Construction method of anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material
A stent material and artificial blood vessel technology, which is applied in the construction field of anticoagulant artificial vascular stent materials, can solve the problems affecting the persistence of NO release, the fast release rate of NO, and the phenomenon of burst release, so as to improve the phenomenon of catalytic NO burst release , overall performance optimization, the effect of inducing and promoting angiogenesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1. The construction method of anticoagulant artificial vascular stent material, comprises the following steps successively:
[0025] ① Preparation of P3HB4HB electrospinning solution with P3HB4HB and Cu 2+ Mixed electrospinning solution of -Cyclen complex:
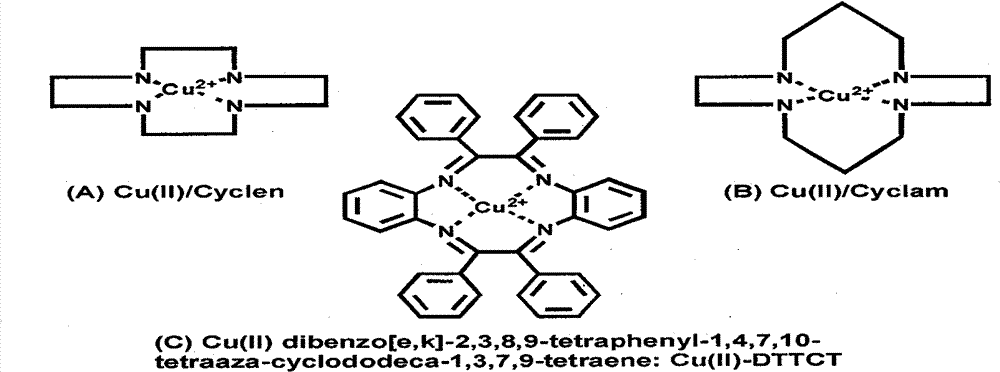
[0026] Weigh 300mg of 12% P3HB4HB, dissolve in 6ml solvent (dichloromethane:methanol=9:1); prepare three parts; one part is dissolved in 1.2mg Cu 2+ -Cyclen complexes;
[0027] ② Preparation of porous vascular stent material with three-layer structure by electrospinning technology:
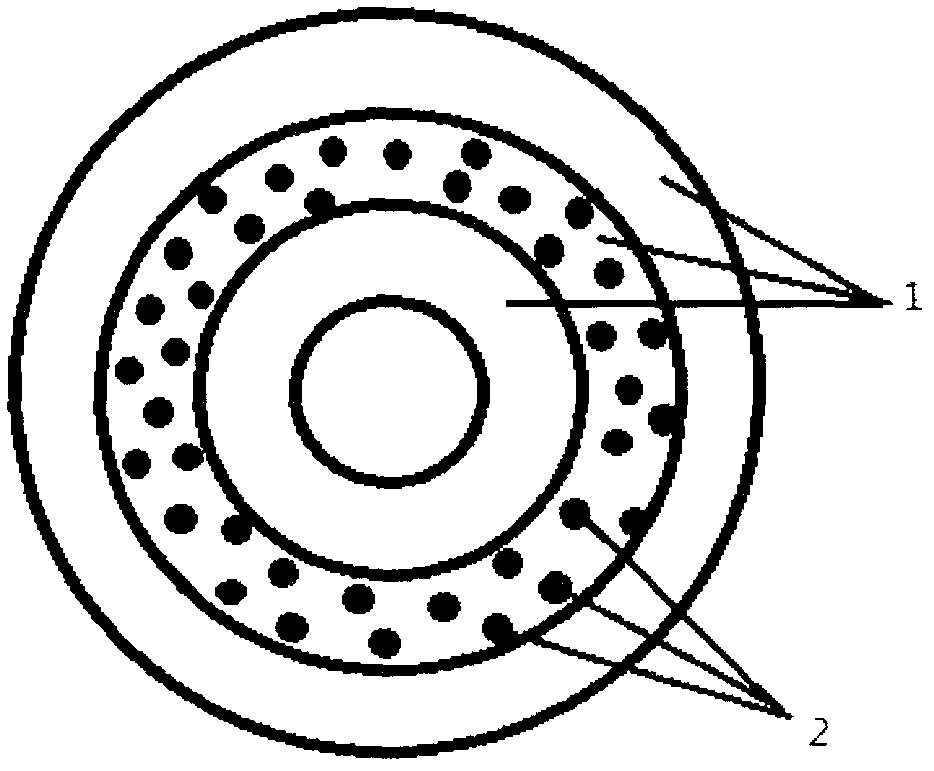
[0028] Using a stainless steel tube with an inner diameter of 3 mm as the electrospinning receiver, the above-mentioned P3HB4HB electrospinning liquid, P3HB4HB and Cu 2+ -Cyclen complex mixed electrospinning solution, and P3HB4HB electrospinning solution electrospun on the tubular receiver to form figure 1 The artificial vascular stent shown;
[0029] Electrospinning conditions: the temperature is 25°C, the air humidity ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2. The construction method of anticoagulant artificial vascular stent material, comprises the following steps successively:
[0032] ①Preparation of PCL electrospinning solution with PCL and Cu 2+ - Mixed electrospinning solution of Cyclam complex:
[0033] Weigh PCL, 300mg, dissolve in 6ml solvent (dichloromethane:methanol=9:1); prepare three parts; one part is dissolved in 1.2mg Cu 2+ - Cyclam complexes;
[0034] ② Preparation of porous vascular stent material with three-layer structure by electrospinning technology:
[0035]Using a stainless steel tube with an inner diameter of 3mm as the electrospinning receiver, the above-mentioned PCL electrospinning solution, PCL and Cu 2+ -Cyclam complex mixed electrospinning solution, and PCL electrospinning solution electrospun on the tubular receiver to form figure 1 The artificial vascular stent shown;
[0036] Electrospinning conditions: the temperature is 25°C, the air humidity is 40%, the flow rate is 1ml / ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3. The construction method of anticoagulant artificial vascular stent material, comprises the following steps successively:
[0039] ① Preparation of PCL and PLGA mixed electrospinning solution, PCL and PLGA and Cu 2+ - Mixed electrospinning solution of DTTCT complex: Weigh 150 mg each of PCL and PLGA, dissolve in 6 ml solvent (dichloromethane: methanol = 9: 1); prepare three parts; one part is dissolved in 1.2 mg Cu 2+ - DTTCT complex;
[0040] ② Preparation of porous vascular stent material with three-layer structure by electrospinning technology:
[0041] Using a stainless steel tube with an inner diameter of 3 mm as the electrospinning receiver, the above-mentioned PCL and PLGA electrospinning solution, PCL and PLGA and Cu 2+ -Cyclam complex mixed electrospinning solution, and PCL and PLGA electrospinning solution are electrospun on the tubular receiver to form figure 1 The artificial vascular stent shown;
[0042] Electrospinning conditions: the temp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com