Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Auditory brainstem response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
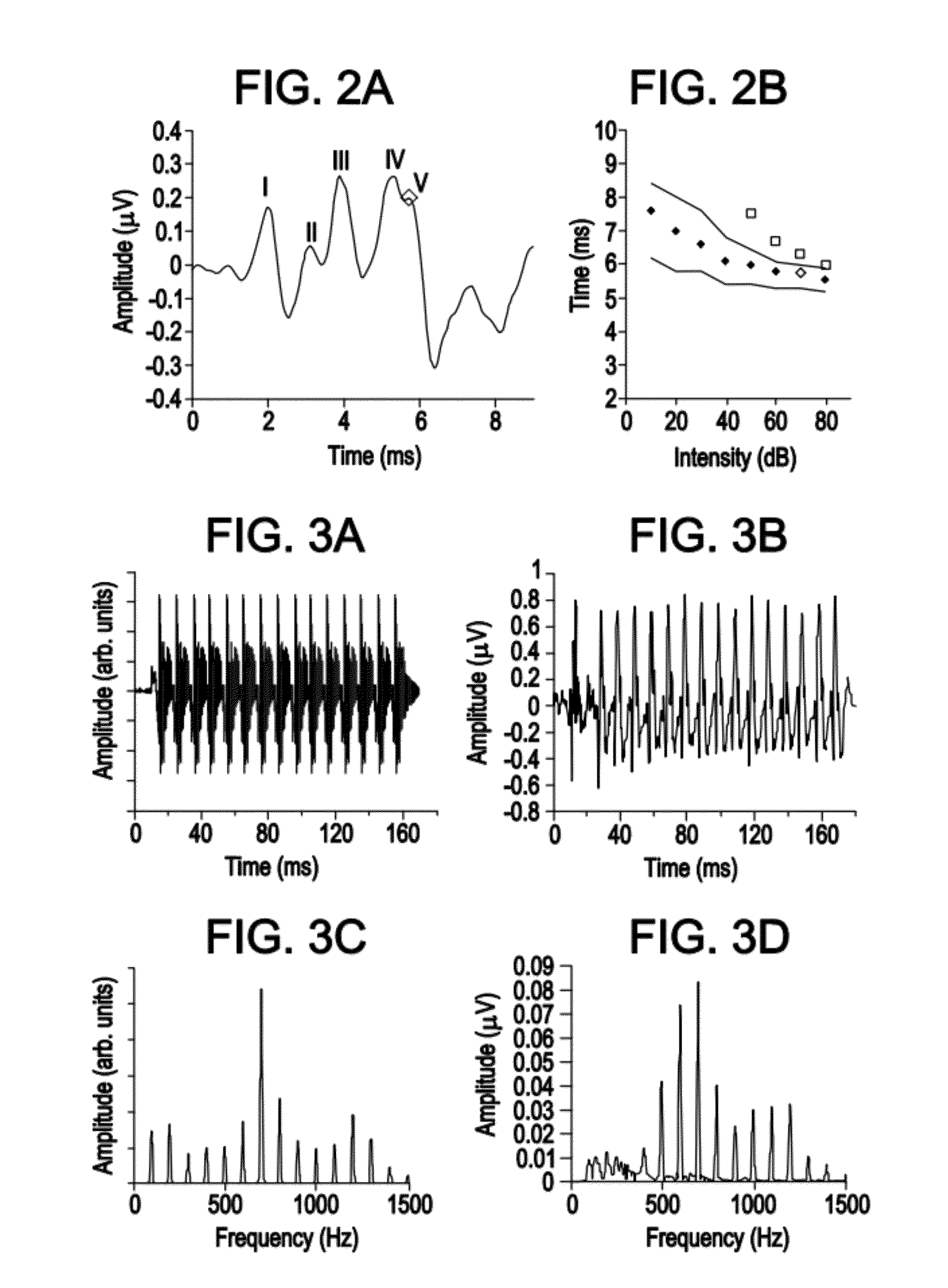
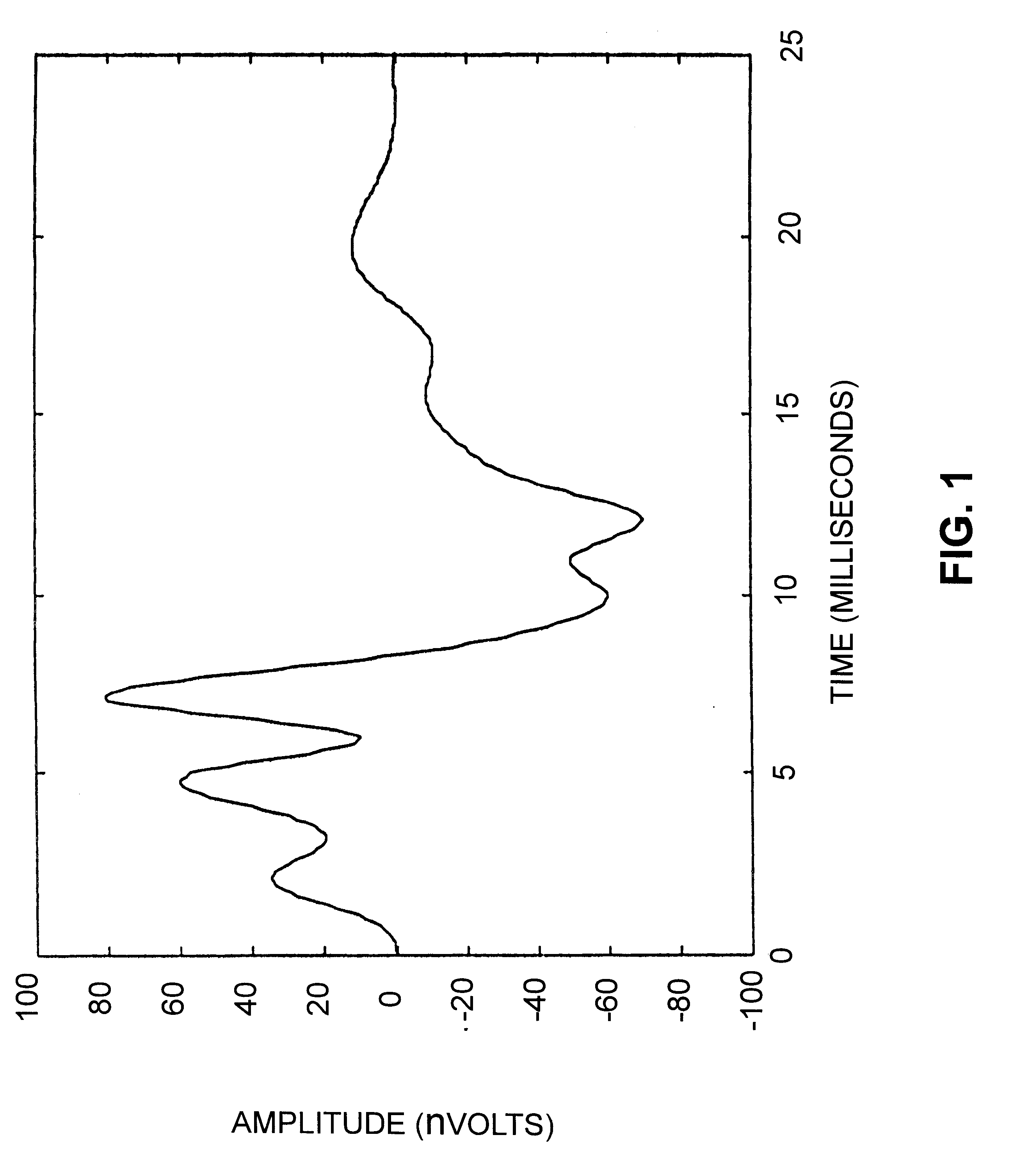
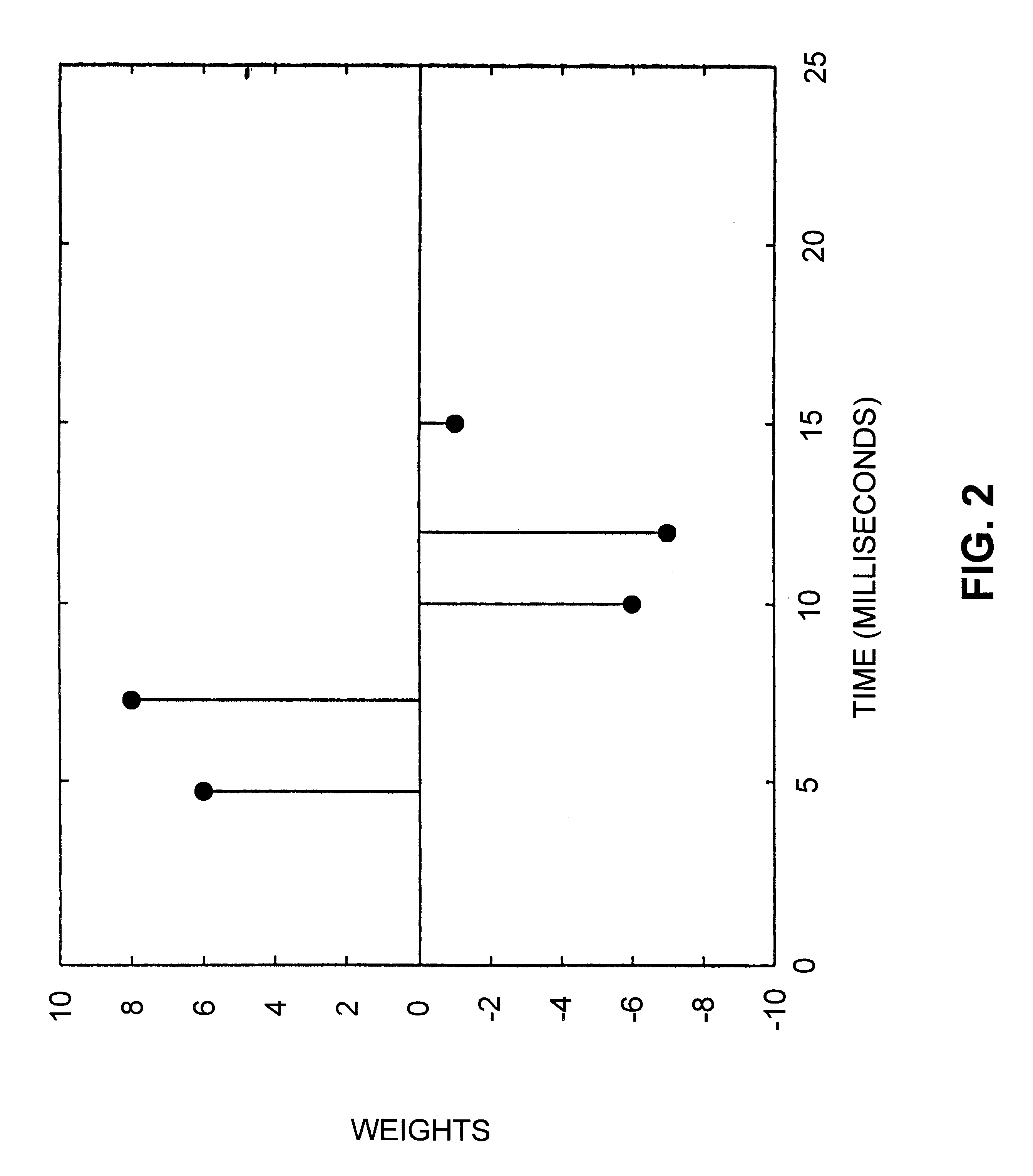
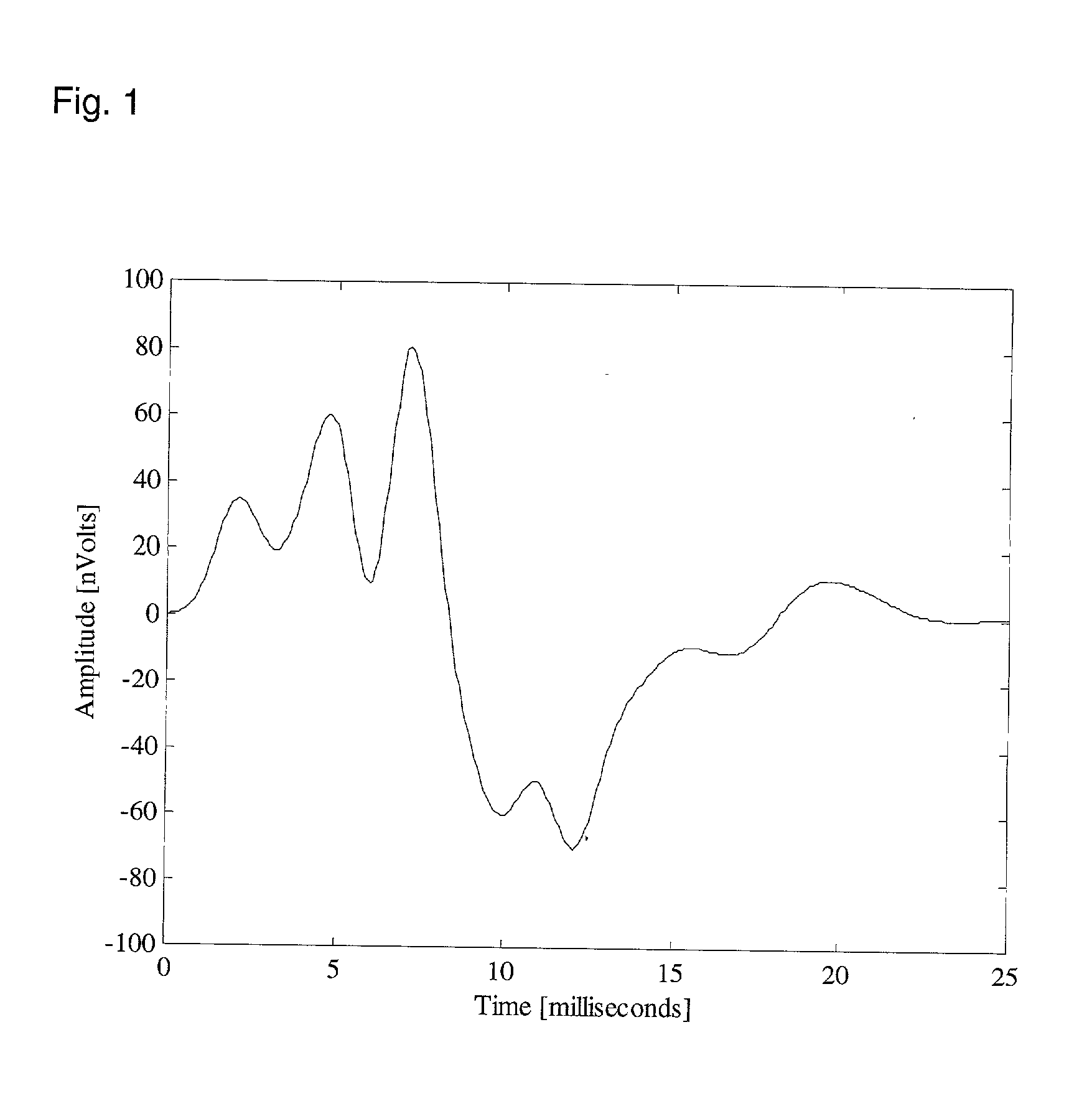
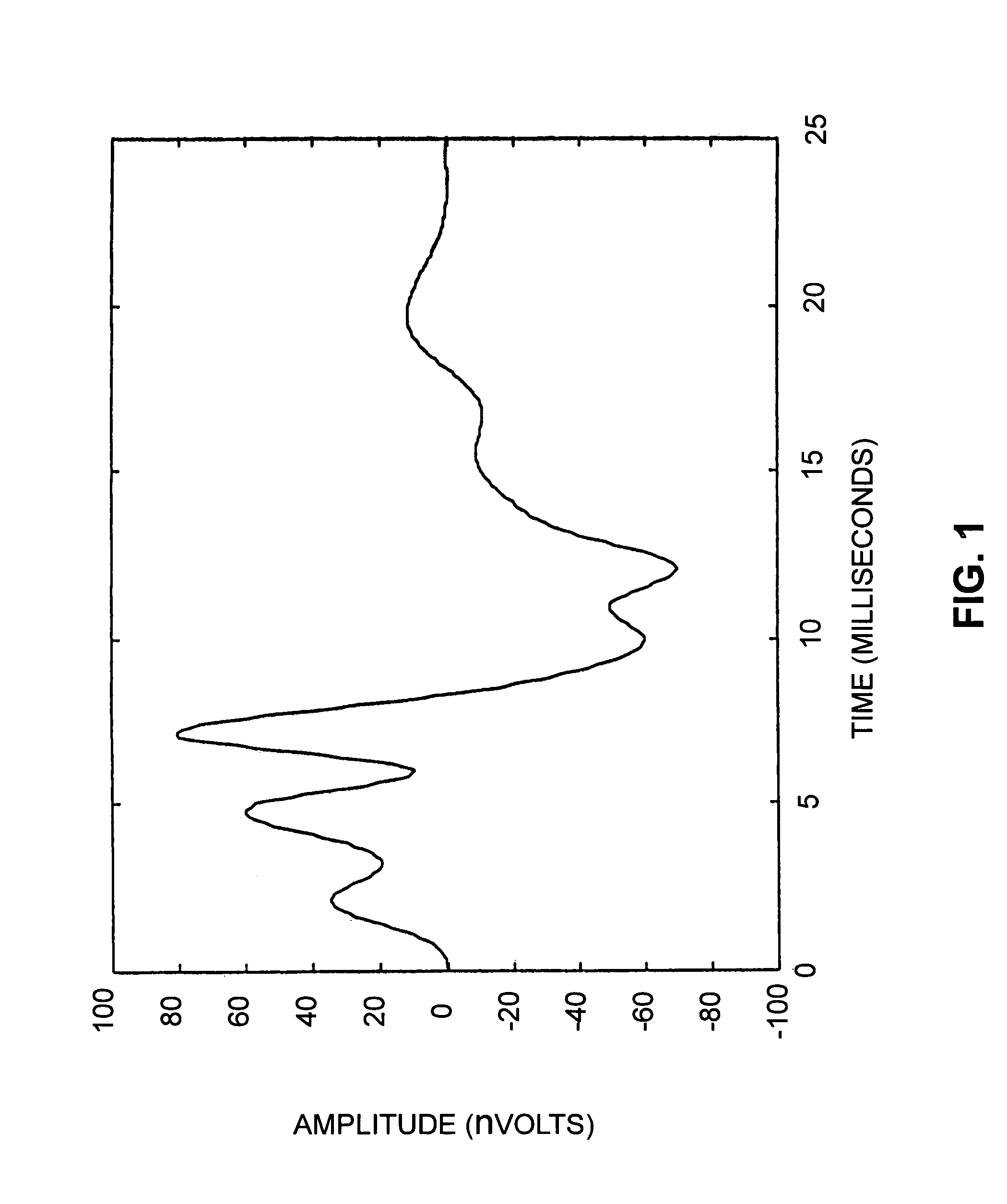
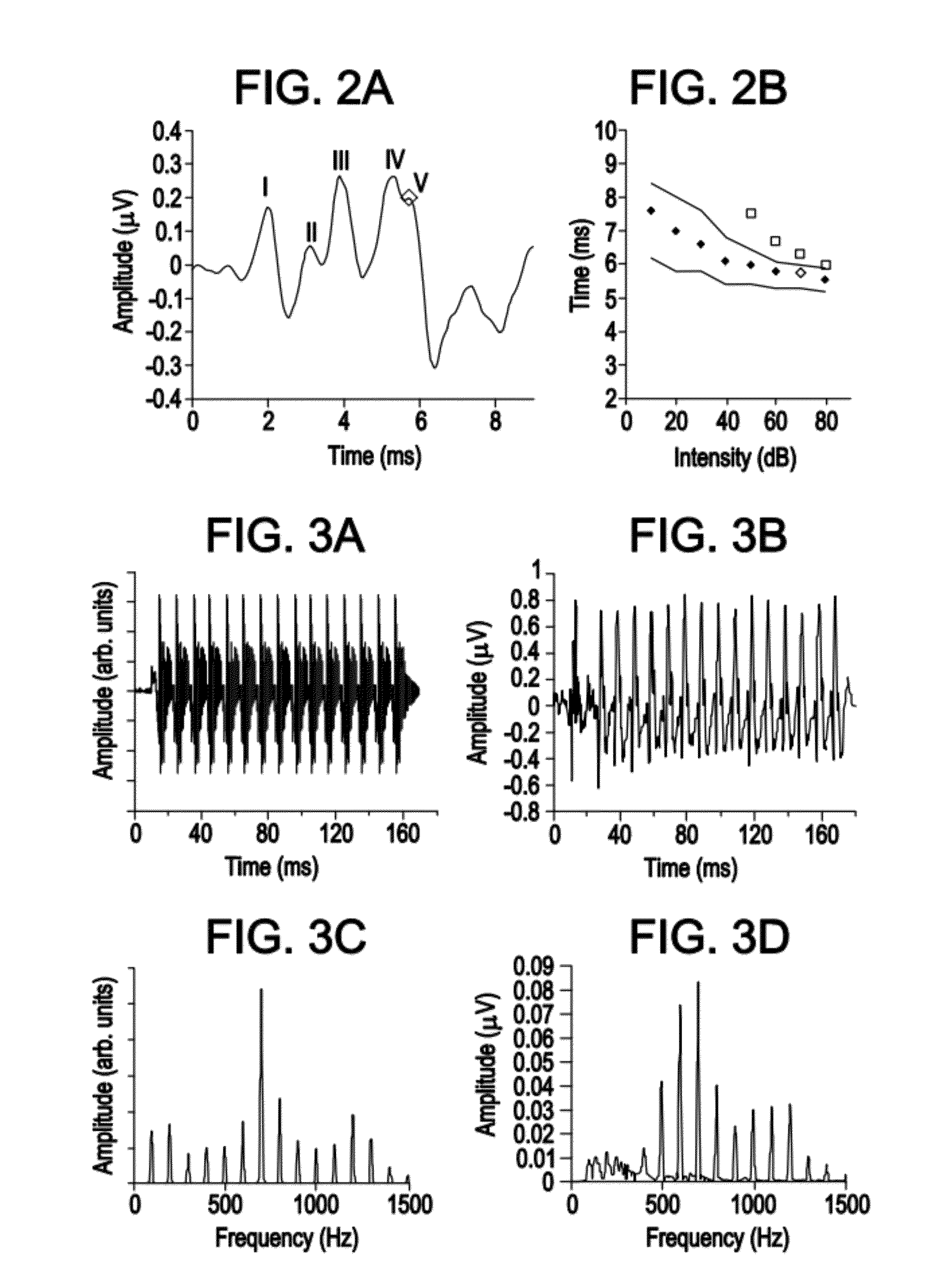
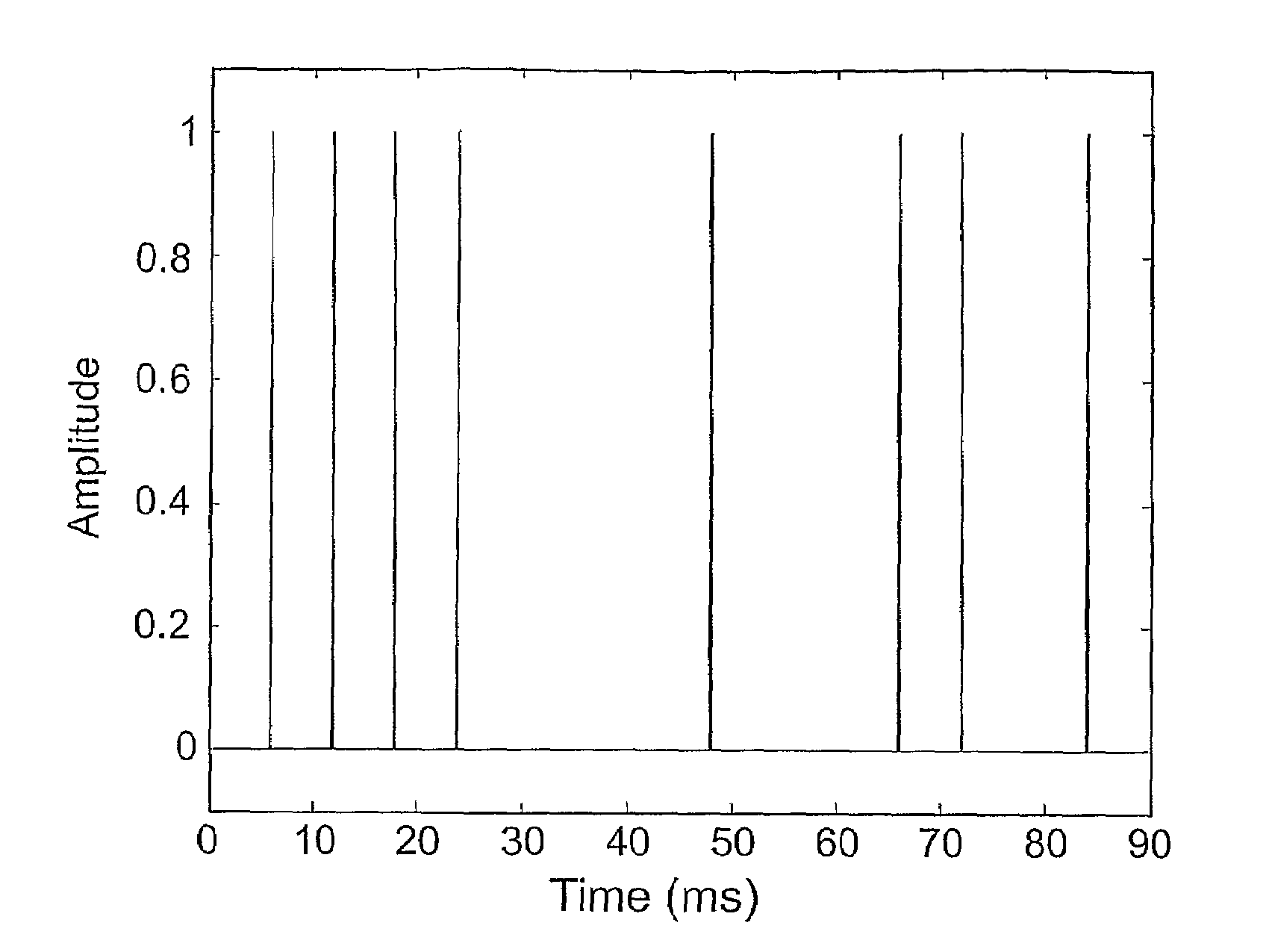
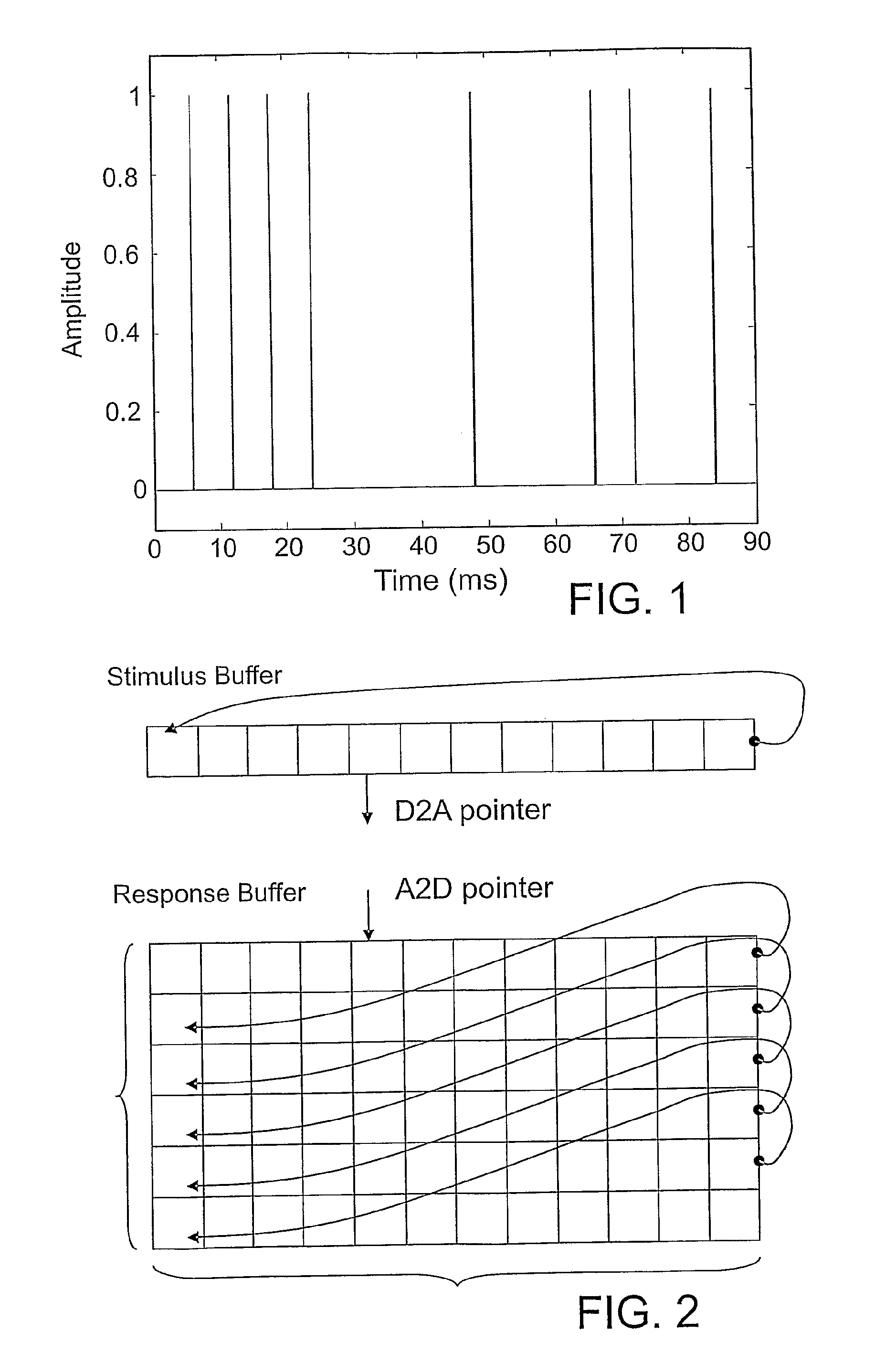
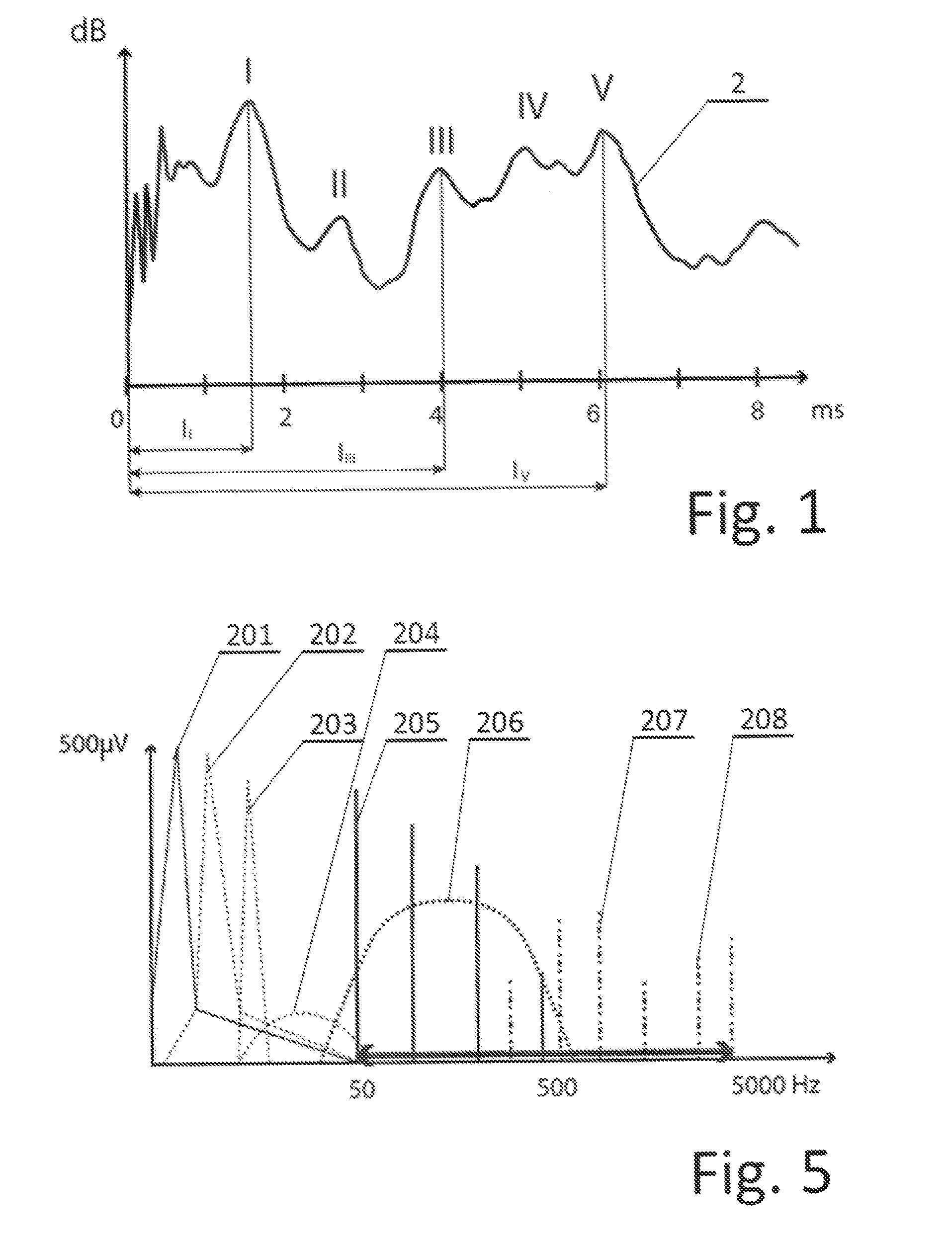
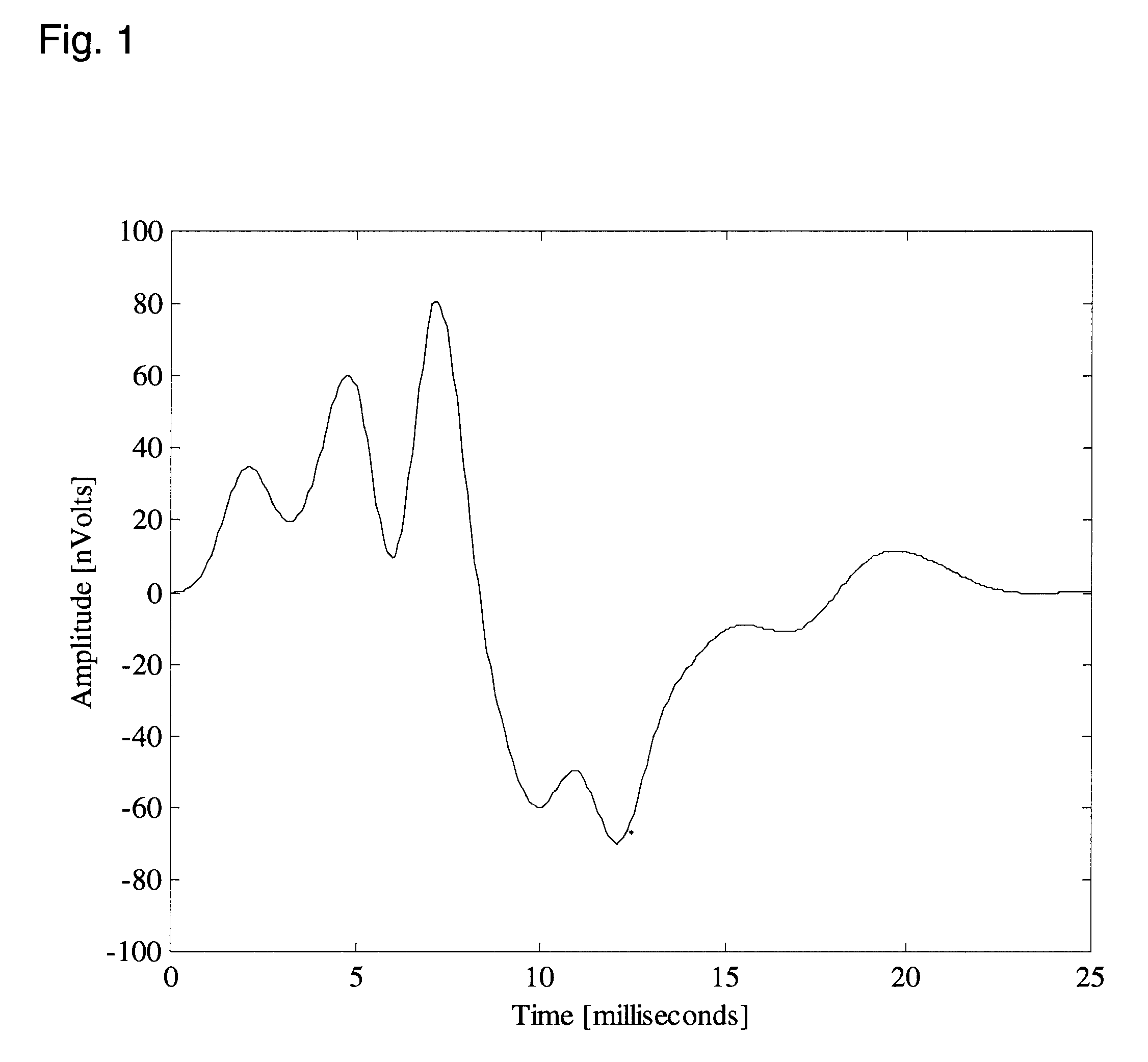
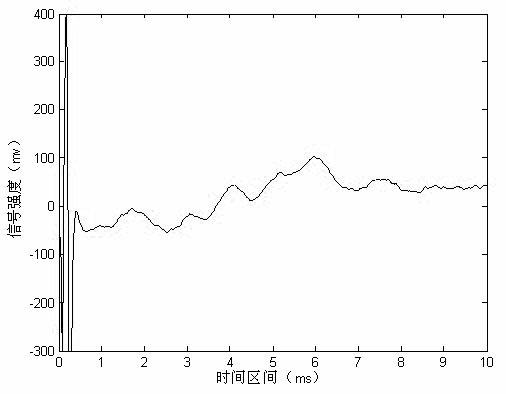
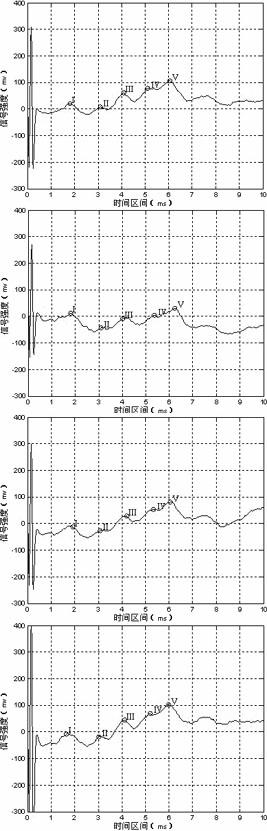
The auditory brainstem response (ABR) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. These waves, labeled with Roman numerals in Jewett and Williston convention, occur in the first 10 milliseconds after onset of an auditory stimulus. The ABR is considered an exogenous response because it is dependent upon external factors.
Systems and methods for measuring complex auditory brainstem response
Certain examples provide a method of collecting and analyzing complex auditory brainstem response. The example method includes presenting at least one complex auditory stimulus to a subject and acquiring the subject's complex auditory brainstem response. The example method includes averaging complex auditory brainstem responses from the subject in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain to form a collected response. The example method includes analyzing the collected response using a signal processor to process the collected response to provide a processed output and to adapt the response for comparison to the at least one complex auditory stimulus. The example method includes performing statistical computations on the processed output to generate visual and data feedback for a user.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
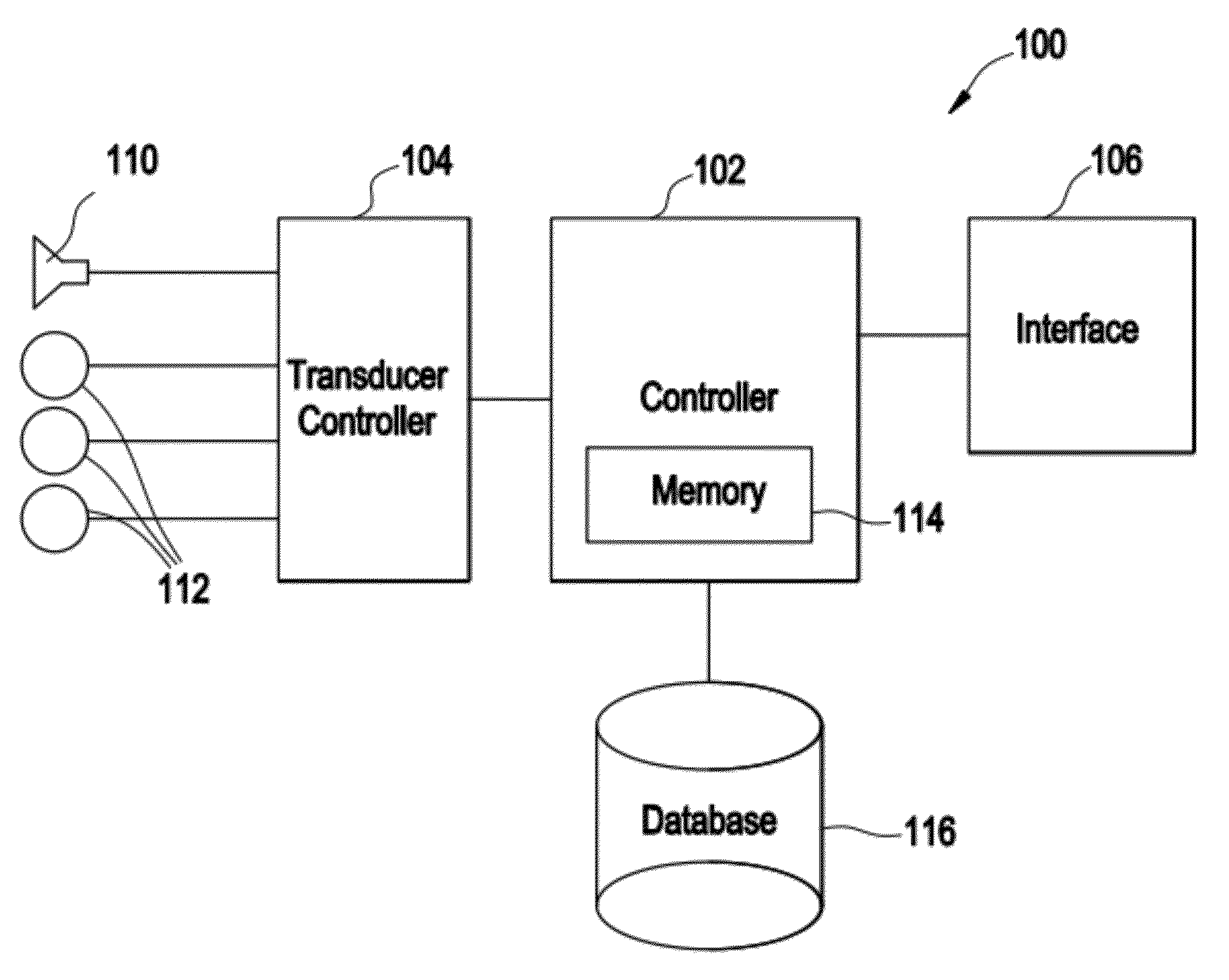
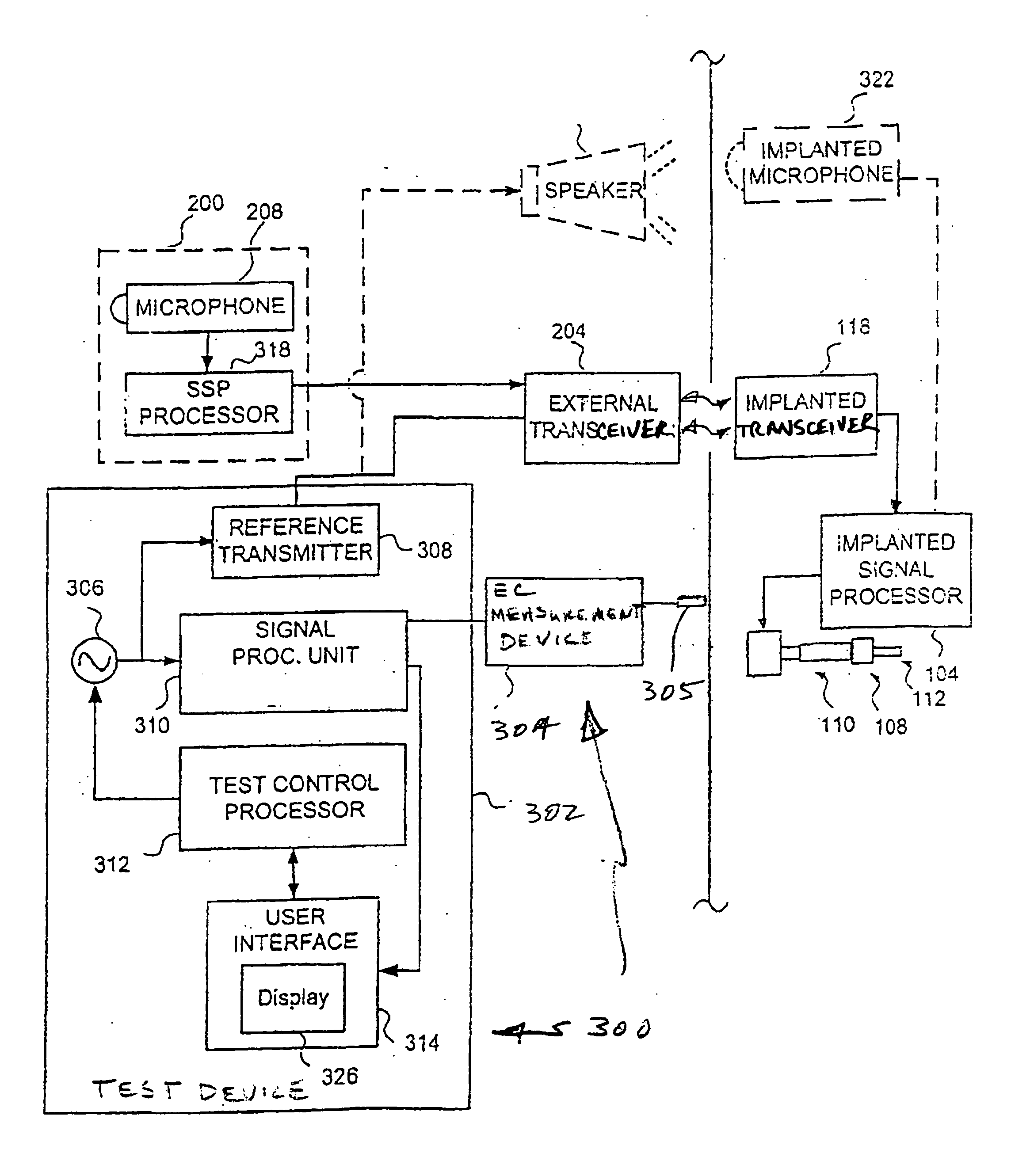
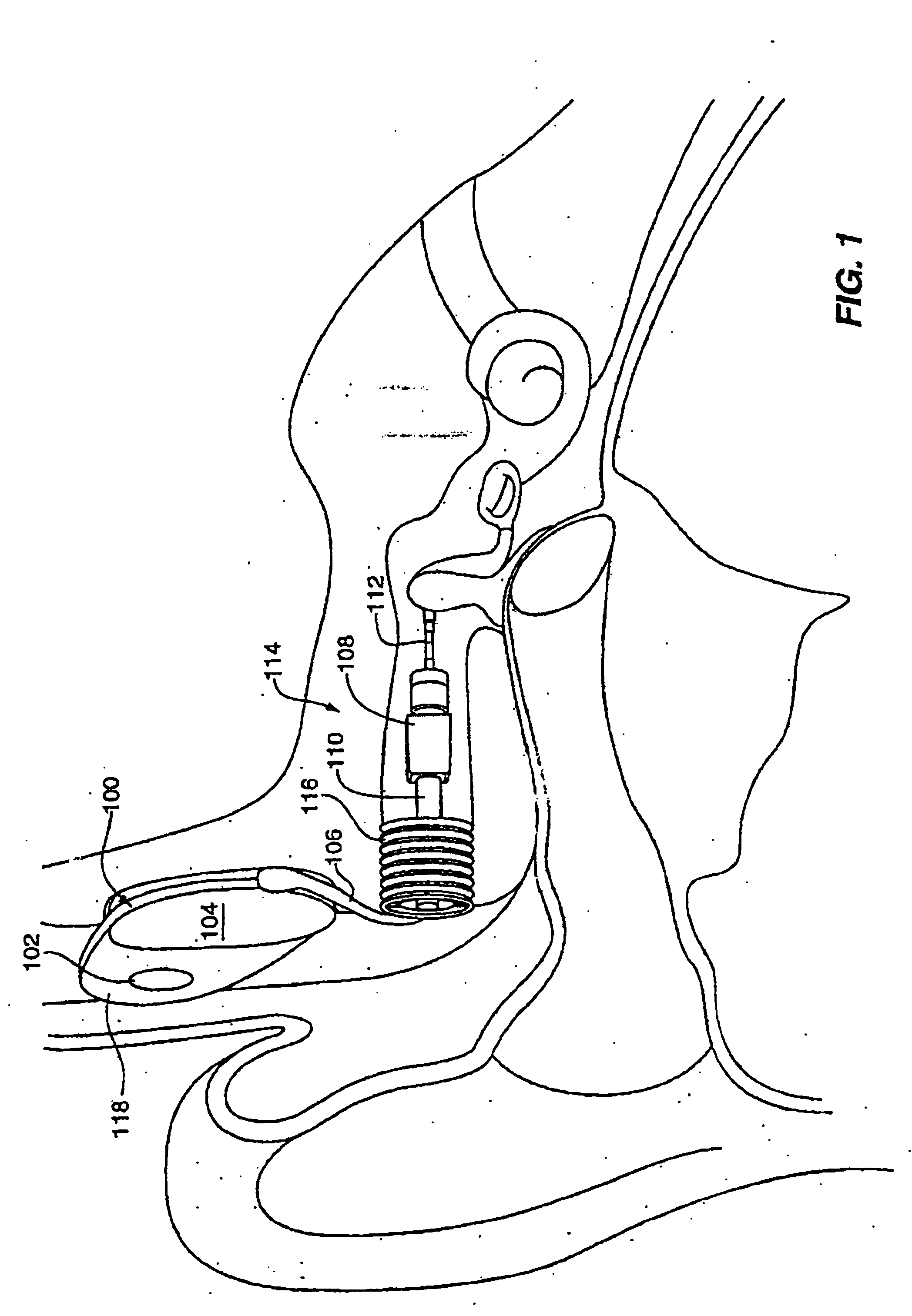
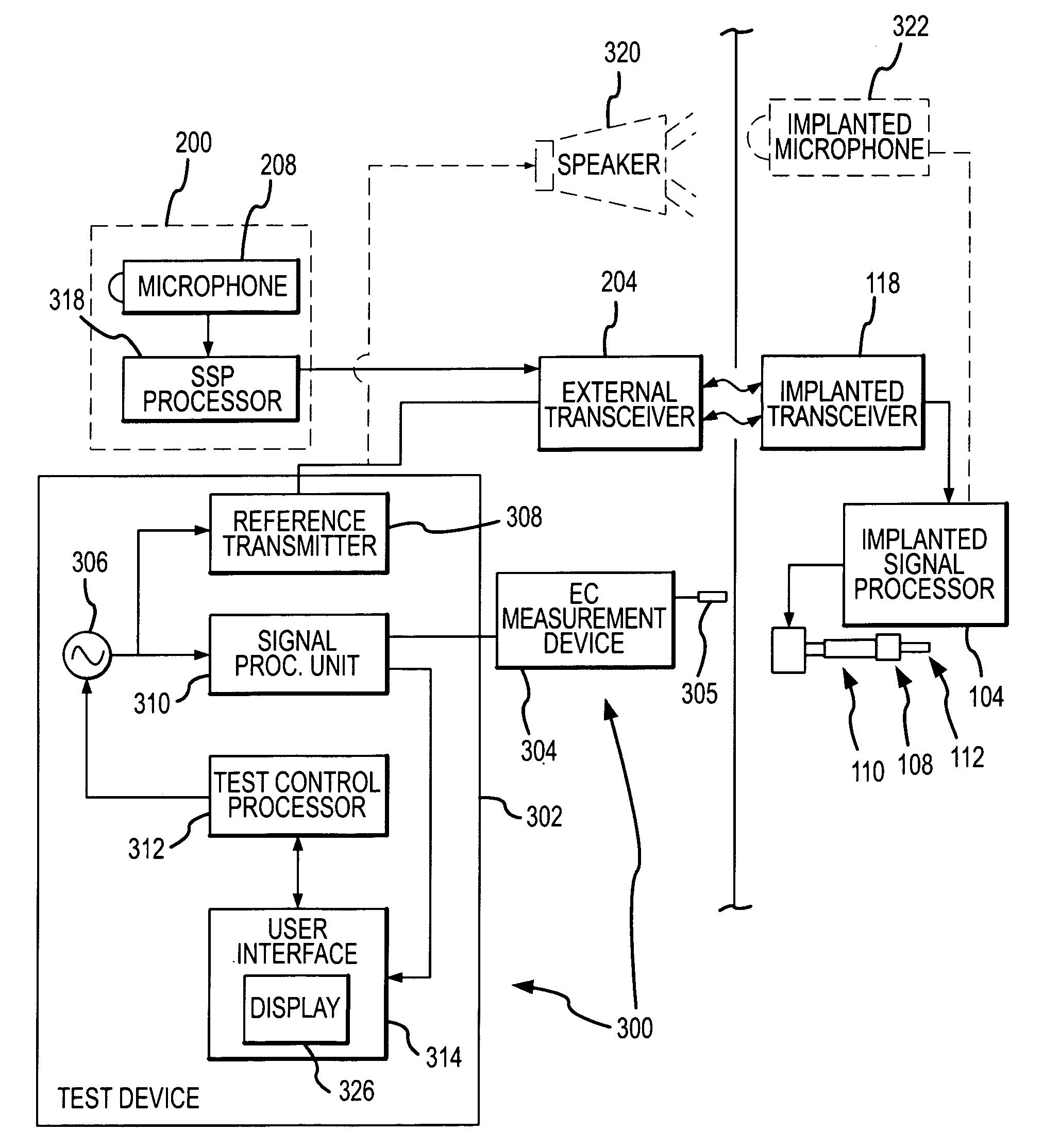
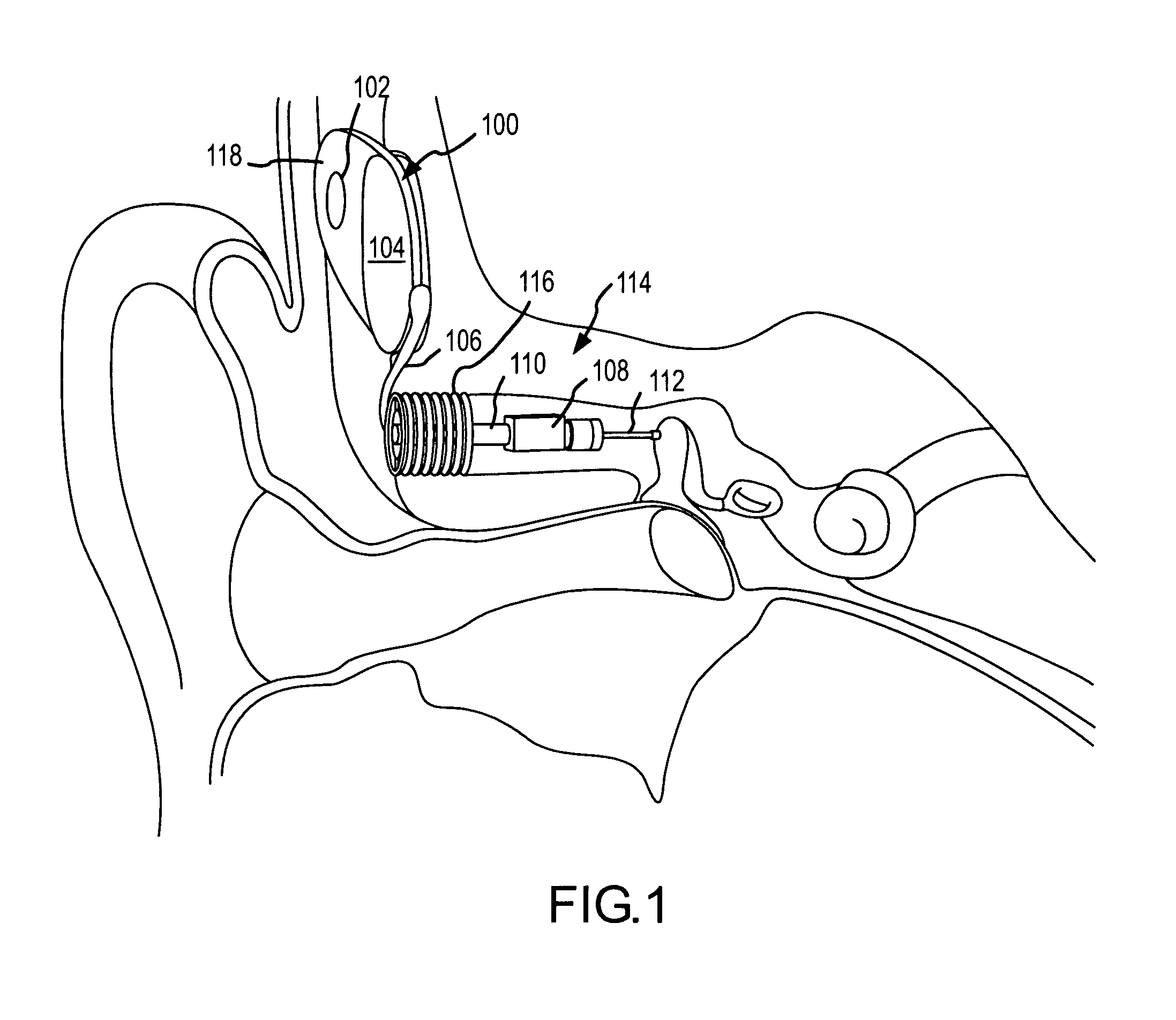
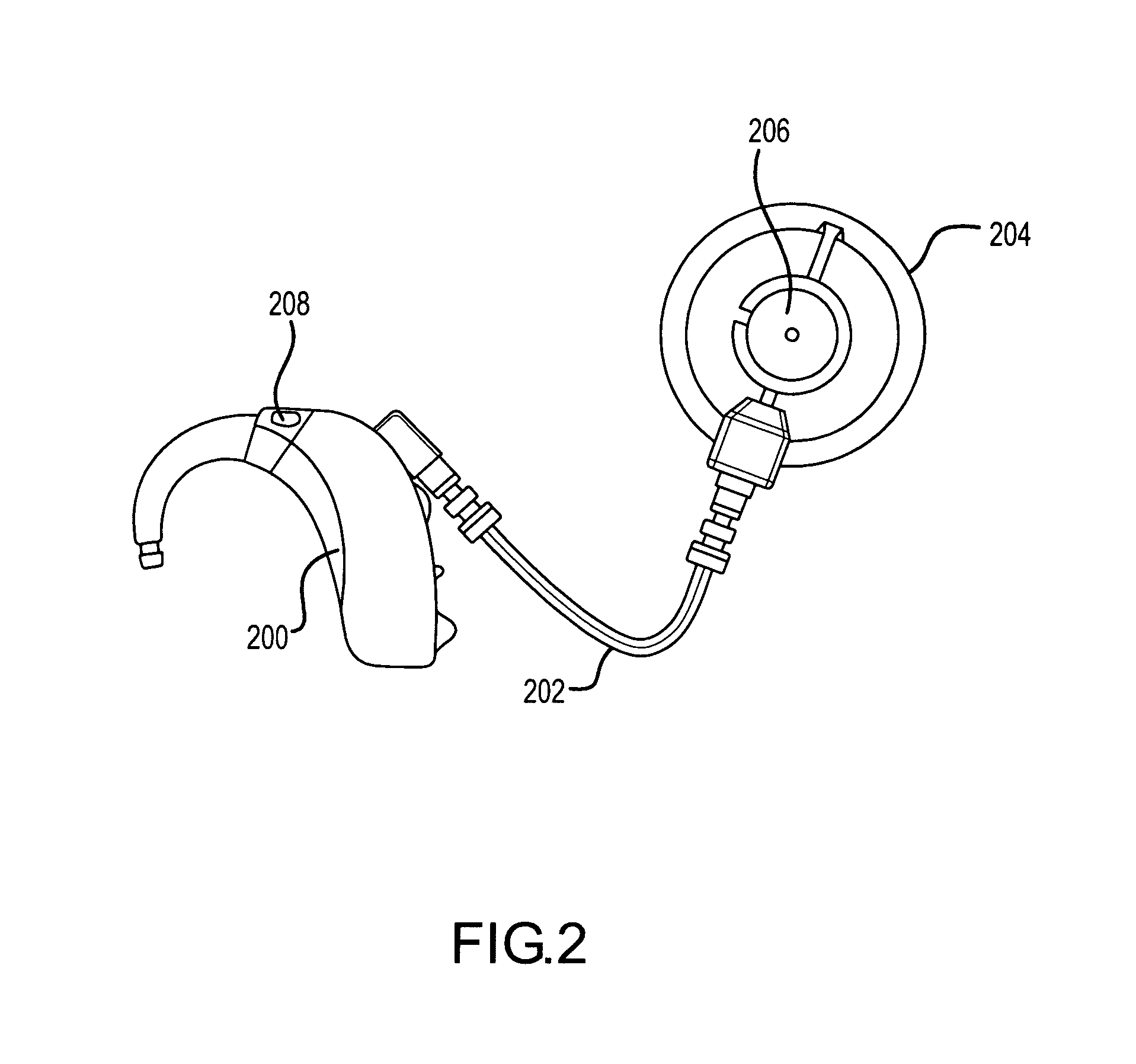
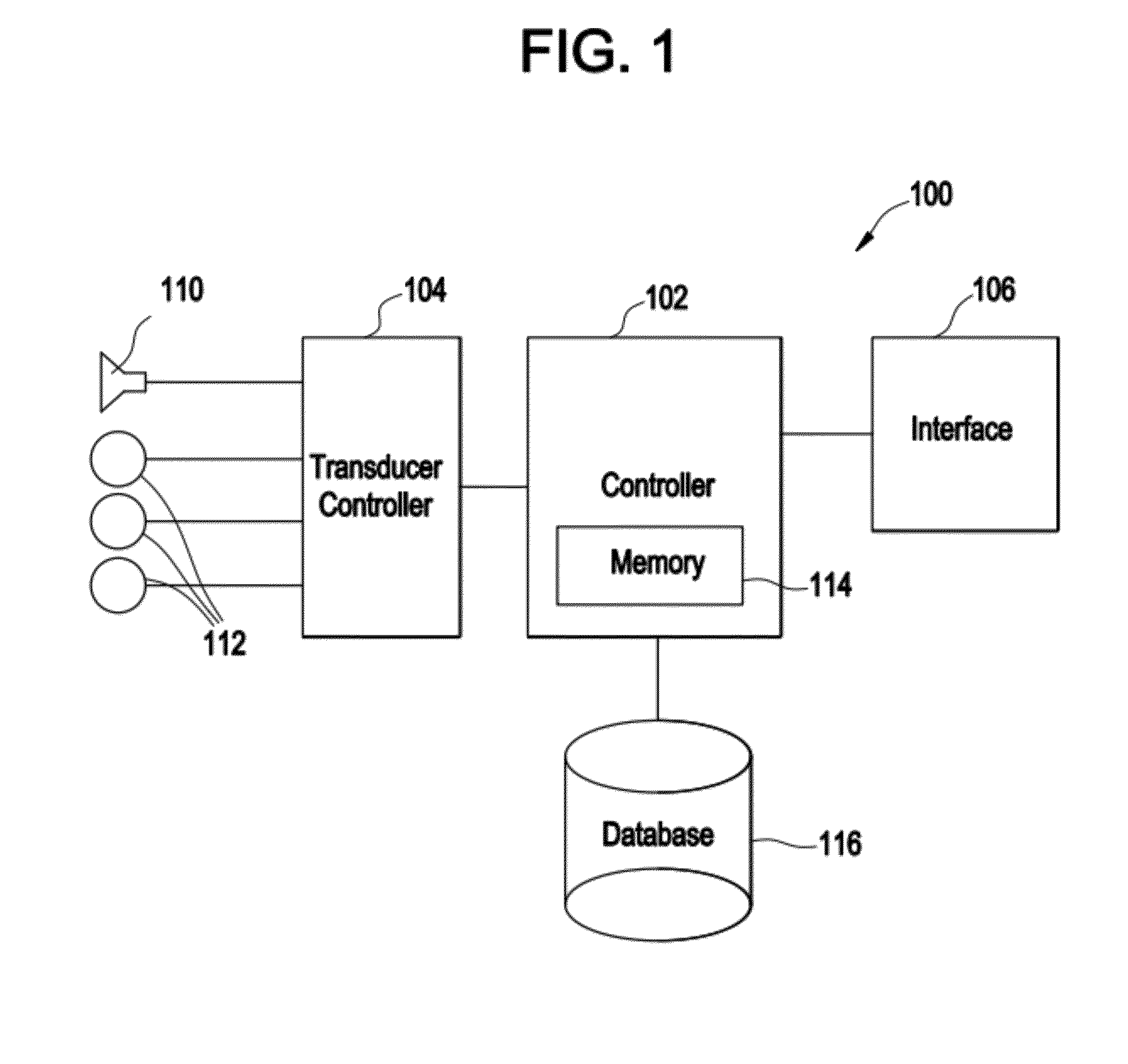
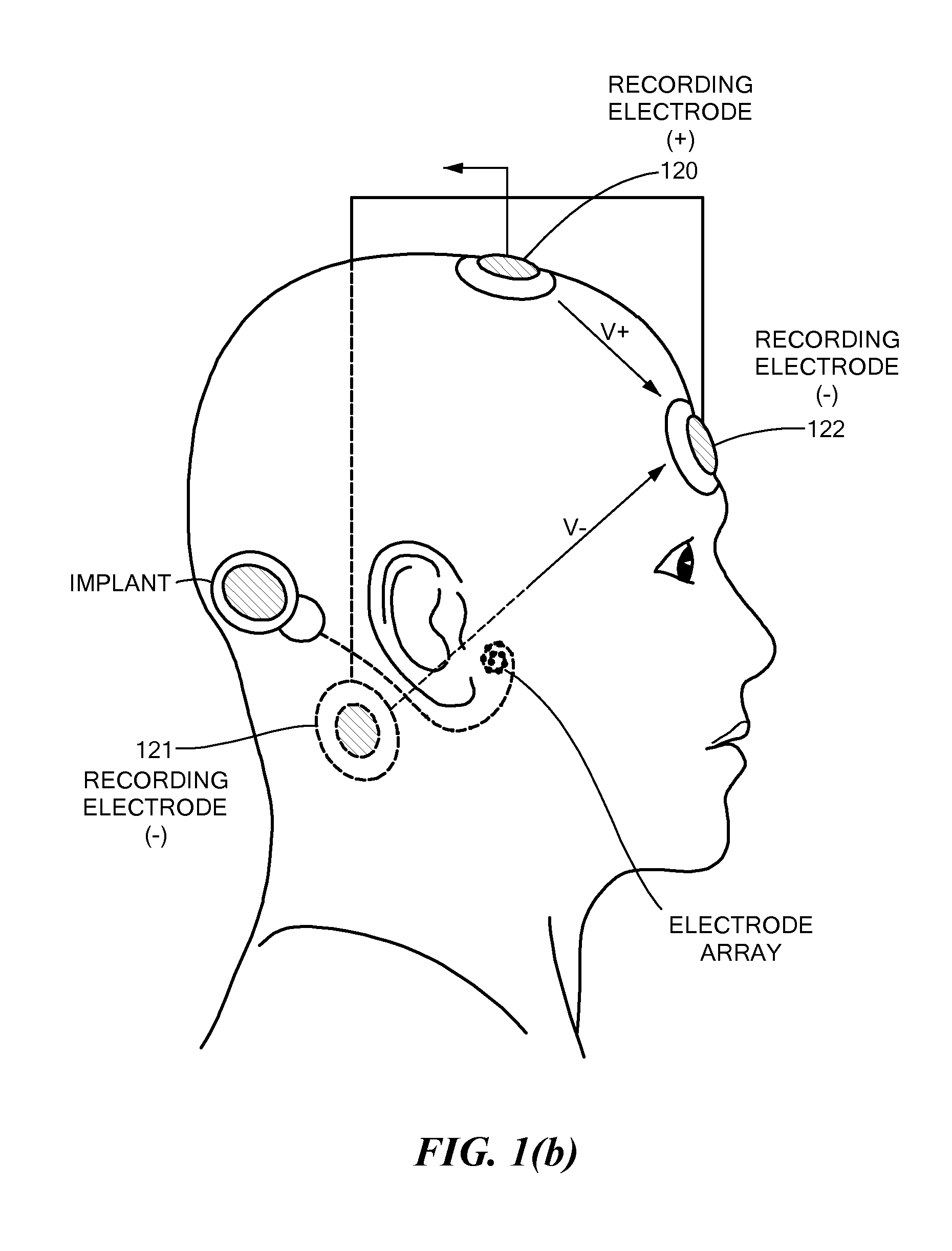
Electrophysiological measurement method and system for positioning an implantable, hearing instrument transducer
ActiveUS20050131272A1Help positioningEasily employedElectroencephalographySensorsPotential measurementMeasurement device
An electrophysiological measurement method and system is provided for positioning an implantable transducer of a hearing instrument relative to a middle ear component or inner ear of a patient. The method and system employ electrophysiological measurement signals obtained in response to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In one embodiment, the electrophysiological measurements are obtained by an electrocochleography measurement device that measures the cochlear summating potential and / or action potential responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In another embodiment, an auditory brainstem response measurement device is utilized to obtain electrical potential measurement signals responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
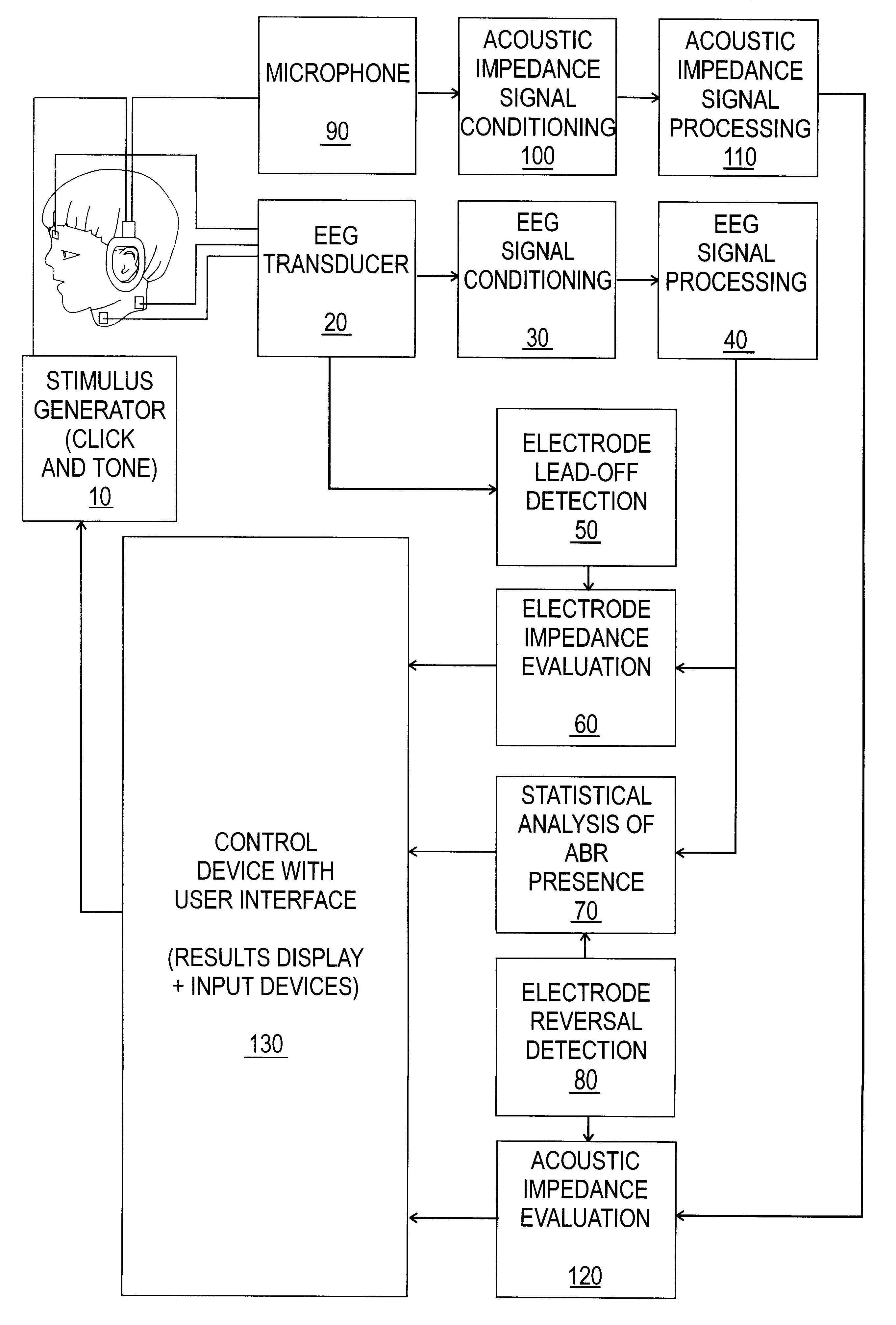
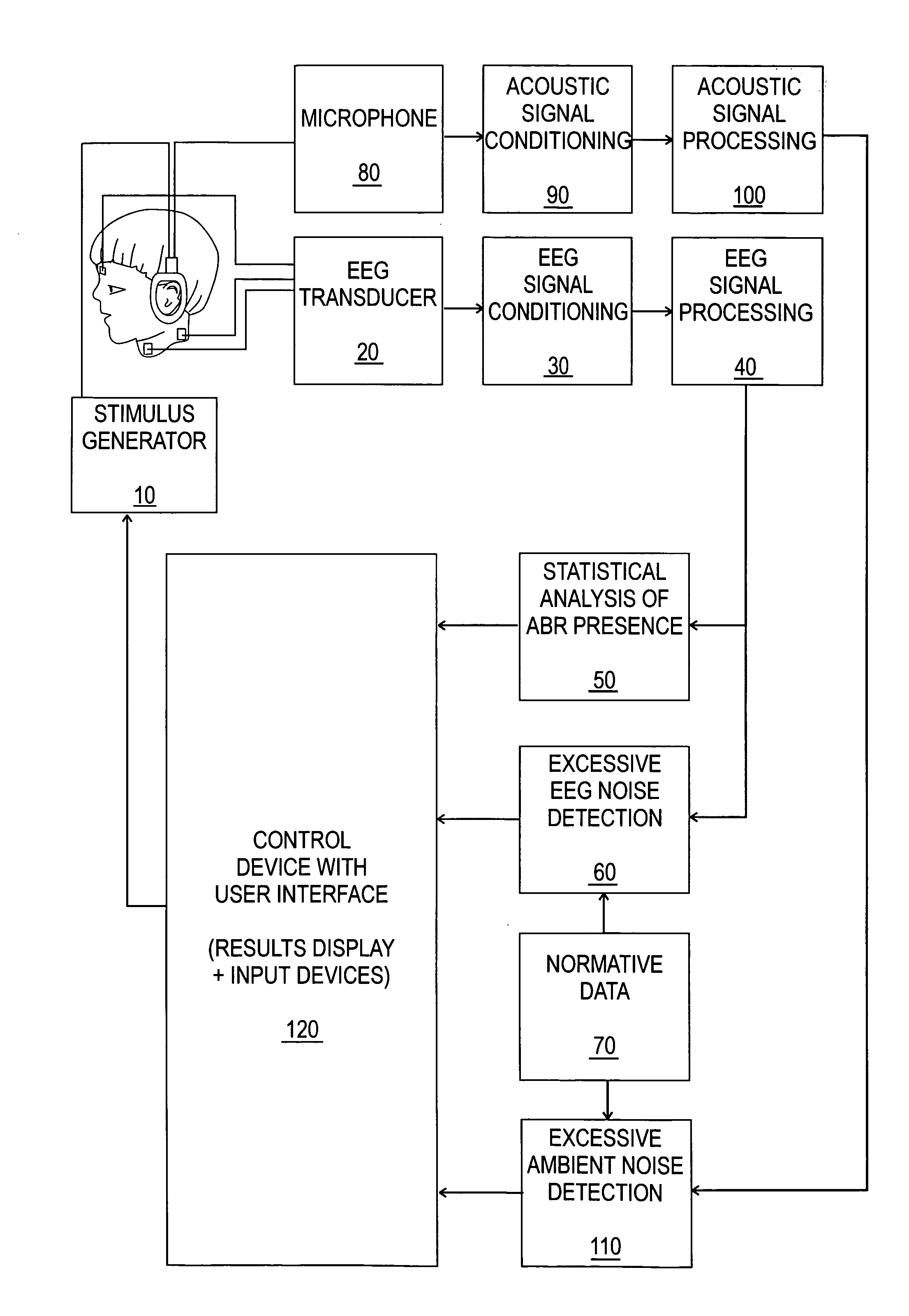
Hearing evaluation device with patient connection evaluation capabilities
InactiveUS6475163B1Test data can be compromisedInhibition formationElectroencephalographyAudiometeringElectrophonic hearingHeadphones
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear iteratively administered click stimuli. The present invention evaluates the sufficiency of the patient connections, namely earphones and electrodes, to the evaluation device. More particularly, the present invention determines if the earphones are detached or deformed, if the electrodes have been reversed, or if the electrodes have become detached.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Hearing evaluation device with noise-weighting capabilities
InactiveUS20030073920A1Conserving evaluation timeSave resourcesElectroencephalographyAudiometeringElectrophonic hearingEngineering
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear repeatedly administered click stimuli. In order to optimize evaluation, the present invention uses normative data to accurately weight the auditory responses, so that evaluation will be possible in different or changing noise conditions.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Electrophysiological measurement method and system for positioning an implantable, hearing instrument transducer
ActiveUS7137946B2Easily employedHelp positioningElectroencephalographySensorsMiddle ear functionPotential measurement
An electrophysiological measurement method and system is provided for positioning an implantable transducer of a hearing instrument relative to a middle ear component or inner ear of a patient. The method and system employ electrophysiological measurement signals obtained in response to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In one embodiment, the electrophysiological measurements are obtained by an electrocochleography measurement device that measures the cochlear summating potential and / or action potential responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer. In another embodiment, an auditory brainstem response measurement device is utilized to obtain electrical potential measurement signals responsive to test signals applied to an implanted transducer.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Hearing evaluation device with noise detection and evaluation capability
InactiveUS7133715B1Improve determinationImprove test efficiencyElectroencephalographyAudiometeringNoise detectionEngineering
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear click stimuli that are repeatedly administered. In order to facilitate efficient differentiation of the ABR from the accompanying noise, normative data is used to detect test conditions where physiological, non-physiological, and ambient acoustic noise would interfere with the progression of test.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Systems and methods for measuring complex auditory brainstem response
Certain examples provide a method of collecting and analyzing complex auditory brainstem response. The example method includes presenting at least one complex auditory stimulus to a subject and acquiring the subject's complex auditory brainstem response. The example method includes averaging complex auditory brainstem responses from the subject in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain to form a collected response. The example method includes analyzing the collected response using a signal processor to process the collected response to provide a processed output and to adapt the response for comparison to the at least one complex auditory stimulus. The example method includes performing statistical computations on the processed output to generate visual and data feedback for a user.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method and apparatus for signal encoding evoked responses
InactiveUS20070167857A1Improve performanceElectroencephalographyAudiometeringEngineeringSignal encoding
A method and apparatus for utilizing the benefits of encoded signal transmission and reception to enhance the performance of medical testing devices (100) adapted to evoke and measure biological response signals such as auditory evoked potentials (AEP), and the auditory brainstem response (ABR) signals in particular. Auditory stimuli, such as clicks, are presented to the ear of a human patient, in a predetermined encoded sequence, resulting in the generation of auditory responses and bio-electric response signals in the human patient. These response signals from the patient are acquired and observed, and are processed according to the predetermined encoded sequence in which the auditory stimuli were presented to the patient's ear in order to extract the desired auditory evoked potential signals or ABR signals.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
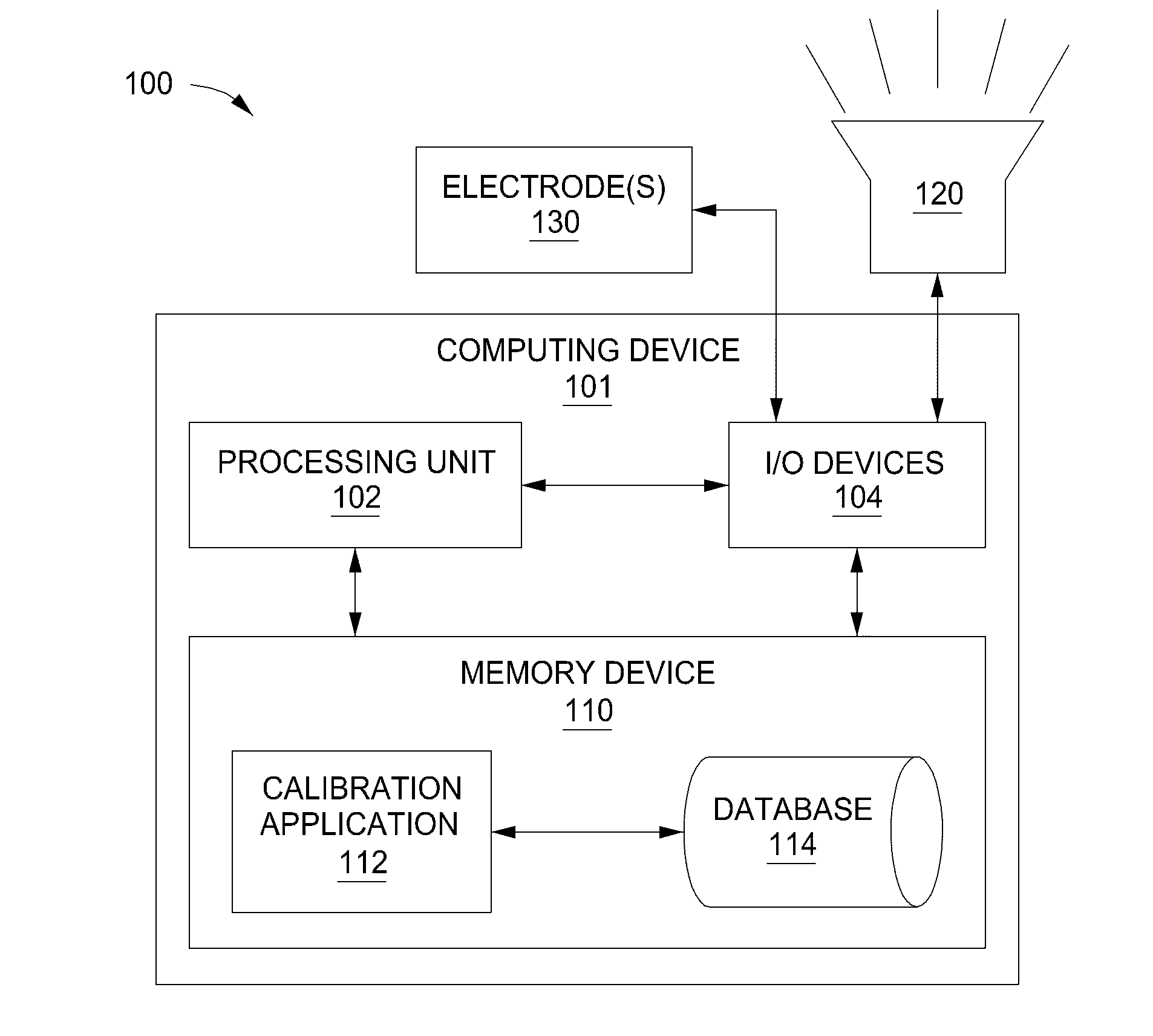
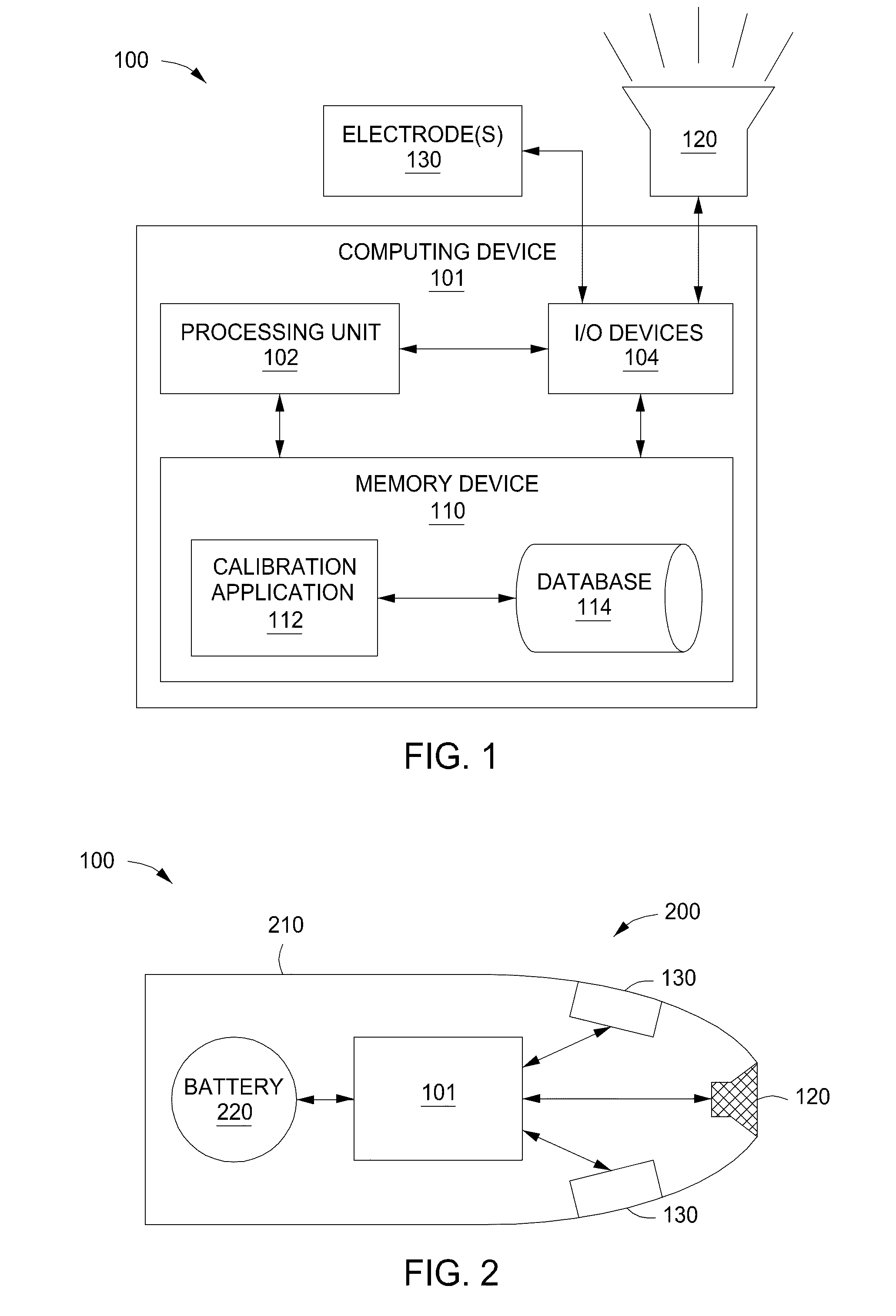
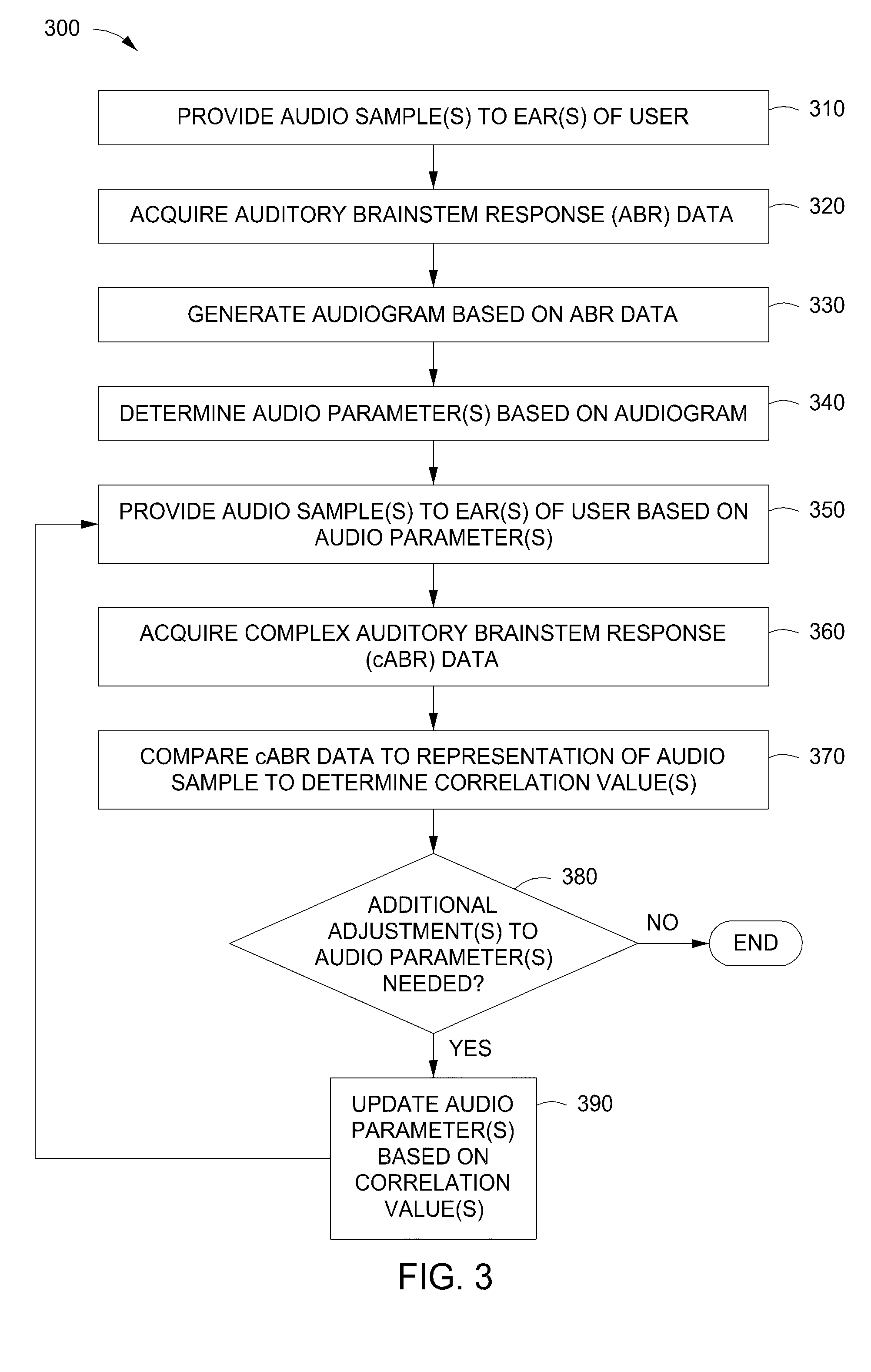
Automatic sound equalization device
ActiveUS20160112022A1Efficiently determinedAccurately determinedInput/output for user-computer interactionStereophonic circuit arrangementsEqualizationAudio frequency
A technique for determining one or more equalization parameters includes acquiring, via one or more electrodes, auditory brainstem response (ABR) data associated with a first audio sample and determining, via a processor, one or more equalization parameters based on the ABR data. The technique further includes reproducing a second audio sample based on the one or more equalization parameters, acquiring, via the one or more electrodes, complex auditory brainstem response (cABR) data associated with the second audio sample, and comparing, via the processor, the cABR data to at least one representation of the second audio sample to determine at least one measure of similarity. The technique further includes modifying the one or more equalization parameters based on the at least one measure of similarity.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Method of acquiring a physiological response
InactiveUS20100030096A1Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyElectroencephalographySensorsEngineeringElectro physiology
A method for acquiring a physiological response from a test subject, particularly an auditory brainstem response, by presenting a plurality of stimuli, such as a Maximum Length Sequence, detecting electrophysiological signals in response to the stimuli, generating a recover signal based on the stimuli and determining the physiological response from the electrophysiological signals and the recovery signal.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
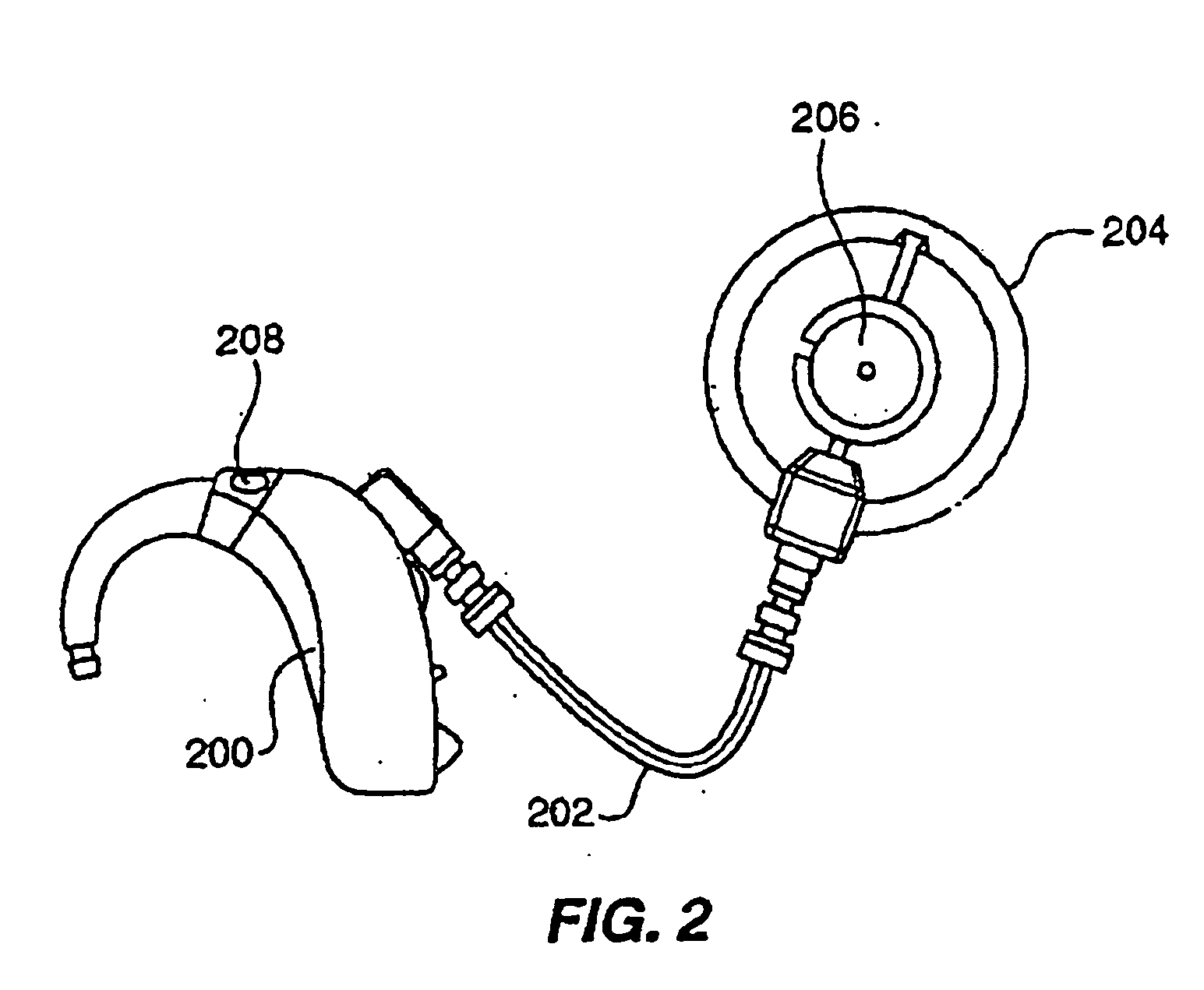
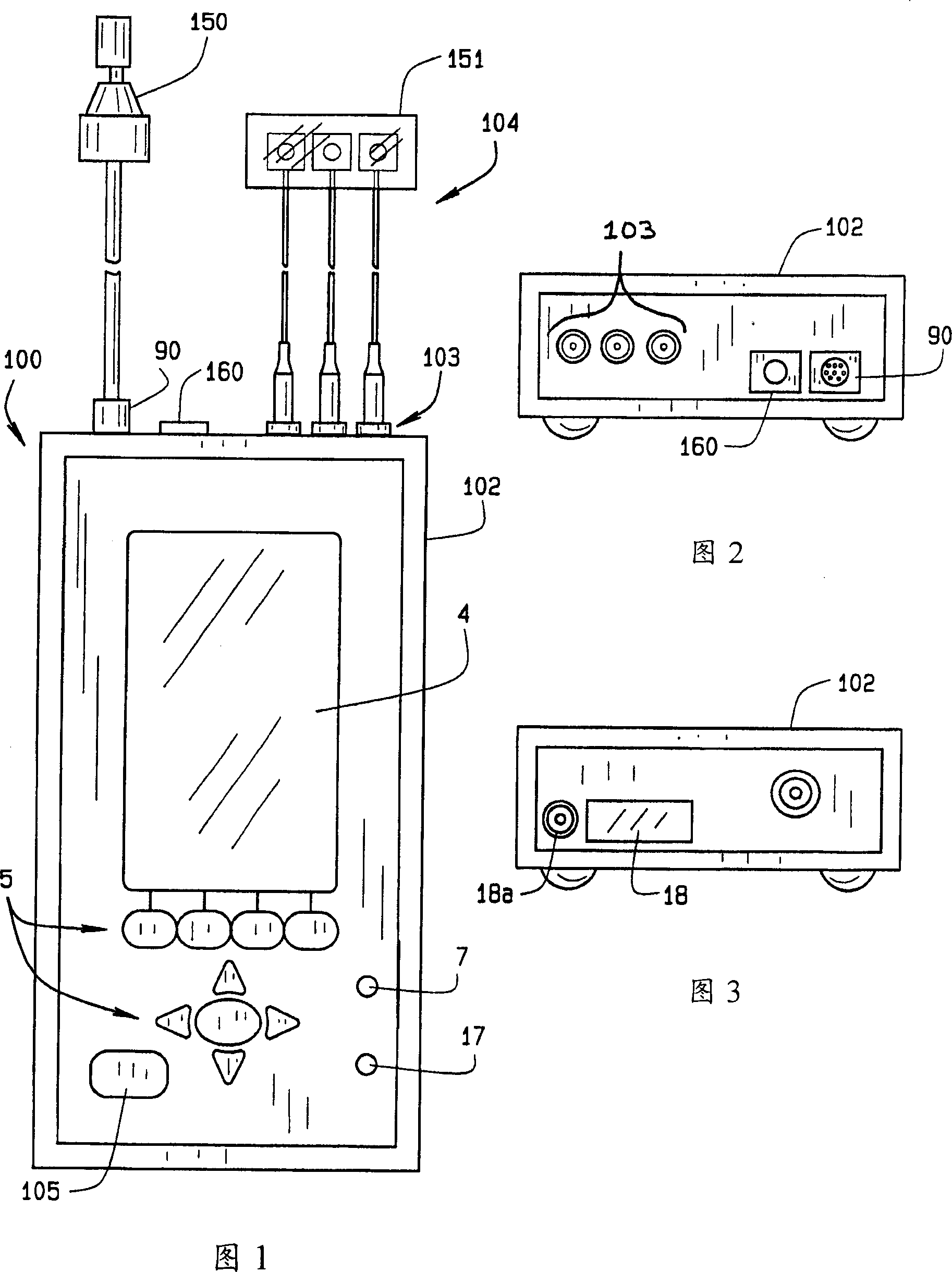
Handheld audiometric device and method for hearing testing
InactiveUS20060074341A1Effective auditory screeningAudiometeringSensorsDigital signal processingHearing test
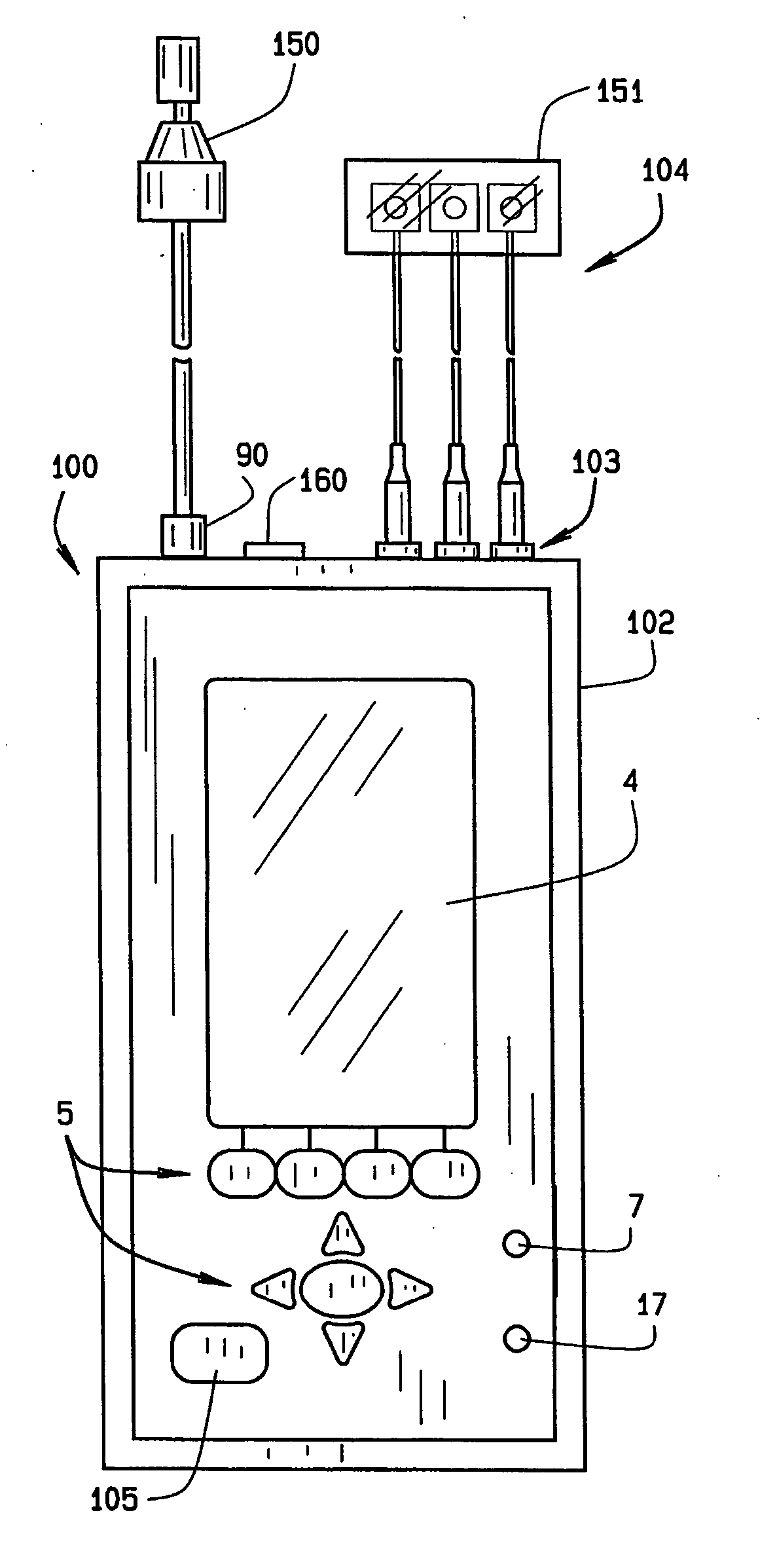
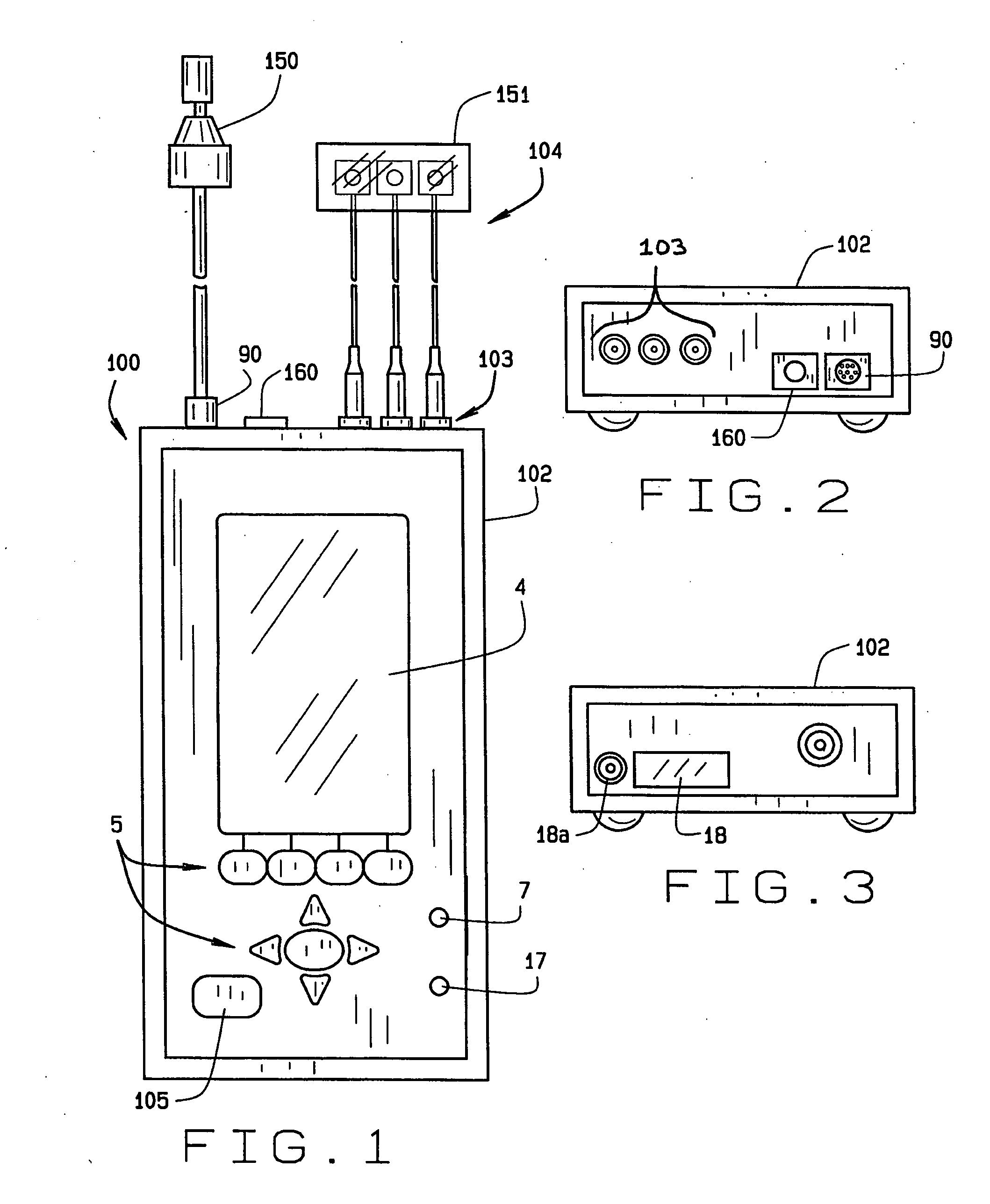
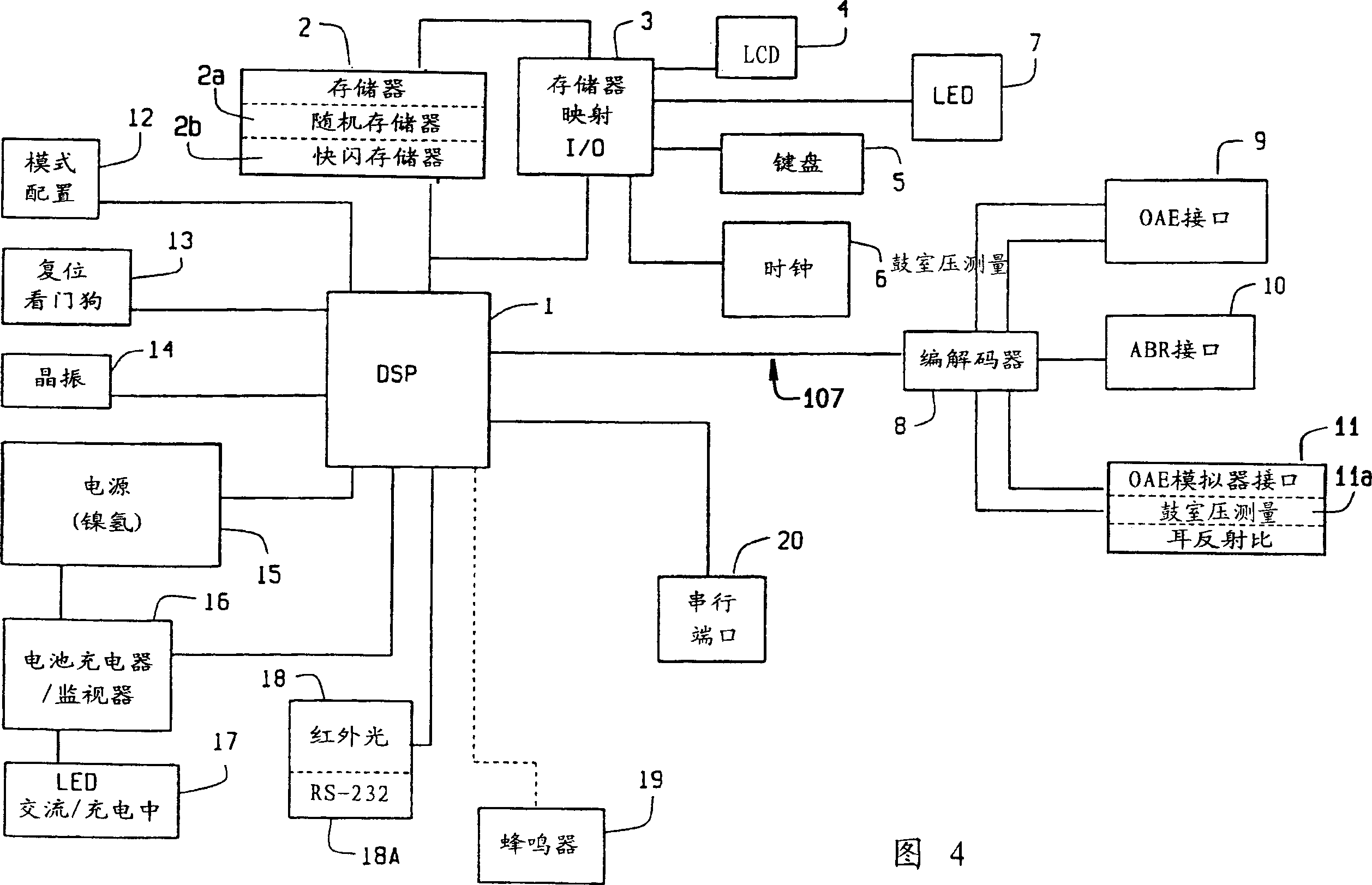
A handheld apparatus and method for comprehensive hearing testing with pass / refer results applicable for large scale neonatal screening, adult screening, or full hearing diagnostic. The apparatus contains a signal processor, integral ear probe, and remote ear and scalp probes all packaged as a single handheld battery operated device. The apparatus preferably performs a range of tests, either independently or combined: otoacoustic measurements utilizing a novel digital signal processing method for evoked otoacoustic signal processing, auditory brain stem response test, tympanometry, and otoreflectance. Algorithms for automatic test sequence, and pass / refer indication for the tests are provided.
Owner:CAREFUSION 202
System for recording and processing signal for diagnosing auditory system and method for recording and processing signal for diagnosing auditory system
InactiveUS20150065813A1Designed for simplicity and ease of useSimple signal analysisElectroencephalographyAudiometeringElectricityAuditory system
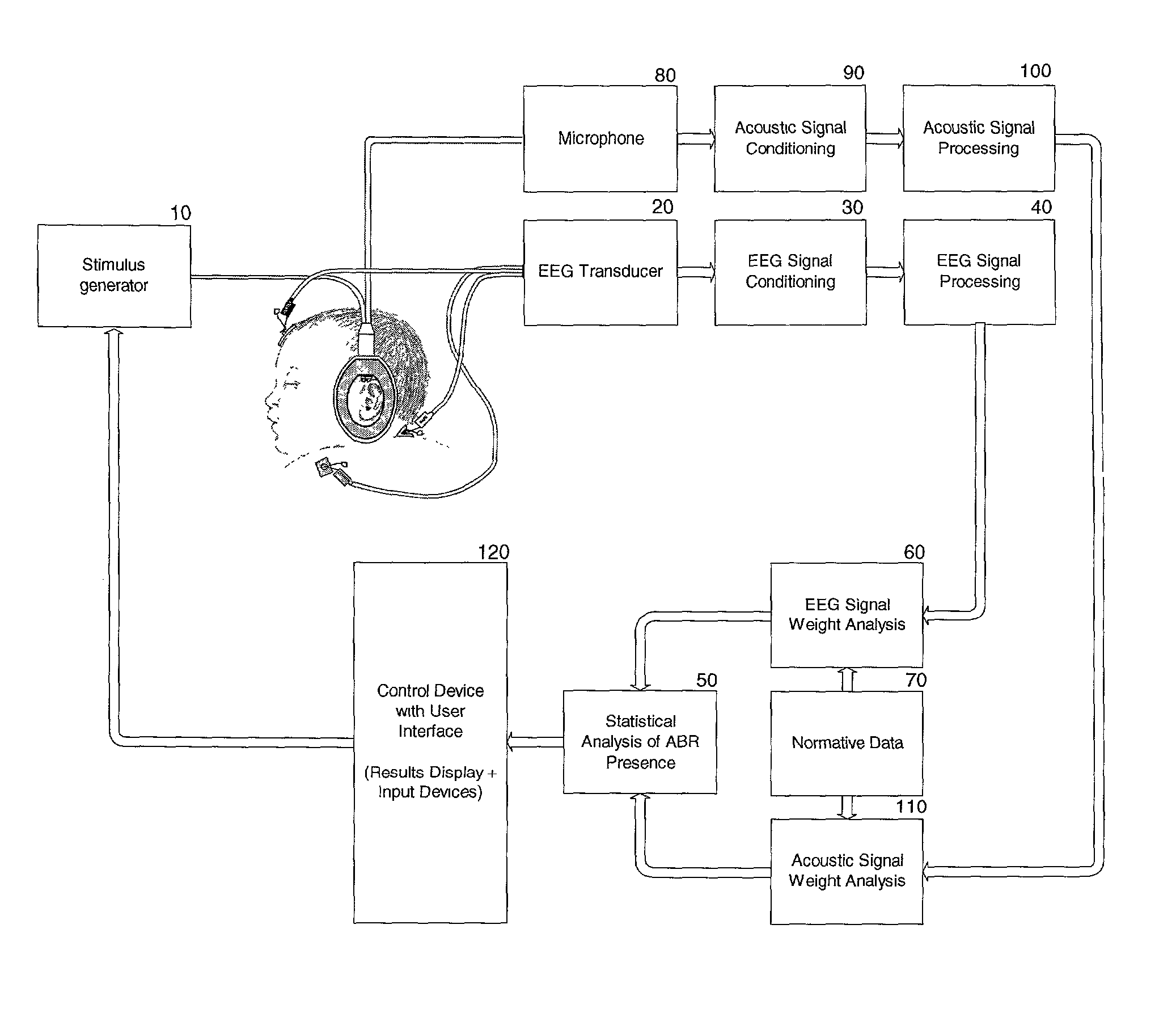
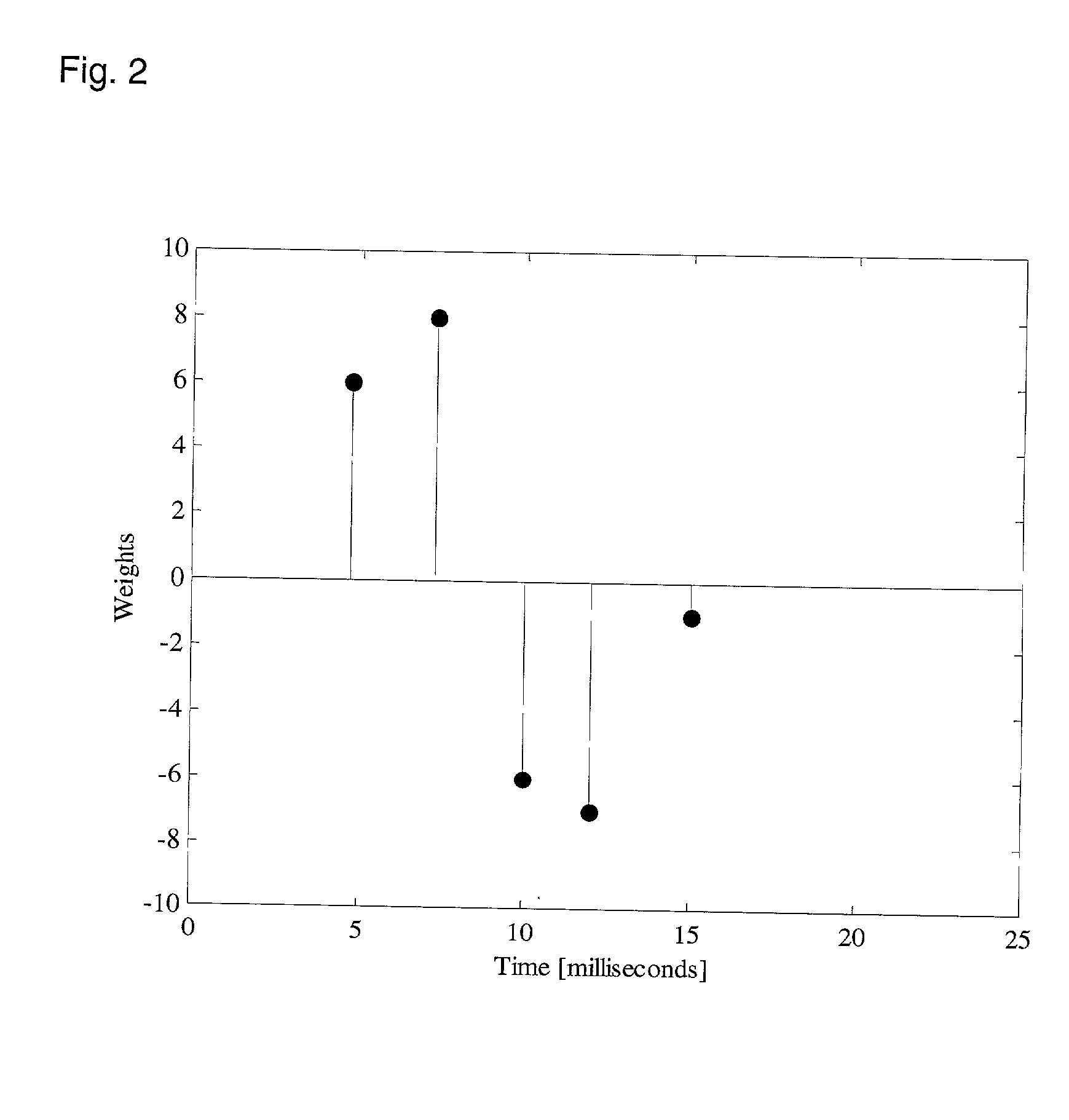
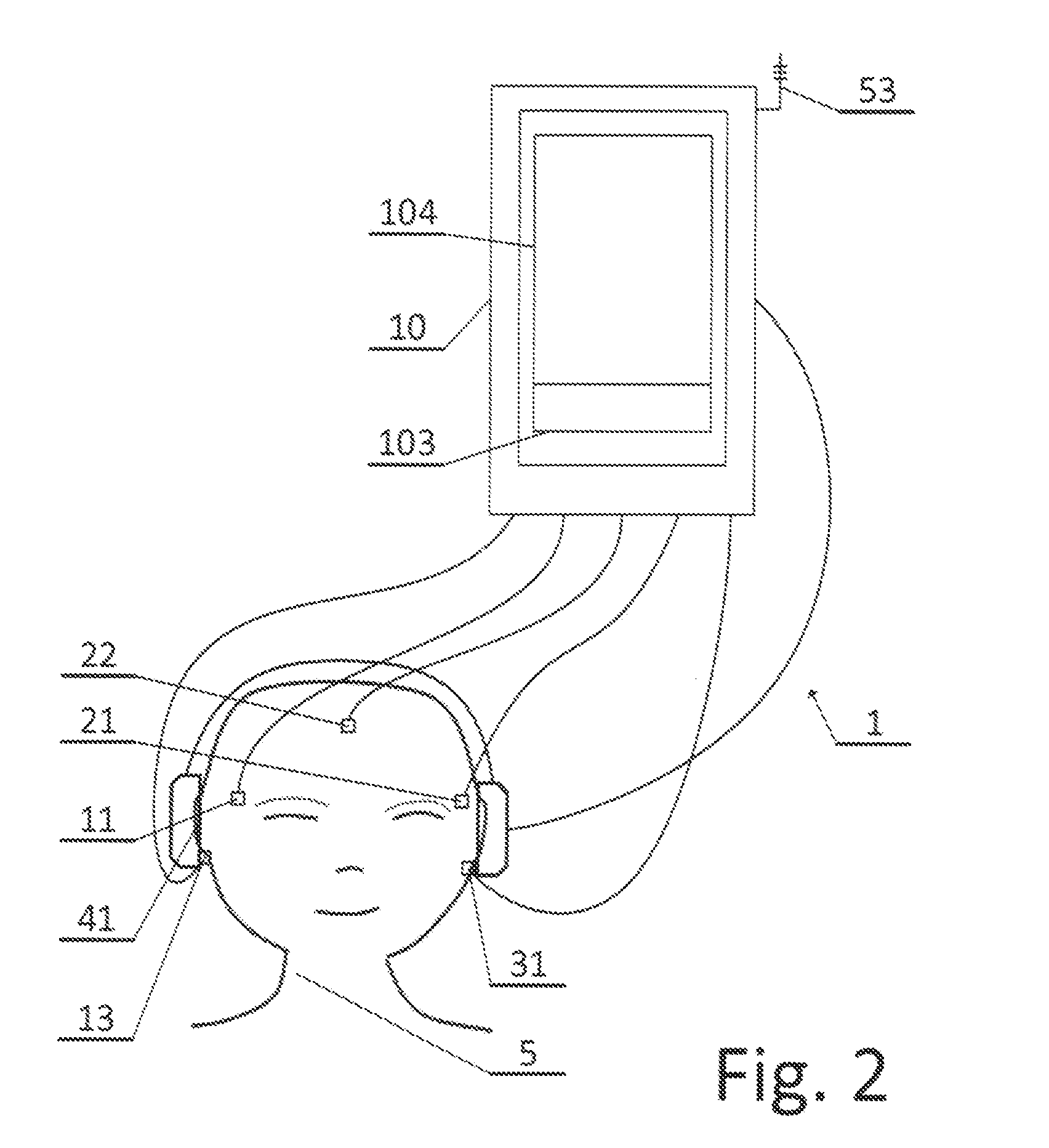
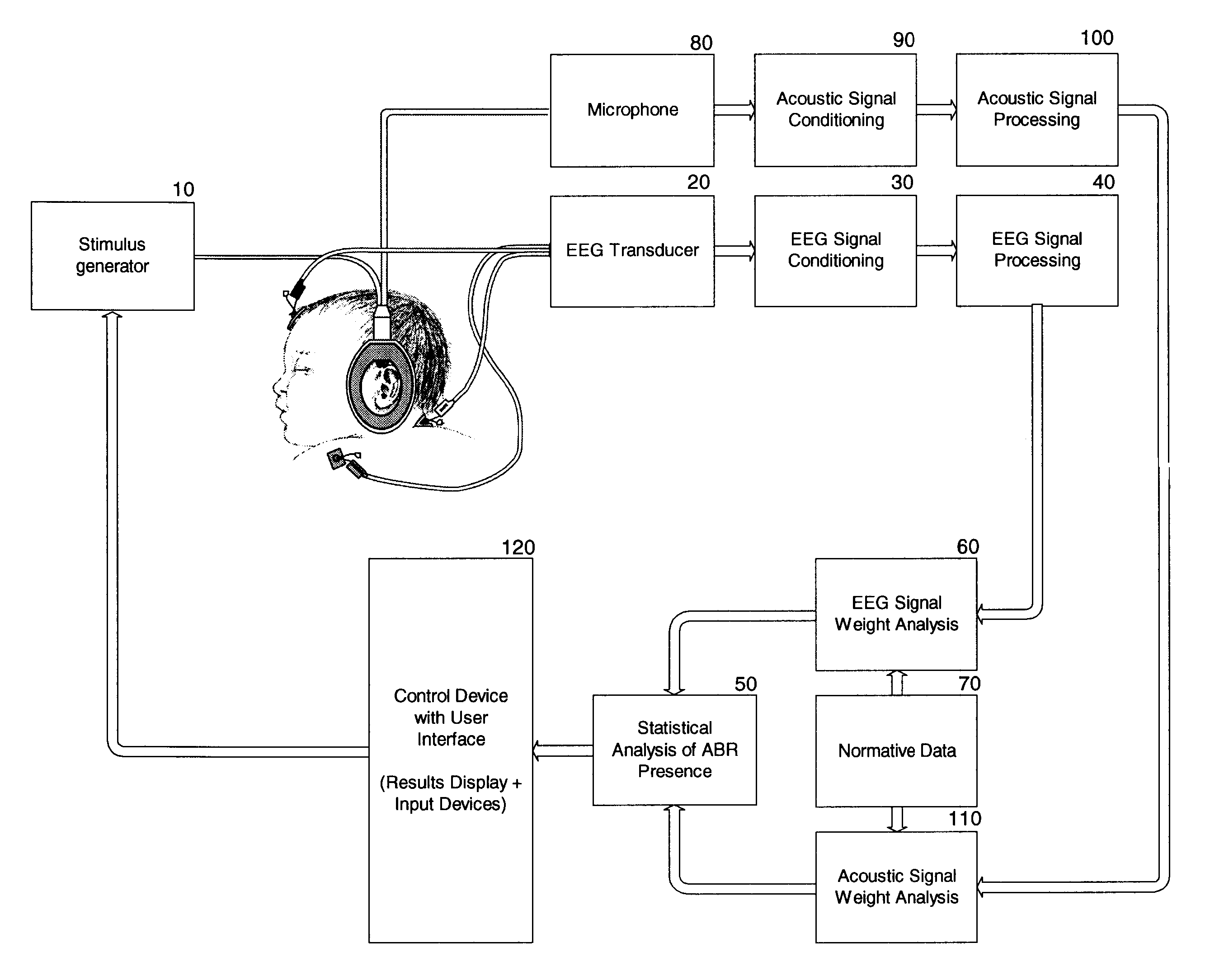
In system for recording and processing a signal for diagnosing an auditory system, a system for measuring signals of bioelectric activity of brain (EEG signal) or eye (EOG signal) or muscle (EMG signal) or their combination obtained from electrodes (11, 21, 22) attached to head skin of a person to be tested communicates with system (105) informing about sleep phase occurrence through an input (27). A system for measuring an auditory brainstem response signal (ABR signal) evoked by acoustic stimulation is automatically activated by a circuit (106) for automatic activation connected to the system (105) informing about sleep phase occurrence and measures the ABR signal. The system also includes a recording system (101, 102) of the ABR signal in a configurable period of time measured from the time of acoustic stimulation and system (103) to present the ABR signal in graphical form.
Owner:SILVERMEDIA SPOLKA Z OGRANICZONA ODPOWIEDZIALNOSCIA
Hearing evaluation device with noise-weighting capabilities
InactiveUS6620100B2Improve accuracySave resourcesElectroencephalographyAudiometeringEngineeringElectrophonic hearing
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear repeatedly administered click stimuli. In order to optimize evaluation, the present invention uses normative data to accurately weight the auditory responses, so that evaluation will be possible in different or changing noise conditions.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
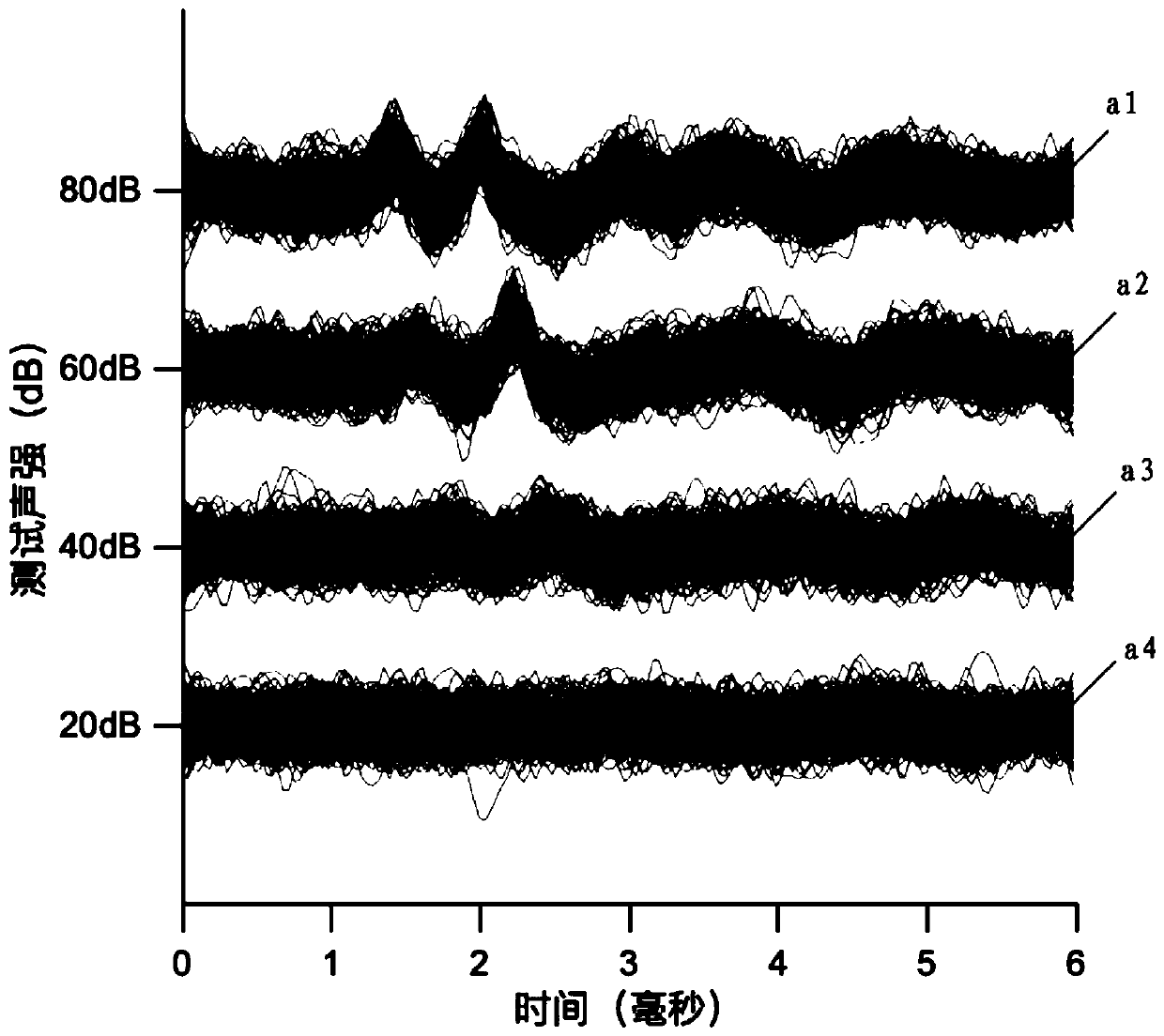
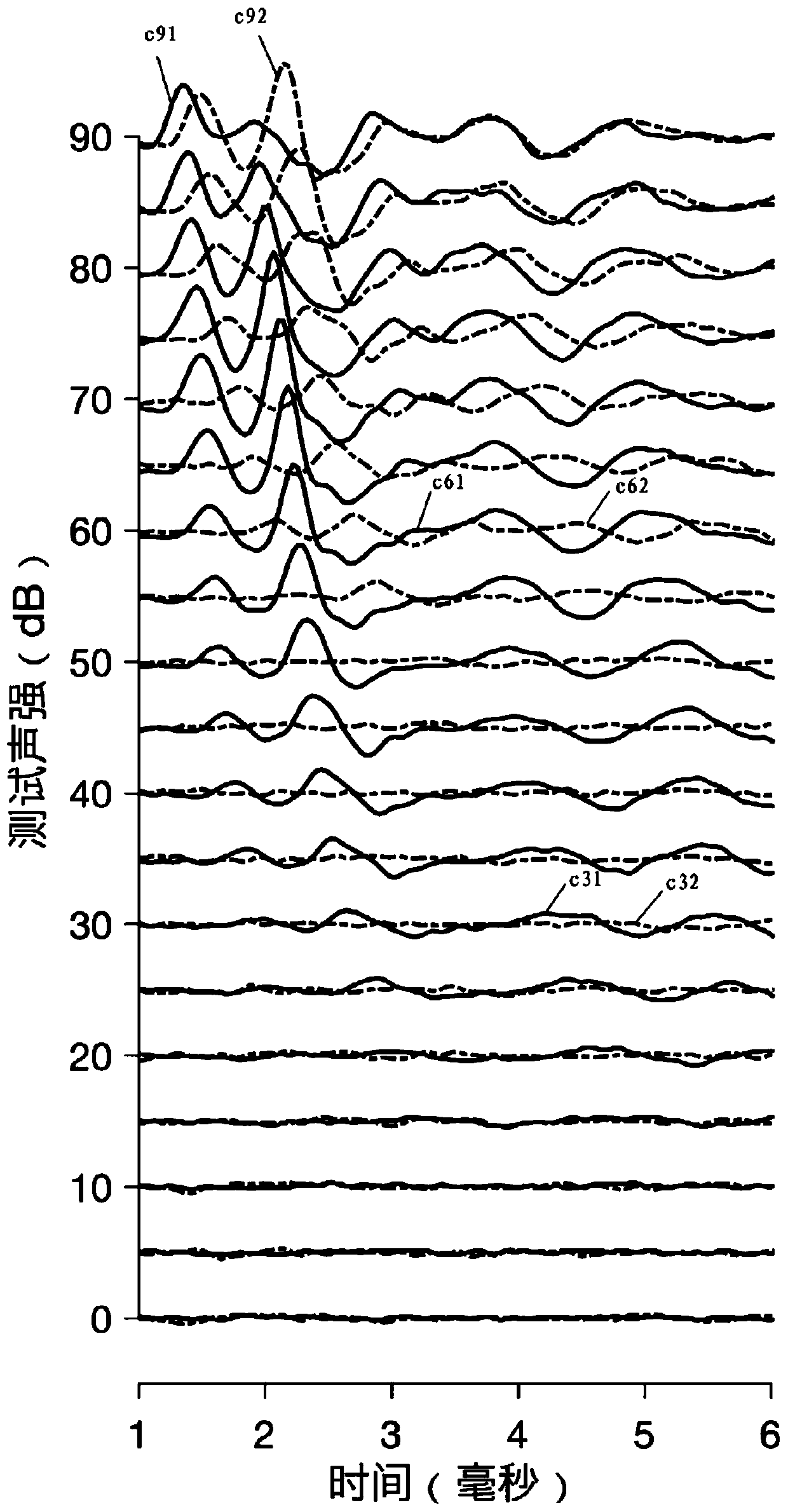
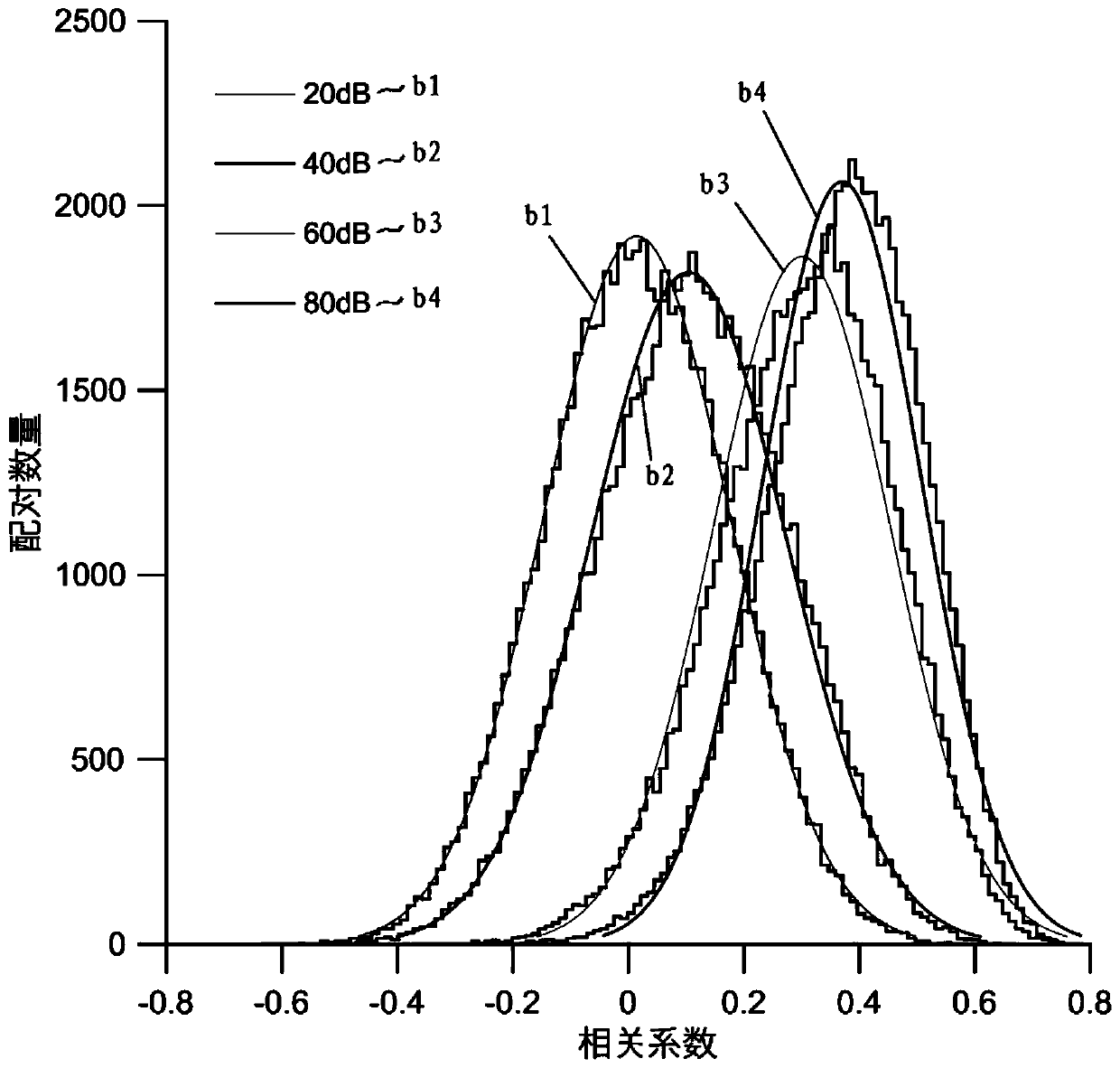
Brand-new algorithm for ABR (auditory brainstem response) signal crest detection
InactiveCN102217932AEasy to detectAccurate detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSurgical operationWave form
The invention relates to a brand-new algorithm for ABR (auditory brainstem response) signal crest detection. A superposition average technology is adopted to denoise an acquired original ABR signal, then automatic identification is carried out on crest detection of an ABR wave, no matter whether the ABR signal is a sensation level signal or a hearing level signal, all the crests in a wave form can be easily and accurately detected by adopting the method, each ABR subwave can be independently analyzed, and effective ABR parameters are provided for hearing threshold evaluation and surgical operation monitoring.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for signal encoding evoked responses
InactiveUS7976473B2Improve performanceElectroencephalographyAudiometeringAuditory stimuliHuman patient
A method and apparatus for utilizing the benefits of encoded signal transmission and reception to enhance the performance of medical testing devices (100) adapted to evoke and measure biological response signals such as auditory evoked potentials (AEP), and the auditory brainstem response (ABR) signals in particular. Auditory stimuli, such as clicks, are presented to the ear of a human patient, in a predetermined encoded sequence, resulting in the generation of auditory responses and bio-electric response signals in the human patient. These response signals from the patient are acquired and observed, and are processed according to the predetermined encoded sequence in which the auditory stimuli were presented to the patient's ear in order to extract the desired auditory evoked potential signals or ABR signals.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Electrophysiological test method of automatic auditory brainstem implant
ActiveCN110226929AImprove the efficiency of electrode testingImprove test efficiencyElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAuditory systemElectrical stimulations
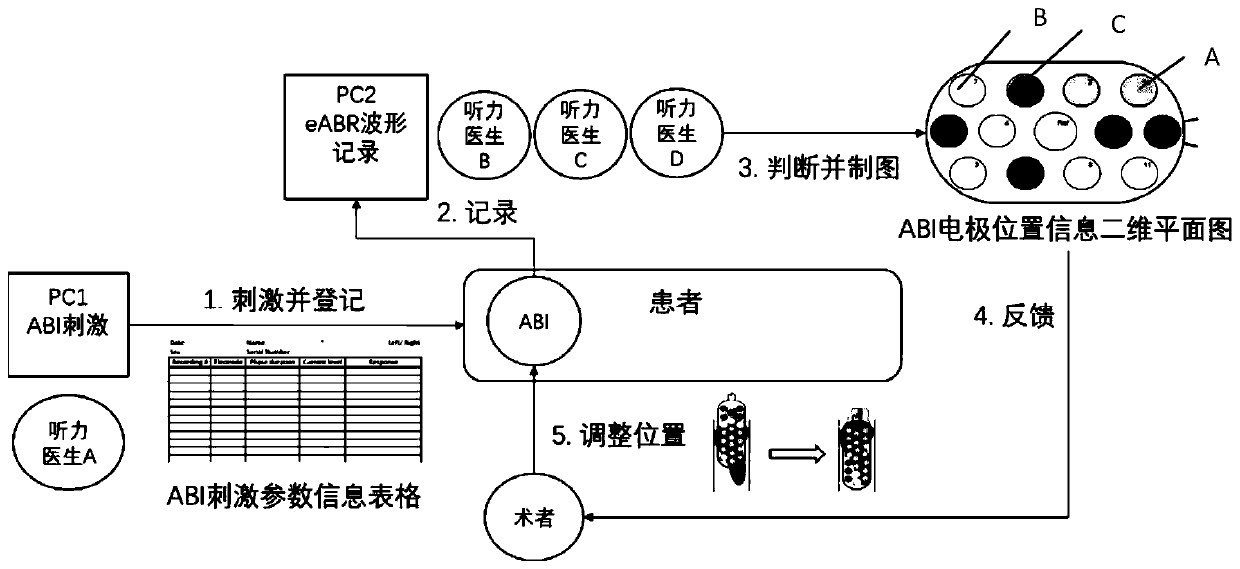
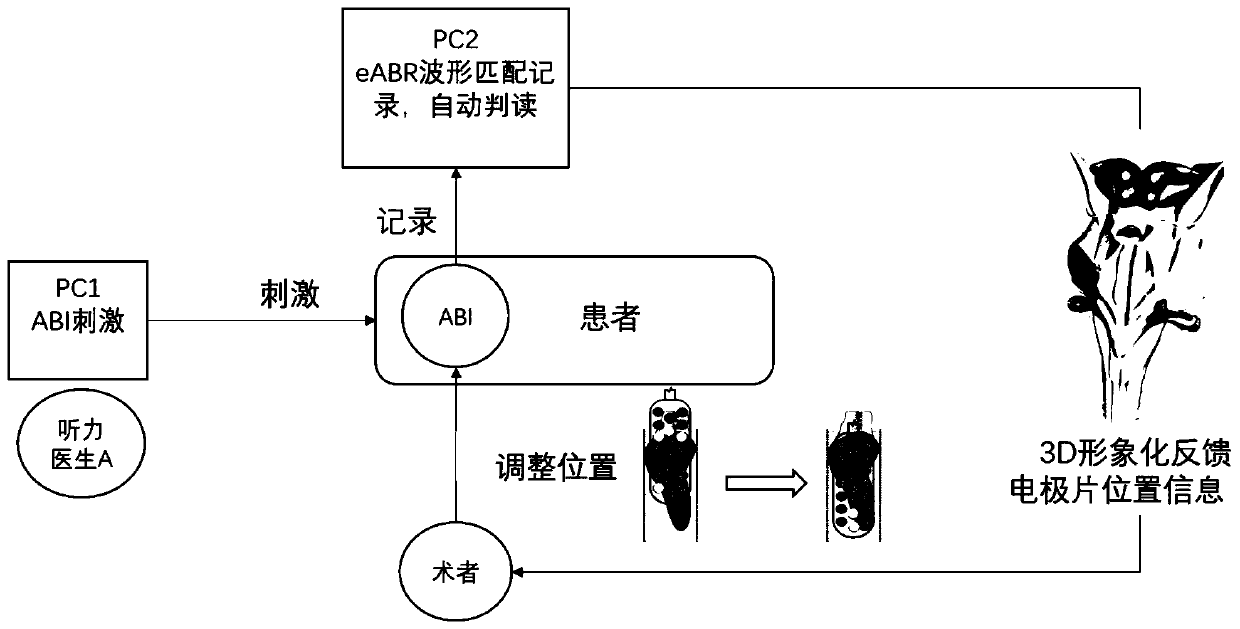
The invention discloses an electrophysiological test method of an automatic auditory brainstem implant ABI. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, a stimulation generator electrically stimulates a plurality of ABI electrodes; step 2, each ABI electrode correspondingly receives an electrical stimulation signal and stimulates a central auditory system to generate an electrical stimulationauditory brainstem response, and a recording electrode in a patient records the electrical stimulation auditory brainstem response; and step 3, a signal receiving device is connected to a signal acquisition device and a signal processing device respectively and receives the electrical stimulation auditory brainstem response which is recorded by the recording electrode and acquired by the signal acquisition device, and the signal processing device judges whether the corresponding ABI electrode has the target waveform of the electrical stimulation auditory brainstem response or not through signal superposition and waveform automatic identification, then summarizes the reaction results of all the ABI electrodes, and visually displays the results in a 3D mode. The method simplifies the electrode testing process in operation, obviously improves the testing efficiency, shortens the operation time of patients, and has great application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Automatic sound equalization device
ActiveUS9787274B2Accurately determinedInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrotherapyEqualizationComputer science
A technique for determining one or more equalization parameters includes acquiring, via one or more electrodes, auditory brainstem response (ABR) data associated with a first audio sample and determining, via a processor, one or more equalization parameters based on the ABR data. The technique further includes reproducing a second audio sample based on the one or more equalization parameters, acquiring, via the one or more electrodes, complex auditory brainstem response (cABR) data associated with the second audio sample, and comparing, via the processor, the cABR data to at least one representation of the second audio sample to determine at least one measure of similarity. The technique further includes modifying the one or more equalization parameters based on the at least one measure of similarity.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Detection method and device for brainstem auditory evoked potentials
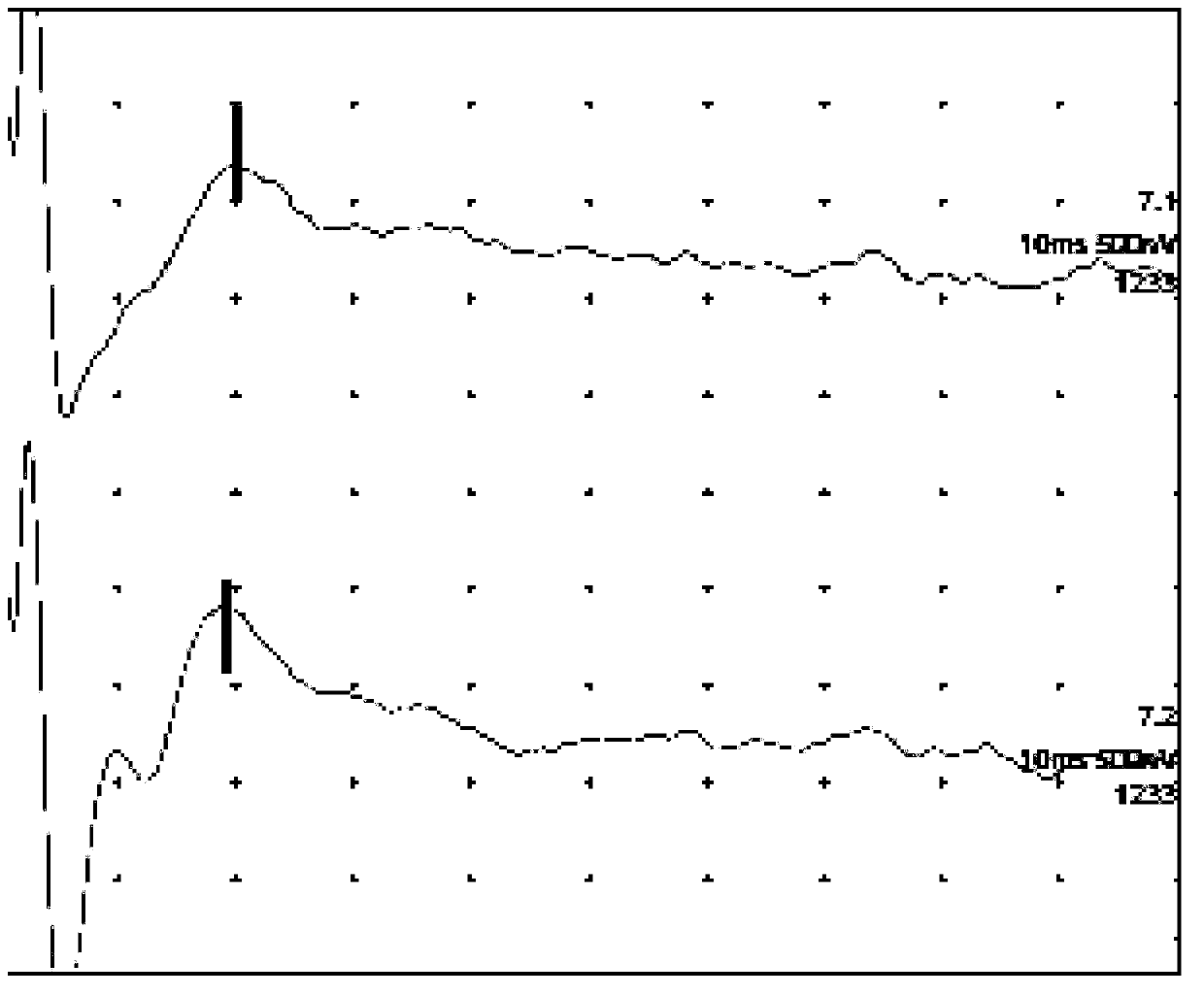
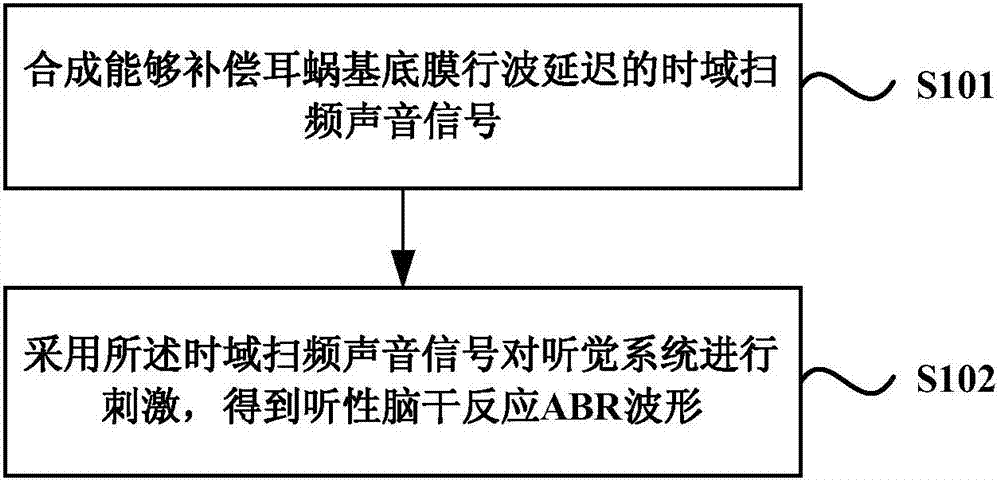
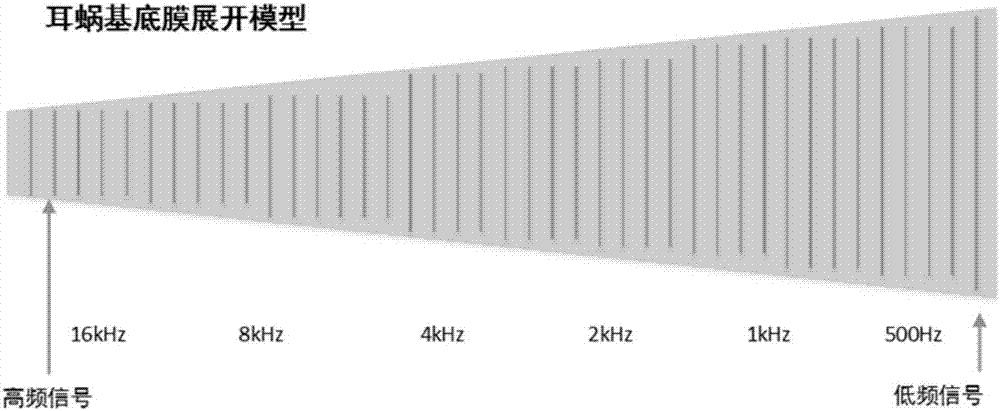
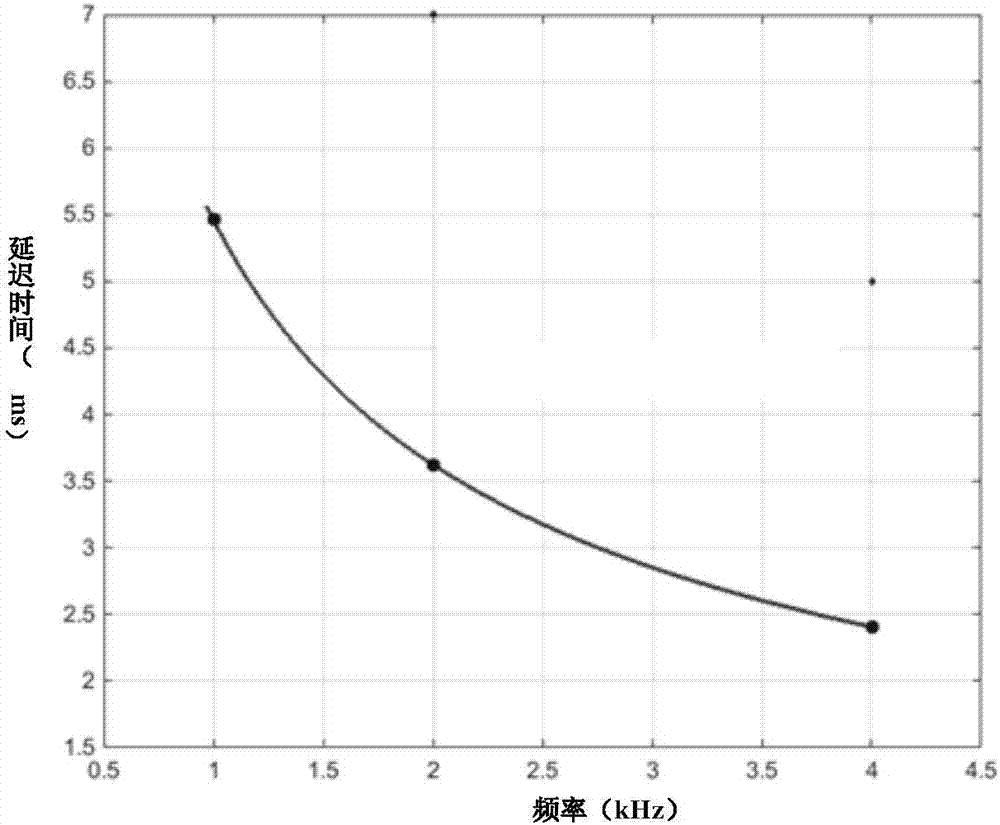
ActiveCN107049309AAccurate ABR WaveformDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime domainAuditory system
The embodiment of the invention discloses a detection method and device for brainstem auditory evoked potentials. The method comprises the following steps: compounding time-domain frequency sweep sound signals capable of compensating basilar membrane traveling wave delay; utilizing time-domain frequency sweep sound signals to simulate an audio system and obtaining auditory brainstem response ABR waveforms. The detection method and device for brainstem auditory evoked potentials have the following beneficial effects: by compounding time-domain frequency sweep sound signals capable of compensating basilar membrane traveling wave delay and utilizing time-domain frequency sweep sound signals to simulate an audio system, accurate ABR waveforms can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
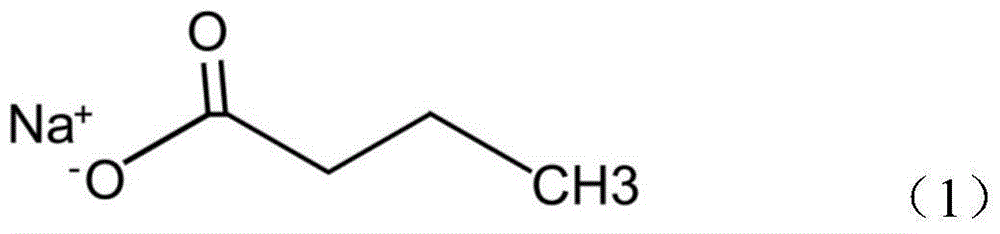
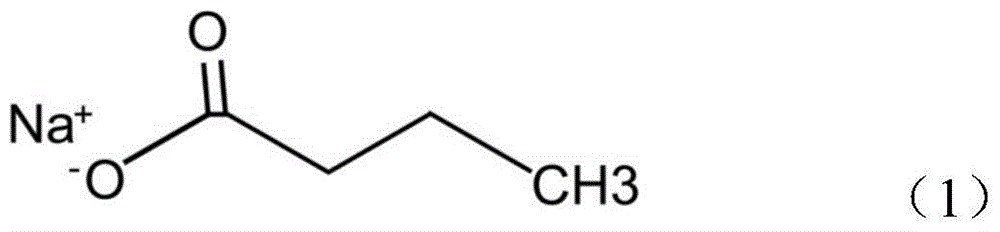
Application of sodium butyrate for preventing noise-induced hearing loss
ActiveCN104546815AConvenient researchReduced evoked potential threshold shiftSenses disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsDiseaseNoise-induced hearing loss
The invention provides an application of sodium butyrate for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. According to the application of sodium butyrate for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, in the noise-induced hearing loss experiment of mice models, sodium butyrate can reduce the auditory brainstem response threshold shift after noise exposure, increase the survival rate of cochlear hair cells after noise exposure, has excellent noise-induced hearing loss preventing effect on noises at multiple frequencies, especially has excellent preventative effect on noise-induced hearing loss, explosive hearing loss and other diseases, can be used for preparing drugs and / or healthcare products for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, has good research and application prospects, and can fill in the gap of drugs for preventing noise-induced hearing loss at present.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
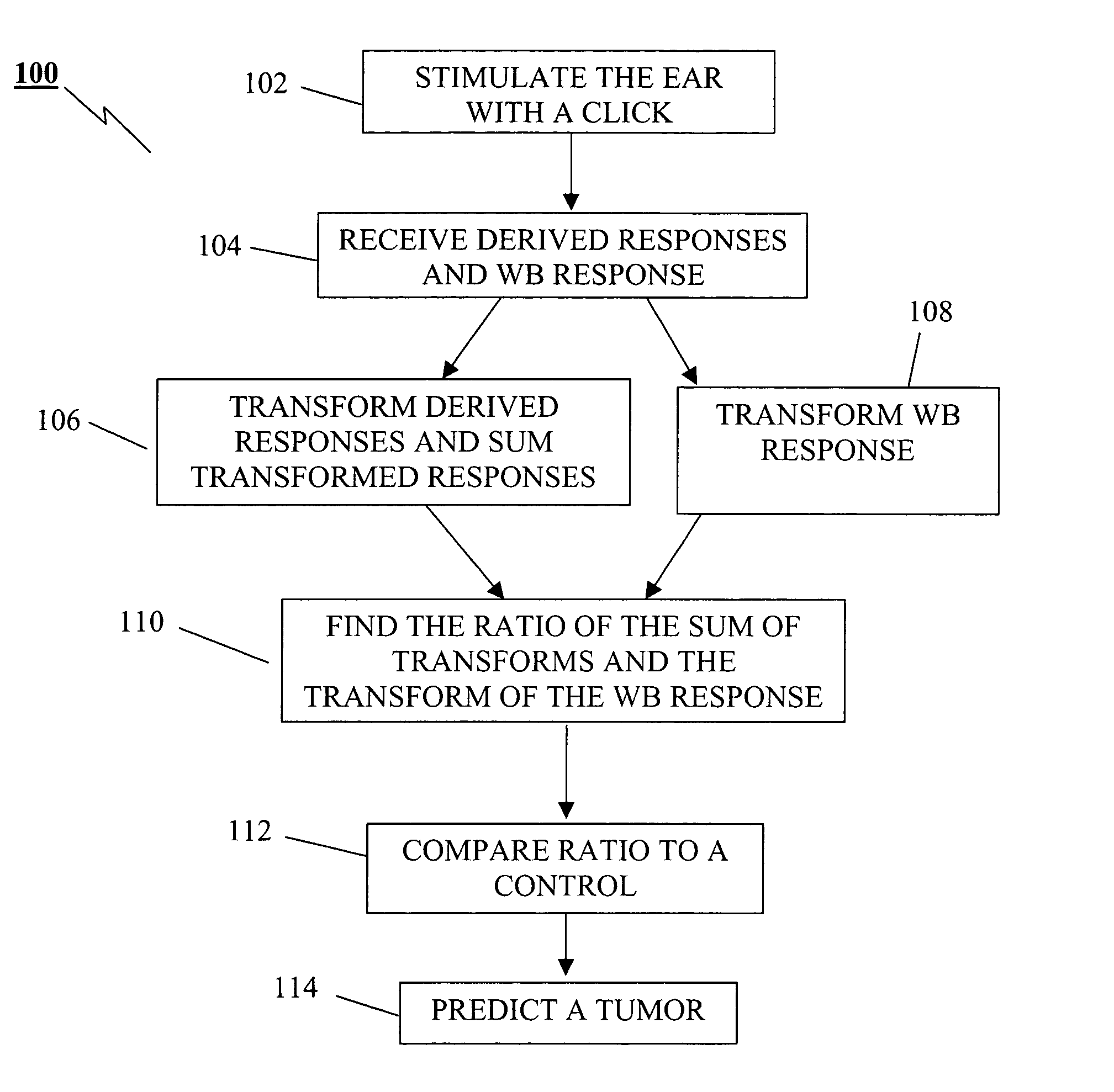
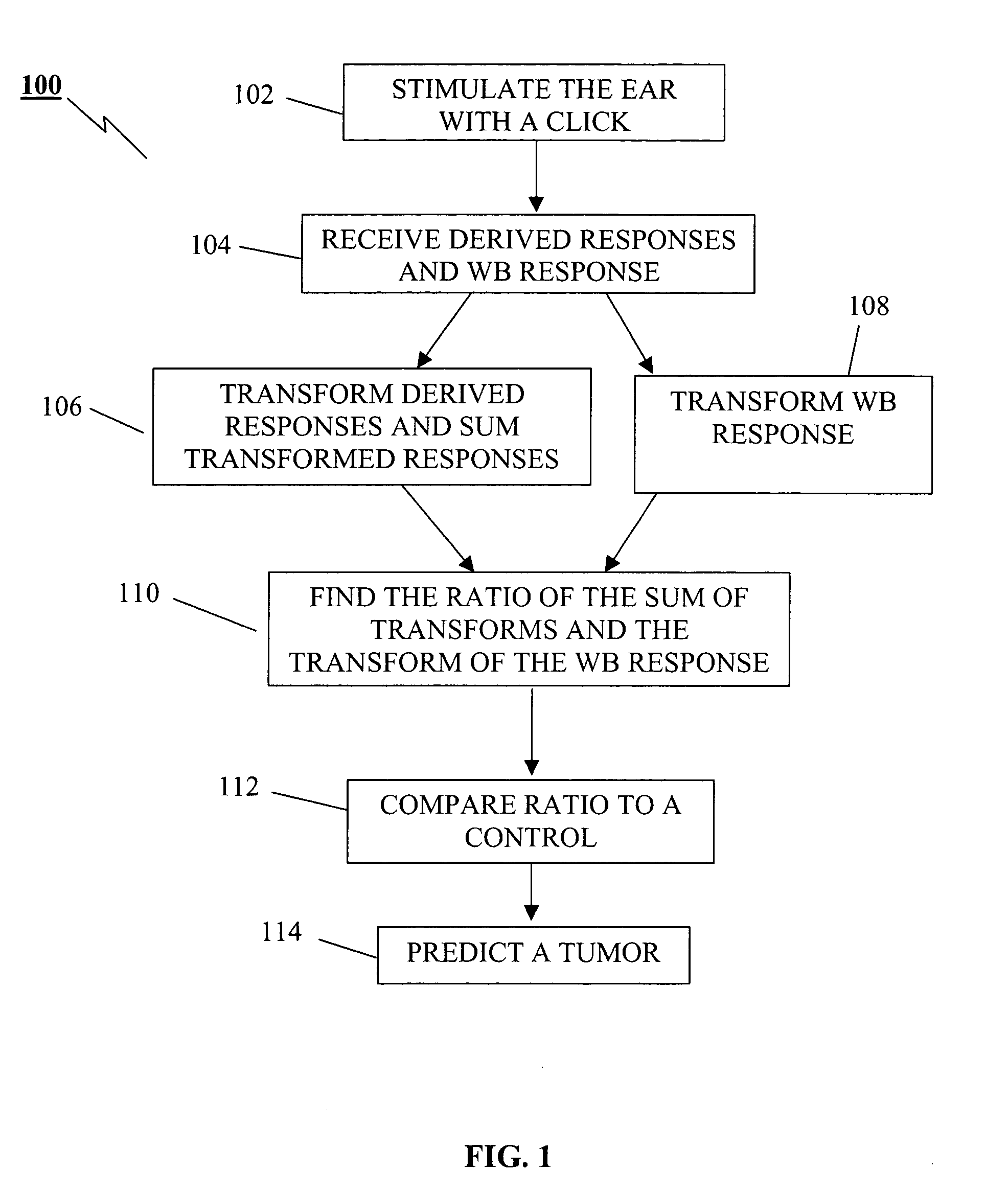
Detection of acoustic nerve tumors
InactiveUS20050137492A1Increase probabilityElectroencephalographySensorsAcoustic Nerve TumorFungating tumour
A method of predicting a tumor of the auditory nerve based on the latency of the auditory brainstem response (ABR) in the presence of a tumor. The ABR is masked using white noise and derived bands are calculated. The wideband (WB) response is also recorded. The derived bands are transformed and summed to form a SUM, and the transform of the WB is also taken. The ratio SUM / WB is taken, and the result is compared to normal ratios to predict the presence of a tumor.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT
Handheld audiometric device and method of testing hearing
InactiveCN100360075CFull graphic displayEnhanced noise filteringAudiometeringSensorsDigital signal processingEngineering
Handheld apparatus (100), and method for comprehensive hearing testing with pass / refer results applicable for large scale neonatal screening, adult screening, or full hearing diagnostic is disclosed. The apparatus (100) contains a signal processor (1), integral ear probe (150), and remote ear, and scalp probes (104) all packaged as a single handheld battery operated device (100). The apparatus (100) preferably performs a battery of tests, either independently or combined: oto-acoustic measurements utilizing a novel digital signal processing method for evoked oto-acoustic signal processing, auditory brain stem response test, tympanometry, and oto-reflectance. Algorithms for automatic test sequence, and pass / refer indication for the tests are provided.
Owner:埃尔维·考斯维克 +1
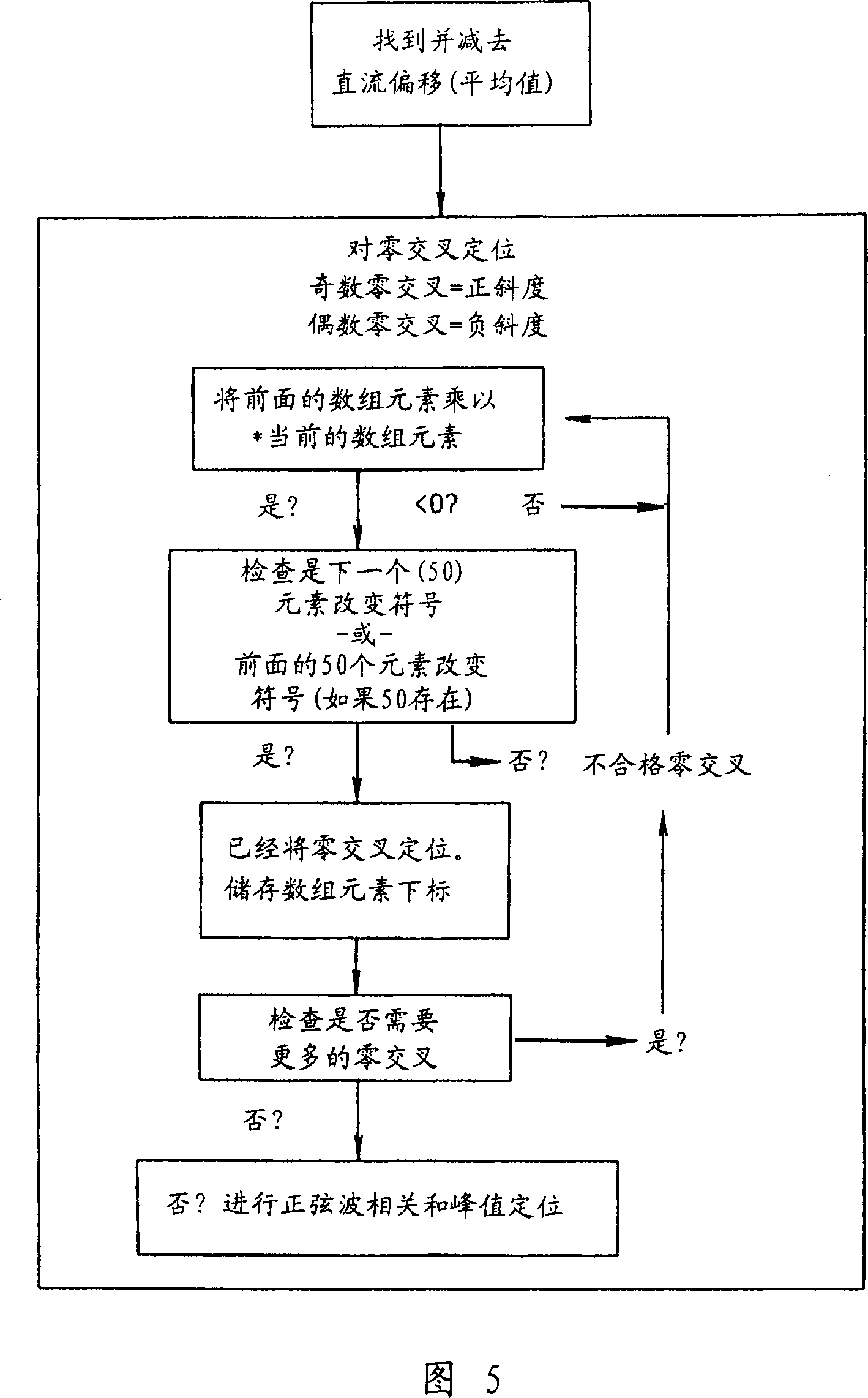
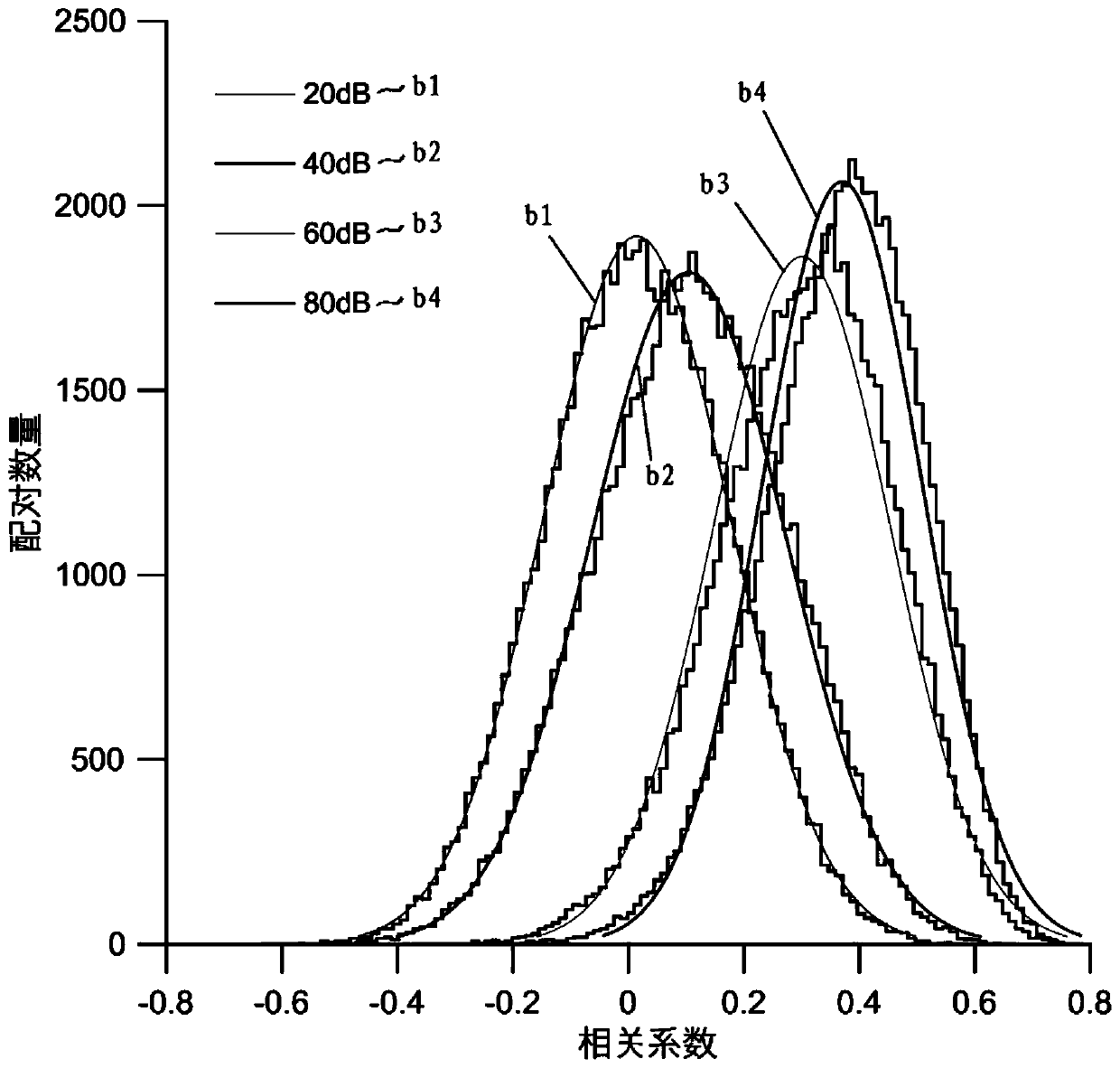
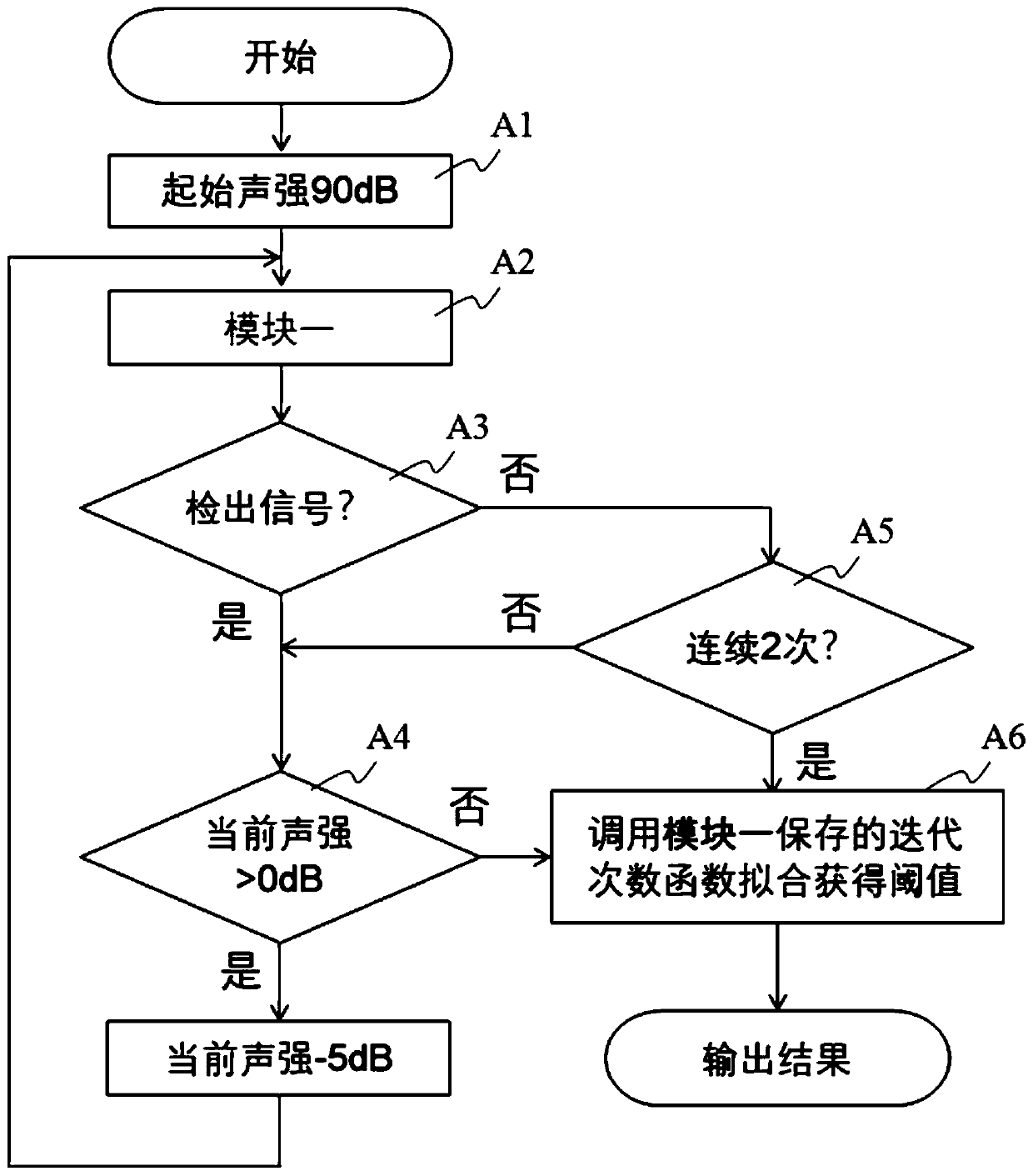
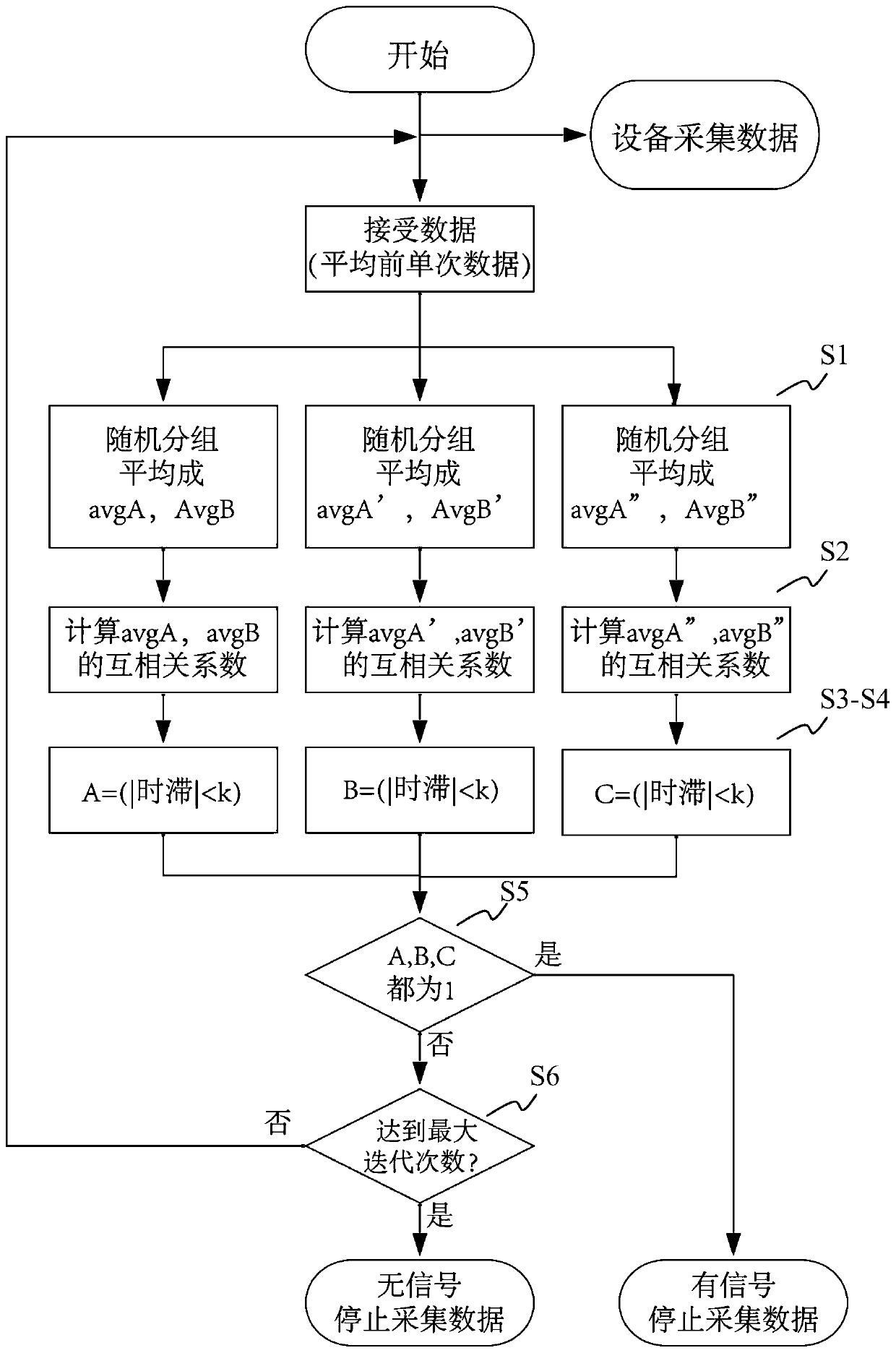
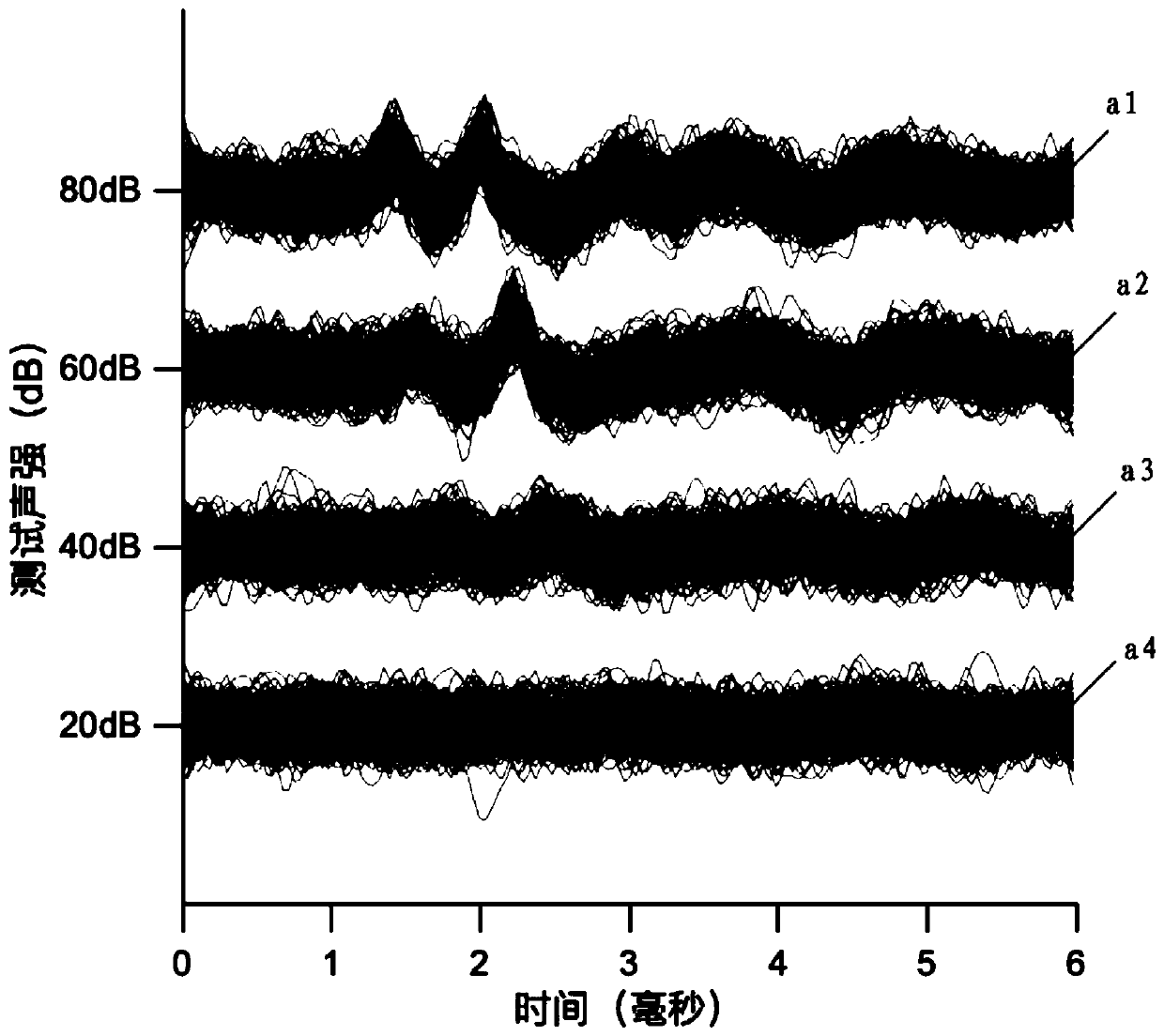
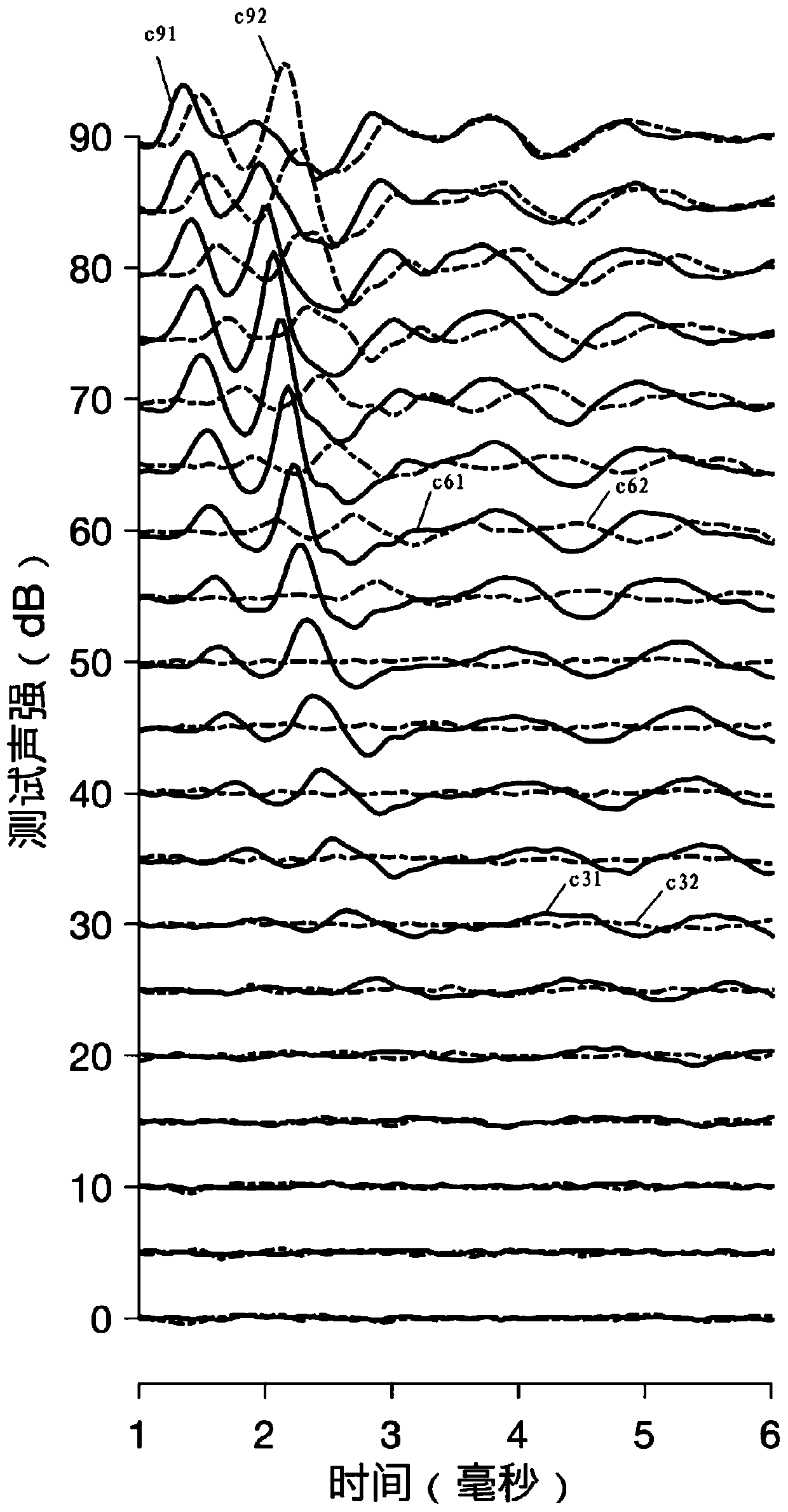
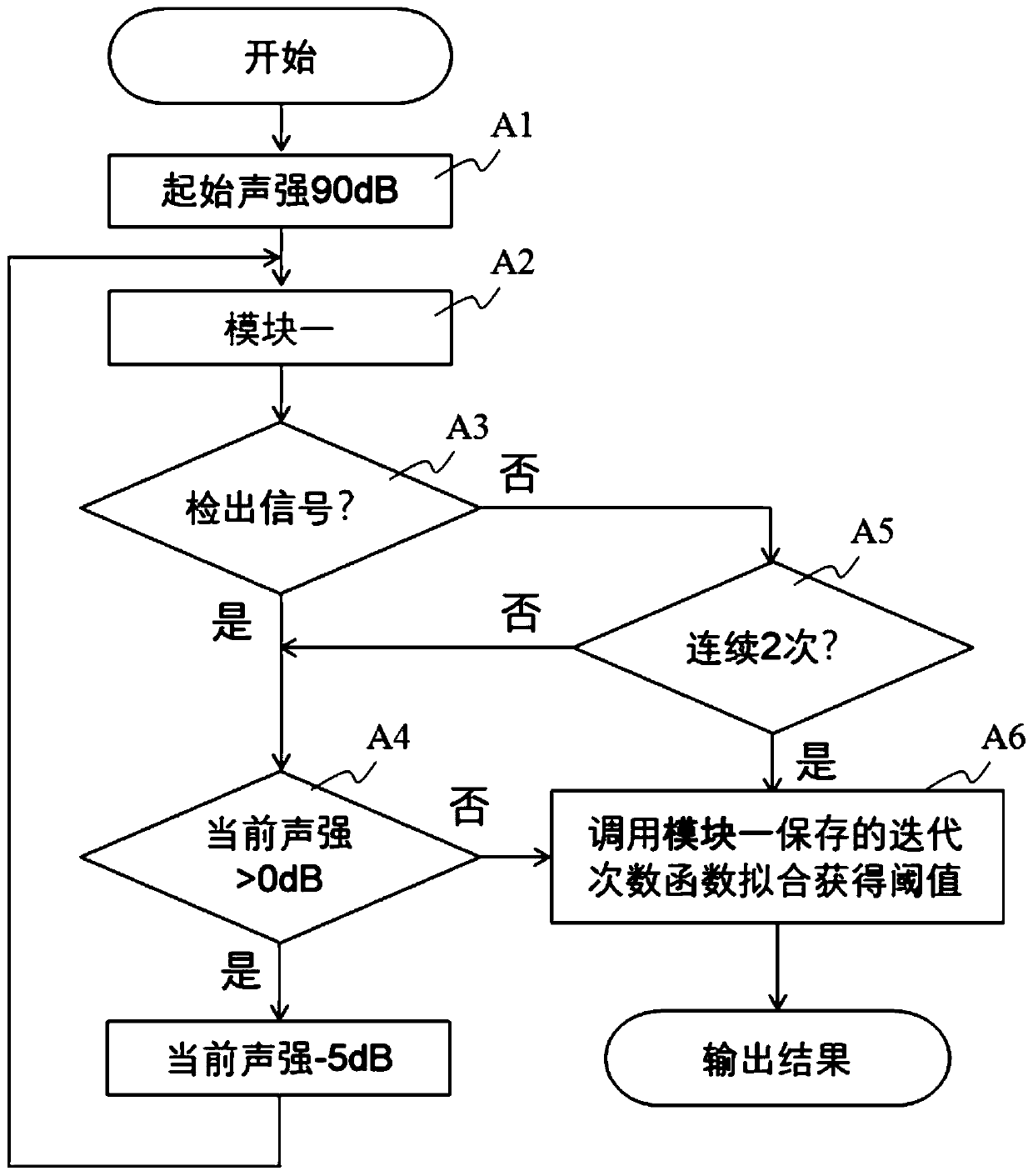
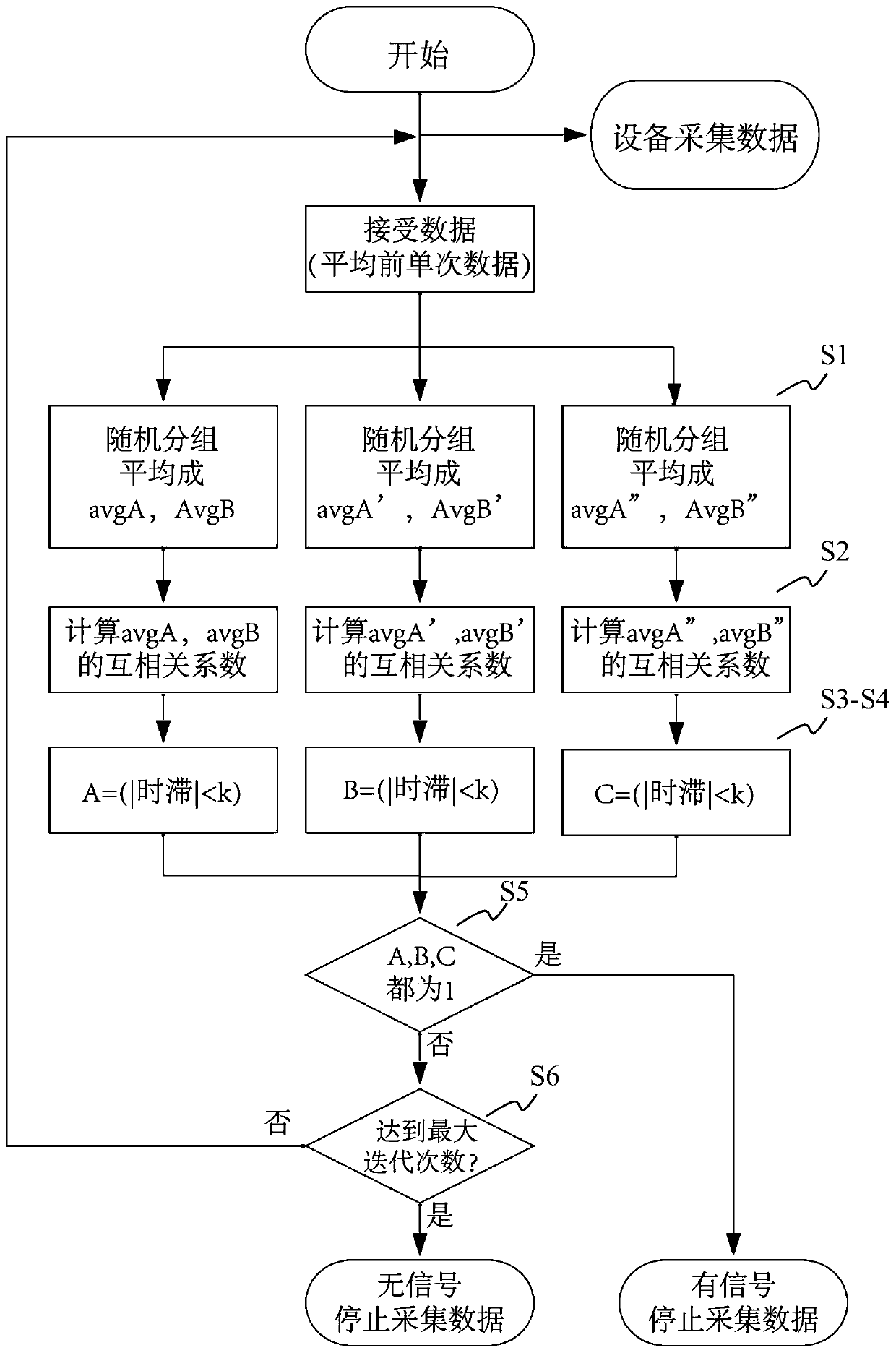
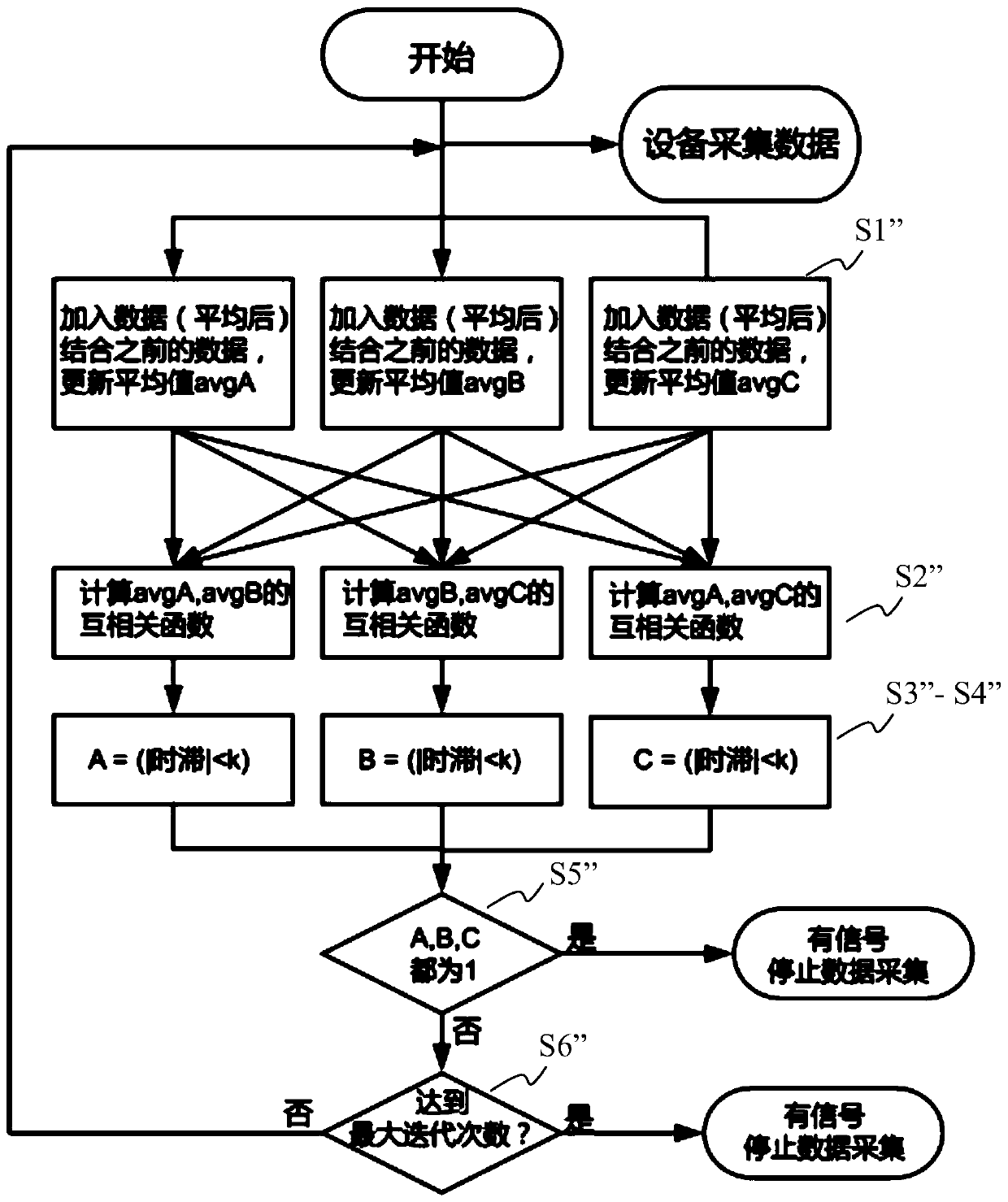
ABR (auditory brainstem response) automatic test method based on self-adaptive average method
ActiveCN110074782ASave duplicate recordsAvoid wastingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAuditory brain stem responseHearing perception
The invention relates to an ABR (auditory brainstem response) automatic test method based on a self-adaptive average method. ABR single-time records collected in batches from high values to low valuesat each test sound intensity are subjected to calculation based on the self-adaptive average method; iteration is performed for increasing the average times of the records step by step; the signal-to-noise ratio is increased until the ABR signal detection conditions are met, i.e., through the ABR single-time records collected in batches and in groups, two groups of average curves are obtained; the located time-lag of the maximum value of a cross-correlation function is calculated; whether ABR signals with the time lock characteristics exist or not is judged according to whether the time-lag deviation is within a specified range or not. A hearing threshold value is obtained through the lowest sound intensity required by detection signals, or the accurate sound intensity corresponding to the hearing threshold value is obtained through a function fitting and interpolation method on the iteration times used at each test sound intensity. According to the method provided by the invention, the detection threshold value efficiency is high; the accuracy rate is close to that of manual judgment; higher objective performance is realized; the repeatability is better; the repeated collection times of the ABR records can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
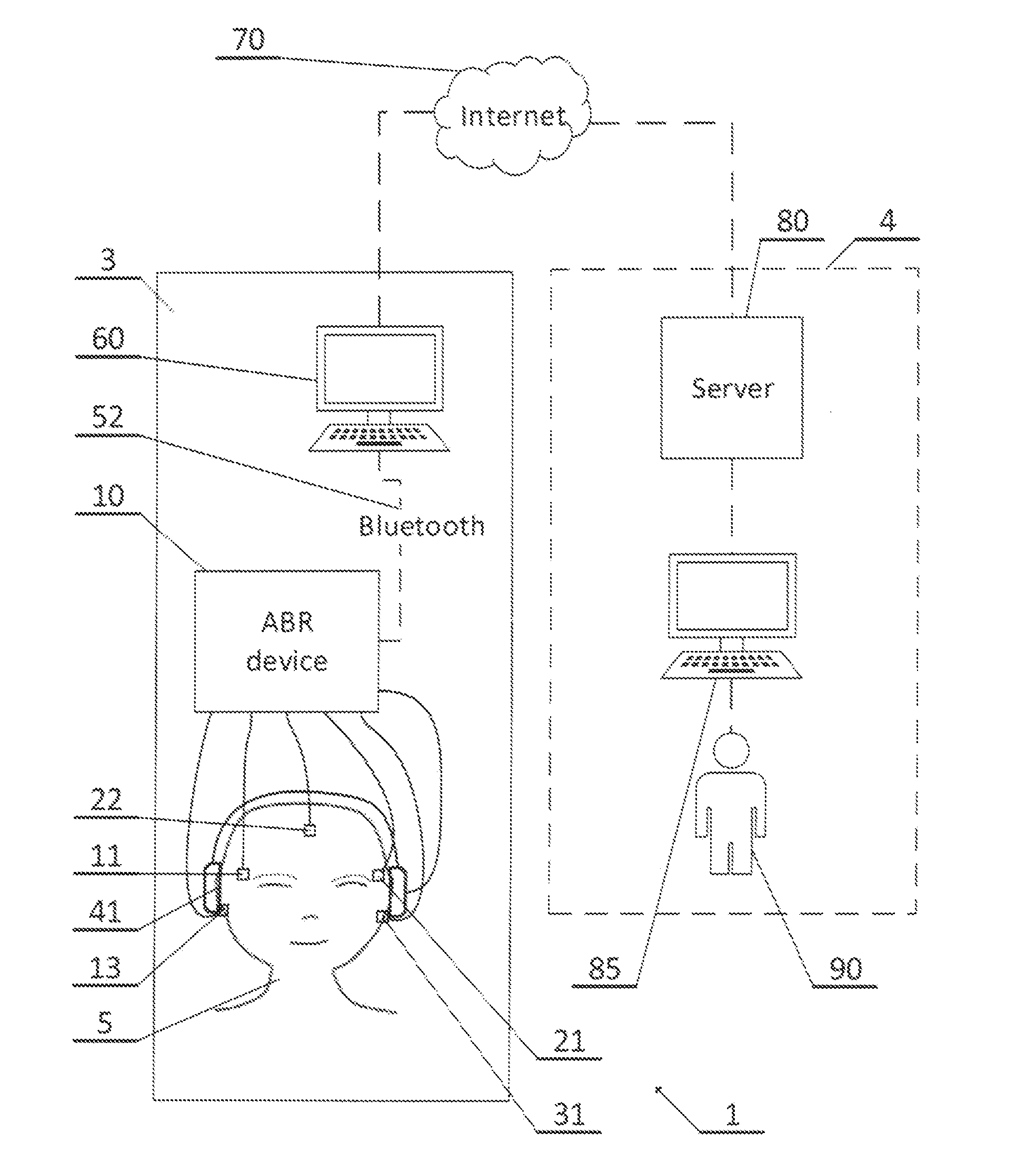
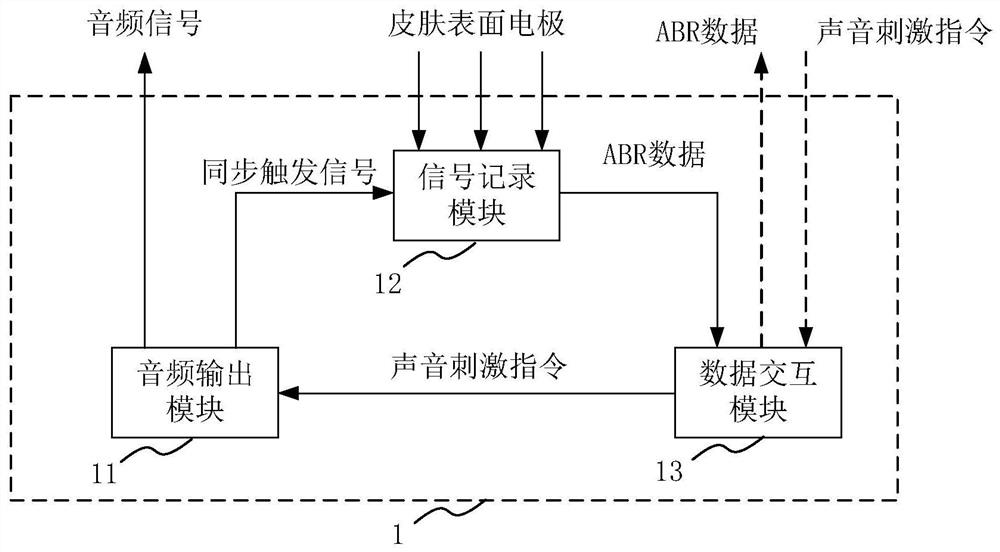
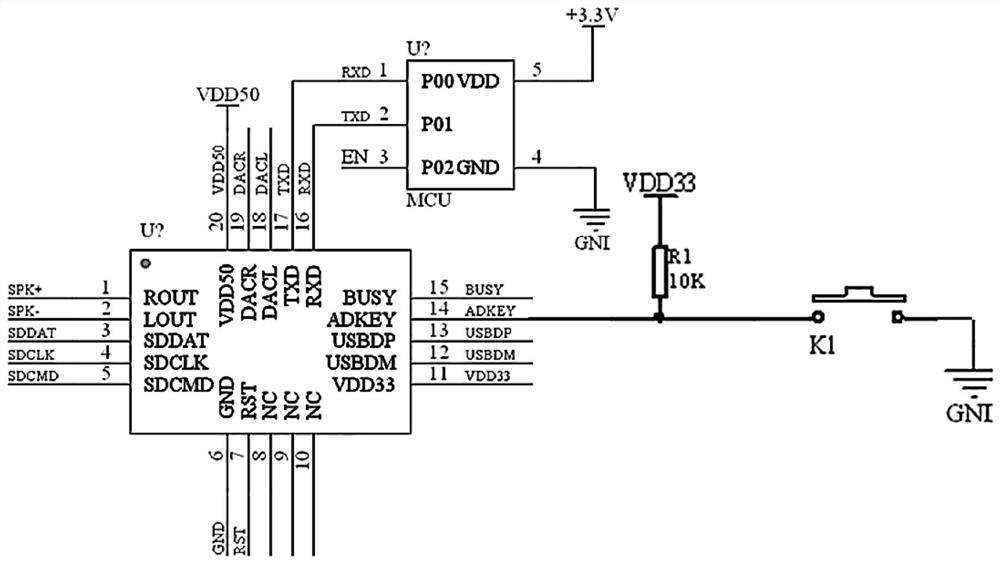
Auditory function test device, wearable device and auditory function test system
PendingCN113069107AWill not be disturbed by psychological factorsWill not be disturbedAudiometeringSensorsAuditory functionsSOUND STIMULATION
The invention provides an integrated auditory function test device, a wearable device and an auditory function test system. The integrated auditory function test device comprises an audio output module, a signal recording module and a data interaction module, wherein the audio output module is used for obtaining a matched audio signal according to a sound stimulation instruction, outputting the audio signal to a first external device and sending a synchronous trigger signal to the signal recording module when outputting the audio signal; the signal recording module is used for amplifying and recording an auditory brainstem reaction signal from a skin surface electrode under the triggering of the synchronous trigger signal, and sending the auditory brainstem reaction signal to the data interaction module; and the data interaction module is used for sending the auditory brainstem reaction signal to a second external device, receiving an externally input sound stimulation instruction and sending the sound stimulation instruction to the audio output module. The test result obtained based on the auditory function test device is not interfered by psychological factors of subjects.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
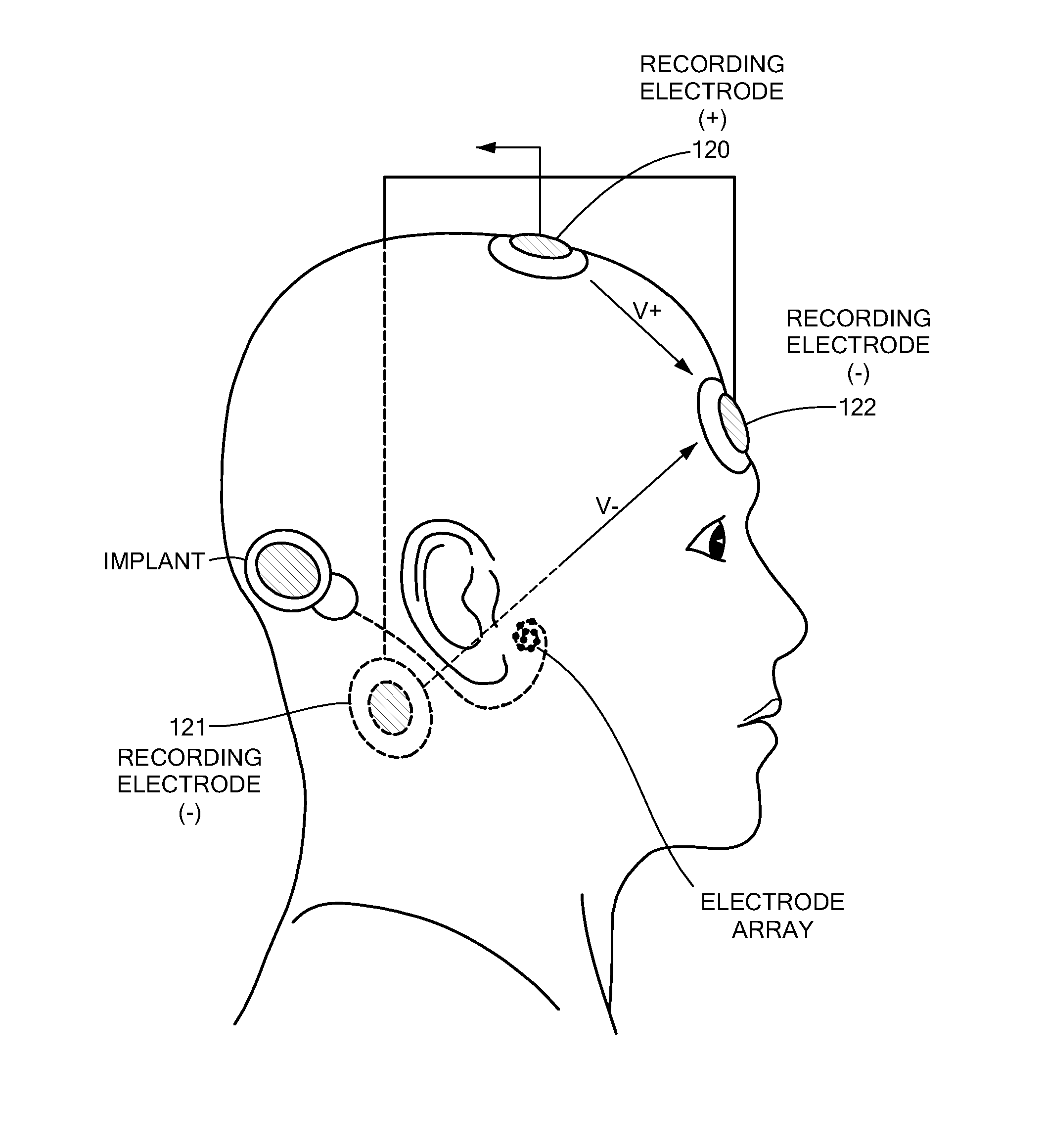
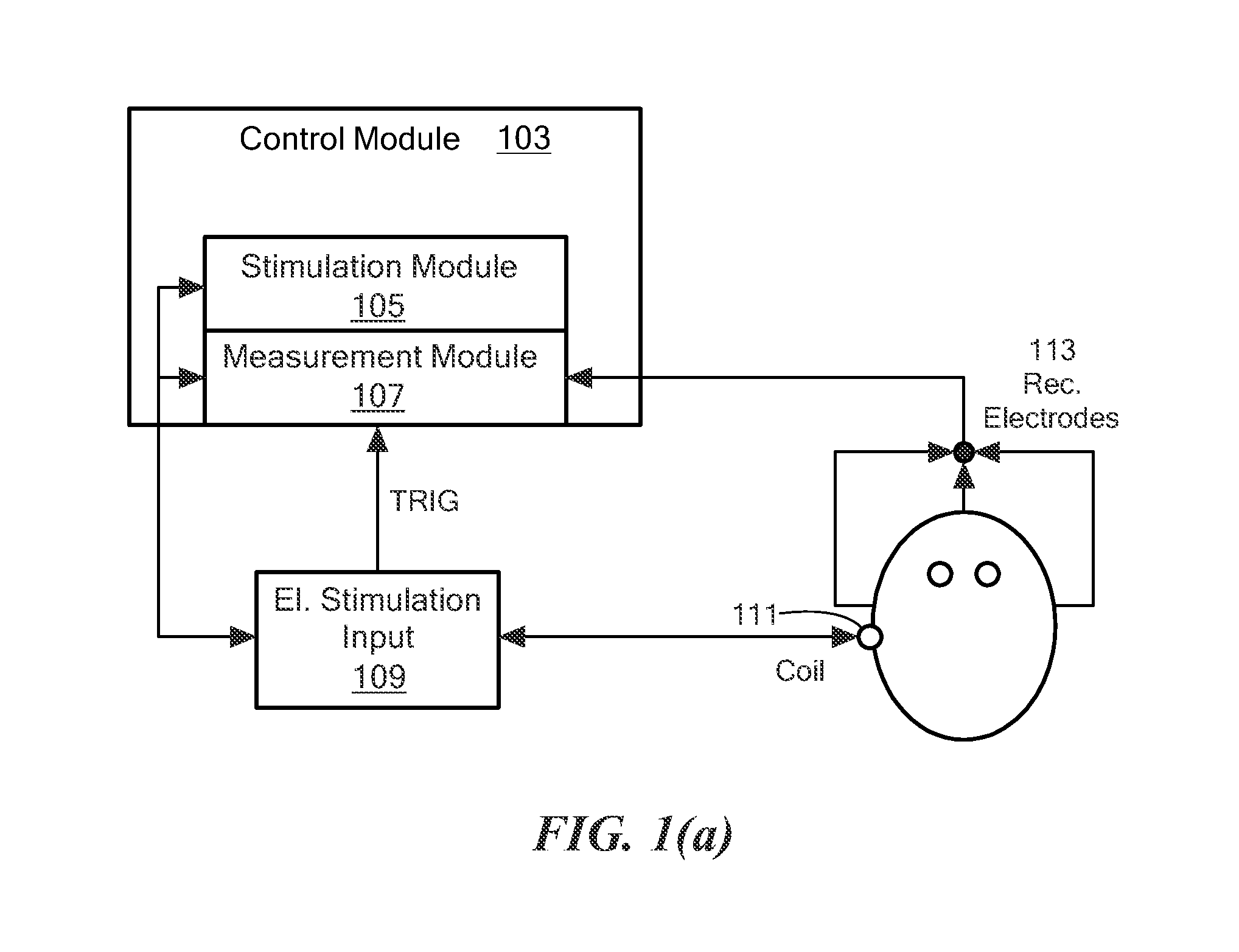
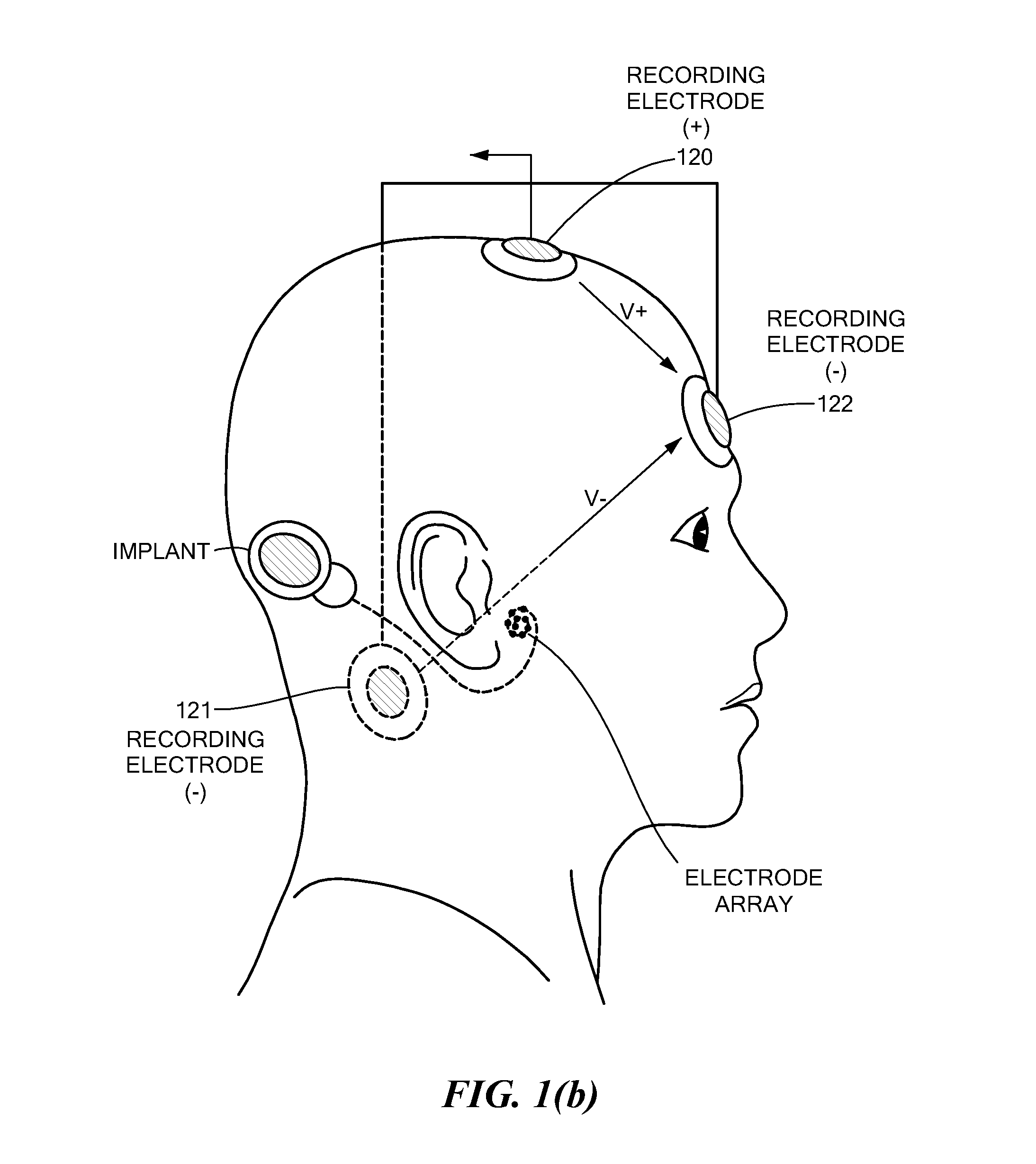
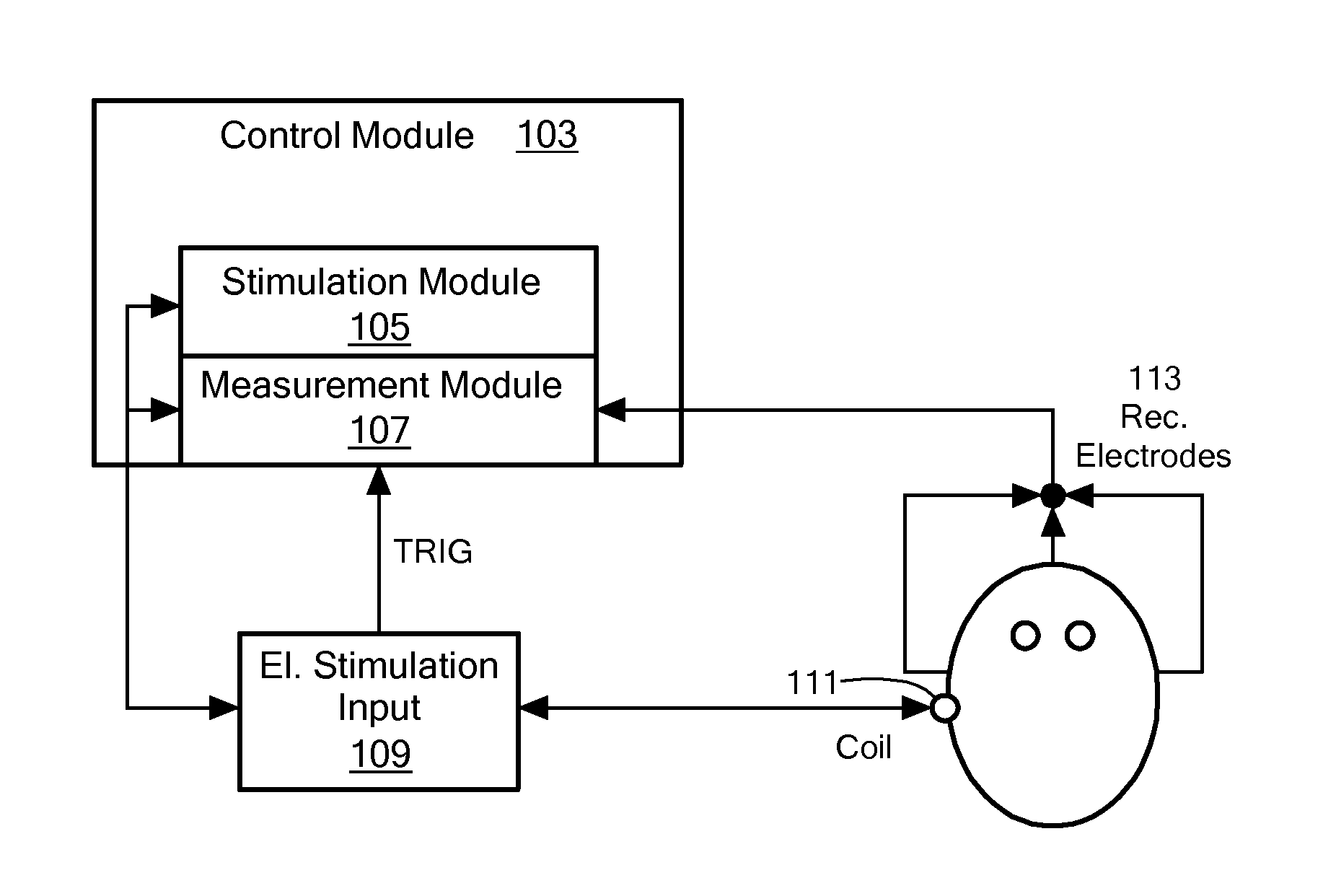
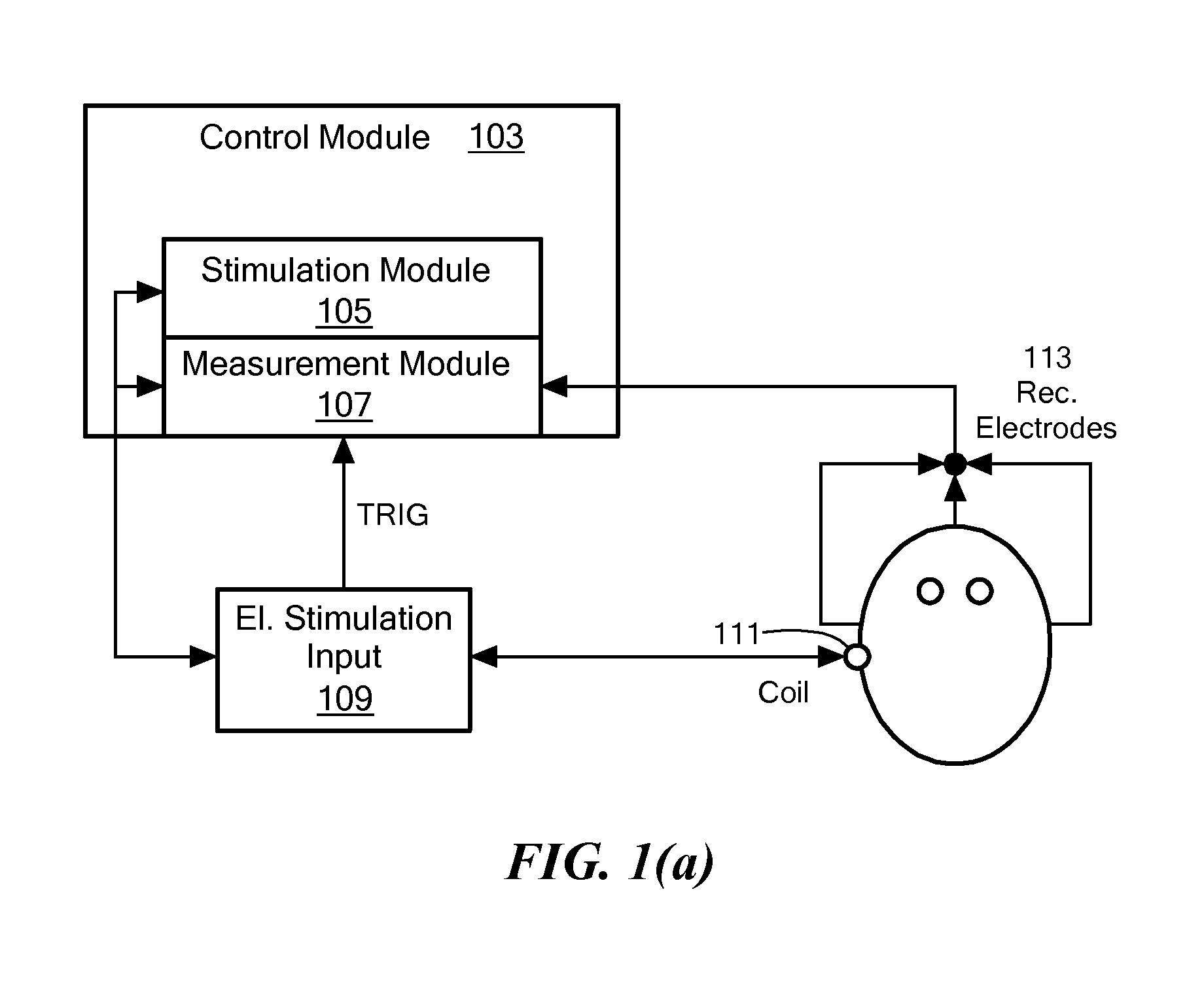
Electrically evoked brainstem response measurements via implant prothesis
A method of measuring electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses of a patient or animal body is provided. The method includes surgically implanting an auditory prosthesis having an electrode array, the electrode array positioned either intracochlear or substantially proximate a brainstem of the body. At least one electrode is stimulated in the electrode array. Electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses resulting from said stimulation are recorded using, at least in part, an electrode in the electrode array as a negative electrode, and a positive electrode positioned substantially proximate the vertex of the head of the body.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Automatic test device and method for auditory brainstem response
ActiveCN109998539ASave duplicate recordsAvoid wastingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime lagSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to an automatic test device and method for an auditory brainstem response (ABR). On the basis of the calculation of an adaptive averaging method, the average number of records isiteratively increased for the ABR records which are respectively collected under multiple sound intensities, and the signal to noise ratio is increased until ABR signal detection conditions are satisfied, wherein an average curve is obtained according to the ABR records collected in groups and batches, the time lag of the maximum values of cross-correlation functions between the groups is calculated, and it is judged whether or not there are ABR signals having time locking characteristics according to the fact whether or not the deviation of the time lag is within a specified range. The iteration is terminated when the ABR signals are detected or no ABR signals are detected after a maximum iteration number is reached. The minimum sound intensity required to detect the signals is adopted as a hearing threshold value, or the iteration number used under each sound intensity is subjected to function fitting, and the accurate sound intensity corresponding to the hearing threshold value isobtained by means of an interpolation method. According to the automatic test device and method, the efficiency of detecting the threshold value is high, the accuracy rate is approximate to that of manual judgment and is more objective, the repeatability is better, and the repeated collection number of the ABR records can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Electrically Evoked Brainstem Response Measurements via Implant Prosthesis
A method of measuring electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses of a patient or animal body is provided. The method includes surgically implanting an auditory prosthesis having an electrode array, the electrode array positioned either intracochlear or substantially proximate a brainstem of the body. At least one electrode is stimulated in the electrode array. Electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses resulting from said stimulation are recorded using, at least in part, an electrode in the electrode array as a negative electrode, and a positive electrode positioned substantially proximate the vertex of the head of the body.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Automatic Data Processing Method Based on Adaptive Averaging Method in Auditory Brainstem Response Test
ActiveCN110074782BSave duplicate recordsAvoid wastingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNoiseCorrelation function
An auditory brainstem response automatic test method based on an adaptive averaging method. With regard to auditory brainstem response single records collected in batches under various test sound intensities from high to low, on the basis of calculation performed using an adaptive averaging method, the average number of records is increased gradually by means of iteration, and a signal-to-noise ratio is increased until an auditory brainstem response signal detection condition is met, the condition involving obtaining two groups of average curves by means of auditory brainstem response single records collected in groups and in batches, calculating a time lag where the maximum value of a cross-correlation function of the two groups of average curves is located, and determining, according to whether the deviation of the time lag is within a specified range, whether there is an auditory brainstem response signal with a time locking characteristic. A hearing threshold value is obtained by means of the minimum sound intensity required for detecting a signal; or an accurate sound intensity corresponding to the hearing threshold value is obtained by performing function fitting on the number of iterations used in each test sound intensity and by means of an interpolation method. The method has a high efficiency in detecting a threshold value, has an accuracy close to that of manual determination, is more objective, has a better repeatability, and can effectively reduce the number of times that an auditory brainstem response record is repeatedly collected.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
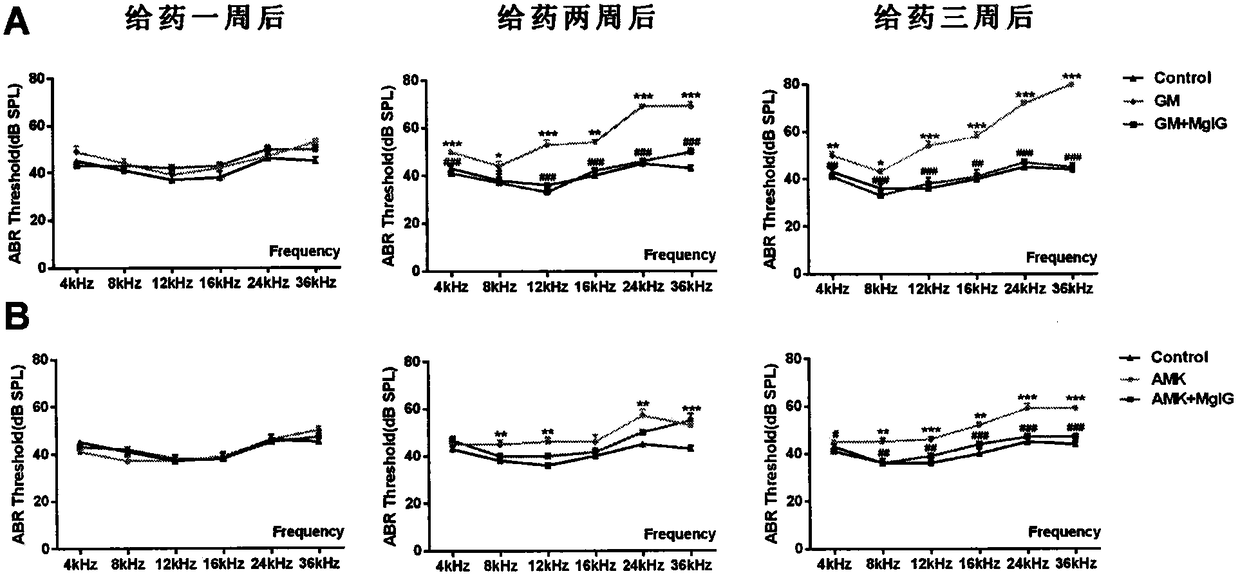
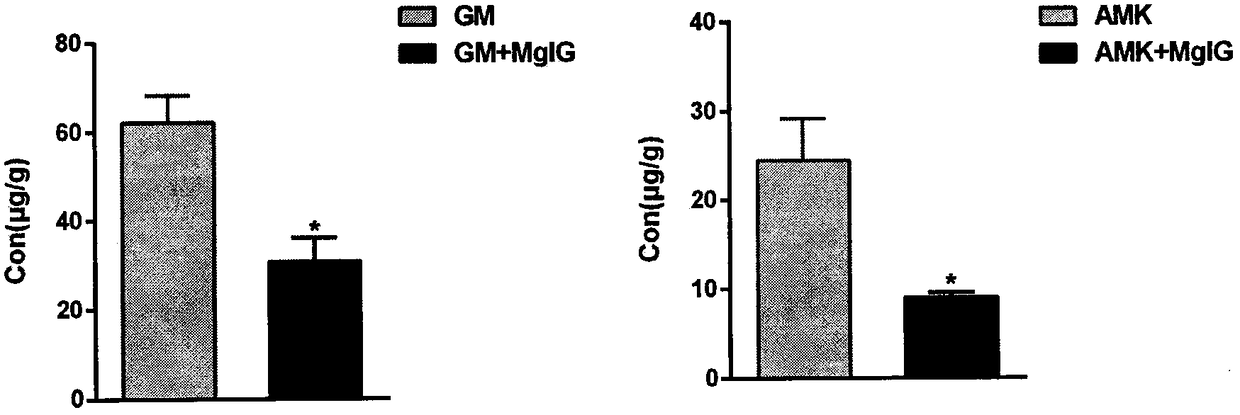
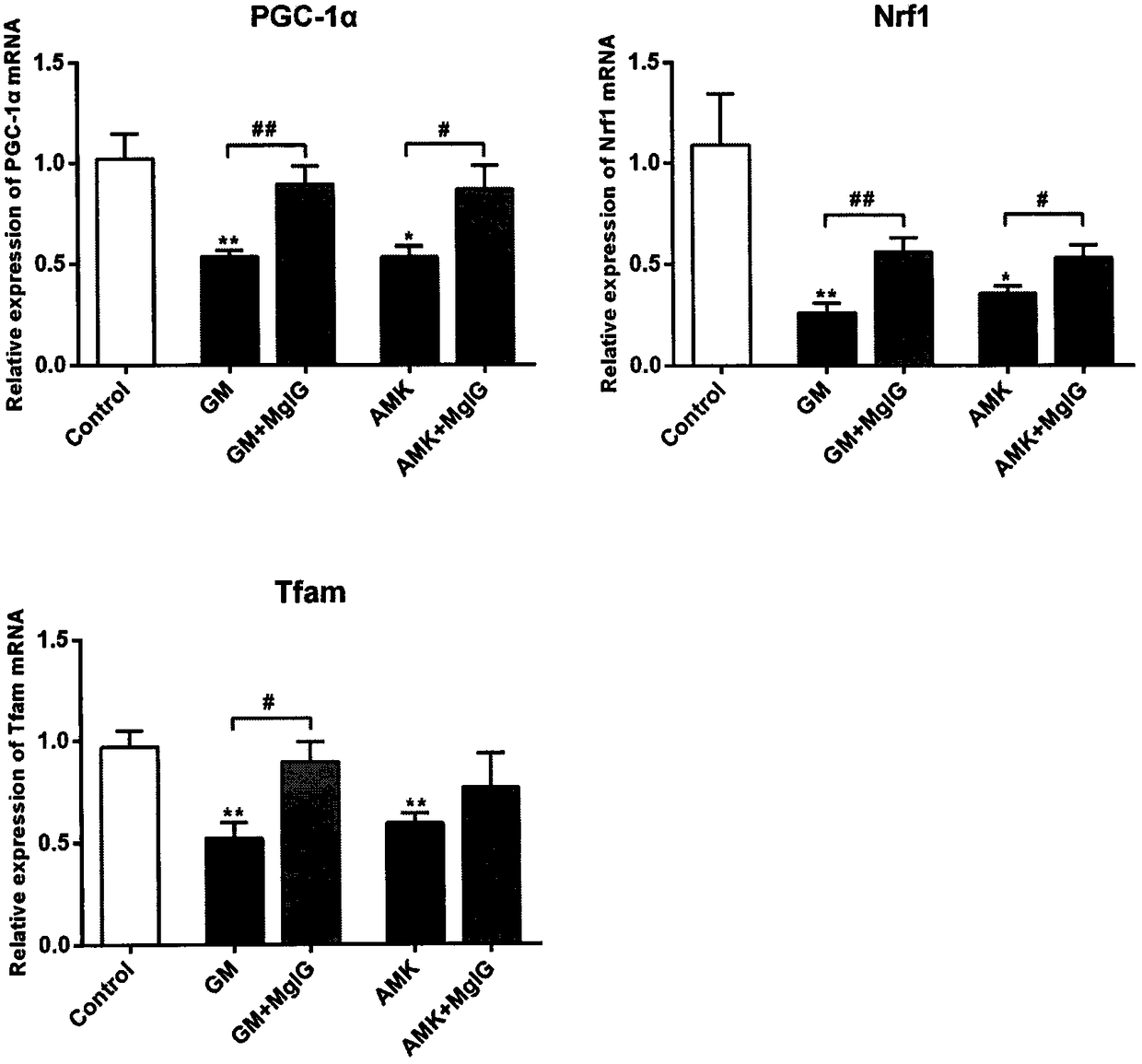
Application of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate to preparation of medicine for lowering ototoxicity caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics
InactiveCN108309996AReduce distributionReduce ototoxic side effectsOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAntibiotic YOtotoxicity
The invention discloses application of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG) to the preparation of a medicine for lowering the ototoxicity caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics, and relates to the fieldof natural medicines. A rat ototoxicity model caused by an aminoglycoside antibiotic gentamicin (GM) and amikacin (AMK) is established; discovering that by jointly using the MgIG, the MgIG can be usedfor effectively ameliorating the threshold value increment of the auditory brainstem response (ABR) caused by the aminoglycoside antibiotisc, and meanwhile, is used for lowering the concentration ofan aminoglycoside medicine in the tissue of an inner ear of a rat and reversing the dysfunction, which is caused by the medicine, of a mitochondrion in the tissue of the inner ear, and the MgIG in theapplication provided by the invention can be used cooperatively to antagonize the ototoxicity caused by the aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
An automatic test device for auditory brainstem response
ActiveCN109998539BSave duplicate recordsAvoid wastingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWhispered voiceNoise
The present invention relates to a kind of auditory brainstem response (ABR) automatic test device, for the ABR records collected separately under multiple sound intensities, based on the calculation of the adaptive average method, the average number of records is increased by iteration, and the signal-to-noise ratio is improved until Meet the conditions for ABR signal detection: obtain the average curve based on the ABR records collected in batches by group, calculate the time lag at which the maximum value of the cross-correlation function between groups is located, and judge whether there is a time-locking characteristic according to whether the deviation of the time lag is within the specified range ABR signal. When the ABR signal is detected or the maximum number of iterations is reached and no ABR signal is detected, the iteration is terminated. The minimum sound intensity required to detect the signal is used as the hearing threshold; or, the function fitting is performed on the number of iterations used under each sound intensity, and the accurate sound intensity corresponding to the hearing threshold is obtained by interpolation. The present invention has high detection threshold efficiency, accuracy close to manual judgment, more objective and better repeatability, and can effectively reduce the number of repeated acquisitions of ABR records.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Application of sodium butyrate in preparation of medicine for preventing noise-induced hearing loss
ActiveCN104546815BConvenient researchReduced evoked potential threshold shiftSenses disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsDiseaseNoise-induced hearing loss
The invention provides an application of sodium butyrate for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. According to the application of sodium butyrate for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, in the noise-induced hearing loss experiment of mice models, sodium butyrate can reduce the auditory brainstem response threshold shift after noise exposure, increase the survival rate of cochlear hair cells after noise exposure, has excellent noise-induced hearing loss preventing effect on noises at multiple frequencies, especially has excellent preventative effect on noise-induced hearing loss, explosive hearing loss and other diseases, can be used for preparing drugs and / or healthcare products for preventing noise-induced hearing loss, has good research and application prospects, and can fill in the gap of drugs for preventing noise-induced hearing loss at present.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com