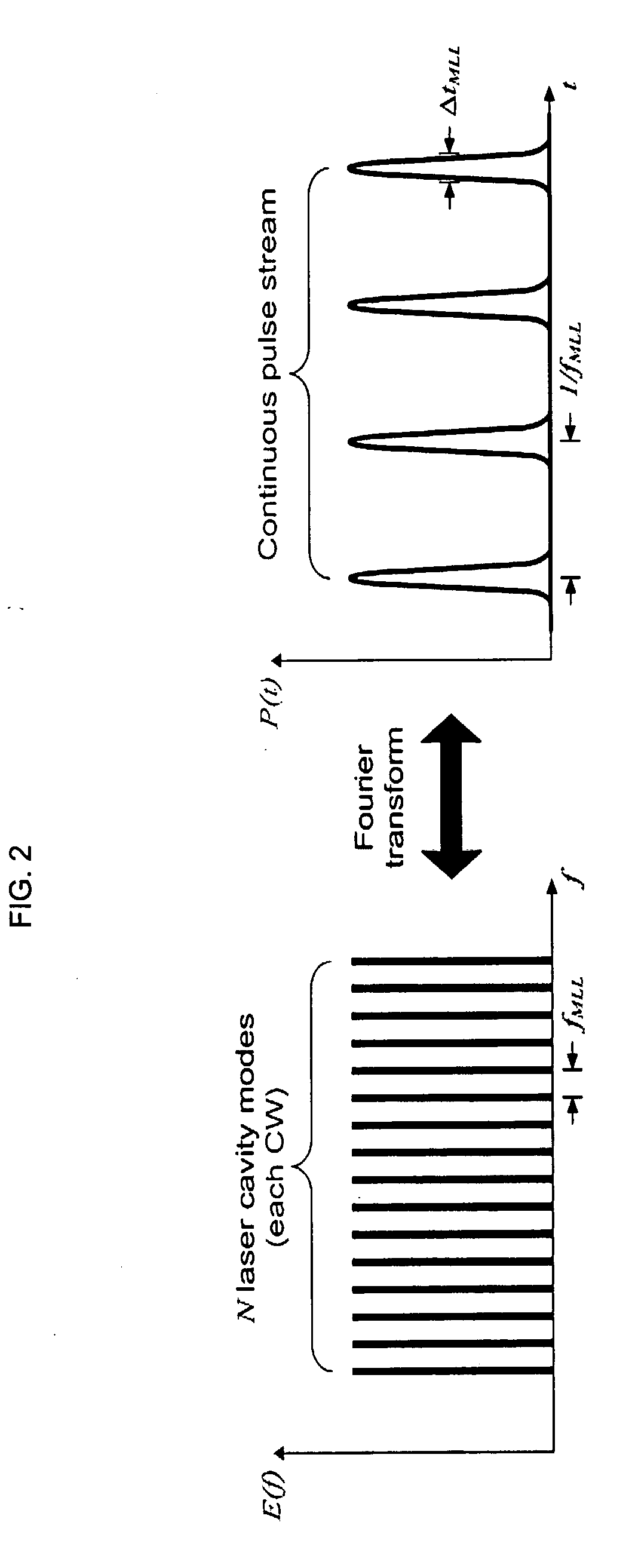
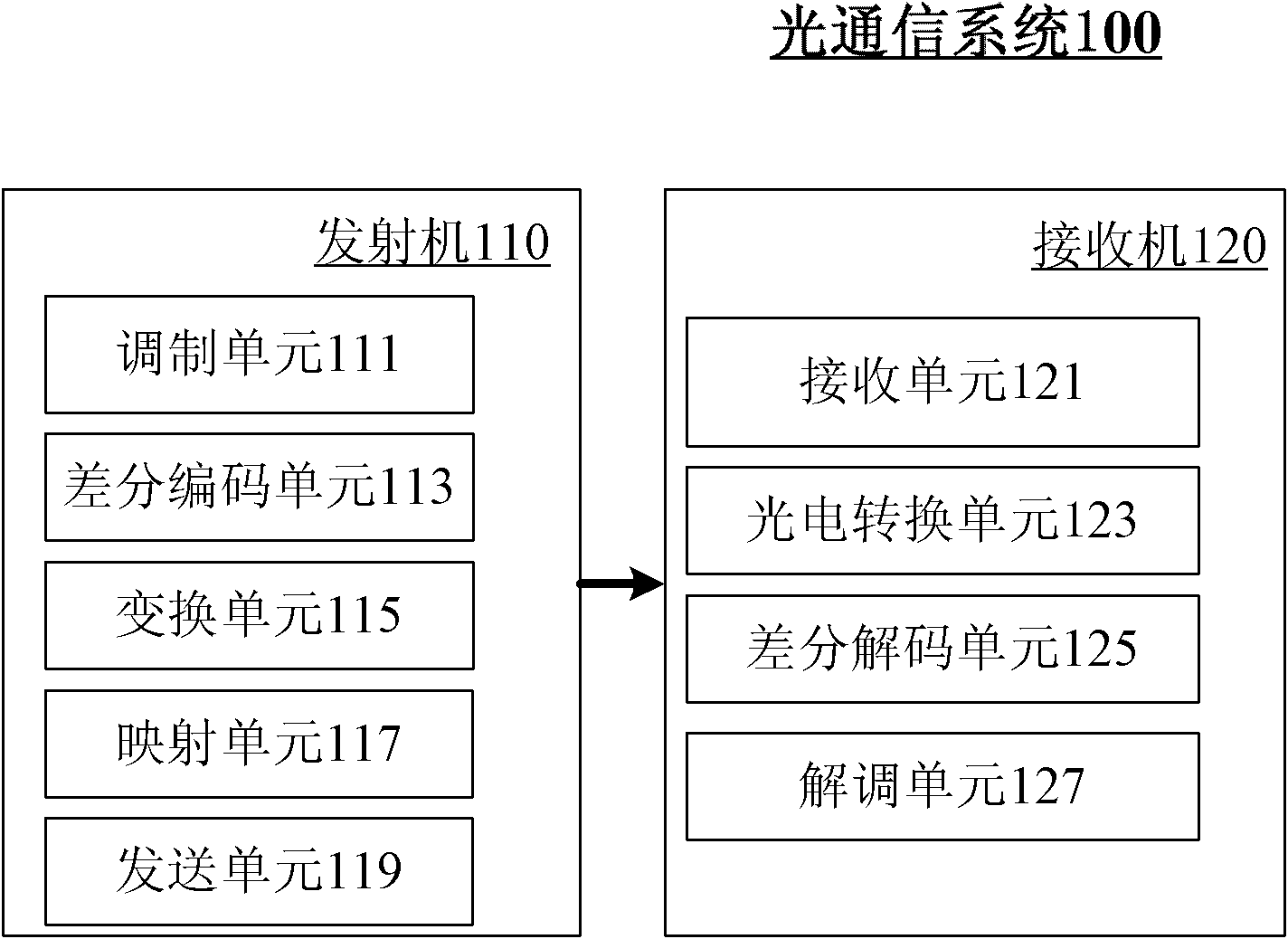
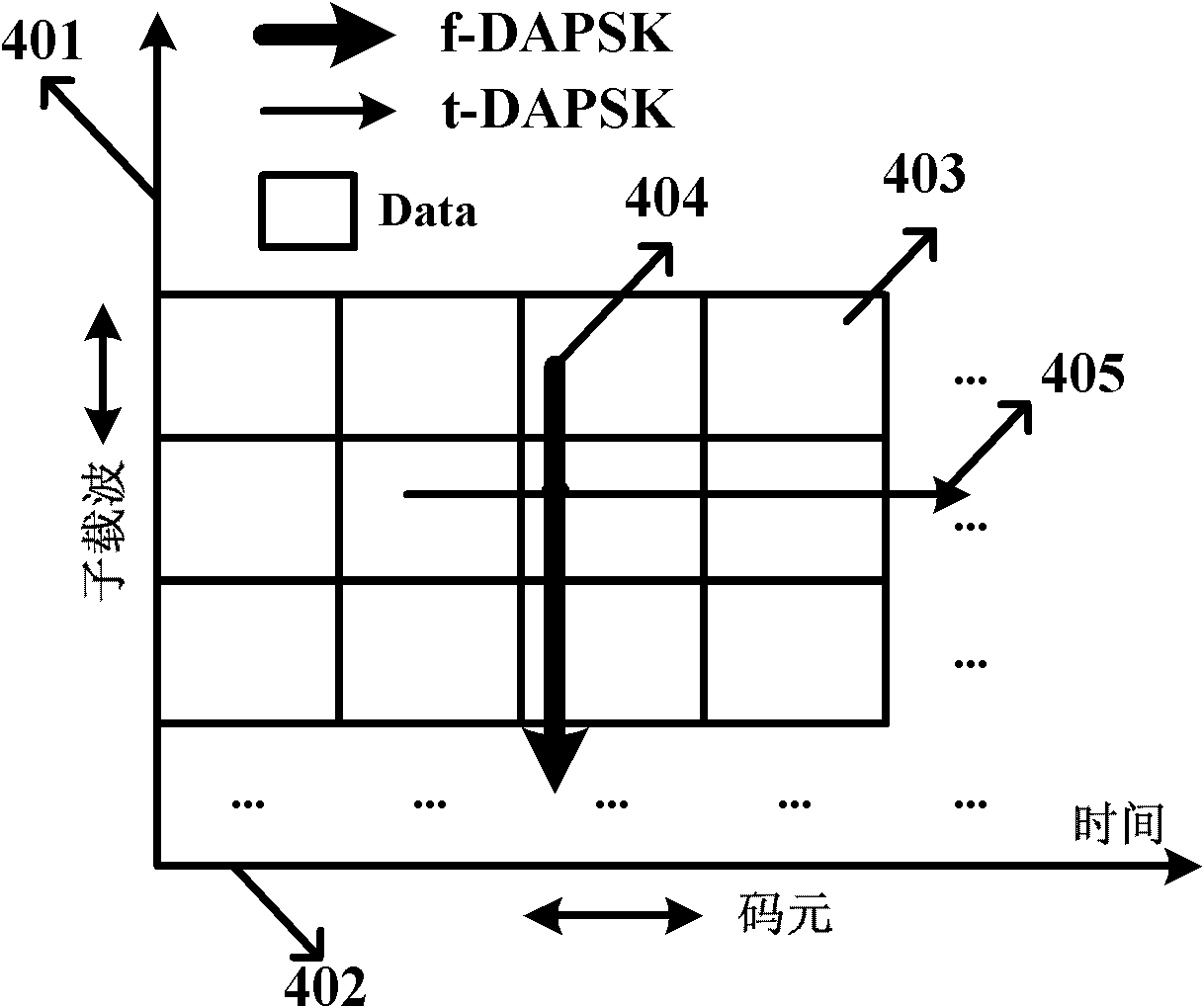
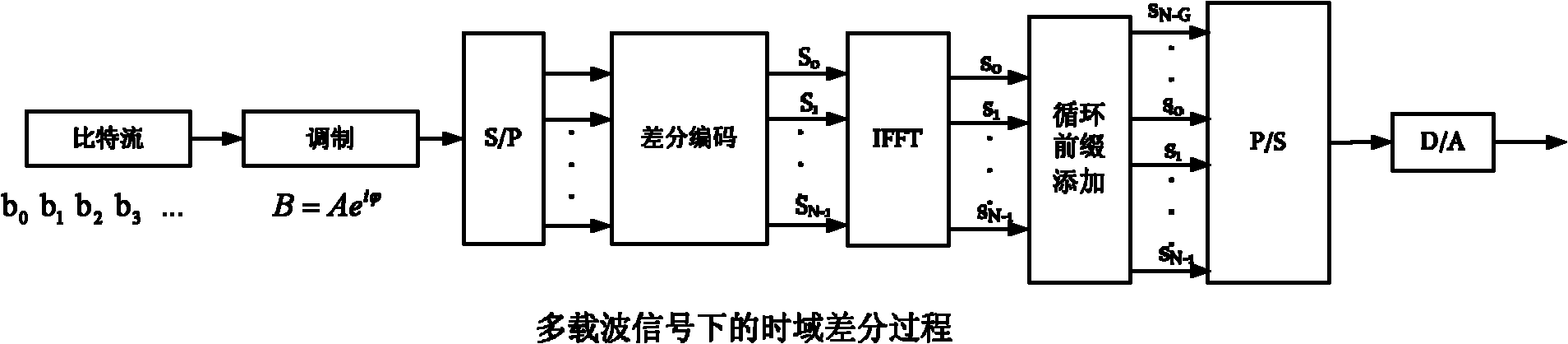
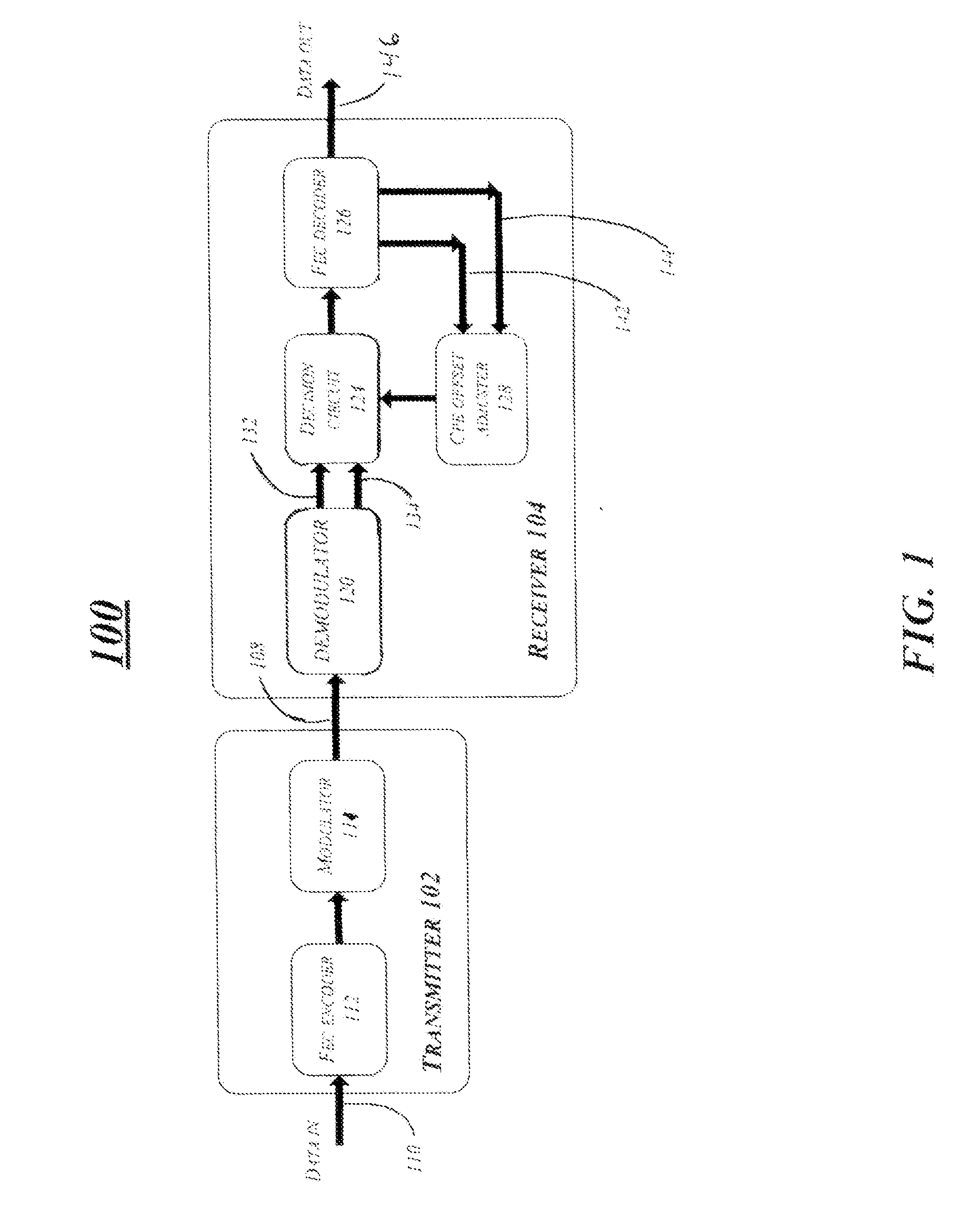
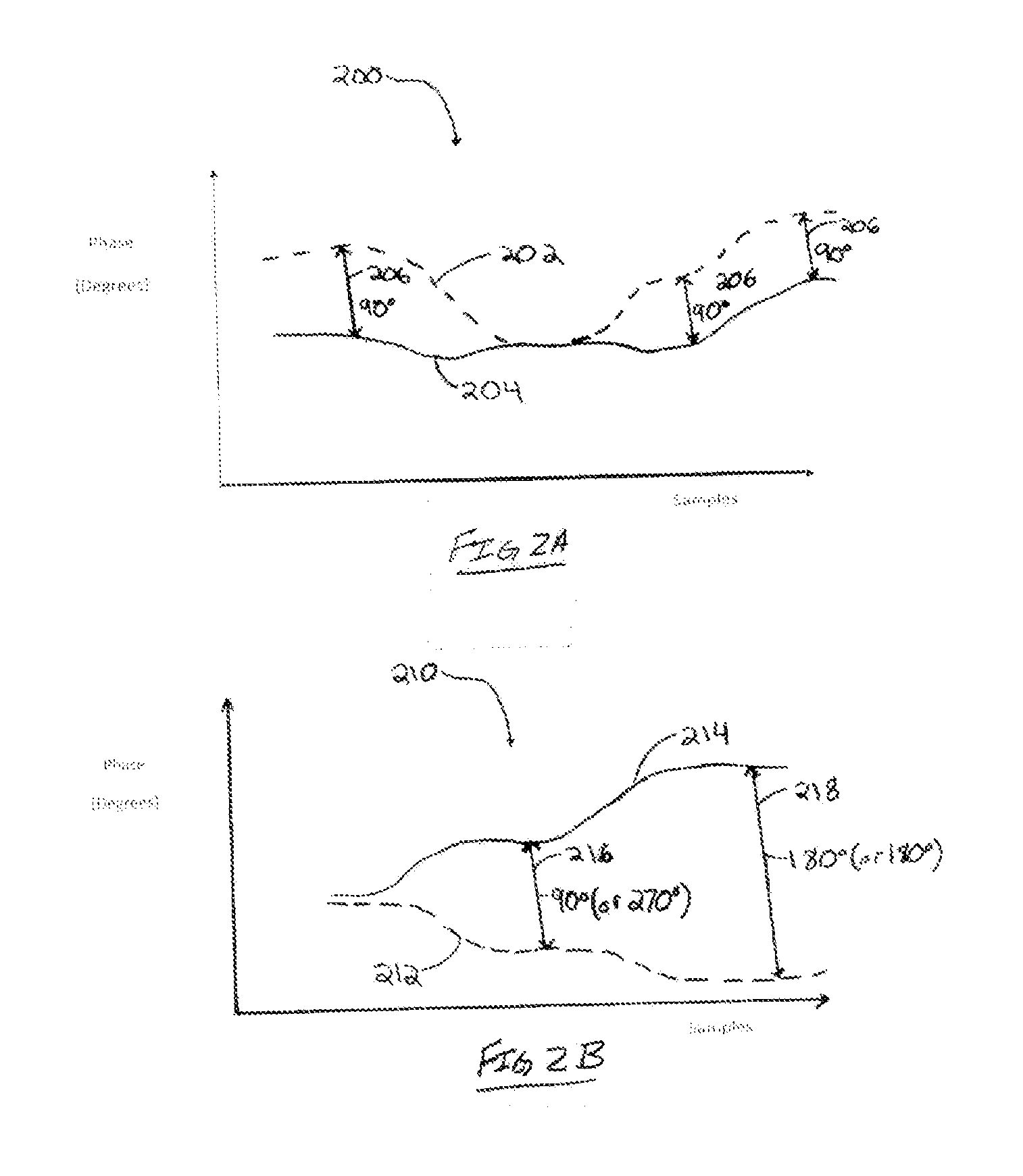
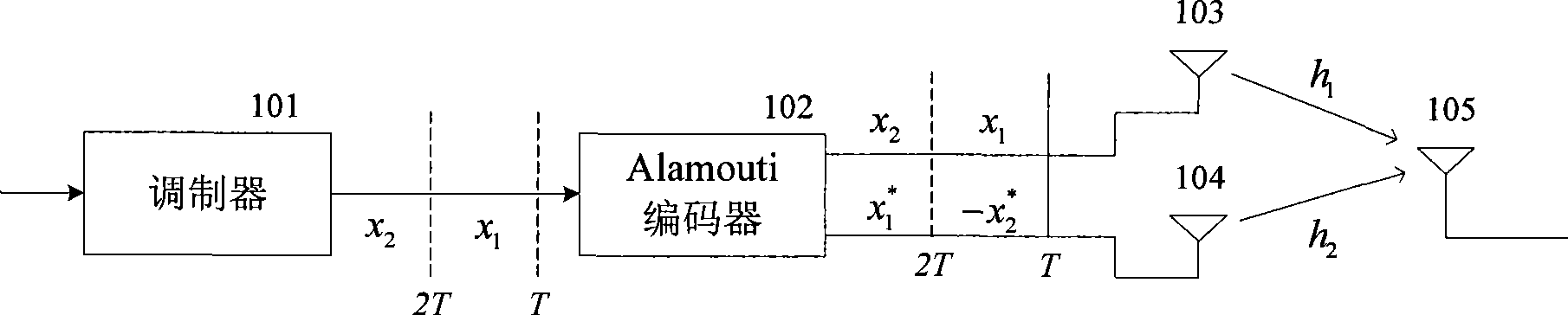
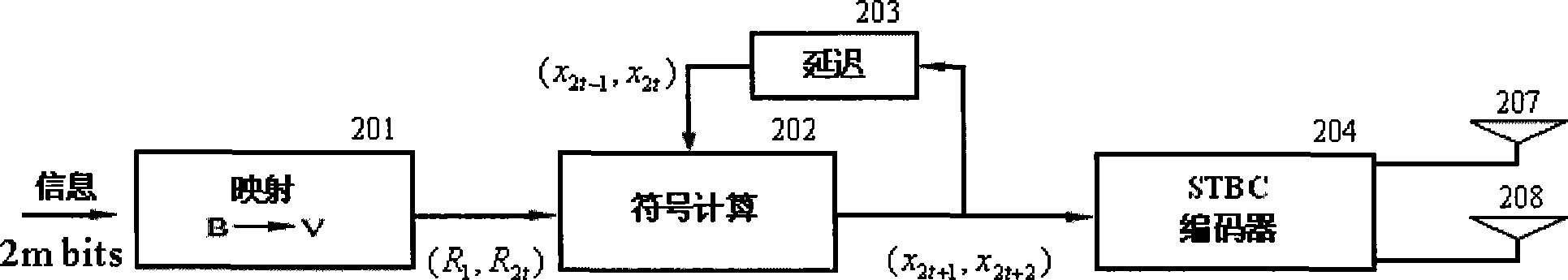
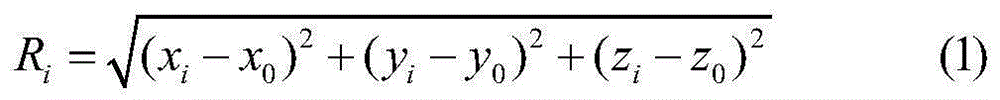Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246 results about "Differential coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In digital communications, differential coding is a technique used to provide unambiguous signal reception when using some types of modulation. It makes data to be transmitted to depend not only on the current signal state (or symbol), but also on the previous one.
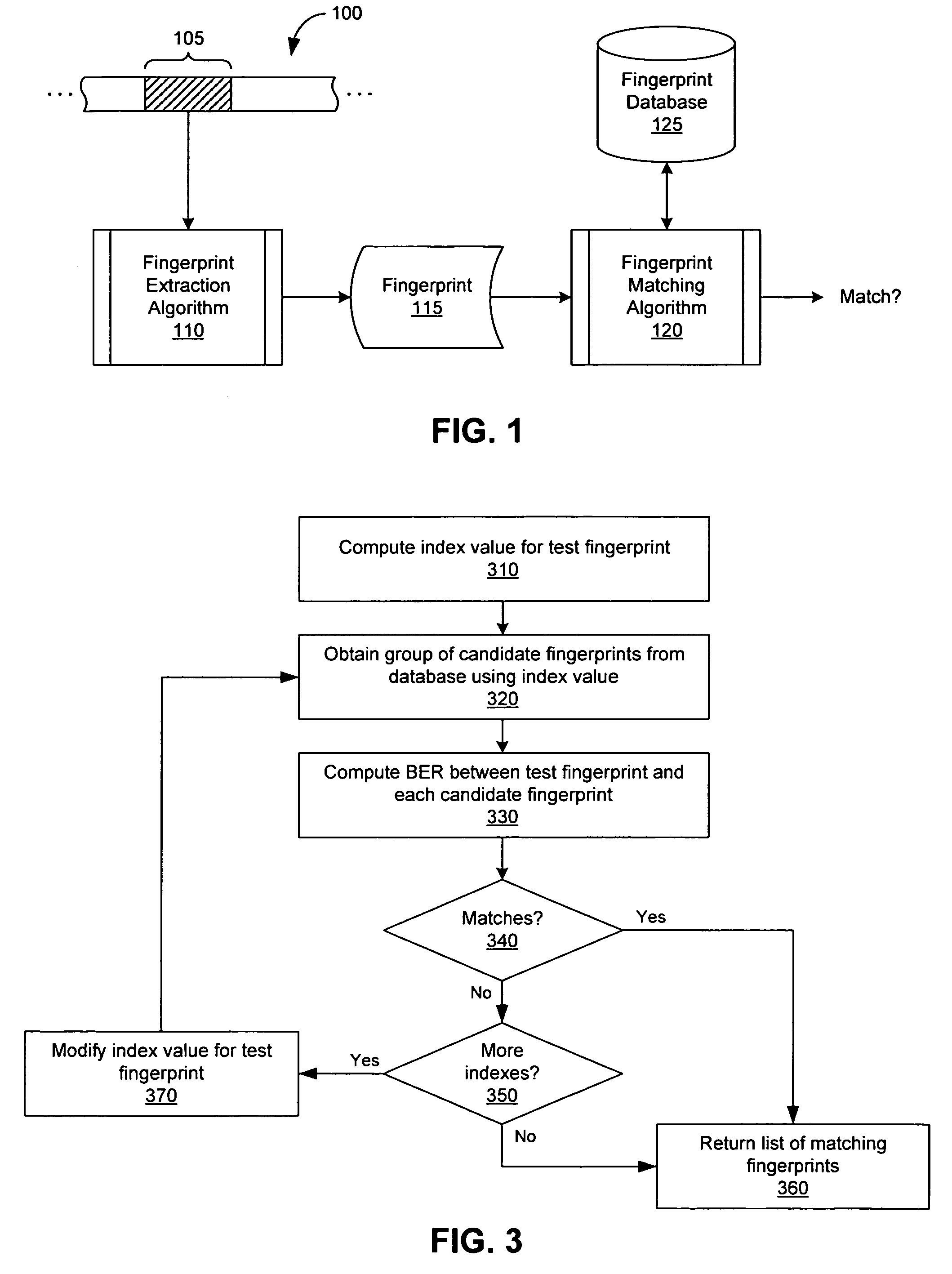
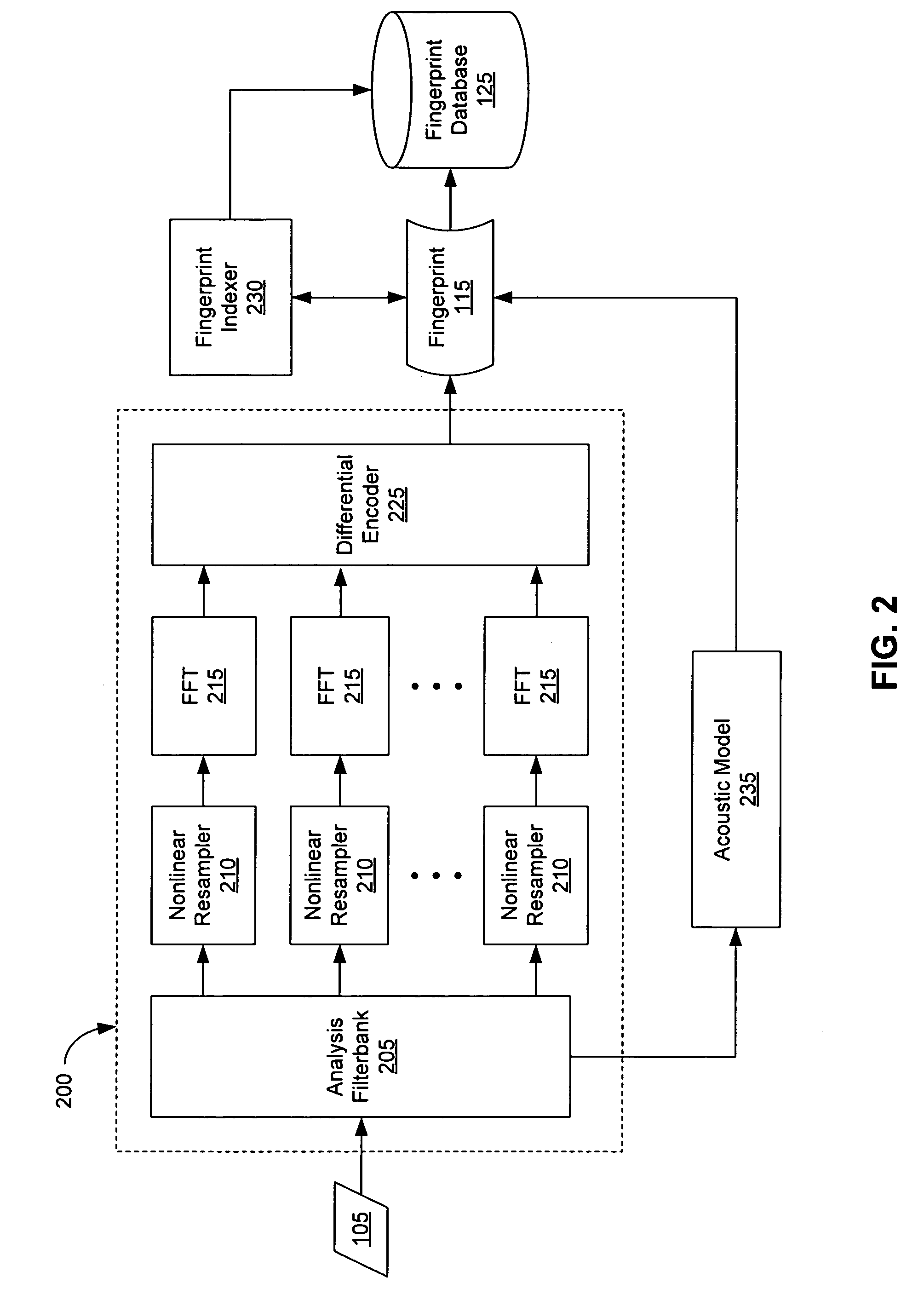
Extraction and matching of characteristic fingerprints from audio signals
InactiveUS20070055500A1Efficient and real-time medium content auditingEfficient and real-time and other reportingDigital data information retrievalSpeech analysisFeature vectorDifferential coding
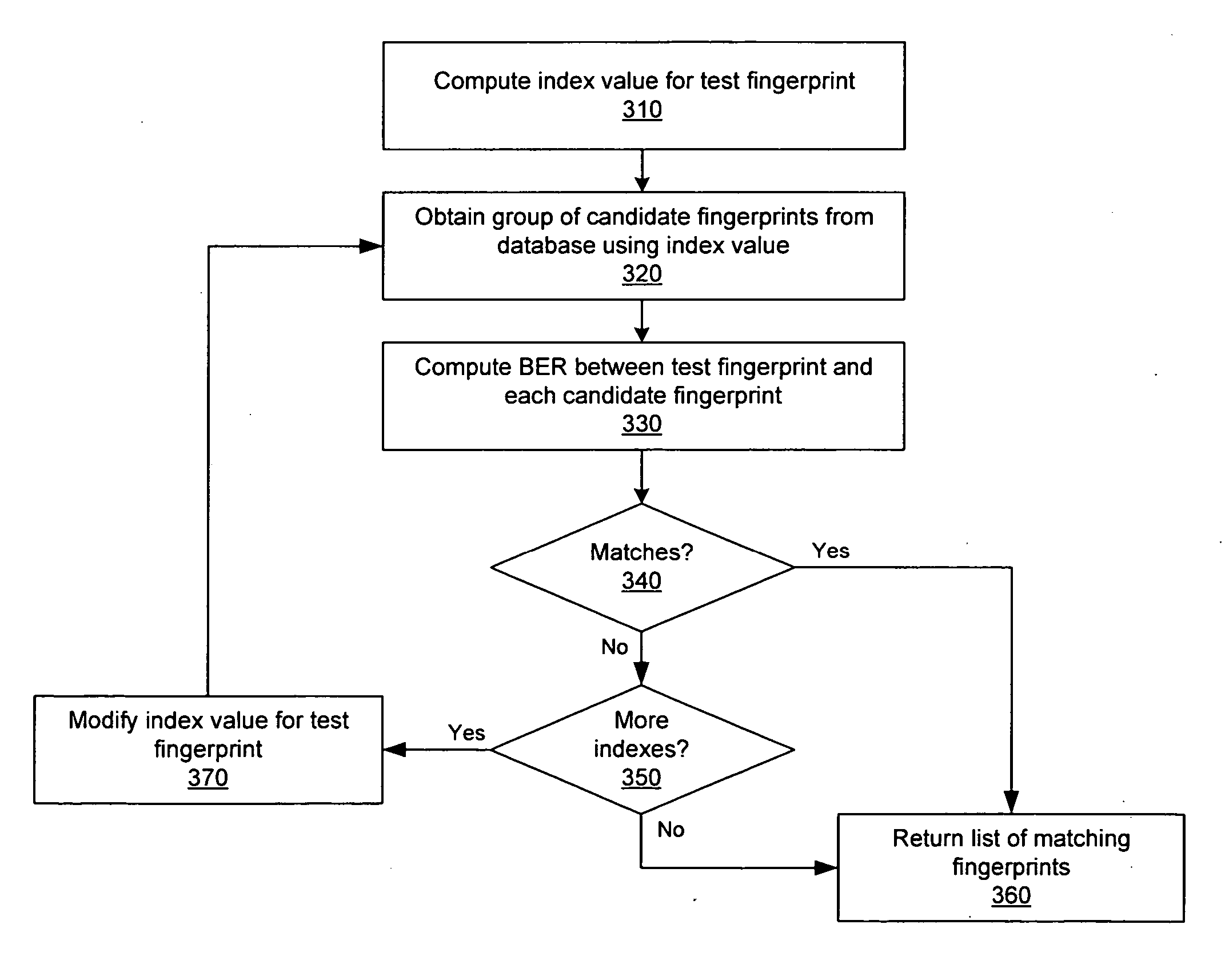
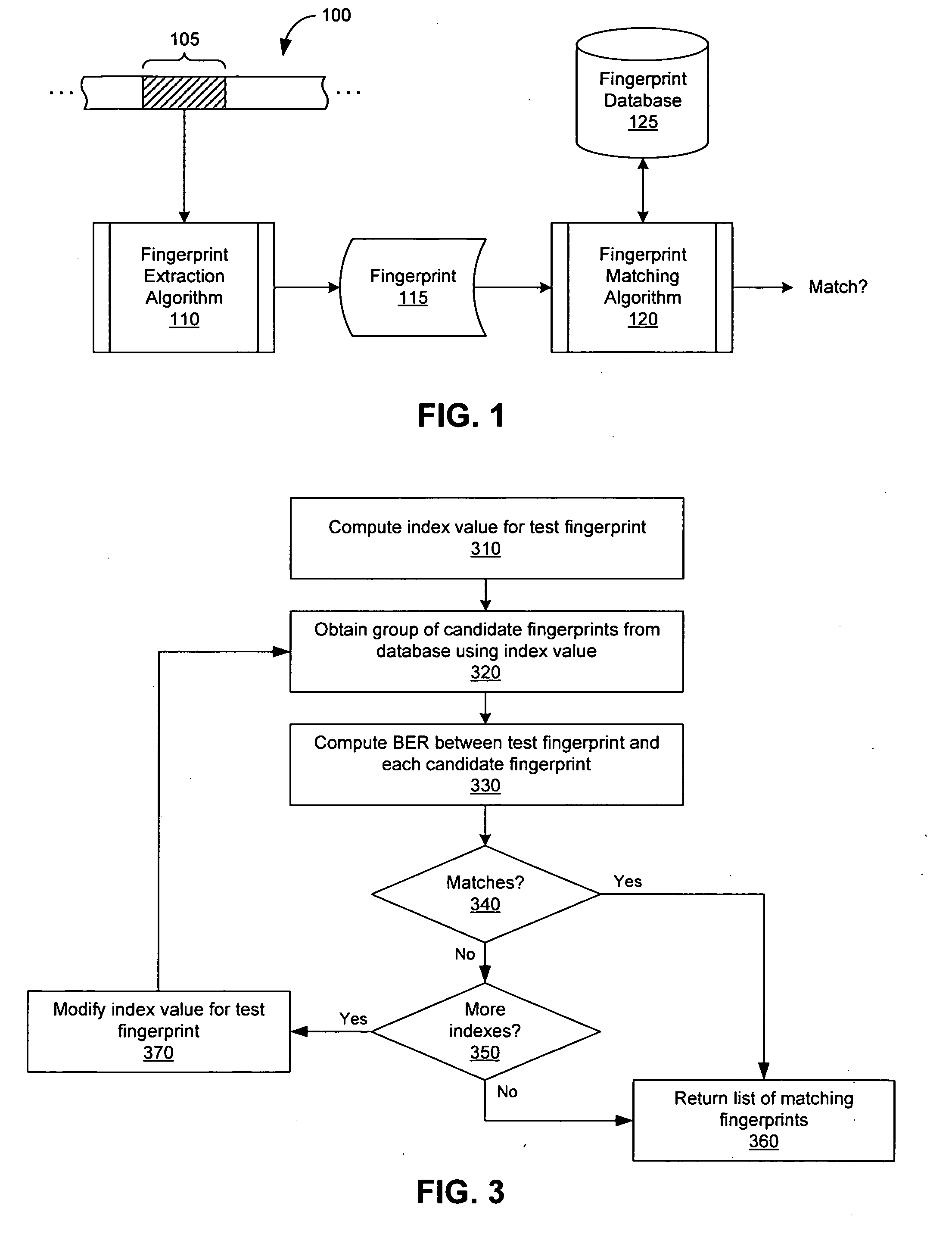
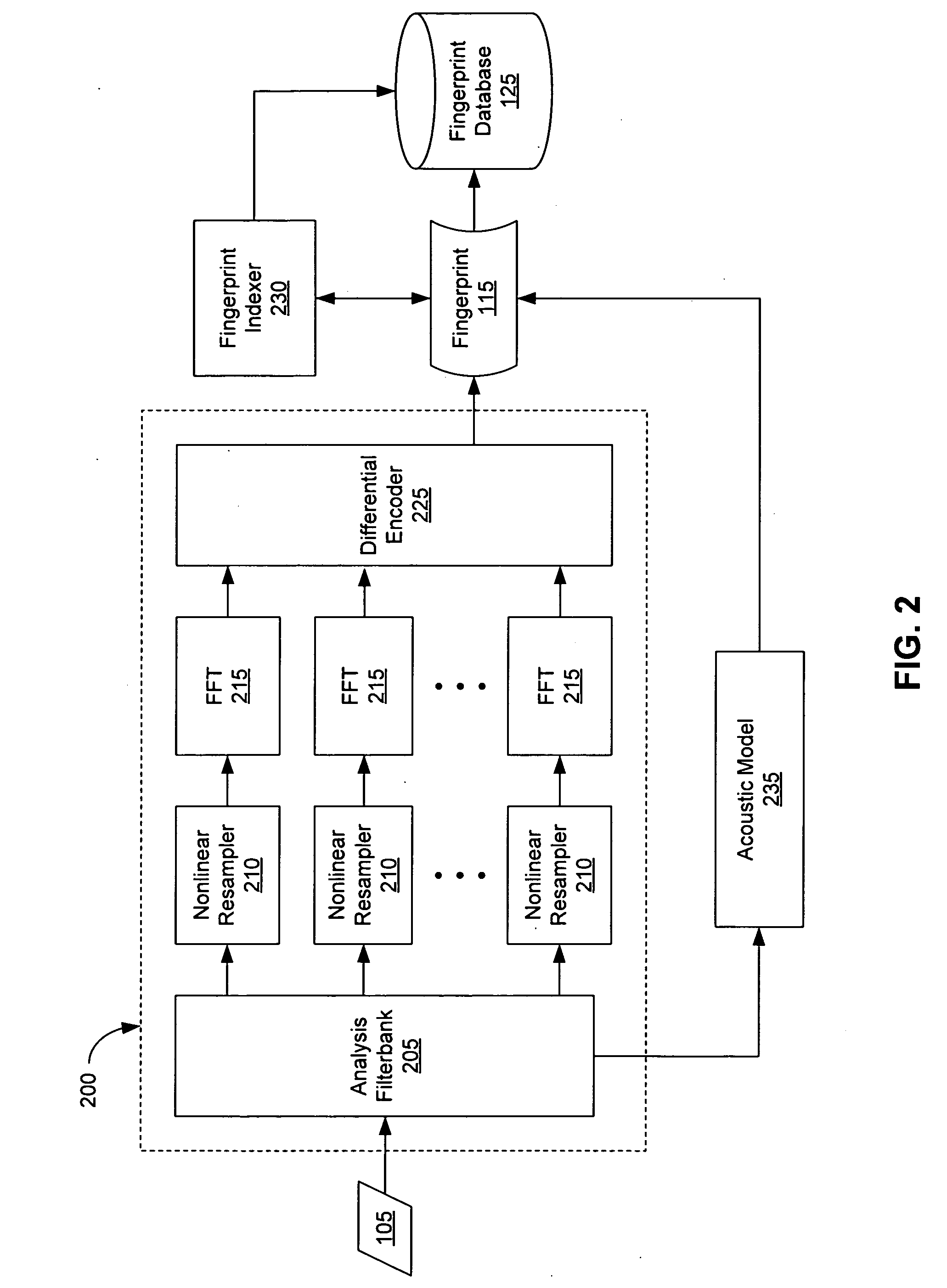
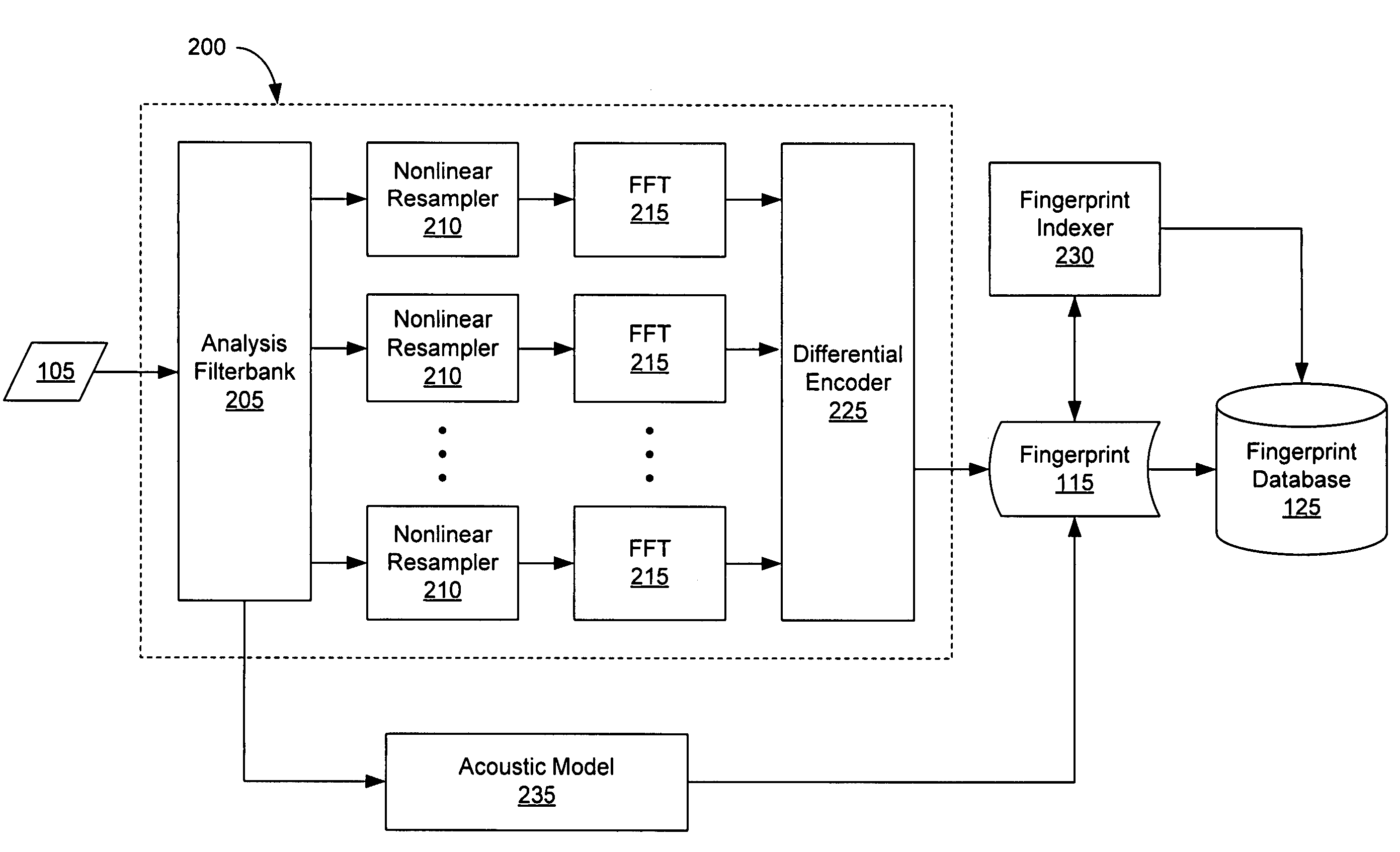
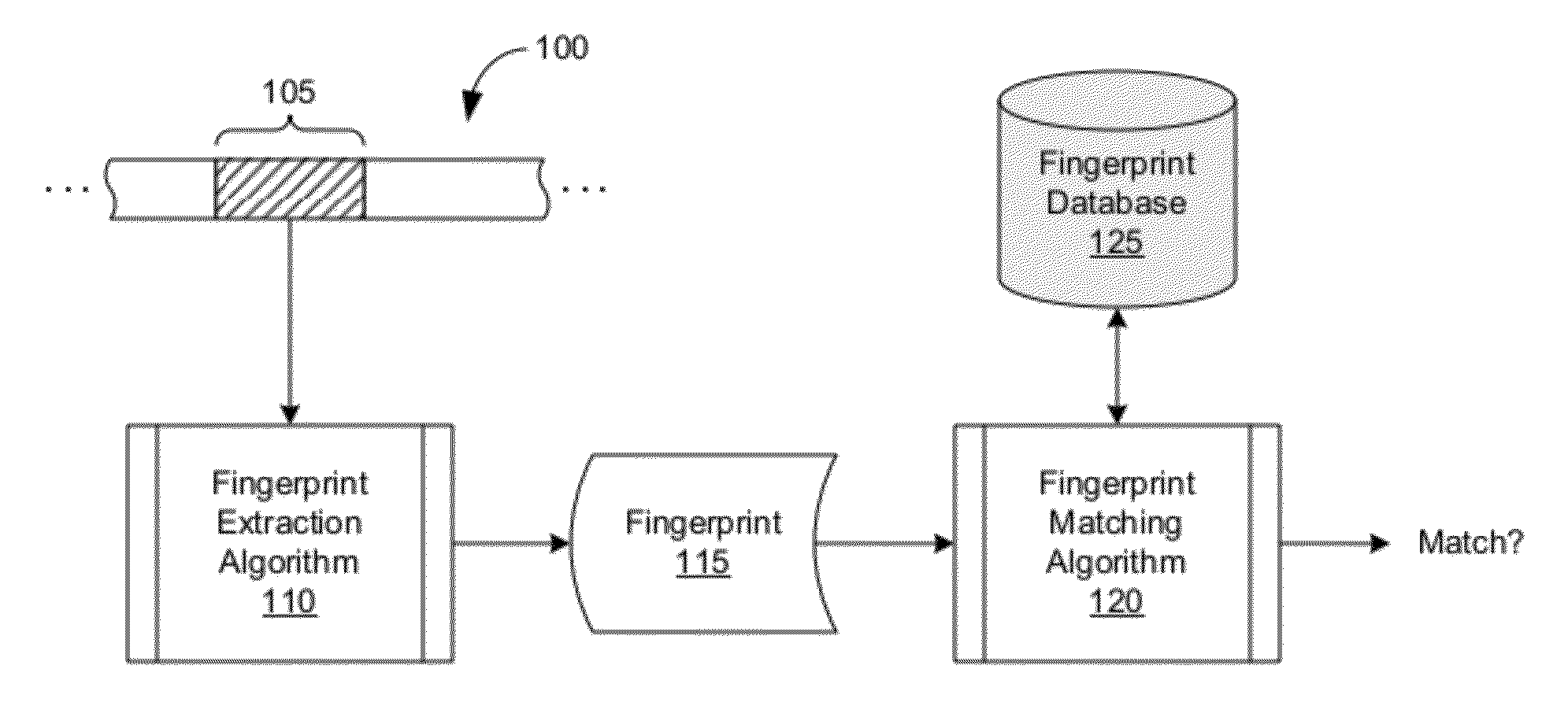
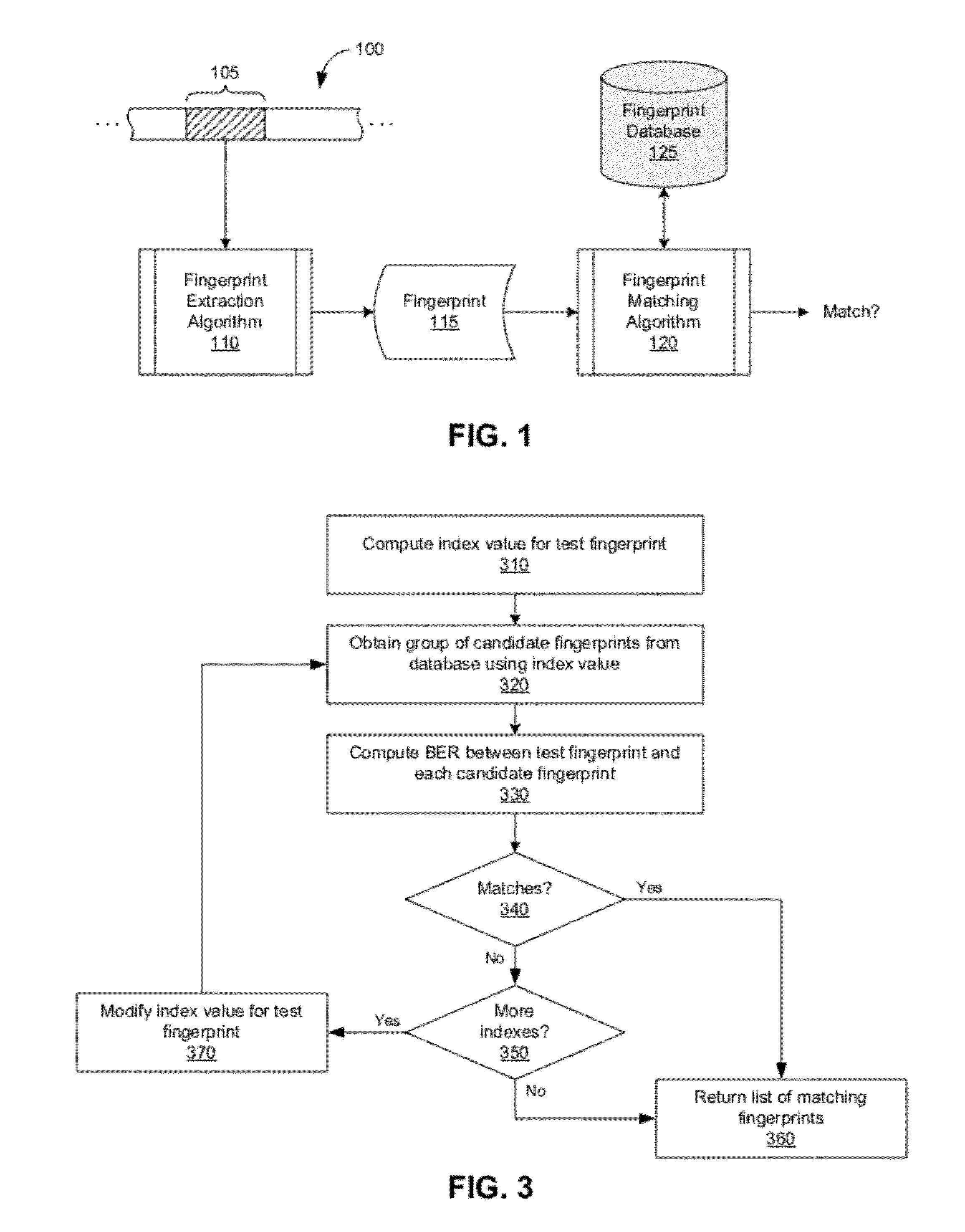
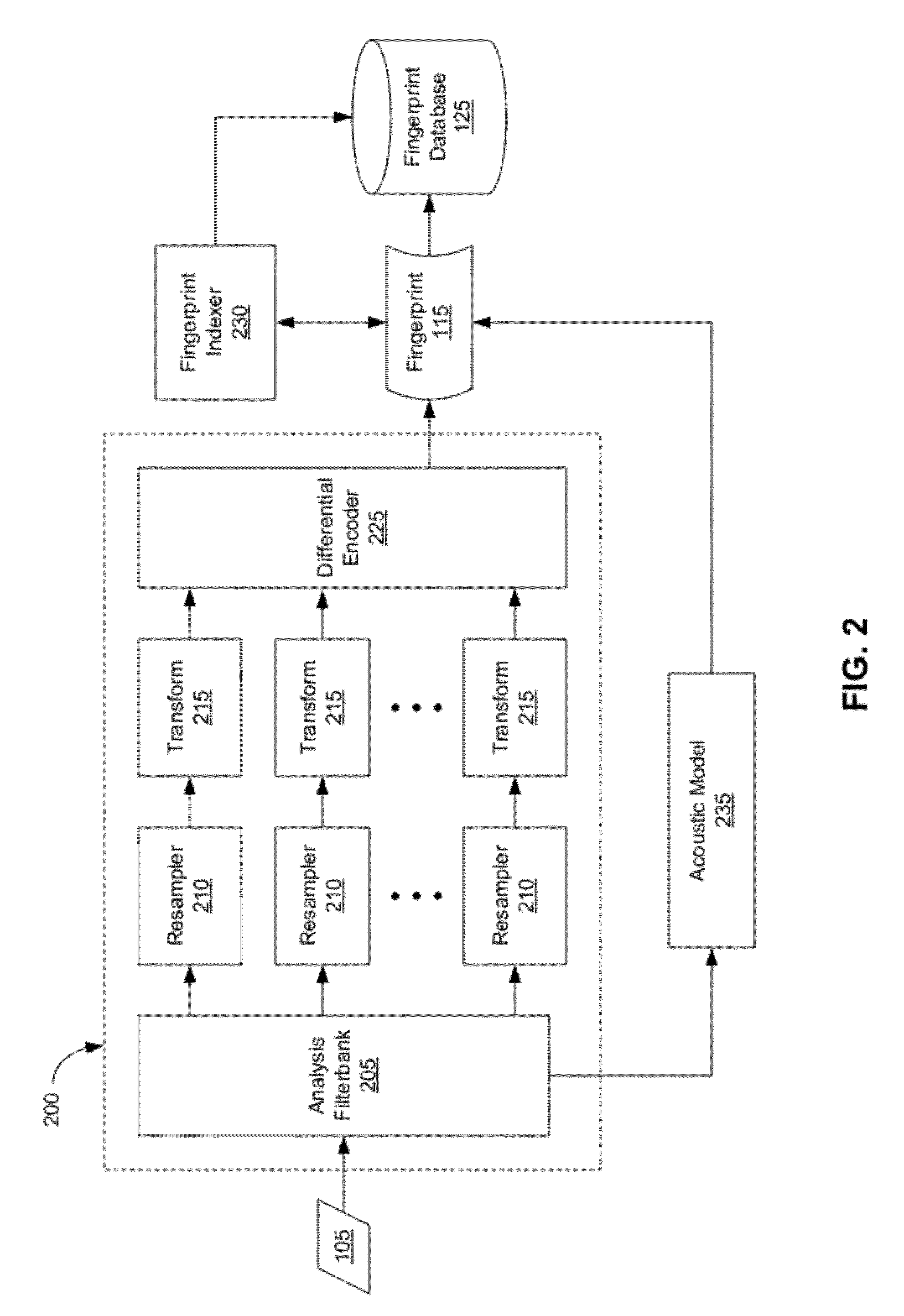
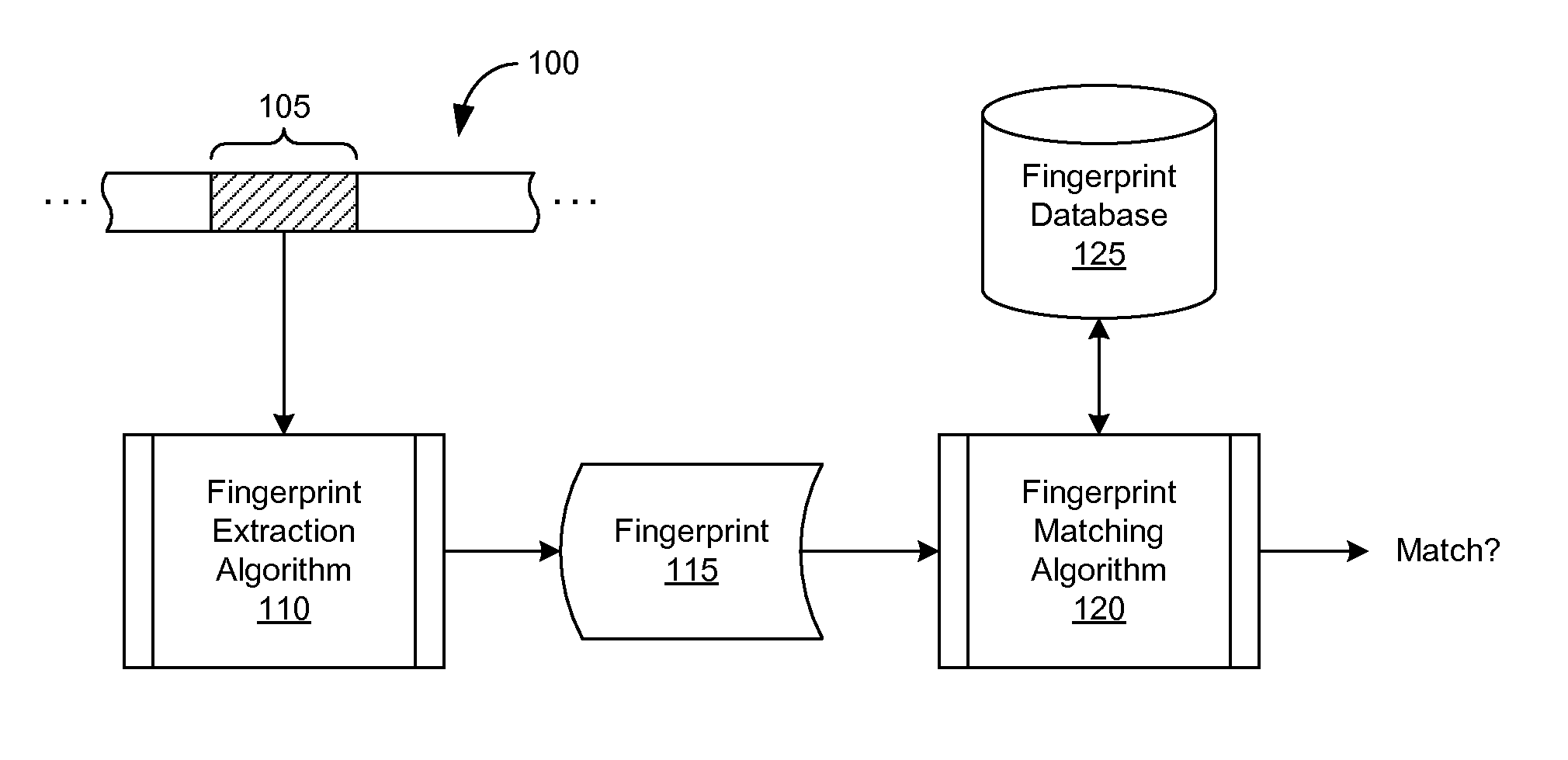
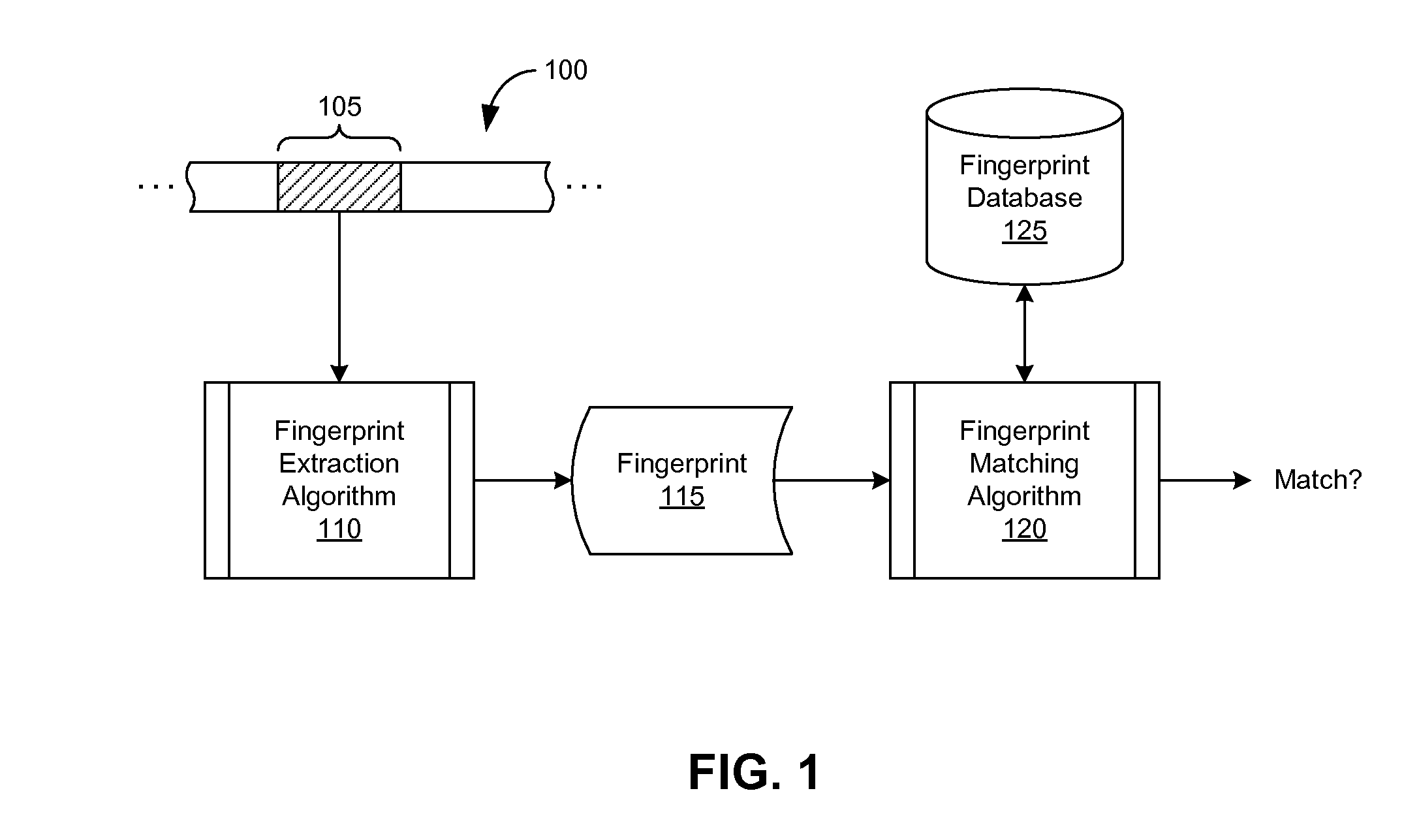
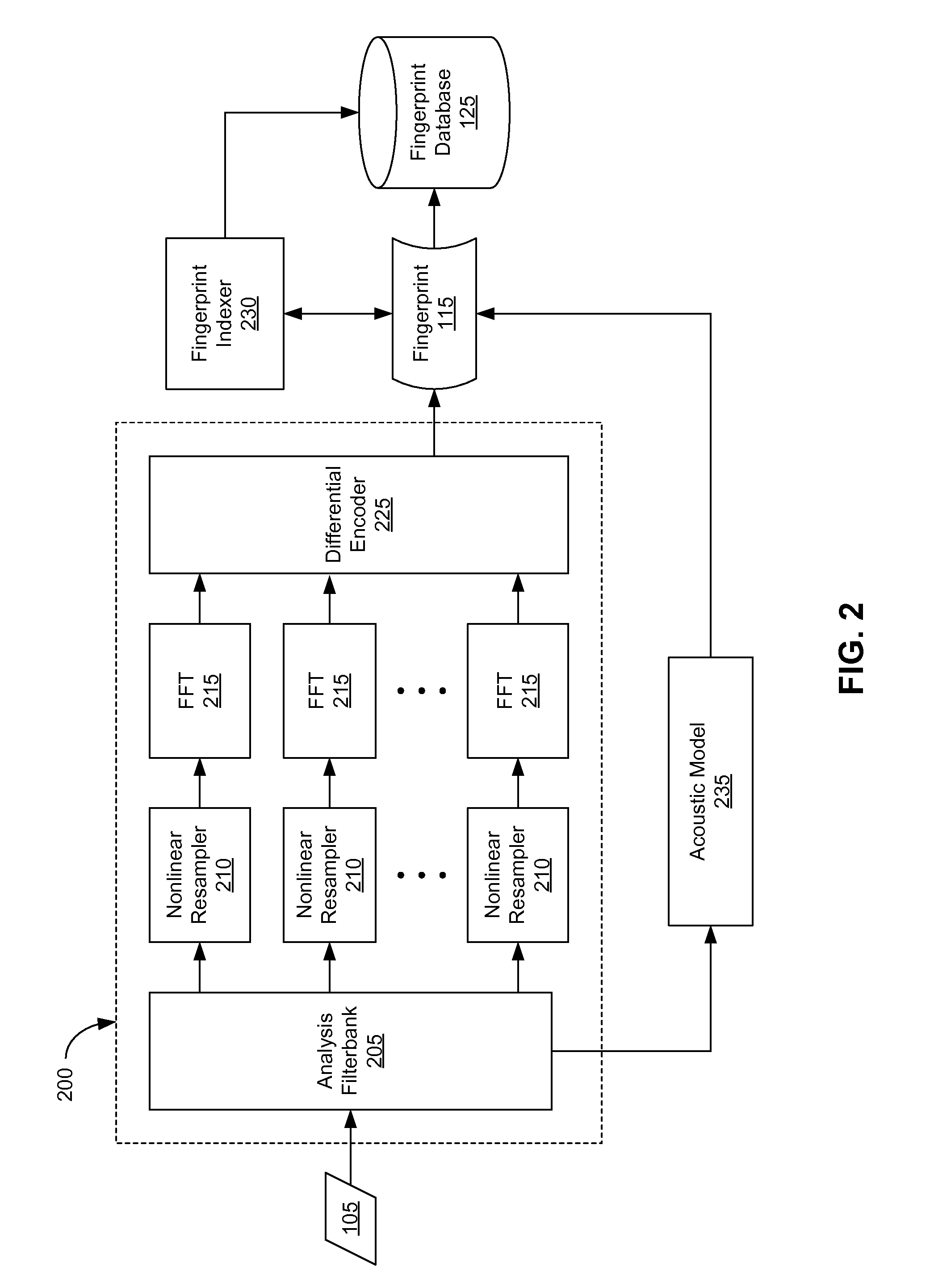
An audio fingerprint is extracted from an audio sample, where the fingerprint contains information that is characteristic of the content in the sample. The fingerprint may be generated by computing an energy spectrum for the audio sample, resampling the energy spectrum logarithmically in the time dimension, transforming the resampled energy spectrum to produce a series of feature vectors, and computing the fingerprint using differential coding of the feature vectors. The generated fingerprint can be compared to a set of reference fingerprints in a database to identify the original audio content.
Owner:AUDITUDE COM +1
Extraction and matching of characteristic fingerprints from audio signals
InactiveUS7516074B2Fast and efficientHighly accurateDigital data information retrievalSpeech analysisFeature vectorDifferential coding
An audio fingerprint is extracted from an audio sample, where the fingerprint contains information that is characteristic of the content in the sample. The fingerprint may be generated by computing an energy spectrum for the audio sample, resampling the energy spectrum logarithmically in the time dimension, transforming the resampled energy spectrum to produce a series of feature vectors, and computing the fingerprint using differential coding of the feature vectors. The generated fingerprint can be compared to a set of reference fingerprints in a database to identify the original audio content.
Owner:AUDITUDE COM +1
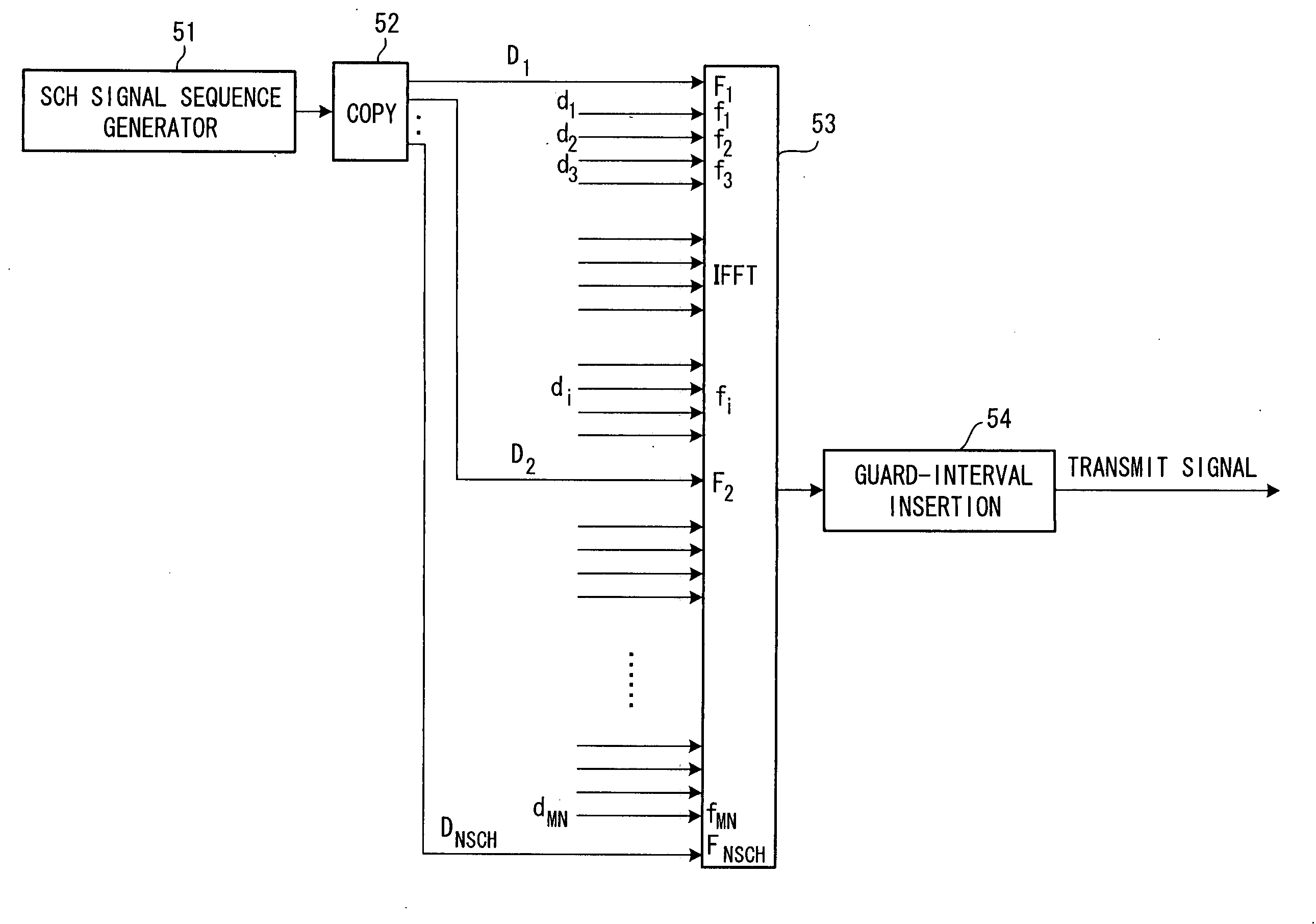
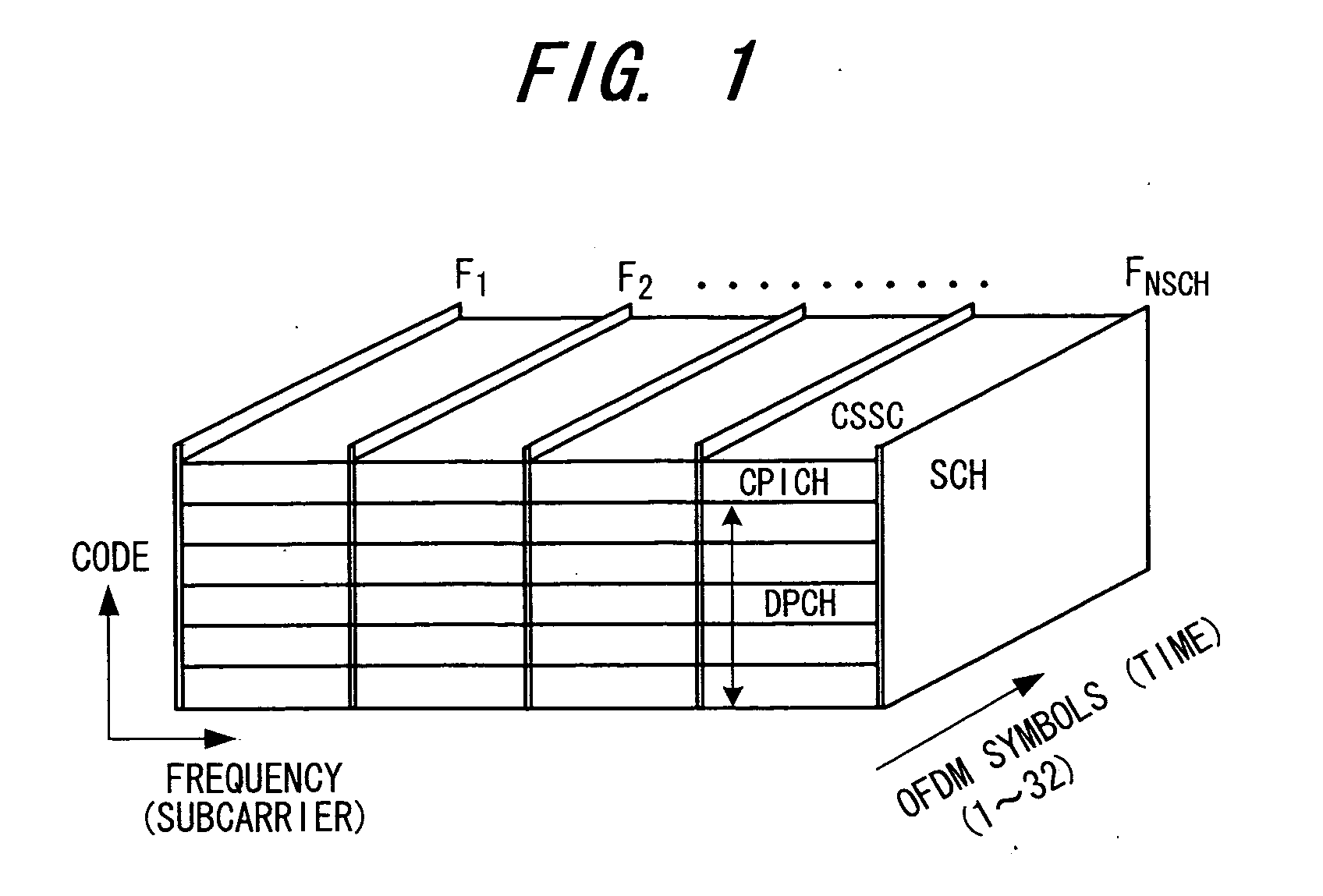
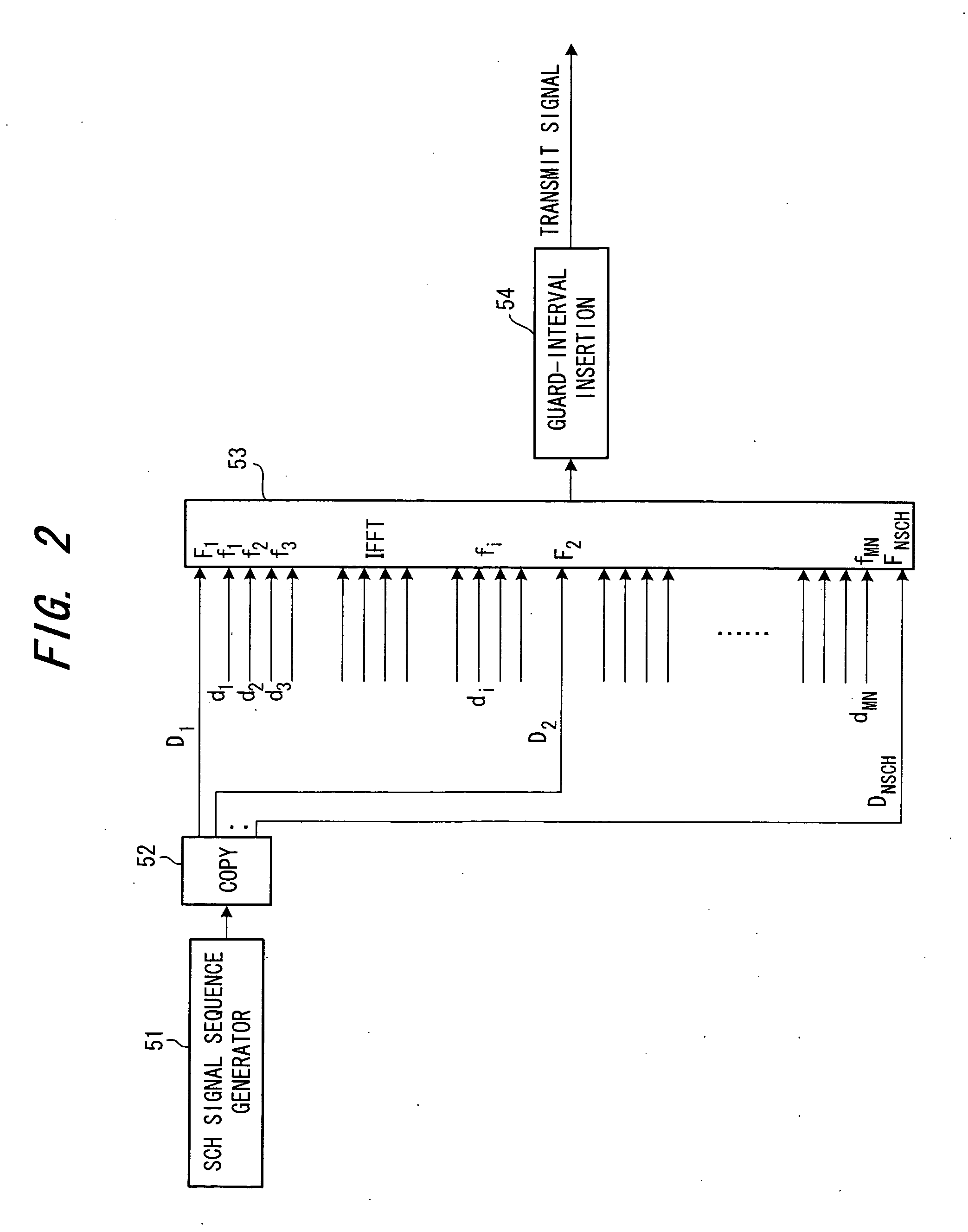
Transceiver apparatus and transceiving method
InactiveUS20050163238A1Accurate detectionResidual carrier-frequency error is not negligibleTransmission path divisionTime-division multiplexTransceiverCarrier signal
In a transmitting method for transmitting a transmit signal sequence by a number of subcarriers, a plurality of subcarriers F1, F2, . . . FNSCH exclusively for a synchronization channel are provided, a signal sequence of synchronization channel SCH is transmitted by the plurality of exclusive subcarriers, and a common pilot CPICH or dedicated signal DPCH is transmitted on the other subcarriers. In this case, the signal sequence of the synchronization channel is subjected to differential encoding processing and the differentially encoded signal sequence is transmitted by the exclusive subcarriers.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
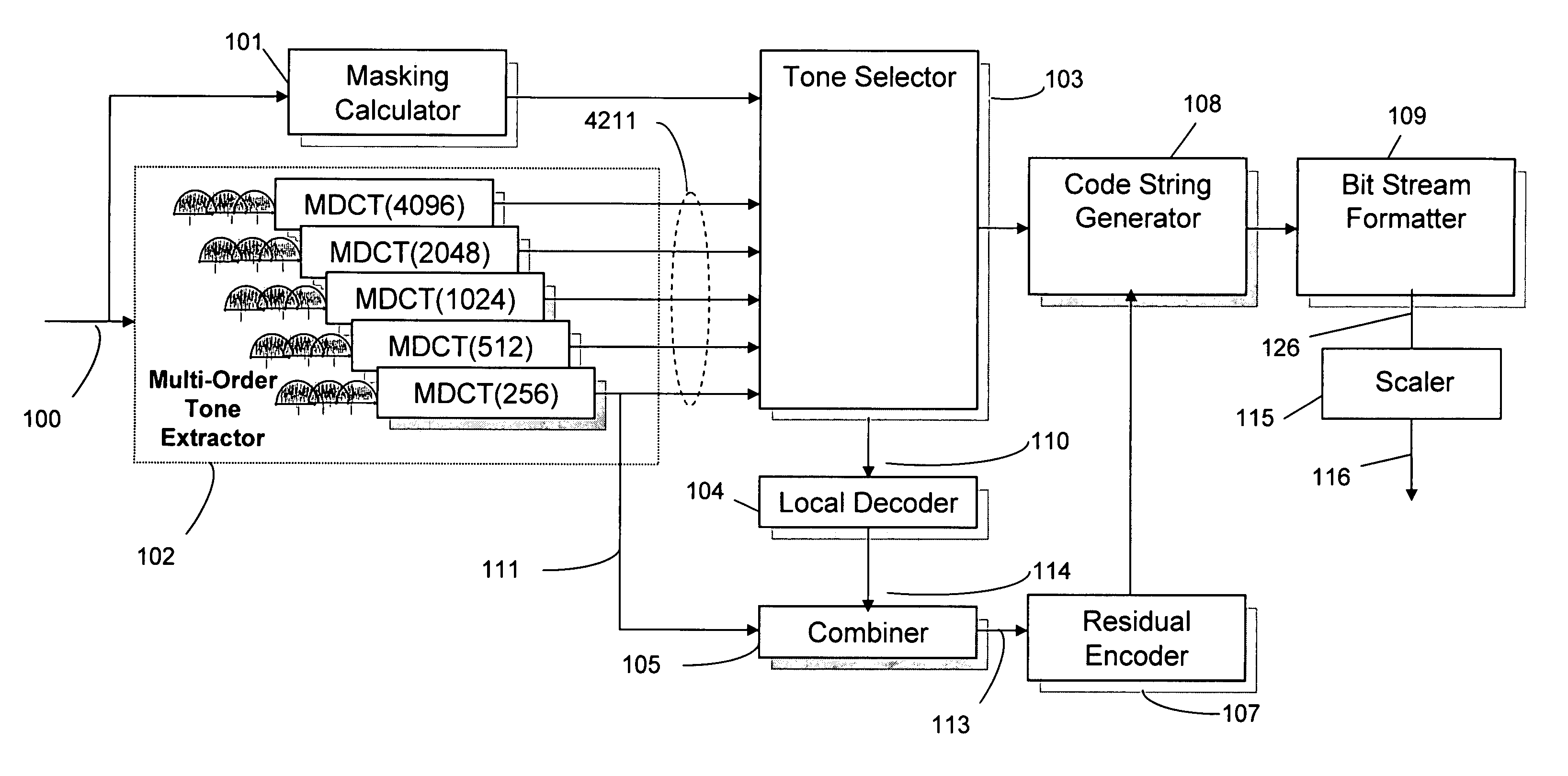
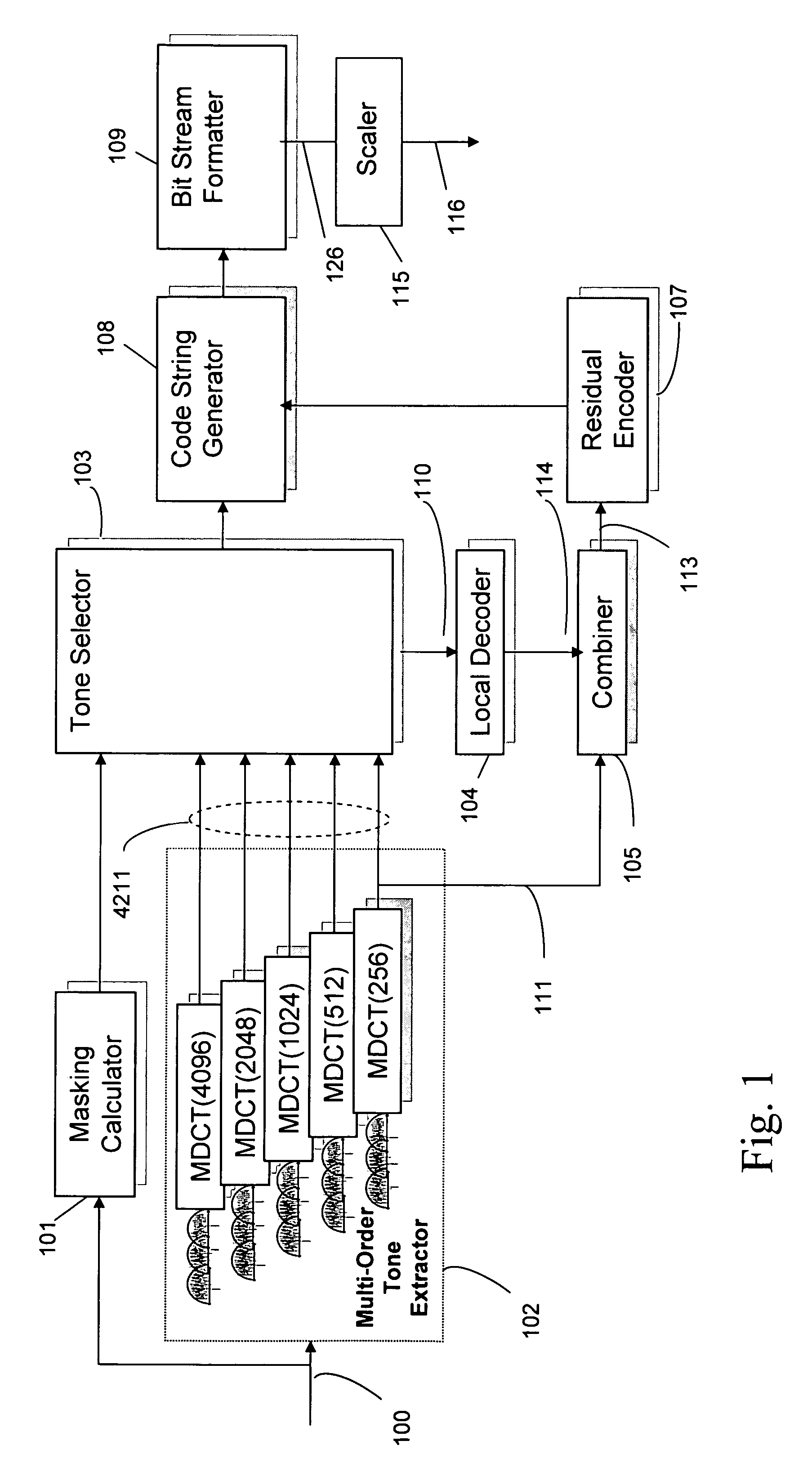
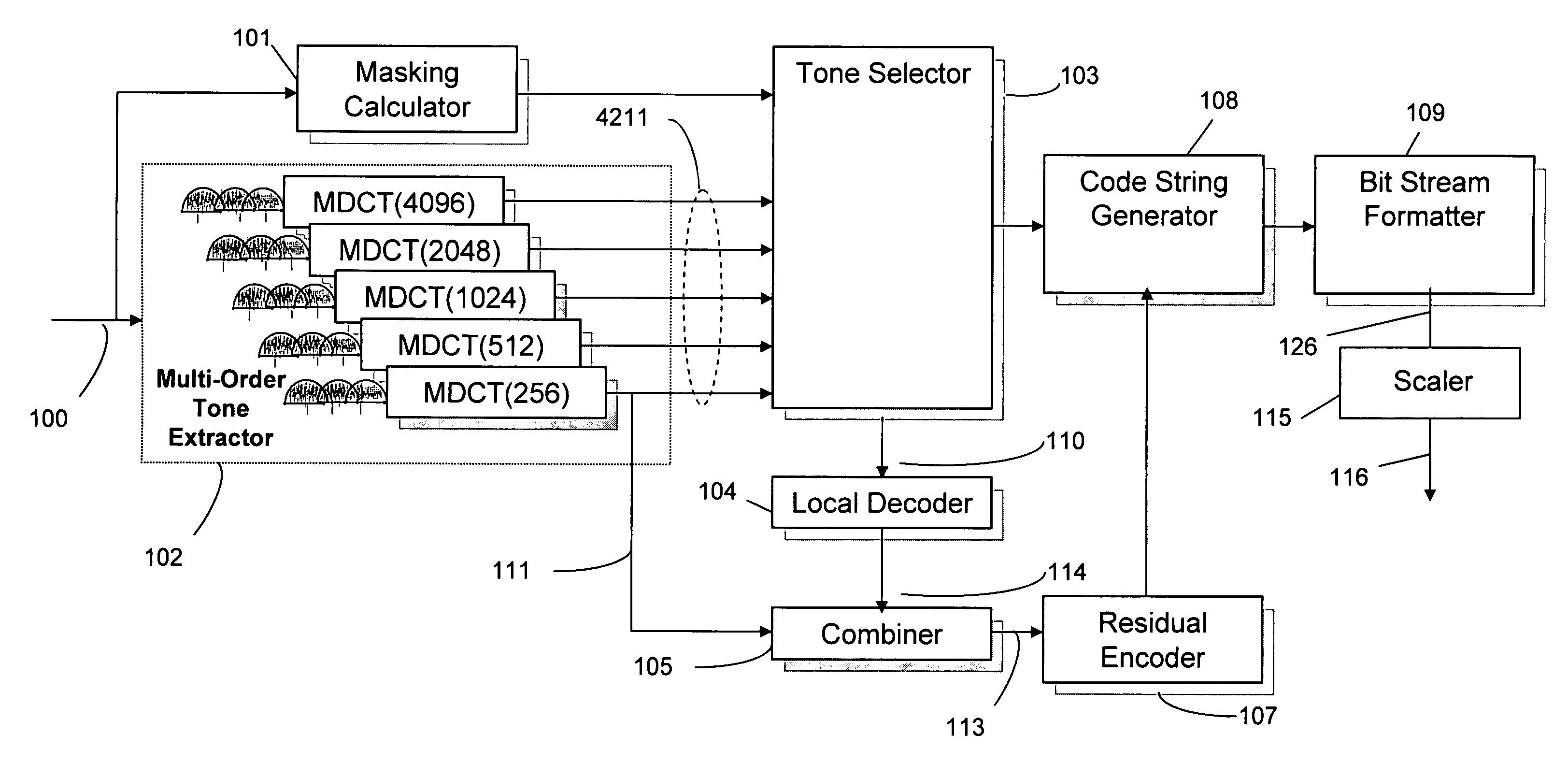
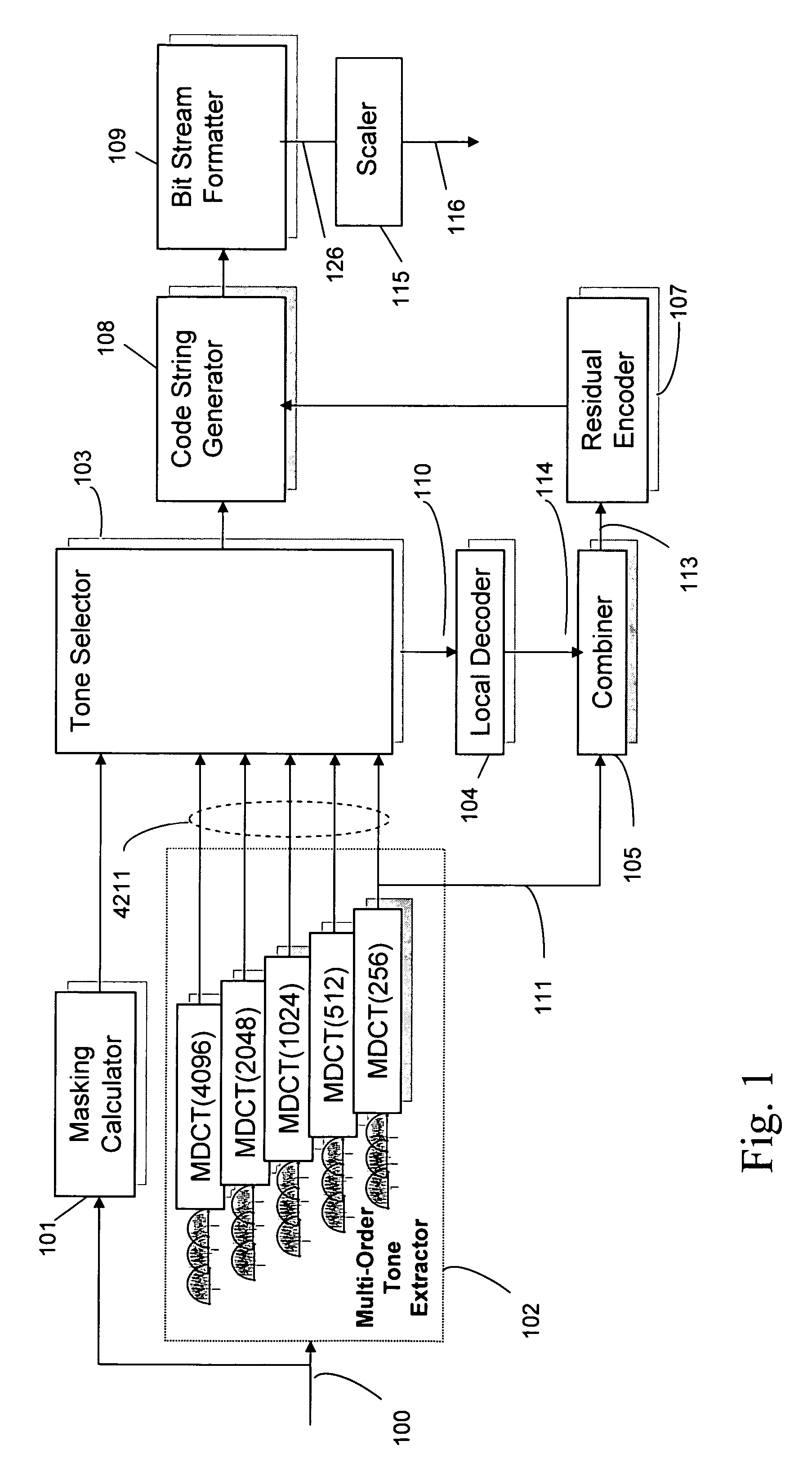
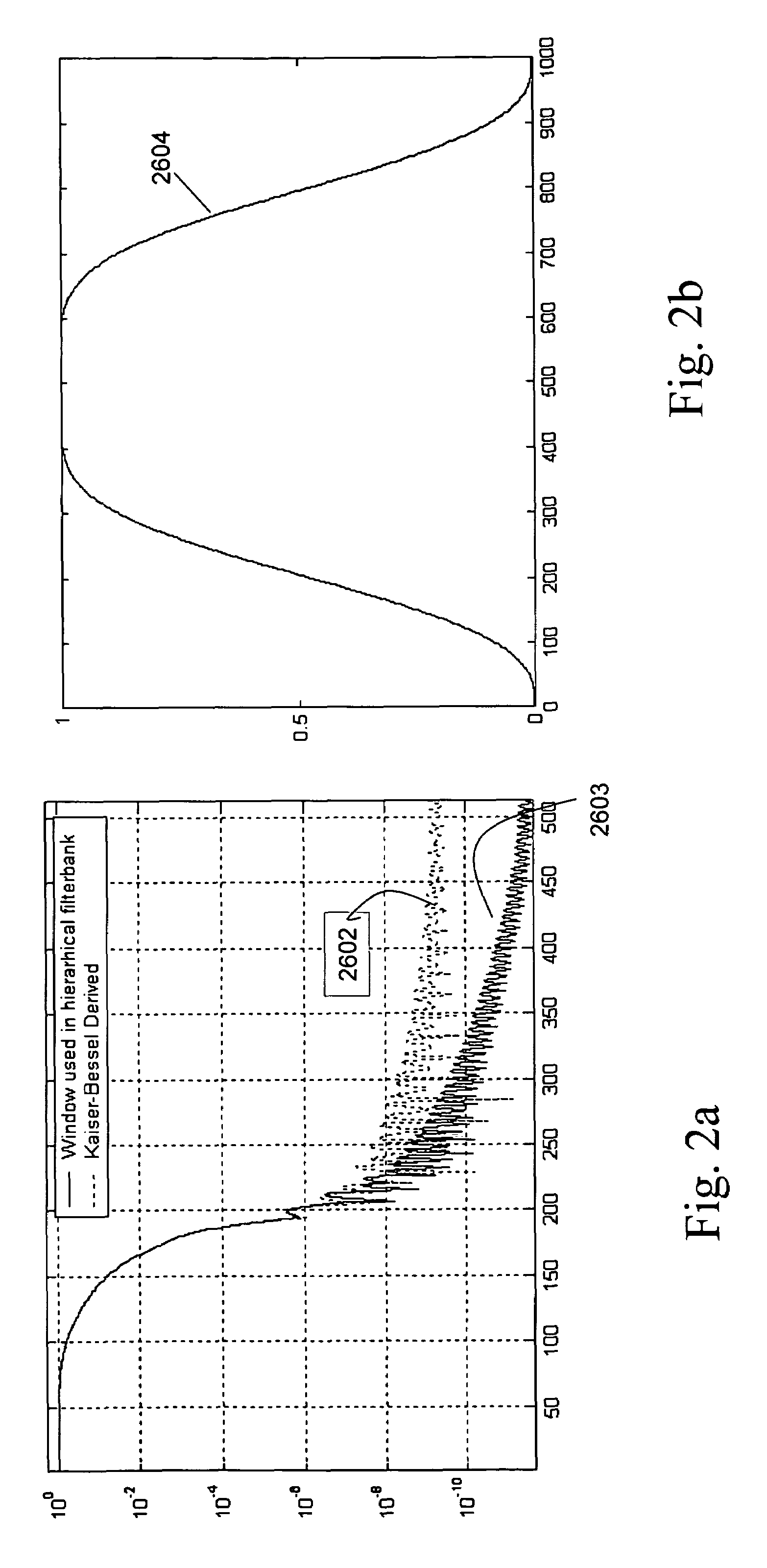
Scalable compressed audio bit stream and codec using a hierarchical filterbank and multichannel joint coding
ActiveUS20070063877A1Facilitate efficient scalingSuitable for useSpeech analysisCode conversionComputer hardwareData rate
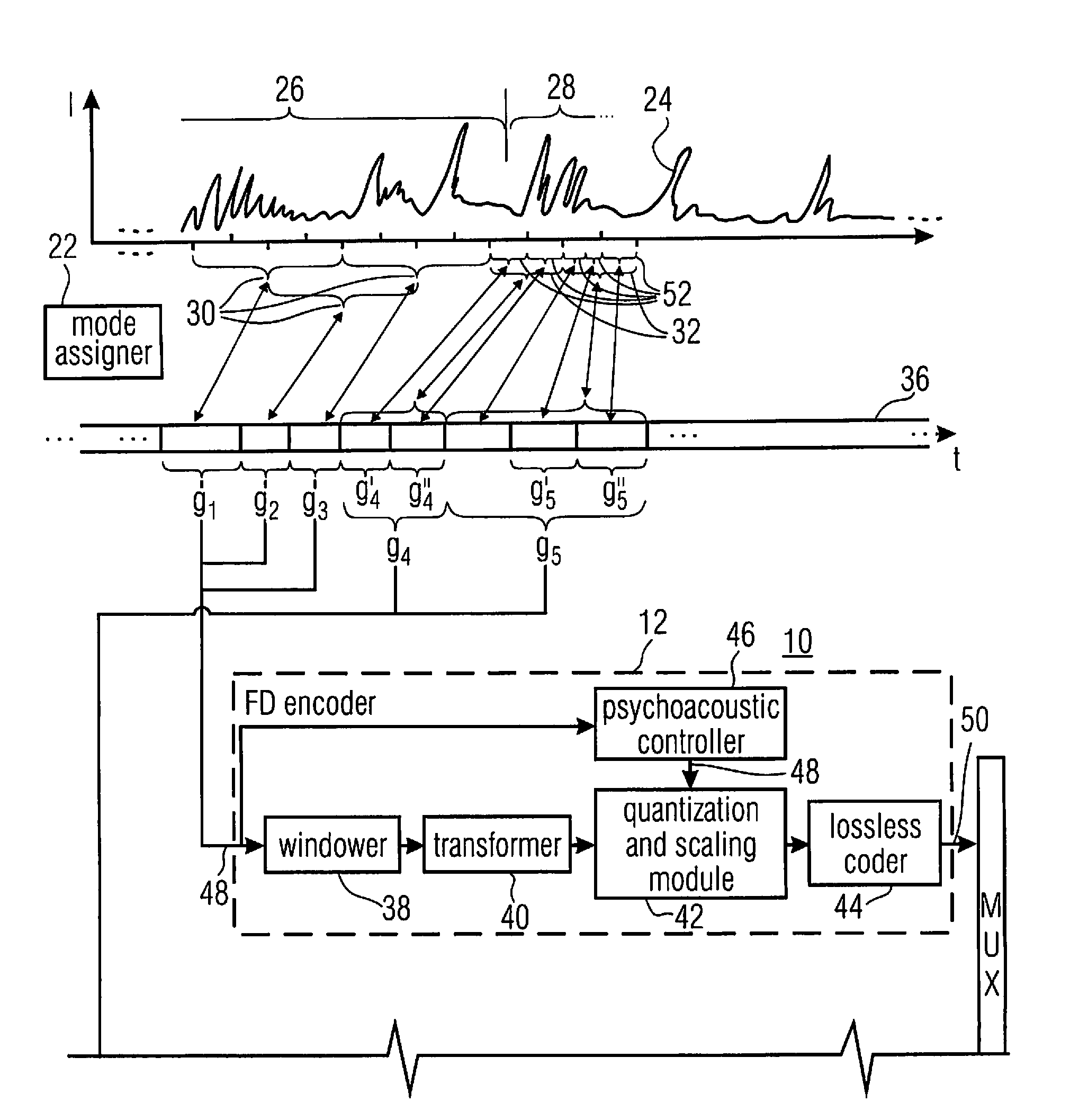
A method for compressing audio input signals to form a master bit stream that can be scaled to form a scaled bit stream having an arbitrarily prescribed data rate. A hierarchical filterbank decomposes the input signal into a multi-resolution time / frequency representation from which the encoder can efficiently extract both tonal and residual components. The components are ranked and then quantized with reference to the same masking function or different psychoacoustic criteria. The selected tonal components are suitably encoded using differential coding extended to multichannel audio. The time-sample and scale factor components that make up the residual components are encoded using joint channel coding (JCC) extended to multichannel audio. A decoder uses an inverse hierarchical filterbank to reconstruct the audio signals from the tonal and residual components in the scaled bit stream.
Owner:DTS
Extraction and Matching of Characteristic Fingerprints from Audio Signals
InactiveUS20120209612A1Fast and efficientHighly accurateSpeech analysisUsing detectable carrier informationFeature vectorDifferential coding
An audio fingerprint is extracted from an audio sample, where the fingerprint contains information that is characteristic of the content in the sample. The fingerprint may be generated by computing an energy spectrum for the audio sample, resampling the energy spectrum, transforming the resampled energy spectrum to produce a series of feature vectors, and computing the fingerprint using differential coding of the feature vectors. The generated fingerprint can be compared to a set of reference fingerprints in a database to identify the original audio content.
Owner:STARBOARD VALUE INTERMEDIATE FUND LP AS COLLATERAL AGENT
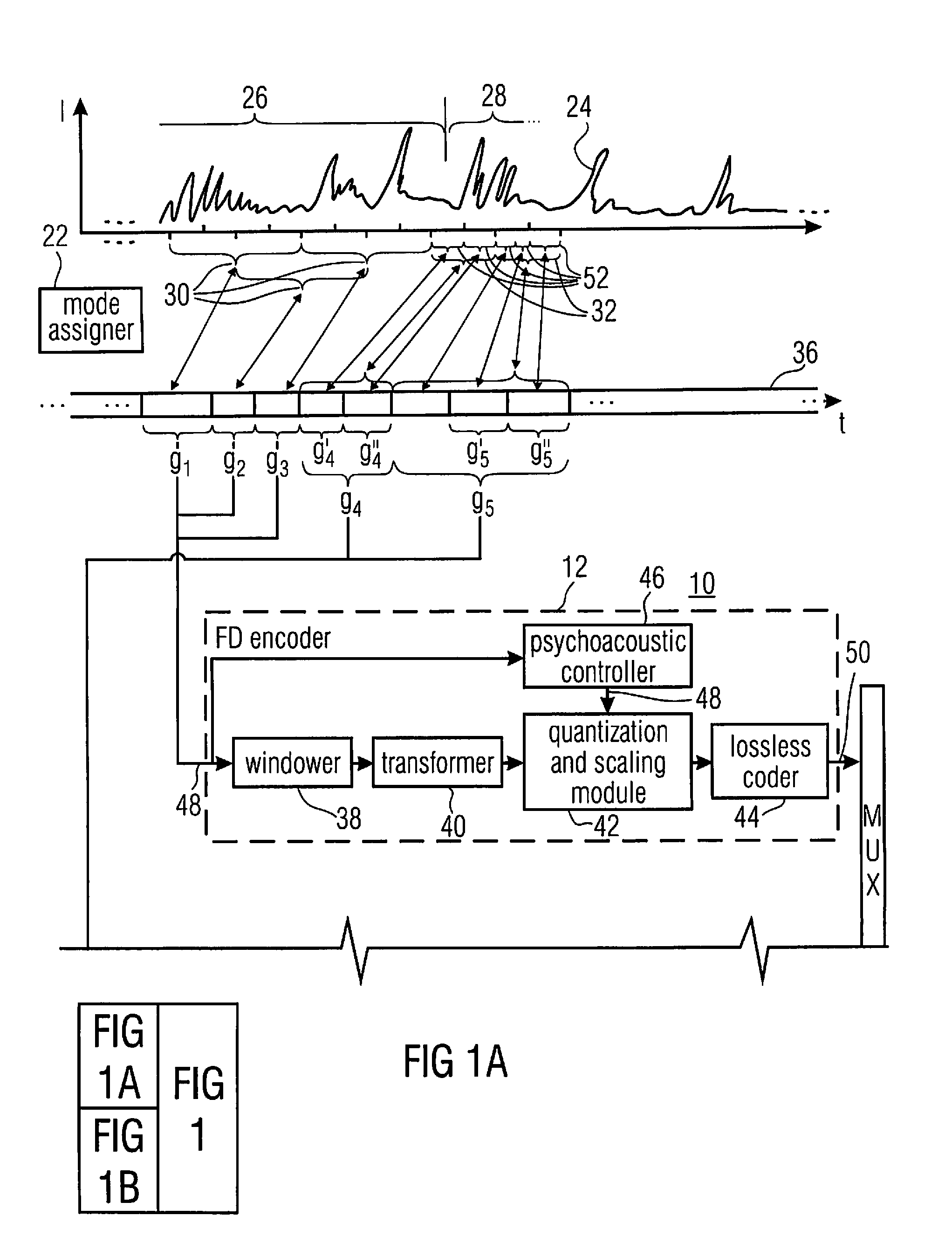
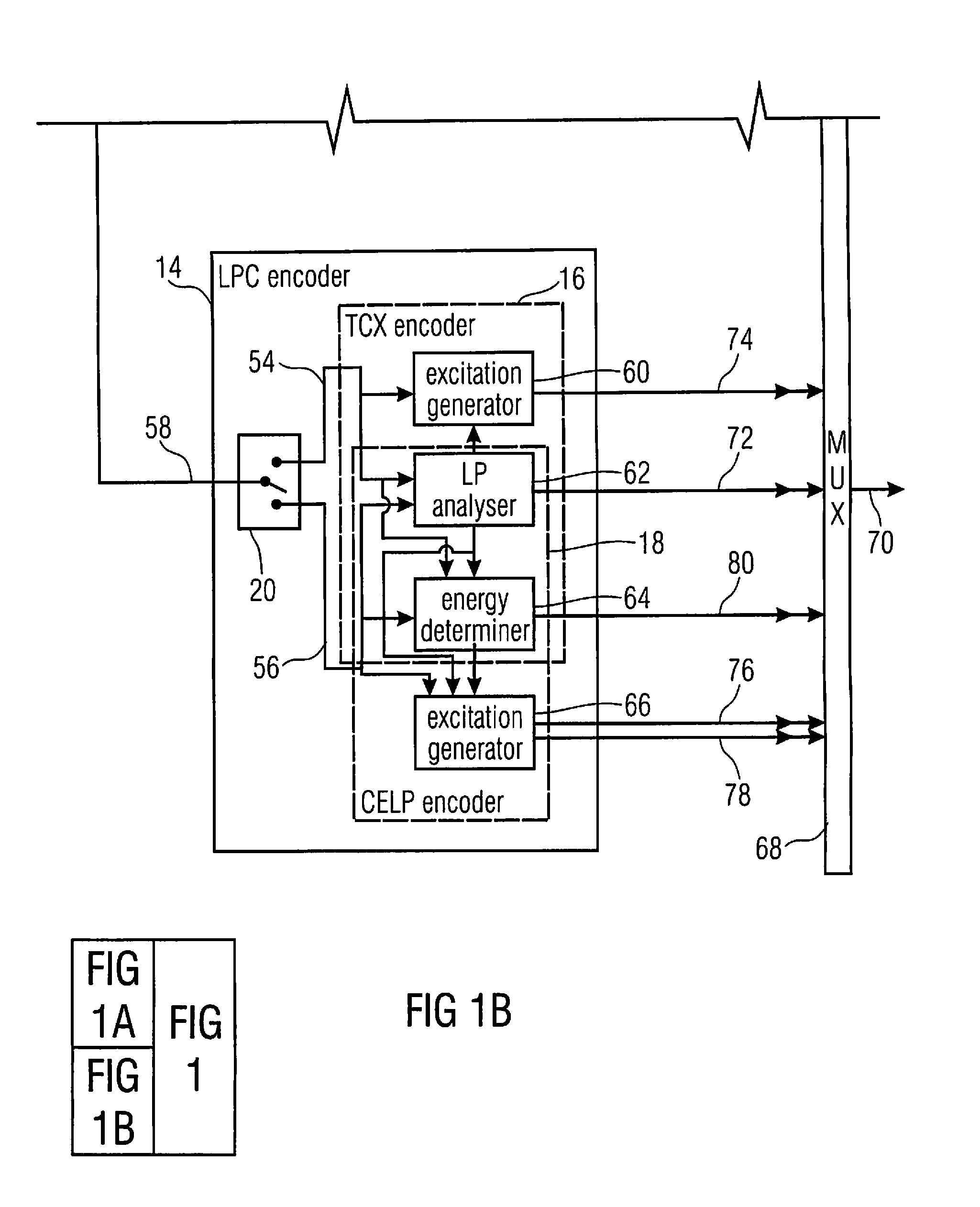
Multi-mode audio codec and celp coding adapted therefore
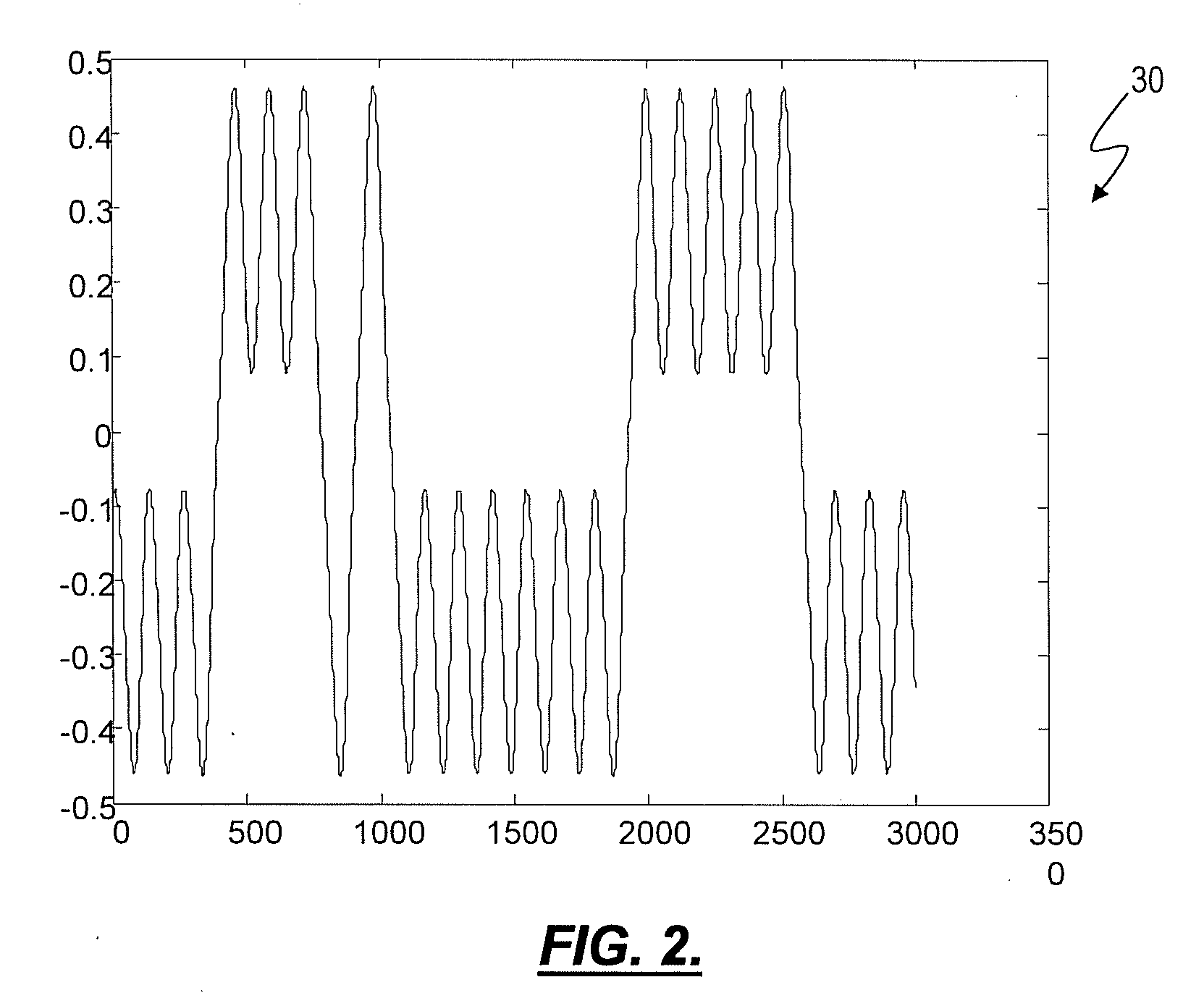
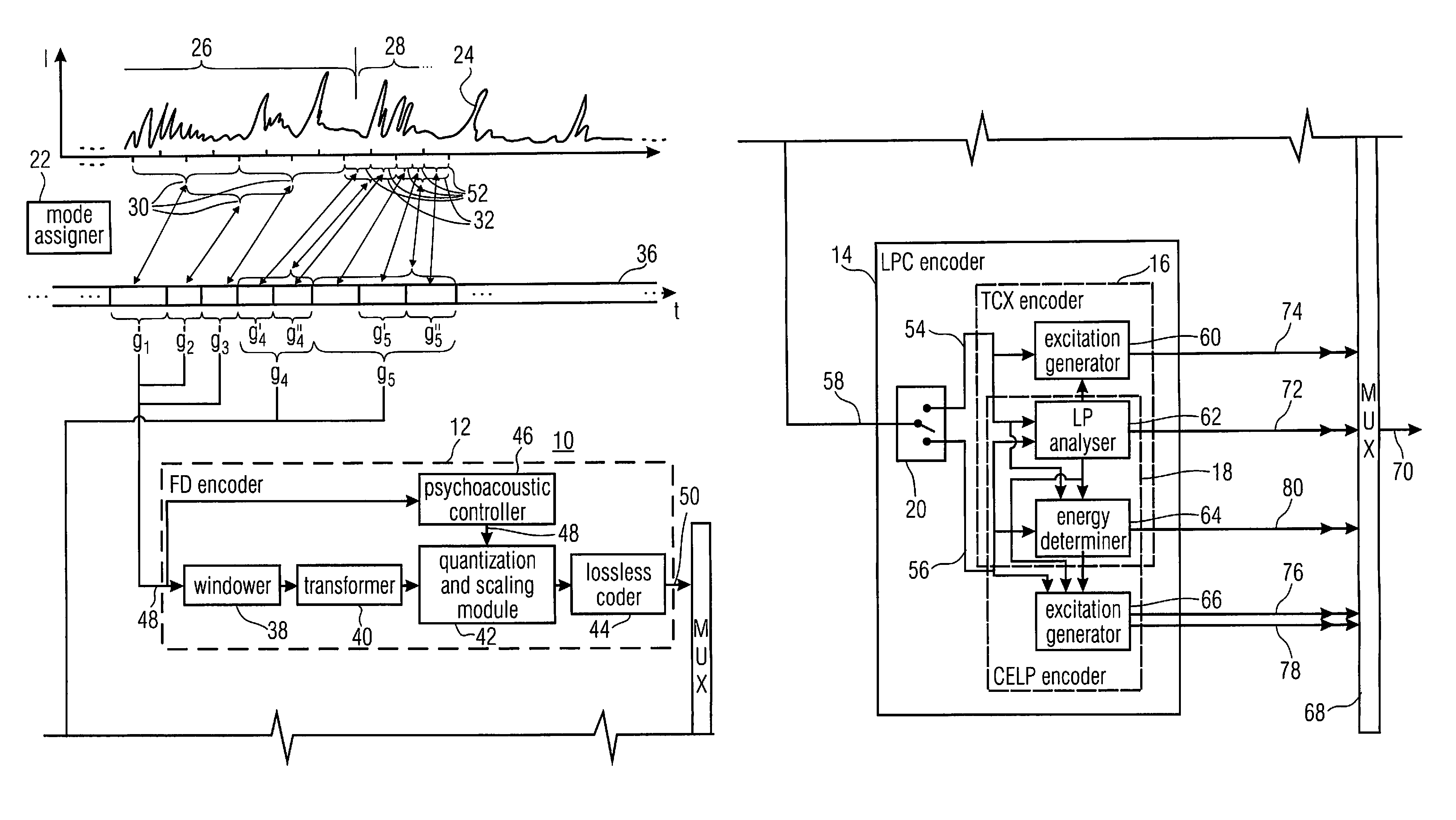
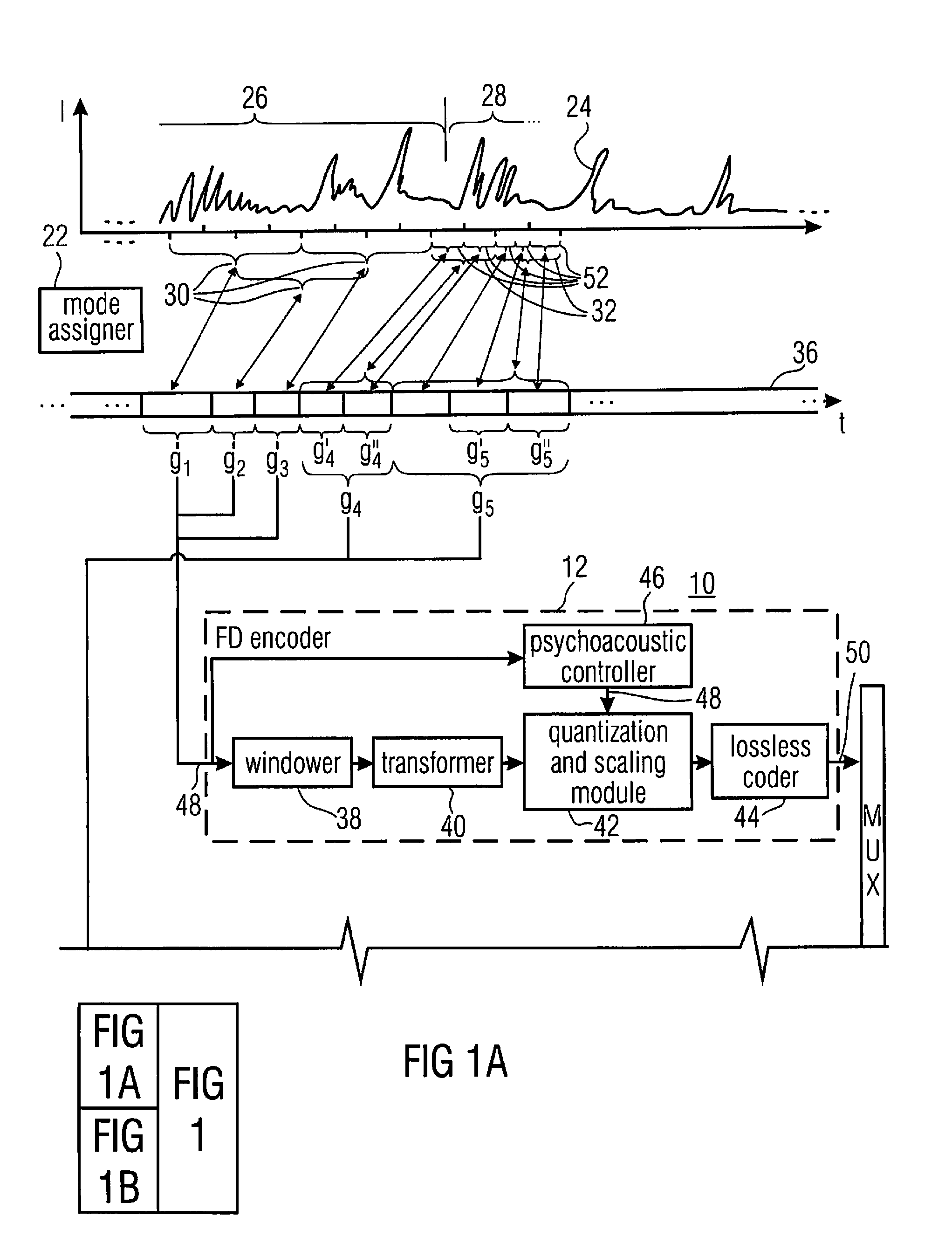
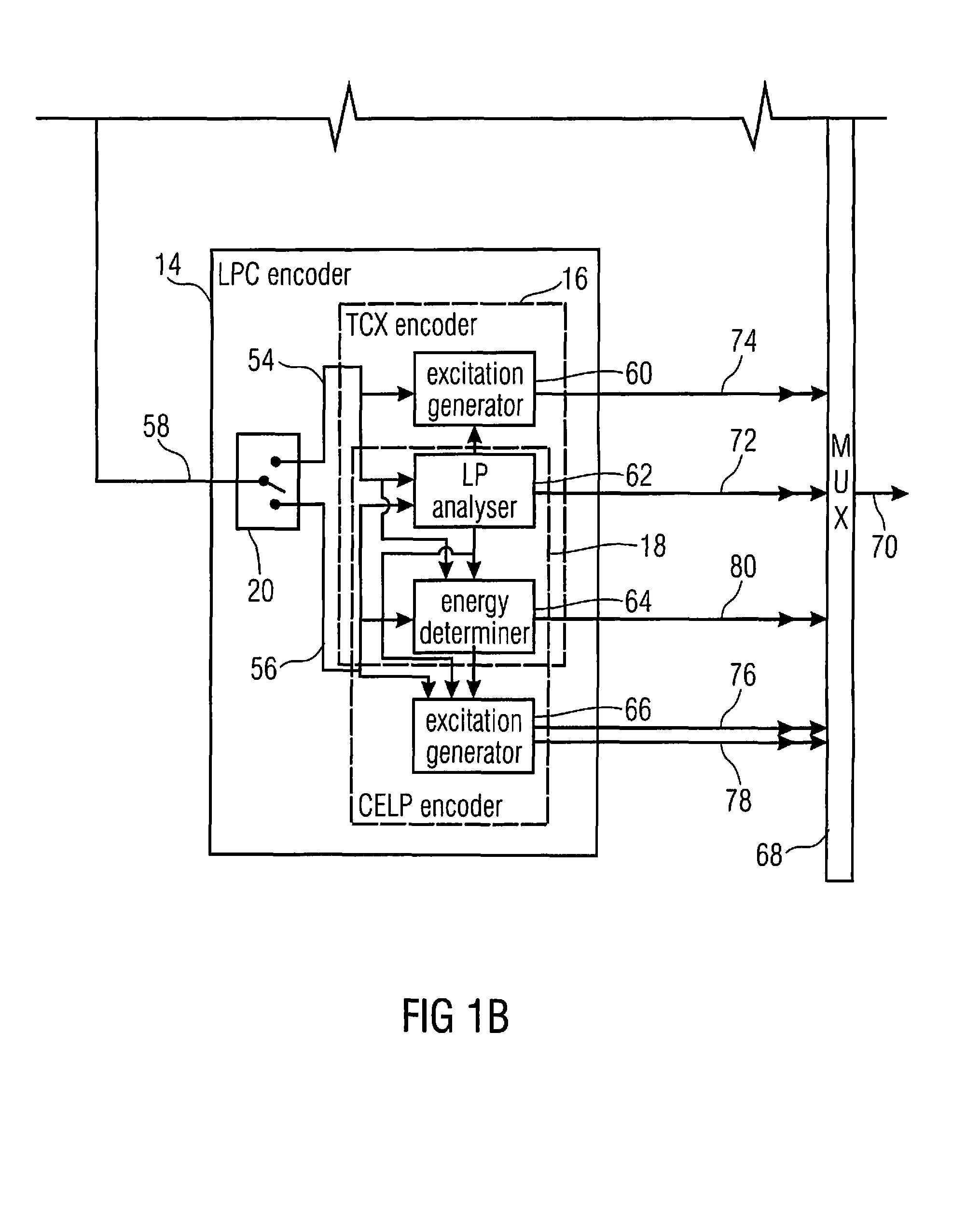
In an embodiment, bitstream elements of sub-frames are encoded differentially to a global gain value so that a change of the global gain value results in an adjustment of an output level of the decoded representation of the audio content. Concurrently, the differential coding saves bits. Even further, the differential coding enables the lowering of the burden of globally adjusting the gain of an encoded bitstream. In another embodiment, a global gain control across CELP coded frames and transform coded frames is achieved by co-controlling the gain of the codebook excitation of the CELP codec, along with a level of the transform or inverse transform of the transform coded frames. In another embodiment, the gain value determination in CELP coding is performed in the weighted domain of the excitation signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
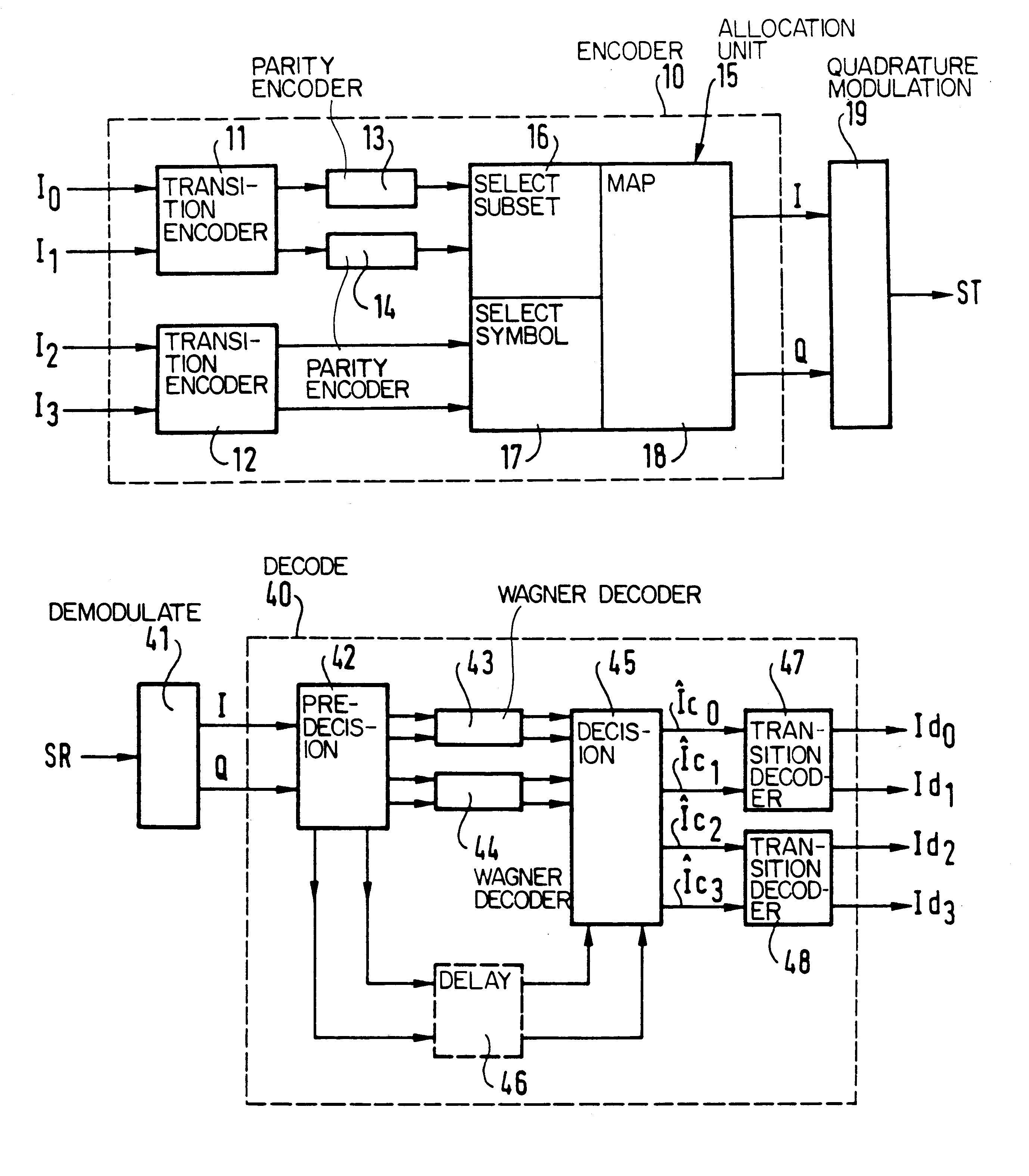
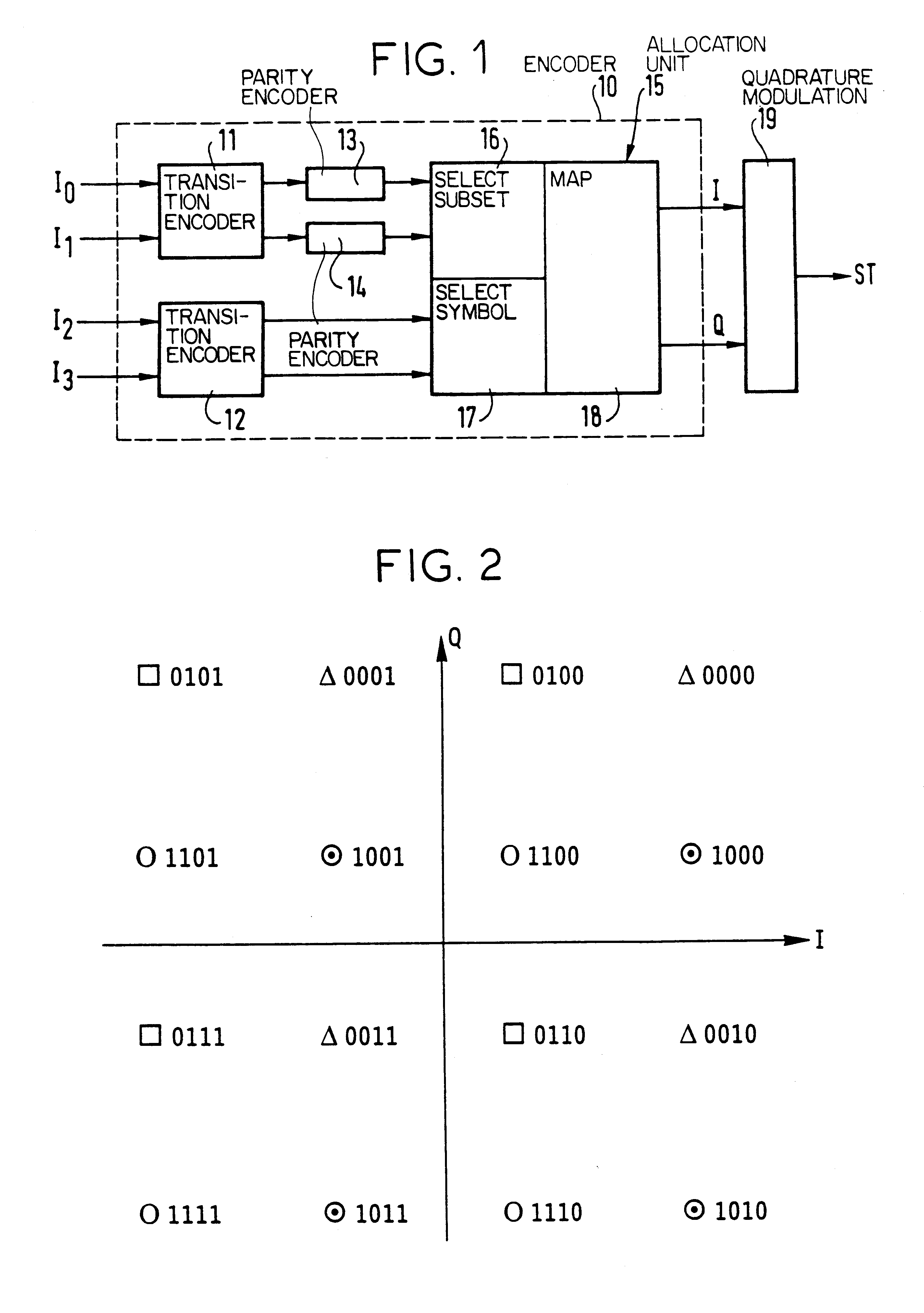
Encoding/decoding system using 16-QAM modulation encoded in multi-level blocks
InactiveUS6195396B1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionQam modulationAlgorithm
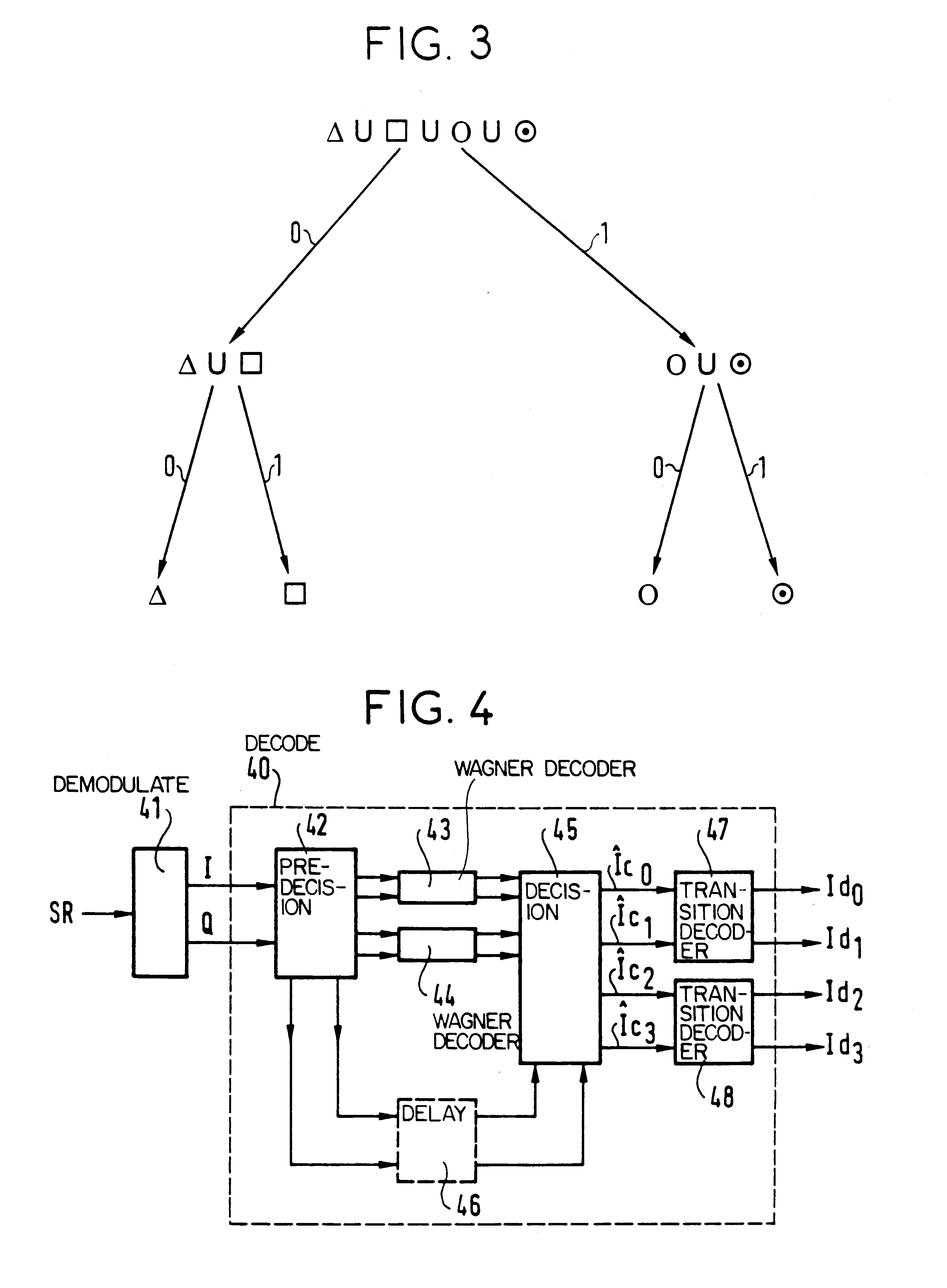
The invention provides a block-encoded modulation scheme using multi-level partitioning techniques. This scheme is made transparent to phase ambiguities of ±pi / 2 and of pi, by means of differential encoding and appropriate mapping, it is applicable to 16-QAM modulation, and it has theoretical encoding gain that is optimal for the rate of the code. The decoder associated with this scheme uses the Wagner algorithm which is much less complicated to implement than the Viterbi algorithm or than the Reed-Solomon algorithm.
Owner:ALCATEL TELSPACE
Extraction and Matching of Characteristic Fingerprints from Audio Signals
InactiveUS20090157391A1Fast and efficientHighly accurateDigital data information retrievalSpeech analysisFeature vectorDifferential coding
An audio fingerprint is extracted from an audio sample, where the fingerprint contains information that is characteristic of the content in the sample. The fingerprint may be generated by computing an energy spectrum for the audio sample, resampling the energy spectrum logarithmically in the time dimension, transforming the resampled energy spectrum to produce a series of feature vectors, and computing the fingerprint using differential coding of the feature vectors. The generated fingerprint can be compared to a set of reference fingerprints in a database to identify the original audio content.
Owner:STARBOARD VALUE INTERMEDIATE FUND LP AS COLLATERAL AGENT
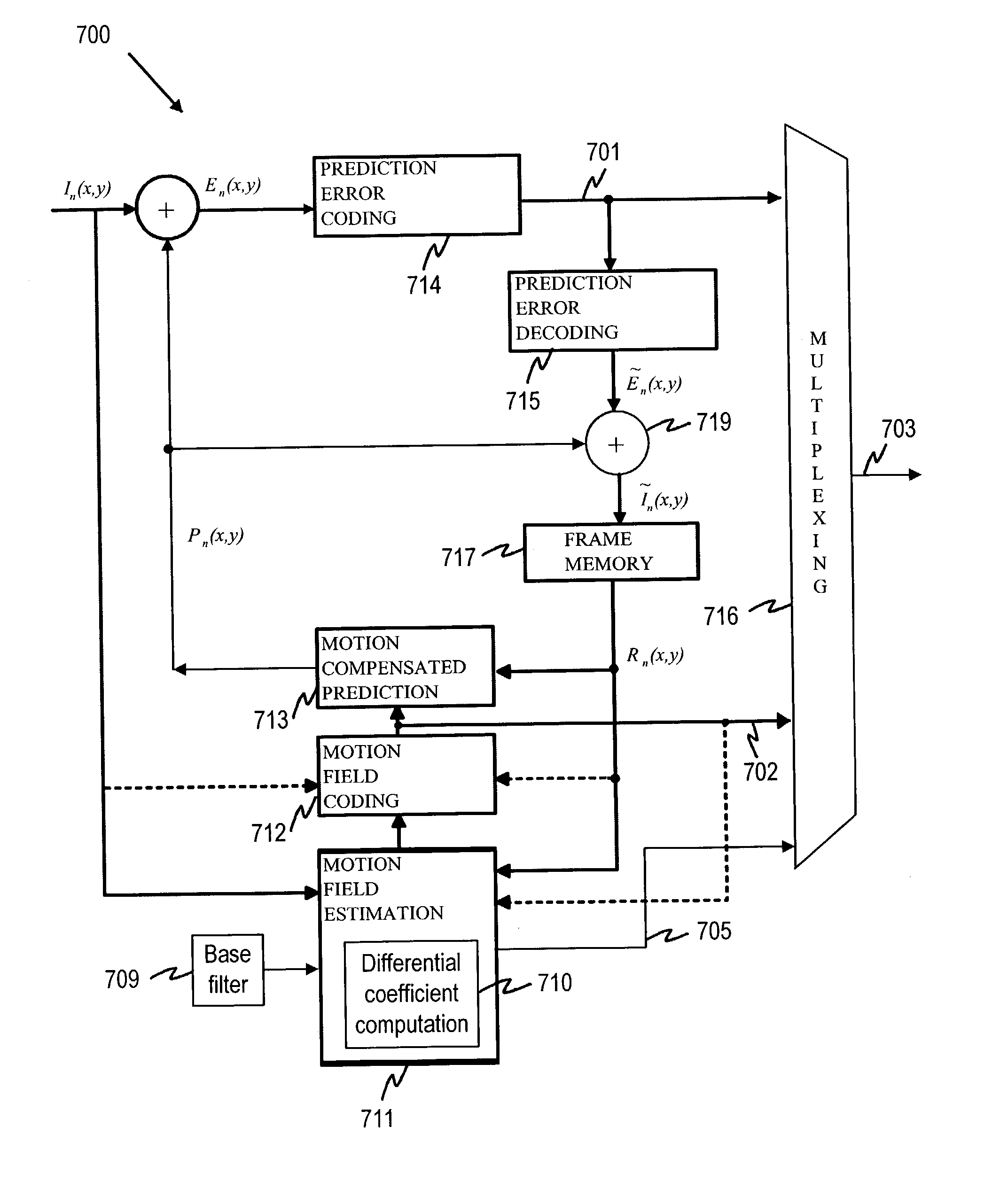
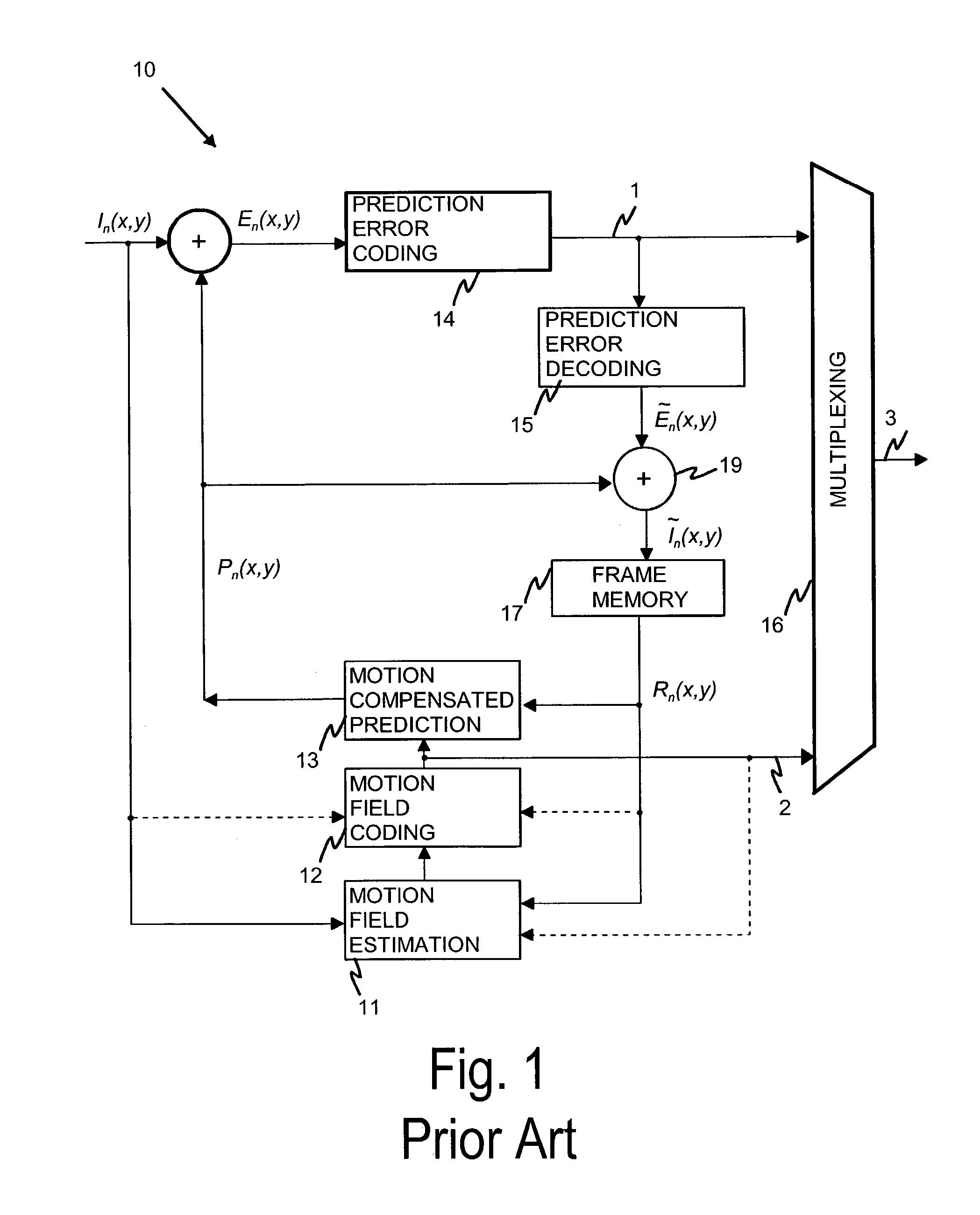
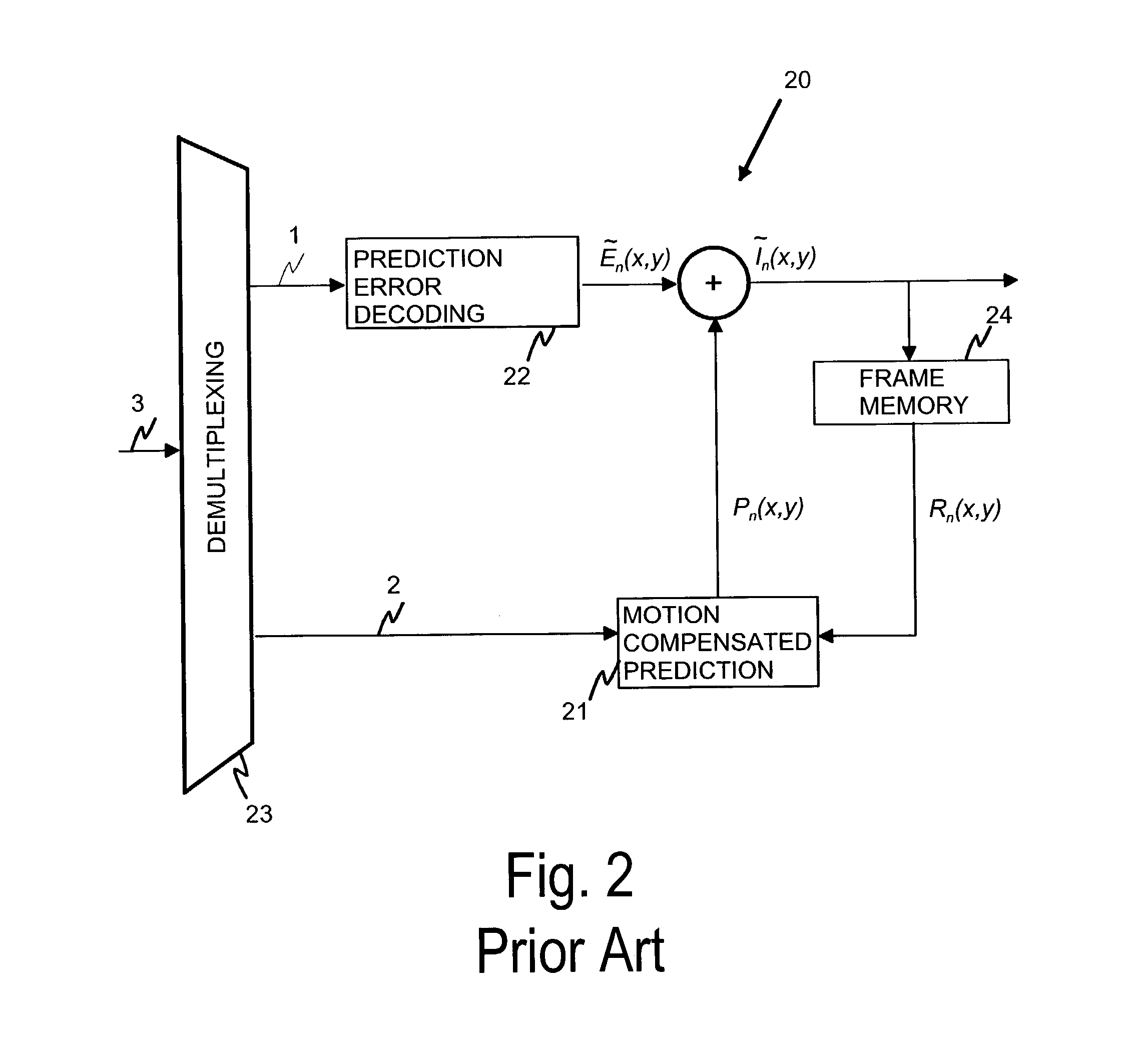
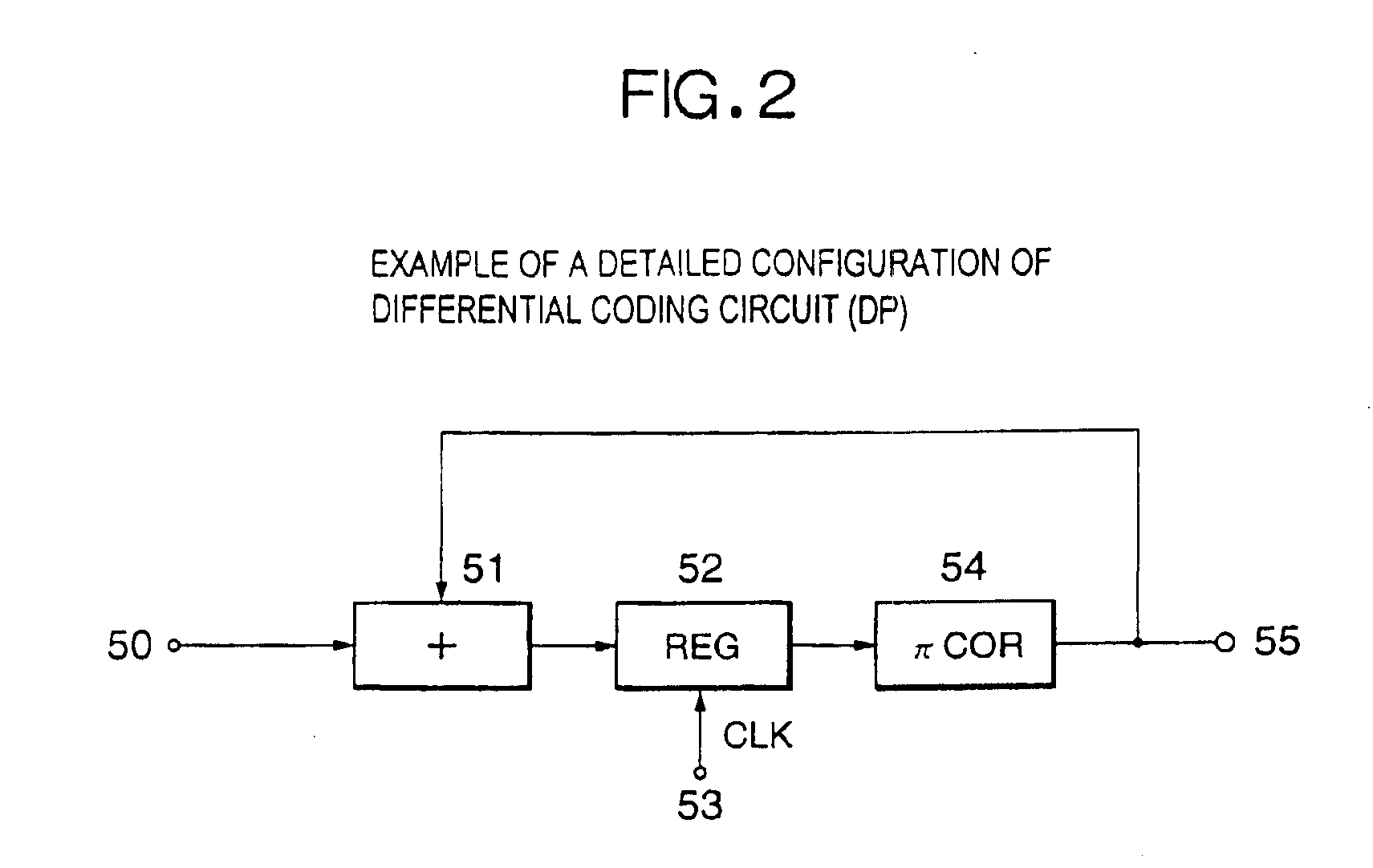
Differential coding of interpolation filters
ActiveUS7379501B2Improve coding efficiencyReduce the amplitudePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionDifferential codingVideo sequence
A video coding system for coding a sequence of video frames each having an array of pixel values is provided. The system includes an interpolation filter to reconstruct sub-pixel values for use in the inter-frame prediction process. The coefficients of an interpolation filter are obtained differentially with respect to a predefined base filter in order to provide a set of difference values. As the base filter coefficients are known to both encoder and decoder and they are statistically close to the actual filters used in the video sequence, the decoder can reconstruct the pixel values based on the set of difference values.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
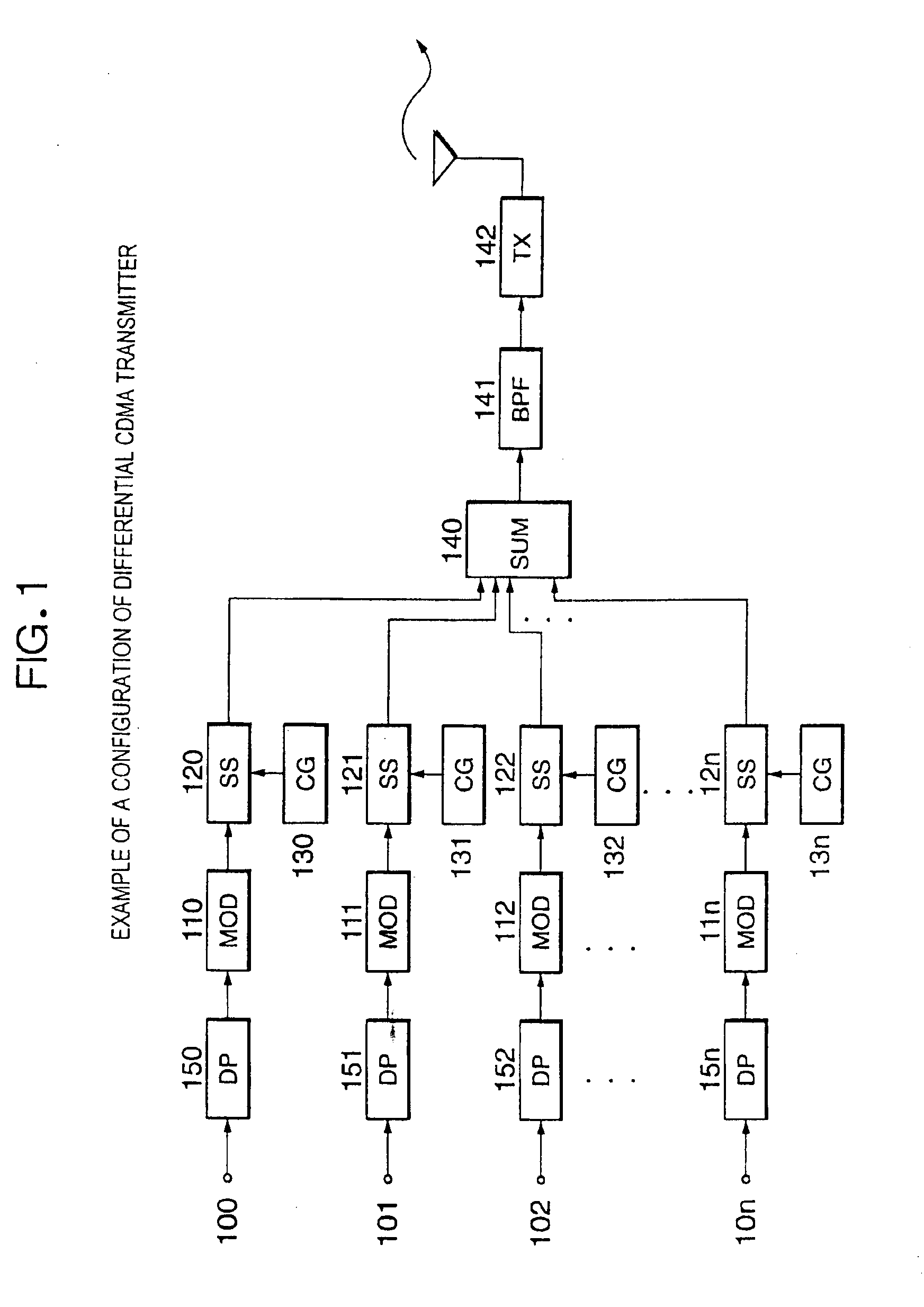
Code division multiple access (CDMA) transmission system
InactiveUS6888813B1Improve communication qualityImprove noise immunityCode division multiplexRadio transmissionTransport systemPhase difference
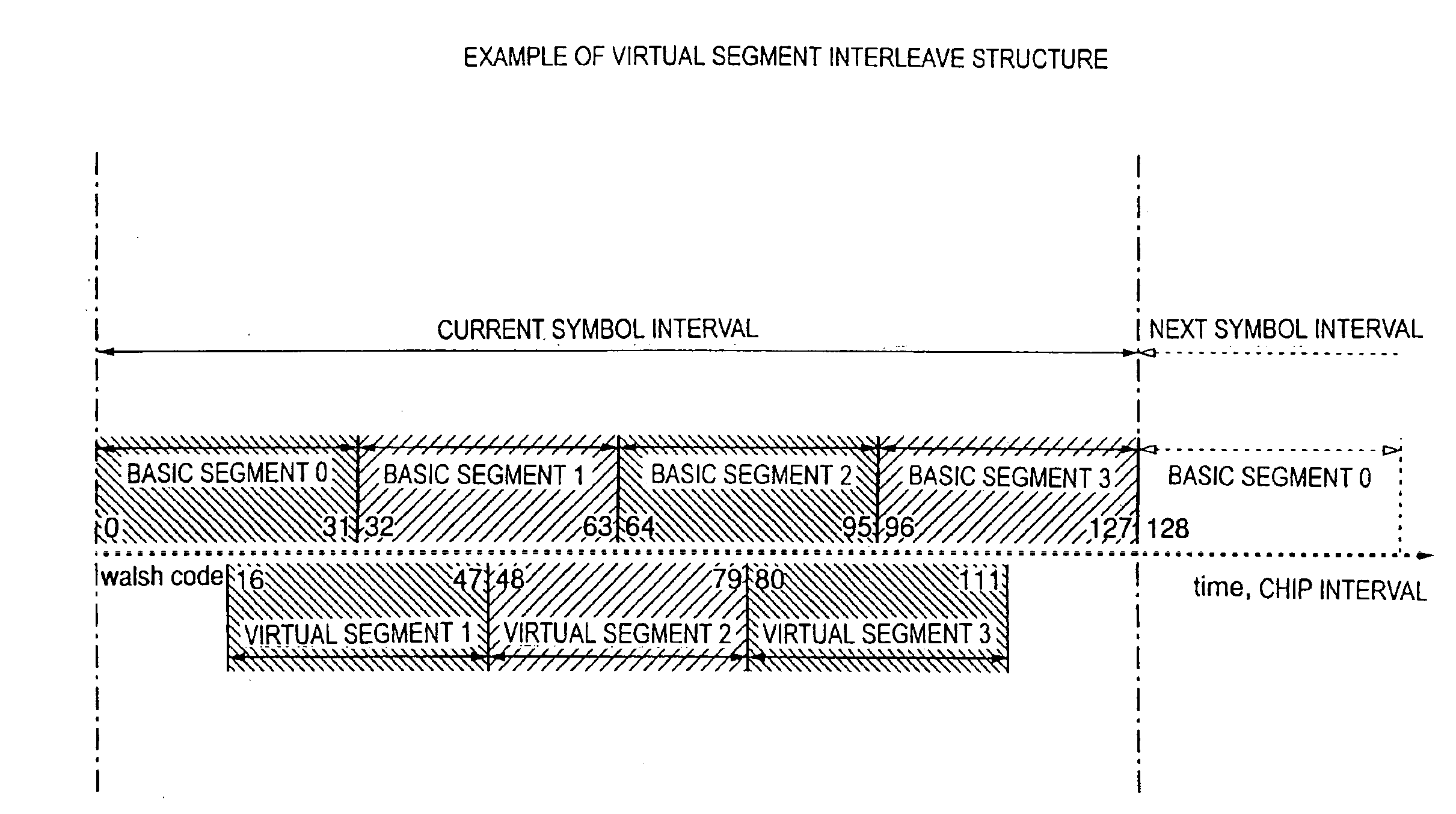
A large-capacity CDMA transmission system that can realize communication with a moving unit such as an automobile, transmitting more quantity of information than the conventional system without increasing the occupied band width, using the same or narrower frequency band width.This system assumes the code division multiple access (CDMA) transmission system for simultaneous multiple communication, which performs phase modulation on a carrier signal while maintaining a phase of the carrier signal in a predetermined period at a predetermined value, so as to generate a primary modulated wave, and then, multiplies the obtained primary modulated wave by a spread code sequence. On the transmitting side, a differential coding phase modulation (DPSK) is employed to generate a primary modulated wave. On the other hand, on the receiving side, a quasi-synchronous detection and difference operation are utilized to detect the phase difference between the last symbol interval and the current symbol interval, and the detected phase difference is given as the information of the current symbol interval.
Owner:KISHI MASAHICHI
Scalable compressed audio bit stream and codec using a hierarchical filterbank and multichannel joint coding
ActiveUS7548853B2Effectively scaledSuitable for useSpeech analysisCode conversionComputer hardwareDifferential coding
A method for compressing audio input signals to form a master bit stream that can be scaled to form a scaled bit stream having an arbitrarily prescribed data rate. A hierarchical filterbank decomposes the input signal into a multi-resolution time / frequency representation from which the encoder can efficiently extract both tonal and residual components. The components are ranked and then quantized with reference to the same masking function or different psychoacoustic criteria. The selected tonal components are suitably encoded using differential coding extended to multichannel audio. The time-sample and scale factor components that make up the residual components are encoded using joint channel coding (JCC) extended to multichannel audio. A decoder uses an inverse hierarchical filterbank to reconstruct the audio signals from the tonal and residual components in the scaled bit stream.
Owner:DTS
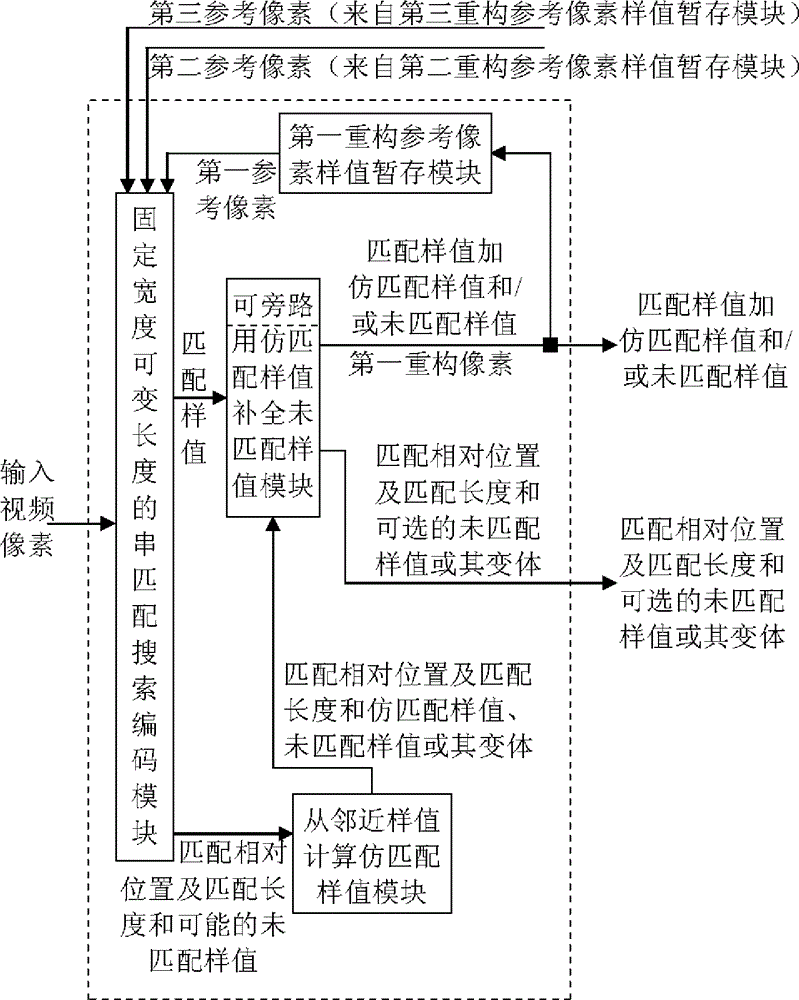
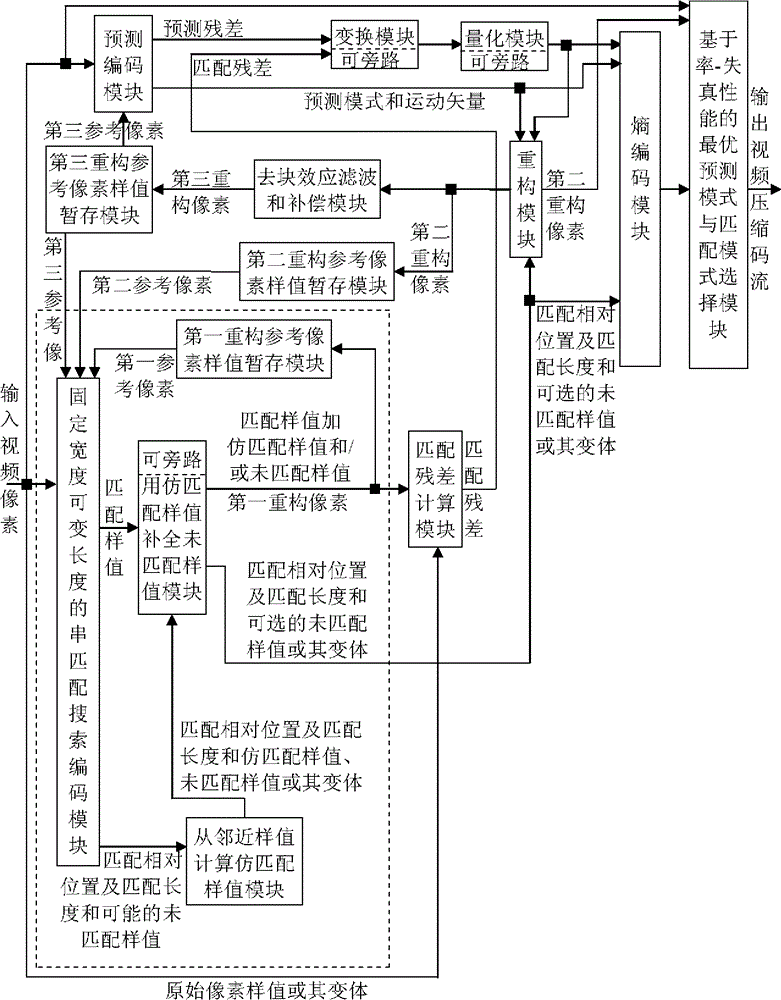
Fixed-width variable-length pixel sample value string matching strengthened image compression method and device
Provided are an image compression method and device. When coding a coding block, within a first, a second, and a third reconstructed reference pixel sample sets, the position labels whereof do not intersect, one or a plurality of optimal fixed-width, variable-length pixel sample matching strings are searched for and obtained, according to predetermined evaluation criteria. Each matching string is characterized by a matching relative position and a matching length. A pseudo matching sample is calculated from neighbouring samples for samples for which no match is found. A matching string search can be performed within a single pixel component plane or within a stacked format pixel space in which the three components are in a single crossed arrangement. Quantization or transformation-quantization coding, predictive coding, differential coding or entropy coding can then be performed on the matching relative position, the matching length and a matching residual error. The matching may have a variety of sample division modes and arrangement modes, an optimal one being selecting therefrom. Hybrid coding based on traditional prediction coding is performed simultaneously on a same coding unit, and an optimal coding mode is finally chosen.
Owner:上海天荷电子信息有限公司
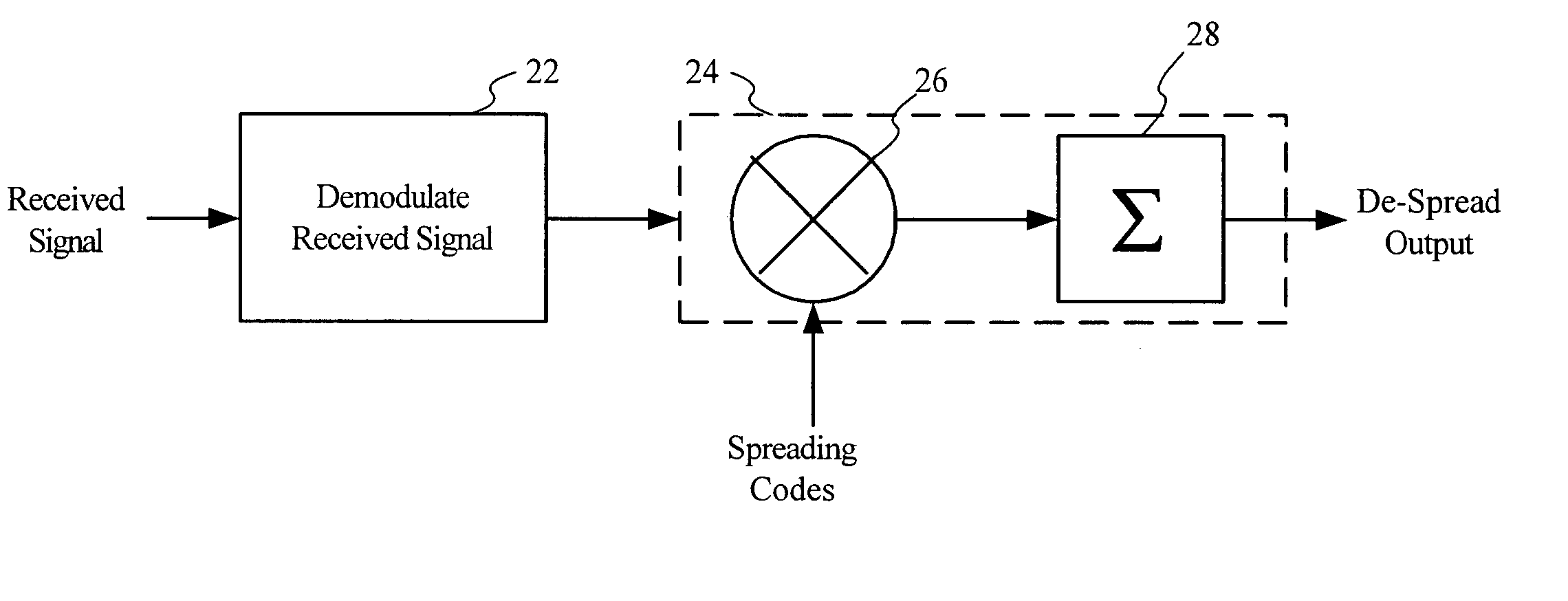
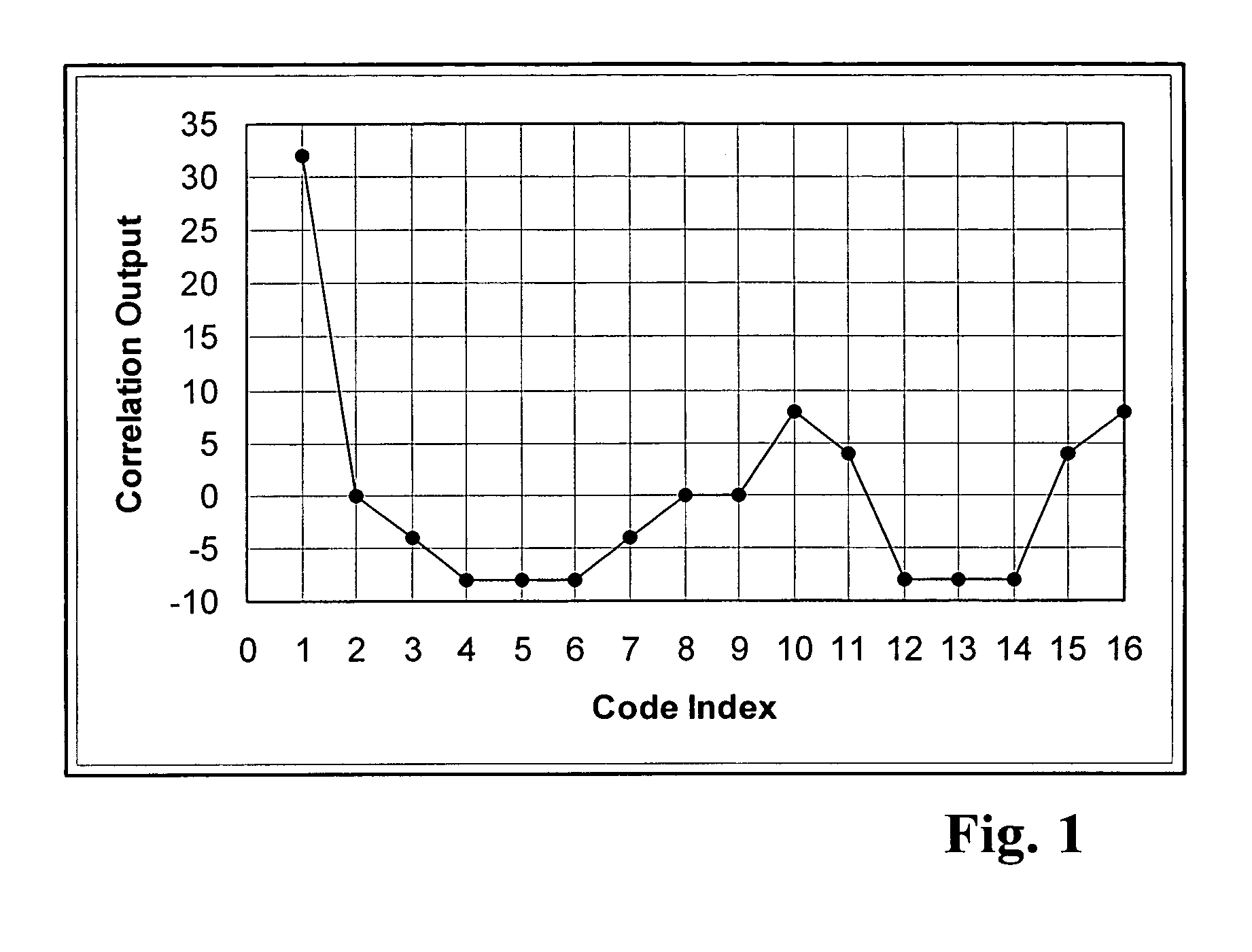
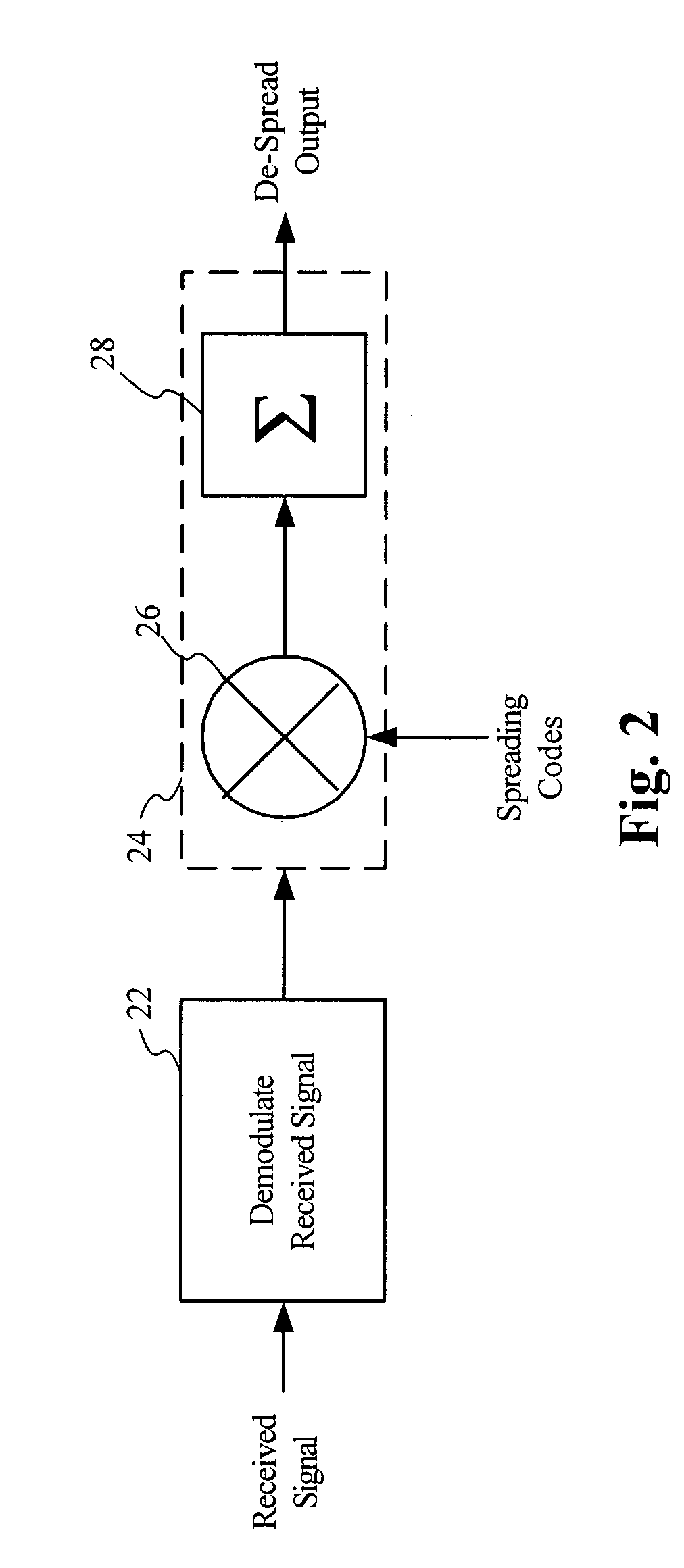
Chip-to-symbol receiver despreader architechtures and methods for despreading spread spectrum signals
ActiveUS20050105597A1Simple methodSignal being spreadDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCode division multiplexProgramming languageShift register
In a spread spectrum system, methods and despreader architectures for despreading the received spreaded codes with the use of a single correlator and a single correlation code is provided. Before despreading the incoming received spreaded codes, a single correlation code is generated using a symbol from a set of symbols that has been mapped into a set of differential encoded PN codes. Despreading output samples for each received spreaded code are obtained by correlating the received spreaded code with this single correlation code. Correlation is accomplished by multiplying each received sample of the received spreaded codes with the correlation code samples and accumulating the products of this multiplication. After correlation, the index for the maximum or minimum peak of the despreading output samples for each code is identified. This index can then be mapped into a symbol corresponding to the transmitted information. Corresponding despreader architectures comprise of a number of taps attached to a series of shift registers. Received samples of each received spreaded codes are inputted into the shift registers. The despreader architectures accumulates the products of multiplication of the value of the shift register with a predetermined value associated with each tap to produce the despreading output samples of a received spreaded code. It identifies the despreading output index producing the maximum of the absolute value of the despreading output and maps said index into a symbol corresponding to the transmitted information.
Owner:UNIBAND ELECTRONICS CORP
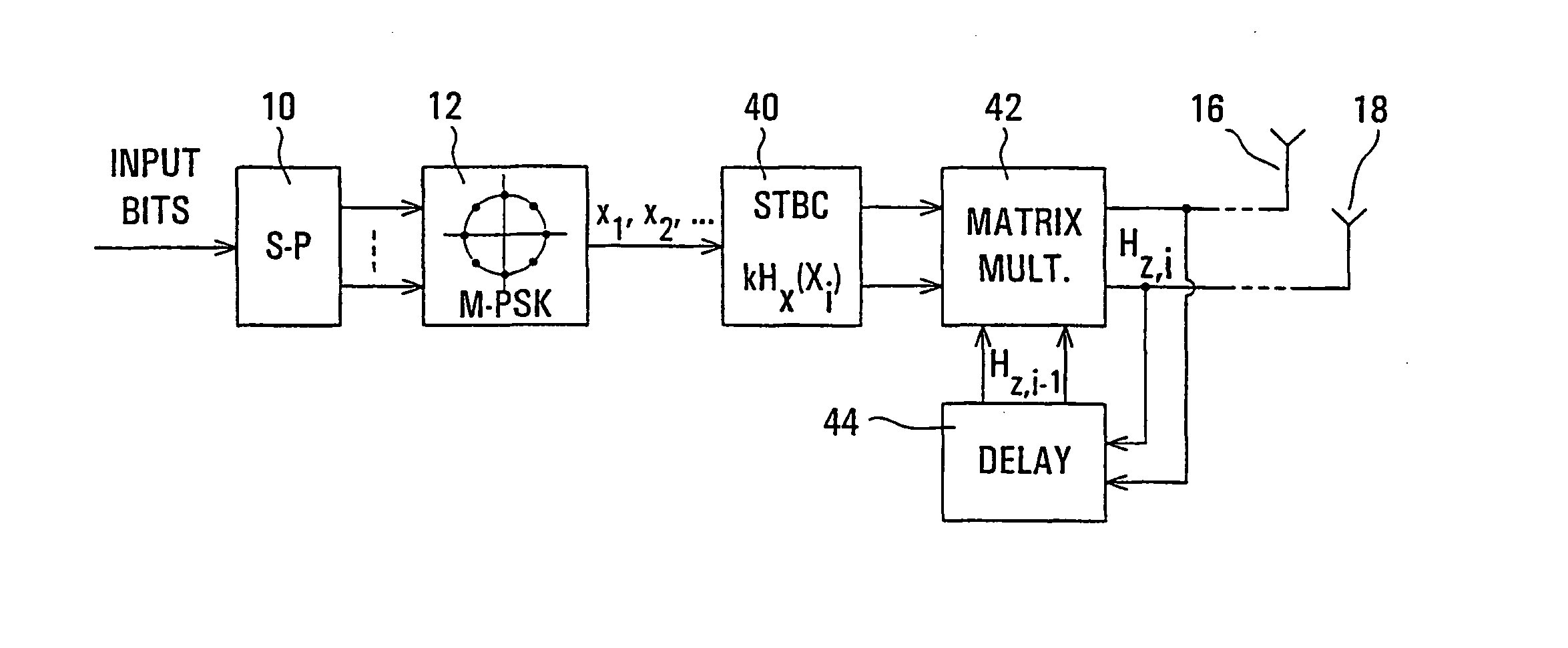
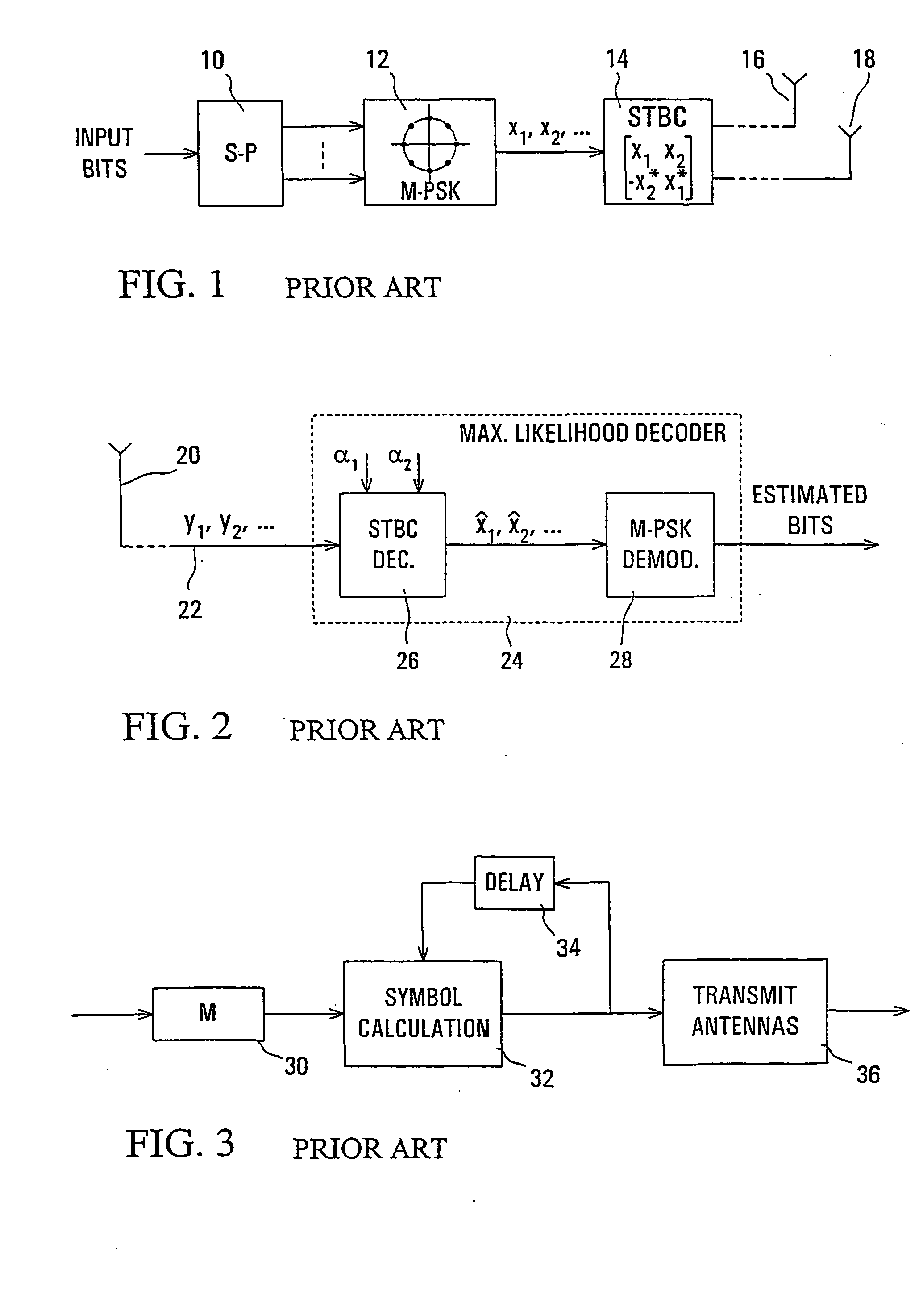
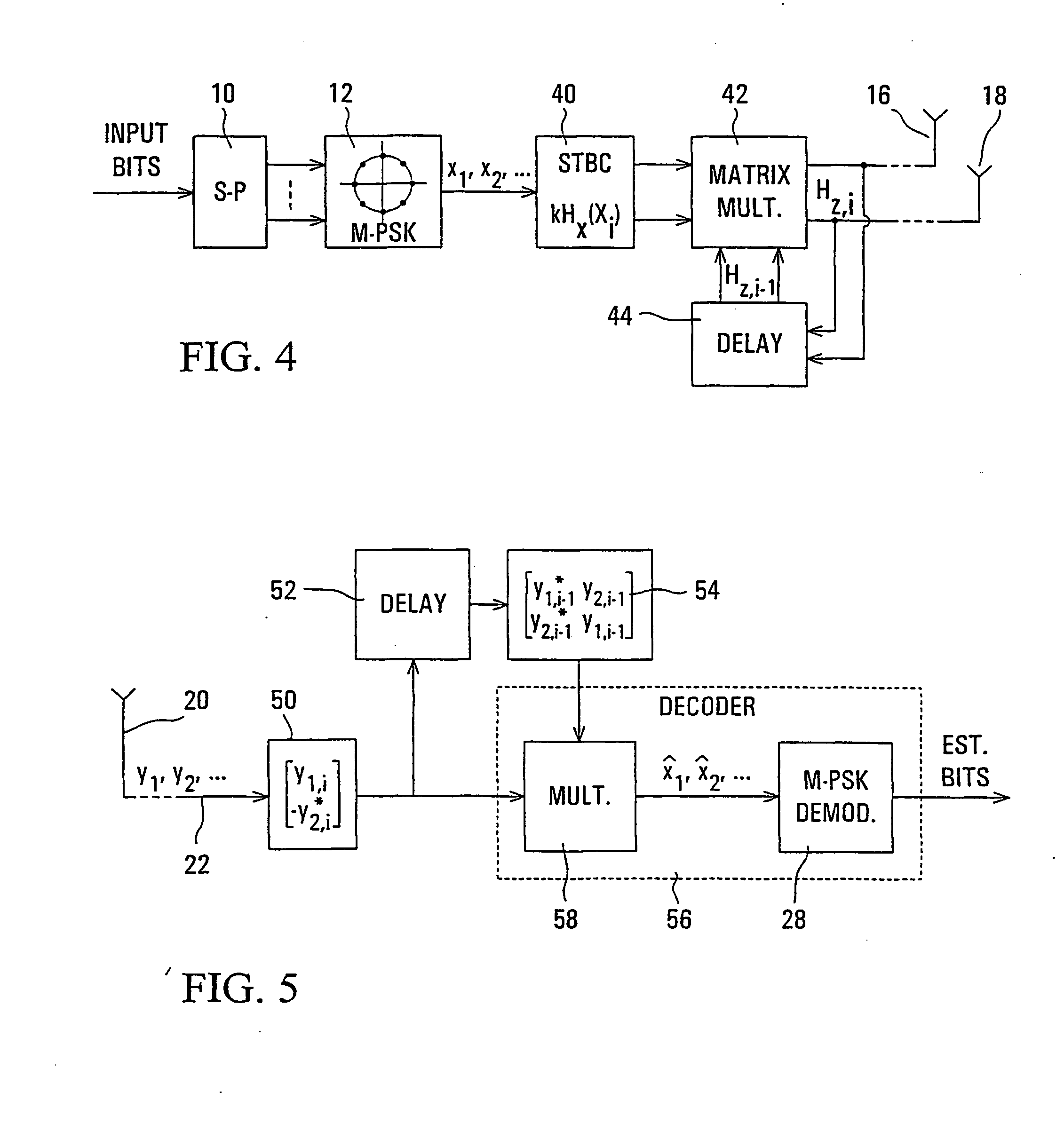
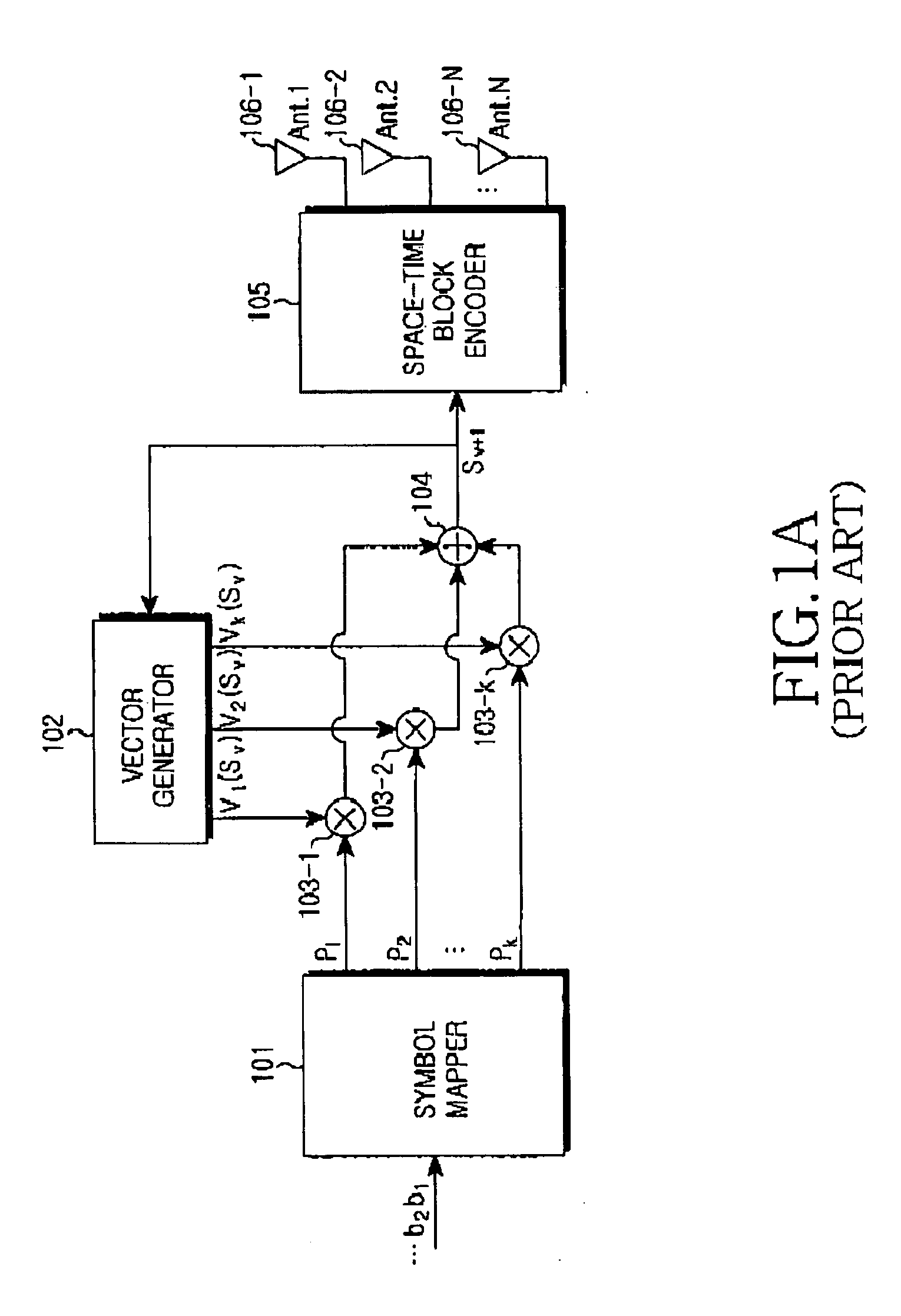
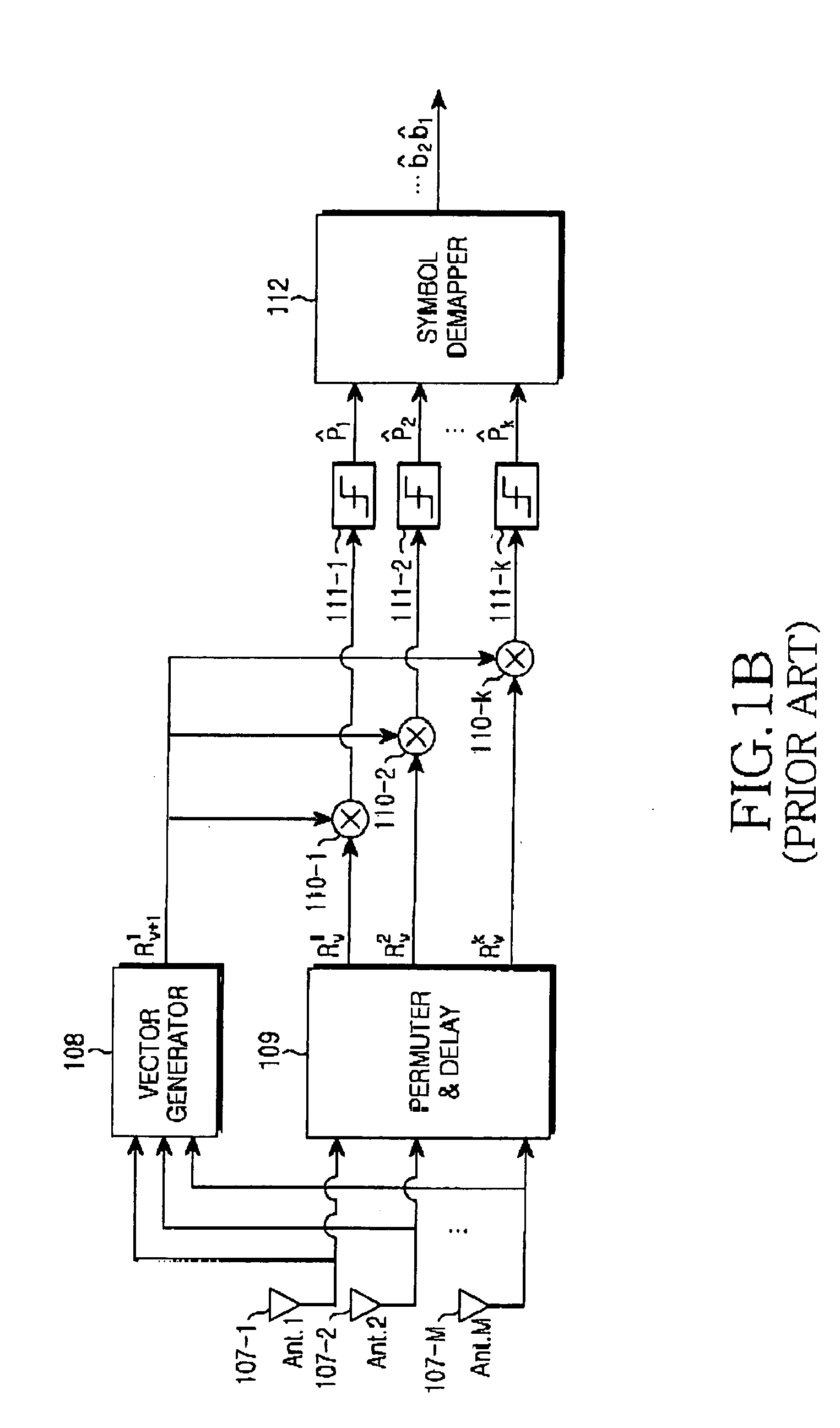
Differential space-time block coding
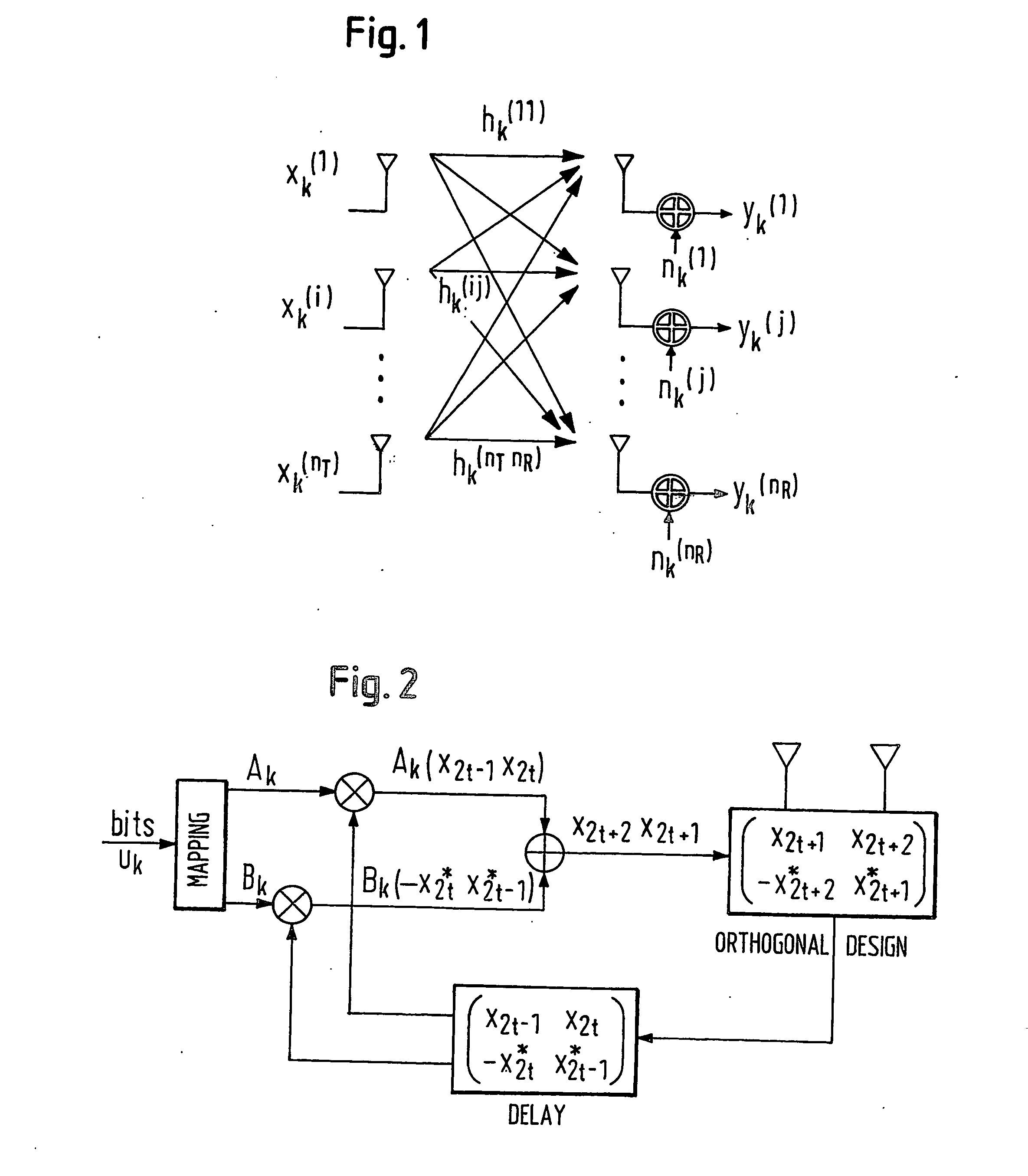
InactiveUS20050063483A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDifferential space timeCommunications system
A differential space-time block coder produces successive space-time blocks of symbols from M-PSK symbols to be encoded, in accordance with an orthogonal matrix and a normalization factor. Differentially encoded space-time output blocks, for transmission via a plurality of transmit antennas (16, 18) of a wireless communications system, are produced by multiplying (42) each space-time block from the space-time block coder (40) by the respective previous (44) differentially encoded space-time output block. Decoding is independent of channel estimation, and the arrangement is simple, avoids error propagation, and is applicable to different numbers of transmit antennas.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
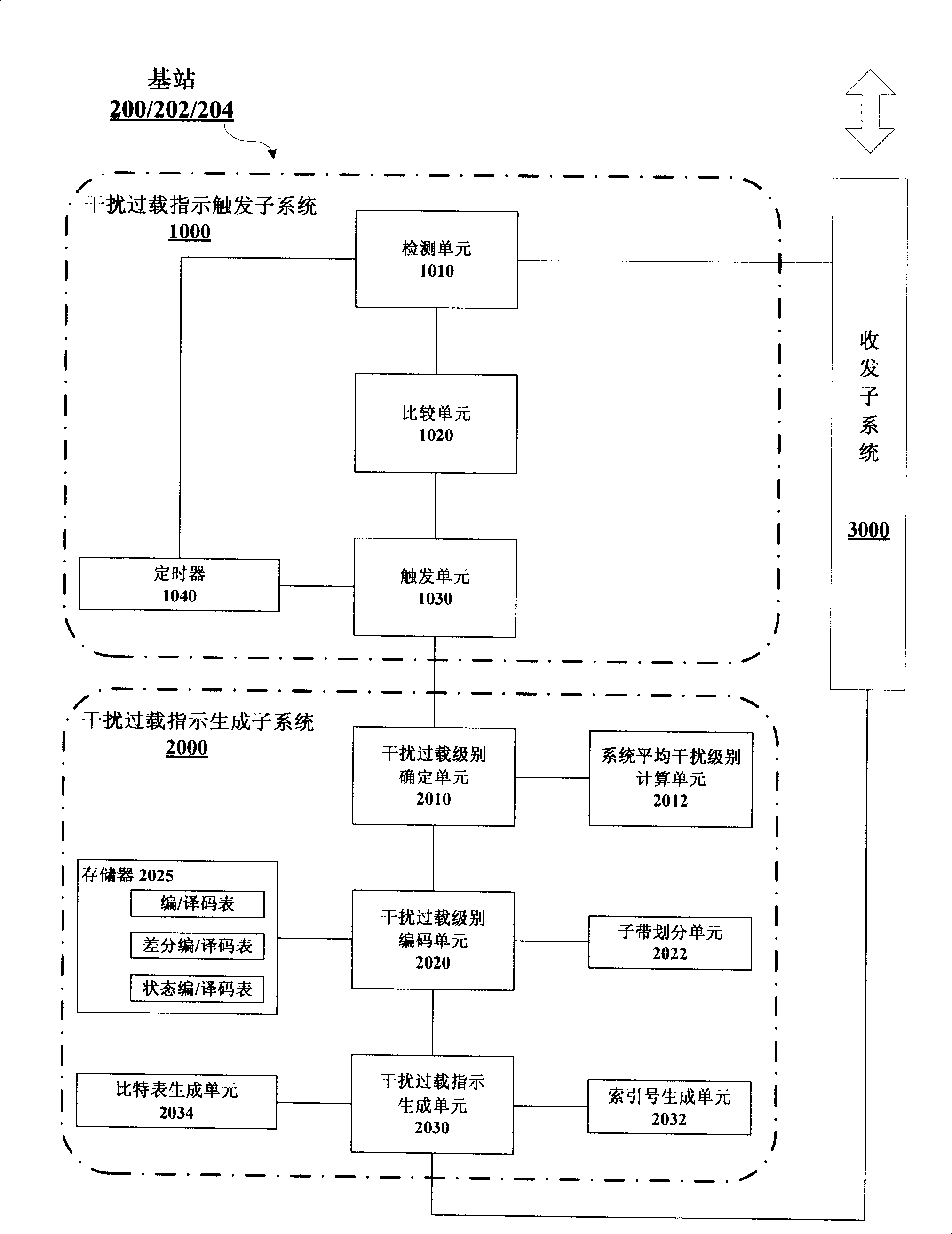
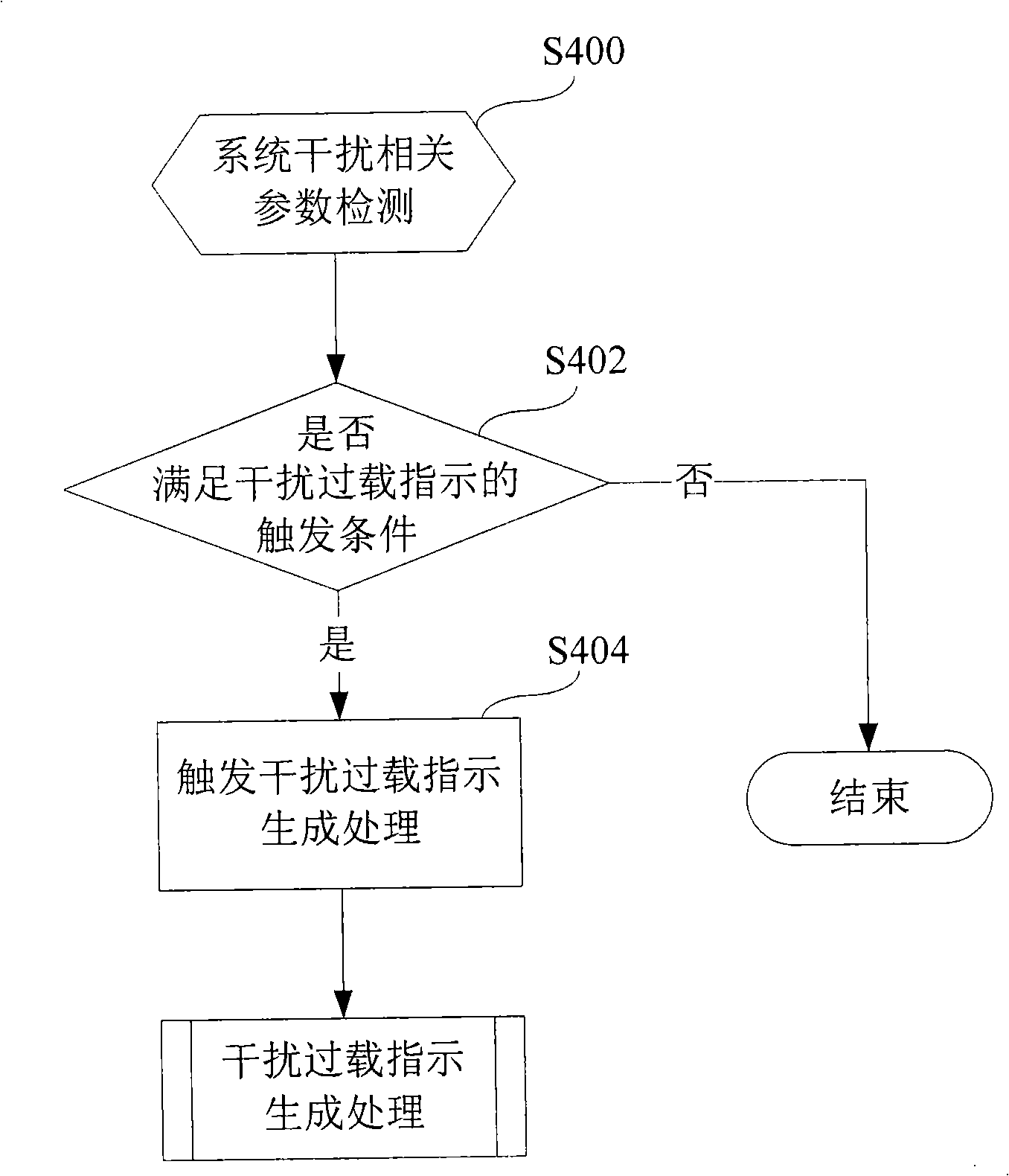
Interference overload indication generating method, interference overload indication triggering method, interference overload indication method and base station
InactiveCN101541012ANetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionInterference (communication)Cellular communication systems
The invention provides an interference indication generating method, an interference indication triggering method, an interference indication method and a base station using the methods for an uplink FDMA cellular communication system. The base station comprises an interference overload indication triggering subsystem (1000), an interference overload indication generating subsystem (2000) and a transceiving subsystem (3000). The interference overload indication triggering subsystem (1000) firstly judges whether a triggering condition of interference indication is met. Only when the condition is met, the interference overload indication generating subsystem (2000) is triggered to operate so as to reduce the signaling overhead of the interference indication; and in order to further reduce the signaling overhead, interference indication signaling is generated and sent by adopting methods of differential coding, state coding, bit tables and the like. The invention has the advantages that a triggering mechanism of the interference indication is simple, the signaling overhead of the interference indication is lower, and the like.
Owner:SHARP KK
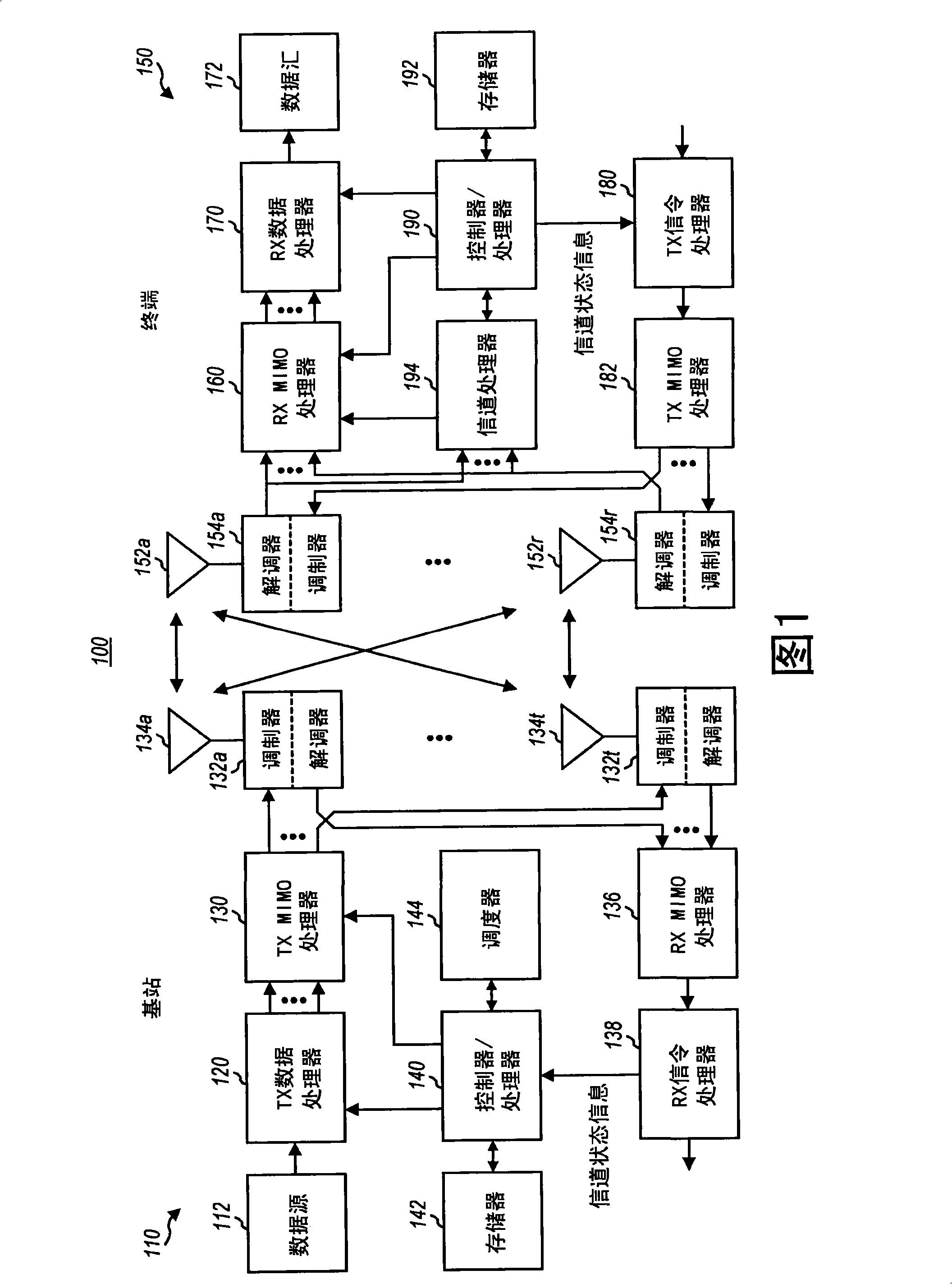
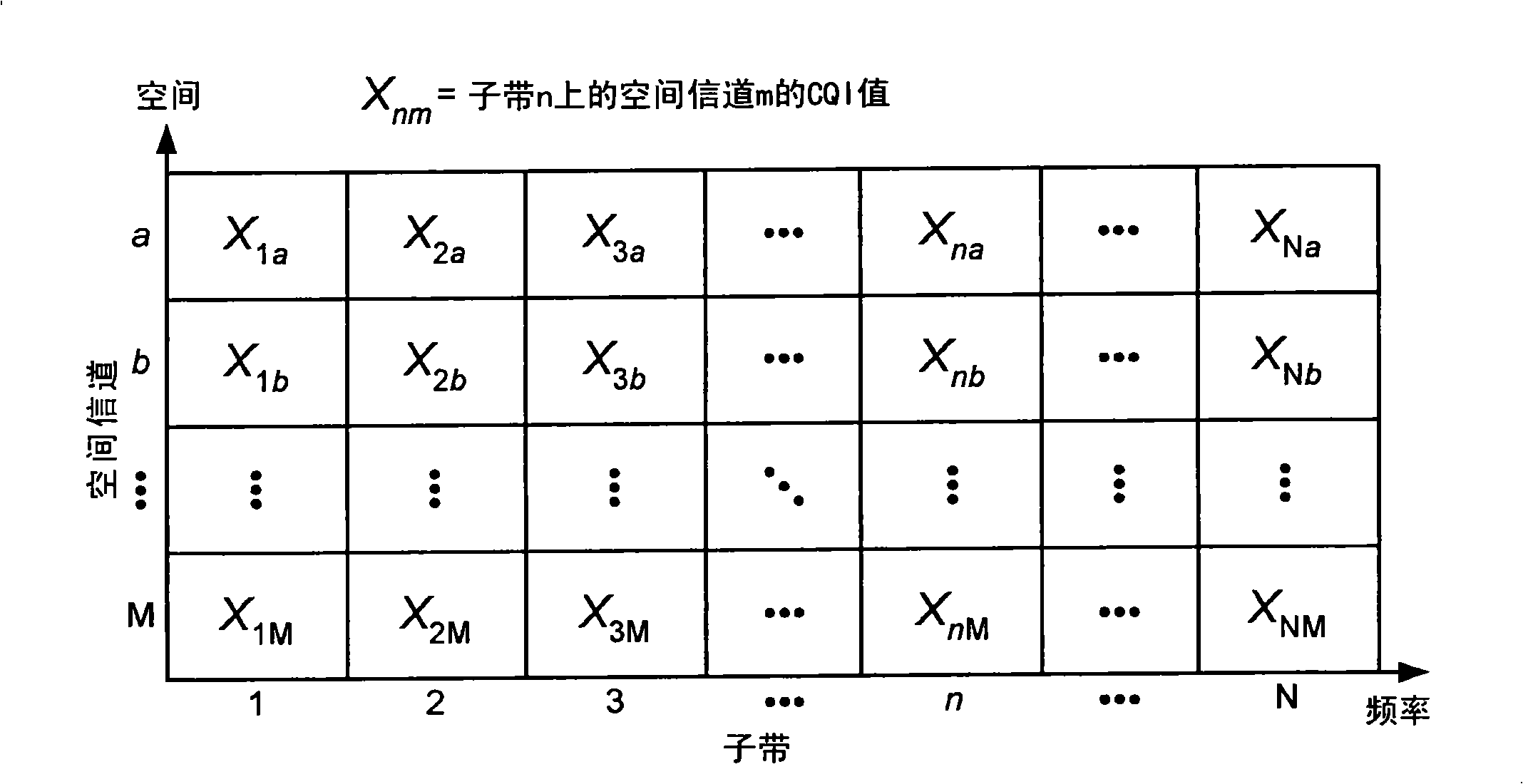
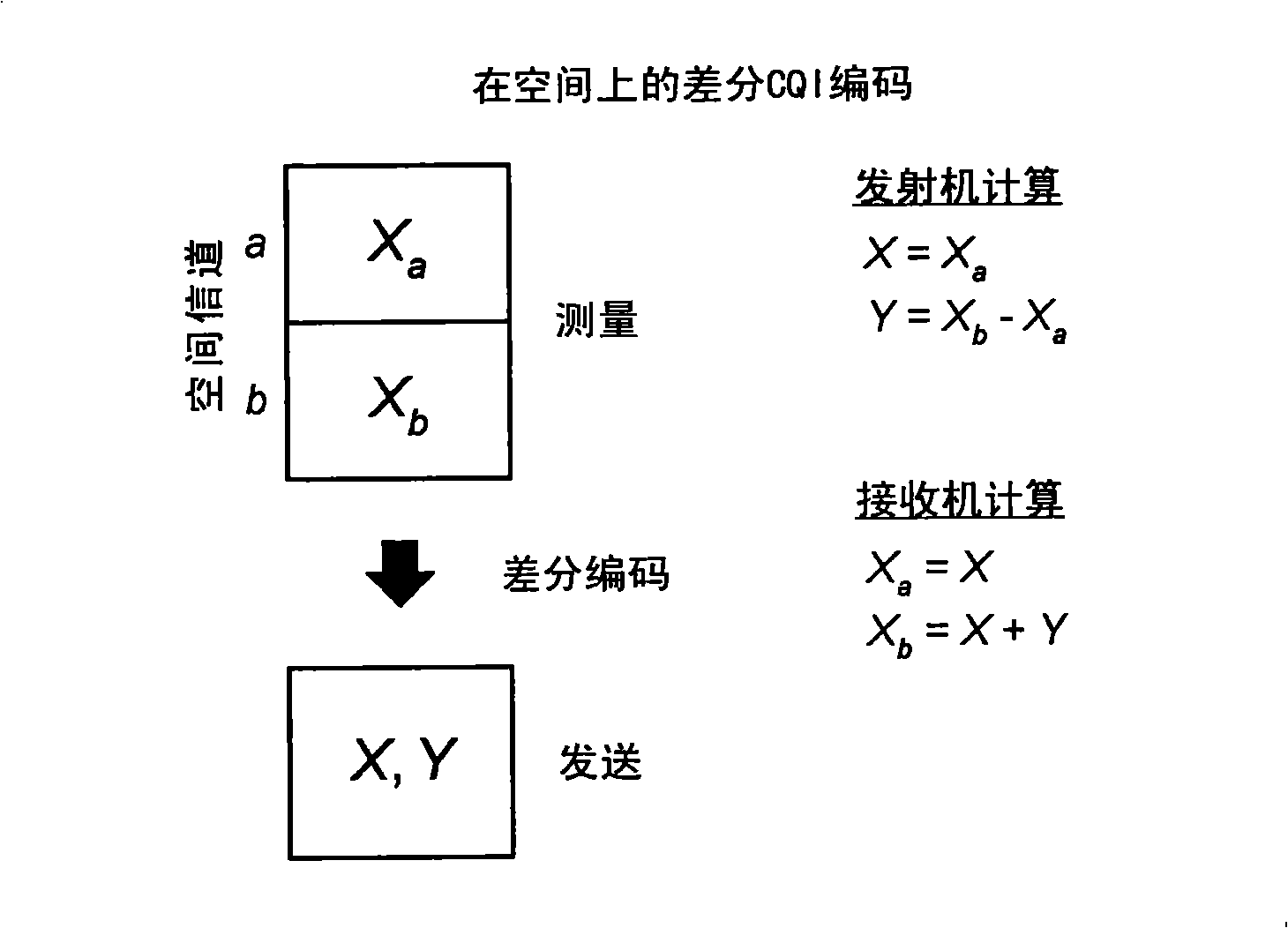
Feedback of channel state information for MIMO and subband scheduling in a wireless communication system
ActiveCN101411110ASpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsChannel state informationPrecoding
Techniques for efficiently sending channel state information using differential encoding are described. Differential encoding may be performed across space, across frequency, across space and frequency, across space, frequency and time, or across some other combination of dimensions. In one design, spatial state information may be determined for multiple spatial channels on multiple subbands. The spatial channels may correspond to different antennas, different precoding vectors, etc. Channel quality indicator (CQI) values may be obtained for the multiple spatial channels on the multiple subbands. The CQI values may be differentially encoded across the multiple spatial channels and the multiple subbands to obtain differential CQI information. In another design, CQI values may be obtained for multiple spatial channels on the multiple subbands in multiple time intervals and may be differentially encoded across space, frequency and time. The differential CQI information and the spatial state information may be sent as feedback.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
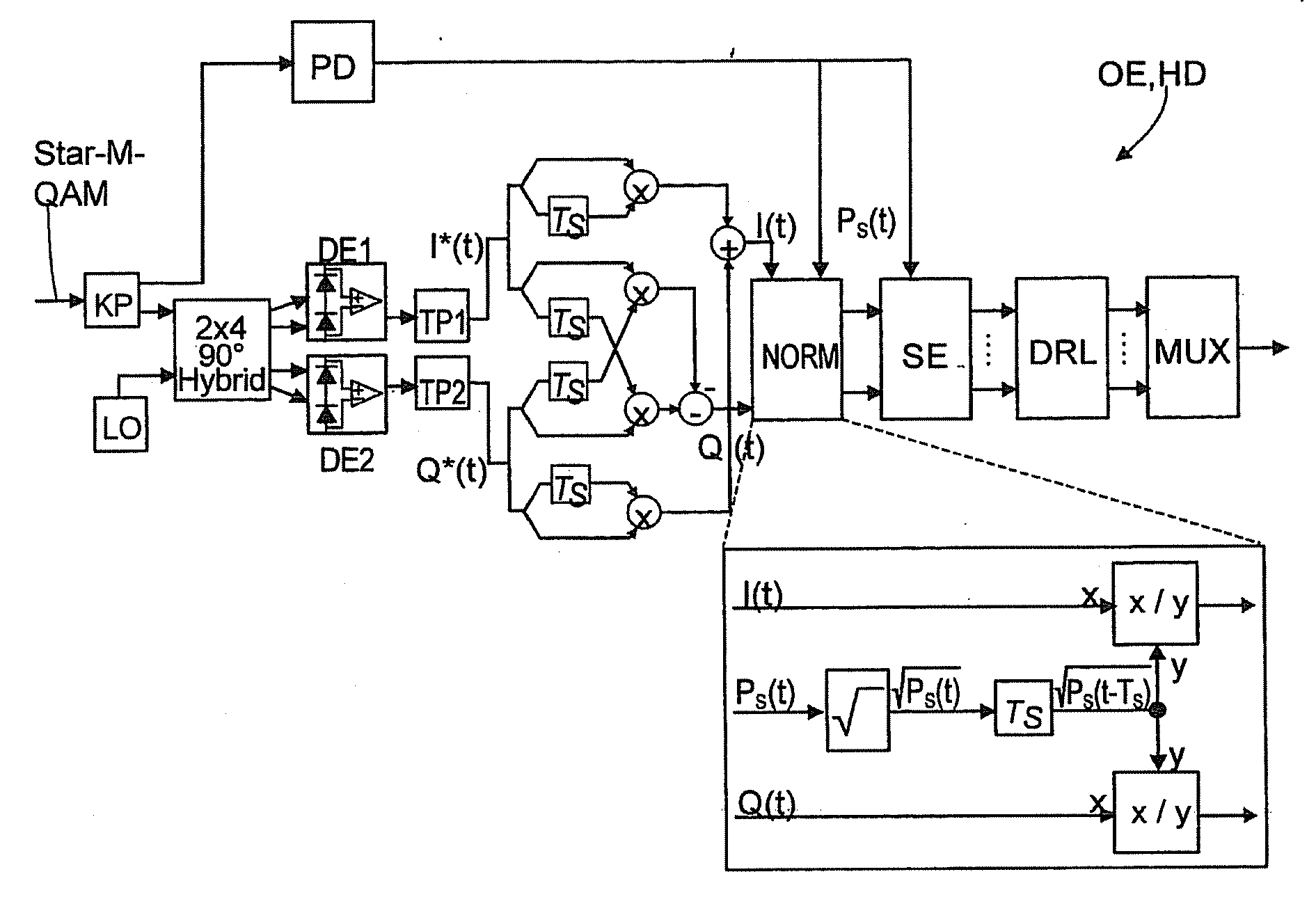
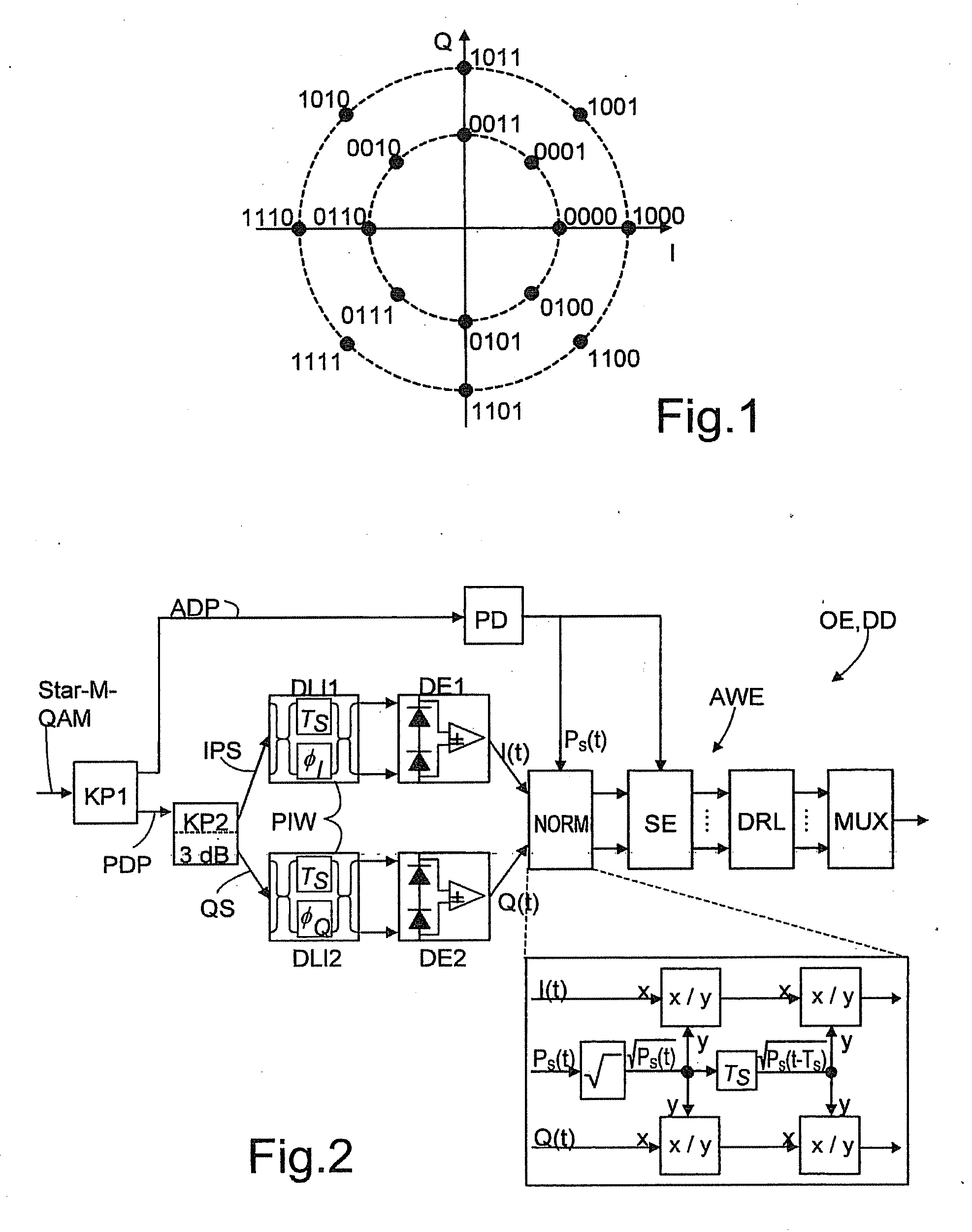
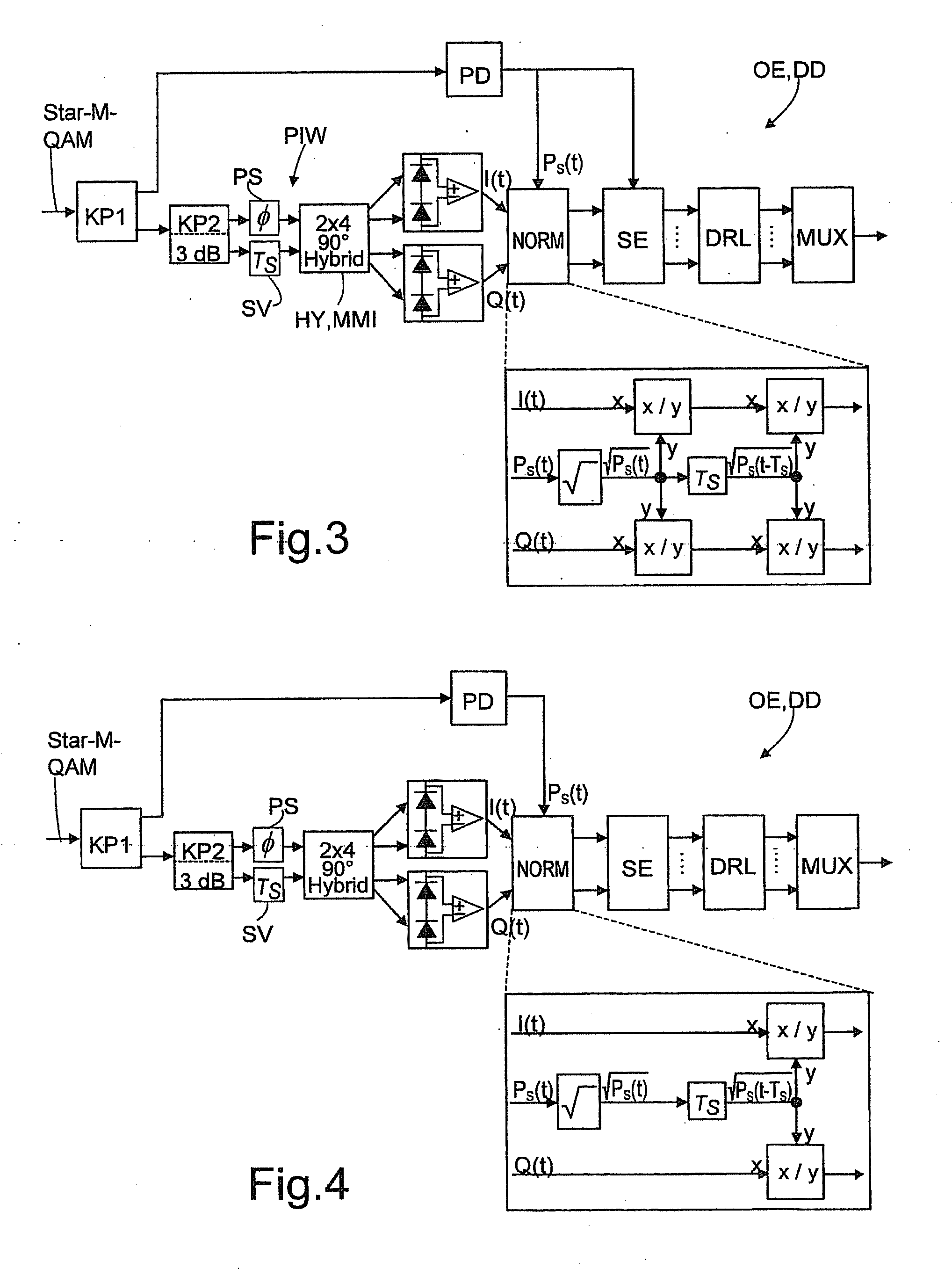
Optical Receiver For Receiving A Signal With M-Valued Quadrature Amplitude Modulation With Differential Phase Coding And Application Of Same
InactiveUS20090129788A1Loss of performancePermit useElectromagnetic receiversMultiple carrier systemsDiscriminatorDifferential phase
Optical data signal receiver having an optical separation of the received data signal into two signal paths, namely, an amplitude detection path and a phase detection path, wherein the phase detection path is split into an in-phase signal path generating in-phase-signals and a quadrature-signal path generating quadrature-signals, and both the in-phase-signal path and the quadrature-signal path, as well as the amplitude detection path, are connected to an analysis unit for demodulation of the received data signal, in which a normalizer and thereafter a symbol discriminator and a data reconstruction logic are arranged in the analysis unit. In the receiver, a connection is provided at least from the amplitude detection path to the normalizer, the normalizer normalizing the in-phase and quadrature-signals with the aid of the signal output from the amplitude detection path, the symbol discriminator discriminating the symbols output from the normalized in-phase and quadrature-signals. Additional connections can be provided from the amplitude detection path signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
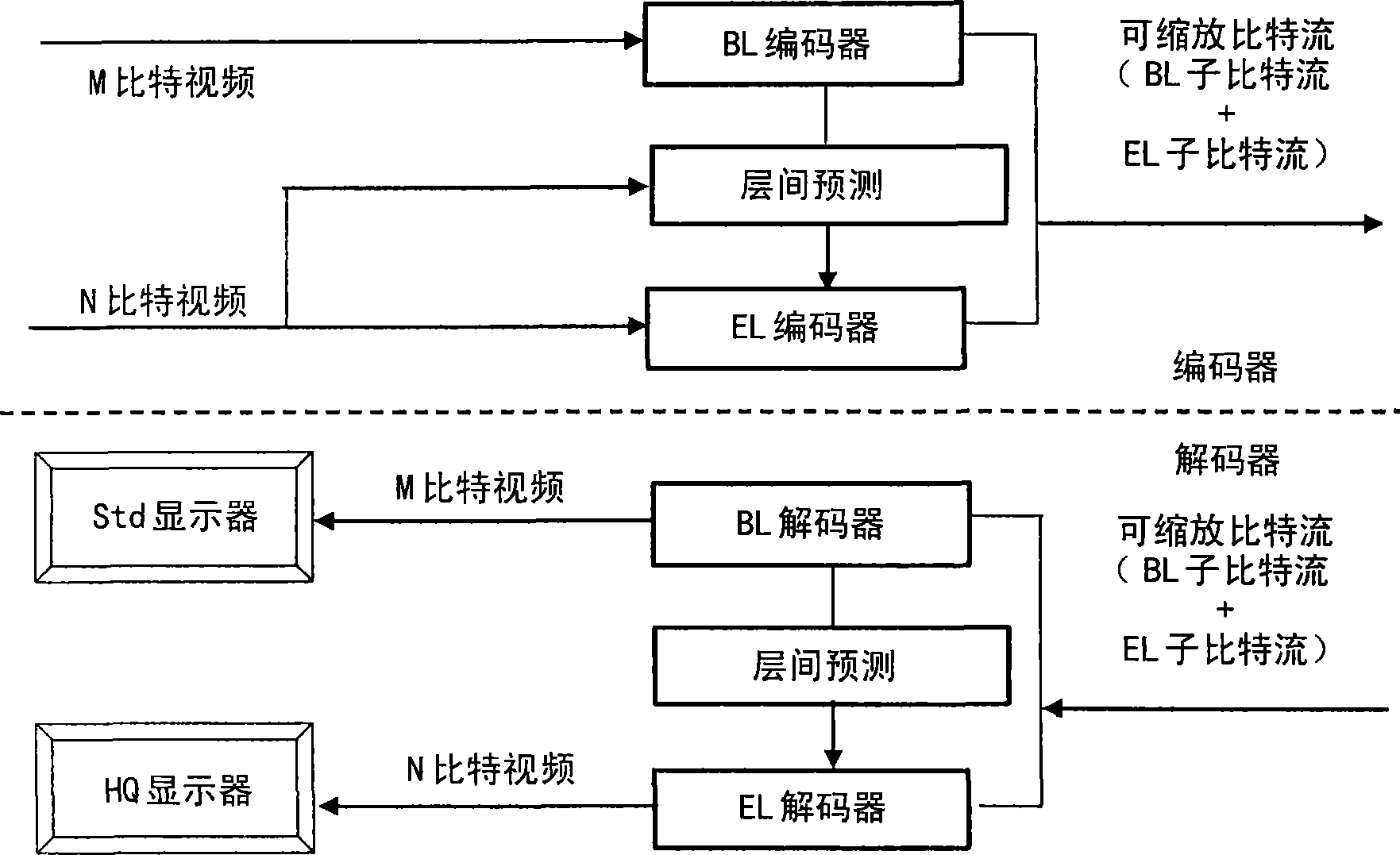
Enhancement layer residual prediction for bit depth scalability using hierarchical luts
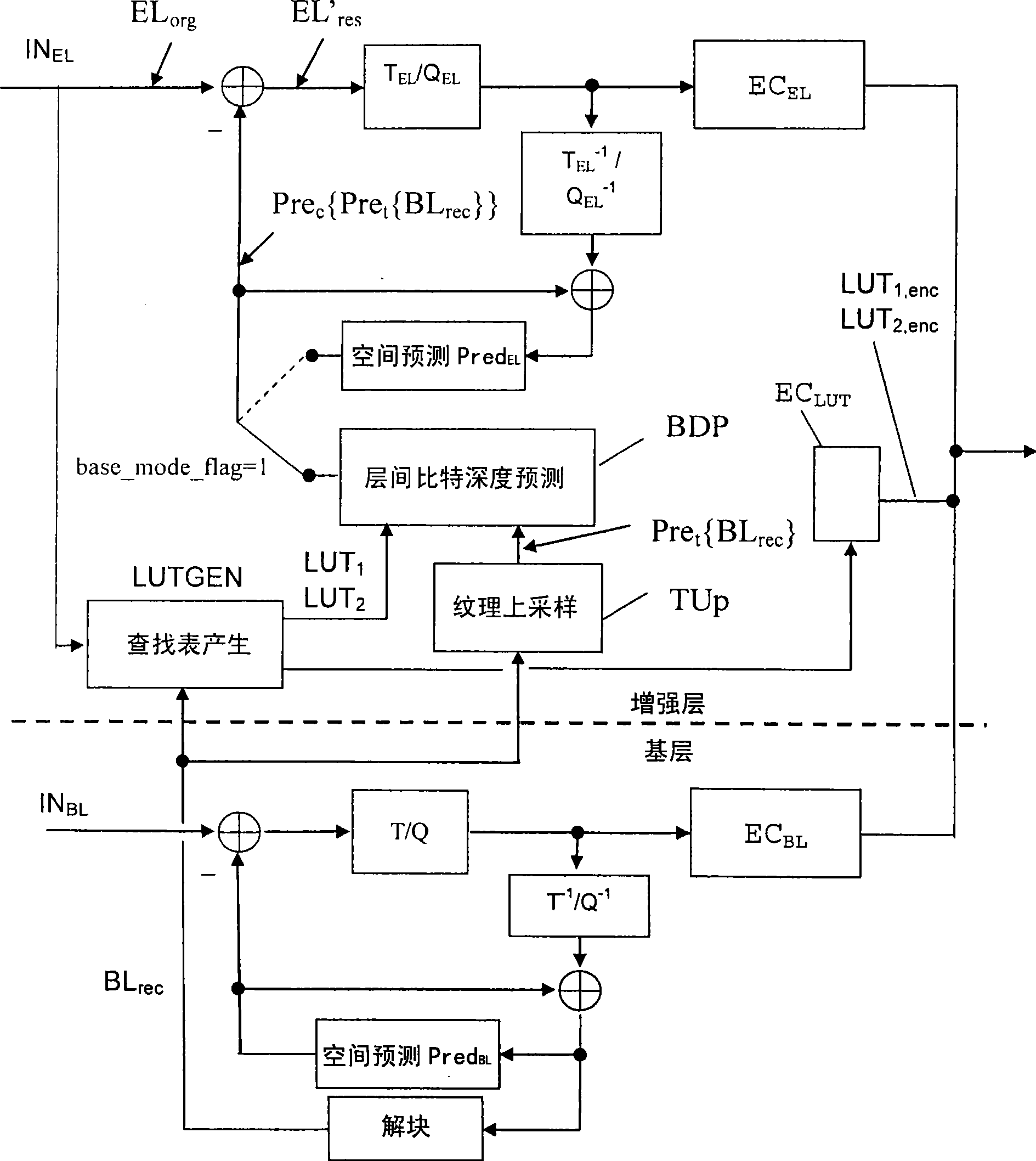
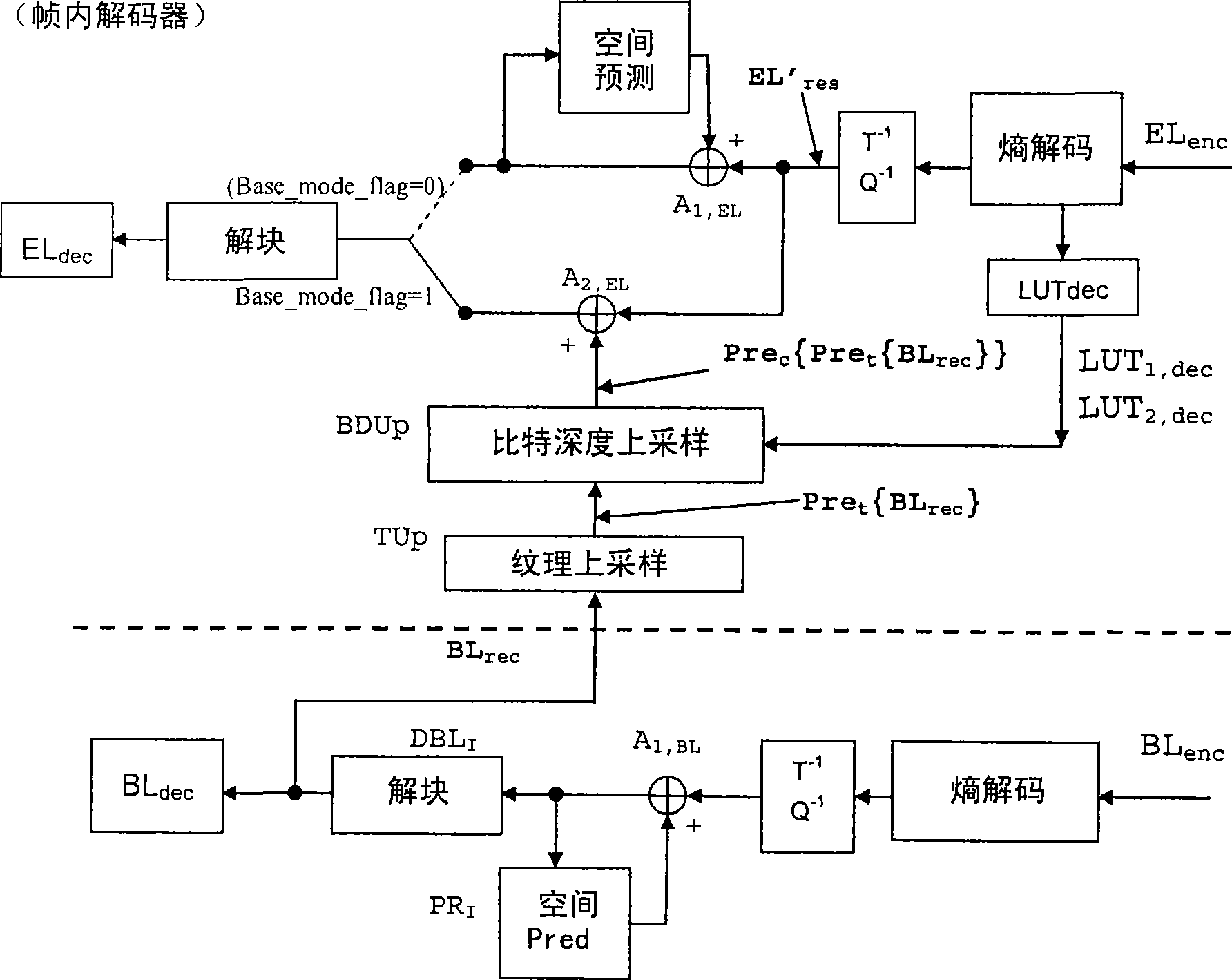
ActiveCN101415120AColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo bitstreamTone mapping
The invention discloses a method for the predication of residual error of classified-LUT-used and bit-depth-scalable enhanced layer. The scalable video bit stream may have H264 / AVC compatible basic layer and scalable enhanced layer, wherein the scalability relates to the color bit depth. According to the invention, BL information carries out bit depth up-sampling using single search table mapped by reverse tone on two or more levels which are image level, image bar level and MB level. The search table is carried out differential coding and contained in the head information. The process of the bit depth up-sampling (BDUp) is as follows: the process enhances the number of the value of each pixel and relative to the colour intensity of the pixel. Based on the search table, the data of the basic layer after the up-sampling is used for predicting the enhance layer in the relative position. The up-sampling is finished at a coder, and a decoder by the same mode, wherein the up-sampling relates to time, space and bit depth. Therefore, the bit depth up-sampling (BDUp) is compatible with the texture up-sampling (TUp).
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
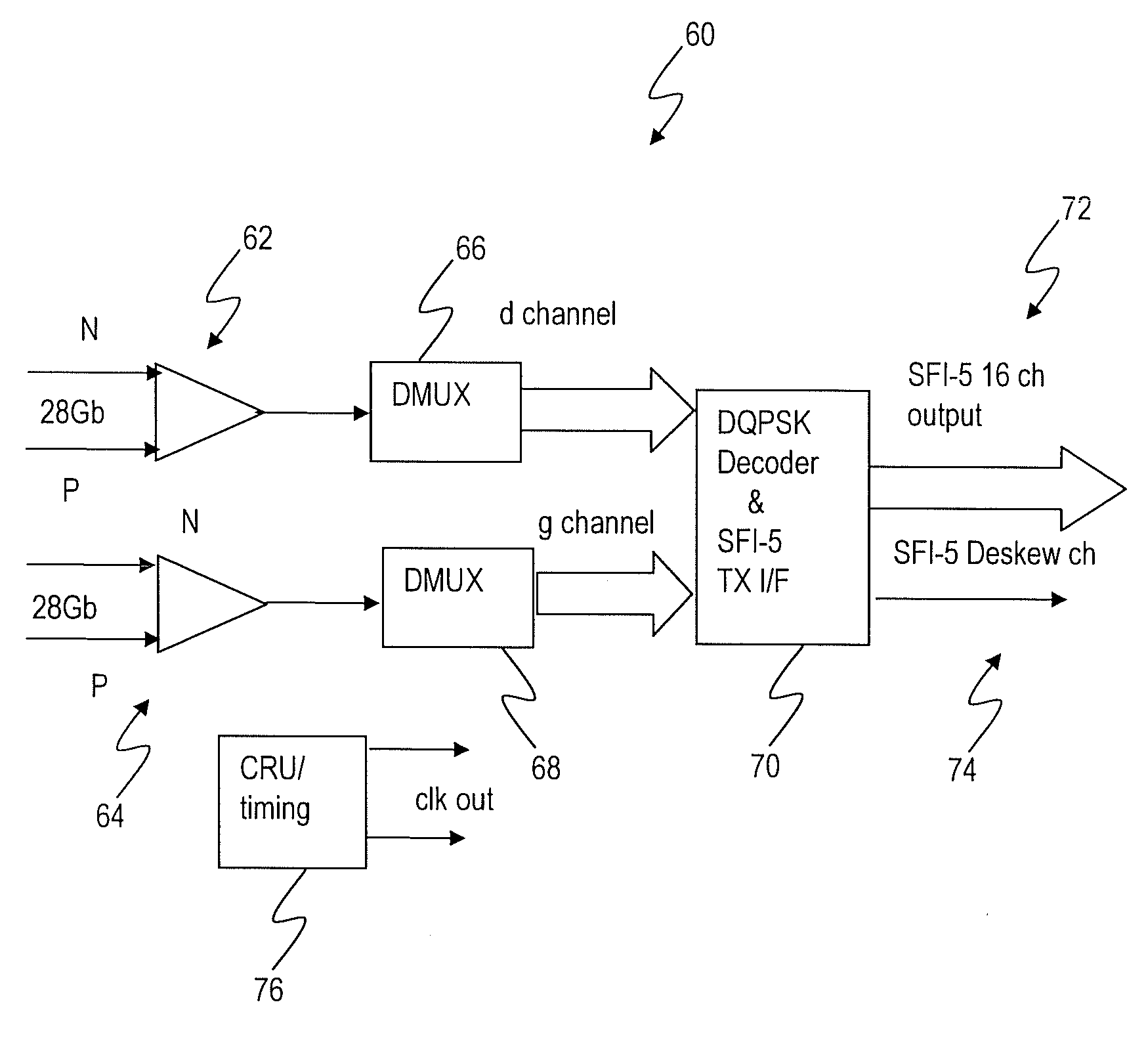
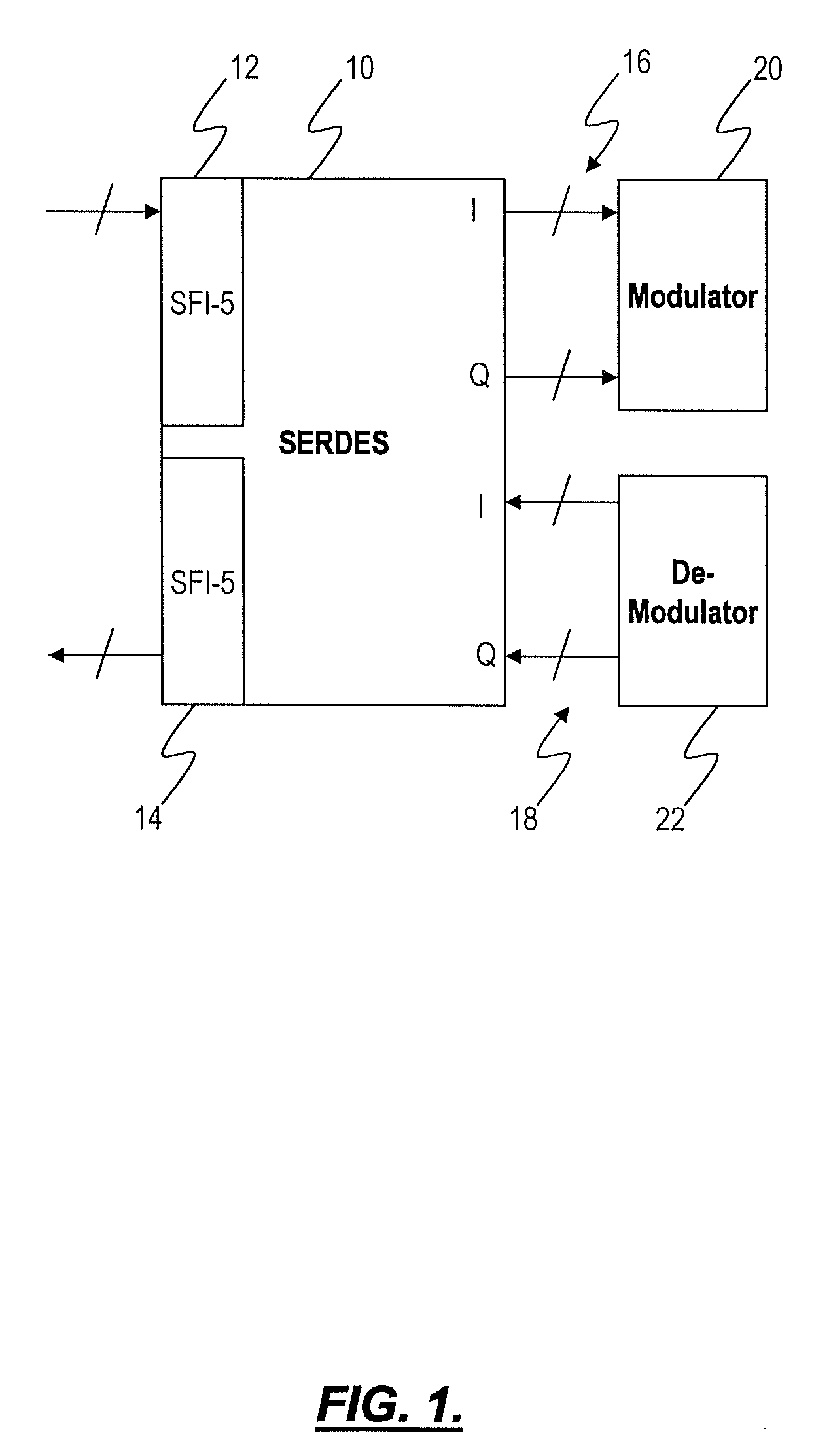
Serializer-deserializer circuit with multi-format and multi-data rate capability
The present invention provides a serializer / deserializer (SERDES) circuit that can cover both client- and network-side interfaces for high-speed data rates. The present invention leverages commonality between the client and network (also known as line) side, and accommodates differences in a flexible manner. In one exemplary embodiment, the present invention provides a four-channel implementation to meet the requirement of both interfaces. The SERDES circuit can be capable of supporting both 40 Gb / s and 56 Gb / s data rates, can include an integrated DQPSK pre-coder and I / Q input / output signals, and can support RZ clock recovery. Additionally, the SERDES circuit can include differential coding support, electronic pre-emphasis, receiver-side electronic dispersion compensation, and the like.
Owner:CIENA
Multi-mode audio codec and CELP coding adapted therefore
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Differential multiple-length transmit and reception diversity
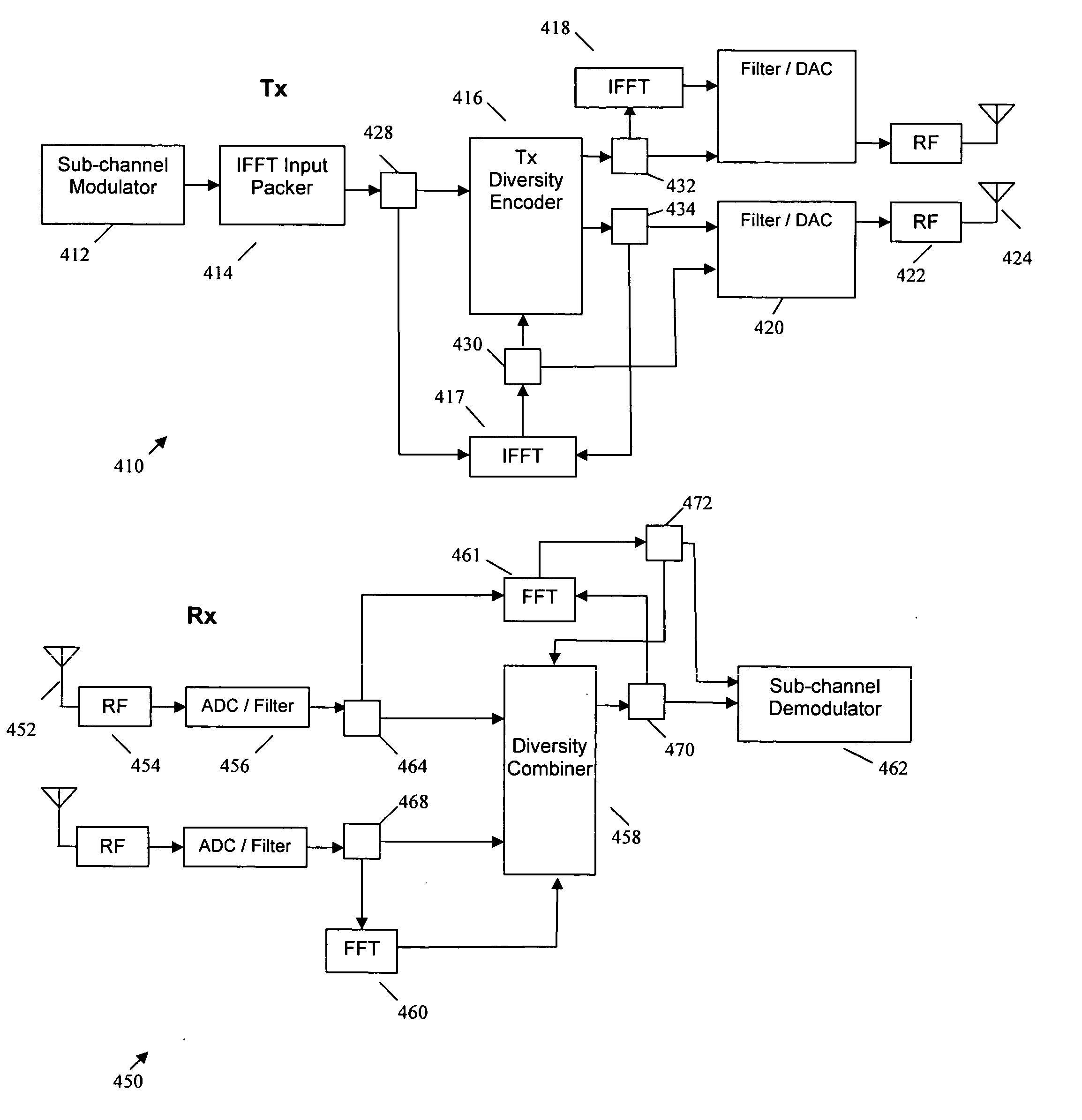
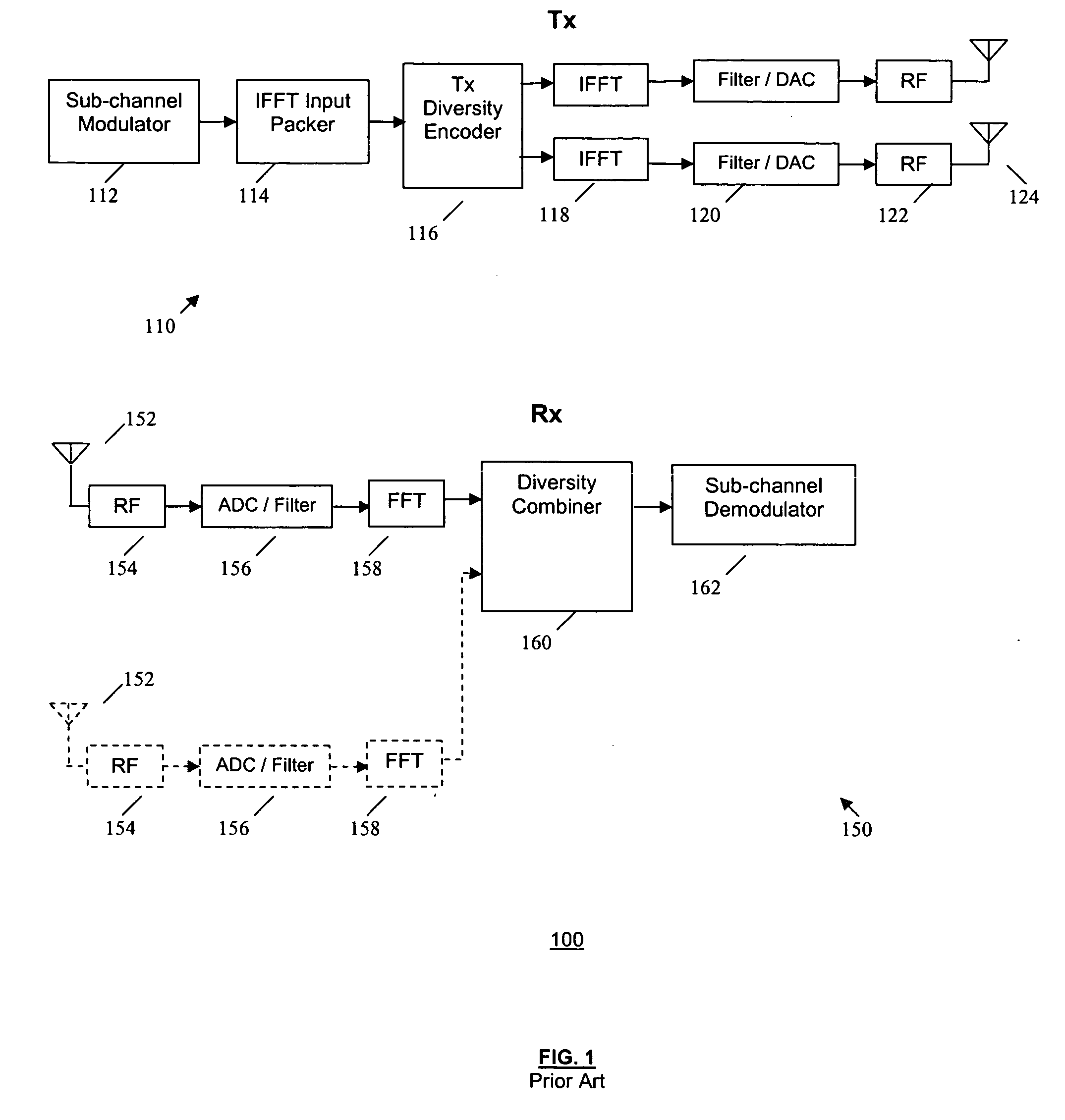
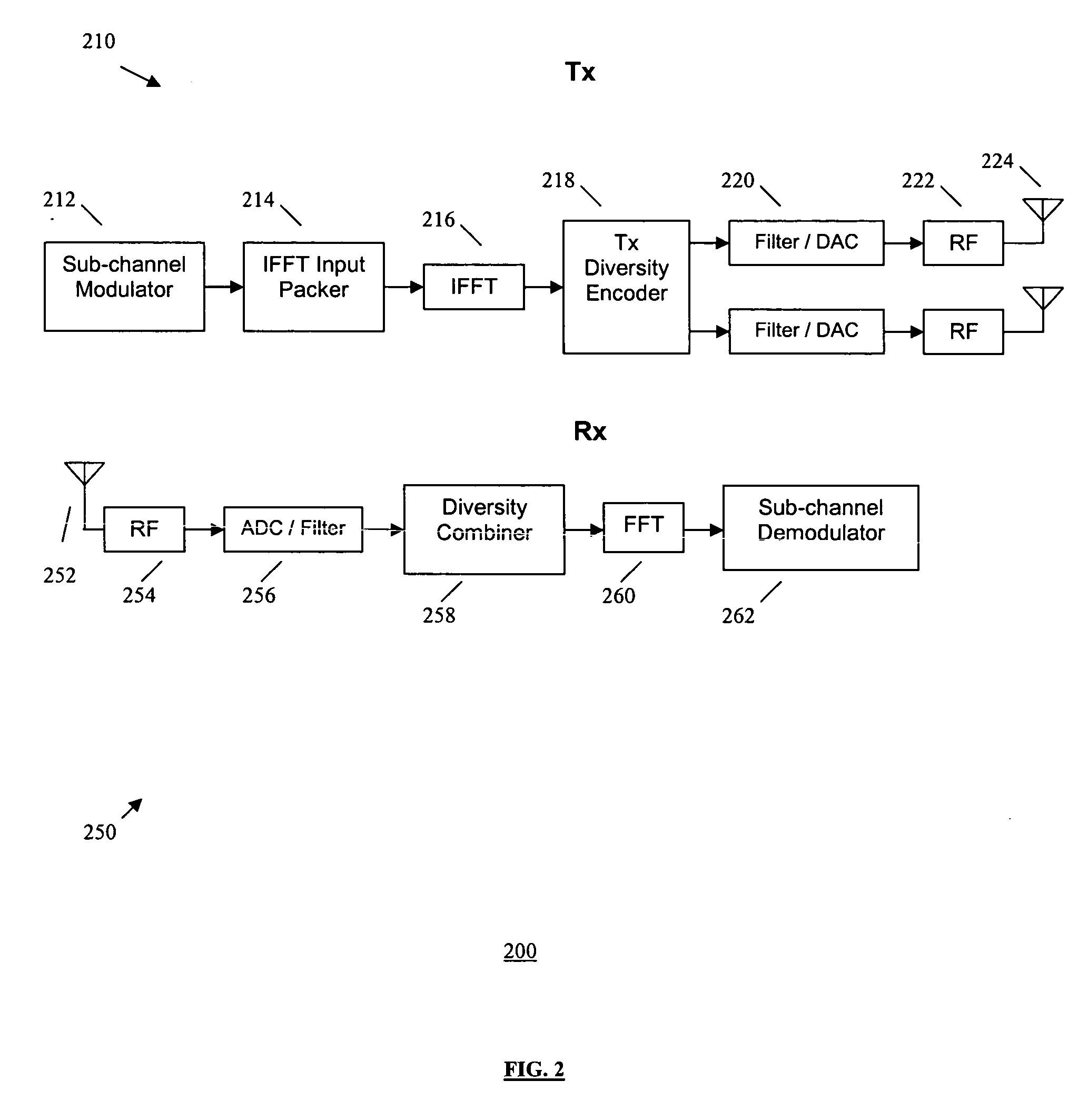
ActiveUS20060274846A1Much more flexibel range of data ratesReduce detectionSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationDifferential codingDiversity scheme
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC +1
Dual-mode real-time pseudo-range differential positioning system and pseudo-range correction data generation method
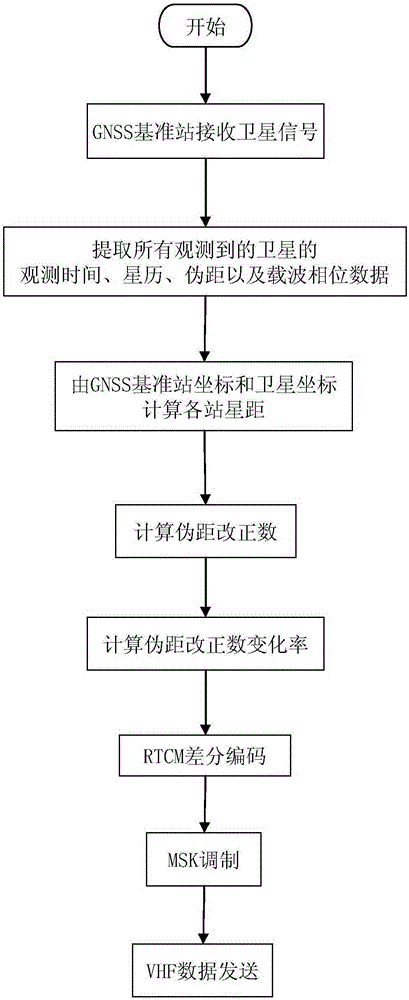
InactiveCN105182384AIncrease flexibilityImprove real-time navigation and positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingCode moduleReal time navigation
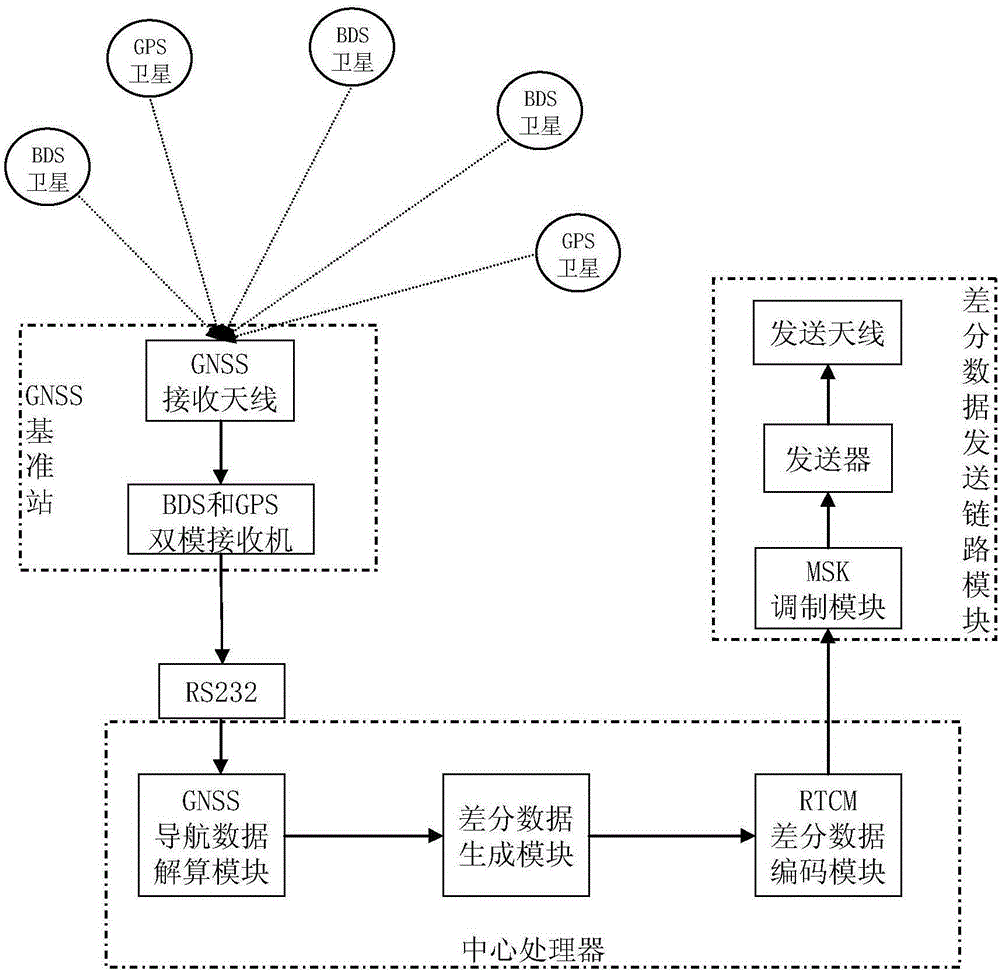
The invention relates to a dual-mode real-time pseudo-range differential positioning system and a pseudo-range correction data generation method. The system comprises a central processor, a GNSS reference station, and a differential data transmitting link module, wherein the GNSS reference station and the differential data transmitting link module are connected with the central processor. The GNSS reference station comprises a BDS, a GPS dual-mode receiver, and a GNSS receiving antenna, wherein the coordinate precision of installation points is known. The central processor comprises a GNSS navigation data resolving module, a differential data generation module, and an RTCM differential data coding module. The differential data transmitting link module comprises an MSK modulation module, a transmitter, and a transmitting antenna, wherein the MSK modulation module, the transmitter and the transmitting antenna are connected sequentially. The method comprises the steps: enabling the GNSS reference station to receive the ephemeris and navigation data, obtained through observation at the same moment, of all GPS and BDS satellites, and transmitting the data to the central processor in real time; extracting data of all satellites; calculating the distances from the station to the satellites; obtaining a pseudo-range correction value and a pseudo-range correction value change rate; and transmitting the data to a peripheral GNSS user after RTCM differential coding and MSK modulation. The system and method greatly improve the real-time navigation positioning precision.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
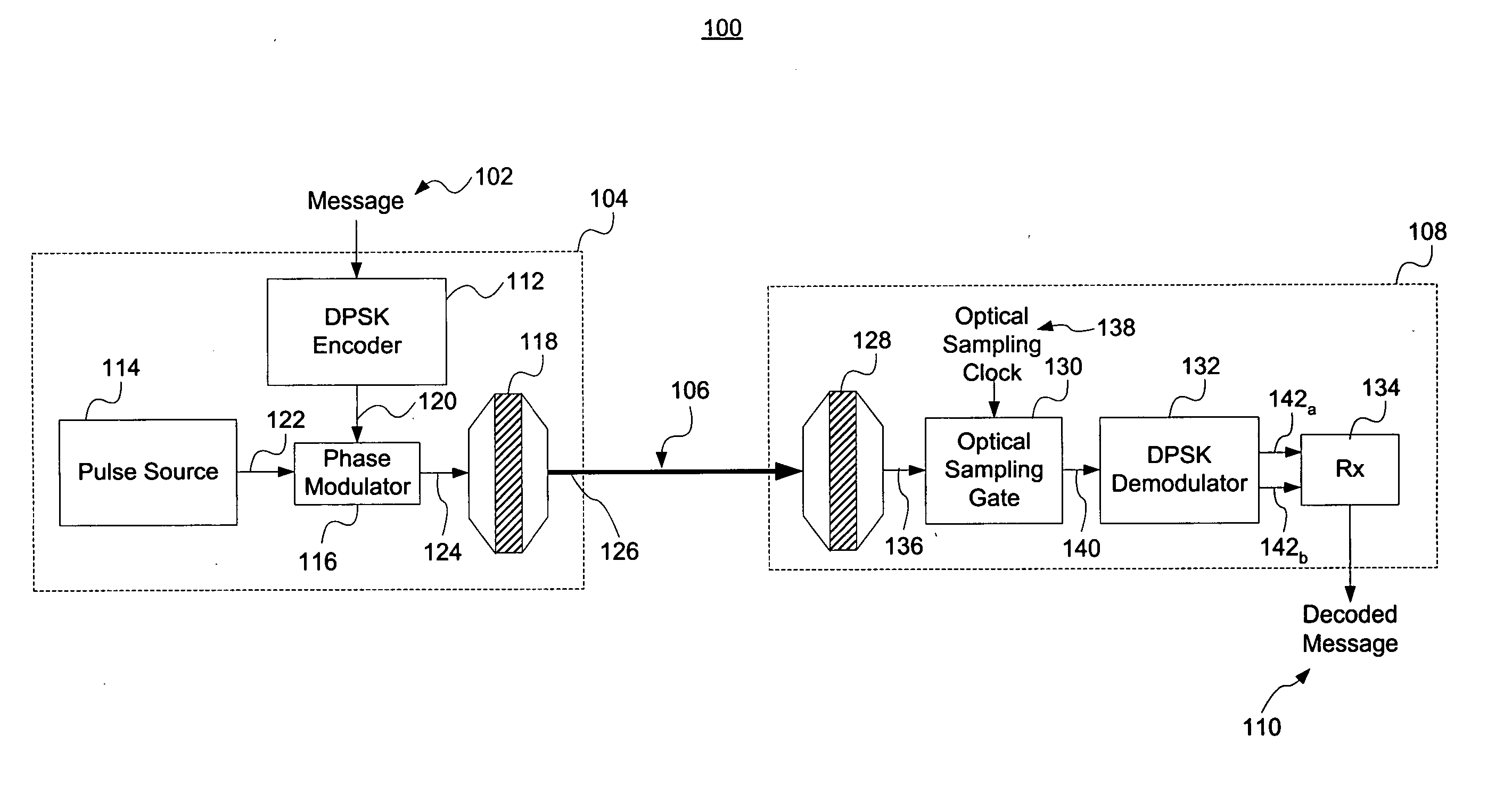
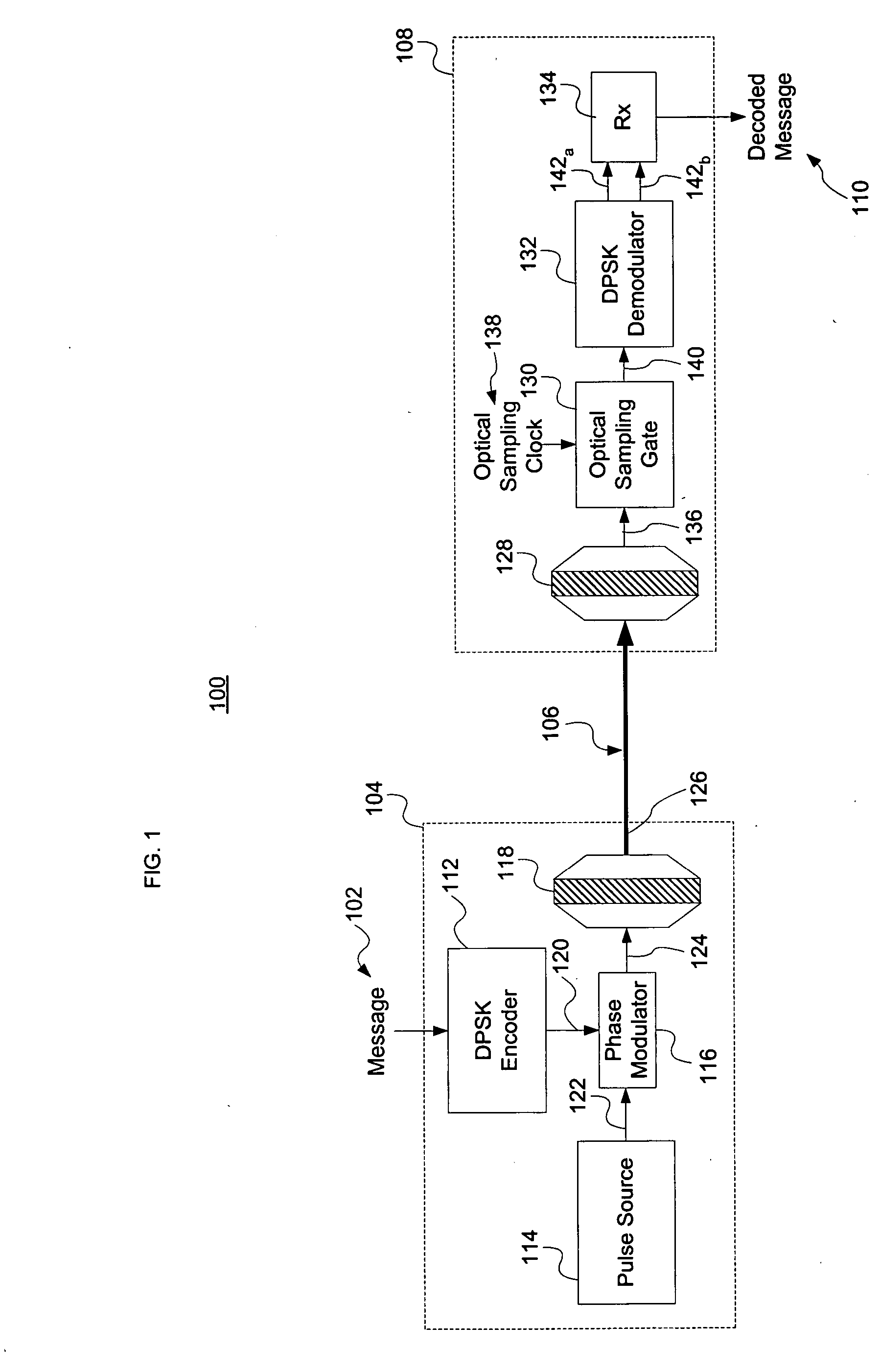
Multi-wavelength optical CDMA with differential encoding and bipolar differential detection
ActiveUS20060171722A1Improve securityTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexOptical cdmaFrequency spectrum
The present invention relates generally to an optical CDMA transmission system and method employing differential optical encoding and bipolar decoding. Differential encoding and bipolar decoding may be performed at the bit level, wherein differential phase encoding and decoding occurs on an entire composite signal. Differential encoding and bipolar decoding may also be performed at the chip level, wherein differential phase encoding and decoding occurs on individual spectral components of a given signal.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Optical communication method and system
InactiveCN102427387AIncrease line widthEnhanced ability to resist inter-carrier interferenceBaseband system detailsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumStream data
The invention provides an optical communication method which comprises the steps of: modulating obtained bit stream data to obtain a modulating signal; carrying out differential coding on the modulating signal to obtain a differential coding signal; converting the differential coding signal into an electrical signal; mapping the electrical signal on an optical carrier to form an optical signal; and then transmitting the optical signal. By using the method, on the premise that a frequency spectrum utilization rate is not reduced, the system capability of resisting disturbance among carriers is enhanced; thus, the tolerance of the existing optical communication sysem for resisting laser linewidth, quick change PMD (Physical Media Dependent), nonlinear fiber, disturbance among channels and other damage is enhanced; and system performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Differential multiple-norm transmit diversity with forward error correction and related diversity reception
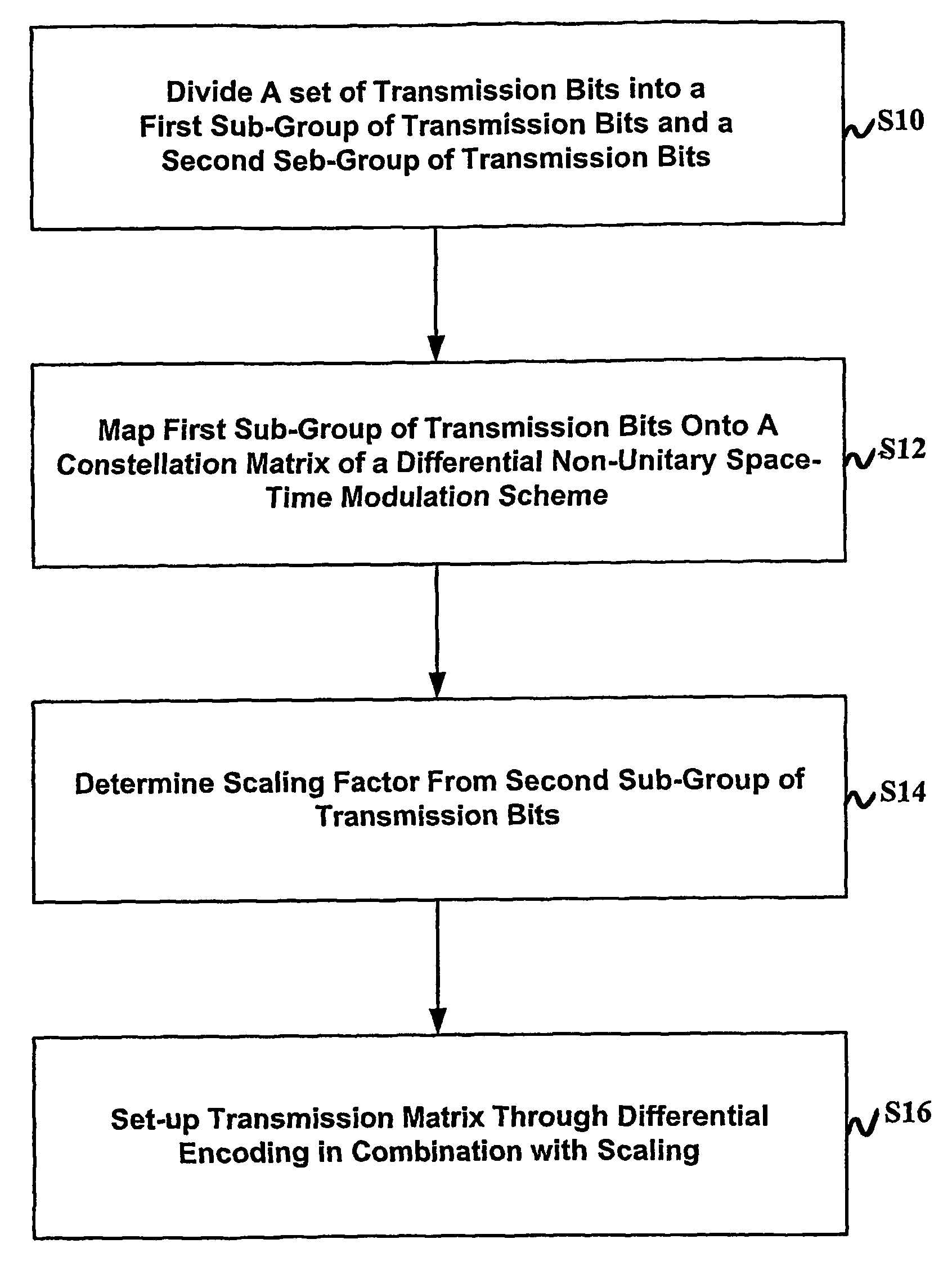
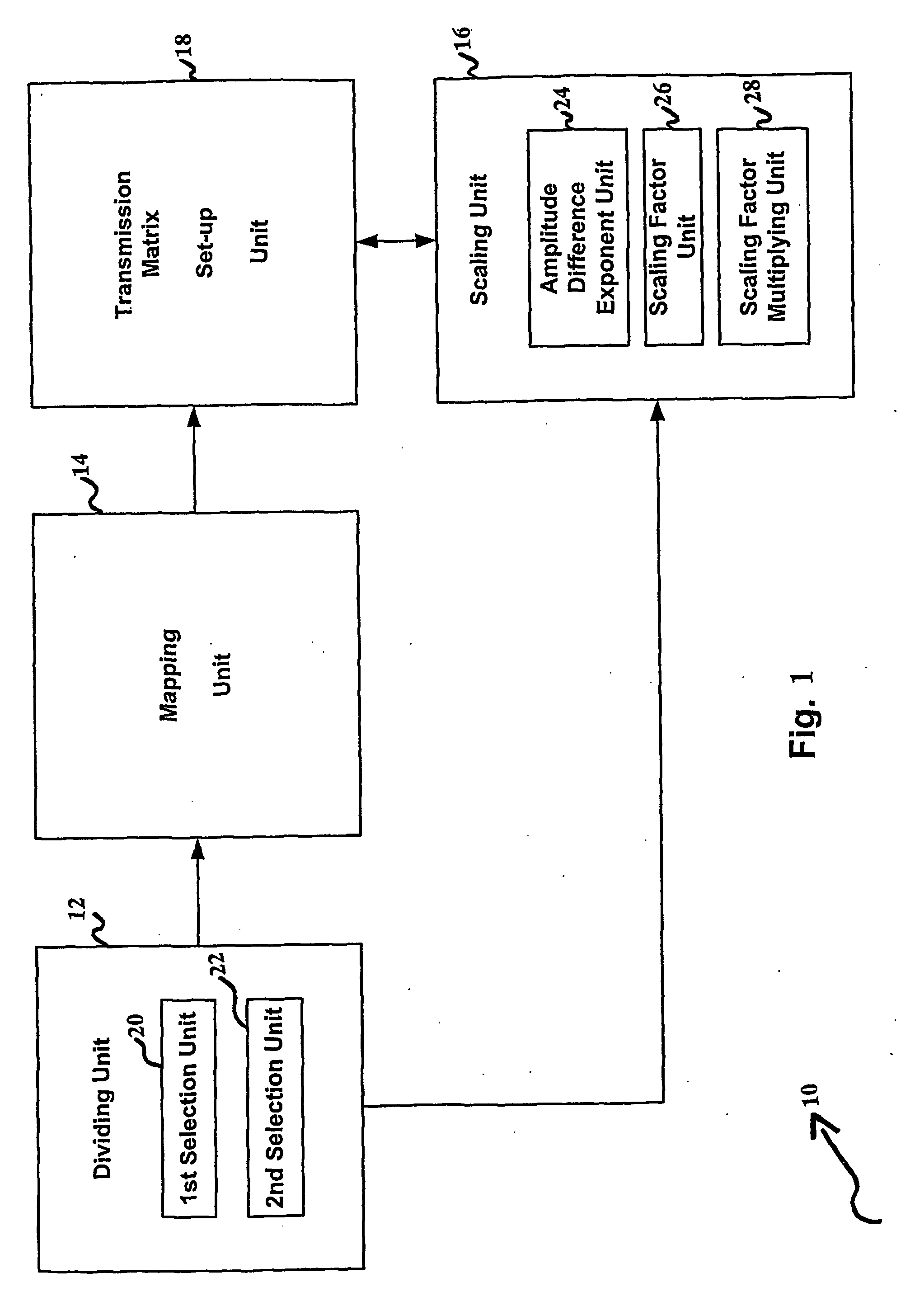
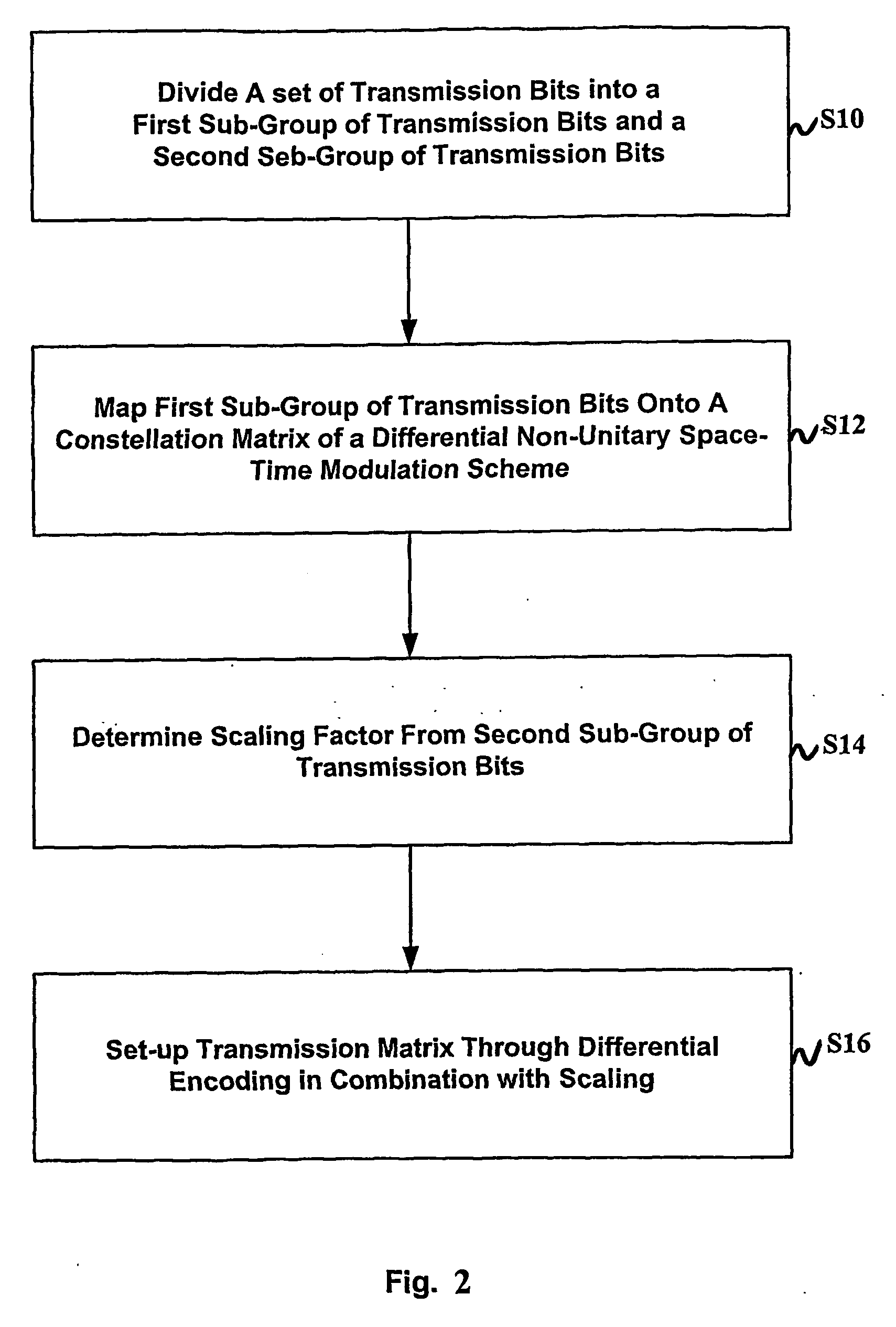
ActiveUS20060232416A1Improves distance propertyMore range of dataSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationSpace time transmit diversityUnitary space time modulation
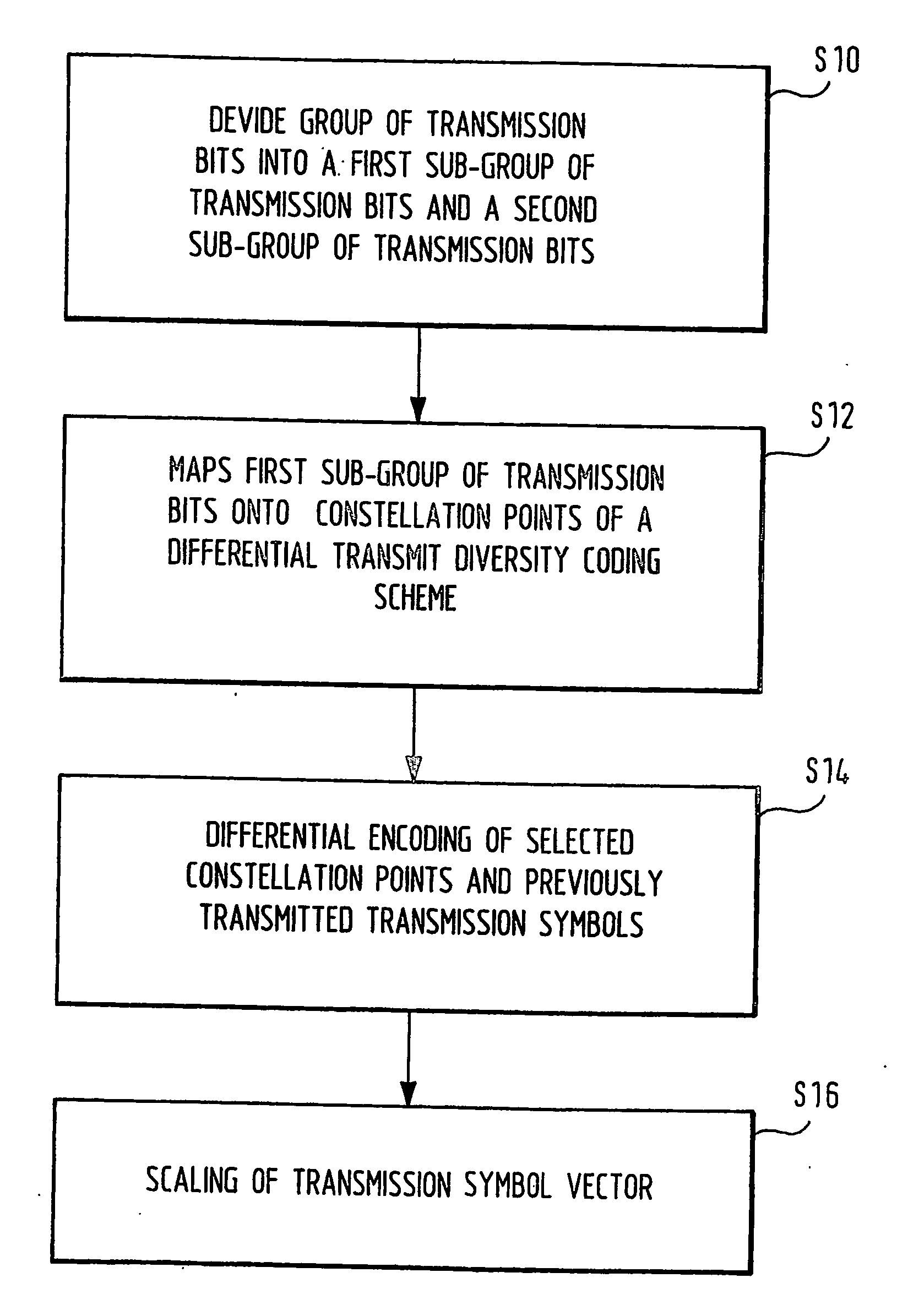
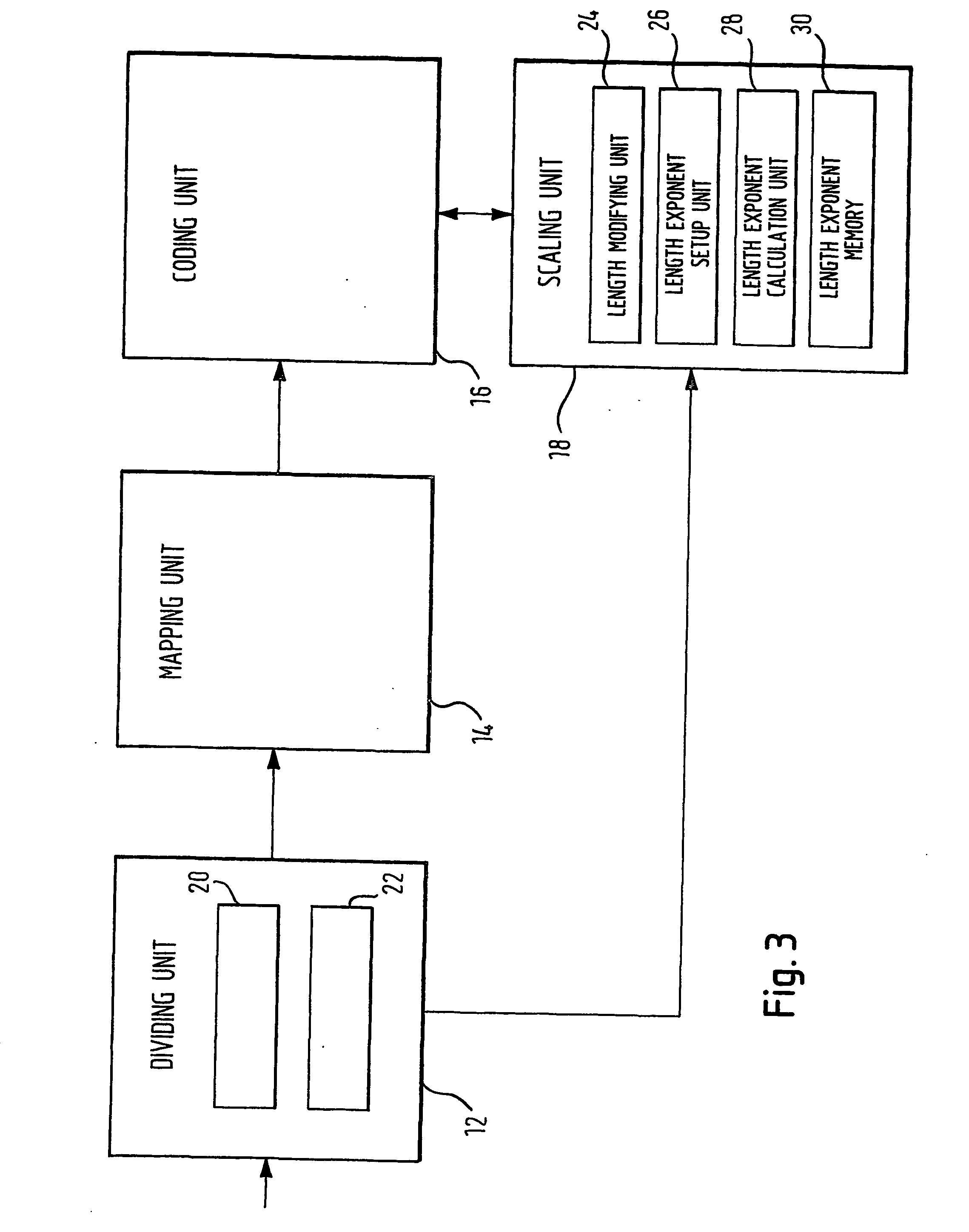
To provide transmission and reception diversity schemes for a powerful, flexible and less complex bandwidth-efficient space-time modulation scheme there is proposed a method of and apparatus for differential multiple-norm space-time transmit diversity from a unitary space-time modulation scheme using at least two transmit antennas. In a first step a group of transmission bits is divided into a first sub-group of transmission bits and a second sub-group of transmission bits. In a second step the first sub-group of transmission bits is mapped onto a constellation matrix of a differential unitary space-time modulation scheme. In a third step a scaling factor is determined from the second sub-group of transmission bits. In a fourth step a transmission matrix is sep up through differential encoding of the constellation matrix and a previously determined transmission matrix in combination with scaling by the scaling factor. The differential multiple-norm transmit diversity according to the present invention improves distance properties of the modulation scheme which are relevant for achievable error rates and extends higher order modulation also to the area of differential transmit diversity schemes from unitary designs.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Differential space-time block coding apparatus using eight or less transmit antennas
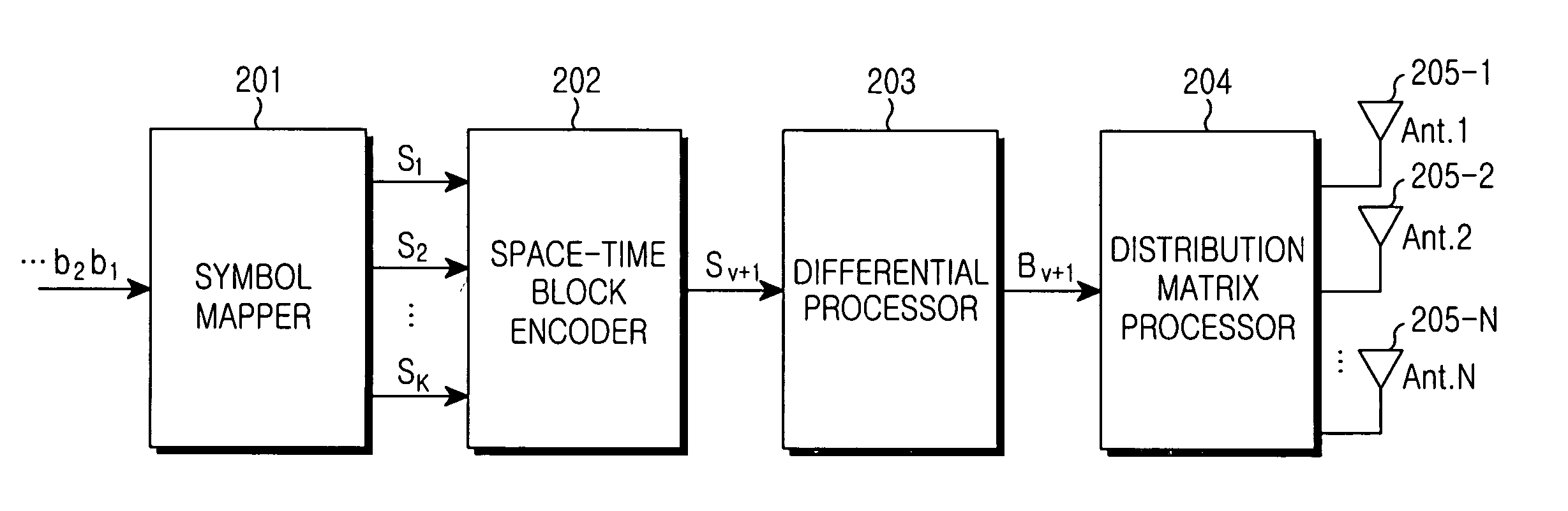
ActiveUS20050135499A1Spatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsDistribution matrixDifferential space time
A differential STBC transmitting / receiving apparatus in a multiple antenna system using eight or less transmit antennas is provided. In the differential STBC transmitting apparatus, a symbol mapper receives binary data and generates a number of symbols from the binary data, each symbol having a number of bits. A space-time block encoder generates an STBC by encoding the symbols. A differential processor differentially encodes the STBC through feedback and delay. A distribution matrix processor substitutes the differentially coded STBC into a distribution matrix preset according to the number of transmit antennas, and outputs the differential STBC code of the distribution matrix to the transmit antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication
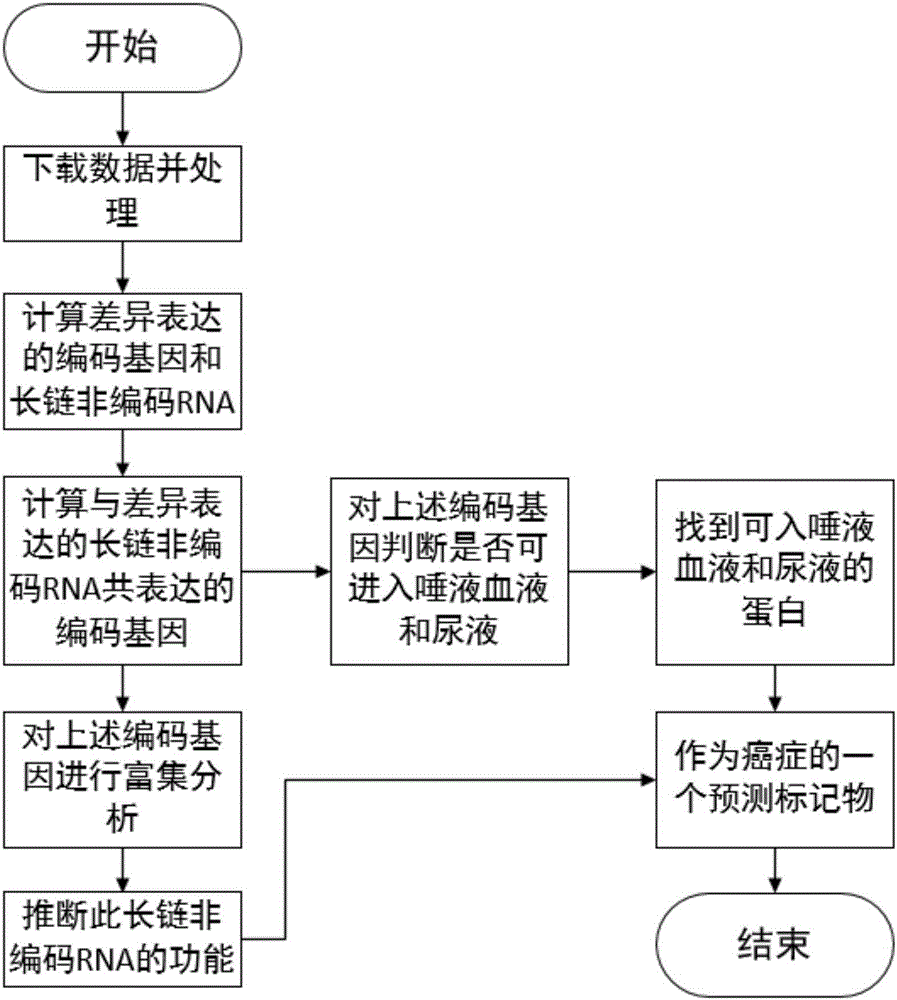
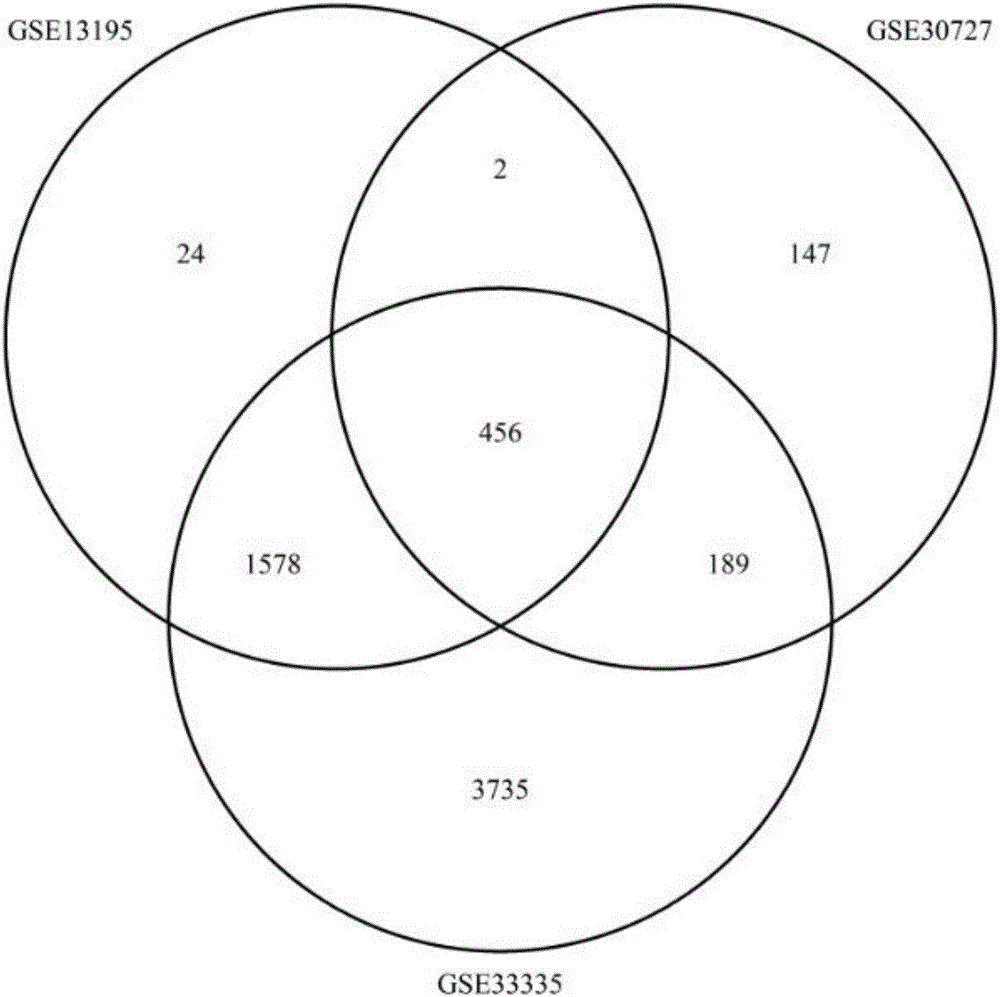
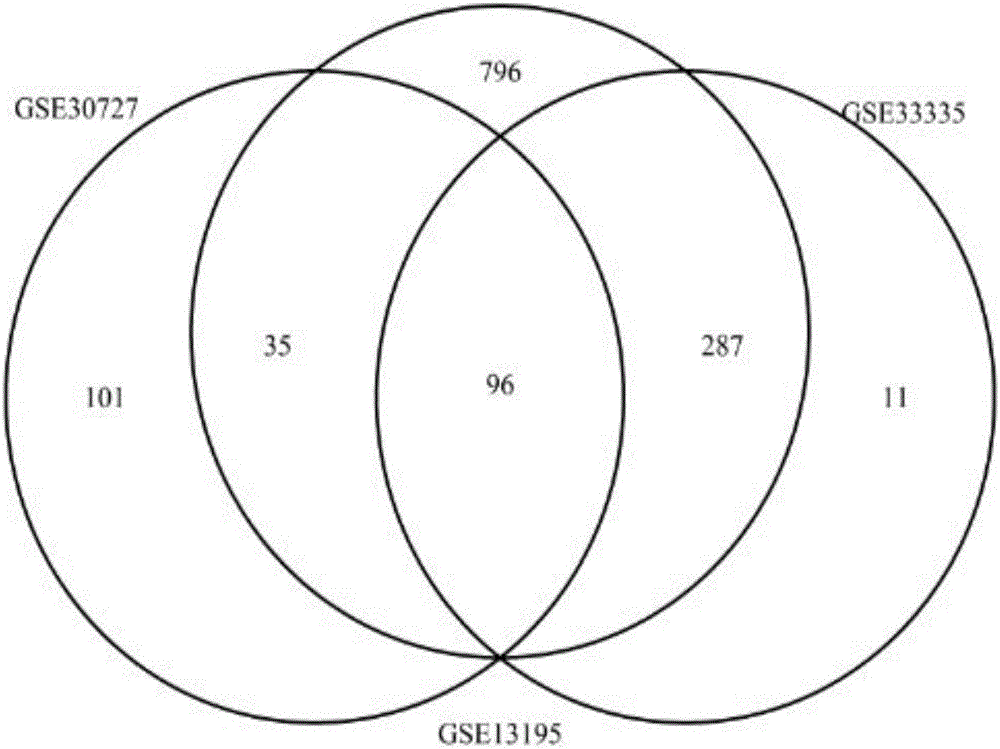
InactiveCN106295246ASimple processSimple methodBiostatisticsProteomicsDifferential codingPredictive marker
The invention relates to tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication. By taking differential expression of IncRNA in tumors as diagnosis references, a process for finding a relation between IncRNA and tumors includes: step one, downloading data from GEO database, processing the data to obtain expression data of part of IncRNA and exons; step two, subjecting the processed expression data to differential expression analysis; step three, analyzing co-expression and differential coding genes and IncRNA for IncRNA in differential expression; step four, subjecting the coding genes to probe platform annotation; step five, further screening the IncRNA in differential expression to select out most obviously differential IncRNA; step six, performing enrichment analysis to obtain a GOBP process and pathyway, and speculating IncRNA functions through coding gene related biological processes; step seven, analyzing whether common coding genes obtained at the step six can enter blood, saliva and urine or not, analyzing genes which are allowed to enter, and taking the genes and IncRNA as potential predication marks of cancers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method and system for time-domain transmission diversity in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
InactiveUS20060056281A1Spatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsDigital dataTime domain
A method of provided for transmitting and receiving OFDM data signals via multiple outputs of a channel including multiple sub-channels. Transmit data streams are modulated by de-multiplexing the data streams into multiple parallel frequency-domain sub-channel data for conversion into time-domain data; and frequency-domain data for each sub-channel is converted into time-domain data. For each sub-channel, the corresponding time-domain data is differentially encoded to obtain differentially encoded time-domain data; and transmitting the differentially encoded time-domain data. The received signals are converted into digital data signals, and for each sub-channel, corresponding time-domain data from the data signals is differentially decoded to obtain differentially decoded time-domain data. The time-domain data for each sub-channel is converted into frequency-domain data and the frequency-domain data is demodulated into data streams by de-multiplexing the data streams into multiple parallel frequency-domain sub-channel data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Joint carrier phase estimation and forward error correction
InactiveUS20120096327A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionCommunications systemAmbiguity
Methods and systems for processing an optical signal in a communication system are disclosed. The disclosed methods yield benefits for estimation and tracking of carrier phase of received signals at a digital coherent receiver without the use of differential coding. Specifically, phase ambiguity is removed by calculating the slope of the CPE at a location where the CPE begins to lose track of the received carrier phase signal. As such, a CPE offset adjustment may be applied in accordance with the calculated slope to reduce the number of ones and zeros corrected by a FEC decoder. Thus, the FEC aided CPE scheme may be a feed forward scheme that requires no training.
Owner:SUBCOM LLC
Differential space-time transmission diversity system in multi-carrier modulation system and implementing method
InactiveCN101453257AImprove spectral efficiencyDiversity gain at altitudeSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalCyclic prefix
The invention provides a system for a differential space time transmit diversity in a multicarrier modulation system and an implement method thereof, wherein the implement method comprises the following steps: A, a modulation signal is subjected to differential coding by a differential space time coder and is output to two paths; and B, one path of signal in the step A passes through an OFDM modulator and a cyclic prefix insertion device and is transmitted by an antenna, the other path of coding signal passes through another OFDM modulator and is transmitted to a time delay delta unit, after the signal is subjected to cyclic time delay with delta delayed time, the signal is transmitted to the cyclic prefix insertion device, inserted with cyclic prefix and transmitted by an antenna. On the premise of ensuring the transmission speed, the system can obtain high space time diversity gain and effectively improve system performance.
Owner:ACAD OF BROADCASTING SCI SARFT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com