Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Policy-based routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer networking, policy-based routing (PBR) is a technique used to make routing decisions based on policies set by the network administrator. When a router receives a packet it normally decides where to forward it based on the destination address in the packet, which is then used to look up an entry in a routing table. However, in some cases, there may be a need to forward the packet based on other criteria. For example, a network administrator might want to forward a packet based on the source address, not the destination address. This permits routing of packets originating from different sources to different networks even when the destinations are the same and can be useful when interconnecting several private networks.
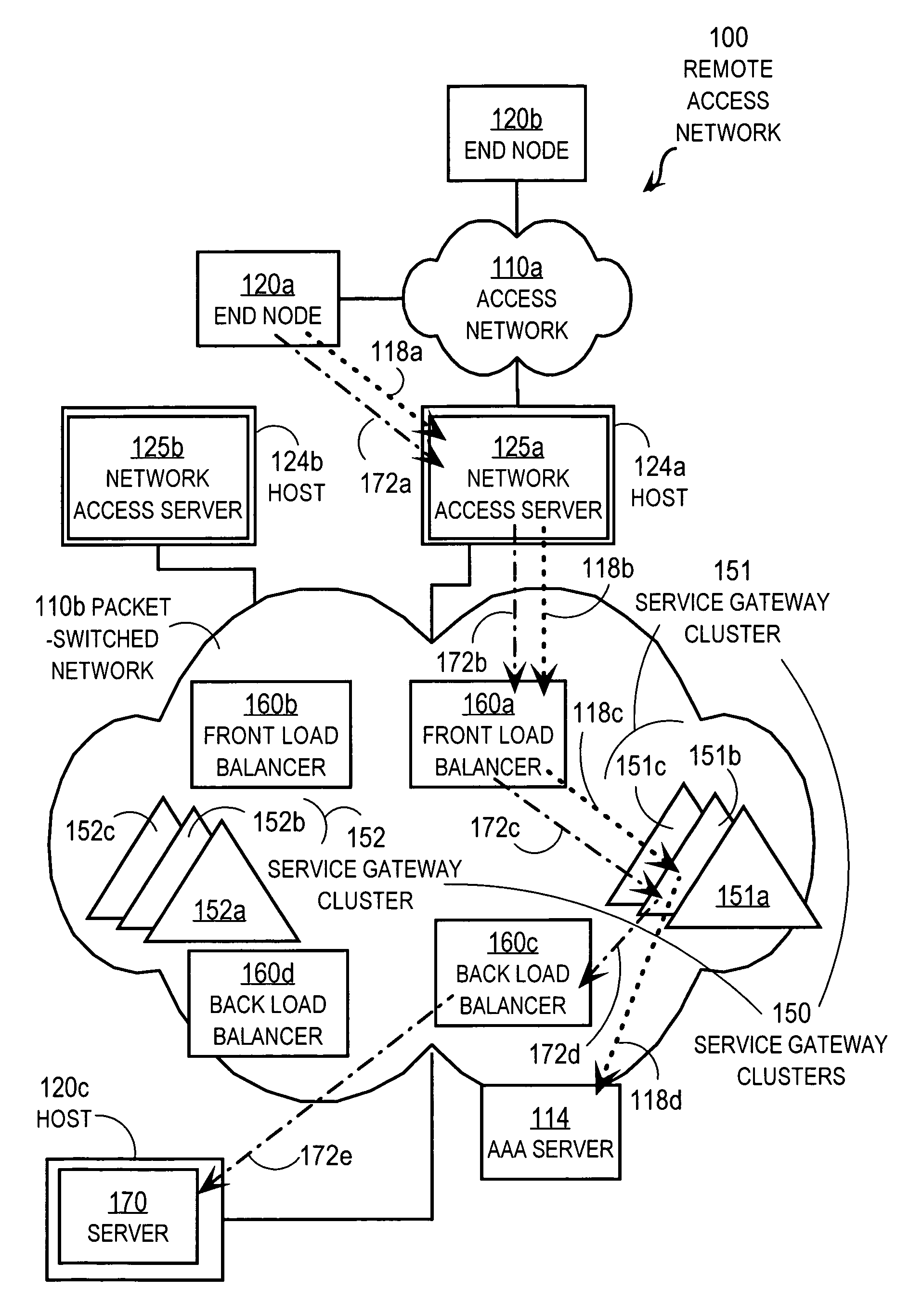
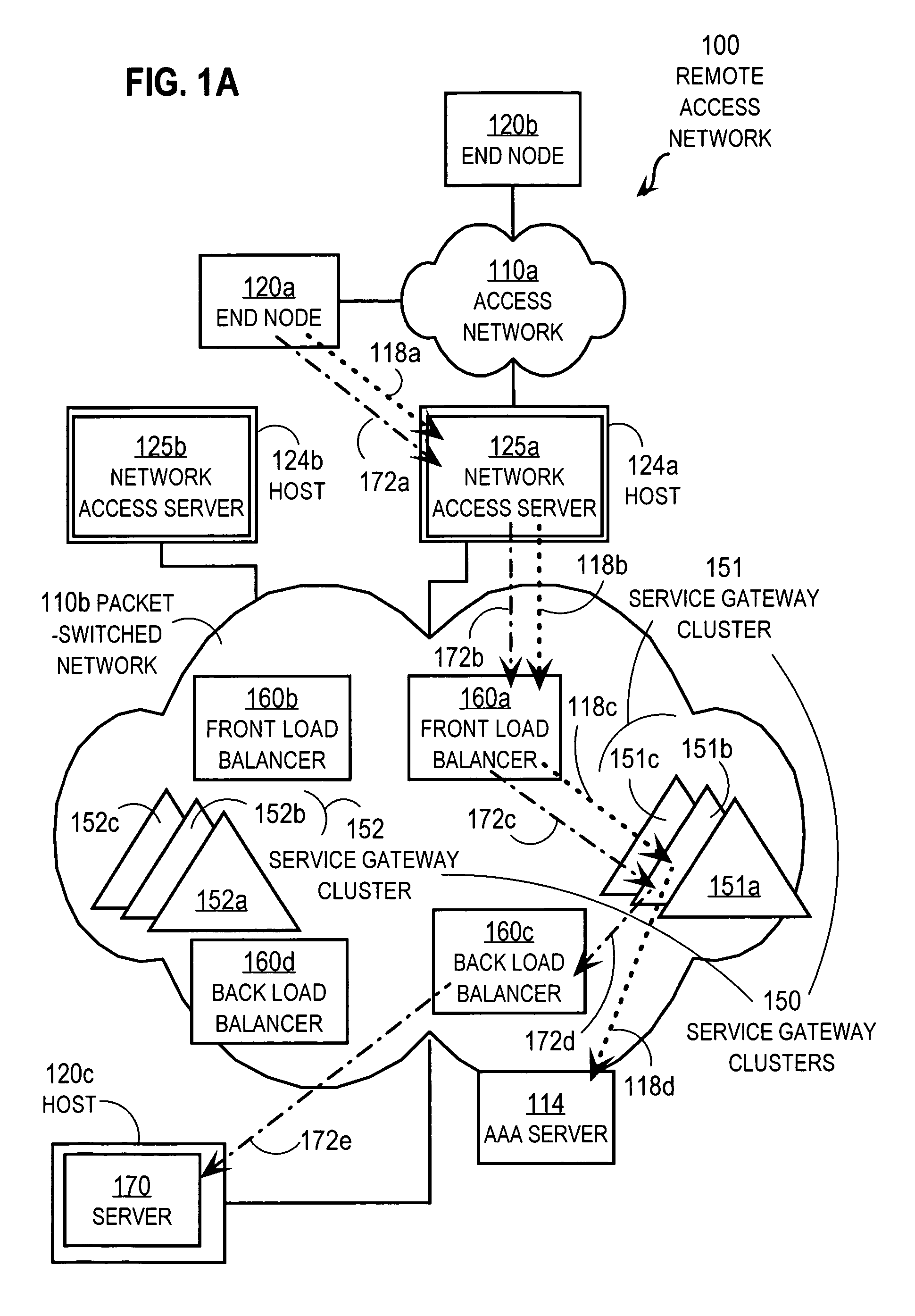
Techniques for load balancing over a cluster of subscriber-aware application servers
InactiveUS20070165622A1Digital computer detailsNetwork connectionsApplication serverDistributed computing
Techniques for distributing control plane traffic, from an end node in a packet switched network to a cluster of service gateway nodes that host subscriber-aware application servers, include receiving a control plane message for supporting data plane traffic from a particular subscriber. A particular service gateway node is determined among the cluster of service gateway nodes based on policy-based routing (PBR) for the data plane traffic from the particular subscriber. A message based on the control plane message is sent to a control plane process on the particular service gateway node. Thereby, data plane traffic and control plane traffic from the same subscriber are directed to the same gateway node, or otherwise related gateway nodes, of the cluster of service gateway nodes. This approach allows currently-available, hardware-accelerated PBR to be used with clusters of subscriber-aware service gateways that must also monitor control plane traffic from the same subscriber.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
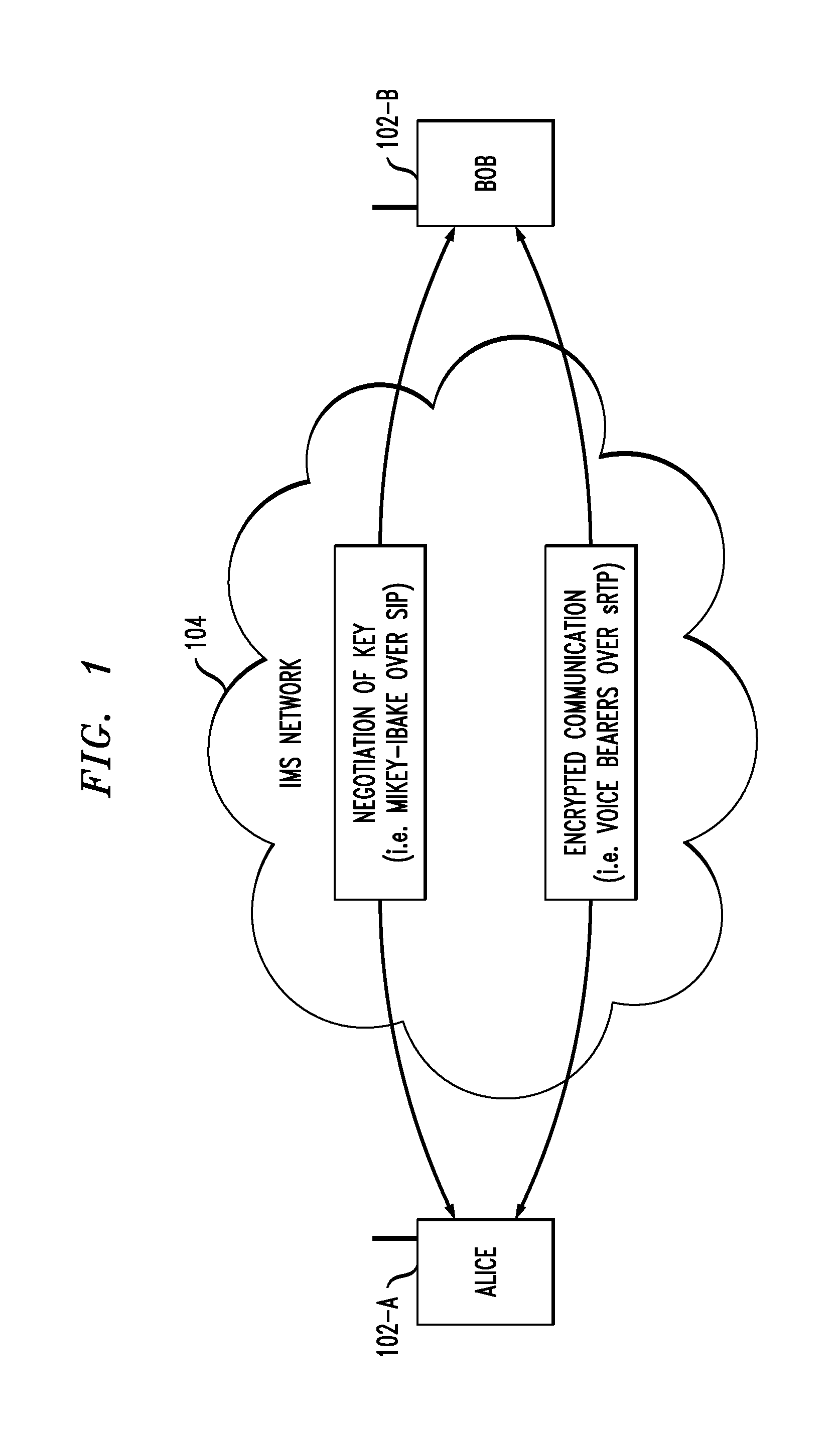
Policy routing-based lawful interception in communication system with end-to-end encryption
Techniques are disclosed for lawfully intercepting information in communication environments with end-to-end encryption. For example, a method for intercepting encrypted communications exchanged between a first computing device and a second computing device in a communication network, wherein the interception is performed by a third computing device in the communication network, comprises the following steps. The third computing device obtains one or more packets having a packet address associated with one of the first computing device and the second computing device. The one or more packets are obtained by the third computing device, in response to at least one interception routing policy being implemented in at least one element in the communication network, such that the one or more obtained packets may be decrypted so as to obtain data contained therein. The third computing device preserves the packet address of the one or more obtained packets. The third computing device forwards the one or more packets toward a packet-destination one of the first computing device and the second computing device such that the packet-destination one of the first computing device and the second computing device is unable to detect from the one or more packets that the one or more packets were intercepted by the third computing device.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
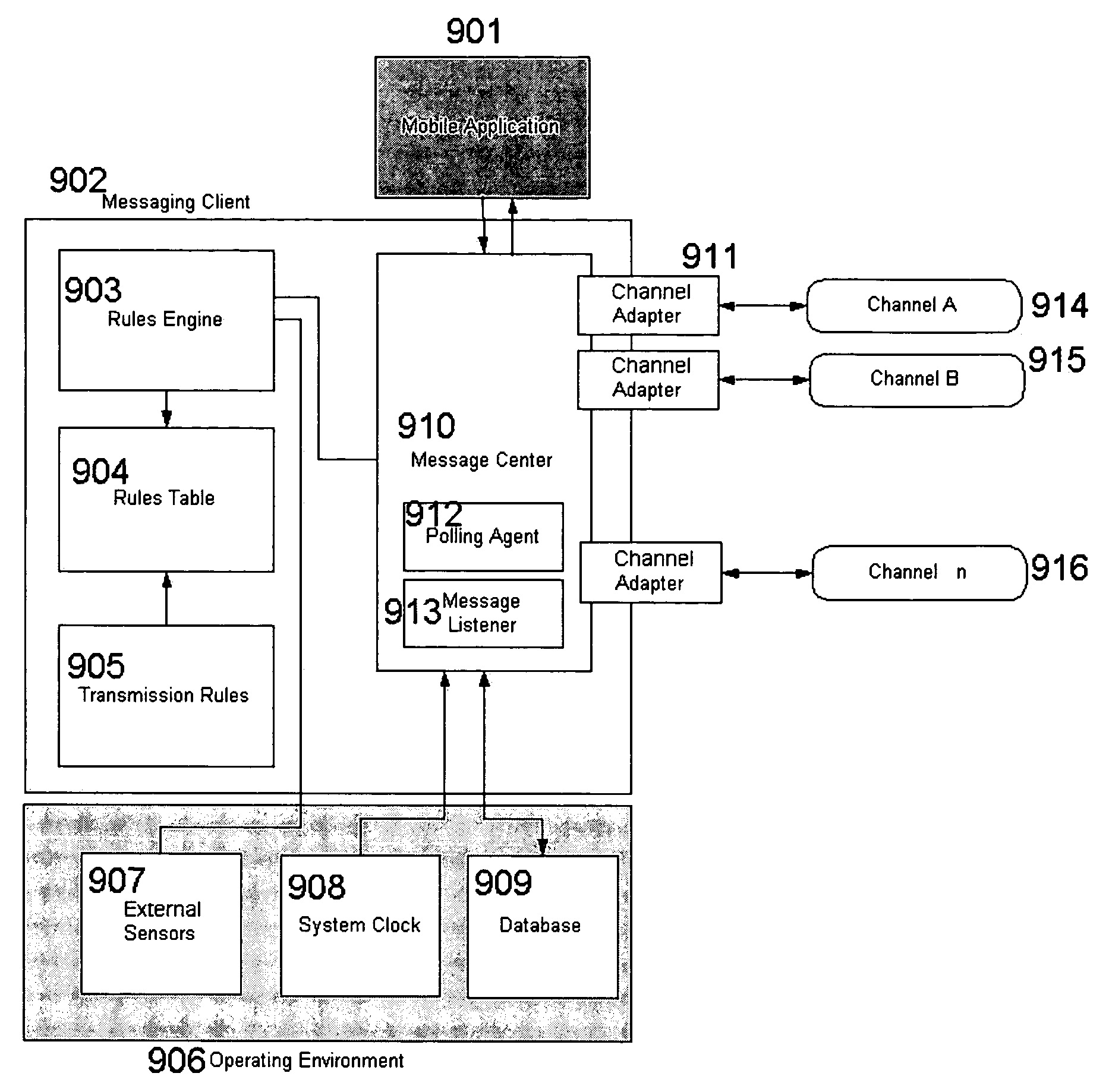
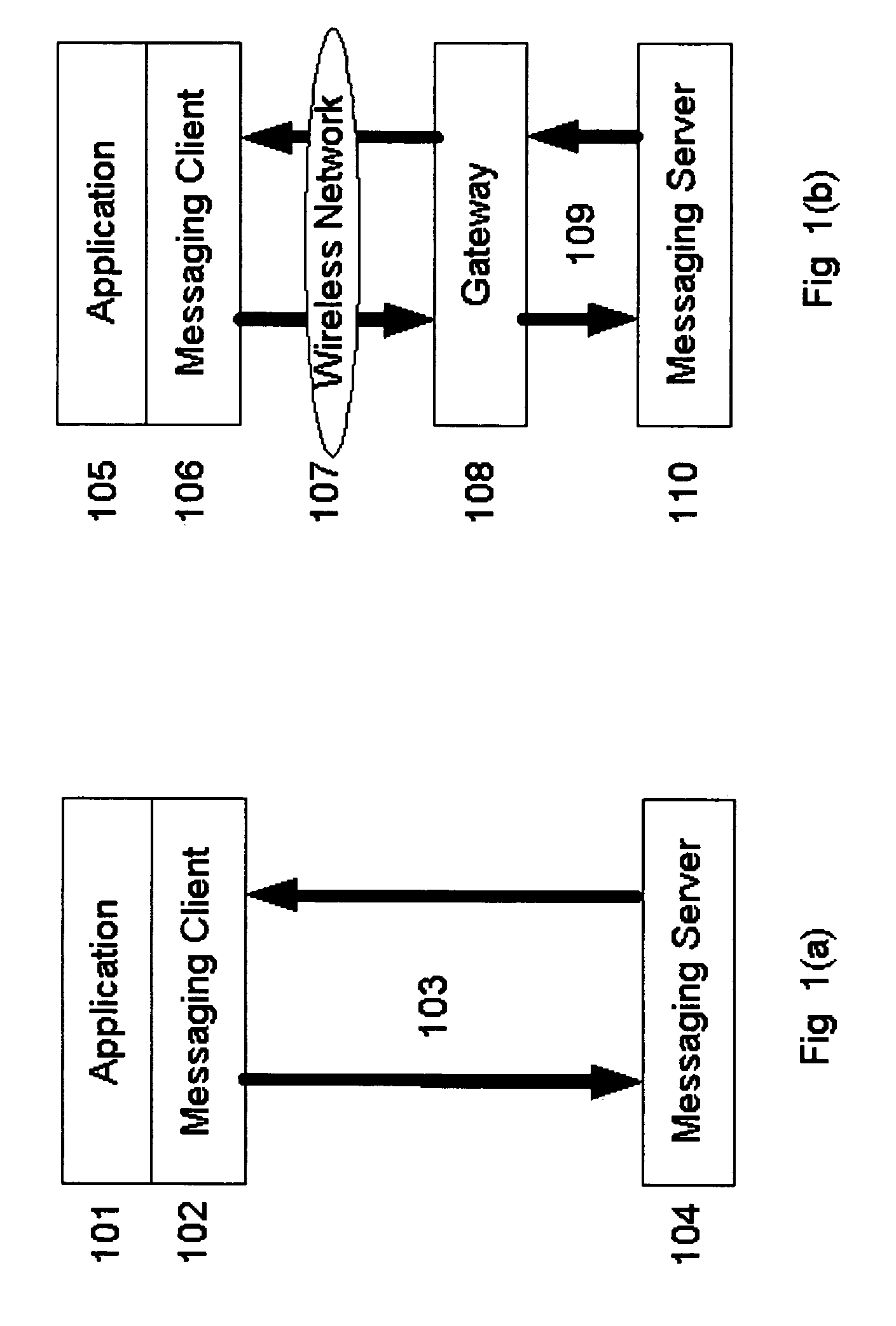
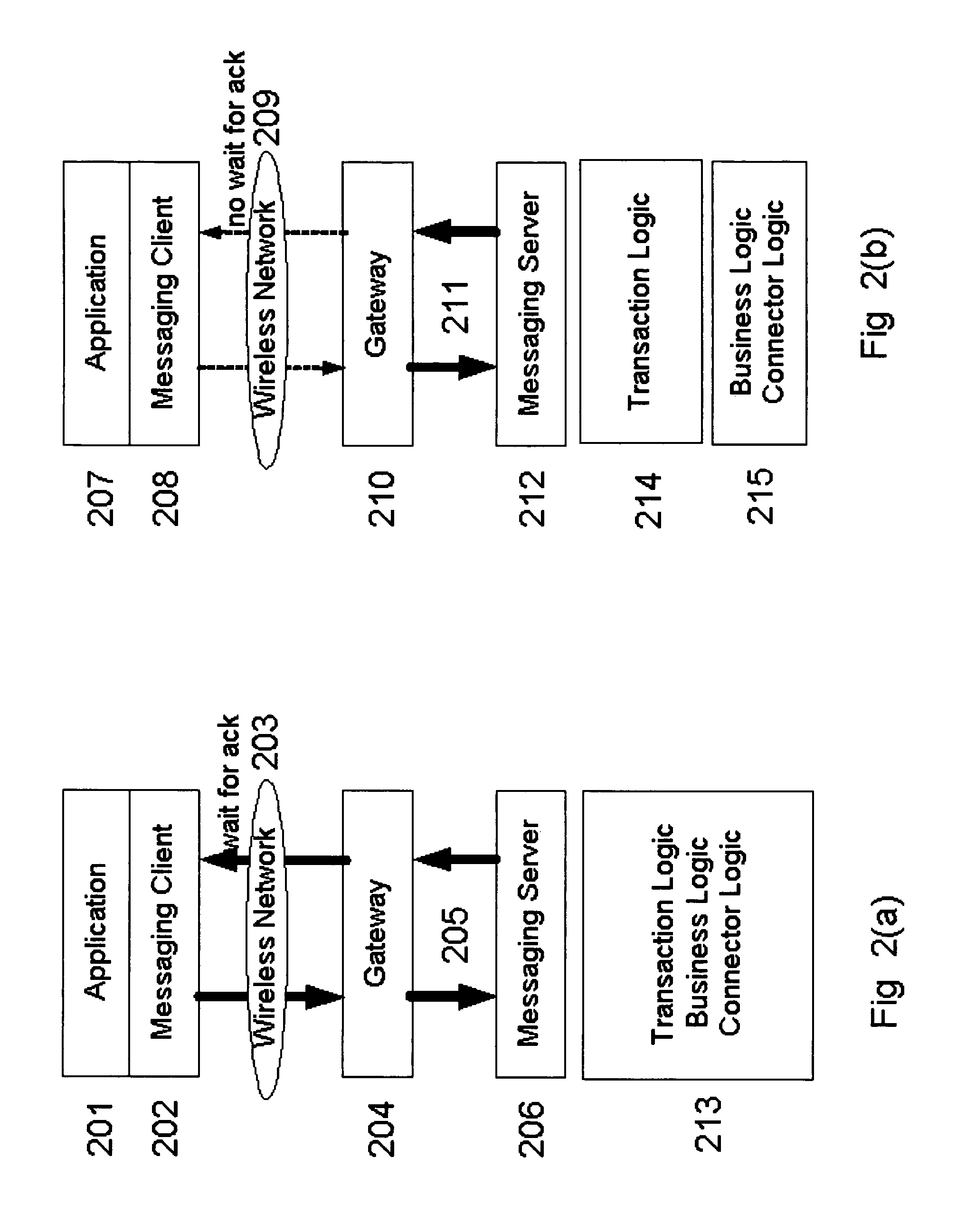
Efficient transactional messaging between loosely coupled client and server over multiple intermittent networks with policy based routing
InactiveUS7702739B1Simplify deploymentSimplifies developmentError preventionAccounting/billing servicesClient-sideMessage passing
Systems and methods are disclosed for reducing the cost of sending messages over an intermittent network of computing devices via multiple communication channels by creating a first message on a first device, the message intended to be sent to a second device over the network multiple communication channels; applying a first policy to reduce the cost of sending messages over the intermittent network of computing devices, the first policy containing one or more rules to determine whether to send the first message to the second device, each rule being a function of one or more messaging attributes of messages, channels or the system environment; and dynamically updating the first policy by sending a second message to the first device, the second message being a system message that results in the addition, deletion or other modification of the rules contained in the policy to reduce the cost of sending messages over the intermittent network of computing devices.
Owner:TRAN BAO
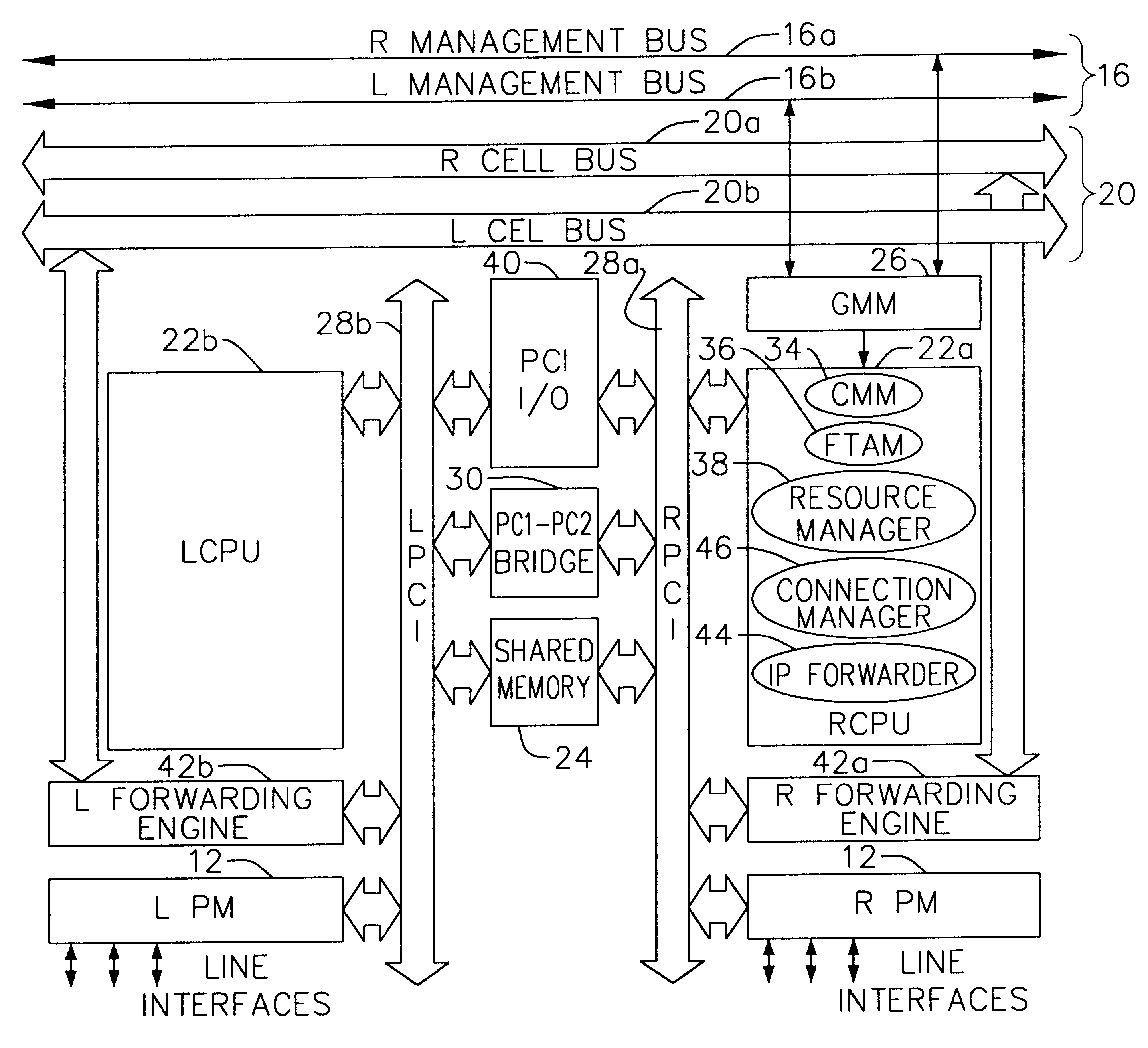
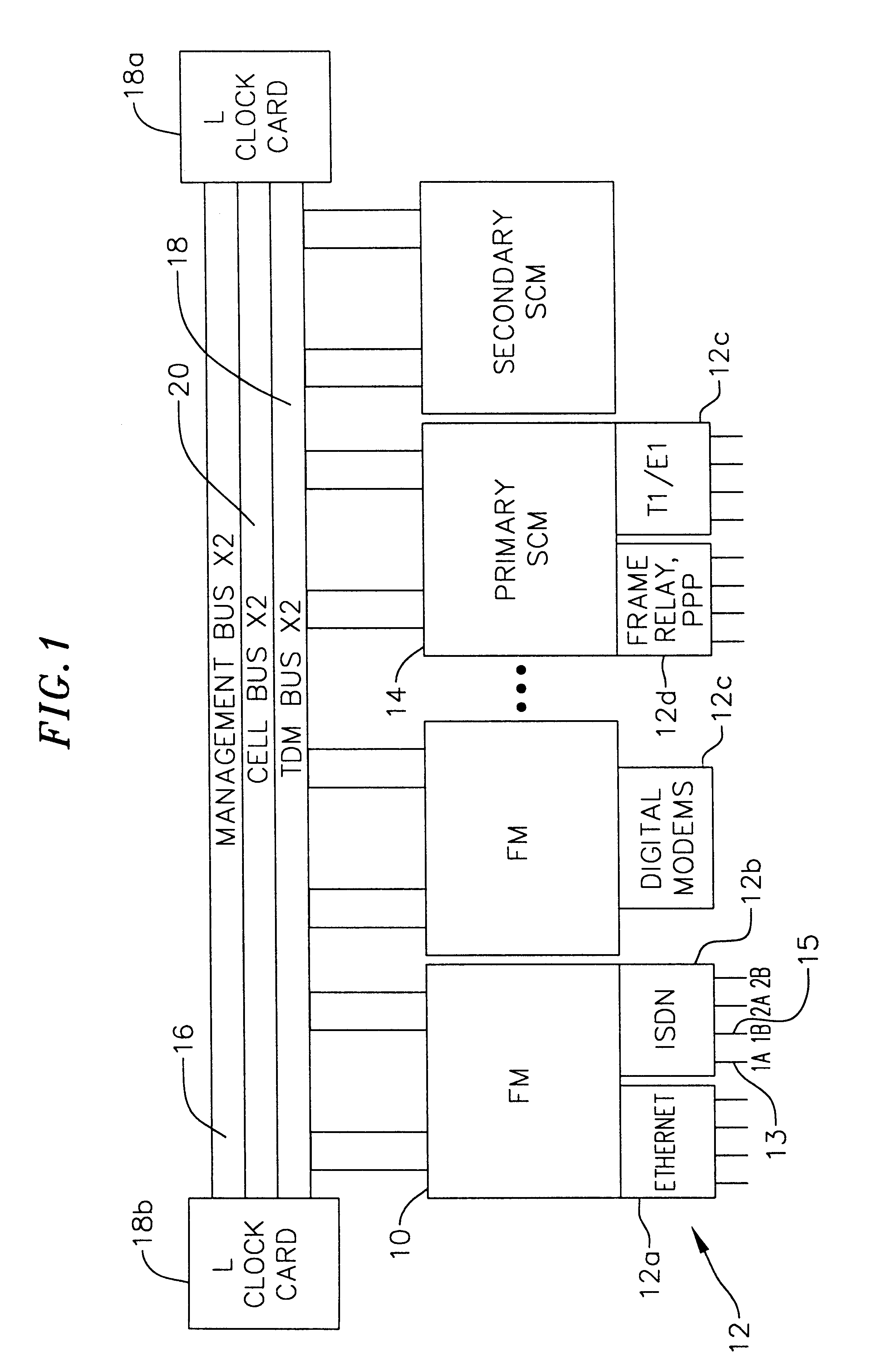
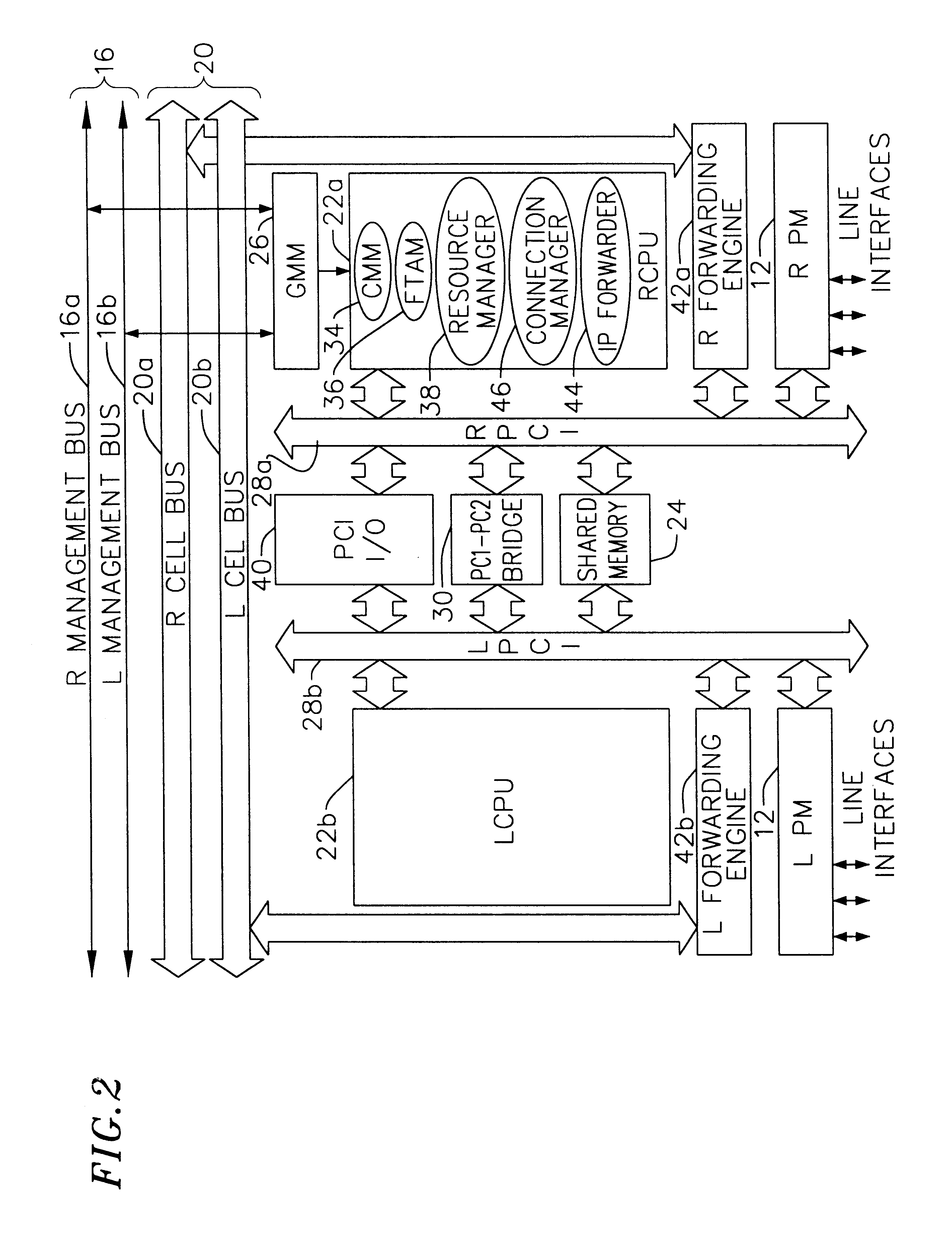
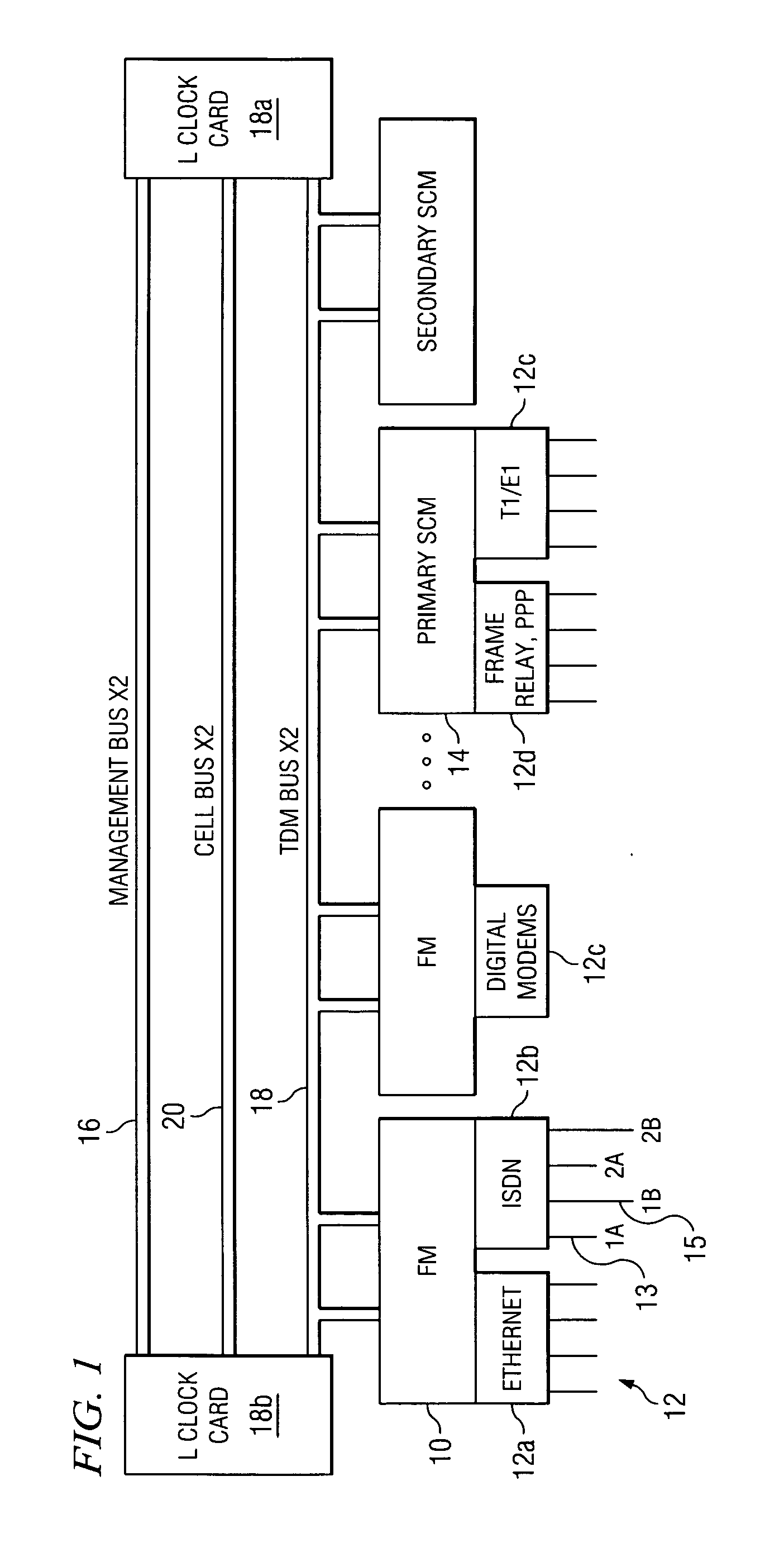
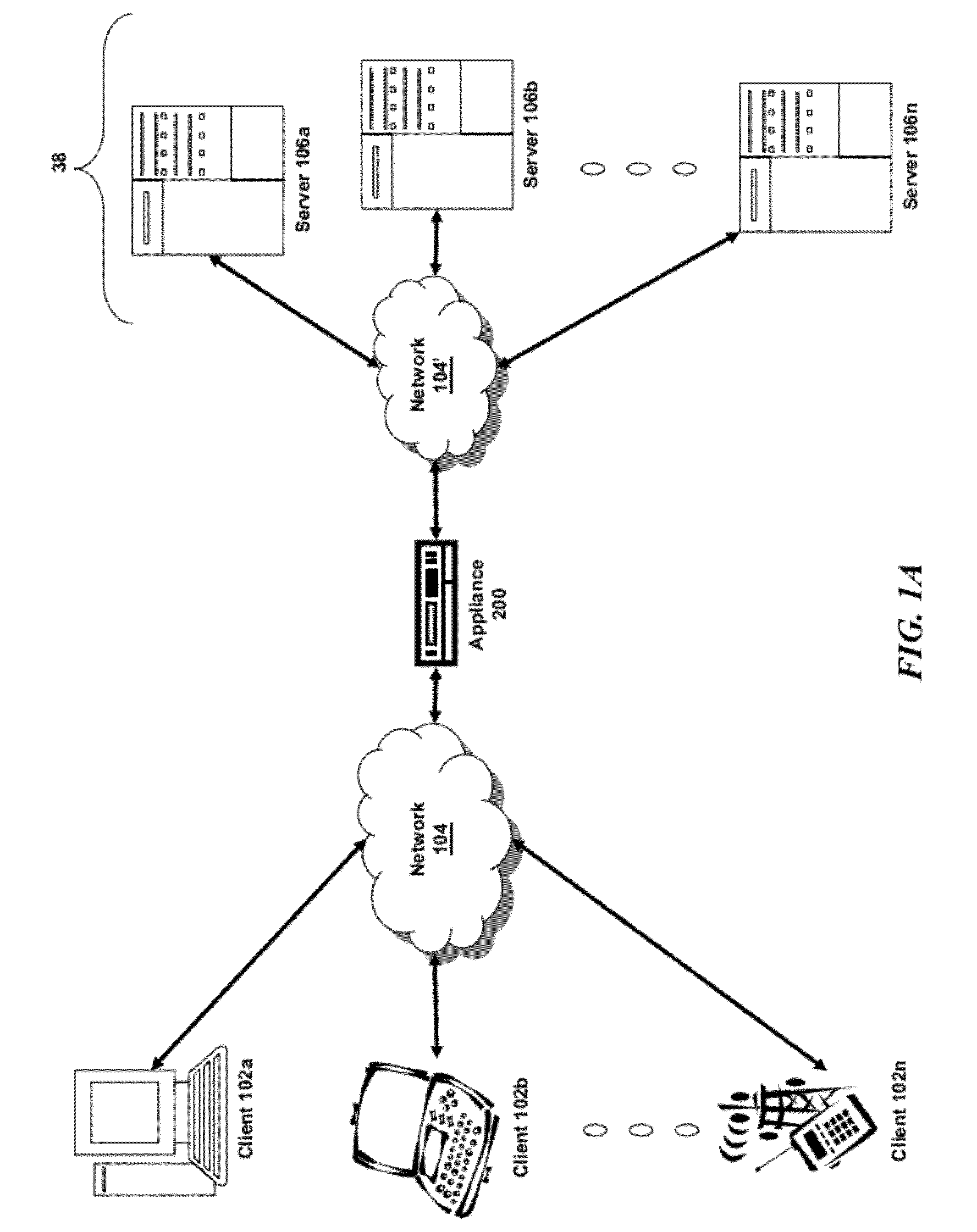
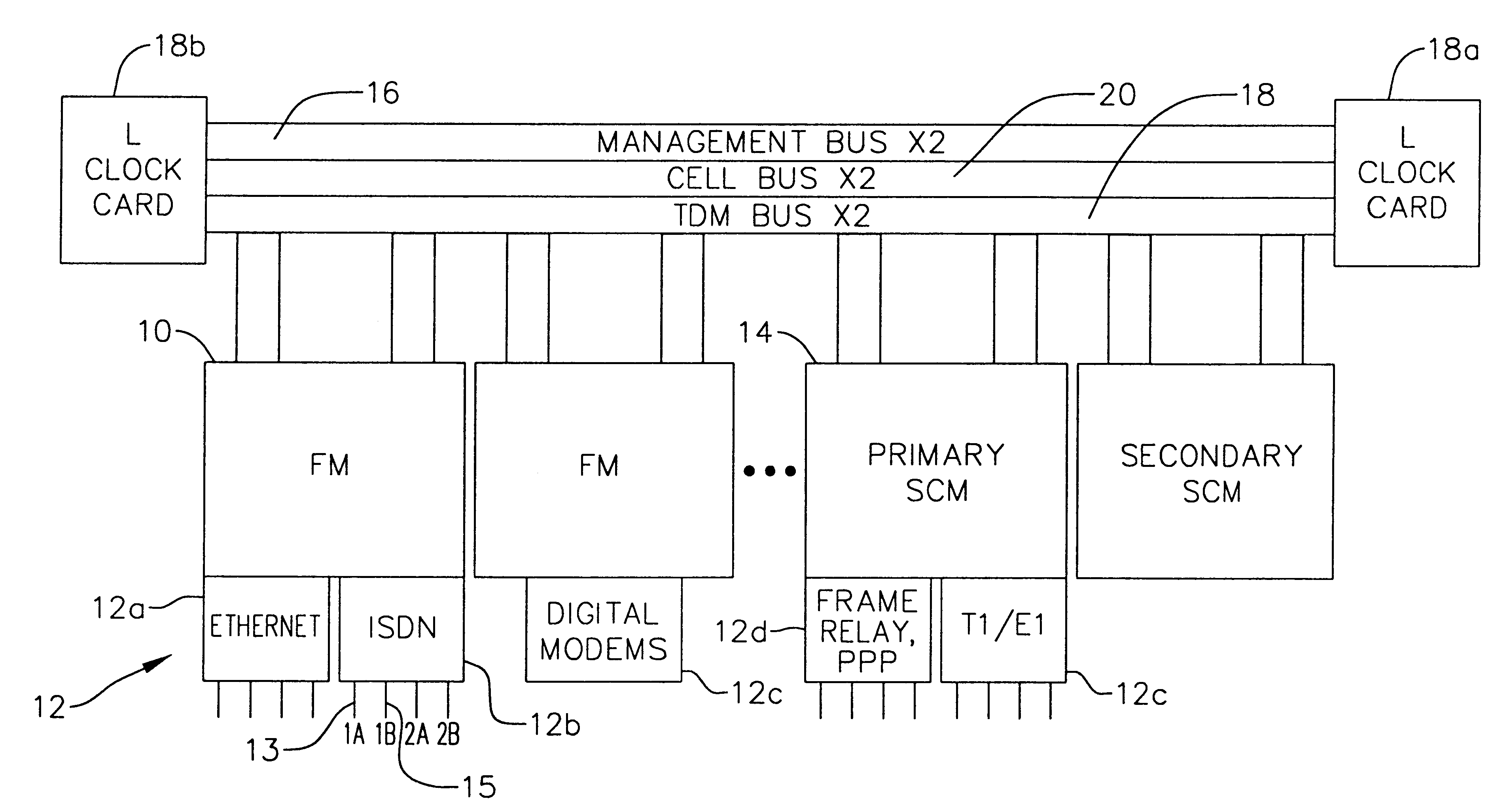
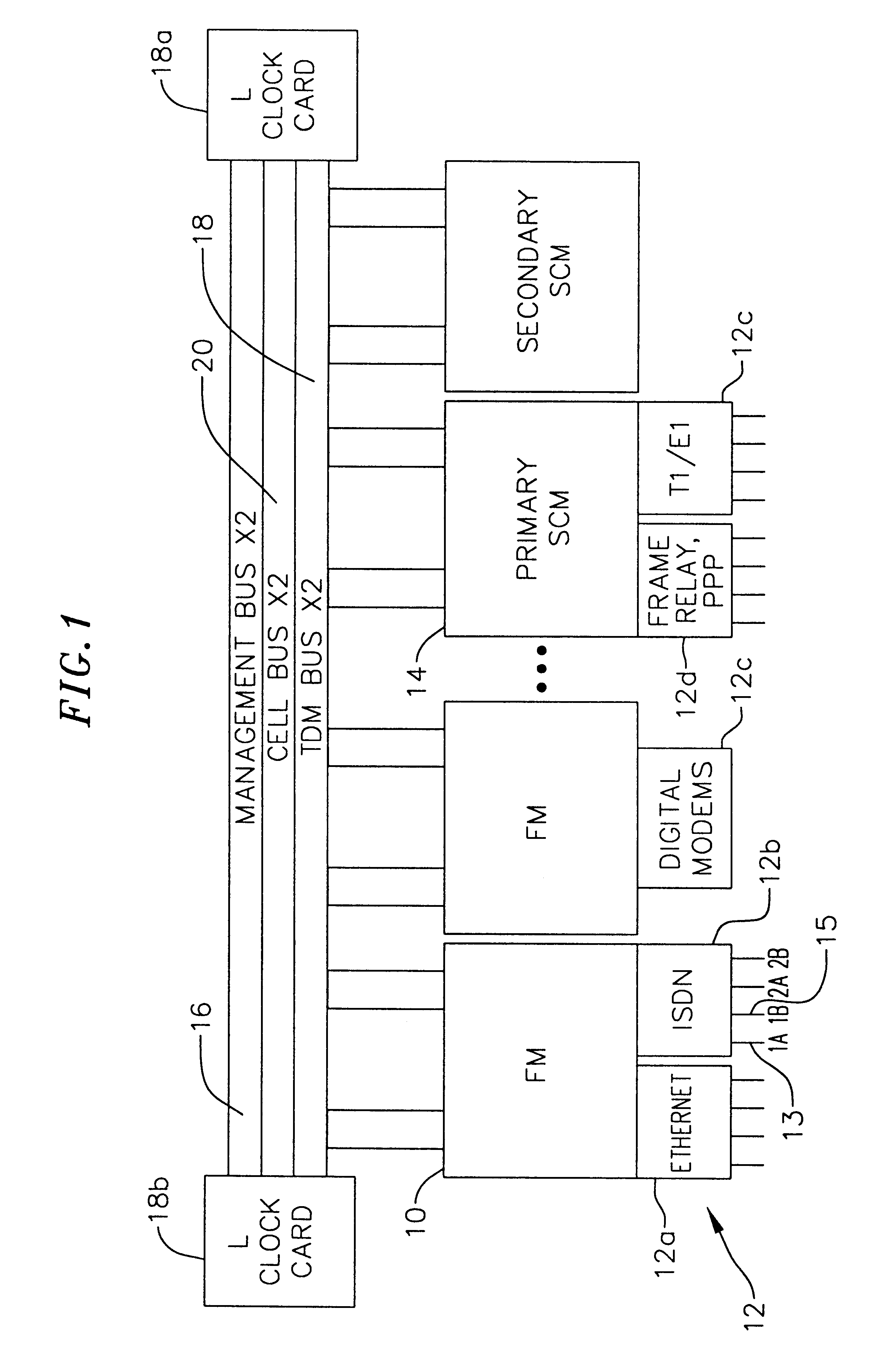
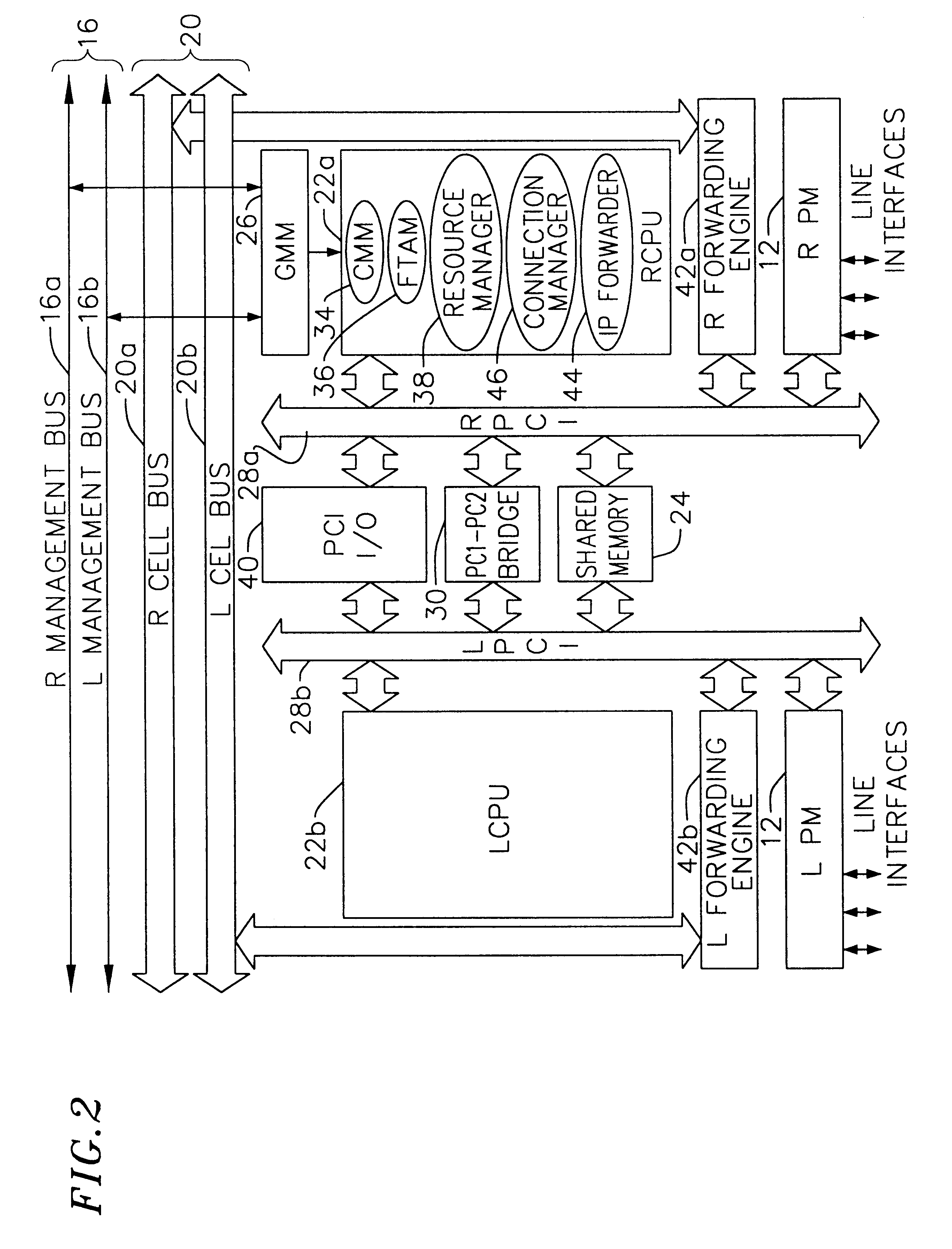
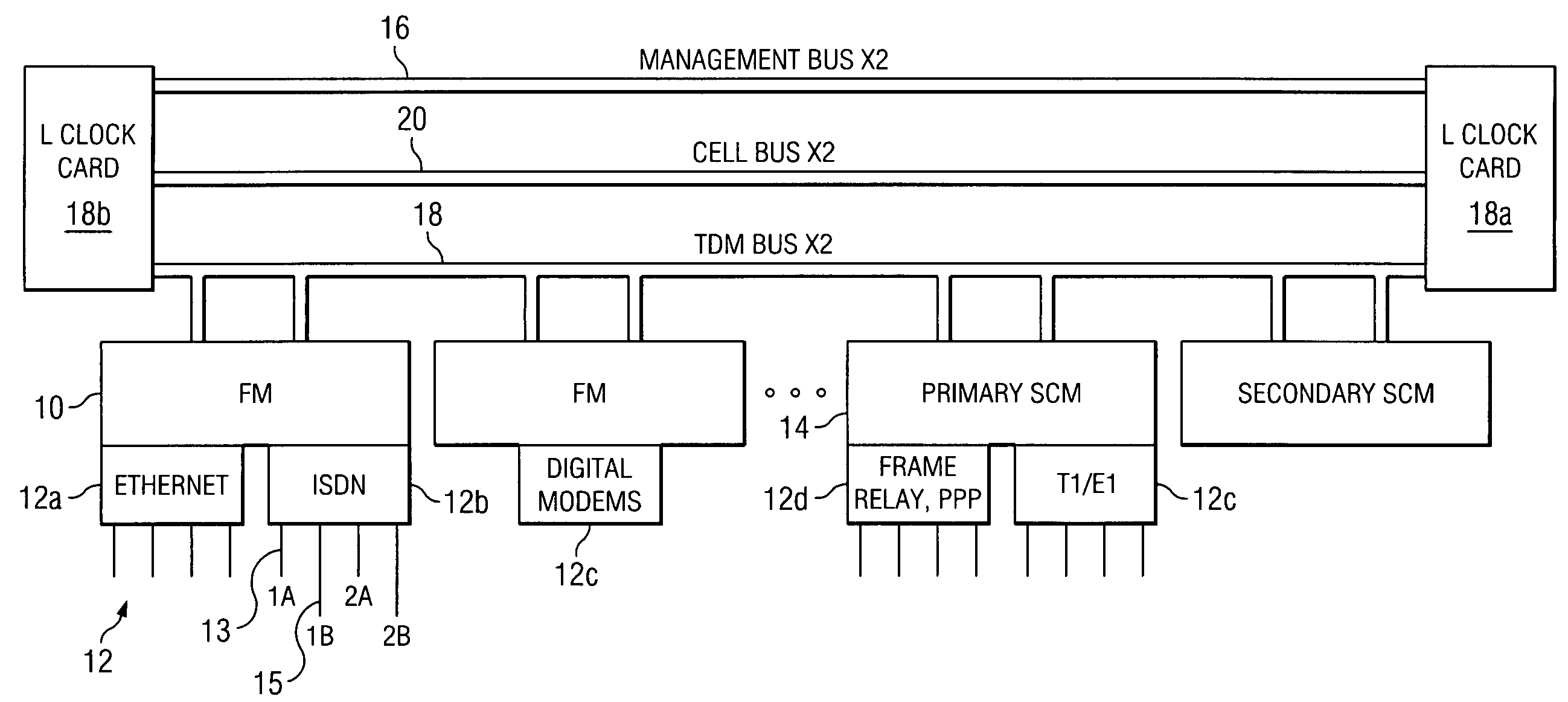
Multi-service network switch
InactiveUS6850531B1Raise priorityReduce dependenceData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDomain nameModem device
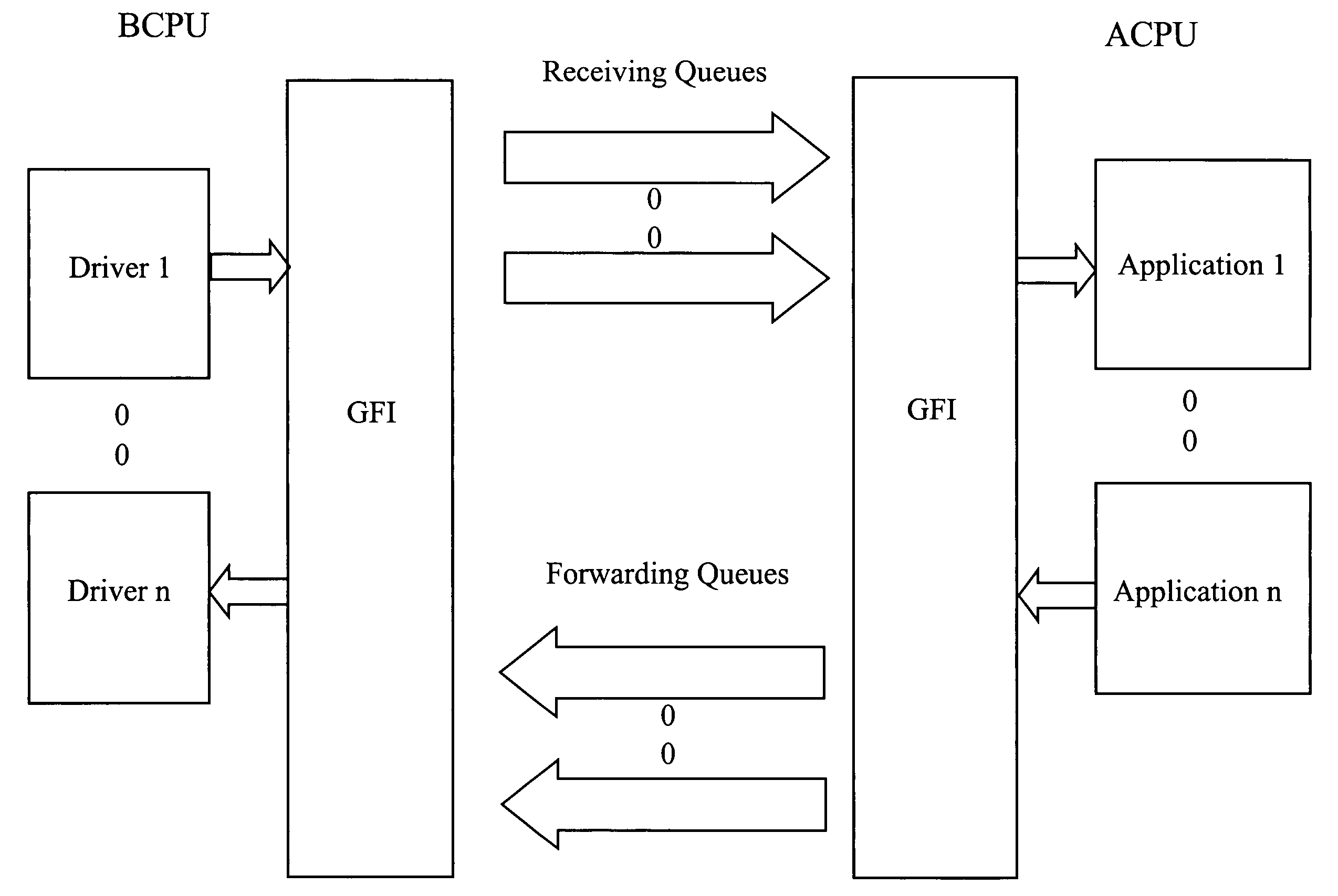
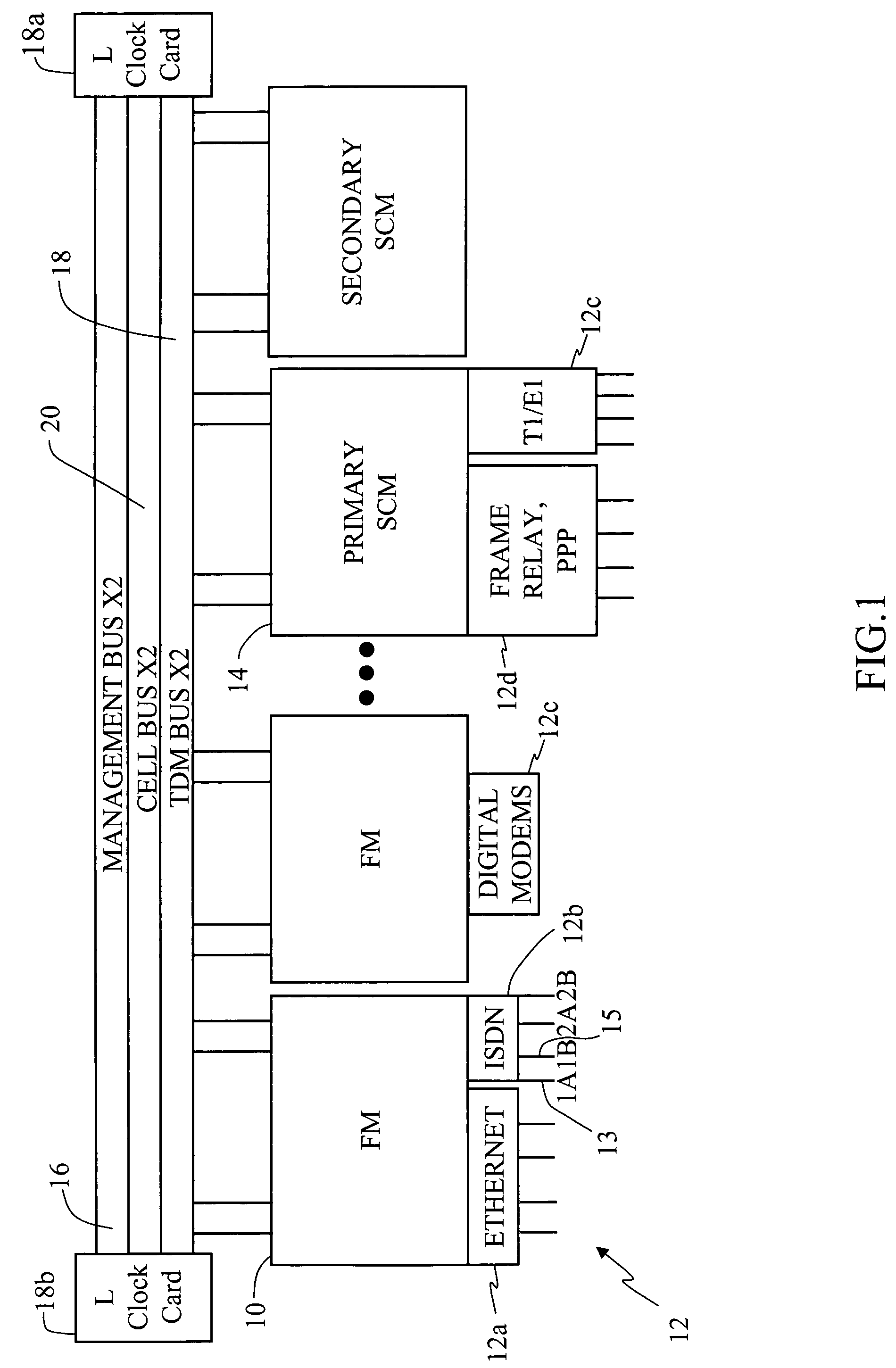
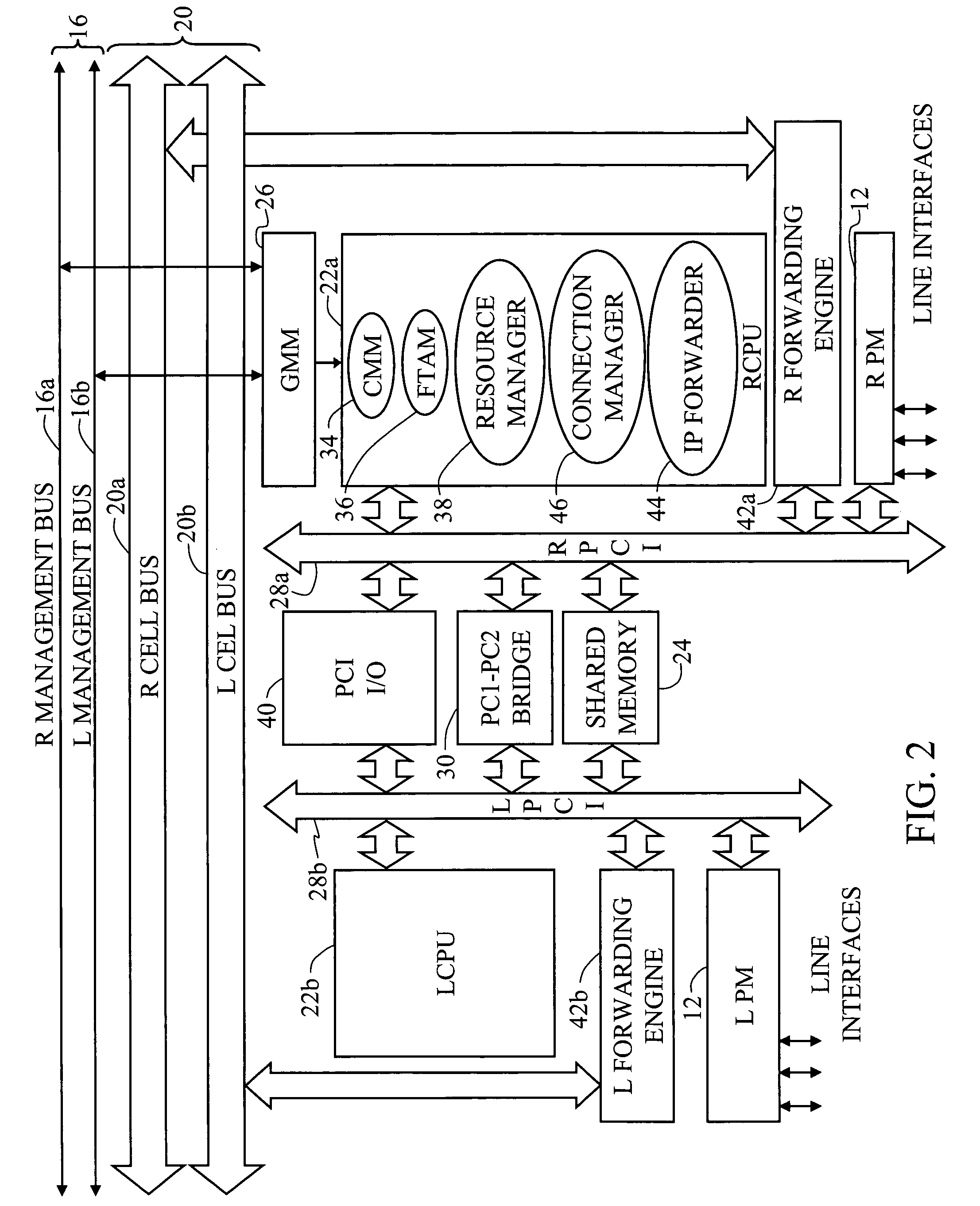
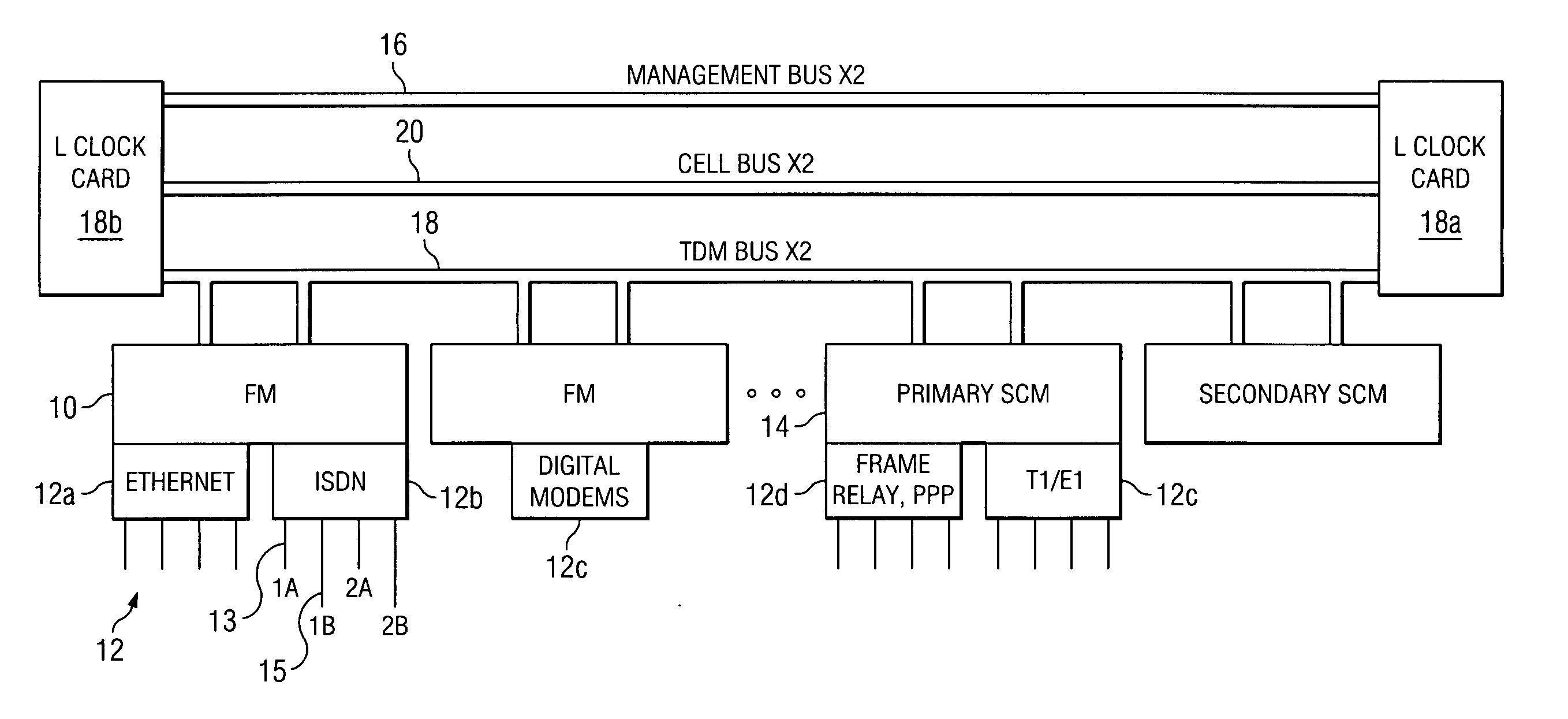
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Systems and methods for point of interaction based policy routing of transactions
InactiveUS8195565B2Convenient transactionHand manipulated computer devicesFinanceComputer scienceAuthorization
Facilitating commercial transactions using a payment system directory are disclosed. A payment directory and / or wireless point of sale (POS) device may be configured to use predetermined rules, a multitude of data items and / or conditions to locate a payment system, and transmit a payment authorization request from a remote location to at least one payment system, either directly, or via a payment system directory and / or a SSL Gateway.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Multi-service network switch with a generic forwarding interface
InactiveUS7116679B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameModem device
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
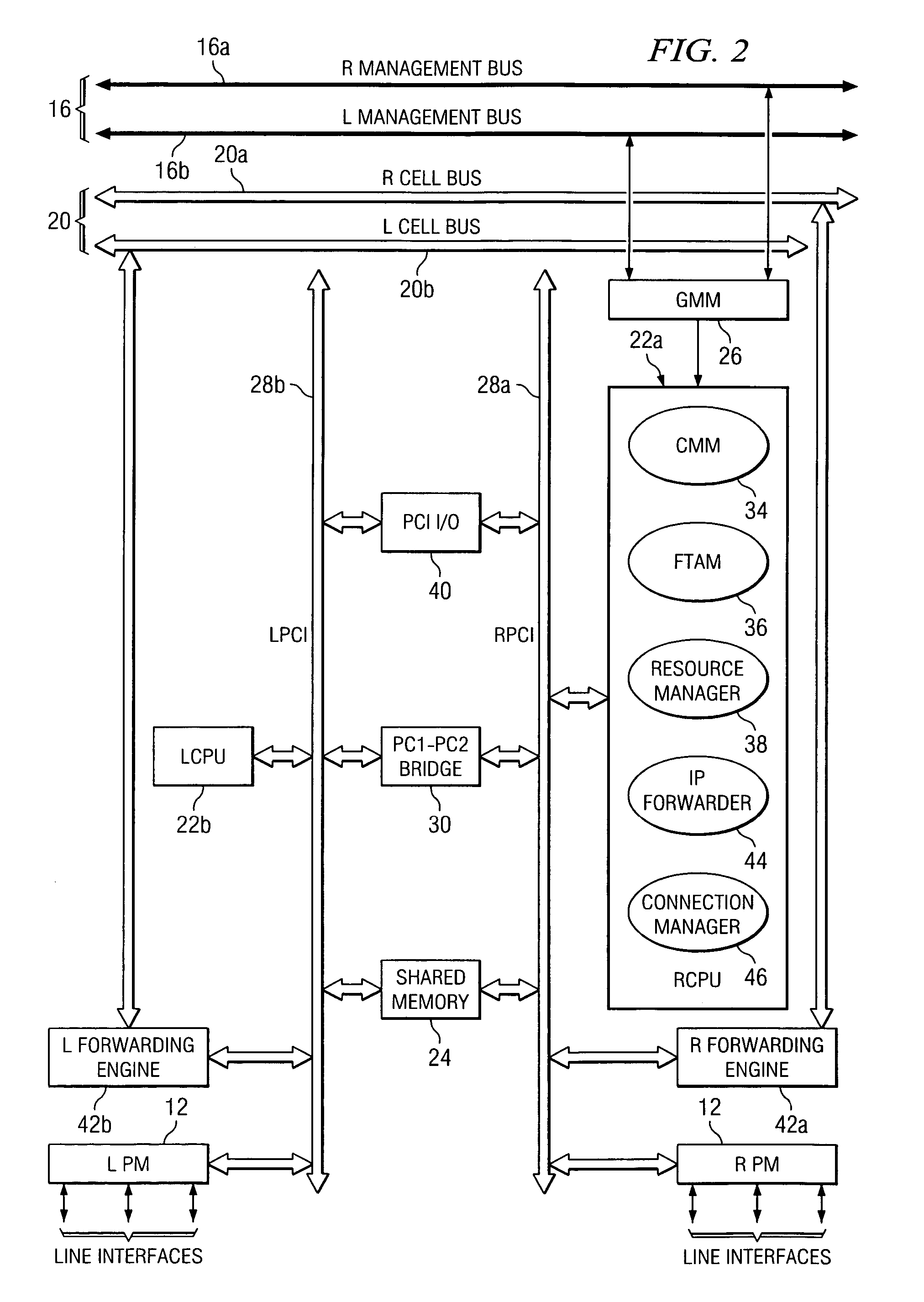
Multi-service network switch with independent protocol stack architecture
InactiveUS20050180429A1Reduce bottlenecksImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDomain nameRouting table
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
One arm data center topology with layer 4 and layer 7 services
ActiveUS7571470B2Expensive to operateExpensive to setComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityData center
A one-arm data center topology routes traffic between internal sub-nets and between a sub-net and an outside network through a common chain of services. The data center topology employs layer 4 services on a common chassis or platform to provide routing and firewall services while reducing the number of devices necessary to implement the data center and simplifying configuration. Load balancing is provided by a load balancing device. In the one-arm topology, policy based routing or client network address translations or NAT pushes traffic to the CSM.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and Methods for Policy Based Routing for Multiple Hops
ActiveUS20120163180A1Provide reliabilityBalance traffic loadError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic characteristicIp address
The present application is directed towards policy based routing for intelligent traffic management via multiple next hops. In some embodiments, the systems and methods disclosed herein may provide management of inbound and outbound traffic across multiple network links, and may further provide reliability in case of link failure, and provide balancing of traffic, responsive to the latency and bandwidth requirements of various applications. Accordingly, these systems and methods may provide intelligent policy-based routing and network and port address translation, sensitive to application traffic types, protocols, source IP addresses and ports, destination IP addresses and ports, or any combination thereof, and can balance traffic loads among multiple available paths based on multiple traffic characteristics. The routing may performed on a packet-by-packet basis, a transaction-by-transaction basis, or a session-by-session basis, and the systems and methods may include capabilities for application-aware health monitoring of available network paths.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Multi-service network switch with modem pool management
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
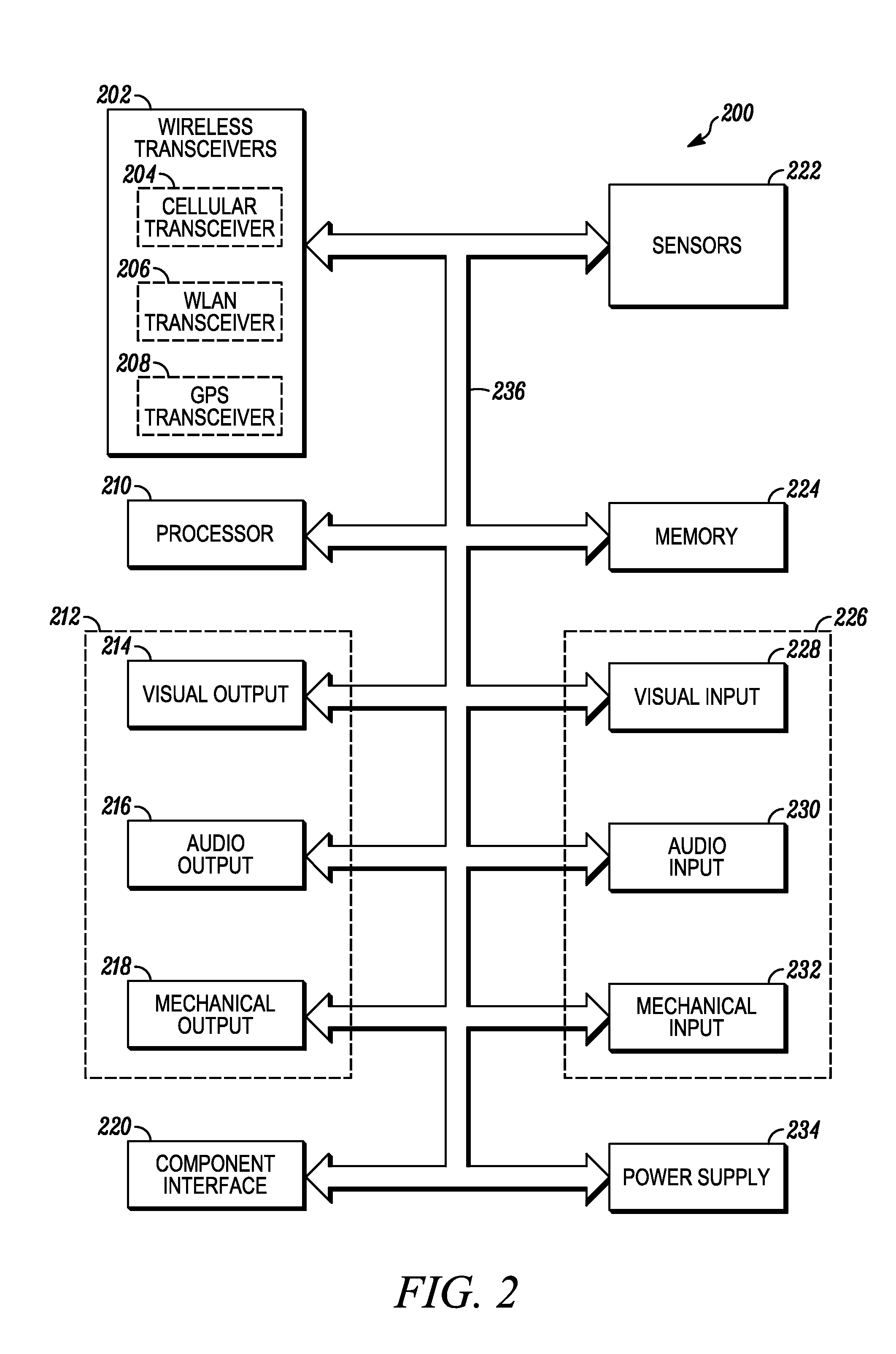
Network device continuity
ActiveUS20070097874A1Error preventionTransmission systemsCommunication interfaceNetwork Access Device
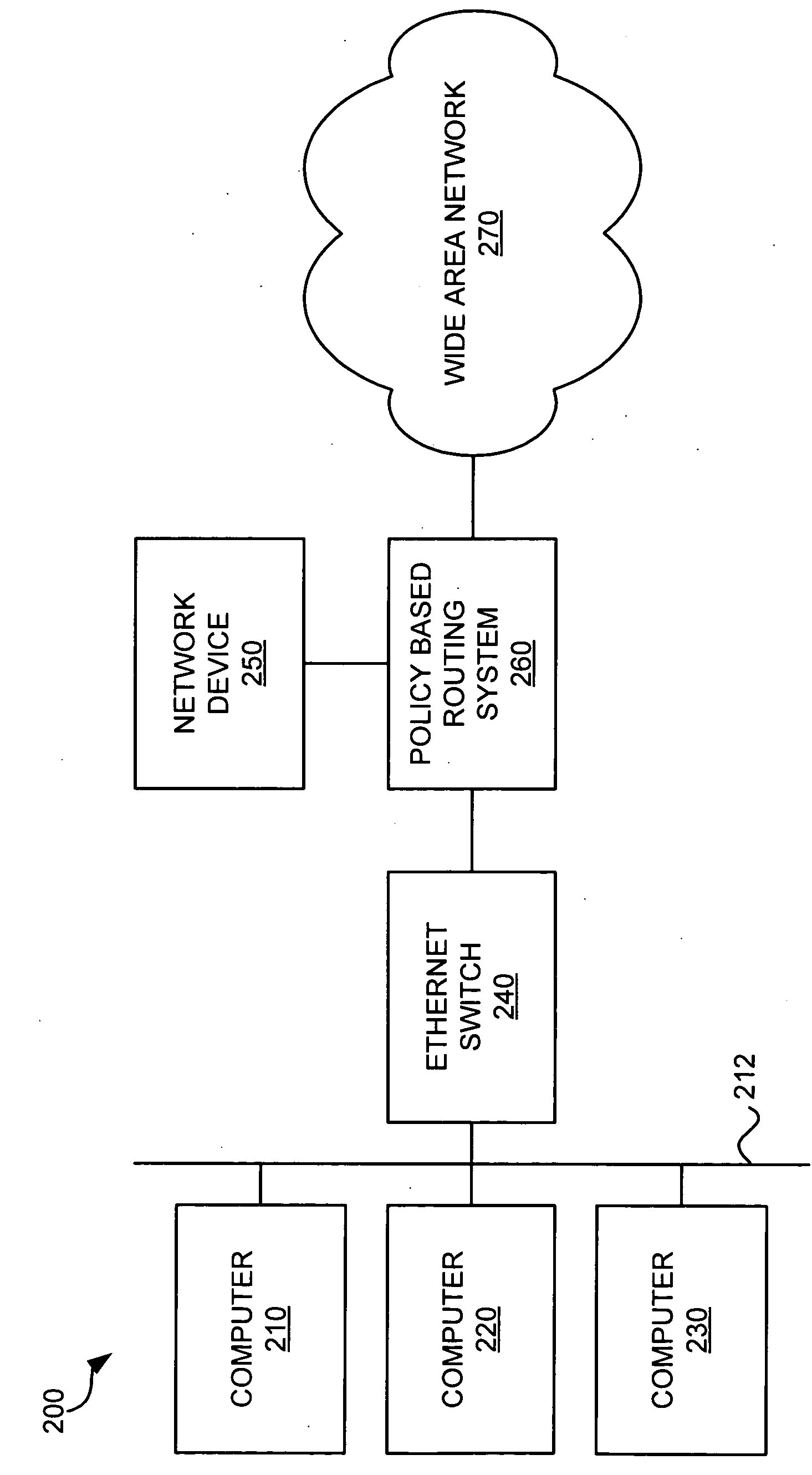
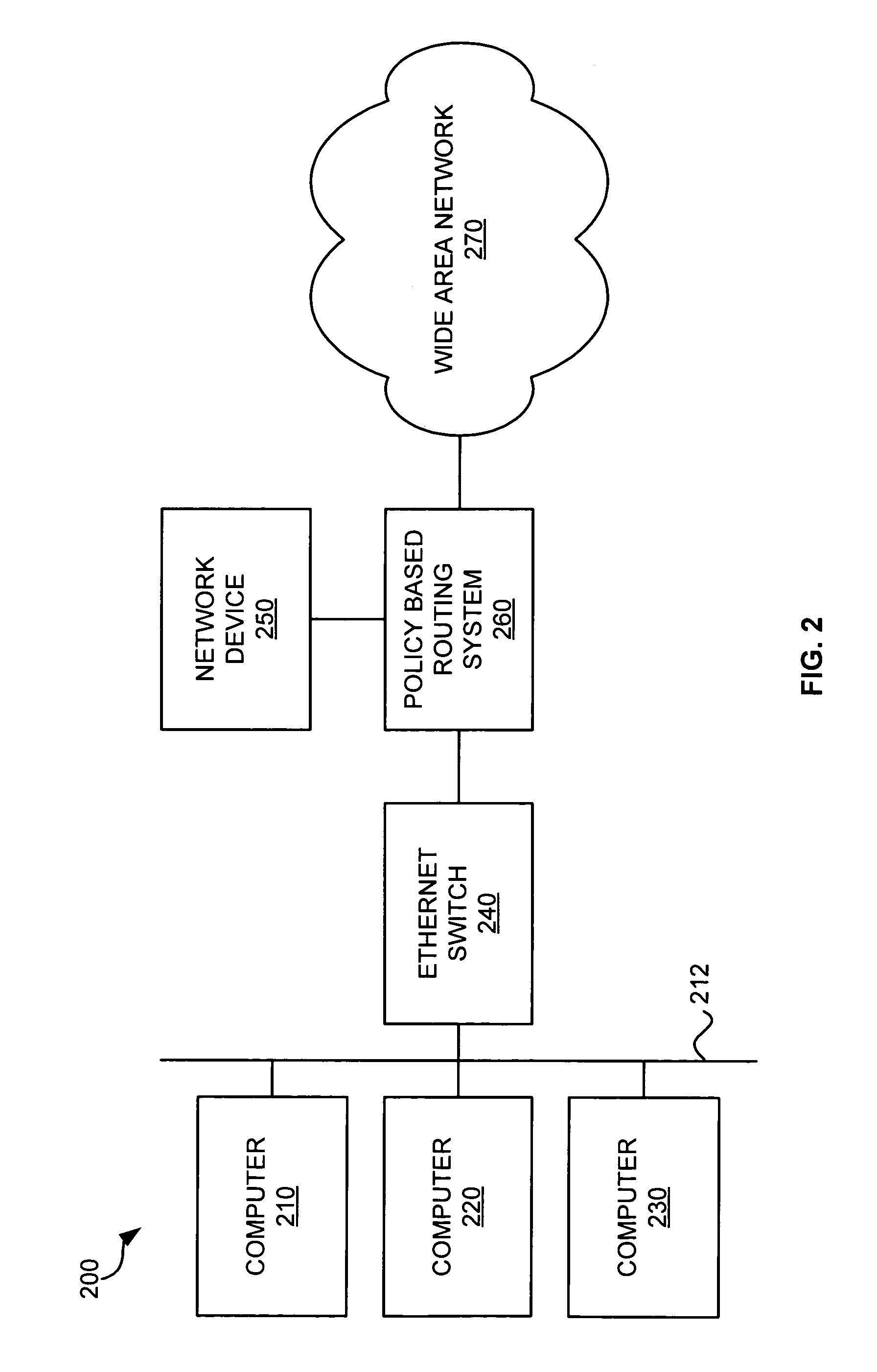
A network device that ensures network continuity includes a processor and a communications interface. The processor determines whether the network device is functioning properly. The processor then generates a signal indicating whether the network device is functioning properly and transmits the signal to the communications interface. The communications interface is coupled to the processor and a policy based routing system. The communications interface processes the signal to activate or deactivate a link to the policy based routing system.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Network device continuity
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
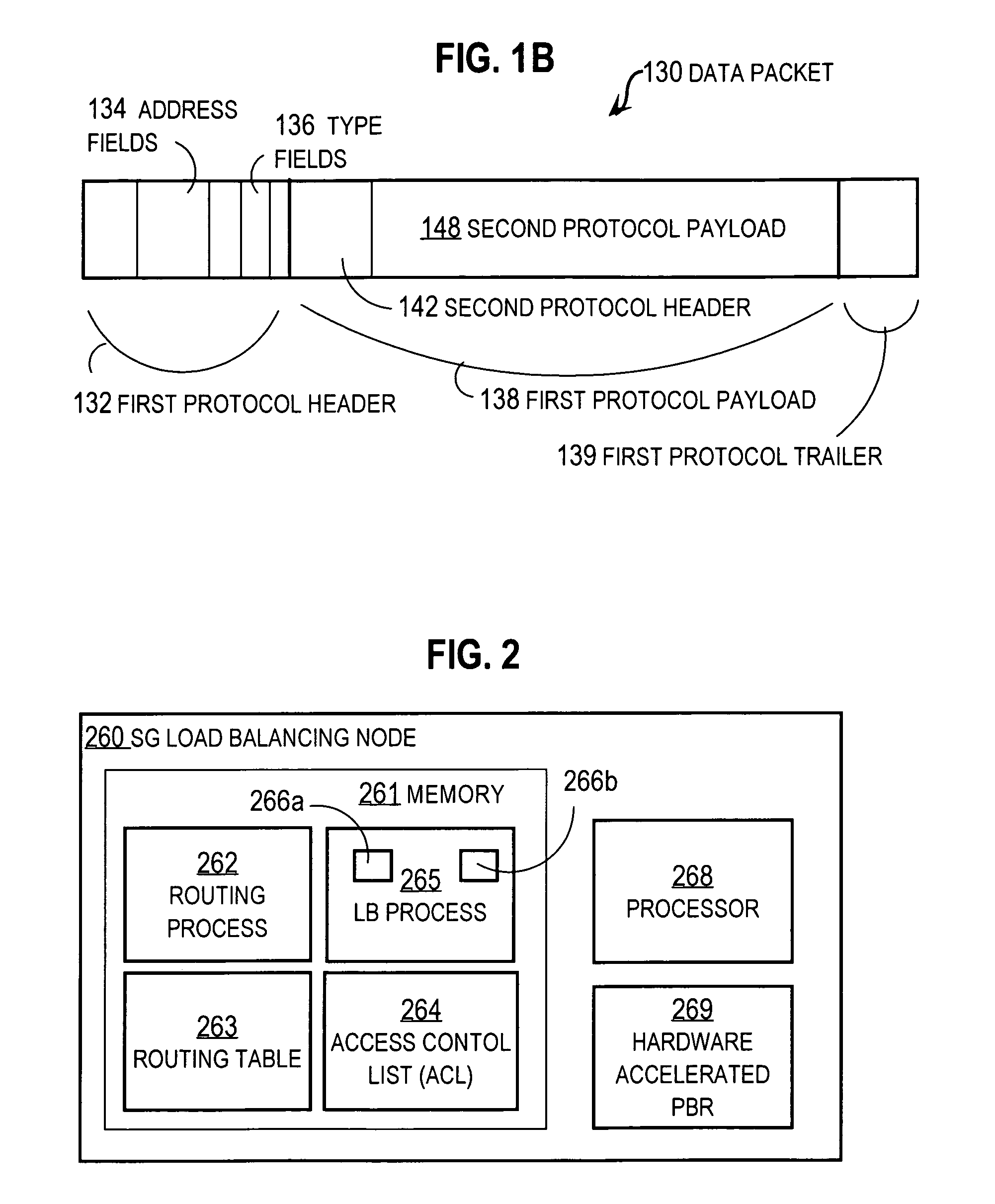
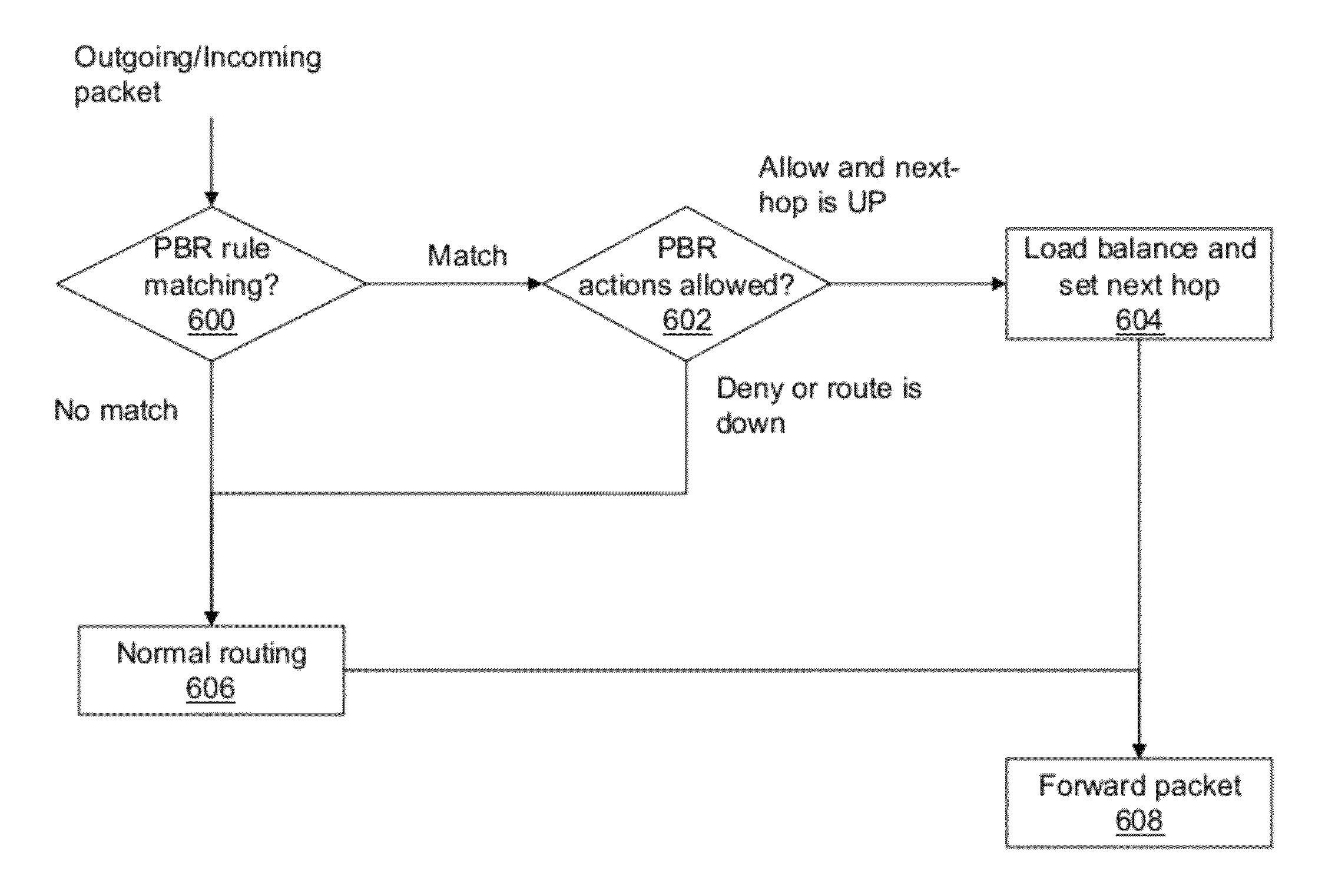
Policy based routing using a fast filter processor
A network device for processing packets. The network device includes applying specific fields from a packet to an associated memory device and comparing means for comparing input to the memory device with entries in the memory device. The network device also includes enabling means for enabling selection of bits, by the memory device, that are required to match exactly with bits from the input to the memory device. The network device further includes outputting means for outputting an address for a matched entry by the memory device and applying means for applying a match from the memory device to an associated entry in a table for applying actions from the table that are associated with the match to the packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
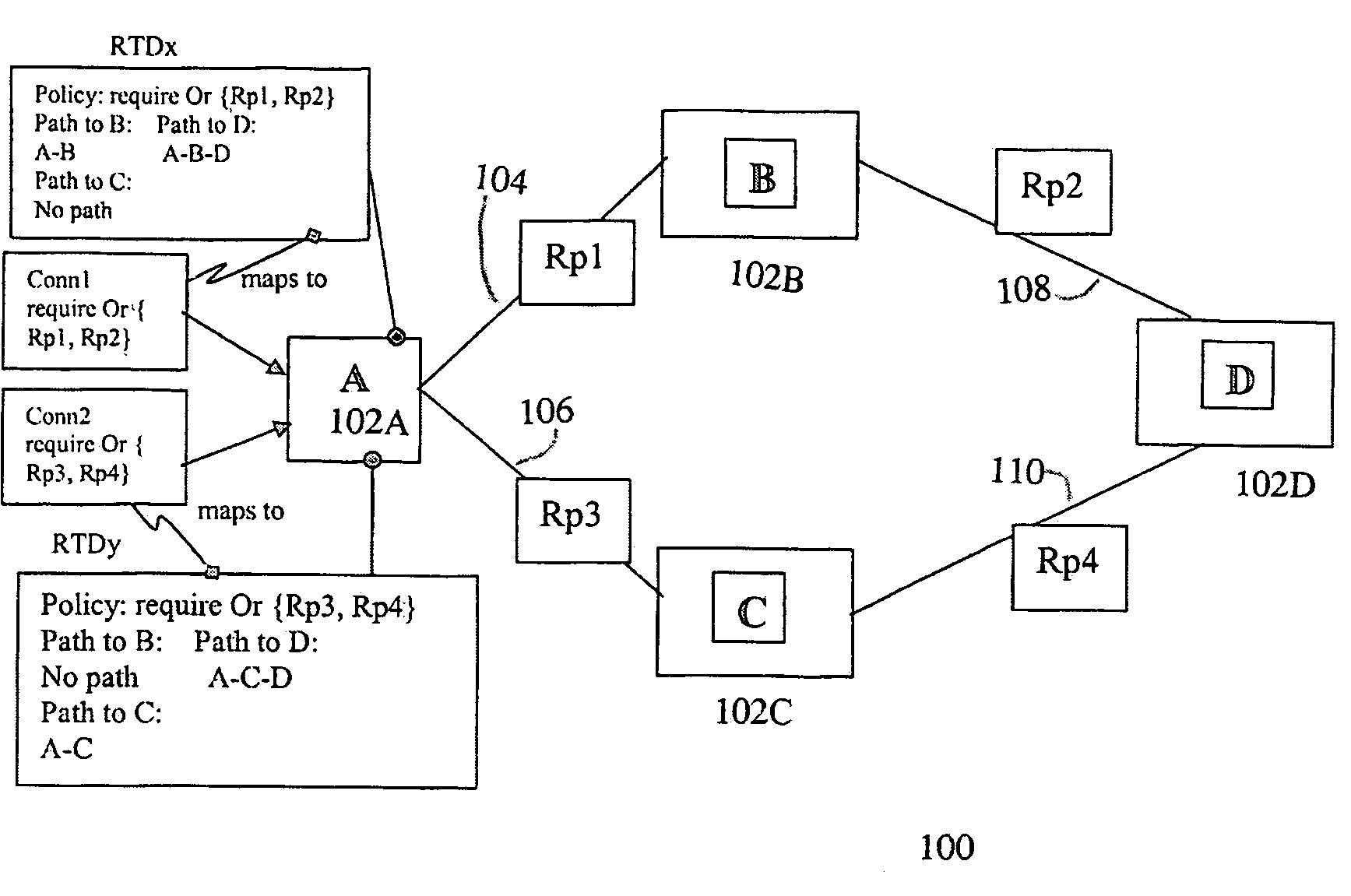
System and method for identifying pre-computed paths in a policy-based routing network
ActiveUS20060153191A1Reduce the numberError preventionTransmission systemsReal-time computingPolicy-based routing
The invention provides a system and method for identifying a pre-computed path for an incoming connection at a node in a policy-based routing network. The method comprises: examining requirements of the incoming connection; examining policies associated with routes available from the node; identifying at least one policy of the policies which meets the requirements of the incoming connection; and utilizing that one policy for the pre-computed path for the incoming connection.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for policy based routing for multiple next hops
ActiveUS9178805B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic characteristicIp address
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method and device for policy-based routing
A mobile device performs a method for policy-based routing. The method includes creating a first set of marking rules based on routing policy data provisioned in the mobile device, wherein each marking rule indicates labeling for packets, wherein the labeling is used in selecting one of a plurality of active network interfaces in the mobile device to route the packets over a set of access networks available to the mobile device. The method further includes creating a first set of routing tables corresponding to the labeling indicated by the first set of marking rules, wherein each routing table directs the mobile device to a different one of the active network interfaces of the plurality of active network interfaces.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for identifying pre-computed paths in a policy-based routing network
ActiveUS7463587B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingPolicy-based routing
The invention provides a system and method for identifying a pre-computed path for an incoming connection at a node in a policy-based routing network. The method comprises: examining requirements of the incoming connection; examining policies associated with routes available from the node; identifying at least one policy of the policies which meets the requirements of the incoming connection; and utilizing that one policy for the pre-computed path for the incoming connection.
Owner:RPX CORP
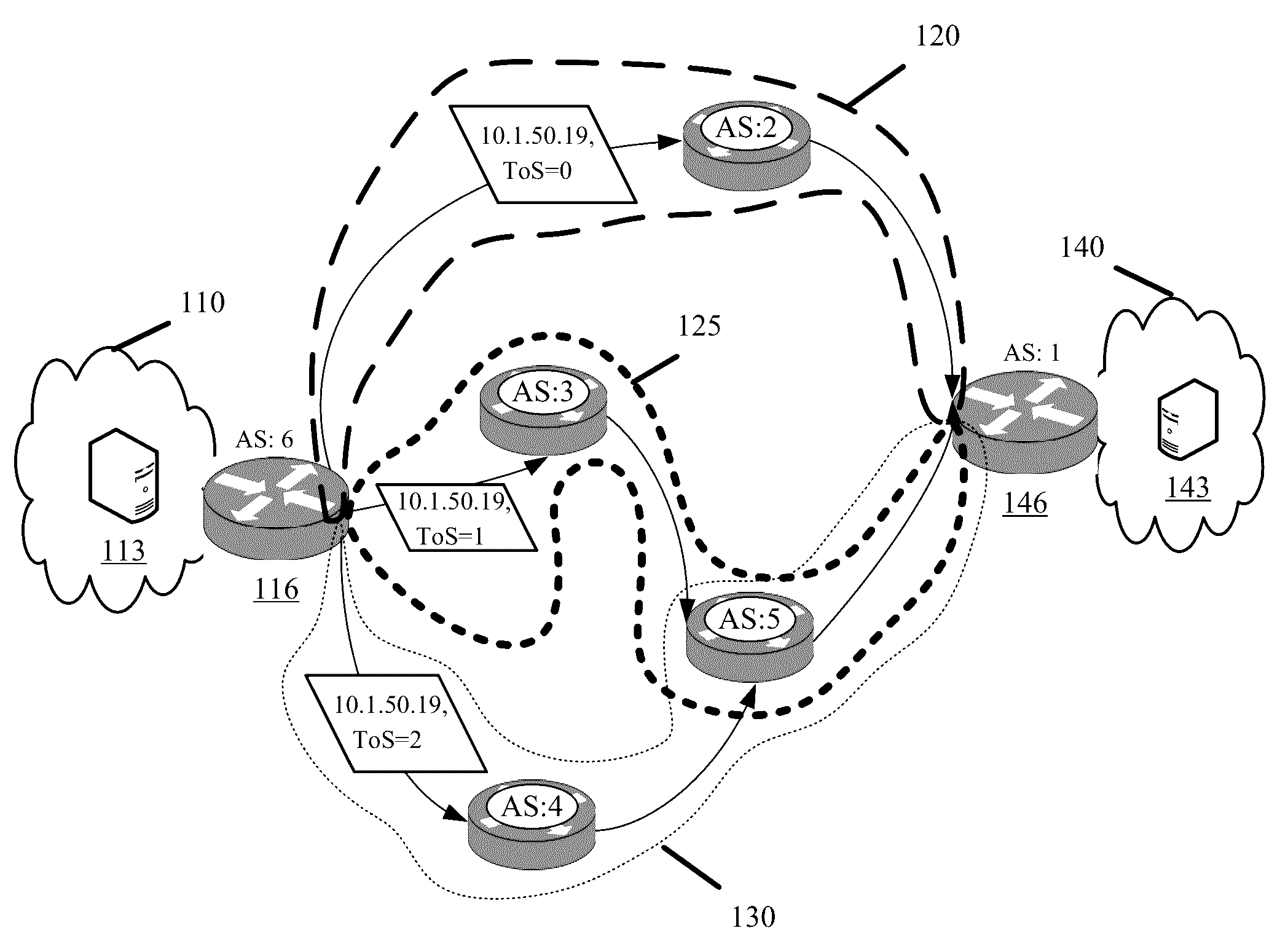
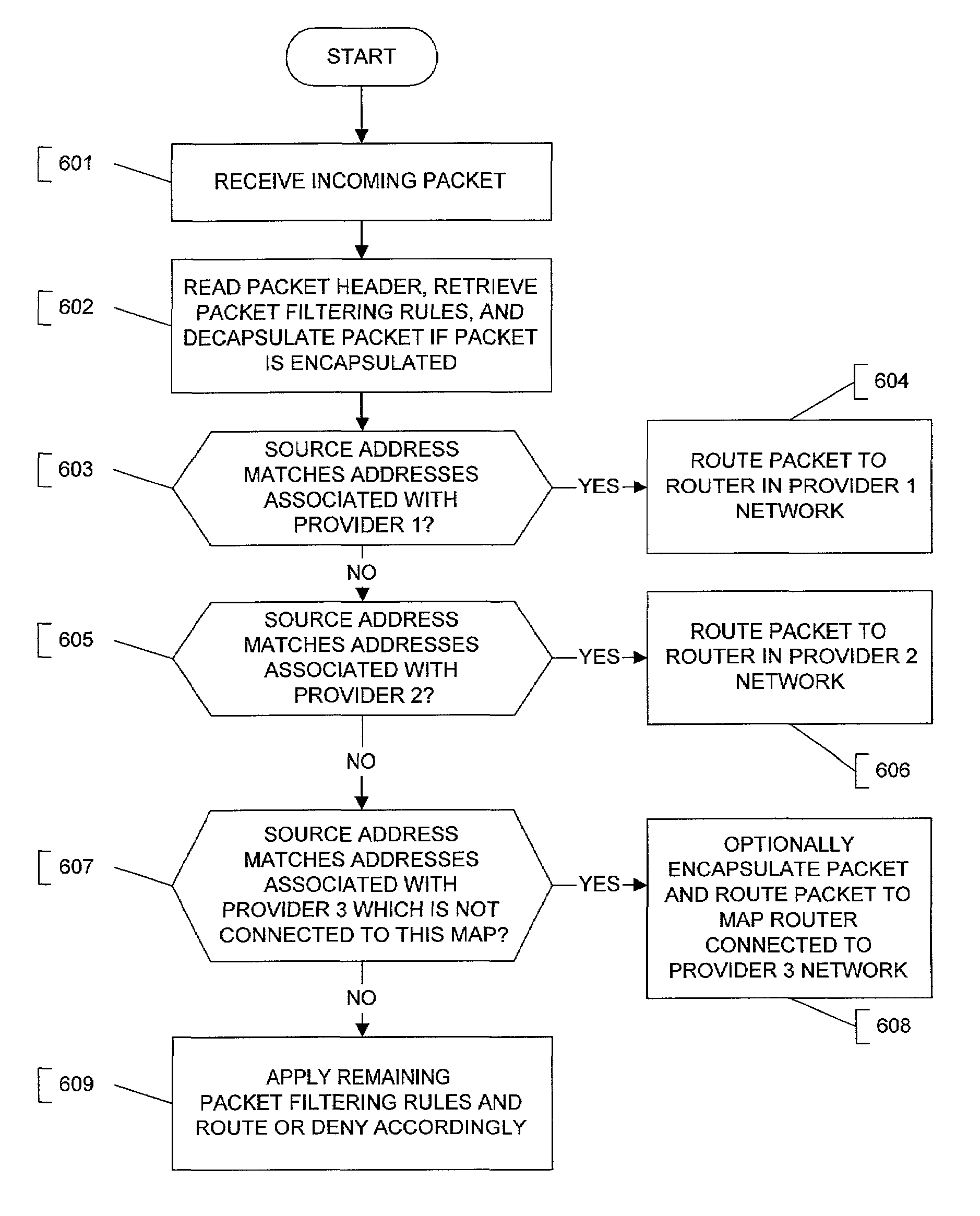
Application Controlled Path Selection Based on Type-of-Service
Some embodiments override network or router level path selection with application or server controlled path selection by repurposing the type-of-service (ToS) or differentiated services header field. A mapping table maps different ToS values to different available transit provider paths to a particular destination. A server generating a packet to the destination selects one of the available paths according to any of load balanced, failover, or performance optimization criteria. The server sets the packet header ToS field with the value assigned to the selected path. A router operating in the same network as the server is configured with policy based routing rules that similarly map the ToS values to different transit provider paths to the particular destination network. Upon receiving the server generated packet, the router routes the packet to the destination network through the transit provider path identified in the packet header by the server set ToS value.
Owner:EDGIO INC
Method and system for packet classification with reduced memory space and enhanced access speed
InactiveUS20090185568A1Reduced amount of accessReduce access operationsData switching by path configurationData setAccess time
A method and system for packet classification is proposed for applications such as firewalls, intrusion detection, policy-based routing, and network service differentiations, within network systems such as Internet or intranet / extranet systems. The proposed method and system is characterized by the use of protocol-oriented rule rearrangement, the probable bit vector (PBV) based on the aggregated bit vectors (ABV) and folded bit vectors (FBV), an ABV-FBV index table dataset whose data structure is based on a featured split full-tree schema, and a DCBV (Don't-Care Bit Vector) dataset for packet classification. The combination of these features allows the packet classification to be implemented with a reduced amount of memory and access time during operation.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Efficient transactional messaging between loosely coupled client and server over multiple intermittent networks with policy based routing
InactiveUS20140098758A1Same quality of serviceSimple and straighError preventionAccounting/billing servicesClient-sideMobile device
A system includes a server; a plurality of wireless networks coupled to the server; and one or more mobile devices coupled to the wireless networks with intermittent access to the wireless networks, the plurality of wireless networks providing data communication between client and server applications over multiple intermittent connections.
Owner:TRAN BAO
Multi-service network switch with independent protocol stack architecture
InactiveUS7327757B2Reduce bottlenecksImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDomain nameRouting table
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for realizing chain circuit polymer function based on strategy route
InactiveCN1553628AImprove primary and backup functionsSimplify configuration workTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNetwork connectionsStreaming dataLink aggregation
This invention discloses a method for implementing link aggregation based on policy-based routing. It includes following steps: the user sends the PPP calling to the wideband access server, the above sever completes the service access, transmits process and service reversing of PPF / IP, when the state of gate exit link turns on, sends the user data to the router, the down stream data is sent to the wideband access server through the router. When the gateway exit link turns off , the user data is sent to backup router, the down stream user data is sent the wide band server through the backup router. The invention can implement the configuration management for the exit of main rout reliably and high efficiently.
Owner:ZTE CORP
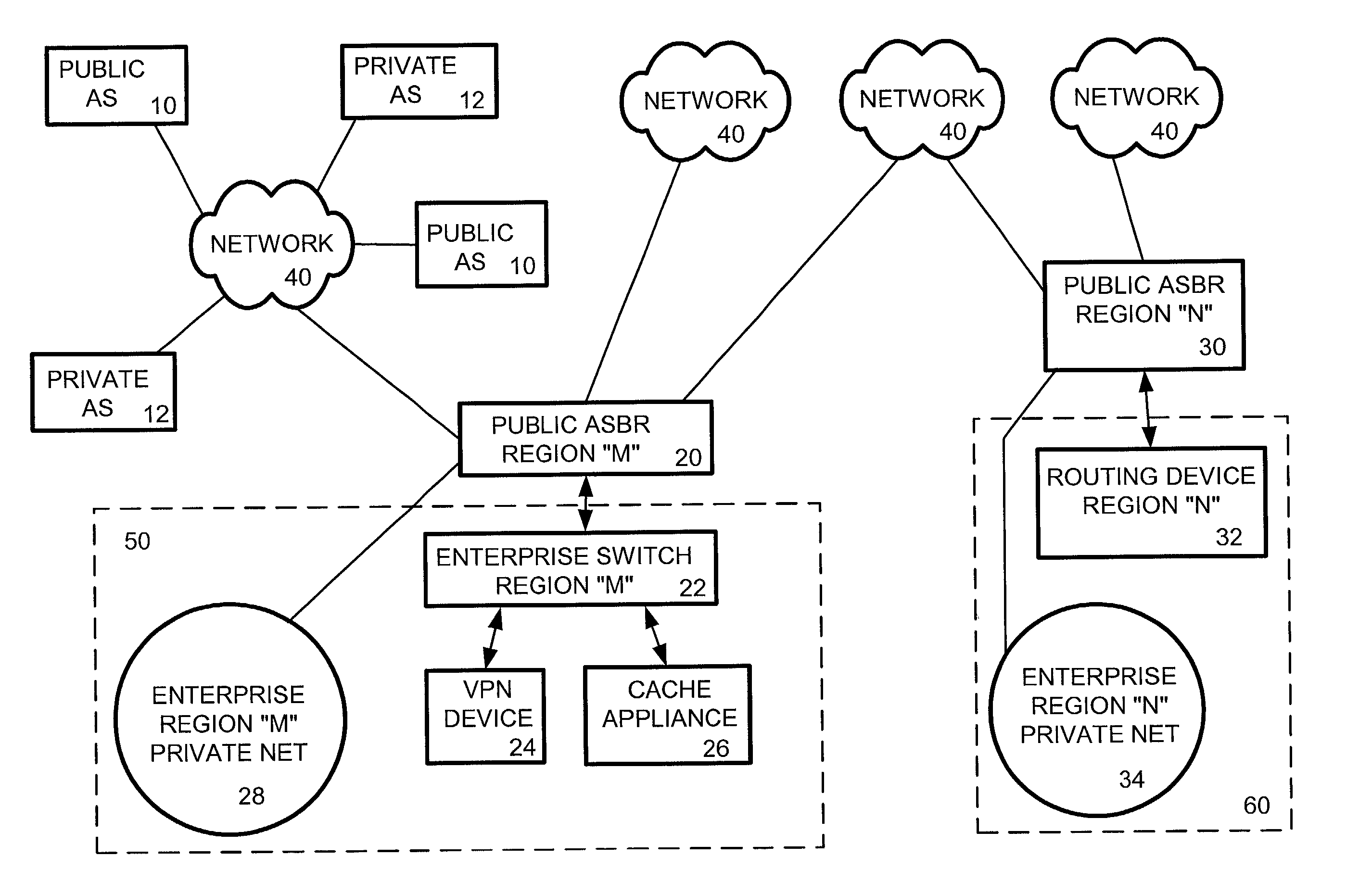
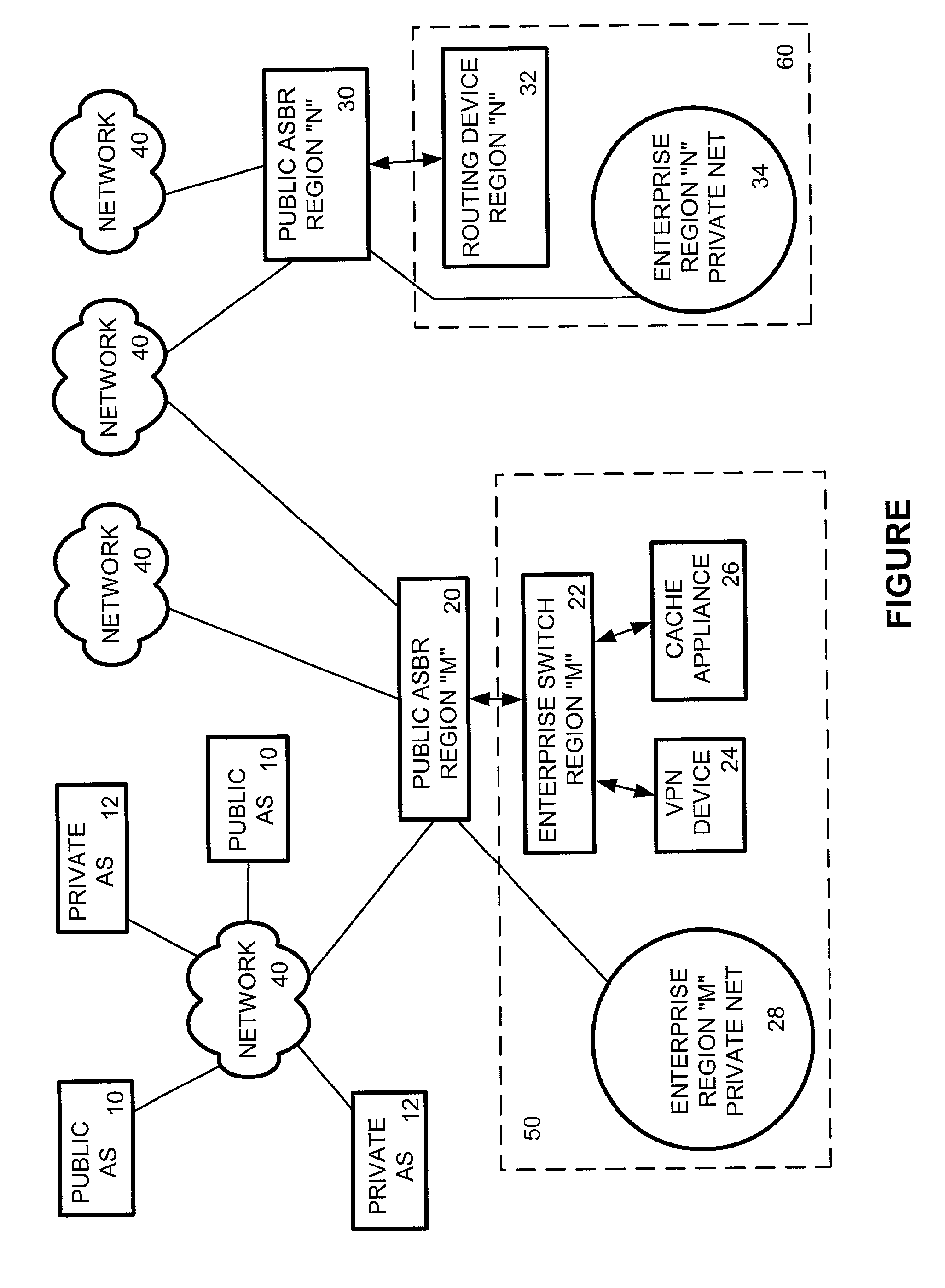
Policy based routing system and method for caching and VPN tunneling
ActiveUS7069336B2Increase specializationEfficient networkingMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityApplication software
An enterprise network router interface communicates with a public regional Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR). The ASBR only forwards the enterprise network traffic to the router interface. The router interface redirects data packets to data highly specialized packet processing appliances for parallel processing of VPN and cache application traffic. Policy based routing instructions are imposed on the ASBR for subsequent secure, tunneled transmission. This enterprise routing system and method used within an enterprise imposes routing instructions superseding gateway protocol routing thus allowing VPN and content caching applications to be run efficiently and securely without resort to an enterprise dedicated backbone.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Systems and methods for policy based routing for multiple next hops
The present application is directed towards policy based routing for intelligent traffic management via multiple next hops. In some embodiments, the systems and methods disclosed herein may provide management of inbound and outbound traffic across multiple network links, and may further provide reliability in case of link failure, and provide balancing of traffic, responsive to the latency and bandwidth requirements of various applications. Accordingly, these systems and methods may provide intelligent policy-based routing and network and port address translation, sensitive to application traffic types, protocols, source IP addresses and ports, destination IP addresses and ports, or any combination thereof, and can balance traffic loads among multiple available paths based on multiple traffic characteristics. The routing may performed on a packet-by-packet basis, a transaction-by-transaction basis, or a session-by-session basis, and the systems and methods may include capabilities for application-aware health monitoring of available network paths.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System, device and method for carrying out policy-based routing mode
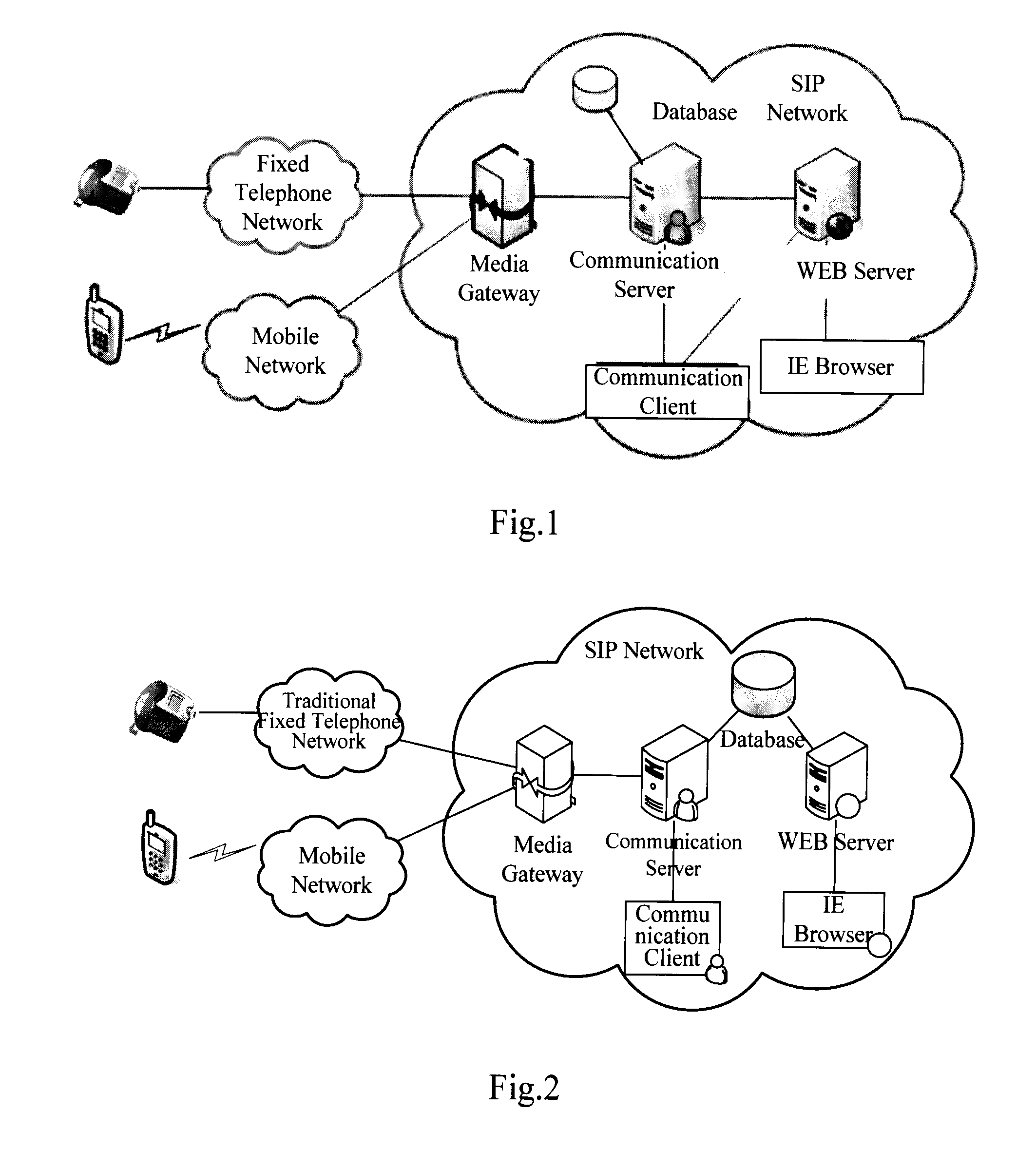
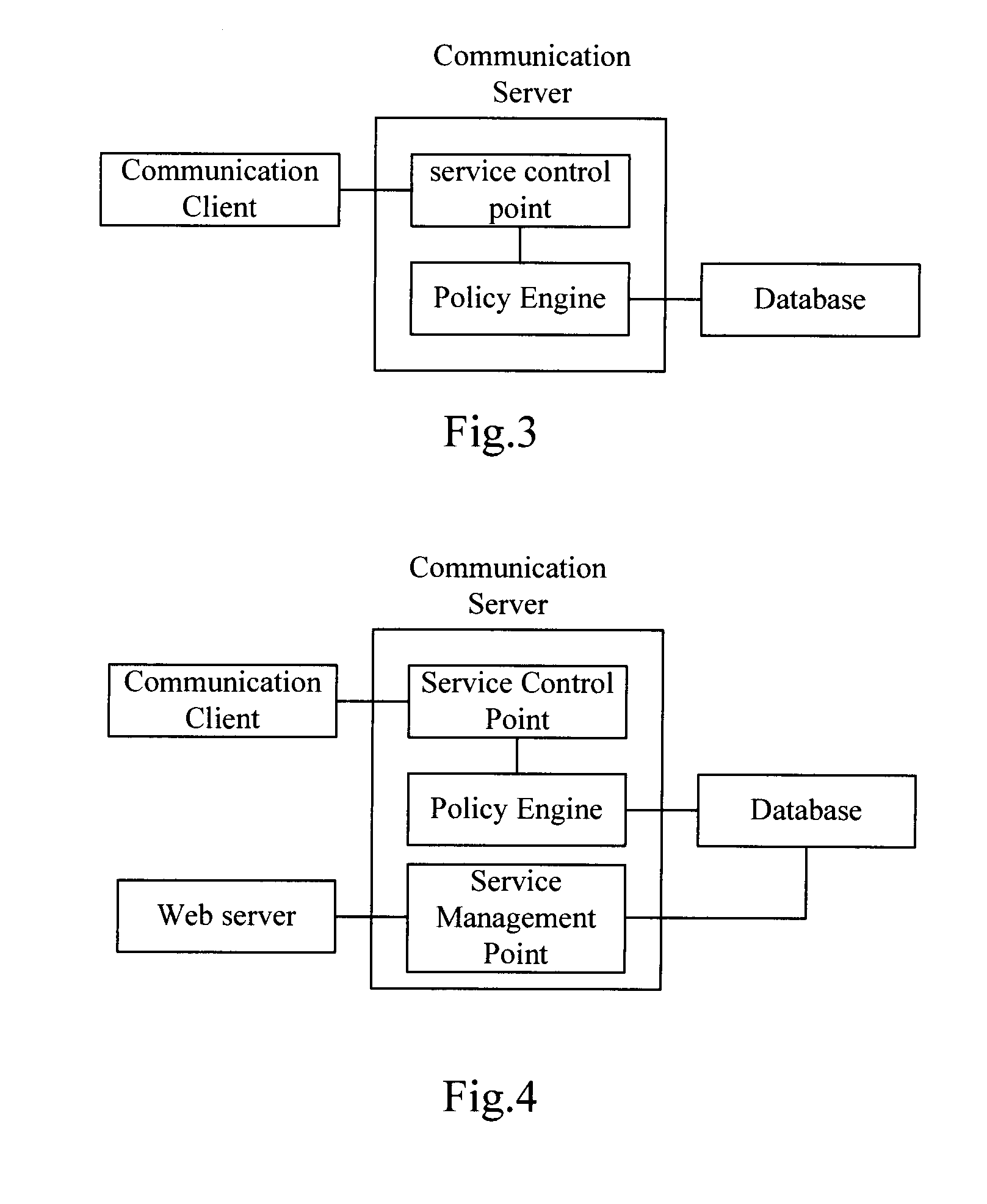
InactiveUS20090265327A1Improve service qualitySpecial data processing applicationsSecuring communicationWeb serviceUnified communications
A system, device and method for carrying out policy-based routing mode are provided; the system in this invention contains database, for storing multiple routing policies set by user, and storing one of the routing policy as current routing policy; communication server, inquiring current routing policy of the user in the database in calling process, and implementing calling based on current routing policy. The system also contains Web server, which receives multiple routing policies of user, and sends them to the database. This invention carries out that the user relies on multiple policies to guide system to flexibly select routing calling through the different user attributes as routing policy evidences, which reaches the aim of enriching uniform communication service content and improving uniform communication service quality.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Service selection in a shared access network using policy routing
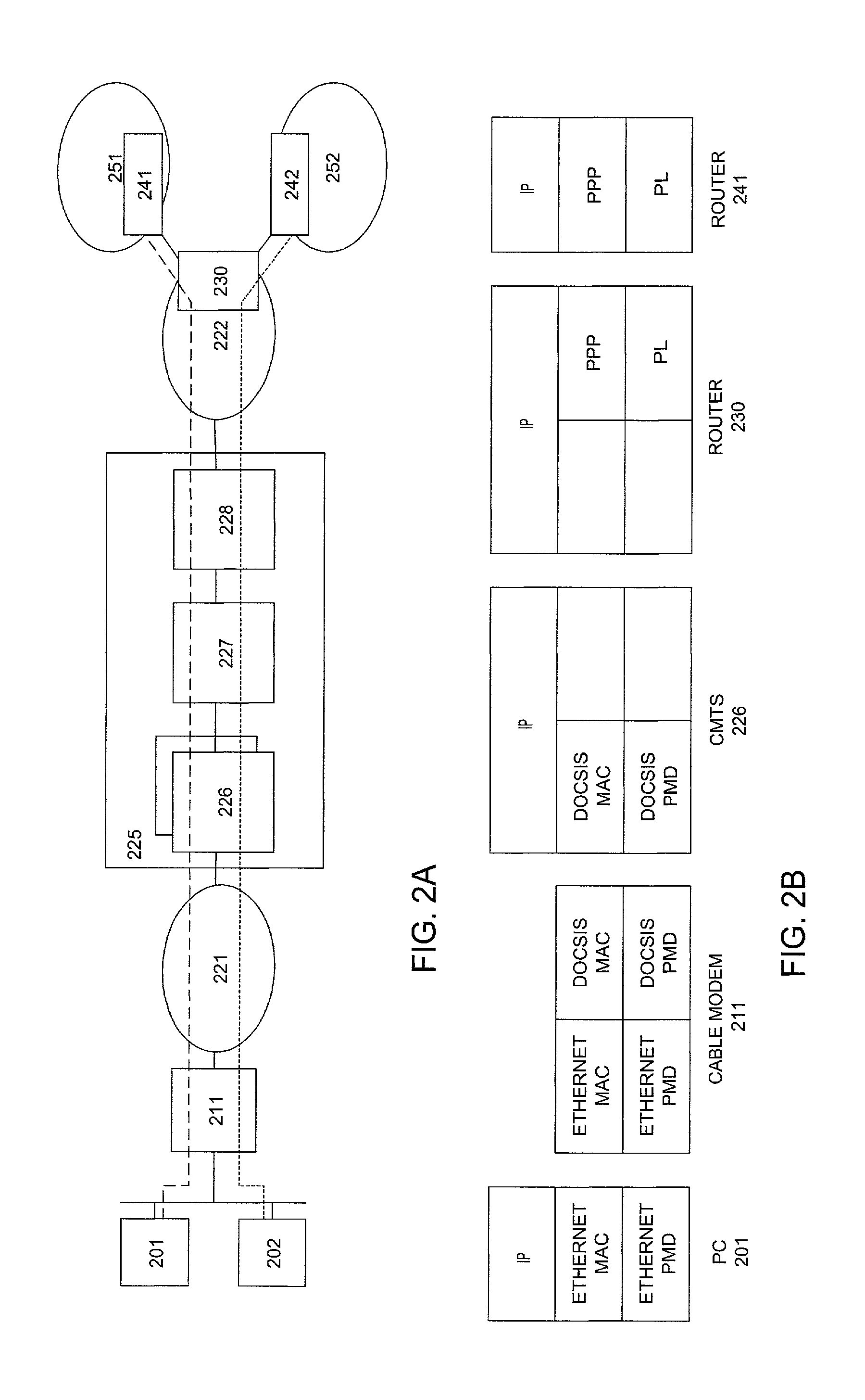
InactiveUS7065578B2Broadband local area networksMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork access serverRadio access network
It is an object of the invention to enable multiple services or service providers to share the facilities of an access network infrastructure providing physical connectivity to subscribers. A network access device advantageously may be used in communication network services with a service or service provider that is separate from the operator of the access network infrastructure.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
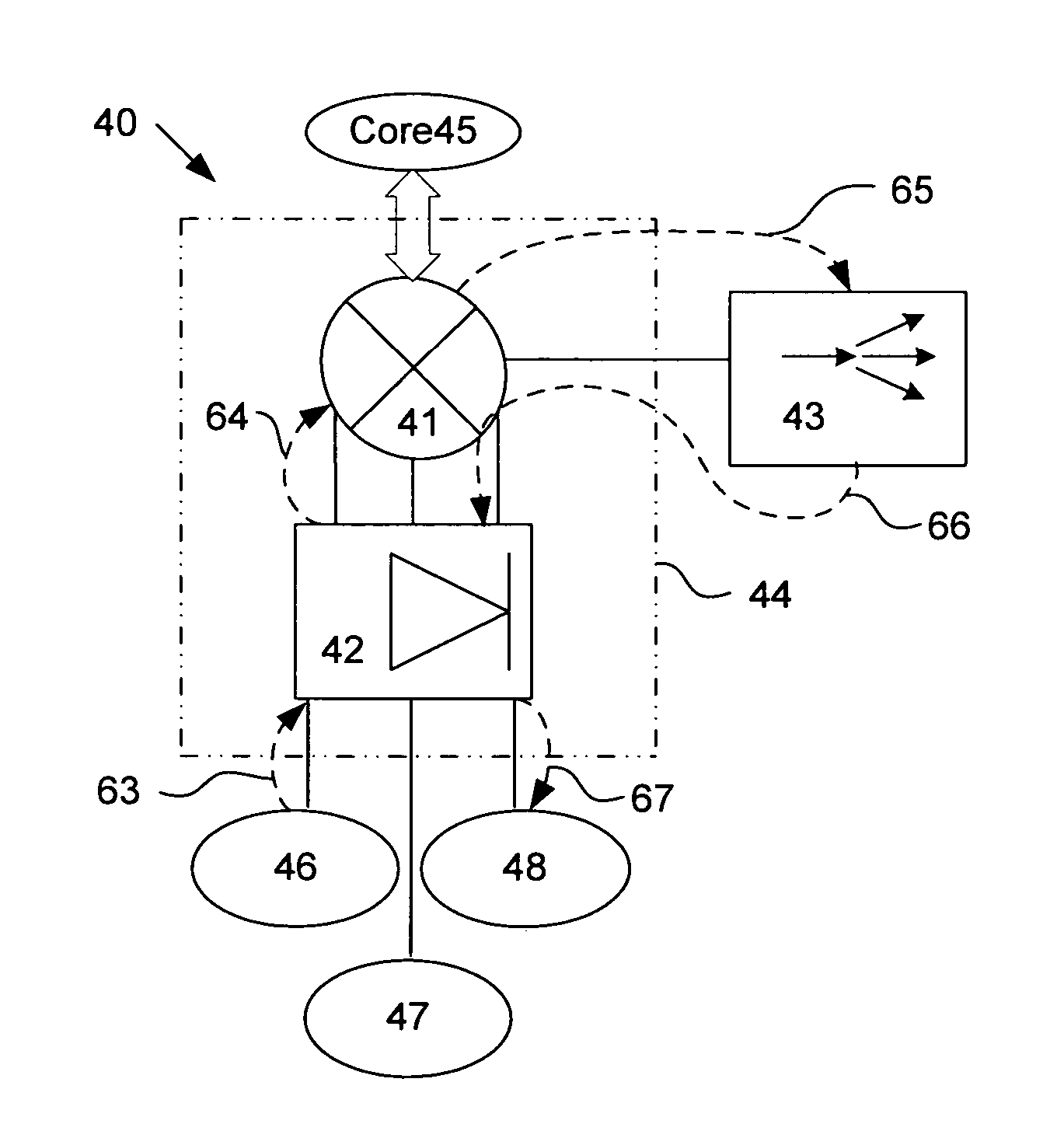
System and method of a data processing pipeline with policy based routing
A method and apparatus of a network element that processes data by a network element with a data processing pipeline is described. In an exemplary embodiment, the network element receives network data and performs a policy-based routing lookup using one or more characteristics of the network data to retrieve a next hop identifier. In addition, the network element generates a key for the next hop identifier and performs a longest prefix match lookup to retrieve a forwarding result. The network element further determines a next hop interface based on the forwarding result.
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
Method and device for realizing policy routing in Ethernet switch chip
InactiveCN103227752AImprove forwarding efficiencyIncrease flexibilityData switching networksDifferentiated servicesQos quality of service
The invention discloses a method and device for realizing policy routing in an Ethernet switch chip, which relates to the technical field of network communication, and solves the problem that the message forwarding efficiency is low since the existing policy routing needs to obtain the IP (Internet protocol) address of a network application server and perform routing information conversion. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: configuring a policy routing table based on the information such as a message source-based IP address, a TCP / UDP (transmission control protocol / user datagram protocol) source port number, a TCP / UDP destination port number, a DSCP (differentiated services code point) value and the like to obtain the second exit information of corresponding policy routing; and searching a common routing table to obtain corresponding first exit information. The method and device disclosed by the invention can conveniently realize policy routing based on different user sources, different network applications and different service quality requirements, and also can flexibly select the common routing result information or policy routing information; and the realization is simple, the system cost is low, and the routing flexibility and message forwarding efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
Techniques for load balancing over a cluster of subscriber-aware application servers
Techniques for distributing control plane traffic, from an end node in a packet switched network to a cluster of service gateway nodes that host subscriber-aware application servers, include receiving a control plane message for supporting data plane traffic from a particular subscriber. A particular service gateway node is determined among the cluster of service gateway nodes based on policy-based routing (PBR) for the data plane traffic from the particular subscriber. A message based on the control plane message is sent to a control plane process on the particular service gateway node. Thereby, data plane traffic and control plane traffic from the same subscriber are directed to the same gateway node, or otherwise related gateway nodes, of the cluster of service gateway nodes. This approach allows currently-available, hardware-accelerated PBR to be used with clusters of subscriber-aware service gateways that must also monitor control plane traffic from the same subscriber.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for Diagnosing the Router Which Supports Policy-Based Routing
ActiveUS20070248019A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsService flowPolicy-based routing
A route diagnosis method which supports policy-based routing is applied in the network which includes a router supporting policy-based routing, which comprises: adding stream description information of service stream in diagnosis-protocol-message, and containing a router warning option in IP head of the said diagnosis-protocol-message; based on the router supporting policy-based routing receiving said diagnosis-protocol-message, routing according to said stream description information in the said diagnosis-protocol-message; said diagnosis-protocol-message is processed as standard diagnosis-protocol-message by the router which is independent of policy-based routing. Employing the method of the present invention, the middle router which supports policy-based routing is able to transfer the message independent of IP head of the said diagnosis-protocol-message, but select routing according to said stream description information included in the message, thereby being capable of keeping the consistency between the diagnosis-protocol-message and routing of the service stream. The purpose that is actually diagnosing routing or correctly diagnosing route is achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com