Low-orbit satellite two-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method
A degree of freedom, low-orbit technology, applied in space navigation equipment, space navigation equipment, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the uncertainty of satellite attitude control system, the inability of solar wings to obtain energy, and the interruption of satellite work process. , to reduce the coupling effect, ensure the stability of the attitude, and reduce the management cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] In order to make the technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
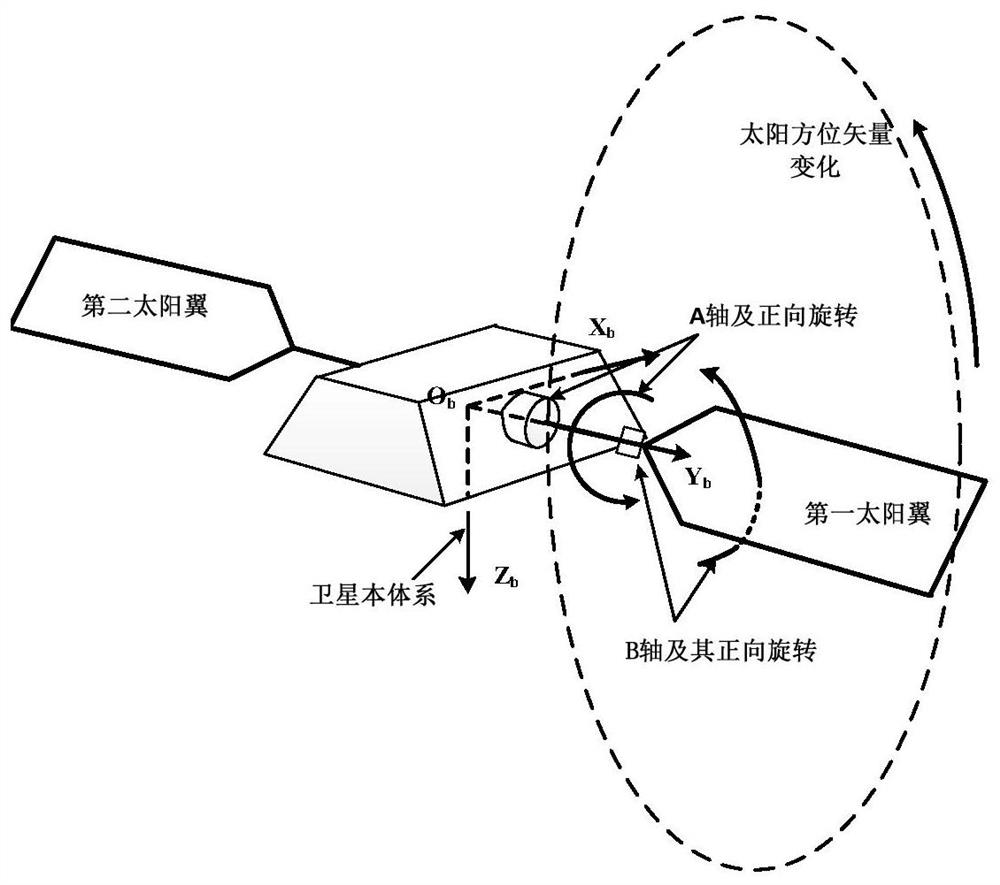
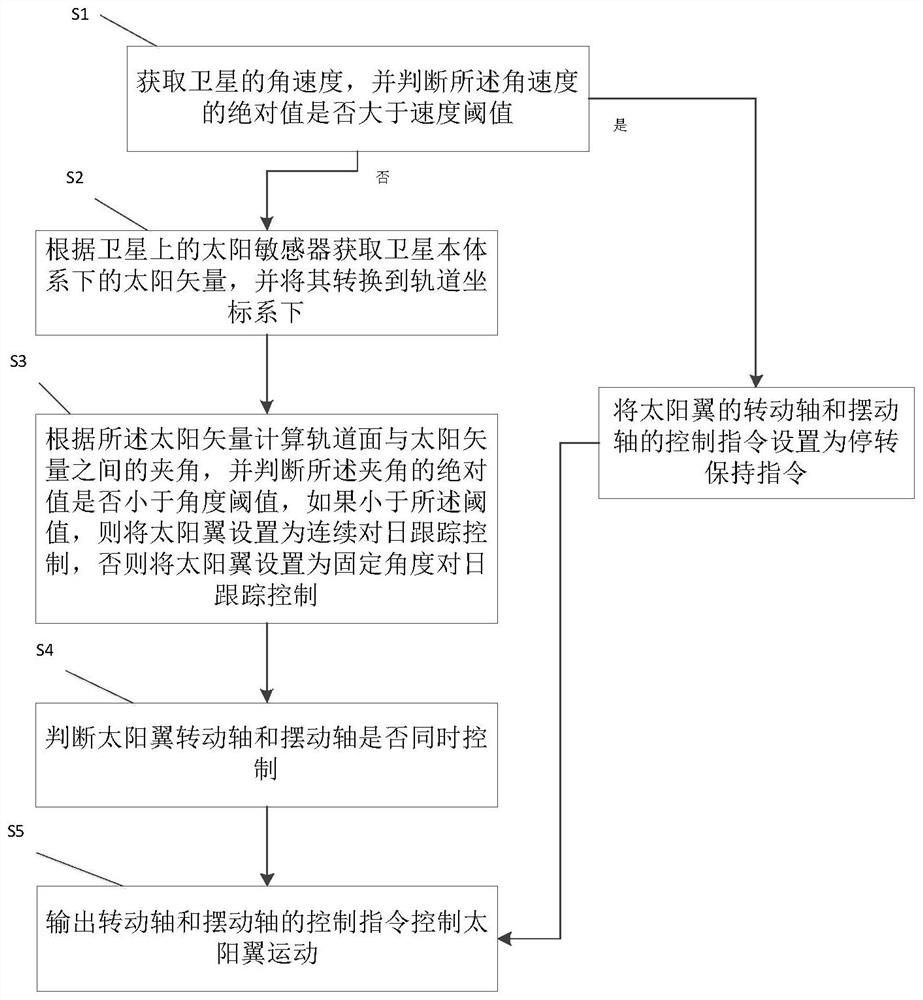
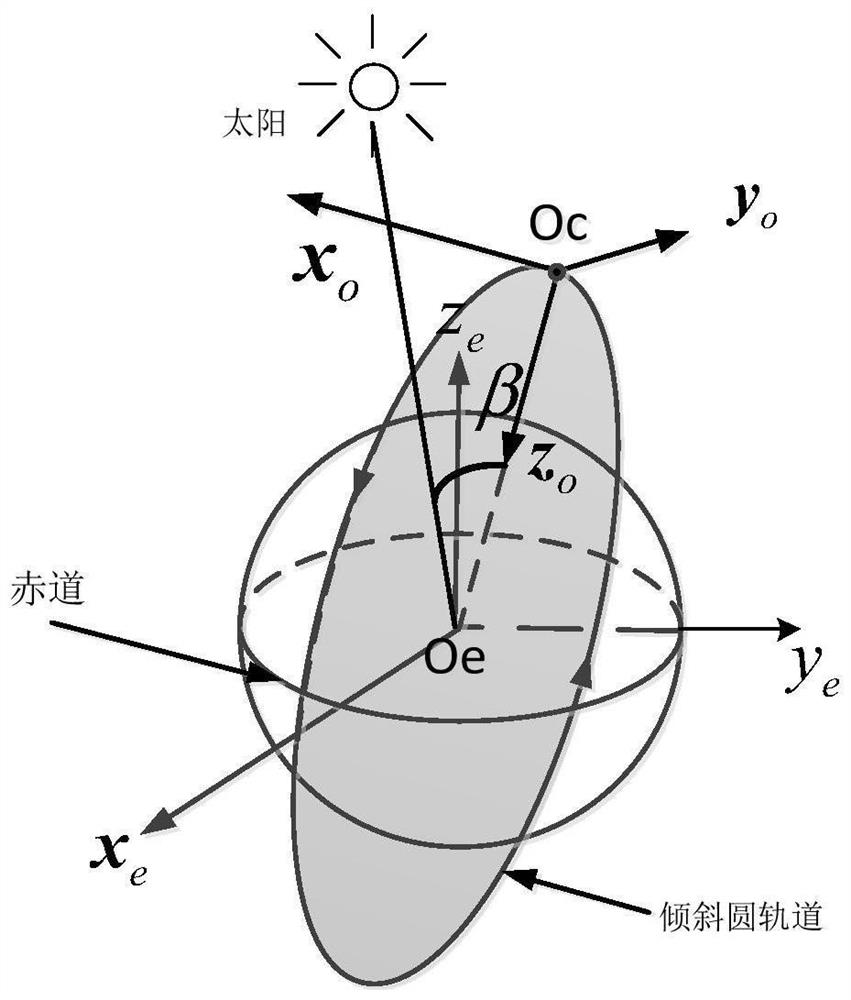
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, a structure diagram of a low-orbit satellite dual-degree-of-freedom solar wing, the solar wing refers to the solar wing in the ±Y-axis direction of the satellite system, and is defined as the first solar wing and the second solar wing respectively, and the double-freedom degree refers to the solar wing with two degrees of freedom of rotation and swing, the axis of rotation and the axis of swing are respectively figure 1 A-axis and B-axis. The rotation axis is consistent with the rotation axis of the single-degree-of-freedom solar wing; the swing axis is located on the extension rod of the output shaft of the rotation axis, and the rotation axis can drive the swing axis to rotate together, and the rotation d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com