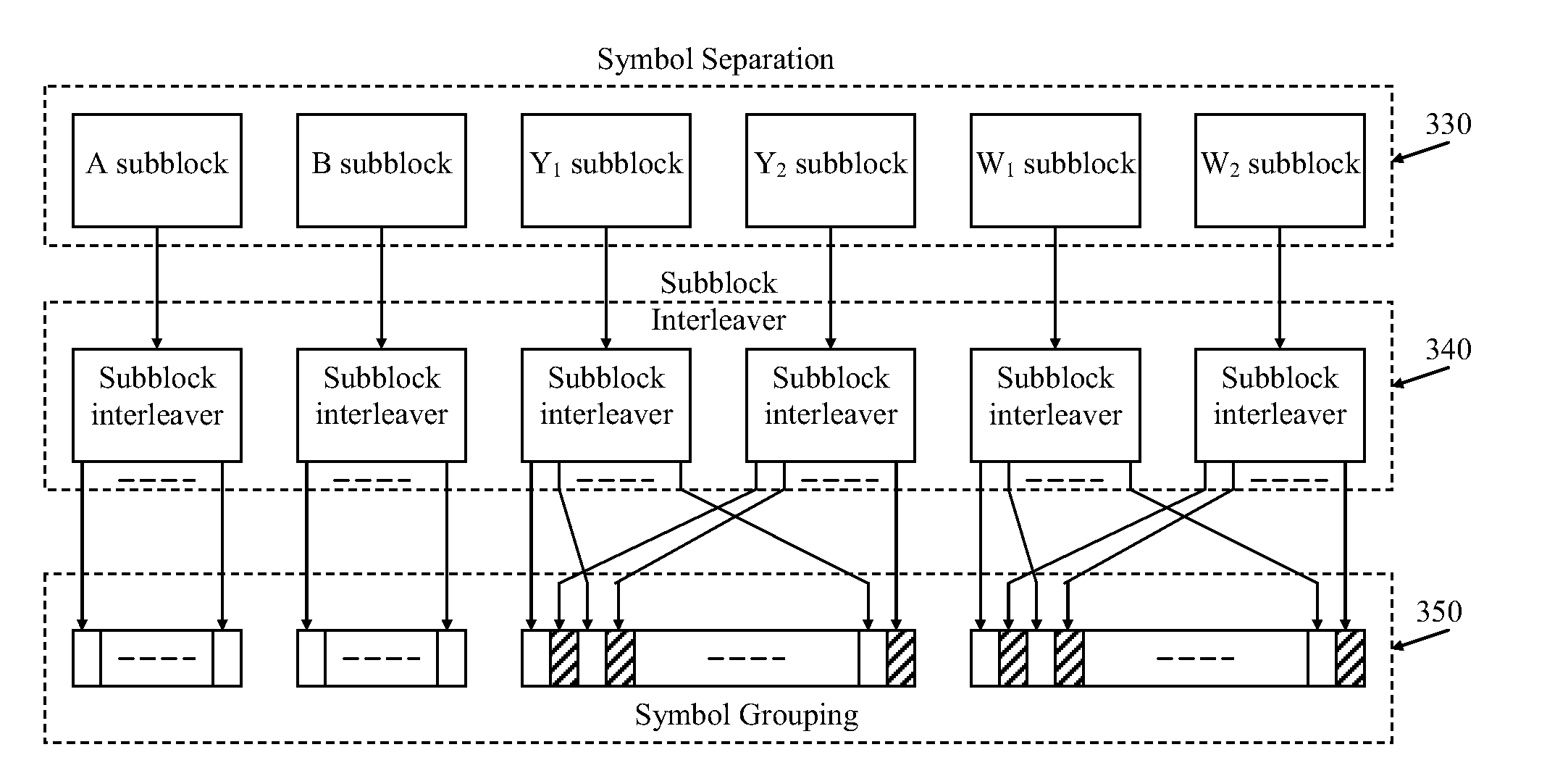
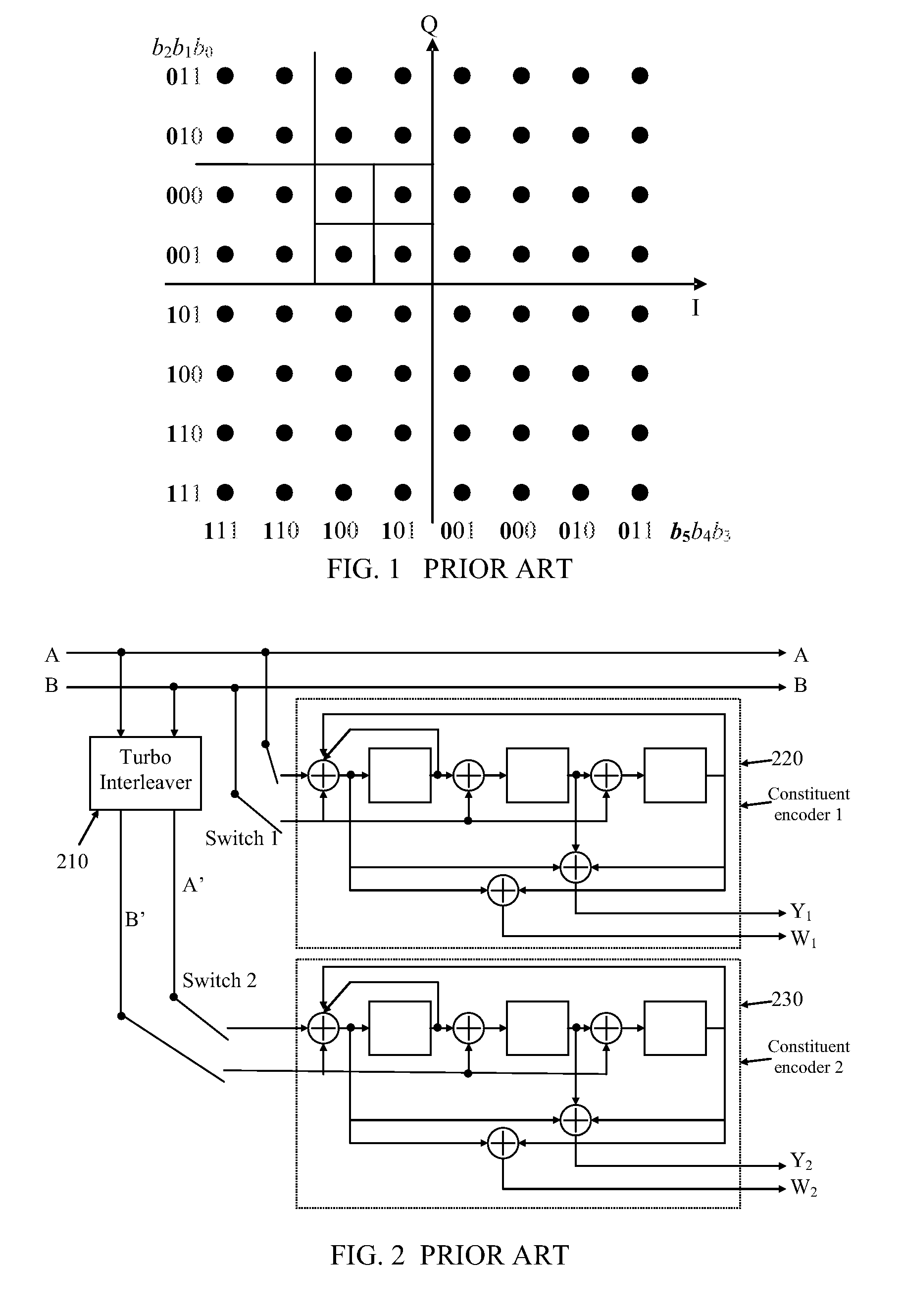
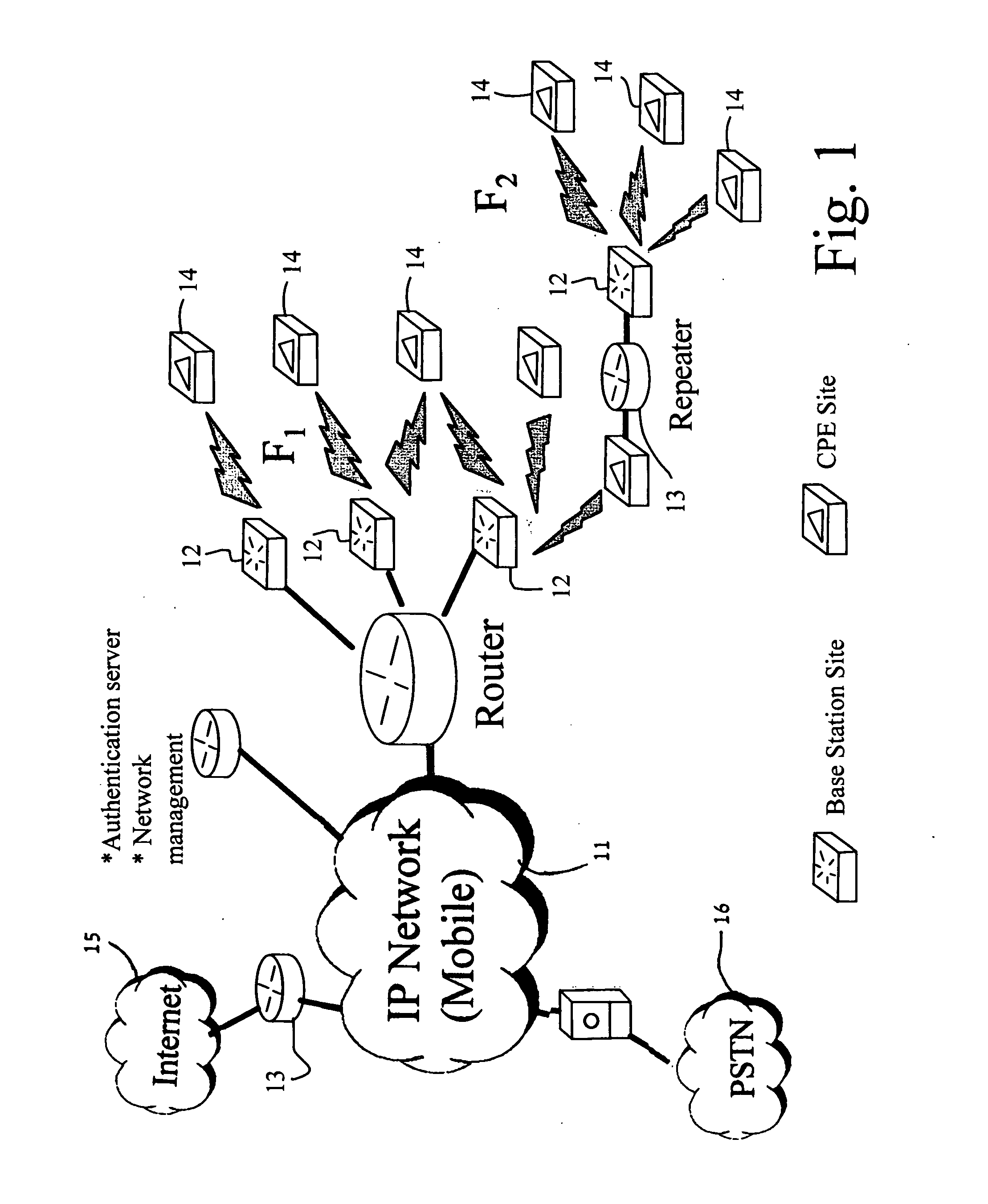
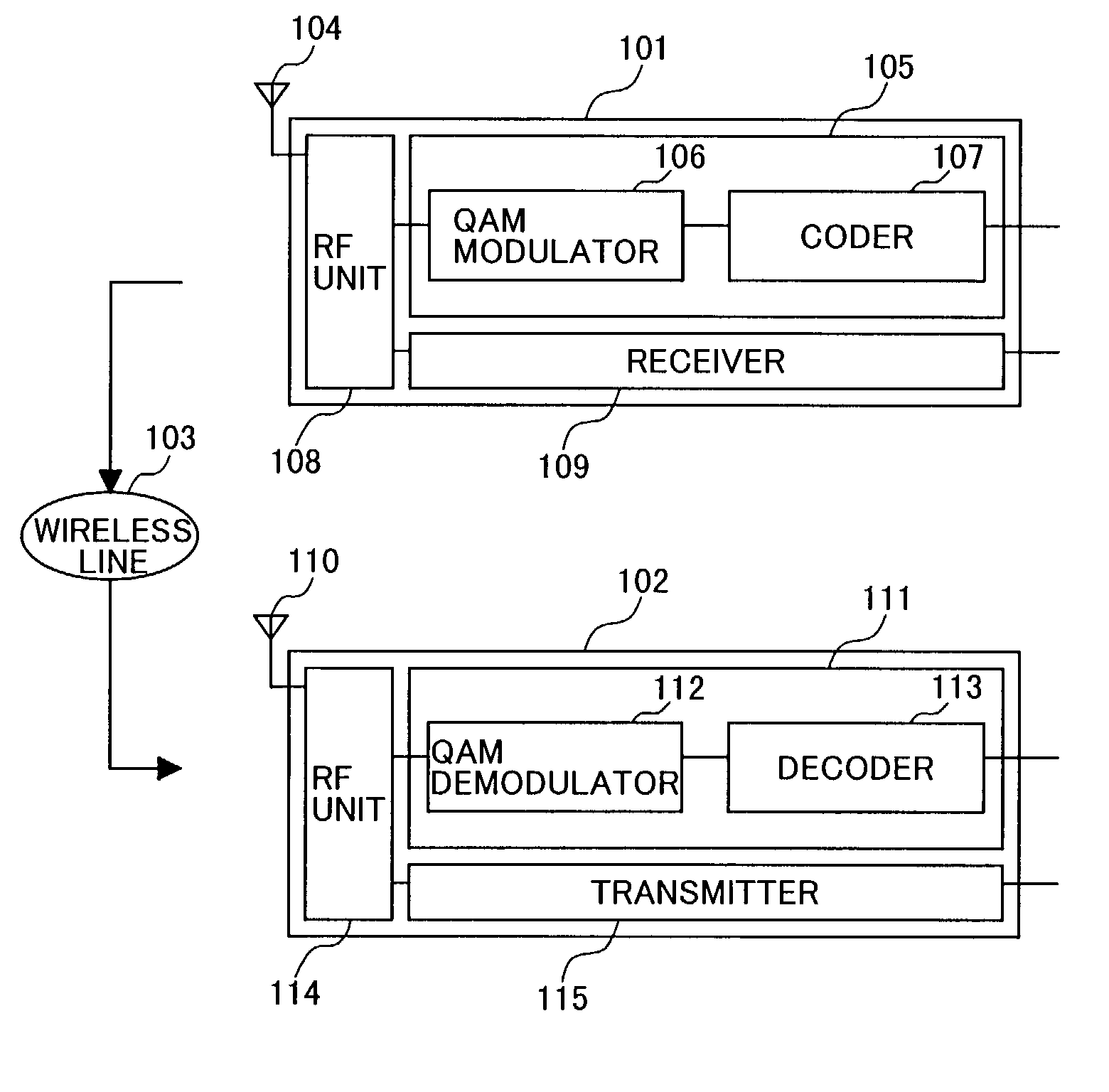
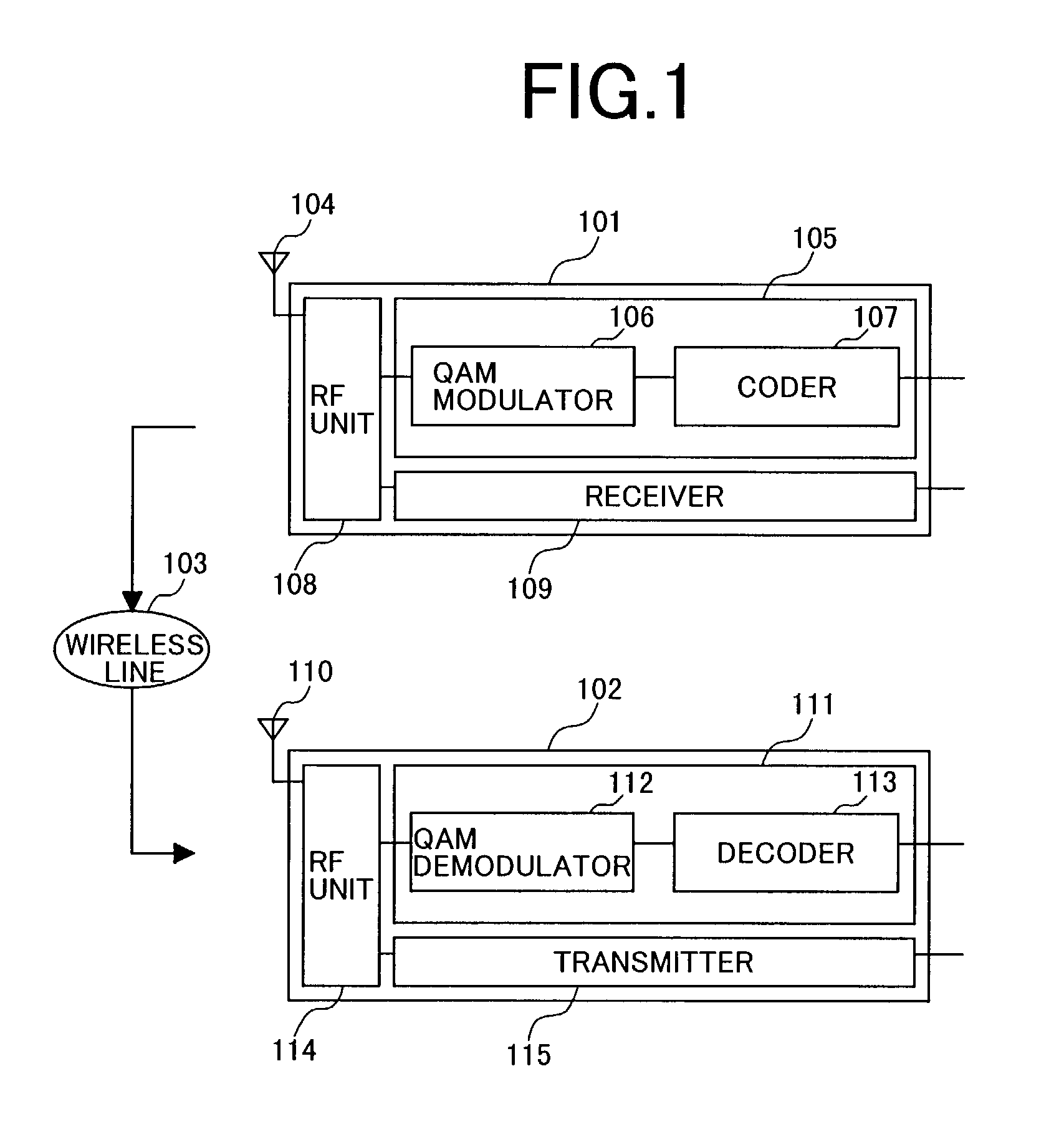
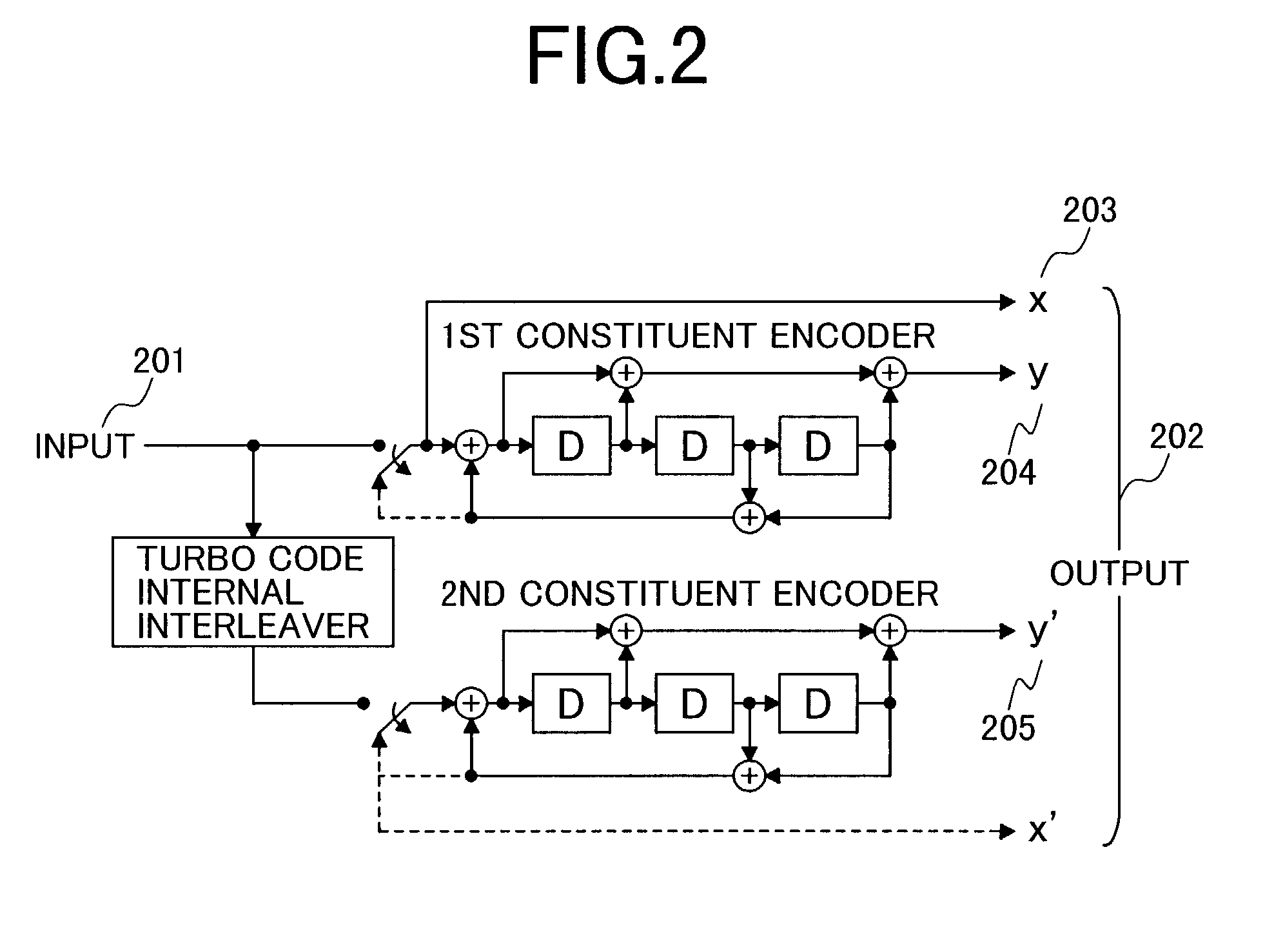
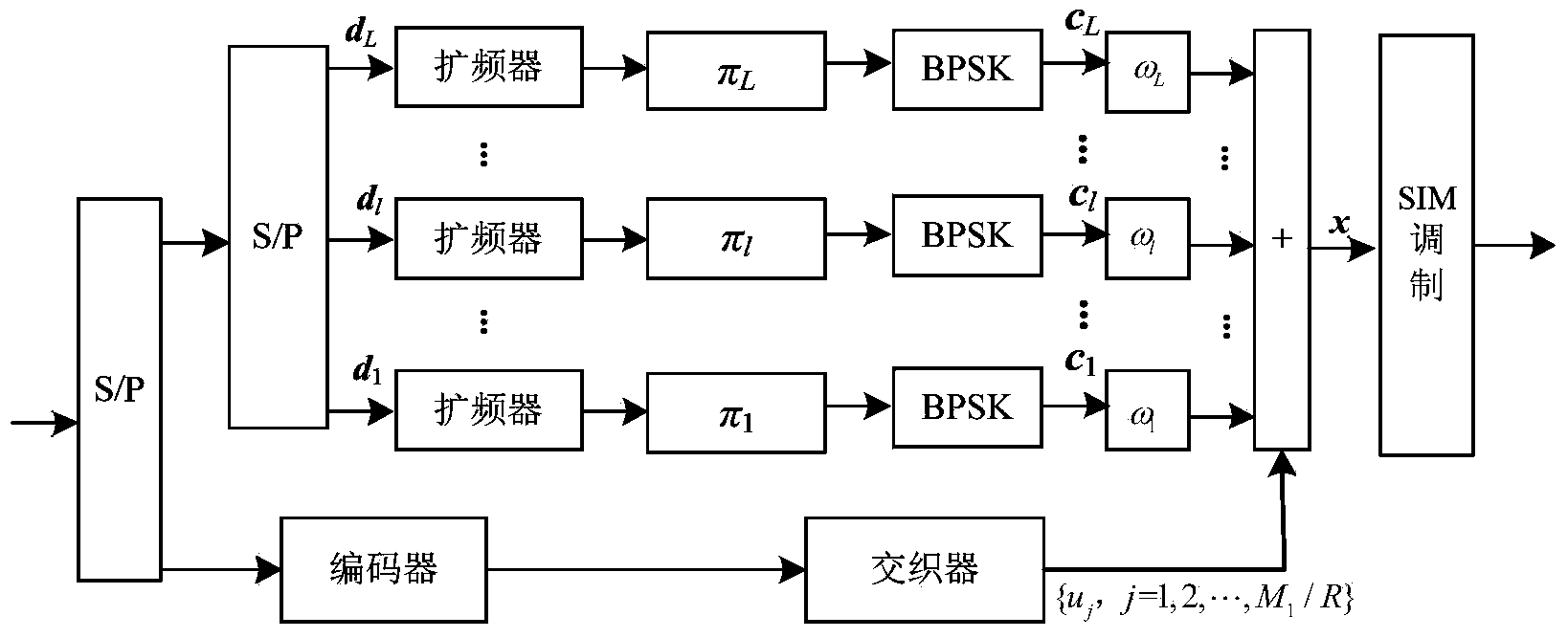
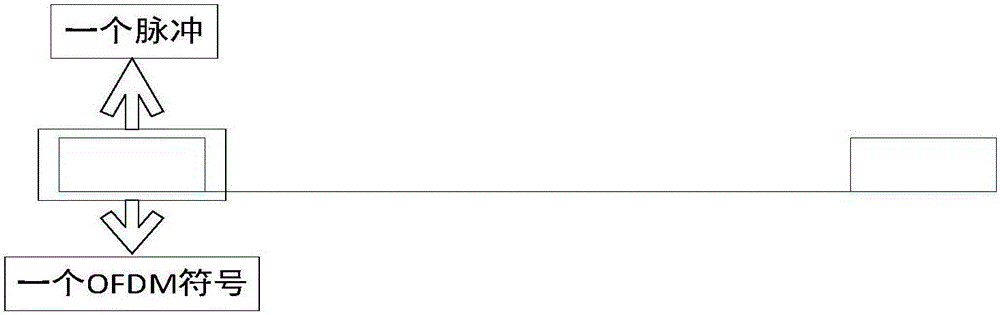Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
304 results about "Qam modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
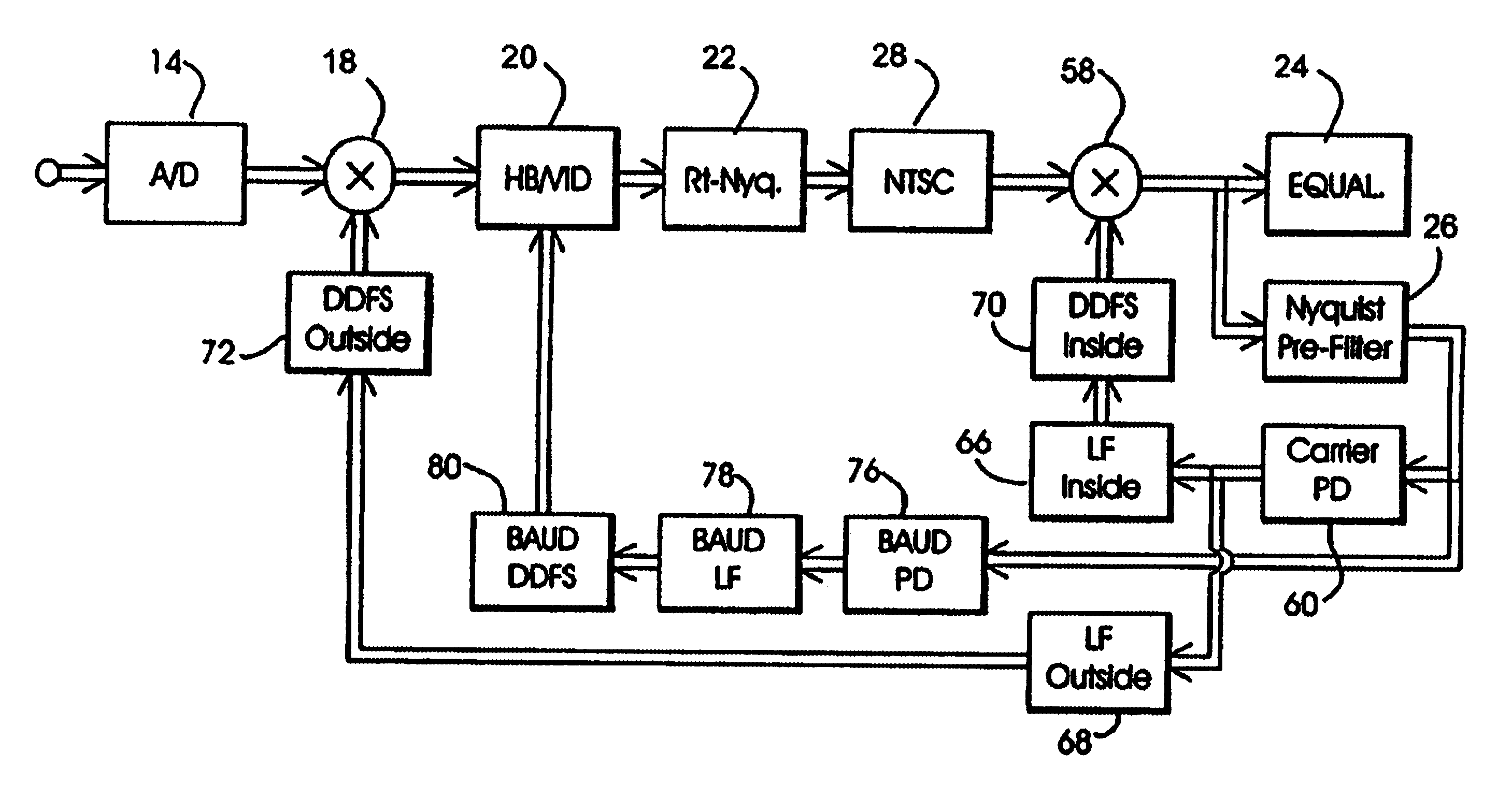
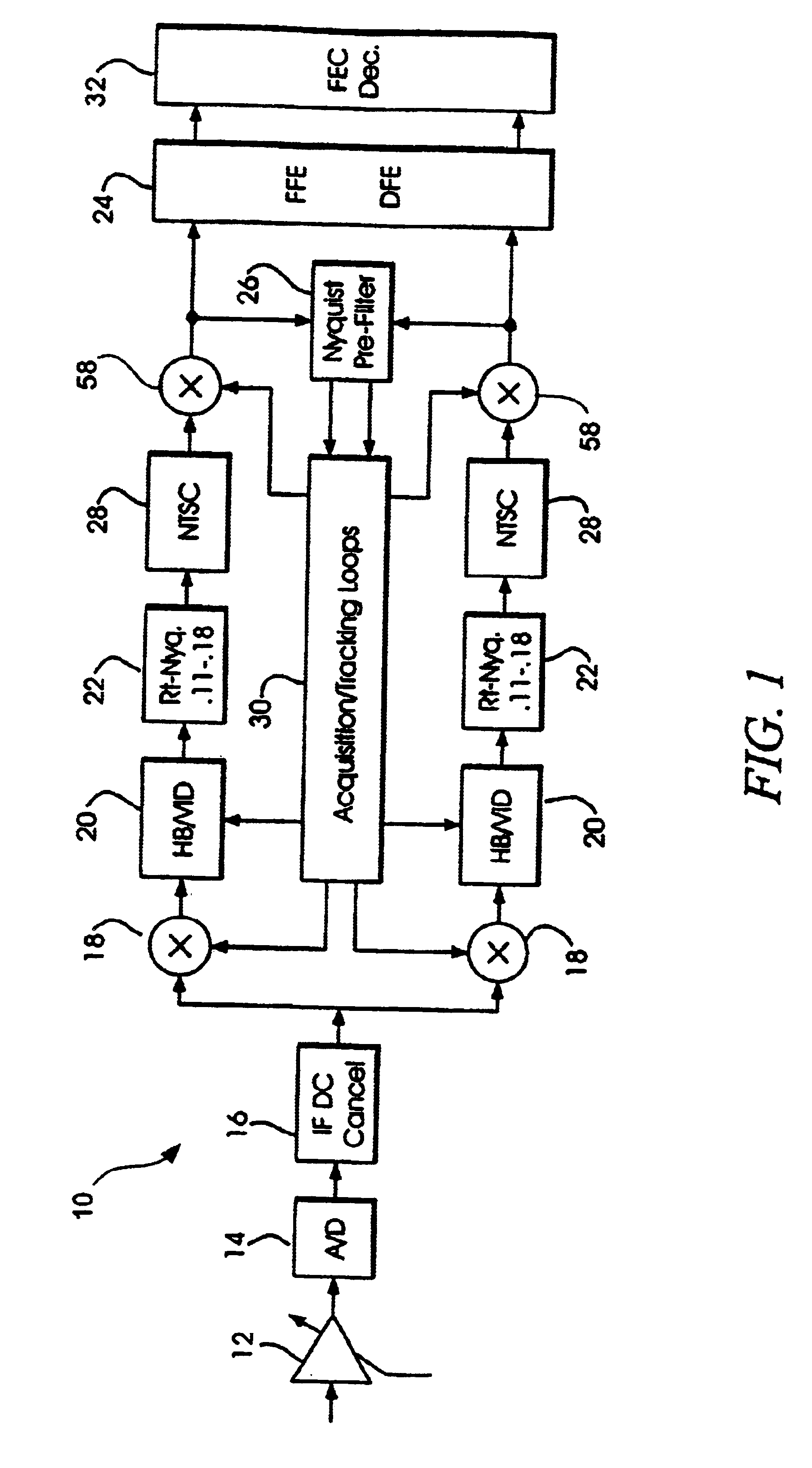
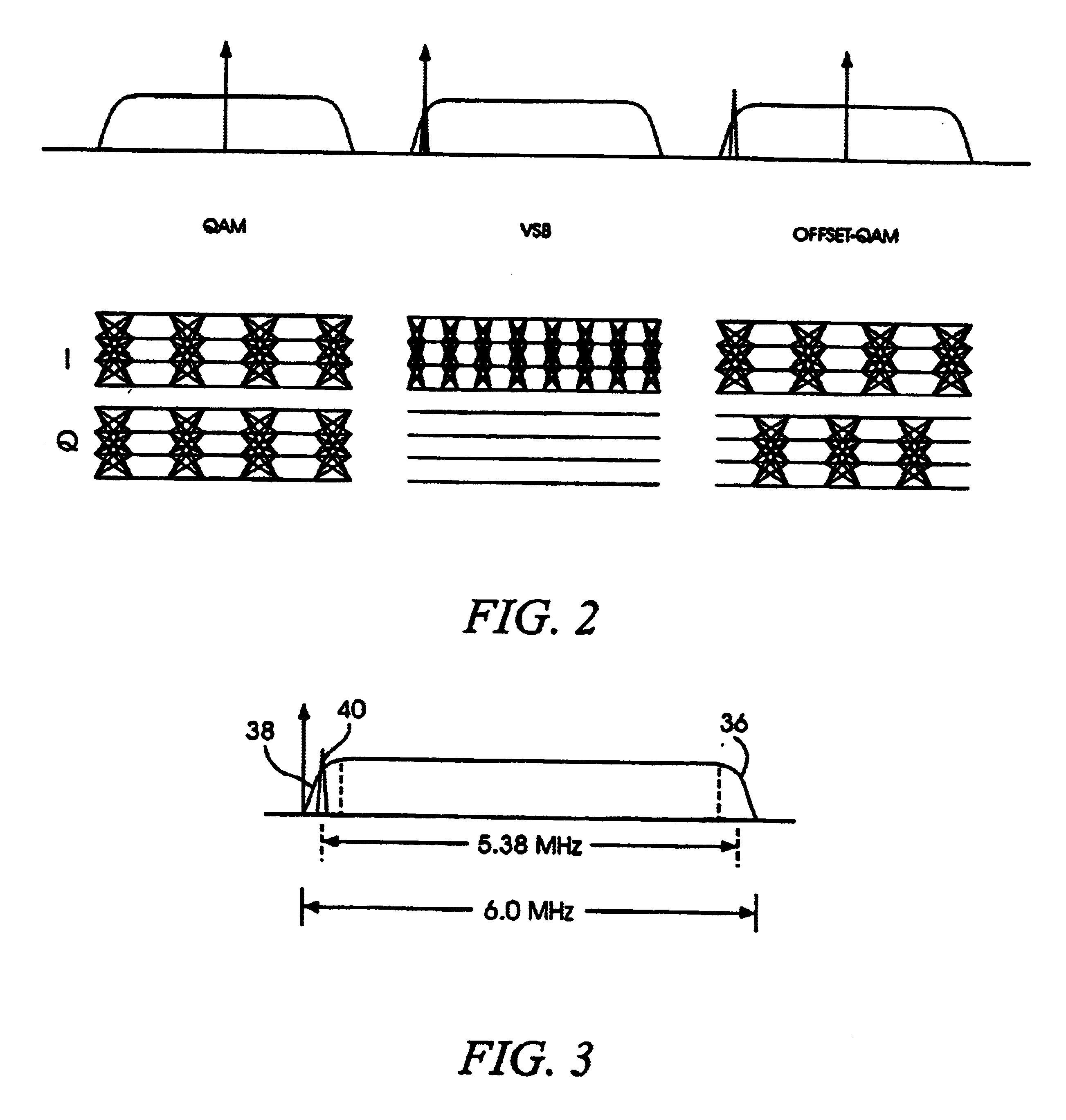
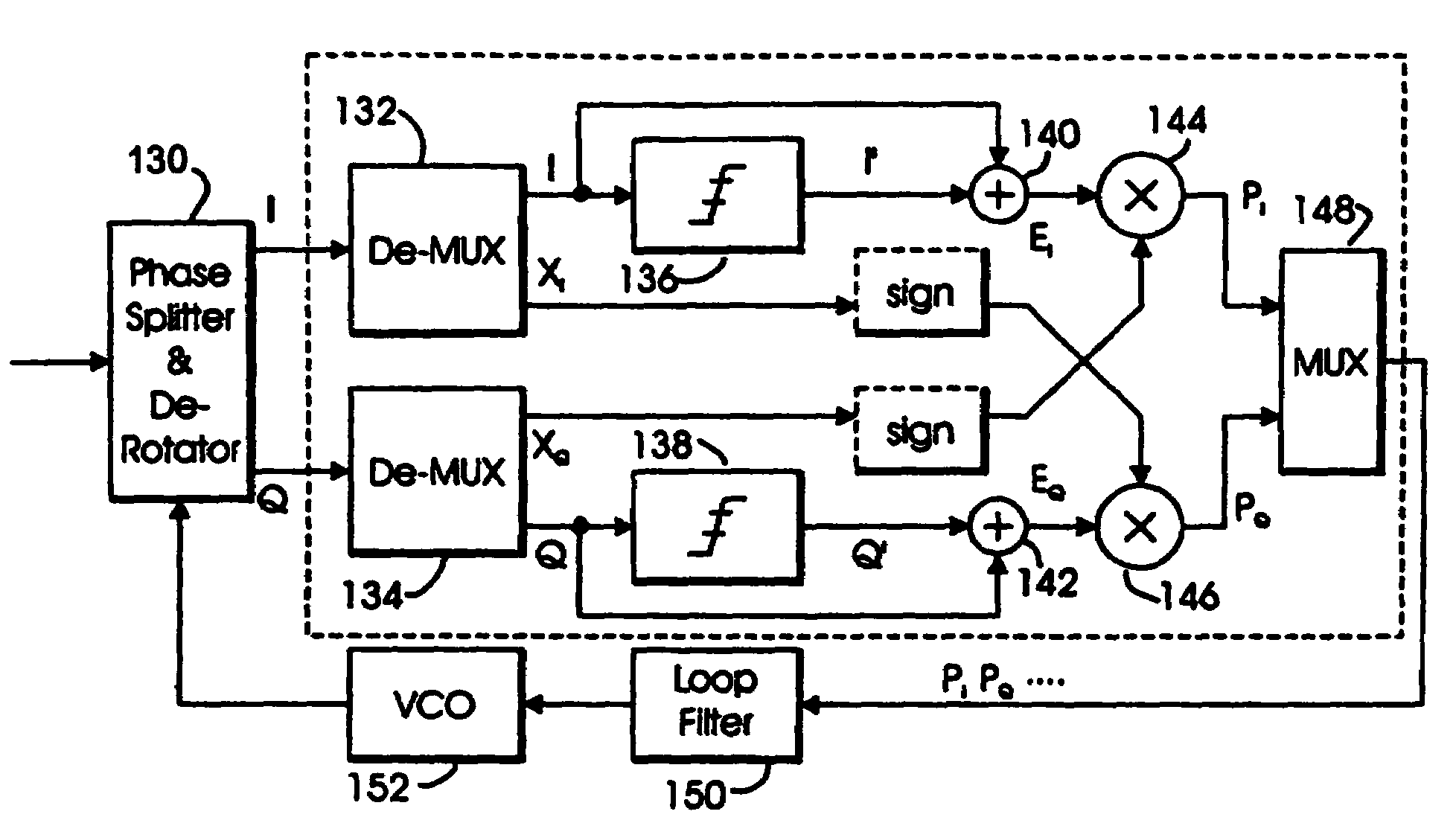
Dual mode QAM/VSB receiver
InactiveUS6842495B1Enhanced reliability symbolic decisionFacilitate decision-makingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhase detectorTelevision receivers
A television receiver system capable of receiving and demodulating television signal information content that has been modulated and transmitted in accordance with a variety of modulation formats is disclosed. In particular, the system is able to accommodate receipt and demodulation of at least 8 and 16-VSB modulated signals in order to support US HDTV applications, as well as 64 and 256-QAM modulated signals, for European and potential US CATV implementations. The system includes carrier and timing recovery loops adapted to operate on an enhanced pilot signal as well as decision directed carrier phase recovery loops. Phase detectors operate on I and Q rail signals, or generate a Q rail from a Hilbert transform of the I rail. Decision directed loops incorporate a trellis decoder in order to operate on sequence estimated decisions for improved reliability in poor SNR environments.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Complexity reduced feed forward carrier recovery methods for m-qam modulation formats
InactiveUS20120155890A1Improve performanceReduce effortCarrier regulationElectromagnetic receiversQam modulationCarrier frequency offset
The present disclosure provides a method of carrier phase error removal associated with an optical communication signal. The method includes estimating and removing a first phase angle associated with an information signal using coarse phase recovery, the information symbol being associated with a digital signal, the digital signal representing the optical communication signal; estimating a carrier frequency offset between a receiver light source and a transmitter light source by using the estimated first phase angle, the carrier frequency offset being associated with the information signal; removing carrier phase error associated with the carrier frequency offset; and estimating and removing a second phase angle associated with the information signal, the estimated second phase angle being based on the estimated first phase angle and the estimated carrier frequency offset.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
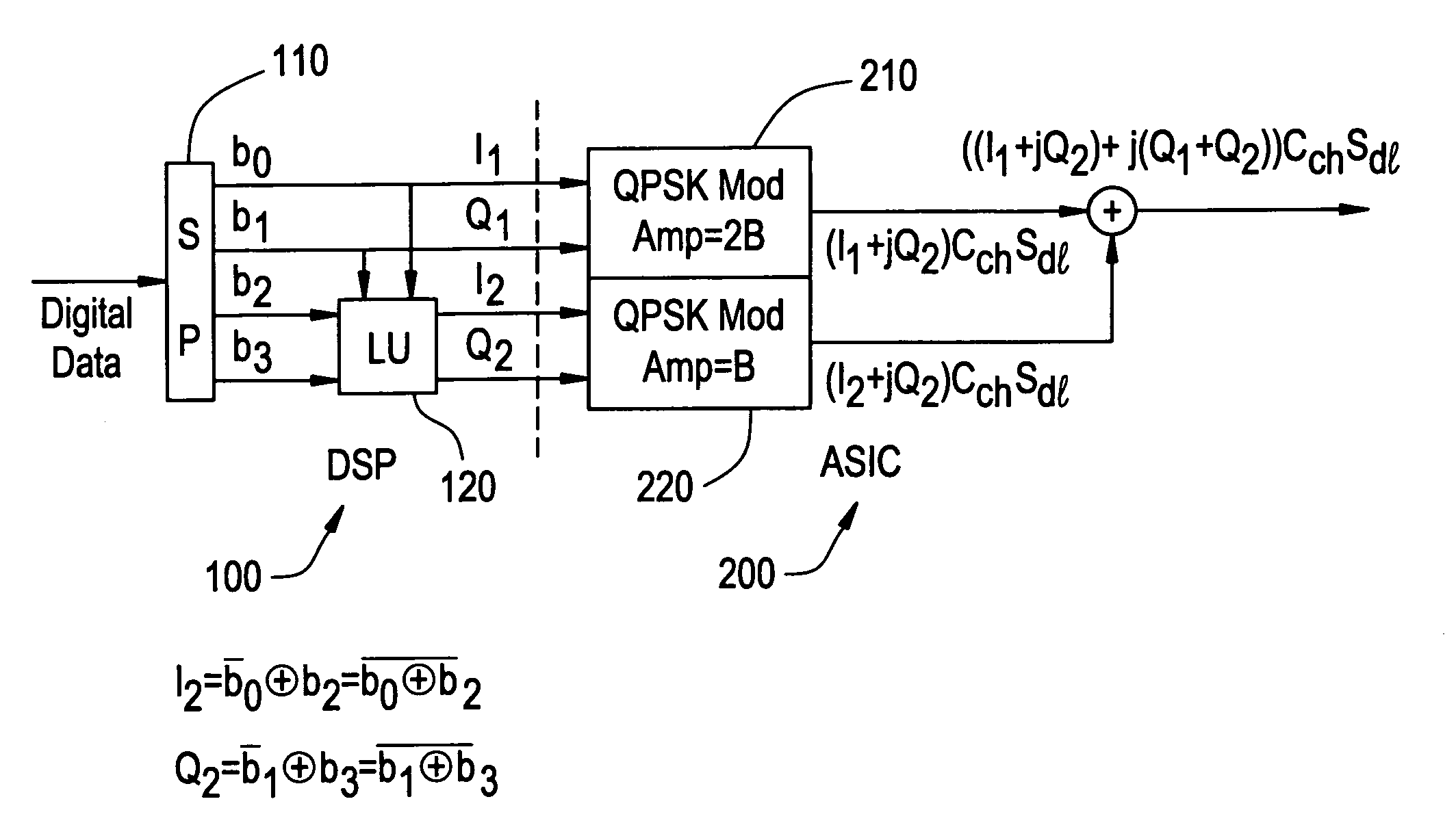
16 QAM modulator and method of 16 QAM modulation
In one embodiment, the 16-quadrature amplitude modulation QAM modulator includes a logic operation device performing a logic operation on first-fourth bits of received data to generate first and second logic outputs. A first quadrature phase shift keying QPSK modulator receives the first and second bits of received data and generates a first QPSK signal. A second QPSK modulator receives the first and second logic outputs and generates a second QPSK signal. A combiner combines the first and second QPSK signals to generate a 16-QAM signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for sending channel quality indication
ActiveCN102624501AImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple carrier systemsCurrent channelQam modulation
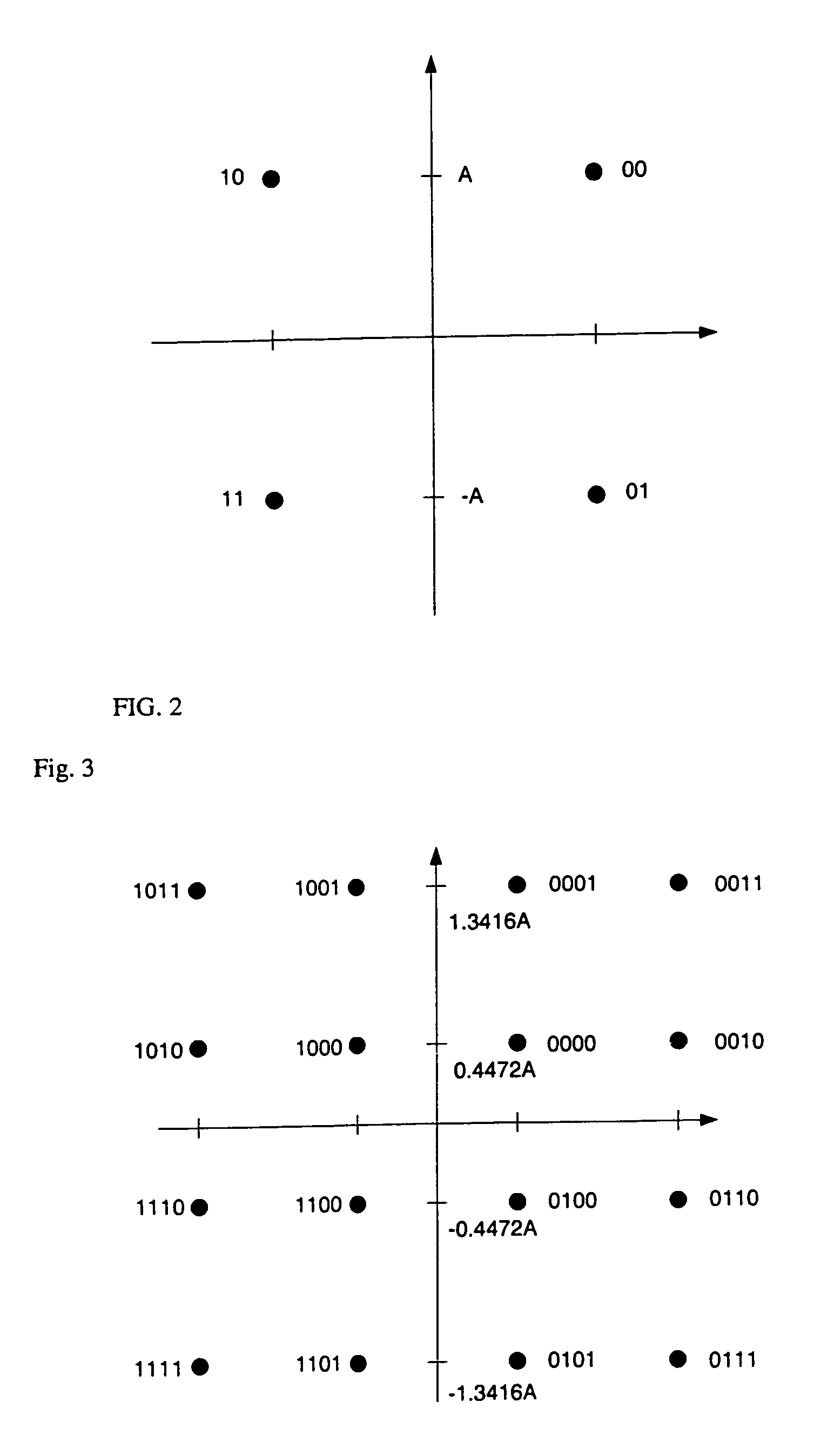
The invention provides a method for sending channel quality indication. The method comprises that: channel quality indication supporting a 256 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) mode is newly increased; and user equipment receives a pilot signal sent by a base station, carries out channel measurement according to the pilot signal and feedbacks current channel quality indication to the base station. Besides, provided is an apparatus for sending channel quality indication. According to the invention, a 256 QAM modulation mode is supported and the system throughput is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Dual mode QAM/VSB receiver
InactiveUS7403579B2Facilitate decision-makingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhase detectorTelevision receivers
A television receiver system capable of receiving and demodulating television signal information content that has been modulated and transmitted in accordance with a variety of modulation formats is disclosed. In particular, the system is able to accommodate receipt and demodulation of at least 8 and 16-VSB modulated signals in order to support US HDTV applications, as well as 64 and 256-QAM modulated signals, for European and potential US CATV implementations. The system includes carrier and timing recovery loops adapted to operate on an enhanced pilot signal as well as decision directed carrier phase recovery loops. Phase detectors operate on I and Q rail signals, or generate a Q rail from a Hilbert transform of the I rail. Decision directed loops incorporate a trellis decoder in order to operate on sequence estimated decisions for improved reliability in poor SNR environments.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
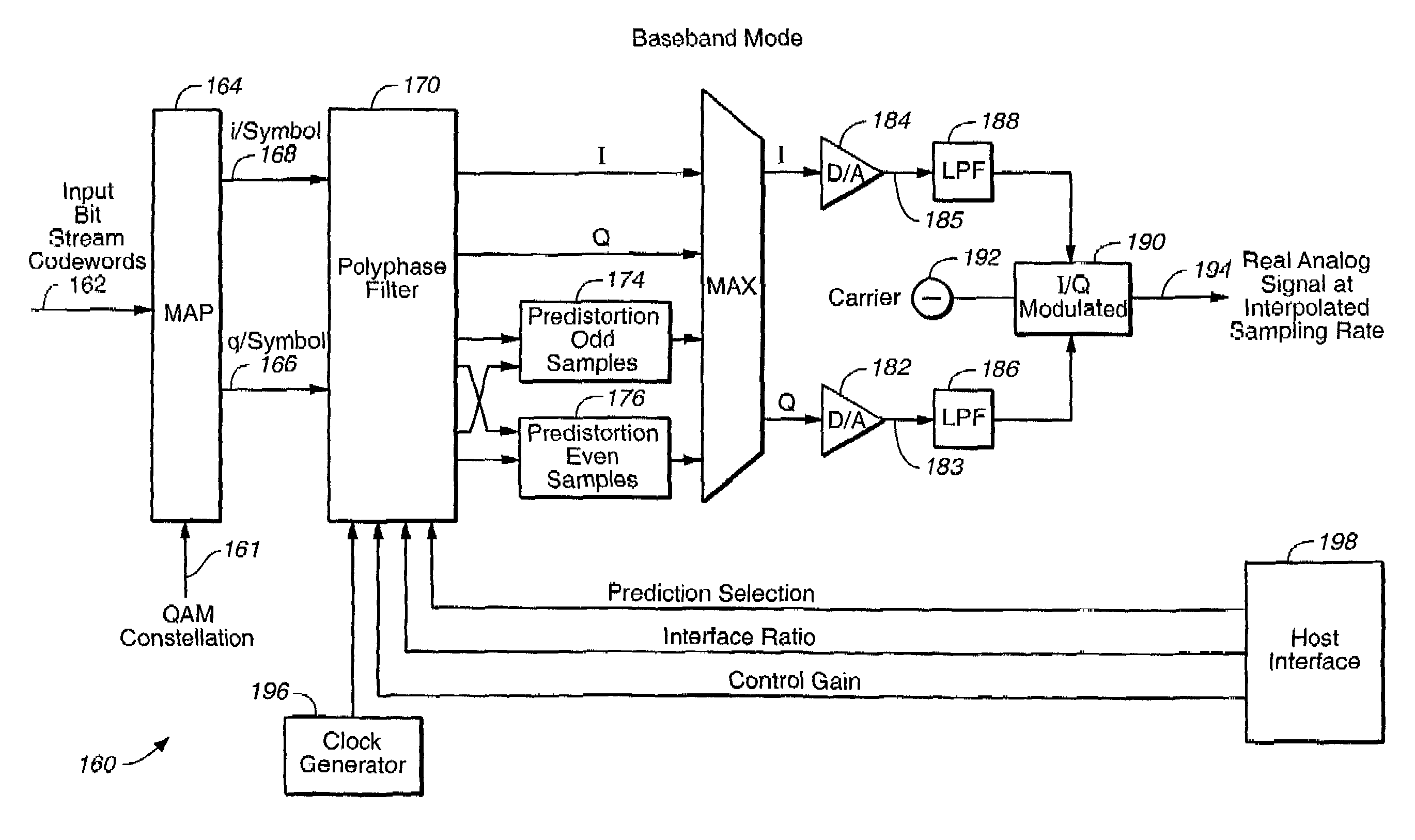
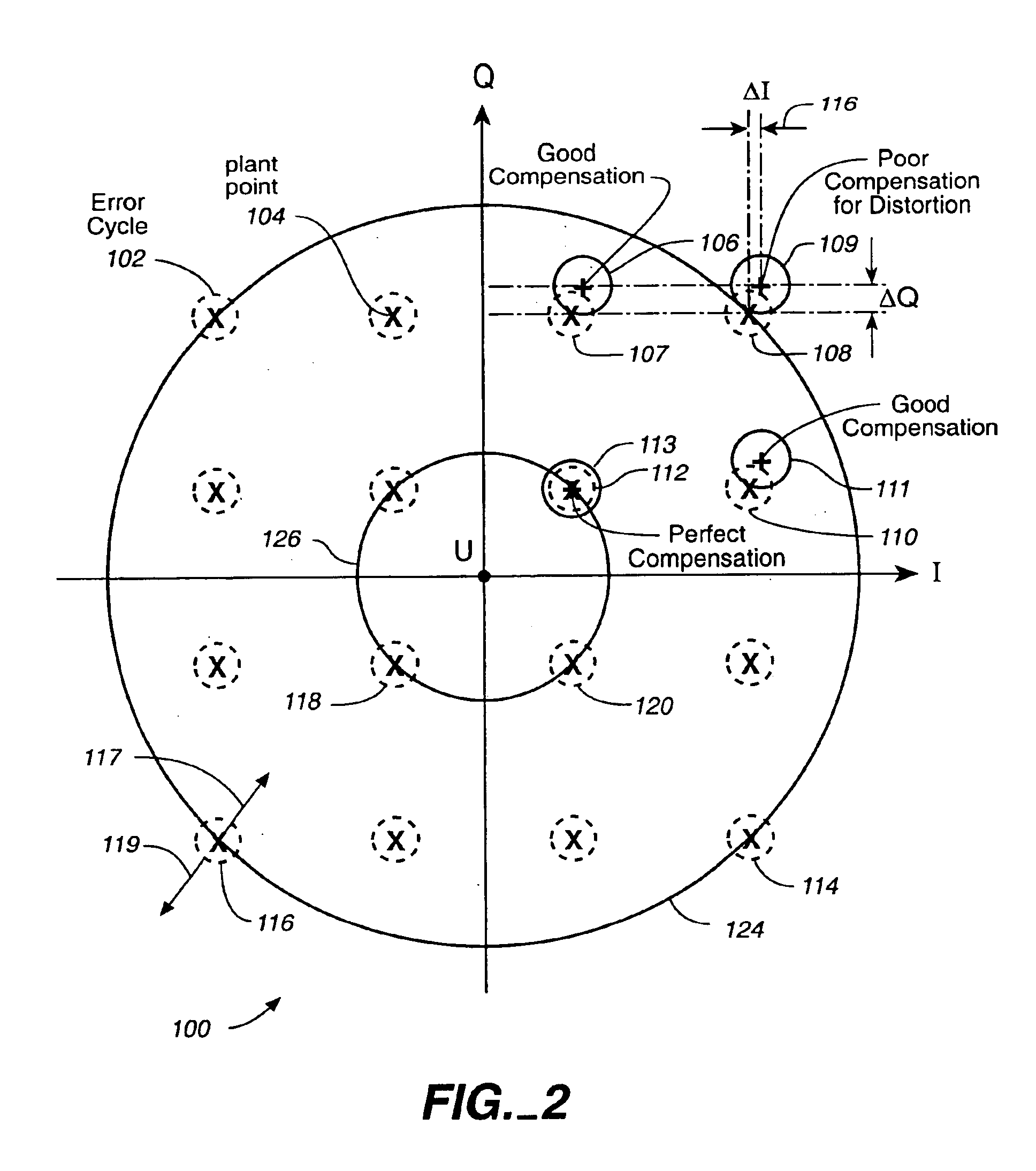
Flexible multimode QAM modulator
InactiveUS6973141B1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle modulationQam modulationTransmission channel
A method of baseband / passband digital modulation for a data transmission system wherein a plurality of data symbols is transmitted over a transmission channel at a symbol rate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) generating a plurality of I and Q components of symbols by mapping an input bit stream comprising a plurality of digital codewords into a QAM constellation; (2) selecting a passband or a baseband mode; and (3) generating an analog output signal in the passband or baseband mode. The step of selecting the passband or the baseband mode depends on the complexity of QAM constellation. If QAM constellation includes less than 64 QAM plant points, the passband mode is selected, and if QAM constellation includes more than 64 QAM plant points, the baseband mode is selected. If the QAM constellation includes less than 64 QAM plant points, initially selecting the passband mode until a D / A conversion speed reaches a maximum passband conversion speed, and until an output symbol rate reaches a maximum passband symbol output rate, and subsequently switching to the baseband mode in order to double the maximum passband conversion speed and to double the maximum passband symbol output rate.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
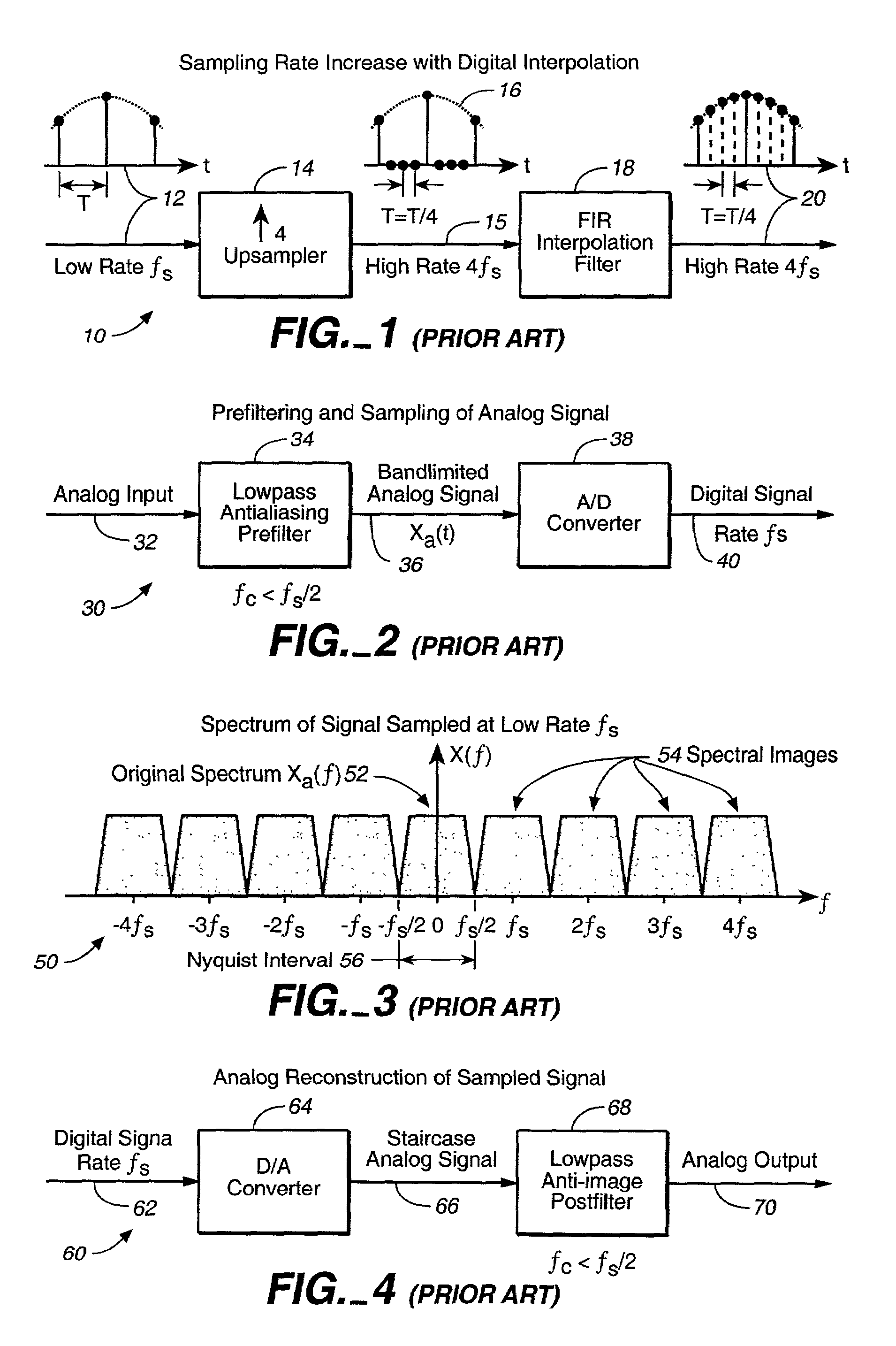
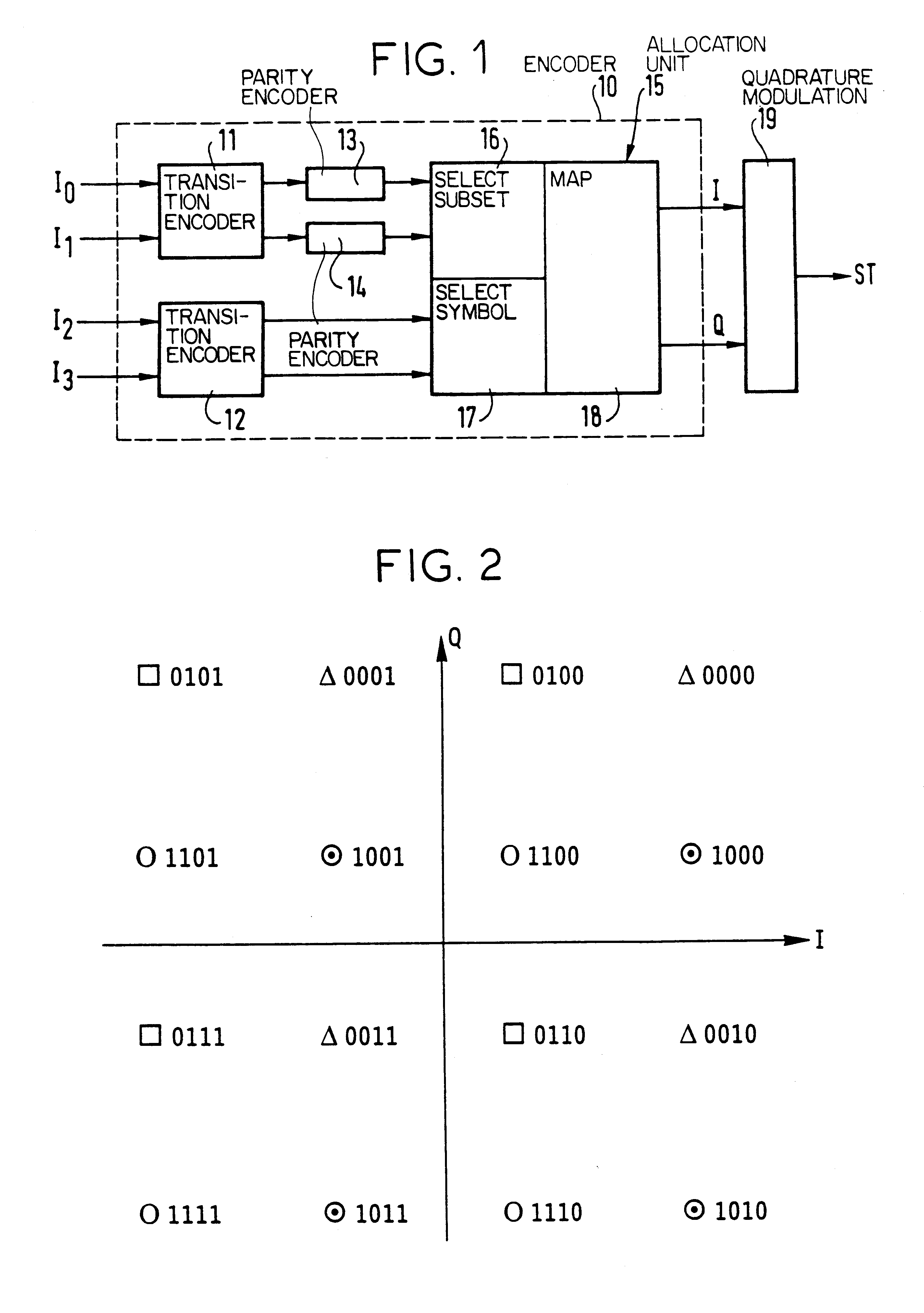
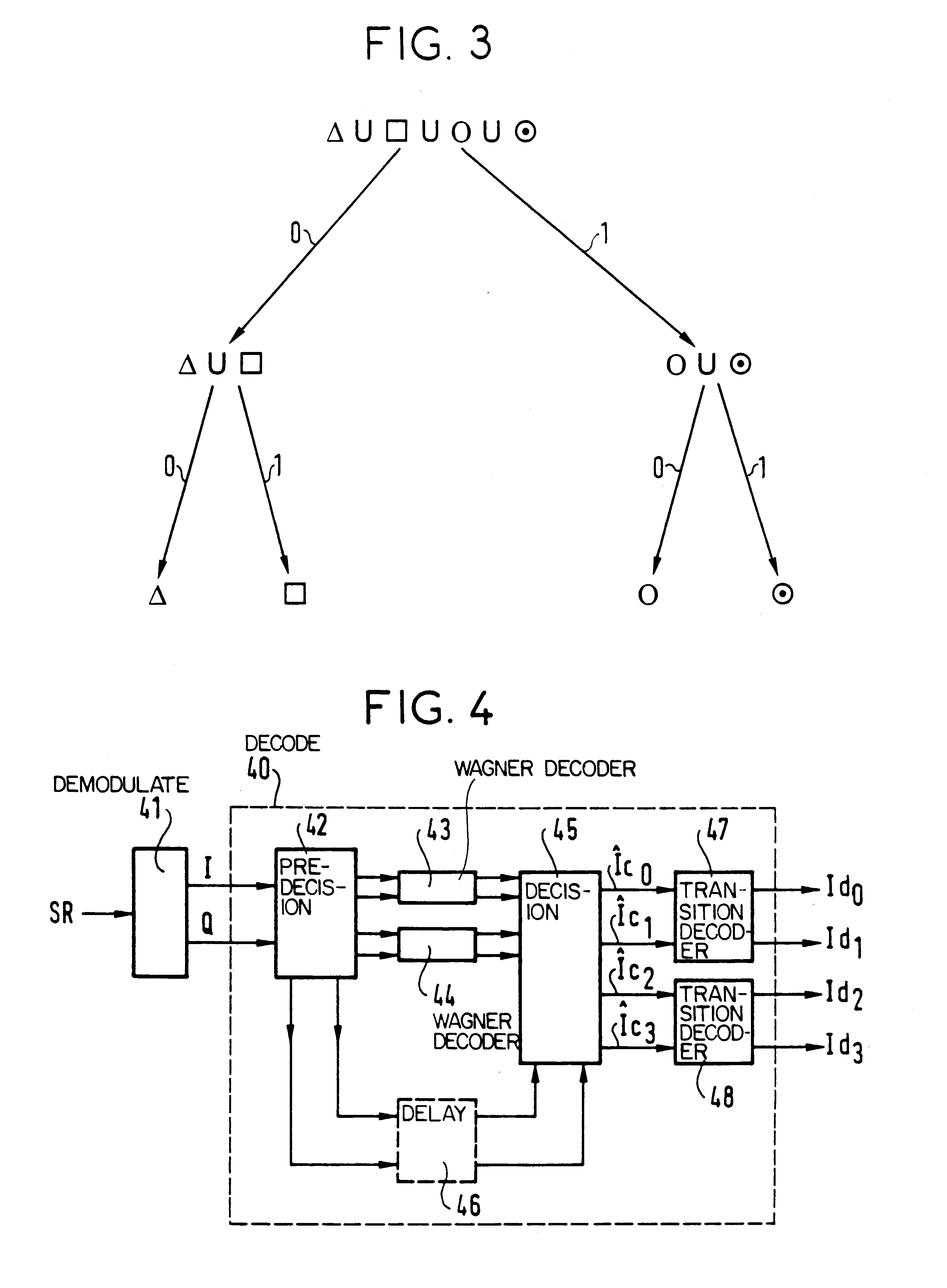
Encoding/decoding system using 16-QAM modulation encoded in multi-level blocks
InactiveUS6195396B1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionQam modulationAlgorithm
The invention provides a block-encoded modulation scheme using multi-level partitioning techniques. This scheme is made transparent to phase ambiguities of ±pi / 2 and of pi, by means of differential encoding and appropriate mapping, it is applicable to 16-QAM modulation, and it has theoretical encoding gain that is optimal for the rate of the code. The decoder associated with this scheme uses the Wagner algorithm which is much less complicated to implement than the Viterbi algorithm or than the Reed-Solomon algorithm.
Owner:ALCATEL TELSPACE
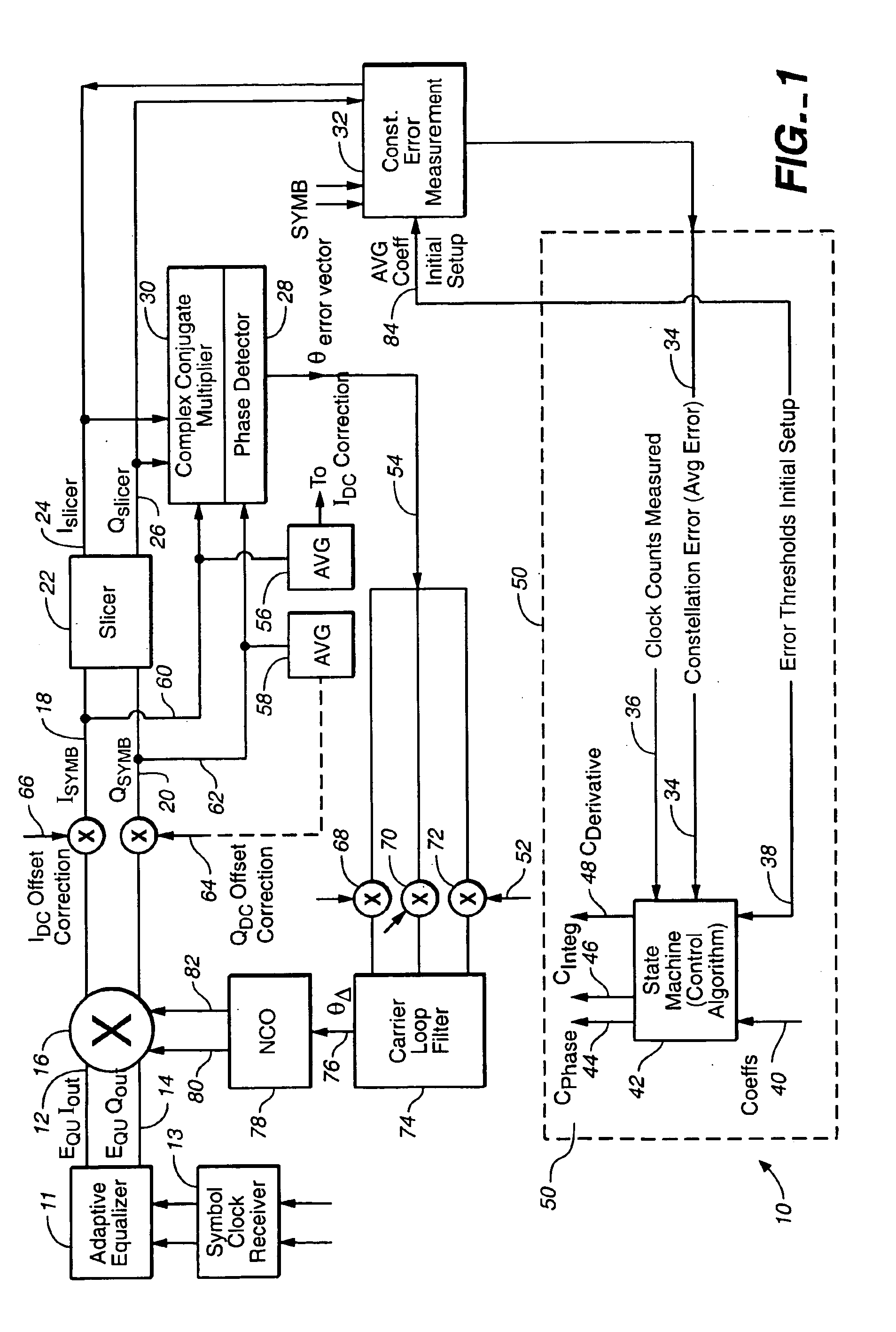
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
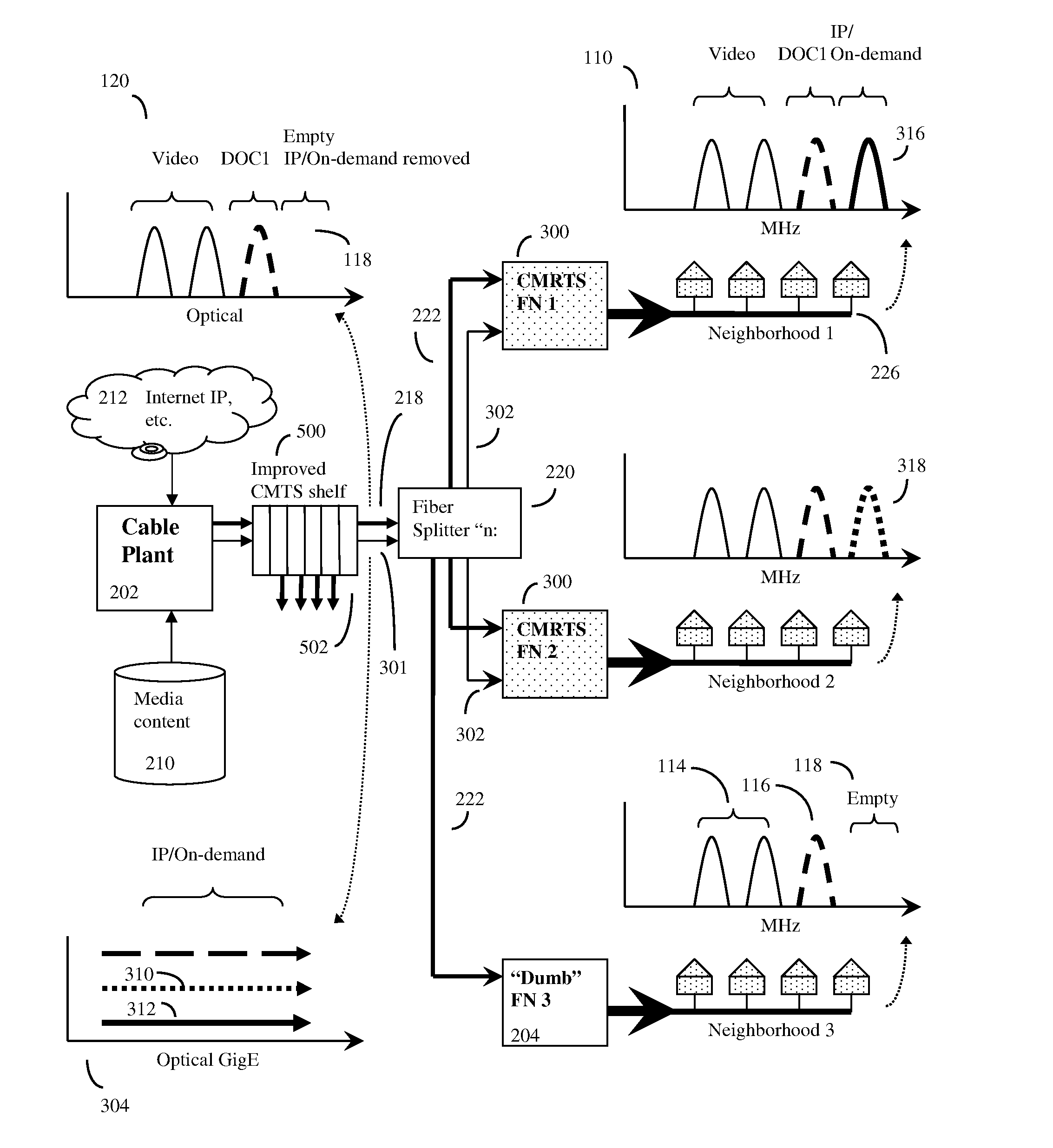
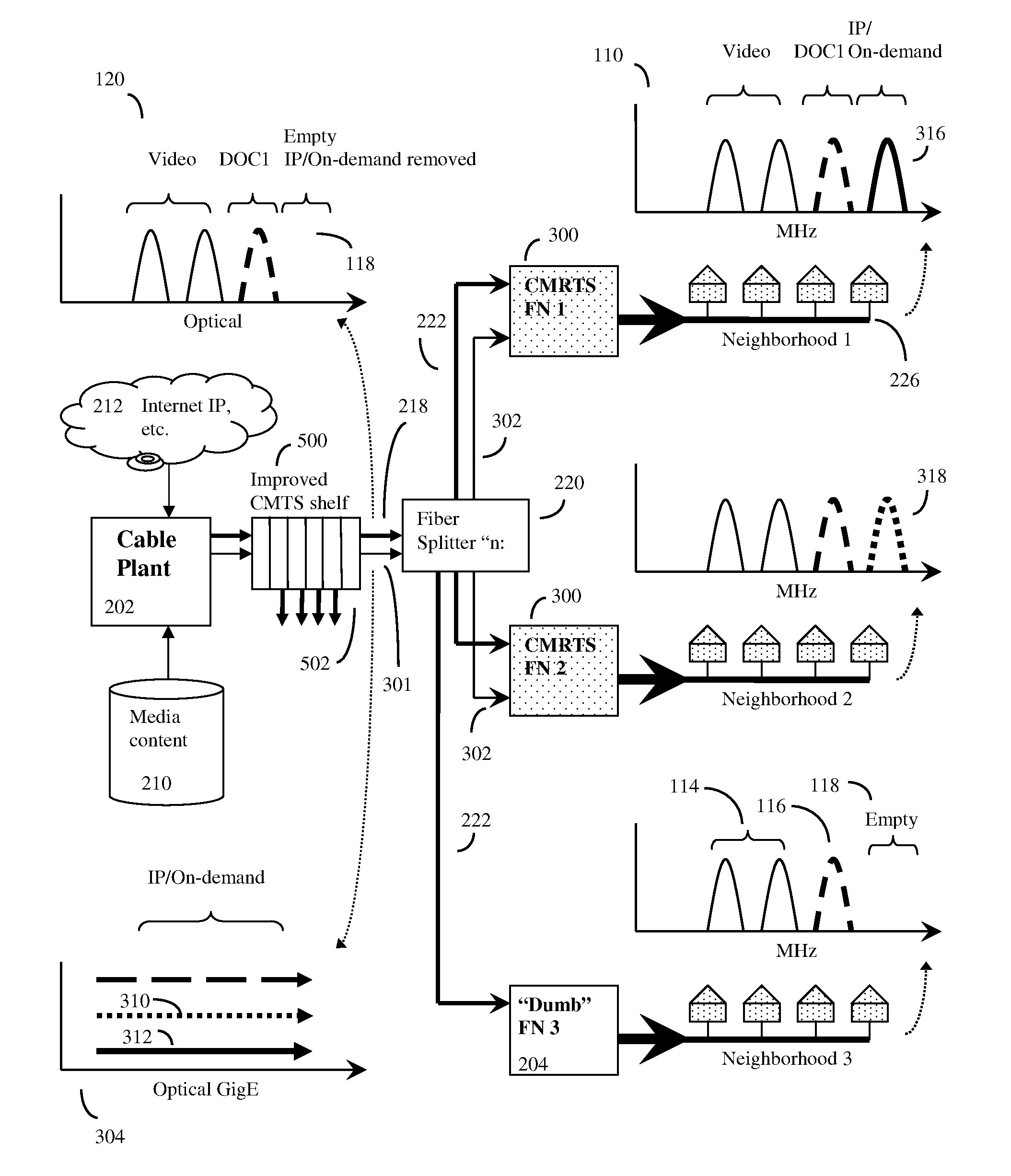
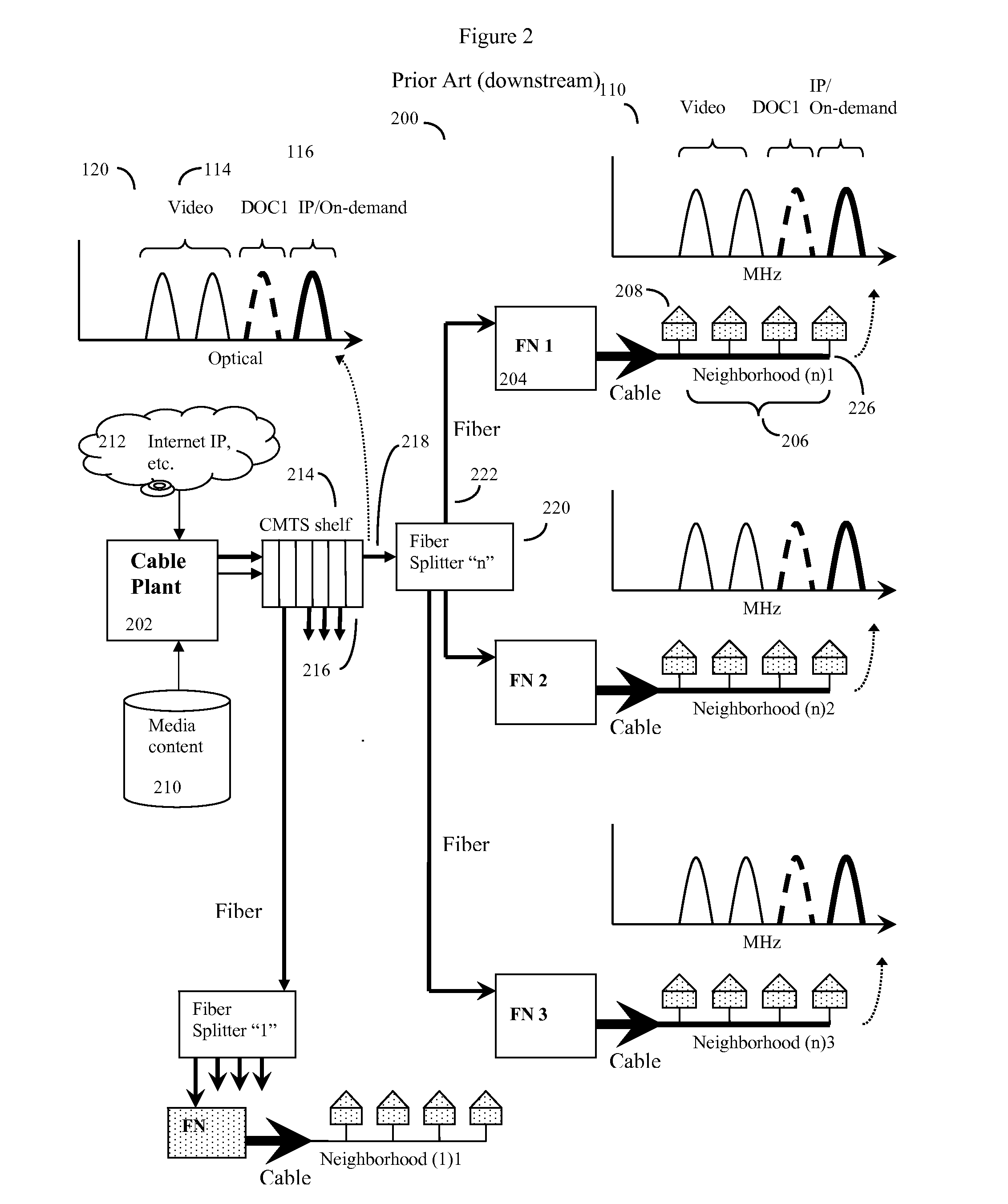
Distributed cable modem termination system
ActiveUS20110182583A1Highly software configurableFunction increaseError preventionBroadband local area networksFiberQam modulation
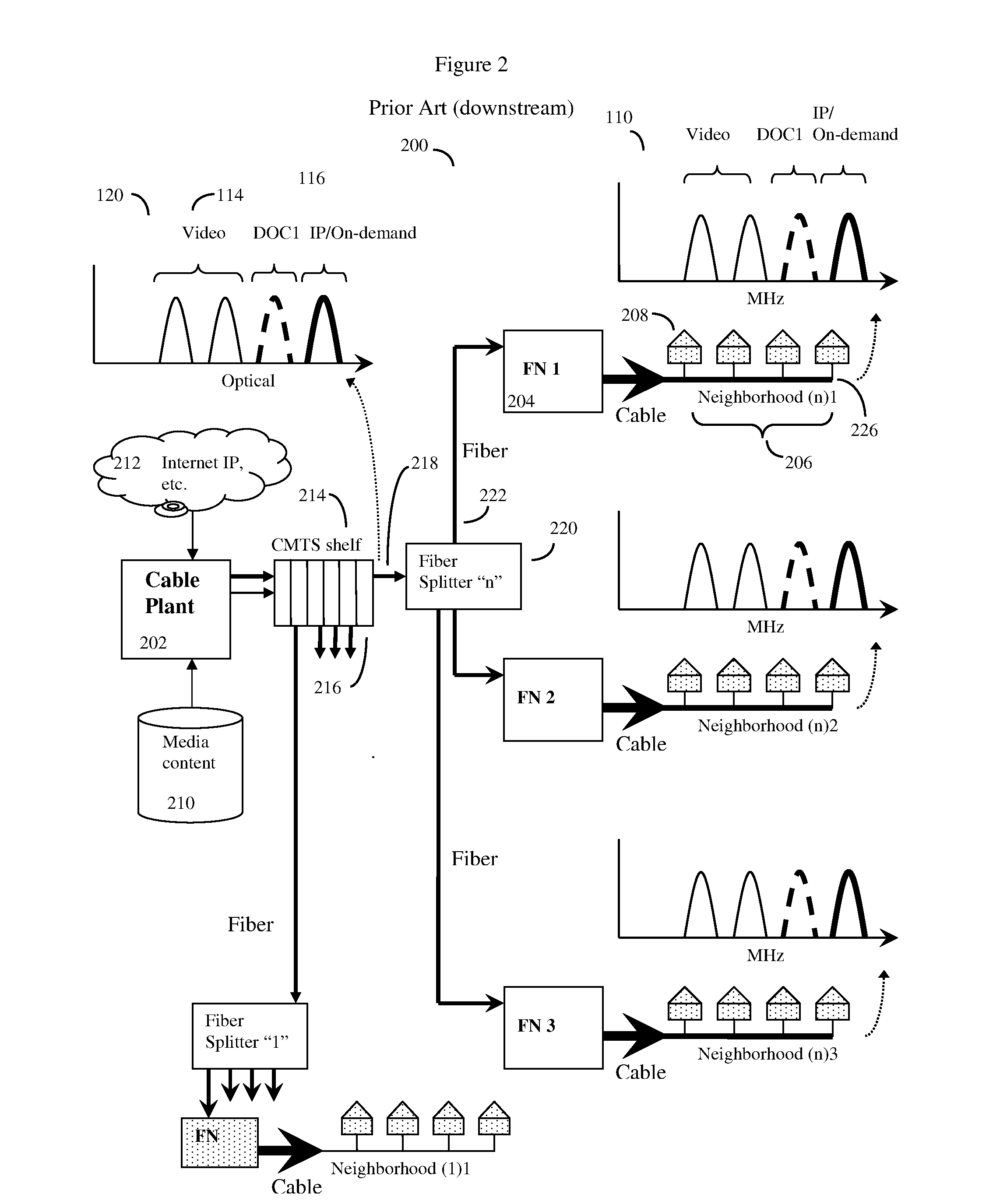
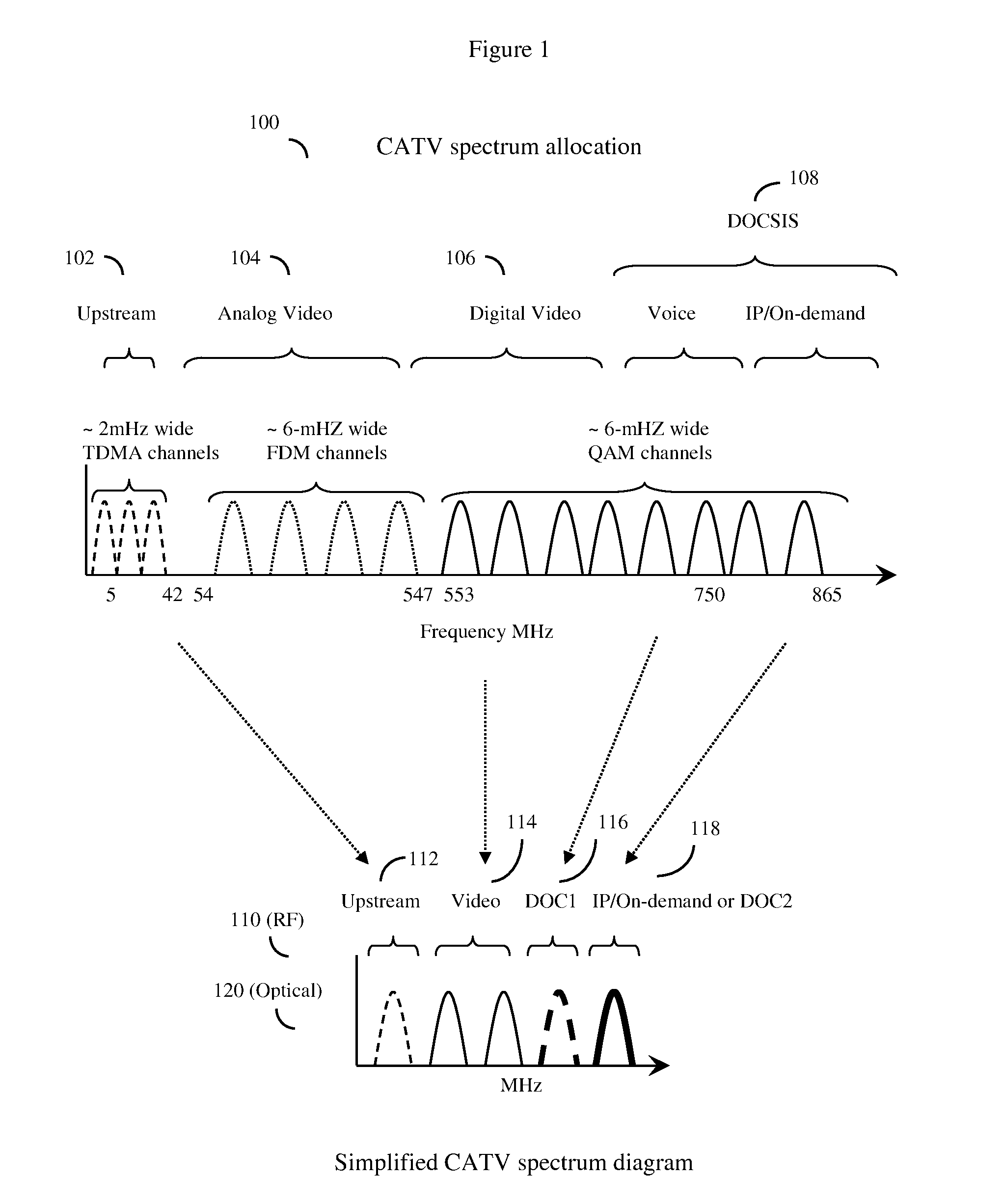
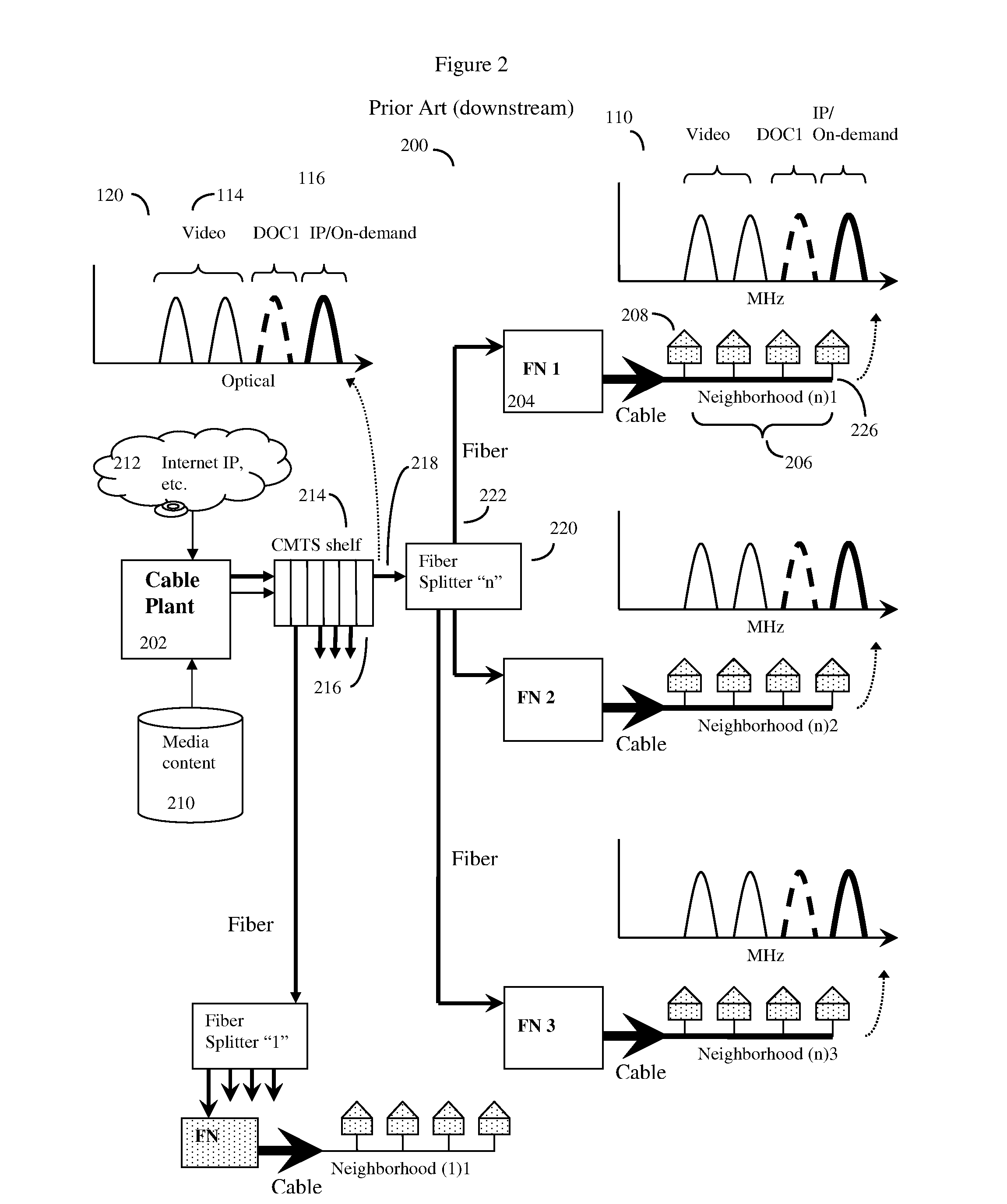
Distributed CMTS device for a HFC CATV network serving multiple neighborhoods by multiple individual cables, in which the QAM modulators that provide data for the individual cables are divided between QAM modulators located at the cable plant, and remote QAM modulators ideally located at the fiber nodes. A basic set of CATV QAM data waveforms may be transmitted to the nodes using a first fiber, and a second set of IP / on-demand data may be transmitted to the nodes using an alternate fiber or alternate fiber frequency, and optionally other protocols such as Ethernet protocols. The nodes will extract the data specific to each neighborhood and inject this data into unused QAM channels, thus achieving improved data transmission rates through finer granularity. A computerized “virtual shelf” control system for this system is also disclosed. The system has high backward compatibility, and can be configured to mimic a conventional cable plant CMTS.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Downstream transmitter and cable modem receiver for 1024 QAM
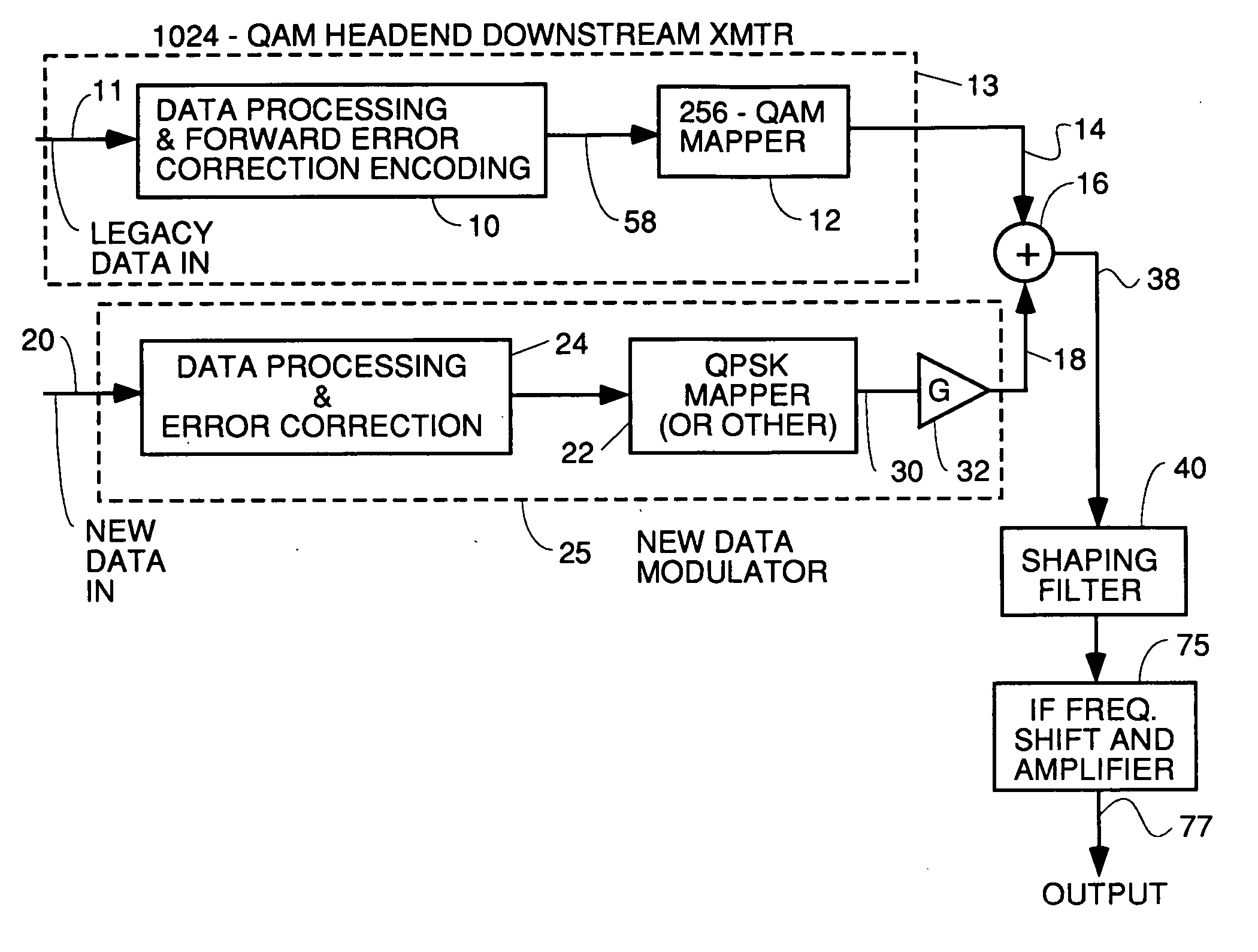
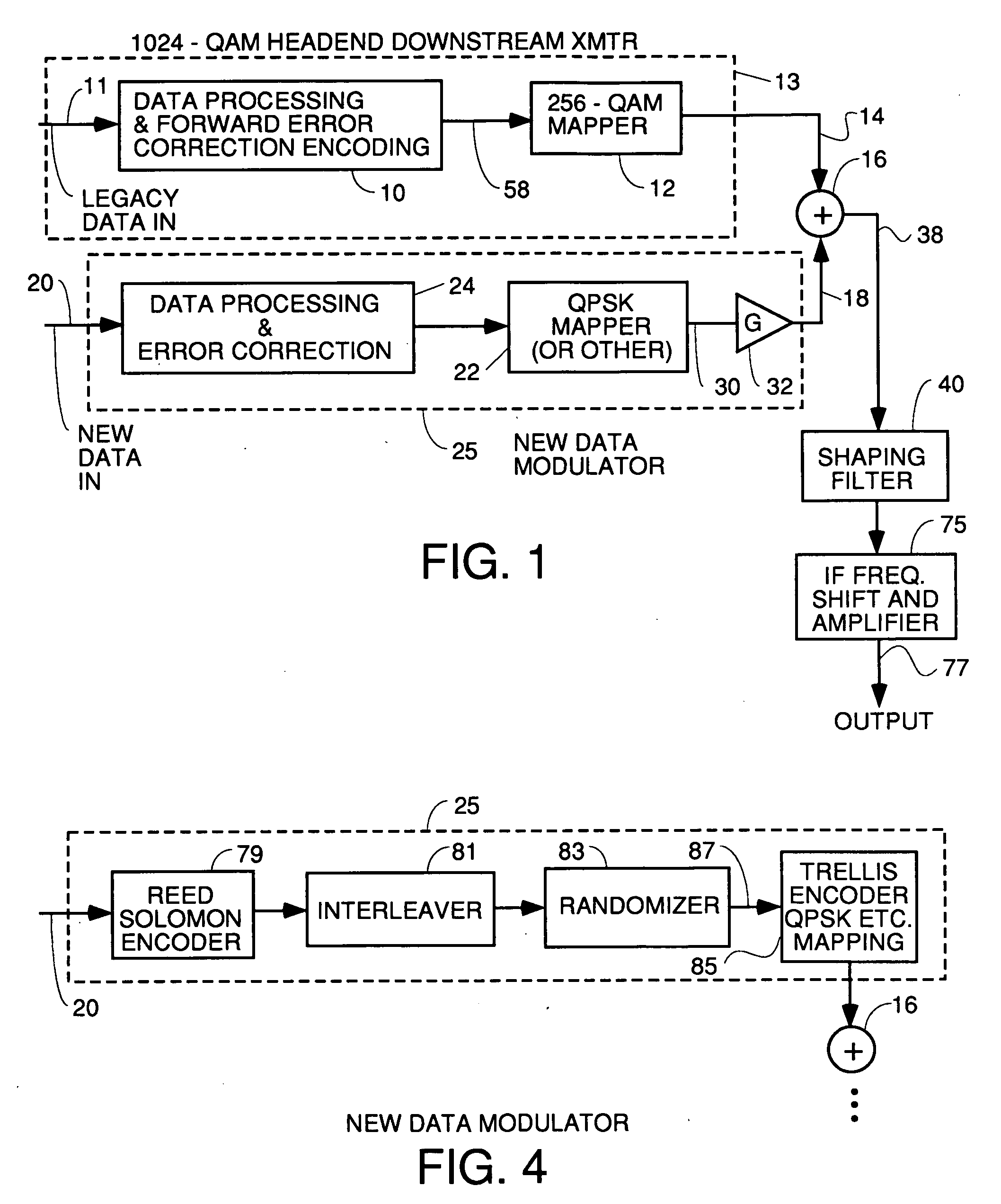
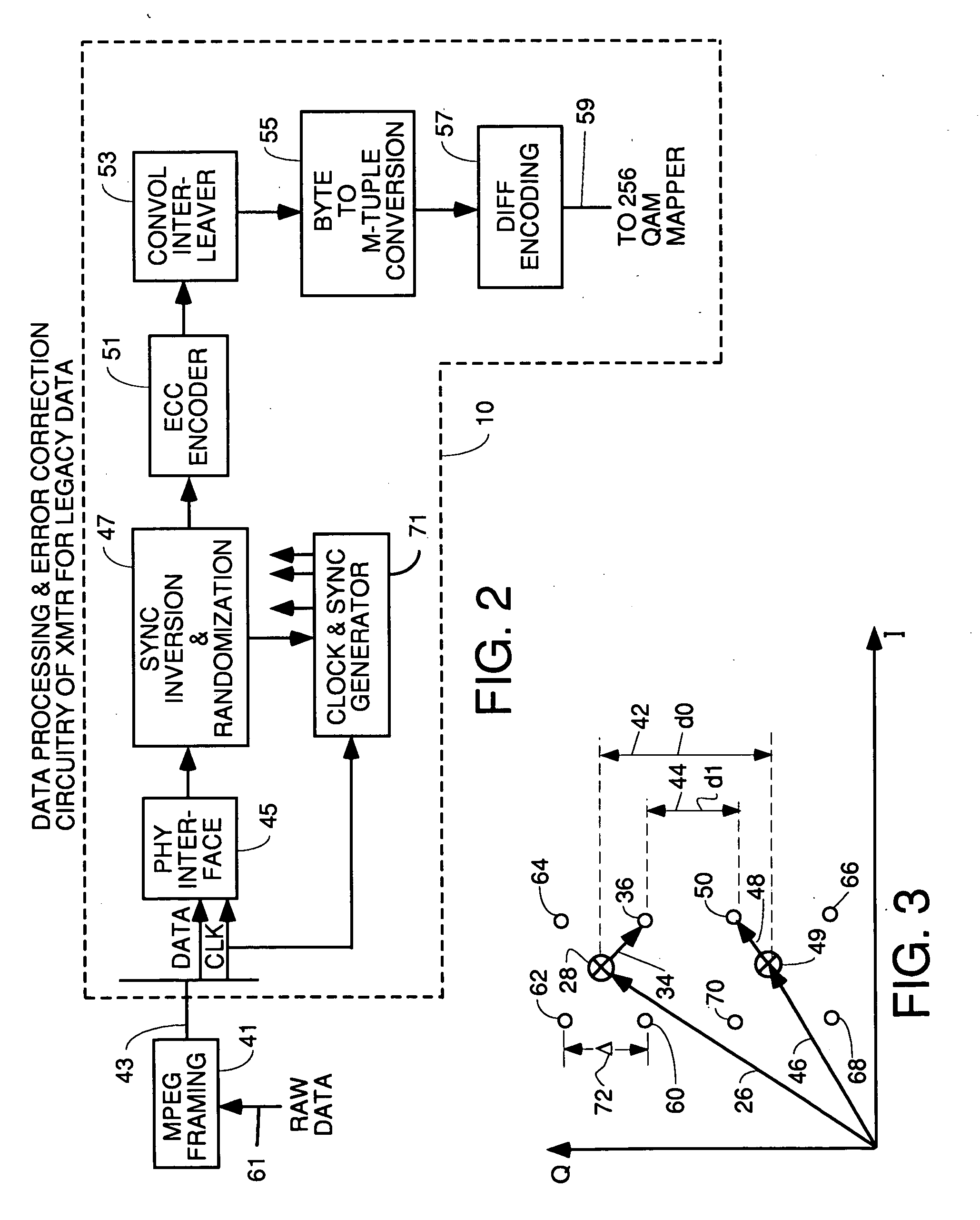
InactiveUS20060085727A1Shortening HFC lengthMinimize reflectionSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationData representation error detection/correctionModem deviceAudio power amplifier
A headend transmitter that transmits 1024 QAM including a 256 QAM modulator which has been modified to have more aggressive forward error correction processing. The 256 QAM modulator outputs 256 QAM points to a summer. Another data modulator receives additional data to be transmitted in a separate, substantially less complex constellation. This modulator processes the additional data to do forward error correction thereon and then maps the encoded data into a less complex constellation such as QPSK, 16 QAM etc. The additional data constellation points are then amplified in a variable gain amplifier and fed to a summer where each additional data point is added by vector summation to one 256 QAM point. The output 1024 QAM point is filtered and shifted to the desired transmission frequency. Legacy cable modem receivers can still receive the 256 QAM point since the addition of the new data just appears to be noise which they can overcome using the parity bits encoded in the transmitted symbols. 1024 QAM cable modem receivers receive both the 256 QAM points and the new data points and output both.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Bit Reverse Interleaving Methods for QAM Modulation in a Wireless Communication System
ActiveUS20090113274A1Efficient mappingEasy to operateError detection/correctionCode conversionCommunications systemQam modulation
In a communication method, a sequence of information bits is encoded into systematic bits and parity bits. The systematic bits and the parity bits are grouped in output blocks, each output block to be assigned to an address of a constellation scheme. The addresses include addresses that are more prone to error and address that are less prone to error so that the symbols are grouped such that bits in groups of consecutive bits of the sequence of information bits are not all assigned to addresses that are more prone to error.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
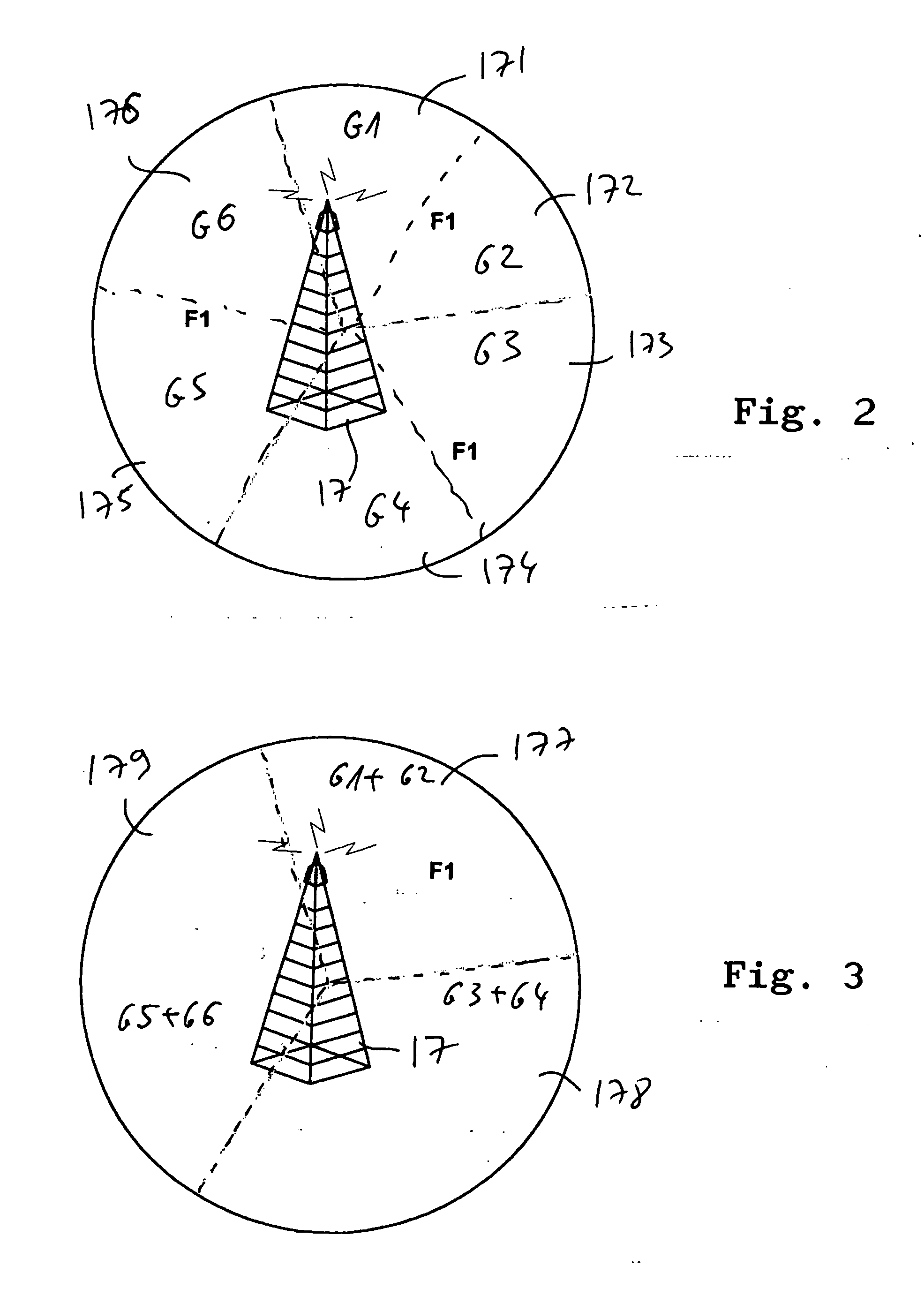
Cellular network system and method
InactiveUS20050002323A1Easy to useFine granularityNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationExtensibilityQam modulation
A Cellular network system wherein the physical layer as defined in 802.16a includes means for its optimization for mobile operators for improved reliability, coverage, capacity, user location, fully scalability, and mobility from 2-6 Ghz, while working in a reuse of 1. The same RF frequency is allocated to all sectors in the cell. The system further includes means for its operation in a Coordinated Synchronous mode, wherein permutations, collisions and averaging interferences from other cells cause limitations on the use of high QAM modulations, which sometimes can increase capacity up to three times (64 QAM instead QPSK).
Owner:HADAD ZION
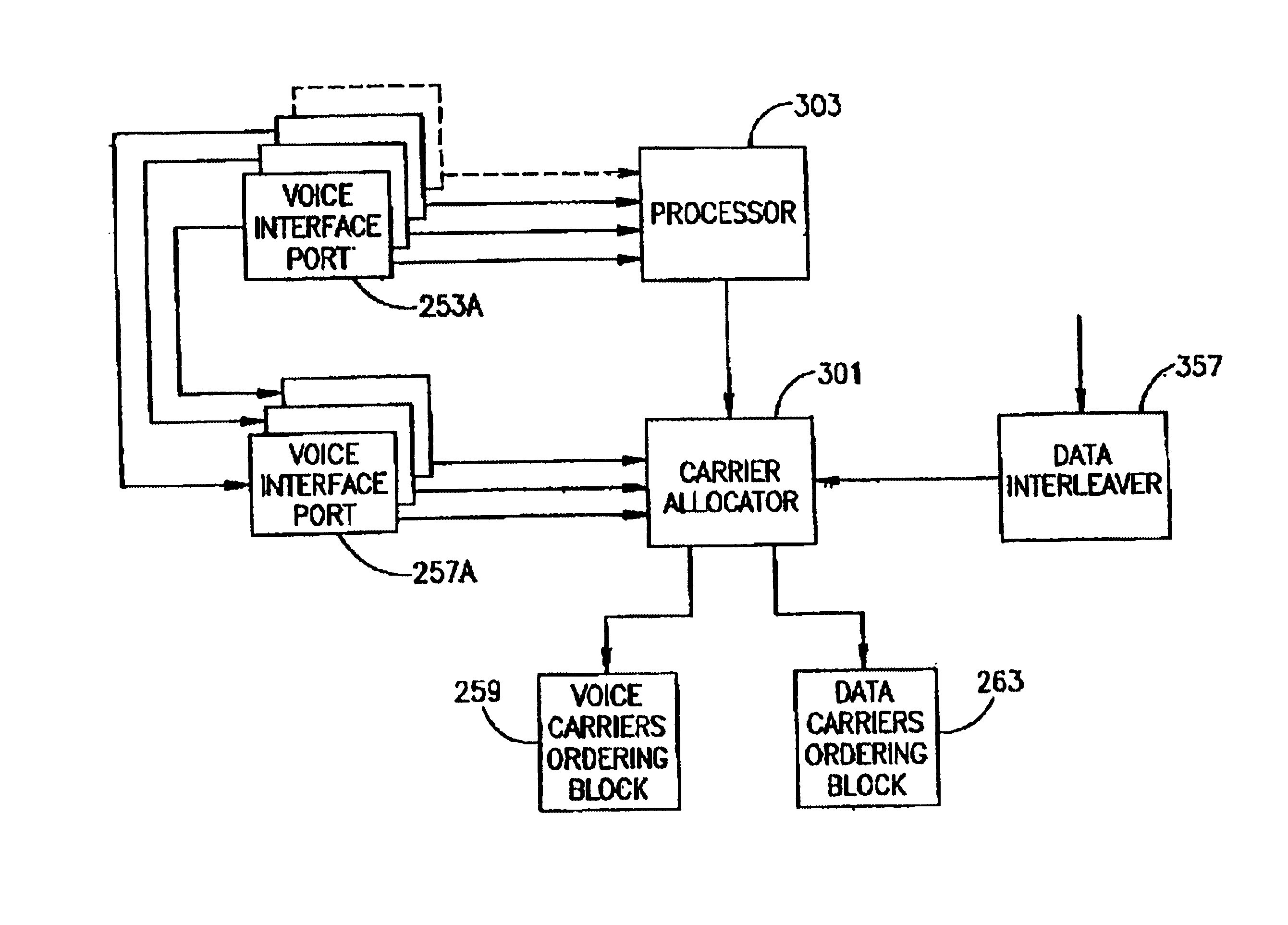
Communication systems conveying voice and data signals over standard telephone lines
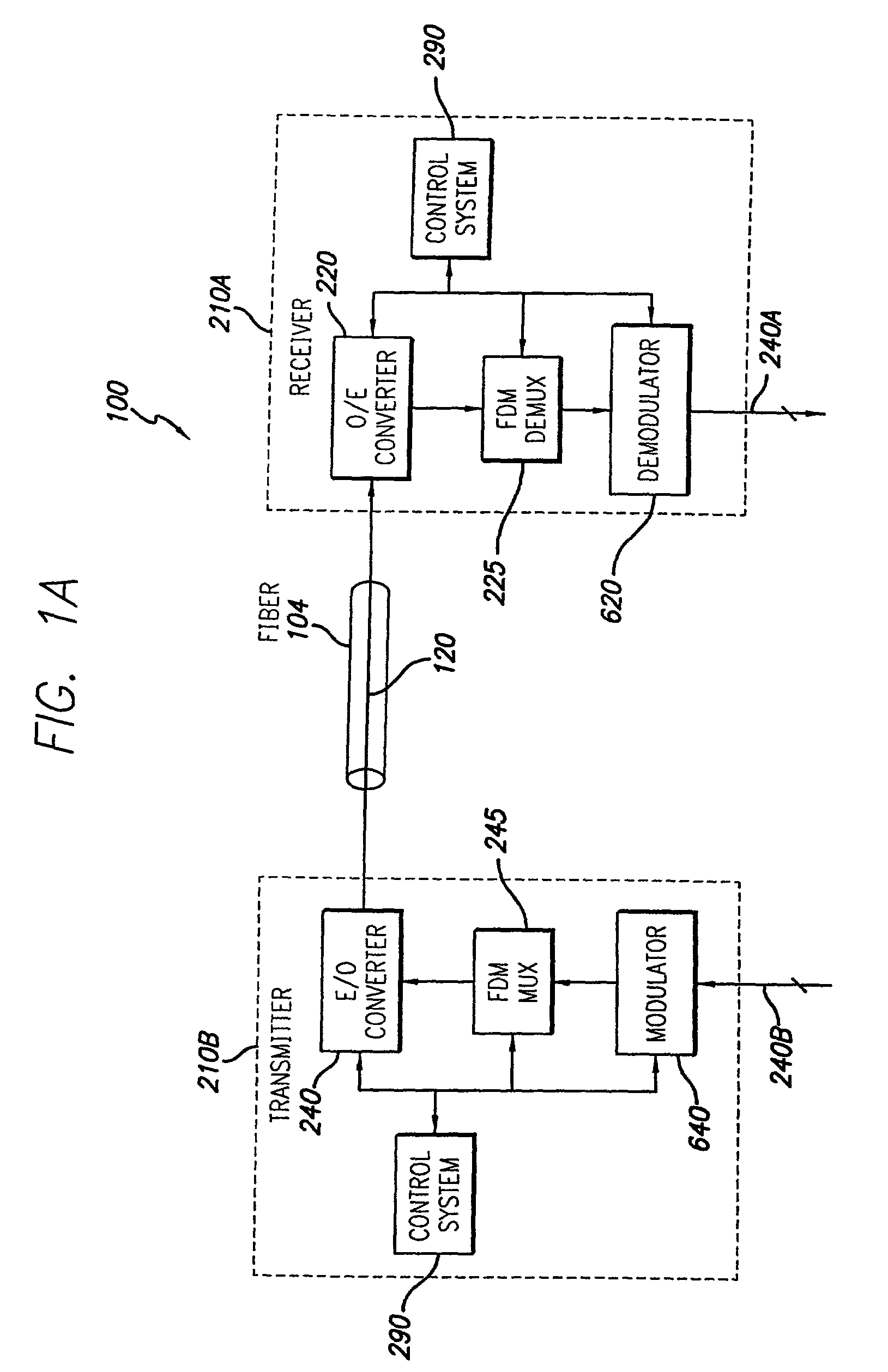
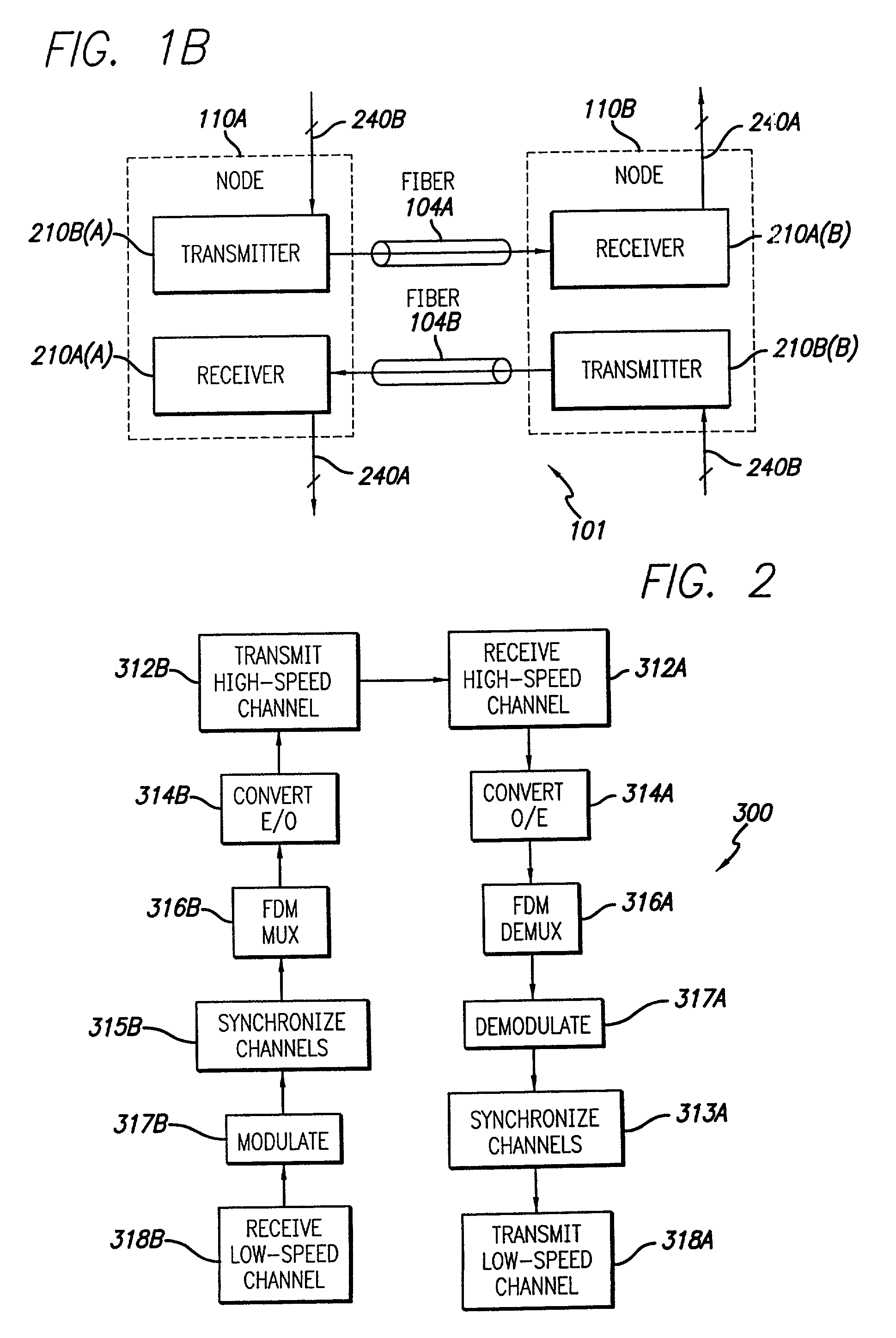
A method for conveying over telephone lines digitized voice signals simultaneously with digital data signals by means of a communication system, having a transmitter having a discrete multi-tone unit yielding a plurality of carriers of different frequency, several of which are assigned to the voice signals and others to the data signals. The carriers for transmitting voice are selected on the basis of their signal-to-noise ratio characteristics, which carriers can be reallocated dynamically to data transmission. A first tone ordering circuit assigns data streams to data carriers, and a second tone ordering circuit assigns voice streams to voice carriers. Each carrier is modulated by QAM modulation, the data carriers by a sequence of QAM symbols representing data and the voice carriers by a sequence of QAM symbols representing voice. QAM modulation is carried out by a first constellation encoder that modulates the data carriers and a second constellation encoder that modulates the voice carriers.
Owner:SIGMA DESIGNS ISRAEL S D I
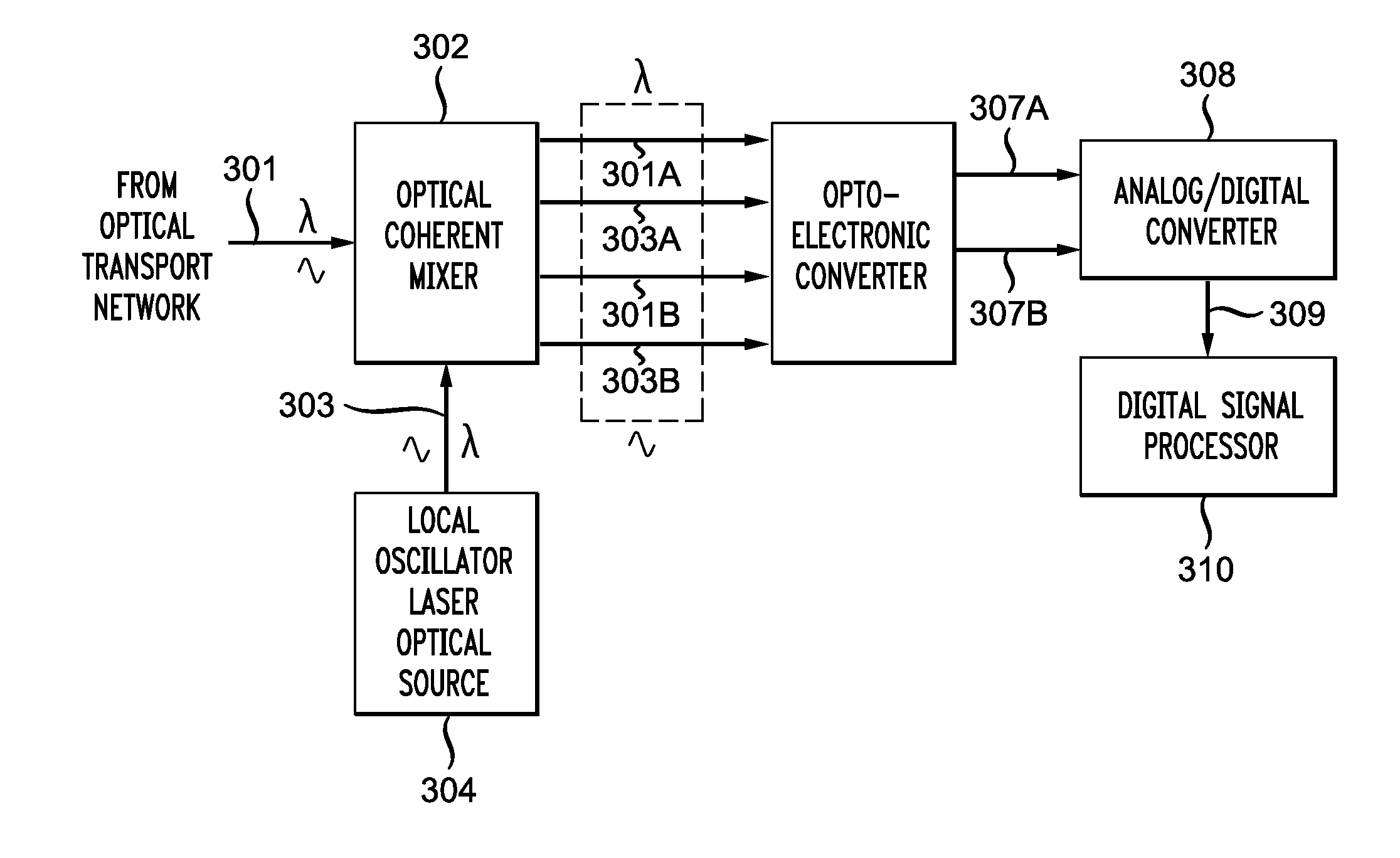
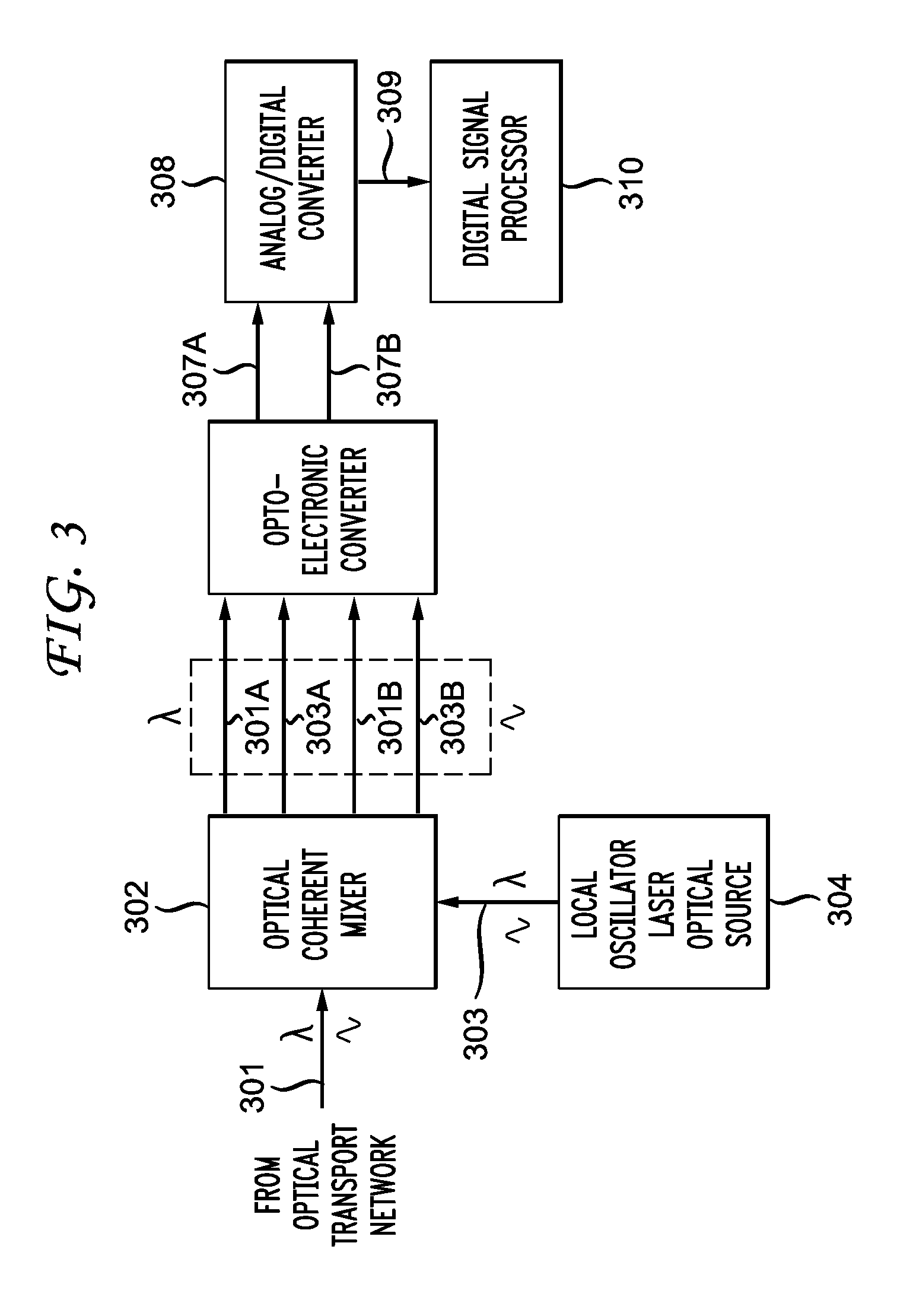
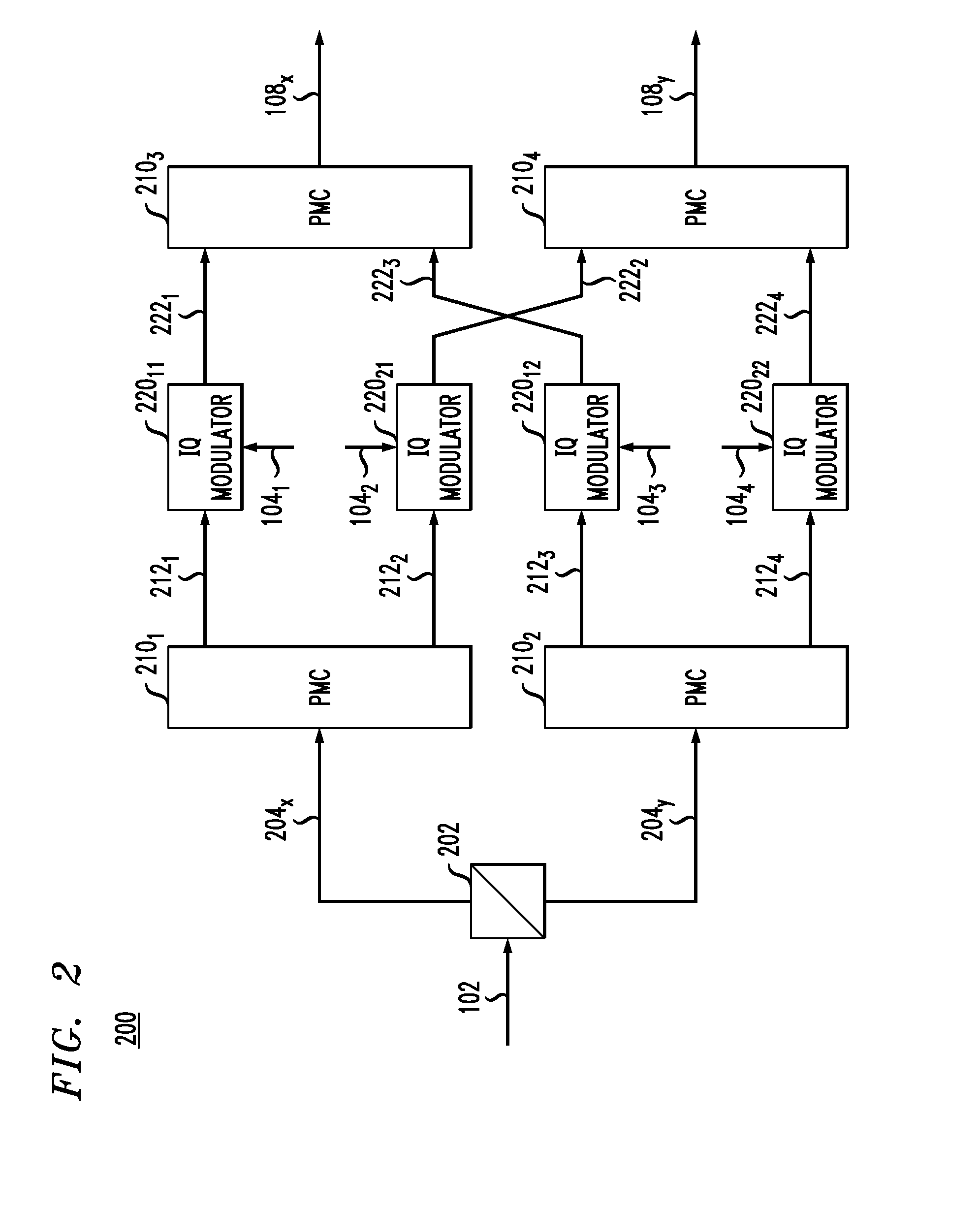
Generation of an optical local-oscillator signal for a coherent-detection scheme
An optical receiver having an optical IQ modulator configured to generate an optical local-oscillator (OLO) signal for optical homodyne detection of an optical input signal applied to the optical receiver. The optical receiver further has (i) a phase detector configured to generate an electrical measure of the phase difference between the OLO signal and a carrier wave of the optical input signal and (ii) a phase-lock loop configured to drive the optical IQ modulator using the electrical measure. In an embodiment, the phase detector is configured to generate the electrical measure using both I and Q components of the homodyne-detected signal and in a manner that enables the optical receiver to be compatible with the M-QAM modulation format.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Distributed cable modem termination system
ActiveUS8311412B2Highly software configurableEasily saturatedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFiberQam modulation
Distributed CMTS device for a HFC CATV network serving multiple neighborhoods by multiple individual cables, in which the QAM modulators that provide data for the individual cables are divided between QAM modulators located at the cable plant, and remote QAM modulators ideally located at the fiber nodes. A basic set of CATV QAM data waveforms may be transmitted to the nodes using a first fiber, and a second set of IP / on-demand data may be transmitted to the nodes using an alternate fiber or alternate fiber frequency, and optionally other protocols such as Ethernet protocols. The nodes will extract the data specific to each neighborhood and inject this data into unused QAM channels, thus achieving improved data transmission rates through finer granularity. A computerized “virtual shelf” control system for this system is also disclosed. The system has high backward compatibility, and can be configured to mimic a conventional cable plant CMTS.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Additional modulation information signaling for high speed downlink packet access
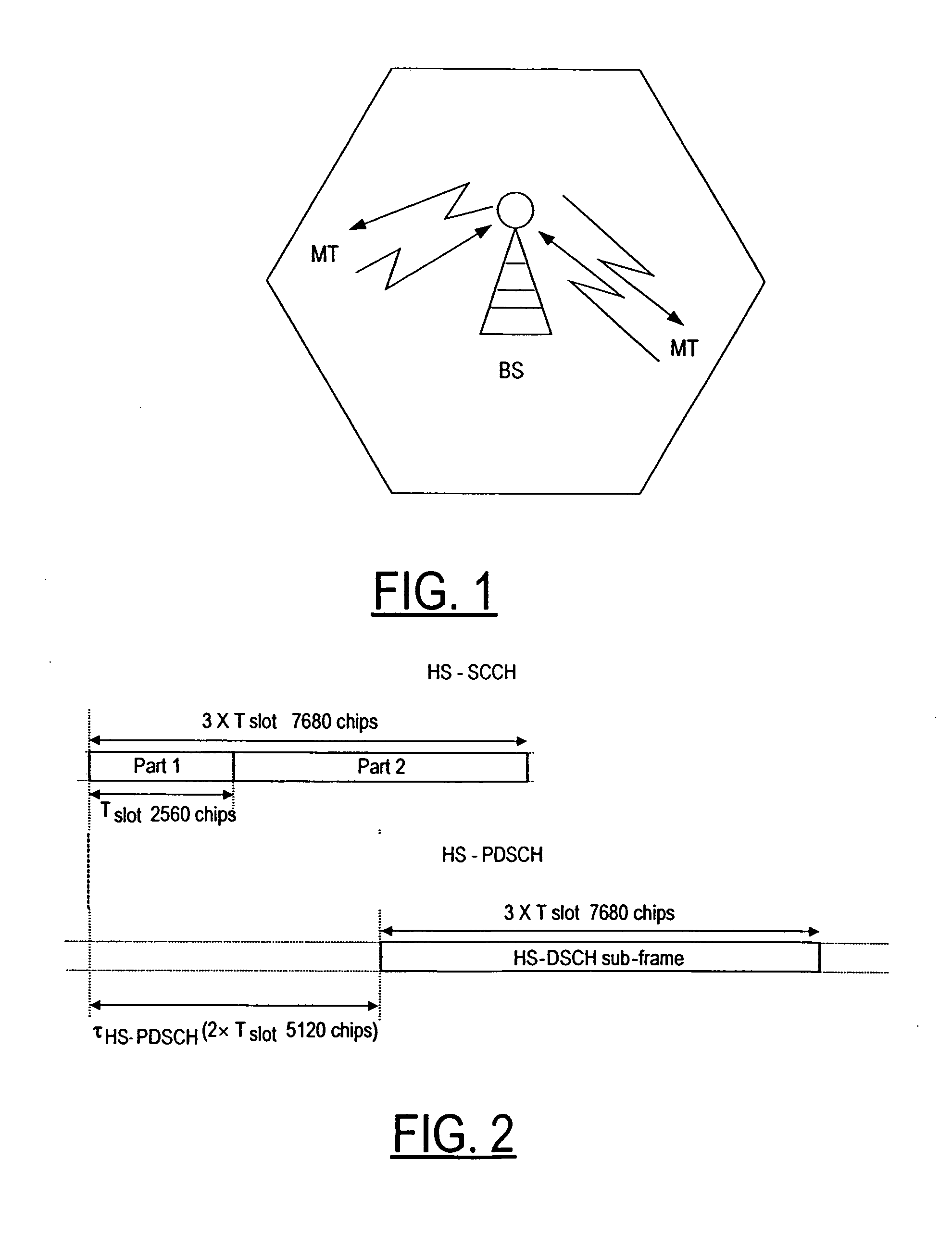
ActiveUS20080117873A1Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer hardwareQam modulation
The modulation indication bit is interpreted as a QPSK / xQAM modulation indication if both the user equipment and the serving cell support 64QAM modulation, such that if QPSK is indicated, the 7 code-set information bits in the HS-SCCH part 1 structure is interpreted as is presently interpreted today as defined in the 3GPP release 5 specification, and if xQAM is indicated, the 7 code-set information bits in the HS-SCCH part 1 structure is interpreted such that only 6 bits are used for code information and one bit is stolen for use for the 16QAM / 64QAM selection.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for determining the distance between a base station and a mobile object, in addition to a base station and identification system for a method of this type
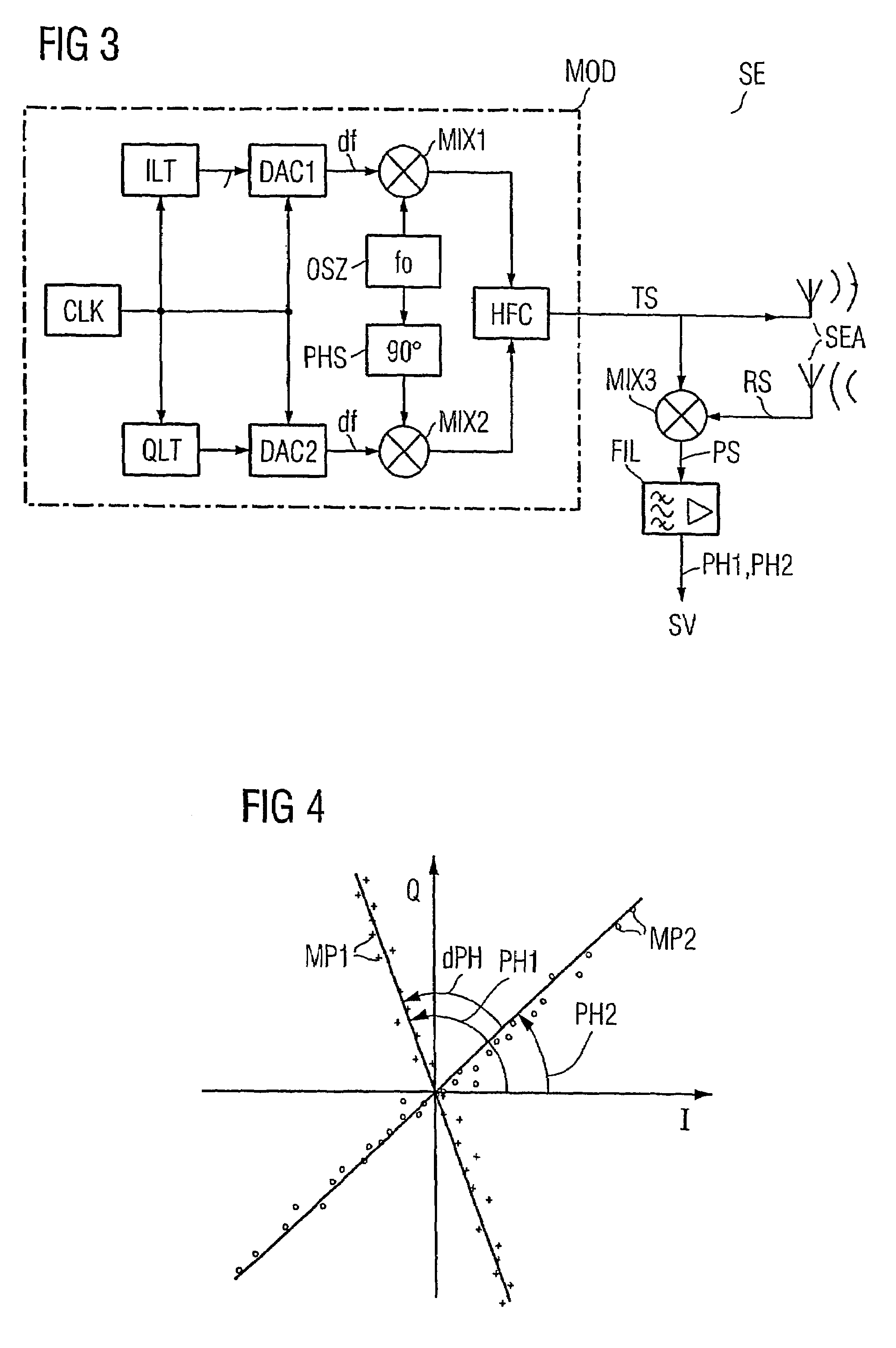
InactiveUS7205931B2Measurement time is requiredEasy to measureRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQam modulationCarrier signal
A method for determining the distance between a base station (SLG) and a mobile object (DT1–DT3). A HF carrier frequency and an offset frequency (df) are predetermined for a QAM modulation. The HF carrier frequency is increased and decreased by the offset frequency in sequence over time in such a way that the HF carrier base frequencies (fo+df, fo−df) resulting in an HF carrier signal (TS) thus modulated exhibit an identical phase when the frequency is changed. The HF carrier signal is subsequently transmitted and simultaneously mixed (MIX) with an HF carrier signal (RS) that has been backscattered by the mobile object to obtain a carrier phase signal (PS). The corresponding carrier phase (PH1, PH2) for the two HF carrier base frequencies is determined in sequence over time. The difference (dPH) between these phases is used to calculate the distance between the base station and the respective mobile object.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Hybrid polar/cartesian digital modulator
ActiveUS7532679B2Reconfigurable analogue/digital convertersAnalogue conversionControl powerQam modulation
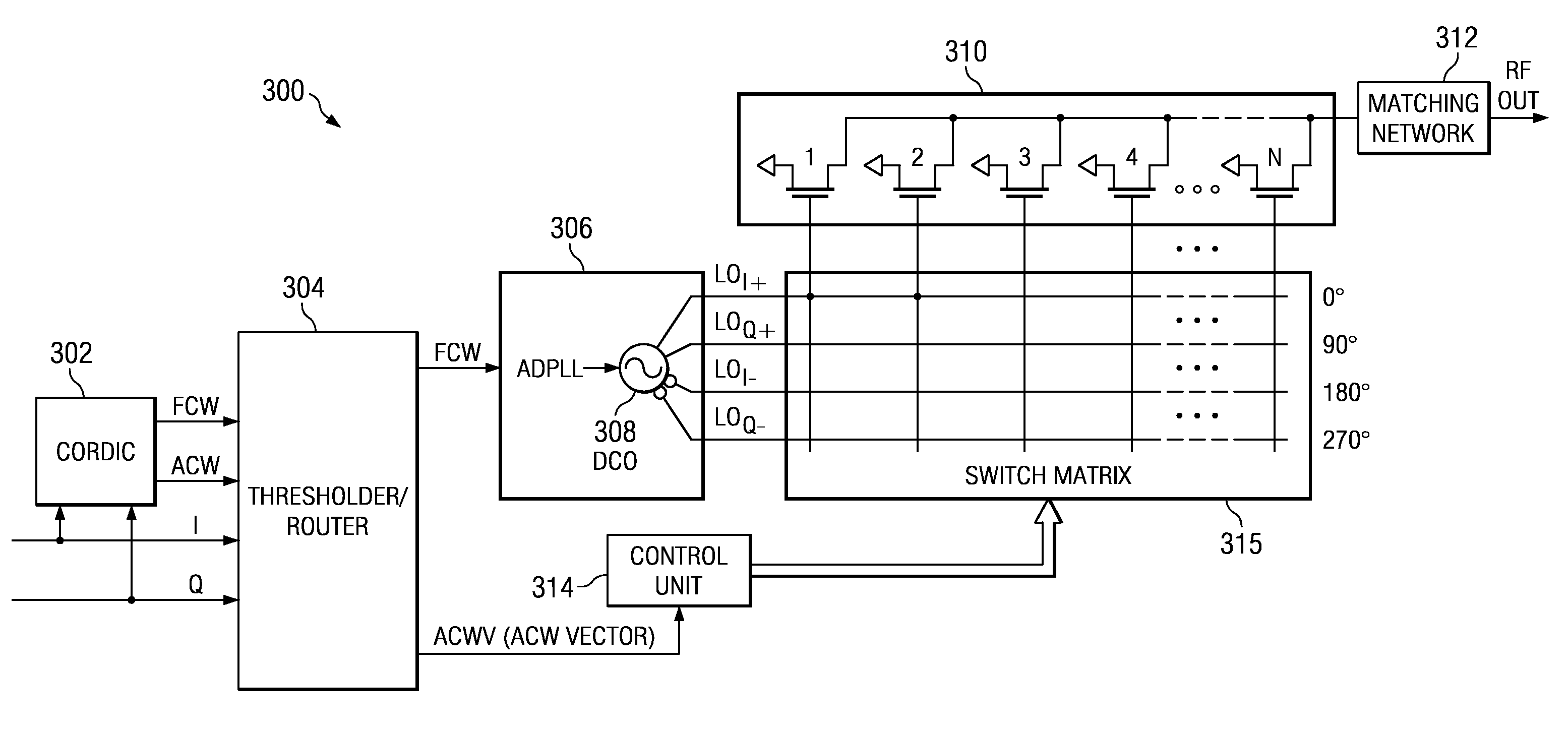
A novel apparatus and method for a hybrid Cartesian / polar digital QAM modulator. The hybrid technique of the present invention utilizes a combination of an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) that features a wideband frequency modulation capability and a digitally controlled power amplifier (DPA) that features interpolation between 90 degree spaced quadrature phases. This structure is capable of performing either a polar operation or a Cartesian operation and can dynamically switch between them depending on the instantaneous value of a metric measured by a thresholder / router. In this manner, the disadvantages of each modulation technique are avoided while the benefits of each are exploited.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Distributed cable modem termination system with software reconfiguable mac and phy capability
ActiveUS20120291084A1Highly software configurableEasily saturatedOptical transmission adaptationsTwo-way working systemsQam modulationControl system
Distributed and highly software reconfigurable CMTS (CMRTS) device, based on MAC and PHY units with FPGA and DSP components, for a HFC CATV network. The various CATV RF modulators, such as QAM modulators, may be divided between QAM modulators located at the cable plant, and remote QAM modulators ideally located at the fiber nodes. A basic set of CATV QAM data waveforms may optionally be transmitted to the nodes using a first fiber, and a second set of IP / on-demand data may be transmitted to the nodes using an alternate fiber or alternate fiber frequency, and optionally using other protocols such as Ethernet protocols. The nodes will extract the data specific to each neighborhood and inject this data into unused QAM channels, thus achieving improved data transmission rates through finer granularity. A computerized “virtual shelf” control system for managing and reconfiguring the FPGA and DSP based CMTRS units is also disclosed.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
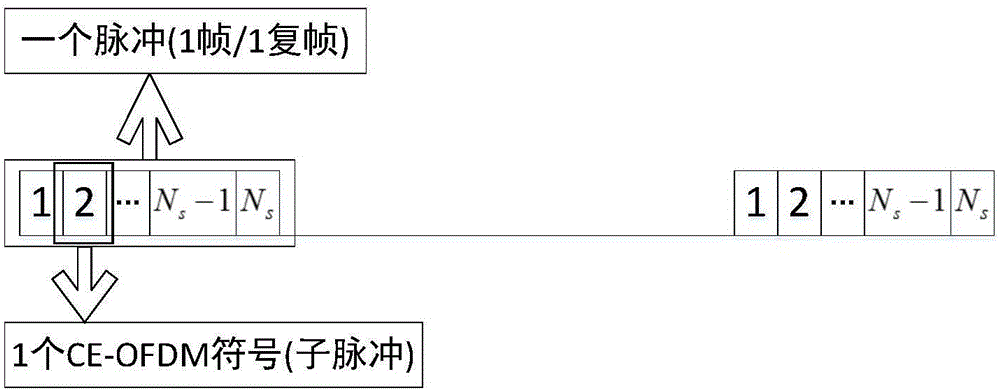
CE-OFDM (Constant Envelope Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) based radar communication integration system
ActiveCN106249231AIncrease transfer rateSolve the problem of highRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQam modulationMultiple signal classification
The invention belongs to the field of radar technologies, and relates to a CE-OFDM (Constant Envelope Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) based radar communication integration system. The invention is a CE-OFDM based super-resolution radar communication integration scheme which is provided on the basis of a traditional OFDM radar communication integration scheme, compensated through communication information, and capable of improving the effective data transmission rate and solving a problem that the PAPR of OFDM signals is too high. A transmitting terminal firstly turns data to be transmitted into CE-OFDM symbol frames through QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) and phase modulation, and a single pulse in a pulse repetition period is replaced by using a CE-OFDM symbol, so that the data transmission rate is improved, and the problem that the PAPR of transmitted signals is too high is solved. At a receiving terminal, received waveform pulses are demodulated, an inverse process of the transmitting process of the CE-OFDM system is carried out on the signals, and data can be demodulated; and the transmitting waveform is known, pulse compression processing is carried out on received echo waves, and super-resolution estimation for the distance and the speed of a target can be accomplished through decorrelation processing and an MUSIC algorithm after information compensation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Cost-effective multi-channel quadrature amplitude modulation
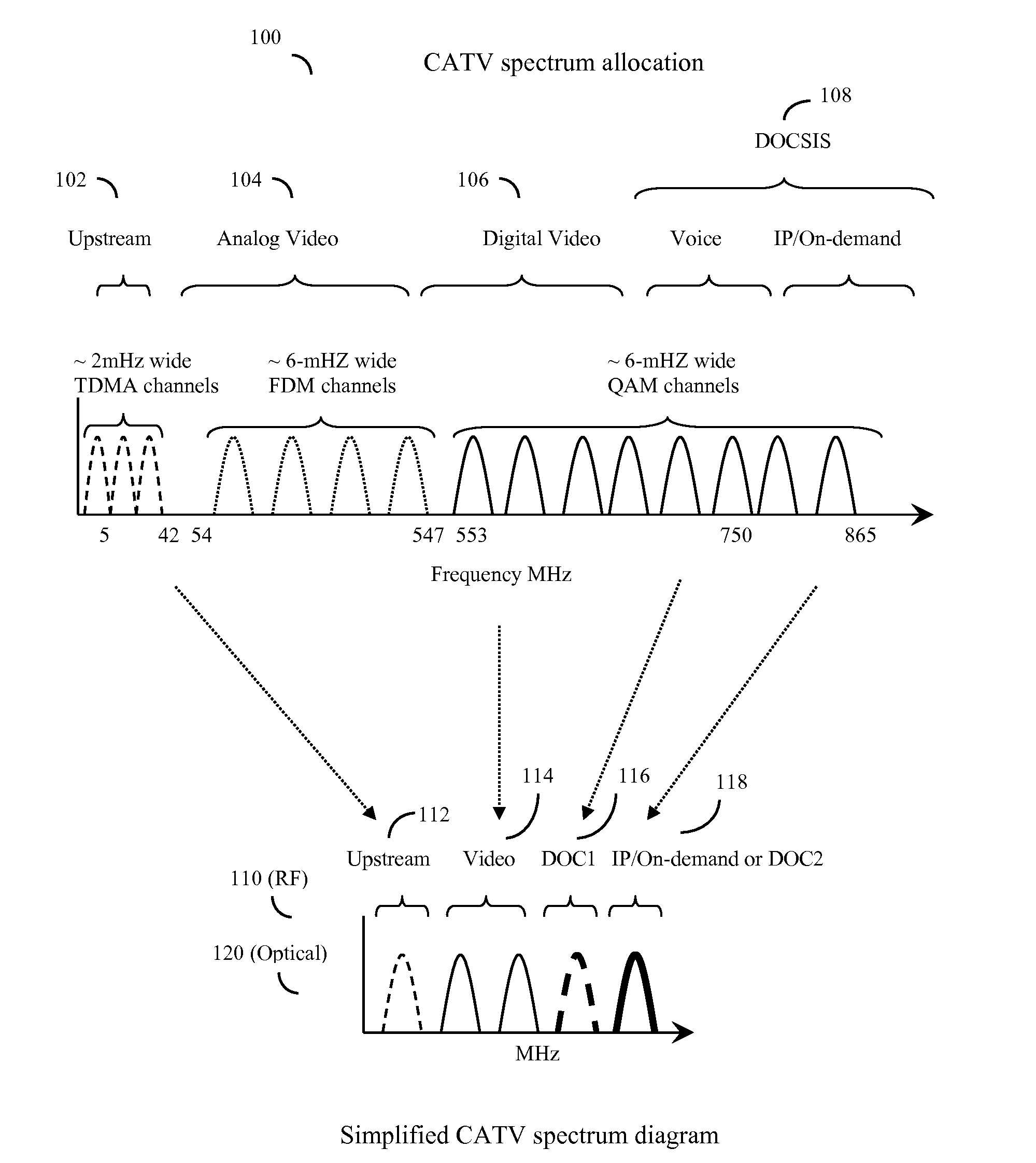
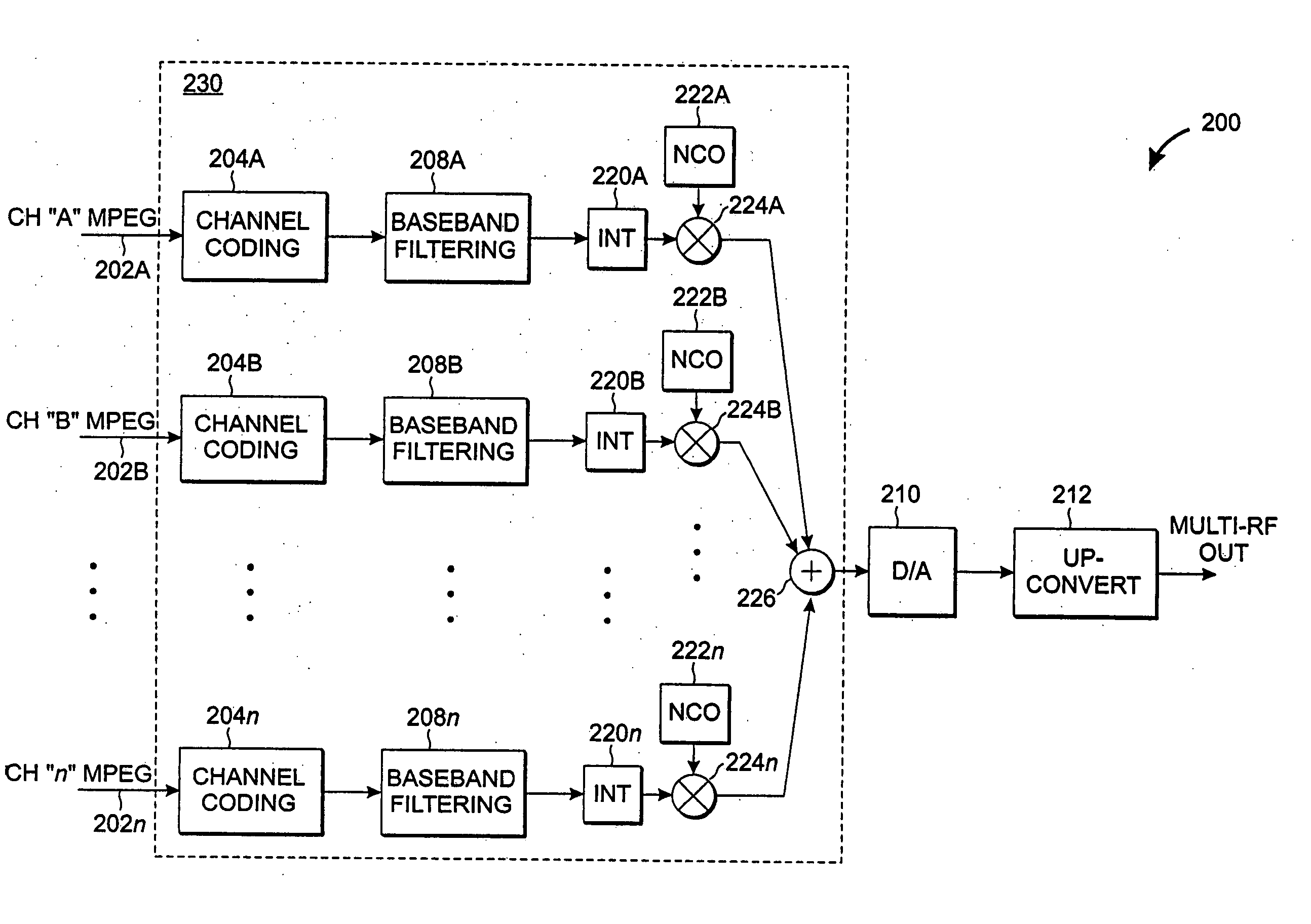
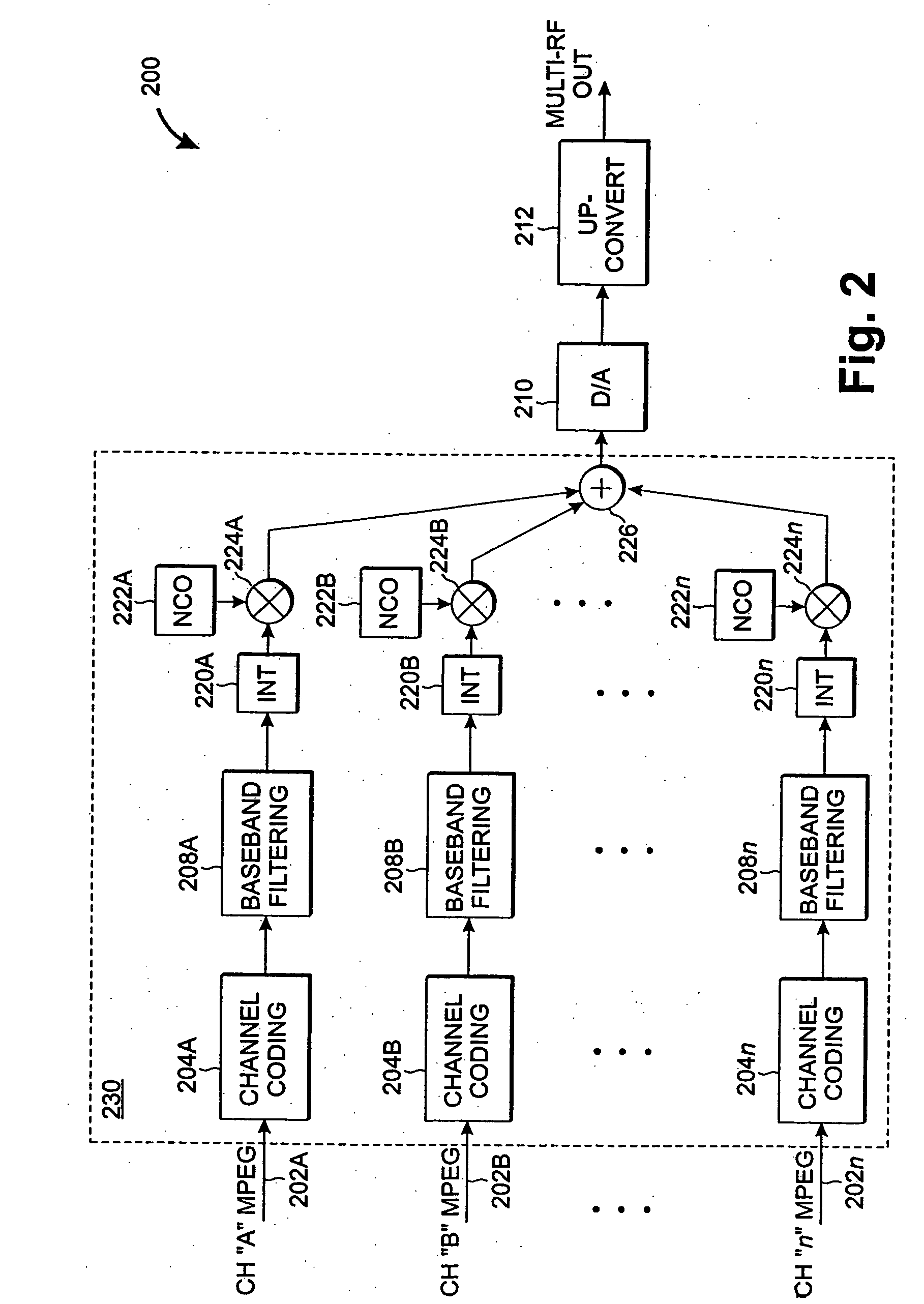
A highly-efficient, cost-effective technique for multi-channel QAM modulation is described. The technique employs an inverse fast-Fourier transform (IFFT) as a multi-channel modulator. QAM encoding expresses QAM symbols as constellation points in the complex plane such that each QAM symbol represents a specific phase and amplitude of a carrier frequency to which it is applied. In multi-channel systems, the carrier frequencies are generally uniformly spaced at a channel-spacing frequency (6 MHz, for digital cable systems in the United States). The IFFT accepts a set of complex frequency inputs, each representing the complex frequency specification (i.e., phase and amplitude) of a particular frequency. The inputs are all uniformly spaced, so assuming that the IFFT is sampled at a rate to provide the appropriate frequency spacing between its frequency-domain inputs, the IFFT will produce a time domain representation of QAM symbols applied to its various inputs modulated onto carriers with the desired channel separation. Since the channel spacing and the symbol rate are different due to excess channel bandwidth, interpolation is used to rectify the difference. An efficient scheme for combining this interpolation with baseband filtering and anti-imaging filtering is described.
Owner:RGB NETWORKS
Modulation Processing Method And Device
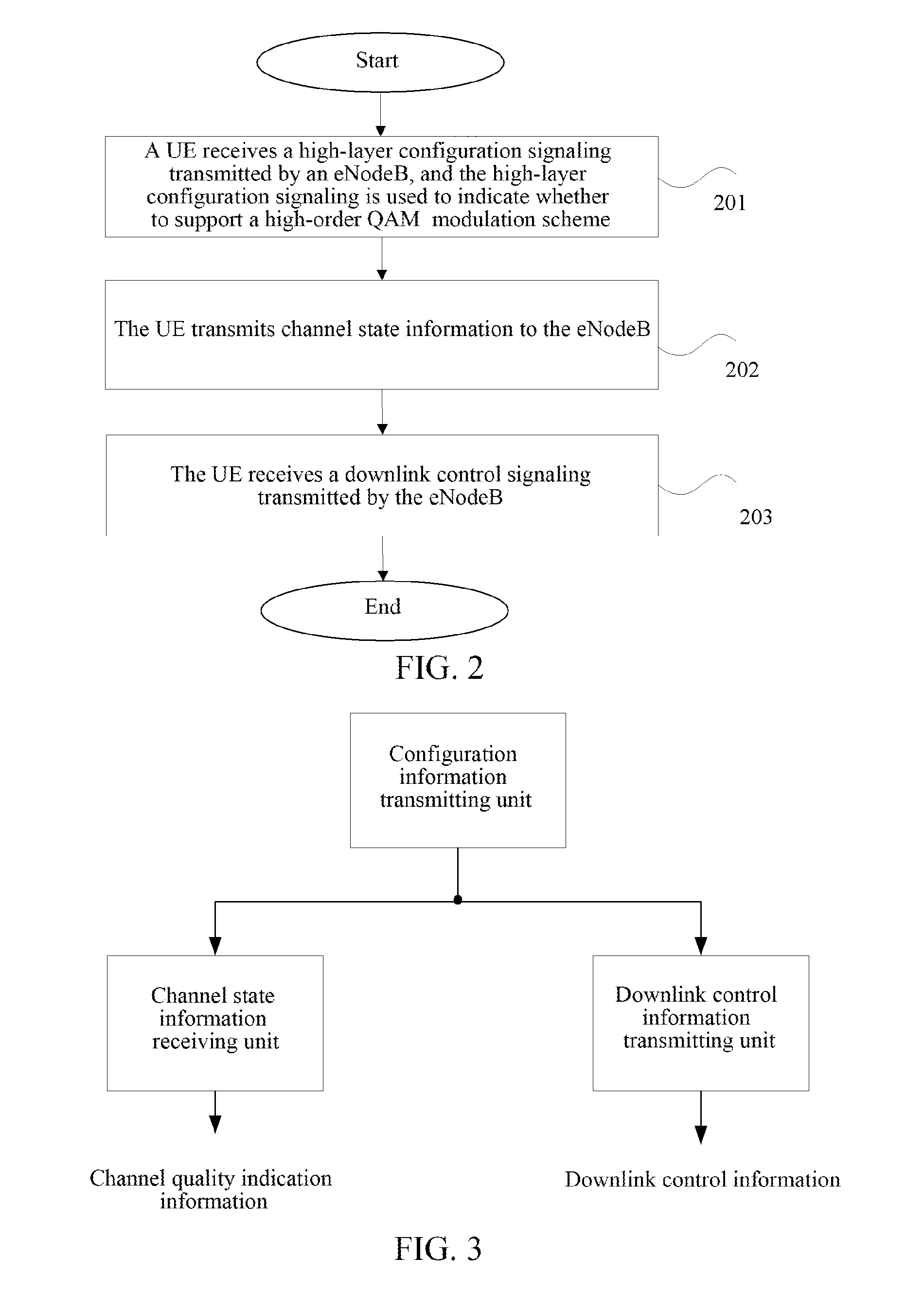
ActiveUS20150372784A1Increase system frequency efficiencyIncrease data peak rateSpatial transmit diversitySignalling characterisationFrequency spectrumWireless transmission
A modulation processing method, a UE and a base station are disclosed; wherein, the base station transmits a high-layer configuration signaling to the UE, wherein the high-layer configuration signaling is used to indicate whether to support a high-order Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) modulation scheme, wherein the high-order QAM modulation scheme is a modulation scheme of M QAM, wherein M is a number greater than 64. With a high-layer configuration signaling indicating whether to support the high-order QAM, the high-order QAM modulation scheme is supported on the basis of being compatible with existing wireless transmission networks, and the peak data rate and the spectral efficiency are improved
Owner:ZTE CORP
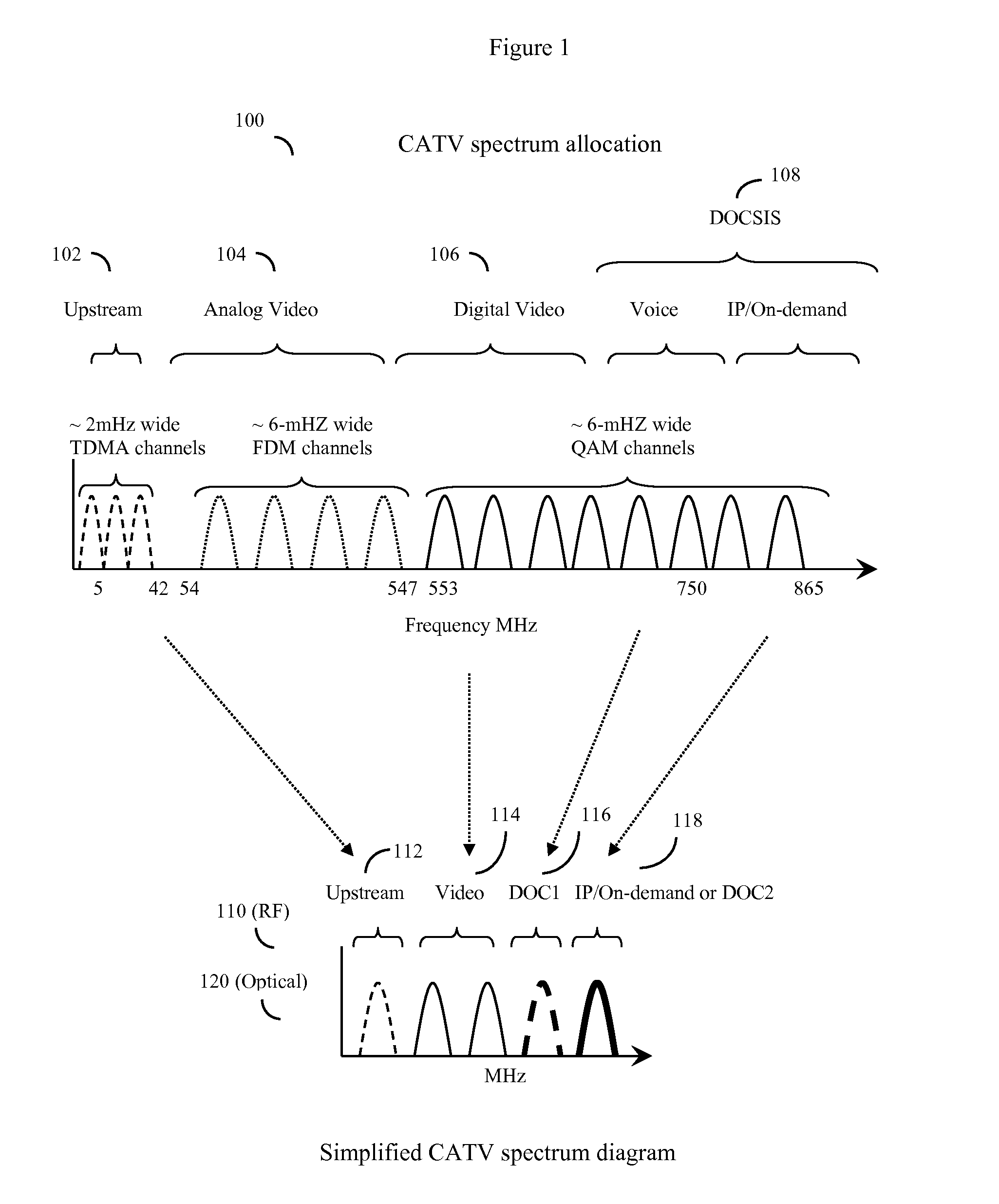
Hfc cable system with wideband communications pathway and coax domain nodes
ActiveUS20120110631A1Achieve backward compatibilityImprove data carrying capacityBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsDigital dataQam modulation
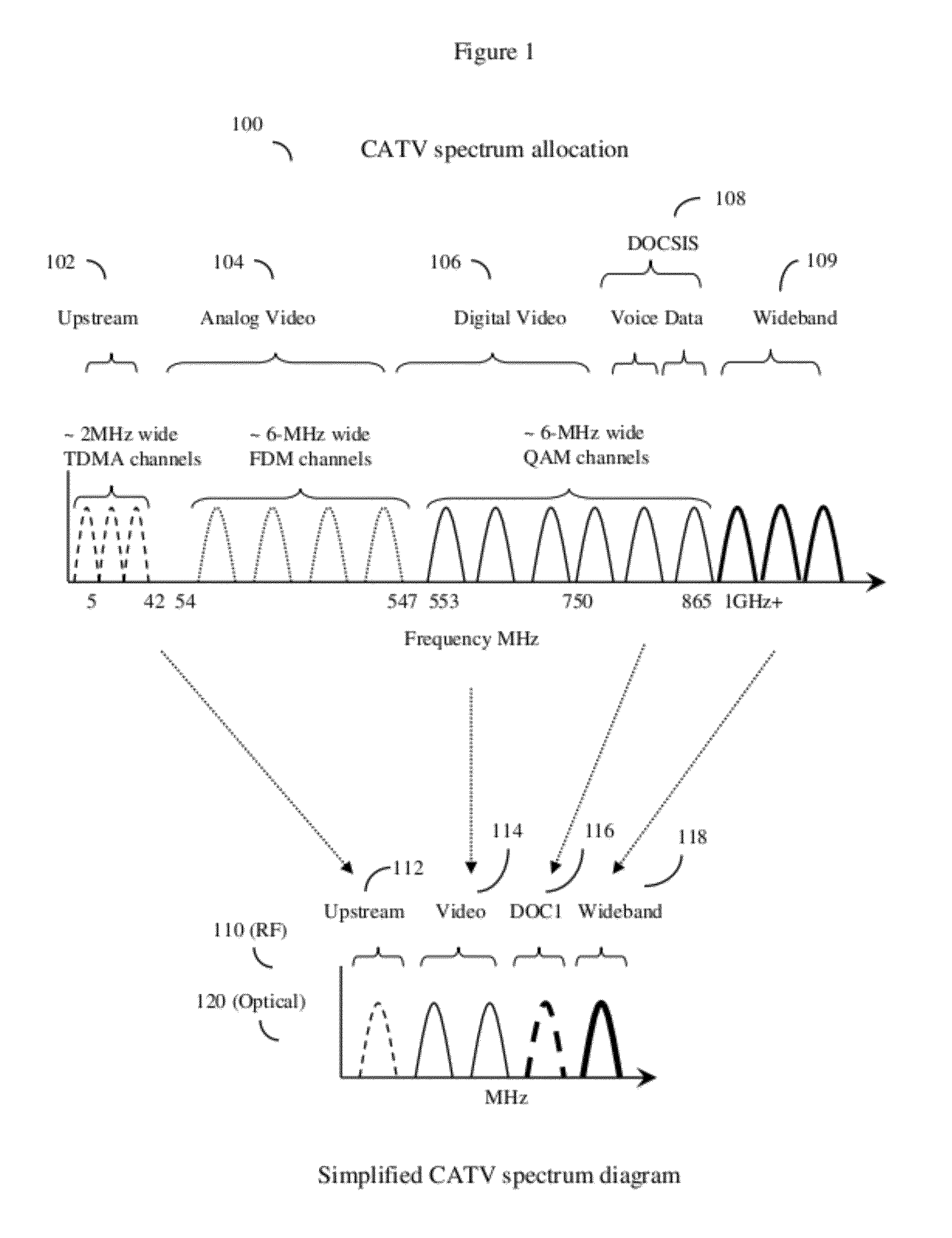
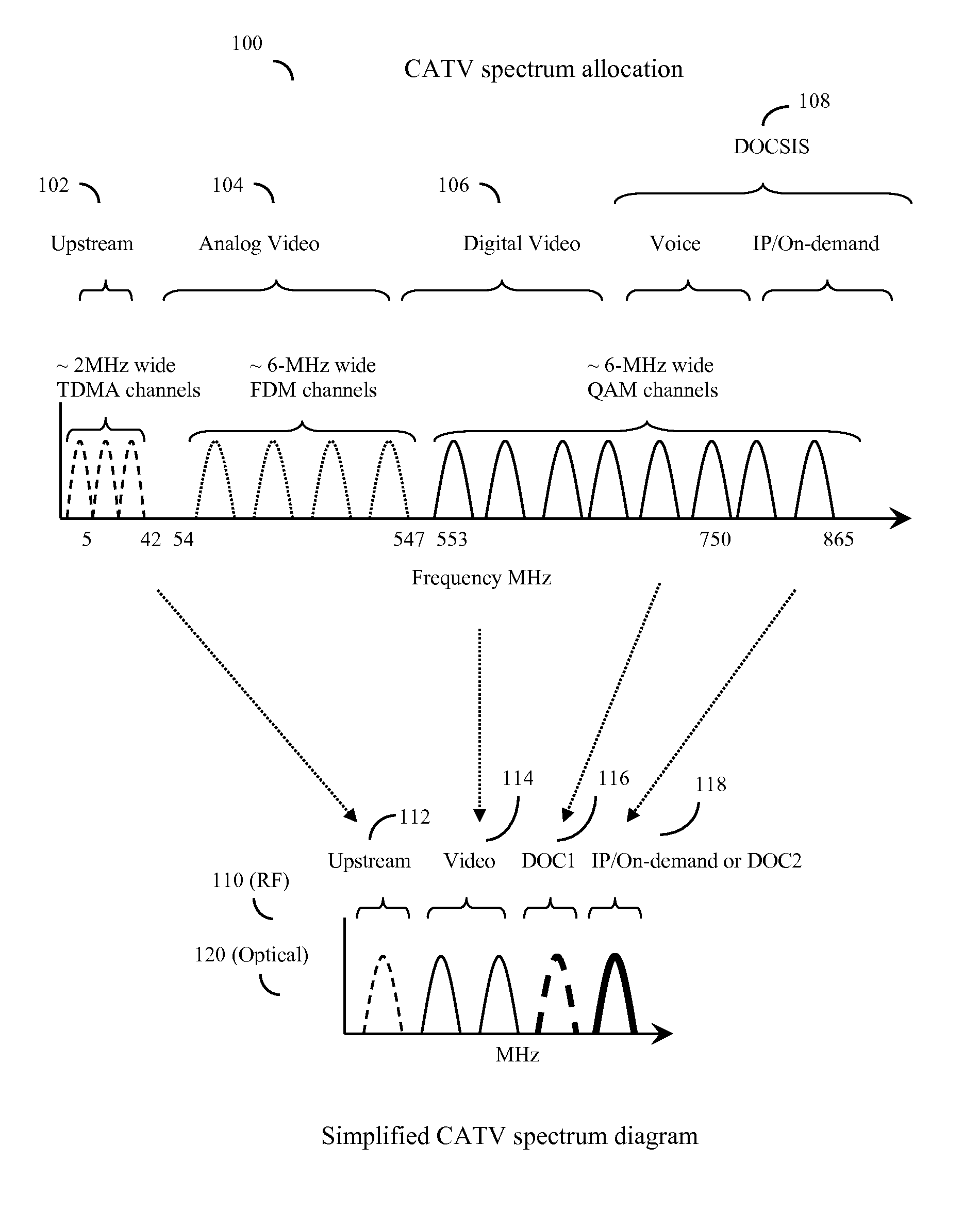
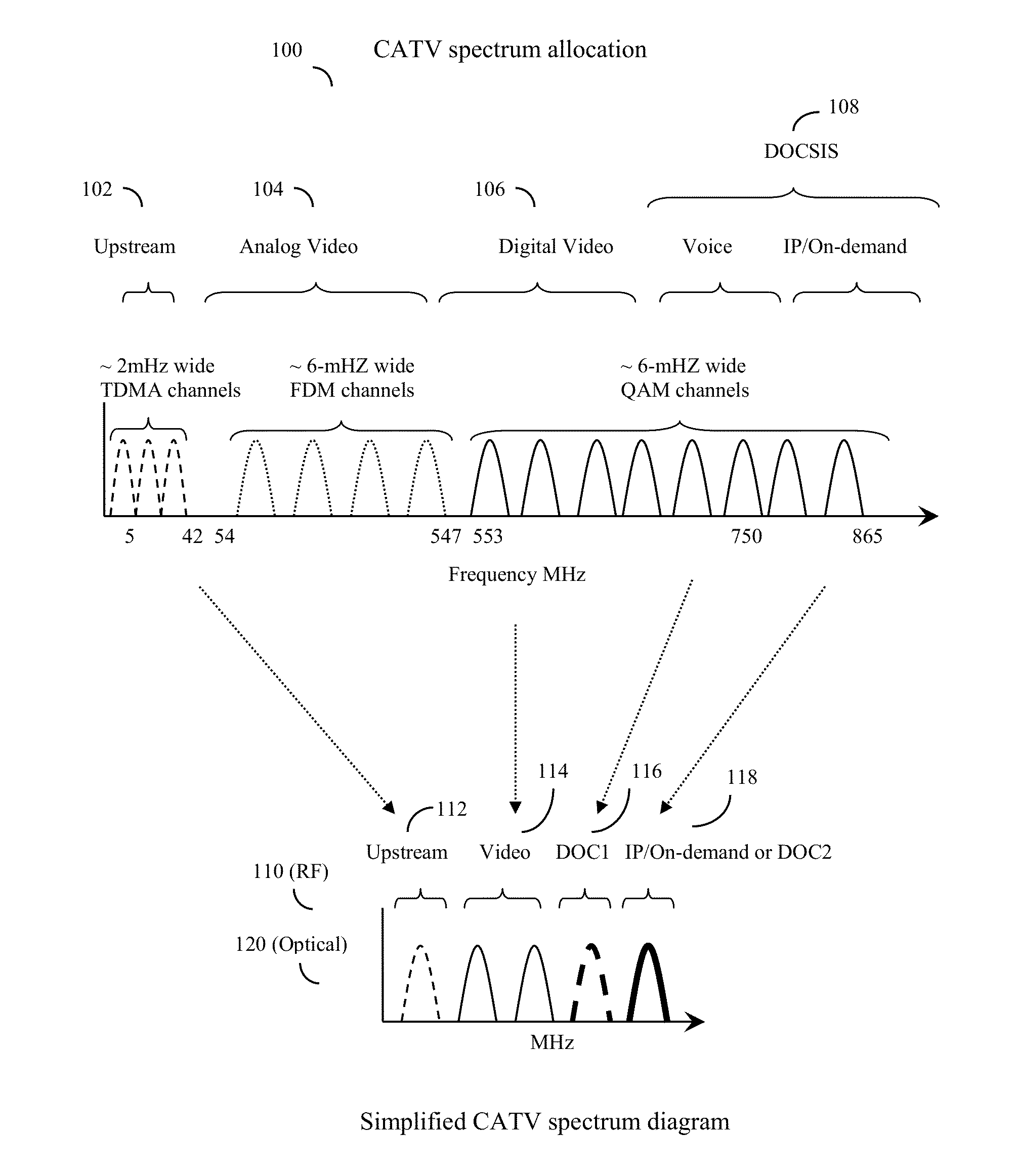
System and method to extend the data carrying capacity of a hybrid fiber cable (HFC) network by adding wideband RF signal capability above 1 GHz, and replacing at least some CATV active devices such as amplifiers with a new type of Coax Domain Node (CDN) device that acts to segment the CATV cable portion of the HFC network into a series of smaller domains. The CDN generally filter RF signals from 5-865 MHz, while amplifying and passing RF signals over 1 GHz. Upstream capability is enhanced because the CDN intercept 5-42 MHz upstream signals from each domain and convert to 1 GHz+ signals. Downstream capability is also enhanced because the CDN can take efficiently encoded 1 GHz+ digital data, QAM modulate it, and locally inject into each domain without crosstalk between domains. The system pushes data management and downstream from the head end to the CDN, creating more throughput.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Timing recovery device and method for telecommunications systems
InactiveUS6856655B1Avoid driftingModulated-carrier systemsSynchronisation error detectionQam modulationComputer science
A timing recovery device for CAP / QAM modems includes an equalizer filter designed to monitor the movement of the filter coefficients within a memory buffer and to adjust the relative position of the filter coefficients within the memory buffer so that the coefficients remain substantially centered within the buffer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Hybrid all digital fiber to CATV cable system and method
ActiveUS20140137177A1Low costEasy to sortBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsFiberCarrying capacity
Producing advanced HFC CATV cable systems while easing the burden of backward compatibility. The system improves CATV data carrying capacity by moving RF QAM modulators from the cable head end to various individually or group addressed optical fiber nodes supplying neighborhood CATV cables, and sending data from the cable head IP backbone to the nodes over optical fiber as IP data packets. For high backward compatibility, the system digitizes legacy RF waveforms, or demodulates legacy QAM waveforms to QAM symbols, also transmits these over the optical fiber as IP data packets, and then reconstitutes back to original waveforms as needed. The system is thus able to easily handle legacy NTSC, FM, QPSK waveforms and do partial (QAM symbol level) compression of legacy QAM waveforms to and from multiple nodes without requiring additional optical fiber wavelengths. The system may use non-standard upstream / downstream CATV frequency splits, filter bank receivers, and FPGA / DSP / ASIC methods.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Virtual ccap cable modem termination system with software reconfiguable mac and phy capability
ActiveUS20140150047A1Highly software configurableAvoid interferenceTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionModem deviceControl system
Distributed and software reconfigurable remote CMTS (CMRTS) device, based on MAC and PHY units with FPGA and DSP components, for a HFC CATV network. The various CATV RF modulators, such as QAM modulators, may be located entirely at the fiber nodes if desired. Although a basic set of CATV QAM data waveforms may optionally be transmitted to the nodes using a first fiber, in a preferred embodiment, all data may be transmitted to the nodes using other protocols such as Ethernet protocols. The nodes will extract the data specific to each neighborhood and inject this data into the cable portion of the system as RF waveforms, such as RF QAM channels. A computerized “virtual shelf” control system for managing and reconfiguring the FPGA and DSP based CMTRS units, as well as a new type of edge router based all-digital virtual head end (virtual converged cable access platform) is also disclosed.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
Mapping method of code word with QAM modulation
ActiveUS7277498B2Large weightImprove error resistanceData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionCommunication qualityCommunications system
In the code word mapping operation of a radio communication system, mapping patterns are provided for different S / N ratios, the code word bits produced from a coder are not equally assigned to multi-level modulation bits, but weighted according to the resistance of multi-level modulation bits to error before being assigned, and the mapping patterns are switched in accordance with S / N. Since the code word mapping method is updated so that the error rate can be always minimized according to the situations of a propagation path and S / N ratio, communication can be made with high communication quality.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Superposition coded modulation method based on subcarrier index modulation (SIM)-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)
InactiveCN104113393AFew overlaysReduce complexityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTechnology communicationTime domain
The invention relates to the technical field of communication anti-jamming, in particular to a superposition coded modulation (SCM) technology communication system, subcarrier index modulation (SIM) and related time domain detecting technologies. According to an SCM method based on SIM-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), ideas of SIM-OFDM and spatial modulation (SM) are used as reference, a part of a string of bit data is used for transmission, the other part of the string of bit data is used as indexing bits, and the indexing bits are respectively coded. During transmission in an OFDM system, particular subcarrier is selected for transmitting data according to the bit data after coding of the indexing bits. A maximum likelihood method is used at a receiving end to obtain soft information of the indexing bits, and the indexing bits are decoded. Compared with prior SCM methods, the SCM method based on the SIM-OFDM has the advantages that the SCM superposition layers are reduced, the complexity is reduced, and error rate performances can be maintained or even improved to a certain degree. Meanwhile, the SCM is used for replacing quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), and performances can be improved under the same transmission efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Cloud base station in fixed-mobile converged access network and operation method thereof
InactiveUS20140003819A1Low costModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionQam modulationCloud base
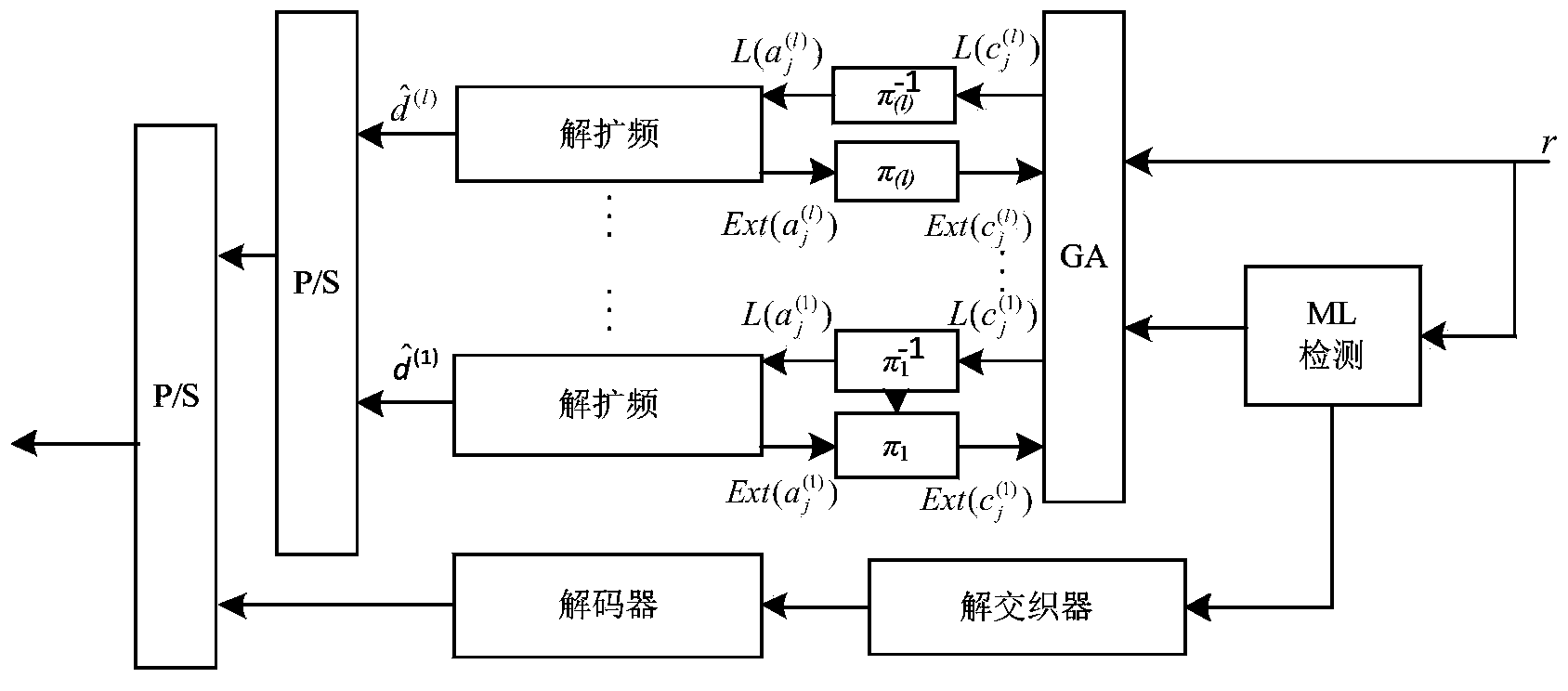
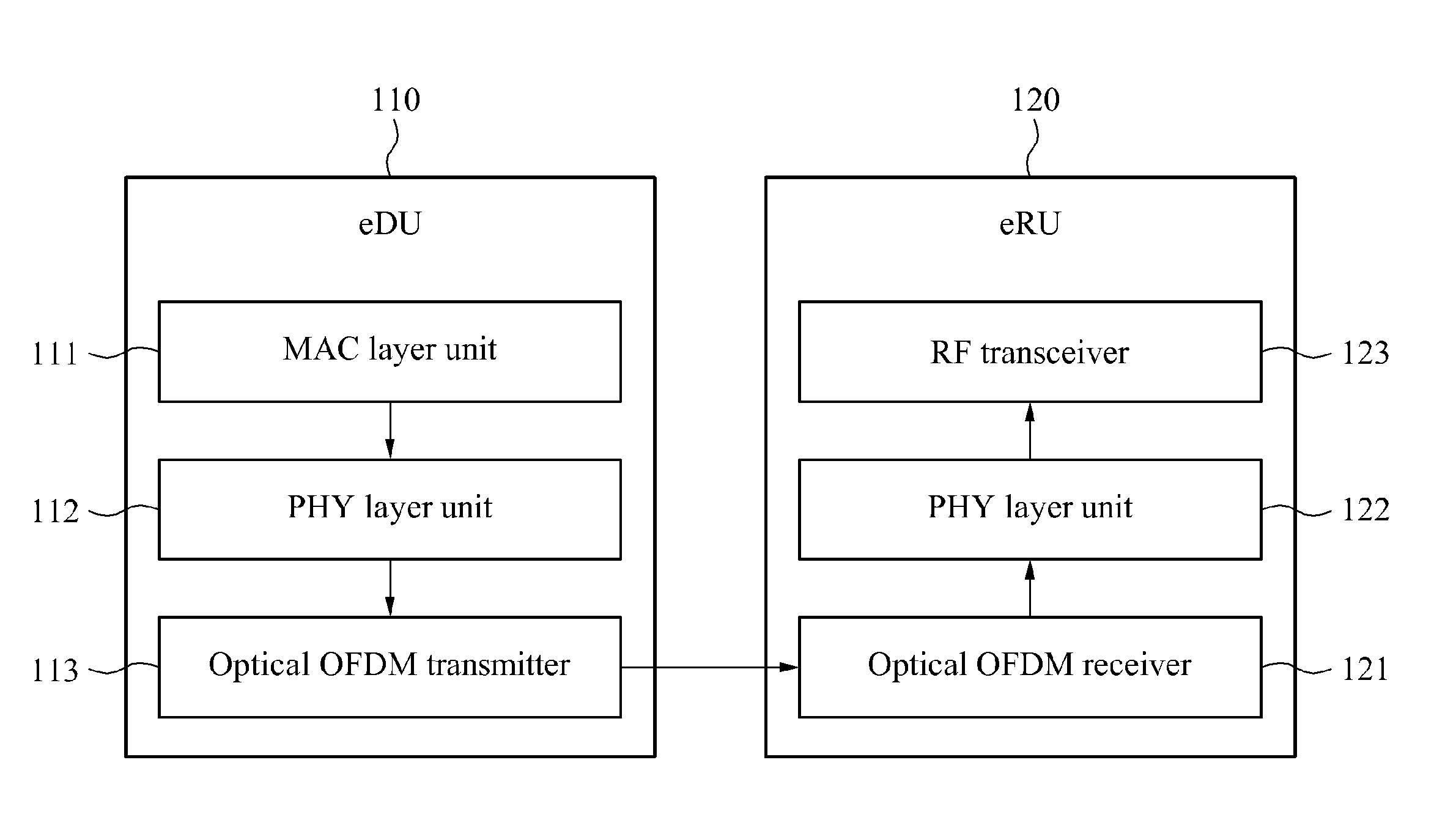
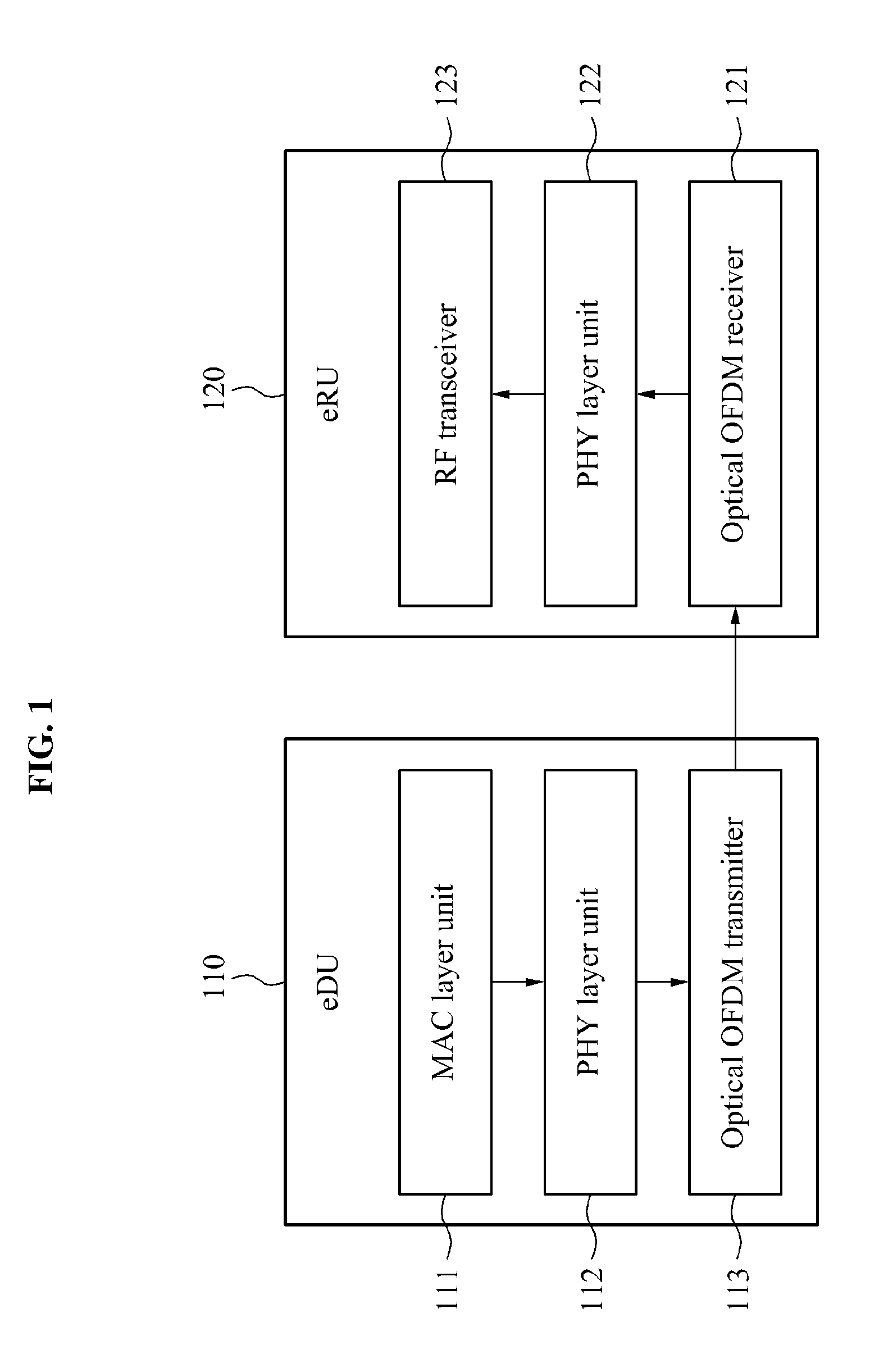
Disclosed is a cloud base station in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)-based fixed-mobile converged access network and an operation method thereof. The cloud base station may include a physical (PHY) layer unit to perform a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of a parallel signal received from a media access control (MAC) layer per subcarrier, and an optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) transceiver to transform the QAM modulated subcarriers into a time domain to generate an OFDM sample per subcarrier, add a cyclic prefix (CP) and control information to for operating an enhanced radio unit (eRU) to the OFDM sample per subcarrier to generate a downstream signal, and transmit the downstream signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
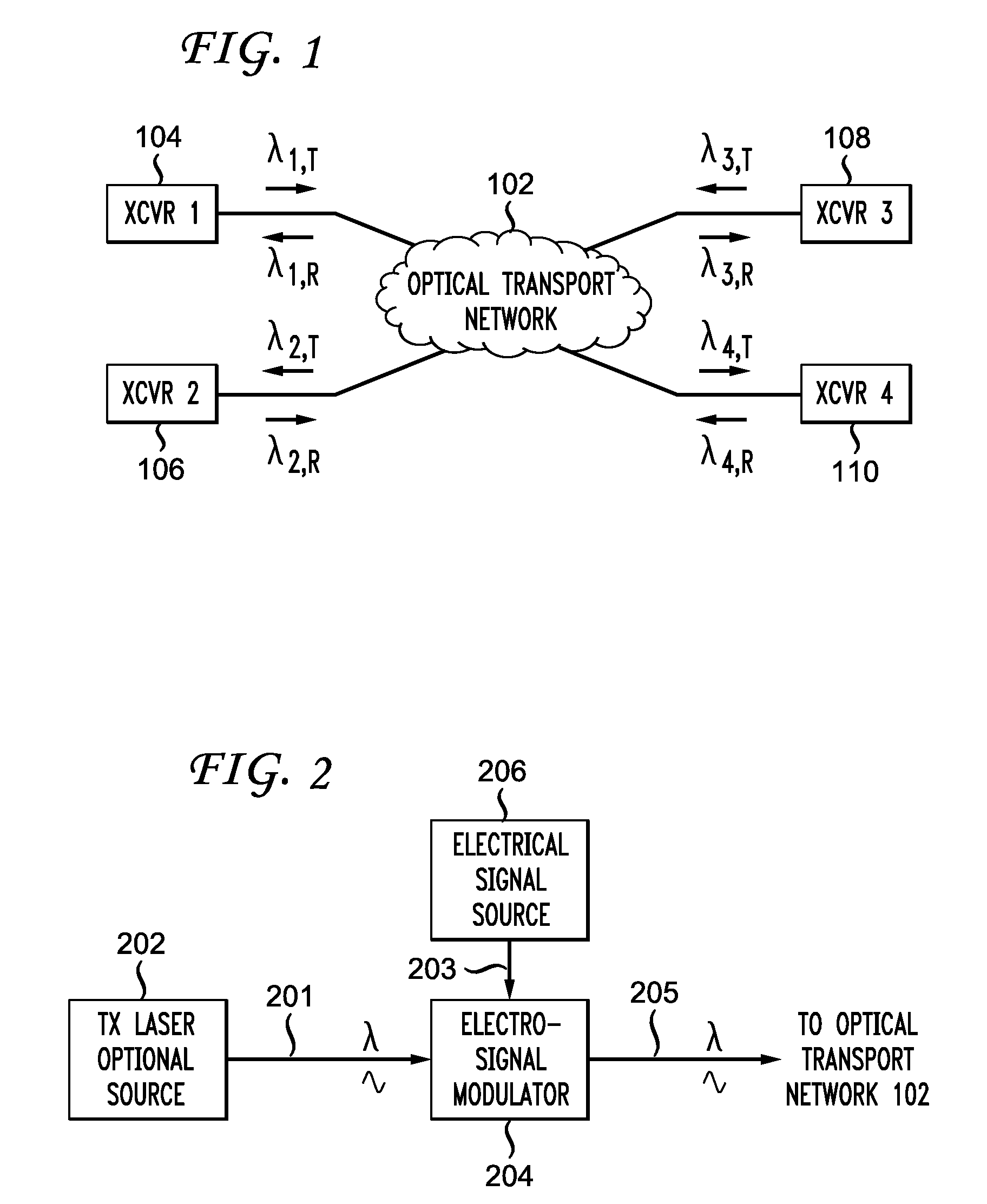
Through-timing of data transmitted across an optical communications system utilizing frequency division multiplexing
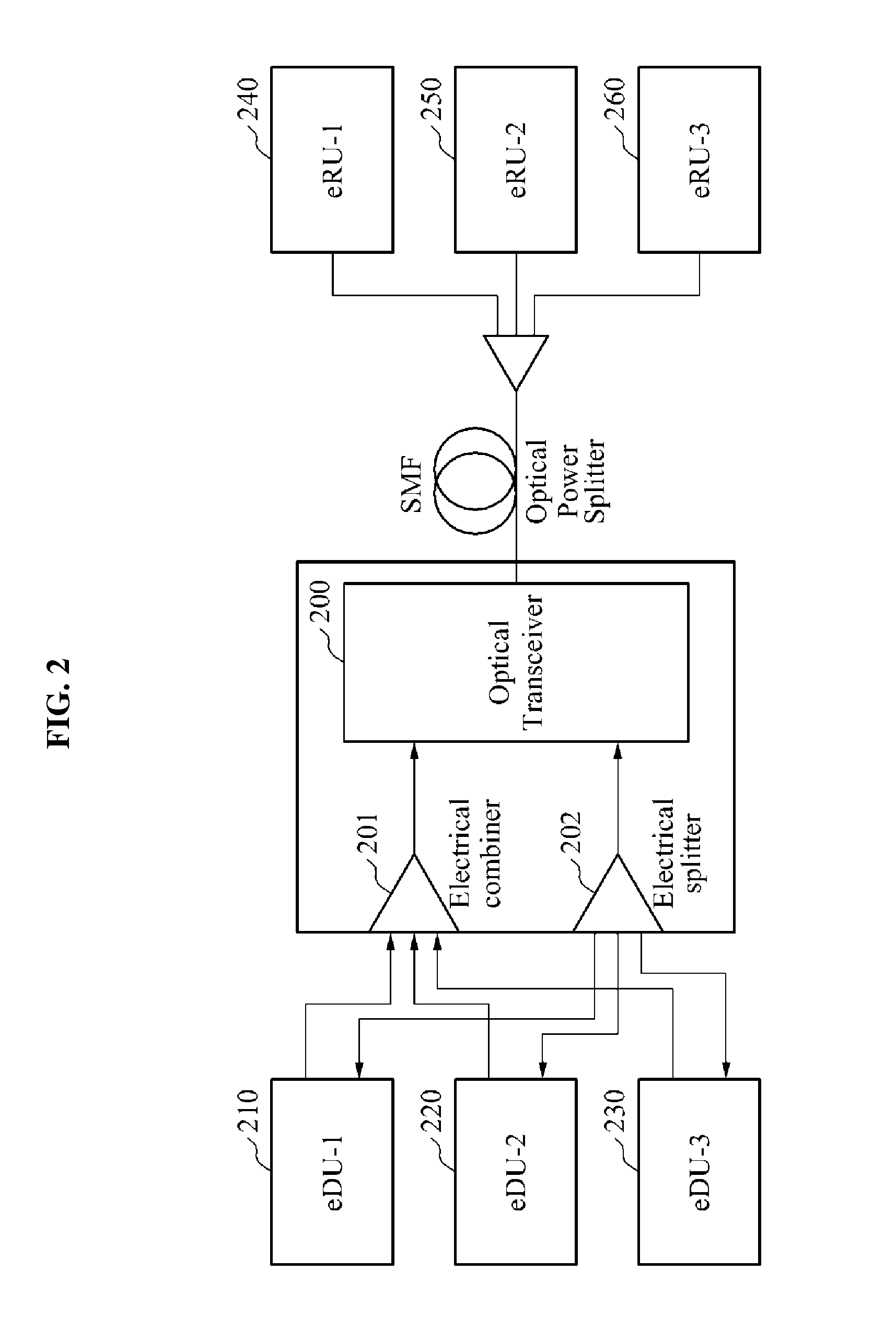
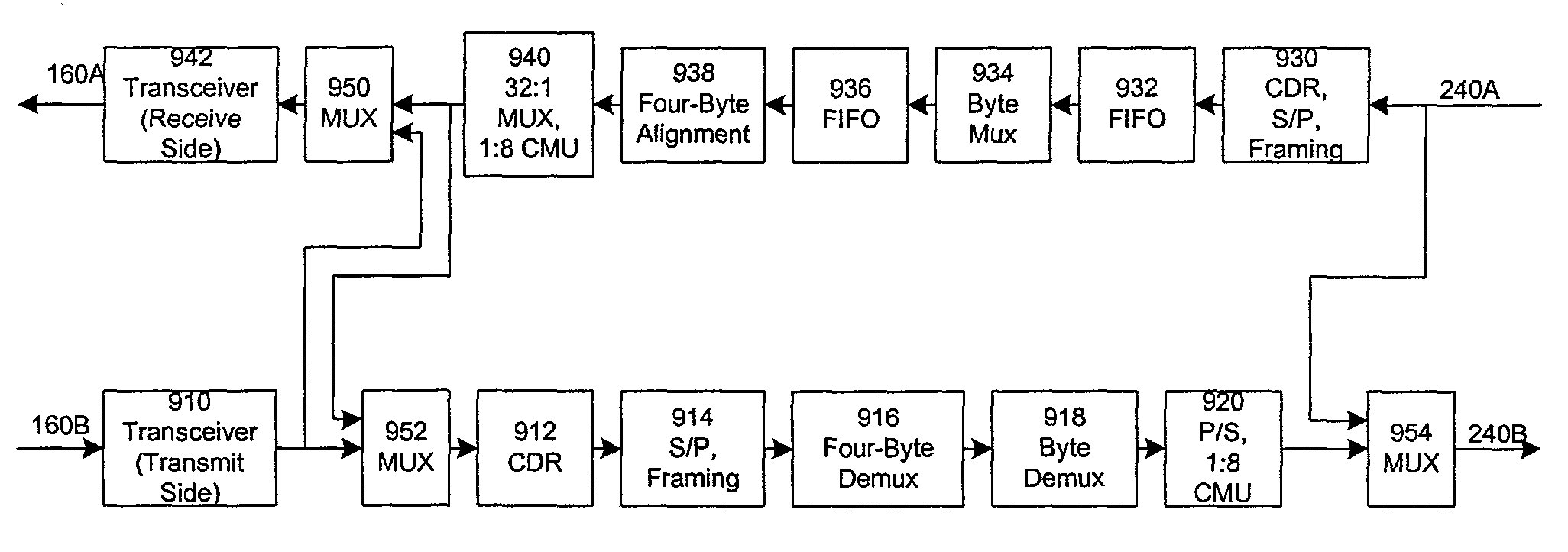
InactiveUS7154914B1Remove unwanted jitterRemove unwantedError preventionTime-division multiplexFiberLow speed
Data is transmitted across an optical fiber communications system by splitting an incoming tributary into multiple low-speed data channels, modulating each of these into a stream of symbols (e.g., by using QAM modulation) and then frequency division multiplexing a number of symbol streams into a single high-speed channel to be transmitted across a fiber. The receiver reverses this process. In order to preserve the jitter tolerance for the overal system, reference clocks are used to remove unwanted jitter in the timing of the system.
Owner:FAR NORTH PATENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com