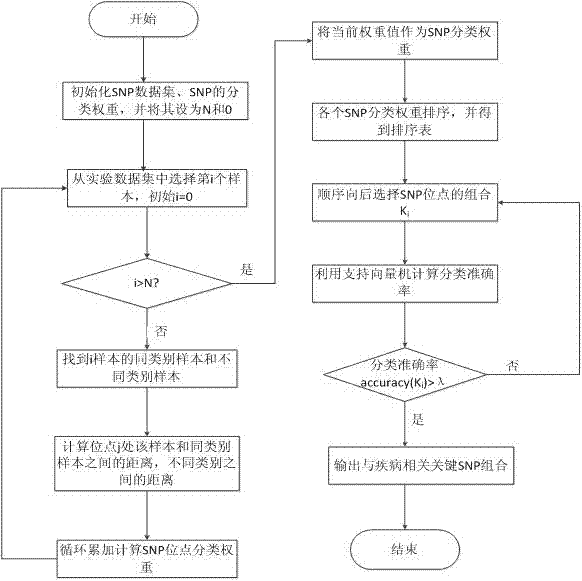
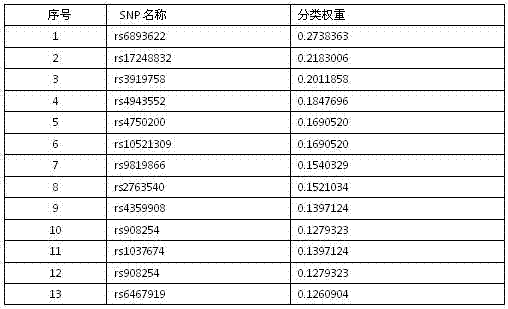
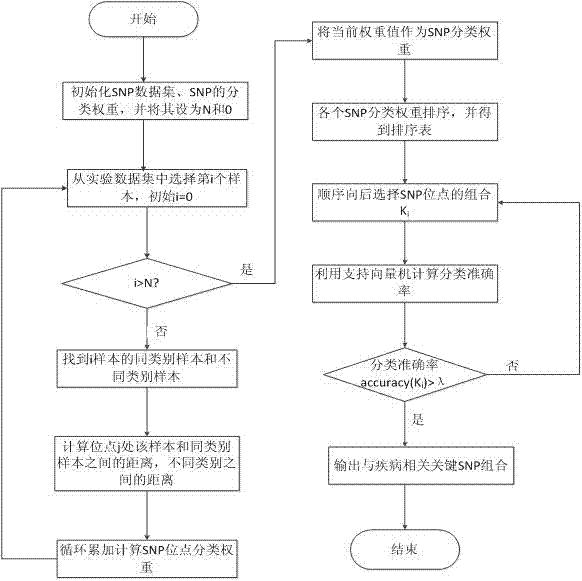
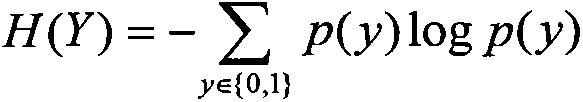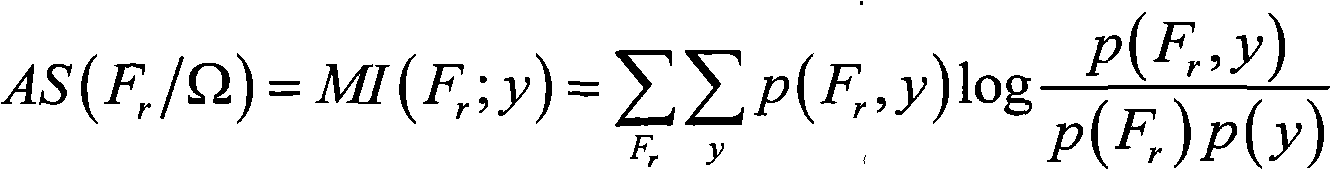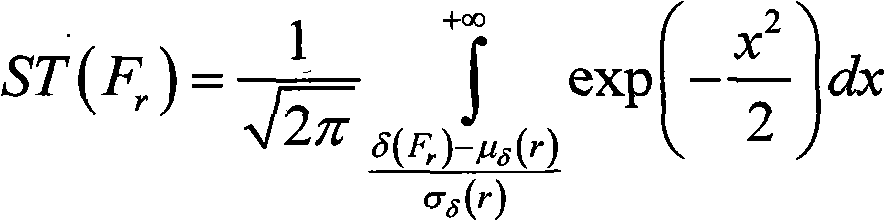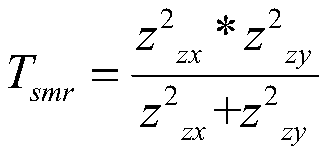Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Snp data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for single cell classification and screening and device therefor
ActiveCN102952854AAvoid marked actionsImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genesData set
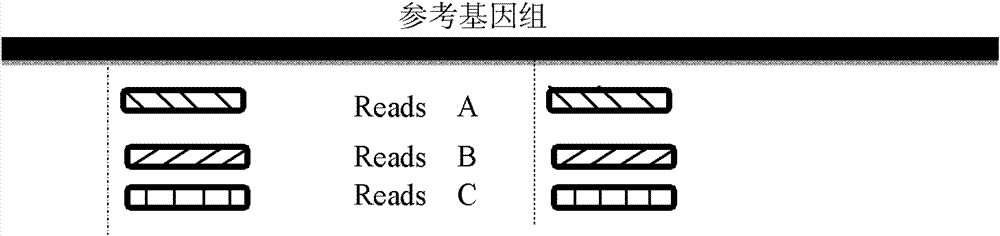
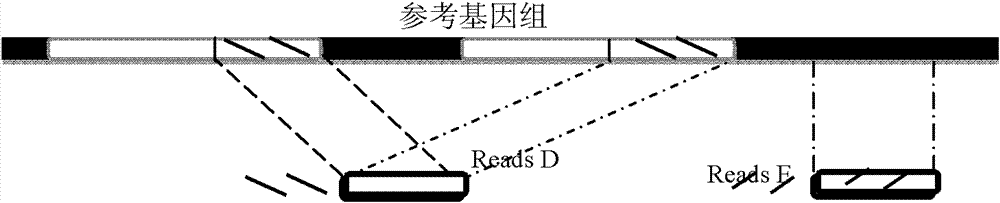
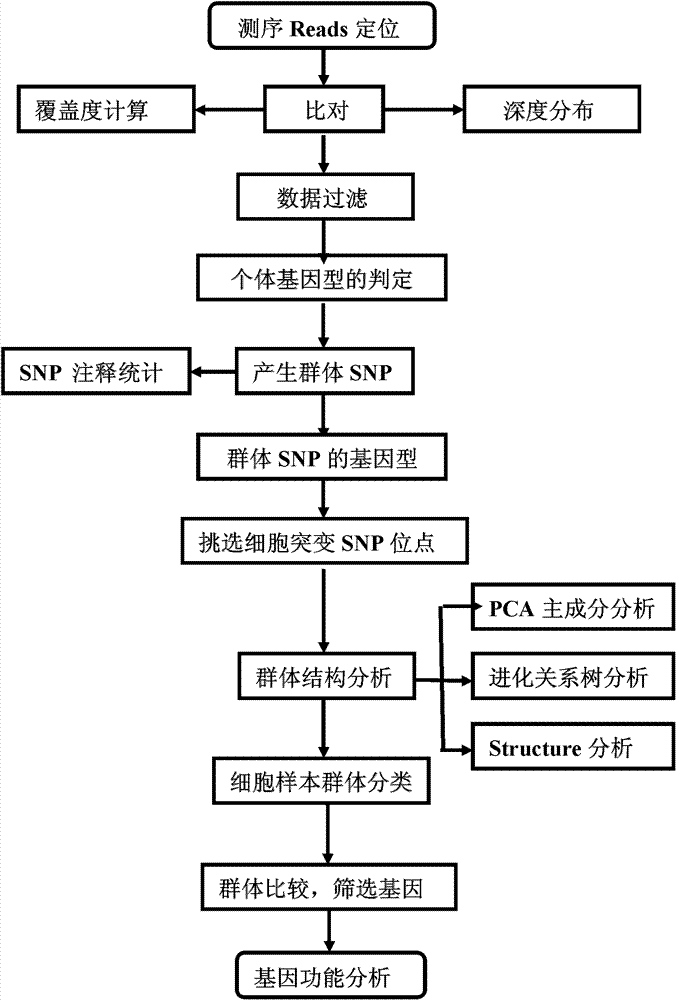
The invention provides a method for single cell classification and screening and a device therefor. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out comparison of reads obtained by sample sequencing and a reference genome, carrying out data filtration of a comparison result, determining a consistent genotype of all single cell samples according to filtered data, saving the consistent genotype of the all single cell samples into a SNP data set, extracting genotype files of loci corresponding to reference genome SNP data set positions from the saved SNP data set, selecting a cell mutation SNP locus, and carrying out cell classification and functional gene screening according to a genotype file of the cell mutation SNP locus. The method and the device avoid cell marking, solve the problem that the traditional single cell classification method can not realize classification of a certain cell subset having no corresponding specific markers, realize complete analysis of genetic variation information of a single cell genome, and greatly improve the accuracy of cell subset classification.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
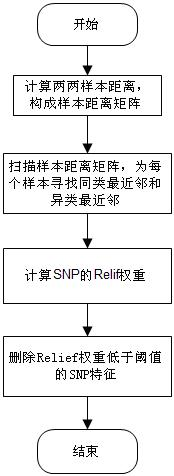
Feature selection method facing to SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) data
InactiveCN102629305ASolve the problem of low efficiency of feature selectionSolve selection inefficienciesSpecial data processing applicationsSmall sampleAlgorithm
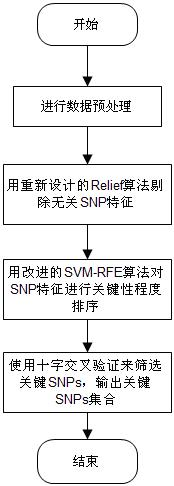
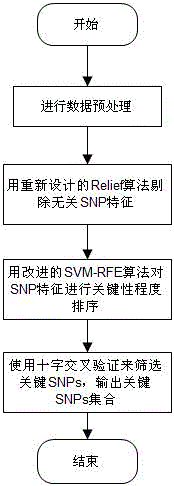
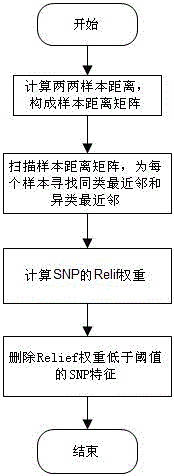
The invention discloses a feature selection method facing to SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) data, which specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out data pre-processing; secondly, removing unrelated SNP features by using a newly-designed Relief algorithm; thirdly, carrying out critical degree sorting on the SNP features by using an improved SVM-RFE algorithm; and finally, screening the critical SNP sorting by using cross validation. The feature selection method has the beneficial effects that the advantages of Filter feature selection and Wrapper feature selection are combined, and a secondary division method is used in the machine learning process, so that the problems of a high-dimensional small sample in the SNP feature selection and a SNP pathogenic combination mode are solved, and the analysis efficiency and the accuracy are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Polymorphisms in mitochondrial transcription factor A ("TFAM") gene and their associations with measures of marbling and subcutaneous fat depth in beef cattle
ActiveUS20070065843A1Increase productivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationZooidMitochondrial transcription
The physiological regulation of intake, growth and energy partitioning in animals is under the control of multiple genes, which may be important candidates for unraveling the genetic variation in economically relevant traits in beef production. The present invention relates to the identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the bovine gene encoding mitochondrial transcription factor A (“TFAM”) and their associations with economically relevant traits in beef production. The invention further encompasses methods and systems, including network-based processes, to manage the SNP data and other data relating to specific animals and herds of animals, veterinarian care, diagnostic and quality control data and management of livestock which, based on genotyping, have predictable meat quality traits, husbandry conditions, animal welfare, food safety information, audit of existing processes and data from field locations.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
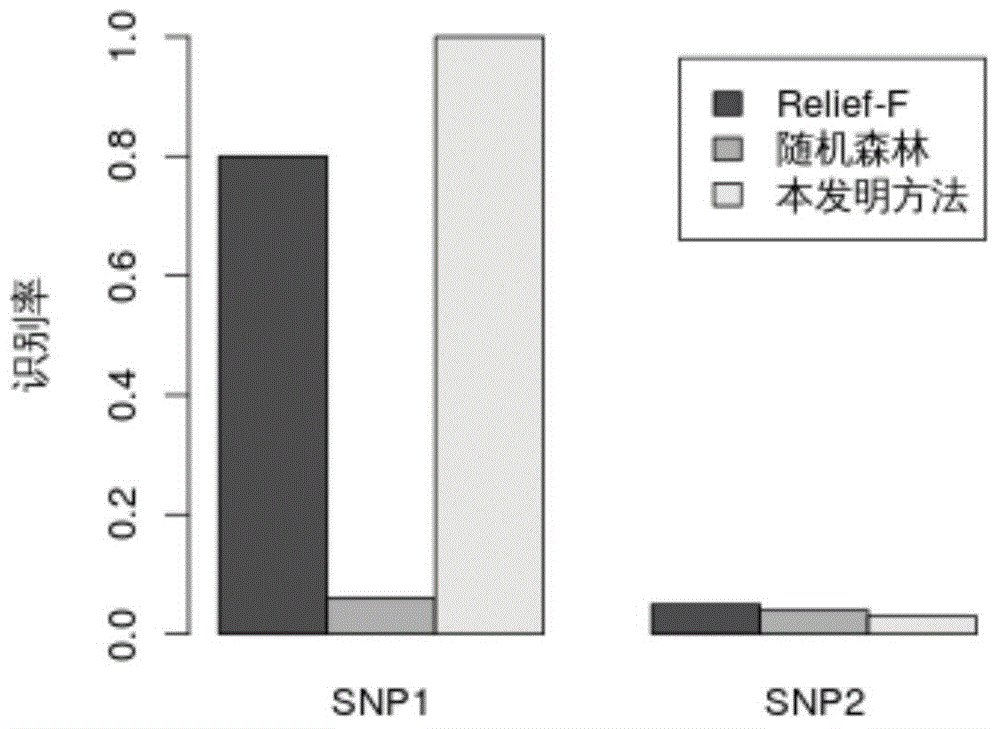
Genome-wide SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site analysis method based on combination of random forest and Relief-F
ActiveCN104462868AProblem with low rankingEasy to handleSpecial data processing applicationsBiological drugsSnp data
The invention discloses a genome-wide SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site analysis method based on combination of random forest and Relief-F. The method includes: primarily screening SNP sites with a generalized linear model; processing SNP interactive capability with Relief-F; preliminarily putting SNP sites, which are interactive, to the front of a queue; ranking the SNP sites at the rear of the queue with the random forest to recognize edge action of each single SNP site so as to obtain an SNP rank queue; removing the SNP sites at the tail of the queue; performing processing again with the Relief-F and the random forest; allowing iteration to obtain a ranking result of the SNP sites. The method has the advantages that the action of each single SNP site and interaction of the SNP sites are comprehensively considered, genome-wide SNP data can be processed so as to find those related to complex diseases, and the method is significant to the research on pathogenesis of the complex diseases, prediction on risk of diseases, development of biological drugs and the like.
Owner:西安电子科技大学重庆集成电路创新研究院
Single cell classification method, gene screening method and device thereof
InactiveUS20140206006A1Improve accuracyReduce stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData setClassification methods
Provided are a single cell classification method, a gene screening method and a device for implementing the method. In that, the single cell classification method includes the following steps: sequencing the whole genomes of a plurality of single cell samples from the same group, respectively, so as to obtain reads from each single cell sample; aligning the reads from each single cell sample to the sequence of a reference genome, respectively, and performing data filtering on said reads; on the basis of the filtered reads, determining a consistent genotype of each single cell sample, in which consistent genotypes of all the single cell samples constitute an SNP dataset of said group; aimed at said each single cell, on the basis of the SNP dataset of said group, determining a corresponding genotype for each cell at a site corresponding to a position in an SNP dataset of the reference genome; and selecting an SNP site associated with cell mutation, and on the basis of the genotype of said single cell at the site, classifying said single cell.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Polymorphisms in fatty acid binding protein 4 ("FABP4") gene and their associations with measures of marbling and subcutaneous fat depth in beef cattle
ActiveUS20070020658A1Increase productivityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementZooidSnp data
The physiological regulation of intake, growth and energy partitioning in animals is under the control of multiple genes, which may be important candidates for unraveling the genetic variation in economically relevant traits in beef production. The present invention relates to the identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the bovine genes encoding fatty acid binding proteins and their associations with economically relevant traits in beef production. The invention further encompasses methods and systems, including network-based processes, to manage the SNP data and other data relating to specific animals and herds of animals, veterinarian care, diagnostic and quality control data and management of livestock which, based on genotyping, have predictable meat quality traits, husbandry conditions, animal welfare, food safety information, audit of existing processes and data from field locations.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
MHC completion database, and establishment method and application thereof
ActiveCN105512514AImprove accuracyReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsData setTyping
The invention discloses a MHC completion database, and an establishment method and application thereof. The MHC completion database comprises a genotype dataset, a HLA typing type dataset, an amino acid changing information dataset, and a HLA haplotype dataset combined together. In the establishment process of the database, LD and HWE are used for the first time for filtering a variation result, and data accuracy is improved. A simple method which is easy to operate is used to obtain SNP distinguishing datasets in least number, and MHC haplotype information is obtained through phasing analysis. Compared with using the whole SNP dataset to perform phasing, the establishment method saves more time, and reduces CPU and memory use, and obtained haplotype information is more accurate. The MHC completion database comprises various datasets in a MHC region, and can effectively complete sites, and lays foundation for deep research of the MHC region.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
Genome information assisted breeding method-breeding parent selection based on SNP clustering information and PAV variation information
InactiveCN106169034AAccurately and effectively obtainReduce workloadBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome information assisted breeding method for parent selection by means of SNP clustering and PAV variation. The essence of the genome information assisted breeding method is to obtain genome sequencing information of candidate parents with the help of genomic and bioinformatics methods; on one hand, a high-quality SNP data set is obtained through sequence alignment, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate parents is calculated, and the affinity between the candidate parents is judged with the help of a clustering tree; on the other hand, a Denovo assembled candidate parent contig is positioned to a reference genome, and the PAV variation of candidate parent target trait related genes is obtained according to the physical location. By combining the PAV variation and affinity information based on SNP, a parent subset is screened out from a large number of candidate parents for phenotype identification; finally, a selected breeding parent is determined by combining the phenotype identification result of the parent subset. The genome information assisted breeding method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding, the range of the materials for phenotype identification can be effectively narrowed from the large number of the candidate parents, the workload of phenotype identification is reduced, and the breeding work efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
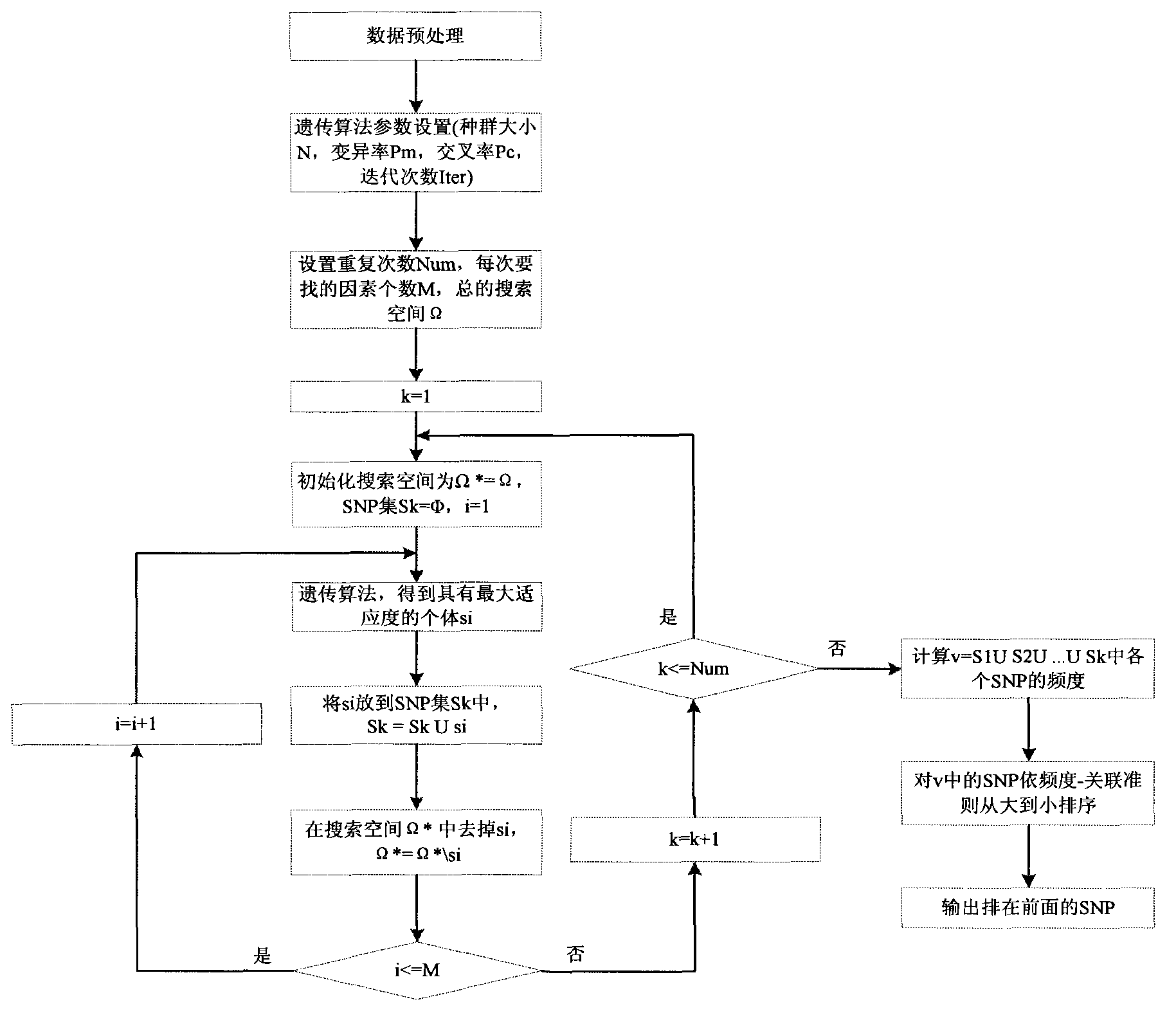
Method for filtering SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) unrelated to complex diseases from whole-genome
InactiveCN103366100ASearch guaranteeGuaranteed stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFactor baseHomologous chromosome
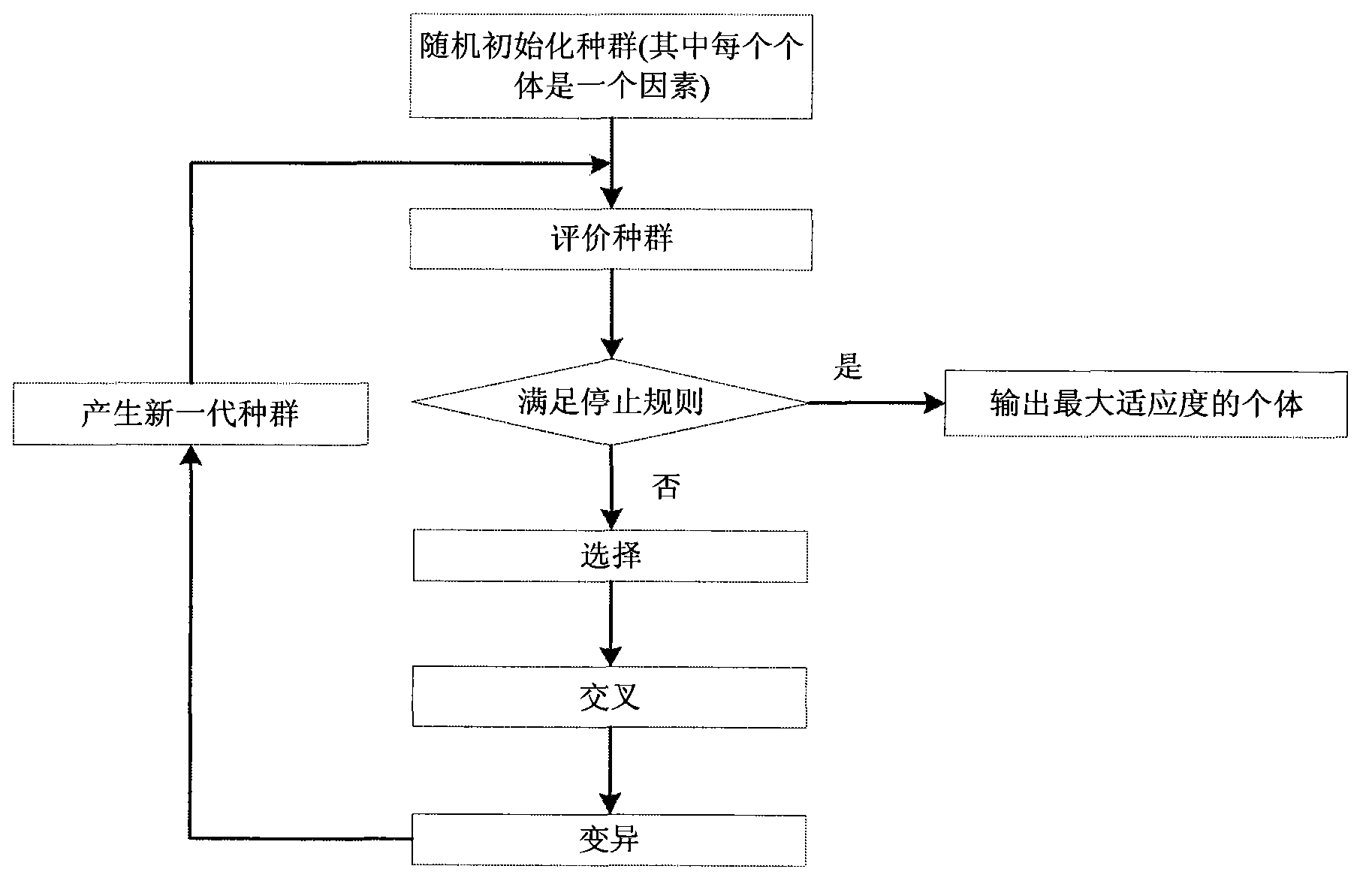
A method for filtering SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) unrelated to complex diseases from a whole-genome is used for the pathogenetic mechanism research of complex diseases, the early diagnosis and biological medicine development. The method comprises the following steps: (1), pre-processing and initializing SNP data, and processing the SNP data into data only including 0, 1, 2, 3 as per the principle that the influence of the variation of a random gene among the alleles of homologous chromosomes on diseases can be in equal treatment; (2), defining the relevance measure, namely defining the relevance I (Y;X) between the SNP subset X and the diseases Y as mutual information MI (Y;X) between X and Y; (3), searching SNP groups of the candidate suspected pathogenesis in the SNP set by adopting an FGSA (factor based genetic search algorithm) method; (4), selecting the SNP group of which the occurrence frequency of frequentness exceeds a threshold value in the set of SNP groups of the candidate suspected pathogenesis according to the frequentness-relevance priority criterion; (5), outputting the SNP of which the frequentness is larger than the threshold value and ranking at the headmost. According to the invention, the method can reserve the SNP corresponding to the pathogenesis covered by other pathogenesis, so as to lay a foundation for the discovery of the follow-up pathogenesis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Transcriptome-referenced association study and application thereof
InactiveCN108004302AMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCandidate Gene Association StudyExpression gene
The invention relates to a transcriptome-referenced association study. The method includes the steps that 1), a reference group is established, the transcriptome sequence of all individuals of the reference group is measured to obtain a reference transcript; 2), high throughput RNA sequencing is performed on the predicted group, and the obtained sequencing data is compared and spliced with the reference transcript, the group transcriptome sequencing results are obtained; 3), the group SNP data is obtained by analyzing the sequencing results of the group transcriptome, the association analysisis conducted by adopting the group SNP and interested characters, and the area of the target gene is determined; and then the gene expression variation in the target area is used to associate with thecharacters, the candidate gene of the target character is obtained. Compared with GWAS, the sequence of the transcriptome is cheap and rapid, and unconstrained by the complexity of the genome. In theory, the transcriptome-referenced association study can achieve to carry out the character association analysis in all species, whether the specie has the reference genome or not, and the genome is complicated or not.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method of discovering SNP group related to complex disease from SNP information
InactiveCN101894216ADescribe linear statistical relationshipsDescribe nonlinear statistical relationshipsSpecial data processing applicationsData setOrganism
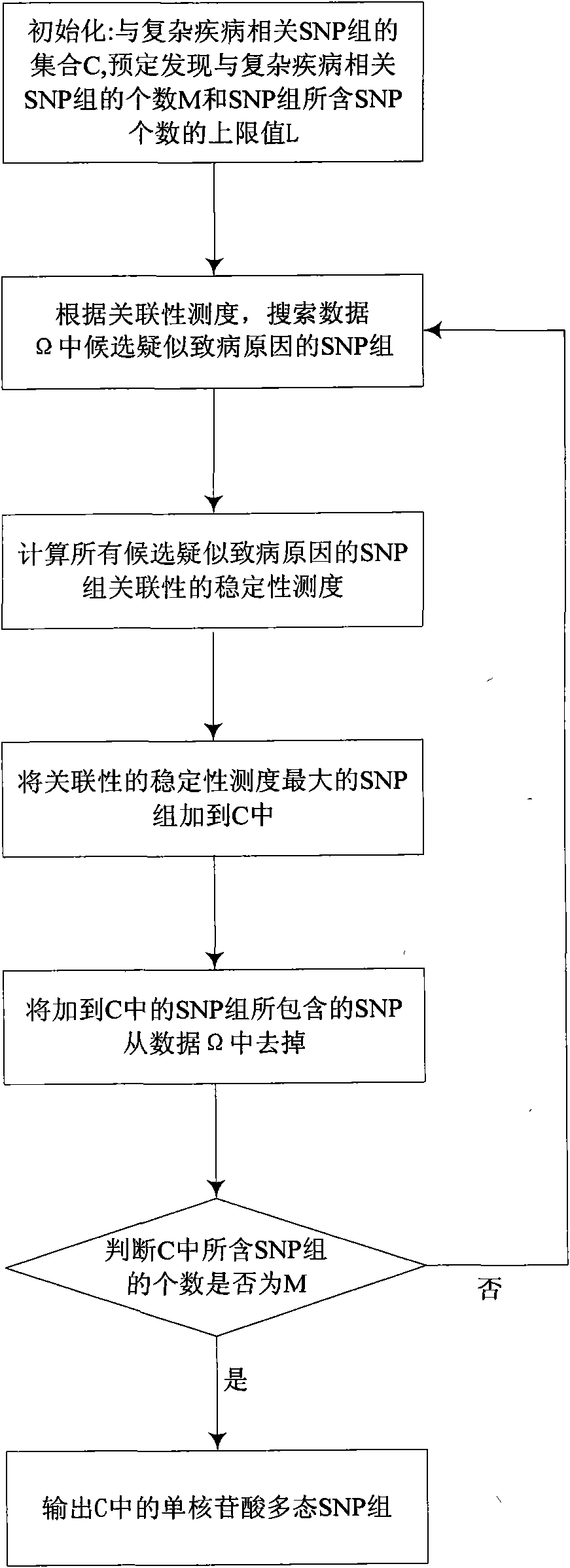
The invention discloses a method of discovering SNP group related to complex disease from SNP information, solving the that problem that the multiple nosogenesis of susceptibilitytodiseases and SNP combination related to each reason can not be found in the SNP data of the complex disease in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of: preprocessing an SNP data set of the complex disease; searching an SNP group of candidate suspected nosogenesis in the preprocessed data set according to the measure of the relevance of the SNP group; calculating the stability measure of the relevance of the SNP group of all candidate suspected nosogenesis; adding the SNP group with maximum relevance stability measure as the suspected nosogenesis into a set of the SNP groups related to the complex disease; and outputting the SNP group in the set of the SNP groups related to the complex disease, and evaluating the degree of the SNP groups being the suspected nosogenesis by using the degree of the relevance stability close to 1. The invention can simultaneously find a plurality of nosogenesis SNP groups hidden in the data, and can be used for the pathogenic mechanism research and the early diagnosis of the complex disease and the development of the biomedicine.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method applied to identification of pacific oyster family
ActiveCN103605913AGood repeatabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSolubilityPacific ocean
The invention discloses a method applied to identification of pacific oyster family and belongs to the technical field of genomic molecular markers. The method comprises the following steps: (1) searching type I and type II SNP mutation sites in an SNP database acquired by an Illumina GoldenGate method; (2) establishing genotype database files of filial generations and parents, and acquiring genetic parameters of each SNP site by utilizing Cervus 3.0 software; (3) performing family simulation identification and analysis according to the allele frequency of each site by utilizing the Cervus 3.0 software, performing actual family identification and analysis, calculating a LOD value of a candidate parental pair, and selecting parents with the highest LOD value being positive value as real parents. According to the invention, an SNP marking method applied to identification of pacific oyster family is developed, and the reaction system and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification conditions are optimized. The experiments prove that the primers have the characteristics of high repeatability, high stability, high solubility curve resolution and the like, and a foundation is laid for breeding of the pacific oyster family.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotype with feed intake and feed efficiency in beef cattle
ActiveUS20080177597A1Increase productivityImprove feeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementResourcesSnp dataLivestock
The physiological regulation of intake, growth and energy partitioning in animals is under the control of multiple genes, which may be important candidates for unraveling the genetic variation in economically relevant traits in beef production. The present invention relates to the identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and their haplotypes, across the bovine genome in genes encoding polypeptides associated with feed efficiency, and their associations with residual feed intake in beef production. The invention further encompasses methods and systems, including network-based processes, to manage the SNP data, haplotype data and other data relating to specific animals and herds of animals, veterinarian care, diagnostic and quality control data and management of livestock which, based on genotyping, have predictable meat quality traits, husbandry conditions, animal welfare, food safety information, audit of existing processes and data from field locations.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) data filtering method
InactiveCN102567652AClassification weight values are accurateImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineDisease
The invention relates to an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) data filtering method, which includes the following steps: firstly, computing SNP classification weight by means of the action of a single SNP and the interaction among the SNPs; and secondly, filtering SNP loci by means of a support vector machine. The action of the single SNP is taken into consideration, and the interaction among the SNPs is sufficiently researched, so that reliability in filtering of the SNPs relevant with diseases is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for clustering single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data
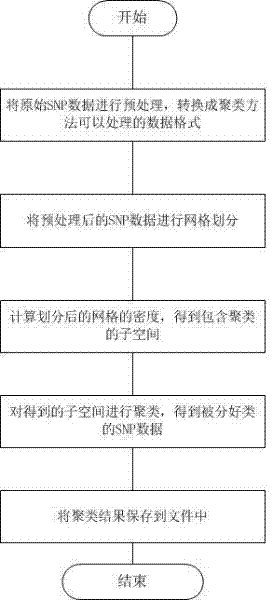
InactiveCN102419774ASolving clustering problemsReduce processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsVolumetric Mass DensitySnp data
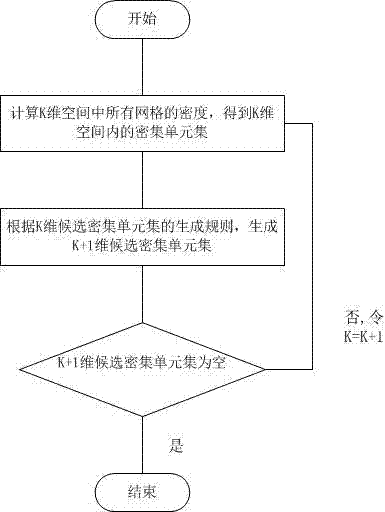
The invention discloses a method for clustering single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, pre-processing original SNP data, and converting the format of the original SNP data into data format which can be processed by using the method; secondly, performing grid division on the pre-processed SNP data, and dividing each dimension of the SNP data into three grids according to an expression value, in each sample, of each SNP site; thirdly, calculating the density of the divided grids to obtain a sub-space which comprises clusters; fourthly, clustering the obtained sub-space to obtain the classified SNP data, wherein each cluster is a set of co-expression SNP sites; and finally, storing a clustering result into a file. By adoption of the method, the problem of clustering of high-dimension classification data is solved, and the SNP data can be quickly clustered with high quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) classification method and application based on PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
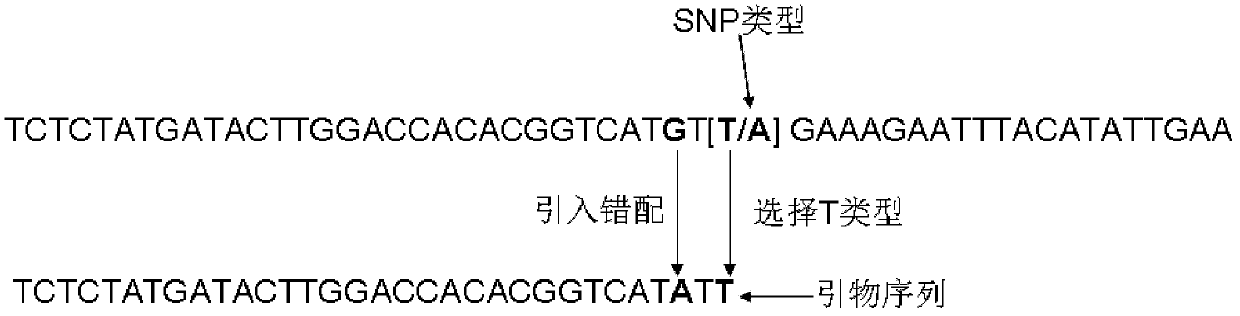
ActiveCN103290102ASimple methodSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGenomic DNA
The invention provides an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) classification method and application based on PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). The SNP classification method comprises the steps of: (1) selecting a plant sample for experiment-tissues of a plurality of strains of certain species; (2) extracting genomic DNA of the tissues; (3) purifying the genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification; (4) selecting AT type SNP in an SNP database of the species; (5) screening out SNP of which the third base before the SNP locus is G; (6) using primer 3 software to design a primer so that the last base of a positive primer is at the SNP locus and the last base is T; (7) introducing mispairing, and changing the antepenultimate base of the positive primer into A; (8) performing PCR amplification; (9) treating the PCR products by means of modified polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic separation; and (10) observing whether amplification band exists. The invention further provides application of the SNP classification method based on PCR in pyramiding breeding; the method is easy to implement, simple, convenient, and low in cost; the detection is simple and efficient; the classification success rate of SNP is as high as 91%.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Data mining of SNP databases for the selection of intragenic SNPs
ActiveUS8725418B2Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsCandidate Gene Association StudySnp data
The present invention relates to data mining of SNP databases for the selection of intragenic SNPs. The present invention provides methodologies for annotating SNPs onto candidate genes based on appropriate sequence comparison software or algorithms such as a BLAST search of SNP databases. Additionally, the present invention provides methodologies useful in the selection of intragenic SNPs for genotyping in genetic studies.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
Method for constructing photosynthetic pathway gene regulation network
ActiveCN106599607ABuild accurate and reliableSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsCandidate Gene Association StudyPhenotypic trait
The invention provides a method for constructing a photosynthetic pathway gene regulation network. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining SNP data of photosynthetic pathway genes of species; 2) measuring phenotypic traits of the species to obtain phenotypic data; 3) performing inter-genetic locus epistasis mode detection by utilizing the SNP data obtained in the step 1) and the phenotypic data obtained in the step 2), and determining an interaction relationship between every two genes; 4) verifying the correlation among the genes obtained in the step 3); and 5) constructing the gene regulation network by taking the correlative genes obtained in the step 3) as candidate genes, wherein the step 1) and the step 2) are free from time sequence limitation. According to the construction method provided by the invention, genetic locus mutation and biotic population phenotypes are comprehensively considered; the gene regulation network is constructed more accurately by calculating inter-locus epistasis; and the method has important theoretical significances and practical values for research and improvement of a photosynthesis mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Genome-information-assisted breeding method II, breeding parent selection method based on whole-genome SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) beneficial haplotype mining
ActiveCN108376210AReduce workloadImprove breeding efficiencyBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome-information-assisted breeding method to select breeding parents via HT (haplotype) variation information and SNP clustering grouping information. The method is substantially to acquire massive genome sequencing information of candidate breeding parents via methods of genomics and biological informatics; on one hand, a high-quality SNP dataset is acquired through sequence comparing and analyzing, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate breeding parents is calculated on such basis, an SNP cluster tree is constructed, and the candidate parents are grouped according to genetic relational degrees; on the other hand, important related gene sites are selected according to target traits set by a breeding plan, HT variation information of the candidate parents is acquired, and differences of the parents having different types of HT variations in terms of target trait are compared. Through integration of the HT variation information and based on SNP cluster parent grouping information, candidate parents to identify repeated phenotypes of the target traits is acquired by screening the massive candidate breeding parents. The method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding; the parent material range can be effectively narrowed from the massive candidate breeding parents via database information mining, phenotype repeats identification work is reduced, and breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
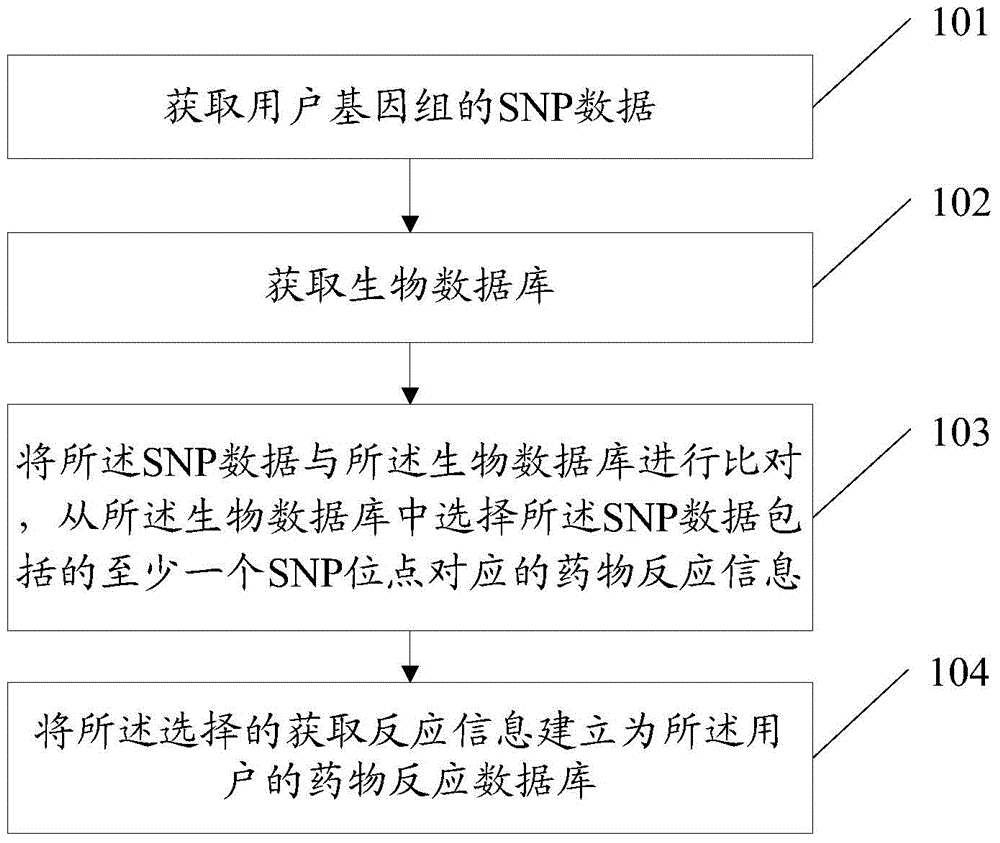
Method and device for establishing drug reaction database
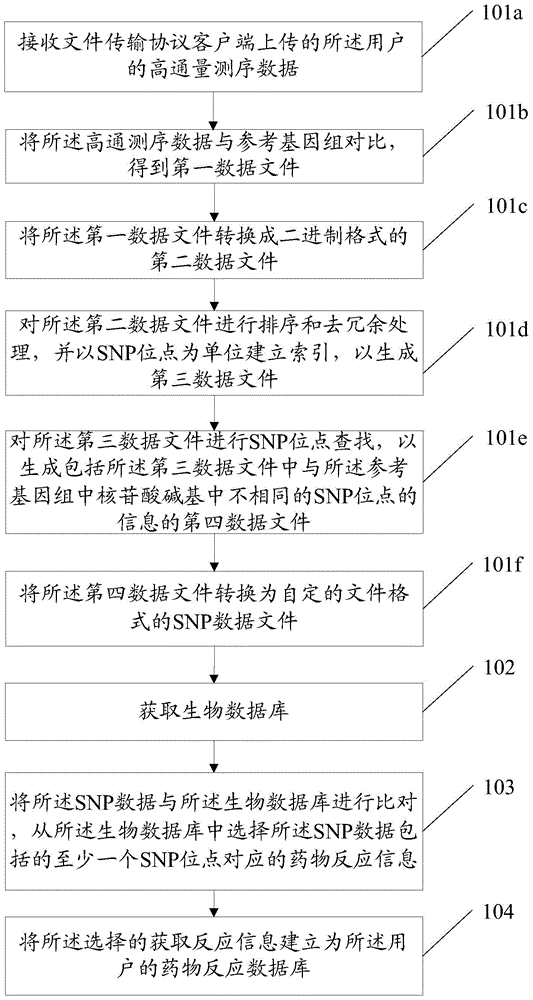
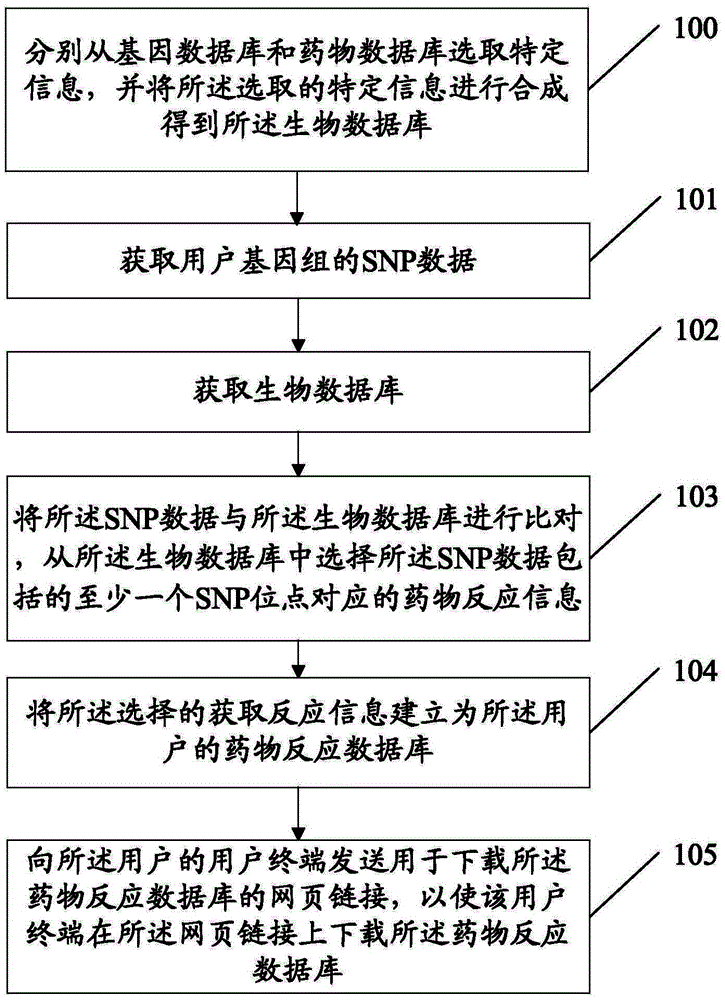
InactiveCN103955631ASolve the problem of establishing an associationSpecial data processing applicationsGene typeDrug reaction
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA +1
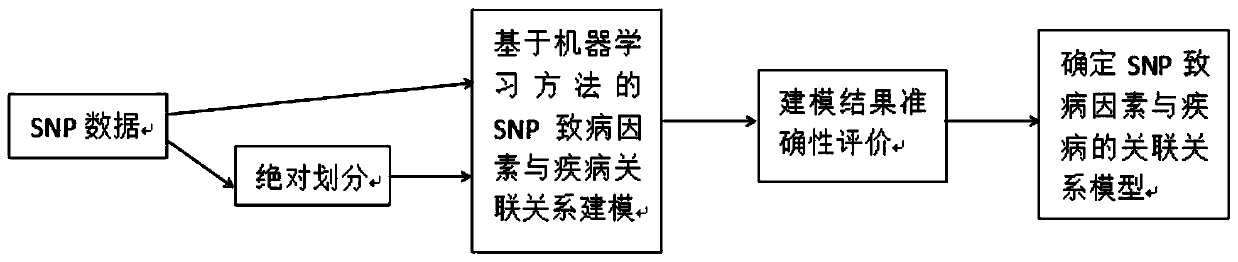
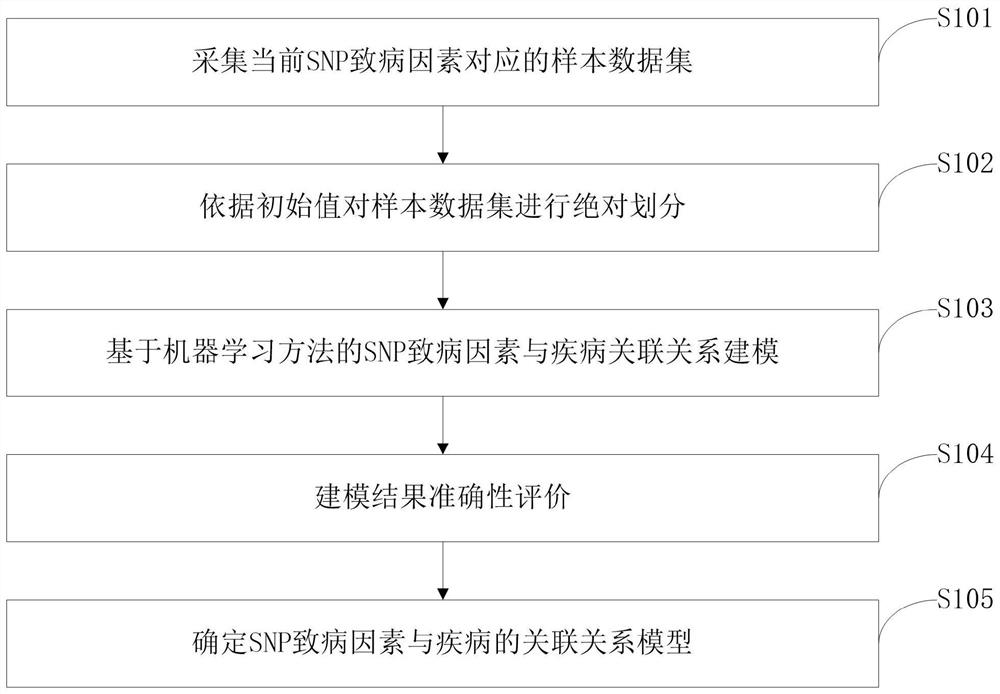
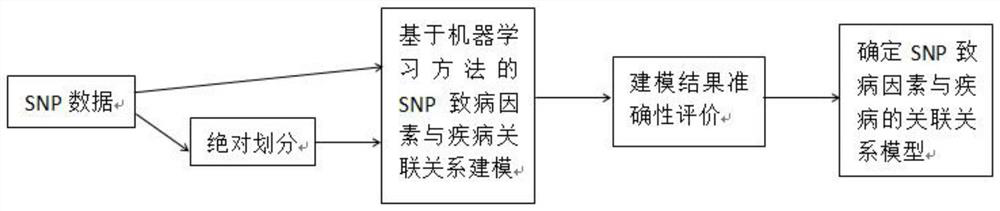
Construction method of models of association relationships of SNP pathogenic factors and disease
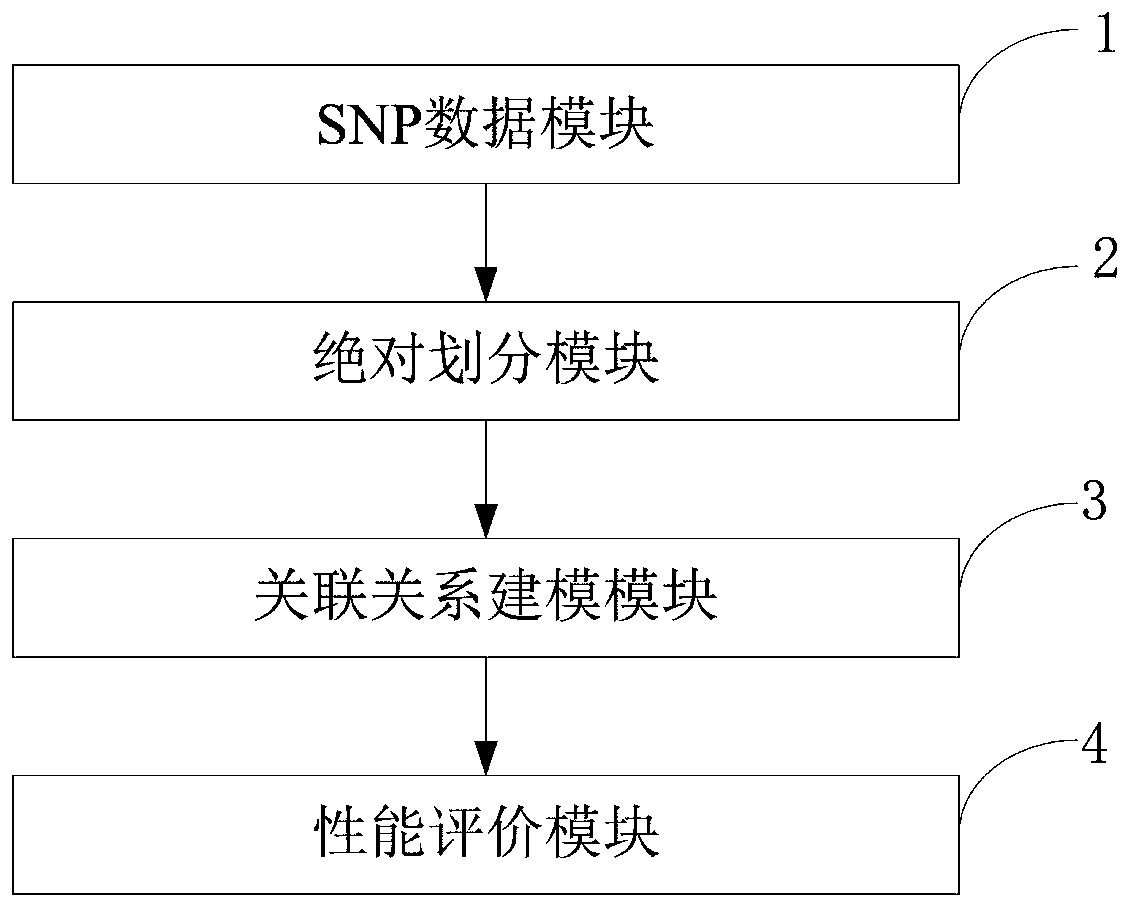
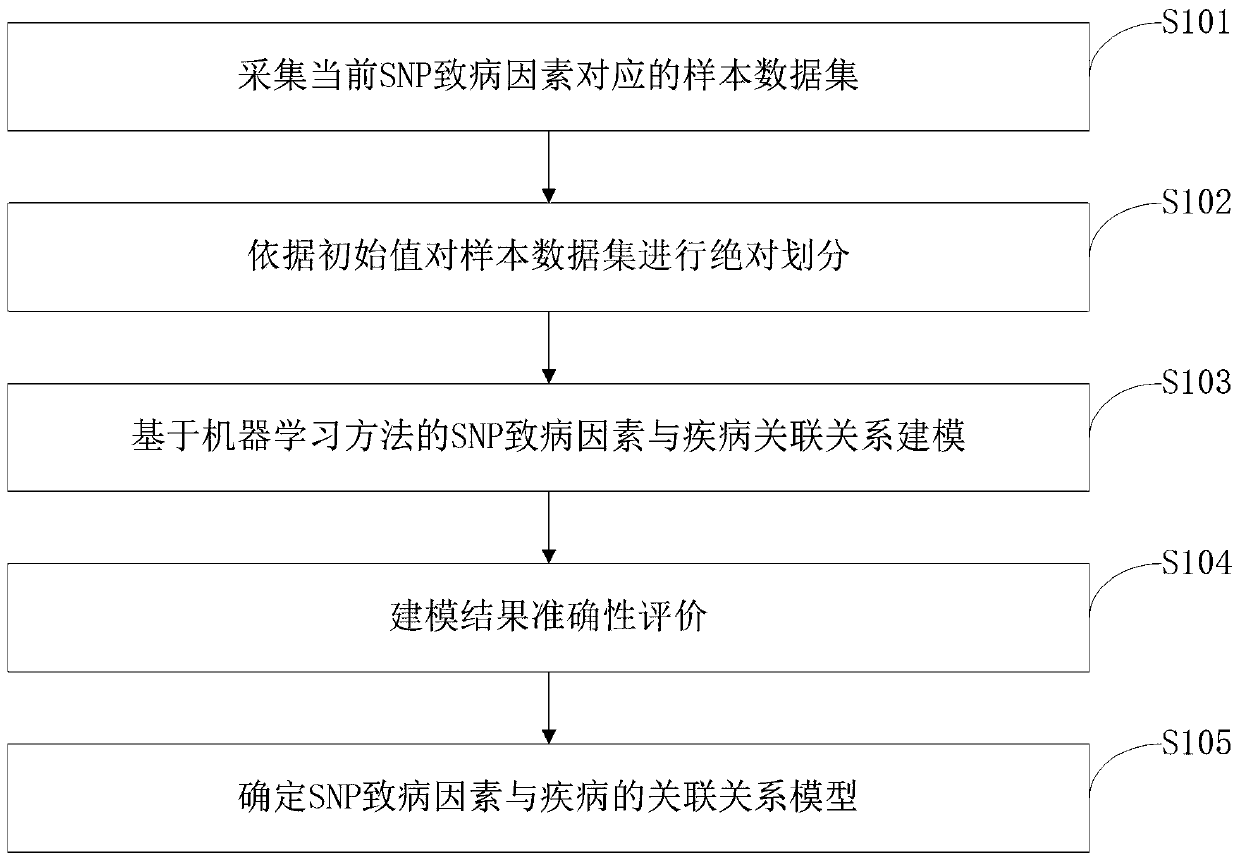
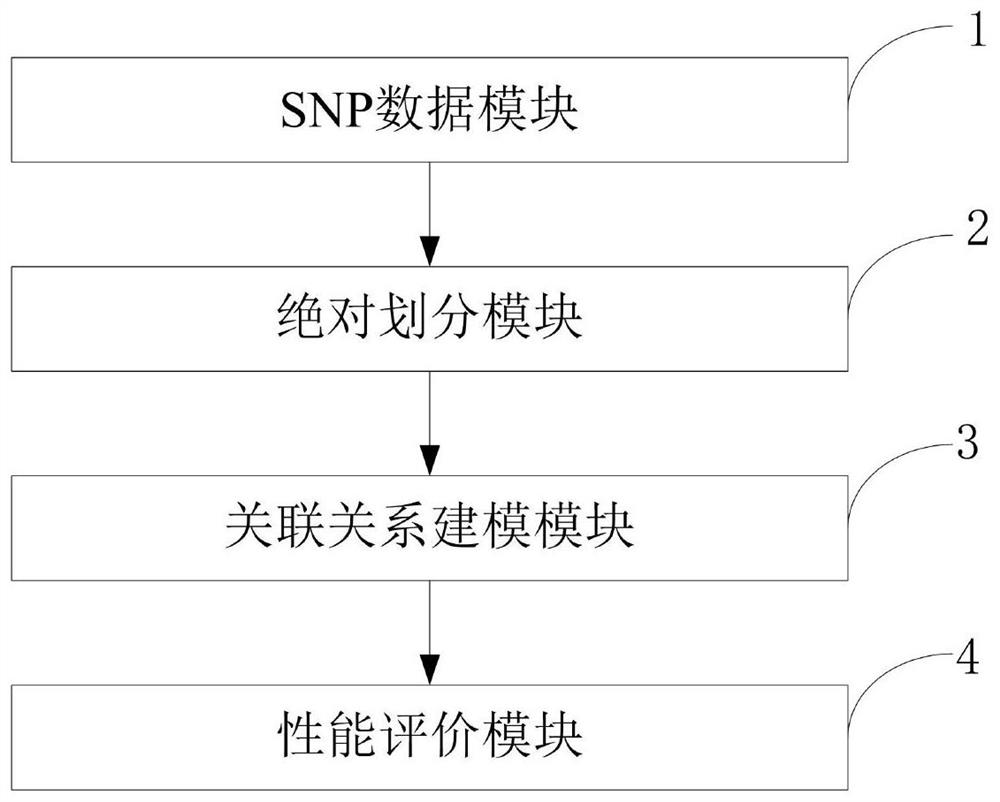
ActiveCN110459266AReduce the degree of interactionThe relationship model is accurateBiostatisticsProteomicsDiseaseData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of data processing, and discloses a construction method of models of association relationships of SNP pathogenic factors and a disease. A sample data set corresponding to the current SNP pathogenic factor is collected; according to an initial value, absolute dividing is conducted on the sample data set; the association relationship of the current SNP pathogenic factor and the disease is modeled based on a machine learning method; the modeling result accuracy is evaluated; the model of the association relationship of the current SNP pathogenic factorand the disease is determined. According to the method, through the absolute dividing method, the degree of mutual influence among all the SNP pathogenic factors is reduced, so that the constructed model of the association relationship of each SNP pathogenic factor and the disease is more accurate. The method is easy to implement, the accurate models of the association relationships of the SNP pathogenic factors and the disease can be obtained simply by inputting original SNP data and all the SNP pathogenic factors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
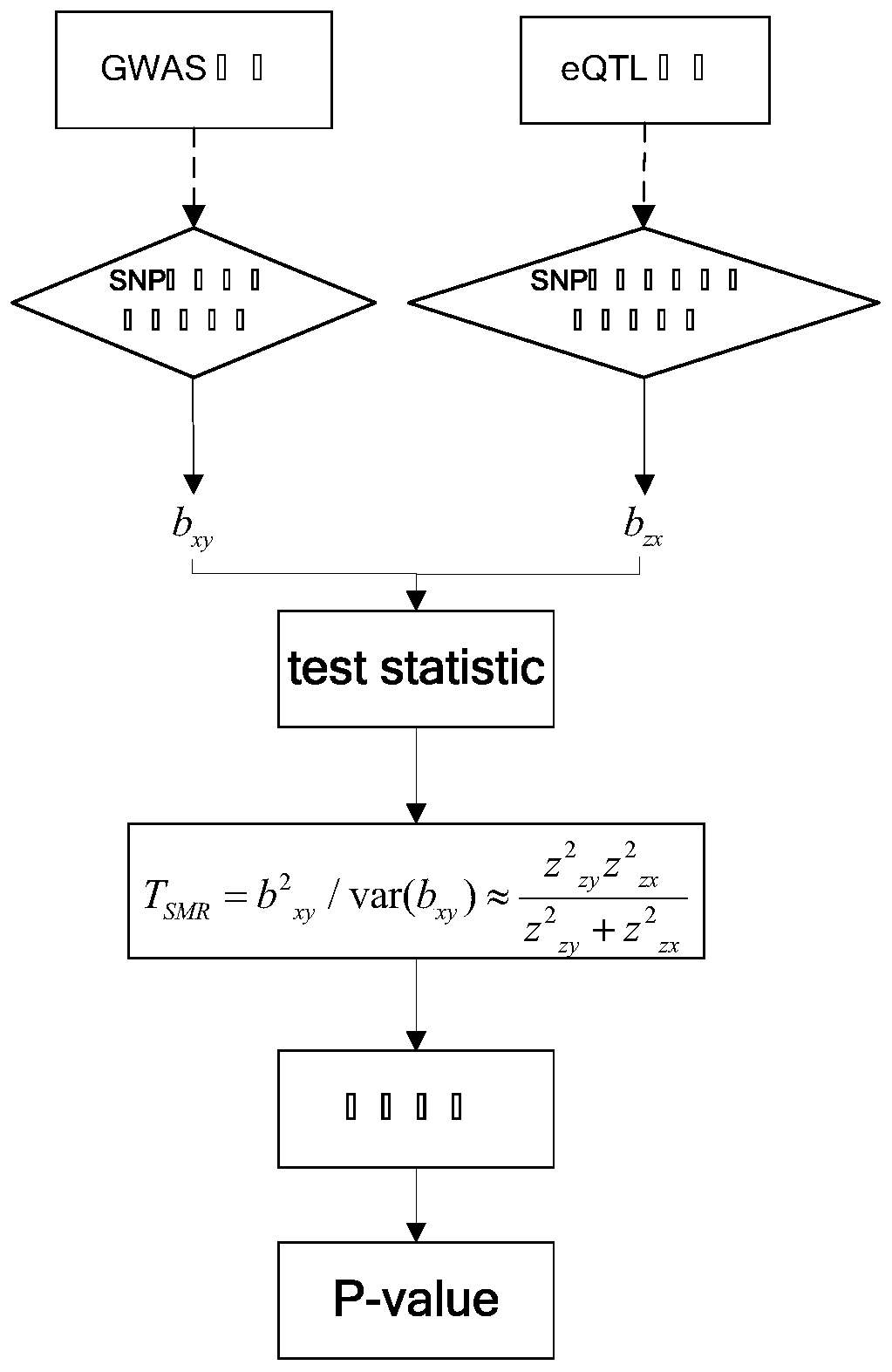
Senile dementia gene and site screening method based on improved Mendelian randomization
The invention provides a senile dementia gene and site screening method based on improved Mendelian randomization, and belongs to the field of Alzheimer's disease related gene and site screening. Themethod comprises the specific steps: taking GWAS data as x, taking eQTL data as y, and taking SNP data as z; obtaining the effect bxy of x on y, the effect bzx of z on x, and the effect bzy of z on y;defining bxy: bxy = bze / bzx; calculating Z-score of SNP in an eQTL dataset; calculating Z-score of corresponding SNPs in a GWAS dataset; calculating a statistic Tsmr and obeying chi-square distribution with a degree of freedom of 1; performing the chi-square test of Tsmr and solution of P-value; and screening the values according to the sizes of the P-value. More genes and sites related to AD arediscovered, the risk of illness can be predicted during gene screening, and the method has extremely important significance for research and development of gene targeted drugs. Under the extreme condition, a gene knockout operation can be carried out to enable a patient to recover.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
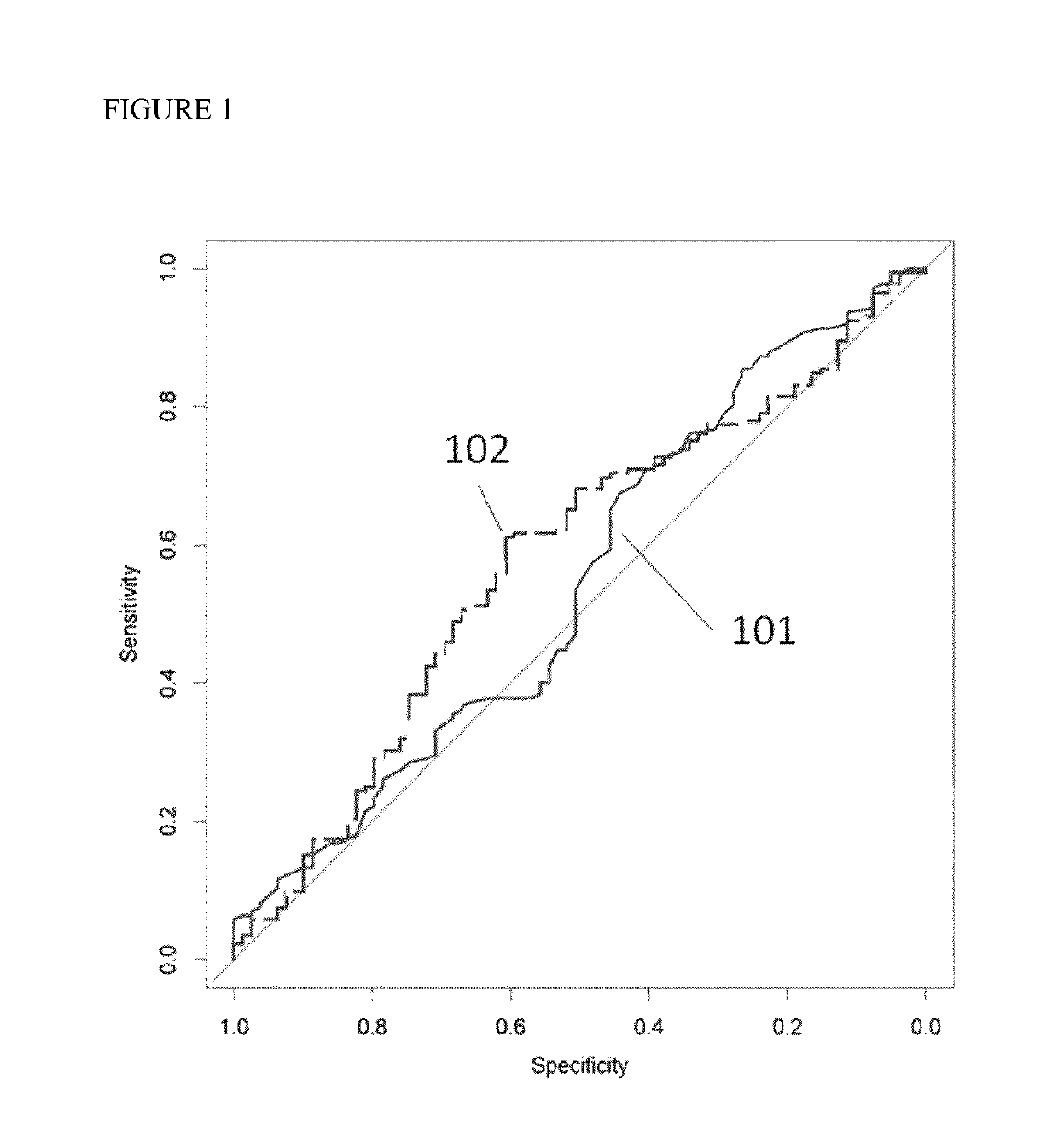
Prognostic Method for Individuals with Prostate Cancer
ActiveUS20150284804A1Improve abilitiesSimple treatmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProstate cancerSnp data
The present invention relates generally to the detection and identification of various forms of genetic markers, and various forms of proteins, which have the potential utility as diagnostic markers. By determining the level of a plurality of biomarkers and genetic markers in a patient sample, and combining the obtained values according to a predefined formula, it is possible to forecast if it is likely that the prostate cancer patient will require active therapy like radiation therapy or surgery. A method based on a redundantly designed combination of data is disclosed for estimating if prostate cancer is aggressive or indolent. Said method combines SNP data to form a composite value, wherein at least 5% of the SNPs can be disregarded.
Owner:PHADIA AB
SNP selection method based on improved fuzzy clustering algorithm
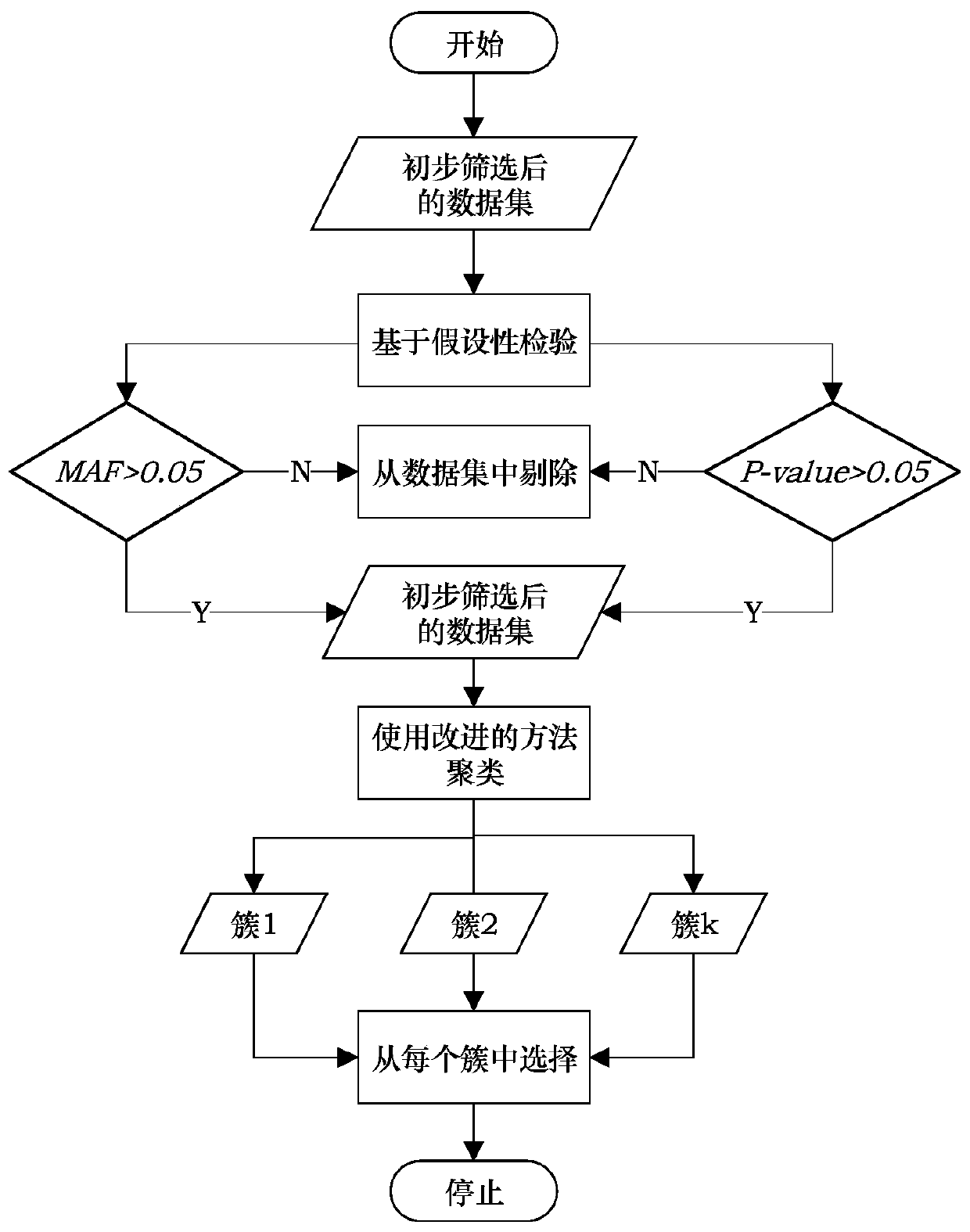
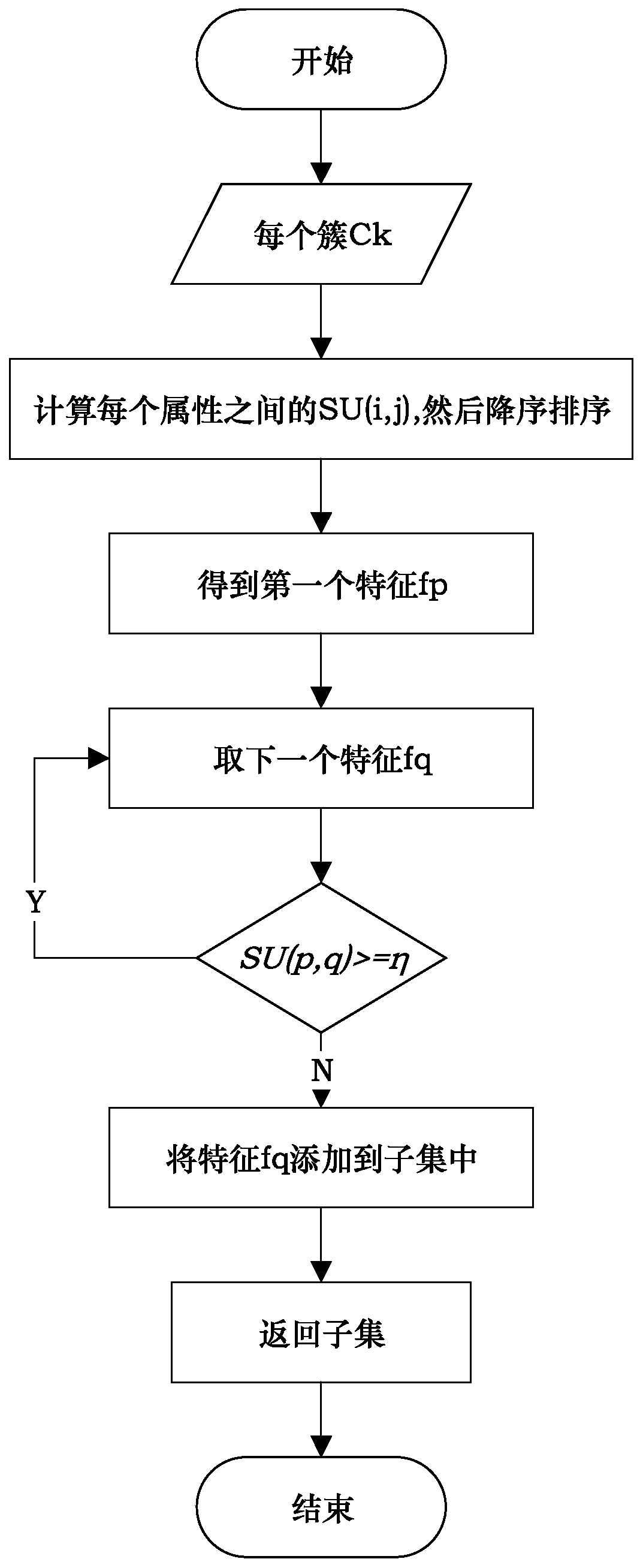
ActiveCN109801681AEasy to digEasy to classifyBiostatisticsInstrumentsCanopy clustering algorithmNucleotide
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) selection method based on an improved fuzzy clustering algorithm. The SNP selection method includes the steps: obtaining an SNP data set; preprocessing the obtained SNP data, including cleaning and re-encoding the data; performing preliminary screening on the pre-processed data based on a hypothesis test; for the preliminarily screened data, respectively calculating the importance degree of each SNP; clustering the SNPs by using the improved fuzzy clustering algorithm; and further screening each cluster obtained from the clustering according to the principle of symmetrical imbalance, and constructing SNP subsets. The SNP selection method based on an improved fuzzy clustering algorithm focuses on the SNP data, considers the influence of a single SNP on the classification result while considering the correlation between the local area SNPs, and fully exploits the information inside the SNPs while achieving dimensionality reduction on the data. The SNP subsets constructed by using the SNP selection method based on an improved fuzzy clustering algorithm has a better classification effect than other selection methods and can be applied to the selection of SNP data.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV +1
Polymorphisms in growth hormone receptor, ghrelin, leptin, neuropeptide Y, and uncoupling protein 2 genes and their associations with measures of performance and carcass merit in beef cattle
ActiveUS8003318B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideDense Core Vesicles
The physiological regulation of intake, growth and energy partitioning in animals is under the control of multiple genes, which may be important candidates for unraveling the genetic variation in economically relevant traits in beef production. The present invention relates to the identification of a single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the bovine genes encoding growth hormone receptor (GHR), ghrelin, leptin, neuropeptide Y (NPY), and Uncoupling Protein 2 (UCP2) and their association with economically relevant traits in beef production. The invention further encompasses methods and systems, including network-based processes, to manage the SNP data and other data relating to specific animals and herds of animals, veterinarian care, diagnostic and quality control data and management of livestock which, based on genotyping, have predictable meat quality traits, husbandry conditions, animal welfare, food safety information, audit of existing processes and data from field locations.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Feature selection method facing to SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) data
InactiveCN102629305BSolve the problem of low efficiency of feature selectionSolve selection inefficienciesSpecial data processing applicationsSmall sampleAlgorithm
The invention discloses a feature selection method facing to SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) data, which specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out data pre-processing; secondly, removing unrelated SNP features by using a newly-designed Relief algorithm; thirdly, carrying out critical degree sorting on the SNP features by using an improved SVM-RFE algorithm; and finally, screening the critical SNP sorting by using cross validation. The feature selection method has the beneficial effects that the advantages of Filter feature selection and Wrapper feature selection are combined, and a secondary division method is used in the machine learning process, so that the problems of a high-dimensional small sample in the SNP feature selection and a SNP pathogenic combination mode are solved, and the analysis efficiency and the accuracy are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
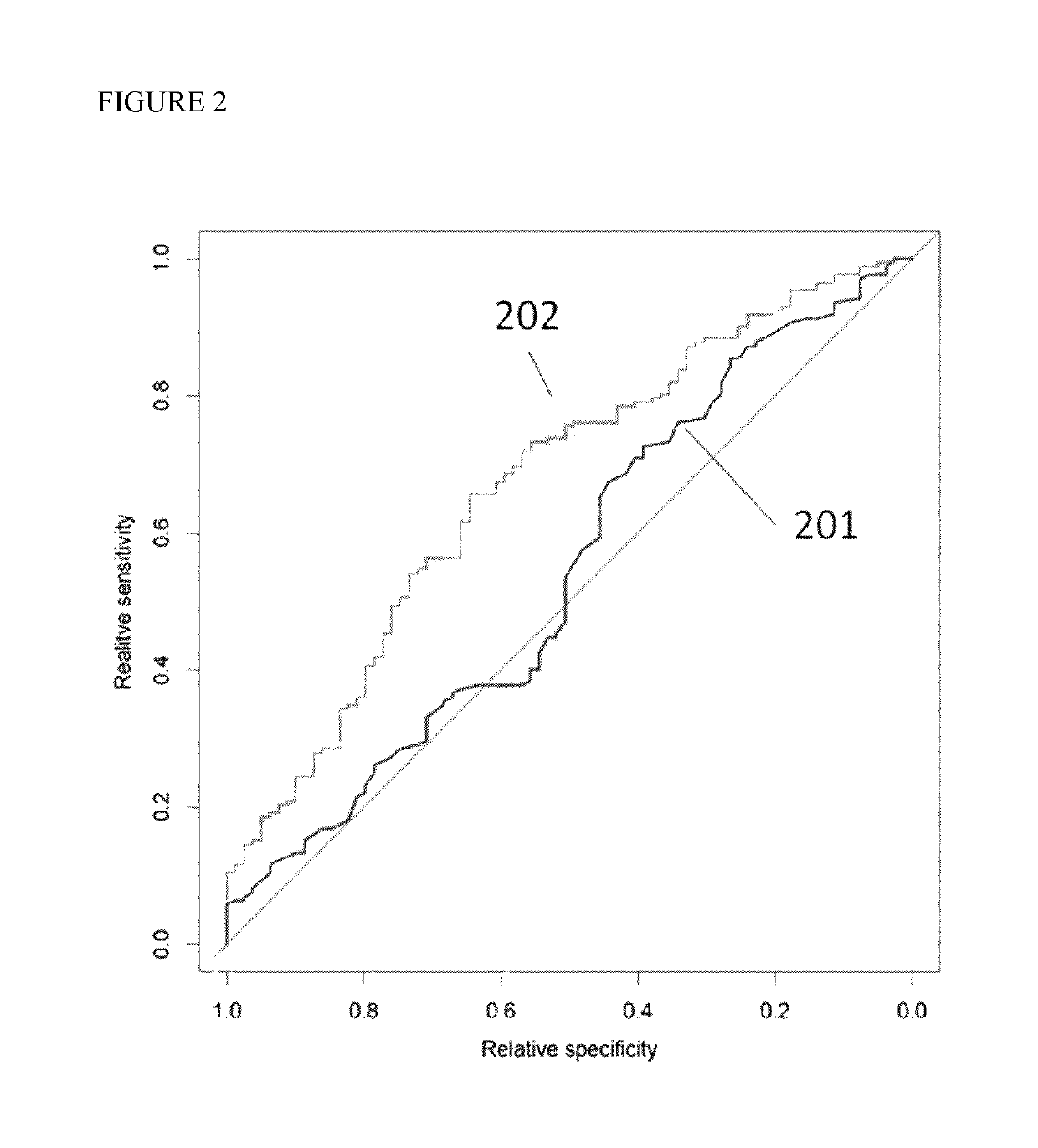
Prognostic method for individuals with prostate cancer
ActiveUS10428385B2Easy to determineSimple treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsProstate cancerBiologic marker
The present invention relates generally to the detection and identification of various forms of genetic markers, and various forms of proteins, which have the potential utility as diagnostic markers. By determining the level of a plurality of biomarkers and genetic markers in a patient sample, and combining the obtained values according to a predefined formula, it is possible to forecast if it is likely that the prostate cancer patient will require active therapy like radiation therapy or surgery. A method based on a redundantly designed combination of data is disclosed for estimating if prostate cancer is aggressive or indolent. Said method combines SNP data to form a composite value, wherein at least 5% of the SNPs can be disregarded.
Owner:PHADIA AB
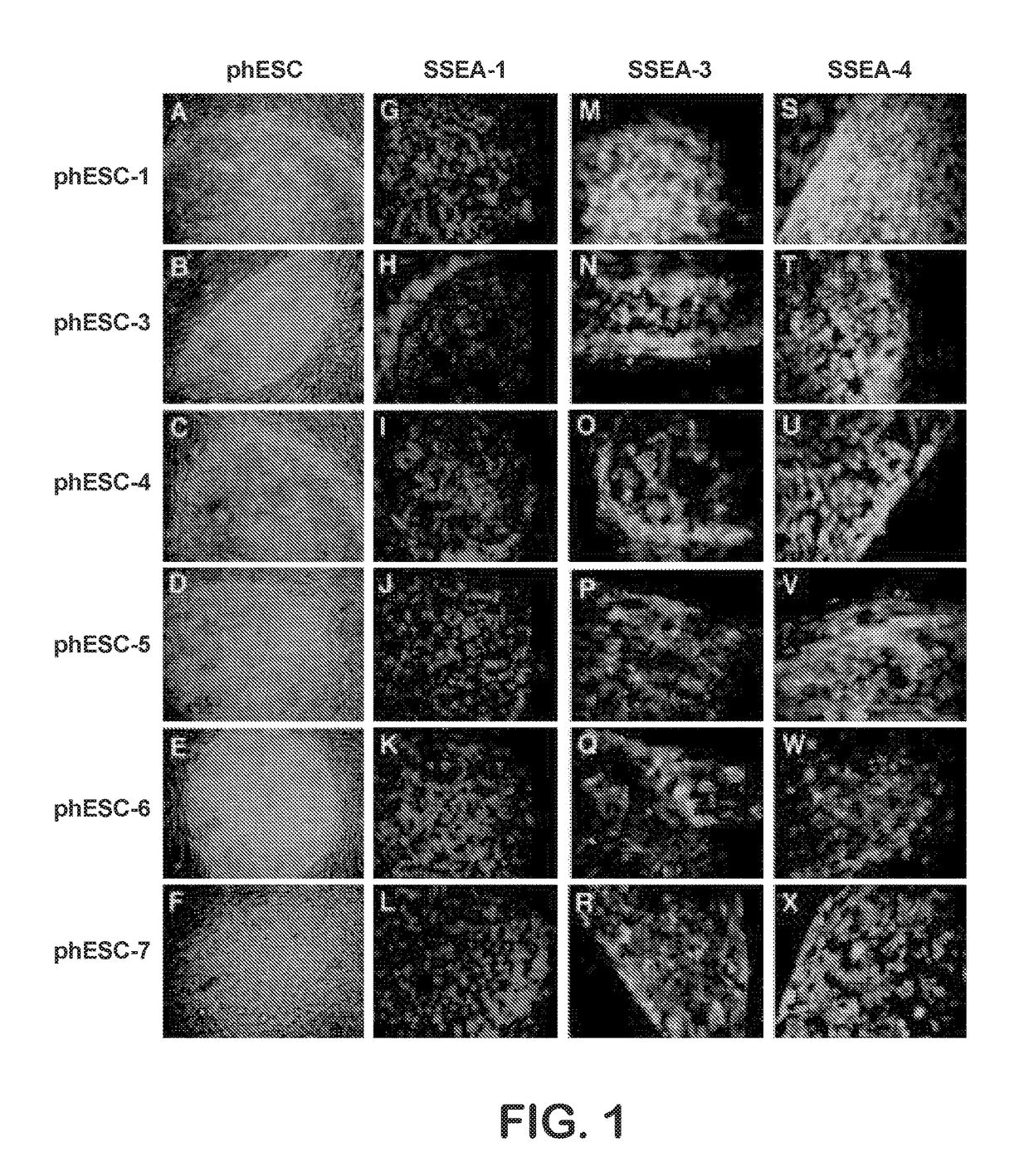
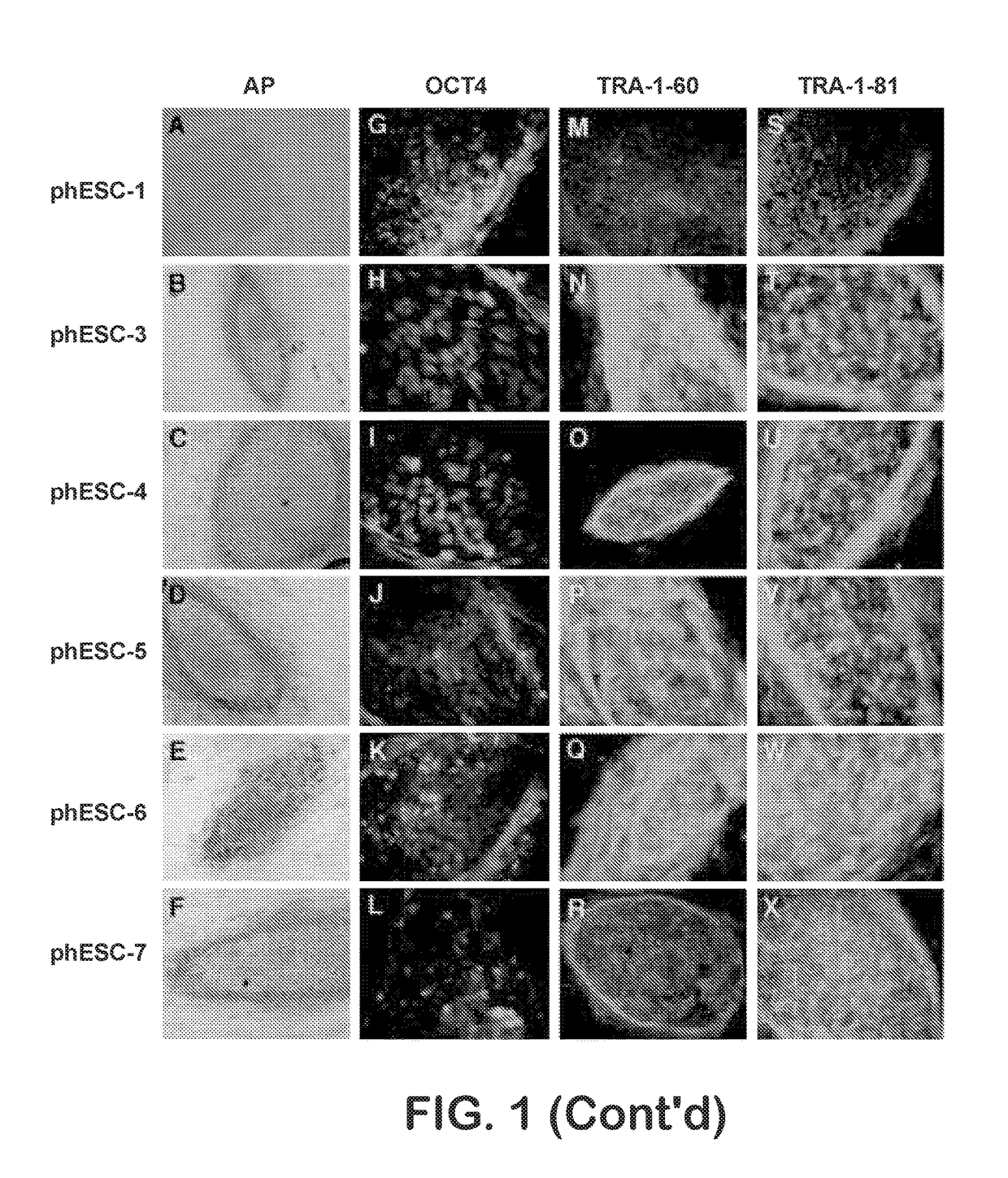
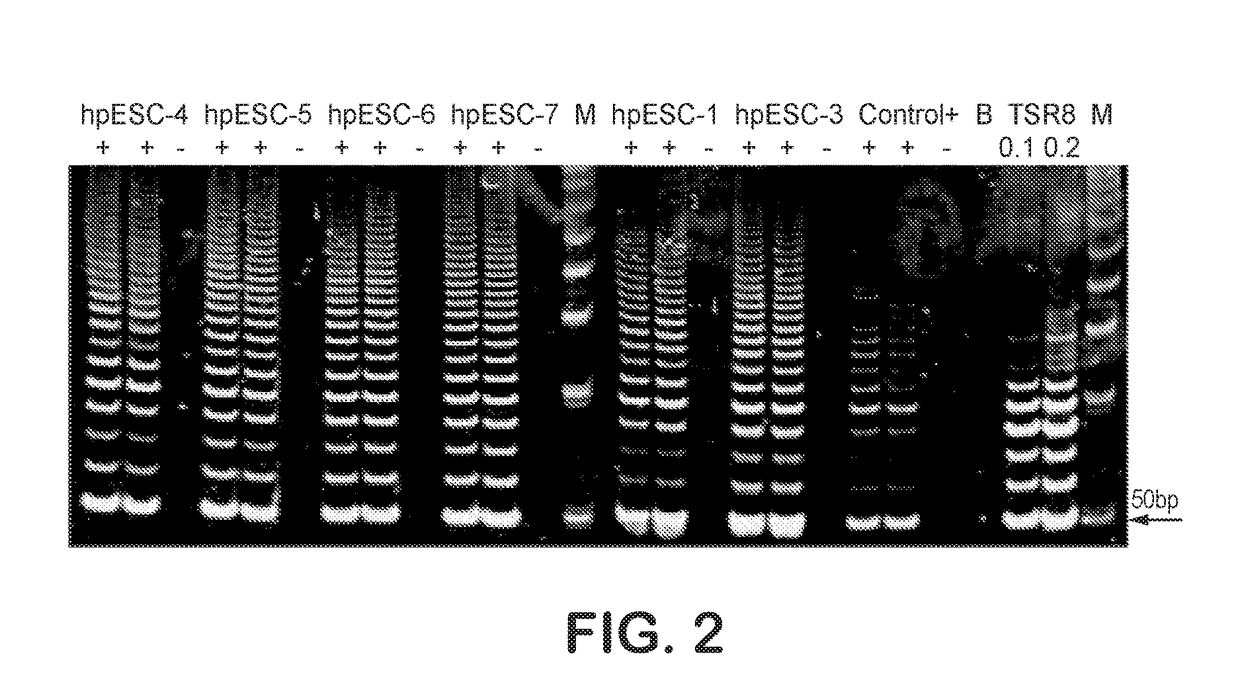
Patient-specific stem cell lines derived from human parthenogenetic blastocysts
Methods are disclosed for generating HLA homozygous parthenogenetic human stem cell (hpSC-Hhom) lines from both HLA homozygous and HLA heterozygous donors. These hpSC-Hhom lines demonstrate typical human embryonic stem cell morphology, expressing appropriate stem cell markers and possessing high levels of alkaline phosphatase and telomerase activity. Additionally, injection of these cell lines into immunodeficient animals leads to teratoma formation. Furthermore, in the case of HLA heterozygous donors, the hpSC-Hhom lines inherit the haplotype from only one of the donor's parents. SNP data analysis suggests that hpSC-Hhom lines derived from HLA heterozygous oocyte donors are homozygous throughout the genome as assessed by single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis. The protocol as disclosed minimizes the use of animal-derived components, which makes the stem cells more practical for clinical application.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Genome Information Assisted Breeding Method I-Breeding Parent Selection Based on SNP Clustering Information and Pav Variation Information
InactiveCN106169034BAccurately and effectively obtainReduce workloadBiostatisticsInstrumentsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome information assisted breeding method for parent selection by means of SNP clustering and PAV variation. The essence of the genome information assisted breeding method is to obtain genome sequencing information of candidate parents with the help of genomic and bioinformatics methods; on one hand, a high-quality SNP data set is obtained through sequence alignment, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate parents is calculated, and the affinity between the candidate parents is judged with the help of a clustering tree; on the other hand, a Denovo assembled candidate parent contig is positioned to a reference genome, and the PAV variation of candidate parent target trait related genes is obtained according to the physical location. By combining the PAV variation and affinity information based on SNP, a parent subset is screened out from a large number of candidate parents for phenotype identification; finally, a selected breeding parent is determined by combining the phenotype identification result of the parent subset. The genome information assisted breeding method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding, the range of the materials for phenotype identification can be effectively narrowed from the large number of the candidate parents, the workload of phenotype identification is reduced, and the breeding work efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP pathogenic factors and disease association model establishment method
ActiveCN110459266BReduce the degree of interactionThe relationship model is accurateBiostatisticsProteomicsDiseaseSnp data
The invention belongs to the technical field of data processing, and discloses a method for establishing a correlation model between SNP pathogenic factors and diseases, collecting sample data sets corresponding to current SNP pathogenic factors; absolutely dividing the sample data sets according to initial values; based on machine learning Methods SNP pathogenic factors and disease association modeling; modeling results accuracy evaluation; determine the SNP pathogenic factors and disease association model. The present invention reduces the degree of interaction among various SNP pathogenic factors through the method of absolute division, so that the established correlation model between each SNP pathogenic factor and the disease is more accurate. The present invention is simple to operate, only needs to input the original SNP data and all SNP pathogenic factors, and can obtain a more accurate correlation model between each SNP pathogenic factor and the disease.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com