Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
674results about "Petrochemical industry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
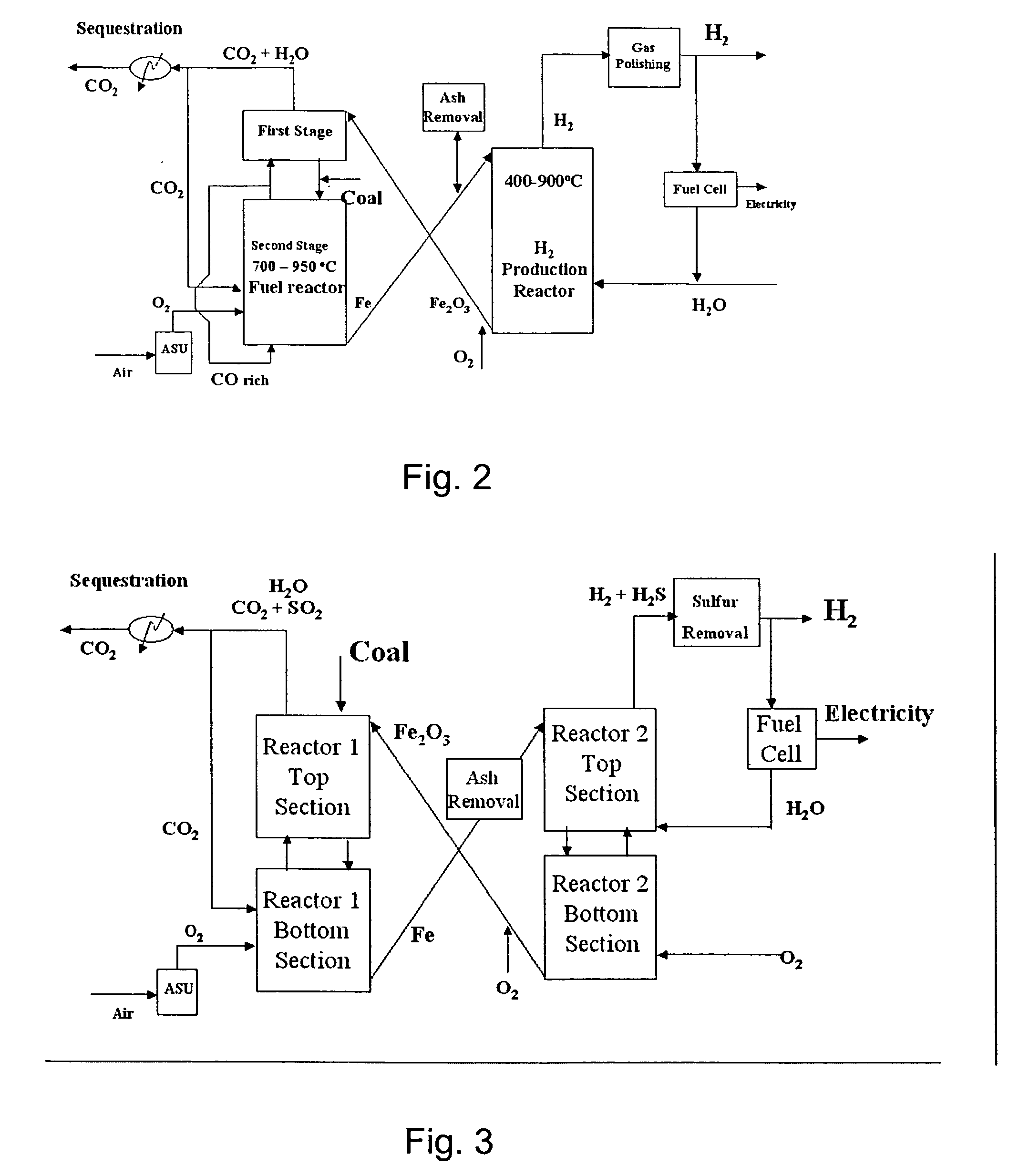
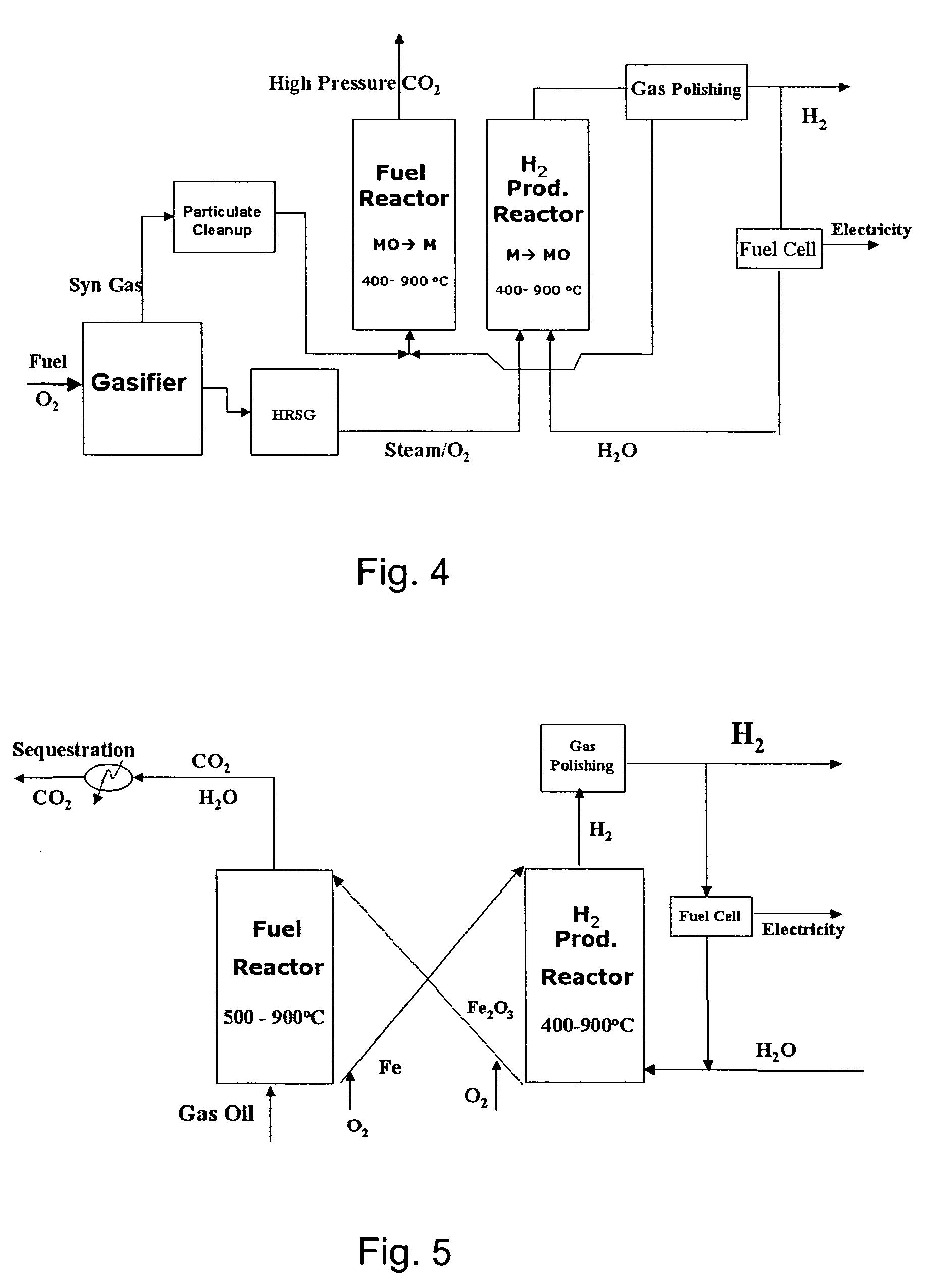
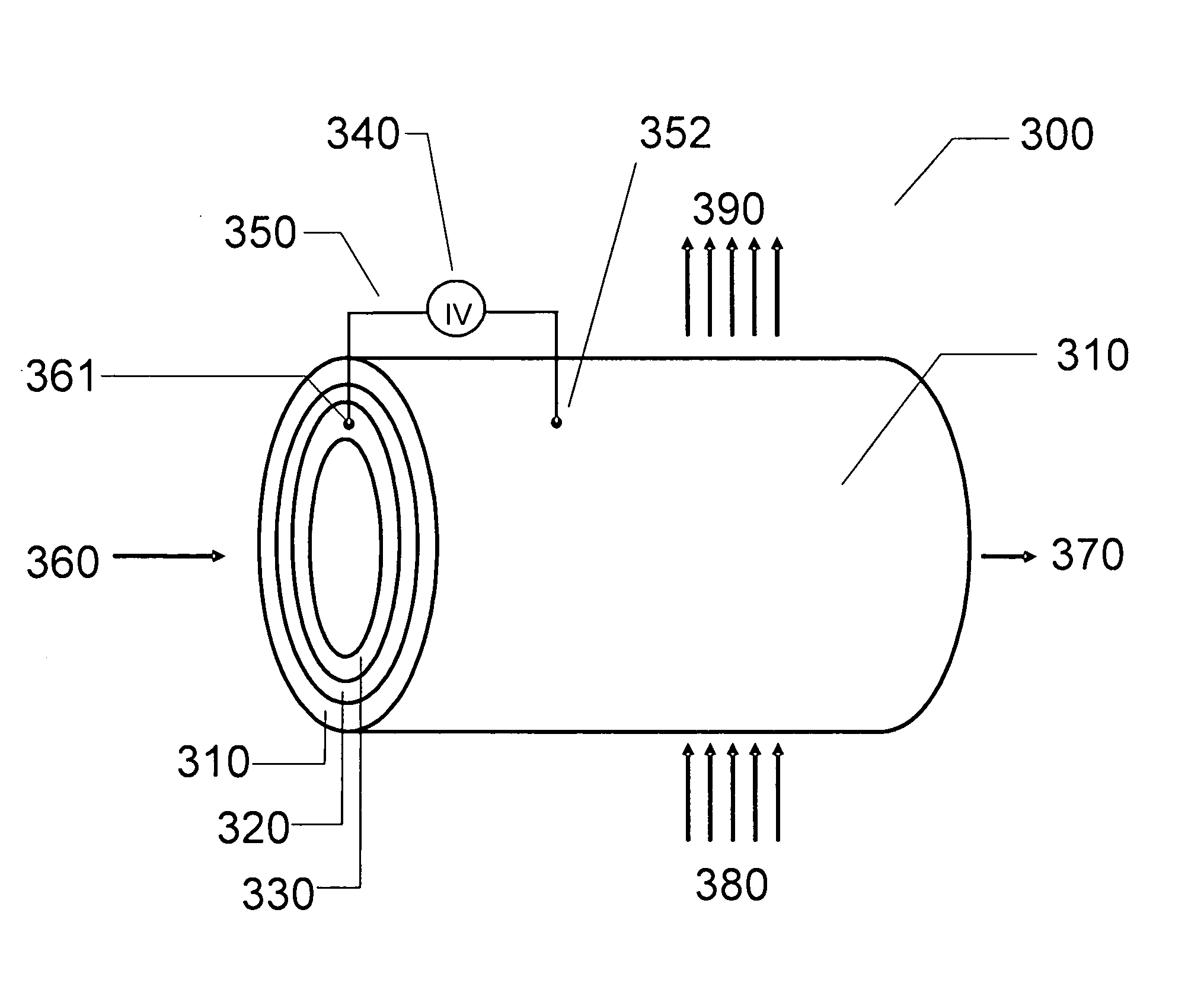
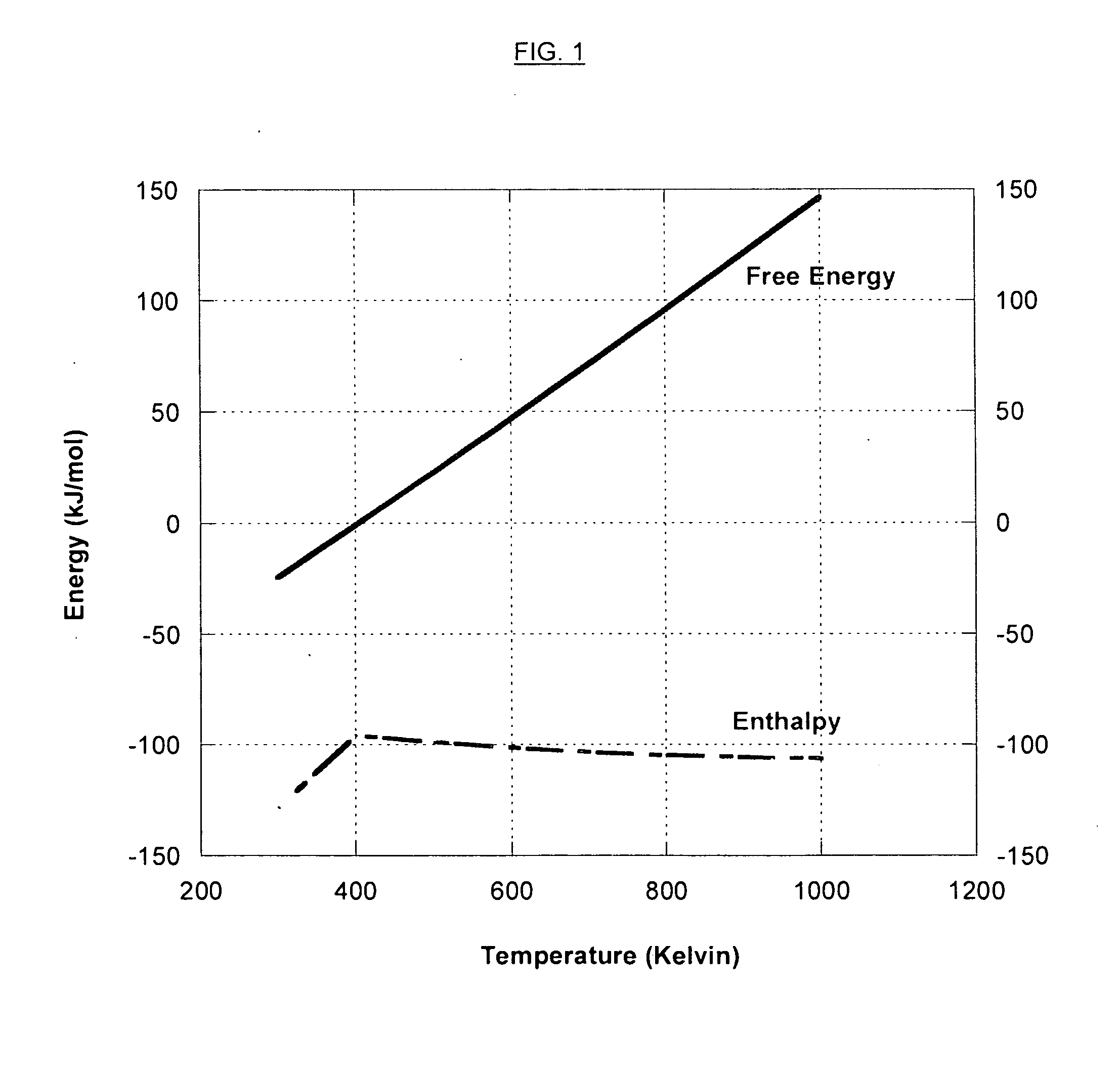
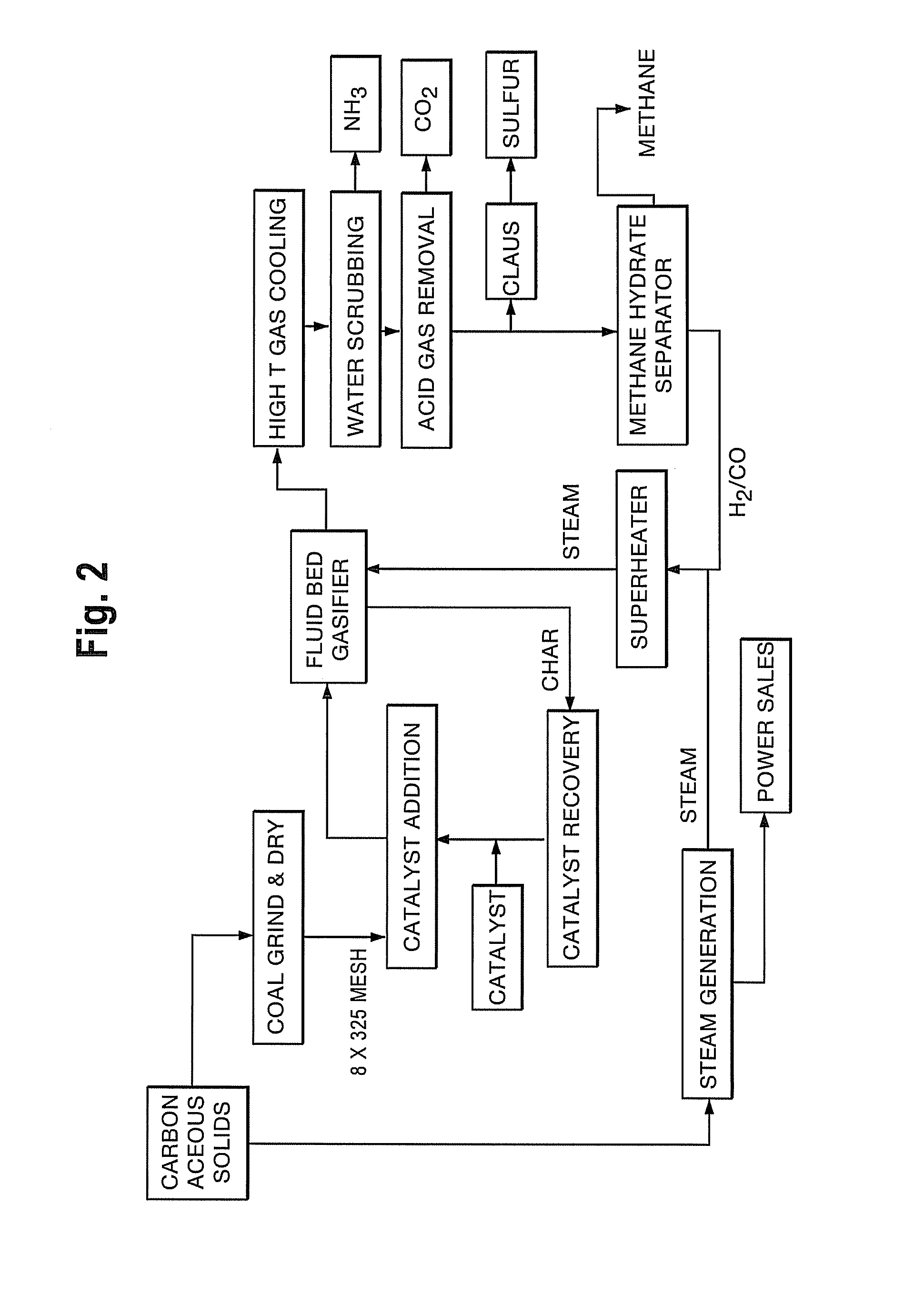
Hydrogen production from carbonaceous material
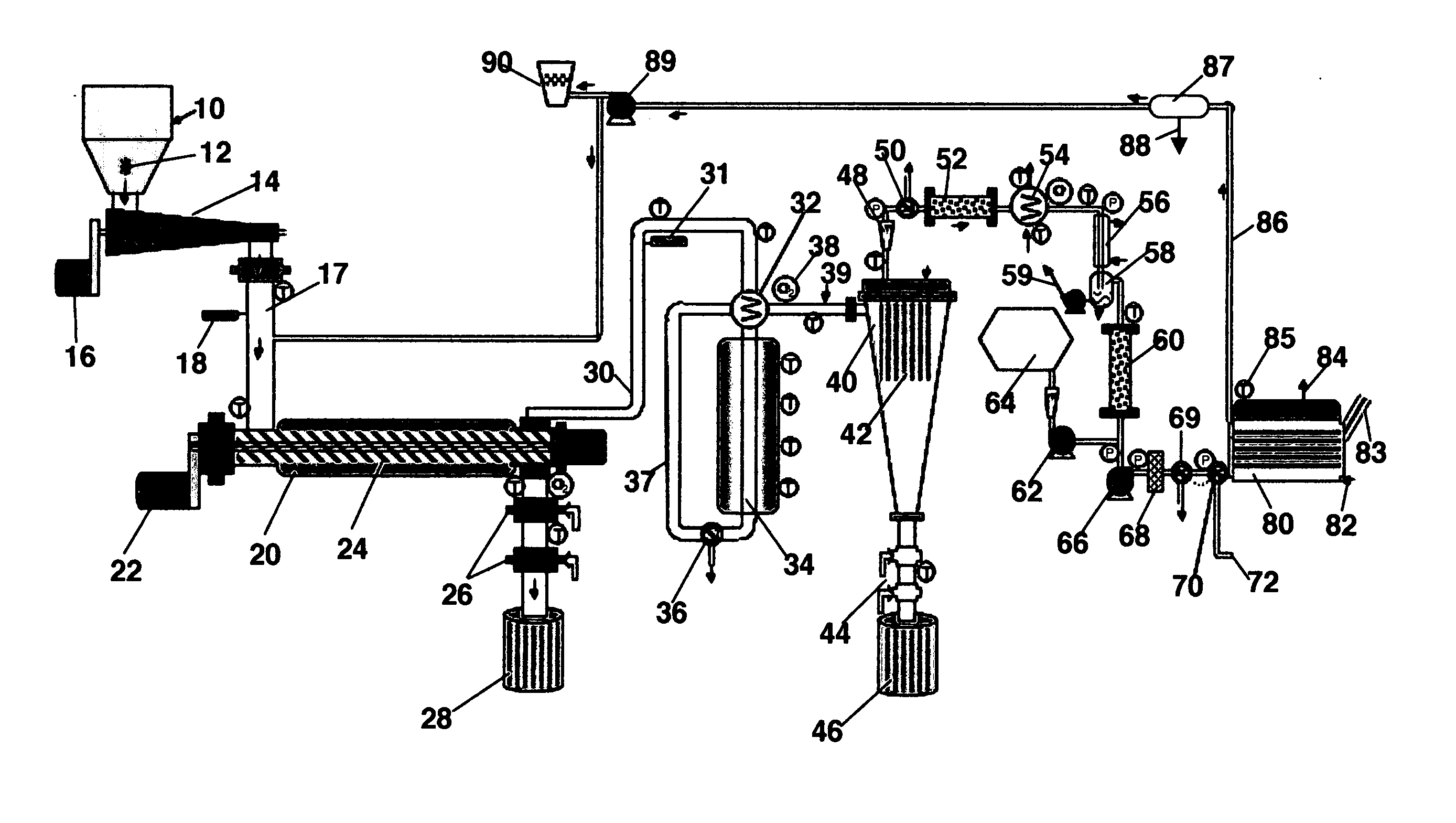
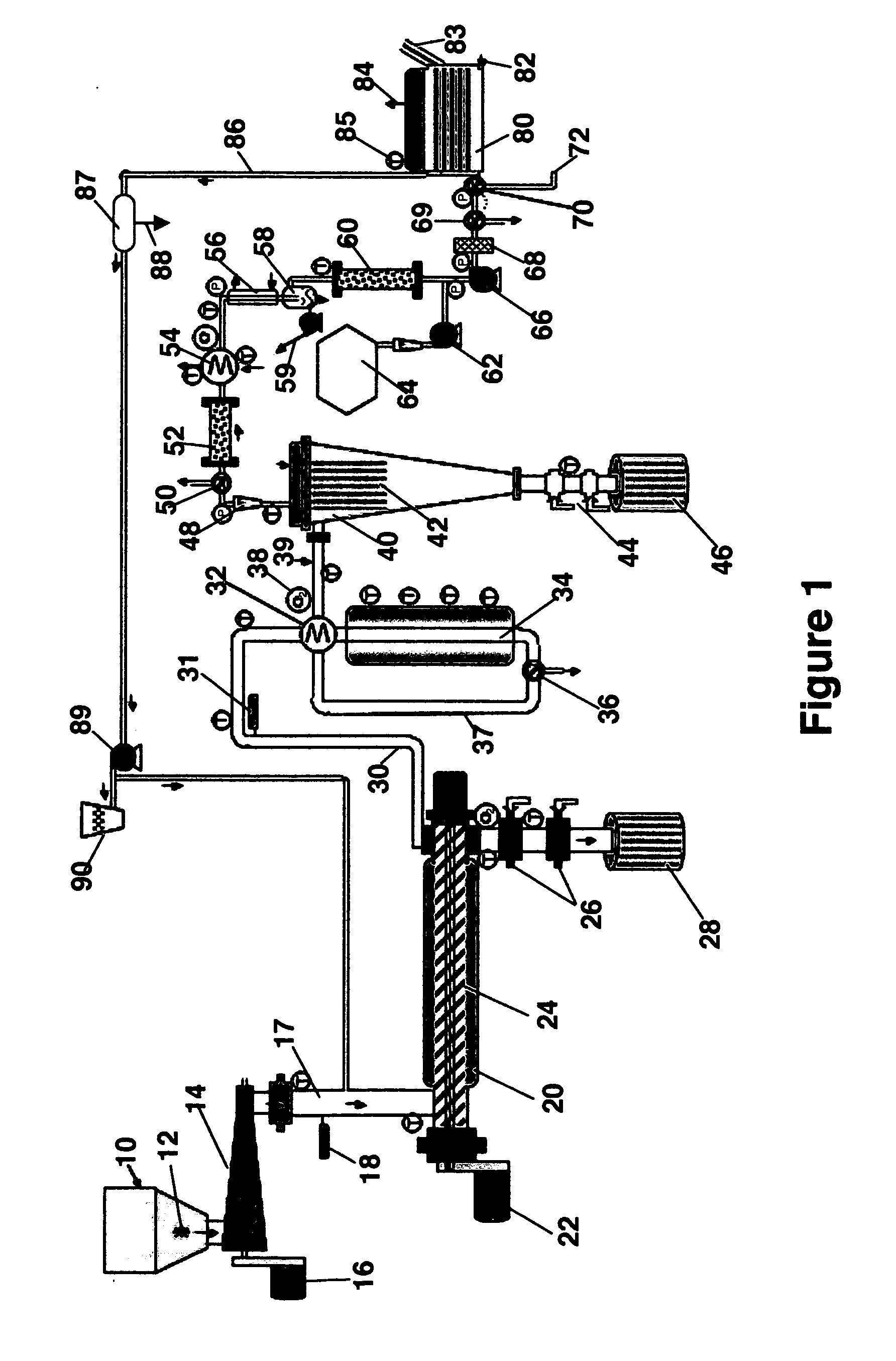
InactiveUS6790430B1Avoid the needCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesGas turbine plantsCalcinationExothermic reaction
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE +1
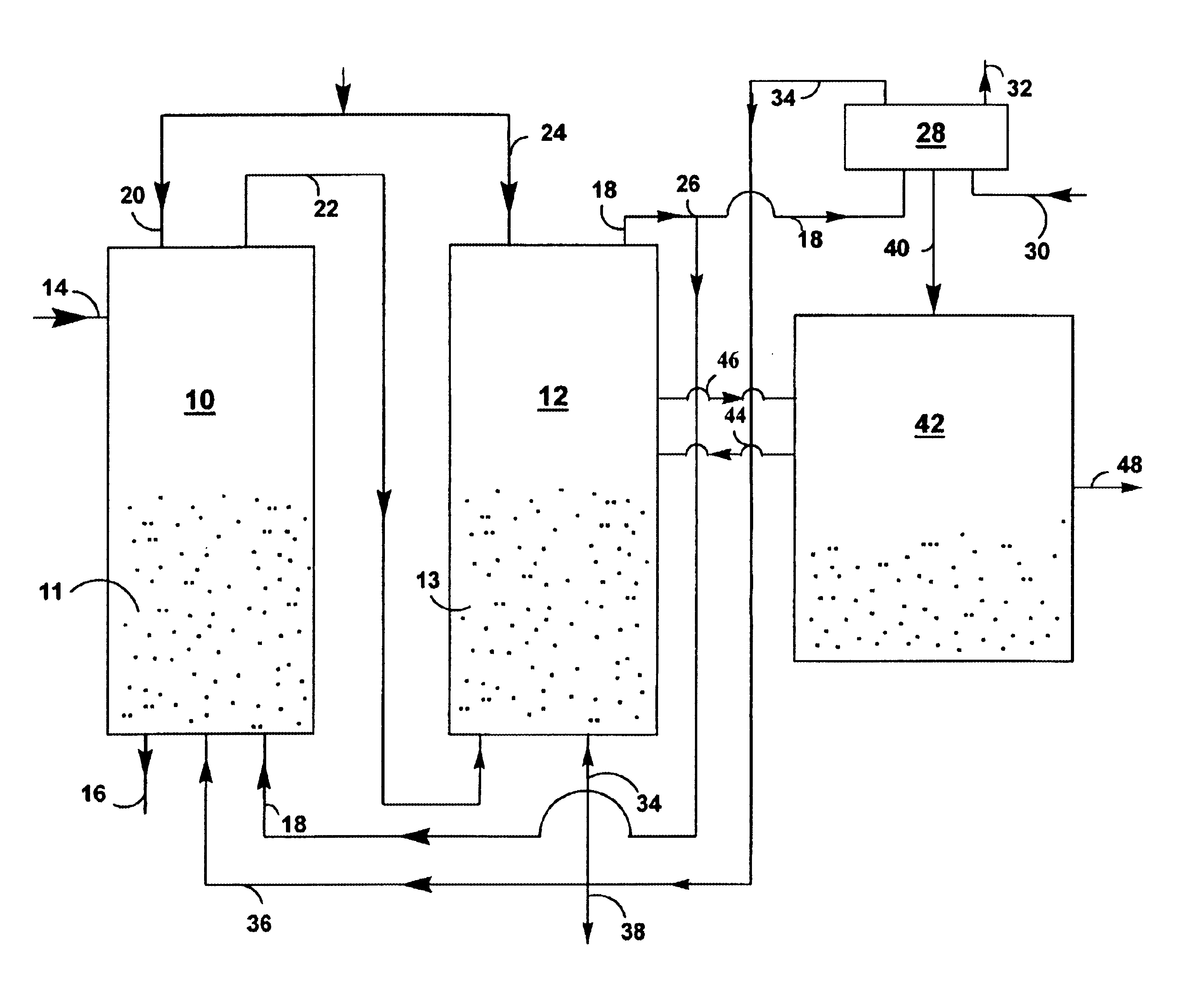
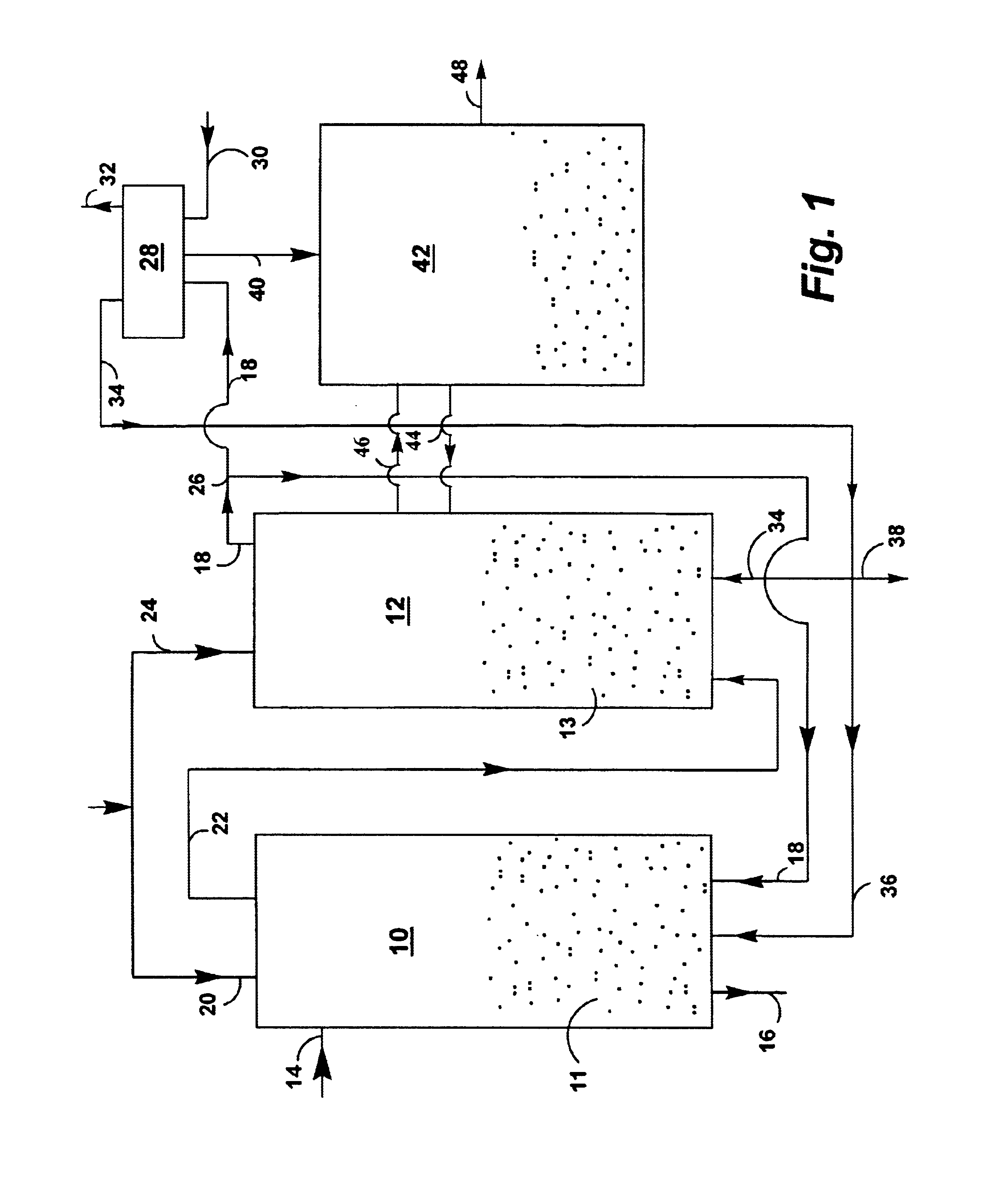
Combustion looping using composite oxygen carriers
ActiveUS20050175533A1Increase surface areaImprove energy conversion efficiencyHydrogen productionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationHydrogenCombustion
A method for producing hydrogen gas is provided and comprises reducing a metal oxide in a reduction reaction between a carbon-based fuel and a metal oxide to provide a reduced metal or metal oxide having a lower oxidation state, and oxidizing the reduced metal or metal oxide to produce hydrogen and a metal oxide having a higher oxidation state. The metal or metal oxide is provided in the form of a porous composite of a ceramic material containing the metal or metal oxide. The porous composite may comprise either a monolith, pellets, or particles.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Methods and devices for the production of Hydrocarbons from Carbon and Hydrogen sources
InactiveUS20080283411A1Reduce the environmentEasy to controlPhotography auxillary processesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
Devices and methods are described for converting a carbon source and a hydrogen source into hydrocarbons, such as alcohols, for alternative energy sources. The influents may comprise carbon dioxide gas and hydrogen gas or water, obtainable from the atmosphere for through methods described herein, such as plasma generation or electrolysis. One method to produce hydrocarbons comprises the use of an electrolytic device, comprising an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte. Another method comprises the use of ultrasonic energy to drive the reaction. The devices and methods and related devices and methods are useful, for example, to provide a fossil fuel alternative energy source, store renewable energy, sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, counteract global warming, and store carbon dioxide in a liquid fuel.
Owner:PRINCIPLE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Energy efficient gas separation for fuel cells
InactiveUS20020142208A1Improve efficiencyReduce the ratioFuel cell heat exchangeFused electrolyte fuel cellsEngineeringDelivery system
An electrical current generating system is disclosed that includes a fuel cell operating at a temperature of at least about 250° C. (for example, a molten carbonate fuel cell or a solid oxide fuel cell), a hydrogen gas separation system or oxygen gas delivery system that includes a compressor or pump, and a drive system for the compressor or pump that includes means for recovering energy from at least one of the hydrogen gas separation system, oxygen gas delivery system, or heat of the fuel cell. The drive system could be a gas turbine system. The hydrogen gas separation system or the oxygen gas delivery system may include a pressure swing adsorption module.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
ActiveUS20070099038A1High hydrogen contentFuel cells groupingHydrogen separation using solid contactPetroleum cokePetroleum
The process of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process uses a steam / CO2 reformer operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900°0 F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen that contains poisons and the compounds that poison fuel cells. The syngas is sent to an interface zone to remove these poisons and other fouling compounds that are electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
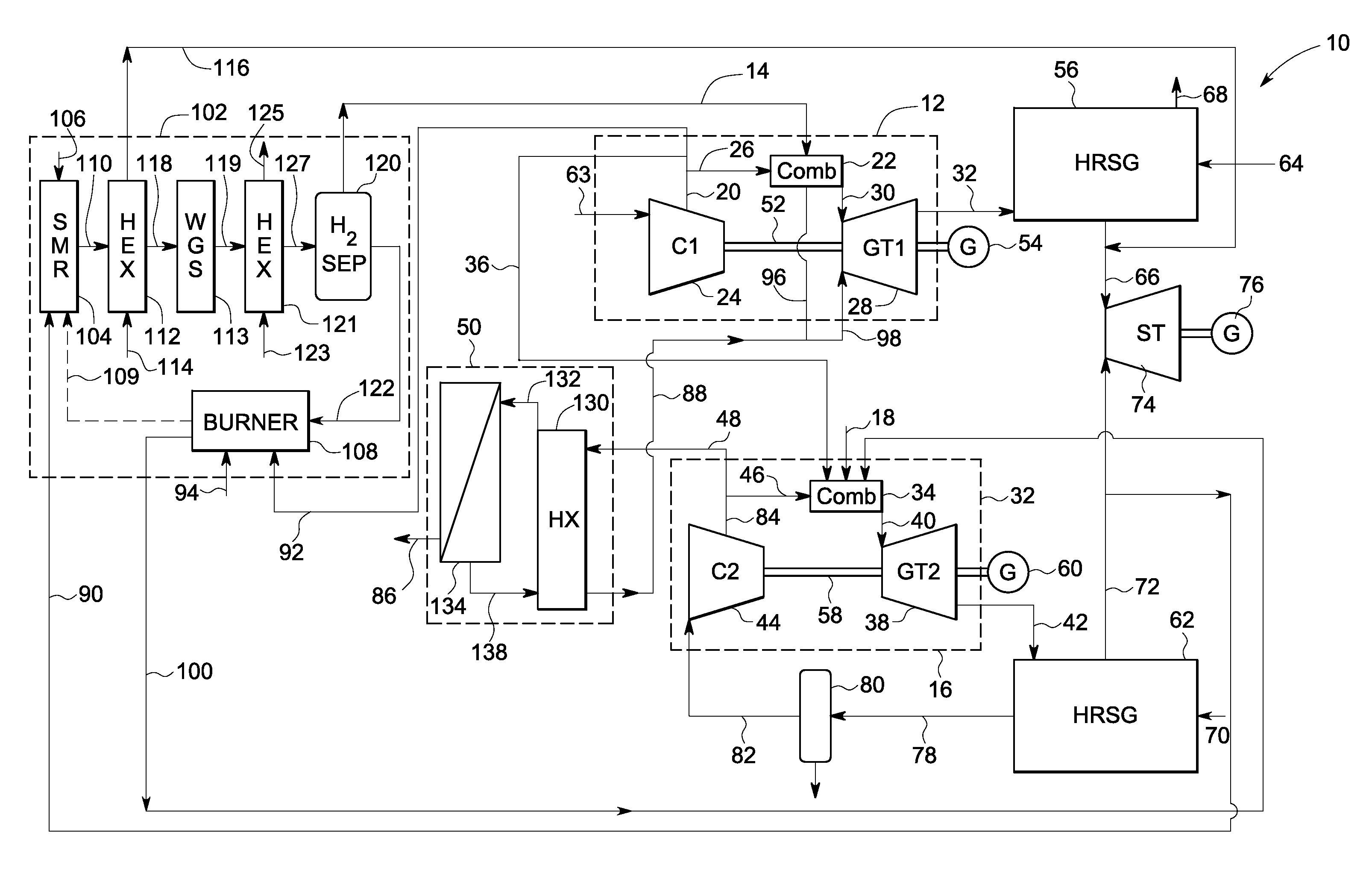
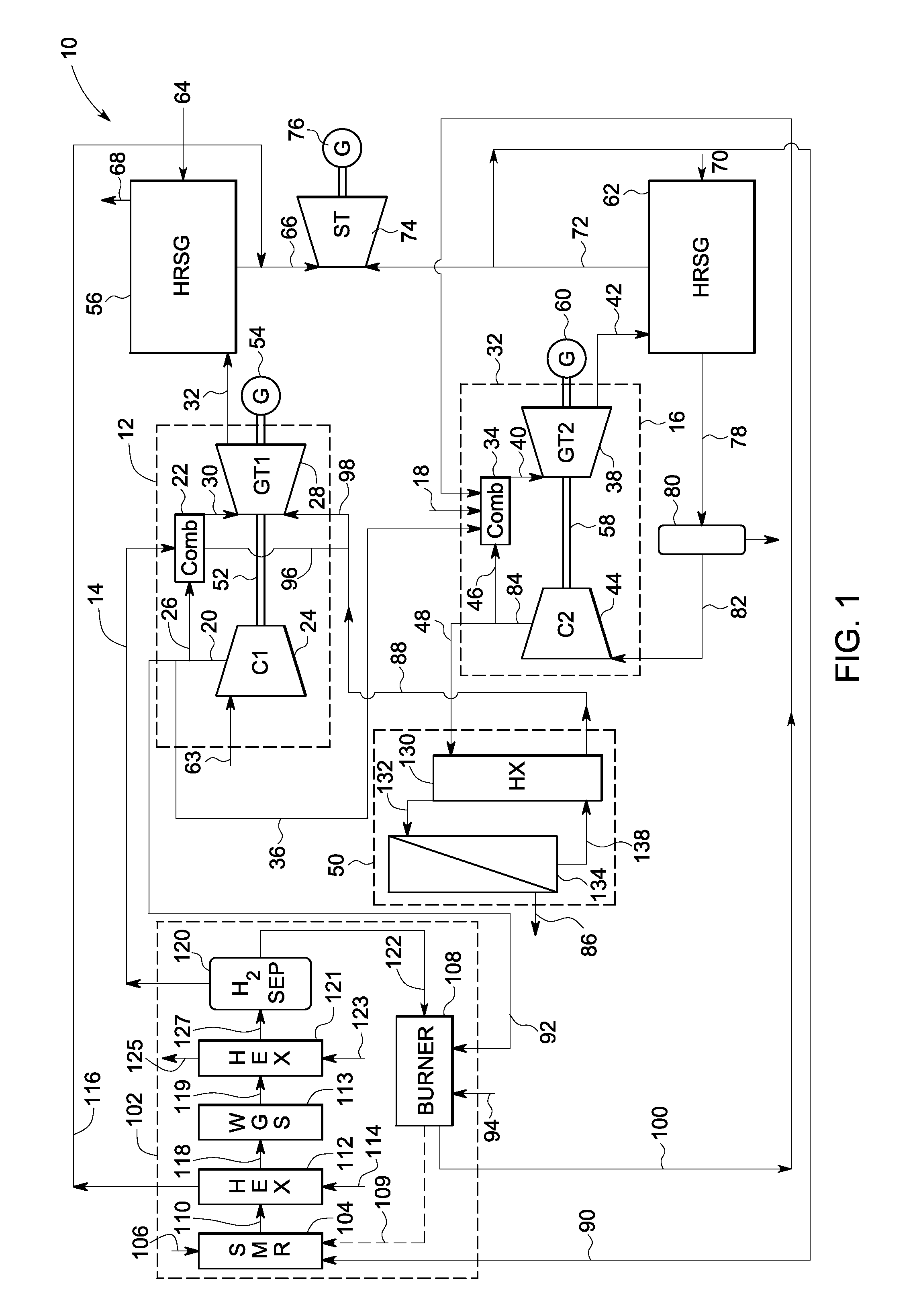
Reforming system for combined cycle plant with partial CO2 capture
A combined cycle system includes, a pre-steam-methane-reformer operating at a temperature of less than about 800 degrees Celsius to reform a mixed fuel stream to generate a first reformate stream, a water-gas-shift reactor to convert carbon monoxide in the first reformate stream to carbon dioxide and form a second reformate stream, a carbon dioxide removal unit for removing carbon dioxide from the second reformate stream and form a carbon dioxide stream and a third reformate stream; wherein less than about 50 percent of the carbon contained in the mixed fuel stream is recovered as carbon dioxide by the removal unit, a gas turbine unit for generating power and an exhaust stream, and a steam generator unit configured to receive the exhaust stream, wherein the heat of the exhaust stream is transferred to a water stream to generate the steam for the mixed fuel stream and for a steam turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Process and Apparatus for the Separation of Methane from a Gas Stream
InactiveUS20090260287A1Combustible gas chemical modificationHydrogen separation using liquid contactHydrogenWater vapor
Processes for conversion of a carbonaceous composition into a gas stream comprising methane are provided, where an energy-efficient process and / or apparatus is used to separate methane out of a gas stream comprising methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen. Particularly, methane can be separated from hydrogen and carbon monoxide using novel processes and / or apparatuses that generate methane hydrates. Because hydrogen and carbon monoxide do not readily form hydrates, the methane is separated from a gas stream. The methane can be captured as a substantially pure stream of methane gas by dissociating the methane from the hydrate and separating out any residual water vapor.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
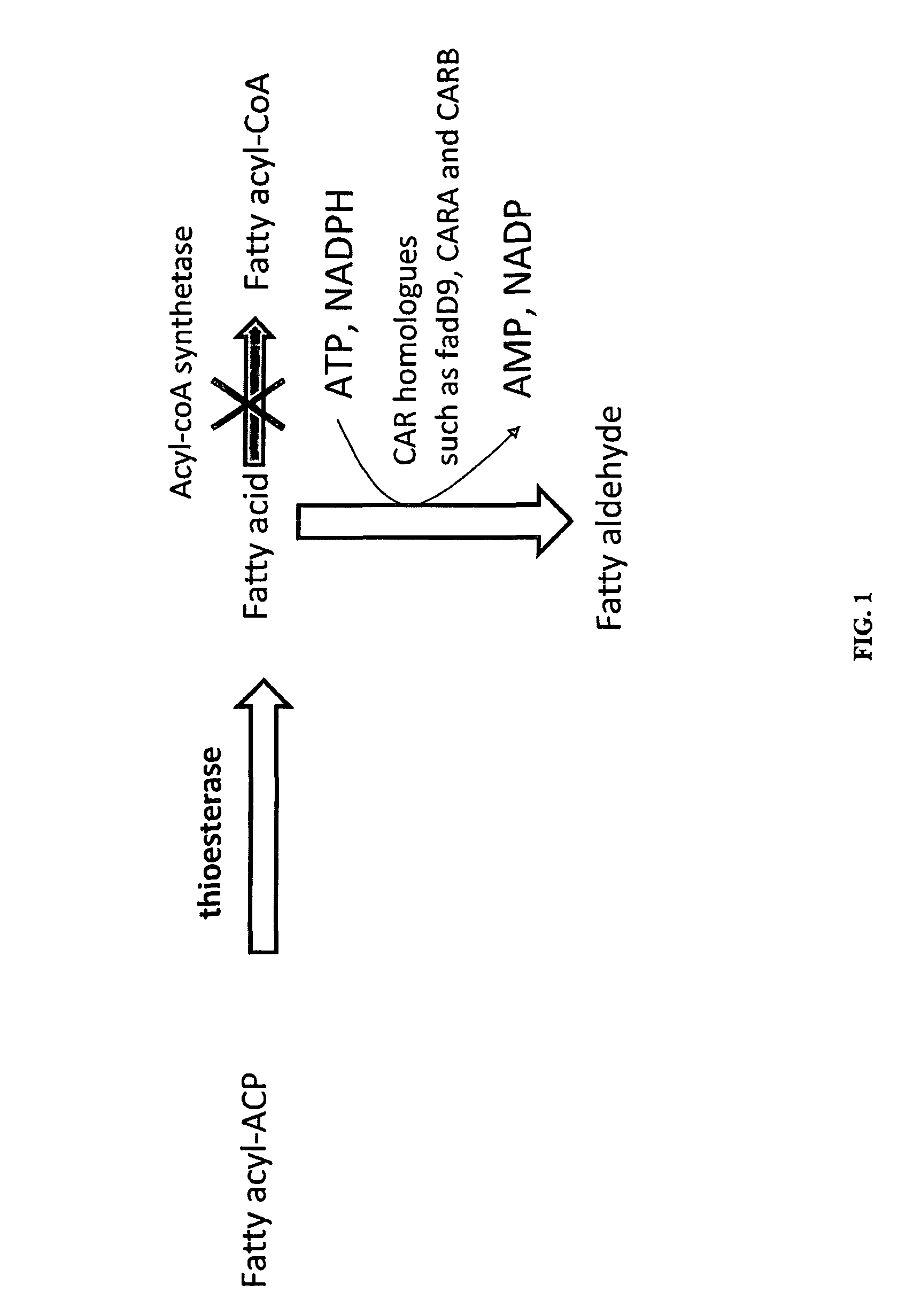
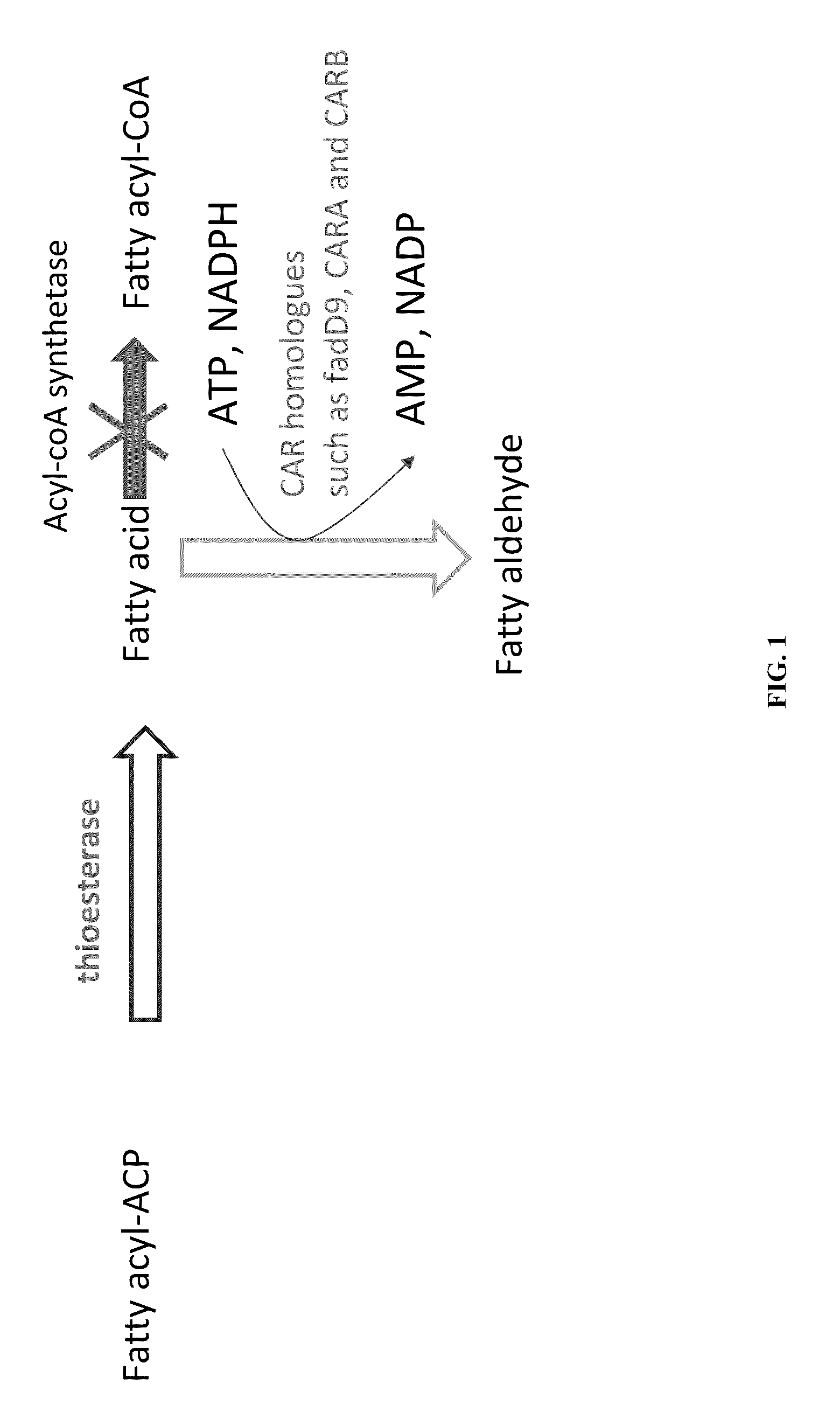
Methods and compositions for producing fatty aldehydes
Methods and compositions, including nucleotide sequences, amino acid sequences, and host cells, for producing fatty aldehydes are described.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
ActiveUS20110088896A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processMethane
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or methane reforming, involving combined capture and recycle of carbon dioxide from both processes.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Processes for hydromethanation of a carbonaceous feedstock
InactiveUS20110031439A1Increase the amount of carbonIncrease volumeCombustible gas chemical modificationHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular a hydrogen product stream and optionally a methane product stream, via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and a hydromethanation catalyst.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Method and apparatus for treating a sour gas
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Integrated hydromethanation combined cycle process
InactiveUS20110062721A1Easy to understandCombustible gas catalytic treatmentHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHydrogenCombustible gas
The present invention relates to an integrated process for preparing combustible gaseous products via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, a hydromethanation catalyst and optionally oxygen, and generating electrical power from those combustible gaseous products as well as a hydrogen and / or methane by-product stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
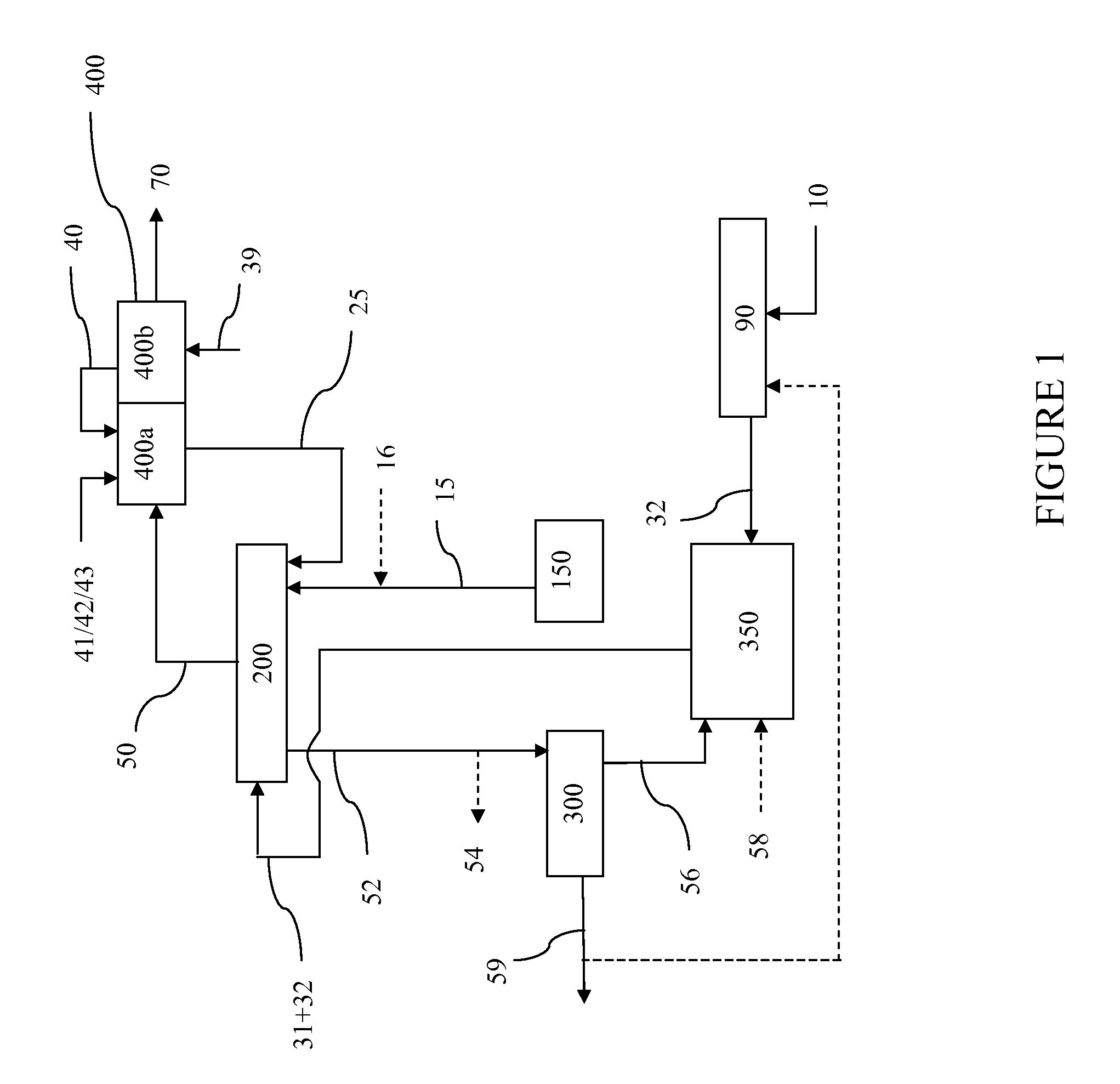
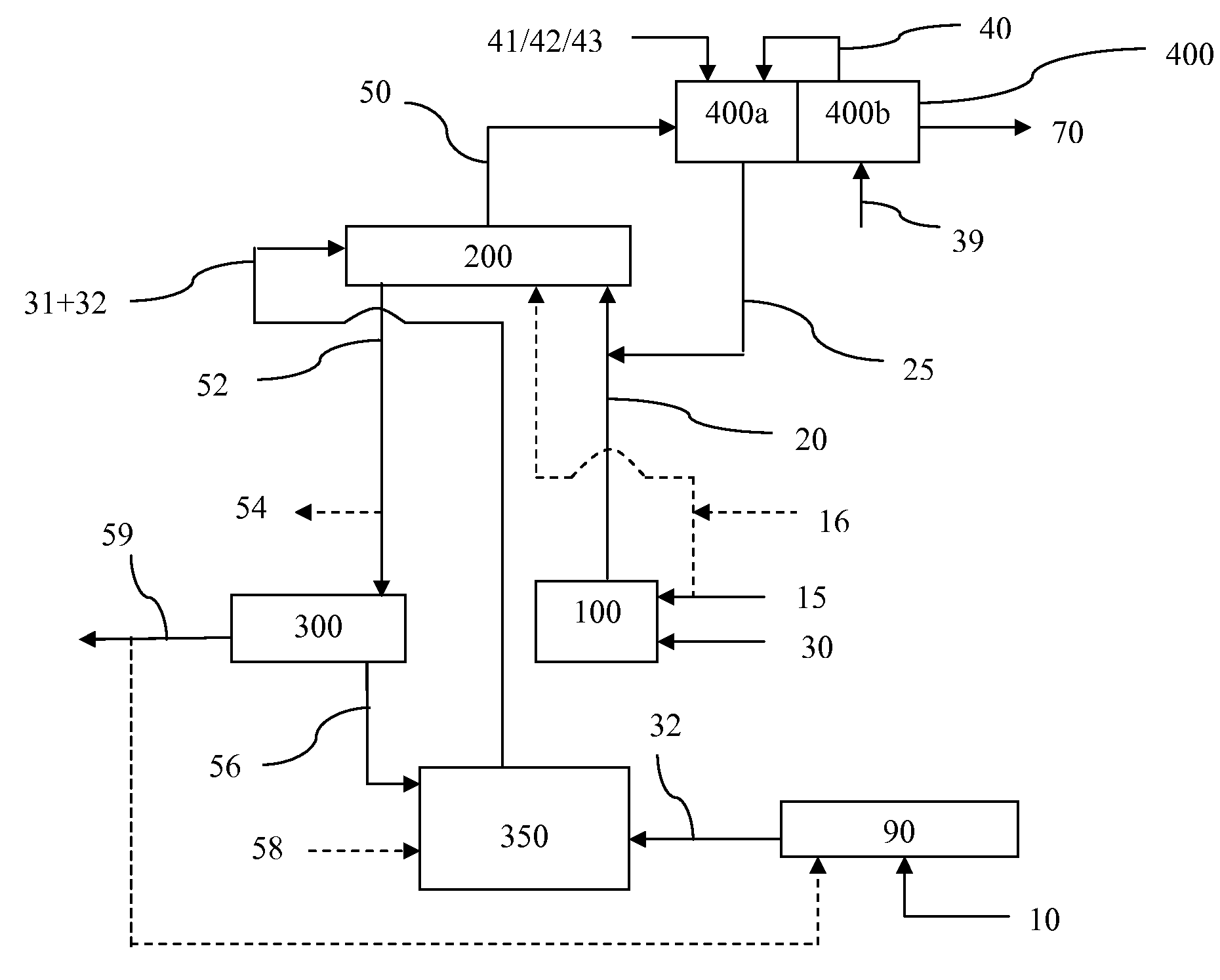
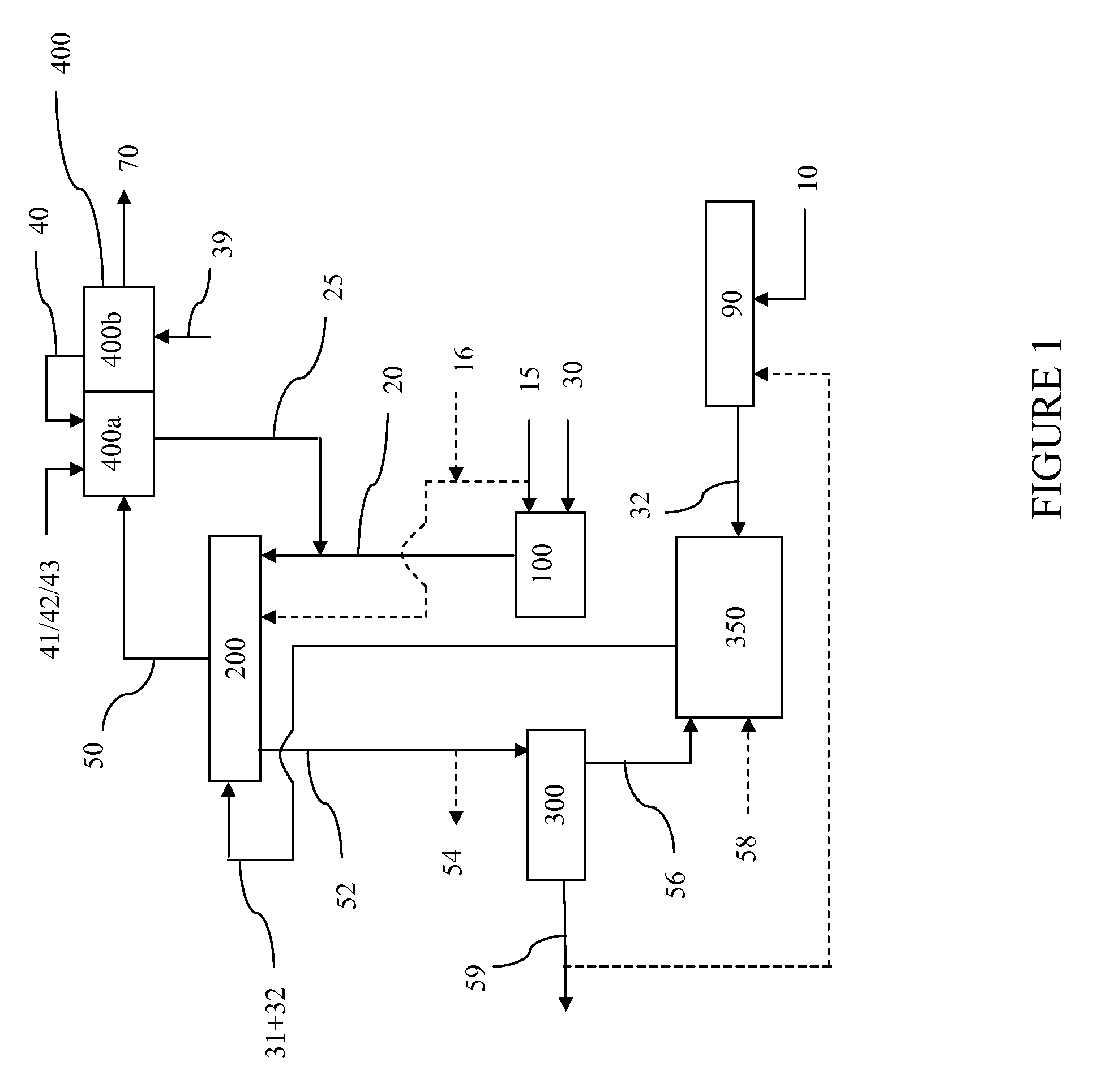
Apparatus and process for production of high purity hydrogen
InactiveUS20060248800A1High purityEnhanced overall recoveryCarbon compoundsIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationSteam reformingCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a new and improved process and apparatus for the production of high purity hydrogen by steam reforming. The apparatus is an integrated flameless distributed combustion-membrane steam reforming (FDC-MSR) or reactor for steam reforming of a vaporizable hydrocarbon to produce H2 and CO2, with minimal CO, and minimal CO in the H2 stream. The flameless distributed combustion drives the steam reforming reaction which pro-vides great improvements in heat exchange efficiency and load following capabilities. The reactor may contain multiple flameless distributed combustion chambers and multiple hydrogen-selective, hydrogen-permeable, membrane tubes. The feed and reaction gases may flow through the reactor either radially or axially. A further embodiment of the invention involves producing high purity hydrogen by dehydrogenation using an integrated FDC-membrane de-hydrogenation reactor. A still further embodiment of the invention involves a zero emission hybrid power system wherein the produced hydrogen is used to power a high-pressure internally manifolded molten carbonate fuel cell. In addition, the design of the FDC-SMR powered fuel cell makes it possible to capture good concentrations of CO2 for sequestration or use in other processes.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods and compositions for producing fatty aldehydes
Methods and compositions, including nucleotide sequences, amino acid sequences, and host cells, for producing fatty aldehydes are described.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
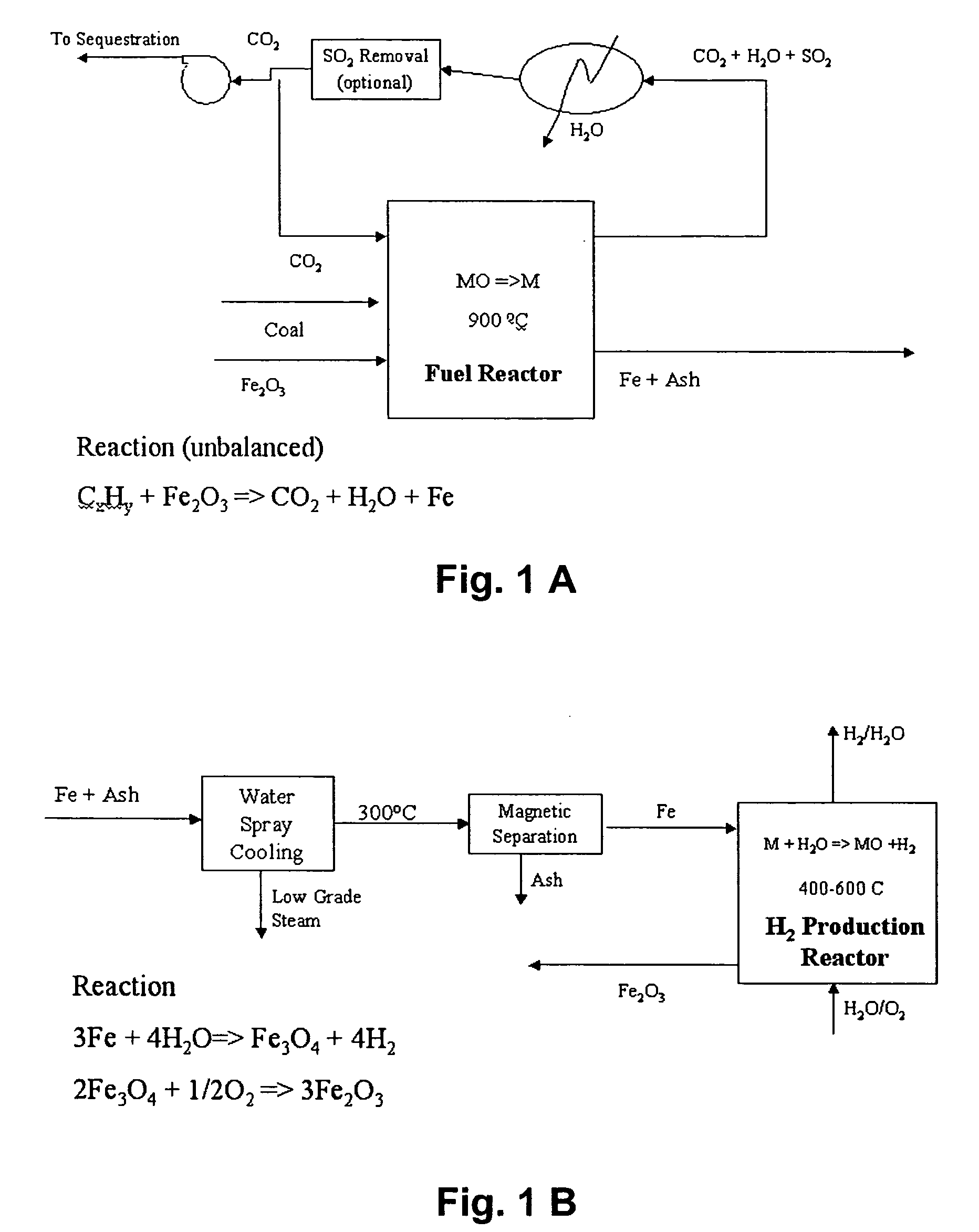
Production of hydrogen and removal and sequestration of carbon dioxide from coal-fired furnaces and boilers
InactiveUS7282189B2Increase ratingsValue maximizationOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsHydrogenProcess engineering
Methods for reducing and eliminating carbon dioxide from the emissions of solid fuel fired power plants, particularly coal fired power plants, and to sequester the carbon dioxide, typically by using existing equipment. In some embodiments, the methods involve pyrolyzing the solid fuel to remove volatile matter and using the volatile matter to produce hydrogen. Additionally, the methods may involve burning the solid fuel or pyrolized solid fuel at very fuel rich stoichiometric conditions. Sequestration may include the production of a carbon dioxide-containing solution and the pumping of the solution into the ground, particularly in areas high in limestone.
Owner:ZAUDERER BERT
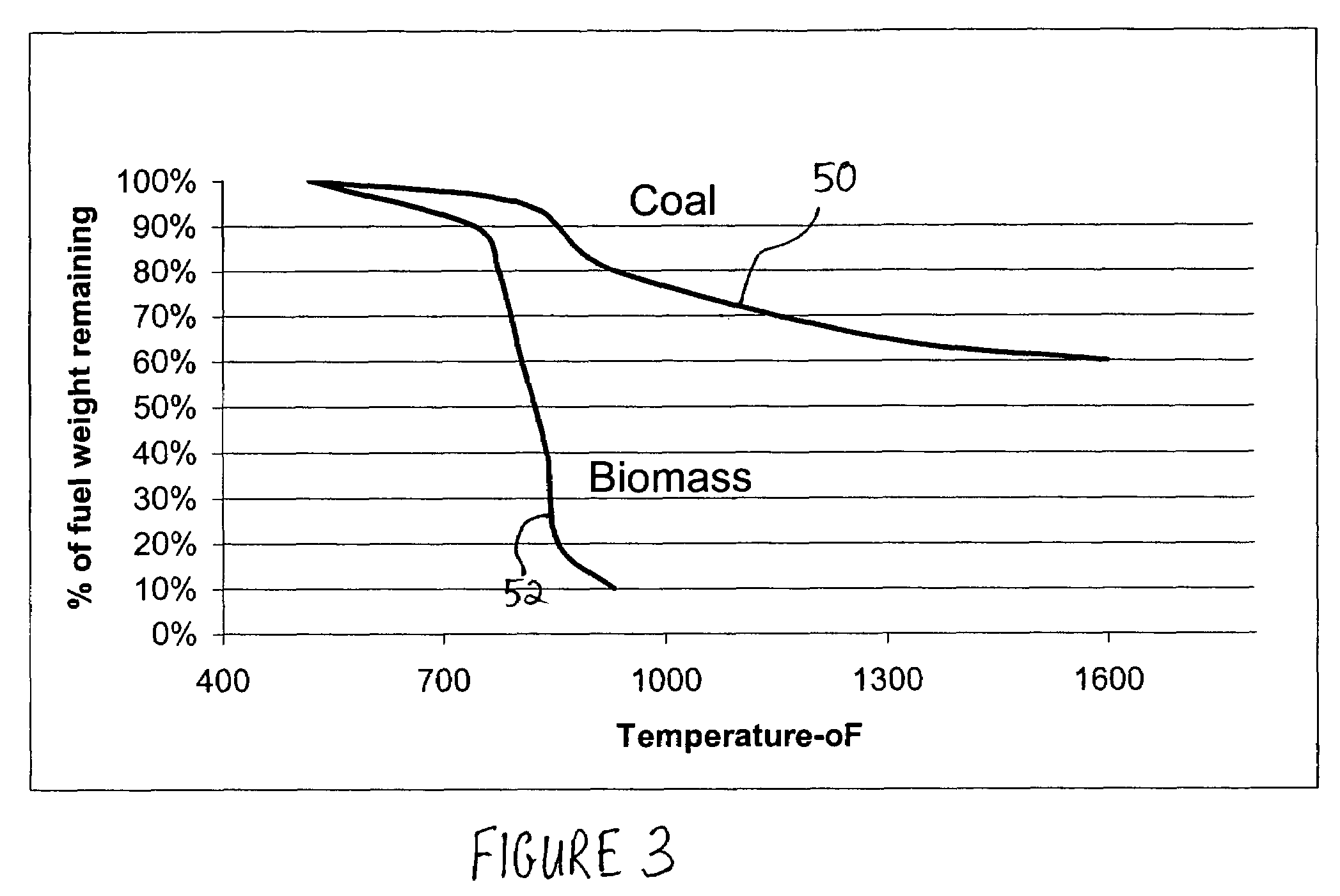
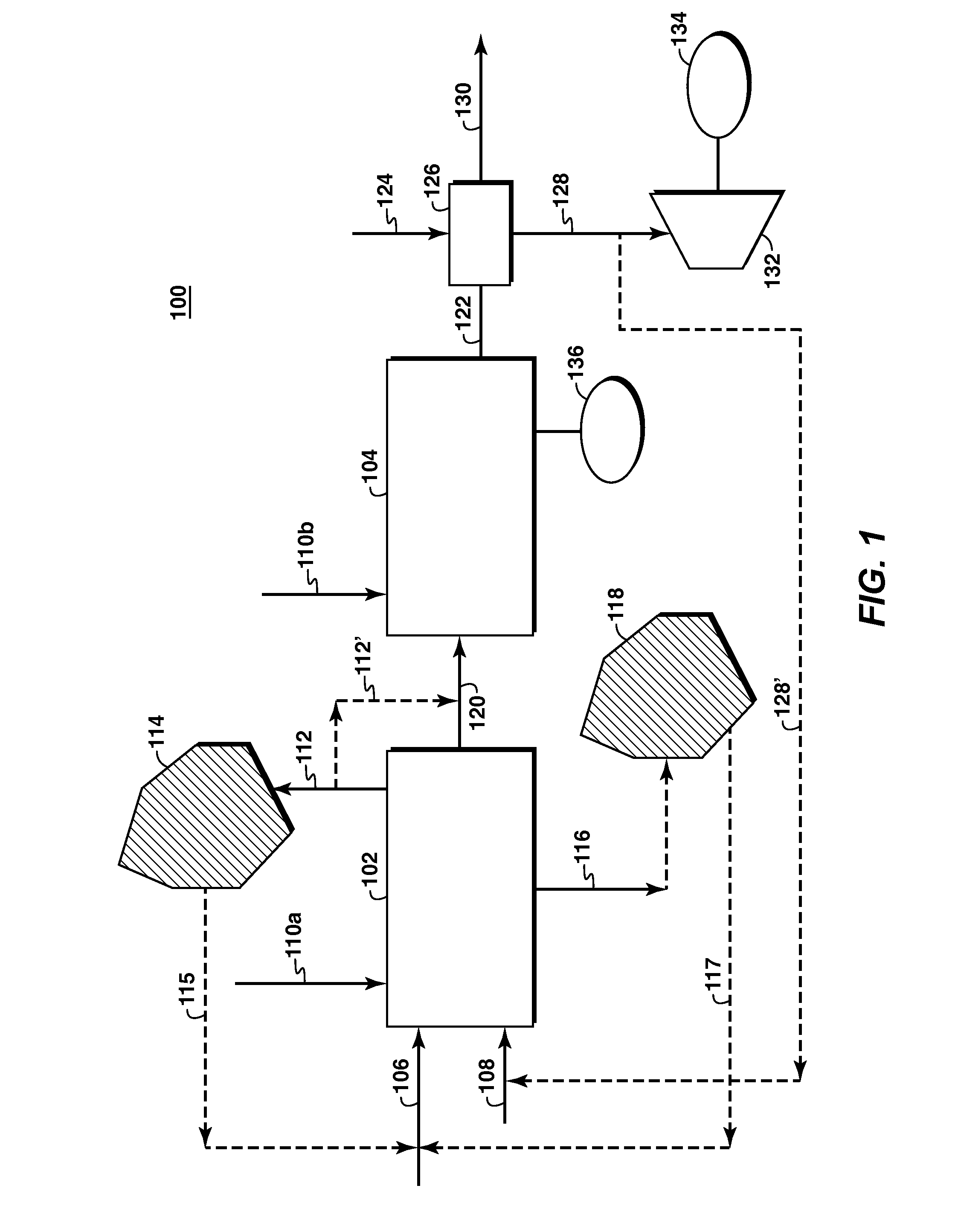
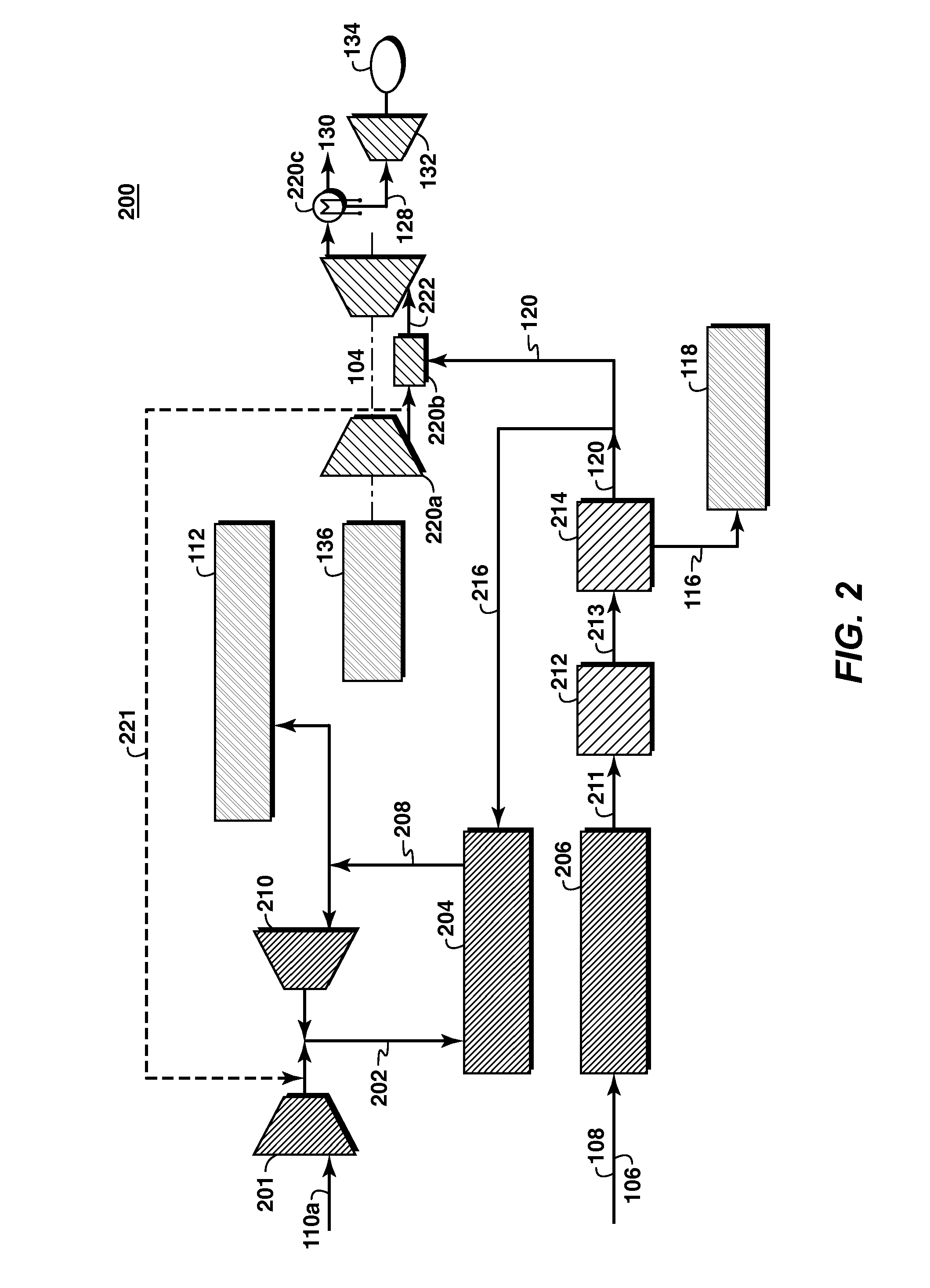
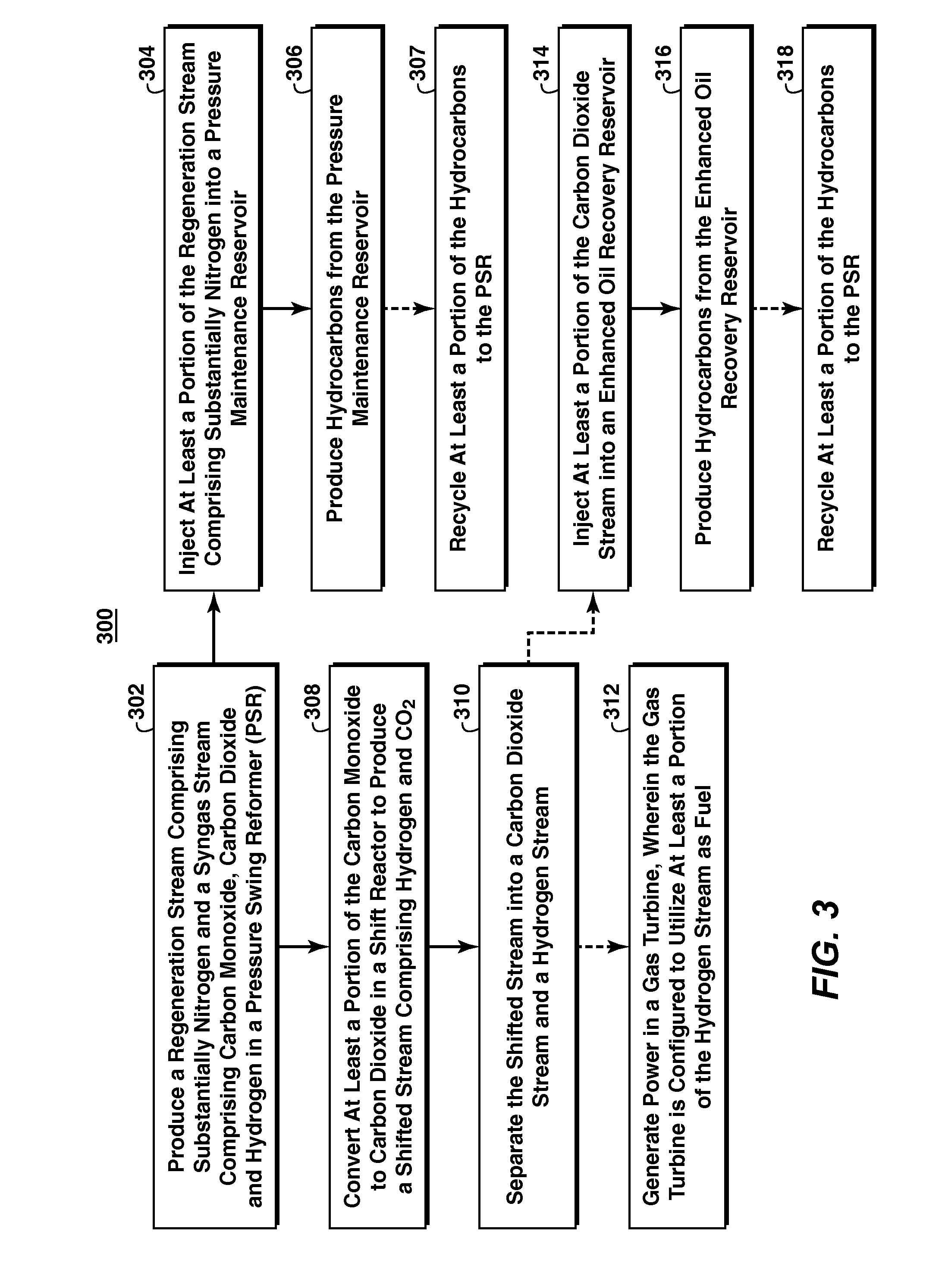
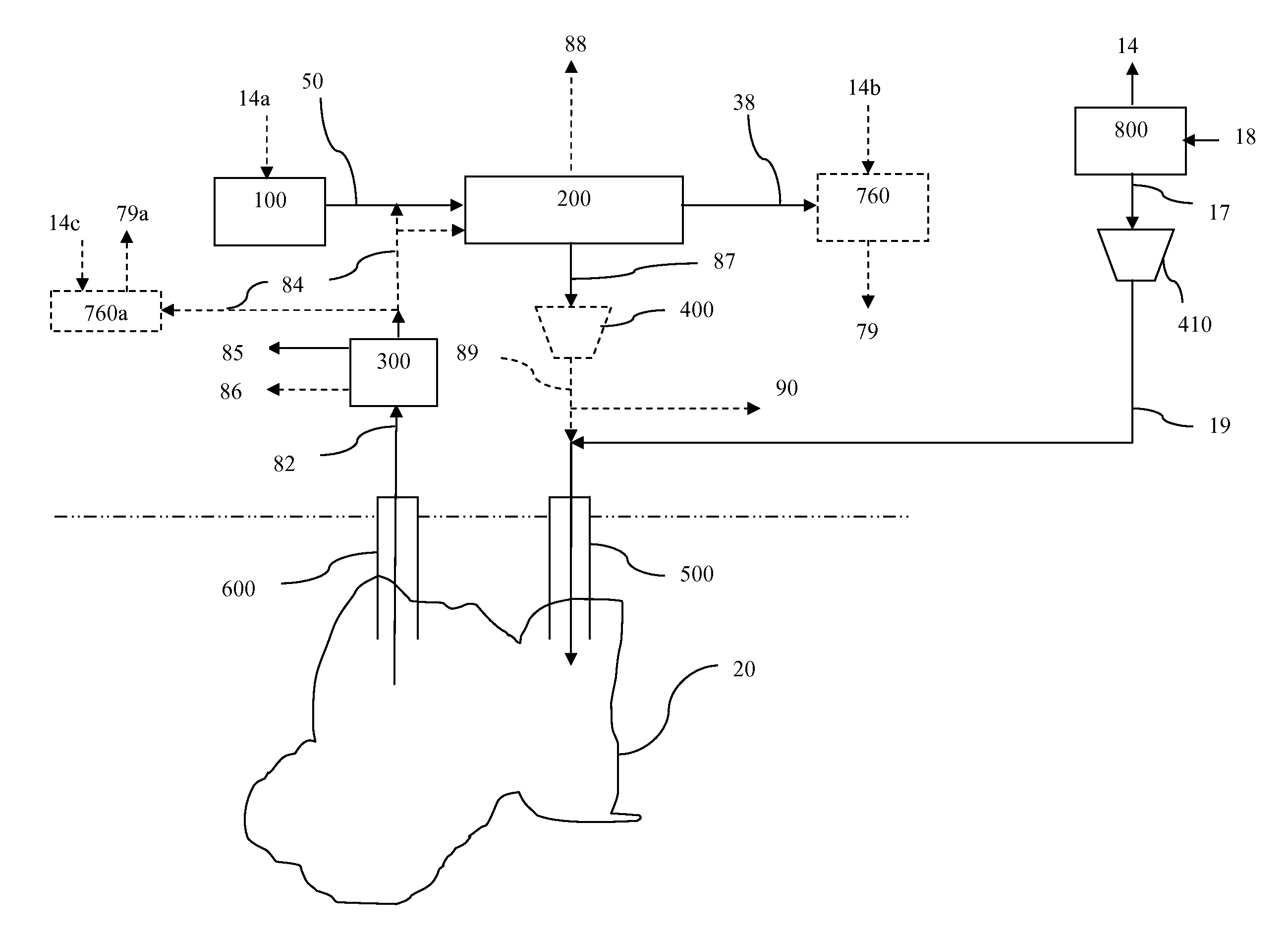
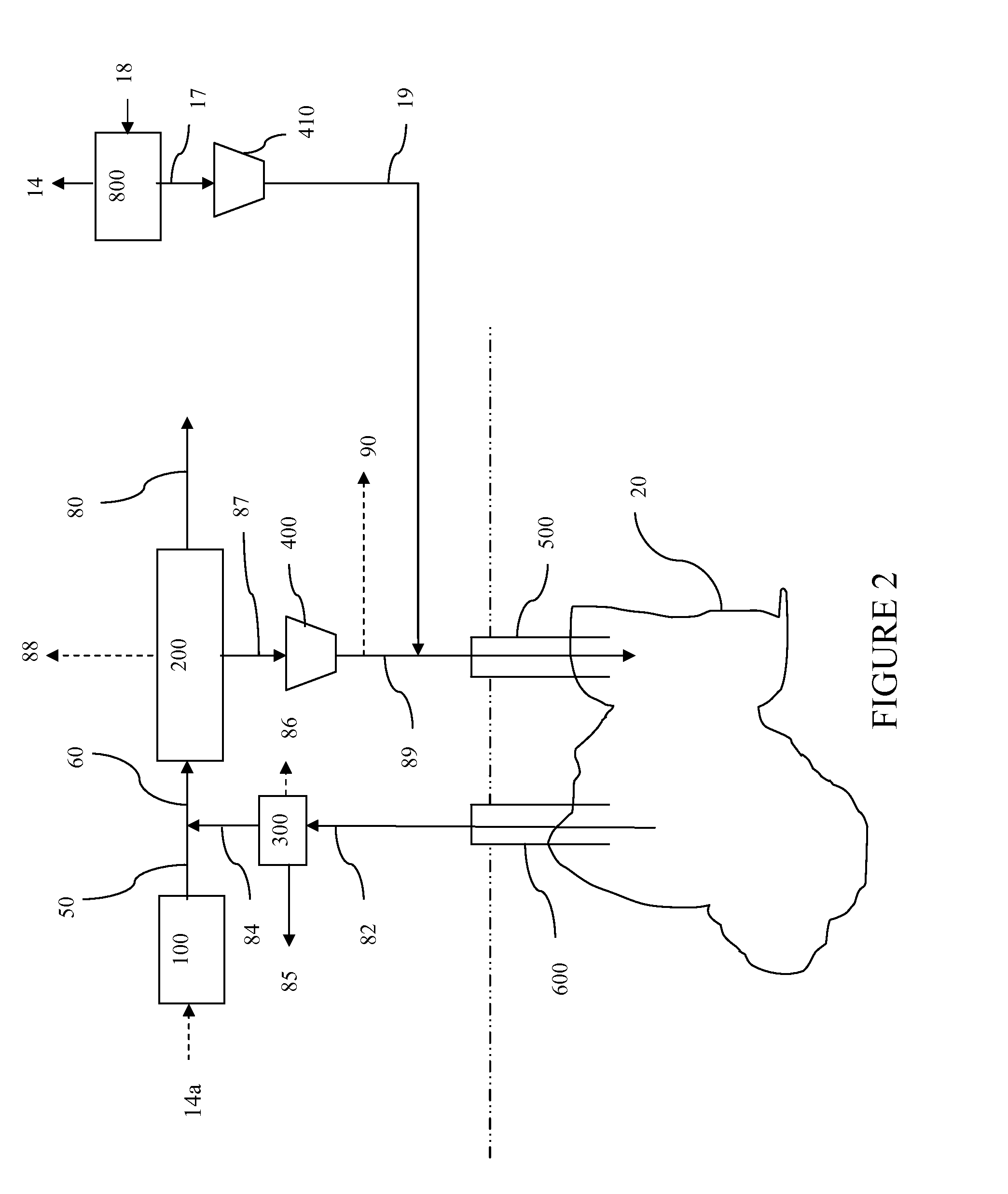
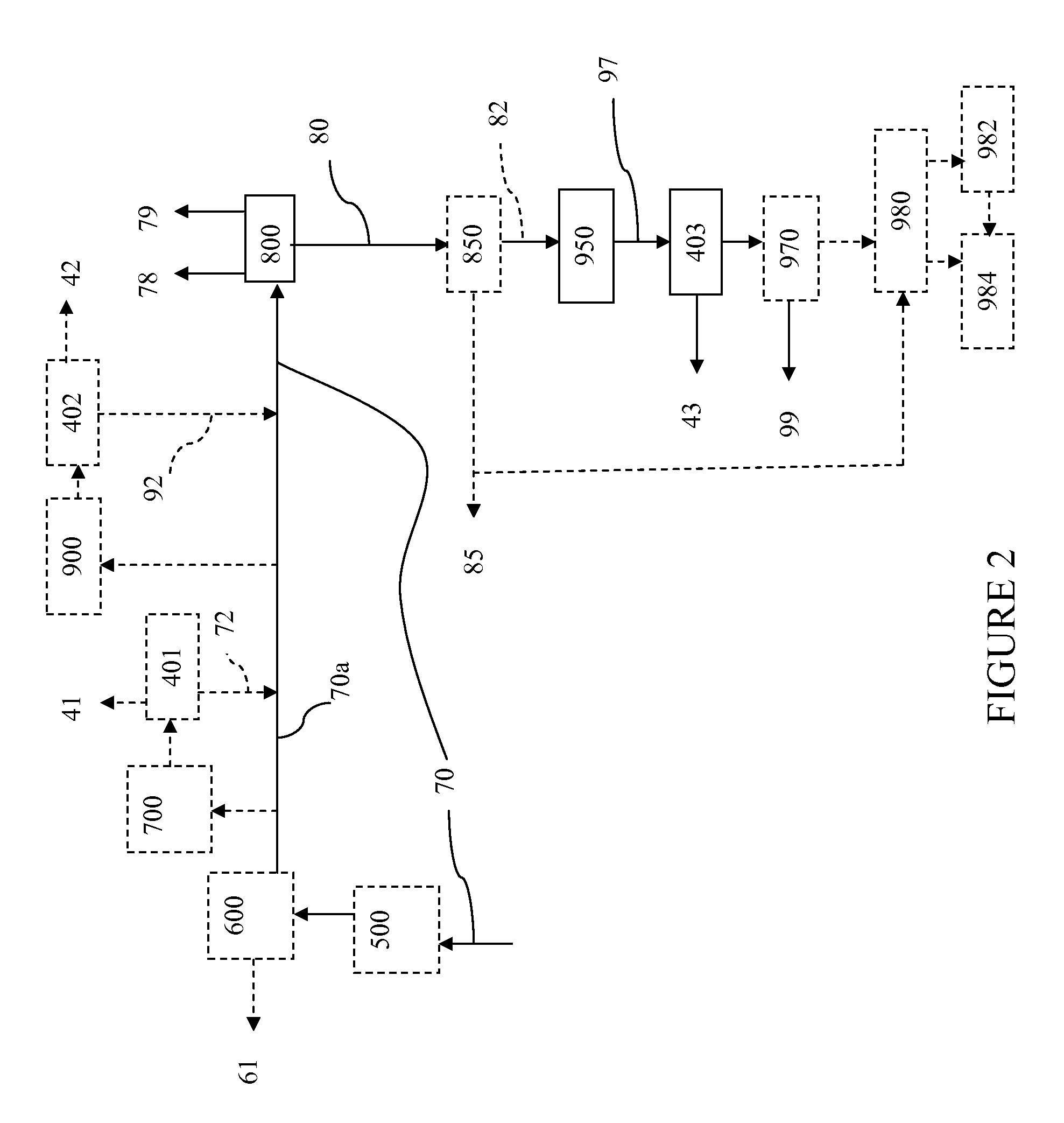
Low Emission Power Generation and Hydrocarbon Recovery Systems and Methods
Methods and systems for low emission power generation in hydrocarbon recovery processes are provided. One system includes integrated pressure maintenance and miscible flood systems with low emission power generation. The system may also include integration of a pressure swing reformer (PSR), air-blown auto-thermal reformer (ATR), or oxygen-blown ATR with a gas power turbine system, preferably a combined cycle gas power turbine system. Such systems may be employed to capture and utilize greenhouse gases (GHG) and generate power for use in hydrocarbon recovery operations.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Two-mode process for hydrogen production
InactiveUS20110064648A1Increase the amount of carbonIncrease volumeGaseous fuelsGasification processes detailsHydrogen productionMethane
The present invention relates to a 2-mode processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular a hydrogen product stream, via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and a hydromethanation catalyst in a first mode, and a partial oxidation of methane in a second mode.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
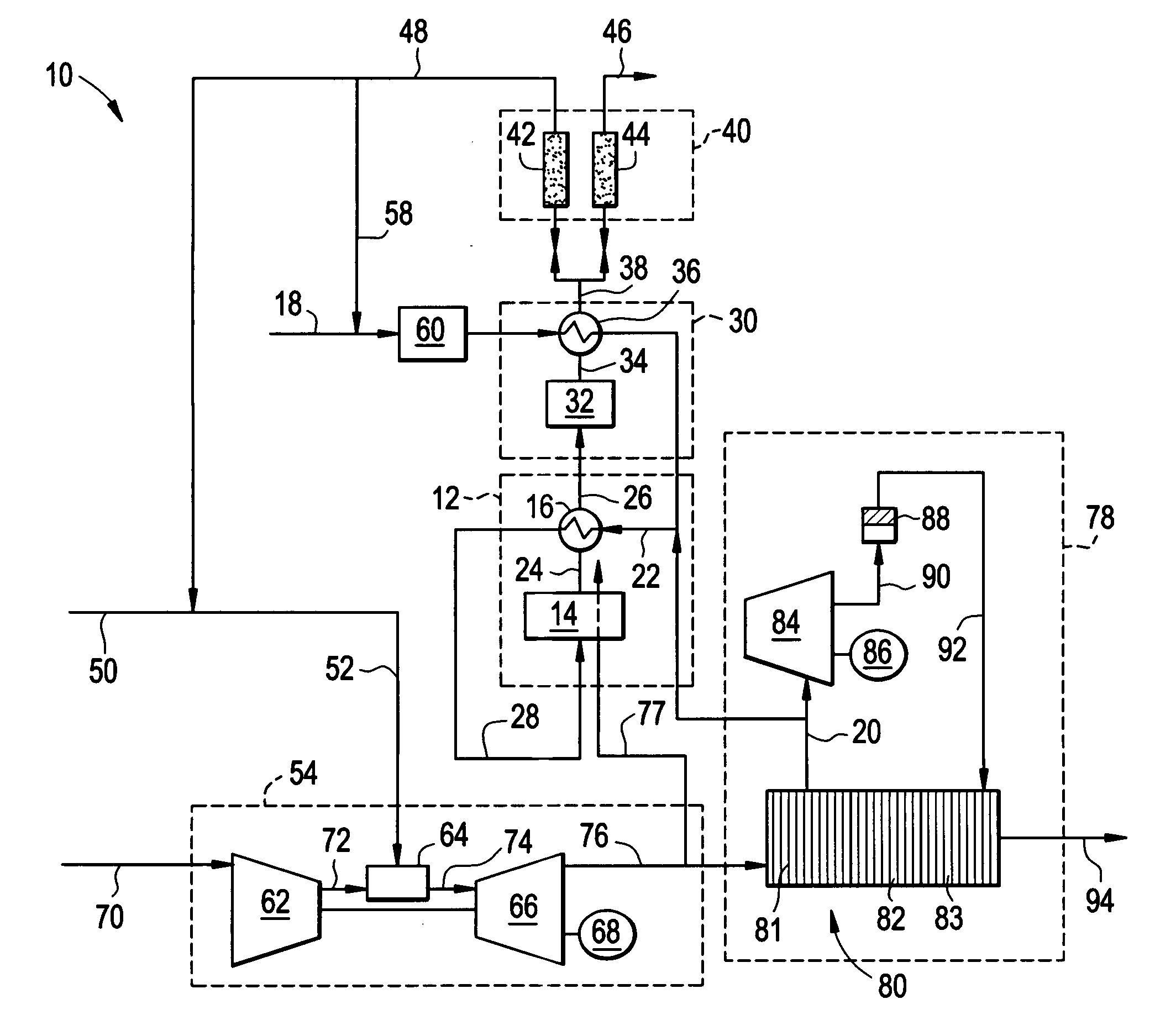
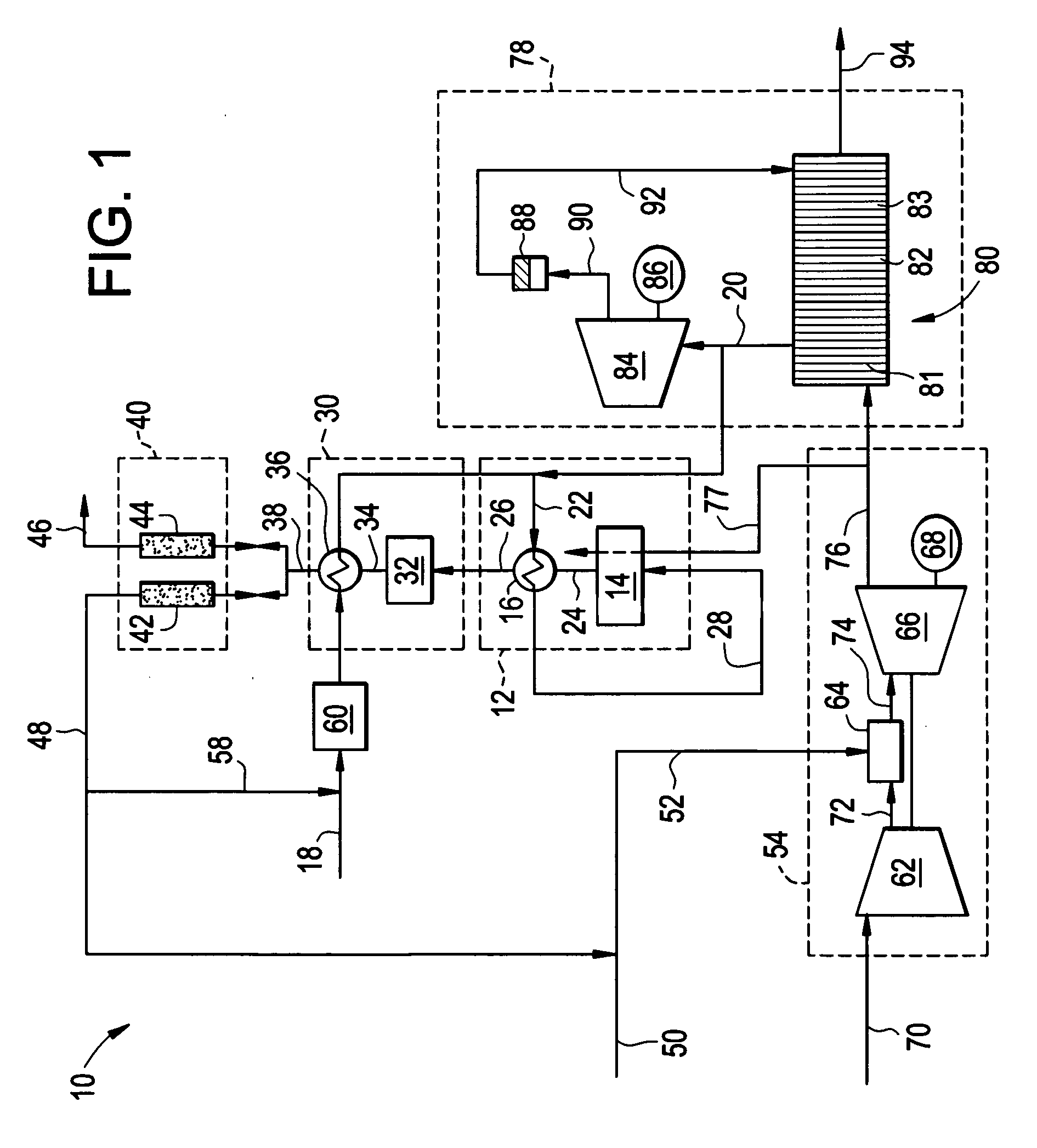
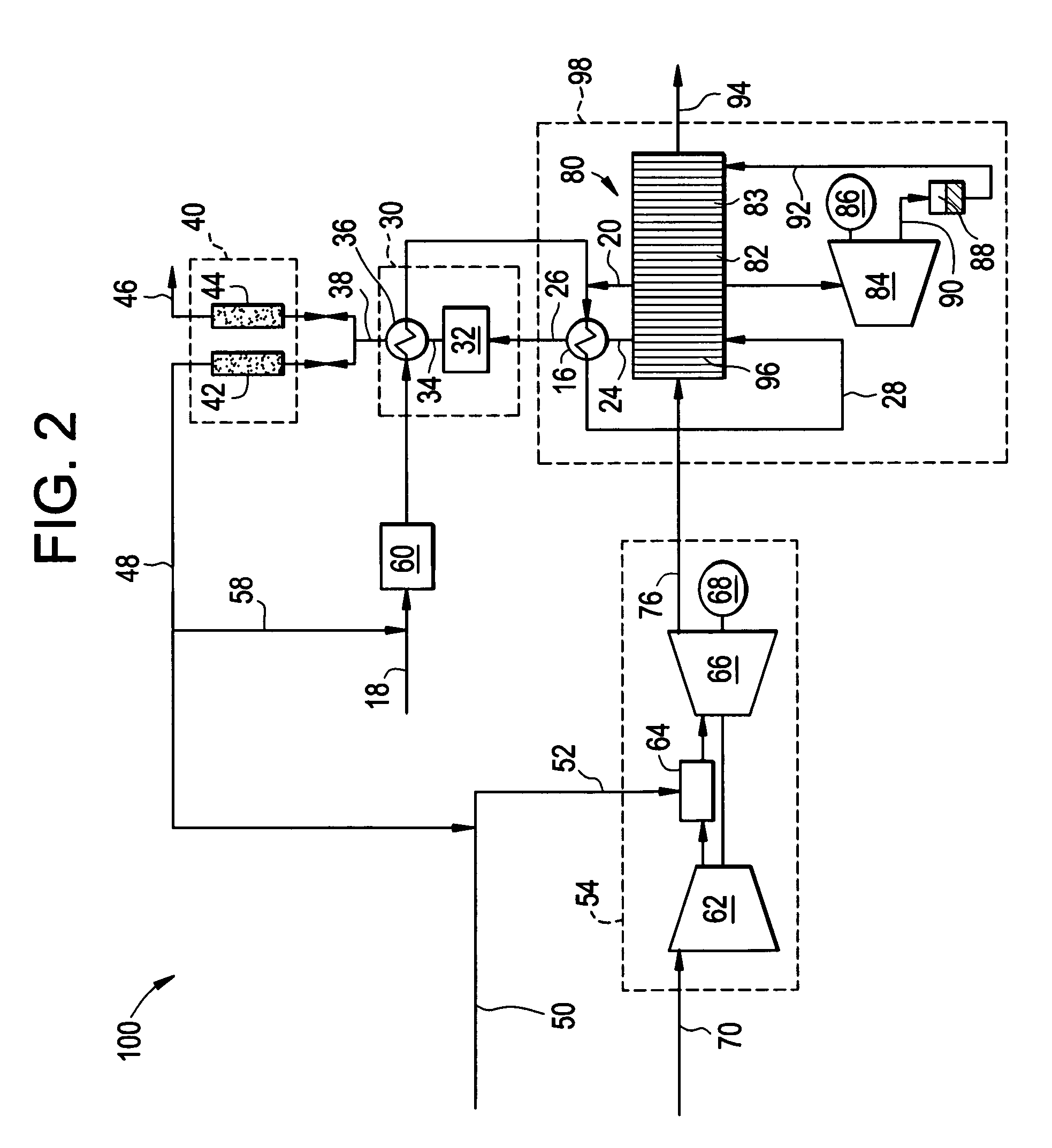
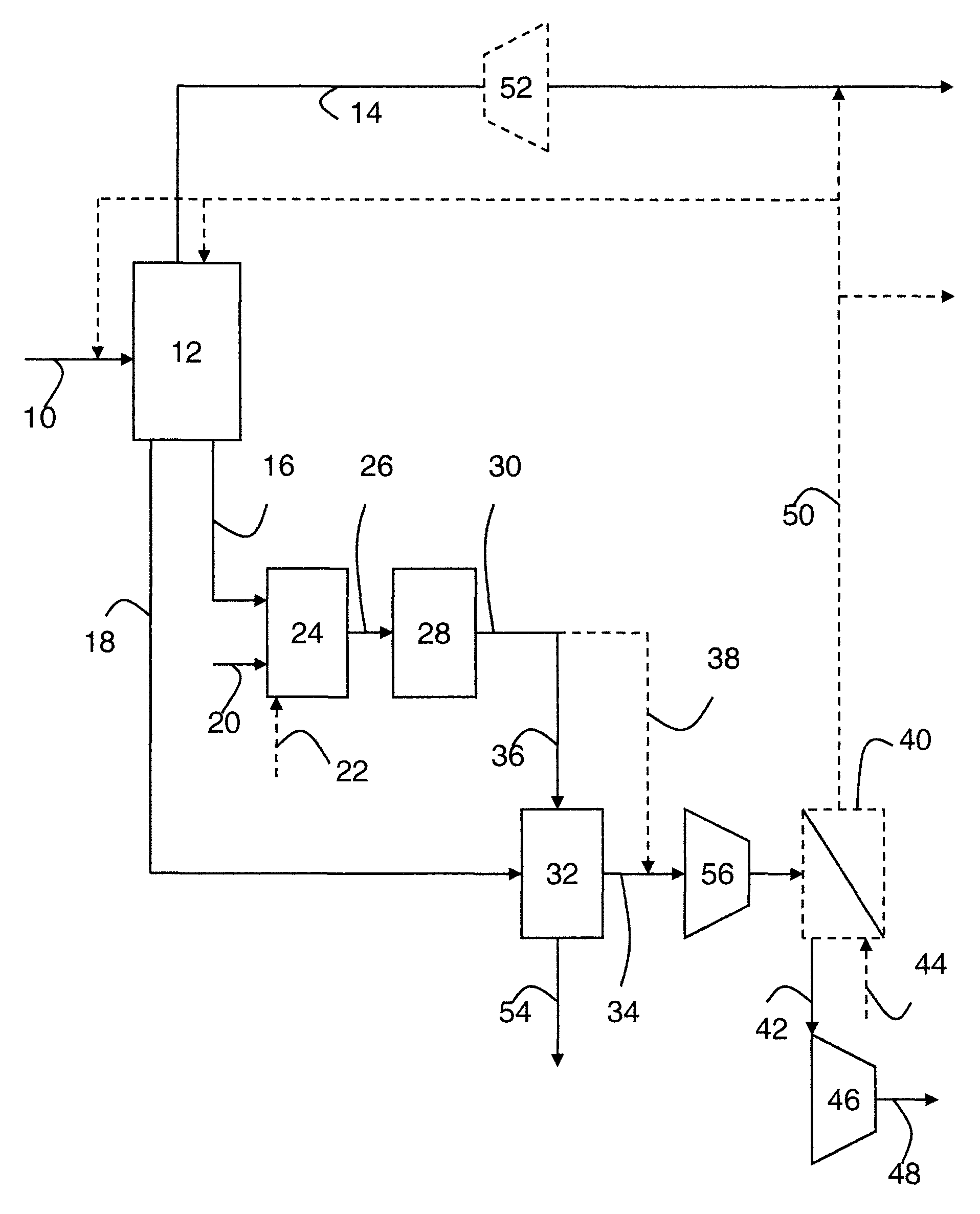
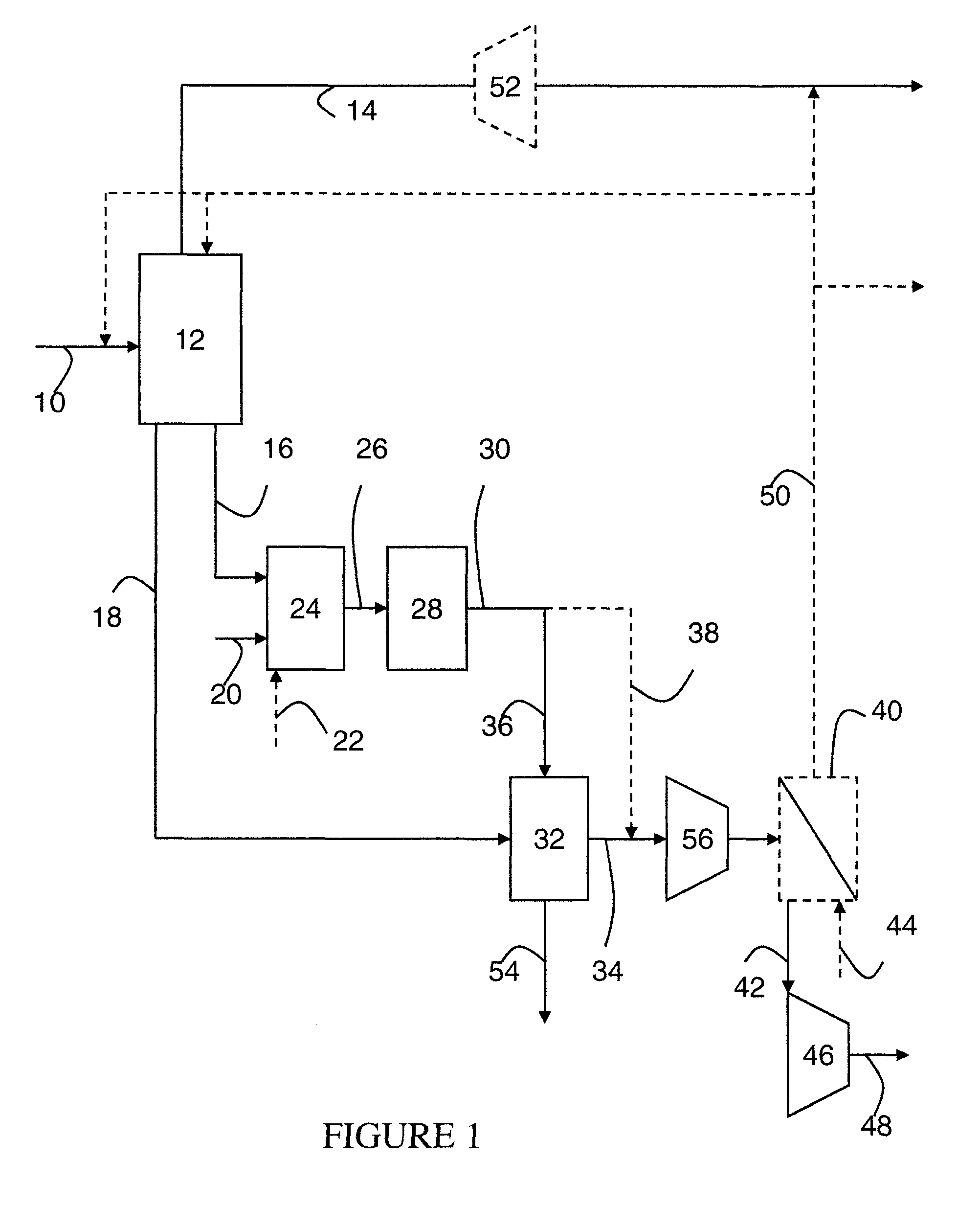
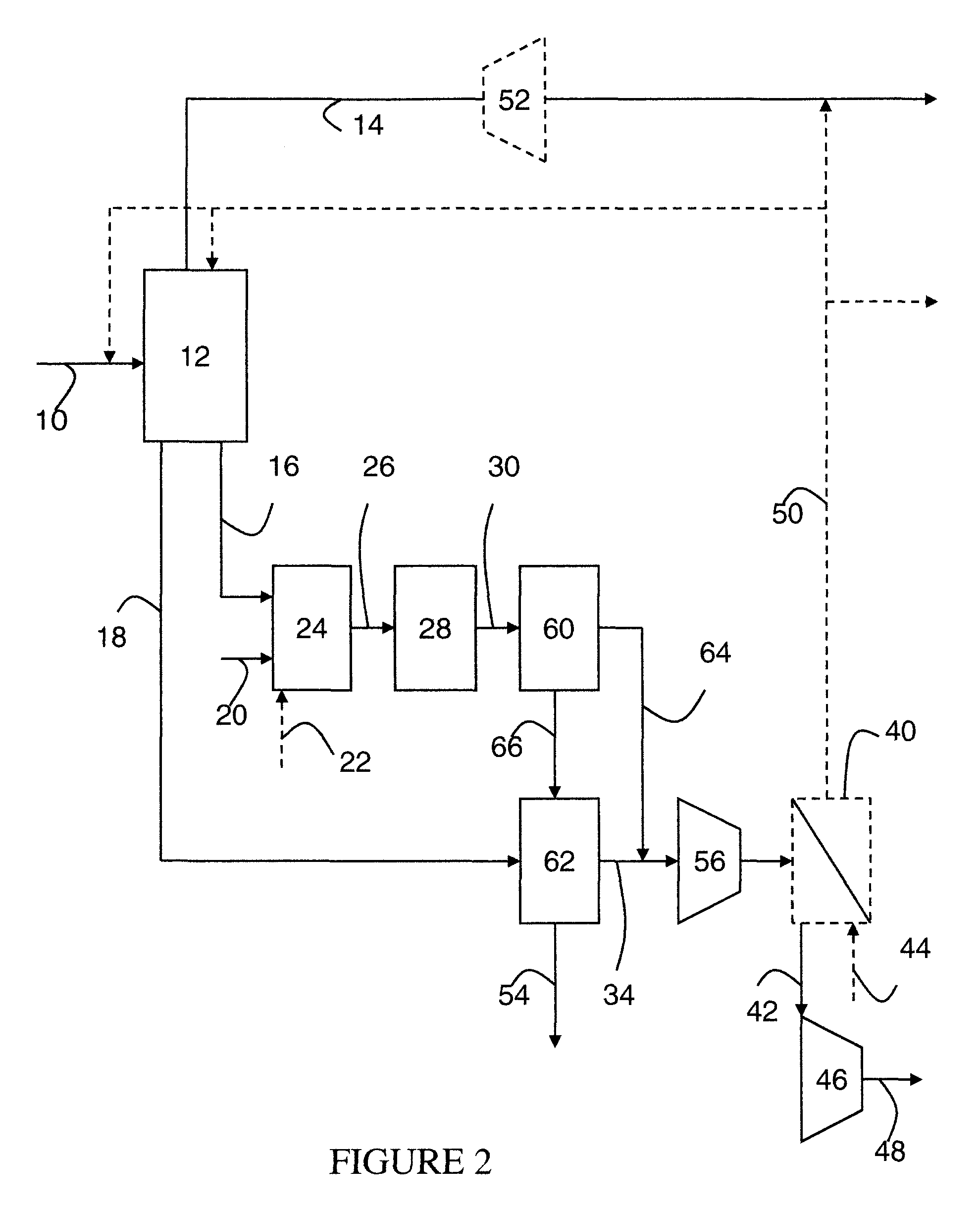
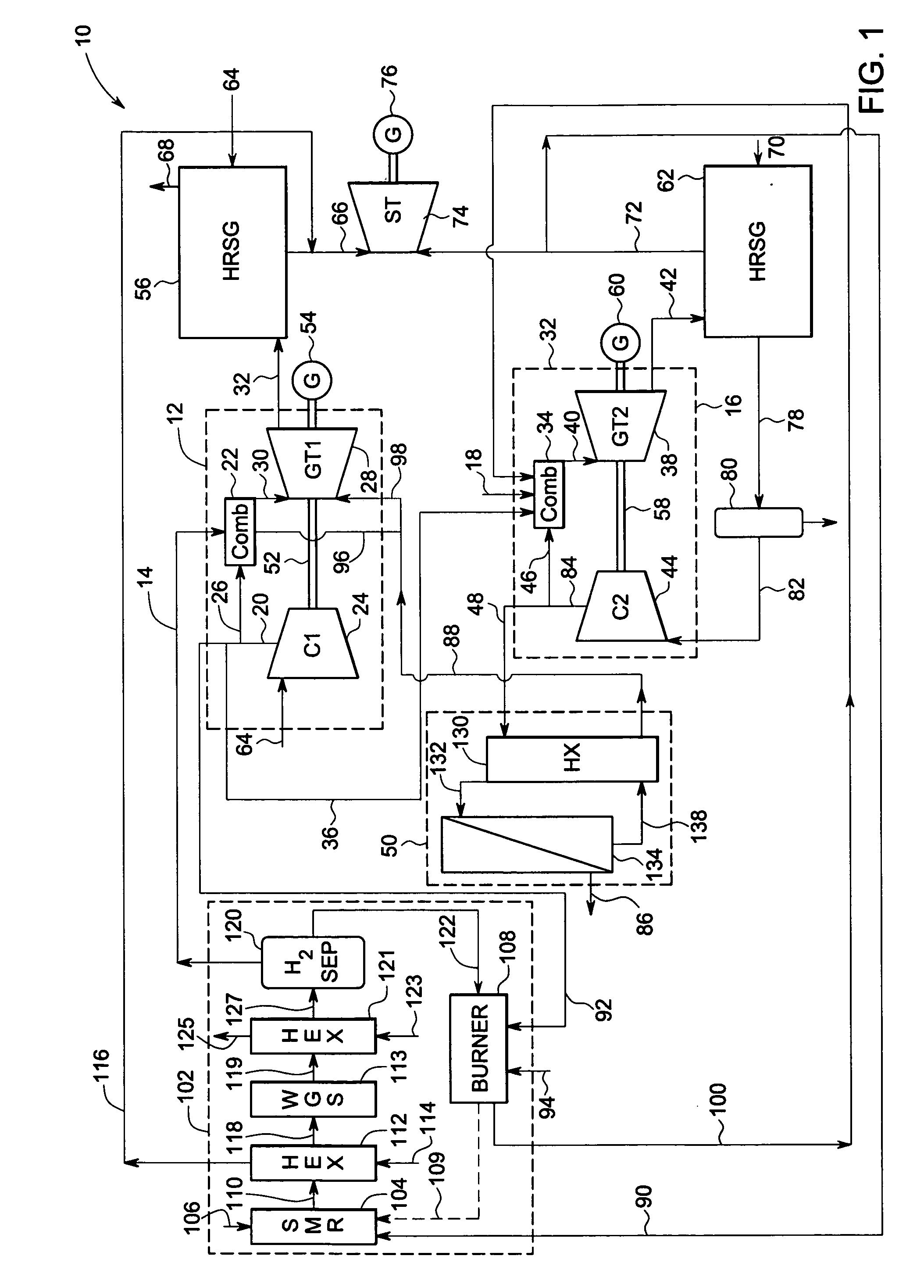
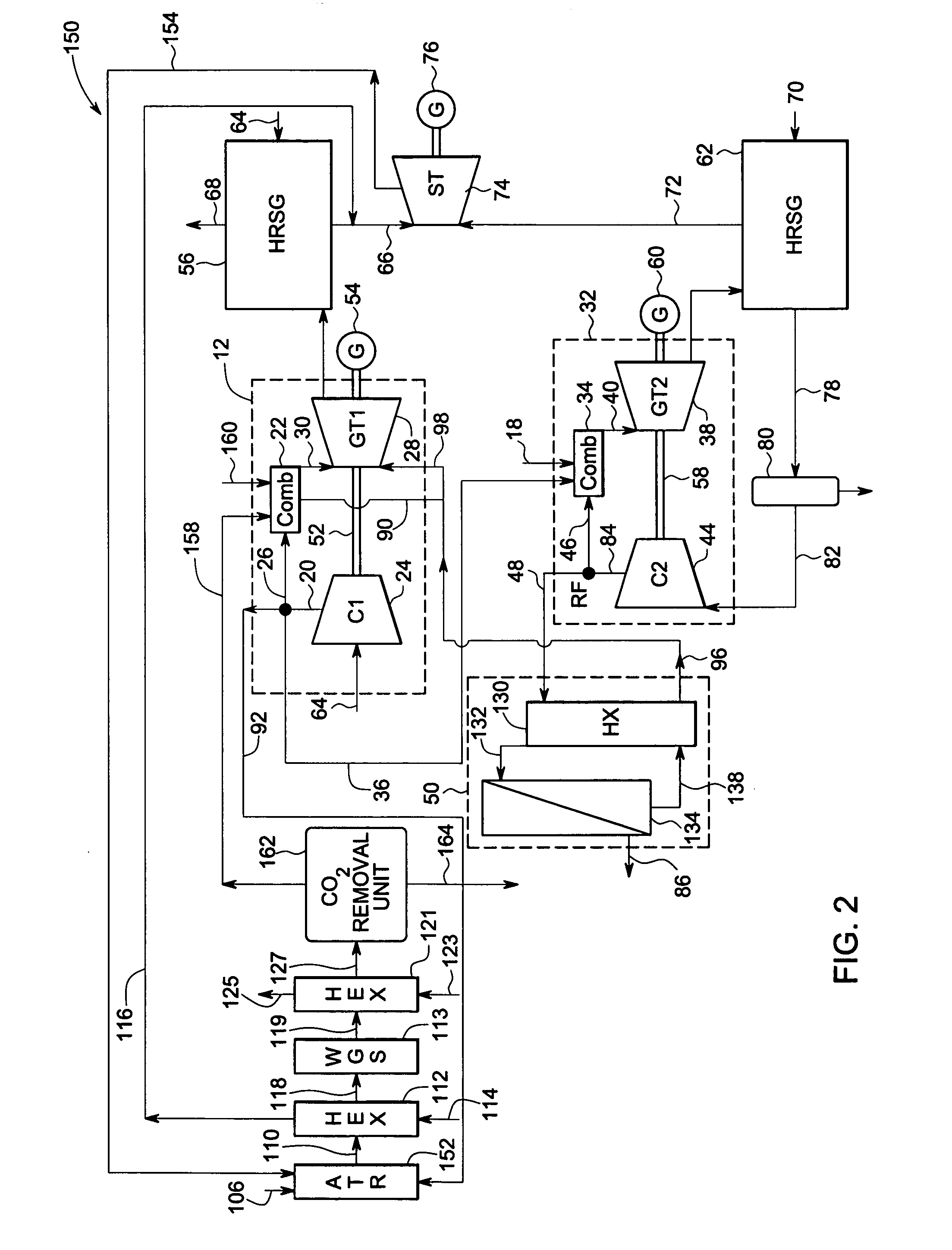
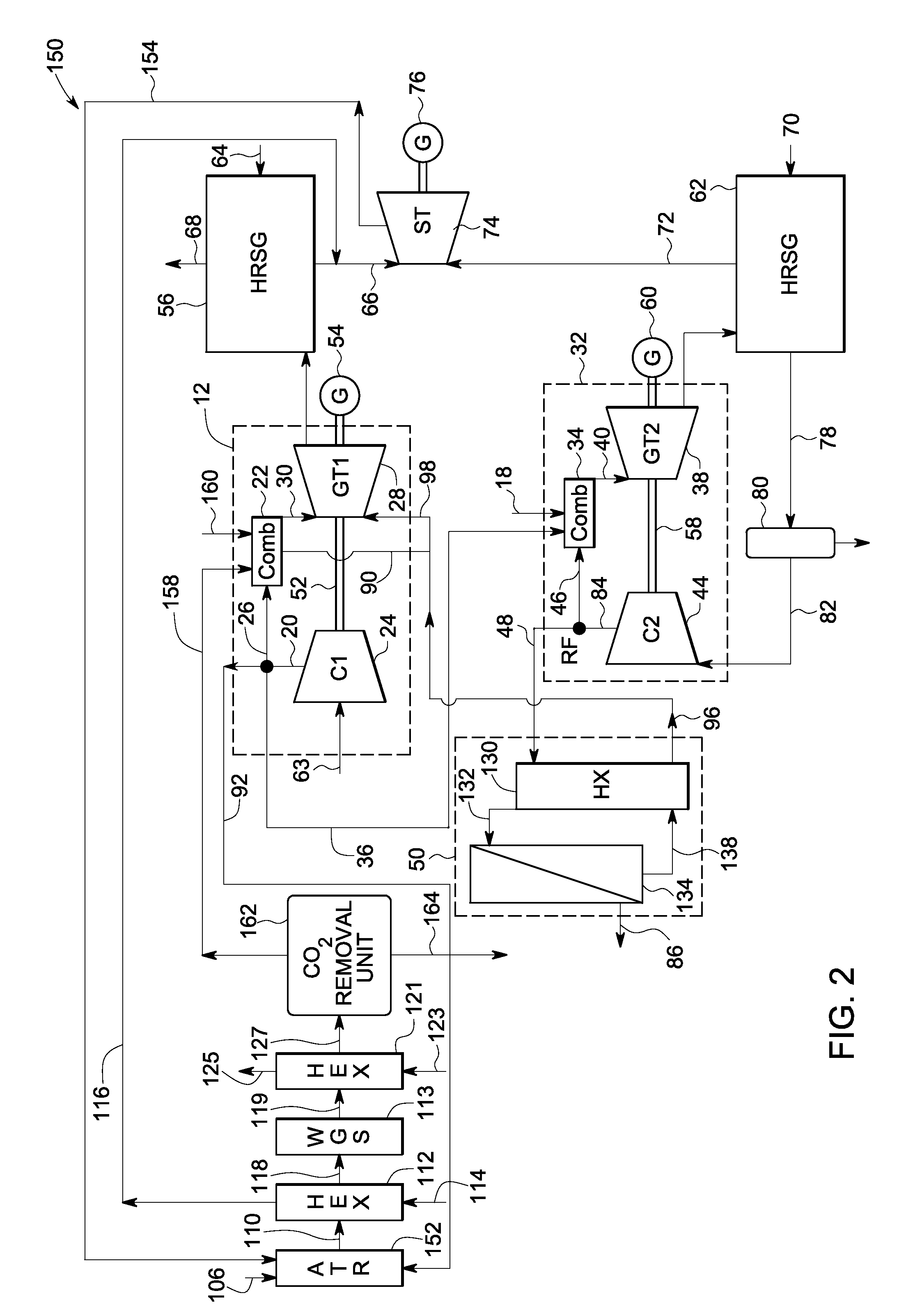
Systems and methods for power generation and hydrogen production with carbon dioxide isolation
A power generation system includes a first gas turbine system. The first turbine system includes a first combustion chamber configured to combust a first fuel stream of primarily hydrogen that is substantially free of carbon-based fuels, a first compressor configured to supply a first portion of compressed oxidant to the first combustion chamber and a first turbine configured to receive a first discharge from the first combustion chamber and generate a first exhaust and electrical energy. The power generation system further includes a second gas turbine system. The second turbine system includes a second combustion chamber configured to combust a second fuel stream to generate a second discharge, wherein the first compressor of the first gas turbine system is configured to supply a second portion of compressed oxidant to the second combustion chamber and a second turbine configured to receive the second discharge from the second combustion chamber to generate a second exhaust and electrical energy. A second compressor is configured to receive the second exhaust comprising carbon dioxide and to discharge a recycle stream to the second combustion chamber and a split stream to a separator system adapted to recover carbon dioxide. The power generation system also includes a hydrogen generation system configured to receive a third fuel and steam to generate the first fuel and a third exhaust gas, wherein the third exhaust gas is recycled into the second combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
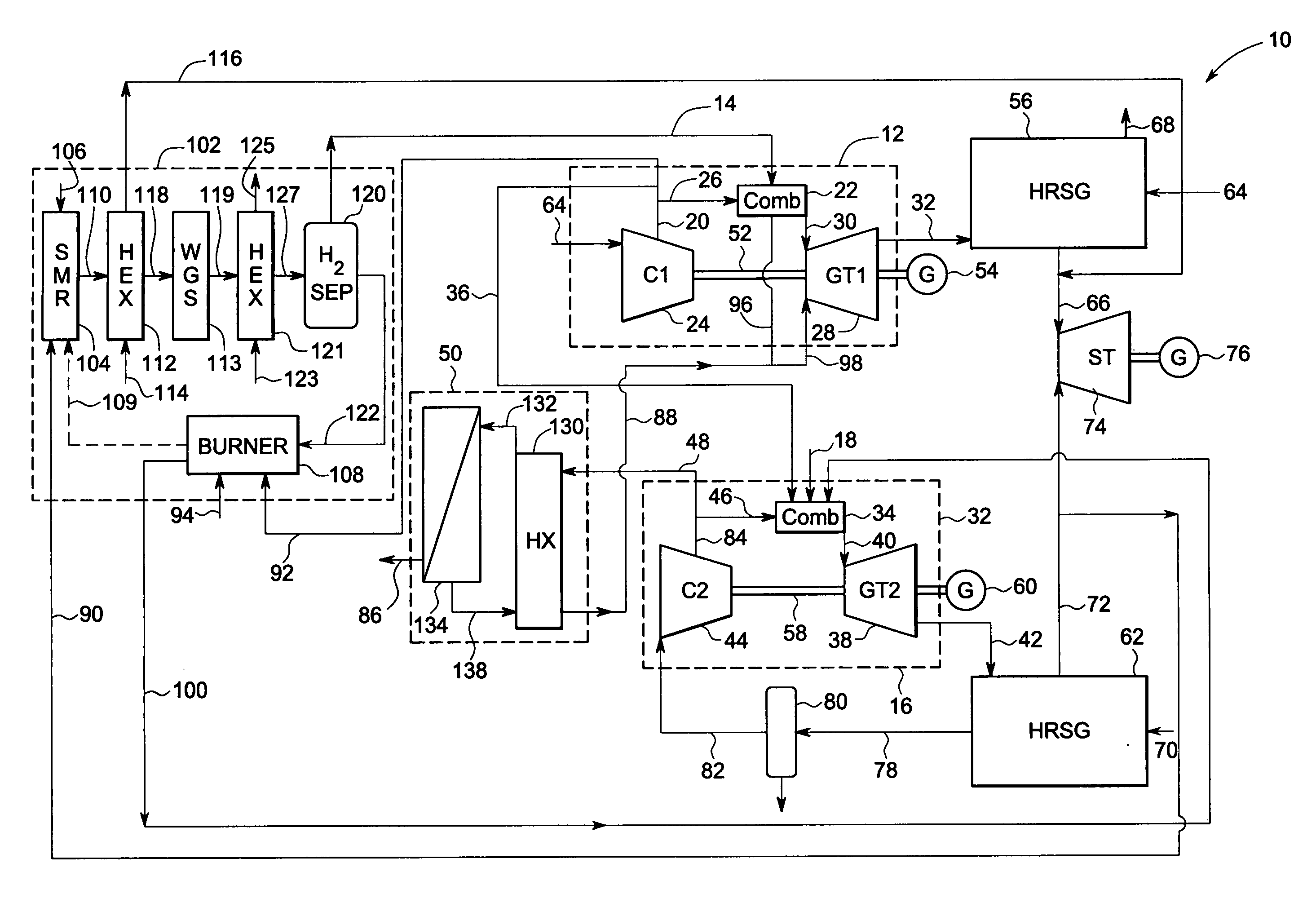
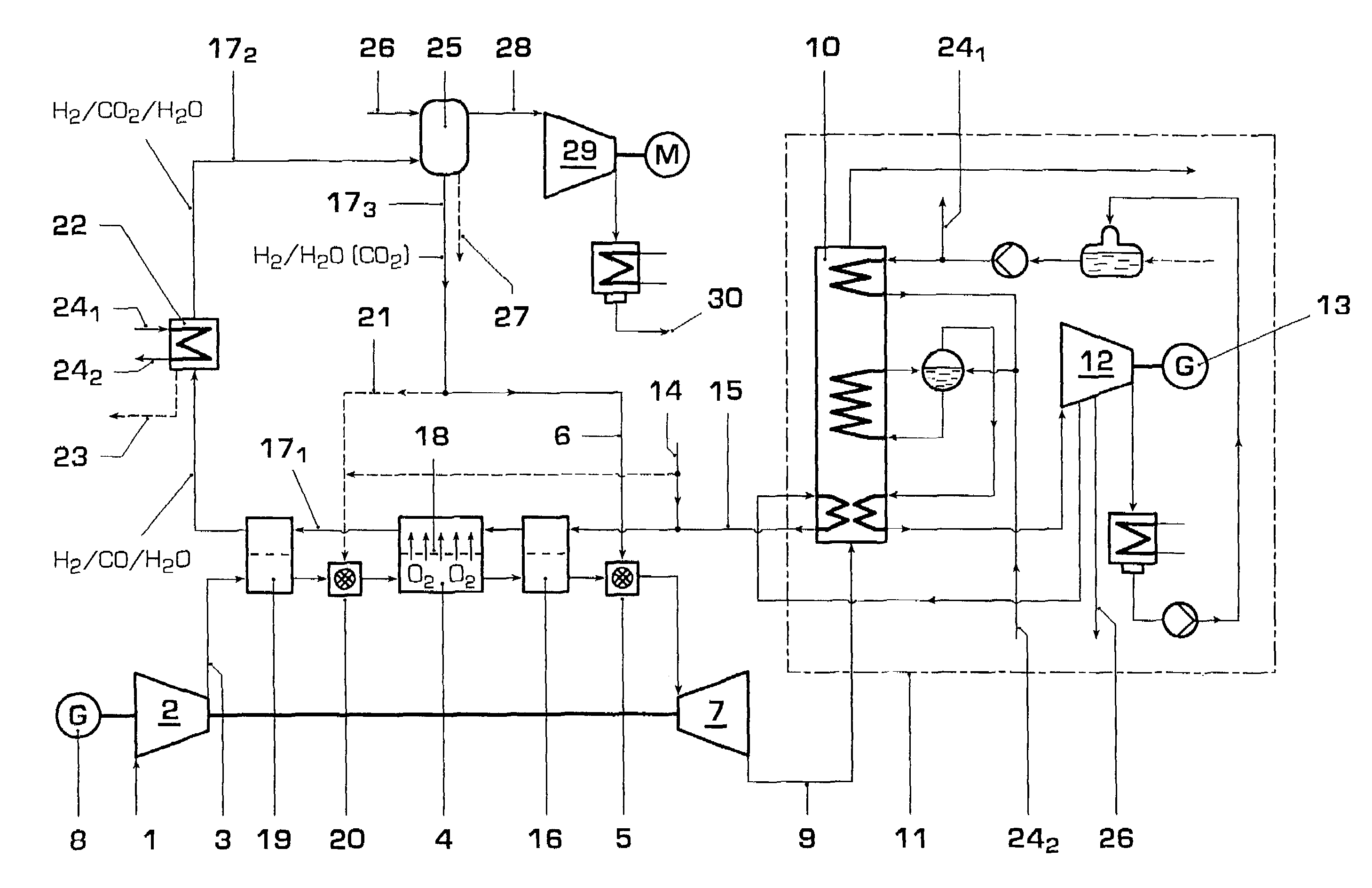
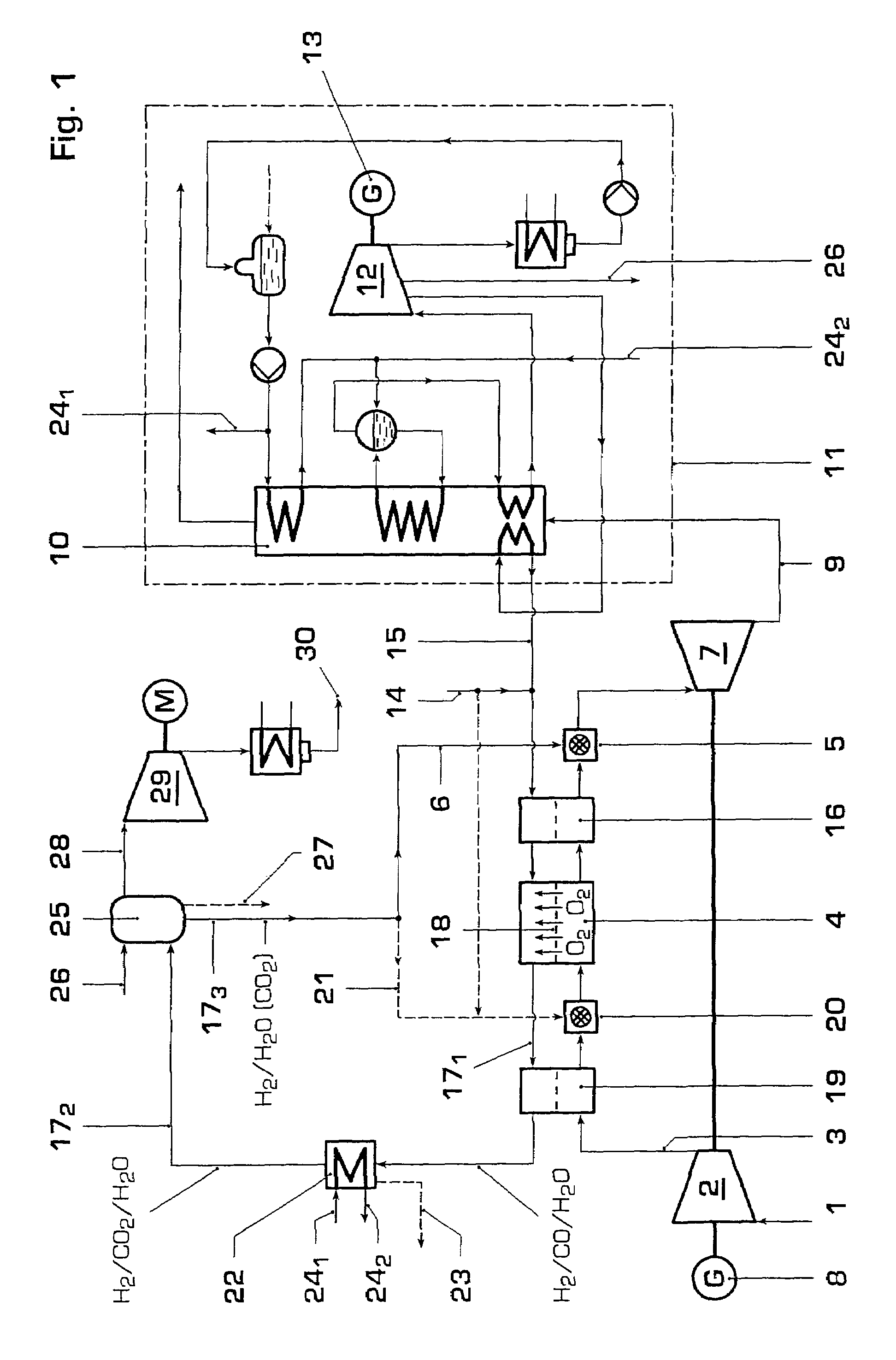
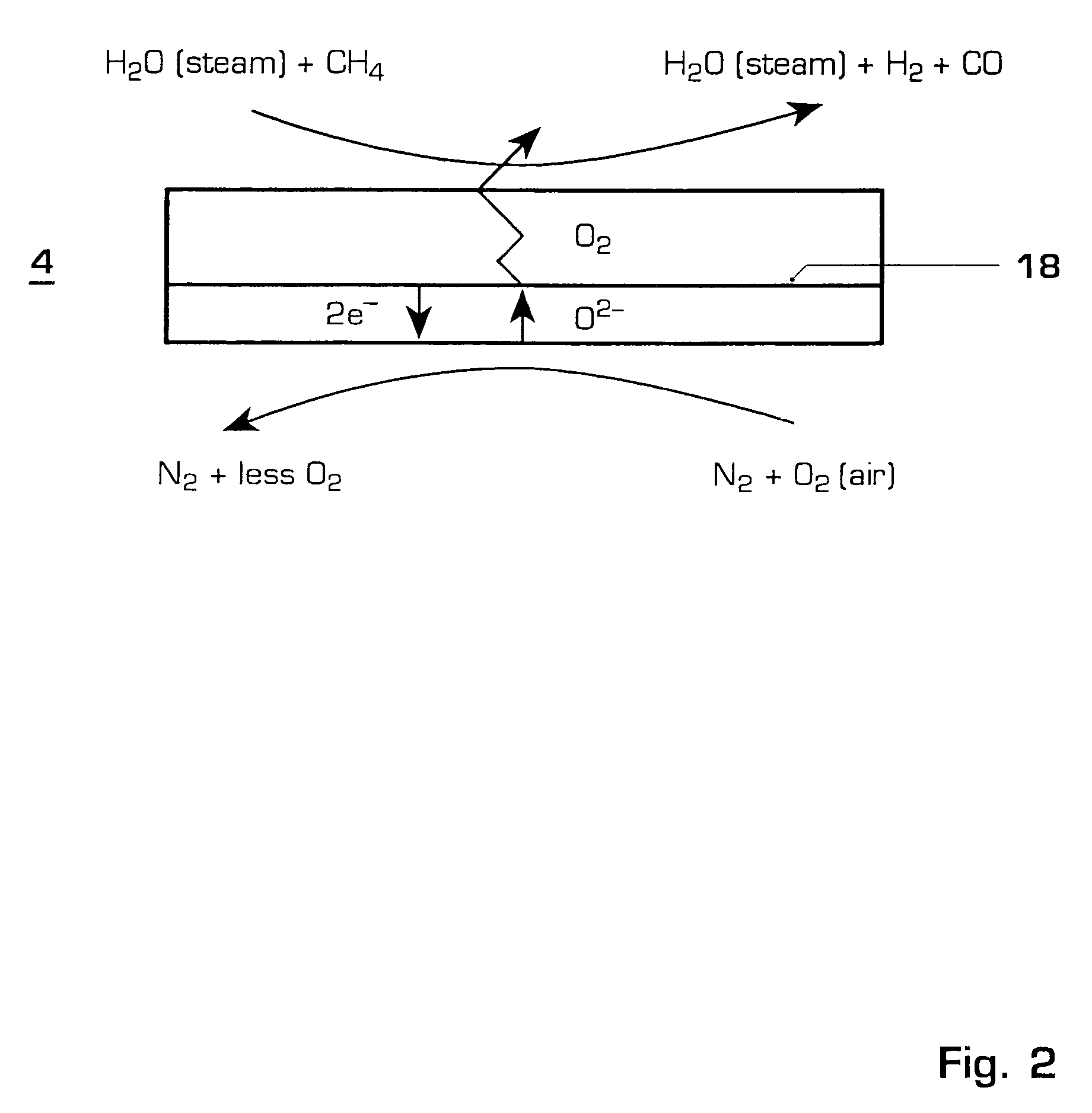
Gas turbine power plant and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7363764B2Improve efficiencyAvoid disadvantagesHydrogenOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSyngasPartial oxidation
A method of operating a gas turbine power plant and gas turbine power plant are disclosed wherein hydrogen for the combusting process is produced by feeding natural gas mixed with steam through a membrane / partial oxidation reactor and converting the natural gas at least to H2 and CO. Thereby oxygen is transferred from the compressed air through the membrane of the membrane / partial oxidation reactor and the oxygen is used for the partial oxidation process of the natural gas. The process is followed by converting the syngas in a CO shift reactor and a CO shift reactor to a CO2 removal equipment to mainly hydrogen.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
InactiveUS20110146978A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processSyngas
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or reforming, and an air separation process for generating (i) an oxygen stream for use, for example, in the syngas process or a combustion process, and (ii) a nitrogen stream for EOR use.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Processes for Hydromethanation of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
ActiveUS20100287835A1Increase the amount of carbonIncrease volumeHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrogen separationMethanationOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular methane, via the hydromethanation of a carbonaceous feedstock in the presence of steam, syngas, a hydromethanation catalyst and an oxygen-rich gas stream.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Processes for Hydromethanation of a Carbonaceous Feedstock
ActiveUS20100287836A1Hydrogen separation at low temperatureCarbon compoundsMethanationHydromethanation
The present invention relates to processes for preparing gaseous products, and in particular methane, via the hydromethanation of carbonaceous feedstocks in the presence of steam, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and a hydromethanation catalyst.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Integrated oxygen generation and carbon dioxide absorption method apparatus and systems
InactiveUS20050031522A1Improvement in mission durationLower acquisition costsFuel cell auxillariesMachines/enginesChemical speciesCo2 absorption
A method for producing oxygen and absorbing carbon dioxide in a single operation using a solution that contains an oxygen source and a redox partner that can react to form oxygen and a chemical species that can form an insoluble carbonate to precipitate and chemically store carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is introduced into the solution and the carbonate precipitates as the oxygen is generated. In particular, the invention uses an aqueous solution of permanganate and hydrogen peroxide that react in the presence of a catalyst to produce oxygen and manganese (II) ions. Carbon dioxide gas introduced into the solution reacts with the manganese (II) ions to precipitate manganese carbonate. Other cations capable of reacting with carbon dioxide to form an insoluble carbonate, for example calcium, barium and magnesium, may also be added to the solution to precipitate carbonate salts. Calcium permanganate may used as a source of both calcium and permanganate.
Owner:CAPITAL MANAGEMENT +1
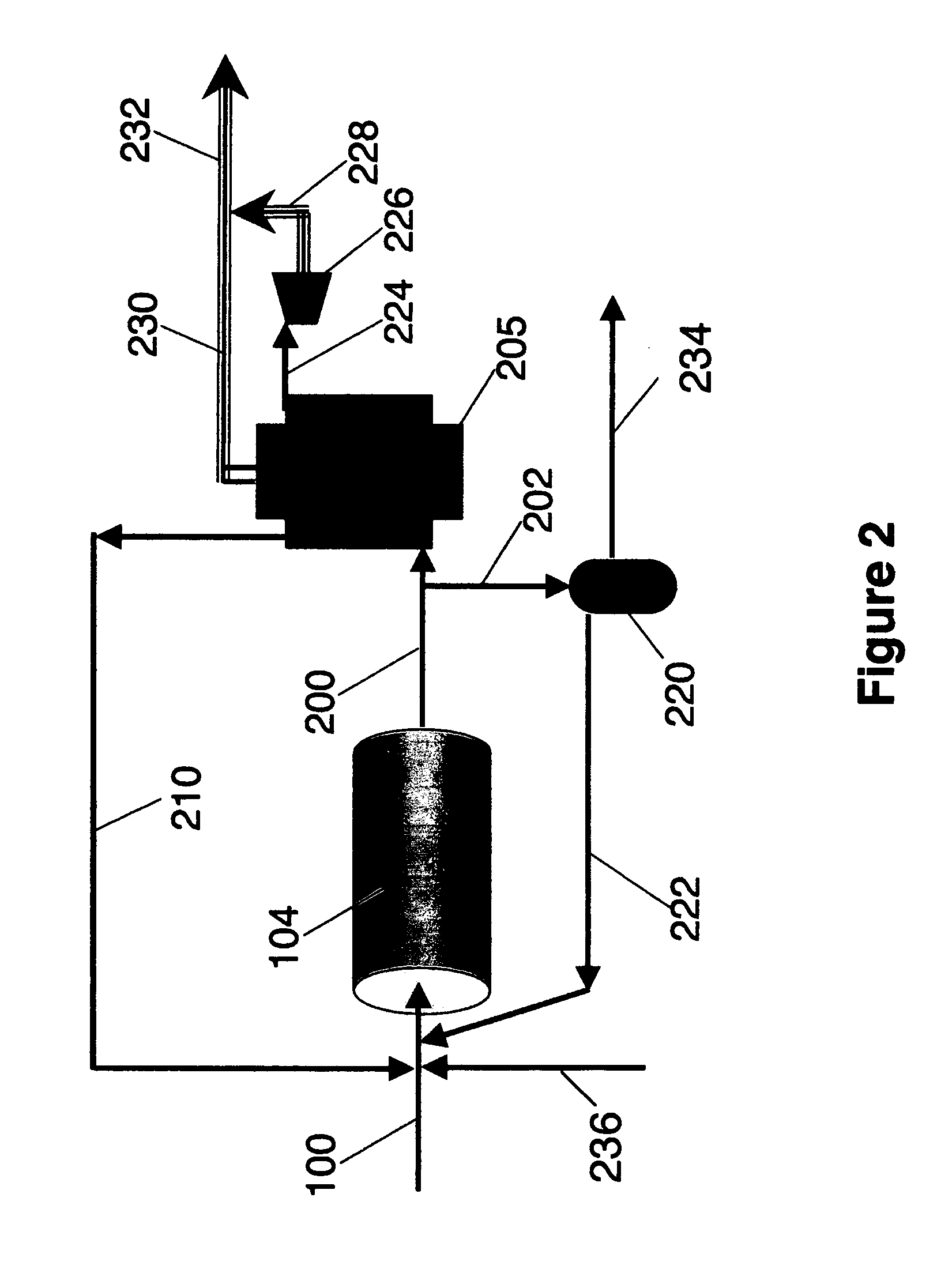
Carbon dioxide production method
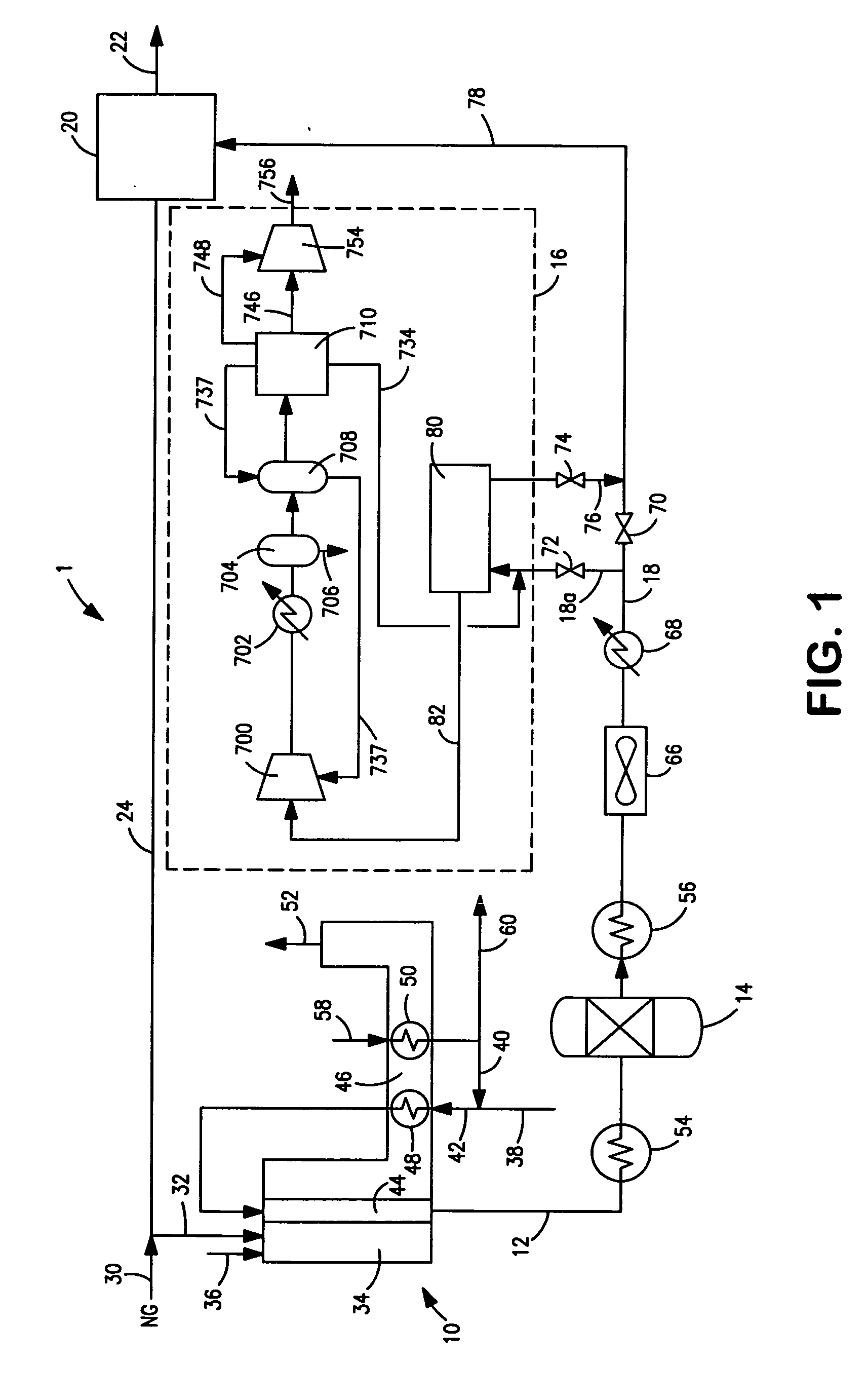
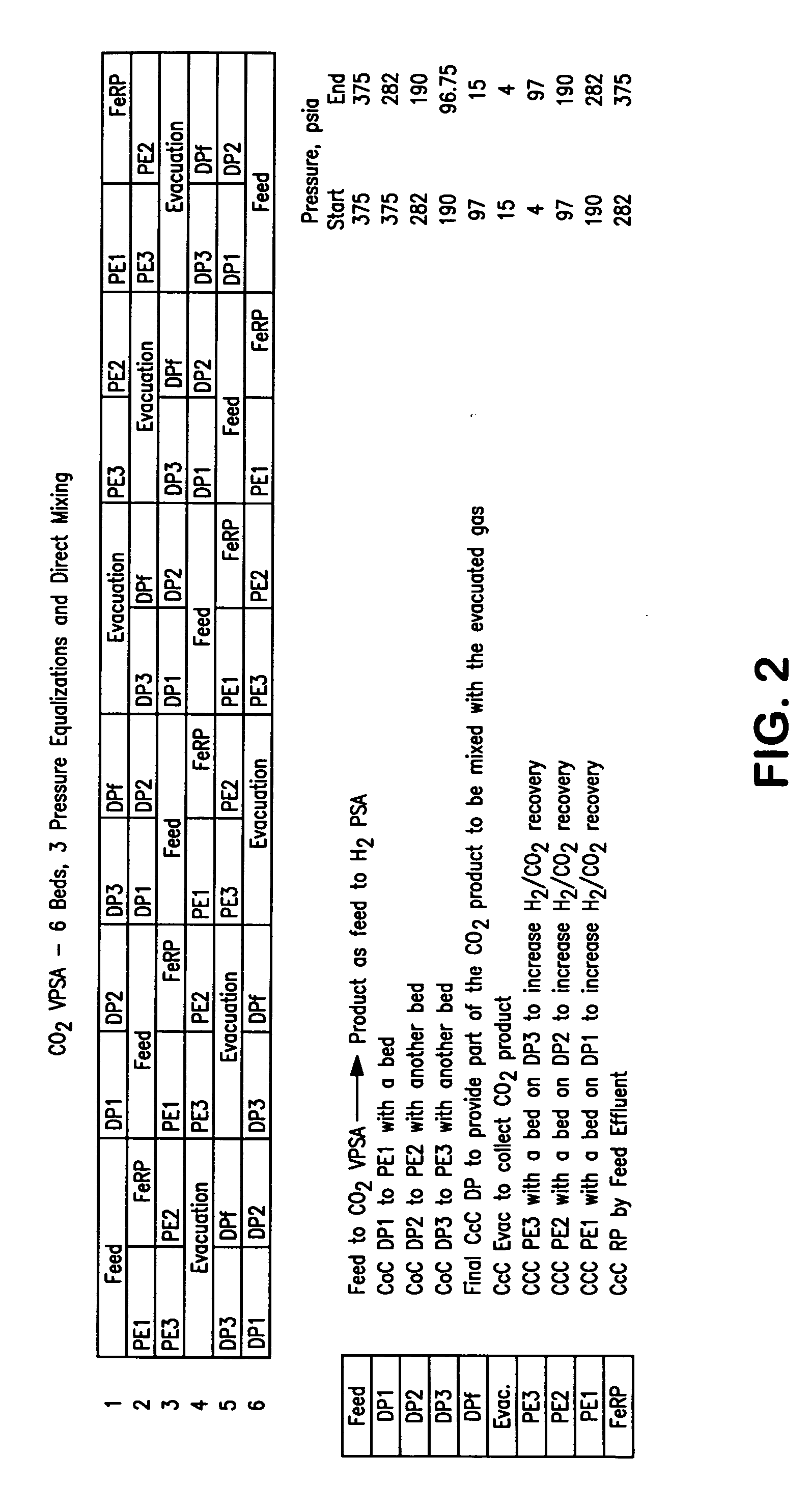
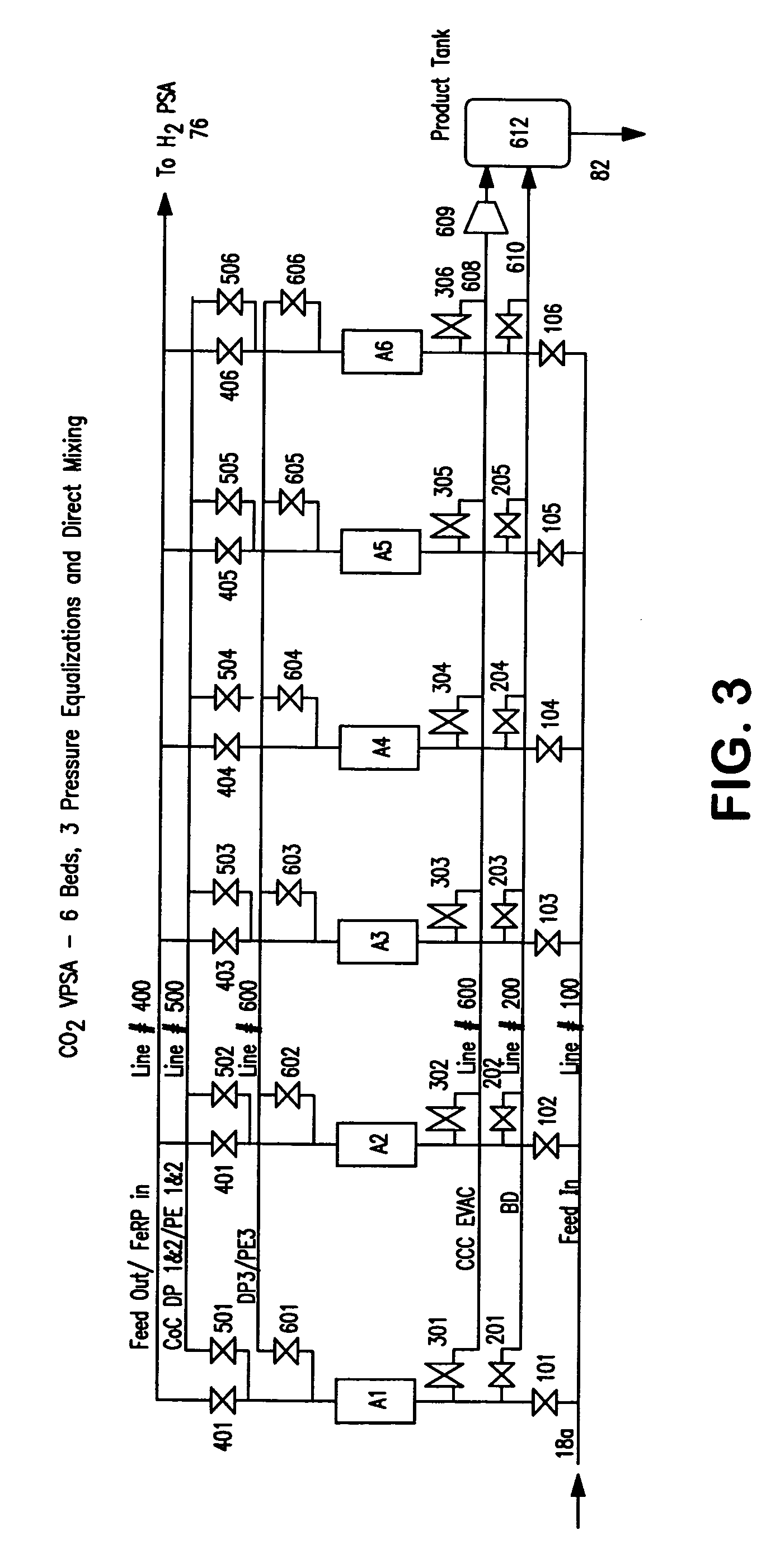
ActiveUS20070232706A1Increased hydrogen recoveryPromote recoverySolidificationLiquefactionVacuum pressureCarbon dioxide production
A method of producing a carbon dioxide product stream from a synthesis gas stream formed within a hydrogen plant having a synthesis gas reactor, a water-gas shift reactor, located downstream of the synthesis gas reactor to form the synthesis gas stream and a hydrogen pressure swing adsorption unit to produce a hydrogen product recovered from the synthesis gas stream. In accordance with the method the carbon dioxide from the synthesis gas stream by separating the carbon dioxide from the synthesis gas stream in a vacuum pressure swing adsorption system, thereby to produce a hydrogen-rich synthesis gas stream and a crude carbon dioxide stream and then purifying the crude carbon dioxide stream by a sub-ambient temperature distillation process thereby to produce the carbon dioxide product. A hydrogen synthesis gas feed stream to the hydrogen pressure swing adsorption unit is formed at least in part from the hydrogen rich stream.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method and apparatus for stimulating heavy oil production
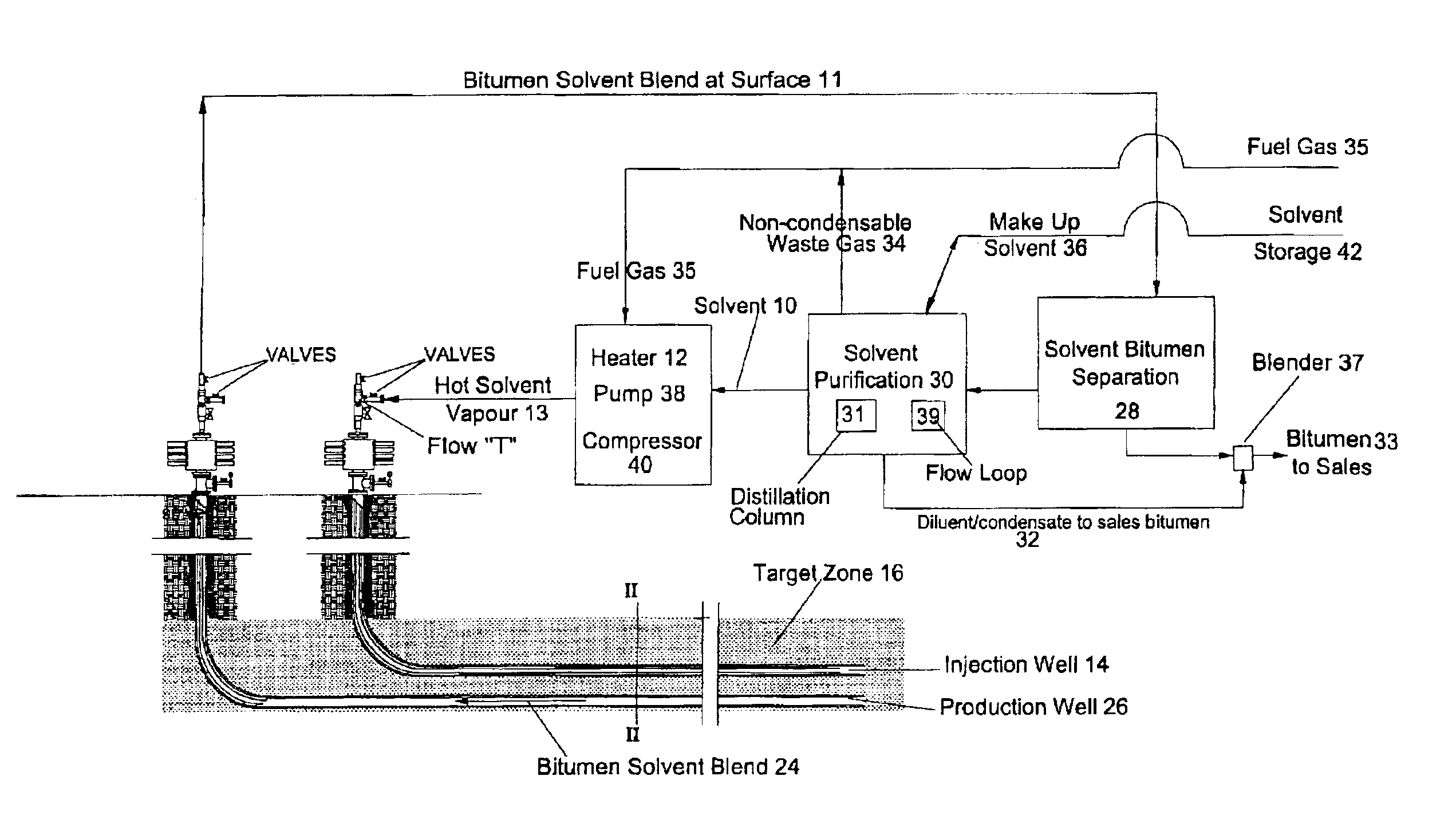
InactiveUS6883607B2Reduce the total massReduce transferInsulationFluid removalFuel oilOil production
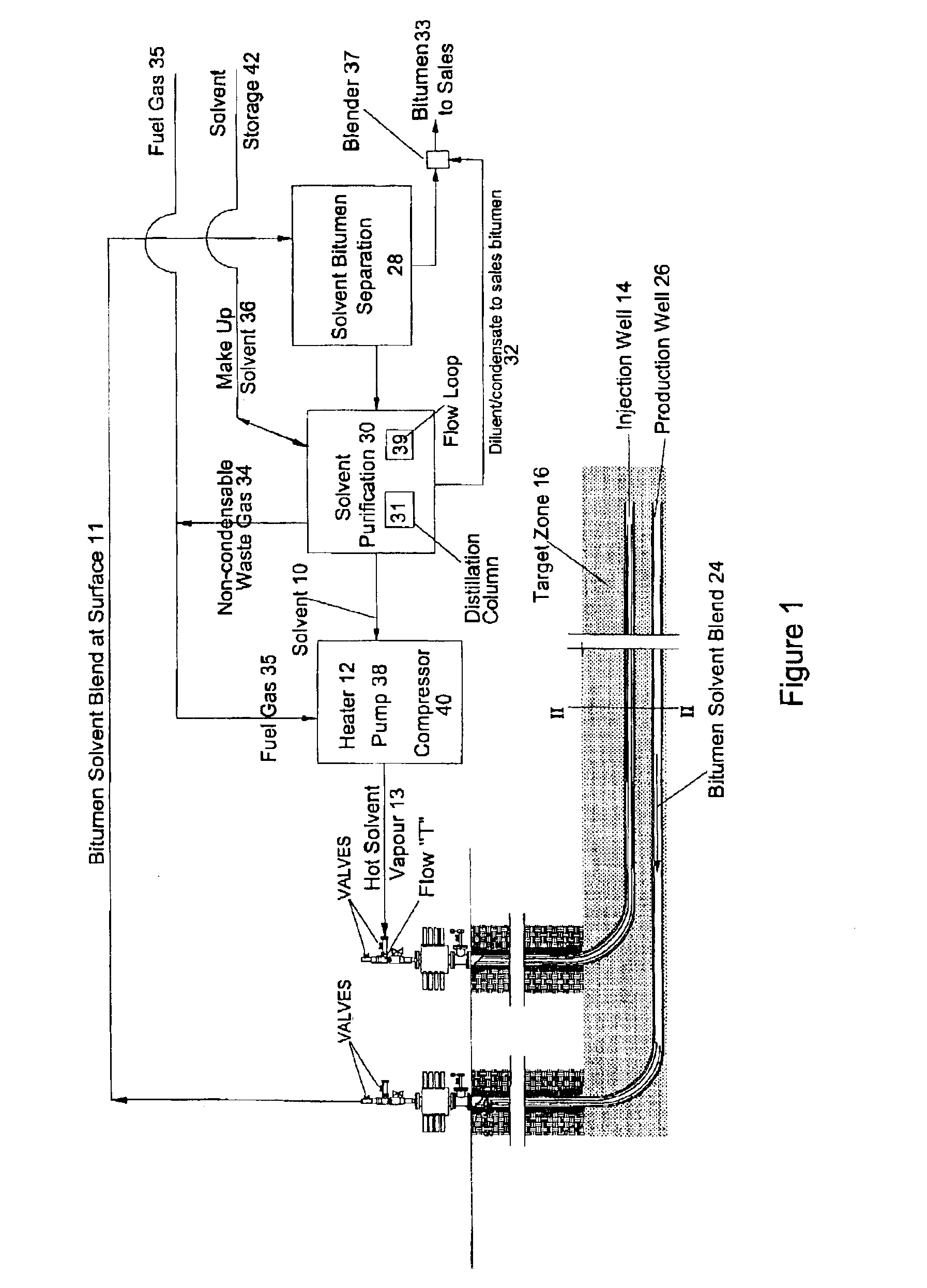
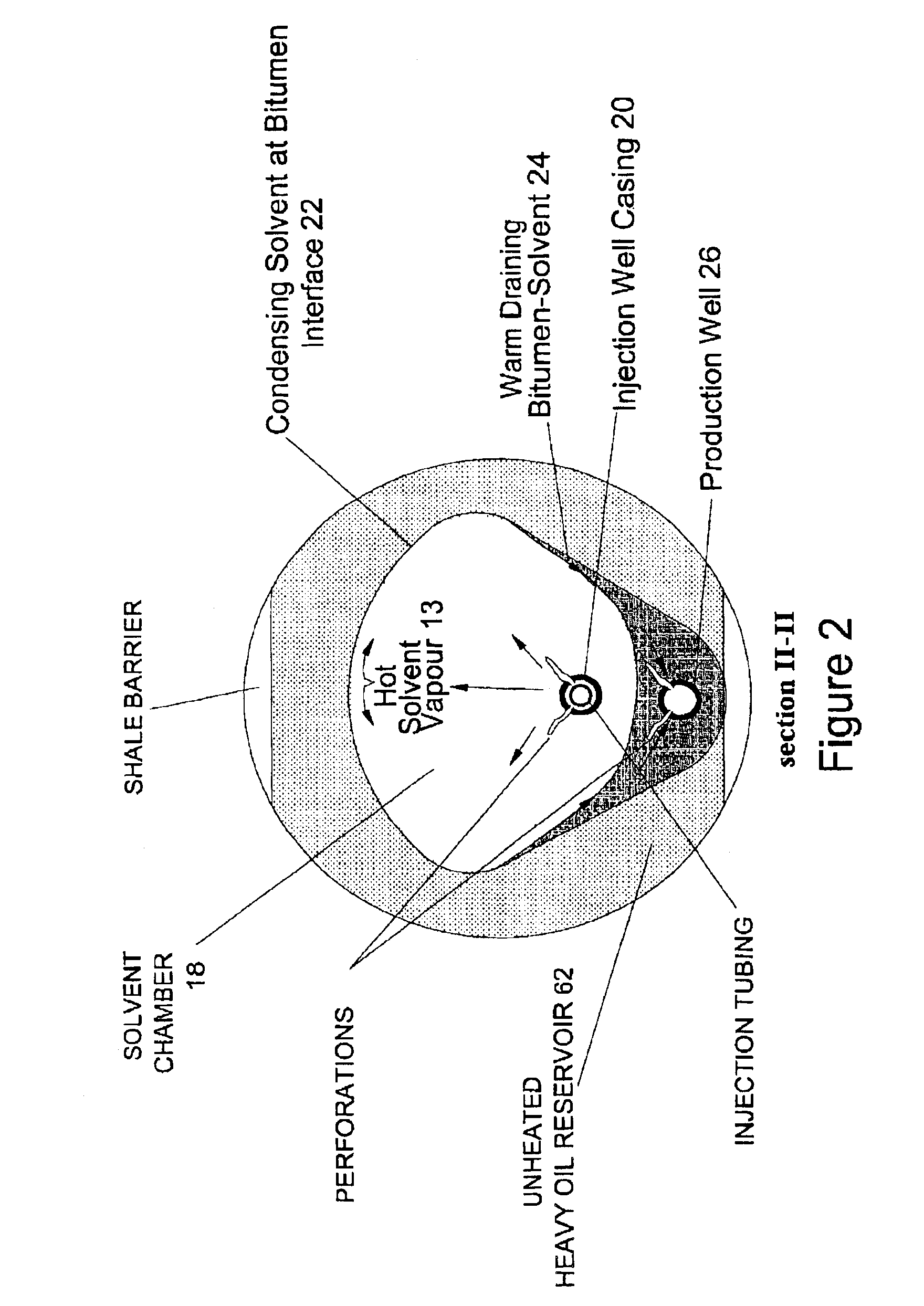
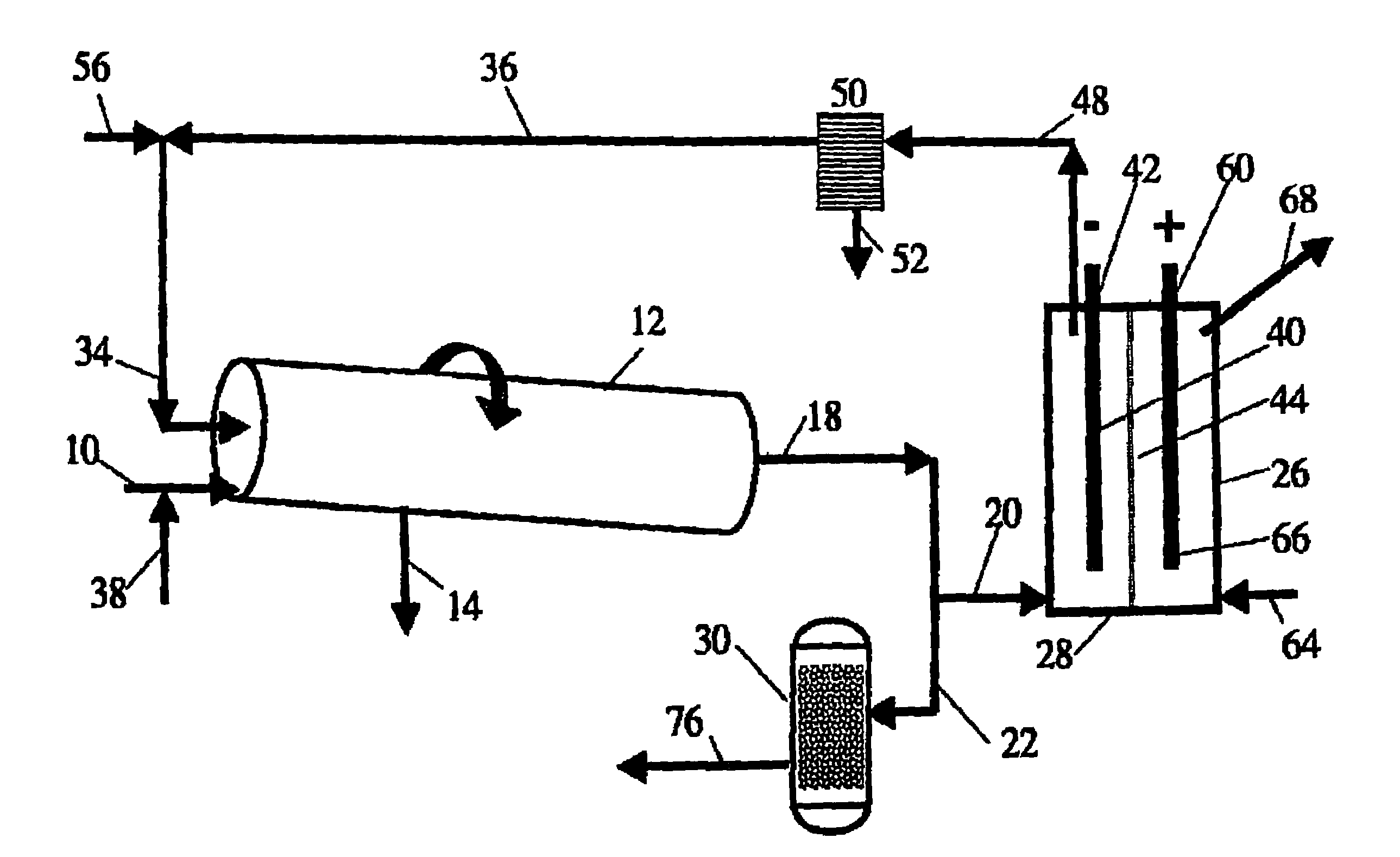
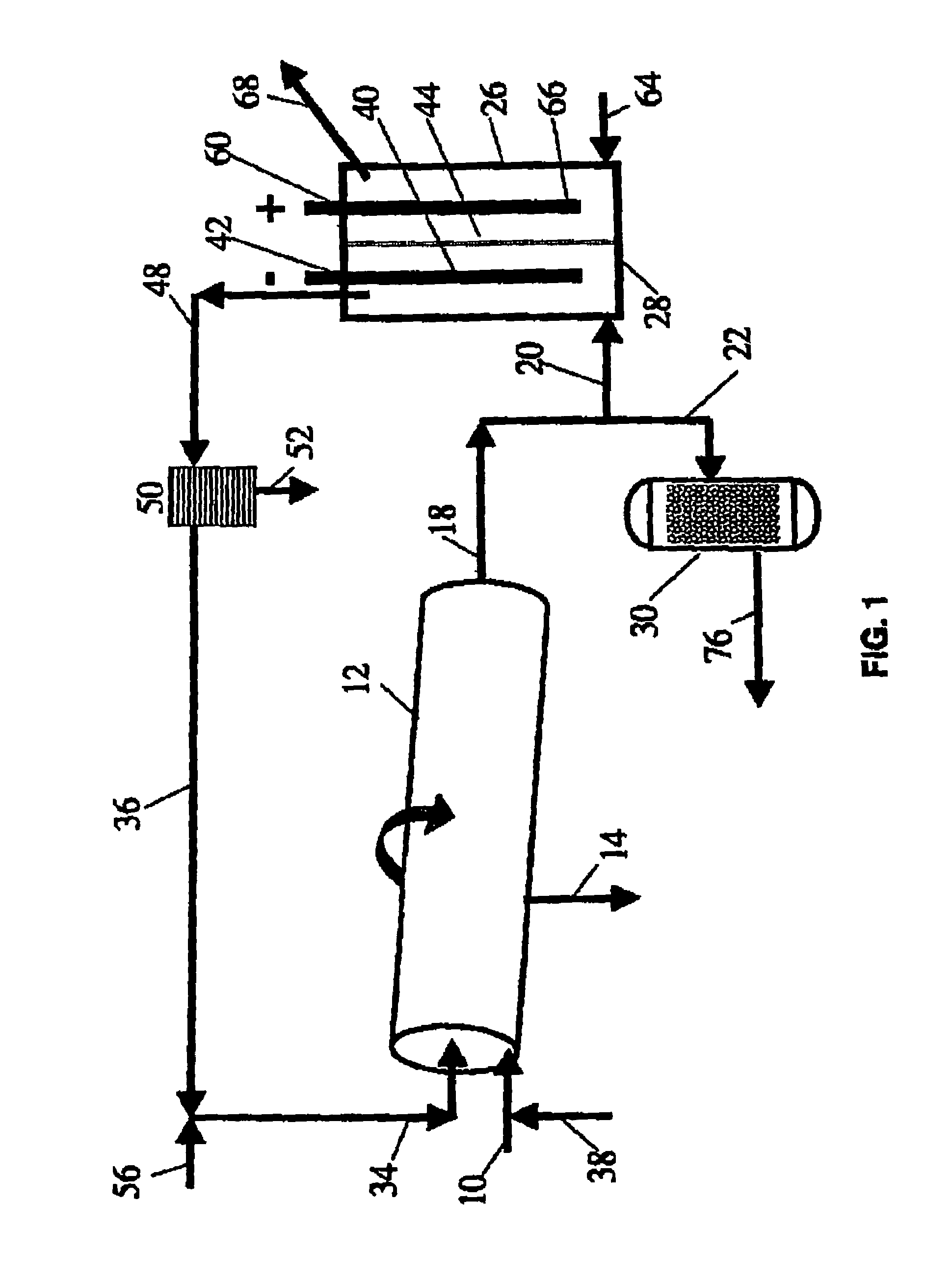
A process for the recovery of hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon bearing formation having an extraction chamber where the extraction chamber has an extraction surface. The process has the steps of heating a solvent, such as propane, and then placing the solvent into the extraction chamber at a temperature and a pressure sufficient for the solvent to be in a vapor state in the chamber and to condense on the extraction surface. The next step is to produce a liquid blend of solvent and heavy oil and then to separate the solvent from said heavy oil. Then the solvent is purified, before being re-injected into the formation again. The purification step removes less condensable fractions from the solvent to ensure a purity that is high enough to support continued heat transfer at extraction conditions. The pressure and temperature are set to levels to cause less condensable fractions to drain away with the liquid bitumen and solvent blend that is produced, thus mitigating heat transfer poisoning.
Owner:HATCH LTD
Process and system for converting carbonaceous feedstocks into energy without greenhouse gas emissions
InactiveUS7220502B2Improve efficiencyHigh hydrogen contentFuel cell auxillariesWaste based fuelPetroleum cokeToxic industrial waste
The process and system of the invention converts carbonaceous feedstock such as coal, hydrocarbon oil, natural gas, petroleum coke, oil shale, carbonaceous-containing waste oil, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing military waste, carbonaceous-containing industrial waste, carbonaceous-containing medical waste, carbonaceous-containing sewage sludge and municipal solid waste, carbonaceous-containing agricultural waste, carbonaceous-containing biomass, biological and biochemical waste, and mixtures thereof into electrical energy without the production of unwanted greenhouse emissions. The process and system uses a combination of a gasifier, e.g., a kiln, operating in the exit range of at least 700° to about 1600° C. (1300-2900° F.) to convert the carbonaceous feedstock and a greenhouse gas stream into a synthesis gas comprising mostly carbon monoxide and hydrogen without the need for expensive catalysts and or high pressure operations. One portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier becomes electrochemically oxidized in an electricity-producing fuel cell into an exit gas comprising carbon dioxide and water. The latter is recycled back to the gasifier after a portion of water is condensed out. The second portion of the synthesis gas from the gasifier is converted into useful hydrocarbon products.
Owner:RAVEN SR INC
Apparatus, methods, and systems for extracting petroleum using a portable coal reformer
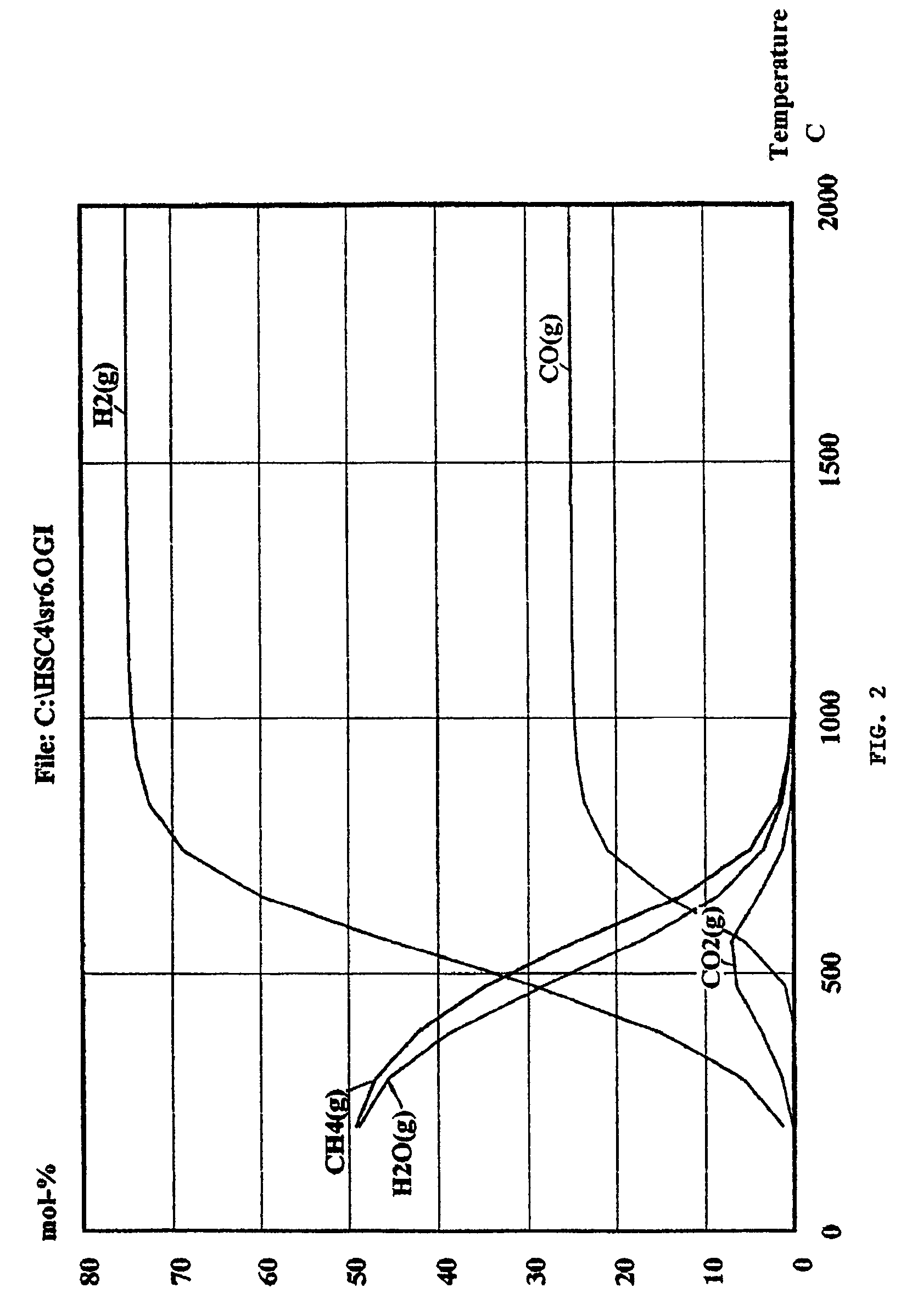
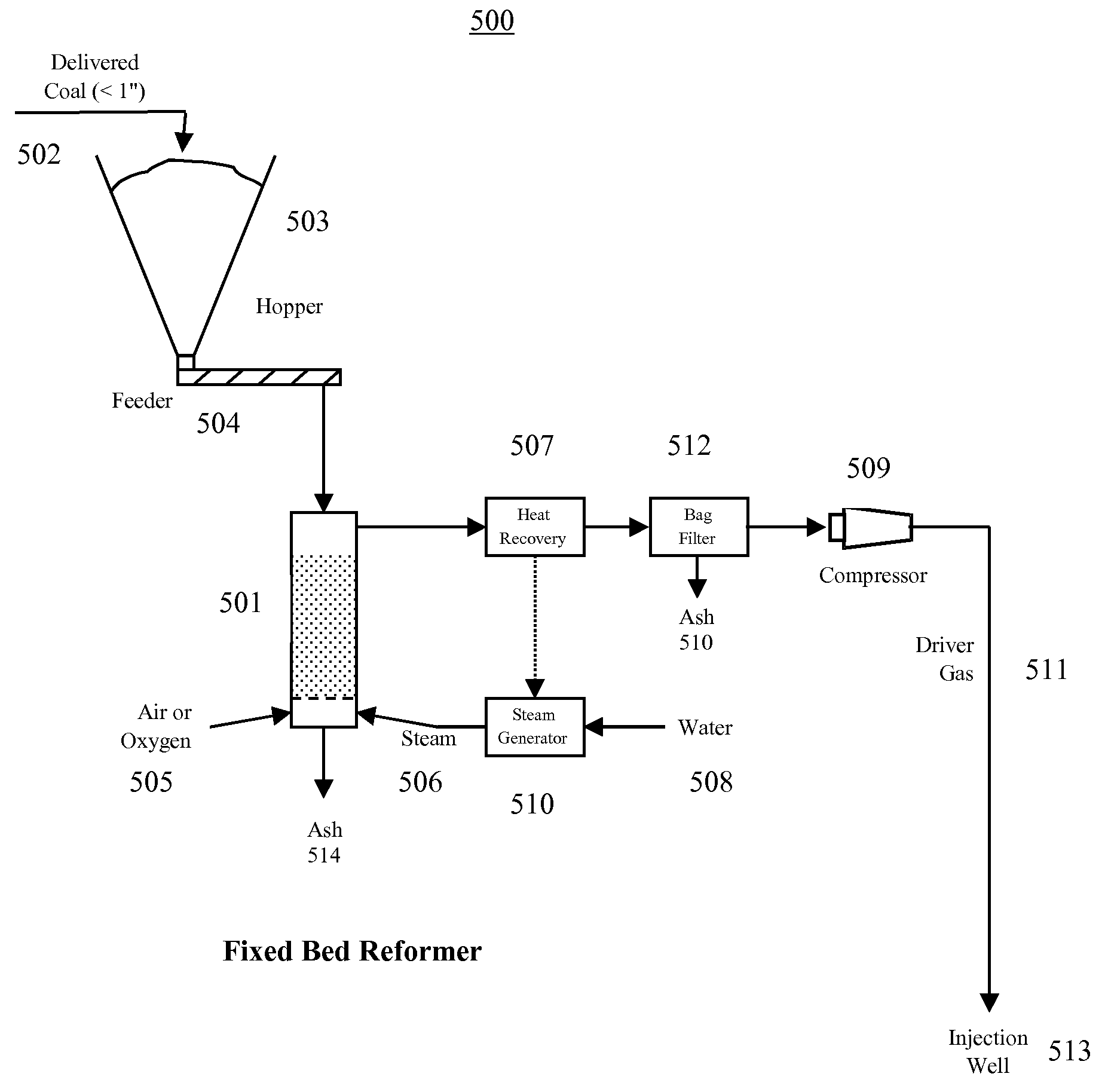
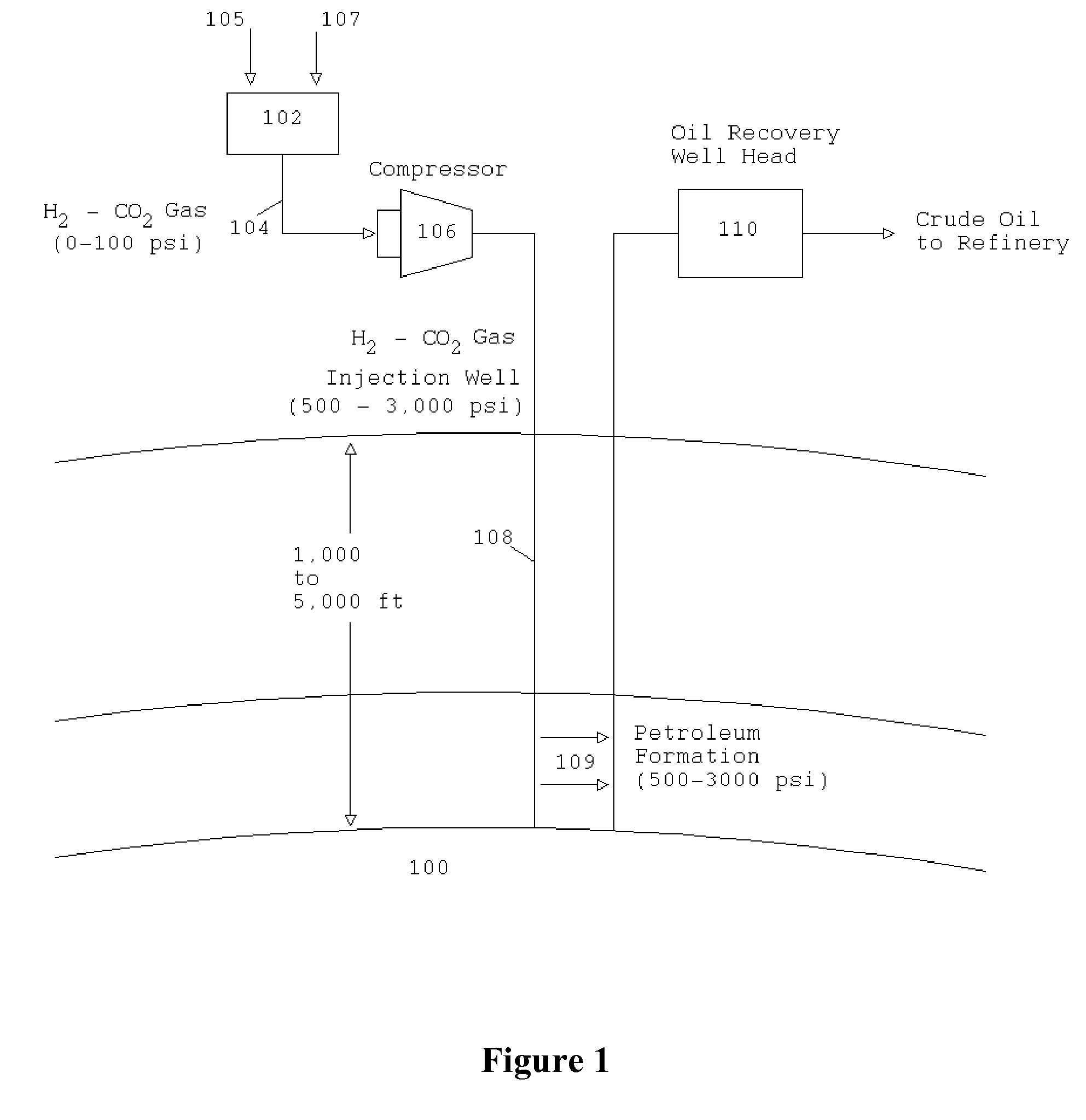
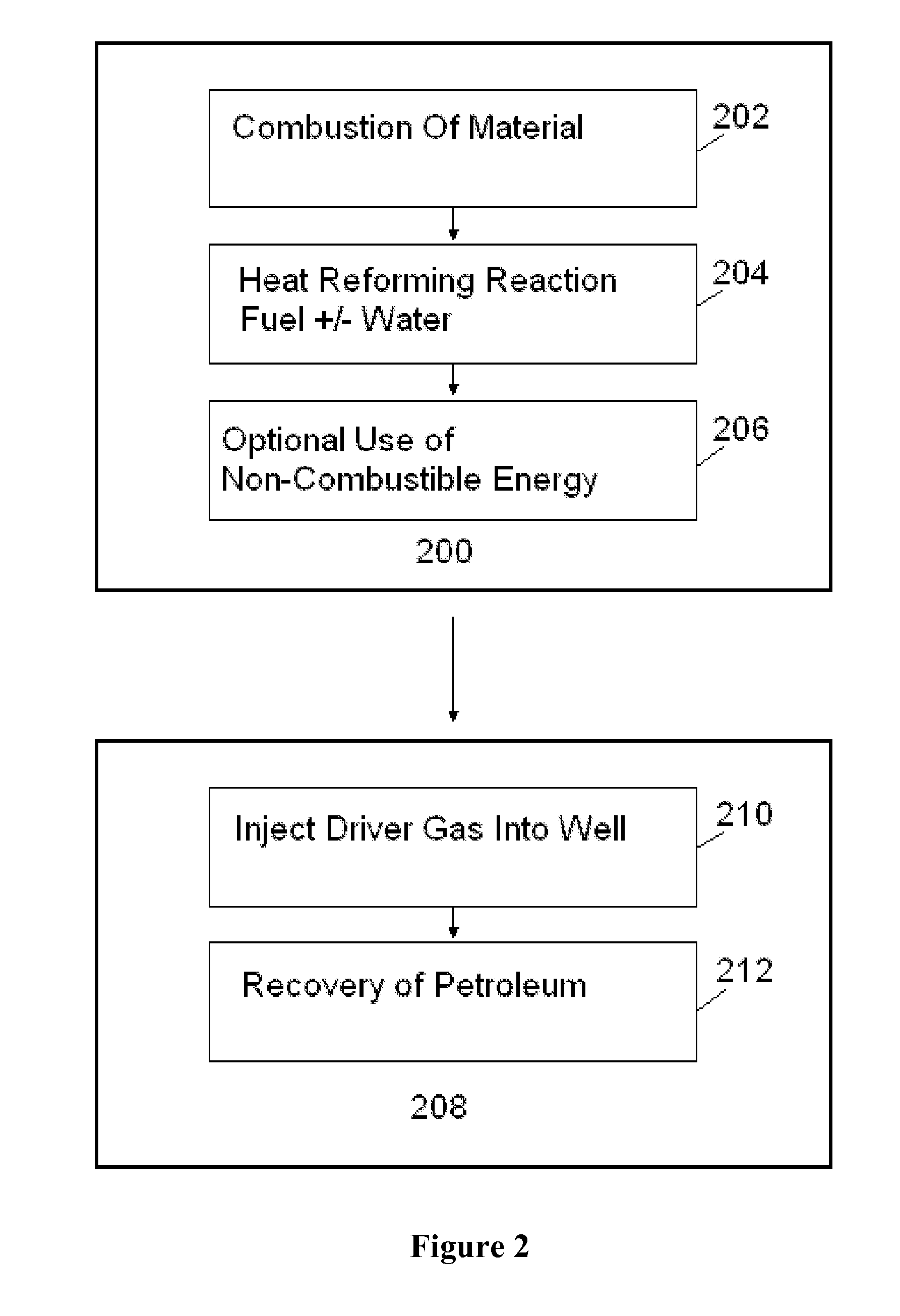
InactiveUS7654330B2Highly economicalVast supplyDrilling rodsHydrogen separation using solid contactPetroleumCoal
Apparatus, methods, and systems for extracting oil or natural gas from a well using a portable coal reformer. In one example, the method may include reforming coal by reaction with water to generate driver gas (comprising carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas), and injecting the driver gas into the well. The driver gas reduces the viscosity and pressurizes the oil to help extract the oil from the oil well. The coal reforming operation may include combusting coal or other combustible material with ambient oxygen to release energy, and heating coal and water with the energy released to a temperature above that required for the coal reforming reaction to proceed, thereby reforming coal and water into driver gas. The driver gas may be purified by filtering out particles and sulfur before injecting into the well. A portion of the hydrogen gas may be separated from the driver gas and used to generate electrical power.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Systems and methods for power generation and hydrogen production with carbon dioxide isolation
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
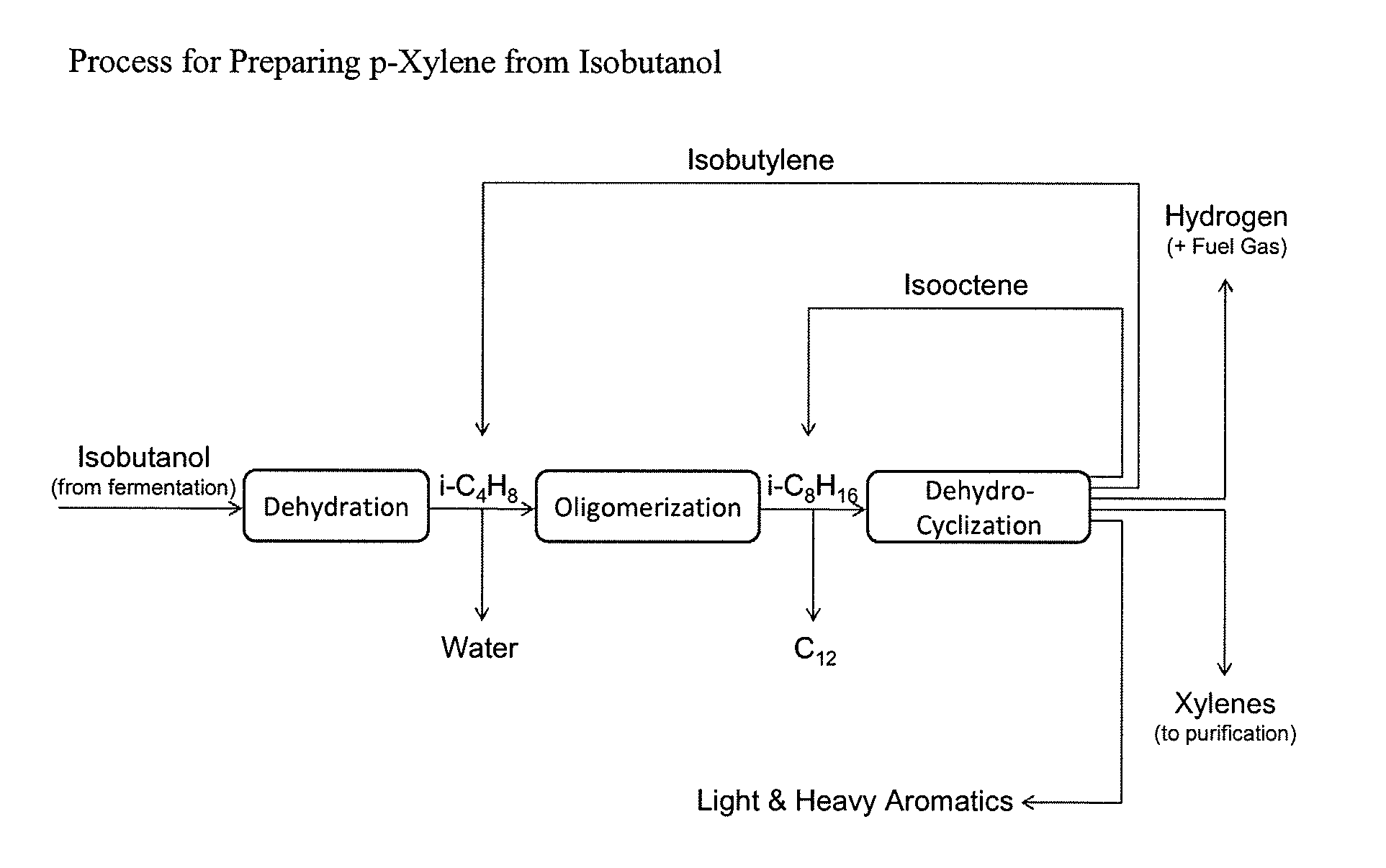
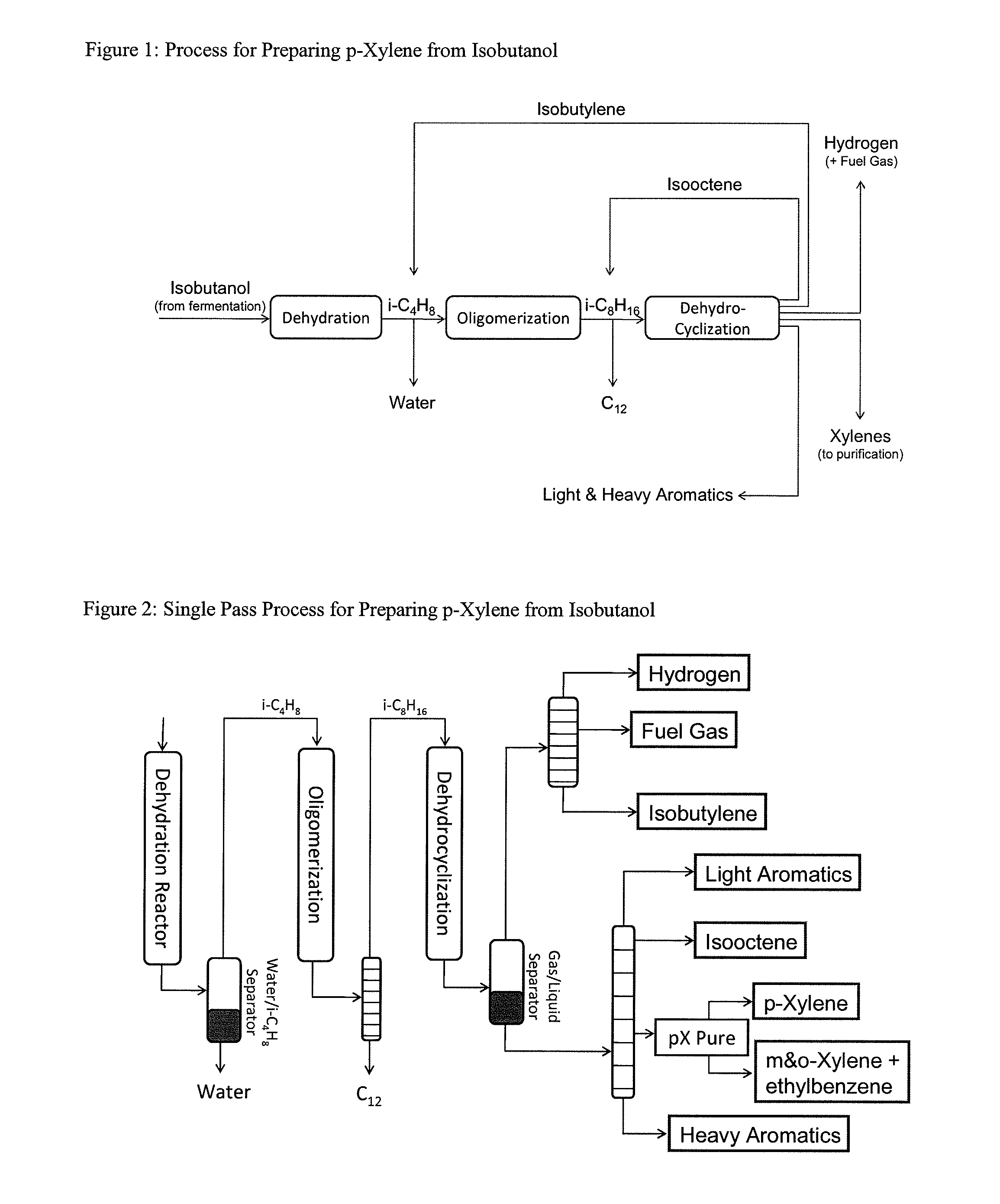
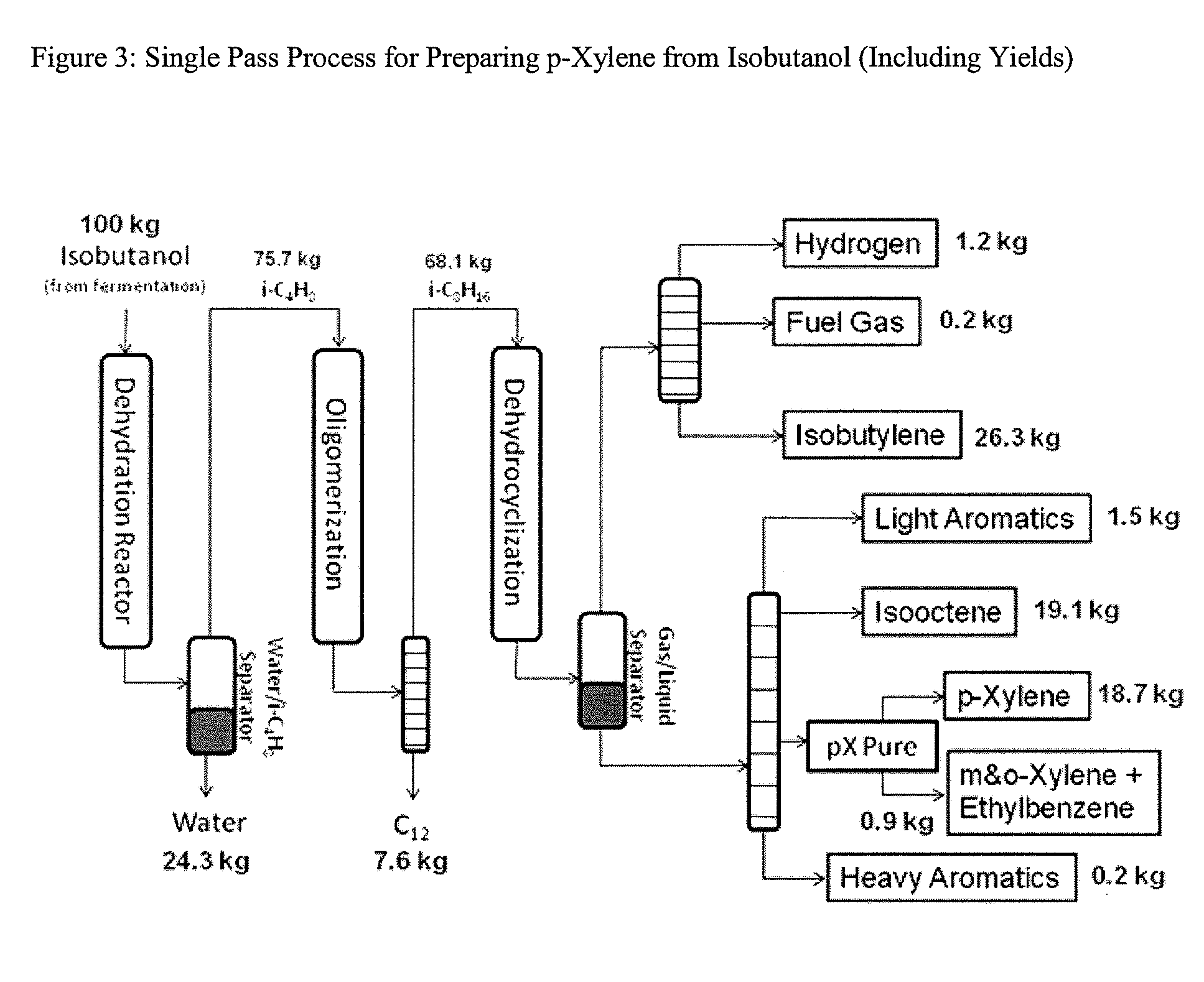
Integrated Process to Selectively Convert Renewable Isobutanol to P-Xylene
The present invention is directed to a method for preparing renewable and relatively high purity p-xylene from biomass. For example, biomass treated to provide a fermentation feedstock is fermented with a microorganism capable of producing a C4 alcohol such as isobutanol, then sequentially dehydrating the isobutanol in the presence of a dehydration catalyst to provide a C4 alkene such as isobutylene, dimerizing the C4 alkene to a form one or more C8 alkenes such as 2,4,4-trimethylpentenes or 2,5-dimethylhexene, then dehydrocyclizing the C8 alkenes in the presence of a dehydrocyclization catalyst to selectively form renewable p-xylene in high overall yield. The p-xylene can then be oxidized to form terephthalic acid or terephthalate esters.
Owner:GEVO INC
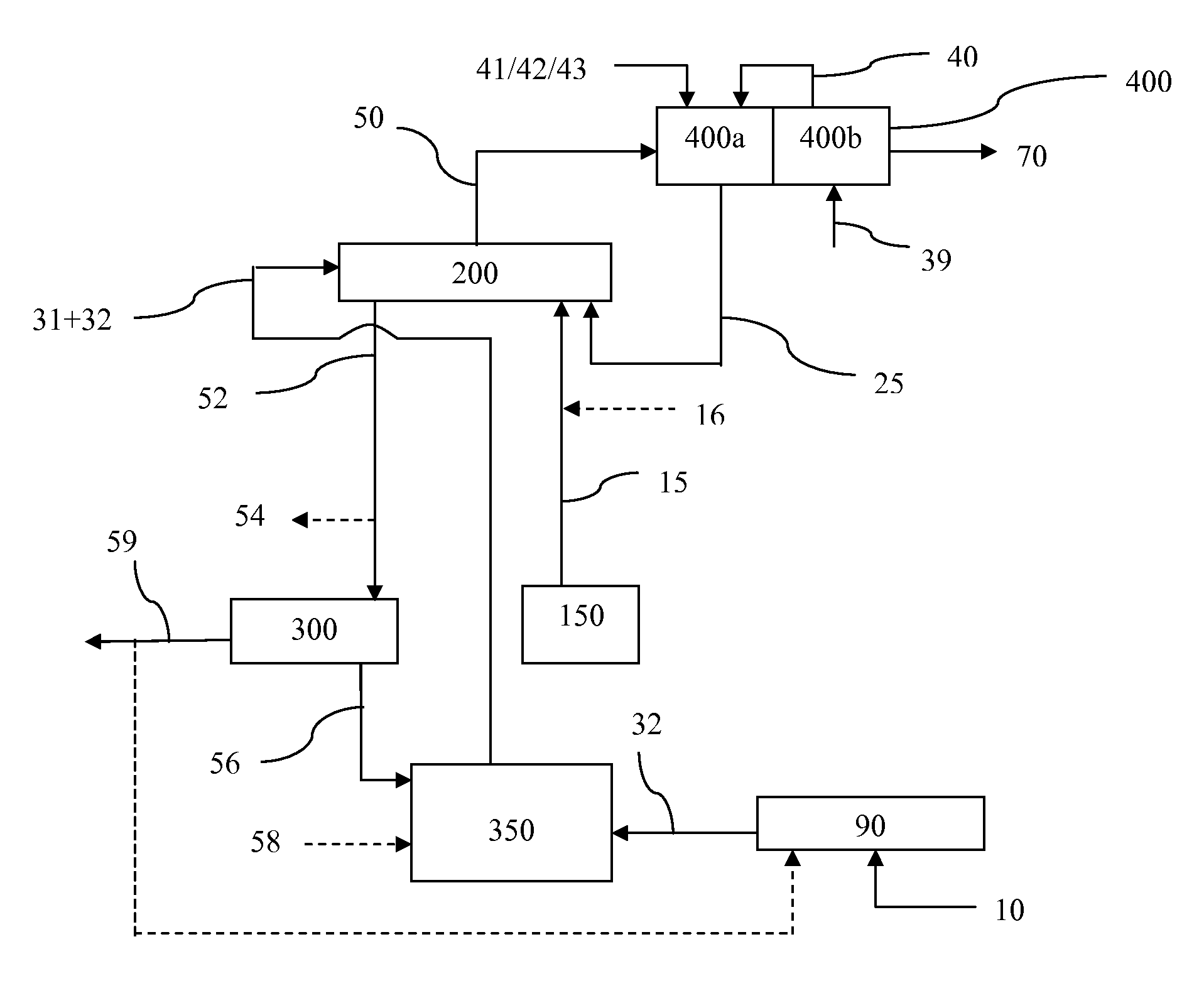
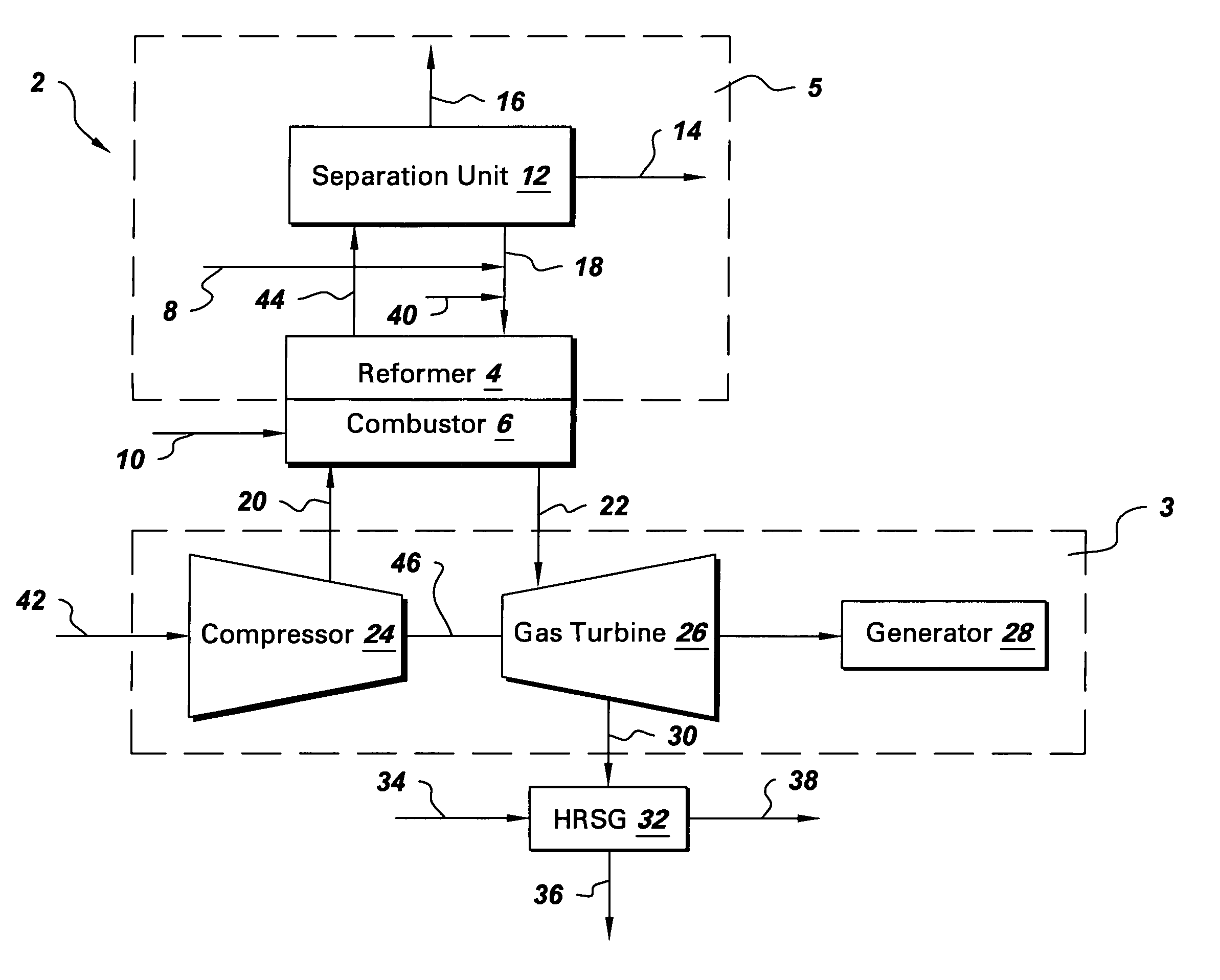
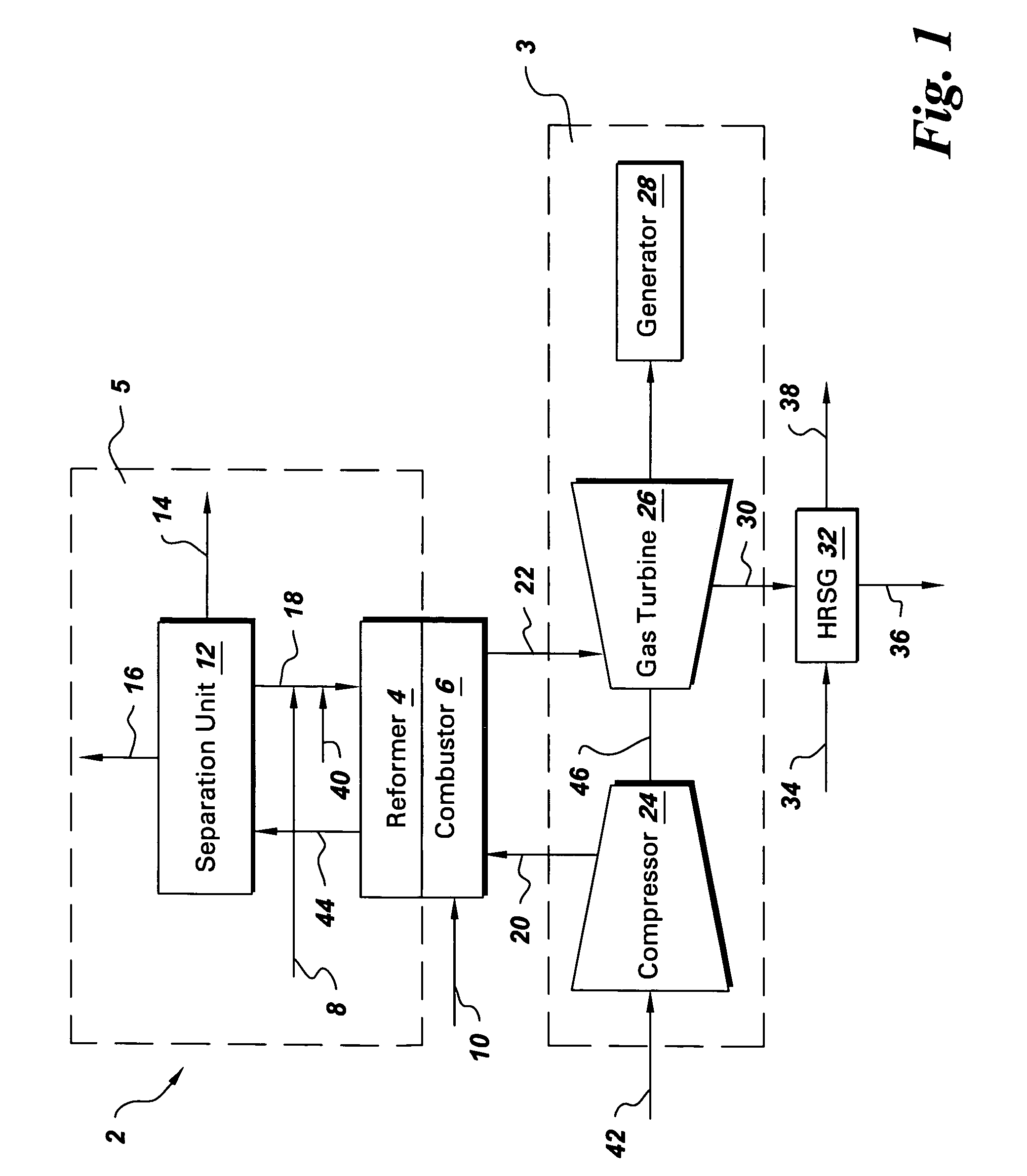
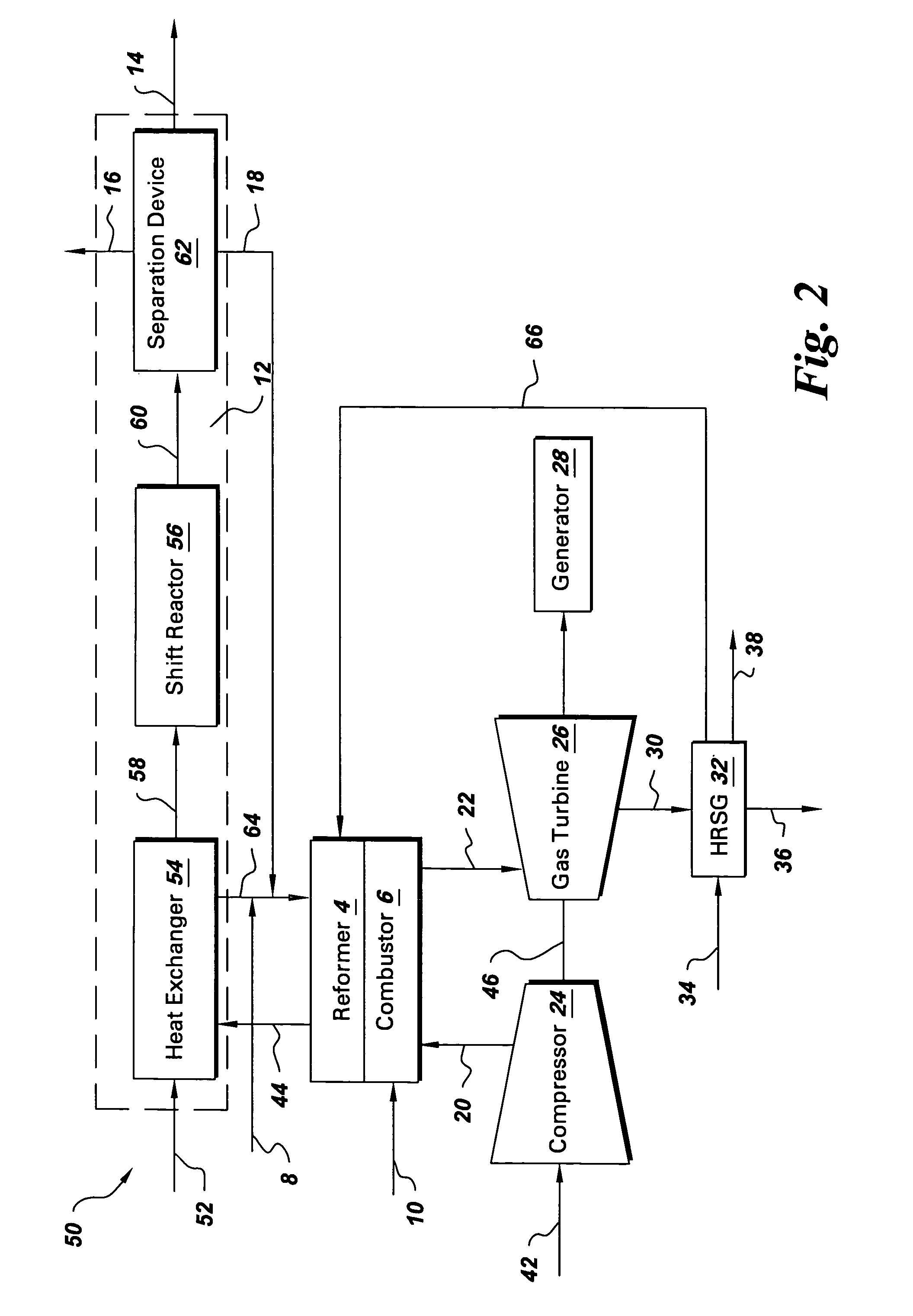
System and method for co-production of hydrogen and electrical energy
A system for co-production of hydrogen and electrical energy comprising a reformer configured to receive a reformer fuel and steam and produce a reformate rich in hydrogen. The system further comprises a separation unit in fluid communication with the reformer wherein the separation unit is configured to receive the reformate to separate hydrogen from the reformate and produce an off gas. The system also includes a combustor configured to receive a fuel for combustion and produce heat energy and a hot compressed gas, wherein the combustor is coupled with the reformer. A gas turbine expands the hot compressed gas and produces electrical energy and an expanded gas; wherein at least a part of the heat energy from the combustor is used to produce the reformate in the reformer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com