Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
279 results about "Evoked potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
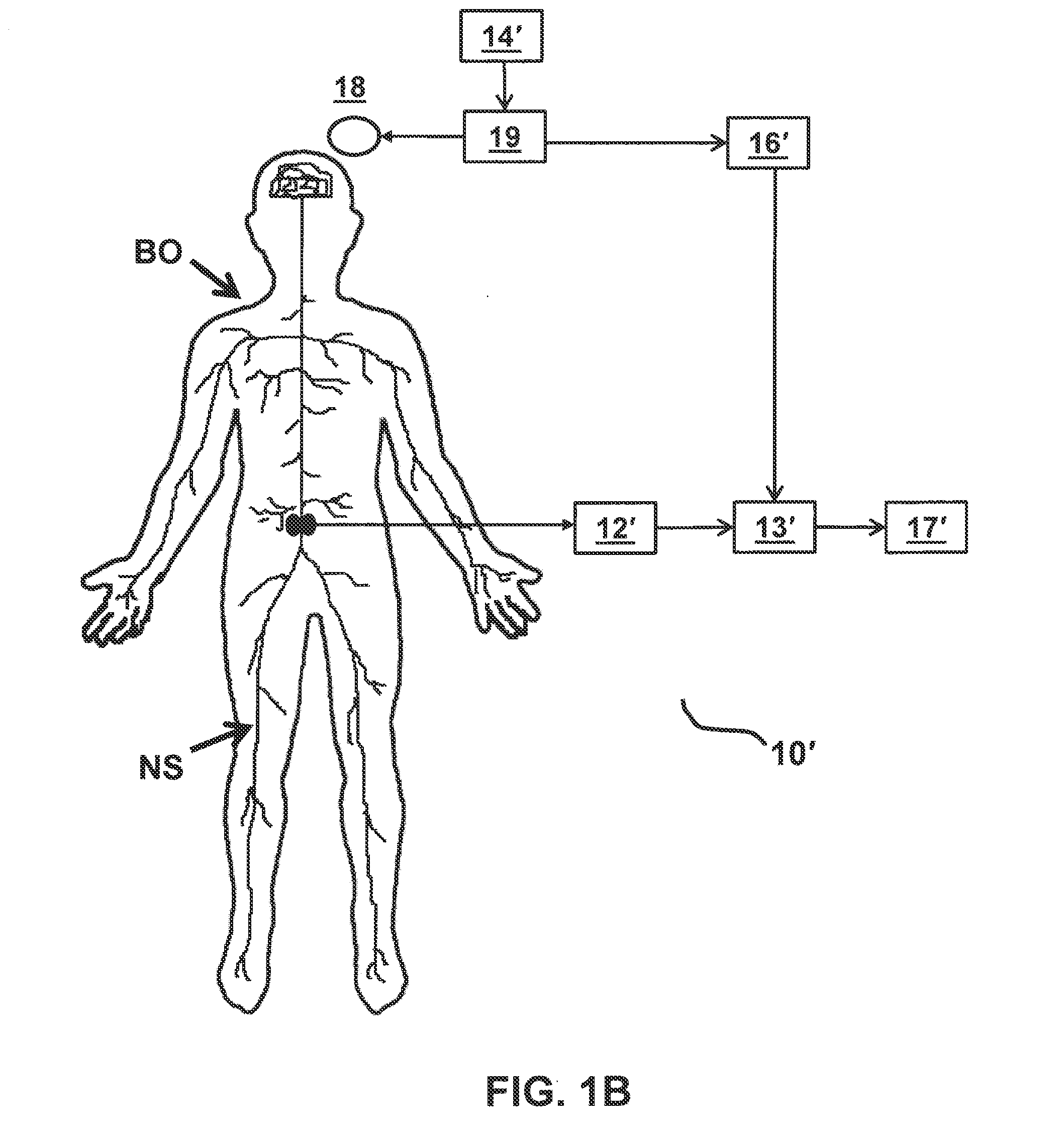
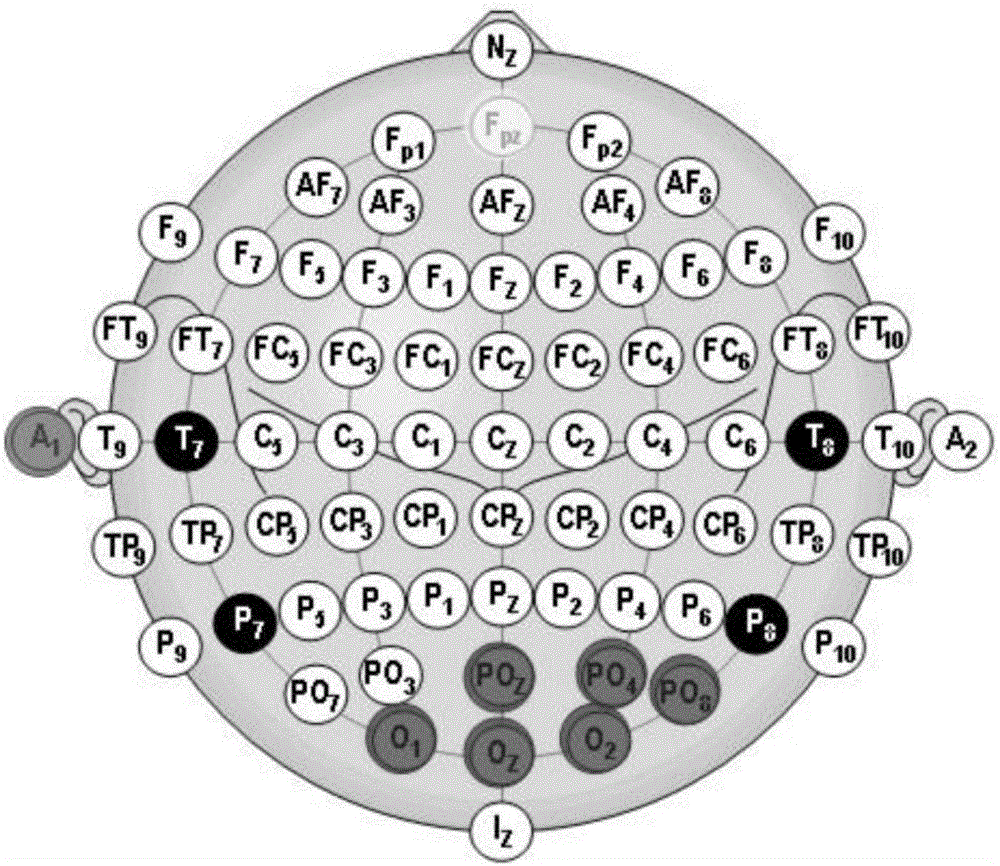
An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential in a specific pattern recorded from a specific part of the nervous system, especially the brain, of a human or other animals following presentation of a stimulus such as a light flash or a pure tone. Different types of potentials result from stimuli of different modalities and types. EP is distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), or other electrophysiologic recording method. Such potentials are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring that include detections of disease and drug-related sensory dysfunction and intraoperative monitoring of sensory pathway integrity.
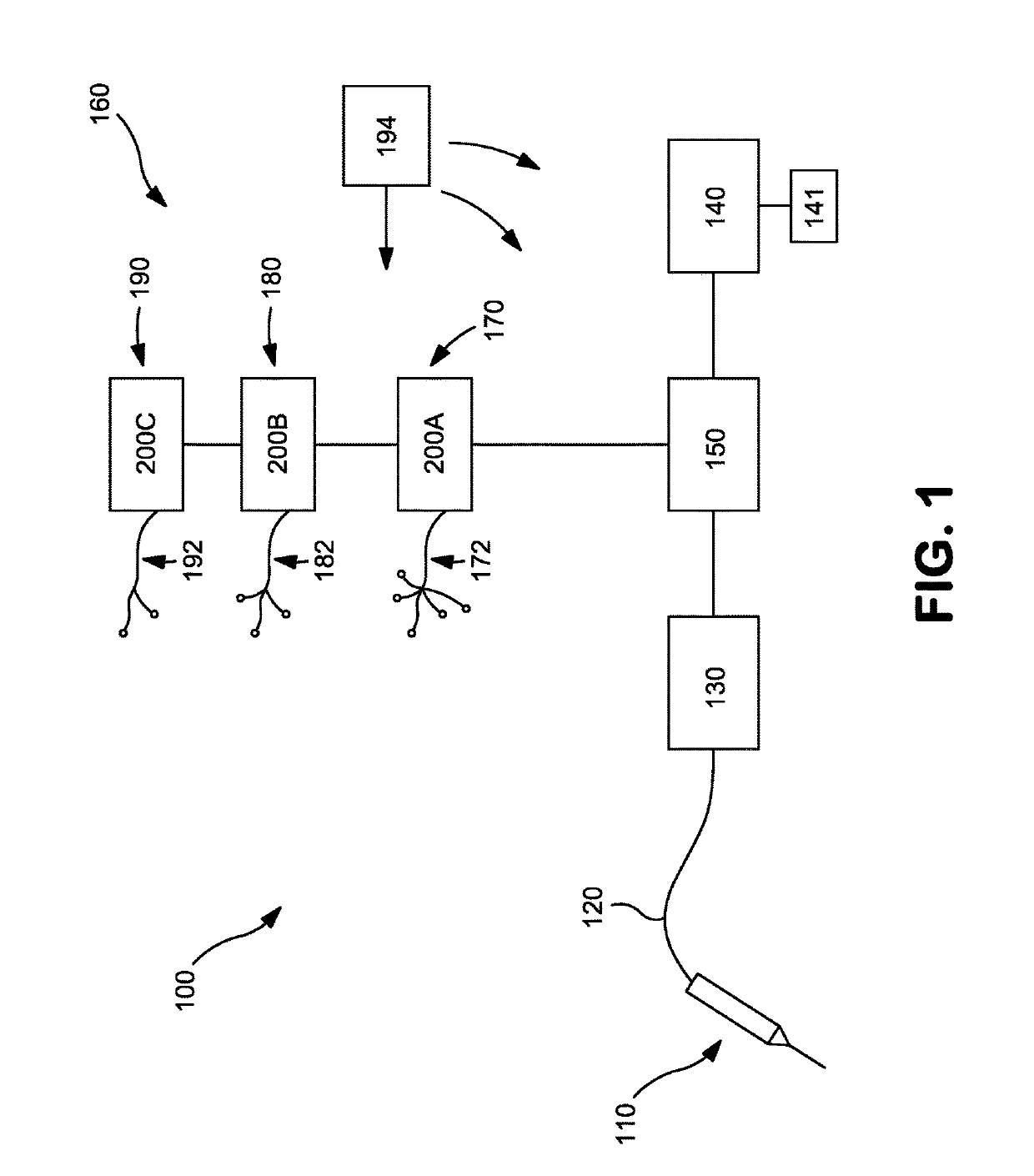
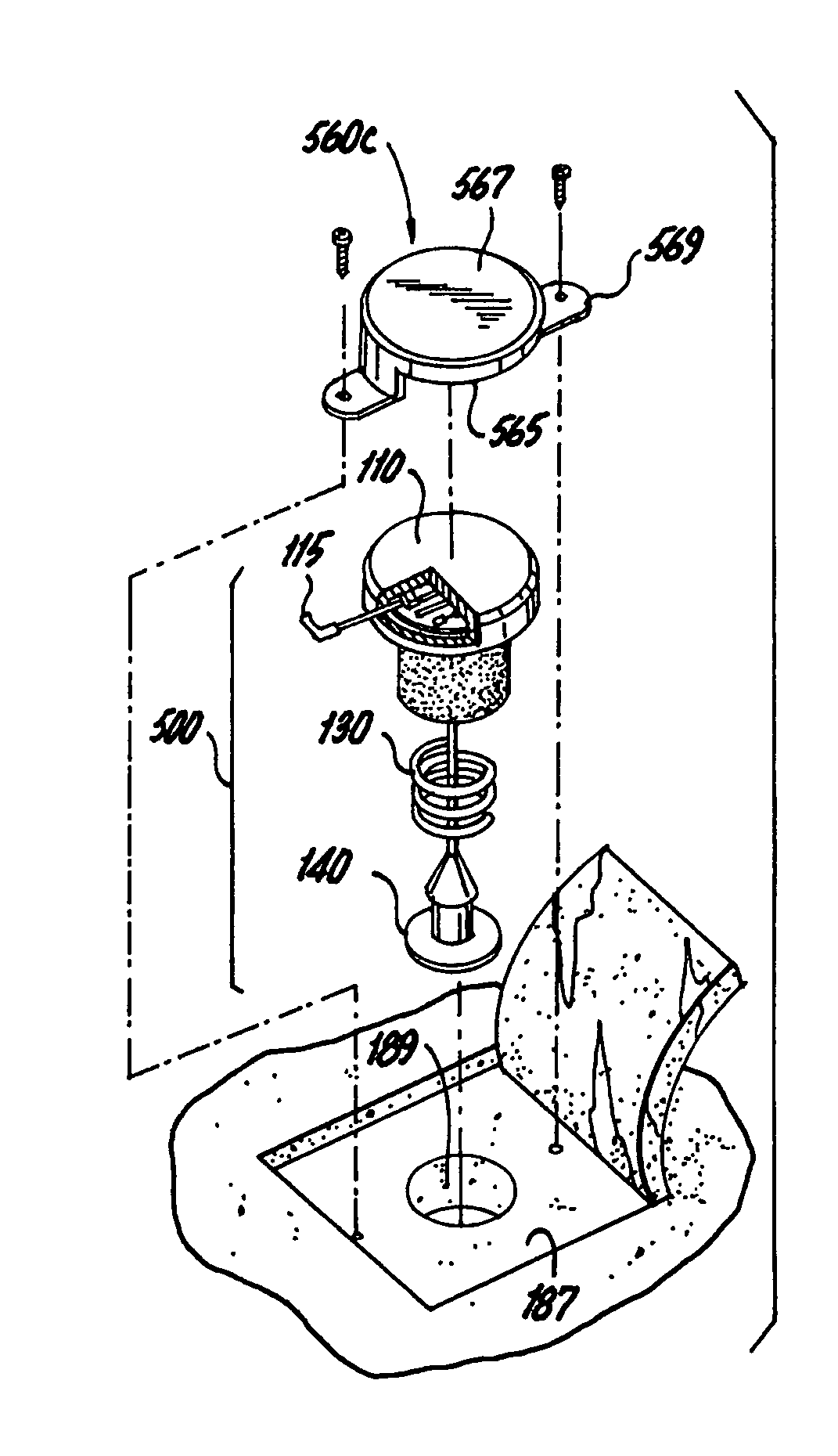
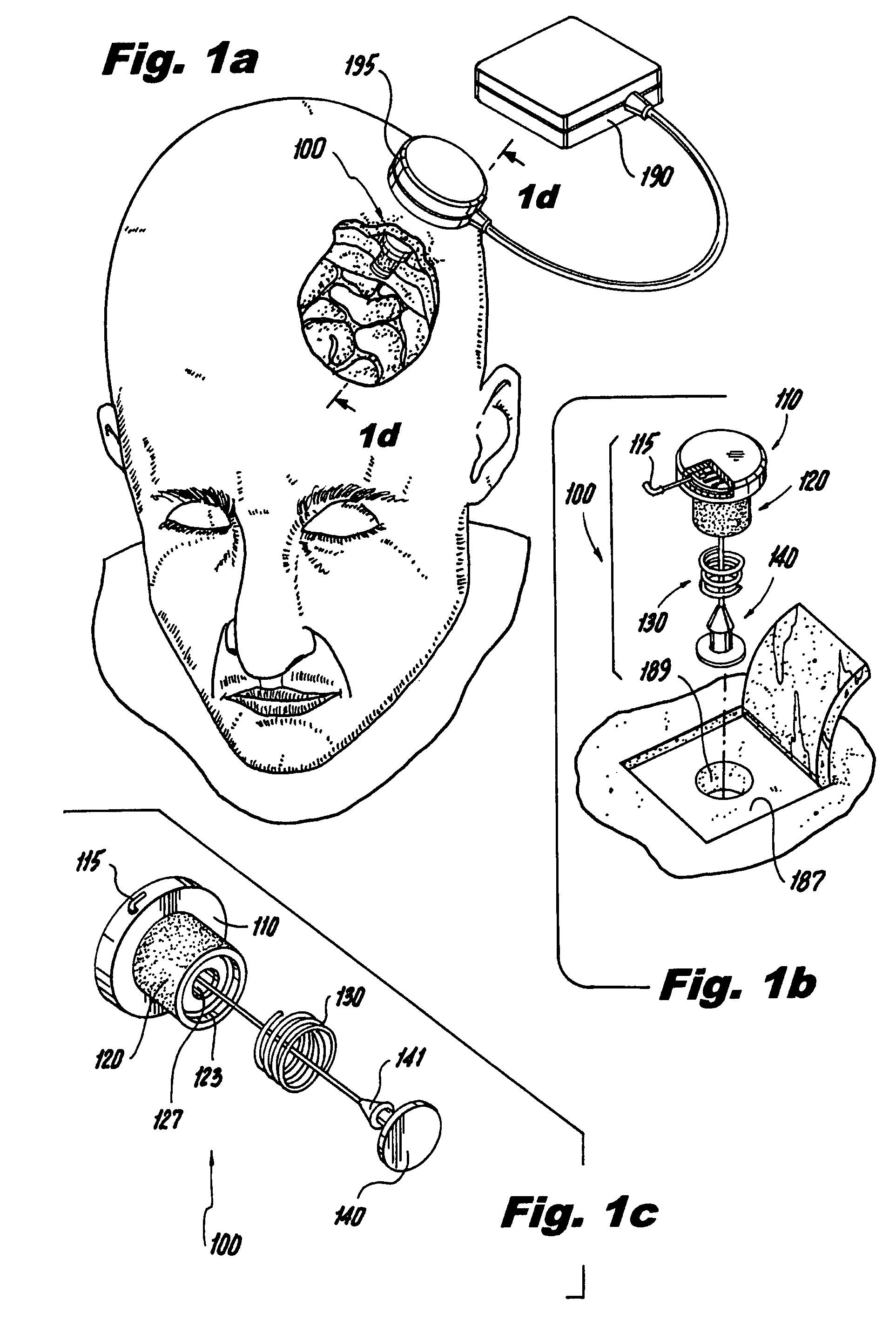
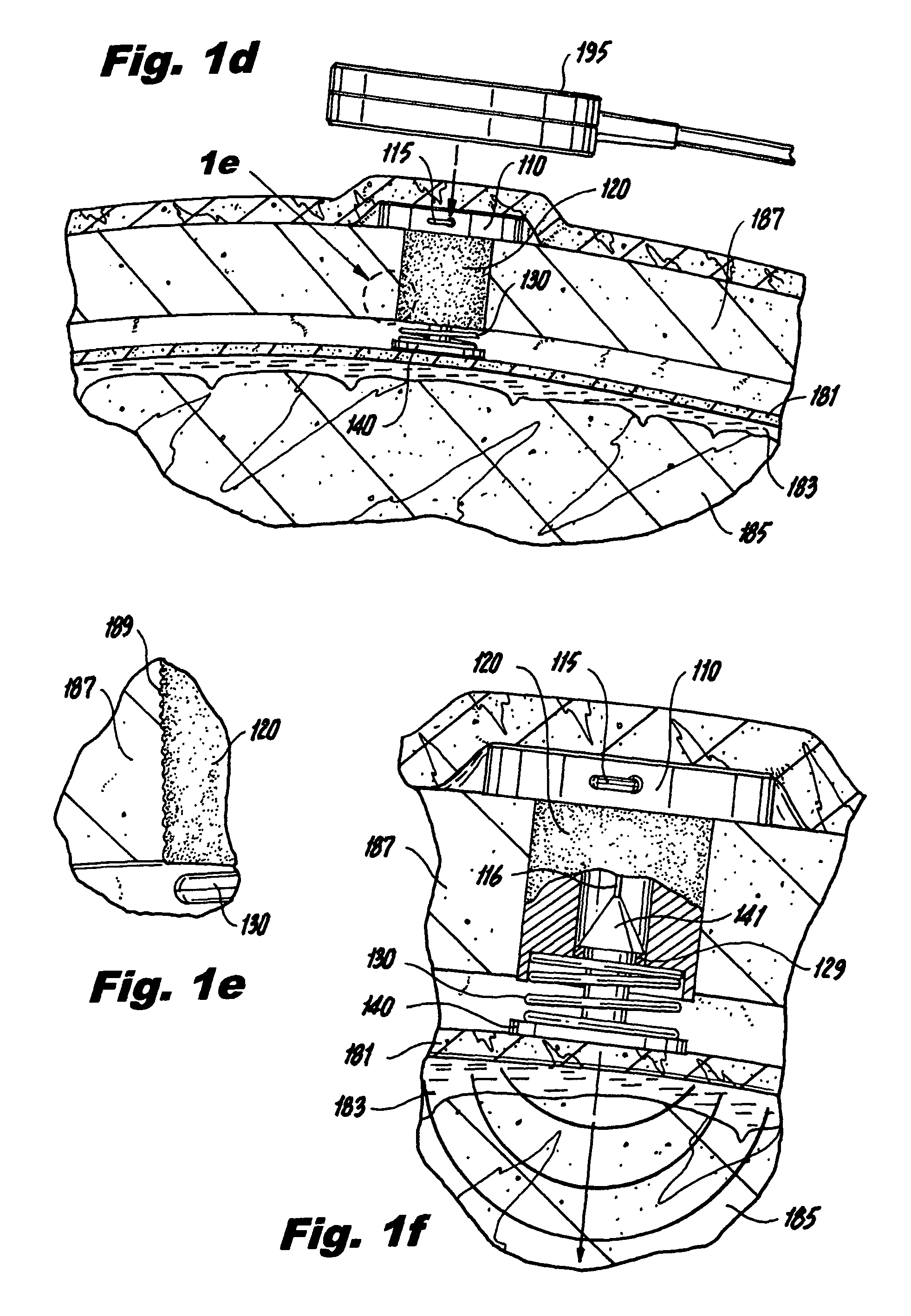
Method for assessing brain function and portable automatic brain function assessment apparatus
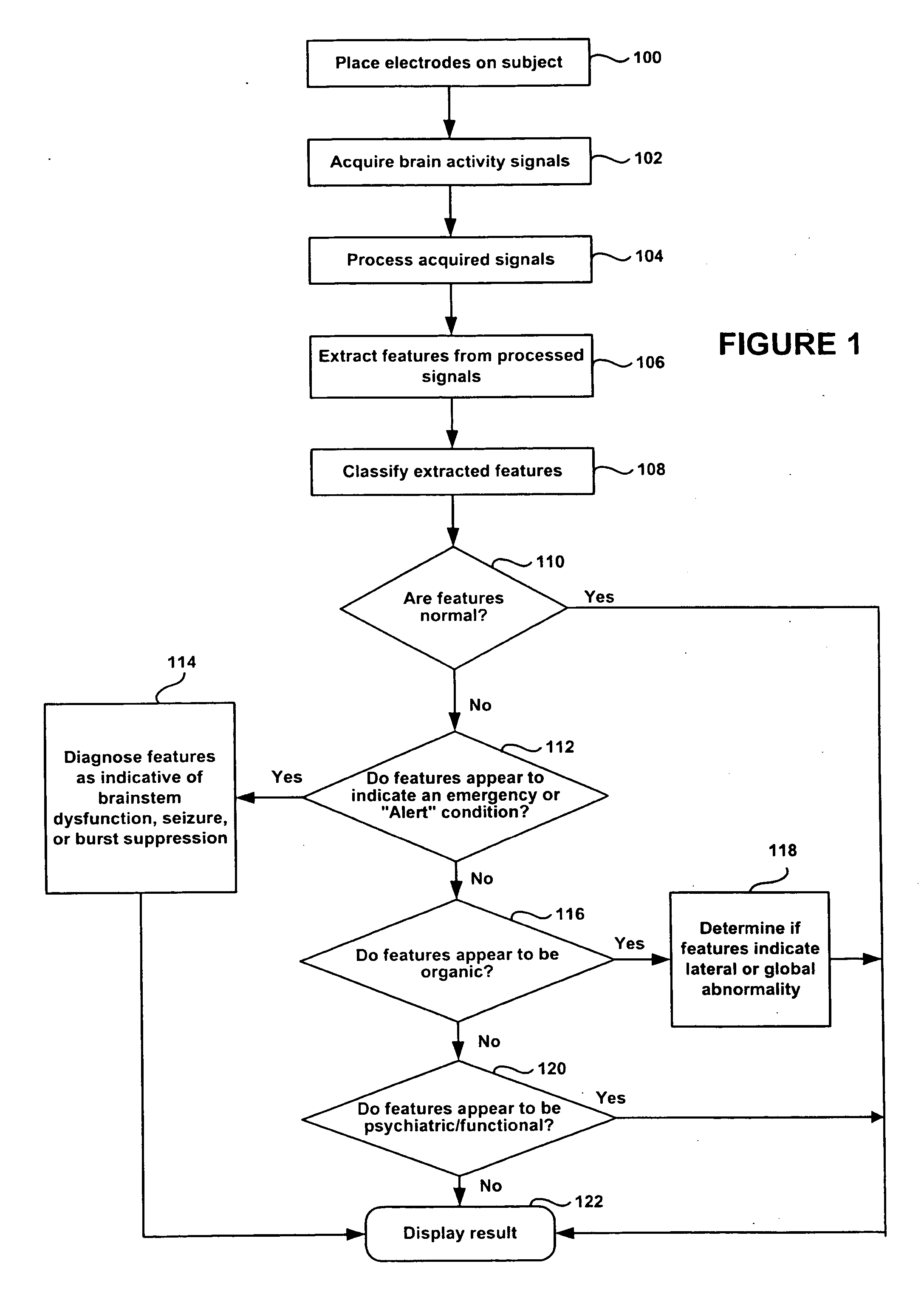
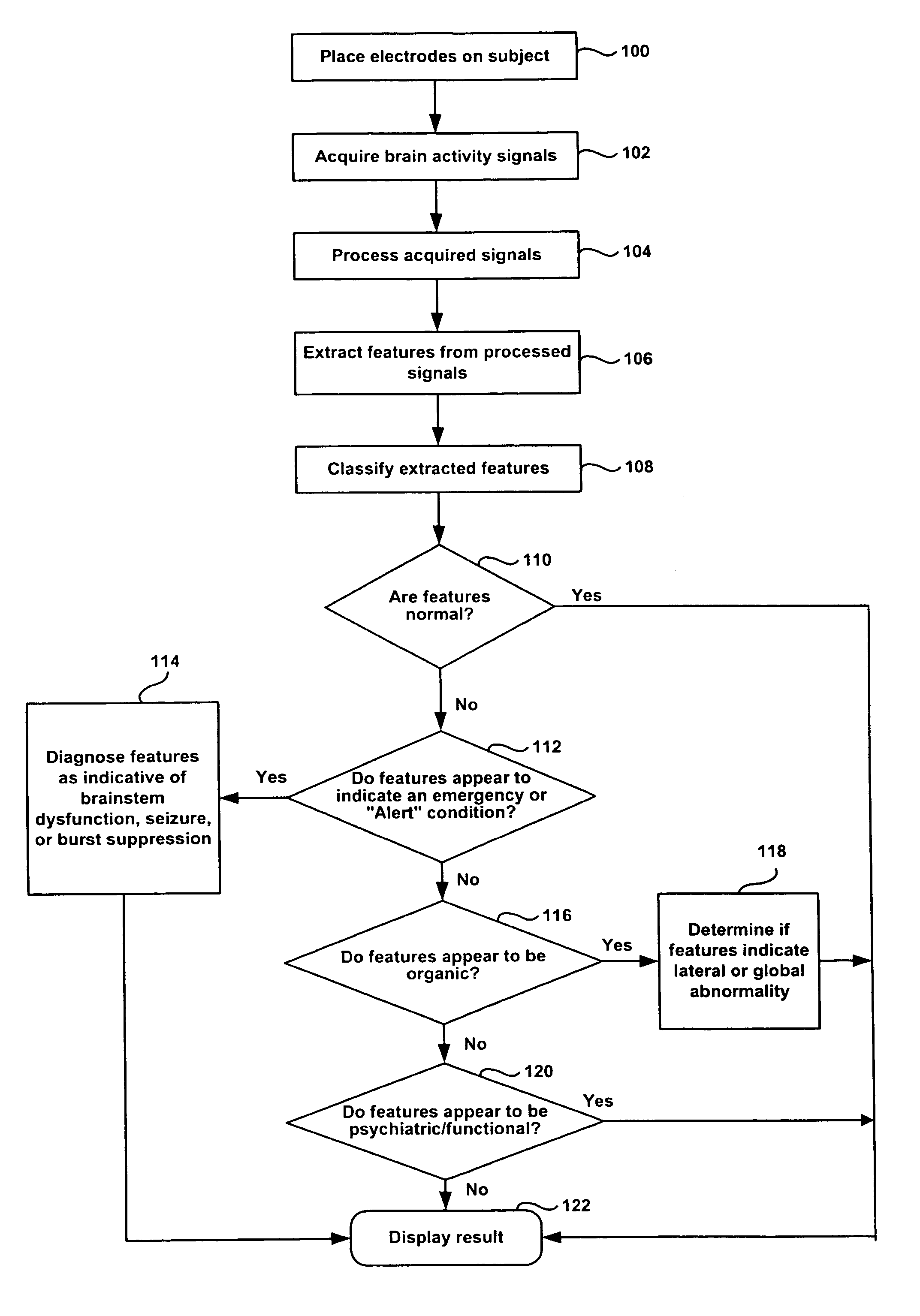
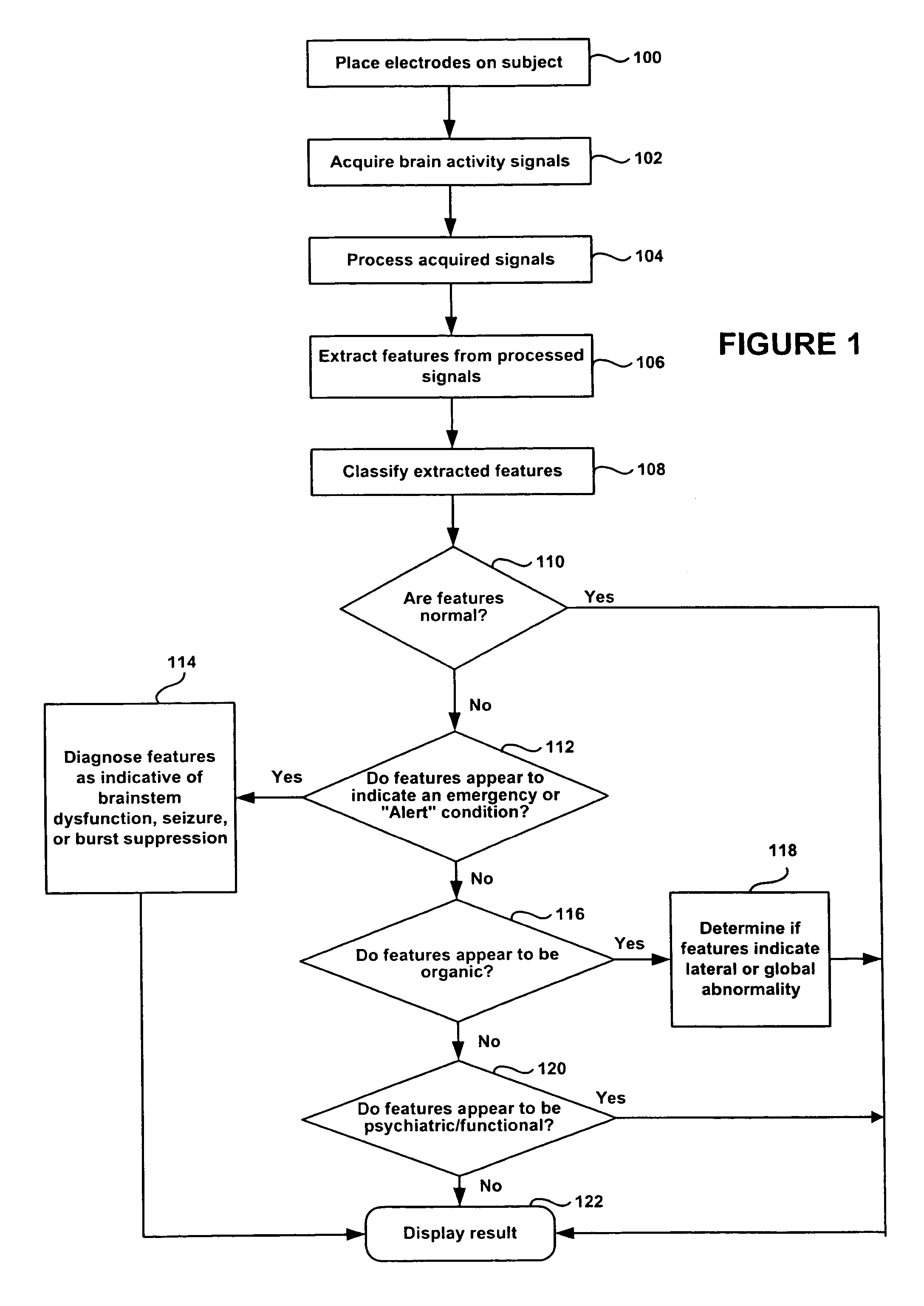
A method and apparatus for performing rapid brain assessment may provide emergency triage to head trauma patients by analyzing a combination of spontaneous and evoked brain potentials. The spontaneous and evoked potentials are analyzed, and the results classified, to present a real-time assessment of a patient's brain, diagnosing any potential abnormalities therein.
Owner:BS HLDG +2
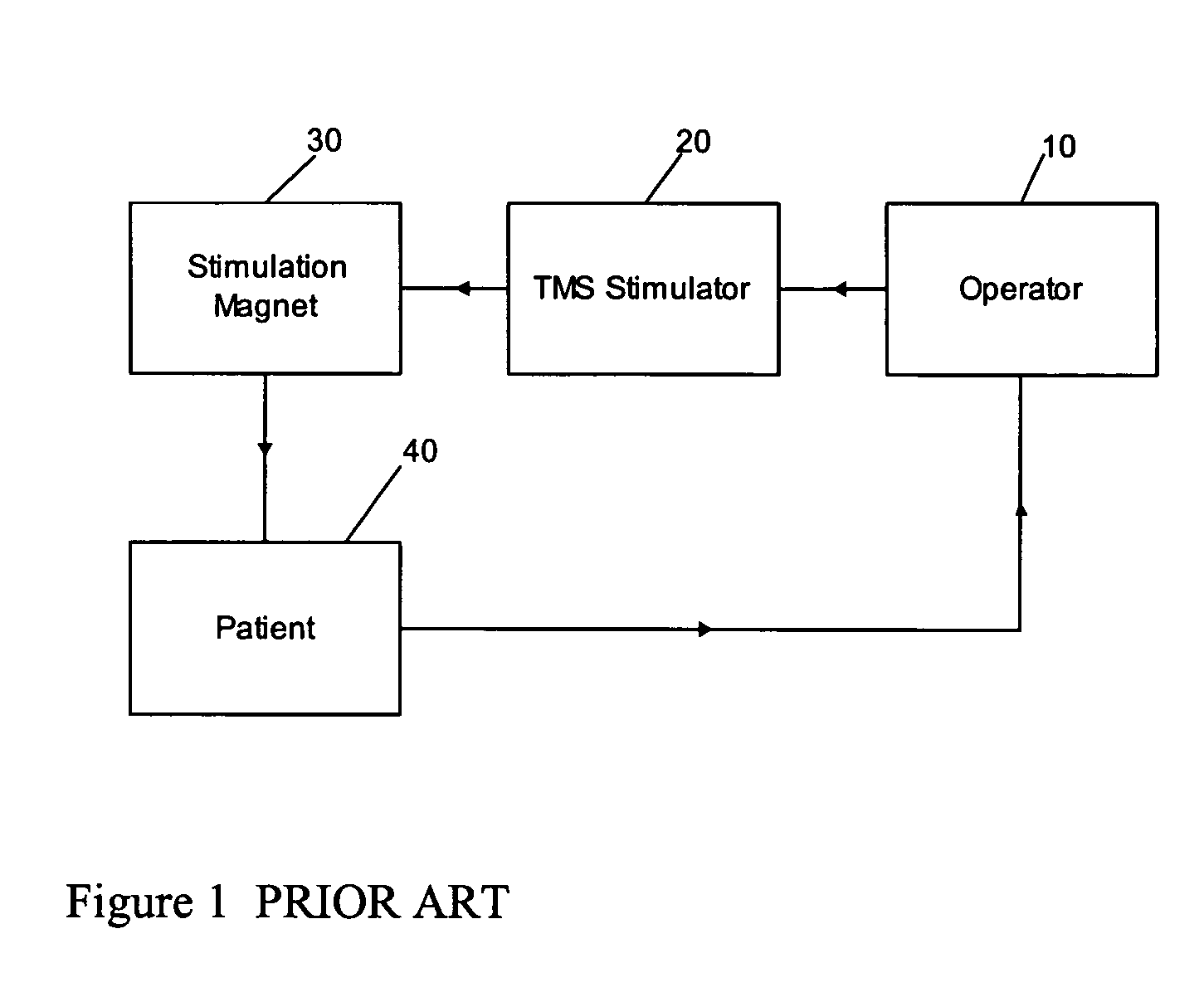
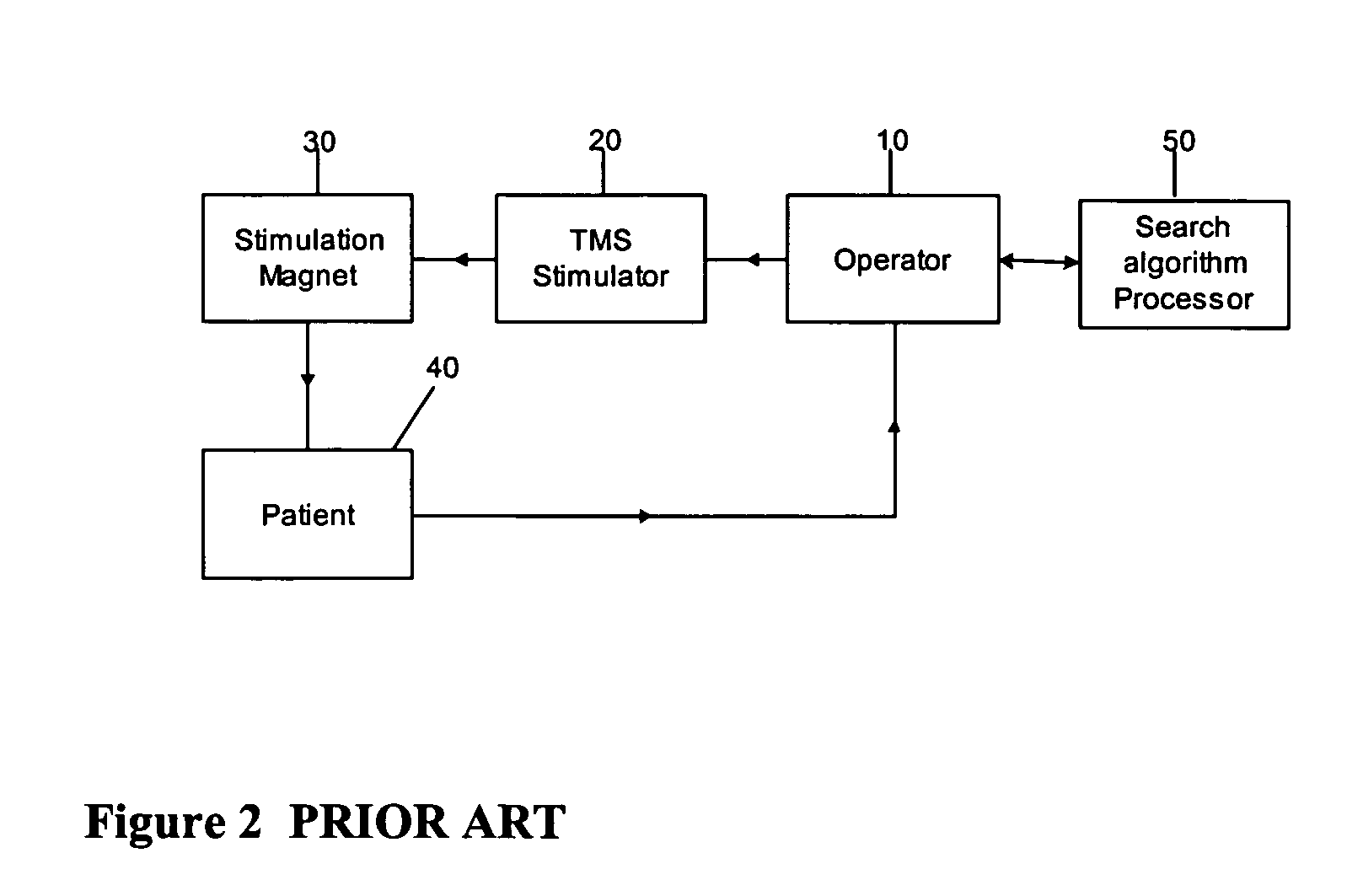
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
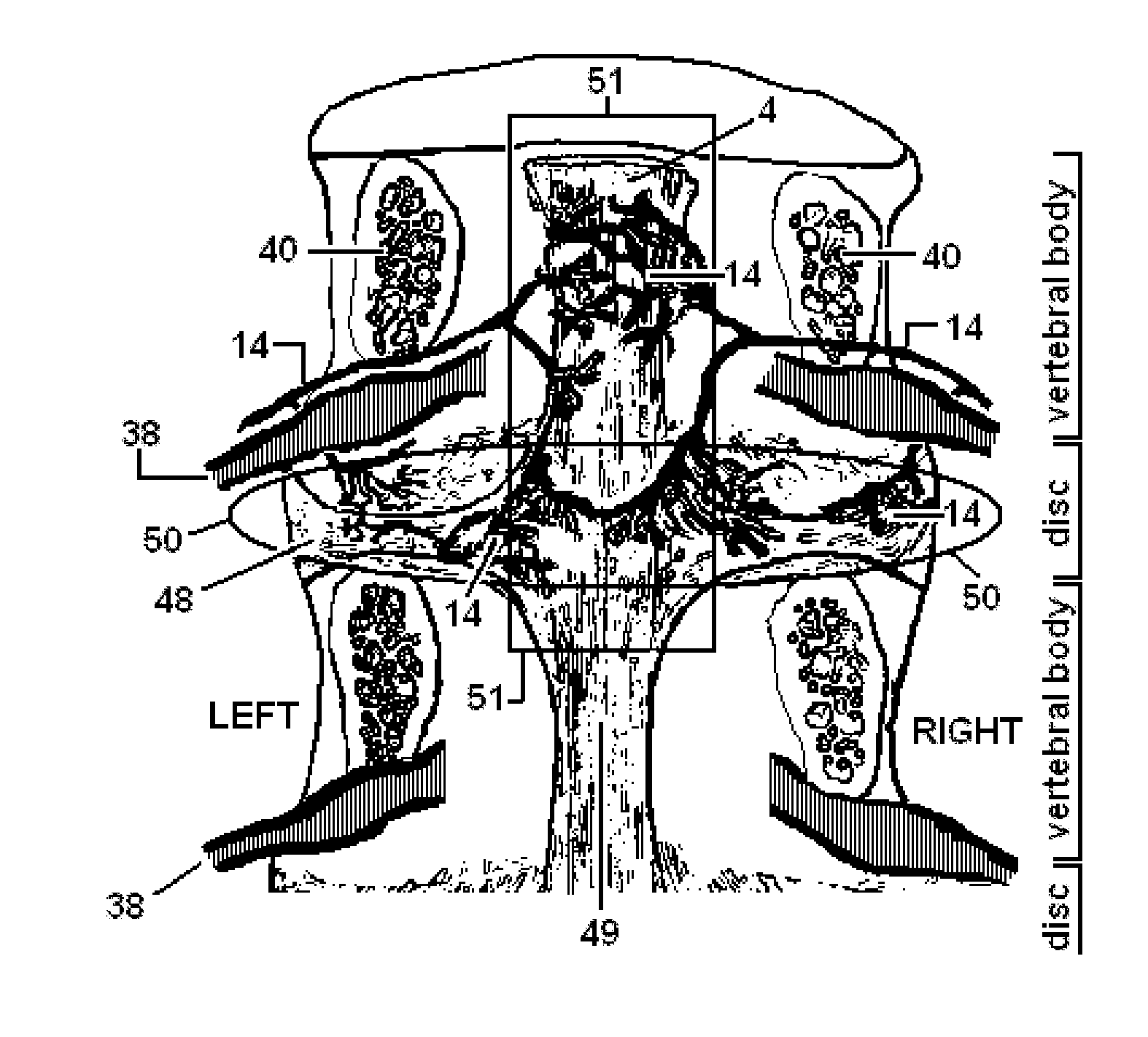
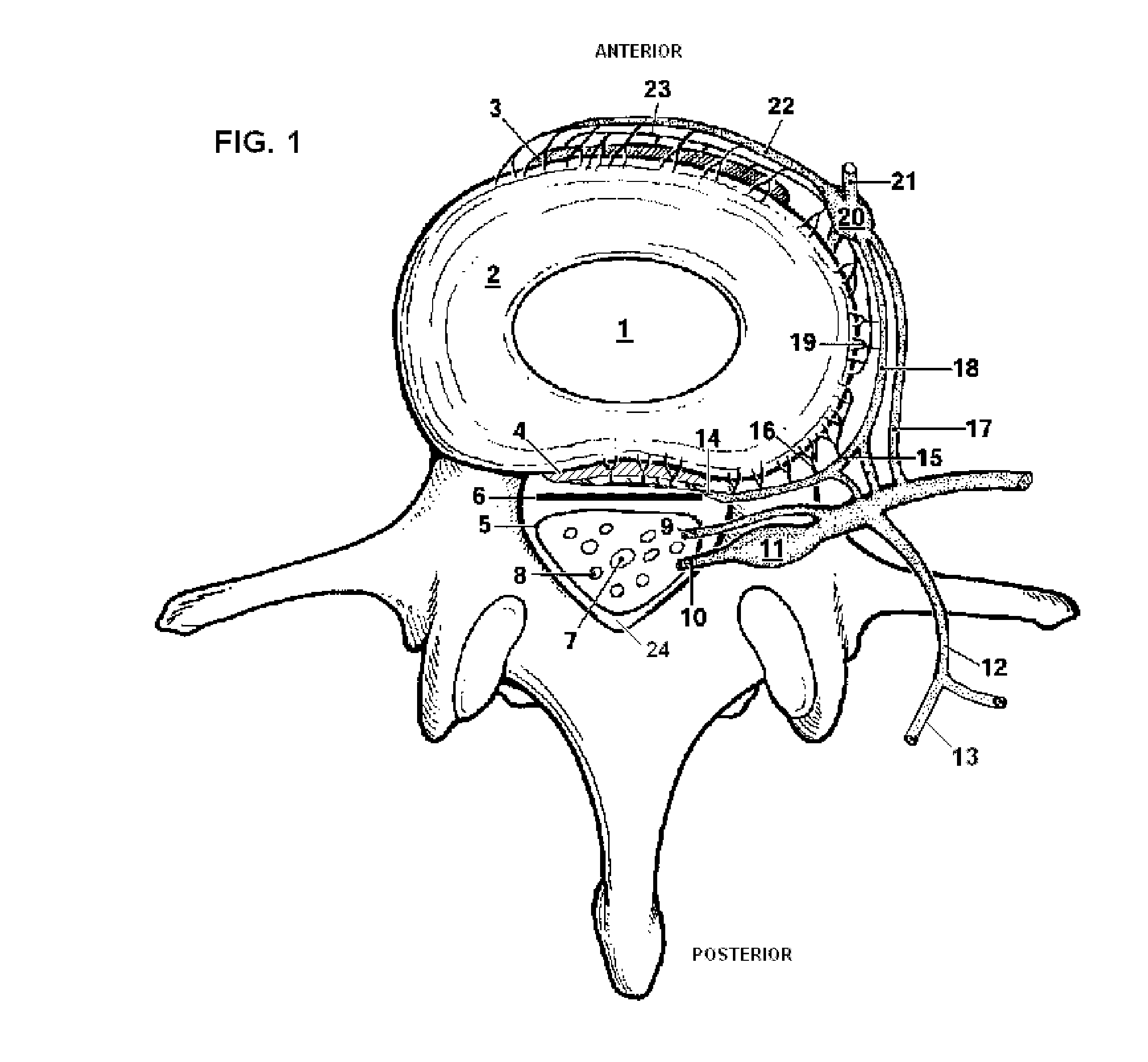
System and Methods for Diagnosis and Treatment of Discogenic Lower Back Pain
ActiveUS20150005680A1Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsClosed loopElectrical impulse
Methods and devices to treat discogenic lumbar back pain are disclosed. Electrodes are implanted within the anterior epidural space of the patient. A pulse generator that is connected to the electrodes delivers electrical impulses to sympathetic nerves located within the posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) of the lumbar spine and outer posterior annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. In alternate embodiments, energy directed to nerves in the PLL may be from light or mechanical vibrations, or the nerves may be cooled. The electrodes may also be used diagnostically to correlate spontaneous nerve activity with spinal movement, fluctuations in autonomic tone and the patient's experience of pain. The electrodes may also be used to generate diagnostic evoked potentials. The diagnostic data are used to devise parameters for the therapeutic nerve stimulation. Automatic analysis of the data may be incorporated into a closed-loop system that performs the nerve stimulation automatically.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
Method and system for identification of source of chronic pain and treatment
A method for identifying and treating a neural pathway associated with chronic pain via nerve stimulation and brain wave monitoring of a mammalian brain includes positioning a probe to stimulate a target nerve, wherein the target nerve is suspected of being a source of chronic pain; delivering a first nerve stimulation from the probe to the target nerve, wherein the first nerve stimulation is sufficient to elicit a chronic pain response in the brain; and monitoring for evoked potential activity in the brain as a result of the first nerve stimulation. The method can also include delivering second and third nerve stimulations to confirm the correct identification of the neural pathway and to treat the chronic pain, respectively. A system and apparatus for performing a procedure to identify and treat a nerve that is the source of chronic pain are also described.
Owner:AVENT INC
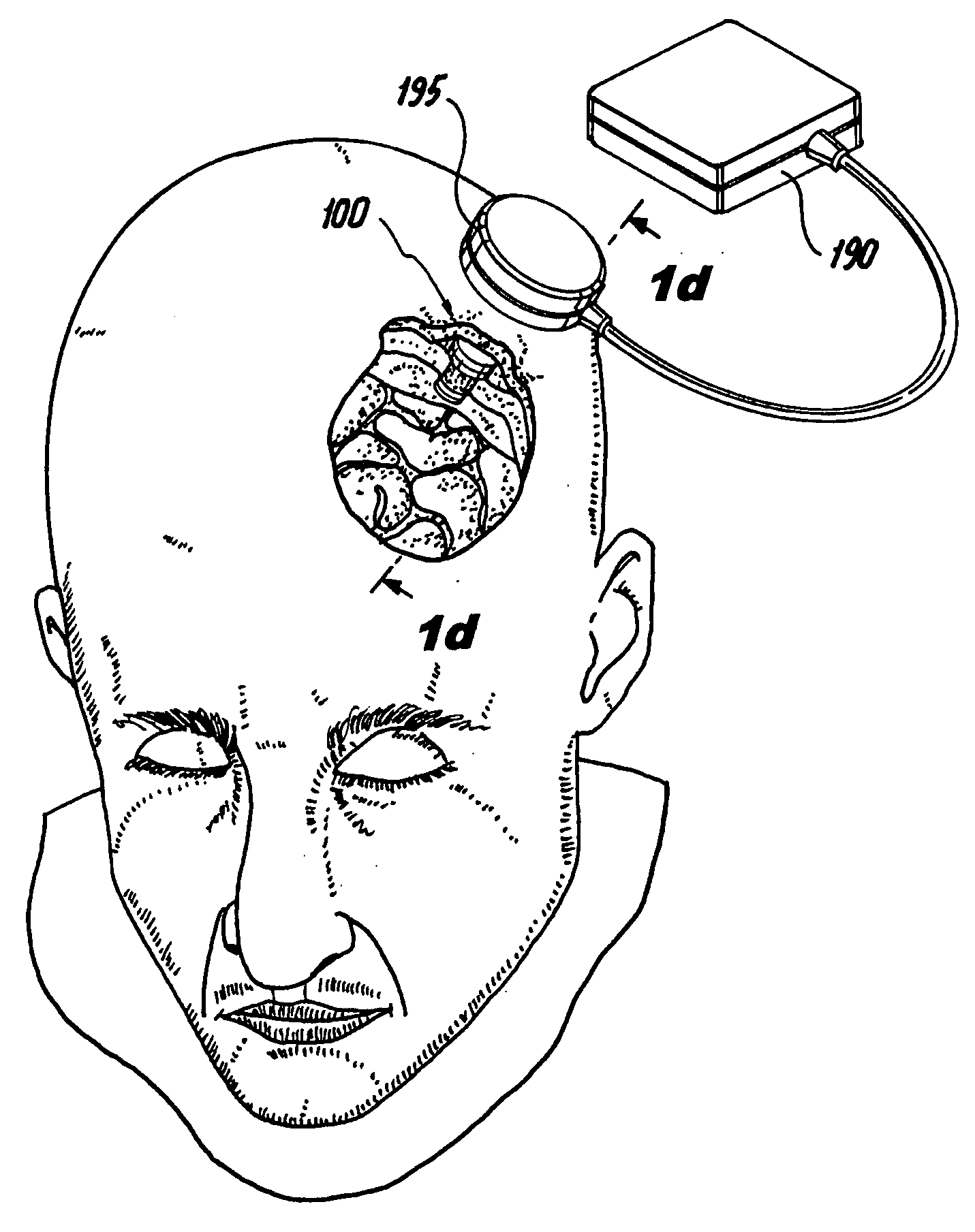
Implantable neurostimulation systems
ActiveUS20080004676A1Reduce excitabilityHigh-frequency ACHead electrodesExternal electrodesInjury brainMotor evoked potentials monitoring
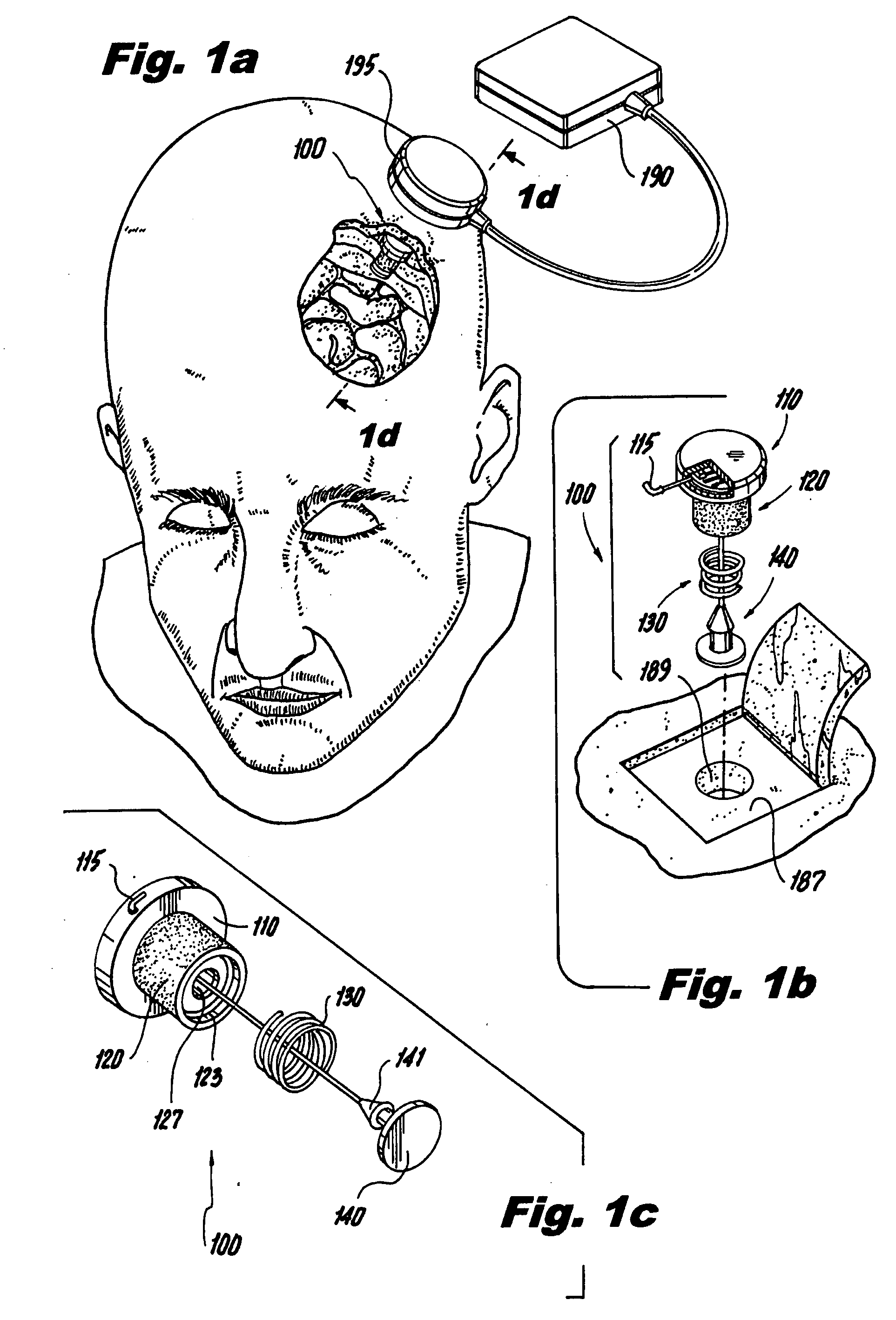
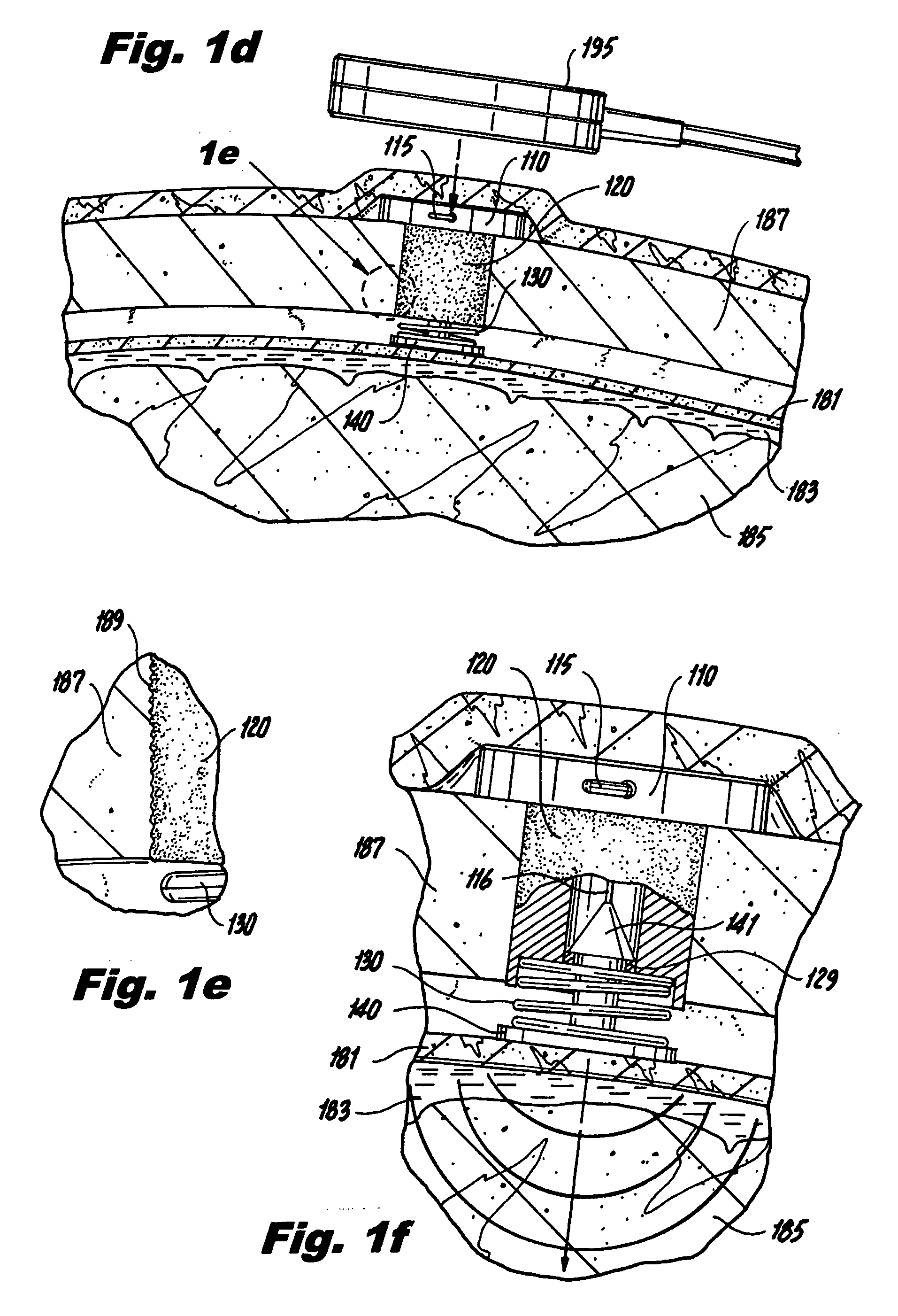
The subject invention is directed to new and useful neurostimulation systems that include an implantable pulse generator dimensioned and configured for implantation in the skull of a patient. The implantable pulse generator has an electrode operatively associated with a distal end portion thereof and can be provided with adjustment means, such as an adjustable biasing member or spring arranged between the electrode to the distal end portion of the pulse generator. The subject invention is also directed to systems involving networked neurostimulators that are configured and adapted to work jointly in accordance with prescribed treatment protocol to effect a desired recovery from brain injury. Such networked neurostimulation systems are particularly advantageous for effecting relatively large and / or relatively distant regions of the brain. The subject invention is further directed to systems and methods for motor-evoked potential (MEP)-based neuromodulation. Further, AC and / or DC stimulation can be utilized, depending on the precise implementation.
Owner:NEUROPOINT MEDICAL
Systems and methods for monitoring muscle rehabilitation
ActiveUS20160106994A1Accurate temporal averagingSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsUser inputMedicine
System and method for rehabilitating a muscle and monitoring such rehabilitation are provided, the system including a user input receiver for receiving stimulation parameter inputs from a user, a stimulator for generating stimulations to be applied to a patient's body based on the stimulation parameter inputs, a signal receiver to receive, detect, and record a signal containing an evoked potential generated by the body in response to the stimulations, a signal processor for processing the recorded signal, for example, by amplifying, filtering, digitizing and temporal averaging the recorded signal, a trigger detector to alert the signal processor module when stimulations are generated to enable synchronization of the response signal with the stimulus for accurate temporal averaging, and an output display for providing data representative of the evoked potential to the user.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
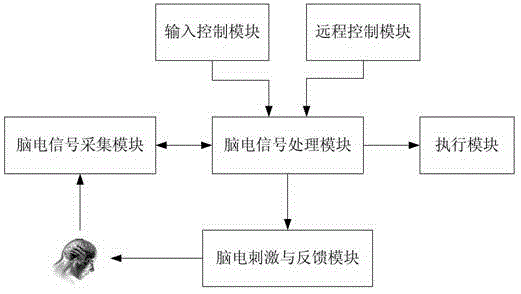
System and method for controlling brain computer interface (BCI) based on multimode fusion
InactiveCN102866775AReduce transfer rateImprove information transfer rateInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingBrain computer interfacingCrowds
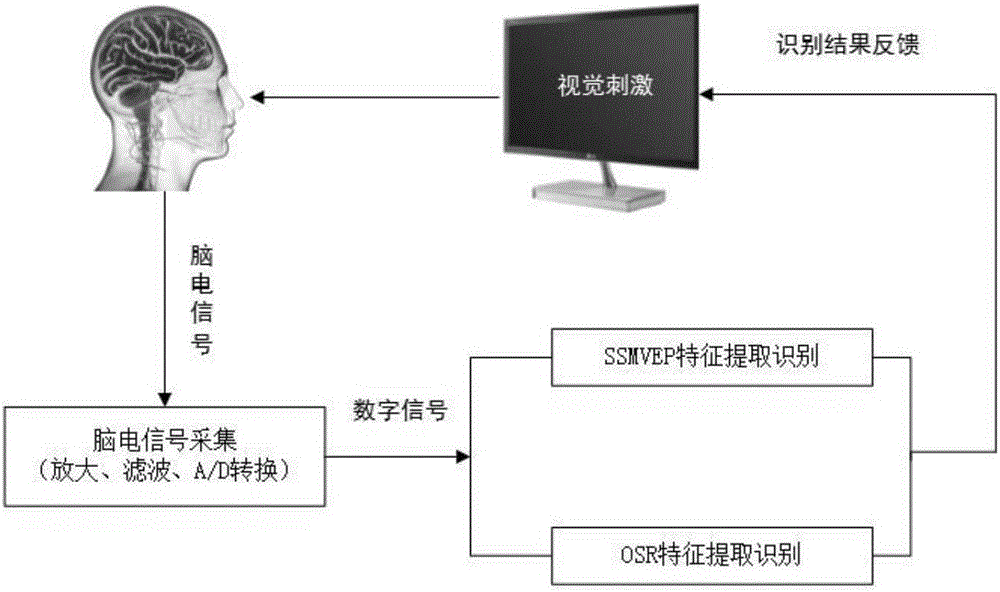
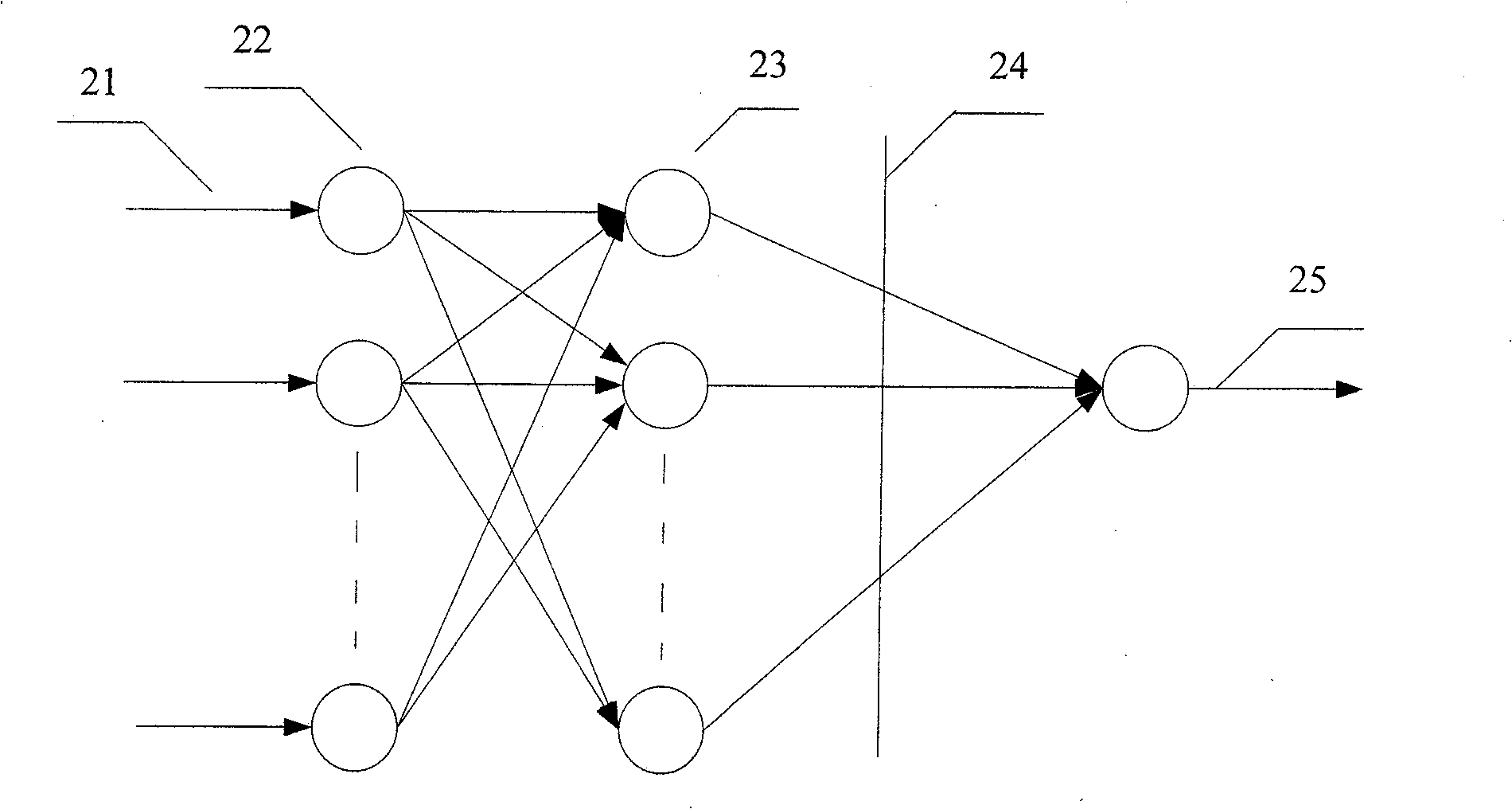
The invention provides a system and method for controlling a brain computer interface (BCI) based on multimode fusion. The system comprises a brain electrostimulation and feedback module, an electroencephalogram (EEG) signal acquisition module, an EEG signal processing module and an execution module, wherein the brain electrostimulation and feedback module is used for evoking an SSVEP (Steady State Visual Evoked Potential) and inducing an MI (Motor Imagery); the EEG signal acquisition module is used for acquiring EEG signals; the EEG signal processing module is used for extracting, identifying and classifying SSVEP characteristics and MI EEG characteristics in the EEG signals and feeding classified results which respectively correspond to the SSVEP characteristics and the MI EEG characteristics back to the brain electrostimulation and feedback module; and the execution module is used for executing the classified results. According to the system and the method, a multimode fusion BCI is constructed, so that the information transmission rate, reliability and flexibility of a control system are improved, the low information transmission rate of a BCI in a single MI mode is reduced, meanwhile, the visual burden under a single SSVEP task is reduced, and the adaptation crowds of the BIC-based control system are increased.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
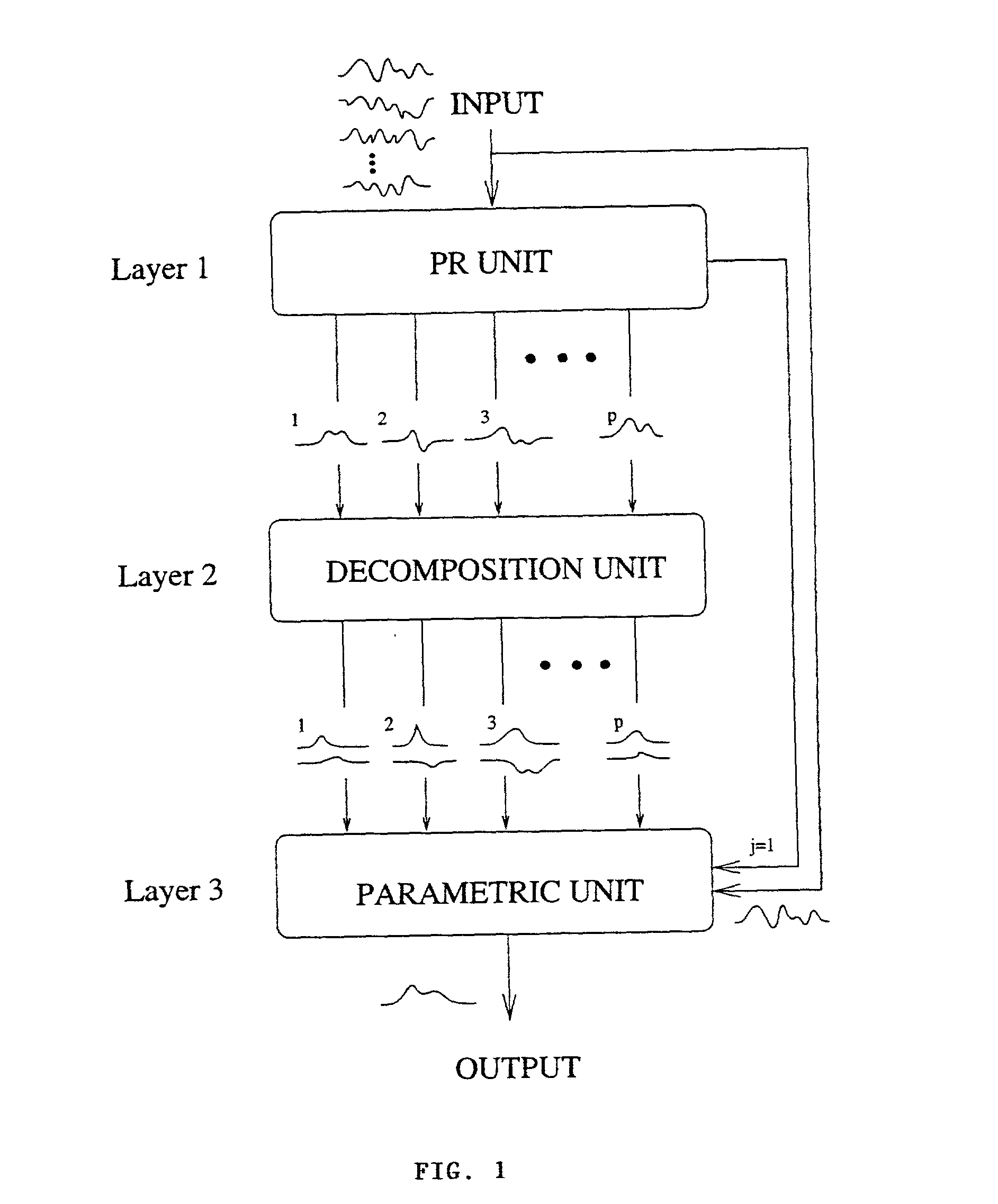
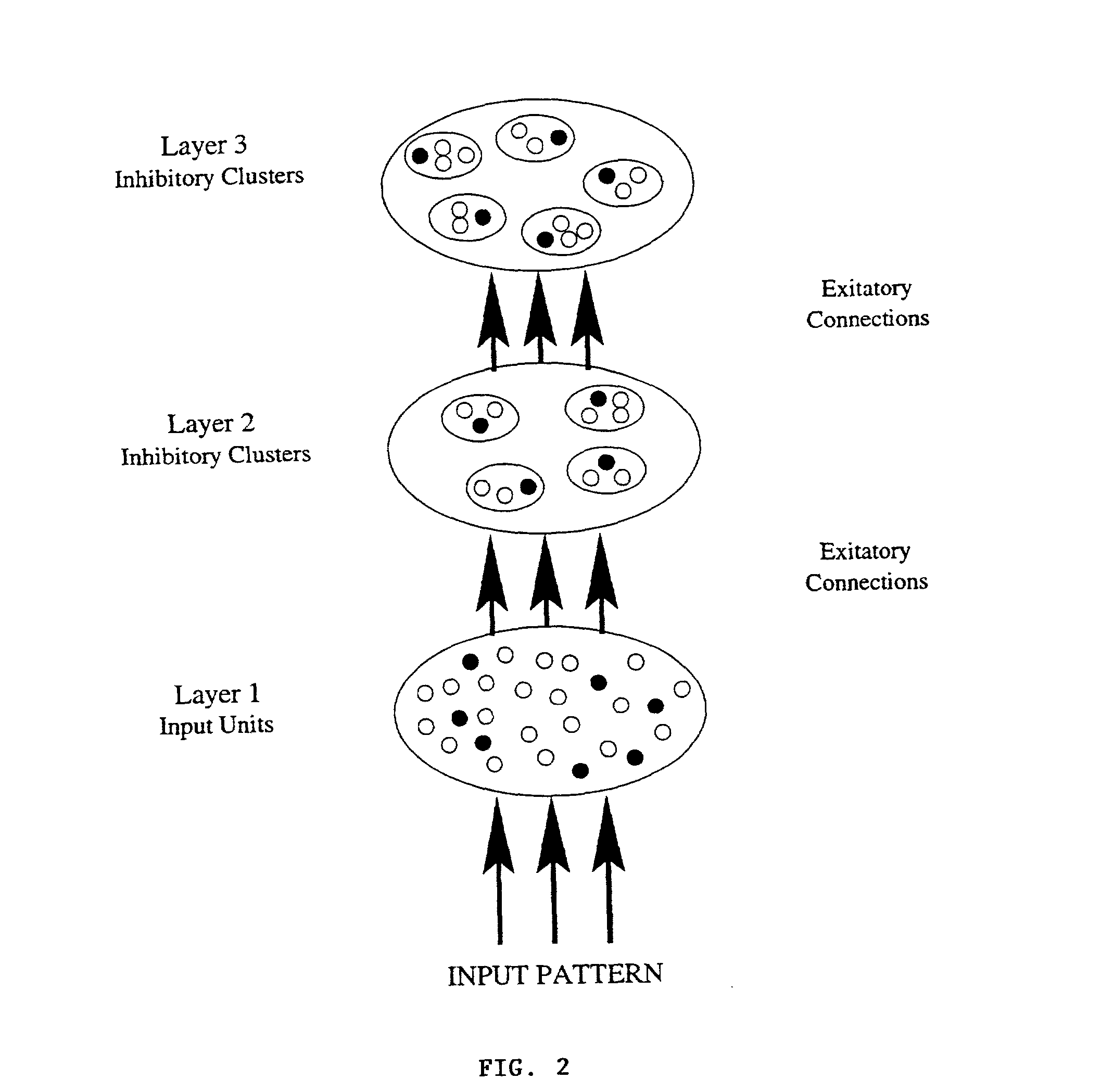
Method and apparatus for extracting low SNR transient signals from noise
InactiveUS6898582B2Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsMotor evoked potentials monitoringComputer science
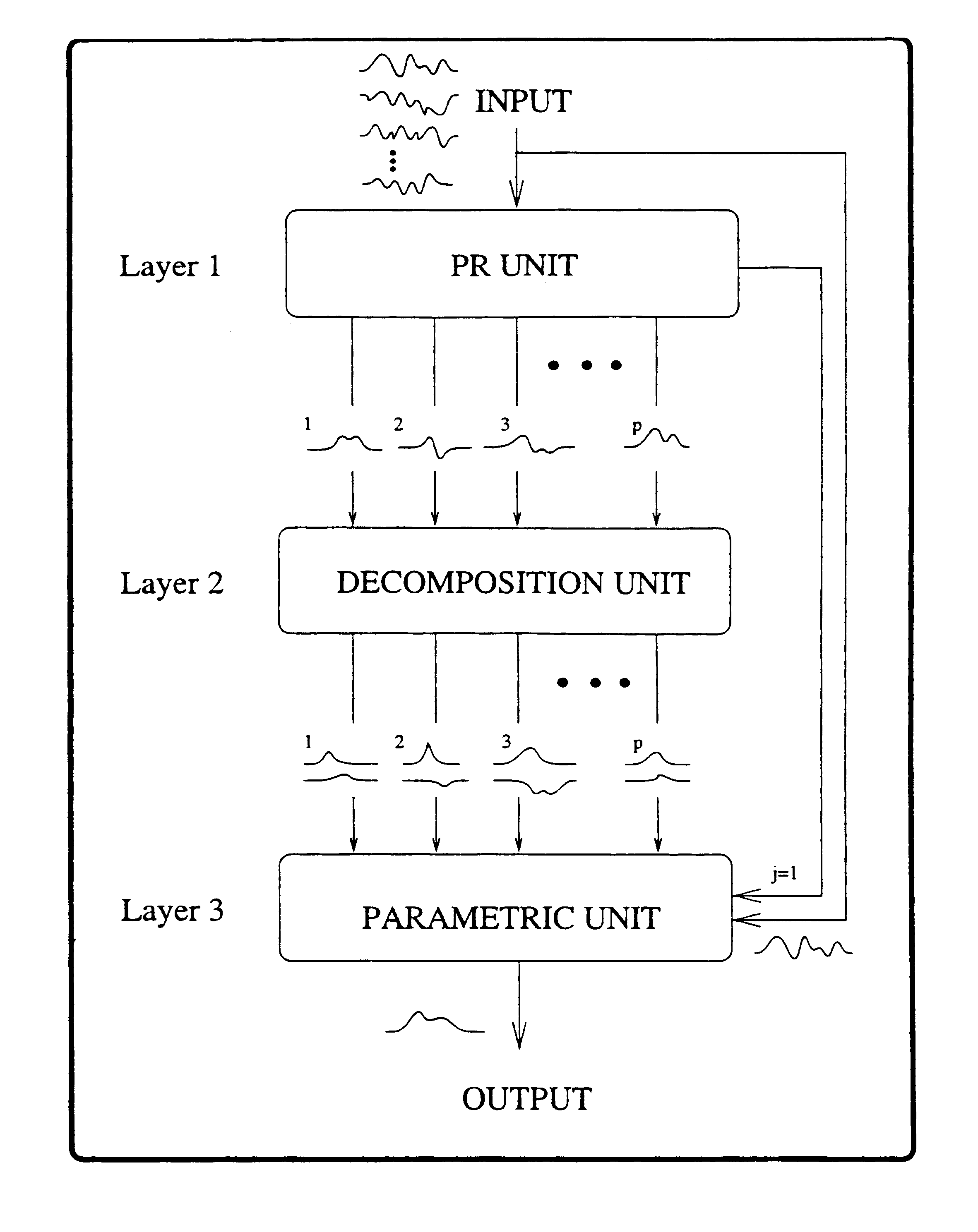
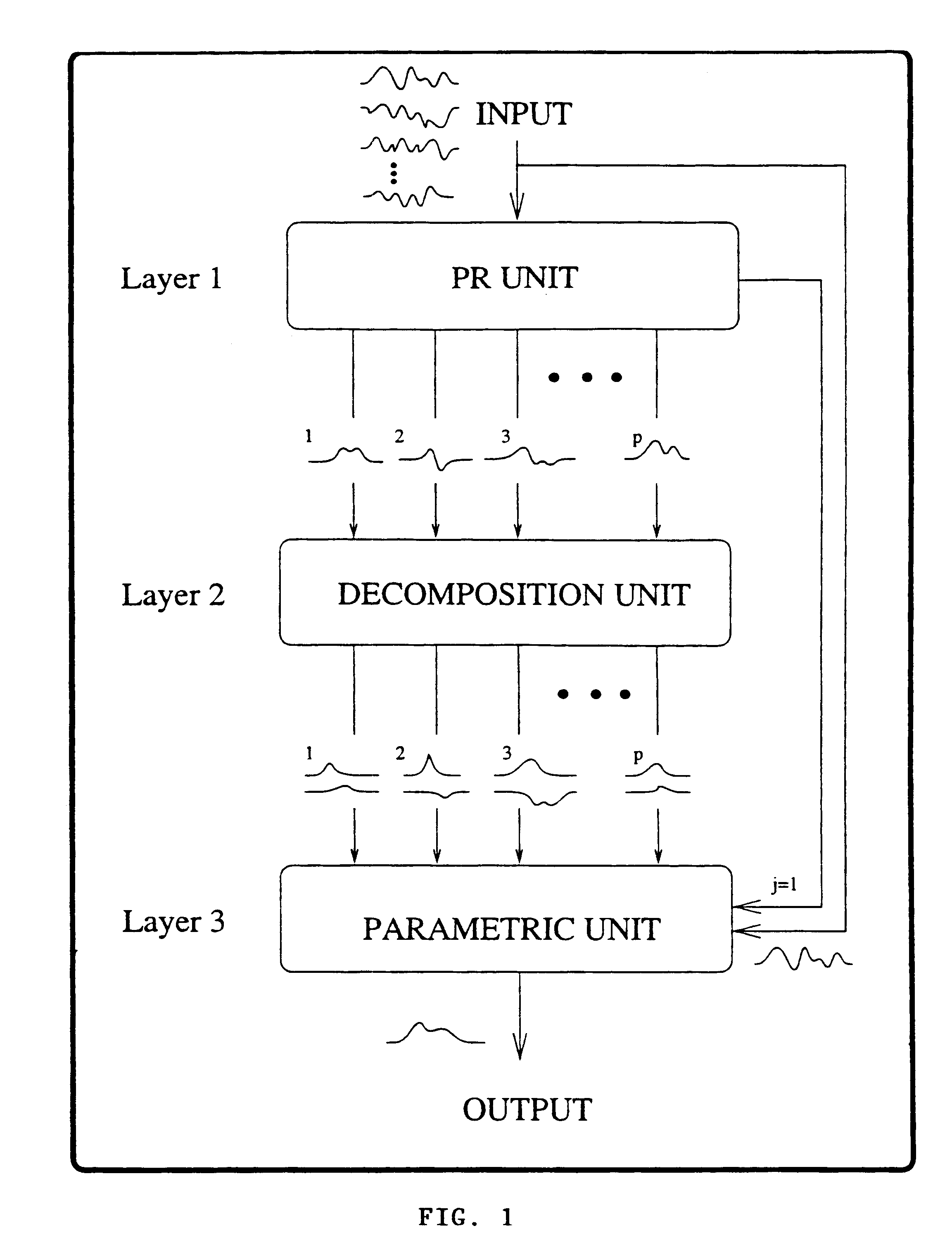
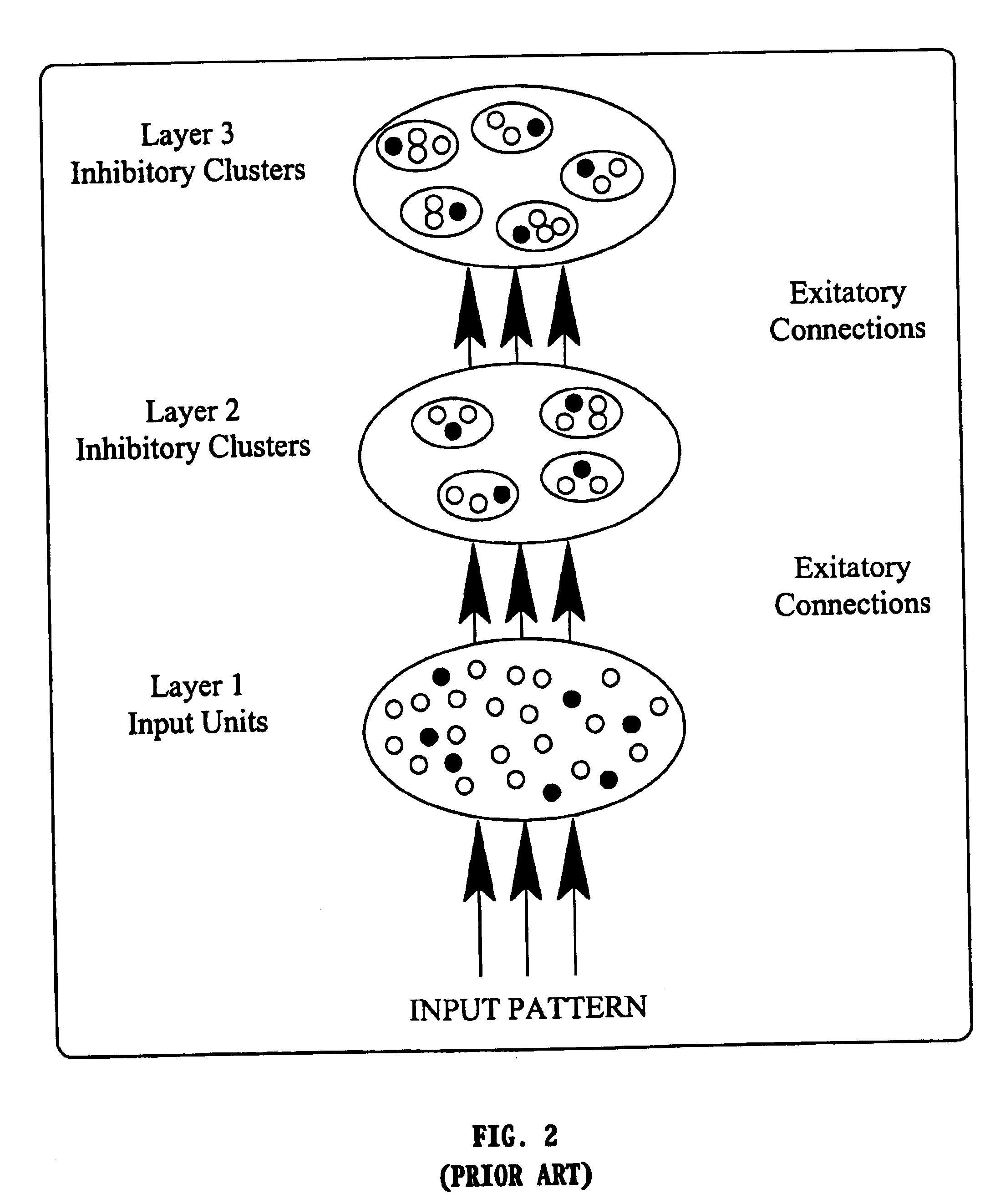
A method and apparatus for processing a composite signal generated by a transient signal generation mechanism to extract a repetitive low SNR transient signal, such as an evoked potential (EP) appearing in an electroencephalogram (EEG) generated in response to sensory stimulation, by: (a) dynamically identifying, via a learning process, the major transient signal types in the composite signal; (b) decomposing the identified major transient signal types into their respective constituent components; (c) synthesizing a parametric model emulating the transient signal generation mechanism; and (d) utilizing the model and the constituent components to identify and extract the low SNR transient signal from the composite signal.
Owner:ALGODYNE
Method for assessing brain function and portable automatic brain function assessment apparatus
A method and apparatus for performing rapid brain assessment may provide emergency triage to head trauma patients by analyzing a combination of spontaneous and evoked brain potentials. The spontaneous and evoked potentials are analyzed, and the results classified, to present a real-time assessment of a patient's brain, diagnosing any potential abnormalities therein.
Owner:BS HLDG +2
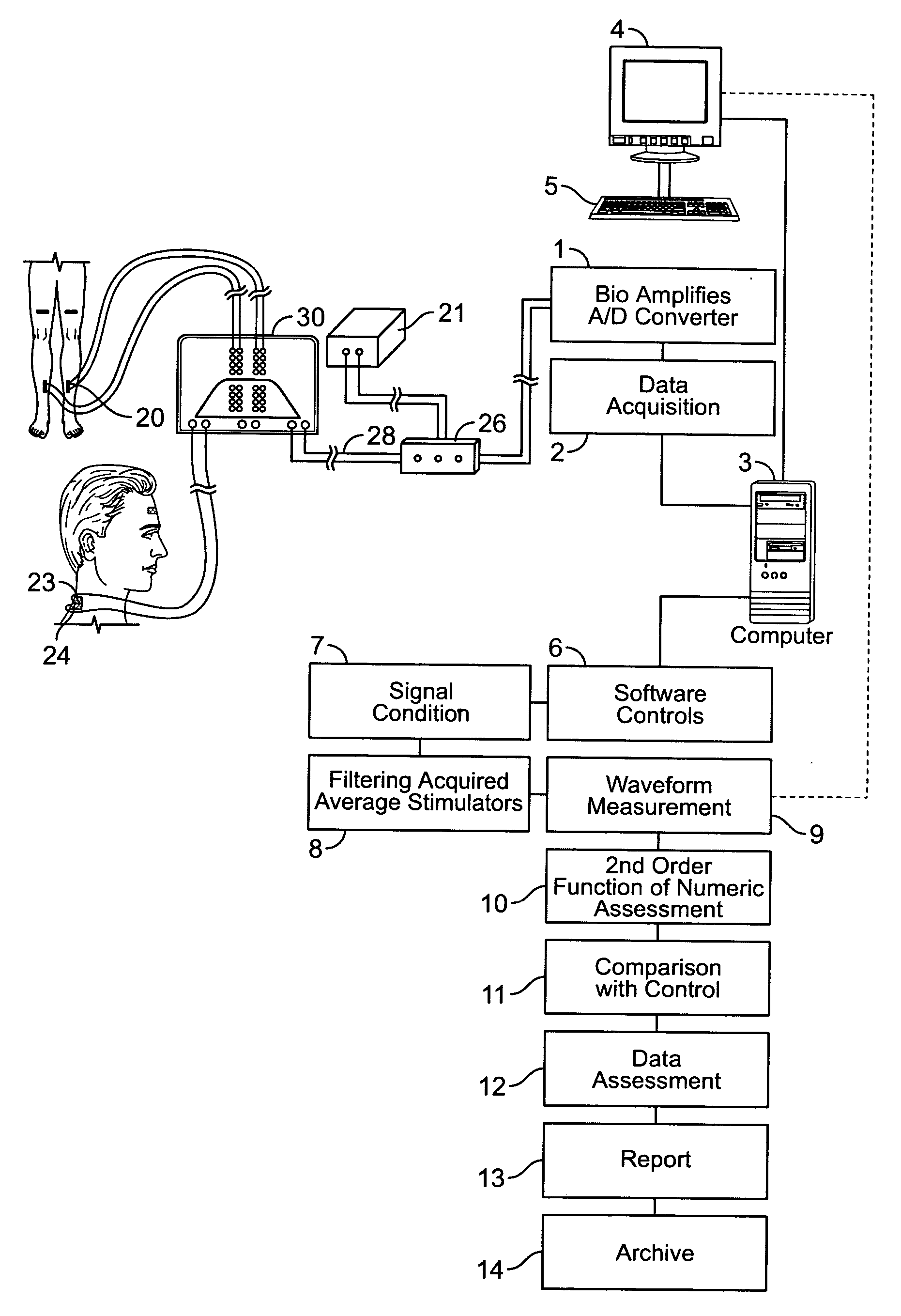
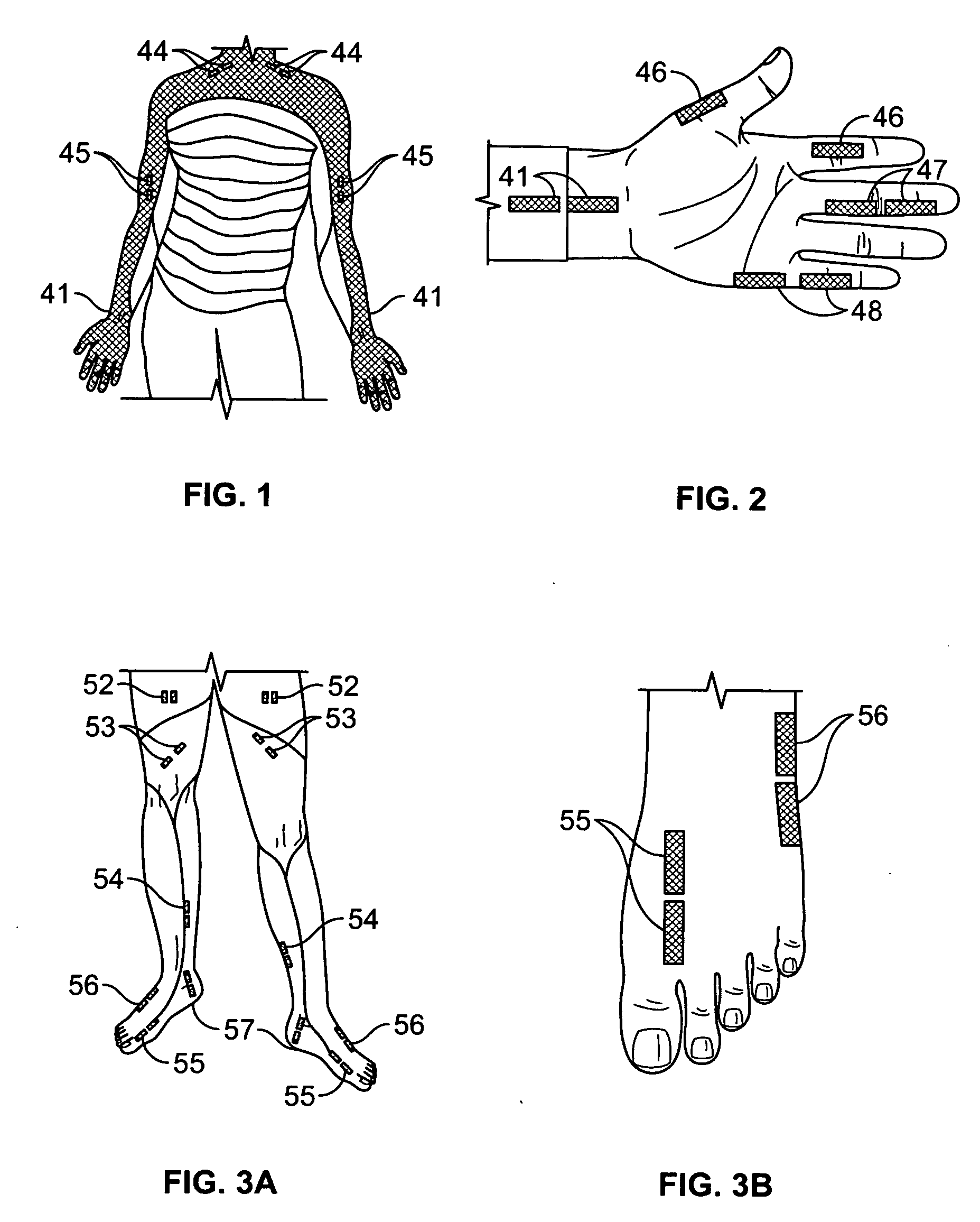
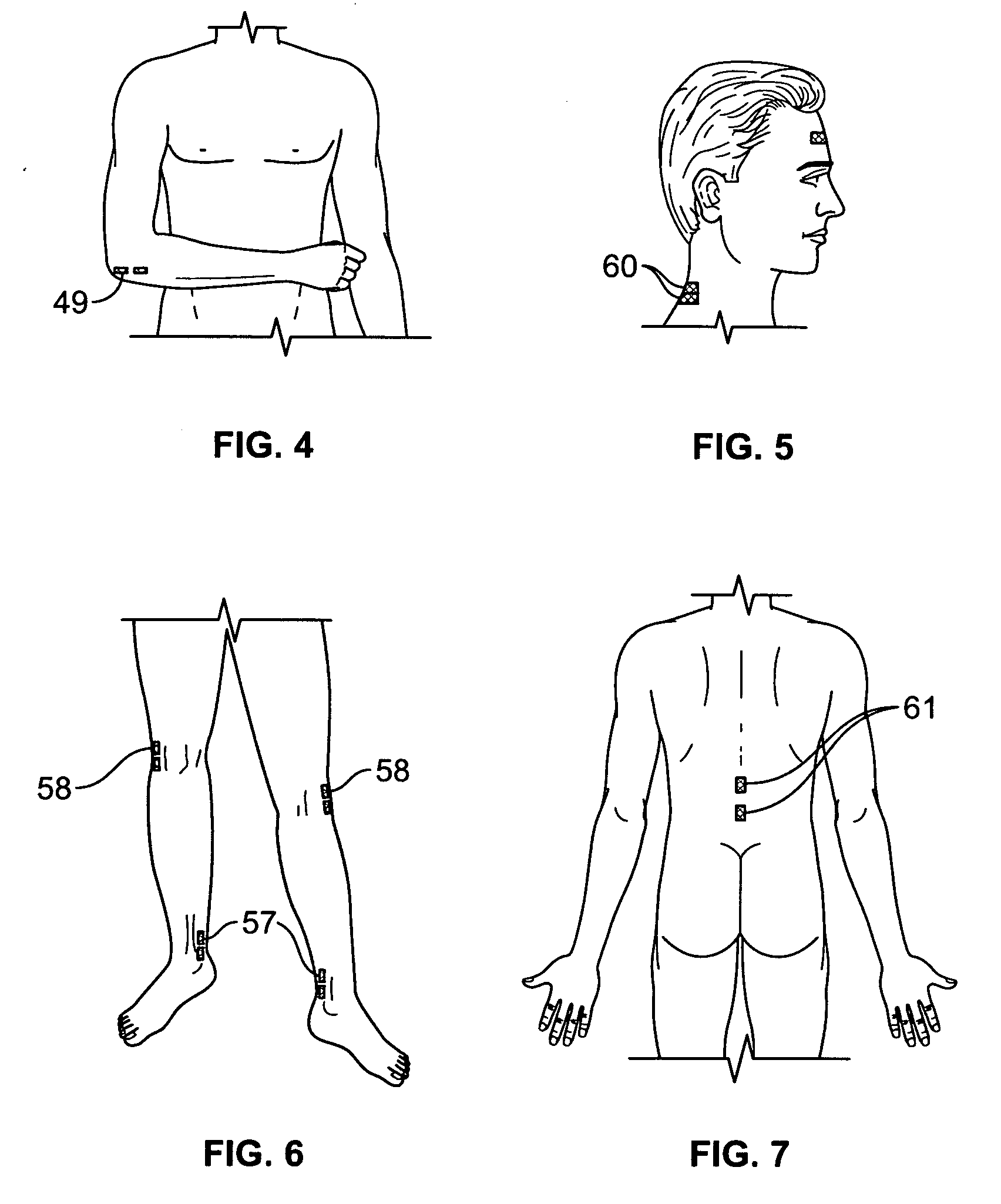
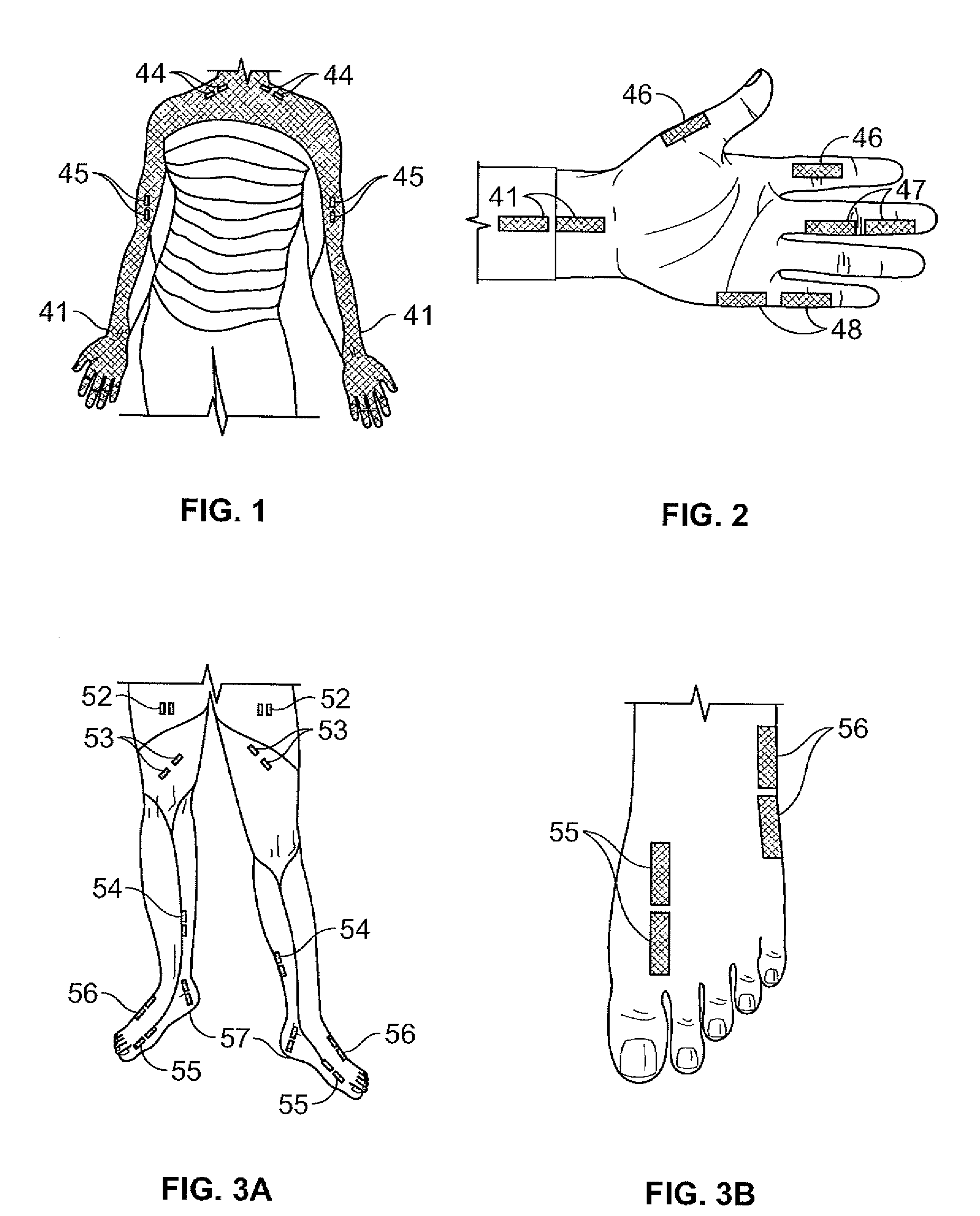
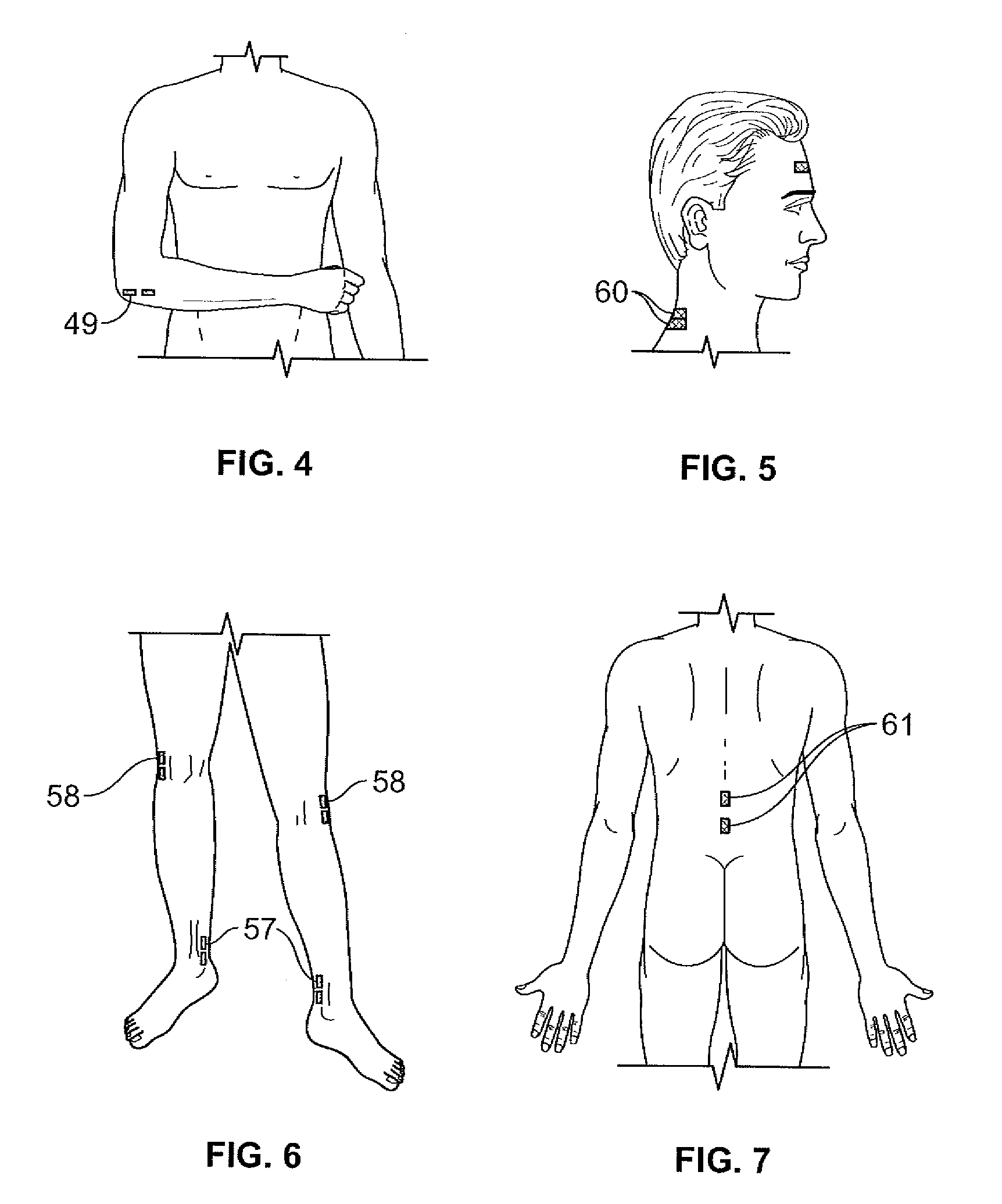
Method of using dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials in real-time for surgical and clinical management
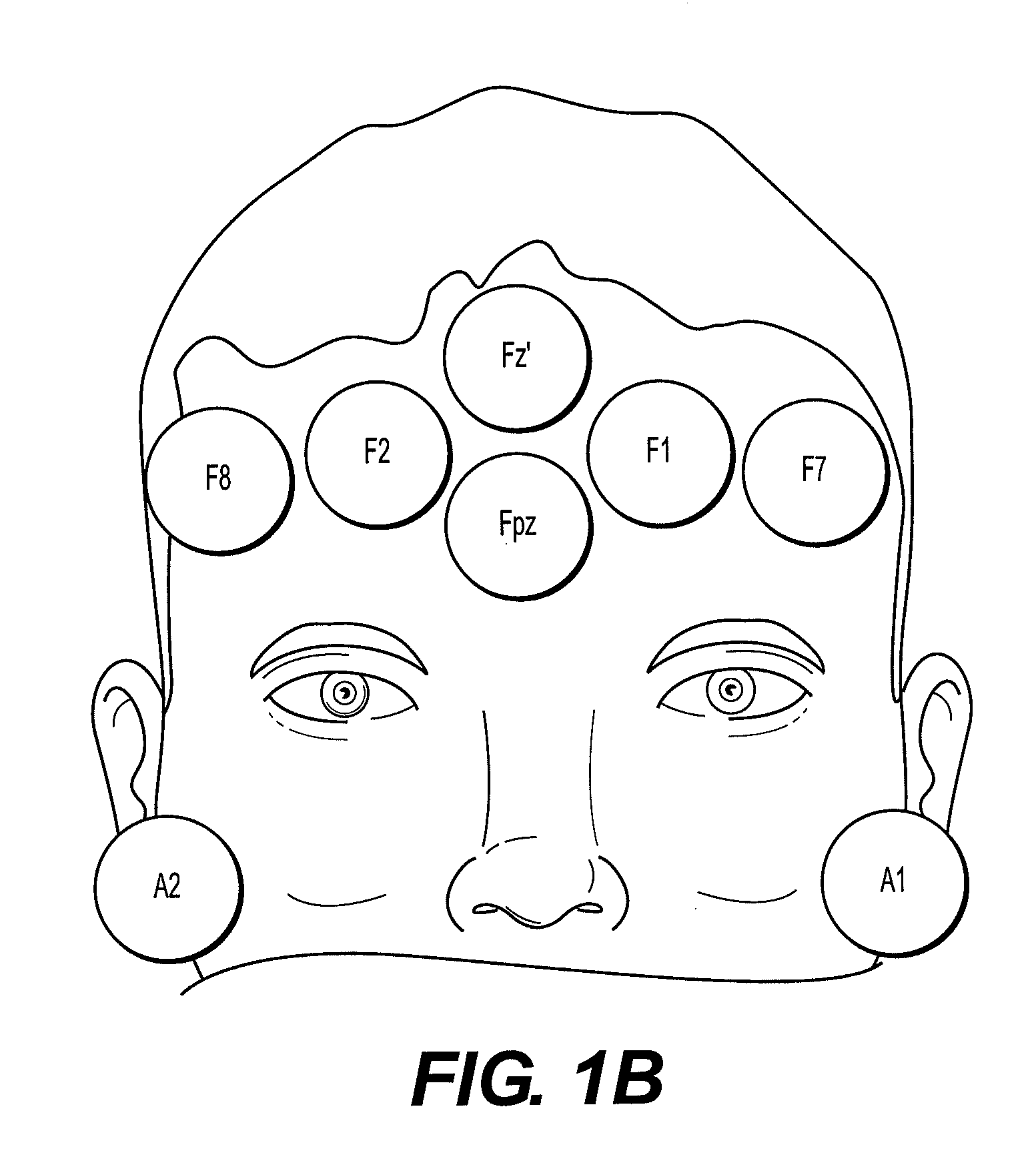
Methods, computer systems and apparatus are provided for neurophysiological assessment, specifically evaluation of mixed and dermatomal nerve conduction latencies and amplitudes, as well as electrophysiological evaluation of spontaneous electromyogram. Software guides the user through protocol selection, electrode placement, baseline determinations, comparisons to normal data, post-manipulation comparisons, displayed warning of pathological changes, archiving of data and report generation.
Owner:NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS
Implantable neurostimulation systems
ActiveUS8116875B2Promote ingrowthPrevent unintentional relative translationHead electrodesExternal electrodesMotor evoked potentials monitoringBiomedical engineering
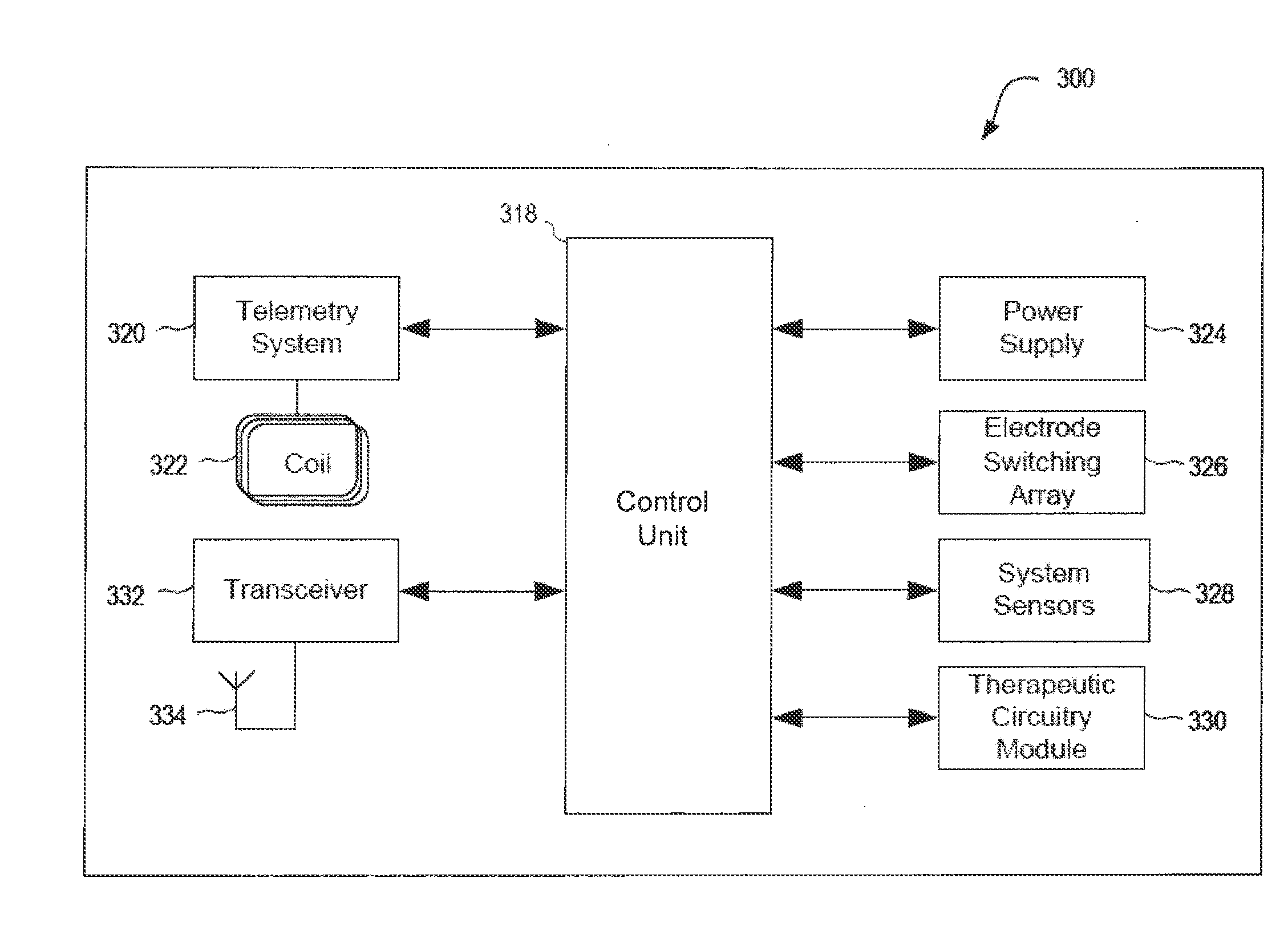
New and useful neurostimulation systems are provided that include an implantable pulse generator dimensioned and configured for implantation in the skull of a patient. The implantable pulse generator has an electrode operatively associated with a distal end portion thereof and can be provided with adjustment means, such as an adjustable biasing member or spring arranged between the electrode to the distal end portion of the pulse generator. Also provided are systems involving networked neurostimulators that are configured and adapted to work jointly in accordance with prescribed treatment protocol to effect a desired recovery from brain injury. Such networked neurostimulation systems are particularly advantageous for effecting relatively large and / or relatively distant regions of the brain. Additionally, systems and methods for motor-evoked potential (MEP)-based neuromodulation are provided. Further, AC and / or DC stimulation can be utilized, depending on the precise implementation.
Owner:NEUROPOINT MEDICAL
Systems and Methods For Neurological Evaluation and Treatment Guidance
InactiveUS20090247894A1Improve acquisitionSimple processElectroencephalographySensorsPoint of careAnalysis data
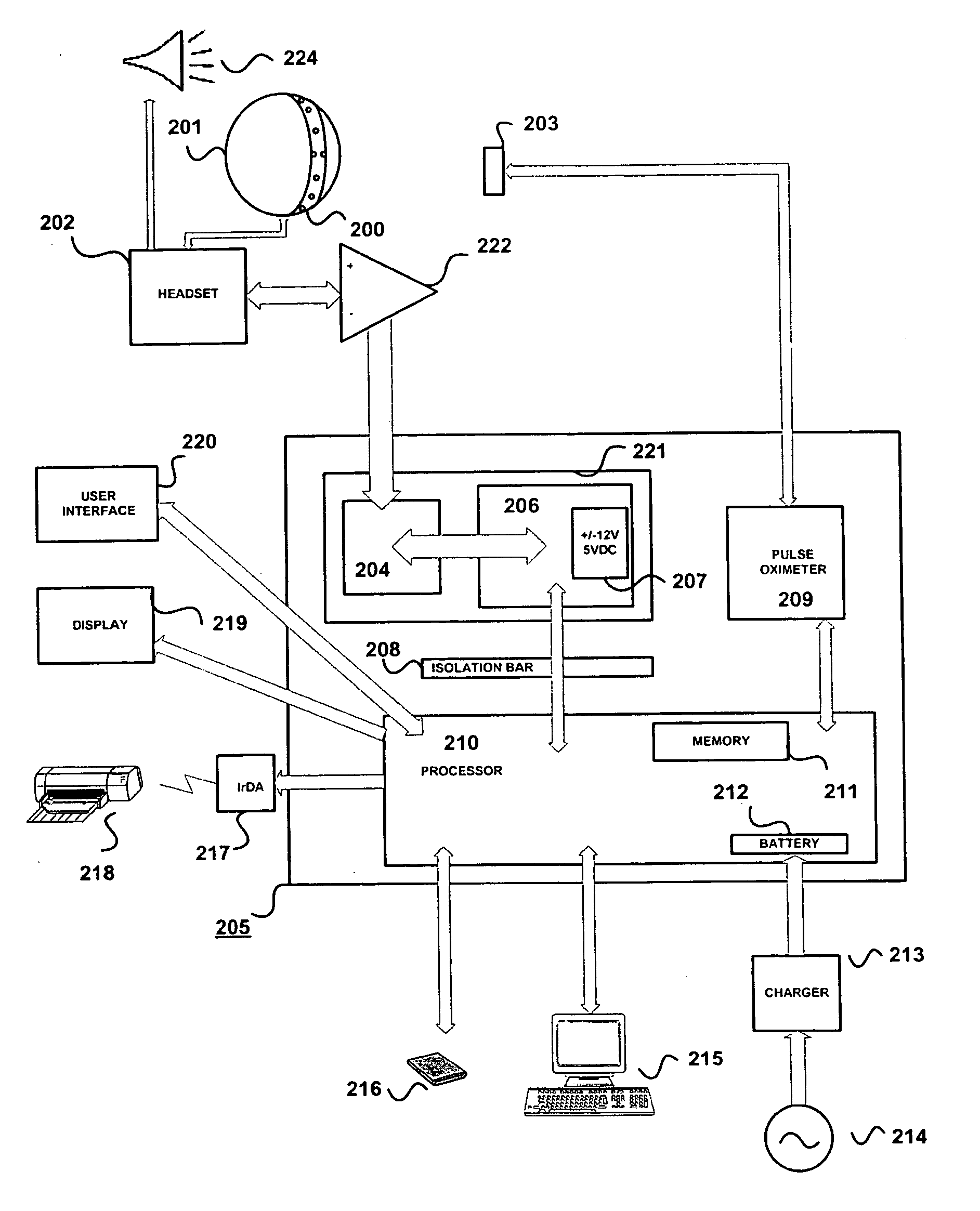
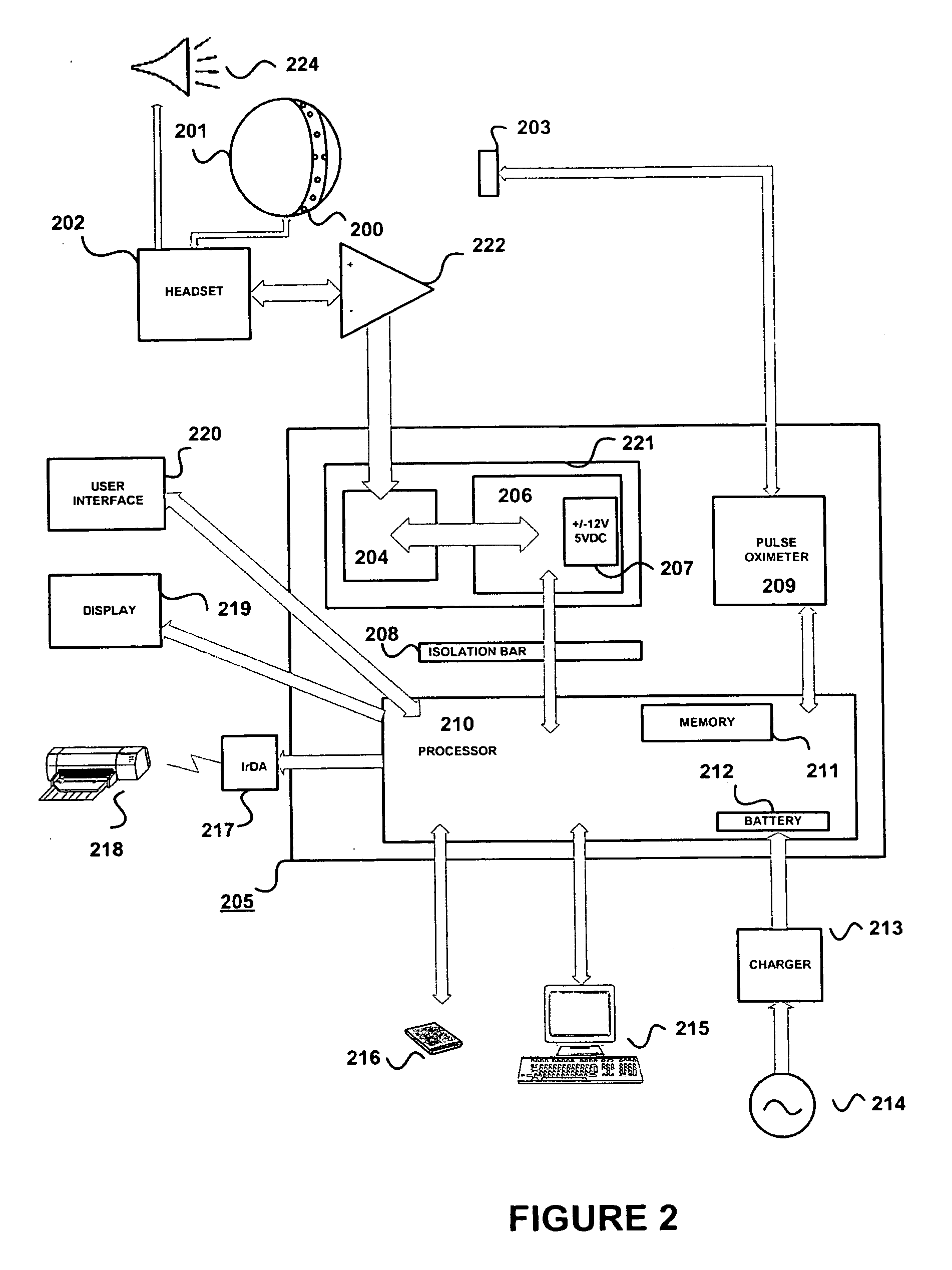
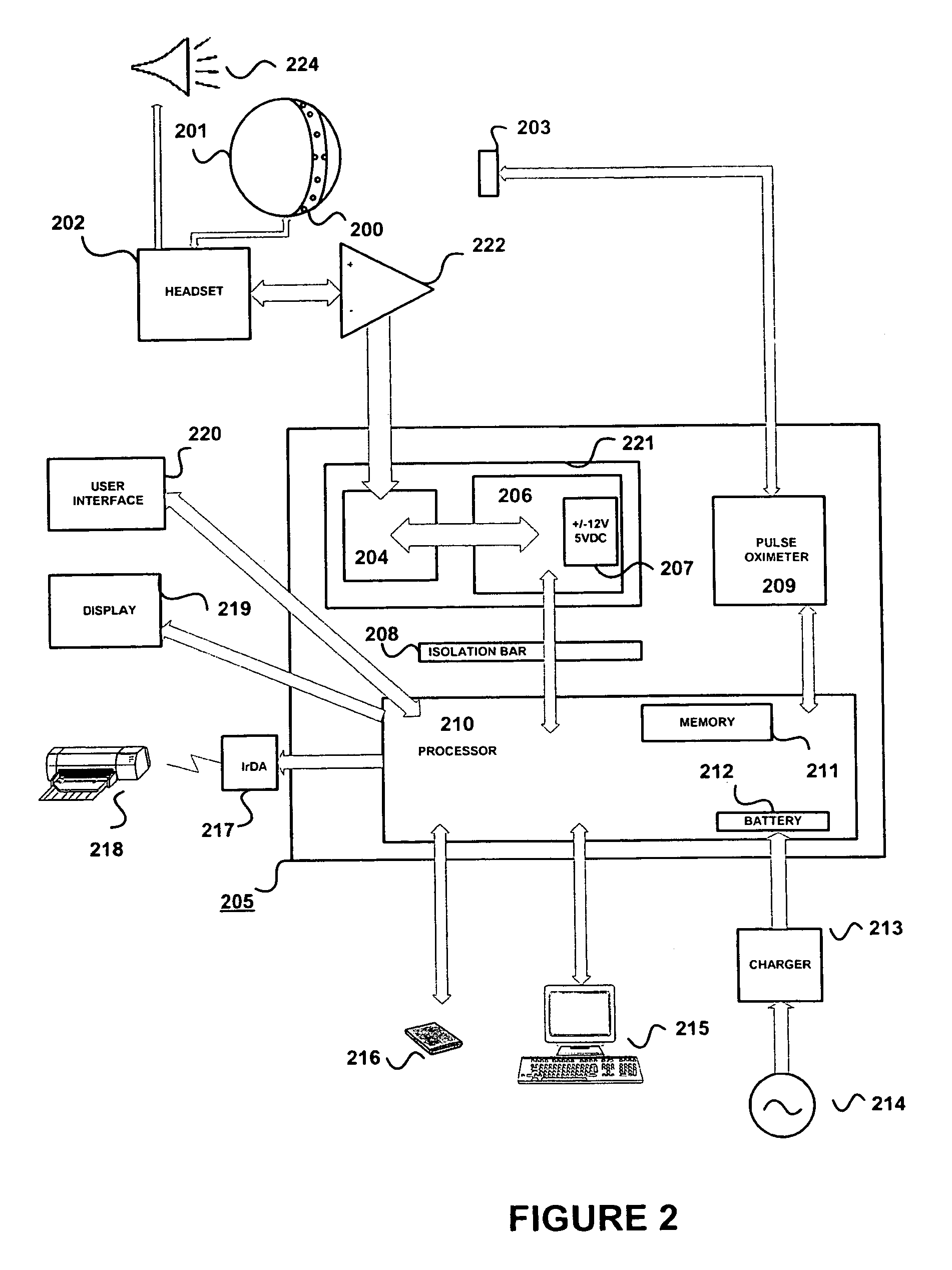
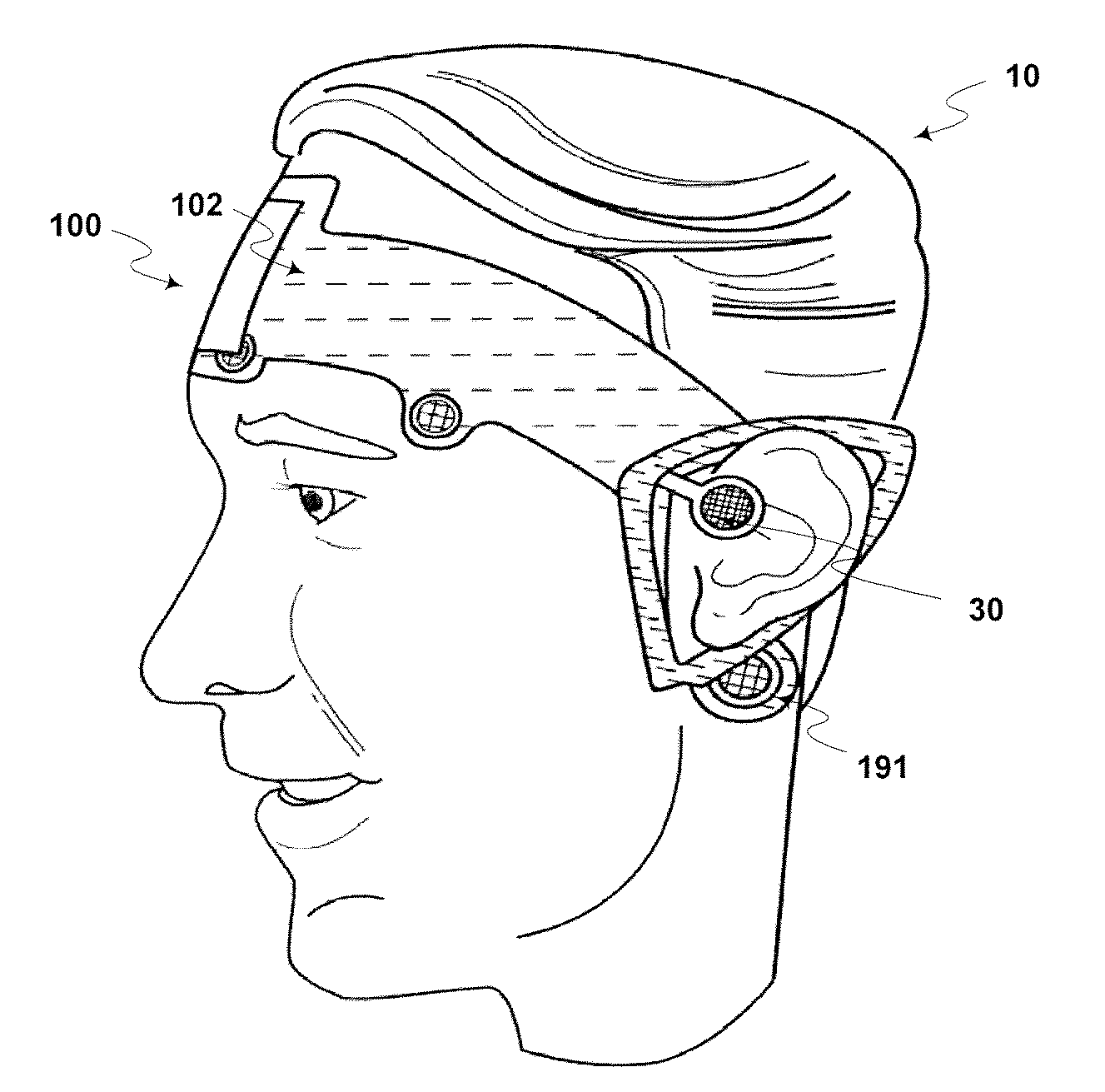
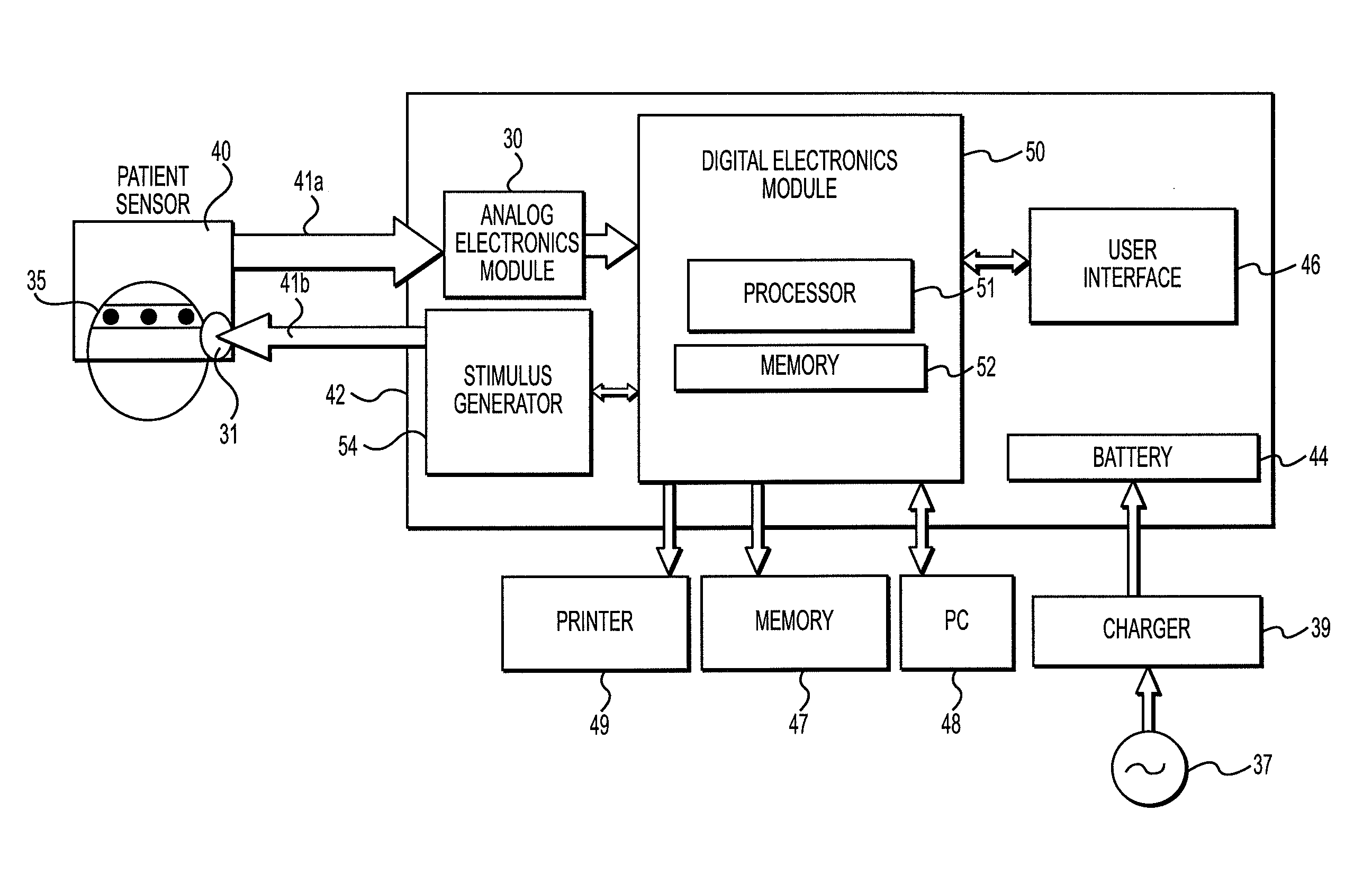
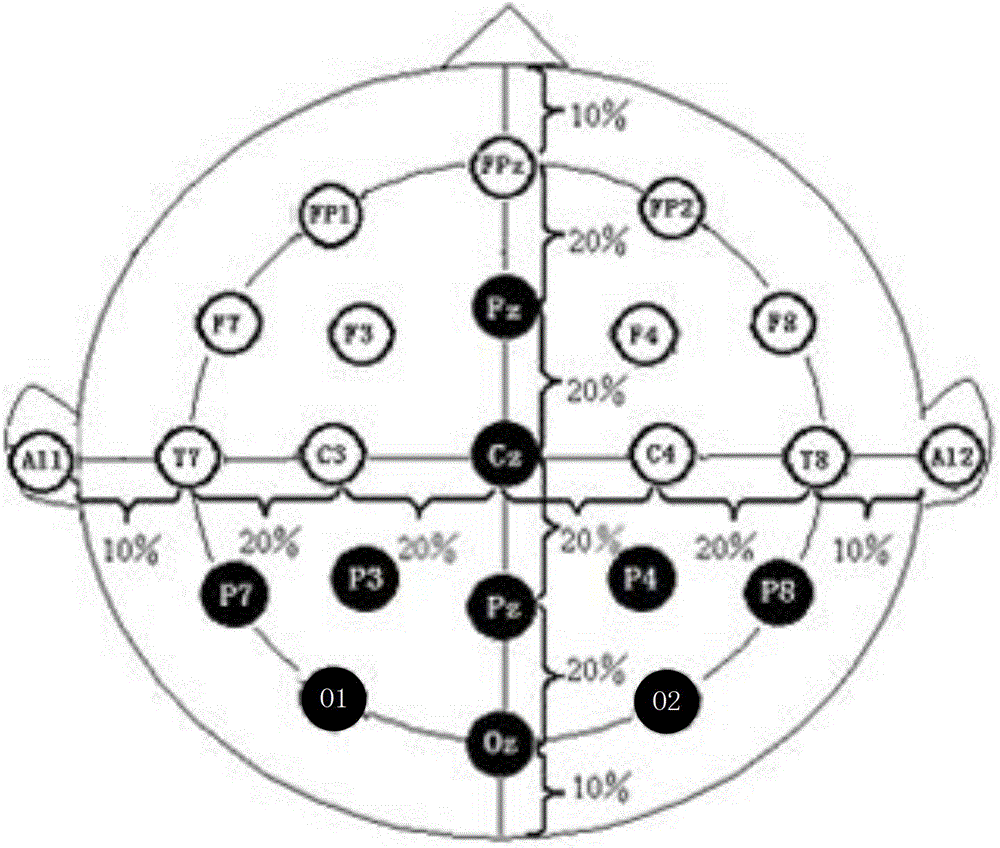
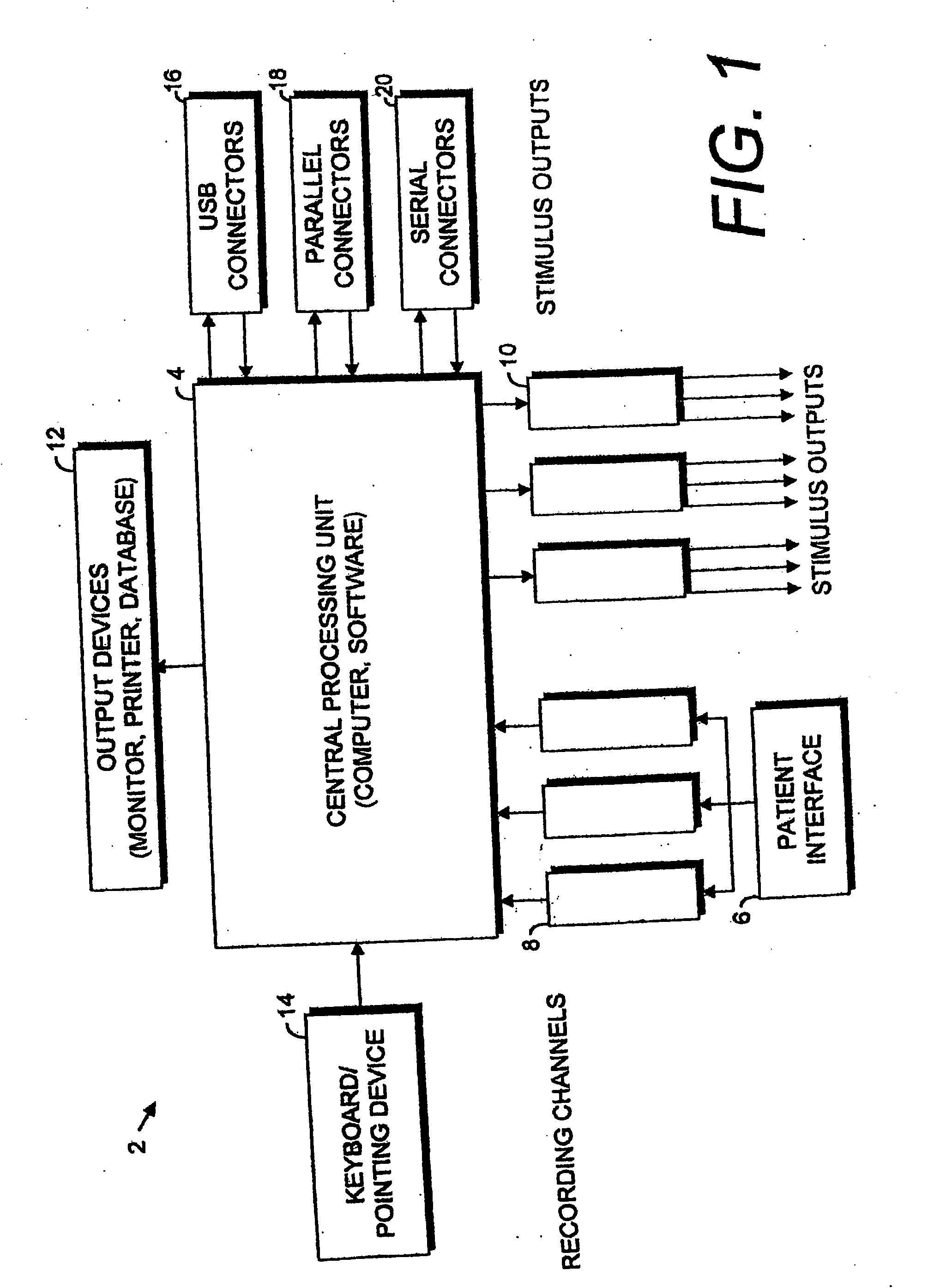
A system for acquiring and processing a subject's brain electrical activity is provided. The system includes at least one electrode, at least one analog amplifier channel, an analog-to-digital converter, a stimulus generator, and a digital signal processor configured to perform a harmonic signal analysis algorithm. The at least one analog amplifier channel, the analog-to-digital converter, and the digital signal processor are configured on a single integrated physical circuit. All the components of the system are configured to reside on a common portable unit to make the system easily applicable at the point-of-care. The system records and processes a subject's spontaneous neuroelectric signals as well as evoked potentials in real-time, and generates analyzed data representative of a subject's neurophysiological condition.
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC
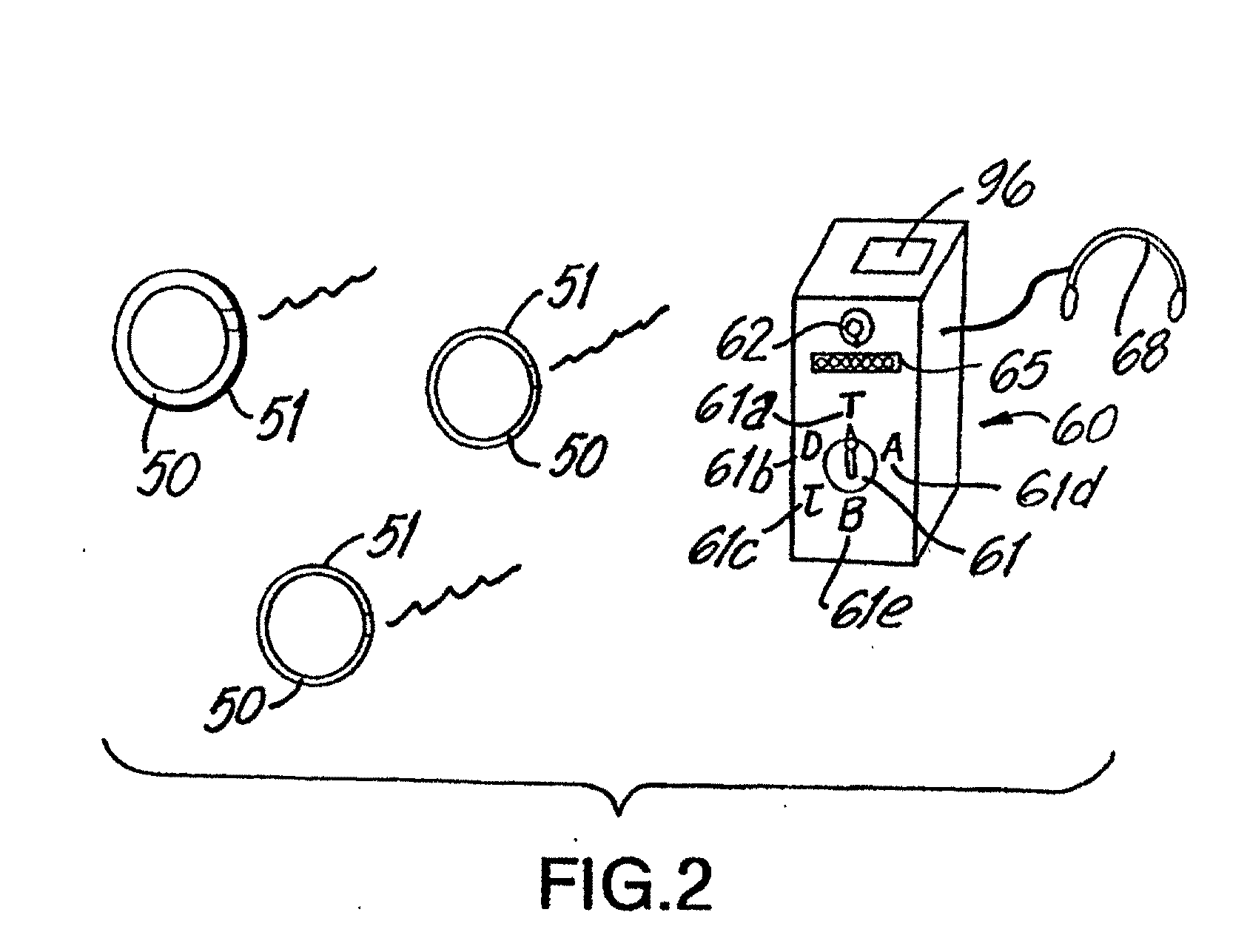
Method and device for point-of-care neuro-assessment and treatment guidance
A method and apparatus for providing an objective assessment of the neurological state of a patient using a field-portable neuro-assessment device is described. The method includes placing an electrode set on the patient's head, acquiring spontaneous brain electrical signals and evoked potential signals from the patient through the electrode set, processing the signals using a handheld base unit, and displaying a result indicating the probability of the patient's neurological signal being normal or abnormal. The neuro-assessment device allows for a rapid, on-site neurological evaluation by an emergency medical technician, triage nurse, or any other medical personnel to identify patients with neurological disorders who may require immediate medical attention.
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC +1
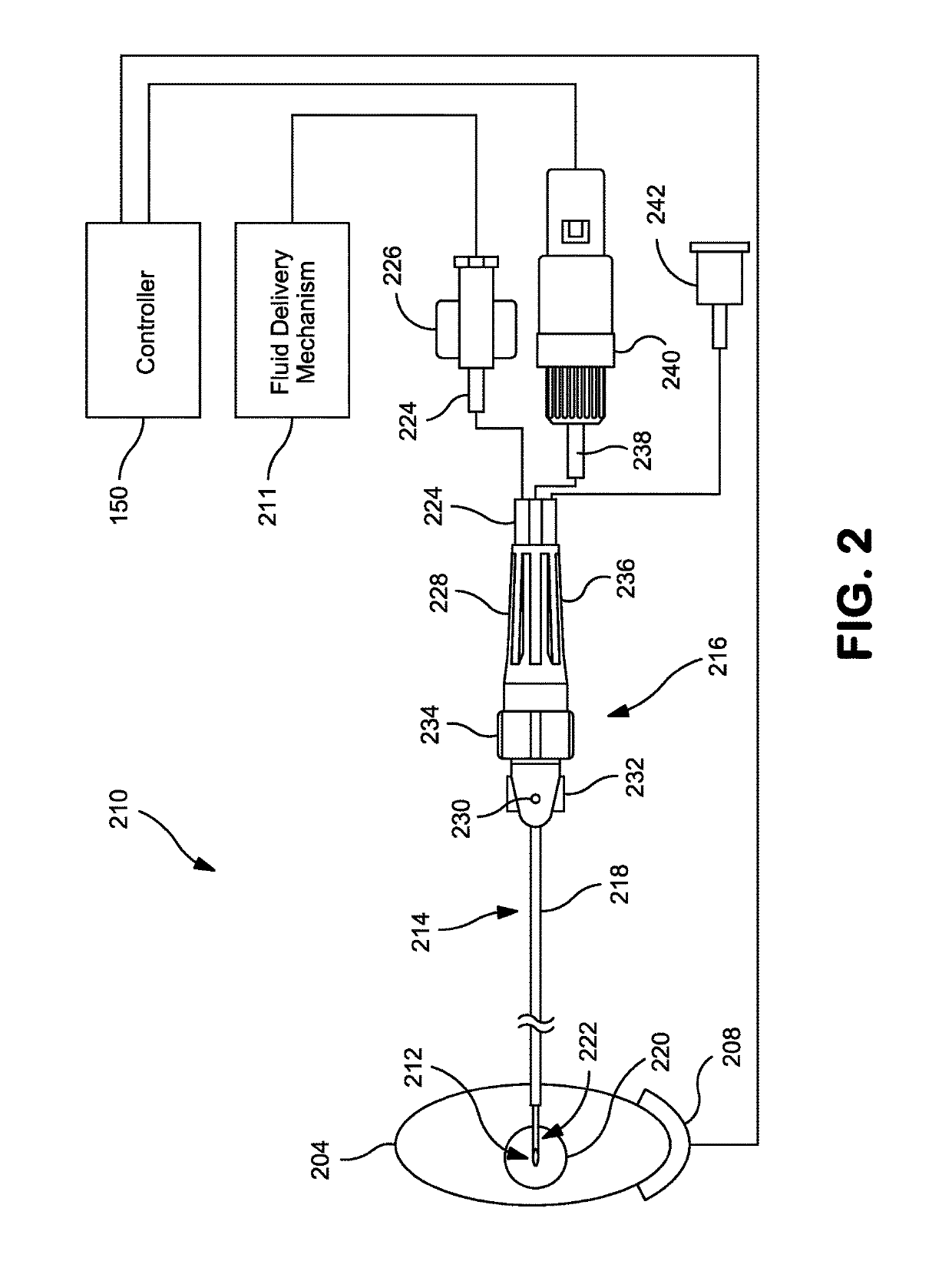
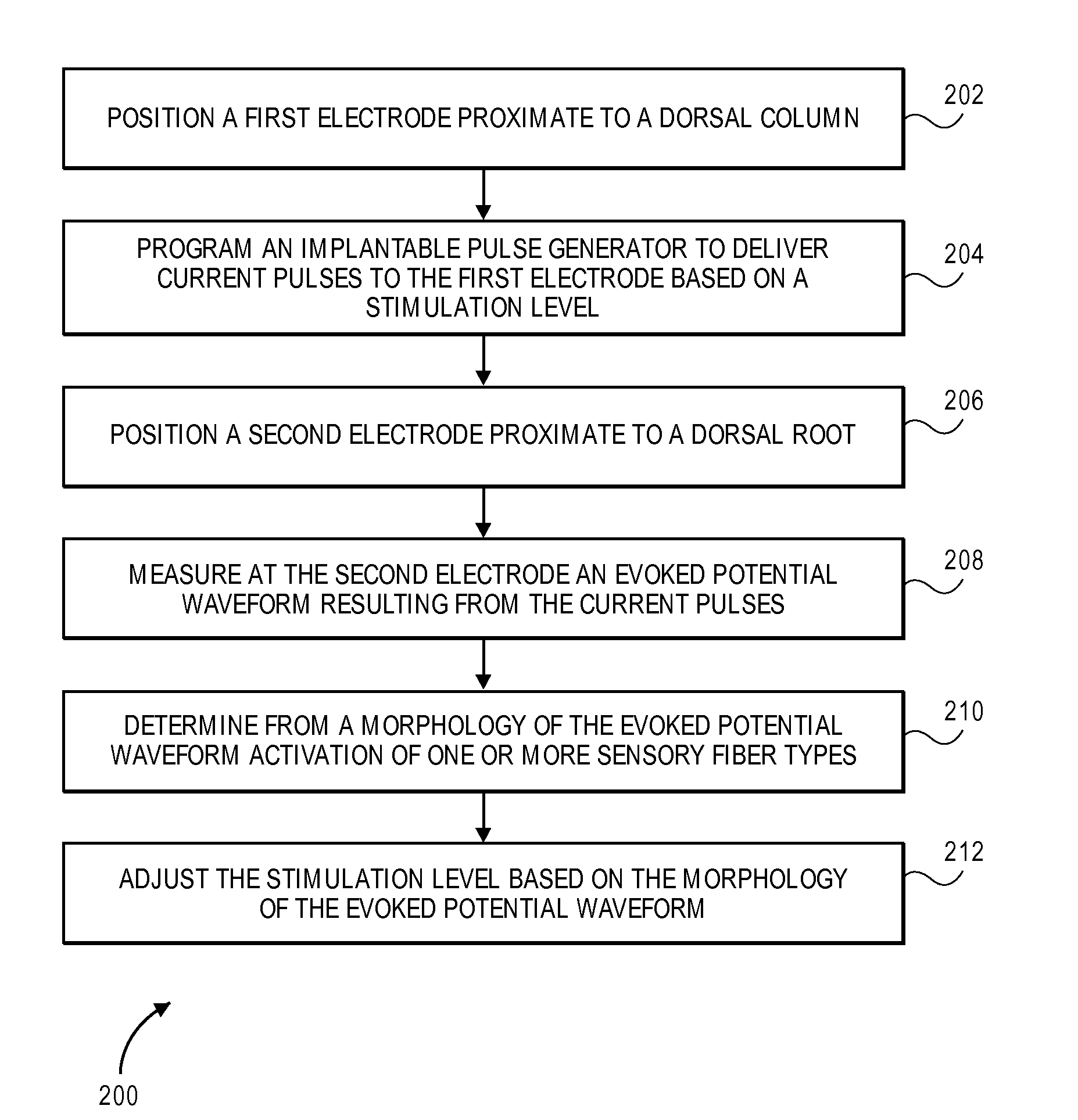
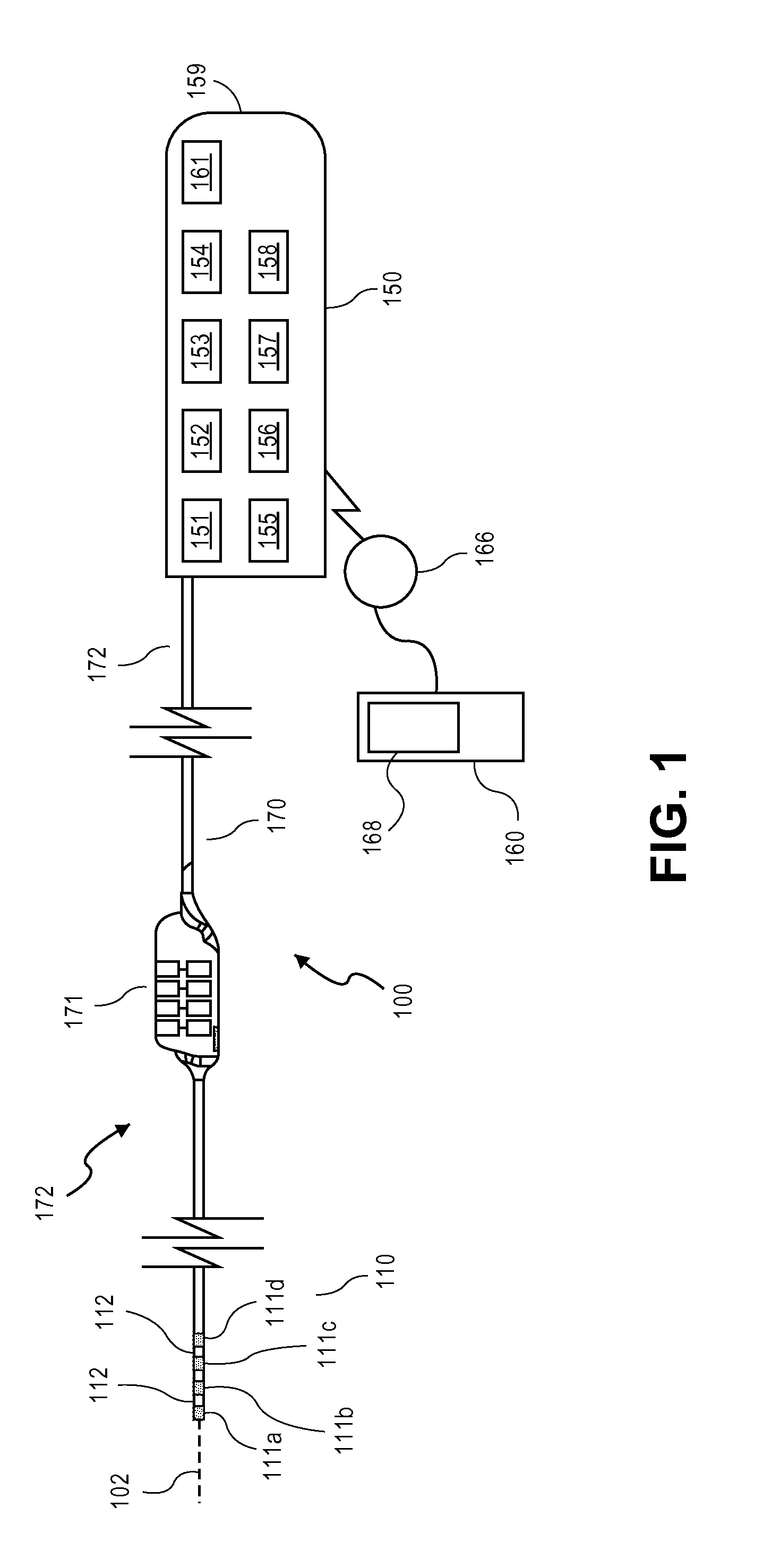
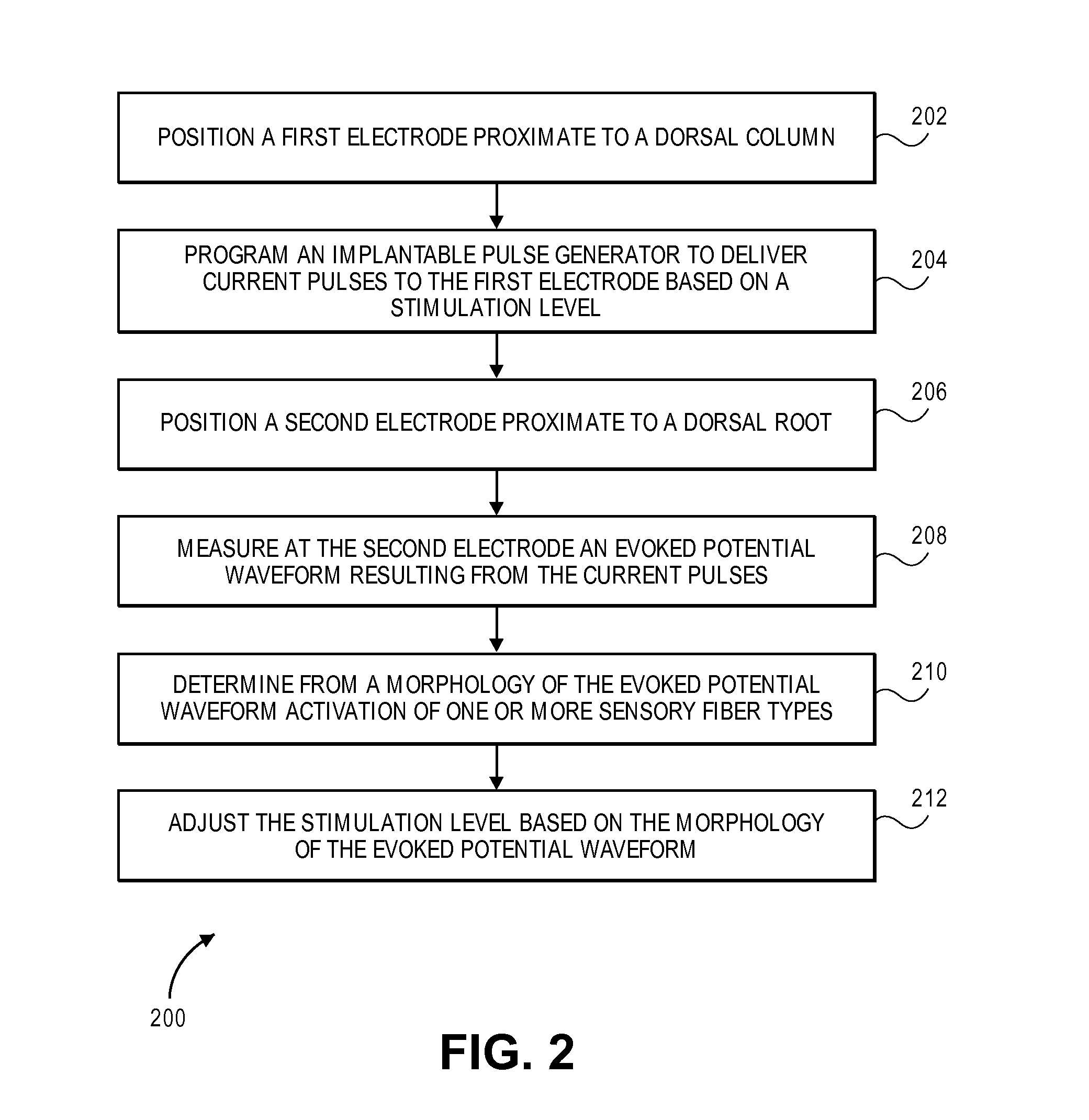
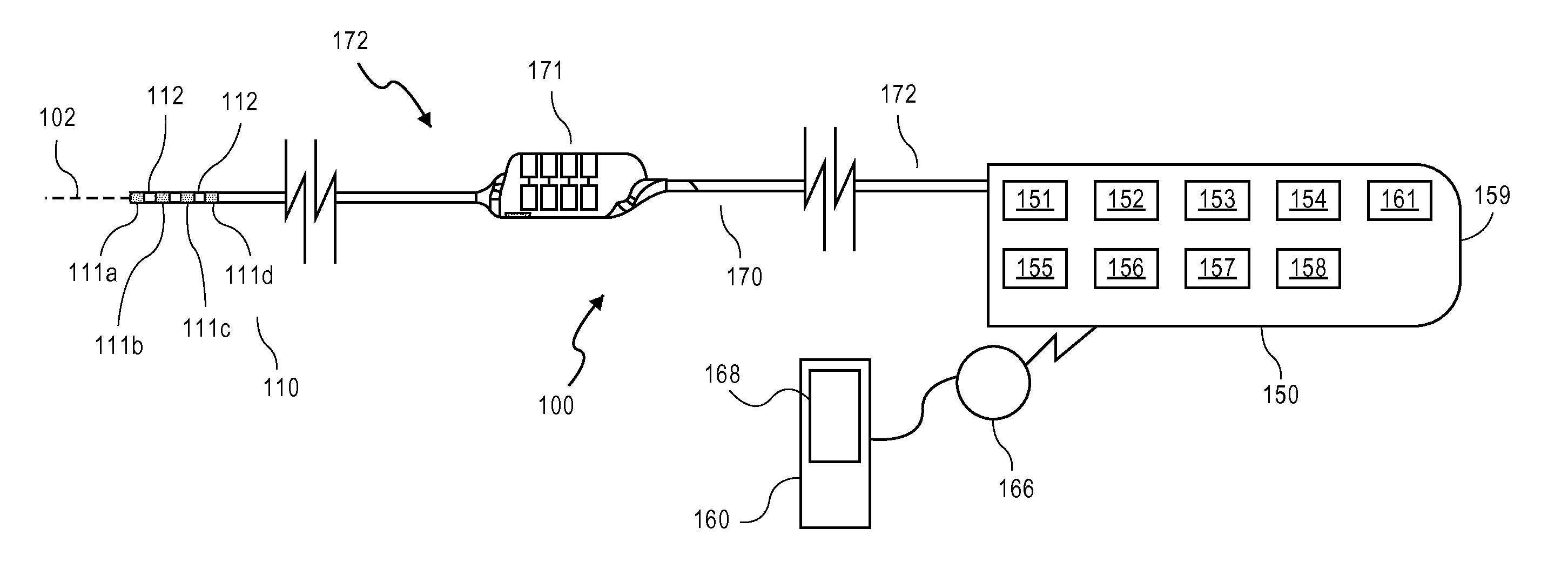
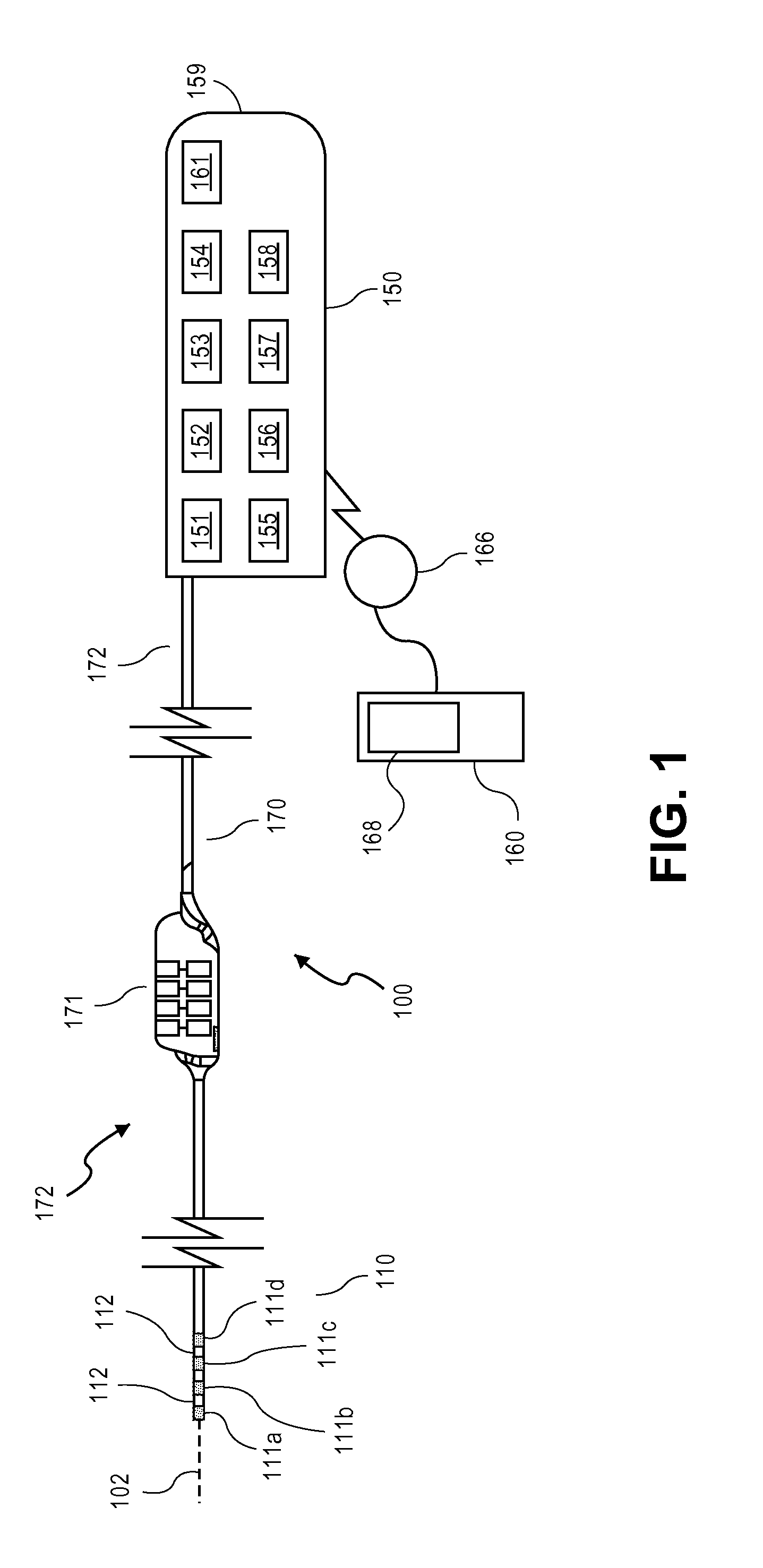
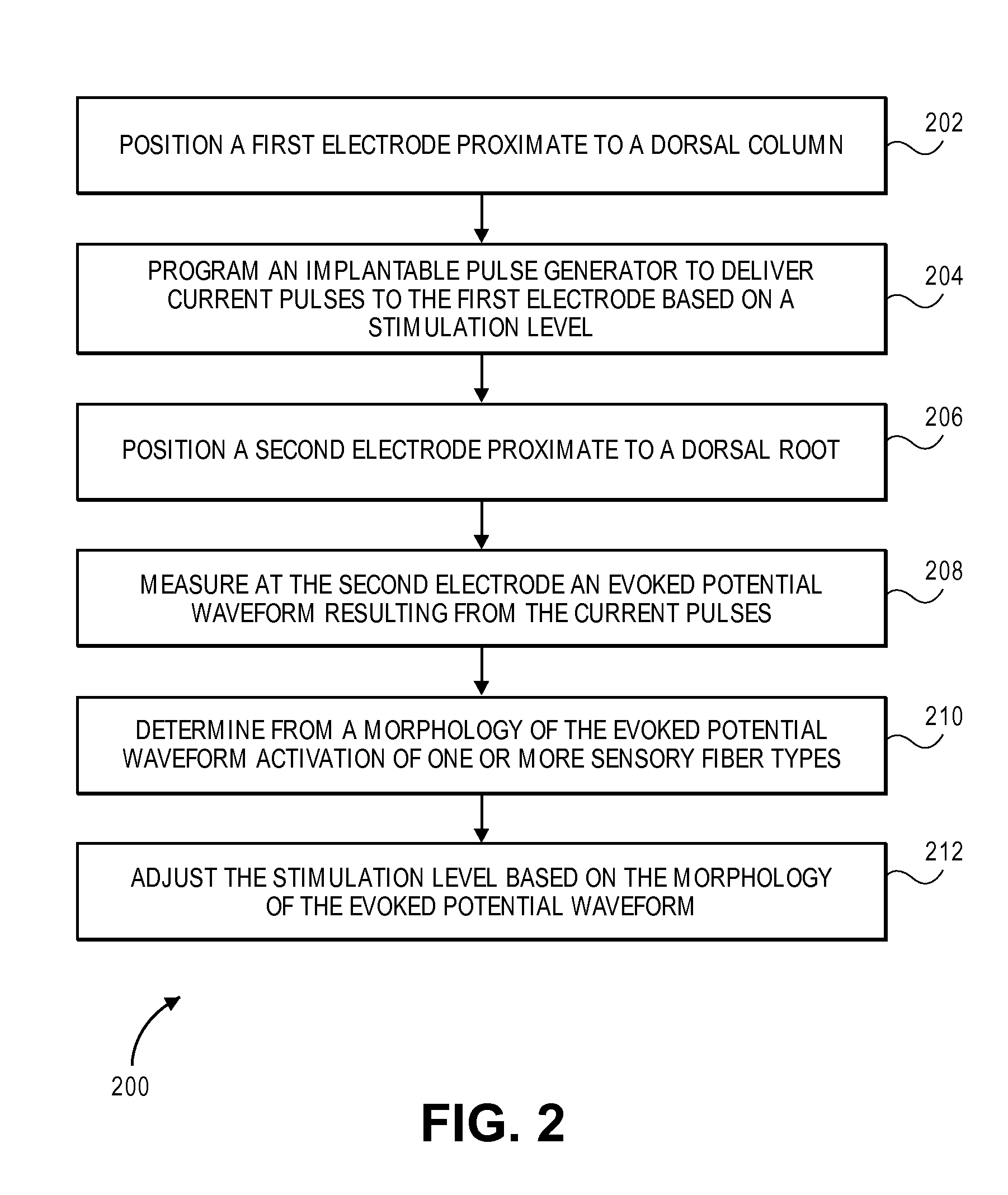
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
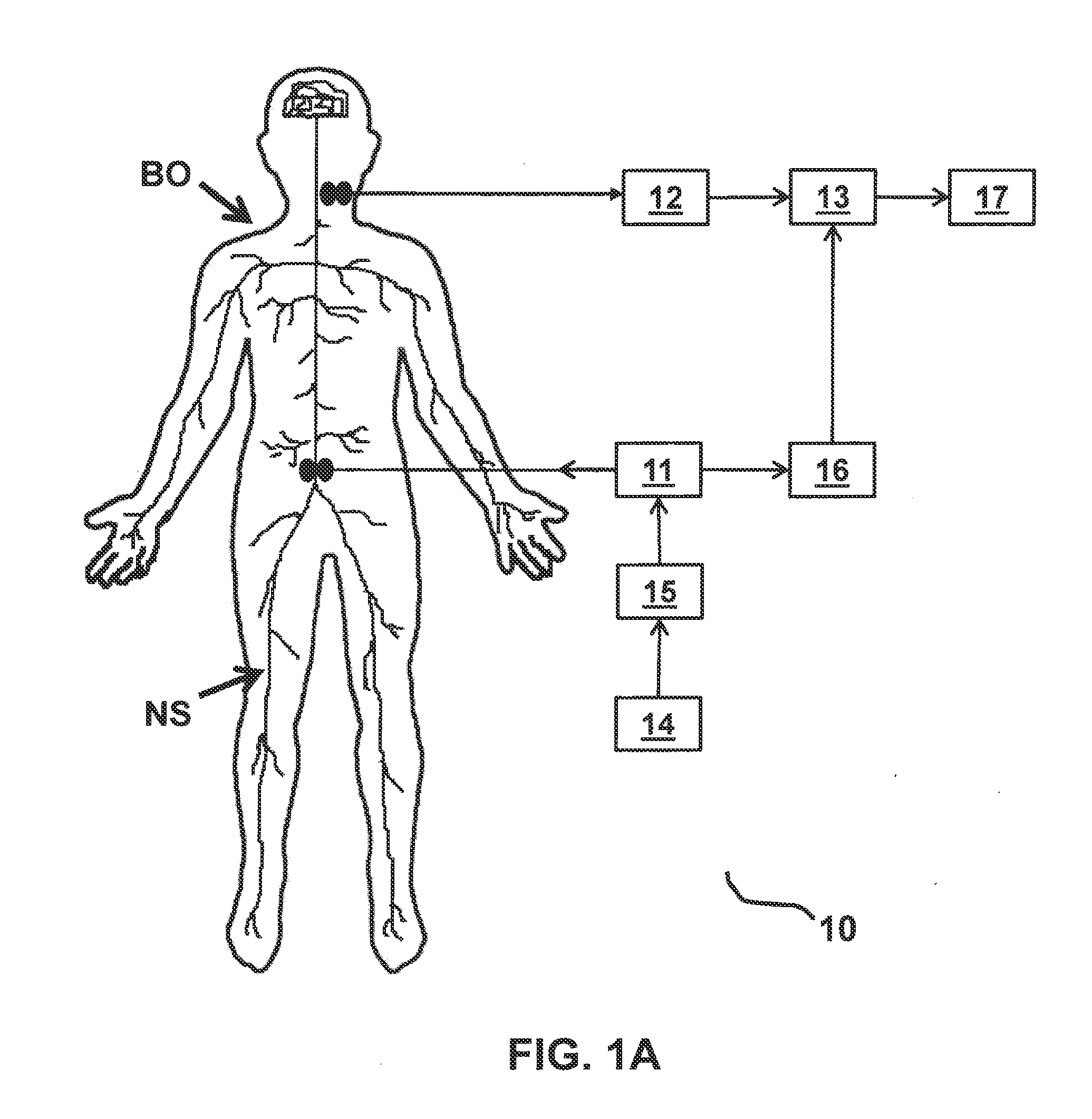
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Brain-controlling animal robot system and brain-controlling method of animal robot
ActiveCN103885445AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsRobotic systemsElectricity
The invention discloses a brain-controlling animal robot system and a brain-controlling method of an animal robot. A corresponding control instruction is generated by collecting brain electrical signals of the brain and processing the brain electrical signals, the corresponding control instruction is used for controlling the animal robot to move, and a brain-to-brain normal form of two mixed modes can effectively control the brain-to-brain animal robot. The brain-controlling animal robot system and the brain-controlling method of the animal robot adopt two control modes, namely the mixed control mode based on ocular electricity / myoelectricity characteristics and motion imagery characteristics of the brain electrical signals and the mixed control mode based on visual evoked potential characteristics and the motion imagery characteristics, select a proper control mode according to the state of a user, and largely improve the real-time performance and reliability of control. The brain-controlling animal robot system can be applied to the fields of unknown environment exploration, brain function mechanism research, brain-to-brain network communication, life assistance and entertainment for the disabled and the like.
Owner:浙江浙大西投脑机智能科技有限公司
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
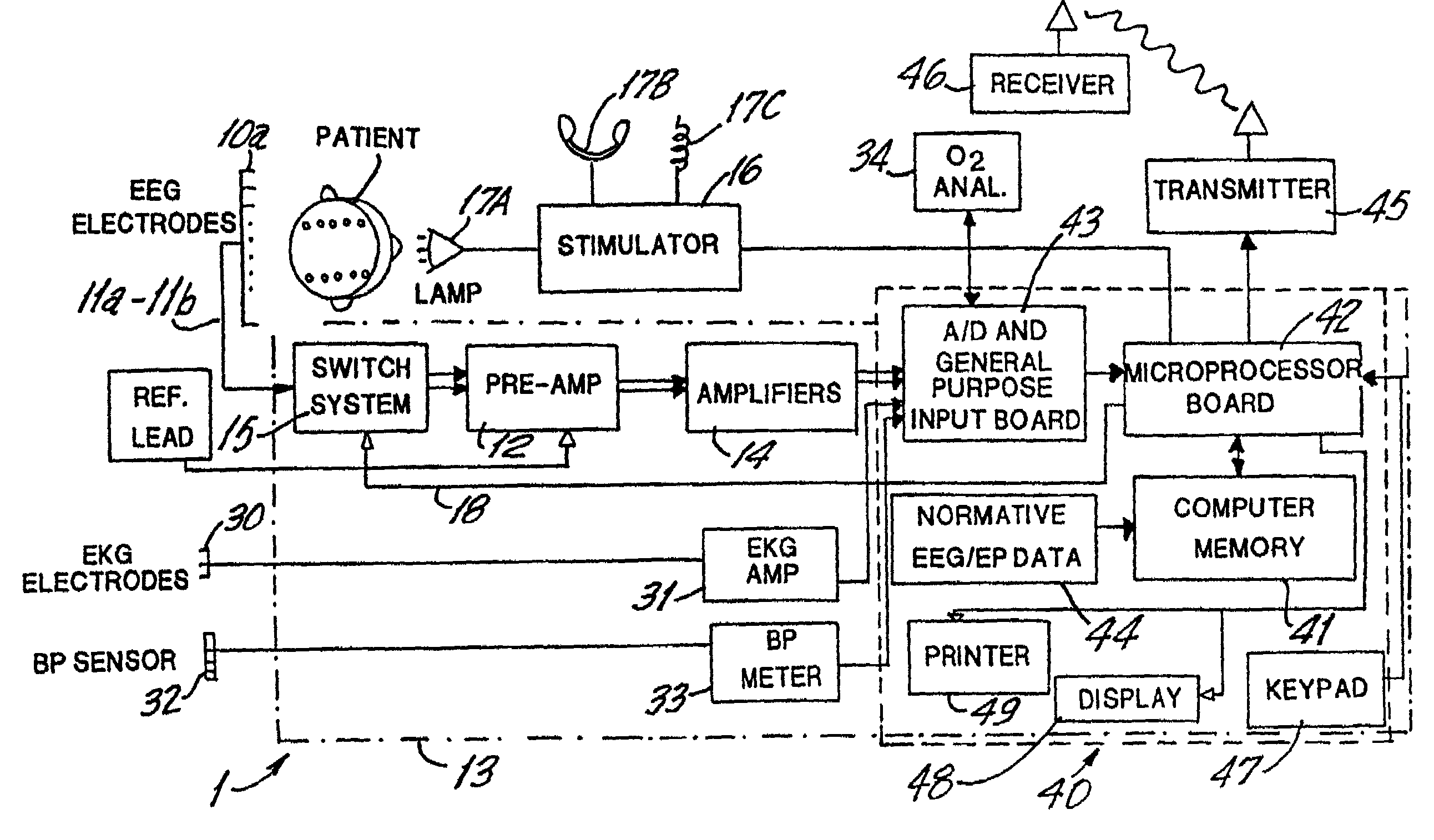
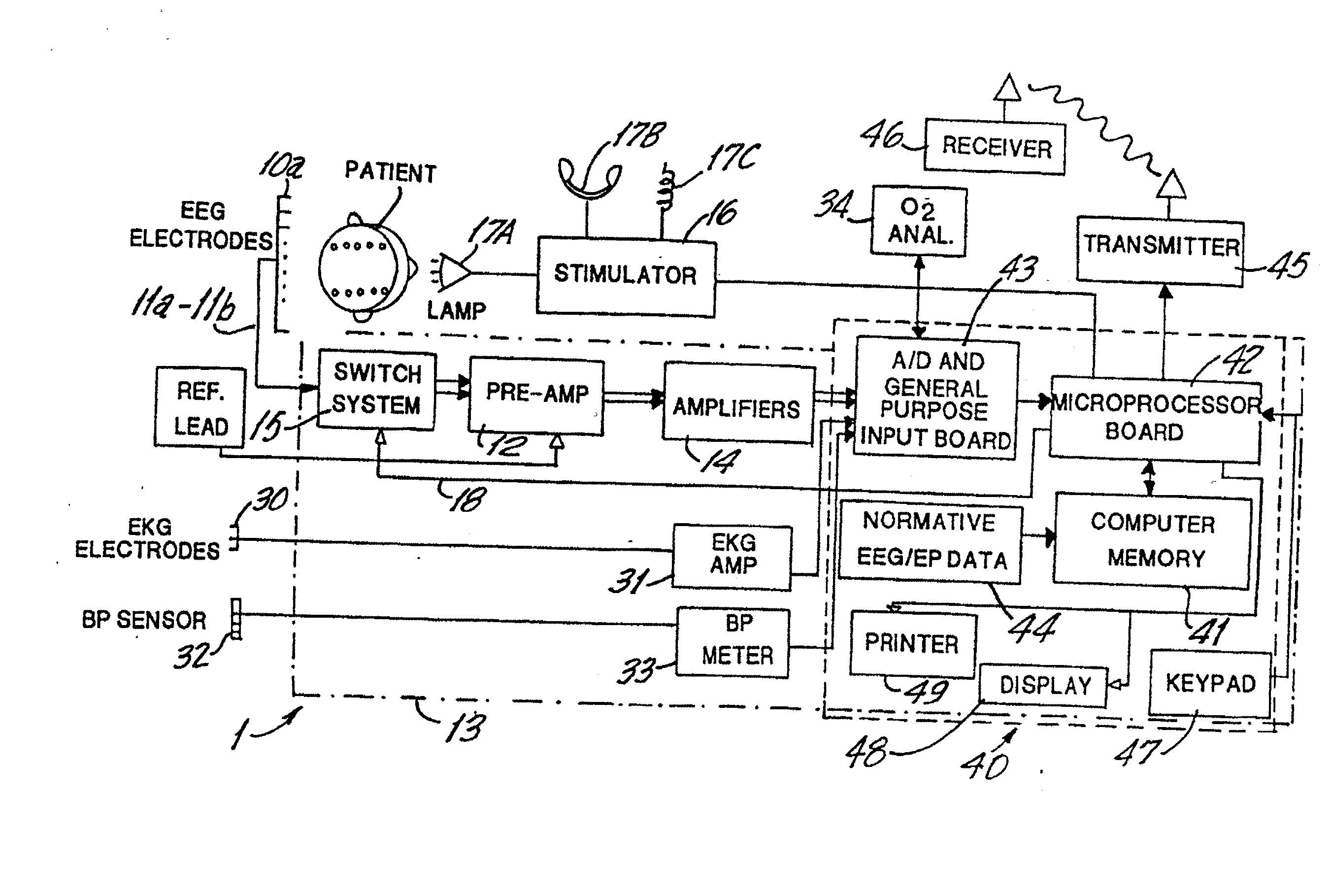
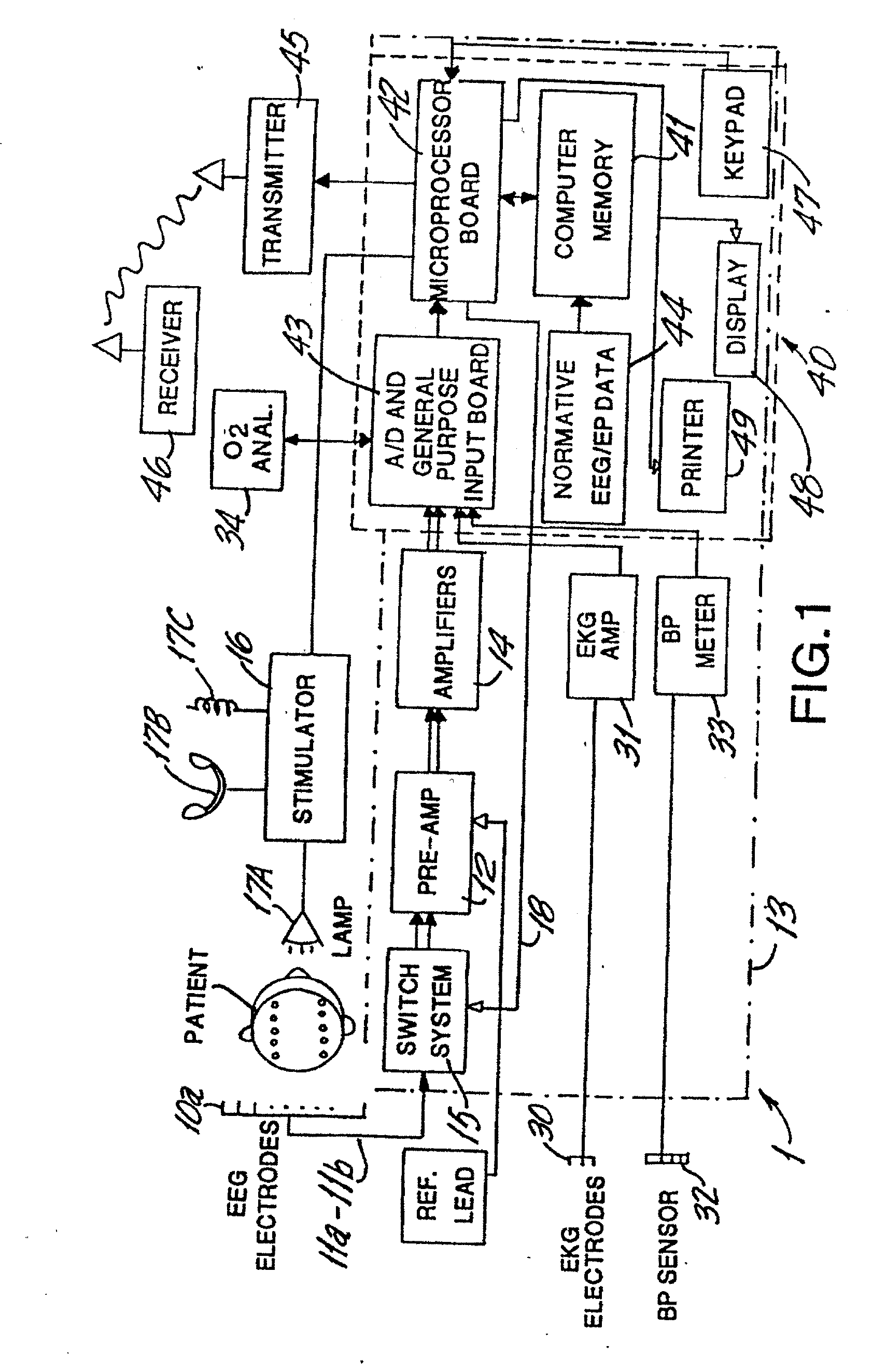
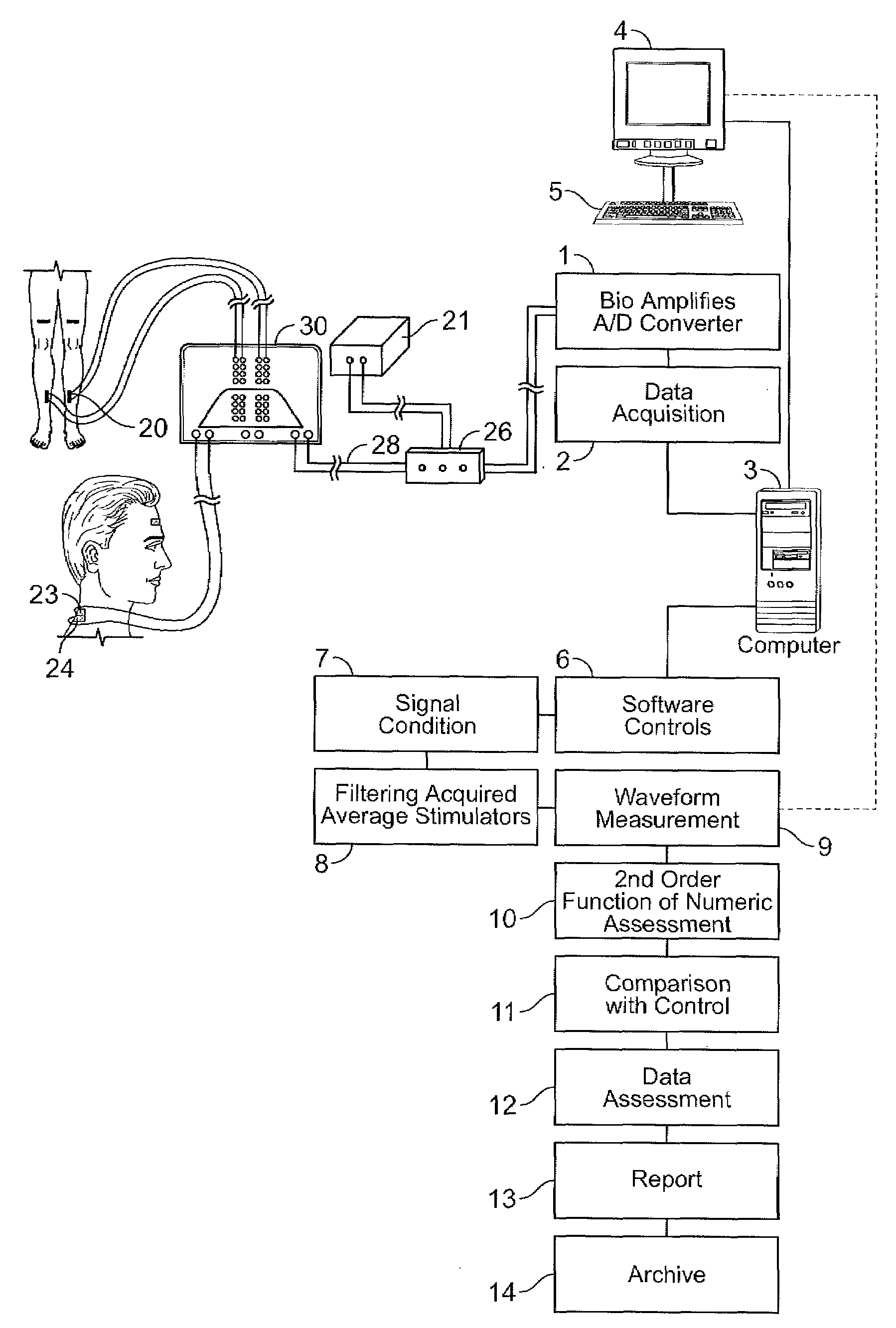
Brain function scan system
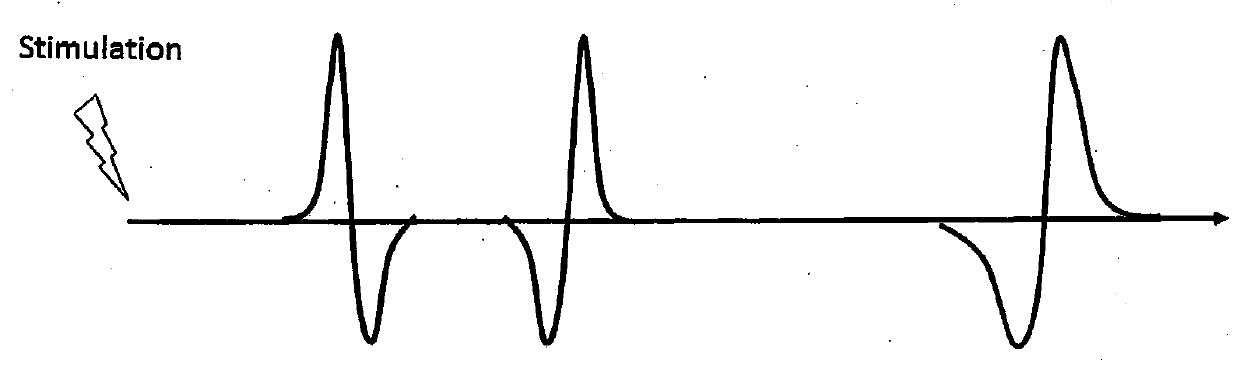
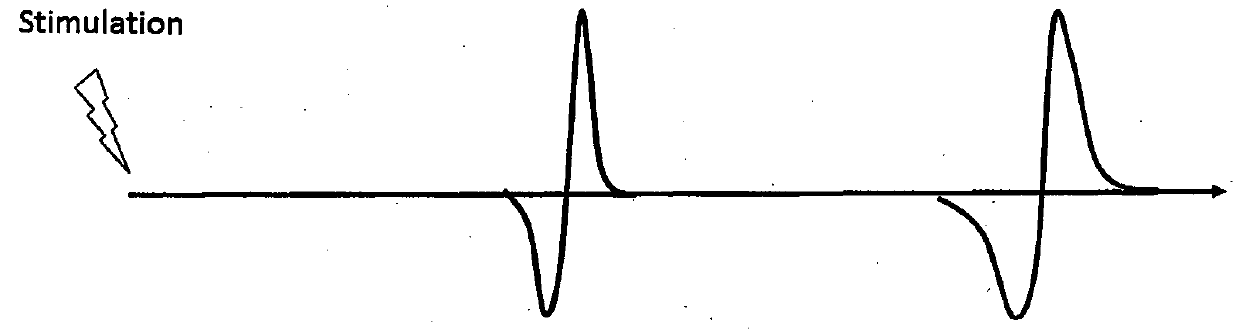
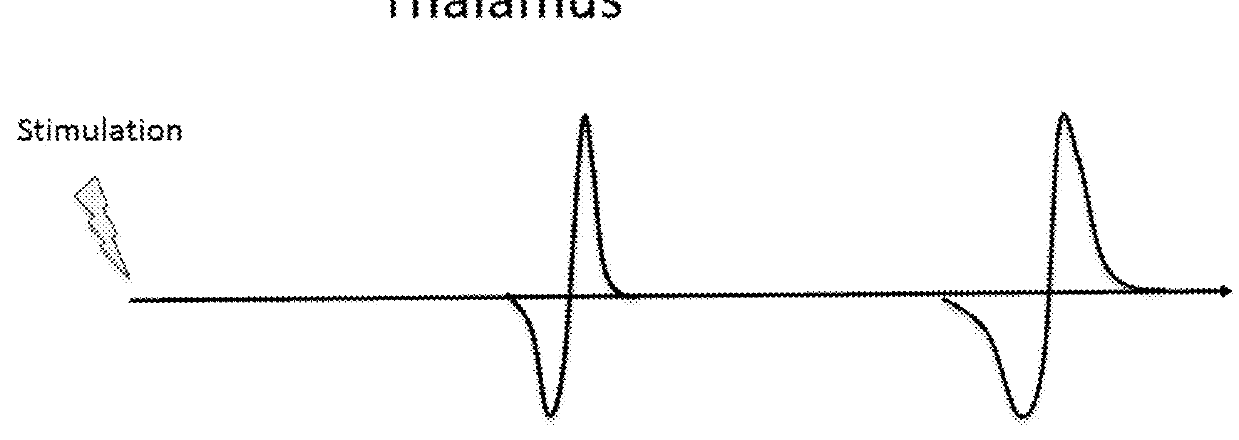
A portable EEG (electroencephalograph) instrument, especially for use in emergencies and brain assessments in physicians' offices, detects and amplifies brain waves and converts them into digital data for analysis by comparison with data from normal groups. In one embodiment, the EEG electrodes are in a headband which broadcasts the data, by radio or cellular phone, to a local receiver for re-transmission and / or analysis. In another embodiment, the subject is stimulated in two modes, i.e., aural and sensory, at two different frequencies to provide the subject's EPs (Evoked Potentials), assessing transmission through the brainstem and thalamus.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
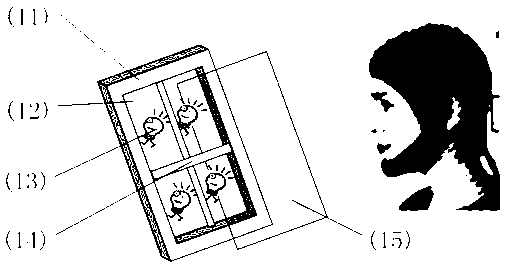
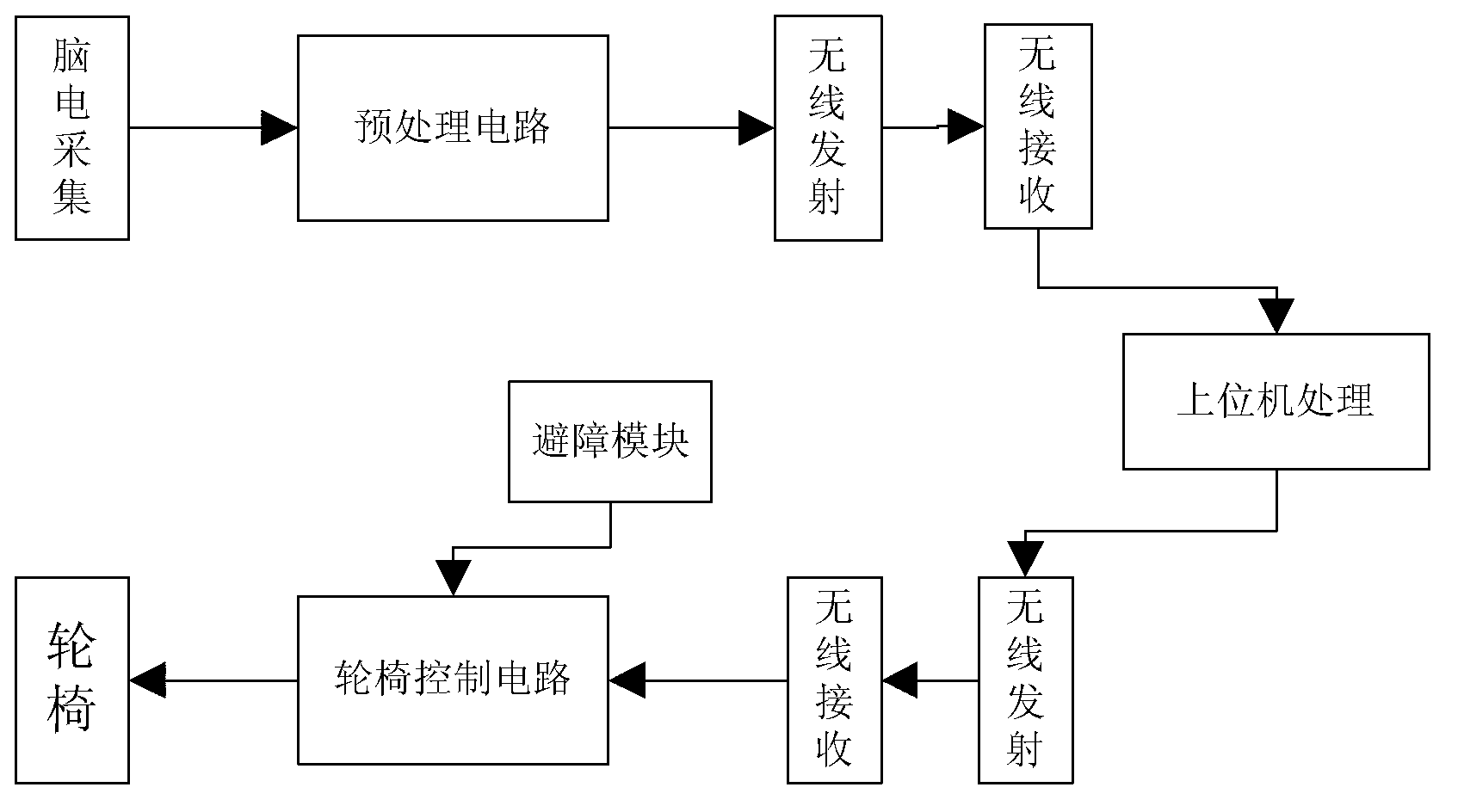
Intelligent wheelchair system based on SSVEP (steady-state visual evoked potential)
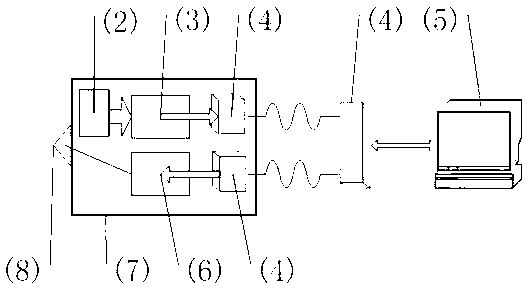
InactiveCN103263324AImprove use valueReduce workloadWheelchairs/patient conveyanceVisual evoked potentialsWheelchair
The invention discloses an intelligent wheelchair system based on SSVEP (steady-state visual evoked potential), and aims to solve the problems of high requirements on a user, less control commands and imperfect wheelchair functions of existing device during the process of using electroencephalogram to control a wheelchair. The intelligent wheelchair system comprises an LED strobe stimulator (1), an electrode cap (2), an electroencephalogram pre-processing circuit (3), a wireless transmission system (4), an upper computer (5), a wheelchair control circuit (6), an electric wheelchair (7), and an automatic obstacle avoidance module (8). Electroencephalogram signals collected by the electrode cap (2) are pre-processed through the electroencephalogram pre-processing circuit (3) and then are transmitted to the upper computer (5) through the wireless transmission system (4) to process and generate control signals, and the control signals are transmitted through the wireless transmission system (4) to the wheelchair control circuit (6) to control the wheelchair. The intelligent wheelchair system has the advantages of convenience in operation and safety in use, and can serve as an assisting tool for the old and the disabled.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
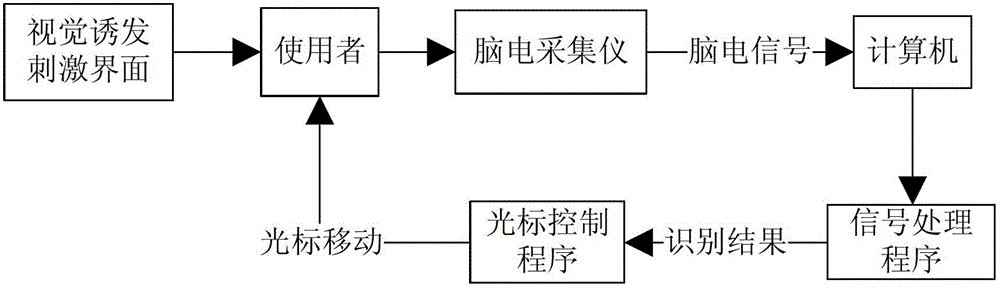
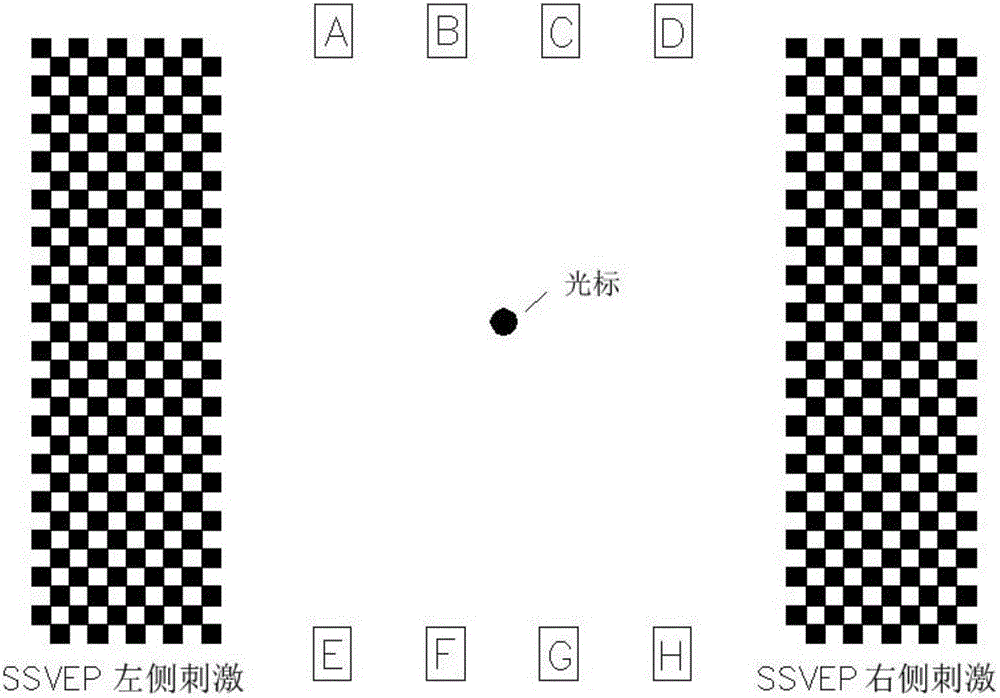
System and method for cursor control based on brain-computer interface
ActiveCN103150023AEasy to useImprove accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual evoked potentialsBrain computer interfacing
The application provides a system and a method of cursor control based on a brain-computer interface. The system comprises a visual evoked simulation module, an electroencephalogram acquisition instrument and a processor, wherein the visual evoked simulation module is used for providing P300 evoked potential stimulation and SSVEP (Steady State Visual Evoked Potential) stimulation for a user in an interface display manner; the electroencephalogram acquisition instrument is used for acquiring the electroencephalogram signal of the user in real time and carrying out amplification and analog-to-digital conversion, and carrying out signal transmission through data wires and the processor; and the processor is used for receiving and processing the electroencephalogram signal, and judging the control purpose of the user and controlling cursor movement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and apparatus for stimulus artifact suppression
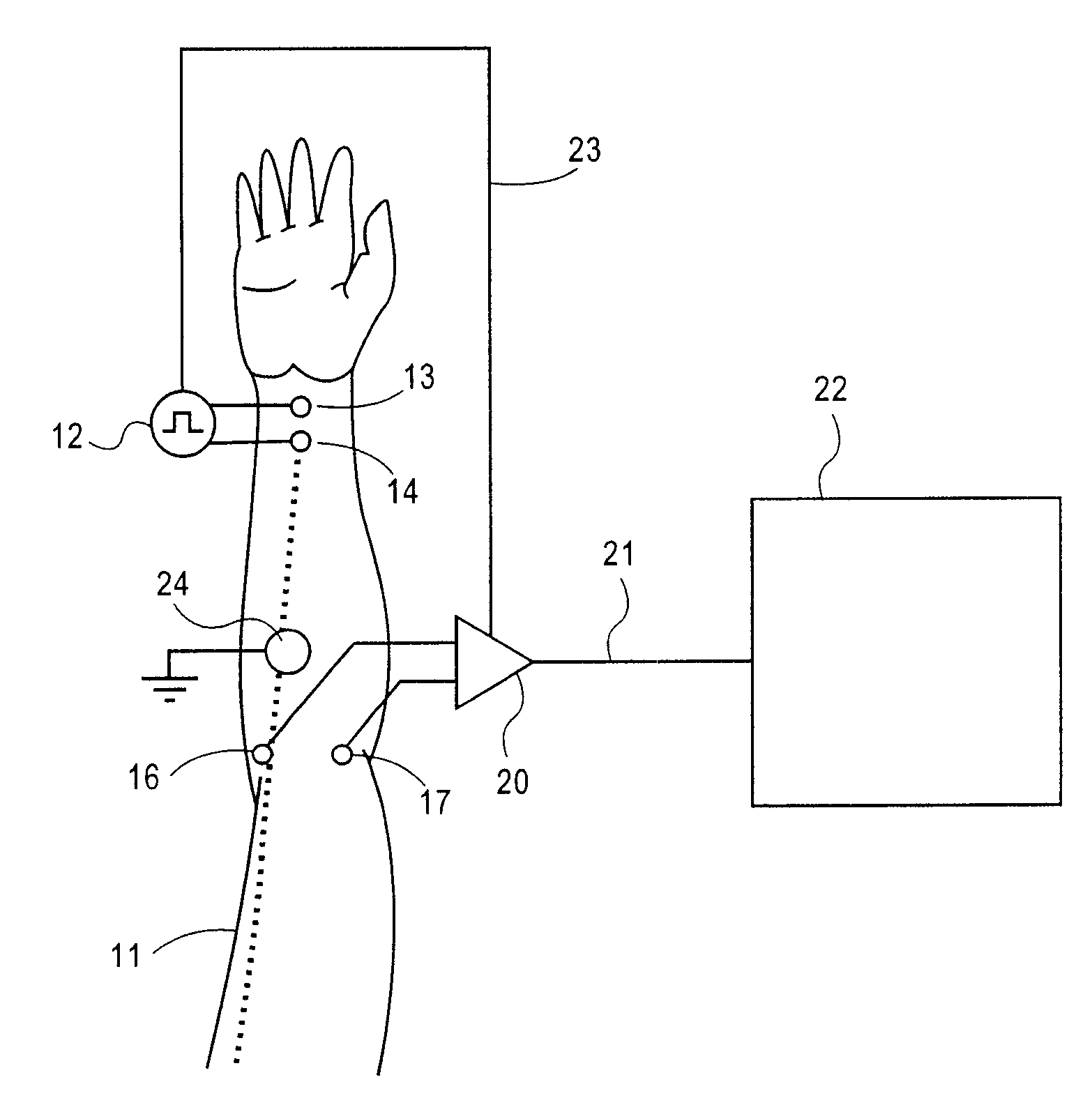
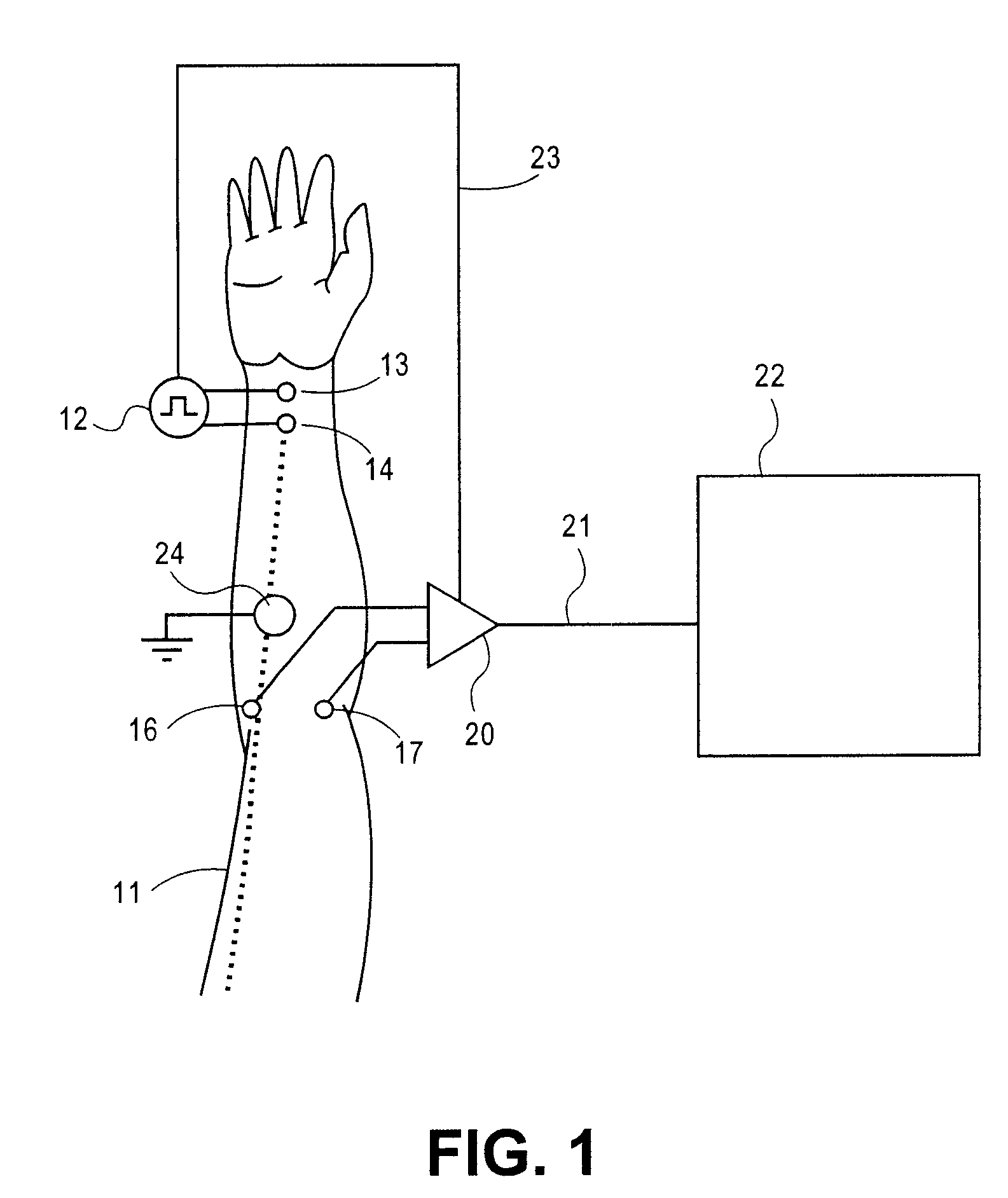
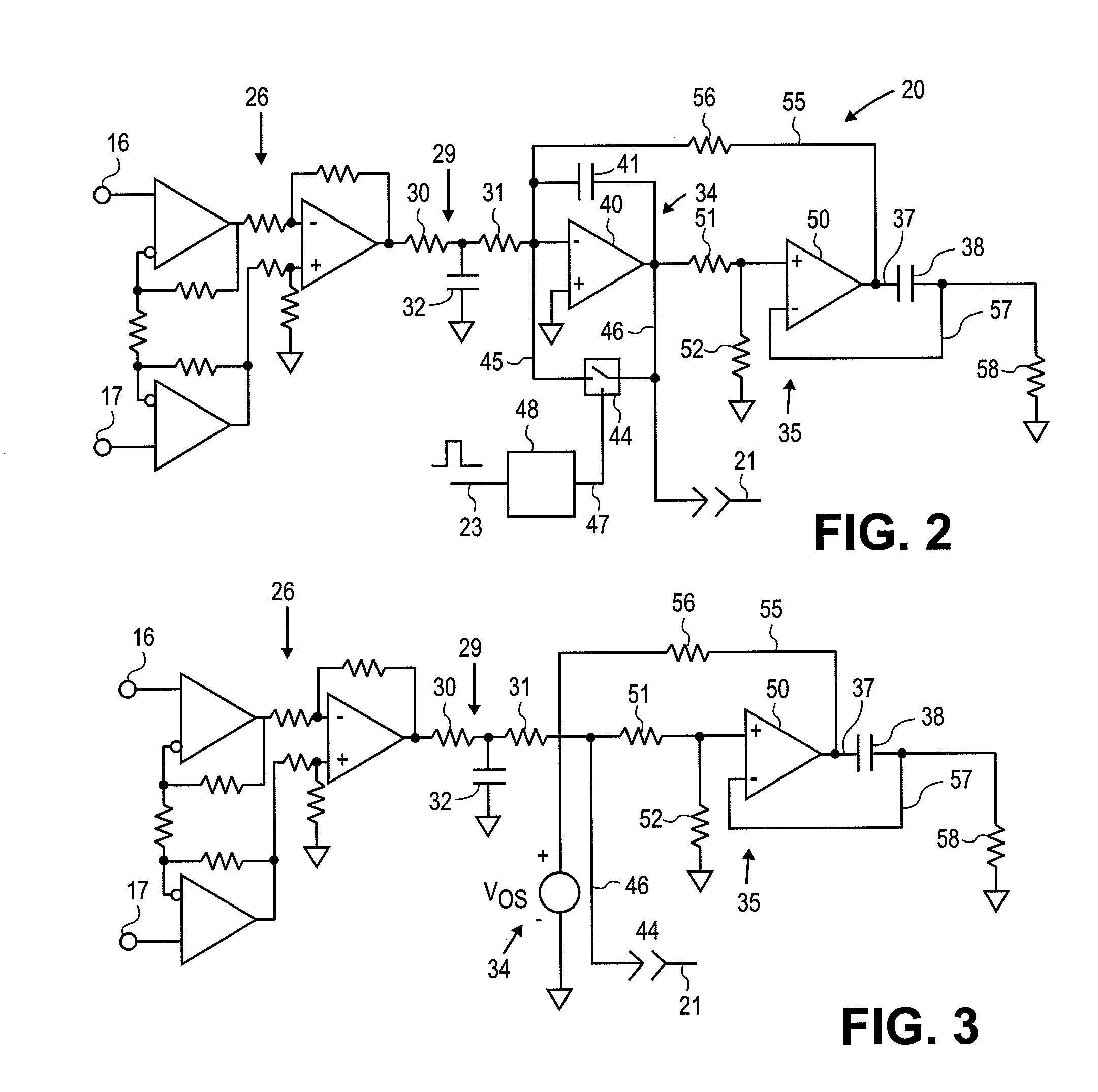
Amplification of an evoked potential signal is carried out utilizing a high pass filter implemented as an integrator in a feedback loop which drives the DC offset voltage to zero. As a result, the feed-forward amplifier circuit has almost zero volts at its output since the only voltage remaining is the offset voltage of the operational amplifier, which is selected so as to maintain this parameter as low as possible. Because the voltage impressed across the feed-forward amplifier section is close to zero, the gain of this section can be set to zero during the time that the electrical stimulus pulse is present without introducing any additional artifacts and subsequent amplifier stages are not driven into saturation. When the electrical stimulus potential is no longer present or is significantly reduced in amplitude and before the time of receipt of the response signal, the feed-forward amplifier is brought back into the circuit to provide the high gain required to amplify the response signal, which can be measured without interference from saturation of any of the amplifier stages as they recover to baseline.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Method and System For Physiological Target Localization From Macroelectrode Recordings and Monitoring Spinal Cord Function
ActiveUS20160051812A1Improve detection rateReduce excitabilityHead electrodesElectromyographyAnatomical structuresNervous system
Provided herein are a method and system are provided for the localization of clinically relevant electrophysiological signals necessary for the proper placement of the electrodes for nervous system stimulation. The system provides electrical and mechanical means to stimulate or excite neural structures in order to elicit specific neural responses. The method can include mechanical vibratory stimulation, cutaneous electrical stimulation, electrical stimulation of the peripheral nerves, or photic stimulation, and recording of local field potentials and extracting evoked potentials in response to stimulation. The method also includes extracting components of the evoked potentials that relate the signal in the evoked potentials to specific anatomical structures and localization of the source of the evoked potentials recorded so as to identify the location of the source relative to the recording electrode with high resolution by sampling the evoked potentials with a relative large (macro) electrode that is moved in small incremental steps.
Owner:GREENVILLE NEUROMODULATION CENT
Hybrid brain-computer interface method based on steady state motion visual evoked potential and default stimulation response
ActiveCN105938397AReduce the numberImprove transfer rateInput/output for user-computer interactionPhysical realisationMATLABEvoked potential feature
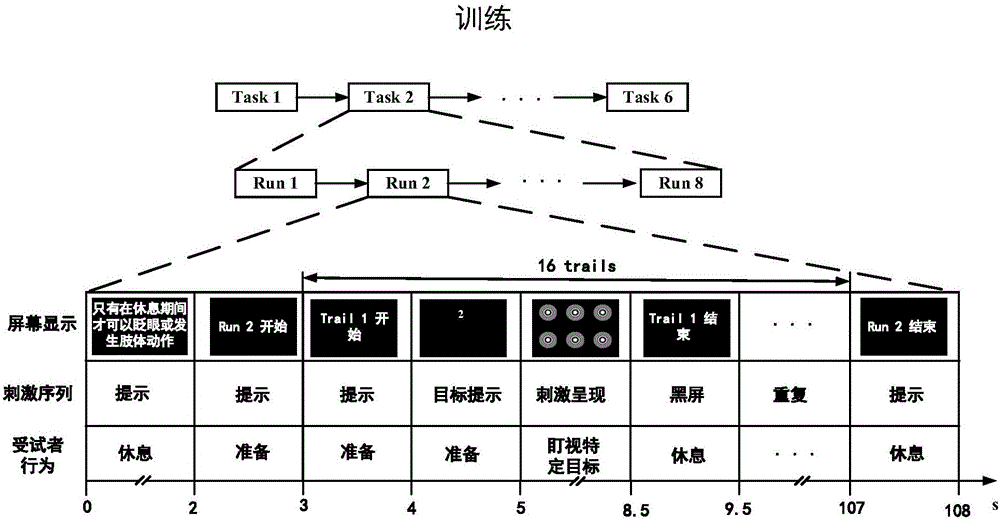
The invention discloses a hybrid brain-computer interface method based on steady state motion visual evoked potential and default stimulation response. The method includes the steps that 1, a testee wears an electrode cap, a reference electrode, a ground electrode and a testing electrode on the electrode cap make contact with the head of the testee, and the vision and the computer screen are in the eye level through visual inspection; 2, a steady state motion visual evoked potential and default stimulation response mixed normal form program is compiled through MATLAB in advance, the testee selects a stimulation target to stare according to a target prompt, and electroencephalogram signals acquired by the electrode cap are stored in a computer; 3, steady state motion visual evoked potential features and default stimulation response features are subjected to feature extraction respectively, and then the stimulation target is subjected to classified recognition; 4, the computer screen displays the stimulation target recognition result, and visual feedback is conducted on the testee; 5, the steps are repeated, and the next round is conducted till the program is ended. According to the hybrid brain-computer interface method, two types of feature recognition information is adopted, and the method has the advantages that operation is simple, less training time is needed, and less electrodes are needed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Identity identification method based on visual evoked potential (VEP)
InactiveCN101828921AValid descriptionImprove recognition accuracyPerson identificationSensorsVision basedFeature parameter
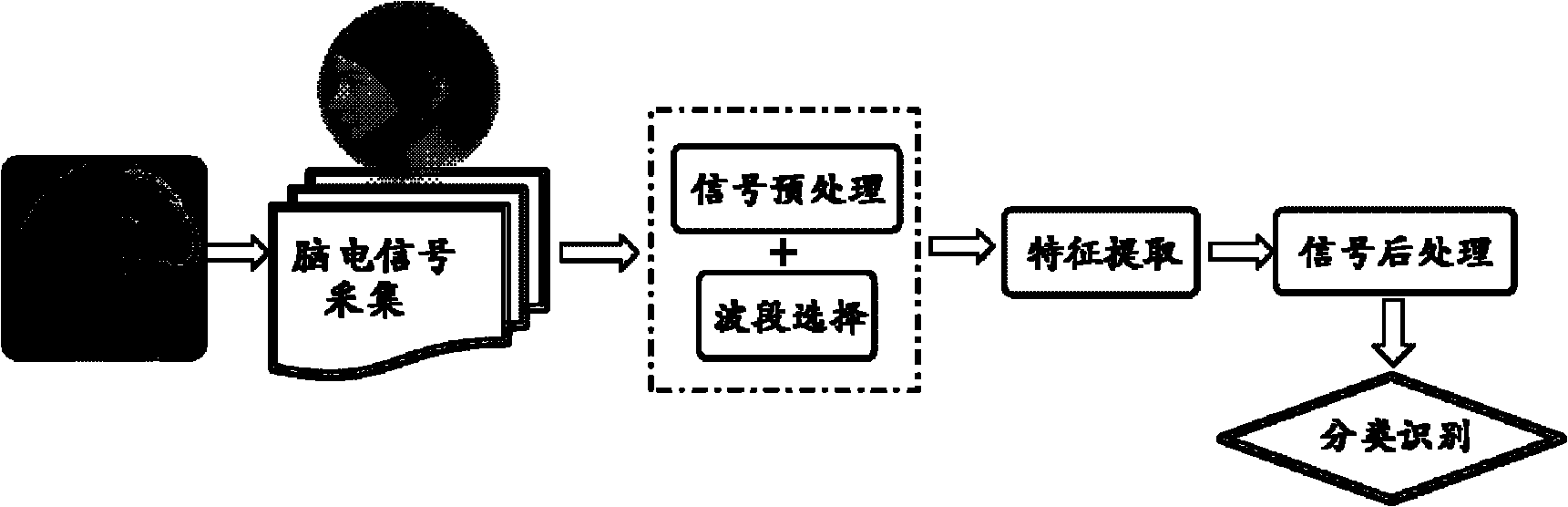
The invention belongs to the field of brain electricity and identity identification, providing an identity identification method which can effectively describe the components of the characteristic of the brain electricity and can achieve the requirement for improving the identification rate. The technical scheme is that the identity identification method based on visual evoked potential (VEP) comprises the following steps of: applying some image stimulation to a subject; selecting a proper scalp leading electrode to capture the visual evoked potential of the subject; preprocessing an original brain electricity signal in a de-noising way; extracting a gamma wave band power spectrum to be taken as the characteristic of the brain electricity to be researched; processing the characteristic of the brain electricity with Fisher linear discrimination; and studying and testing the optimized characteristic parameter in a classifying way through a BP neural network to realize the identity identification. The method is mainly applied to the identity identification.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
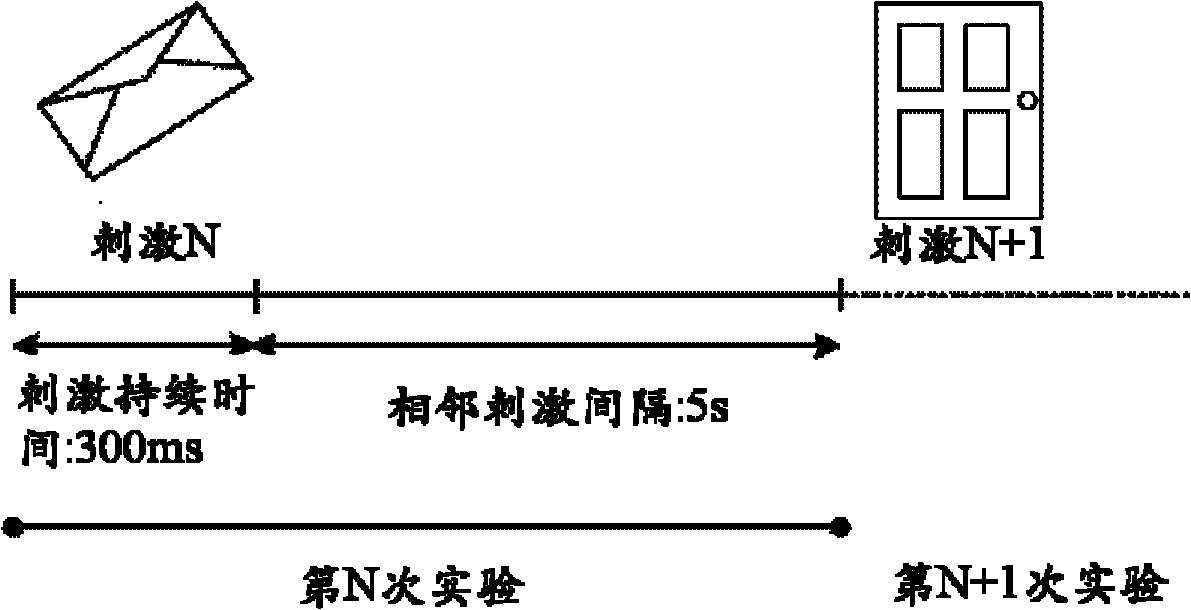
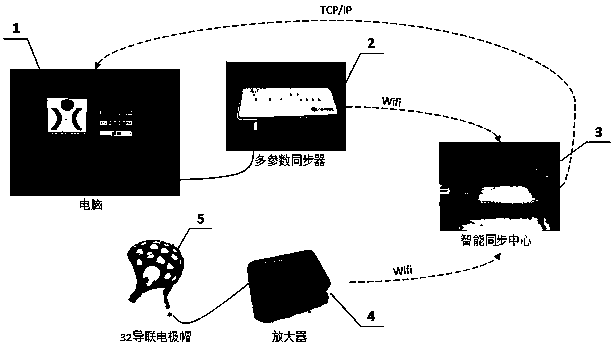
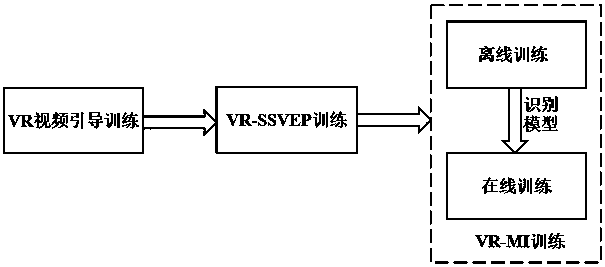
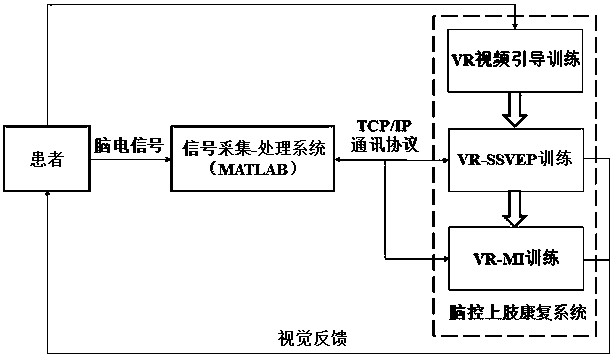
Three-stage brain-controlled upper limb rehabilitation method combining steady-state visual evoked potential and mental imagery
InactiveCN108597584AImprove securityImprove immersion effectMedical simulationMental therapiesPatient needUpper limb rehabilitation
The invention relates to a three-stage brain-controlled upper limb rehabilitation method combining steady-state visual evoked potential and mental imagery (MI). The method comprises the following steps: (1) the first stage of VR video guidance training: a patient is made to be familiar with upper limb rehabilitation movements through VR video guidance; (2) the second stage of VR-SSVEP training: the patient needs to concentrate to observe pictures that represent different upper limb movements and flicker with a specific frequency, EEG signals of the patient are collected in real-time to analyzeintentions of the patient, and visual feedback is provided to the patient through VR animation to make the patient learn to concentrate; and (3) the third stage of VR-MI training: EEG signals of theleft and right upper limbs of the patient during MI are collected during off-line training, and a mental imagery intention recognition model is established. The EEG signals of mental imagery of the patient are analyzed according to the model during online training, movement intentions of the patient are recognized, and movements of a 3D character in an interface are controlled in real time, so that brain central nerve remodeling is facilitated through MI. The method exhibits a good immersion property, enables active rehabilitation to be realized, enables rehabilitation to proceed step by step,and is a new method for upper limb rehabilitation of a cerebral stoke patient.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
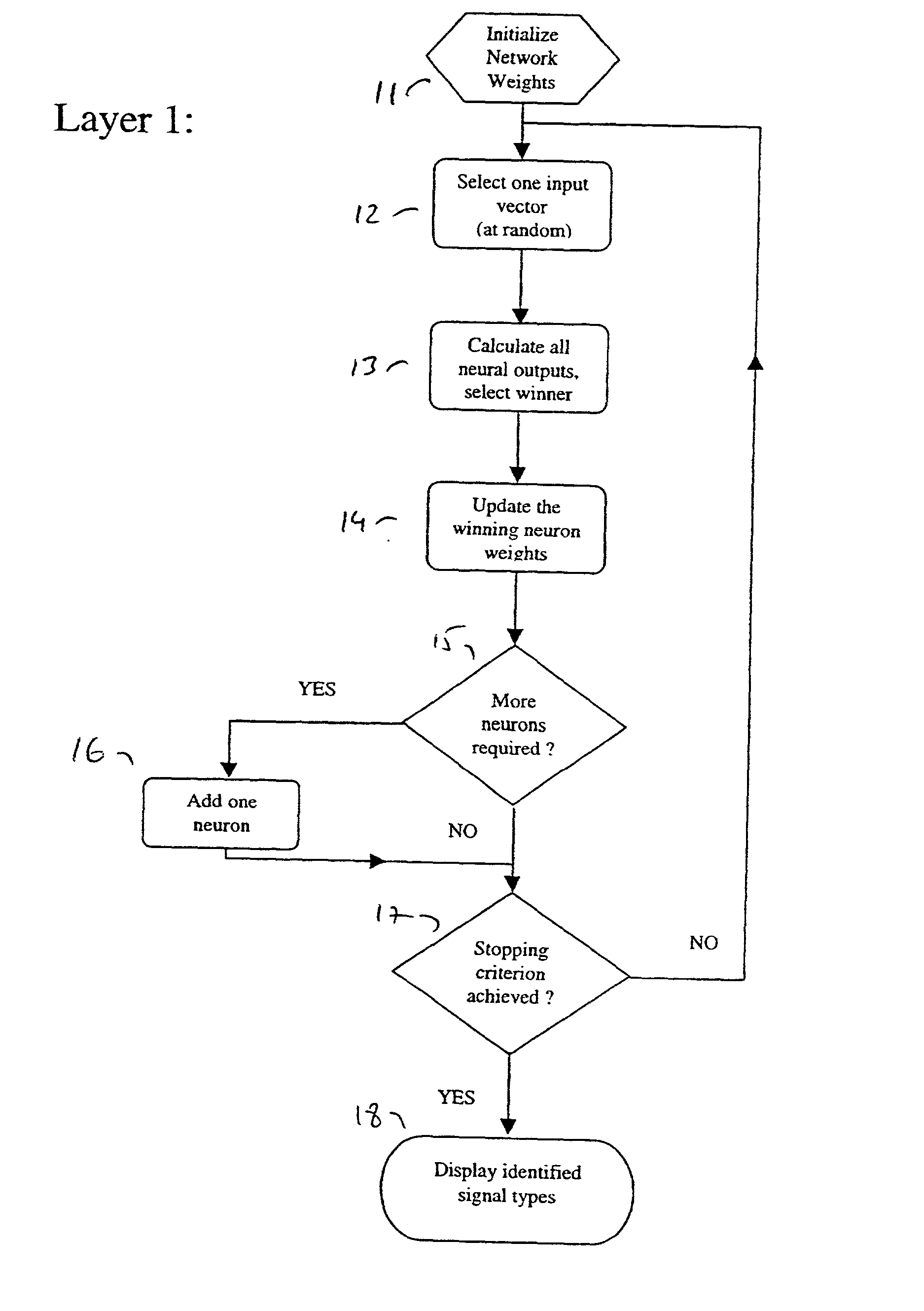
N400 evoked potential lie detection method based on improved extreme learning machine
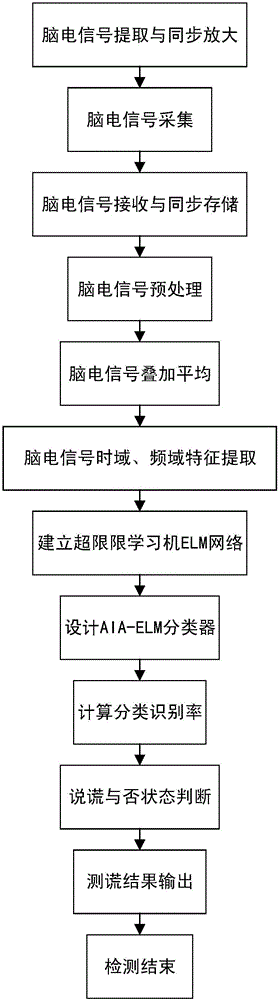
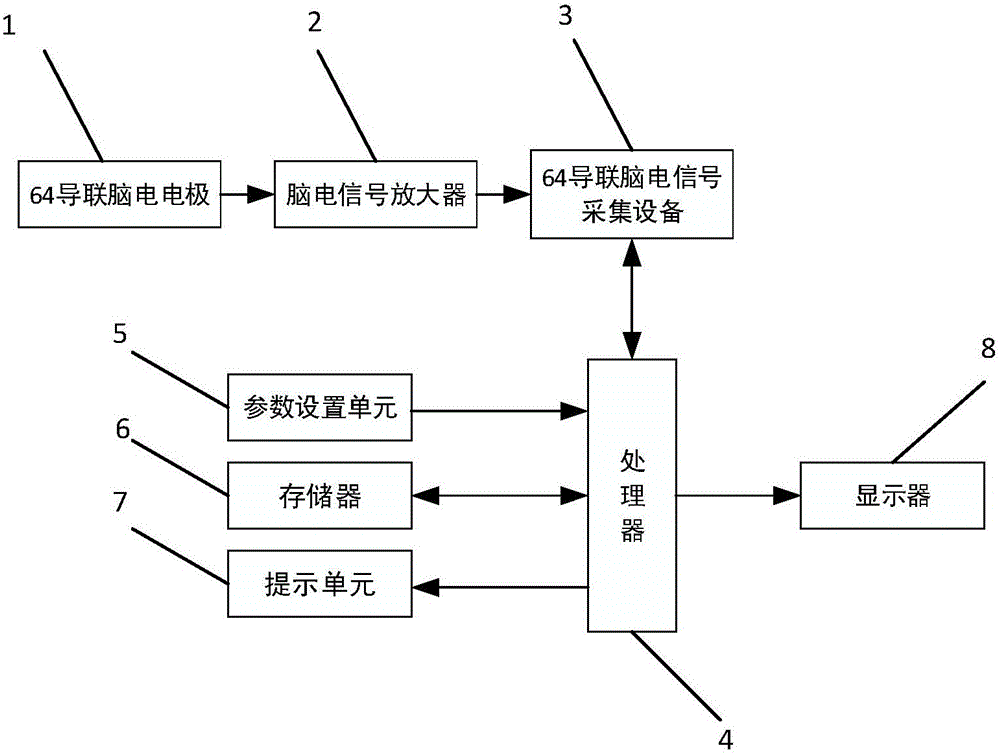
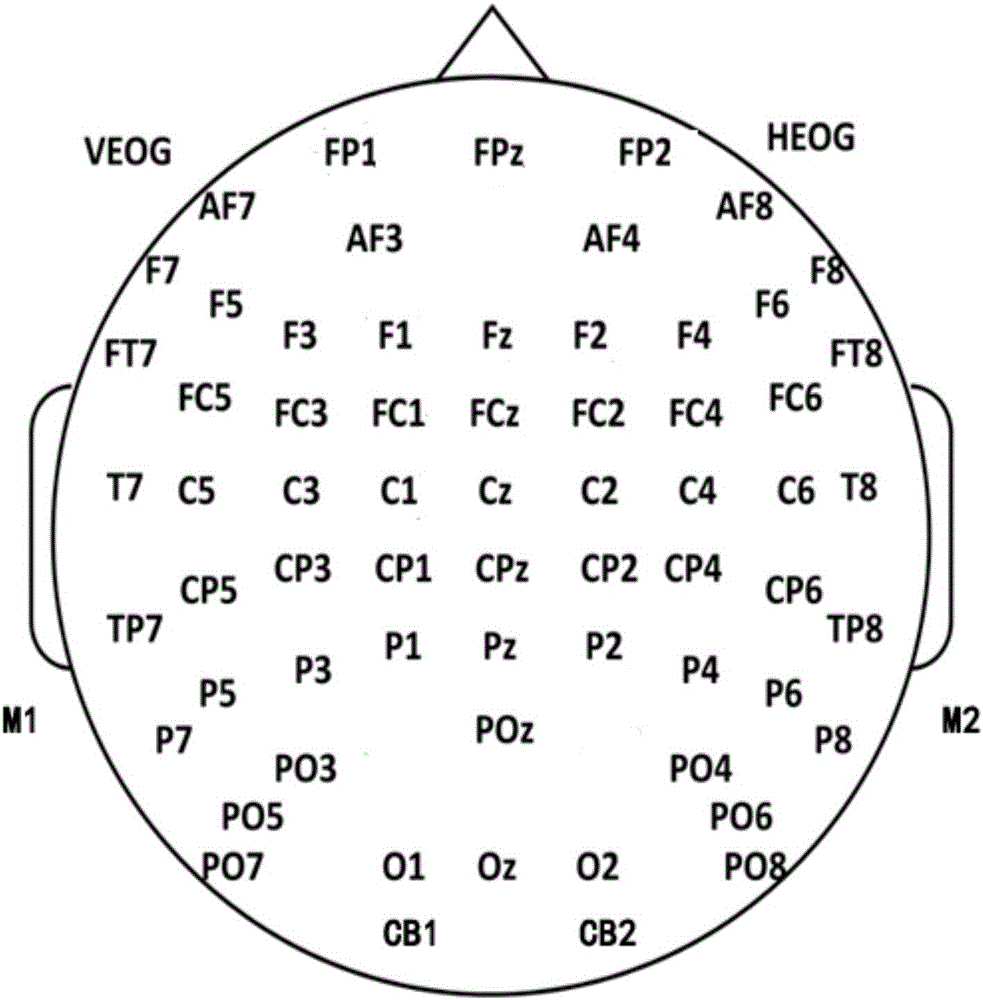
ActiveCN105852885AStable lie recognition accuracyImprove classification recognition rateSensorsPsychotechnic devicesGeometric propertyTime domain
The invention provides an N400 evoked potential lie detection method based on an improved extreme learning machine; random parameters of the extreme learning machine are optimized on the basis of an artificial immune algorithm, and the electroencephalogram lie detection method based on an N400 evoked potential and the improved extreme learning machine is proposed; by virtue of the improved extreme learning machine, classification recognition rates of crime group subjects and control group subjects to detection stimulation and unassociated stimulation are calculated, and the classification recognition rates of the two groups of subjects are calculated and analyzed, so that a threshold parameter for distinguishing whether a subject lies or not is found out; and detection stimulation and unassociated stimulation time domain and frequency domain characteristics of 40 channel N400 induced electroencephalogram signals are extracted, so that the extracted electroencephalogram signal characteristics are more comprehensive; therefore, shortcomings in the prior art which conducts lie detection and judgment on the basis of a few of channels and by taking induced potential waveform geometric properties as characteristic parameter are overcome; and the lie detection method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that a stable lie identification right rate is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for extracting low SNR transient signals from noise
InactiveUS20040015894A1Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsMotor evoked potentials monitoringEvoked potential
A method and apparatus for processing a composite signal generated by a transient signal generation mechanism to extract a repetitive low SNR transient signal, such as an evoked potential (EP) appearing in an electroencephalogram (EEG) generated in response to sensory stimulation, by: (a) dynamically identifying, via a learning process, the major transient signal types in the composite signal; (b) decomposing the identified major transient signal types into their respective constituent components; (c) synthesizing a parametric model emulating the transient signal generation mechanism; and (d) utilizing the model and the constituent components to identify and extract the low SNR transient signal from the composite signal.
Owner:ALGODYNE
Brain Function Scan System
InactiveUS20090227889A2Accurately and reliably and continuously and quickly determinePermit separationElectroencephalographySensorsDigital dataPortable EEG
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Dermatomal somatosensory evoked potential (DSSEP) apparatus for real time nerve root function diagnosis in surgical and clinical situations
A dermatomol somatosensory evoked potential (DSSEP) diagnositic apparatus for evaluating nerve root functions in a mammalian subject is presented. The DSSEP apparatus includes an electrical stimulator, a stimulus site selector switchbox, a connection box, a plurality of stimulating electrodes, a plurality of recording electrodes, a computer system, and a software package. The stimulating electrodes are configured to receive and to apply an electrical stimulus onto a dermal stimulation site of the mammalian subject. The recording electrodes are configured to receive an evoked potential induced by the applied electrical stimulus such that the evoked potential response passes through nerves from the dermal stimulation site to the dermal recording site. The computer system and software package process the results.
Owner:MCGINNIS WILLIAM C +1
Target selecting method based on transient visual evoked electroencephalogram
InactiveCN101515200AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEasy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionBiological neural network modelsTimestampCPU time
The invention relates to a target selecting method based on transient visual evoked electroencephalogram, comprising the following steps: VC + + writing visual stimulator evokes an electroencephalogram signal, 16-lead collecting device collects an electroencephalogram signal VEP which is amplified by an electroencephalogram amplifier and A / D converted, so that the signal is input into a computer and memorized in a memorizer in a way of signal voltage magnitude; B sample band biorthogonal wavelet method is used for extracting an electroencephalogram characteristic signal, in addition, corresponding results are classified, identified and output by the self-learning ability of BP neuronic network; wherein, the method also comprising the following steps of: designing the accurate timing visual stimulator by CPU timestamp; answering the output impulse of paralled port; collecting the electroencephalogram signal VEP by a collecting device; pretreating the collected signal; extracting the electroencephalogram signal by the B sample band biorthogonal wavelet method; and classifying characteristic quantity by the BP neuronic network. The method has the advantage that the BP neuronic network is used for effectively improving signal to the noise ratio and the recognition rate of visual evoked potential VEP.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
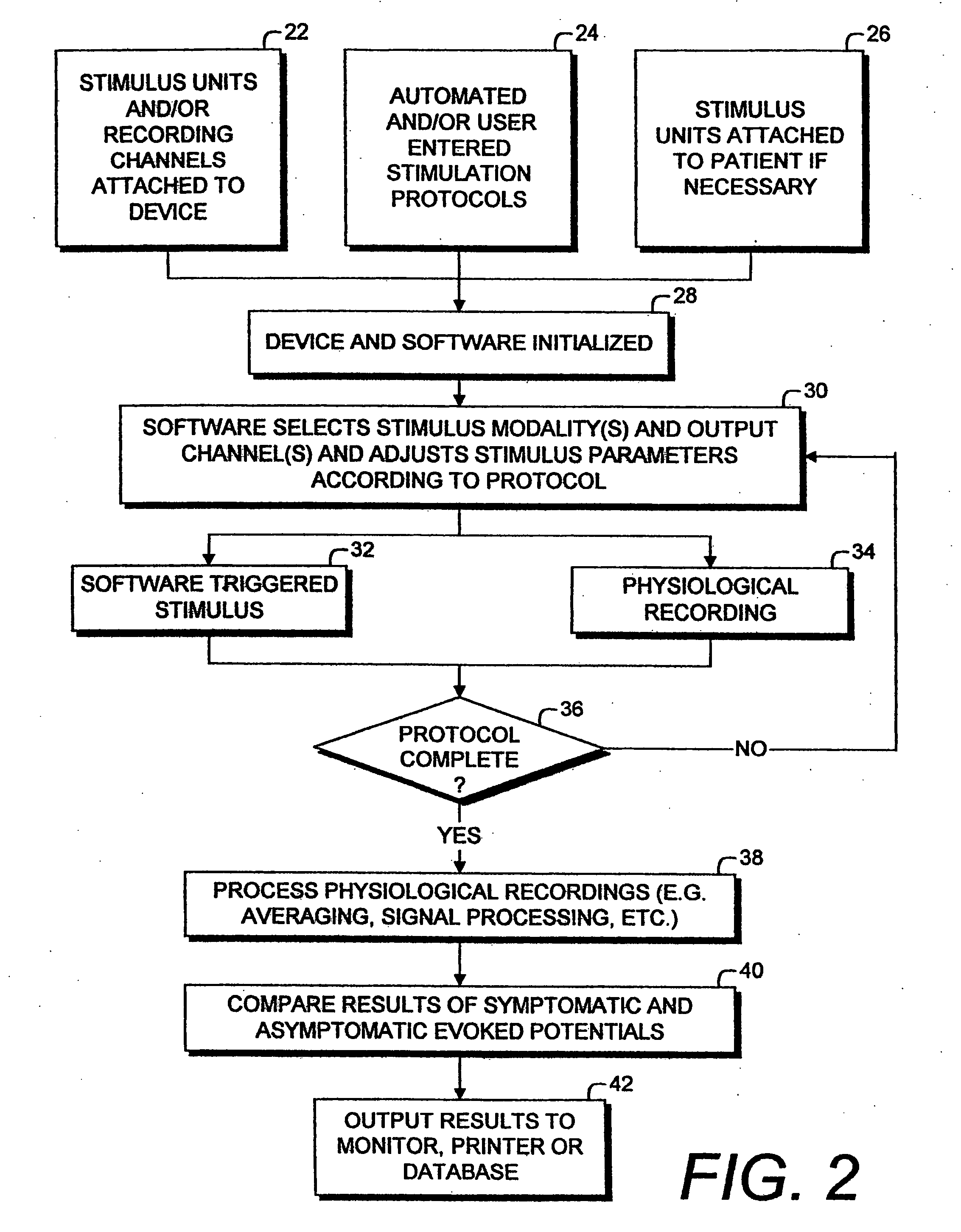
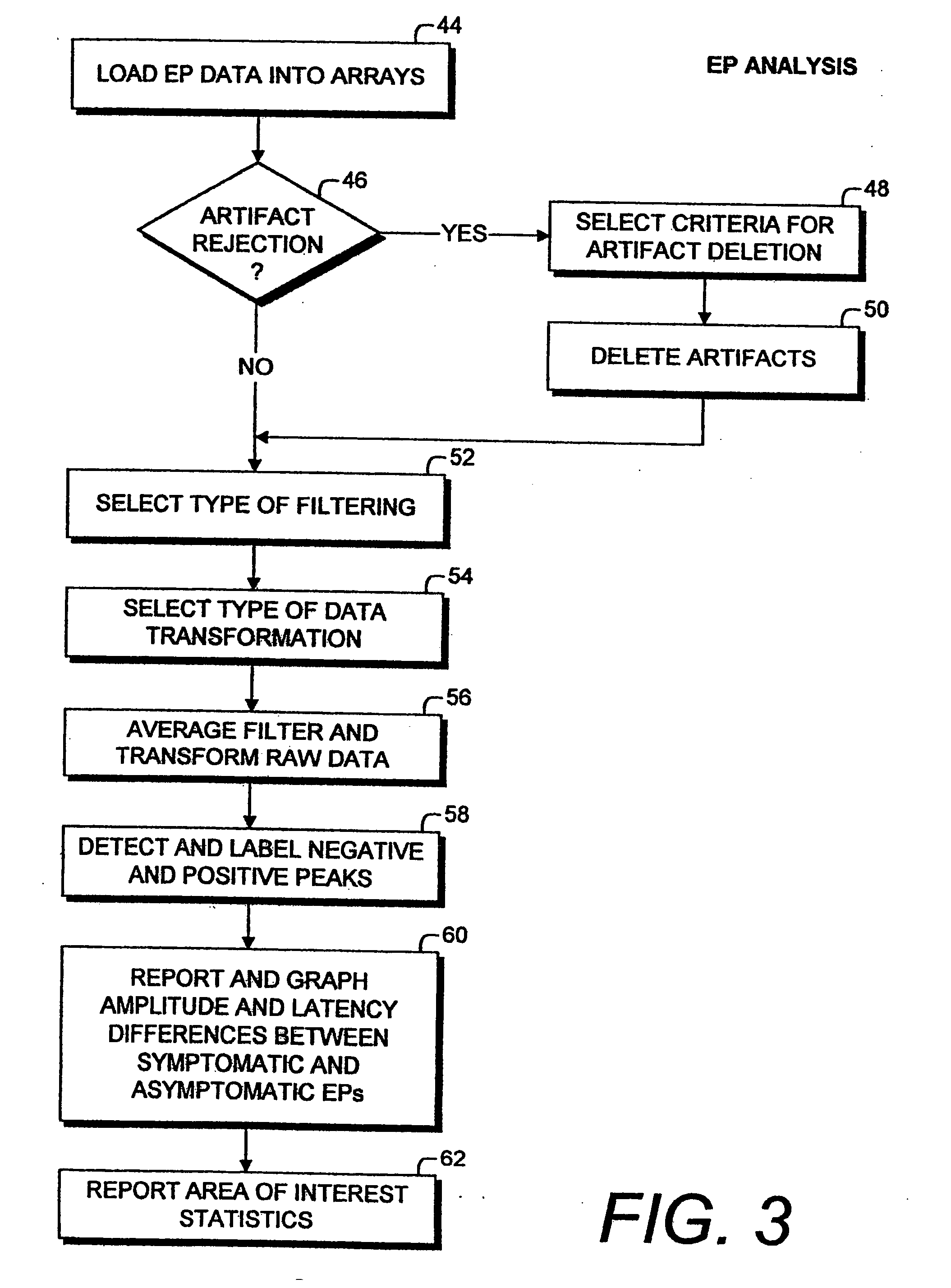
Physiological assessment system and method
InactiveUS20060116556A1Improve reliabilityImprove validityElectroencephalographySensorsClinical psychologyTherapeutic intent
A system and method for physiological assessment utilizes electrophysiological techniques, such as evoked potential (EP) data. Symptomatic and asymptomatic sensory areas are stimulated and EP data are collected. Artifacts can optionally be deleted from the raw EP data, which can then be appropriately filtered and transformed using software filtering and signal processing transformation techniques. Points of interest are detected and labeled on the resulting traces, which are output for analysis, diagnosis and treatment purposes. Differences between symptomatic and asymptomatic EPs provide objective, quantitative, repeatable information about pathological conditions.
Owner:DUHAMEL PAUL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com