Voice frequency signal frame loss compensation method and device
A compensation method and technology for speech and audio, applied in the field of speech and audio coding and decoding, can solve the problems of insignificant frame loss compensation effect in transform domain, high computational complexity and general compensation effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
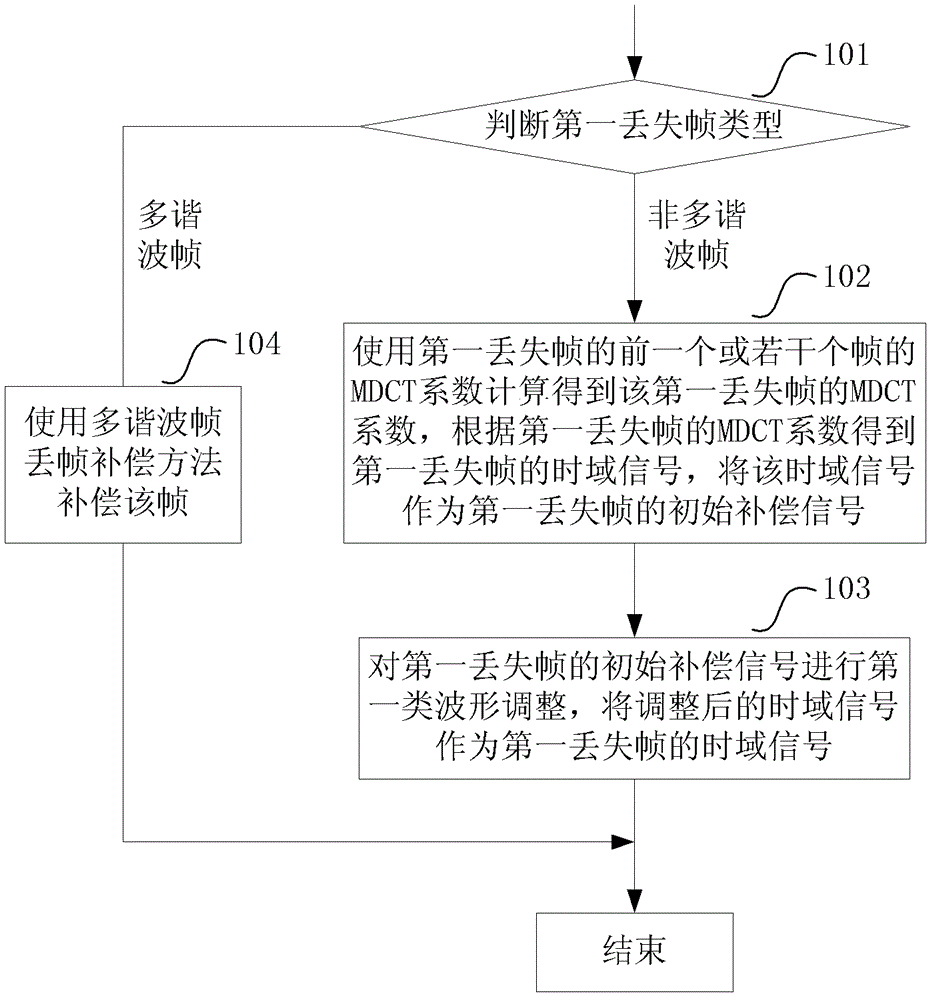
[0086] This embodiment describes the compensation method when the first frame following the correctly received frame is lost, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0087] Step 101: Determine the type of the first lost frame, and execute step 102 when the first lost frame is a non-multiharmonic frame, otherwise execute step 104;
[0088] Step 102: When the first lost frame is a non-multiharmonic frame, use the MDCT coefficients of one or several frames before the first lost frame to calculate the MDCT coefficients of the first lost frame, according to the MDCT coefficients of the first lost frame obtaining a time-domain signal of the first lost frame, and using the time-domain signal as an initial compensation signal of the first lost frame;
[0089]The following methods can be used to calculate the MDCT coefficient value of the first lost frame: for example, the weighted average of the MDCT coefficients of the previous frames can be used and the value after...
Embodiment 2
[0166] This embodiment describes the compensation method when more than two consecutive frames are lost immediately following the correctly received frame, as in Figure 6 shown, including the following steps:
[0167] Step 201: determine the type of the lost frame, and execute step 202 when the lost frame is a non-multiharmonic frame, otherwise execute step 204;
[0168] Step 202: When the lost frame is a non-multiharmonic frame, calculate the MDCT coefficient value of the current lost frame using the MDCT coefficients of one or several frames before the current lost frame, and then obtain the MDCT coefficient value of the current lost frame according to the MDCT coefficient of the currently lost frame A time-domain signal, using the time-domain signal as an initial compensation signal;
[0169] Preferably, the weighted average of the MDCT coefficients of the previous frames and the value after proper attenuation can be used as the MDCT coefficient of the current lost frame,...
Embodiment 3
[0176] This embodiment describes the recovery processing flow after frame loss when only one non-multi-harmonic frame is lost in the frame loss process. In the case of multiple frame loss or when the frame loss type is a multi-harmonic frame, this process operation is not required. Such as Figure 7 As shown, in this embodiment, the first lost frame is the first lost frame immediately following the correctly received frame, and the first lost frame is a non-multiharmonic frame, and the correctly received frame is immediately followed by the first lost frame A correctly received frame includes the following steps:
[0177] Step 301: Decoding to obtain the time domain signal of the correctly received frame;
[0178] Step 302: Adjust the estimated value of the pitch period used when compensating for the first lost frame. The specific adjustment methods include:
[0179] Note that the estimated value of the pitch period used when compensating for the first lost frame is T, and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com