Methods and systems for solution based sequence enrichment
a technology of sequence enrichment and solution, applied in the field of methods and systems for the capture and enrichment of target nucleic acids and analysis, can solve the problems of reducing arduous and often fruitless task of identifying such snps, and using genomes to reduce the complexity of the genom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Discovery of New Polymorphisms and Mutations in Large Genomic Regions
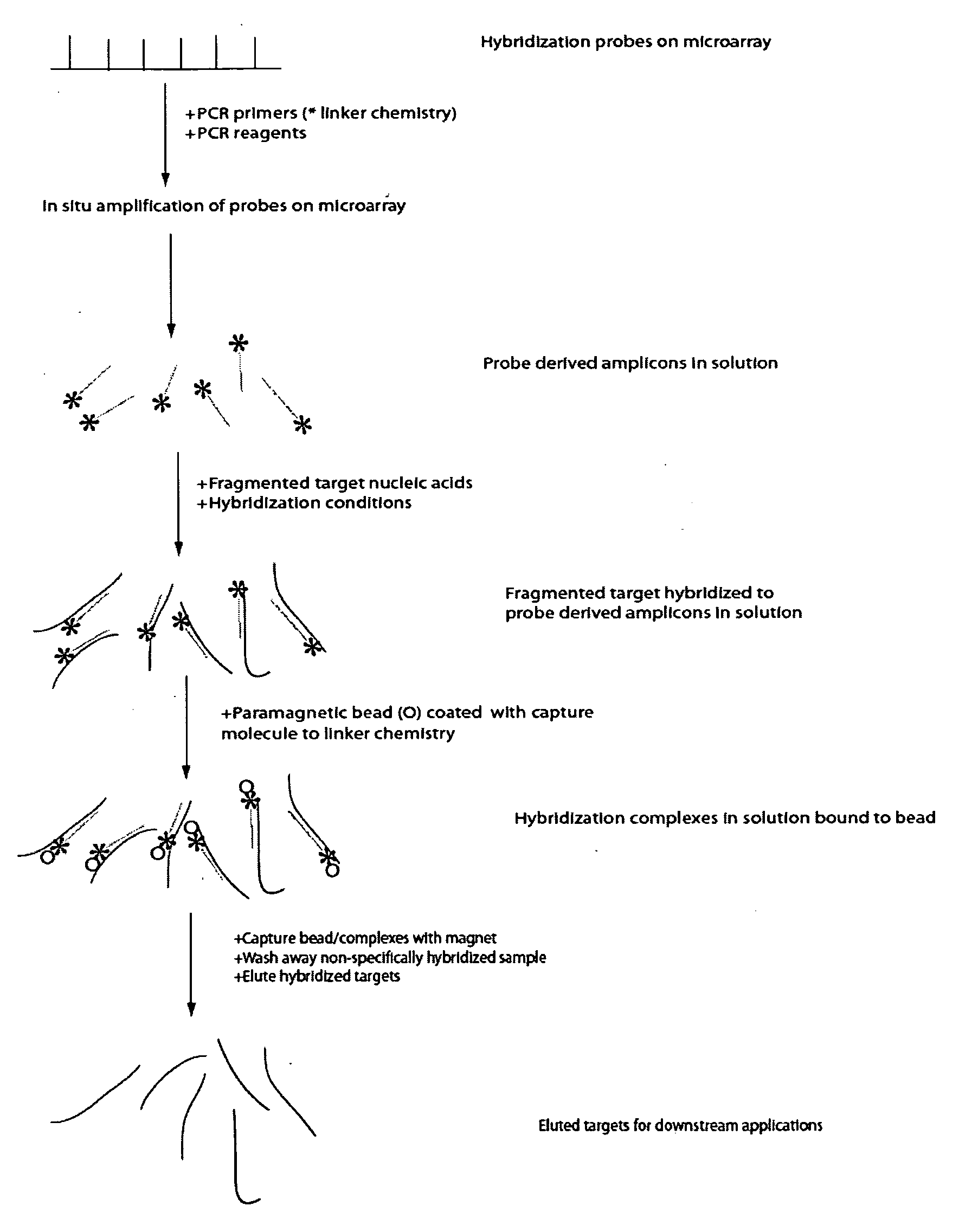
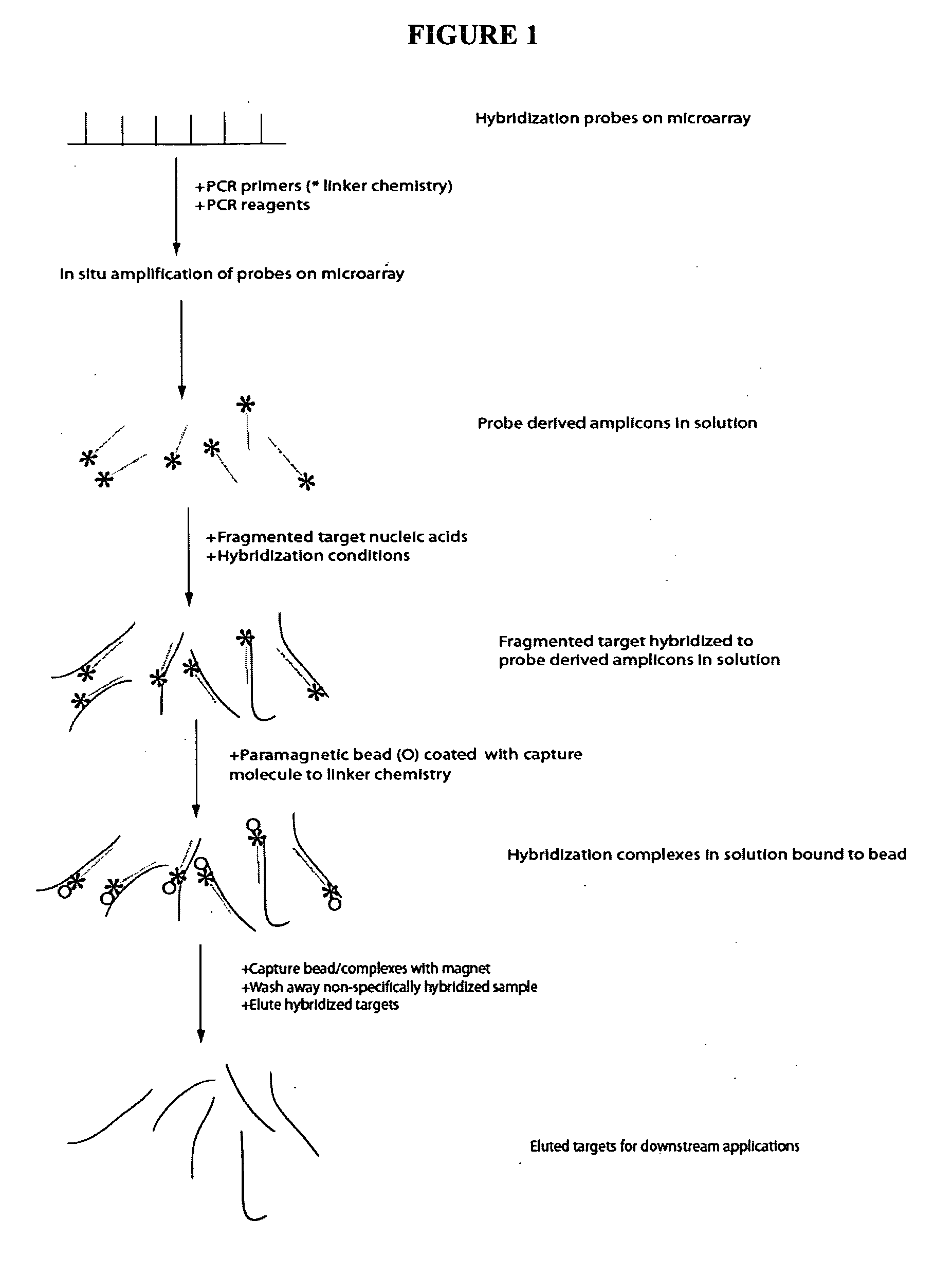
[0083]This generic example describes how to perform selection that allows for rapid and efficient discovery of new polymorphisms and mutations in large genomic regions. Microarrays having immobilized probes are used in one- or multiple rounds of hybridization selection with a target of total genomic DNA, and the selected sequences are amplified by LM-PCR
a) Preparation of the Genomic DNA and Double-Stranded Linkers
[0084]DNA is fragmented using sonication to an average size of 500 base pairs. A reaction to polish the ends of the sonicated DNA fragments is set up:
DNA fragments41 μlT4 DNA Polymerase20 μlT4 DNA polymerase reaction mix20 μlWater10 μl
[0085]The reaction is incubated at 11° C. for 30 min. The reaction is then subjected to phenol / chloroform extraction procedures and the DNA is recovered by ethanol precipitation. The precipitated pellet is dissolved in 10 μl water (to give a final concentration of 2 μg / μl).
[0...
example 2
Array-Targeted Resequencing
[0098]A series of high-density oligonucleotide microarrays that capture short segments that correspond to 6,726 individual gene exon regions of at least 500 base pairs were chosen from 660 genes distributed about the human genome (sequence build HG17) (approximately 5 Mb of total sequence) were synthesized according to standard Roche NimbleGen, Inc. microarray manufacturing protocols. Overlapping microarray probes of more than 60 bases each on the array spanned each target genome region, with a probe positioned each 10 bases for the forward strand of the genome.
[0099]Highly-repetitive genomic regions were excluded by design from the capture microarrays, to reduce the likelihood of non-specific binding between the microarrays and genomic nucleic acid molecules. The strategy for identifying and excluding highly-repetitive genomic regions was similar to that of the WindowMasker program (Morgulis et al.). The average 15-mer frequency of each probe was calculat...
example 3
Sequence Variation Captured by Genomic Enrichment and Resequencing
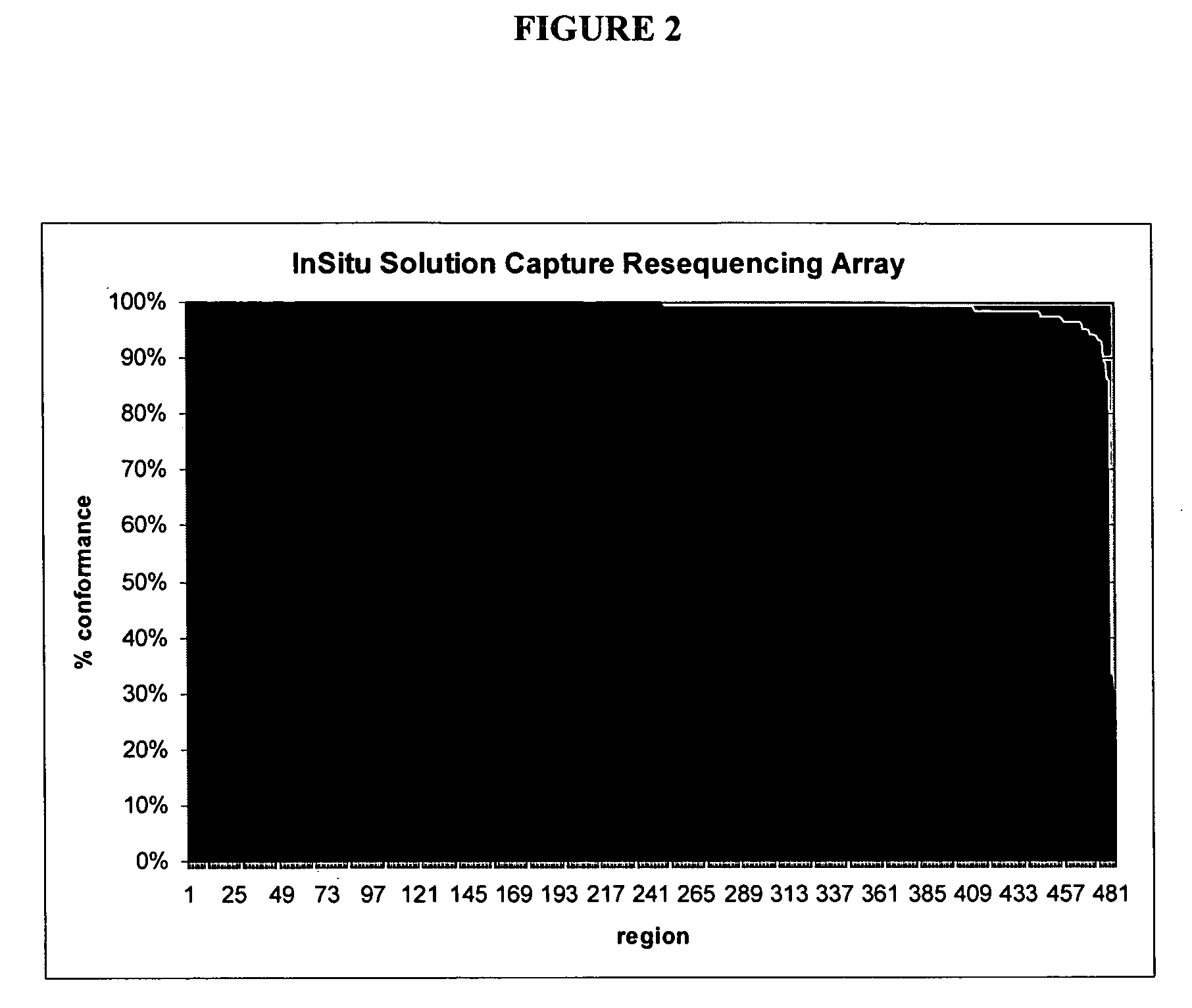
[0106]To ascertain the ability to discern variation in the human genome, genomic DNA samples from four cell types in the human HapMap collection (CEPH / NA11839, CHB / NA18573, JPT / NA18942, YR1 / NA18861, Coriell) were captured on the exon arrays of the prior examples, eluted and sequenced, as disclosed herein, except that the genomic DNAs were not whole genome amplified before capture. The capture results (shown in Table 1, rows 4-7) were similar to those above, except that sequence coverage was consistently more uniform than before, suggesting a bias introduced during WGA.
[0107]The sequence from the four HapMap samples was assembled and mutations were identified and compared to the HapMap SNP data for each sample (Tables 1 and 2). The total number of positions in the target regions that were genotyped in the HapMap project was 8103 (CEU), 8134 (CHB), 8134 (JPT), 8071 (YR1) for each of the four genomes. Of these, most (˜60...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com