Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
638 results about "Trust relationship" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
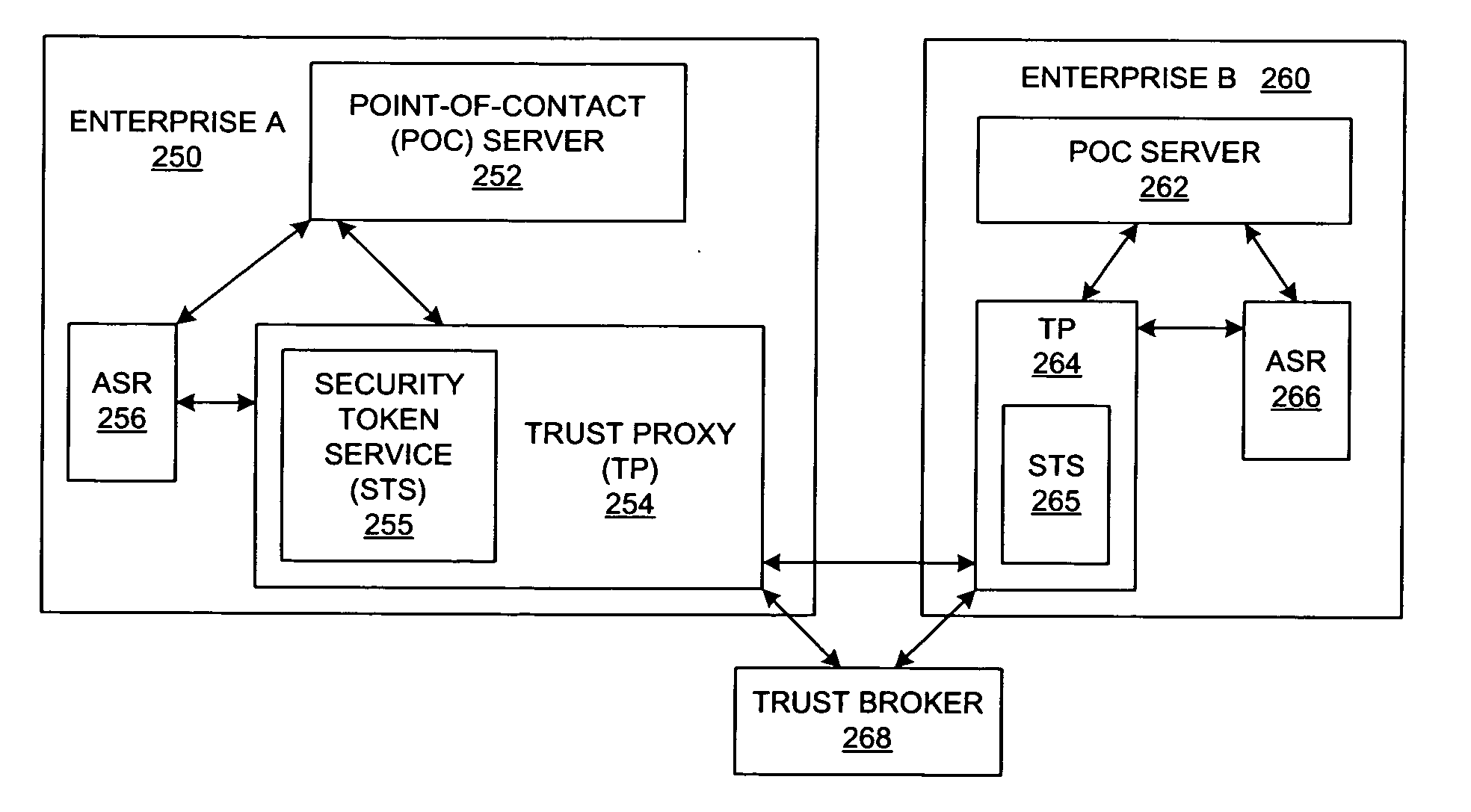
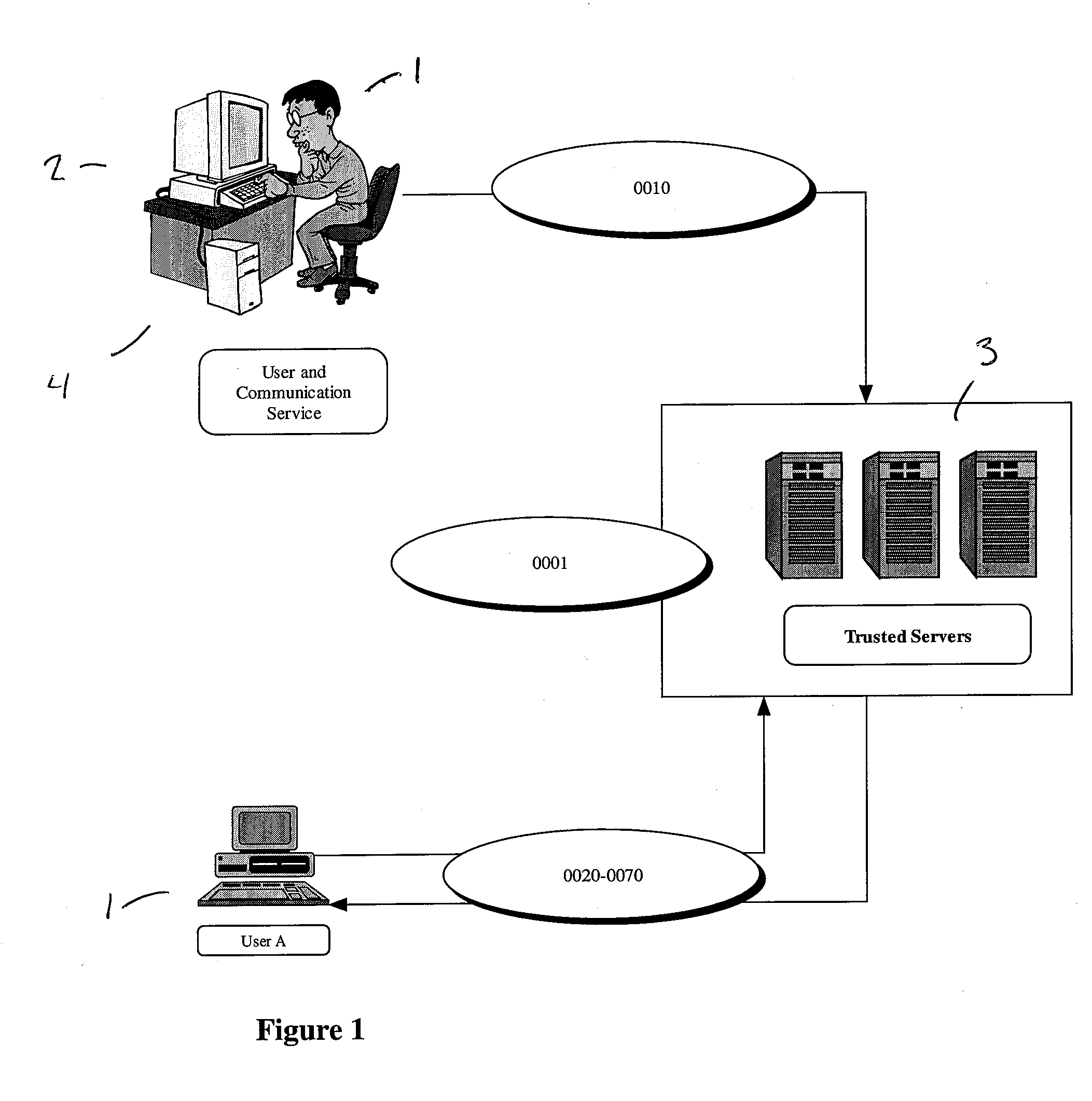
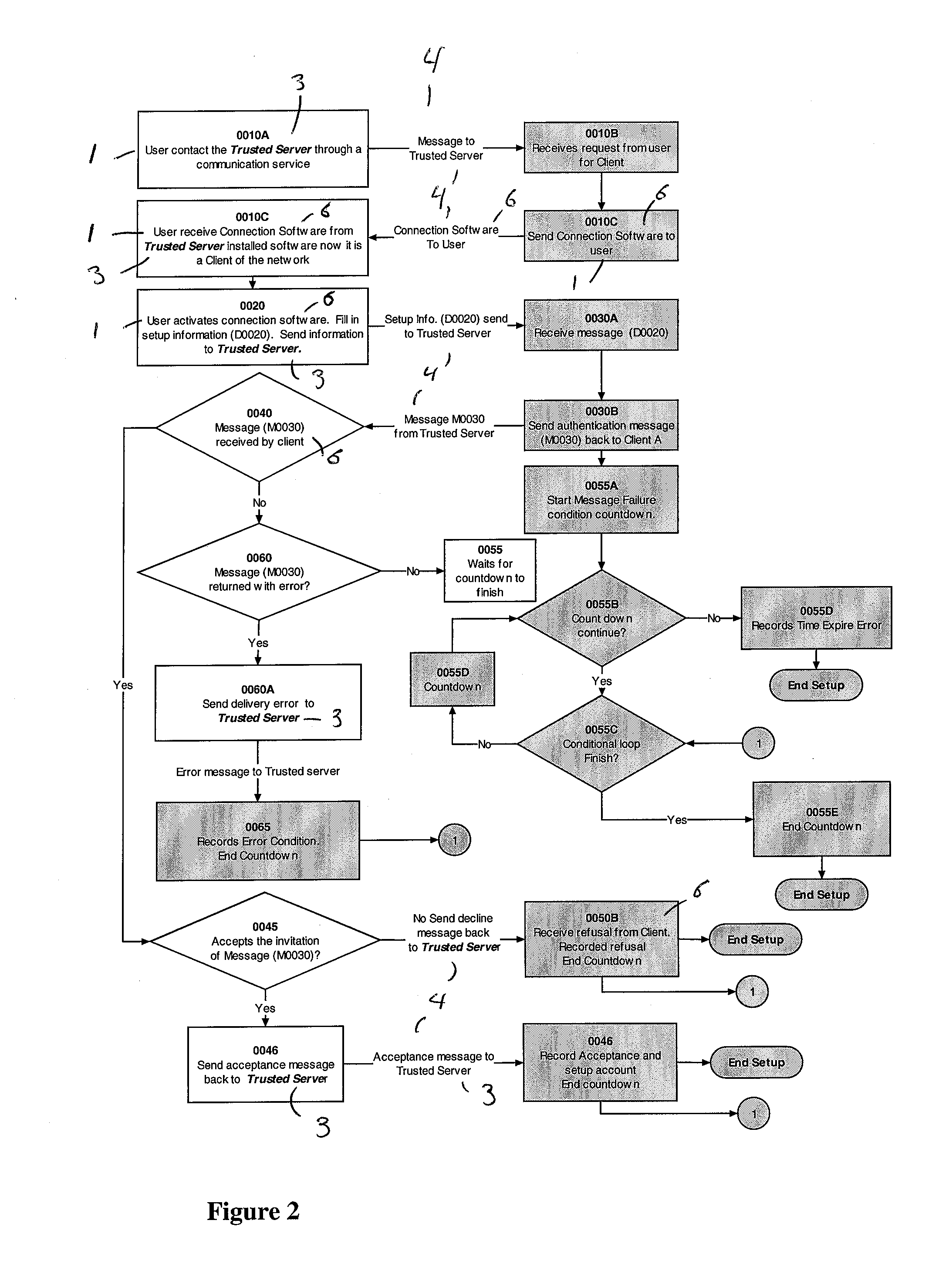
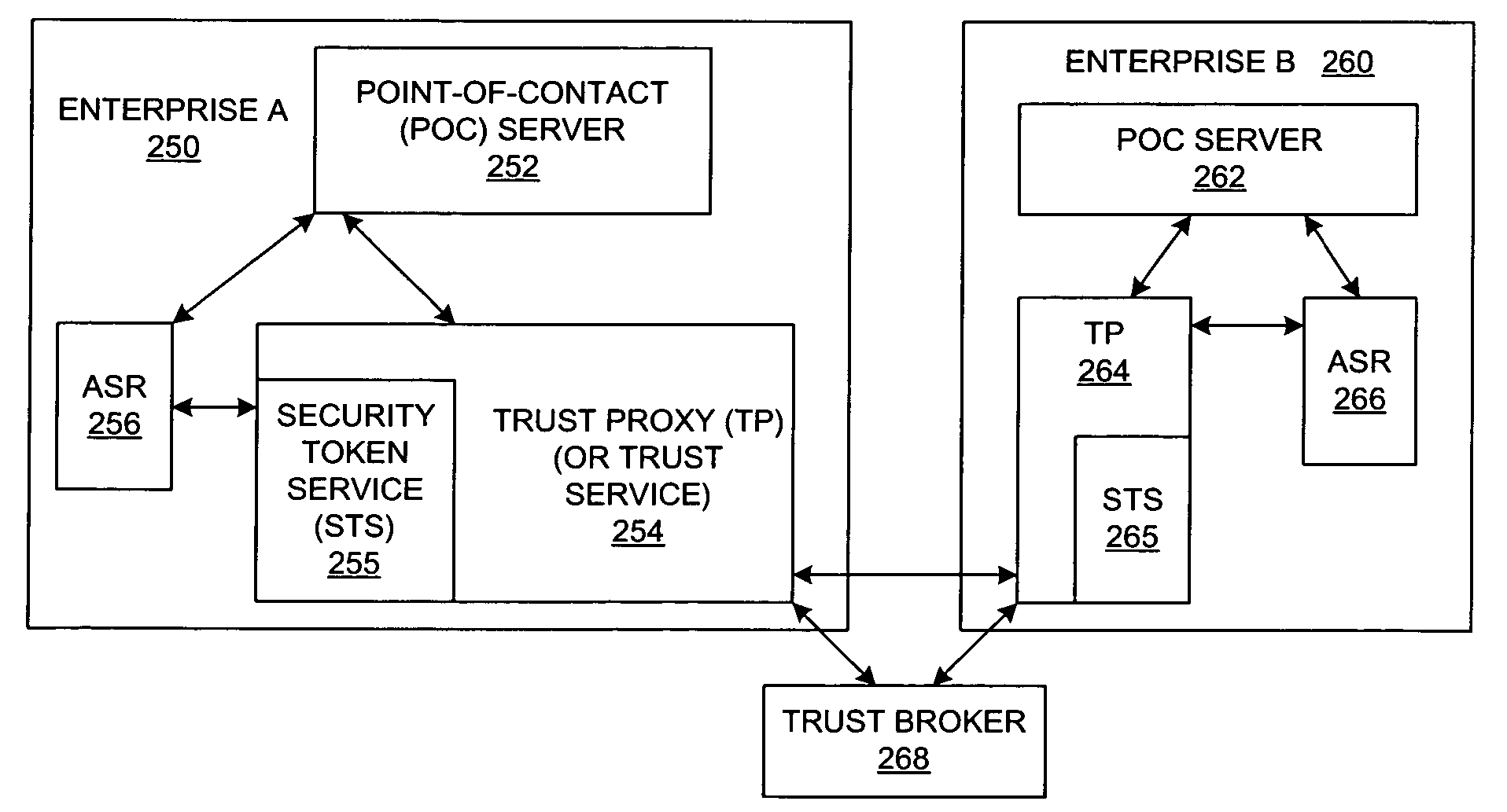
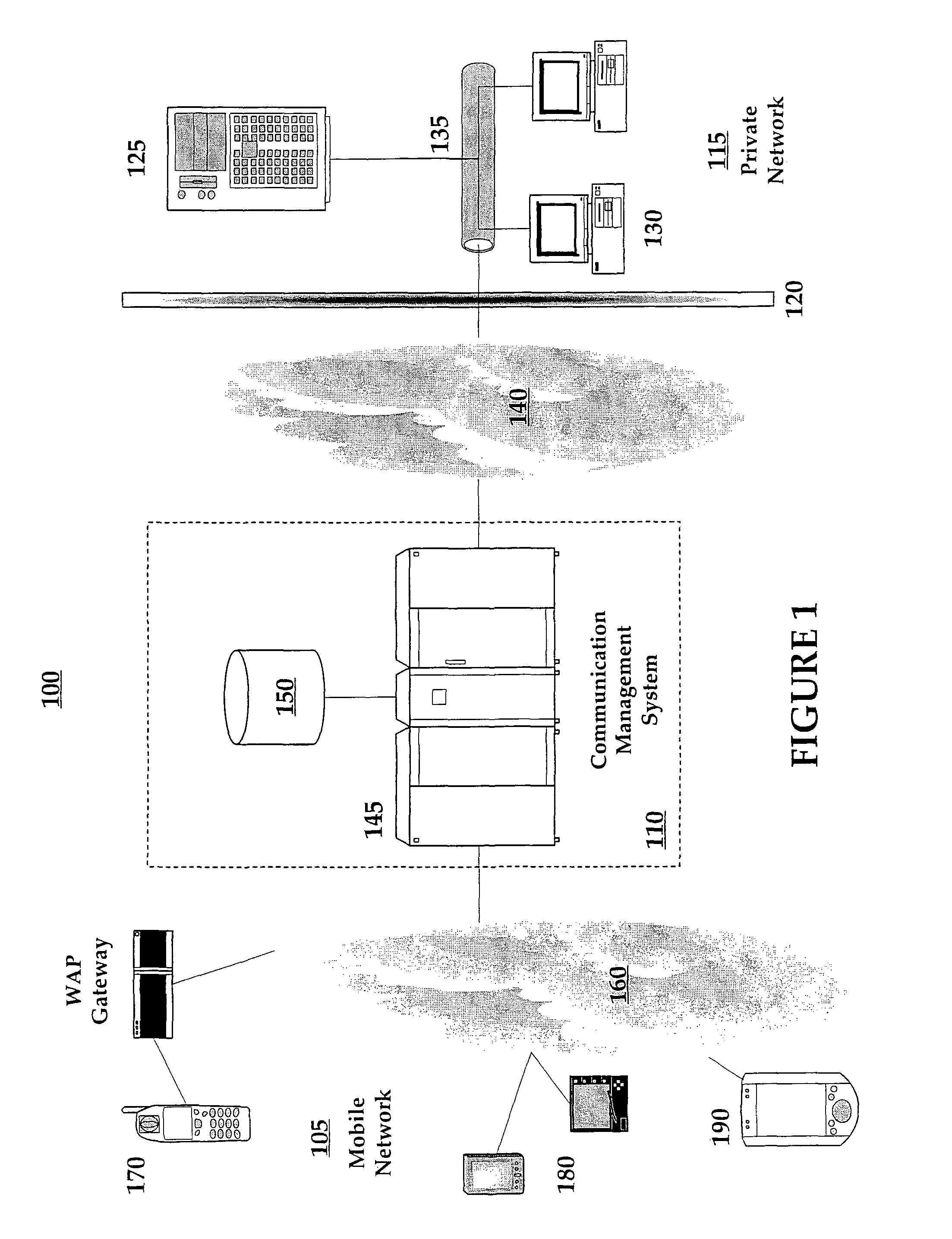
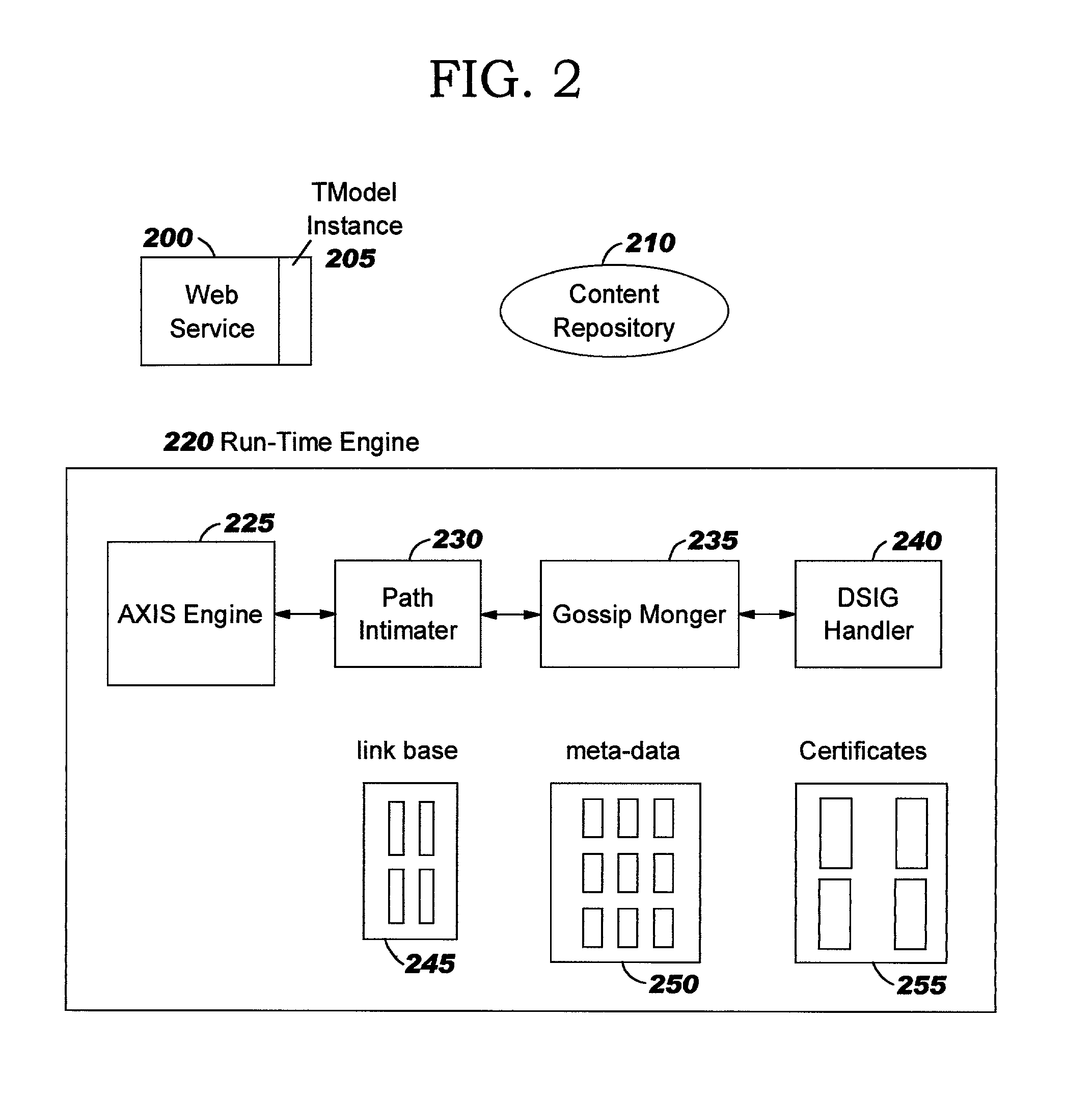
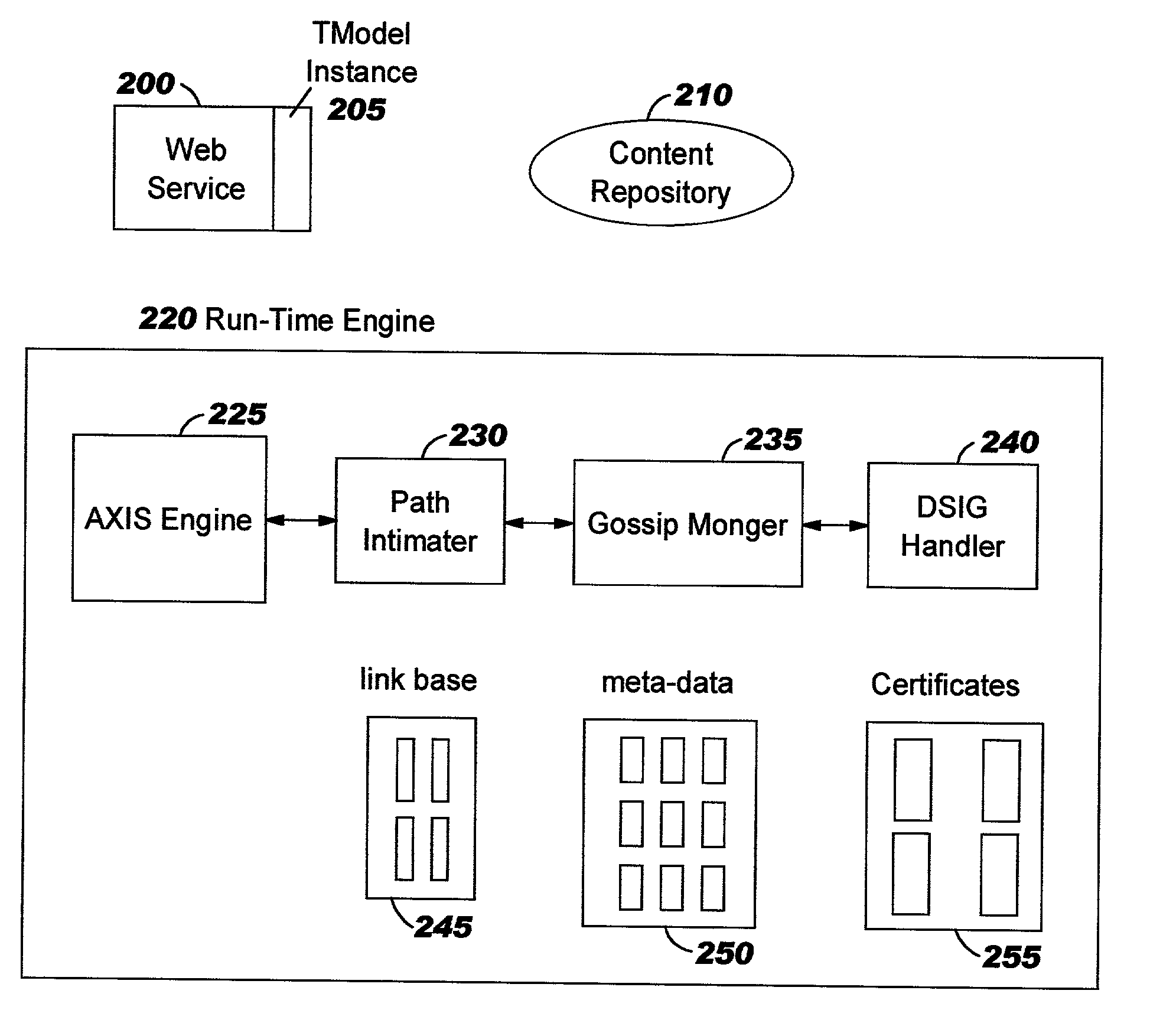
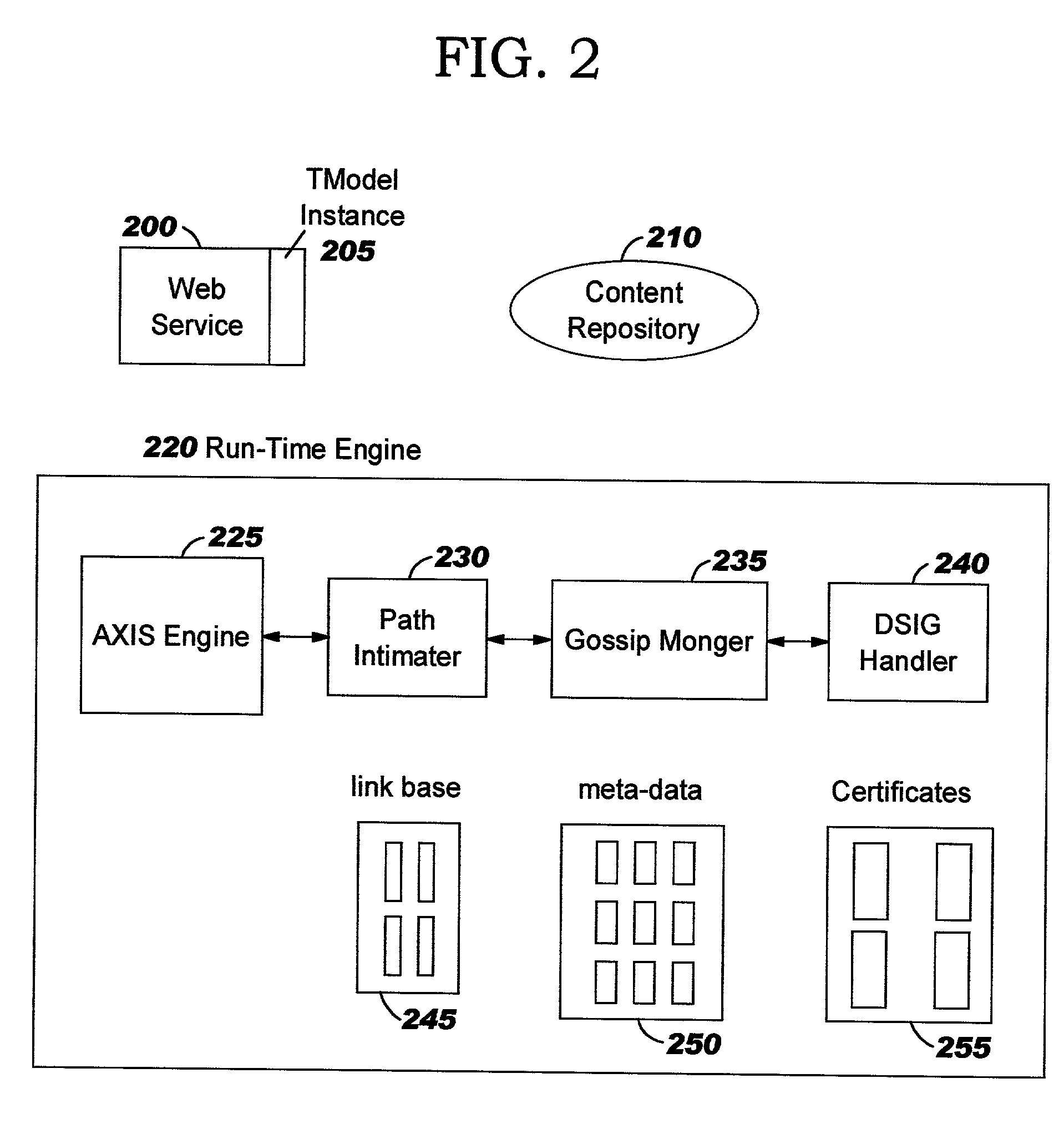
Method and system for federated provisioning
ActiveUS20060021019A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyTrust relationship
A method and a system are presented in which federated domains interact within a federated environment. Domains within a federation can initiate federated single-sign-on operations for a user at other federated domains. A point-of-contact server within a domain relies upon a trust proxy within the domain to manage trust relationships between the domain and the federation. Trust proxies interpret assertions from other federated domains as necessary. Trust proxies may have a trust relationship with one or more trust brokers, and a trust proxy may rely upon a trust broker for assistance in interpreting assertions. When a user is provisioned at a particular federated domain, the federated domain can provision the user to other federated domains within the federated environment. A provision operation may include creating or deleting an account for a user, pushing updated user account information including attributes, and requesting updates on account information including attributes.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
System, method and apparatus for federated single sign-on services
ActiveUS20030163733A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsCyber operationsService domain
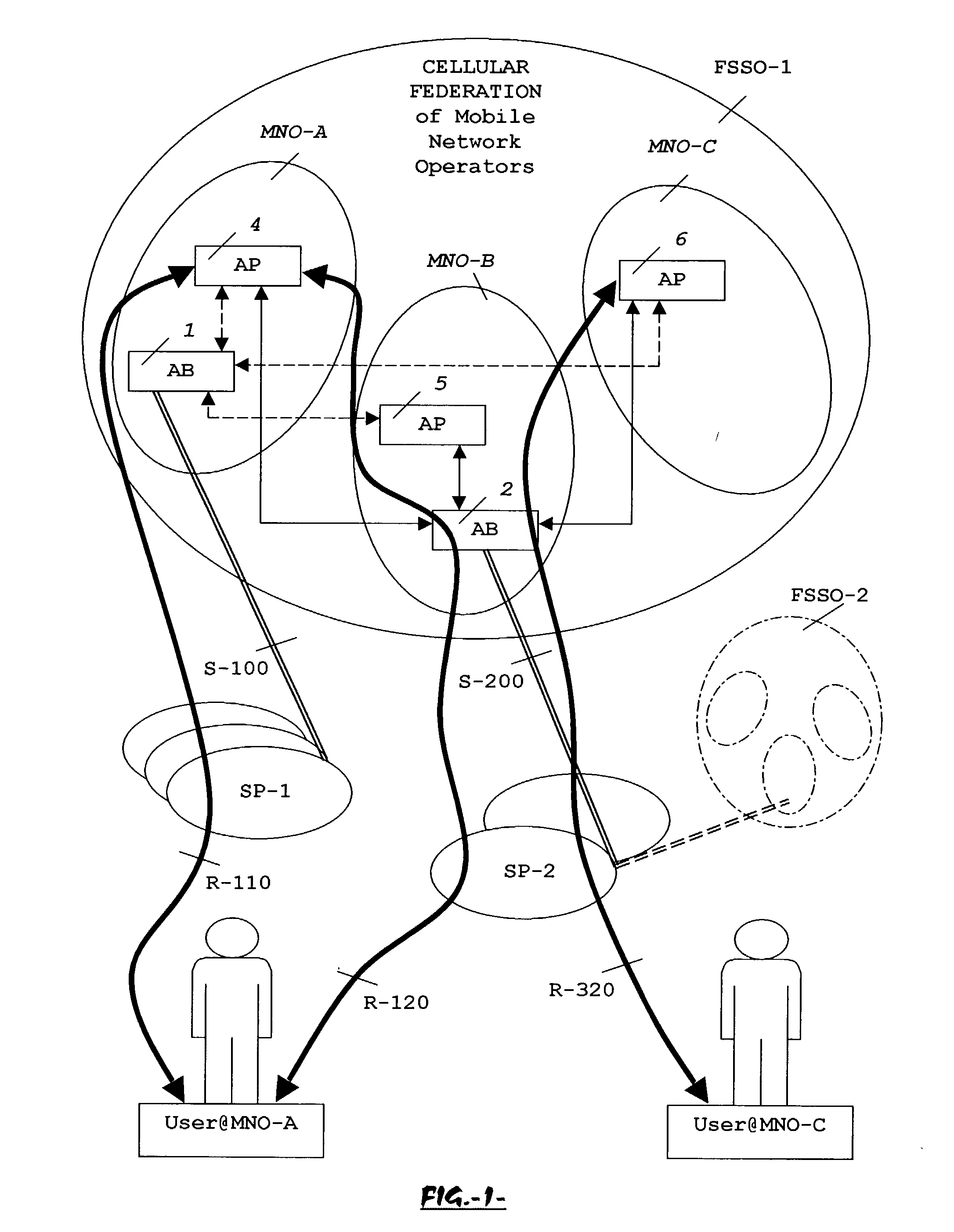
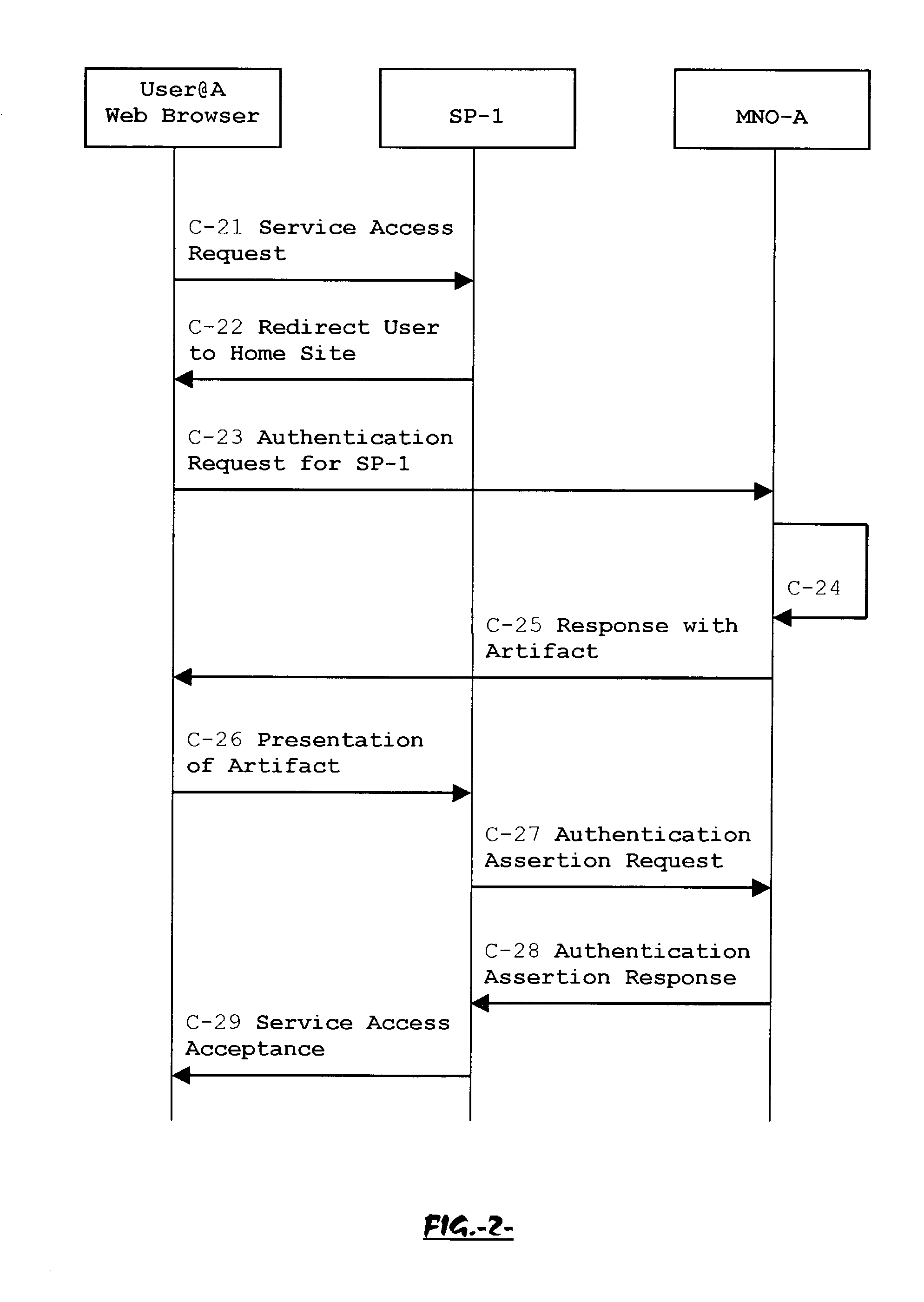
The advent of new and sophisticated web services provided by Service Providers to users, services that individually require authentication of user and authorization of access, brings the needs for a new service to facilitate such authentication and access, a service referred to as Single Sign-On (SSO). The basic principle behind SSO is that users are authenticated once at a particular level, and then access all their subscribed services accepting that level of authentication. The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus wherein a cellular Federation of mobile network operators becomes an SSO authentication authority for subscribers of this Federation accessing Service Providers having such agreement with a mobile network operator of the Federation. In accordance with this invention, mobile network operators can leverage their operator-subscriber trust relationship in order to act as SSO authentication authority for those subscribers accessing Service Providers in a service domain other than the mobile network domain.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
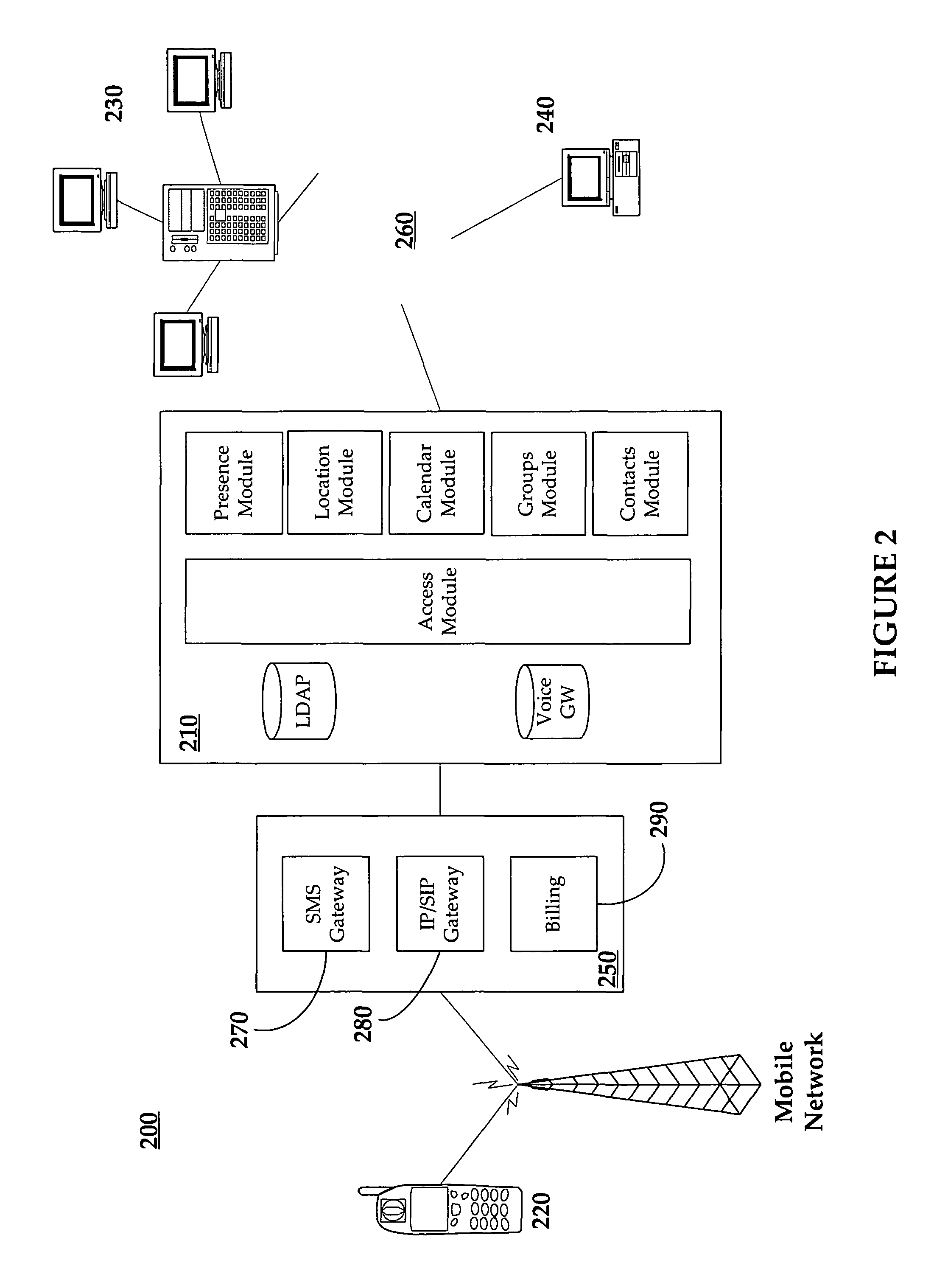
Automated Access, Key, Certificate, and Credential Management
ActiveUS20150222604A1Effective rotationLow costMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationCredential managementTrust relationship
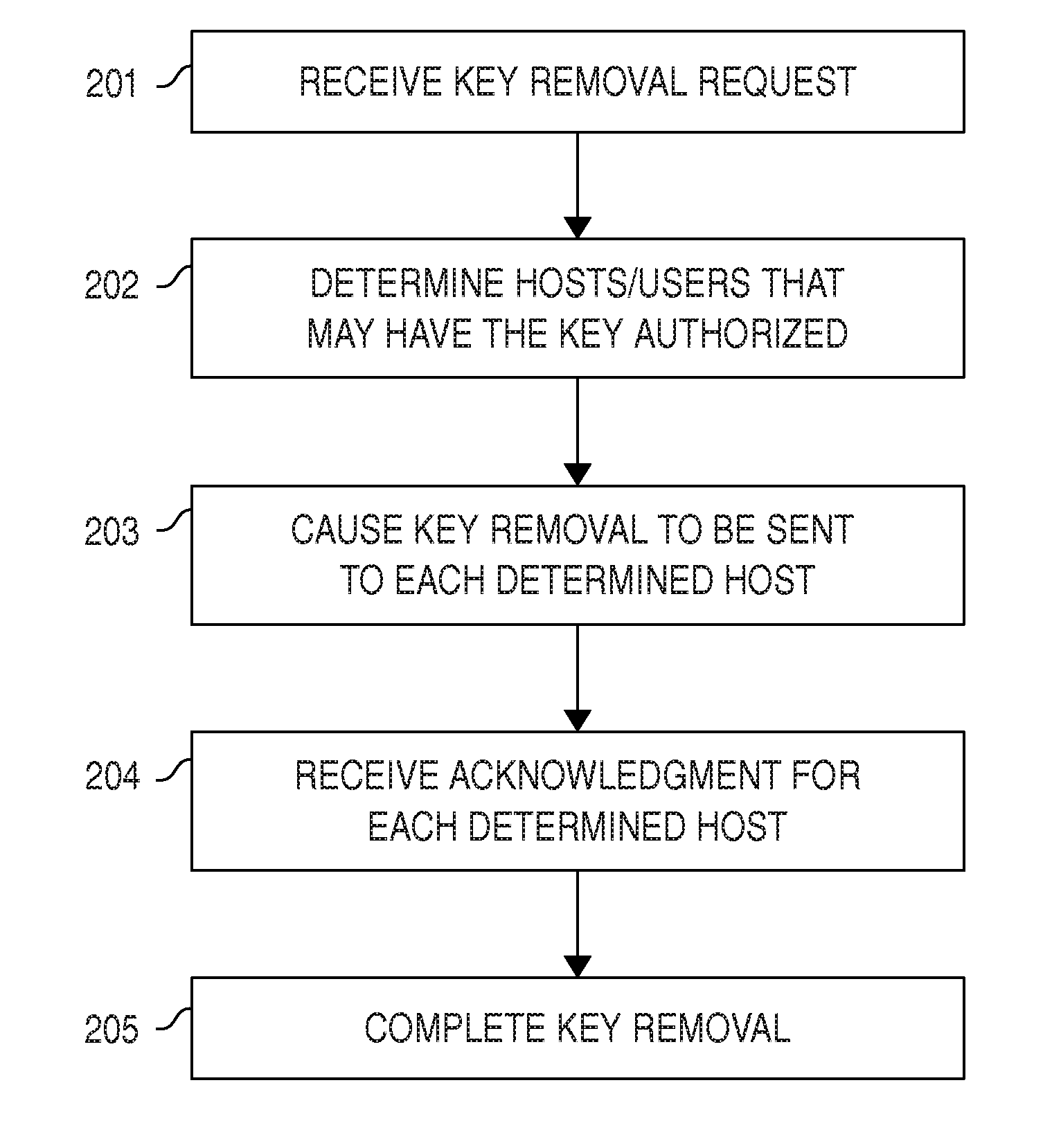
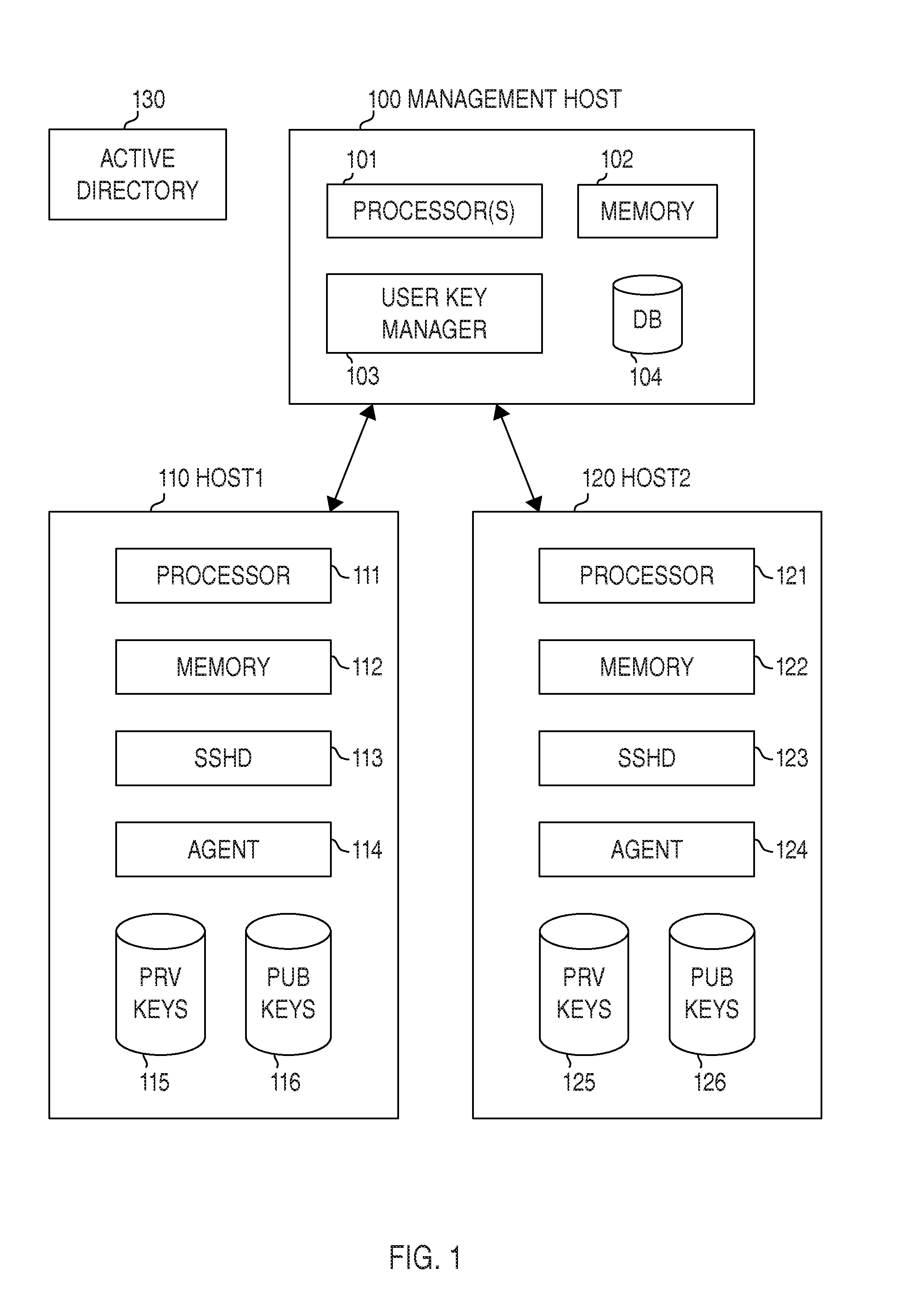
Certain embodiments provide means for managing automated access to computers, e.g., using SSH user keys and other kinds of trust relationships. Certain embodiments also provide for managing certificates, Kerberos credentials, and cryptographic keys. Certain embodiments provide for remediating legacy SSH key problems and for automating configuration of SSH keys, as well as for continuous monitoring.
Owner:SSH COMMUNICATIONS SECURITY
Method, system and service for conducting authenticated business transactions
InactiveUS6957199B1Fast authenticationImprove securityComputer security arrangementsCommerceService provisionThe Internet
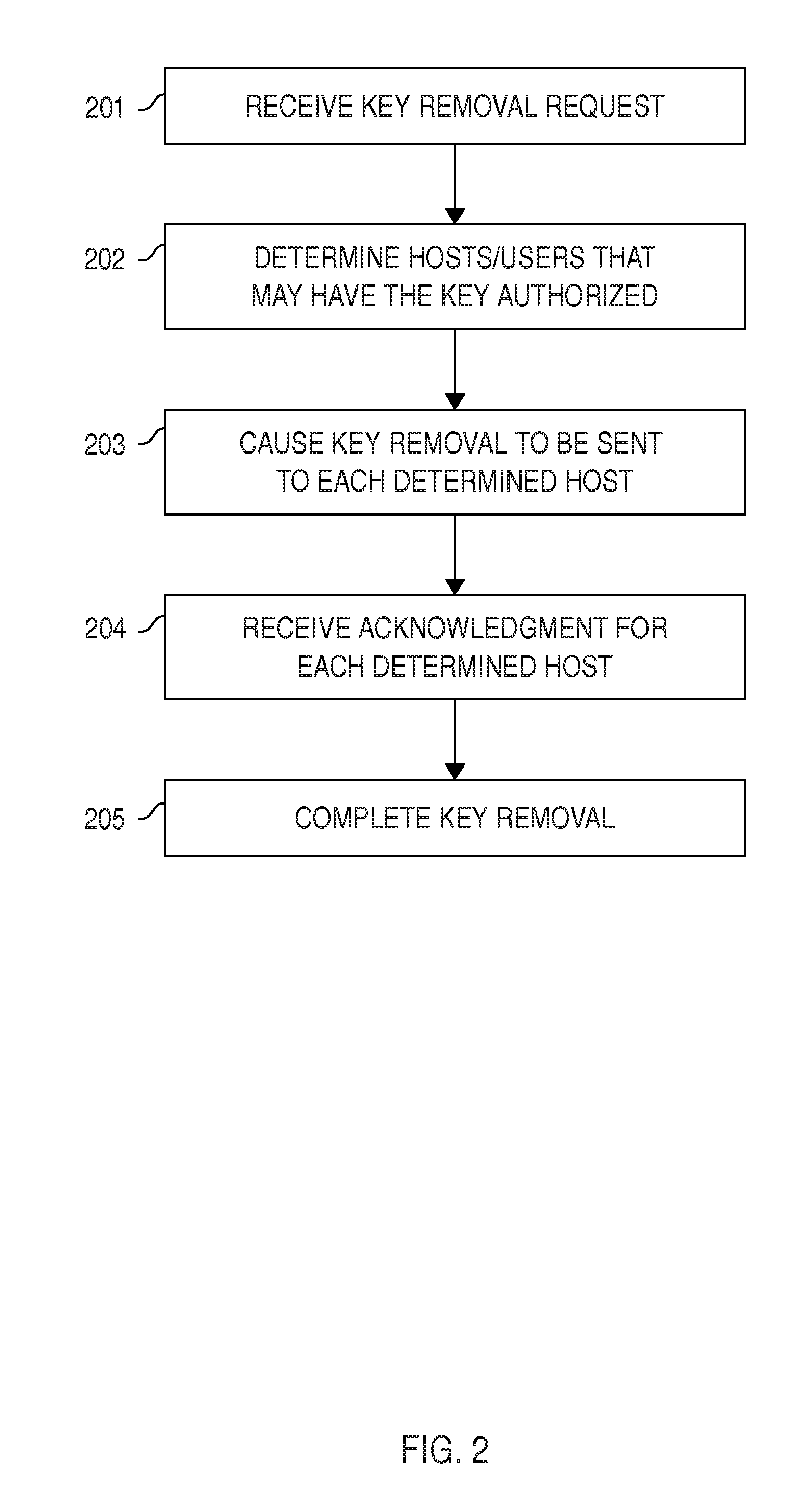
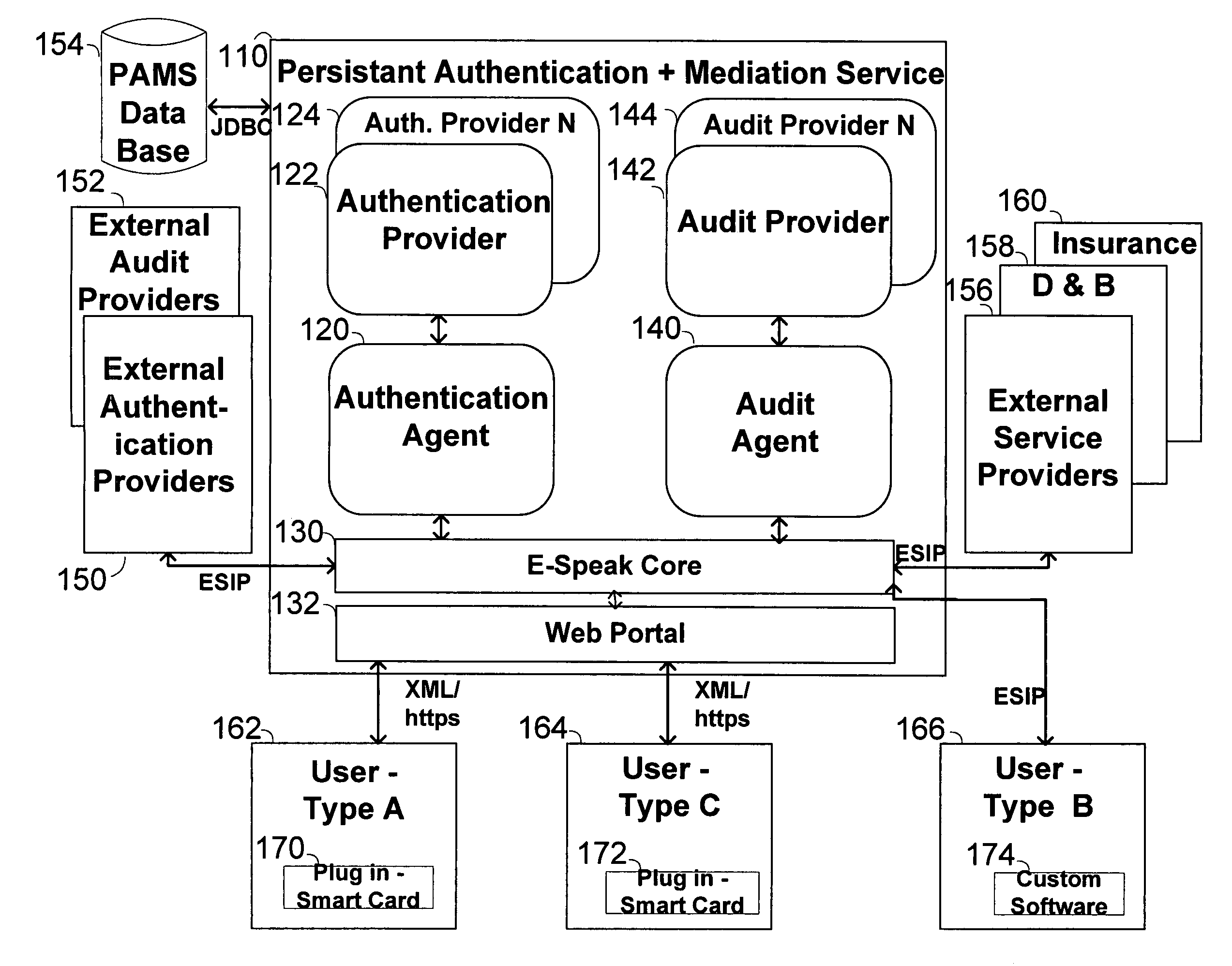
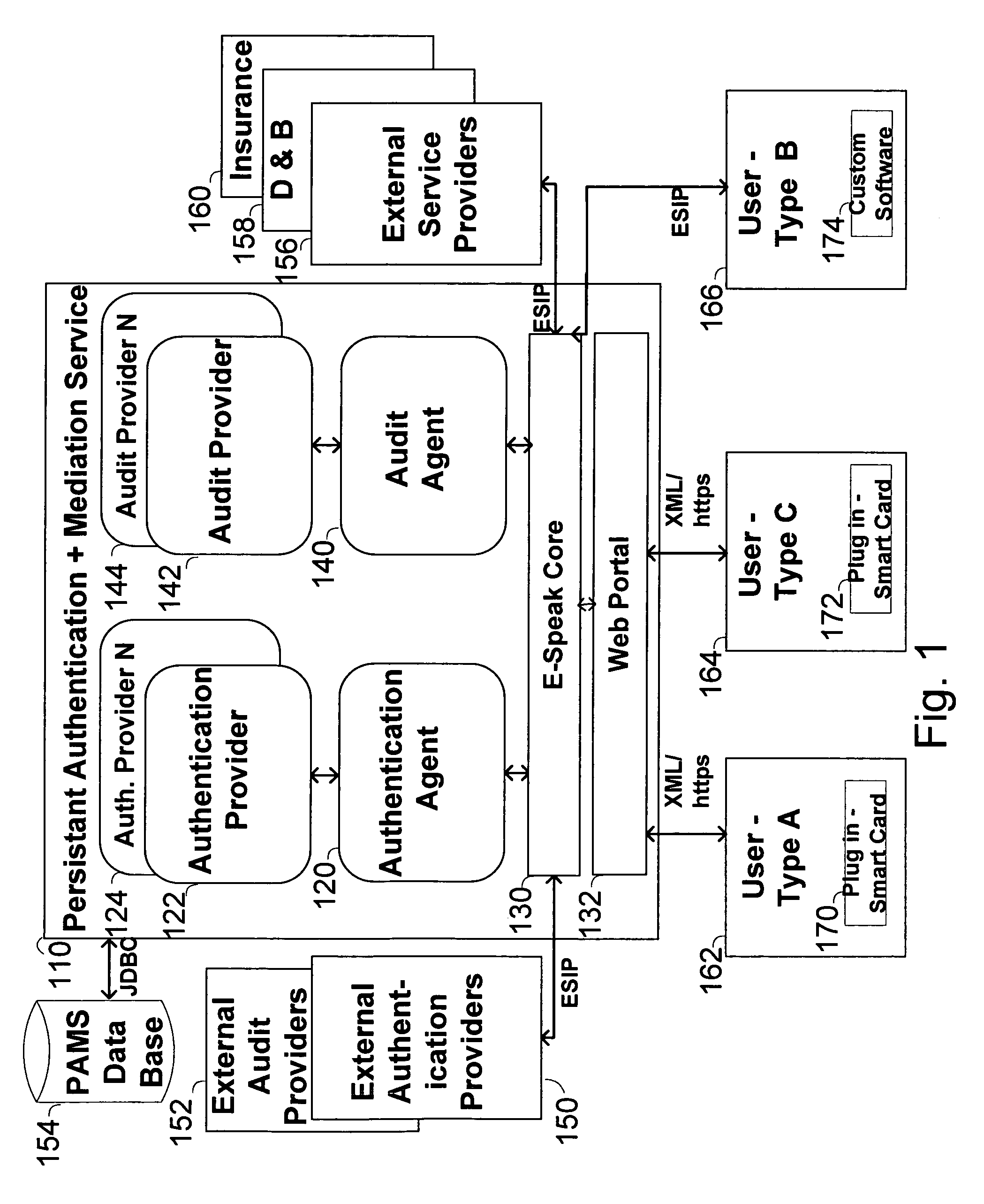
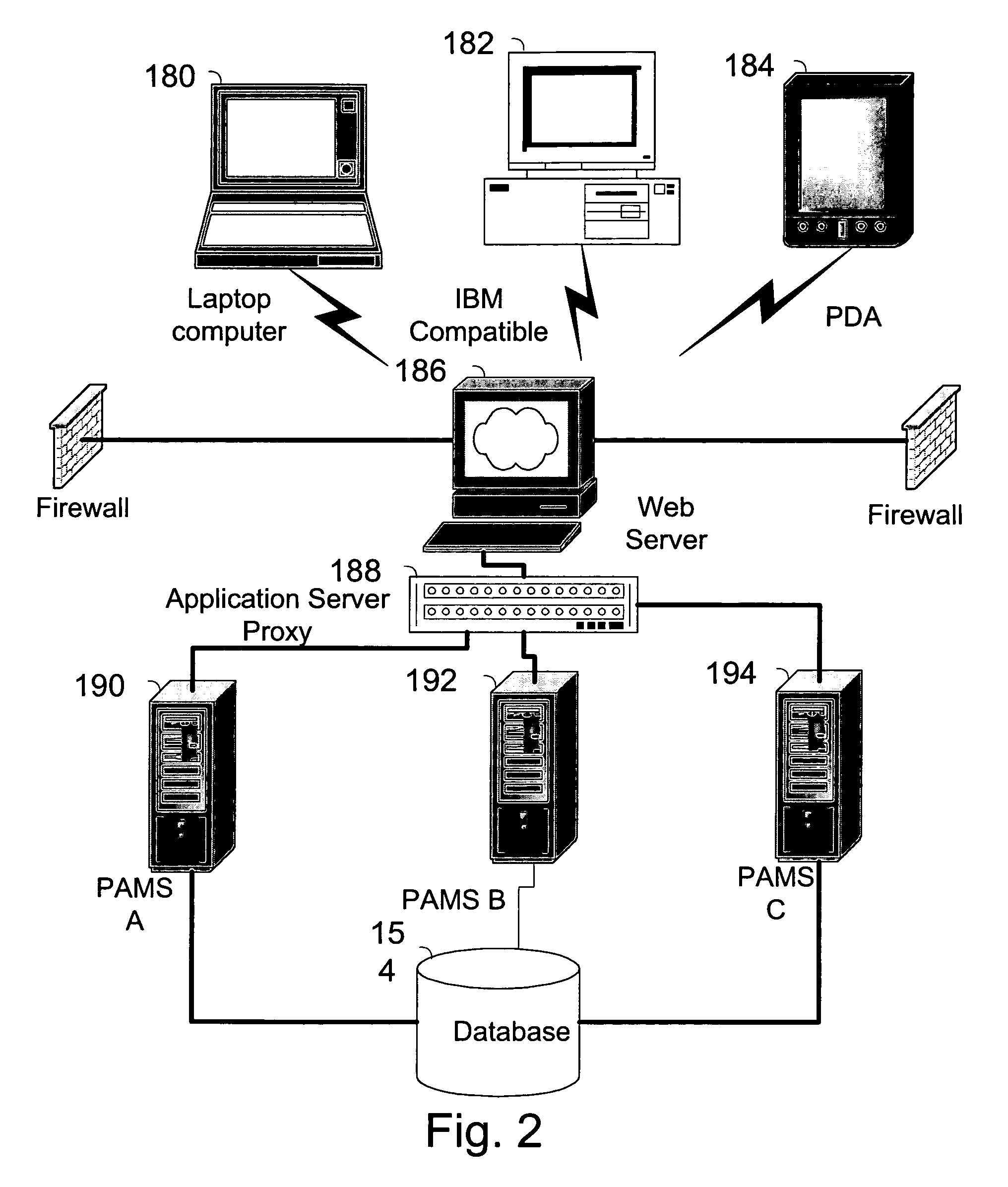
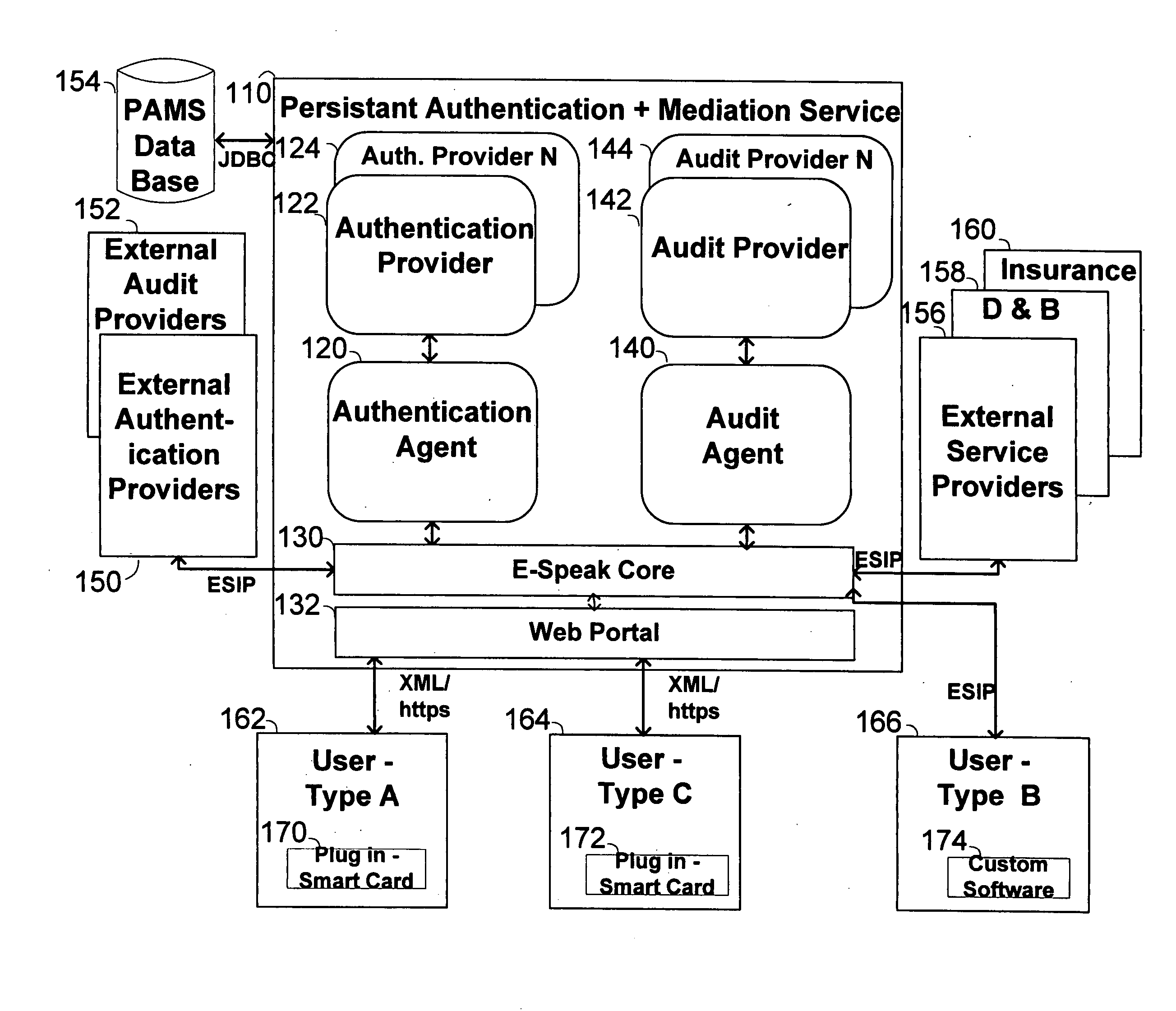
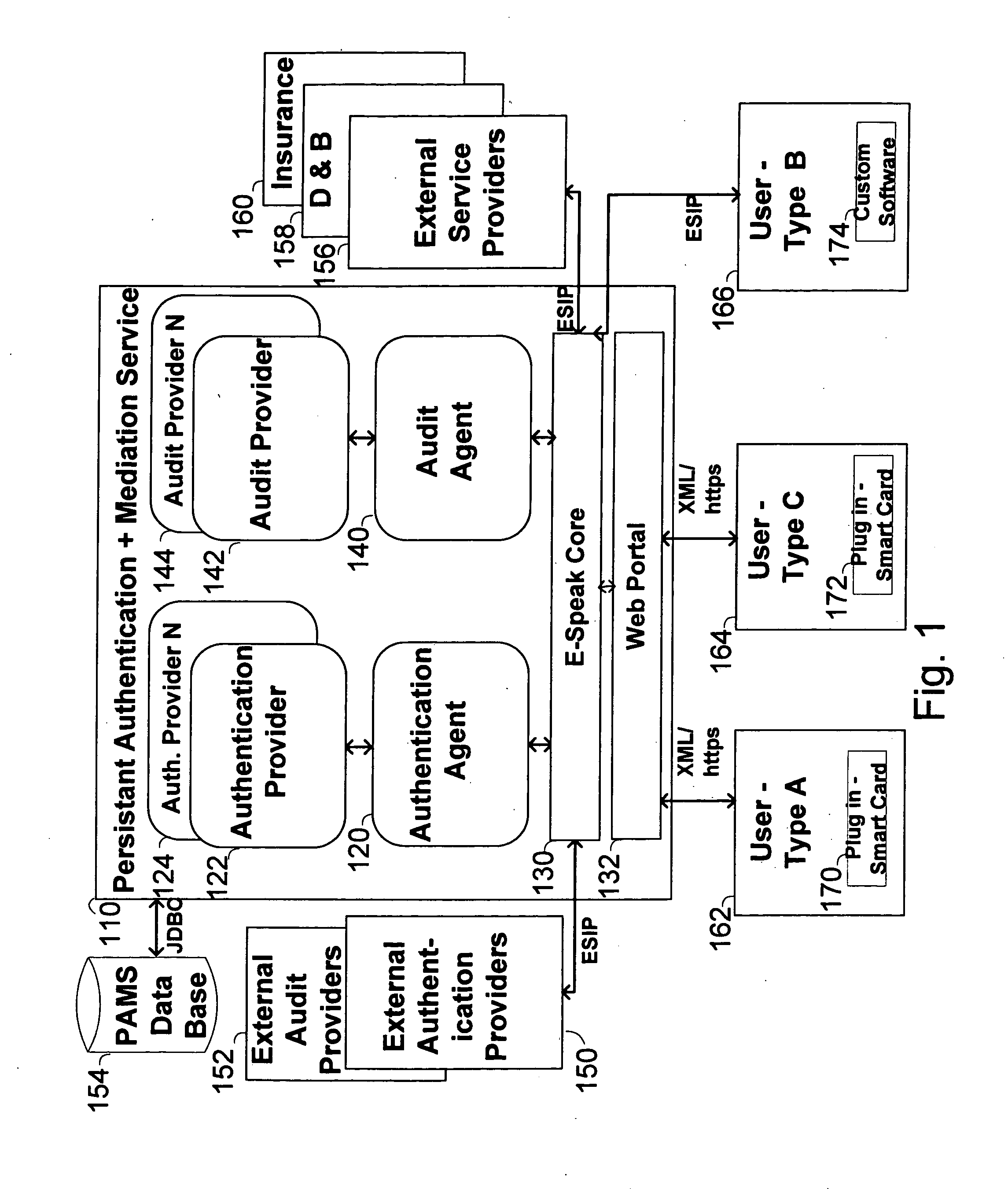
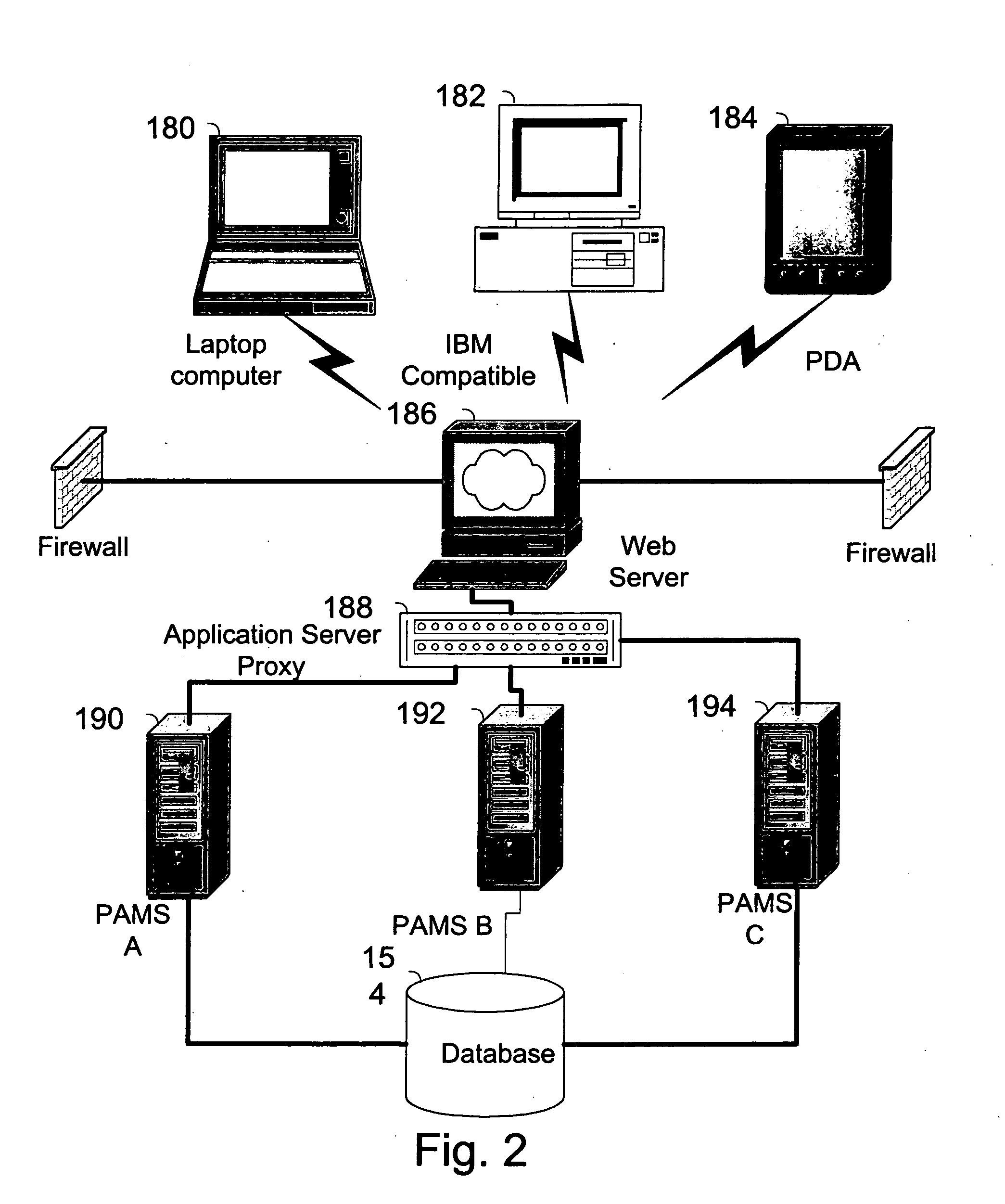
The invention pertains to a method, online service, and system, for creating partnerships based on trust relationships over a public network, authenticating trade partners, infrastructure providers and collaborators to each other, and providing users with an environment suitable for conducting transactions requiring a high level of trust. A service according to the invention is a persistent authentication and mediation service (PAMS) which is provided as an on-line service. One embodiment is a method for conducting authenticated business transactions involving microprocessor equipped devices over the Internet comprising:A. providing an on-line authentication service available on the distributed network;B. authenticating a plurality of users to said on-line authentication service using a closed authentication system to produce a plurality of authenticated users; andC. connecting a group of at least two of said plurality of authenticated users under persistent mediation of said on-line authentication service, producing a connected group of authenticated users.
Owner:FISHER DOUGLAS
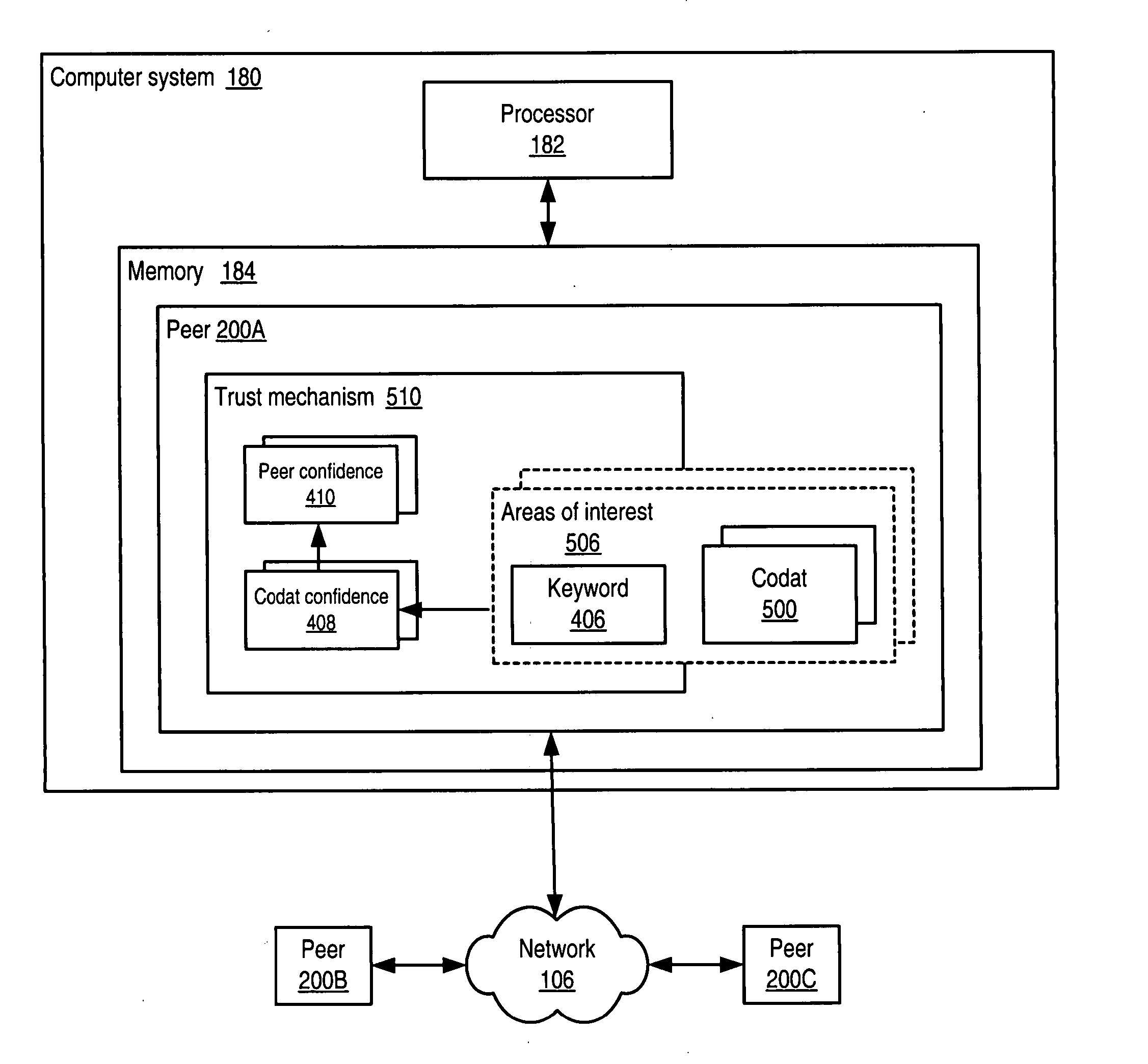
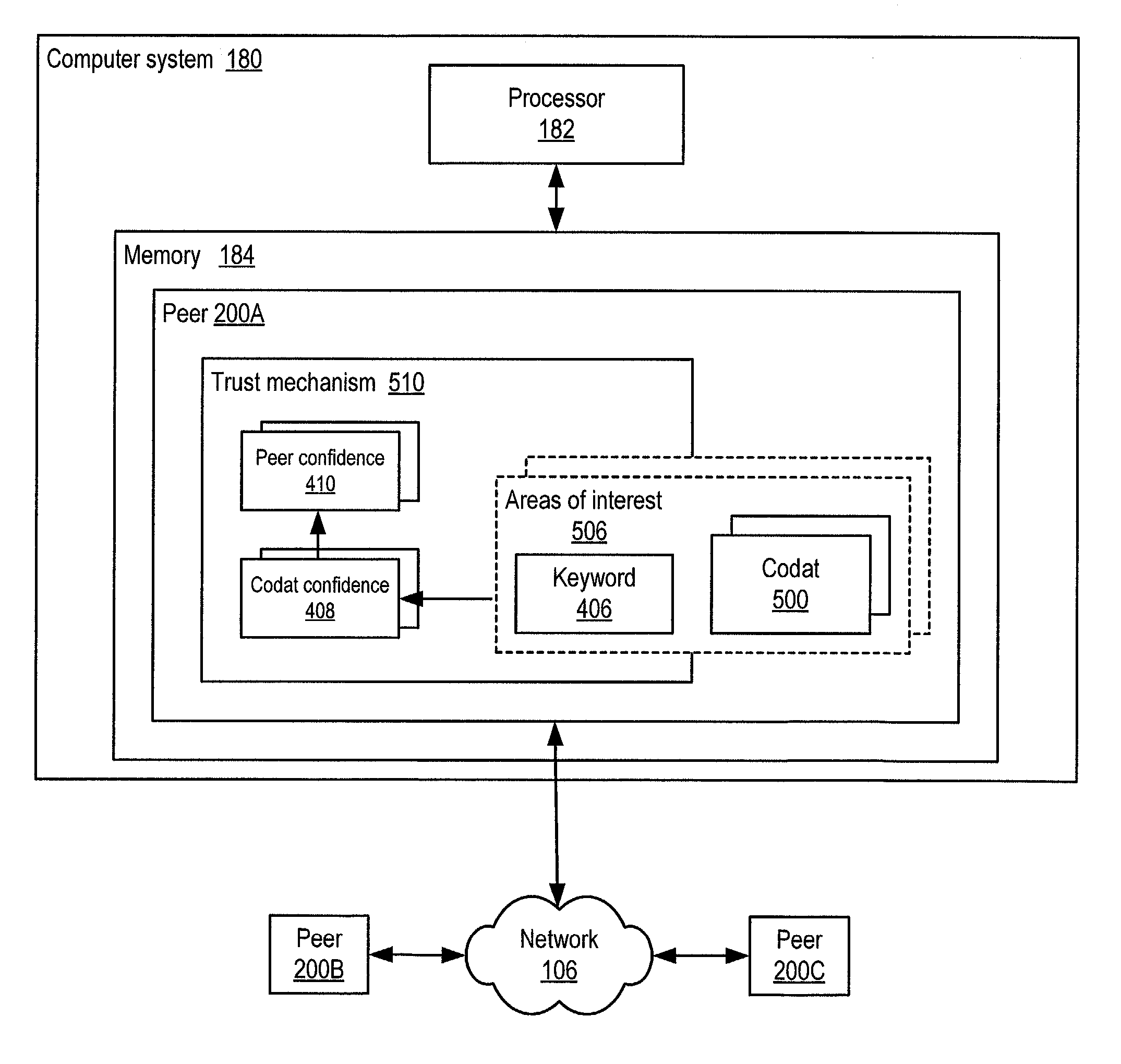
Trust mechanism for a peer-to-peer network computing platform
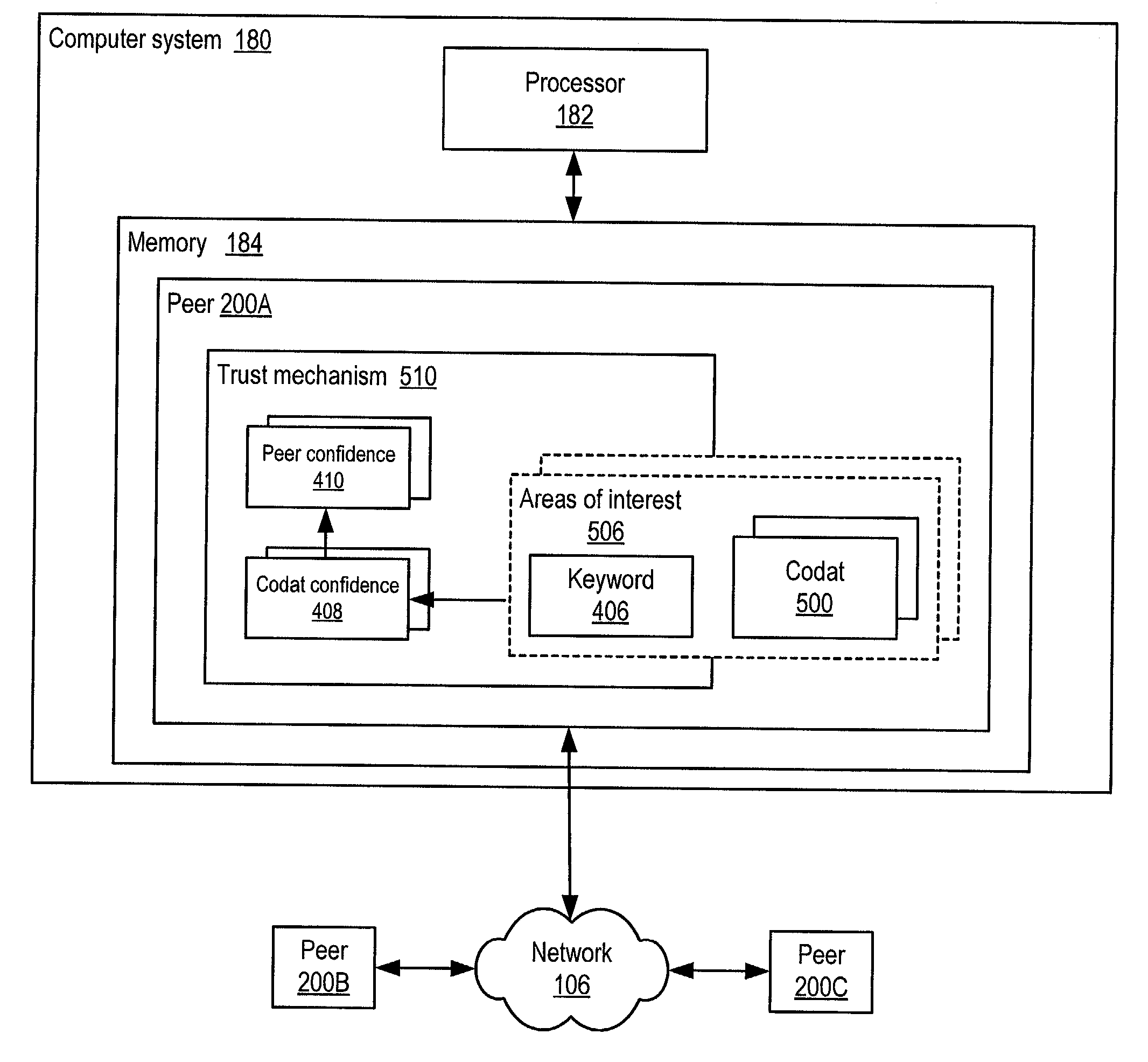
ActiveUS20050086300A1Generate and confidenceMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust relationshipDatabase
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for creating a secure trusted social network
InactiveUS20060259957A1FinanceDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyElectronic communication
A system for a plurality of users to share resources with access, control and configuration based on pre-defined relationships of trust between the users of the system. A computer-based authority provides the services of authentication, identification and verification of each user within network. Processes are described that leads to the formation of an electronic community, which facilitates electronic communication and transactions in a defined manner.
Owner:TAM CHUNG +2
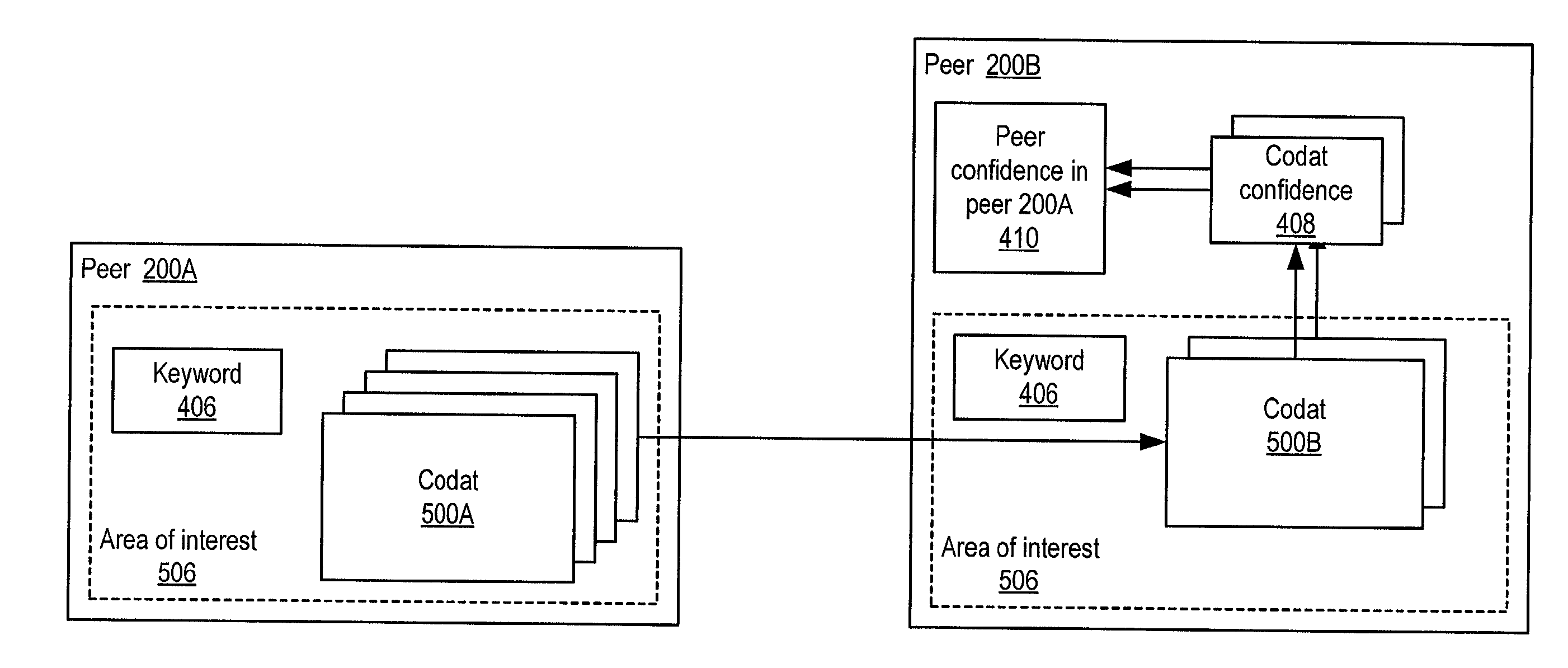
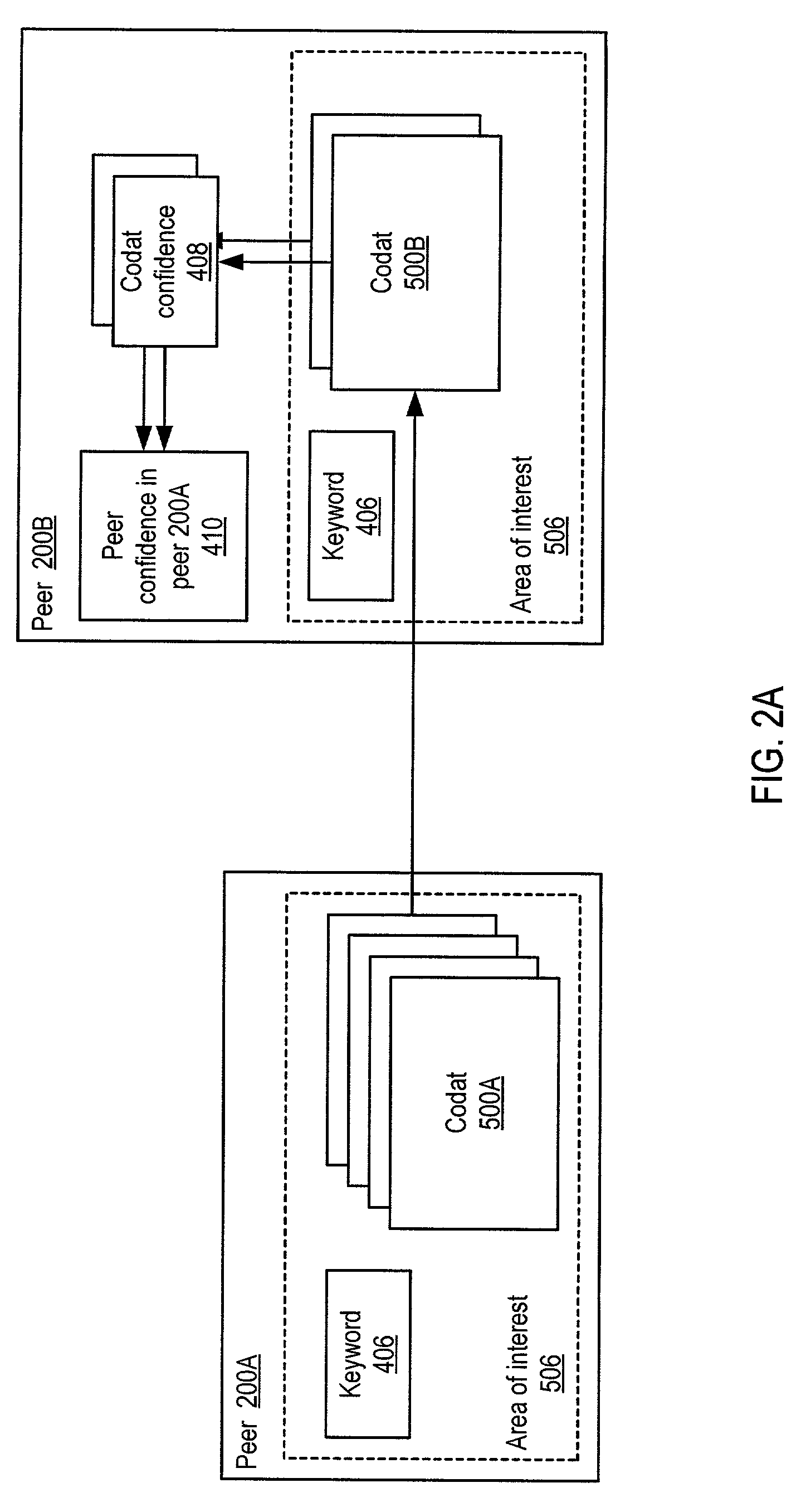
Propagating and updating trust relationships in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20030055898A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet privacyTrust relationship
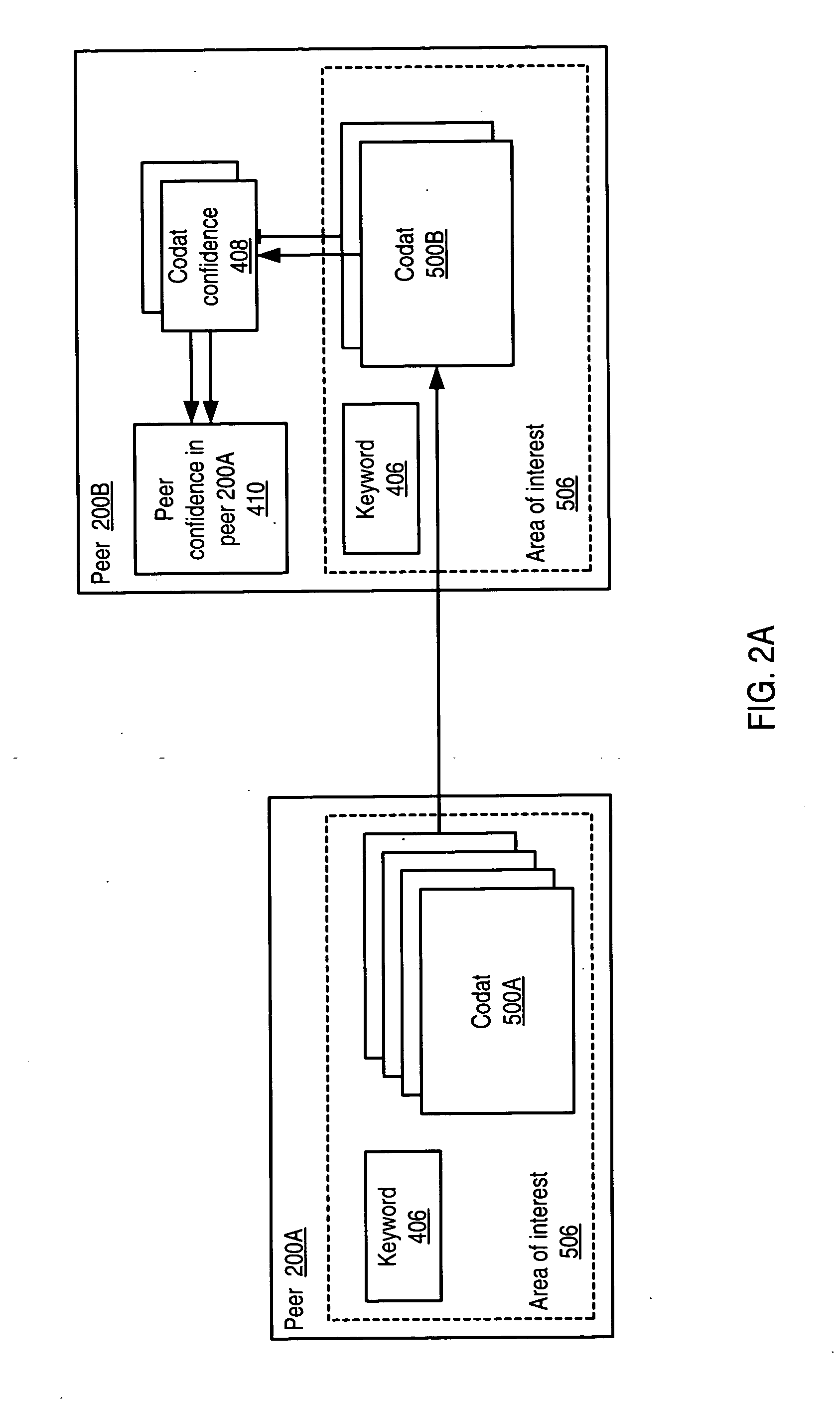
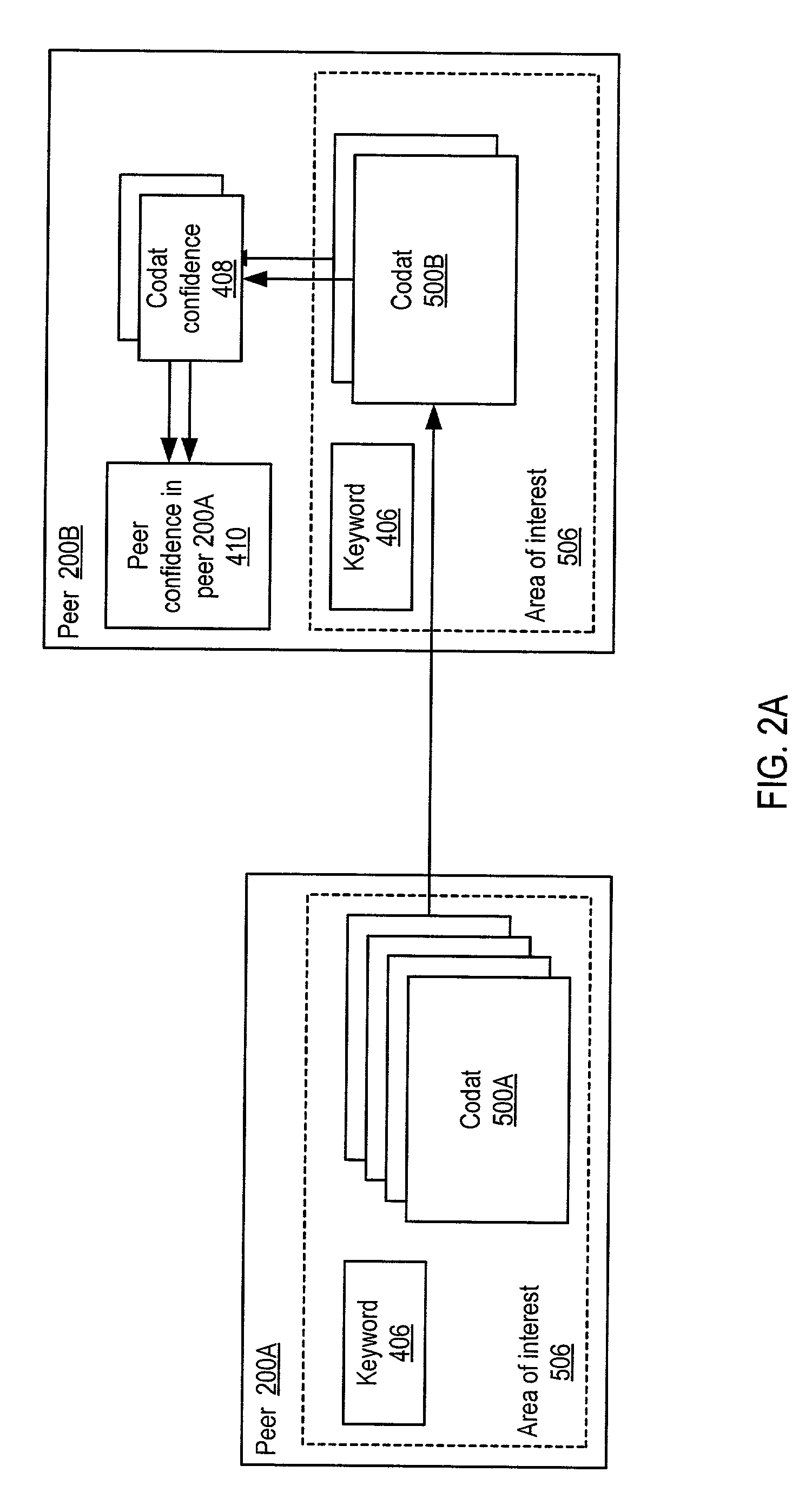
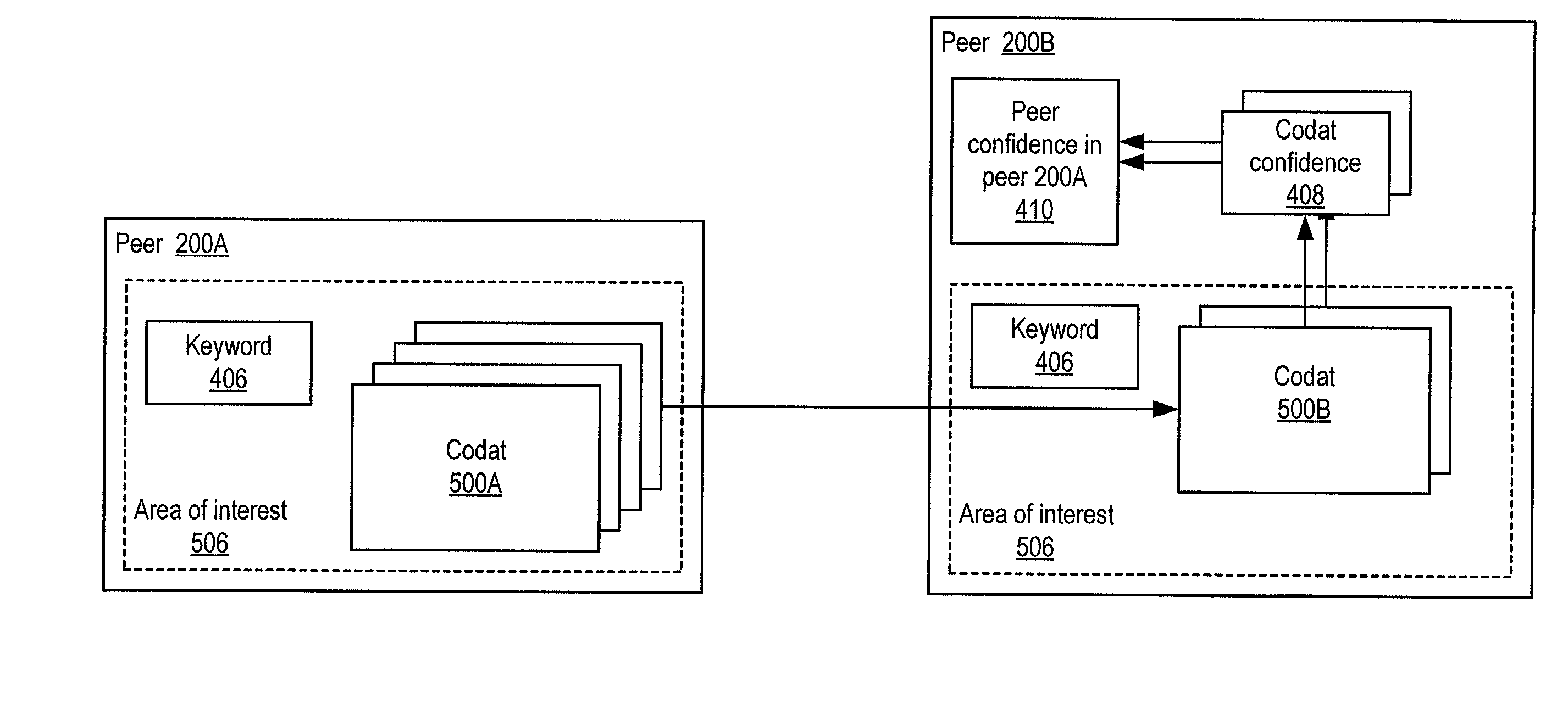
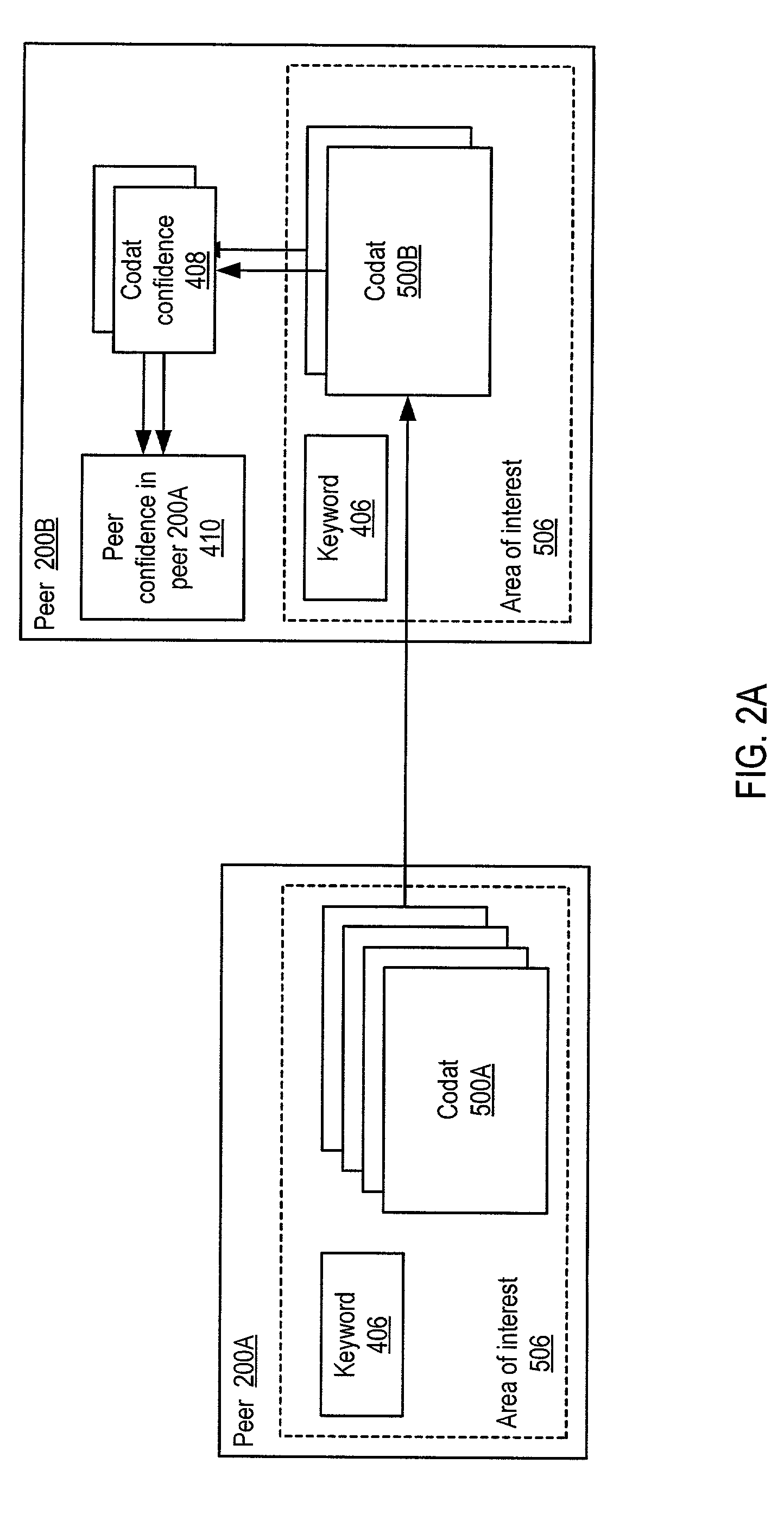
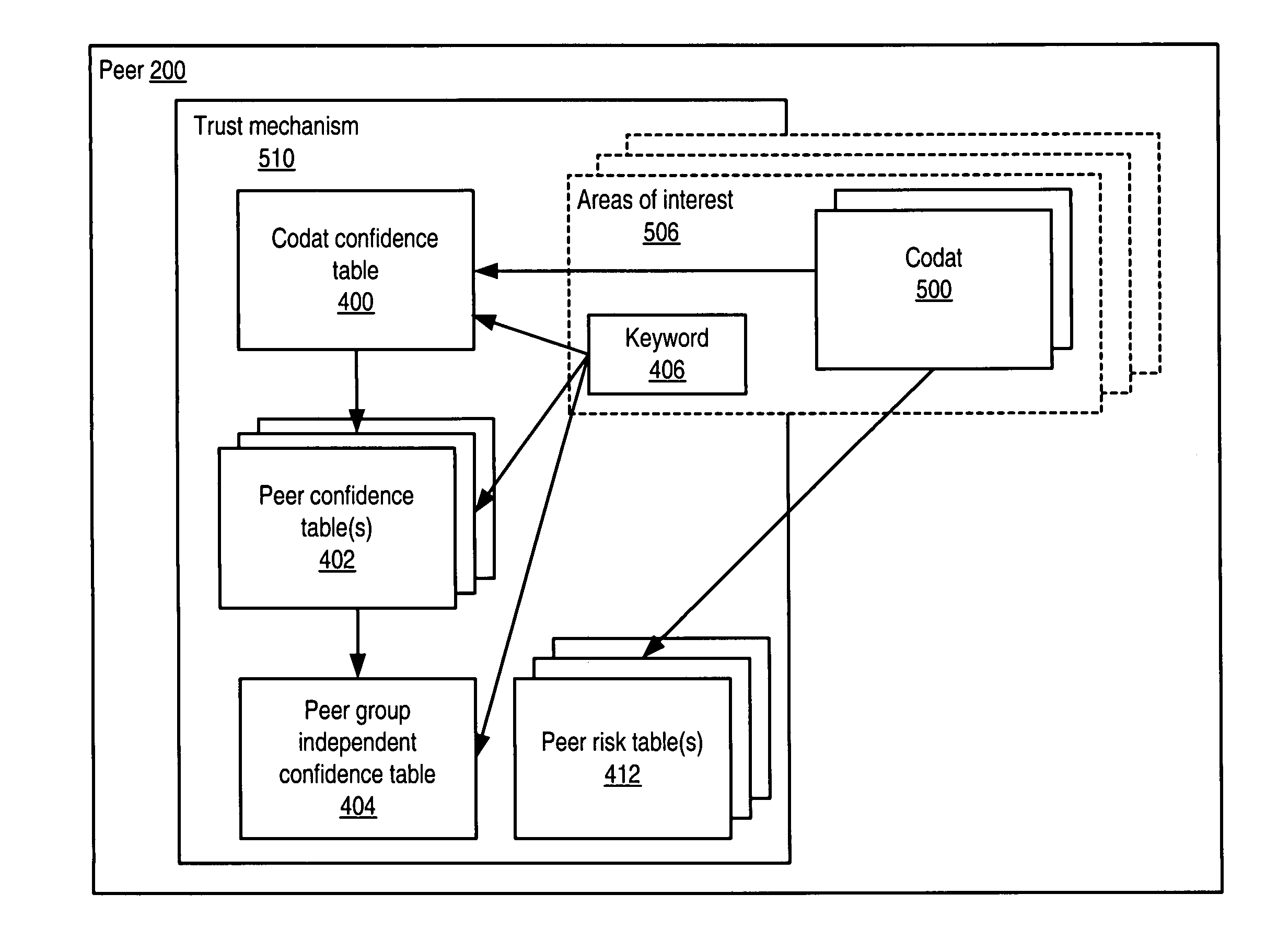
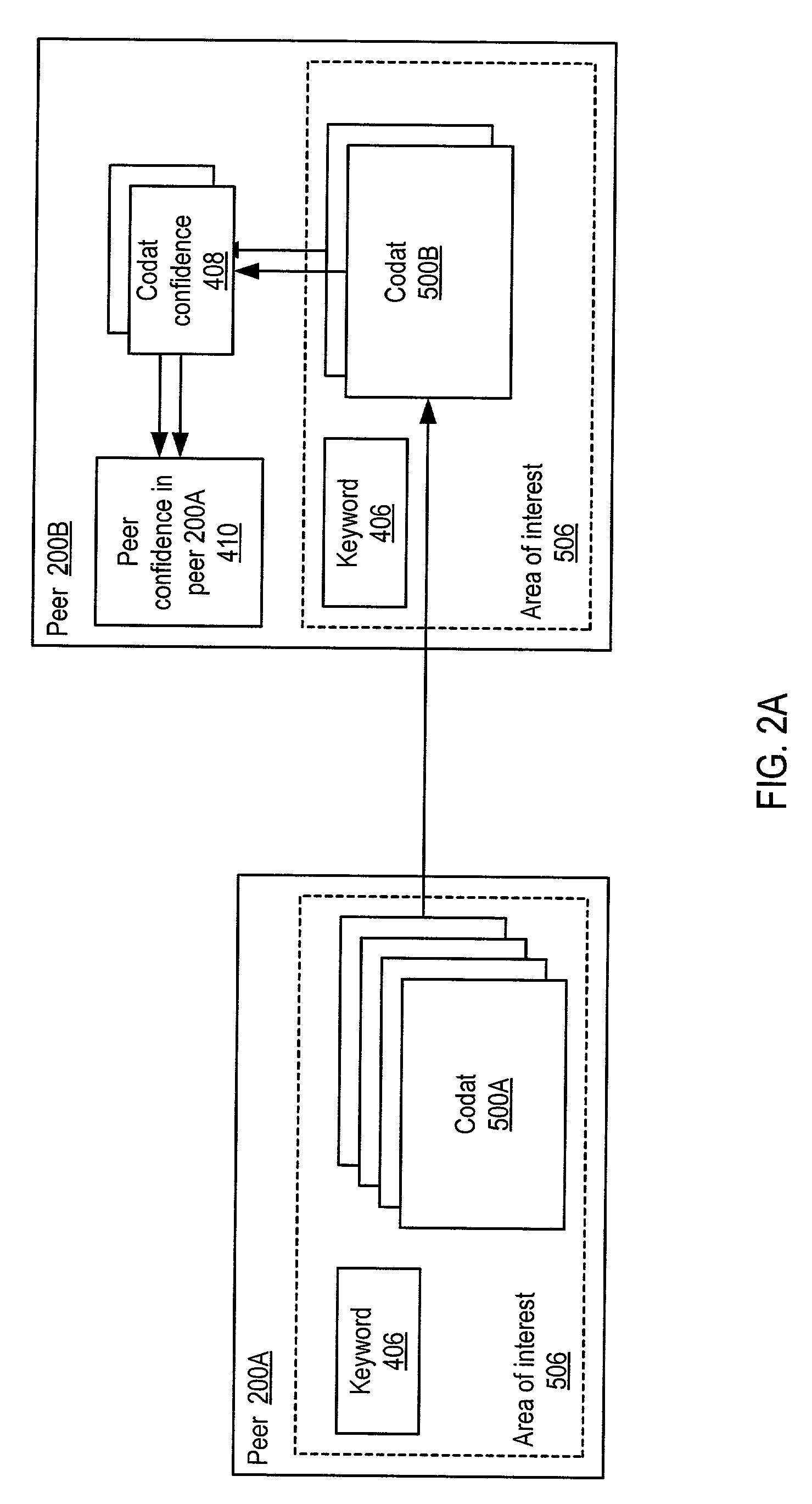
System and method for representing and rate the trustworthiness of peers as providers of content and data (codats) relevant to the peers' interests. In one embodiment, trust may be propagated through transaction pipes (paths) along which codats located in a search for codats relevant to an area of interest may be accessed by the requestor. In some embodiments, the trust a peer has in another peer as a provider of codats may be a function of the trust values of the provider peer and all other peers on a path. If there are multiple paths, trust in the provider peer may be an average of the trust values for all the paths. Trust in a provider peer may be used to determine confidence in codats provided by the peer. Embodiments may provide mechanisms for feeding back trust information to the providing peer and for propagating trust information to other peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Trust spectrum for certificate distribution in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20030070070A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsFrequency spectrumMaximum level
Embodiments of a decentralized, distributed trust mechanism that may be used in peer-to-peer platforms, to implement trust relationships based on data relevance between peers on a network and to implement trust relationships between peers and content and data (codat). In one embodiment, the trust mechanism may provide a trust spectrum of multiple levels wherein unique peer identities may be established to enable authentication and the assignment of the peers' associated access policies within a peer group. In one embodiment, the trust spectrum may have Certificate Authority signed certificates as a maximum level of security, and self-signed certificates as a minimum level of security. Since a certificate is one form of codat, in one embodiment the trust mechanism may be applied to a peer group member's collection of signed certificates for a given peer group.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
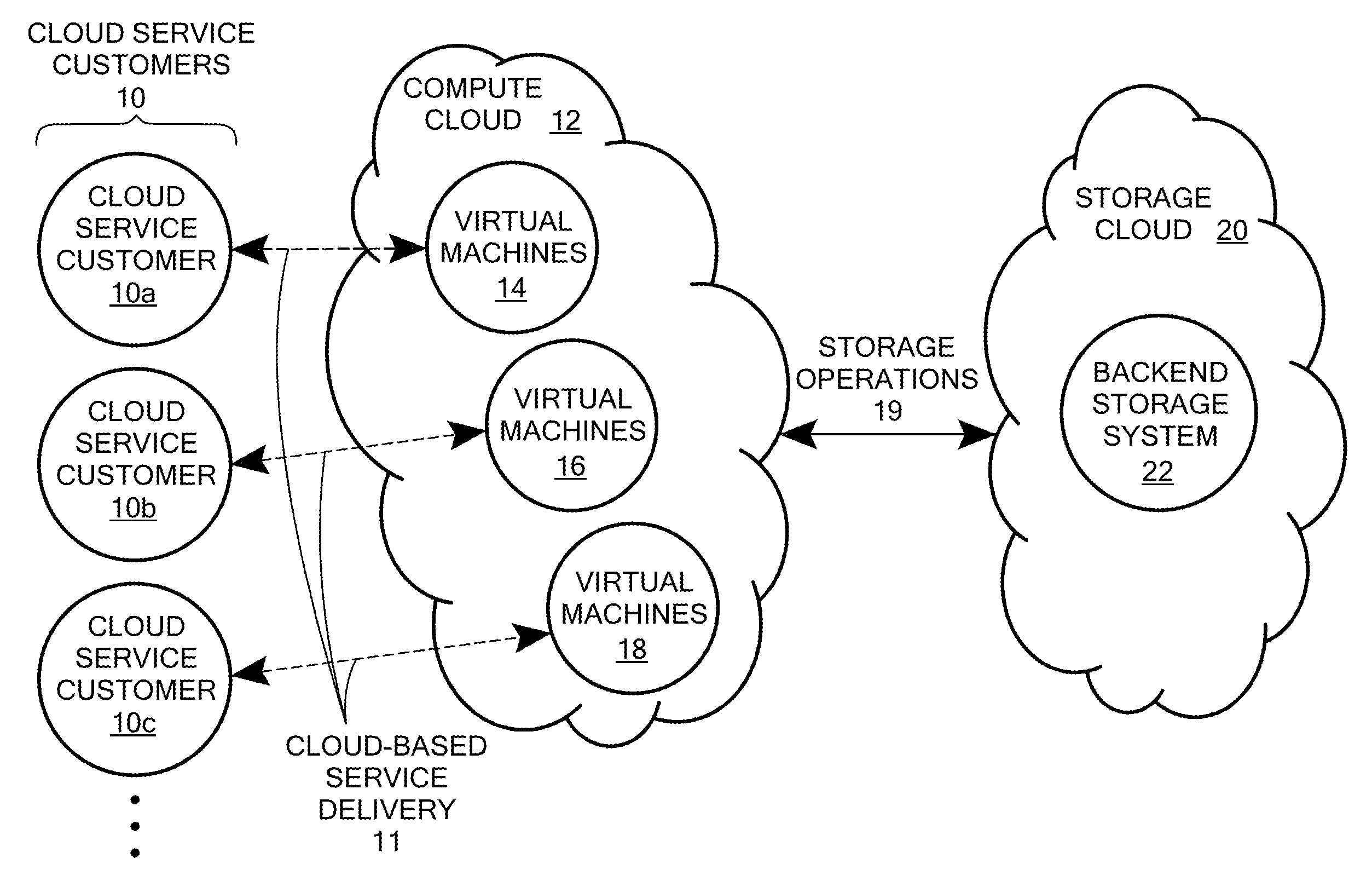
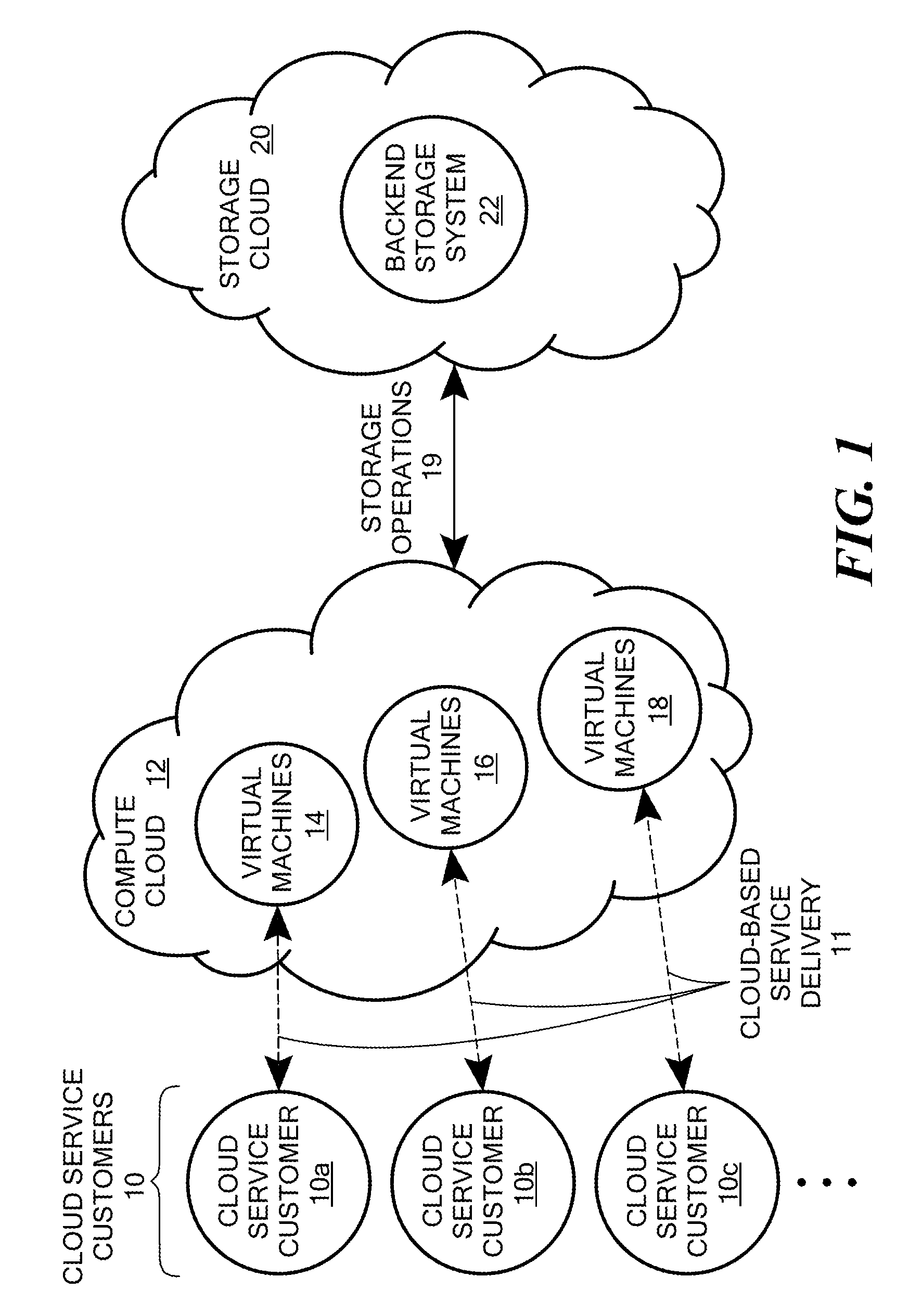
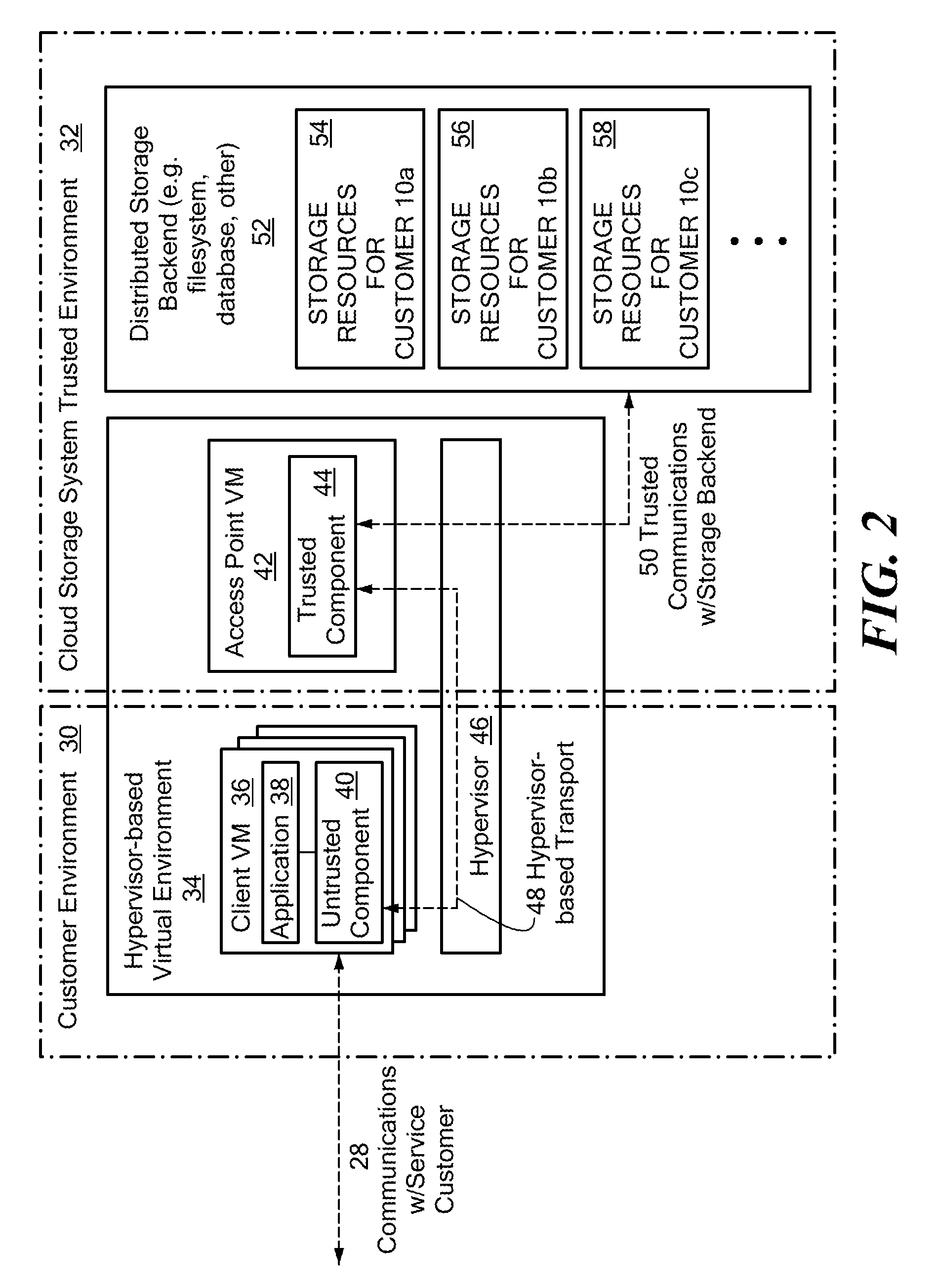
Scalable and secure high-level storage access for cloud computing platforms
ActiveUS8352941B1Effective segmentationImprove the level ofMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTrusted componentsTrust relationship
An untrusted component exposing a high level storage object interface within an untrusted client virtual machine accepts application level storage object operations. Responsive to a storage object operation, the untrusted component passes a message through the underlying hypervisor to an associated trusted component. The trusted component processes the message by authenticating the client virtual machine and locating an internal mapping between the client virtual machine and an associated customer-specific set of backend storage resources to which the requested storage object operation is to be applied. The trusted component uses a trust relationship with the backend storage system to securely communicate the storage object operation to the backend storage system, and passes the operation results through the hypervisor back to the untrusted component in the source client virtual machine from which the storage object request originated.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
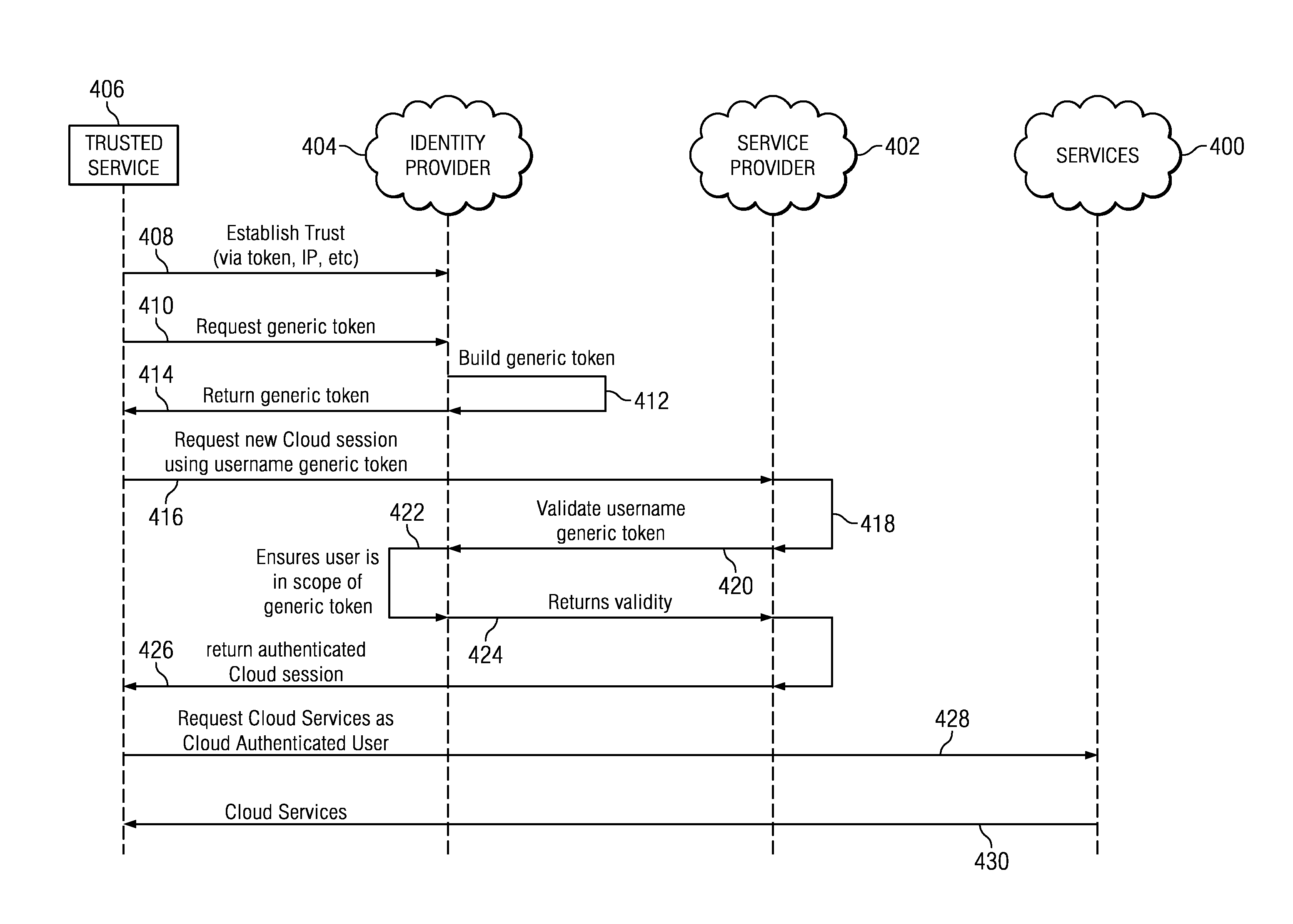
User impersonation/delegation in a token-based authentication system
ActiveUS20120254957A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyTrust relationship
A “trusted service” establishes a trust relationship with an identity provider and interacts with the identity provider over a trusted connection. The trusted service acquires a token from the identity provider for a given user (or set of users) without having to present the user's credentials. The trusted service then uses this token (e.g., directly, by invoking an API, by acquiring another token, or the like) to access and obtain a cloud service on a user's behalf even in the user's absence. This approach enables background services to perform operations within a hosted session (e.g., via OAuth-based APIs) without presenting user credentials or even having the user present.
Owner:IBM CORP
Secure interprocess communications binding system and methods
InactiveUS20050182966A1Inhibit exchangeFlexible performanceDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust relationshipInter-process communication
The secure trust relationship between communicating programs is established at any policy defined level down to individual program instances. Policy enforcement modules installed on host computer systems support qualified encrypted communications channels between discretely selected program instances. Program instances are qualified to establish communication channels, each defined by a unique session encryption key, based on an evaluation of security data including the individual process execution contexts, user authorizations, and access attributes of the program instances. A security appliance server performs the policy-based qualification based on a mutually interdependent evaluation of the security data for both the communications channel source and target program instances.
Owner:PHAM DUC +3
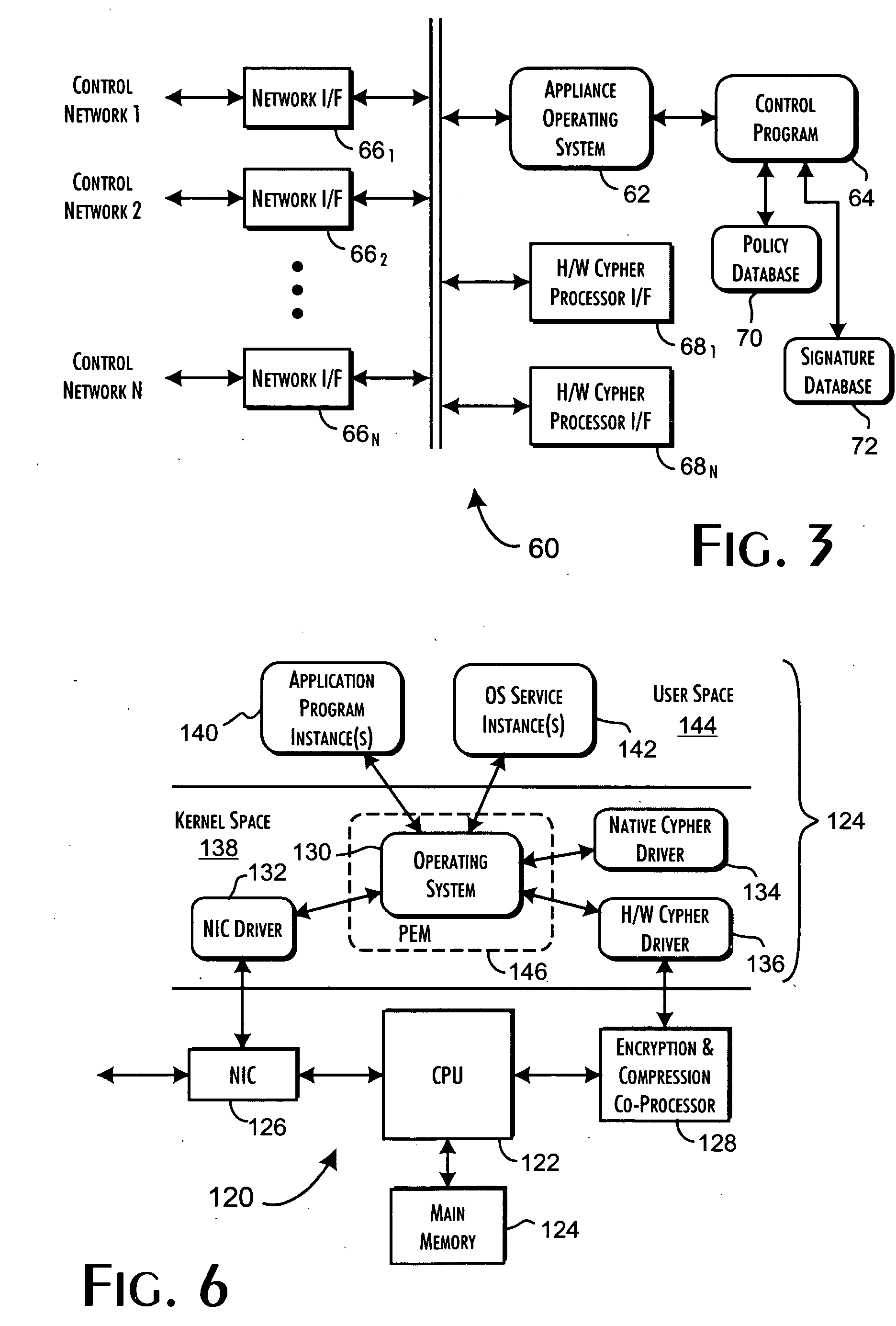
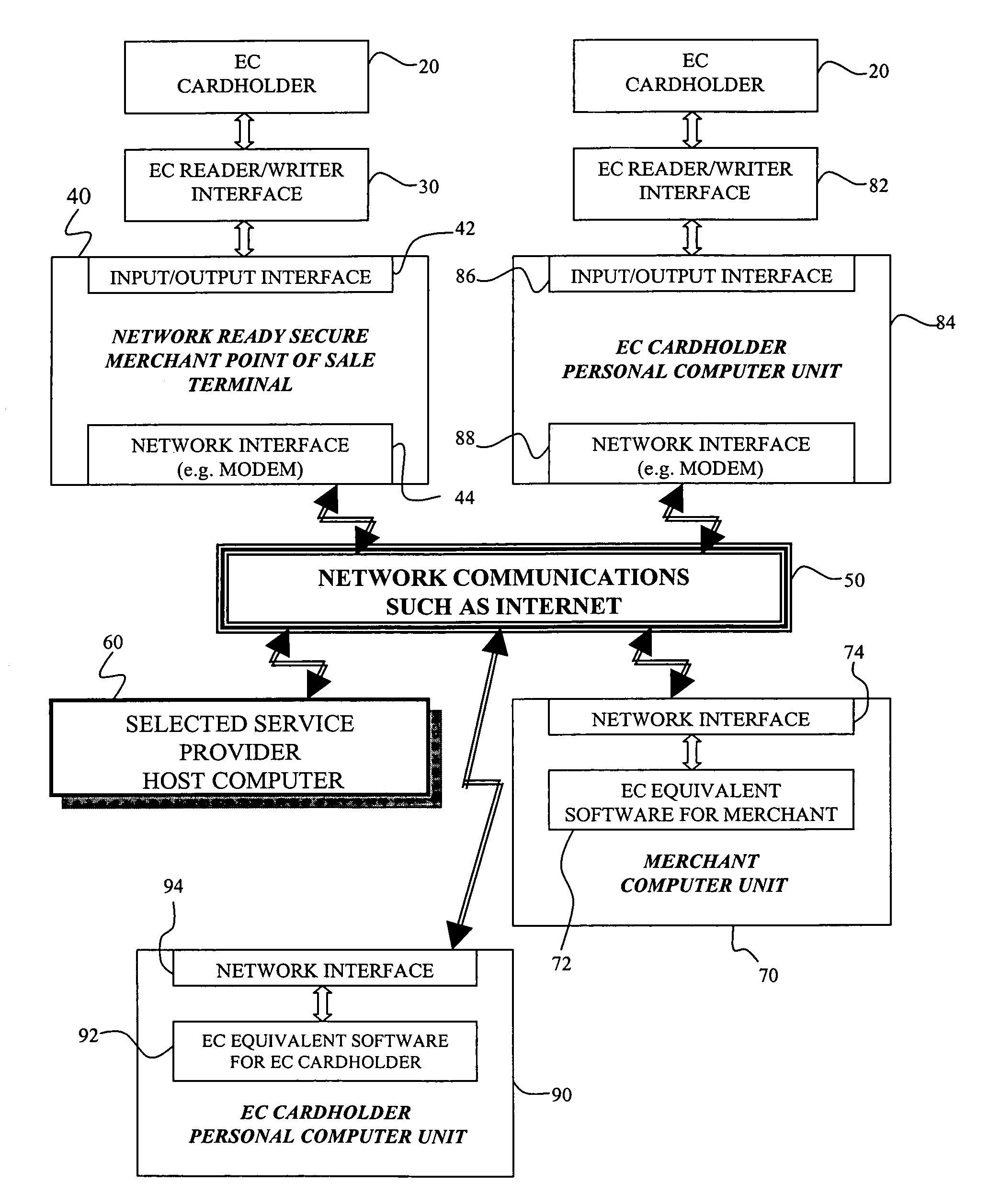
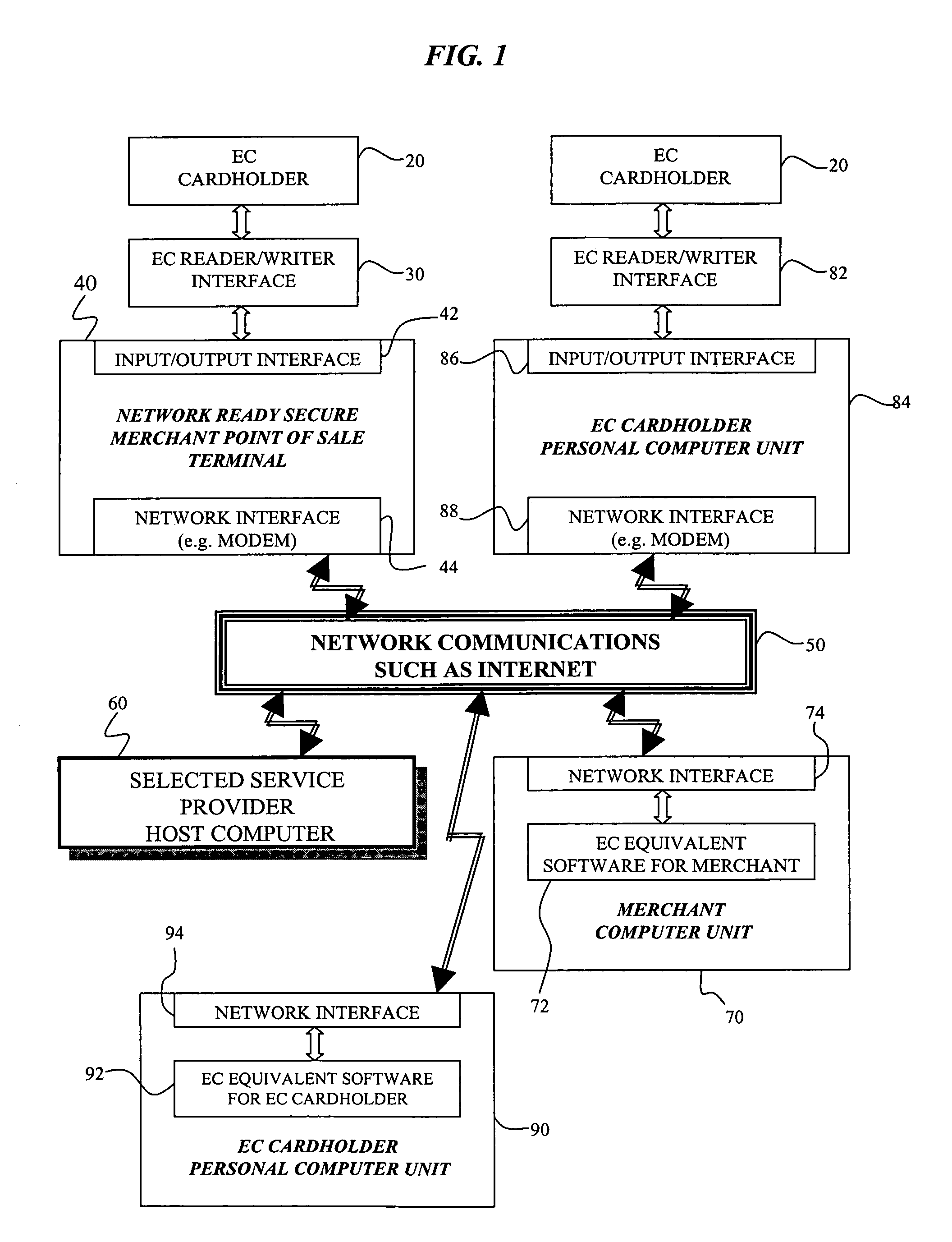
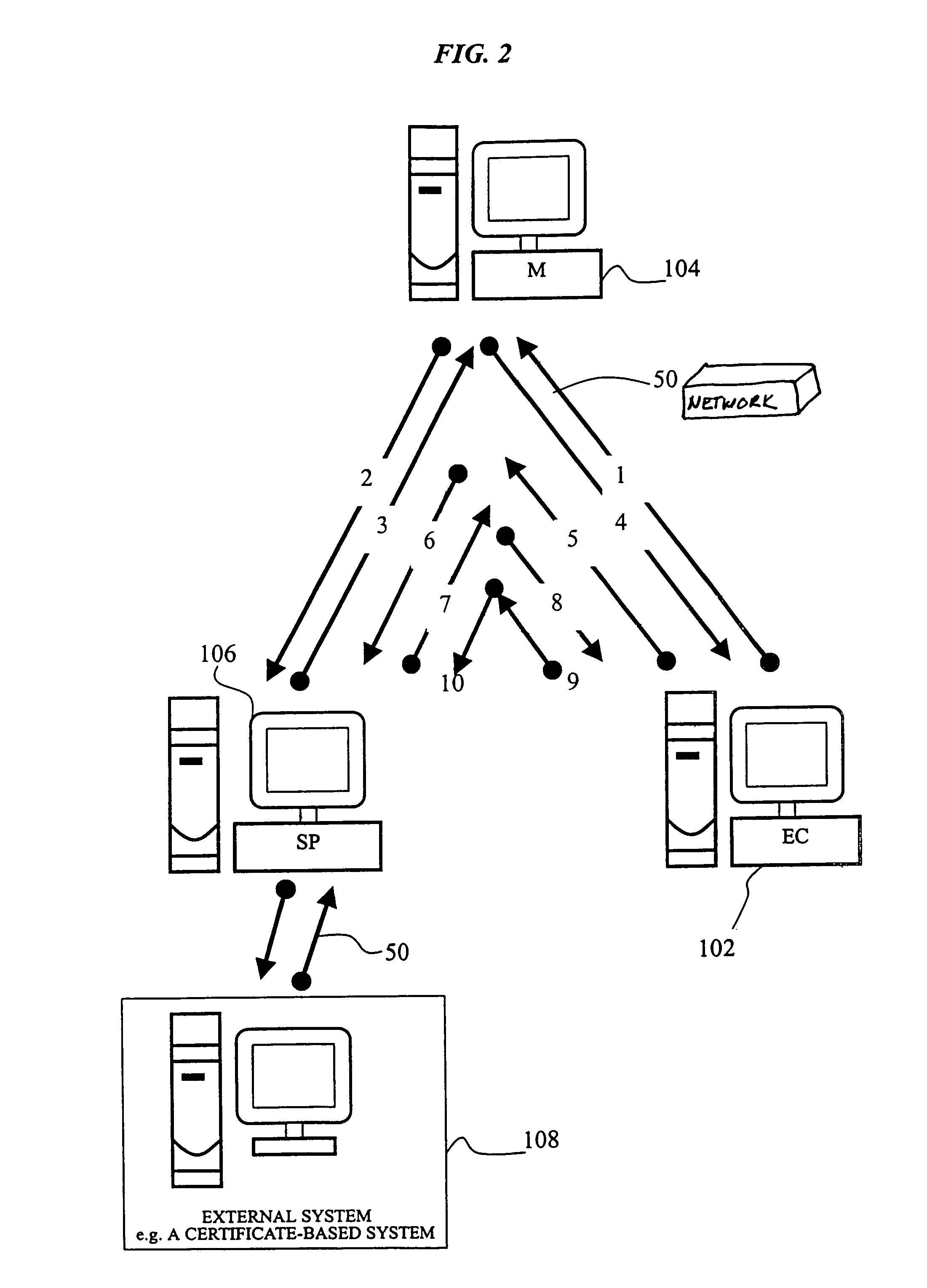
Cryptographic system and method for electronic transactions
InactiveUS7096494B1Key distribution for secure communicationFinanceCredit cardSecure Electronic Transaction
An electronic transaction system, which facilitates secure electronic transactions among multiple parties including cardholders, merchants, and service providers (SP). The system involves electronic cards, commonly known as smart cards, and their equivalent computer software package. The card mimics a real wallet and contains commonly seen financial or non-financial instruments such as a credit card, checkbook, or driver license. A transaction is protected by a hybrid key cryptographic system and is normally carried out on a public network such as the Internet. Digital signatures and challenges-responses are used to ensure integrity and authenticity. The card utilizes secret keys such as session keys assigned by service providers (SPs) to ensure privacy for each transaction. The SP is solely responsible for validating each participant's sensitive information and assigning session keys. The system does not seek to establish a trust relationship between two participants of a transaction. The only trust relationship needed in a transaction is the one that exists between individual participants and the SP. The trust relationship with a participant is established when the SP has received and validated certain established account information from that particular participant. To start a transaction with a selected SP, a participant must have the public key of the intended SP. Since the public key is openly available, its availability can be easily established by the cardholder. The SP also acts as a gateway for the participants when a transaction involves interaction with external systems.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Method, system and service for conducting authenticated business transactions
The invention pertains to a method, on-line service, and system, for creating partnerships based on trust relationships over a public network, authenticating trade partners, infrastructure providers, and collaborators to each other, and providing users with an environment suitable for conducting transactions requiring a high level of trust. A service according to the invention is a persistent authentication and mediation service (PAMS) which is provided as an on-line service. One embodiment is a method for conducting authenticated business transactions involving microprocessor equipped devices over the Internet comprising: A. Providing an on-line authentication service available on the distributed network; B. Authenticating a plurality of users to said on-line authentication service using a closed authentication system to produce a plurality of authenticated users; and C. Connecting a group of at least two of said plurality of authenticated users under persistent mediation of said on-line authentication service, producing a connected group of authenticated users.
Owner:FISHER DOUGLAS
Trust mechanisms for a peer-to-peer network computing platform
ActiveUS7275102B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust relationshipDatabase
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Trust spectrum for certificate distribution in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS7383433B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsMaximum levelSelf-signed certificate
Embodiments of a decentralized, distributed trust mechanism that may be used in peer-to-peer platforms, to implement trust relationships based on data relevance between peers on a network and to implement trust relationships between peers and content and data (codat). In one embodiment, the trust mechanism may provide a trust spectrum of multiple levels wherein unique peer identities may be established to enable authentication and the assignment of the peers' associated access policies within a peer group. In one embodiment, the trust spectrum may have Certificate Authority signed certificates as a maximum level of security, and self-signed certificates as a minimum level of security. Since a certificate is one form of codat, in one embodiment the trust mechanism may be applied to a peer group member's collection of signed certificates for a given peer group.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for enabling trust infrastructure support for federated user lifecycle management
InactiveUS20060021018A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrust relationshipKey management
A method and a system are presented in which computing environments of different enterprises interact within a federated computing environment. Federated operations can be initiated at the computing environments of federation partners on behalf of a user at a different federated computing environment. A point-of-contact service relies upon a trust service to manage trust relationships between a computing environment and computing environments of federation partners. The trust service employs a key management service, an identity / attribute service, and a security token service. A federated user lifecycle management service implements federated user lifecycle functions and interacts with the point-of-contact service and the trust service.
Owner:IBM CORP
Universal data aggregation
InactiveUS20070027930A1Productive controlBridging of information communities and organizationsDigital data processing detailsTransmissionData sourceData aggregator
A system for aggregating and managing PIM data from multiple sources is provided. By aggregating various sources of data, the present system allow for the bridging of networked communities and organizations. Limitations of data aggregation as a result of proprietary and / or protocol concerns are overcome through the development of trusted relationships amongst users of the data aggregation and management system.
Owner:SEVEN NETWORKS INC
Access control systems and methods using visibility tokens with automatic propagation
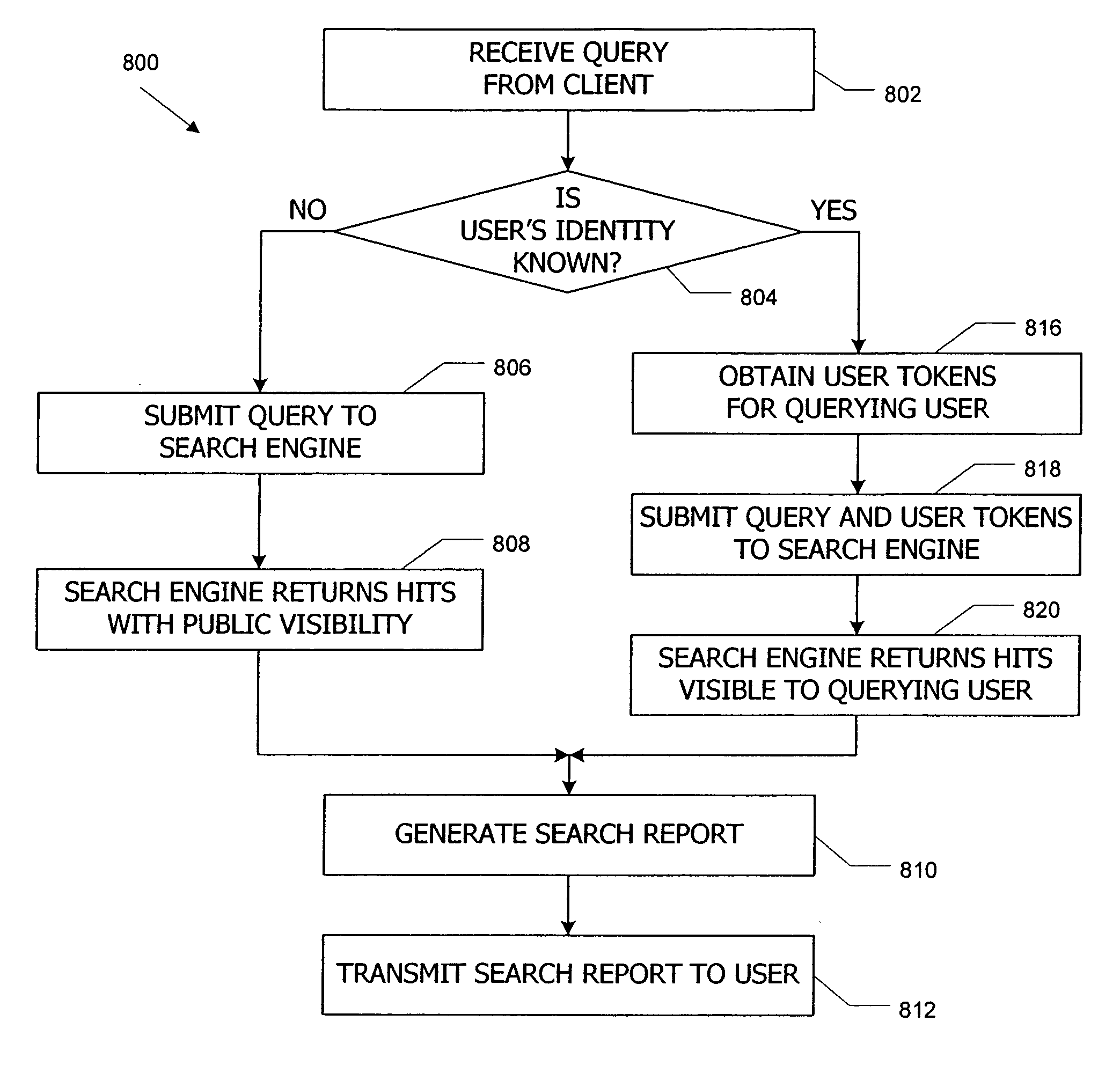
ActiveUS20060294192A1Improved search response timeShort response timeDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVisibilityControl system
Access control systems and methods regulate access to shared content items in a corpus using visibility tokens. A user provides other users with access to a content item by associating a content token with the content item and associating a matching user token with each user who is to be granted access. A user who attempts to access the content item succeeds only if that user has a user token matching the content token associated with the content item. User tokens can be propagated automatically from one user to another, e.g., based on trust relationships among the users. Content tokens can be indexed with content items so that when a user searches the corpus, a search engine can detect matches between user tokens and content tokens and filter the search results based on whether they are visible to the querying user.
Owner:SLACK TECH LLC
Propagating and updating trust relationships in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS7203753B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet privacyTrust relationship
System and method for representing and rate the trustworthiness of peers as providers of content and data (codats) relevant to the peers' interests. In one embodiment, trust may be propagated through transaction pipes (paths) along which codats located in a search for codats relevant to an area of interest may be accessed by the requestor. In some embodiments, the trust a peer has in another peer as a provider of codats may be a function of the trust values of the provider peer and all other peers on a path. If there are multiple paths, trust in the provider peer may be an average of the trust values for all the paths. Trust in a provider peer may be used to determine confidence in codats provided by the peer. Embodiments may provide mechanisms for feeding back trust information to the providing peer and for propagating trust information to other peers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
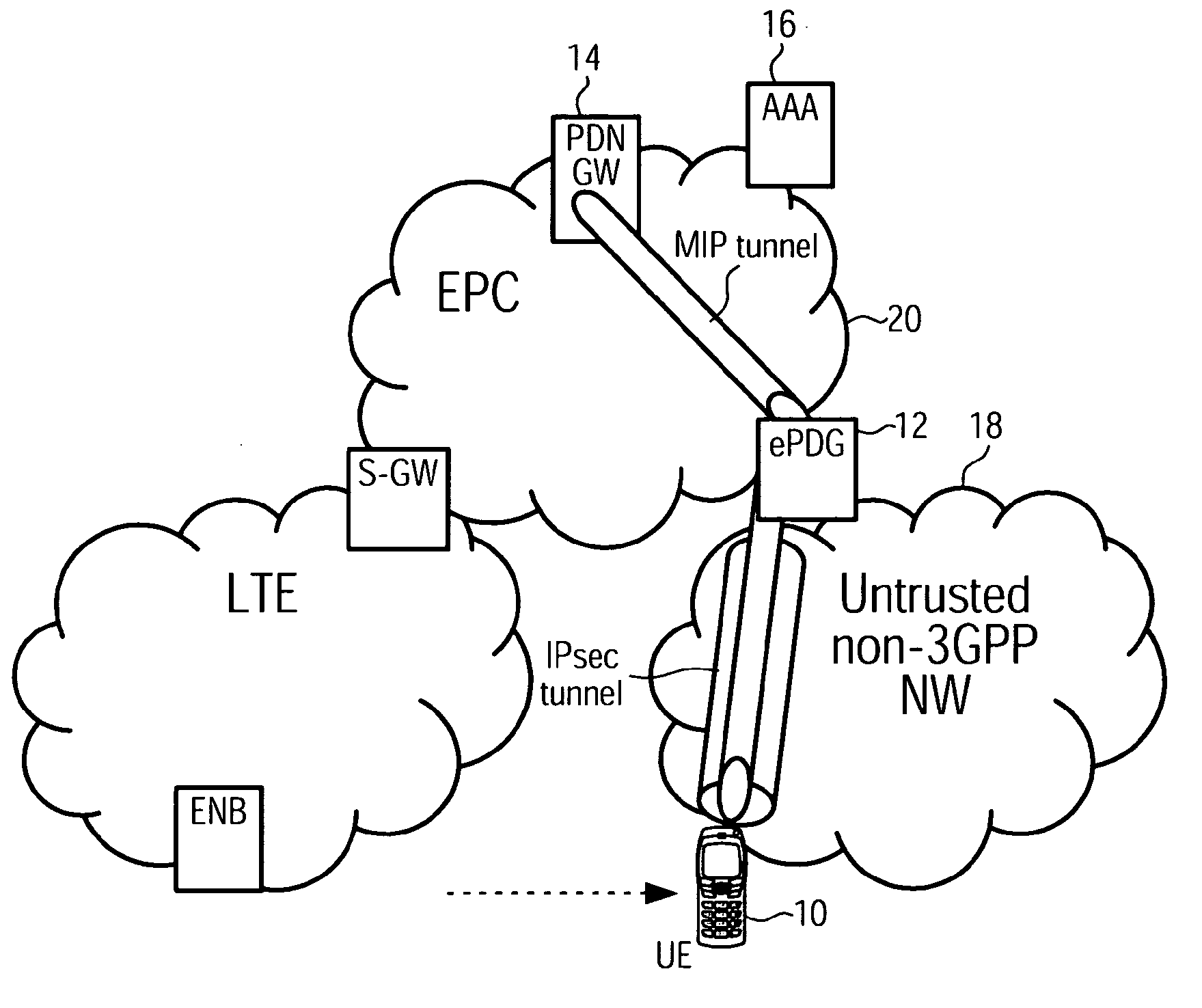
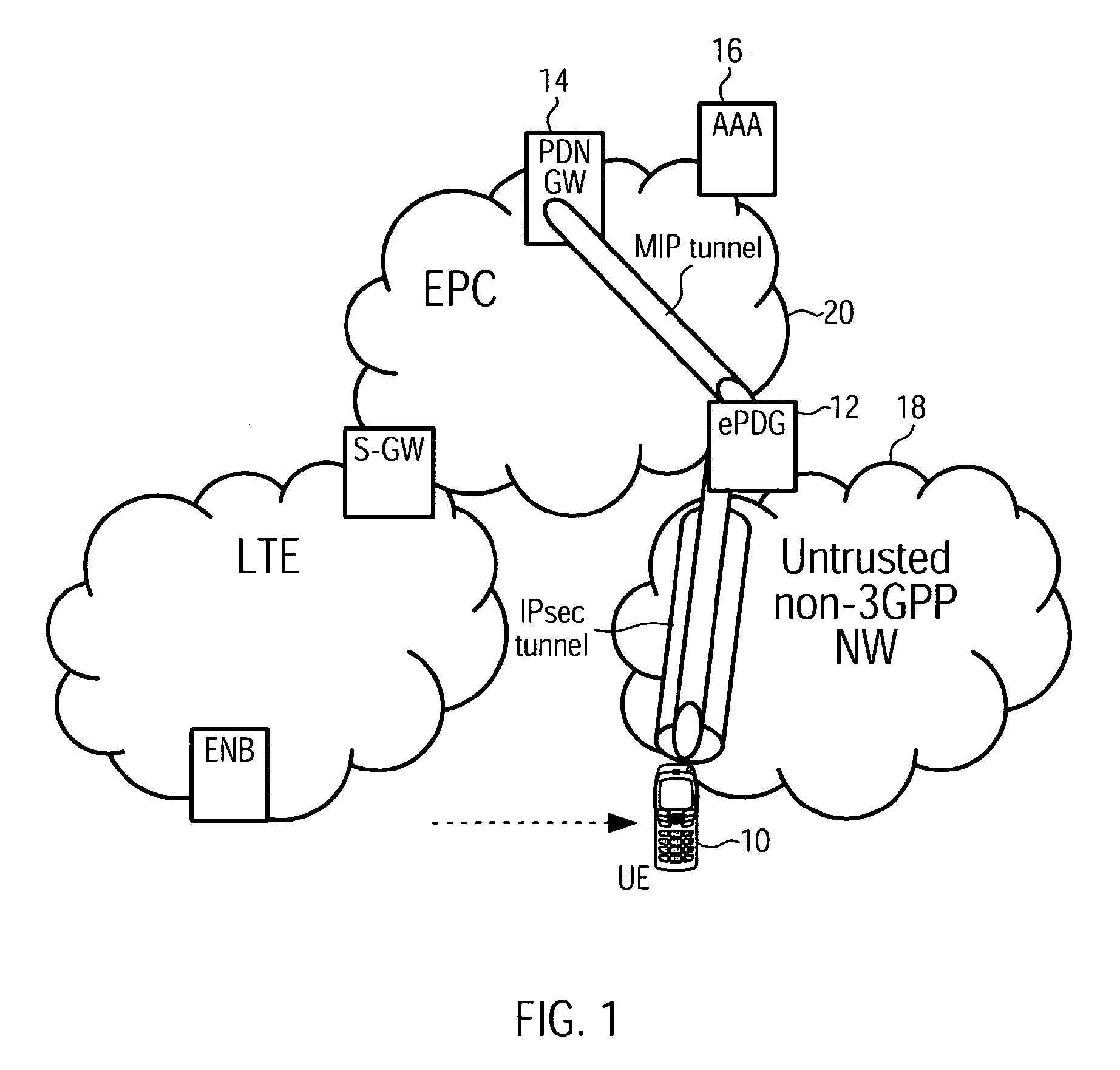
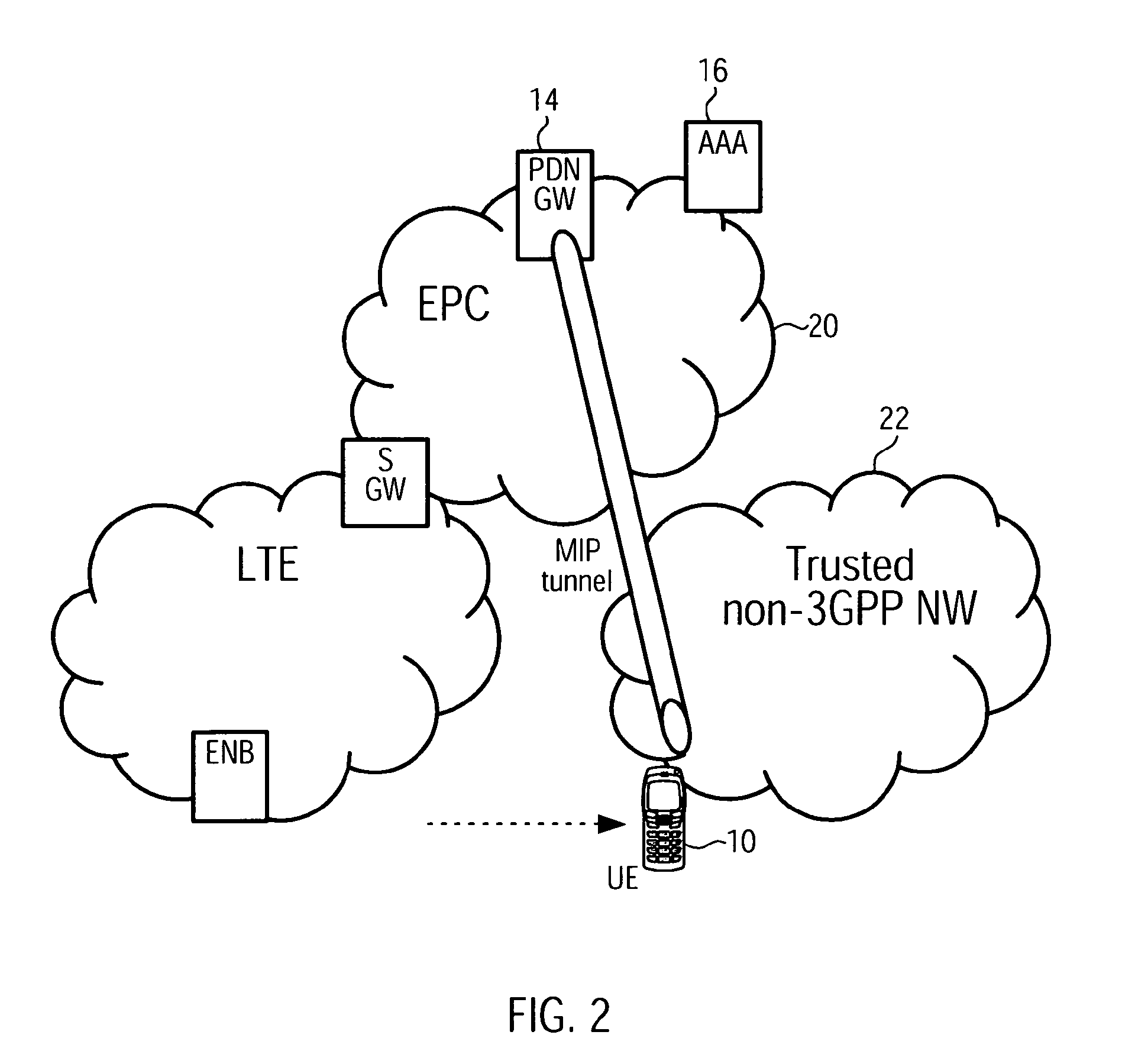
Access-Network to Core-Network Trust Relationship Detection for a Mobile Node
InactiveUS20100199332A1Sure easyEfficiently signaledError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAccess networkIp address
The invention provides a method for trust relationship detection between a core and access network for a user equipment. The gist is that a security tunnel establishment procedure is used so one entity, be it part of the core network or be it the user equipment itself, is provided with information to determine whether the access network is trusted or untrusted. The information may comprise a first IP address / prefix, which is initially assigned to the user equipment, upon attaching to the access network. The necessary information may further comprise a second IP address / prefix, which is an address / prefix that is allocated at a trusted entity of the core network. Depending which entity determines the trust relationship of the access network, it might be necessary to transmit either the first IP address / prefix or the second IP address / prefix or the first and the second IP address / prefix using the security tunnel establishment procedure.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
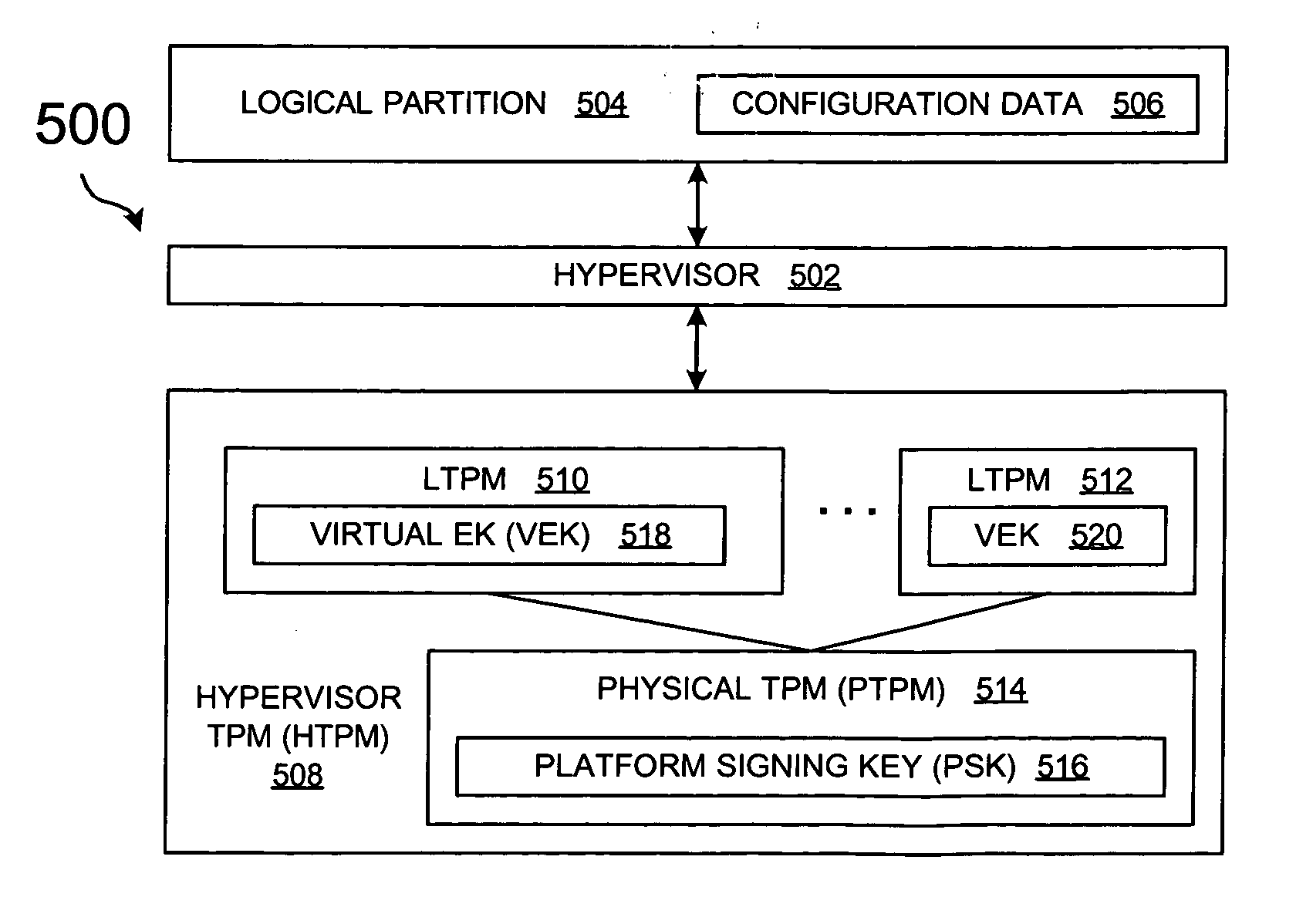
Method and system for virtualization of trusted platform modules
ActiveUS20050246552A1User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtualizationData processing system
A method, an apparatus, a system, and a computer program product is presented for virtualizing trusted platform modules within a data processing system. A virtual trusted platform module along with a virtual endorsement key is created within a physical trusted platform module within the data processing system using a platform signing key of the physical trusted platform module, thereby providing a transitive trust relationship between the virtual trusted platform module and the core root of trust for the trusted platform. The virtual trusted platform module can be uniquely associated with a partition in a partitionable runtime environment within the data processing system.
Owner:IBM CORP
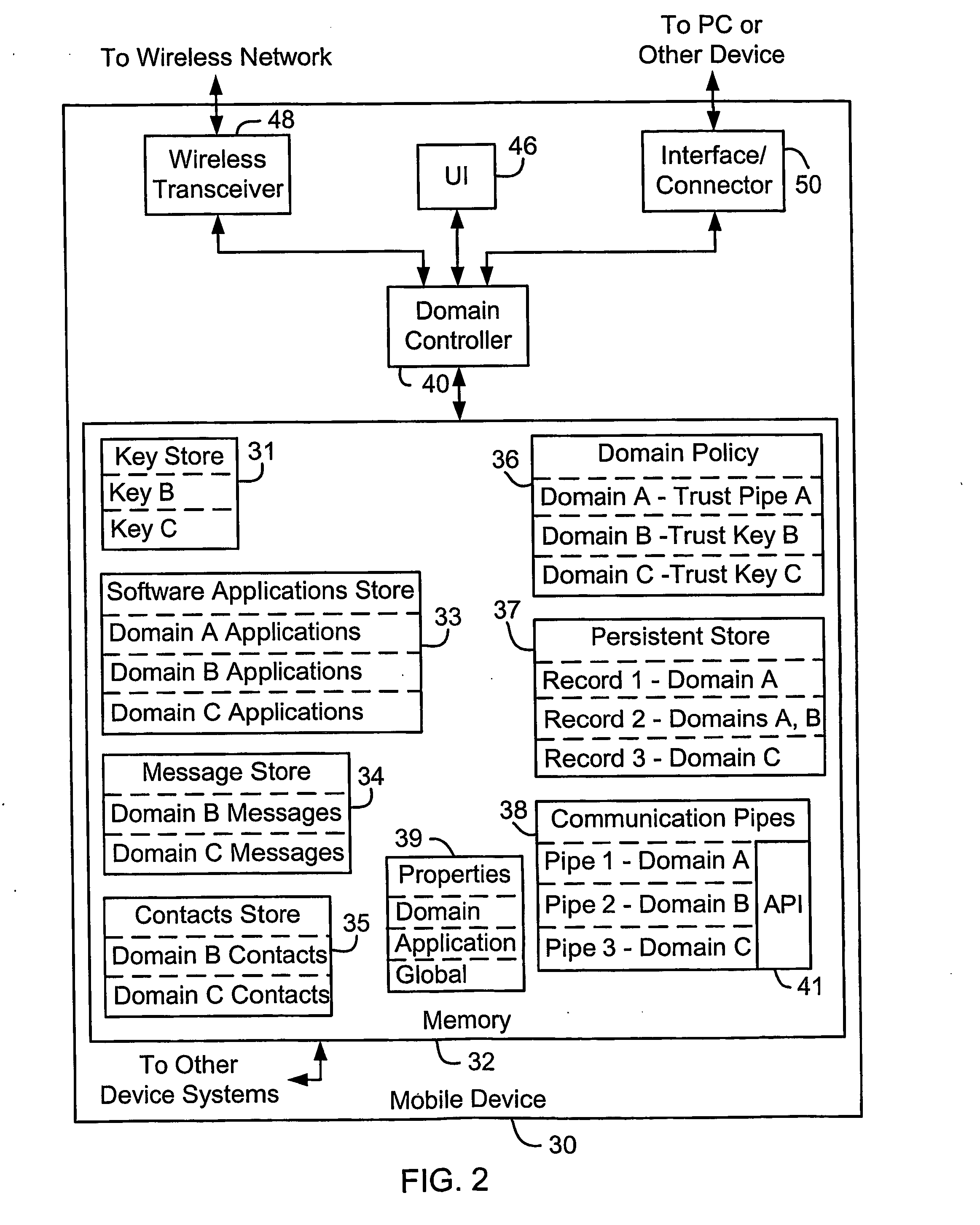
System and method for secure control of resources of wireless mobile communication devices
ActiveUS20050213763A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrust relationshipCommunication device
Systems and methods for secure control of a wireless mobile communication device are disclosed. Each of a plurality of domains includes at least one wireless mobile communication device asset. When a request to perform an operation affecting at least one of the assets is received, it is determined whether the request is permitted by the domain that includes the at least one affected asset, by determining whether the entity with which the request originated has a trust relationship with the domain, for example. The operation is completed where it is permitted by the domain. Wireless mobile communication device assets include software applications, persistent data, communication pipes, and configuration data, properties or user or subscriber profiles.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Managing storage resources in decentralized networks
InactiveUS7251689B2Avoiding drawback and limitationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationPersistent identifierWeb service
Methods, systems, and computer program products are disclosed for managing storage resources in decentralized networks. Persistent identifiers are defined for nodes, allowing nodes to be identified across sessions and invocations, even though they re-enter the network with a different network address. Paths taken by content resources as they traverse the network (e.g. which nodes forwarded the content) are persisted, along with reputation information about nodes (e.g. indicating how successful they are at answering queries from peers). Trust relationships can be derived using the persisted information. A tiered broadcast strategy is defined for reducing the number of messages exchanged. Preferred embodiments leverage a web services implementation model.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and Method to Enable PKI- and PMI- Based Distributed Locking of Content and Distributed Unlocking of Protected Content and/or Scoring of Users and/or Scoring of End-Entity Access Means - Added
ActiveUS20150312233A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTrust relationshipThin client
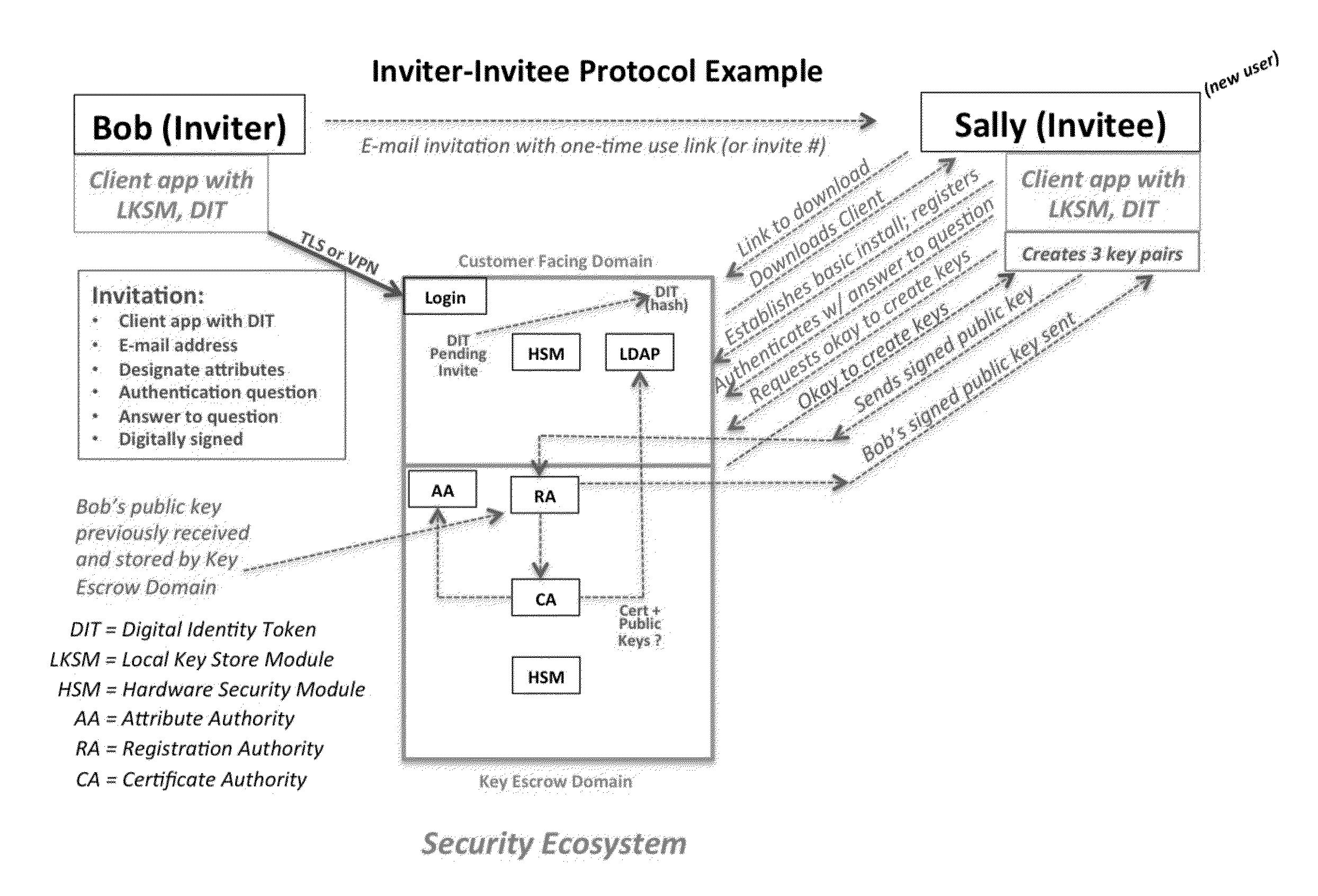
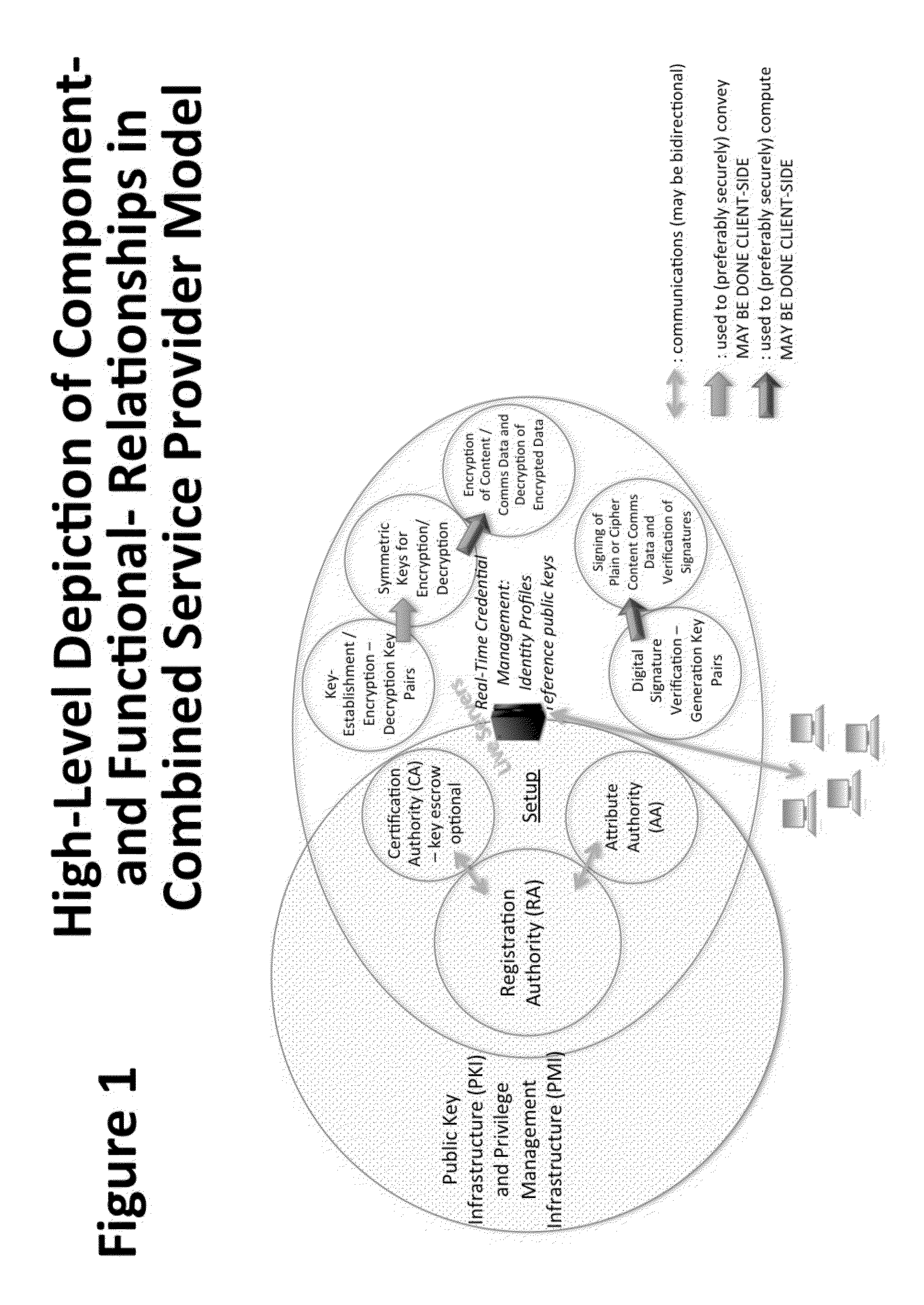
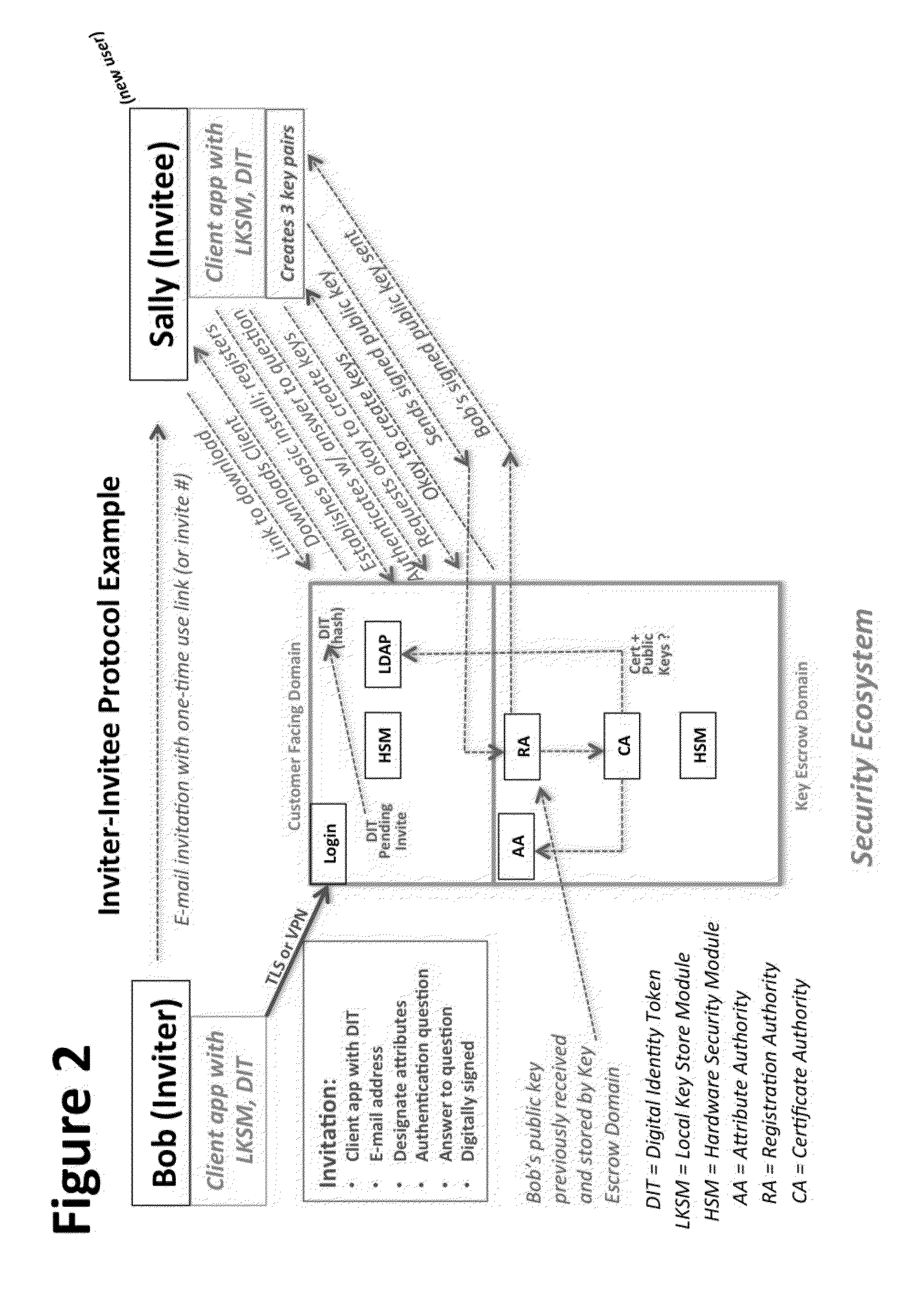
A central server configured with an Attribute Authority (“AA”) acting as a Trusted Third Party mediating service provider and using X.509-compatible PKI and PMI, VPN technology, device-side thin client applications, security hardware (HSM, Network), cloud hosting, authentication, Active Directory and other solutions. This ecosystem results in real time management of credentials, identity profiles, communication lines, and keys. It is not centrally managed, rather distributes rights to users. Using its Inviter-Invitee protocol suite, Inviters vouch for the identity of Invitees who successfully complete the protocol establishing communication lines. Users establish and respond to authorization requests and other real-time verifications pertaining to accessing each communication line (not end point) and sharing encrypted digital files. These are auditable, brokered, trusted-relationships where such relationships / digital agreements can each stand-alone (for privacy) or can leverage build-up of identity confidence levels across relationships. The service is agnostic to how encrypted user content is transported or stored.
Owner:T CENT
Universal data aggregation
A system for aggregating and managing PIM data from multiple sources is provided. By aggregating various sources of data, the present system allow for the bridging of networked communities and organizations. Limitations of data aggregation as a result of proprietary and / or protocol concerns are overcome through the development of trusted relationships amongst users of the data aggregation and management system.
Owner:SEVEN NETWORKS INC
Providing management functions in decentralized networks
InactiveUS7039701B2Avoiding drawback and limitationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationPersistent identifierWeb service
Methods, systems, and computer program products are disclosed for providing management functions in decentralized networks. Persistent identifiers are defined for nodes, allowing nodes to be identified across sessions and invocations, even though they re-enter the network with a different network address. Paths taken by content resources as they traverse the network (e.g. which nodes forwarded the content) are persisted, along with reputation information about nodes (e.g. indicating how successful they are at answering queries from peers). Trust relationships can be derived using the persisted information. A tiered broadcast strategy is defined for reducing the number of messages exchanged. Preferred embodiments leverage a web services implementation model.
Owner:IBM CORP
Persisting node reputations in transient communities
Methods, systems, and computer program products are disclosed for persisting node reputations in a transient peer-to-peer networking environment where communities have ad hoc participants. Persistent identifiers are defined for nodes, allowing nodes to be identified across sessions and invocations, even though they re-enter the network with a different network address. Paths taken by content resources as they traverse the network (e.g. which nodes forwarded the content) are persisted, along with reputation information about nodes (e.g. indicating how successful they are at answering queries from peers). Trust relationships can be derived using the persisted information. A tiered broadcast strategy is defined for reducing the number of messages exchanged. Preferred embodiments leverage a web services implementation model.
Owner:IBM CORP
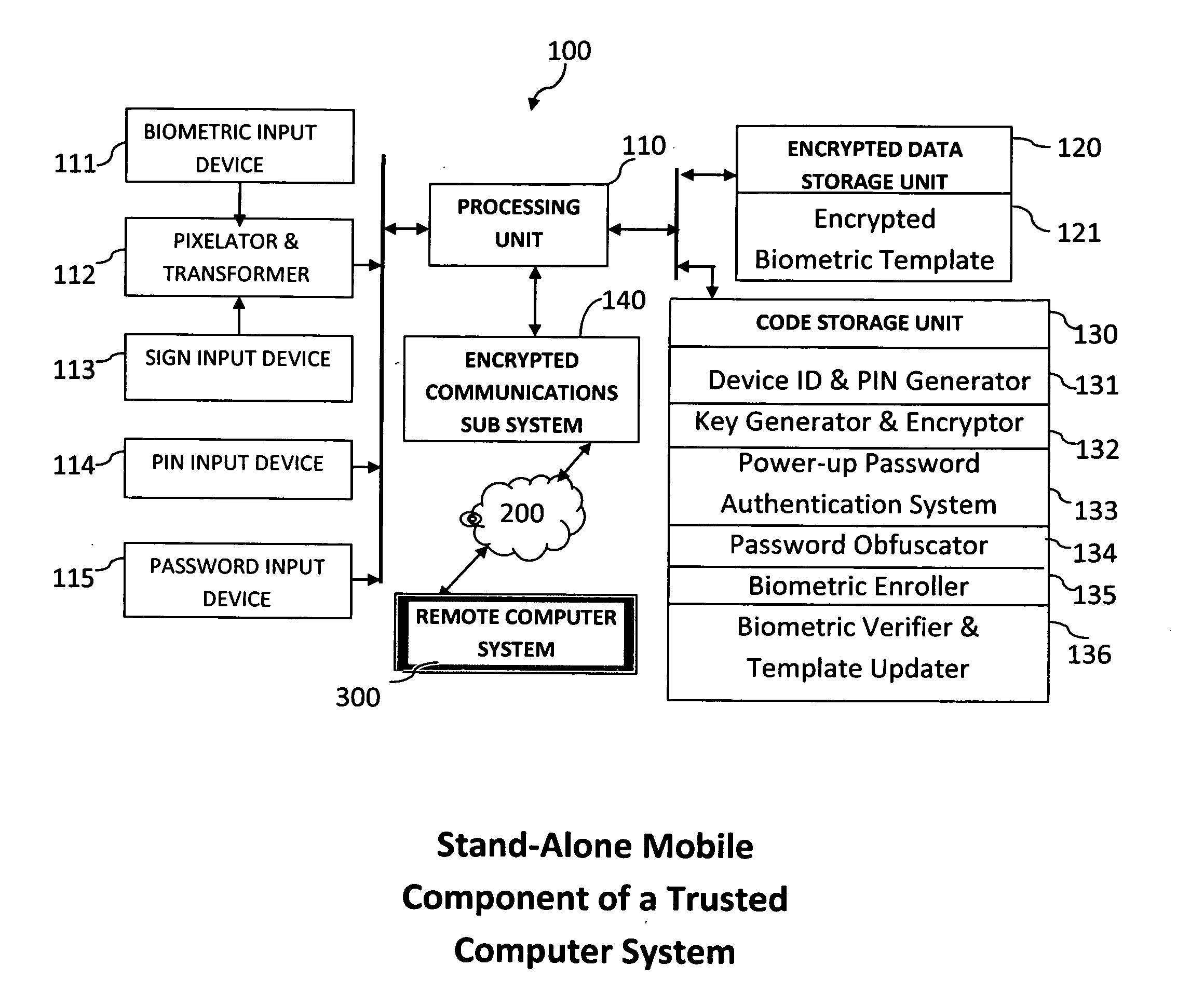
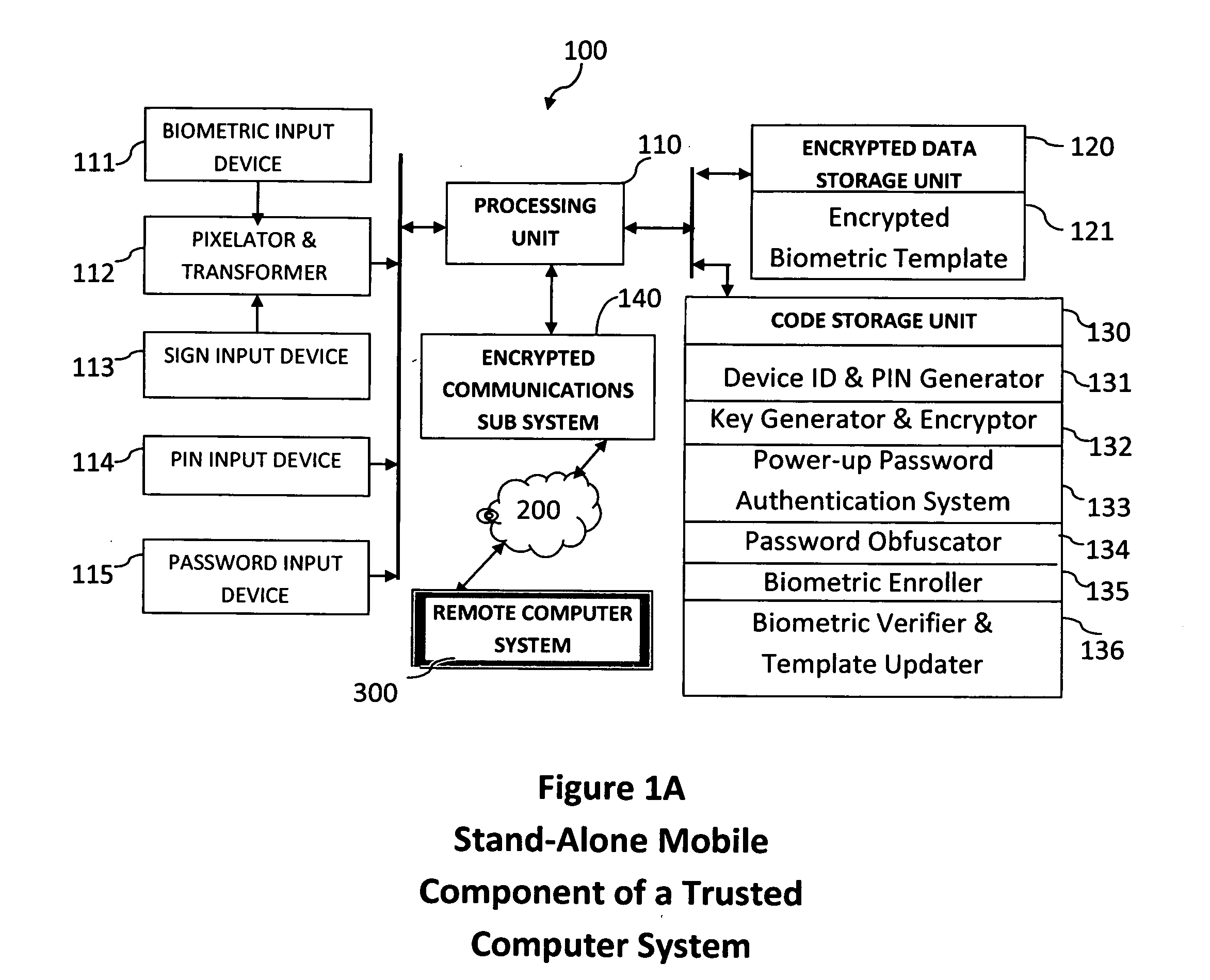
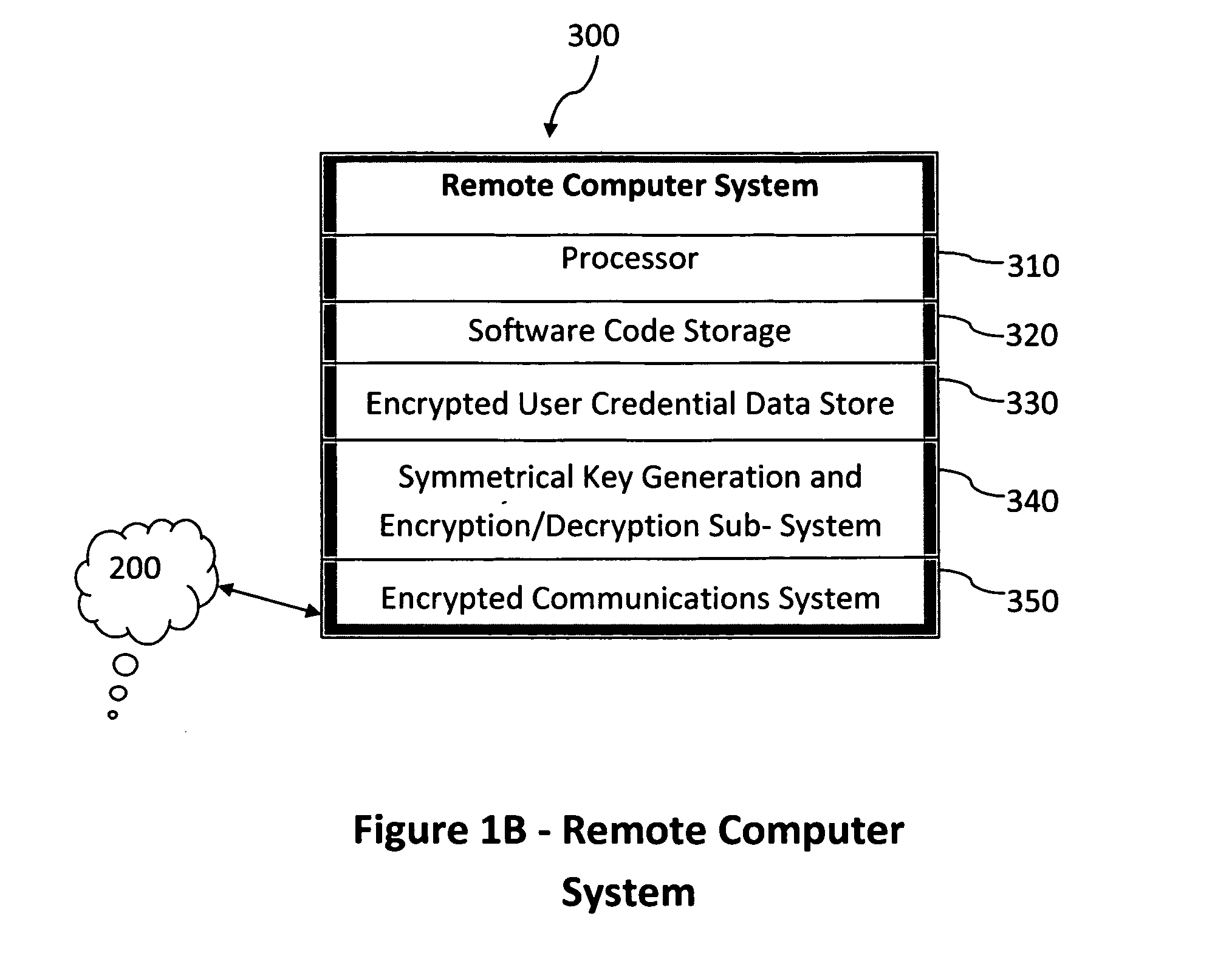
Method and system for combining a PIN and a biometric sample to provide template encryption and a trusted stand-alone computing device
ActiveUS20110126024A1Secure EncryptionEasy to useDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationBiometric dataTrust relationship
Biometric data, suitably transformed are obtained from a biometric input device contained within a stand-alone computing device and used in conjunction with a PIN to authenticate the user to the device. The biometric template and other data residing on the device are encrypted using hardware elements of the device, the PIN and Password hash. A stored obfuscated password is de-obfuscated and released to the device authentication mechanism in response to a successfully decrypted template and matching biometric sample and PIN. The de-obfuscated password is used to authenticate the user to device, the user to a remote computer, and to encrypt device data at rest on the device and in transit to and from the remote computer. This creates a trusted relationship between the stand-alone device and the remote computer. The system also eliminates the need for the user to remember and enter complex passwords on the device.
Owner:BIOCRYPT ACCESS LLC
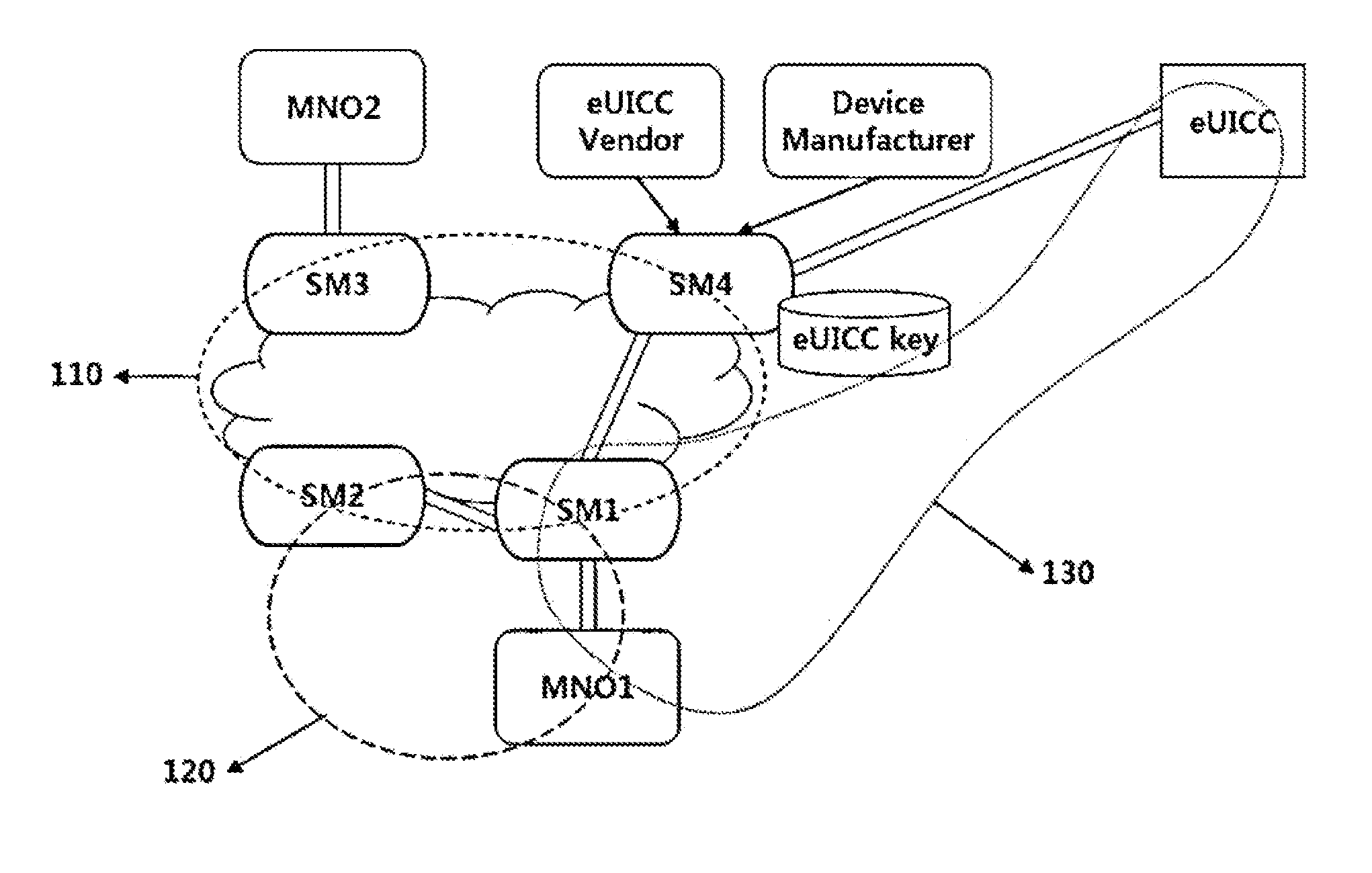
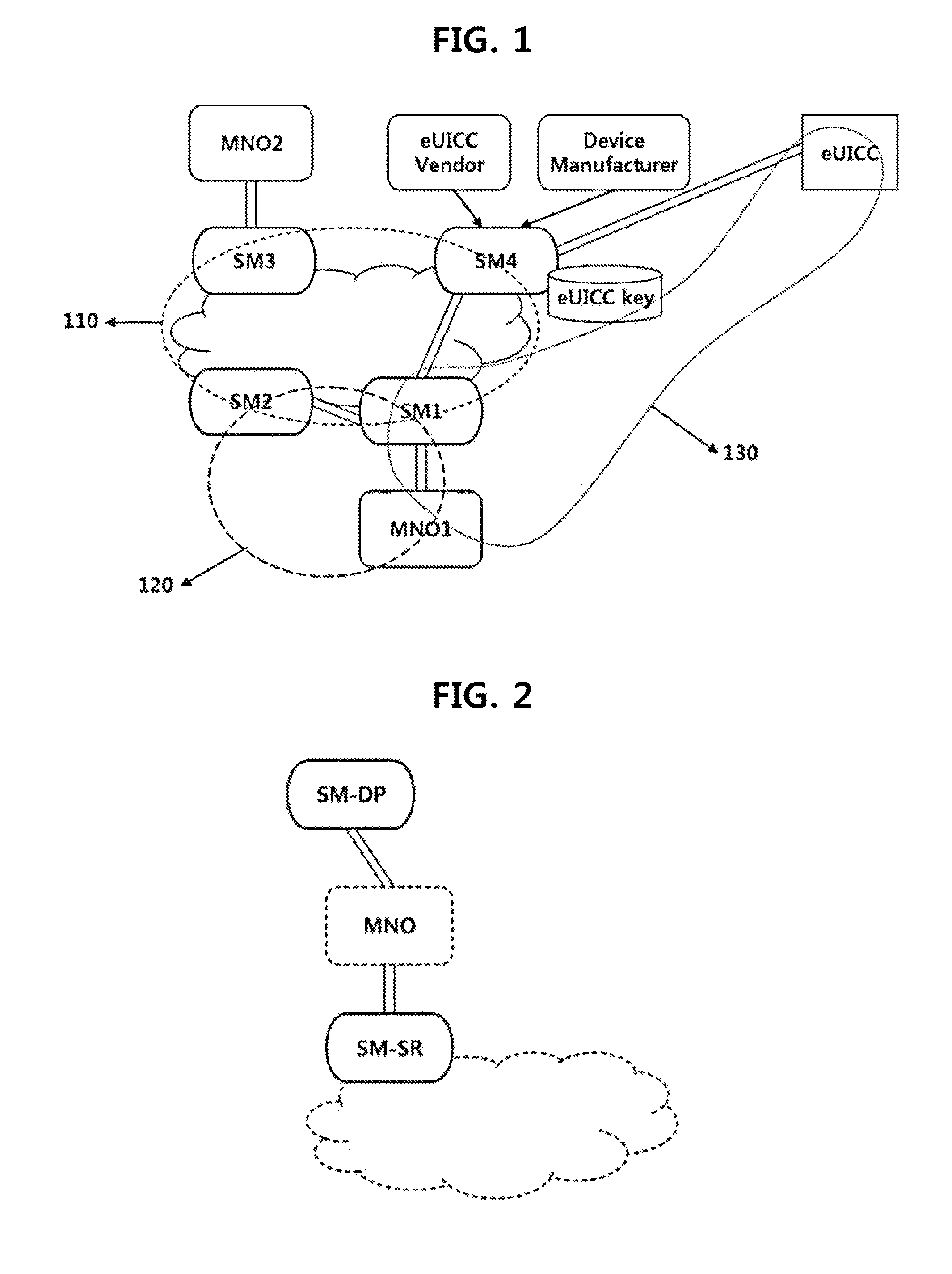
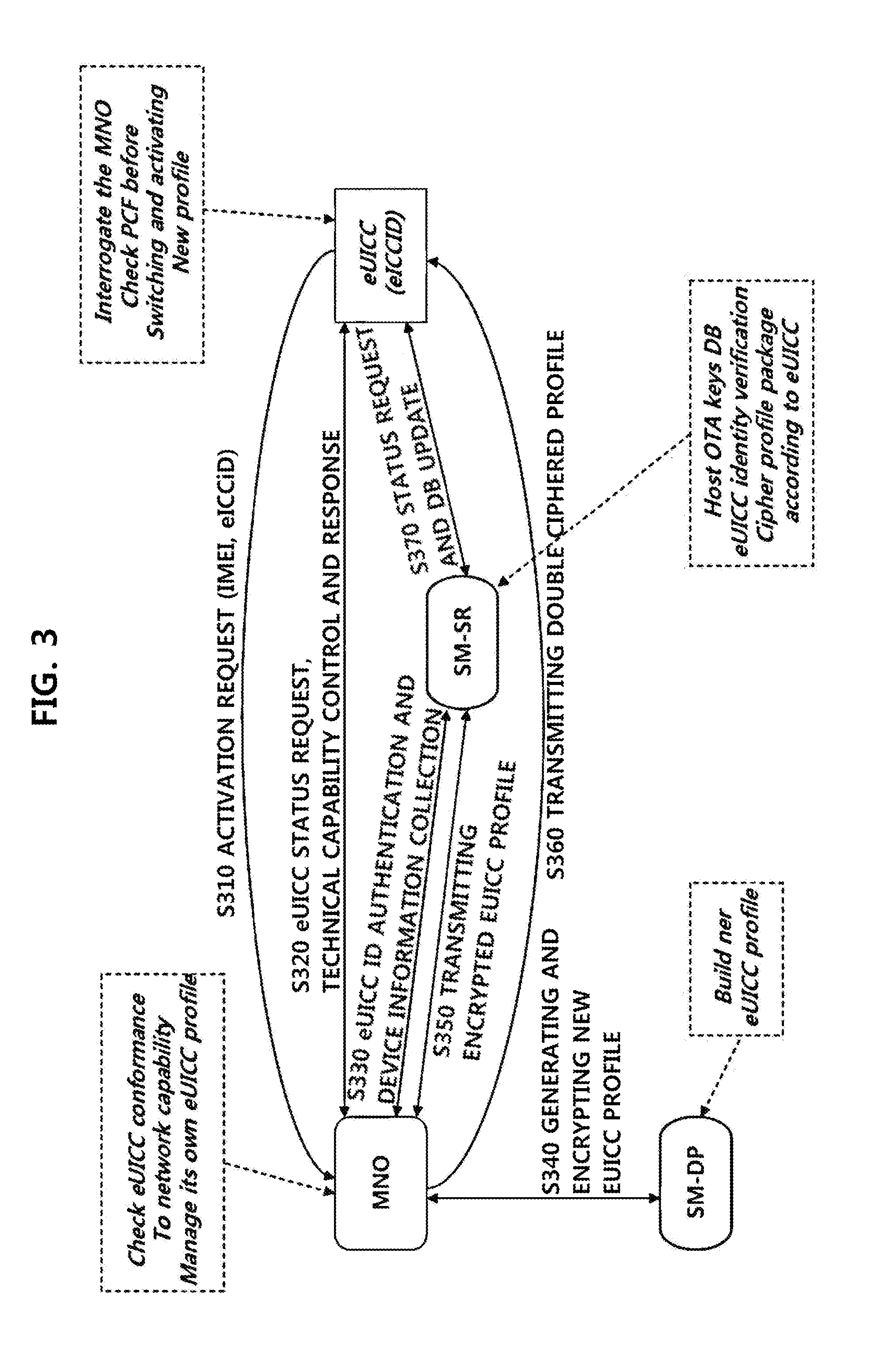
Method for forming a trust relationship, and embedded uicc therefor
ActiveUS20140287725A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemTrust relationship
The present invention relates to a method for forming a trust relationship among an MNO, an SM, and an eUICC in a communication system in which the SM is defined as an entity for managing the eUICC, as well as to an embedded UICC therefor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
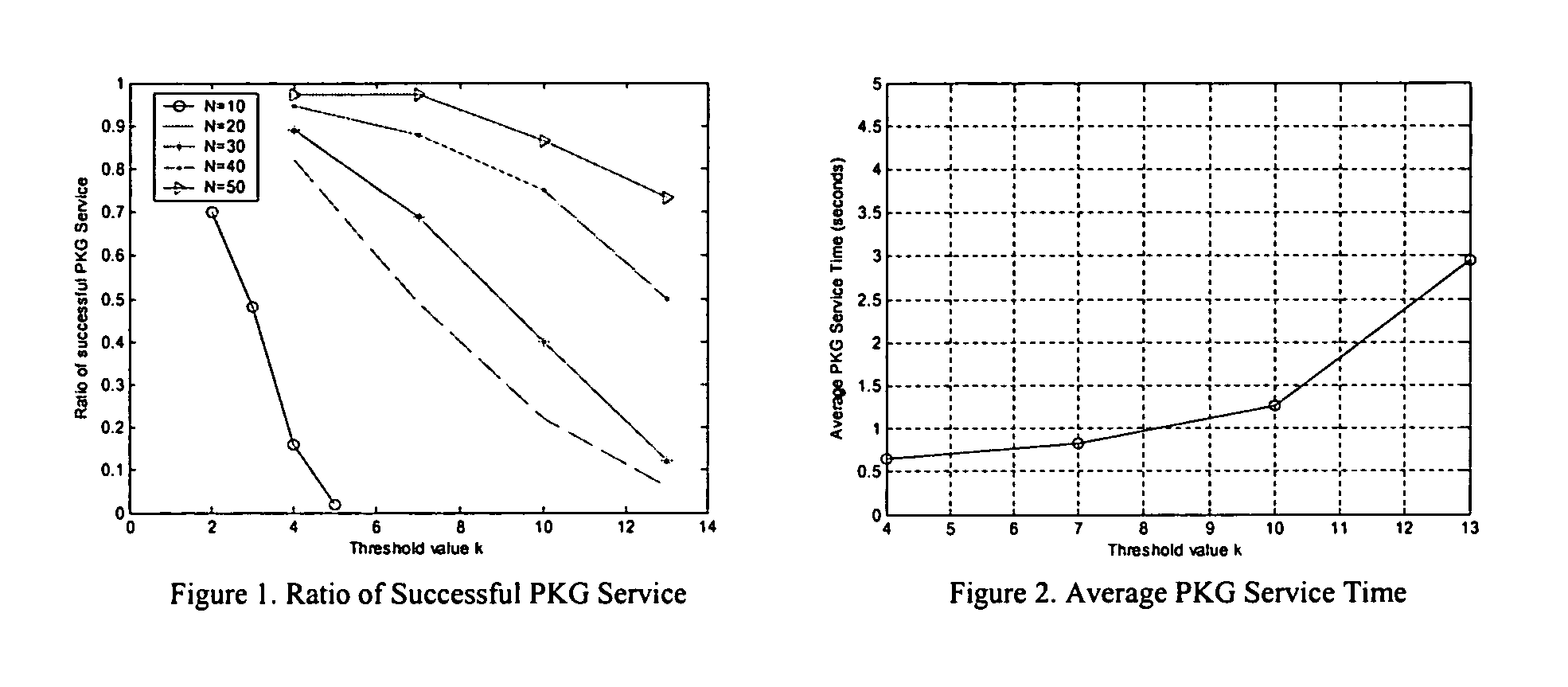
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20060023887A1Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityWireless ad hoc network
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com