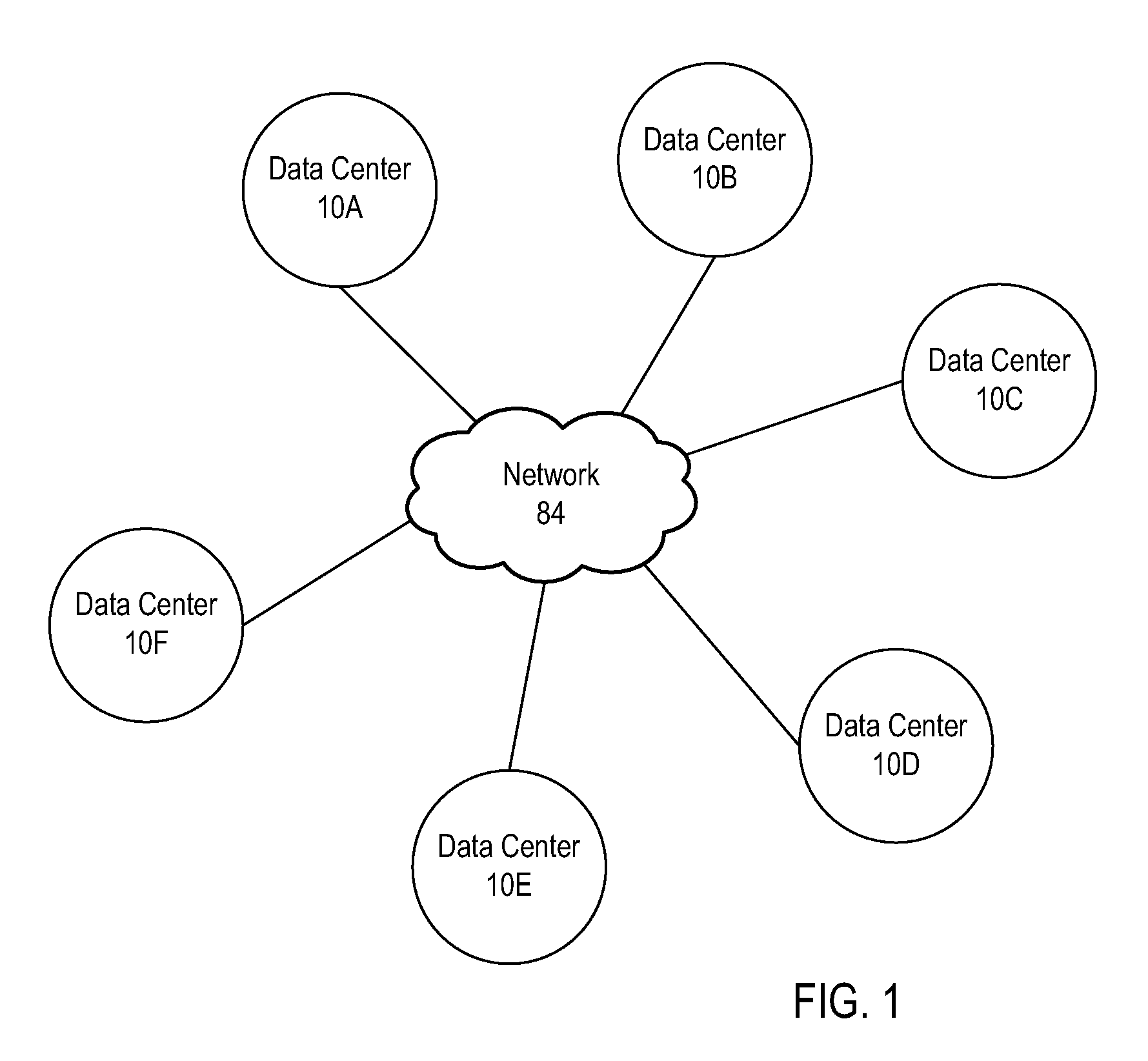
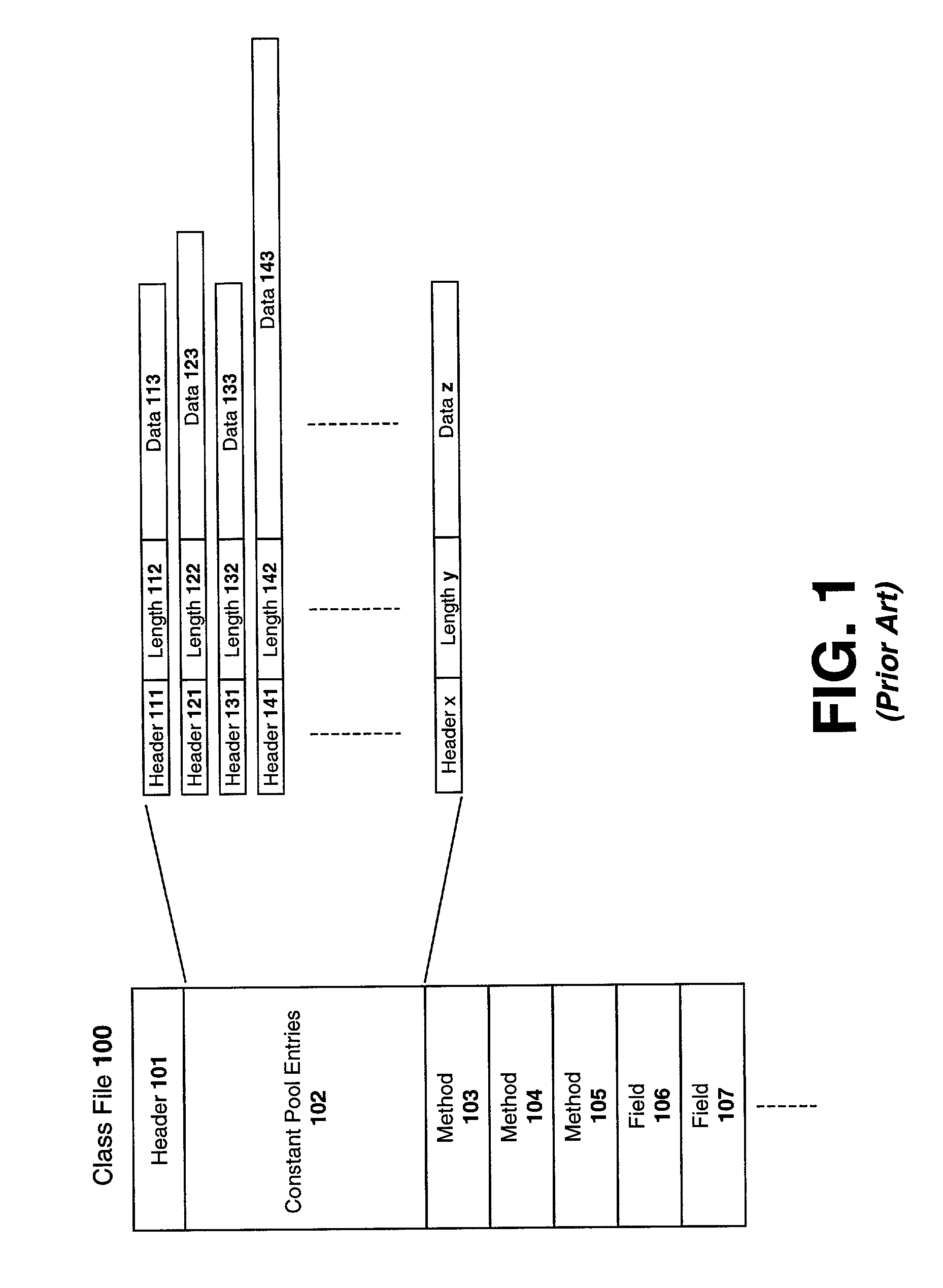
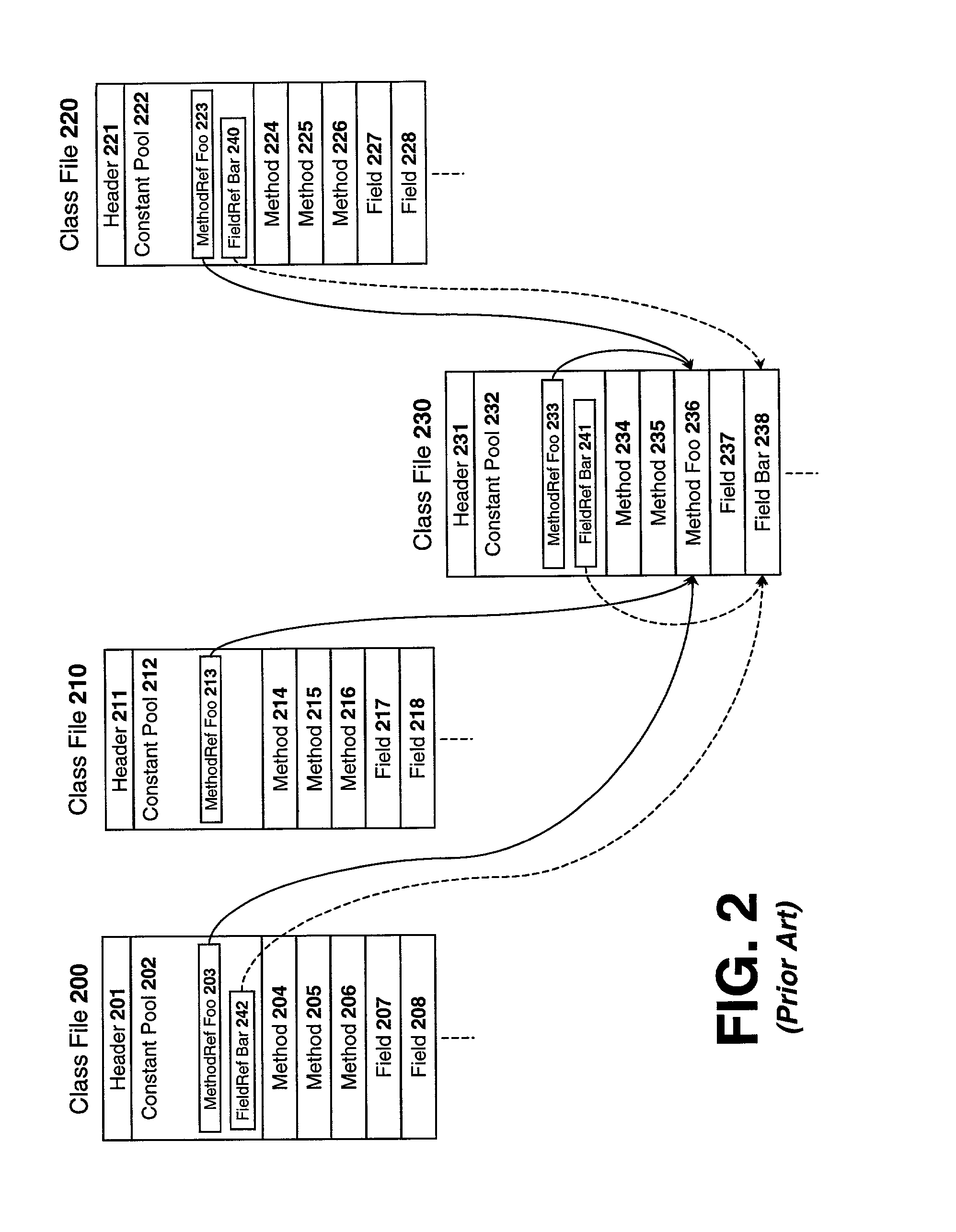
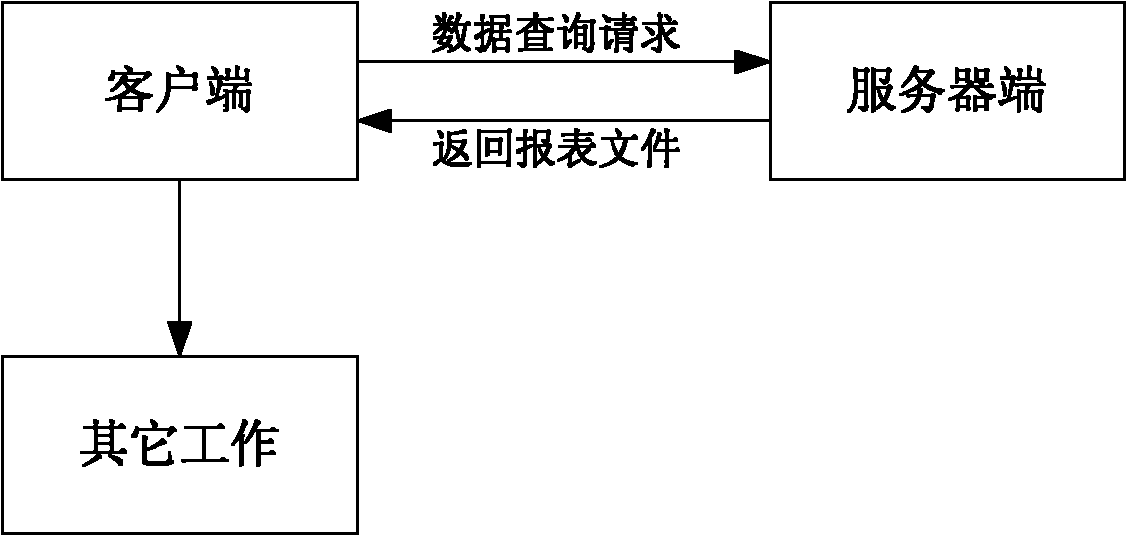
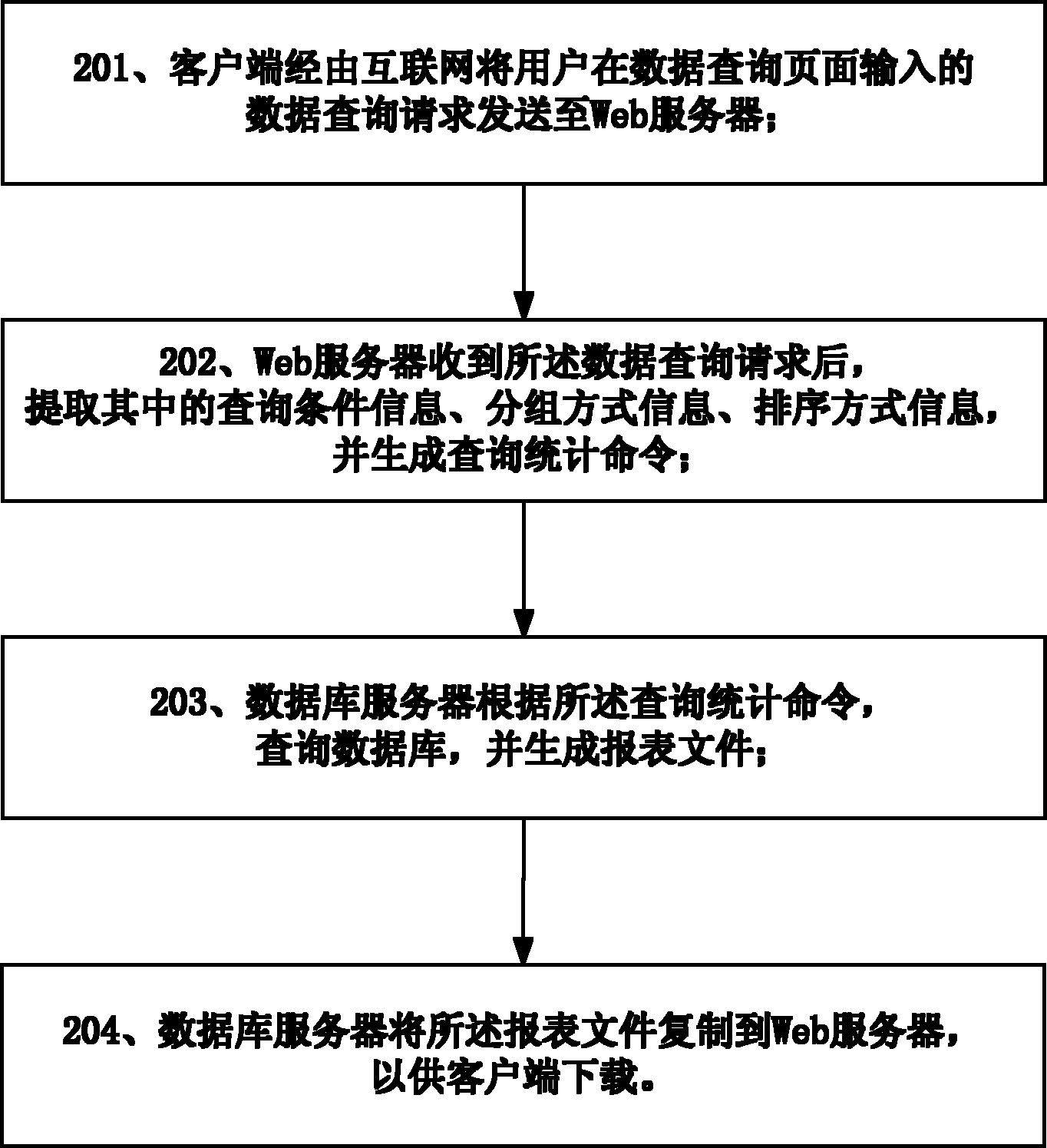
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "File replication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
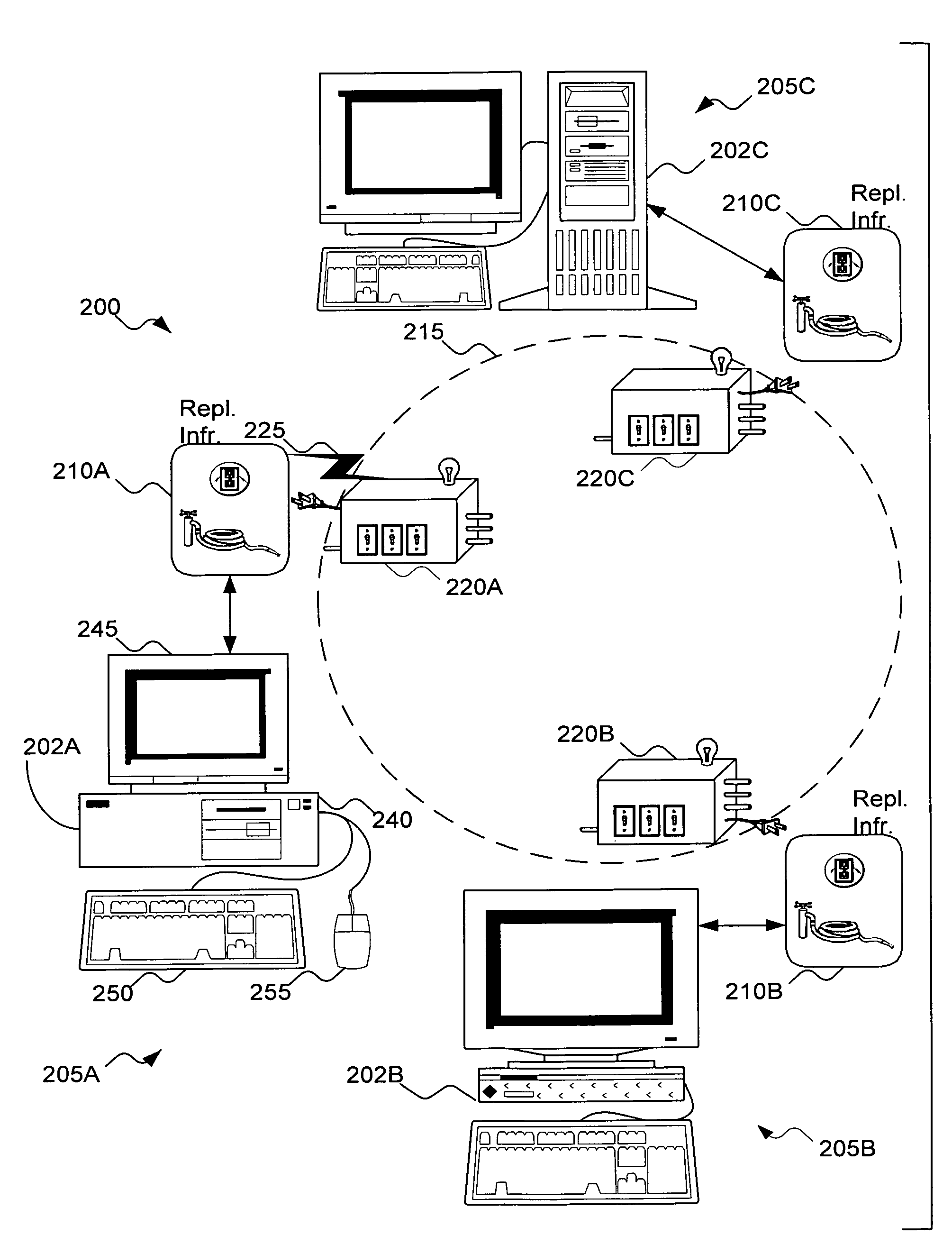
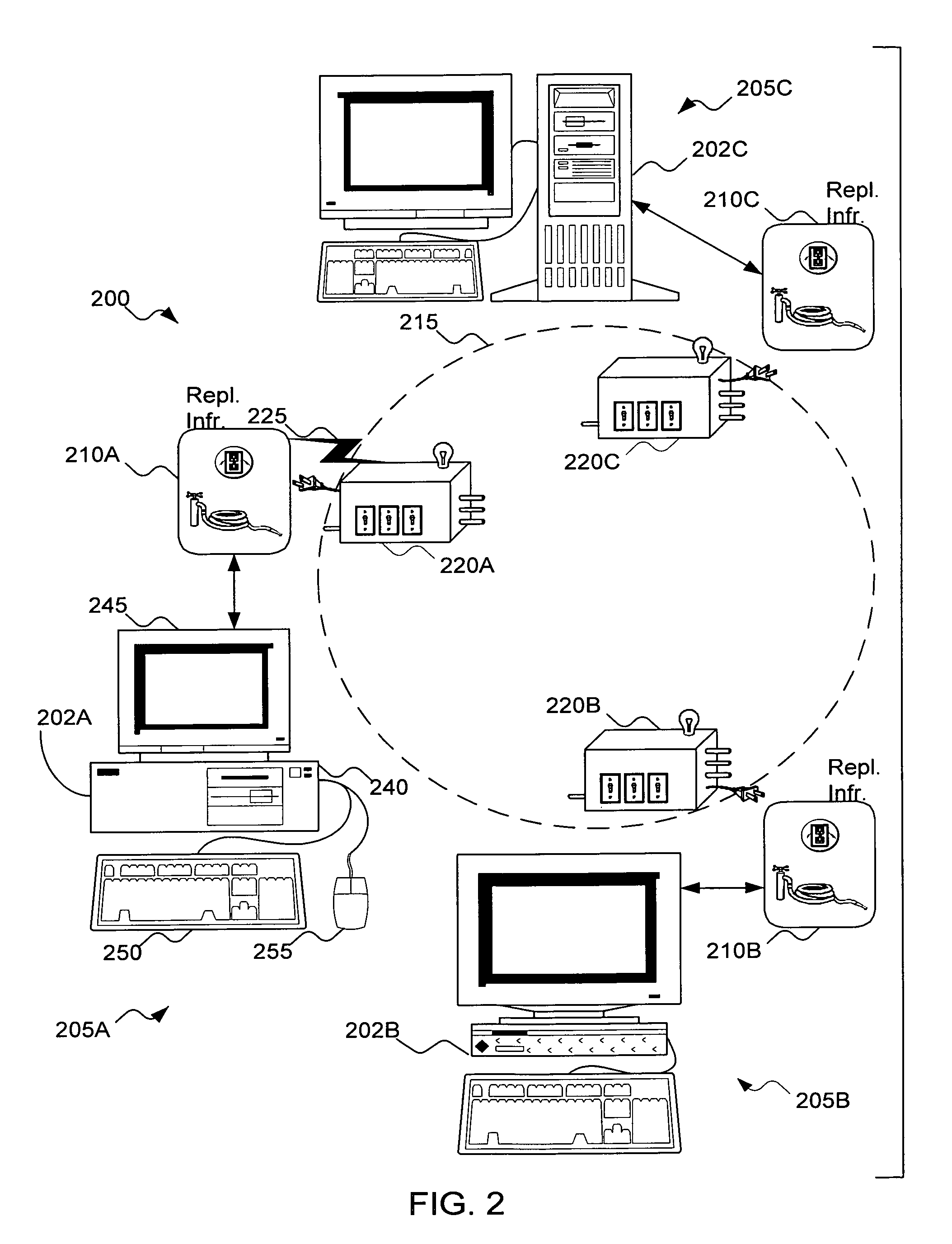
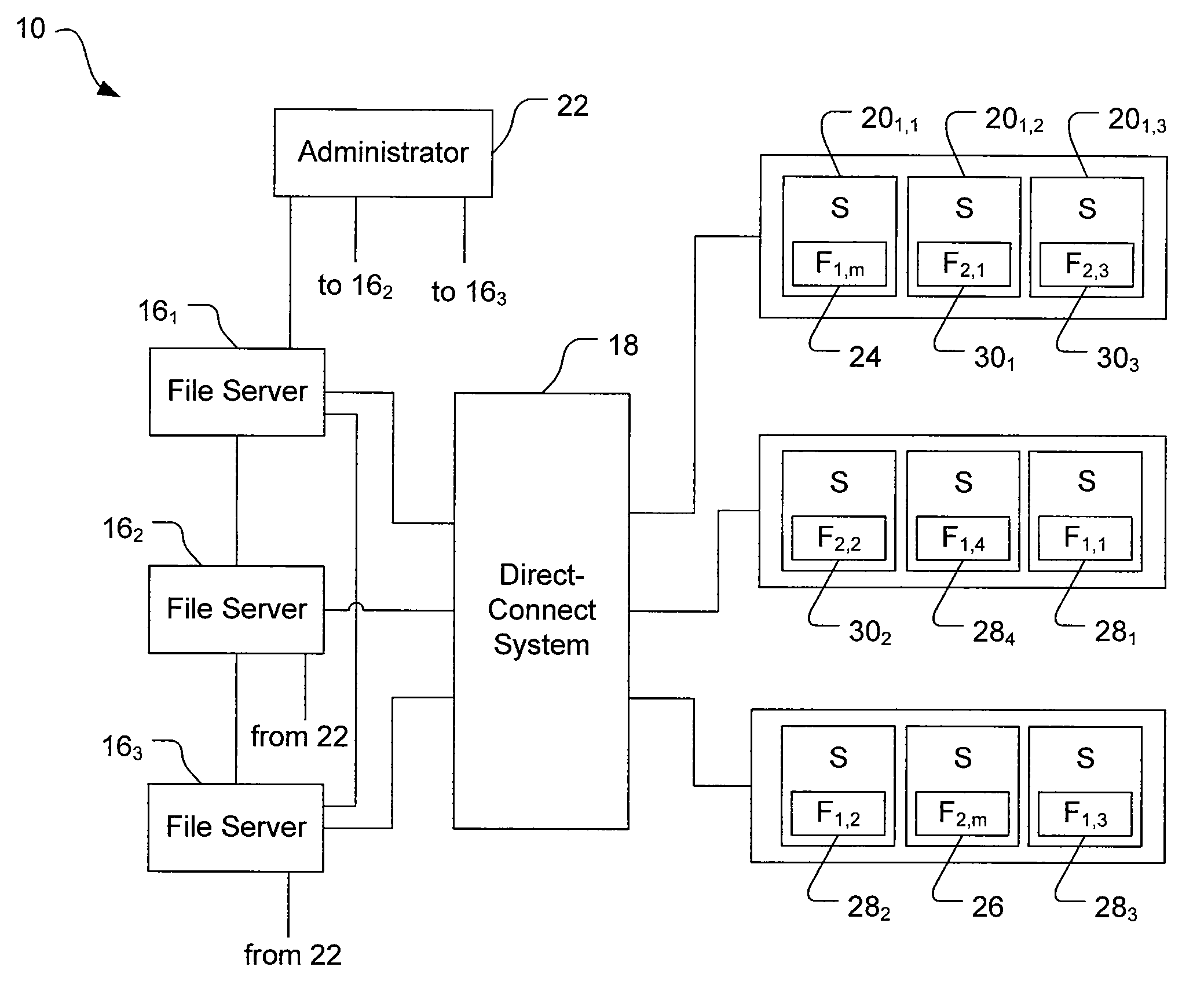
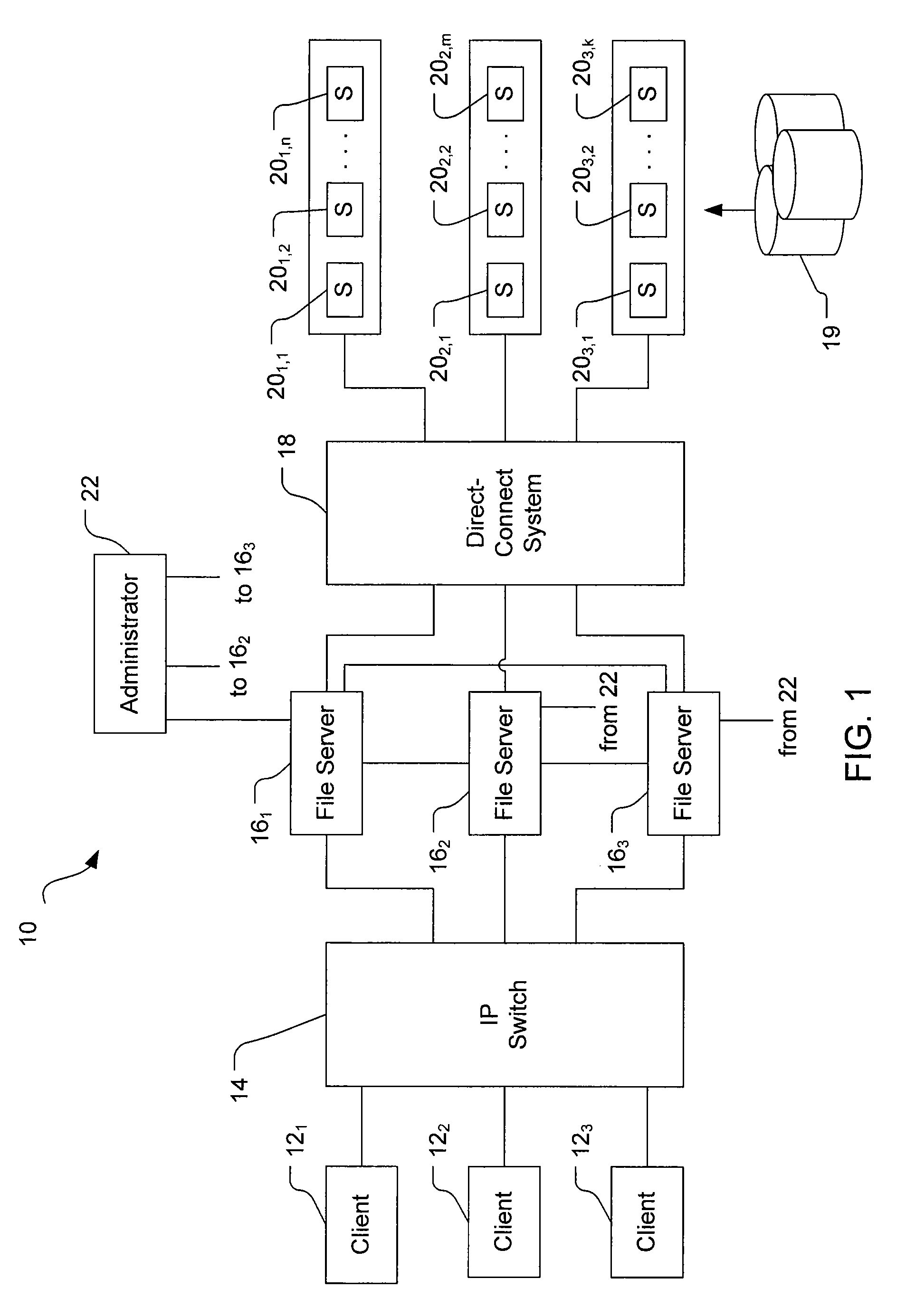
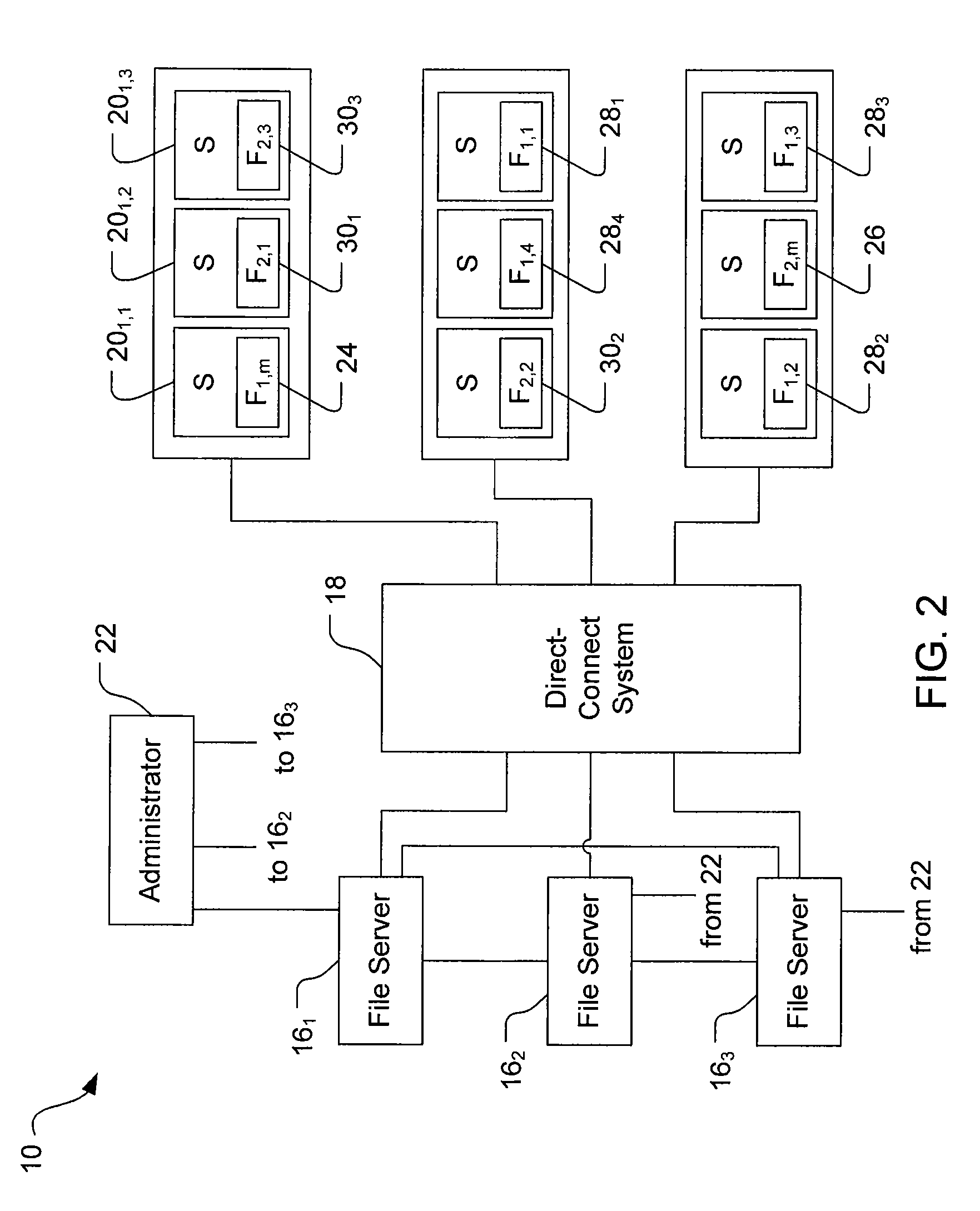
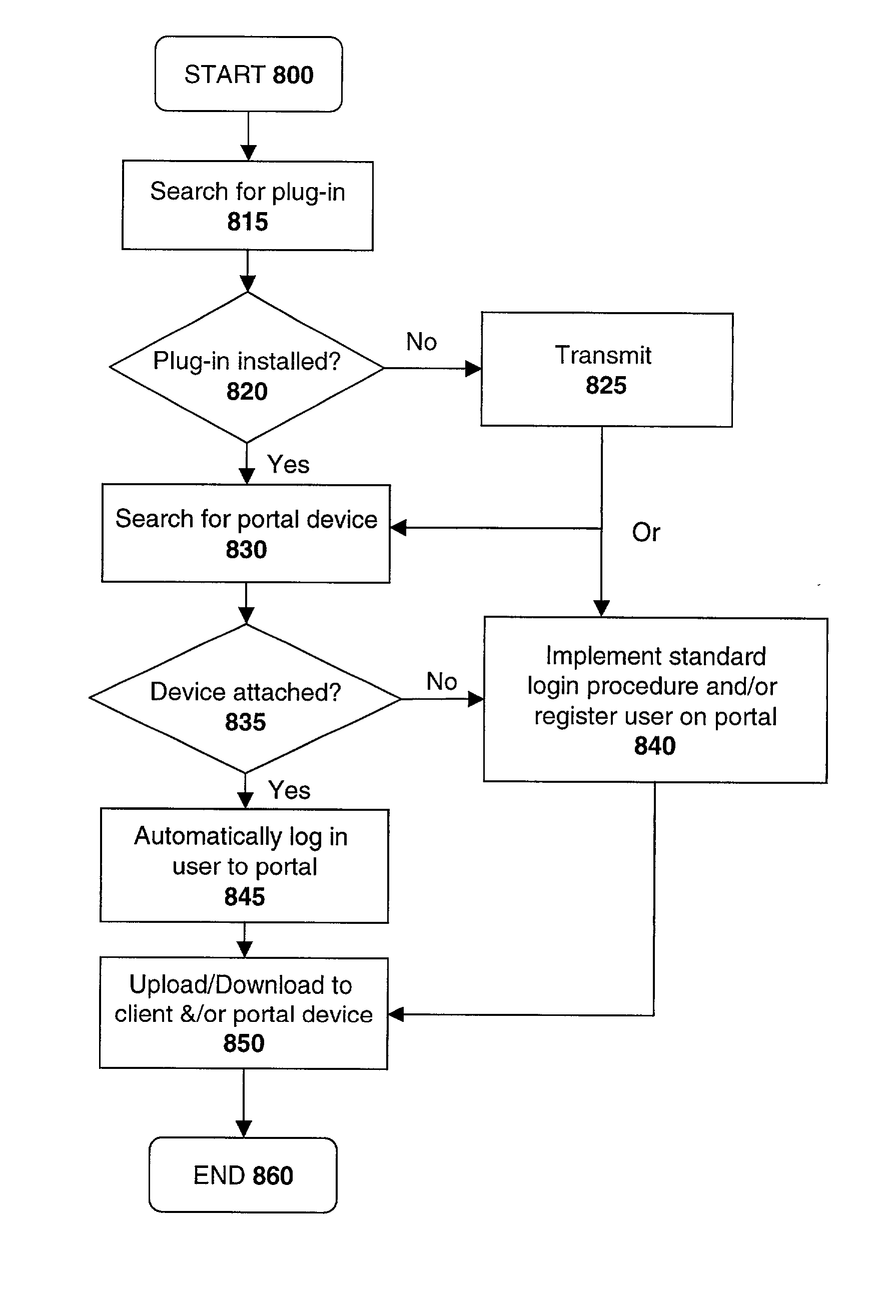
File Replication Service (FRS) is a Microsoft Windows Server service for distributing shared files and Group Policy Objects. It replaced the (Windows NT) Lan Manager Replication service, and has been partially replaced by Distributed File System Replication. It is also known as NTFRS after the name of the executable file that runs the service.
Multi-protocol sharable virtual storage objects
ActiveUS20050044162A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUnixFile replication
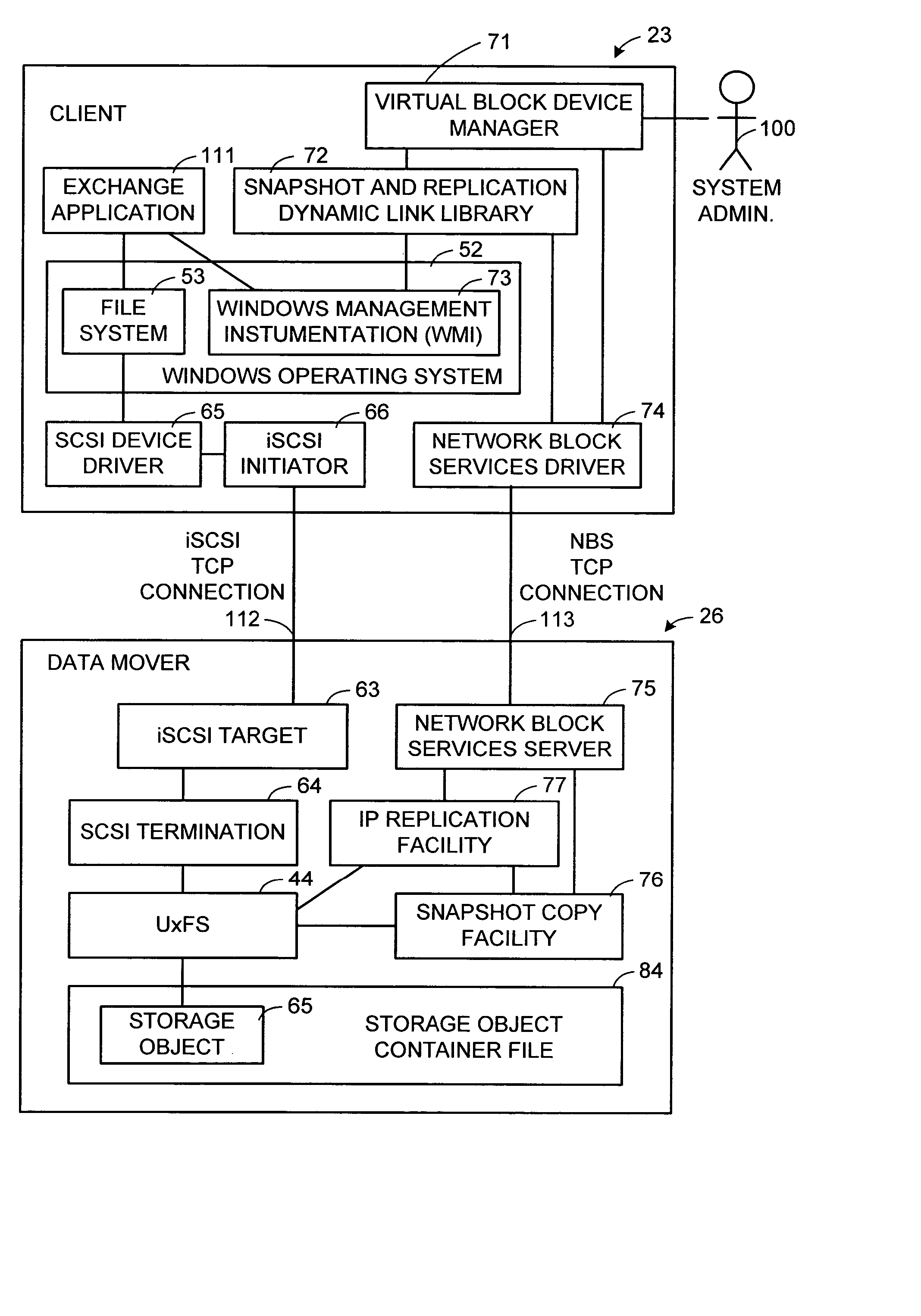
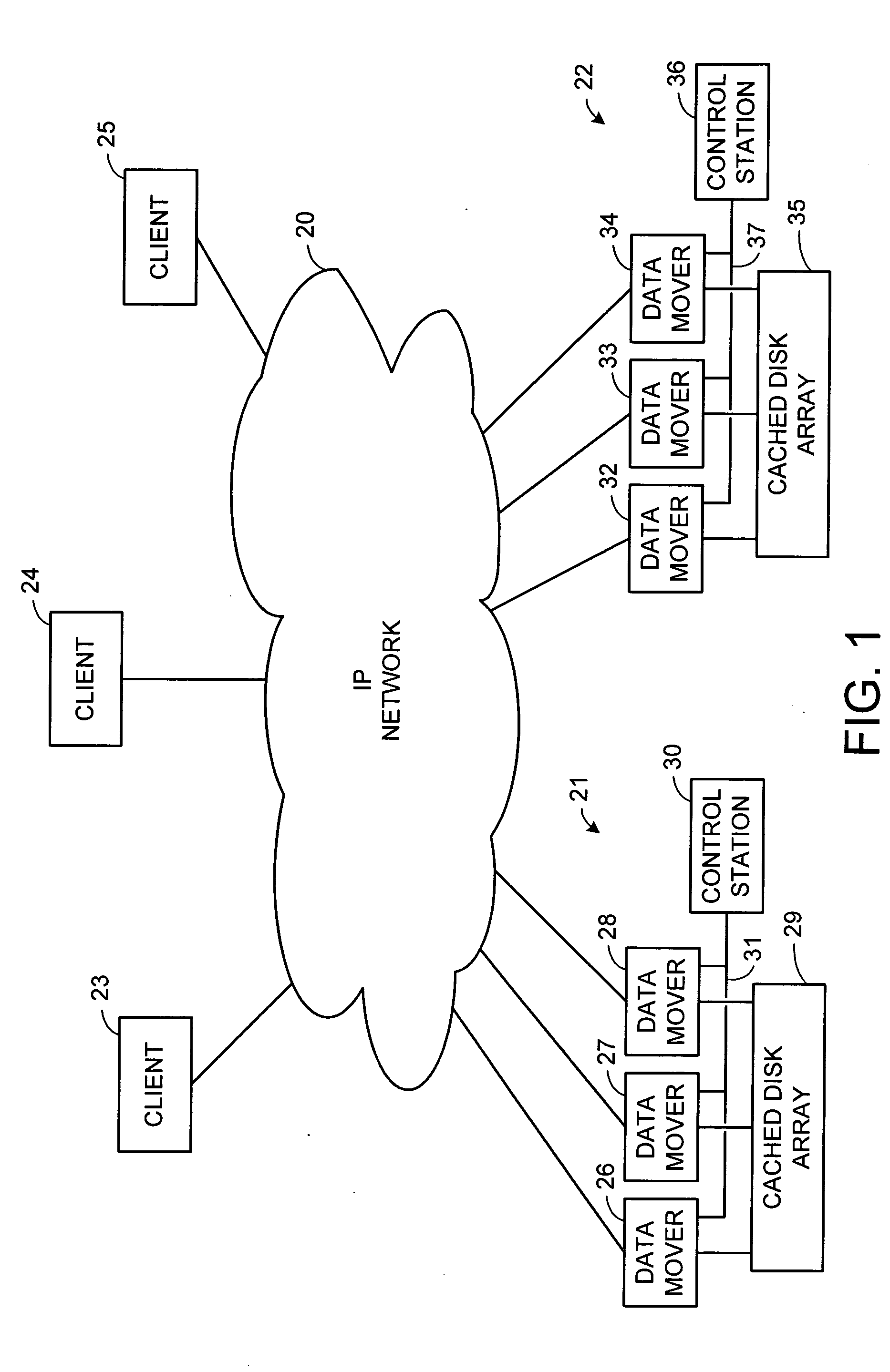
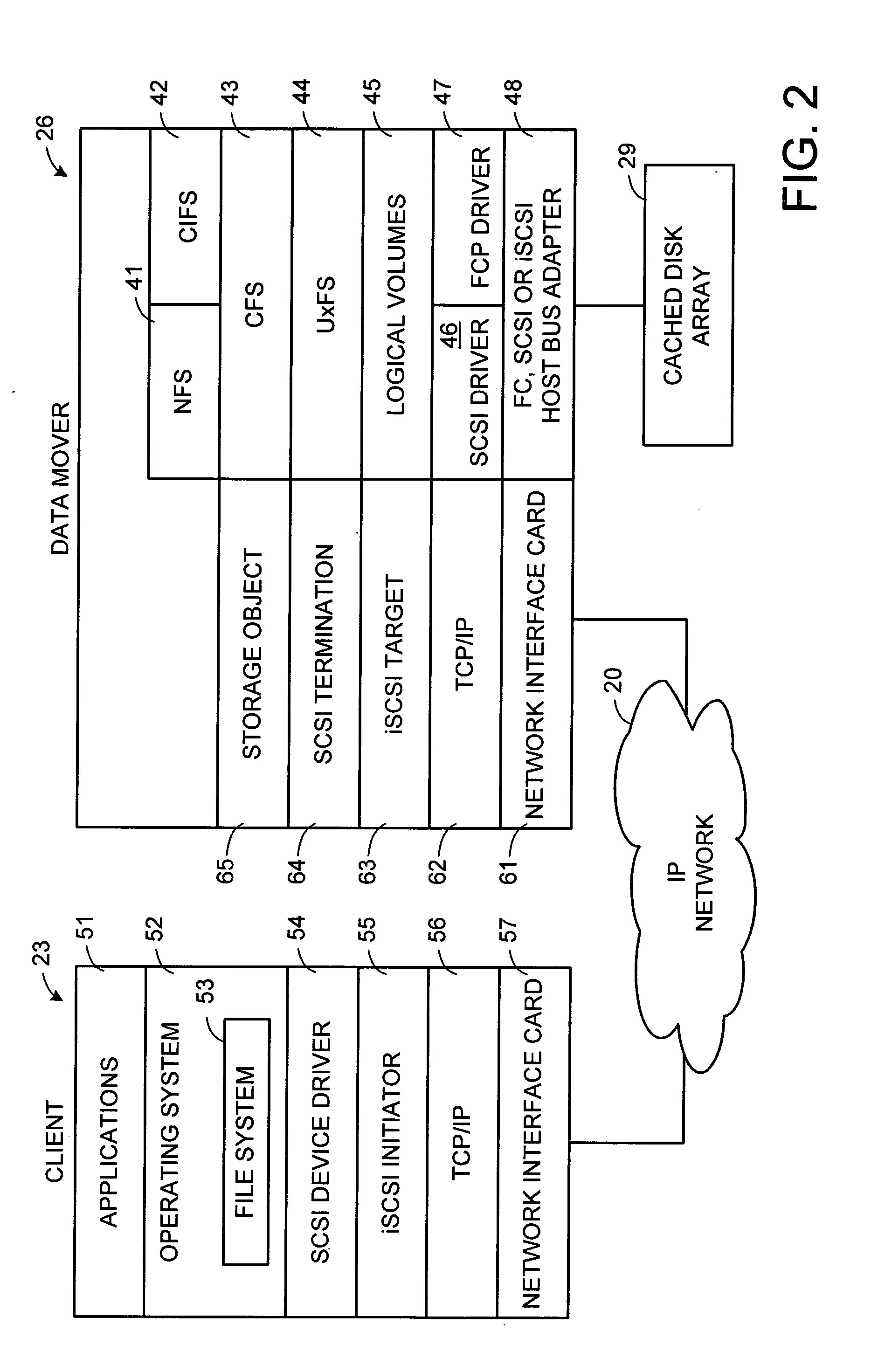
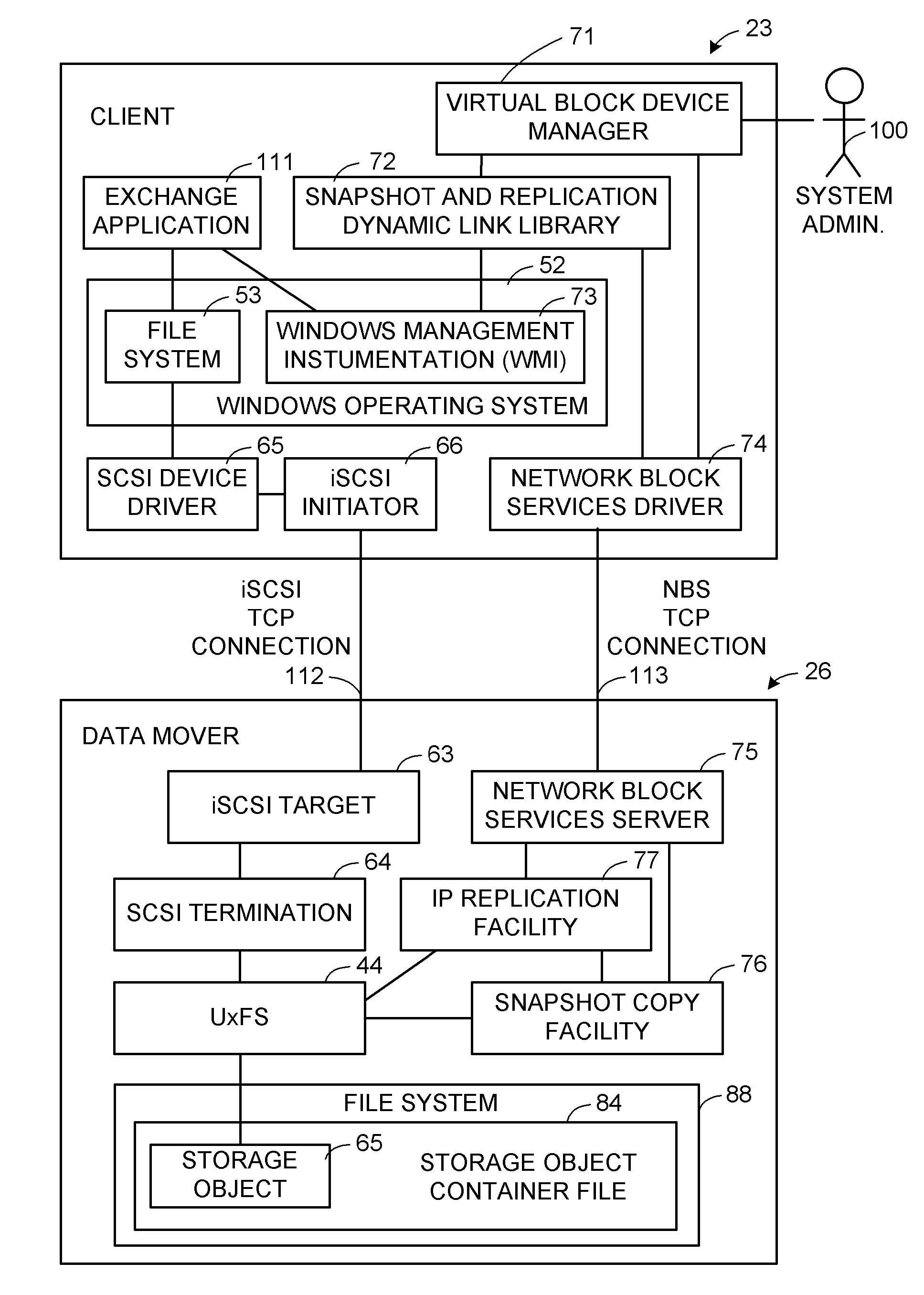
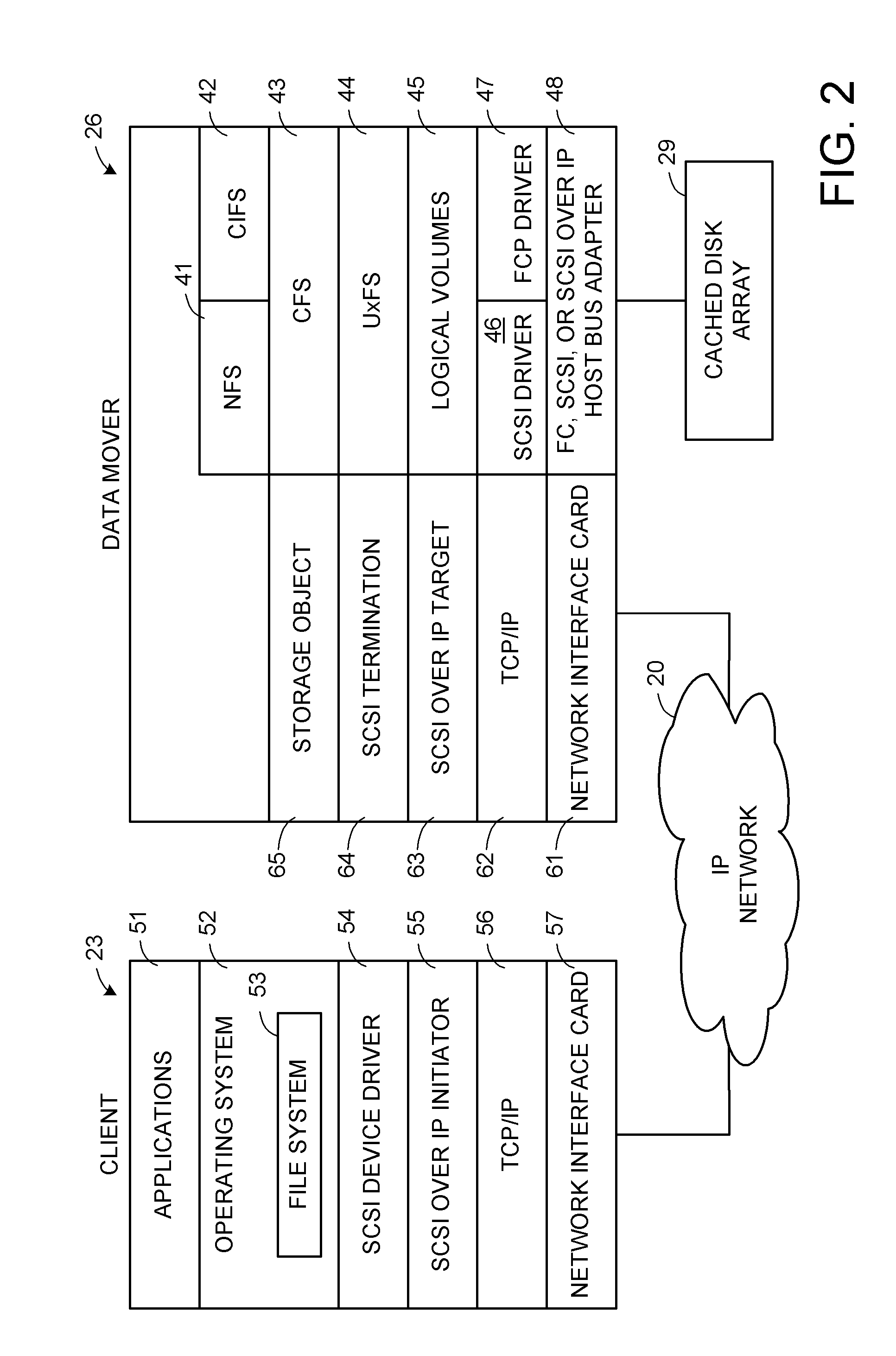
A storage object such as a virtual disk drive or a raw logical volume is contained in a UNIX compatible file so that the file containing the storage object can be exported using the NFS or CIFS protocol and shared among UNIX and MS Windows clients or servers. The storage object can be replicated and backed up using conventional file replication and backup facilities without disruption of client access to the storage object. For client access to data of the storage object, a software driver accesses the file containing the storage object. For example, a software driver called a virtual SCSI termination is used to access a file containing a virtual SCSI disk drive. Standard storage services use the iSCSI protocol to access the virtual SCSI termination. An IP replication or snapshot copy facility may access the file containing the virtual SCSI disk drive using a higher-level protocol.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Data replication facility for distributed computing environments
ActiveUS7054910B1Avoid configurationAvoid point of failureDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile replicationDistributed Computing Environment
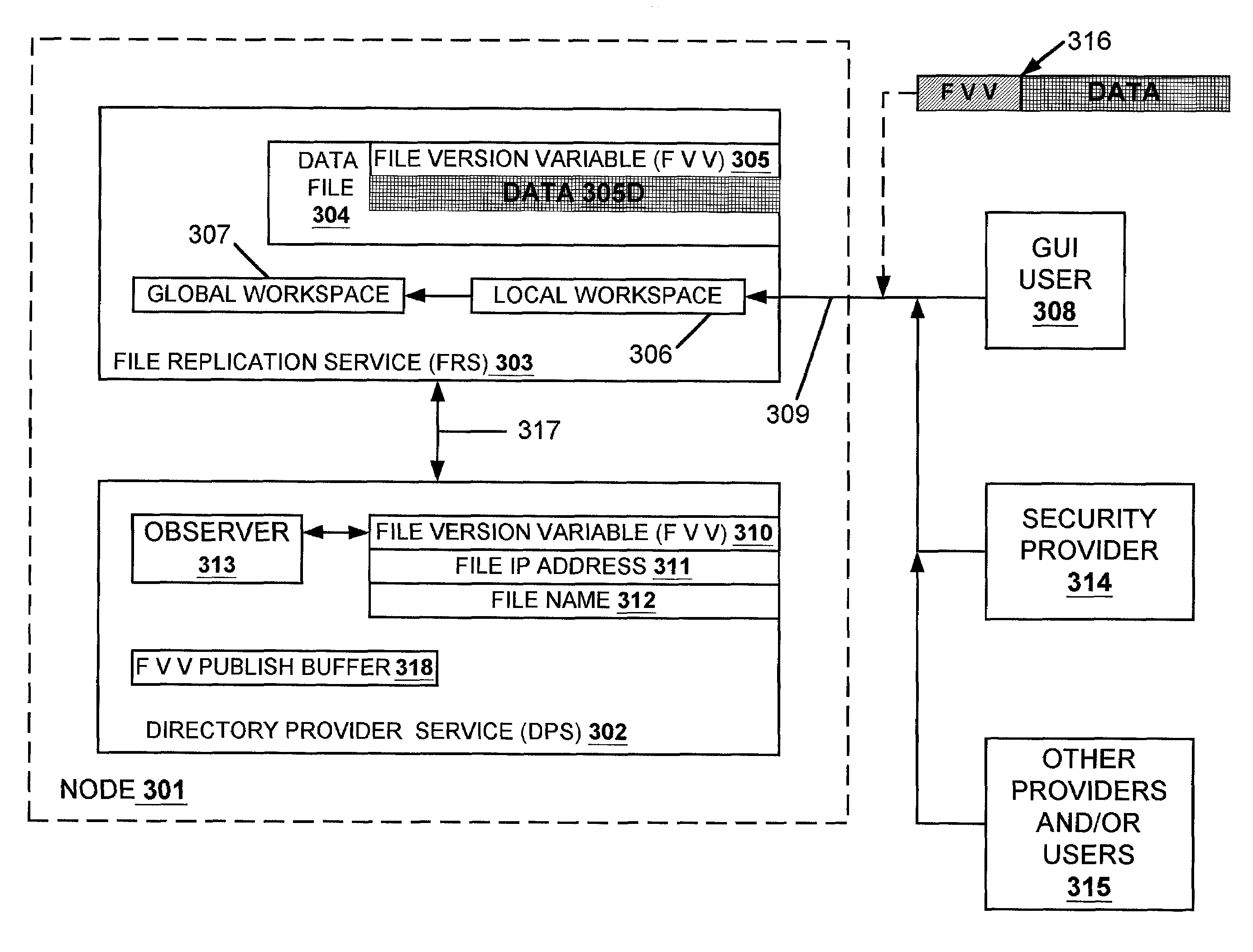
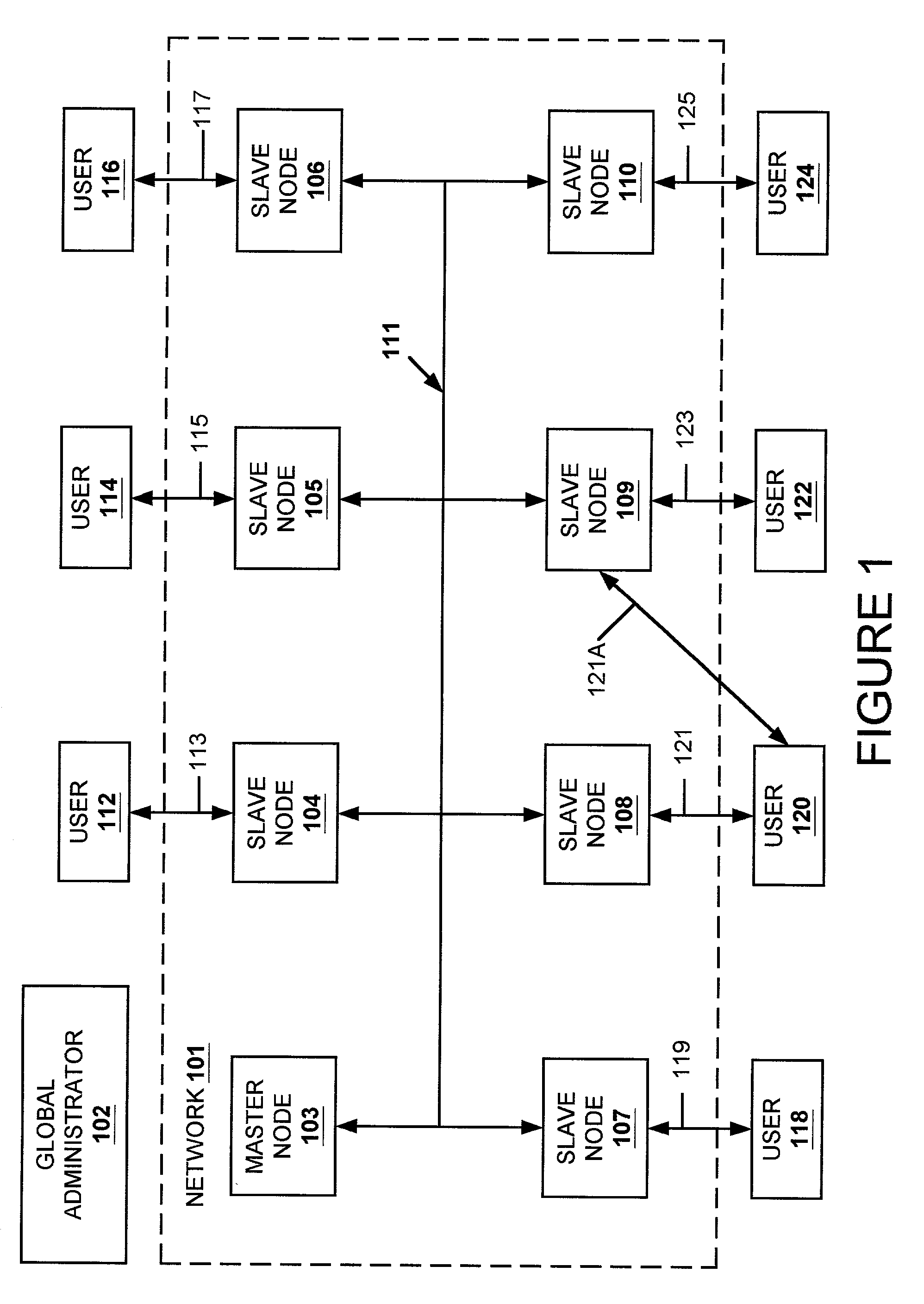
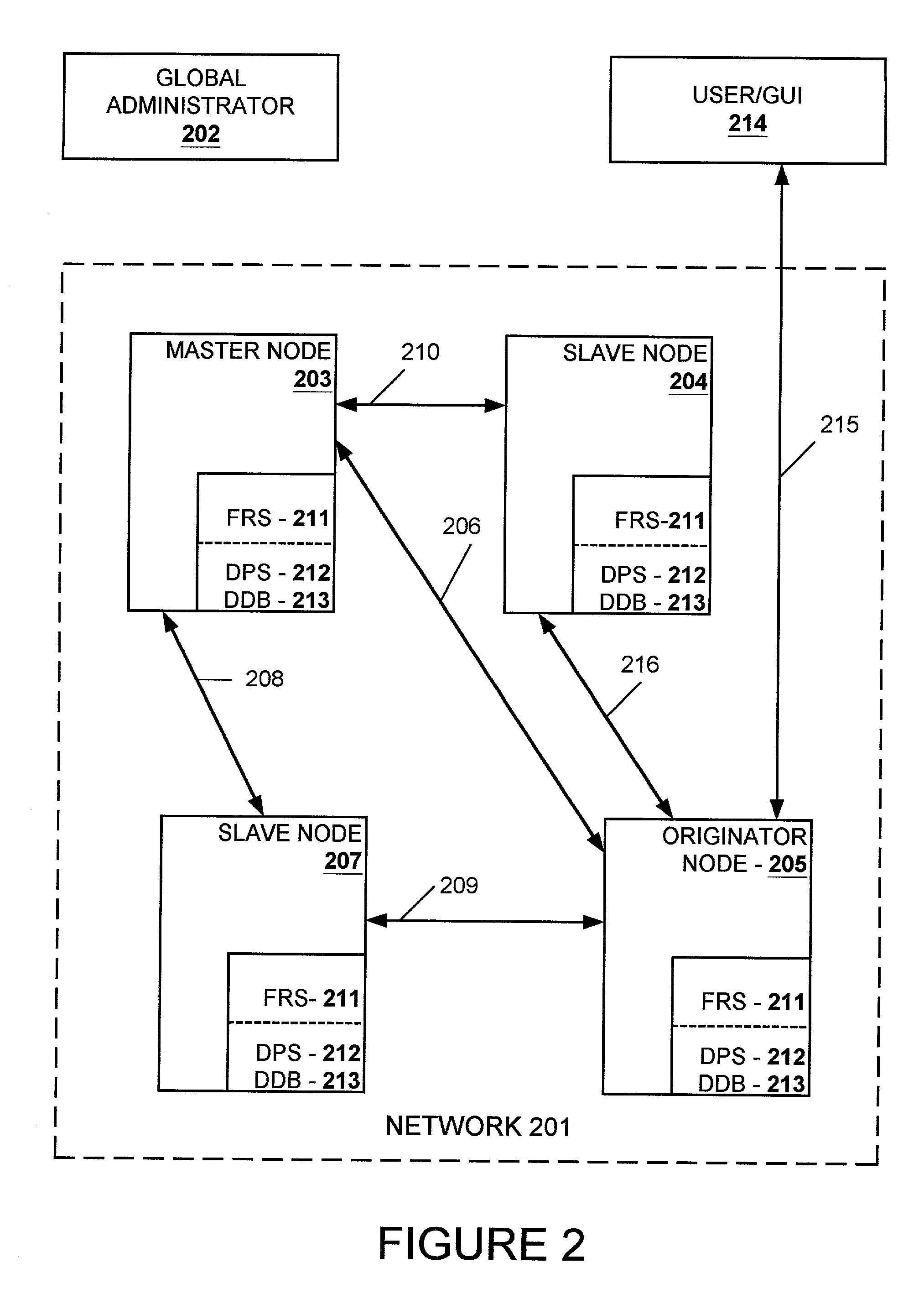
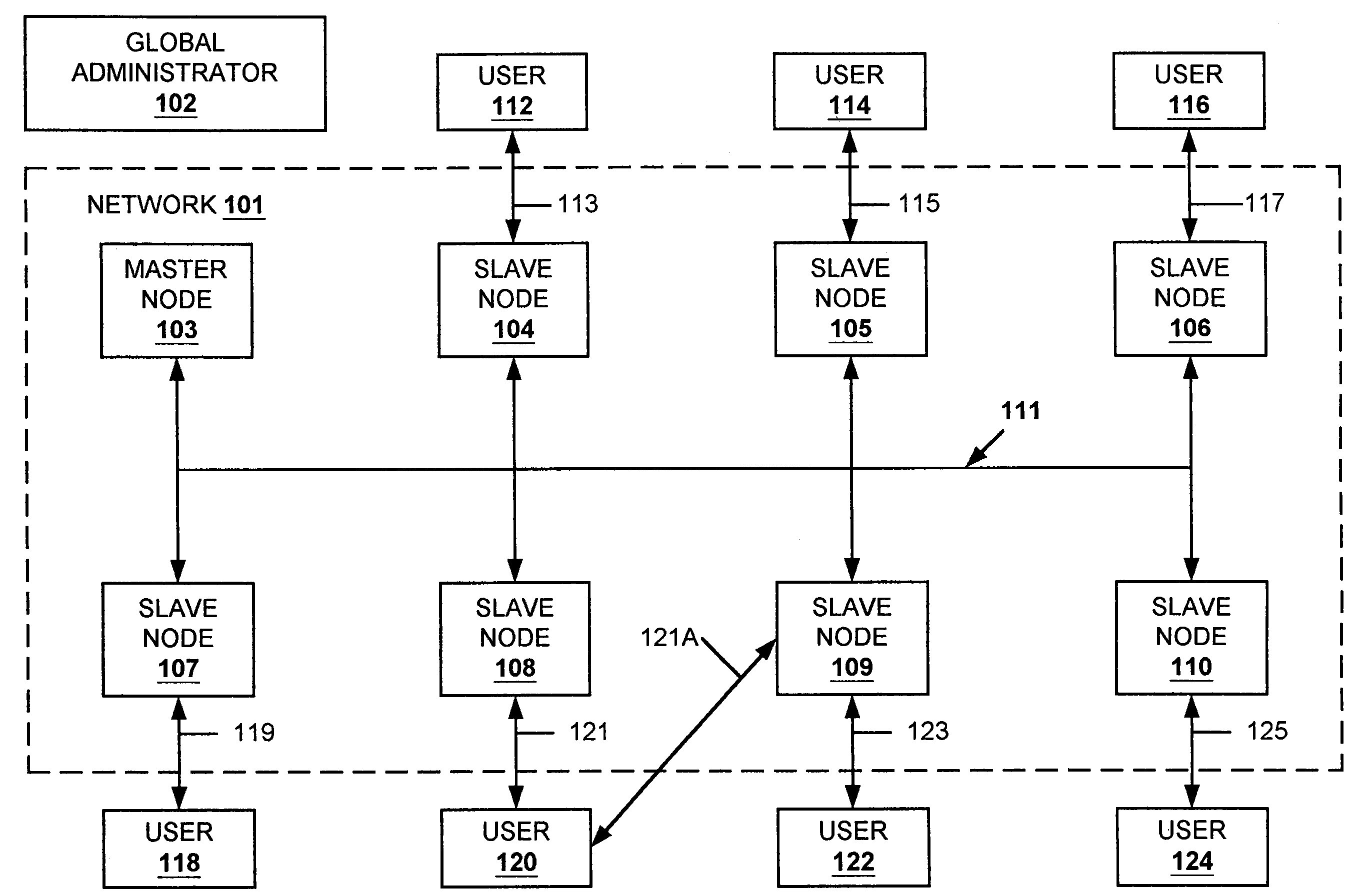
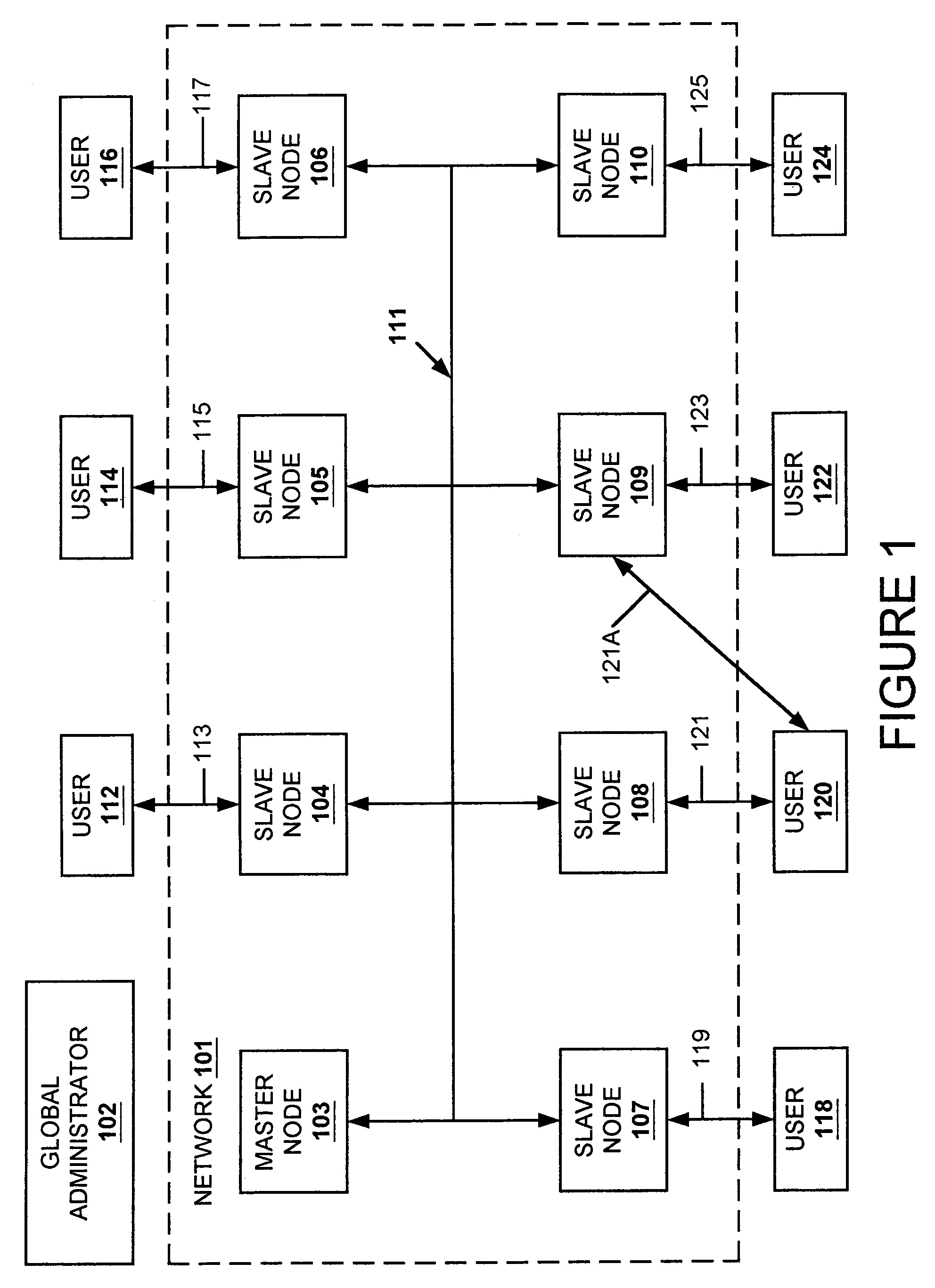
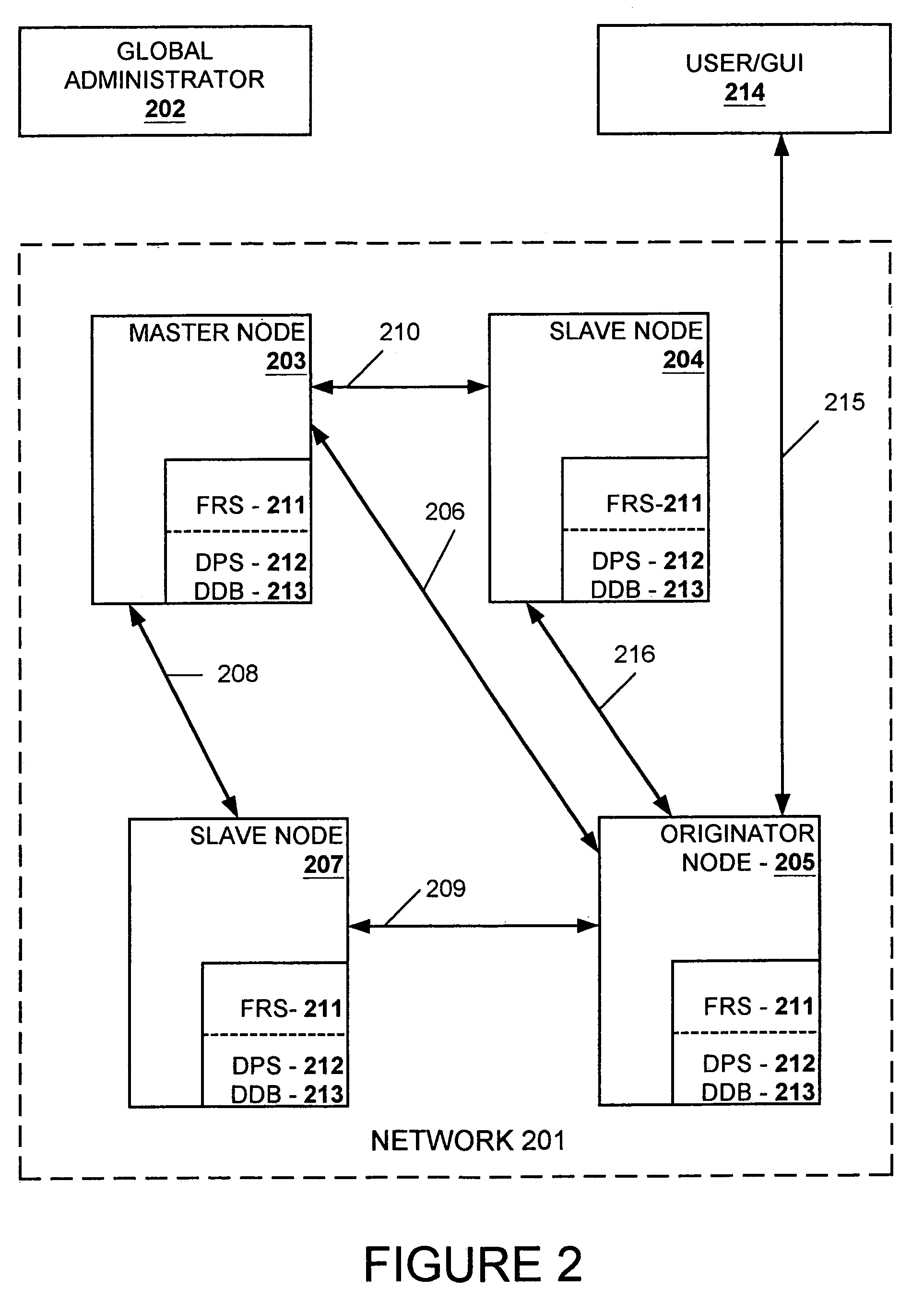
A data replication facility for distributed computing environments. A computer network having a plurality of network nodes utilizes a distributed directory provider service (DPS) having an established master node. The DPS supports a file replication service (FRS). The FRS establishes one of the nodes as originator node which receives new or updated files from one or more user / GUIs and / or from one or more software providers such as a security provider. The originator node in cooperation with the master node establish a backup copy of the new or updated file in the master node. Thereafter, the originator node publishes a File Version Variable (FVV) representation of the new or updated file to other network nodes (slave nodes) which obtain such file from the originator or, if need be, from the backup master node. Object observers are utilized to determine changes to the file version variables thereby triggering the downloading of new or updated files into the network nodes, whereby data file replication is accomplished throughout the network. In addition to avoiding a single point of failure, embodiments of the present invention also are network-topology independent. Additional syncing threads are employed as part of the file replication service to further ensure synchronization of the network nodes' data files within a predetermined interval, regardless of network failure modes. Embodiments of the present invention are particularly useful with networks of the client-server storage network variety.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
File replication system, replication control method, and storage medium
InactiveUS20010039548A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalFile replicationCopy control
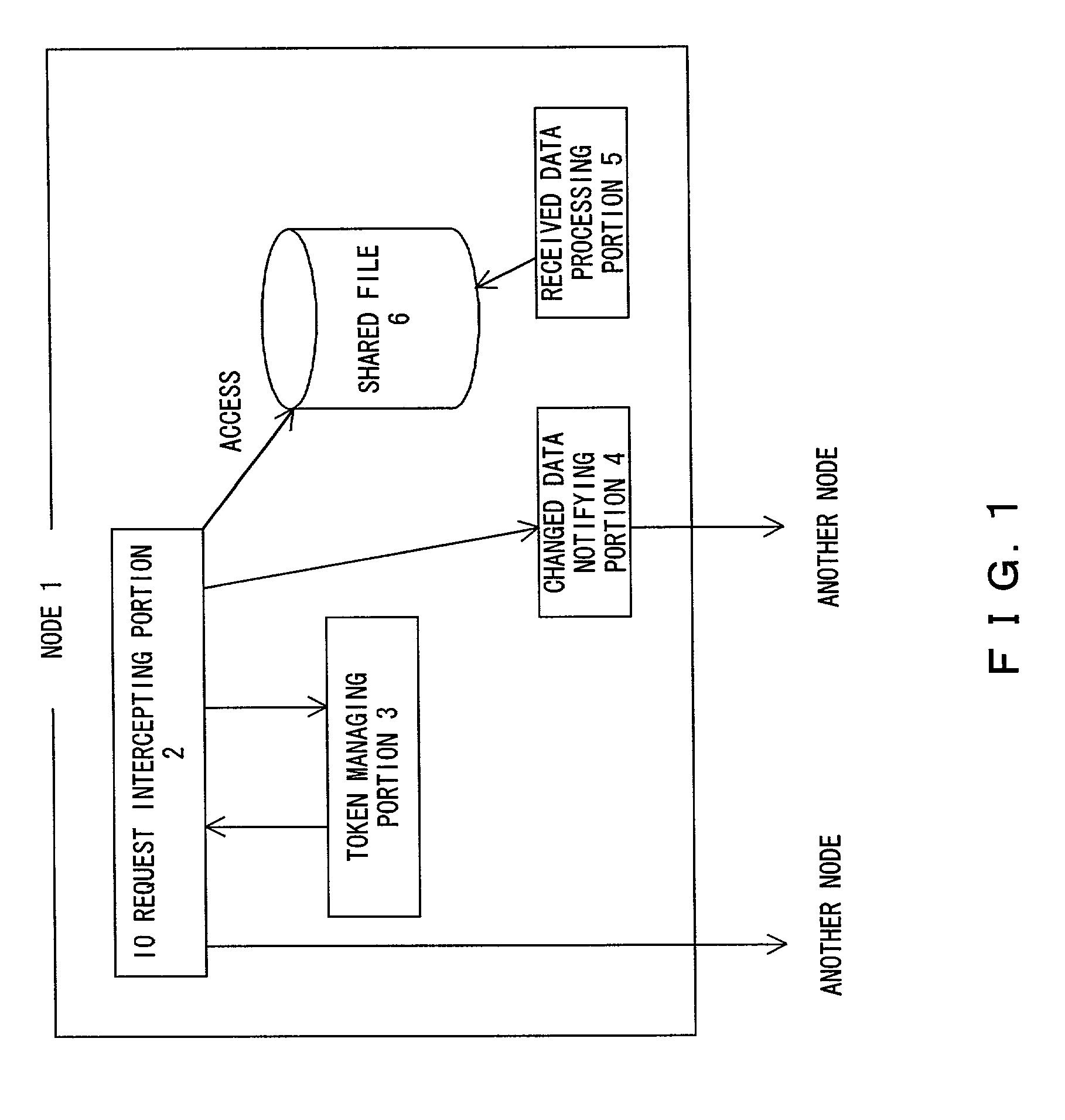
A token managing portion manages an access request for a shared file. An IO request intercepting portion asks the token managing portion to acquire access permission for the shared file in response to an access request for the shared file in the node itself. The token managing portion notifies the IO request intercepting portion of a node that has update permission in response to the access request of the IO request intercepting portion. The IO request intercepting portion asks the node that has the update permission to access the shared file when the IO request intercepting portion is not capable of acquiring the access permission. Thus, with a file consistent assurance control, a file replication system as an improved application of a file replication can be accomplished.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Peer-to-peer enterprise storage
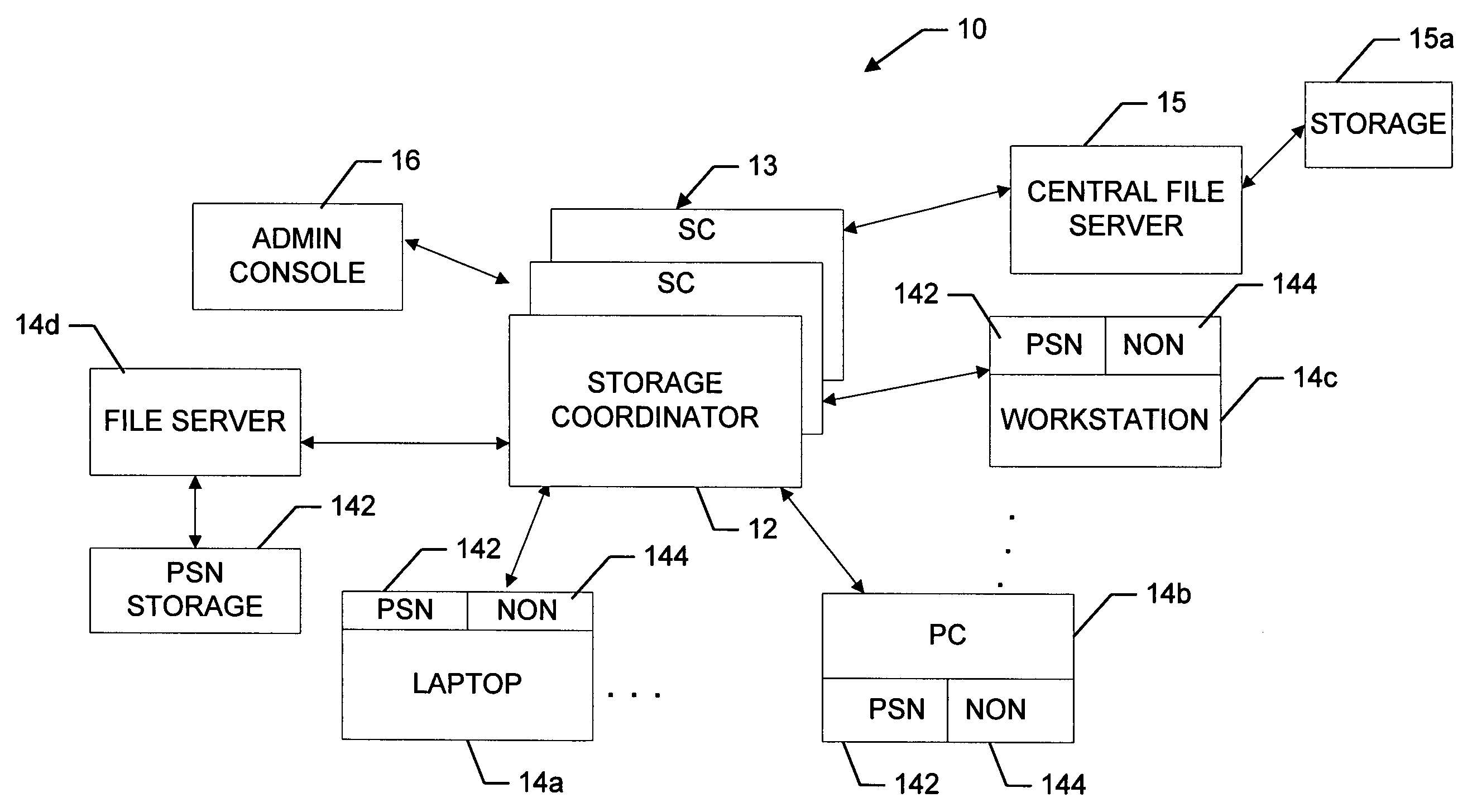
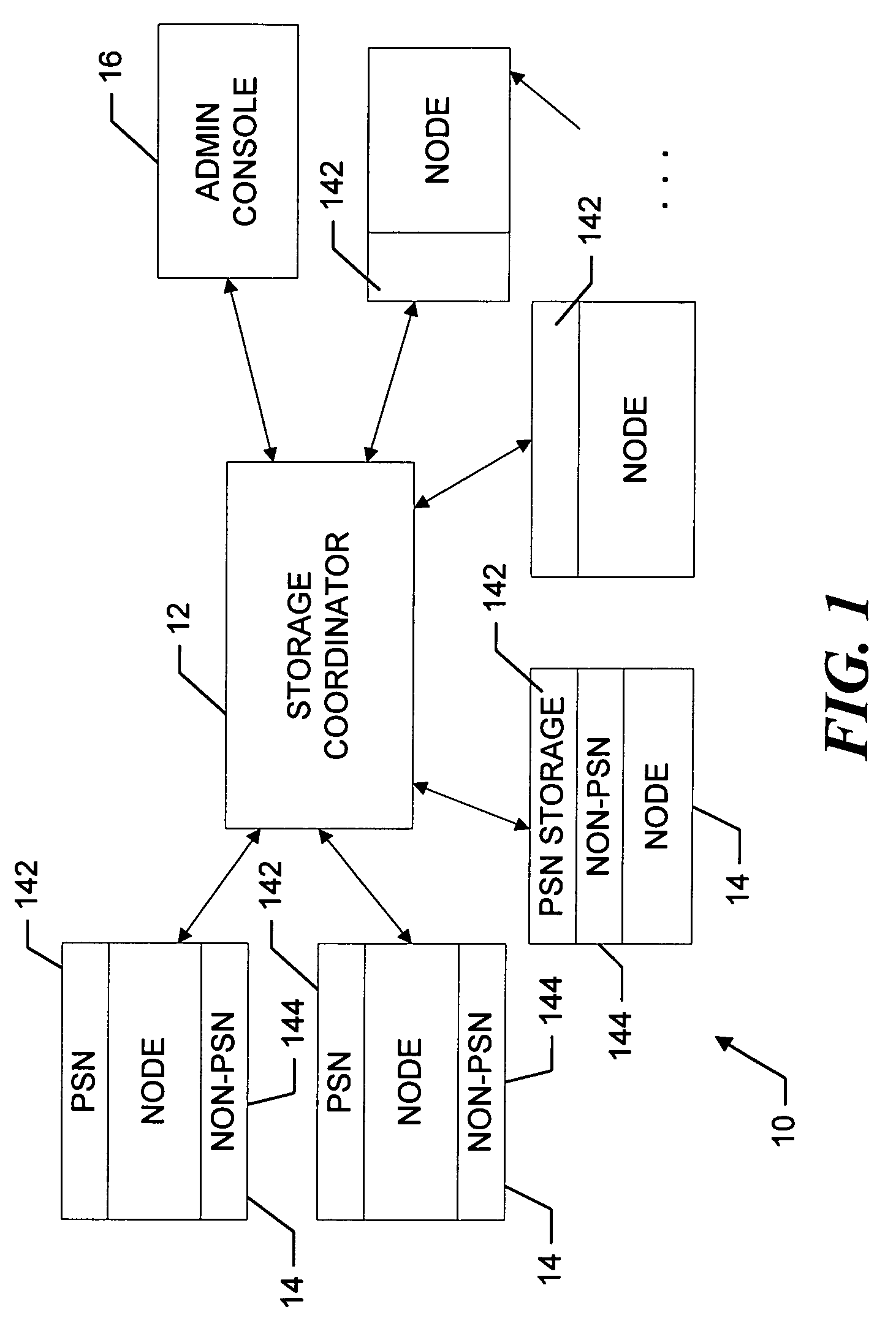
InactiveUS7069295B2Quantity minimizationMaximize rangeDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationFile replicationNear neighbor
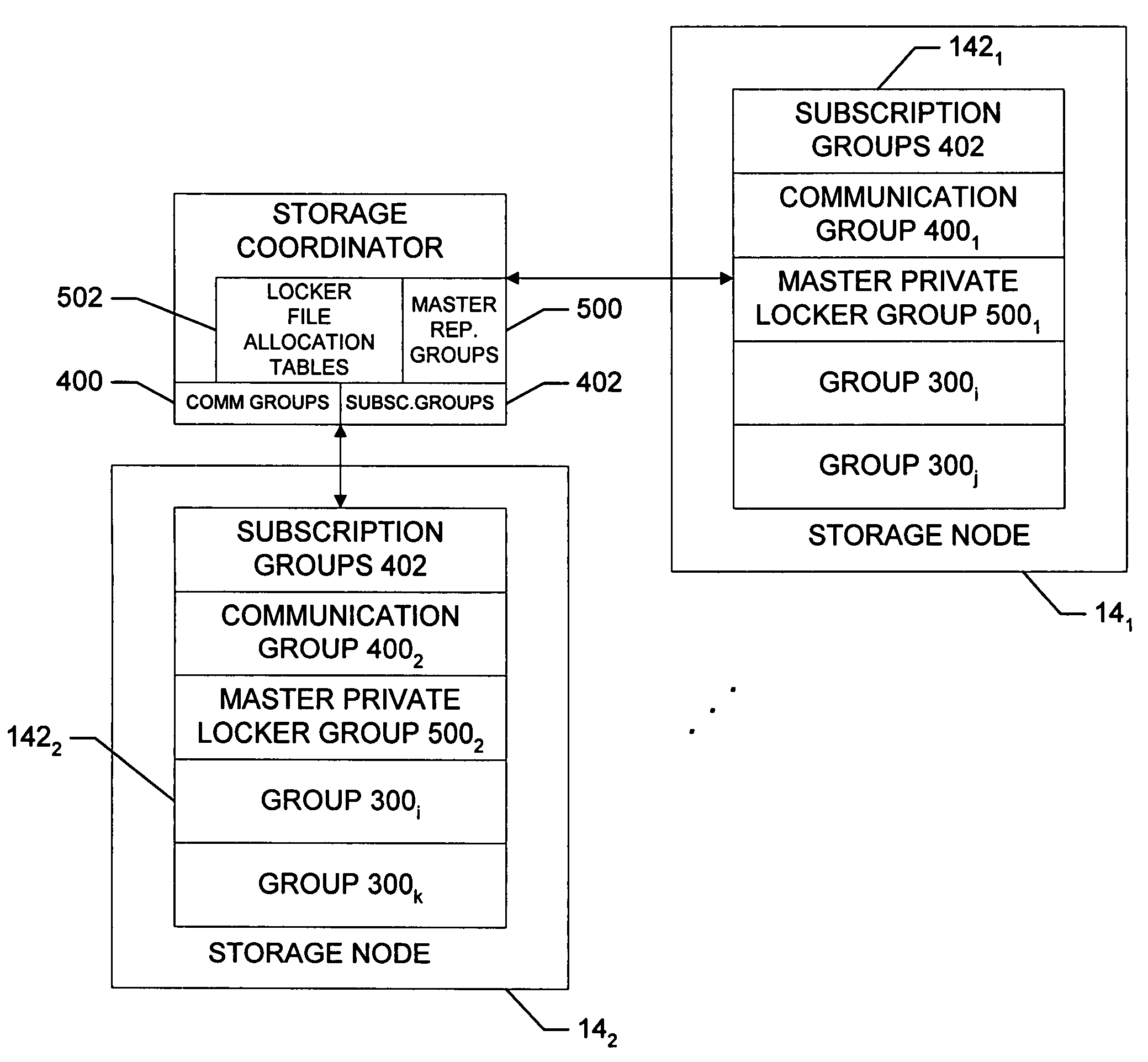
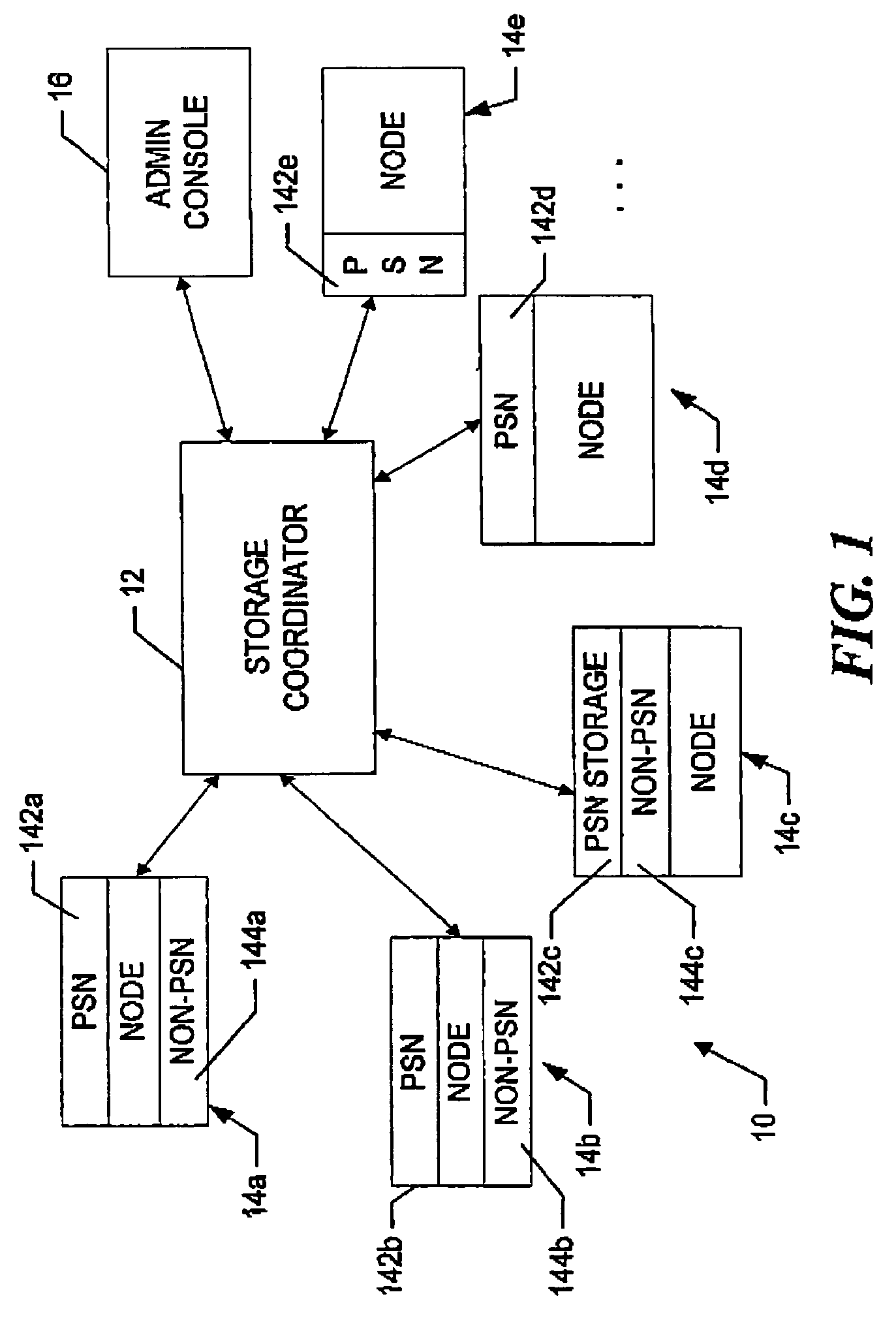
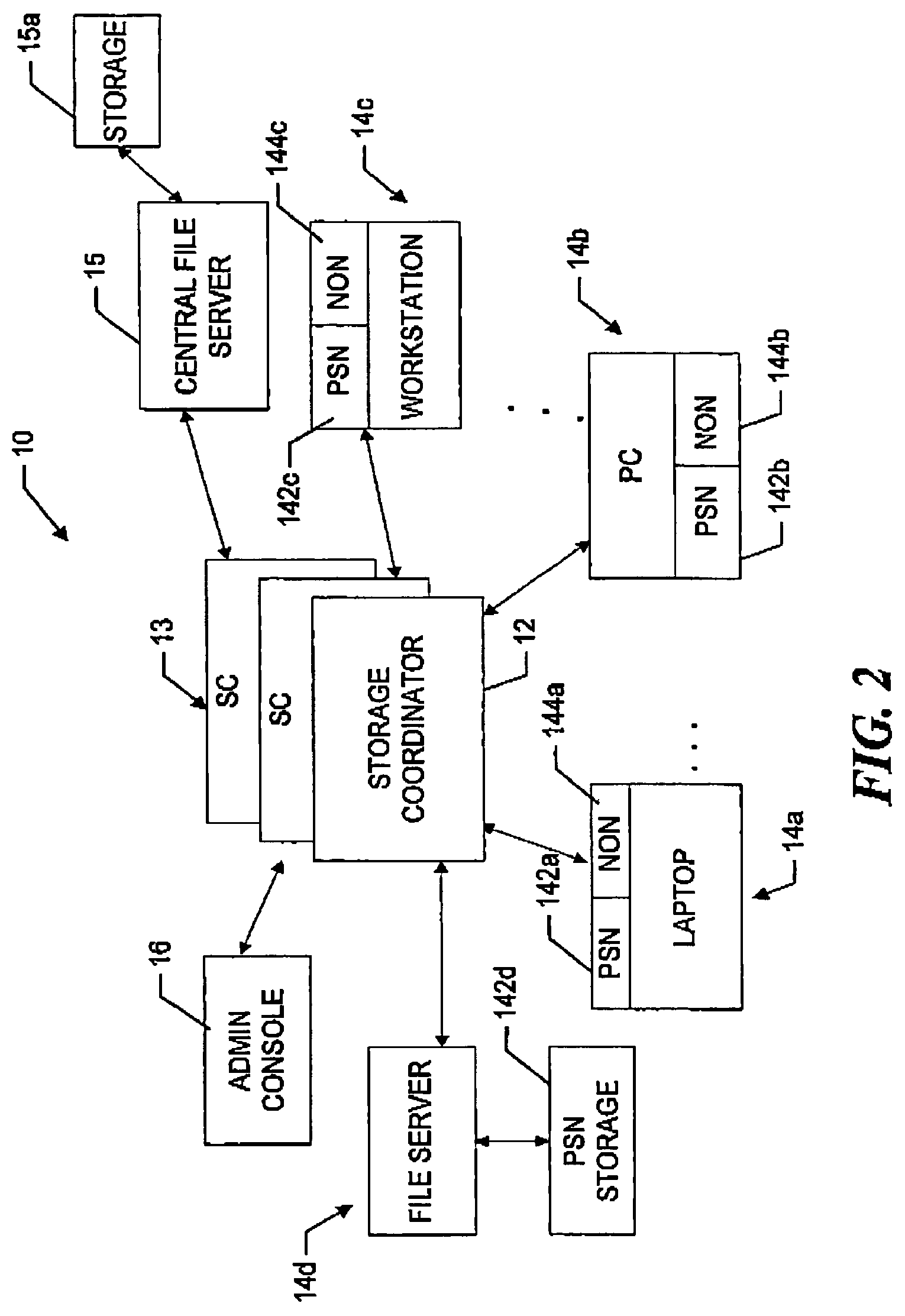
A peer-to-peer storage system includes a storage coordinator that centrally manages distributed storage resources in accordance with system policies administered through a central administrative console. The storage resources, or “nodes,” are otherwise unused portions of storage media, e.g., hard disks, that are included in the devices such as personal computers, workstations, laptops, file servers, and so forth, that are connected to a corporate computer network, and are thus otherwise available only individually to the respective devices. The storage coordinator assigns the nodes to various “replication groups” and allocates the storage resources on each of the nodes in a given group to maintaining dynamically replicated versions of the group files. The storage nodes in a given group perform dynamic file replication and synchronization operations by communicating directly, that is, peer-to-peer, using a message-based protocol. The storage coordinator also manages distributed searches of file content on the network by selecting one node from each group to search through the associated group files. The selected nodes report the search results back to the storage coordinator, which organizes the results and provides them to the user. Thereafter, in response to a request for various files by the user, the storage coordinator instructs the nodes that are near neighbors of the user to provide the requested files. The storage coordinator thus ensures that the amount of the network bandwidth consumed by the search operation is minimized.
Owner:ESCHER GROUP
Methods and systems for file replication utilizing differences between versions of files
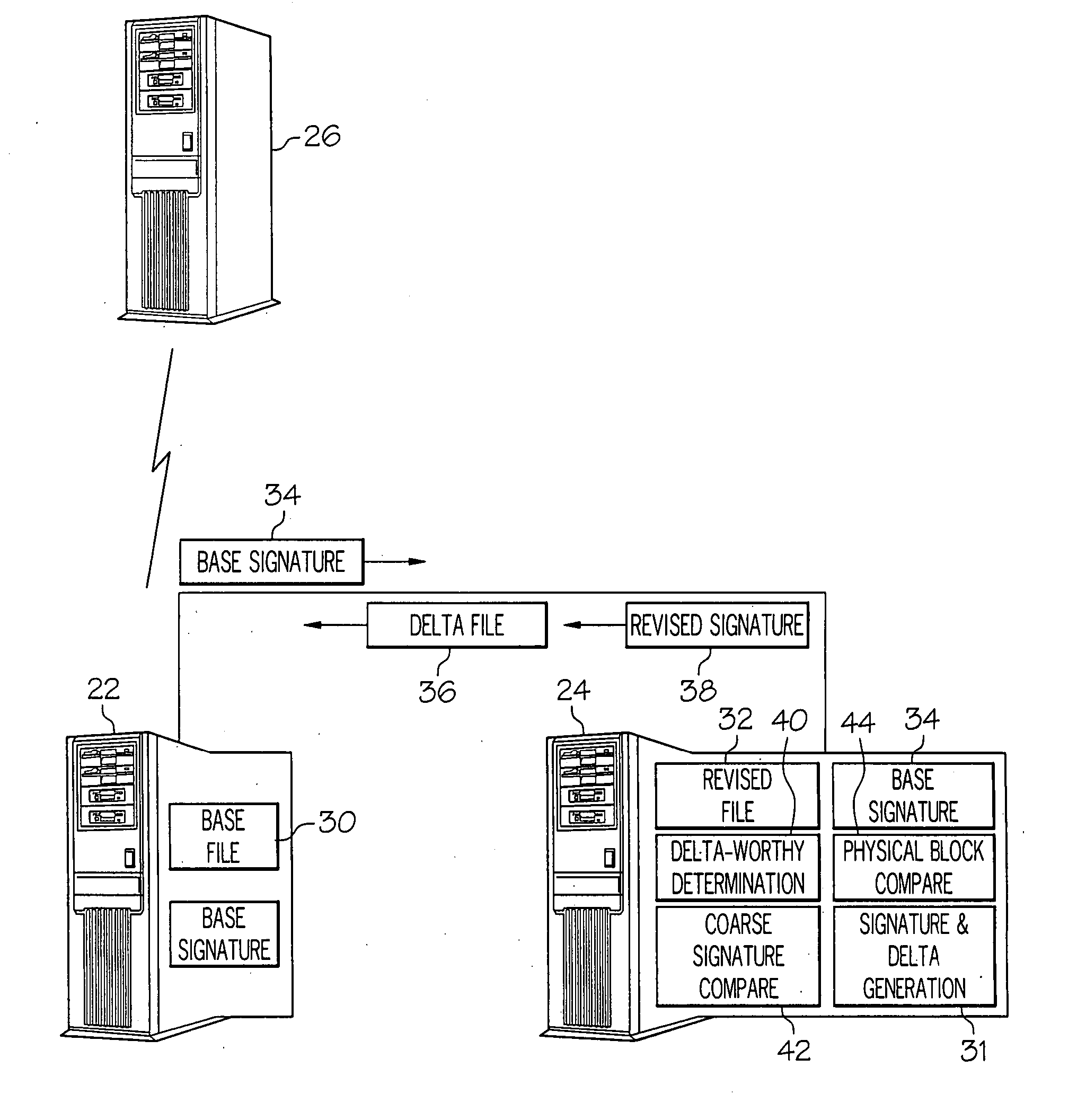
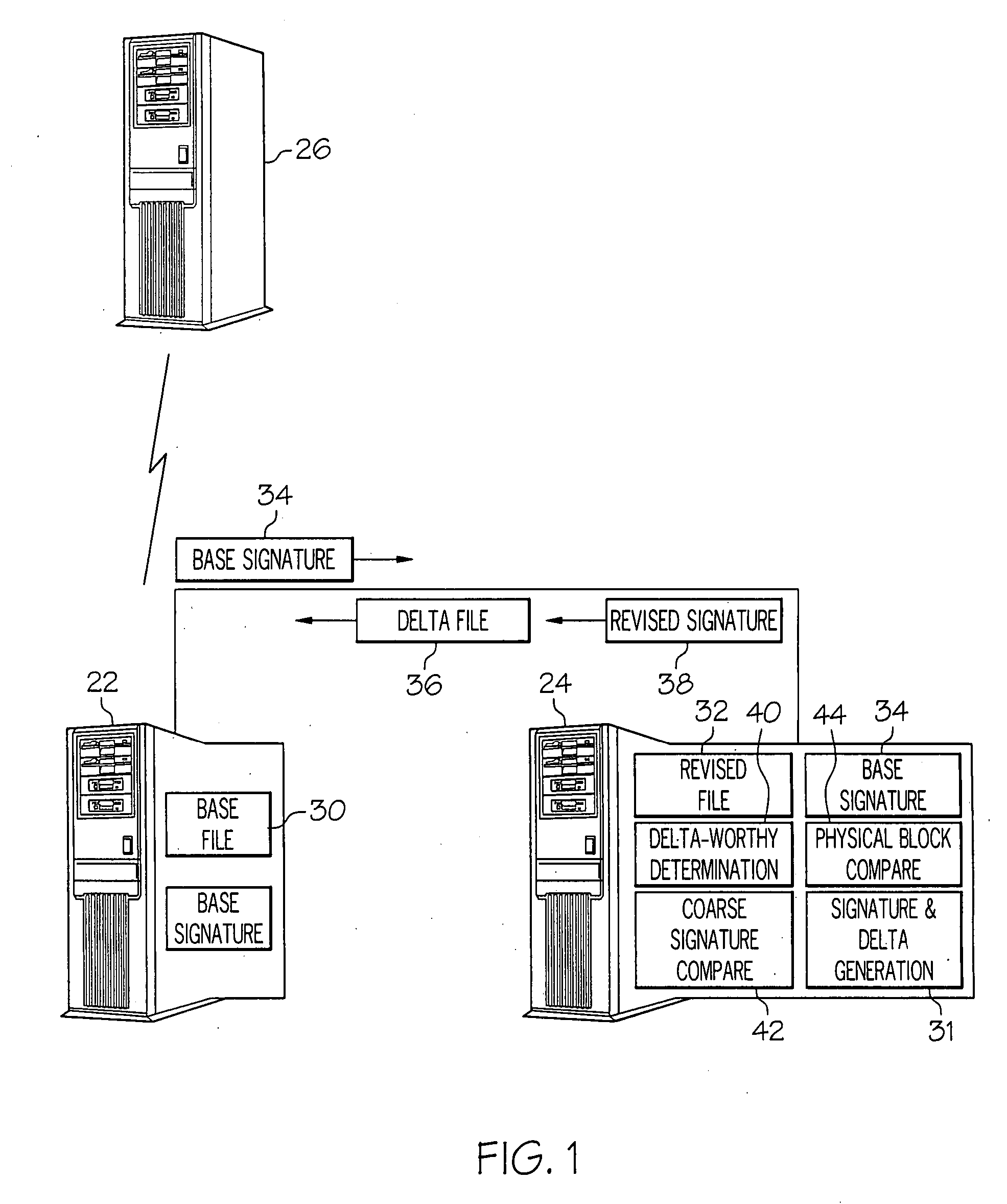
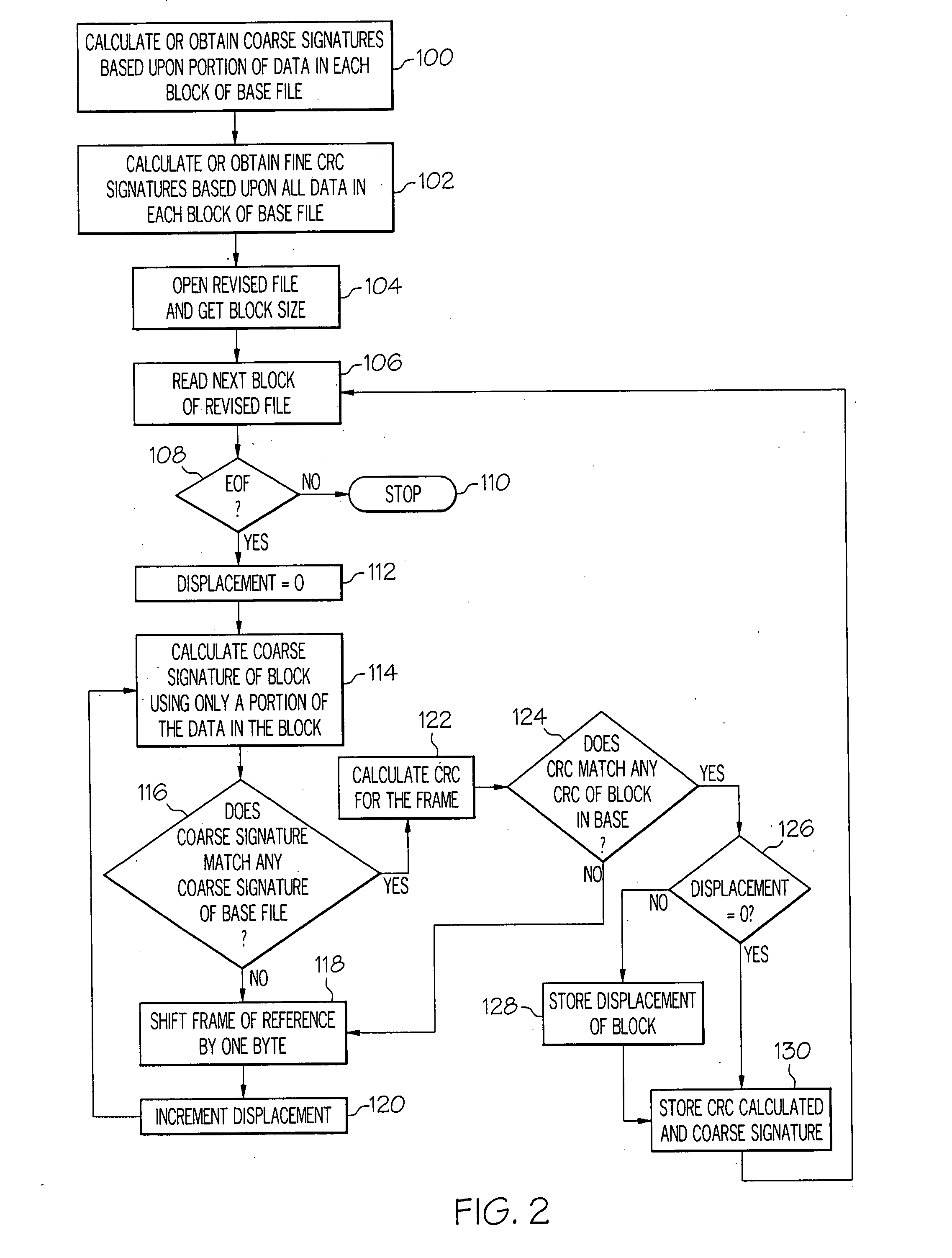
ActiveUS20070288533A1Block completeData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputer hardware
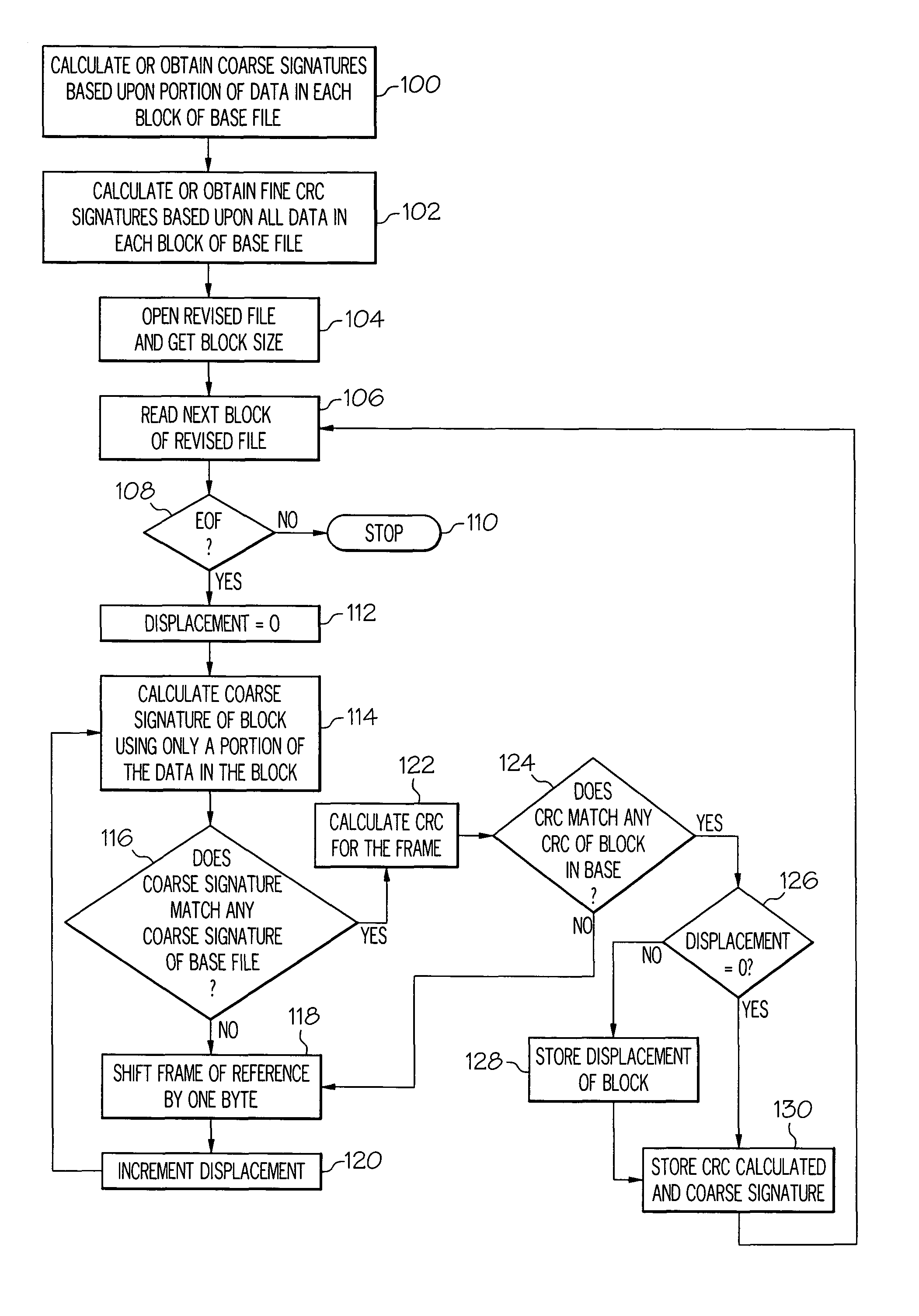
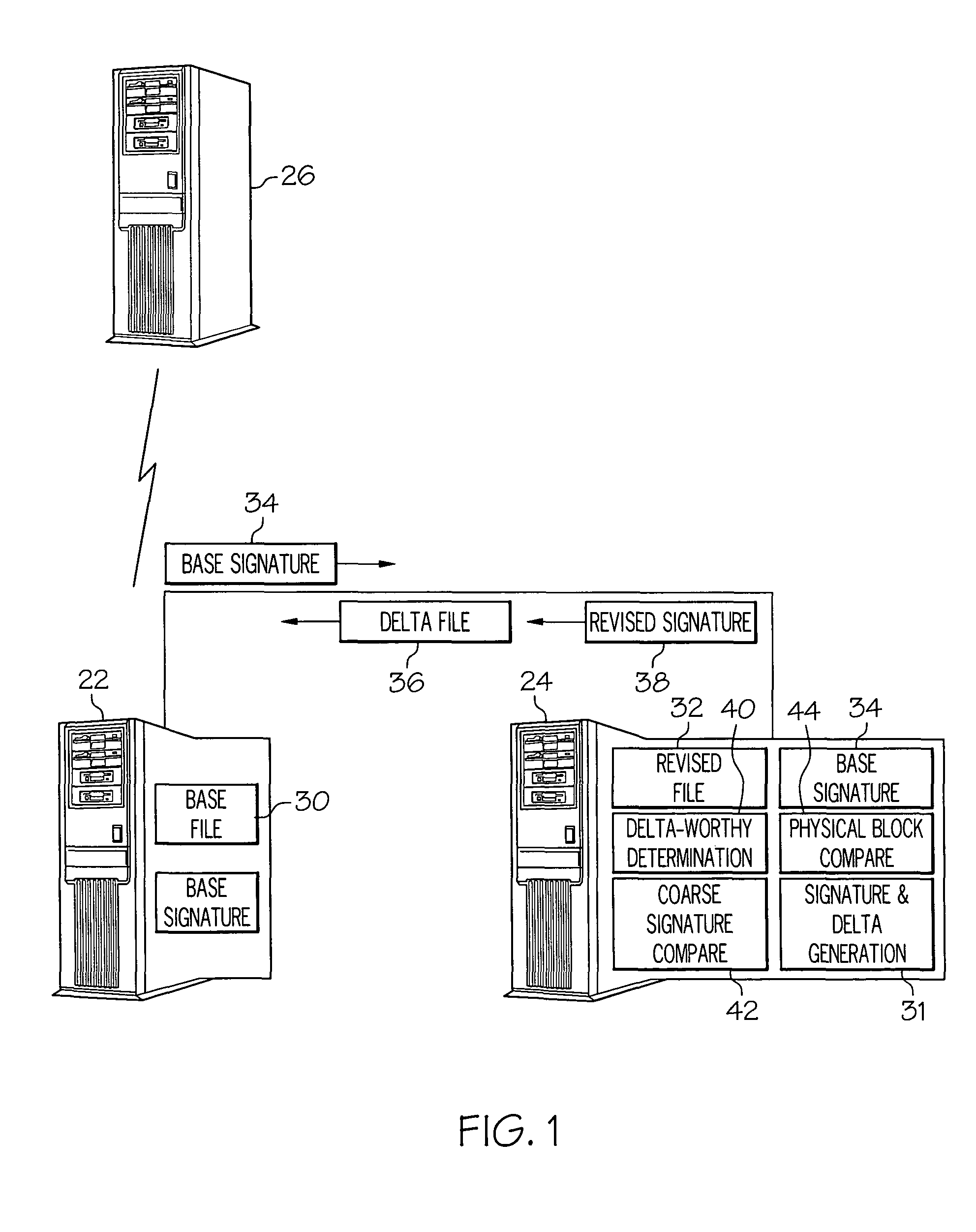
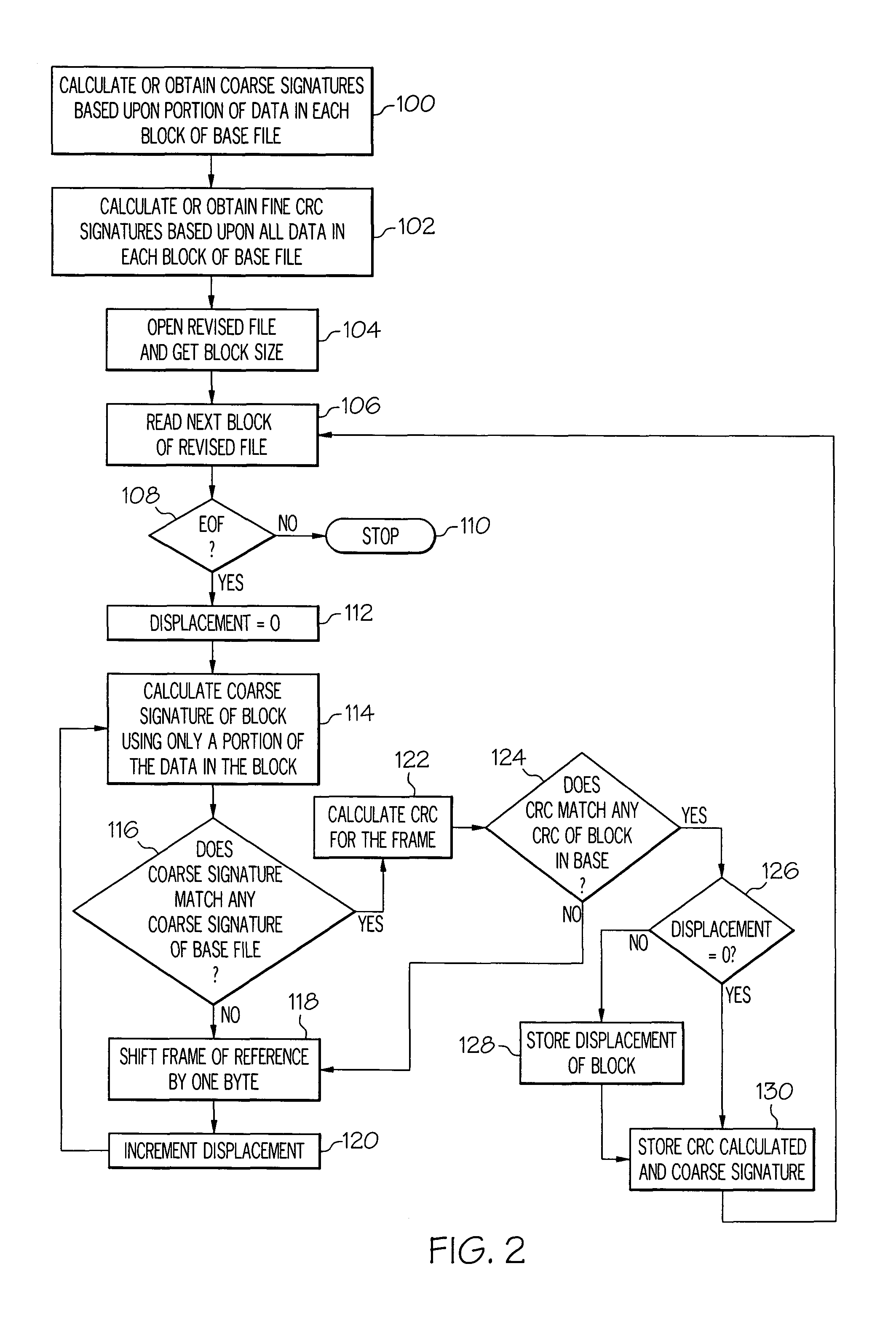
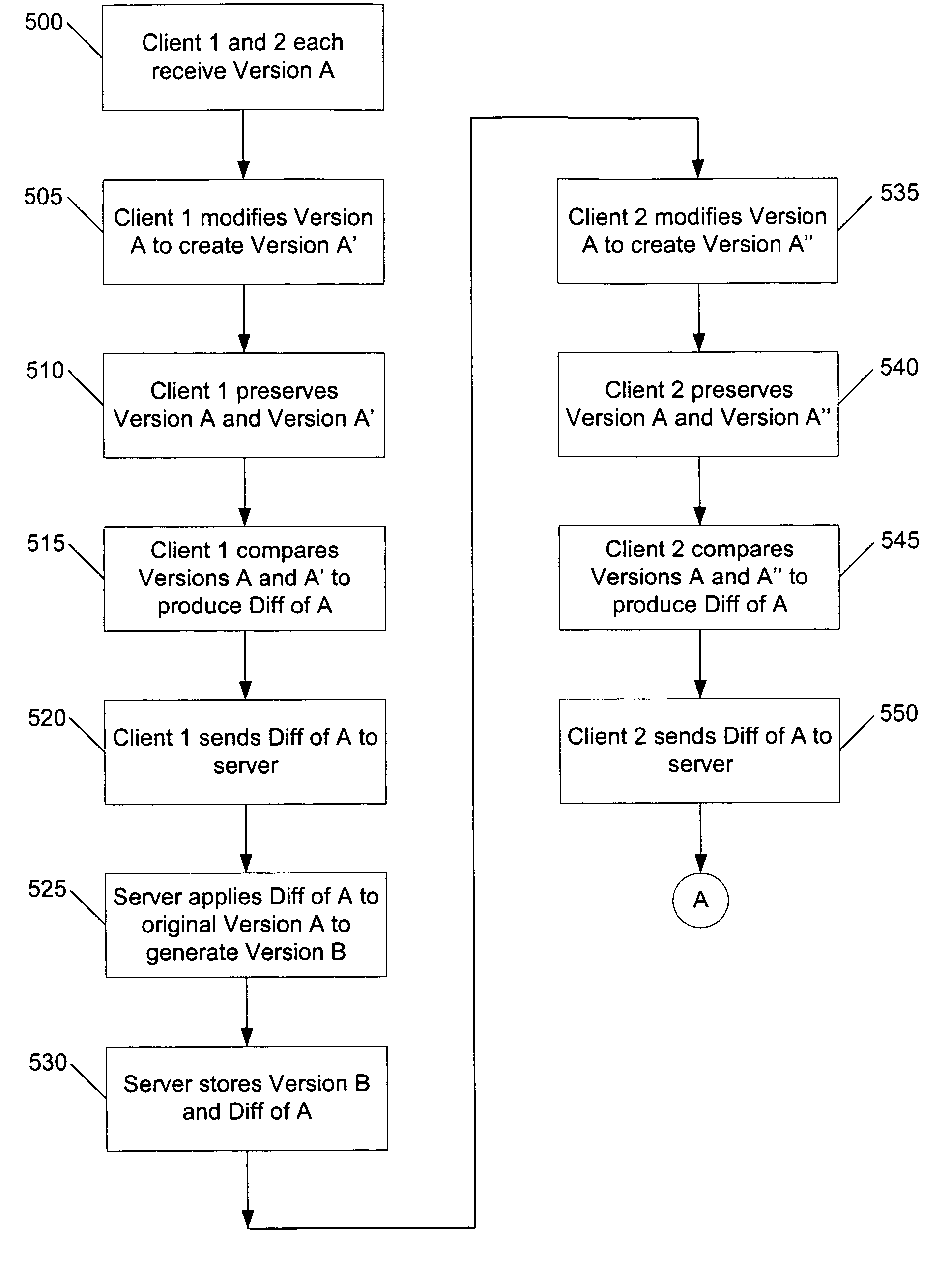
Methods and systems for efficient file replication are provided. In some embodiments, one or more coarse signatures for blocks in a base file are compared with those coarse signatures for blocks of a revised file, until a match is found. A fine signature is then generated for the matching block of the revised file and compared to a fine signature of the base file. Thus, fine signatures are not computed unless a coarse signature match has been found, thereby minimizing unneeded time-consuming fine signature calculations. Methods are also provided for determining whether to initiate a delta file generation algorithm, or whether to utilize a more efficient replication method, based upon system and / or file parameters. In accordance with additional embodiments, the lengths of valid data on physical blocks are obtained from physical block mappings for the files, and these lengths and mappings are utilized for delta file generation, to minimize unnecessary signature computations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
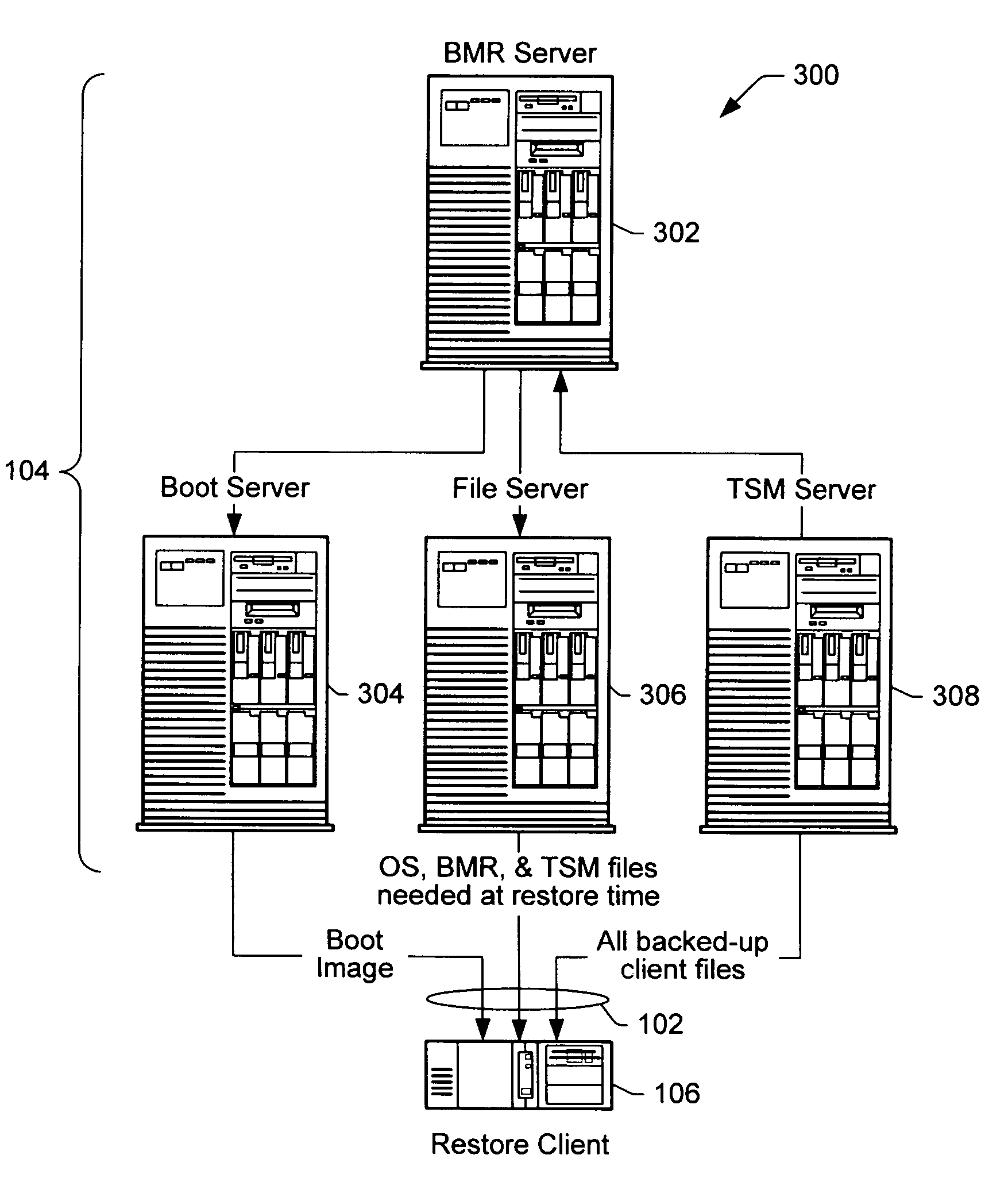
Computer restoration systems and methods
A method restores a client device of a network on major failure of the client device. The client device is incapable of automatically booting on its own. The network includes a server computer. The method includes booting the client device over the network in the restoration operation, configuring the client device according to the boot program and saved configuration states for the client device, and copying files to the client device in accordance with the configuration. The client computer has access to a storage manager application, such as a server computer of the network operating a storage management software program. All client files, including configuration files, as well as application and data files, of the client device are saved on the network by the storage manager application. The client device is booted over the network, rather than locally to the client device by boot disk or otherwise. The boot program is loaded to the client device, and the client device retrieves configuration and file information over the network from the storage manager application. The client device configures its disk according to the configuration information, and then all other files and data of the client device at the time of failure of the client device are saved on the disk substantially in the condition and state just prior to the failure and as most recently backed up to the storage manager application. Alternatively, the client device is reset and booted via a control device either locally or otherwise connected to the client device, and substantially according to the method of the network boot.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Method for backing up a disk array system
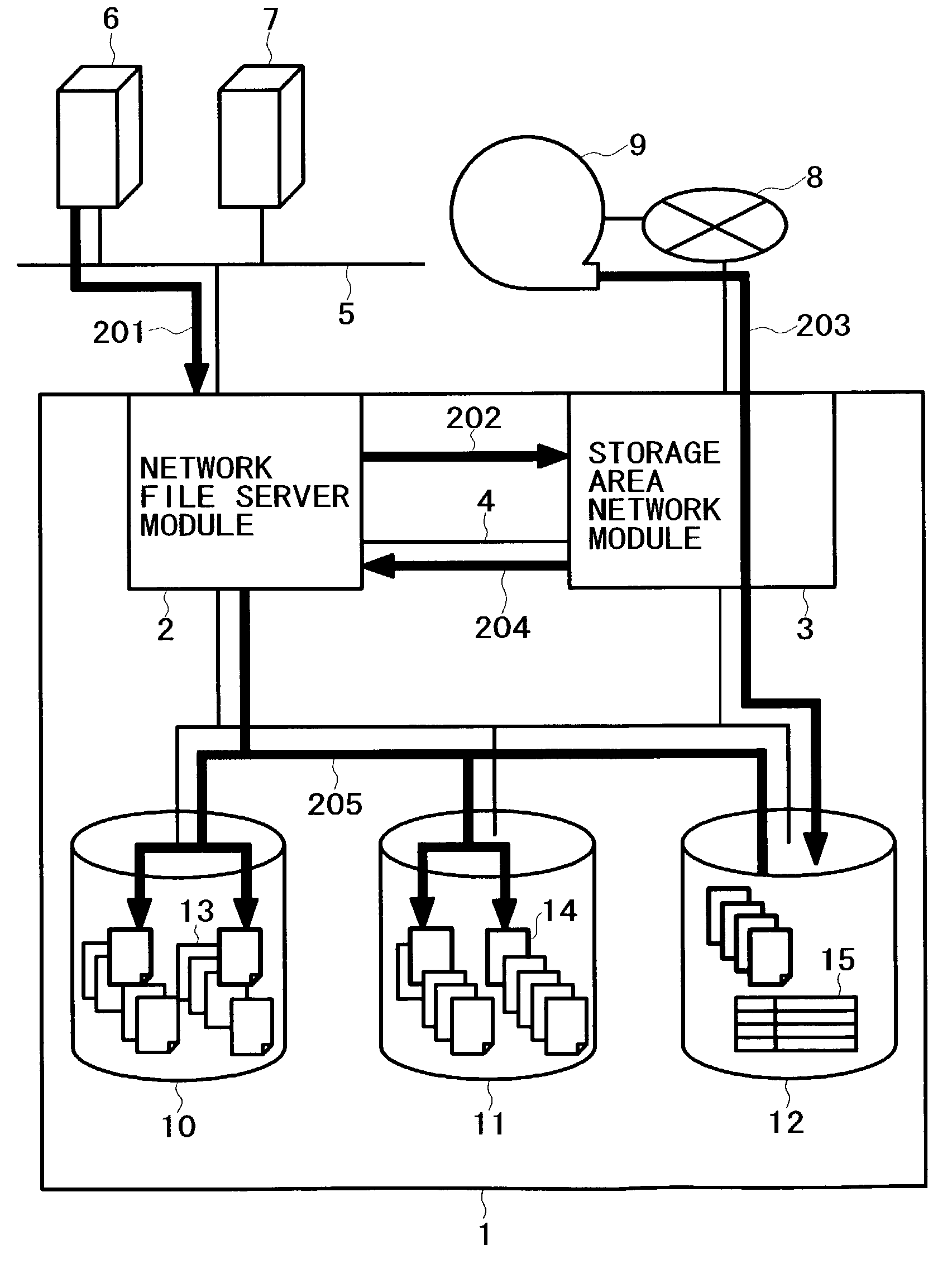
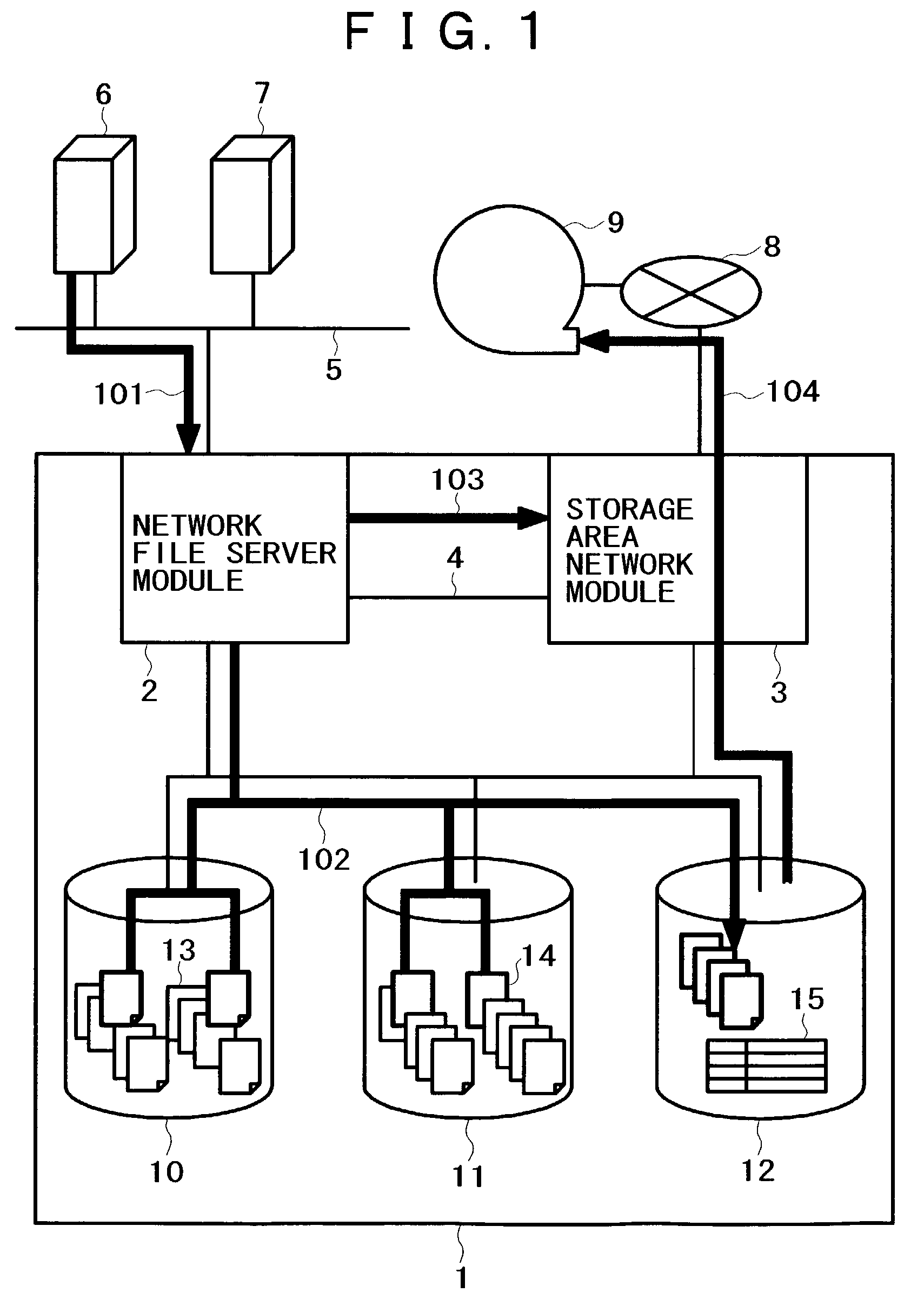
InactiveUS7099901B2Simple processIncrease loadData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersFile replicationExternal storage
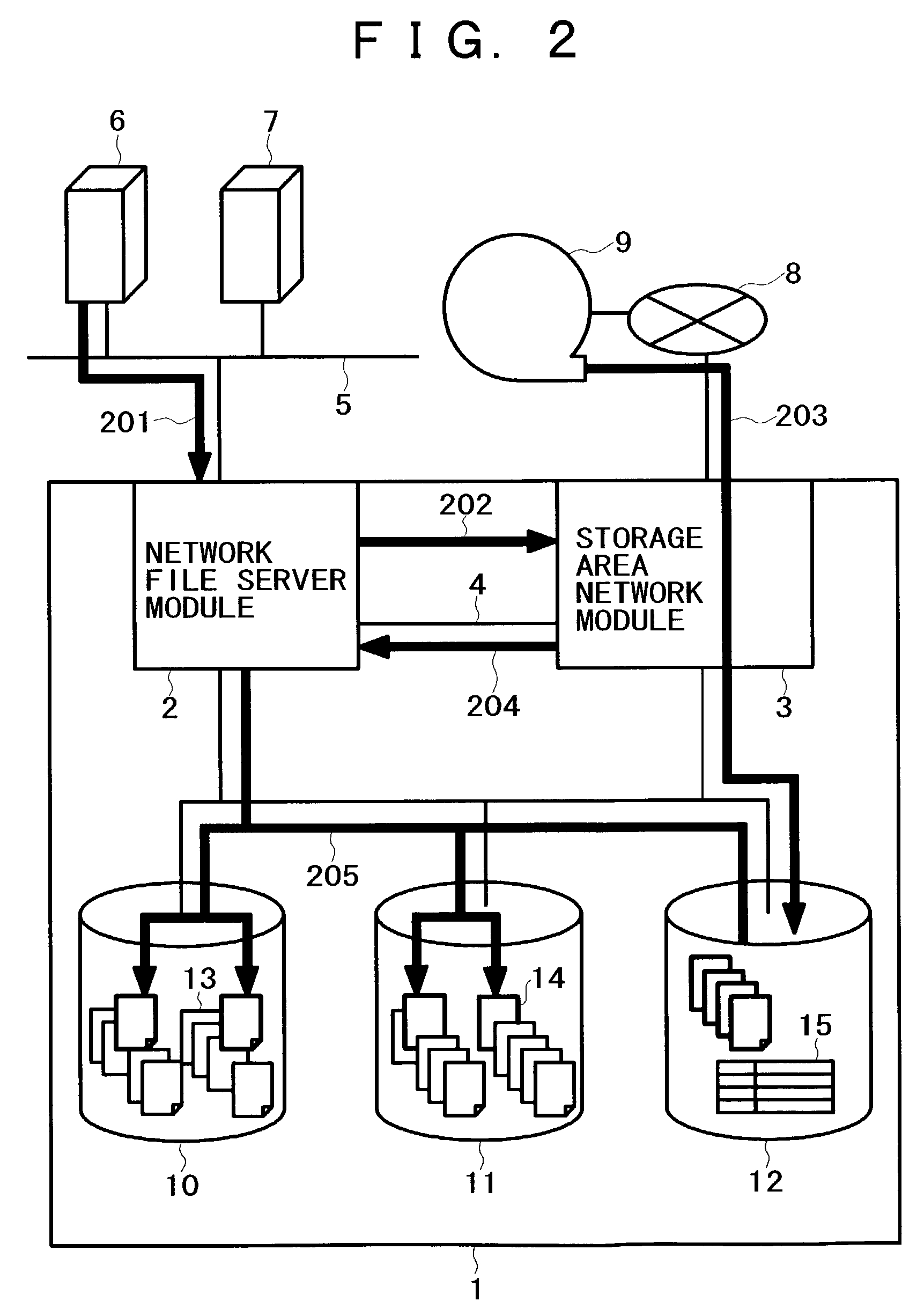
A method for backing up the data of a disk array system having network file server and storage area network functions easily and rapidly without using a route for data to be not backed up. Upon receipt of a backup request, a network file server module copies files on the disk array system's regular volumes to a backup volume. The network file server module then requests a storage area network module to copy the files to an external storage device. Finally, the storage area network module copies the current contents of the backup volume to the external storage device. The network file server module can limit the data to be backed up, thereby reducing the backup time requirements. The load on a LAN does not increase because the storage area network module acquires the data to be backed up. The processing speed increases thanks to backup load distribution within the disk array system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Transparent file replication using namespace replication
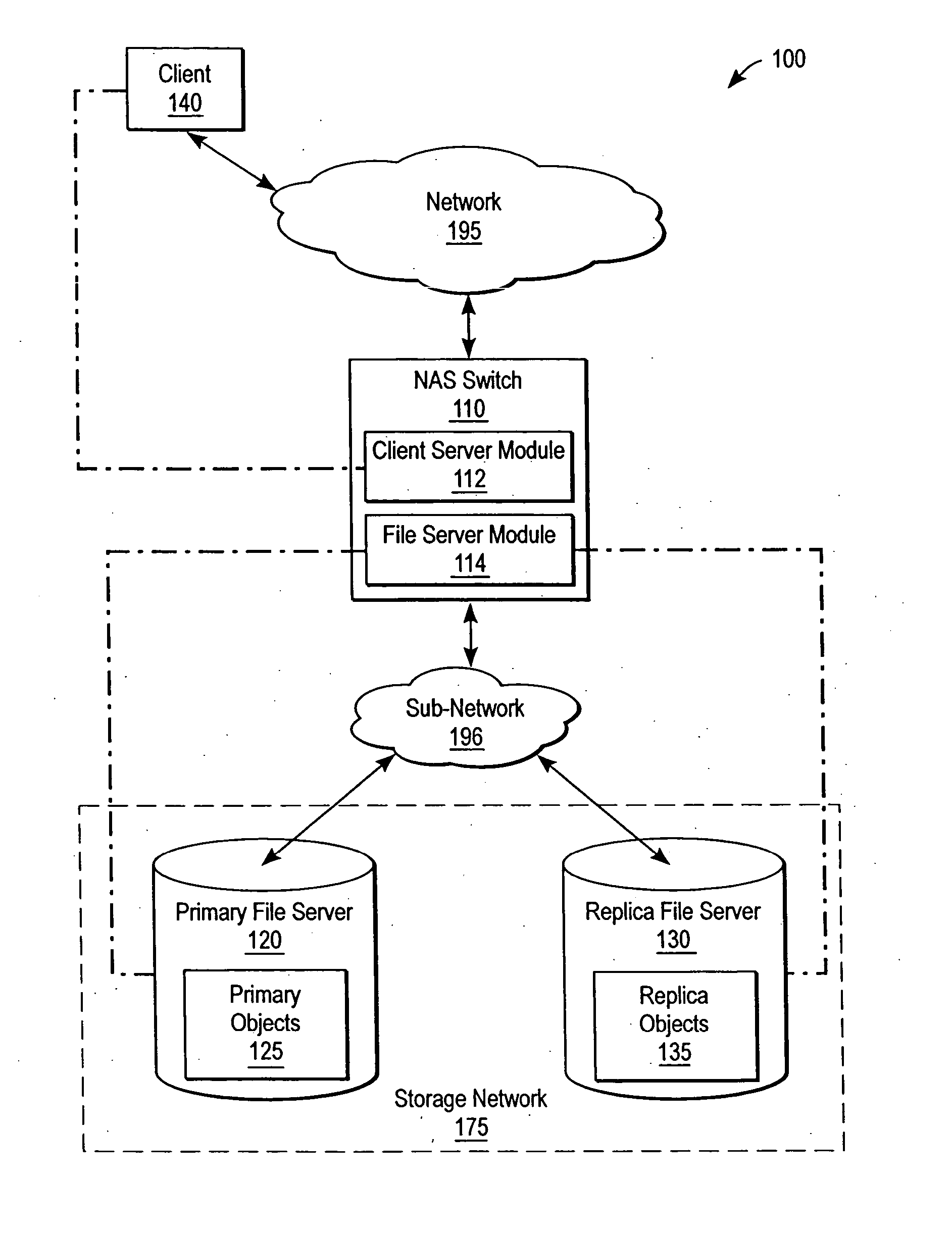
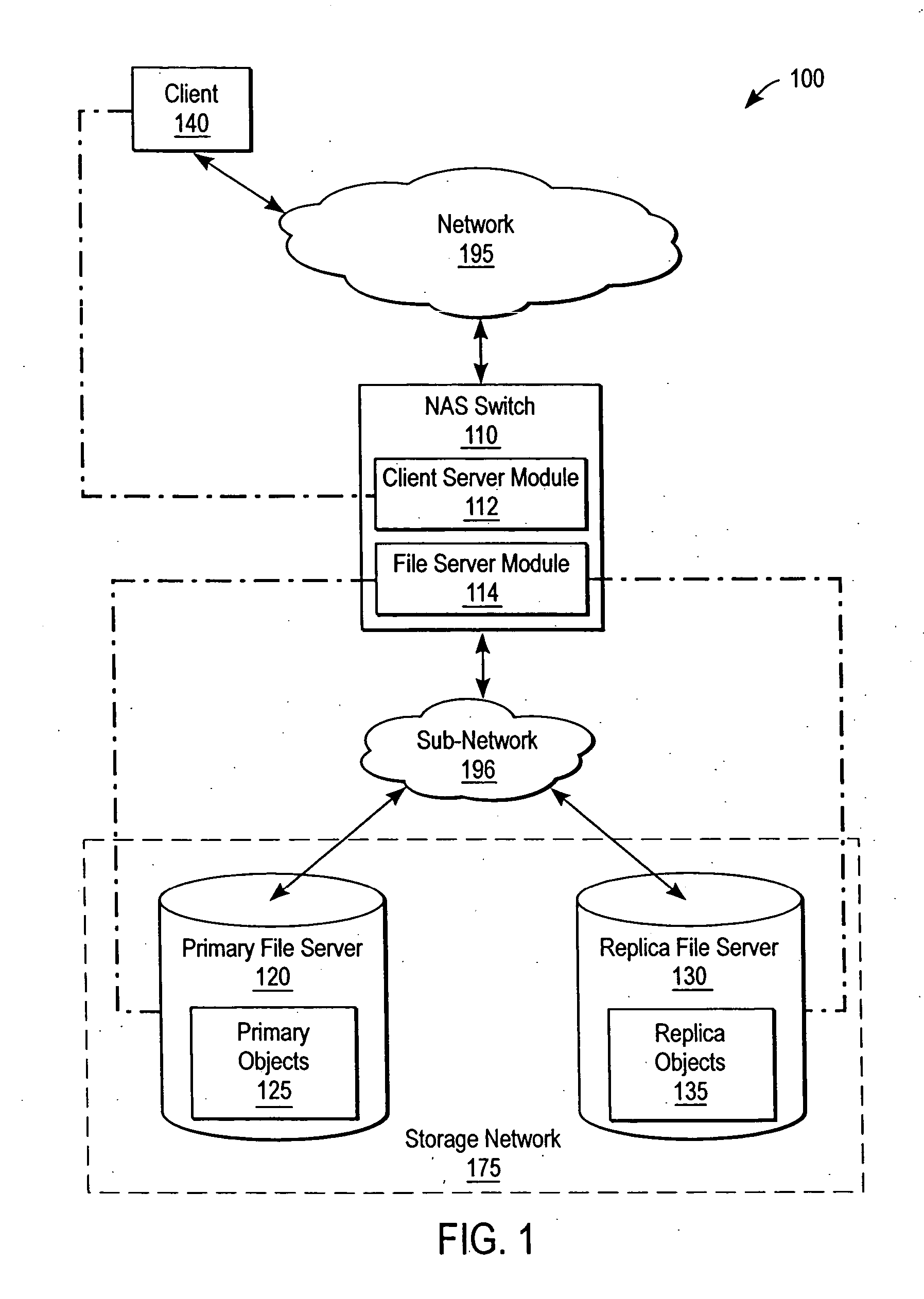
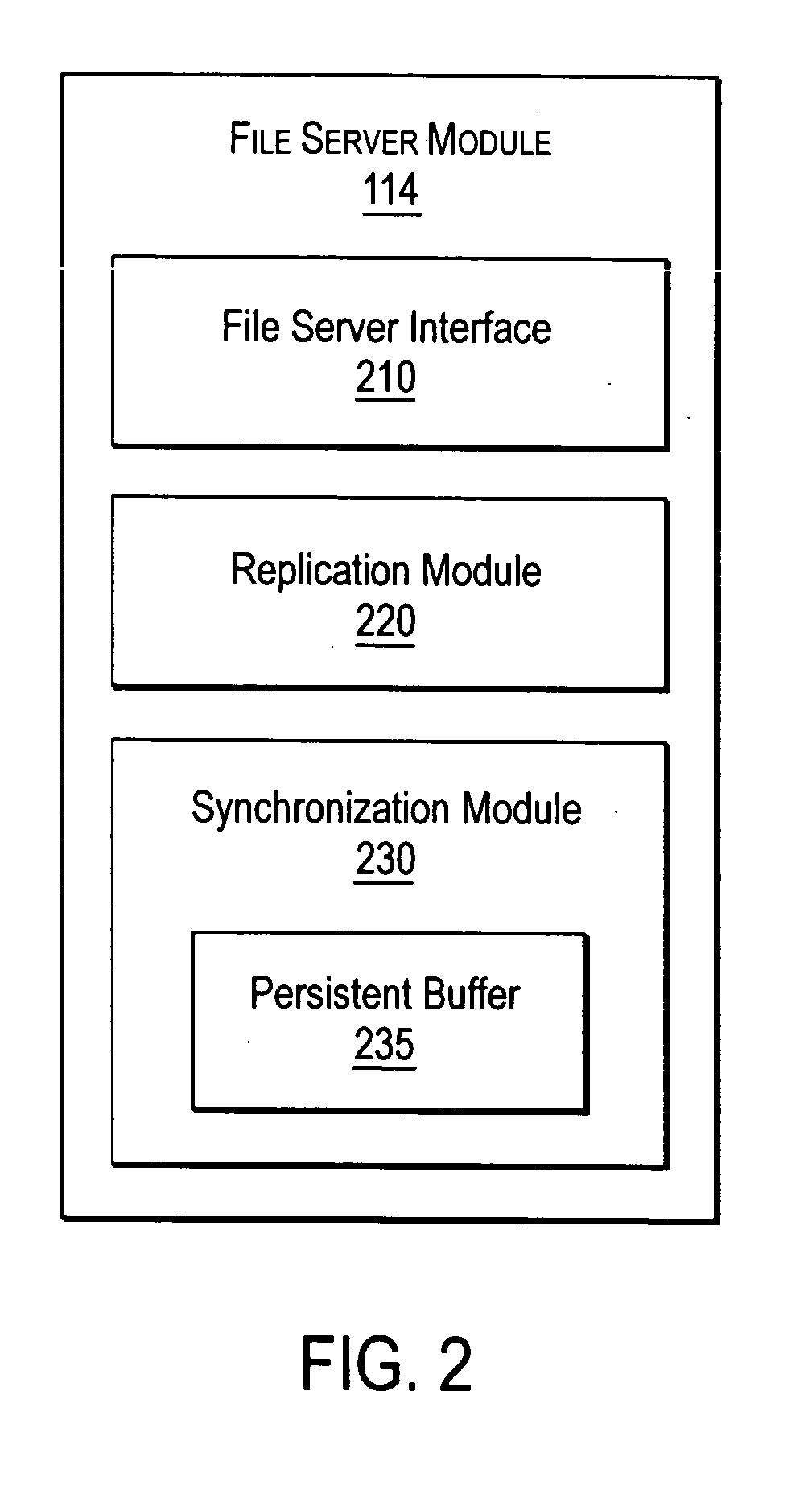
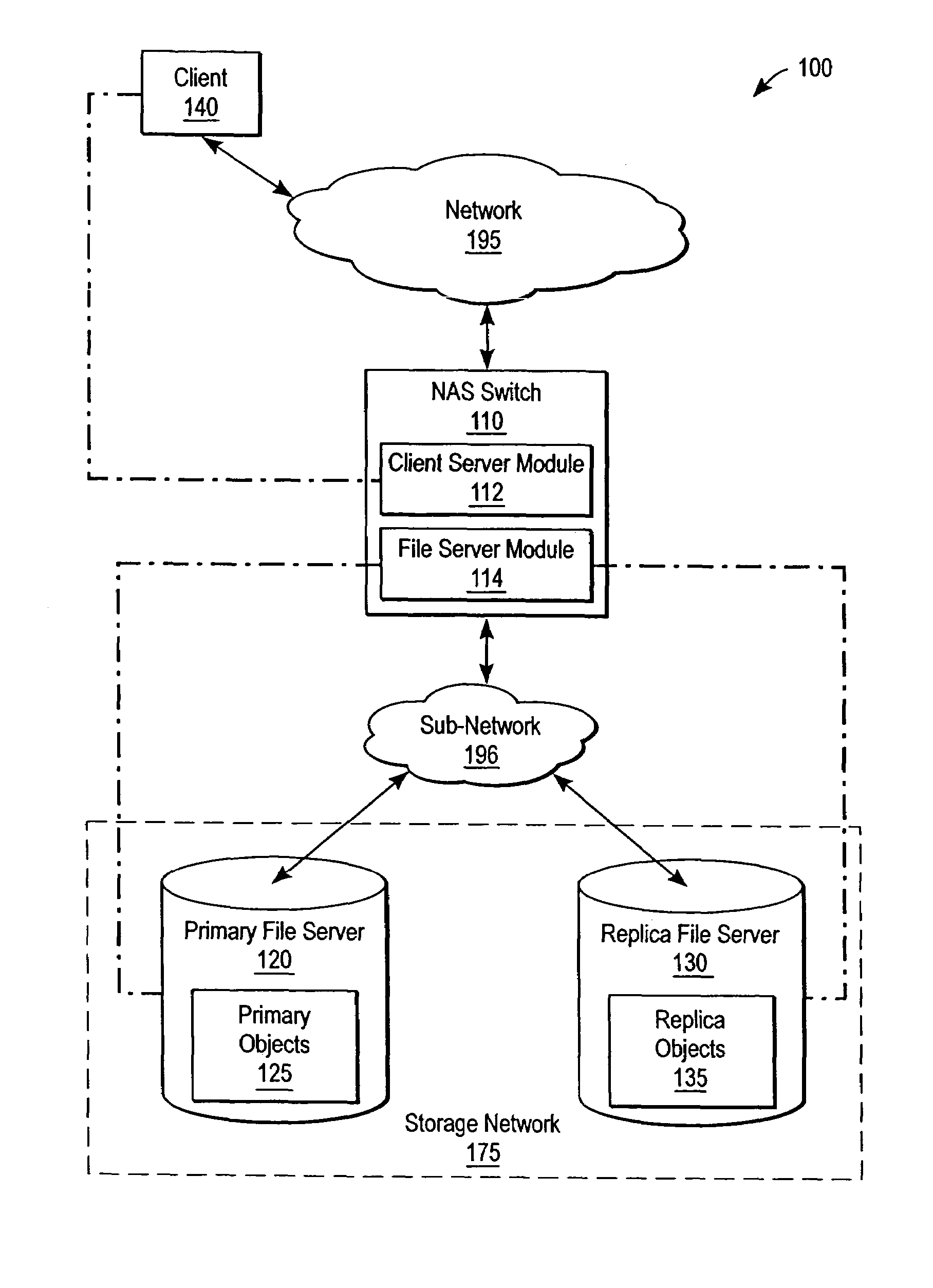
InactiveUS20040267752A1Maintain consistencyProviding serviceData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideFile replication
A NAS switch, in the data path of a client and a NAS file server on the storage network, provides a centralized point of reconfiguration after a network change that alleviates the need for reconfiguration of each connected client. The client uses a NAS request to access a storage object to the NAS switch using a switch file handle that is independent of object location and that can be used to locate the primary and its replica storage objects if the object is subsequently replicated. A replication module replicates a namespace separately from data contained therein. Afterwards, synchronicity module looks-up the switch file handle in a file handle replication table to determine if the object has been replicated and, if so, sends one of the replica NAS file handles. The synchronicity module also maintains synchronicity between the primary and replica file servers through critical NAS requests that modify objects such as create, delete, and the like.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Peer to peer enterprise storage system with lexical recovery sub-system
InactiveUS7243103B2Promote recoveryAvoid disruption and disruptionData processing applicationsData switching networksFile replicationSystems management
A peer-to-peer storage system includes a storage coordinator that centrally manages distributed storage resources in accordance with system policies administered through a central administrative console and a lexical recovery sub-system that automatically creates versions of files that are thereafter maintained by the system. The storage resources, or “nodes,” are otherwise unused portions of storage media, e.g., hard disks, that are included in the devices such as personal computers, workstations, laptops, file servers, and so forth, that are connected to a corporate computer network, and are thus otherwise available only individually to the respective devices. The storage coordinator assigns the nodes to various “replication groups” and allocates the storage resources on each of the nodes in a given group to maintaining dynamically replicated current and previous versions of the group files. The storage nodes in a given group perform dynamic file replication and synchronization operations by communicating directly, that is, peer-to-peer, using a message-based protocol. The storage coordinator also manages distributed searches of file content on the network by selecting one node from each group to search through the associated group files. The selected nodes report the search results back to the storage coordinator, which organizes the results and provides them to the user. The user may then restore or recover a previous version of a file or review a current version of the file by selecting the desired file version from the search results.
Owner:ESCHER GROUP
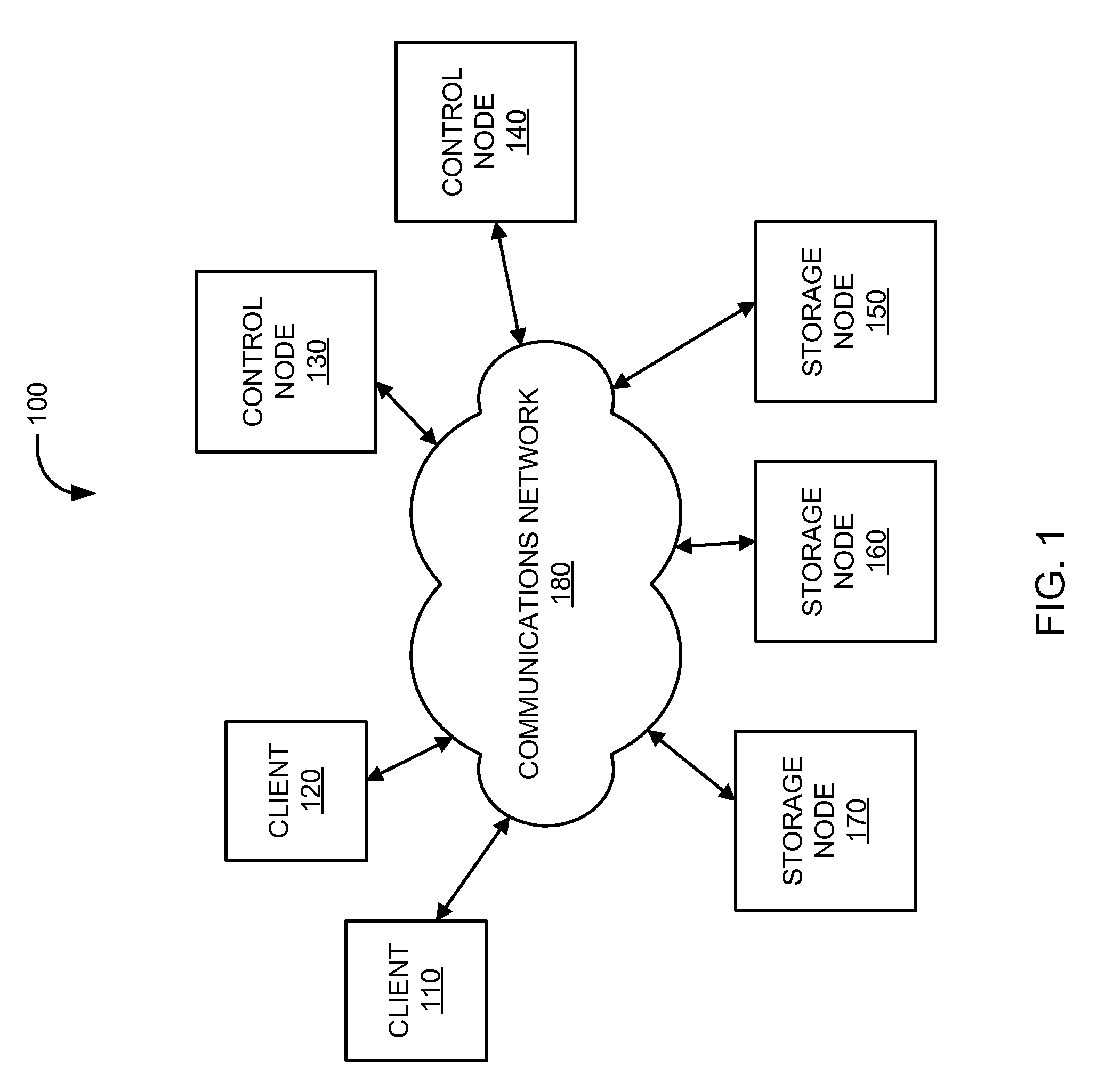
Asynchronous file replication and migration in a storage network
ActiveUS7571168B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile replicationStorage area network
File system independent techniques and mechanisms for replicating files on multiple devices are provided, migrating files from one device to another (for purposes of reliability, increased bandwidth, load balancing, capacity expansion, or reduced cost), and propagating updates from a master copy to remote replicas. The mechanisms involve work queues and asynchronous file migration daemons that operate independently from and in parallel with the primary client-server and network protocol to on-disk storage data paths.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
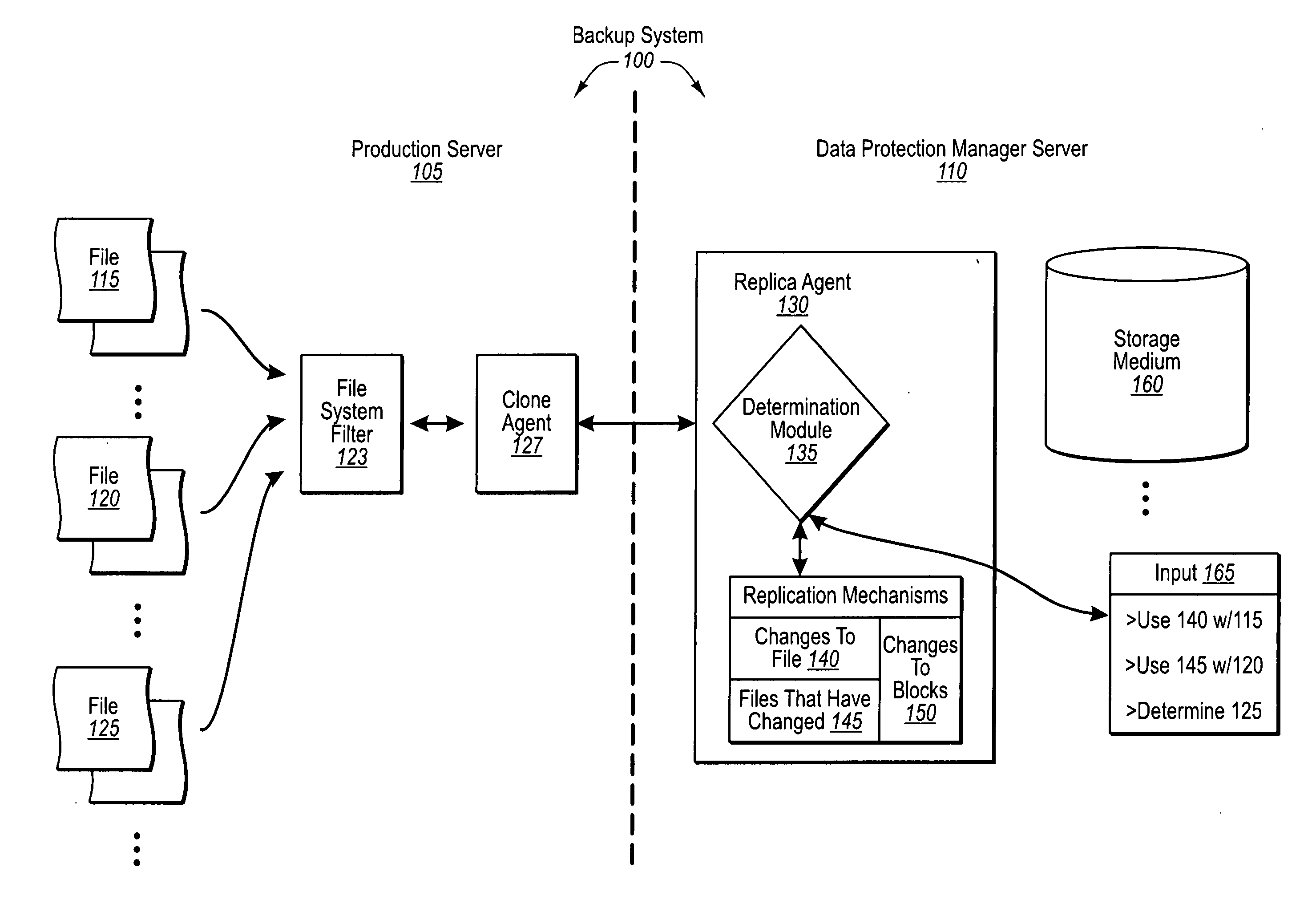
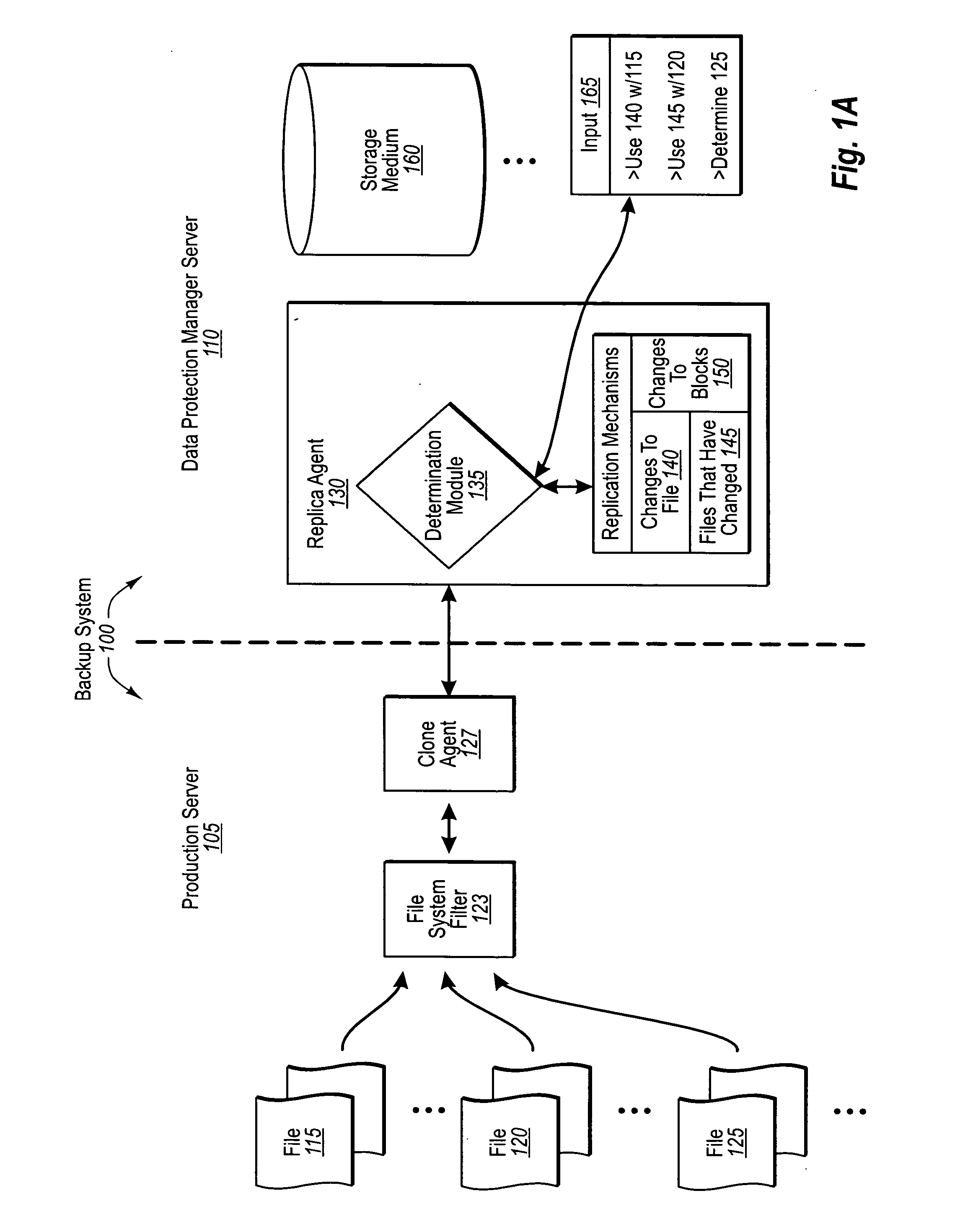
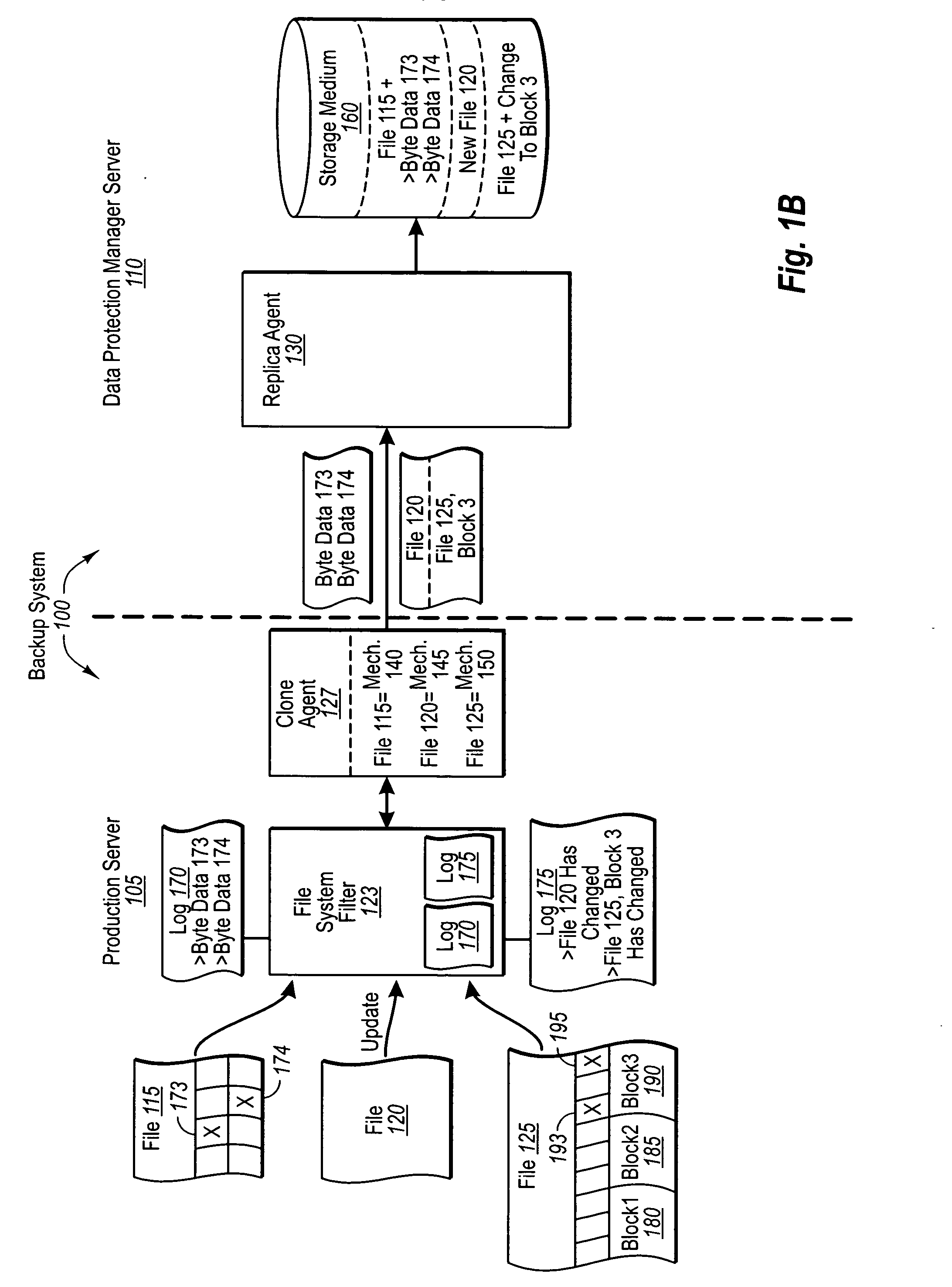
Automatically determining file replication mechanisms
InactiveUS20070192386A1Effective judgmentProgram control using stored programsMemory loss protectionFile replicationByte
A backup administrator can backup files from a production server on any of a plurality of different bases. In particular, some files can be replicated on a changed-byte basis. In other cases, files can be backed up by replicating updated copies of the entire file, or even byte blocks of the file. Determinations as to how a replication agent will back up a certain file or set of files can be made by a backup administrator, automatically through a predefined logic, or dynamically based on defined criteria. Corresponding agents at the production server can then flag these files as indicated. Thus, at a later point, when the DPM server requests the updates of each file, the production server can either send over copies of the changed file bytes, entire copies of the changed file itself, or even changed blocks of a file, as appropriate.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and systems for file replication utilizing differences between versions of files
ActiveUS7320009B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputer hardware
Methods and systems for efficient file replication are provided. In some embodiments, one or more coarse signatures for blocks in a base file are compared with those coarse signatures for blocks of a revised file, until a match is found. A fine signature is then generated for the matching block of the revised file and compared to a fine signature of the base file. Thus, fine signatures are not computed unless a coarse signature match has been found, thereby minimizing unneeded time-consuming fine signature calculations. Methods are also provided for determining whether to initiate a delta file generation algorithm, or whether to utilize a more efficient replication method, based upon system and / or file parameters. In accordance with additional embodiments, the lengths of valid data on physical blocks are obtained from physical block mappings for the files, and these lengths and mappings are utilized for delta file generation, to minimize unnecessary signature computations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data replication facility for distributed computing environments
InactiveUS7624155B1Avoid configurationAvoid point of failureData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile replicationDistributed Computing Environment
A data replication facility for distributed computing environments. A computer network having a plurality of network nodes utilizes a distributed directory provider service (DPS) having an established master node. The DPS supports a file replication service (FRS). The FRS establishes one of the nodes as originator node which receives new or updated files from one or more user / GUIs and / or from one or more software providers such as a security provider. The originator node in cooperation with the master node establish a backup copy of the new or updated file in the master node. Thereafter, the originator node publishes a File Version Variable (FVV) representation of the new or updated file to other network nodes (slave nodes) which obtain such file from the originator or, if need be, from the backup master node. Object observers are utilized to determine changes to the file version variables thereby triggering the downloading of new or updated files into the network nodes, whereby data file replication is accomplished throughout the network. In addition to avoiding a single point of failure, embodiments of the present invention also are network-topology independent. Additional syncing threads are employed as part of the file replication service to further ensure synchronization of the network nodes' data files within a predetermined interval, regardless of network failure modes. Embodiments of the present invention are particularly useful with networks of the client-server storage network variety.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Optimizing file replication using binary comparisons
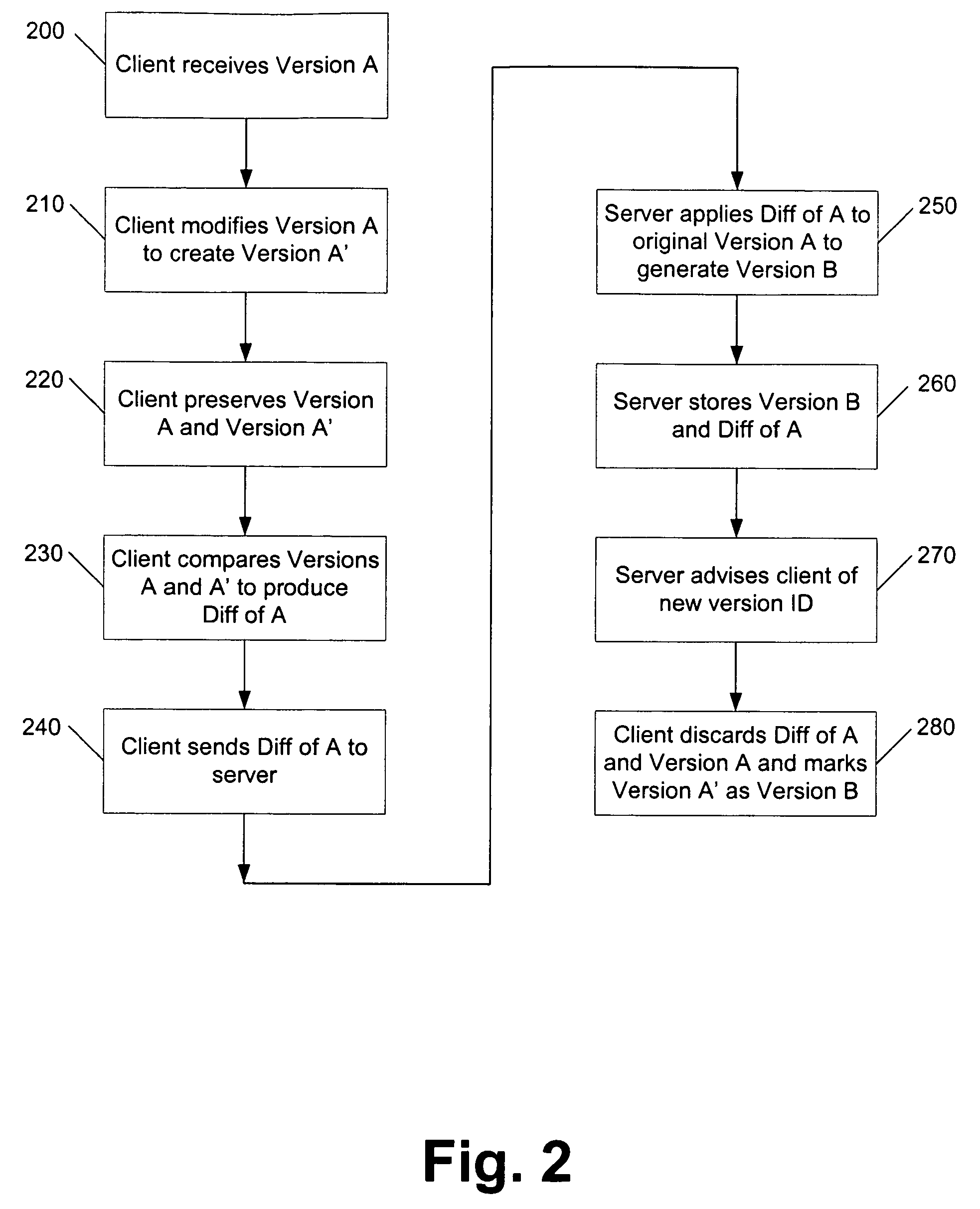
Client and server based copies of a file are maintained in synchronicity as changes are made to the file. Data is compared to a previous version known to both the client and server and a highly compressed representation of the differences between the two is generated. These differences, or “diffs”, are then transmitted, and may use extensions to the HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) protocol.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Transparent file replication using namespace replication
InactiveUS7587422B2Maintain availabilityMaintain consistencyData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsFile replicationClient-side
A NAS switch, in the data path of a client and a NAS file server on the storage network, provides a centralized point of reconfiguration after a network change that alleviates the need for reconfiguration of each connected client. The client uses a NAS request to access a storage object to the NAS switch using a switch file handle that is independent of object location and that can be used to locate the primary and its replica storage objects if the object is subsequently replicated. A replication module replicates a namespace separately from data contained therein. Afterwards, synchronicity module looks-up the switch file handle in a file handle replication table to determine if the object has been replicated and, if so, sends one of the replica NAS file handles. The synchronicity module also maintains synchronicity between the primary and replica file servers through critical NAS requests that modify objects such as create, delete, and the like.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Intelligent replication method
InactiveUS6973464B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile replicationReplication method
A replication method supports file replication across a plurality of file servers by tracking the changes to the local volume on the storage system. Each change is then ranked according to a number of criteria. Each criterion is weighted, and an overall ranking is determined for each change. The changes are then ordered according to their ranks, and each change is transmitted to remote storage systems for remote duplication of the change.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Two-level structured overlay design for cluster management in a peer-to-peer network
InactiveUS20080177767A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksFile replicationLevel structure
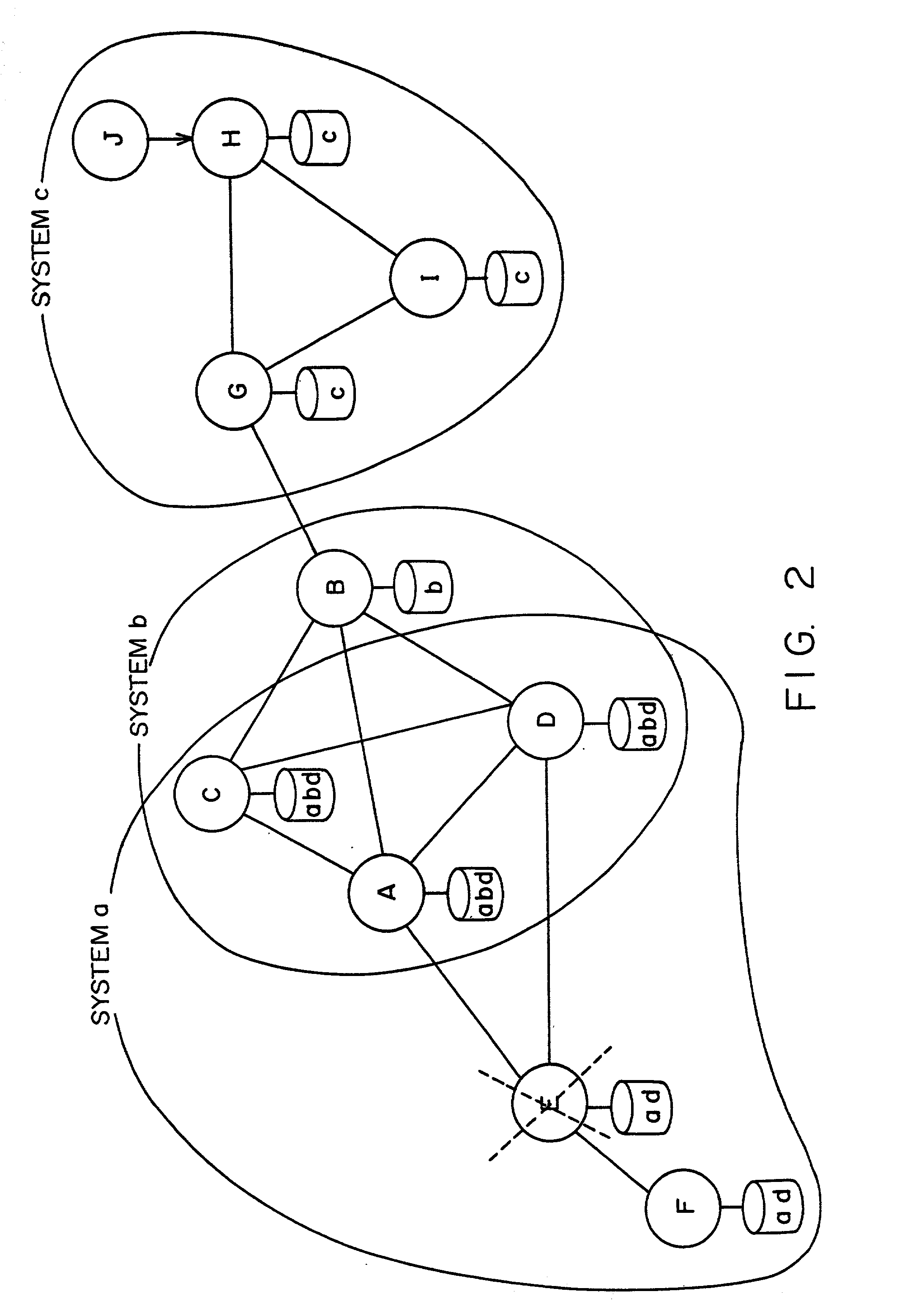
A method and system for designing file replication schemes in file sharing systems consider node storage constraints and node up / down statistics, file storage costs, and file transfer costs among the nodes, user request rates for the files, and user specified file availability requirements. Based on these considerations, a systematic method for designing file replication schemes can be implemented. The method first determines the number of copies of the files to be stored in the system to achieve the desired goal (e.g., to satisfy file availability requirements, or to maximize the system hit rate), and then selects the nodes at which to store the file copies to minimize the total expected cost. The file replication scheme for a peer-to-peer file sharing system in a distributed and adaptive manner can scale to a large number of nodes and files and can handle changes in the user request pattern over time.
Owner:XEROX CORP
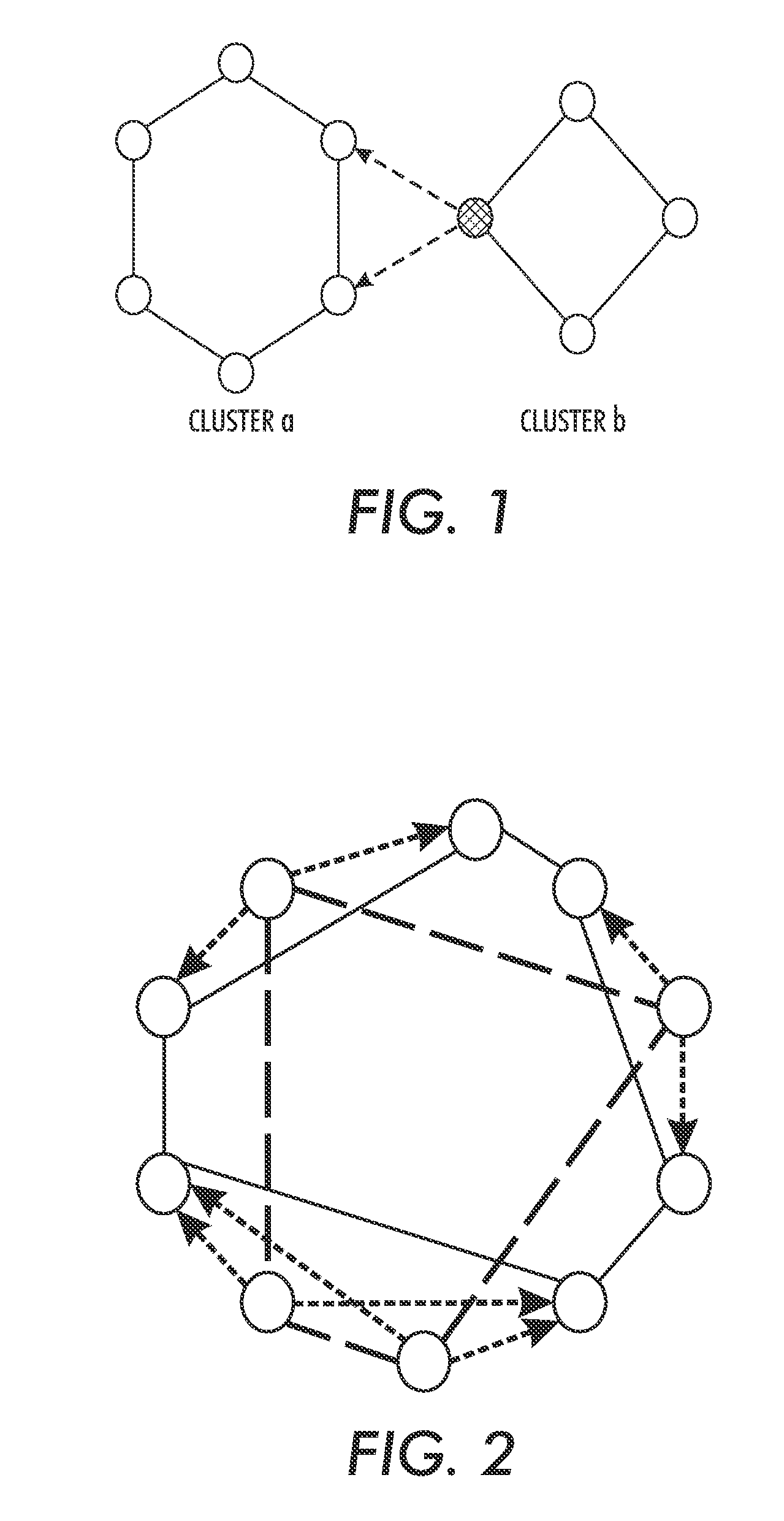
Pull Model for File Replication at Multiple Data Centers
ActiveUS20090083342A1Digital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionFile replicationData center
Various embodiments of a system and method for replicating a file over multiple data centers are described. The method may comprise creating a plurality of file records in a database at a data center that initially receives the file. Each record may correspond to a destination data center at which the file should be stored. The file records may be replicated to respective databases at each of the destination data centers, and each respective destination data center may pull a copy of the file to the respective destination data center. When a file is pulled to a given destination data center, the file record corresponding to the copy of the file at the given destination data center may be updated, and the updated file record may be communicated to the other destination data centers.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Detecting malicious software through file group behavior
ActiveUS7594272B1Prevents file replicationPrevents other malicious behaviorMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputerized system
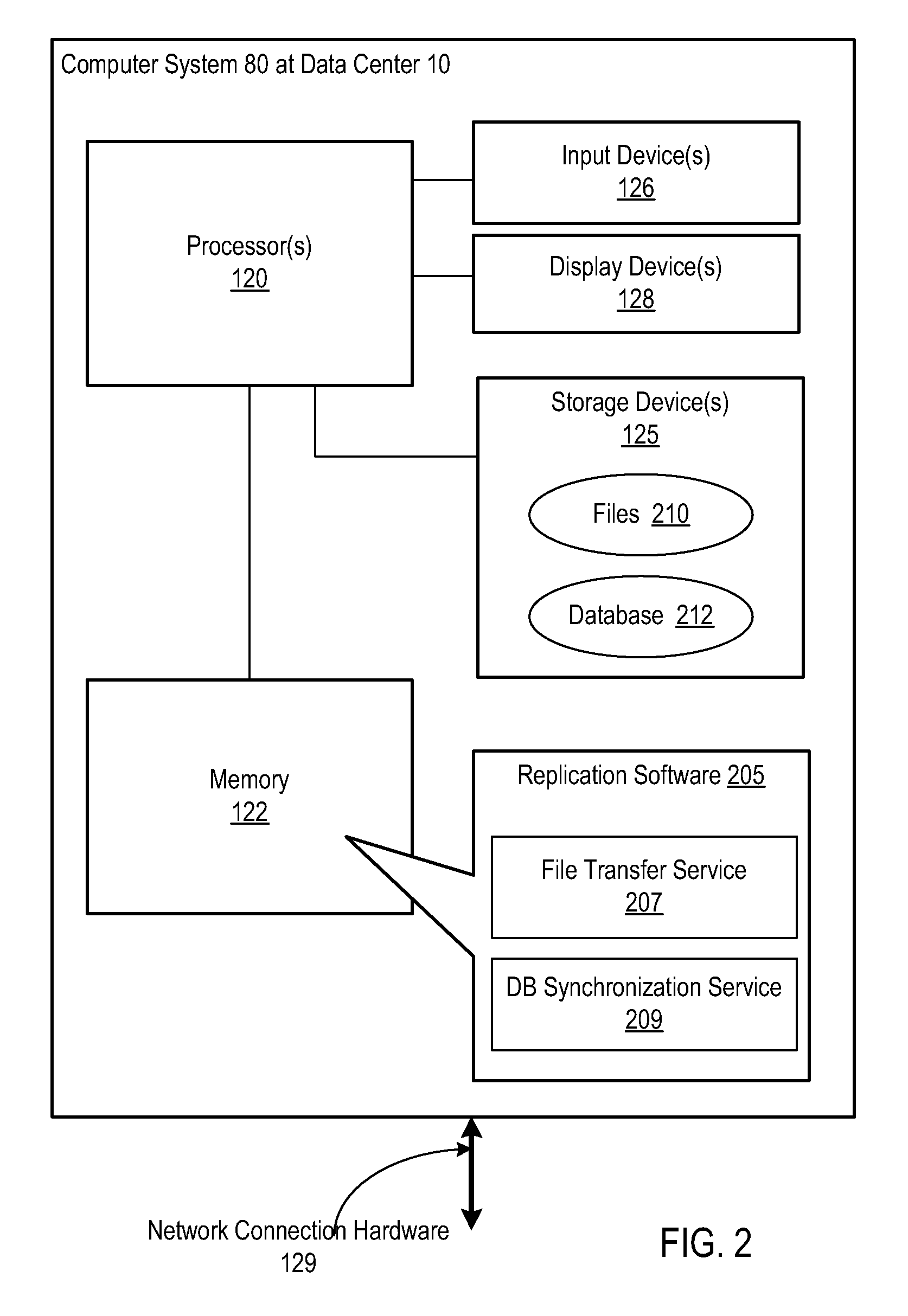
A malicious software detection module (MSDM) detects worms and other malicious software. The MSDM executes on a computer system connected to a network. The MSDM monitors a storage device of the computer system for the arrival of software from a suspicious portal. The MSDM designates such software as suspicious. The MSDM tracks the set of files that are associated with the suspicious software. If the files in the set individually or collectively engage in suspicious behavior, the MSDM declares the suspicious software malicious and prevents file replication and / or other malicious behavior.
Owner:NORTONLIFELOCK INC
Multi-protocol sharable virtual storage objects
ActiveUS7953819B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUnixFile replication
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method to share licensed applications between virtual machines
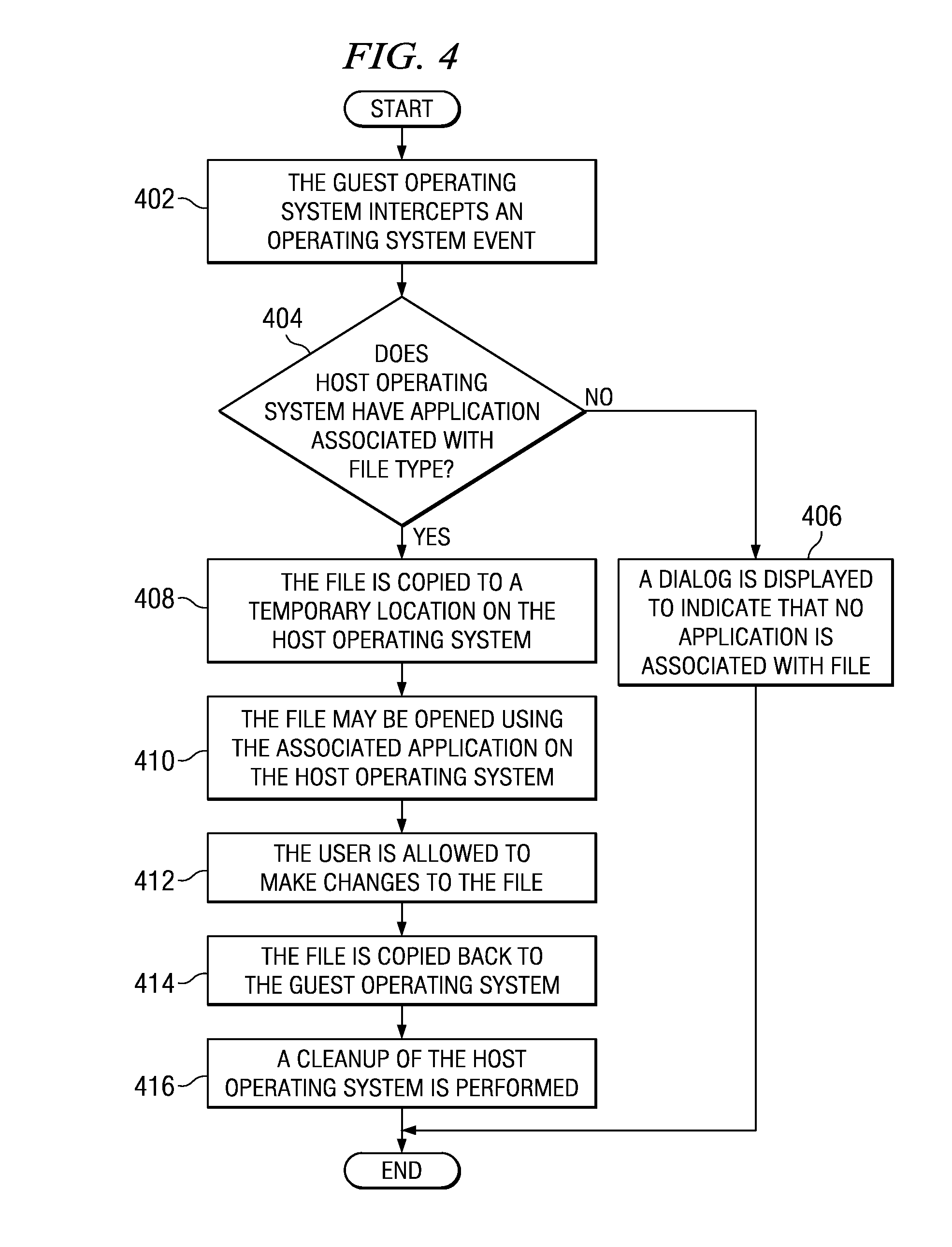
InactiveUS20080098391A1Multiprogramming arrangementsComputer security arrangementsFile replicationOperational system
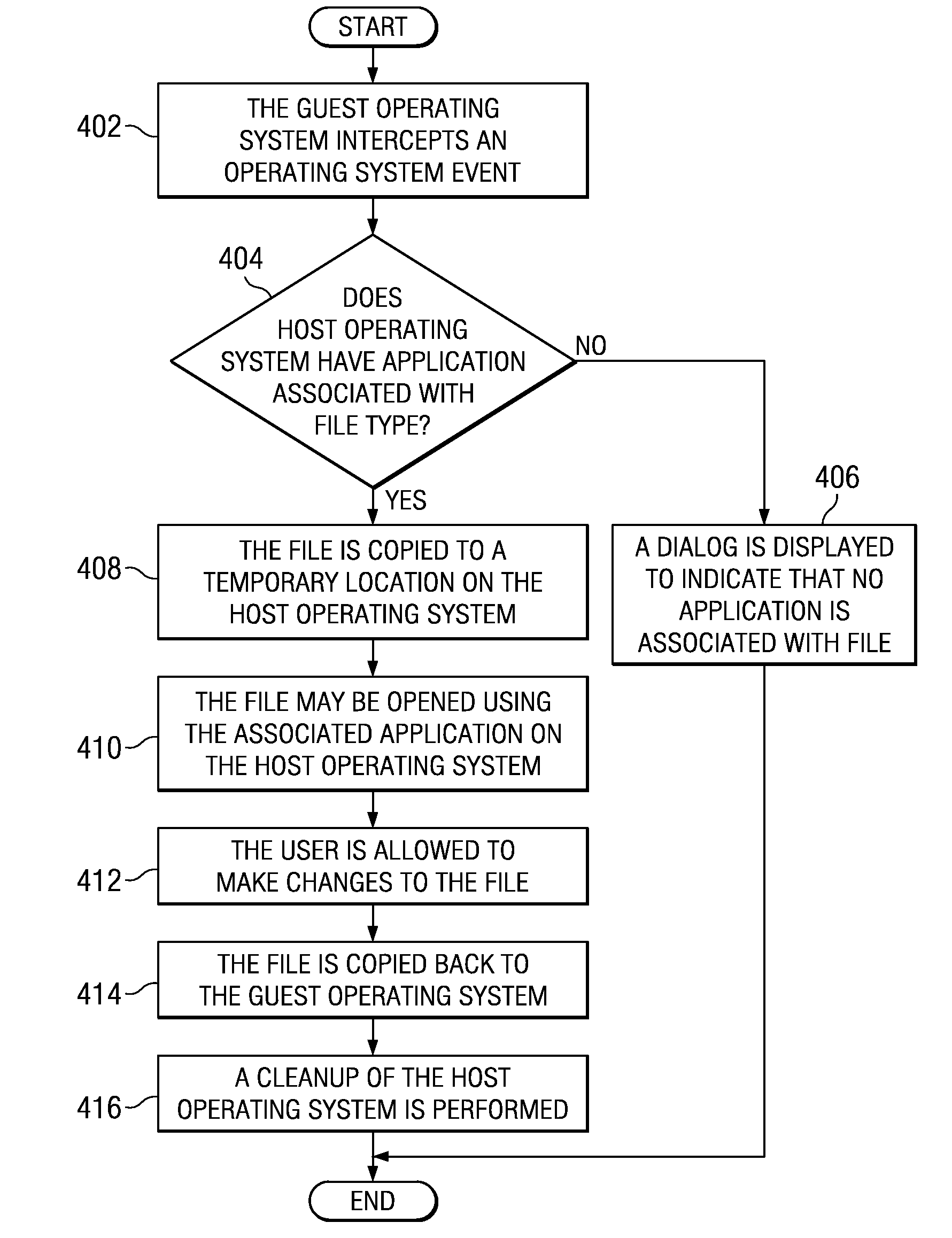
A computer implemented method and computer program product for sharing licensed applications between virtual machines. When an event is intercepted which comprises an attempted access of a file stored in a hard disk of a guest operating system, wherein the file type has no association with any application installed on the guest operating system, an application installed on a host operating system capable of opening the file is identified. An association of the file type with an application on the host operating system is established, and the file is copied from the hard disk of the guest operating system to a temporary location on the host operating system. The file is opened and accessed using the associated application on the host operating system. The file is then copied back to the hard disk of the guest operating system.
Owner:SNAP INC
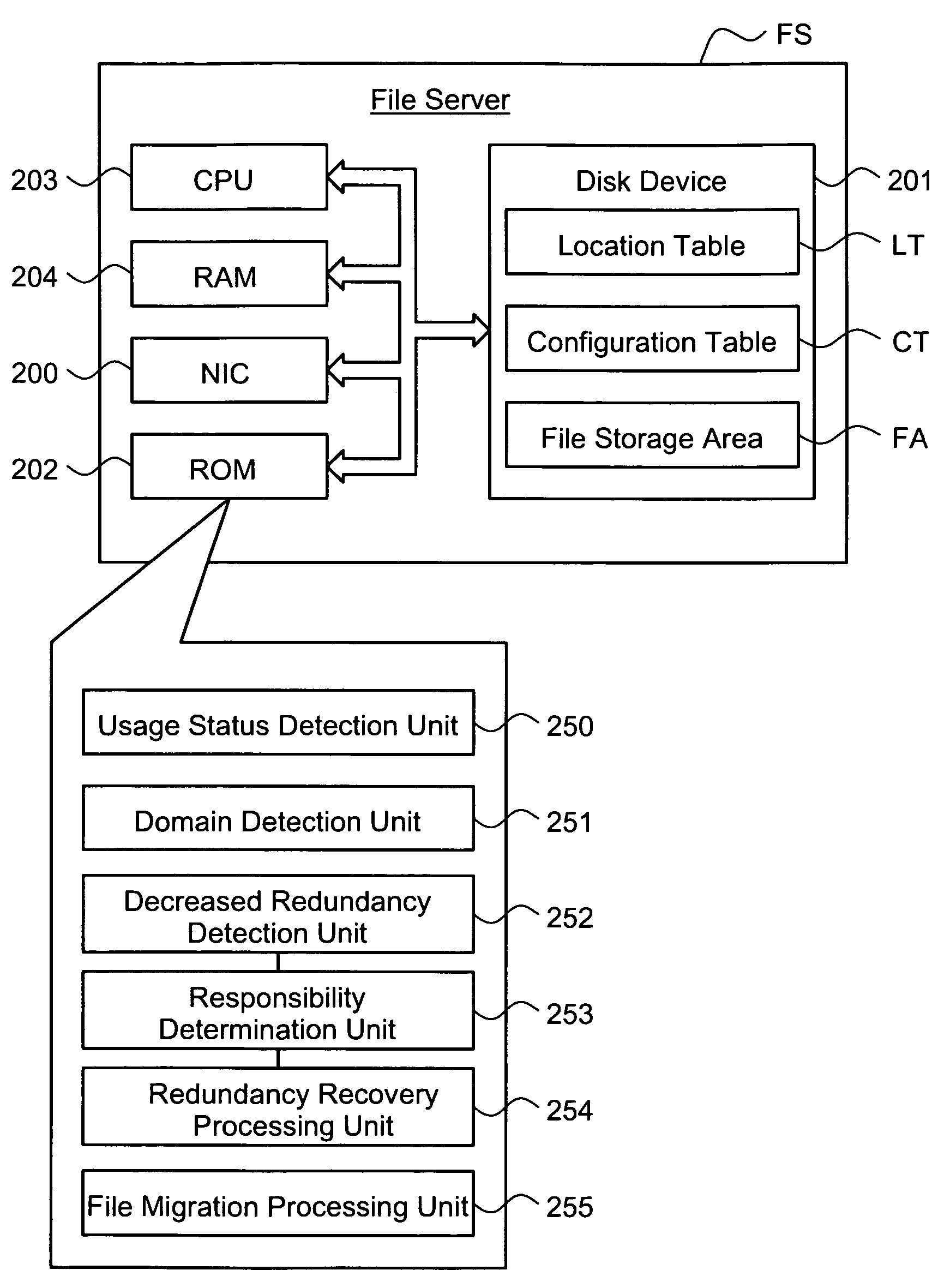
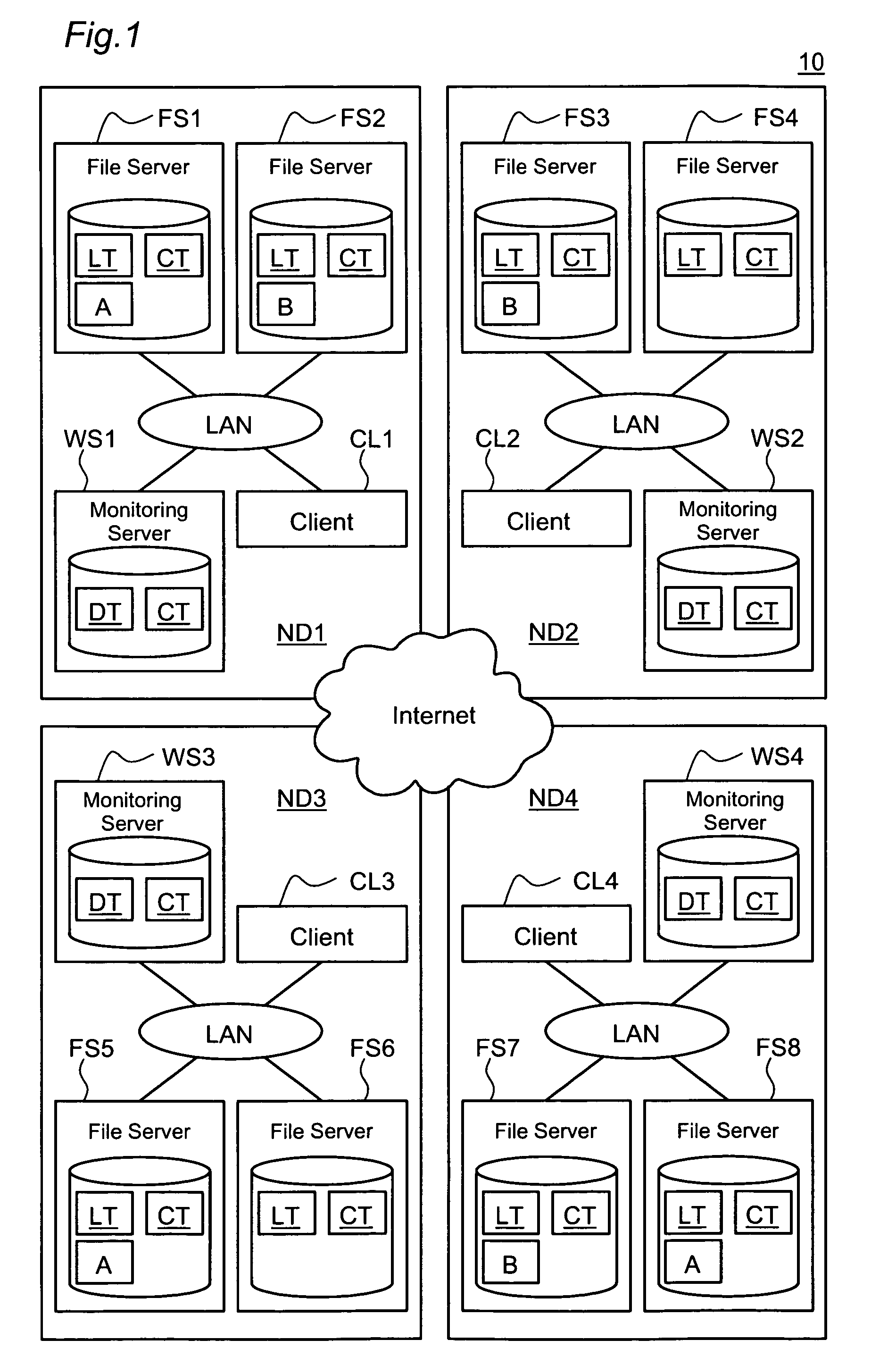
File server and file server controller
InactiveUS7146368B2Maintaining redundancyReduce distanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsFile replicationServer replication
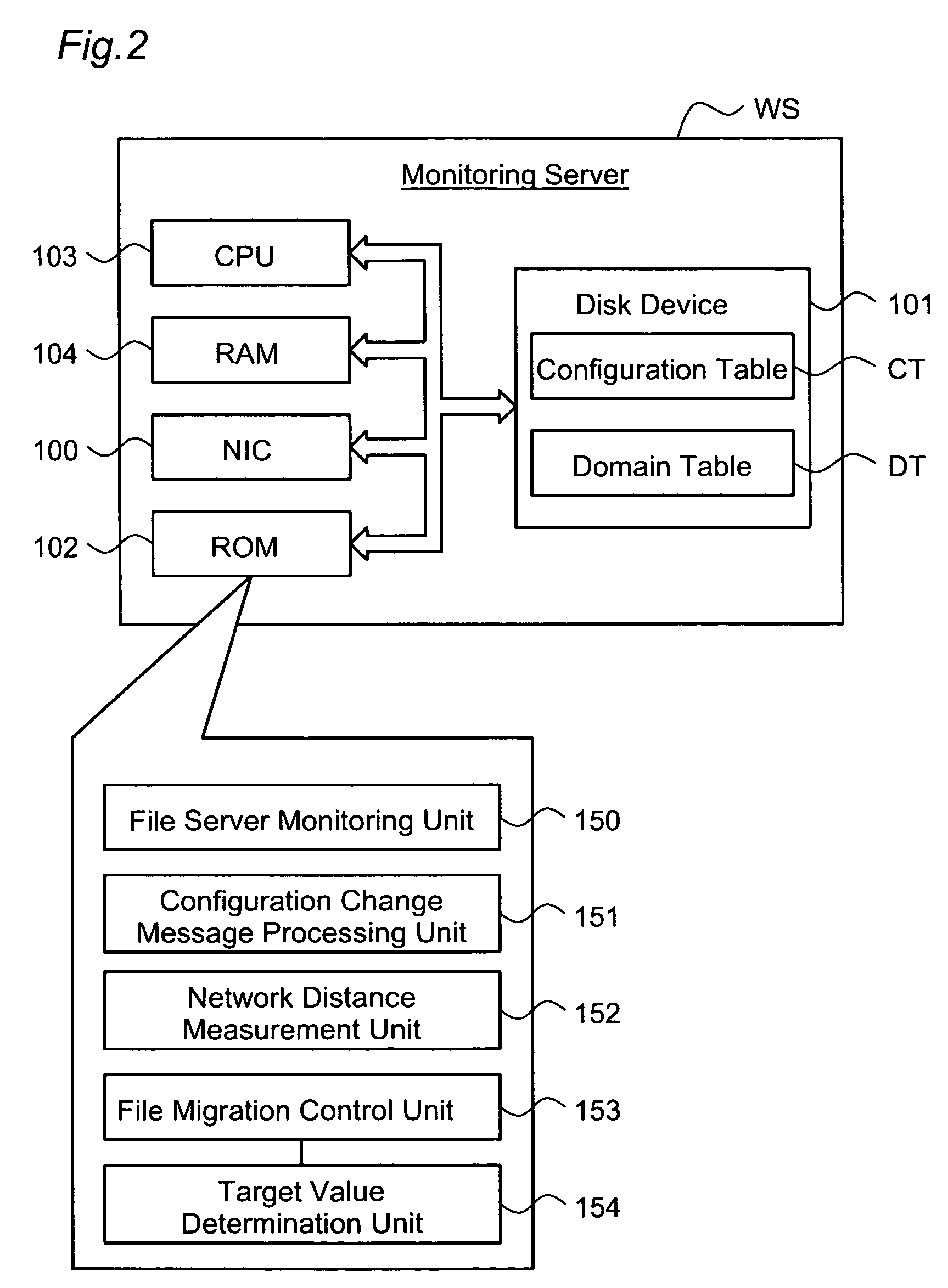
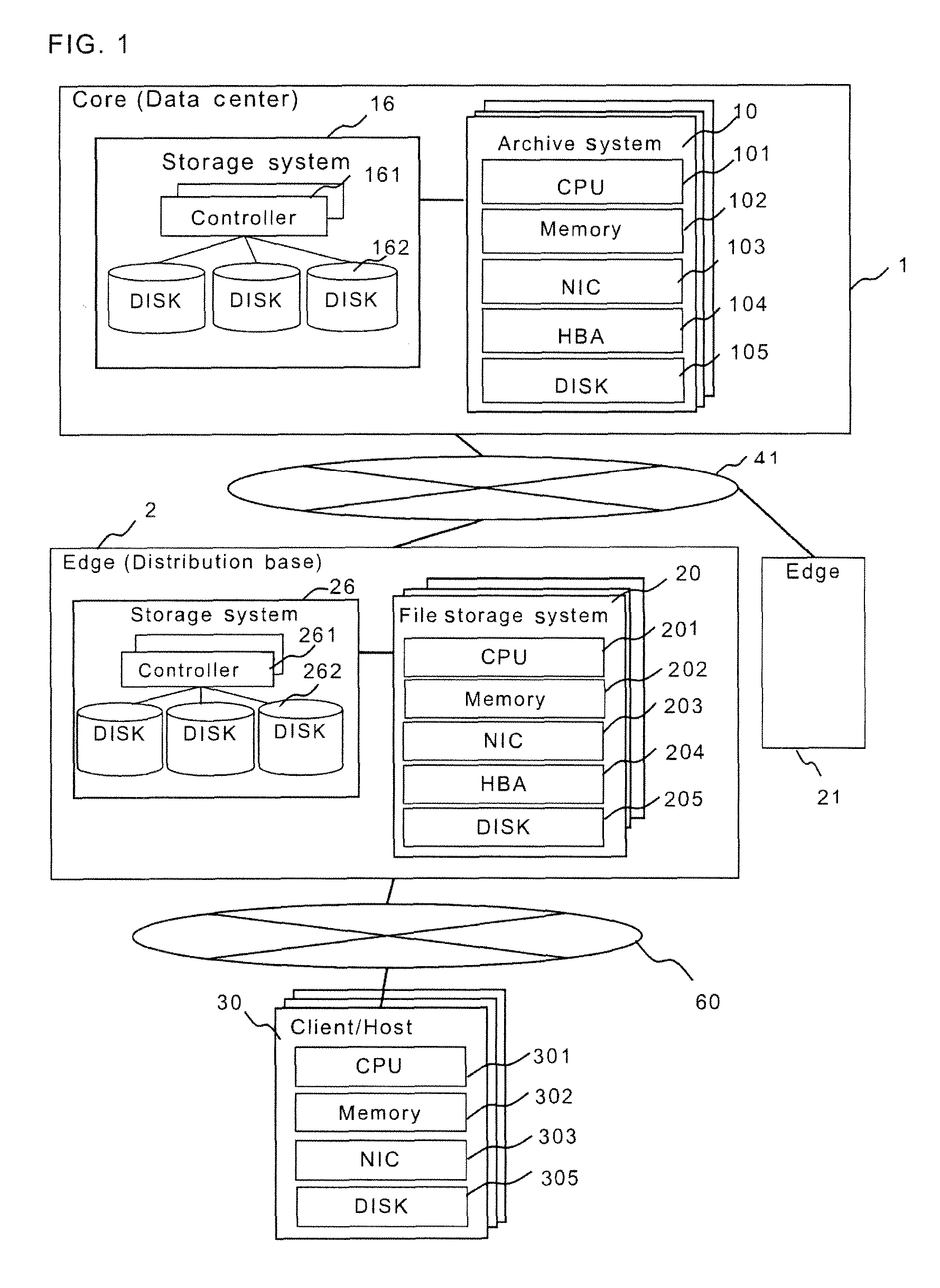
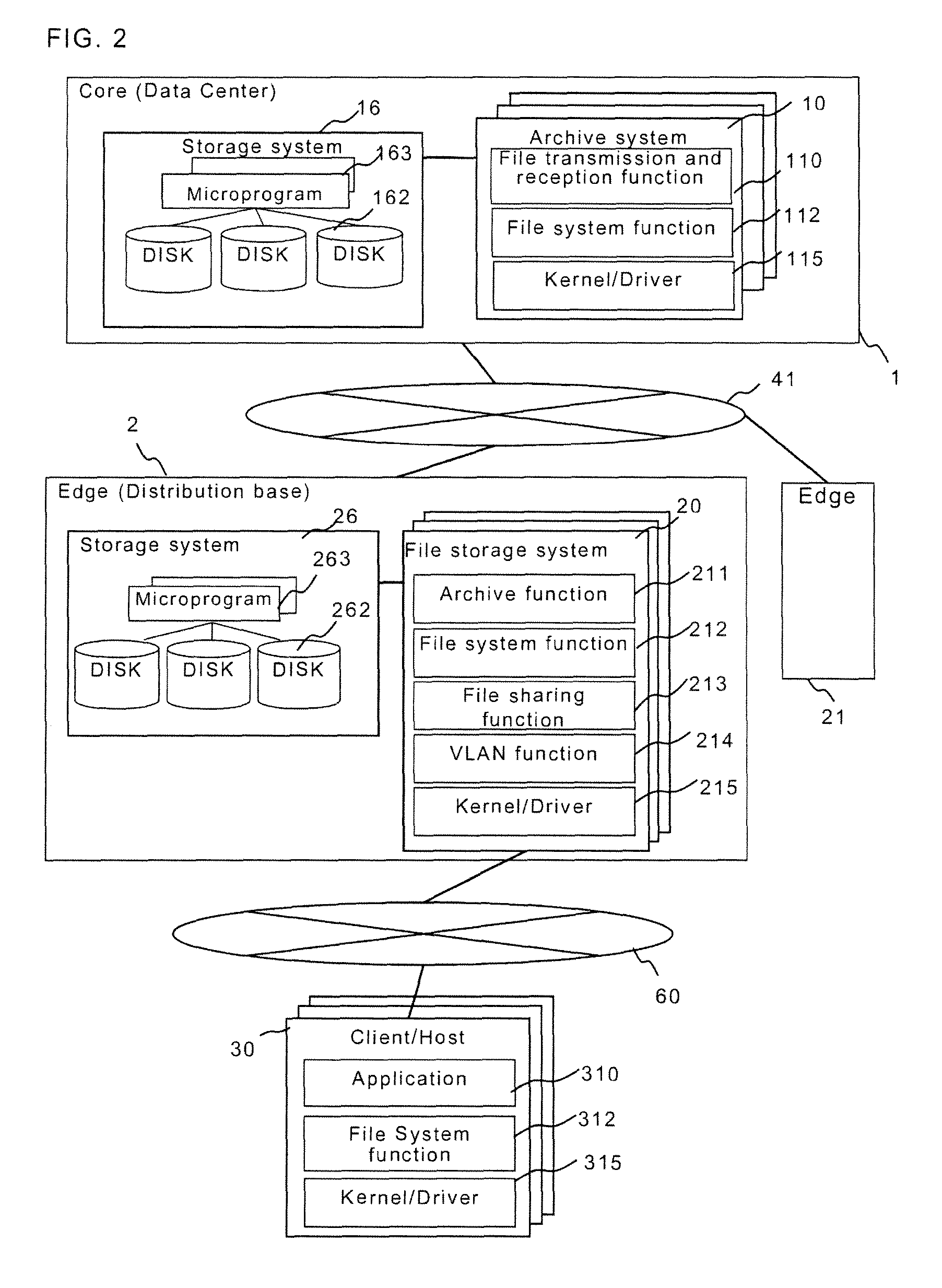
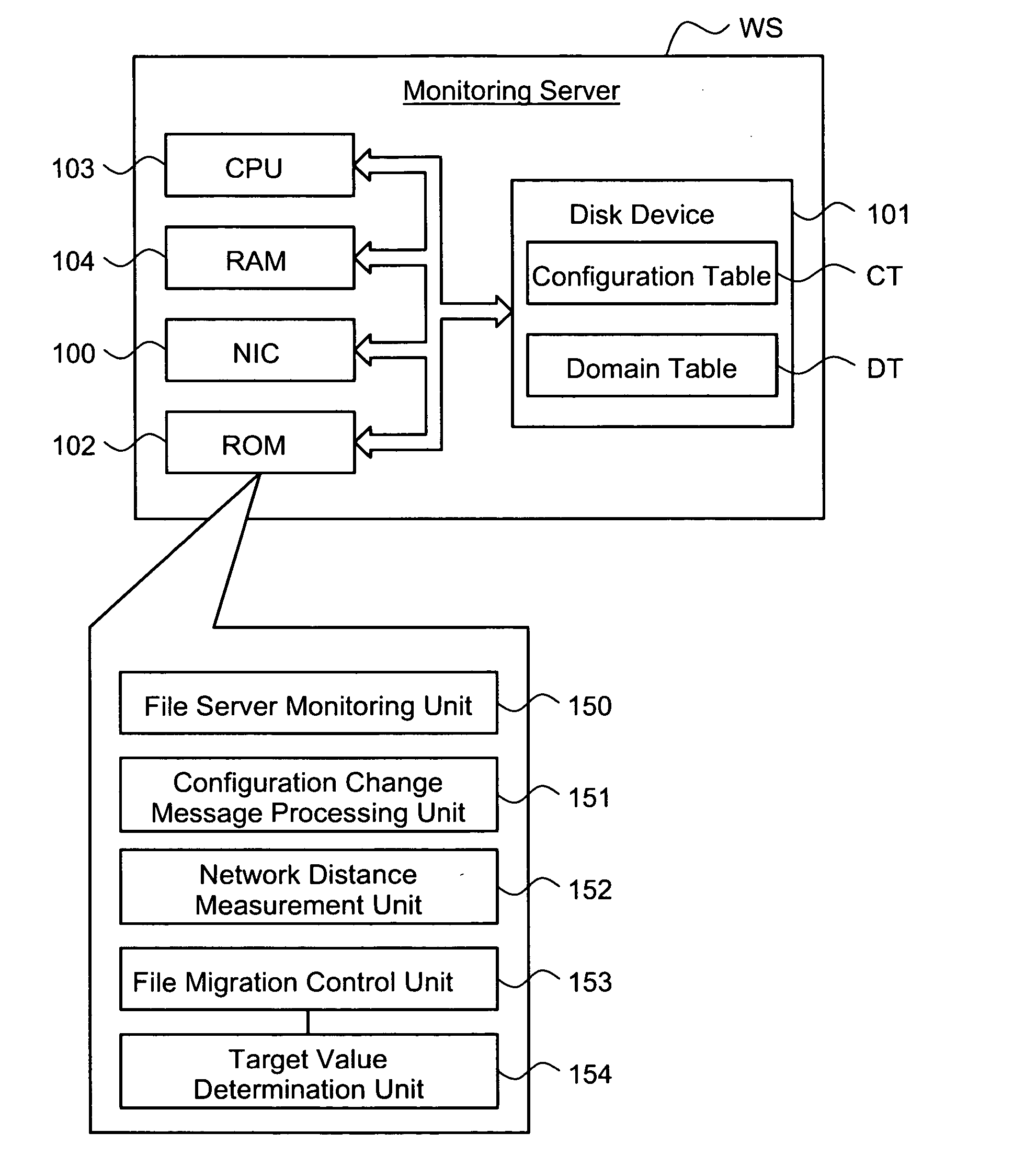
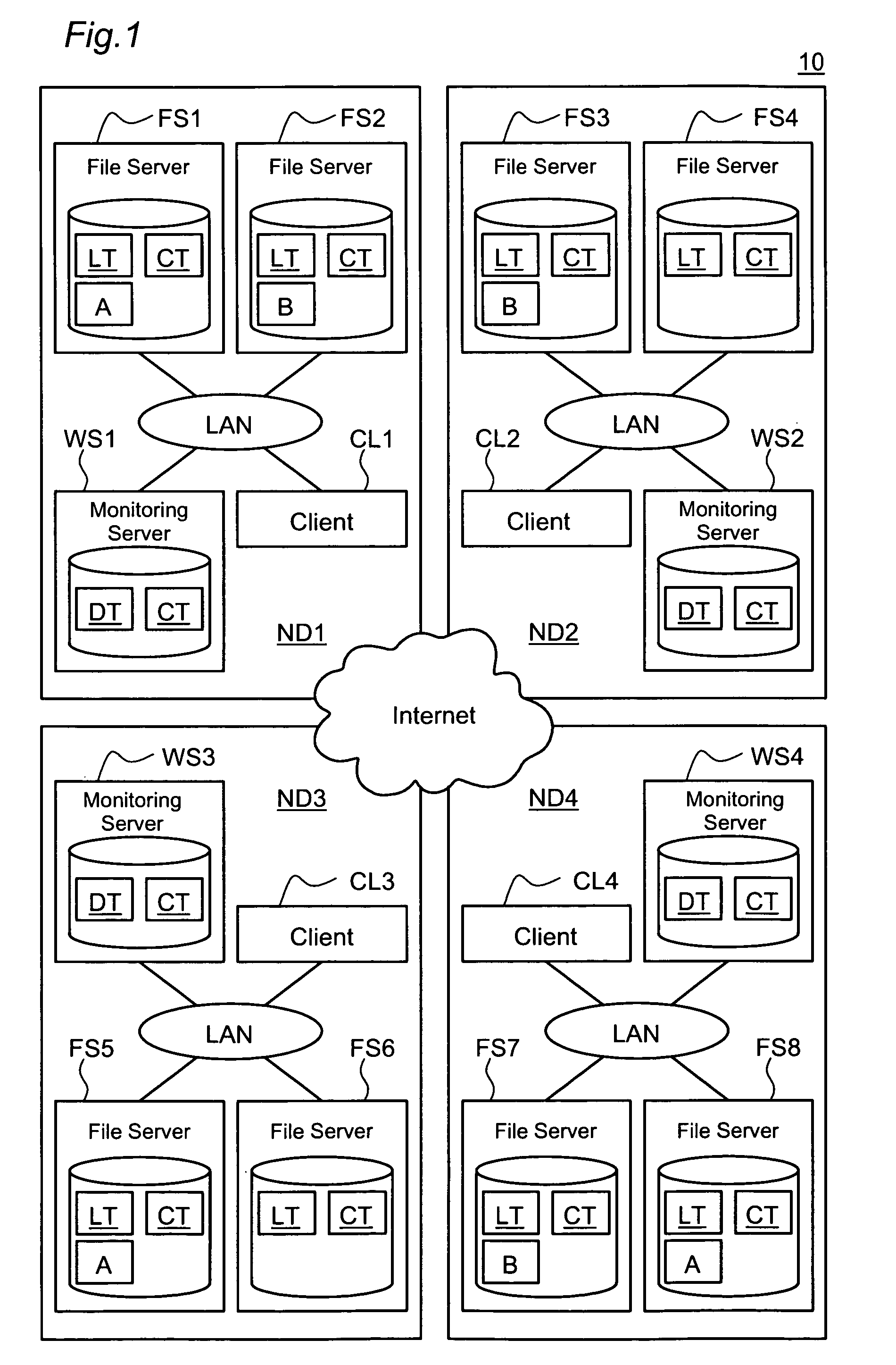
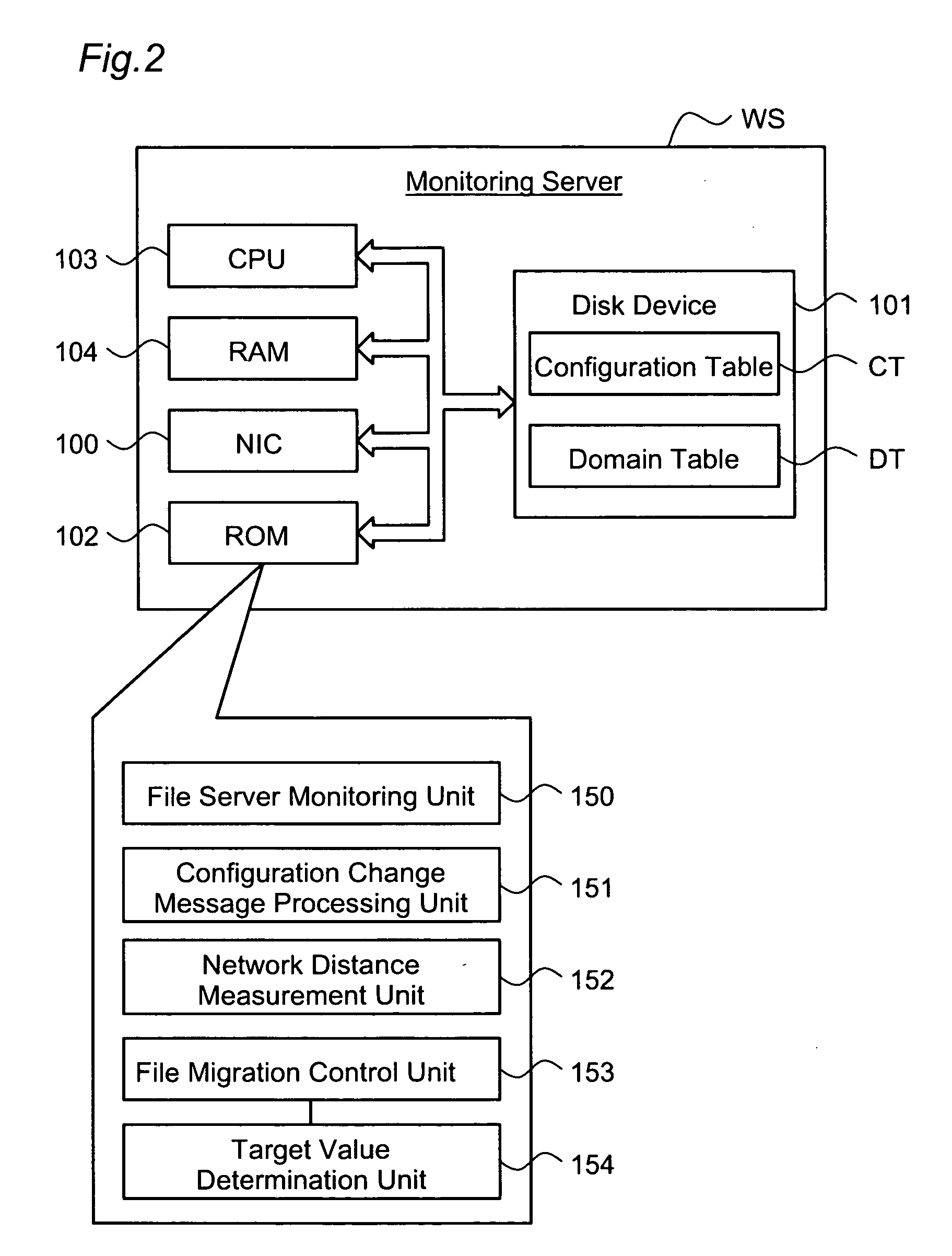
The redundancy of a file is maintained without using a centralized controller in a system where file servers are connected via a network. Each domain ND within a file storage system includes a file server FS, a monitoring server WS, and a client CL, which are connected via a LAN. When the file server FS detects a failure in another file server FS in the system, it considers that redundancy of a file stored in the failed file server FS has decreased, and then determines whether or not it is responsible for recovering the redundancy. If the file server FS has determined that it is responsible for recovering the redundancy, it selects a file server FS as a file copy source and a file server FS as a file copy destination, and then copies the identical file from the copy source server to the copy destination server.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
File storage system for transferring file to remote archive system
InactiveUS20130024421A1Raise priorityIncrease speedDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsTime informationFile copying
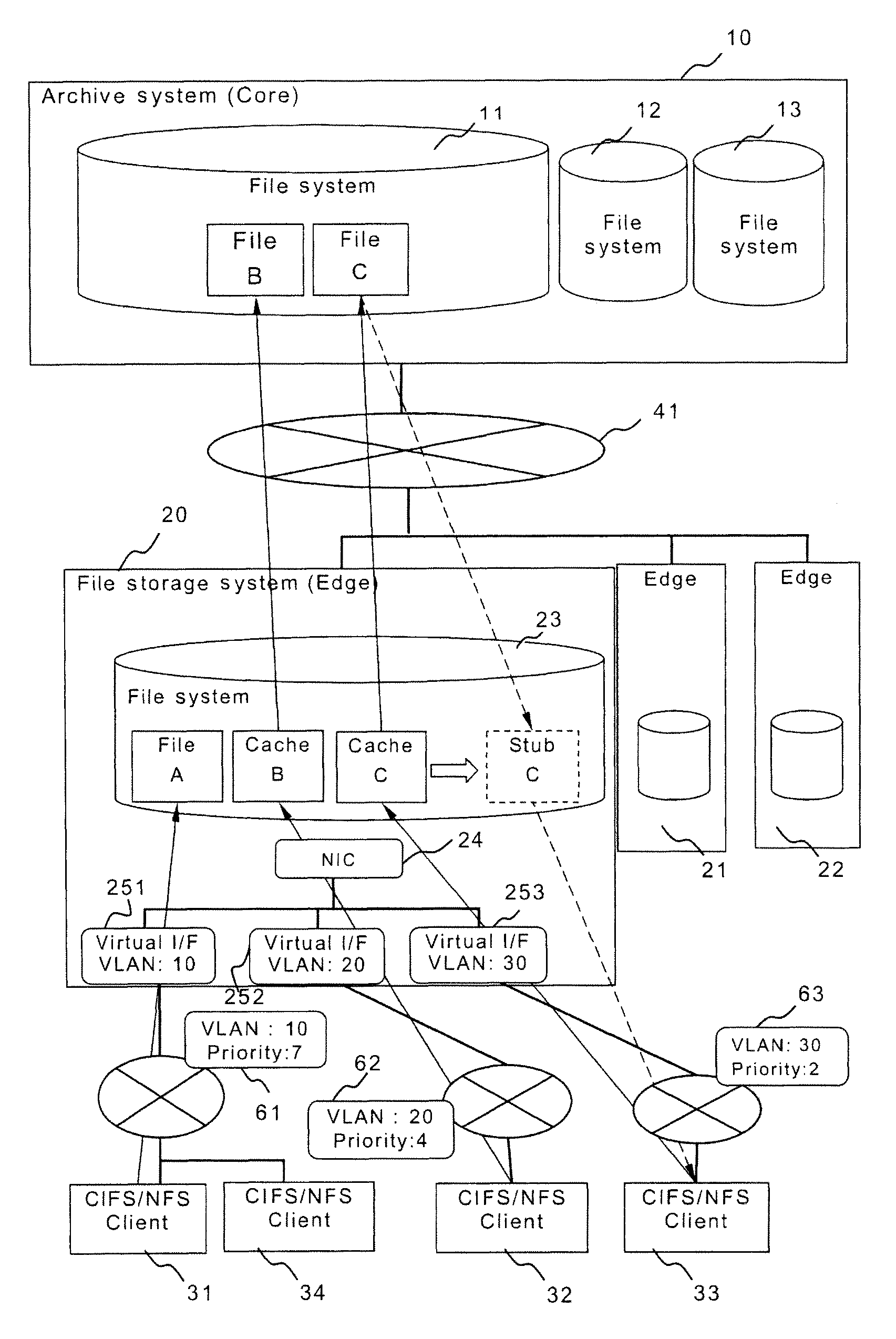
An archive system and a file storage system are connected via a communication network, wherein the file storage system (a) replicates a file to the archive system; (b) manages the replicated file as a file to be stubbed; (c) updates the priority information of a metadata based on a result computed from the priority information of metadata of an already stored file and the priority information of the access request; (d) retains an access date and time information of the access request in the metadata; (e) monitors a used capacity of the file storage system; and (f) starts a deleting process of a file to be stubbed using either the priority information or the date and time information in the metadata when the used capacity exceeds an upper limit set in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
File replication in a distributed segmented file system
InactiveUS7836017B1Expand accessDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile replicationFile system
A system includes storage configured to store file system entities, including directories and files, residing in segments of a distributed, segmented single file system, file servers configured to implement the single file system with separate ones of the file servers controlling metadata of separate ones of the segments, and a controller configured to control storage of files in the file system such that for a master file stored in a first segment, a first replica of the master file will be stored in a second segment that is physically separate from the first segment, the controller being further configured to control storage of directories in the file system such that a single directory will include identifiers for the master file and the first replica.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and method for transforming object code
InactiveUS20020170047A1Software engineeringProgram loading/initiatingFile replicationProgramming language
A unified programming object is described comprising: a shared constant pool comprising global constant pool entries mapped from local constant pool entries of two or more class files; and a plurality of object code copied from the two or more class files to the unified programming object and identified by the global constant pool entries.
Owner:DANGER RES
Method and system for querying data and exporting report
InactiveCN103034658AShorten the timeImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsFile replicationDatabase server
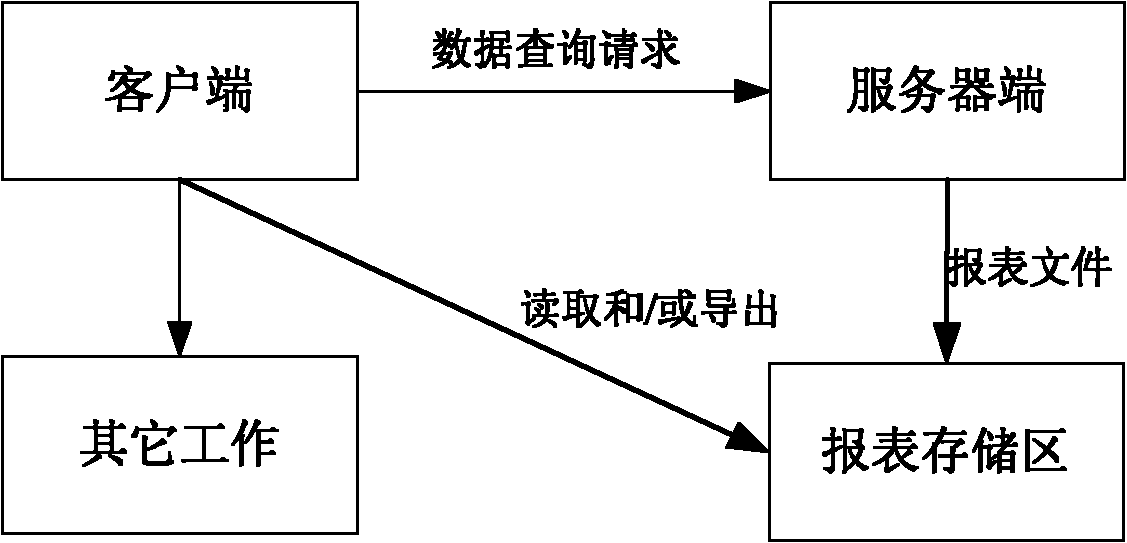
The invention discloses a method and a system for querying data and exporting a report. The method comprises the following steps: a client side sends a data querying request input by a user at a data querying page through an internet to a Web server; the Web server receives the data querying request, extracts query condition information, packet mode information and sorting mode information of the data querying request, and generates a querying statistics command; a database server queries a database according to the querying statistics command and generates a report file; and the database server duplicates the report file to the Web server for the client side to download. According to the method and the system for querying the data and exporting the report, the system resource can be saved; the working efficiency is improved; the valuable time is saved for the user; and the higher benefit can be brought for the enterprises.
Owner:FUJIAN RAYNEN TECH
File server and file server controller
InactiveUS20050102289A1Easy to useCapacity remains stableData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersFile replicationServer replication
The object of the present invention is to maintain redundancy of file without using a centralized controller in a system where a plurality of file servers are connected with each other via a network. Each domain ND within a file storage system 10 includes a file server FS, a monitoring server WS, and a client CL, which are connected with each other via a LAN. When the file server FS detects a failure having occurred in another file server FS included in the system, it considers that redundancy of a file stored in the failed file server FS has decreased, and then determines whether or not it is responsible for recovering the redundancy. If the file server FS has determined that it is responsible for recovering the redundancy, it selects a file server FS as a file copy source and a file server FS as a file copy destination, and then copies based on the selection the identical file from the copy source server to the copy destination server.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and device for web application debugging
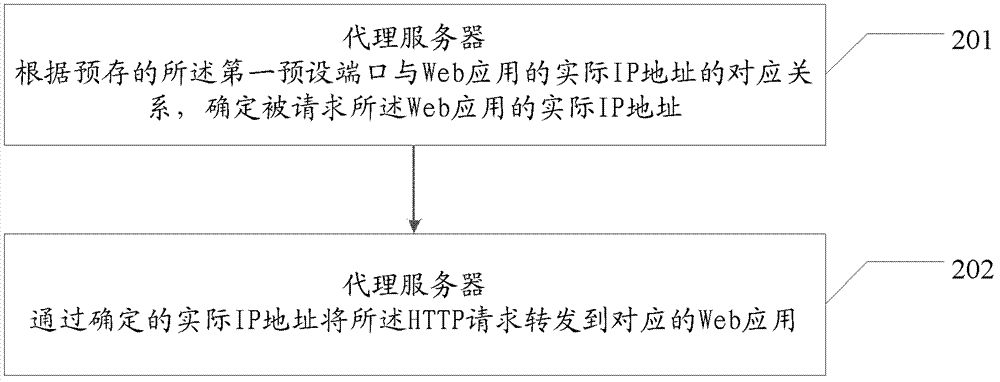
ActiveCN103095783AEliminate remote file copyingOmit operabilityTransmissionFile replicationDomain name
The invention provides a method and a device for web application debugging. The method for the web application debugging comprises the following steps: analyzing a first hyper text transport protocol (HTTP) request through the obtaining of the first HTTP request of a default request port; confirming a first realm name of the first HTTP request; confirming a first preset transmission port corresponding to the first realm name; transmitting the first HTTP request to a corresponding web application through the first preset transmission port; receiving a response content returned by the web application; and returning the response content to a browser which sends the first HTTP request through the default request port. A plurality of web applications in a distributed web system can be simultaneously debugged on a same computer, remote file replication and remote switch operation among a plurality of computers are eliminated, and then operation efficiency of the deployment and the deployment for the web applications in the distributed web system is improved.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
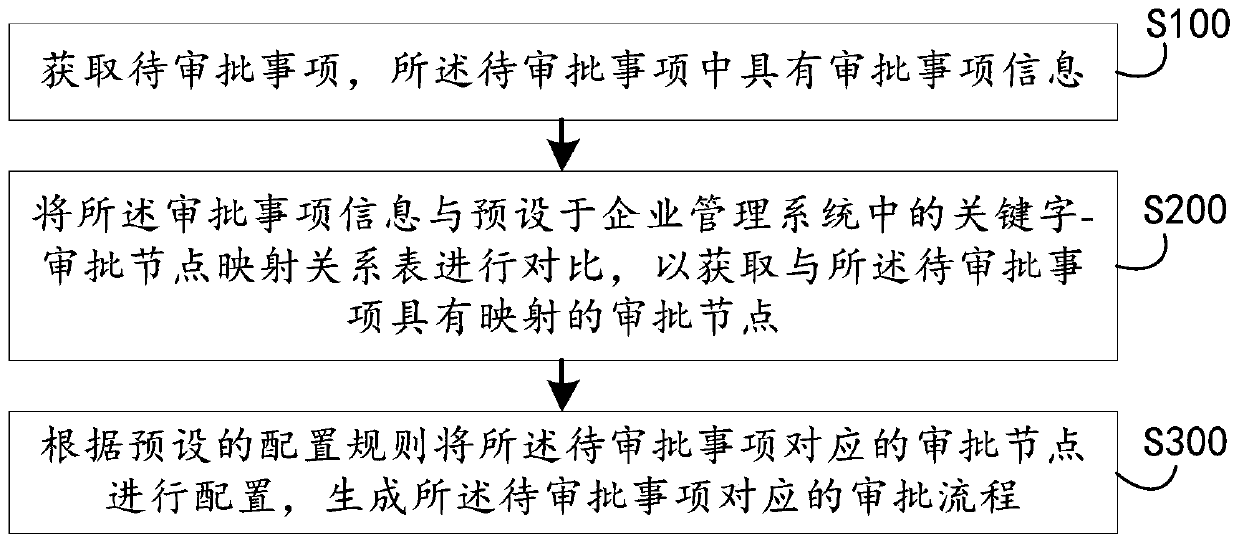
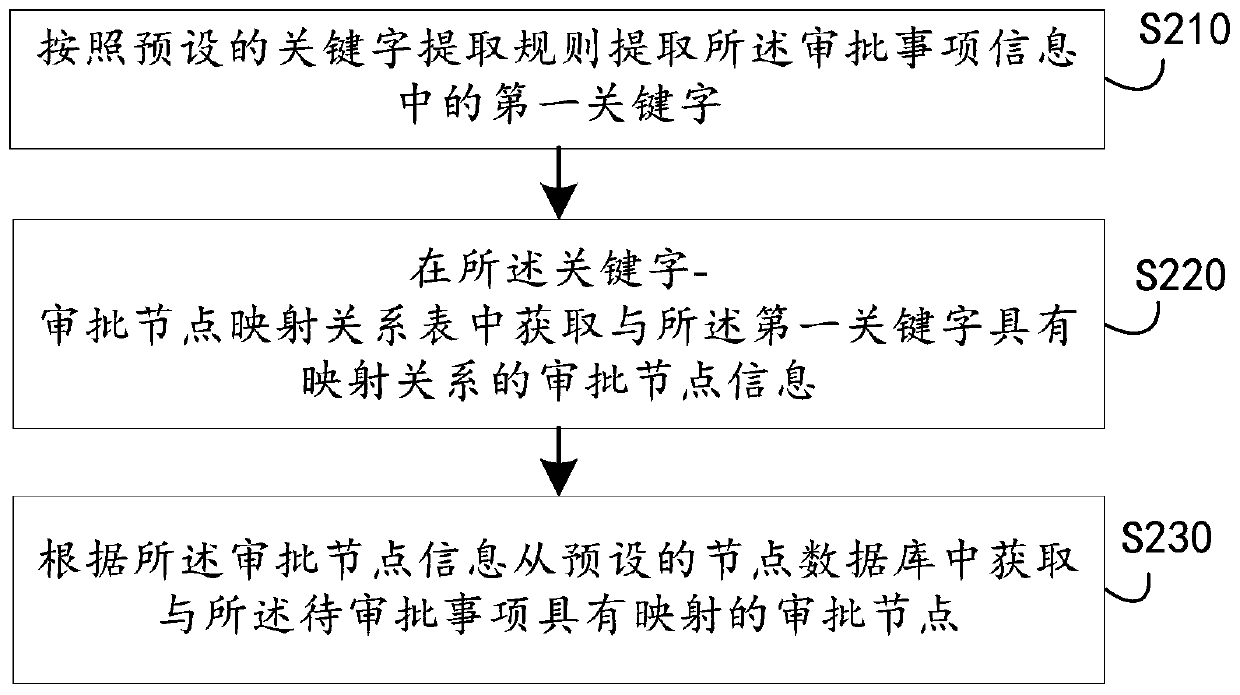
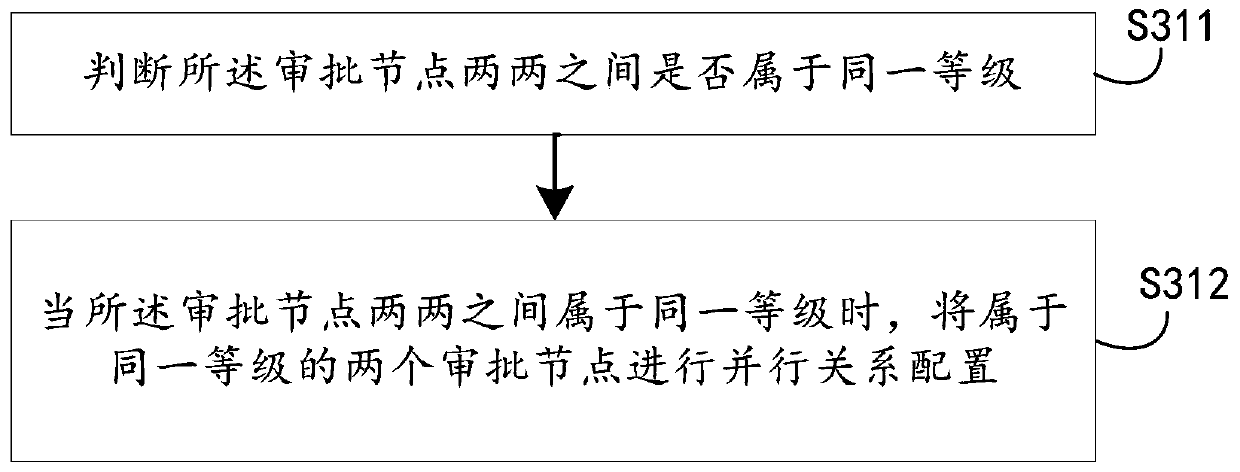
Examination and approval process dynamic configuration method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN109784829AFlexible configurationImprove general performanceOffice automationFile replicationProcess dynamics
The invention discloses an approval process dynamic configuration method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises: acquiring a to-be-approved item, wherein the to-be-approved item contains approval item information; comparing the approval item information and a keyword-approval node mapping relation table preset in an enterprise management system to obtain an approval node having mapping with the to-be-approved item; And configuring the approval node corresponding to the to-be-approved item according to a preset configuration rule, and generating an approval process corresponding to the to-be-approved item. As the approval process corresponding to the to-be-approved item is dynamically generated according to the approval item information, the method has thecharacteristics of flexible configuration, wide application scene, high universality and the like. The approval node can also be set to be an approval node group with a plurality of sub-nodes, circulation between the nodes and the node group and circulation between the node group and the node group are supported, and the efficiency of file replication and the efficiency of related workers can beimproved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
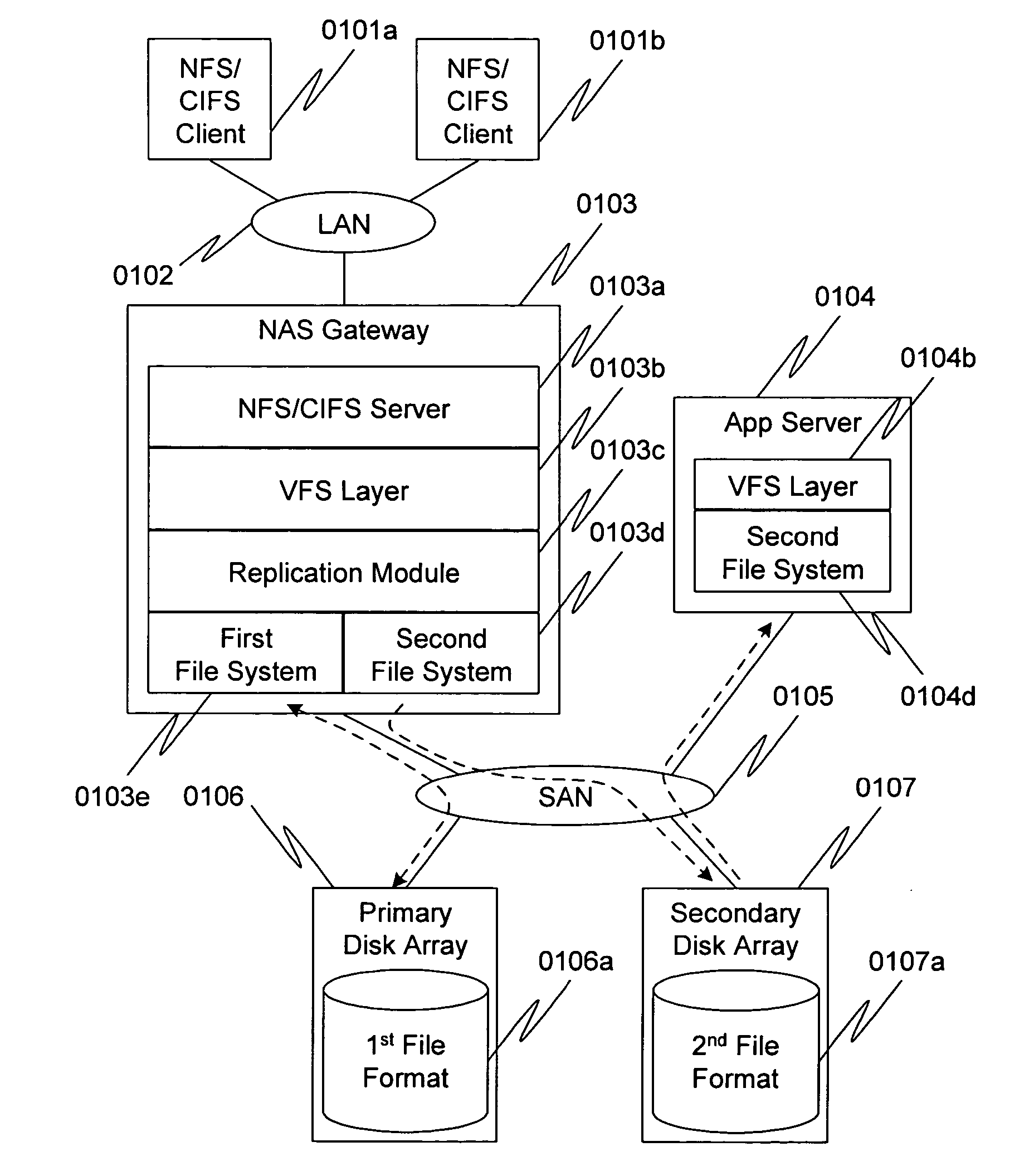
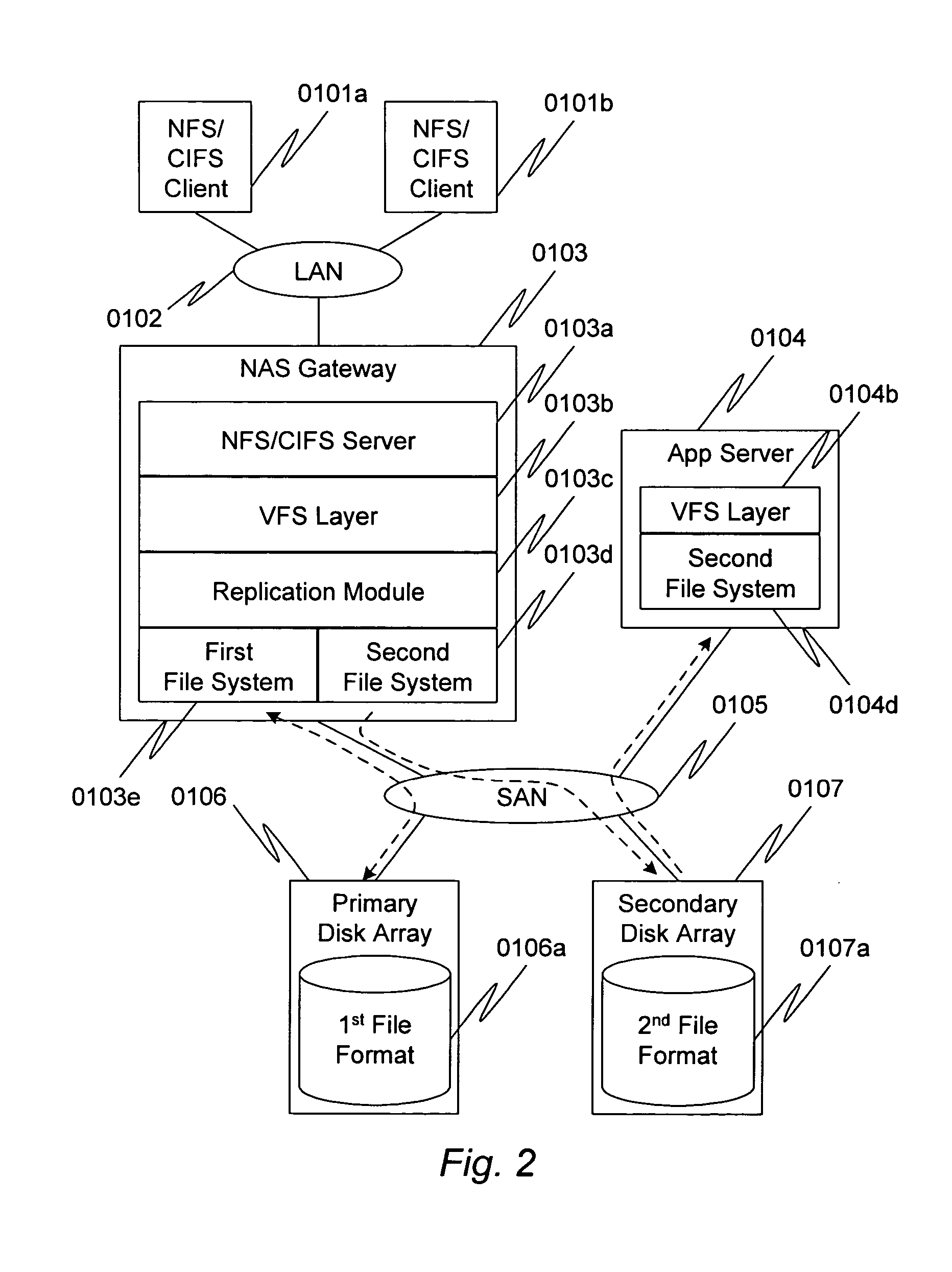
Method and apparatus for file replication with a common format
InactiveUS20050086294A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsPaymentFile replication
File requests sent to a file server that supports a proprietary file system are selectively performed on a second file system, in addition to being performed on the first file system. The second file system is not proprietary, but rather is designed around a publicly known format. Access to the second file system does not require obtaining permission from the vendor of the first file system; e.g., licensing, payment of royalties, and so on.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com