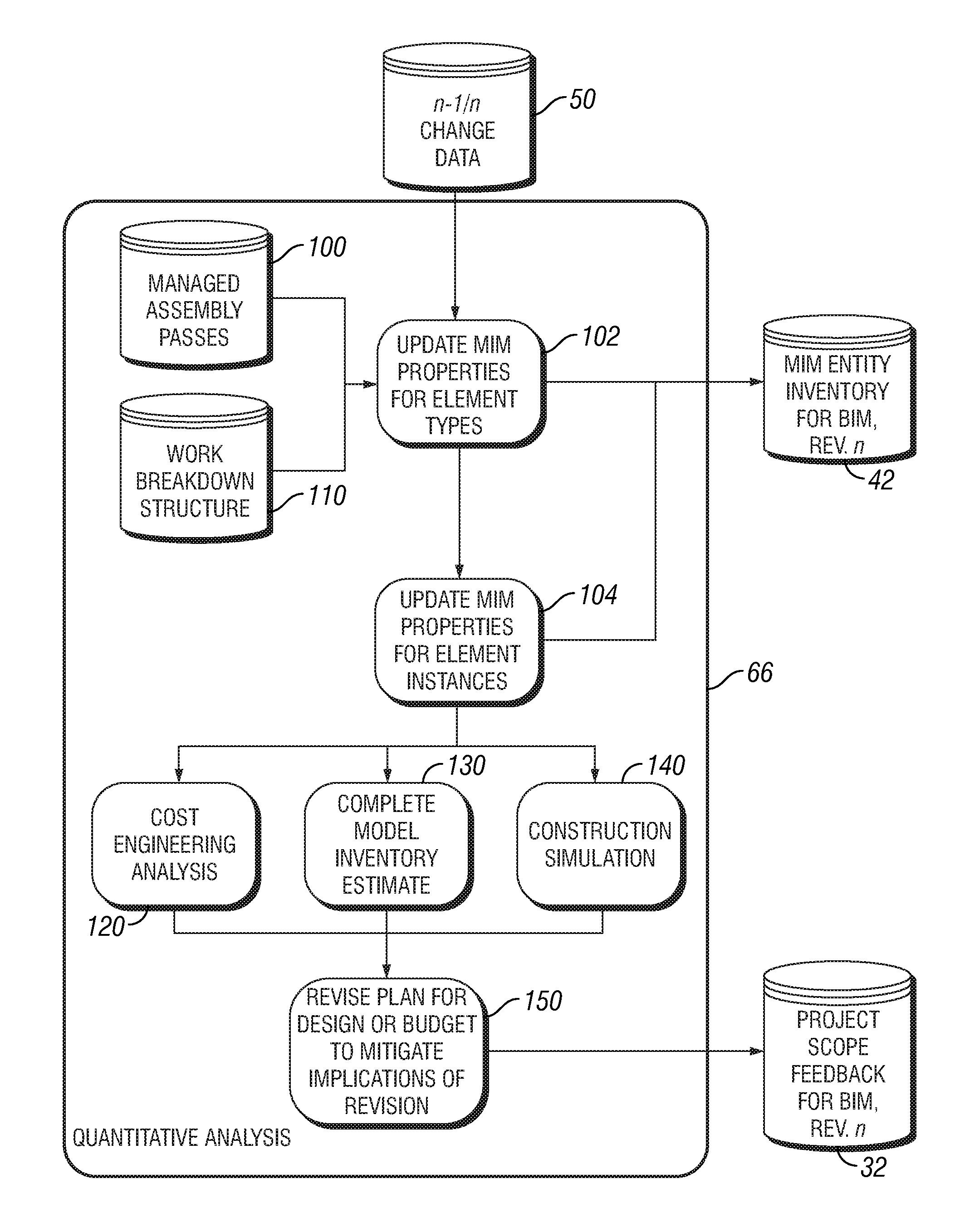
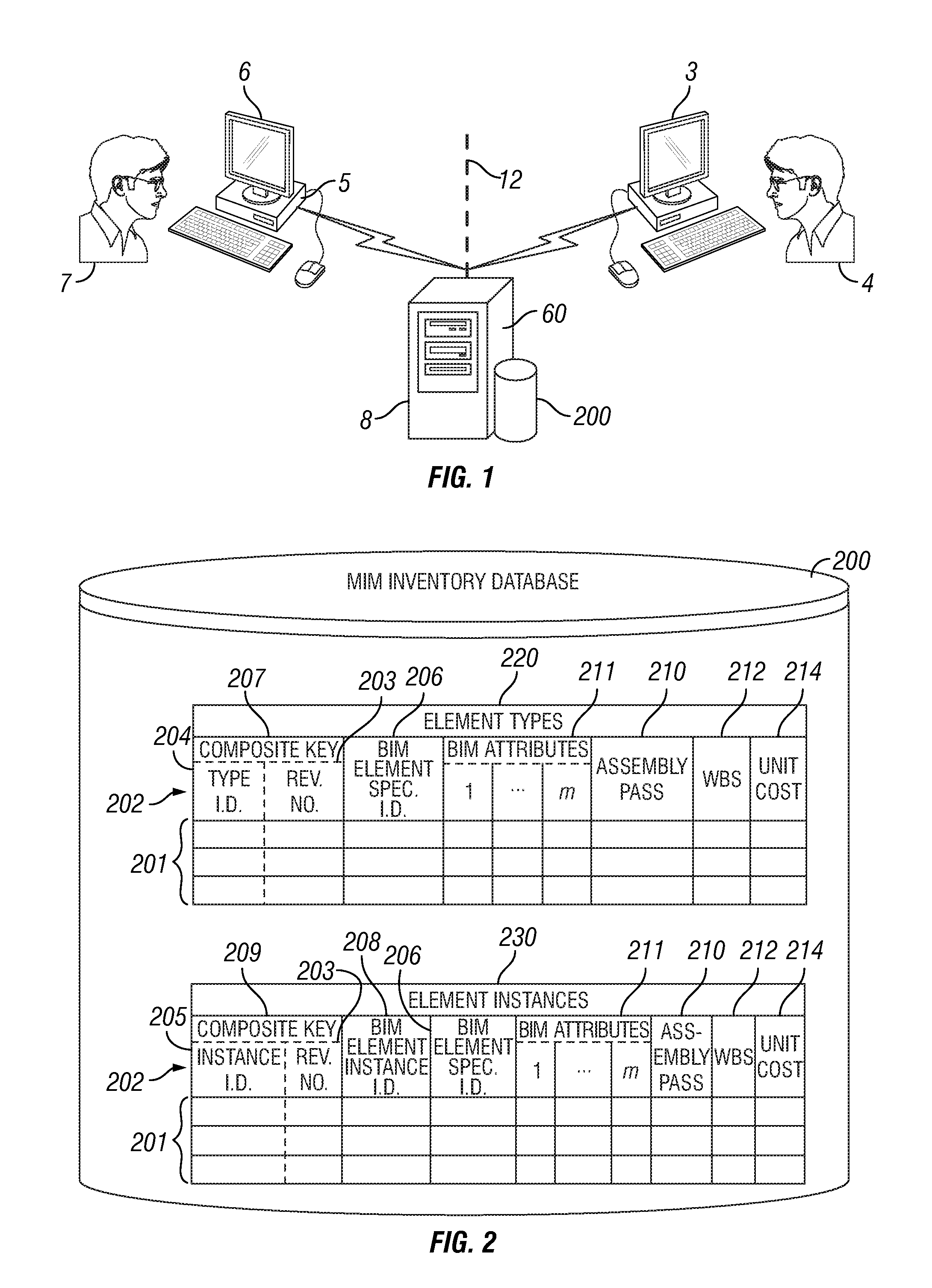
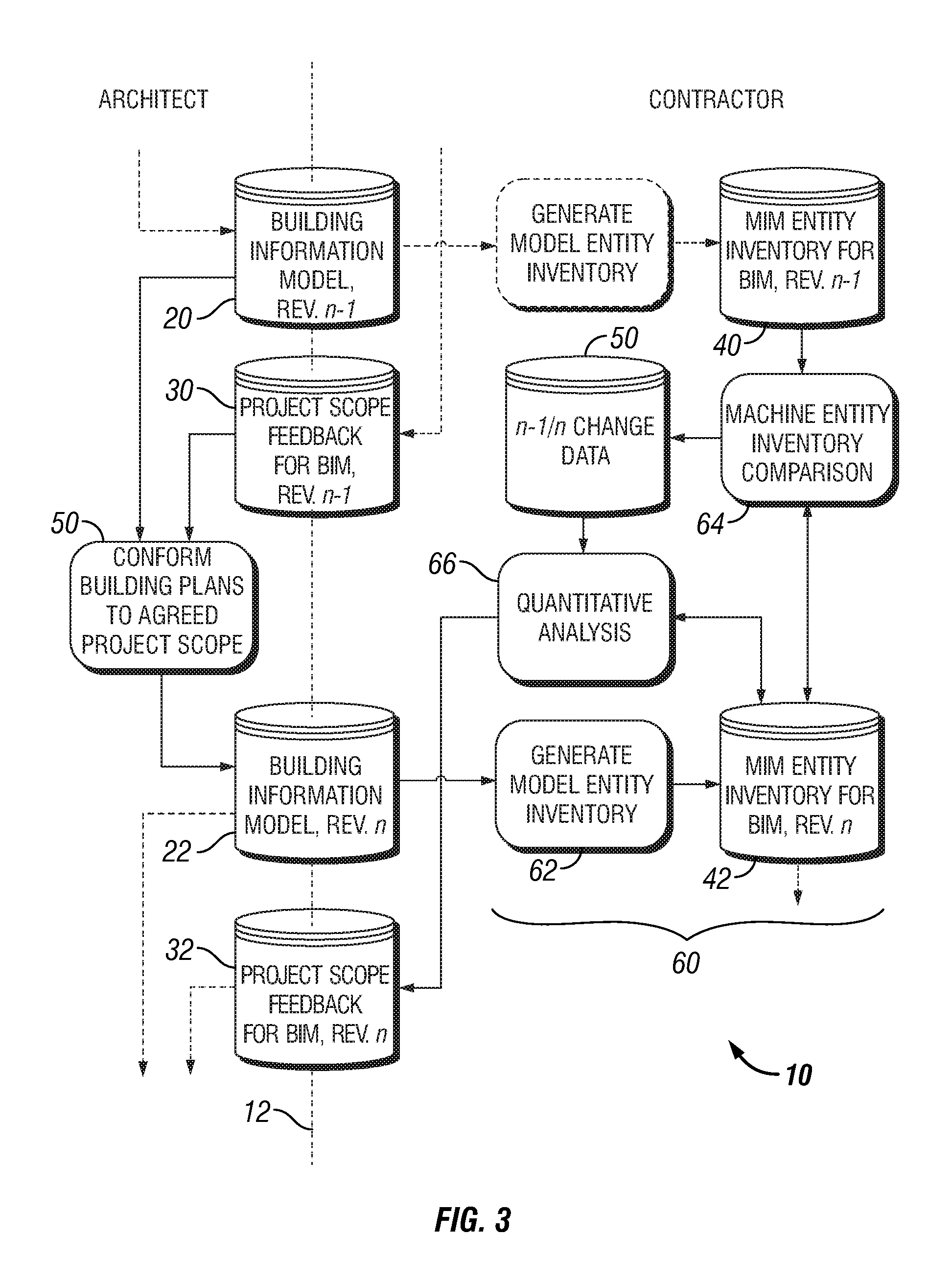
InactiveUS20110307281A1Quick understandingQuick analysisGeometric CADDigital data processing detailsData setInventory management
A method and apparatus for managing a building model inventory, including a database structured for storing element specification and instance data from both a previous version and a latter revision of building information modeling datasets, respectively. In addition to the building information modeling element data, the database associates completed assembly pass, unit cost, work breakdown structure, and other inventory management data with the element type definitions and element instance data. Application software compares the first and second inventory revisions to identify all changes, additions and / or deletions of building elements between the previous version and the latter revision of the building information modeling datasets. By tracking the elements that change, the changes that affect the construction schedule and quantity, configuration and specification of materials are identified. An engineering cost analysis based on the changed data provides a rapid understanding of the implications of any design change.
Owner:ASSEMBLE SYST
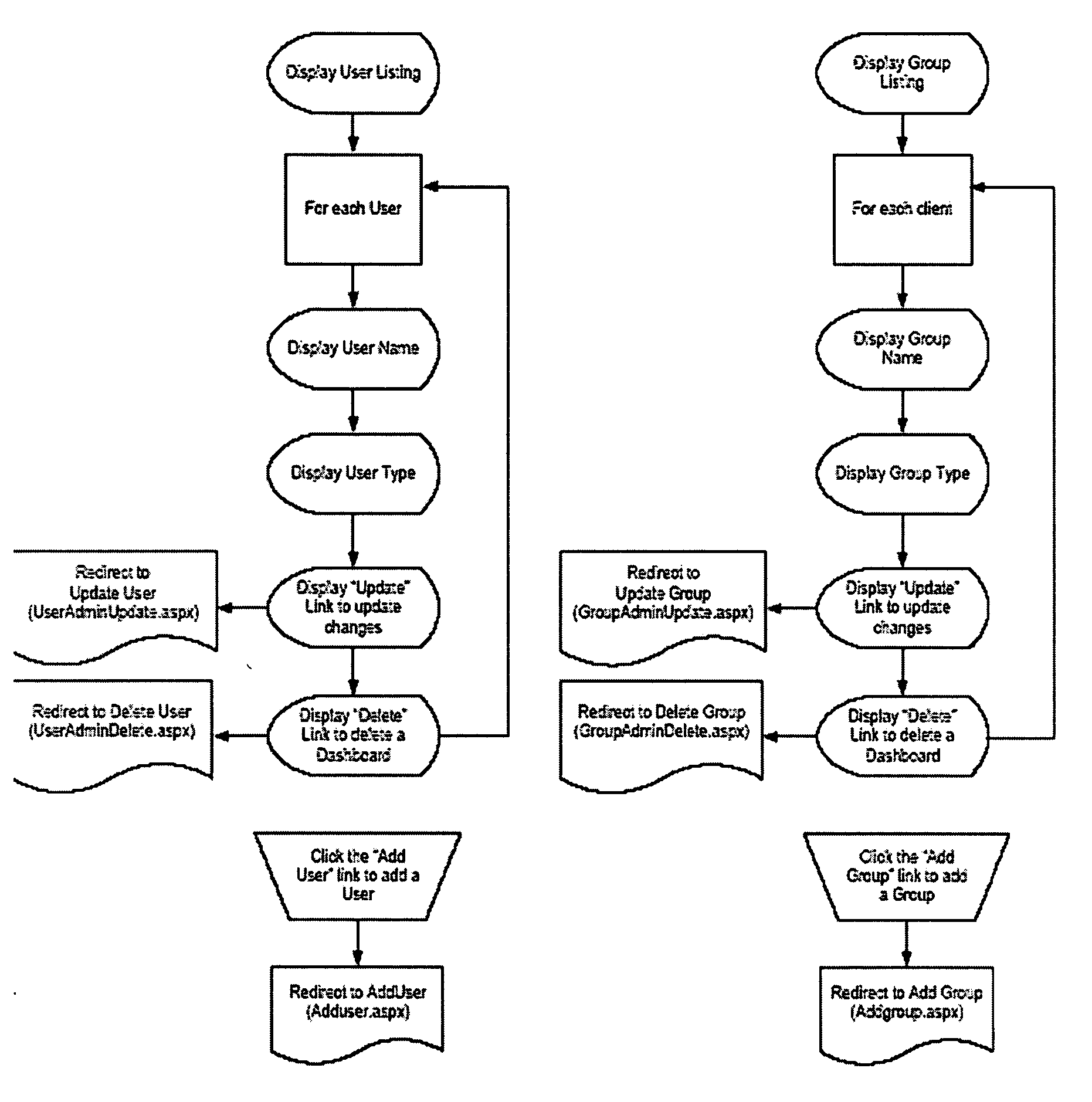
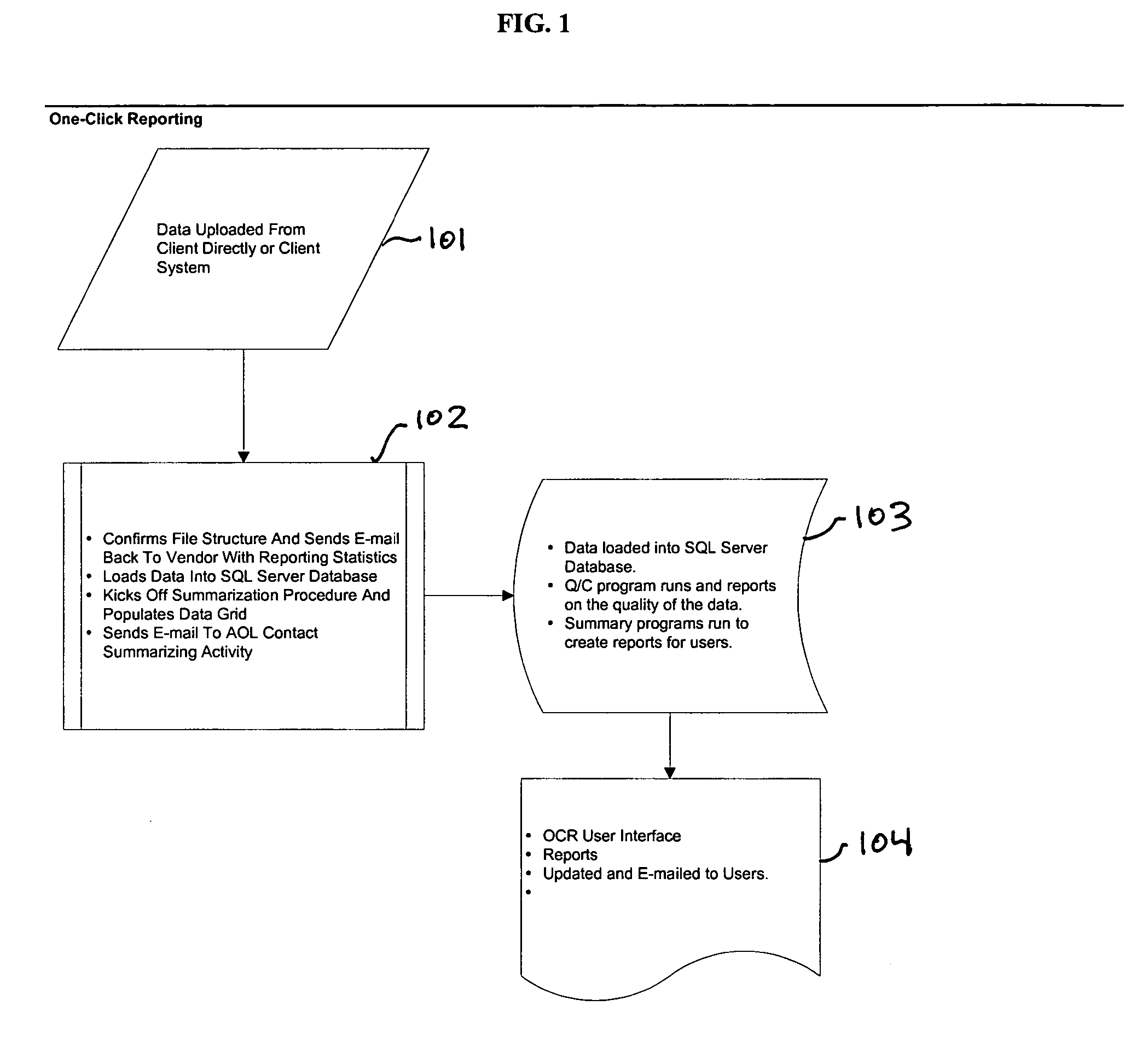
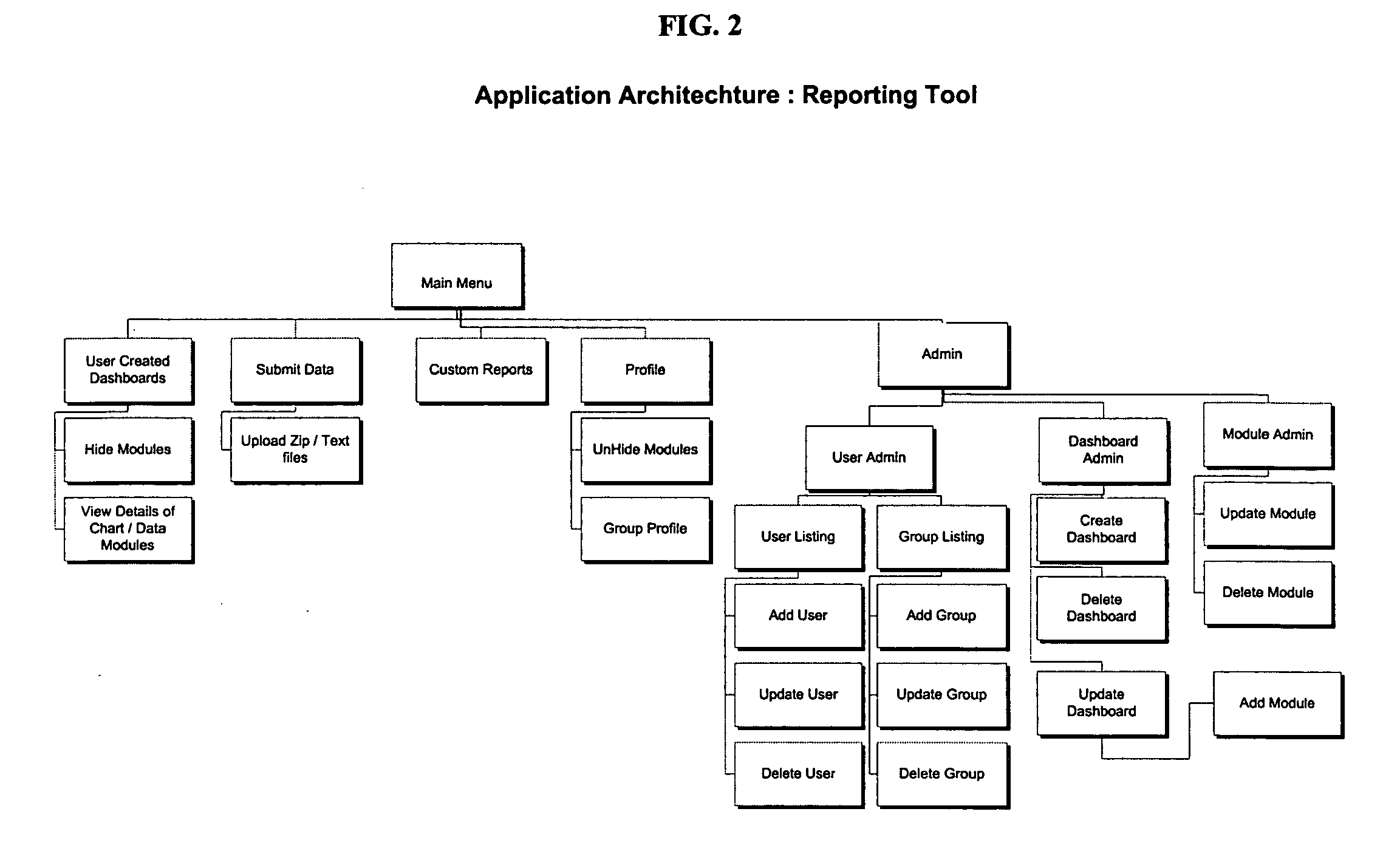
Integrated tool set for generating custom reports
InactiveUS20050004947A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTime range
A process and graphical user interface for generating and modifying customized reports based on criteria specified by a user. After uploading data supplied by the user to a customer unique database structure having predefined data elements, report data elements are selected from the predefined data elements. Timeframes and variables associated with the report data elements are then selected, and the table layout is formatted. A report is generated, and afterwards, the user can easily change the report by changing any one of the report data elements, timeframes or variables, without reprogramming a database program or application processing software associated with generating the report.
Owner:EMLET JAMES L +1
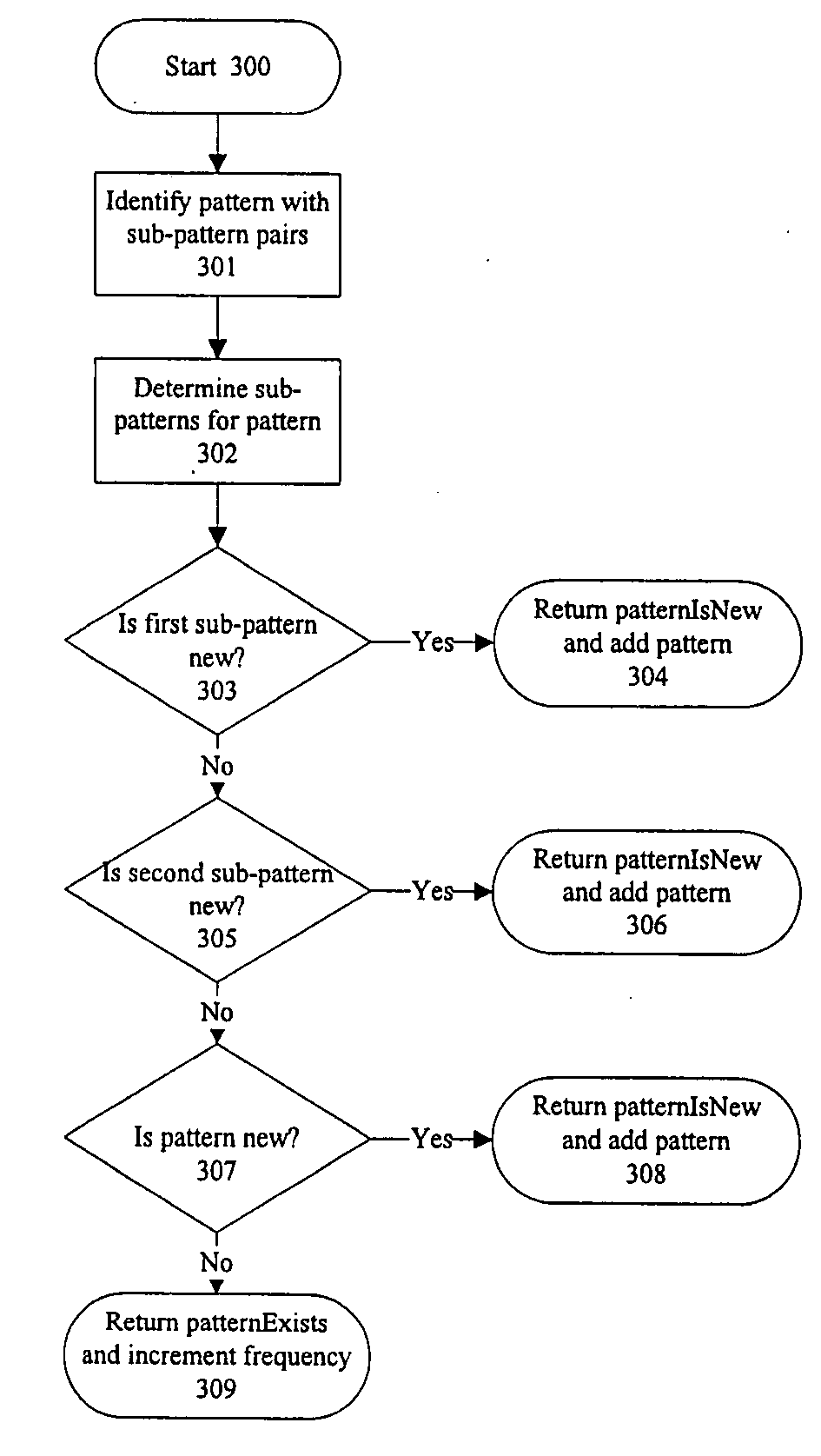
Method and system for implementing an enhanced database
A database is created from a set of data by identifying the patterns in the data set, storing the patterns in a memory device, and generating a representation of the database structure using pointers to the stored patterns. The use of pointers to store the patterns can greatly reduce the amount of memory or other space required to store the data set by replacing duplicate patterns with additional pointers, which are normally considerably smaller in size. In addition, the use of pointers may allow for more rapid searching, sorting, and other operations on the database. The representation of the database may use pointers in a tree structure to identify nodes and reduce searching and other operations. A tree structure representation of a table may use a pointer to a pattern for the base leaf node (e.g., nodes that do not branch) while using pointer pairs to represent branching nodes.
Owner:TERADATA US
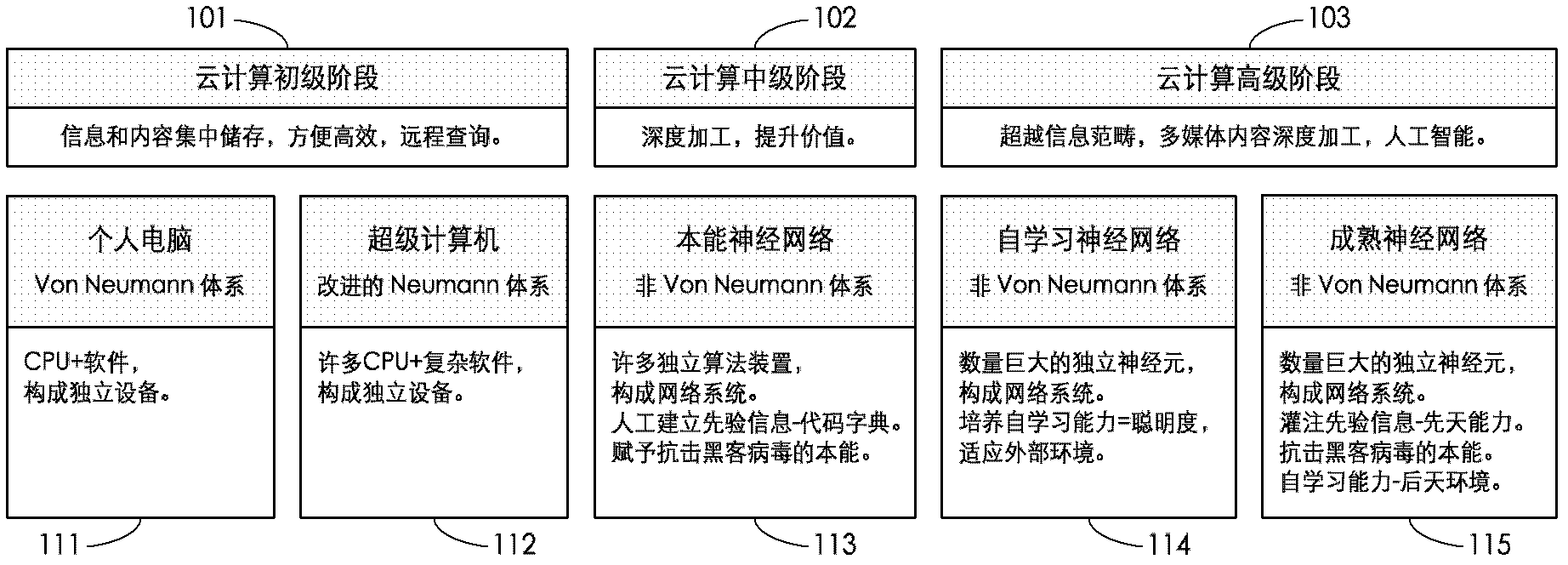
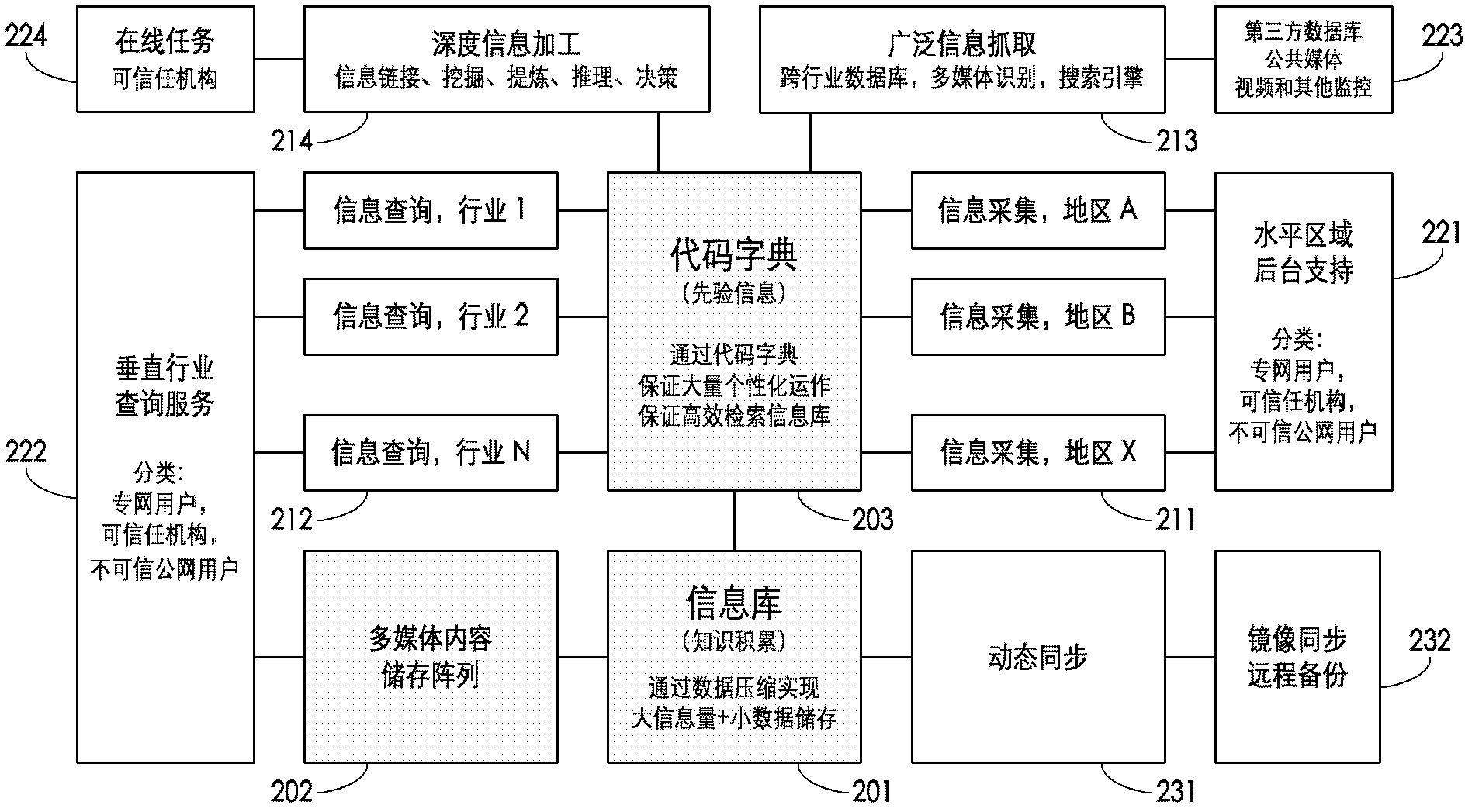
Neural network-based cloud intelligent machine system
InactiveCN102496060ABreak through the bottleneck of computing powerPrevent hackingTransmissionPhysical realisationSelf-healingArray data structure
The invention relates to a neural network-based cloud intelligent machine system of cloud operation, data mining, the neural network, information security and the like. The system comprises a neural network-based computer structure, a generalized database structure and a data structure over software and hardware boundaries. The system provides and uses a plurality of novel technologies, including an algorithm engine structure, an instinctual neural network, information compression, a limited network protocol, a security system, a cross platform data structure and the like, wherein the computer system structure described in the invention can easily be over thousands times of the cluster computing power of a current top server, and break through the bottleneck of the computing capacity of a future cloud computing center. The system has immunization and self-healing ability, and is prevented from being attacked by virus hackers. The system grows and metabolizes like organisms, defines new constantly changing tasks, and completes upgrading and expansion, and can be applied to a large-scale information center, an out-sourcing enterprise management, E-business and other cloud computing centers.
Owner:高汉中
Software re-engineering system
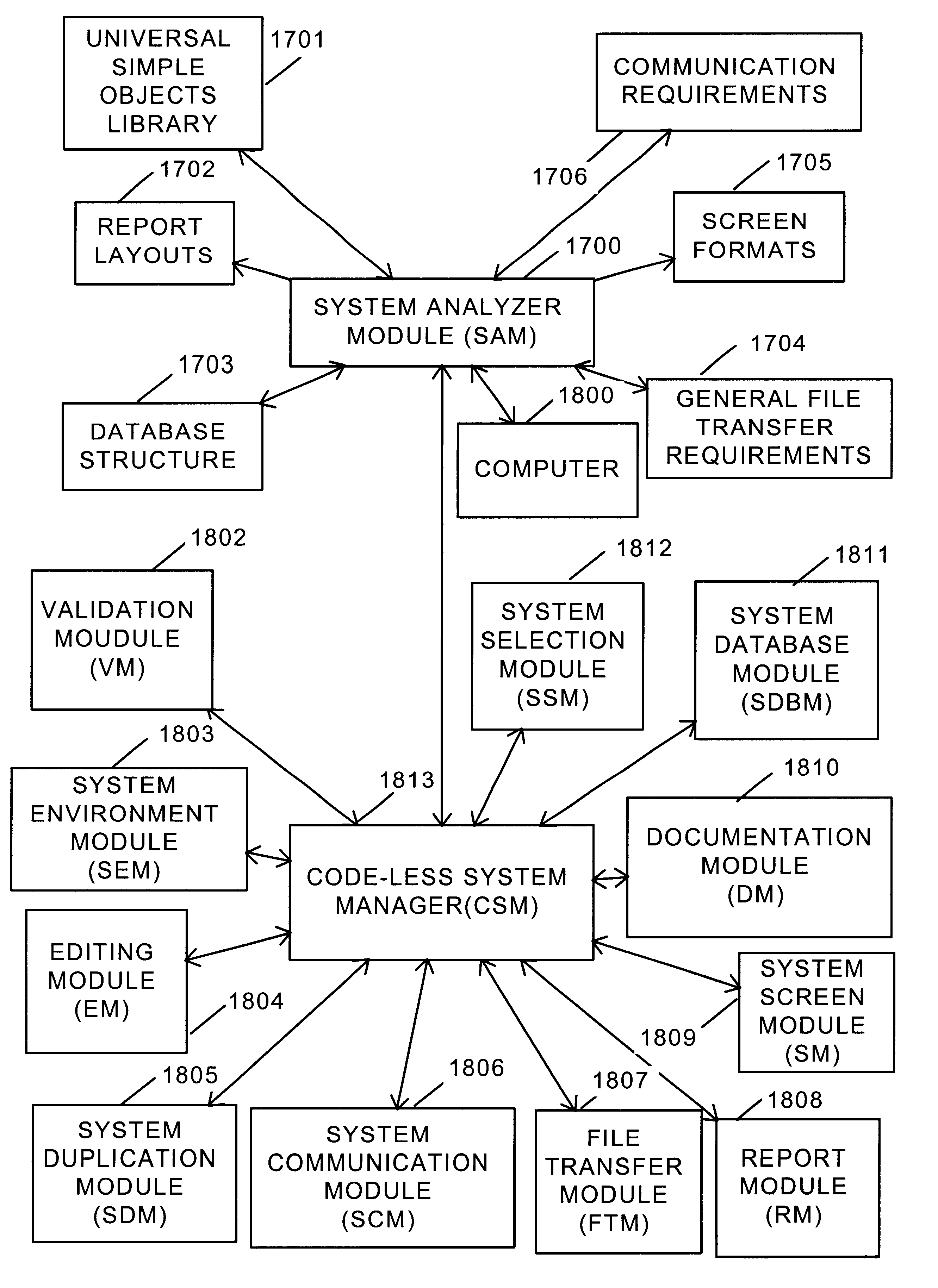
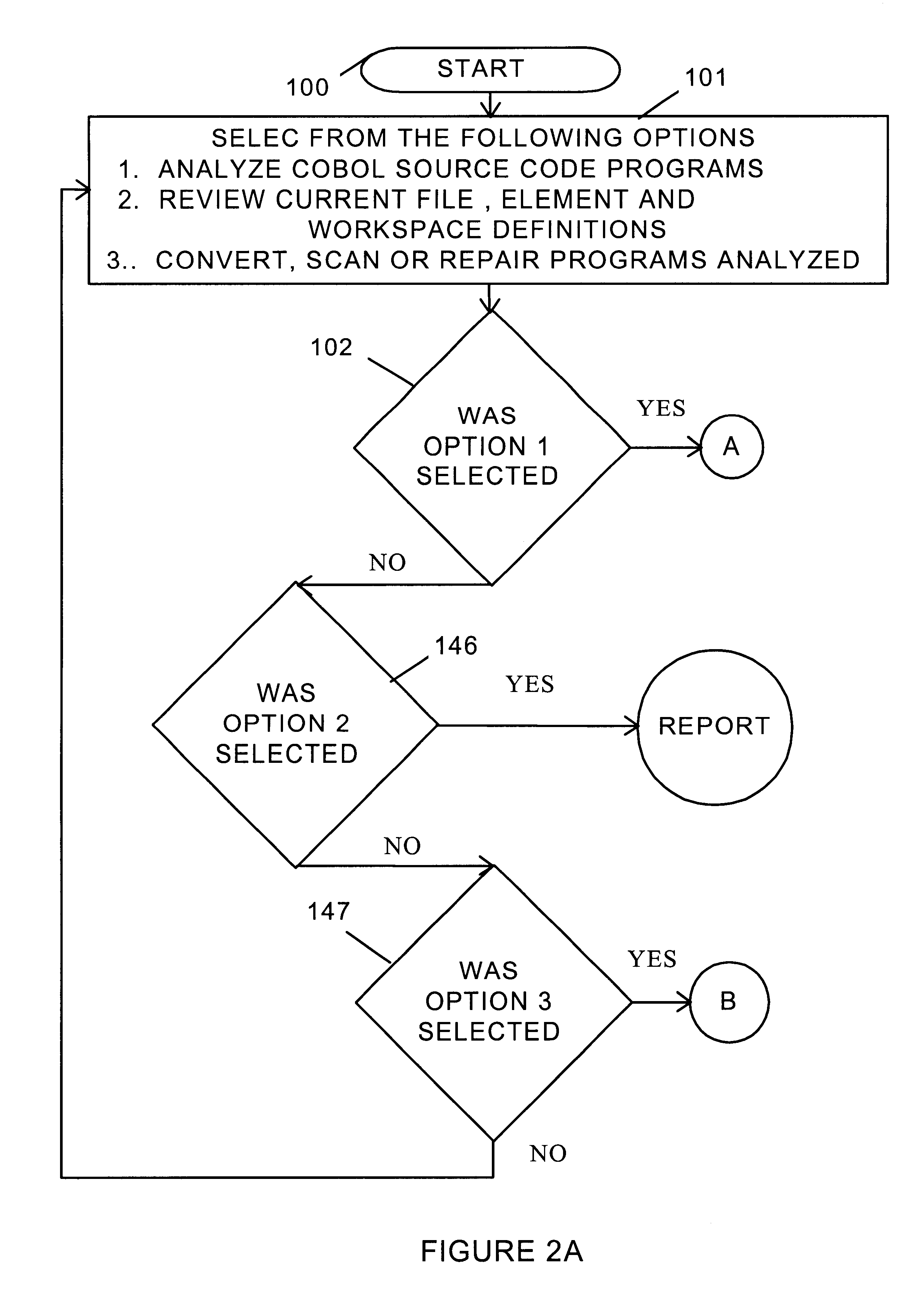
InactiveUS6269474B1Improve system performanceSoftware maintainance/managementProgram loading/initiatingData fileApplication software
An optimization system including an option to convert existing code to a code-less environment or to create a codeless environment by the establishment of all essential application elements in files. The code-less environment is created through a design and analysis step, an environmental step and an installation step. An application map is prepared during the design and analysis step which defines where information enters into the system, where information is used, and where used information is changed. The application map is also used to verify that all information is accounted for. The design and analysis step also includes the generation of default database structures, screen formats, print layouts, file transfer protocols, validation tables and communication specifications. The environmental step includes modifying specifications in accordance with user preferences, simulating performance of the specifications with test data, preparing existing data files for conversion to the code-less system, and implementing parallel processing. The installation step includes final testing of selected hardware platforms and maintenance on a development system.
Owner:INT VERONEX RESOURCES
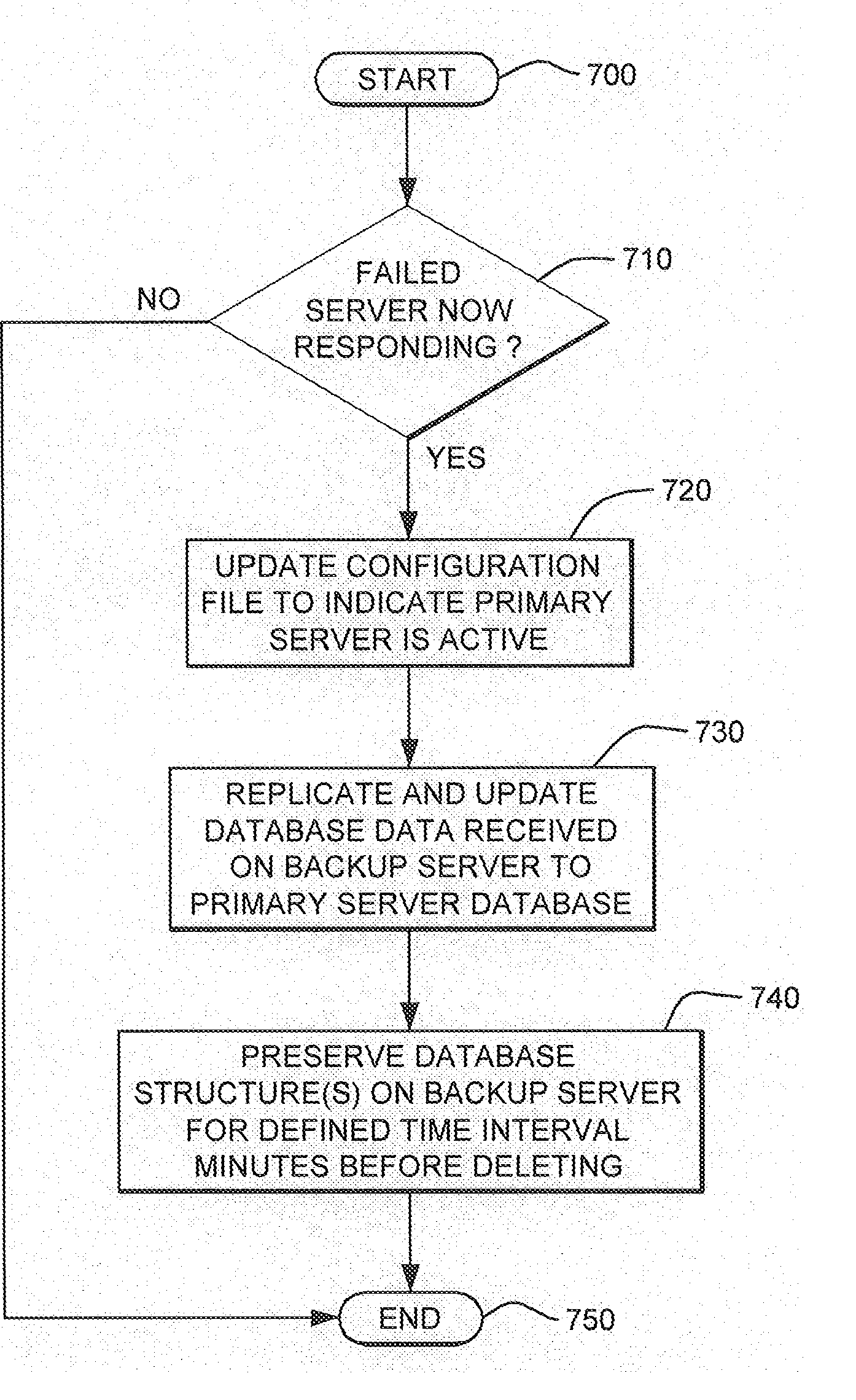
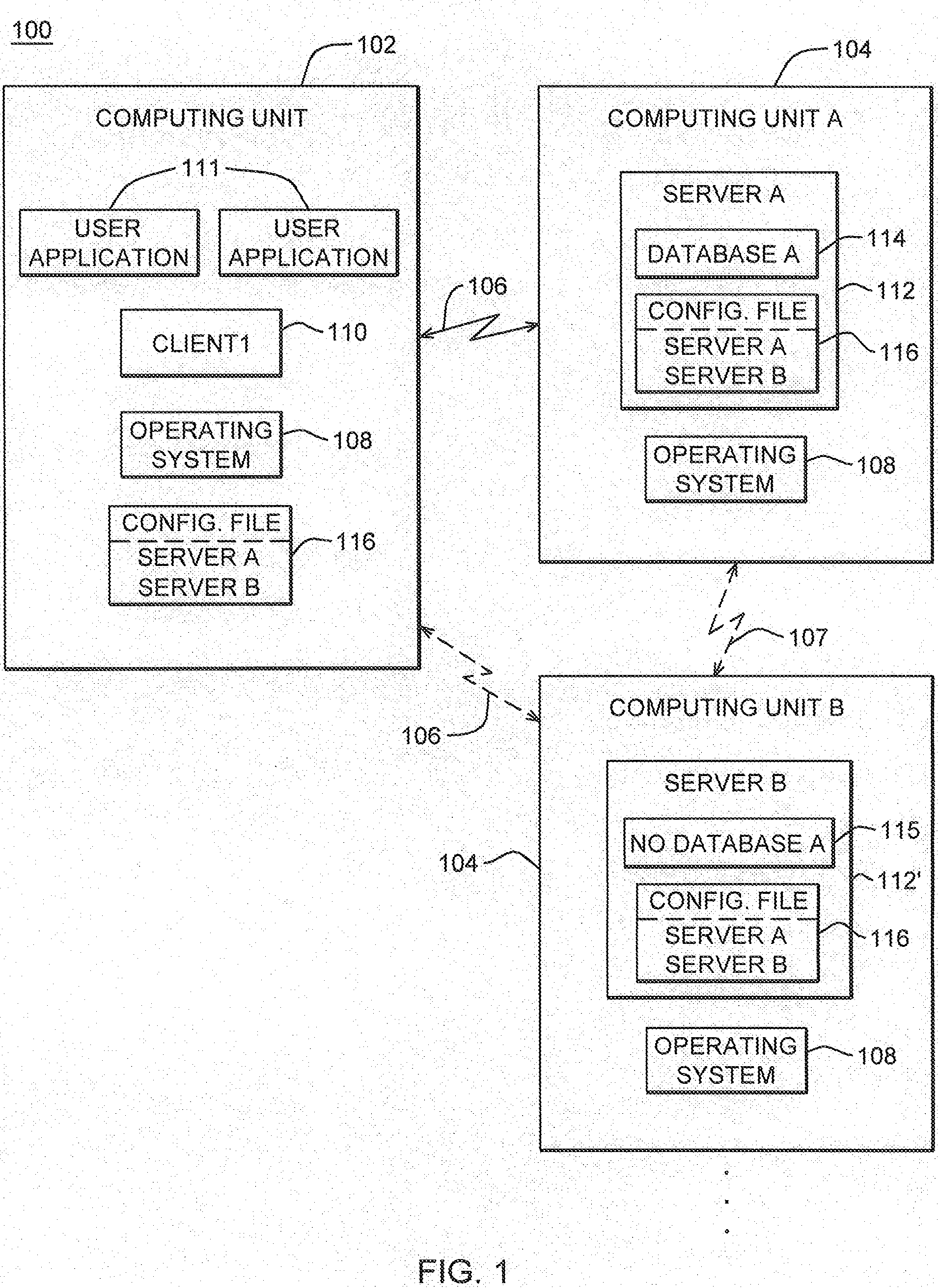
Transitioning of Database Service Responsibility Responsive to Server Failure in a Partially Clustered Computing Environment
A facility is provided for transitioning a database service from a failing, primary server to another server of a computing environment including a plurality of servers, at least some of which have a common database service capability, but not commonly replicated supporting databases. The facility includes, responsive to detection of failure at the primary server, selecting another server of the plurality of servers to function as database service backup for the primary server, updating at least one configuration file of the computing environment to indicate that the another server is to function as database service backup for the primary, failing server, and dynamically creating at least one database structure at the another server. The dynamically created at least one database structure supports the database service backup function at the another server and corresponds to a database structure of a database supporting the database service at the primary server.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for a mobile business application development and deployment platform
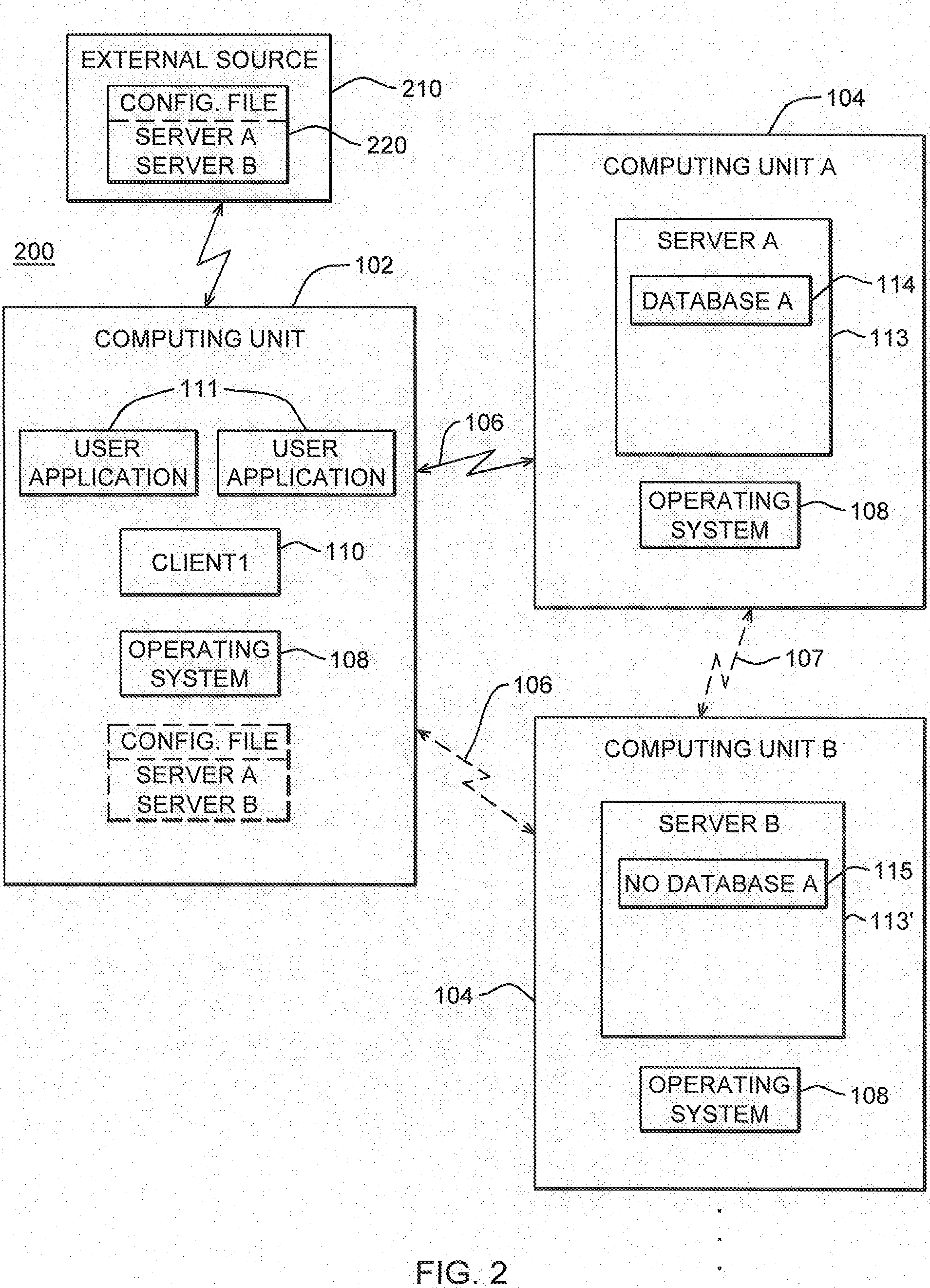
ActiveUS20130247005A1Improve customizabilityHigh degreeVersion controlSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemMobile business
Systems and methods for developing, customizing, and deploying mobile device business applications are provided through a mobile application development and deployment platform. Preferably, these systems and methods are implemented in an Internet based environment that allows non-technical users to build highly-customizable cross-platform mobile applications. The platform allows users to select, input, create, customize, and combine various content, design characteristics, database structure, and application components, such as modules, some of which allow an end user to store and access data in an end user database for business applications. In certain embodiments, the platform allows users to compile and generate a configuration file for the mobile application that can be distributed to end users for execution on various mobile devices and mobile operating systems. When the mobile application is installed on, or executed by the mobile device, the configuration file may enable the retrieval of data associated with the mobile application.
Owner:MEDIA DIRECT
Method and Apparatus for Optimizing the Evaluation of Semantic Web Queries
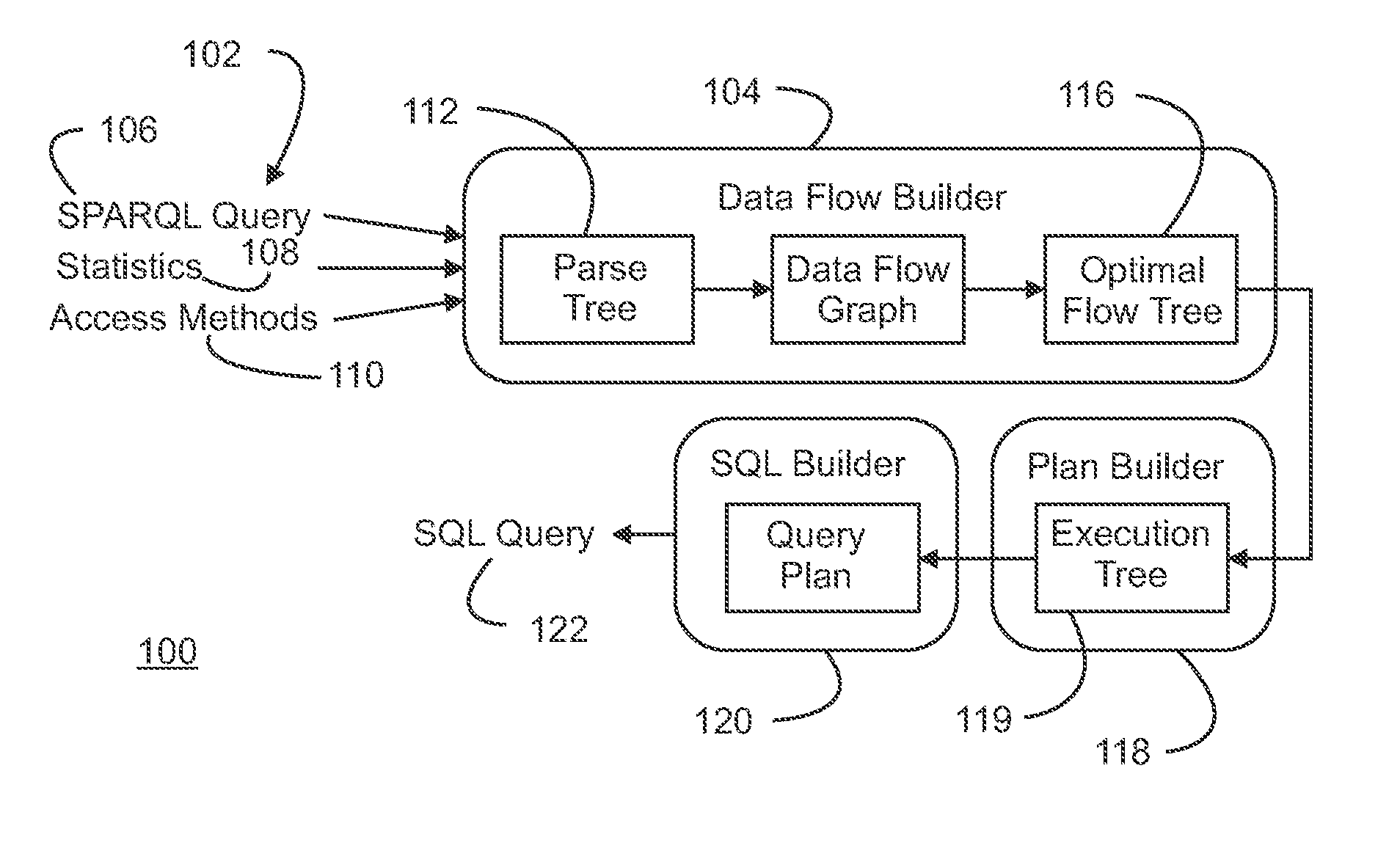
InactiveUS20140304251A1Effective evaluationAmenable to optimizationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuery planAccess method
A semantic query over an RDF database is received with RDF database statistics and access methods for evaluating triple patterns in the query. The semantic query is expressed as a parse tree containing triple patterns and logical relationships among the triple patterns. The parse tree and access methods create a data flow graph containing a plurality of triple pattern and access method pair nodes connected by a plurality of edges, and an optimal flow tree through the data flow graph is determined such that costs are minimized and all triple patterns in the semantic query are contained in the optimal flow tree. A structure independent execution tree defining a sequence of evaluation through the optimal flow tree is created and is transformed into a database structure dependent query plan. This is used to create an SQL query that is used to evaluate the semantic query over the RDF database.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and apparatus for defect reduction analysis
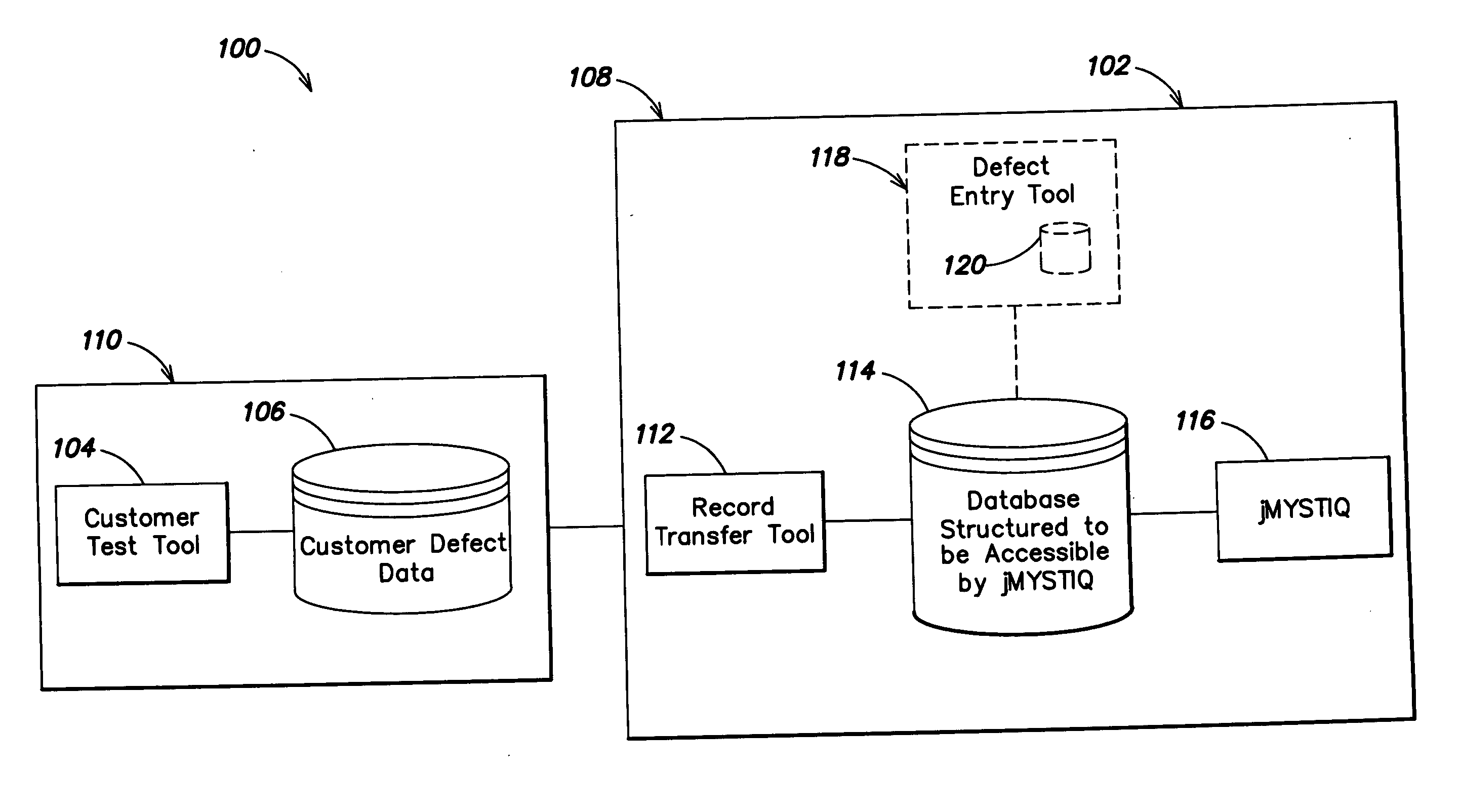
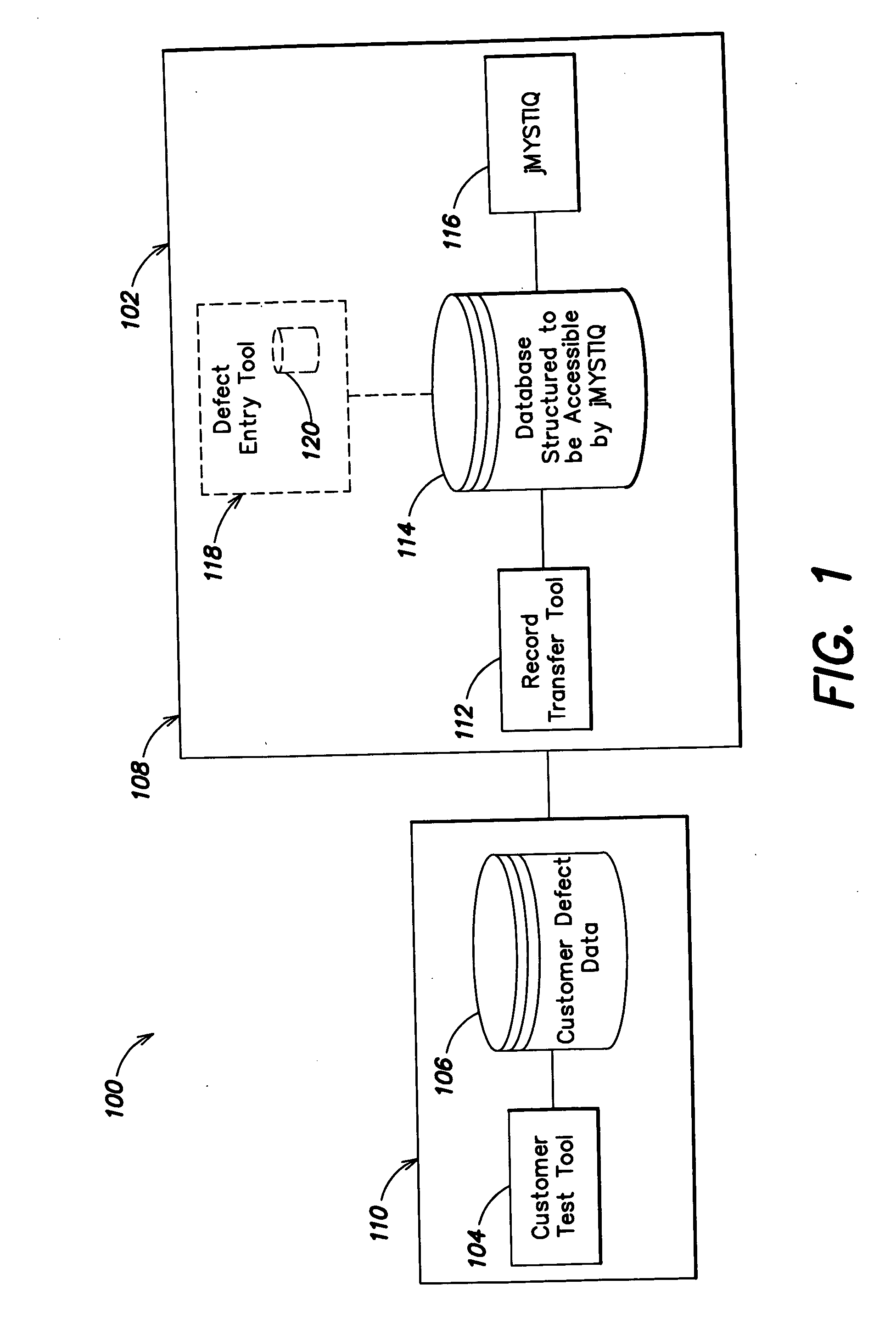
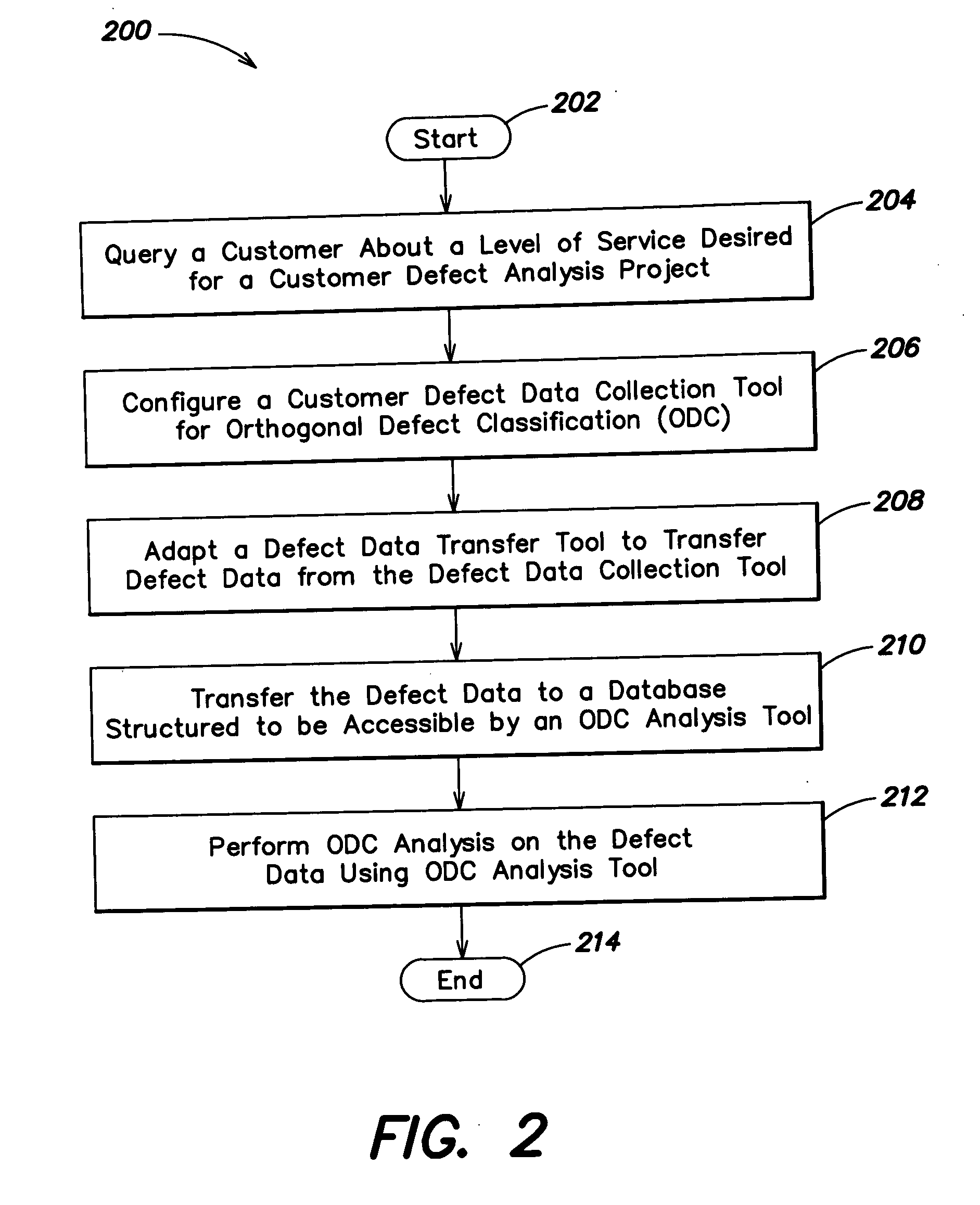
In a first aspect, a first method is provided for providing a service for performing Orthogonal Defect Classification (ODC) analysis. The first method includes the steps of (1) querying a customer about a level of service desired for a customer defect analysis project; (2) configuring a customer defect data collection tool for ODC; (3) adapting a defect data transfer tool to transfer defect data from the defect data collection tool; (4) transferring the defect data to a database structured to be accessible by an ODC analysis tool; and (5) performing ODC analysis on the defect data using the ODC analysis tool. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Classification engine for managing attribute-based data
A classification engine provides flexible support for manipulation of attribute-based data by dynamic generation of SQL with classifiers constructed from different schema objects representing different database schemas. The classifiers may be constructed by defining classifiers corresponding to the database schema, and mapping the classifiers to columns on tables in the database. The invention also allows a classification system to modify the database structure and easily conform the classification engine to the modified structure without recompiling the engine or rewriting the application that use the classification system. The engine is conformed to the new structure by constructing a second schema object for the modified database. The schema objects are preferably defined using a field-based language such as extensible markup language (XML).
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com