Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Elastin tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
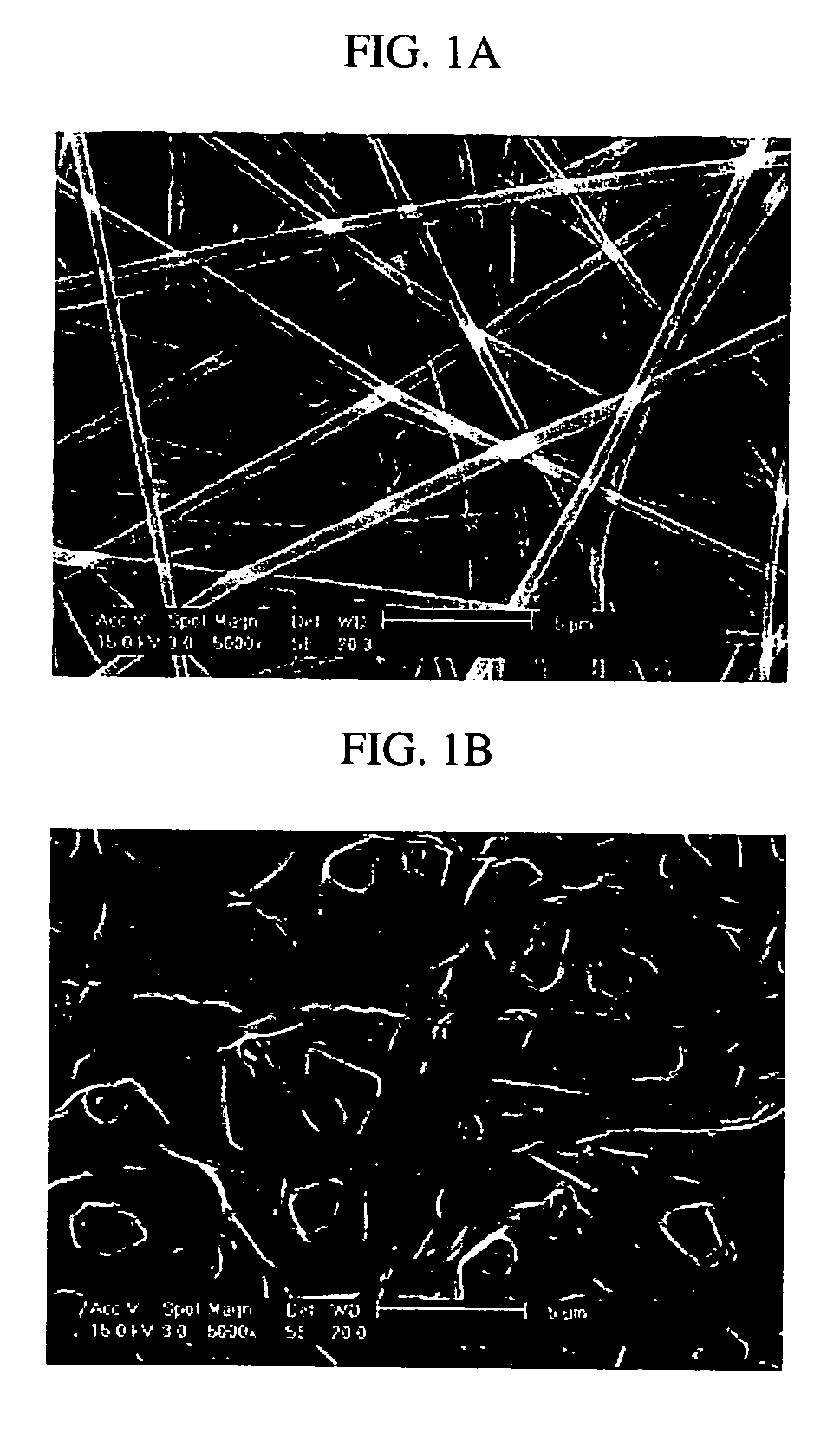
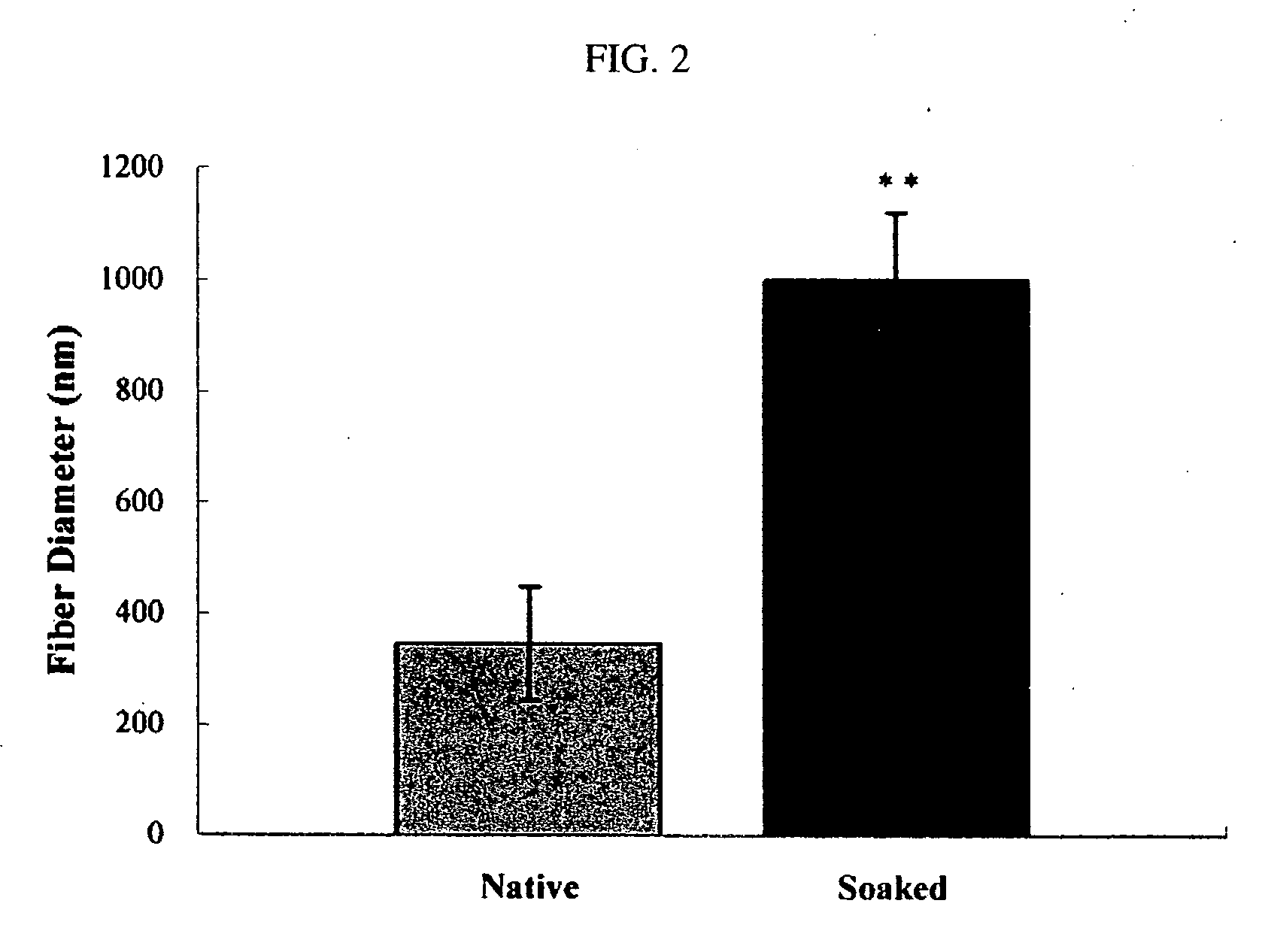
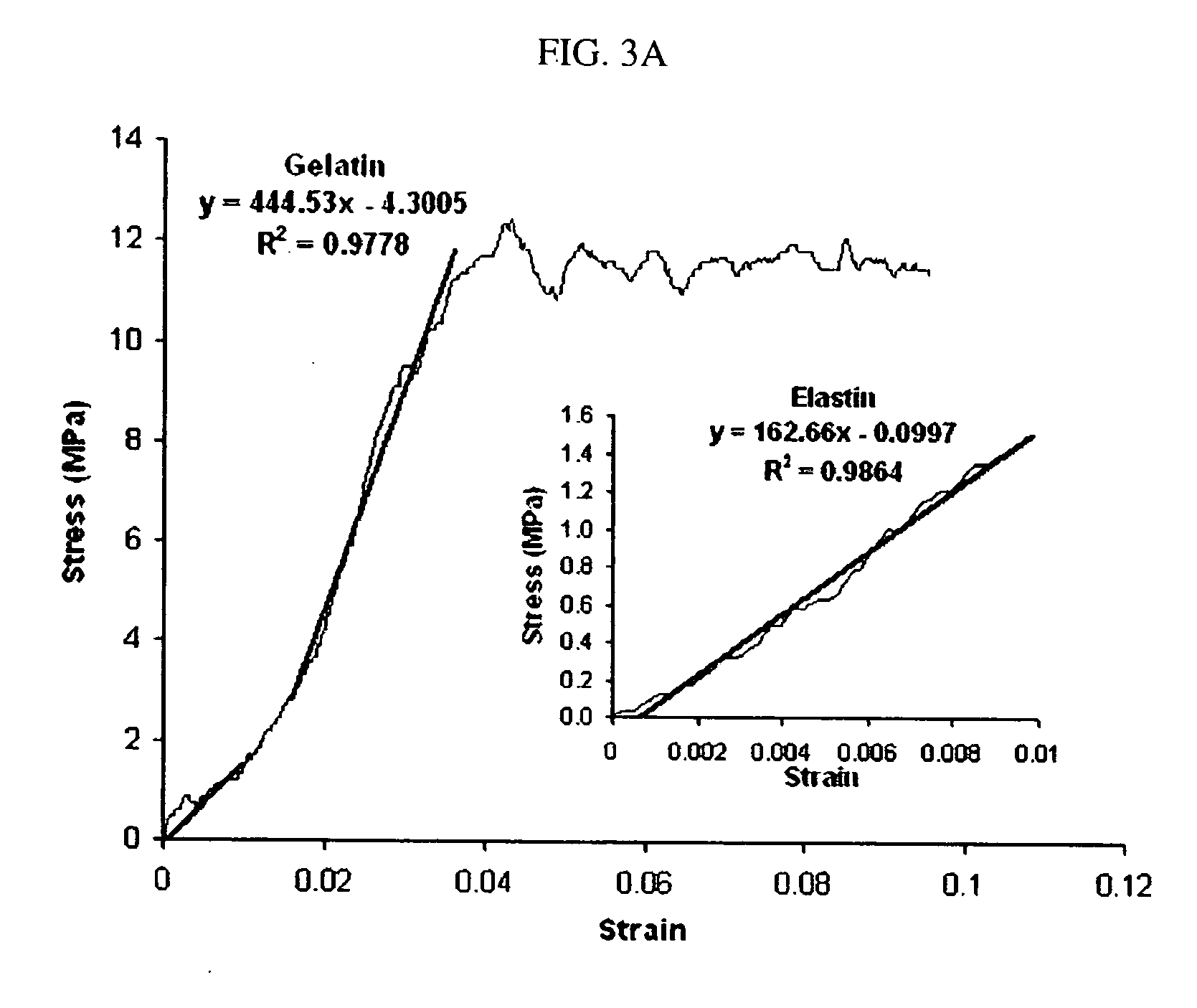
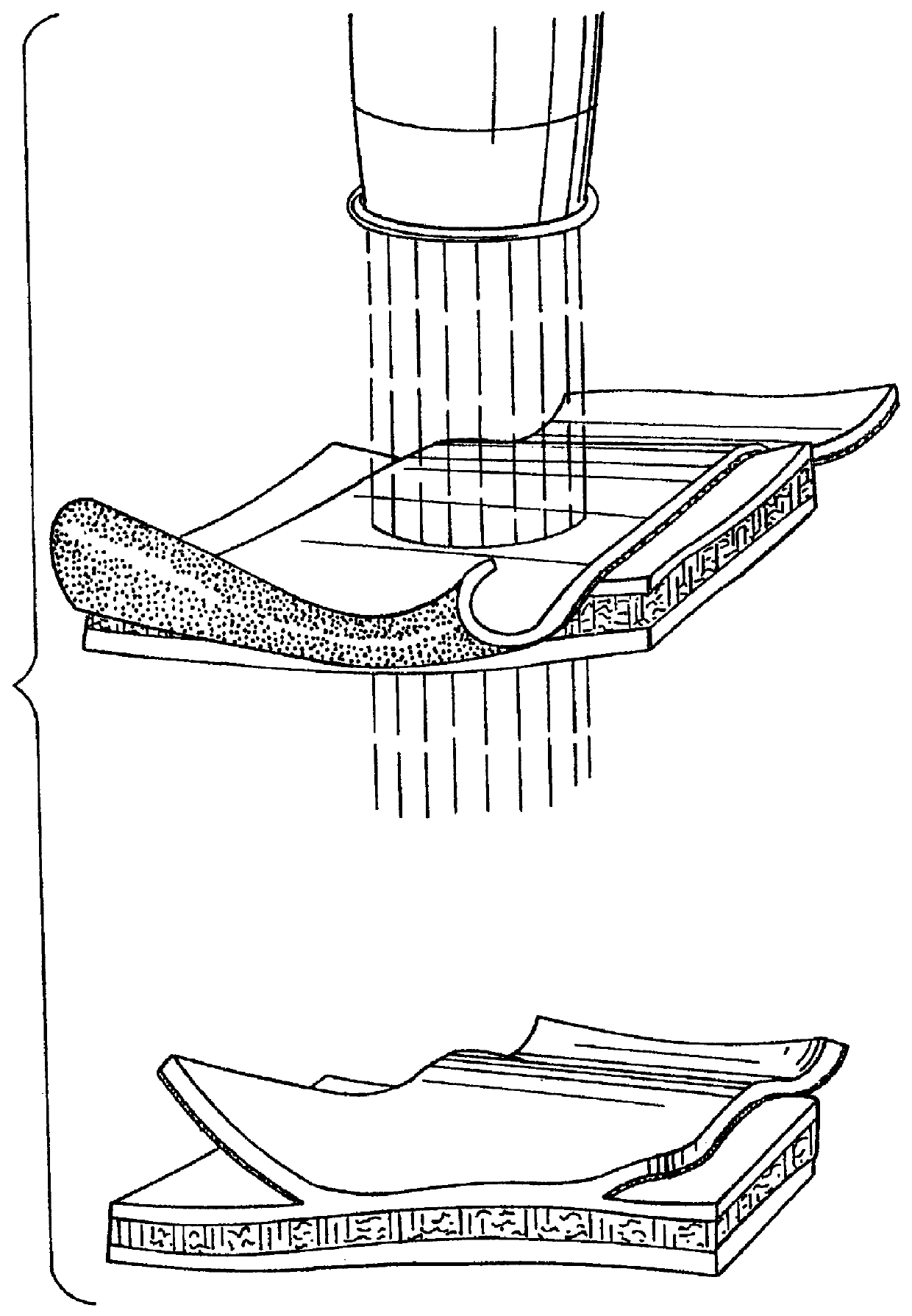
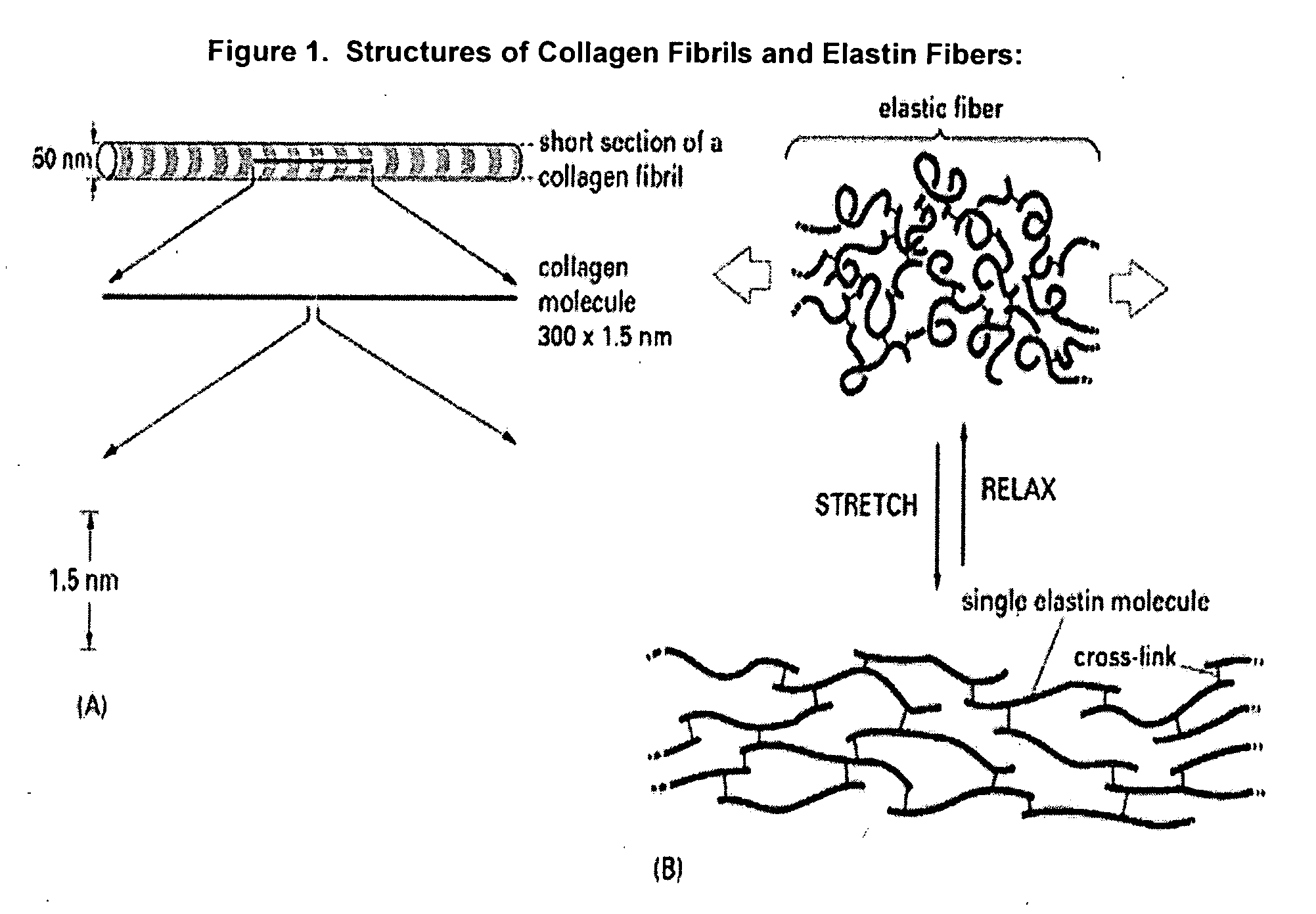
Elastin is part of connective tissue. It is an elastic protein which allows many tissues in the body to go back to their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin return to its original position when handled. Elastin is also used in places where mechanical energy is stored.
Synovial fluid barrier
InactiveUS20060178743A1Improve regenerative healingImprove responseSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSynovial jointsSacroiliac joint
A composite tissue formed in situ is provided. The composite tissue includes a synovial joint tissue; and a barrier material adhered thereto for sealing the synovial joint tissue against synovial fluid. Also provided is a method for regenerating synovial joint tissue in situ by excluding synovial fluid therefrom. The method includes providing a synovial joint tissue having a defect; and placing a barrier material in intimate contact with the defect for sealing the defect against synovial fluid. The barrier material includes a curable protein copolymer. The method further includes curing the protein copolymer in situ. The barrier material can include a crosslinked network, or a self gelled network of repeating elastin-like and fibroin-like polymer chains.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Tissue material and process for bioprosthesis
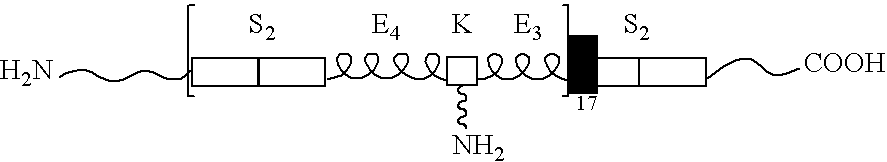
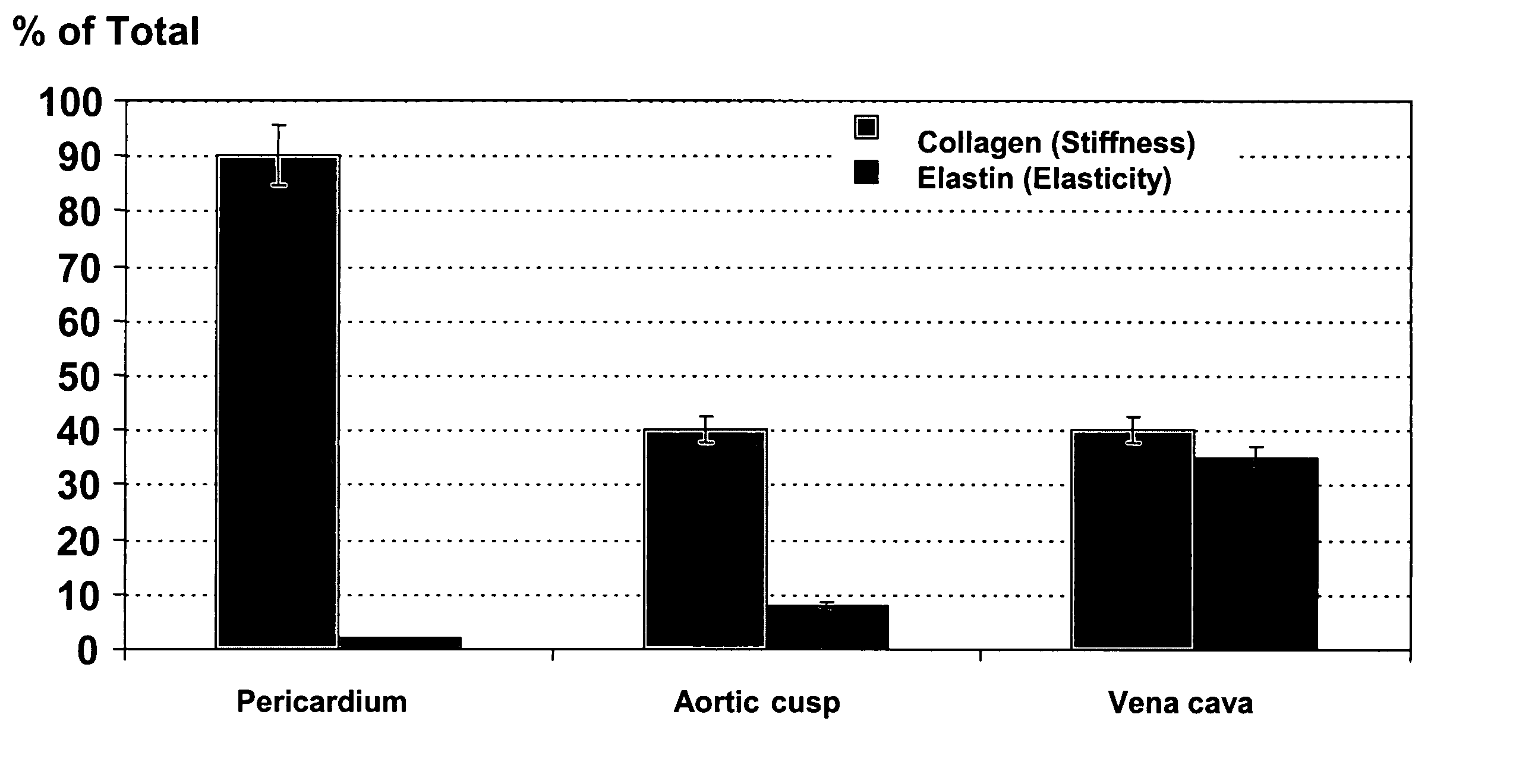
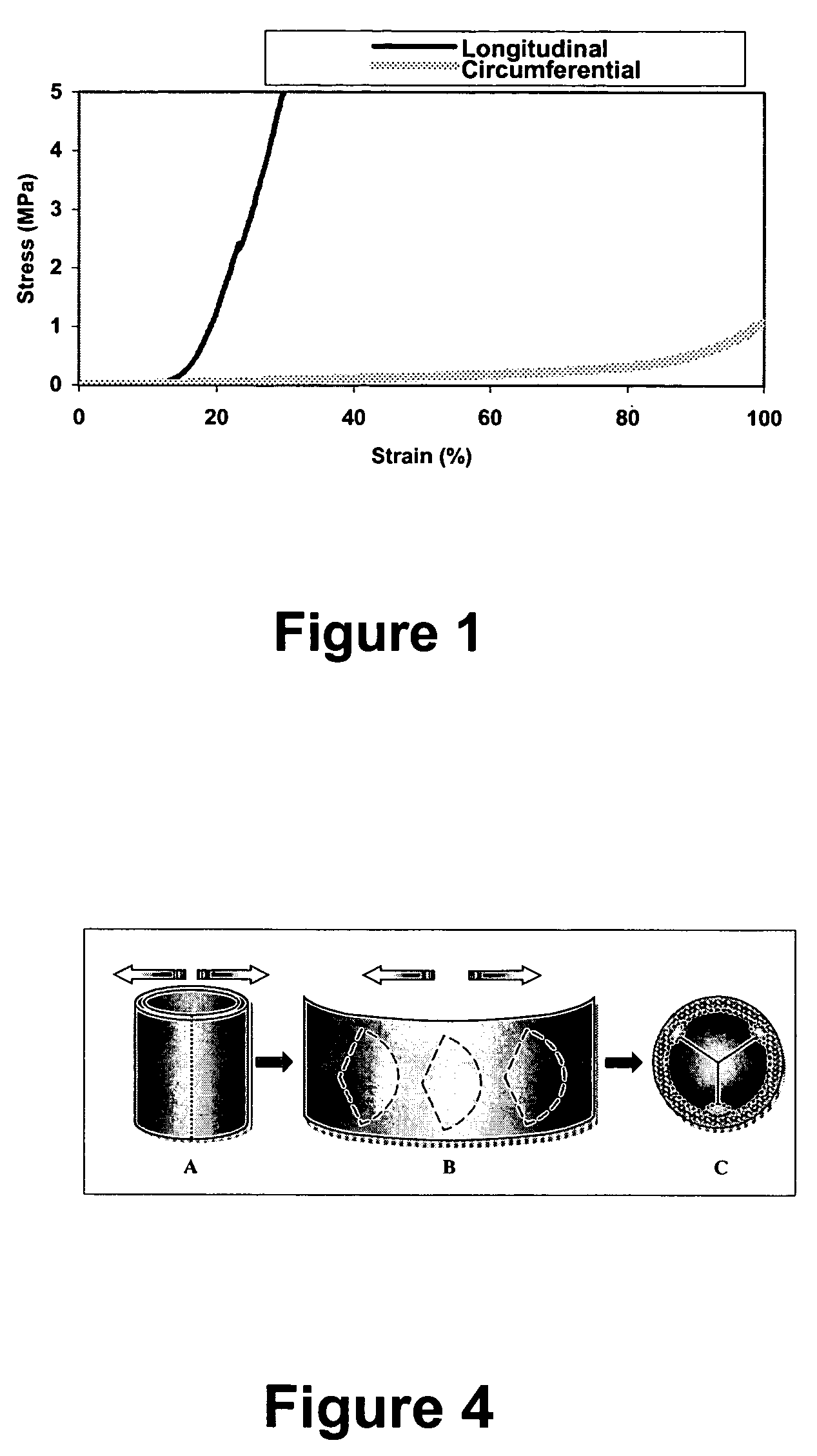
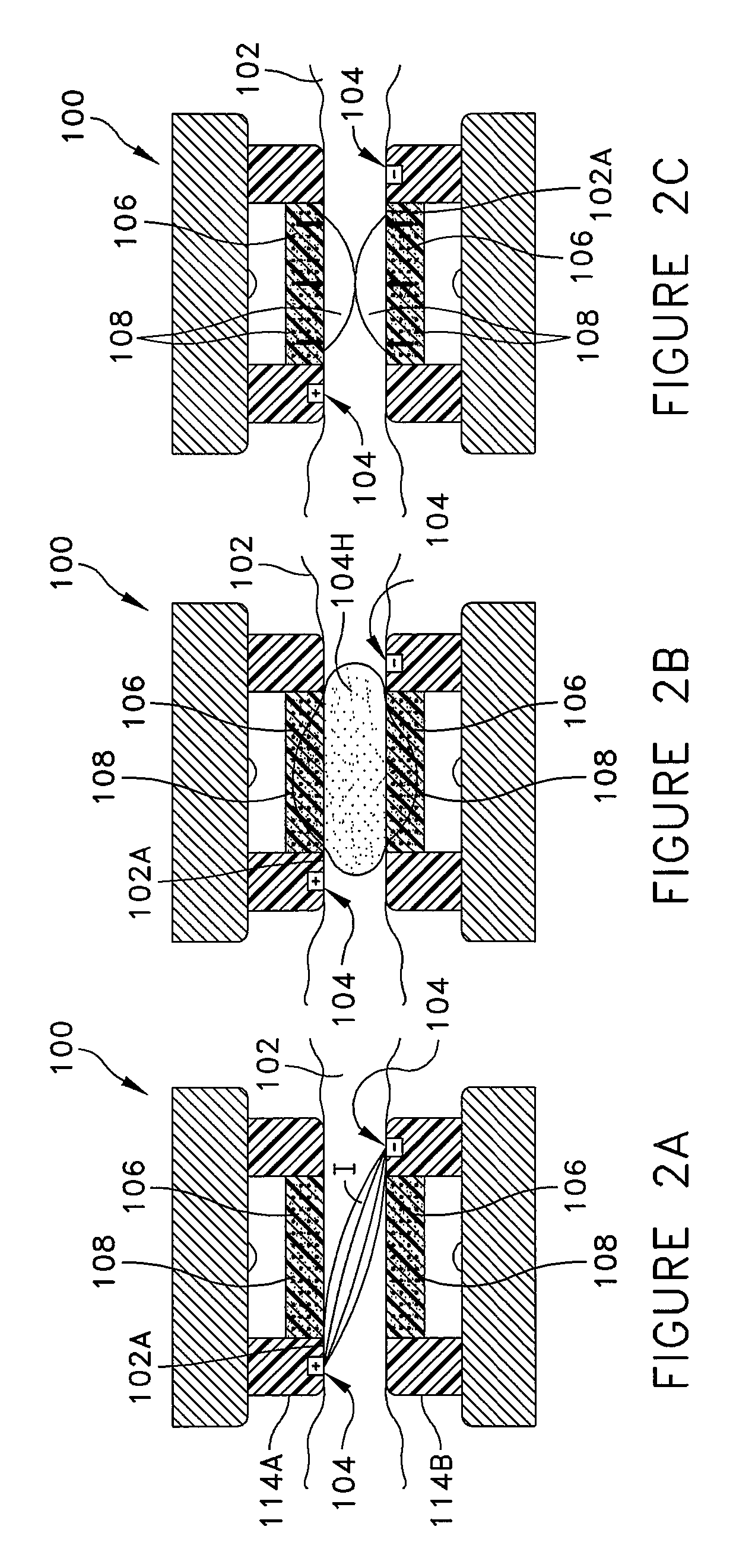
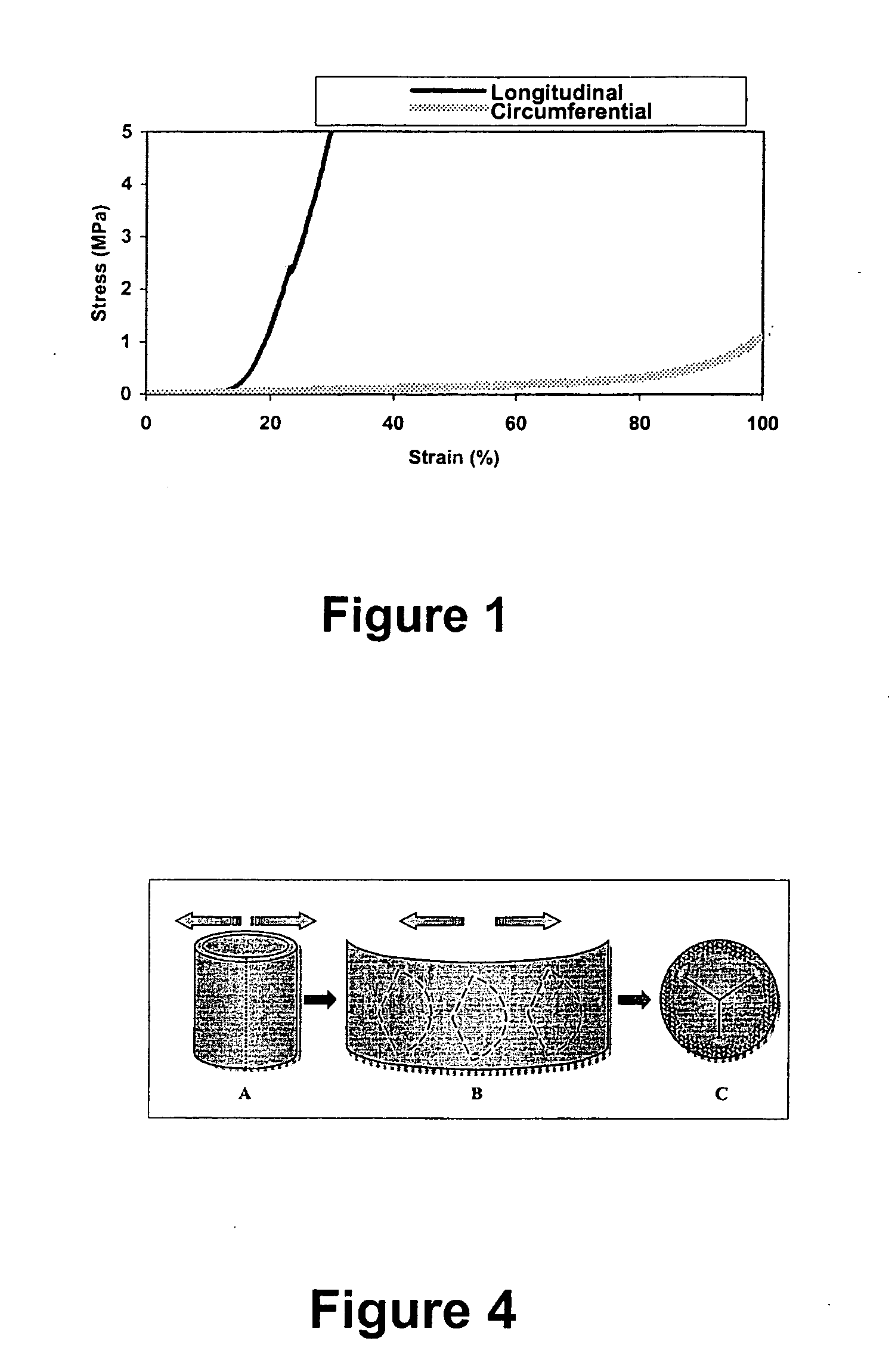
A biomaterial useful for bioprostheses such as bioprosthetic heart valves is provided in which the fixed tissue has improved elastic properties. The high elastin-containing biomaterial is further characterized by having anisotropic properties wherein the biological material has a greater stiffness in one direction and a greater elasticity in a cross direction. For instance, the biological material has an elastin content of about 30% by weight. In one embodiment, the biological material is vena cava tissue.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Electrospun blends of natural and synthetic polymer fibers as tissue engineering scaffolds
InactiveUS20060263417A1Facilitate cell penetrationFacilitate proliferationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberPolymer science
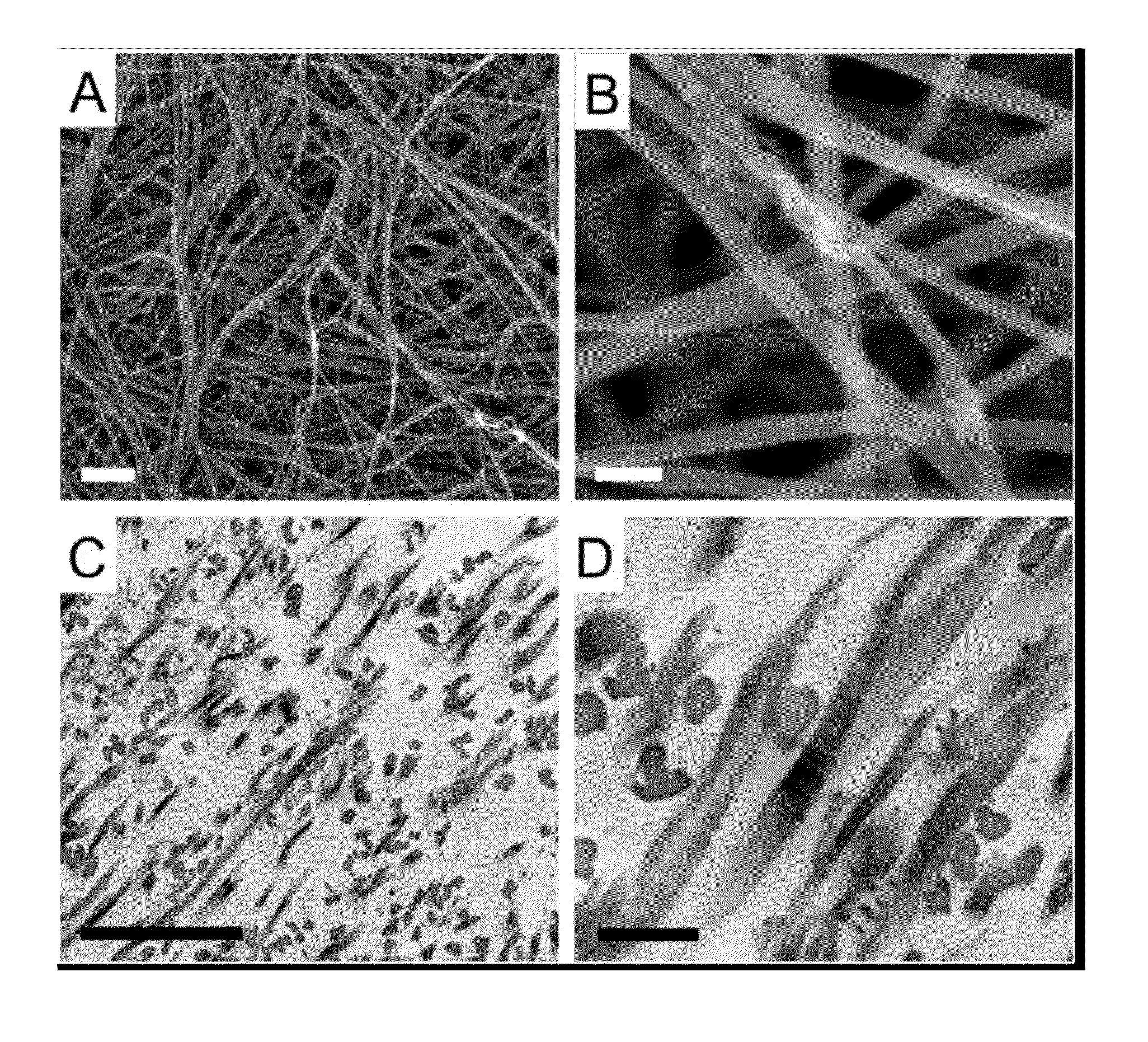
Non-woven fibrous scaffolds made by electrospinning from the synthetic biodegradable polymer such as, for example, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) and natural proteins, such as, for example, gelatin (denatured collagen) and elastin and a method of making thereof.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Elastin and elastin-based materials
It is a general object of the invention to provide a method of effecting repair or replacement or supporting a section of a body tissue. Specifically to provide an elastin or elastin-based biomaterial suitable for use as a stent, for example, a vascular stent, or as conduit replacement, as an artery, vein or a ureter replacement. The biomaterial can also be used as a stent or conduit covering or coating or lining. It is also an object of the invention to provide a method of securing an elastin or elastin-based biomaterial to an existing tissue without the use of sutures or staples.
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON AN OREGON NONPROFIT CORP +2
Apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, apparatus for reinforcement of tissue, methods of attaching and reinforcing tissue, and methods of reinforcing tissue
There are disclosed methods and apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, and methods and apparatus for reinforcement of tissue. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an energy applicator configured to apply energy to generate heat within a target tissue to evaporate water to create dried tissue, and denature at least one of collagen and elastin to attach portions together, and a biopolymer applicator configured for to receive the heat generated to allow biopolymer material to change from solid to molten, and to allow the biopolymer to fill dried tissue to reinforce portions of the target tissue and provide a hermetic seal.In another embodiment, the method includes applying energy to tissue surfaces with an energy applicator, and applying a biopolymer material into the tissue surfaces with a biopolymer applicator disposed on a housing in connection with the energy applicator. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHECHTER DAVID A
Biomaterials with enhanced properties and devices made therefrom
ActiveUS20120059487A1Reduce thicknessLow profile insertionHeart valvesSurgeryCell membraneLong term durability
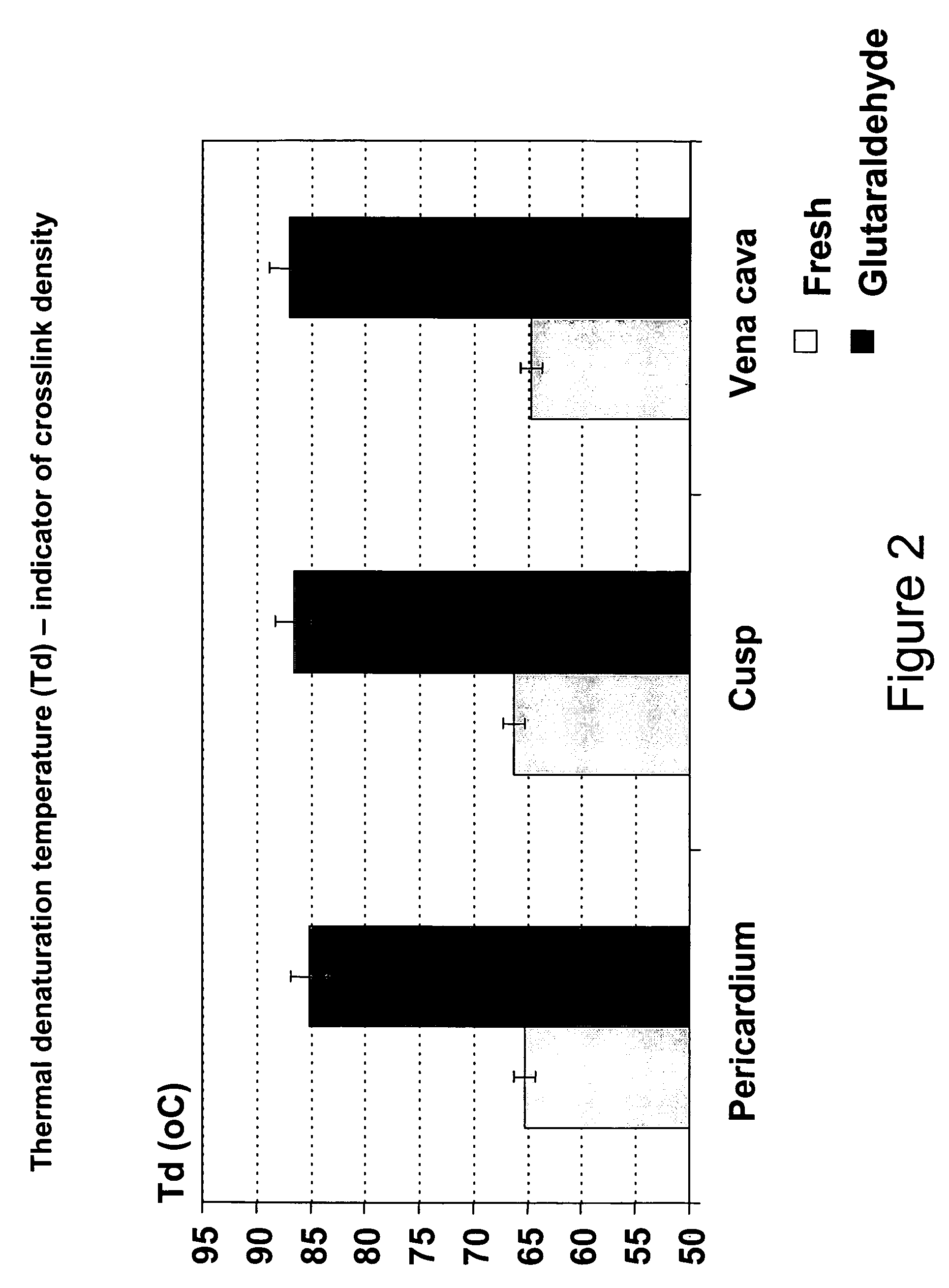
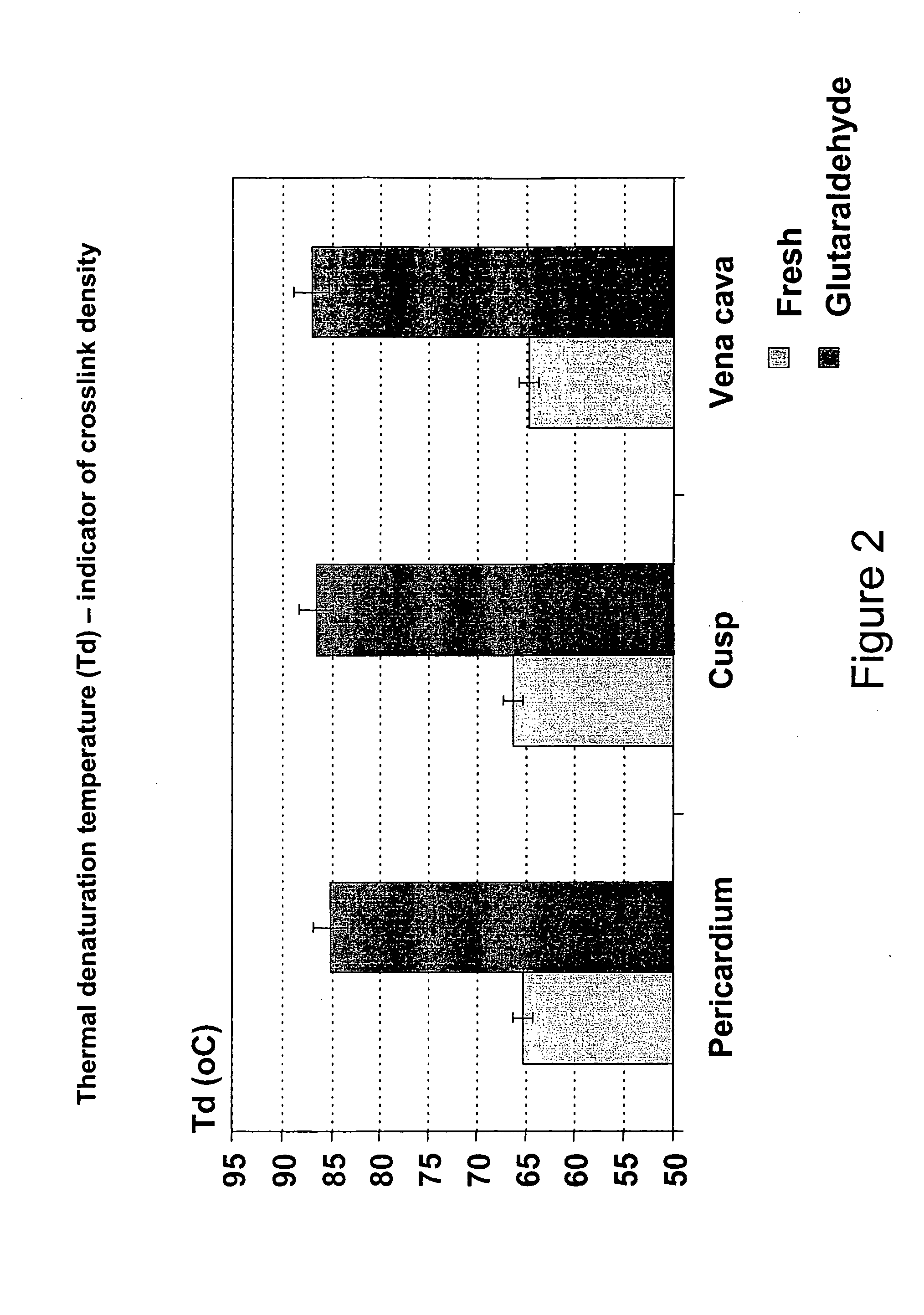
Biomaterials with enhanced properties such as improved strength, flexibility, durability and reduced thickness are useful in the fabrication of biomedical devices, particularly those subjected to continuous or non-continuous loads where repeated flexibility and long-term durability are required. These enhanced properties can be attributed to elevated levels of elastin, altered collagen types, and other biochemical changes which contribute to these enhanced properties. Examples of devices which would be improved by use of such tissue include heart valves, including percutaneous heart valves, and vascular grafts, patches and the like. Such enhanced materials can be sourced from specific populations of animals, such as neonatal calves, or in range-fed adult cattle, or can be fabricated or created from cell populations exhibiting such properties. In one embodiment, glutaraldehyde-fixed neonatal pericardial tissue is used to create leaflets in a percutaneous heart valve, and may be used without chemical fixation, with or without processes to remove residual cellular membranes, and utilized as a scaffold material for tissue engineering.
Owner:SOUTHERN LIGHTS VENTURES 2002
Tissue material and process for bioprosthesis
ActiveUS20070005132A1Increase stiffnessIncrease elasticityHeart valvesTubular organ implantsTissue materialProsthesis
A biomaterial useful for bioprostheses such as bioprosthetic heart valves is provided in which the fixed tissue has improved elastic properties. The high elastin-containing biomaterial is further characterized by having anisotropic properties wherein the biological material has a greater stiffness in one direction and a greater elasticity in a cross direction. For instance, the biological material has an elastin content of about 30% by weight. In one embodiment, the biological material is vena cava tissue.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Medical device with coating that promotes endothelial cell adherence
InactiveUS20050043787A1Prevent restenosisPreventing other thromboembolic complicationMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPolyethylene glycol
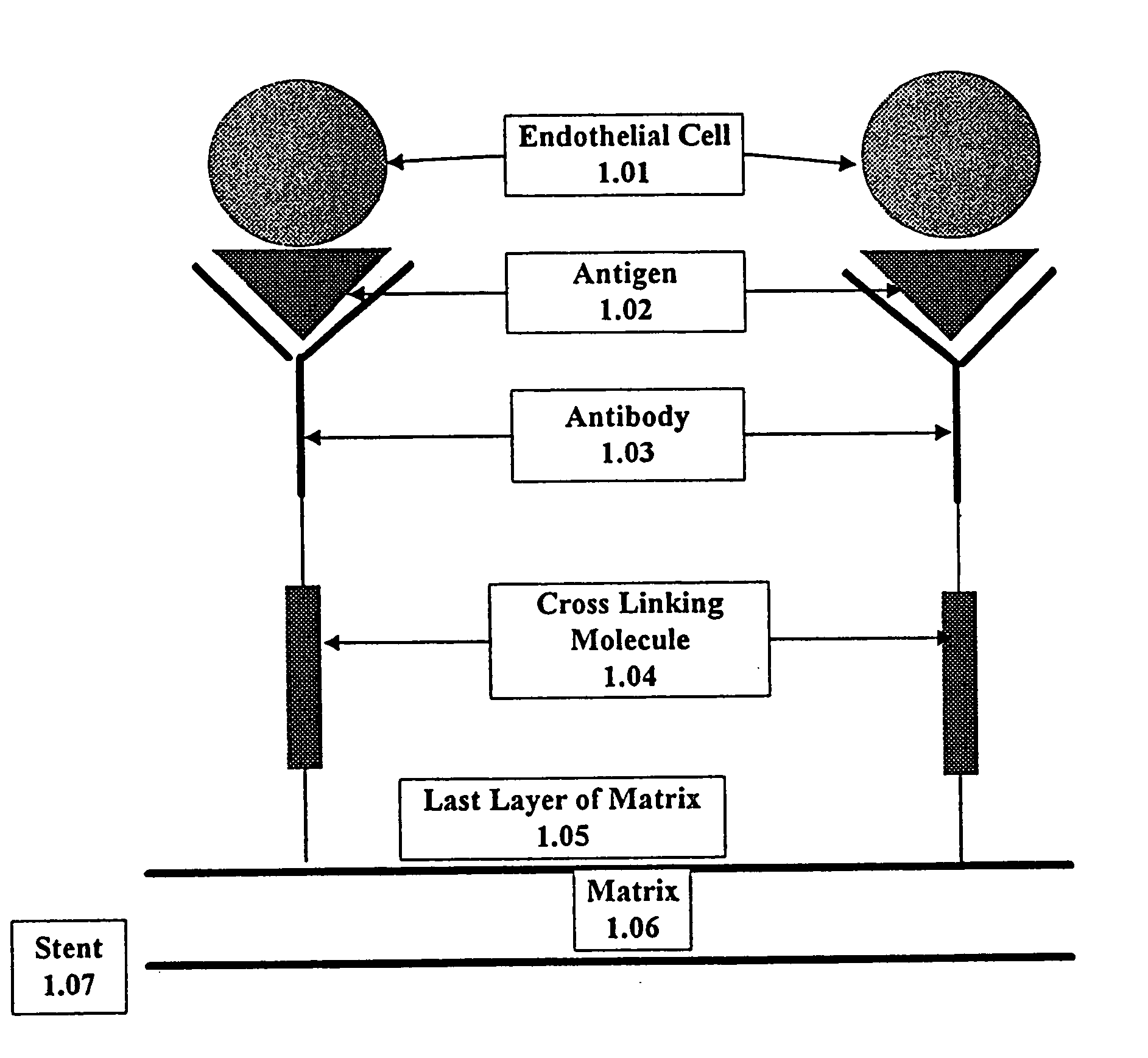
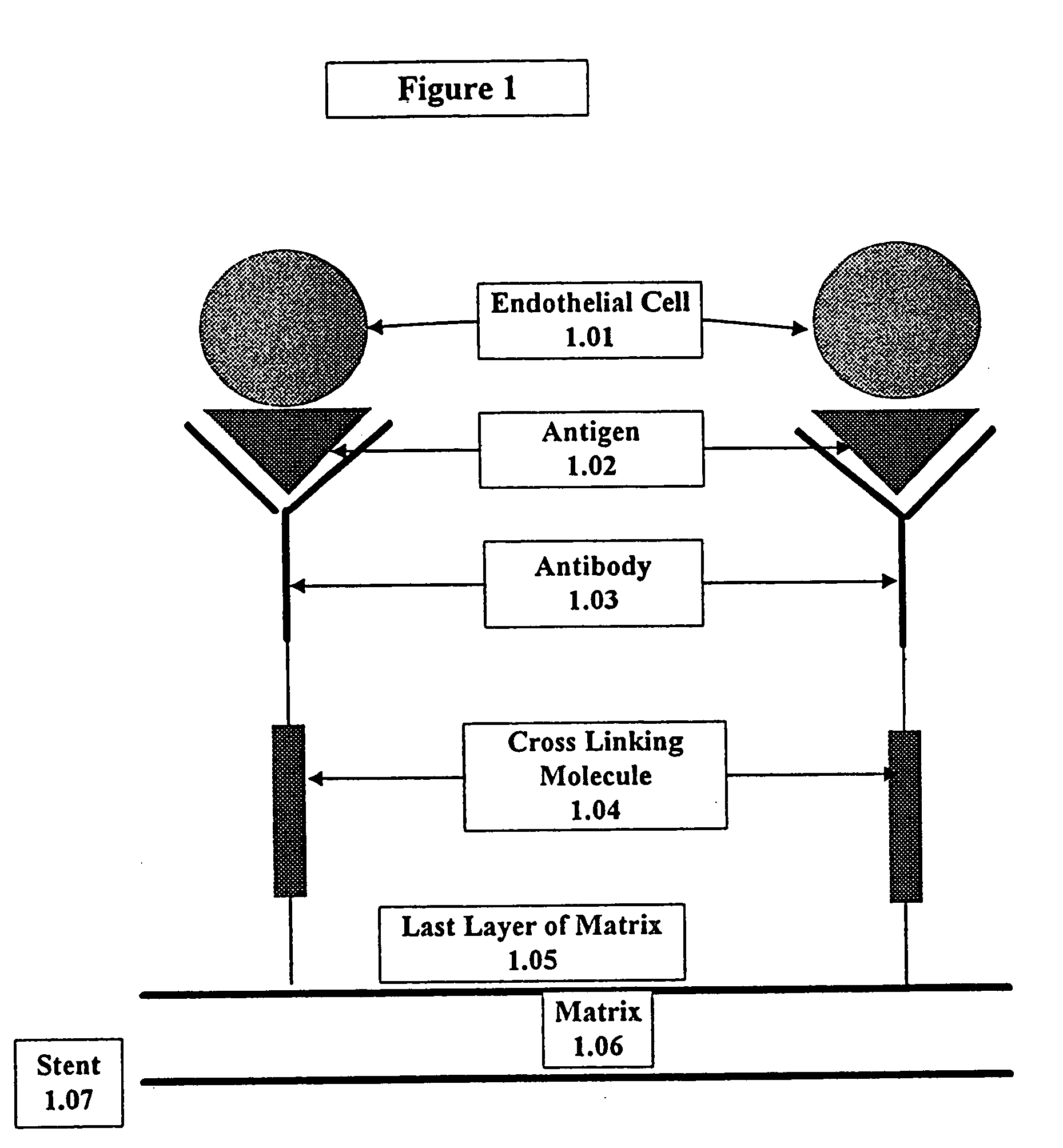
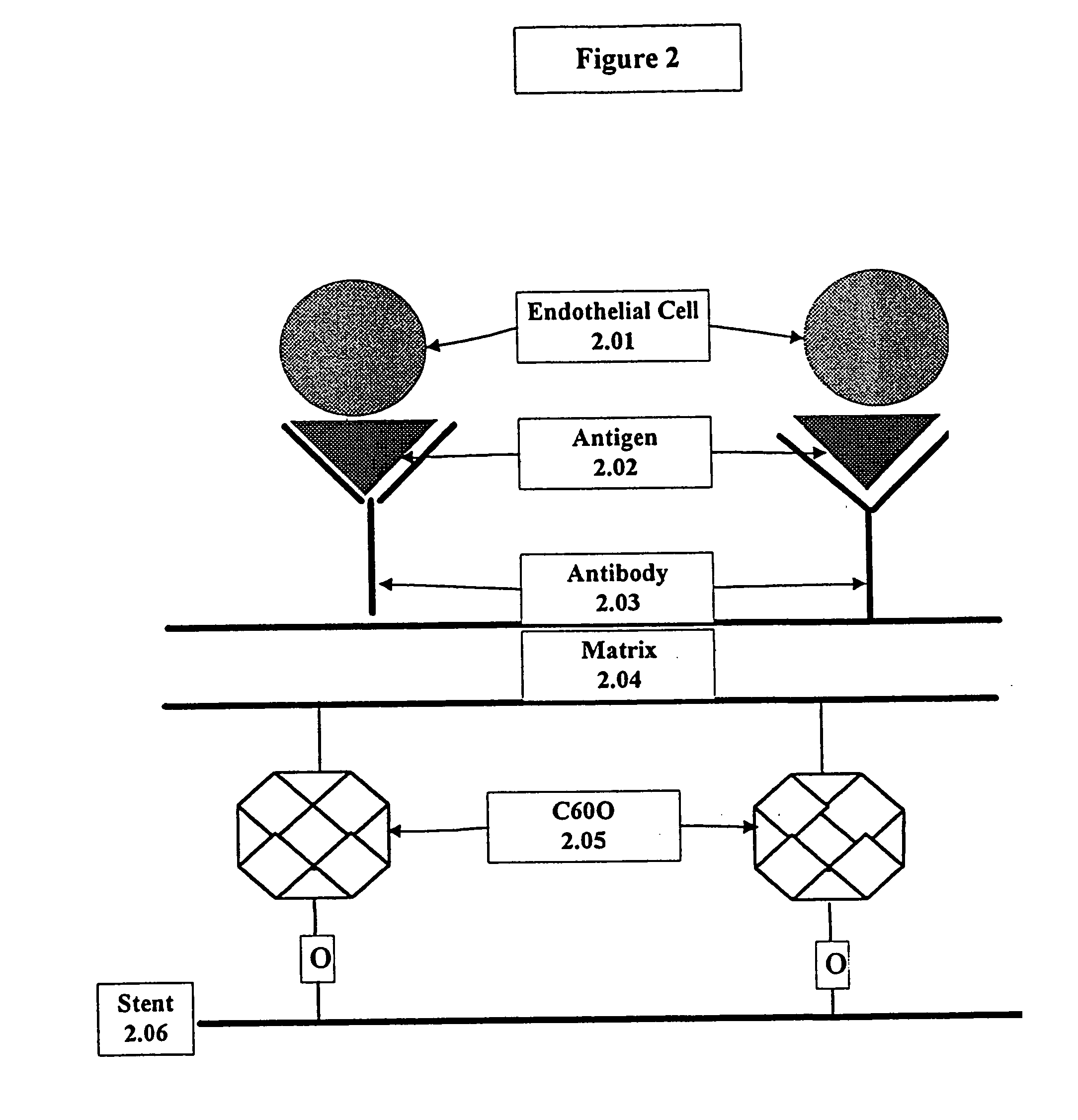
This invention provides compositions and methods for producing a medical device coated with a matrix and an antibody which reacts with an endothelial cell antigen. The matrix coating the medical device may be composed of synthetic material, such as polyurethane, poly-L-lactic acid, cellulose ester or polyethylene glycol. In another embodiment, the matrix is composed of naturally occurring materials, such as collagen, fibrin, elastin, amorphous carbon. In a third embodiment, the matrix may be composed of fullerenes. The fullerenes range from about C60 to about C100. The medical device may be a stent or a synthetic graft. The antibodies promote adherence of endothelial cells on the medical device. The antibodies may be mixed with the matrix or covalently tethered through a linker molecule to the matrix. Following adherence to the medical device, the endothelial cells differentiate and proliferate on the medical device. The antibodies may be different types of monoclonal antibodies. Methods of preparing such composition and methods of treating a mammal with atherosclerosis or other types of vessel obstruction are disclosed. By facilitating adherence of endothelial cells to the surface of the medical device, the methods and compositions of this invention will decrease the incidence of restenosis as well as other thromboembolic complications resulting from implantation of medical devices.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Intra-serum and intra-gel for modeling human skin tissue
InactiveUS6475800B1Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsConfocalCrosslinking reagent
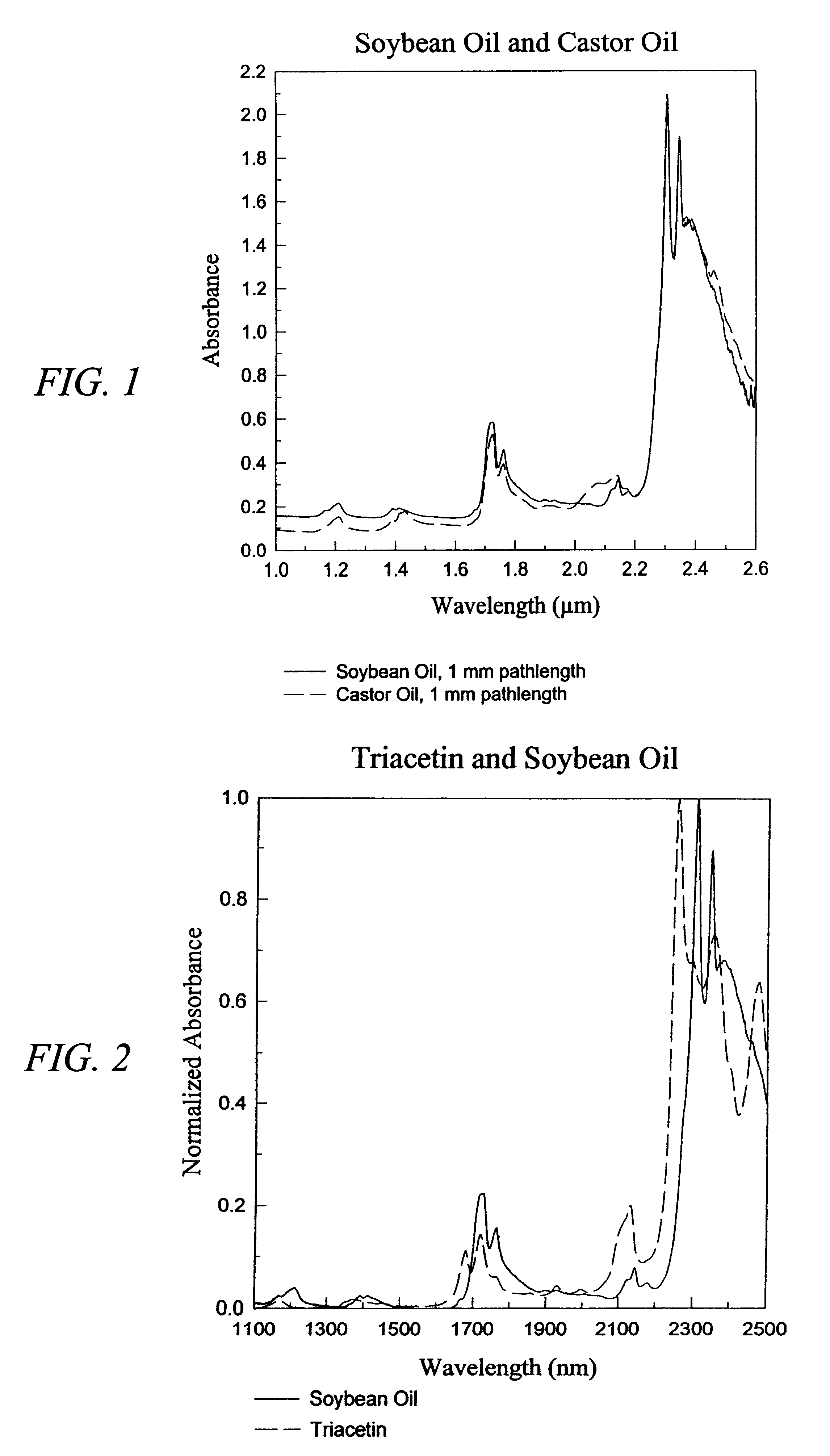
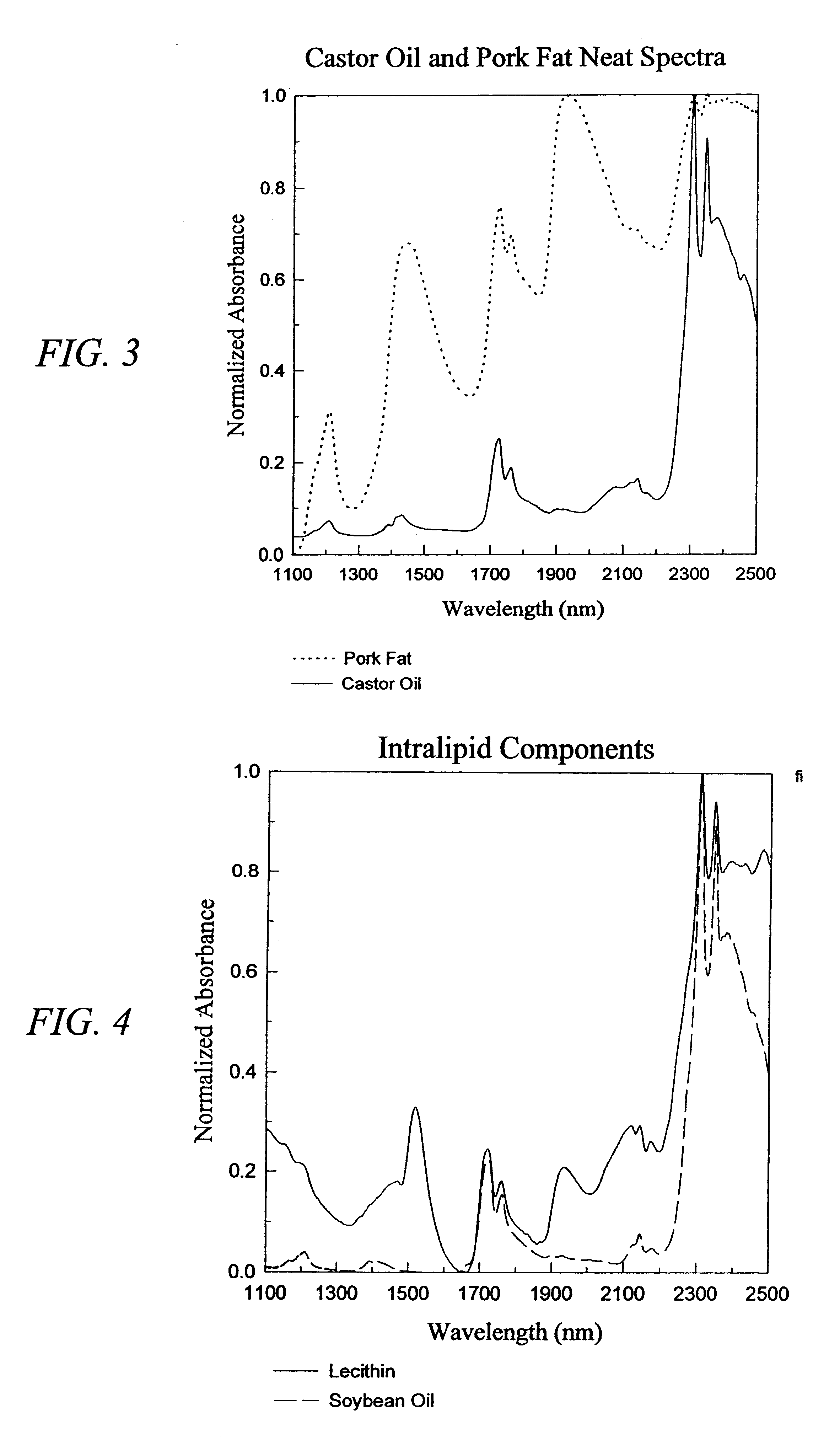
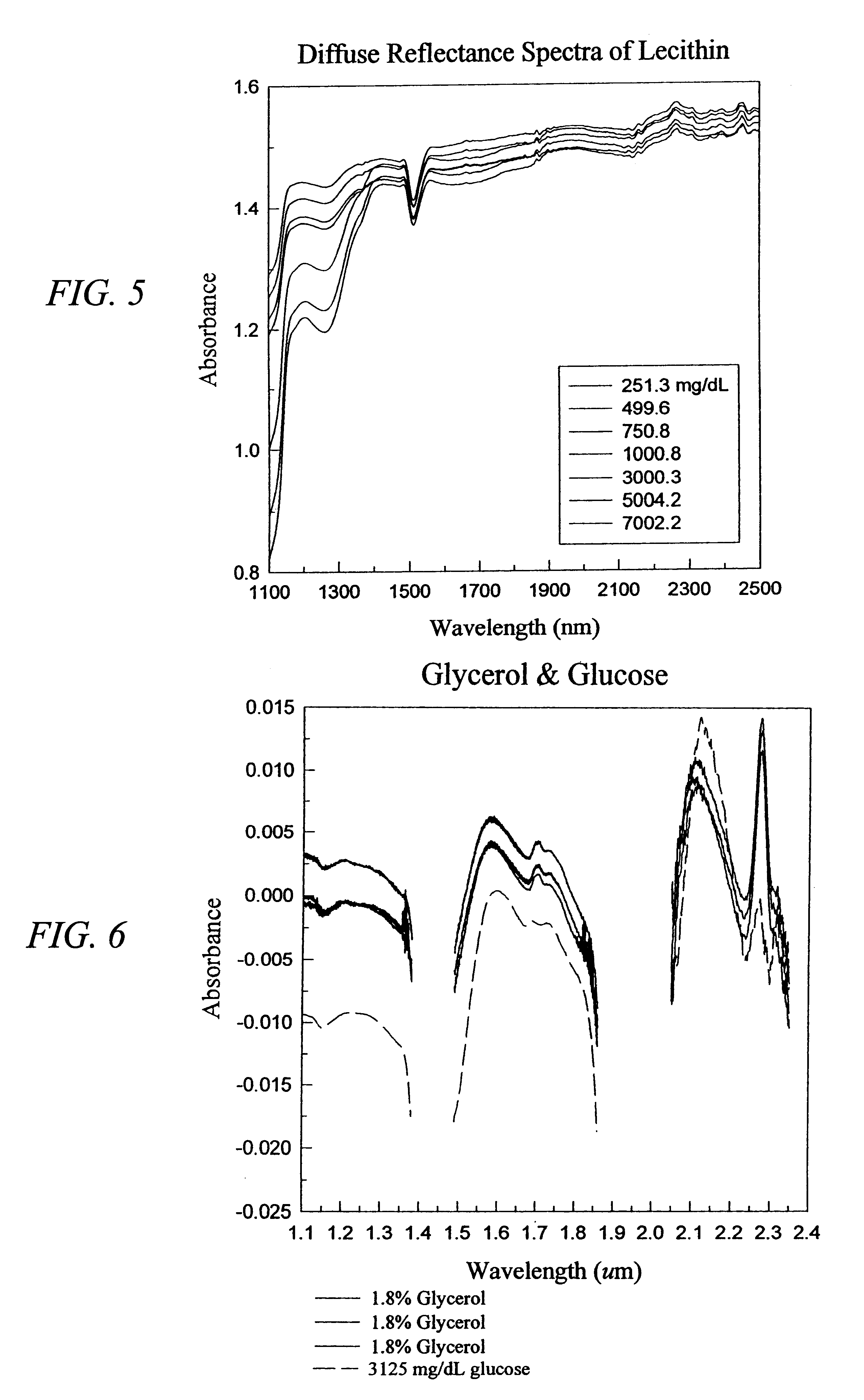
The invention provides a class of samples that model the human body. This family of samples is based upon emulsions of oil in water with lecithin acting as the emulsifier. These solutions that have varying particle sizes may be spiked with basis set components (albumin, urea and glucose) to simulate skin tissues further. The family of samples is such that other organic compounds such as collagen, elastin, globulin and bilirubin may be added, as can salts such as Na+, K+ and Cl-. Layers of varying thickness with known index of refraction and particle size distributions may be generated using simple crosslinking reagents, such as collagen (gelatin). The resulting samples are flexible in each analyte's concentration and match the skin layers of the body in terms of the samples reduced scattering and absorption coefficients, mums and muma. This family of samples is provided for use in the medical field where lasers and spectroscopy based analyzers are used in treatment of the body. In particular, knowledge may be gained on net analyte signal, photon depth of penetration, photon radial diffusion, photon interaction between tissue layers, photon density (all as a function of frequency) and on instrument parameter specifications such as resolution and required dynamic range (A / D bits required). In particular, applications to delineate such parameters have been developed for the application of noninvasive glucose determination in the near-IR region from 700 to 2500 nm with an emphasis on the region 1000 to 2500 nm (10,000 to 4,000 cm-1).
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, apparatus for reinforcement of tissue, methods of attaching and reinforcing tissue, and methods of reinforcing tissue
There are disclosed methods and apparatus for attachment and reinforcement of tissue, and methods and apparatus for reinforcement of tissue. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an energy applicator configured to apply energy to generate heat within a target tissue to evaporate water to create dried tissue, and denature at least one of collagen and elastin to attach portions together, and a biopolymer applicator configured for to receive the heat generated to allow biopolymer material to change from solid to molten, and to allow the biopolymer to fill dried tissue to reinforce portions of the target tissue and provide a hermetic seal.In another embodiment, the method includes applying energy to tissue surfaces with an energy applicator, and applying a biopolymer material into the tissue surfaces with a biopolymer applicator disposed on a housing in connection with the energy applicator. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHECHTER DAVID A
Method for preparing biological scaffold materials
InactiveUS20080027562A1Maintain mechanical strengthLess degree of cross-linkingHeart valvesDead animal preservationProsthesisElastin tissue
A method for preparing a scaffold material for use in the prosthesis therapy is disclosed. The method comprises (a) lyophilizing a segment of native soft tissue of mammalian origin, heating the lyophilized tissue at a temperature of 100-200° C., and incubating the tissue with elastase to selectively remove elastin leaving the extracellular components mainly comprised of collagen.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis of diseases of the aorta
InactiveUS20070224643A1Facilitate patient treatmentConvenient treatmentDiagnosticsSurgeryAortic dissectionSmooth Muscle Myosins
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for symptom-based differential diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects. In particular, the invention relates to the use of biomarkers, either individually or in combinations with one another to rule in or out diseases of the aorta and its branches, most particularly aortic aneurysm and / or aortic dissection, and for risk stratification in such conditions. Preferred markers include one or more of creatine kinase-BB (CK-BB), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), acidic calponin, basic calponin, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), NT-proBNP, proBNP, BNP79-108, BNP3-108, caldesmon, caspase-3, D-dimer, soluble elastin fragments, endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule (ESAM), fibrillin-1, heart-type fatty acid binding protein, MMP-9, myeloperoxidase, myoglobin, smooth muscle myosin, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, TIMP-1, free cardiac troponin I, complexed cardiac troponin I, free and complexed cardiac troponin I, free cardiac troponin T, complexed cardiac troponin T, and free and complexed cardiac troponin T, and preferred assays are configured to detect these markers.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
Method and composition for restoration of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body
InactiveUS20060073178A1Restoring age related tissue lossEasy to produceCosmetic preparationsBiocideInsulin-like growth factorThyroid hormones
A treatment method for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face or selected areas of the body is disclosed which includes injecting an injectable composition containing a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier into the dermis, the hypodermis, or both, in various areas of the face, or selected areas of the body of a person to stimulate collagen, elastin, or fat cell production, thereby restoring age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body. Further disclosed is an injectable composition for restoring of age related tissue loss in the face and selected areas of the body, which contains a growth factor and hyaluronic acid as a carrier for providing time release of the growth factor into tissues. The growth factor can be insulin, insulin-like growth factor, thyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor, estrogen, retinoic acid, or their combinations.
Owner:CELLHEALTH TECH
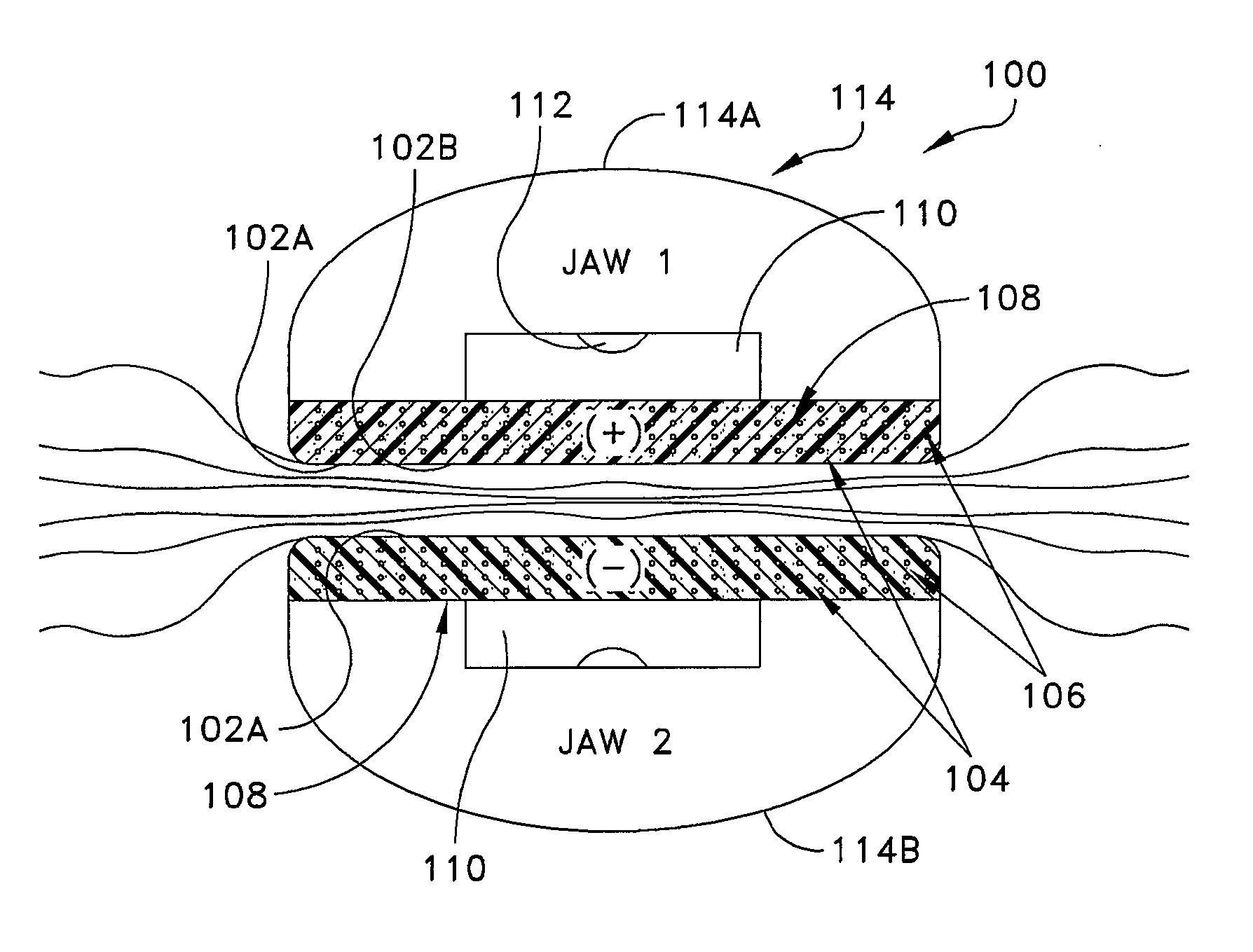
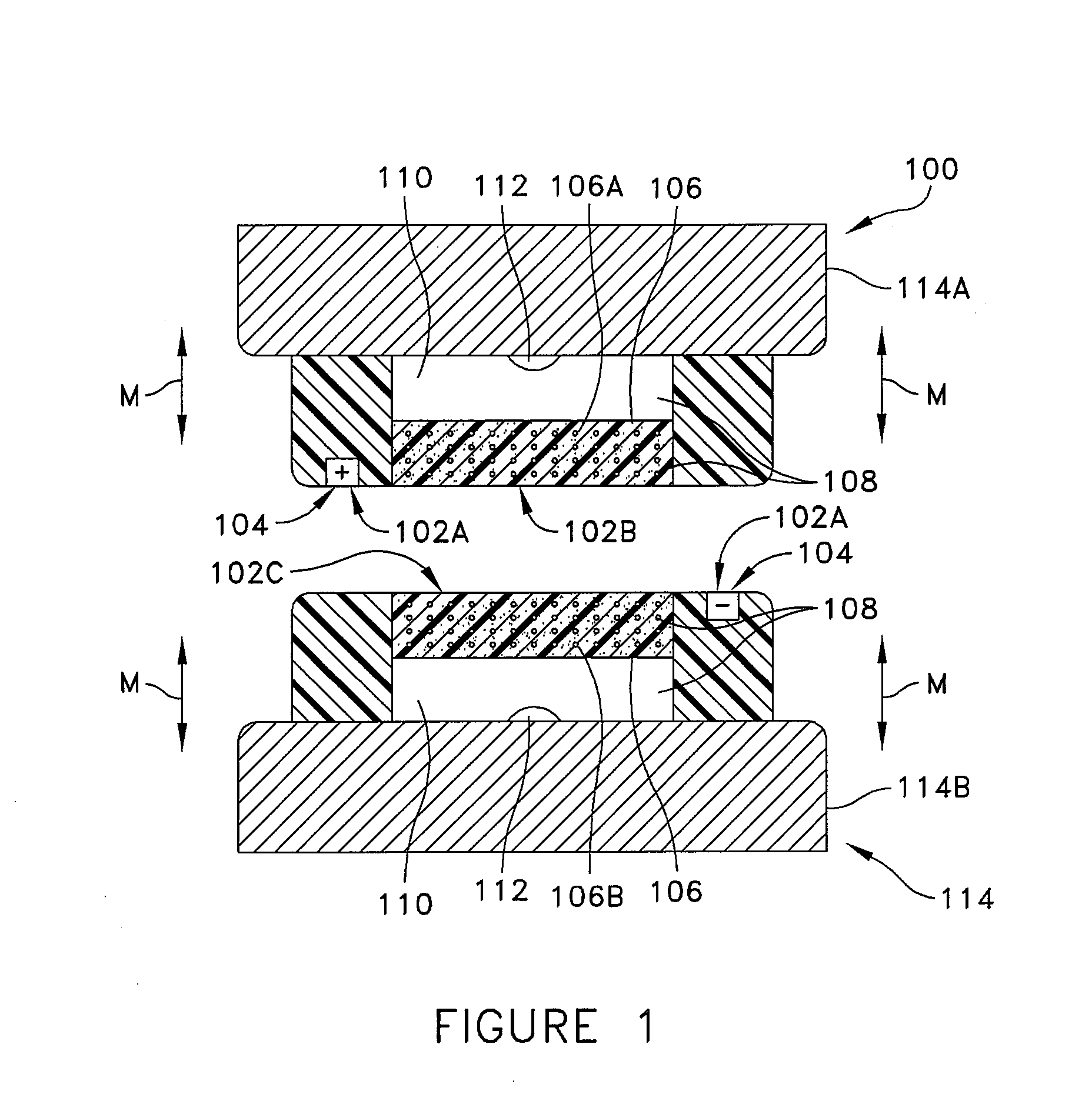
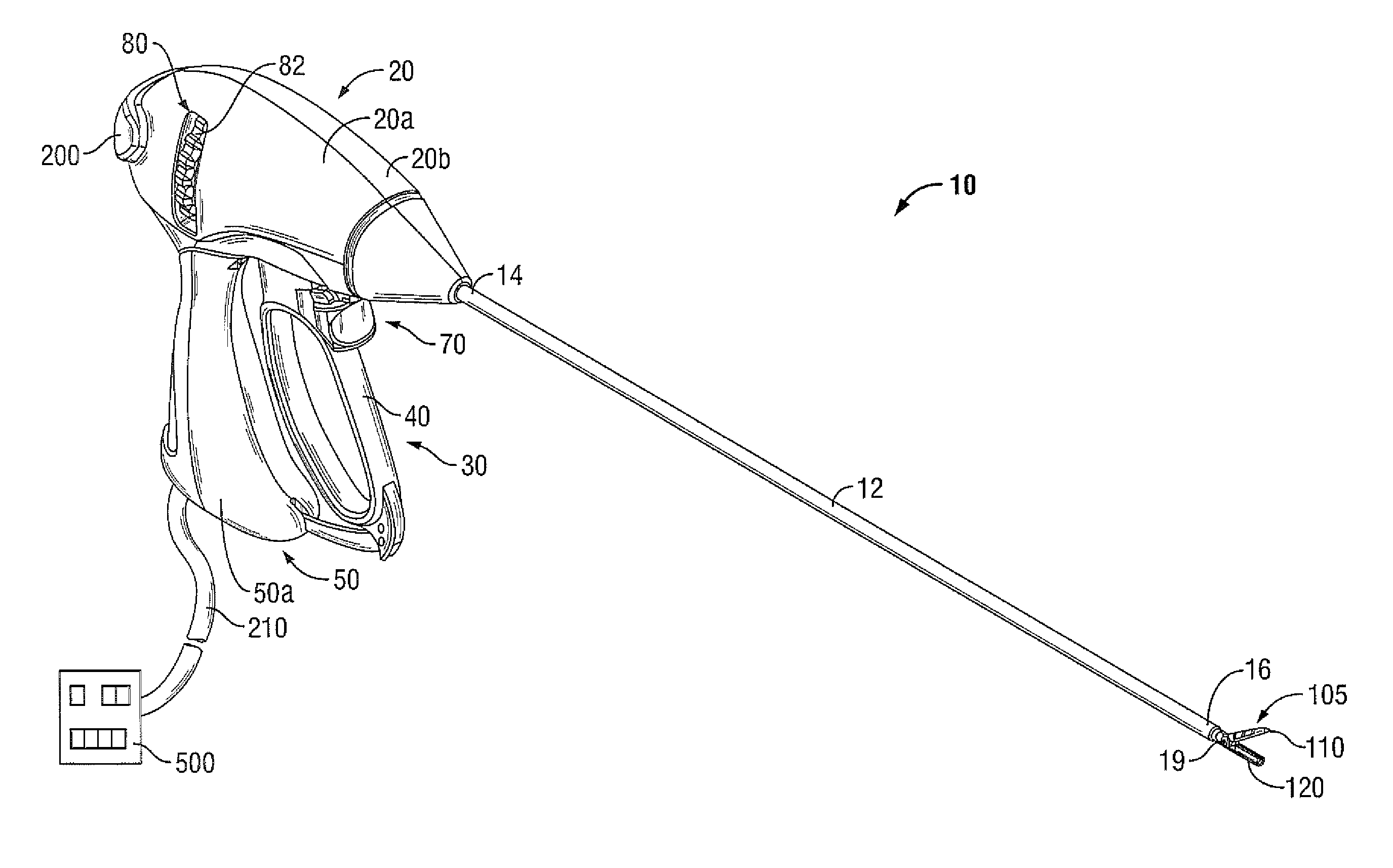
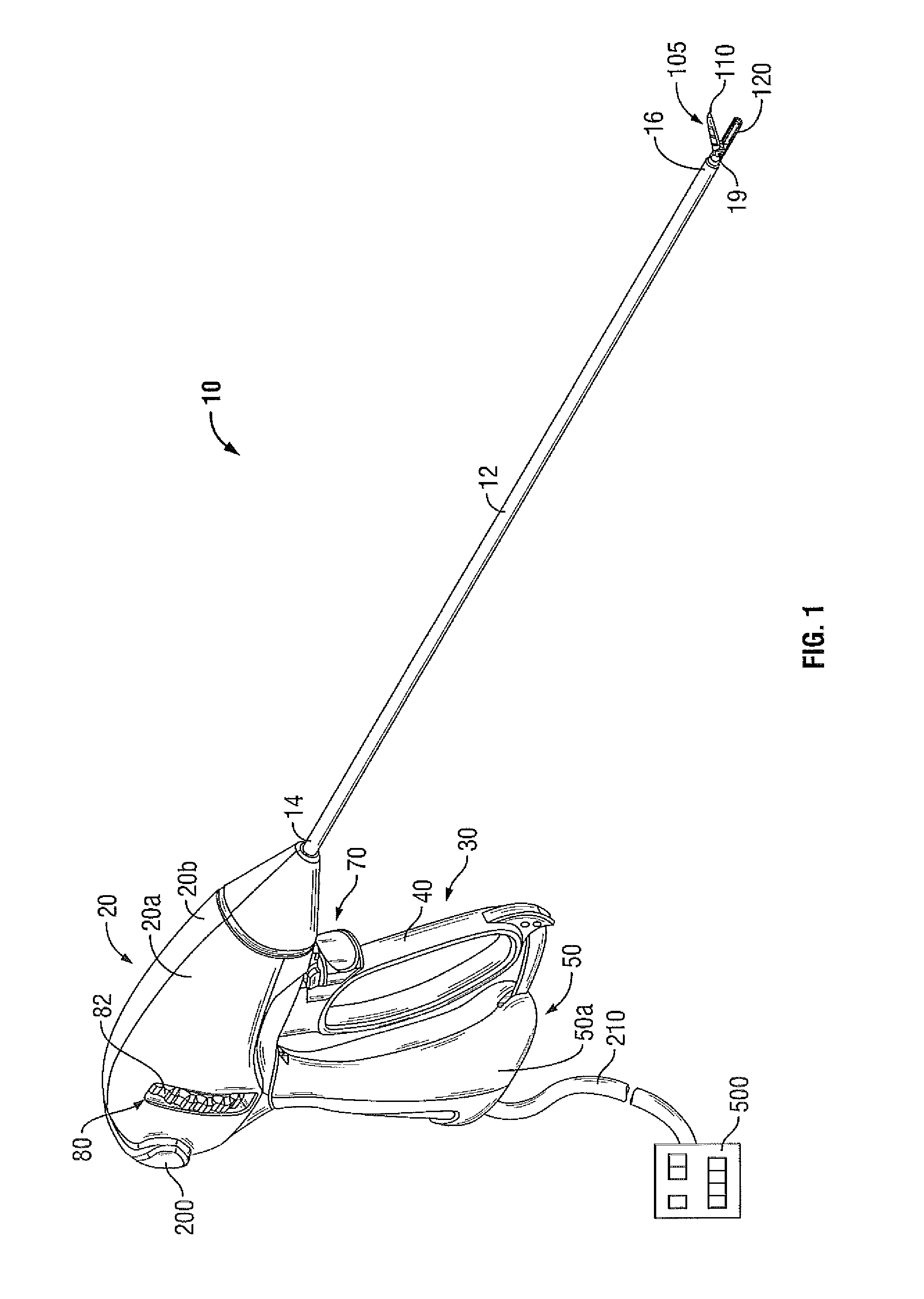
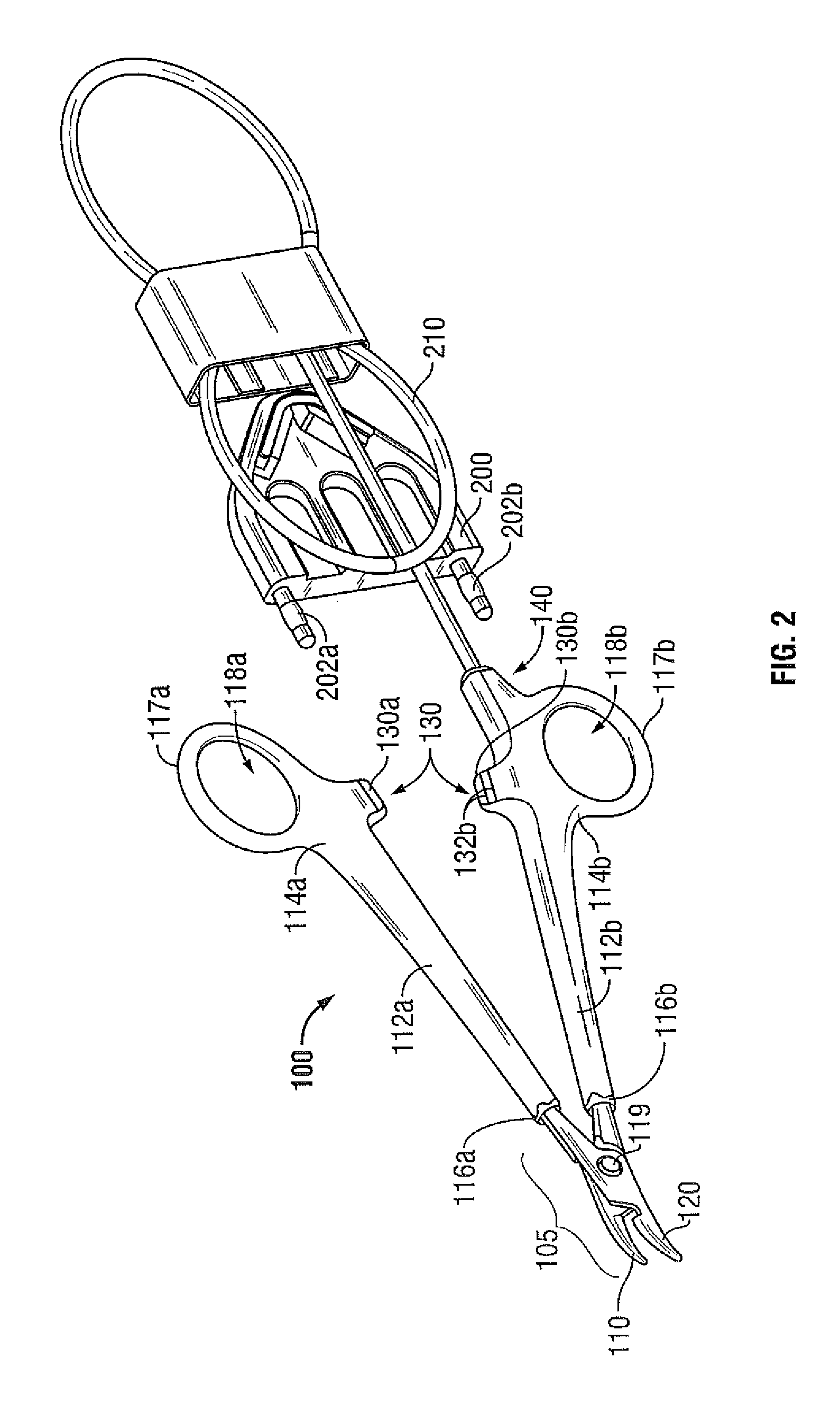
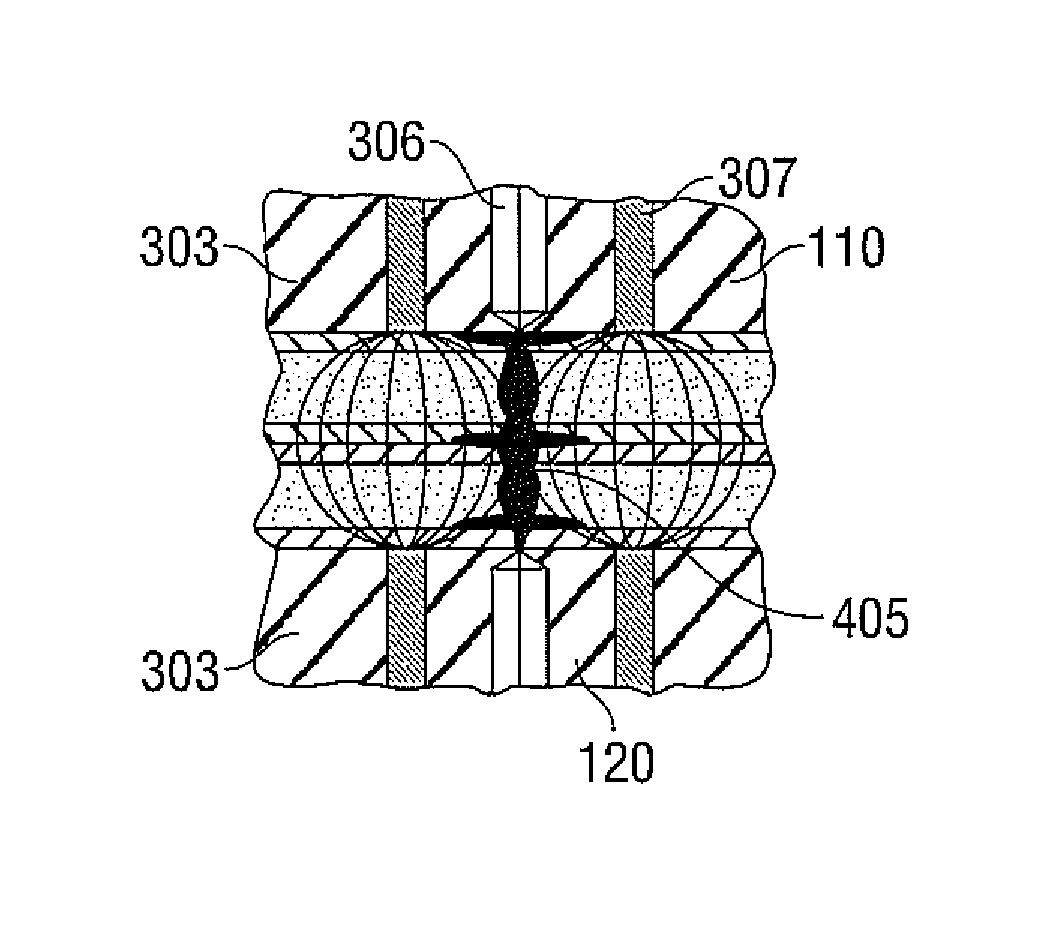
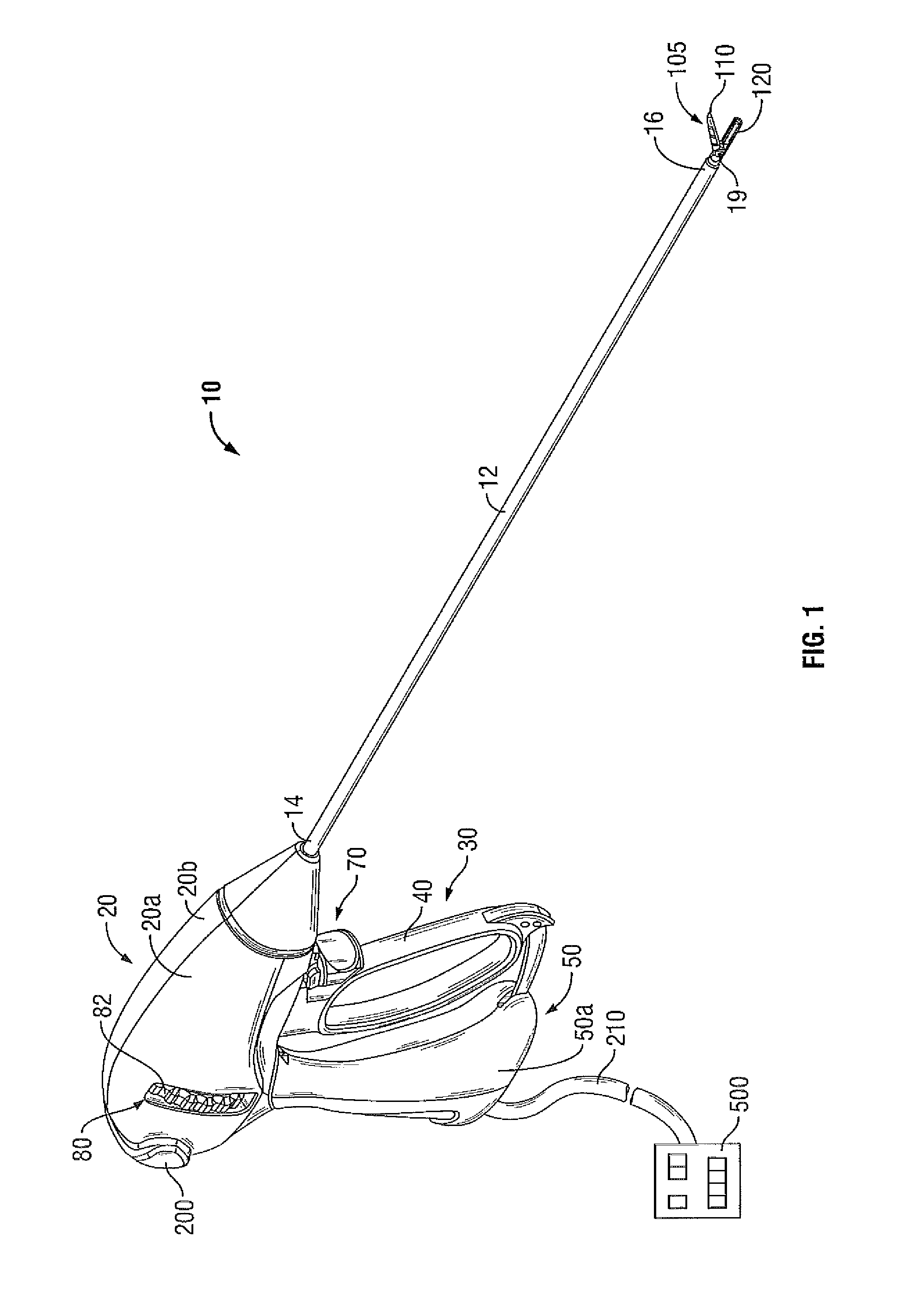
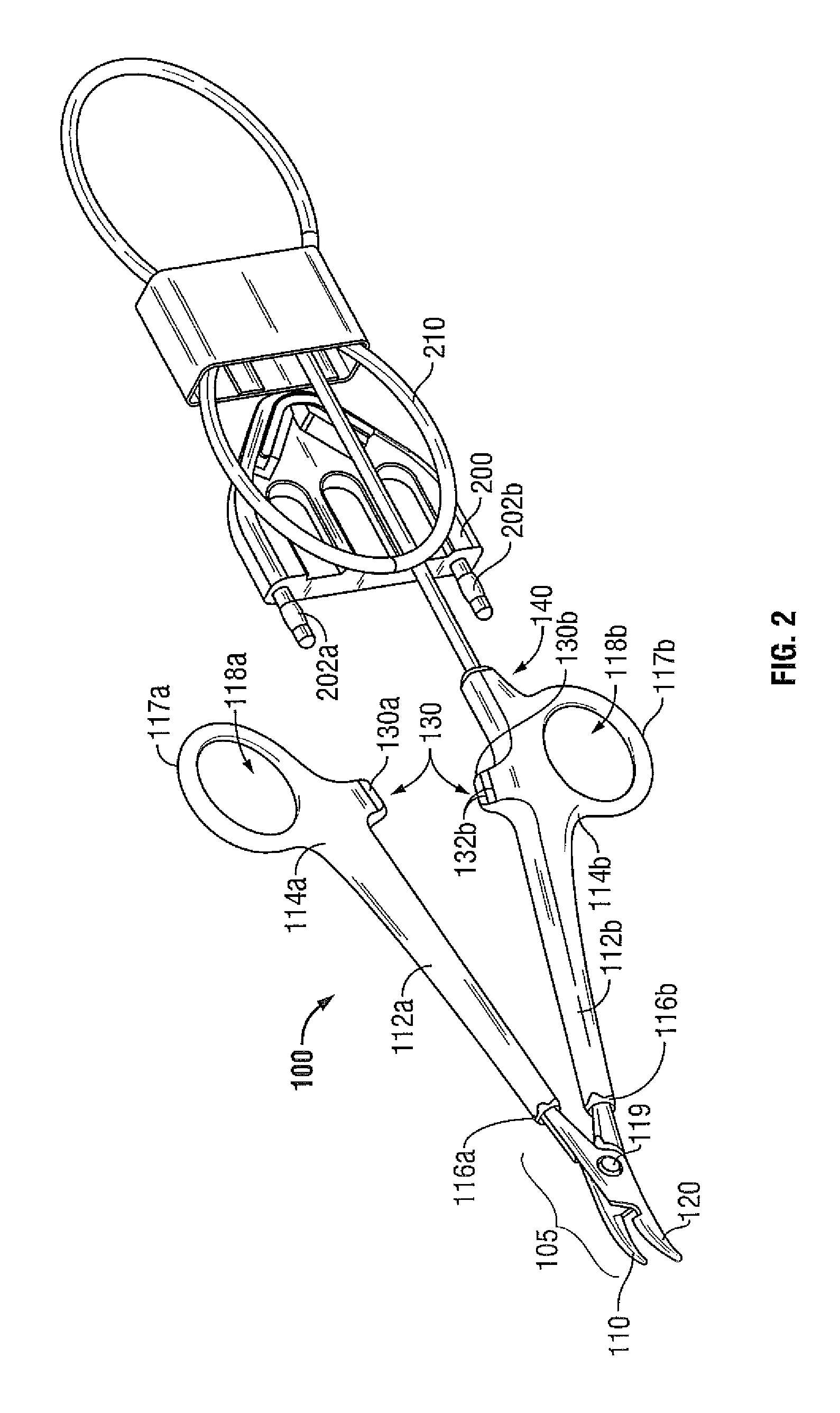
Method and Apparatus for Vascular Tissue Sealing with Reduced Energy Consumption
ActiveUS20120123402A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
An end effector assembly for use with an electrosurgical instrument is provided. The end effector assembly includes a pair of opposing jaw members configured to grasp tissue therebetween. Each of the opposing jaw members includes a non conducting tissue contact surface and an energy delivering element configured to perforate the tissue to create an opening, extract elastin and collagen from the tissue and denaturize the elastin and the collagen in the vicinity of the opening.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for vascular tissue sealing with reduced energy consumption
An end effector assembly for use with an electrosurgical instrument is provided. The end effector assembly includes a pair of opposing jaw members configured to grasp tissue therebetween. Each of the opposing jaw members includes a non conducting tissue contact surface and an energy delivering element configured to perforate the tissue to create an opening, extract elastin and collagen from the tissue and denaturize the elastin and the collagen in the vicinity of the opening.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
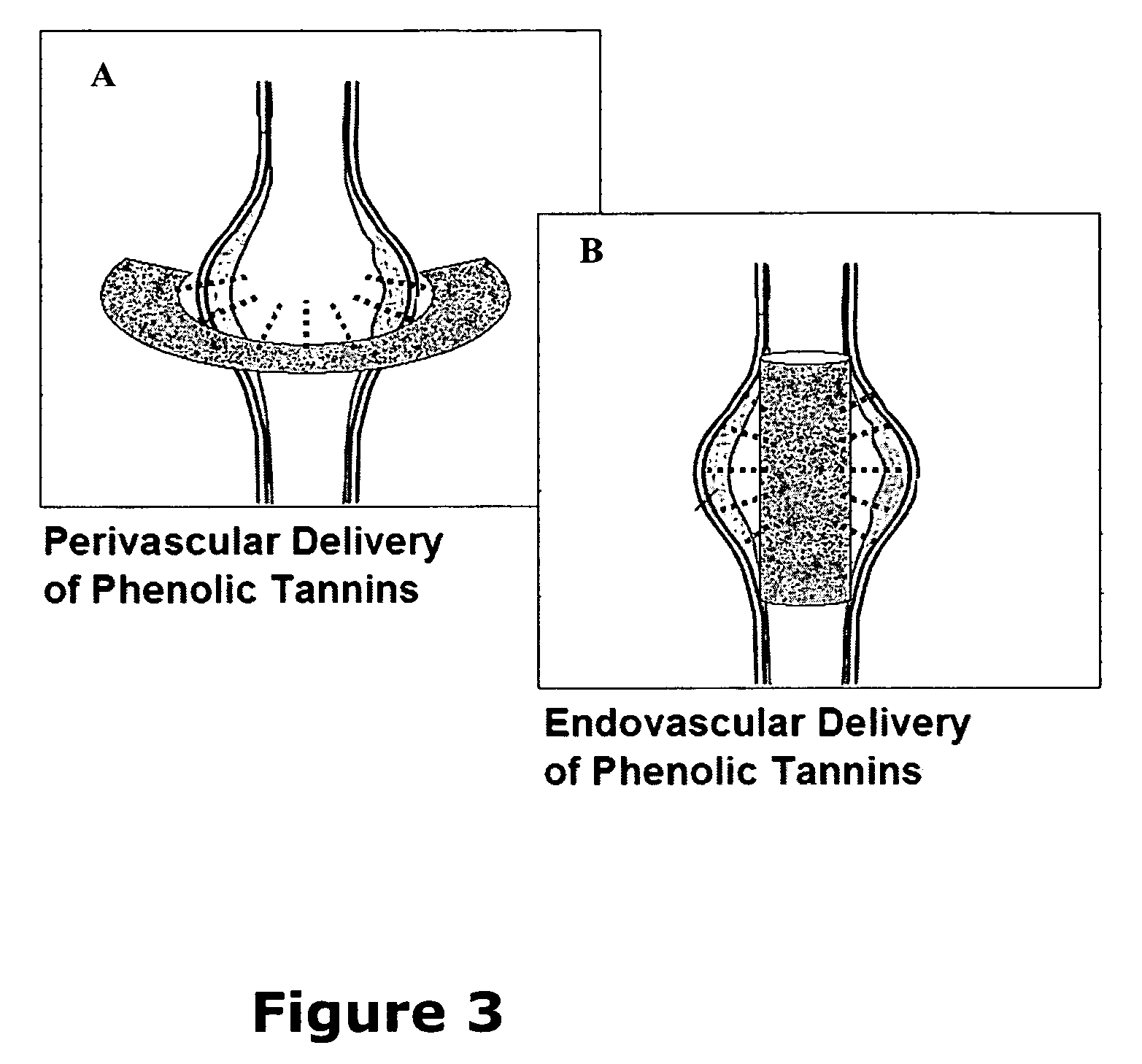
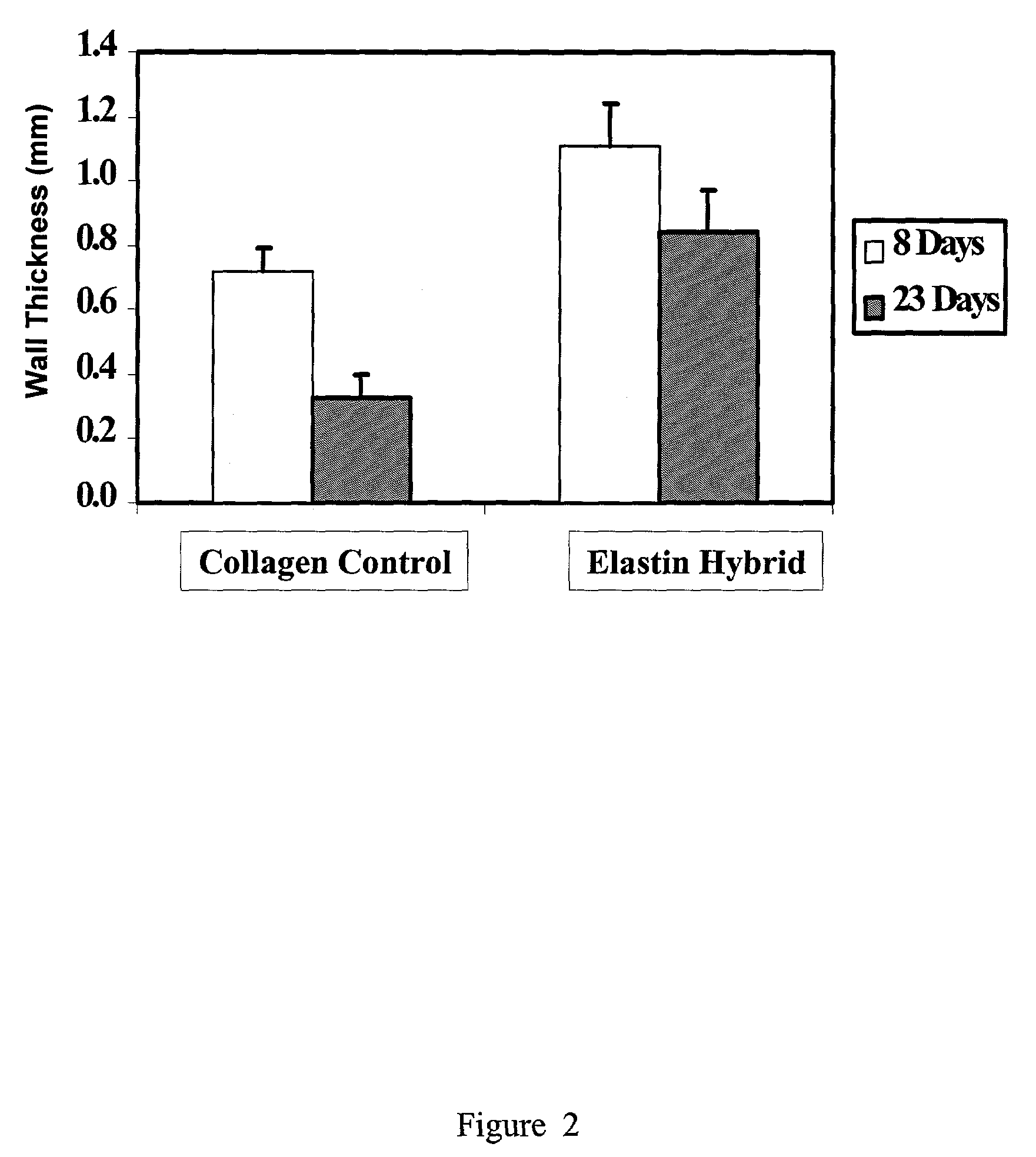
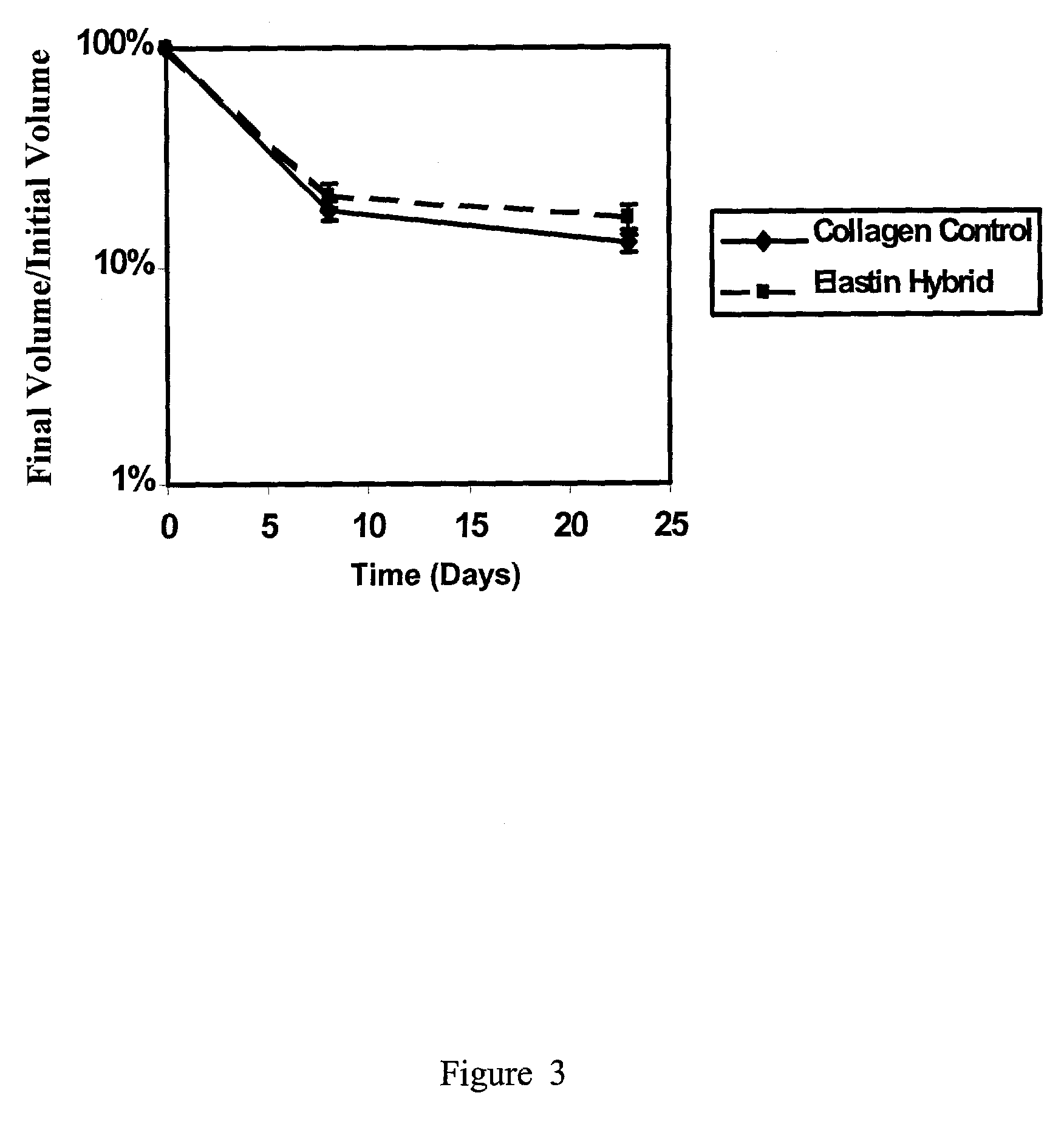
Elastin stabilization of connective tissue
A method and product are provided for the treatment of connective tissue weakened due to destruction of tissue architecture, and in particular due to elastin degradation. The treatment agents employ certain unique properties of phenolic compounds to develop a protocol for reducing elastin degradation, such as that occurring during aneurysm formation in vasculature. According to the invention, elastin can be stabilized in vivo and destruction of connective tissue, such as that leading to life-threatening aneurysms in vasculature, can be tempered or halted all together. The treatment agents can be delivered or administered acutely or chronically according to various delivery methods, including sustained release methods incorporating perivascular or endovascular patches, use of microsphere carriers, hydrogels, or osmotic pumps.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Tubular construct for implantation
InactiveUS7029689B2Growth inhibitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyStructural protein
The present invention is directed to devices for repair, replacement or augmentation of soft tissues in an organism. The devices comprise cellular compositions comprising cells and preferably, structural proteins such as collagen or elastin. The devices can also be used in methods for testing the effects of agents on soft tissues.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
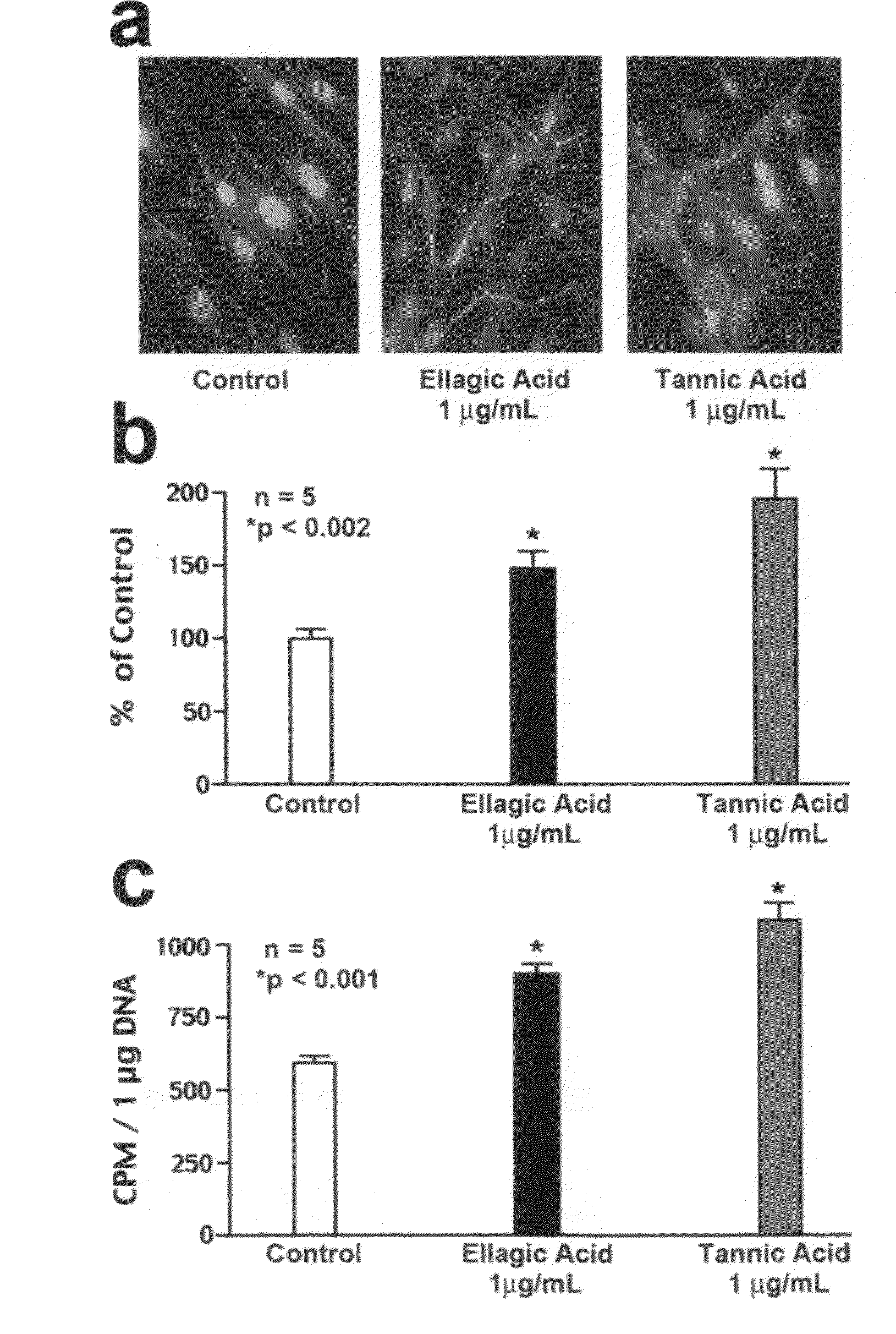
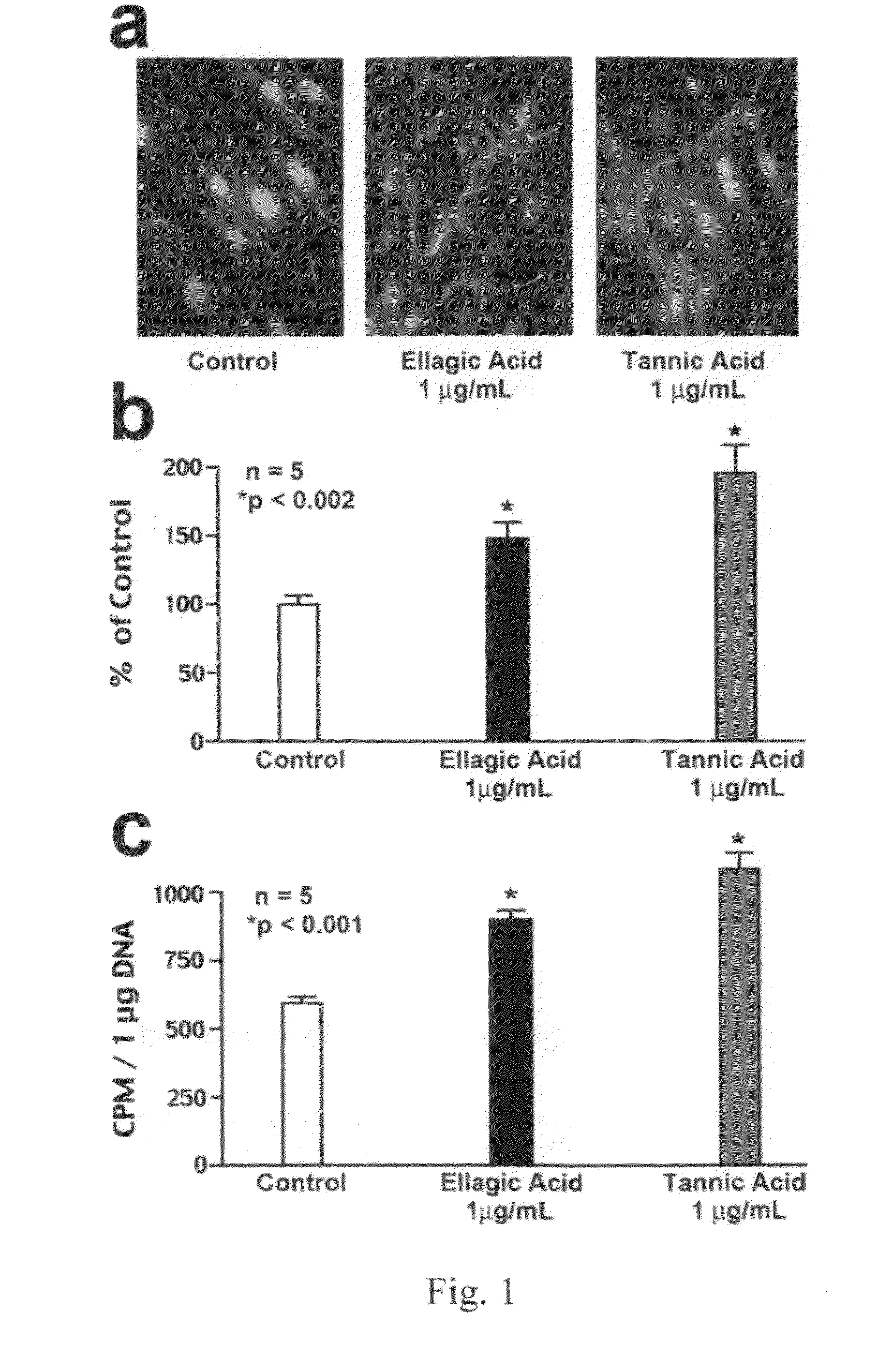
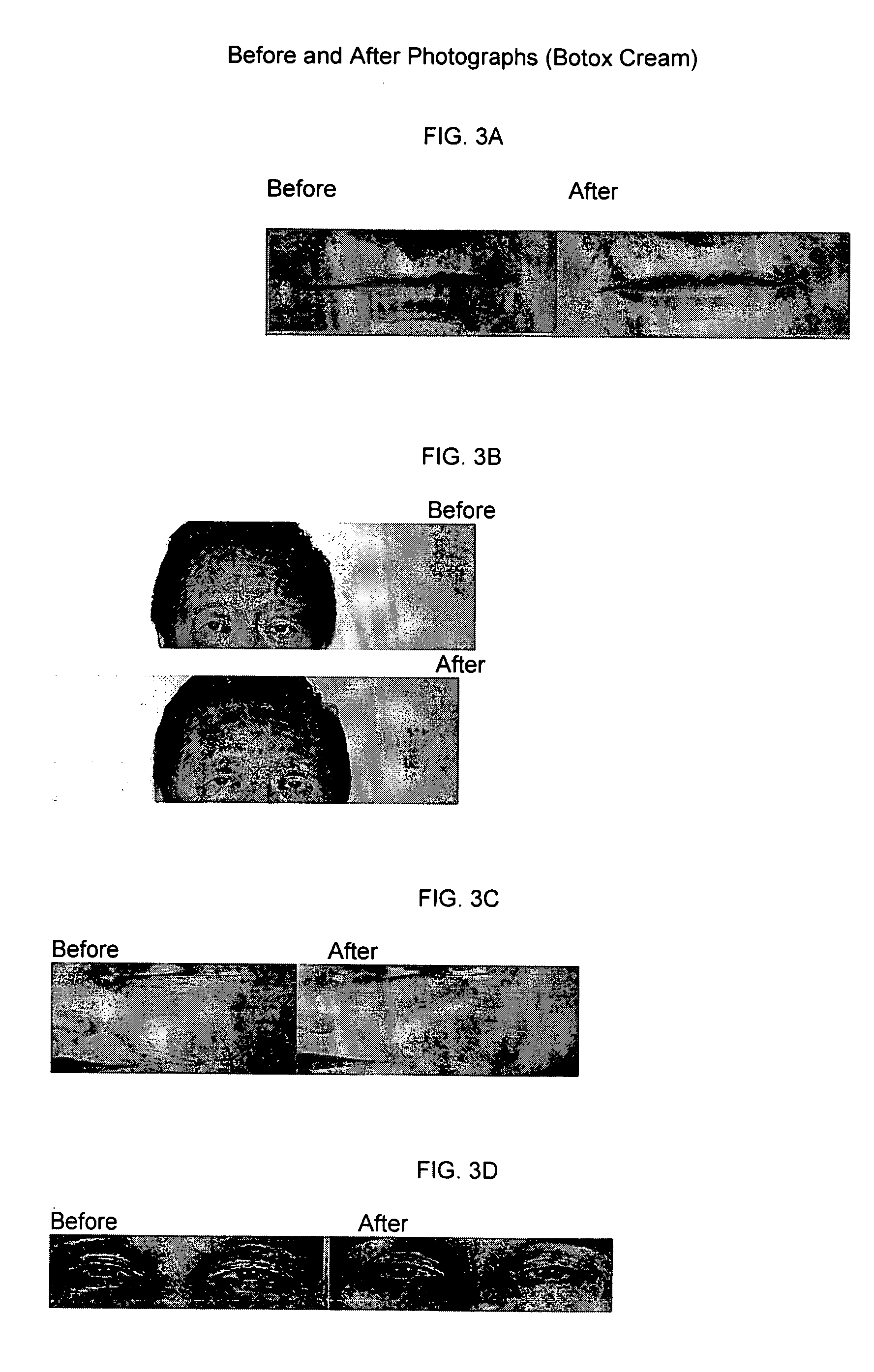
Elastin protective polyphenolics and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20090110709A1Prevent premature proteolyticEfficient elastogenesisCosmetic preparationsBiocideFiberPolyphenol
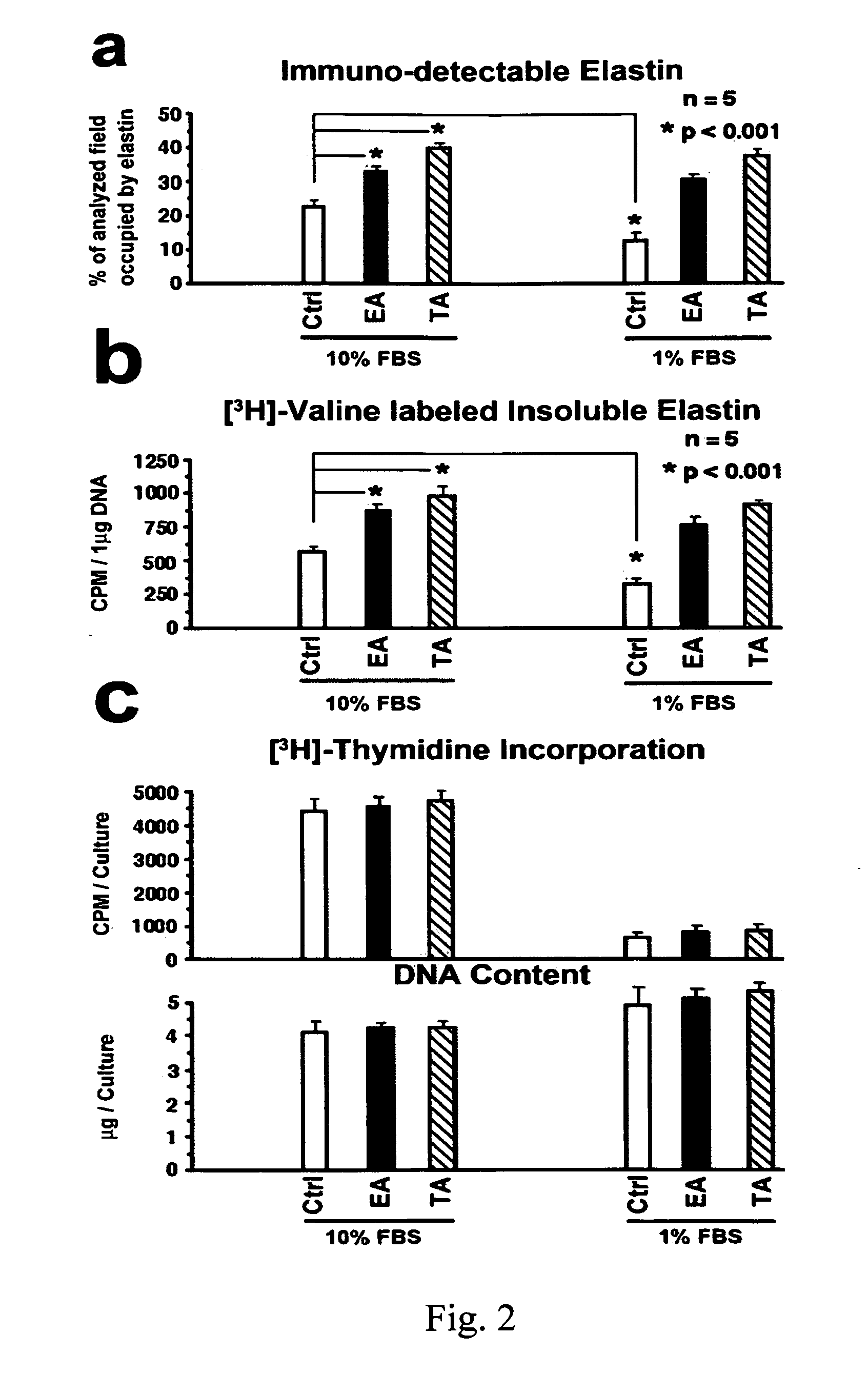
Dermal fibroblasts permanently loose their ability to synthesize elastin, the major component of elastic fibers, shortly after puberty. This progressive loss of elastic fibers cannot be replaced, resulting in the physical signs of aging. The present invention provides methods and compositions containing the polyphenols ellagic acid and / or tannic acid for protection against degradation of cutaneous elastic fibers by the elastolytic enzymes. The use of ellagic acid and / or tannic acid increased the overall deposition of elastic fibers in healthy and damaged skin cells. The protection of both intra-tropoelastin and extra-cellular mature elastic fibers from proteolytic enzymes by ellagic acid and tannic acid caused an increase in the net deposition of elastic fibers. Therefore, embodiments of the present invention provide methods and composition for the treatment of skin and prevention and treatment of degradation of dermal elastic fibers.
Owner:ELASTOGENESIS LLC +1
Stabilized compositions for topical administration and methods of making same
InactiveUS20060182794A1Easy to useCost-effective and simple useOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsActive agentBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A stabilizing composition that also enhances permeation is provided for the topical or transdermal administration of an active ingredient. The composition preferably comprises collagen, elastin, sphingoside and cerebroside. Also provided are pharmaceutical or cosmetic formulations comprising an effective amount of an active agent and the stabilizing composition as well as methods of administering active agents topically or transdermally.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL
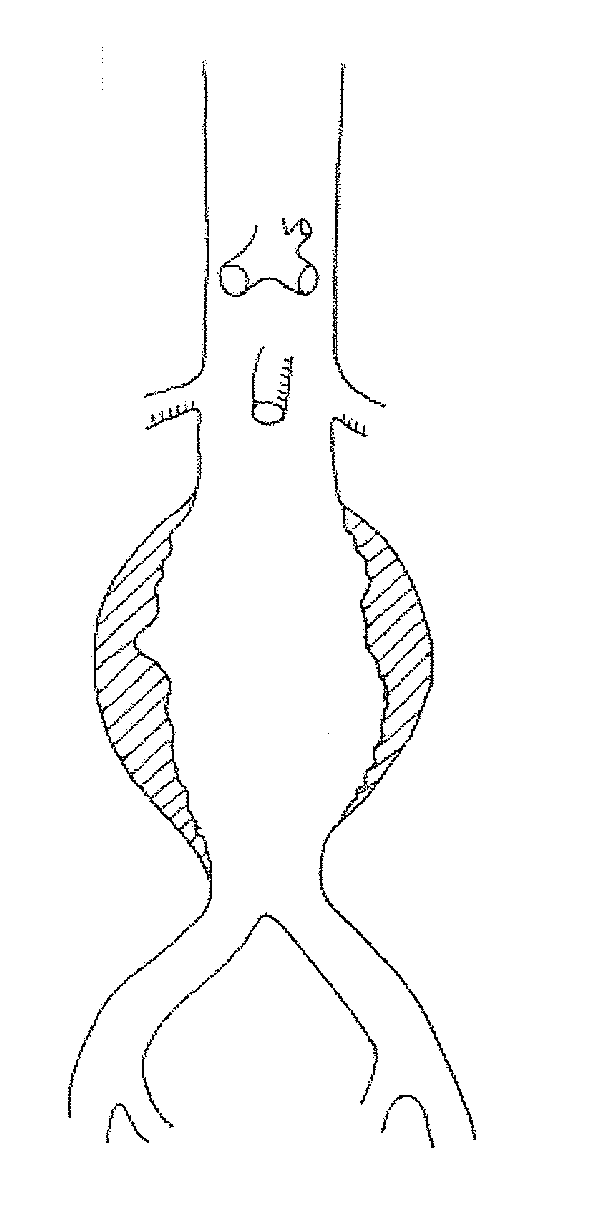
Treatment of aneurysm with application of connective tissue stabilization agent in combination with a delivery vehicle
Delivery vehicles for controlled release of connective tissue stabilization agent for the treatment of vascular aneurysms are described. The delivery vehicle generally is combined with a connective tissue stabilization agent to form a therapeutic composition. The treatment of an aneurysm can be achieved through release of connective tissue stabilization agent from the delivery vehicle to the aneurysm. The connective tissue stabilization agent can be collagen stabilization agent, elastin stabilization agent, or a combination thereof. The aneurysm can be treated individually, simultaneously or sequentially with collagen stabilization agent and elastin stabilization agent embedded in separate delivery vehicles.
Owner:VATRIX MEDICAL INC
Dermal retraction with intersecting electromagnetic radiation pathways
InactiveUS9050116B2Avoid excessive injuryLevel of disruption to the dermal layerUltrasound therapyElectrotherapySubcutaneous fatty tissueLight beam
A method and device for stimulating human dermal tissue retraction and collagen and elastin production is provided. One or more lasers or other electromagnetic radiation devices produce at least two output beams (split or independent beams) that can be directed to deliver electromagnetic energy to a desired subsurface depth of dermal tissue, thereby disrupting the same, without causing excessive damage to the adjacent epidermis, subcutaneous fatty tissue, or blood vessels of the skin.
Owner:HOMER GREGG S
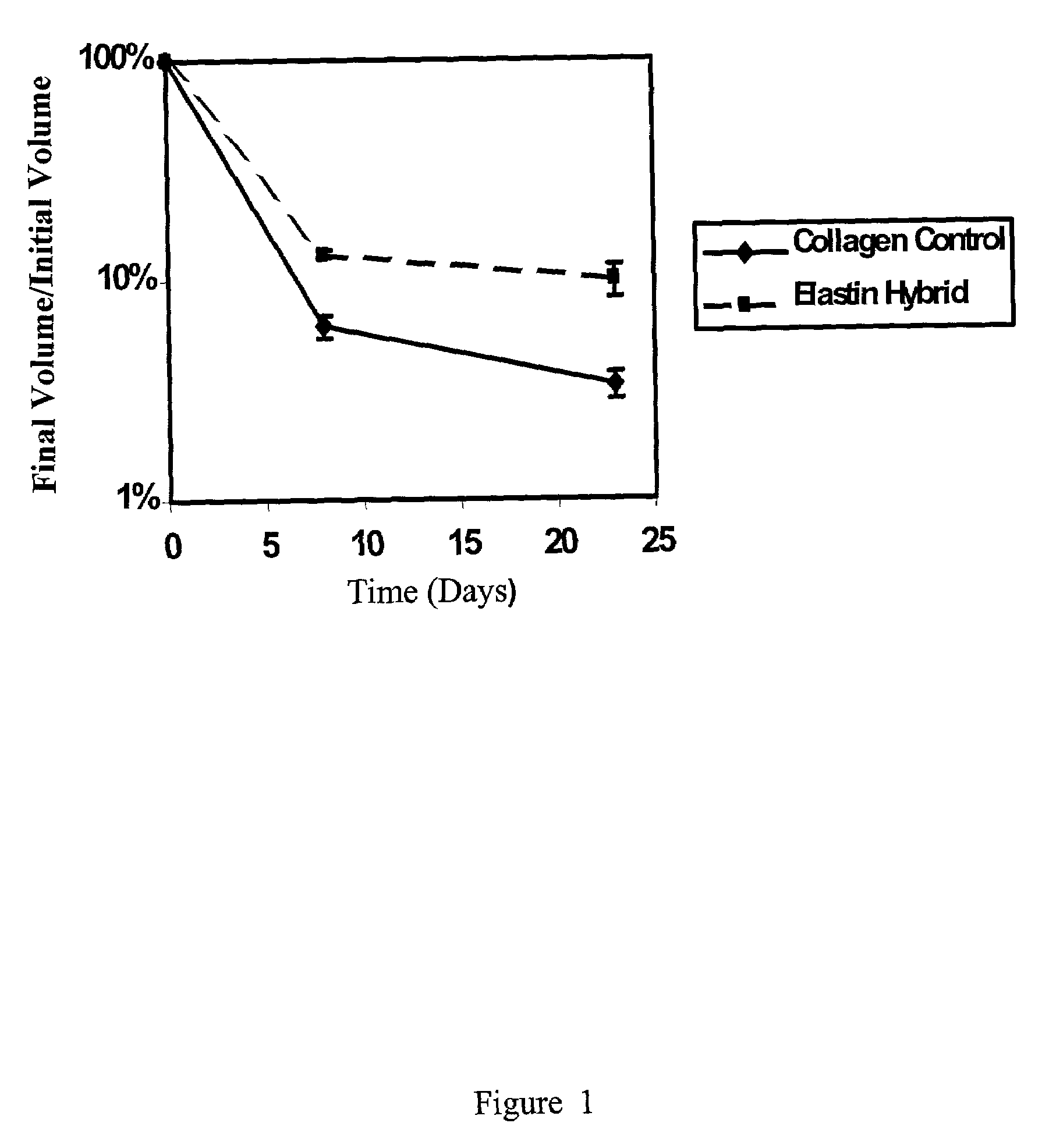
Collagen based materials and uses related thereto
InactiveUS20140193477A1Reduce inflammationPrevent coagulationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue repairMedicine
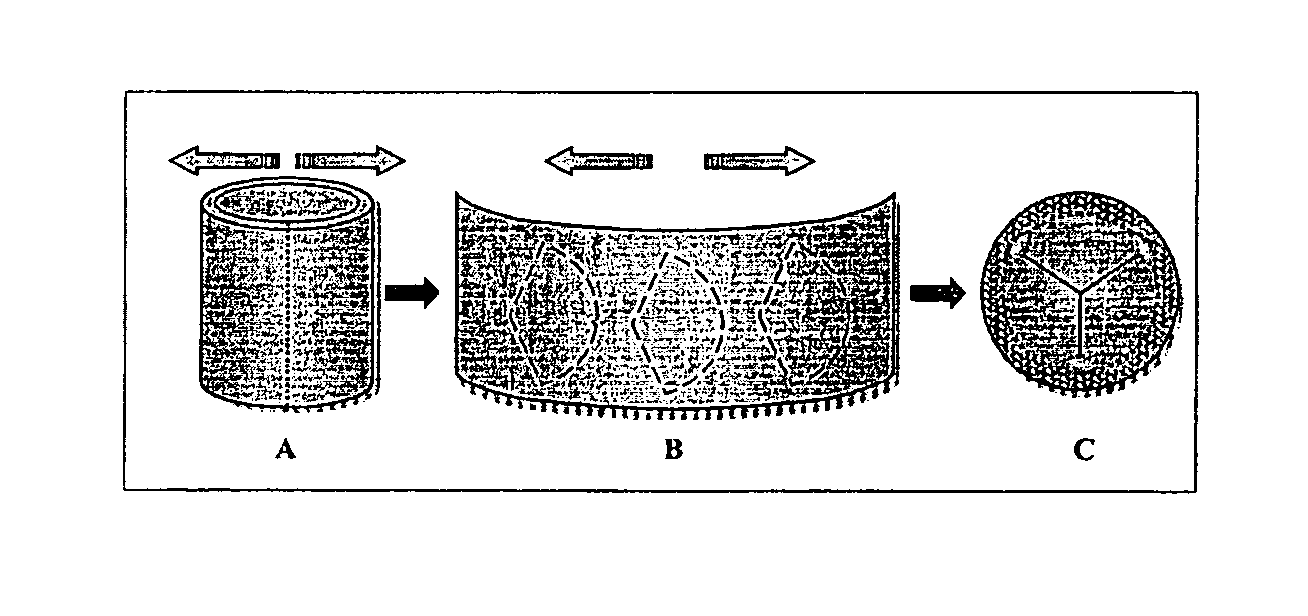
This disclosure relates to materials fabricated from collagen and uses relates thereto. Typically, layers of collagen are stretched during a curing period and optionally coated or impregnated with an elastin like protein. In certain embodiments, these materials can be used in tissue repair or arranged into cylinders and utilized as a prosthetic vascular graft.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +2
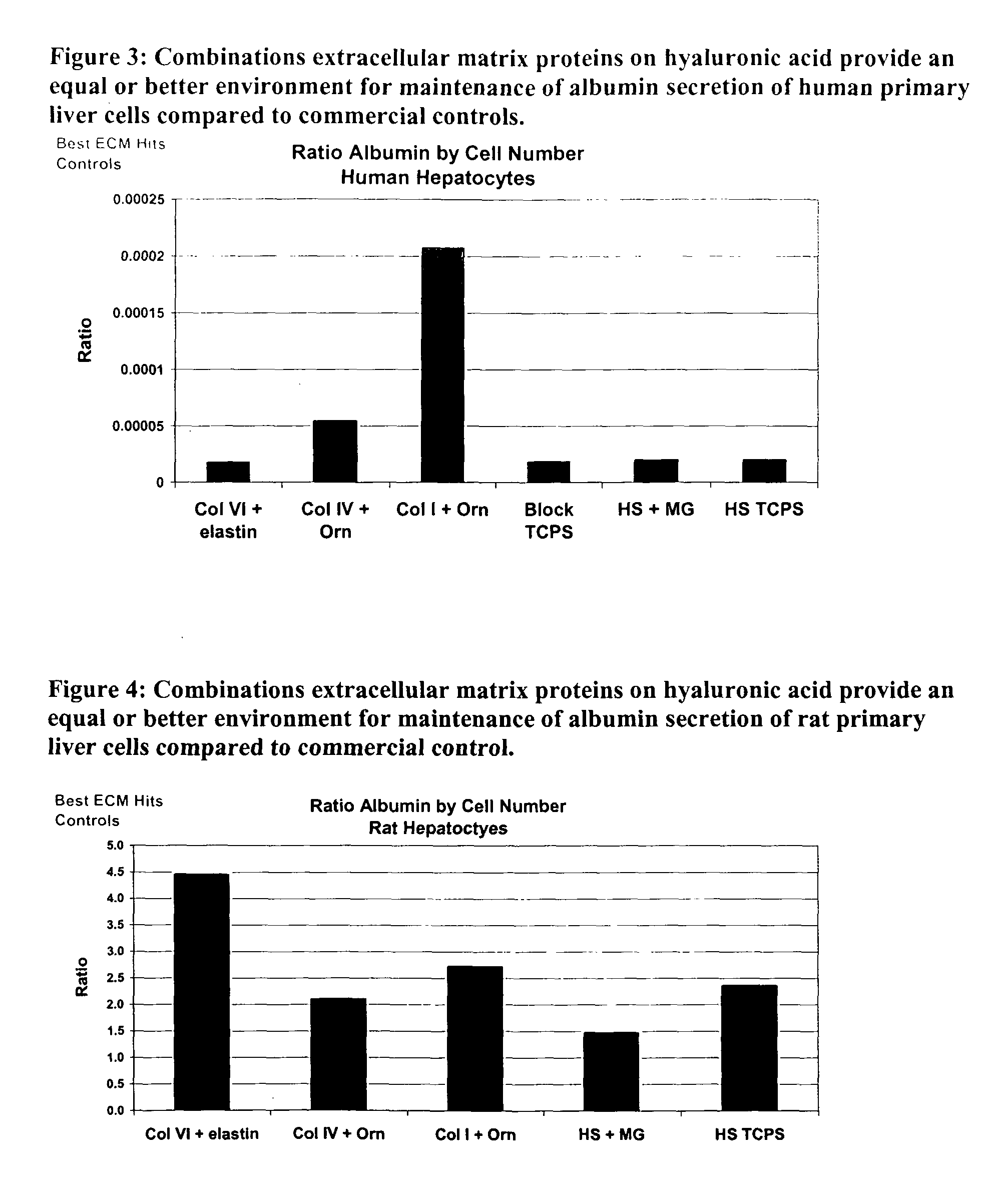
Environments that maintain function of primary liver cells
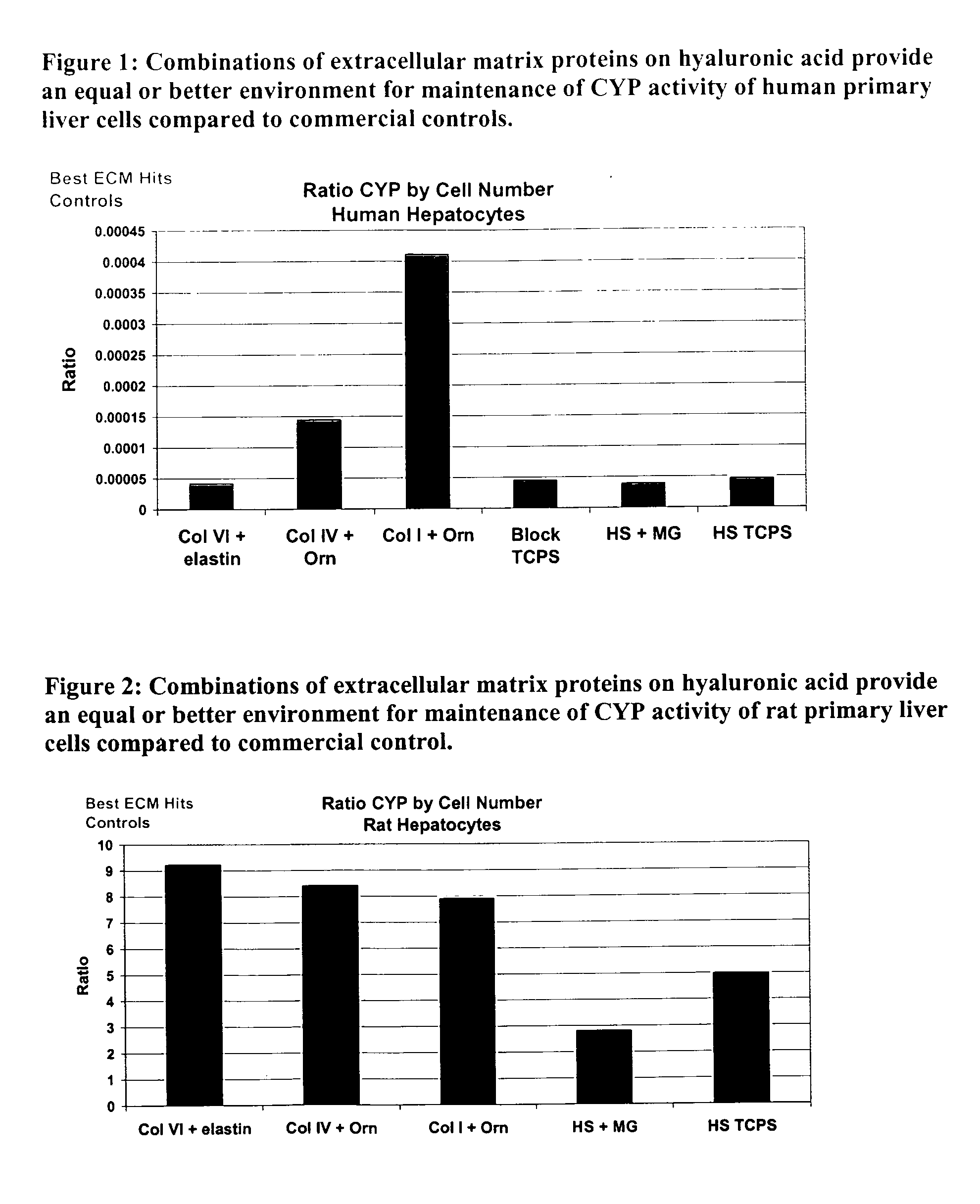
InactiveUS20050059150A1Good adhesionEasy maintenanceHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsECM ProteinL-Ornithine
Surfaces useful for cell culture comprise a support to which is bound a CAR material, and, bound to the CAR material, an ECM protein, or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof such as elastin, fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, collagen I, collagen III, collagen IV, and collagen VI. Also, optionally present on the surface is an active factor, preferably a polycationic polymer or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof, such as polyethyleneimine (PEI), poly-D-lysine (PDL), poly-L-lysine (PLL), poly-D-ornithine (PDO) or poly-L-ornithine (PLO). This surface is used in cell culture to promote cell attachment, survival, and / or proliferation of primary liver cells. The invention also relates to methods utilizing this surface, such as methods for attachment, survival, and / or proliferation of cells. Further disclosed is the use of the surface in cell culture with serum-free medium. Methods of screening using the surface of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Elastin stabilization of connective tissue
A method and product are provided for the treatment of connective tissue weakened due to destruction of tissue architecture, and in particular due to elastin degradation. The treatment agents employ certain unique properties of phenolic compounds to develop a protocol for reducing elastin degradation, such as that occurring during aneurysm formation in vasculature. According to the invention, elastin can be stabilized in vivo and destruction of connective tissue, such as that leading to life-threatening aneurysms in vasculature, can be tempered or halted all together. The treatment agents can be delivered or administered acutely or chronically according to various delivery methods, including sustained release methods incorporating perivascular or endovascular patches, use of microsphere carriers, hydrogels, or osmotic pumps.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
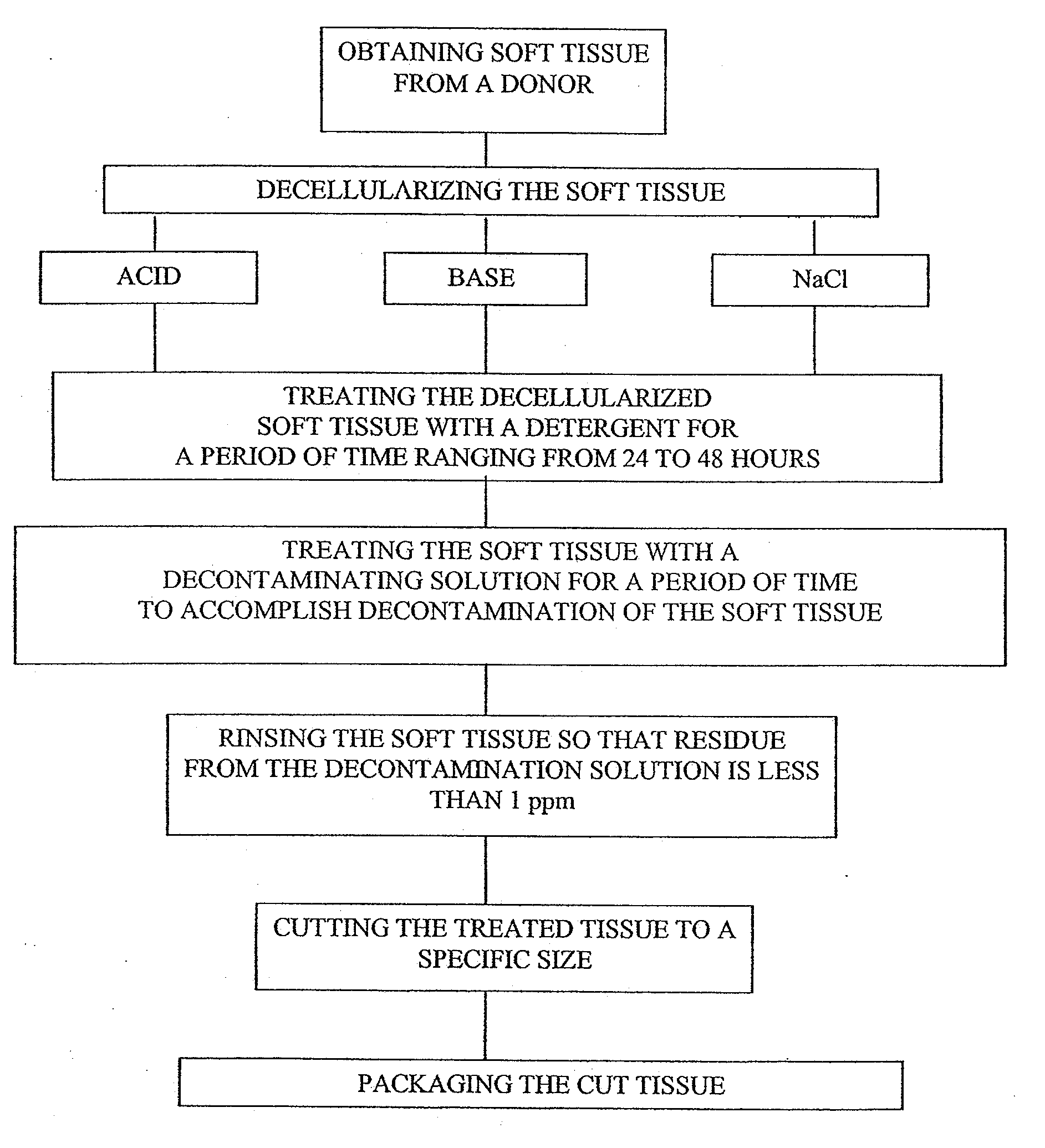
Processing soft tissue, methods and compositions related thereto
InactiveUS20100112543A1Long-term durabilityLong-term functionVertebrate cellsDead animal preservationCellular componentMedicine
In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to a process for preparing skin removed from a human donor, including a living human donor, and removing cellular components and forming a decellular matrix having as major components collagens and elastins while disinfecting the tissue. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to a process for treating a decellularized soft tissue by freezing the same at a plurality of decreasing temperatures at atmosphere or higher such that there is formation of ice crystals having a size greater than 2.0 and lyophilizing the soft tissue under vacuum to remove the water to less than 6% forming a porous matrix.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Plant based formulations for improving skin moisture, texture, and appearance
ActiveUS20060198810A1Increase moistureImprove textureCosmetic preparationsBiocideLipid formationAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to formulations of ingredients that are useful for improving the appearance, texture and / or moisture of skin. In particular, the formulations of the present invention stimulate collagen, elastin, and lipid synthesis and / or inhibit or minimize the loss of collagen, elastin, and lipids in the skin. Additionally, the formulations of the present invention inhibit matrix metalloproteases, such as MMP-1, MMP-9, collagenase, or elastase.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Devices for the Treatment of Vascular Aneurysm
Devices for the treatment of vascular aneurysms are described. The treatment is achieved through the delivery of an effective amount of elastin stabilization agent to an isolated volume at the aneurysm. The elastin stabilization agent maybe embedded in a delivery composition. The device optionally has an aspiration means to improve the effectiveness of the treatment.
Owner:VATRIX MEDICAL INC
Compositions for elastrogenesis and connective tissue treatment
ActiveUS20050208150A1Increase elasticityGood lookingHeavy metal active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsArterial smooth muscle cellsFiber
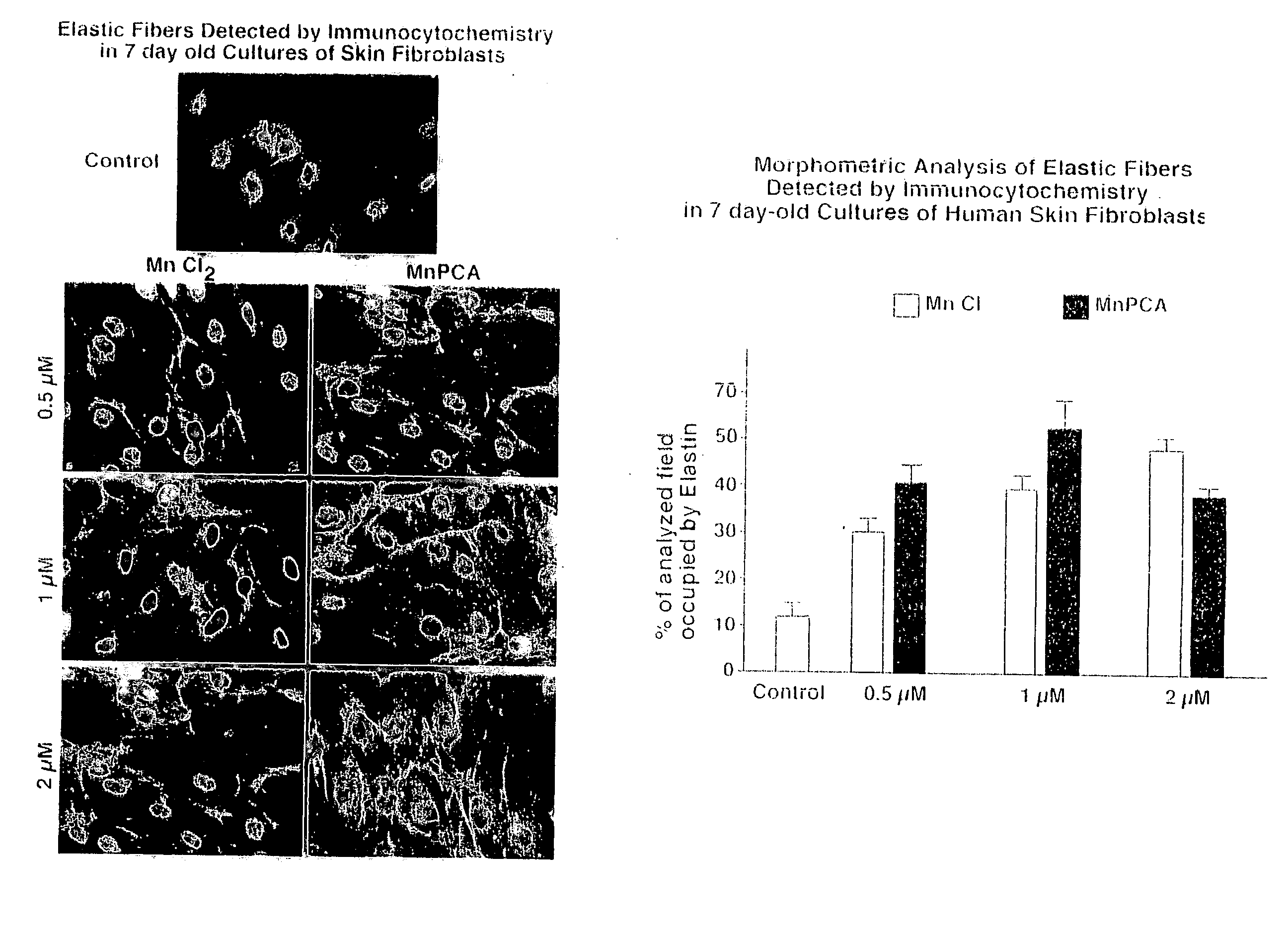
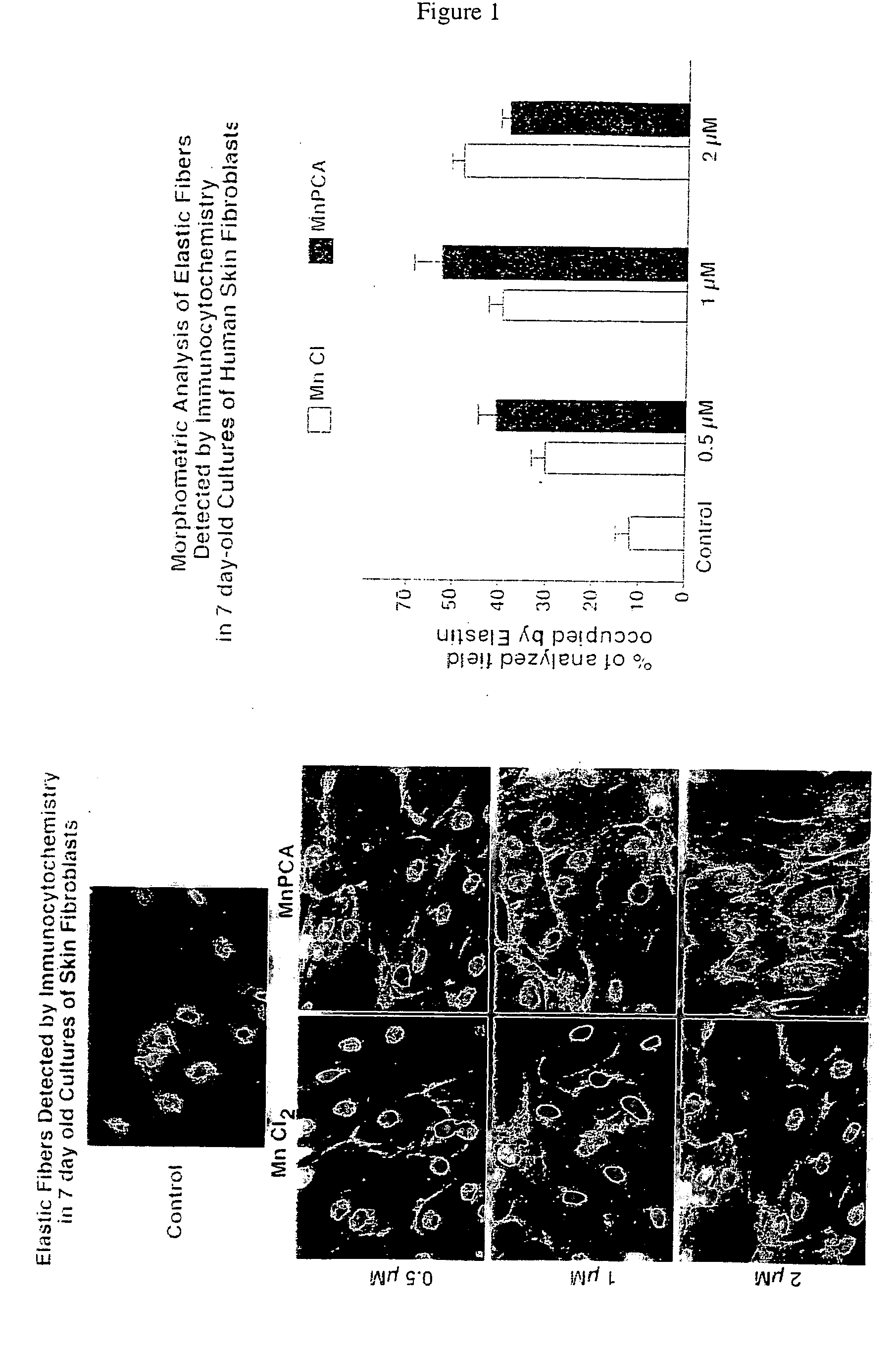
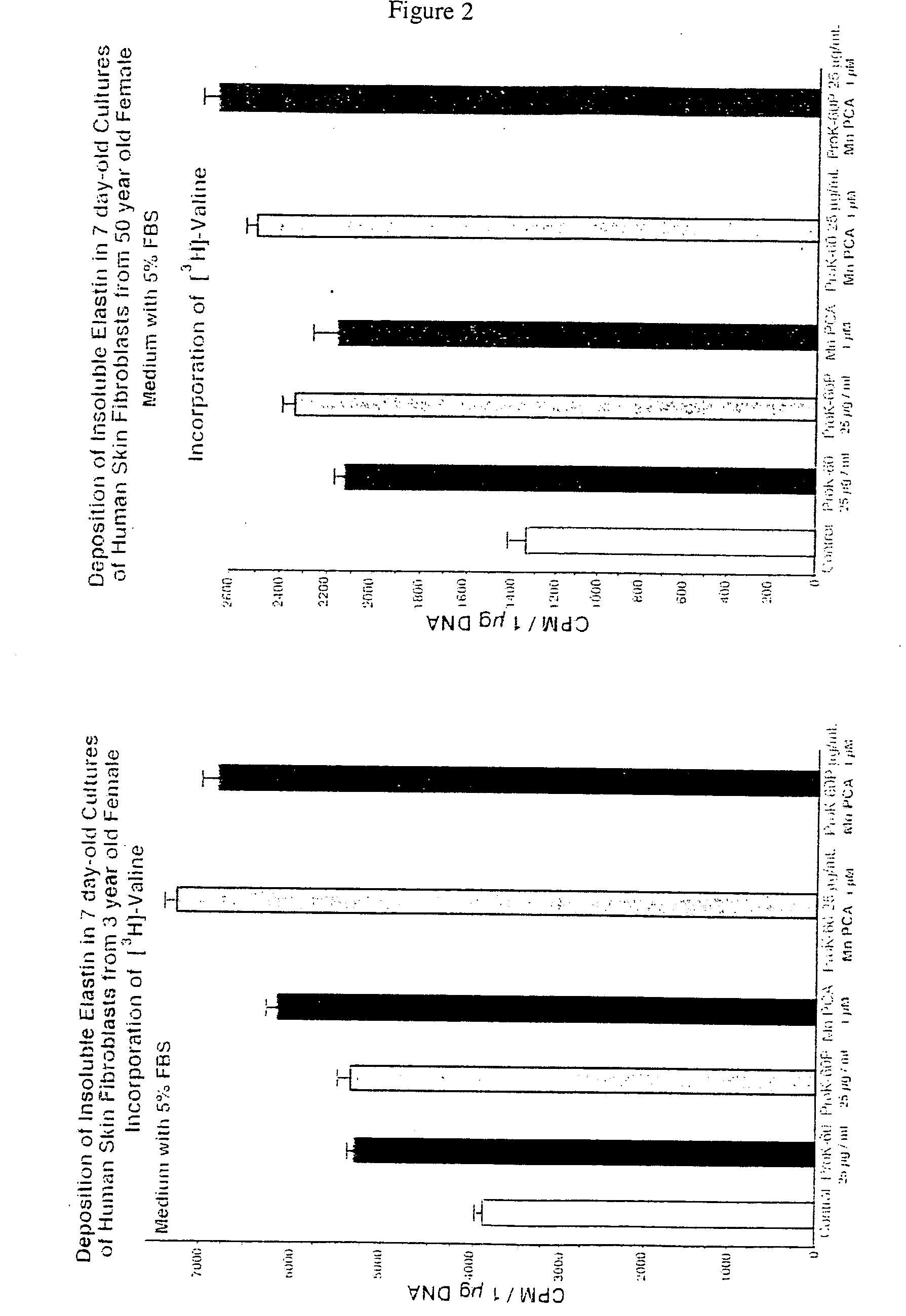
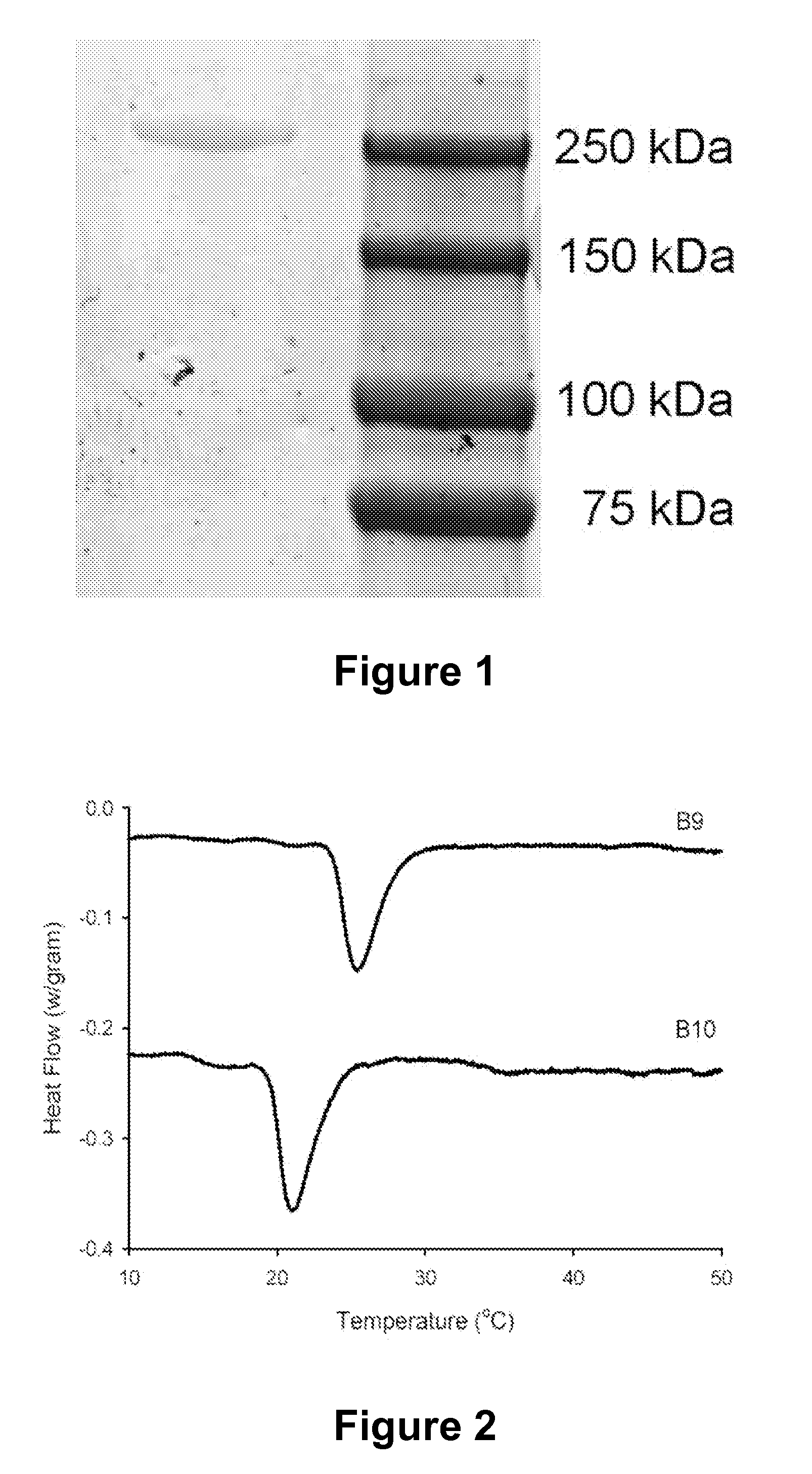
The present invention describes therapeutic compositions comprising one or more minerals, including trivalent iron, divalent manganese and salts thereof, suitable in facilitating synthesis and deposition of connective tissue matrix, particularly rich of elastin and collagen, and mitogenic potential in human dermal fibroblasts. It also describes the phenomenon in which stimulation of elastogenesis by arterial SMC associates with a net decrease in proliferation of these cell types. The present invention also describes methods of treatment of human skin fibroblasts and arterial smooth muscle cells. The therapeutic compositions of the present invention comprise one or more of trivalent iron or divalent manganese or salts thereof and may be combined with an elastic tissue digest.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN +1
Modified Protein Polymers
ActiveUS20100048473A1Suitable mechanical propertyDifferent mechanical propertyElectric discharge heatingPeptide/protein ingredientsMechanical propertyCopolymer
In an embodiment, a number of synthetic protein triblock copolymers are provided comprising first and second end hydrophobic blocks separated by a central hydrophilic block. In particular, the synthetic proteins are elastin-mimetic proteins having improved mechanical characteristics and related methods of making the proteins with the capability of providing precise control over the mechanical properties. Provided are proteins used in a number of medical devices such as artificial blood vessels, shunts, stents or as embolic agents in situations where it is desired to stop or reduce blood flow or pressure in a localized region.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
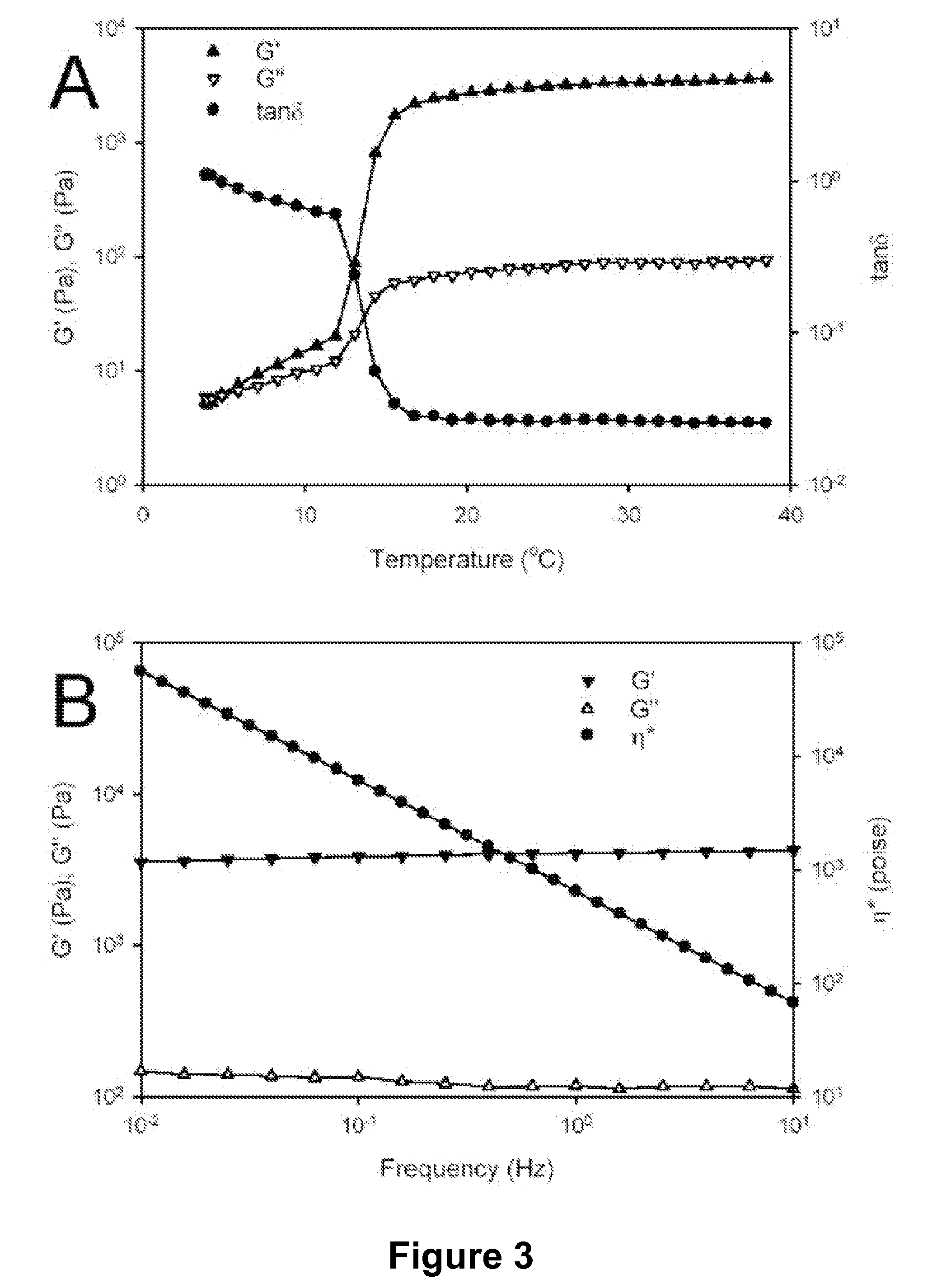
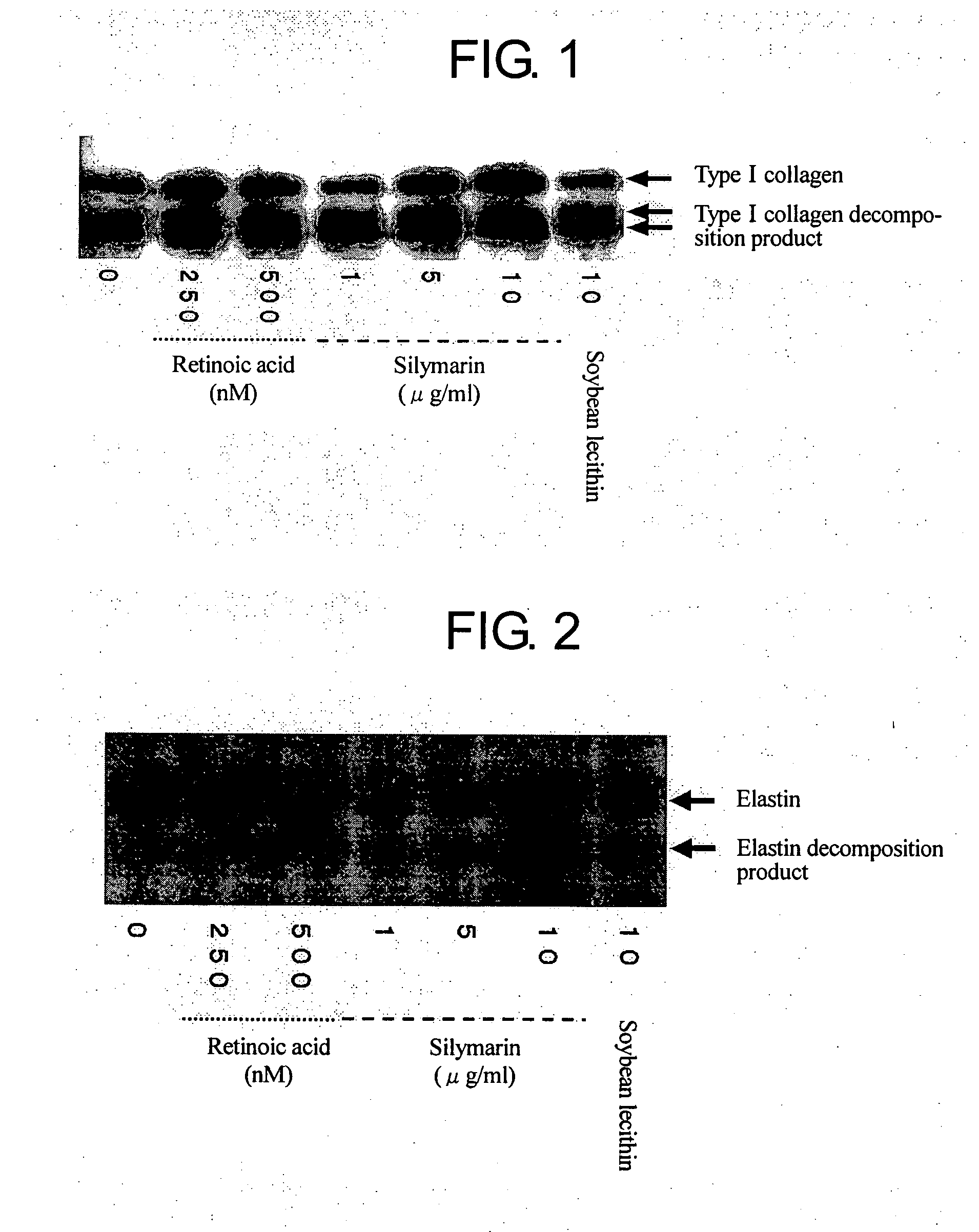
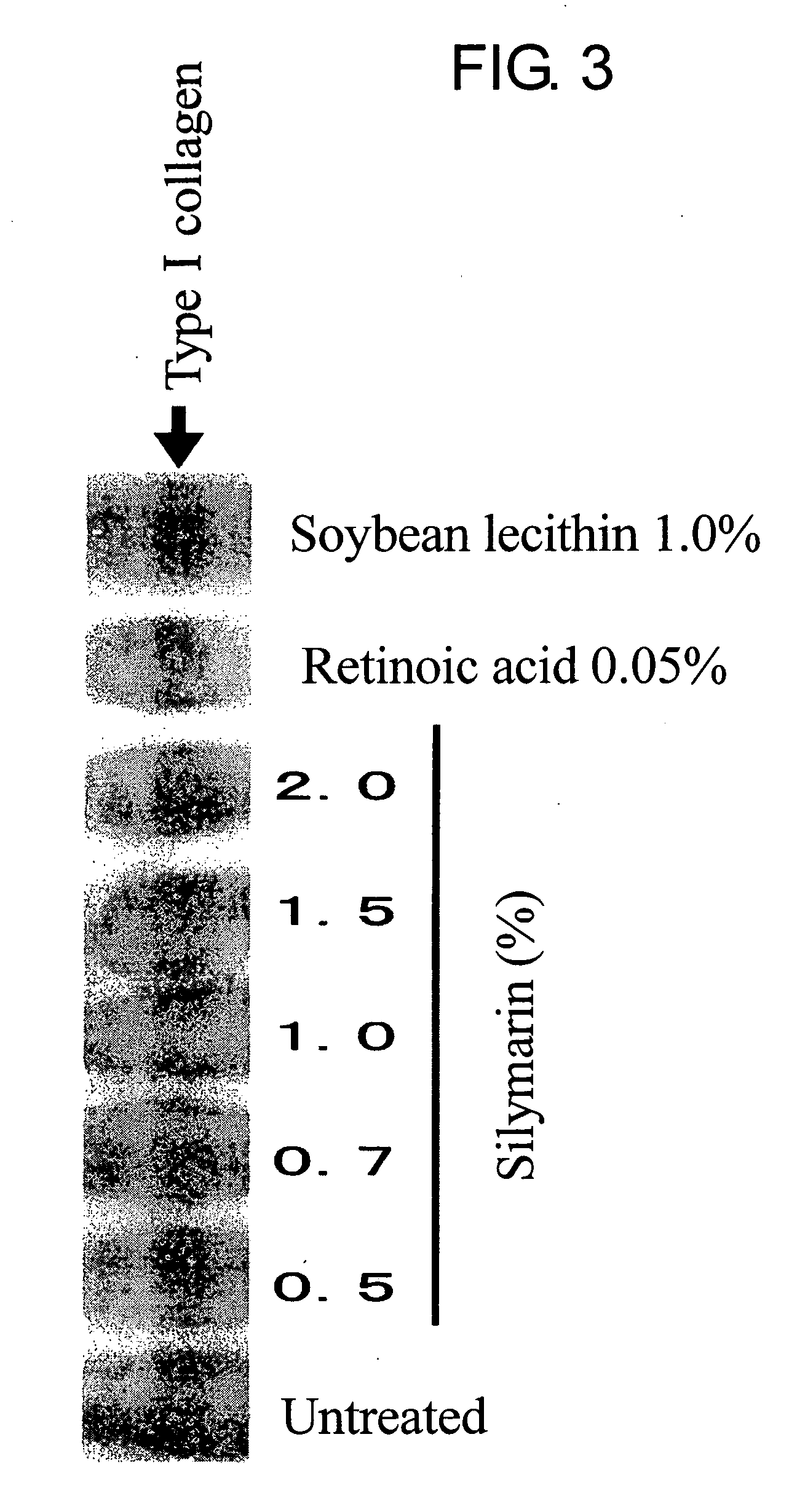
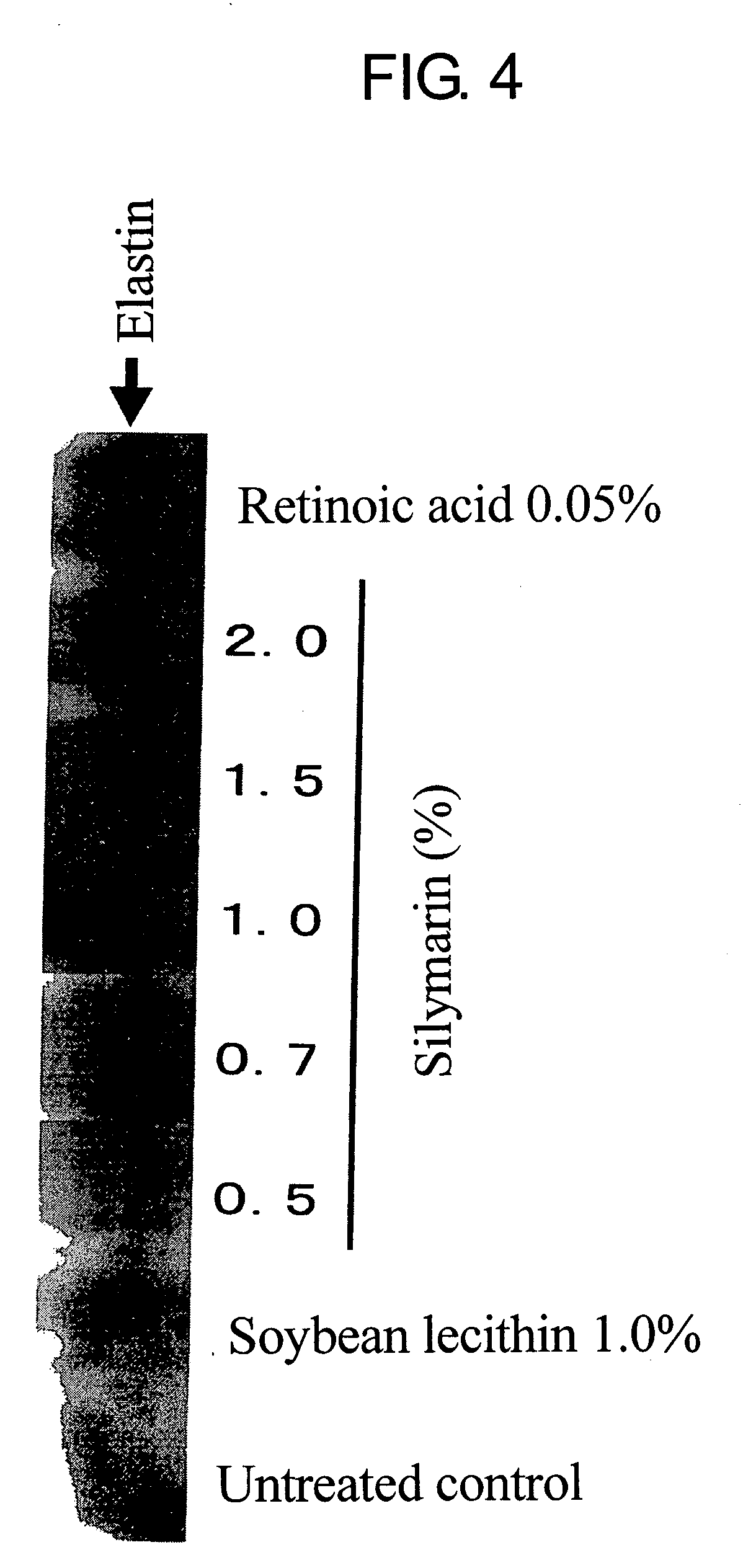
Composition for promoting production of type 1 collagen and/or elastin
InactiveUS20060233738A1Easy to produceImproves suppleness and elasticity of skinBiocideCosmetic preparationsWrinkle skinMedicine
This invention aims to provide a composition that promotes the production of type I collagen and / or elastin in the human skin fibroblast cells, wherein the composition improves the suppleness and elasticity of the skin, is amply effective in preventing and improving wrinkles and sagging, and is also very safe to the skin. The present invention relates to a composition that contains silymarin, which is a general term for flavonolignans such as silybin, silydianin, silychristin and isosilybin, wherein the aforementioned composition has a property to promote the production of type I collagen and / or property to promote the production of elastin. It also relates to a composition containing silymarin derived from a silymarin-containing plant and / or extract of such plant, wherein the aforementioned composition also has a property to promote the production of type I collagen and / or property to promote the production of elastin.
Owner:FUAN KERU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com