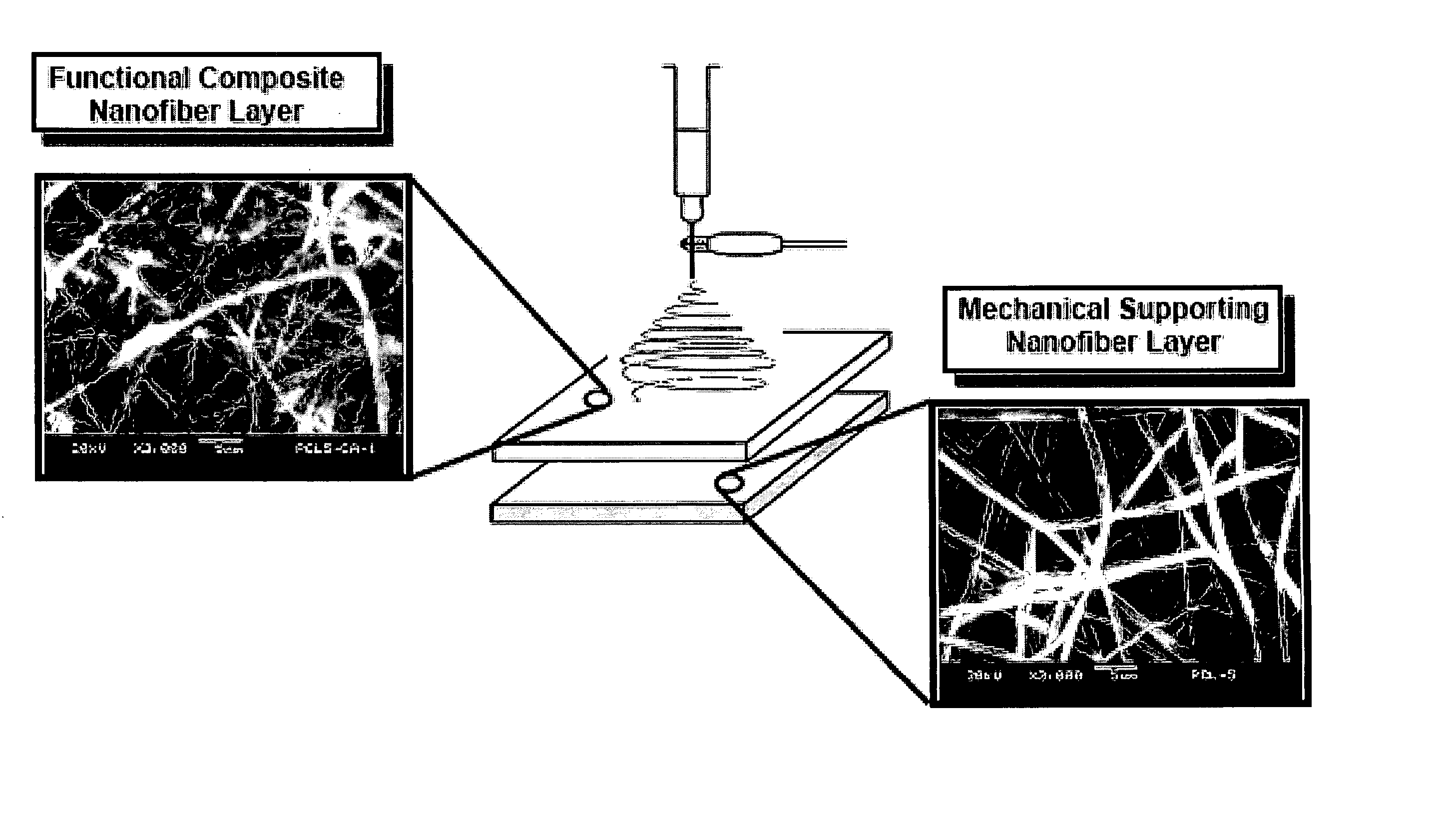
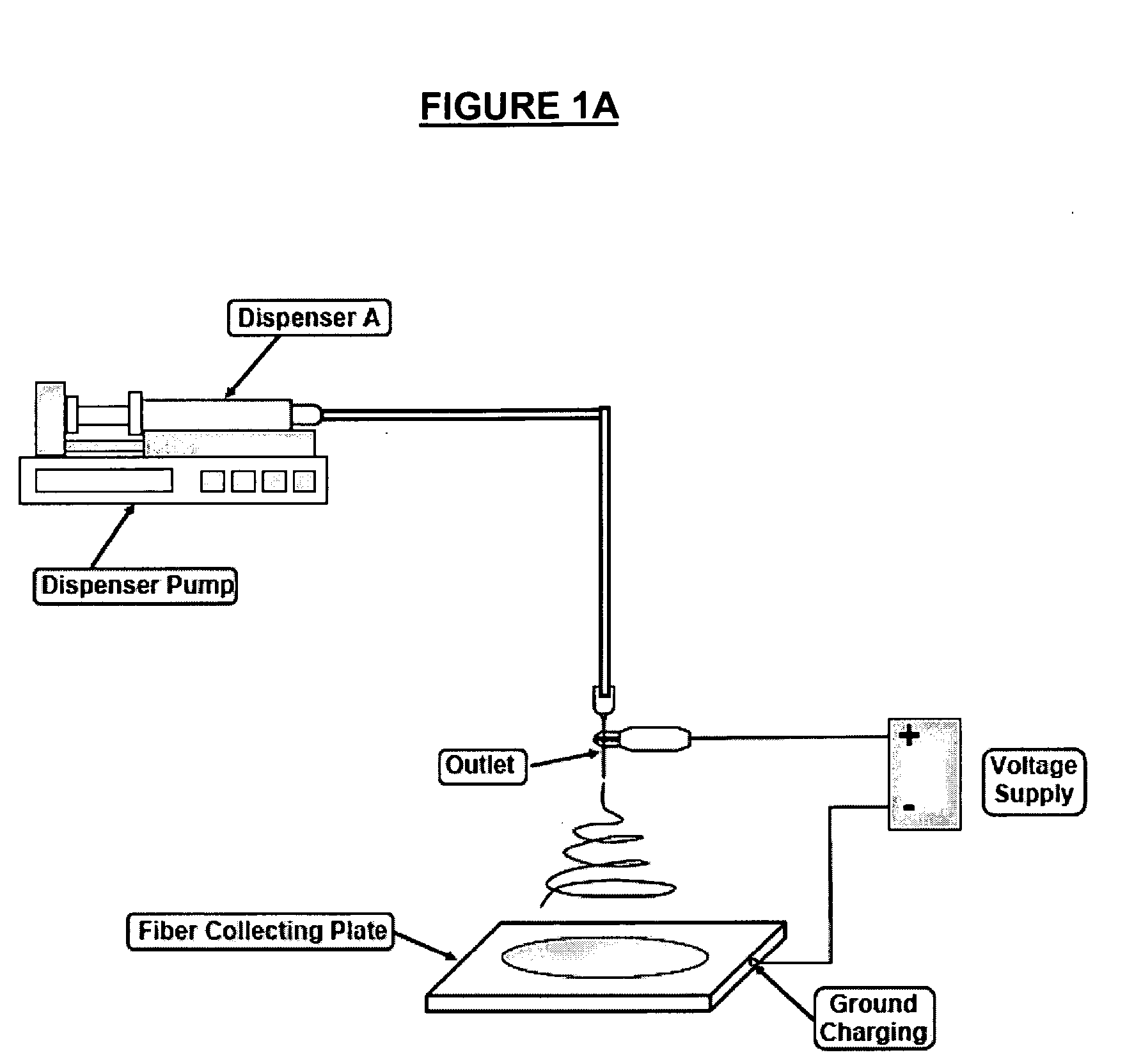
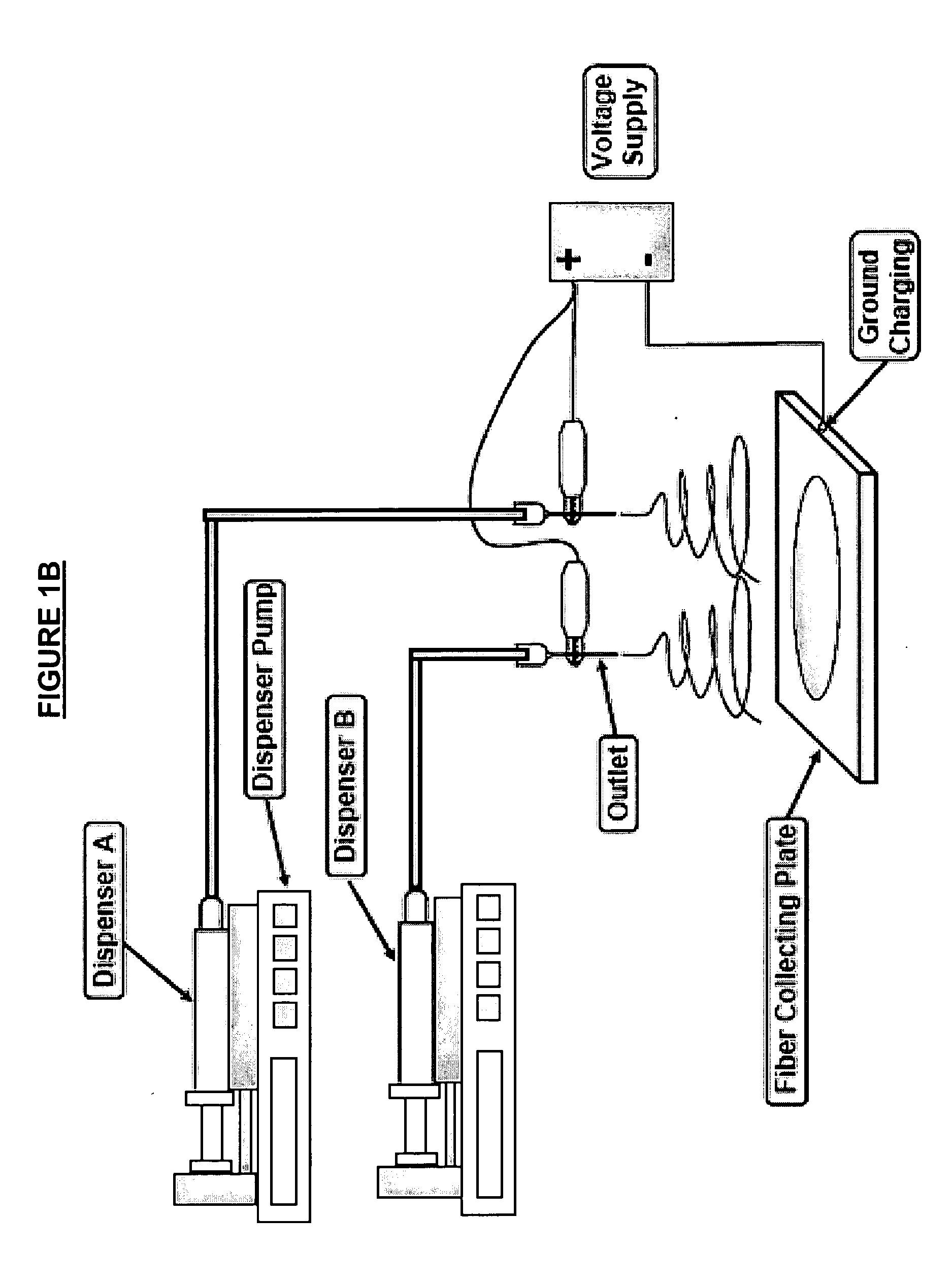
Nanofiber construct and method of preparing thereof
a nanofiber and construct technology, applied in the field of nanofiber constructs and methods of preparing them, can solve the problems of inability to use implants, decrease in the tensile property of these membranes, etc., and achieve the effects of enhancing the hydrophilicity of composite nanofiber constructs, enhancing cell attachment, and enhancing the osteoconductive property of nanofibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0116] In the present invention, the composite nanofiber constructs were prepared by ε-polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibers and a composite of PCL and calcium carbonate nanoparticles (CaCO3) nanofibers with a particular weight ratio, i.e., PCL:CaCO3=25:75 wt %). The materials used were PCL pellet (Mn=80,000) purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Singapore Pte. Ltd., and CaCO3 nanoparticles (average particle size=40 nm: cubic type) supplied from NanoMaterials Technology Pte. Ltd. Singapore. For PCL nanofibers, the PCL pellet was first dissolved in a mixture of solvent comprising 75 wt % chloroform and 25 wt % methanol. The concentration of PCL solution was 7.5 wt % to ensure fine fiber morphology in the resulting nanofibers. For PCL / CaCO3 composite nanofibers, CaCO3 nanoparticles were first dissolved in a mixture of solvent and subsequently, the PCL pellet was dissolved. The concentration of PCL in the resulting mixture was 5 wt %. The outlet was a needle with 0.21 mm inner diameter. The feed ra...
example 2
[0118] Please note that with reference to this example, GBR membrane (A) refers to nanofiber (A) and GBR membrane (B) refers to nanofiber (B).
2.1 Fabrication of Composite Nanofibrous Construct
2.1.1 Electrospinning
[0119] In this example, composite nanofibrous constructs were designed by epsilon-polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibers and PCL / CaCO3 composite nanofibers with two different weight ratios (i.e. PCL:CaCO3=75:25 wt % and 25:75 wt %). The materials used were PCL pellet (Mn=80,000) purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Singapore Pte. Ltd., and CaCO3 nanoparticles (average particle size of 40 nm, cubic type) supplied by NanoMaterials Technology Pte. Ltd. Singapore.
[0120] For PCL nanofibers, the PCL pellet was first dissolved in a mixture of 75 wt % chloroform and 25 wt % methanol. In order to obtain fine fiber morphology, the concentration of PCL solution was varied in the range from 3 wt % to 7.5 wt %.
[0121] For PCL / CaCO3 composite nanofibers, CaCO3 nanoparticles were first dissolved...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com