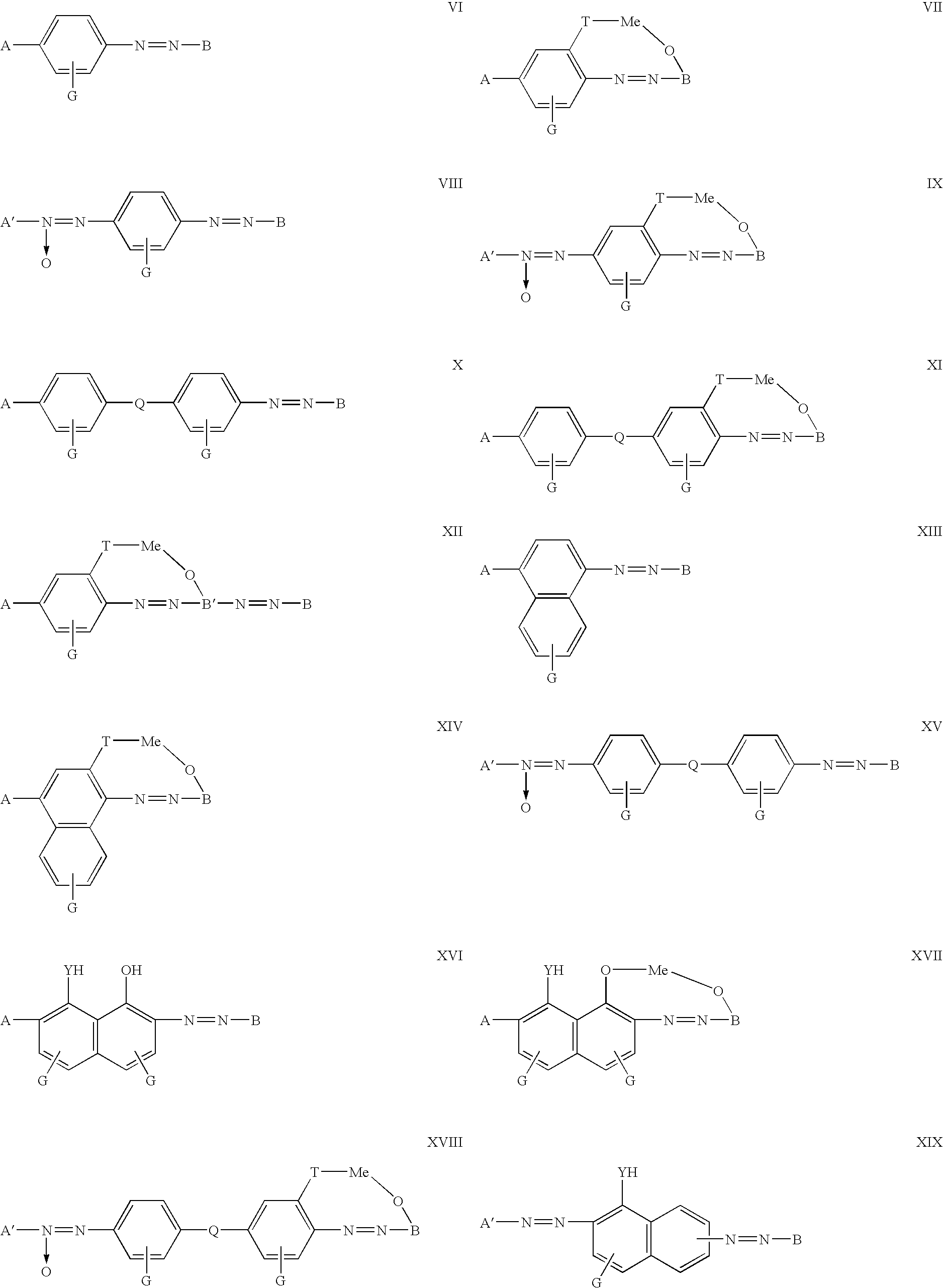Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Optical transition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
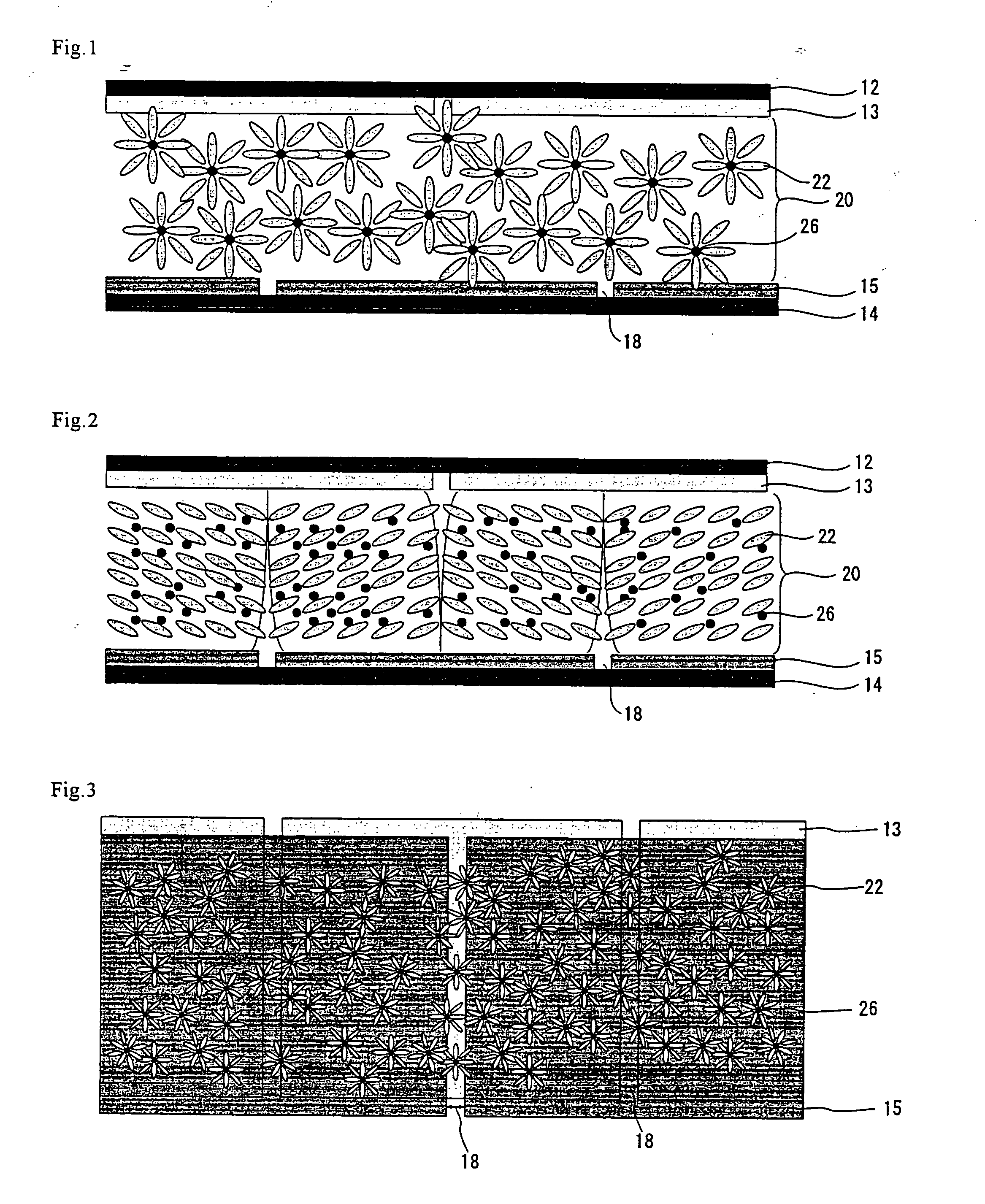
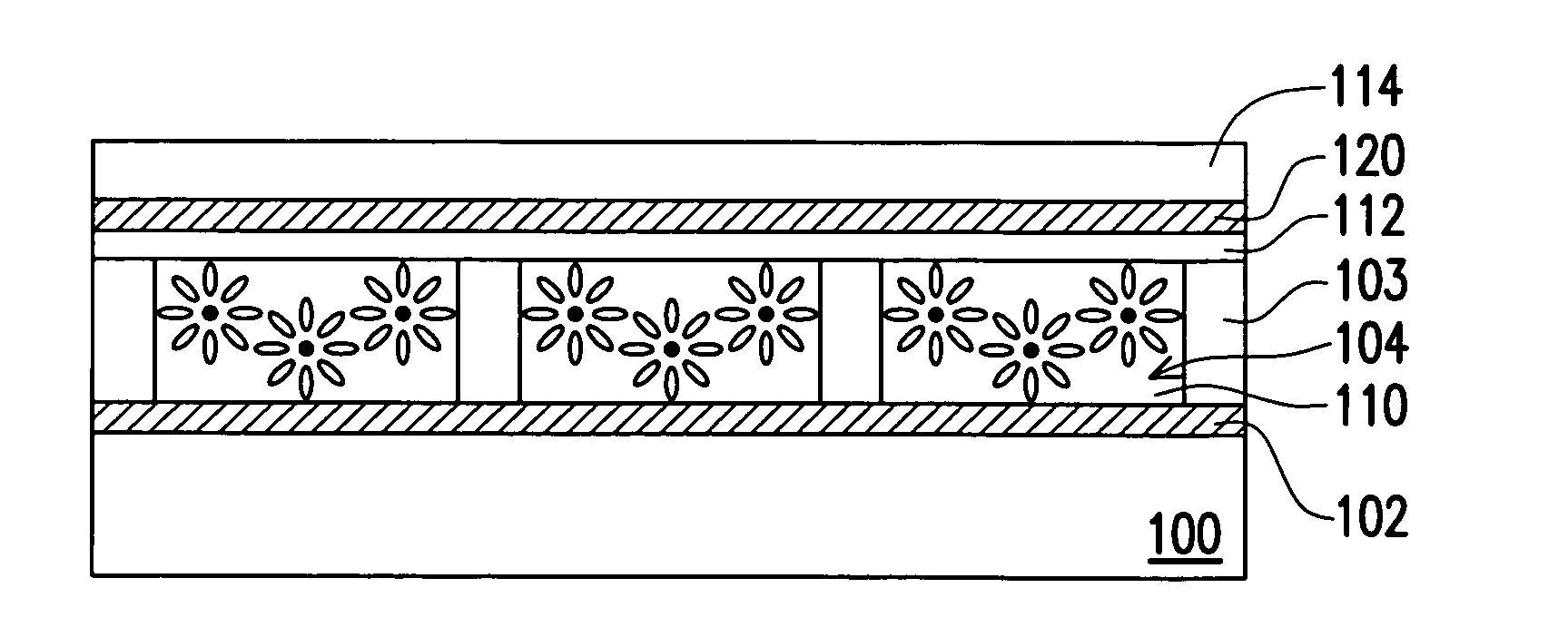
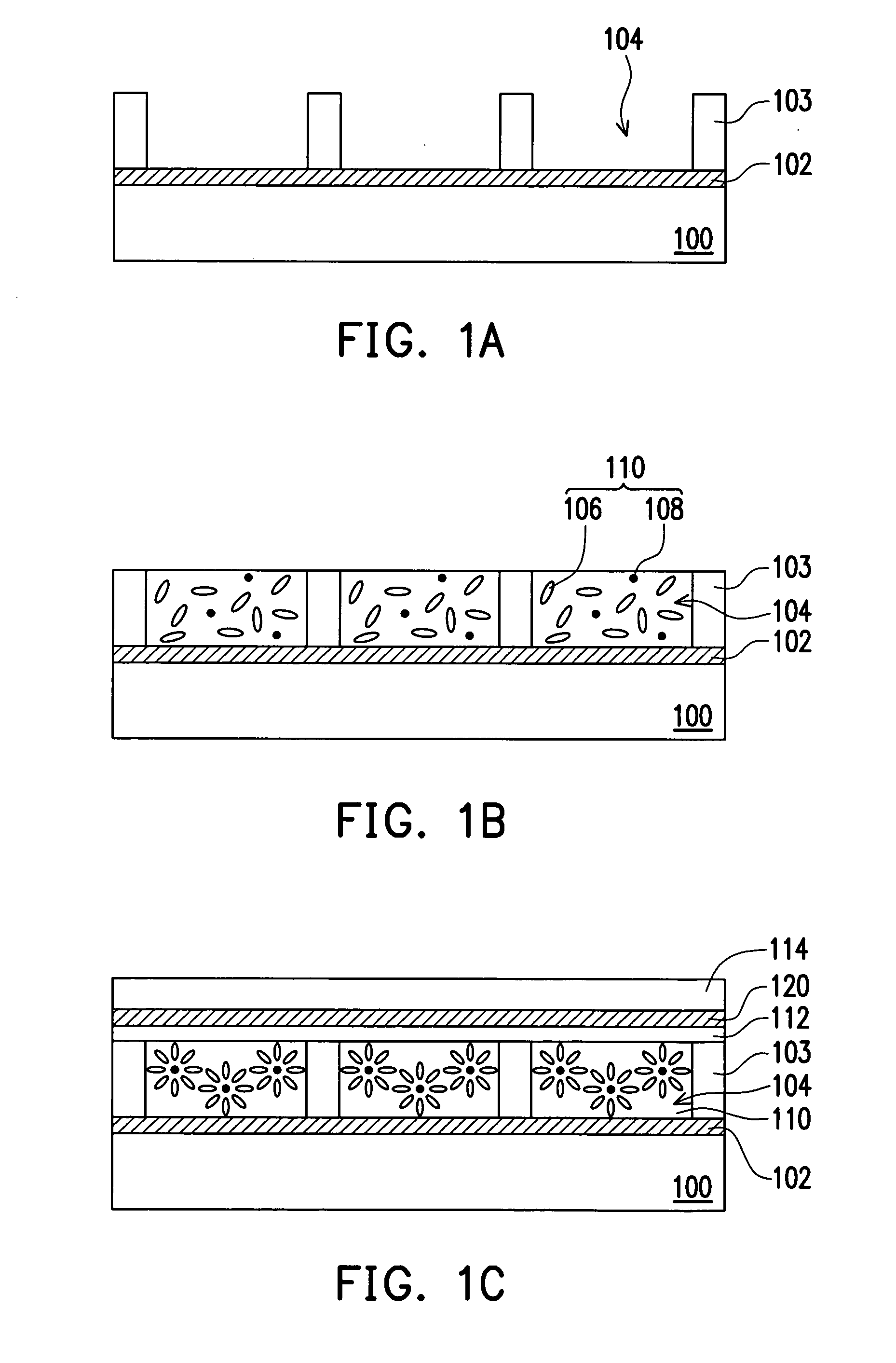
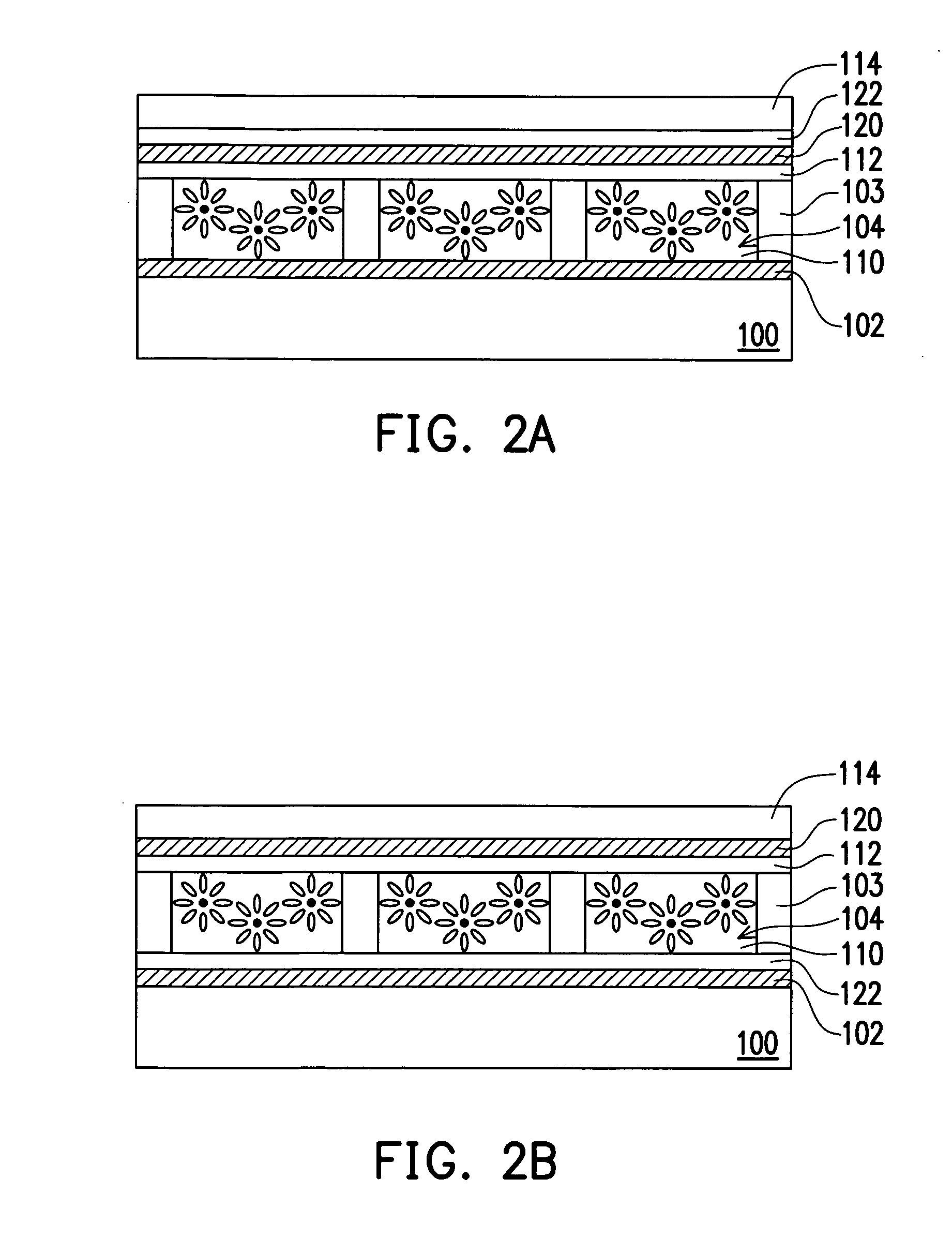
Light-emitting nanoparticles and method of making same
InactiveUS6846565B2Reduce aggregationResist formationMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH +1
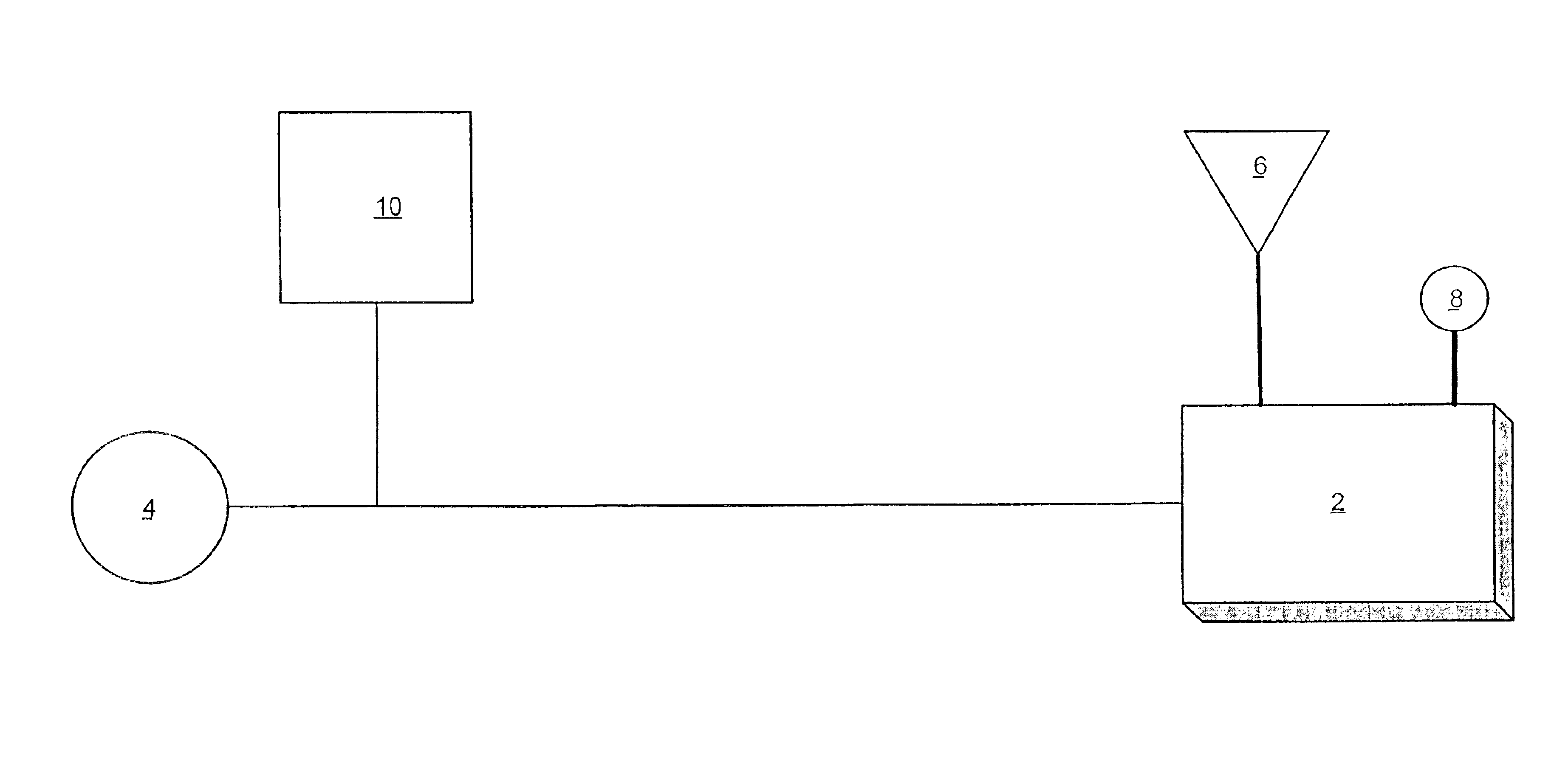
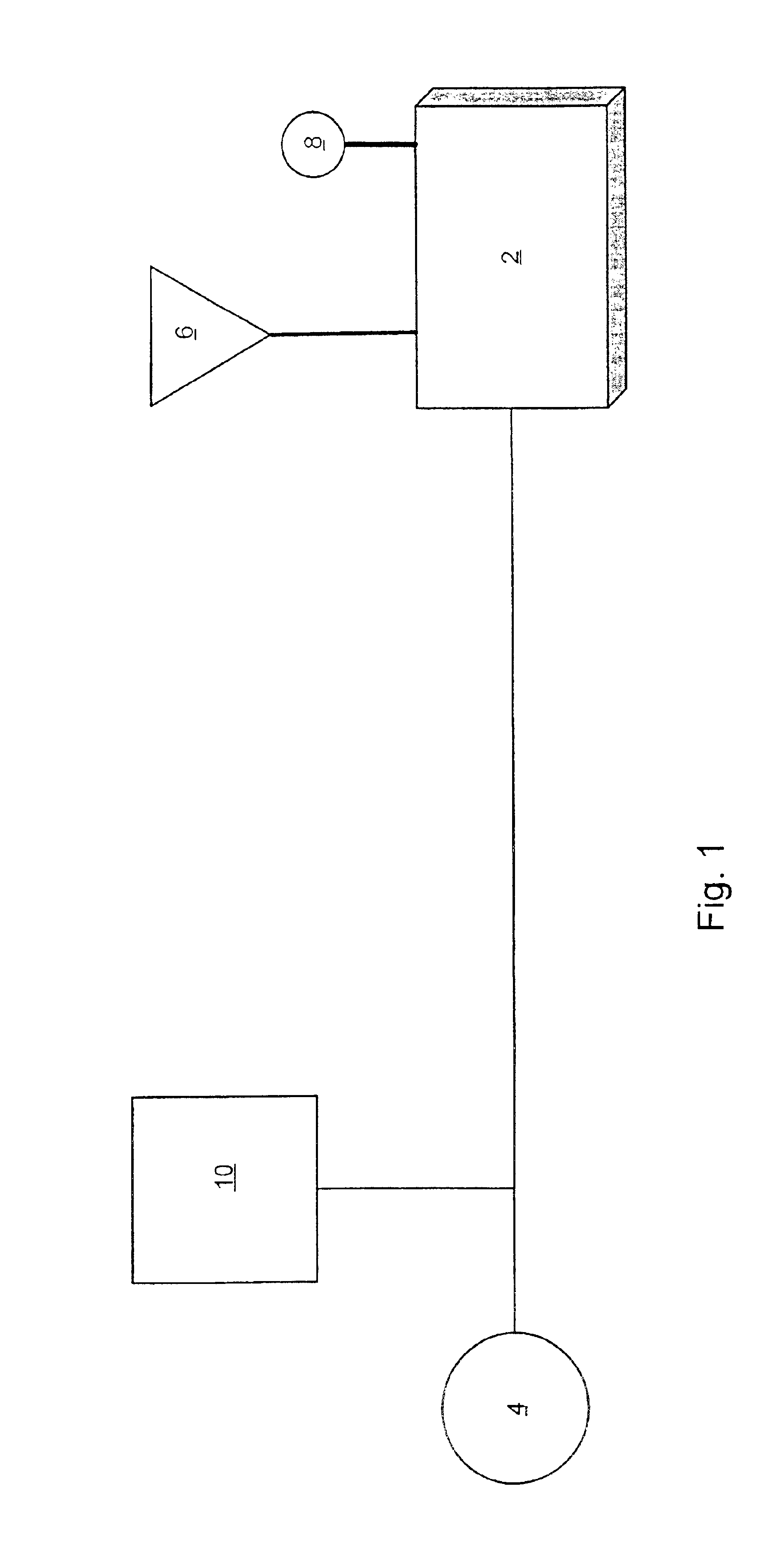
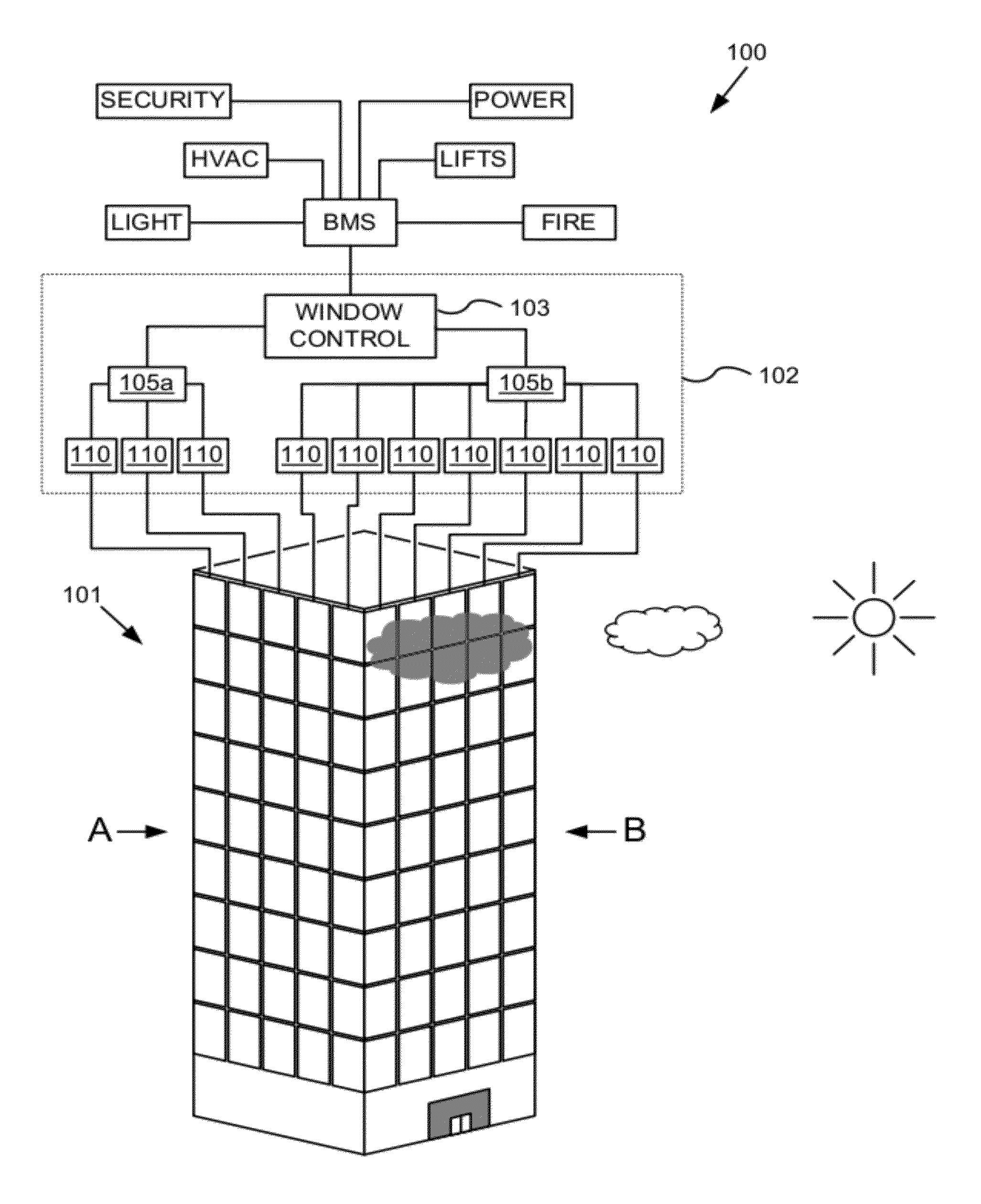
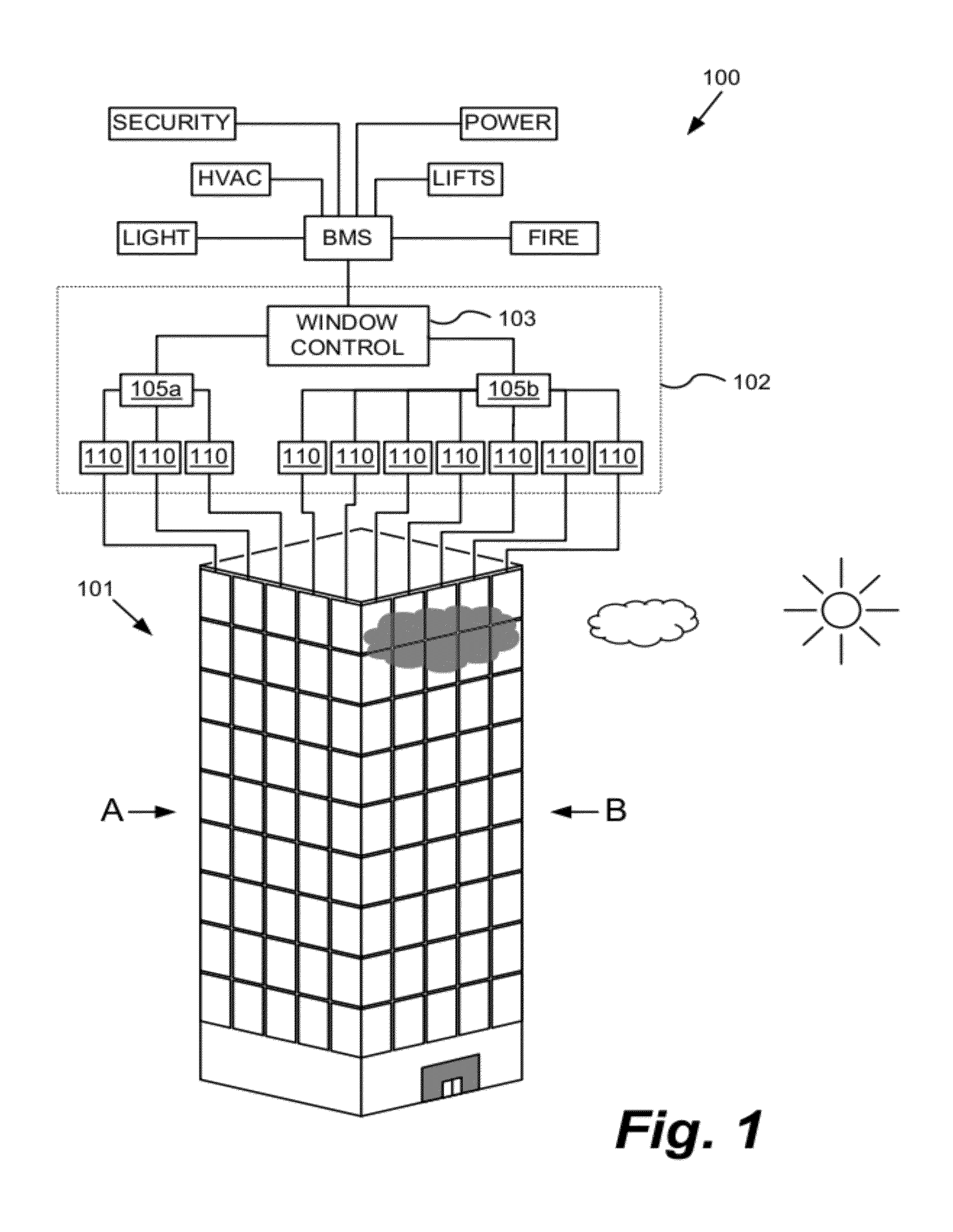
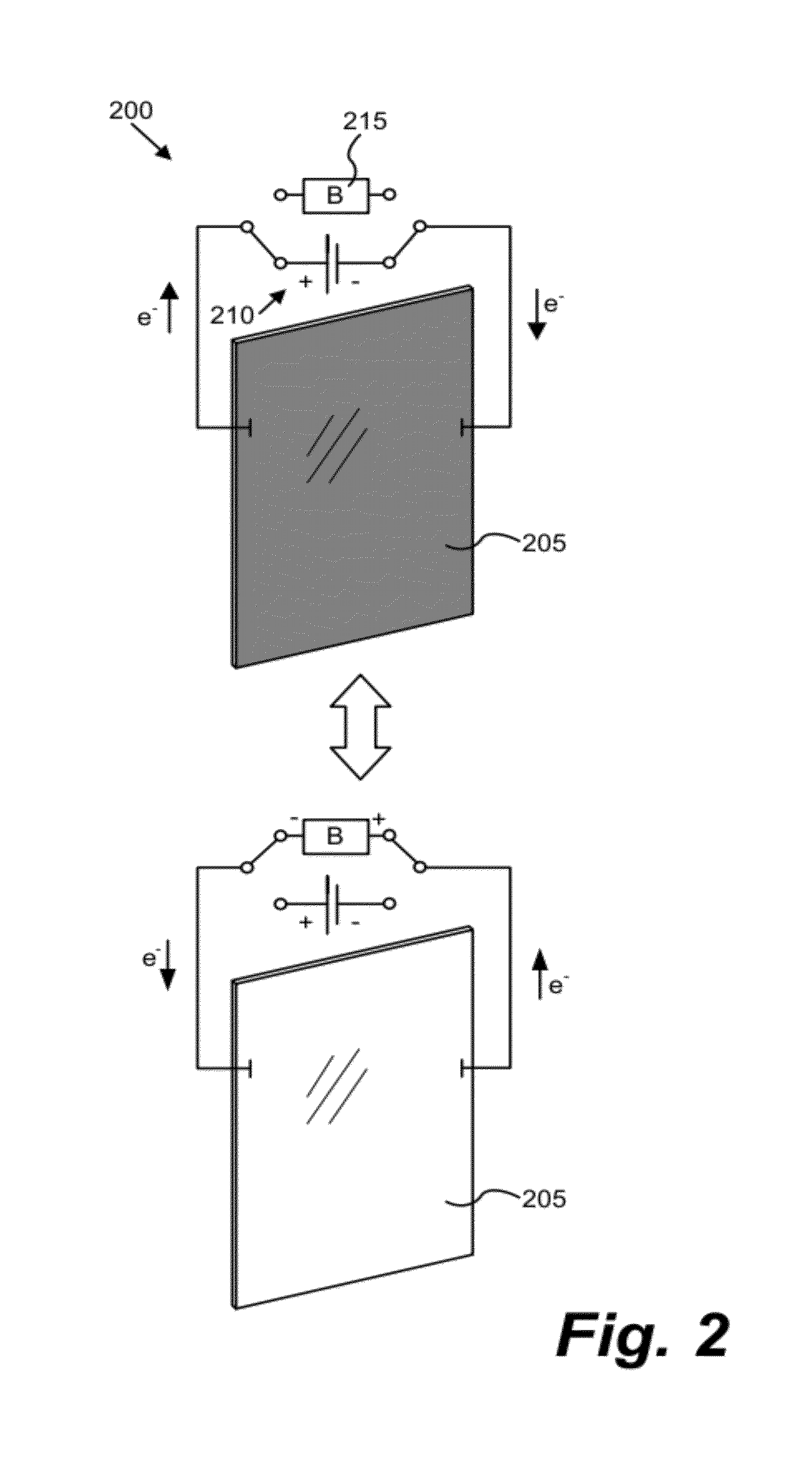
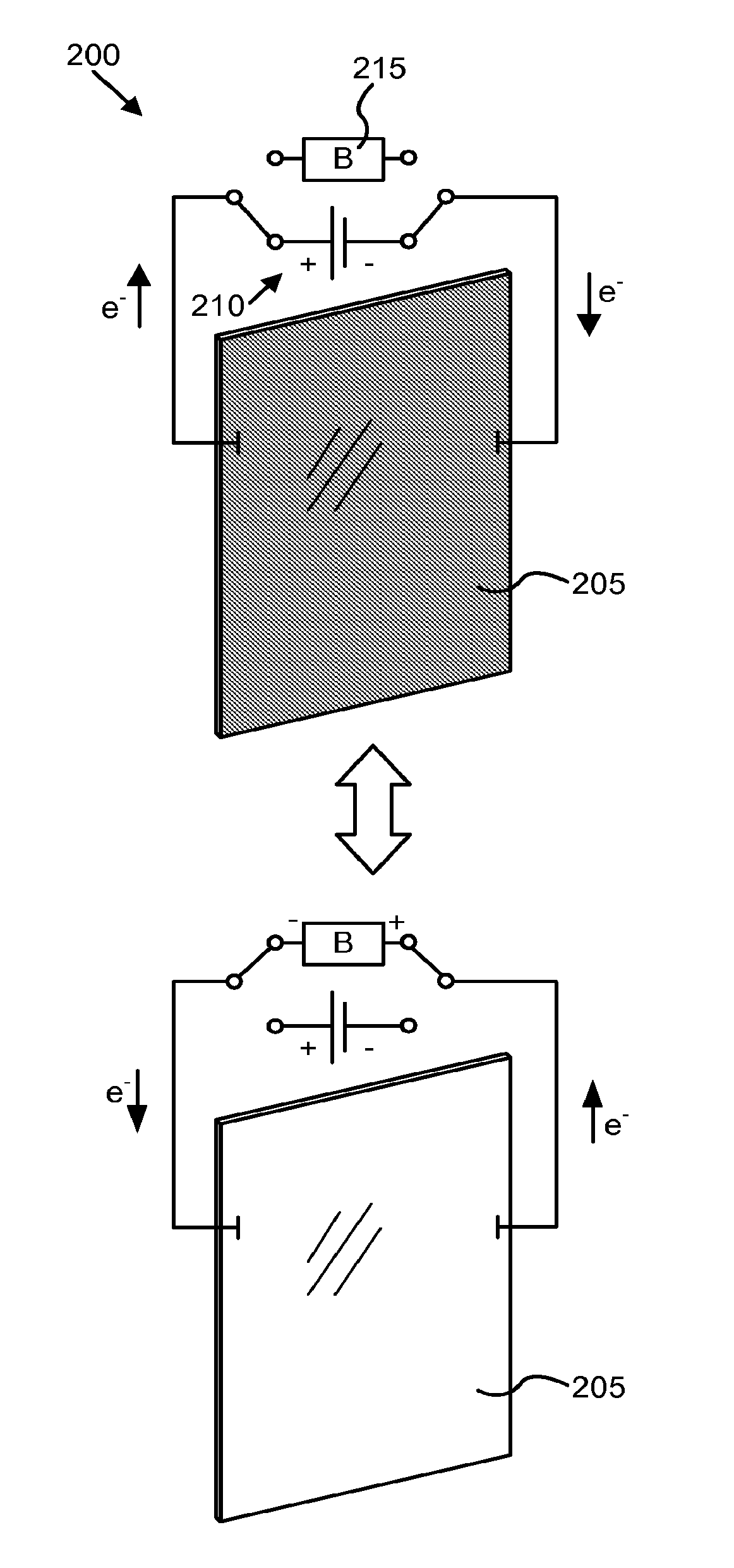
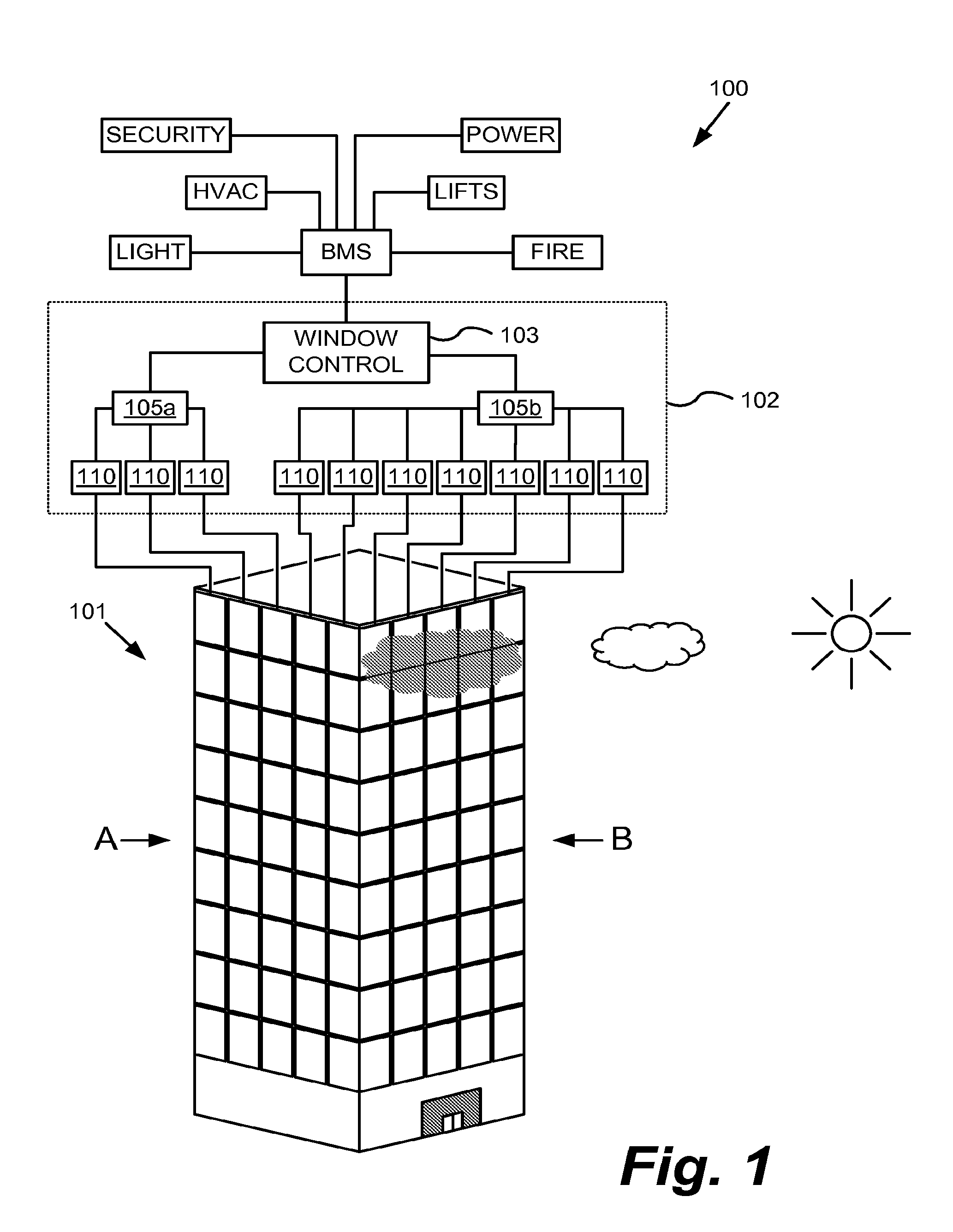
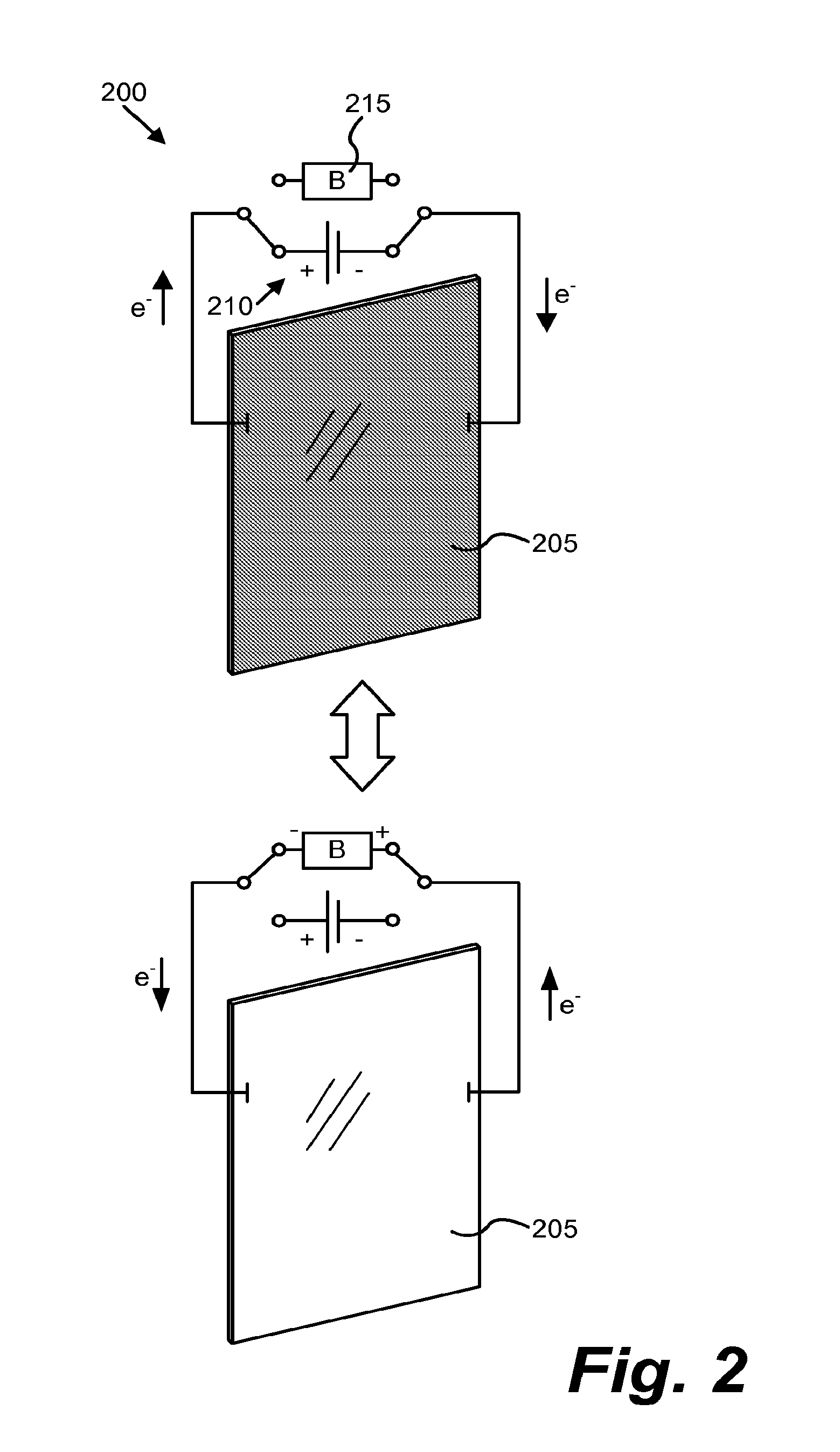
Multipurpose controller for multistate windows
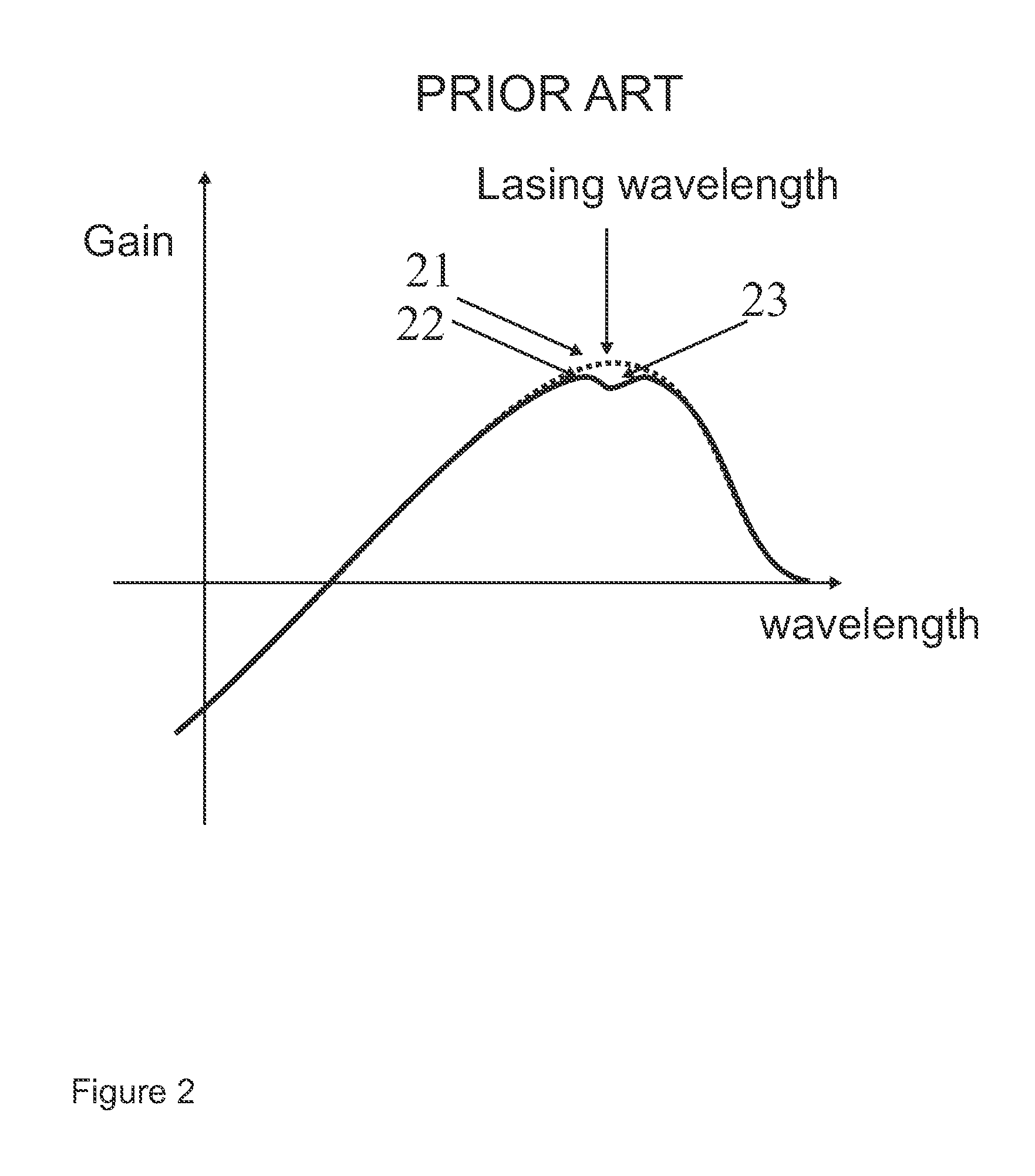
ActiveUS20120239209A1Improve the environmentSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlTransmittanceLocal environment
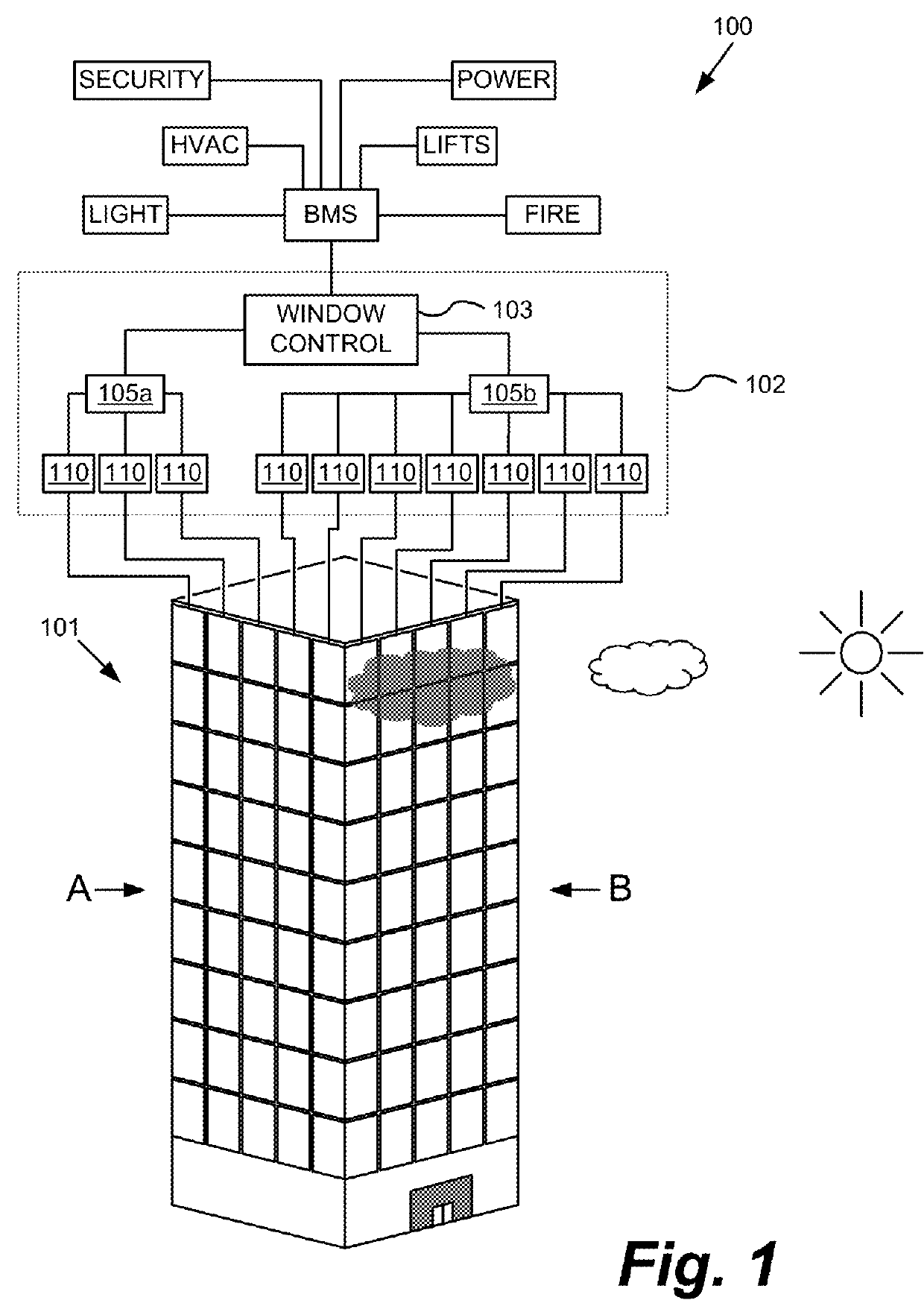
“Smart” controllers for windows having controllable optical transitions are described. Controllers with multiple features can sense and adapt to local environmental conditions. Controllers described herein can be integrated with a building management system (BMS) to greatly enhance the BMS's effectiveness at managing local environments in a building. The controllers may have one, two, three or more functions such as powering a smart window, determining the percent transmittance, size, and / or temperature of a smart window, providing wireless communication between the controller and a separate communication node, etc.
Owner:VIEW INC
Applications of light-emitting nanoparticles
InactiveUS6918946B2Reduce aggregationResist formationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:KORGEL BRIAN A +1
Multipurpose controller for multistate windows
ActiveUS20140160550A1Improve the environmentLight protection screensNon-linear opticsTransmittanceEngineering
“Smart” controllers for windows having controllable optical transitions are described. Controllers with multiple features can sense and adapt to local environmental conditions. Controllers described herein can be integrated with a building management system (BMS) to greatly enhance the BMS's effectiveness at managing local environments in a building. The controllers may have one, two, three or more functions such as powering a smart window, determining the percent transmittance, size, and / or temperature of a smart window, providing wireless communication between the controller and a separate communication node, etc.
Owner:VIEW INC
Three-level air-clad rare-earth doped fiber laser/amplifier
InactiveUS6987783B2Facilitates dopingLower effective refractive indexOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsThree levelAudio power amplifier
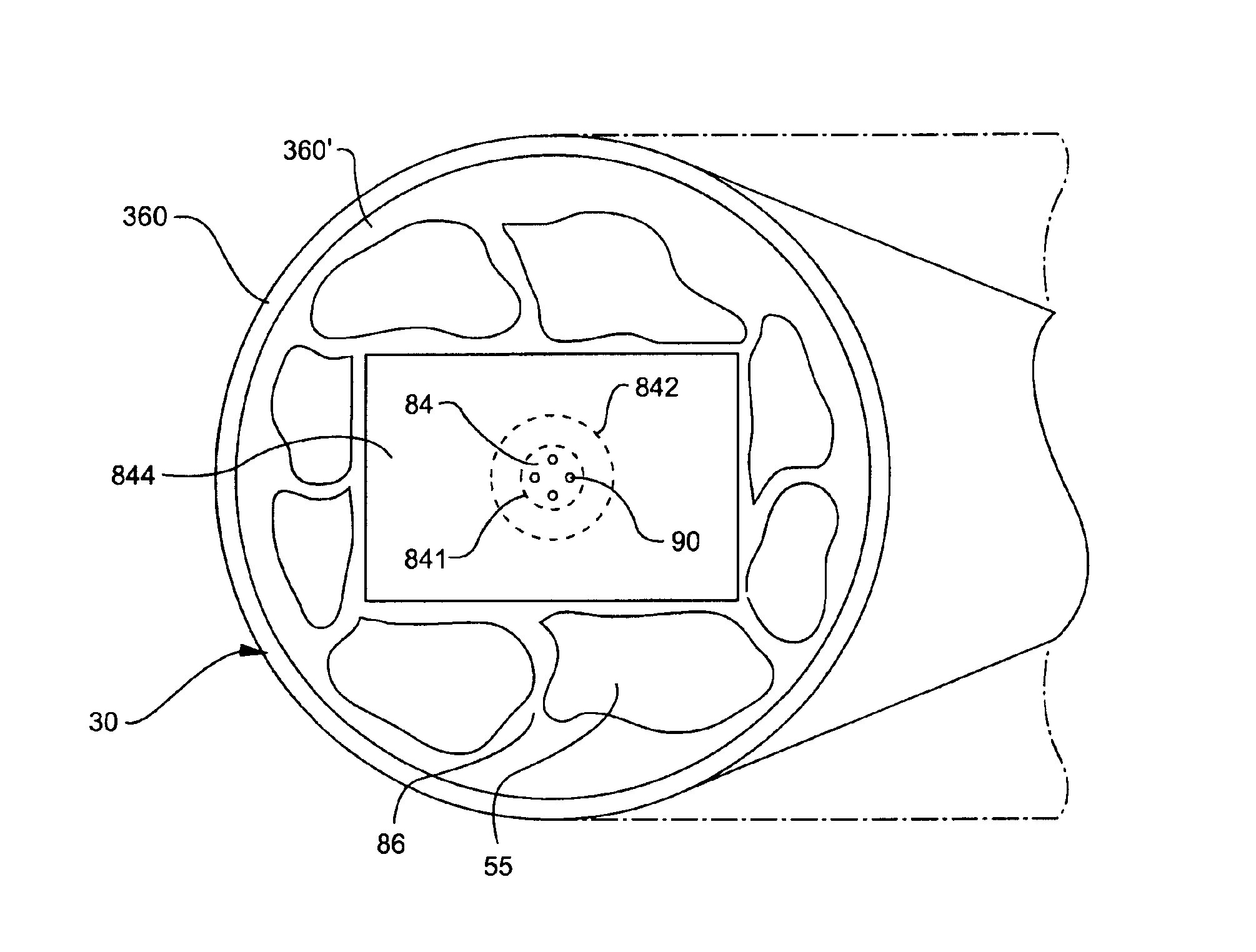
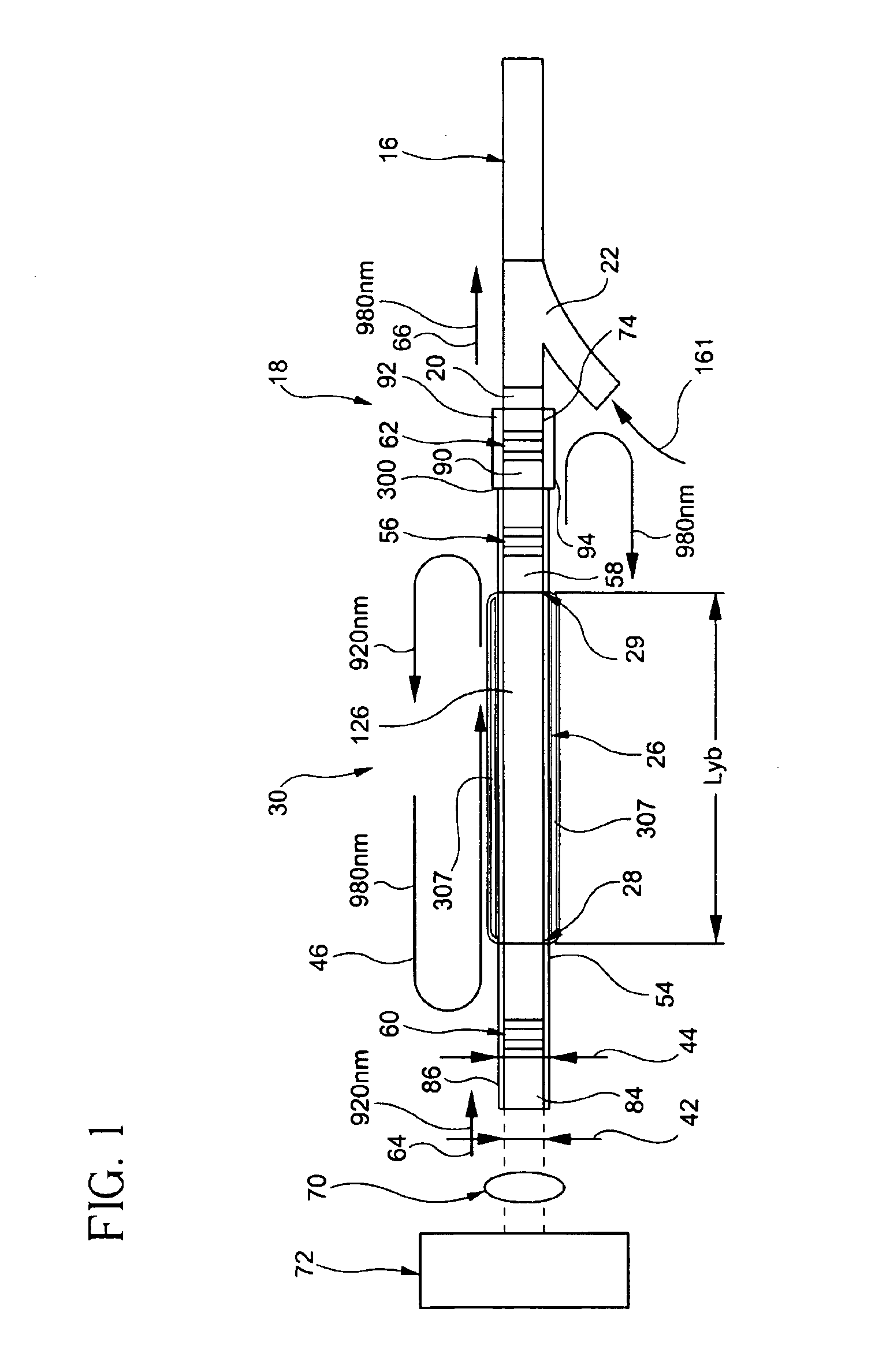
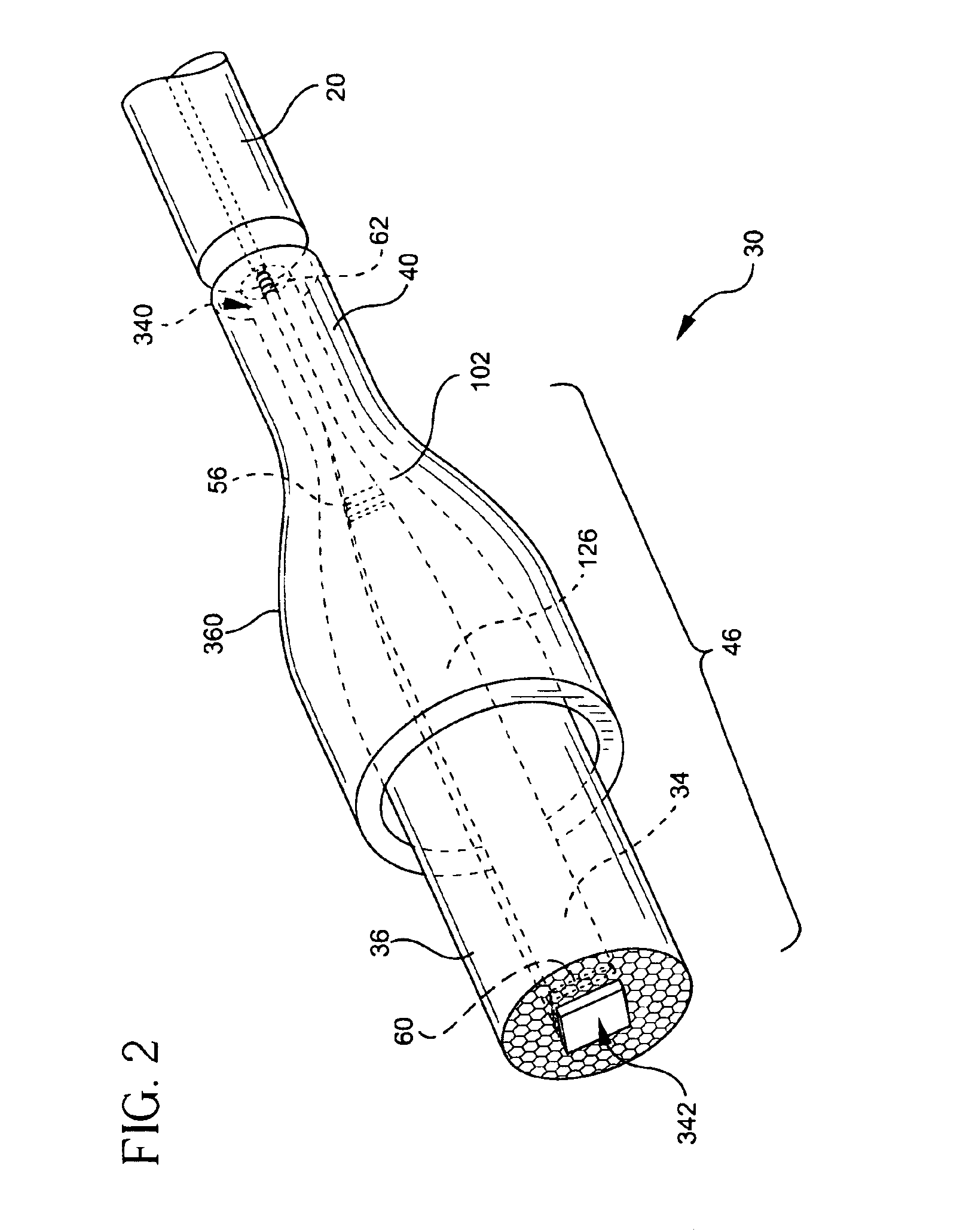
An optically-active air-clad fiber (30) includes a core (34, 84) that facilitates doping with an ion optically excitable and having a three-level optical transition when pumped at a first end (28) of an optical cavity (46) by a multimode pump source (72) at a pump wavelength (64) for lasing at a signal wavelength (66) different than the pump wavelength (64) at a second end (29) of the optical cavity (46), the core (34, 84) having a refractive index, wherein the core (34, 84) is transformed from the first end to proximate the second end (29) thereof such that the optically-active fiber (30) is multimode at the pump wavelength proximate to the first end (28), and is single-mode at the signal wavelength proximate to the second end (29). An air-clad (36, 86) surrounds at least one portion of the core (34, 84) and has a lower effective refractive index than the refractive index of the core (34, 84).
Owner:CORNING INC
Multipurpose controller for multistate windows
ActiveUS20160054634A1Improve the environmentStatic indicating devicesLight protection screensOperating energyControl engineering
“Smart” controllers for windows having controllable optical transitions are described. Controllers with multiple features can sense and adapt to local environmental conditions. Controllers described herein can be integrated with a building management system (BMS) to greatly enhance the BMS's effectiveness at managing local environments in a building. The controllers may have one, two, three or more functions such as powering a smart window, determining the percent transmittance, size, and / or temperature of a smart window, providing wireless communication between the controller and a separate communication node, etc.
Owner:VIEW INC
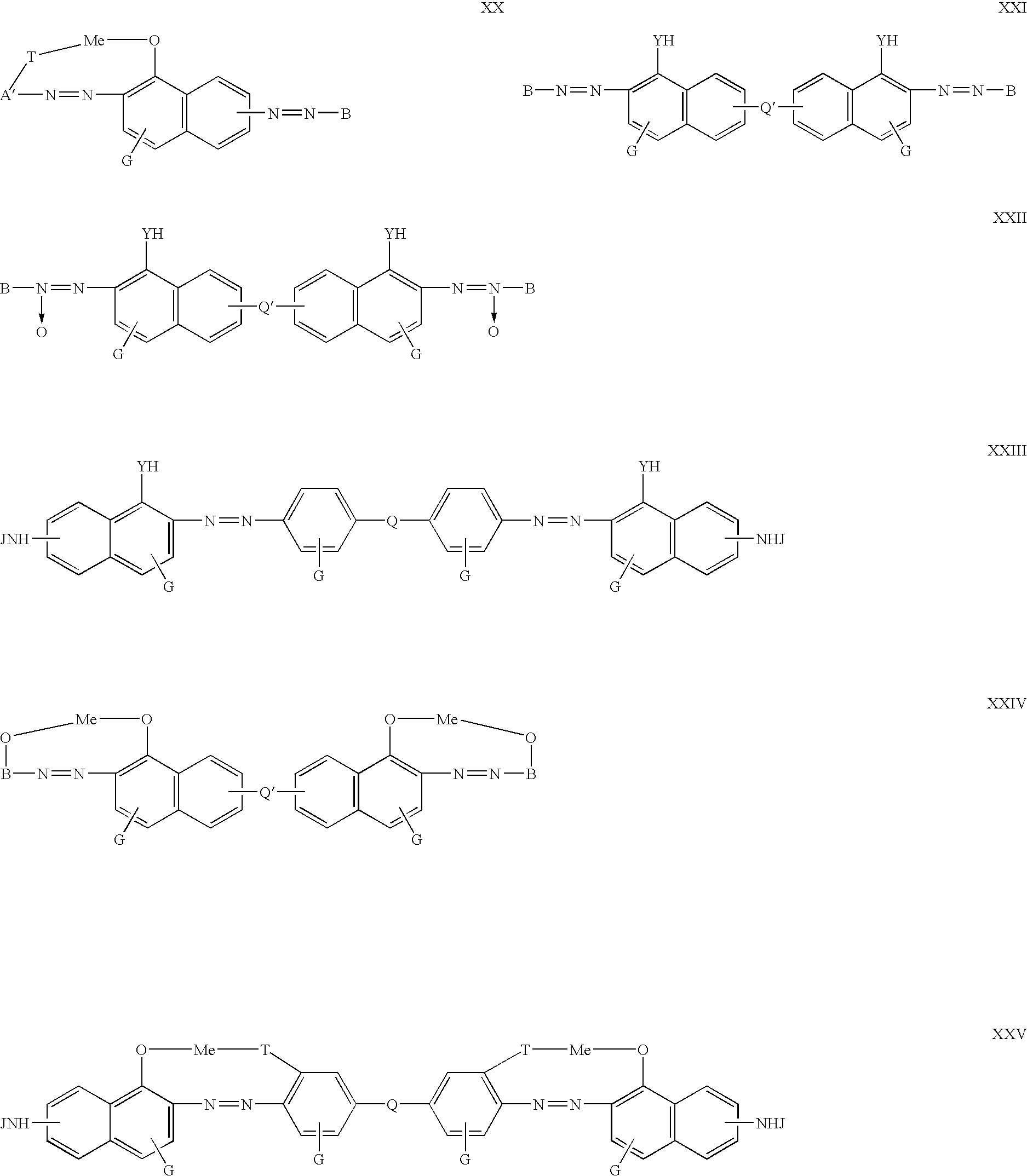
Optical device
InactiveUS20040232394A1Liquid crystal compositionsMethine/polymethine dyesPolarizerElectromagnetic radiation
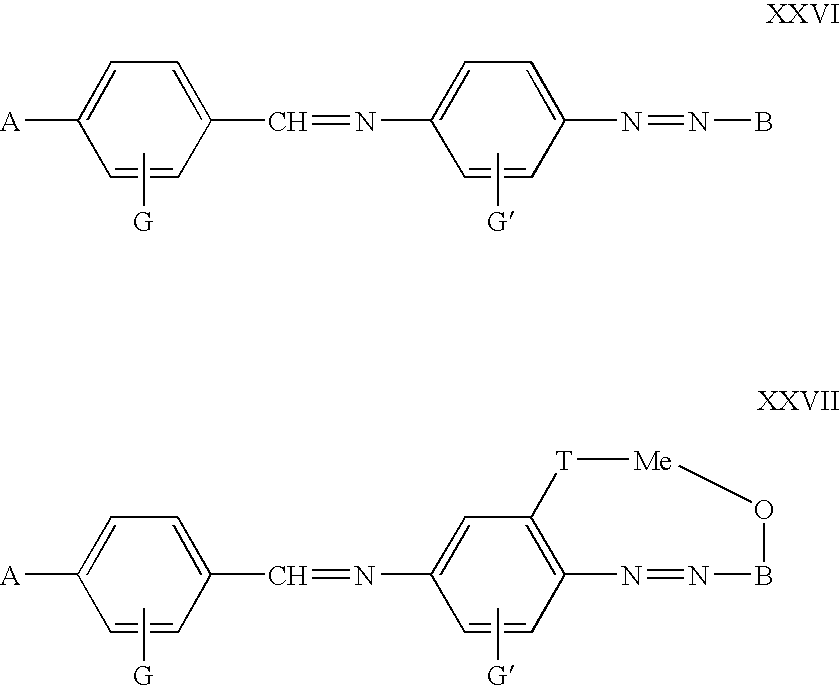
The invention relates to optical devices for producing and / or transforming polarised electromagnetic emission by means of anisotropic absorption and / or optical rotation effects and / or birefringence and can be used as different polarizers (dichroic, reflecting), lagging layers (retarders), liquid-crystal displays and indicators and also for producing polarising glass for building construction and for sun and antiglare glasses, masks, aprons and faceplates. The inventive optical device is based on at least one molecularly oriented layer of a low-molecular or oligomeric dichroic material which can form a stable lyotropic liquid crystal structure. The projection of at least one anisotropically absorbing fragment of a molecule of the dichroic material on the surface of the molecularly oriented layer of a dipole moment of optical transition is disposed in a parallel position to the optical axis of the molecularly oriented layer at least within several ranges of wavelength of the electromagnetic emission.
Owner:IR GVON KHAN
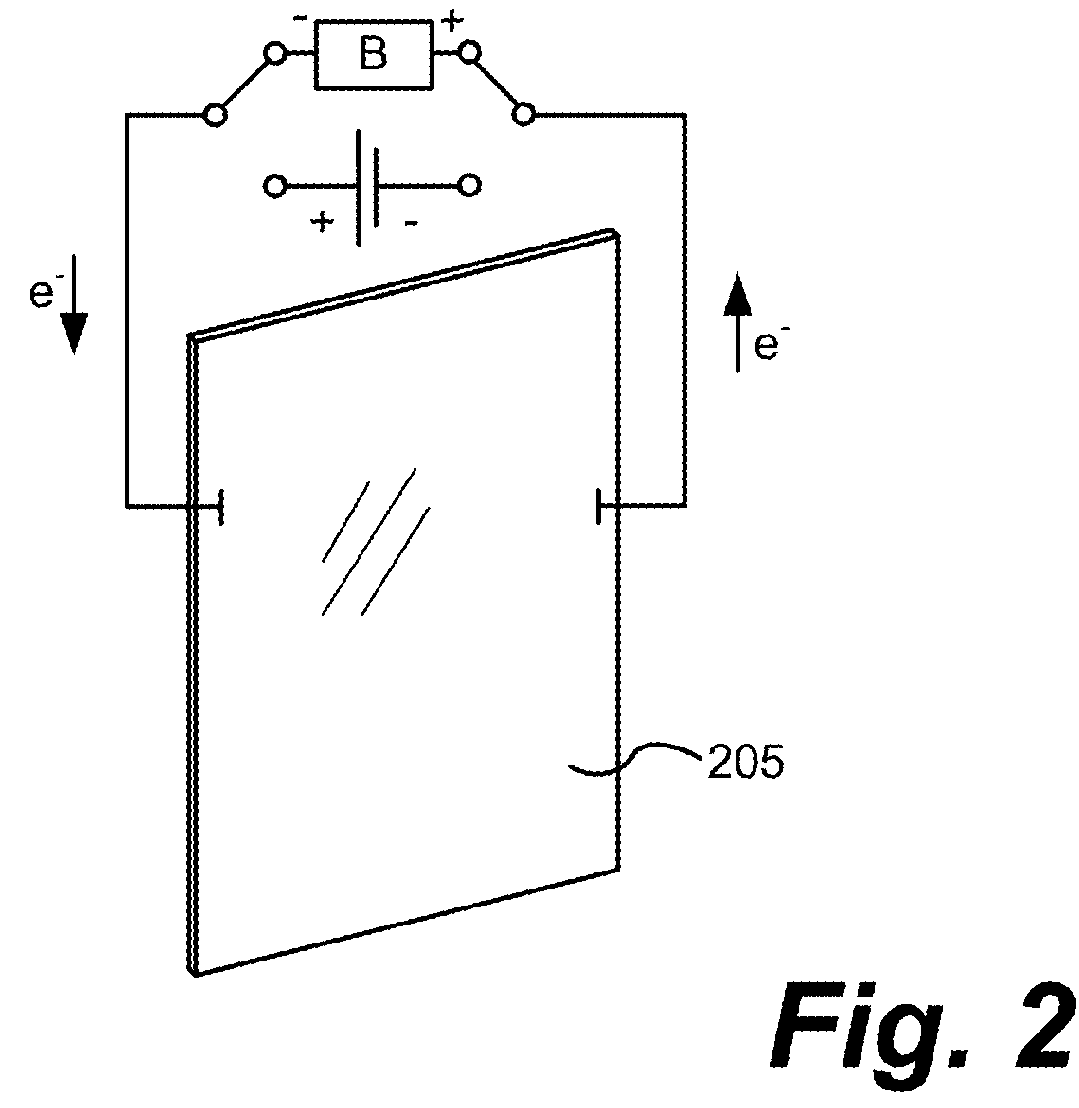
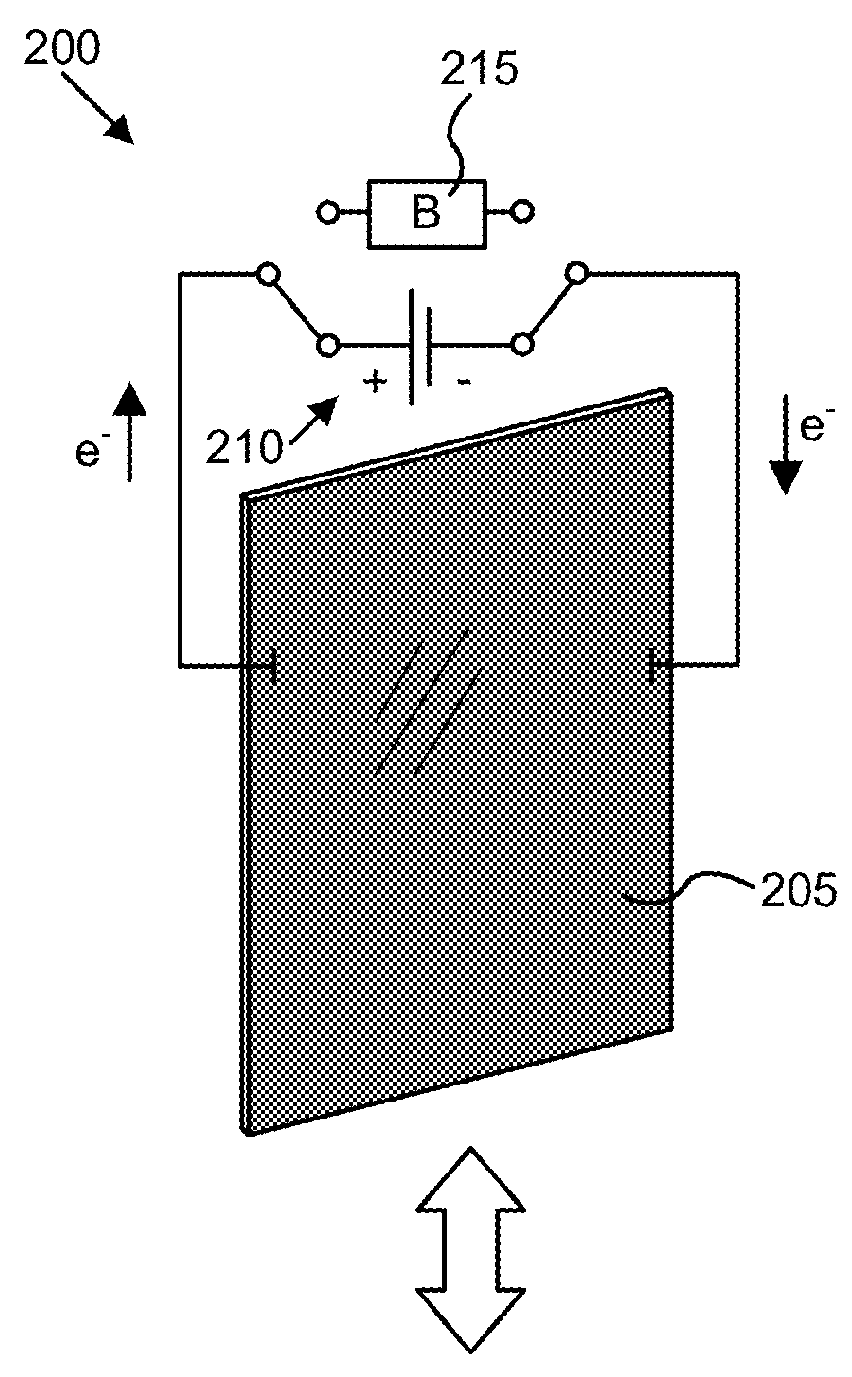
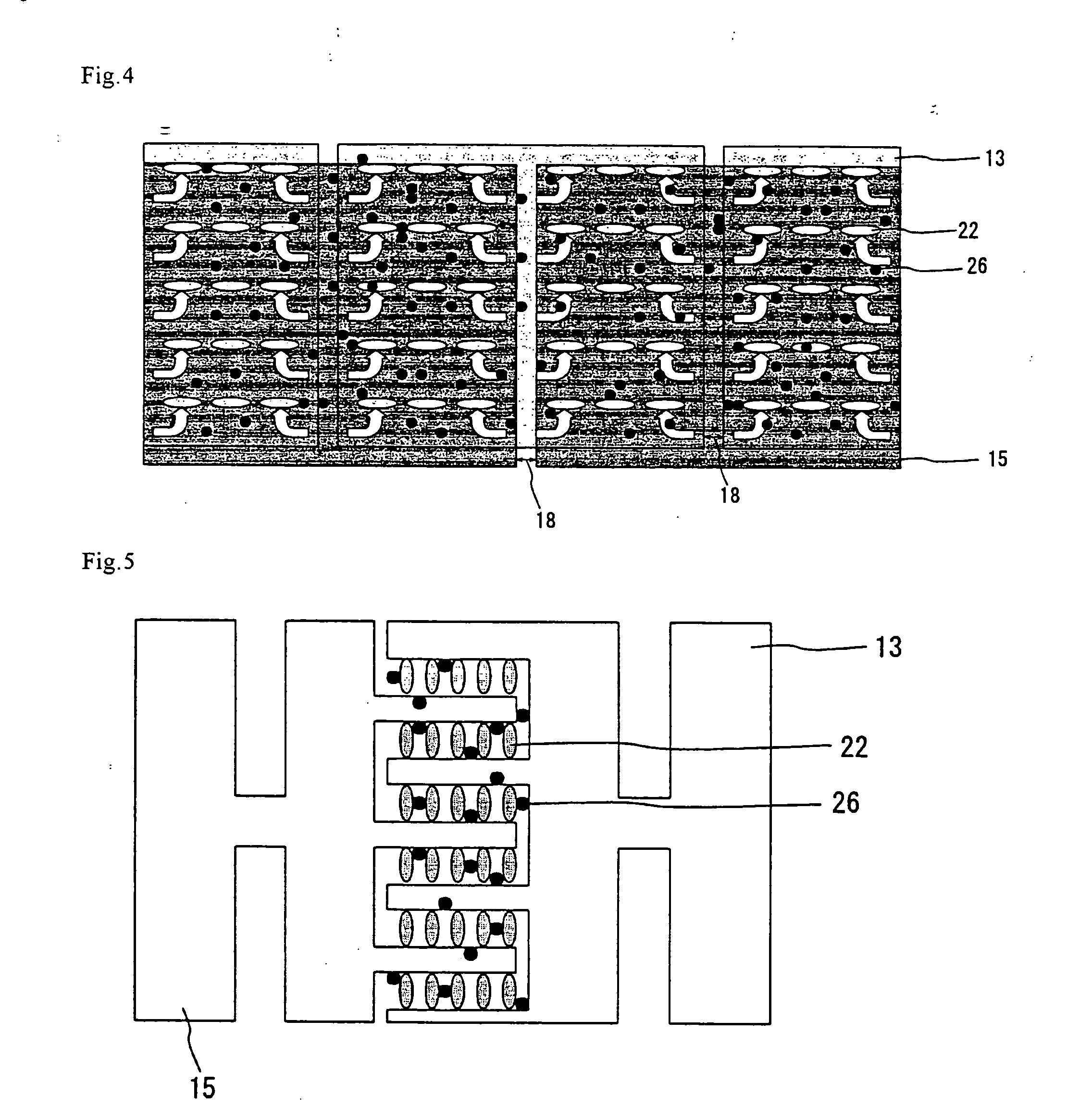
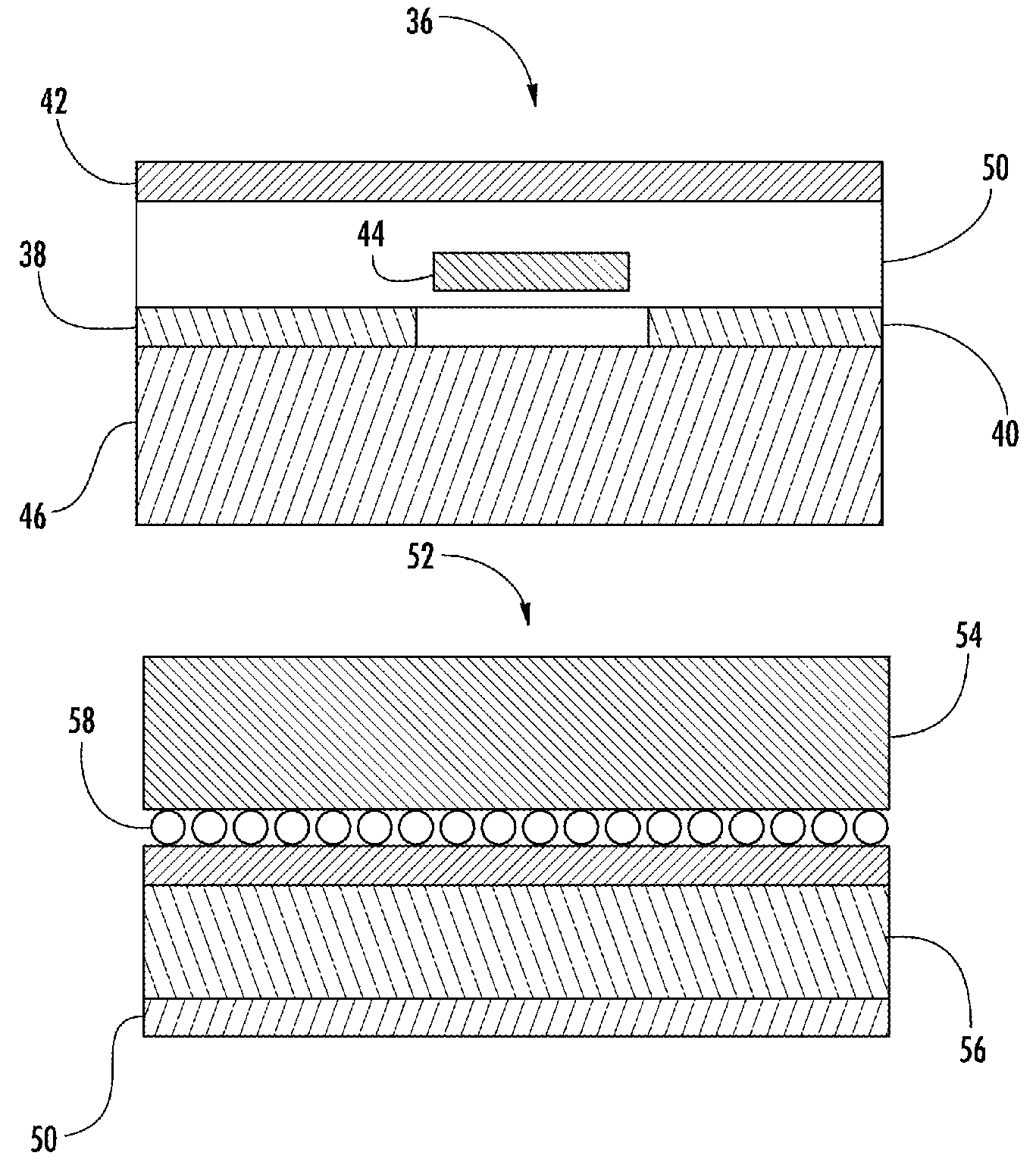
Electrophoretic or bi-stable display device and driving method therefor
InactiveUS20060170648A1Lower Level RequirementsStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisDisplay device
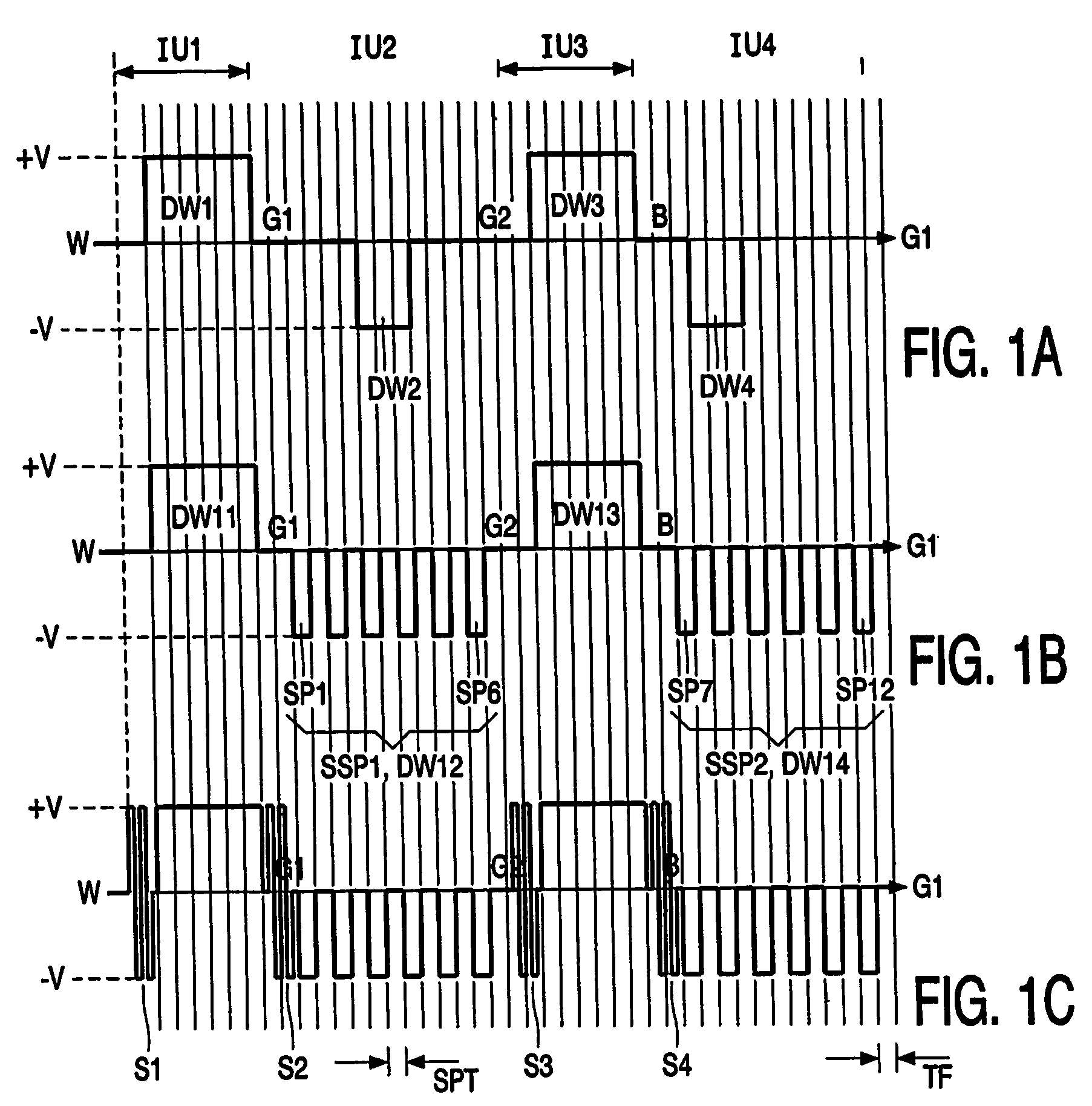
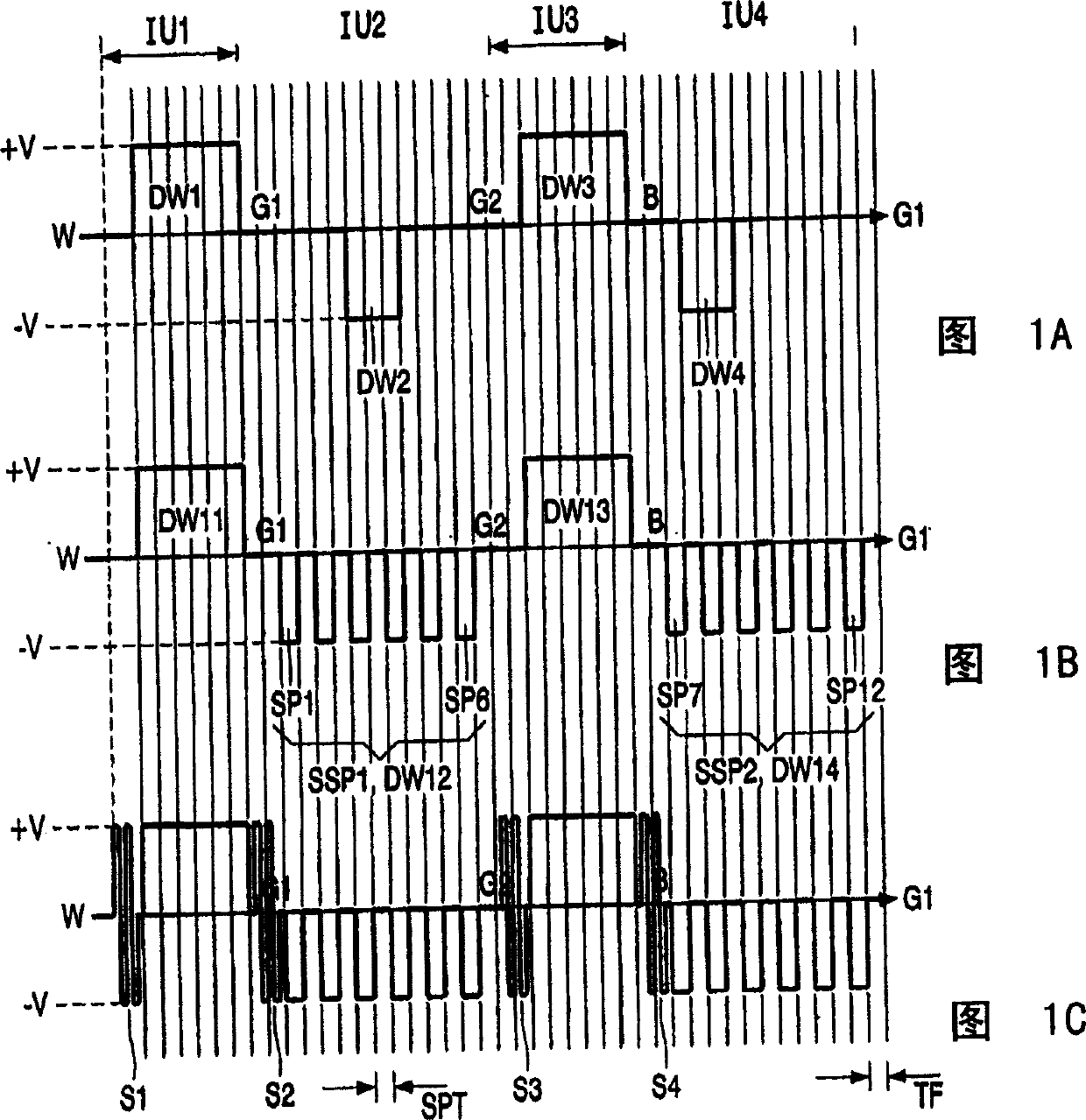
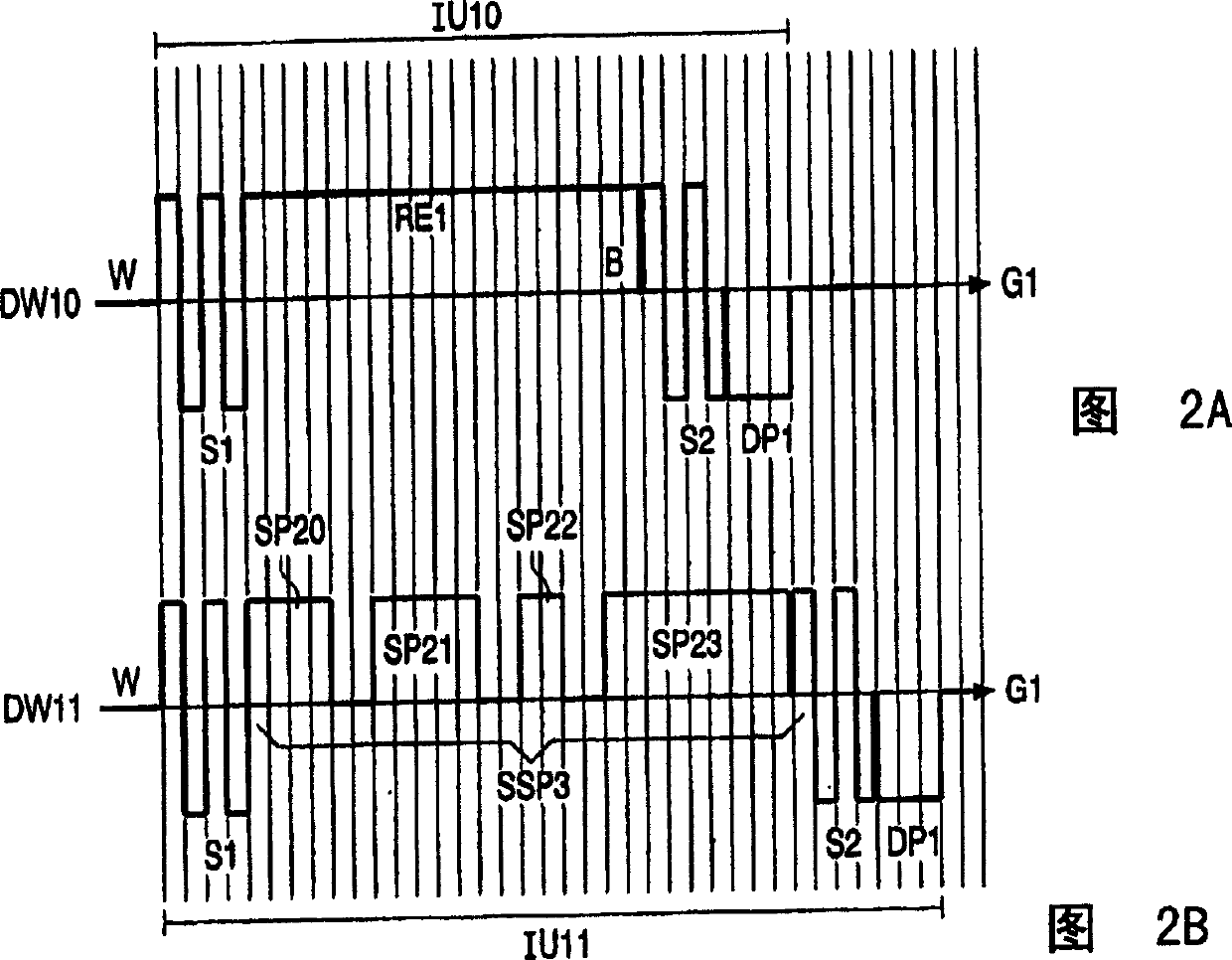
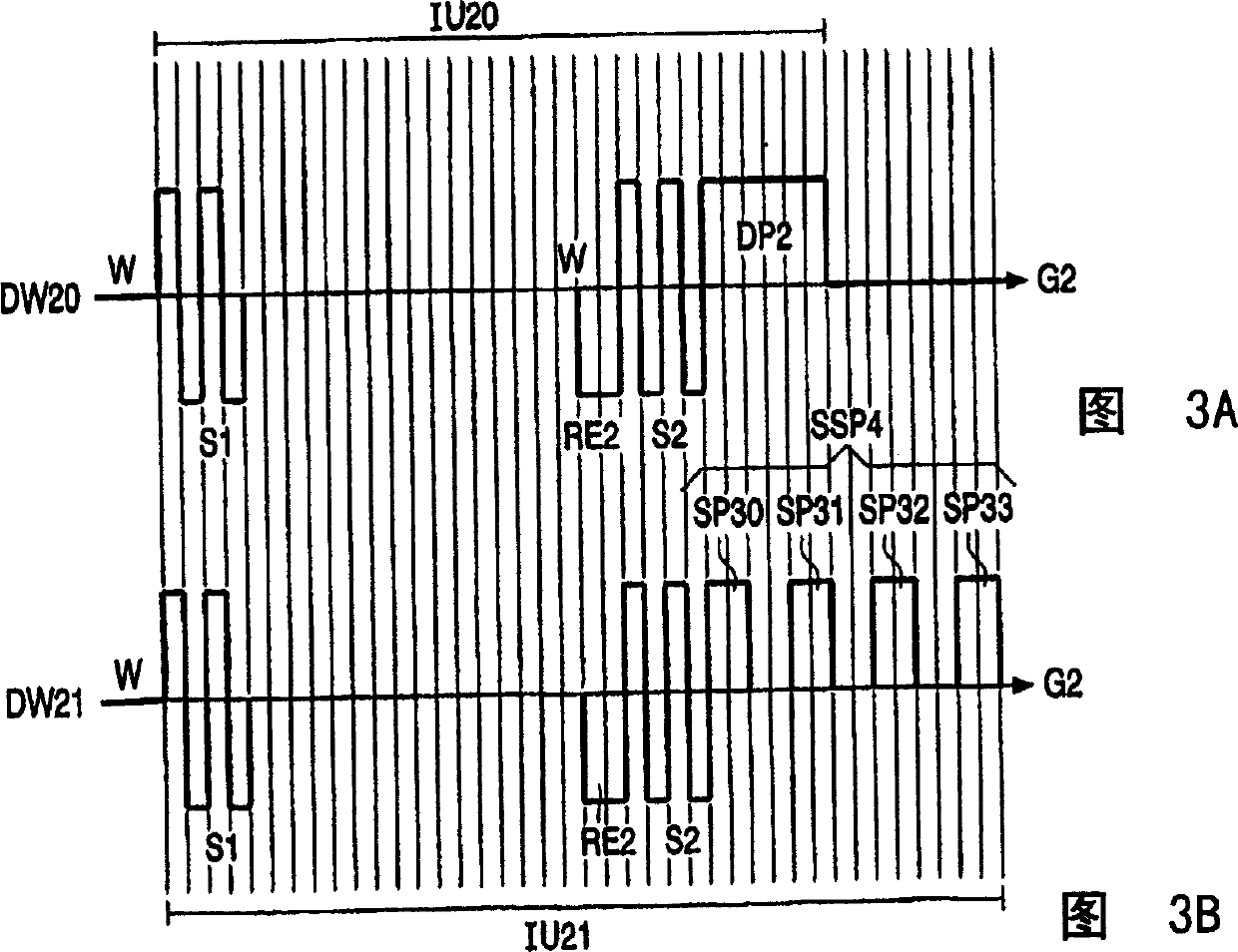
A drive circuit for a bi-stable display comprises: a driver (101, 102) which supplies drive waveforms (DWk) to the pixels (Pij) of the display during an image update period (IUk) wherein the image presented by the pixels (Pij) is updated. A controller (103) controls the driver (101, 102) to supply, during the image update period (IUk) wherein a particular optical transition of a particular one of the pixels (Pij) is required, an associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) to the particular one of the pixels (Pij). The associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) comprises a sequence of a particular number of pulse, (SPk), wherein consecutive ones of the pulses (SPk) of the sequence are separated by a separation period of time (SPT). The particular number of said pulses (SPk), and / or a duration of said pulses (SPk), and / or a duration of the separation period (SPT) of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) is determined to obtain the particular optical transition at a desired energy of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) to decrease an average value of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Light-emitting nanoparticles and method of making same
InactiveUS20050266697A1Reduce aggregationResist formationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanoparti clesSilicon nanoparticle
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:KORGEL BRIAN A +1
CMOS compatible integrated dielectric optical waveguide coupler and fabrication
ActiveUS7738753B2Efficient preparationPerformance is not affectedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsDielectricRefractive index
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method and apparatus for spatially limited excitation of an optical transition
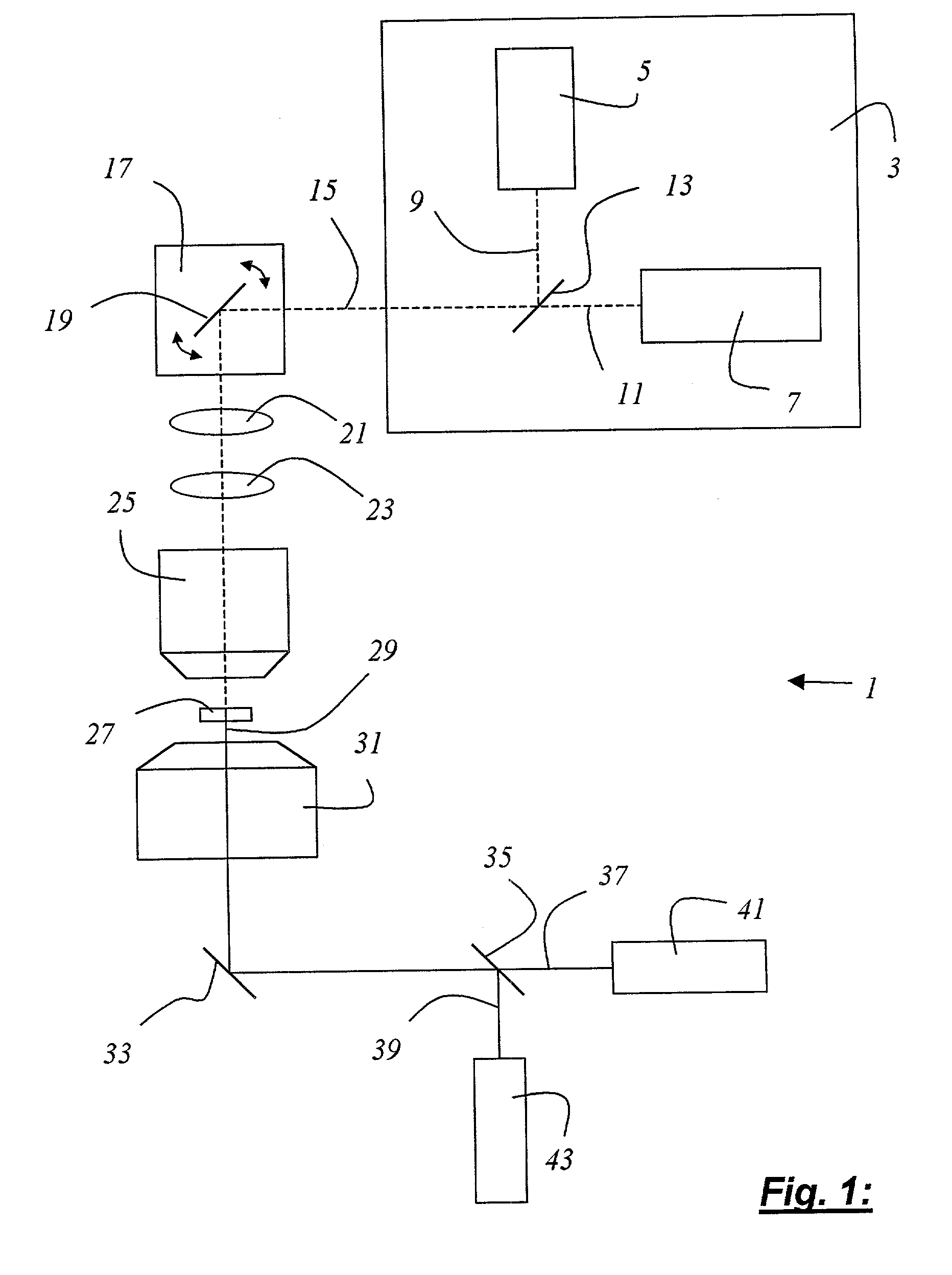
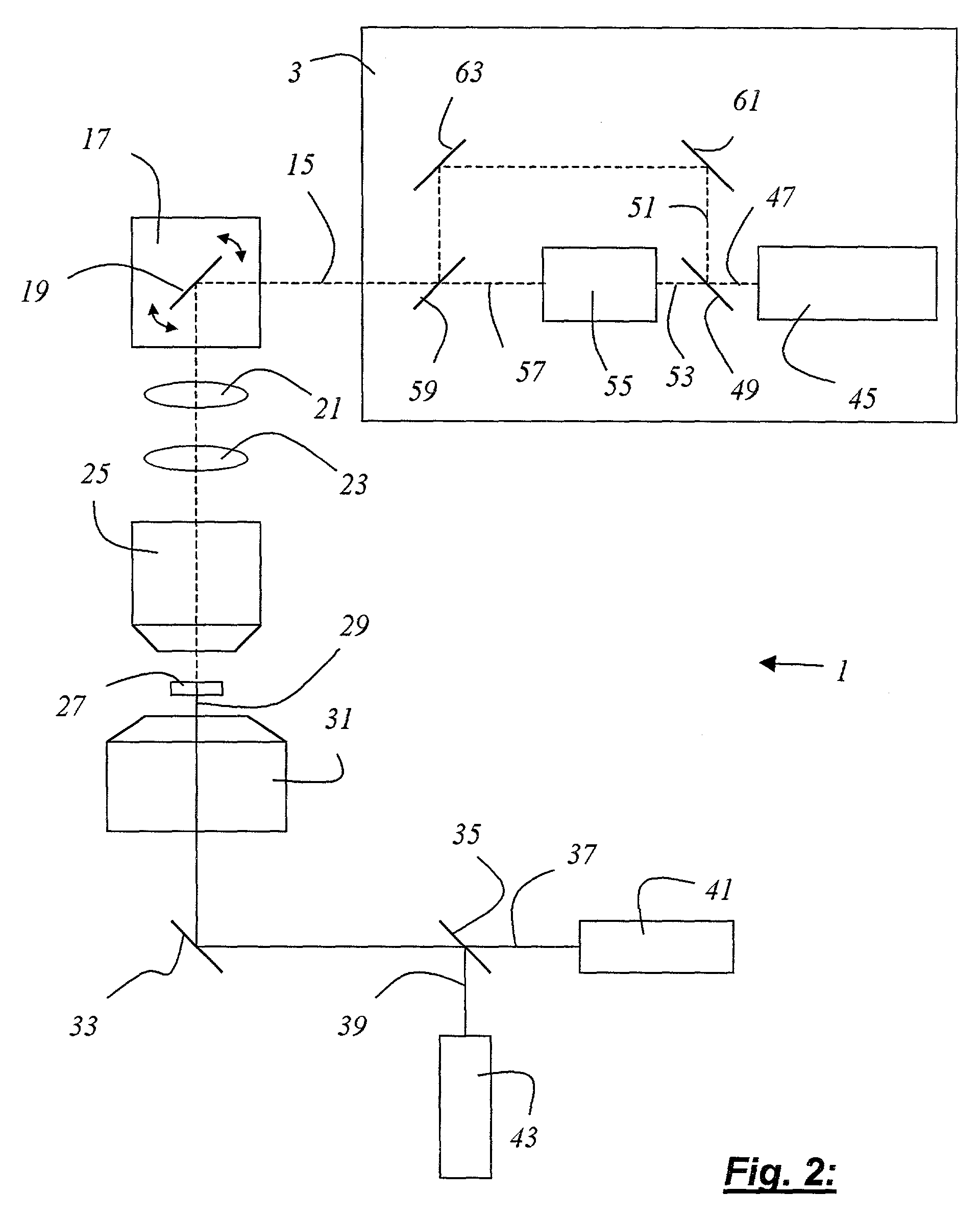
InactiveUS7253893B2High strengthImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyRelative phaseLight beam
A method of exciting an optical transition in a narrowly limited area of a material comprising the steps of focusing an excitation light beam whose wavelength is tuned to the optical transition to be excited into a focal area extending beyond a focal point; splitting up a de-excitation light beam which is at least somehow influencing the optical transition into at least two partial beams; focusing the at least two partial beams of the de-excitation light beam out of different directions onto the focal point to form a spatially extending interference pattern in the focal area; adjusting a relative phase of the at least two partial beams of the de-excitation light beam so that the interference pattern has an intensity minimum at the focal point and a plurality of intensity maxima on different sides of the focal point; and aberrating the wave fronts of the at least two partial beams of the de-excitation light beam so that the intensity maxima of the interference pattern on different sides of the focal point are spatially expanded without eliminating the intensity minimum at the focal point.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Nanophotonic devices based on quantum systems embedded in frequency bandgap media
InactiveUS7076138B2Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyQuantum computersLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsBinding state
The present invention describes nanophotonic materials and devices for both classical and quantum optical signal processing, transmission, amplification, and generation of light, which are based on a set of quantum systems having a discrete energy levels, such as atoms, molecules, or quantum dots, embedded in a frequency bandgap medium, such as artificial photonic crystals (photonic bandgap materials) or natural frequency dispersive media, such as ionic crystals, molecular crystals, or semiconductors, exhibiting a frequency (photonic) bandgap for propagating electromagnetic modes coupled to optical transitions in the quantum systems. If the frequency of one of optical transitions, called the working transition, lies inside the frequency bandgap of the medium, then spontaneous decay of the working transition into propagating photon modes is completely suppressed. Moreover, the excitation of the working transition and a photon form a photon-quantum system bound state lying inside the photonic bandgap of the medium, in which radiation is localized in the vicinity of the quantum system. In a quantum system “wire” or a quantum system “waveguide”, made of spatially disordered quantum systems, or in a chain quantum system waveguide made of a periodically ordered identical quantum systems, wave functions of the photon-quantum system bound states localized on different quantum systems overlap each other and develop a photonic passband lying inside bandgap of the photonic bandgap medium.
Owner:ALTAIR CENT
Light-emitting nanoparticles and method of making same
ActiveUS20110171789A1Reduce aggregationResist formationSilicon organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Laser source with broadband spectrum emission
ActiveUS20070189348A1Easy to manufactureEmission spectrumOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsFrequency spectrumLaser source
A quantum dot laser operates on a quantum dot ground-state optical transition. The laser has a broadband (preferably ≧15 nm) spectrum of emission and a high output power (preferably ≧100 mW). Special measures control the maximum useful pump level, the total number of quantum dots in the laser active region, the carrier relaxation to the quantum dot ground states, and the carrier excitation from the quantum dot ground states. In one embodiment, a spectrally-selective loss is introduced into the laser resonator in order to suppress lasing on a quantum dot excited-state optical transition, thereby increasing the bandwidth of the emission spectrum.
Owner:INNOLUME
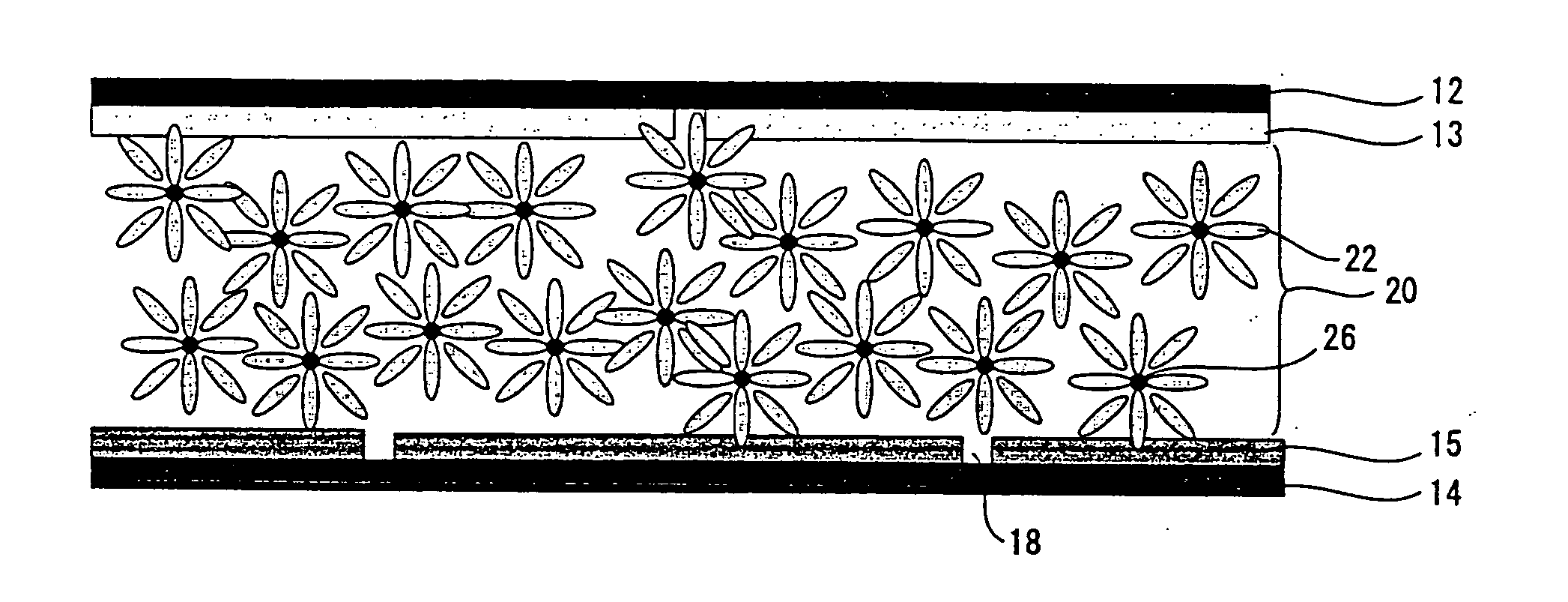
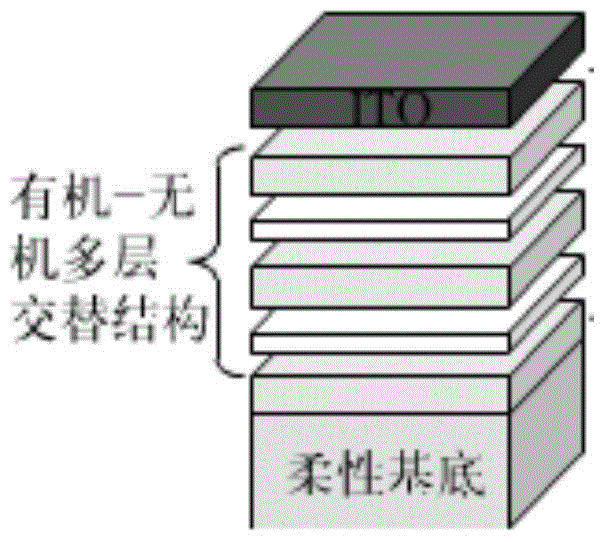
Optical transition layer material, optical substrate/packaging layer, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveCN102751447AReduce reflection lossImprove light extraction efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible organic light-emitting diodeReflection loss
The invention relates to an organic electroluminescent technology and discloses a method for improving the luminous efficiency. The method can be applied to various types of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) devices of bottom emission, top emission, transparency and the like. The invention provides an optical transition layer material, an optical substrate (packaging layer), an OLED, and manufacturing methods thereof. If the OLED is the bottom-emission OLED, an optical transition layer is manufactured on the substrate; if the OLED is the top-emission OLED, the optical transition layer is manufactured on the packaging layer; and if the OLED is the transparent OLED, the optical transition layer can be independently or simultaneously manufactured on the substrate or the packaging layer. An organic material main body with high light transmittance and moderate refractive index and an inorganic nano grain with the high light transmittance and low absorption rate are selected; the inorganic nano grain is used as a scattering medium to be scattered into the organic material main body to prepare the optical transition layer material; and the optical transition layer material is used for preparing an optical transition layer on the substrate (packaging layer) including glass and the like, so that the full-reflection loss of emergent light is effectively reduced and the luminous efficiency of the OLED is improved by 20-50%.
Owner:TRULY SEMICON
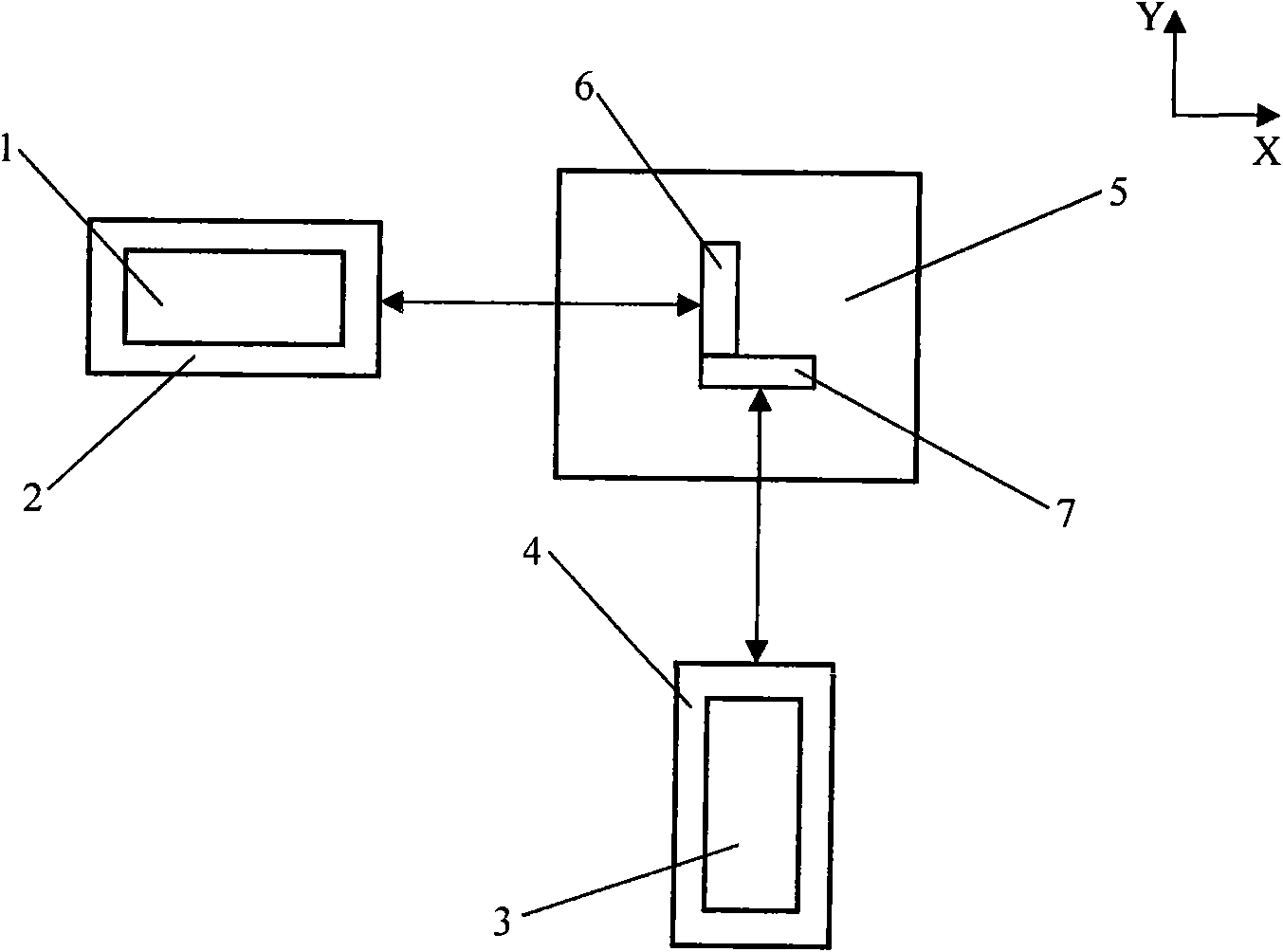
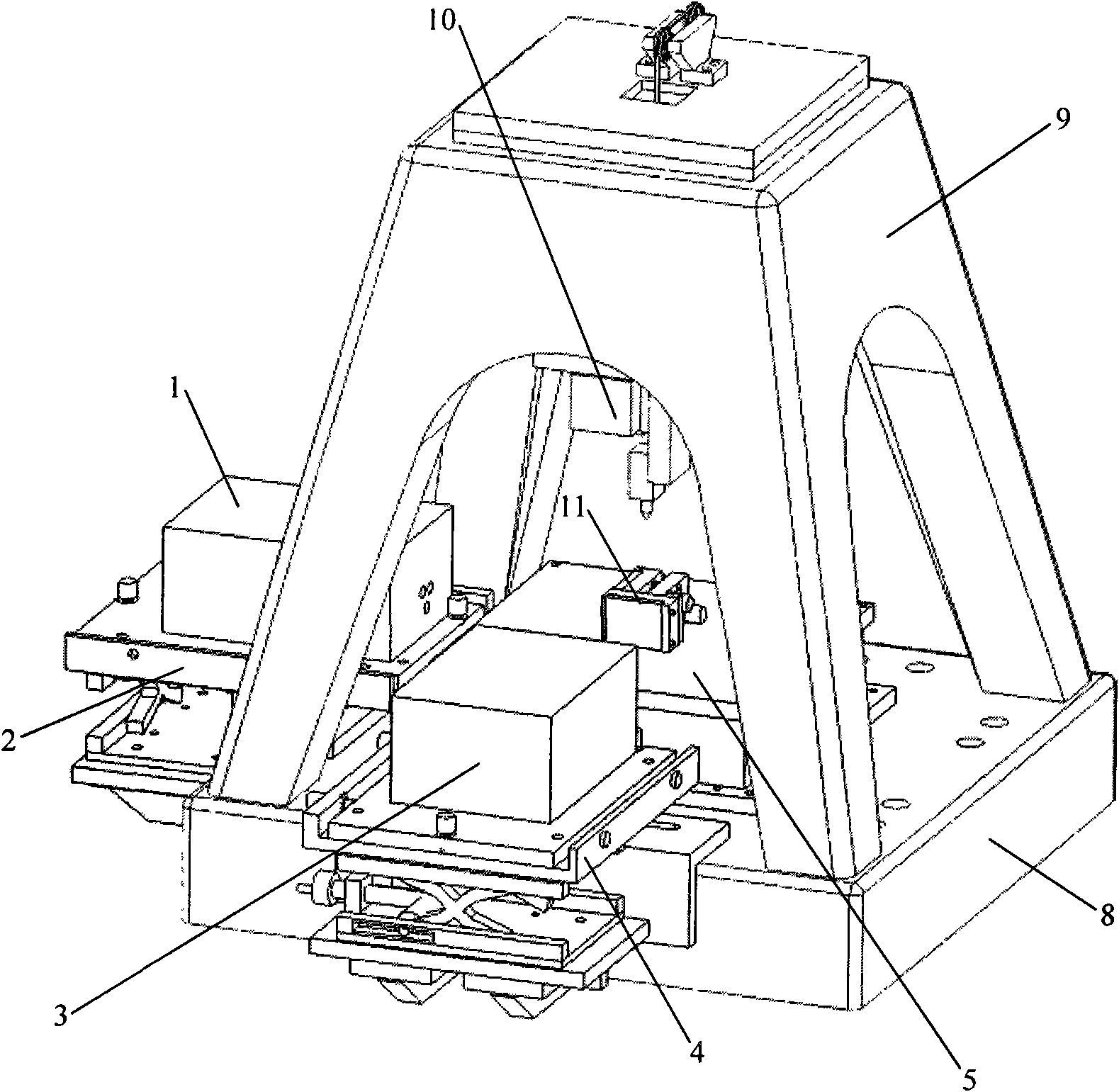
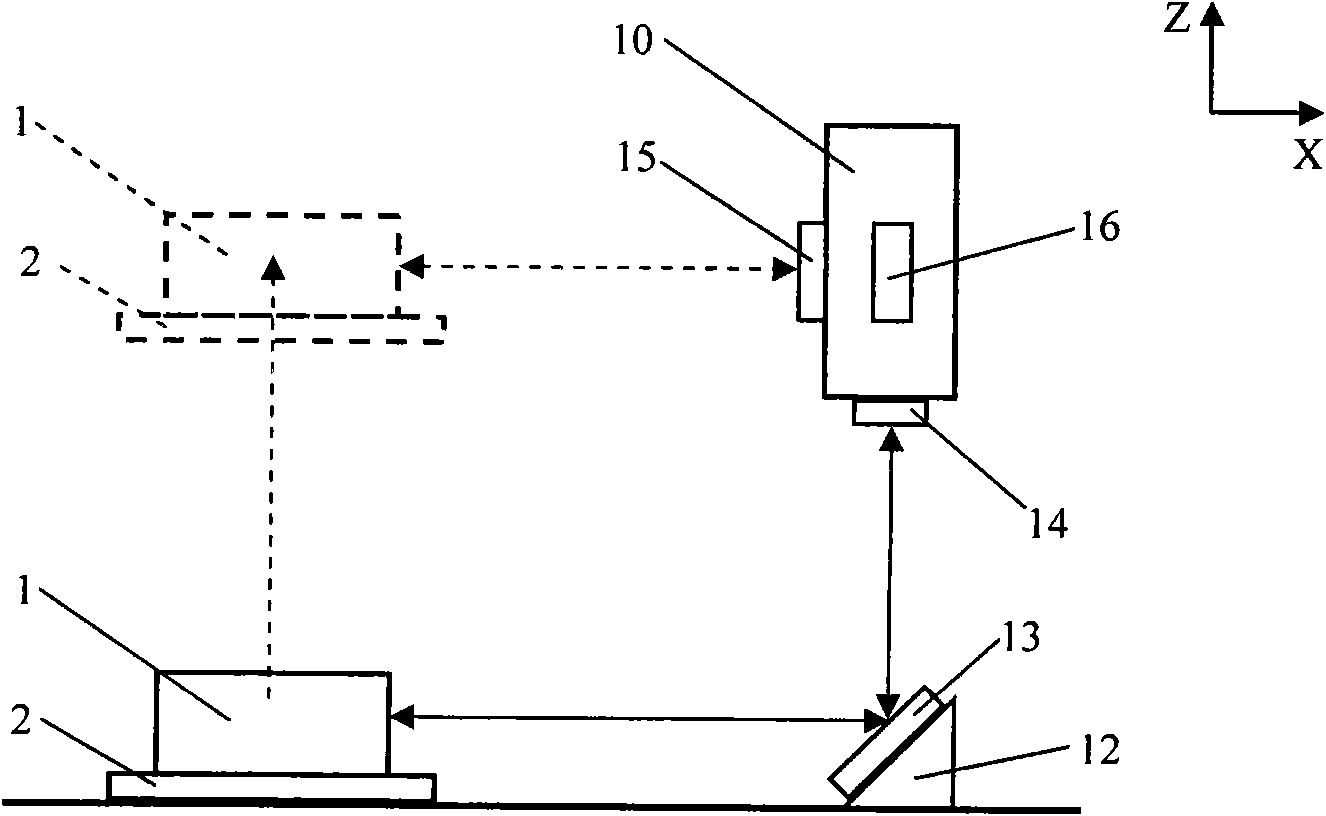
Error detecting system of minitype high accuracy three coordinate measuring machine
InactiveCN101571374AImprove test efficiencySimplify verification stepsUsing optical meansVertical edgeOptical axis
The invention relates to an error detecting system of a minitype high accuracy three-coordinate measuring machine, which is characterized by comprising an X / Y axis target lens, an optical transition target lens, a Z axis target lens, a vertical edge laser interferometer having optical axis being parallel to X axis direction and a transverse edge laser interferometer having optical axis being parallel to Y axis direction. The error detecting system is synchronously tested by multiple items of high accuracy geometrical error, and can realize nanoscale precision detection for the geometrical error of the three-coordinate measuring machine. Furthermore, the error detecting system has high working efficiency and simple operating way.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050062927A1Quick responseIncrease opening ratioLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesContrast ratioHigh contrast
It is an object of the present invention to provide a liquid crystal display device in which a liquid crystal layer may form a stable transparent state and, in addition, which provides for a black display with an excellent viewing angle characteristic, as well as a high contrast ratio and a high response speed in liquid crystal display. The present invention is directed to a liquid crystal display device comprising an electrode and a liquid crystal layer between substrates, said liquid crystal layer consists of a liquid crystalline material containing liquid crystal molecules and fine particles, and is optically isotropic when the voltage applied to the electrode is lower than a threshold value and undergoes optical transition due to change in the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules when the applied voltage is not lower than the threshold value.
Owner:SHARP KK
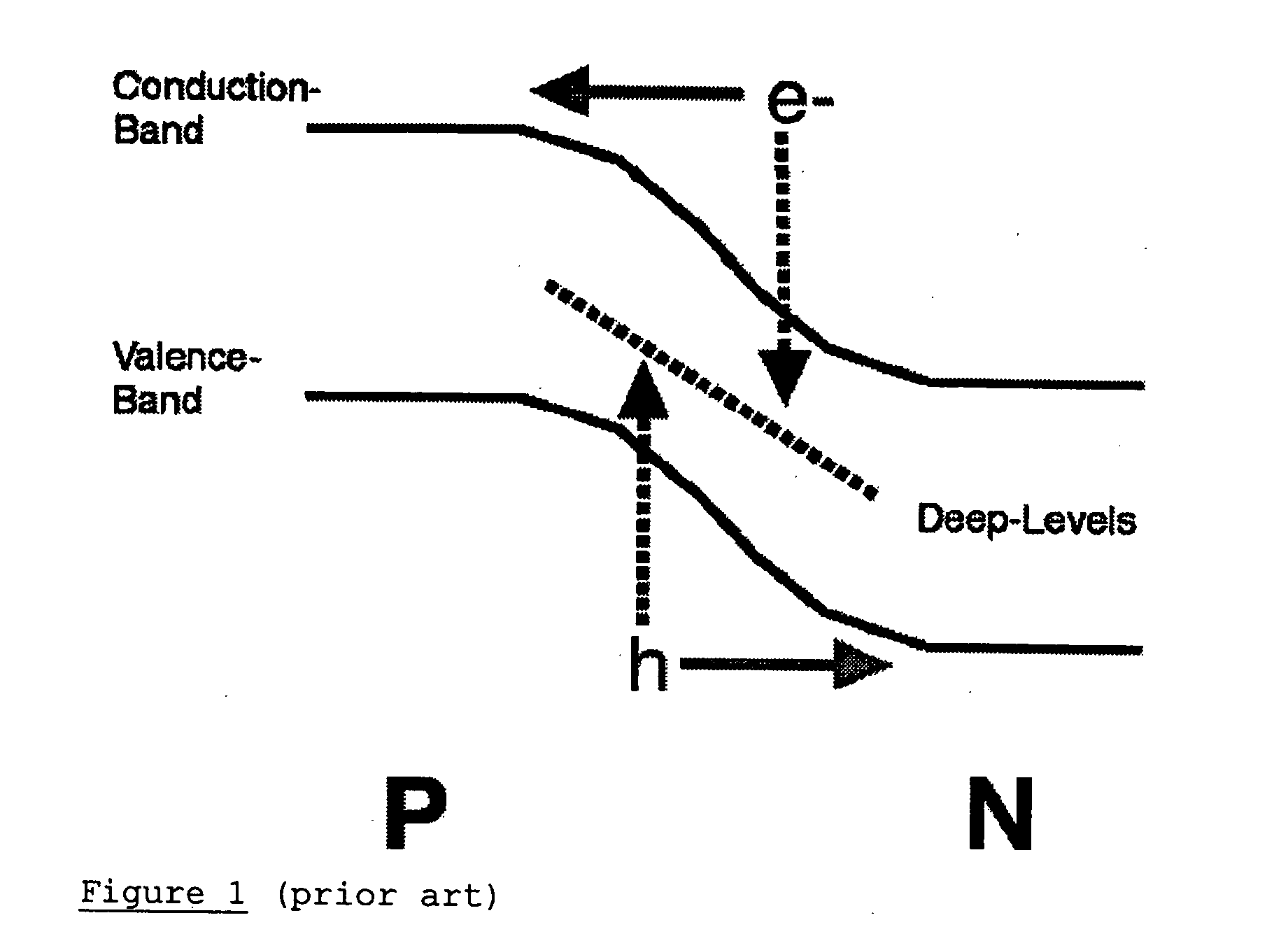
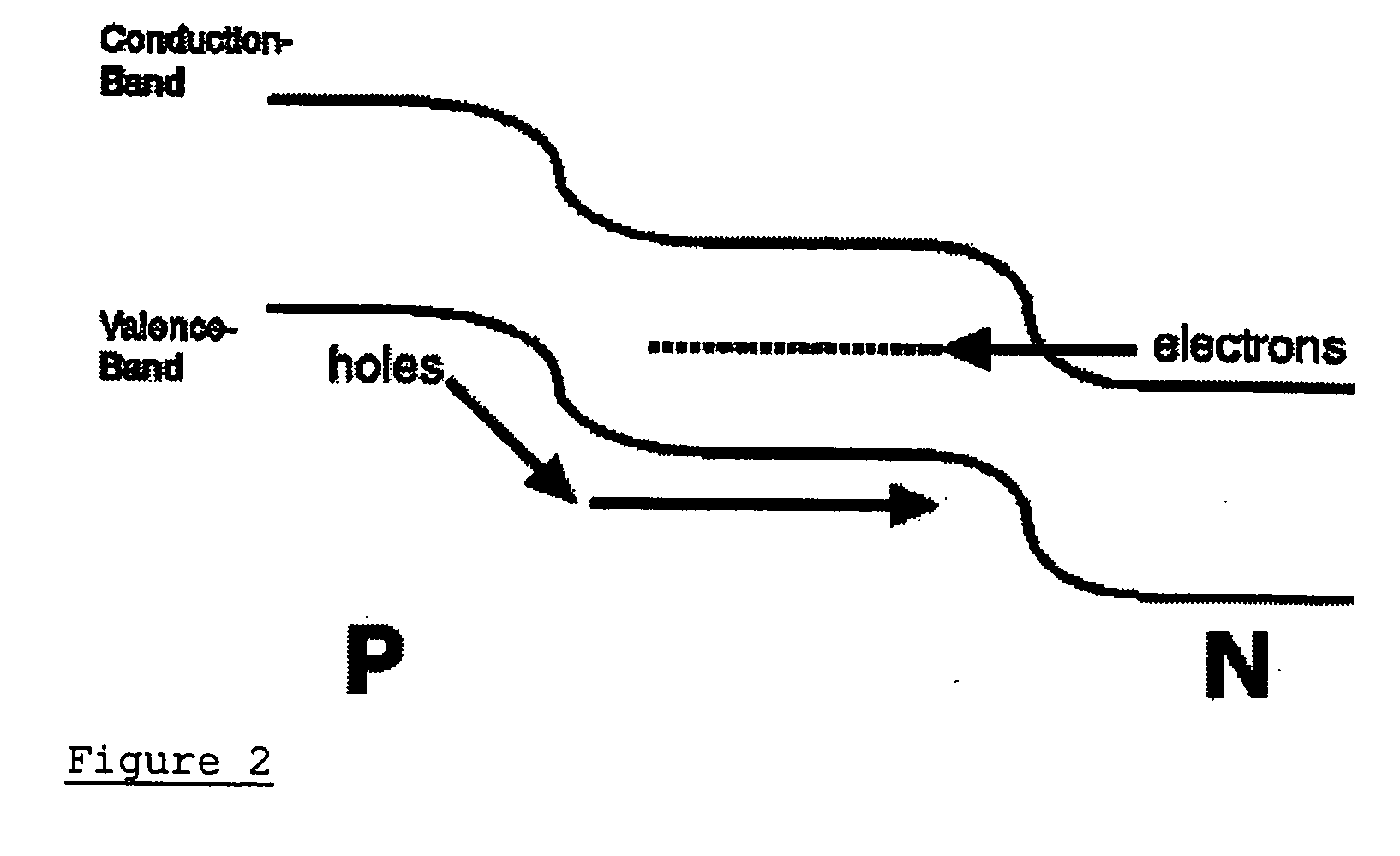
Use of deep-level transitions in semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20050056864A1Easy to useDesigning can be facilitatedLaser detailsLaser active region structureDevice materialEngineering
The invention relates to the design, fabrication, and use of semiconductor devices that employ deep-level transitions (i.e., deep-level-to-conduction-band, deep-level-to-valence-band, or deep-level-to-deep-level) to achieve useful results. A principal aspect of the invention involves devices in which electrical transport occurs through a band of deep-level states and just the conduction band (or through a deep-level band and just the valence band), but where significant current does not flow through all three bands. This means that the deep-state is not acting as a nonradiative trap, but rather as an energy band through which transport takes place. Advantageously, the deep-level energy-band may facilitate a radiative transition, acting as either the upper or lower state of an optical transition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
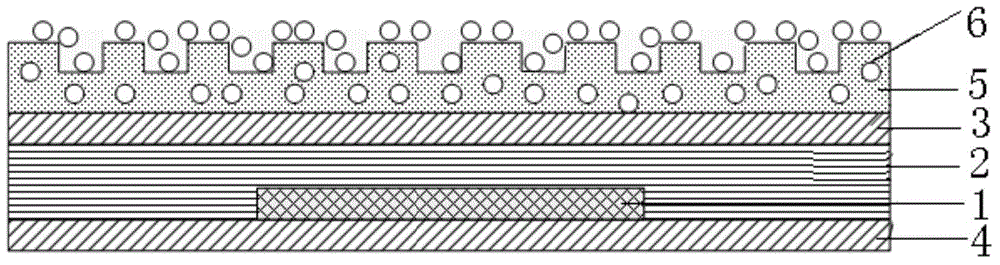
Waterproof anti-reflection flexible OLED device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105226198AWaterproofBoth anti-reflection effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicro structureNanoparticle
The invention relates to an OLED device and a preparation method thereof. The OLED device is composed of an OLED device, a device encapsulation layer, an upper flexible substrate, and a lower flexible substrate. Besides, an anti-reflection layer is arranged at the outer side of the upper flexible substrate; inorganic nanometer particles are deposited on the surface of the anti-reflection layer. According to the invention, the inorganic nanometer particles with high light transmittance and low absorptivity are selected to be scattered in an organic material with high light transmittance and moderate refractive index; and because of a formed optical transition layer, the anti-reflection effect can be improved by 20% to 50%. Moreover, a concave-convex micro structure is formed on the surface of the organic main body and the inorganic nanometer particles cover the micro structure, so that a bonding force of the organic main body and the inorganic nanometer particles is provided and the waterproof effect is also realized. According to the technical scheme, the OLED device has the waterproof and anti-reflection effect and the overall thickness is low.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Light-emitting nanoparticles and method of making same
ActiveUS8163633B2Reduce aggregationResist formationSilicon organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticle compositionHigh pressure
A method for the production of a robust, chemically stable, crystalline, passivated nanoparticle and composition containing the same, that emit light with high efficiencies and size-tunable and excitation energy tunable color. The methods include the thermal degradation of a precursor molecule in the presence of a capping agent at high temperature and elevated pressure. A particular composition prepared by the methods is a passivated silicon nanoparticle composition displaying discrete optical transitions.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
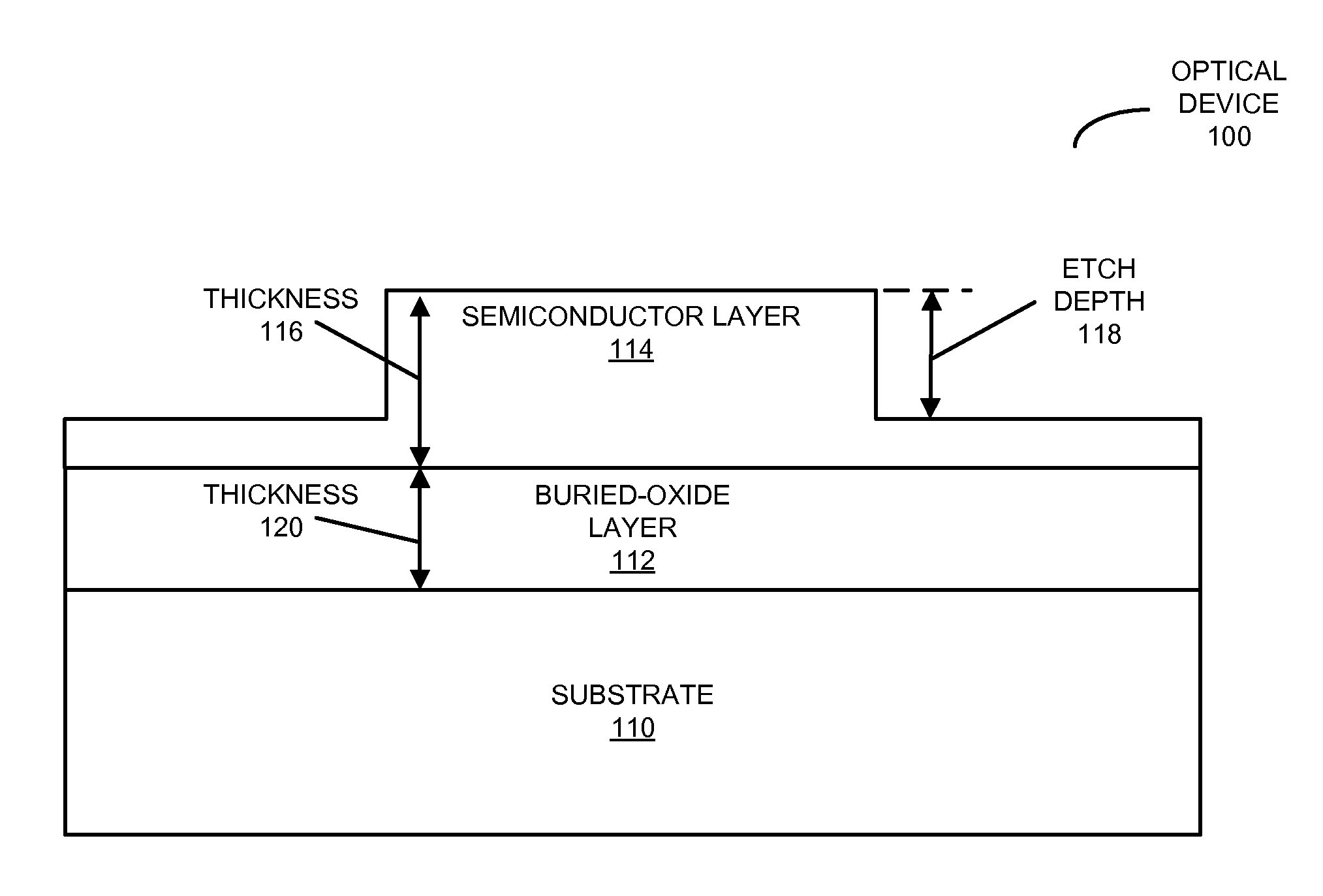
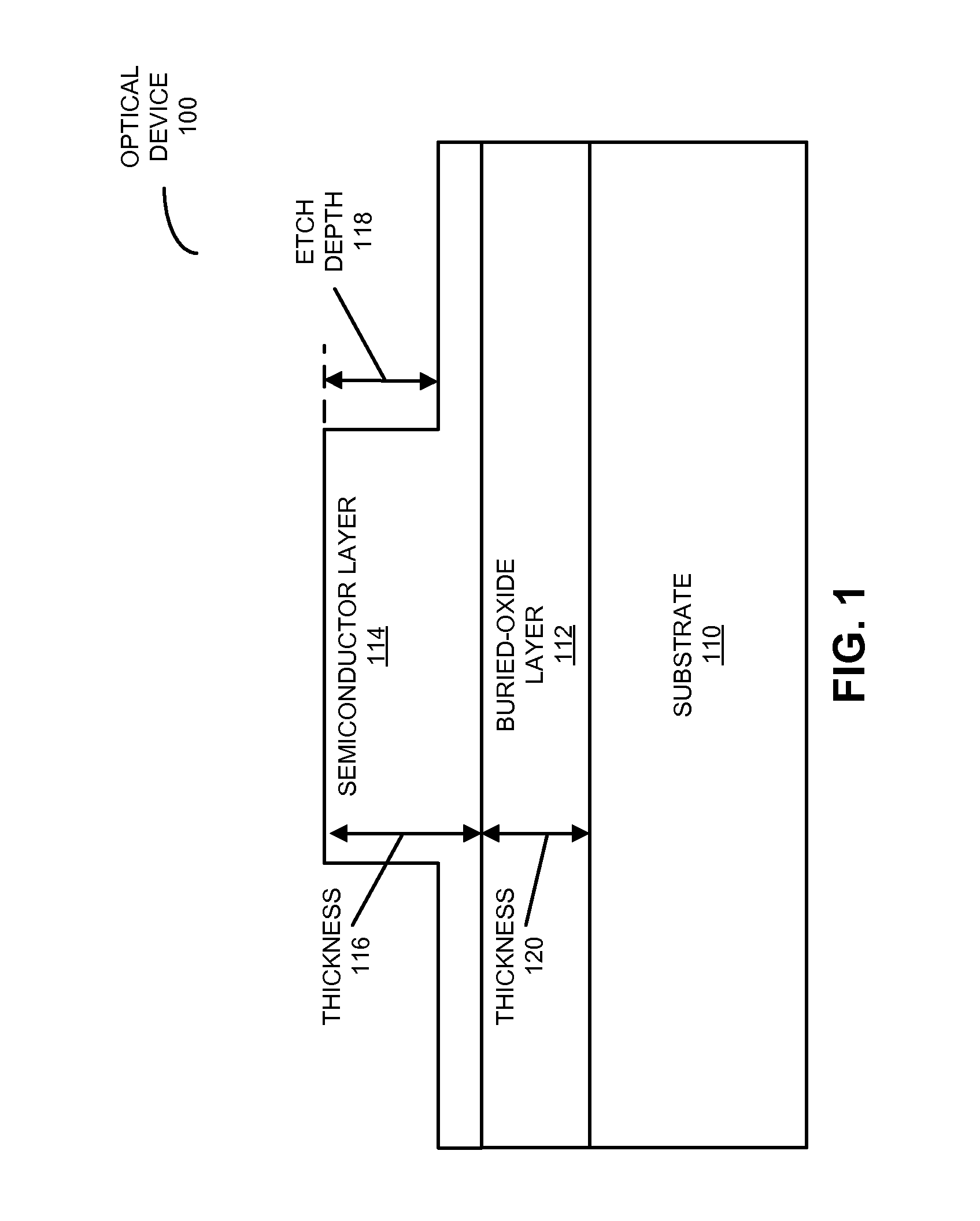
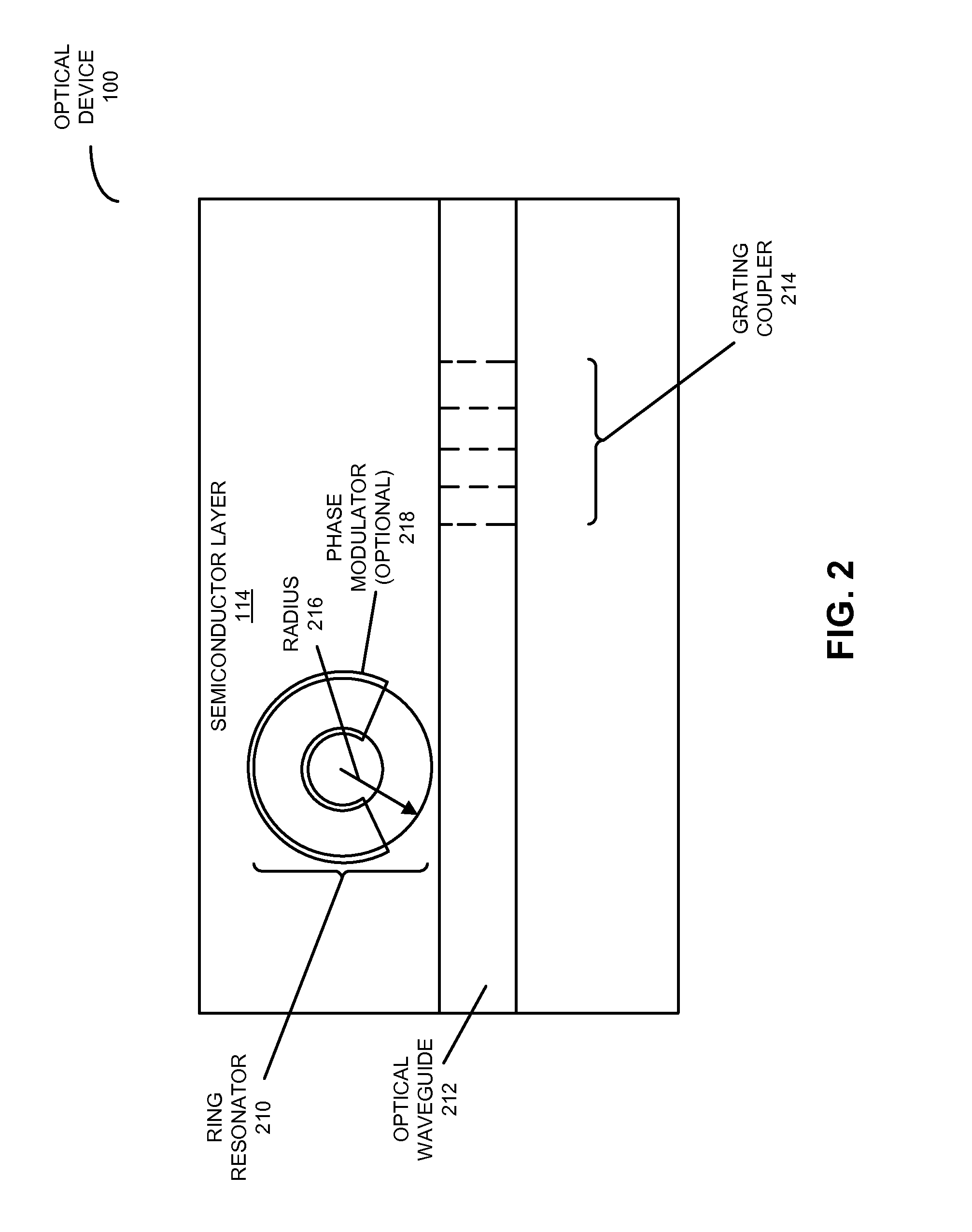
Optical components having a common etch depth
ActiveUS20130301981A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideGratingGrating coupling
An optical device is described. This optical device includes multiple components, such as a ring resonator, an optical waveguide and a grating coupler, having a common etch depth (which is associated with a single etch step or operation during fabrication). Moreover, these components may be implemented in a semiconductor layer in a silicon-on-insulator technology. By using a common etch depth, the optical device may provide: compact active devices, multimode ultralow-loss optical waveguides, high-speed ring resonator modulators with ultralow power consumption, and compact low-loss interlayer couplers for multilayer-routed optical links. Furthermore, the single etch step may help reduce or eliminate optical transition loss, and thus may facilitate high yield and low manufacturing costs.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
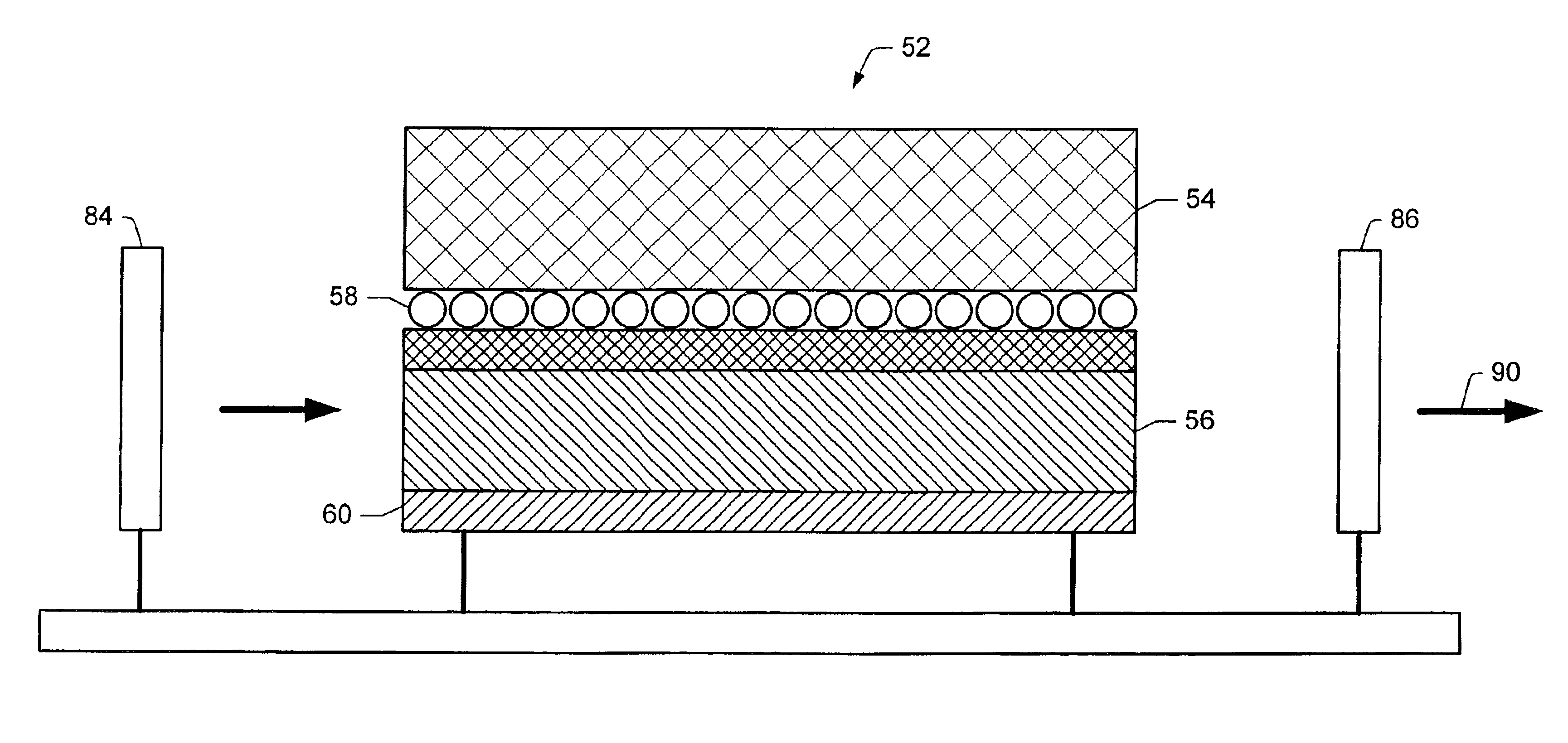
Electrophoretic or bi-stable display device and driving method therefor
A drive circuit for a bi-stable display comprises: a driver (101, 102) which supplies drive waveforms (DWk) to the pixels (Pij) of the display during an image update period (IUk) wherein the image presented by the pixels (Pij) is updated. A controller (103) controls the driver (101, 102) to supply, during the image update period (IUk) wherein a particular optical transition of a particular one of the pixels (Pij) is required, an associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) to the particular one of the pixels (Pij). The associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) comprises a sequence of a particular number of pulse., (SPk), wherein consecutive ones of the pulses (SPk) of the sequence are separated by a separation period of time (SPT). The particular number of said pulses (SPk), and / or a duration of said pulses (SPk), and / or a duration of the separation period (SPT) of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) is determined to obtain the particular optical transition at a desired energy of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk) to decrease an average value of the associated one of the drive waveforms (DWk).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for examining a specimen, and scanning microscope system
InactiveUS6961124B2Improved bleaching characteristicImprove power densitySpectrum investigationLuminescent dosimetersScanning electron microscopeLength wave
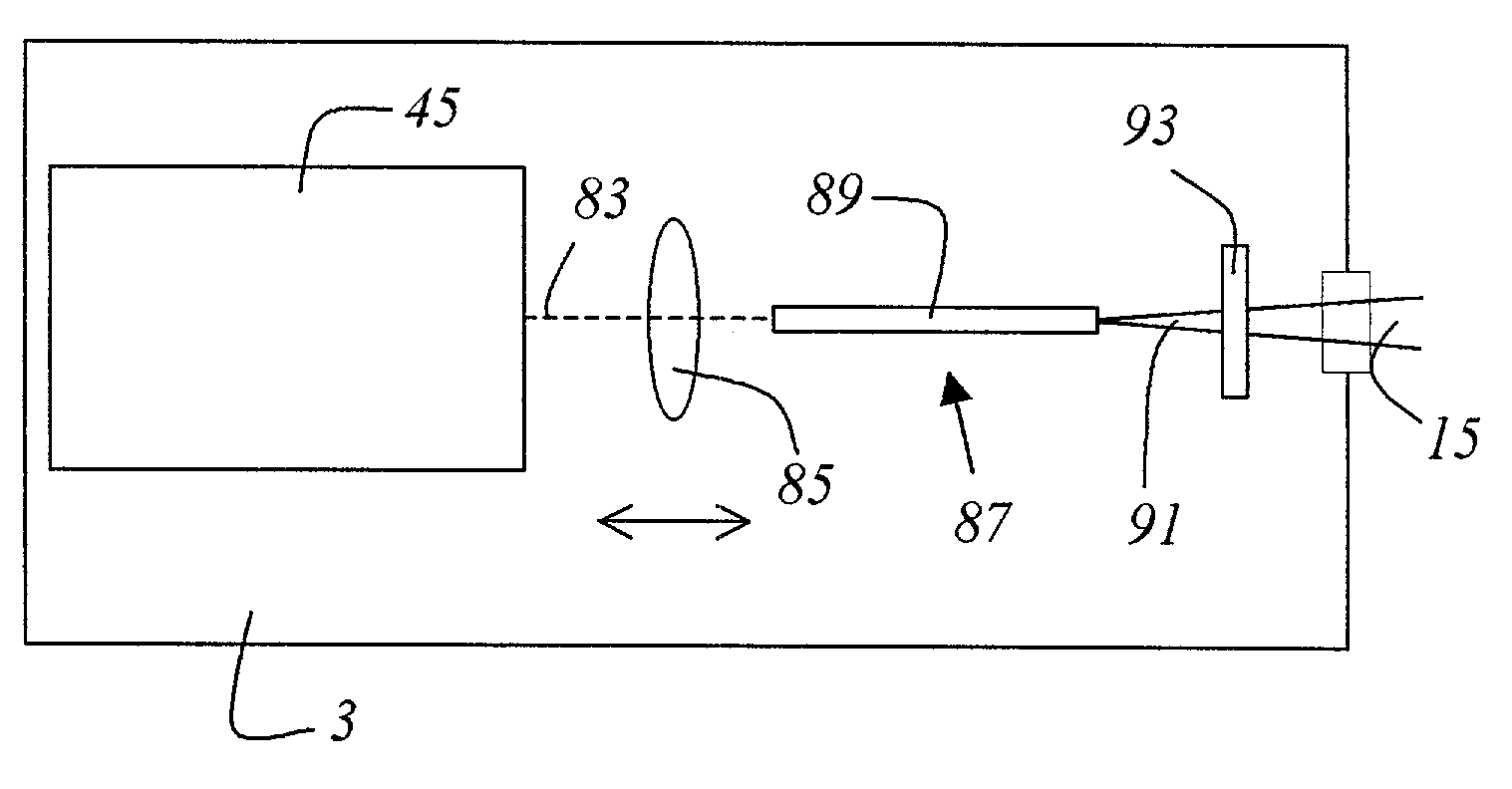
A method for examining a specimen (27) that exhibits at least two optical transition lines and is optically excitable at least with light of a first and light of a second wavelength is characterized by the step of illuminating the specimen (27) with illuminating light (15) that generates at least a multiple of the first wavelength and a multiple of the second wavelength; and by the step of detecting the detected light (29) proceeding from the specimen (27).Also disclosed is a scanning microscope system (1) having at least one light source (3) that emits illuminating light (15) for illumination of a specimen (27), the specimen (27) exhibiting at least two optical transition lines and being optically excitable at least with light of a first and light of a second wavelength, having at least one detector (41, 43, 65, 77, 79) for detection of the detected light (29) proceeding from the specimen (27) and an objective (25) for focusing the illuminating light (15) onto a subregion of the specimen (27). The scanning microscope system is characterized in that the illuminating light (15) generates at least a multiple of the first wavelength and a multiple of the second wavelength.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
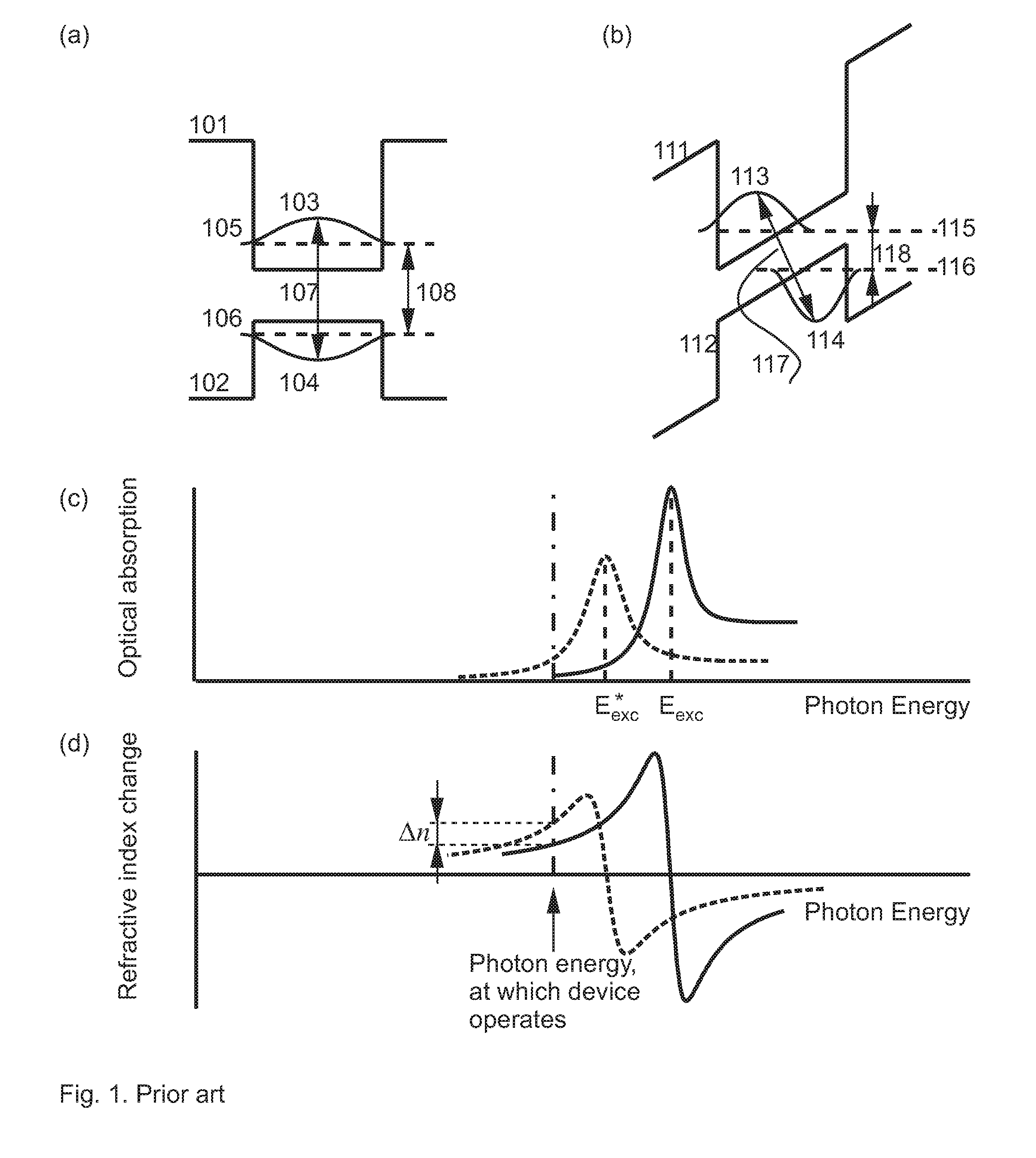
Anti Stark Electrooptic Medium and Electrooptically Modulated Optoelectronic Device Based Thereupon
ActiveUS20090041464A1Increase overlapIncrease oscillator strengthWavelength-division multiplex systemsSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionOscillator strength
Semiconductor electrooptic medium shows behavior different from a medium based on quantum confined Stark Effect. A preferred embodiment has a type-II heterojunction, selected such, that, in zero electric field, an electron and a hole are localized on the opposite sides of the heterojunction having a negligible or very small overlap of the wave functions, and correspondingly, a zero or a very small exciton oscillator strength. Applying an electric field results in squeezing of the wave functions to the heterojunction which strongly increases the overlap of the electron and the hole wave functions, resulting in a strong increase of the exciton oscillator strength. Another embodiment of the novel electrooptic medium includes a heterojunction between a layer and a superlattice, wherein an electron and a hole in the zero electric field are localized on the opposite sides of the heterojunction, the latter being effectively a type-II heterojunction. Yet another embodiment has a heterojunction between two superlattices, wherein an electron and a hole in a zero electric field are localized on the opposite sides of the heterojunction, the latter operating effectively as a type-II heterojunction. A further embodiment has an ultrathin quantum well layer confined by barrier layers, having an essentially different barrier heights and a thick layer, wherein, in a zero electric field, a charged particle of one sign having a large effective mass is localized in this ultrathin layer, and a particle having a different sign of the charge, having a small effective mass is not localized in this ultrathin layer, but is localized mainly in the neighboring thick layer. Thus, the heterojunction between the two layers operates effectively as a type-II heterojunction. Applying an electric field to all types of the electrooptic medium of the present invention results in a dramatic increase of the exciton oscillator strength and, therefore, in a large positive refractive index change at the photon energies below the exciton absorption peak. A very strong increase in the optical transition photon energy can be achieved, when necessary.
Owner:CONNECTOR OPTICS
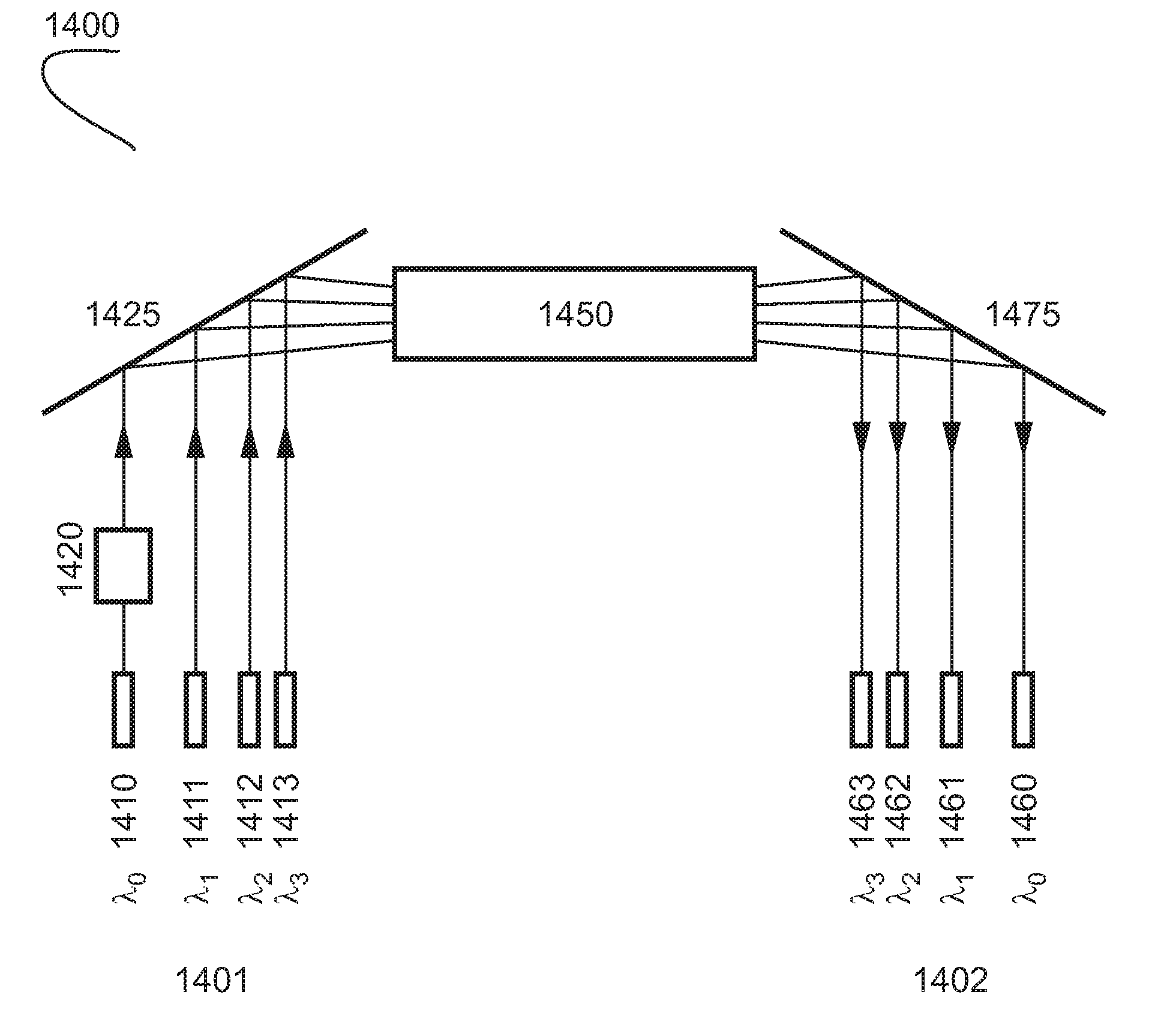
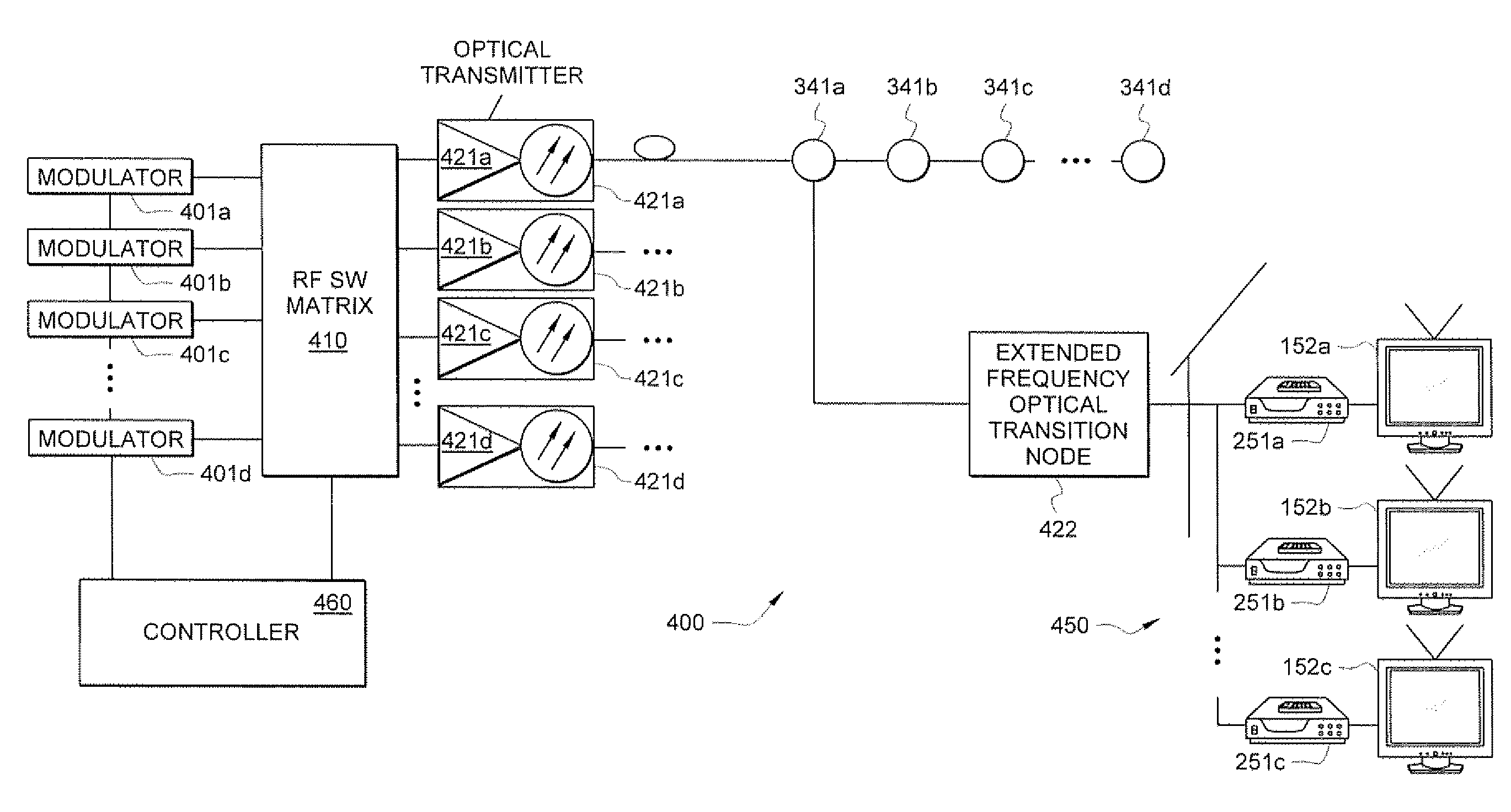
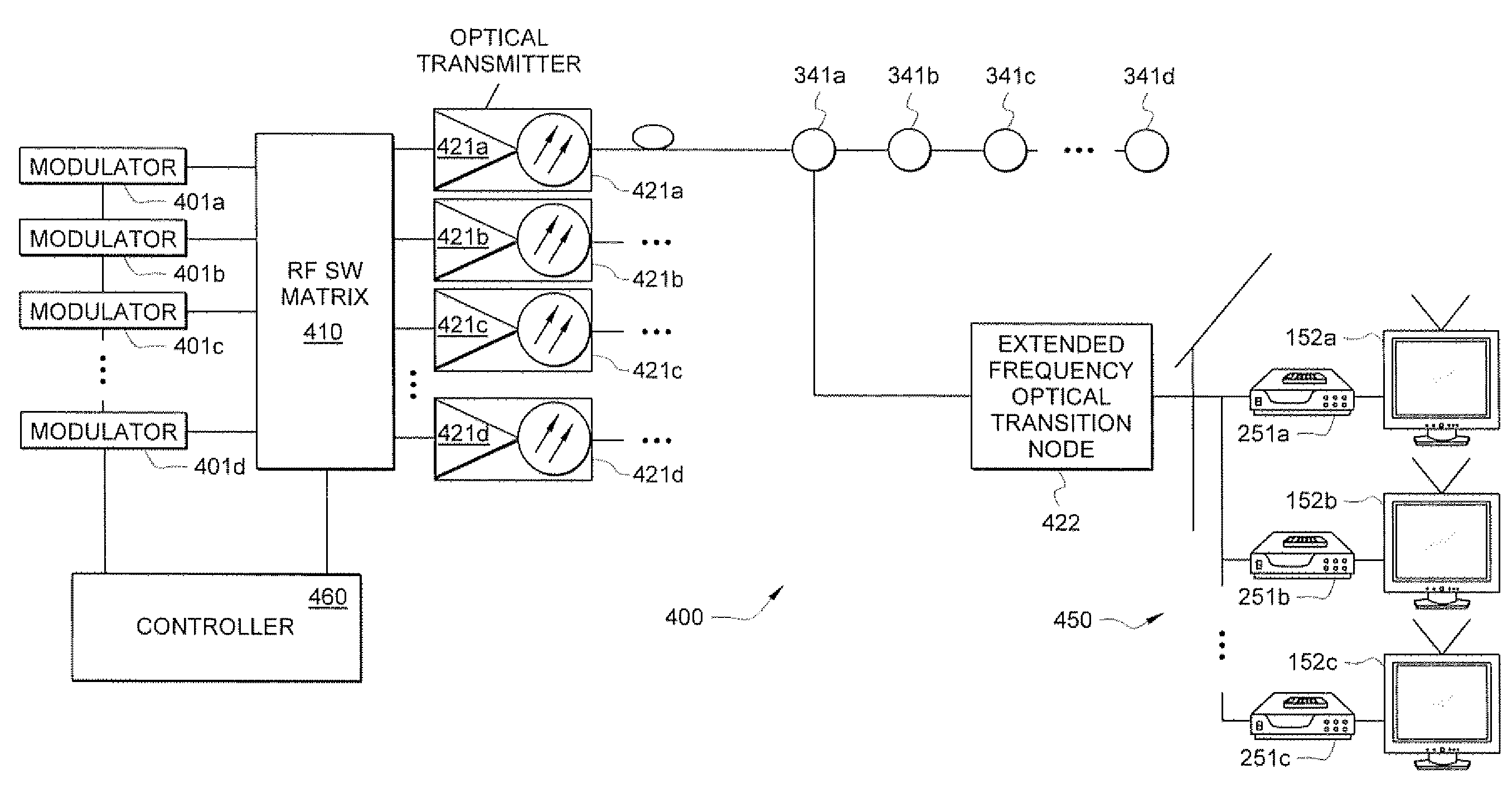
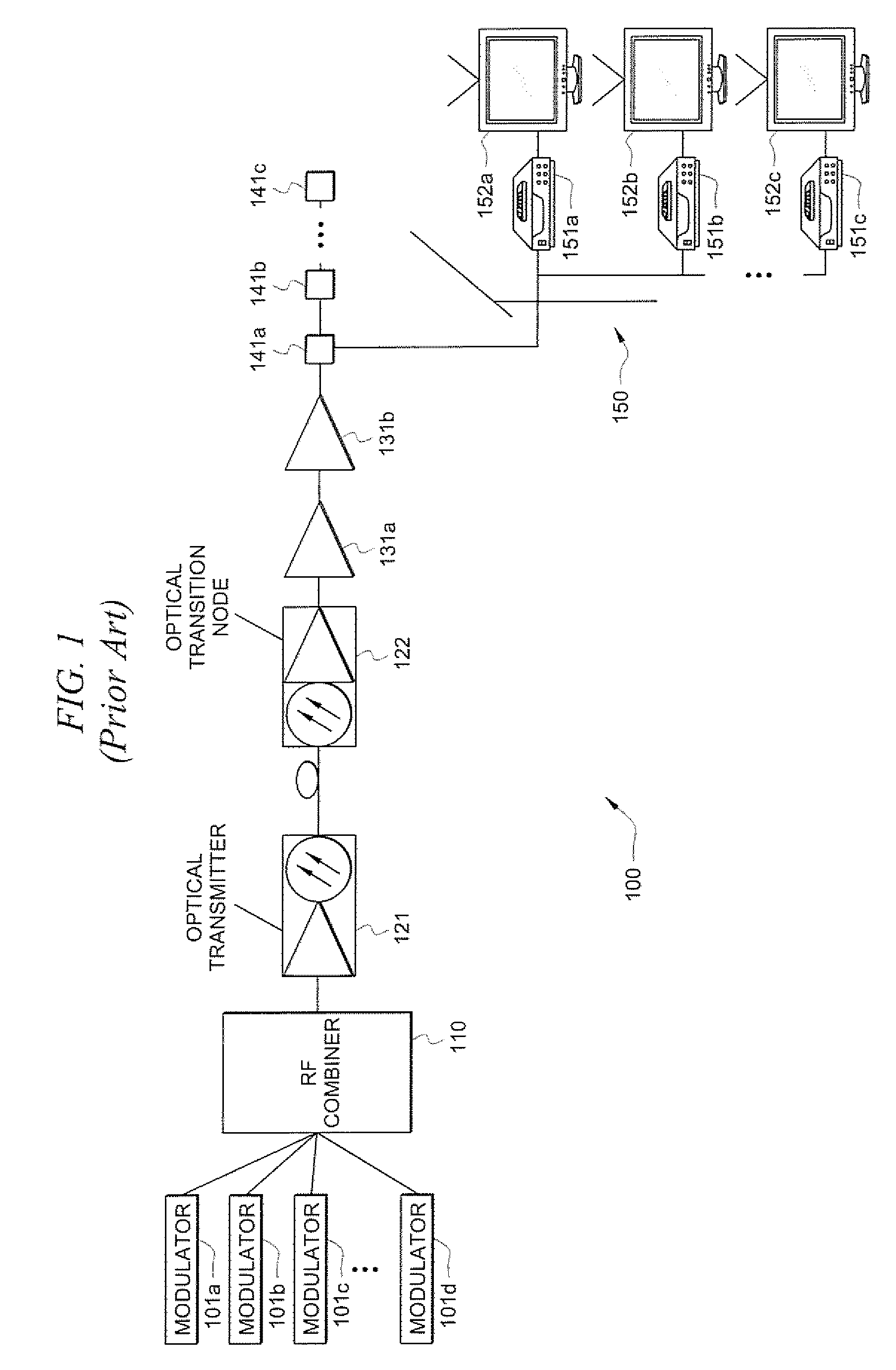
Systems and methods for broadband transmission of signals
InactiveUS8019221B2Improve abilitiesTelevision system detailsTime-division optical multiplex systemsBroadband transmissionFrequency conversion
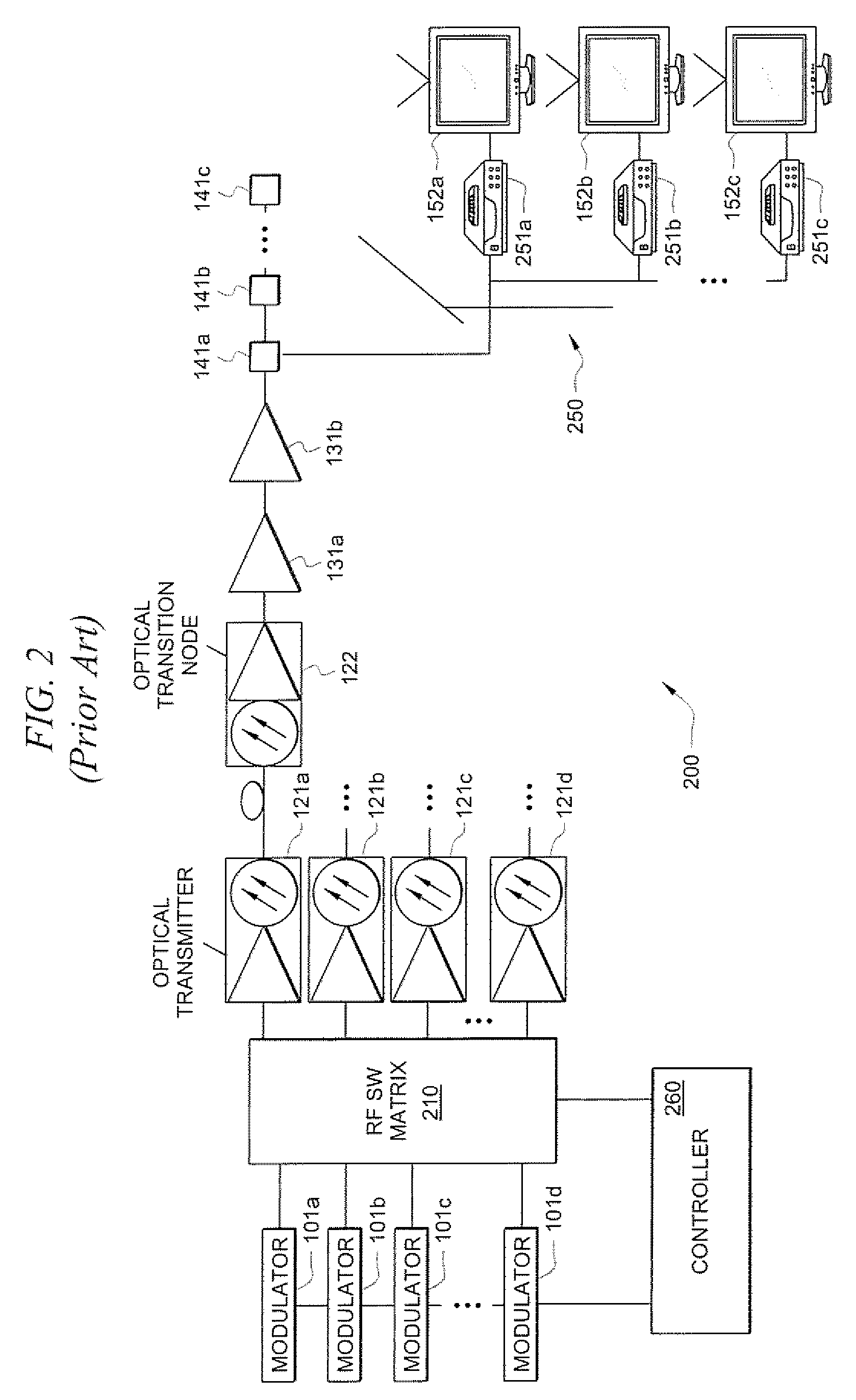
Systems and methods which facilitate broadband transmission of signals using a delivery point tuning technique to provide a extended frequency passive optical network (EF-PON) are shown. Embodiments provide an extended frequency optical transition node (EF-OTN) at each of a plurality of delivery points to provide a frequency translation interface between equipment disposed at the delivery point locations and a network utilizing transmission bandwidth which is incompatible with that equipment. The foregoing frequency conversion is preferably transparent to the equipment receiving the network transmissions. Embodiments utilize a single wideband tuner for providing frequency conversion with respect to a plurality of equipment disposed a delivery point. Network head-end modulators are controlled to implement channel grouping such that the signals requested by each piece of subscriber equipment at a delivery point are placed within radio frequency (RF) channels so that each such signal is within the frequency converted band of an EF-OTN tuner.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Liquid crystal device and method for forming the same
InactiveUS20070268446A1Increase contrastDisplay qualityLiquid crystal compositionsLamination ancillary operationsContrast ratioMaterials science
The present invention generally relates to liquid crystal devices and methods for forming the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to liquid crystal devices easy to be fabricated. Such liquid crystal devices exhibit excellent display characteristics such as a high contrast with a simple structure. The liquid crystal liquid crystal device includes a plurality of encapsulated liquid crystal composite filled in between substrates. In particular, the liquid crystal composite comprises liquid crystal molecules and fine-particles, and is optically isotropic when the voltage applied to the electrode layer is lower than a threshold value and undergoes optical transition due to change in the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules when the applied voltage is equal to or higher than the threshold value.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
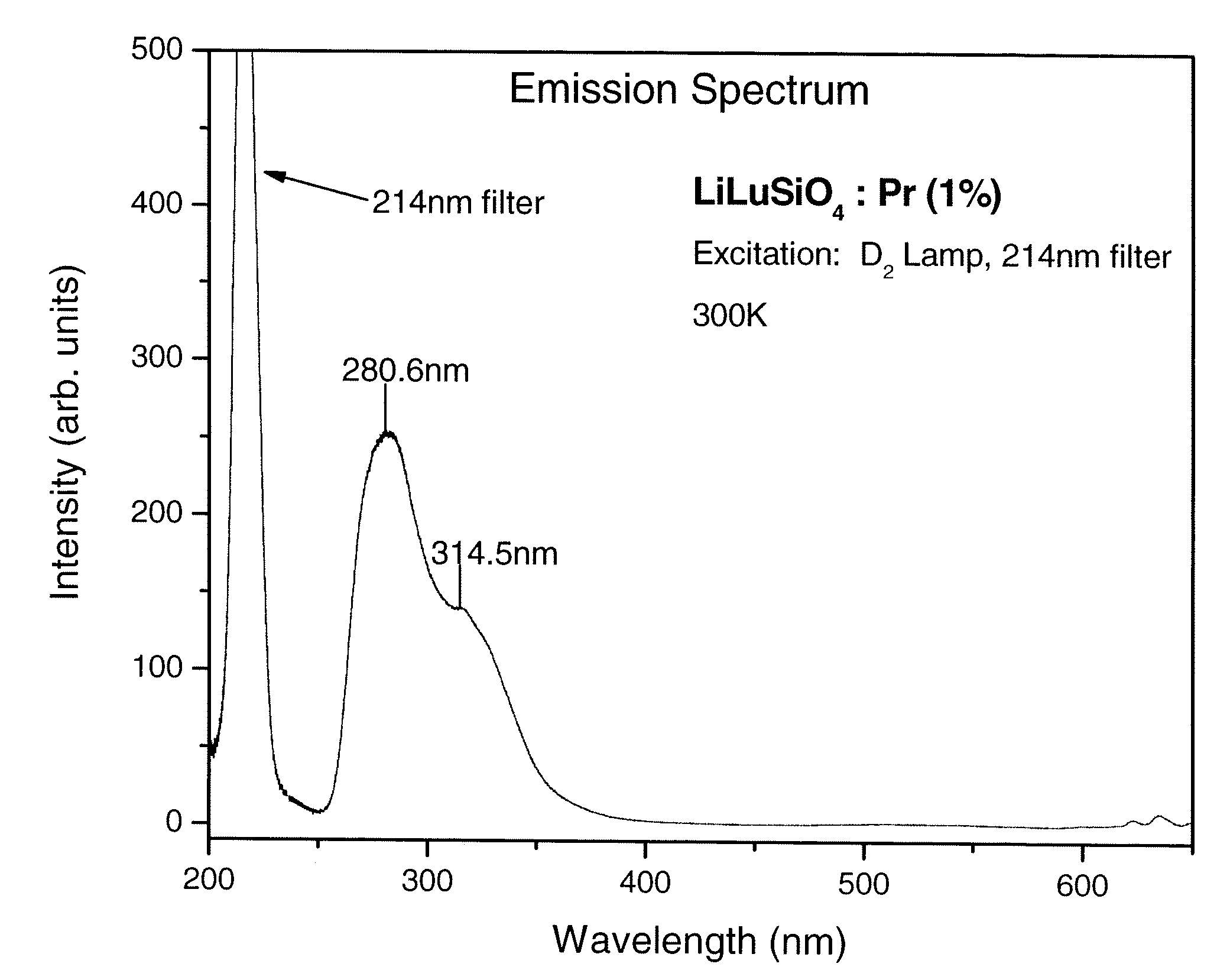
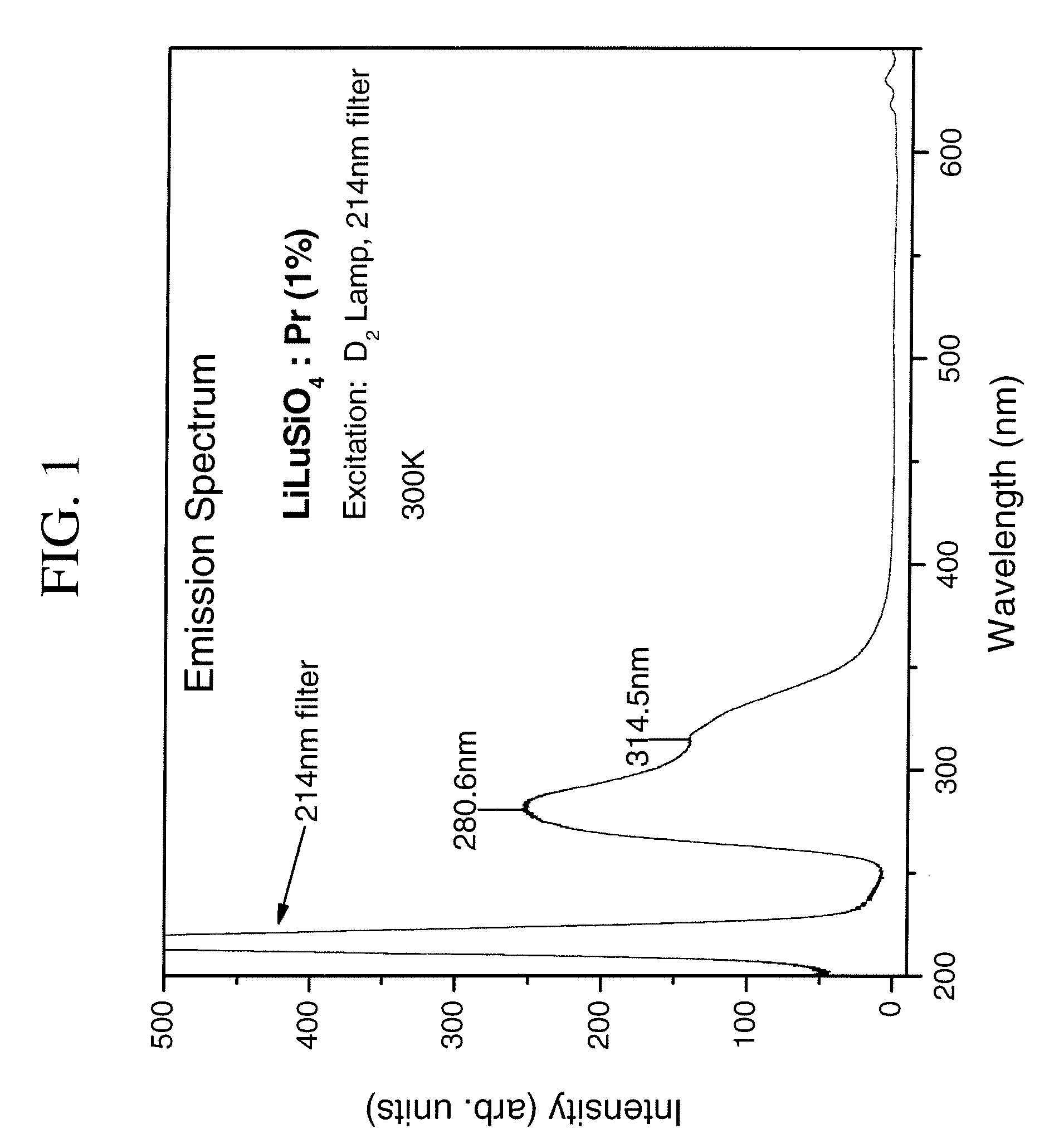
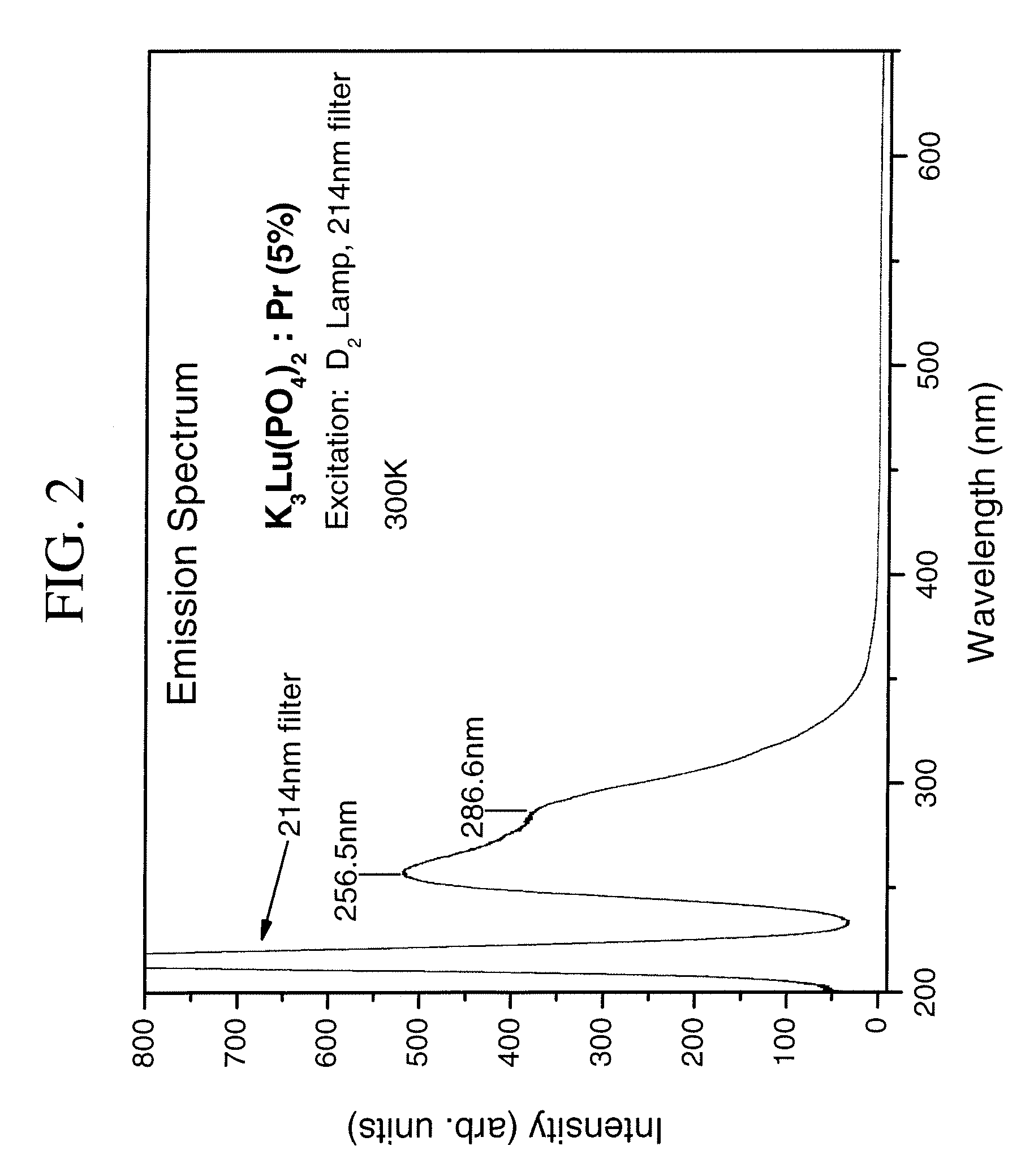
Scintillator materials based on lanthanide silicates or lanthanide phosphates, and related methods and articles
InactiveUS20090146065A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementLithiumHigh energy
A scintillator composition is described. The composition includes a matrix material in the form of a host lattice characterized by a 4f5d→4f optical transition under activation. The matrix material is based on certain lithium-lanthanide silicate compounds or alkali-lanthanide phosphate compounds. The composition also includes a praseodymium (Pr) activator for the matrix material. Radiation detectors which include crystal scintillators are also part of the present invention, as are methods for detecting high-energy radiation, using these devices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for broadband transmission of signals
InactiveUS20090034979A1Improve abilitiesTelevision system detailsTime-division optical multiplex systemsBroadband transmissionEngineering
Systems and methods which facilitate broadband transmission of signals using a delivery point tuning technique to provide a extended frequency passive optical network (EF-PON) are shown. Embodiments provide an extended frequency optical transition node (EF-OTN) at each of a plurality of delivery points to provide a frequency translation interface between equipment disposed at the delivery point locations and a network utilizing transmission bandwidth which is incompatible with that equipment. The foregoing frequency conversion is preferably transparent to the equipment receiving the network transmissions. Embodiments utilize a single wideband tuner for providing frequency conversion with respect to a plurality of equipment disposed a delivery point. Network head-end modulators are controlled to implement channel grouping such that the signals requested by each piece of subscriber equipment at a delivery point are placed within radio frequency (RF) channels so that each such signal is within the frequency converted band of an EF-OTN tuner.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Photonic device comprising a laser optically connected to a silicon waveguide and method for manufacturing such a photonic device
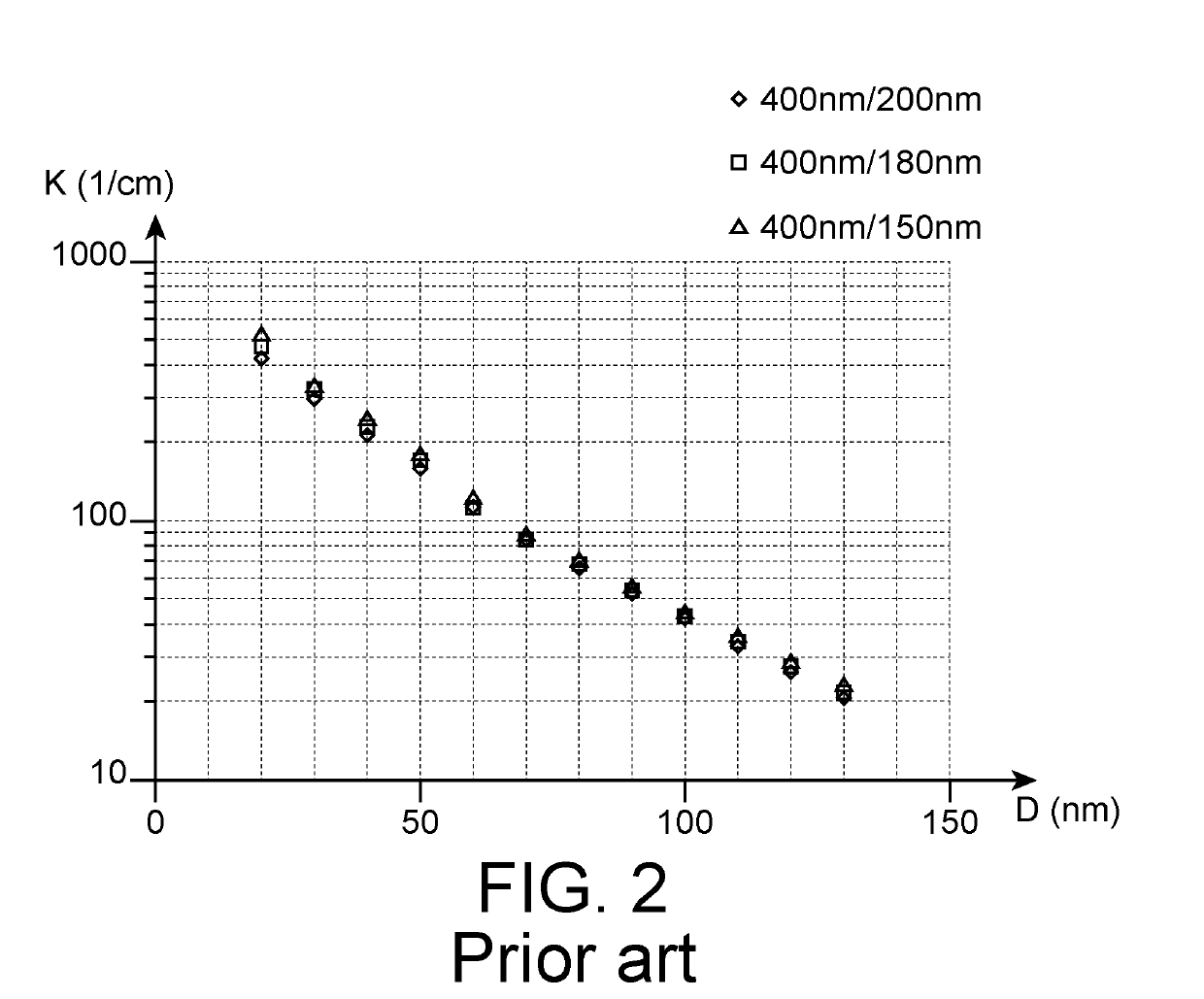
A photonic device comprising: a support; an intermediate layer (; an optical guiding level including a waveguide and a first to a fifth waveguide section. The photonic device further includes a first dielectric layer covering the optical guiding level and a gain structure in contact with the first dielectric layer. The second and fourth waveguide sections and the first and second ends of the gain structure form a first and a second zone of optical transition between a laser hybrid waveguide, and respectively the first and the fifth waveguide sections. A pattern forming a Bragg grating is arranged over a first part of the thickness of the third waveguide section which is away from the gain structure.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
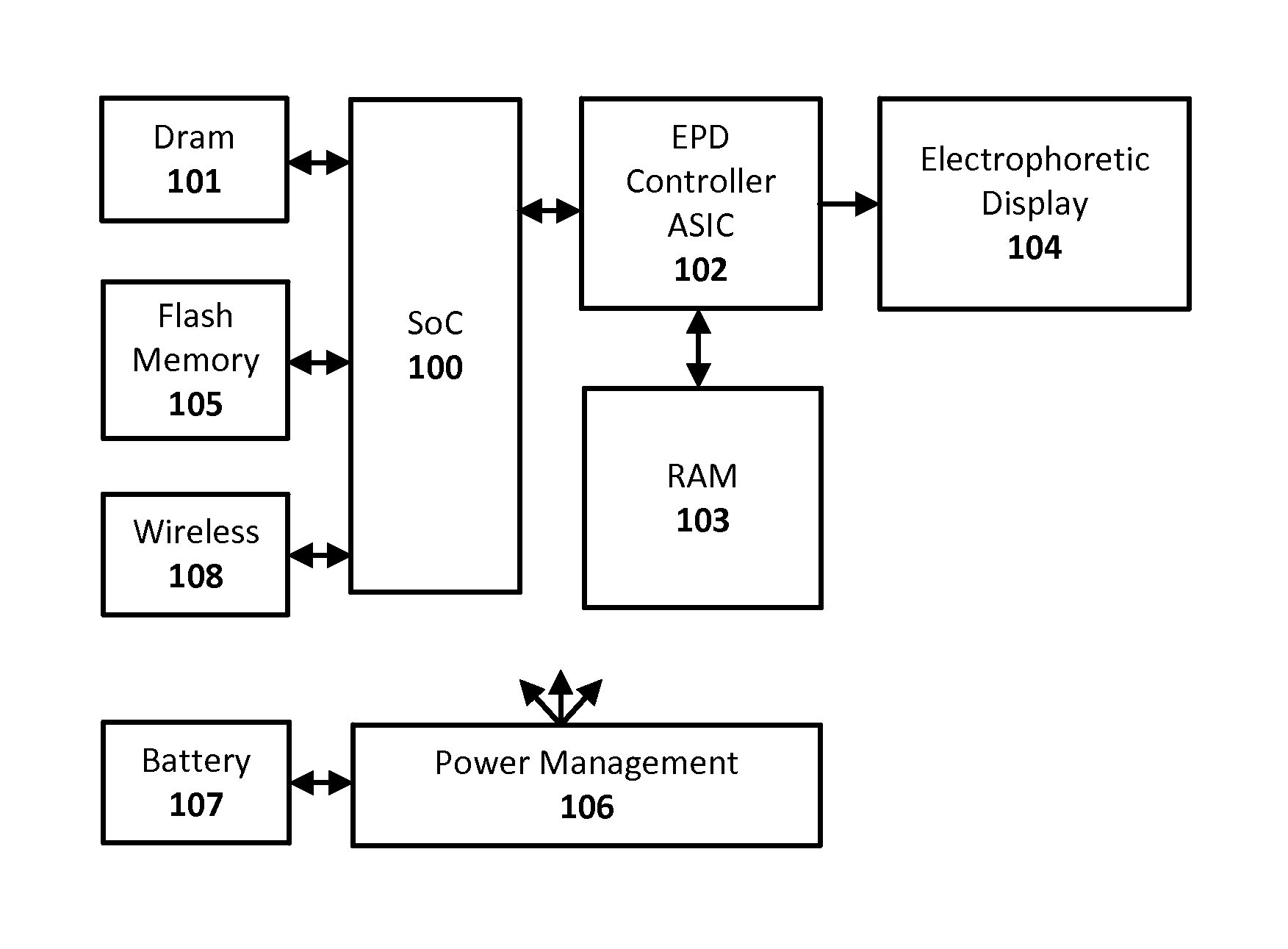
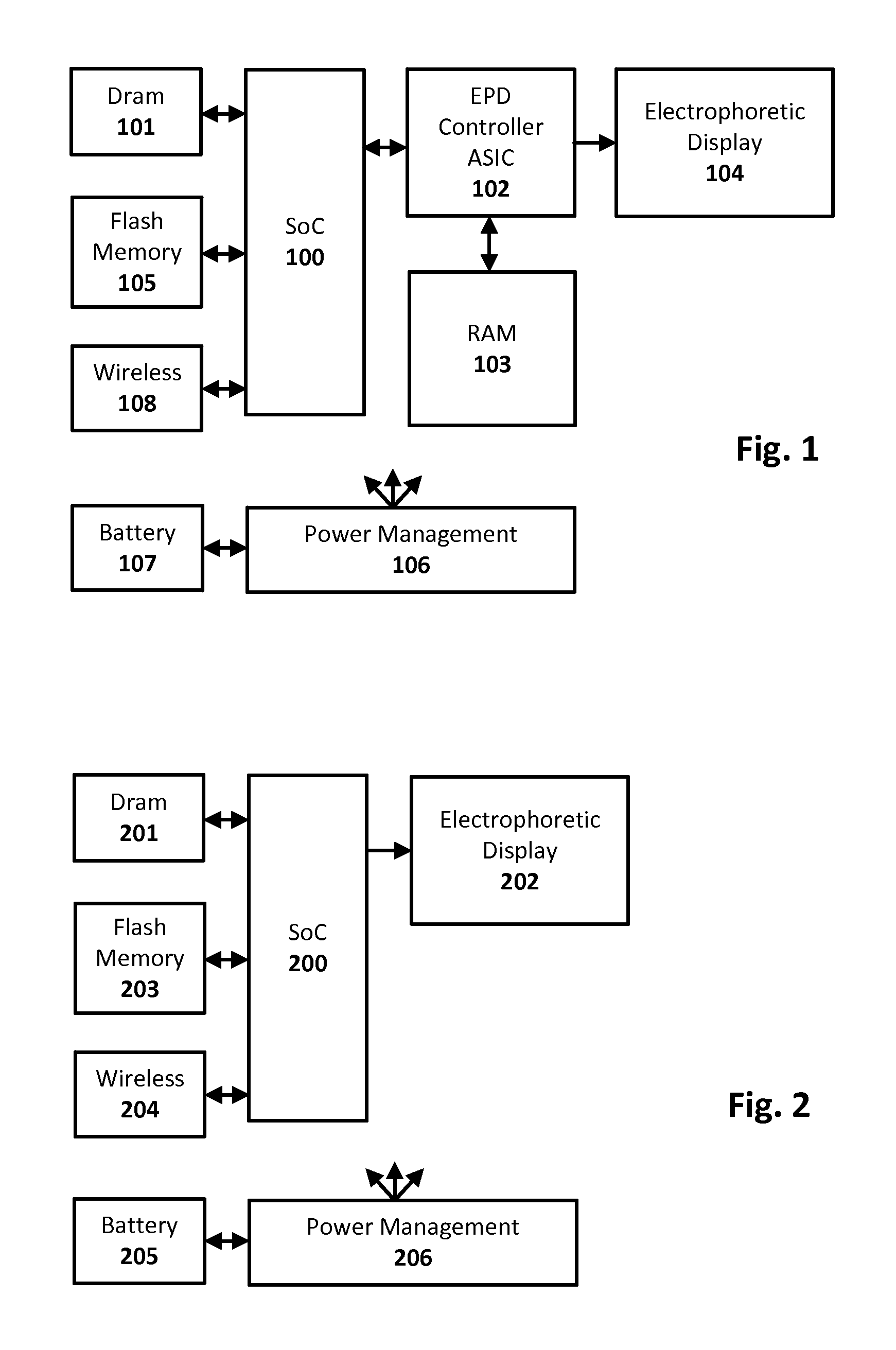
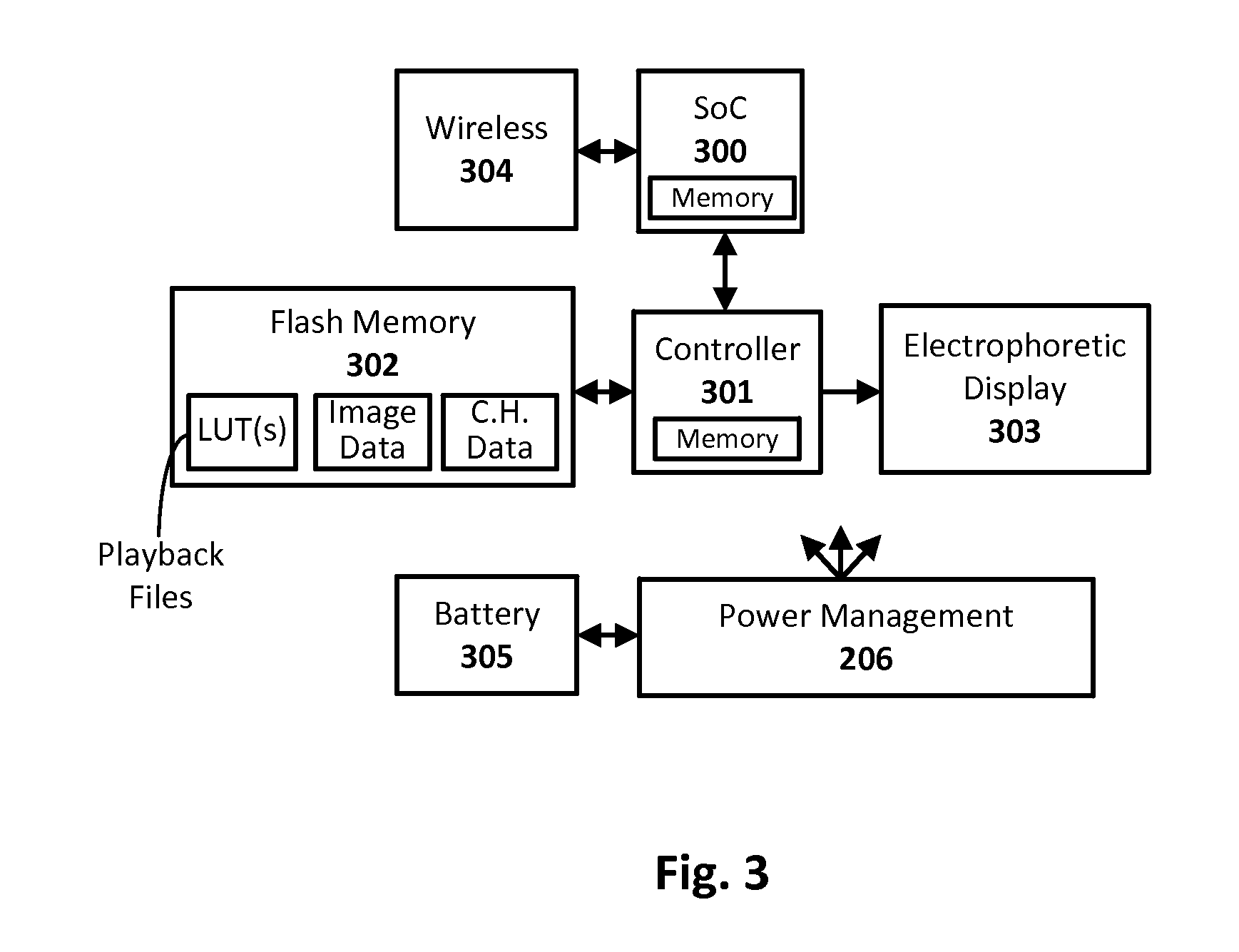
Electrophoretic display drive techniques
ActiveUS20160284323A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsComputer graphics (images)Electrophoresis
Techniques for updating an electrophoretic display or other integrating display are provided. A first image data representing the current optical state of the display is combined with a second image data representing the desired next optical state of the display along with a third data representing the charge history of the display to form a compact intermediate representation of the electrical drive signals required to transition the display. Such compact intermediate representations can be provided for each pixel of the display and stored in flash memory. Once determined, these representations of the drive signals can be rapidly replayed from flash memory and further processed to drive the display and affect the desired optical transition from current image to next image while correcting for DC imbalances.
Owner:NOOK DIGITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com