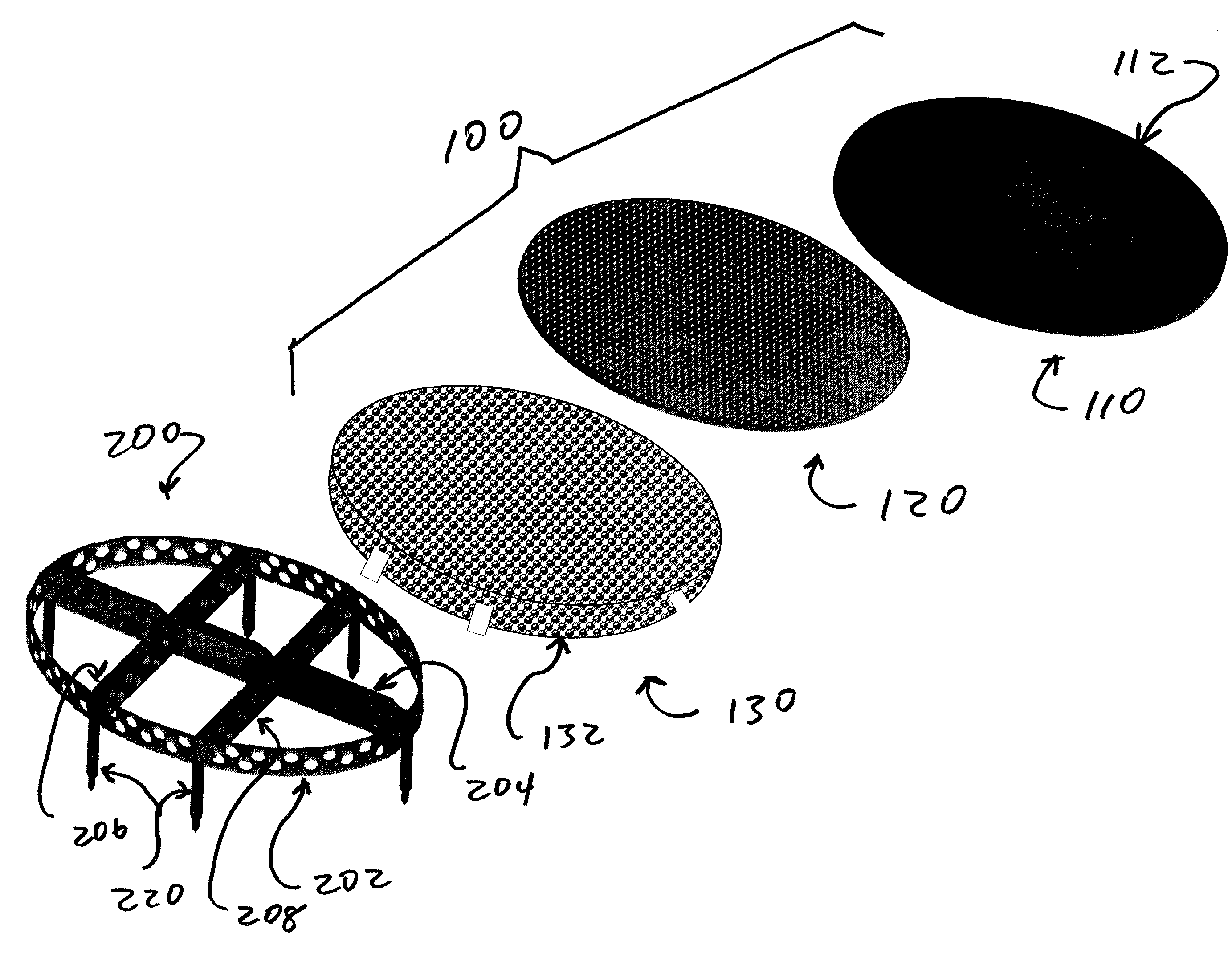
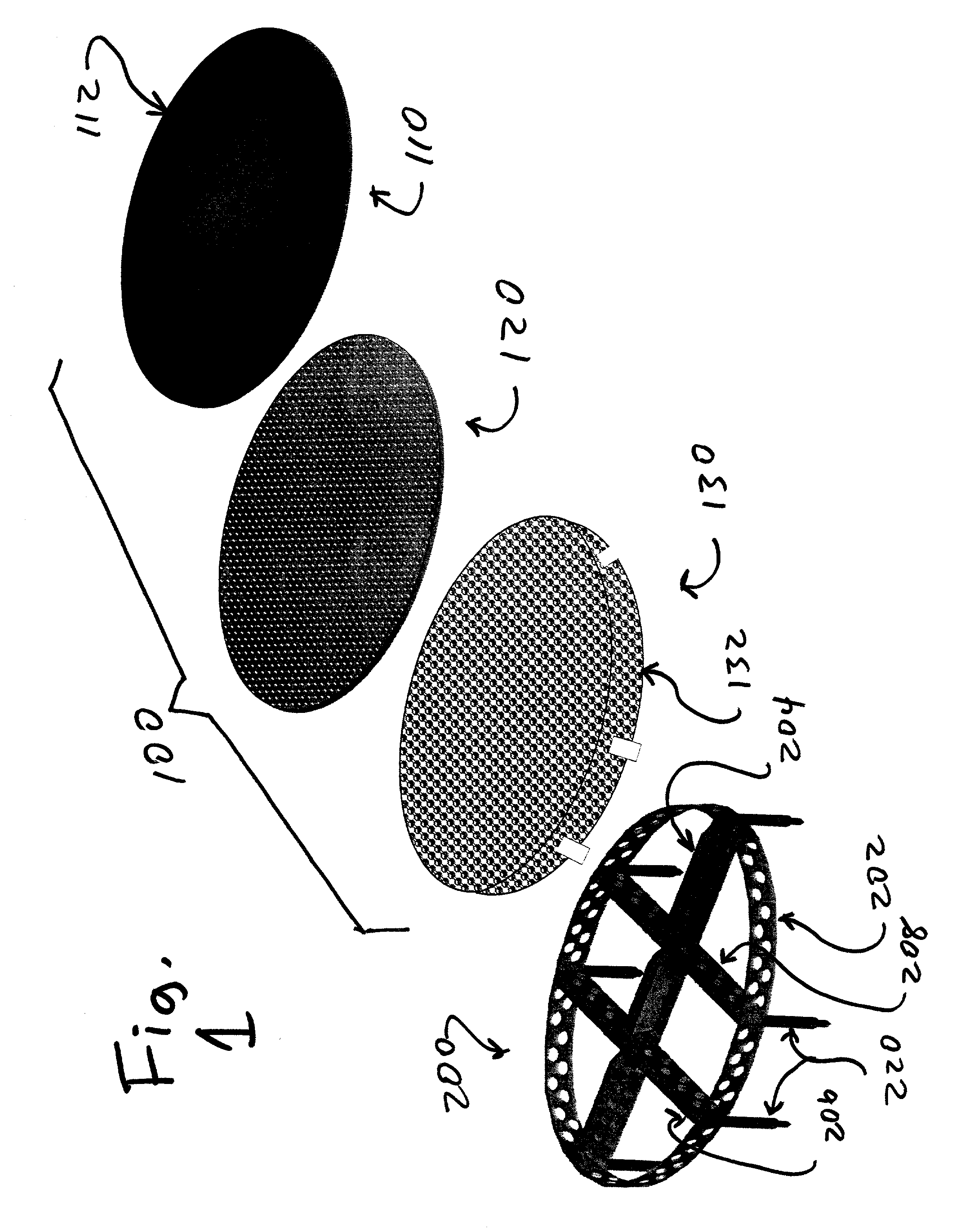
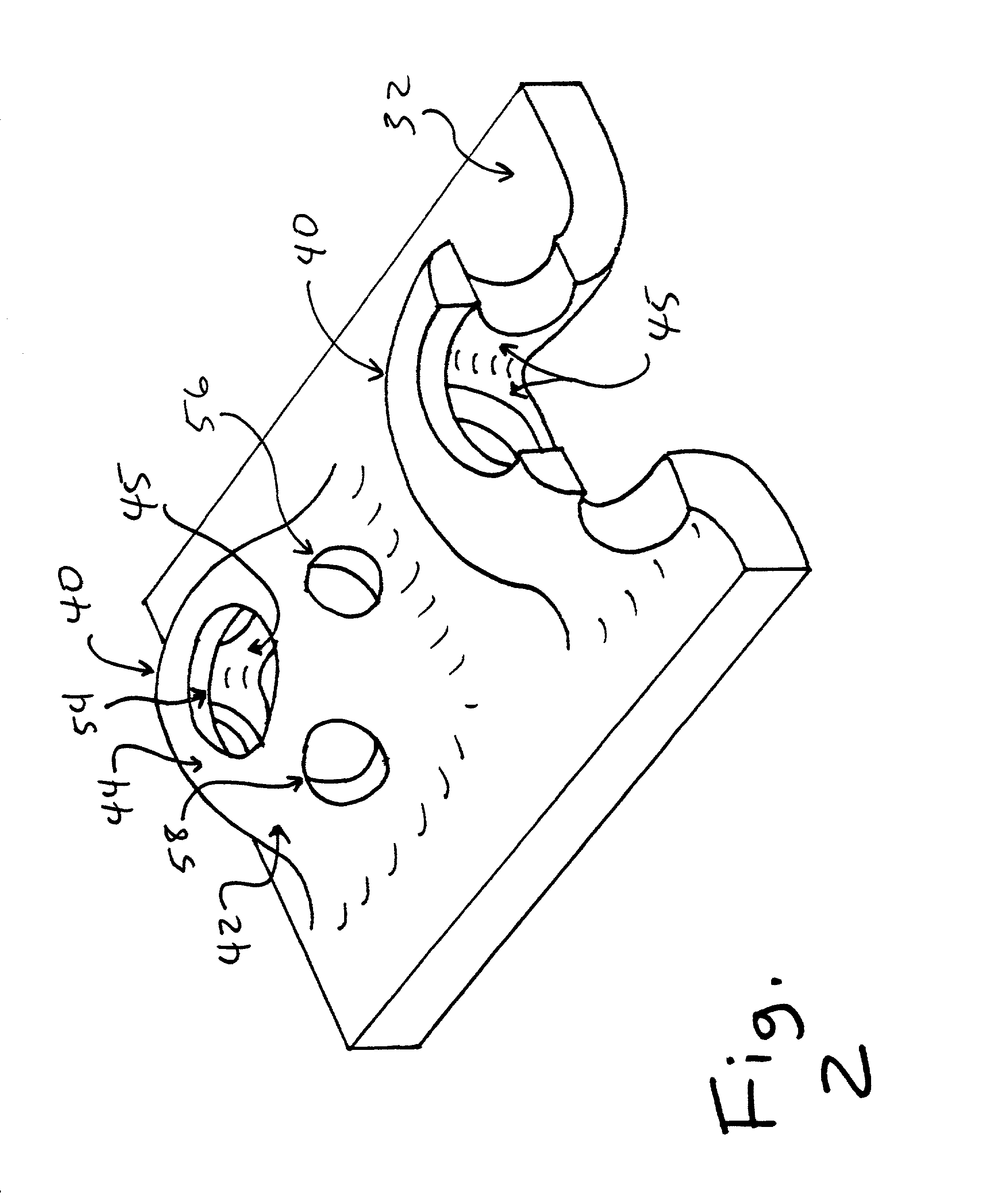
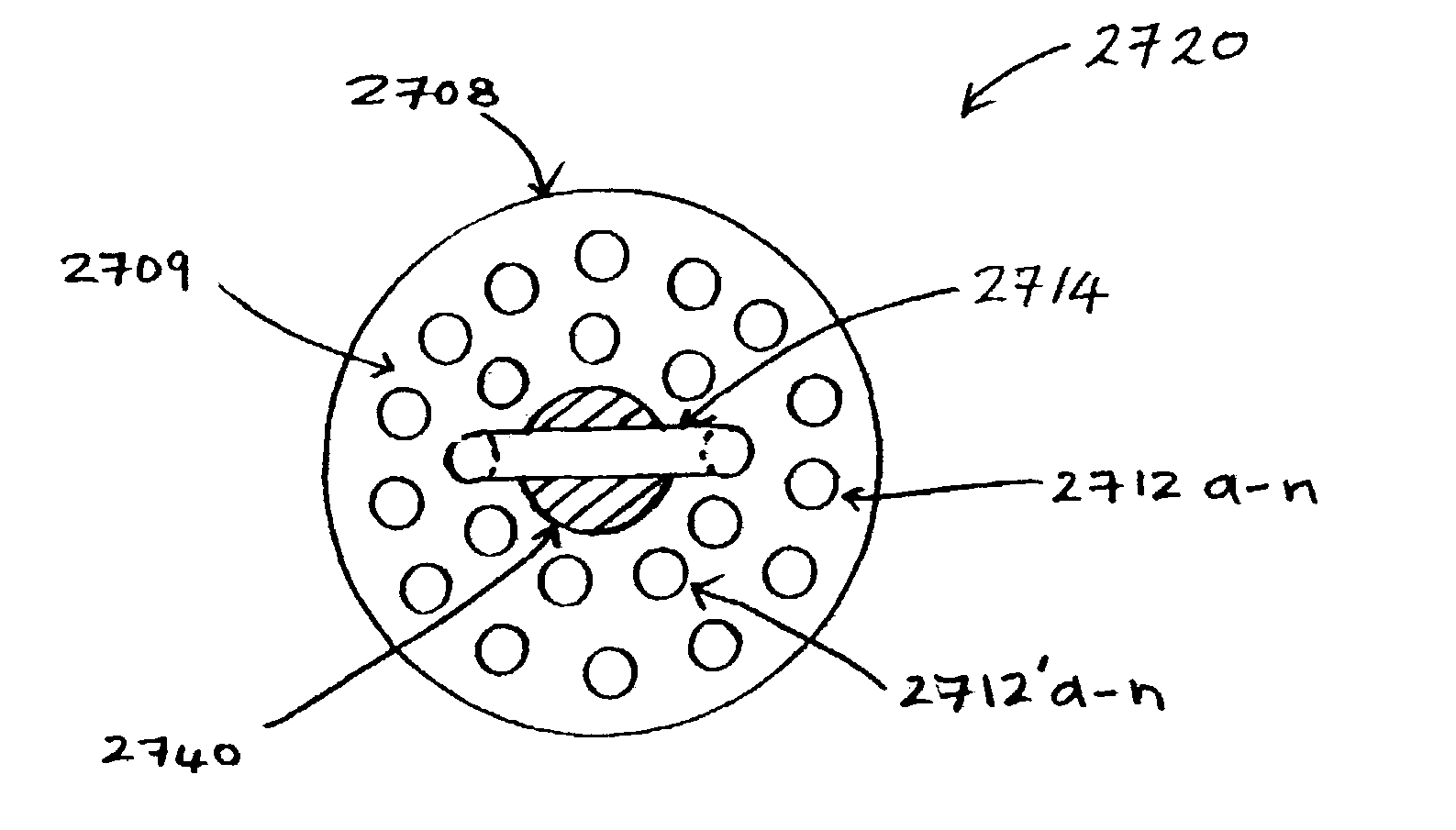
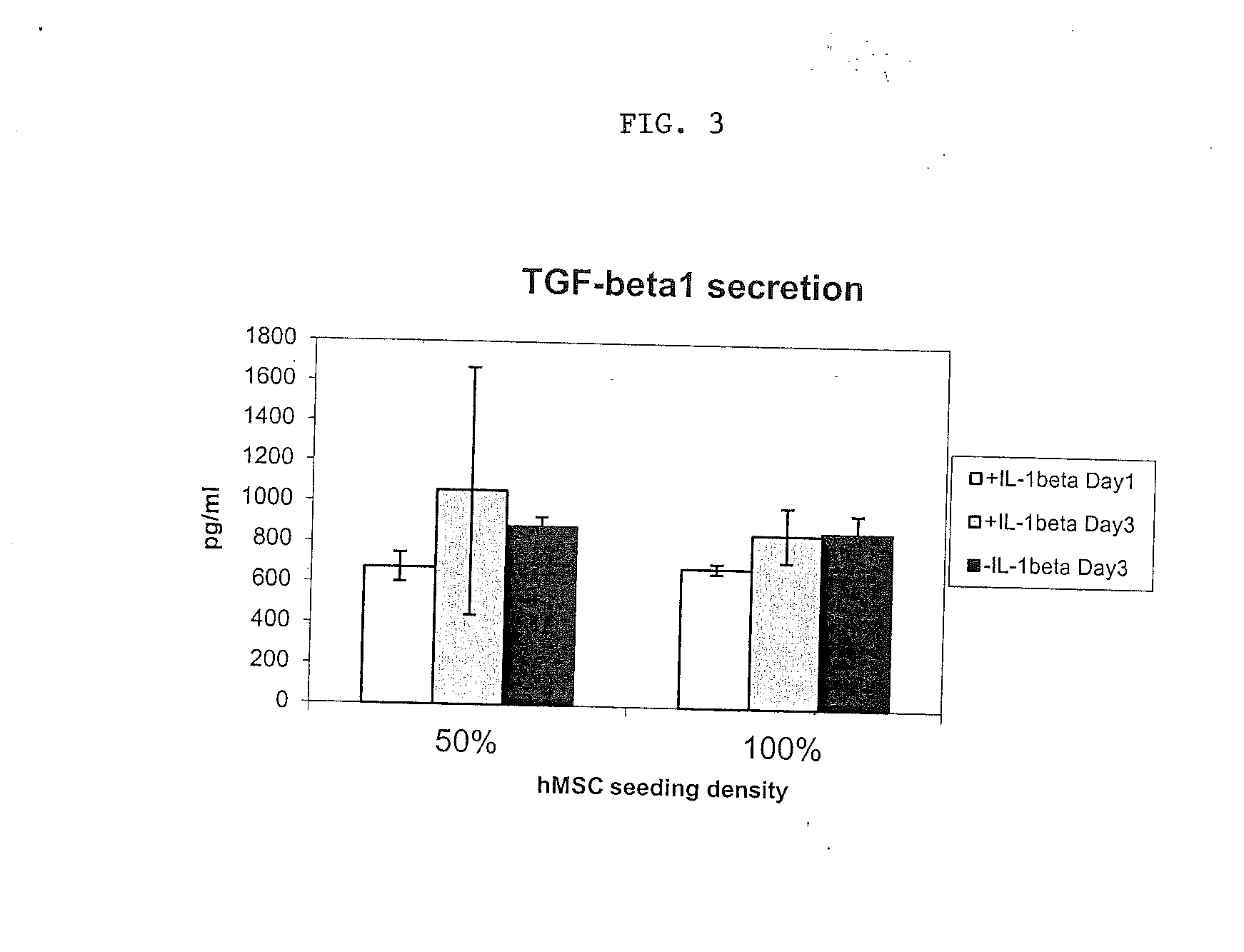
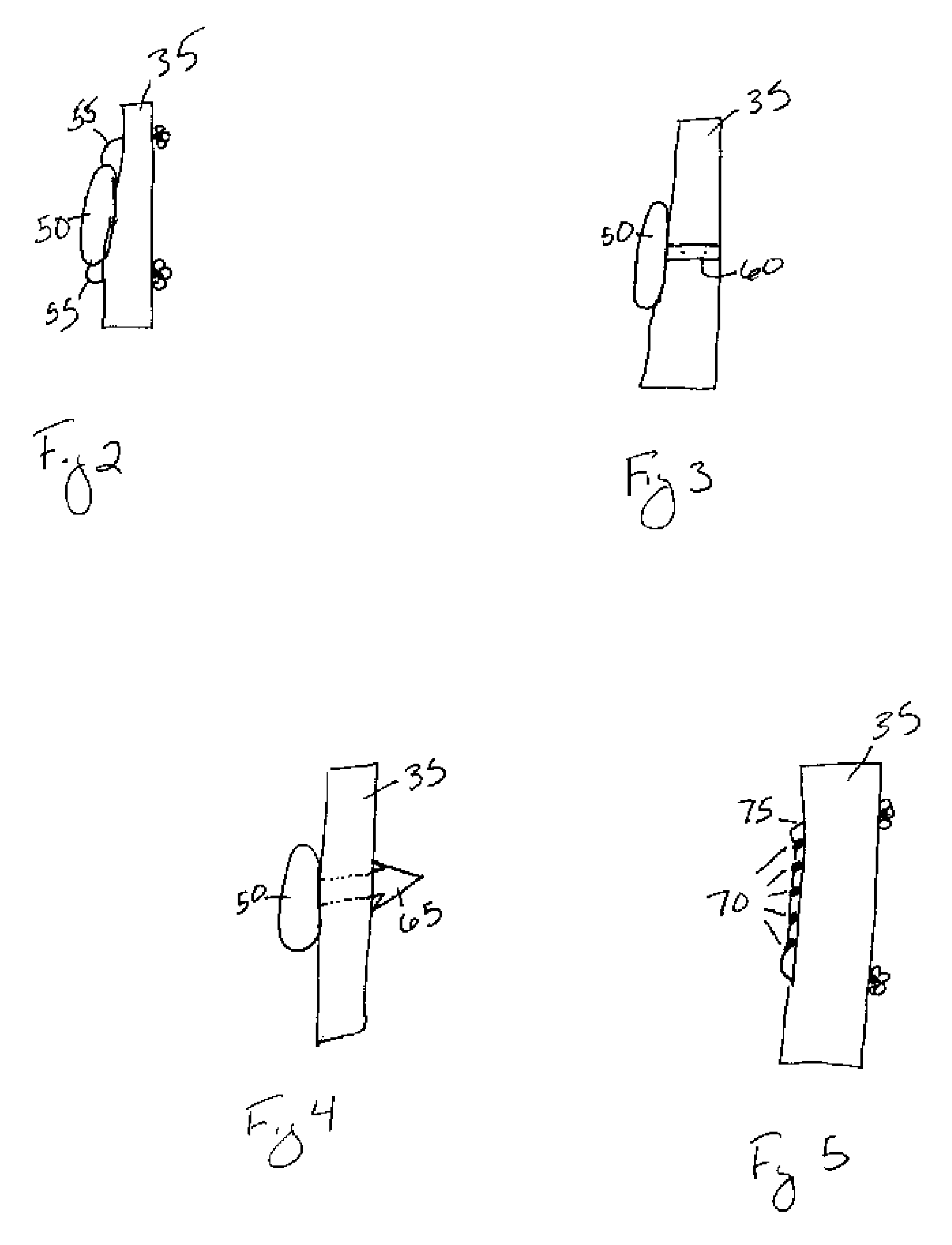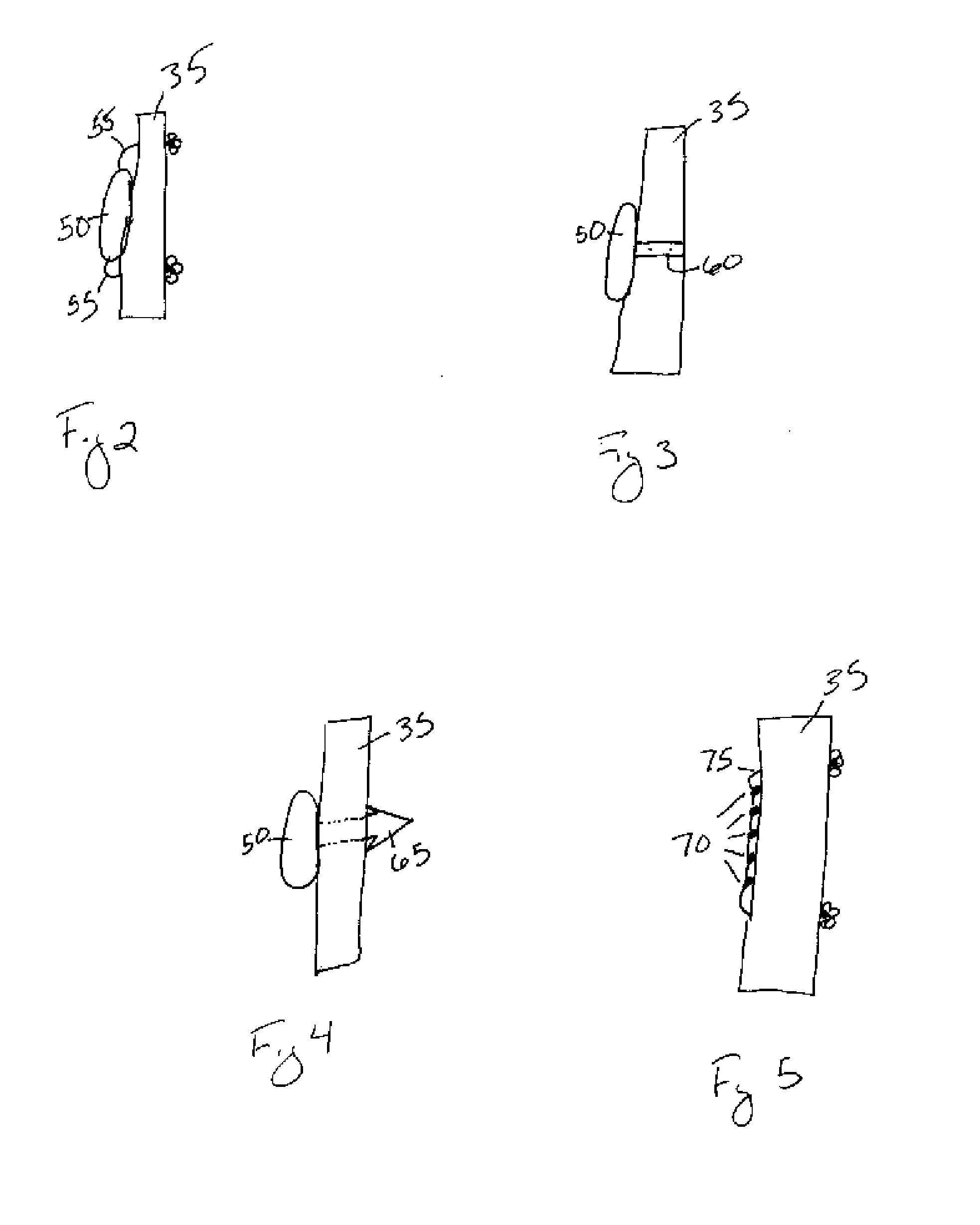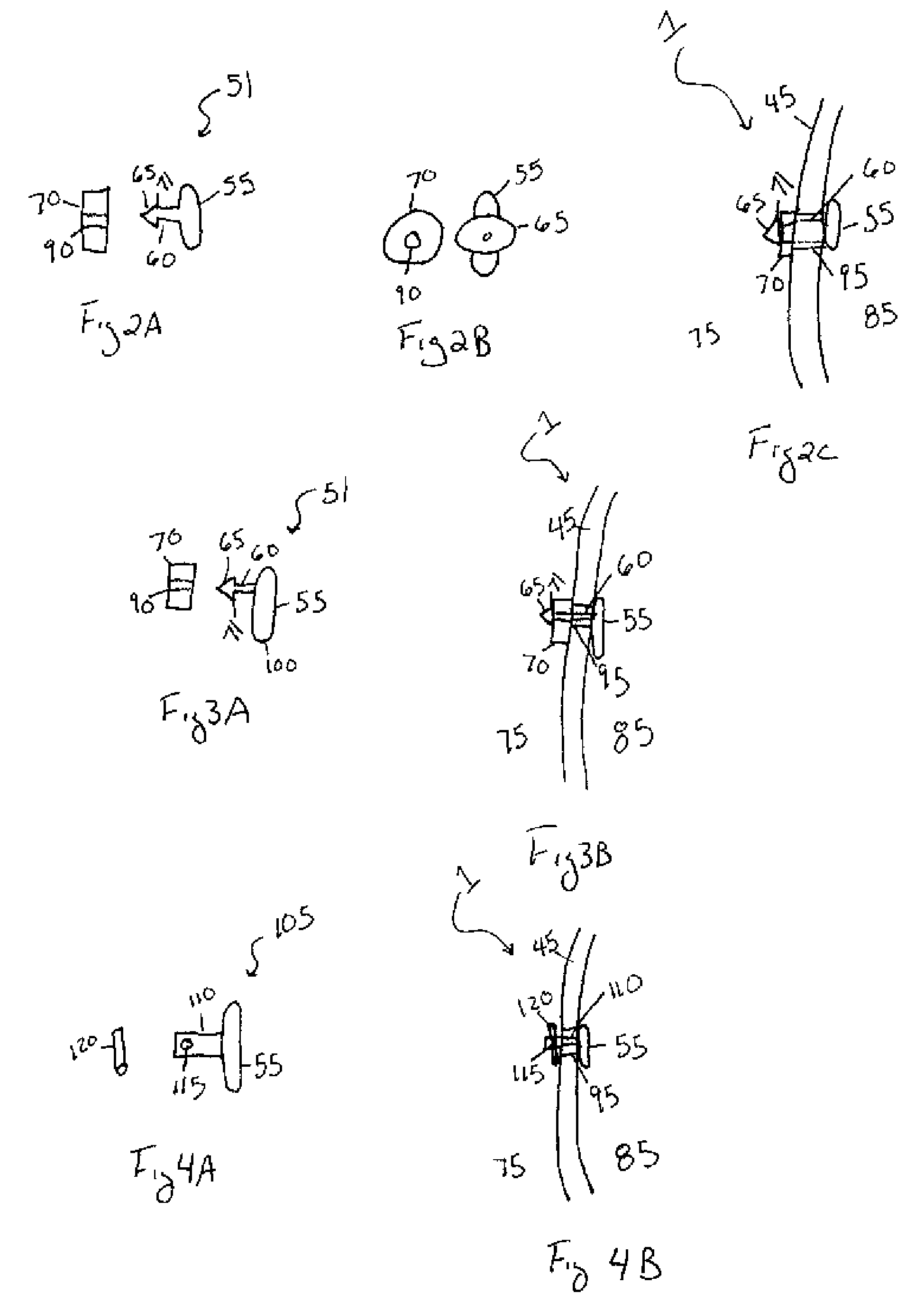Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Synovial joints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
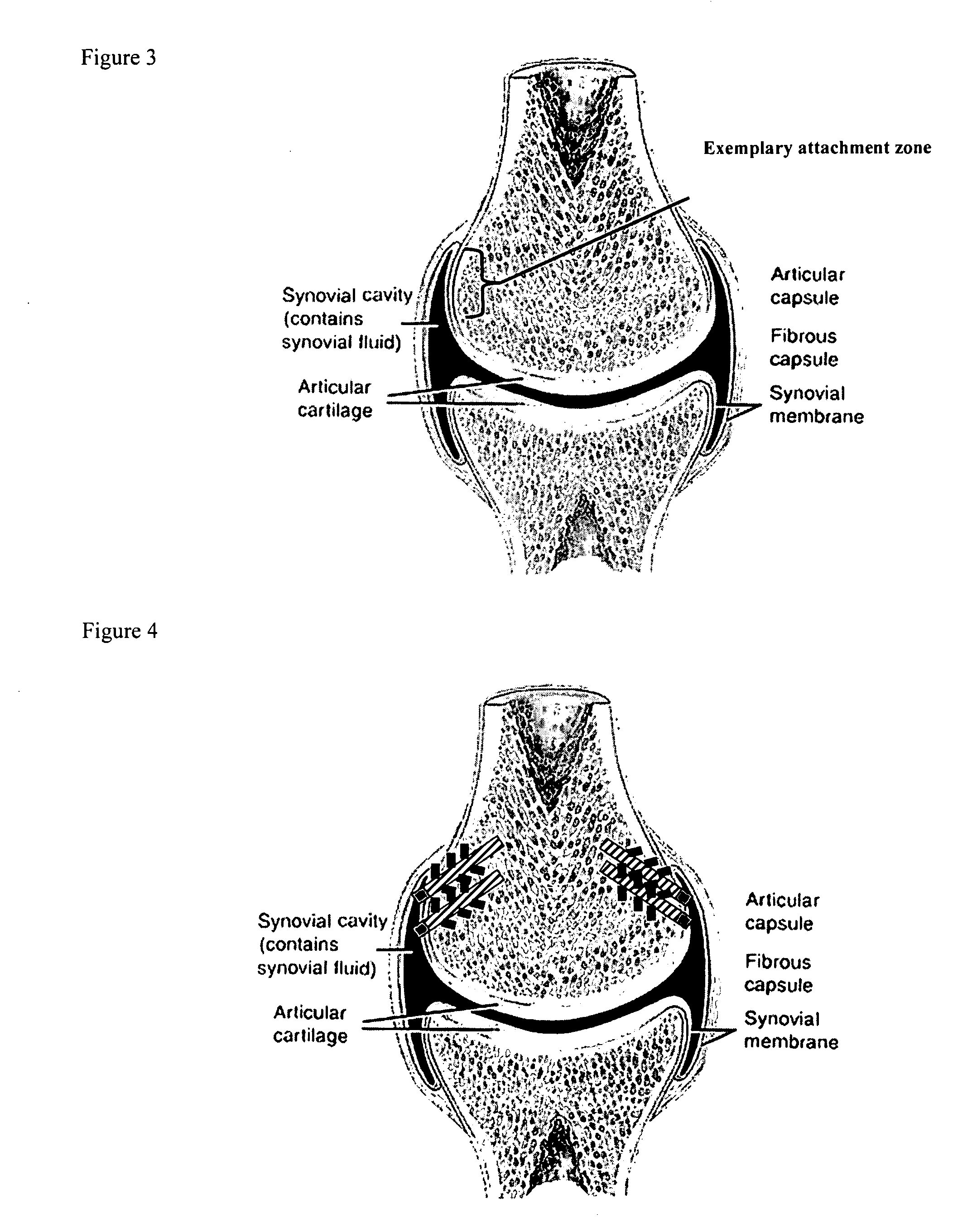
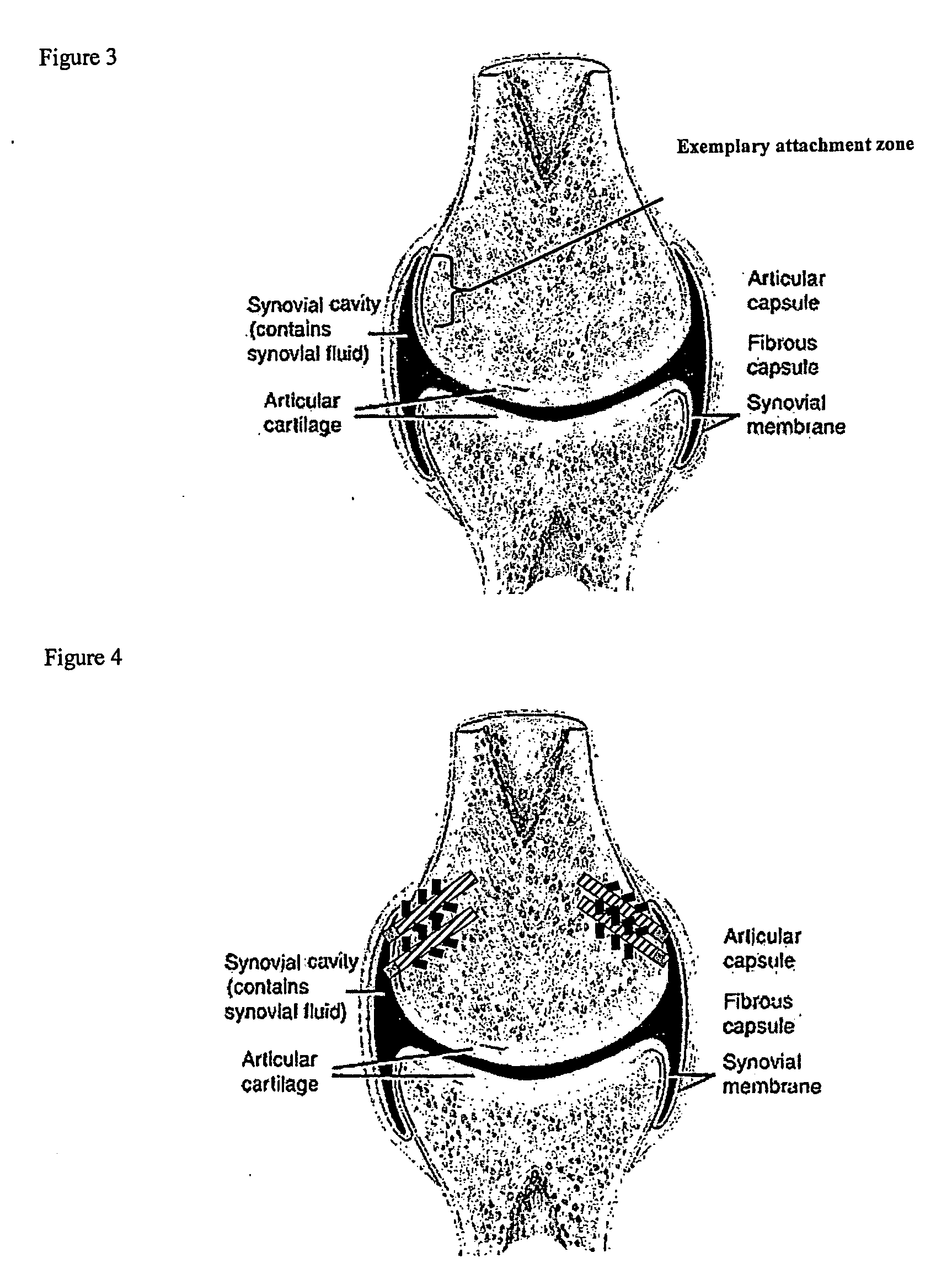
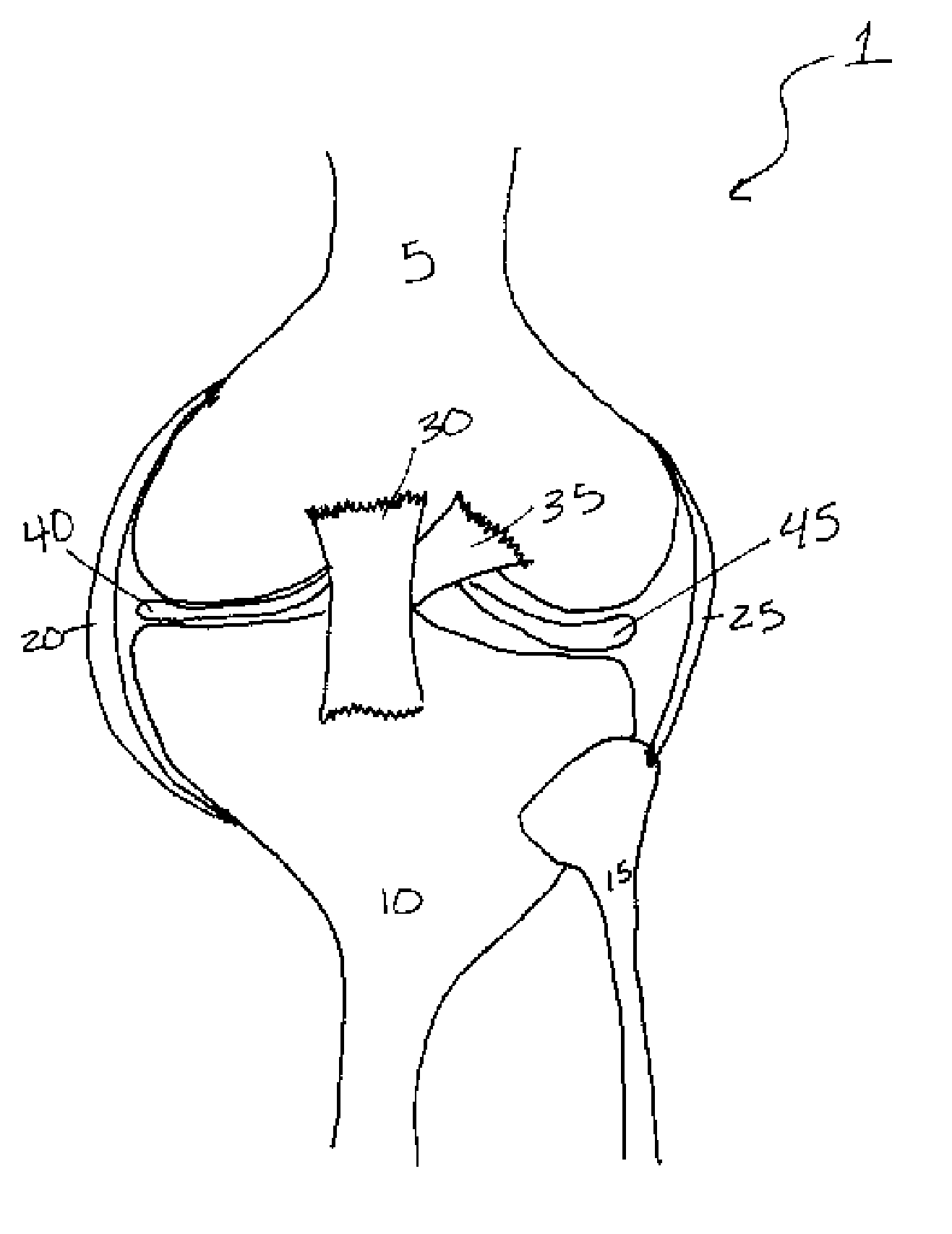
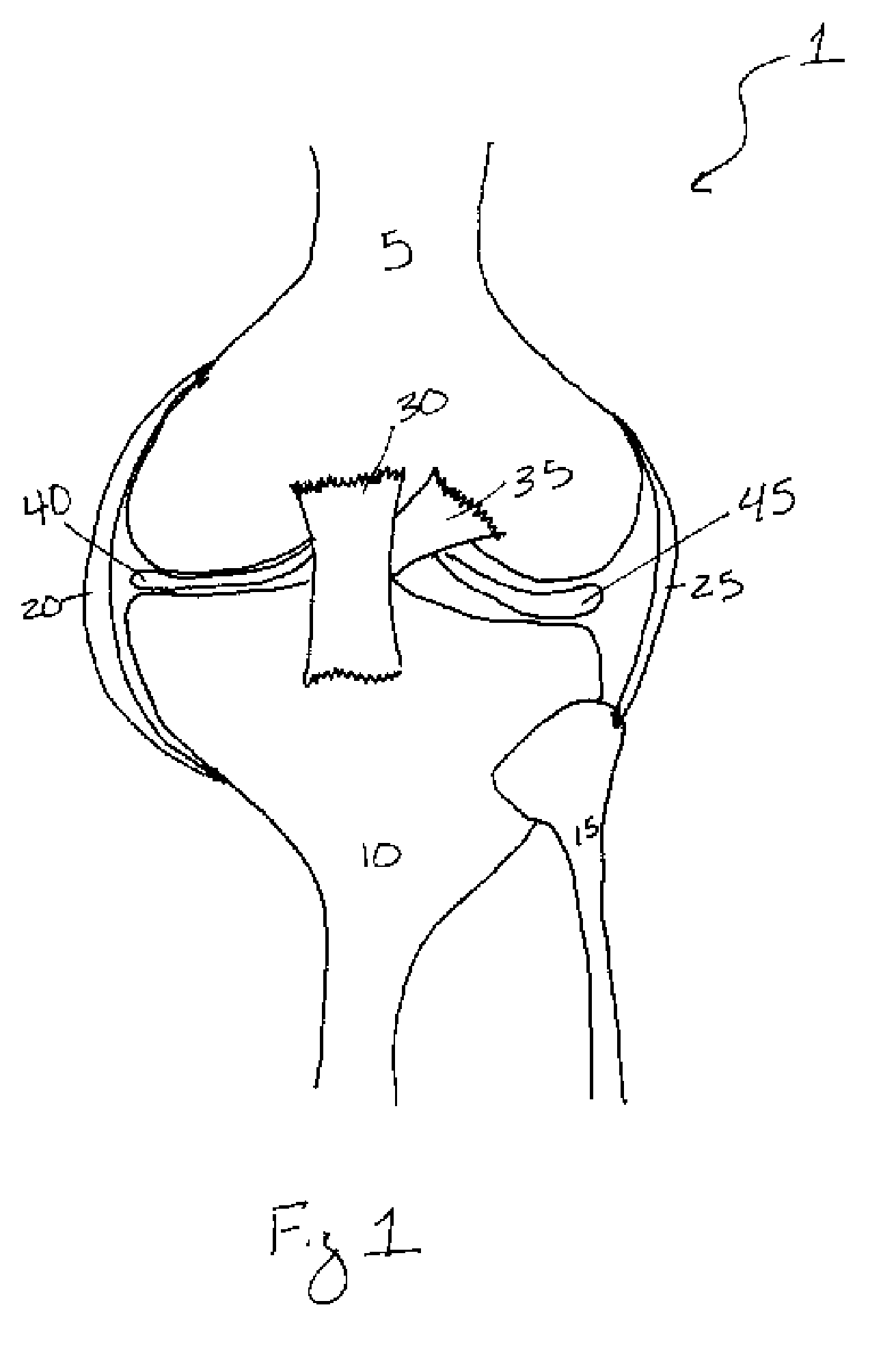
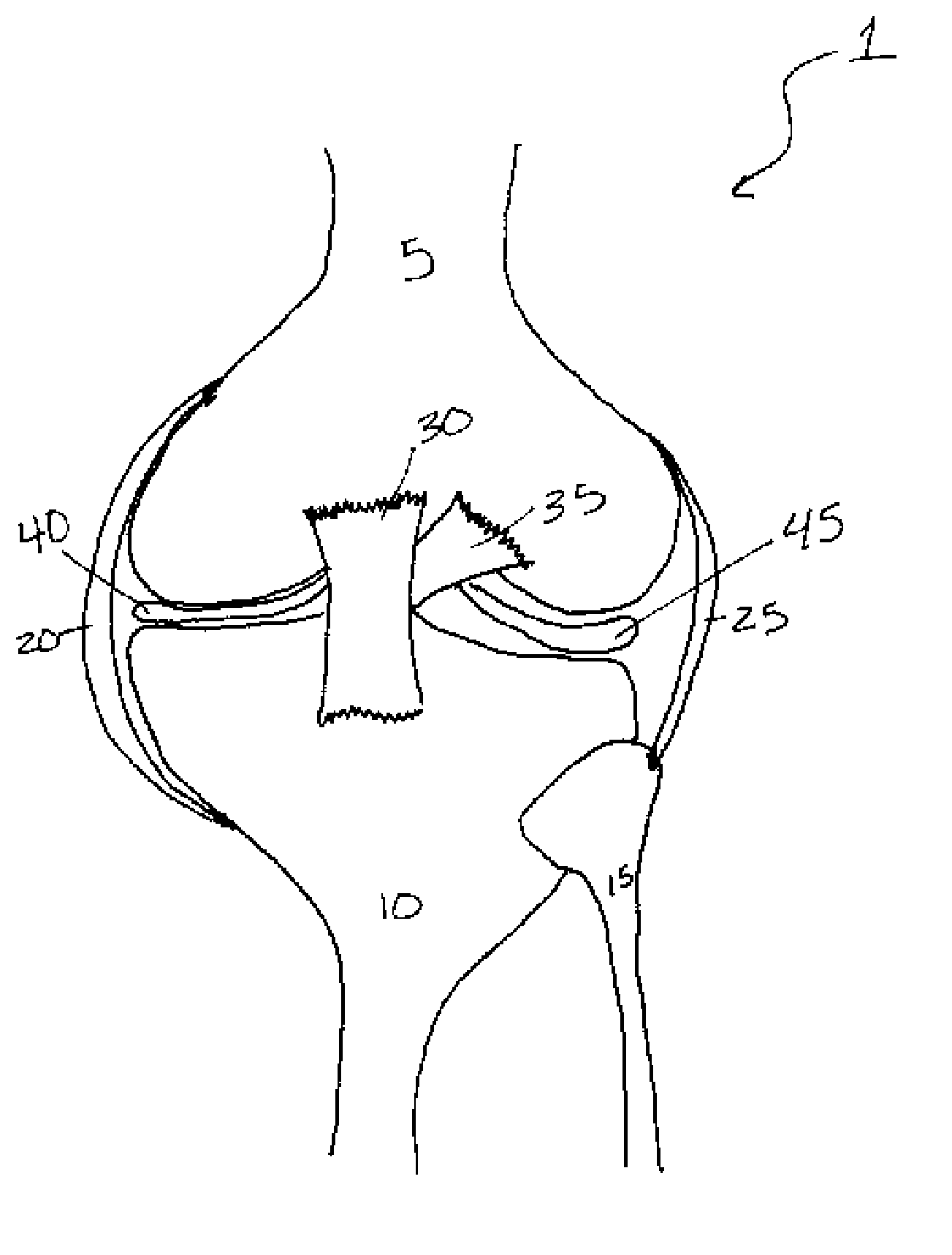
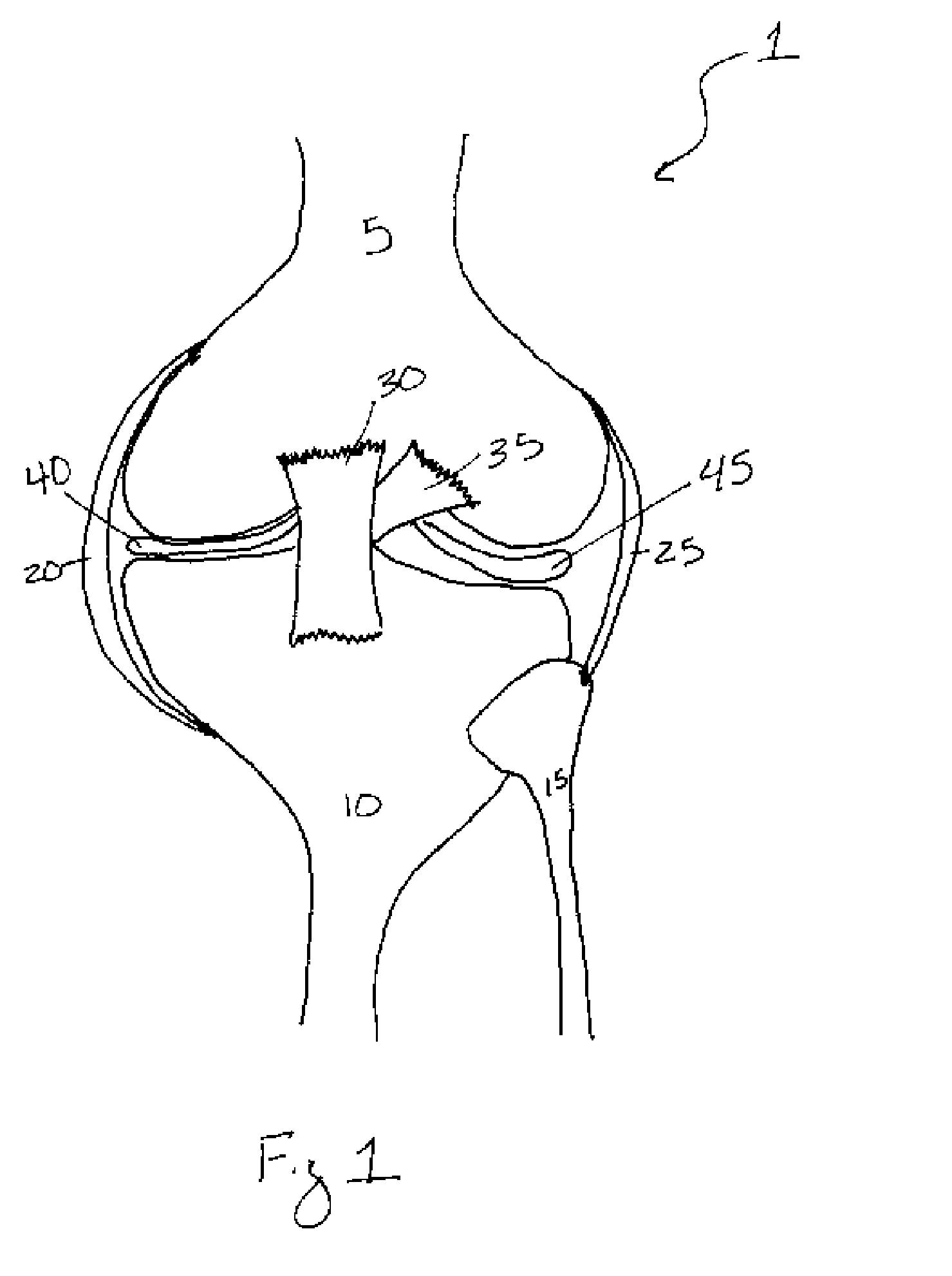
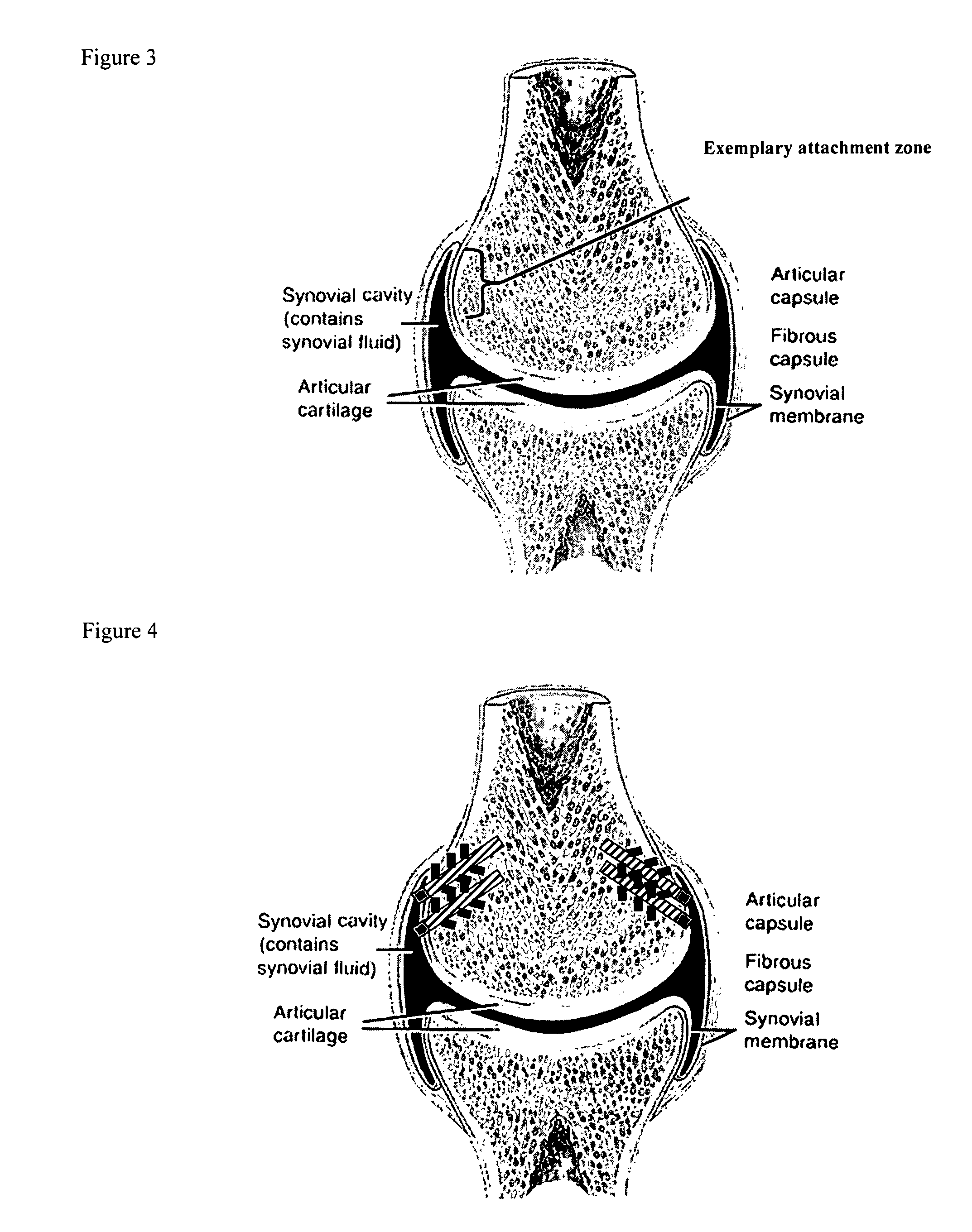
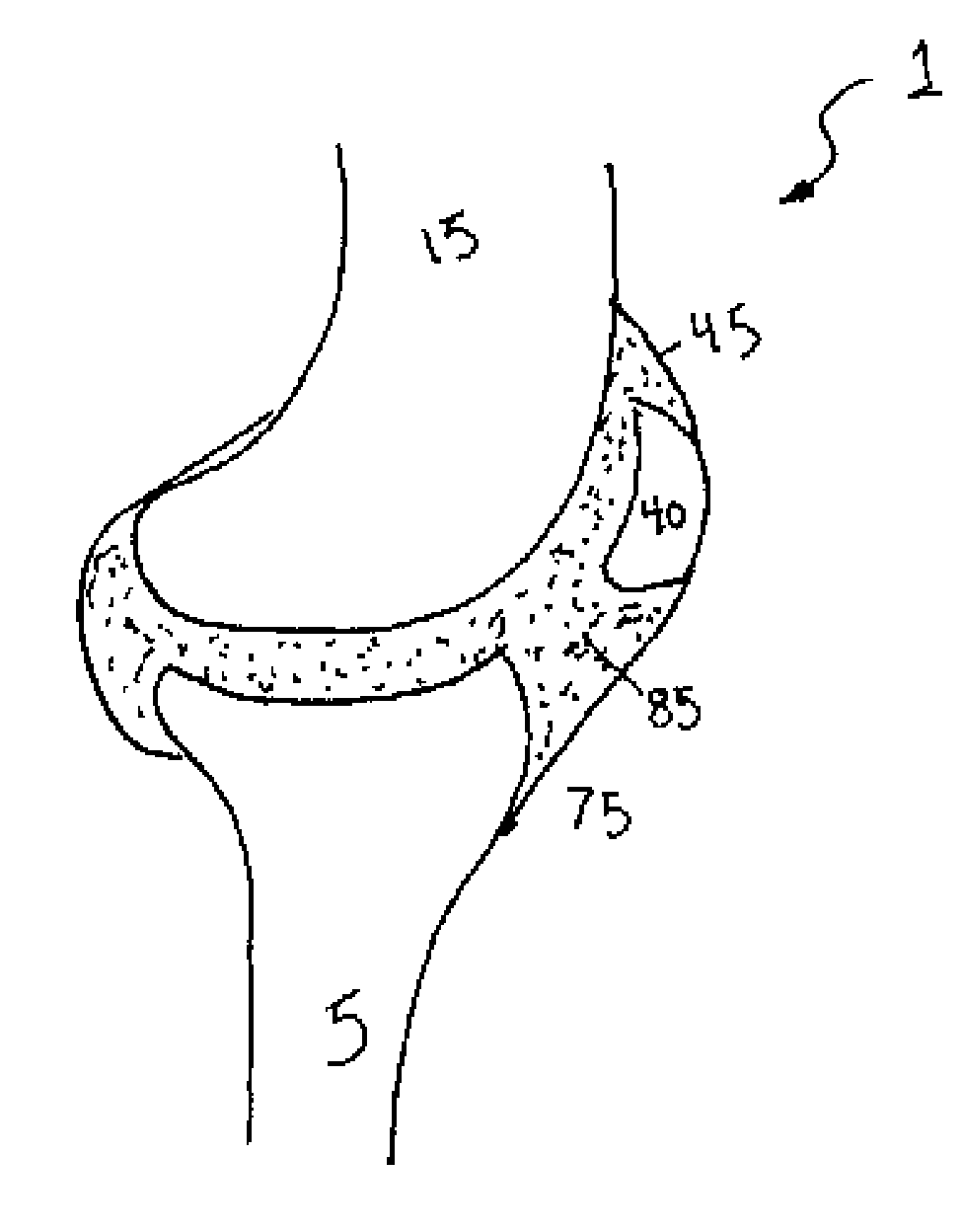
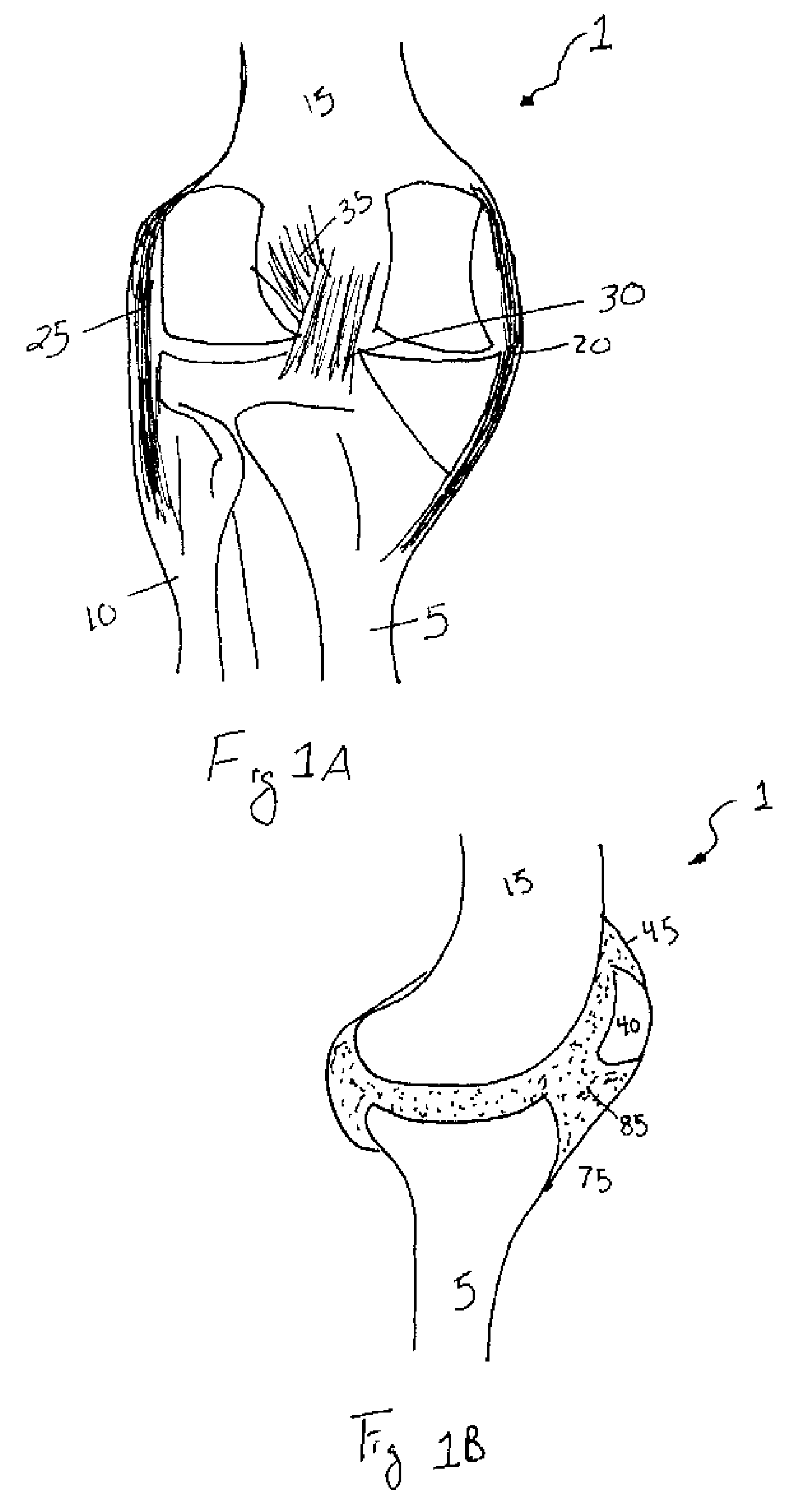
A synovial joint is the most movable and most widespread type of joint throughout the body. It sometimes is referred to as a diarthroses. The term "synovial" refers to the tissue involved in the joint, and "diarthroses" refers to the movement enabled. Some examples of these joints are those found in the wrist, elbow, hip and knee.
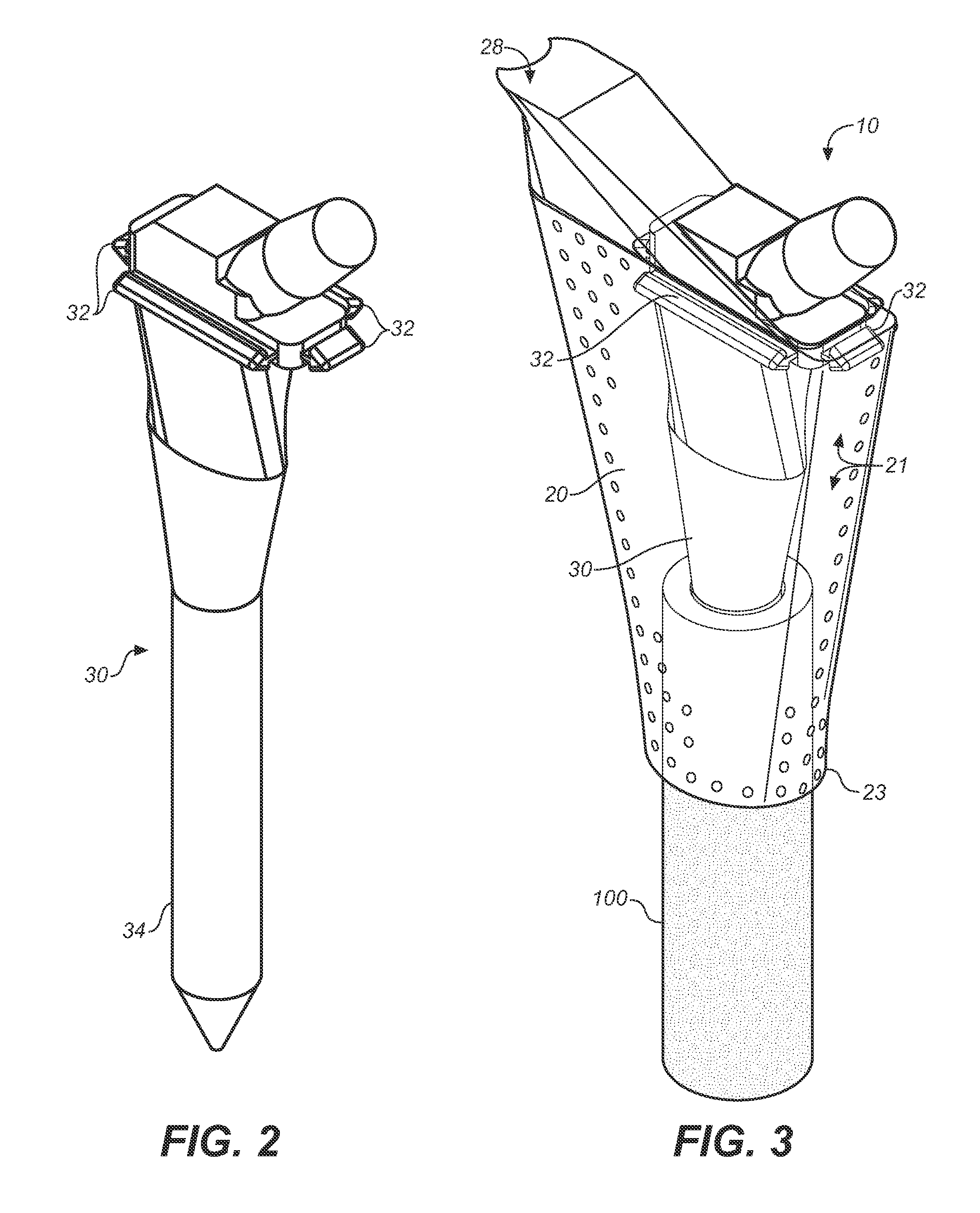
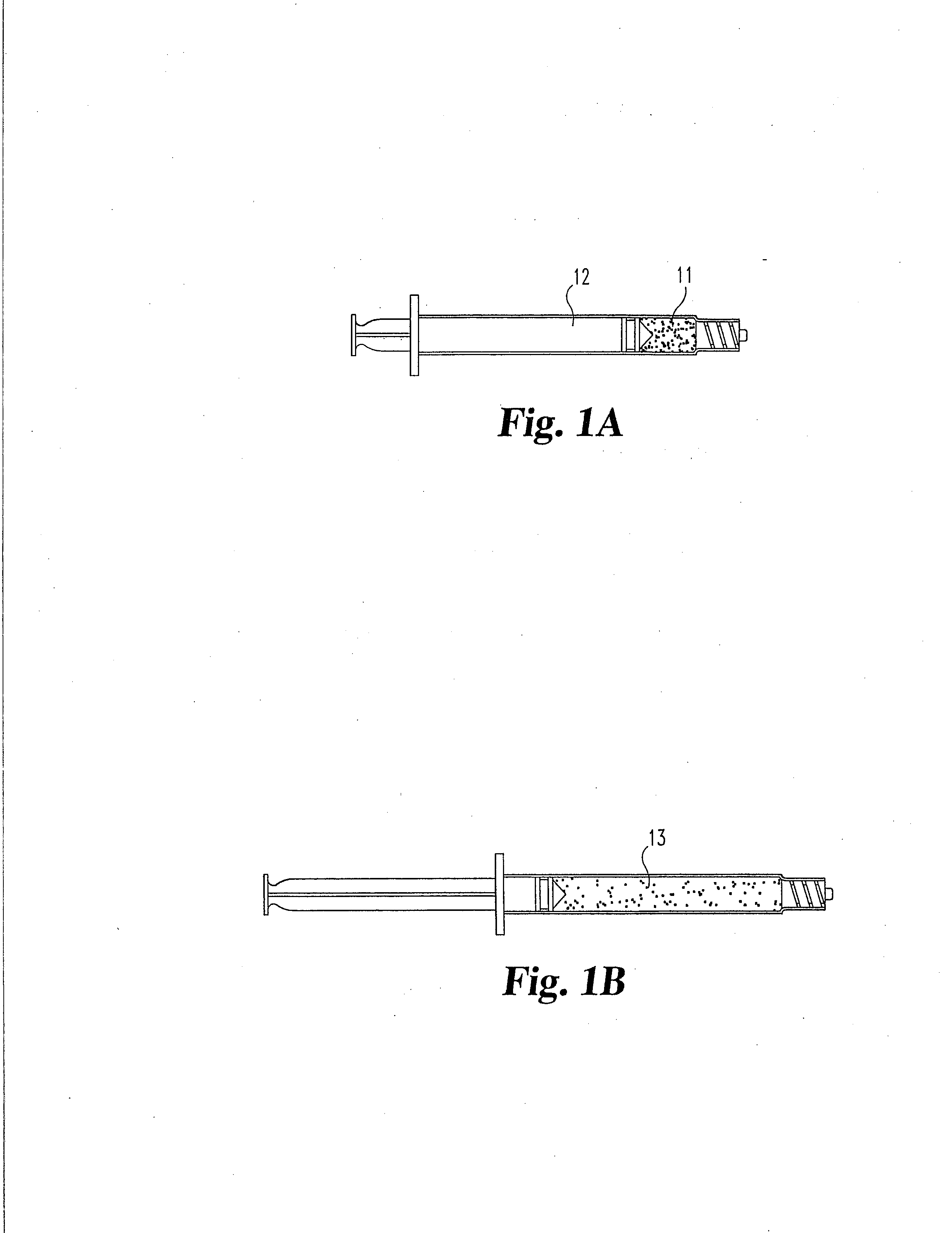
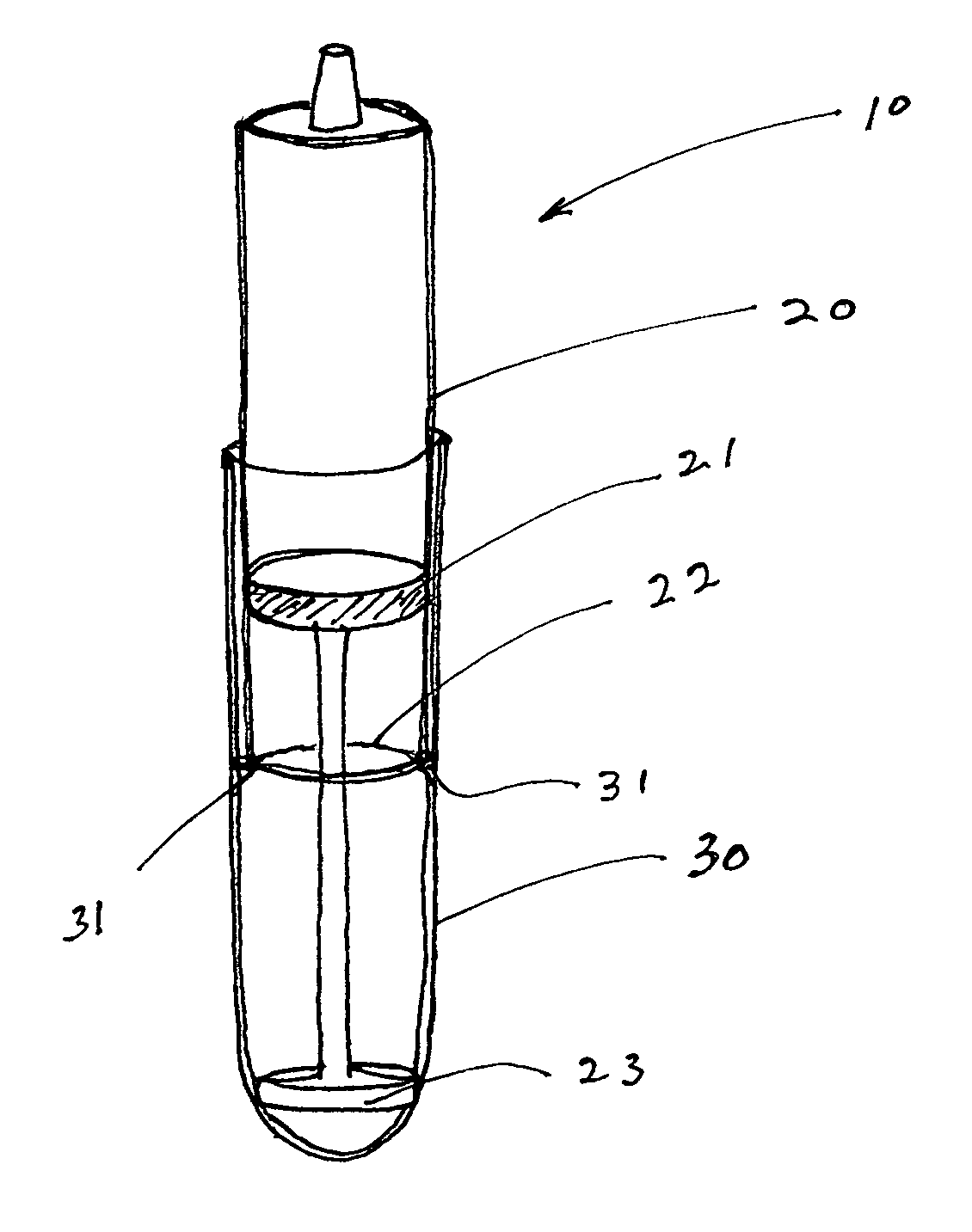
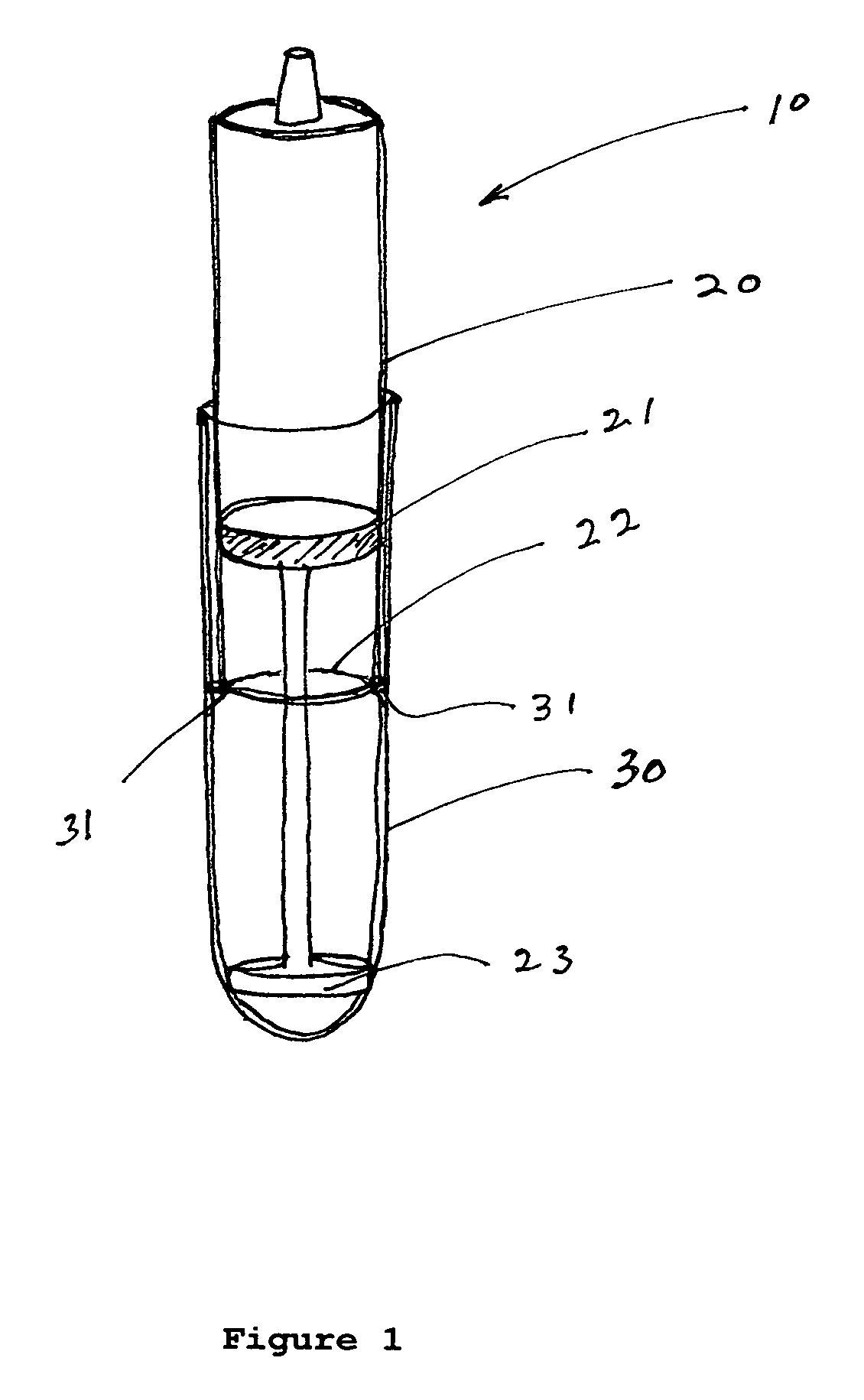
Cartilage repair implant with soft bearing surface and flexible anchoring device
InactiveUS9050192B2Strong and more permanent fixationSoft and bendableJoint implantsHip jointsCartilage repairSurgical implant
A surgical implant for replacing hyaline cartilage in a knee or other articulating synovial joint has an anchoring side on one side of the implant adapted for fixing the implant to one of the bones in the joint, and a bearing surface on the opposite side of the implant for lubricious rubbing and sliding contact with another bone in the joint. The anchoring side can be configured with an irregular surface for tissue ingrowth. The bearing side can include hydrogel. The implant can be rolled up from an original shape and surgically inserted by arthroscopic means, and opens into its original shape when released inside the joint.
Owner:FORMAE
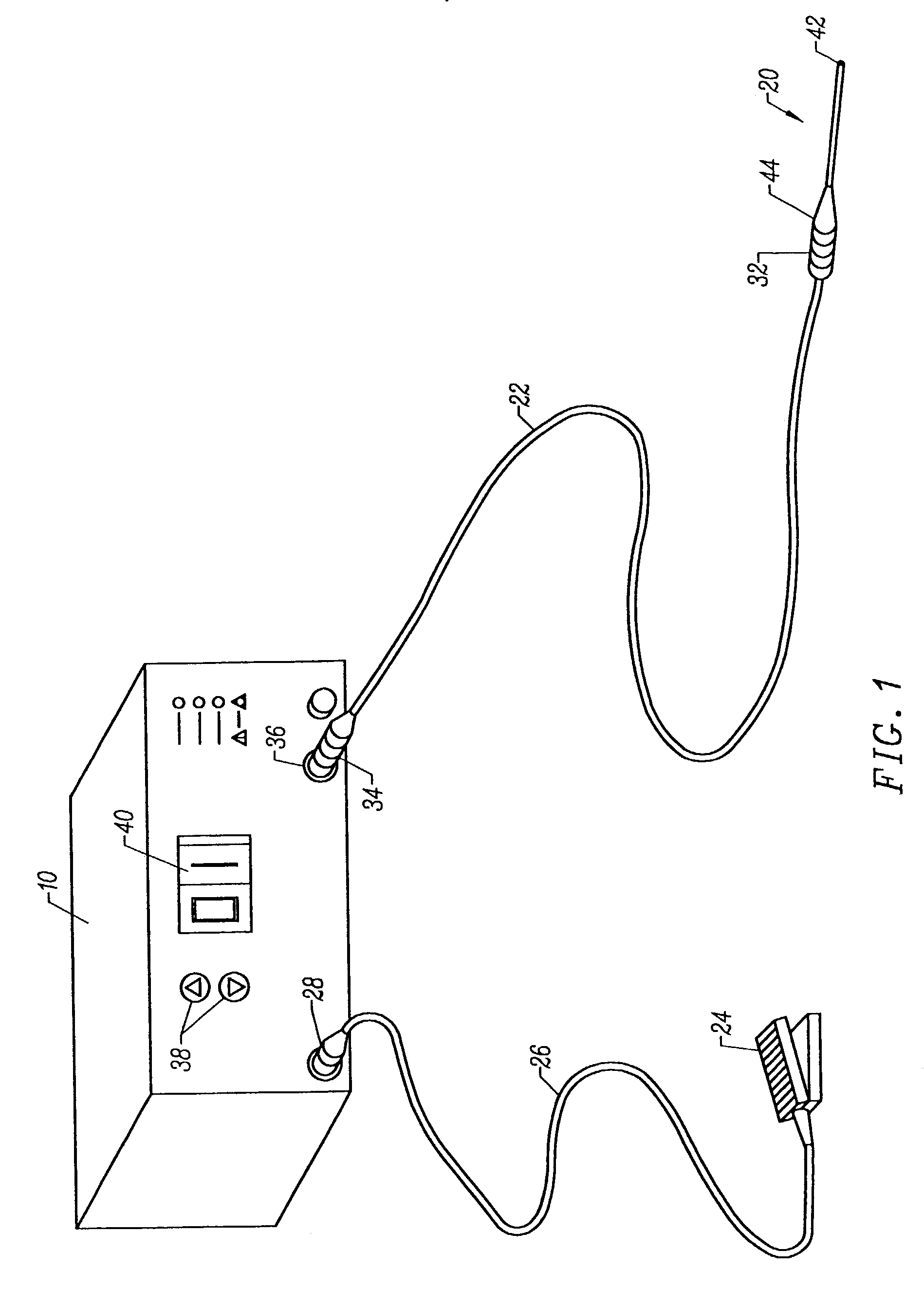
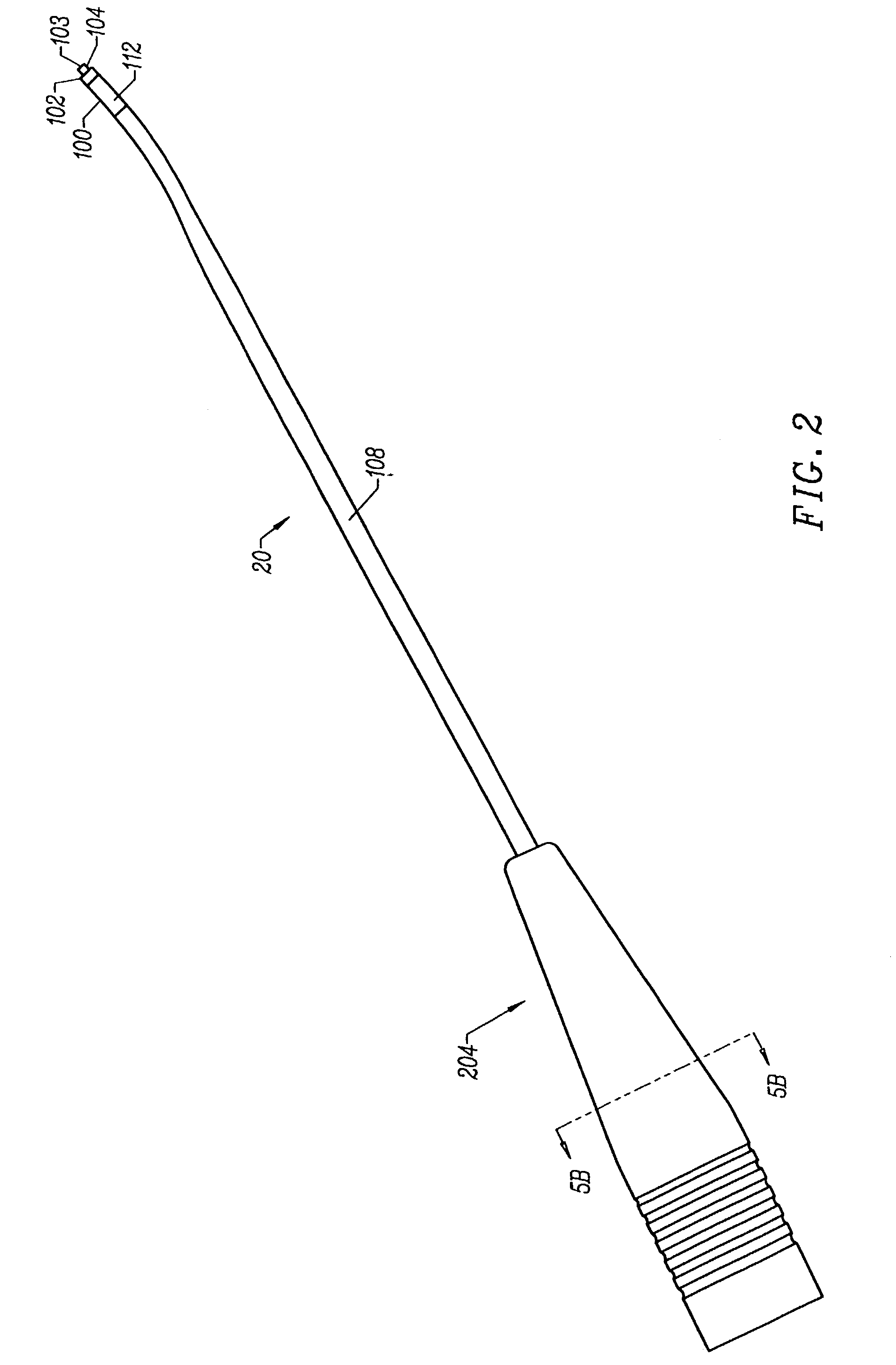
Electrosurgical probe having circular electrode array for ablating joint tissue and systems related thereto
InactiveUS6991631B2Low aspiration rateIncrease inhalation rateSurgical instruments for heatingTherapyMeniscal tissueElectrode array
Electrosurgical methods, systems, and apparatus for the controlled ablation of tissue from a target site, such as a synovial joint, of a patient. An electrosurgical probe of the invention includes a shaft, and a working end having an electrode array comprising an outer circular arrangement of active electrode terminals and an inner circular arrangement of active electrode terminals. The electrode array is adapted for the controlled ablation of hard tissue, such as meniscus tissue. The working end of the probe is curved to facilitate access to both medial meniscus and lateral meniscus from a portal of 1 cm. or less.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Synovial fluid barrier
InactiveUS20060178743A1Improve regenerative healingImprove responseSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSynovial jointsSacroiliac joint
A composite tissue formed in situ is provided. The composite tissue includes a synovial joint tissue; and a barrier material adhered thereto for sealing the synovial joint tissue against synovial fluid. Also provided is a method for regenerating synovial joint tissue in situ by excluding synovial fluid therefrom. The method includes providing a synovial joint tissue having a defect; and placing a barrier material in intimate contact with the defect for sealing the defect against synovial fluid. The barrier material includes a curable protein copolymer. The method further includes curing the protein copolymer in situ. The barrier material can include a crosslinked network, or a self gelled network of repeating elastin-like and fibroin-like polymer chains.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
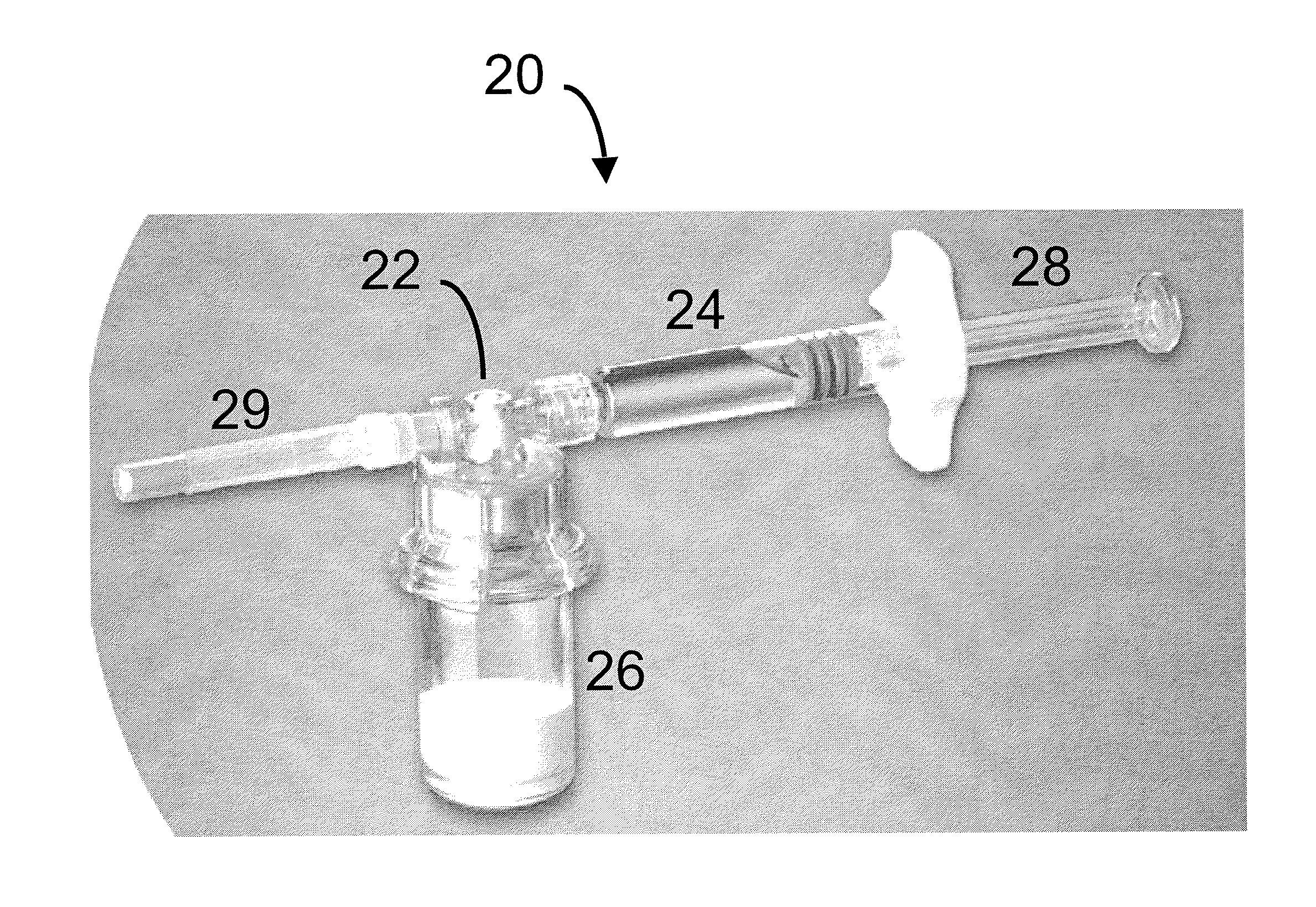
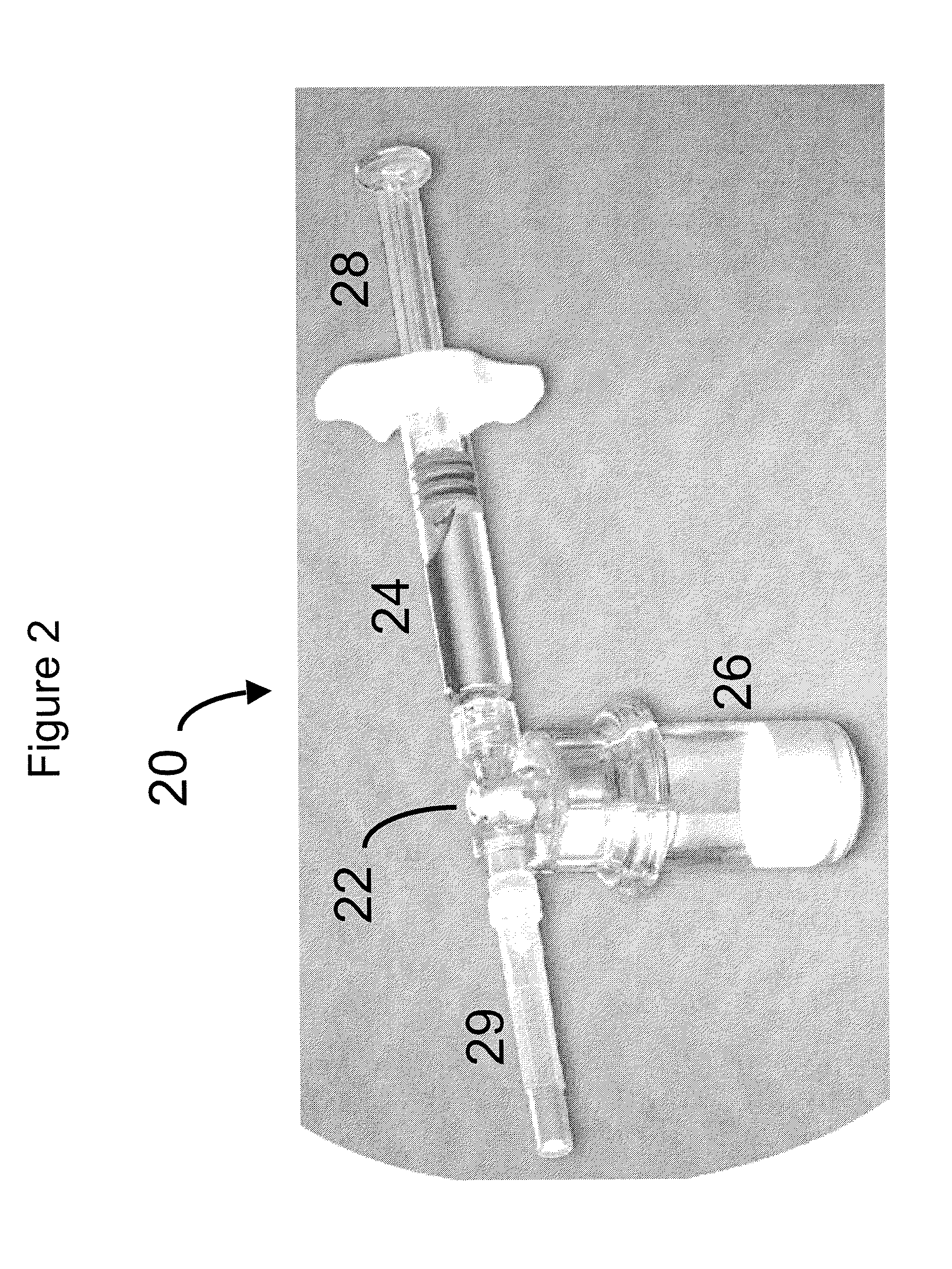
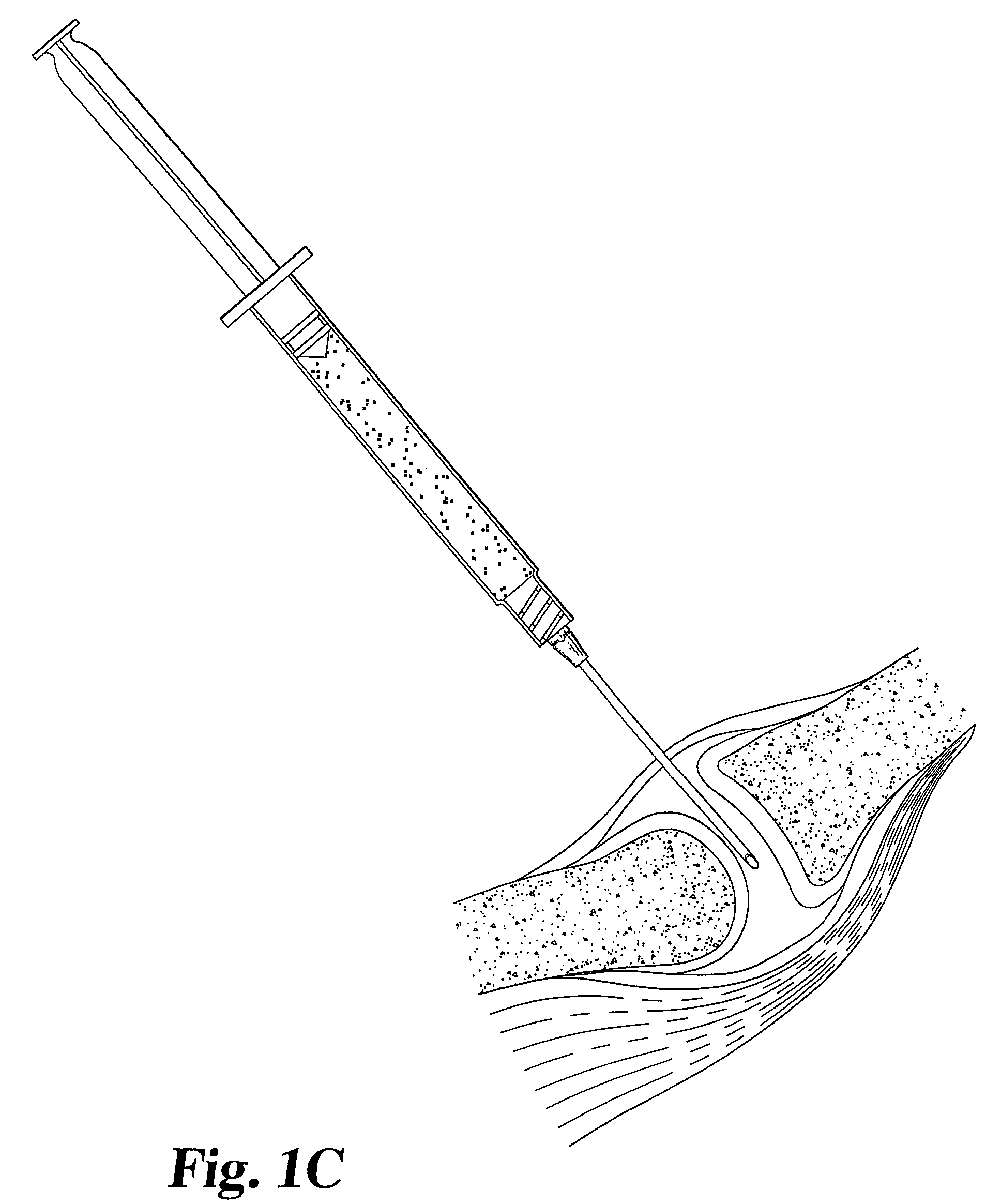
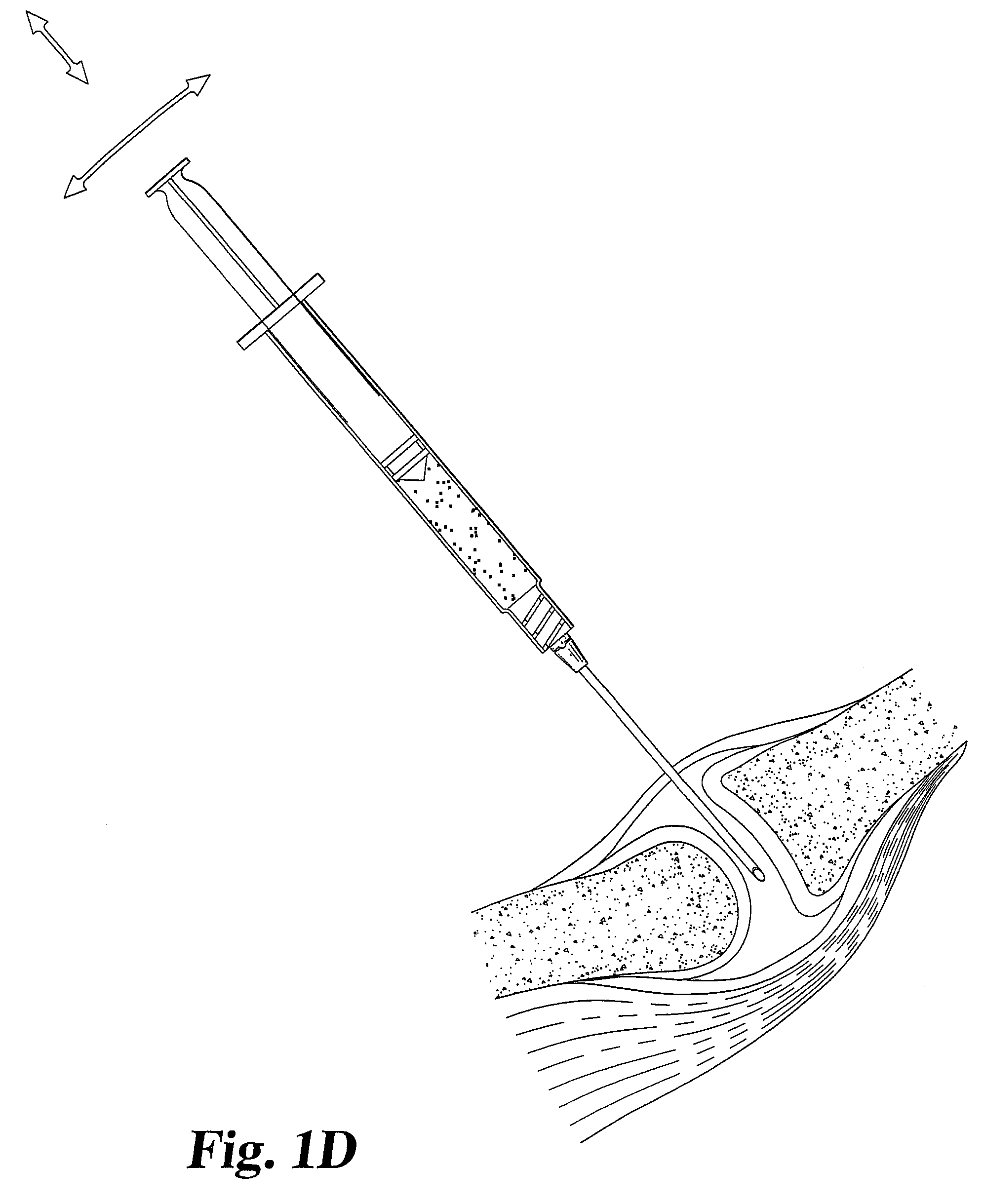
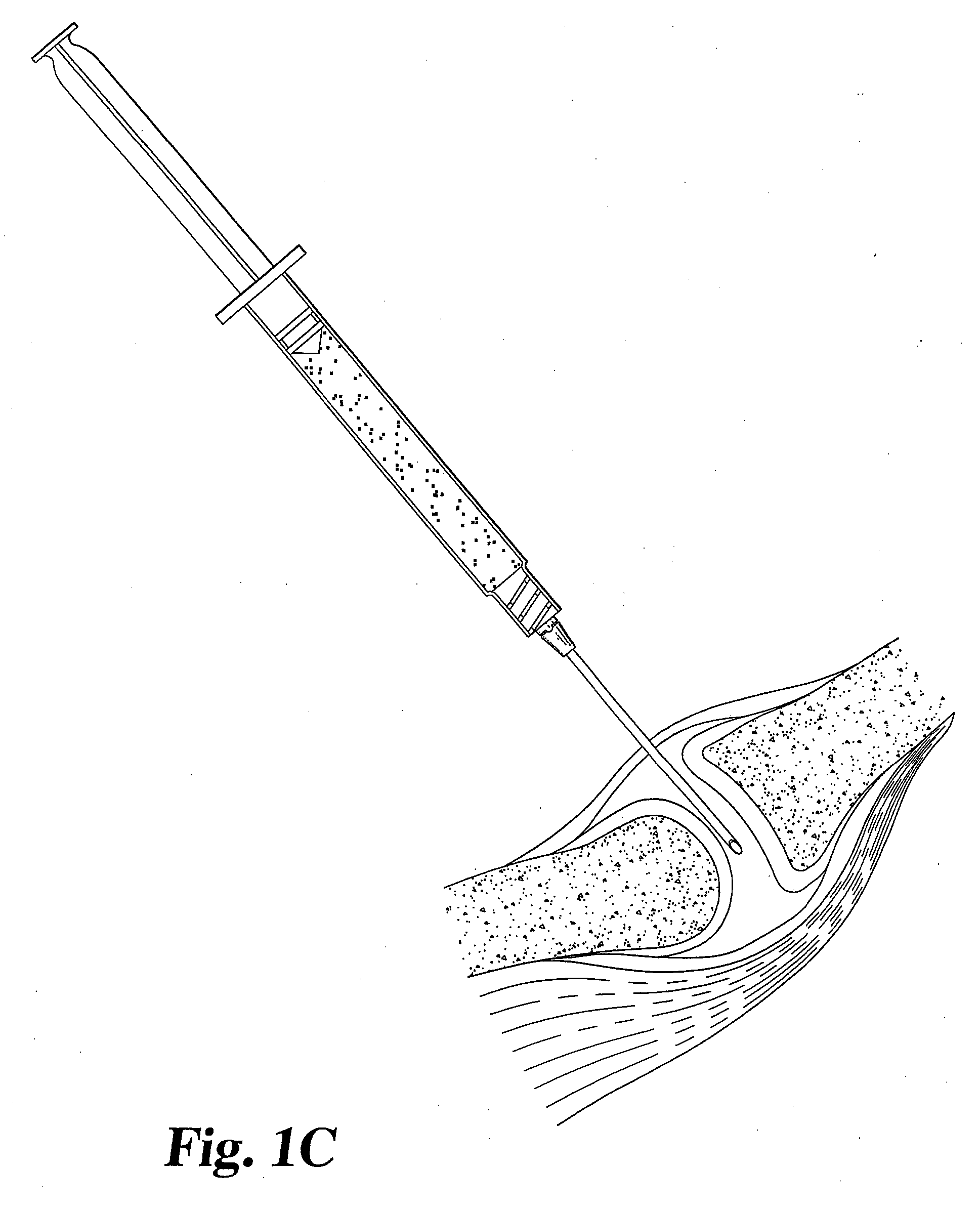
Drug delivery to a joint
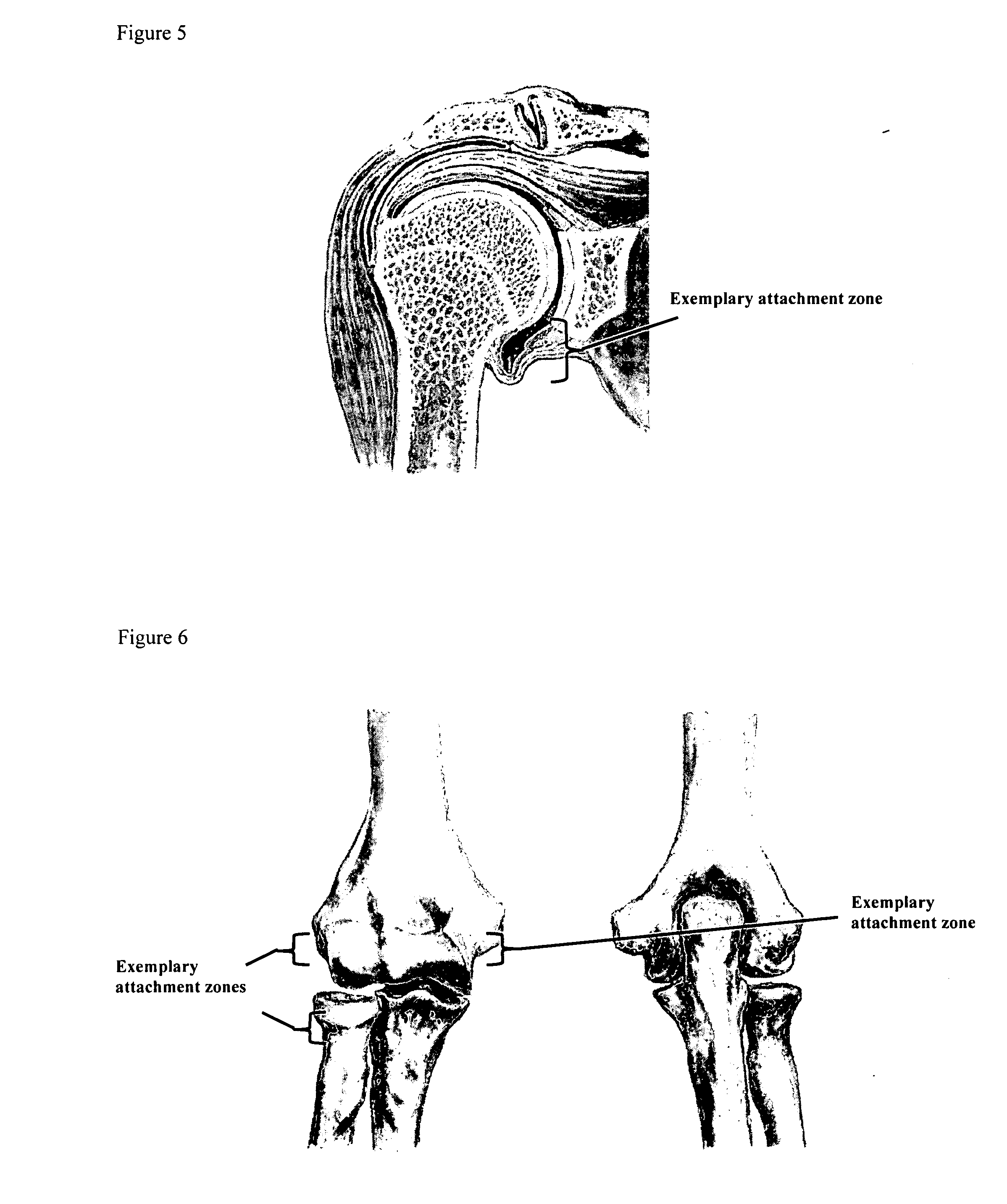
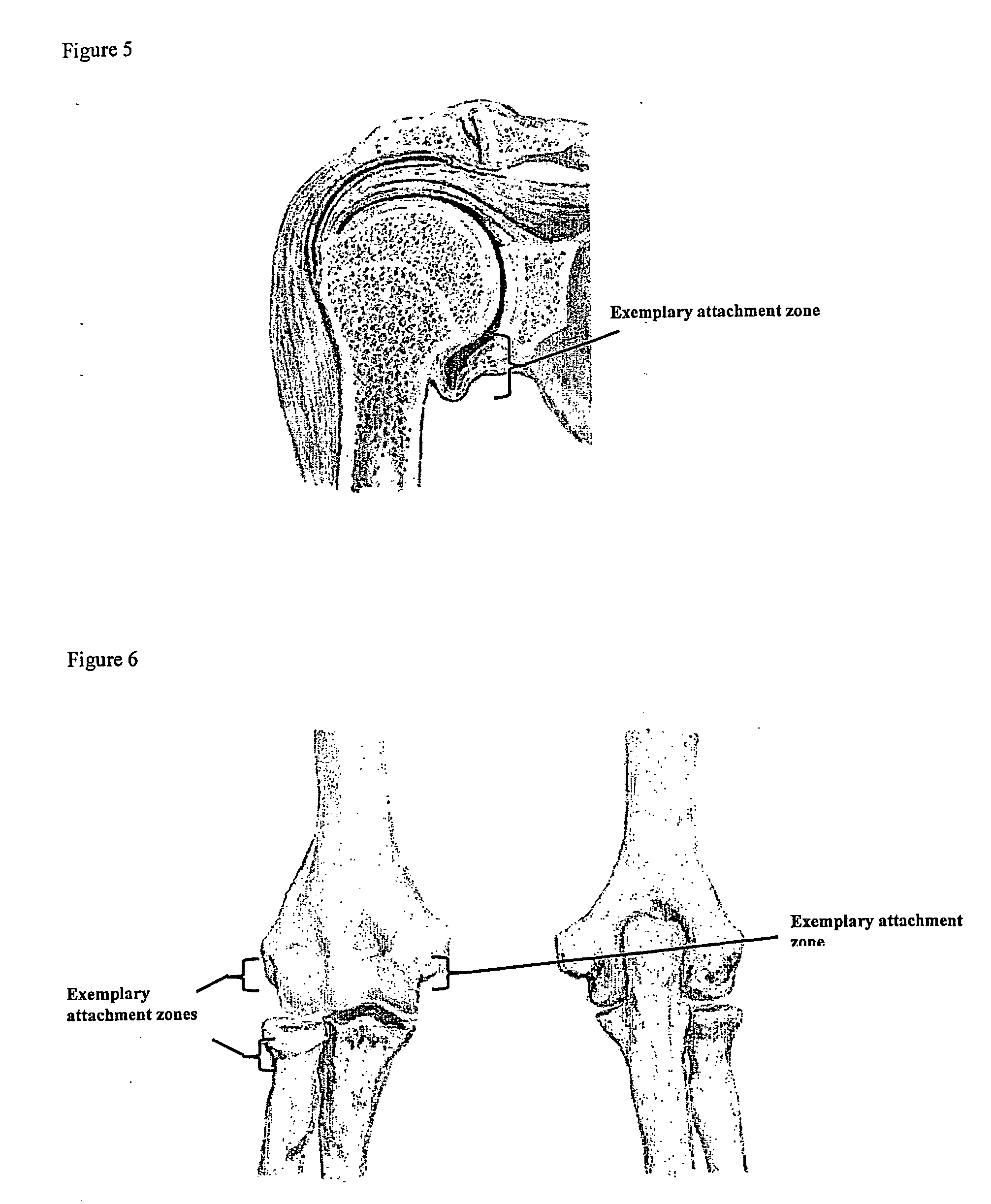
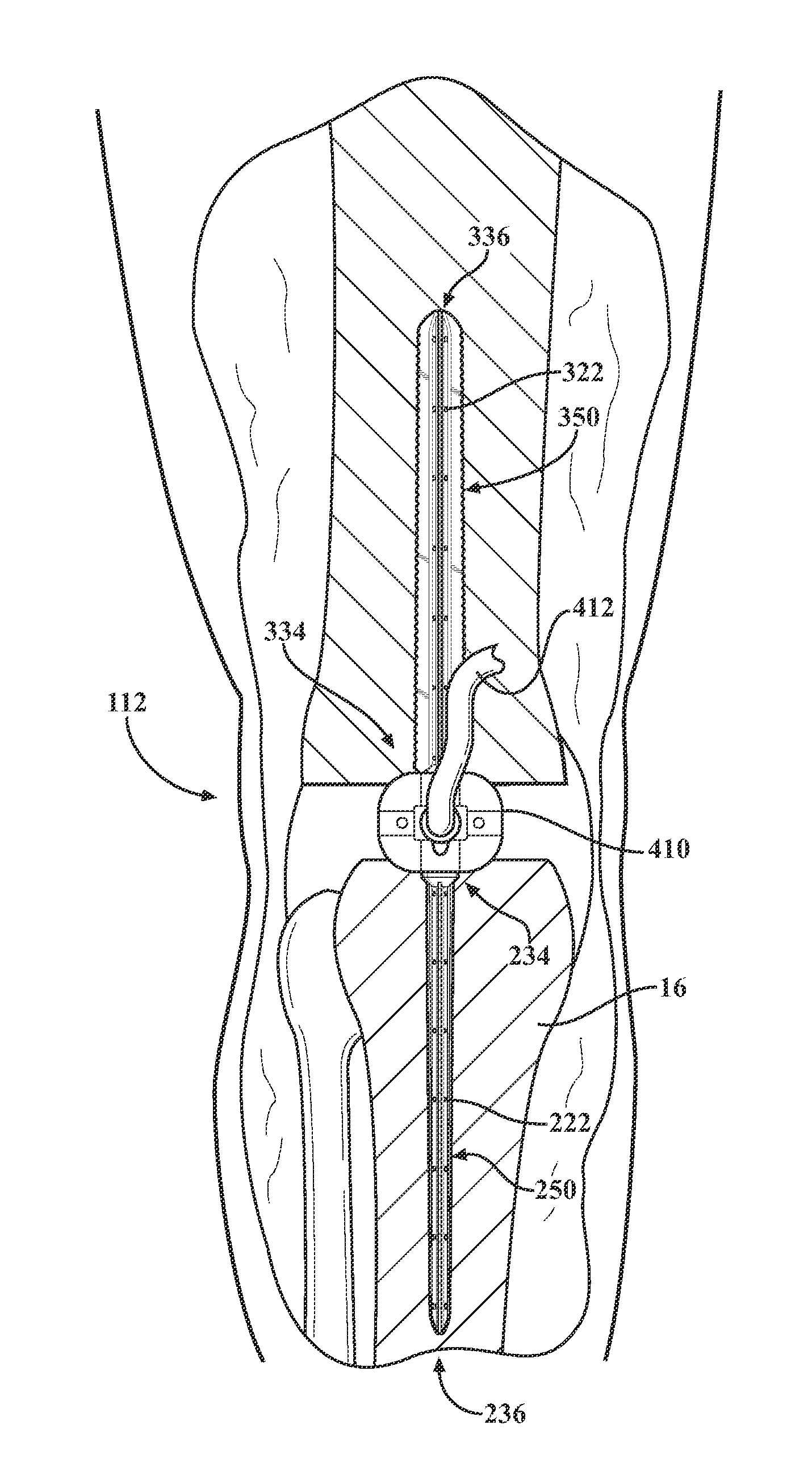
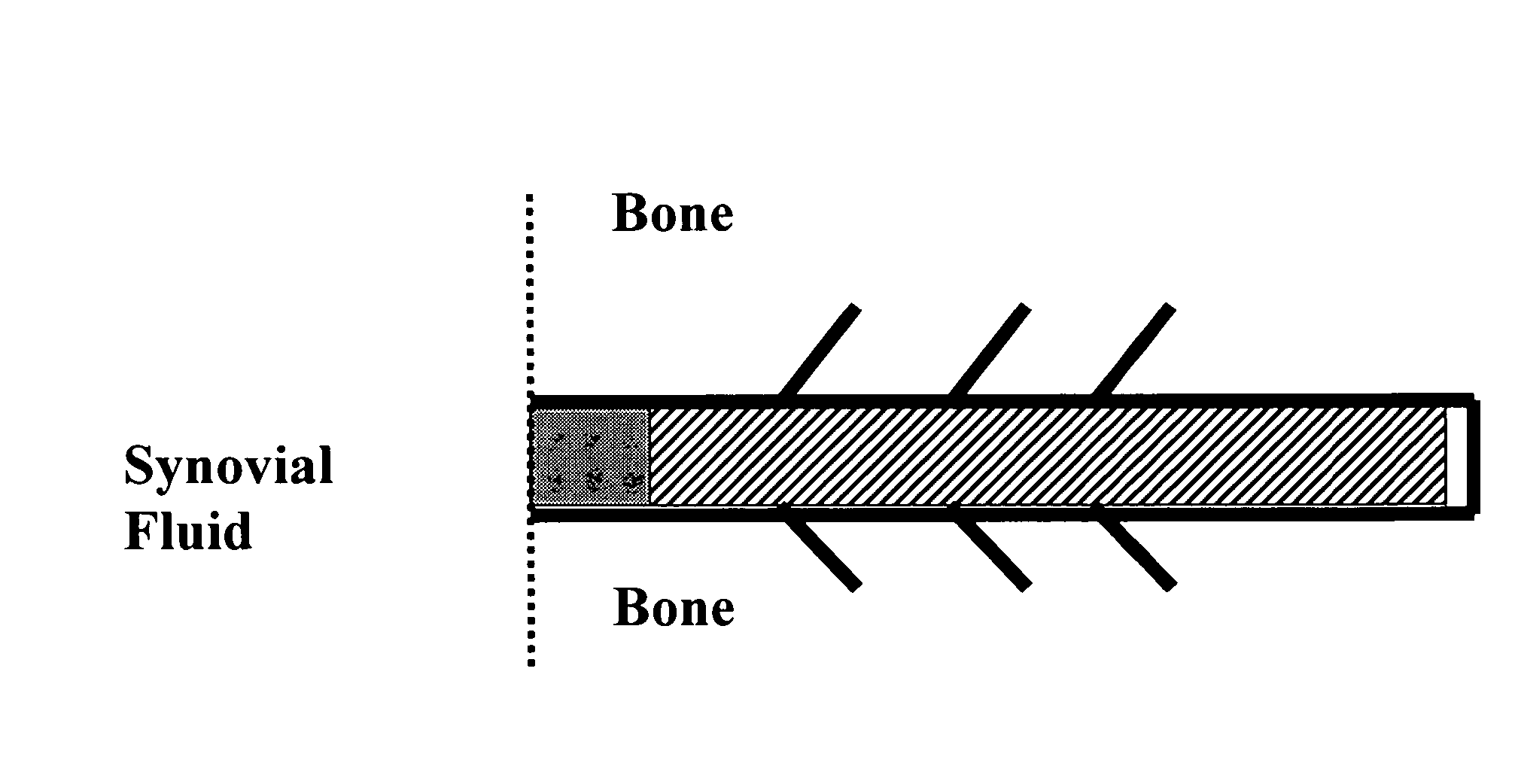
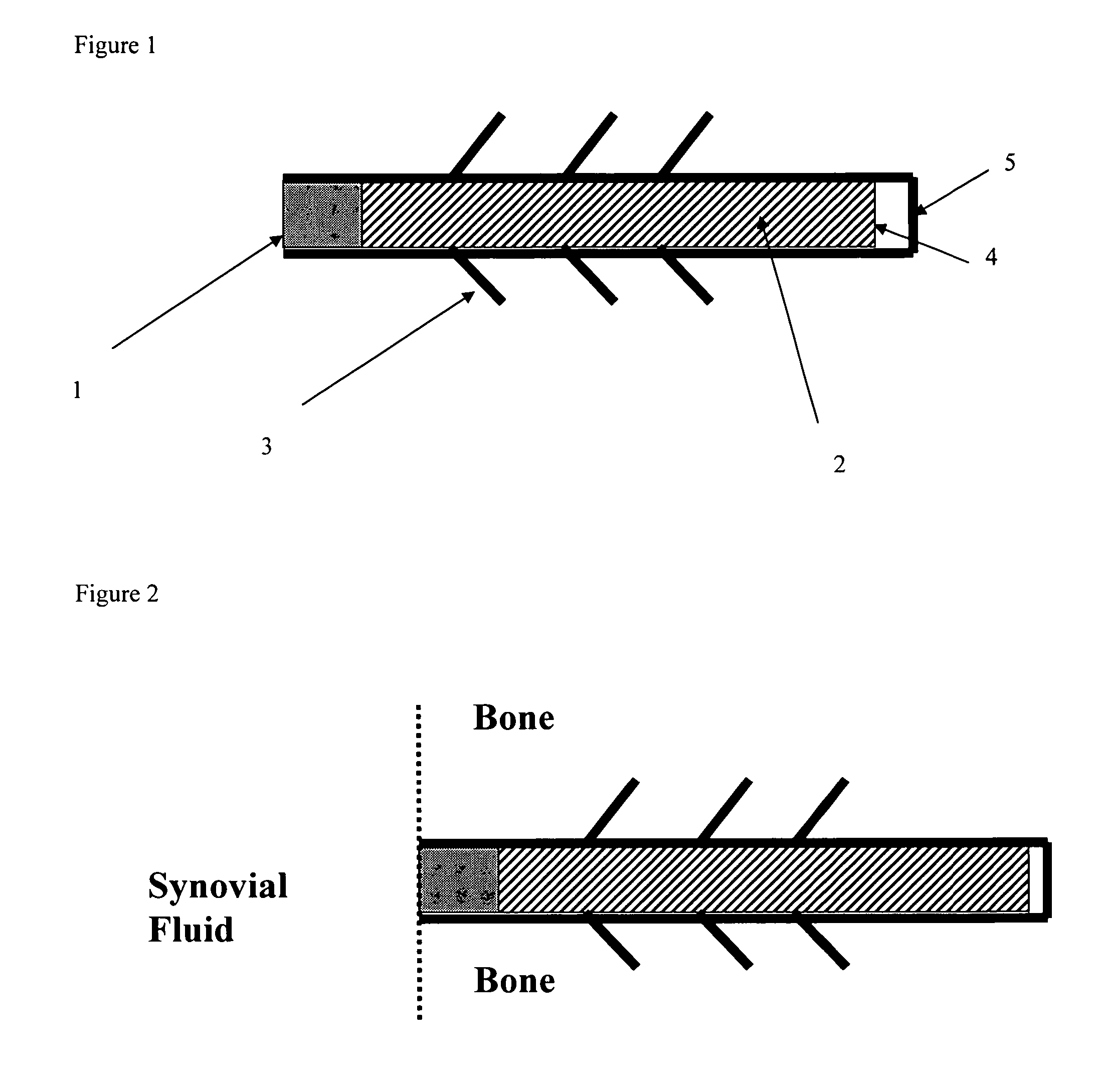
A method of intra-articular drug delivery may include selecting an attachment zone in a synovial joint; affixing a drug release device in the attachment zone, the drug release device comprising a base affixable in the attachment zone, a sustained-release drug carrier, and a drug, the device positioned so that the device releases the drug into the synovial fluid of the synovial joint, and so that agitation of the synovial fluid facilitates elution of the drug from the drug release device.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
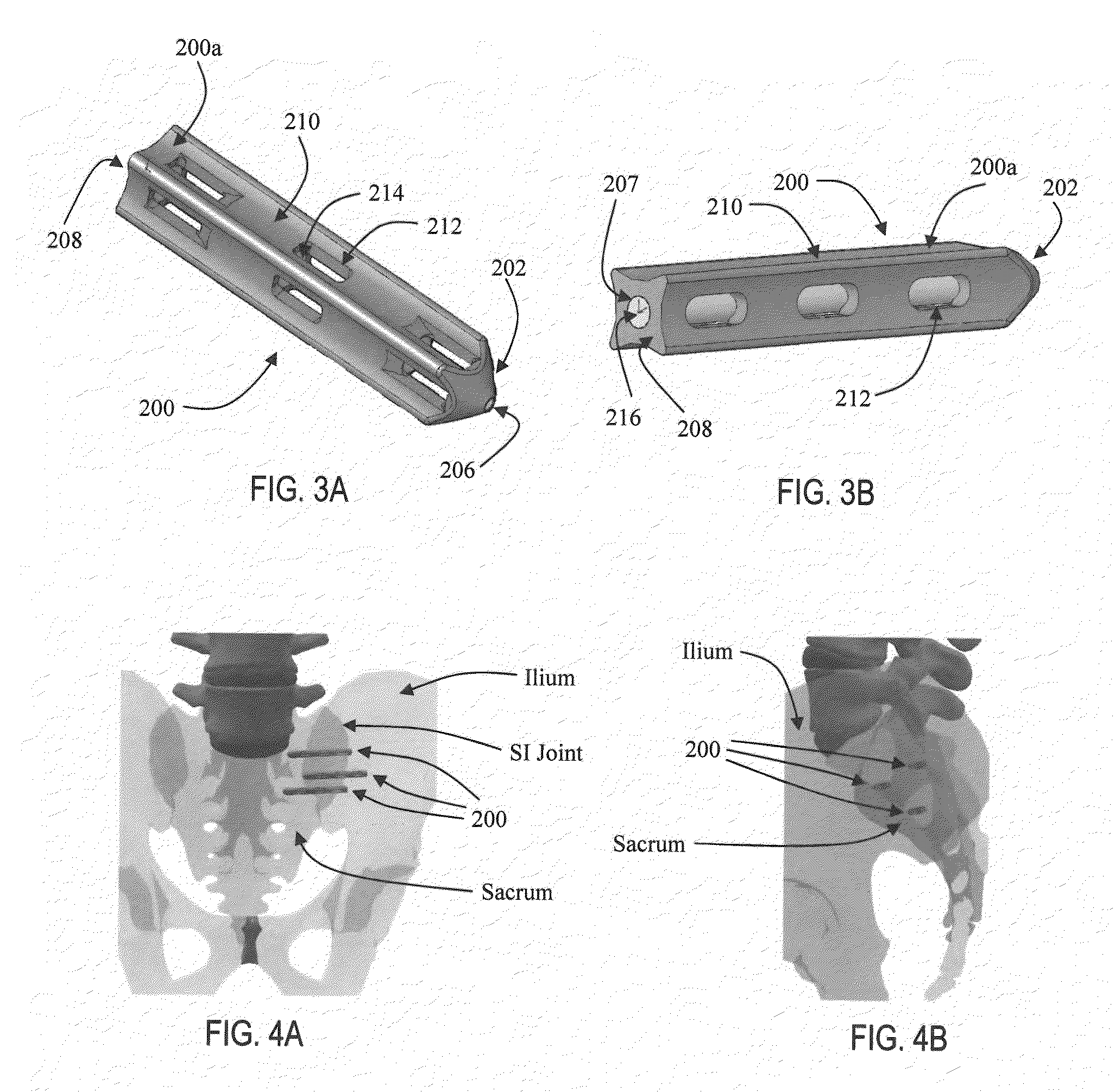
Apparatus and methods for immobilization and fusion of a synovial joint
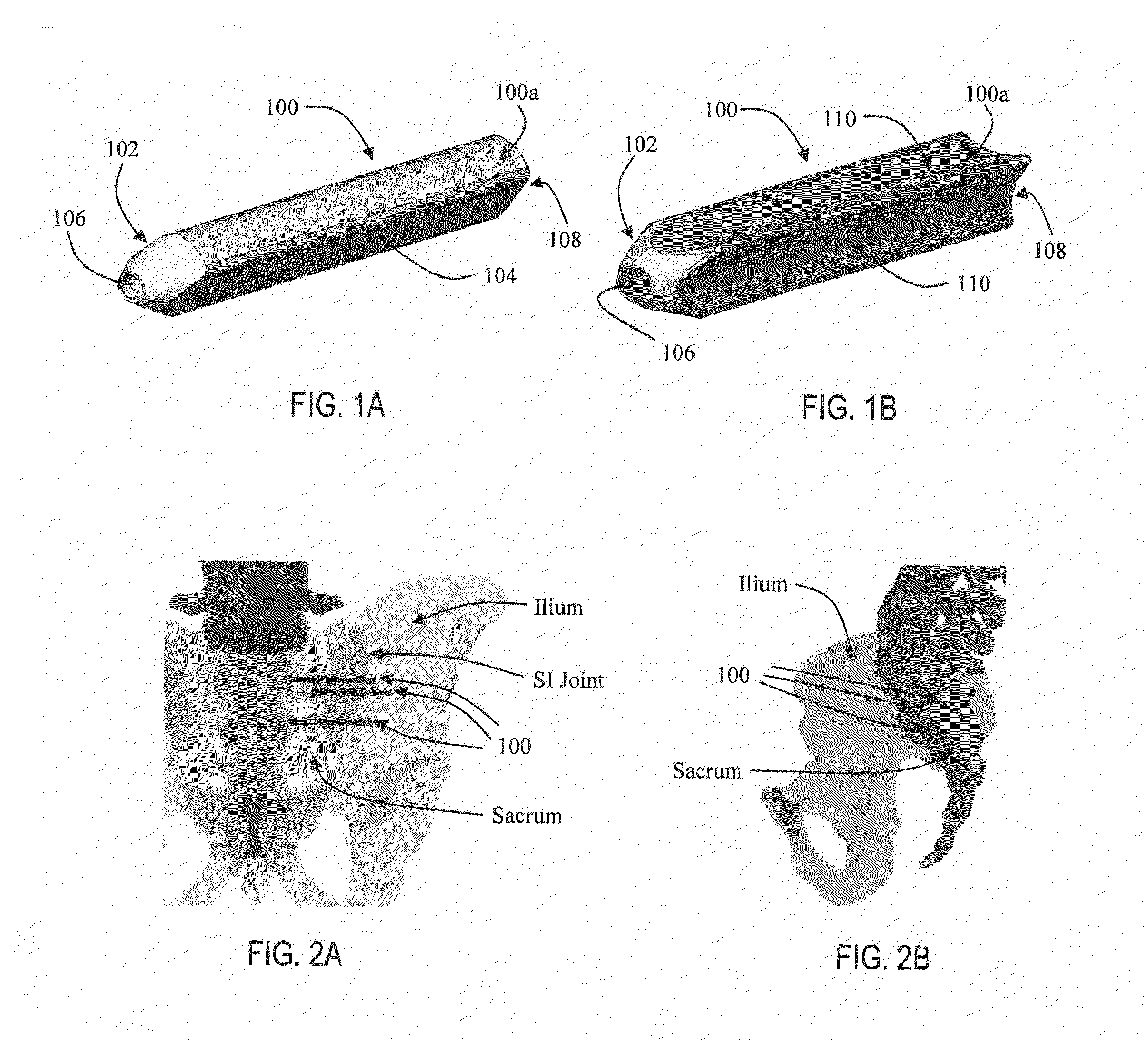
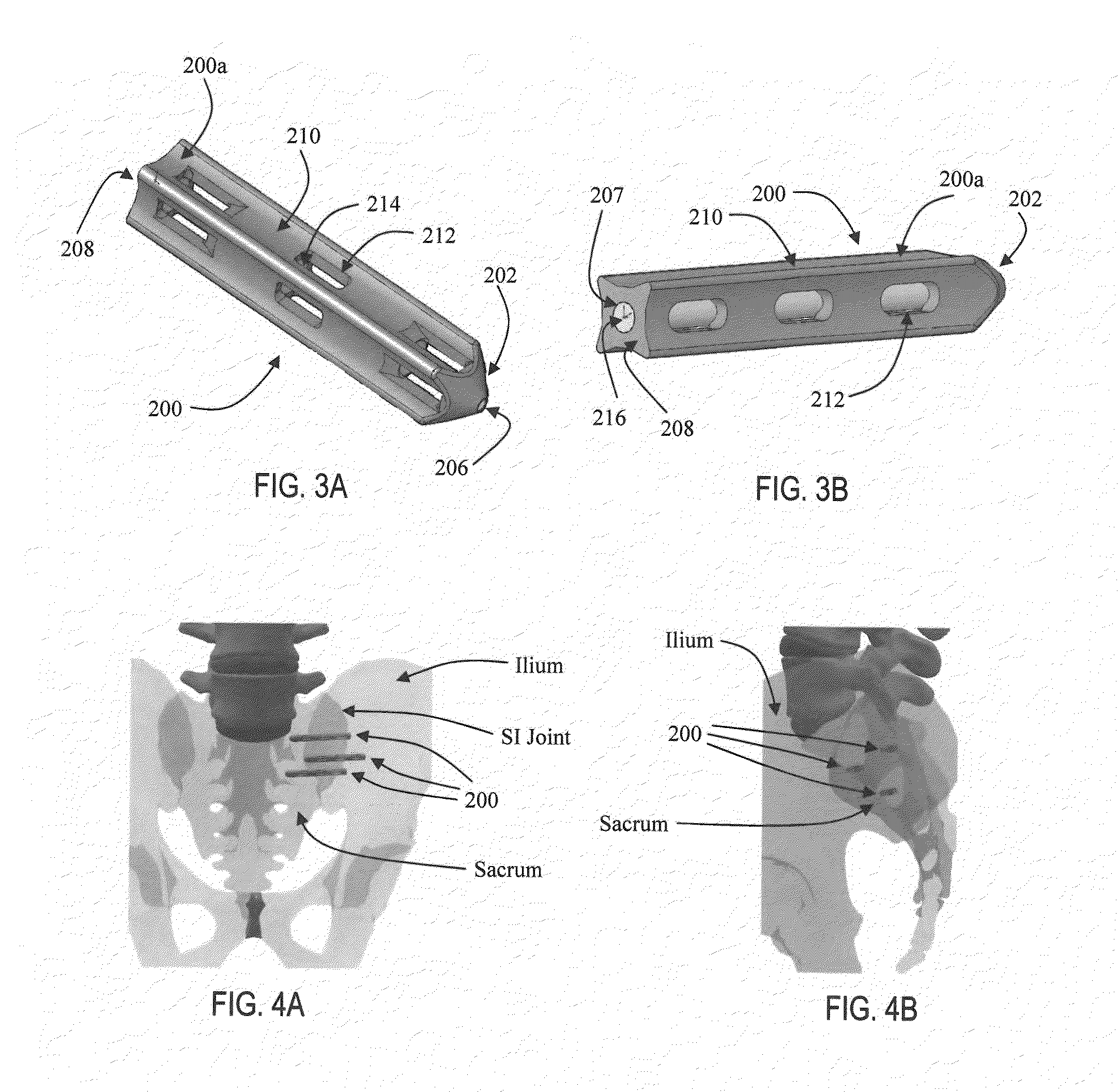
Methods and apparatus for immobilizing a synovial joint, such as a sacroiliac (SI) joint are disclosed. In one form, a multipiece fixation device, such as a dowel, includes multiple expandable fasteners that are configured to fix adjacent bones of a synovial joint with respect to one another. The expandable fasteners include expansion portions that are expanded radially via insertion of another expandable fastener or an expansion device to fix the expandable fasteners to the bone. The fixation device may be configured to provide for compression or distraction of the bones of the synovial joint while at the same time stabilizing the joint.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
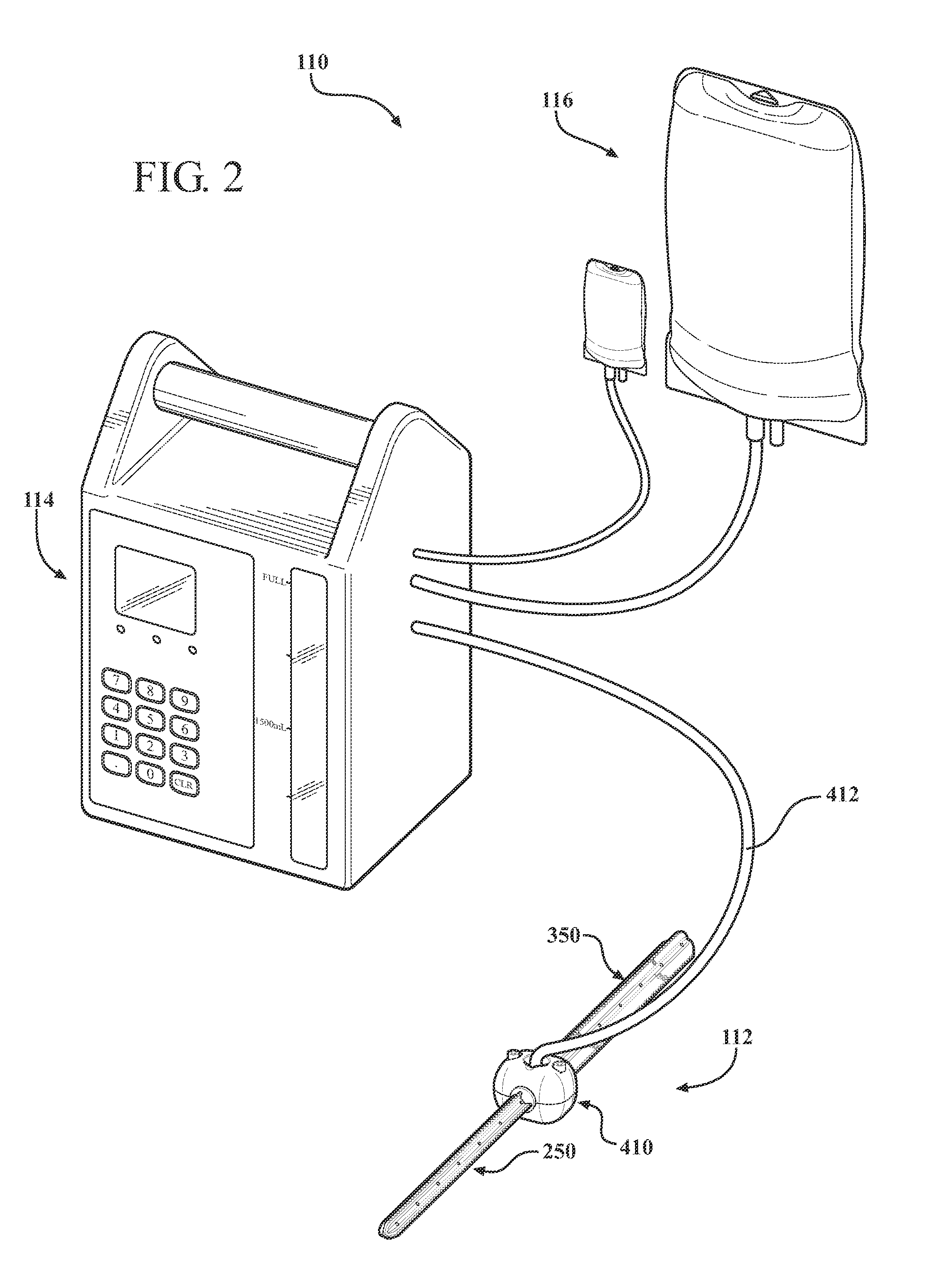
Antibiotic delivery system and method for treating an infected synovial joint during re-implantation of an orthopedic prosthesis
ActiveUS20100217401A1High local joint space and tissue levelRelieve painFinger jointsMedical devicesRe implantationProsthesis
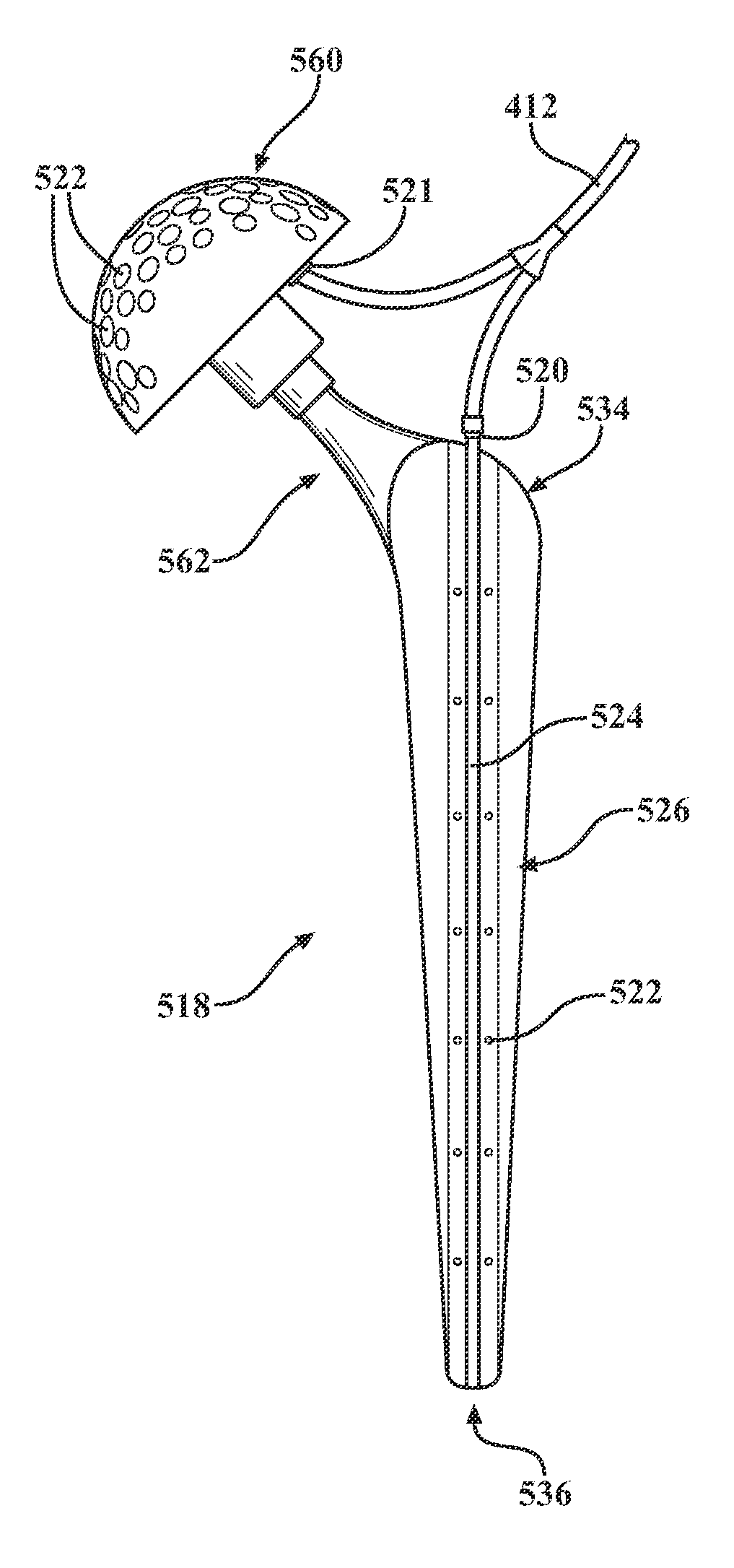
An antibiotic delivery system including an intramedullary stem that is adapted to be removably mounted into a medullary canal of a bone. The stem includes a body having an inlet adapted to be in fluid communication with a source of liquid-borne antibiotic and a plurality of outlets disposed along the stem. A channel extends between the inlet and the plurality of outlets for delivering a fluid-borne antibiotic from the inlet to the plurality of outlets so as to distribute the antibiotic along the medullary canal in a controlled fashion. A method of treating an infected joint during a two-stage re-implantation of an orthopedic implant is also disclosed.
Owner:OSTEAL THERAPEUTICS INC
Drug delivery to a joint
InactiveUS20070053963A1Easy to eluteAntibacterial agentsPowder deliverySustained release drugElution
A method of intra-articular drug delivery may include selecting an attachment zone in a synovial joint; affixing a drug release device in the attachment zone, the drug release device comprising a base affixable in the attachment zone, a sustained-release drug carrier, and a drug, the device positioned so that the device releases the drug into the synovial fluid of the synovial joint, and so that agitation of the synovial fluid facilitates elution of the drug from the drug release device.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Antibiotic delivery system and method for treating an infected synovial joint during re-implantation of an orthopedic prosthesis
ActiveUS8454706B2High local joint space and tissue levelRelieve painFinger jointsMedical devicesRe implantationProsthesis
Owner:OSTEAL THERAPEUTICS INC
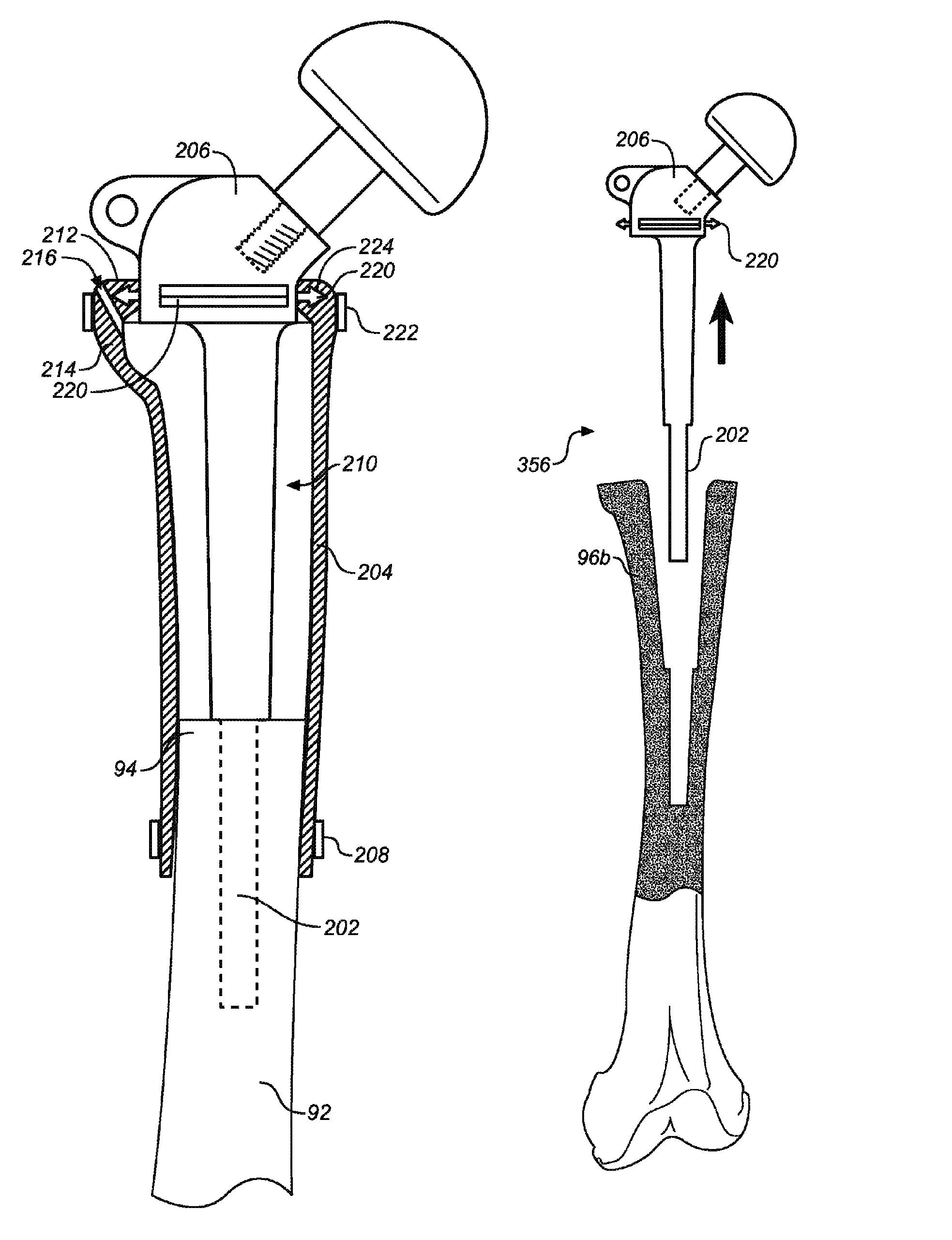
Device and method for reconstruction of osseous skeletal defects
ActiveUS8187336B2Immediate stabilizationSuture equipmentsAnkle jointsTotal knee replacementBone stock
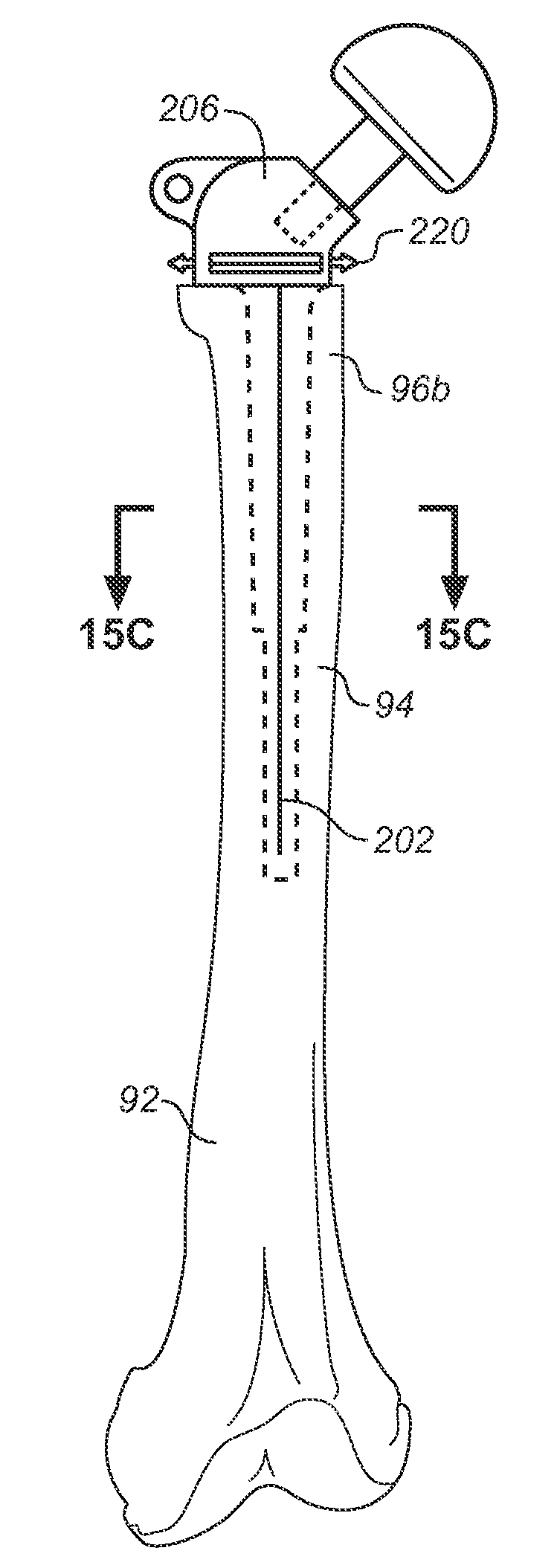
A synovial joint implantable apparatus for the reconstruction of skeletal defects with a flexible member, which is preferably resorbable, attached to a rigid structural prosthesis such as a total hip or total knee replacement implant. The cavitary space defined and surrounded by the flexible member is filled with osteoconductive and / or inductive materials which eventually matures into new column of bone. The prosthesis is supported by the bed of graft material surrounding it and is gradually unloaded as the bed matures into solid bone. The fixation of the prosthesis into native bone depends on the specific implant and the anatomic area of its use. The flexible member is secured to the margins of the prosthesis using rails, runners, sutures, or other attachment devices that prevent the escape of the bone graft and maintain an initial column of support for the implant. Should the metal implant even need removal, the reconstituted bone can be separated from the implant in such a way as to restore bone stock and facilitate future revision surgical procedures.
Owner:JAMALI AMIR A
Methods of treating a trauma or disorder of the knee joint by local administration and sustained-delivery of a biological agent
InactiveUS7910123B2Good treatment effectEliminate needPeptide/protein ingredientsDiagnosticsKnee JointLigament structure
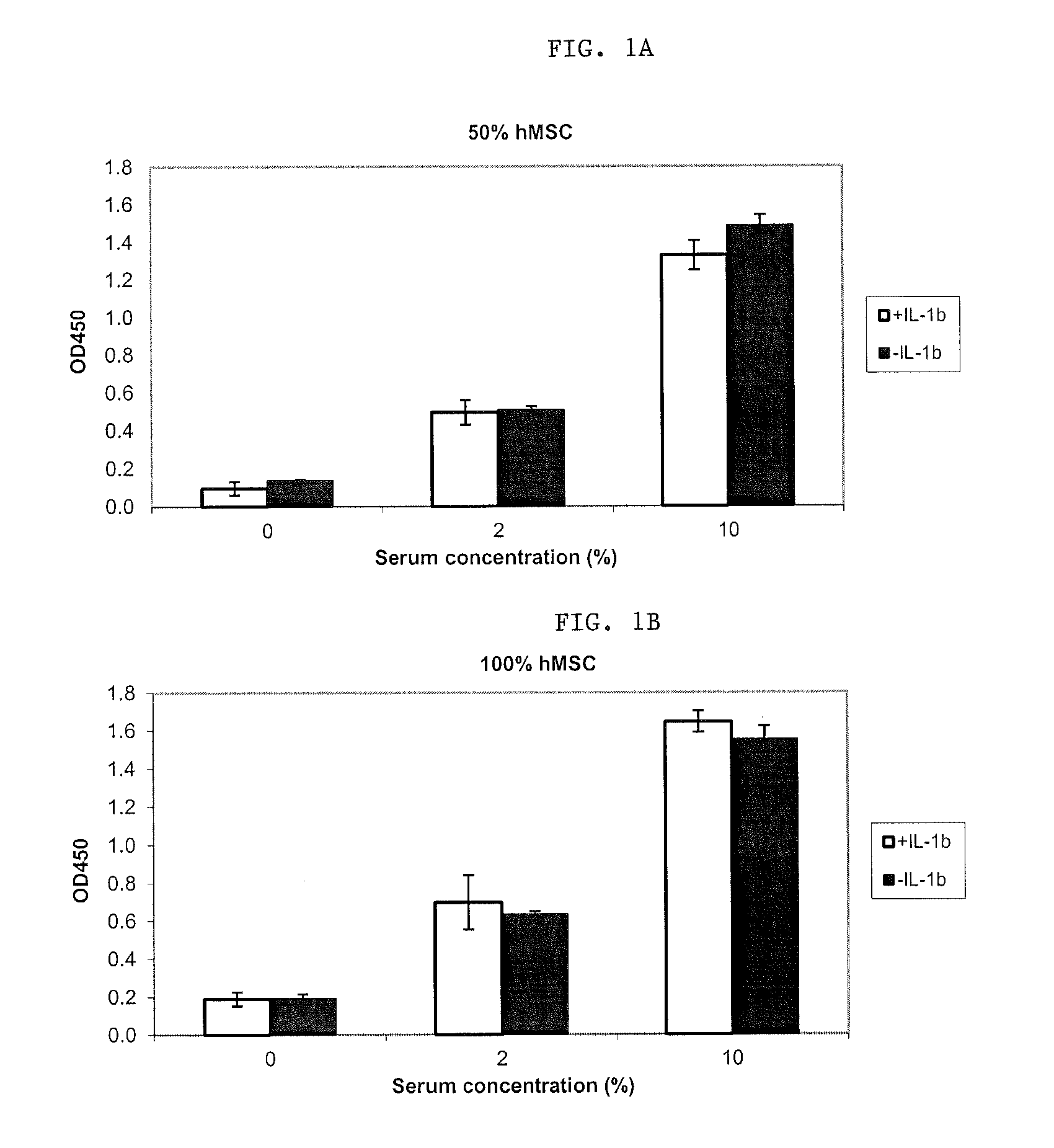
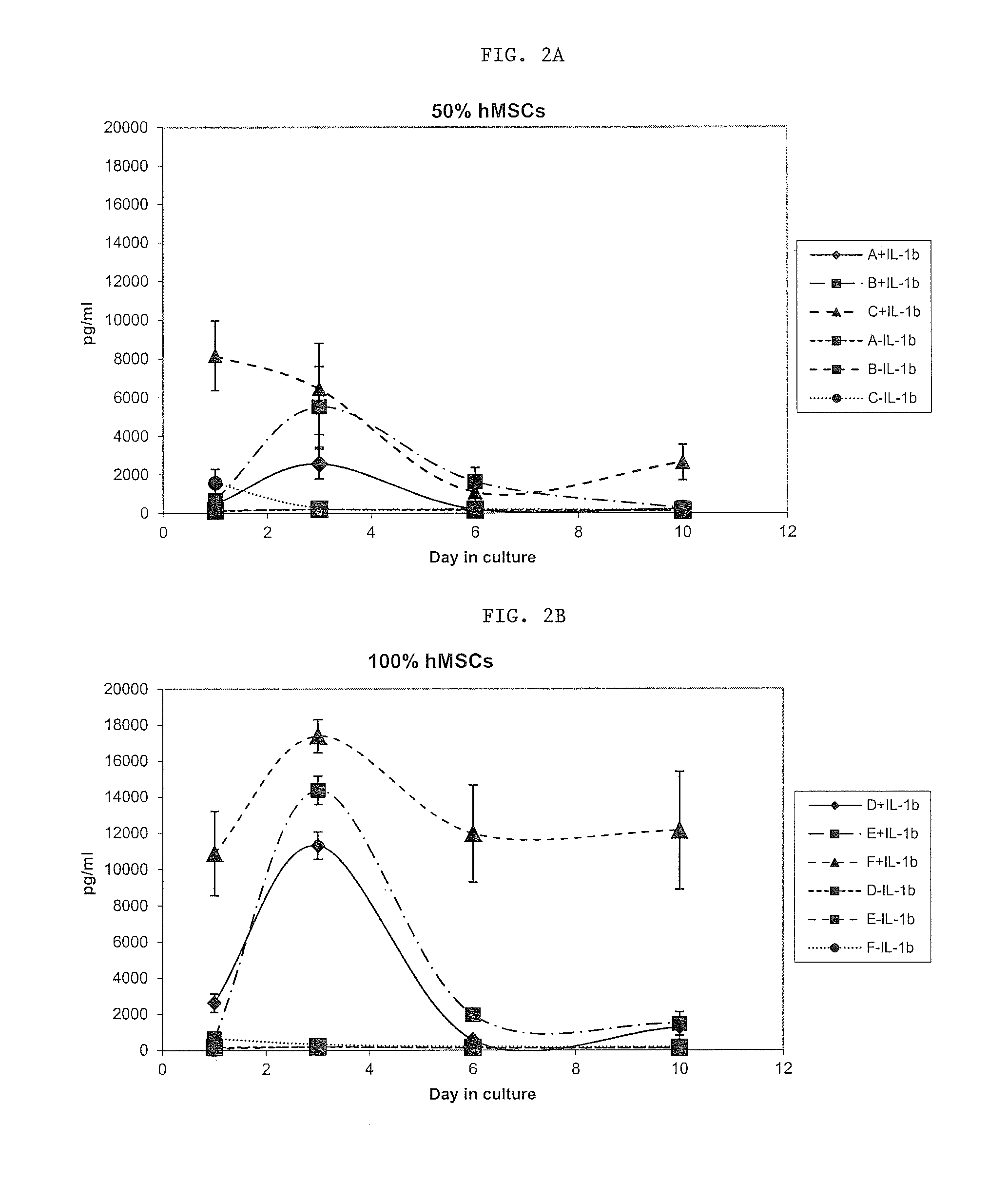
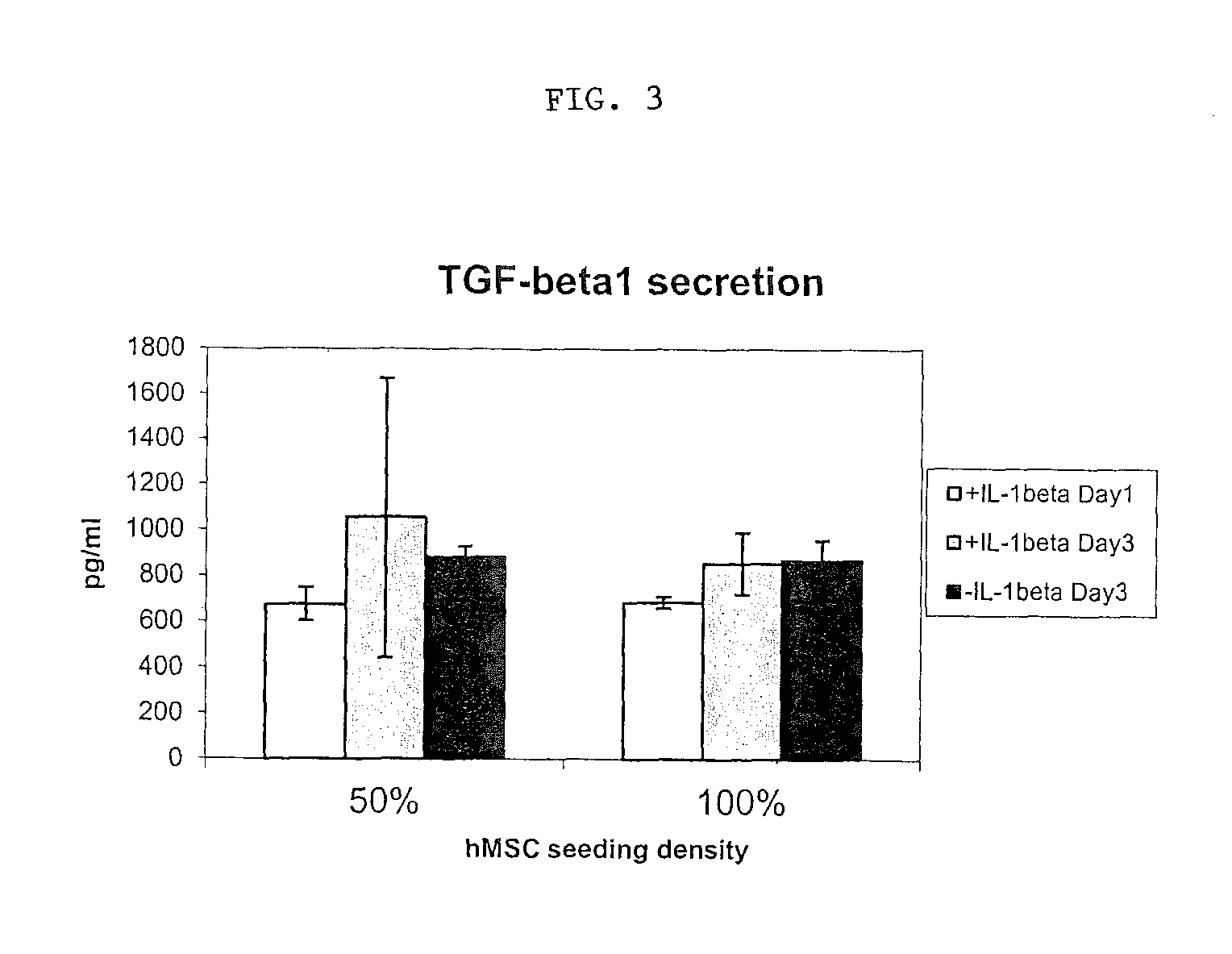
Methods and apparatus of providing a subject with post-operative, sustained-release of a biological agent within a synovial joint is disclosed. These methods involve securing a depot containing the biological agent to a ligament, tendon, muscle within the joint to provide sustained-release of the agent while allowing for normal joint articulation. This methodology may be utilized to provide for sustained-release of a biological agent useful in treating various traumas and disorders of the joint. Such biological agents include antagonists of inflammation-related proteins, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, NF-κB, High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMG-B1), IL-2, IL-15 and steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. Other biological agents include anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, IL-4, IL-13, and TGF-β. The biological agents also include osteogenic and cartilage producing growth factors such as, but not limited to, BMP-2, BMP-4, BMP-6, BMP-7, BMP-8, and MIA CD-RAP. Finally, the biological agents include siRNA and / or therapeutic antibodies.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
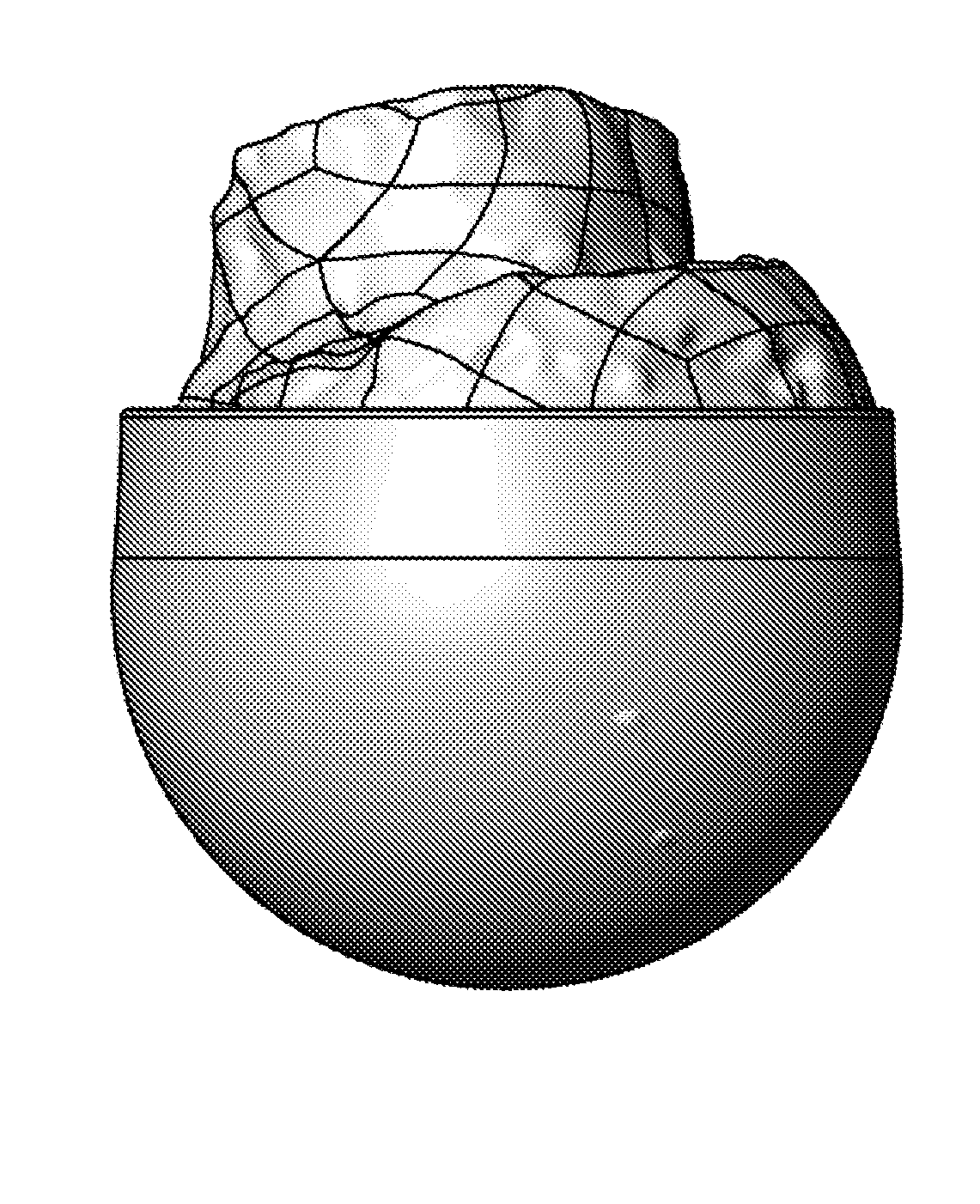
Medical Implant for Reducing Pain in Diseased Joints
ActiveUS20150335437A1Reduce interventionExpense can be limitedSurgeryJoint implantsDiseaseJoint pain
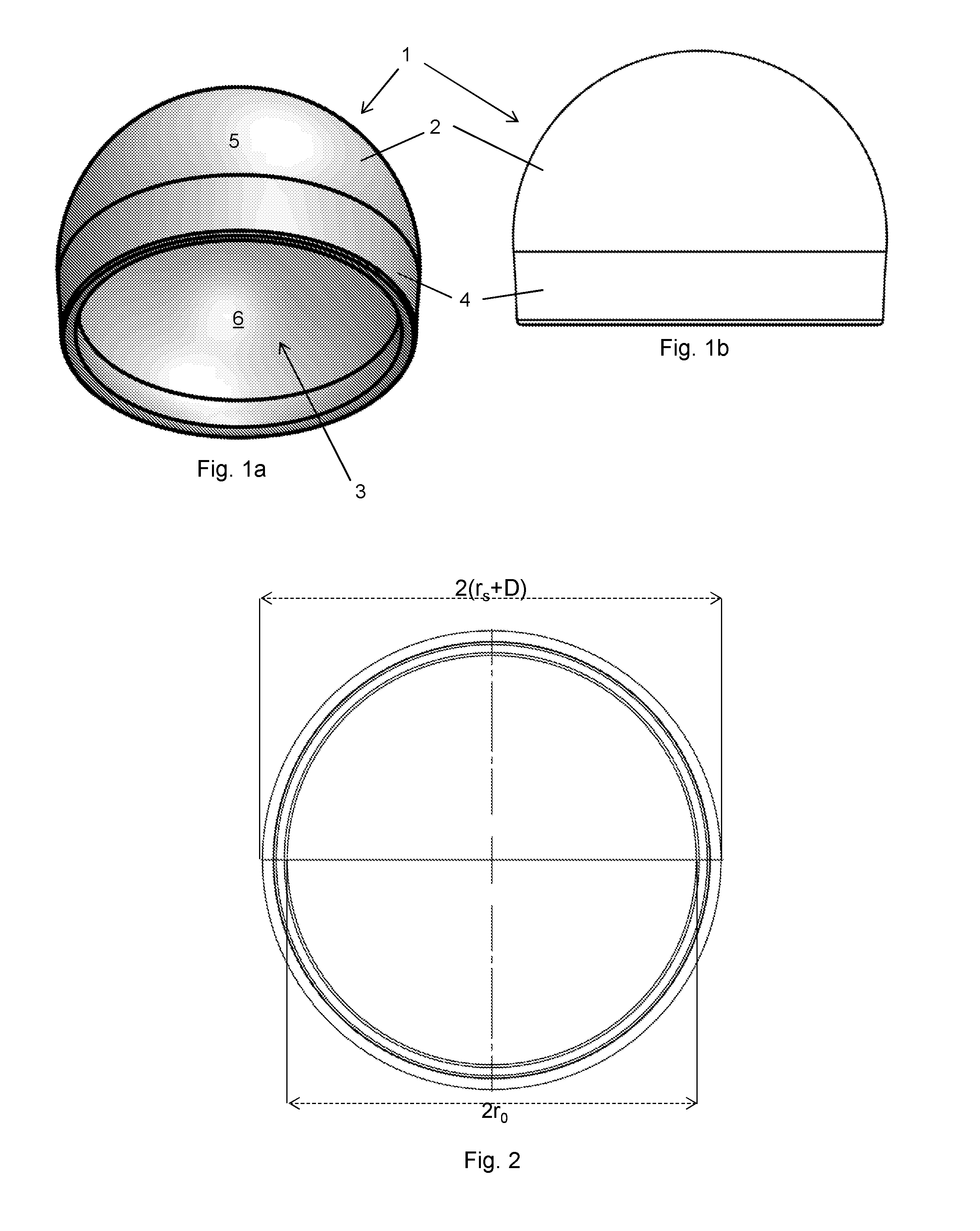
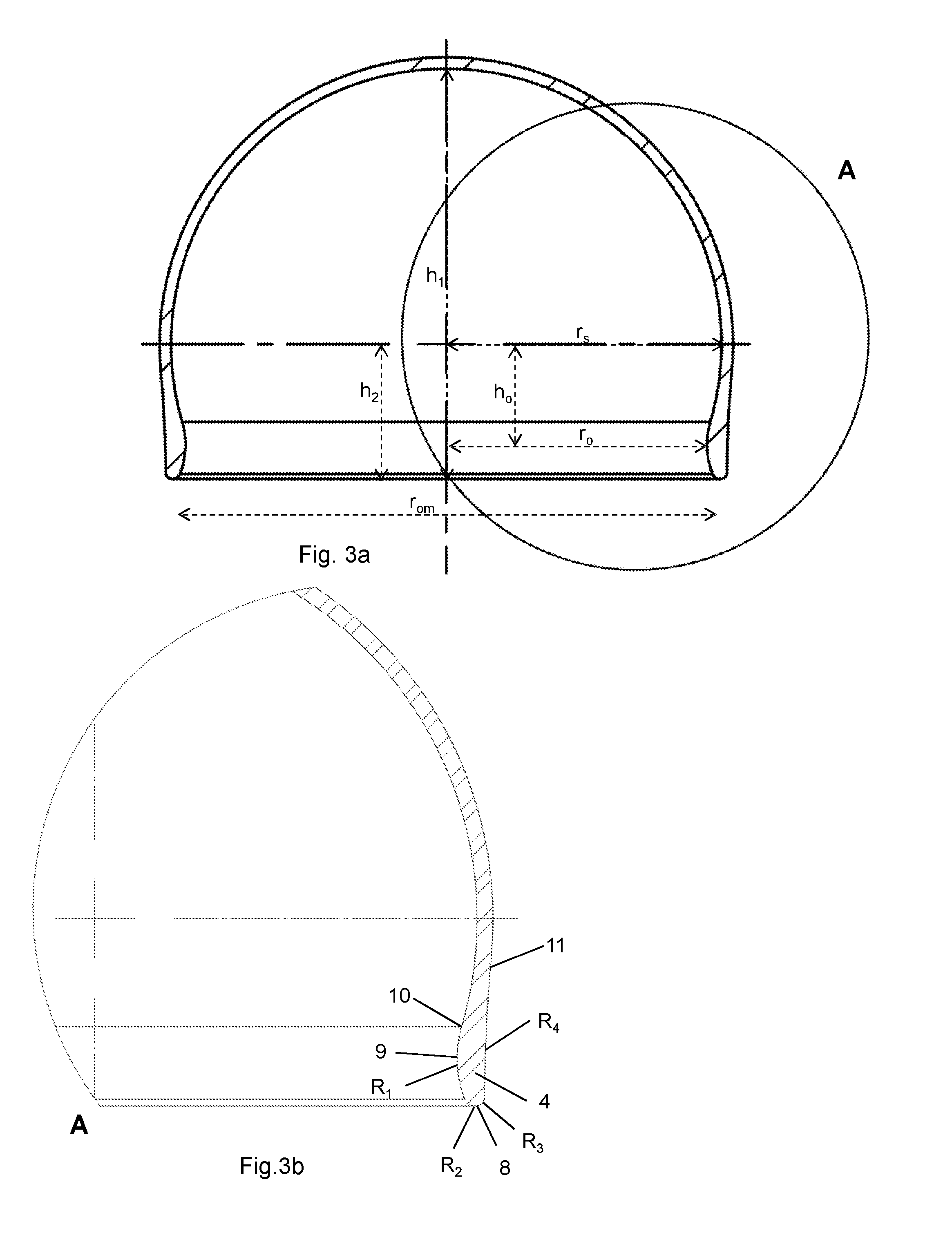
The present invention relates to a medical implant for reducing pain in diseased joints such as synovial joints, in particular ball and socket joints such as the hip joint and the shoulder joint. One embodiment relates to a medical implant for attachment to and at least partly covering the femoral head, said medical implant comprising a dome shaped shell with an orifice, said shell having a height h1, an equatorial shell radius rs and an orifice radius ro wherein the shell radius rs>ro, and h1>rs, and the orifice is defined by a circumferential rounded edge.
Owner:BISPEBJERG HOSPITAL
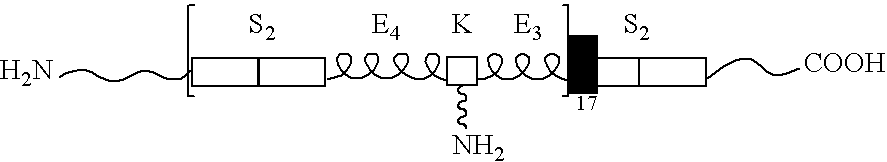
Recombinant lubricin molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS7642236B2Promote generationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPericardium tissueSynovial joints
Recombinant lubricin molecules and uses thereof. Novel recombinant lubricin molecules and their uses as lubricants anti-adhesive agents and / or intra-articular supplements for, e.g., synovial joints, meniscus, tendon, peritoneum, pericardium and pleura are provided.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Apparatus and methods for immobilization and fusion of a synovial joint
Methods and apparatus for immobilizing a synovial joint, such as a sacroiliac (SI) joint are disclosed. In one form, a multipiece fixation device, such as a dowel, includes multiple expandable fasteners that are configured to fix adjacent bones of a synovial joint with respect to one another. The expandable fasteners include expansion portions that are expanded radially via insertion of another expandable fastener or an expansion device to fix the expandable fasteners to the bone. The fixation device may be configured to provide for compression or distraction of the bones of the synovial joint while at the same time stabilizing the joint.
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Methods and compositions are disclosed for an intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis. The methods and compositions comprising combinations of hyaluronic acid and a bone morphogenetic protein, like rhGDF-5, can be useful for any synovial joint, including the knee, shoulder, hip, ankle, hands, spinal facet, or temporomandibular joint, both for the relief of pain and for slowing disease progression.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Methods of treating a trauma or disorder of the knee joint by local administration and sustained-delivery of a biological agent
InactiveUS20090060971A1Good treatment effectEliminate needPeptide/protein ingredientsDiagnosticsKnee JointLigament structure
Methods and apparatus of providing a subject with post-operative, sustained-release of a biological agent within a synovial joint is disclosed. These methods involve securing a depot containing the biological agent to a ligament, tendon, muscle within the joint to provide sustained-release of the agent while allowing for normal joint articulation. This methodology may be utilized to provide for sustained-release of a biological agent useful in treating various traumas and disorders of the joint. Such biological agents include antagonists of inflammation-related proteins, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, NF-κB, High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMG-B1), IL-2, IL-15 and steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. Other biological agents include anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, IL-4, IL-13, and TGF-β. The biological agents also include osteogenic and cartilage producing growth factors such as, but not limited to, BMP-2, BMP-4, BMP-6, BMP-7, BMP-8, and MIA CD-RAP. Finally, the biological agents include siRNA and / or therapeutic antibodies.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Methods and compositions are disclosed for an intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis. The methods and compositions comprising combinations of hyaluronic acid and a bone morphogenetic protein, like rhGDF-5, can be useful for any synovial joint, including the knee, shoulder, hip, ankle, hands, spinal facet, or temporomandibular joint, both for the relief of pain and for slowing disease progression.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Flowable composition that sets to a substantially non-flowable state
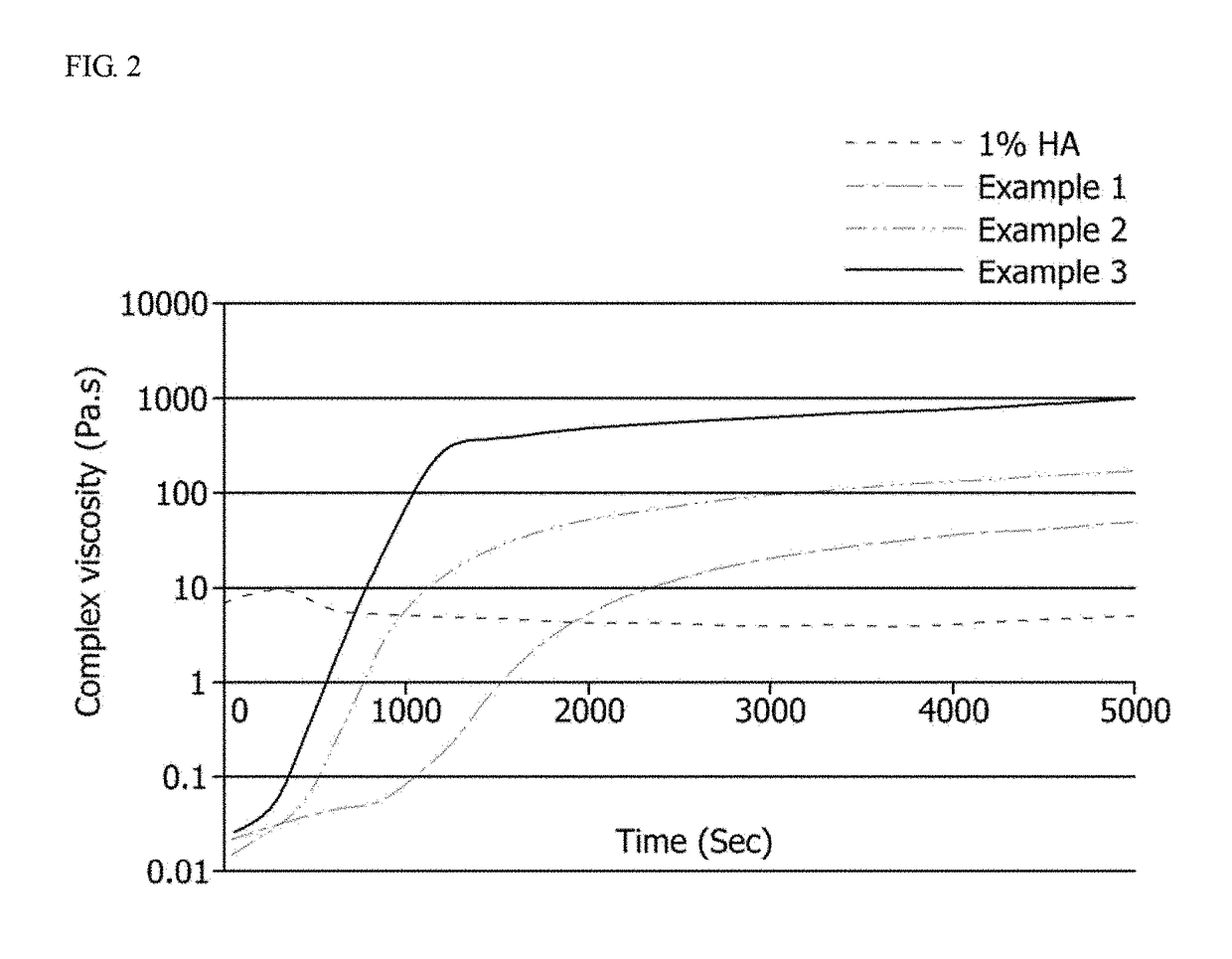
ActiveUS20110104233A1Reduce deliveryHigh viscosityOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsSpinal nerveLigament structure
Flowable compositions and methods are provided for delivering a therapeutic agent at or near a target tissue site beneath the skin of a patient, the flowable composition comprising (i) a solvent, (ii) a polymer and (iii) an effective amount of the therapeutic agent, the flowable composition being capable of setting to form a substantially non-flowable composition at a physiological temperature or as the solvent contacts bodily fluid at or near the target tissue site, wherein the substantially non-flowable composition is capable of releasing the therapeutic agent over a period of at least one day and the target tissue site comprises at least one muscle, ligament, tendon, cartilage, spinal disc, spinal foraminal space near the spinal nerve root, facet or synovial joint, or spinal canal.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Drug delivery to a joint
A method of intra-articular drug delivery may include selecting an attachment zone in a synovial joint; affixing a drug release device in the attachment zone, the drug release device comprising a base affixable in the attachment zone, a sustained-release drug carrier, and a drug, the device positioned so that the device releases the drug into the synovial fluid of the synovial joint, and so that agitation of the synovial fluid facilitates elution of the drug from the drug release device.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Method and apparatus for delivering treatment to a joint
InactiveUS20090062922A1Patient compliance is goodEliminate needSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTargeted therapyTethered Cord
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for treating inflammation and / or infection within a synovial joint. The invention is comprised of a depot, tether and cap. The depot is comprised of a biodegradable polymer which is impregnated with a biological agent targeted to treat the inflammation and / or infection. The depot is inserted into the synovial joint through an incision or hole in the synovial membrane. A tether that extends from the depot is then thread back through the incision or hole and coupled to a cap such that the depot is coupled to the synovial membrane on an interior side of the synovial joint capsule and the cap is secured to the membrane on an exterior side of the synovial joint capsule. Once secured, the depot degrades and gradually releases the biological agent over a sustained time period. The biological agent then treats the targeted inflammation and / or infection.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Device and method for reconstruction of osseous skeletal defects
ActiveUS20100076572A1Immediate stabilizationSuture equipmentsAnkle jointsTotal knee replacementBone stock
A synovial joint implantable apparatus for the reconstruction of skeletal defects with a flexible member, which is preferably resorbable, attached to a rigid structural prosthesis such as a total hip or total knee replacement implant. The cavitary space defined and surrounded by the flexible member is filled with osteoconductive and / or inductive materials which eventually matures into new column of bone. The prosthesis is supported by the bed of graft material surrounding it and is gradually unloaded as the bed matures into solid bone. The fixation of the prosthesis into native bone depends on the specific implant and the anatomic area of its use. The flexible member is secured to the margins of the prosthesis using rails, runners, sutures, or other attachment devices that prevent the escape of the bone graft and maintain an initial column of support for the implant. Should the metal implant even need removal, the reconstituted bone can be separated from the implant in such a way as to restore bone stock and facilitate future revision surgical procedures.
Owner:JAMALI AMIR A
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Methods and compositions are disclosed for an intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis. The methods and compositions comprising combinations of hyaluronic acid and a bone morphogenetic protein, like rhGDF-5, can be useful for any synovial joint, including the knee, shoulder, hip, ankle, hands, spinal facet, or temporomandibular joint, both for the relief of pain and for slowing disease progression.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Means for detecting pathological transformation of the app protein and their uses
InactiveUS20070026527A1Easy to eluteCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSustained release drugElution
A method of intra-articular drug delivery may include selecting an attachment zone in a synovial joint; affixing a drug release device in the attachment zone, the drug release device comprising a base affixable in the attachment zone, a sustained-release drug carrier, and a drug, the device positioned so that the device releases the drug into the synovial fluid of the synovial joint, and so that agitation of the synovial fluid facilitates elution of the drug from the drug release device.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
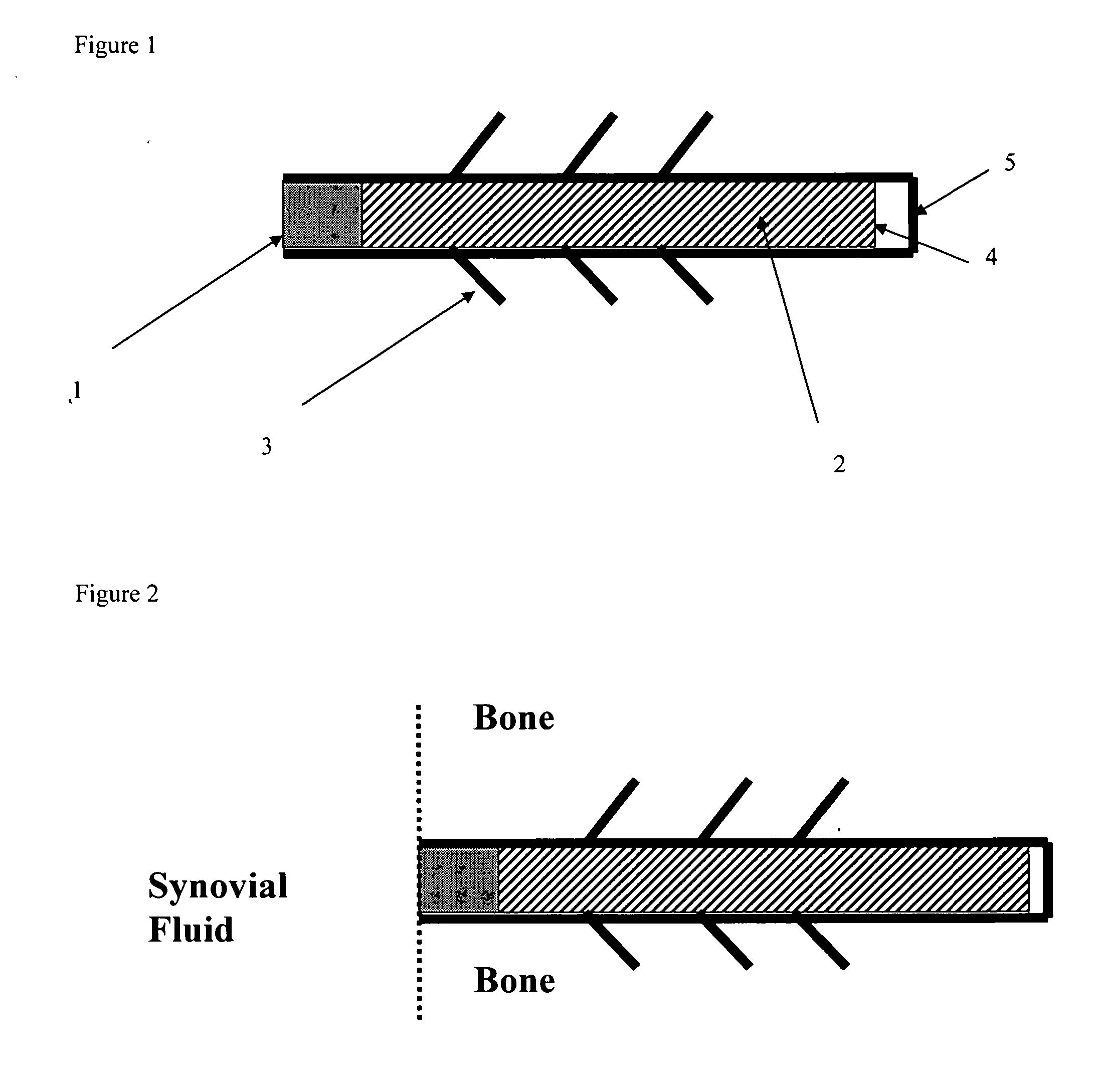
Collagen-based materials and methods for treating synovial joints
ActiveUS7731981B2Enhance the imagePromote collagen crosslinkingAntibacterial agentsBiocideMedicineInjected material
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Collagen-based materials and methods for treating synovial joints
ActiveUS20070134343A1Promote collagen crosslinkingEnhance the imageAntibacterial agentsBiocideMedicineInjected material
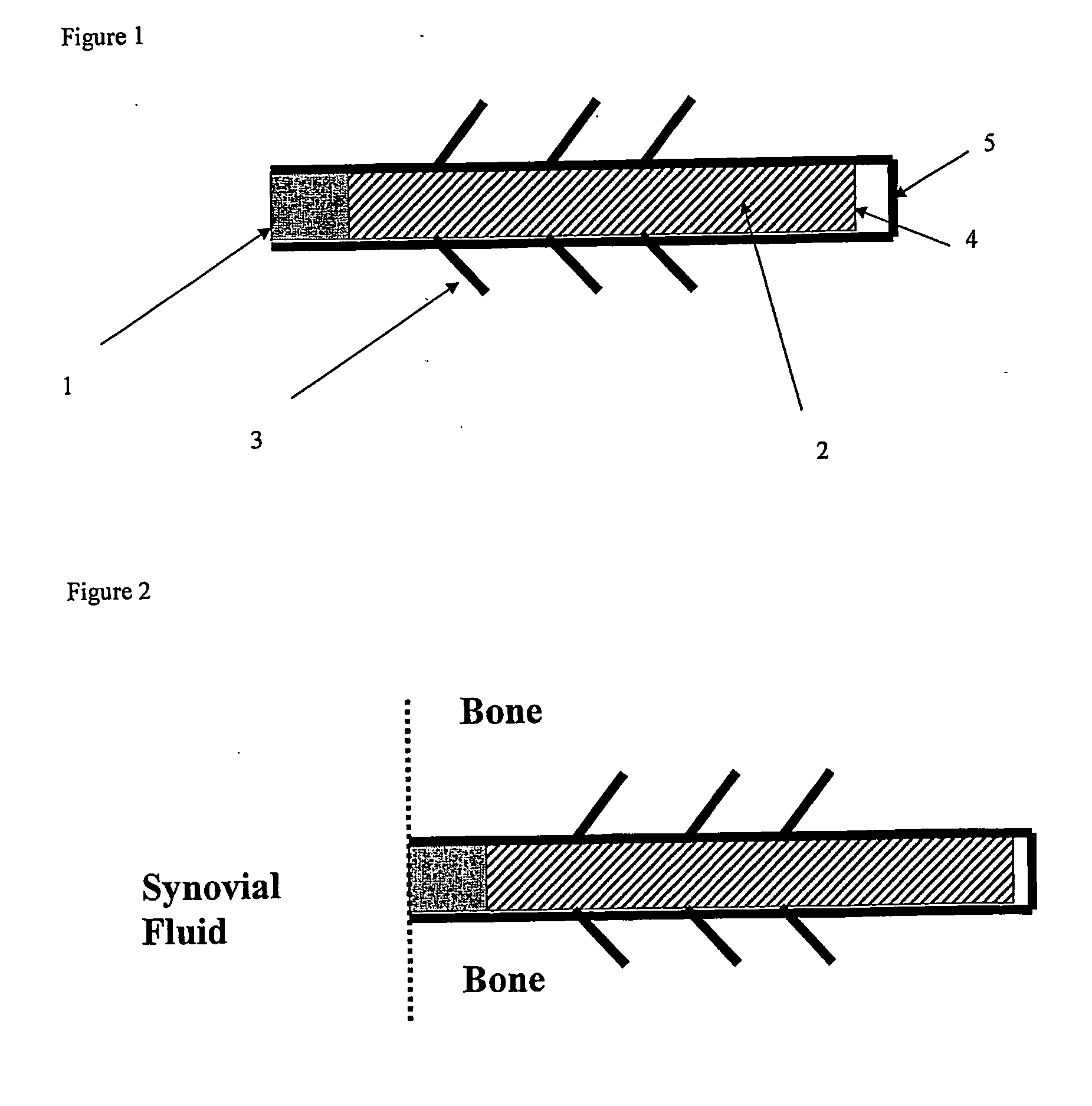
A method of treating a synovial joint by injecting particles of collagen-based material into the joint. The particles may be dehydrated before implantation, and rehydrated after implantation, or they may be implanted in a “wet” state—such as a slurry or gel. Radiocontrast materials may be included to enhance imaging of the injected material. Other additives may include analgesics, antibiotics, proteoglycans, growth factors, and / or other cells effective to promote healing and / or proper joint function.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Use of autologous sediment from fluid aspirates as vehicles for drug delivery
InactiveUS20070059372A1Minimize any inflammatory responsePowder deliveryMammal material medical ingredientsGene vectorCytokine
A method of using fluid aspirates as vehicles for drug delivery by collecting a fluid aspirate such as synovial joint effusion, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, or ascites from a patient and centrifuging the fluid aspirate to provide a supernatant and a sedimented material. The sedimented material can optionally be further purified. One or more factors such as cytokines, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), pharmaceutical drugs and gene vectors are added to the sedimented material or supernatant, optionally also including a biologically compatible medium such as a bioabsorbable sponge, so as to provide a vehicle for the one or more factors for reintroducion into the patient.
Owner:JOHNSON LANNY L
Primed stem cells and uses thereof to treat inflammatory conditions in joints
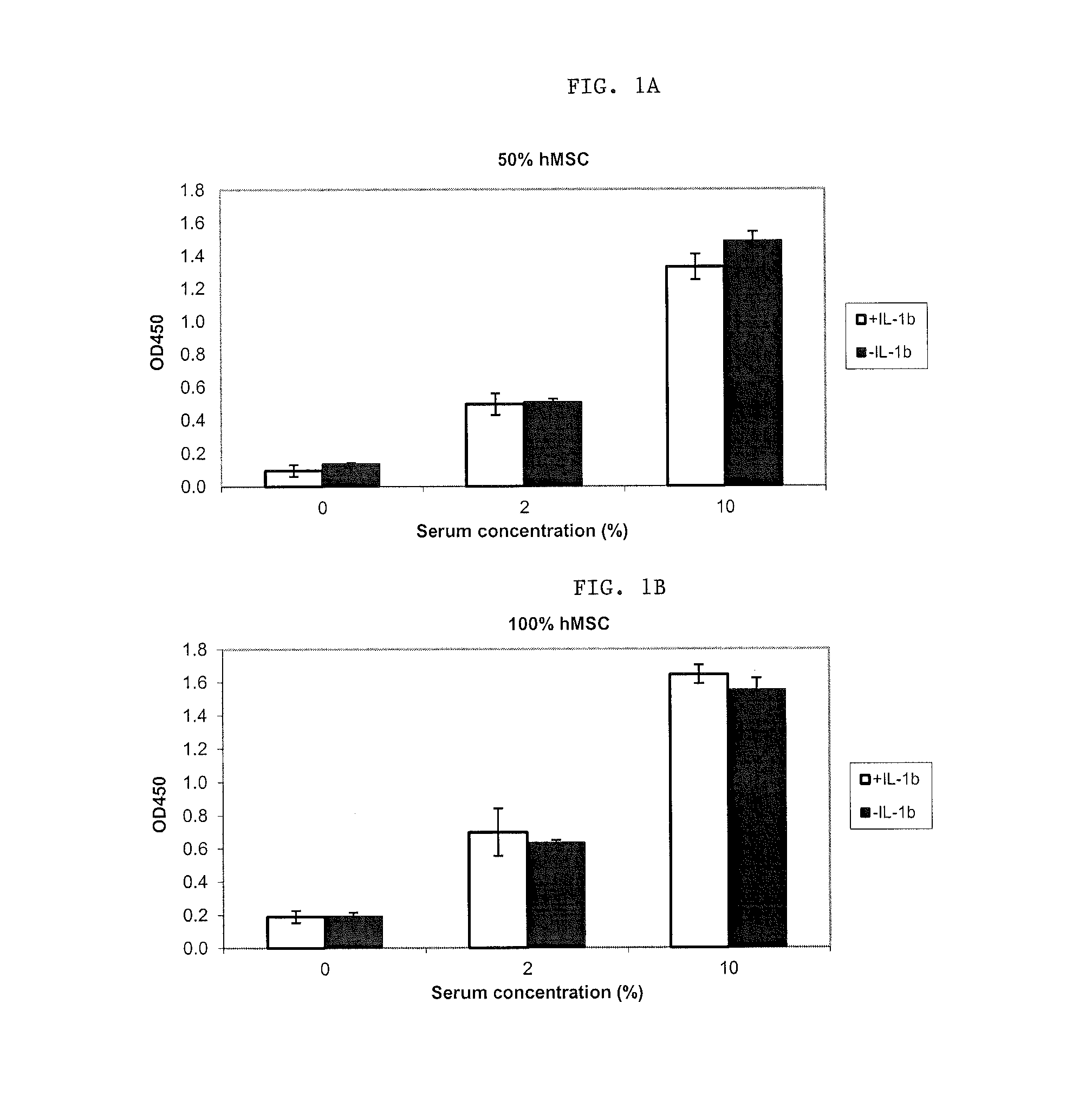
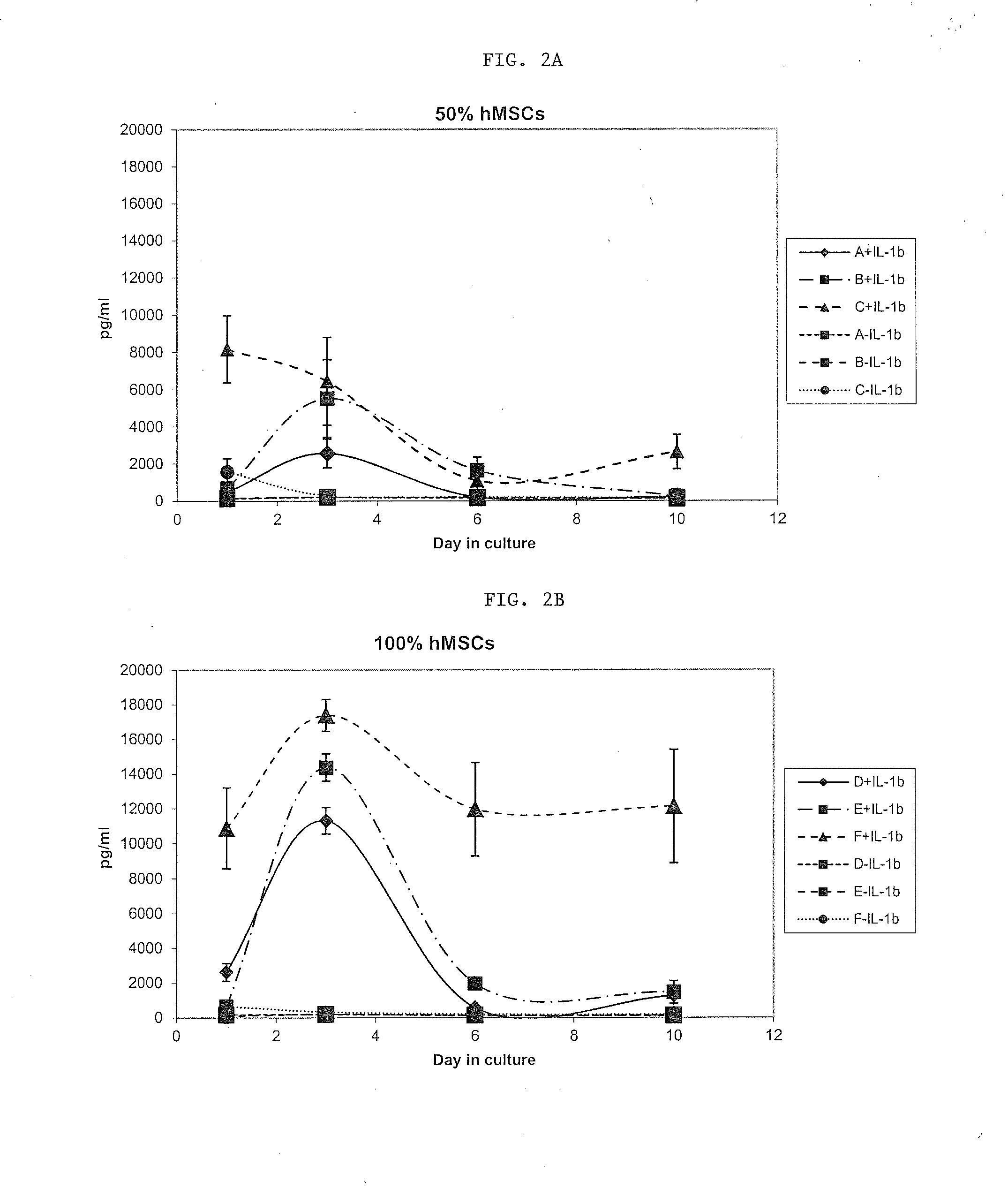
Disclosed are methods of treating inflammation within a synovial joint, comprising administering to the joint a composition comprising primed stem or progenitor cells in an amount effective to enhance recovery, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
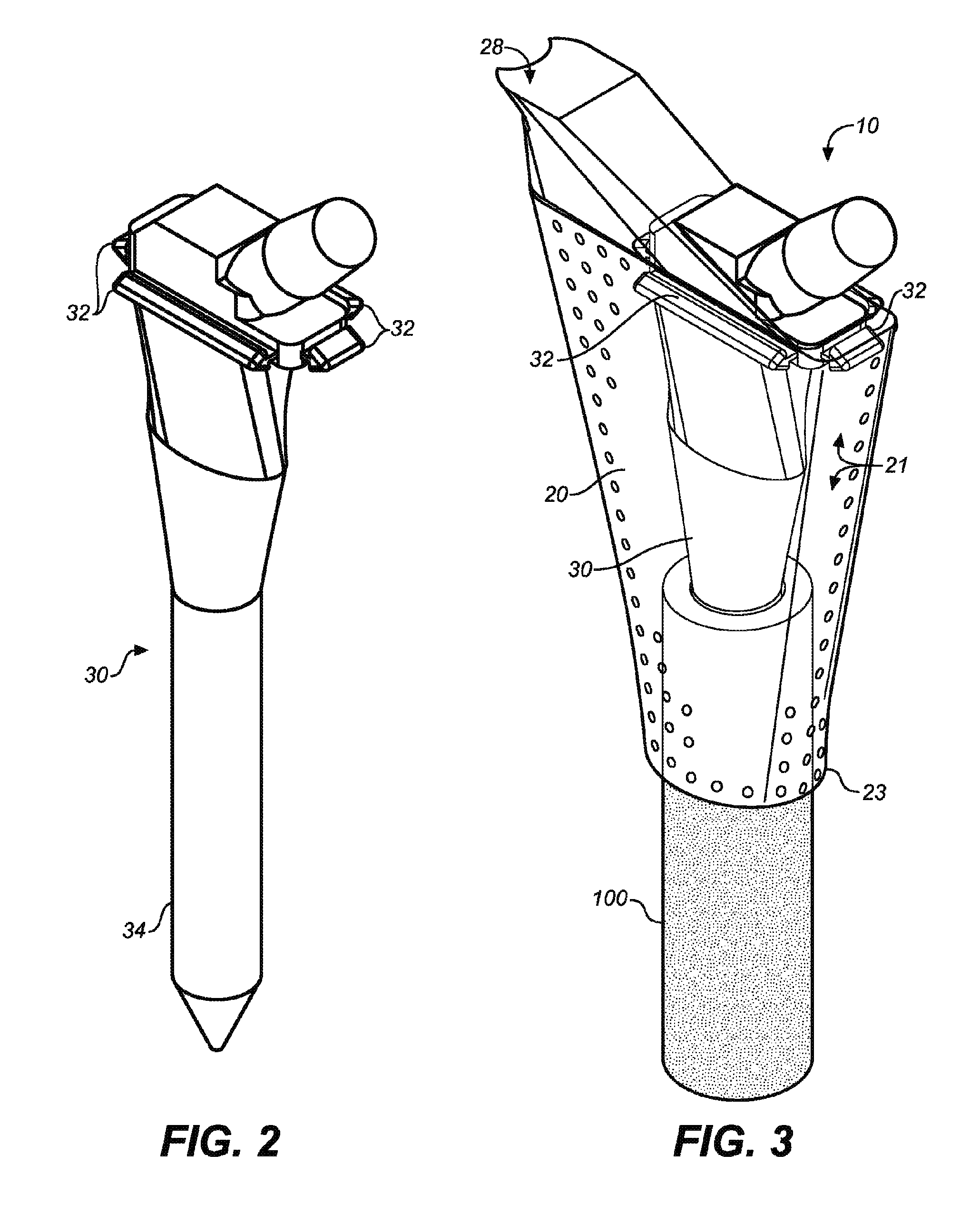
Orthopaedic medical device
InactiveUS20180161022A1Reduce the possibility of damageMore areaSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsOrthopaedic deviceSurgical site
This present invention provides an orthopaedic medical device, in particular an arthroscopic aid, for stimulating the release of cells and / or encouraging migration of cells to a surgical site or an injury site. The invention includes methods of increasing a cell population at a surgical site or injury, a method of improving surgical outcome of synovial joint procedures and methods of delivering intra-operative minimally manipulated cells to a synovial joint.
Owner:UNIV OF LEEDS
Use of autologous sediment from fluid aspirates as vehicles for drug delivery
InactiveUS7927630B2Minimize any inflammatory responsePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsGene vectorCytokine
A method of using fluid aspirates as vehicles for drug delivery by collecting a fluid aspirate such as synovial joint effusion, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, or ascites from a patient and centrifuging the fluid aspirate to provide a supernatant and a sedimented material. The sedimented material can optionally be further purified. One or more factors such as cytokines, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), pharmaceutical drugs and gene vectors are added to the sedimented material or supernatant, optionally also including a biologically compatible medium such as a bioabsorbable sponge, so as to provide a vehicle for the one or more factors for reintroducion into the patient.
Owner:JOHNSON LANNY L
Primed stem cells and uses thereof to treat inflammatory conditions in joints
ActiveUS8709401B2Joint painAvoid loweringBiocideGenetic material ingredientsProgenitorSynovial joints
Disclosed are methods of treating inflammation within a synovial joint, comprising administering to the joint a composition comprising primed stem or progenitor cells in an amount effective to enhance recovery, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Polethylene glycol hydrogel injection
InactiveUS20170340774A1Improving and treating various conditionImprove pain reliefOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismJoint cavityPolythylene glycol
The present invention relates to a polyethylene glycol hydrogel injection, and, more particularly, to an injection to be administered into a joint (a synovial joint cavity) for the improvement of symptoms of arthritis by containing two separate buffer solutions, wherein a solution (1) contains a polyethylene glycol derivative with an electrophilic functional group and a buffer of pH 3.5 to 6, and a solution (2) contains a polyethylene glycol derivative with a nucleophilic functional group, hyaluronic acid, and a buffer of pH 7.5 to 11. The injection of the present invention is highly biocompatible and long-lasting in the joint, showing the efficacy of pain relief, cartilage protection, and inhibition of inflammation, thus offering the effective prevention and treatment of arthritis.
Owner:SUN BIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com